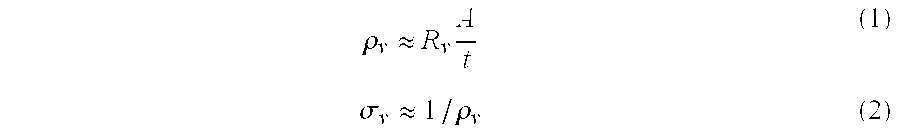Patents
Literature
63 results about "Biomedical sensors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
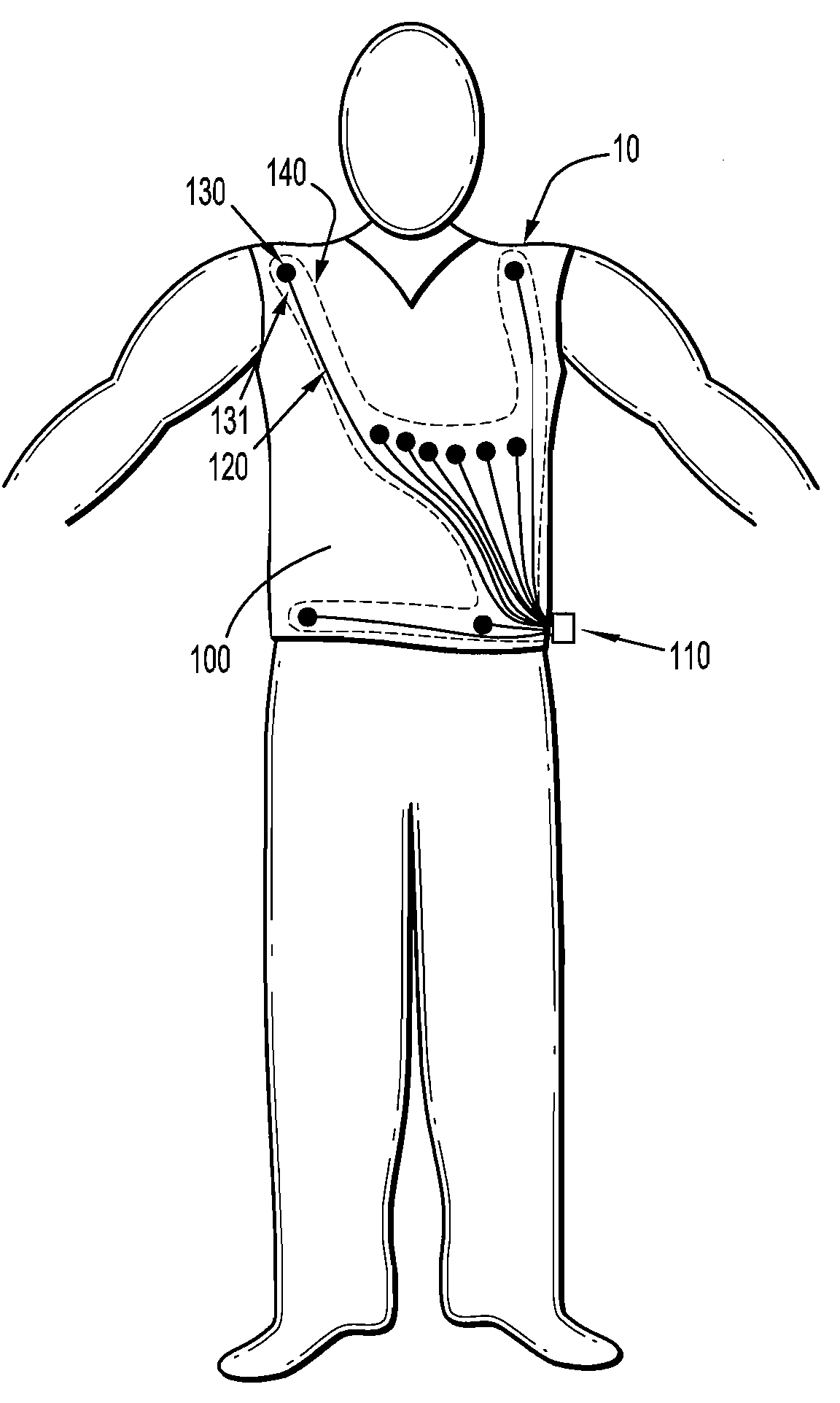
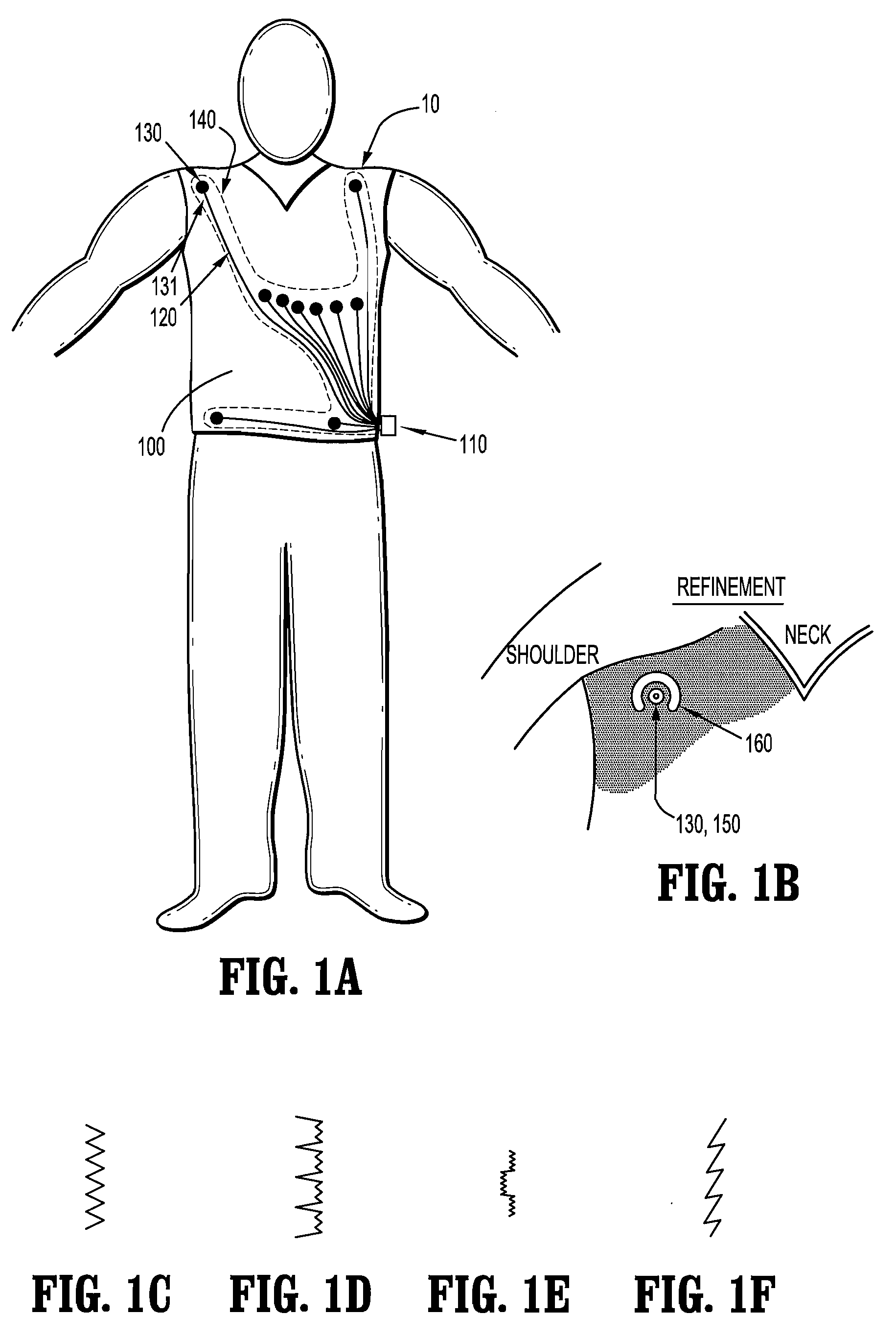
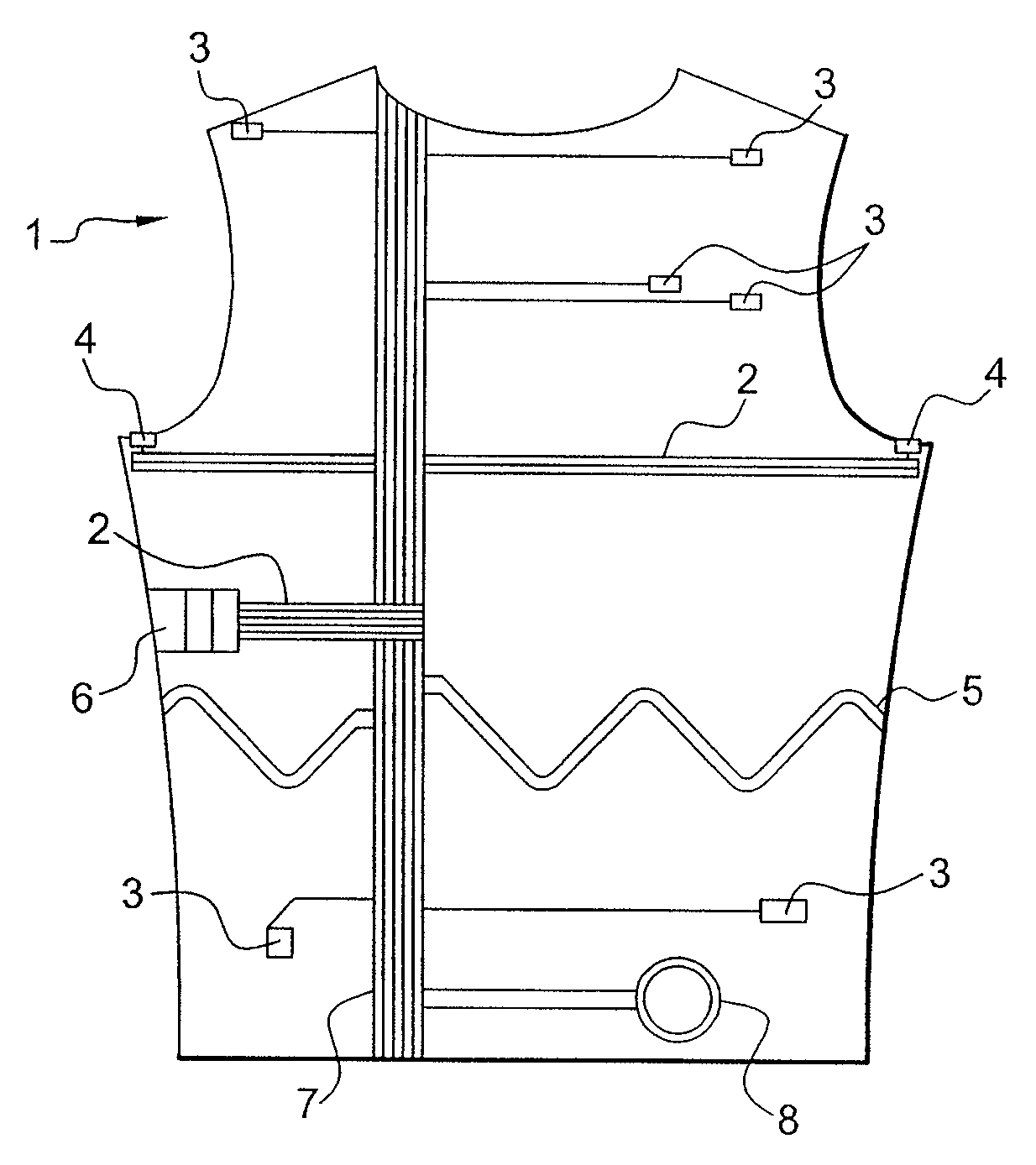
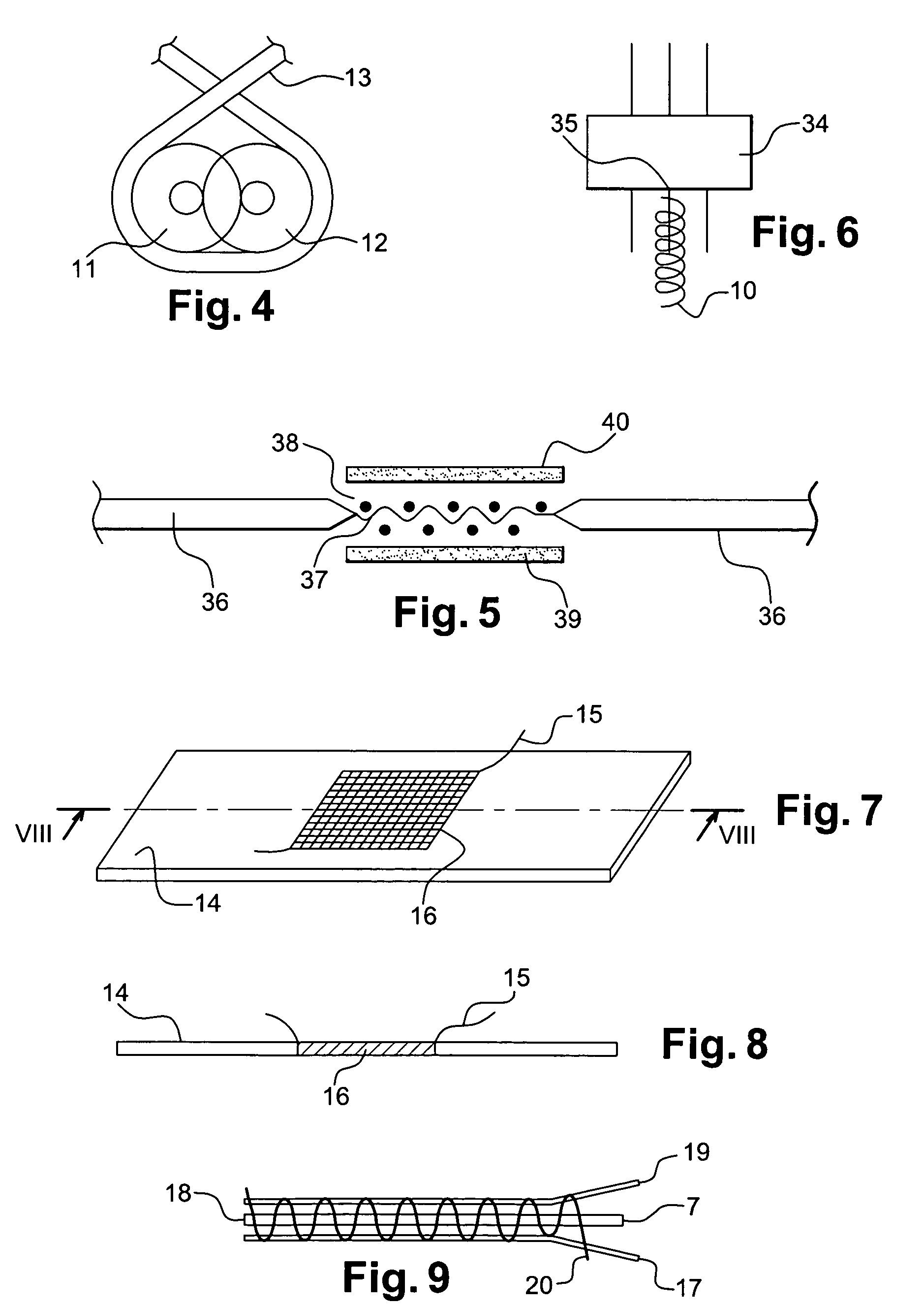
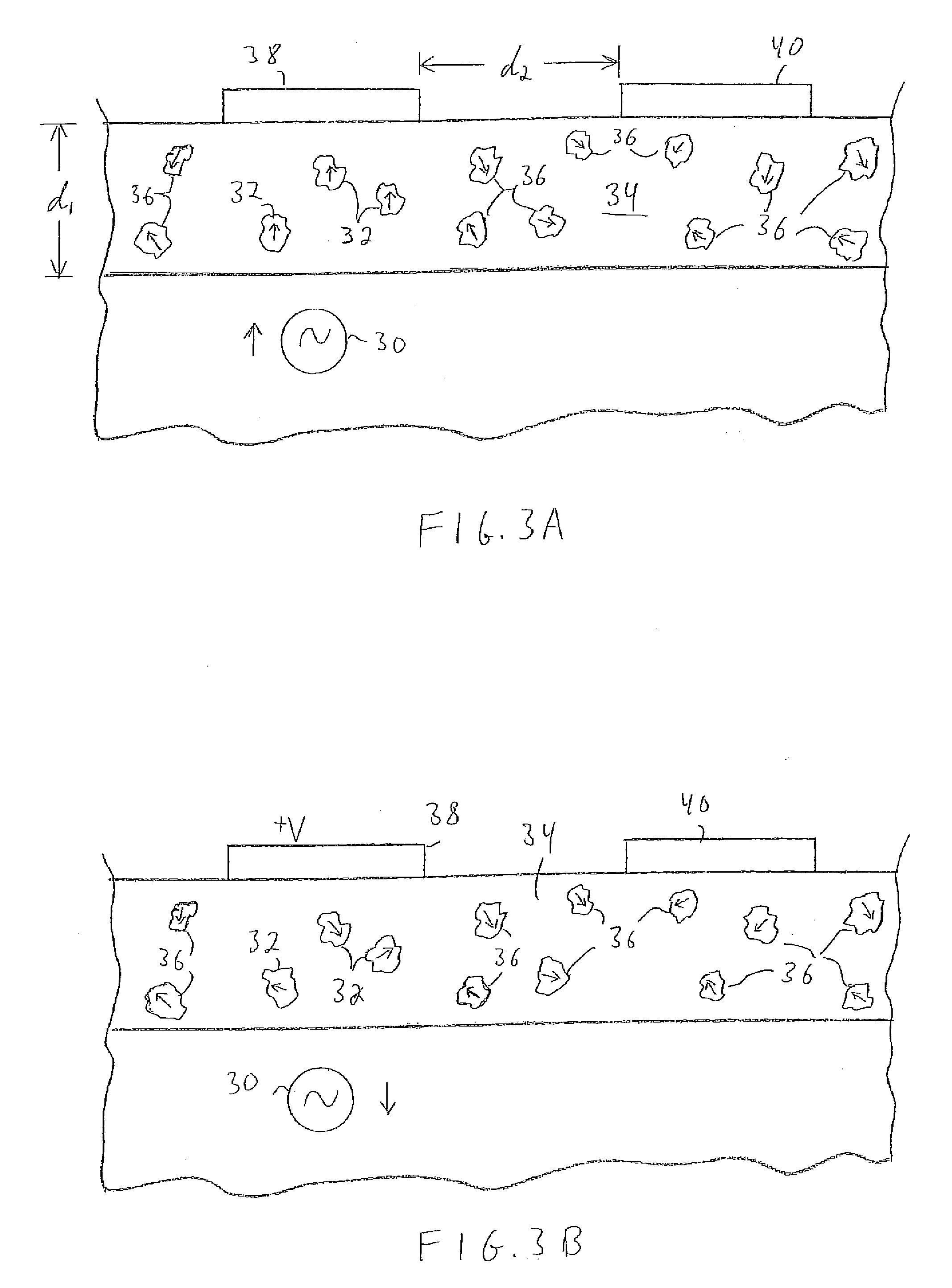
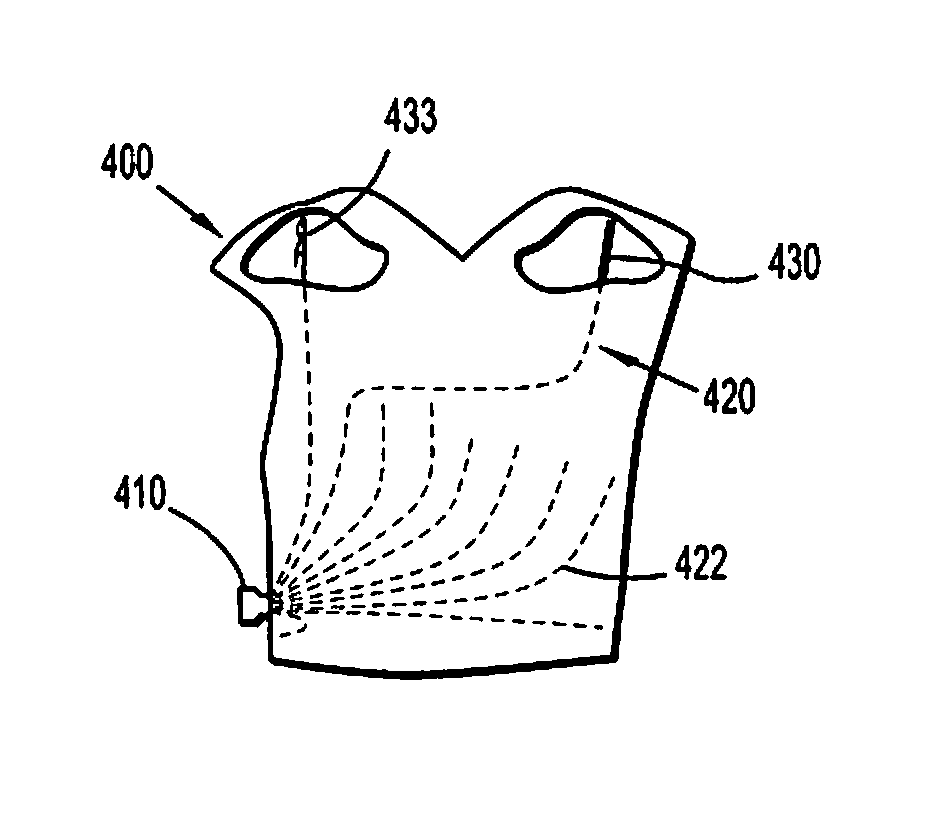
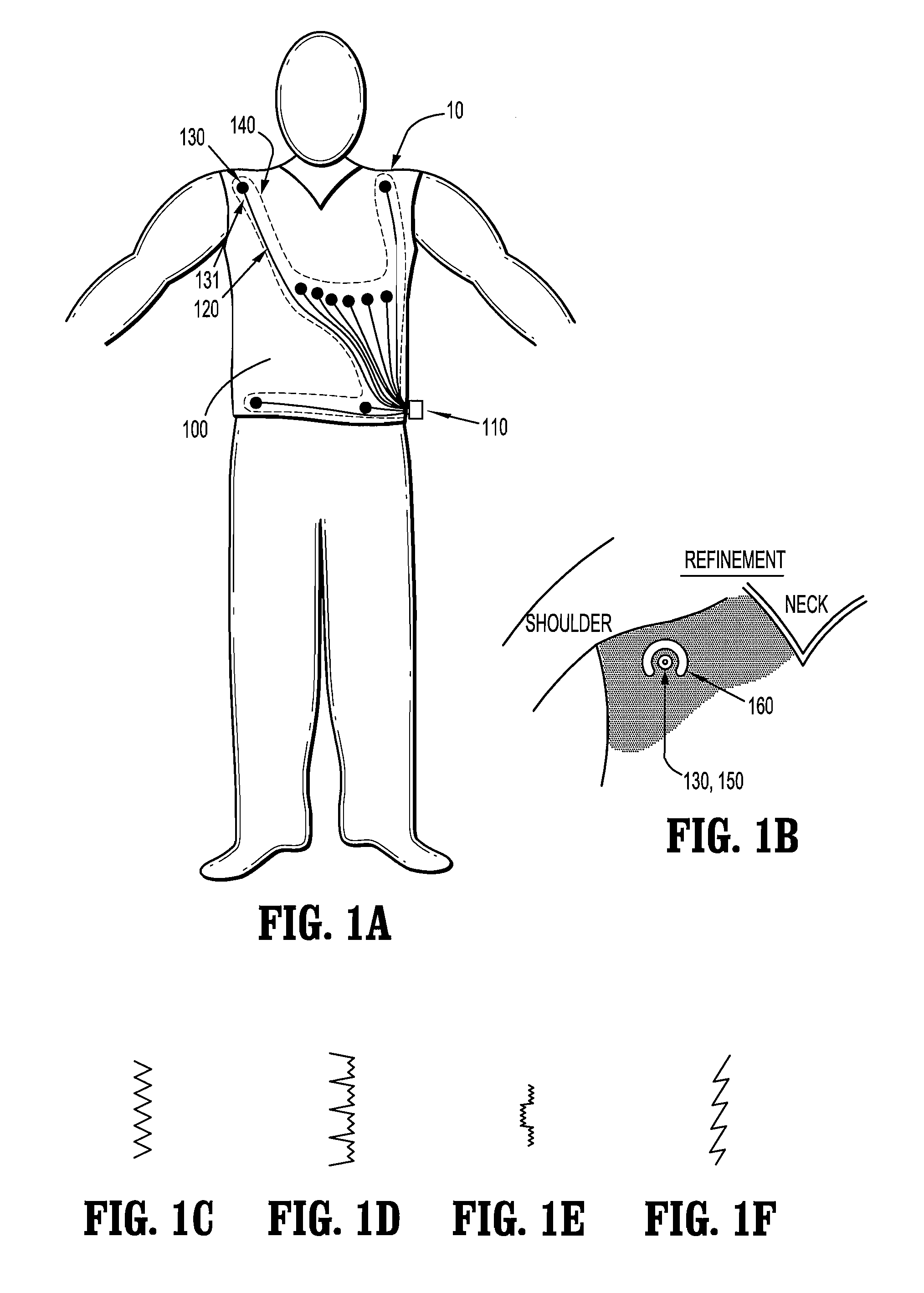
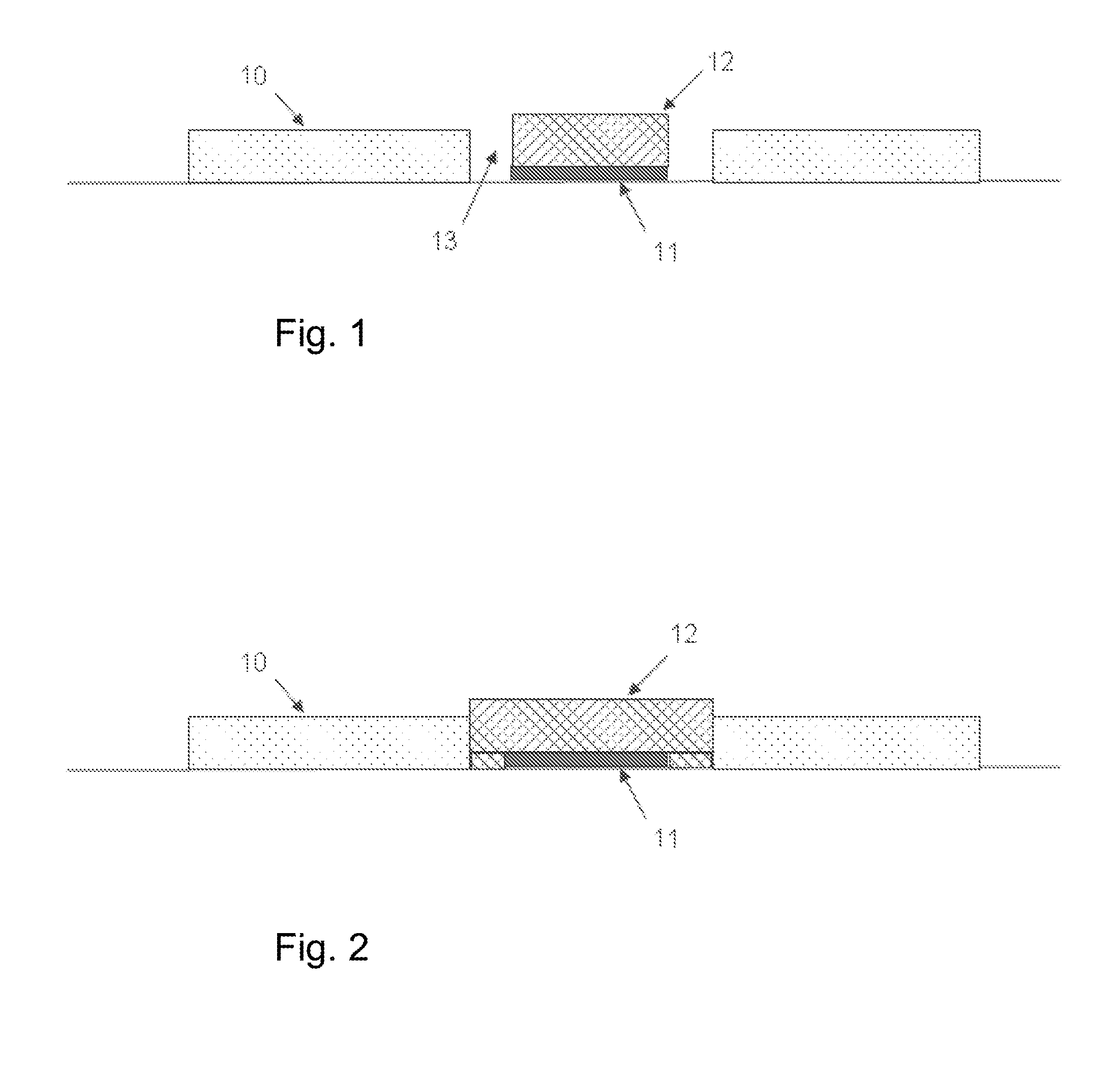
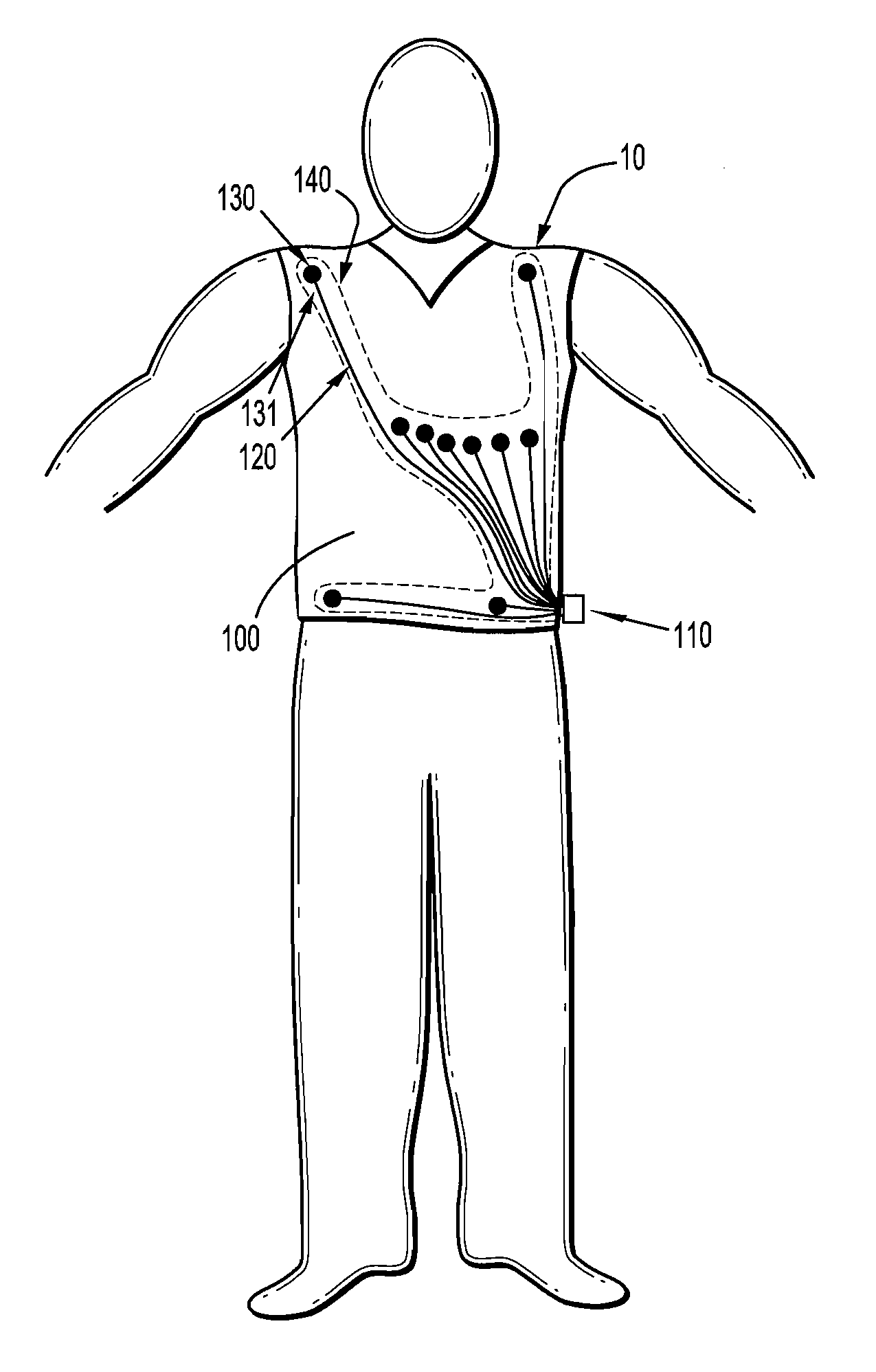
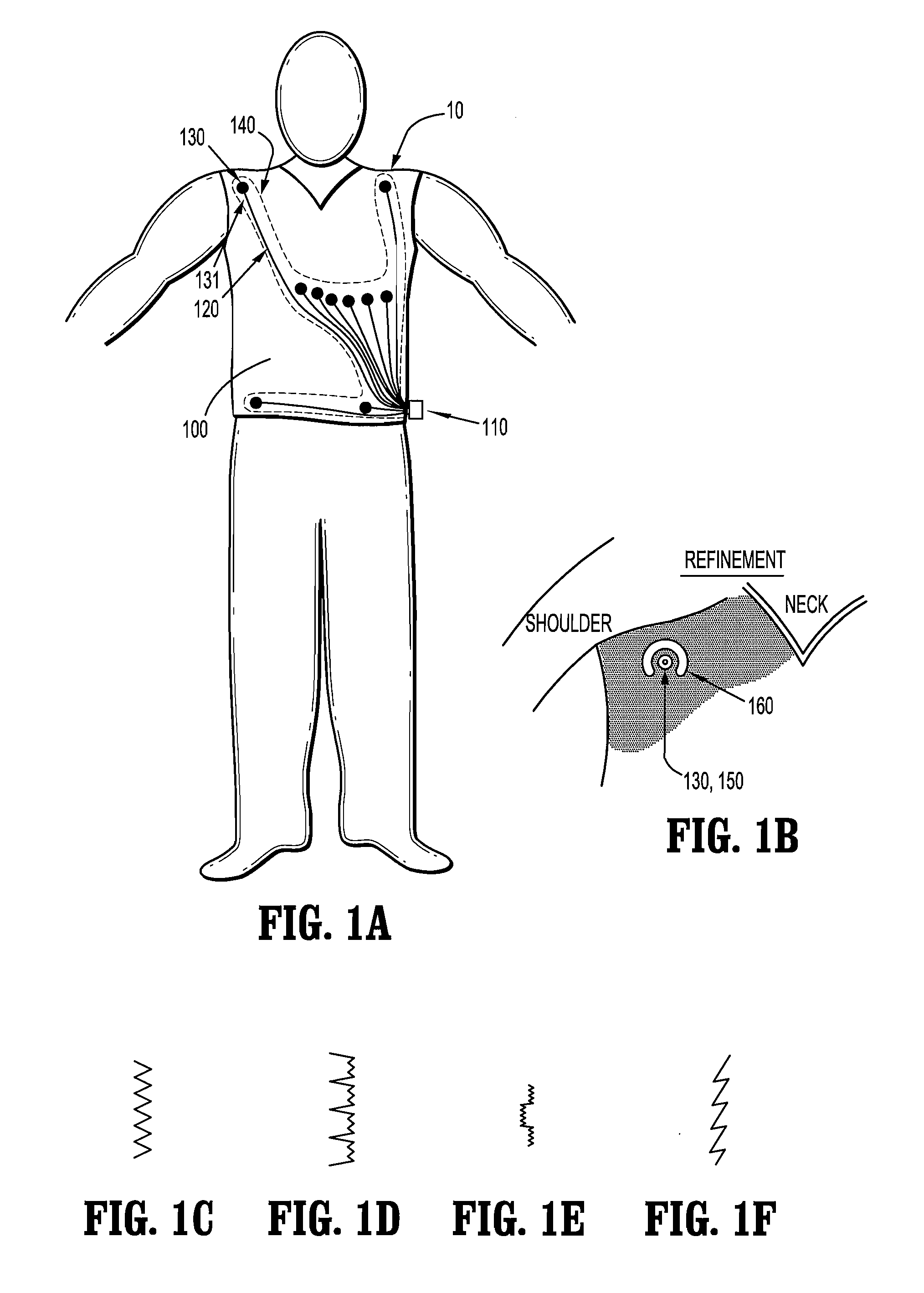
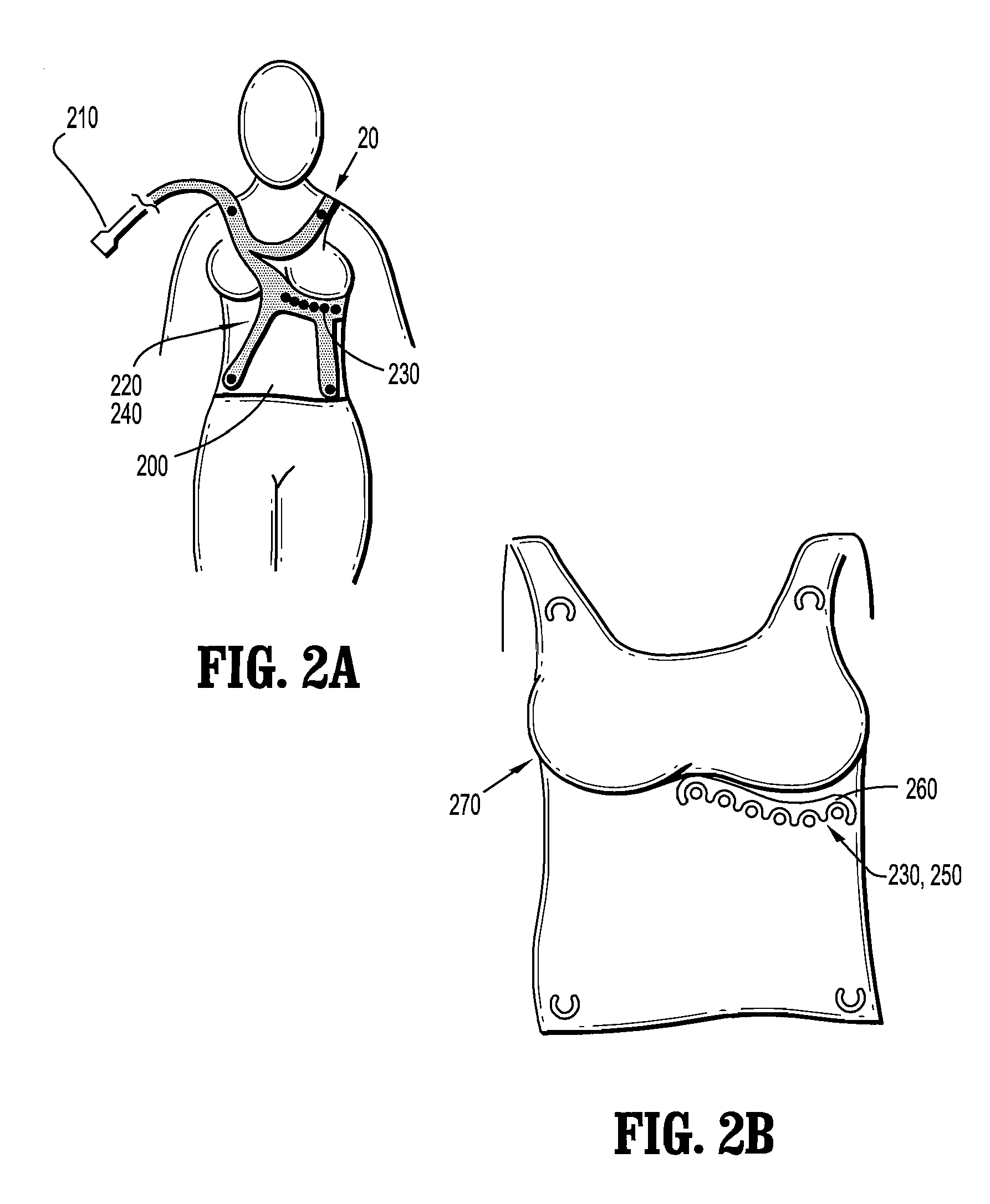
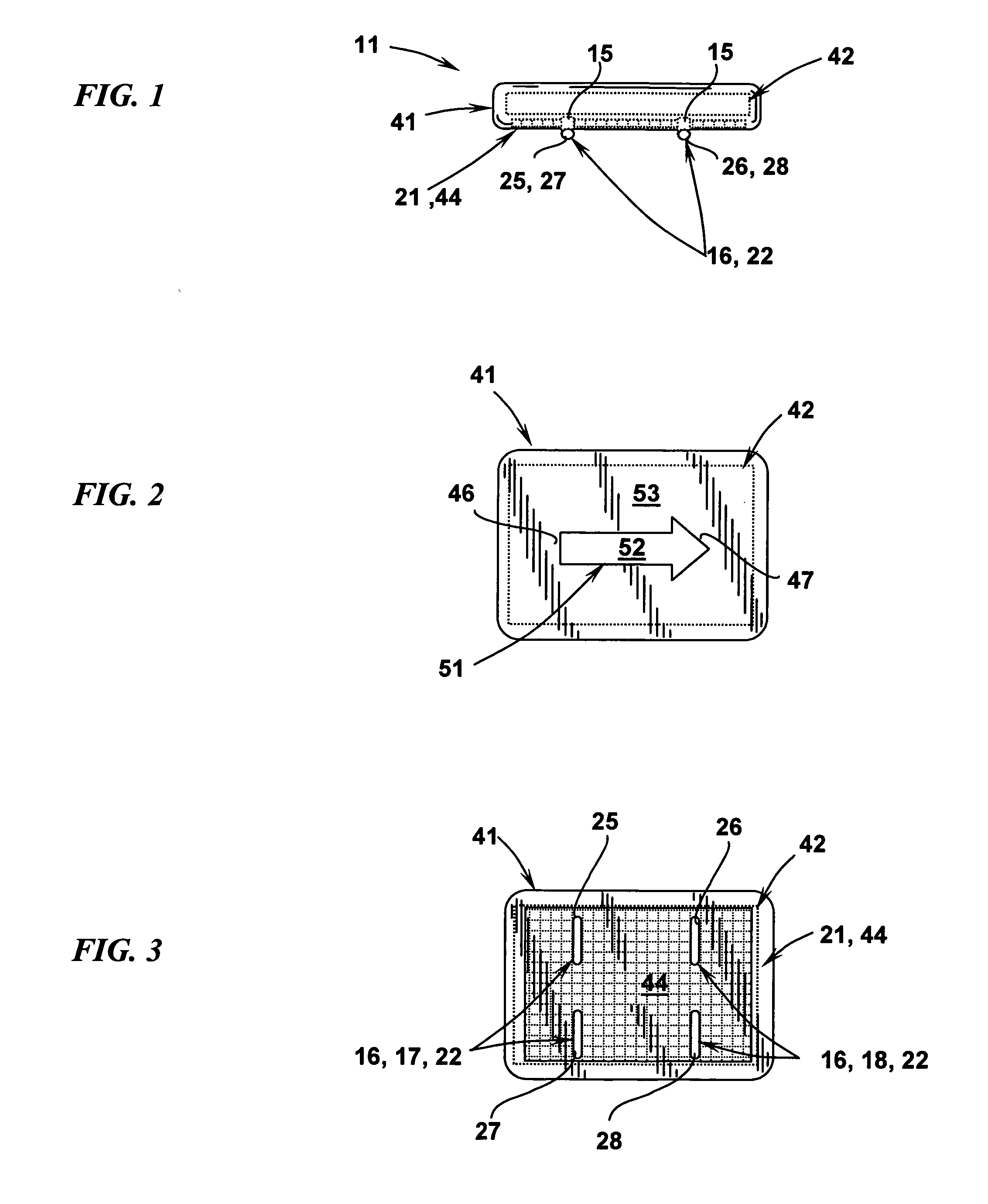
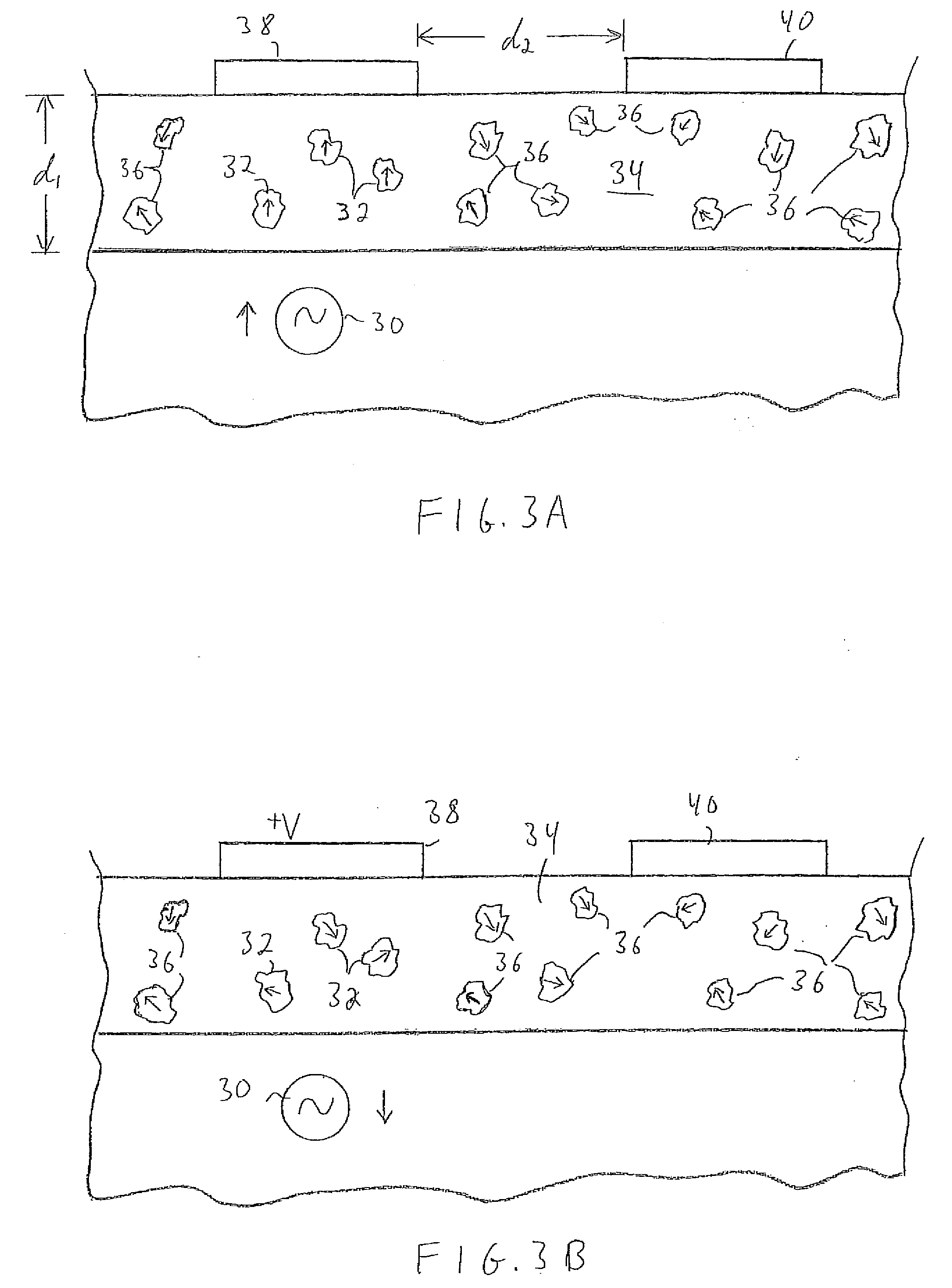
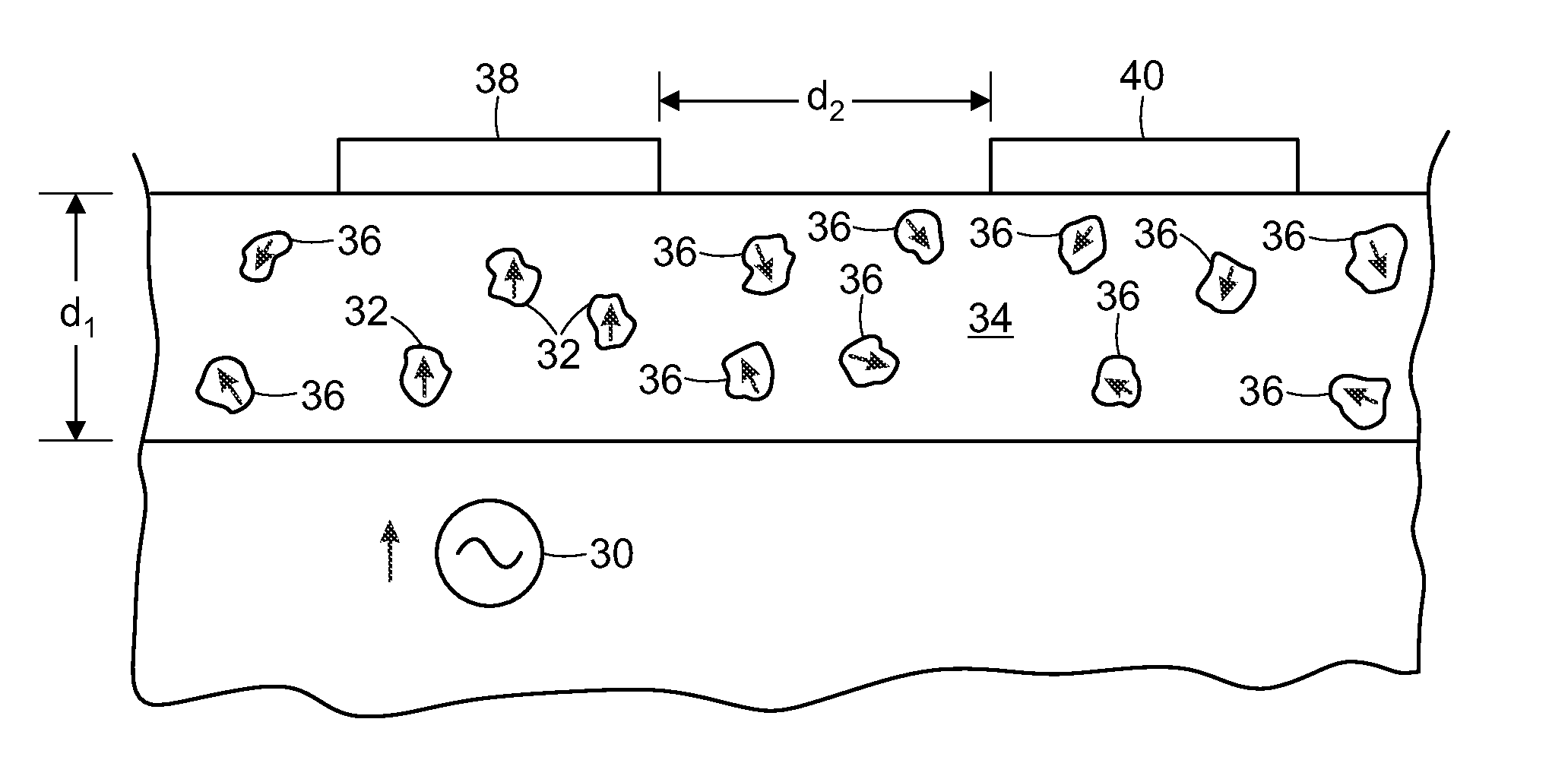
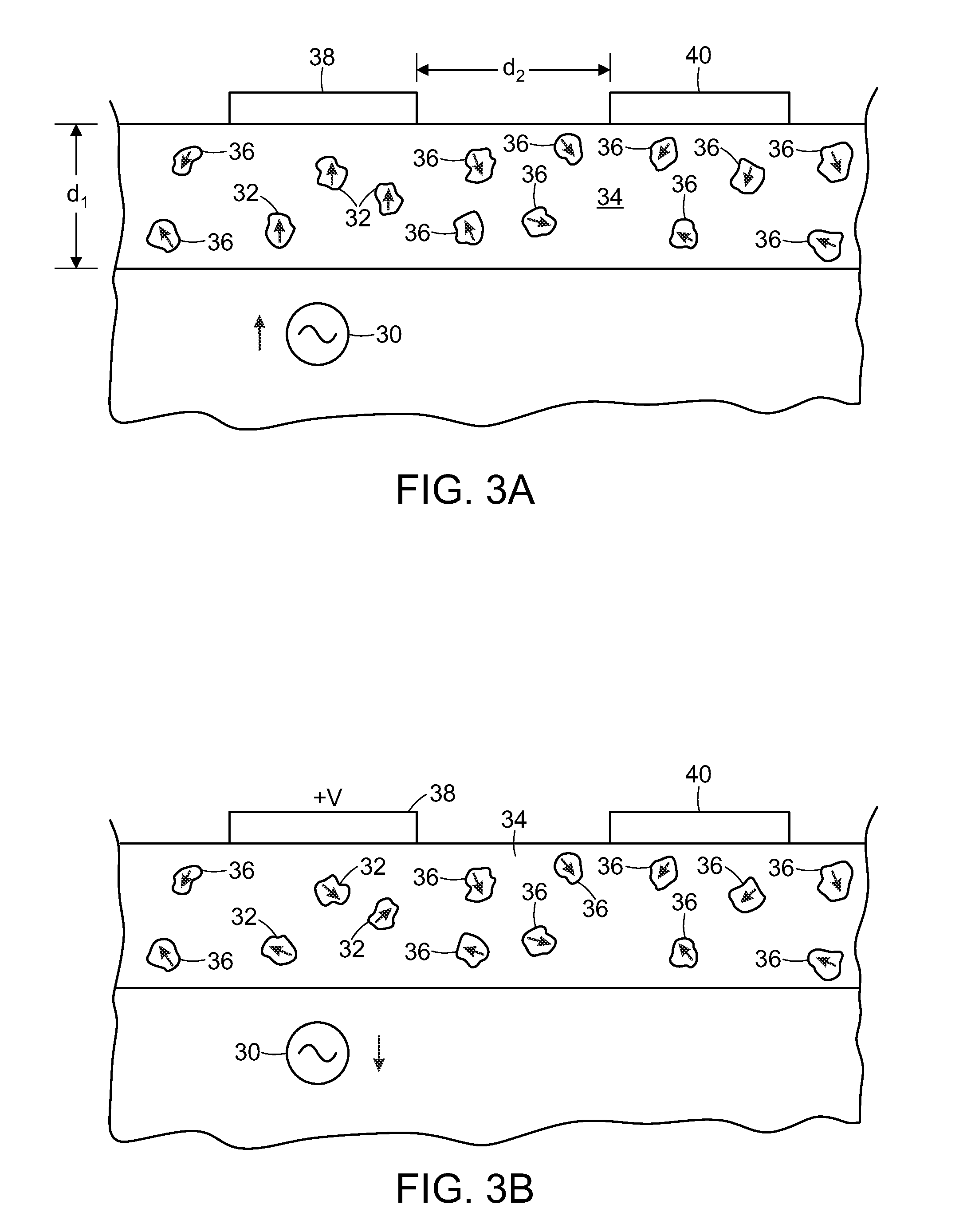
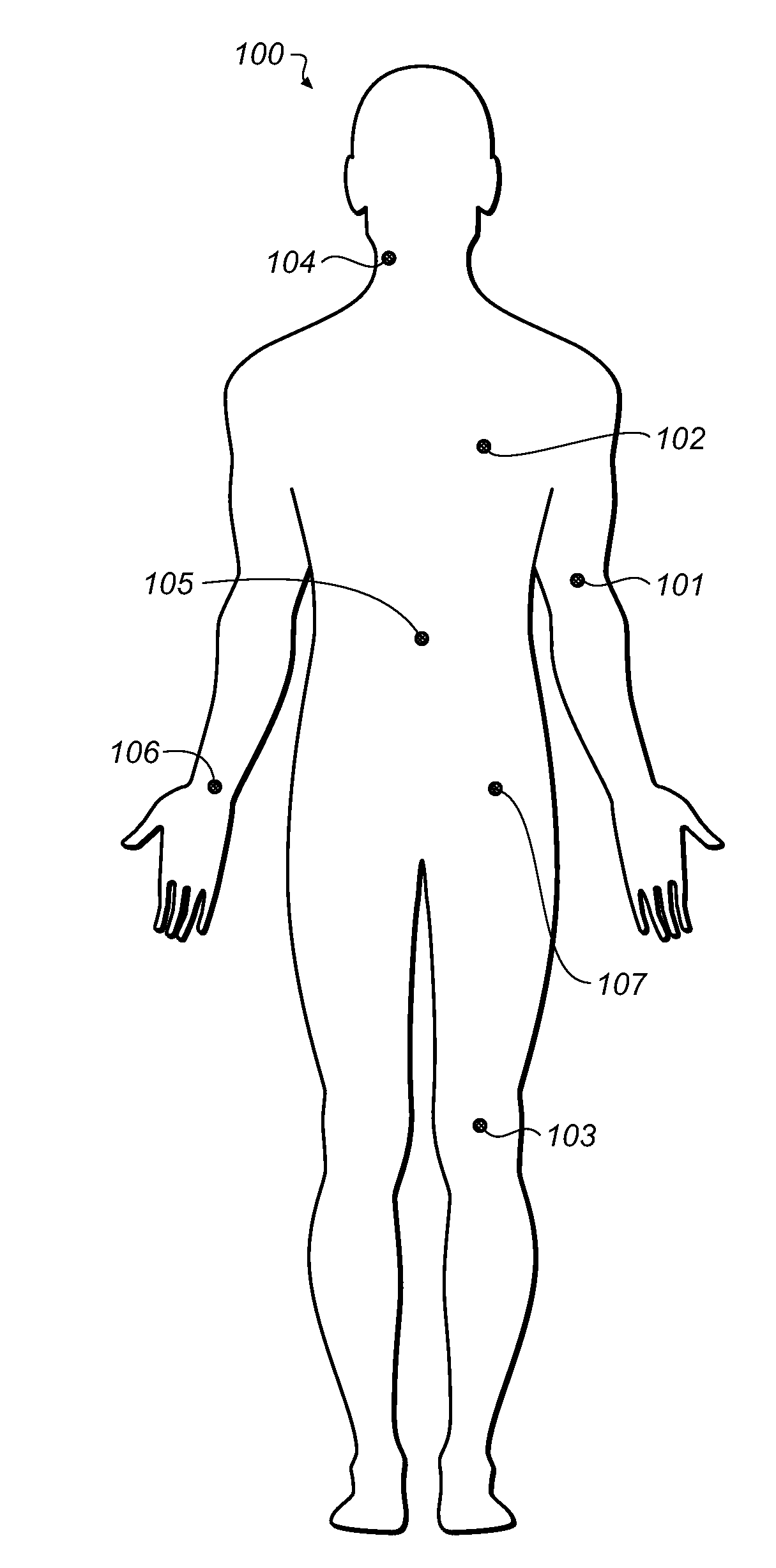
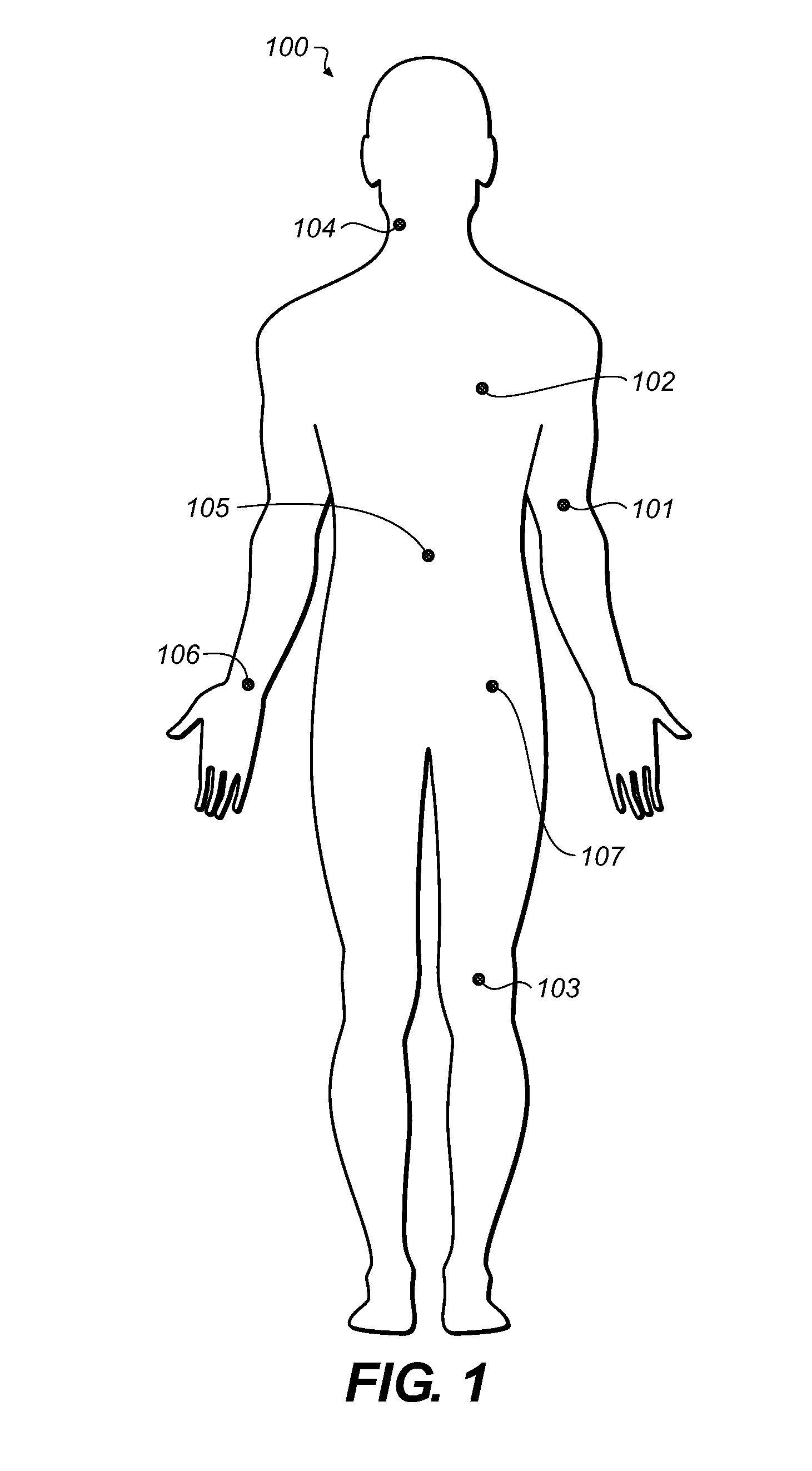
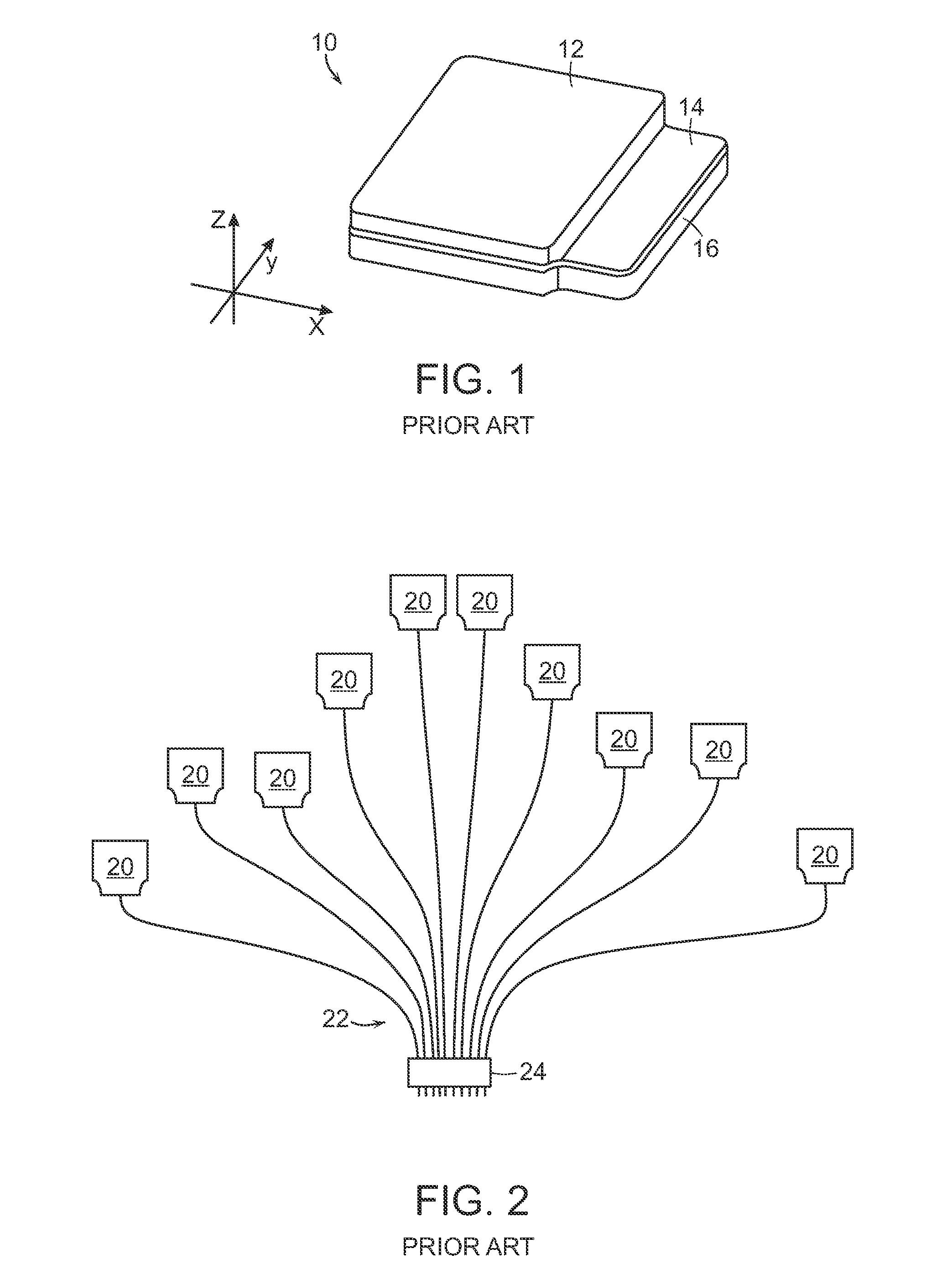
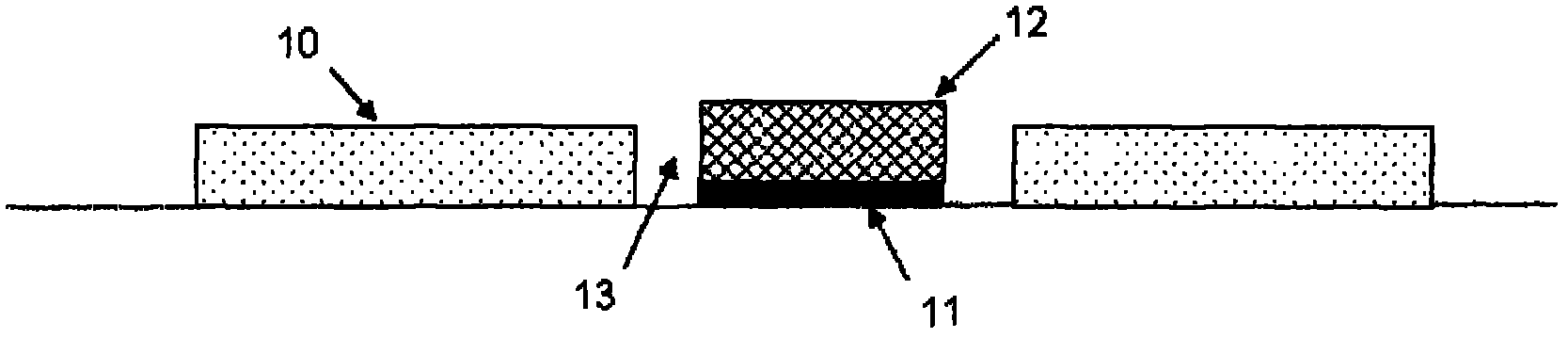
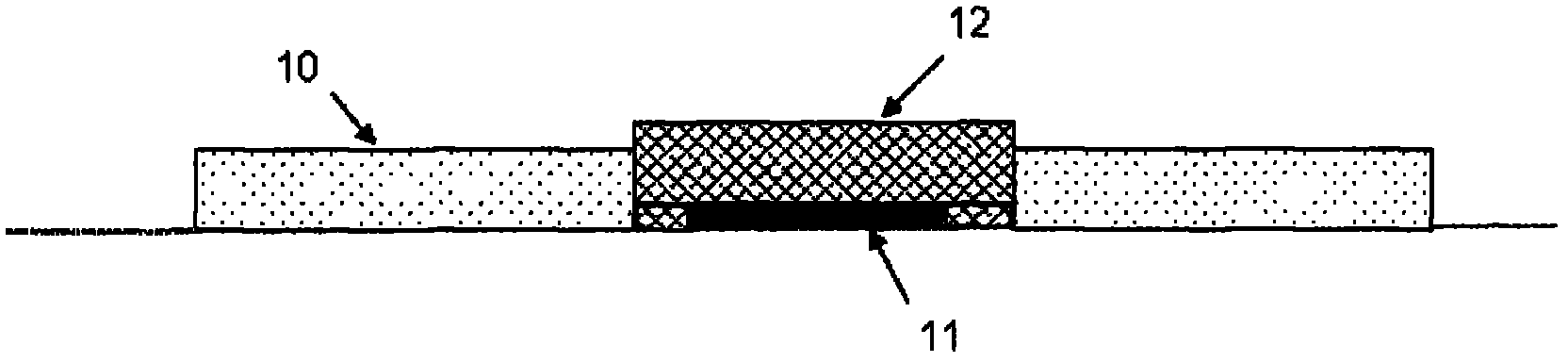
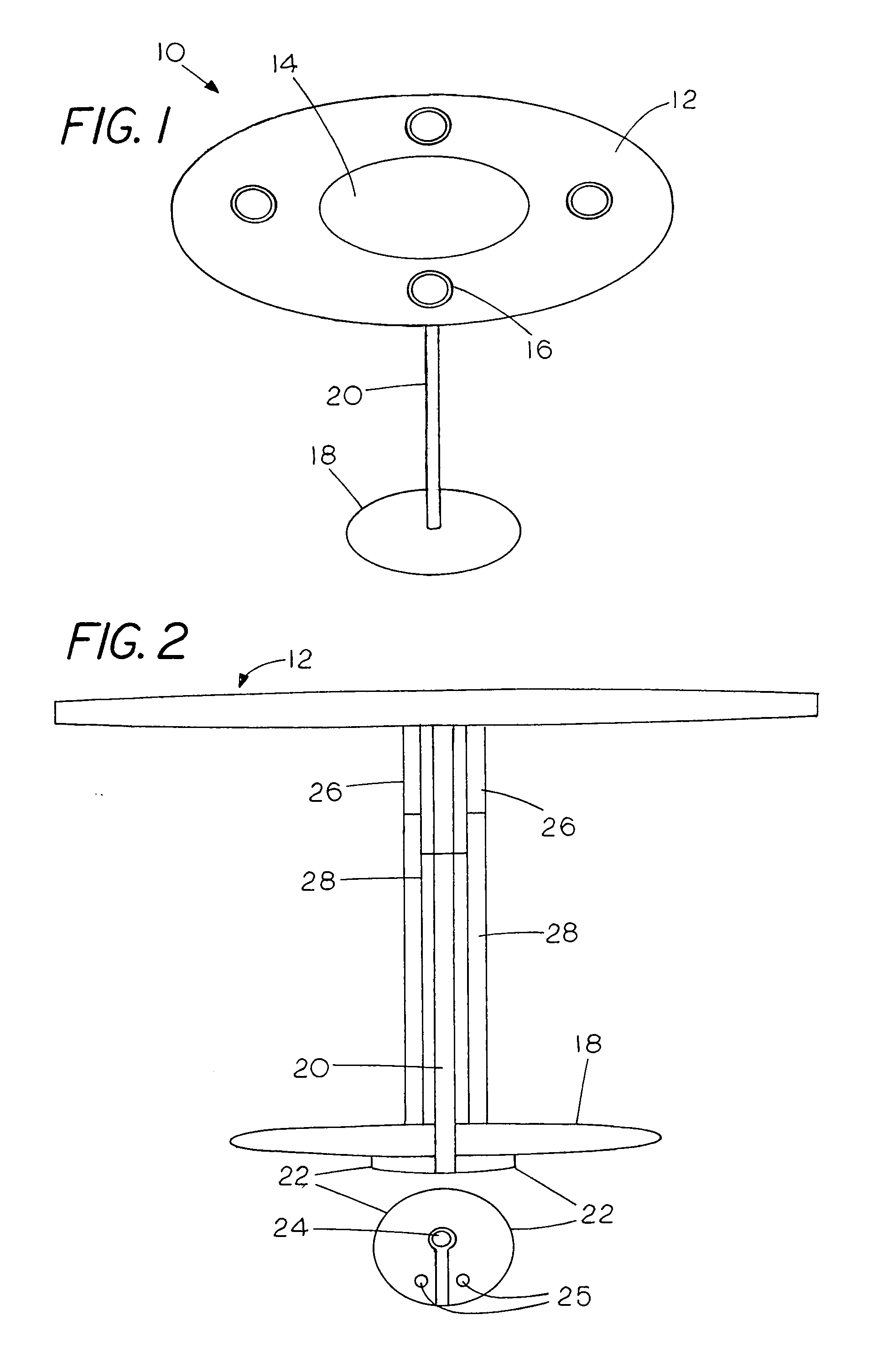
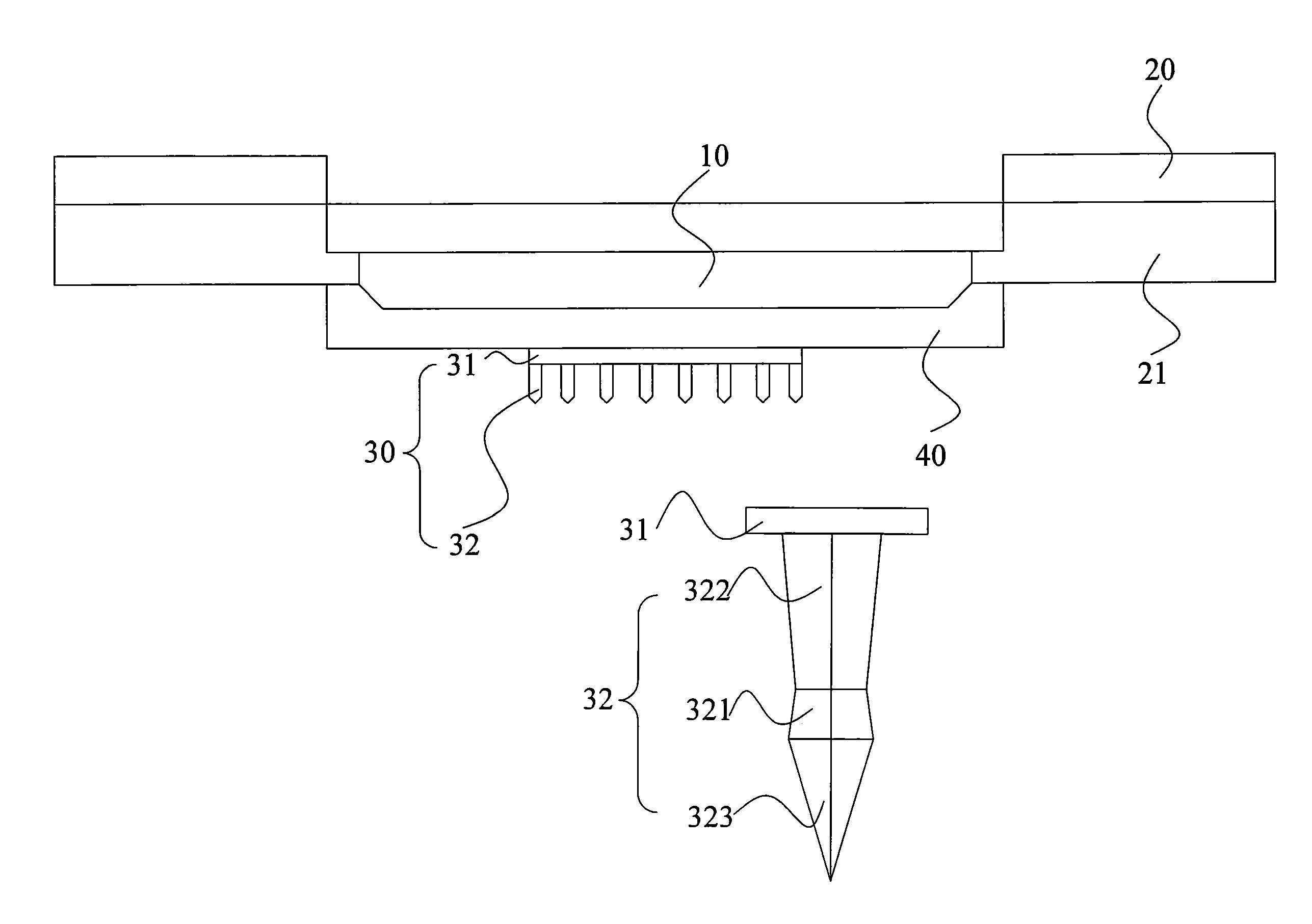
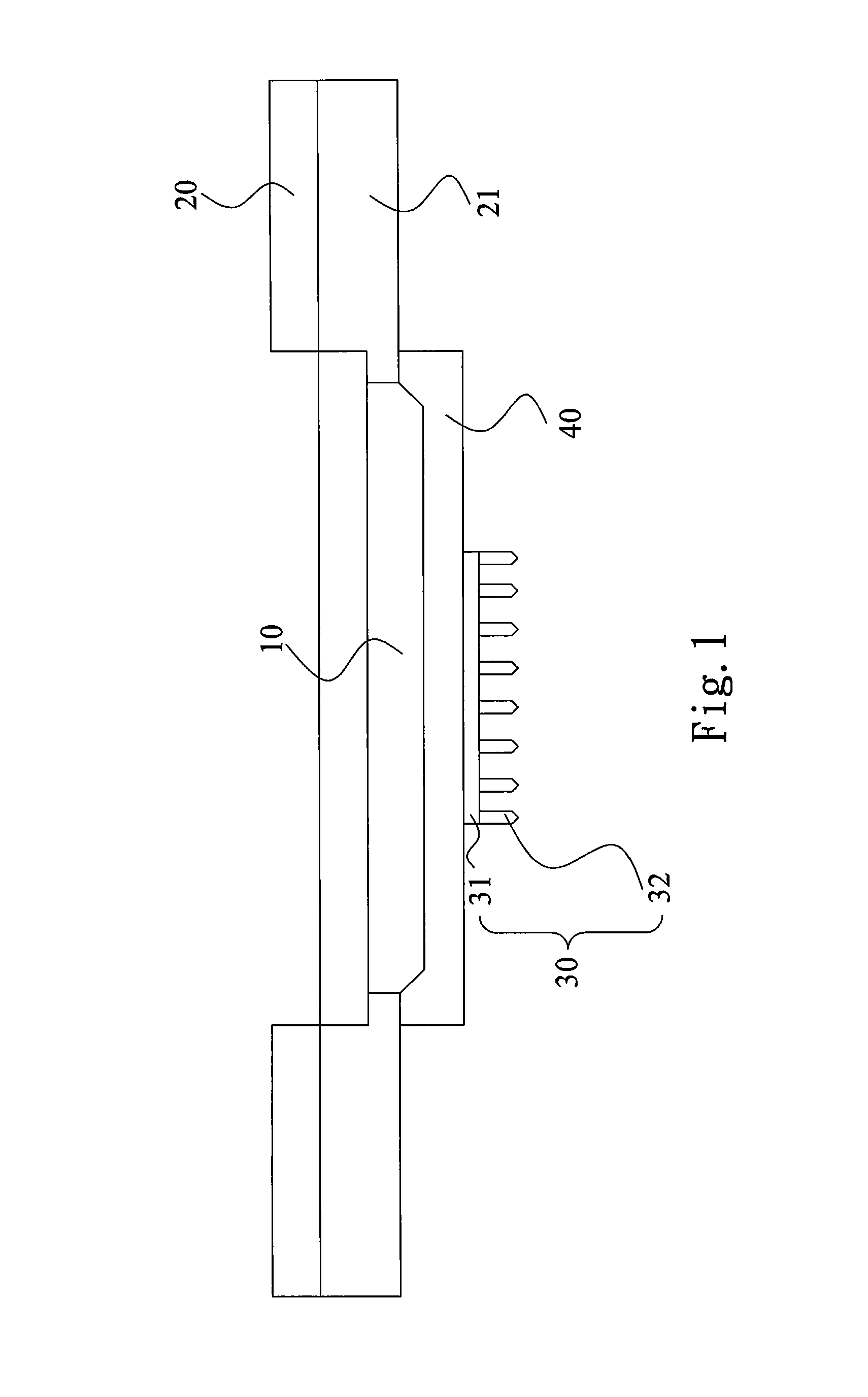
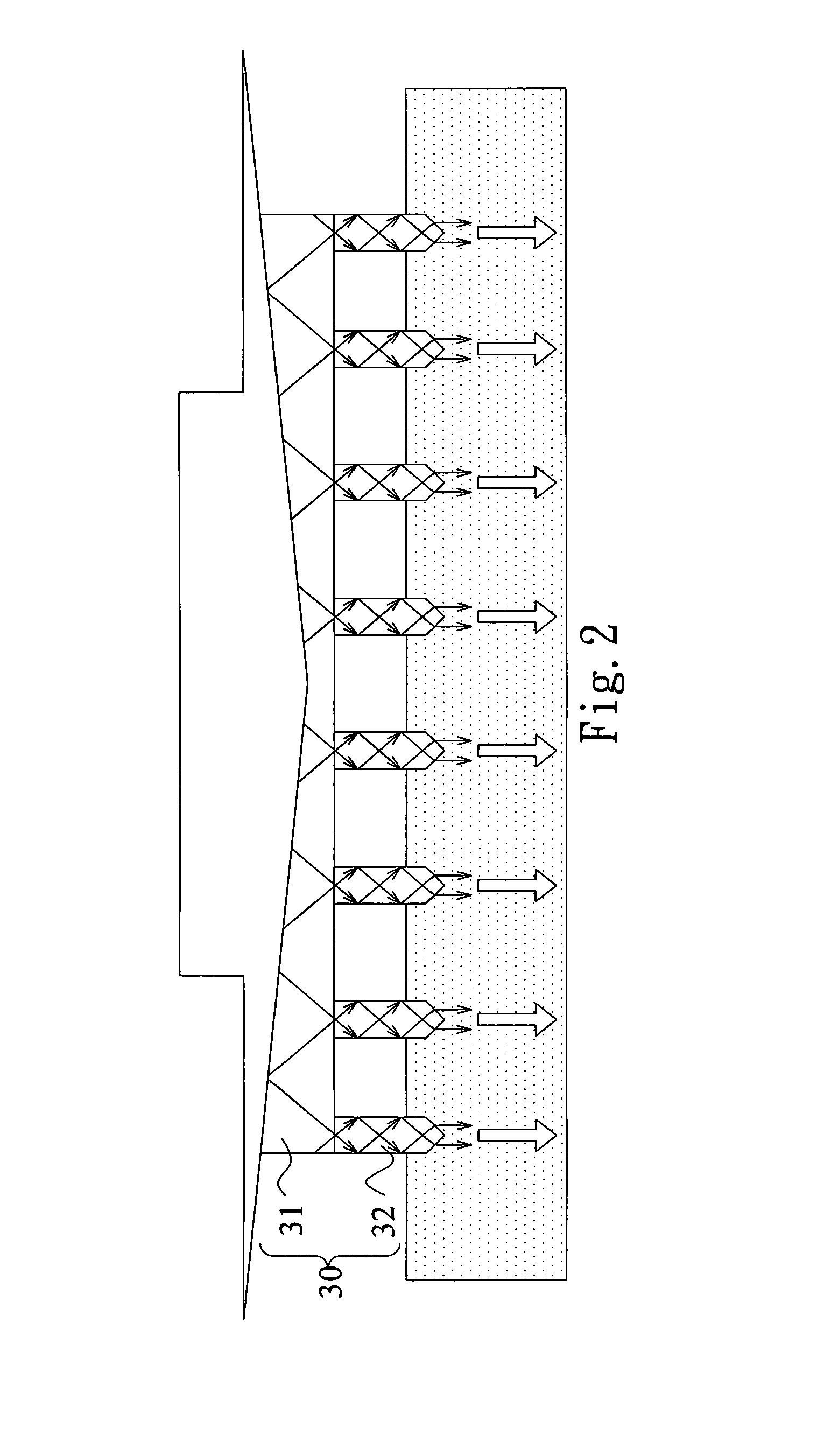
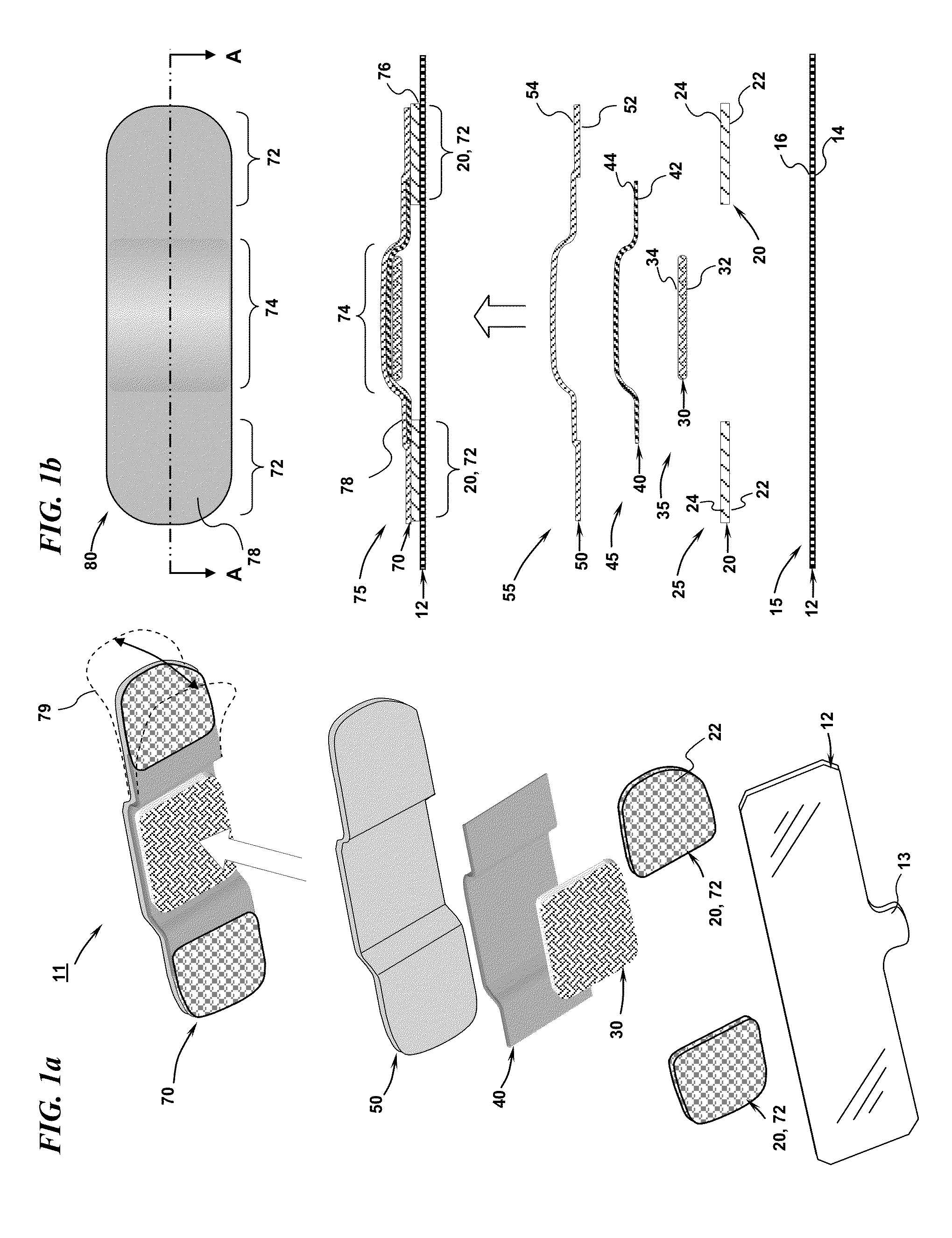
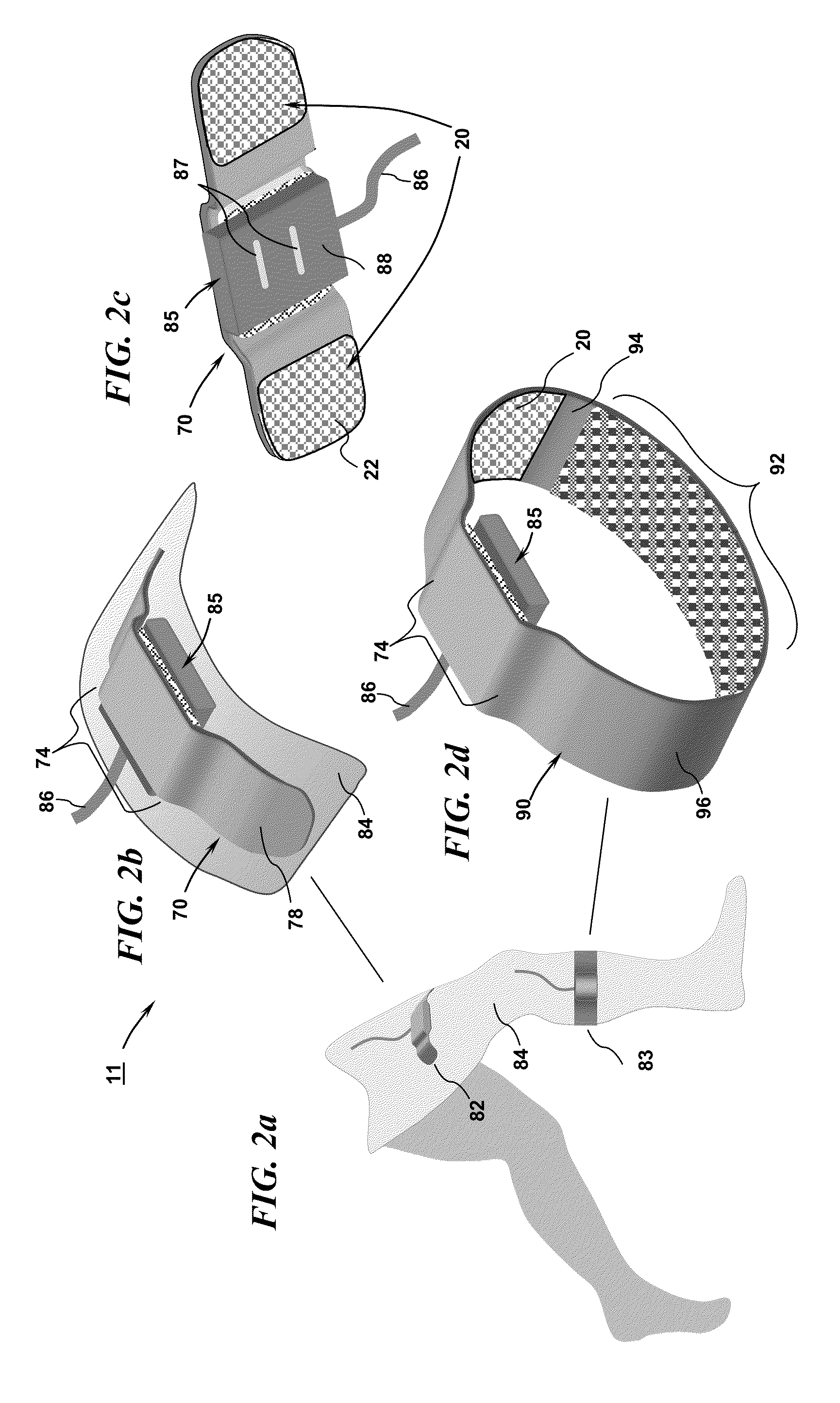
Physiological sensor placement and signal transmission device
InactiveUS20090088652A1Firmly connectedAvoid interferenceElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyElectrode placementBiomedical sensors
A garment is used to facilitate the placement of biomedical sensors or other electrodes on the body. The garment is comfortable and allows freedom of movement much like typical clothing. Textile based electrical components are included in the garment which are capable of transmitting an electrical signal to and from various external electrodes placed on the body. A textile based EMI shield protects the signals from electromagnetic interference. The garment may take any form such as a vest, sports bra, long sleeve shirt, bonnet, or other form and may provide access to an electrode placement site without requiring removal of the garment.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
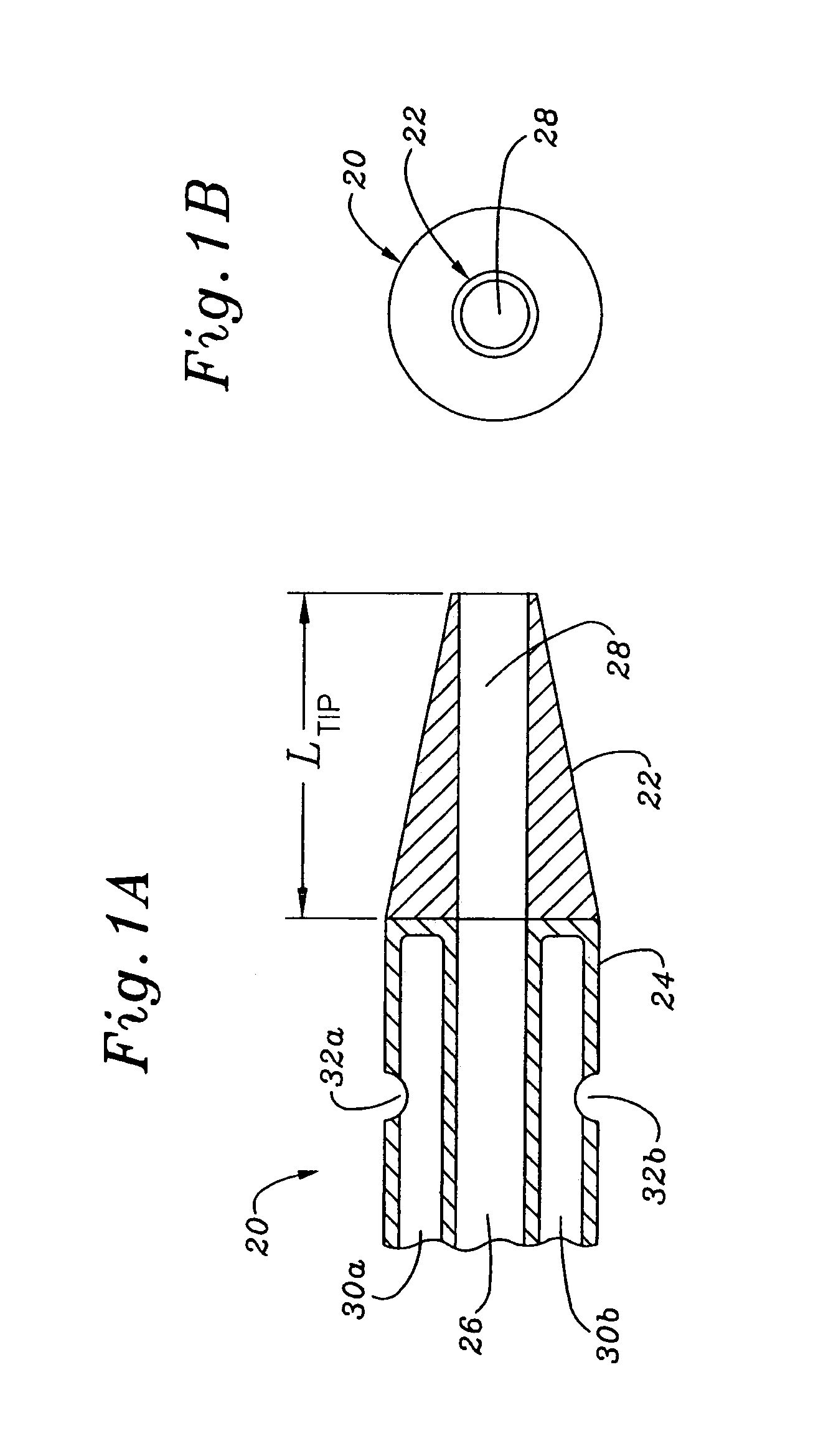
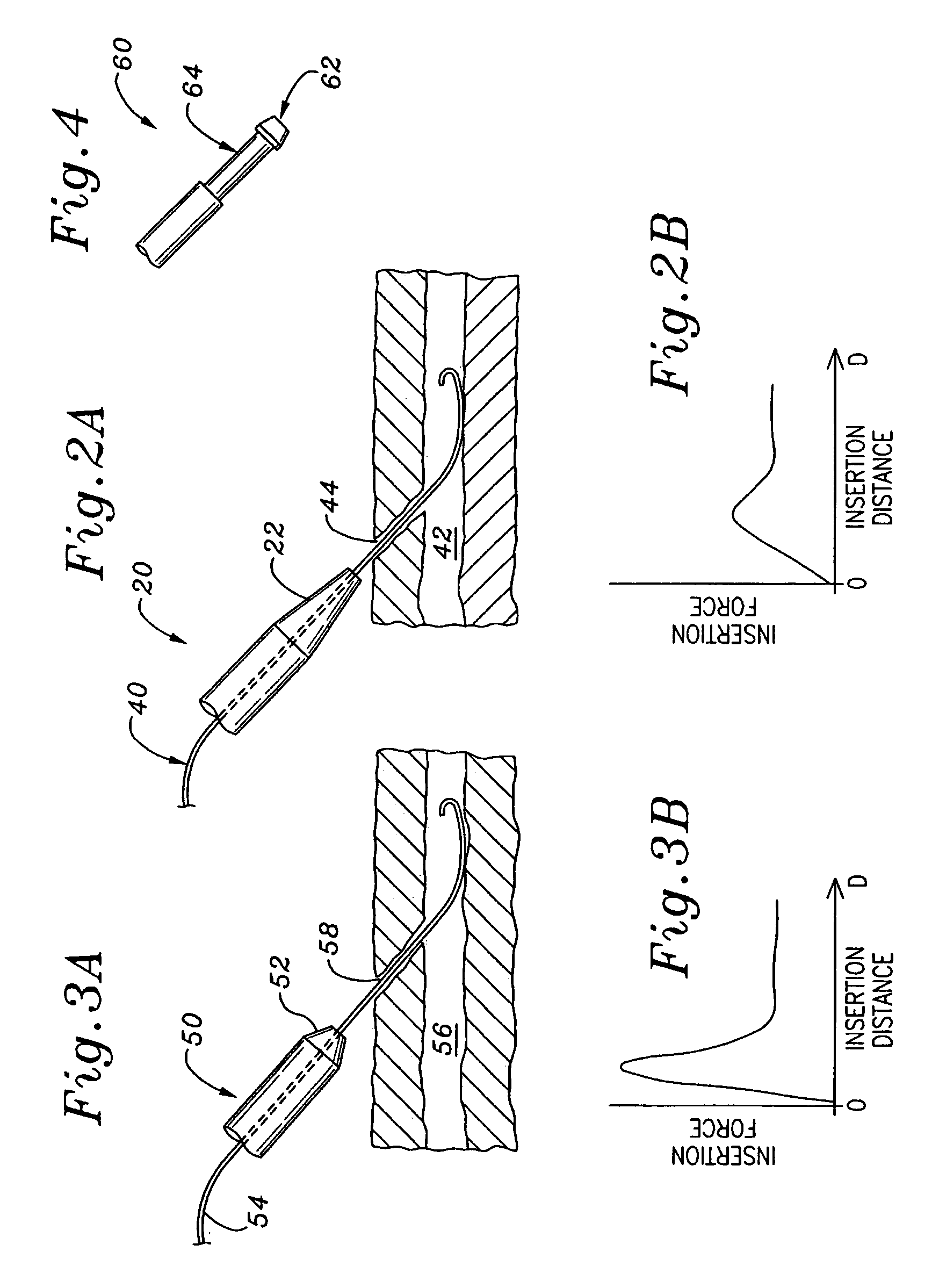
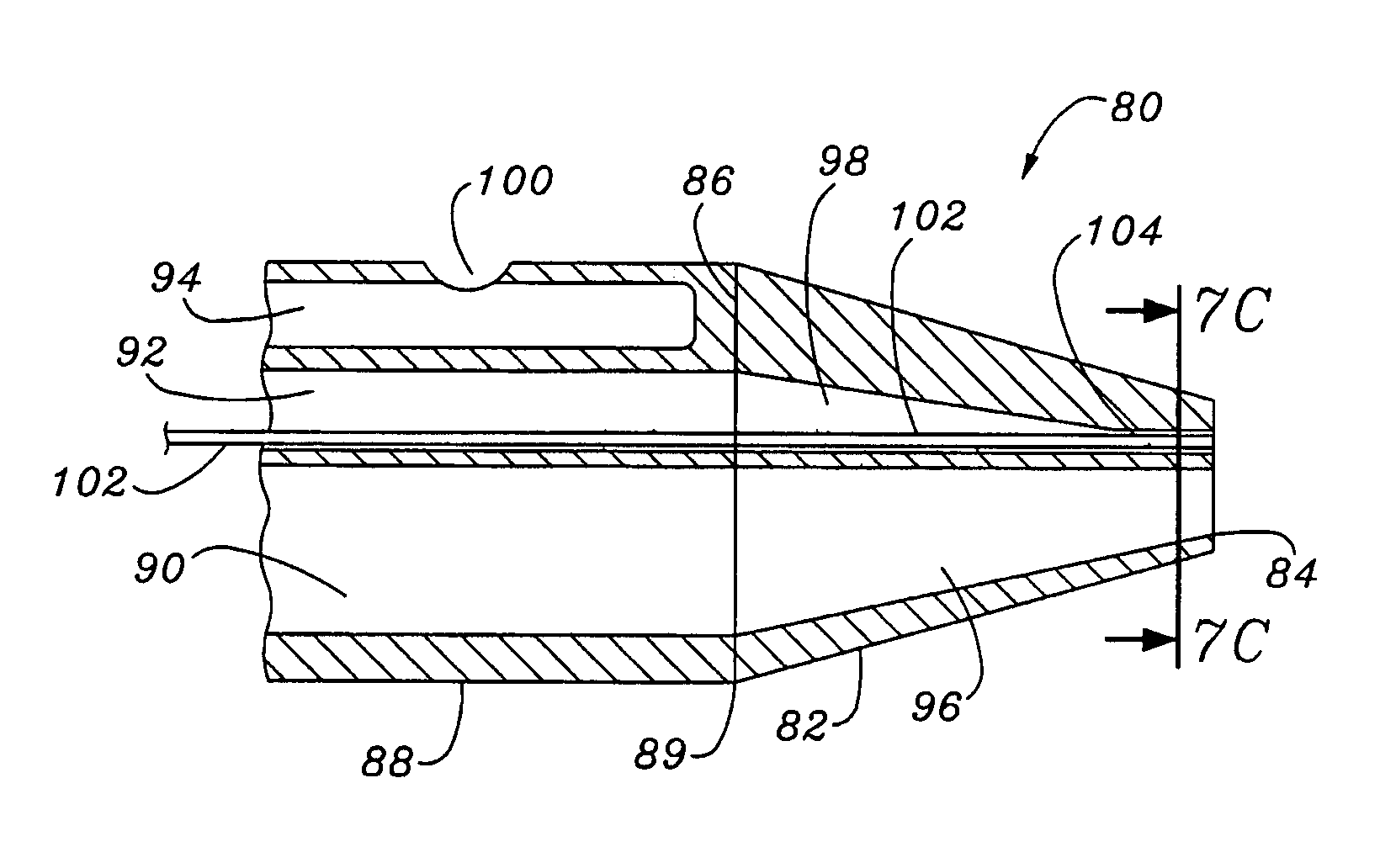
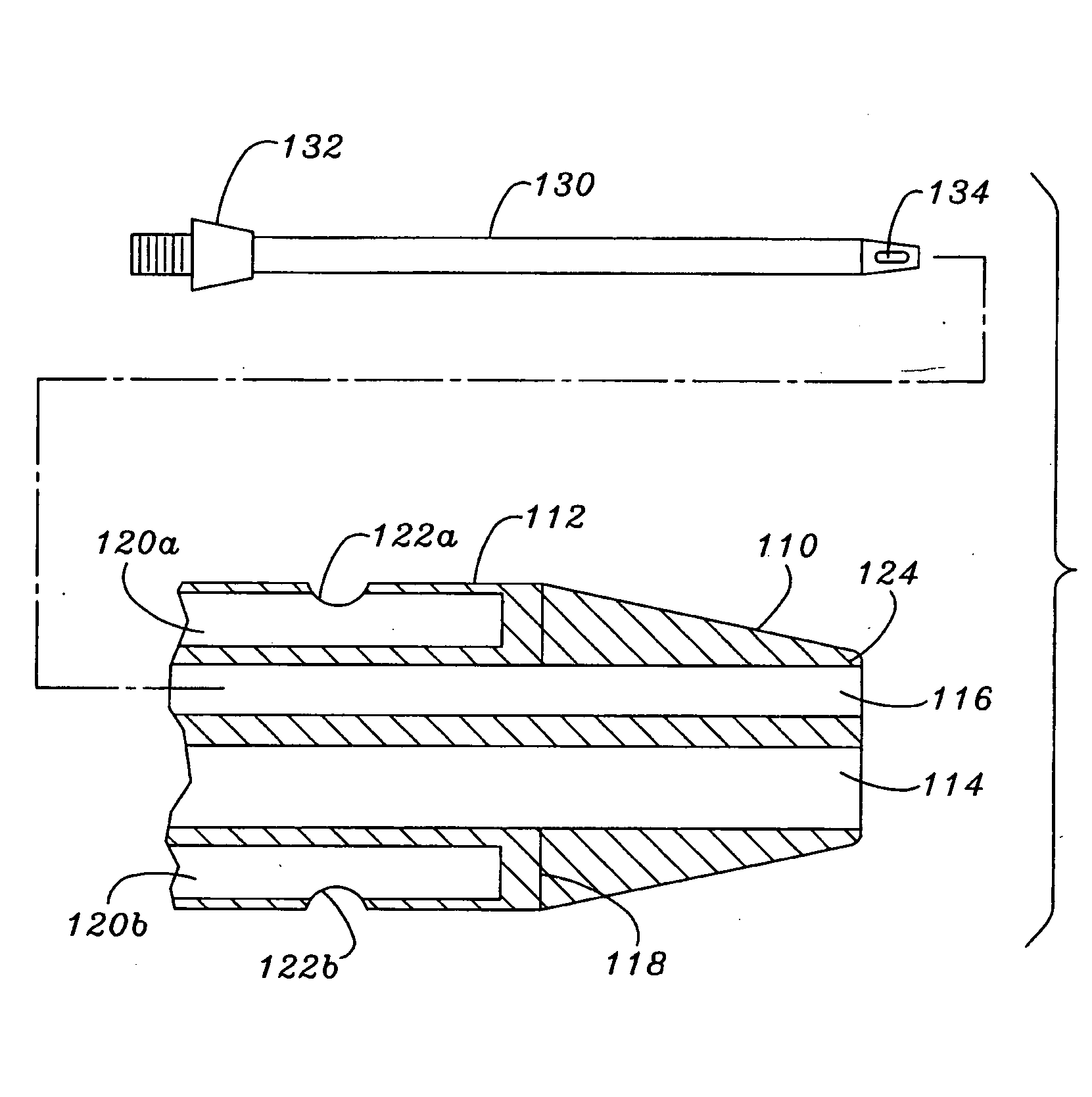
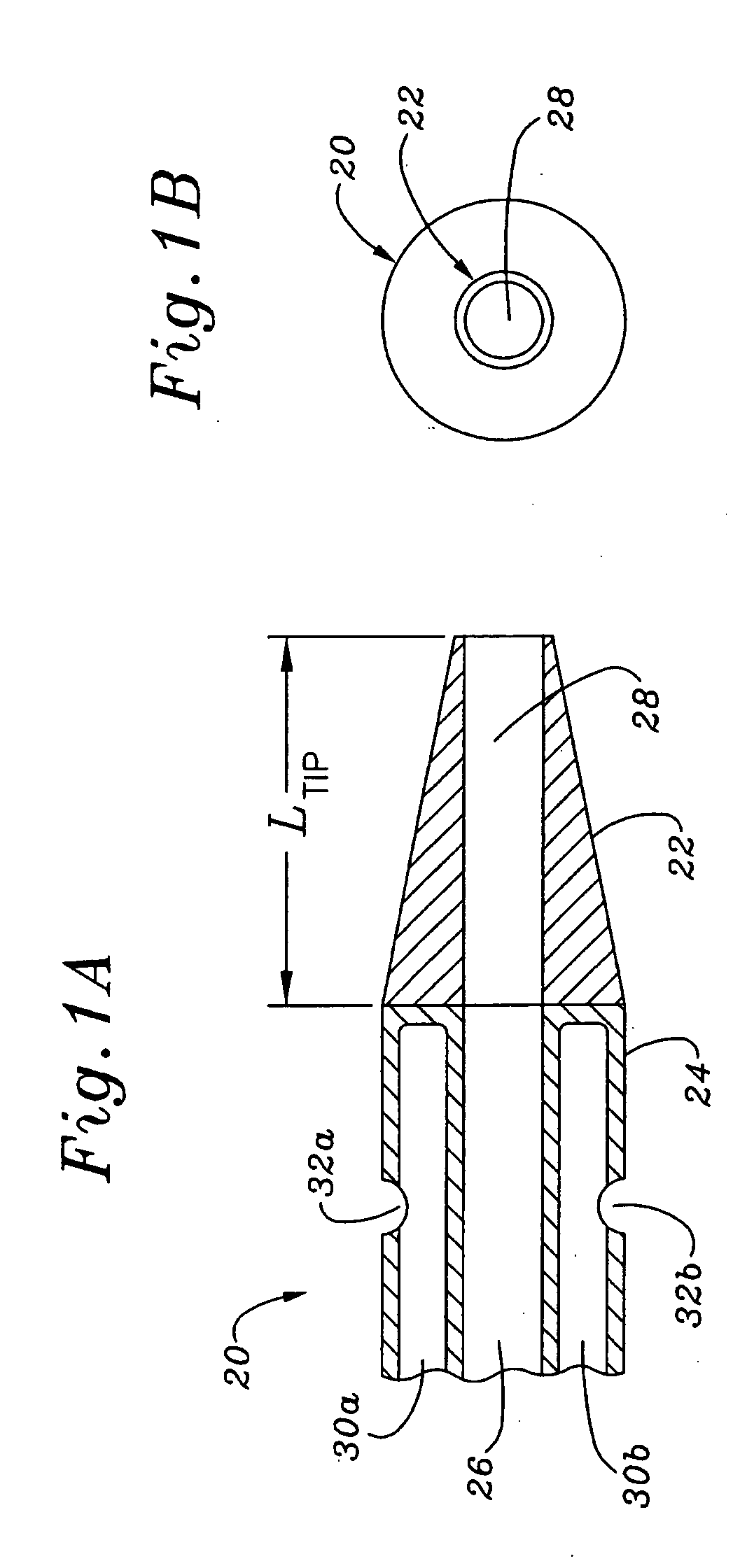
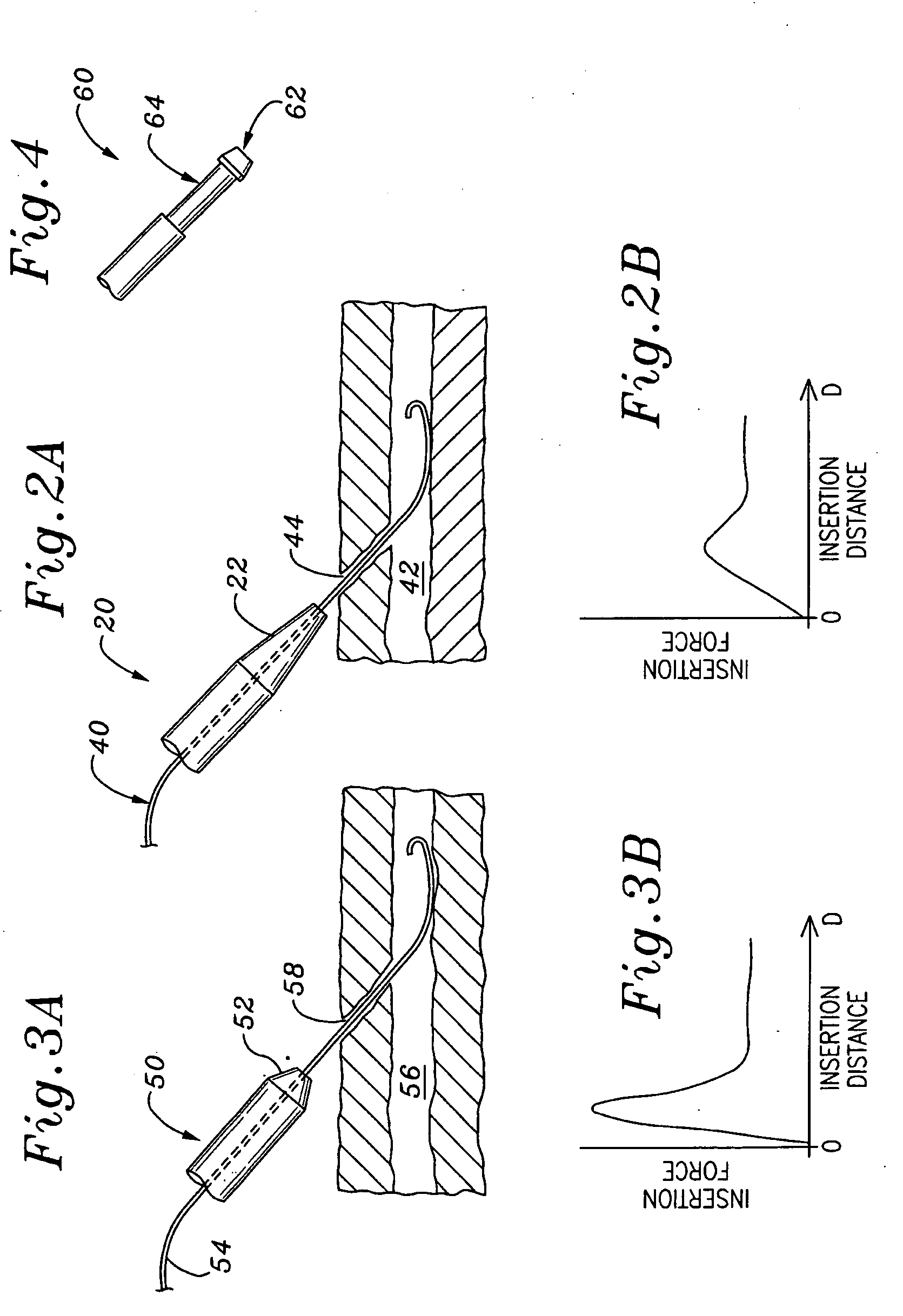
Multiple lumen catheter having a soft tip
A multiple lumen catheter having a soft, tapered multiple lumen distal tip for insertion into a body vessel. One of the lumens is sized to pass over a guidewire such that the catheter can be inserted into the body vessel using the Seldinger technique. At least one medical implement lumen is used for placement or positioning of a biomedical sensor or other medical implement. For example, at least one optical fiber passing through the medical implement lumen may transmit and receive light at the distal tip for measuring oxygen saturation of the blood. The catheter may have a cylindrical catheter body to which the soft distal tip attaches. The soft tip reduces the possibility of vessel or tissue puncture and abrasion. The tip is constructed of a soft plastic or pliable material that yields easily when force is applied. For example, the tip may be made of a softer material than the catheter body, or if made of the same material, the tip can be configured with thinner walls or a higher air-to-material ratio cross-section. Various geometrical configurations and combinations of materials can be used to decrease the flexible resistance of the tip to an applied load. One particular useful application for the catheter of the present invention is as a central venous catheter equipped with fibers for measuring oximetry. The fibers extend to the distal end of the tip and are preferably secured therein with minimal adhesive so as to limit the stiffness added to the tip. One particular useful construction is to secure the fibers within the medical implement lumen using adhesive only along a length of between about 0.5–3.5 mm.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
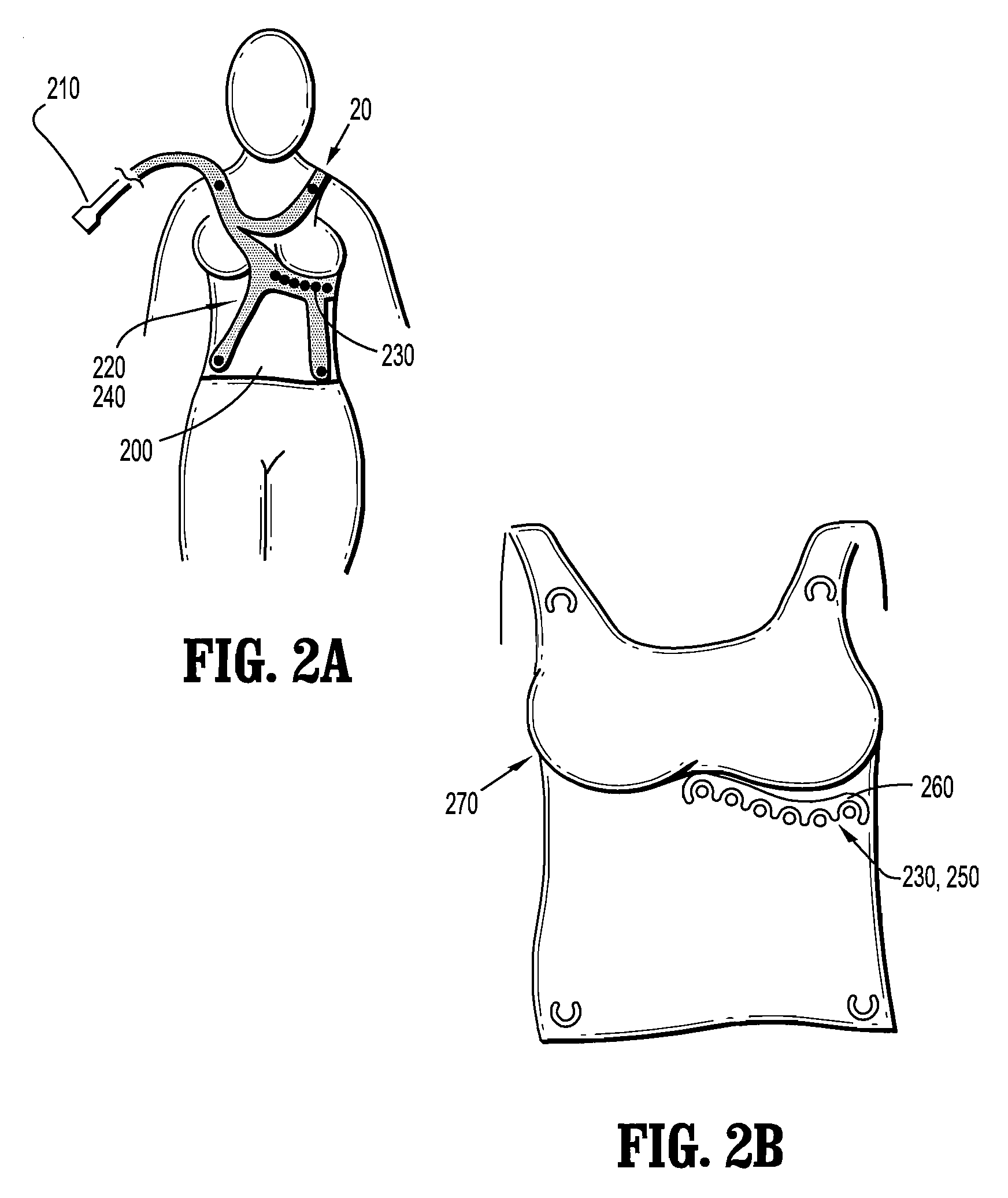
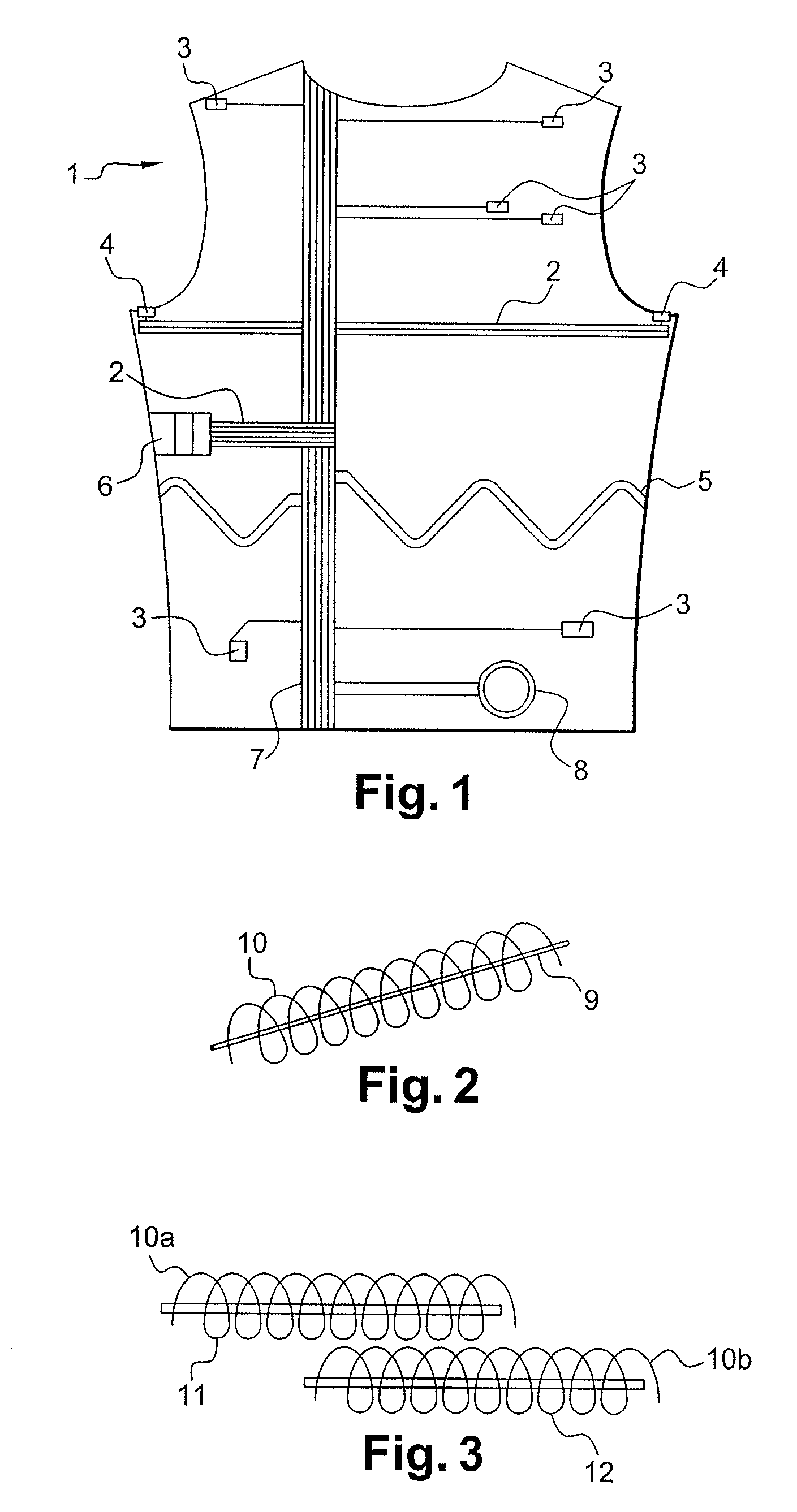
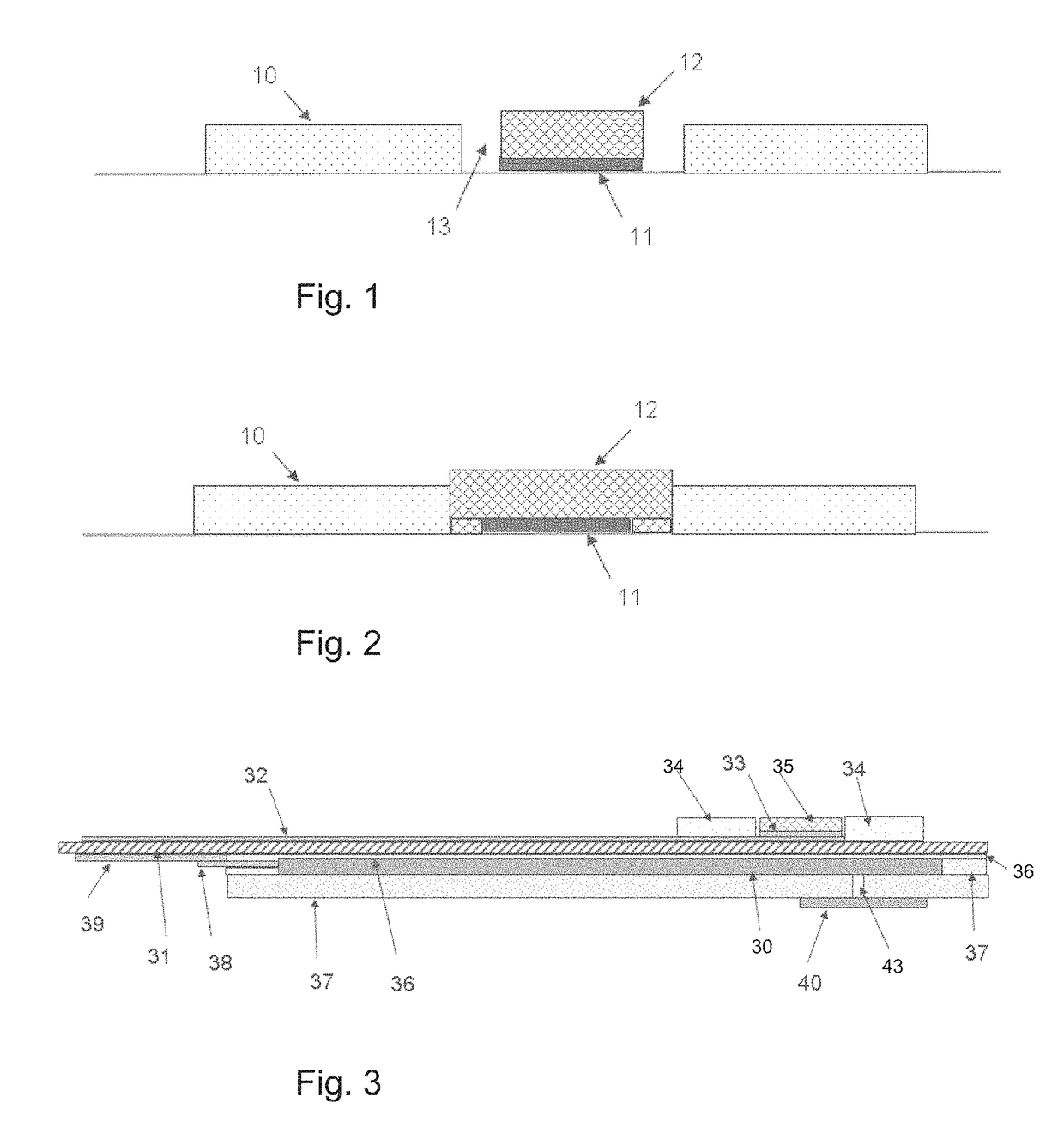
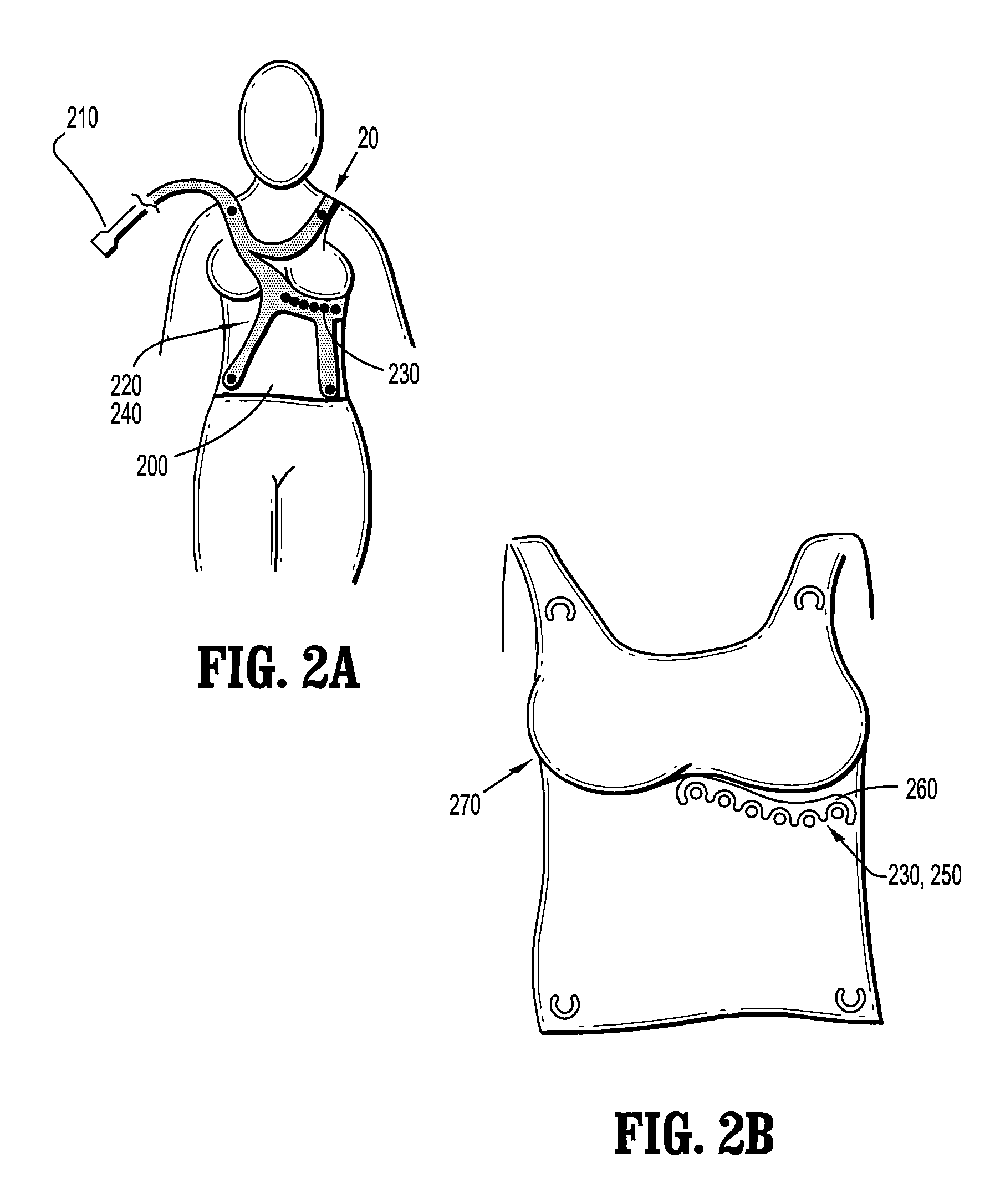
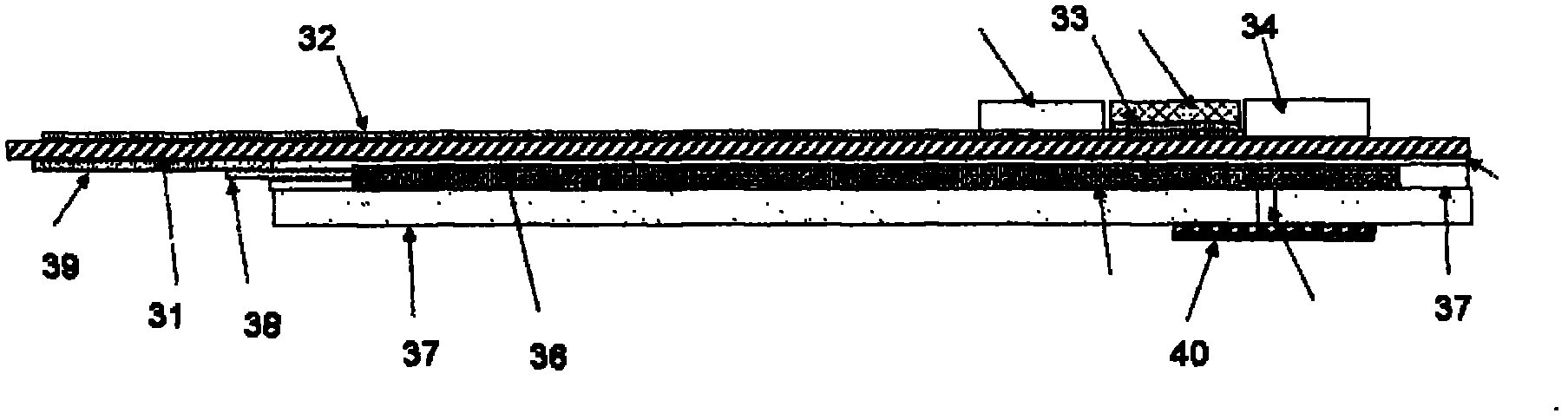
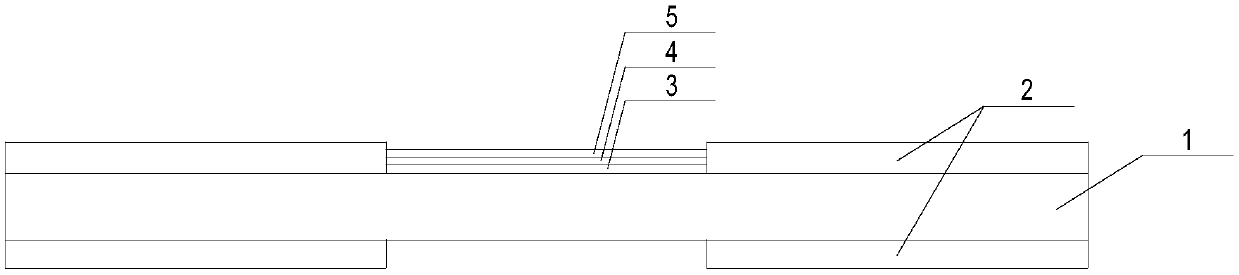
Garment for the medical monitoring of a patient
ActiveUS7319895B2Flexibility and elasticity propertyWeft knittingOrnamental textile articlesYarnBiomedical sensors
A flexible, elastic garment (1) is provided comprising biomedical sensors (3, 4, 5, 6), an electrical power distribution and data transmission bus (2, 7) and a coupling circuit for allowing contactless transmission of power and data between the sensors and a circuit external to the garment. The sensors (3, 4, 5, 6), and the bus (2, 7) for distributing the electrical power and / or transporting the data from the sensors in the garment are formed by elastic conducting yarns integrated into the fabric of the garment.
Owner:BIOSERENITY
Central venous catheter having a soft tip and fiber optics
A multiple lumen catheter having a soft, tapered multiple lumen distal tip for insertion into a body vessel. One of the lumens is sized to pass over a guidewire such that the catheter can be inserted into the body vessel using the Seldinger technique. At least one medical implement lumen is used for placement or positioning of a biomedical sensor or other medical implement. For example, at least one optical fiber passing through the medical implement lumen may transmit and receive light at the distal tip for measuring oxygen saturation of the blood. The catheter may have a cylindrical catheter body to which the soft distal tip attaches. The soft tip reduces the possibility of vessel or tissue puncture and abrasion. The tip is constructed of a soft plastic or pliable material that yields easily when force is applied. For example, the tip may be made of a softer material than the catheter body, or if made of the same material, the tip can be configured with thinner walls or a higher air-to-material ratio cross-section. Various geometrical configurations and combinations of materials can be used to decrease the resistance of the tip to an applied load. One particular useful application for the catheter of the present invention is as a central venous catheter equipped with fibers for measuring oximetry. The fibers extend to the distal end of the tip and are preferably secured therein with minimal adhesive so as to limit the stiffness added to the tip. One particular useful construction is to secure the fibers within the medical implement lumen using adhesive only along a length of between about 0.5–3.5 mm.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
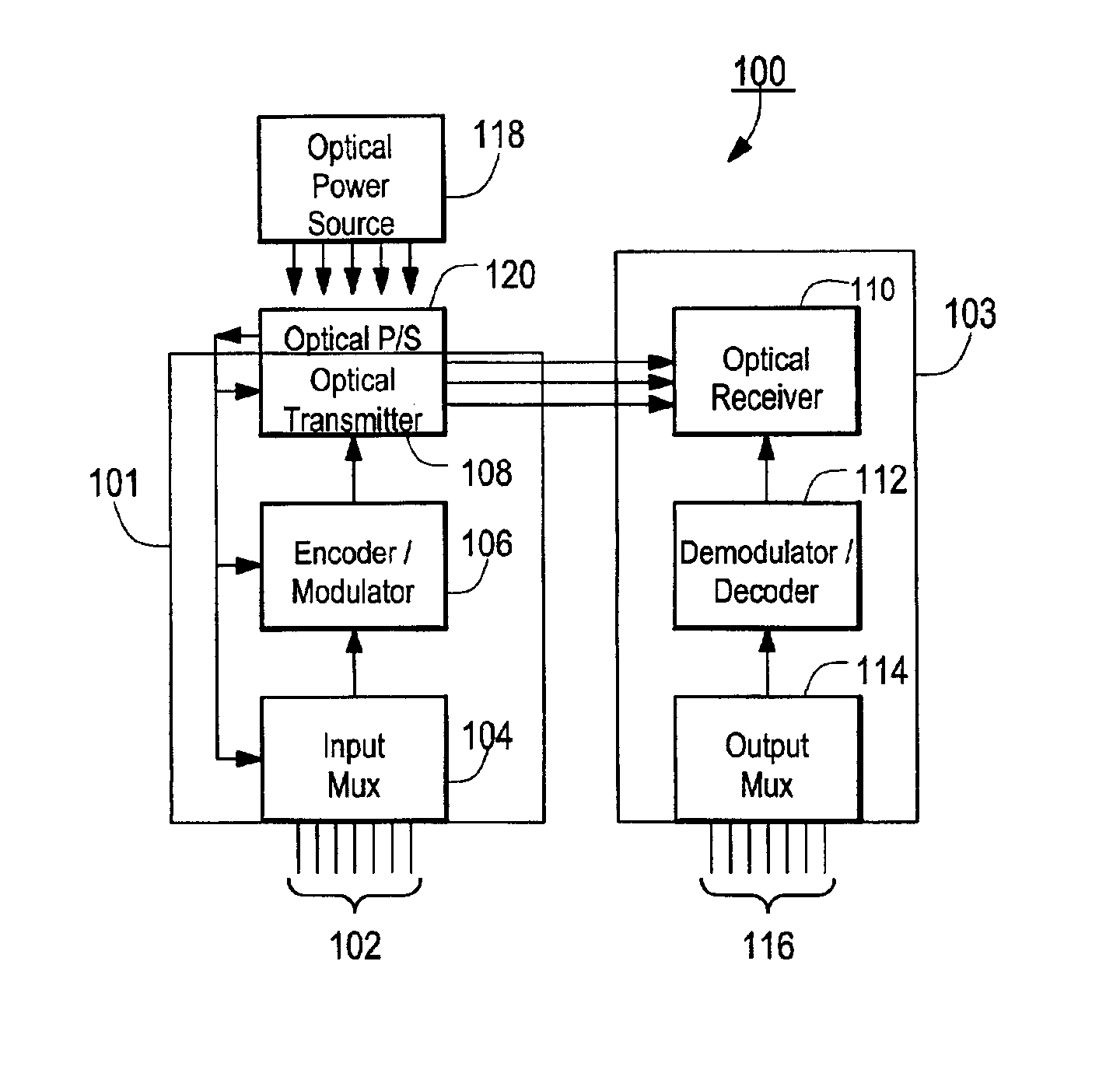
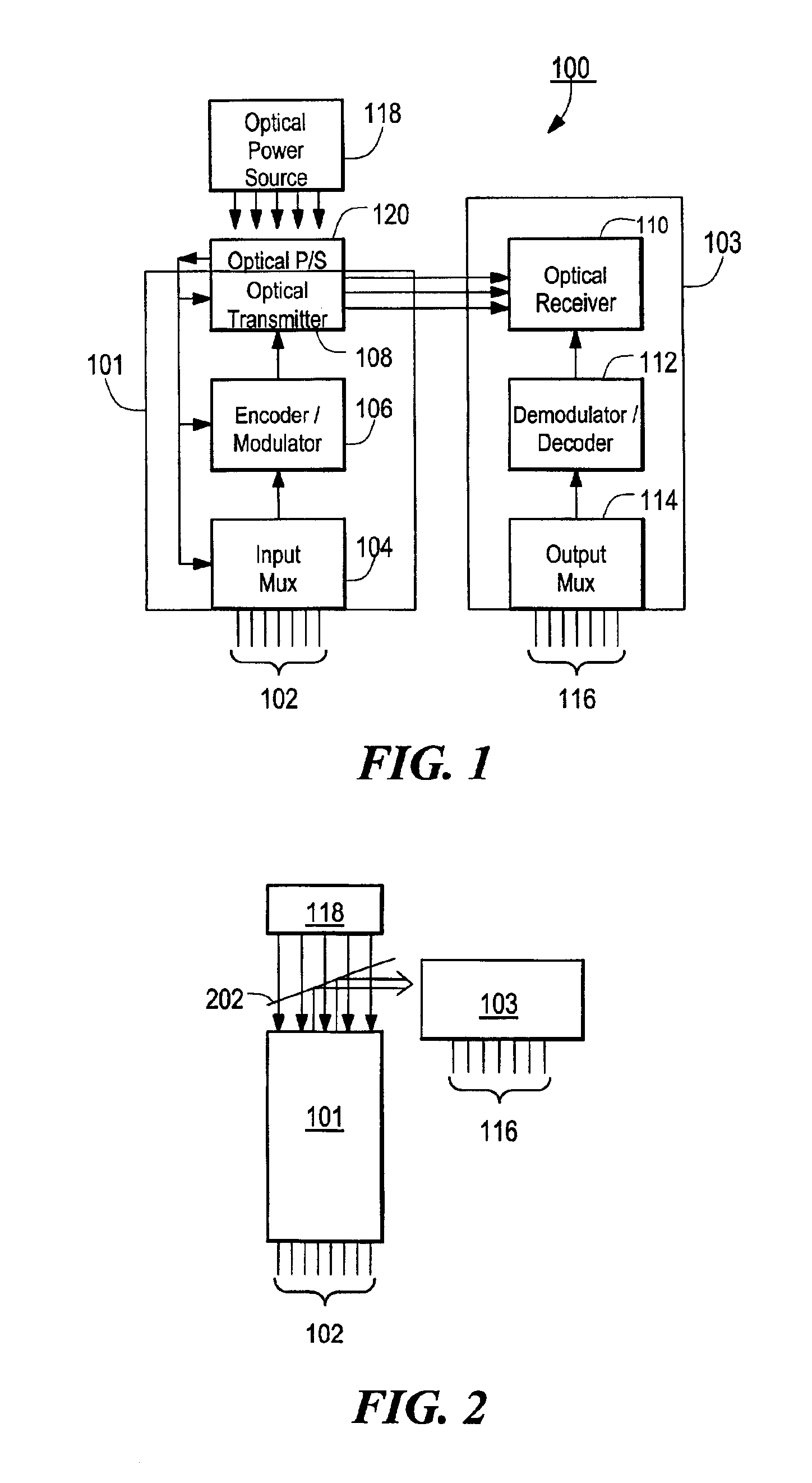
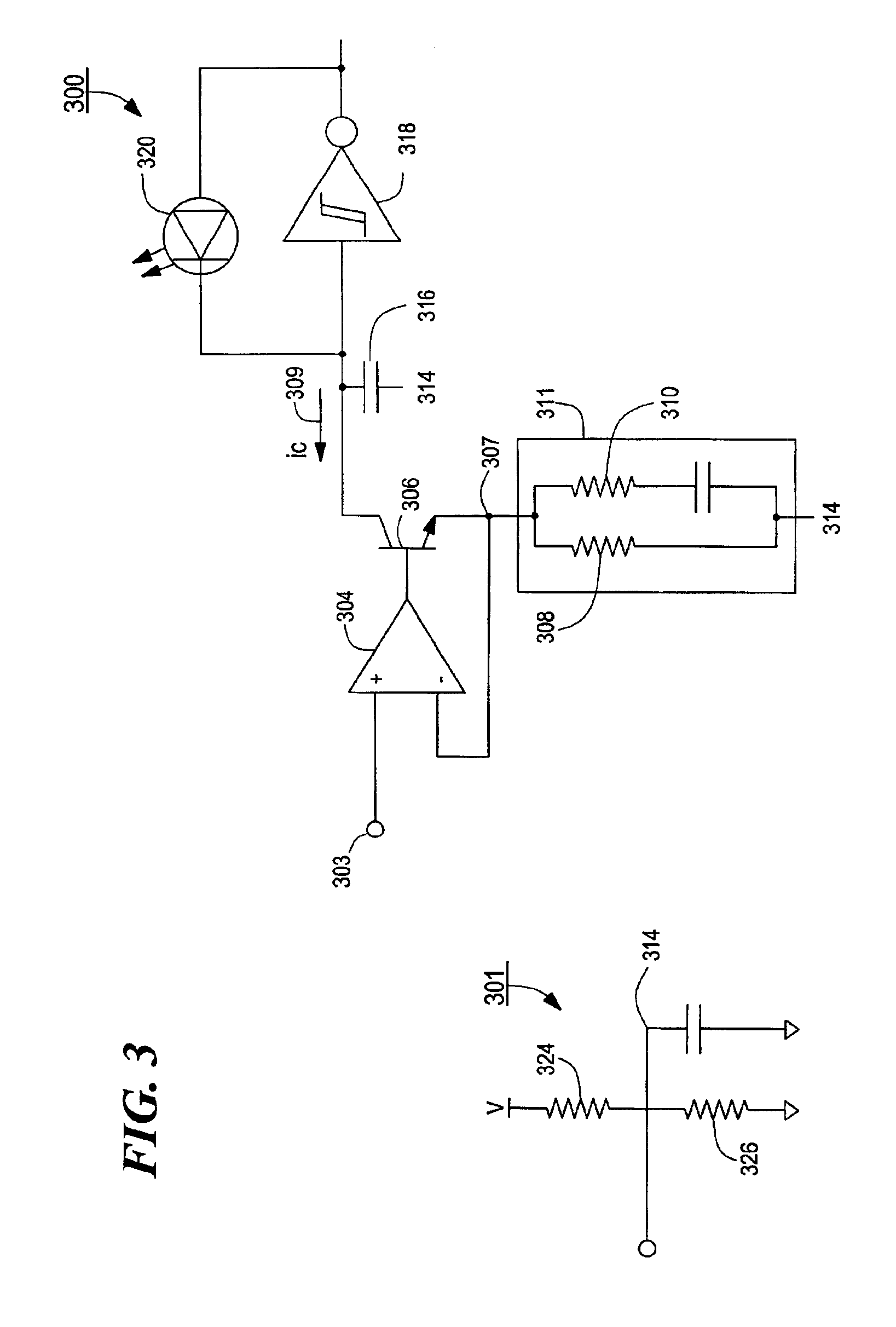
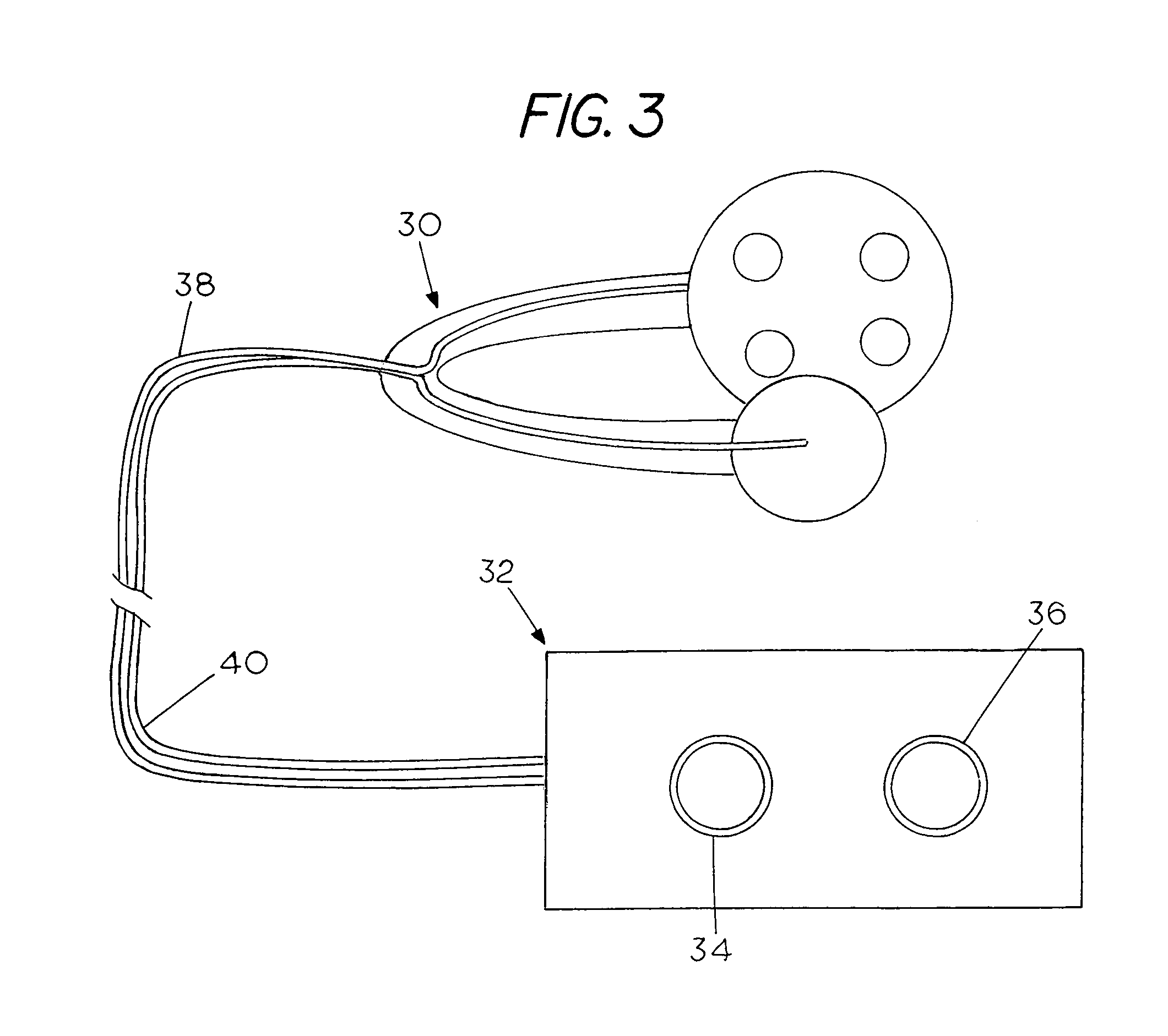
Optical telemetry of data and power for wireless biomedical sensors and actuators
An apparatus and corresponding method for providing data communications to and from a location within a body cavity in which an internal transmitter receives a first data stream from an in vivo sensor, electrode, or transducer. The internal transmitter is configured and arranged to asynchronously modulate the first data stream and to provide as an output a first optical signal carrying the asynchronously modulated first data stream. The apparatus further includes an external receiver that is configured and arranged external to the body cavity such that an optical input to the external receiver is optically coupled to the internal transmitter output and receives the optical signal therefrom. The external receiver asynchronously demodulates the received optical signal and provides as an output at least one signal indicative of the first data stream.
Owner:INNERSEA TECH
High-conductivity polymer carbon nanotube composite material and micro-processing method thereof
InactiveCN102115558AImprove dispersion stabilityImprove conductivityLiquid crystal compositionsSurgeryCooking & bakingBiomedical sensors
The invention discloses a high-conductivity polymer carbon nanotube composite material and a micro-processing method thereof. The invention is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: adding 50-99.95 parts of polymer grain or powder, 0.05-20 parts of carbon nanotube, 0-15 parts of antioxidant and 0-15 parts of dispersant into a micro-extruder, a double-screw extruder or a double-screw extruder / micro-extruder combined facility, extruding at a screw rotation speed of 20-500rpm at a polymer melting or softening temperature of Tm+10 DEG C-Tm+80 DEG C for 1-3 times to obtainuniformly dispersed composite material grains, and carrying out micro extrusion, micro injection or micro compaction on the grains to prepare a high-conductivity micro product; or carrying out isothermal or non-isothermal heat treatment on the product in a baking oven with a temperature of Tm-80 DEG C-Tm+20 DEG C for 5 seconds to 1.5 hours; or carrying out after-treatment on the sample in microwaves, infrared rays or plasma. The high-conductivity polymer carbon nanotube composite material disclosed by the invention is used for preparing micro biomedical devices in minimally invasive operations, and used in the field of micro biomedical sensors, micro electronics, micro electro-mechanics or micro-robots.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Multiple lumen catheter having a soft tip
A multiple lumen catheter having a soft, tapered multiple lumen distal tip for insertion into a body vessel. One of the lumens is sized to pass over a guidewire such that the catheter can be inserted into the body vessel using the Seldinger technique. At least one medical implement lumen is used for placement or positioning of a biomedical sensor or other medical implement. For example, at least one optical fiber passing through the medical implement lumen may transmit and receive light at the distal tip for measuring oxygen saturation of the blood. The catheter may have a cylindrical catheter body to which the soft distal tip attaches. The soft tip reduces the possibility of vessel or tissue puncture and abrasion. The tip is constructed of a soft plastic or pliable material that yields easily when force is applied. For example, the tip may be made of a softer material than the catheter body, or if made of the same material, the tip can be configured with thinner walls or a higher air-to-material ratio cross-section. Various geometrical configurations and combinations of materials can be used to decrease the flexible resistance of the tip to an applied load. One particular useful application for the catheter of the present invention is as a central venous catheter equipped with fibers for measuring oximetry. The fibers extend to the distal end of the tip and are preferably secured therein with minimal adhesive so as to limit the stiffness added to the tip. One particular useful construction is to secure the fibers within the medical implement lumen using adhesive only along a length of between about 0.5-3.5 mm.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method for efficiently preparing graphene-like carbon nitride
ActiveCN106542509ANo preprocessing requiredEasy to makeNitrogen and non-metal compoundsBiomedical sensorsHigh energy
The present invention provides a method for efficiently preparing graphene-like carbon nitride. The method is characterized by comprising: using a nitrogen-rich organic matter as a raw material, adding a microwave absorbing agent, mixing, placing into a ceramic crucible, placing the crucible into the center of an industrial high-energy resonant cavity, vacuumizing, and carrying out high-energy microwave irradiation heating so as to rapidly and efficiently prepare the graphene-like carbon nitride. According to the present invention, the obtained graphene-like carbon nitride has characteristics of high specific surface area, high yield and high purity, and can be used in the fields of degradation of organic matters, hydrogen production through photolysis of water, catalyst carriers, biomedical sensors, and the like.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG DONGDA IND TECH RES INST +1
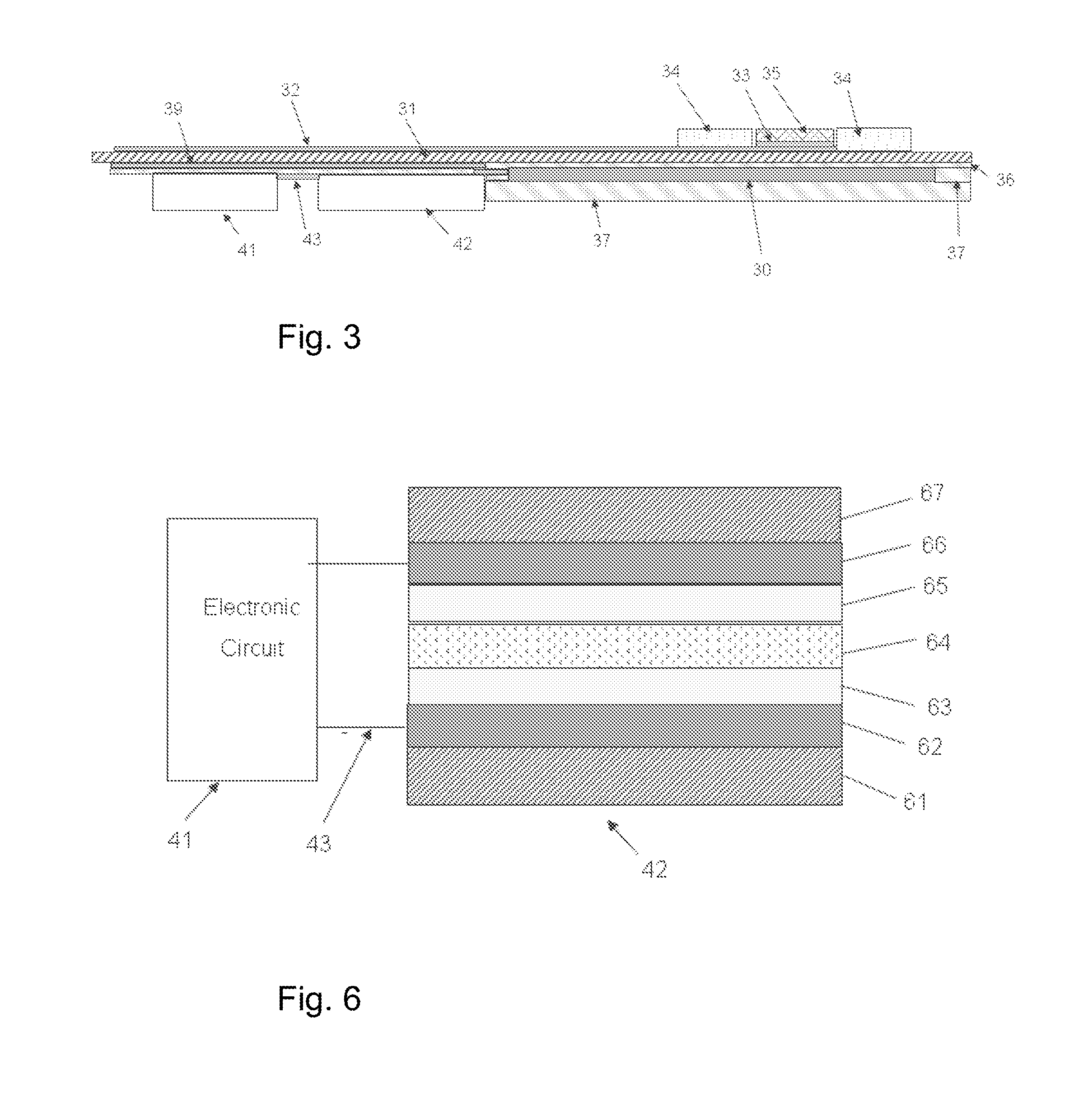
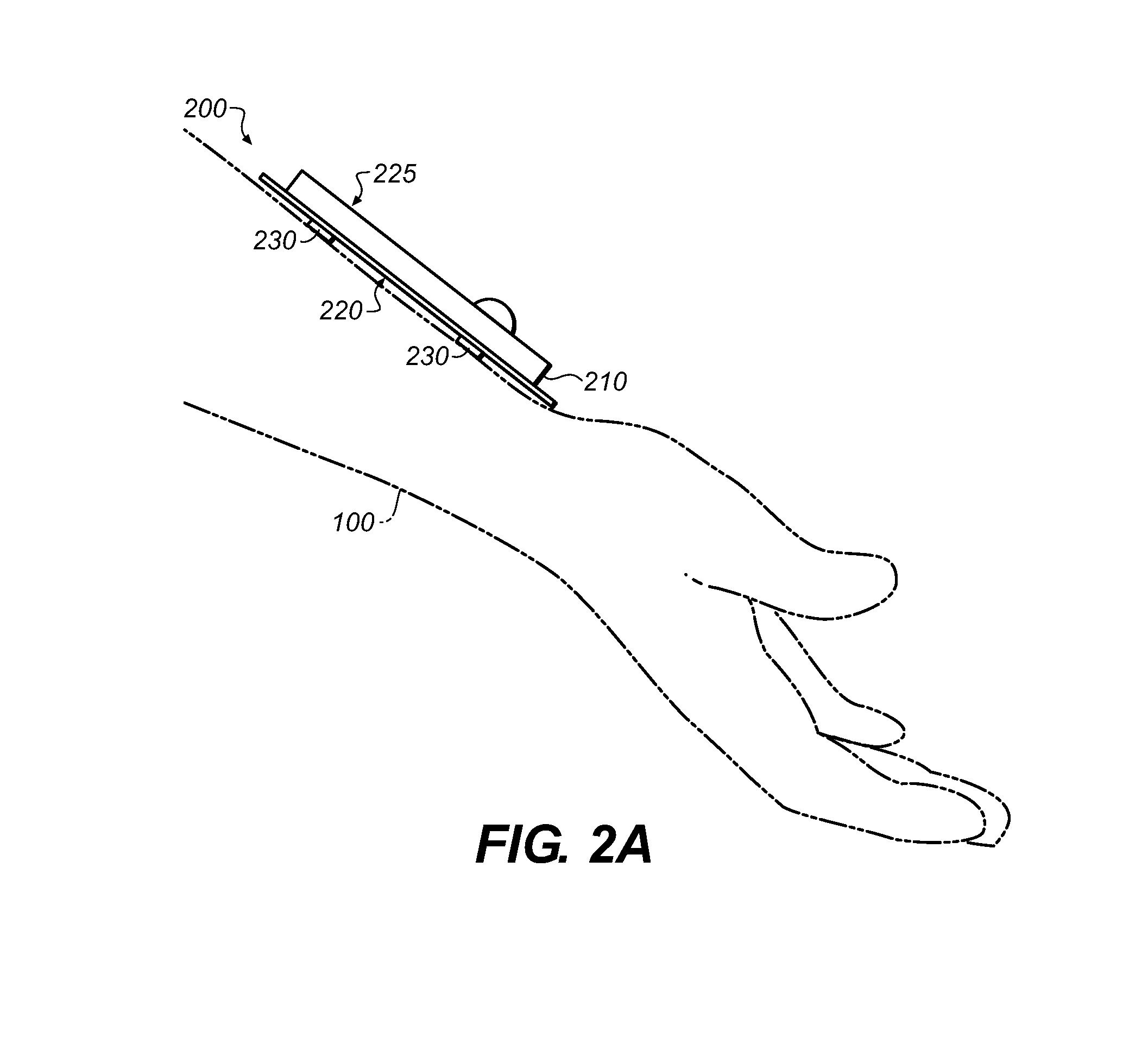
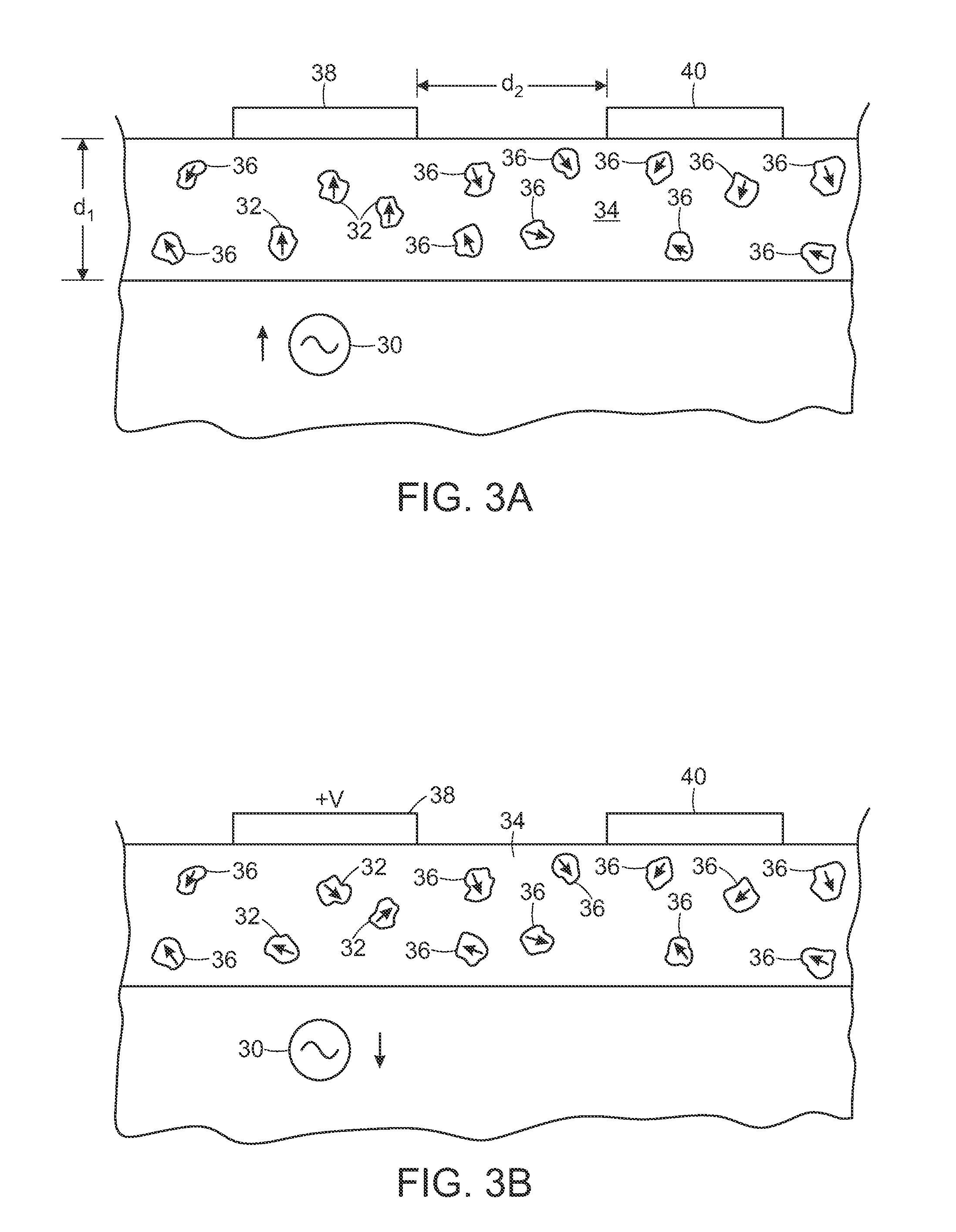
Multiple Electrode Composite Systems and Methods for Use in Electrocardiogram Detection Systems
ActiveUS20100036230A1Less discomfortHigh impedanceElectrocardiographySensorsBiomedical sensorsAdhesive materials
A biomedical sensor system is disclosed that includes a plurality of electrodes and a contiguous adhesive material that is in contact with each of the plurality of electrodes. In certain embodiments a method is provided that includes the step of applying a first surface of adhesive material to a patient wherein the adhesive material includes at least two electrodes on second surface thereof that is opposite the first surface. The method also includes the step of receiving a time varying signal a first electrode of the at least two electrodes at a first location such that the time varying signal is not received at a second electrode of the at least two electrodes.
Owner:FLEXCON
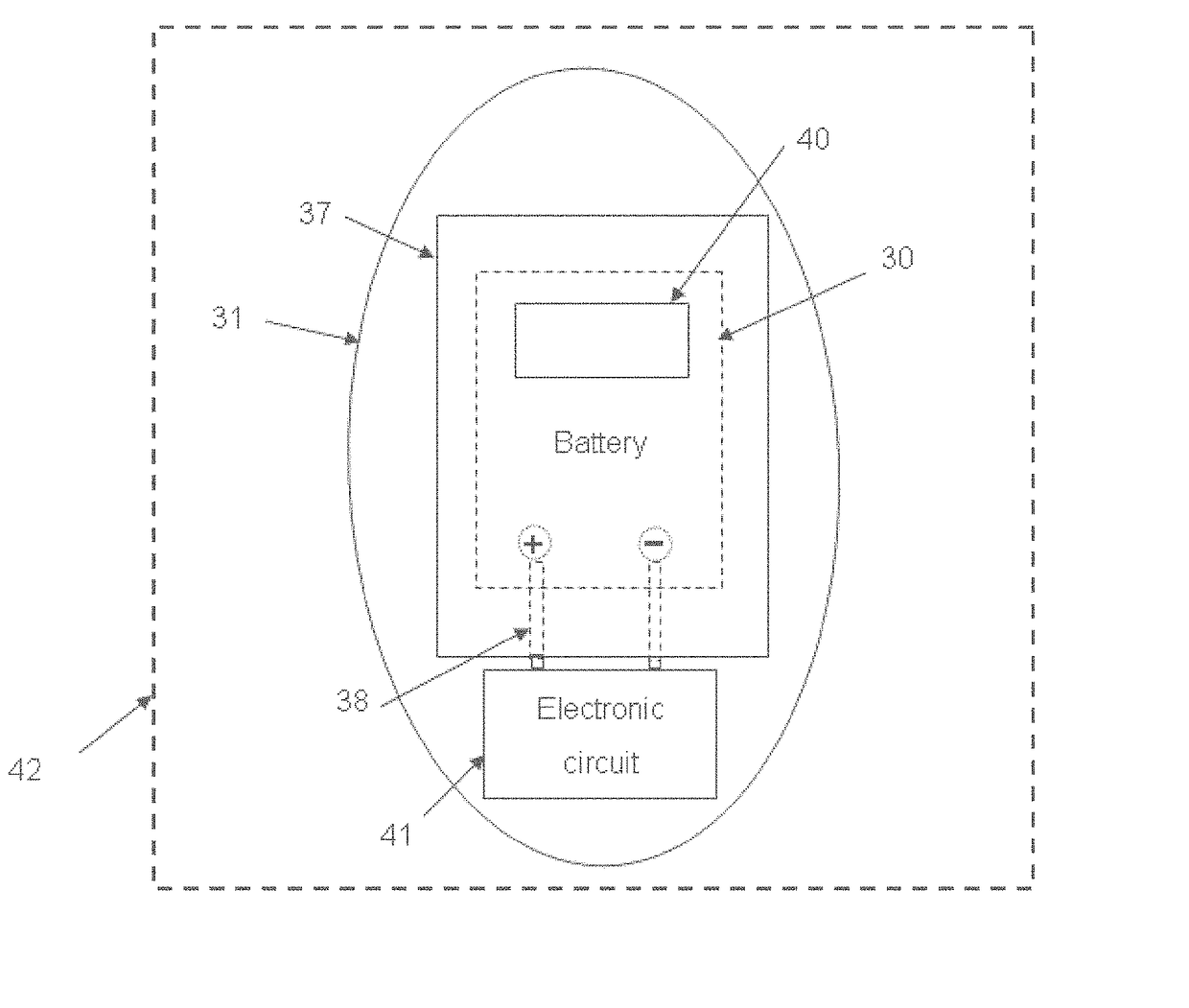
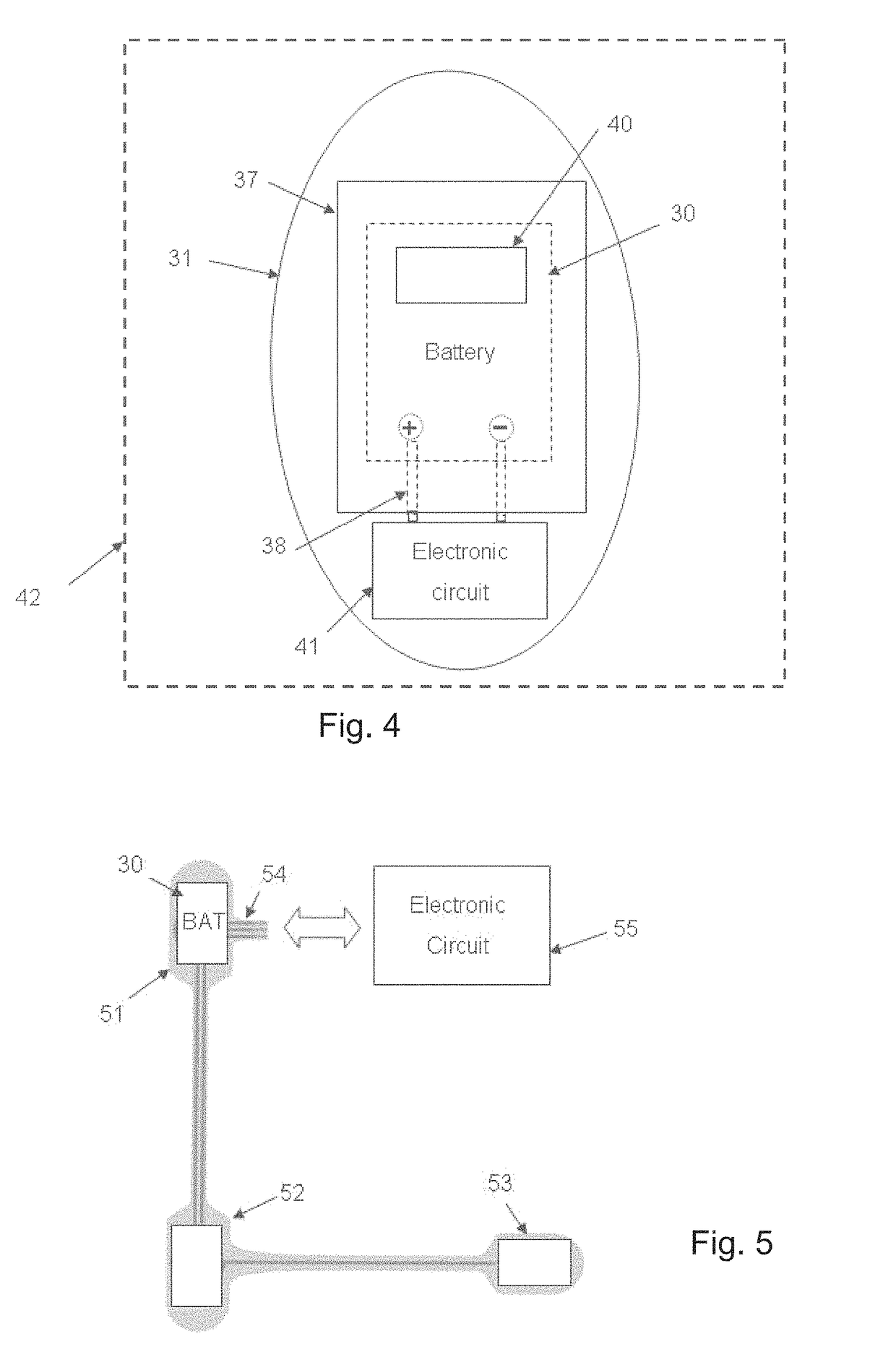
Single-use biomedical sensors
ActiveUS9782095B2Extended shelf lifeElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyPower sensorBiomedical sensors
A disposable self-powered biomedical sensor comprises a printed wet electrode on a substrate sheet. The wet electrode is provided with an electrolyte element to enhance the electrical contact with a surface to be measured. Moreover, a printed battery encapsulated in a hermetically sealed compartment is provided on the substrate sheet. The disposable self-powered sensor can be stored within an enclosure or a package which provides a proper atmosphere to prevent the drying of the electrolyte and prolong the shelf life of the sensors.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Physiological sensor placement and signal transmission device
ActiveUS8798708B2Firmly connectedAvoid interferenceElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyElectrode placementBiomedical sensors
A garment is used to facilitate the placement of biomedical sensors or other electrodes on the body. The garment is comfortable and allows freedom of movement much like typical clothing. Textile based electrical components are included in the garment which are capable of transmitting an electrical signal to and from various external electrodes placed on the body. A textile based EMI shield protects the signals from electromagnetic interference. The garment may take any form such as a vest, sports bra, long sleeve shirt, bonnet, or other form and may provide access to an electrode placement site without requiring removal of the garment.
Owner:KPR U S LLC
Biomedical sensor
A biomedical sensor is provided. The biomedical sensor comprises a printed bio-potential electrode on the biomedical sheet sensor configured to provide an electrical contact with a surface to be measured, and a bi-stable printed electronic ink indicator provided on the biomedical sheet sensor and configured to indicate a loose contact of a bio-potential electrode operation by switching the color of the bi-stable indicator from a first color to a second color when a loose contact is detected.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
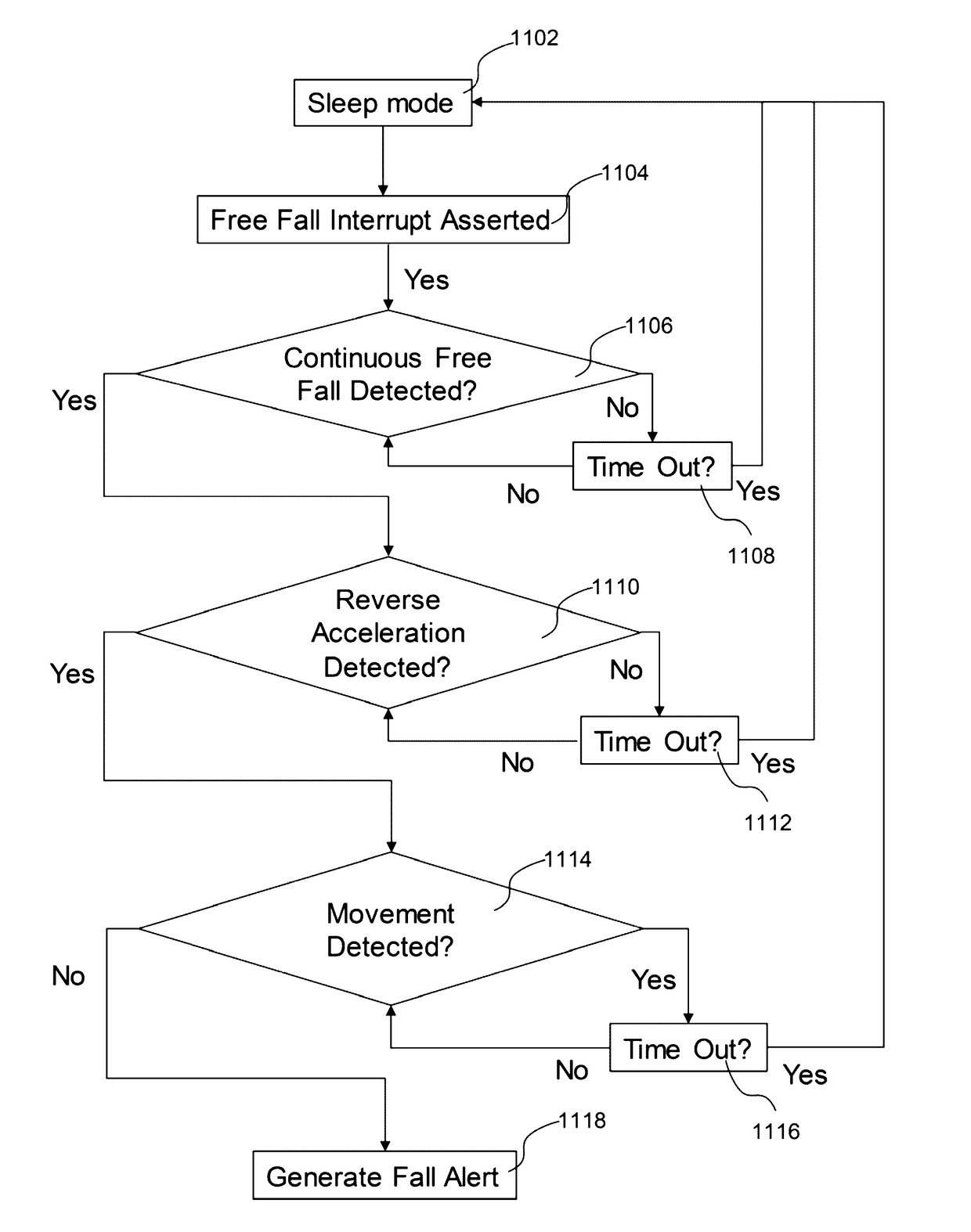
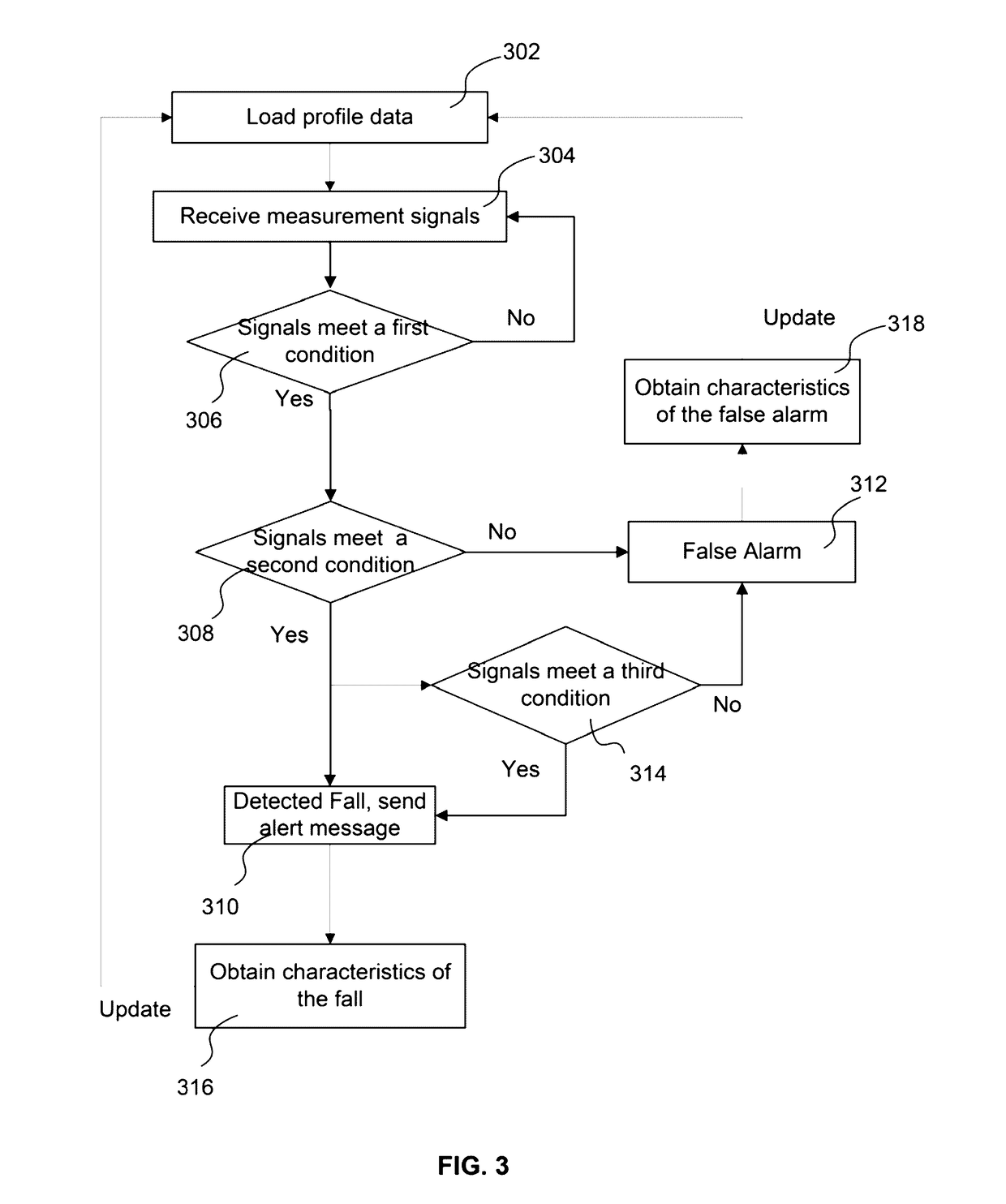
Method and system for fall detection
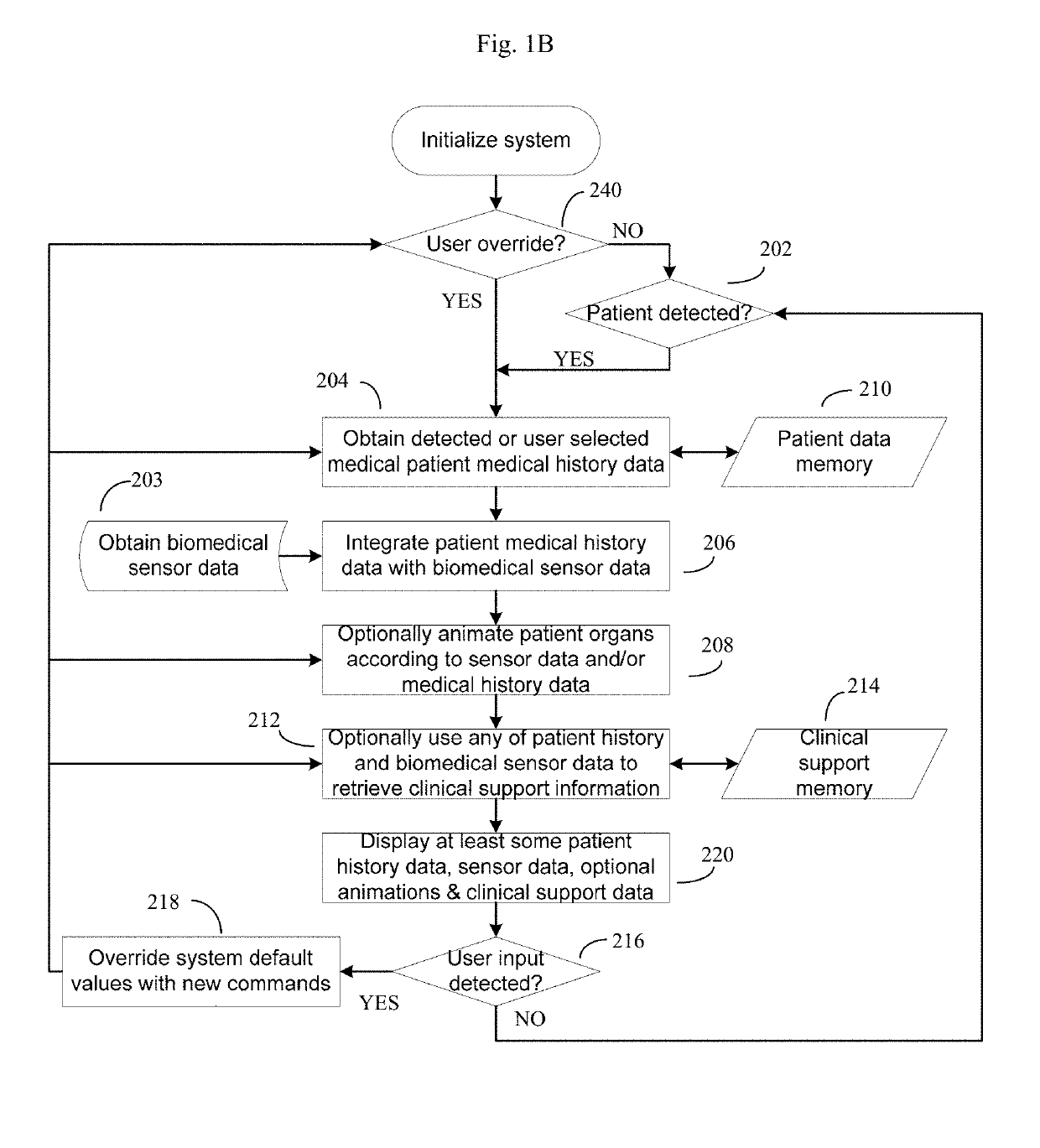
The present disclosure provides a method and a system for fall detection. Measurement signals are received from a plurality of sensors to monitor user activities, the plurality of sensors including a motion sensor for collecting motion information and a biomedical sensor for collecting physiological information. According to a signal processing sequence, whether the measurement signals meet multiple qualifying conditions for a fall incident is determined. The multiple qualifying conditions include: a condition evaluating at least the motion information, and a condition evaluating at least the physiological information. The method further includes: when the measurement signals do not meet the multiple qualifying conditions, continuing to monitor the user activities; and when the measurement signals meet the multiple conditions, determining that a fall incident has occurred, and sending an alert message to a designated contact.
Owner:MPC CORPORATION
Biological signal sensor on a body surface
An electrically conductive fiber and a coupled biomedical sensor are described. An electrically conductive core of the fiber includes a multiplicity of synthetic conductive filaments and an outer nonconductive fiber layer. The sensor area of the electrically conductive fiber is coated by thin film of silver ink and thin film of silver-silver chloride ink. The electrically conductive fiber's porous surface contacts the thin silver ink coating and the silver coating contacts the silver-chloride ink coating. A surface of the biomedical sensor is coated by a thick film of ionically conductive media, containing an electrolyte, in contact with the silver-chloride coating. The electrolyte diffuses into a porous structure of electrically conductive yarn.
Owner:LOBODZINSKI S SUAVE
Physiological Sensor Placement and Signal Transmission Device
ActiveUS20130072777A1Firmly connectedAvoid interferenceElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyElectrode placementBiomedical sensors
A garment is used to facilitate the placement of biomedical sensors or other electrodes on the body. The garment is comfortable and allows freedom of movement much like typical clothing. Textile based electrical components are included in the garment which are capable of transmitting an electrical signal to and from various external electrodes placed on the body. A textile based EMI shield protects the signals from electromagnetic interference. The garment may take any form such as a vest, sports bra, long sleeve shirt, bonnet, or other form and may provide access to an electrode placement site without requiring removal of the garment.
Owner:KPR U S LLC
Biomedical electrode configuration for suppressing movement artifact
ActiveUS20110028823A1Suppression problemProviding mechanical stabilityElectromyographySensorsBiomedical sensorsEngineering
A biomedical sensor for detecting EMG signals may include a non-conducting fixed framework supporting a symmetrical arrangement of four electrode surfaces, configured as two signal detection contacts, each with a respective associated signal reference contact. The mechanical and electrical configuration act together to suppress movement artifact.
Owner:ALTECH INDS
High Impedance Signal Detection Systems and Methods for Use in Electrocardiogram Detection Systems
A biomedical sensor system is disclosed that includes a high impedance conductive electrode having an electrode impedance of at least about 20 kΩ / sq-mil, and a dielectric material on a first side of the electrode for receiving a discharge of an electrical signal from the dielectric material responsive to the presence of a time varying signal adjacent a second side of the dielectric material that is opposite the first side.
Owner:FLEXCON
High impedance signal detection systems and methods for use in electrocardiogram detection systems
ActiveUS8788009B2Less discomfortHigh impedanceElectrocardiographyConductive materialElectricityDielectric
Owner:FLEXCON
Methods, systems, and devices for optimal positioning of sensors
ActiveUS20160317088A1Easy to FeedbackWay accurateElectroencephalographyElectromyographyBiomedical sensorsTest measurement
A biomedical sensor has conducting elements disposed at least partly over a skin-facing surface. A sensing element detects a signal representative of a physiological parameter of a body using the conducting elements. A storage device stores a physiological model. A processor determines sensor placement quality by comparing the signal to the model and operates an indicator to indicate the determined quality. A method of measuring using the sensor includes computing a measurement acceptance criterion using numerous measurements, determining whether a subsequent test measurement corresponds to the measurement acceptance criterion obtained from the computing step, and indicating the results via the indicator. A system for measuring a physiological property of the body includes the sensor, a user interface device to receive measurements from the sensor, and a processor associated with the user interface device and configured to provide feedback if the measurement does not meet a selected acceptance criterion.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Multiple electrode composite systems in electrocardiogram detection systems
ActiveUS8792957B2Less discomfortHigh impedanceElectrocardiographyConductive materialBiomedical sensorsAdhesive materials
Owner:FLEXCON
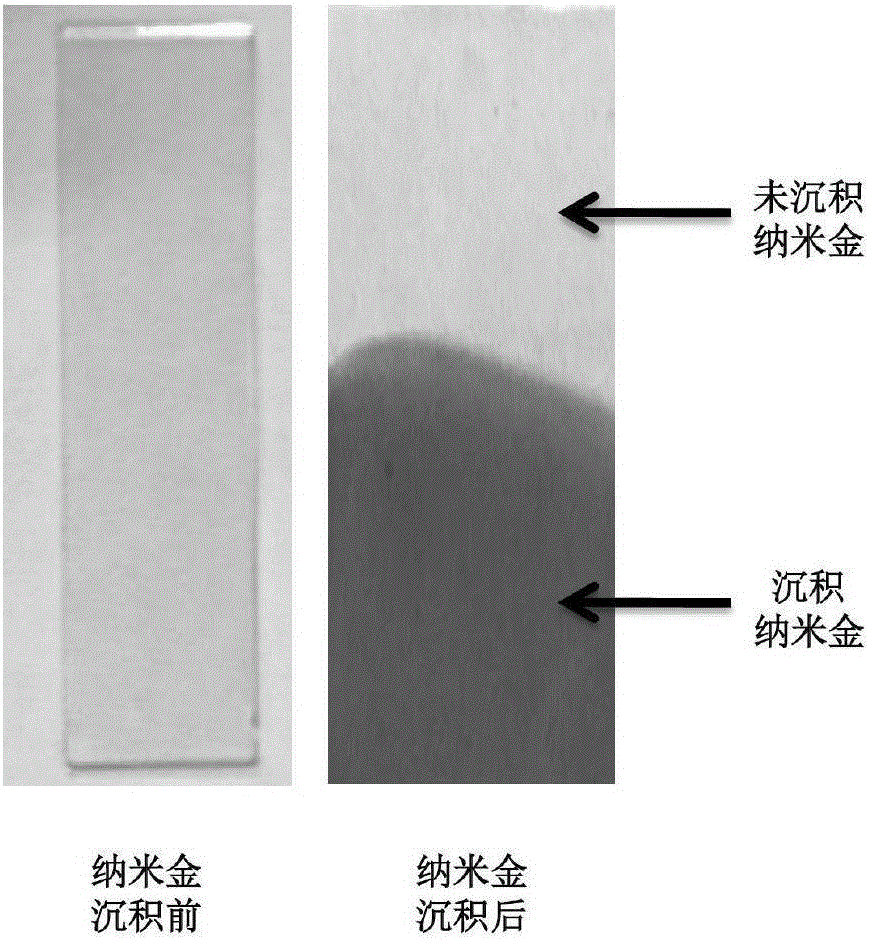
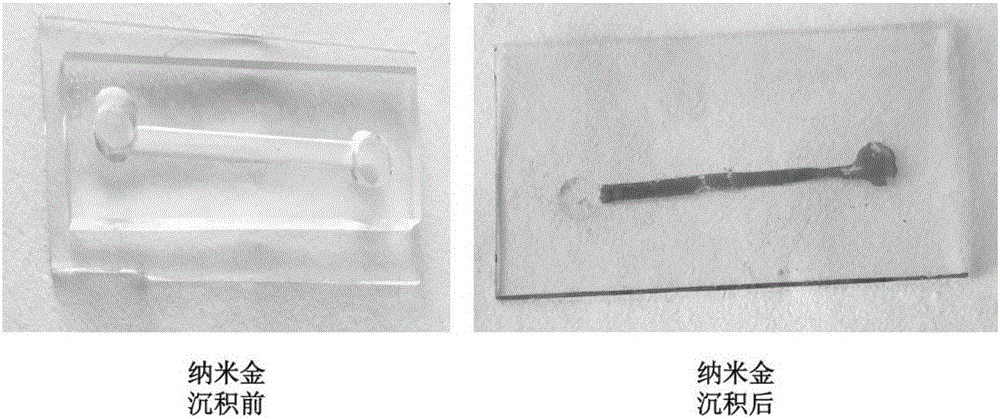
Method for depositing nanogold in microfluidic pore passage
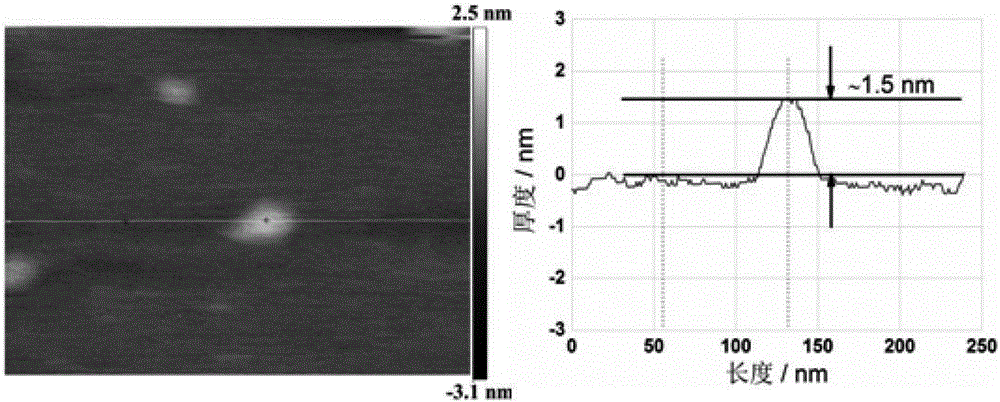
ActiveCN106198659ALow costGood repeatabilityLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesMultilayer membraneBiomedical sensors
The invention relates to a method for depositing nanogold in a microfluidic pore passage. ITO glass provided with a (PDDA / PSS)n self-assembled multilayer membrane is prepared by carrying out pretreatment on ITO glass, the prepared ITO glass is taken as a substrate and is sealed with a chip made from PDMS to form a microfluidic chip, then mixed solution of KAuCl4 and H2SO4 is injected into the microfluidic pore passage, nanogold is deposited in the microfluidic pore passage by virtue of a chronoamperometry, and nanogold surface topography detection shows that uniformly distributed nanogold particles can be seen in the microfluidic pore passage. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of rapidness, simplicity, good repeatability and low cost and has a broad application prospect in the fields of medical biology engineering, biomedical sensors and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
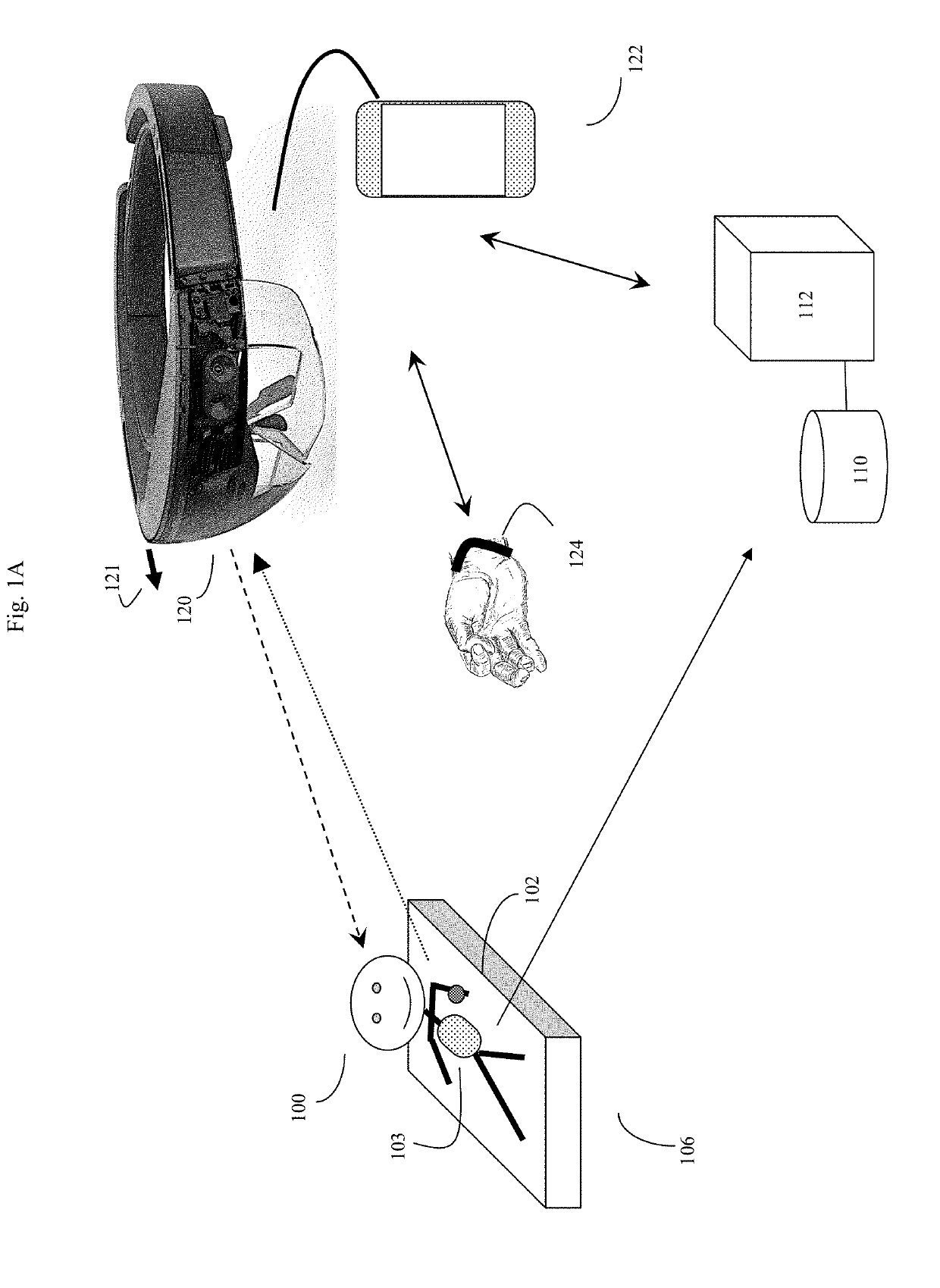
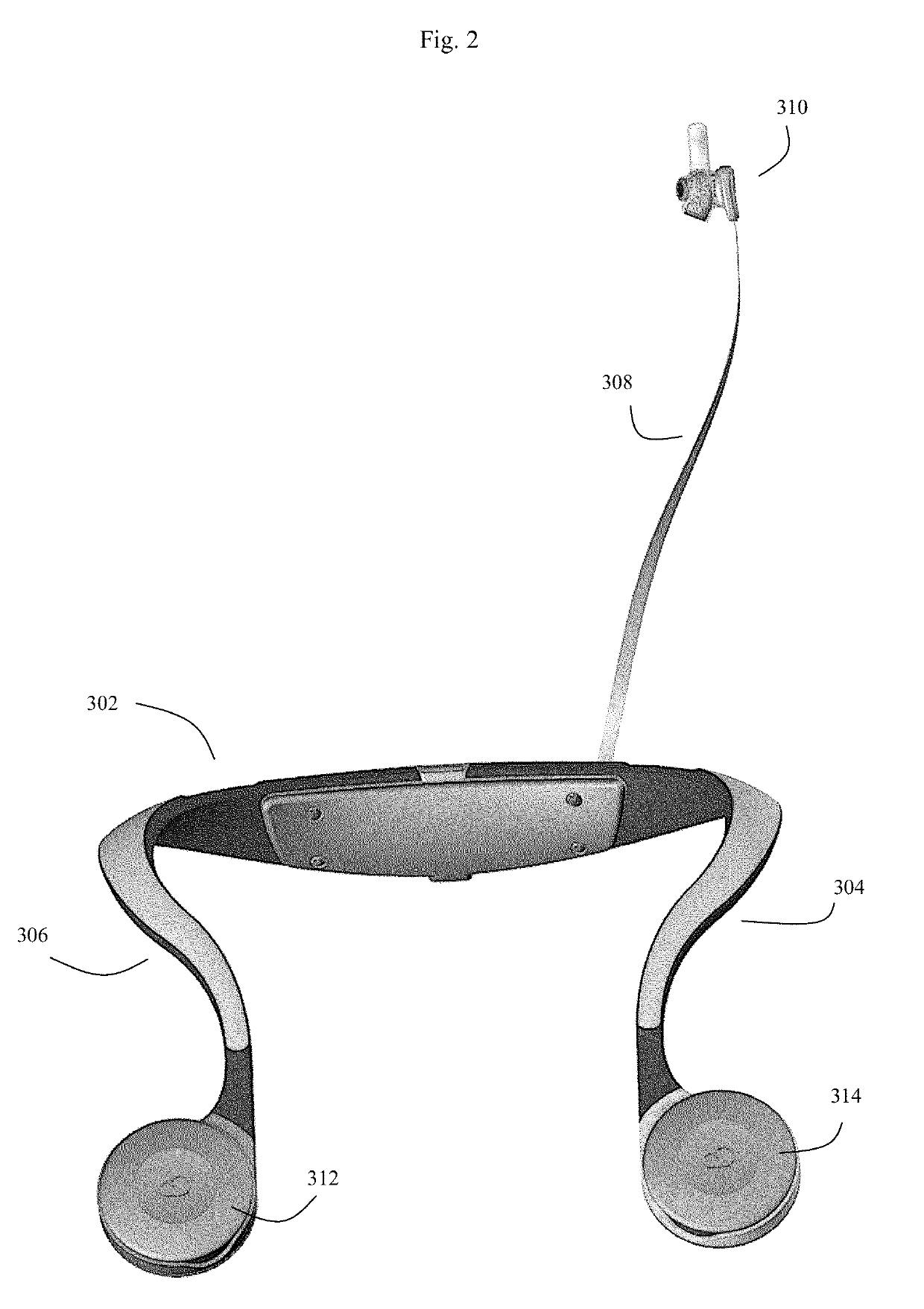
Augmented reality systems for time critical biomedical applications
ActiveUS20190302460A1Improve survivalEasy accessDrug and medicationsPerson identificationUser needsMedical record
An augmented reality system and method configured to automatically provide a user, such as a physician, with a real-time heads-up view of a patient's real-time medical status using an augmented reality headset. The system can automatically identify patients, pull up relevant medical records, obtain real-time biomedical sensor data from the patient, and display this to the user while, at the same time, allowing the user to directly view the patient through the headset's transparent lenses, and leaving the user's hands free to manipulate the patient or perform other functions. The system and method are particularly useful for intensive care units and other emergency medical situations where the user needs to get an almost instant understanding of the patient's status.
Owner:CLOUD DS INC CORP
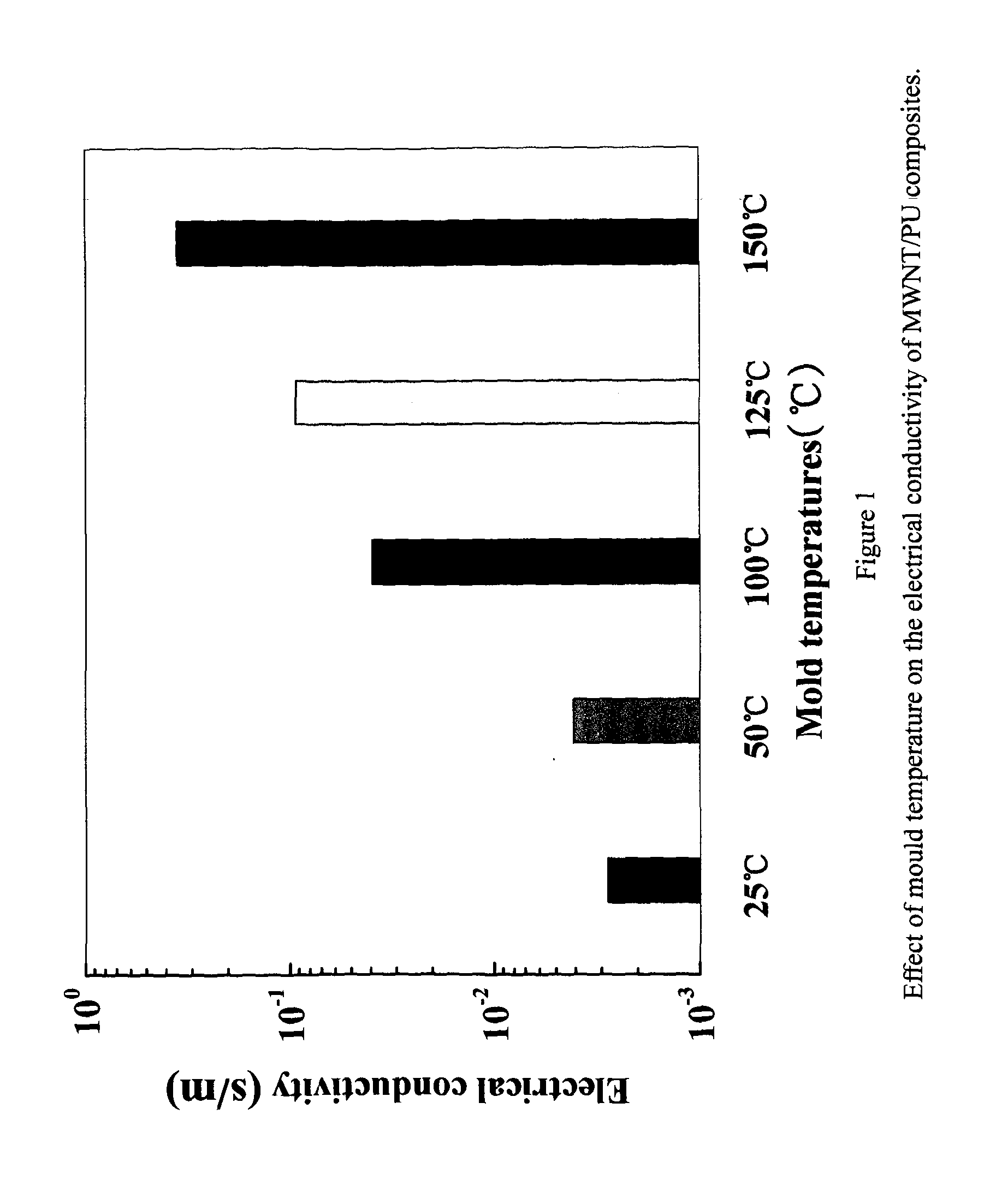
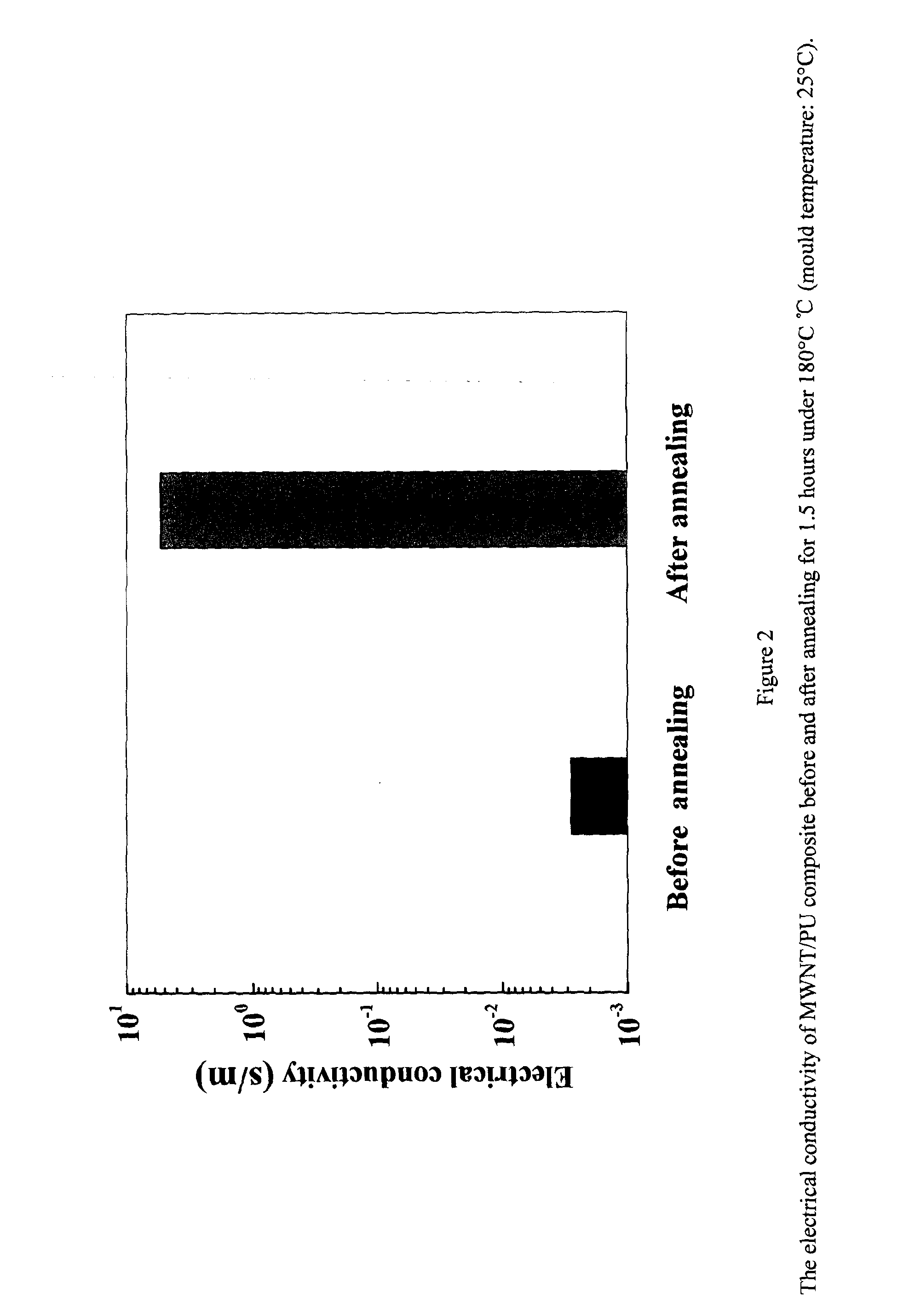
Methods to Improve the Electrical Conductivity for Moulded Plastic Parts
InactiveUS20140001415A1Improve conductivityHigh strain rateNon-metal conductorsMaterial nanotechnologyBiomedical sensorsMicro devices
Disclosed herein are the methods to improve the electrical conductivity for micro-moulded plastic parts containing carbon nanotubes. The polymer / carbon nanotubes composites suitable for polymer micromoulding including 80˜99.95 wt % of a polymer pellet or powder, 0-2 wt % of antioxidant, 0-2 wt % of dispersant agent and 0.05-20 wt % of carbon nanotube with a diameter 0.5-200 nm and a length of 200 nm-20 μm are firstly prepared through melt extrusion. The plastic microparts are prepared by micromoulding of the polymer / carbon nanotubes composites including micro extrusion, micro injection and hot embossing at optimized processing conditions and then are subject to a post thermal treatment to enhance the electrical conductivity. The post thermal treatment methods include electric heating, microwave, infrared or plasma heating. The methods disclosed can be used to prepare electrical conductive biomedical implanted plastic micro devices for minimally invasive surgery, biomedical sensors, microelectrodes, drug delivery devices, automated pipetting systems, breathing tubes, EMI devices etc.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BRADFORD +1
Silver nanothread/silk fibroin composite fiber and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110230113AImprove conductivityGood flexibilityElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureMonocomponent fibroin artificial filamentFiberBiomedical sensors
The invention discloses a silver nanowire / silk fibroin composite fiber and a preparation method thereof. A wet spinning technology is adopted. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a regenerated silk fibroin film; then, synthesizing silver nanowires, and dissolving the prepared silk fibroin film in a silver nanowire / acidic solvent dispersion system to form a silk fibroin / silver nanowire / acidic solvent spinning solution; finally, preparing the single-fibrous silver nanowire / silk fibroin composite fiber with high conductivity and high flexibility. The prepared silver nanowire / silk fibroin composite fiber has huge application prospect in the fields of wearable equipment, biomedical sensors, implantable devices, intelligent clothing, flexible solar cells and medical tissue engineering.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
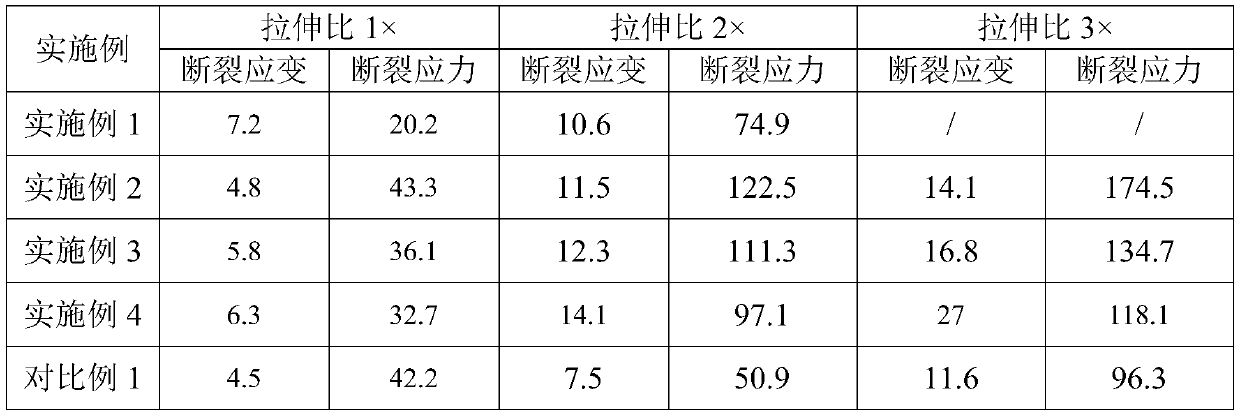
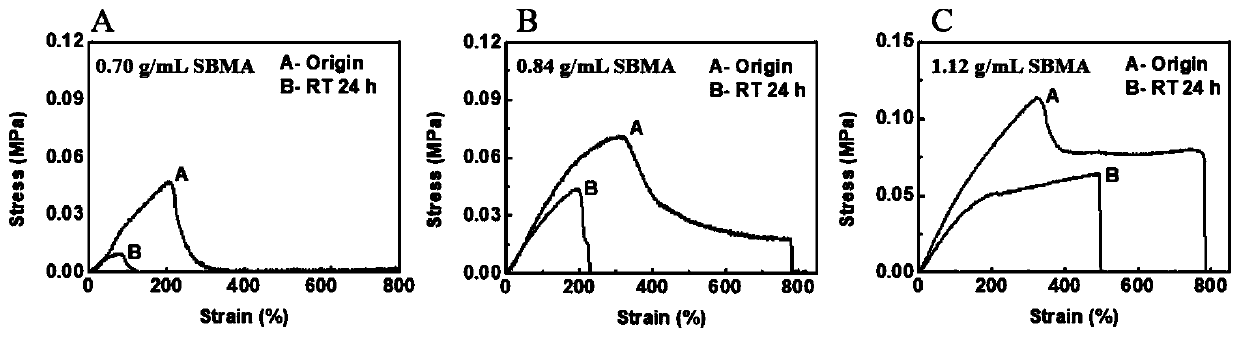
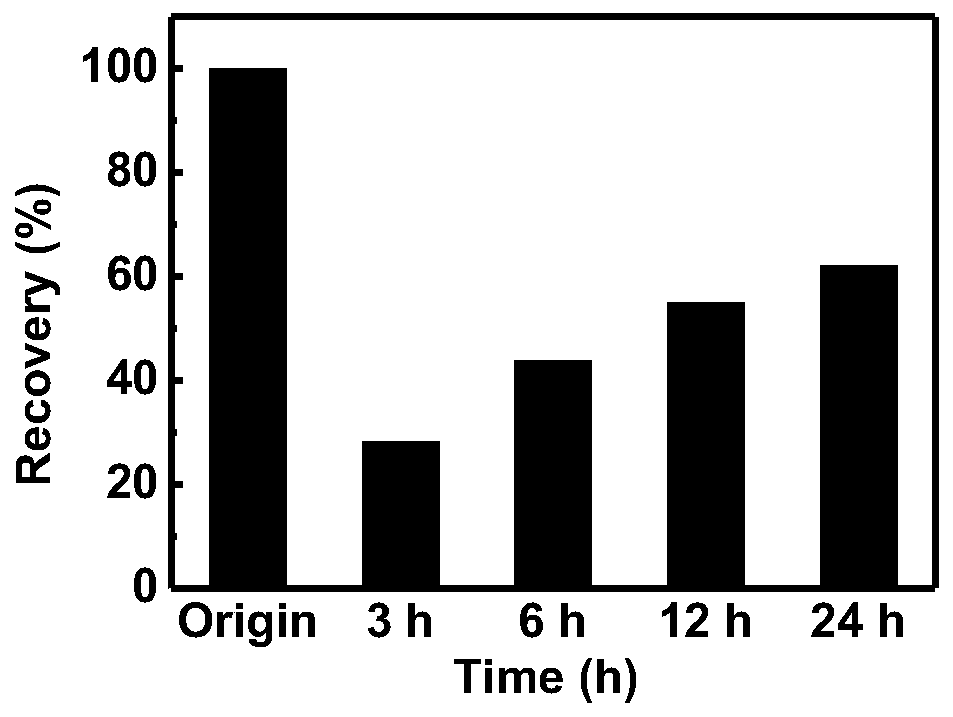
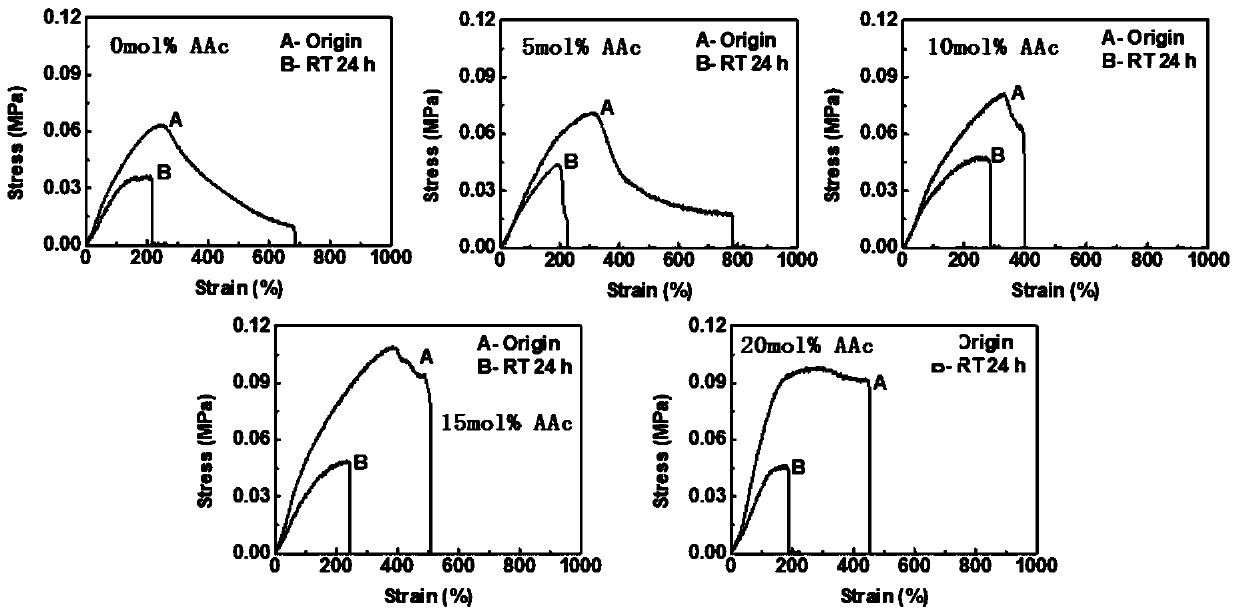
Chitosan/zwitter-ion and acrylic acid copolymer double network self-healing hydrogel and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses chitosan / zwitter-ion and acrylic acid copolymer double network self-healing hydrogel and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of hydrogel. The hydrogel is of a double network structure, and formed by a first network and a second network in a mutually penetrating mode, the first network is a physical cross-linking network formed by chitosan and polyvalent negative ions, the second network is a copolymer network formed by a zwitter-ion monomer and an acrylic acid monomer, the first network intersperses in the second network, the chitosan and the polyvalent negative ions are selected to form the first network, the zwitter-ion monomer and the acrylic acid monomer are selected to form the second network, the double network self-healing hydrogel, obtained by the cross-linking purely physical effect, with the mutually interspersed first network and the second network makes the hydrogel have excellent mechanical performance and self-healing ability, the high relative resistance change rate is provided when deformation occurs, and the chitosan / zwitter-ion and acrylic acid copolymer double network self-healing hydrogel has broad applicationprospects in the field of soft electronics, especially as biomedical sensors.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Single-use biomedical sensors
ActiveCN102525450AImproved infection controlReduce clutterElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyPower sensorBiomedical sensors
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Tongue sensors for monitoring multiple physiological parameters and tongue stimulation
An implantable tongue sensor / stimulator device is disclosed for sensing and monitoring physiological parameters and providing a reactive stimulation to a patient. The device includes a main upper disc member carrying one or more micro-biomedical sensors for sensing multiple physiological parameters and one or more stimulation electrodes for creating stimulating sensations in the tongue, a lower tongue plate member that includes a battery for powering the device circuitry and a locking mechanism for locking the device in place when it is implanted, and an intermediate assembly including a central tongue rod member and conducting tubes for penetrating a tongue and connecting the upper disc with the lower disc. The device contains a wireless transmitter for transmitting data from the device.
Owner:AVITALL BOAZ
Optical fiber surface plasma resonance sensor modified by nano-composite structure
InactiveCN109655515AAchieve coverageSolve the problem of incomplete retouchingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiomedical sensorsPlasma resonance
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical sensors, and discloses an optical fiber surface plasma resonance sensor modified by a nano-composite structure. The optical fiber surface plasma resonance sensor comprises a sensing area arranged on an optical fiber, and the sensing area is composed of a fiber core layer, a bonding layer, a sensing dielectric layer and a two-dimensional nano material layer from inside to outside; and the length range of the sensing area is 15 + / -5 mm. Compared with other structures, the optical fiber surface plasma resonance sensor has the advantages that MoS2-graphene nano composite structure can utilize the characteristics of high optical absorption coefficient of MoS2 and large surface area-volume ratio of graphene, so that the detection performance of the SPR sensor is greatly improved. The optical fiber surface plasma resonance sensor also has the advantages of being small in size, high in sensitivity, non-toxic and pollution-free.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Biomedical sensor device
InactiveUS8543179B2Easy to optimizeFast signalElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyBiomedical sensorsProbe array
A biomedical sensor device includes a light source, a probe array, and a photo detector. The light source is configured for emitting infrared radiation. The probe array is contacted to a user's skin to detect an electric wave signal transmitted through the probe array from the skin. The probe array includes a substrate and a plurality of probes mounted on the substrate, wherein the substrate and the probes are non-opaque so that the infrared radiation may be transmitted through the probe array into the skin. The photo detector is configured to detect an infrared signal by measuring the infrared radiation absorption by the skin.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Disposable protective overlay covering for biomedical sensors
ActiveUS20150080697A1Stable positionReduce the potential for sensor dislodgmentElectromyographySensorsBiomedical sensorsBiomedical engineering
A disposable, low profile sensor overlay covering for use with biomedical sensors and which includes a framework of flexible component layers supporting an arrangement of electrostatic shielding, insulating, cushioning, and electrically conductive adhesive substrate components configured to form a protective covering encasing the sensor. The combination of component layers provides a means to stabilize the relative position of the sensor with respect to the skin and reduce the potential for sensor dislodgment. The mechanical and electrical configurations act in synergy to shield the sensor from external electrical fields and suppress movement artifact.
Owner:ALTECH INDS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com