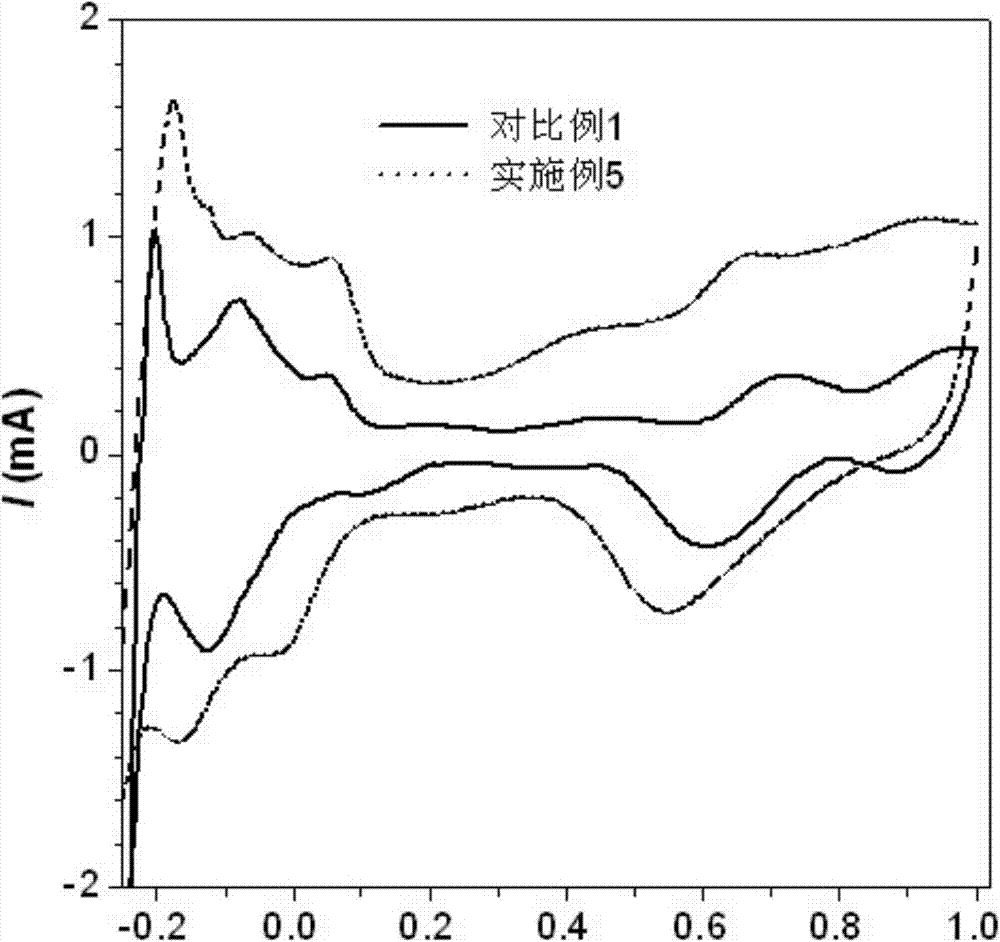
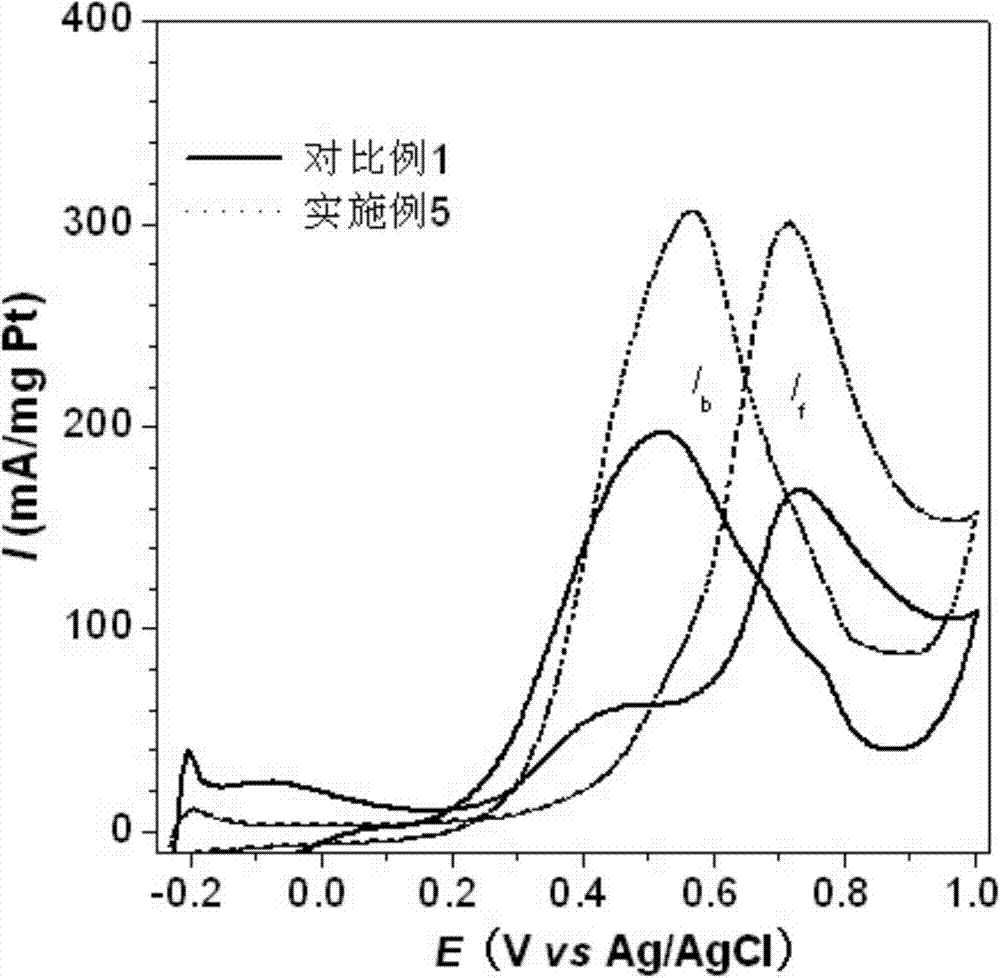
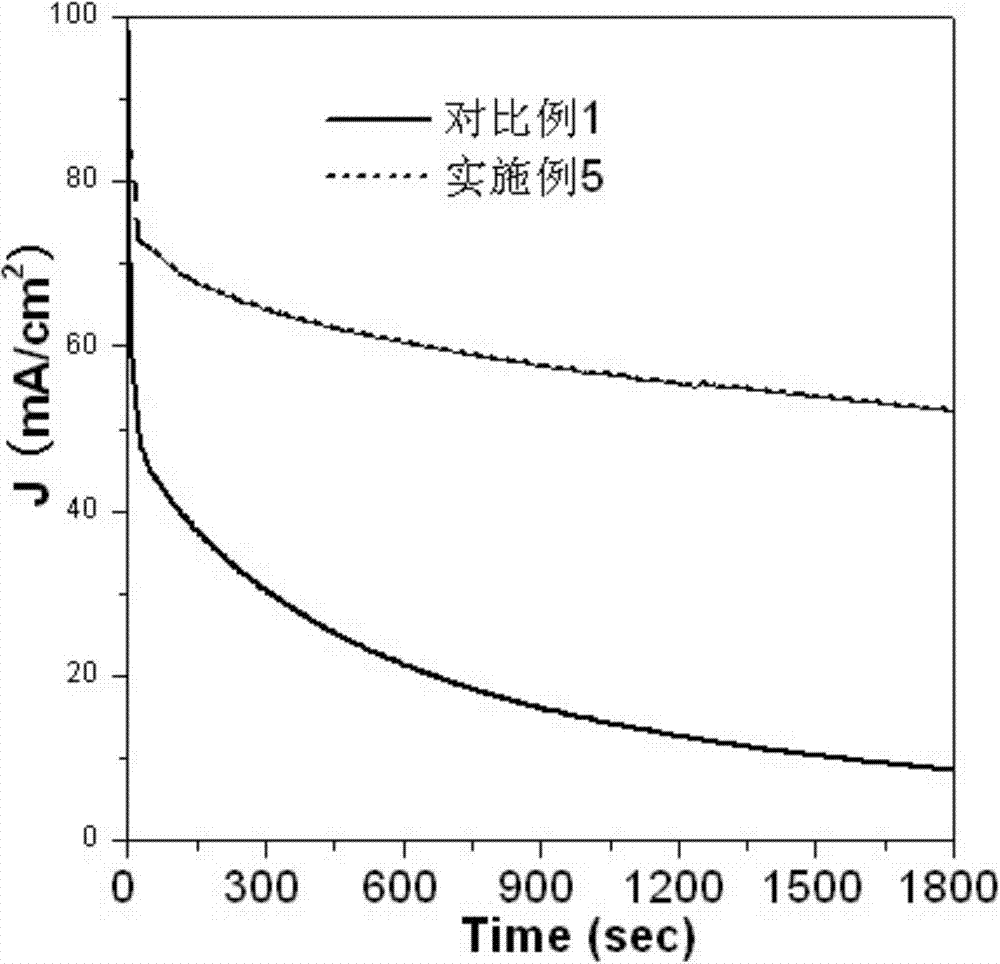
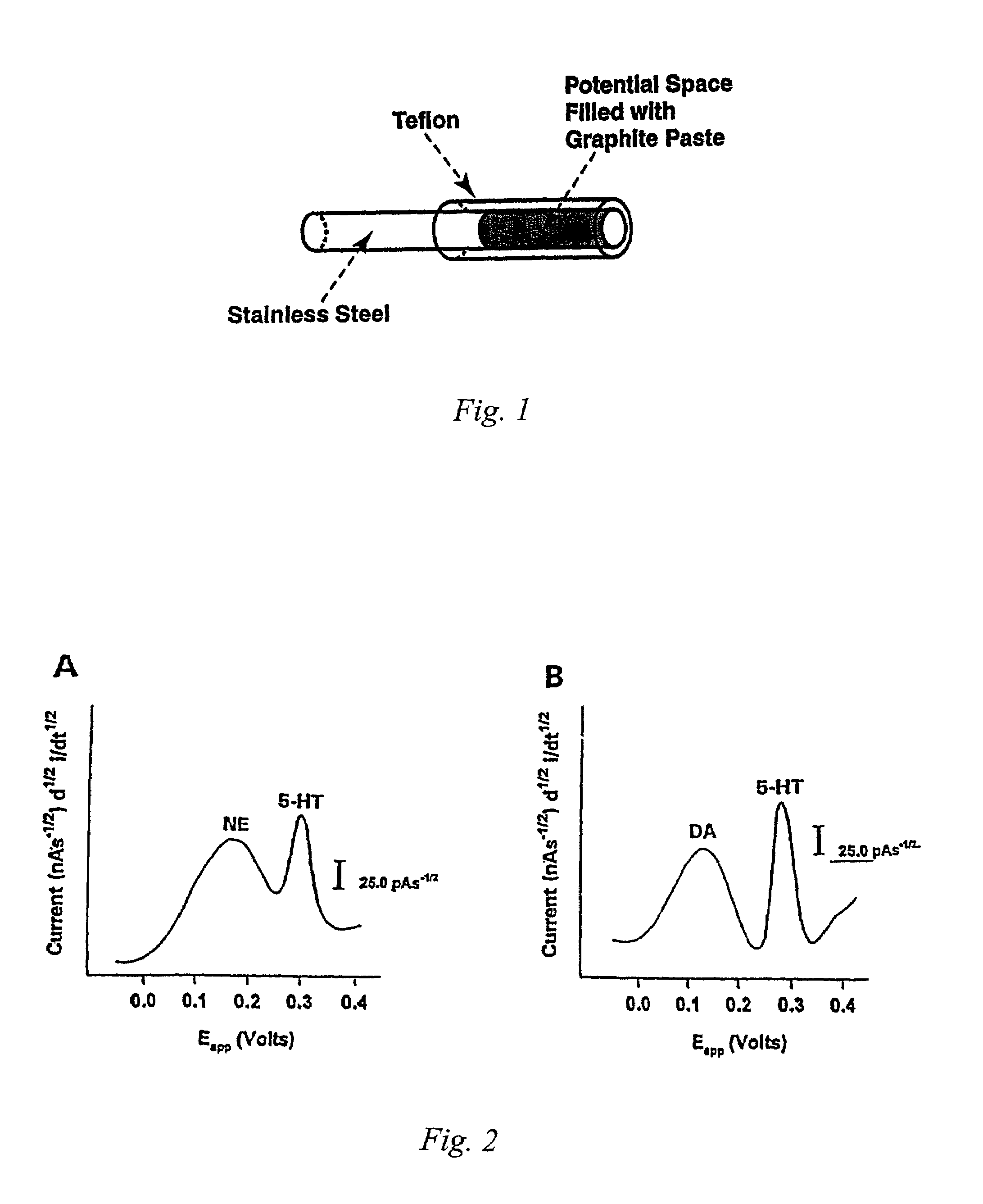
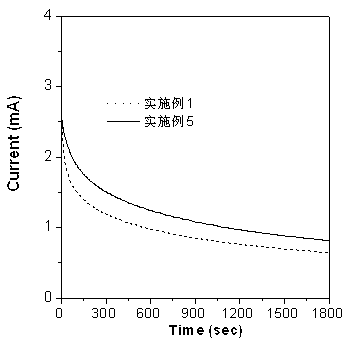
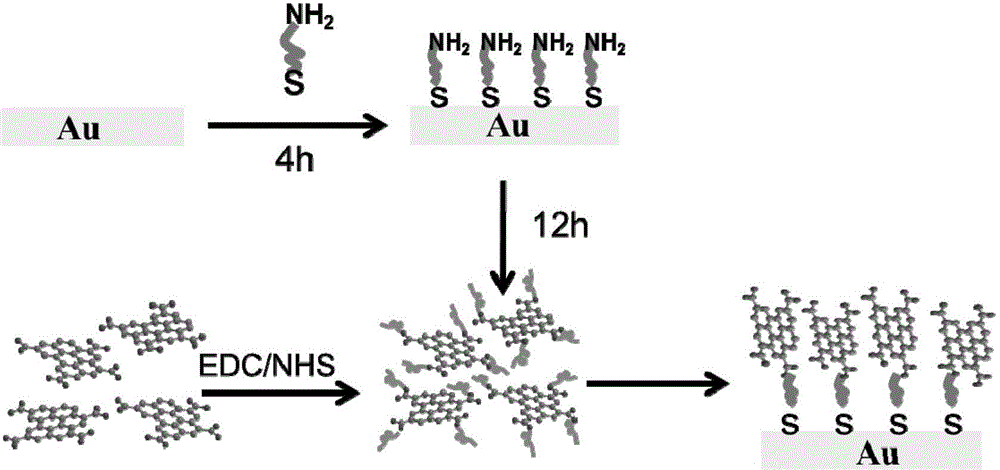
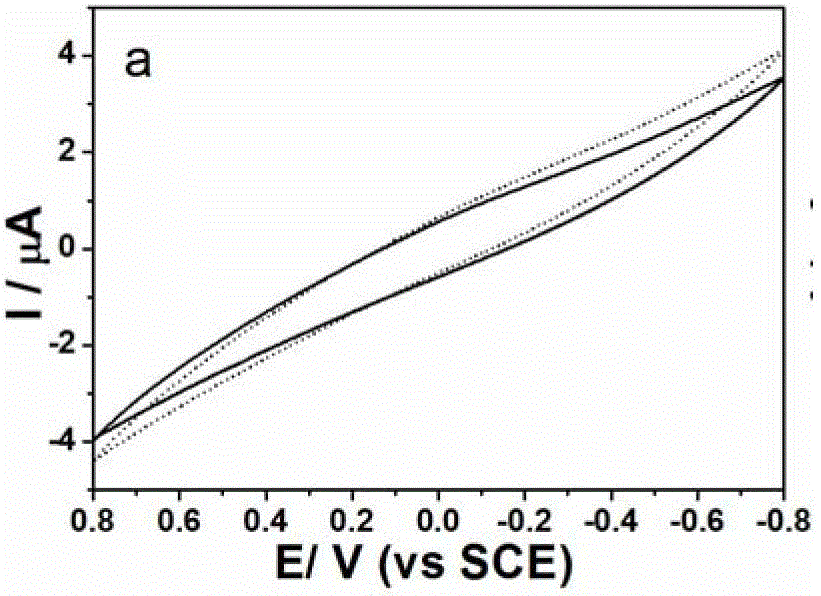
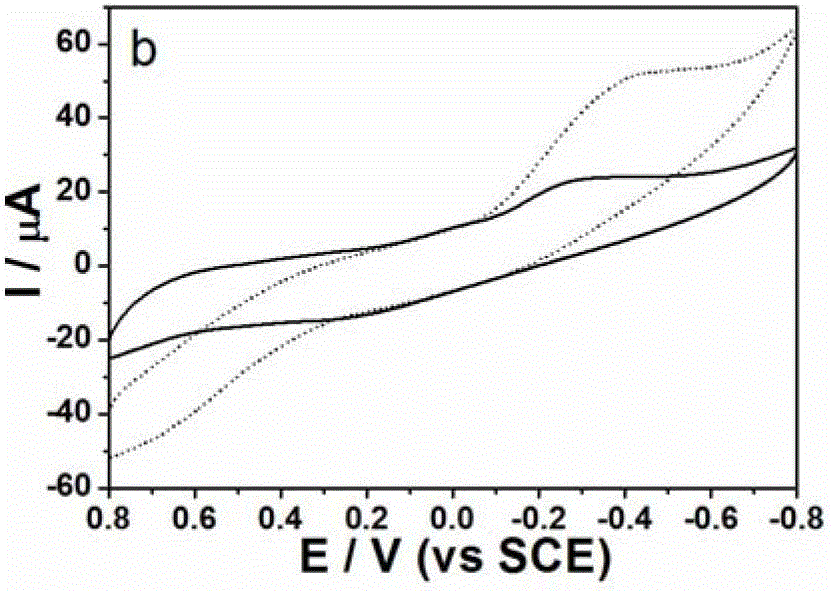
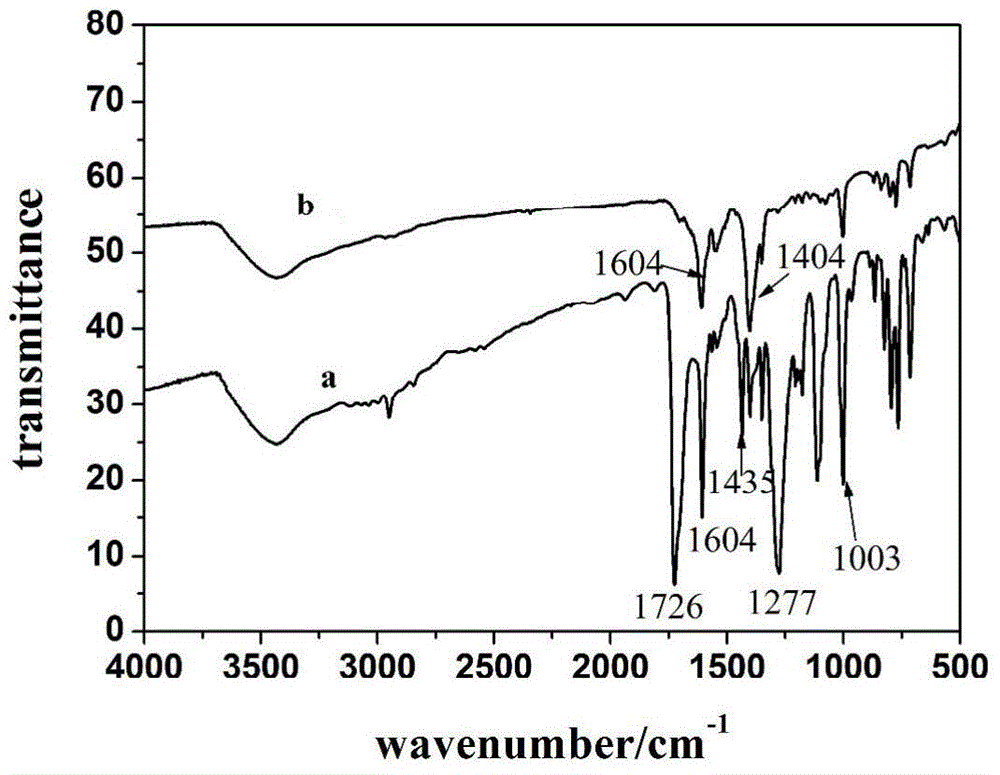
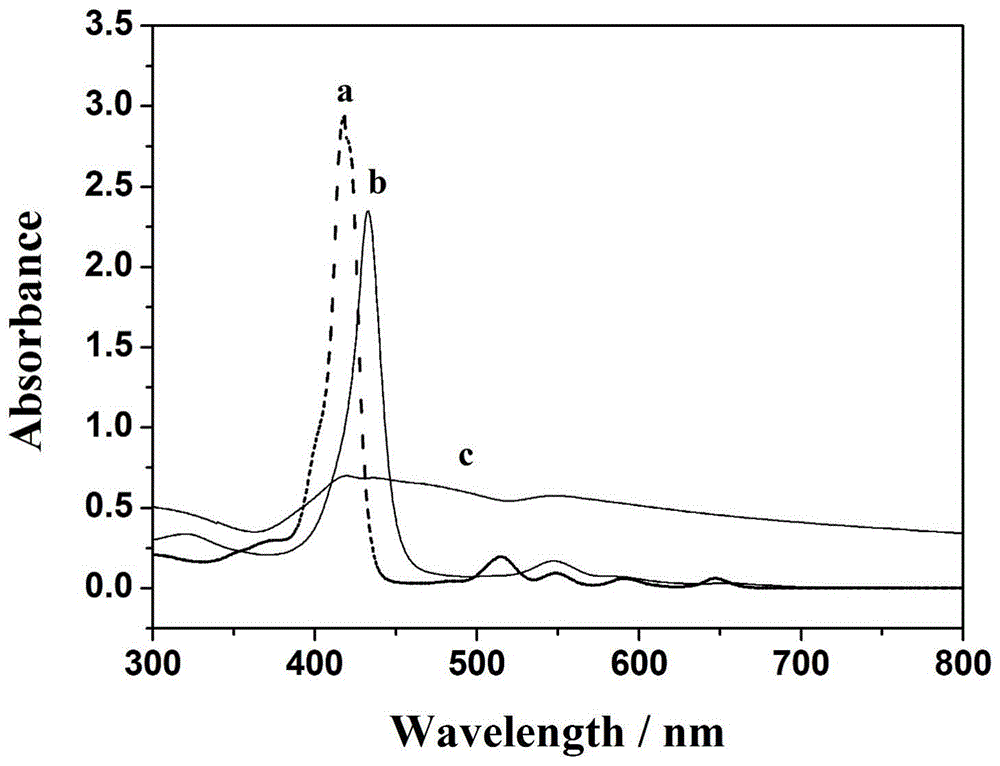
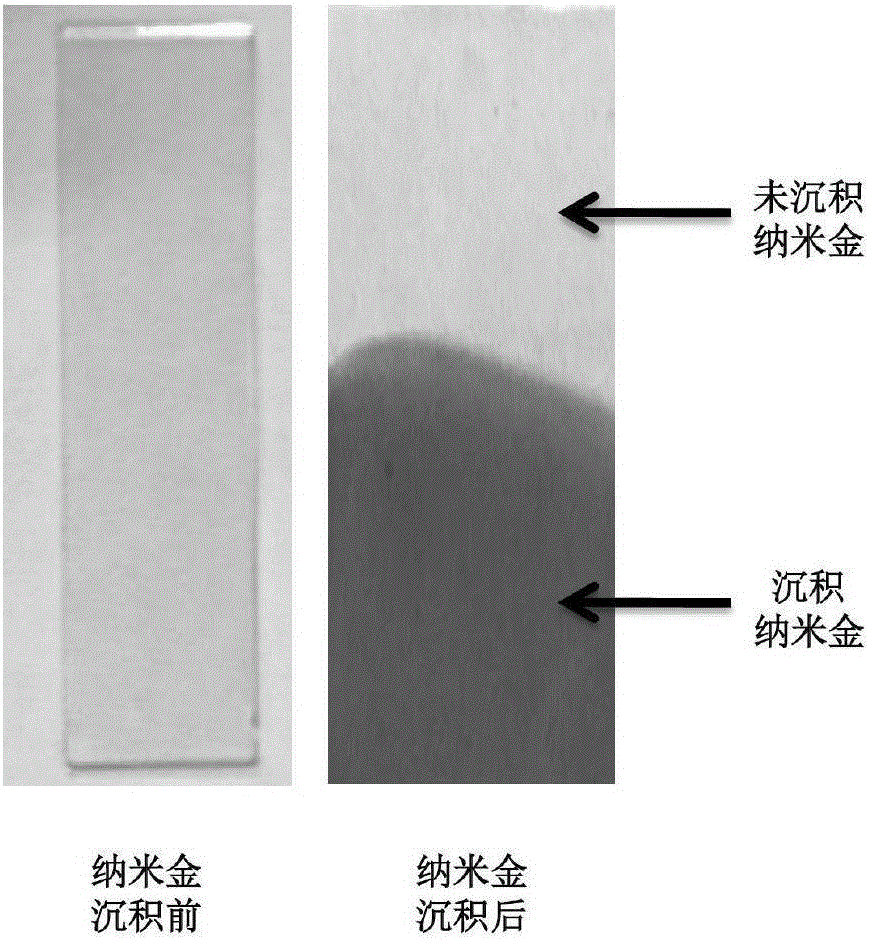
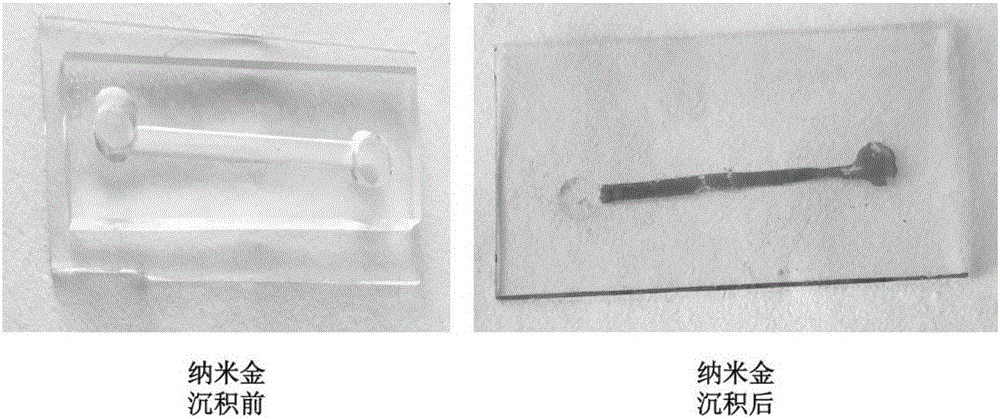
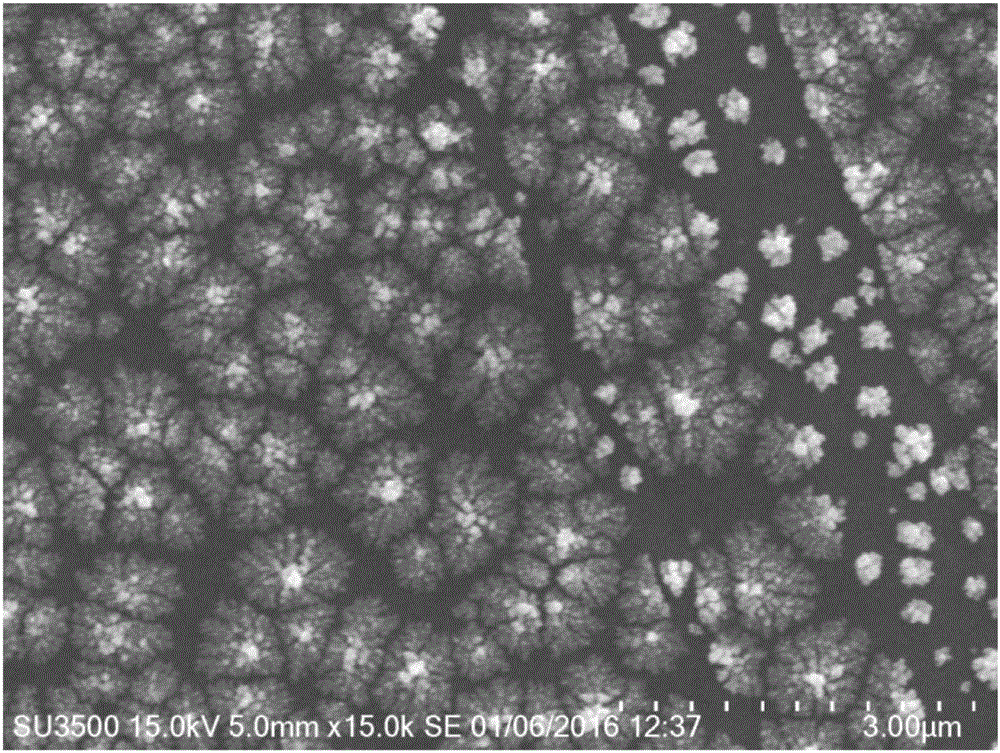
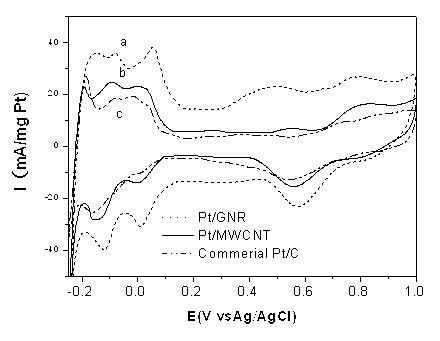
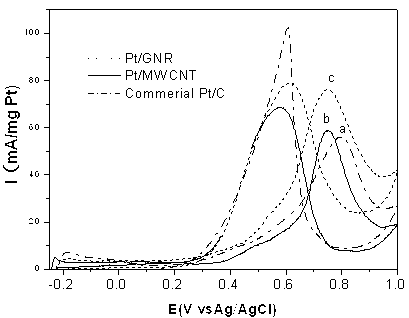
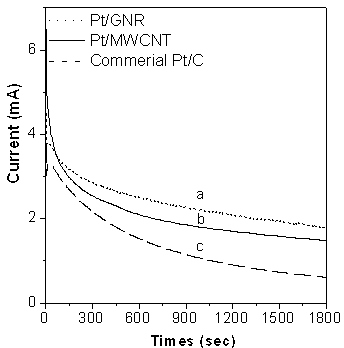
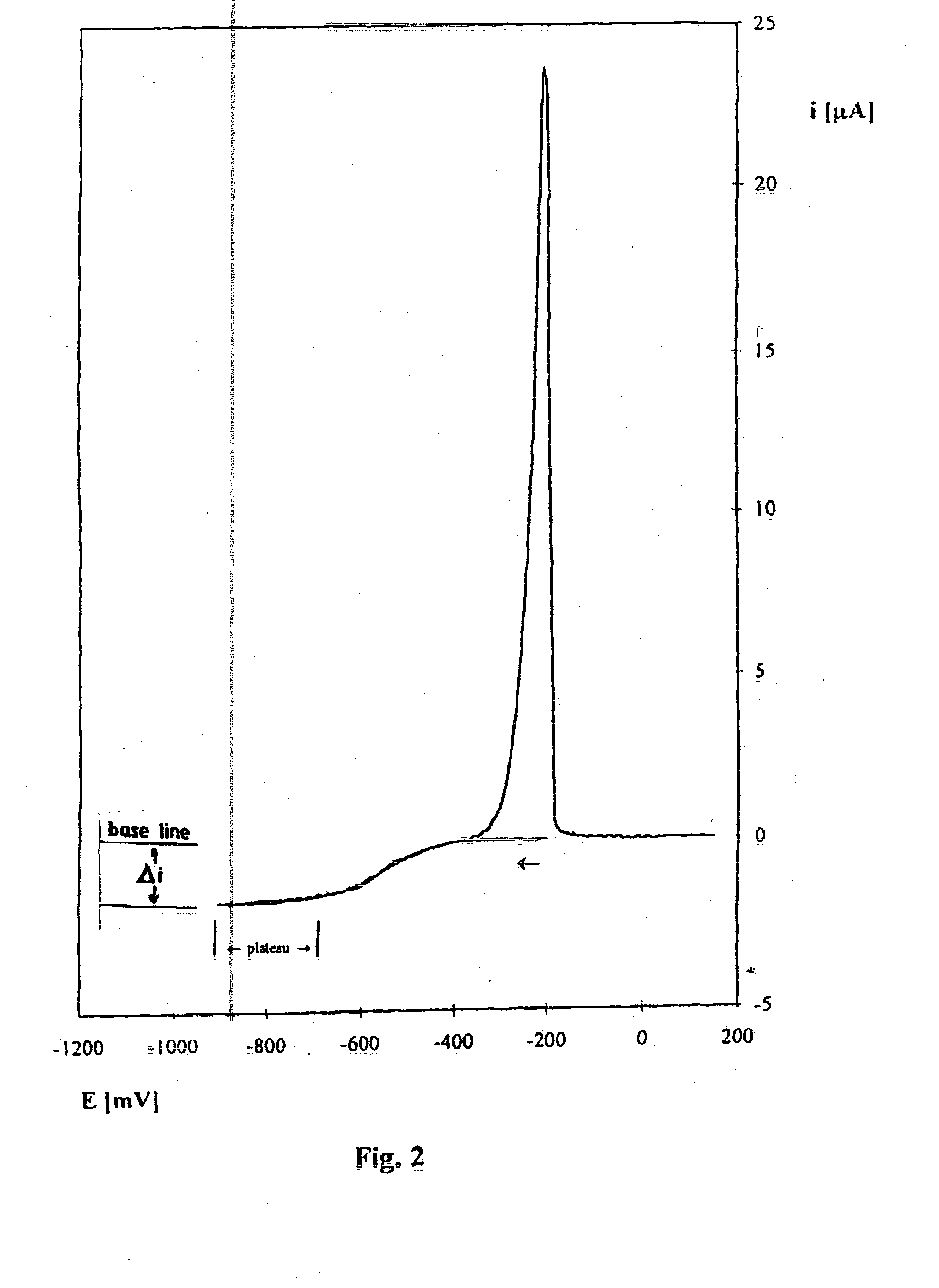
Patents
Literature
129 results about "Chronoamperometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chronoamperometry is an electrochemical technique in which the potential of the working electrode is stepped and the resulting current from faradaic processes occurring at the electrode (caused by the potential step) is monitored as a function of time. The functional relationship between current response and time is measured after applying single or double potential step to the working electrode of the electrochemical system. Limited information about the identity of the electrolyzed species can be obtained from the ratio of the peak oxidation current versus the peak reduction current. However, as with all pulsed techniques, chronoamperometry generates high charging currents, which decay exponentially with time as any RC circuit. The Faradaic current - which is due to electron transfer events and is most often the current component of interest - decays as described in the Cottrell equation. In most electrochemical cells this decay is much slower than the charging decay-cells with no supporting electrolyte are notable exceptions. Most commonly a three electrode system is used. Since the current is integrated over relatively longer time intervals, chronoamperometry gives a better signal to noise ratio in comparison to other amperometric techniques.
Carbon fiber supported metal catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103545536AConducive to loadHigh catalytic activityHybrid capacitor electrodesCell electrodesFiberHigh current density
The invention relates to a carbon fiber supported metal catalyst as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The materials such as graphene nano belt, a multi-arm carbon nano tube and graphene are adopted as graphitization template-based additives, and composite carbon fiber with high graphitization degree and high conductivity is obtained by electrostatic spinning and wet spinning processes and a high-temperature carbonization process, wherein the preferential amount of the template-based additives is 0.5-5% by weight; the high-graphitization composite carbon fiber is used as a carrier of the catalyst, and a metal / carbon nano fiber catalyst for a fuel cell is obtained by reduction; the catalyst has a large initial electrochemical-activity surface area and strong CO toxicity resistance; the current density attenuation is reduced in a 30 minutes of chronoamperometry test, and the catalyst shows higher electrochemical activity, higher current density and better electrochemical stability; and moreover, the catalyst taking the high-graphitization carbon fiber as a carrier shows remarkably high durability.
Owner:上海氢尚新能源科技有限公司
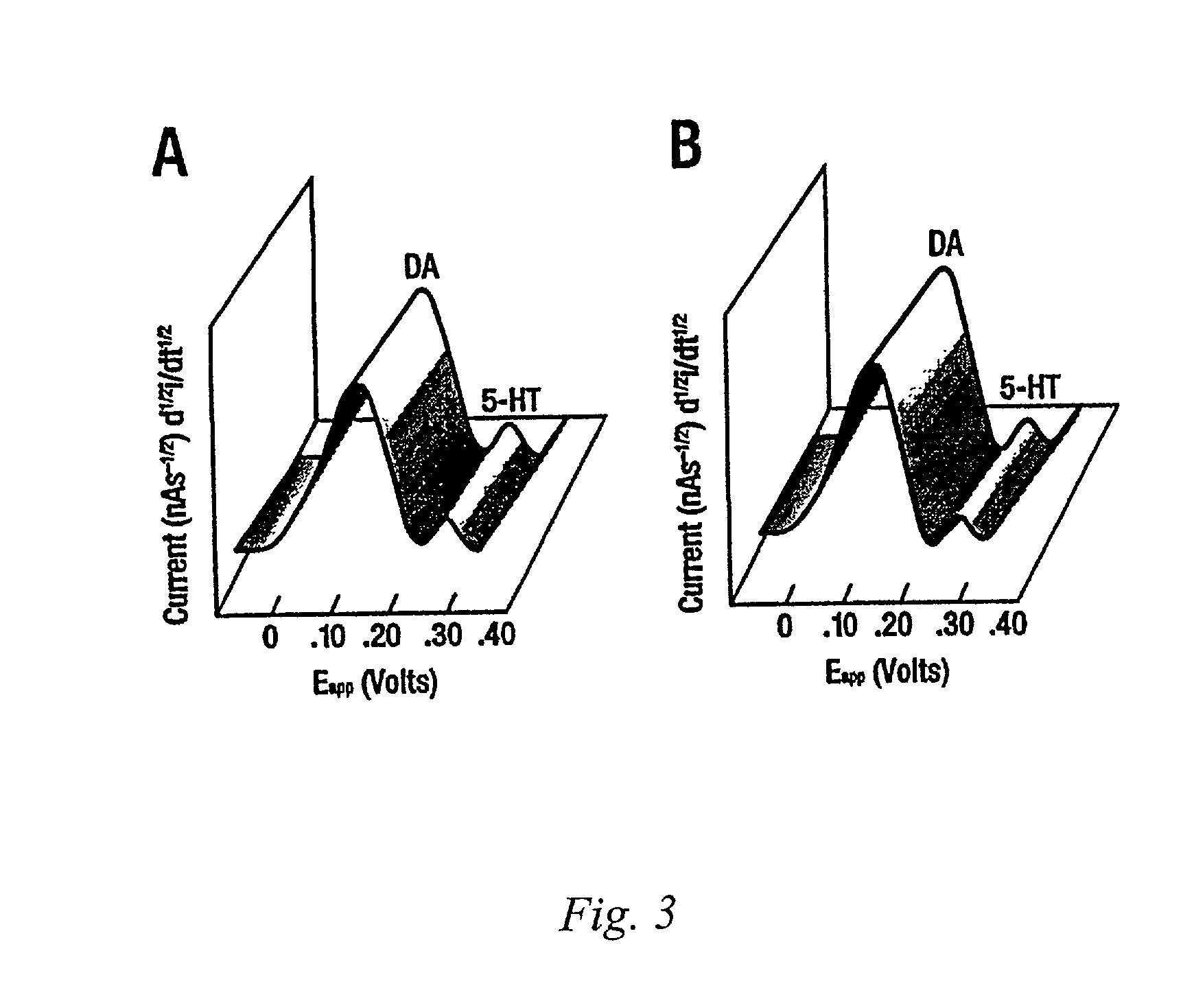
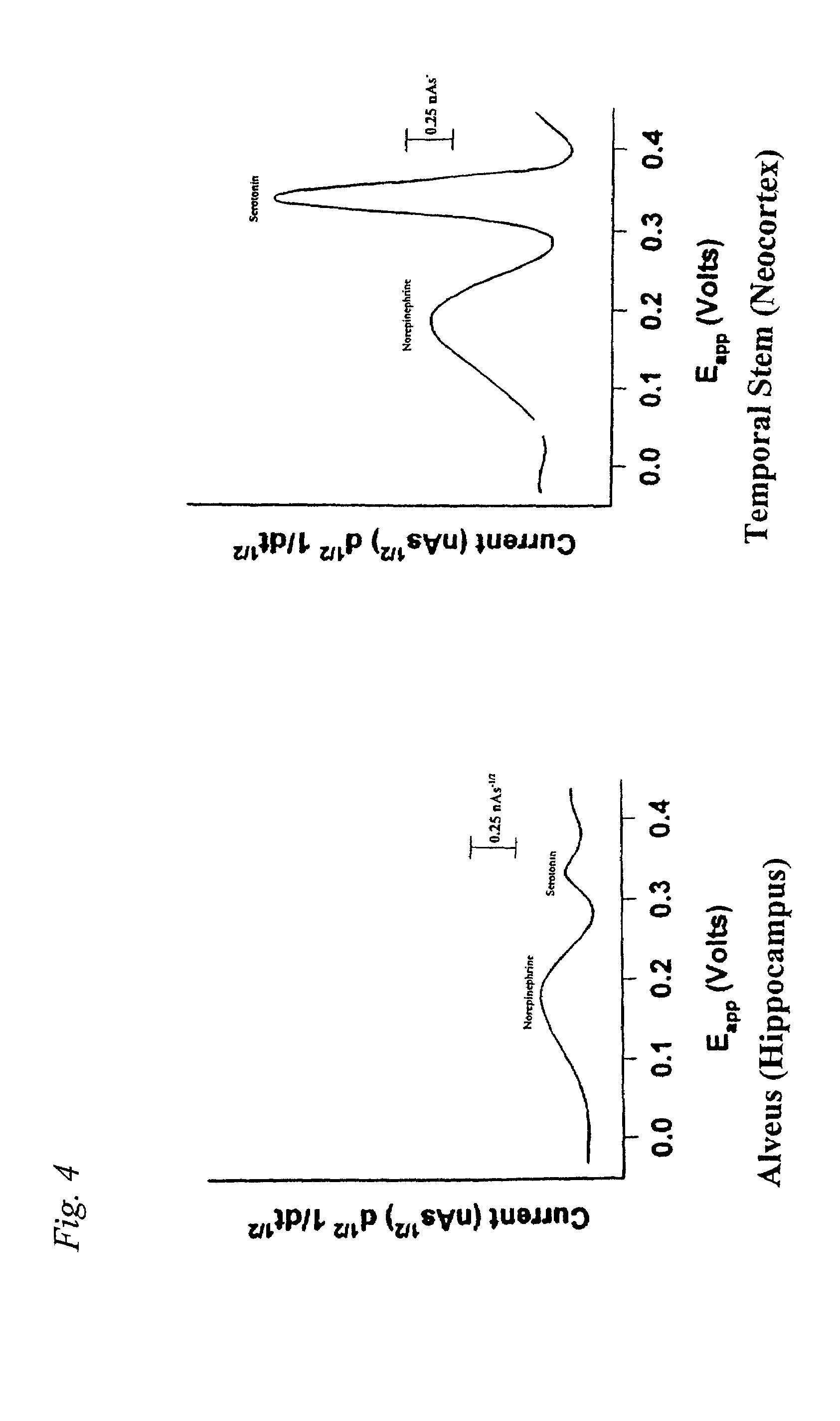
Identification, diagnosis, and treatment of neuropathologies, neurotoxicities, tumors, and brain and spinal cord injuries using microelectrodes with microvoltammetry
InactiveUS7112319B2Reliable distinctionIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteInjury brain
The present invention relates to devices and methods of use thereof for making semiderivative voltammetric and chronoamperometric measurements of chemicals, e.g. neurotransmitters, precursors, and metabolites, in vitro, in vivo, or in situ. The invention relates to methods of diagnosing and / or treating a subject as having or being at risk of developing a disease or condition that is associated with abnormal levels of one or more neurotransmitters including, inter alia, epilepsy, diseases of the basal ganglia, athetoid, dystonic diseases, neoplasms, Parkinson's disease, brain injuries, spinal cord injuries, and cancer. The invention provides methods of differentiating white matter from grey matter using microvoltammetry. In some embodiments, regions of the brain to be resected or targeted for pharmaceutical therapy are identified using Broderick probes. The invention further provides methods of measuring the neurotoxicity of a material by comparing Broderick probe microvoltammograms of a neural tissue in the presence and absence of the material.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Carbon-containing metal catalyst, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103227334AConducive to loadHigh catalytic activityCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHigh resistanceHigh current density
Owner:上海氢尚新能源科技有限公司
Graphene quantum dot modified electrochemical sensor, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102879442AImprove electrochemical responseFast current responseMaterial electrochemical variablesMaterials scienceLinear range
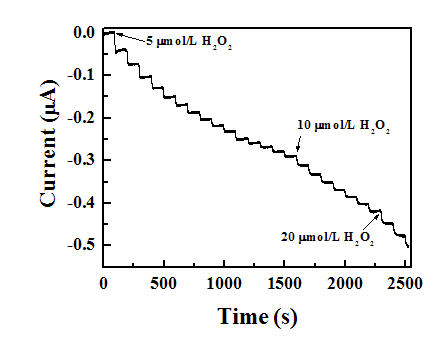
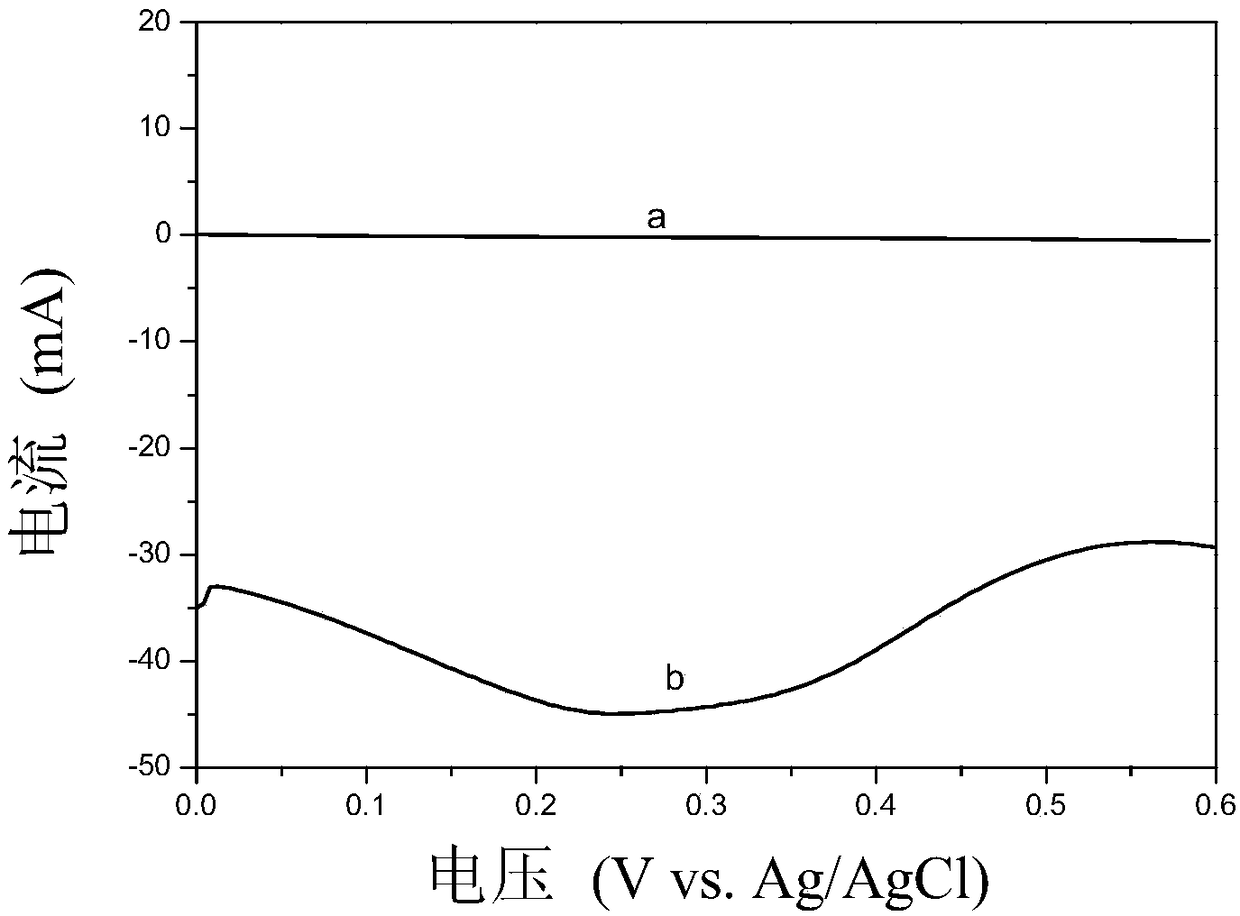
The invention relates to a graphene quantum dot modified electrochemical sensor, and a preparation method and application thereof. A three-electrode system is adopted for the sensor, and a graphene quantum dot modified gold electrode is taken as a working electrode. Chemical bonds are used for bonding carboxylic groups of graphene quantum dots and amino groups on the surface of the modified gold electrode to construct the graphene quantum dot modified electrochemical sensor. The graphene quantum dot modified gold electrode is taken as the working electrode, and chronoamperometry is used for determining a working curve of H2O2 concentration. The linear range of the H2O2 concentration is determined to be 2 mu M to 8mM, and a detection lower limit is 1.3 mu M. In addition, the sensor can be used for detecting the content of H2O2 released by living cells in real time, has the advantages of quick response, wide linear range, low detection lower limit, broad application prospect and the like, and is significant for diagnostic tests in diseases caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Electrochemical biosensor for detecting hydrogen peroxide, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106404873ALarge specific surface areaHigh specific surface areaMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorHemin
The present invention relates to an electrochemical biosensor for detecting hydrogen peroxide, a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of (1) synthesizing the silica-three-dimensional graphene composite material; (2) doping nitrogen and carbon into the synthesized silica-three-dimensional graphene composite material; (3) pretreating a glassy carbon electrode; (4) preparing the glassy carbon electrode modified by the nitrogen-carbon-doped silica-three-dimensional graphene composite material through the dispensing method; (5) putting the glassy carbon electrode into a chloroauric acid solution to prepare gold nanoparticle-nitrogen-carbon-doped silica-three-dimensional graphene glassy carbon electrode through chronoamperometry; (6) dipping the glassy carbon electrode into a double-sulfhydryl-modified GDNA solution and cultivating for 2-4 hours; (7) dipping the composite electrode into a hemin solution for 10-14 hours. The electrochemical biosensor is good in stability and reproducibility, high in specificity and sensitivity, fast and simple and convenient to operate. The electrochemical biosensor can be used for detecting the content of hydrogen peroxide in biological samples, cosmetics and the like.
Owner:广东省汕头市质量计量监督检测所
Method for depositing nano-silver in microfluidic channels
ActiveCN106198660ALow costSimple and easy layer-by-layer assembly methodLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesChronoamperometryEngineering
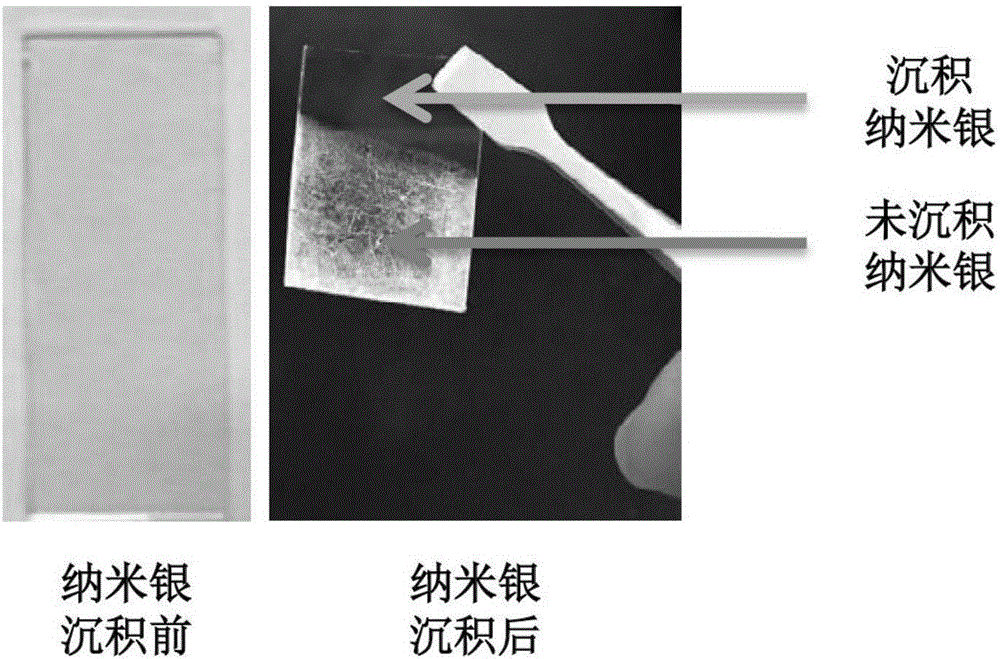
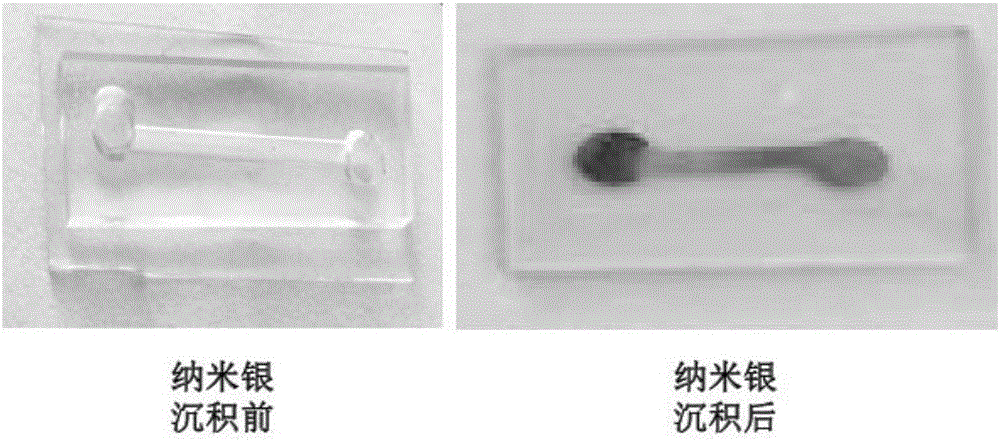
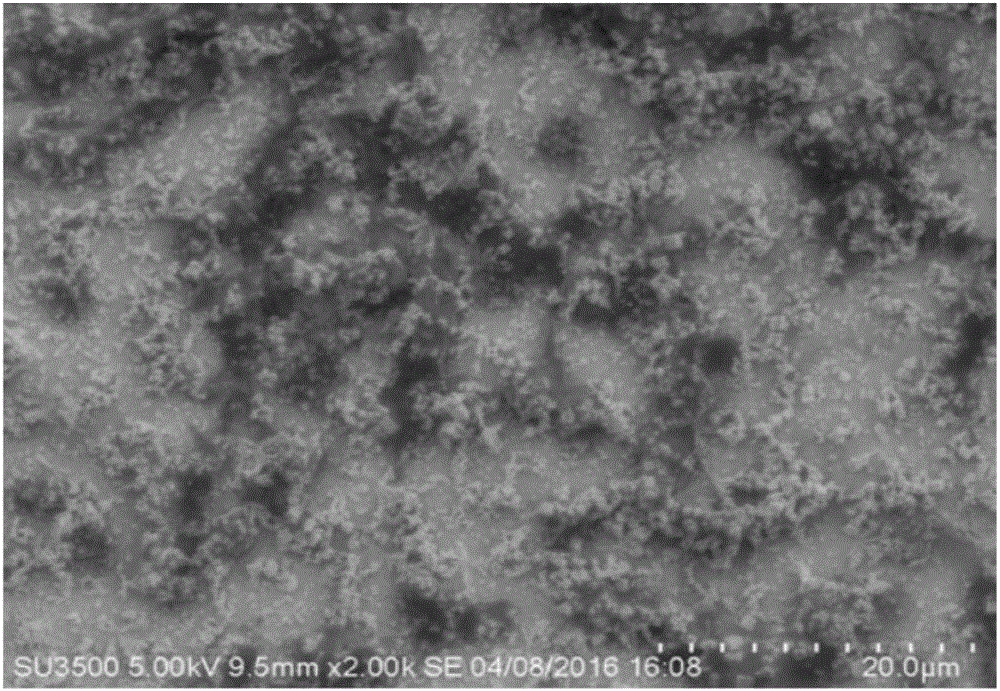
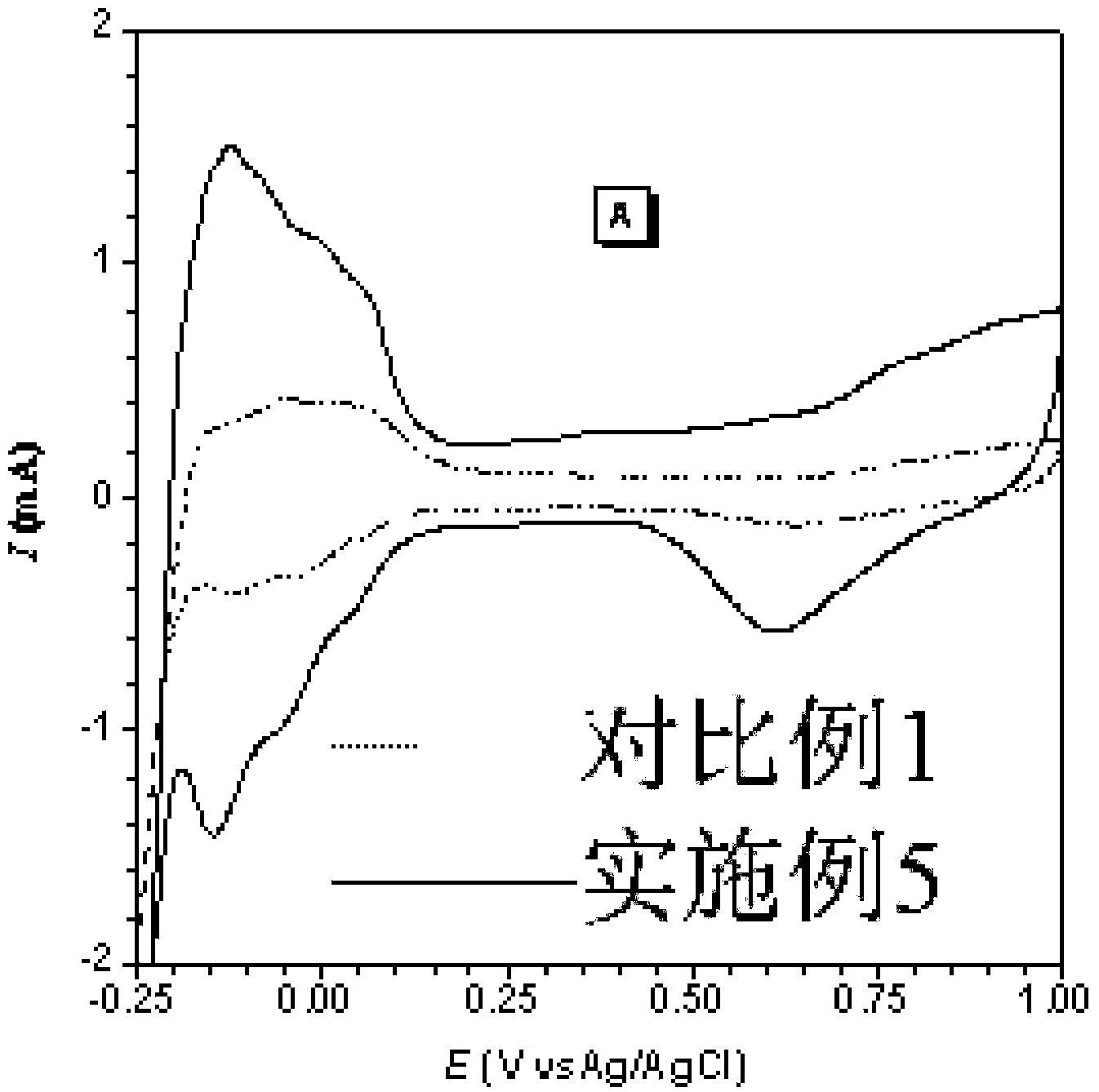
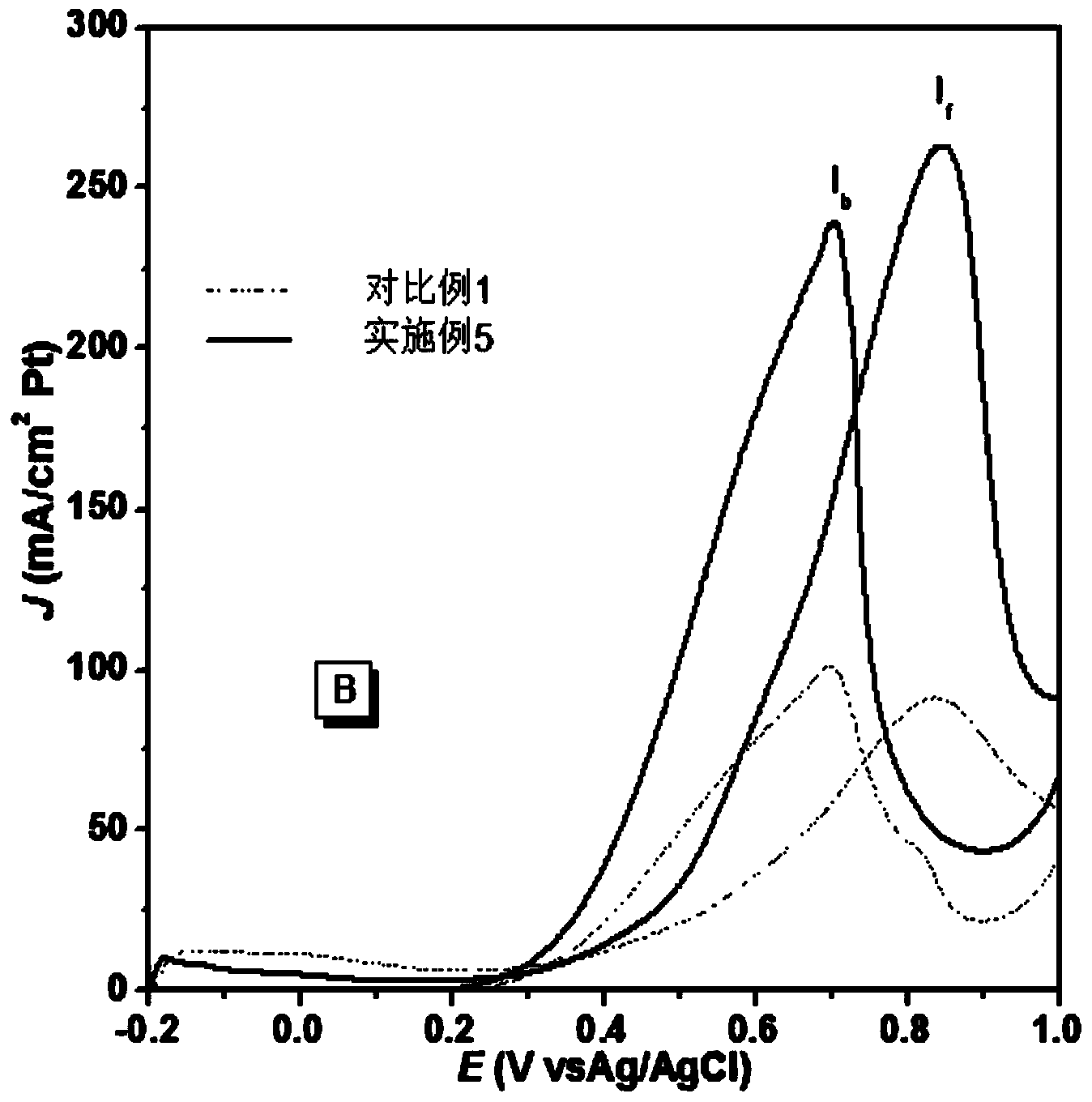
The invention relates to a method for depositing nano-silver in microfluidic channels. The method comprises the steps that ITO glass is pretreated, and ITO glass with (PDDA / PSS) n multilayer self-assembled films is prepared; the ITO glass serves as a substrate and is connected with a chip made of PDMS in an encapsulating mode to form a microfluidic chip, then a NaNO3 and AgNO3 mixed solution is injected into microfluidic channels, nano-silver is deposited in the microfluidic channels with chronoamperometry, and nano-silver surface morphology detection shows that nano-silver particles distributed evenly can be seen in the microfluidic channels. The method has the advantages of being quick, simple, high in repeatability, low in cost and the like, and has wide application prospects in the fields such as medical bio-engineering and medical biosensors.
Owner:DALIAN UNIVERSITY
Composite carbon fiber-loaded metal catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a composite carbon fiber-loaded metal catalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The composite carbon fiber-loaded metal catalyst is high in graphitization degree, good in catalyst metal particle dispersion performance and excellent in catalytic performance and is prepared by adopting a transitional metal oxide as a graphitization enhancer of a carbon material and a metal dispersion loading induction agent. The prepared composite carbon fiber material loaded with the transitional metal oxide is catalyzed through the transitional metal oxide under the high temperature condition to obtain a carbon material with a high graphitization degree, and the transitional metal oxide composite carbon fiber material is used as a catalyst carrier to be reduced by a reduction agent. The catalyst is high in initial electrochemical activity surface area and good in duration, and after the catalyst is cycled for 4500 times, the electrochemical active surface area sill can be maintained at 54 percent. The current density attenuation is reduced in a timing current-method electrochemical test of 120 minutes, the electrochemical activity is high, the current density is high, and the duration is excellent.
Owner:上海氢尚新能源科技有限公司
Apparatus and method for measuring concentration of whole blood samples
ActiveUS20160077037A1Reduce measurement errorEffectively and economically removing and minimizing hindranceImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical biosensorMeasurement device
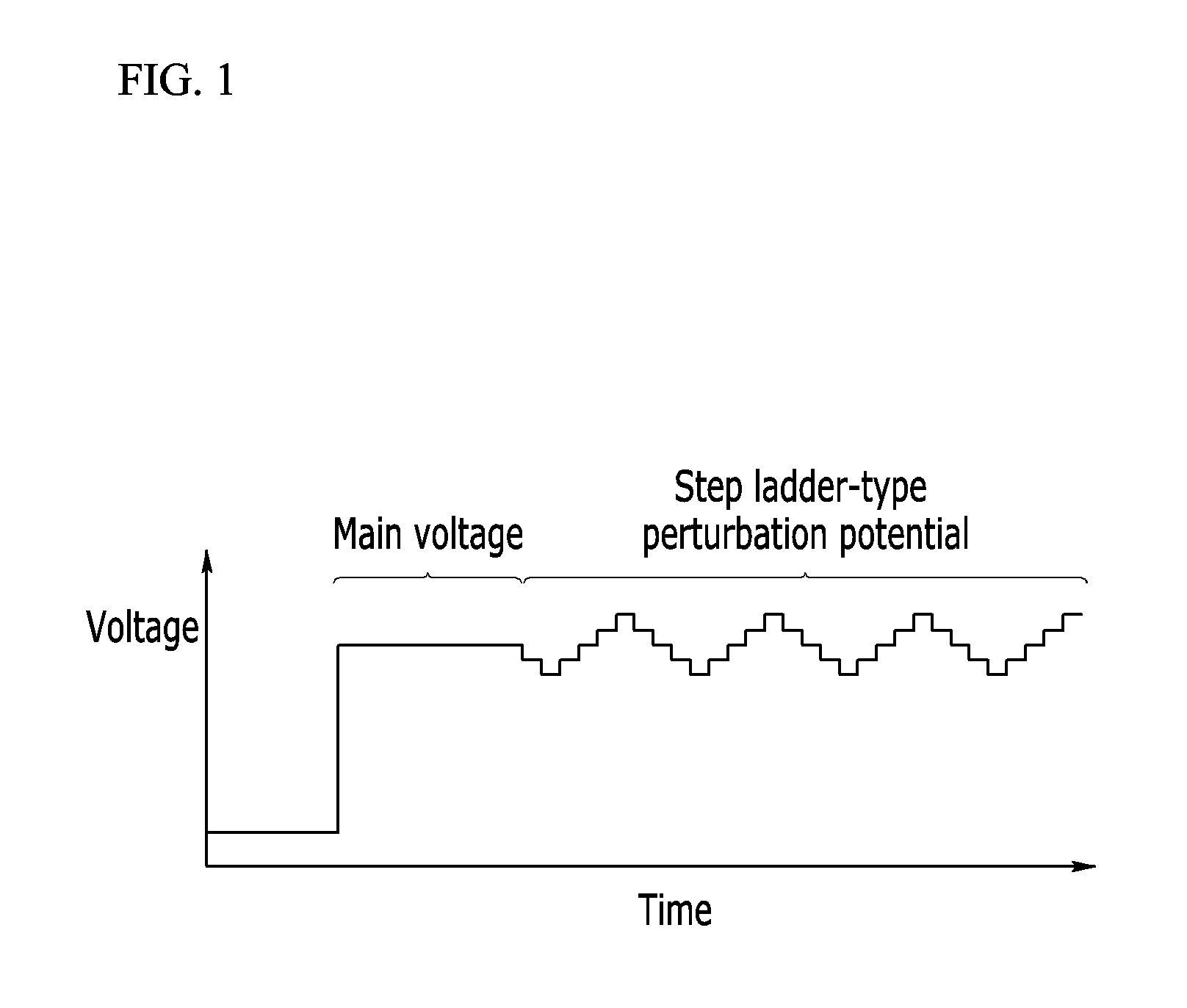
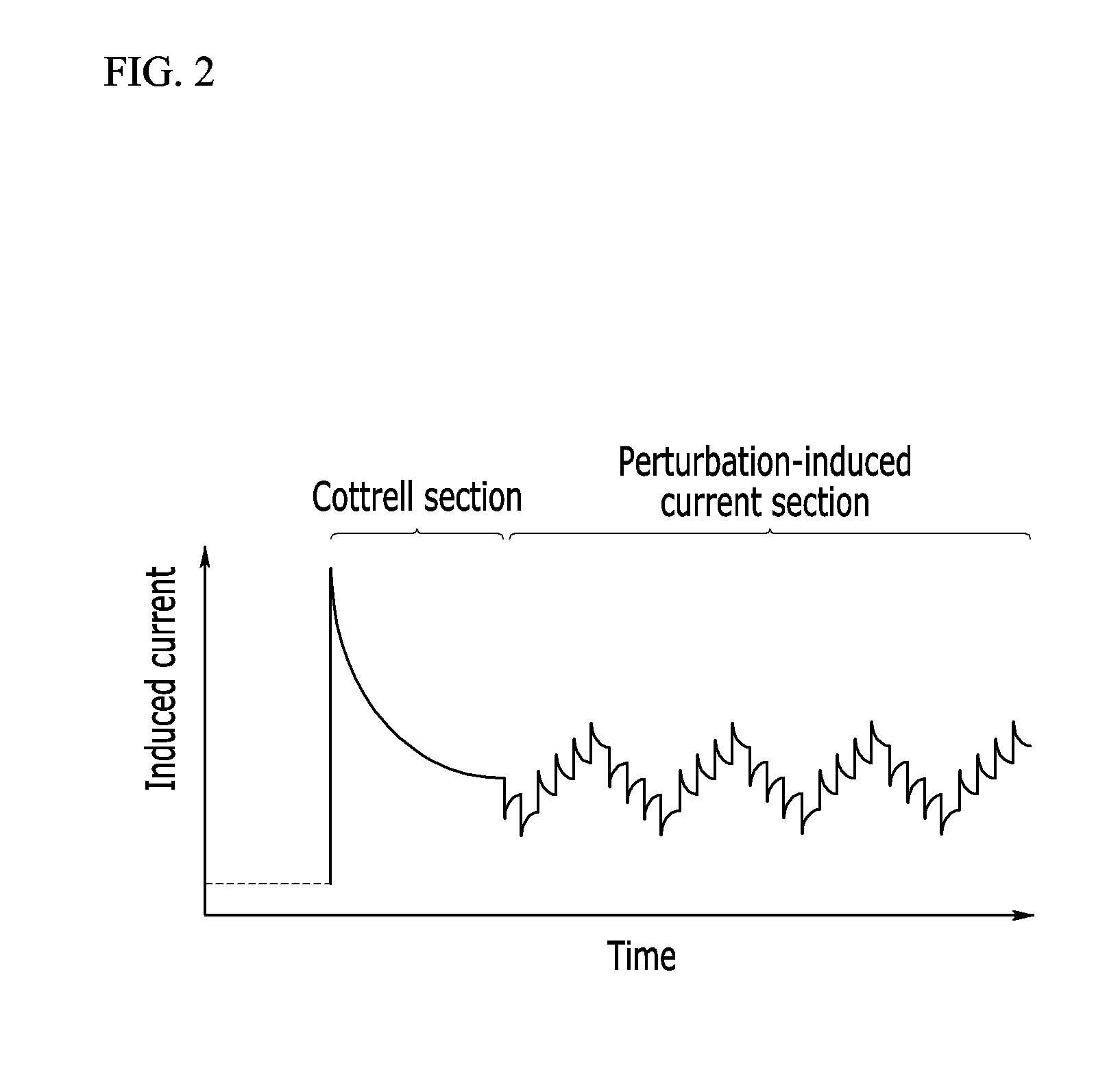
A method for measuring a concentration of an analyte in a bio-sample using an electrochemical bio-sensor according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention is characterized by a step of obtaining predetermined features from induced currents obtained by applying a DC voltage according to chronoamperometry in which, after a whole blood sample is injected to the electrochemical bio-sensor, a concentration of an analyte is obtained from an induced current obtained by applying a DC voltage for a certain time and from all induced currents obtained by further applying several step-ladder perturbation potentials for a short time subsequent to the DC voltage for the certain time, and is also characterized by minimization of a measurement error caused by a hindering material by forming a calibration equation by combining the at least one feature in a function and optimizing various conditions of the bio-sample through Deleted Texts multivariable analysis.With this configuration, a perturbation potential application method added to a conventional measurement method can maintain a bio-sensor and a measuring apparatus already used, a line used in the measuring apparatus, and calibration of amperometry as they are, improve accuracy in measurement by effectively minimizing a matrix interference effect of a background material in a bio-sample, particularly an inaccuracy caused by a change in hematocrit, and also remarkably improve accuracy in measurement by simply upgrading a measurement program of a conventional measuring apparatus.
Owner:I SENS INC
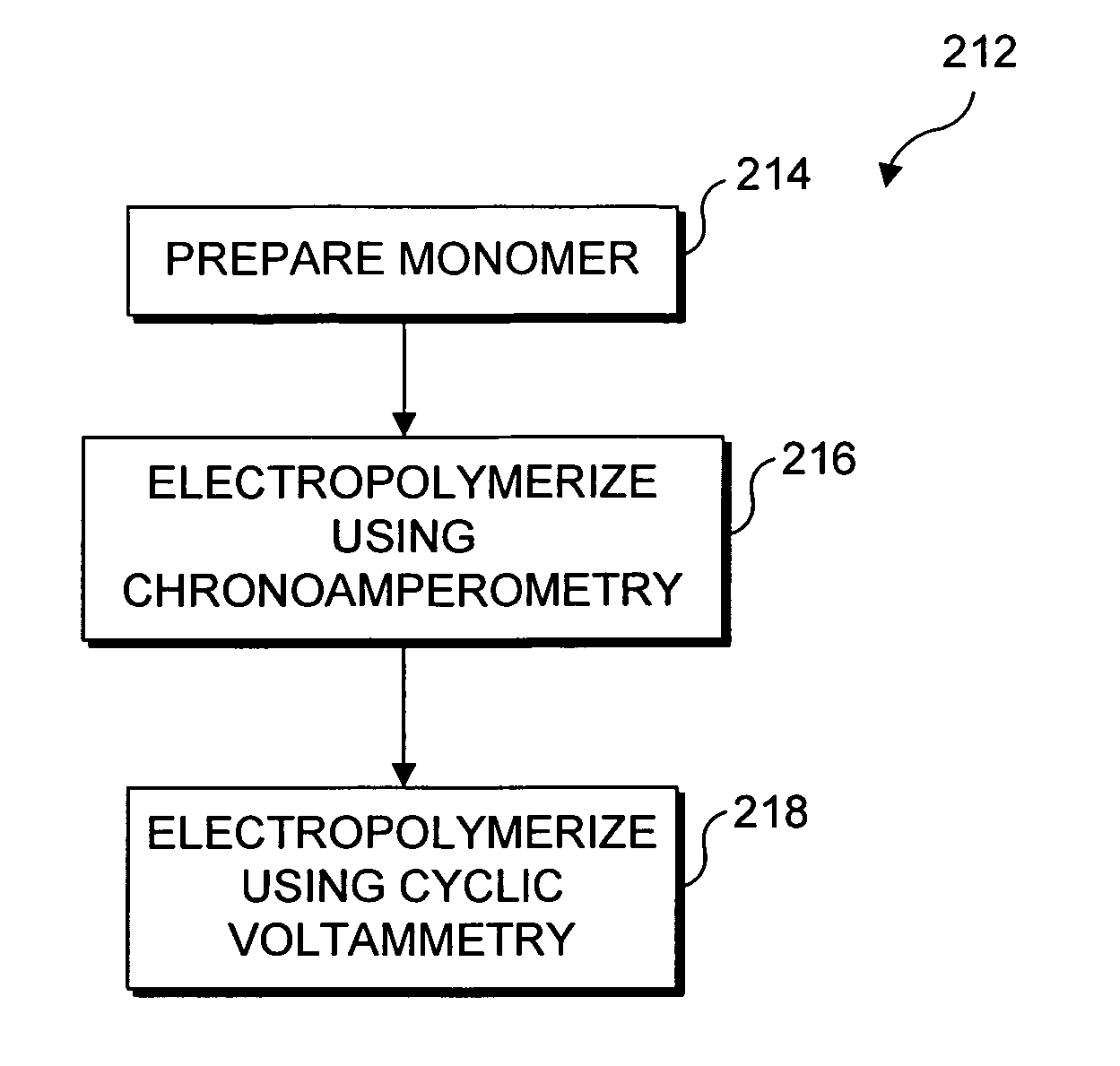
Electropolymerization of enhanced electrochromic (EC) polymer film
ActiveUS7450290B2High resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansTenebresent compositionsChronoamperometryPolymer thin films
Electropolymerization of EC monomers is employed to obtain an EC polymer film deposited on a substrate. A first embodiment of a method to produce the film employs cyclic voltammetry alone, while a second embodiment deposits a very thin homogeneous layer using chronoamperometry, and then cyclic voltammetry is employed to increase the density of the film. Another aspect of the present invention is directed to specific web like configurations for a grid of conductive material deposited onto a transparent substrate. The web like configuration is based either on concentric circles, or on concentric ellipses. Yet another aspect of the present invention is directed to an imaging system including a digital window that is disposed between a prism and a patterned analytic layer.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Au(111)-like nano-particle non-enzyme glucose sensor electrode, and preparation method and application of same
InactiveCN103399059AGood choiceGood detection characteristicsMaterial electrochemical variablesNitrogen gasHydrogen peroxide
The invention belongs to the technical field of electrochemical sensors, and in particular relates to an Au(111)-like nano-particle modified non-enzyme glucose sensor electrode, and a preparation method and application of the same. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, wiping a conductive substrate with alcohol, then, respectively performing ultrasonic washing with acetone, isopropyl alcohol and ultrapure water, adding the conductive substrate in the mixed liquor of deionized water, ammonia water and hydrogen peroxide, heating until boiling, finally, cleaning the conductive substrate with the ultrapure water and blowing the conductive substrate to dry with nitrogen; in the electrolyte solution composed of sodium perchlorate and chloroauric acid solution, firstly, performing electrolytic deposition on the conductive substrate by means of chronoamperometry, then, further performing electrolytic deposition on the conductive substrate by means of cyclic voltammetry, and cleaning the conductive substrate with the deionized water. The non-enzyme glucose sensor electrode is very sensitive to the concentration variation of the glucose and presents better linear relation, moreover, the non-enzyme glucose sensor electrode has better selectivity to the glucose, only needs 1.5s response time to the glucose and can achieve the detection limit of 5mu moL / L.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting hydrogen peroxide and nitrite by electrochemical sensor based on dual-metal porphyrin coordination polymer
InactiveCN104897765AUnique bimetallic electrocatalytic activityImprove electrocatalytic performanceMaterial electrochemical variablesNitritePorphyrin
The invention discloses a method for detecting hydrogen peroxide and nitrite by an electrochemical sensor based on a dual-metal porphyrin coordination polymer. A dual-metal porphyrin coordination polymer (CoTCPP-Cu or CoTCPP-Cu / CNTs) composite material modification electrode is used as a working electrode; hydrogen peroxide or nitrite is detected by a timing current method; CoTCPP-Cu is a coordination polymer assembled by dual metals Co and Cu and tetra-(p-carboxyphenyl) porphyrin. The electrochemical sensor adopted in the method is a current type sensor, has unique dual-metal activity and is high in sensitivity; the method has the advantages of convenience in detection and wide application range; the detection limit for hydrogen peroxide can reach 5.0*10<-7>M and the detection limit for nitrite can reach 2.5*10<-6>. The detection method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of quick on-site detection, high sensitivity, low cost and the like.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for depositing nanogold in microfluidic pore passage
ActiveCN106198659ALow costGood repeatabilityLaboratory glasswaresMaterial electrochemical variablesMultilayer membraneBiomedical sensors
The invention relates to a method for depositing nanogold in a microfluidic pore passage. ITO glass provided with a (PDDA / PSS)n self-assembled multilayer membrane is prepared by carrying out pretreatment on ITO glass, the prepared ITO glass is taken as a substrate and is sealed with a chip made from PDMS to form a microfluidic chip, then mixed solution of KAuCl4 and H2SO4 is injected into the microfluidic pore passage, nanogold is deposited in the microfluidic pore passage by virtue of a chronoamperometry, and nanogold surface topography detection shows that uniformly distributed nanogold particles can be seen in the microfluidic pore passage. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of rapidness, simplicity, good repeatability and low cost and has a broad application prospect in the fields of medical biology engineering, biomedical sensors and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Band-shaped carbon-carrier metal catalyst, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103227336AHigh catalytic activityImprove catalytic stabilityCatalyst carriersCell electrodesHigh current densityBand shape
The invention discloses a carbon-carrier precious metal catalyst for fuel cell, a preparation method thereof and an application thereof. The catalyst uses band-shaped nanometer carbon as the carrier, sodium borohydride, methanol or glycol as a reducing agent, and co-reduces the band-shaped nanometer carbon and the precious metal acid or the precious metal salts to obtain the precious metal / band-shaped nanometer carbon catalyst for the fuel cell, preferably a platinum loading amount being 10-60 wt %. The catalyst is high in initial electrochemical active surface area, relatively small in current density attenuation during a chronoamperometry test, and relatively high in current density during an electrochemical timing current test compared with that of present catalysts, and shows relatively high electrochemical activity, relatively high current density and relatively excellent electrochemical stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Nano-cone structure composite for capturing cancer cells, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107177553AAchieve dopingSimple methodBiomass after-treatmentTumor/cancer cellsCancer cellPolypyrrole
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical biomaterials, and discloses a nano-cone structure composite for capturing cancer cells, and a preparation method and application thereof. The method includes: electrodepositing chlorine-doped polypyrrole on the surface of a conductive substrate by the aid of chronoamperometry; selecting a three-electrode pattern to deposit polypyrrole / biotin material with nano-cone structure on a working electrode by the aid of chronopotentiometry by using a conductive metal as a counter electrode, the polypyrrole-deposited conductive substrate as the working electrode and a buffer solution containing pyrrole and biotin as an electrolyte; activating the working electrode deposited the polypyrrole / biotin material with nano-cone structure, culturing in streptavidin solution, performing grafting reaction with antibodies, and culturing in BSA (bull serum albumin) solution to obtain the nano-cone structure composite. The method is simple and low in cost, the nano-cone structure in the composite is stable, and cancer cells can be effectively captured and nondestructively released.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Supercapacitor electrodes
The present invention relates to a method of producing an electrodeposited metal oxide coating for a supercapacitor electrode. The present invention relates to the chronoamperometric electrodeposition of the metal oxide over a period from a few seconds, up to about 30 seconds leading to superior performance as a result of an increased surface area of the deposit. According to the present invention, the capacitances achieved are typically greater than 1300 F / g, and in some instances, over 4000 F / g.
Owner:NEWCASTE INNOVATION LTD
Method for testing hydrogen peroxide in cell based on horseradish peroxidase-attapulgite nanometer composite material
InactiveCN102147389AGood electrochemical propertiesImprove electrocatalytic performanceNanotechnologyMaterial electrochemical variablesH2O2 - Hydrogen peroxideNanocomposite
The invention relates to a method for testing hydrogen peroxide in a cell based on a horseradish peroxidase-attapulgite nanometer composite material; the method comprises the following steps: horseradish peroxidase is adsorbed on the surface of purified attapulgite so as to prepare the horseradish peroxidase-attapulgite nanometer composite material; a dispensing method is used for applying the composite material to the surface of a glassy carbon electrode so as to construct a horseradish peroxidase-attapulgite nanometer composite material biological sensor; the sensor is used as a working electrode; and a chronoamperometry is used for detecting H2O2 in the cell. The biological sensor adopted by the method for testing the hydrogen peroxide in the cell has good electrical catalytic activity on hydrogen peroxide, can be applied to the detection of H2O2 in the cell and has the advantages of fast response, wide linear range, low detection limit, good repeatability and the like; and a new electrochemistry method based on enzyme sensing for detecting H2O2 in the cell is established.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Electrochemical reduction-oxidation graphene modified electrode and application thereof in detection of heavy metal sexivalent chromium ions in water thereof
InactiveCN108732216AMeet the controllabilityIncreasing the thicknessMaterial electrochemical variablesLinear sweep voltammetryMaterials science
The invention relates to an electrochemical reduction-oxidation graphene modified electrode and application thereof in detection of heavy metal sexivalent chromium ions in water thereof. The modifiedelectrode is prepared by directly depositing electrochemical reduction-oxidation graphene on the surface of a working electrode. The sexivalent chromium ions are detected by using chronoamperometry, linear sweep voltammetry or cyclic voltammetry, the graphene modified electrode serves as a working electrode, an Ag / AgCl electrode serves as a reference electrode, a platinum electrode serves as the counter electrode, and experimental parameter setting is detected. The graphene modified gold electrode serves as the working electrode, the electrode preparation process is simple and convenient, andthe prepared electrode has high electrochemical activity, is capable of realizing rapid detection Cr (VI), wide in detection range (5-2000ug / L) and low in lower limit of detection (0.5 ug / L), has theadvantages of resistance to interference of other metal ions, stability, short detection cycle and the like, and is expected to be applied to actual portable detection application in future.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Electrochemical CF (Carbon Fiber) surface modification method
InactiveCN102002847AImprove microbial fixation performanceIncrease the amount of fixationAnodisationElectrolysis componentsFiberTreatment field
The invention belongs to the fieldss of electrochemistry and fiber materials. In the invention, anodic oxidation treatment or surface electropolymerization treatment are carried out on CF by adopting a chronoamperometry method in an external electric field under an external voltage of 0.5-6 V at a reaction temperature of 20-35 DEG C for a reaction time of 5-150 s. In case of the anodic oxidation treatment, acid, alkali or ammonium salt is adopted as an electrolyte which has the concentration ranging from 0.1-5mol / L. In case of the surface electropolymerization treatment, maleic anhydride is adopted as an elemental solution which has the concentration of 0.1-2mol / L. In the invention, by modifying the CF surface through anodic oxidation or surface electropolymerization, the surface oxygen content and the roughness of the CF surface are improved so that the hydrophilicity and the microbial affinity of the CF surface are improved and the applications of the CF as a biofilm carrier to the sewage treatment field by using a biofilm method are facilitated.
Owner:SICHUAN CITY TRACK TRAFFIC MATERIAL +1
Universal portable detector for electrochemical biosensor
InactiveCN101661015AHighly integratedCompact structureMaterial electrochemical variablesMicrocontrollerElectrochemical biosensor
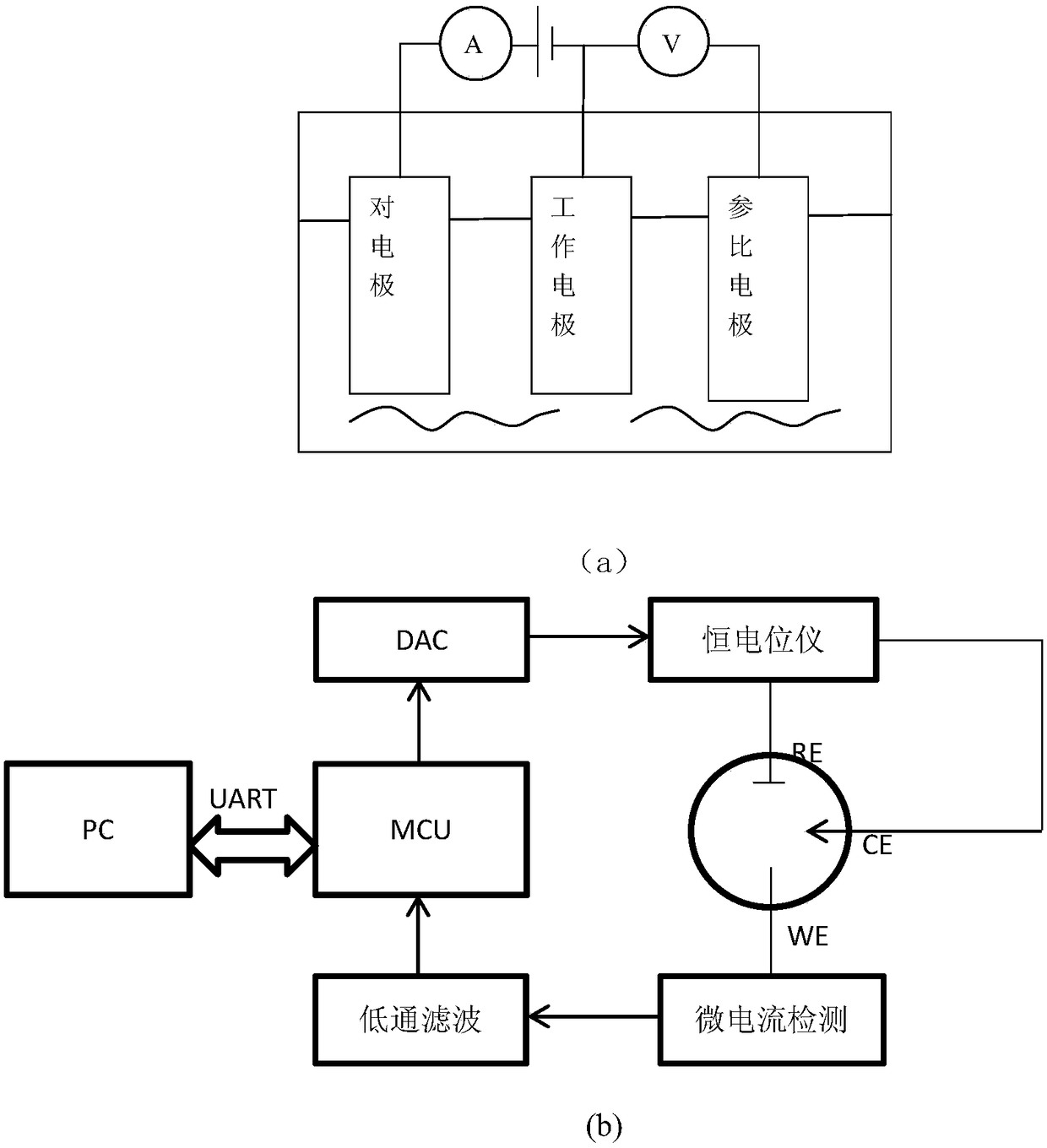
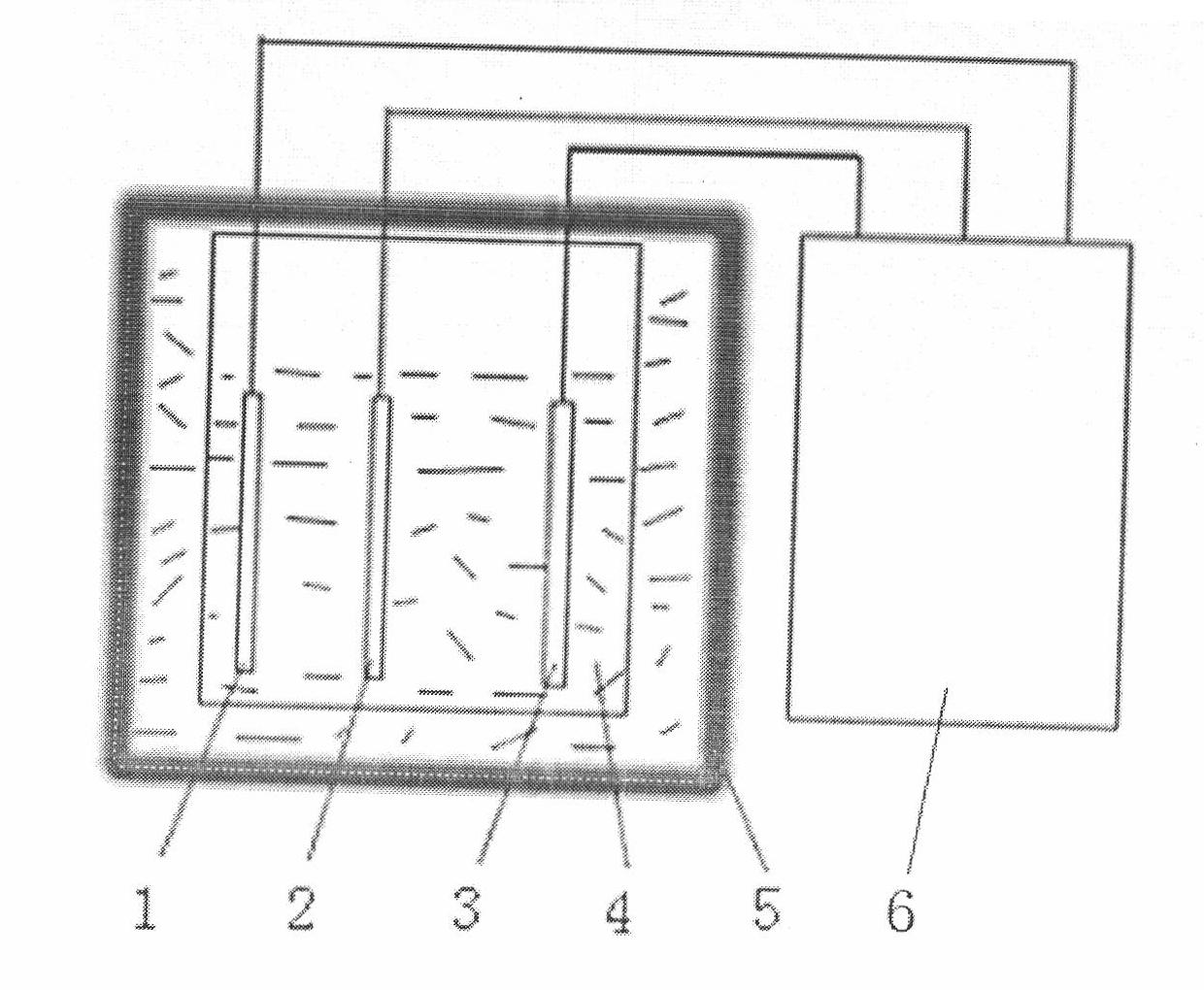
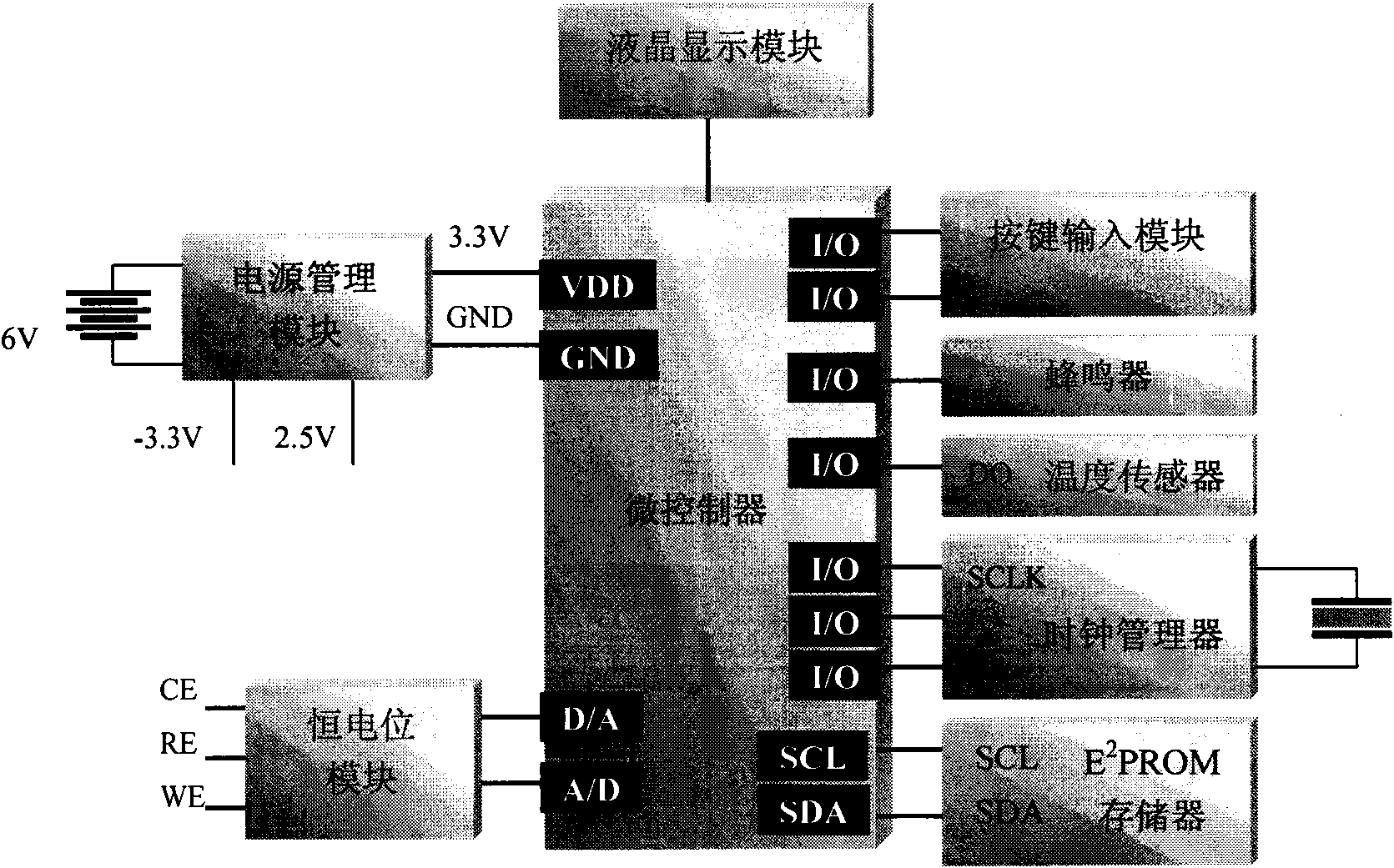
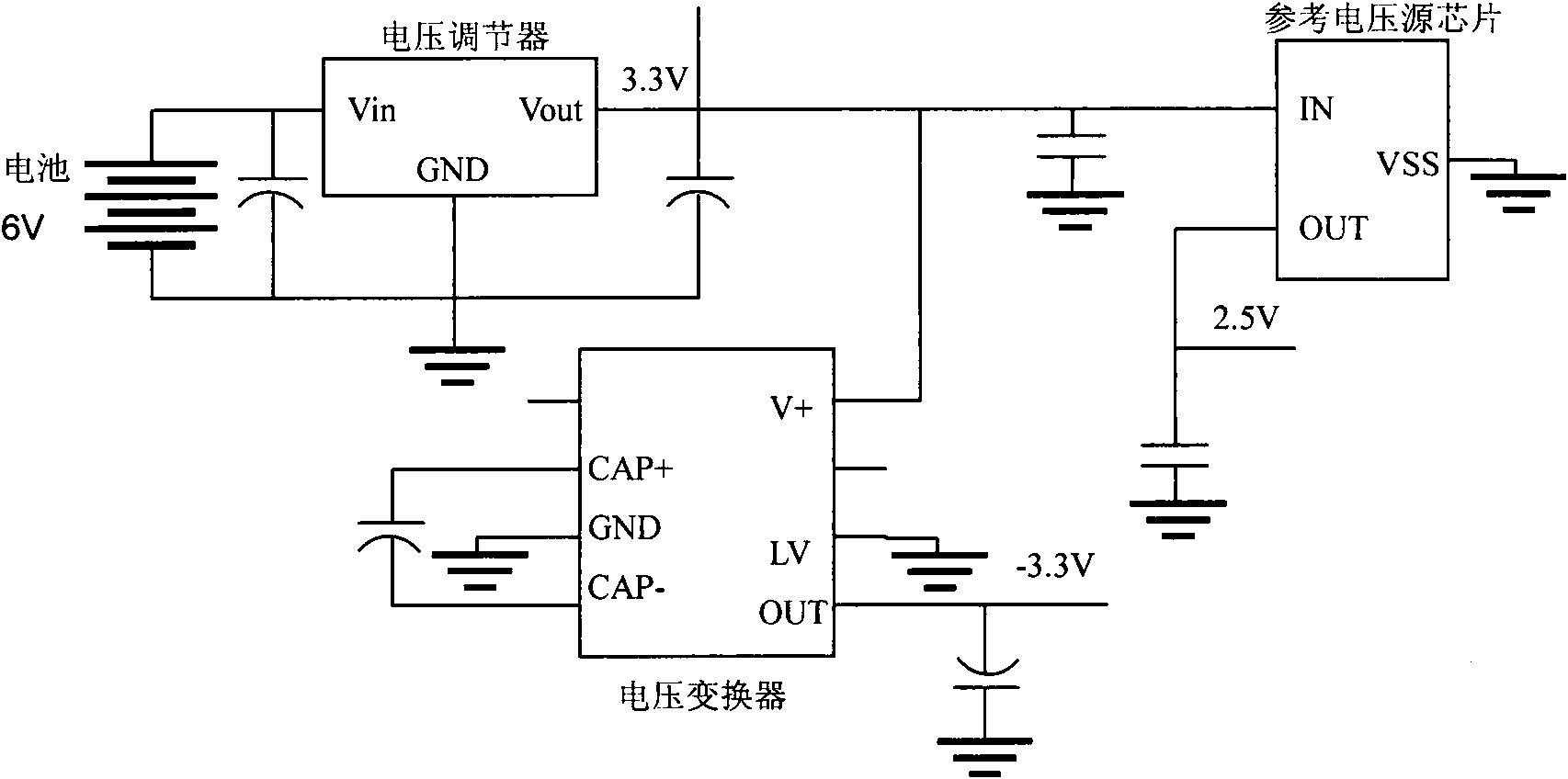
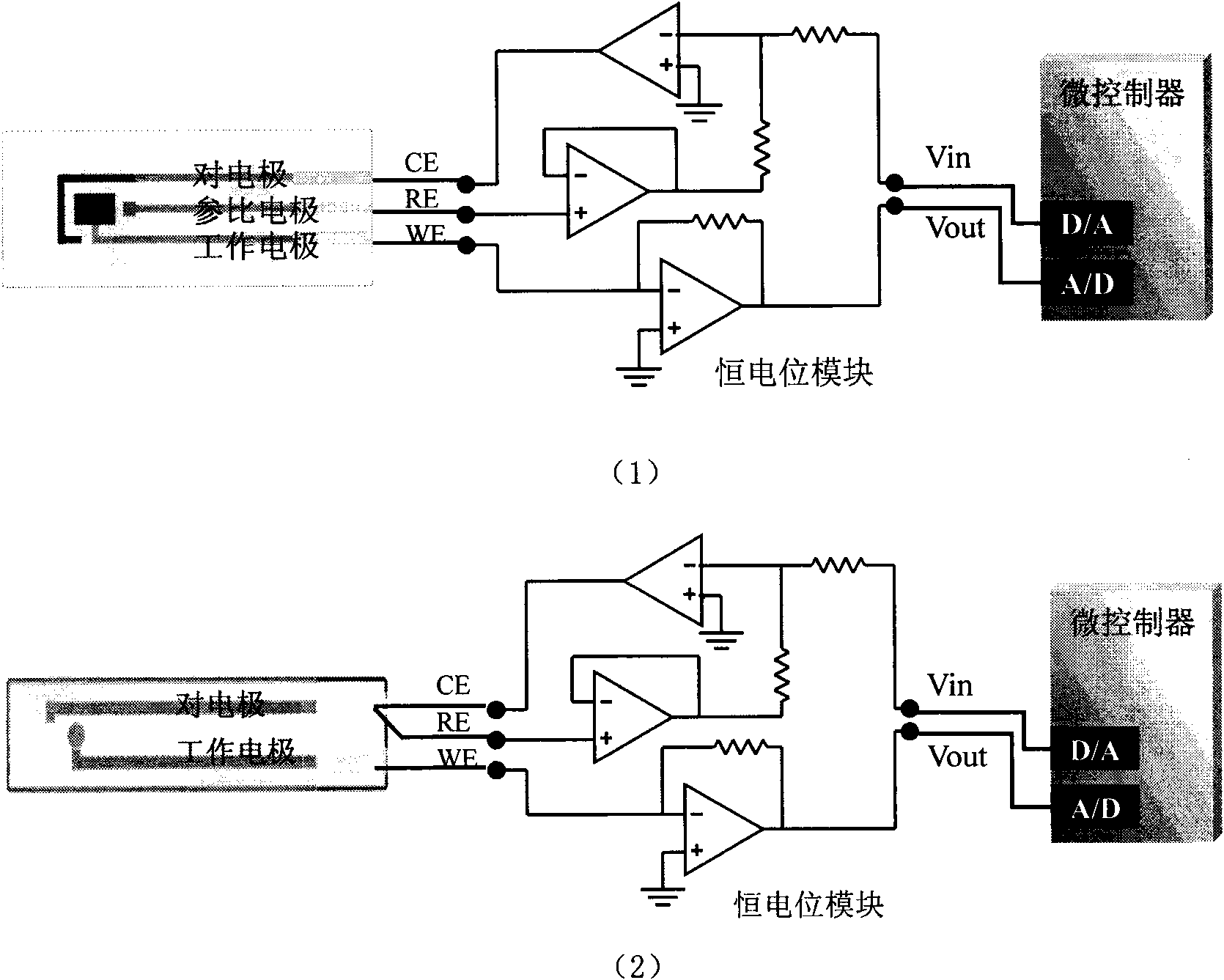
A universal portable detector for an electrochemical biosensor takes a microcontroller integrating functions of digital-to-analog conversion and analog-to-digital conversion together as a core, wherein, a peripheral circuit comprises a power management module, a constant potential module, an E<2>PROM memory, a clock manager, a temperature sensor, a buzzer, a keypad input module and an LCD module;and the universal portable detector can be matched with the common varied electrochemical biosensors with a three-electrode system or a two-electrode system, particularly a chip of the small-sized orminiature electrochemical biosensor to realize chronoamperometry, chronocoulometry and multiple voltammetry detection functions, and meanwhile the detector can perform temperature correction on a detection result. The universal portable detector takes high integration level, low power consumption and practicability as a design principle; the detector has small volume and convenient power supply with a battery, thus having portability; and the detector is applicable to on-spot analysis in the fields such as medical detection, food security, environmental protection and the like, thus meeting the requirement for fast detection.
Owner:上海睿兴实业有限公司 +1
Method for rapidly corroding and patterning indium tin oxide surface by using electrochemical technology
InactiveCN102691093AEasy to operateAccelerated corrosionPhotomechanical apparatusChronoamperometryIndium tin oxide
The invention relates to a method for rapidly corroding and patterning an indium tin oxide (ITO) surface by using an electrochemical technology, belonging to the fields of electrochemistry and micro-nanotechnologies. Aiming at the problem of the traditional ITO-corroding method, the method for rapidly corroding and patterning the indium tin oxide surface by using the electrochemical technology, provided by the invention, comprises the steps as follows: (1) washing the ITO surface; (2) pressing a used photoresist into a protective film on an ITO substrate by using a plastic-envelop machine, directly placing a mask of a used pattern, performing ultraviolet exposure and developing, and forming and washing to form a needed pattern; (3) corroding exposed ITO part of the photoresist on the ITO surface with diluted hydrochloric acid as a corrosive liquid by using cyclic voltammetry or chronoamperometry and the electrochemical technology; and (4) washing an electrochemically corroded ITO glass sheet by using an alkali solution, removing a protective photoresist film; and drying by using N2 to obtain a patterned ITO surface. The method for rapidly corroding and patterning the indium tin oxide surface by using the electrochemical technology has the advantages of simplicity in operation, high speed, good corrosive effect, clearness of borders, low cost and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method of measuring copper ion concentration in industrial electrolytes
InactiveUS20030183539A1High selectivityGood reproducibilityWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementHigh concentrationPlatinum
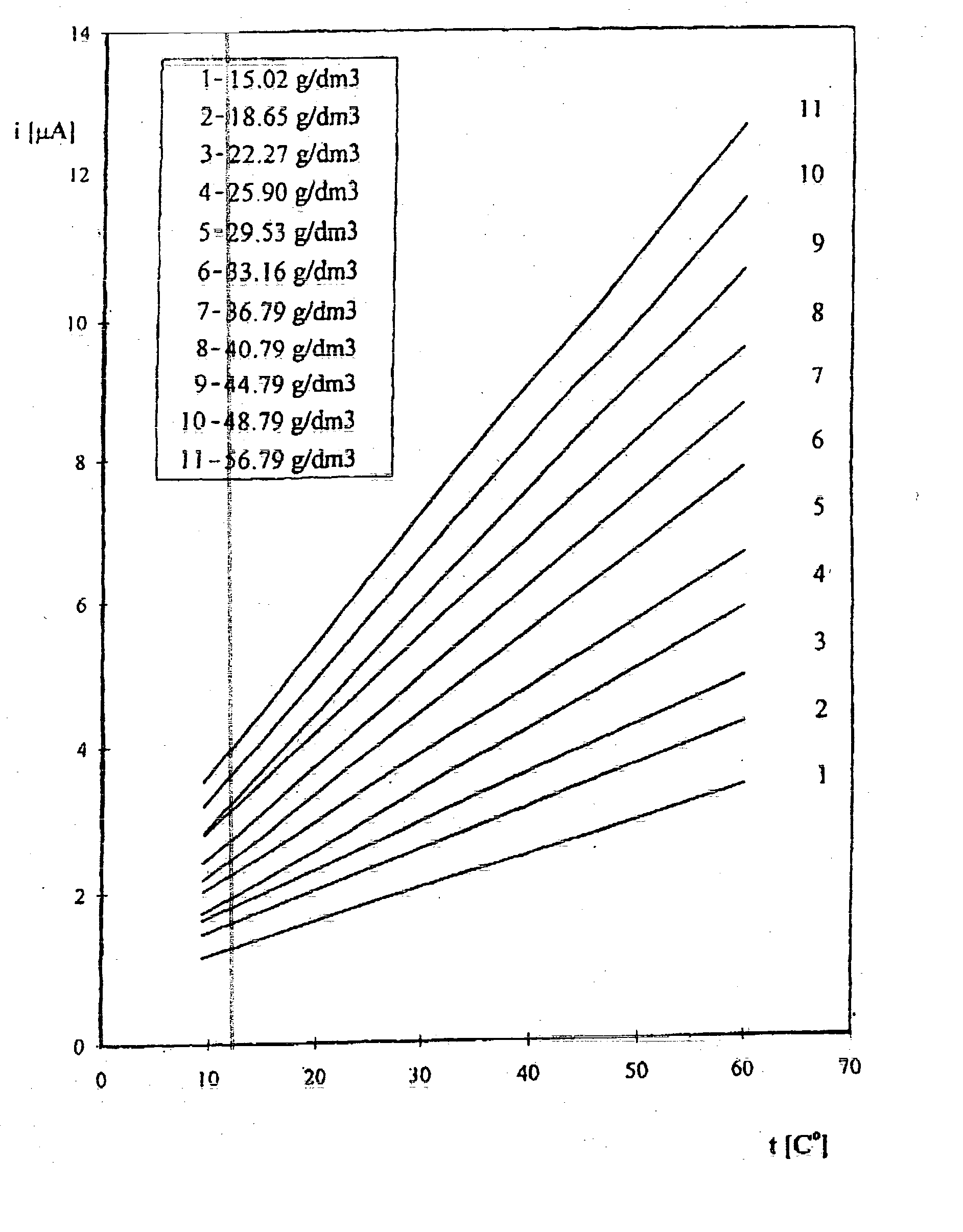
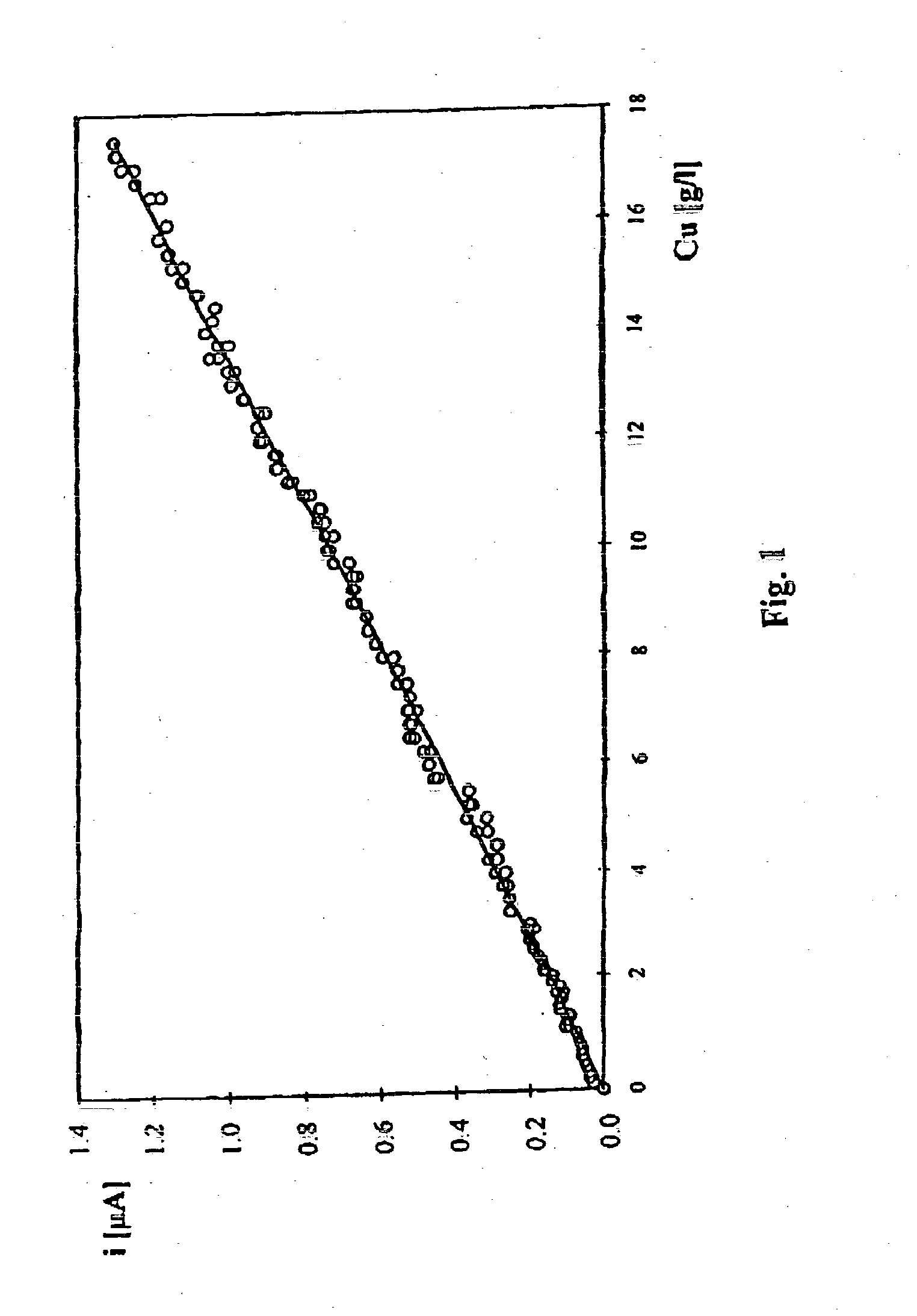
The method consists in registering curves by cyclic voltammetry method in the range of copper ion concentration up to 20 g / l or alternately by chronoamperometric method in the range of concentration from 20 to 60 g / l. A platinum or gold microprobe of a diameter in the range from 1 to 50 um and a copper plate reference electrode are used. The value of current density read off from said curves is compared to the calibration curves previously determined by standard additions method. For high concentration in the range from 20 to 60 g / l the calibration curves obtained in the range of temperatures from 15 to 60° C. are registered.
Owner:K G H M POLSKA MIEDZ SPOKA AKCYJNA
Preparing method for graphene oxide composite coating on surface of magnesium alloy
ActiveCN105350049AImprove corrosion resistanceEasy to operateElectrolytic coatingsElectrolytic agentOxide composite
The invention discloses a preparing method for a graphene oxide composite coating on the surface of a magnesium alloy. The preparing method includes the steps that firstly, a magnesium alloy matrix is preprocessed; then, graphene oxide is prepared and dissolved into a 1-5 ml / L triethanolamine water solution and is subjected to ultrasonic dispersing for 2 hours to serve as an electroplating electrolyte; afterwards, a CHI860D type electrochemical workstation is used for assembling a three-electrode system, the preprocessed magnesium alloy serves as a study electrode, a platinum electrode serves as an auxiliary electrode, a saturated calomel electrode serves as a reference electrode, and the chronoamperometry is selected for conducting electrochemical deposition on the magnesium alloy; and finally, the magnesium alloy is taken out to be dried for 1-2 hours at the temperature ranging from 60 DEG C to 70 DEG C, and the graphene oxide composite coating on the surface of the magnesium alloy is obtained. The method is easy to operate, the surface of the obtained composite coating is even and flat, a typical crumple structure of the graphene oxide exists, low corrosion current density and high electrochemical resistance are achieved, and corrosion resistance of the magnesium alloy can be well improved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots with high dispersion in water phase and application
ActiveCN108037171AThe synthesis process is simpleReduce riskFluorescence/phosphorescenceMaterial electrochemical variablesQuantum yieldElectrolysis
The invention discloses a preparation method of nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots with high dispersion in a water phase and an application. The preparation method comprises the following steps: anaqueous solution of tetrabutylammonium hydroxide is used as an electrolyte; a graphite rod with high purity is used as a working electrode, a platinum wire electrode is used as a counter electrode, acalomel electrode is used as a reference electrode, and fixed potential chronoamperometry is used for electrolysis of the graphite rod; an electrolytic solution is filtered in order to remove a graphene slice layer, a dialysis bag is used for dialysis, in order to obtain the nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots with high dispersion in a water phase. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process, cheap and easily available raw materials, and short preparation time; the nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots have the characteristics of good dispersion in water phase, long fluorescentlifetime, high quantum yield, good biocompatibility, and the like; and the nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots have good application prospects in the fields of fluorescence detection of life samplesand imaging.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Electropolymerization of enhanced electrochromic (EC) polymer film
ActiveUS20070188845A1Increase horizontal resolutionHigh resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansTenebresent compositionsChronoamperometryConductive materials
Electropolymerization of EC monomers is employed to obtain an EC polymer film deposited on a substrate. A first embodiment of a method to produce the film employs cyclic voltammetry alone, while a second embodiment deposits a very thin homogeneous layer using chronoamperometry, and then cyclic voltammetry is employed to increase the density of the film. Another aspect of the present invention is directed to specific web like configurations for a grid of conductive material deposited onto a transparent substrate. The web like configuration is based either on concentric circles, or on concentric ellipses. Yet another aspect of the present invention is directed to an imaging system including a digital window that is disposed between a prism and a patterned analytic layer.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Method for detecting glucose based on cobalt-based metal organic framework enzyme-free glucose sensor
ActiveCN111537589AAccurate detectionThe detection process is fastPreparing sample for investigationMaterial electrochemical variablesGlucose sensorsConcentrations glucose
The invention relates to a method for detecting glucose based on a cobalt-based metal organic framework enzyme-free glucose sensor. The method is carried out by adopting the cobalt-based metal organicframework enzyme-free glucose sensor, and comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a three-electrode system by taking the cobalt-based metal organic framework enzyme-free glucose sensor as a working electrode; (2) fitting and drawing a calibration curve according to a current response value corresponding to glucose concentration; 3) determining the content of glucose in the to-be-determined solution. The method is based on the cobalt-based metal organic framework enzyme-free glucose sensor, and an electrochemical workstation and a three-electrode system are adopted for detection, so rapid and accurate detection of glucose is achieved through a chronoamperometry. The detection method is high in detection speed, stable current can be achieved within 5 seconds, and operation is easy and convenient. The detection limit is low (1.6 [mu]M), the linear range is wide (5-900 [mu]M), the influence of temperature and pH is avoided, the detection range is wide, and the sensitivity can reach 169 [mu]A*mM<-1>*cm<-2>.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
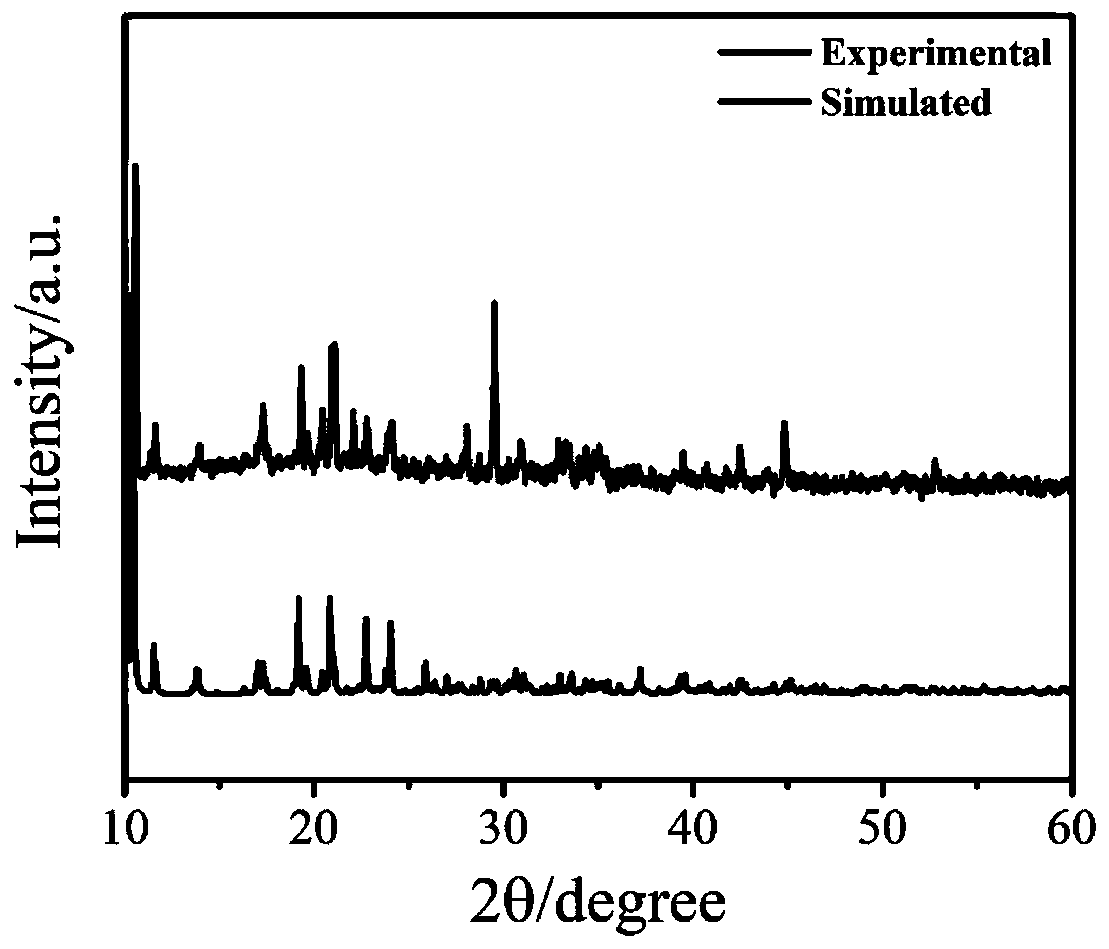
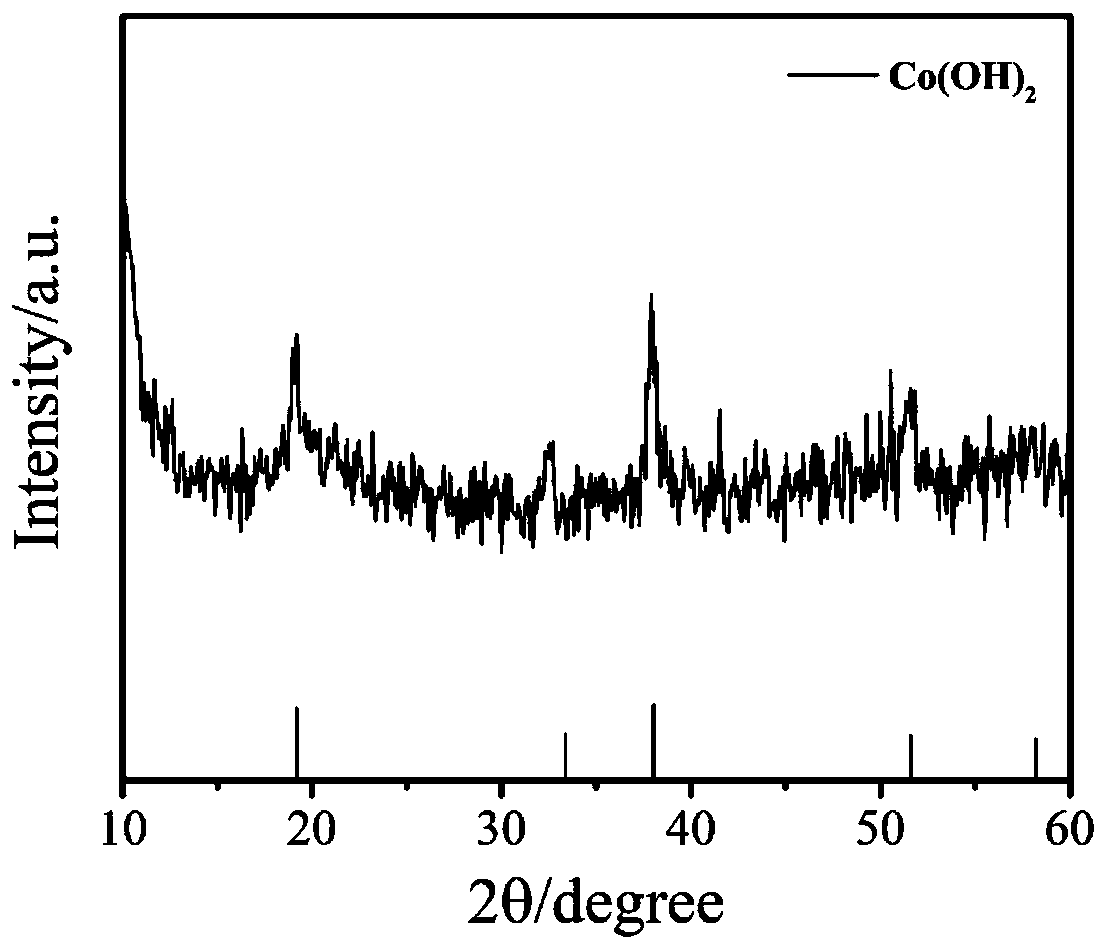
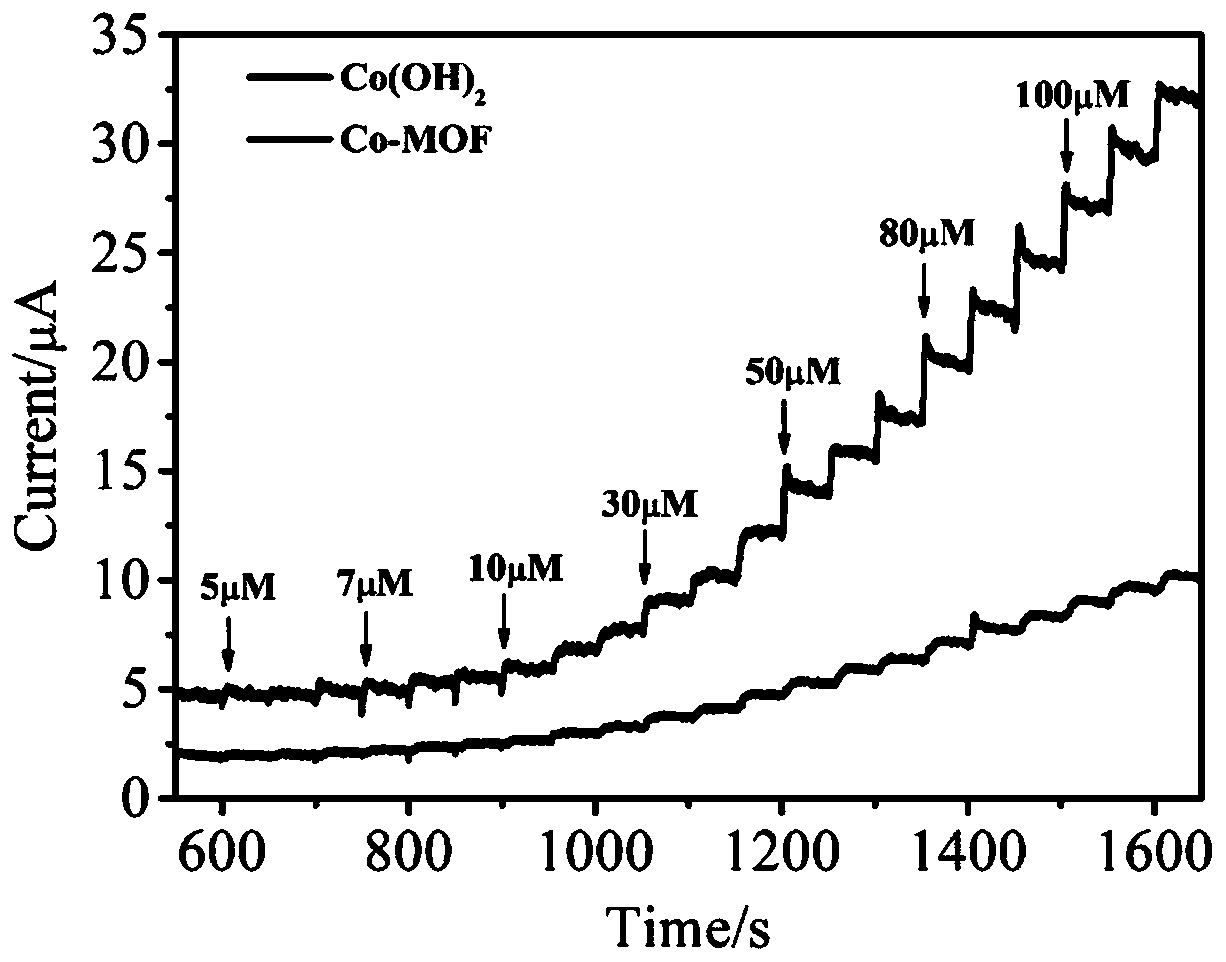
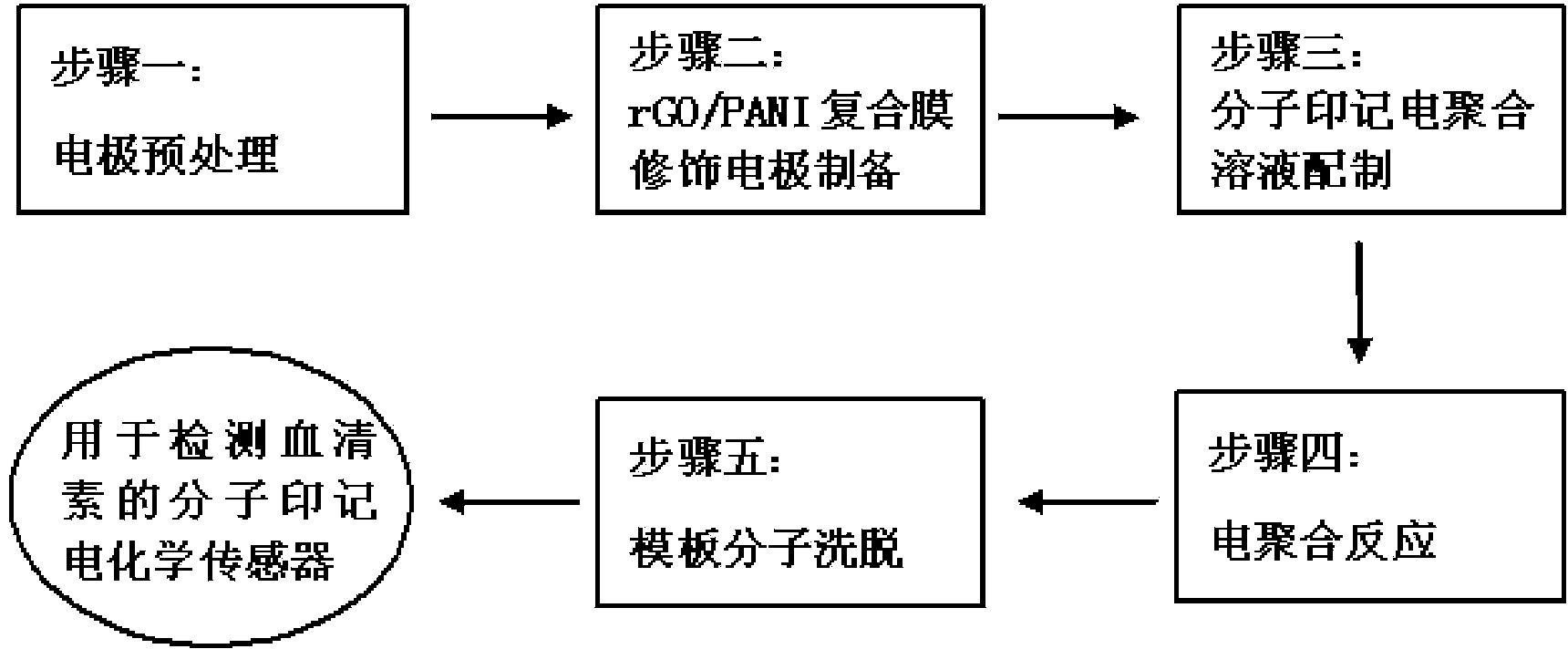
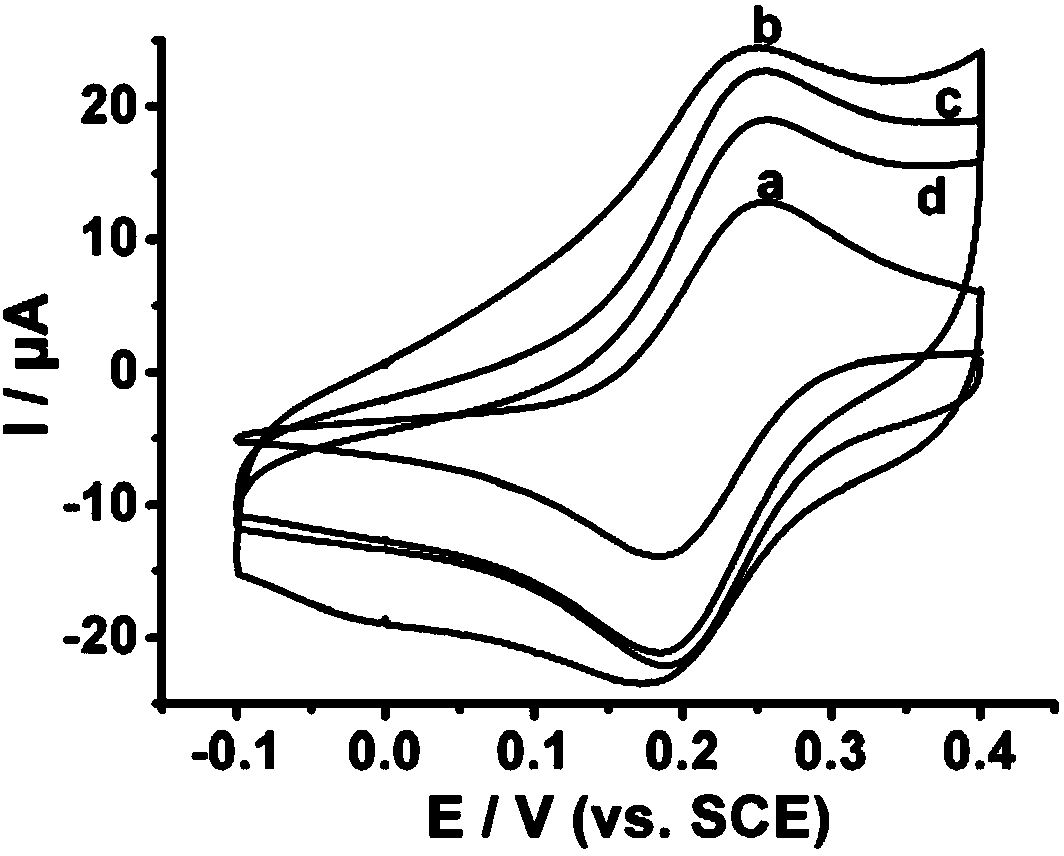
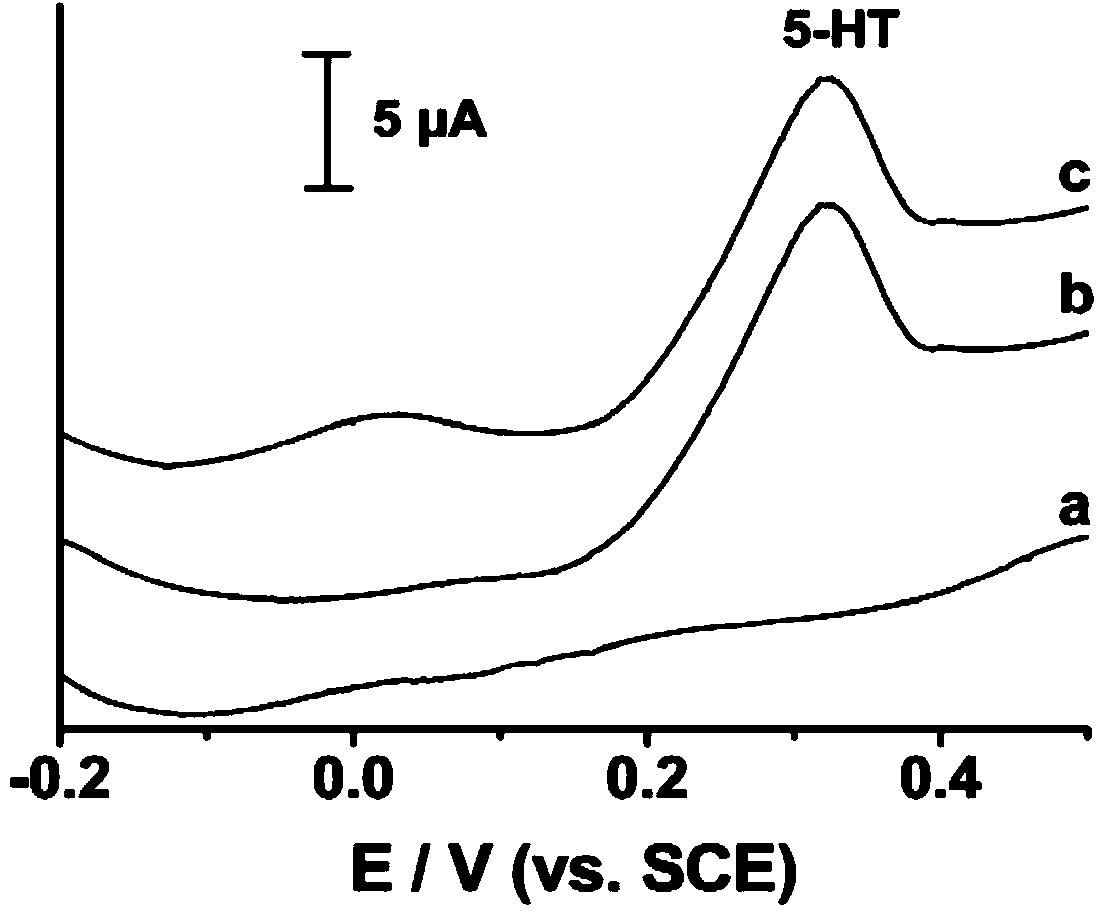
Preparation method of molecular imprinting electrochemical sensor for detecting serotonins
InactiveCN103884748AImprove conductivityHigh selectivityMaterial electrochemical variablesComposite filmPhosphate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a molecular imprinting electrochemical sensor for detecting serotonins. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out polishing and washing pre-treatment on a glassy carbon electrode; preparing a sulfuric acid solution containing rGO; adding aniline and mixing sufficiently to prepare an electric polymerization solution; immersing the glassy carbon electrode into the electric polymerization solution and carrying out electric polymerization reaction; reacting and drying to obtain an rGO / PANI composite film modified electrode; preparing a PBS (Phosphate Buffer Solution) containing functionalized gold nano grains, amino thiophenol and the serotonins and standing the solution to obtain a molecular imprinting self-assembling solution; inserting the rGO / PANI composite film modified electrode into the molecular imprinting self-assembling solution; carrying out the electric polymerization reaction by using a chronoamperometry; and immersing the electrode into the sulfuric acid solution to be treated to obtain the molecular imprinting electrochemical sensor for detecting the serotonins. According to the preparation method, the electrical conductivity of the surface of the electrode is improved by the sensor, the detection sensitivity and the selectivity to the serotonins are improved, and the sensitivity of the molecular imprinting sensor is enhanced.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
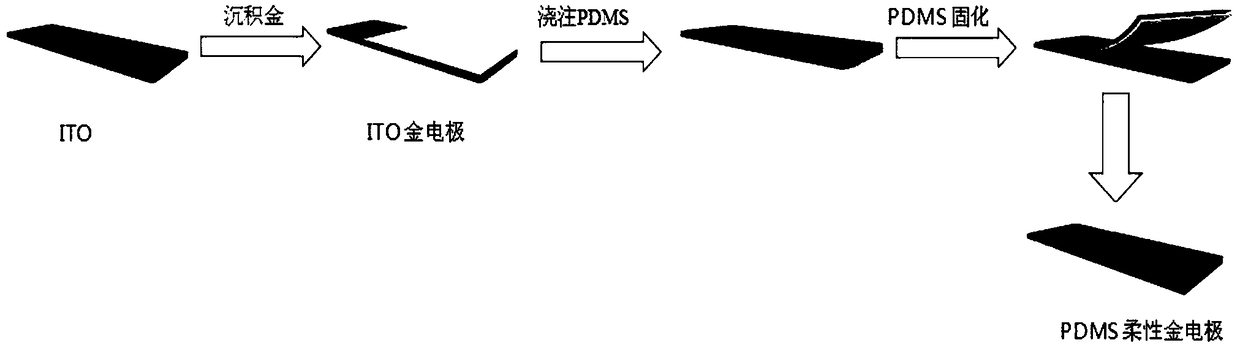
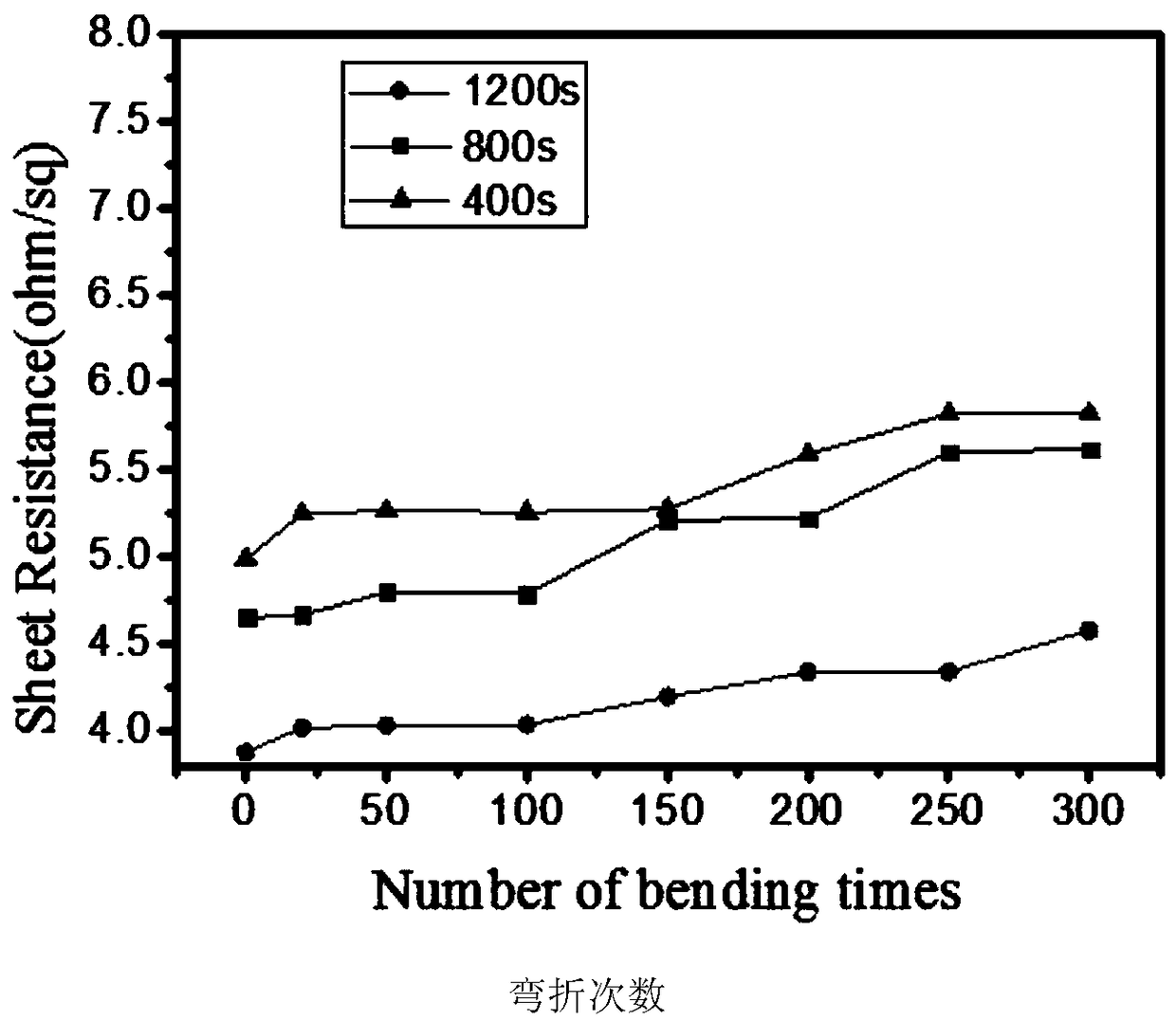
Flexible electrode based on flower-like nanogold structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108982632AImprove conductivityImprove tensile propertiesMaterial electrochemical variablesElectronMaterials science
The invention relates to a flexible electrode based on a flower-like nanogold structure and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of electronic materials. The flexible electrode is characterized in that ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) glass is self-assembled layer by layer, electrochemical gold deposition is carried out on the assembled ITO glass by adopting chronoamperometry, alayer of golden flower-like nanogold will deposit on the ITO glass after the electrochemical deposition, and the golden flower-like nanogold depositing on the ITO glass is called ITO-Au; used electrolyte is a KAuCl4 and H2SO4 mixed solution, a reference electrode is an Ag / AgCl electrode, a counter electrode is a platinum wire, and a working electrode is the assembled ITO glass; the ITO glass requires to be cleaned before assembling. A cleaning process is characterized by carrying out ultrasonic cleaning by respectively using deionized water, acetone and ethanol. The flexible electrode preparedby the invention has lower square resistance, and good electrical conductivity still can be kept after bending for many times and stretching for many times.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Dendritic nano silver structure-based flexible film pressure sensor and preparation method thereof
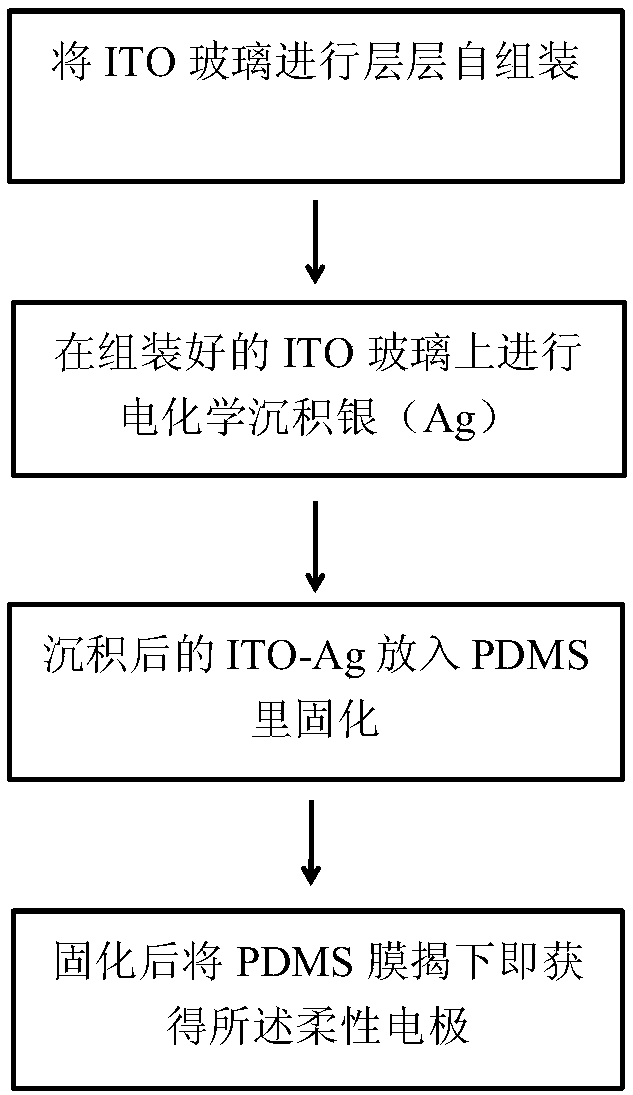
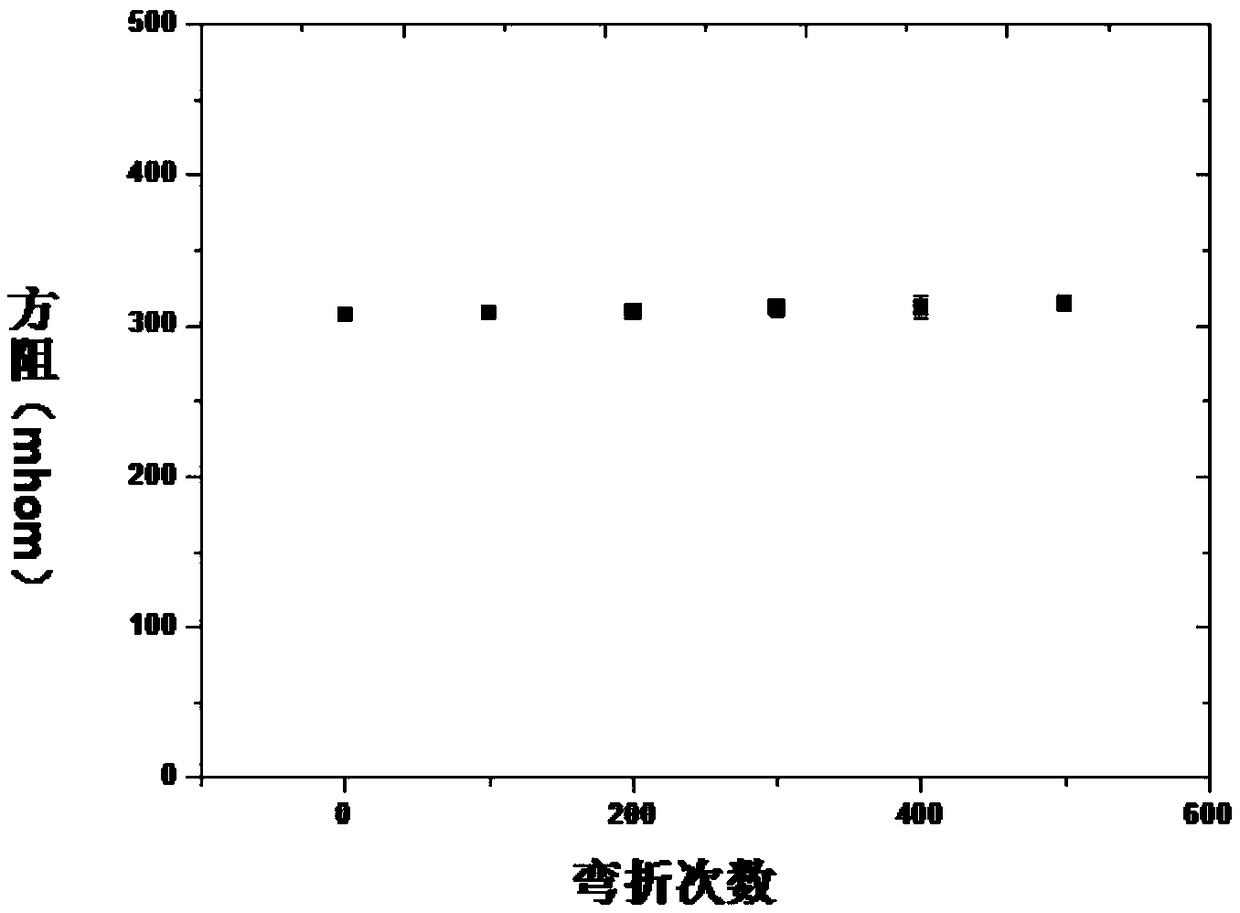
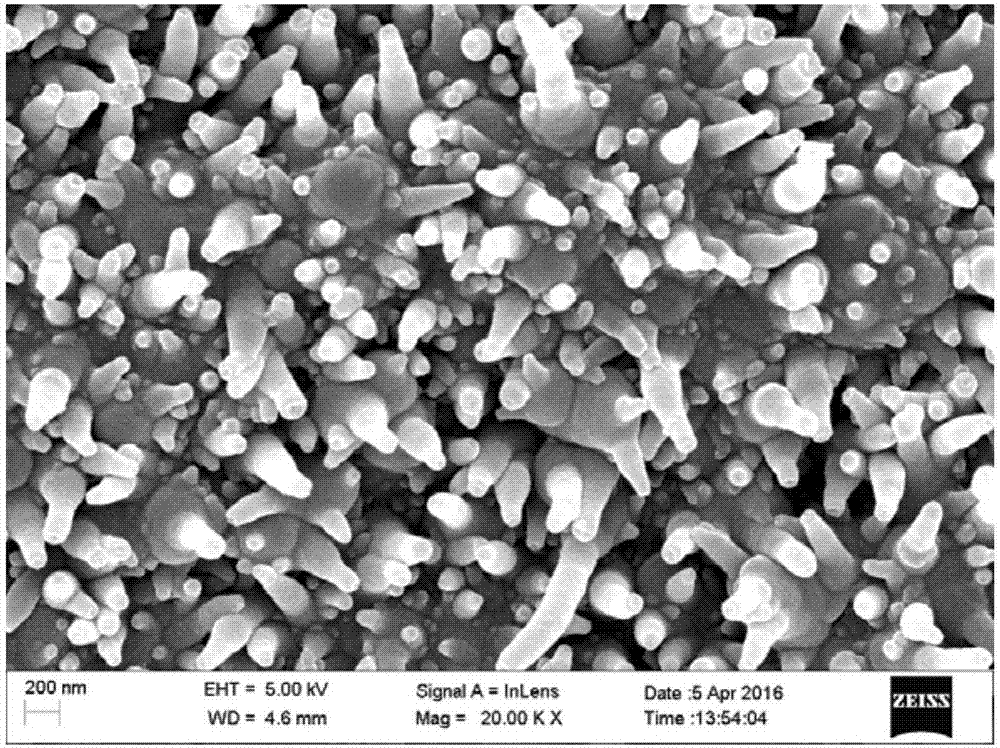
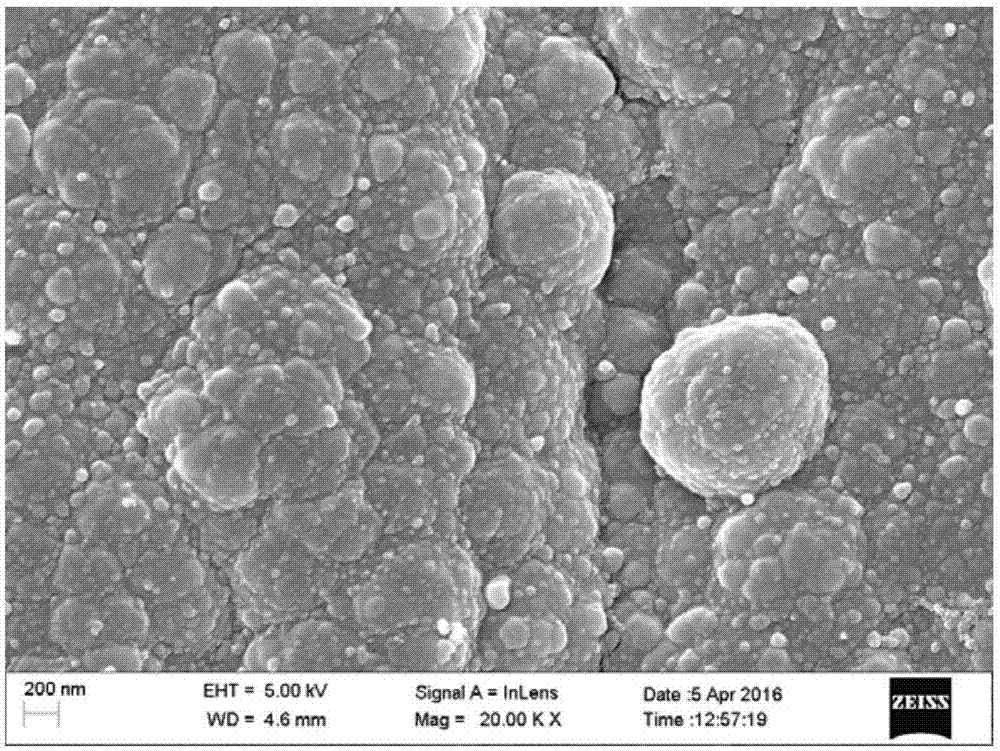
InactiveCN109269709AImprove bending resistanceGood stretch resistanceFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsChronoamperometryBlood pressure
The invention relates to a dendritic nano silver structure-based flexible film pressure sensor and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of electronic materials. According tothe technical schemes of the invention, the preparation method of the dendritic nano silver structure-based flexible film pressure sensor includes the following steps that: the self-assembly of ITO glass layers is realized, electrochemical silver deposition is performed on assembled ITO glass through chronoamperometry, and a white dendritic nano-silver layer is deposited on the ITO glass after the electrochemical deposition is performed, and the ITO glass with the white dendritic nano-silver layer is called ITO-Ag; and the ITO-Ag is immersed in a curing agent-containing PDMS solution, heatingand curing are performed, and a cured PDMS flexible substrate is removed from the ITO-Ag, so that the dendritic nano silver structure-based flexible film pressure sensor can be obtained. The dendritic nano silver structure-based flexible film pressure sensor prepared by the method of the invention has low square resistance and can maintain good electrical conductivity after being bent a pluralityof times and stretched with different ratios. The sensor can monitor human body health basic data online for a wearable smart device, and provide trial conditions in the aspects of pulse, blood pressure, and heartbeat.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Nano-structure polypyrrole/biotin composite material based on conductive base material, preparation method and application
InactiveCN107313093AAchieve dopingSimple methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNano structuringPolypyrrole
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical biomaterials, and discloses a nano-structure polypyrrole / biotin composite material based on a conductive base material, a preparation method and application. The preparation method for the nano-structure polypyrrole / biotin composite material based on the conductive base material comprises the steps that firstly, the chlorine-doped polypyrrole is electro-deposited on the surface of the conductive base material by adopting chronoamperometry; then a three-electrode mode is selected, conductive metal is a counter electrode, the conductive base material with the polypyrrole deposited on the surface is a working electrode, an electrolyte is a buffer solution containing pyrrole and biotin, and chronopotentiometry is adopted so as to obtain the nano-structure polypyrrole / biotin composite material based on the conductive base material; when the buffer solution is neutral, a nano-cone-structure polypyrrole / biotin material is deposited on the surface of the working electrode; and when the buffer solution is acidic or alkaline, a nano-particle-structure polypyrrole / biotin material is deposited on the surface of the working electrode. The preparation method is simple, the cost is low, the nano structure of the prepared composite material is stable, and the preparation method can be used for preparing materials for efficiently capturing and releasing circulating tumor cancer cells.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for detecting uric acid with G-MoS2-Nafion
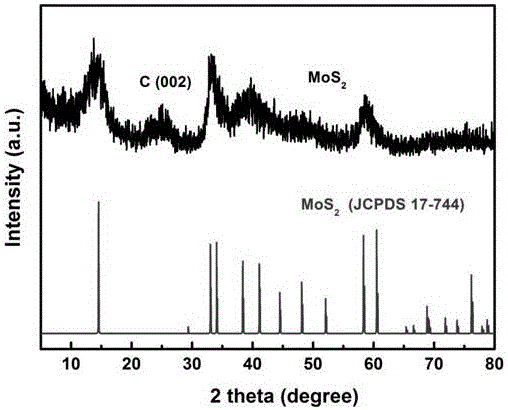
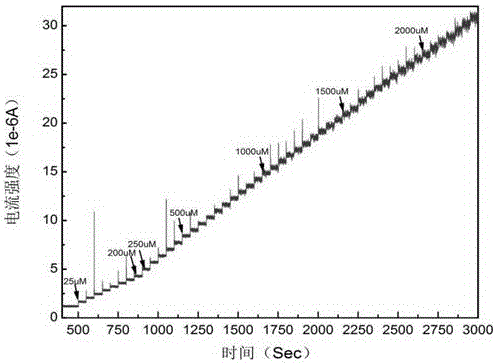
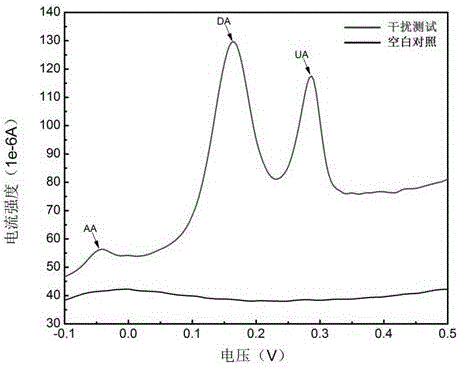
InactiveCN106290500ALow priceHigh detection sensitivityPreparing sample for investigationMaterial electrochemical variablesAlcoholChronoamperometry
The invention discloses a method for detecting uric acid with G-MoS2-Nafion. The method is characterized by including the following steps that firstly, a G-MoS2-Nafion mixture is prepared; secondly, 0.005 ml of G-MoS2-Nafion compound ethyl alcohol suspension is sucked and dropwise added to the surface of a glassy carbon electrode, the glassy carbon electrode is placed at the room temperature to be naturally dried for 30 min, and the glassy carbon electrode modified with G-MoS2-Nafion is obtained; thirdly, the glassy carbon electrode is put into a phosphate buffer solution with the PH of 7.4 to be stabilized for 2 h; fourthly, separated plasma is added into the PBS to be diluted right by 5 folds, stirring is carried out for 20 s, the current value of diluted plasma is measured with the chronoamperometry according to the three-electrode system measurement principle, and the concentration value of uric acid in detected plasma is obtained through conversion.
Owner:川北医学院附属医院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com