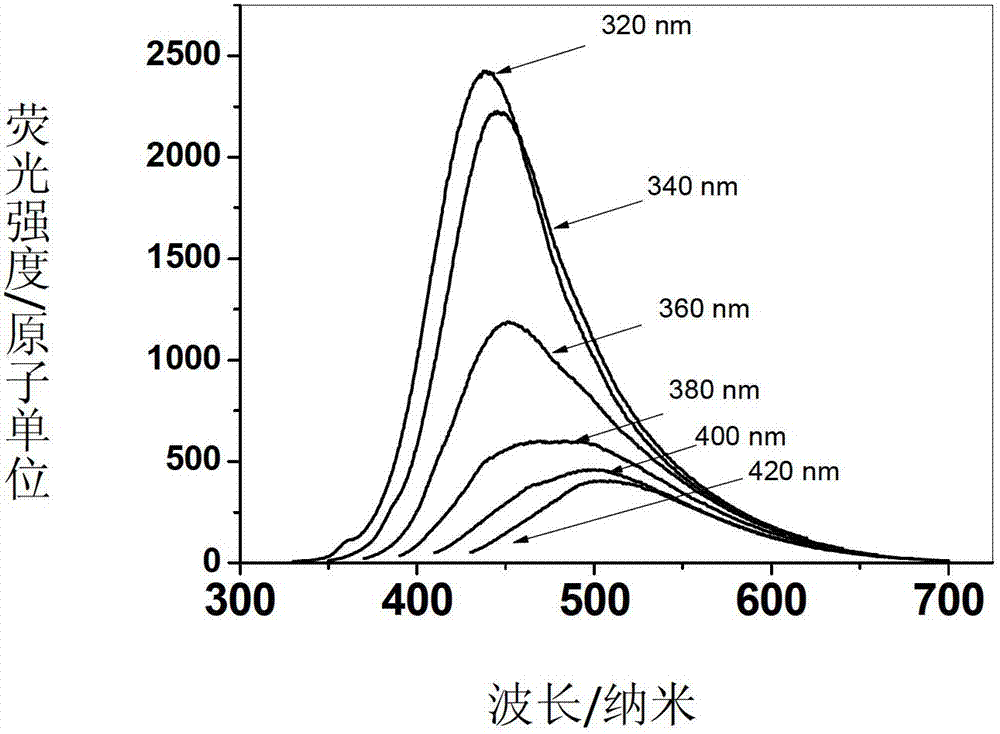
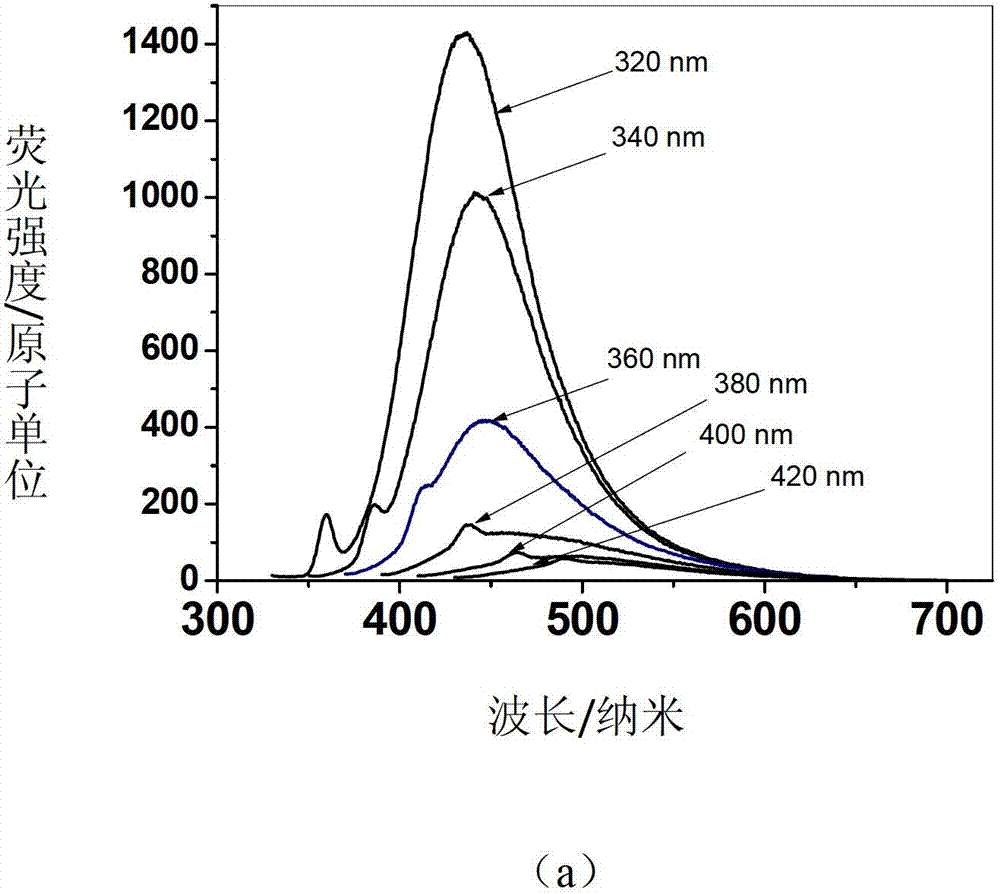
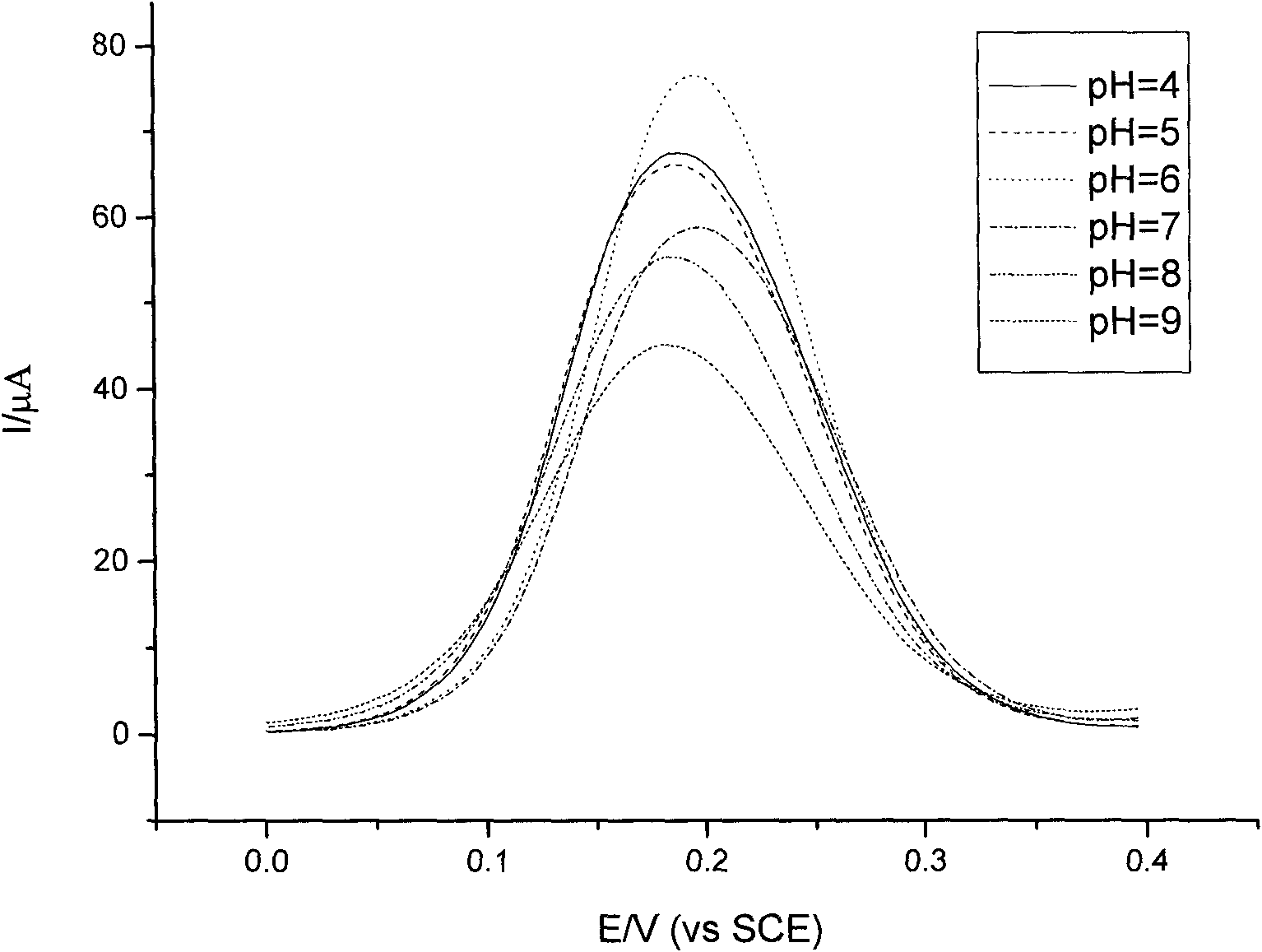
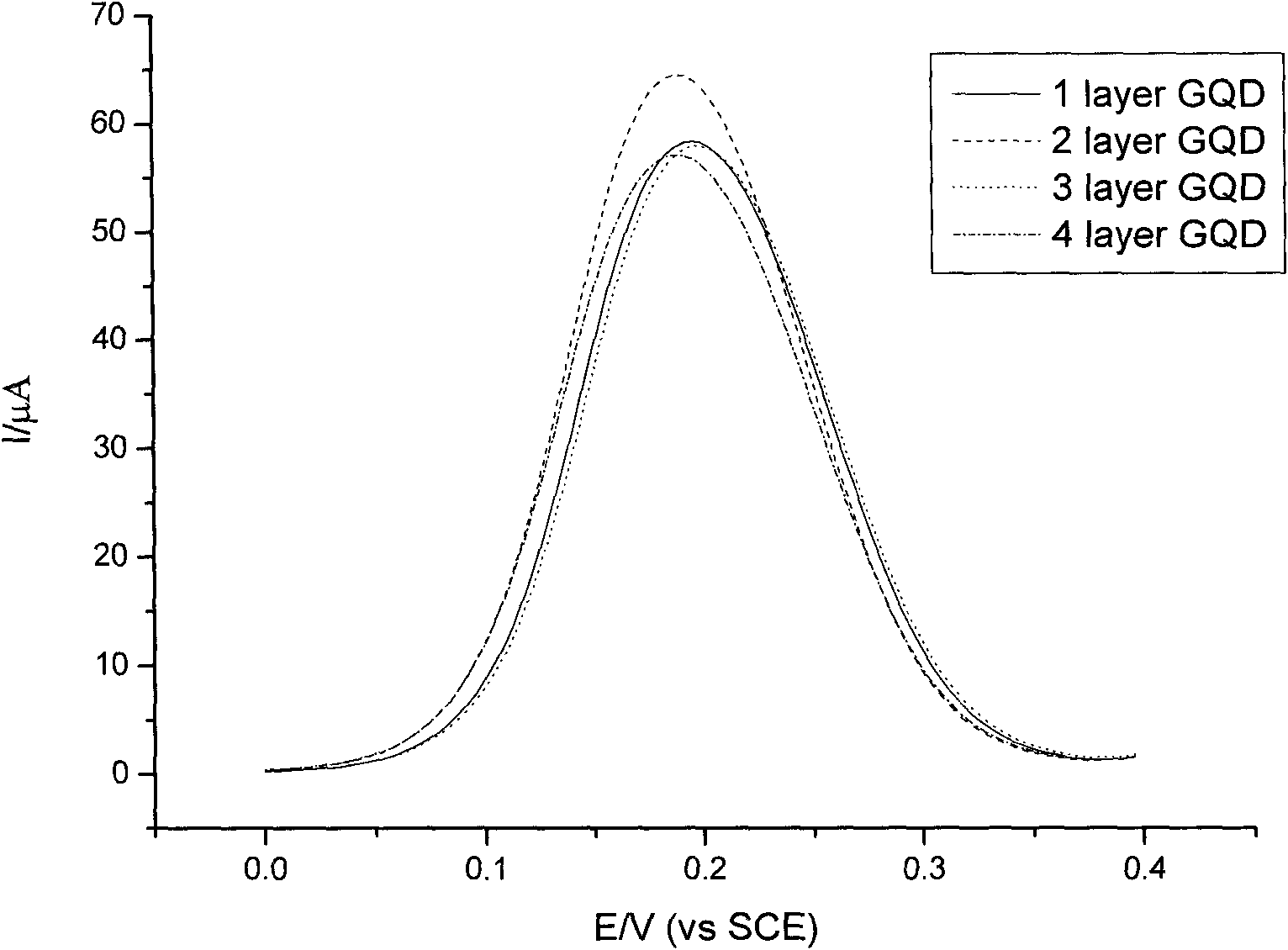
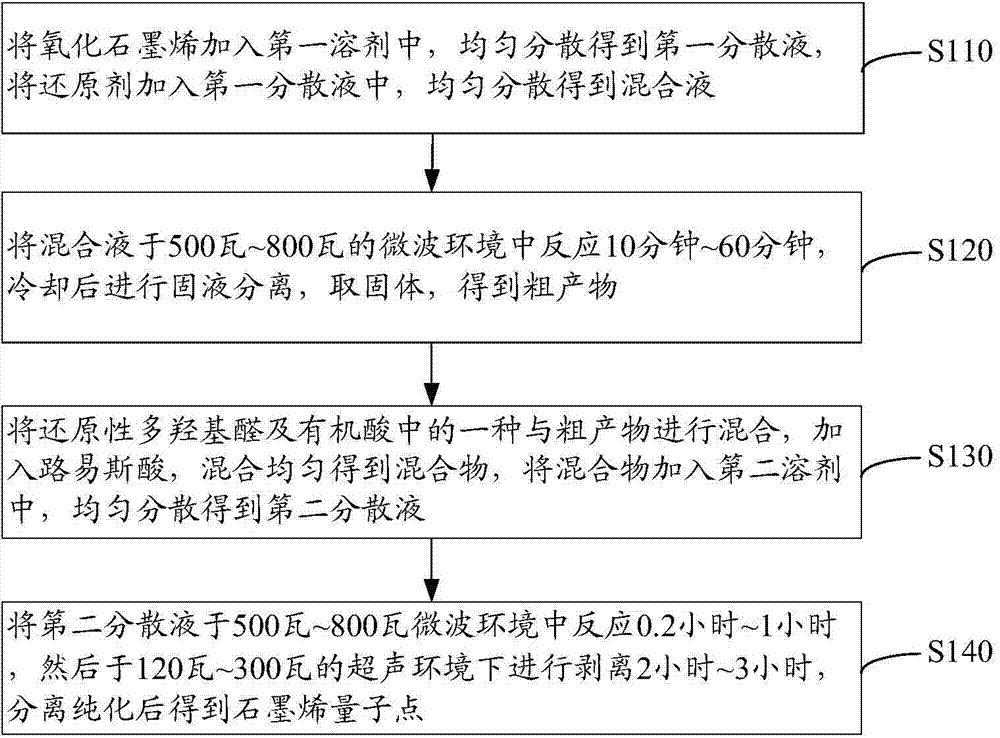
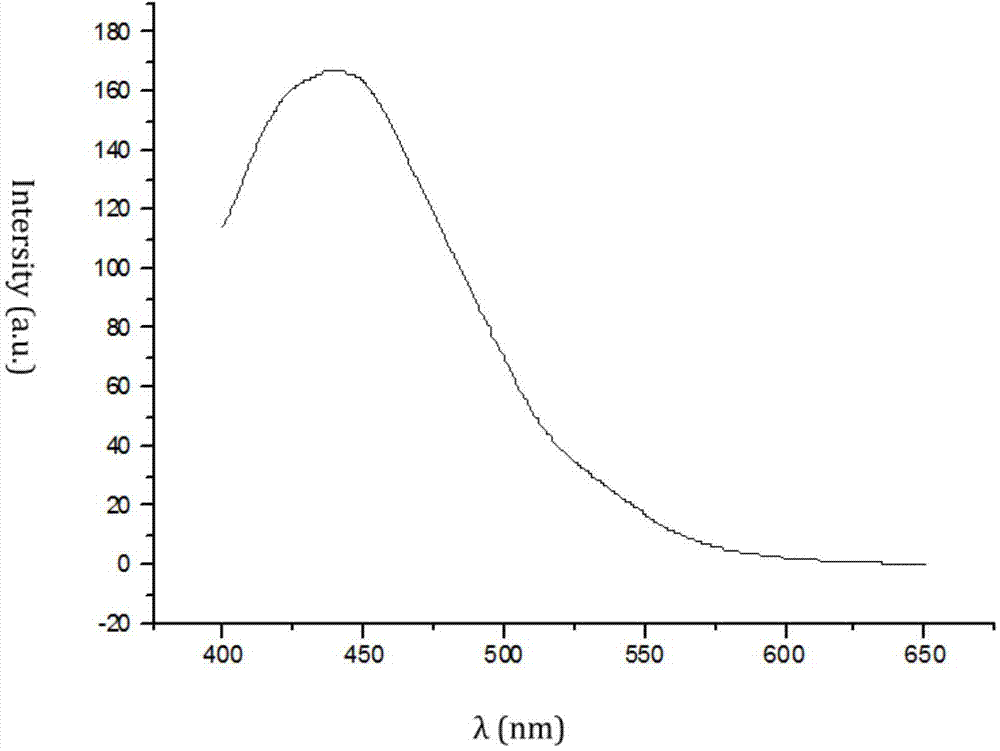
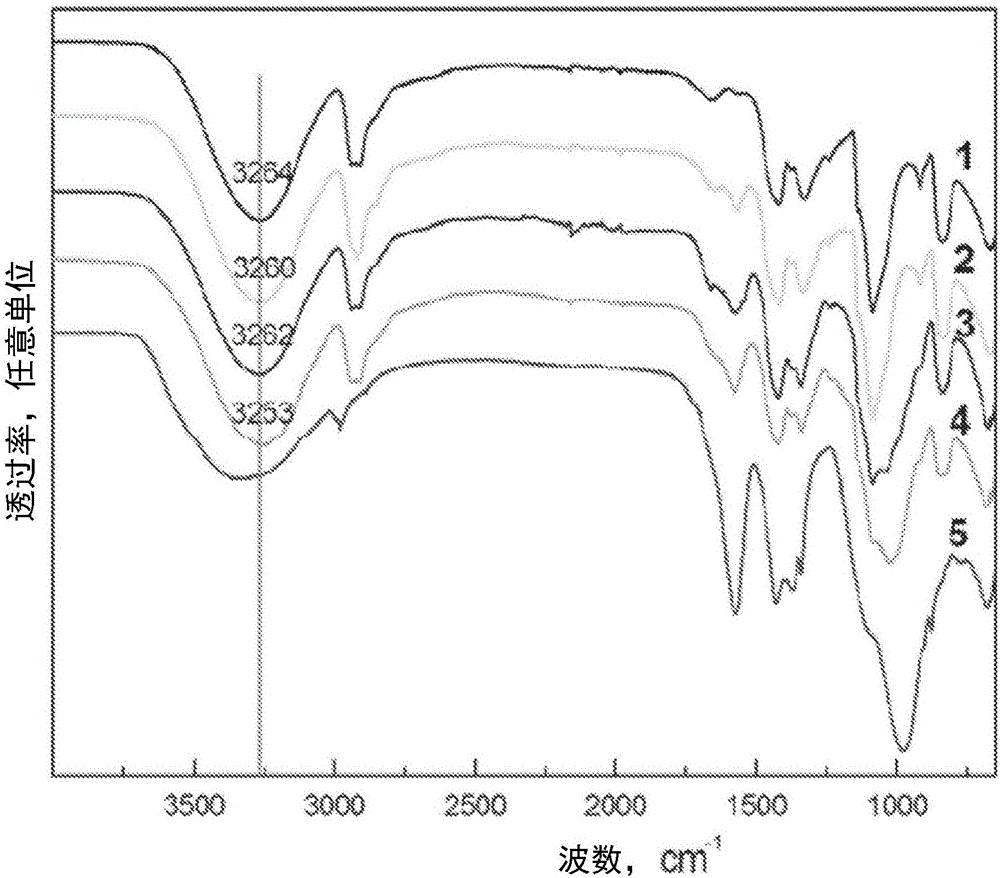
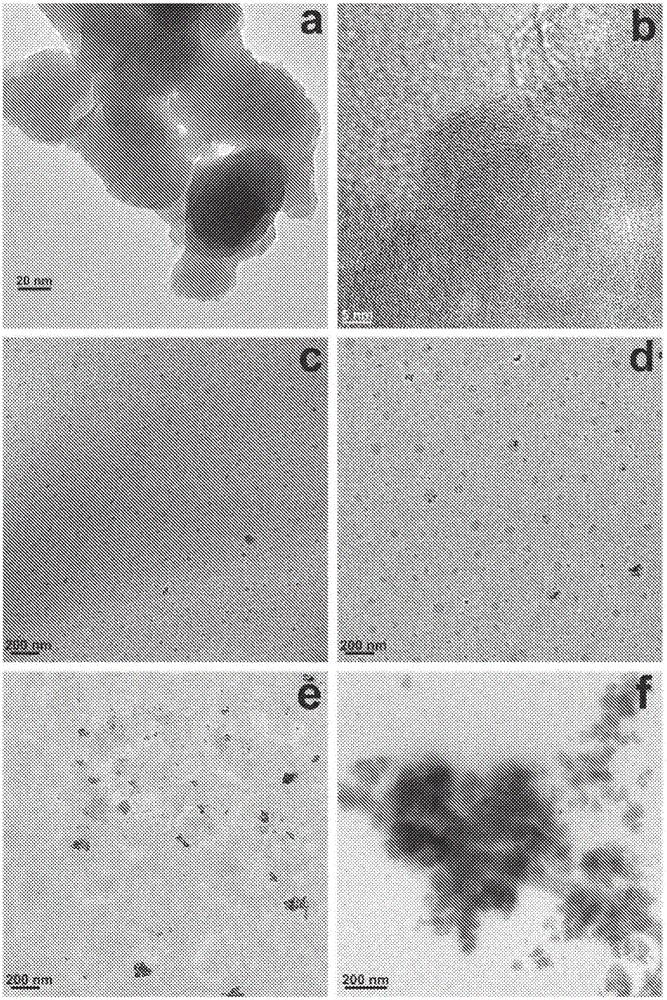
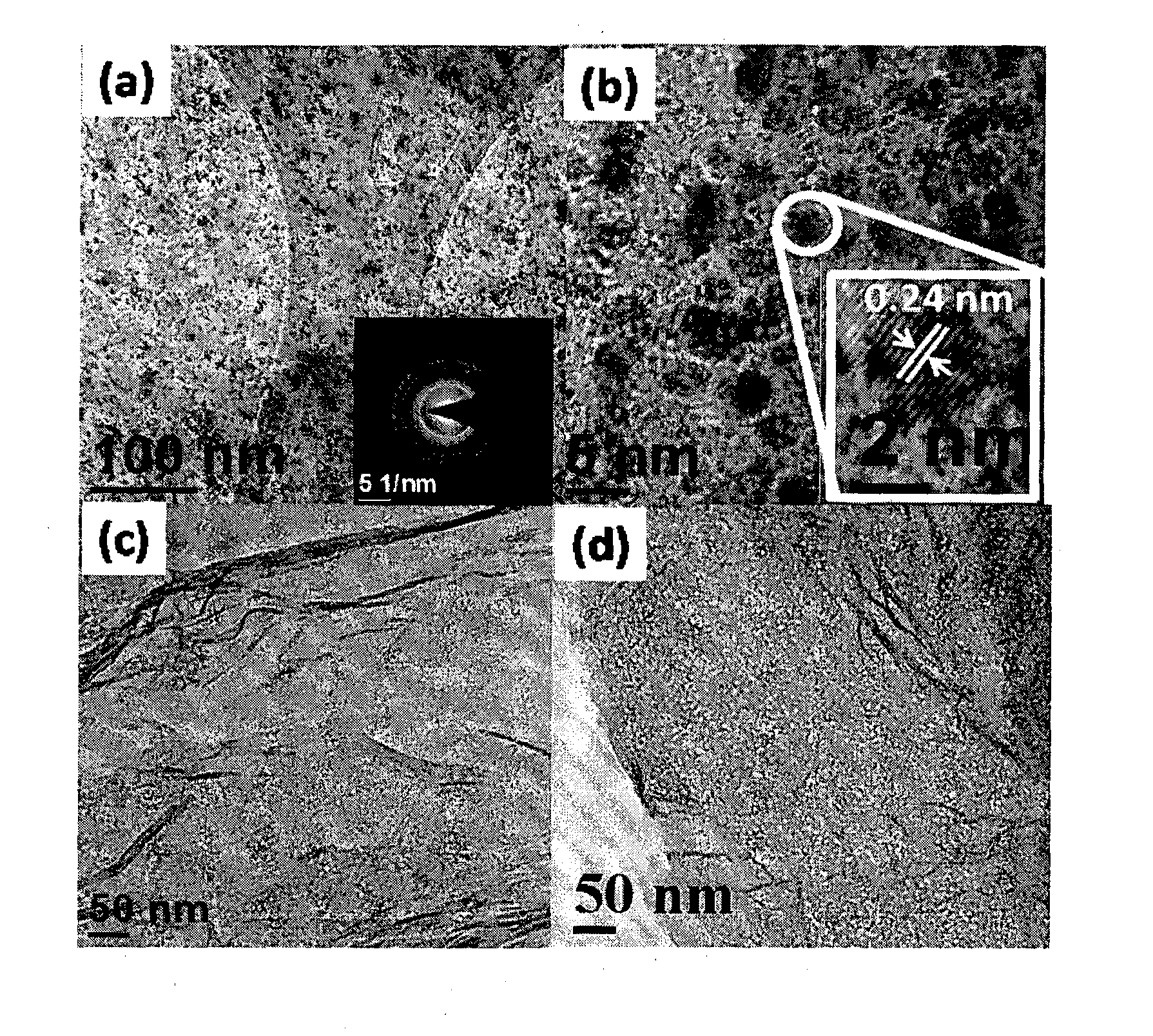
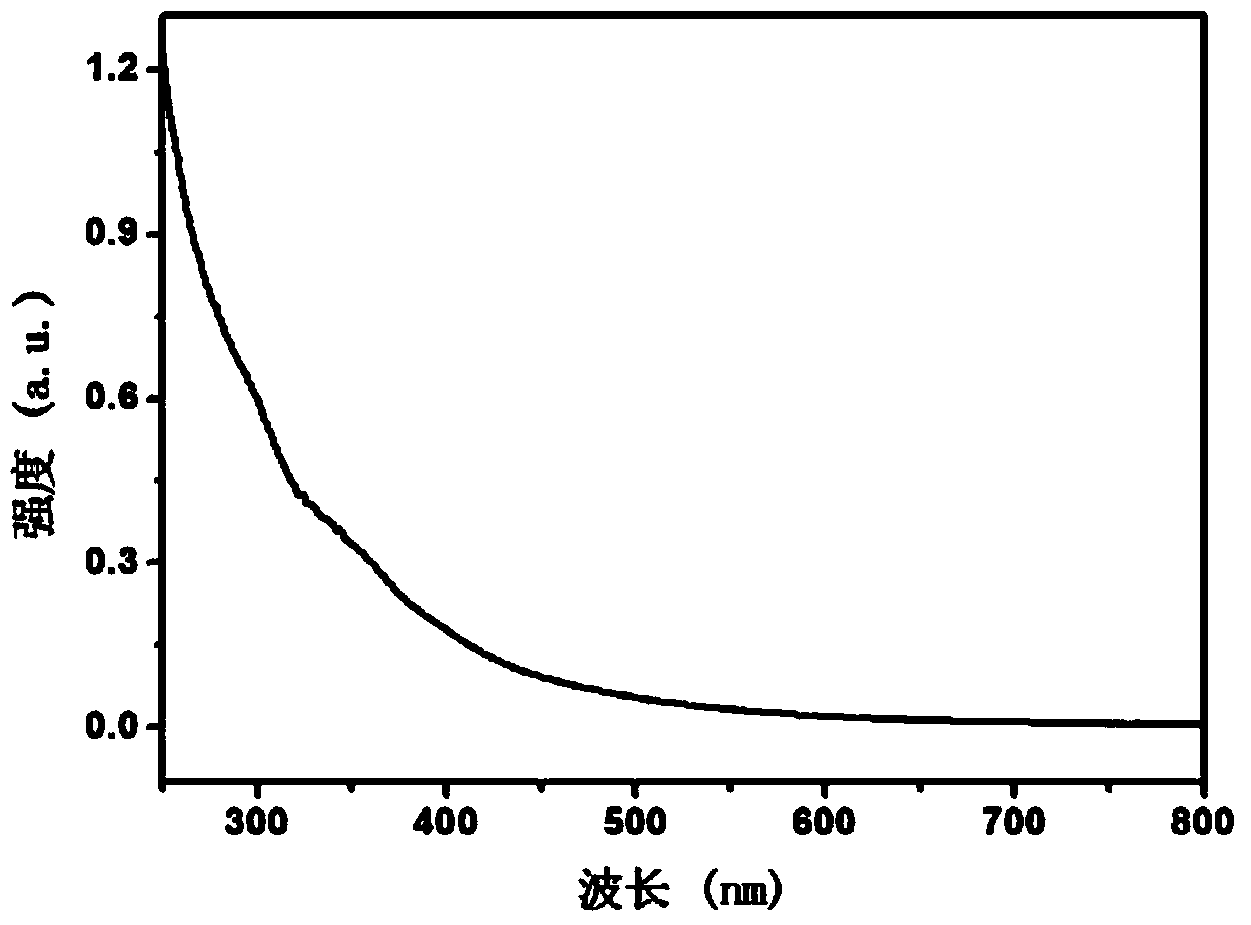
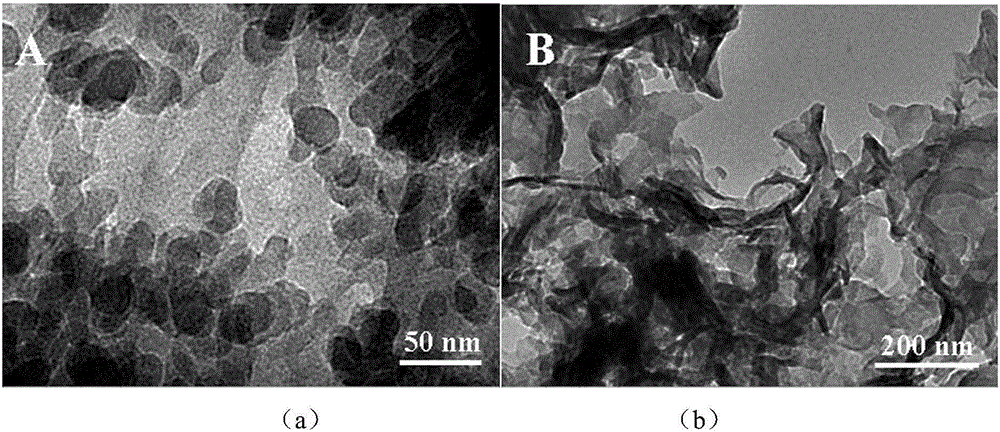
Patents
Literature
1447 results about "Graphene quantum dot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
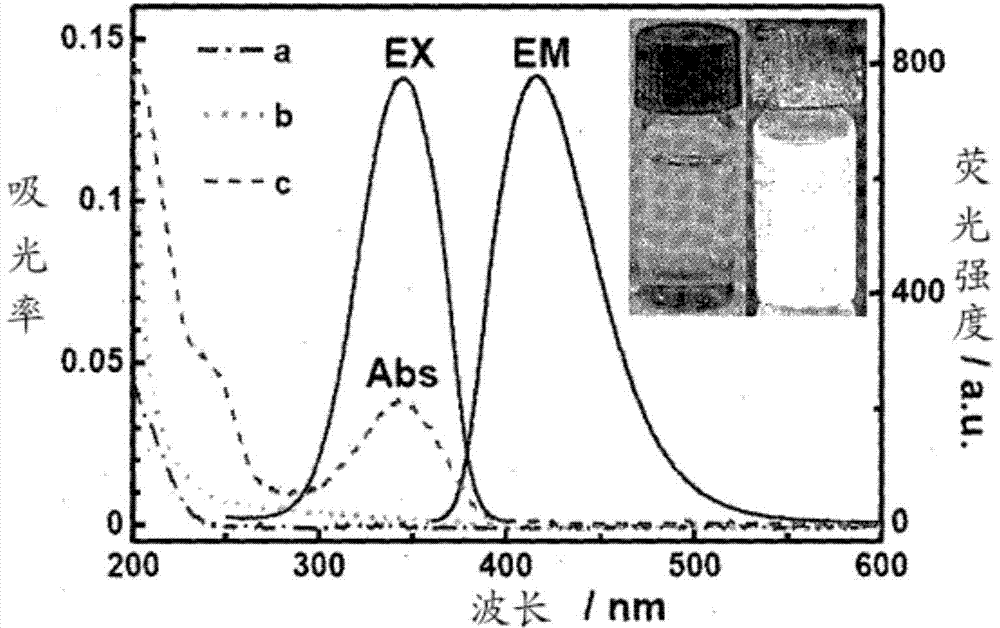
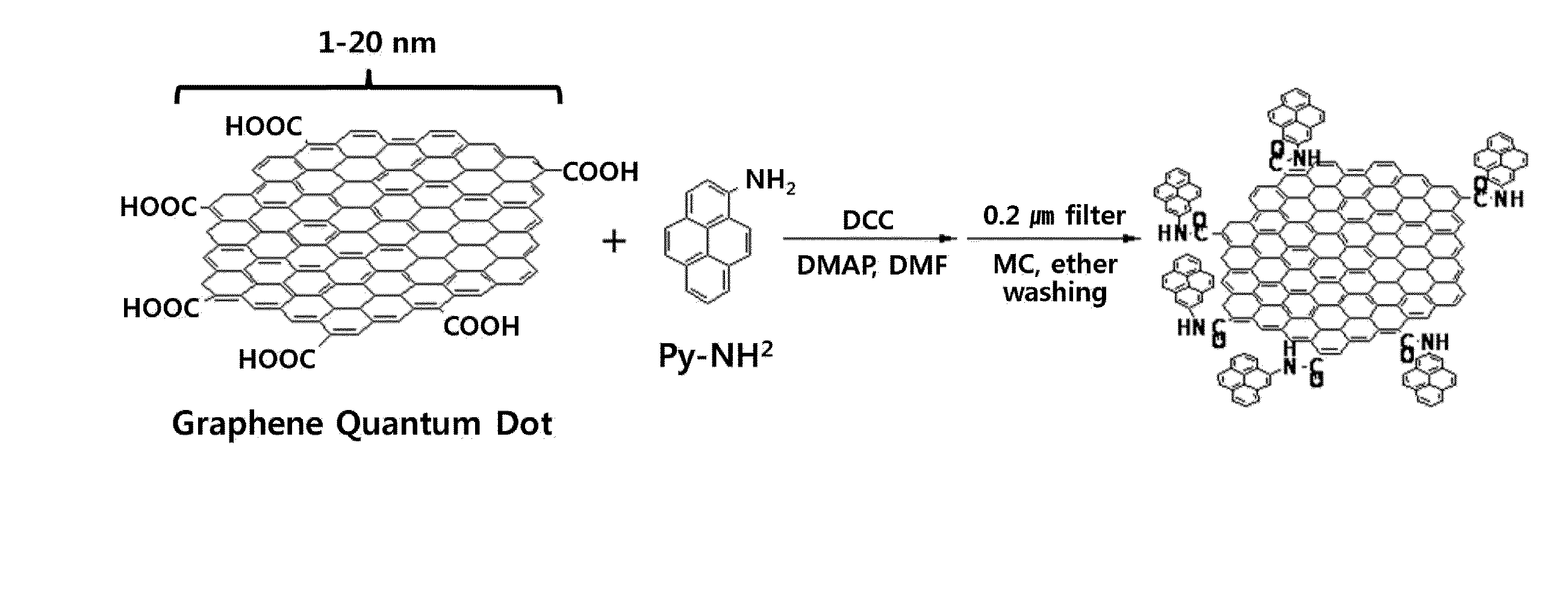
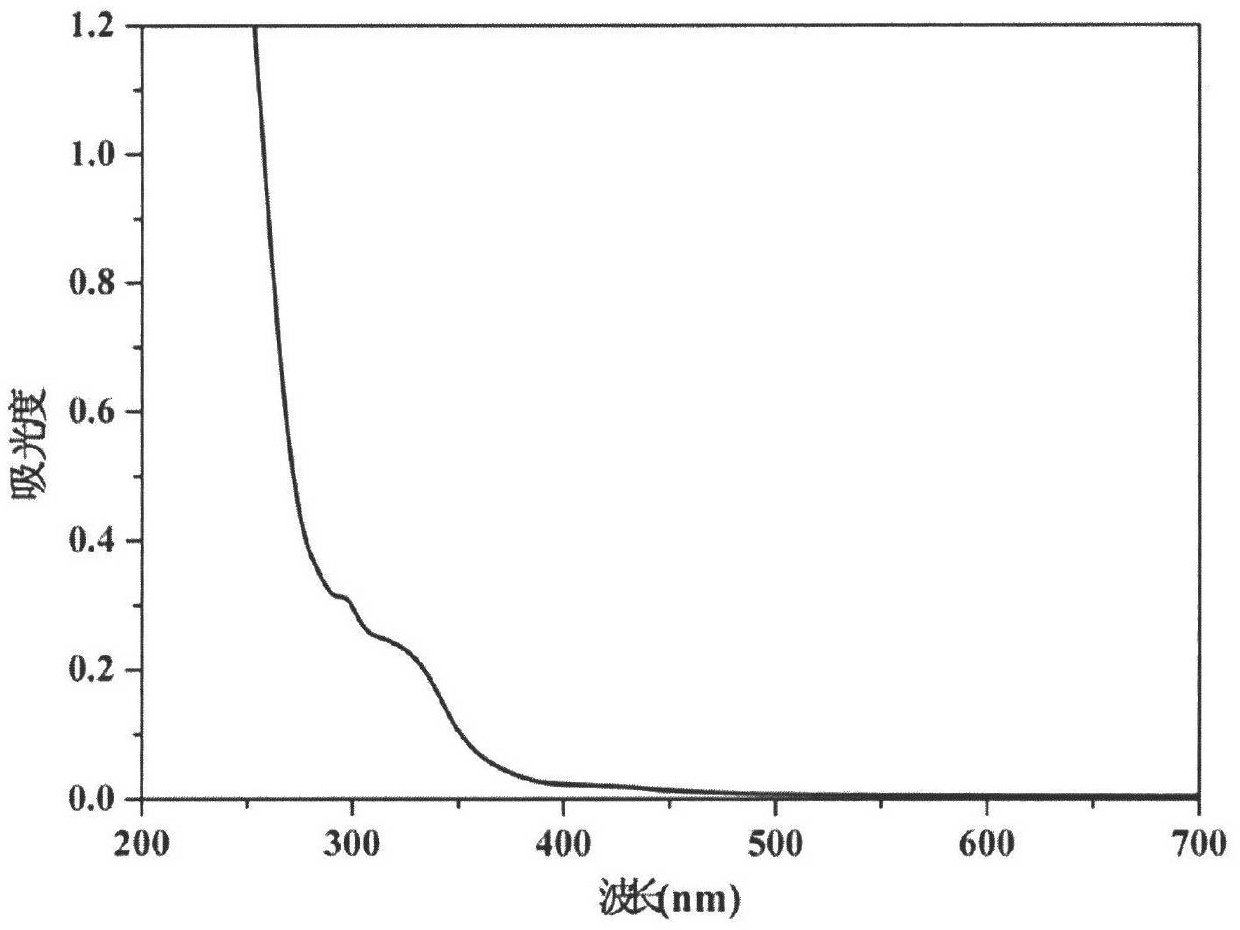
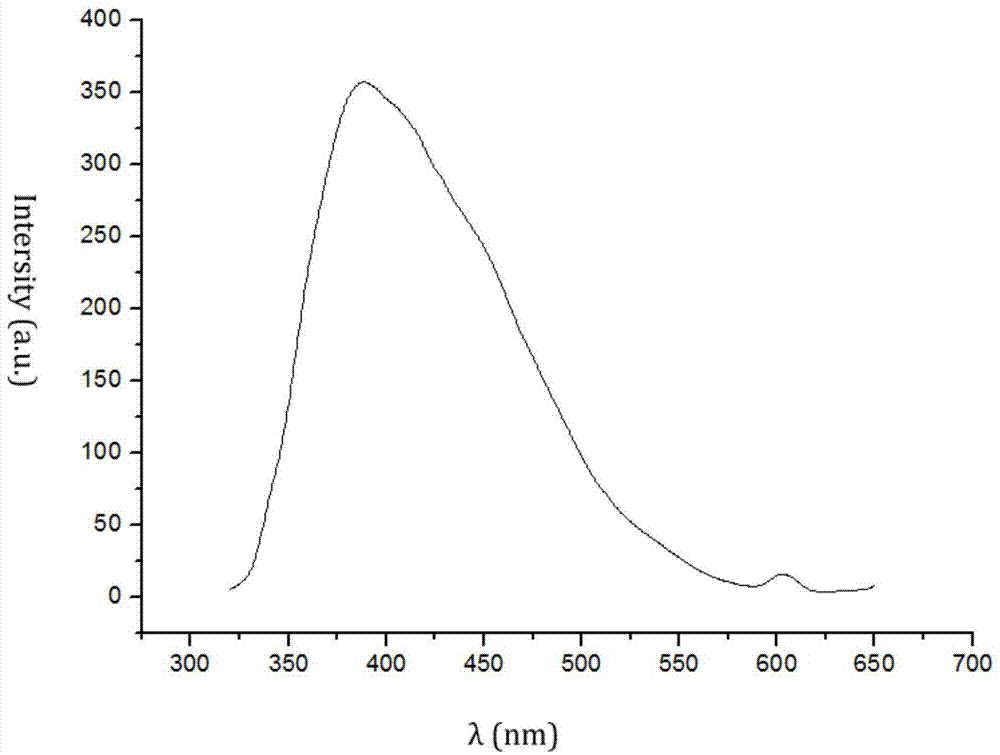
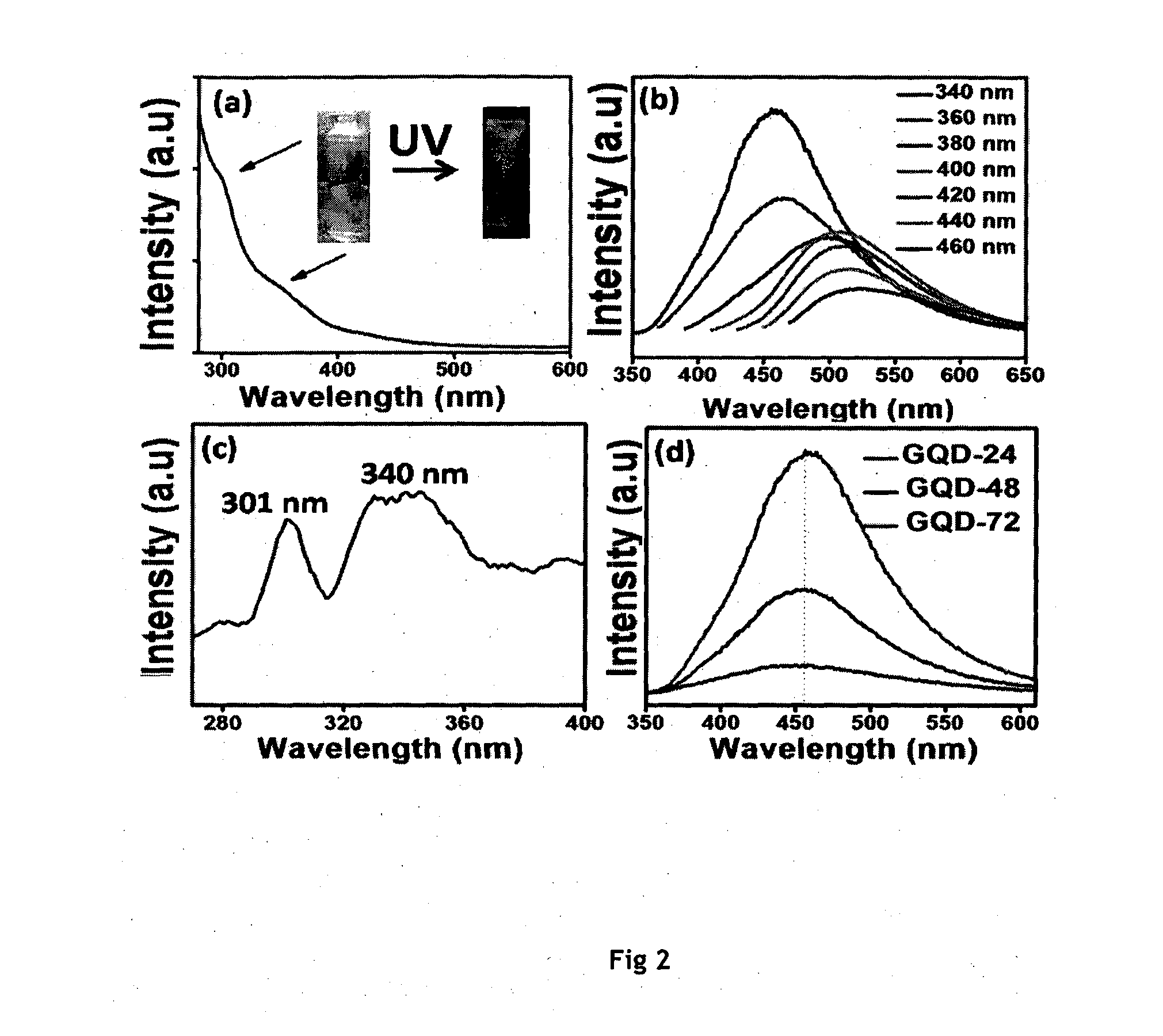
Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) are graphene nanoparticles with a size less than 100 nm. Due to their exceptional properties such as low toxicity, stable photoluminescence, chemical stability and pronounced quantum confinement effect, GQDs are considered as a novel material for biological, opto-electronics, energy and environmental applications.
Preparation method of suspension liquid and powder of graphene quantum dot
The invention discloses a preparation method of a suspension liquid and a powder of graphene quantum dots. The method includes following steps: preparing the suspension liquid of the graphene quantum dots in one step from fullerene in a manner of chemical oxidation cleavage, removing impurity ions from the suspension liquid, and then performing a drying process to obtain the powder of the graphene quantum dots. In the invention, problems of complex technology and high cost in preparation of the suspension liquid and the powder of the graphene quantum dots are solved. The preparation method is simple in operation, can quickly prepare the suspension liquid and the powder of the graphene quantum dots in macro scale in an amplifying manner and is high in yield. The graphene quantum dots are uniform in size distribution and are excellent in water solubility.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Preparation method for graphene quantum dot film
A disclosed preparation method for a graphene quantum dot film comprises the following concrete steps; employing a modified Hummers process to prepare graphite oxide; dispersing graphite oxide in a dispersant, and using a microwave-assisted solvothermal process to prepare graphene quantum dot; and dropwise adding the graphene quantum dot solution on a liner, and performing spinning coating to obtain the graphene quantum dot film. The method is cheap in raw material, simple in equipment and convenient to operate; the obtained graphene quantum dot is good in solubility and uniform in dimension; and the graphene quantum dot film is uniform in thickness and good in electric conductivity, and has considerable application prospect on the aspect of solar cells.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing fluorescent graphene quantum dots by solvothermal method
InactiveCN102660270AHigh degree of oxidationLuminescent compositionsChromatographic separationSurface oxidation
The invention belongs to the technical field of the preparation of graphene quantum dots (GQDs), and particularly relates to a method for preparing fluorescent graphene quantum dots with controllable oxidation degree and fluorescence by a solvothermal method. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps of: 1, preparing graphene oxide; 2, preparing green fluorescent graphene quantum dots by a single-step method starting from the graphene oxide; and 3, preparing the fluorescent graphene quantum dots with the controllable oxidation degree by a column chromatographic separation method. According to the method, the sizes and surface oxidation degree of the graphene quantum dots can be controlled under the synthetic condition, so that the fluorescent properties and surface chemical characteristics of the graphene quantum dots are controlled. The prepared graphene quantum dots are high in chemical stability and biocompatibility, low in biotoxicity, and high in property of applicable upconversion fluorescence, matt and the like and bleaching performance. By the excellent properties, the graphene quantum dots have a wide application range in aspects of biological imaging, photovoltaic devices and sensors, and are novel promising fluorescent nano materials.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
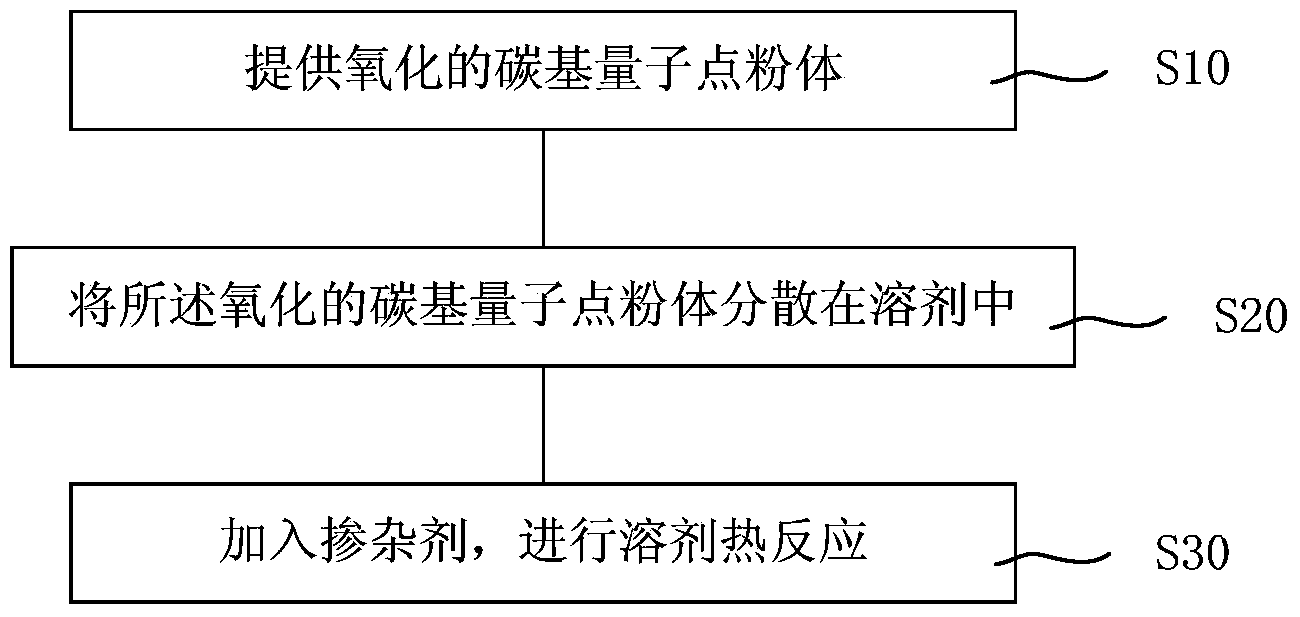
Preparation method for fluorescence carbon-based quantum dot
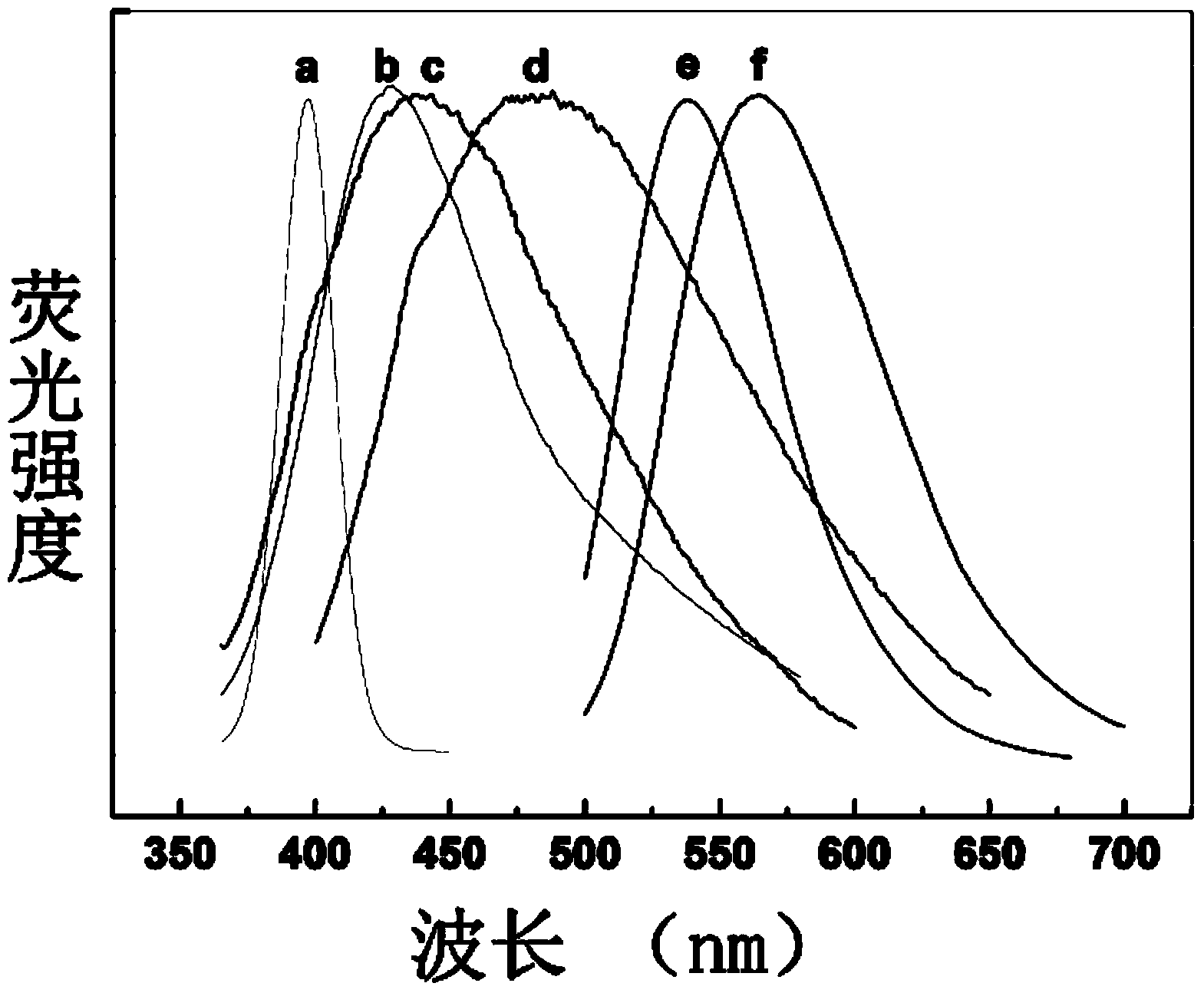
The invention provides a preparation method for a fluorescence carbon-based quantum dot. The preparation method for the fluorescence carbon-based quantum dot at least comprises the steps of providing oxidized carbon-based quantum dot powder; providing a solvent, and dispersing the oxidized carbon-based quantum dot powder into the solvent to obtain the oxidized carbon-based quantum dot solution; adding a doping agent into the oxidized carbon-based quantum dot solution, reducing the oxidized carbon-based quantum dot by utilizing the solvent thermal reaction so as to obtain the doped carbon-based quantum dot. According to the invention, the technical scheme that oxidized carbon-based quantum dot is taken as a raw material and the solvent thermal reduction and doping are synchronously carried out is adopted, the carbon-based quantum dot represented by graphene quantum dot and carbon quantum dot can be reduced and doped by adopting various easily available nonmetal compounds or metal compounds through the solvent thermal reaction, the yield of a product is high, the regulation on the fluorescent spectrum of the carbon-based quantum dot can be realized, and the yield of quantum can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing grapheme-quantum dot composite film and solar battery structured by using same
InactiveCN102176382AControl quantityImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyLight-sensitive devicesFinal product manufactureComposite filmOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a method for preparing a grapheme-quantum dot composite film and a solar battery structured by using the same. The method comprises the following steps of: performing suction filtering on a suspension of grapheme-quantum dot composite powder on a filtering film to obtain a film; and then dissolving the filtering film away with an organic solvent, and transferring the filmto a conductive substrate. The method is characterized in that the ratio of the quantum dot to the grapheme and the thickness of the film can be controlled effectively; in addition, since the film isprepared at normal temperature, the requirement on the conductive substrate is reduced greatly. The prepared film can be used for structuring a novel quantum dot sensitized solar battery. The structured solar battery is of a layer structure, consists of the grapheme-quantum dot film on the conductive substrate, an electrolyte layer and a counter electrode and has the advantages of low cost, simpleness in preparation process, low temperature and stable performance. By the use of the grapheme-quantum dot composite film prepared by the method provided by the invention, the photoelectron transmission performance can be improved, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of a battery can be enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing graphene quantum dots
ActiveCN102807209AHigh puritySmall particle sizeMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneSolubilityFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for preparing graphene quantum dots, which belongs to the technical field of nano-material preparation. The method for preparing grapheme quantum dots comprises the following steps: firstly, utilizing graphite oxide to prepare graphene slices, and dissolving 50mg of graphene slices, 0-30mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, 10-40mL of concentrated nitric acid and the balance of de-ionized water for supplementing to 40mL into a dispersing system with 40mL; filtrating the abovementioned dispersing system, dispersing the solid into the de-ionized water again, adjusting the pH value to 8 with a sodium hydroxide solution, processing for 3 min in a microwave reaction kettle, naturally cooling, filtering with a filter membrane, collecting filtrate and dialyzing the filtrate in a dialysis bag for three days; and drying the dialyzed products to obtain the graphene quantum dots. The method provided by the invention is convenient in synthetic process and high in efficiency, and the obtained graphene quantum dots are high in purity, small in particle size, and strong in fluorescent property, and has monodispersity and water solubility, so that the graphene quantum dots are good in application prospect in the aspects of bioluminescent marks and solar cells.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Multicolor fluorescence fluorescent graphene quantum dot material preparation method
InactiveCN103320125AGood dispersionSimple stepsLuminescent compositionsHigh concentrationPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a preparation method of multicolor fluorescence fluorescent graphene quantum dots. According to the invention, pyrene with a low price is adopted as a precursor; oxygen functionalization is carried out on the surface of pyrene grains under low temperature; and low-temperature hydrothermal dehydrogenation, growth, and in-situ surface functionalization are carried out under the effect of a catalyst hydrazine and ammonia water. With the method provided by the invention, synthesized quantum dots can be stably dispersed in water. The quantum dots are brown under low concentration, and are approximately black under high concentration (the higher the concentration, the deeper the color). Light emitting color or wavelength is adjustable (blue to yellow, 450-535nm). The quantum dots provided by the invention show attractive application prospects in high-tech fields such as environmental protection, bio-nano technology, new energy, nano-device, and the like. The synthesizing method is simple and environment-friendly, and energy consumption is low. The method is suitable for industrial scale-up.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for forming nitrogen and sulfur co-doped graphene quantum dots
ActiveCN104812697AHigh fluorescence quantum yieldExcitation-independentMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneHigh densityDoped graphene
The invention relates to a method for forming graphene quantum dots, and in particular, to doped graphene quantum dots. The graphene quantum dots are co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur. The co-doped elements introduce a new type and high density of surface state of graphene quantum dots, leading to high yield and excitation-independent emission.
Owner:BEIJING XINNA INT NEW MATERIALS TECH CO LTD
Preparation method of graphene
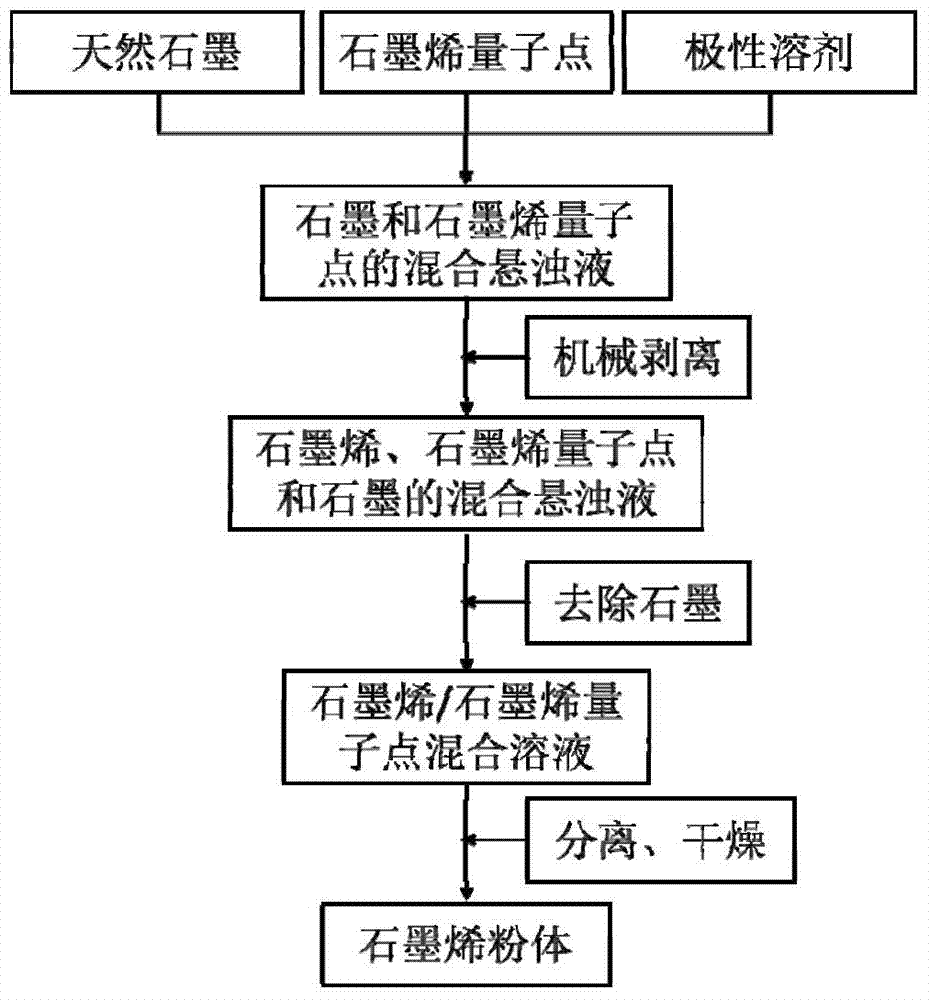
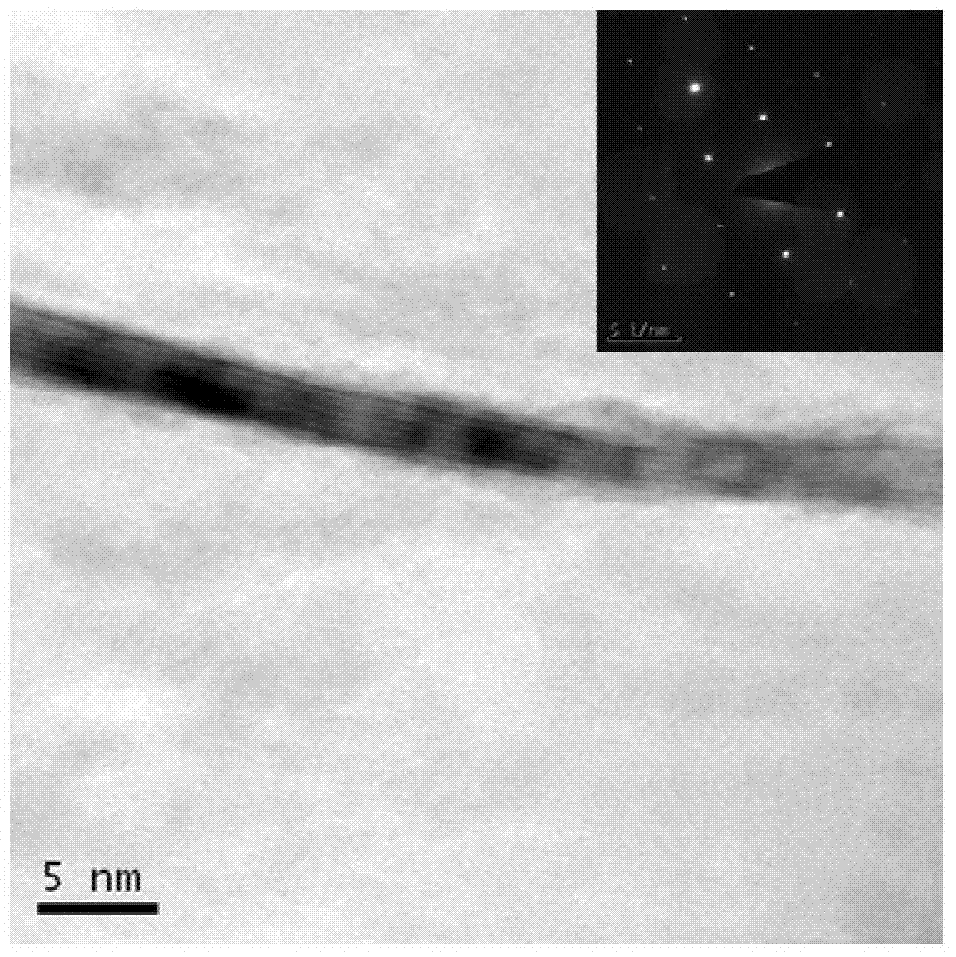
The invention discloses a preparation method of graphene, which is characterized in that natural graphite used as a raw material is subjected to mechanical stripping under the auxiliary action of graphene quantum dots by using a polar solvent as a dispersion medium to prepare the high-quality graphene. The stripping of the natural graphite and dispersion of the graphene nanosheets in the polar solvent are promoted by utilizing the favorable dispersivity of the graphene quantum dots in the polar solvent and the strong non-covalent bond combination between the graphene quantum dots and graphene / graphene laminae, thereby obtaining the high-quality graphene. According to the invention, the graphene powder is directly obtained from the natural graphite under the condition of not introducing any surfactant, inorganic salt, organic salt or any other impurity. Compared with the existing methods, the method is simple in technique, and can be perform in multiple polar solvents; the maximum yield of the obtained graphene can reach 50%, and the quality is good; the graphene quantum dots used for auxiliary stripping can be recycled; and thus, the method is very suitable for mass preparation of graphene.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
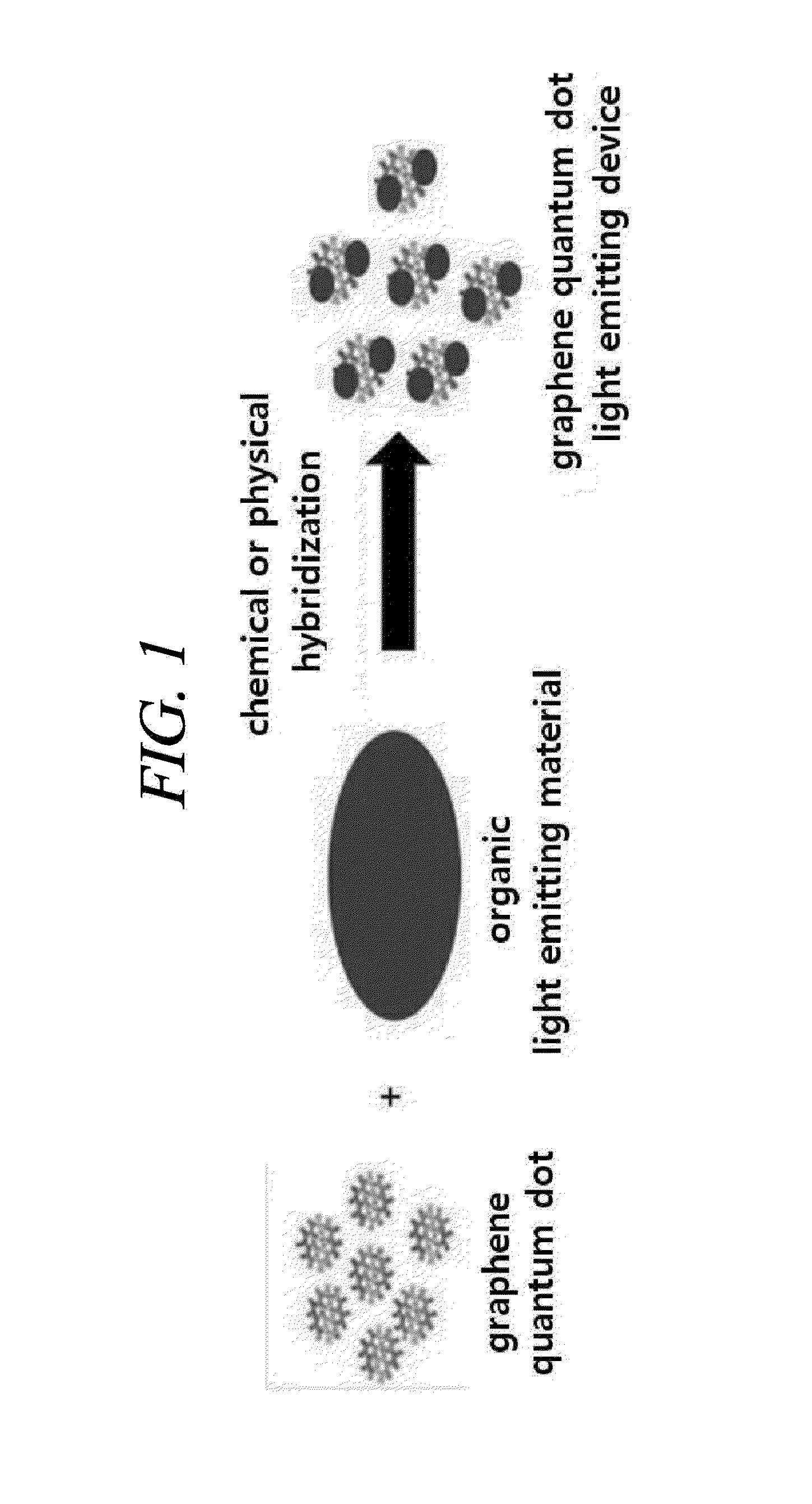
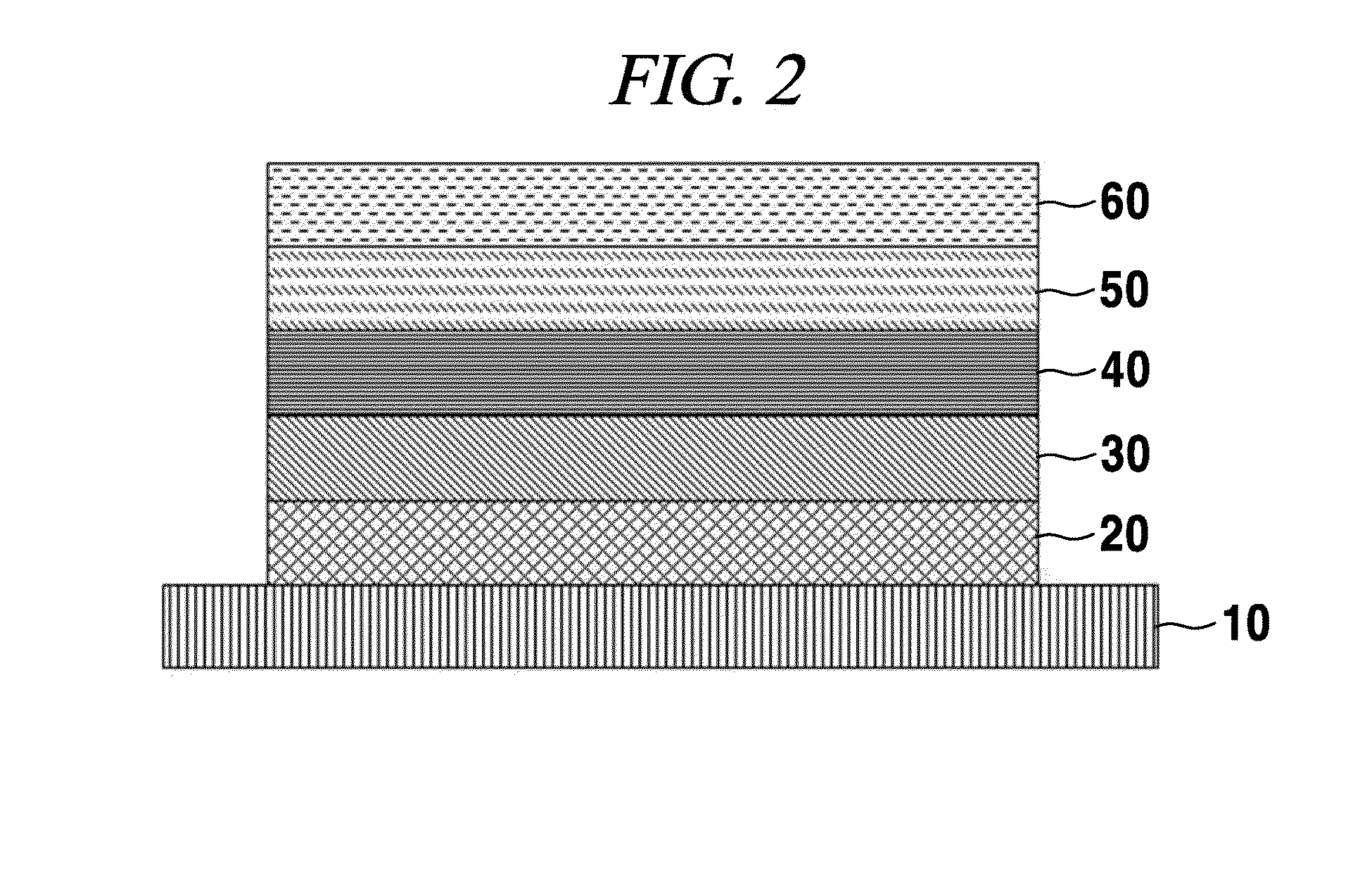
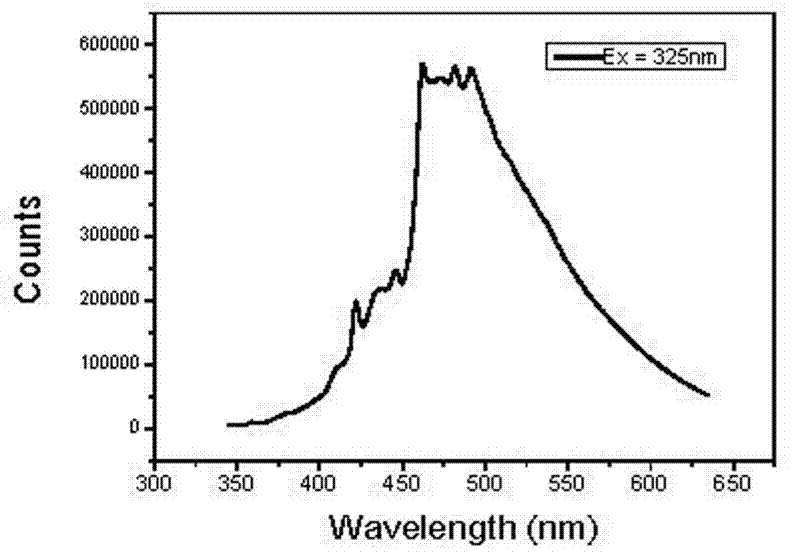
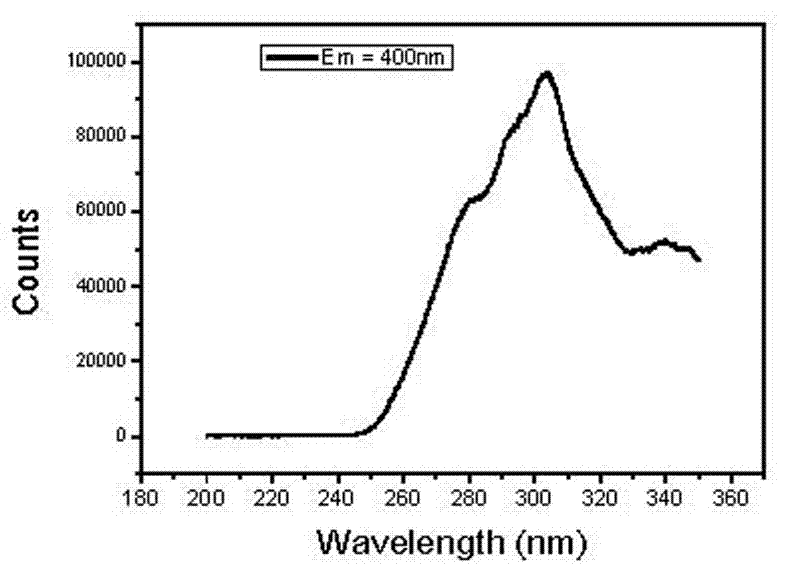
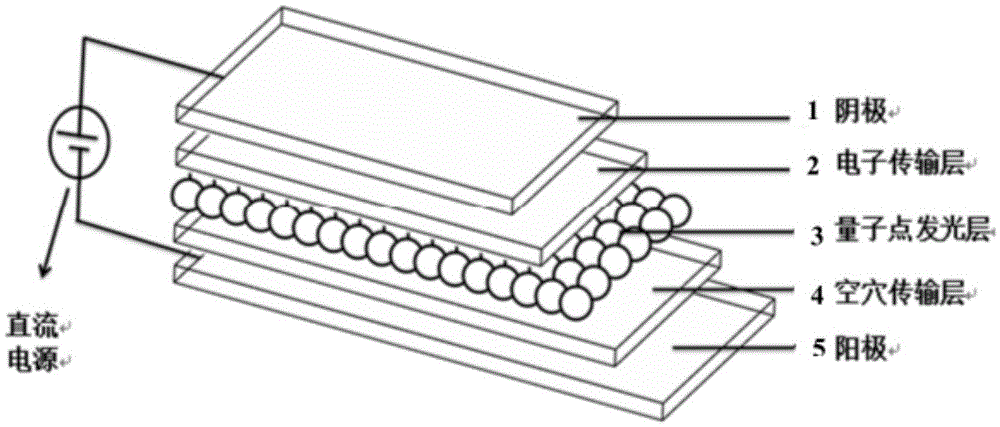
Light emitting device using graphene quantum dot and organic light emitting device including the same
ActiveUS20140145145A1Easy to optimizeGood dispersionNanoopticsSemiconductor devicesOrganic light emitting deviceGraphite
The present disclosure relates to a light emitting device using a graphene quantum dot, and an organic light emitting device including the same.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Supersonic chemical preparation method for grapheme quantum dots
InactiveCN102225758AEasy to operateSimple processNanotechnologyEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesSolubilityUltrasound - action
A supersonic chemical preparation method for grapheme quantum dots relates to a preparation method for grapheme quantum dots, and especially relates to a method for preparing a grapheme quantum dot solution with the characteristics of good monodispersity and luminescence performance using a simple and environmentally friendly process with cheap carbon black or graphite powder as the raw material. The preparation method provided in the invention is characterized by adding a dispersant into carbon black or graphite and obtaining grapheme quantum dots under the action of supersonic wave. The grapheme quantum dot solution prepared in the invention has the characteristics of luminescence, monodispersion, water-solubility, etc.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
Hydrothermal method for preparing water-soluble graphene quantum dots
ActiveCN102190296AGood size controlAverage distribution size narrowNanotechnologySolubilityWater soluble
The invention discloses a hydrothermal method for preparing water-soluble graphene quantum dots. The invention relates to the preparation method of graphene quantum dots, and especially relates to a hydrothermal method for preparing water-soluble graphene quantum dots. The method provided by the present invention is characterized in that: 0.01 to 1.0M of an aqueous solution of polyhydroxyl carbohydrate is added to a hydrothermal reaction vessel; the aqueous solution is heated for 10 to 600 minutes under a temperature of 120 to 220 DEG C; sugar molecules are polymerized into graphene quantum dots with sizes of 1 to 10nm, such that target products are obtained. The graphene quantum dots prepared with the method provided by the present invention has characteristics of water-solubility, monodispersity and special photoelectrical characteristics. The raw materials are cheap, and the sources of the raw materials are wide. With environmental-protective technology, the method is suitable for volume production.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
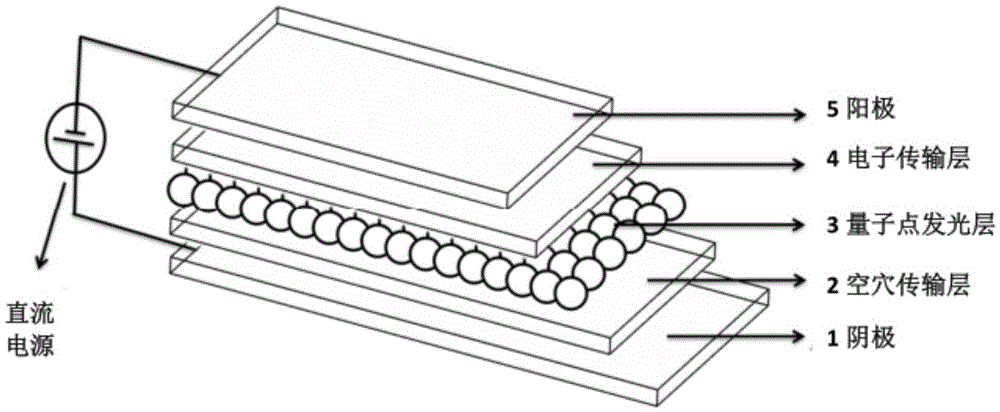
High-efficiency quantum dot light emitting diode with self-assembly polymer hole transmission layer structure
InactiveCN105609651AIncrease transfer rateImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZinc selenidePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The invention discloses and proposes a high-efficiency quantum dot light emitting diode with a self-assembly polymer hole transmission layer structure. Except a positive electrode and a negative electrode, the high-efficiency quantum dot light emitting diode comprises a three-layer structure: a hole transmission layer, a quantum dot light emitting layer and an electron transmission layer, wherein one end of the quantum dot light emitting layer is connected with the hole transmission layer, the other end of the quantum dot light emitting layer is connected with the electron transmission layer, the electron transmission layer is organic nanoparticles after doped, the hole transmission layer is formed by doping a monomer, a polymer, small-molecule, inorganic oxidized metal nanoparticles or a two-dimensional nanometer material into poly(3,4- ethylenedioxythiophene monomer), a quantum dot is quantum dots of zinc sulfide, zinc selenide, cadmium sulfide, cadmium selenide, cadmium telluride, mercury sulfide, mercury selenide, mercury telluride or core-shell nanometer structured cadmium selenide-zinc sulfide, cadmium sulfide-zinc sulfide, cadmium sulfide-zinc selenide and graphene thereof and the like, and the negative electrode is glass or polyethylene terephthalate (PET) with a layer of indium tin oxide (ITO) or fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) or graphene.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Graphene quantum dot preparation method
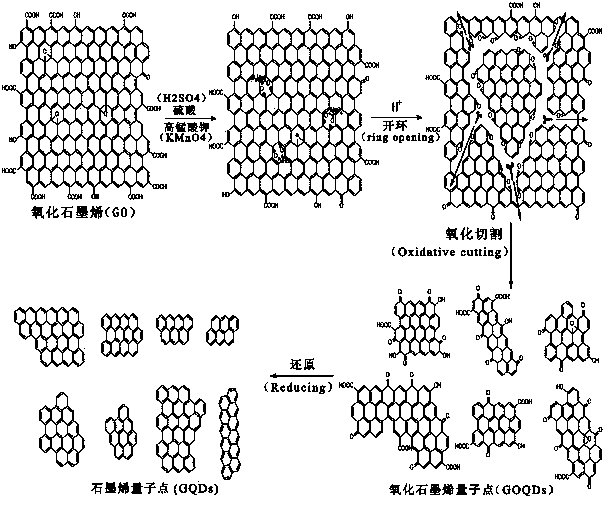
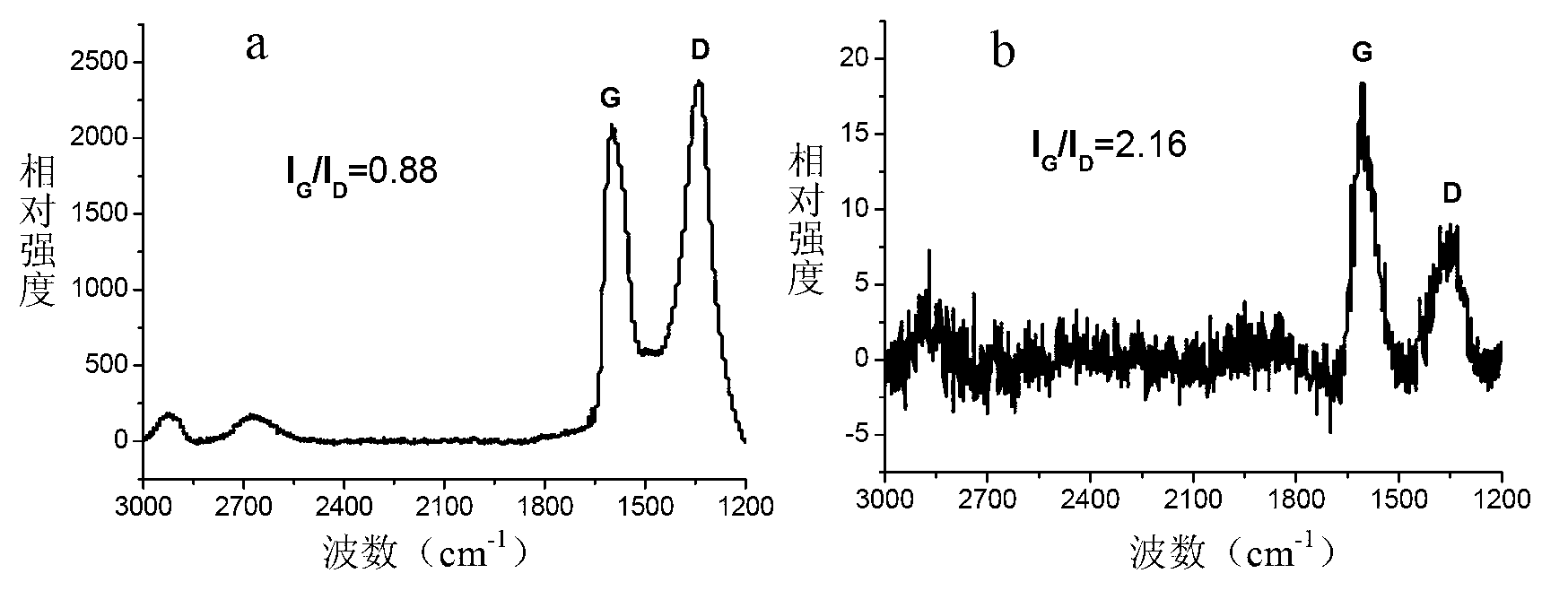
The present invention discloses a graphene quantum dot preparation method, belongs to the technical field of nanometer material preparation, and particularly relates to a graphene quantum dot preparation method. The technical scheme comprises that: a carbon material being subjected to deep oxidation is cut into graphene oxide nano-sheets, C=C bonds and C-C bonds of the graphene oxide are broken to prepare green fluorescence graphene oxide quantum dots, and a reduction or high temperature annealing method is further adopted to prepare the blue fluorescence graphene quantum dots. According to the present invention, the operations are simple, the raw materials are easy to obtain, and the prepared graphene quantum dots have characteristics of excellent monodispersity, good water solubility and strong fluorescence, and have potential application prospects in the fields of supercapacitors, lithium batteries, biological imaging, solar cells, field-effect transistors, OLEDs and the like.
Owner:YANCHENG ZENGCAI SCI & TECH +1
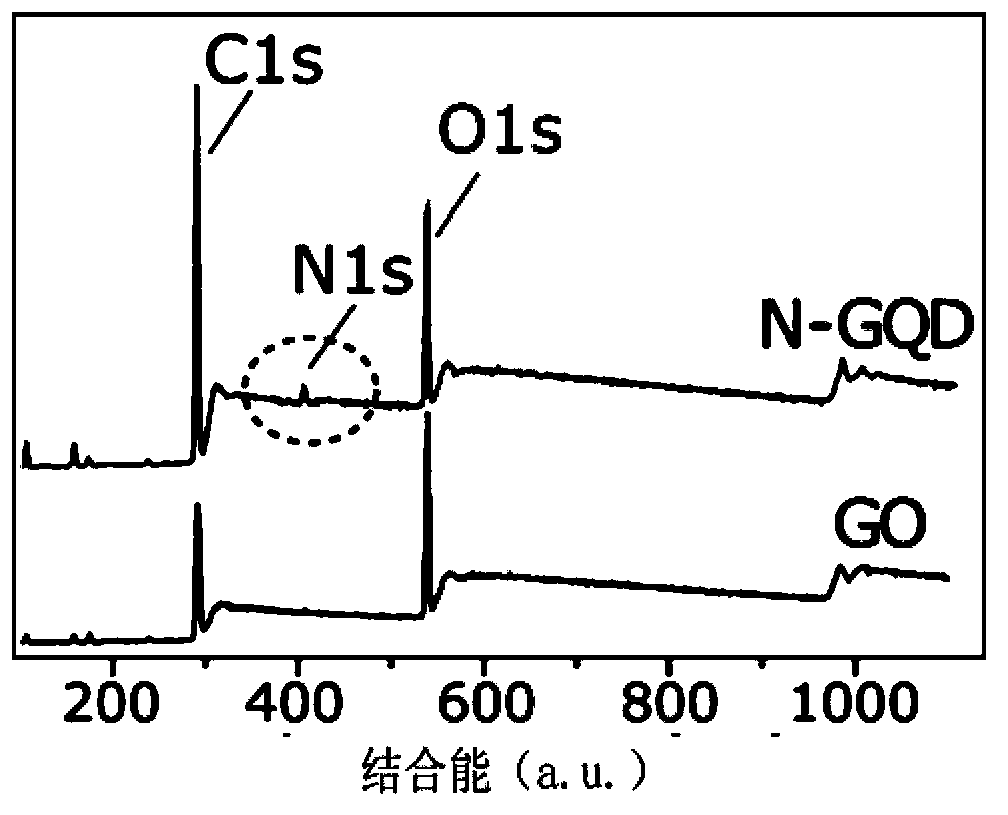
Chemical preparation method for nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot
The invention relates to a chemical preparation method for a nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot, belonging to the technical field of nano materials. The invention particularly relates to a preparation method for the nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, by taking graphite oxide as a carbon source and glycine as a nitrogen source, preparing a nitrogen-doped graphene sheet under a high-temperature annealing condition; then, cutting the deeply oxidized nitrogen-doped graphene sheet into an oxidized nitrogen-doped graphene nano sheet; preparing the nitrogen-doped-graphene quantum dot with super-strong blue fluorescence by way of a hydrothermal reaction. The synthetic method of the nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot provided by the invention is simple in synthetic process, all raw materials are cheap and easy to get in the market, and the prepared nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot is high in purity and yield, mono-dispersible and good in water solubility, has a very strong blue fluorescence performance and has a very good application prospect in the application fields of lithium batteries, micro supercapacitors, biological fluorescent labels, solar batteries and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
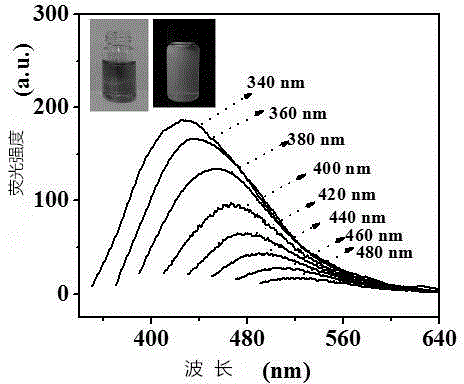
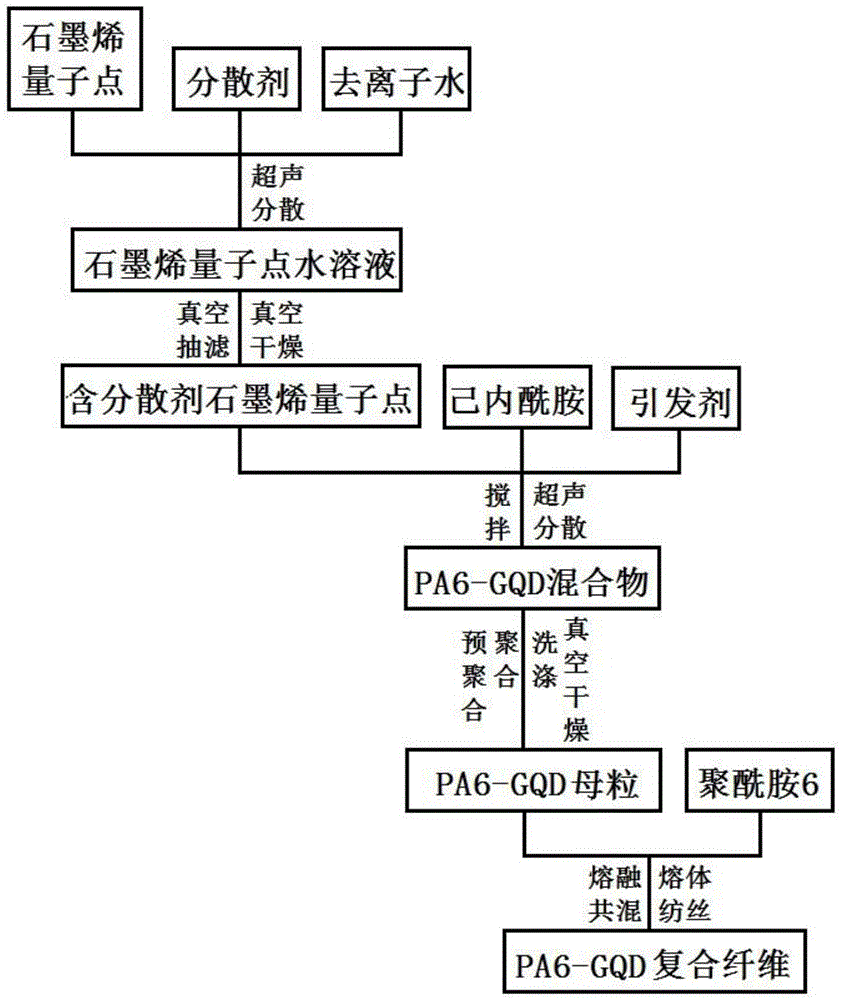
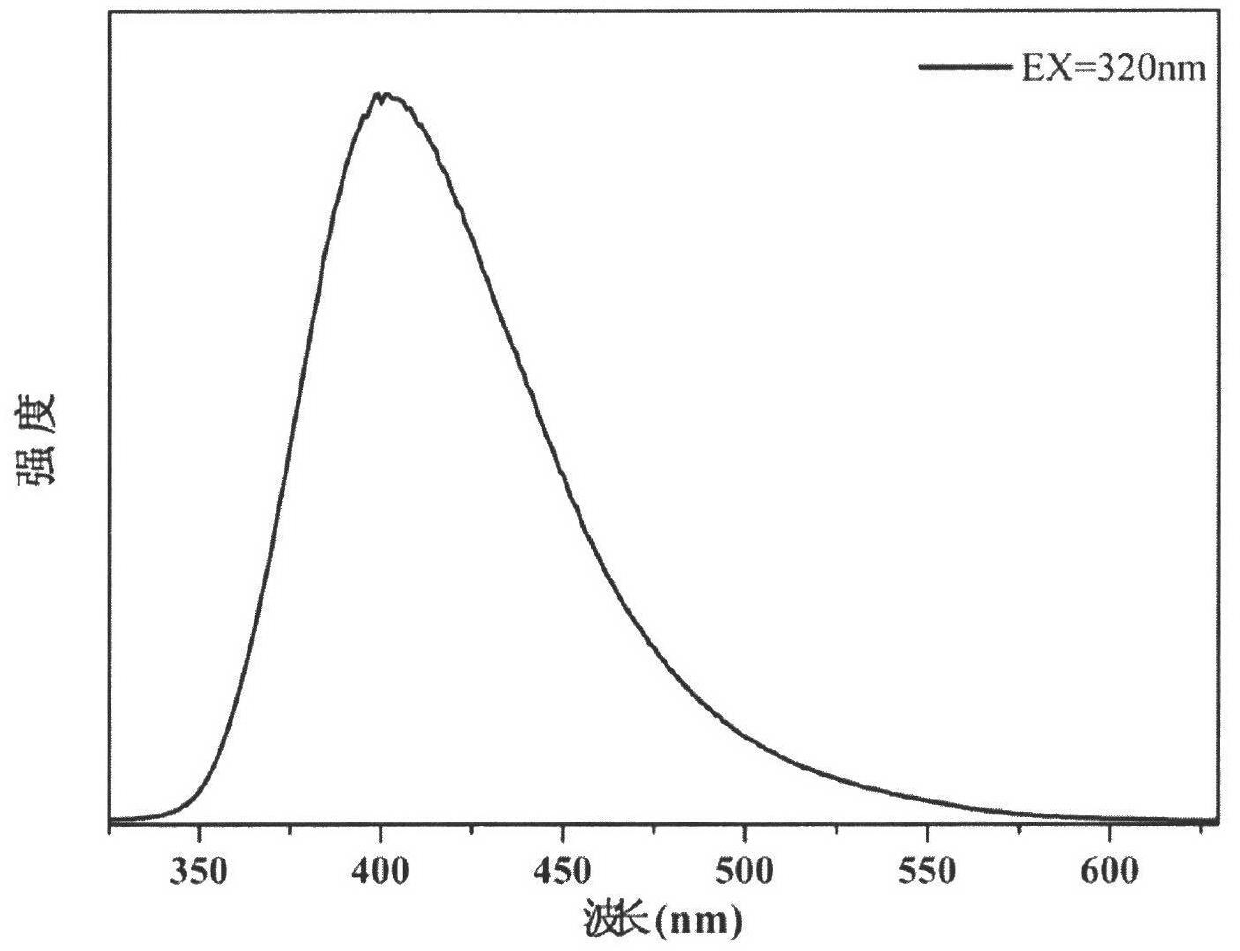
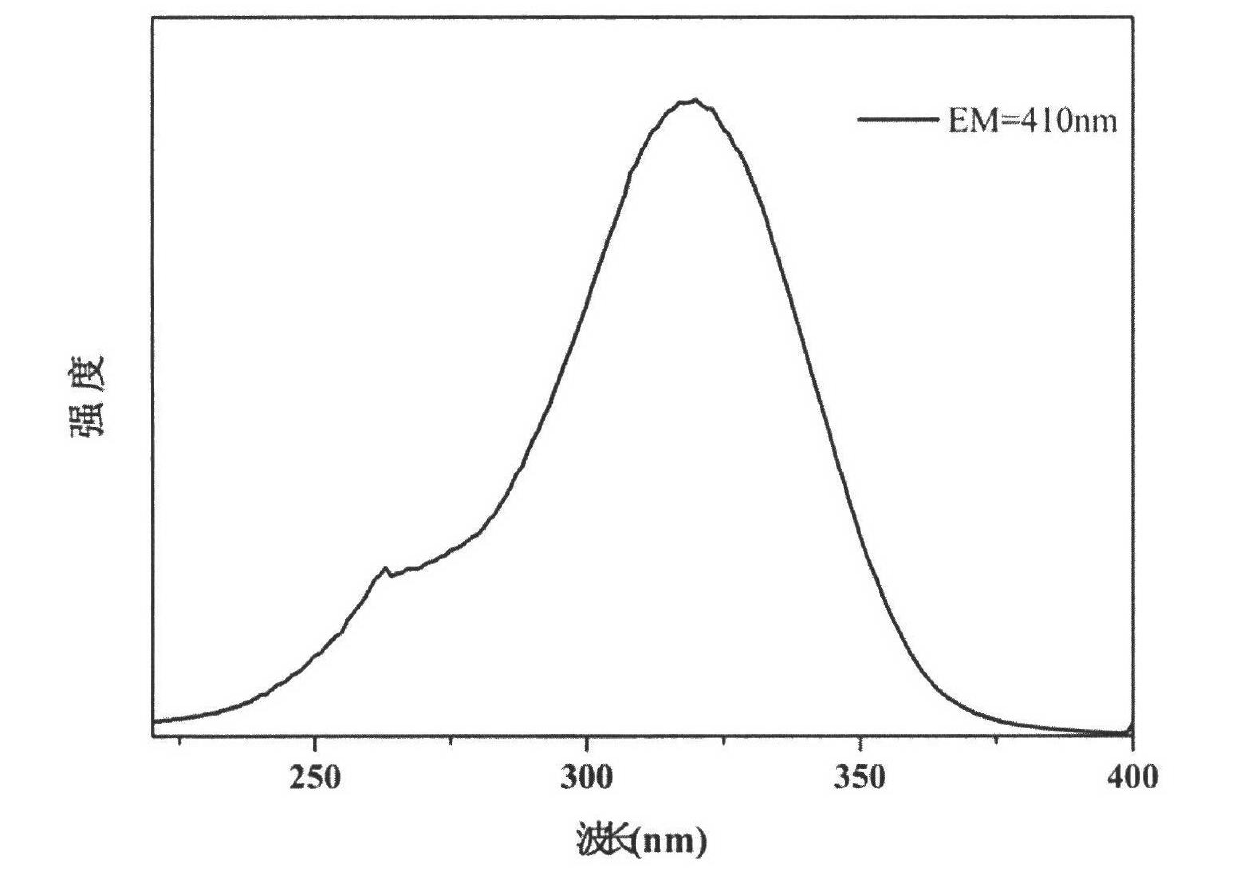
Graphene quantum dot reinforced polyarmide fiber and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105463612AImprove mechanical propertiesGood mechanical propertiesArtifical filament manufactureMonocomponent polyamides artificial filamentPolyamideUltimate tensile strength
The invention provides graphene quantum dot reinforced polyarmide fiber and a preparation method thereof. The mechanical property of PA6 fiber is improved through the molecular template effect of graphene quantum dots and the staggered effect between graphene quantum dots and a PA6 texture structure; the high-strength and high-modulus PA6-GQD compound fiber with tensile strength of 0.72-1.05 GPa and initial modulus of 8-11 GPa is prepared through a traditional mature PA6 melt spinning process. Compared with traditional high-strength and high-modulus PA6 fiber, the graphene quantum dot reinforced polyarmide fiber has the advantages that the mechanical performance is more excellent, the technological process is simple, environment pollution is small, cost is low, the fiber is suitable for being produced on a large scale, an existing PA6 melt spinning process device does not need to be changed, the prepared PA6-GQD fiber has excellent mechanical performance, and the fiber can be used for the fields of tire curtain wires, industrial cloth, clothes, fishing nets and military war industry.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for preparing graphene quantum dot
The invention relates to a method for preparing a graphene quantum dot. The method is mainly characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: adding an amine passivation agent in a suspension of graphene oxide dispersed in water; and then carrying out hydrothermal passivation treatment to obtain the graphene quantum dot with higher quantum yield. The method is very simple and convenient in operation and environment-friendly; the obtained quantum dot has high quantum yield; and the properties are easily regulated and controlled by changing the kinds of the passivation agents; and the method has large-scale preparation potential and wide application prospect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
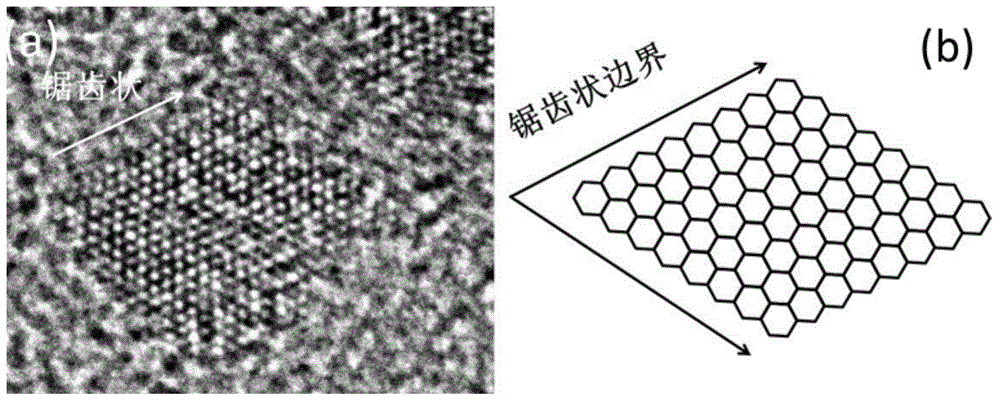
Porous graphene and graphene quantum dot and preparation method of porous graphene and graphene quantum dot
ActiveCN104555999AUniform pore size distributionExcellent oxygen reduction catalytic activityPorous grapheneCvd graphene
The invention discloses porous graphene and a graphene quantum dot. The porous graphene comprises, but is not limited to 2-9 atomic layers, wherein each atomic layer simultaneously comprises crystal lattices and holes of graphene, but is not limited to the holes of which the apertures are 2-10nm; the area of the holes accounts for about 5%-40% of total area of each atomic layer. The graphene quantum dot is characterized by comprising 1-5 atomic layers; the boundary is in a sawtooth shape; and the dimension of the quantum dot is 2-10nm. The porous graphene disclosed by the invention is uniform in aperture distribution, and not equal in interlayer spacing; and the graphene quantum dot has the advantages of high luminous efficacy, good crystal form and few defects.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
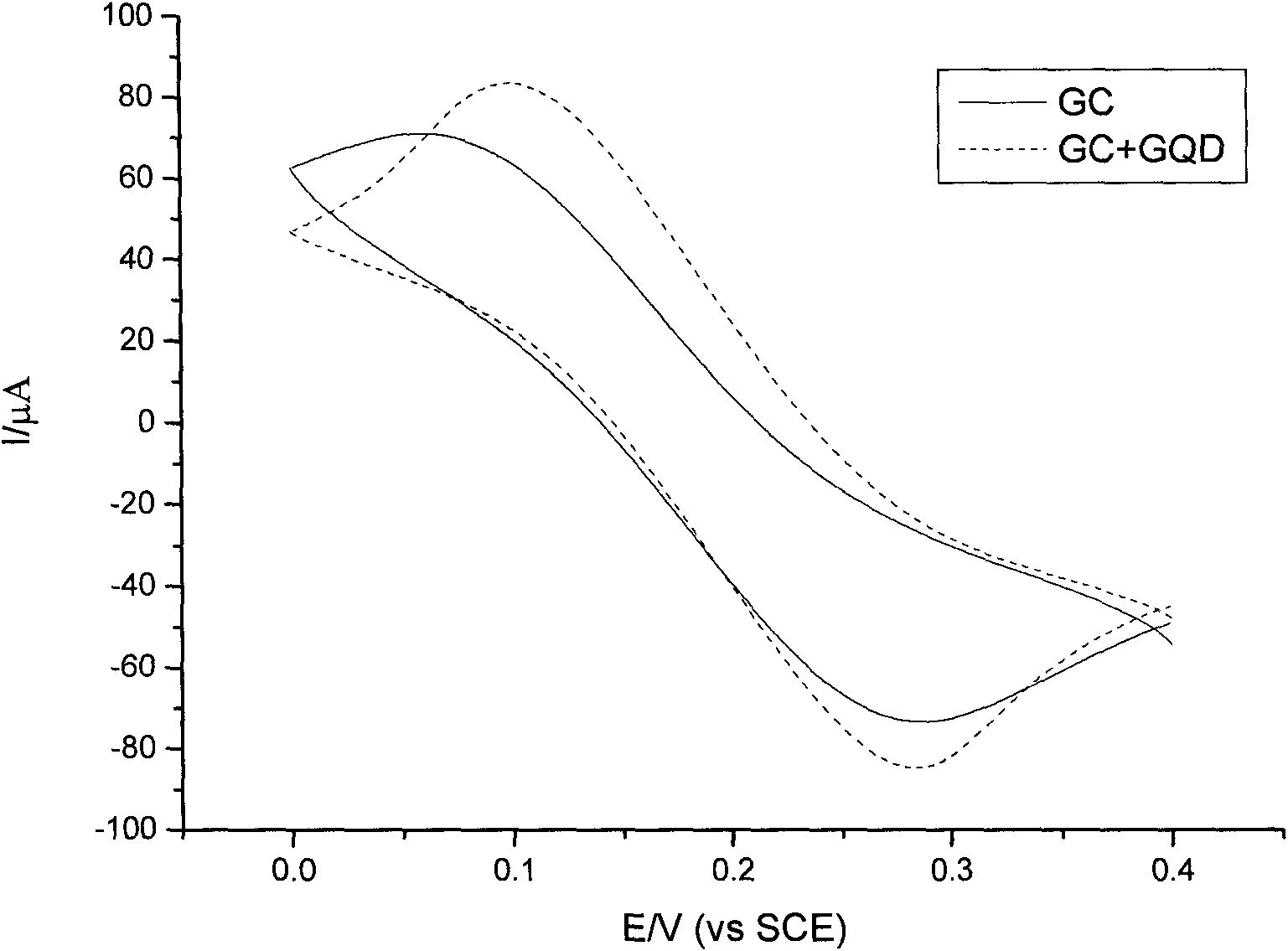
Electrochemical biosensor modified by graphene quantum dot and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an electrochemical biosensor modified by graphene quantum dots and a preparation method thereof. The electrochemical biosensor is a three-electrode system sensor; in a three-electrode, the counter electrode is a platinum electrode, a reference electrode is a saturated calomel electrode, and a working electrode is a glassy carbon electrode the surface of which is coated with 1-4 layers of the graphene quantum dots. The electrochemical biosensor modified by the graphene quantum dots can successfully recognize an objective single-stranded DNA with the lowest concentration of 50nm; in case of the objective single-stranded DNA, equivalent and complementary single-stranded DNA and the objective single-stranded DNA form a double-stranded DNA; an electrochemical signal and the complementary single-stranded DNA have obvious differences so as to make effects on rapidly detecting the objective single-stranded DNA; and the single-stranded DNA section does not need to be modified by sulfydryl or a fluorescence group, thus achieving convenient application. In the invention, the detected single-stranded DNA is nucleic acid of an arbitrary sequence section; and theoretically the invention is applicable to an arbitrary single-stranded nucleic acid sequence which can not form an internal double-strand, thus the single-stranded nucleic acid sequence is displaced into a specific sequential gene related to diseases, i.e. the invention can be used in gene detection related to diseases, thus having wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Large-scale preparation method for graphene quantum dots
The invention provides a large-scale preparation method for graphene quantum dots. The large-scale preparation method comprises the following steps: adding graphene oxide into a first solvent to obtain a first solvent to obtain a first dispersion solution; adding a reducing agent into the first dispersion solution to obtain a mixed solution; reacting the mixed solution in a microwave environment of 500-800W for 10-60 minutes; cooling and carrying out solid-liquid separation and taking solids to obtain a rough product; mixing one of reductive polyhydroxy aldehyde and an organic acid with the rough product; adding Lewis acid and uniformly mixing to obtain a mixture; adding the mixture into a second solvent to obtain a second dispersion solution; reacting the second dispersion solution in the microwave environment of 500-800W for 0.2-1 hour; then stripping in the microwave environment of 120-300W for 2-3 hours; separating and purifying to obtain the graphene quantum dots. The large-scale preparation is finished by a microwave-solvothermal method; the process is simple and the utilization rate of the graphene oxide is high; the yield is high.
Owner:湖北高地石墨烯科技有限公司
3D (three-dimensional) printing graphene-metal composite material, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106744857ALow resistivityHigh hardnessMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesChemical compoundSlurry
The invention relates to a 3D (three-dimensional) printing graphene-metal composite material, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that (1) under the ultrasonic effect, graphene quantum dots and / or graphene microchips and nanometer metal simple substances / nanometer metal compounds are mixed, ground and sheared to prepare a composite slurry material or a composite powder material, wherein the ultrasonic frequency is 10 to 100 KHz, and the weight of the graphene quantum dots and / or graphene microchips accounts for 0.01 to 35 percent of the total weight; (2) the prepared composite slurry material or the powder material is dried. A laser sintering graphene metal substance composite material and a preparation method thereof are provided for the 3D printing; the obtained composite material has the excellent performance of high hardness, high intensity, corrosion resistance, easy-to-process performance and easy-to-use performance; after 3D printing, the laser can be used for sintering and quenching; the particle compaction of the composite material is promoted; crystalline grains are refined, so that the mechanical performance of a 3D printing product is improved.
Owner:尹宗杰 +1
Method for preparing graphene quantum dot powder on large scale
The invention relates to a method for preparing graphene quantum dot powder on a large scale. Proceeding from natural flake graphite, the method for realizing the large-scale preparation of the graphene quantum dot powder comprises the following three steps of: step one. transforming the natural flake graphite into graphite nanometer particles; step two. transforming the graphite nanometer particles into first-order intercalation nanometer graphite oxide; and step three. placing the first-order intercalation nanometer graphite oxide in a non-sealed crucible with a cover, and carrying out thermal treatment in air to obtain the graphene quantum dot powder. The method can be used for realizing the 100% transformation from the intercalation nanometer graphite oxide particles to the graphene quantum dot powder by taking the low-cost natural flake graphite as a raw material in combination of a ball-milling grinding intercalation technology for volume production and a unique thermal treatment technology and breaks through the technical bottleneck that quantum dots can only be obtained in a solution.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
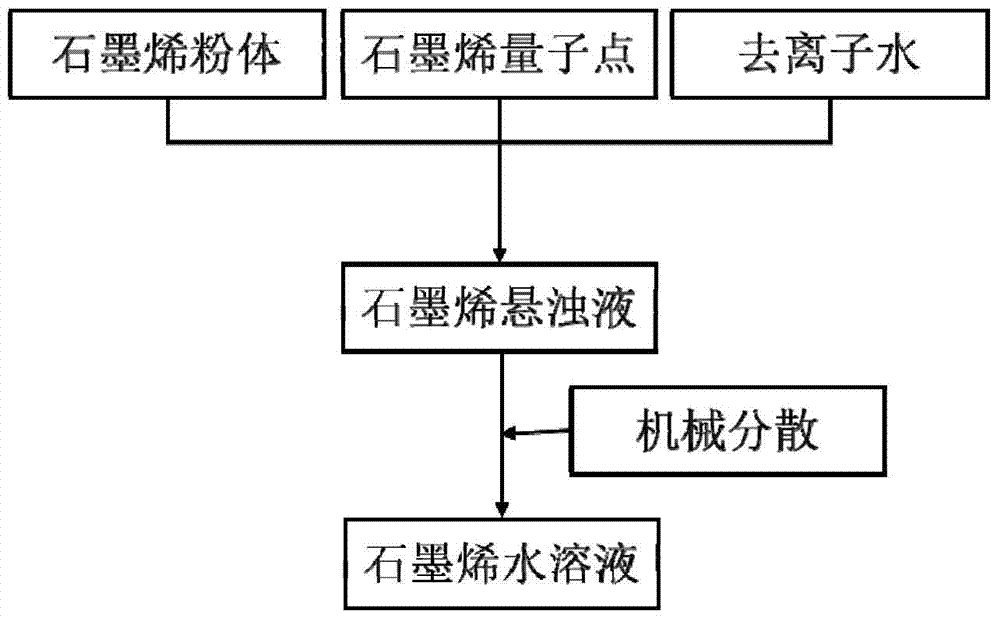
Preparation method of graphene water solution
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene water solution, which is characterized in that graphene quantum dots used as a dispersant and graphene sheets are subjected to non-covalent binding in a water solution to promote dispersion of the graphene in water, thereby obtaining the graphene water solution which can be dispersed stably. The technical scheme is as follows: the method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a mixture of graphene powder and graphene quantum dot water to obtain a graphene suspension; and (2) mechanically dispersing the mixture to obtain the stable graphene water solution. Compared with the existing preparation technique of the graphene water solution, the method disclosed by the invention fully utilizes the dispersivity of the graphene quantum dots in water to assist in dispersing the graphene powder which can not be easily dispersed in water, thereby obtaining the stably-dispersed graphene water solution; and thus, the technique is simple. The method solves the problem that the surfactant, polymer and the like, which must be introduced to disperse the graphite powder in water in the past, are hard to remove; and the method is very suitable for mass production of the graphene water solution.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sulfur-doping graphene quantum dot, preparation method of sulfur-doping graphene quantum dot and application of silver ion detection
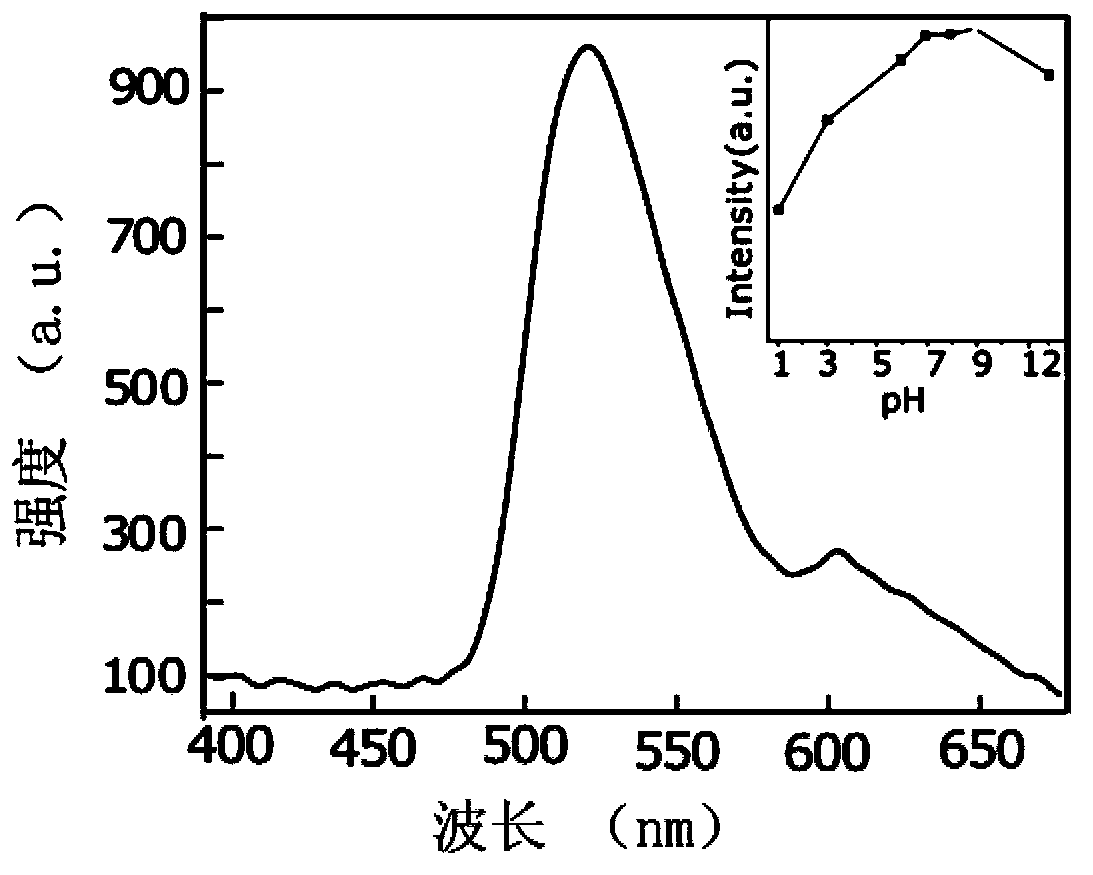
ActiveCN105670618ASpecial lightSpecial selectivityMaterial nanotechnologyFluorescence/phosphorescenceSulfurSilver ion
The invention discloses a sulfur-doping graphene quantum dot, a preparation method of the sulfur-doping graphene quantum dot and application of silver ion detection. The preparation method comprises the following steps of dissolving a carbon source compound and a sulfur source compound into water; performing a hydro-thermal reaction; preparing the sulfur-doping graphene quantum dot, wherein the carbon source compound is 1,3,6-trinitro pyrene, and the sulfur source compound is sulfydryl fatty acid with the carbon atom number being 3 to 4. The prepared sulfur-doping graphene quantum dot has good fluorescence property; when the pH is greater than 4, the stable fluorescence emission is realized; the excitation wavelength independence is realized; when the excitation wavelength of 320 to 360nm is used for excitation, the fluorescence emission peak position is not changed; the result proves that the sulfur-doping graphene quantum dot synthesized by the method provided by the invention has high quality; the obvious selective recognition capability on silver ions is realized; the fast detection on trace silver ions can be realized.
Owner:苏州冉星网络科技有限公司
Compound photocatalyst and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105214635AFull utilizationImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsFull waveTitanium oxide
The invention discloses a compound photocatalyst and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound photocatalyst is formed by compositing metal oxide and quantum dot materials, wherein the metal oxide accounts for, by mass, 80%-99.99% of the photocatalyst, and the quantum dot materials account for, by mass, 0.01%-20% of the photocatalyst, zinc oxide or titanium oxide serves as the metal oxide, and graphene quantum dots serve as the quantum dot materials. The preparation method includes the steps of sequentially conducting stirring, mixing, ultrasonic processing and drying on the metal oxide and the quantum dot materials. The photocatalyst can absorb full-wave-band light of sunlight and can improve the photoelectric conversion efficiency; meanwhile, the photocatalyst can restrain compositing of carriers and comprehensively improve the photocatalytic efficiency; compared with photocatalysts of other types, the photocatalyst has higher catalysis efficiency and a higher catalysis speed for decomposers; the sunlight is more sufficiently and comprehensively used, and the compound photocatalyst has the advantages of being low in price and easy to obtain.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
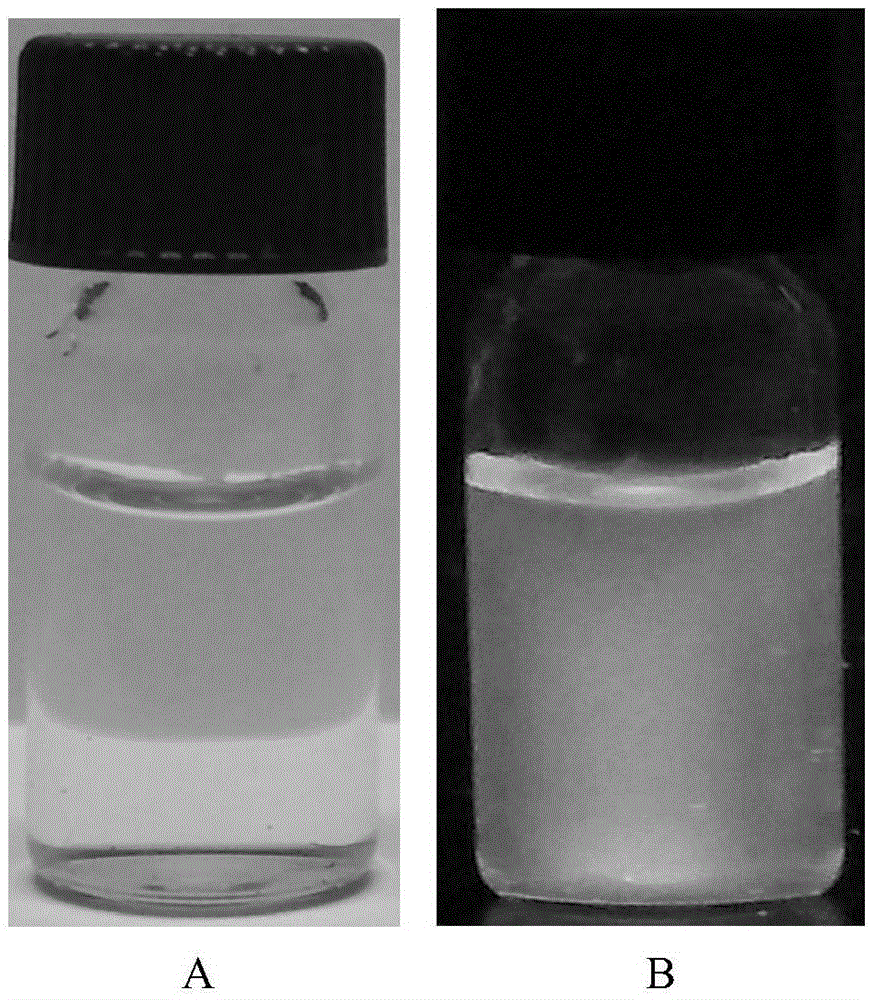
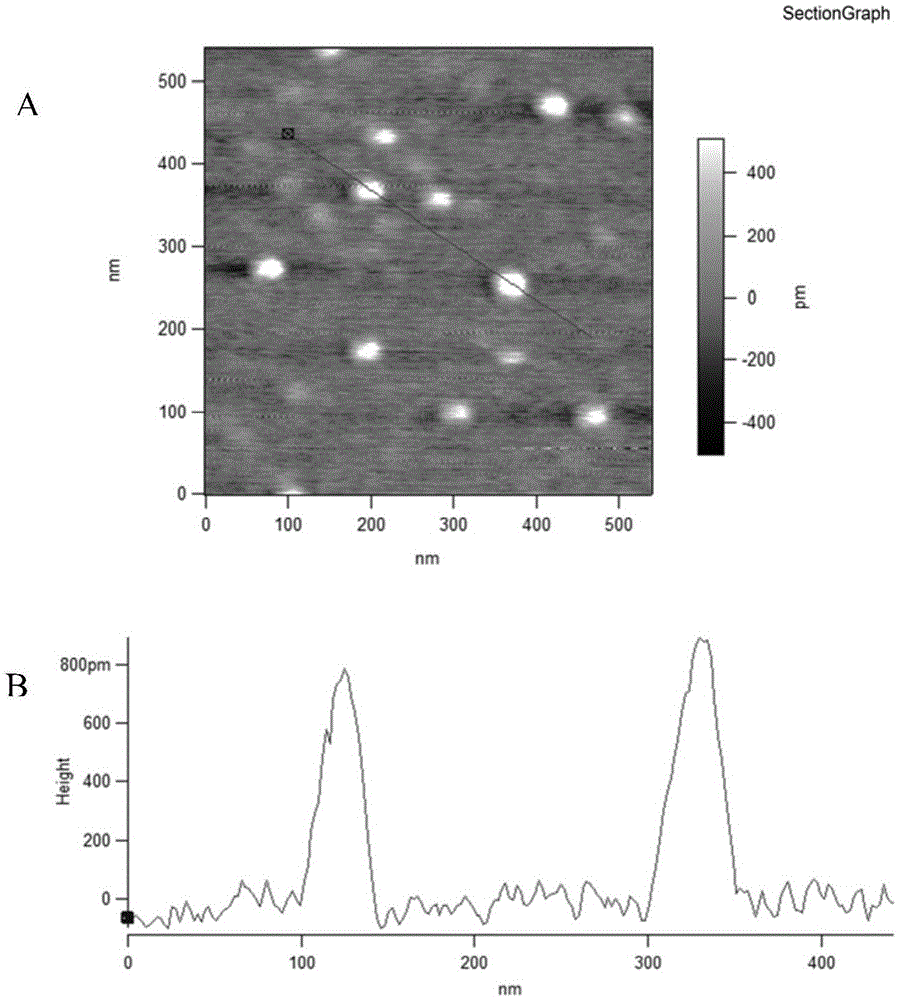
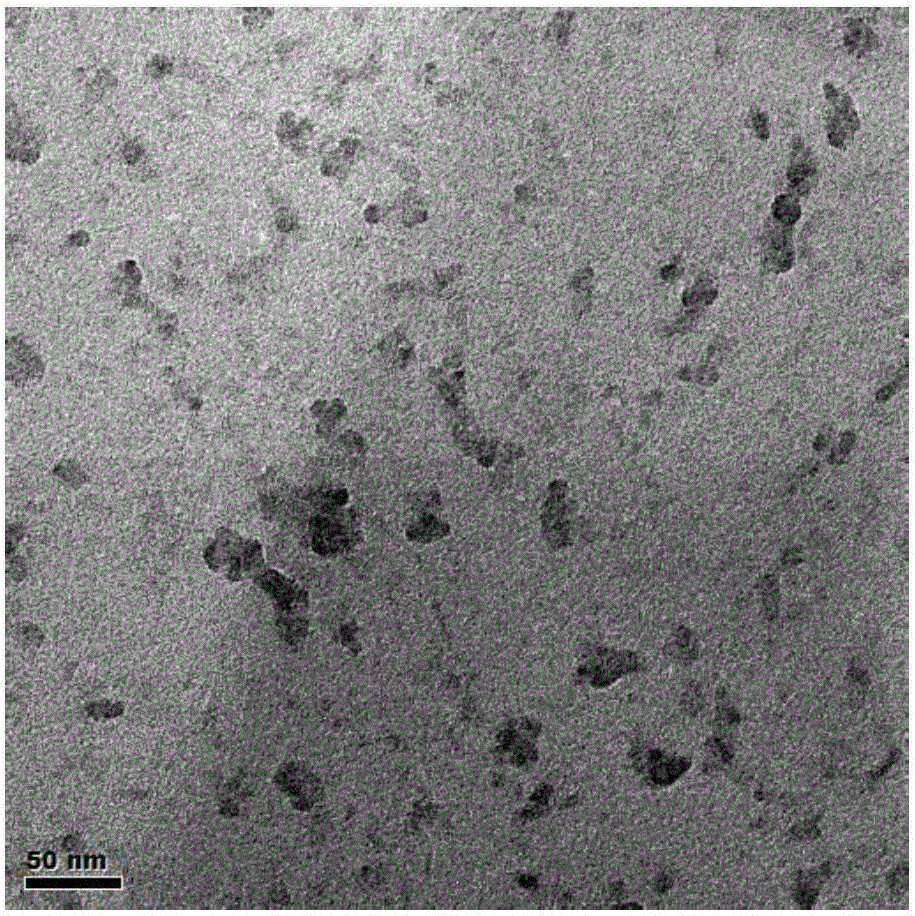
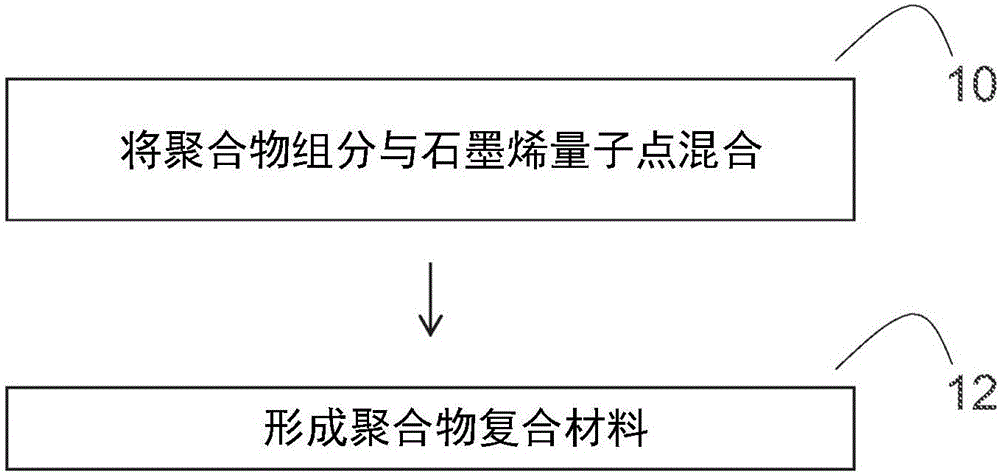
Graphene quantum dot-polymer composites and methods of making the same
Various embodiments of the present disclosure pertain to methods of forming polymer composites that include polymers and graphene quantum dots. The methods occur by mixing a polymer component (e.g., polymers, polymer precursors and combinations thereof) with graphene quantum dots. In some embodiments, the polymers are in the form of a polymer matrix, and the graphene quantum dots are homogenously dispersed within the polymer matrix. In some embodiments, the graphene quantum dots include, without limitation, coal-derived graphene quantum dots, coke-derived graphene quantum dots, unfunctionalized graphene quantum dots, functionalized graphene quantum dots, pristine graphene quantum dots, and combinations thereof. Additional embodiments of the present disclosure pertain to polymer composites that are formed by the methods of the present disclosure. In some embodiments, the polymer composites of the present disclosure are fluorescent and optically transparent. In some embodiments, the polymer composites of the present disclosure are in the form of a film.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Process for preparation of nanoporous graphene and graphene quantum dots
ActiveUS20160130151A1Simple and scalableNo wasteNanotechOther chemical processesPorous grapheneCvd graphene
The present invention discloses a simple and easily scalable process for preparation of two potentially value added carbonaceous materials from graphene. The invention further discloses simultaneous preparation of graphene quantum dots (GQDs,) and porous graphene (pGr) from graphene. The invention further relates to nitrogen doped porous graphene having excellent activity towards electrochemical oxygen reduction reaction (ORR).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Preparation and application of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum-dot two-photon fluorescence
InactiveCN104109534AEasy to prepareNo precipitationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceTwo-photon absorptionNitrogen
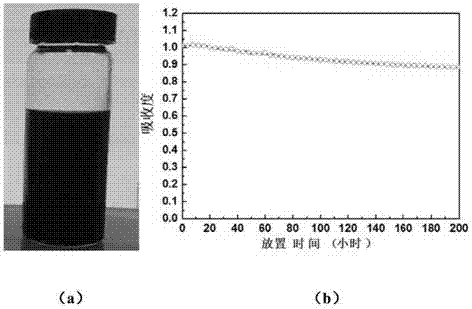
The invention discloses a nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot, a preparation method thereof and application thereof as a two-photon fluorescence probe to imaging of living cells. The nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot is simple in preparation method, is good in imaging effect when applied to two-photon fluorescence imaging of living cells, and has extremely strong two-photon fluorescence in a relatively wide pH scope, and the two-photon absorption cross section can reach 48000 GM; the nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot is extremely easy to dissolve in water, free of toxicity and good in light stability; and a solution of the nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot has extremely strong stability, is capable of keeping stable within 24 months, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
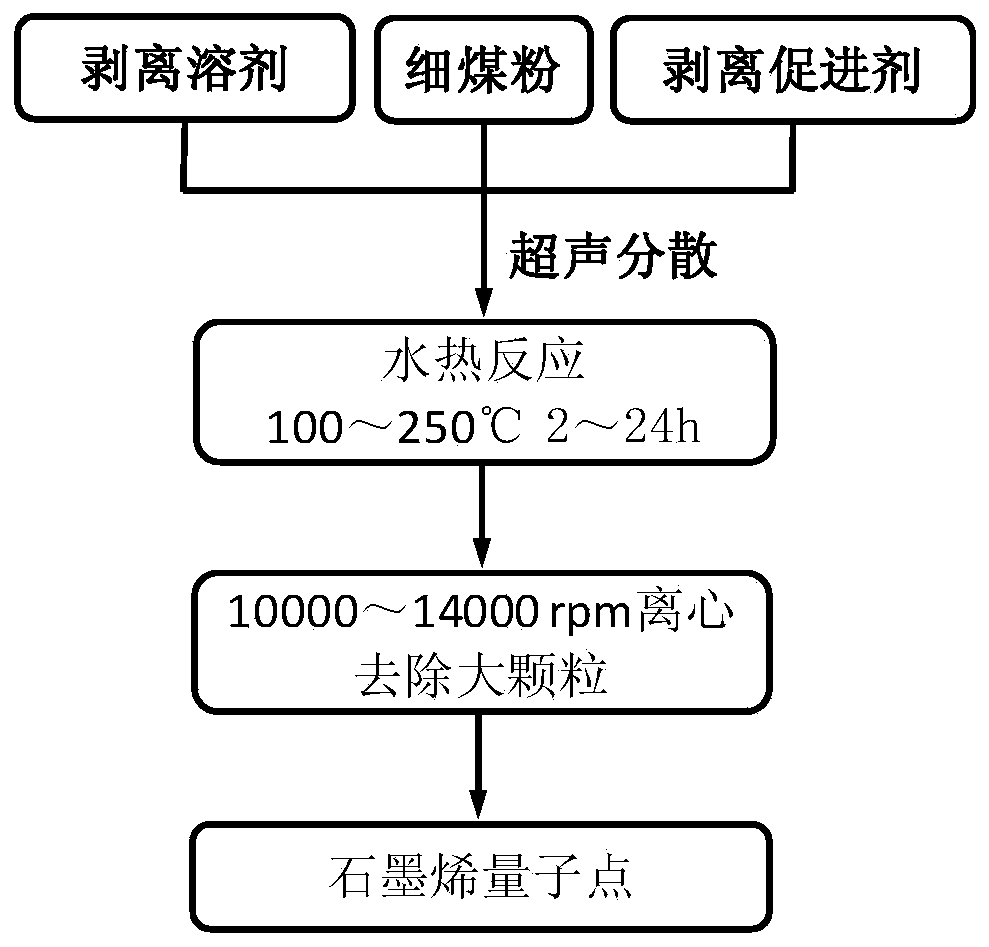
Macro method of coal-based graphene quantum dot
InactiveCN103803538AHigh fluorescence efficiencyGood water solubilityGrapheneLuminescent compositionsSolubilityFluorescence
The invention relates to a macro method of a coal-based graphene quantum dot. The macro method comprises the following steps: mixing crushed coal dust with a peeling solvent and a peeling accelerant, performing ultrasonic dispersion, subsequently transferring into a high-pressure reaction kettle and performing hydrothermal reaction under the continuous magnetic stirring action, cooling down, and performing centrifugal separation to remove unpeeled large grains so as to obtain the graphene quantum dot. According to the macro method, macro preparation of the graphene quantum dot is achieved by controlling parameters including the ratio of the coal dust to the peeling solvent and the peeling accelerant, the hydrothermal reaction temperature and the time; compared with the prior art, the coal-based graphene quantum dot not only has the advantages of good water solubility and high fluorescence efficiency as the organic solvent is adopted to directly peel off coal to prepare the graphene quantum dot, but also is low in preparation cost, simple in process, high in productivity and convenient for industrial volume production.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot and graphite-phase carbon nitride composite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105964286AIncreased visible light response rangeHigh catalytic activityCatalyst activation/preparationCarbon nitrideNitrogen
The invention relates to a nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot and graphite-phase carbon nitride composite photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst consists of the following components in percentage by mass: 95-98% of g-C3N4 and the balance of N-GQDs. The N-GQDs / g-C3N4 composite photocatalyst has the advantages of greater visible light response range, high catalytic activity, good stability, long service cycle and the like. According to the preparation method for the N-GQDs / g-C3N4 composite photocatalyst, precursor urea of N-GQDs and g-C3N4 is adopted to prepare the N-GQDs / g-C3N4 composite photocatalyst by roasting at a high temperature through one step, so that the conventional process of firstly preparing g-C3N4 and then compounding the N-GQDs with the g-C3N4 is reduced; and N-GQDs can be firmly compounded to the surface of g-C3N4, so that the activity and stability of the catalyst are improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com