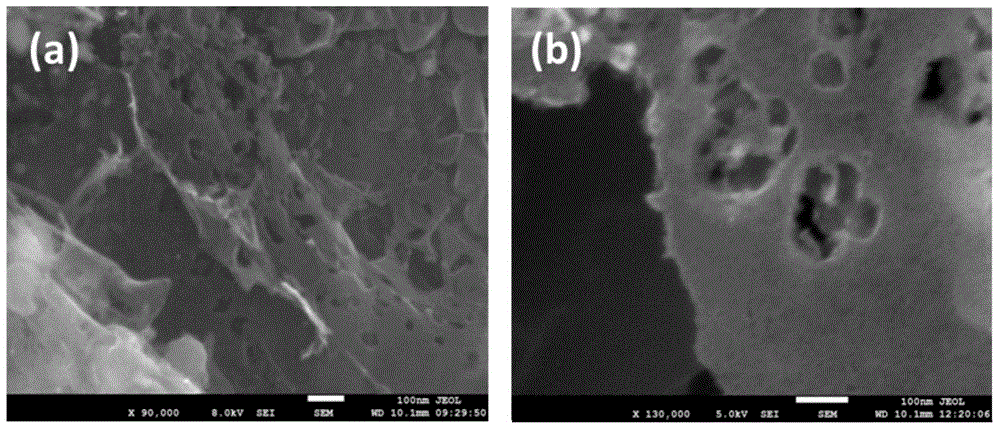
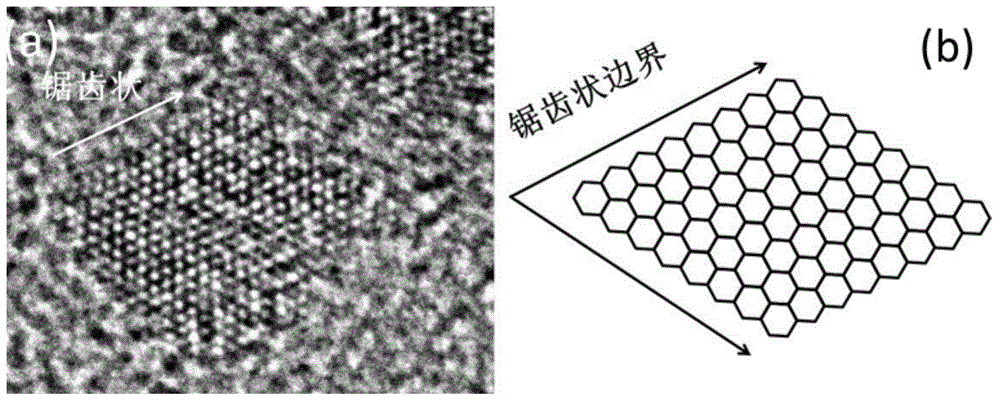
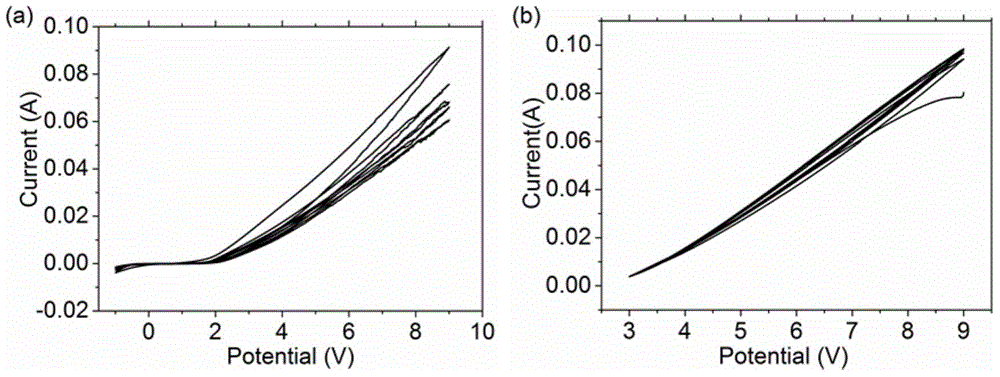
Porous graphene and graphene quantum dot and preparation method of porous graphene and graphene quantum dot
A technology of graphene quantum dots and porous graphene, which is applied in the field of graphene, can solve the problems of affecting the quality of graphene quantum dots, destroying the structural integrity of graphene, and having many defects in graphene quantum dots, so as to achieve good crystal form and high defect less, high luminous efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] (1) Preparation of raw material graphene microsheets
[0071] With flexible graphite paper (the specific surface area of the electrode is 2 square meters per gram (2m 2 / g), resistivity 1 ohm meter) is the electrode material, the distance between the two electrodes is about 20mm, separate the two electrodes with a porous membrane (polypropylene, aperture 1μm), and the ratio of the electrolyte to the graphite is 20ml / g. The DC power supply voltage is -5V—+5V alternately, the electrolyte is composed of cheap sodium perchlorate and dimethyl carbonate aqueous solution, the concentration of sodium perchlorate is 110g / L, and the concentration of water is 2g / L. Programmed charging for 48 hours, changing the charging direction every 30 minutes, the ratio of initial output current density to graphite is 0.01 ampere per gram, and the temperature is 20°C. The flexible graphite paper gradually swells. After the flexible graphite paper is completely swollen, filter out the ele...
Embodiment 2
[0077] (1) Preparation of graphene microsheets
[0078] The specific surface area of the flexible graphite paper electrode is 2 square meters per gram (2m2 / g), the resistivity is 1 ohm m) as the electrode material, and the electrodes are separated by an insulating porous polypropylene film (the average pore size is 0.4 microns). The distance is 10mm and the ratio of electrolyte to graphite is 40ml / g. 16 electrodes form an electrode array and are placed in an electrolytic cell. DC power supply voltage charging -9V—+9V alternately, the electrolyte is composed of cheap sodium perchlorate and dimethyl carbonate aqueous solution, the concentration of sodium perchlorate is 140g / L, and the concentration of water is 5g / L. Programmed charging for 60 hours, changing the charging direction every 1 hour, the ratio of output current density to graphite fluctuates around 0.002 amperes per gram, and the temperature is 40°C. After the flexible graphite paper is completely swollen, press f...
Embodiment 3
[0084] (1) Preparation of graphene microsheets
[0085] The porous electrode material is made of expanded graphite and aluminum foil, with a specific surface area of 3.5 square meters per gram and a resistivity of 10 ohm·m. Separate the graphite electrodes (average pore size is 0.5 micron) with an insulating porous polypropylene bag, and the ratio of the electrolyte to the graphite is 50ml / g. 32 electrodes form an electrode array, and the distance between the electrodes is 5-10mm. They are connected in parallel to form 2 electrolytic cells, each with 16 electrode square arrays. The electrolyte is composed of cheap sodium perchlorate, water and dimethyl carbonate solution, the concentration of sodium perchlorate is 150g / L, the concentration of aqueous solution is 50g / L, and the mass percentage of water is 8%. DC power supply voltage charging -10V and +10V is carried out alternately, programmed charging is 48 hours, and the charging direction is changed every 8 hours. The rat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com