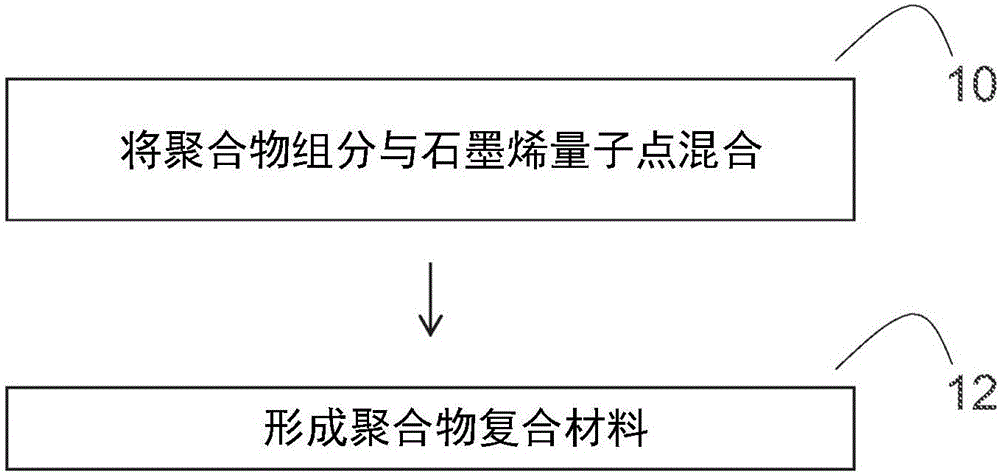
Graphene quantum dot-polymer composites and methods of making the same
A technology of graphene quantum dots and composite materials, applied in the field of graphene quantum dot-polymer composite materials and their preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0112] Example 1. Fluorescent polymer composite film containing coal-derived graphene quantum dots
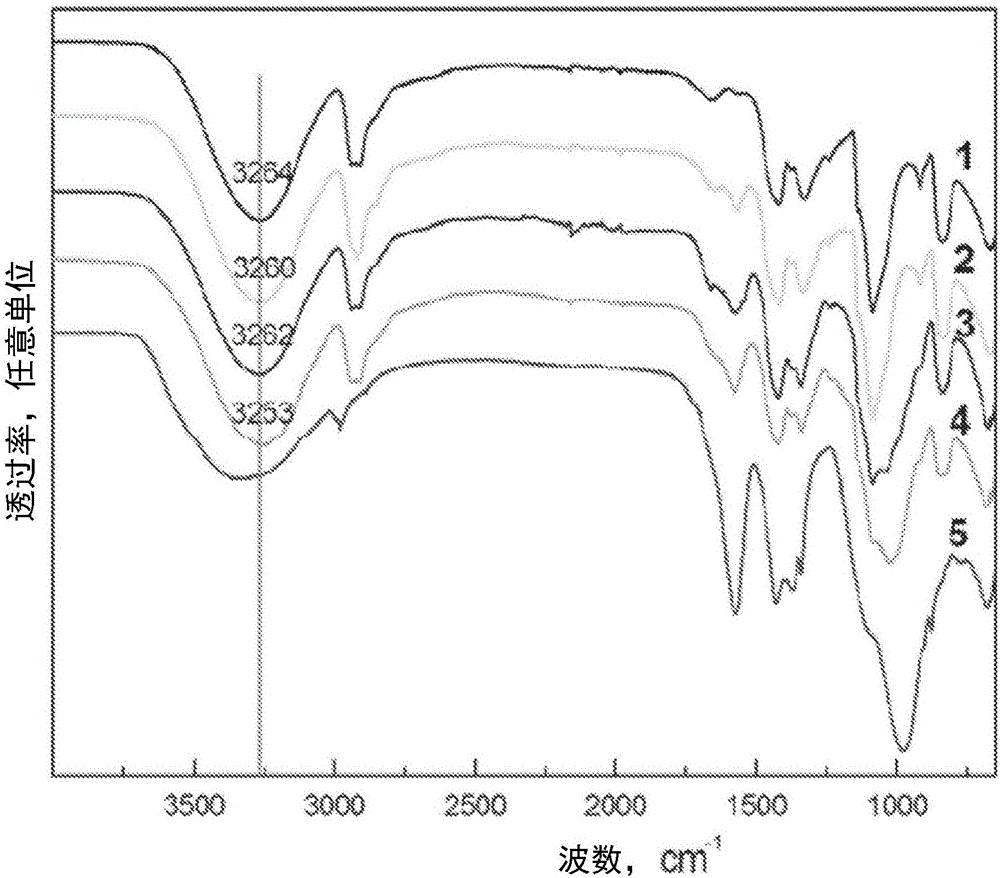
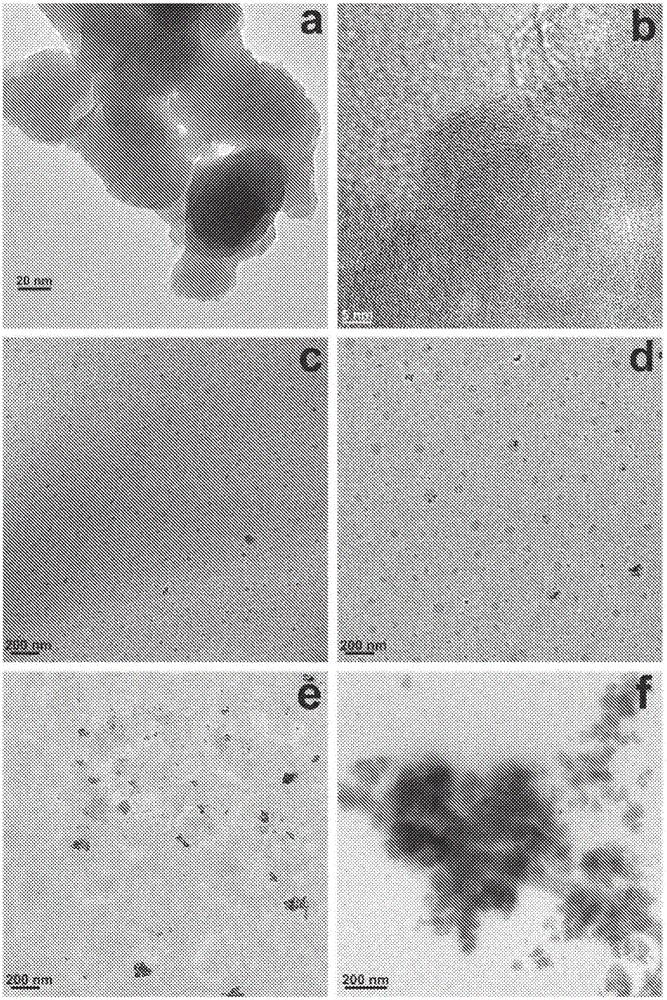
[0113] In this example, the fluorescent polymer composite was prepared by casting from an aqueous solution. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) is used as the polymer matrix. Graphene quantum dots (GQD) derived from coal are mixed with a polymer matrix. The coal-derived GQD imparts fluorescent properties to the polymer matrix, and the prepared composite film shows solid-state fluorescence. The optical, thermal and fluorescent properties of PVA / GQD nanocomposites were studied. The high optical transparency (78%-91%) of the composite film and the best dispersion of the nanoparticles were observed at a GQD concentration of 1% to 5% by weight. The maximum photoluminescence intensity is obtained when the GQD content is 10% by weight.
[0114] In this example, PVA was selected as the matrix polymer because of its hydrophilicity, including water solubility, high optical transparency, good chemica...
Embodiment 11
[0116] Example 1.1. Materials
[0117] Put poly(vinyl alcohol) ( Hydrolysis, molecular weight 89000-98000, Sigma-Aldrich), bituminous coal (Fisher Scientific), sulfuric acid (95-98%, Sigma-Aldrich) and nitric acid (70%, Sigma-Aldrich) Company) use as supplied. Purify GQD with a dialysis bag (Membrane Filtration Products Co., Ltd., product number 1-0150-45 (MembraneFiltration Products, number 1-0150-45)).
Embodiment 12
[0118] Example 1.2. GQD synthesis
[0119] According to the previously described procedure, GQD synthesized from bituminous coal is oxidized in a mixture of sulfuric acid and nitric acid. See, for example, Ye R et al., Nat. Commun. 2013, 4:2943. See also International Patent Application PCT / US2014 / 036604.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com