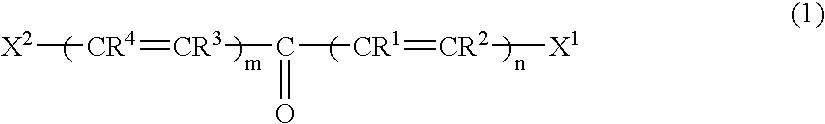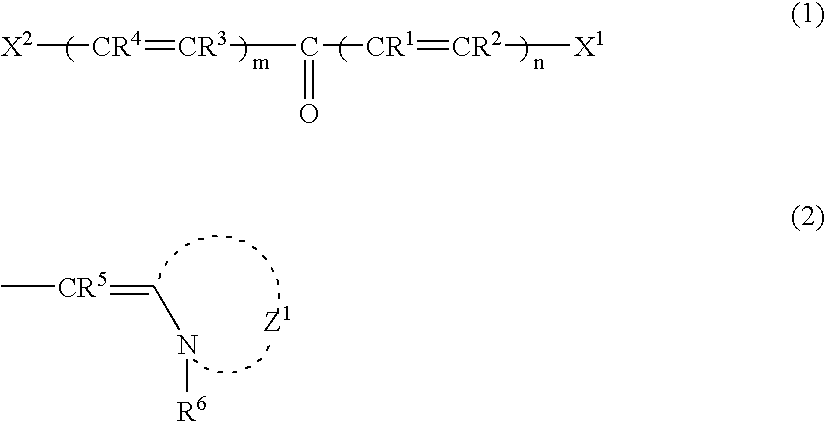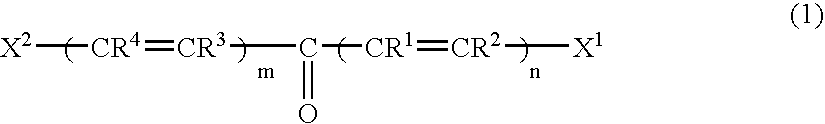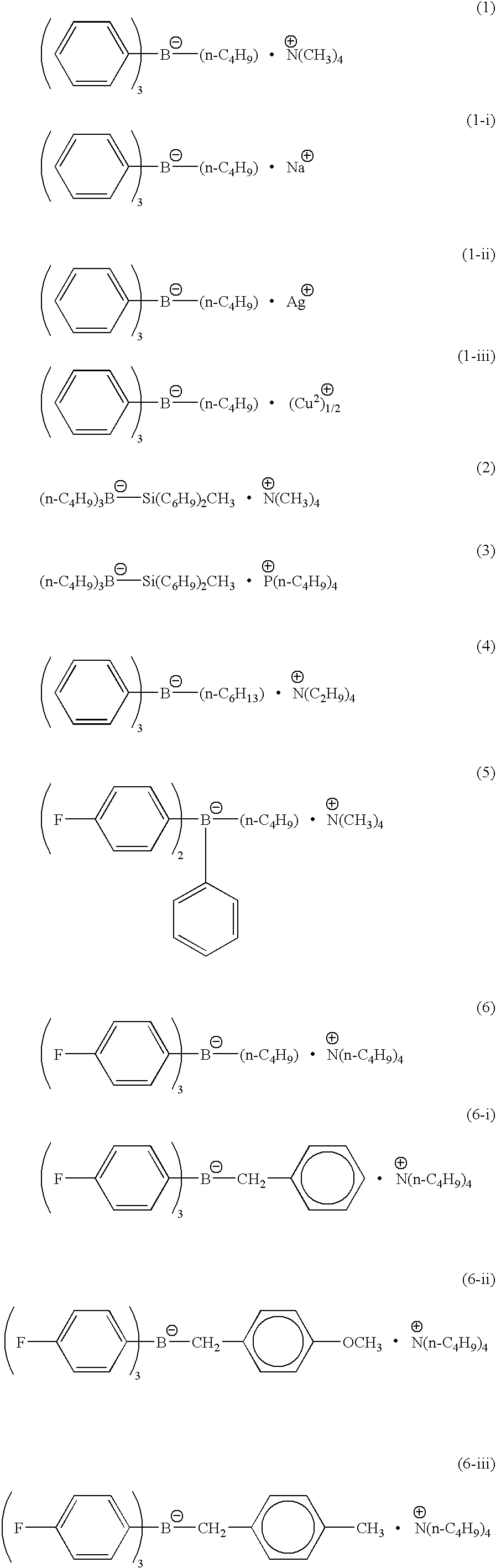Patents
Literature
418 results about "Two-photon absorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
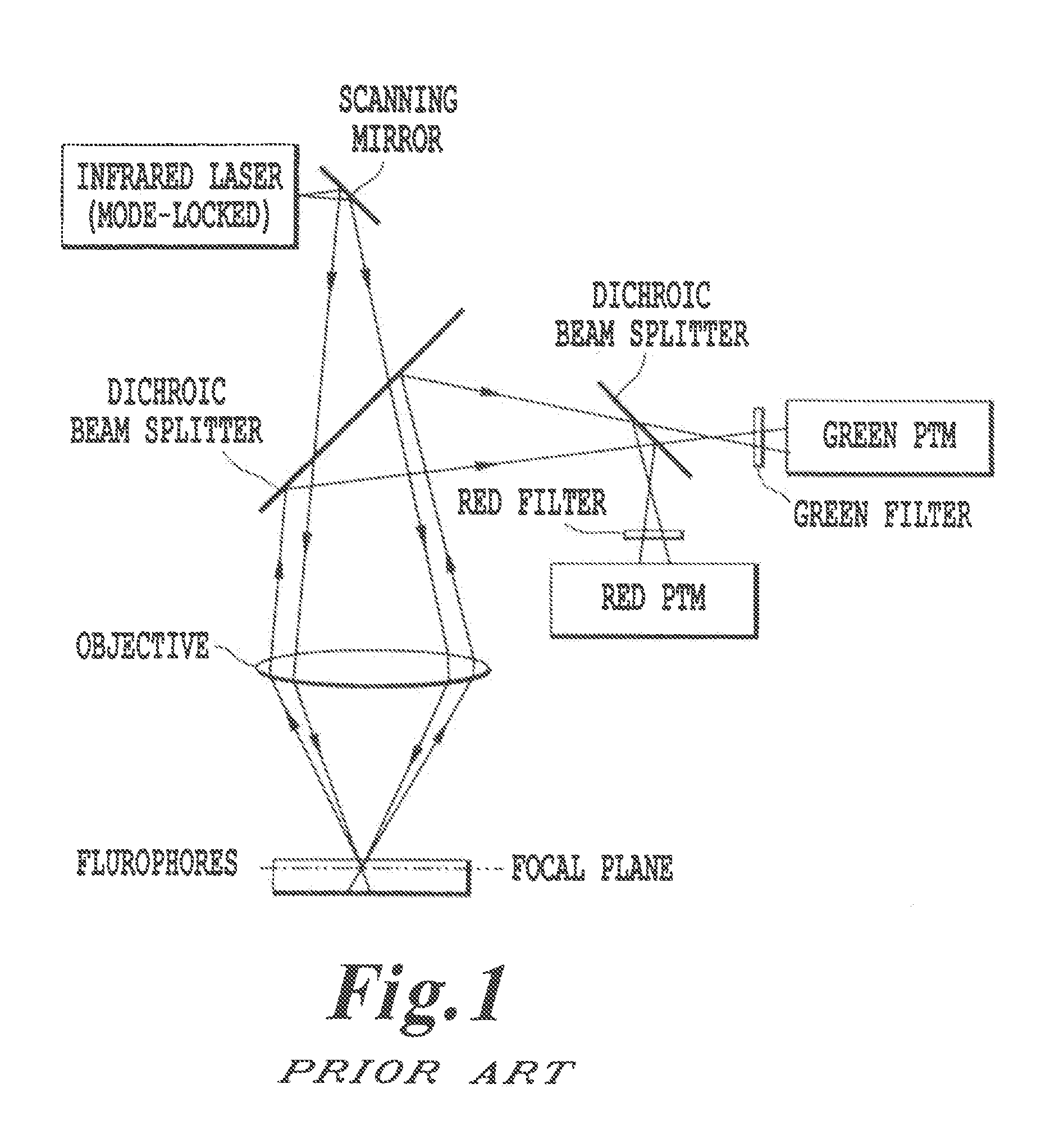
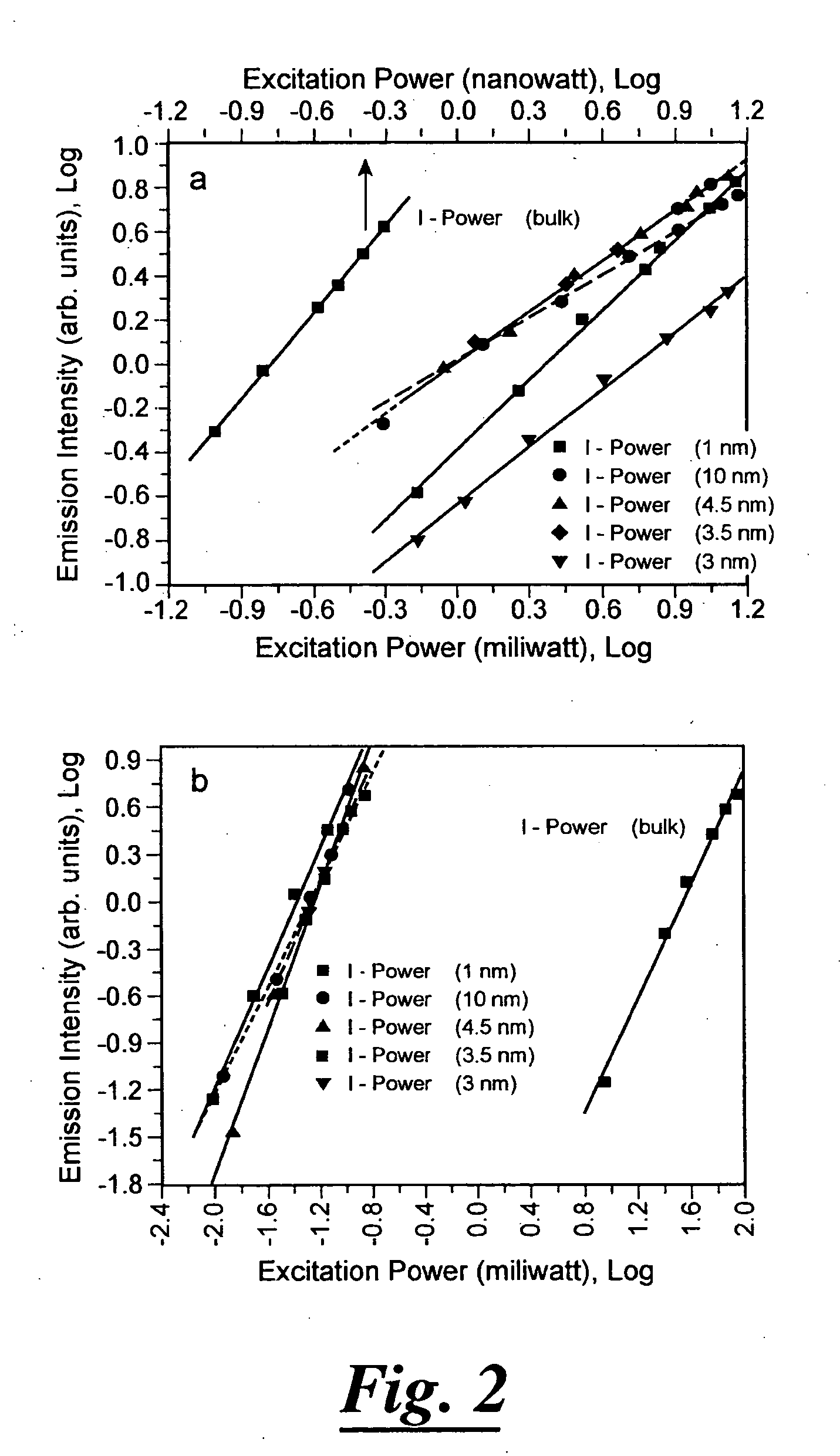
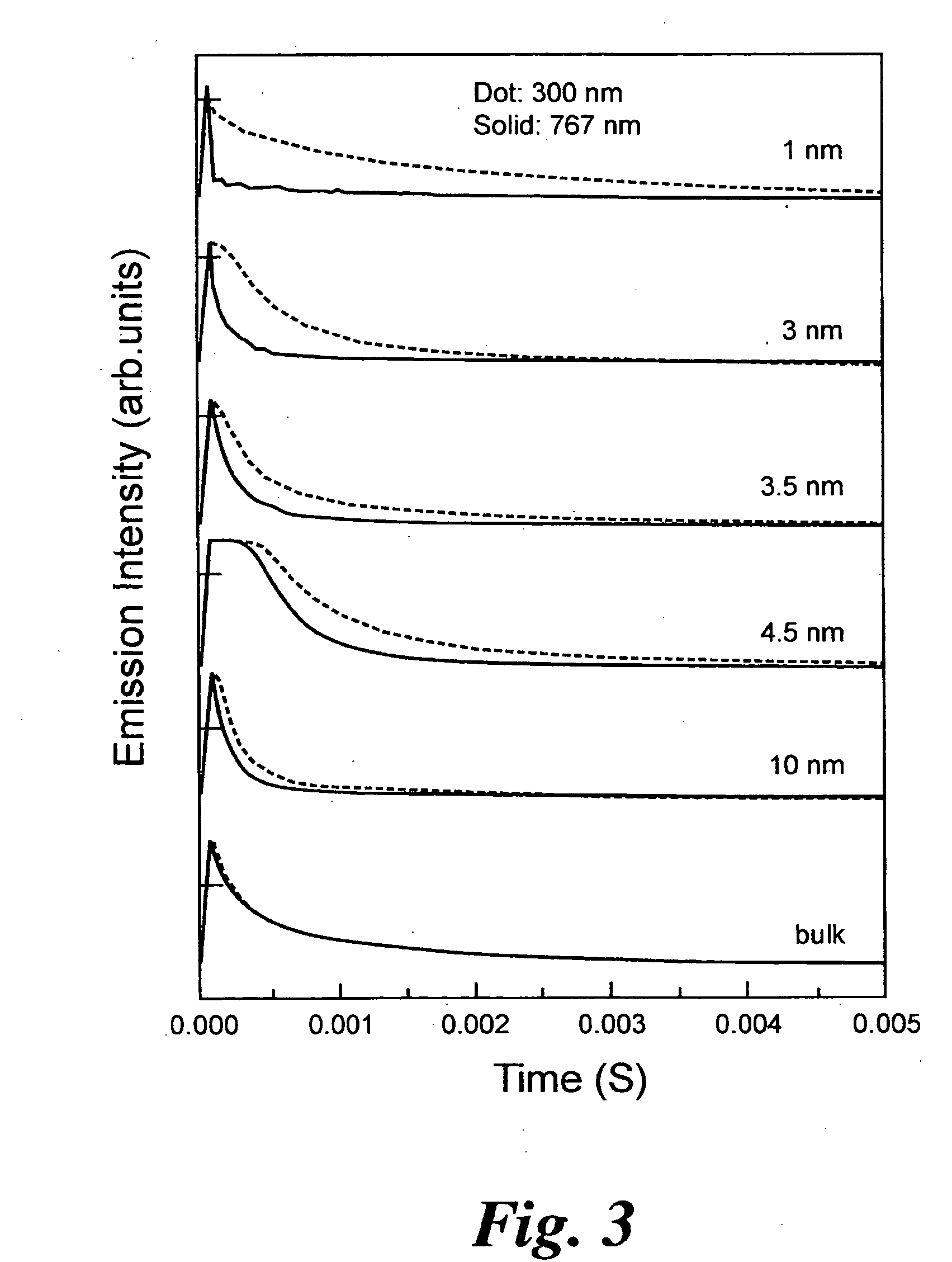
Two-photon absorption (TPA) is the absorption of two photons of identical or different frequencies in order to excite a molecule from one state (usually the ground state) to a higher energy, most commonly an excited electronic state. The energy difference between the involved lower and upper states of the molecule is equal to the sum of the photon energies of the two photons absorbed. Two-photon absorption is a third-order process, typically several orders of magnitude weaker than linear absorption at low light intensities. It differs from linear absorption in that the optical transition rate due to TPA depends on the square of the light intensity, thus it is a nonlinear optical process, and can dominate over linear absorption at high intensities.
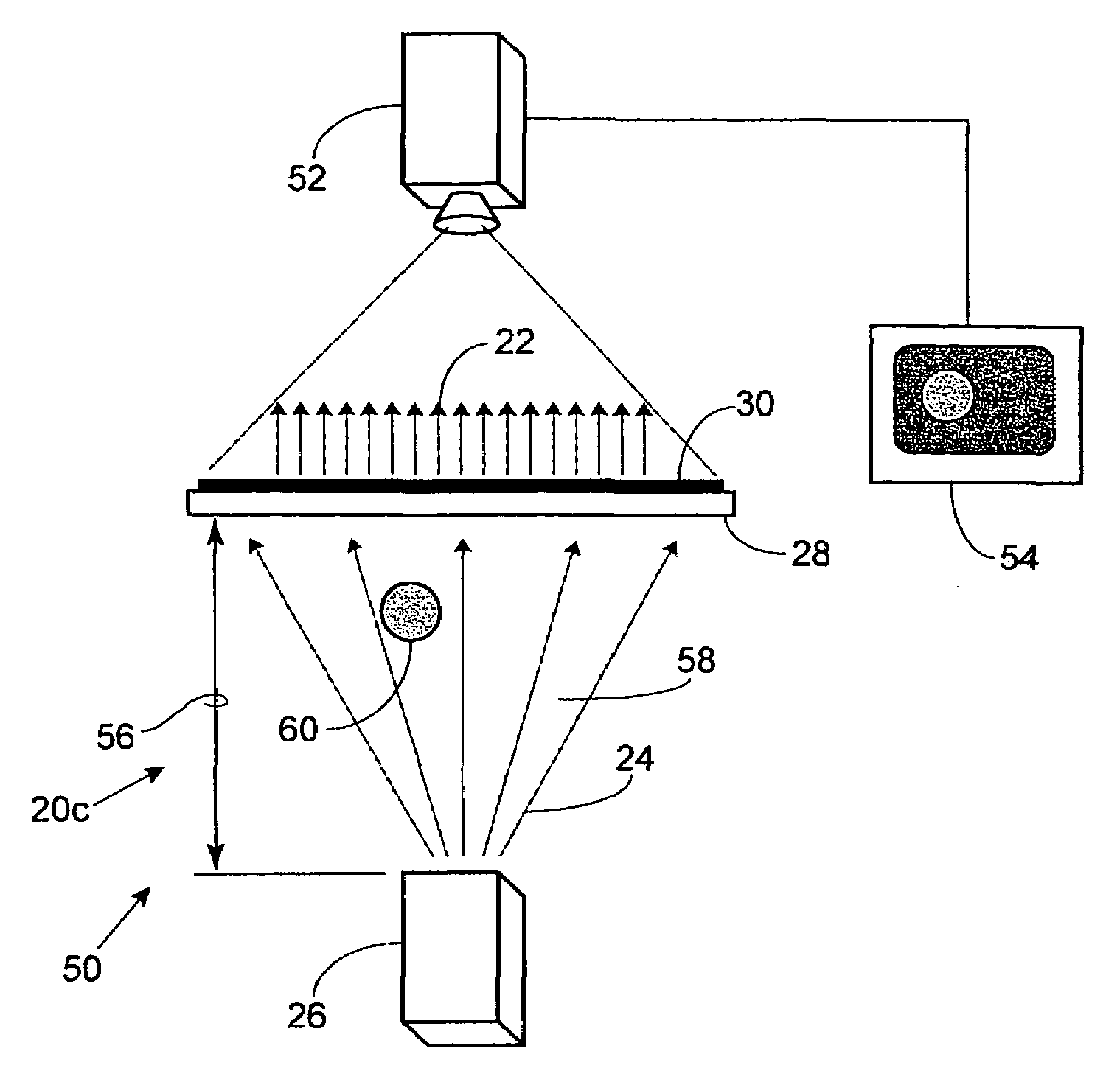
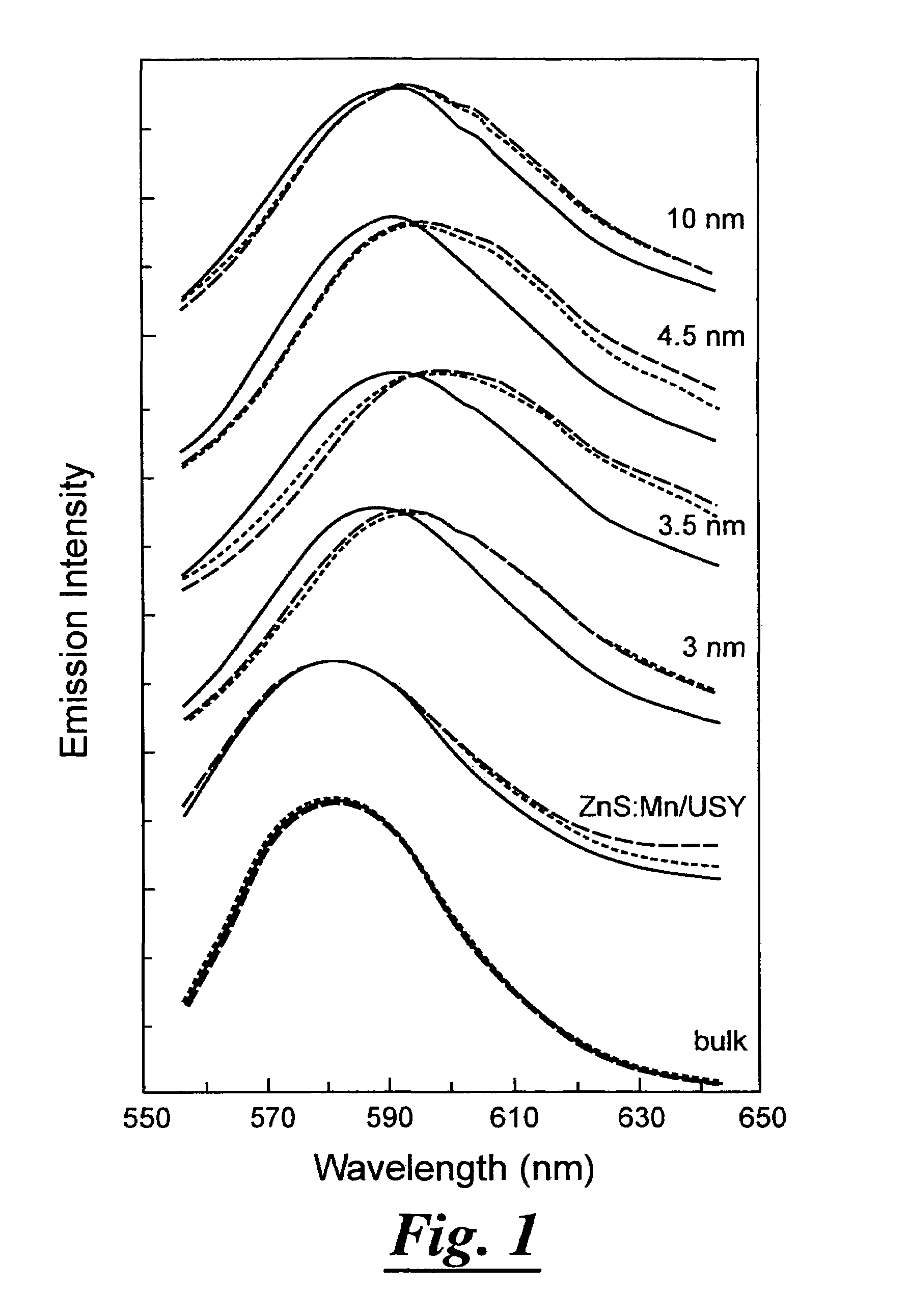
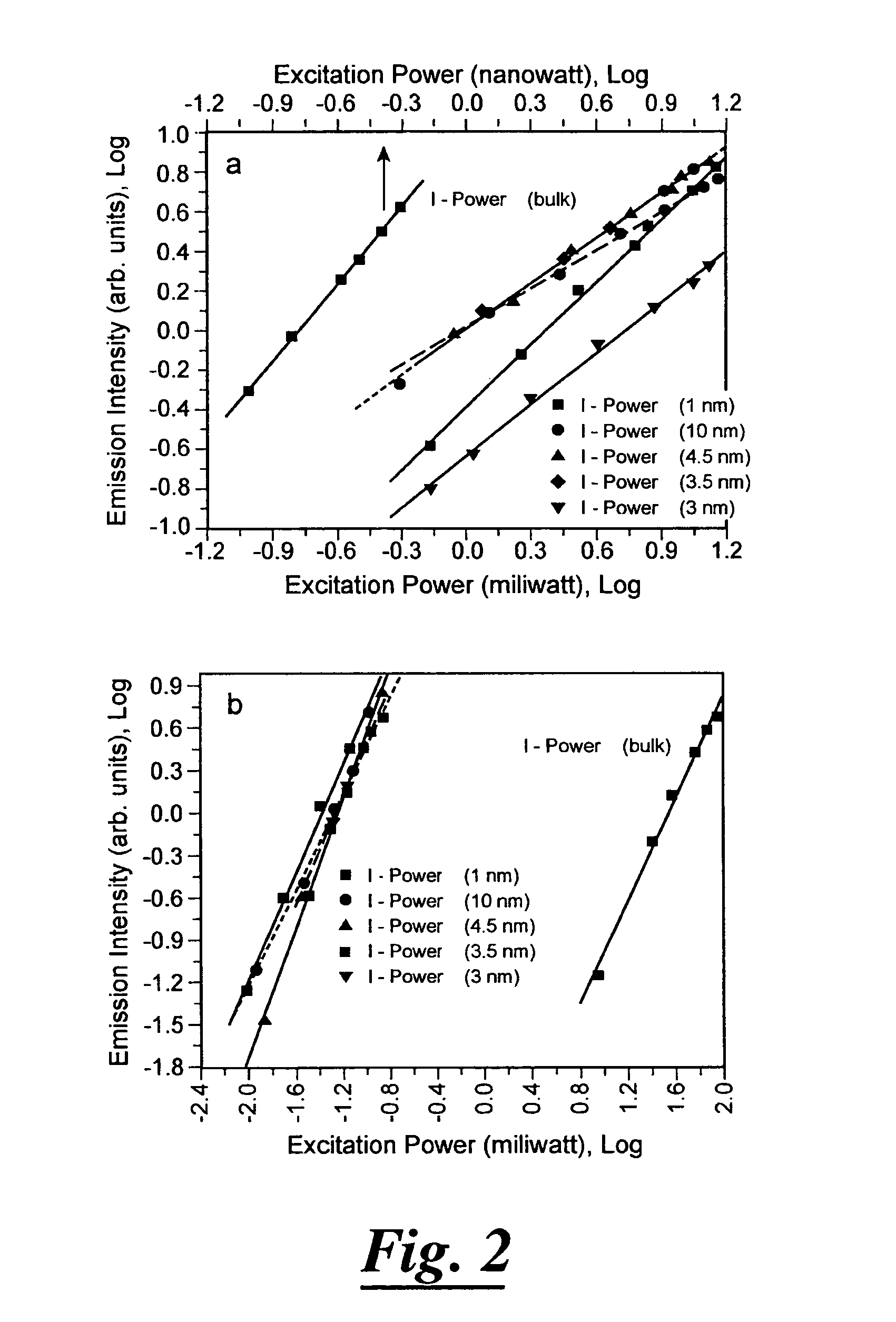
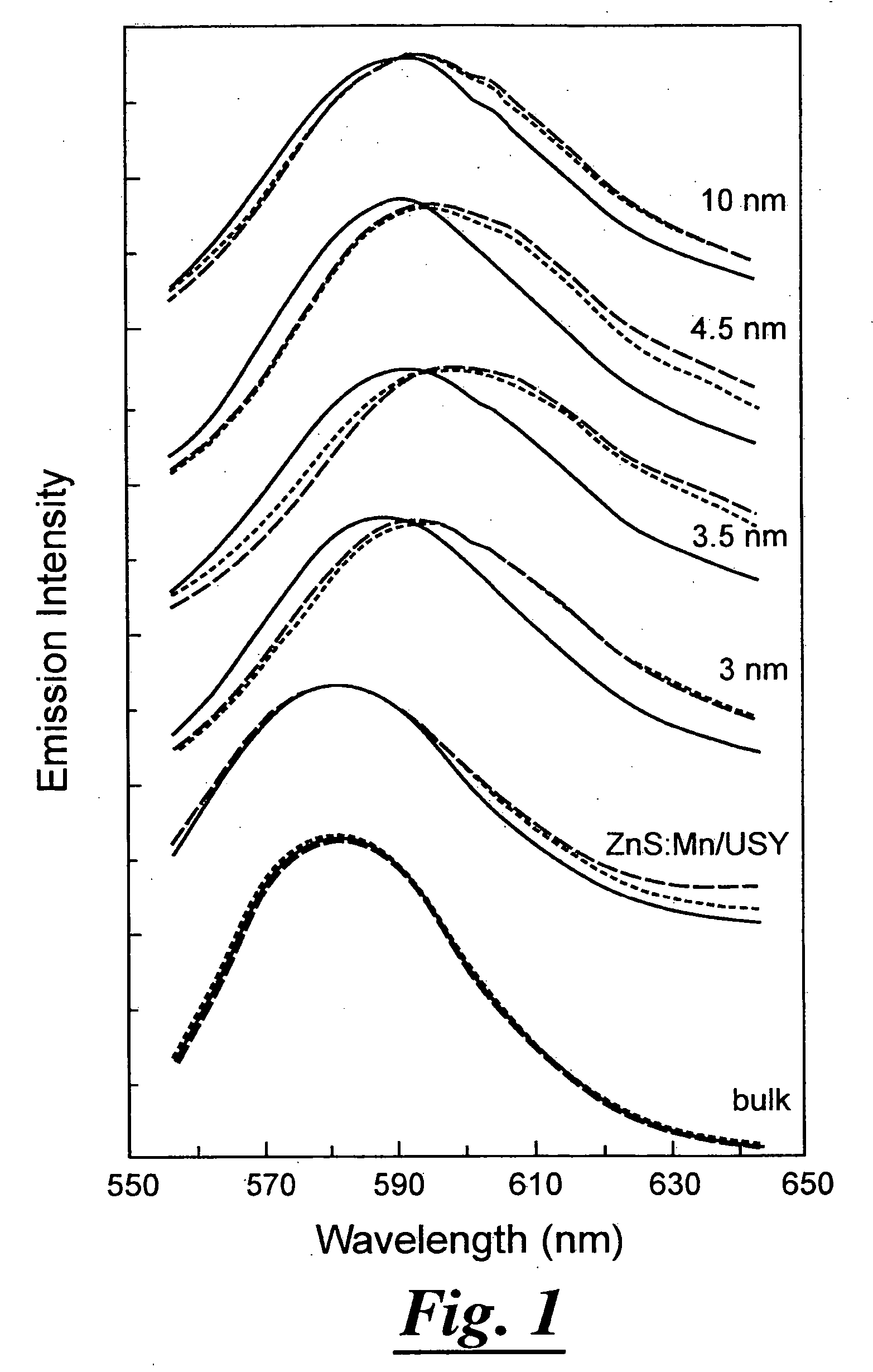
Manganese doped upconversion luminescence nanoparticles
InactiveUS7008559B2PhotometryThermometers using physical/chemical changesTwo-photon absorptionUpconversion luminescence
The present relates in general to upconversion luminescence (“UCL”) materials and methods of making and using same and more particularly, but not meant to be limiting, to Mn2+ doped semiconductor nanoparticles for use as UCL materials. The present invention also relates in general to upconversion luminescence including two-photon absorption upconversion, and potential applications using UCL materials, including light emitting diodes, upconversion lasers, infrared detectors, chemical sensors, temperature sensors and biological labels, all of which incorporate a UCL material.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
Upconversion luminescence materials and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20030030067A1PhotometryThermometers using physical/chemical changesTwo-photon absorptionUpconversion luminescence
The present relates in general to upconversion luminescence ("UCL") materials and methods of making and using same and more particularly, but not meant to be limiting, to Mn2+ doped semiconductor nanoparticles for use as UCL materials. The present invention also relates in general to upconversion luminescence including two-photon absorption upconversion, and potential applications using UCL materials, including light emitting diodes, upconversion lasers, infrared detectors, chemical sensors, temperature sensors and biological labels, all of which incorporate a UCL material.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
Methods and systems for treating cell proliferation disorders using two-photon simultaneous absorption
InactiveUS20090104212A1Avoid the needHigh selectivityAntibacterial agentsBiocideTwo-photon absorptionBiological activation
A method for treating a cell proliferation disorder in a subject, comprising:(1) administering to the subject at least one activatable pharmaceutical agent that is capable of activation by a simultaneous two photon absorption event and of effecting a predetermined cellular change when activated; and(2) applying an initiation energy from an initiation energy source to the subject,wherein the initiation energy is capable of penetrating completely through the subject, and wherein the applied initiation energy activates the activatable agent by the simultaneous two photon absorption event in situ,thus causing the predetermined cellular change to occur, wherein the predetermined cellular change treats the cell proliferation related disorder,and a kit for performing the method, a computer implemented system for performing the method, a pharmaceutical composition useful in the method and a method for causing an autovaccine effect in a subject using the method.
Owner:IMMUNOLIGTHT LLC
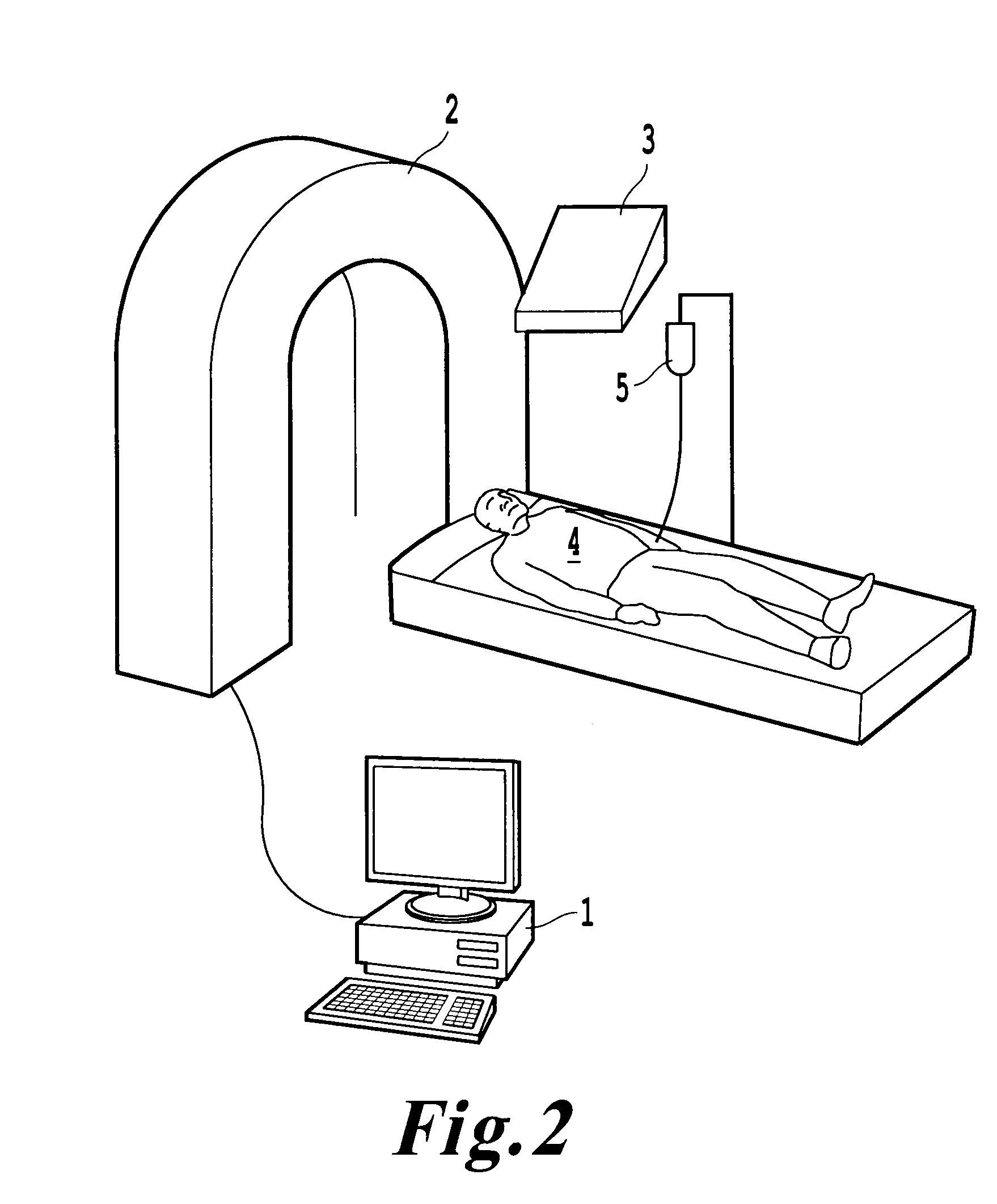
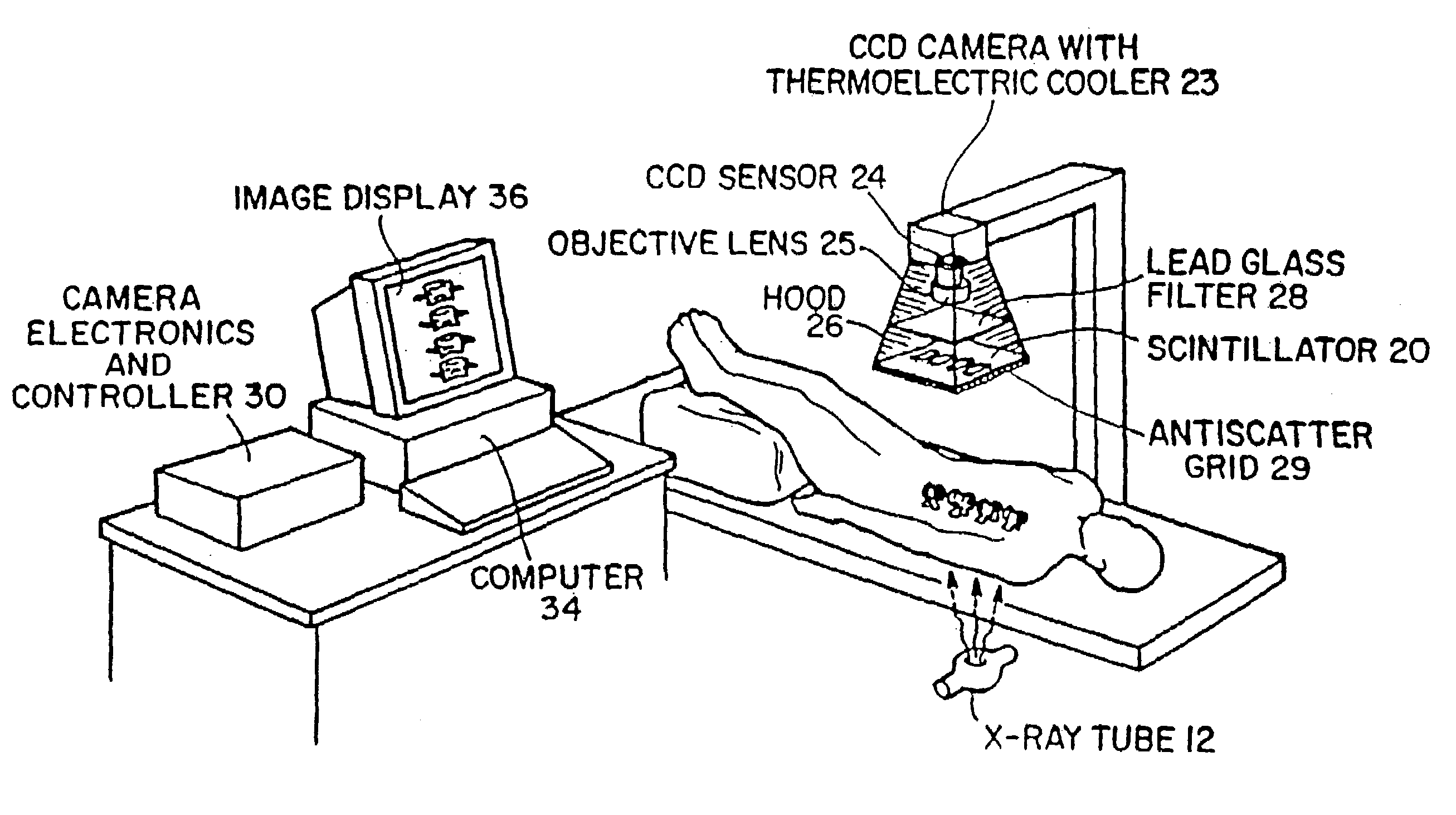
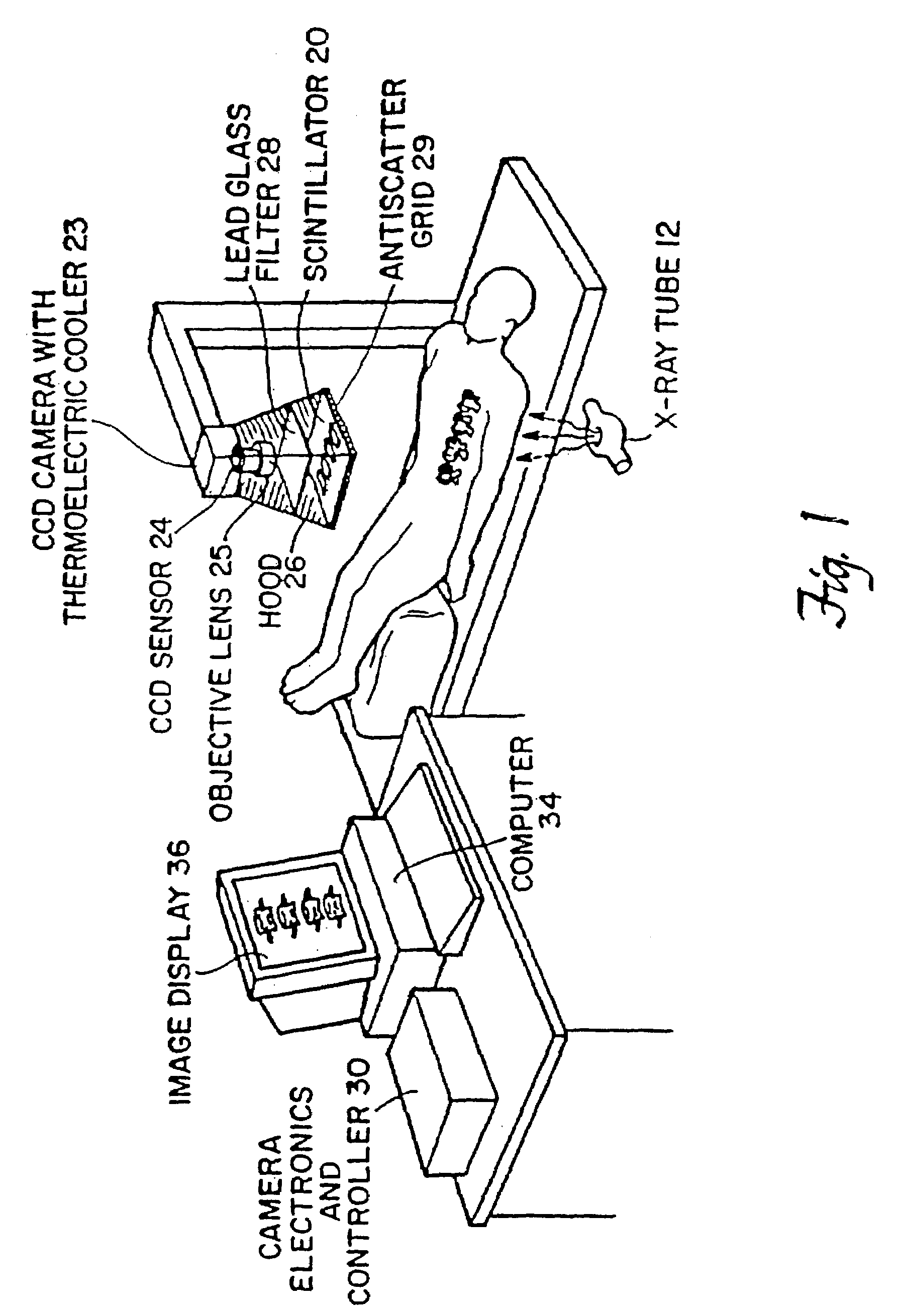
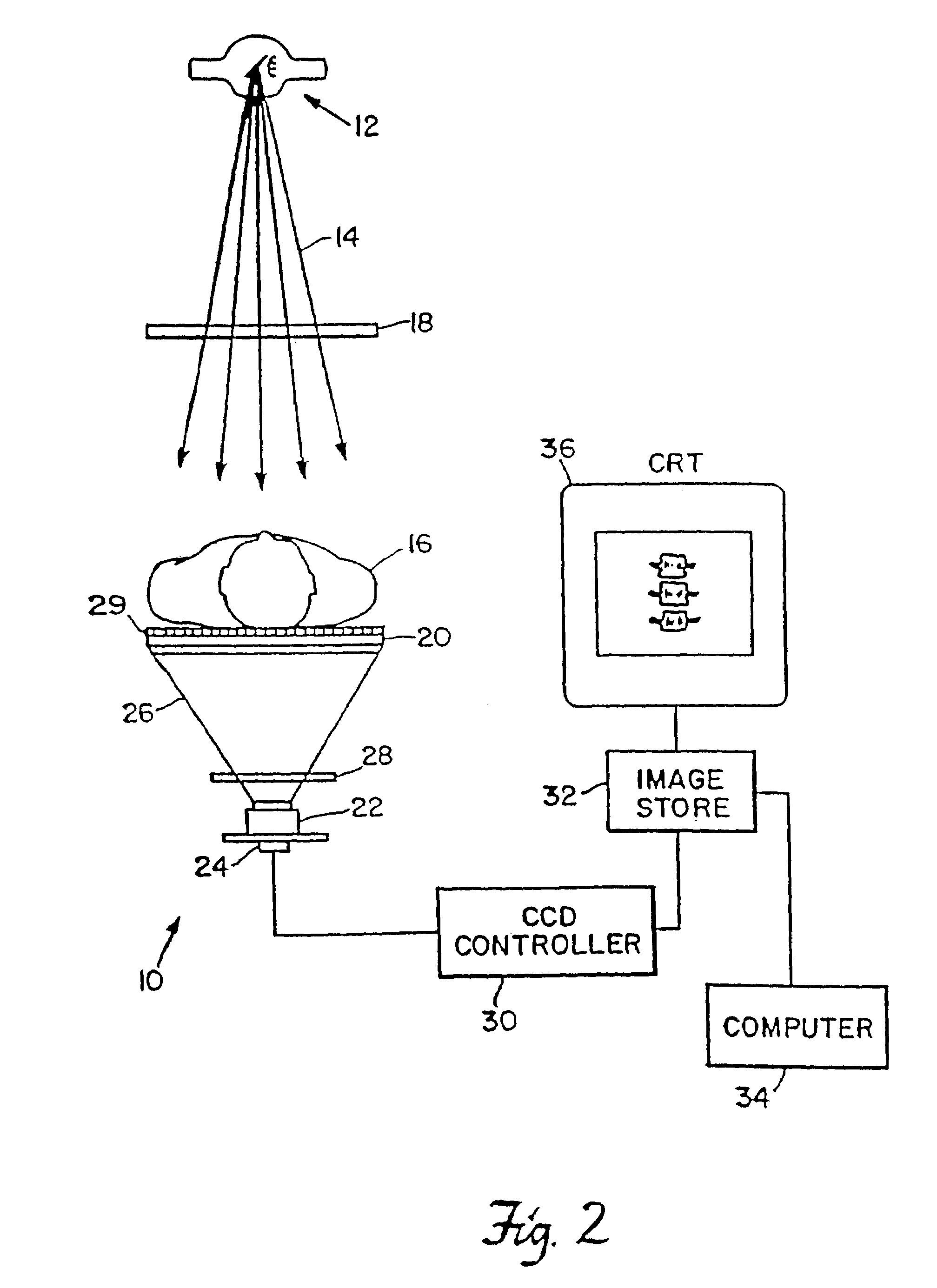
System for quantitative radiographic imaging
InactiveUS7330531B1Reduce and eliminate scattered radiationSuitable for applicationTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayDual energy
A system for spectroscopic imaging of bodily tissue in which a scintillation screen and a charged coupled device (CCD) are used to accurately image selected tissue. Applications include the imaging of radionuclide distributions within the human body or the use of a dual energy source to provide a dual photon bone densitometry apparatus that uses stationary or scanning acquisition techniques. An x-ray source generates x-rays which pass through a region of a subject's body, forming an x-ray image which reaches the scintillation screen. The scintillation screen reradiates a spatial intensity pattern corresponding to the image, the pattern being detected by a CCD sensor. The image is digitized by the sensor and processed by a controller before being stored as an electronic image. A dual energy x-ray source that delivers two different energy levels provides quantitative information regarding the object being imaged using dual photon absorptiometry techniques. Dual scintillation screens can be used to simultaneously generate images of low-energy and high-energy x-ray patterns. Each image is directed onto an associated respective CCD or amorphous silicon detector to generate individual electronic representations of the separate images.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS MEDICAL CENT
Manganese doped upconversion luminescence nanoparticles
InactiveUS7501092B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceNanosensorsTwo-photon absorptionUpconversion luminescence
The present relates in general to upconversion luminescence (“UCL”) materials and methods of making and using same and more particularly, but not meant to be limiting, to Mn2+ doped semiconductor nanoparticles for use as UCL materials. The present invention also relates in general to upconversion luminescence including two-photon absorption upconversion, and potential applications using UCL materials, including light emitting diodes, upconversion lasers, infrared detectors, chemical sensors, temperature sensors and biological labels, all of which incorporate a UCL material.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
Two-photon absorption decolorizable material, two-photon absorption refractive index modulation material, two-photon absorption polymerization material, two-photon absorption polymerization method and three-dimensional optical recording material
InactiveUS20060083890A1Efficient decolorizationIncrease productionSpectales/gogglesPhotosensitive materialsEnergy transferTwo-photon absorption
A two-photon absorption decolorizable material comprising: a two-photon absorption dye executing a two-photon absorption; and a decolorizable dye having a molar absorption coefficient equal to or less than 100 at a wavelength of a light irradiated at the two-photon absorption, wherein the decolorizable dye is decolorized by an electron transfer or an energy transfer utilizing an excitation energy obtained by the two-photon absorption of the two-photon absorption dye.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Laser micromachining method
InactiveUS7169687B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesTwo-photon absorptionHigh energy
A method is described for laser scribing or dicing portions of a workpiece using multi-source laser systems. In one embodiment, a first laser uses multiphoton absorption to lower the ablation threshold of portions of the workpiece prior to a second laser ablating the portions of the workpiece. In an alternative embodiment, a first laser uses high energy single-photon absorption to lower the ablation threshold of portions of the workpiece prior to a second laser ablating the portions of the workpiece.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Advanced methods and systems for treating cell proliferation disorders
ActiveUS20110263920A1Avoid the needHigh selectivityBiocideElectrotherapyTwo-photon absorptionActive agent
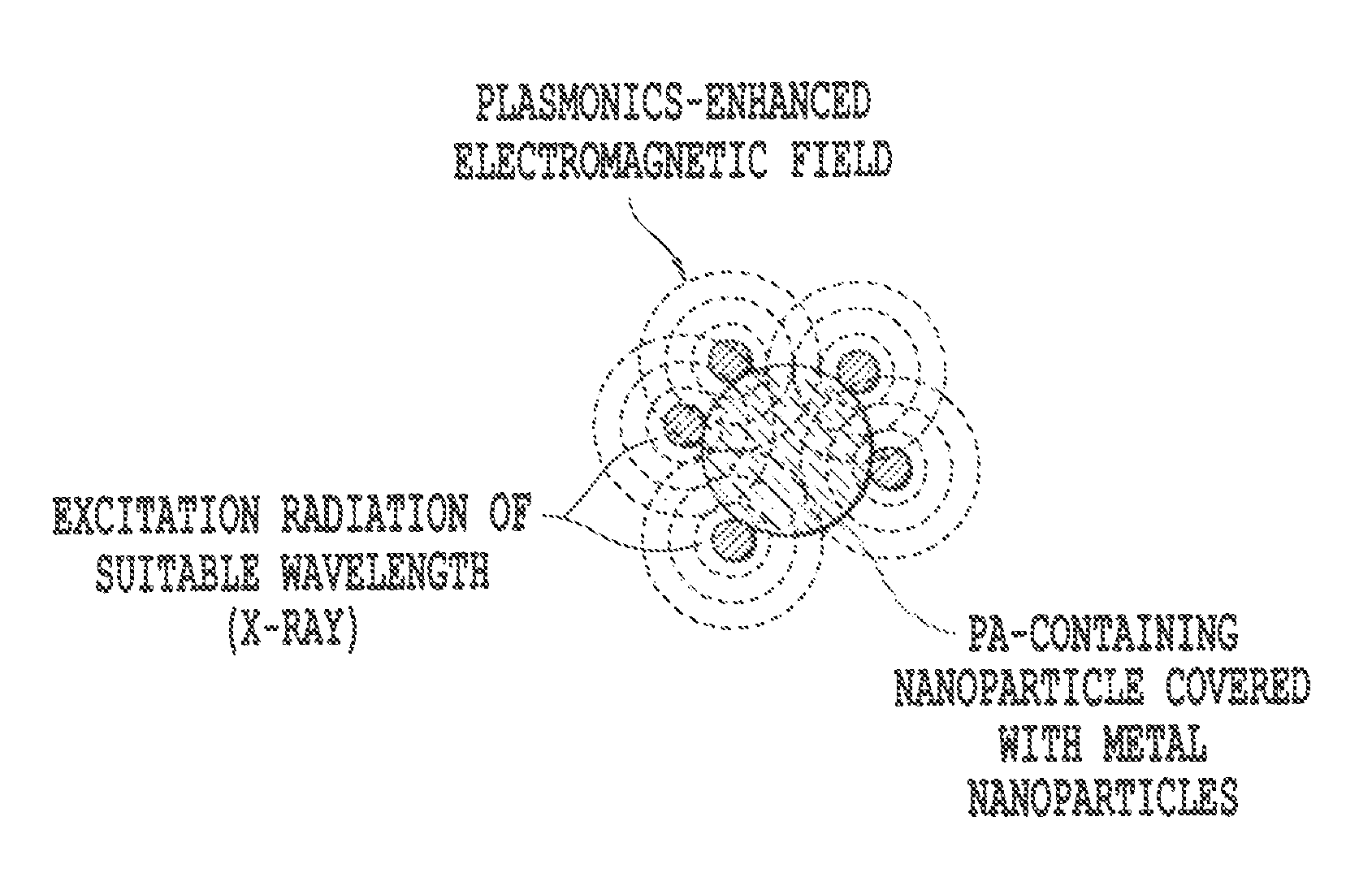
The present invention relates to methods for treating cell proliferation disorders comprising (1) administering to the subject at least one activatable pharmaceutical agent that is capable of activation by a simultaneous two photon absorption event and of effecting a predetermined cellular change when activated, (2) administering at least one plasmonics-active agent to the subject, and (3) applying an initiation energy from an initiation energy source to the subject, wherein the plasmonics-active agent enhances or modifies the applied initiation energy, such that the enhanced or modified initiation energy activates the activatable pharmaceutical agent by the simultaneous two photon absorption event in situ, thus causing the predetermined cellular change to occur, wherein said predetermined cellular change treats the cell proliferation related disorder, and the use of plasmonics enhanced photospectral therapy (PEPST) and exiton-plasmon enhanced phototherapy (EPEP) in the treatment of various cell proliferation disorders, and the PEPST and EPEP agents and probes
Owner:IMMUNOLIGTHT LLC +1
Manganese doped upconversion luminescence nanoparticles
InactiveUS20060140240A1Reduce luminous intensityWeather/light/corrosion resistanceExcitation process/apparatusTwo-photon absorptionUpconversion luminescence
The present relates in general to upconversion luminescence (“UCL”) materials and methods of making and using same and more particularly, but not meant to be limiting, to Mn2+ doped semiconductor nanoparticles for use as UCL materials. The present invention also relates in general to upconversion luminescence including two-photon absorption upconversion, and potential applications using UCL materials, including light emitting diodes, upconversion lasers, infrared detectors, chemical sensors, temperature sensors and biological labels, all of which incorporate a UCL material.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
Nanolithography method and nanolithography device
InactiveCN102866580AControl shapeRegulatory distributionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusNanolithographyTwo-photon absorption
The invention discloses a nanolithography method and a nanolithography device in the technical field of nanolithography. The device comprises a femtosecond laser device, a light transmittance base plate, a photoetching mask plate, photoresist and a substrate. A specific super-diffraction limit graph is formed on the photoetching mask plate through the femtosecond laser device; a plasma excimer excitation structure on the upper surface of the photoetching mask plate is changed, and an exposure wavelength is adjusted by controlling the material of the photoetching mask plate, so that the shape, the distribution and the size of the super-diffraction limit graph can be controlled; moreover, a two-photon absorption phenomenon of the photoresist is introduced; and the line width of an exposure graph of the photoresist is controlled by controlling the power of a femtosecond laser exposure light source.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
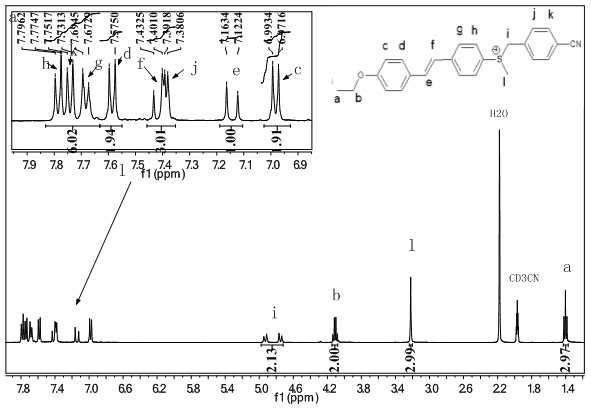
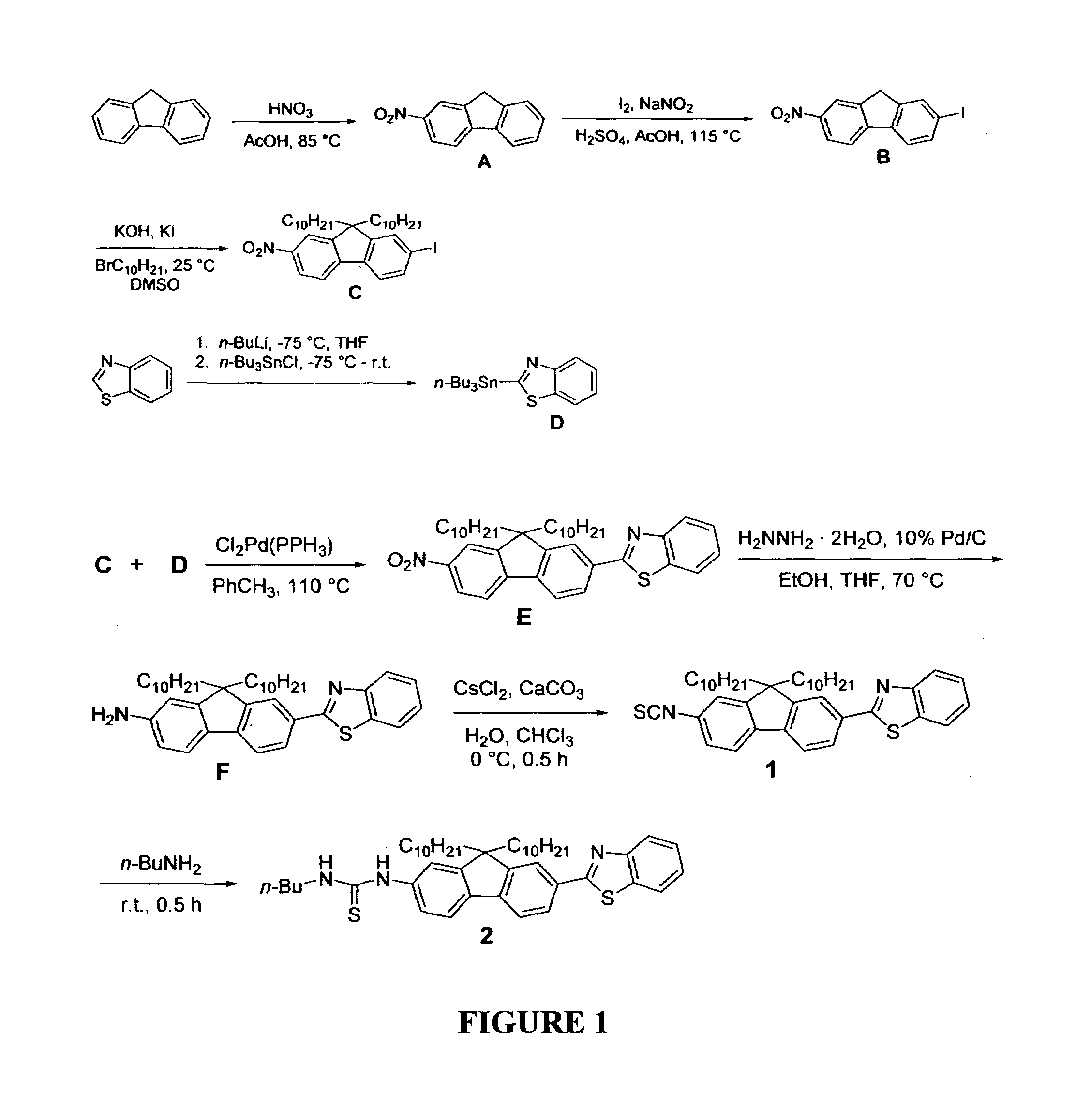
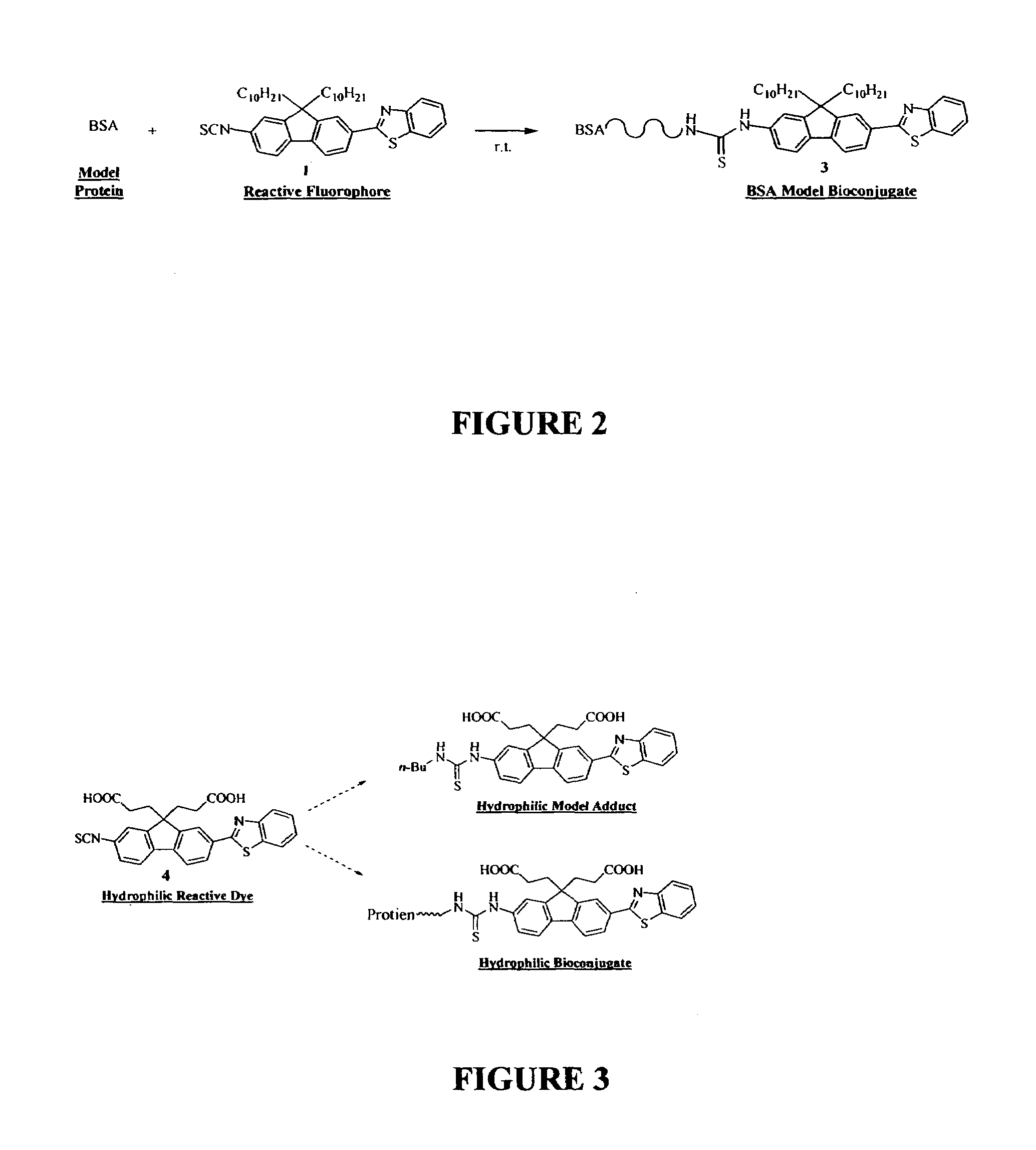
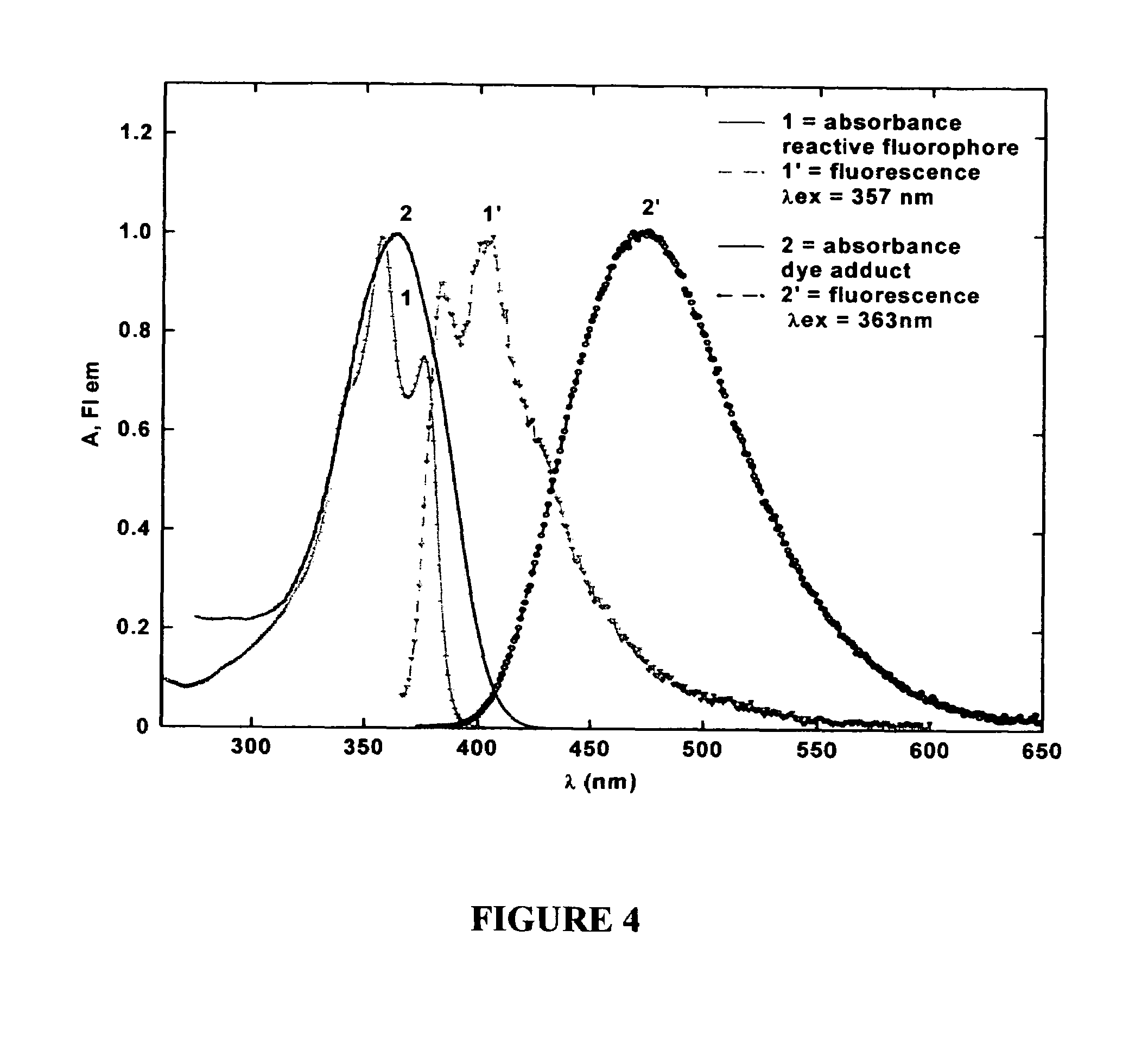
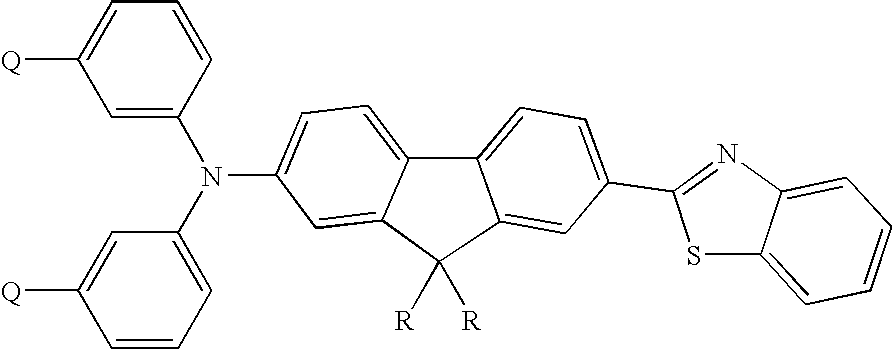
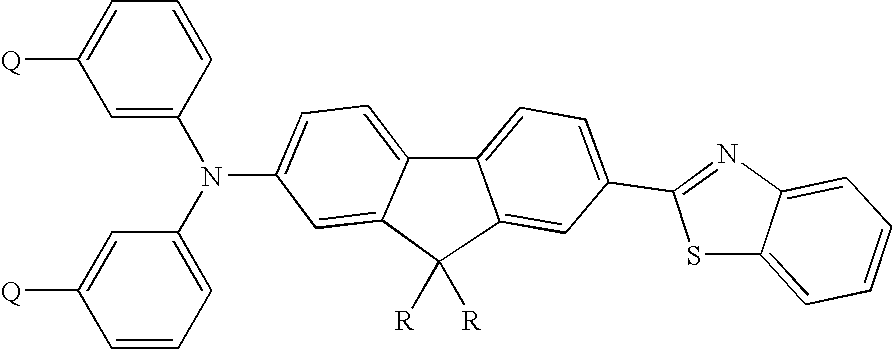
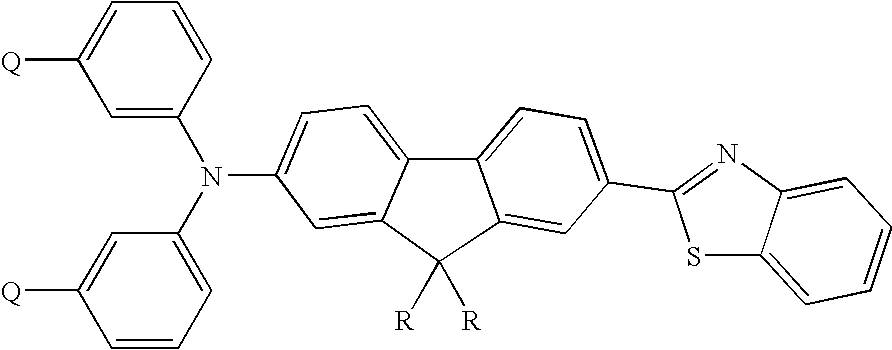
Reactive probes for two-photon fluorescent imaging and sensing
InactiveUS7282514B1High fluorescence quantum yieldBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsQuantum yieldBovine serum albumin
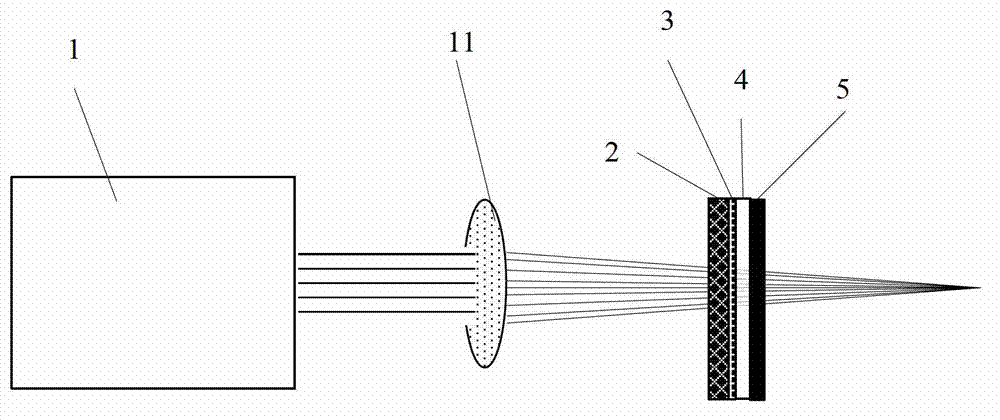
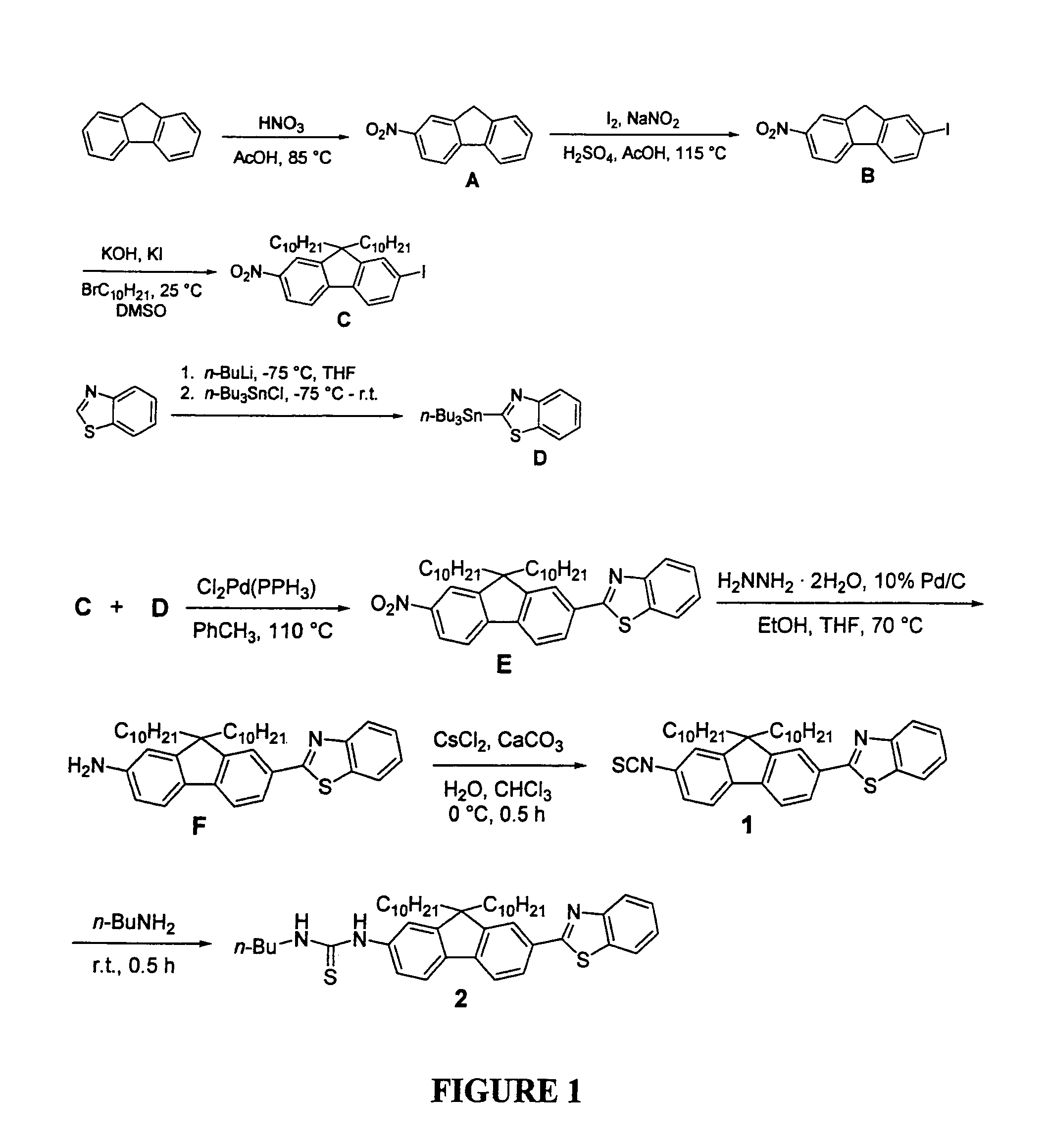
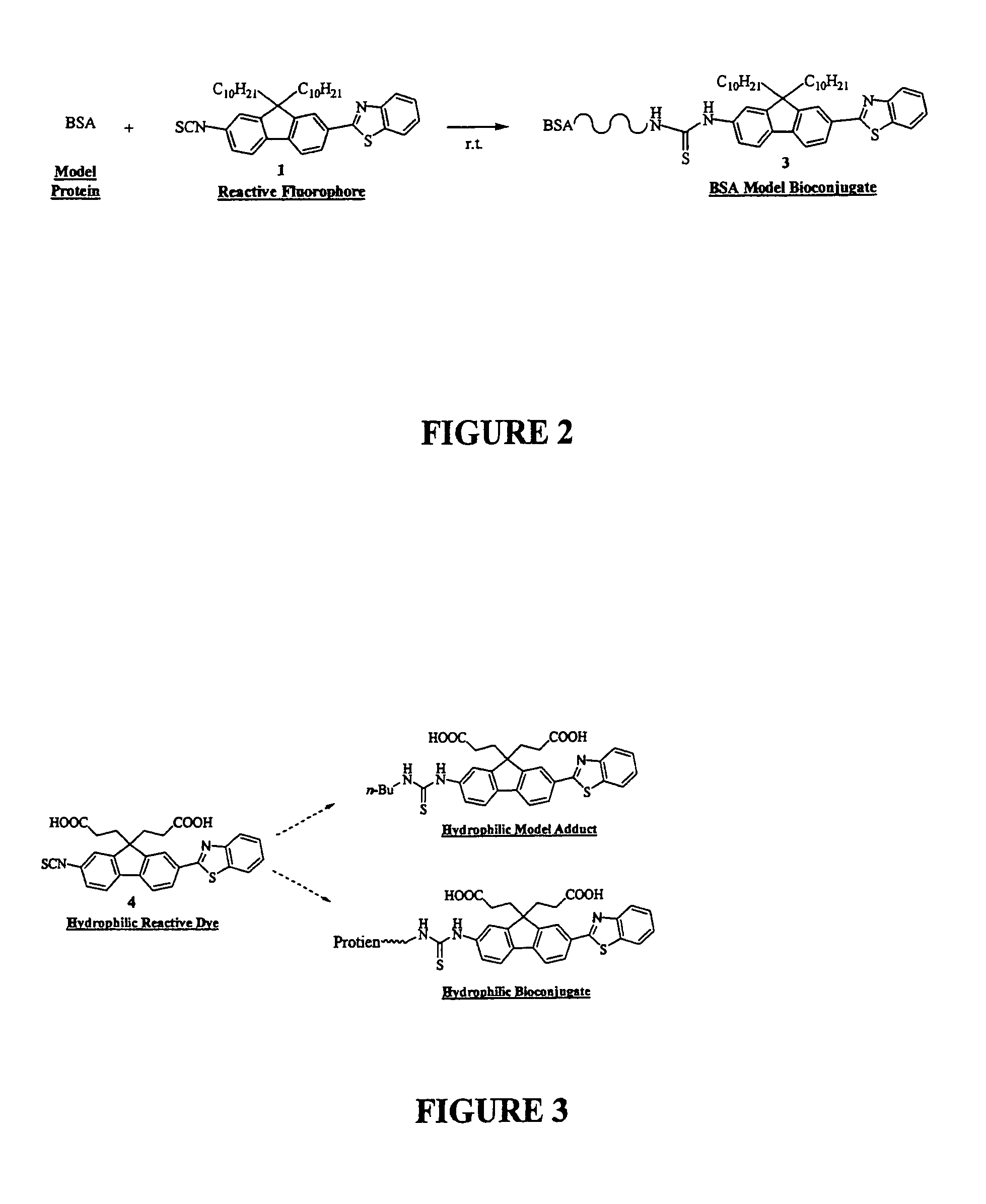
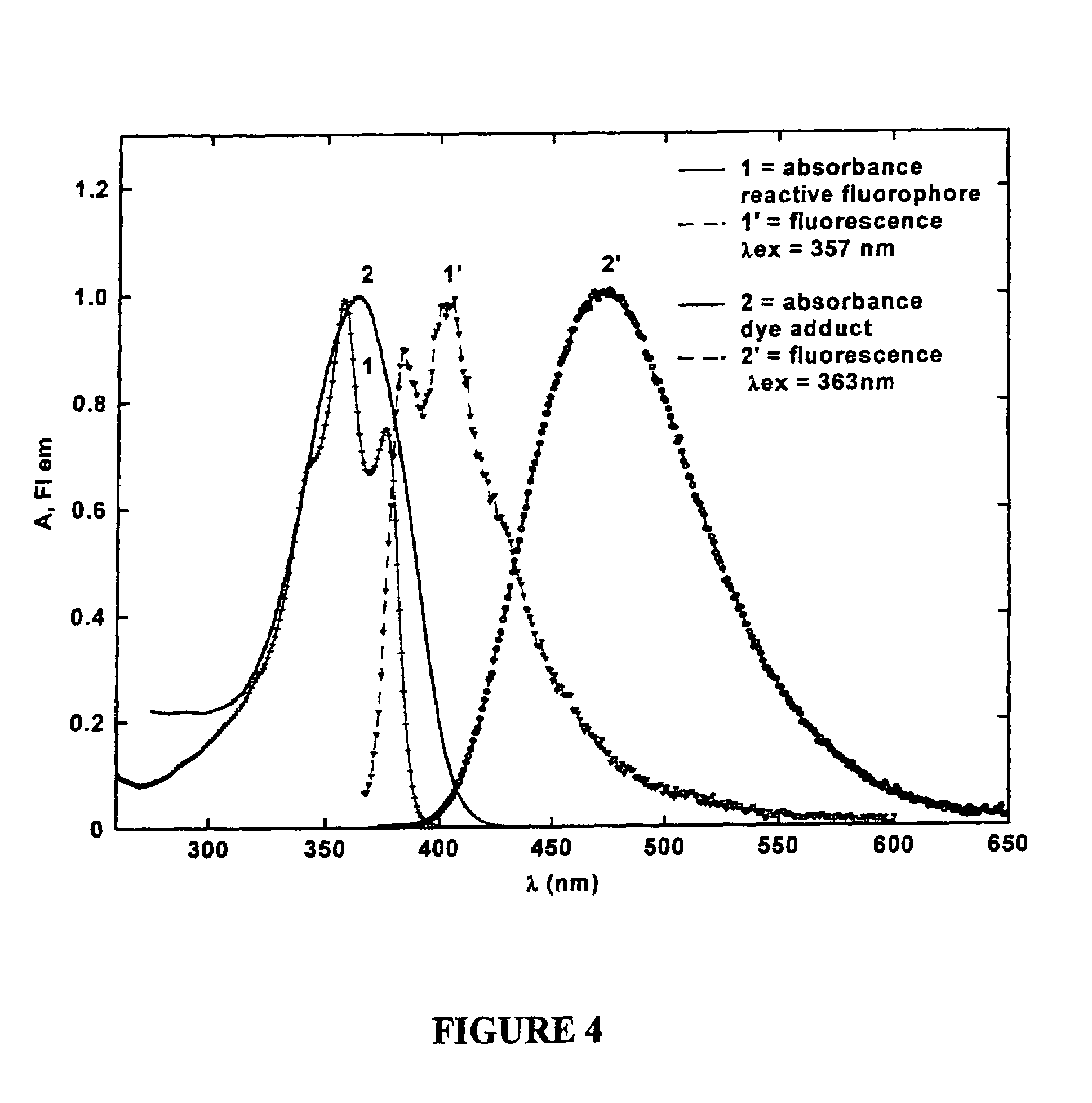
Fluorescent dyes and probes are key components in multiphoton based fluorescence microscopy imaging of biological samples. In order to address the demand for better performing dyes for two-photon based imaging, a new series of reactive fluorophores tailored for multiphoton imaging has been disclosed. These fluorophores are based upon the fluorene ring system, known to exhibit high fluorescence quantum yields, typically >0.7, and possess high photostability. They have been functionalized with moieties to act, e.g., as efficient amine-reactive fluorescent probes for the covalent attachment onto, e.g., proteins and antibodies. The synthesis and the single-photon spectral characteristics, as well as measured two-photon absorption cross sections of the reactive fluorophores in solution are presented. Spectral characterizations of bovine serum albumin (BSA) conjugated with the new reactive probe is presented.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
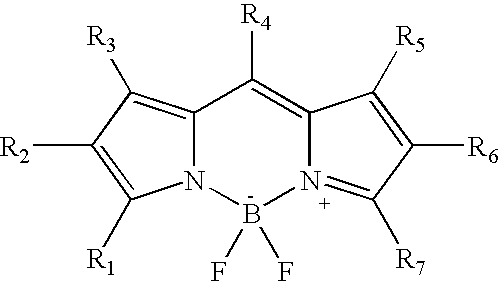
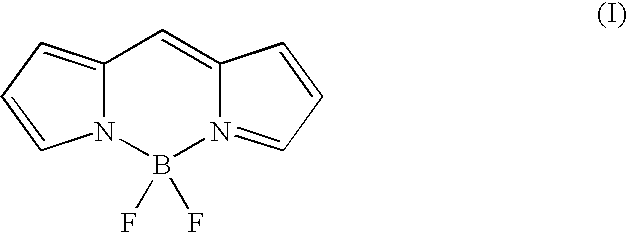
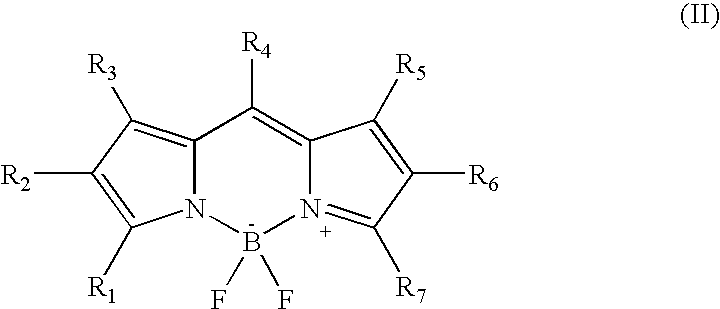
Two-photon absorbing dipyrromethenboron difluoride dyes and their applications
InactiveUS20040157231A1Reduce yieldImprove excitation efficiencySilicon organic compoundsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBenzoxazoleFluorescence
The invention relates to a separation free bioanalytical assay method for measuring an analyte from a biological fluid or suspension comprising of microparticles as a bioaffinity binding solid phase, a biospecific secondary reagent labelled with a two-photon fluorescent dipyrrometheneboron difluoride dye, focusing the laser into the reaction suspension, measuring two-photon excited fluorescence from single microparticles when they randomly float or are guided by the radiation pressure of the excitation laser through the focal volume of the laser beam using a two-photon fluorescent dipyrrometheneboron difluoride dye. The dye has the structure (II): Either at least one of groups R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 and R7 is a substituted or unsubstituted phenyl, thienyl, pyrrolyl, furanyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl oxadiazolyl, imidazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzothiazolyl, benzimidazolyl, benzofuranyl, indolyl, conjugated ethenyl, dienyl or trienyl group, and at least one of the groups R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 or R7 is substituted to yield a chemically reactive group that can be used for selective covalent linkage to other molecules, and at least one of the groups R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 or R7 is substituted to yield a water-solubilizing group, and the remaining groups of R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 and R7 are each independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, alkyl, cyano, carboxy, each of which can optionally be substituted; or groups R1, R2, R3, R5, R6 and R7 are substituted or unsubstituted alkyl groups, R4 is a hydrogen or a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, and at least one of the groups R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 or R7 is substituted to yield a chemically reactive group that can be used for selective covalent linkage to other molecules; and at least one of the groups R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 or R7 is su
Owner:ARCTIC DIAGNOSTICS
Two-photon absorption dye-containing material, three-dimensional refractive index modulation material, three-dimensional absorption index modulation material and three-dimensional optical recording material
InactiveUS20050019711A1Improve preservation qualityImprove spatial resolutionStyryl dyesMonoazo dyesTwo-photon absorptionOptical recording
To provide a two-photon absorption dye-containing material having a great off-resonant two-photon absorption cross section and comprising a two-photon absorption dye capable of decoloring itself through off-resonant two-photon absorption, useful for a three-dimensional refractive index or absorption index modulation material, a three-dimensional optical recording medium, three-dimensional refractive index modulation method and recording and reproducing method for a three-dimensional optical recording medium a two-photon absorption dye-containing material comprising at least a two-photon absorption dye capable of decoloring itself through two-photon absorption.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Two-photon absorbing optical recording material and two-photon absorbing optical recording and reproducing method
InactiveUS20050003133A1High sensitivityBig contrastPhotosensitive materialsLayered productsTwo-photon absorptionPhoto irradiation
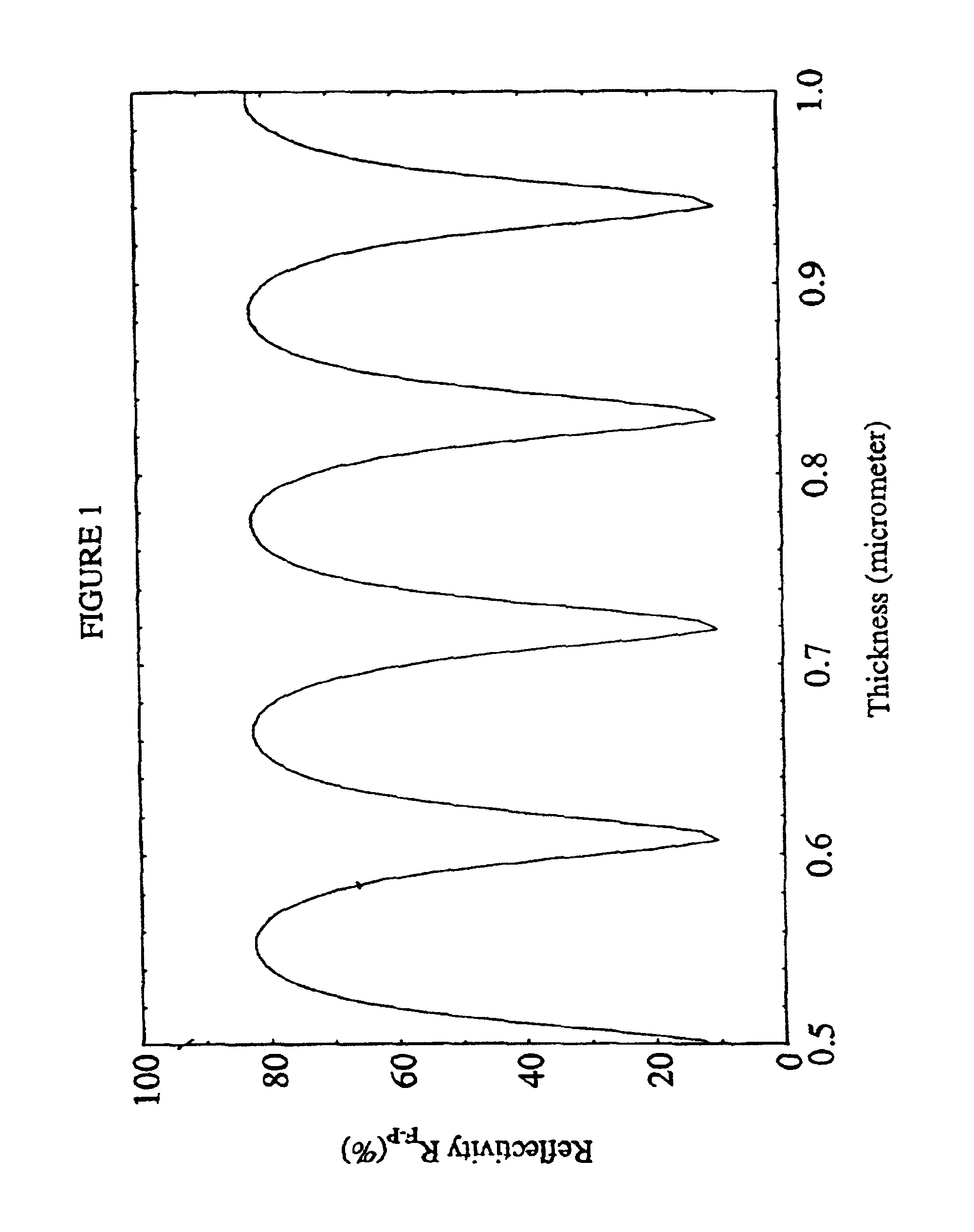
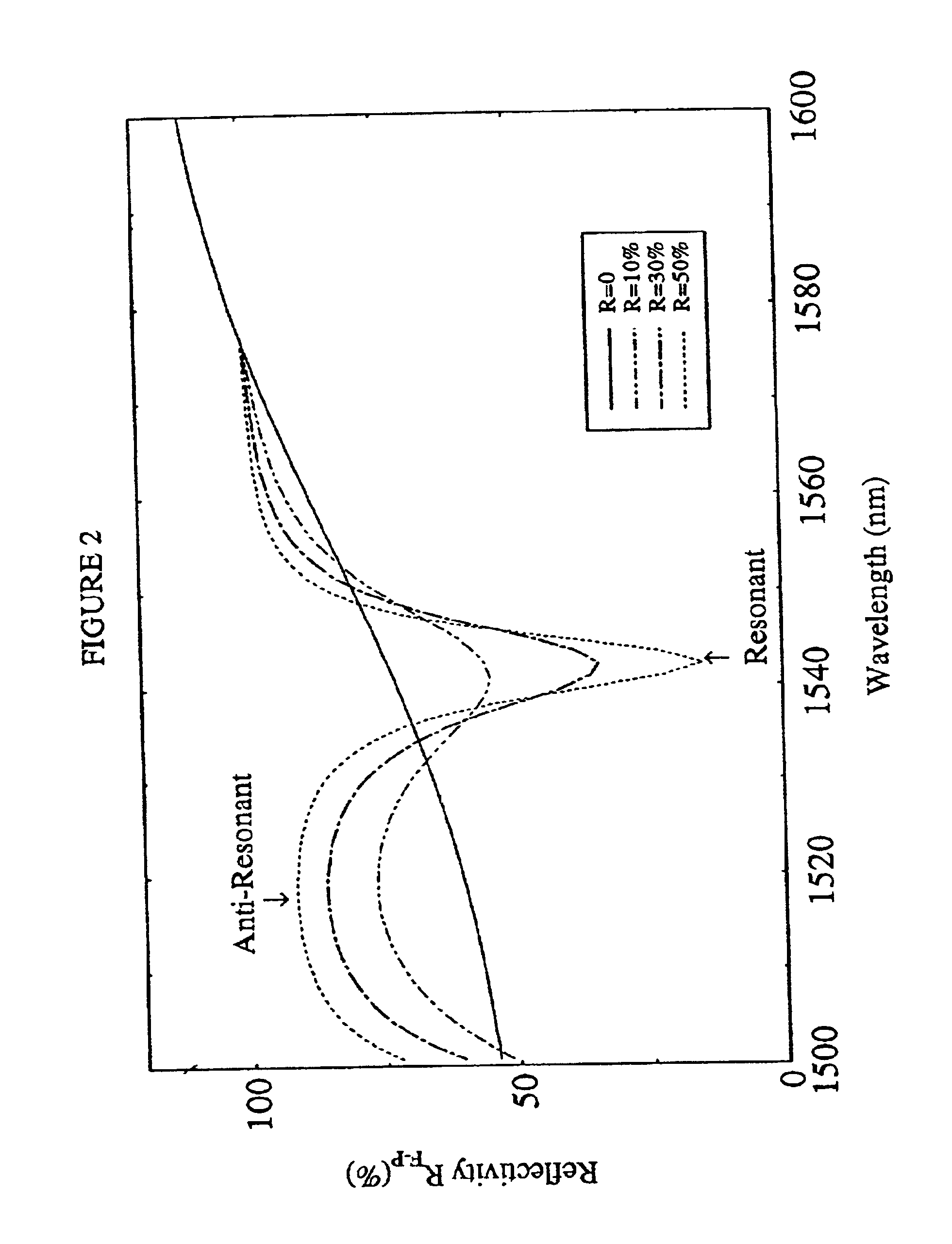
A two-photon absorbing optical recording material comprising at least one two-photon absorbing compound and a recording component is provided. Recording is made on it by utilizing the two-photon absorption of the two-photon absorbing compound in the material, and then the material is irradiated with light to thereby detect the difference in the reflectance between the recorded area and the unrecorded area thereof, and the recorded information is thereby reproduced from the material, and also provided are a photosensitive polymer composition and a photon-mode recording method for the material.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Two-photon absorbing polymerizable composition and polymerization process thereof
InactiveUS7112616B2High sensitivityImprove efficiencyPhotosensitive materialsPretreated surfacesTwo-photon absorptionAryl
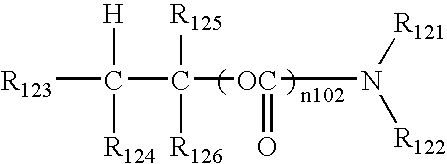
A two-photon absorbing polymerizable composition contains at least a two-photon absorbing compound, a polymerization initiator and a polymerizable compound, the composition being photopolymerizable upon non-resonant two-photon absorption, wherein the two-photon absorbing compound is a methine dye containing a compound represented by the formula (1):wherein R1 to R5 each represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent and some of R1 to R4 may combine with each other to form a ring; n and m each independently represents an integer of 0 to 4, provided that n and m are not 0 at the same time; X1 and X2 each represents an aryl group, a heterocyclic group or a group represented by formula (2); R6 represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, an alkenyl group, an aryl group or a heterocyclic group, and Z1 represents an atomic group for forming a 5- or 6-membered ring.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Quantum steganography
InactiveUS20040258421A1Increase an associated entangled two-photon cross-sectionReduced cross sectionSecret communicationElectromagnetic transmittersTwo-photon absorptionQuantum steganography
A system and method of detecting entangled photon pairs, each pair including a signal photon and an idler photon, is disclosed. Entangled photon pairs are provided having an entanglement time and an entanglement area selected to substantially increase an associated entangled two-photon cross-section of an associated target medium. The entangled photon pairs are also selected to have an energy distribution between the signal photon and the idler photon to substantially decrease an associated random two-photon absorption cross section of the target medium. The entangled photon pairs are directed to the target medium, and at least one entangled-photon pair being absorbed by the target medium is detected. The techniques for detecting entangled photons may be adapted to accommodate hiding information in entangled photons. That is, these techniques may be used for quantum steganography.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS MISSION SYST INC
Preparation and application of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum-dot two-photon fluorescence
InactiveCN104109534AEasy to prepareNo precipitationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceTwo-photon absorptionNitrogen
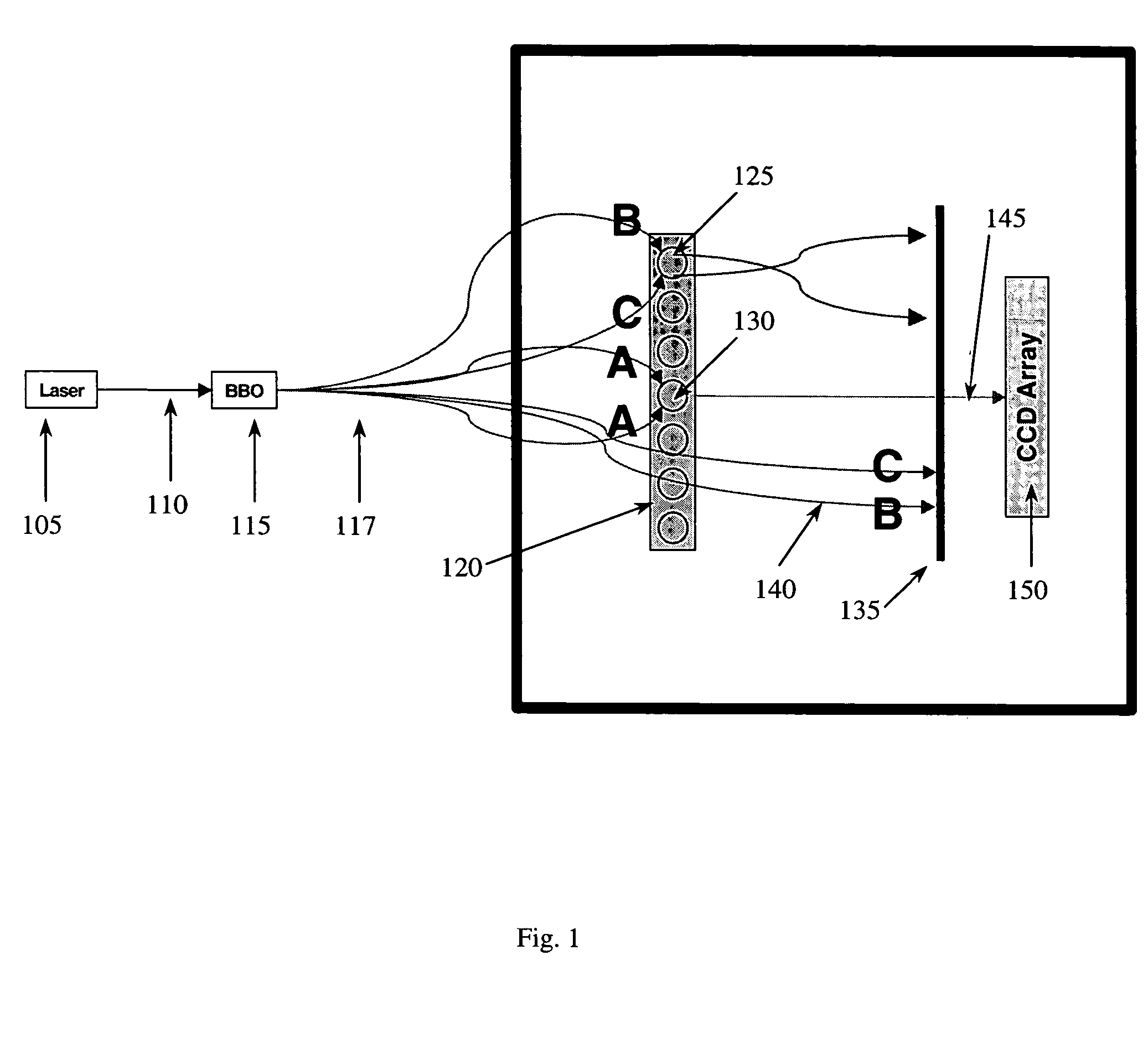
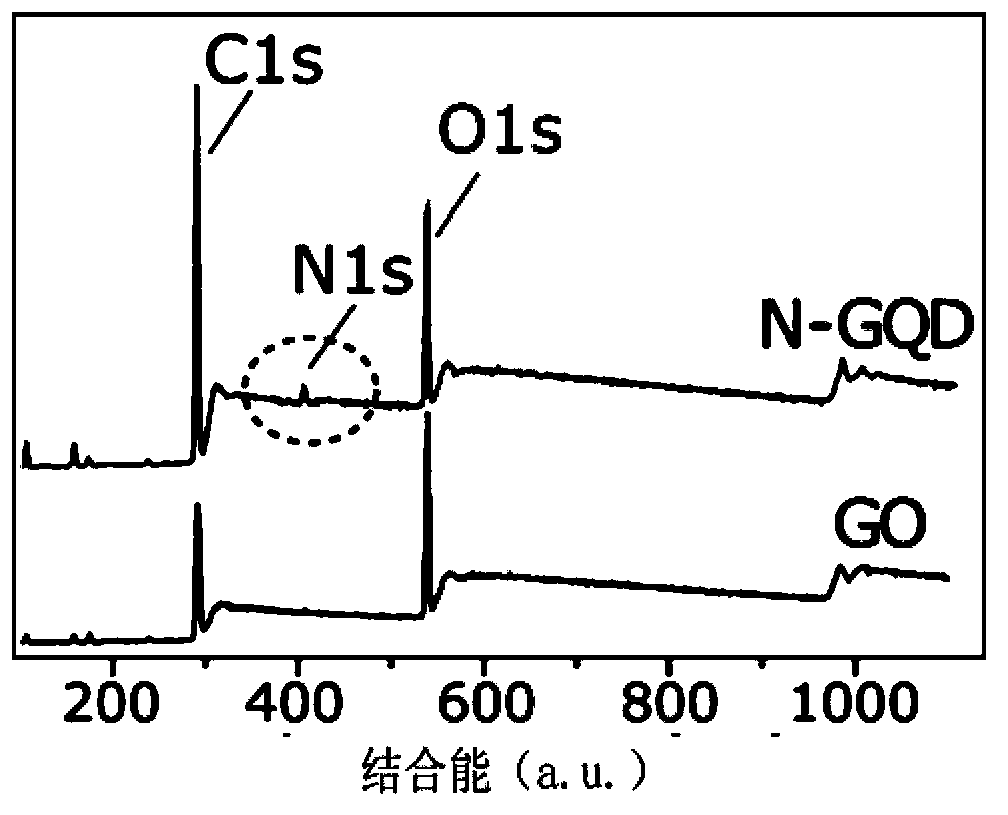
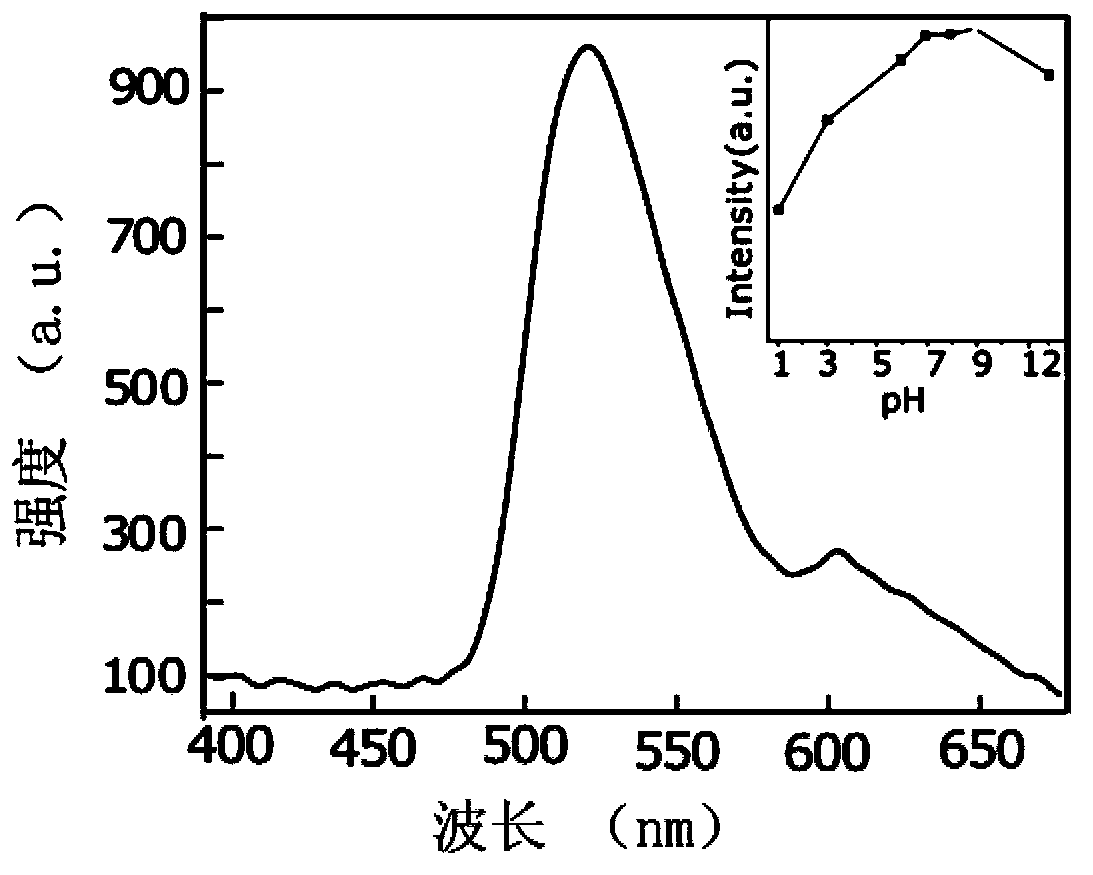
The invention discloses a nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot, a preparation method thereof and application thereof as a two-photon fluorescence probe to imaging of living cells. The nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot is simple in preparation method, is good in imaging effect when applied to two-photon fluorescence imaging of living cells, and has extremely strong two-photon fluorescence in a relatively wide pH scope, and the two-photon absorption cross section can reach 48000 GM; the nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot is extremely easy to dissolve in water, free of toxicity and good in light stability; and a solution of the nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot has extremely strong stability, is capable of keeping stable within 24 months, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Nanoparticles for two-photon activated photodynamic therapy and imaging
InactiveUS20090035576A1Improve behaviorPowder deliveryPhotodynamic therapySinglet oxygenSilicon dioxide
The present invention provides organically modified silica (ORMOSIL) nanoparticles into which have been incorporated two-photon absorption dye molecules. The two photon absorption dye displays a unique aggregation induced fluorescence enhancement behavior. As a result ORMOSIL nanoparticles with high amounts of the dye can be prepared. These particles can be used for imaging. In one embodiment, the nanoparticles can additionally have incorporated therein a photosensitizer. The photosensitzer can be activated by intraparticle fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) from the dye aggregates resulting in enhanced fluorescence and singlet oxygen generation from photosensitizer under two-photon excitation conditions. Such nanoparticles can be used for photodynamic therapy applications.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Enhanced performance mode converter
ActiveUS7242821B2Reduce accumulationPropagation delayCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSemiconductor materialsSchottky barrier
An optical mode converter comprising a slow wave electrode structure and including Schottky barriers for preventing an accumulation of free carriers in the optical waveguide region of the converter. The Schottky barriers are also used for suppressing higher order modes in the waveguide. Low refractive index insulators are used to allow efficient driving of the device without hindering the impedance or the microwave index of the optical mode converter. Two-photon absorption processes are eliminated through the use of a waveguide semiconductor material having a bandgap of at least twice the photon energy of the light beam propagating through the optical mode converter.
Owner:OPTELIAN ACCESS NETWORKS
Method of manufacturing a three dimensional photonic device by two photon absorption polymerization
A method of manufacturing a three dimensional photonic device by two photon absorption polymerization. The method includes several stages, including direct laser writing involving polymerization by two-photon absorption to manufacture a three dimensional photonic device integrating at least two distinct micro-optical components having two optical functions and being aligned with each other so that optical signal can be transmitted from one of said distinct components to the other. The distinct components are built at a same stage of the process flow to improve their relative alignment by direct laser writing involving polymerization by two-photon absorption.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
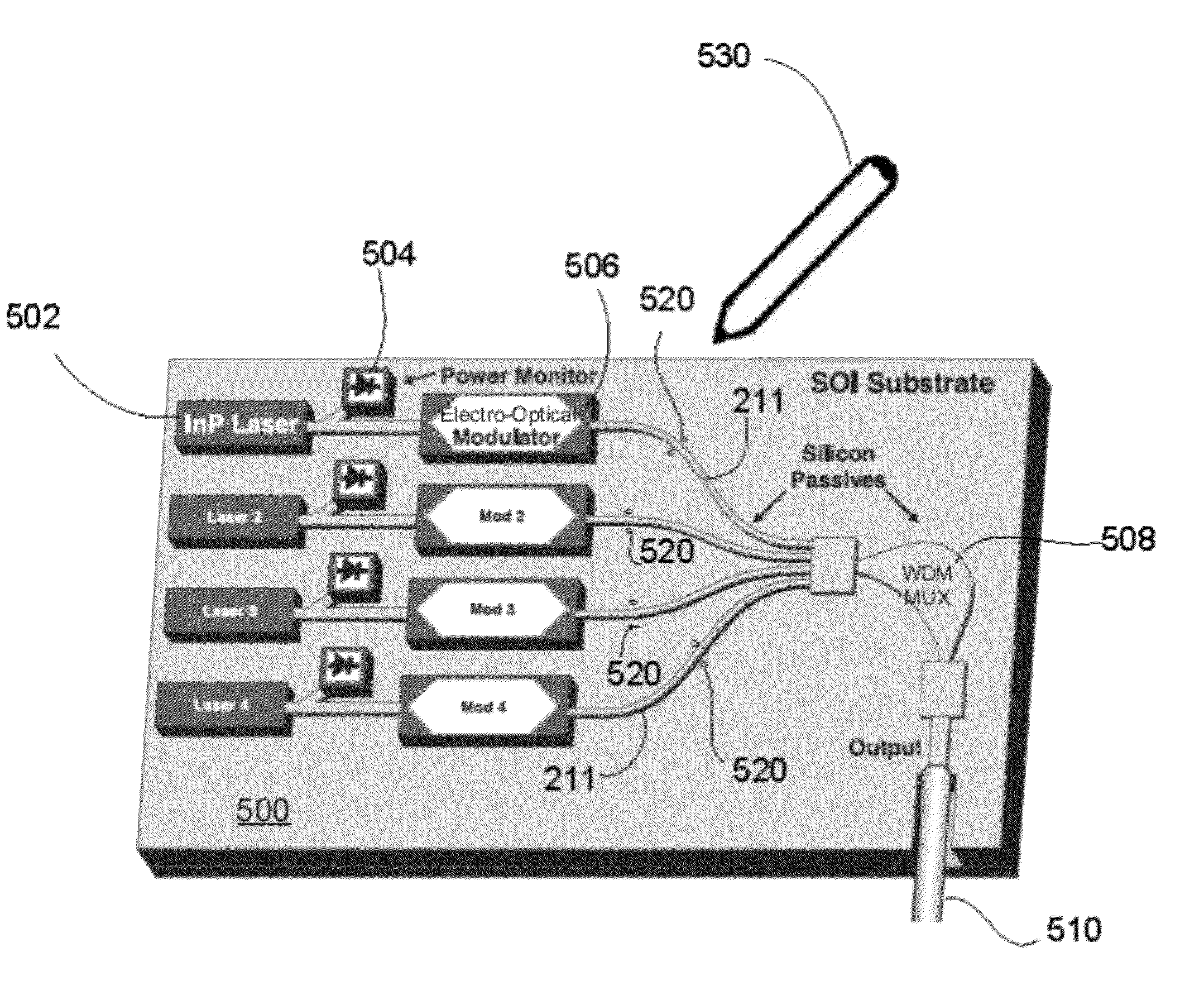
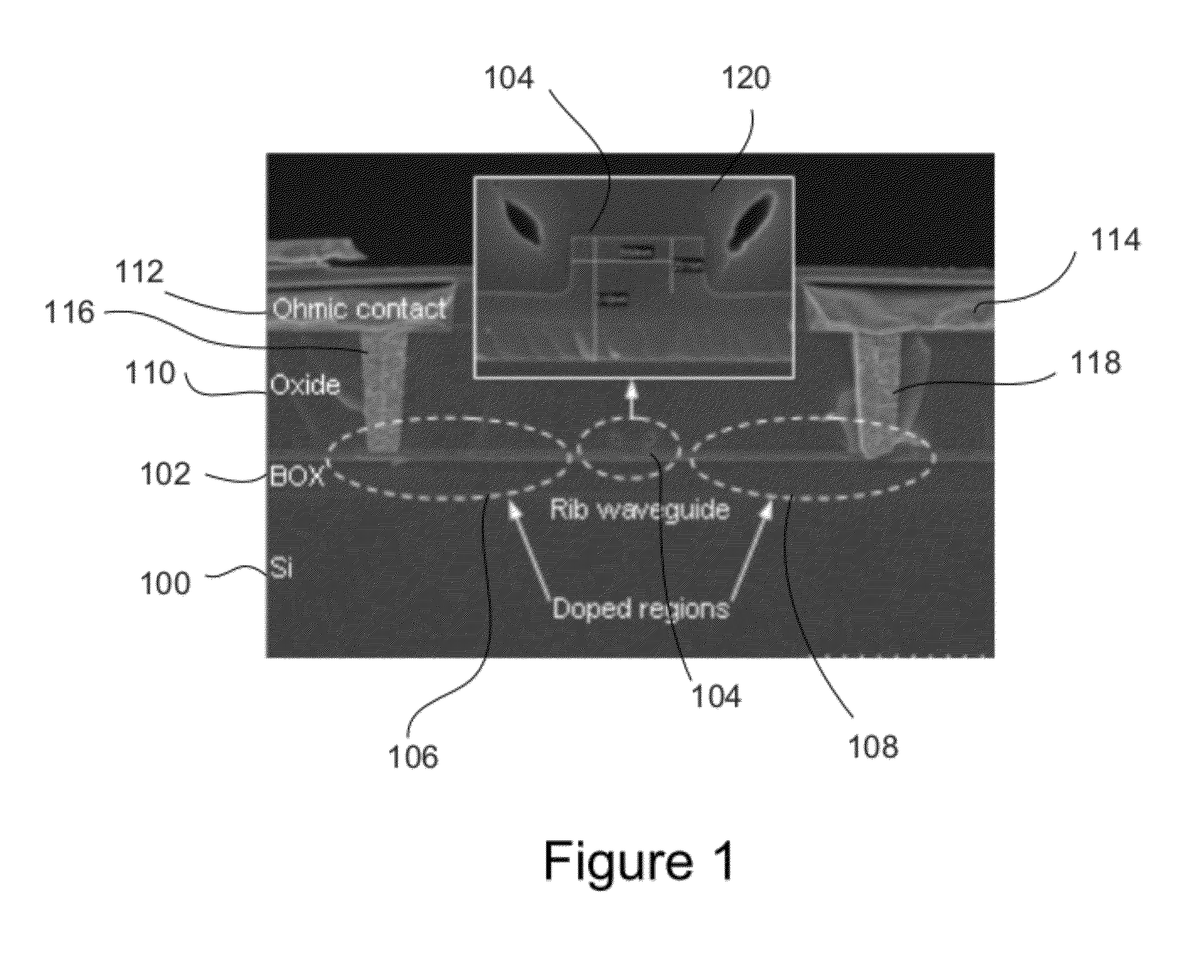
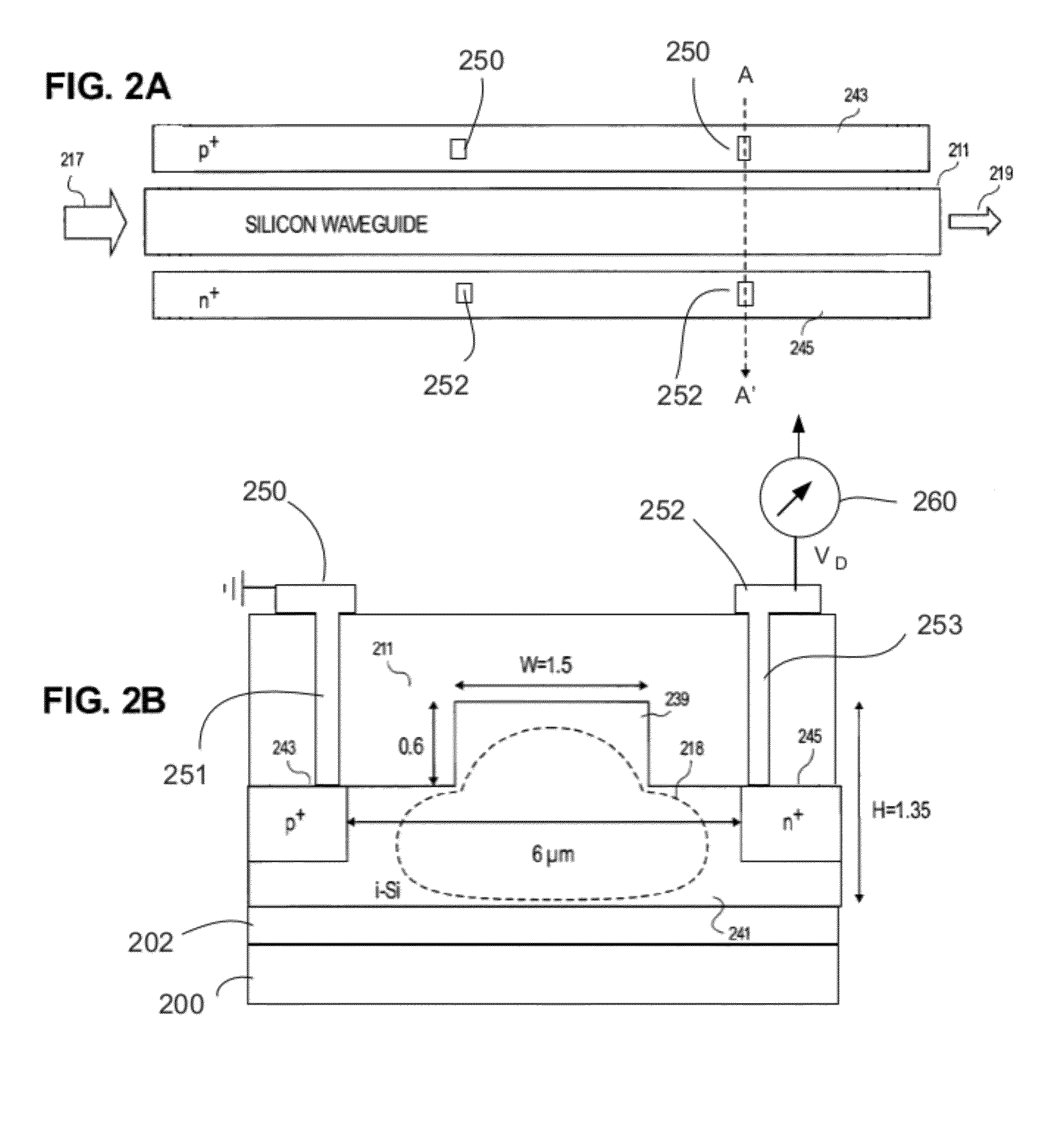
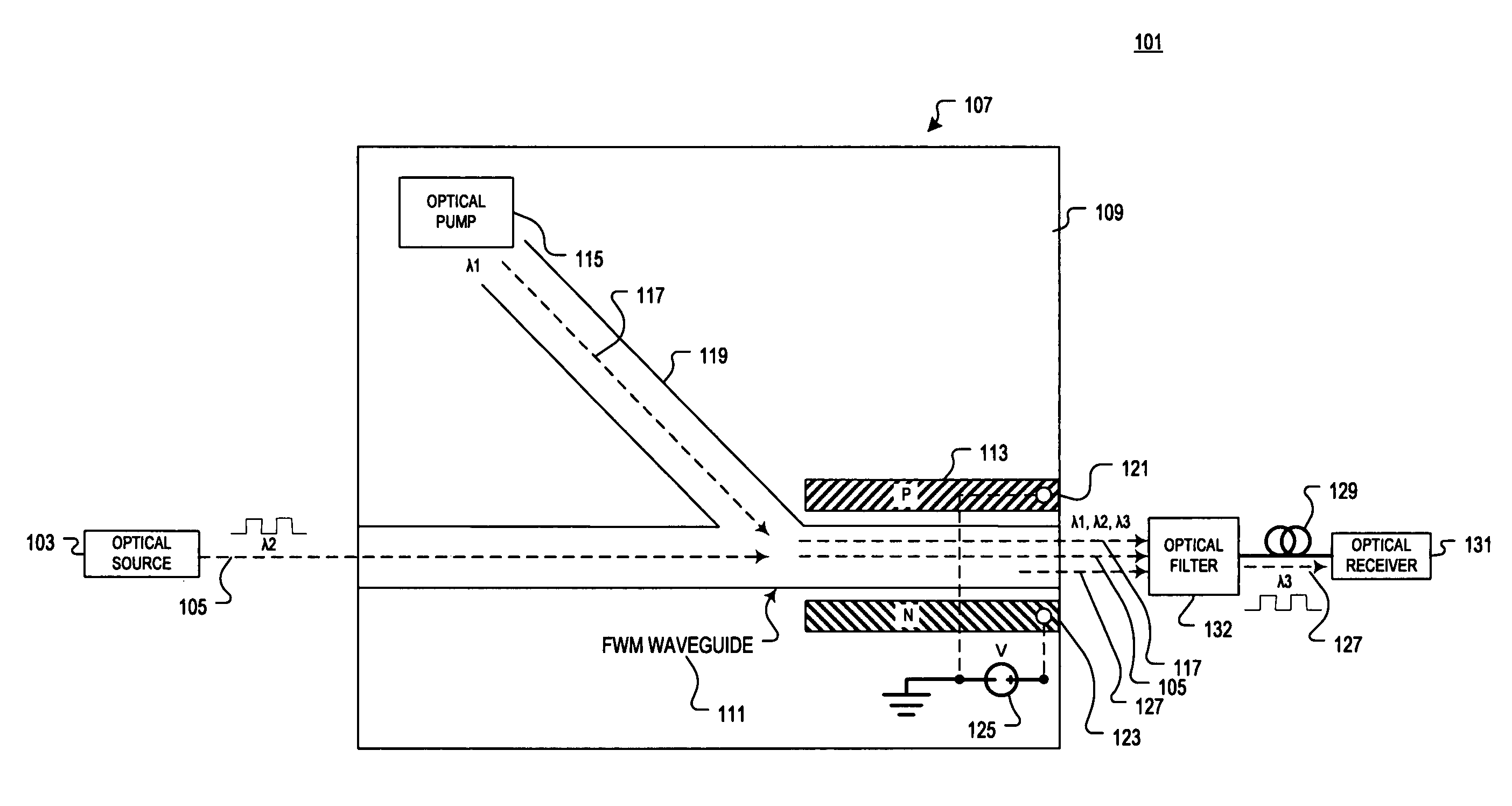
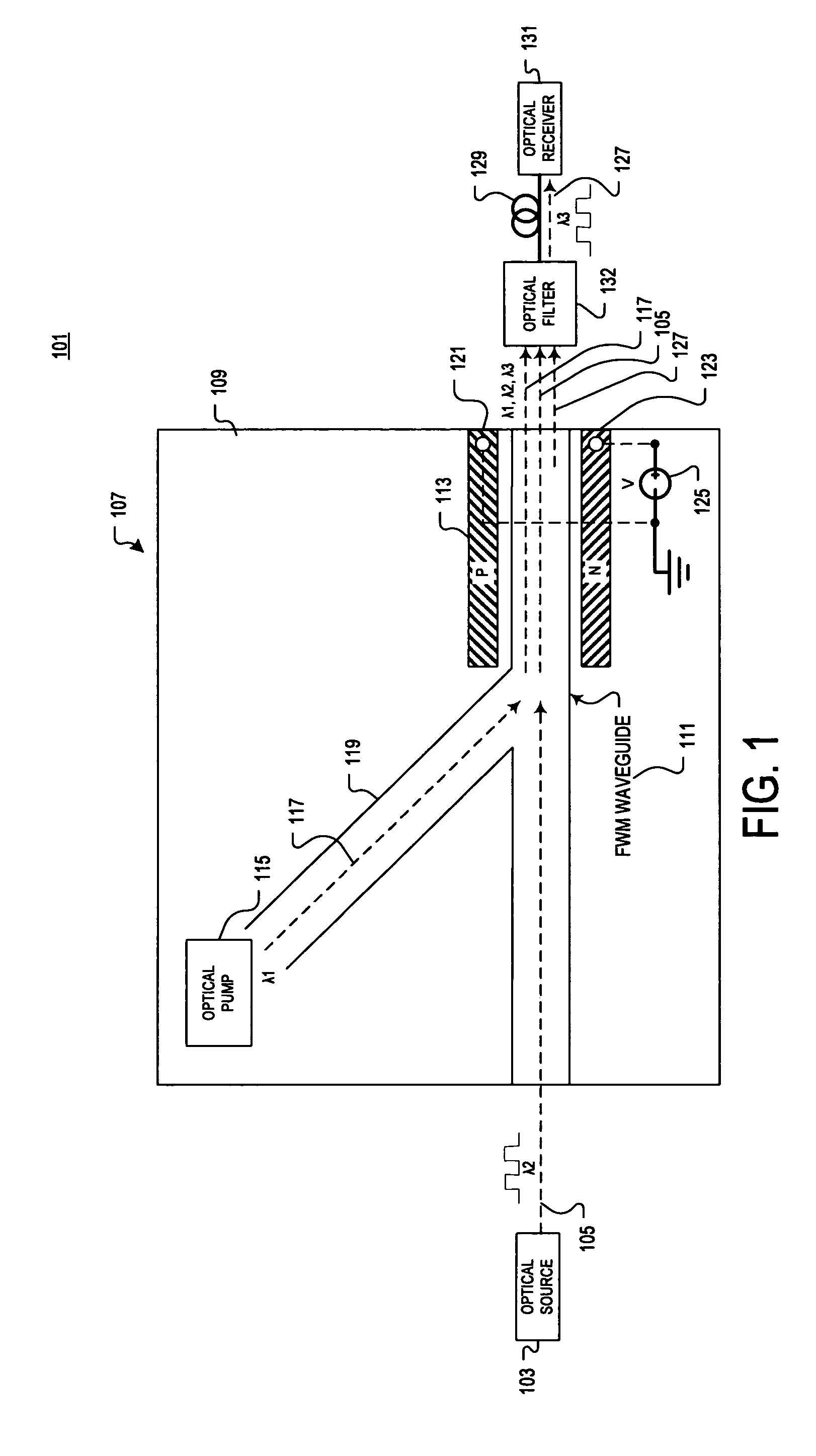
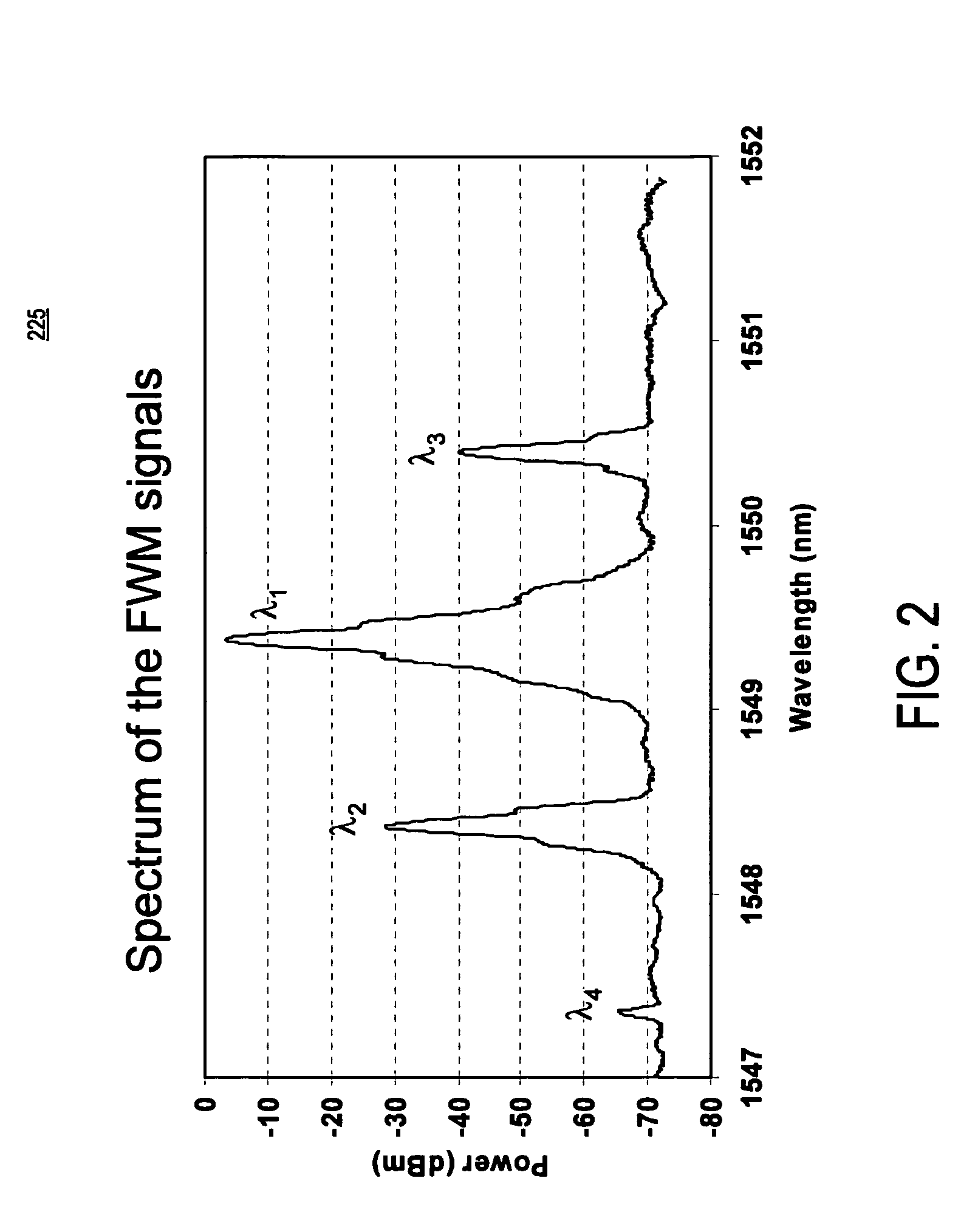
Two-photon-absorption-based silicon waveguide photo-power monitor
InactiveUS20120080672A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTwo-photon absorptionComing out
Instead of monitoring the optical power coming out of a waveguide, a direct method of monitoring the optical power inside the waveguide without affecting device or system performance is provided. A waveguide comprises a p-i-n structure which induces a TPA-generated current and may be enhanced with reverse biasing the diode. The TPA current may be measured directly by probing metal contacts provided on the top surface of the waveguide, and may enable wafer-level testing. The p-i-n structures may be implemented at desired points throughout an integrated network, and thus allows probing of different devices for in-situ power monitor and failure analysis.
Owner:INTEL CORP
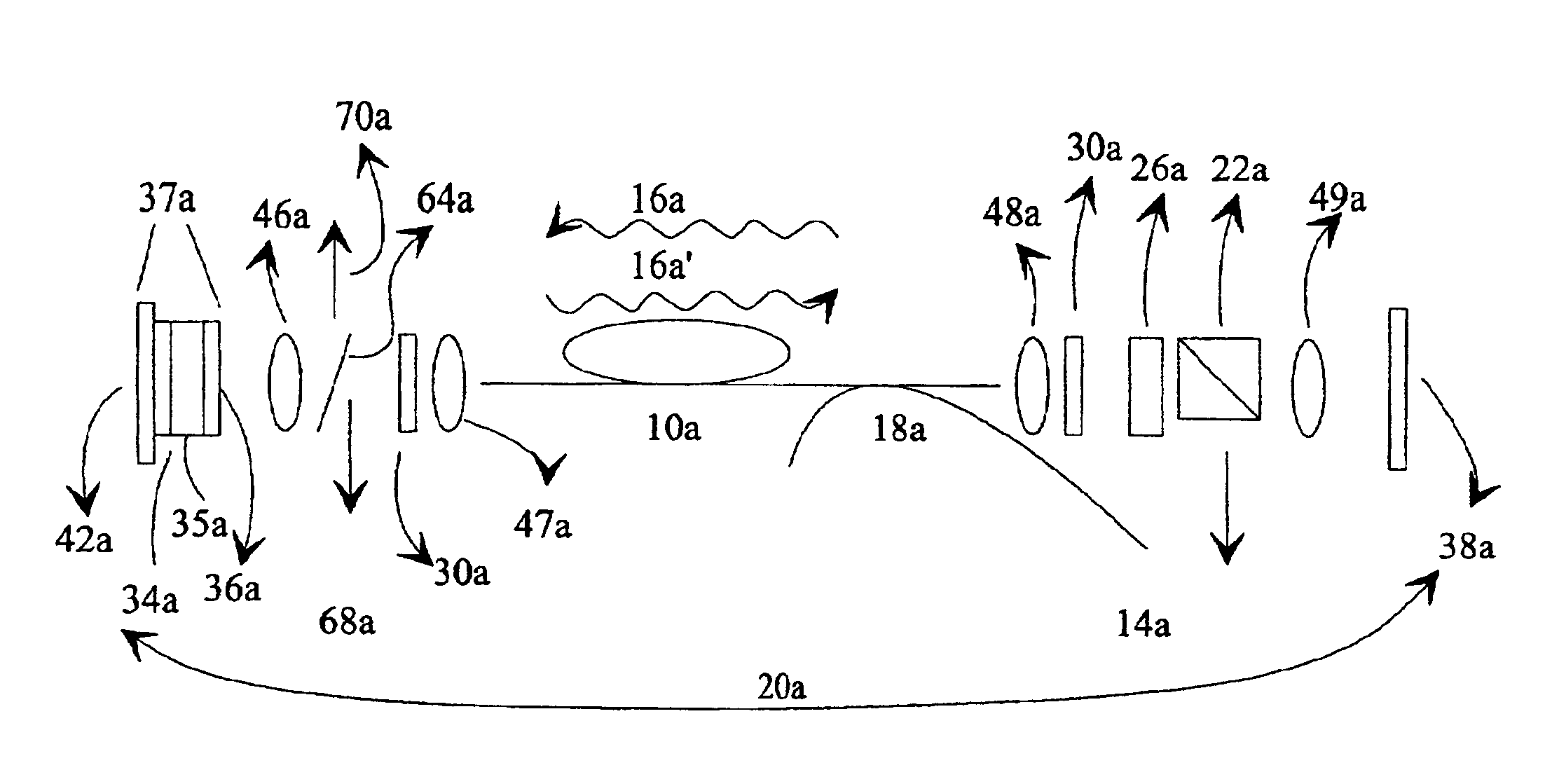
Resonant fabry-perot semiconductor saturable absorbers and two photon absorption power limiters
InactiveUS6956887B2Limit pulse shorteningFacilitating cw modelockingPhotomechanical apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionTwo-photon absorptionQ-switching
An intracavity resonant Fabry-Perot saturable absorber (R-FPSA) induces modelocking in a laser such as a fiber laser. An optical limiter such as a two photon absorber (TPA) can be used in conjunction with the R-FPSA, so that Q-switching is inhibited, resulting in laser output that is cw modelocked. By using both an R-FPSA and a TPA, the Q-switched modelocked behavior of a fiber laser is observed to evolve into cw modelocking.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Sulfonium salt photo-acid generator using stilbene as main body and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101943862AGood acid productionEasy to makeOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusSolubilityElectron donor
The invention relates to a sulfonium salt photo-acid generator using stilbene as the main body and a preparation method thereof, which discloses a design and preparation method of a sulfonium salt photo-acid generator using stilbene chromophore as the main body and having two-photon absorption capability, in particular to a novel photo-acid generator synthesized by using stilbene as the conjugated chain bridge, adding various electron donors on para positions of the benzene ring and using sulfonium salts with different substituent groups as electron acceptors and a preparation method thereof. The photo-acid generator can be well dissolved in a common solvent such as dichloromethane, trichloromethane, acetone and tetrahydrofuran, and has the advantages of simple synthesis procedure, easy purification, high yield and the like. Because the photo-acid generator has a push-pull type molecular structure and the molecule indicates the two-photon absorption properties of the stilbene compound, the photo-acid generator has great application values in the fields of single-photon photoetching and two-photon photoetching.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Semiconductor waveguide based high speed all optical wavelength converter
A semiconductor-based all optical wavelength converter is disclosed. An apparatus according to aspects of the present invention includes an optical waveguide disposed in semiconductor material. An optical pump source is optically coupled to direct an optical pump beam having a first wavelength into the optical waveguide. The optical waveguide is further optically coupled to receive an input optical beam having a second wavelength. The optical waveguide is optically coupled to generate an output optical beam having a third wavelength in response to the optical pump beam and the input optical beam in the optical waveguide. A diode structure is disposed in the optical waveguide. The diode structure includes at least P and N regions. The diode structure is biased to generate an electric field to remove free carriers from an optical path through the optical waveguide generated in response to two photon absorption in the optical waveguide.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Advanced methods and systems for treating cell proliferation disorders
ActiveUS8770203B2High selectivityAvoid the needOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapyTwo-photon absorptionMedicine
Owner:IMMUNOLIGTHT LLC +1
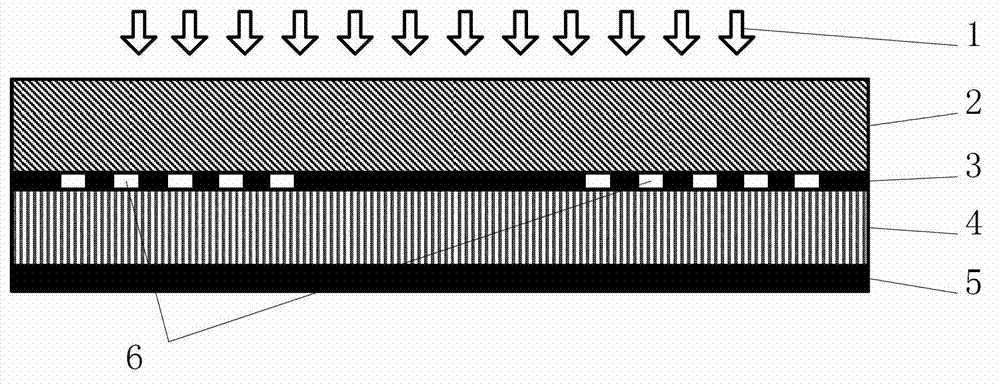
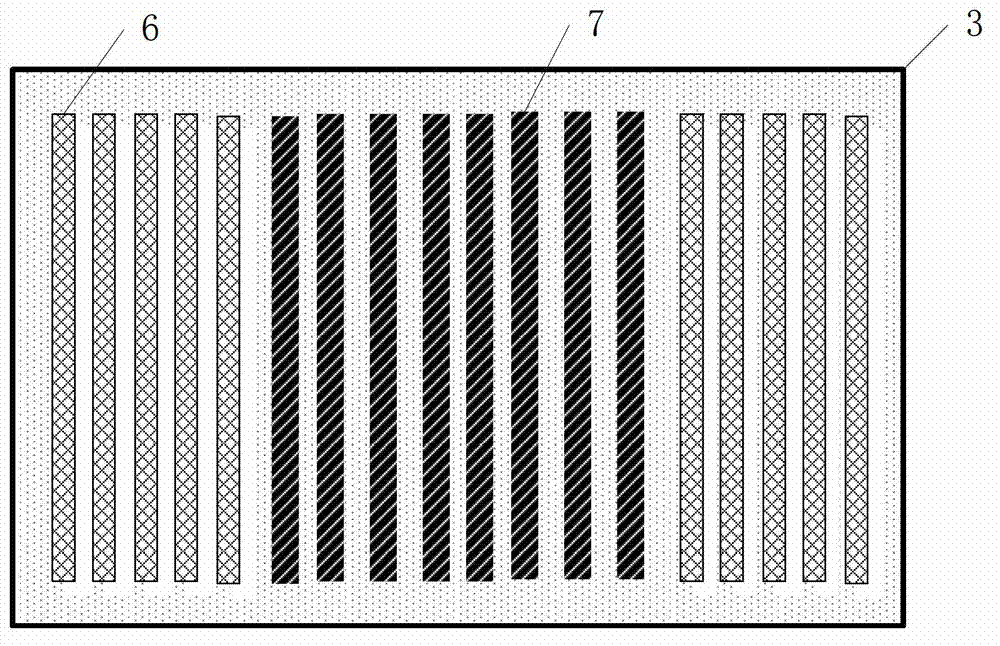
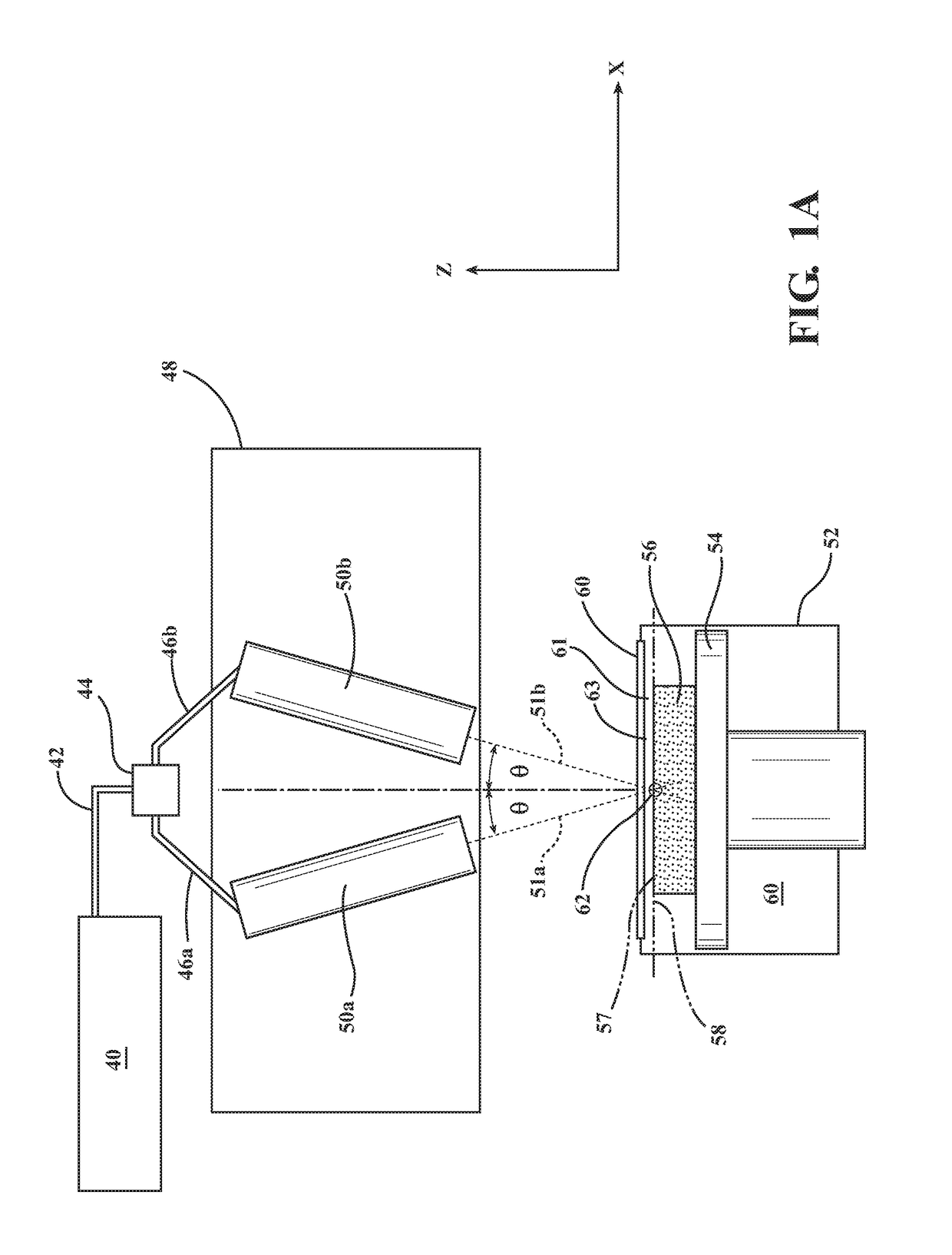
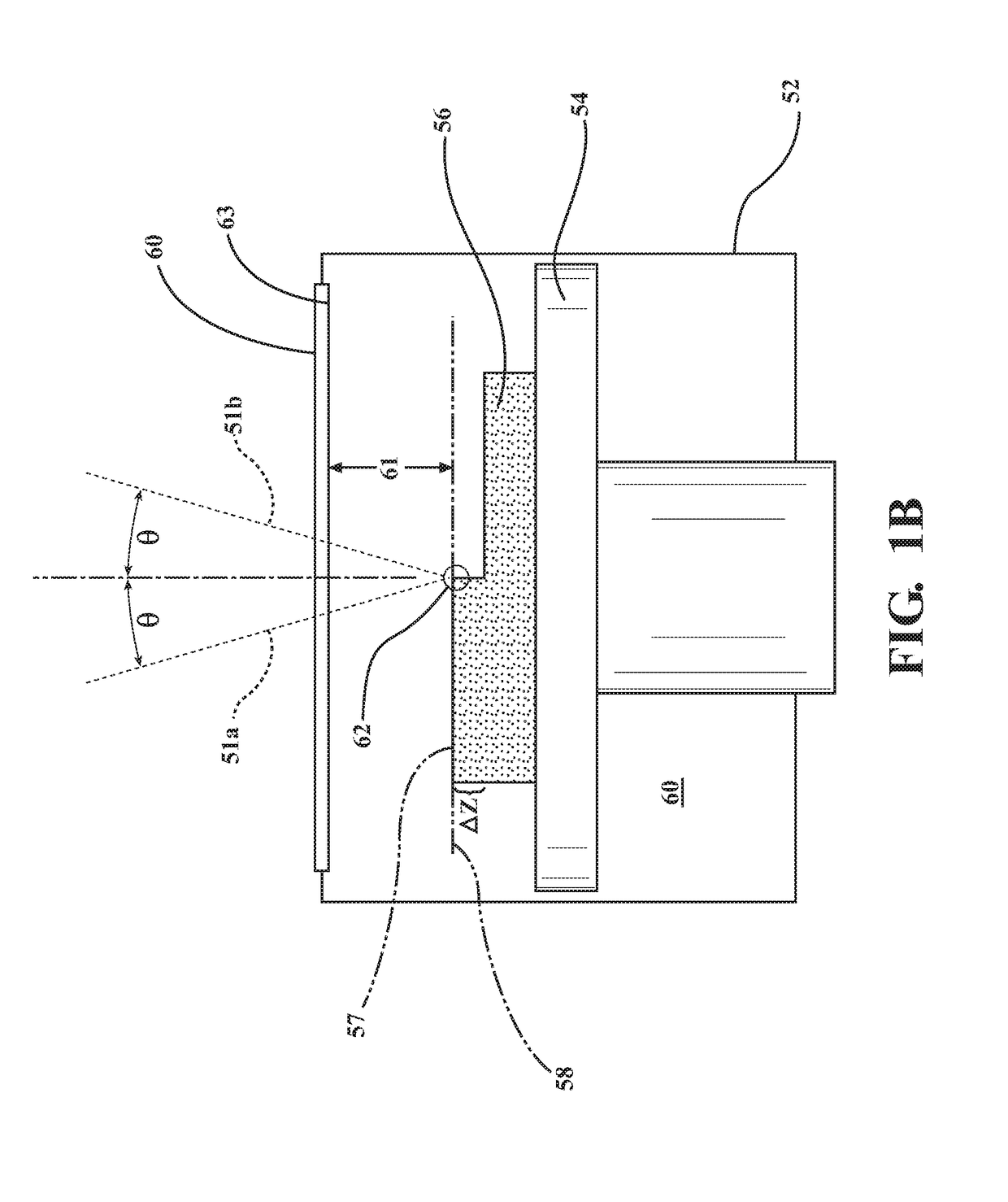
Apparatus and method for forming three-dimensional objects using two-photon absorption linear solidification
InactiveUS20170225393A1Additive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyTwo-photon absorptionImage resolution
An apparatus and method for making a three-dimensional object from a solidifiable material using two photon absorption is described. The use of two photon absorption allows for the creation of a non-solidification zone beneath the exposed surface of a solidifiable material so that no separation is required between the most recently solidified layer of the object and a substrate such as a glass, a film, or a glass / film combination. In addition, when used with a linear scanning device, two photon absorption causes solidification to occur within a small spot area, which provides a means for creating larger, higher resolution objects than DLP systems or laser systems that use single photon absorption.
Owner:GLOBAL FILTRATION SYST
Reactive probes for two-photon fluorescent imaging and sensing
InactiveUS7253287B1High fluorescence quantum yieldImprove light resistanceOrganic chemistryQuantum yieldBovine serum albumin
Fluorescent dyes and probes are key components in multiphoton based fluorescence microscopy imaging of biological samples. In order to address the demand for better performing dyes for two-photon based imaging, a new series of reactive fluorophores tailored for multiphoton imaging has been disclosed. These fluorophores are based upon the fluorene ring system, known to exhibit high fluorescence quantum yields, typically >0.7, and possess high photostability. They have been functionalized with moieties to act, e.g., as efficient amine-reactive fluorescent probes for the covalent attachment onto, e.g., proteins and antibodies. The synthesis and the single-photon spectral characteristics, as well as measured two-photon absorption cross sections of the reactive fluorophores in solution are presented. Spectral characterizations of bovine serum albumin (BSA) conjugated with the new reactive probe is presented.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Thermally cross-linkable two-photon chromophores
Provided are new two-photon absorbing chromophores of the formula:wherein R is an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms and Q is OH, OMe, propargyloxy-(O—CH2—C≡CH), methylpropargyloxy-(O—CH2—C≡C—CH3), allyloxy-(O—CH2—C═CH2),1-methyl-allyloxy(O—CH2—CH═CHCH3) and 3-methyl-allyloxy (O—CH(CH3)—CH═CH2).
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
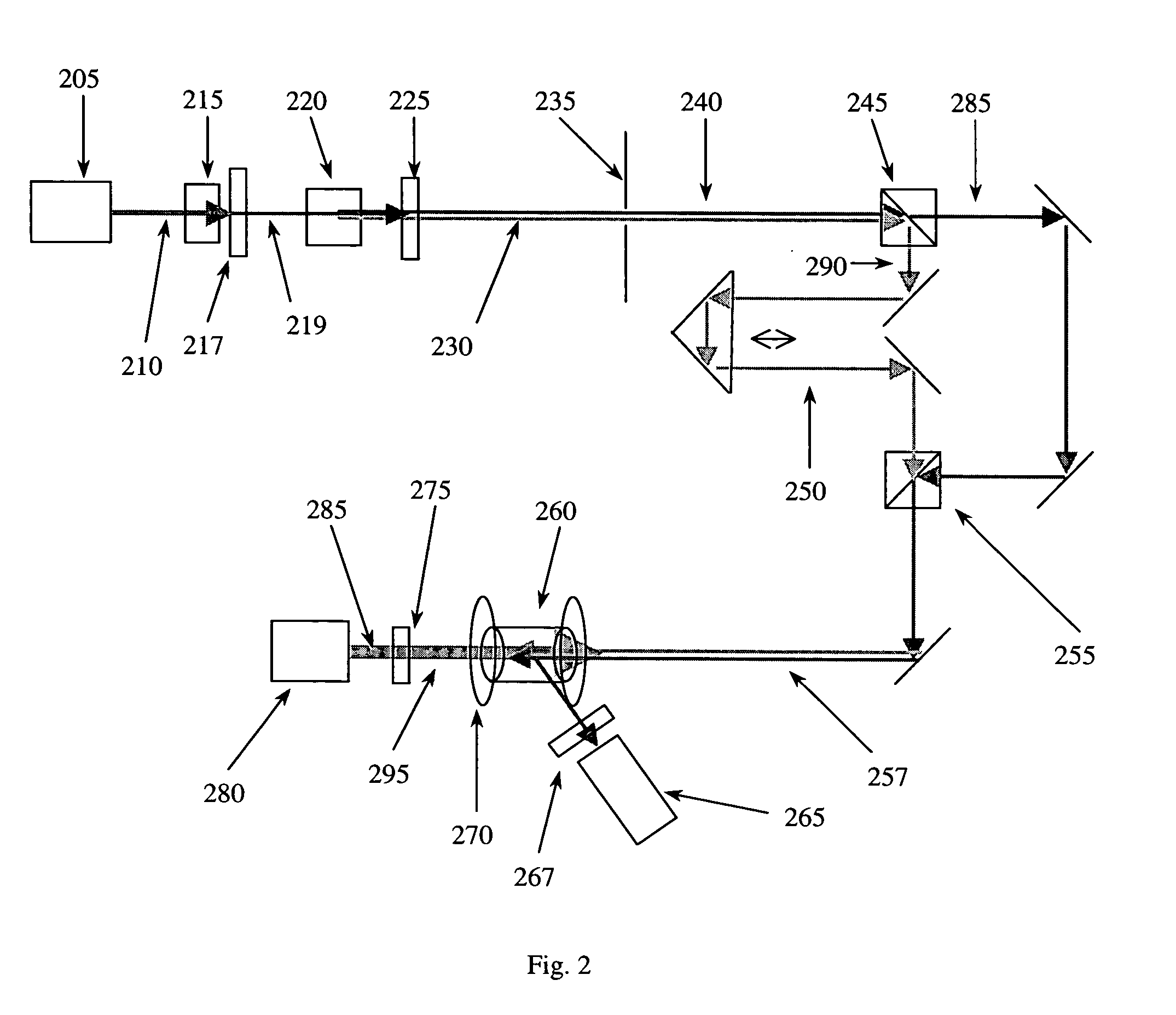
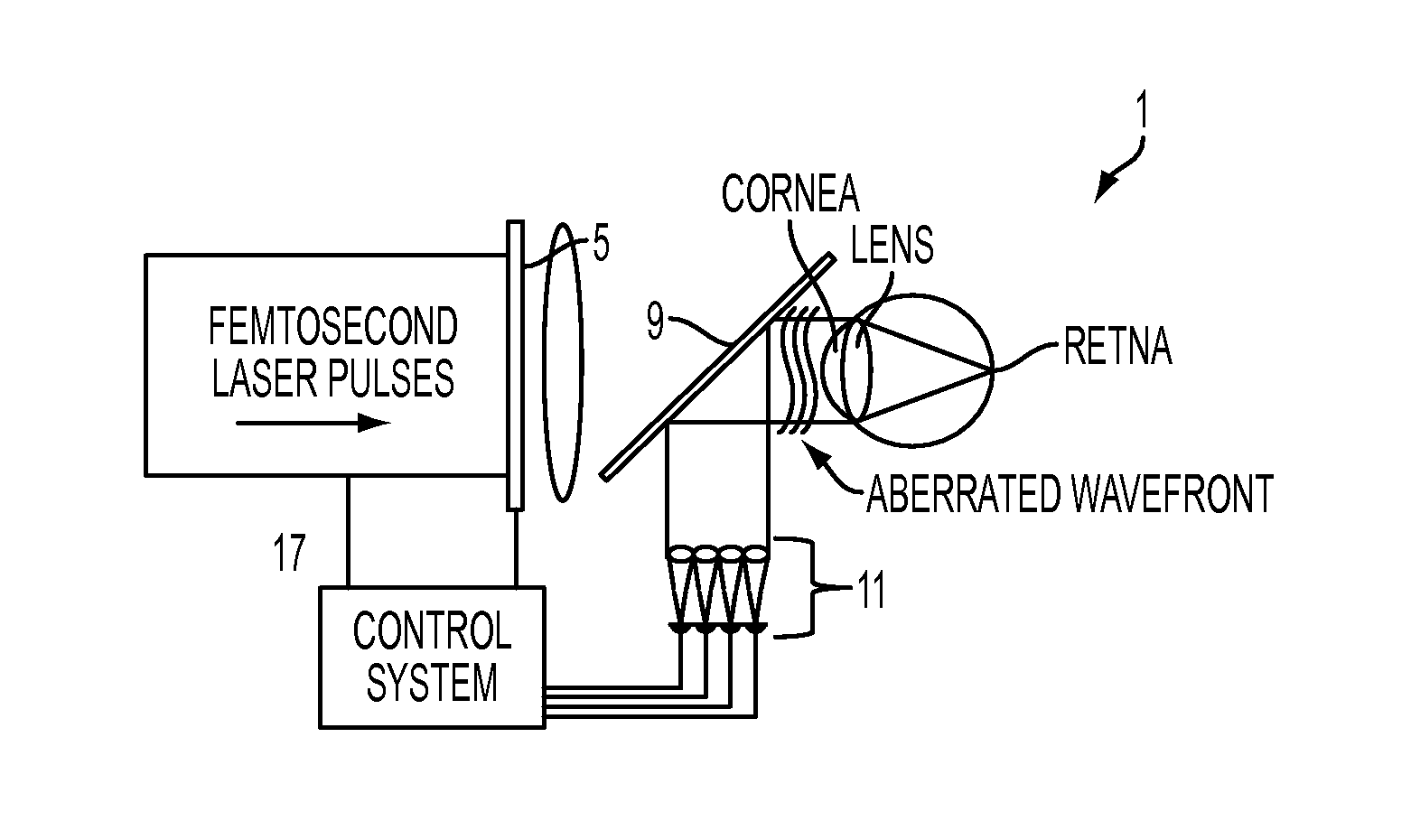
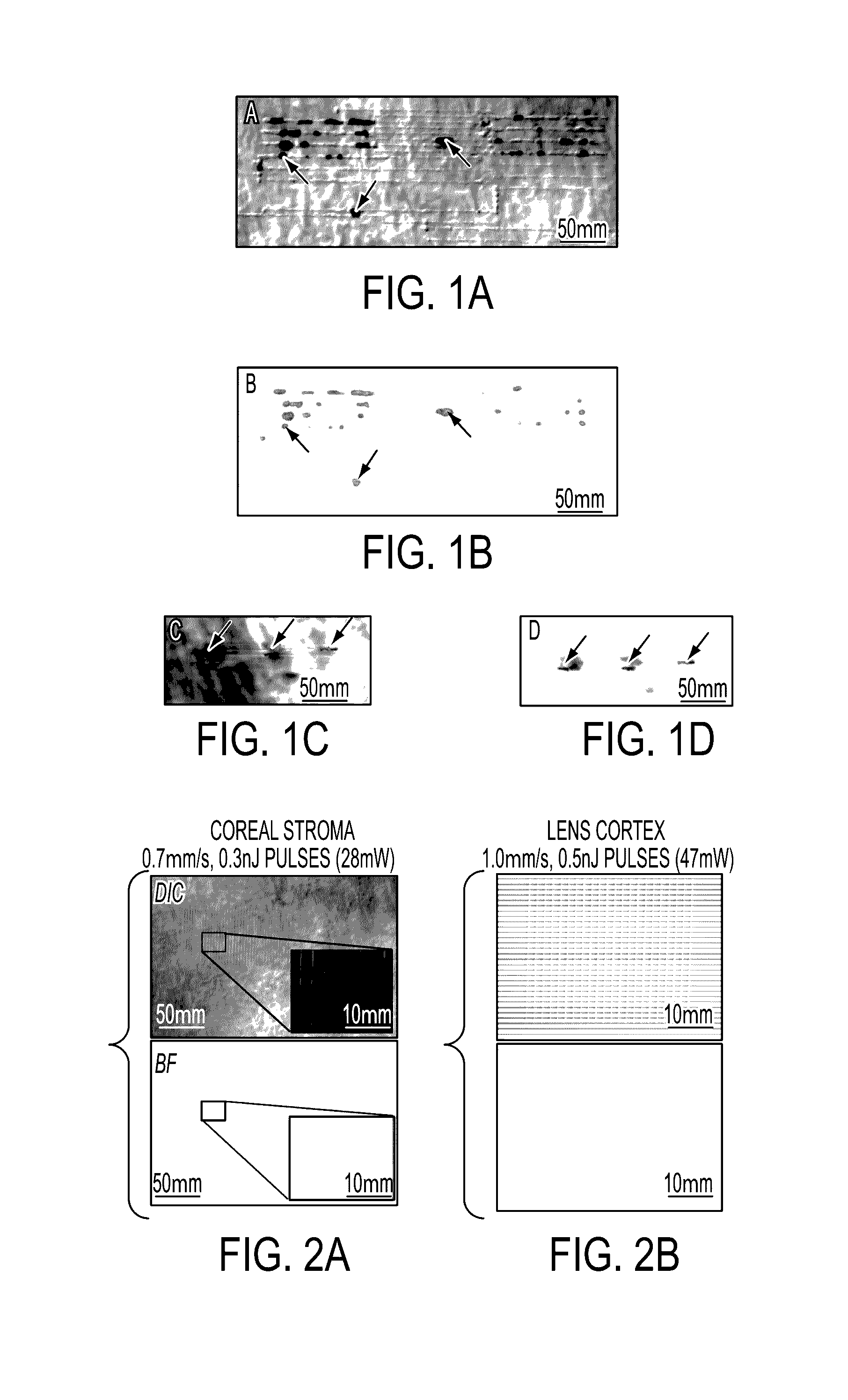
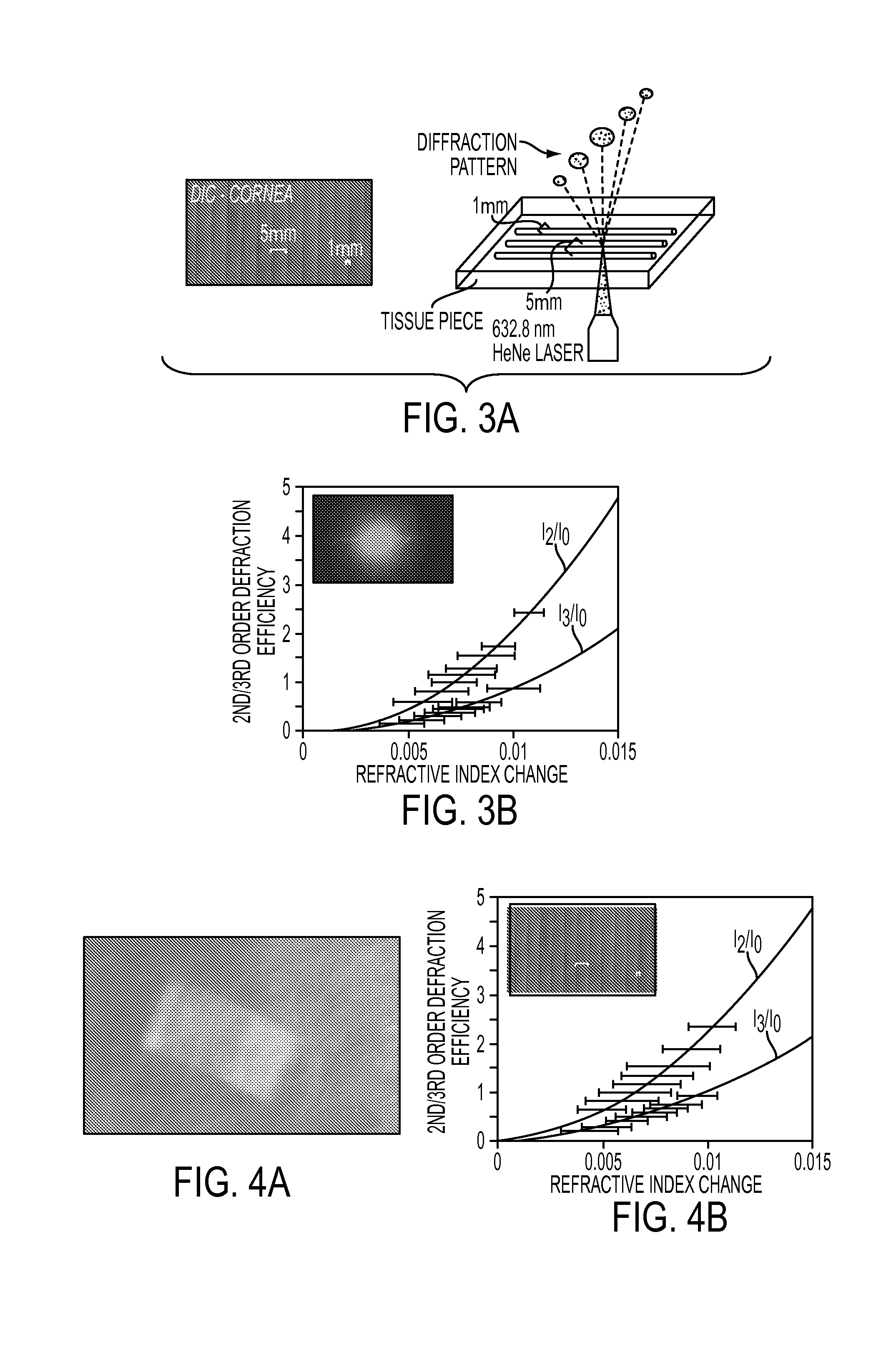
Multi-photon absorption for femtosecond micromachining and refractive index modification of tissues
By adapting femtosecond micromachining approaches developed in hydrogels, we can perform Intra-tissue Refractive Index Shaping (IRIS) in biological tissues. We reduced femtosecond laser pulse energies below the optical breakdown thresholds to create grating patterns that are associated with a change in the refractive index of the tissue. To increase two-photon absorption, we used a two (or more)-photon-absorbing chromophore.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Two-photon recording method, two-photon absorption recording material, two-photon absorption recording-reproduction method and optical recoding medium
InactiveUS20070048666A1High sensitivityImprove storage effectPhotosensitive materialsNanoinformaticsTwo-photon absorptionLuminous intensity
A two-photon recording method is provided and includes: a first step of effecting two-photon absorption to form a latent image in a two-photon absorption recording material; a second step of subjecting the two-photon absorption recording material to heat treatment by which refractive index, absorptivity or luminescence intensity is modulated according to the latent image to effect recording; and a third step of irradiating the two-photon absorption recording material thus heat-treated with light on the entire surface thereof to fix the recording thus formed. The recording can be reproduced without being erased.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com