Patents
Literature
920 results about "Q-switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
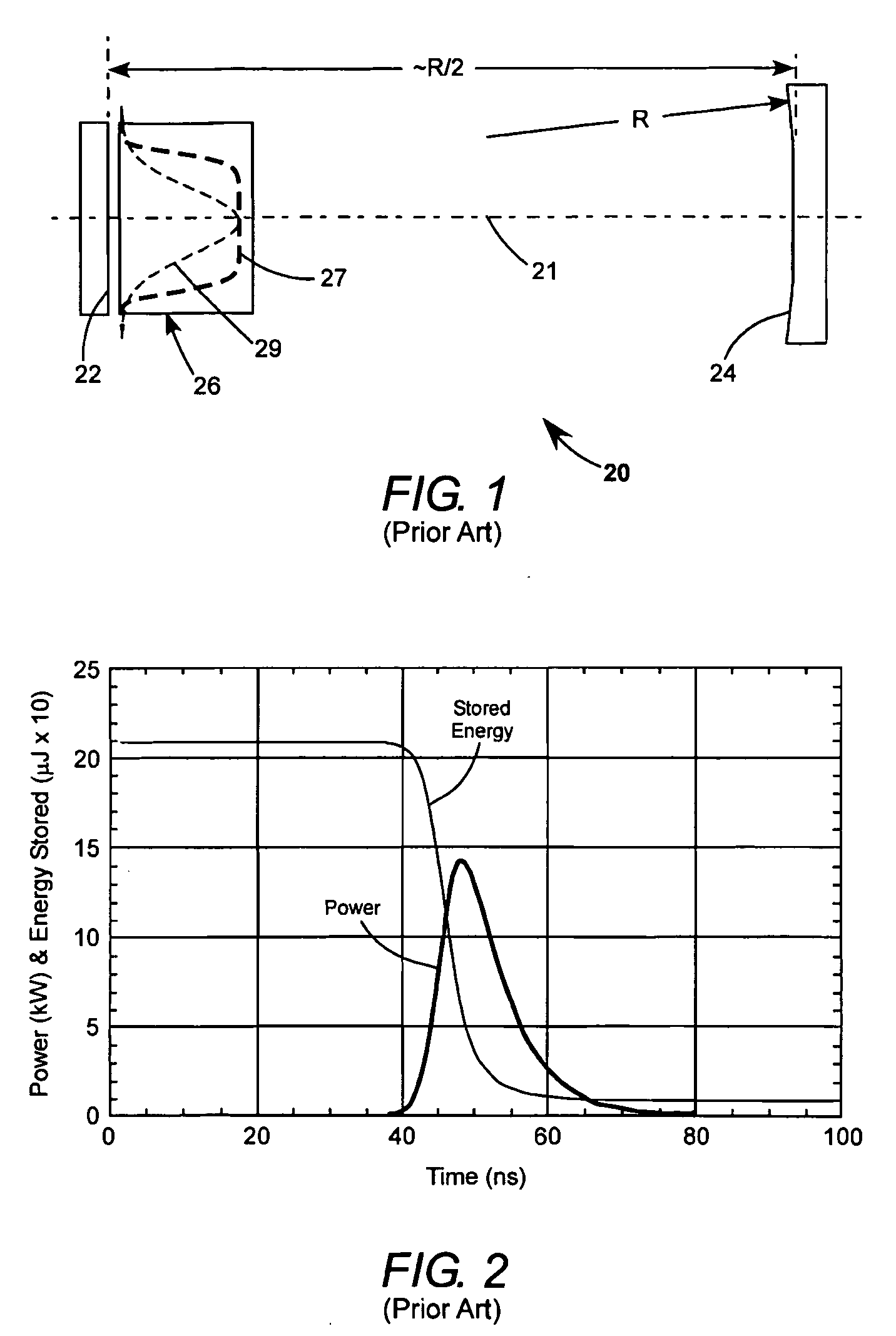
Q-switching, sometimes known as giant pulse formation or Q-spoiling, is a technique by which a laser can be made to produce a pulsed output beam. The technique allows the production of light pulses with extremely high (gigawatt) peak power, much higher than would be produced by the same laser if it were operating in a continuous wave (constant output) mode. Compared to modelocking, another technique for pulse generation with lasers, Q-switching leads to much lower pulse repetition rates, much higher pulse energies, and much longer pulse durations. The two techniques are sometimes applied together.
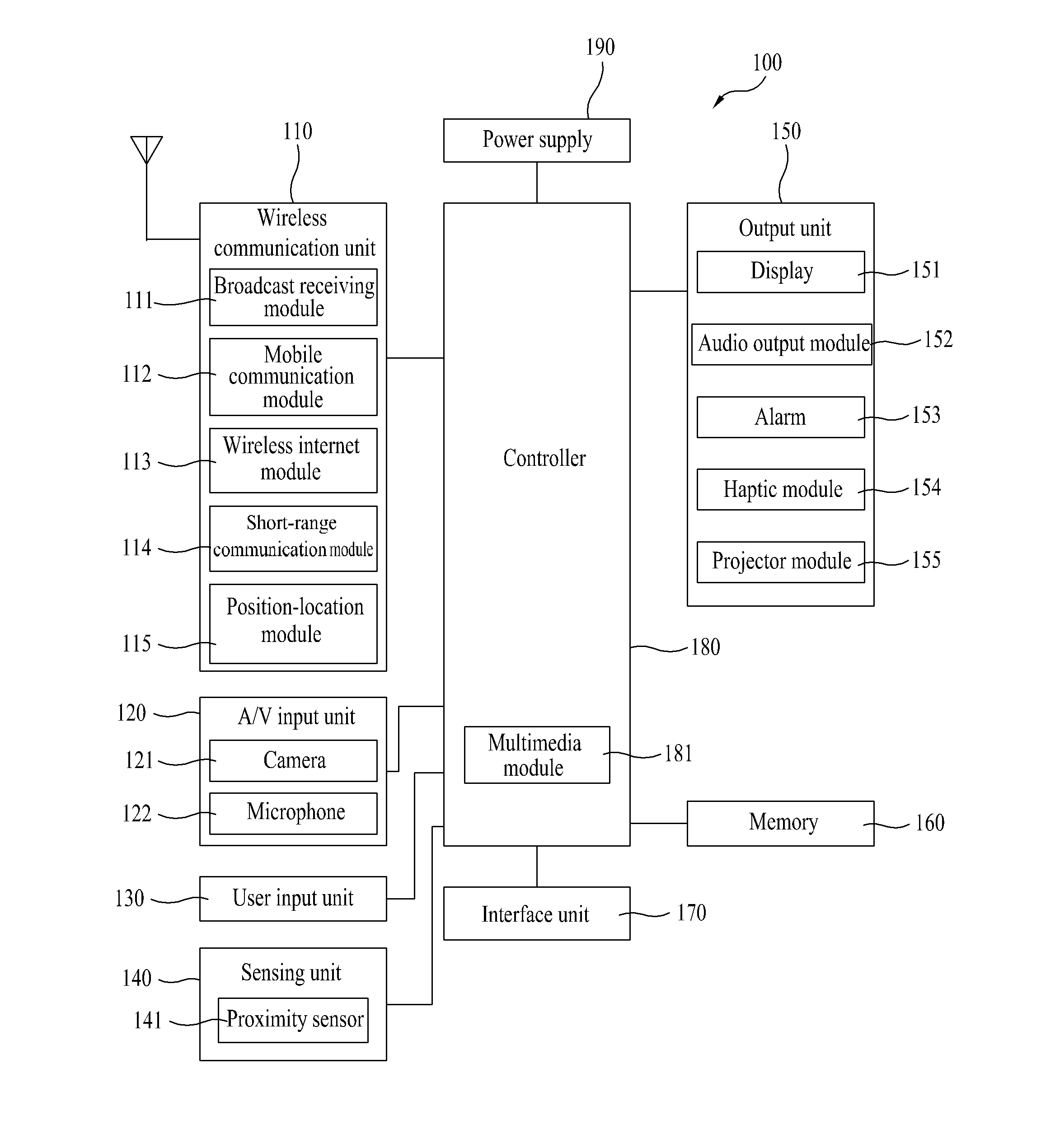
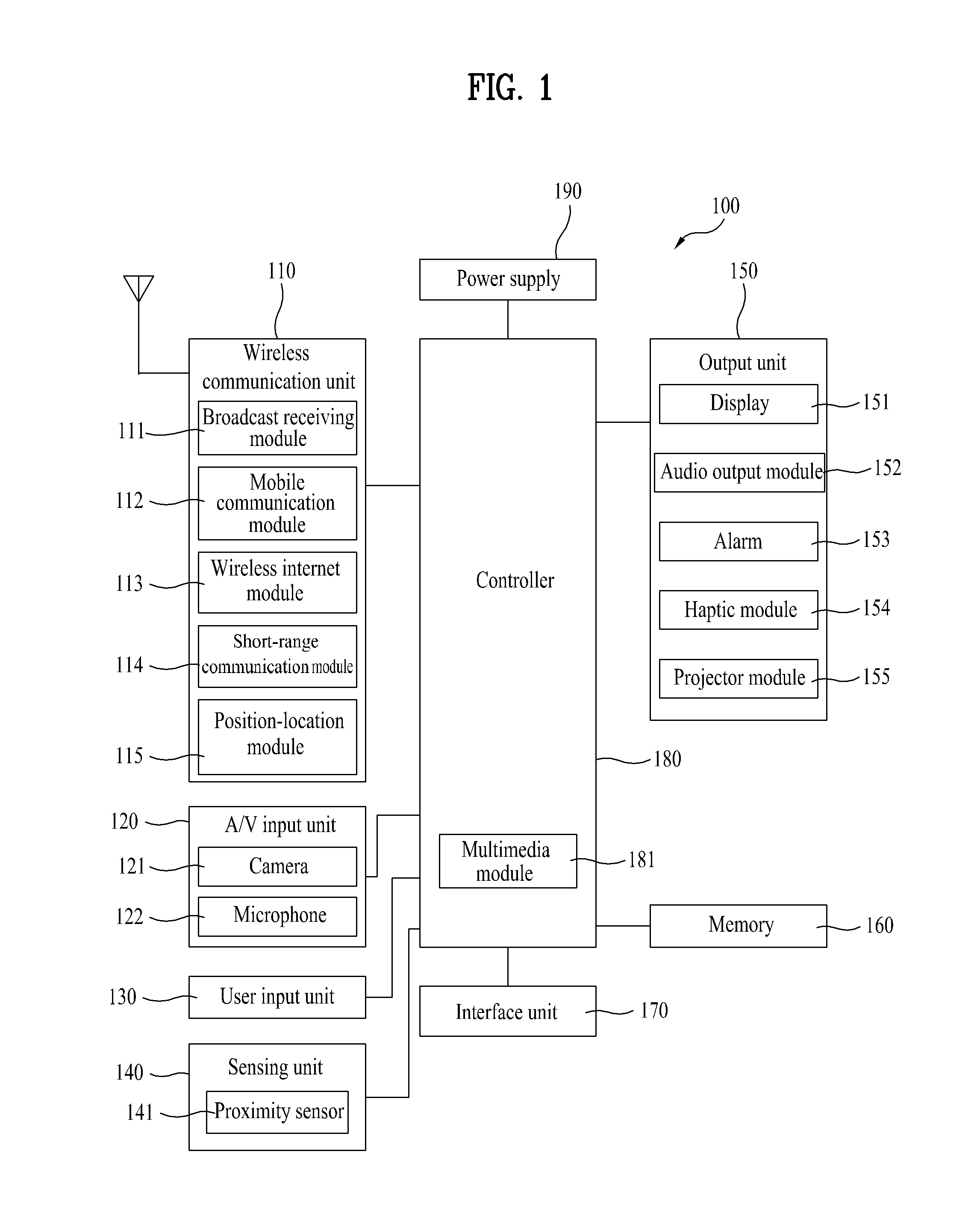
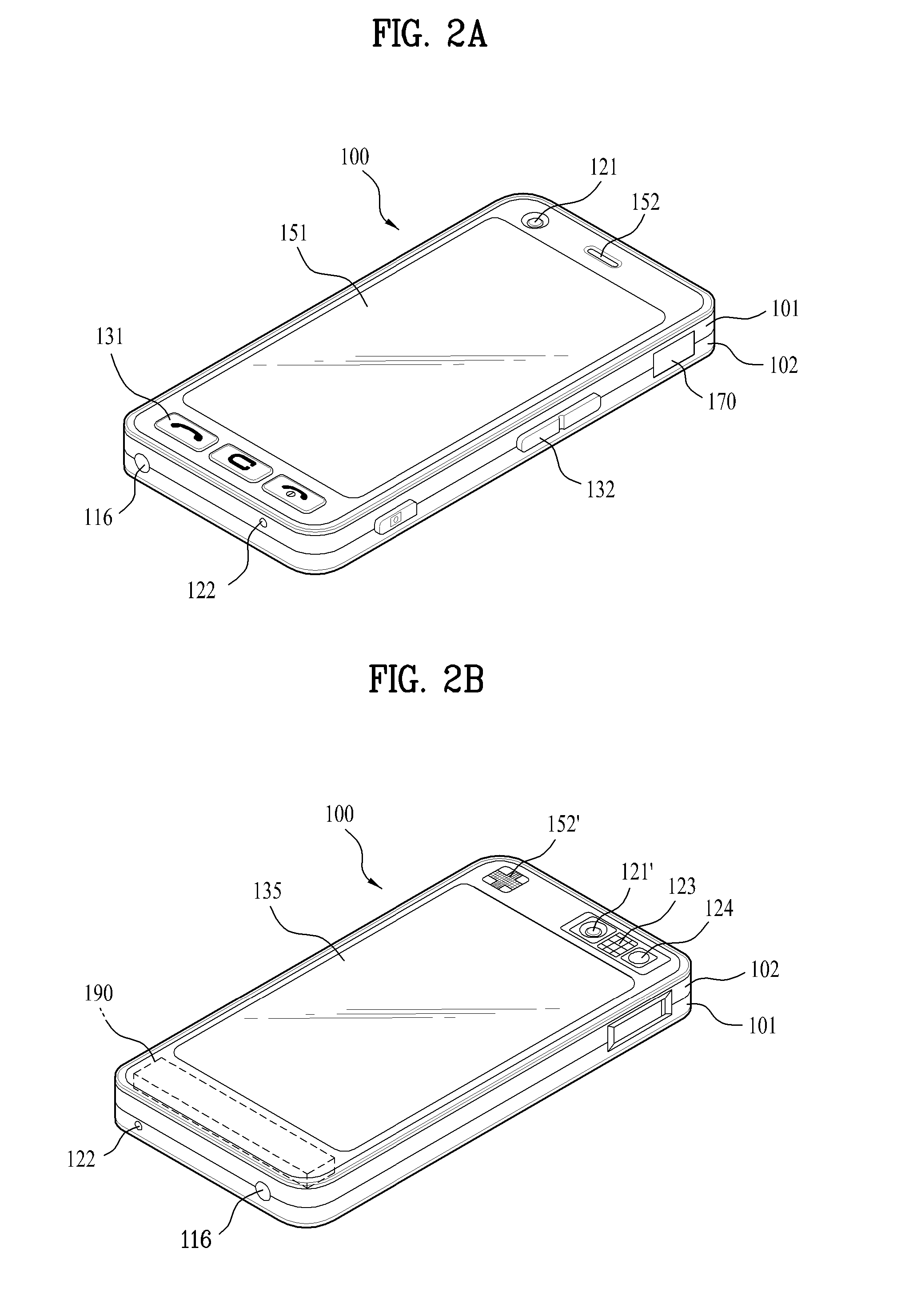
Mobile terminal and method of controlling a mode switching therein
InactiveUS20120154413A1Efficient executionReinforcing inter-mode data securityImage memory managementInternal/peripheral component protectionOperational systemCommunication unit
A mobile terminal including a communication unit configured to communicate with at least one external terminal; a memory configured to store at least a first and second operating system including at least first and second modes, respectively; and a controller configured to execute the first operating system and to activate the first mode corresponding to the first operating system, to display a first information screen on a display unit corresponding to the activated first mode, to receive a switching signal indicating the first mode is to be switched to the second mode, to perform an authentication procedure for authenticating that the first mode can be switched to the second mode, to activate the second mode and deactivate the first mode when the authentication procedure is validly performed, and to display a second information screen on the display unit corresponding to the second mode and that is different than the first information screen.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
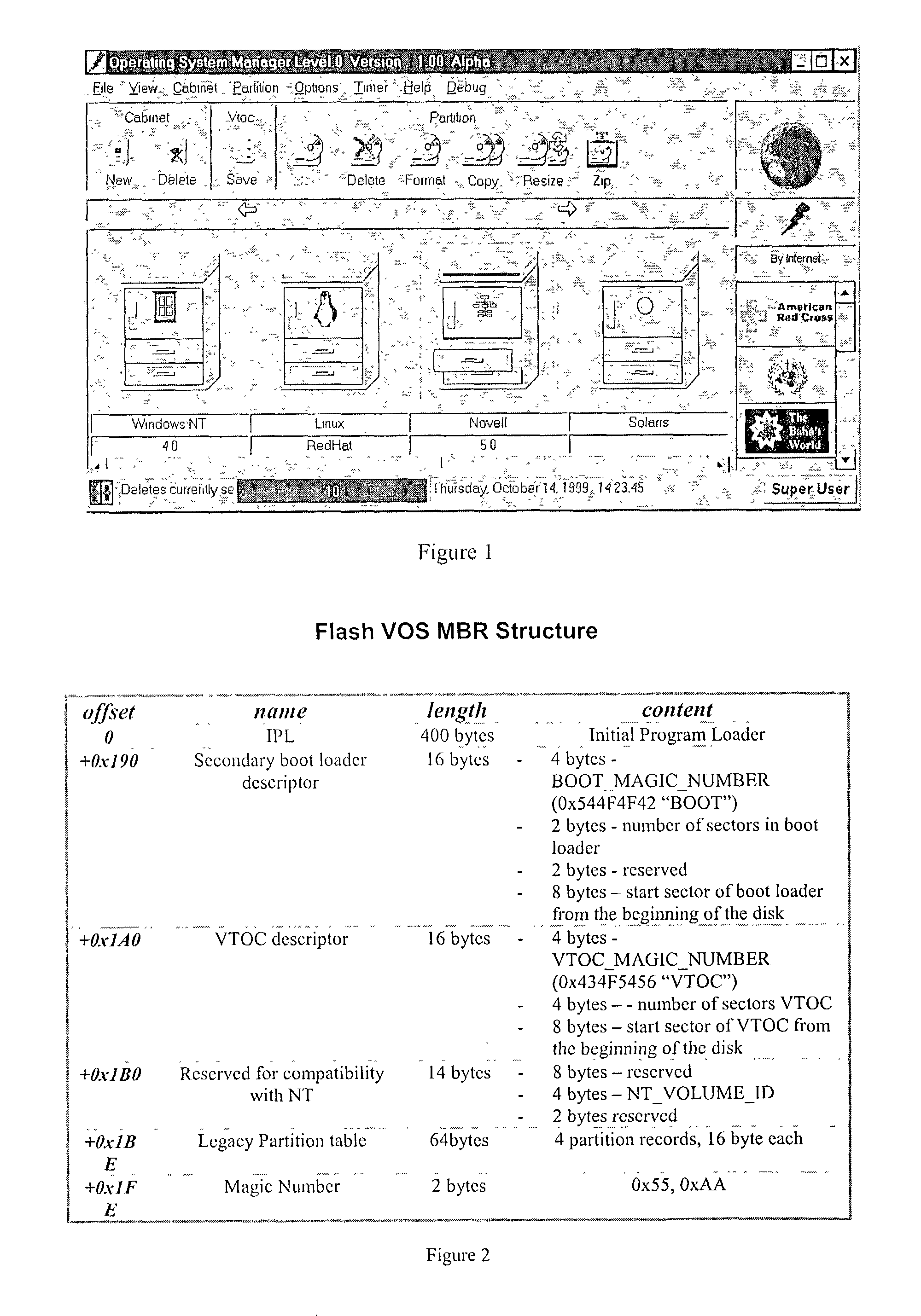
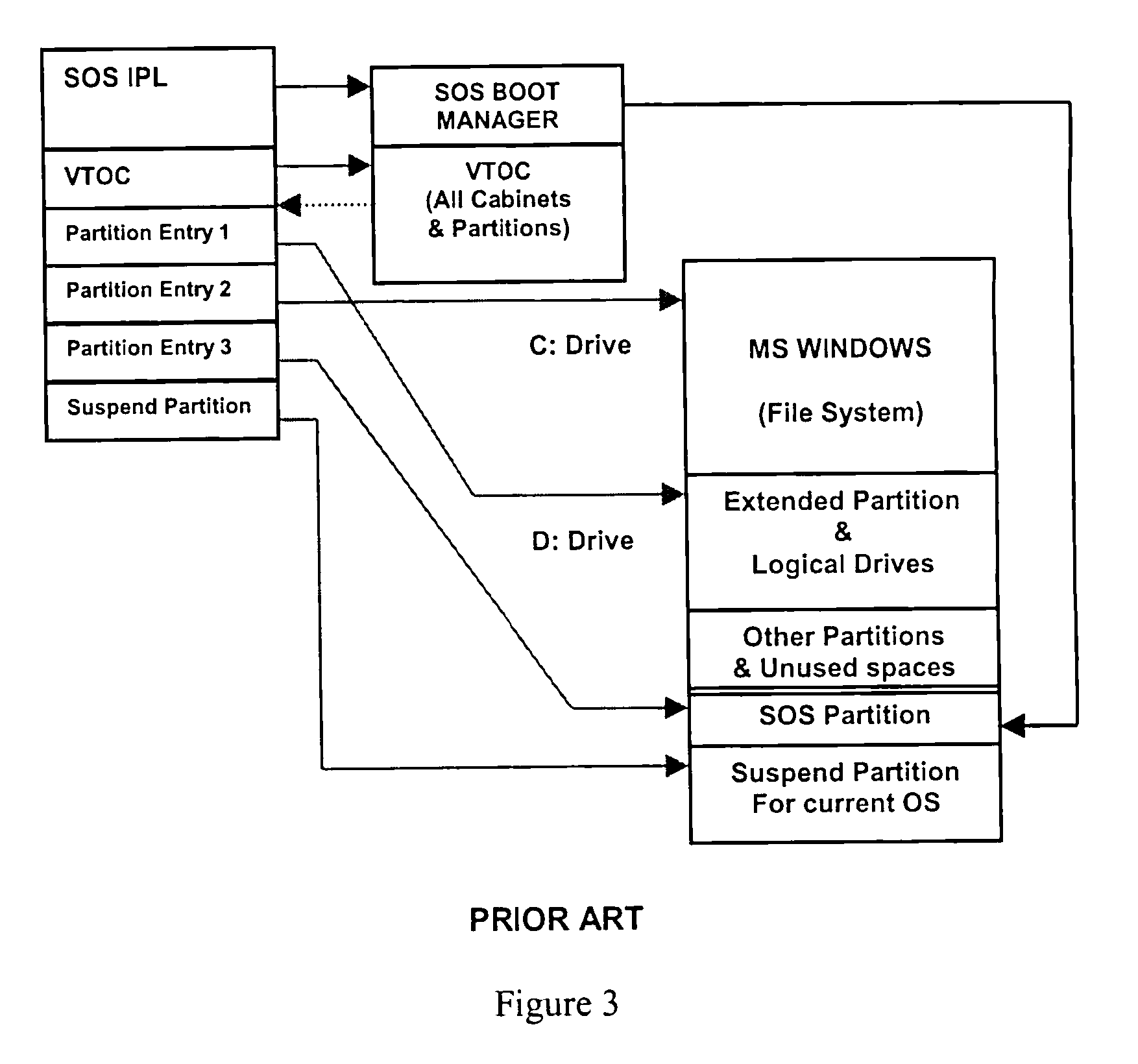
Computer system capable of fast switching between multiple operating systems and applications
ActiveUS7356677B1Fast transferFast shutdownDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsApplication program softwareOperational system
A method and apparatus is presented that allows rapid switching between multiple operating system environments on a single computer, through the use of a Super Operating System operating between the computer system's firmware level and a plurality of bootable operating systems and applications. Relevant data, such as hardware controls, bootable operating systems, and applications software, are grouped onto physical partitions in physical memory. Combinations of compatible partitions can be assigned to a cabinet to create a virtual computer system. A given partition is assignable to multiple cabinets. By operating above the virtual computer systems, the Super Operating System uses the suspend and resume functions of the power management support functions to suspend and hybernate one operating virtual computer system, while activating and operating an alternate virtual computer system on the same computer.
Owner:ONE WORLD LED PTY LTD
Entropy coding supporting mode switching
ActiveUS20140140400A1Increase spectral resolution of spectralImprove coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareData stream
A decoder for decoding a data stream into which media data is coded has a mode switch configured to activate a low-complexity mode or a high-efficiency mode depending on the data stream, an entropy decoding engine configured to retrieve each symbol of a sequence of symbols by entropy decoding using a selected one of a plurality of entropy decoding schemes, a desymbolizer configured to desymbolize the sequence of symbols to obtain a sequence of syntax elements, a reconstructor configured to reconstruct the media data based on the sequence of syntax elements, selection depending on the activated low-complexity mode or the high-efficiency mode. In another aspect, a desymbolizer is configured to perform desymbolization such that the control parameter varies in accordance with the data stream at a first rate in case of the high-efficiency mode being activated and the control parameter is constant irrespective of the data stream or changes depending on the data stream, but at a second lower rate in case of the low-complexity mode being activated.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
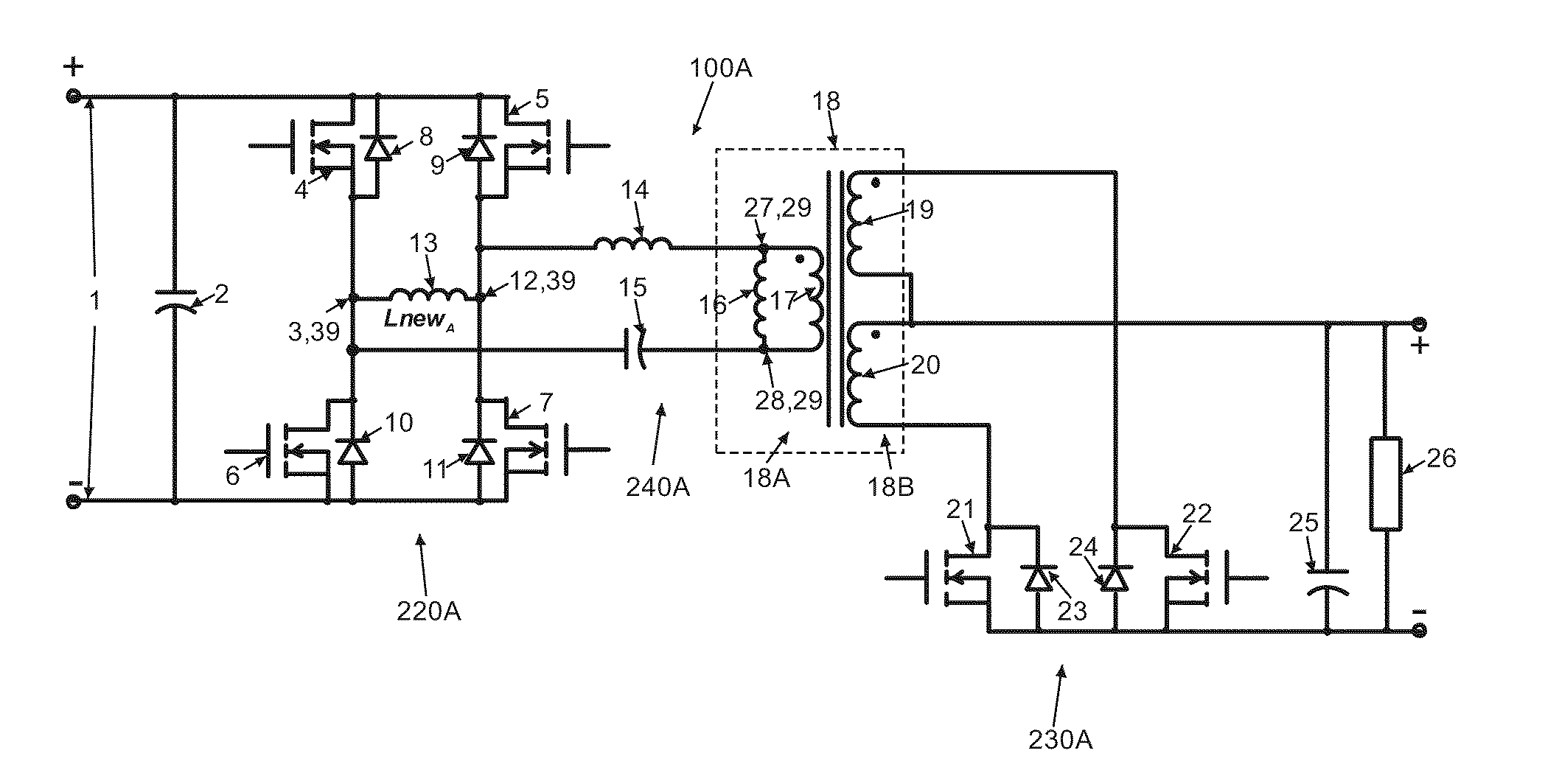
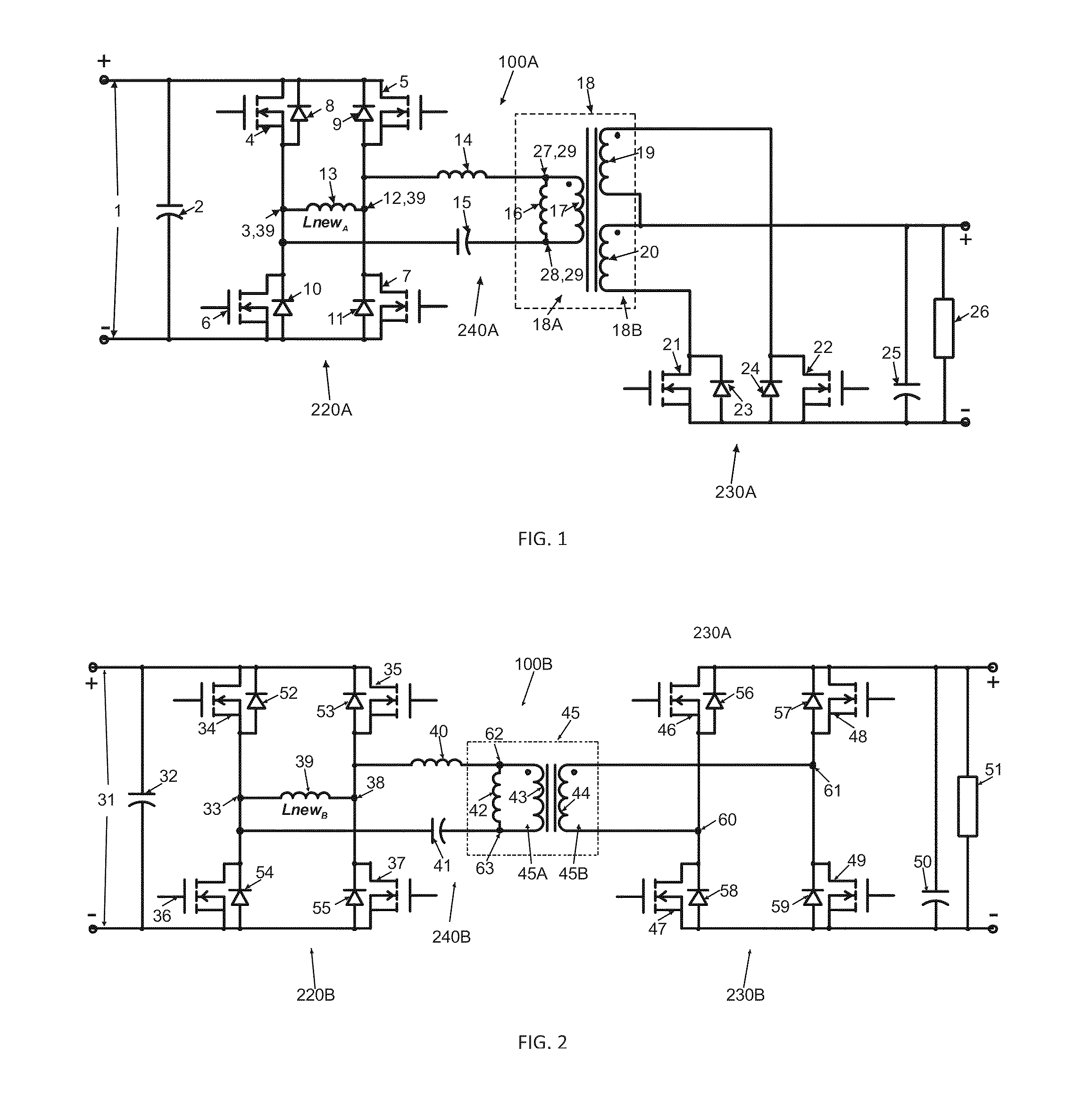
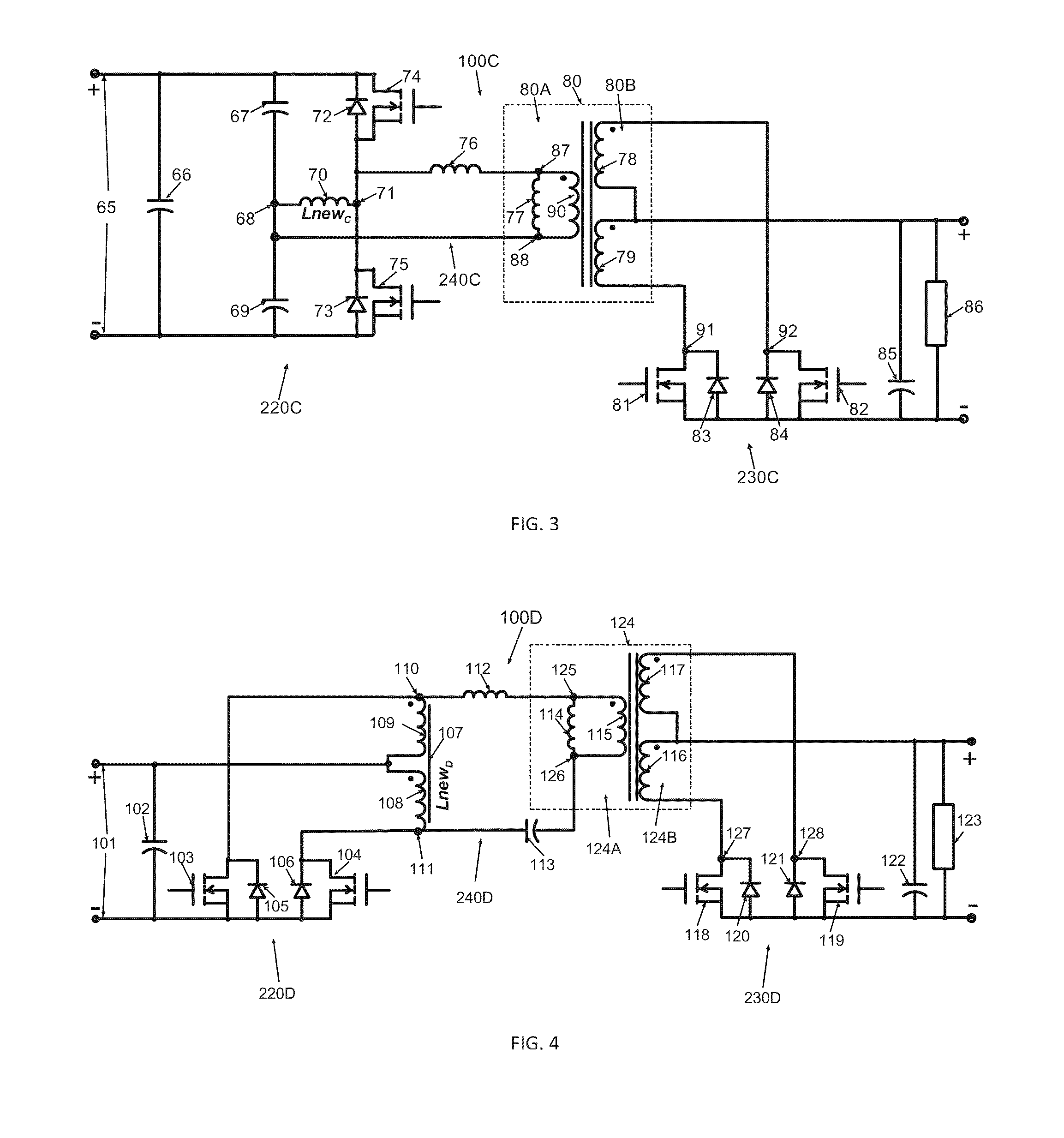
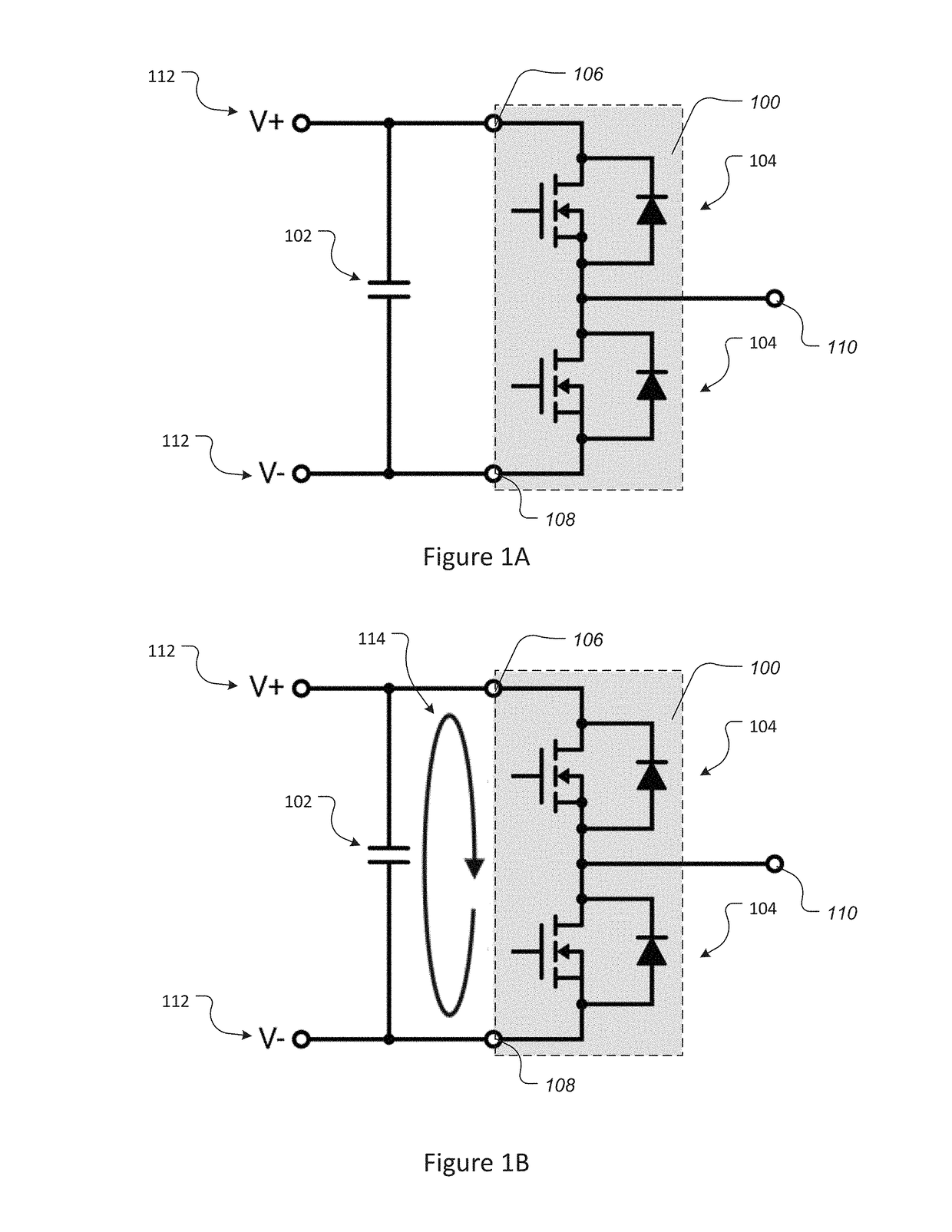
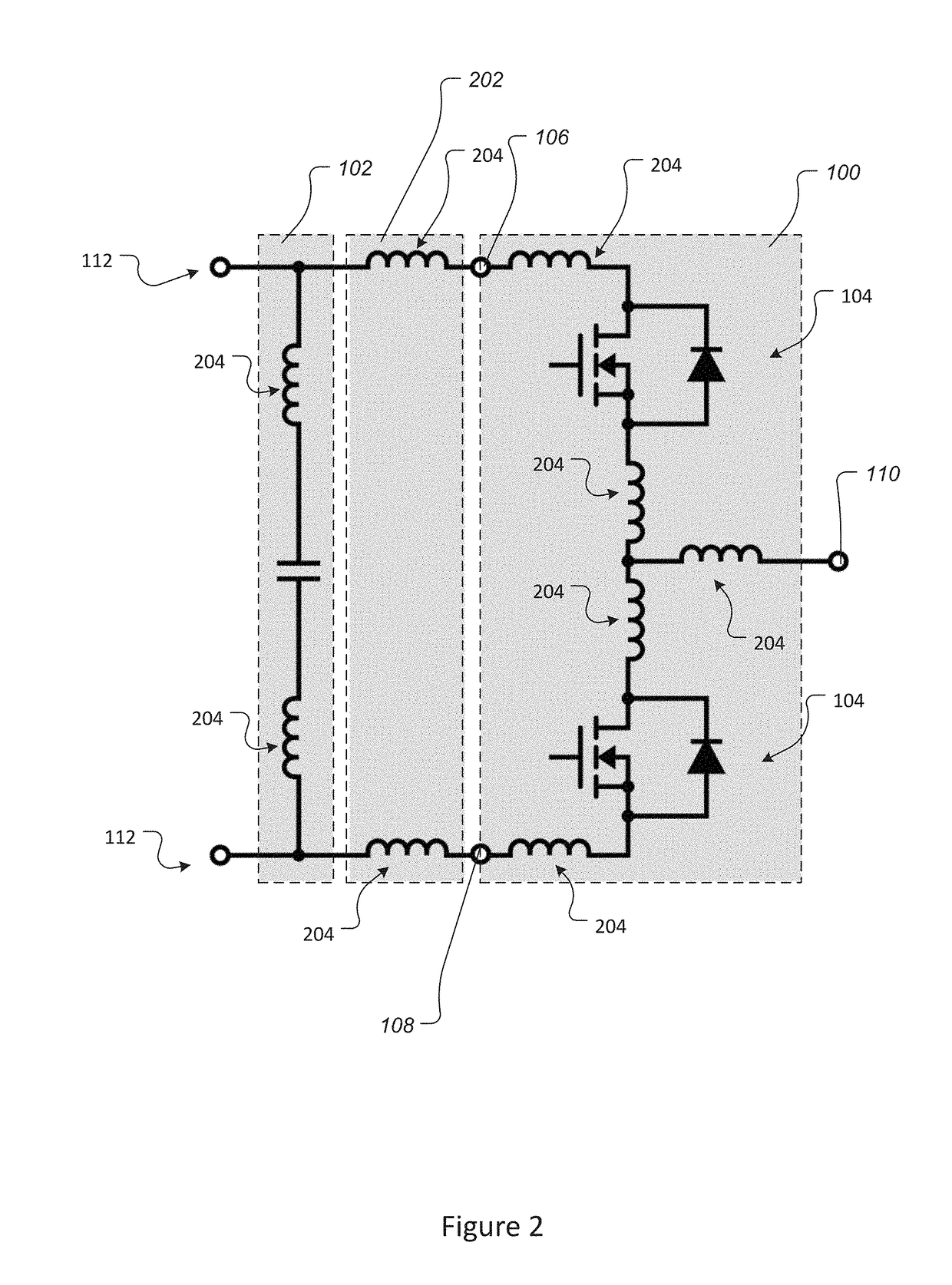
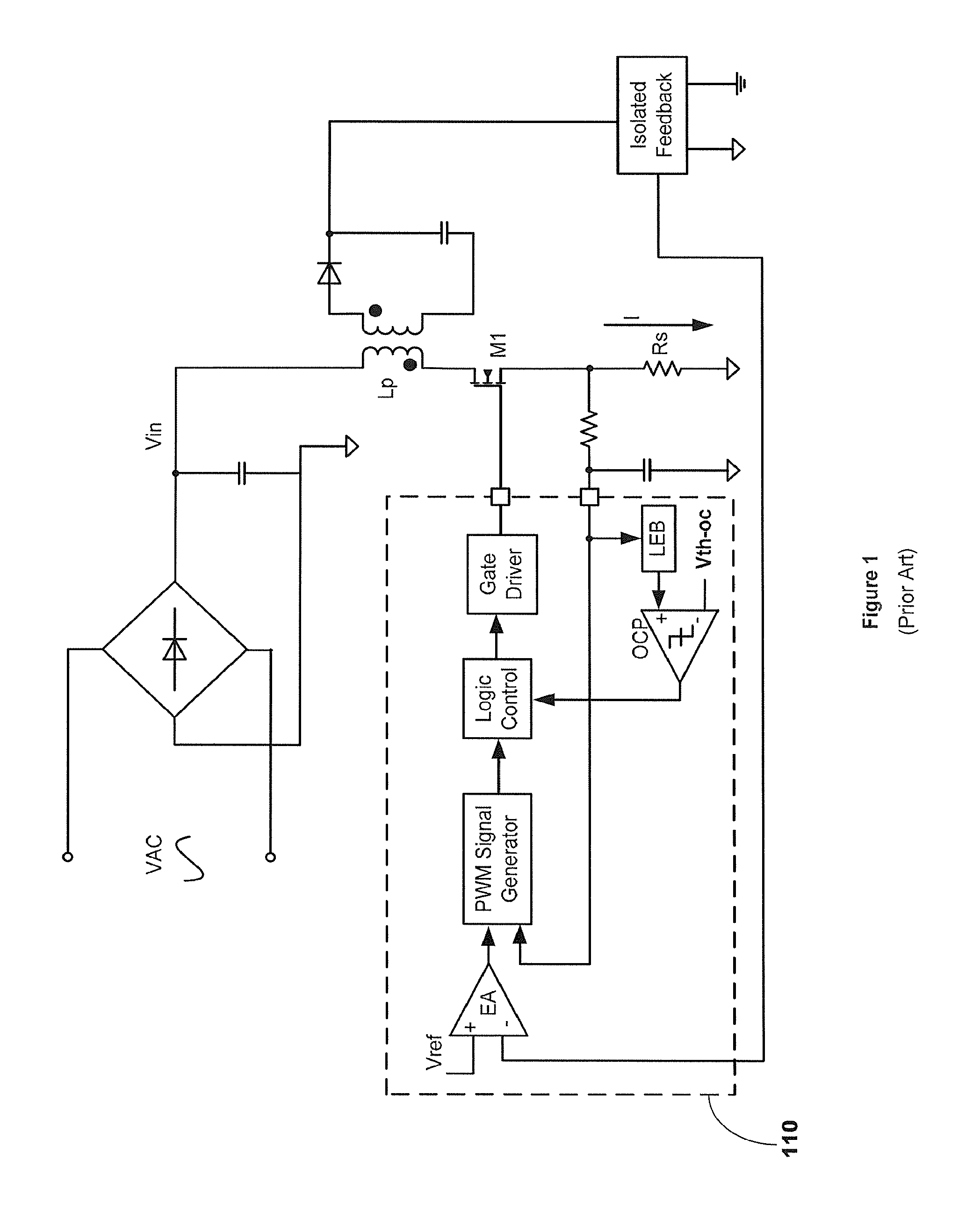
Bi-directional power converter with regulated output and soft switching
ActiveUS20110317452A1Loss-less switchingSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionSoft switchingQ-switching
A resonant, bi-directional, DC to DC voltage converter with loss-less (soft) switching having regulated output and capable of converting power between two, high-potential and low-potential DC voltage sources. The converter's semiconductor and magnetic components provide both, output regulation and soft switching in both (step-down and step-up) directions of power conversion which reduces total component count, cost and volume and enhances power conversion efficiency.
Owner:GREECON TECH
High-repetition rate passively mode-locked solid-state laser
InactiveUS6393035B1Simple designOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersOptical probingMode-locking
A passively mode-locked solid-state laser for emitting a continuous-wave train of electromagnetic-radiation pulses, the fundamental repetition rate of the emitted pulses exceeding 1 GHz, without Q-switching has an optical resonator, a solid-state laser gain element placed inside the optical resonator, an exciter for exciting said laser gain element to emit electromagnetic radiation having the effective wavelength, and a saturable absorber for passive mode locking. The laser gain element preferably consists of a laser material with a stimulated emission cross section exceeding 0.8x10-18 cm-2 at the effective wavelength. Typically, the laser gain element is made of Nd:vanadate. The saturable absorber is preferably a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror device. The laser is simple, robust, compact, efficient, and low-cost. It generates a relatively large average power of 100 mW and higher, which is useful for a number of optical probing and detection applications, in a beam which is substantially a fundamental spatial mode.
Owner:LUMENTUM SWITZERLAND AG
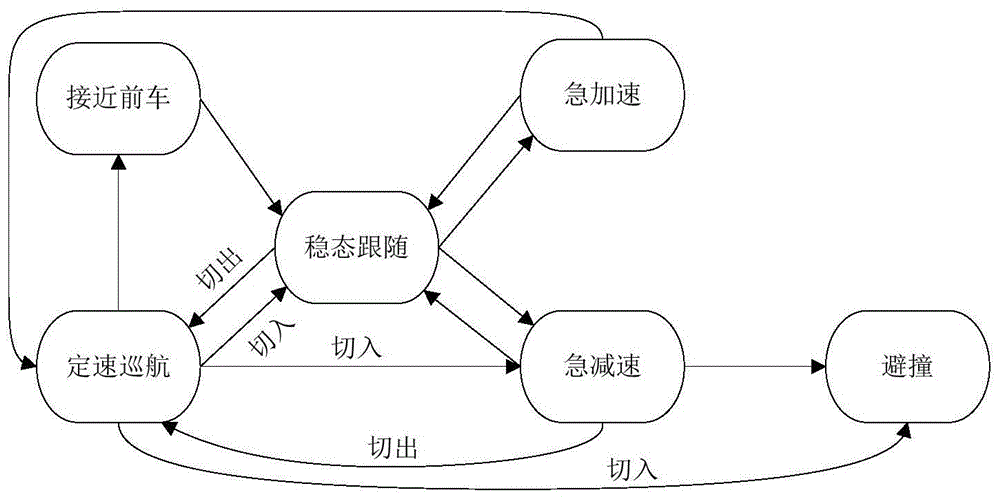
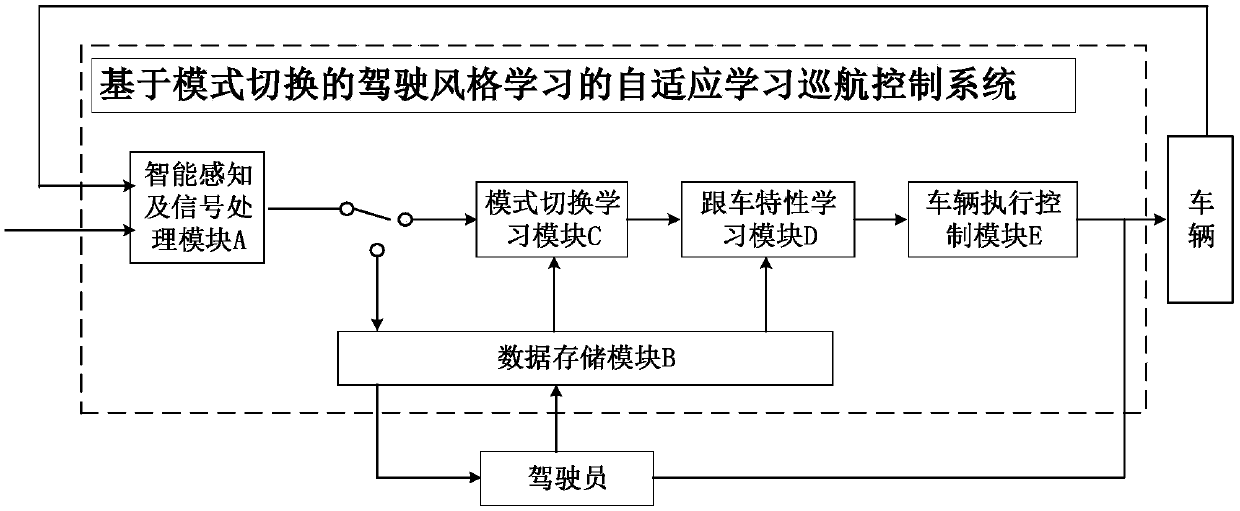
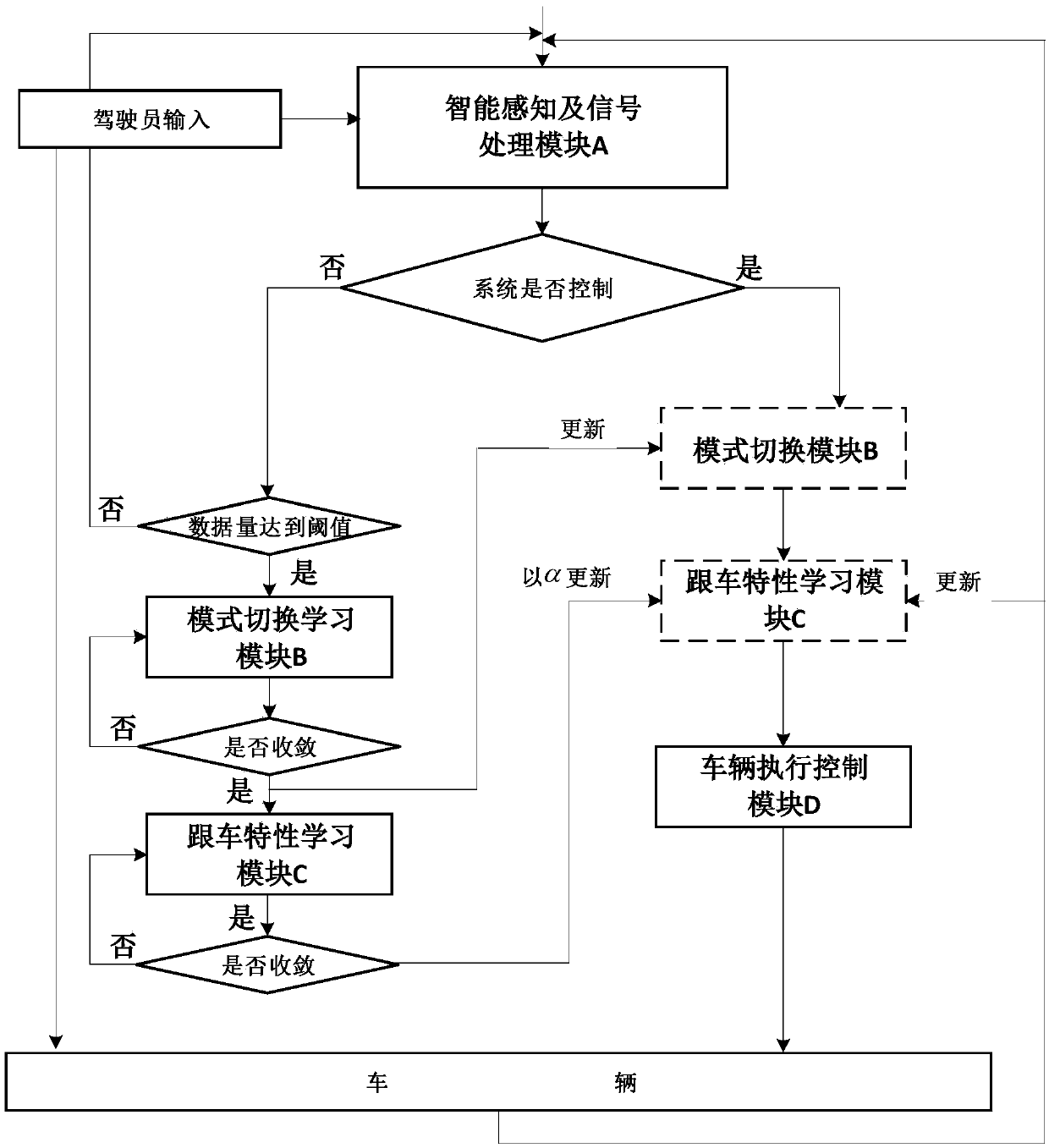
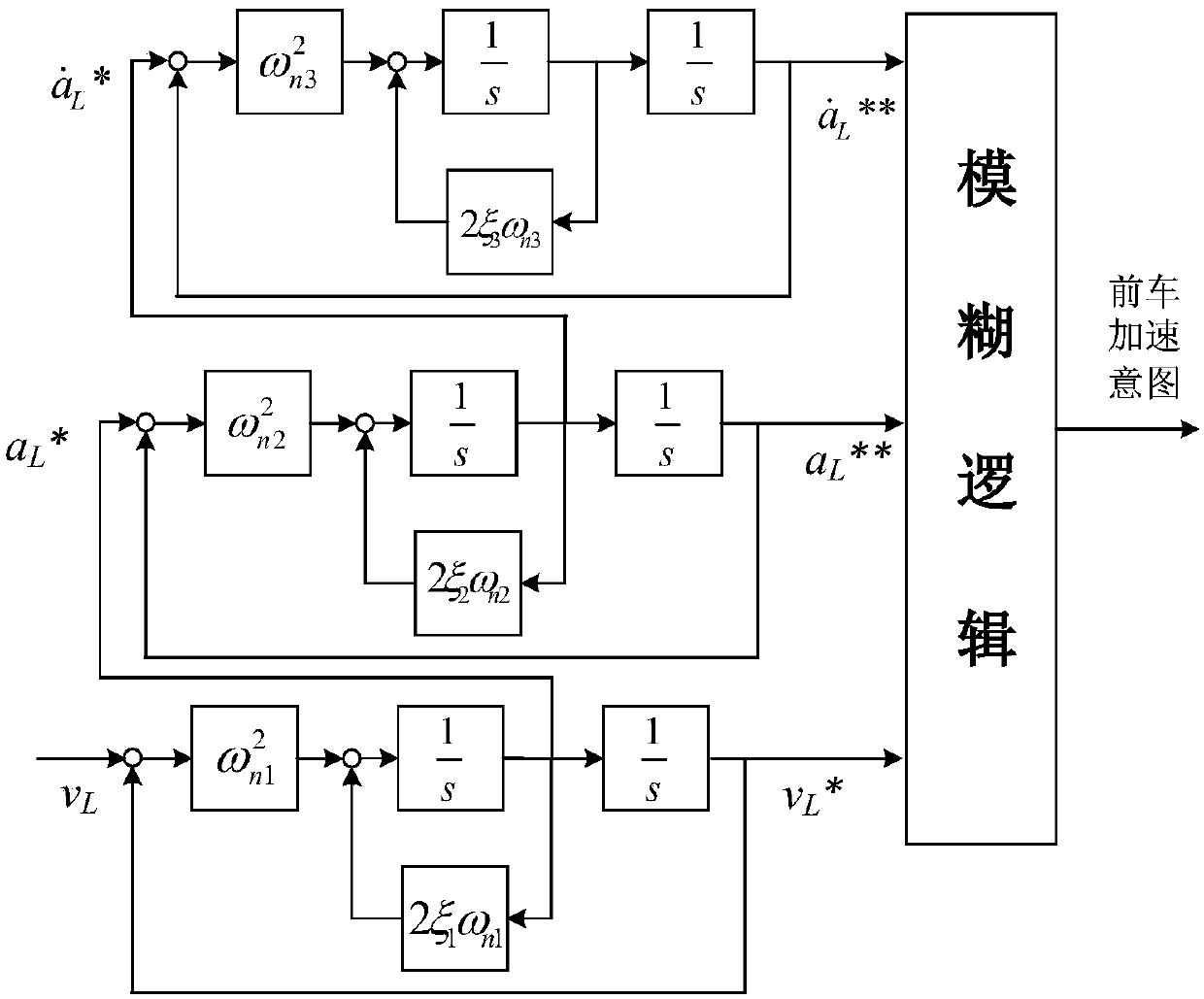
Automotive self-adaptive cruising system with multi-mode switching system and control method thereof
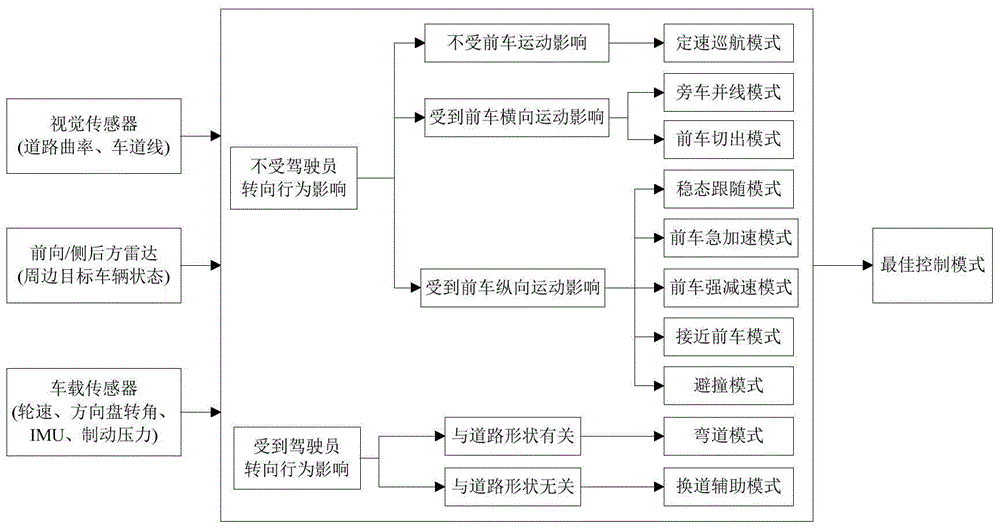
The invention discloses an automotive self-adaptive cruising system with a multi-mode switching system and a control method thereof. The system is divided into three layers of control structures including a mode switching layer, an upper-layer controller and a low-layer controller; a set of automobile traveling mode comprehensively arbitrating and switching mechanism is designed in the mode switching layer and is used for picking out the ideal working mode which is most suitable for the current traveling working condition from ten control modes. The ten control modes include the constant-speed cruising mode, the steady-state automobile following mode, the front automobile approaching mode, the urgent acceleration mode, the forcible deceleration mode, the curve mode, the lane changing assisting mode, the collision avoidance mode, the doubling mode and the switching-out mode. The upper-layer controller is responsible for specifically achieving the corresponding control mode and conducting continuous handling before an expected accelerated speed is output so as to avoid sudden change of the accelerated speed; the lower-layer controller is responsible for tracking the expected accelerated speed by controlling an execution mechanism of the automobile. According to the automotive self-adaptive cruising system with the multi-mode switching system and the control method thereof, the multi-mode switching system is adopted, in this way, the automotive self-adaptive cruising system can be better adapted to a complicated traveling environment, and the acceptability of drivers is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
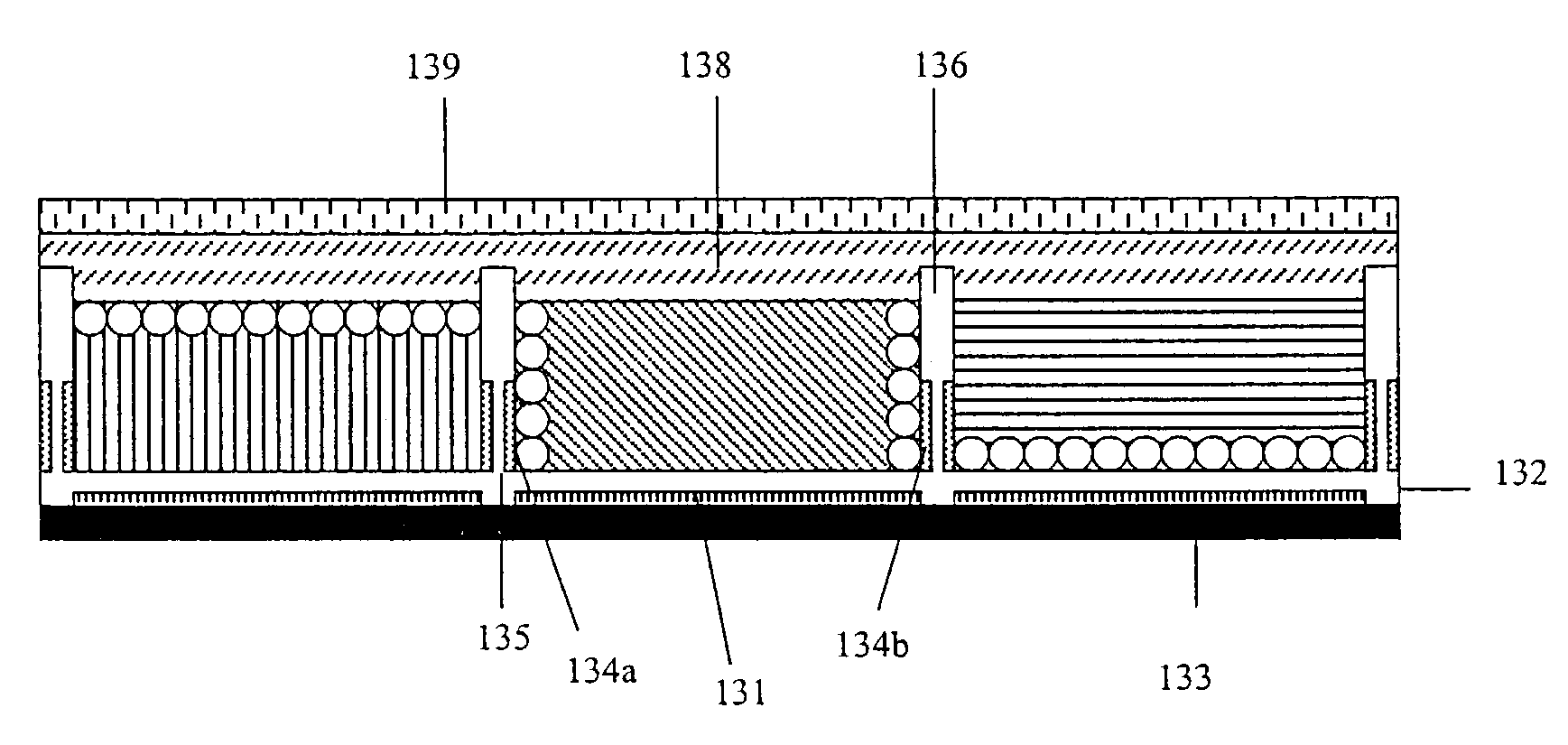
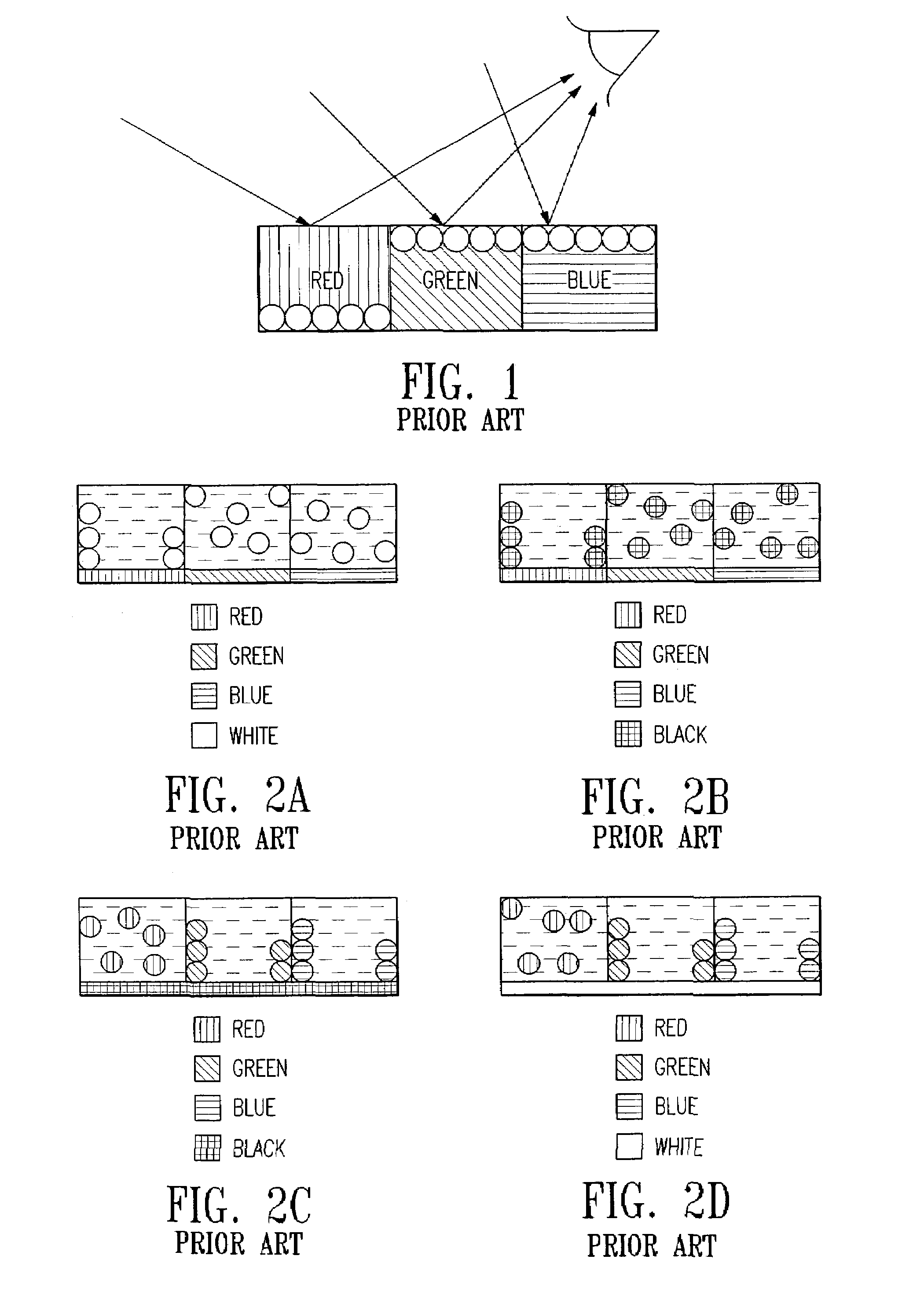
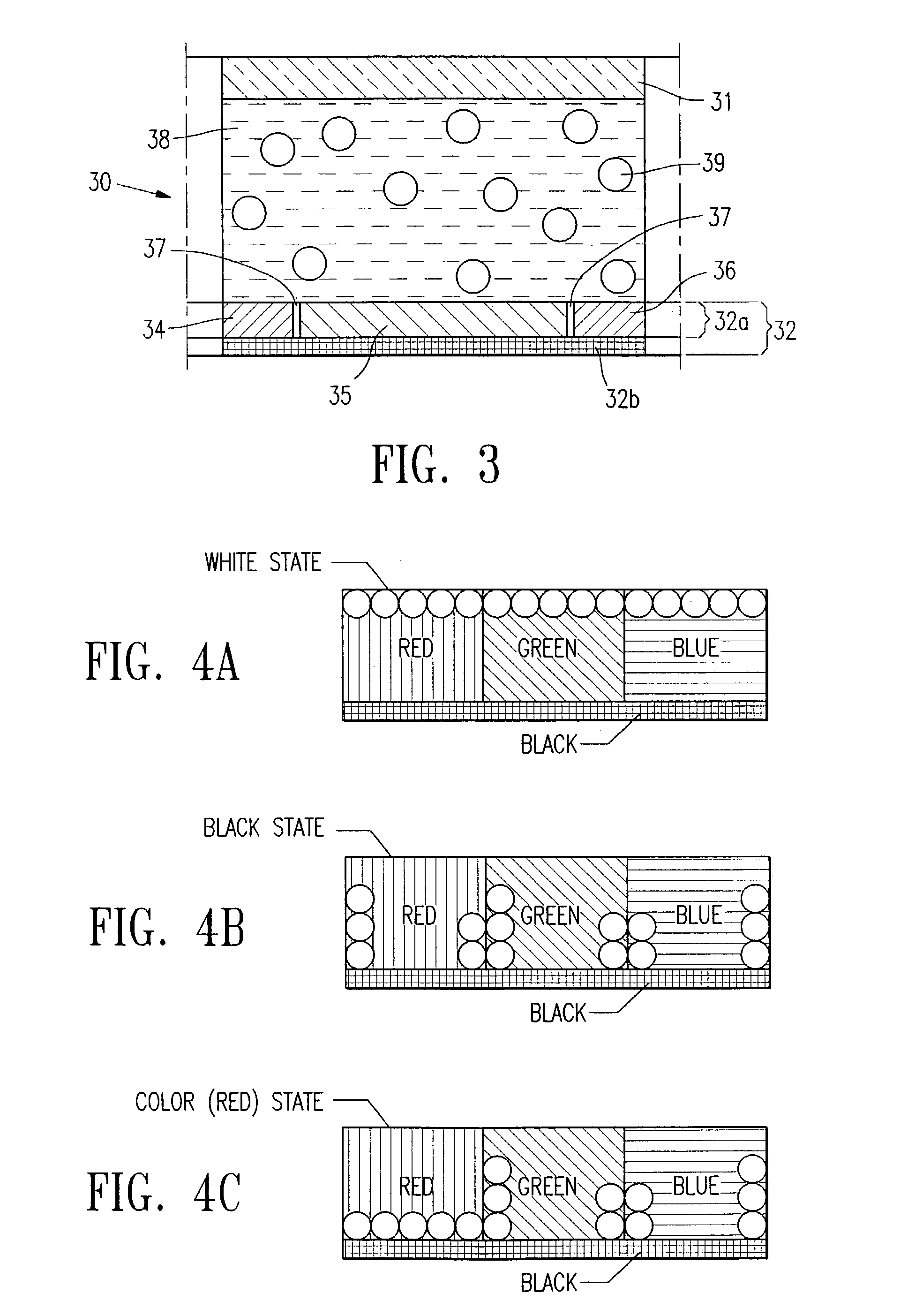
Electrophoretic display with dual-mode switching
InactiveUS7271947B2Increase contrastHigh saturationTransistorStatic indicating devicesIn planeDual mode
The present invention relates to an improved EPD which comprises both the traditional up / down switching and the in-plane switching modes. The monochrome EPDs of the present invention are capable of displaying highlight color of choice which is different from the text. Furthermore, the full color EPDs of the present invention are capable of displaying high contrast images of high color saturation. Both high quality black and white states are possible in the full color displays of the present invention. The EPDs of the present invention do not need complex circuitry design, and are compatible with low cost and high yield roll-to-roll manufacturing processes.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
Method and device of inter-cell switching
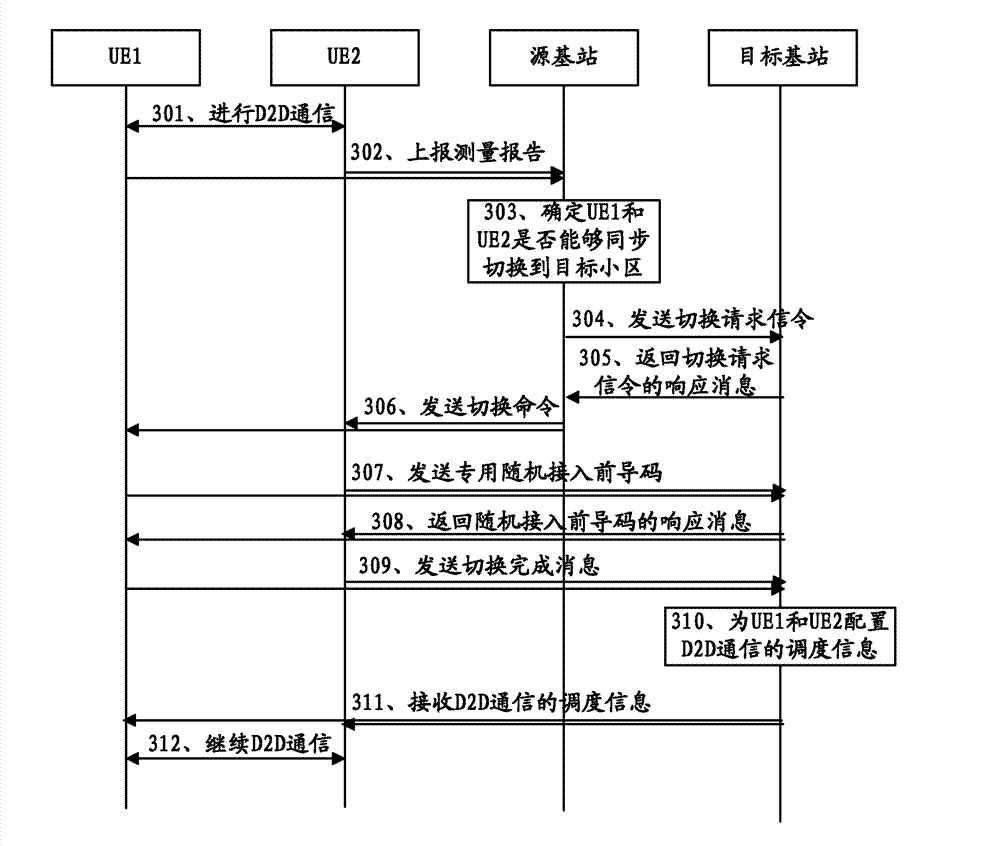
The invention discloses a method, a device and a system of inter-cell switching and relates to the field of communications. The method, the device and the system of the inter-cell switching are used for solving the problem that device-to-device (D2D) communication is interrupted when user equipment carrying out the D2D communication is switched to an adjacent cell. The method includes the following steps: a first set of user equipment submits a measurement report to a source base station, and the measurement report is used for judging whether the first set of user equipment and a second set of user equipment which directly carry out D2D communication among the equipment at present can be switched to a target cell synchronously by the source base station; and when a switching command is received, the first set of user equipment is switched to the target cell from a source cell belonging to the source base station and continues to carry out D2D communication with the second set of user equipment. The method, the device and the system of the inter-cell switching are applicable to the field of communications and used for achieving the inter-cell switching of the D2D communication.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Active antenna adapted for impedance matching and band switching using a shared component
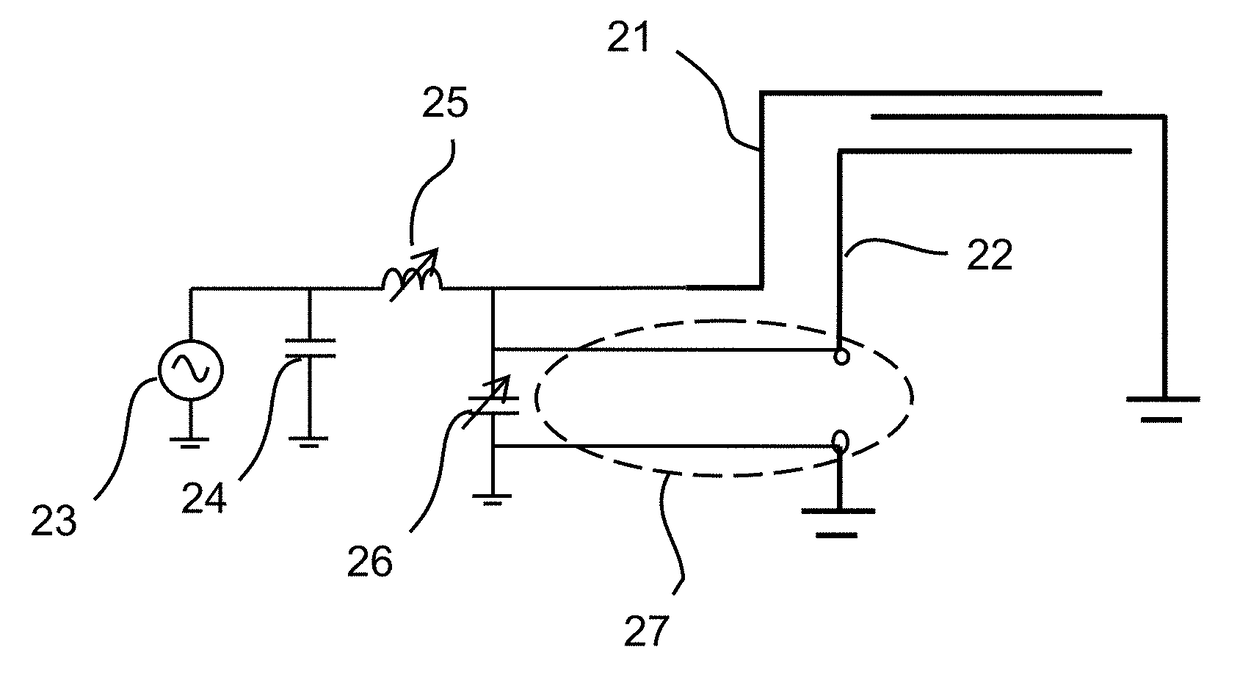
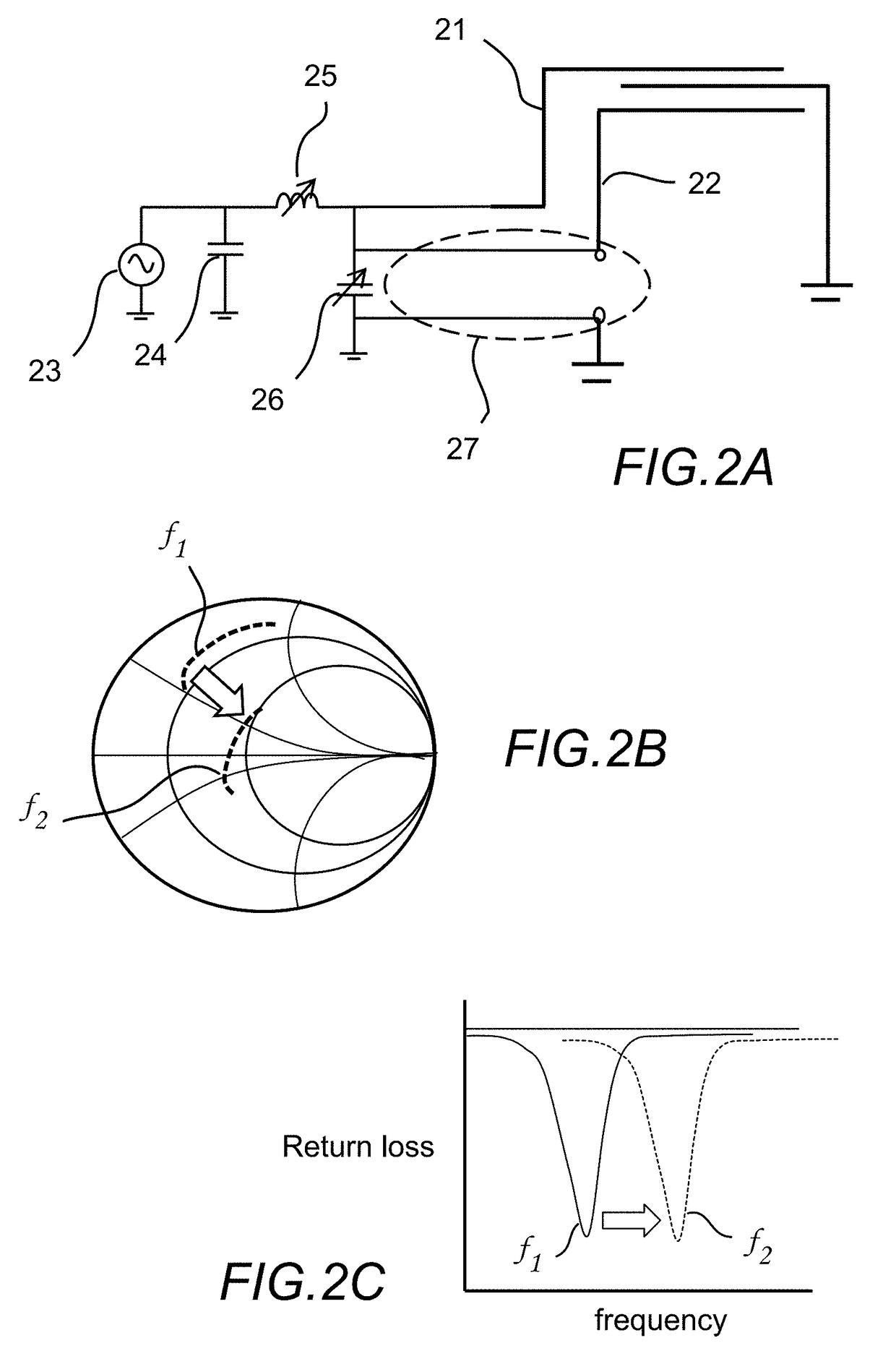
ActiveUS9755305B2Low costMeet cutting requirementsSimultaneous aerial operationsAntennas earthing switches associationImpedance matchingQ-switching
An active antenna and associated circuit topology is adapted to provide active impedance matching and band switching of the antenna using a shared tunable component. Using a shared tunable component, such as a tunable capacitor or other tunable component, the antenna provides a low cost and effective active antenna solution. In certain embodiments, one or more passive components can be further utilized to design band switching of the antenna from a first frequency to a second desired frequency.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
Soft switching interleaved power converter
ActiveUS6979980B1Reduce switching lossesReduced loss diode reverse-recovery lossApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationSoft switchingReverse recovery
There is provided by this invention soft switching interleaved power converters that are suitable for high power and high voltage applications such as plasma processing. They have greatly reduced switching losses and diode reverse-recovery losses which allows operation at high switching frequencies. The peak values of the reverse-recovery currents of the diodes are substantially less then their peak forward operating currents. The power converters incorporate power converter cells that comprise a plurality of switching assemblies that are operated with an interleaved switching pattern, and that are each connected to an input terminal of an inductor assembly that also has a common terminal. The inductance between each pair of input terminals is less than the inductance between each input terminal and the common terminal of the inductor assembly.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
Optical pulse lasers
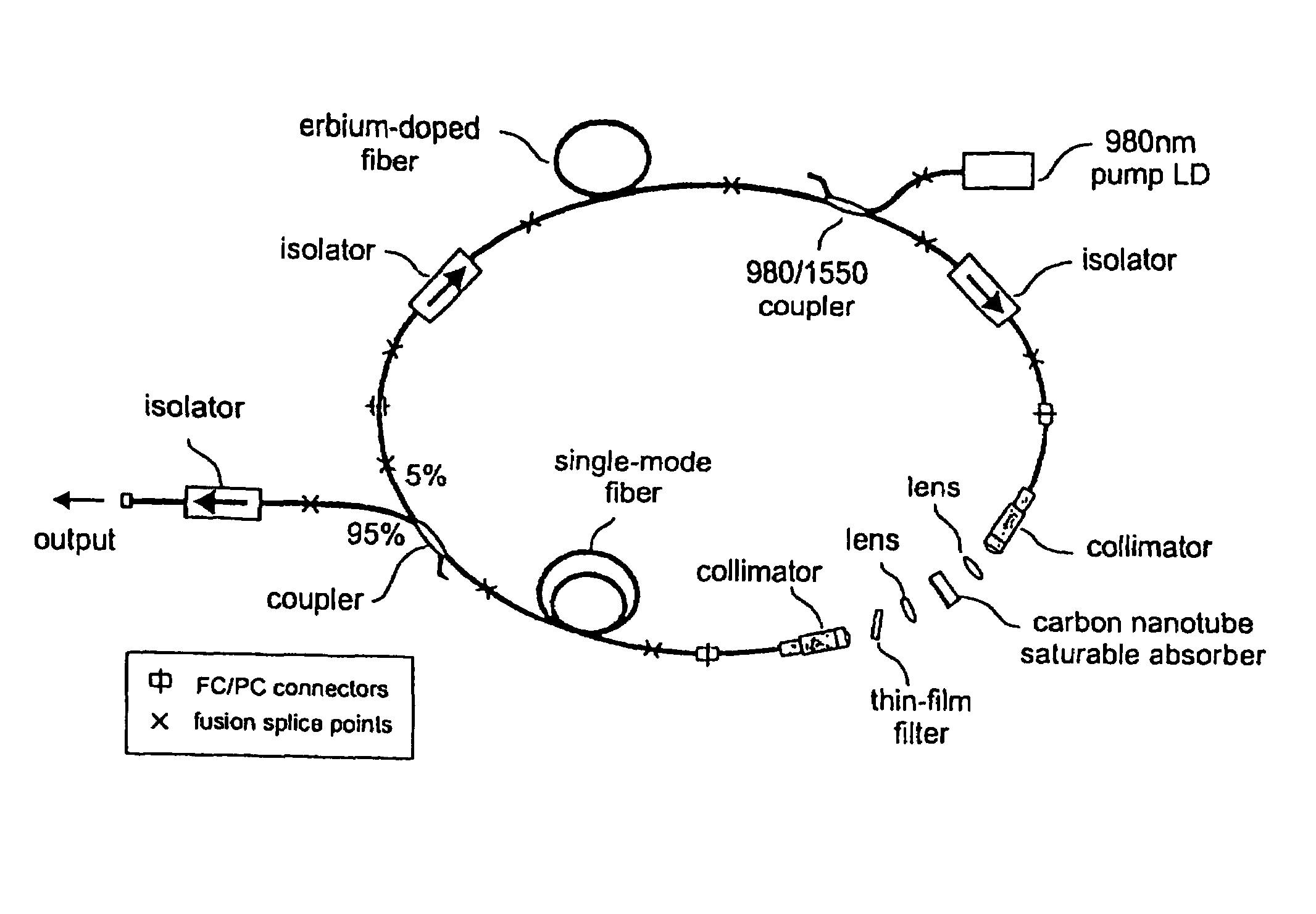
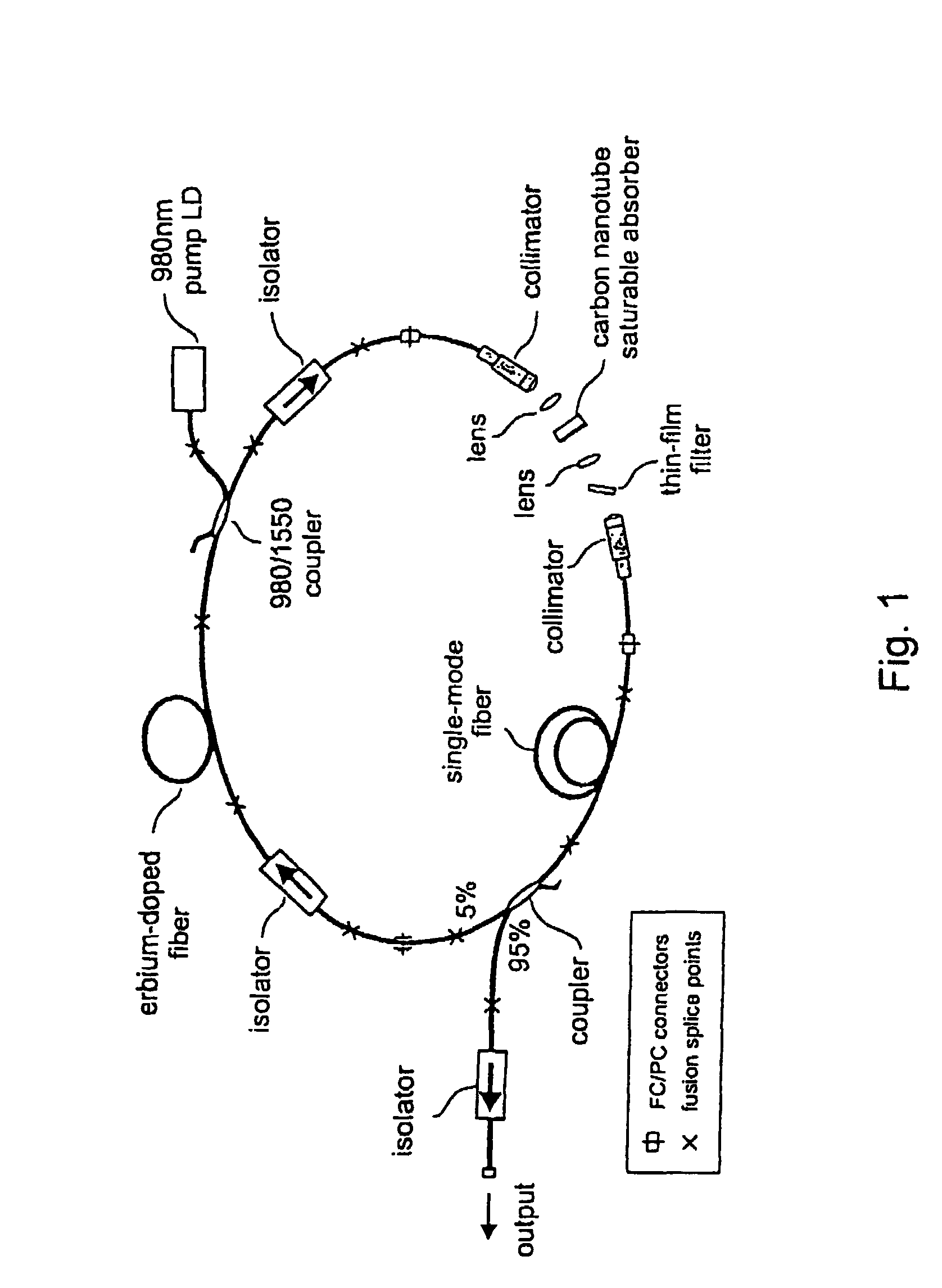
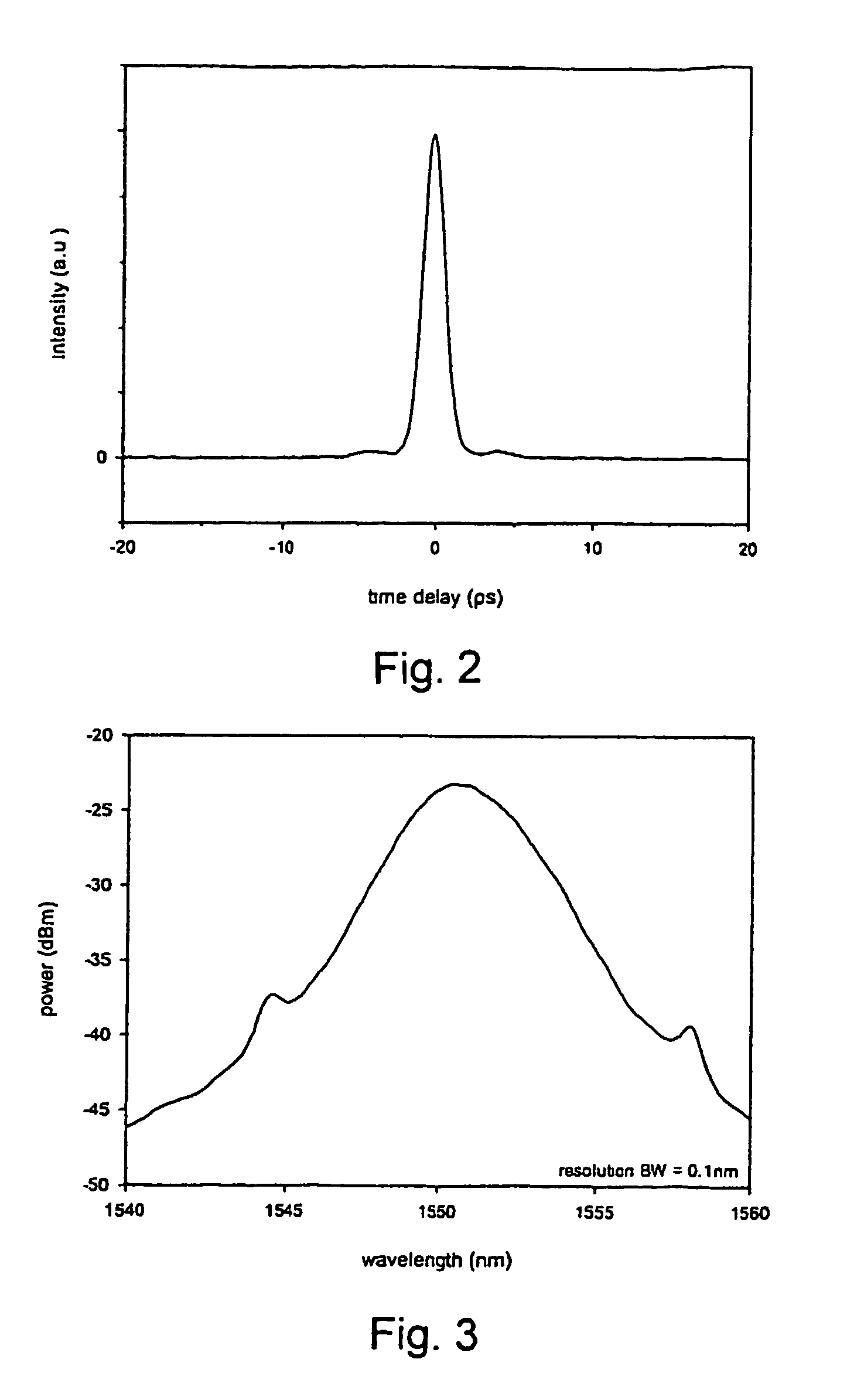
InactiveUS7372880B2Fast recovery timeHigh optical damage thresholdMirrorsNanoinformaticsCarbon nanotubeMode-locking
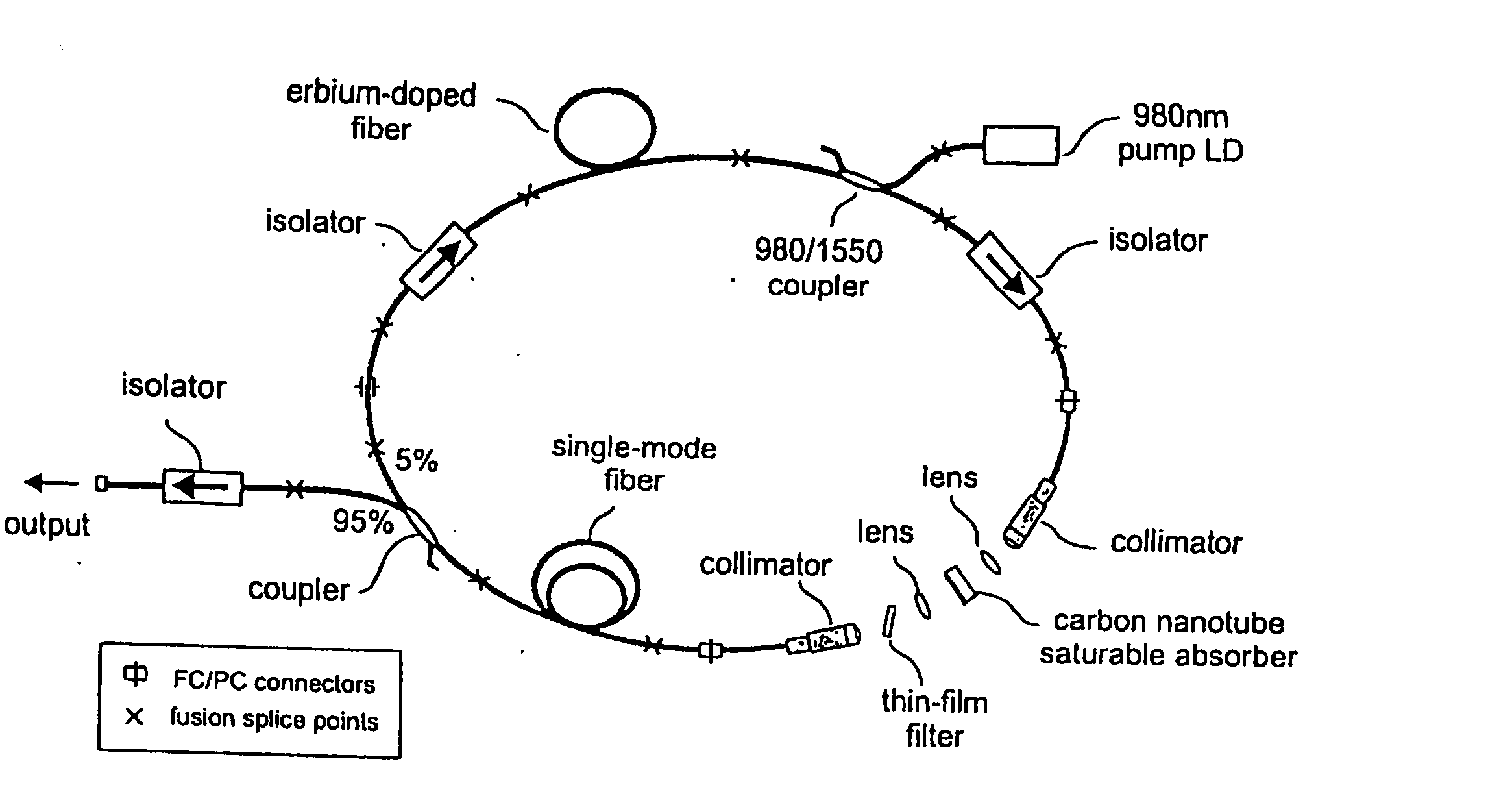
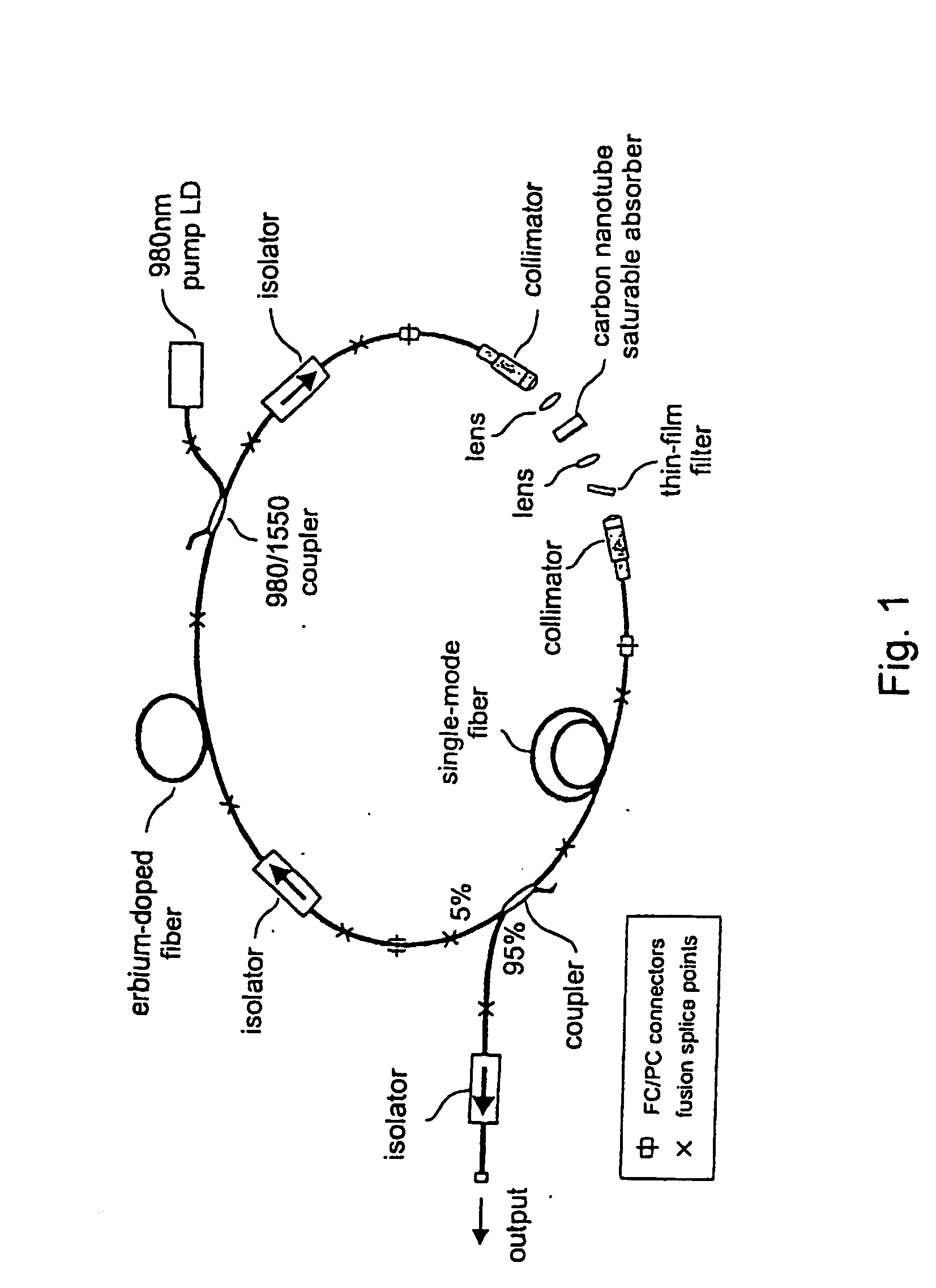
The present invention provides pulsed lasers which employ carbon nanotubes, particularly layers of carbon nanotubes, as saturable absorbers, mode lockers or for Q-switching elements. The present invention also provides methods and materials for mode-locking and Q-switching of lasers in which carbon nanotubes are employed as non-linear optical materials and / or saturable absorbers which facilitate mode-locking and / or Q-switching. The invention further provides mode locker and Q-switching elements or devices which comprise one or more layers containing carbon nanotubes which layer or layers function for mode locking and / or Q-switching.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
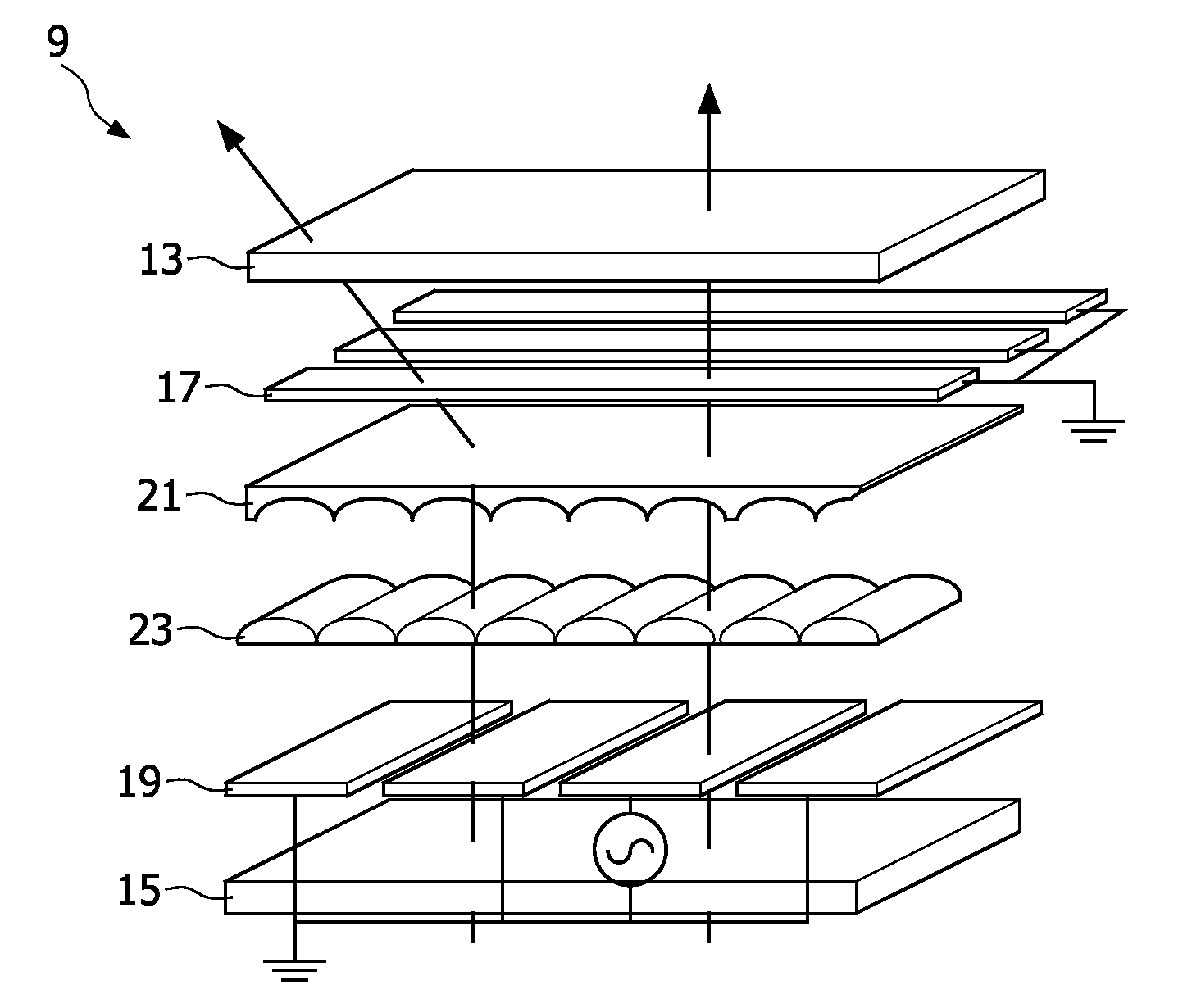
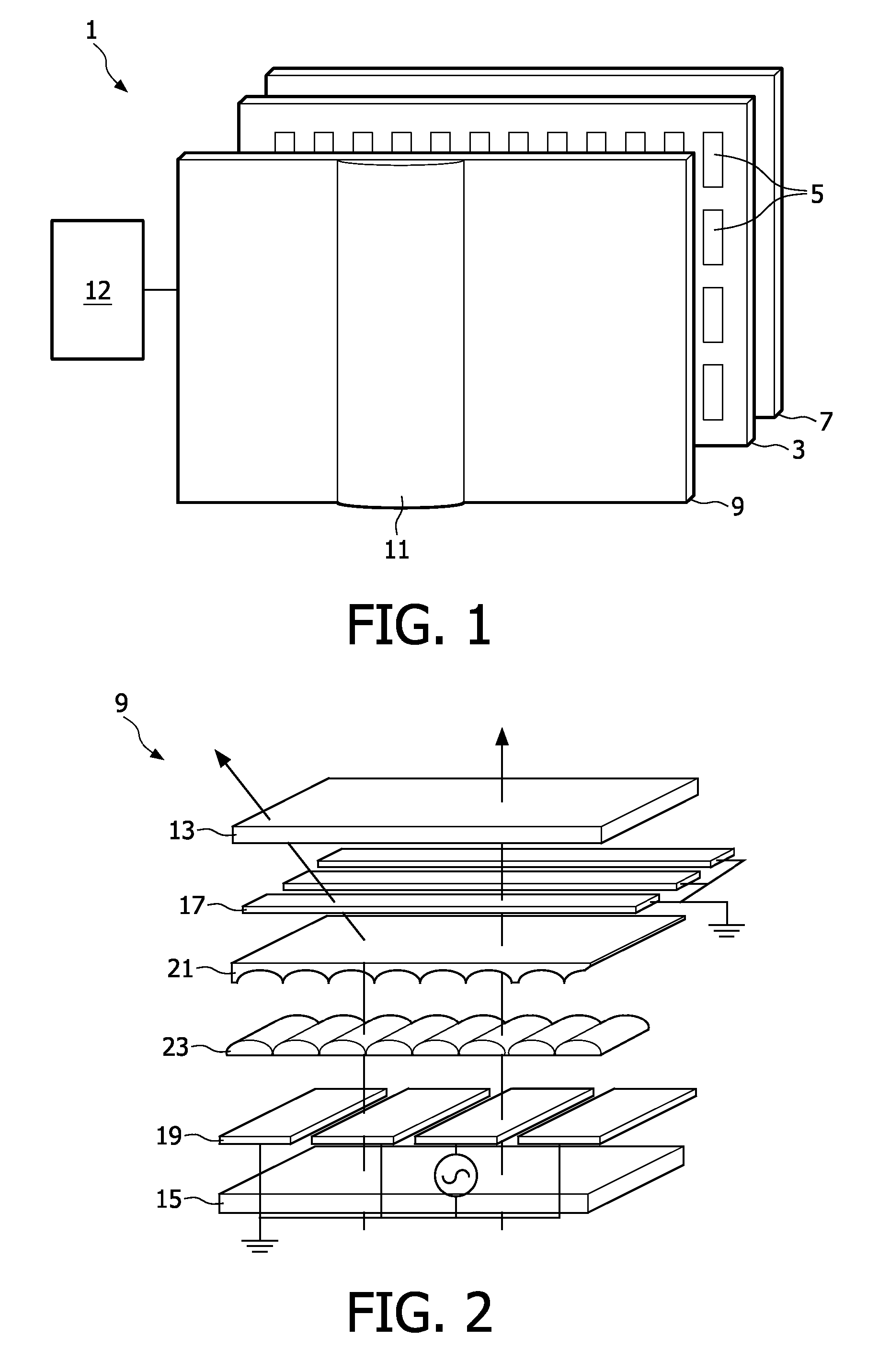
Autostereoscopic display device using controllable liquid crystal lens array for 3d/2d mode switching
ActiveUS20090033812A1Reduce additionalSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsRefractive indexDisplay device
An autostereoscopic display device has an array (9) of lenticular elements (11) overlying a display panel (3), the lenticular elements comprising electro-optic material (23) and being switchable to enable 2D and 3D viewing modes. The electro-optic material, for example liquid crystal material, is contained adjacent an optically transparent layer in the form of a lenticular body (21). A birefringent material is utilized for the lenticular body, preferably with the ordinary and extra-ordinary index of refraction substantially matching that of the electro-optic material.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
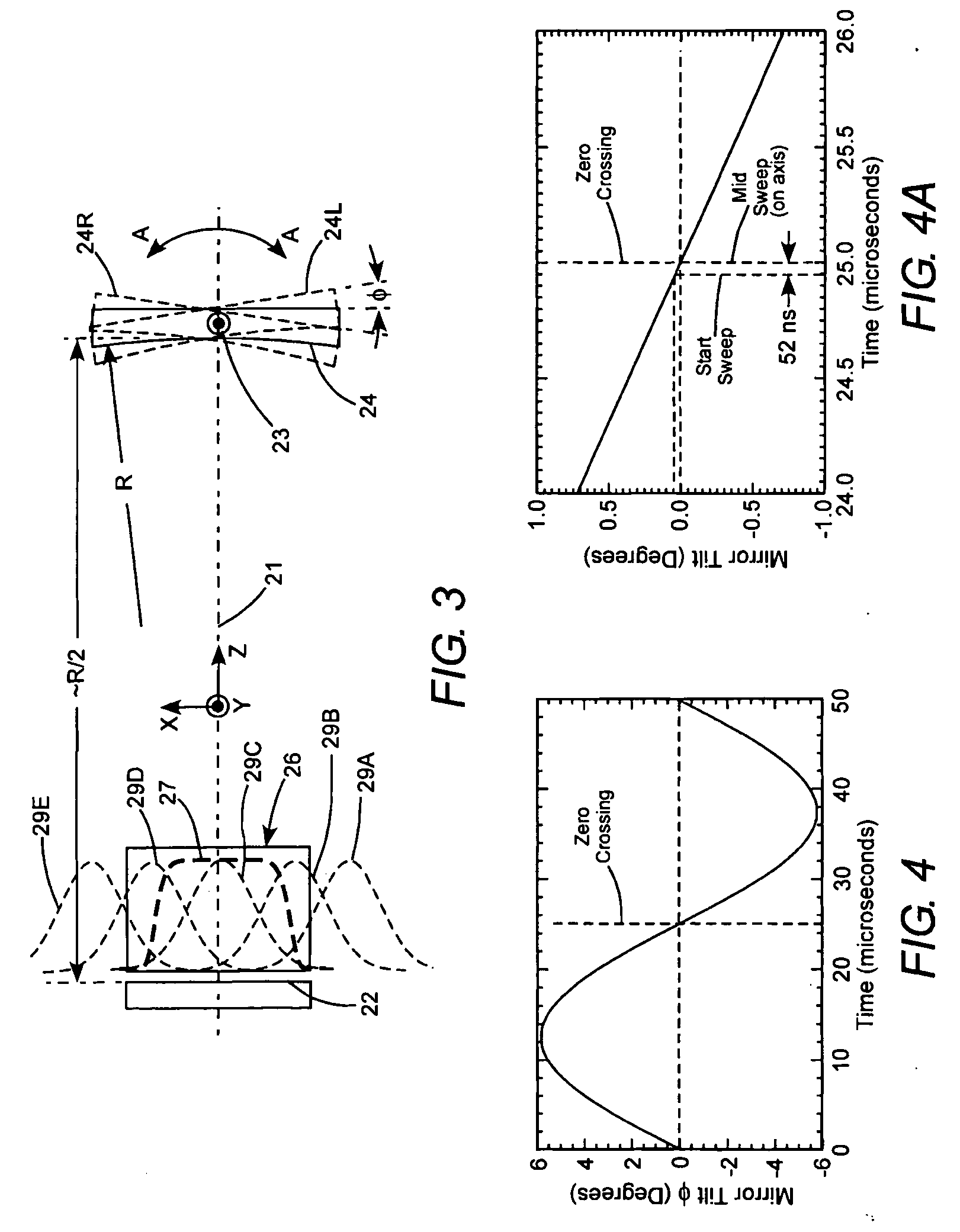
Low power Q-switched solid-state lasers
InactiveUS20070268950A1Increase volumeLow costOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser monitoring arrangementsArm foldingQ-switching
In a miniature Q-switched, pulsed laser, having a two arm folded resonator, Q-switching is effected by rapidly and reciprocally tilting a resonator mirror of the laser about an axis perpendicular to the axis of the laser resonator. The angular excursion of the tilting and the frequency of the tilting are selected cooperative with dimensions of the resonator to maximize energy and symmetry of intensity distribution in Q-switched pulses delivered by the laser. Rapid reciprocal tilting of the mirror is accomplished using a piezoelectrically-driven, MEMS scanner operated in a resonant mode.
Owner:COHERENT INC
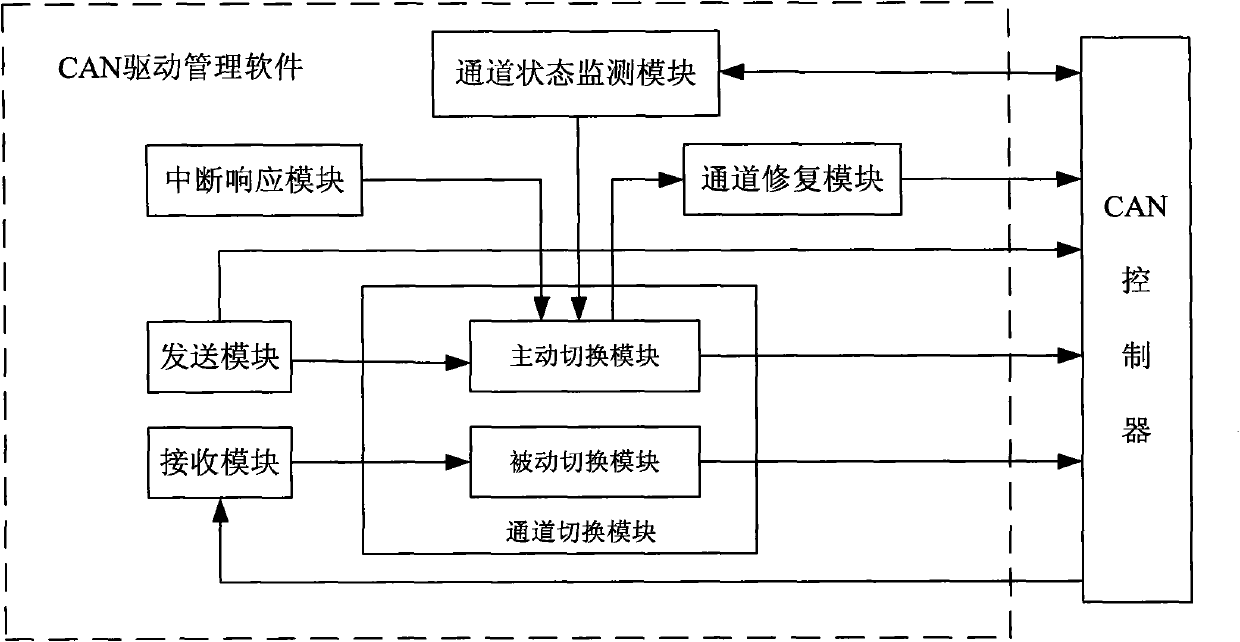
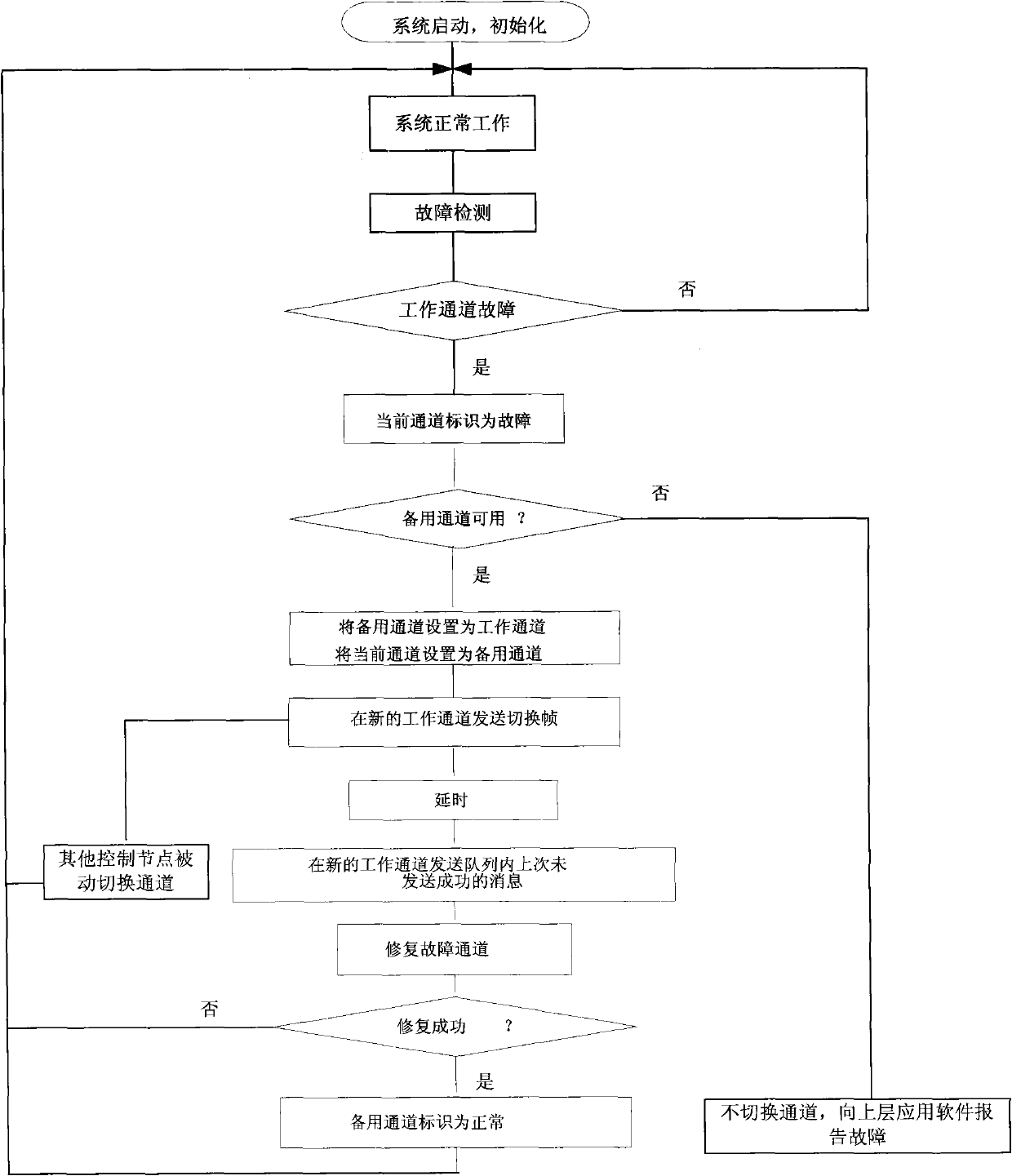
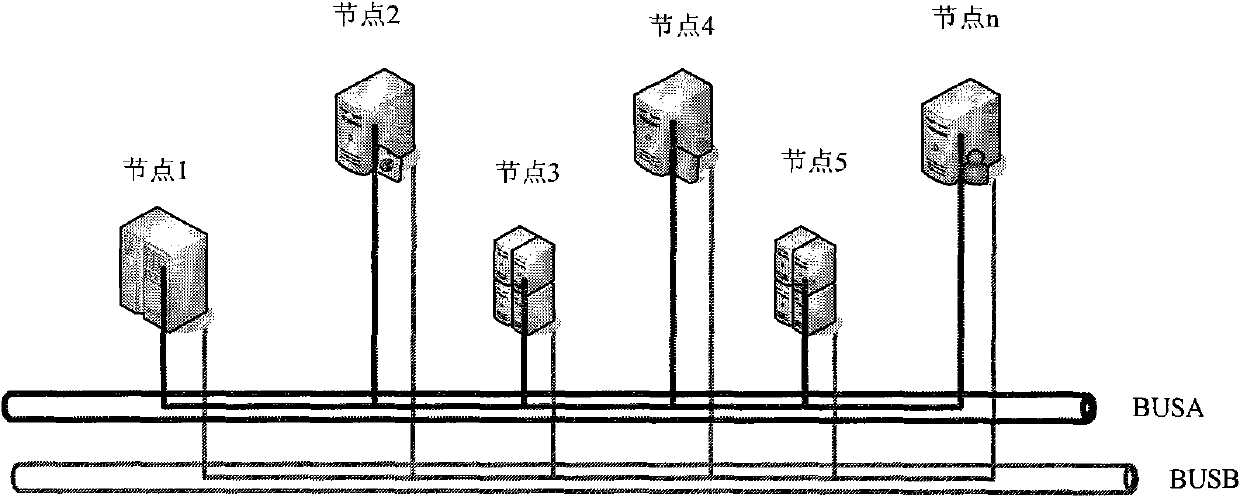
Heat switching system and heat switching method of dual-redundant CAN bus
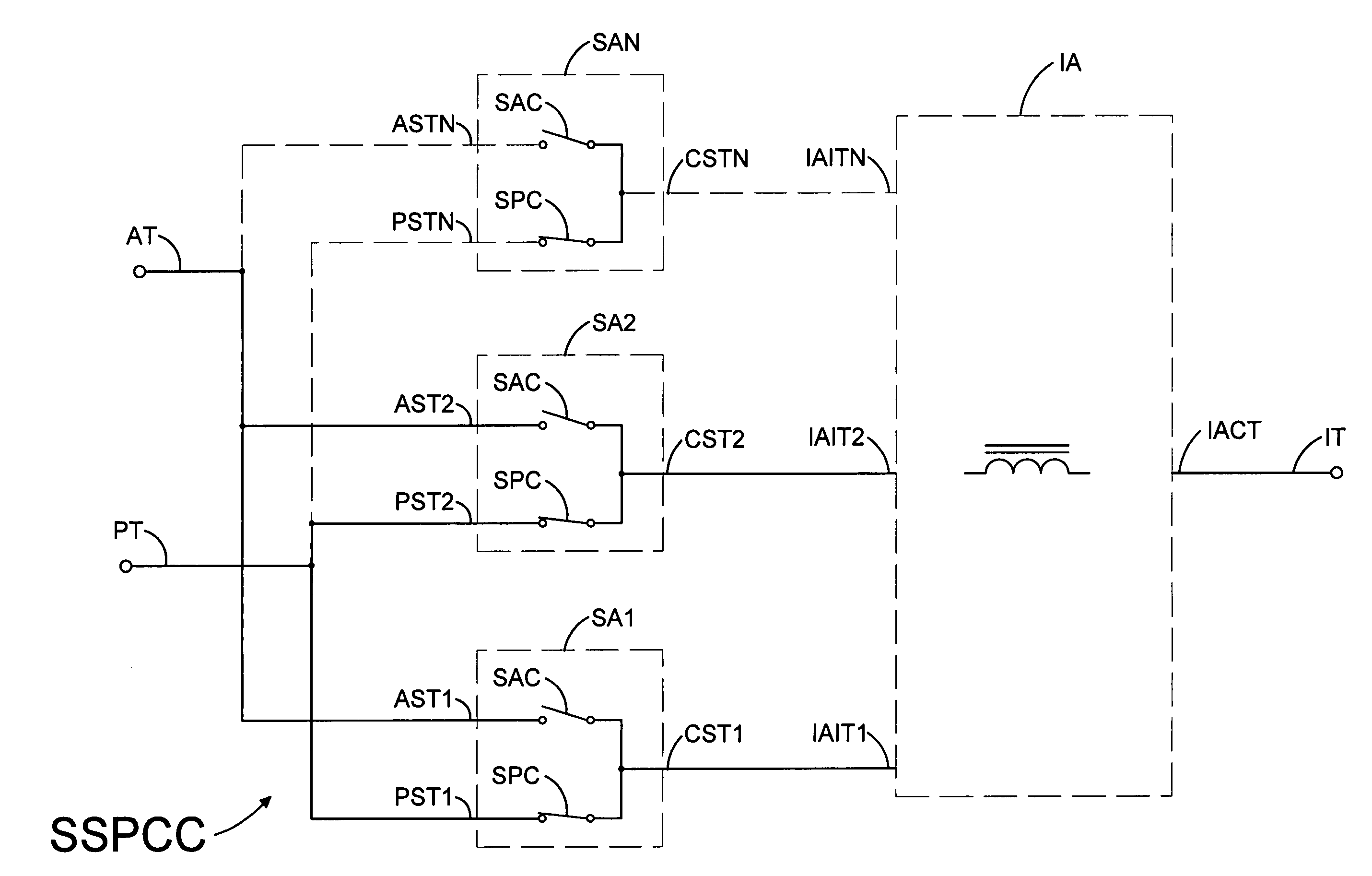
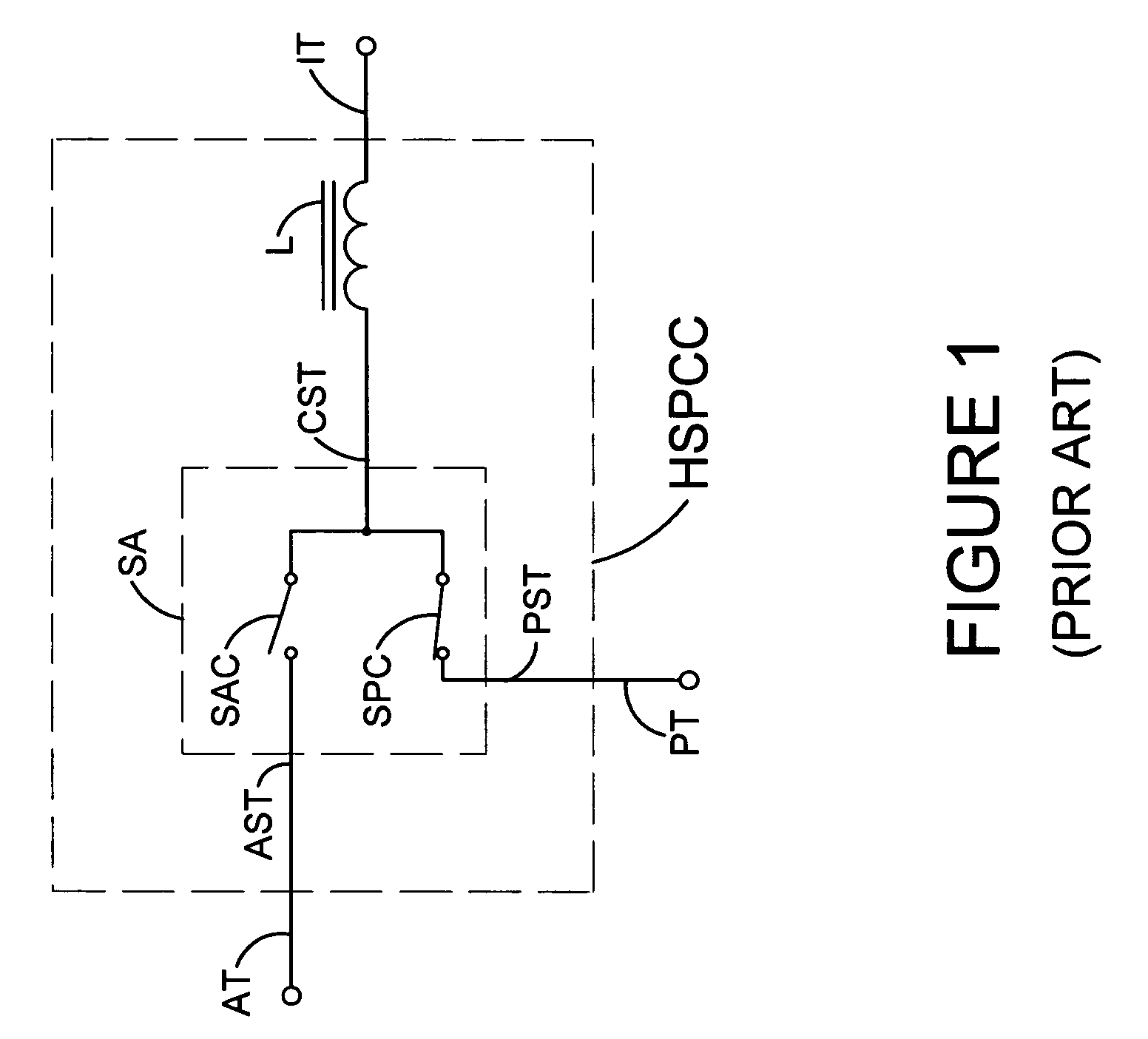
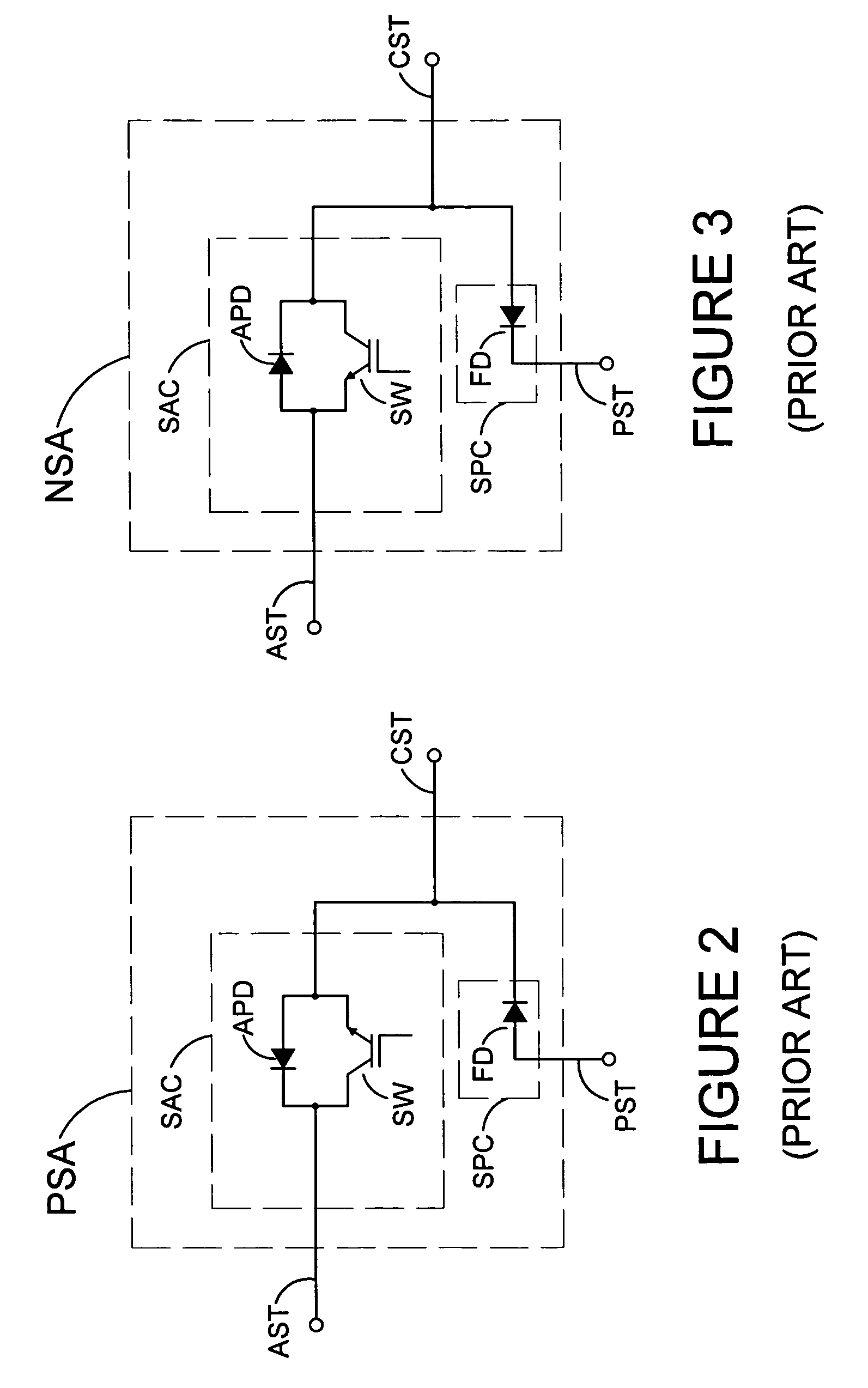
ActiveCN101908974ASupport operationReduce the number of control nodesError preventionBus networksDual busQ-switching
The invention relates to a heat switching system and a heat switching method of a dual-redundant CAN bus, and provides a networking mode of a dual-redundant CAN bus system and a dual-bus heat exchanging method. The networking mode of the dual-redundant CAN bus system is as follows: two bus cables are designed in network; each node unit comprises a microprocessor and two CAN controllers which are respectively connected with two bus cables to form two independent CAN channels. The dual-bus heat switching method is as follows: during operation, one of the channels is a working channel for receiving and transmitting messages and the other channel is used as a reserve channel for only receiving messages; and a CAN drive control software in the node monitors the channel state in real time, switches the reserve channel into a working channel when a fault occurs in the working channel and repairs the original working channel and sets the working channel to be a reserve channel.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACE LAUNCH TECH
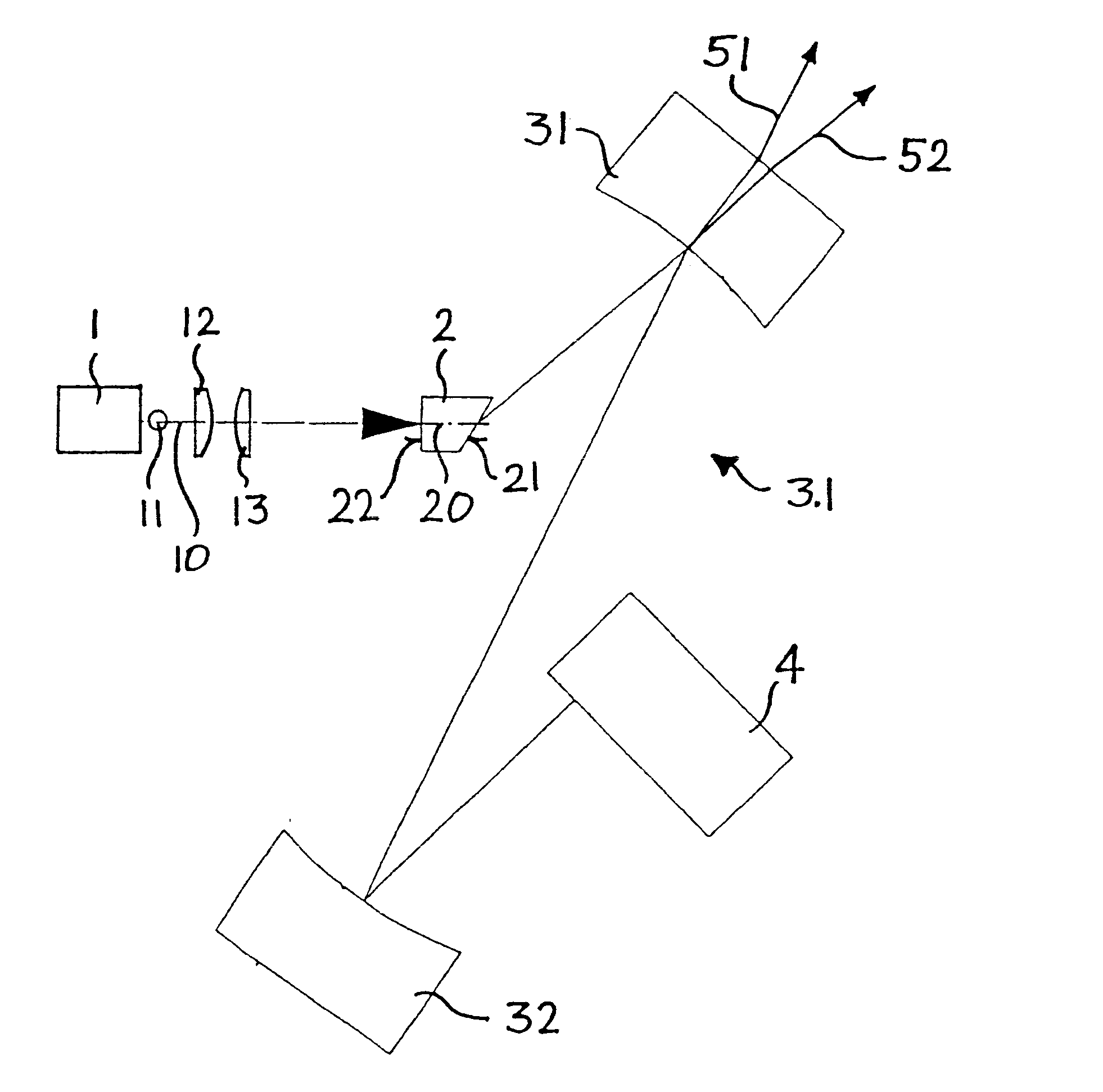
High-repetition-rate passively mode-locked solid-state laser
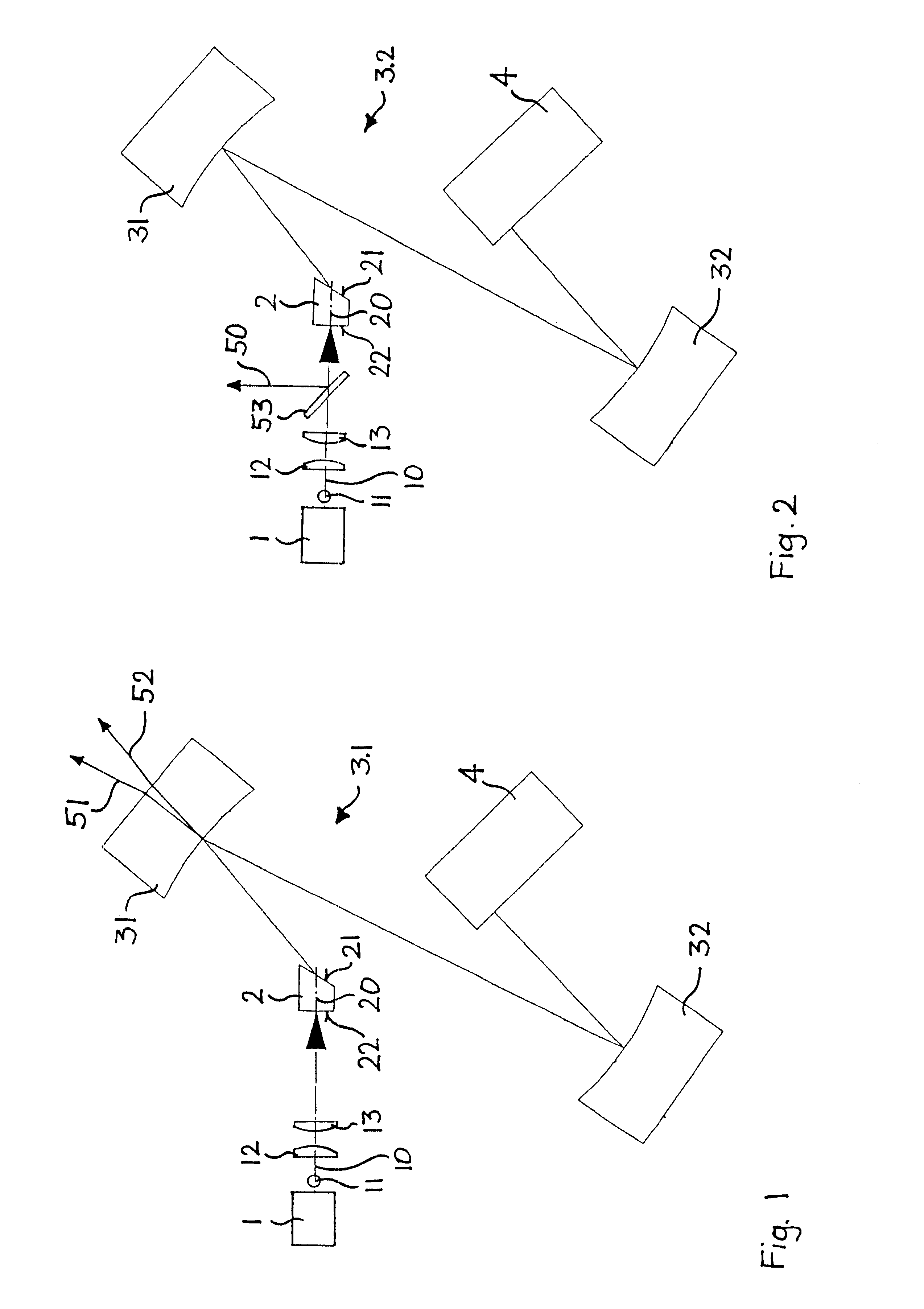
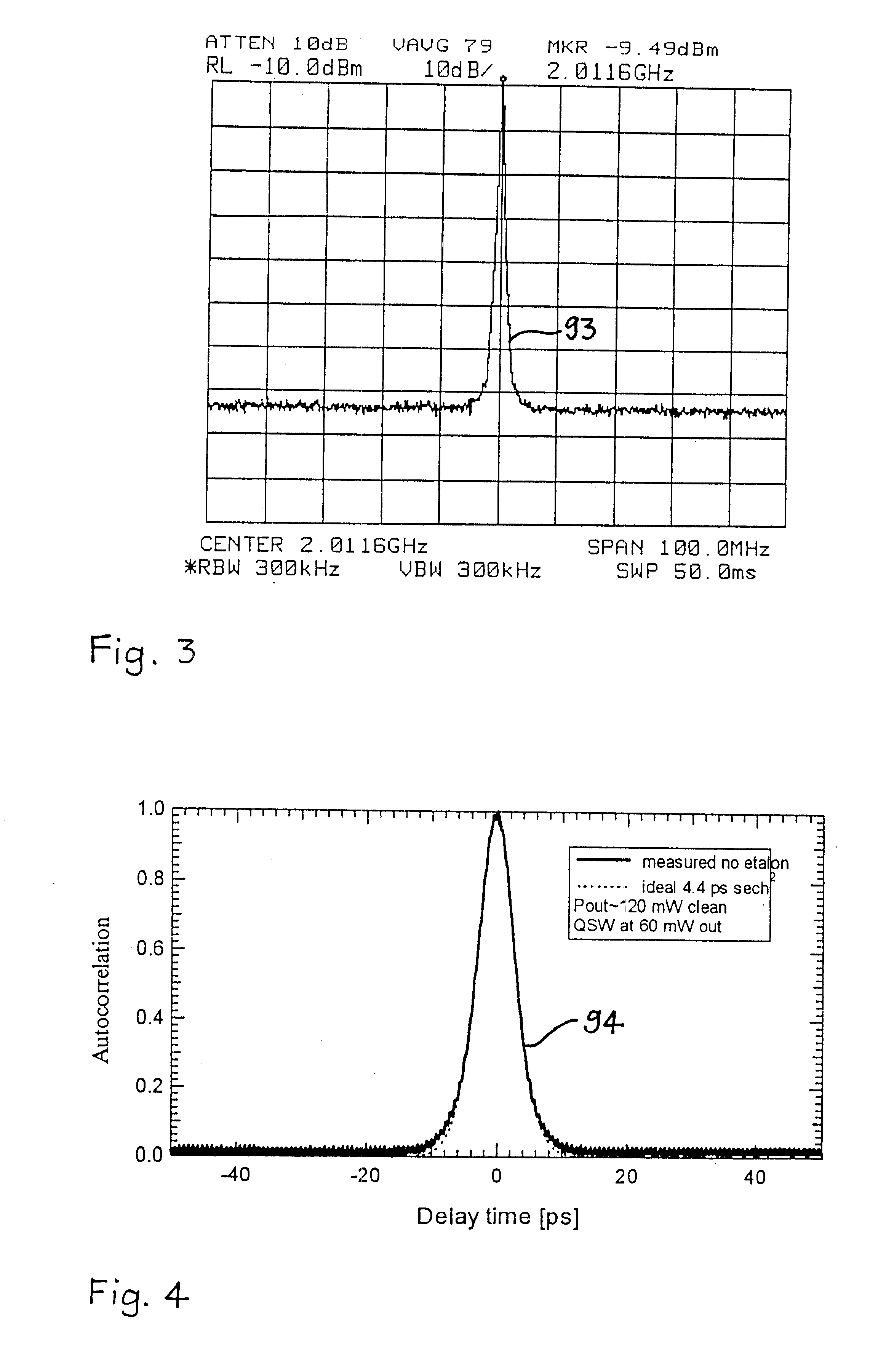
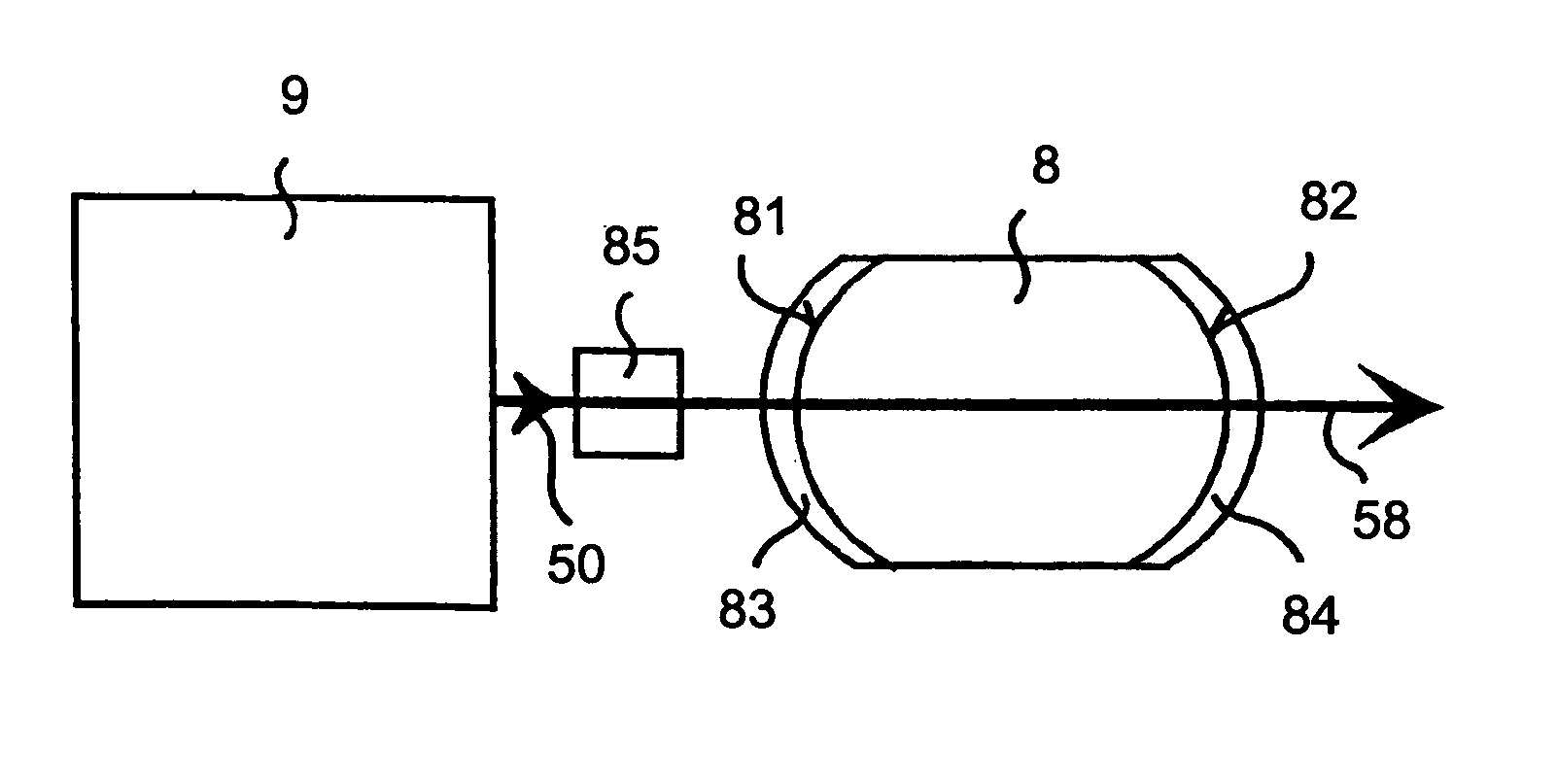
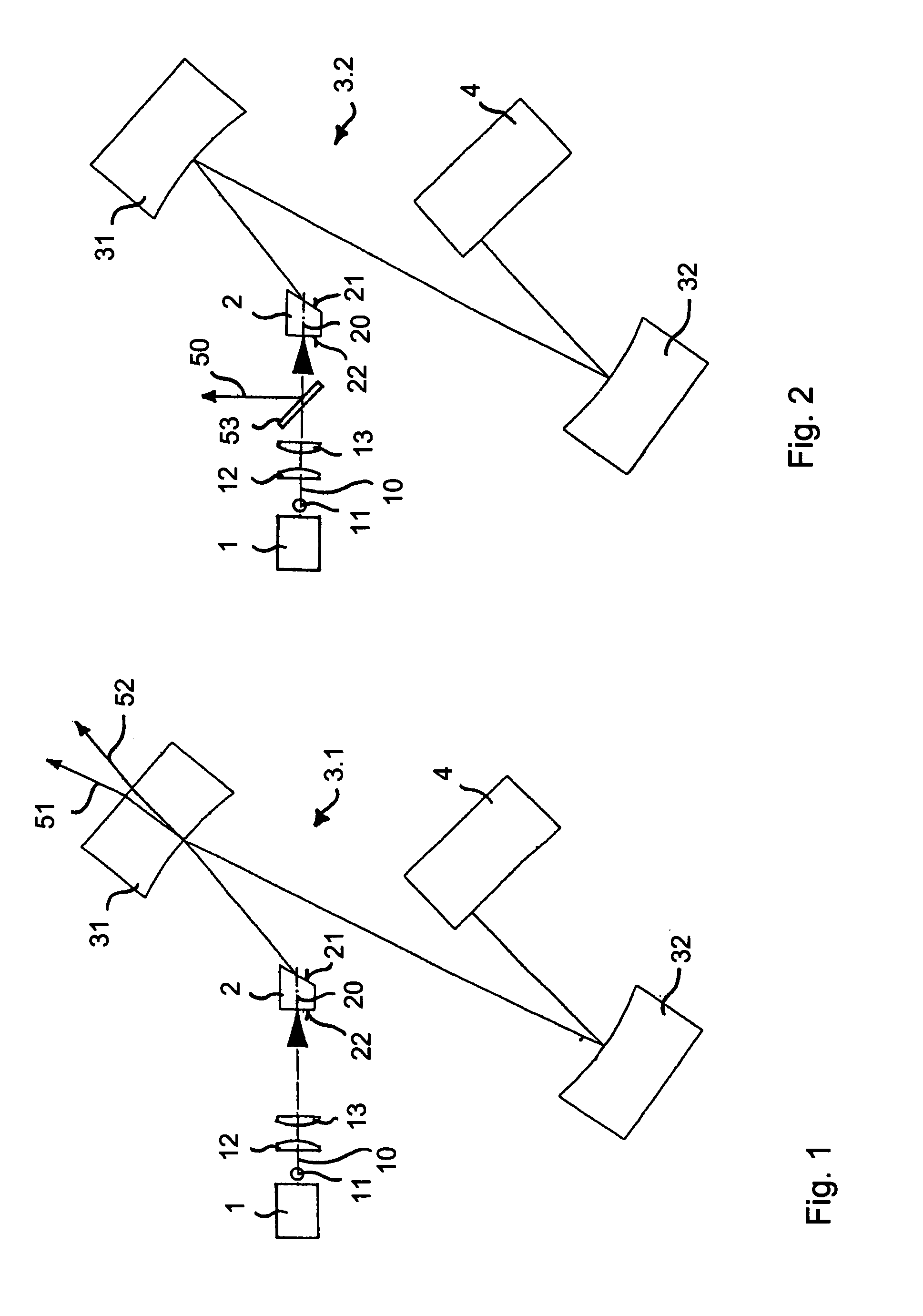
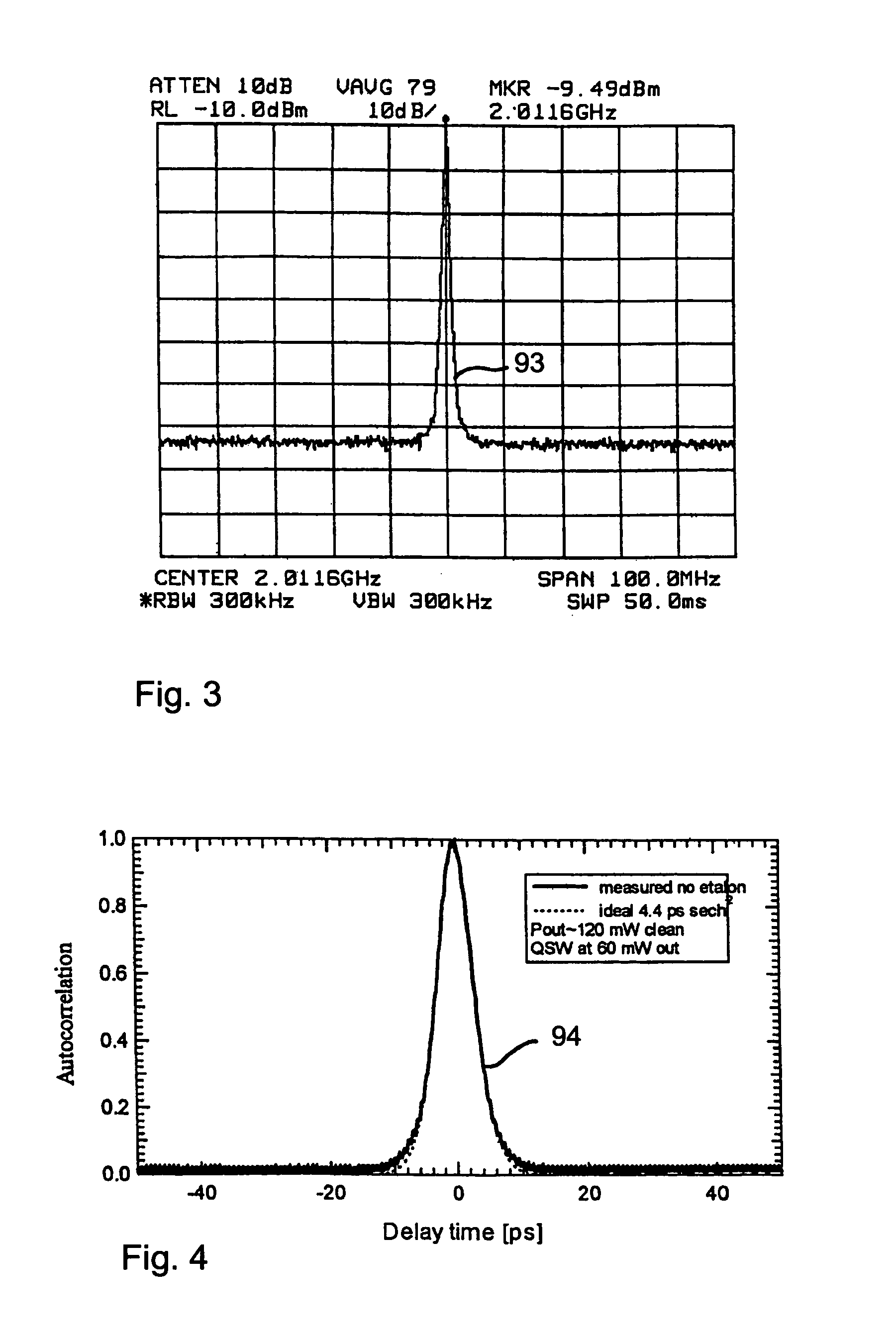
A passively mode-locked solid-state laser is designed to emit a continuous-wave train (51, 52) of electromagnetic-radiation pulses, the fundamental repetition rate of the emitted pulses exceeding 1 GHz, without Q-switching instabilities. The laser includes an optical resonator (3.1), a solid-state laser gain element (2) placed inside the optical resonator (3.1), a device (1) for exciting said laser gain element (2) to emit electromagnetic radiation having the effective wavelength, and a device (4) for passive mode locking including a saturable absorber. The laser gain element (2) is a laser material with a stimulated emission cross section exceeding 0.8×10−18 cm2 at the effective wavelength, and is made of Nd:vanadate. The saturable absorber (4) is preferably a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror (SESAM) device. Even higher repetition rates are achieved by operating the laser in the soliton regime. For use in fiber-optical telecommunication, the laser wavelength is preferably shifted to 1.5 μm by use of an optical parametric oscillator. The laser is simple, robust, compact, efficient, and low-cost. It generates a relatively large average power of 100 mW and higher, which is useful for a number of optical probing and detection applications, in a beam (51, 52) that is substantially a fundamental spatial mode.
Owner:LUMENTUM SWITZERLAND AG
Diode structures with controlled injection efficiency for fast switching
ActiveUS20120193676A1Reduced injection efficiencyReduce chargeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorSemiconductor package
This invention discloses a semiconductor device disposed in a semiconductor substrate. The semiconductor device includes a first semiconductor layer of a first conductivity type on a first major surface. The semiconductor device further includes a second semiconductor layer of a second conductivity type on a second major surface opposite the first major surface. The semiconductor device further includes an injection efficiency controlling buffer layer of a first conductivity type disposed immediately below the second semiconductor layer to control the injection efficiency of the second semiconductor layer.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Optical pulse lasers
InactiveUS20060198399A1Easy to operateFast recovery timeMirrorsNanoinformaticsMode-lockingCarbon nanotube
The present invention provides pulsed lasers which employ carbon nanotubes, particularly layers of carbon nanotubes, as saturable absorbers, mode lockers or for Q-switching elements. The present invention also provides methods and materials for mode-locking and Q-switching of lasers in which carbon nanotubes are employed as non-linear optical materials and / or saturable absorbers which facilitate mode-locking and / or Q-switching. The invention further provides mode locker and Q-switching elements or devices which comprise one or more layers containing carbon nanotubes which layer or layers function for mode locking and / or Q-switching.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
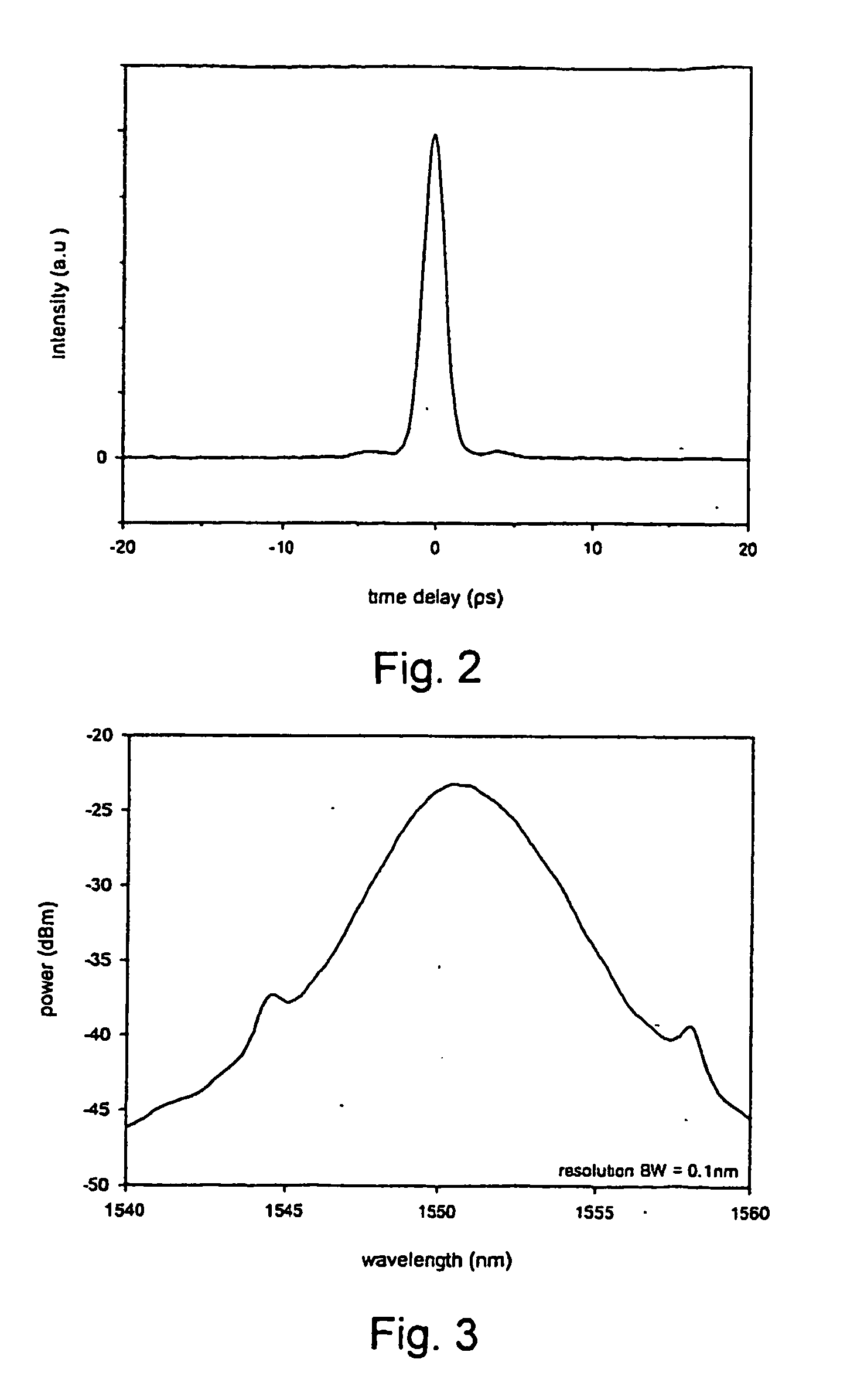
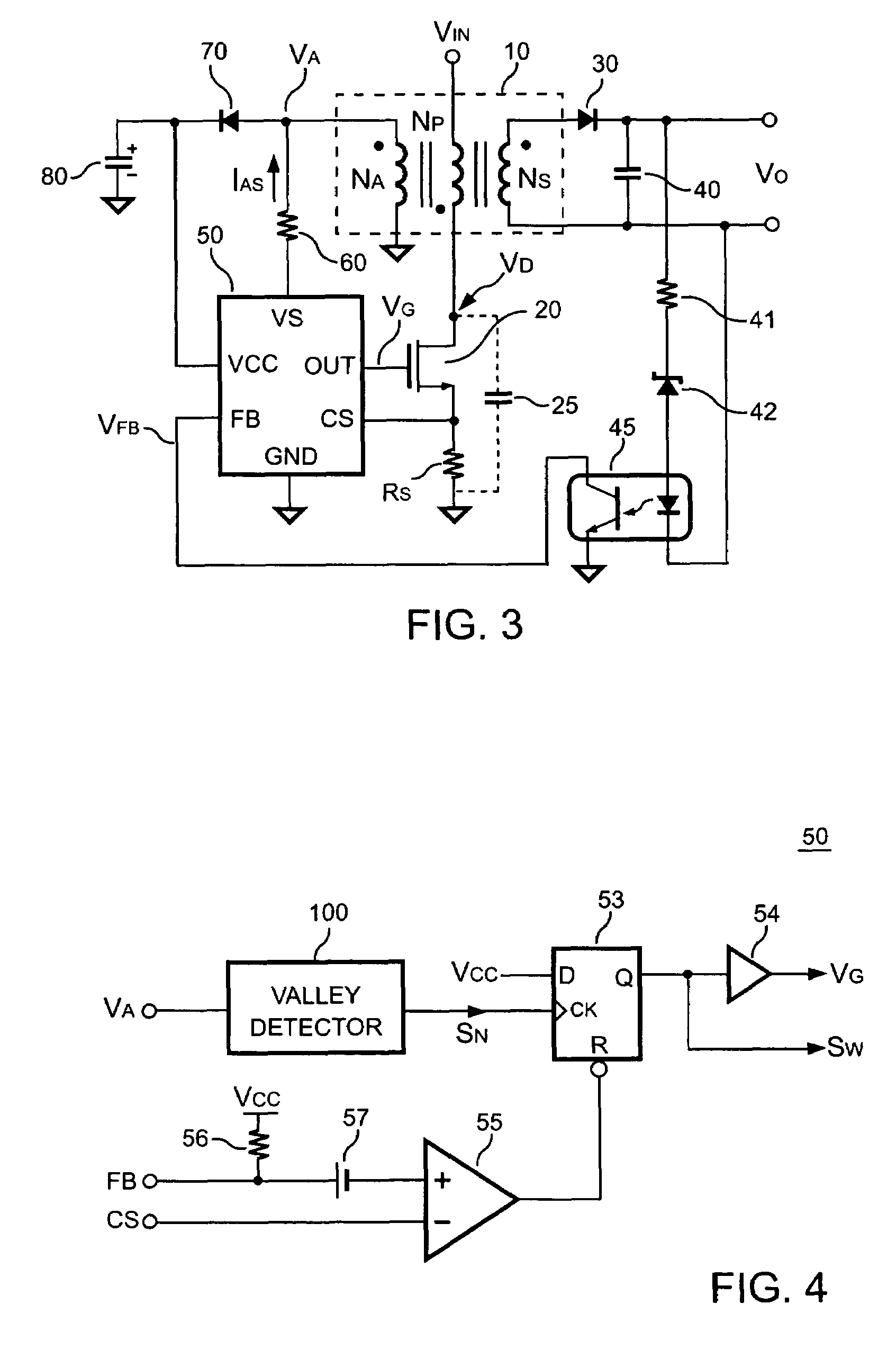
Switching control circuit having a valley voltage detector to achieve soft switching for a resonant power converter
ActiveUS7426120B2Improve efficiencySoft switchingEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSoft switchingControl signal
The present invention provides a switching control circuit having a valley voltage detector to achieve the soft switching and improve the efficiency of a power converter. The switching control circuit includes a control circuit coupled to the feedback signal to generate a switching signal. Through an output circuit, the switching signal drives a switching device for switching a transformer and regulating the output of the power converter. The valley voltage detector is coupled to an auxiliary winding of the transformer for generating a control signal in response to the voltage of the transformer. The control signal is used for enabling the switching signal. The switching signal further turns on the switching device in response to a valley voltage across the switching device.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Perpendicular magnetic recording write head with spin torque oscillator for fast switching of write pole magnetization
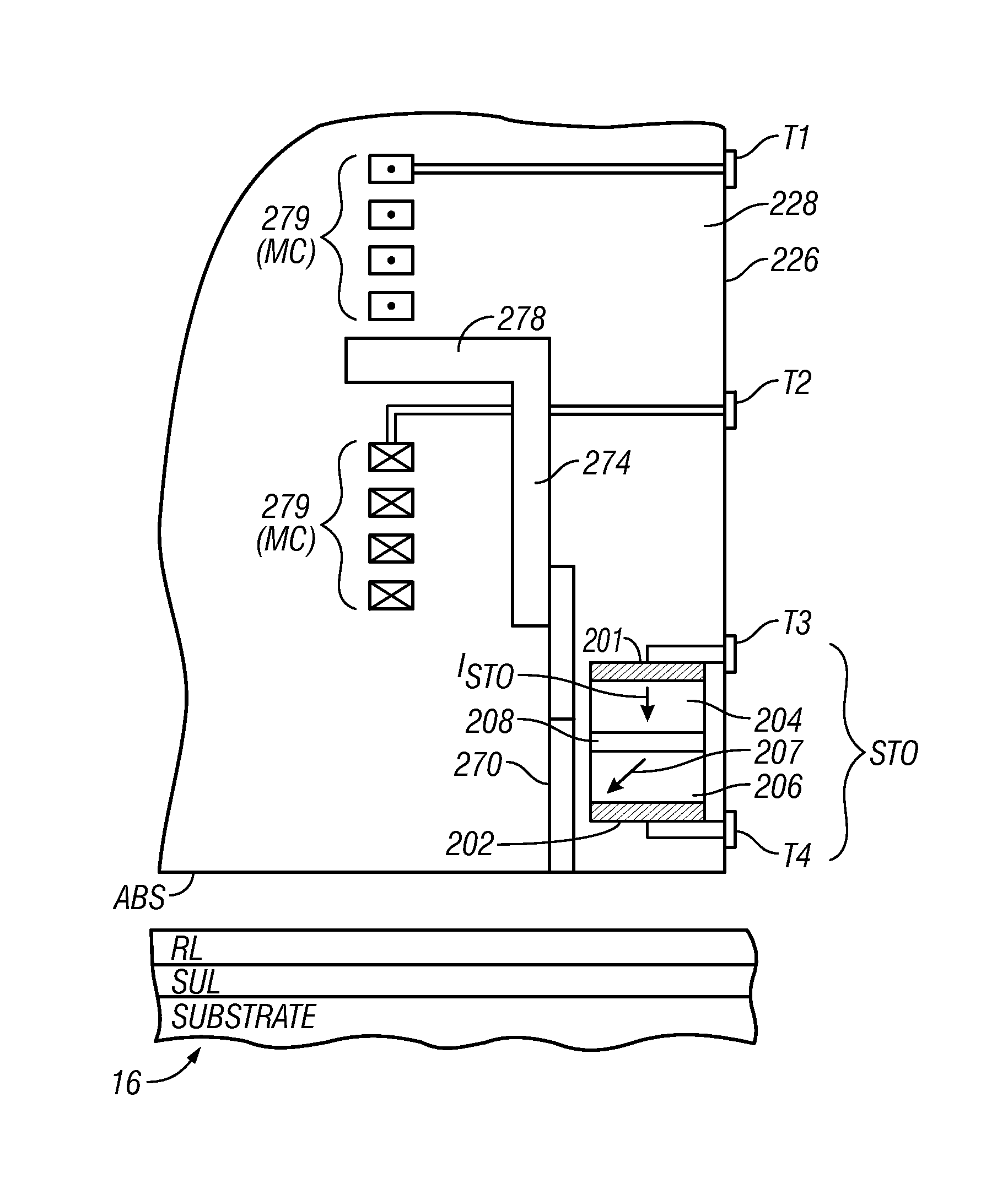
ActiveUS8446690B2Construction of head windingsRecord information storagePower flowSpin torque oscillators
A perpendicular magnetic recording write head that a write pole, an electrically conductive coil coupled to the write pole for generating magnetic flux in the write pole in the presence of electrical write current, and a spin torque oscillator (STO) that injects auxiliary magnetic flux to the write pole in a direction generally orthogonal to the write pole to facilitate magnetization switching of the write pole. The STO comprises a stack of layers including electrodes, a pinned ferromagnetic layer having a fixed, a free ferromagnetic layer having a magnetization free to rotate, and a nonmagnetic spacer layer between the pinned and free layers. The free layer may be oriented either substantially orthogonal to the write pole or substantially parallel to the write pole, in which latter embodiment a flux guide may be located between the free layer and the write pole for directing the auxiliary magnetic flux from the free layer to the write pole.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
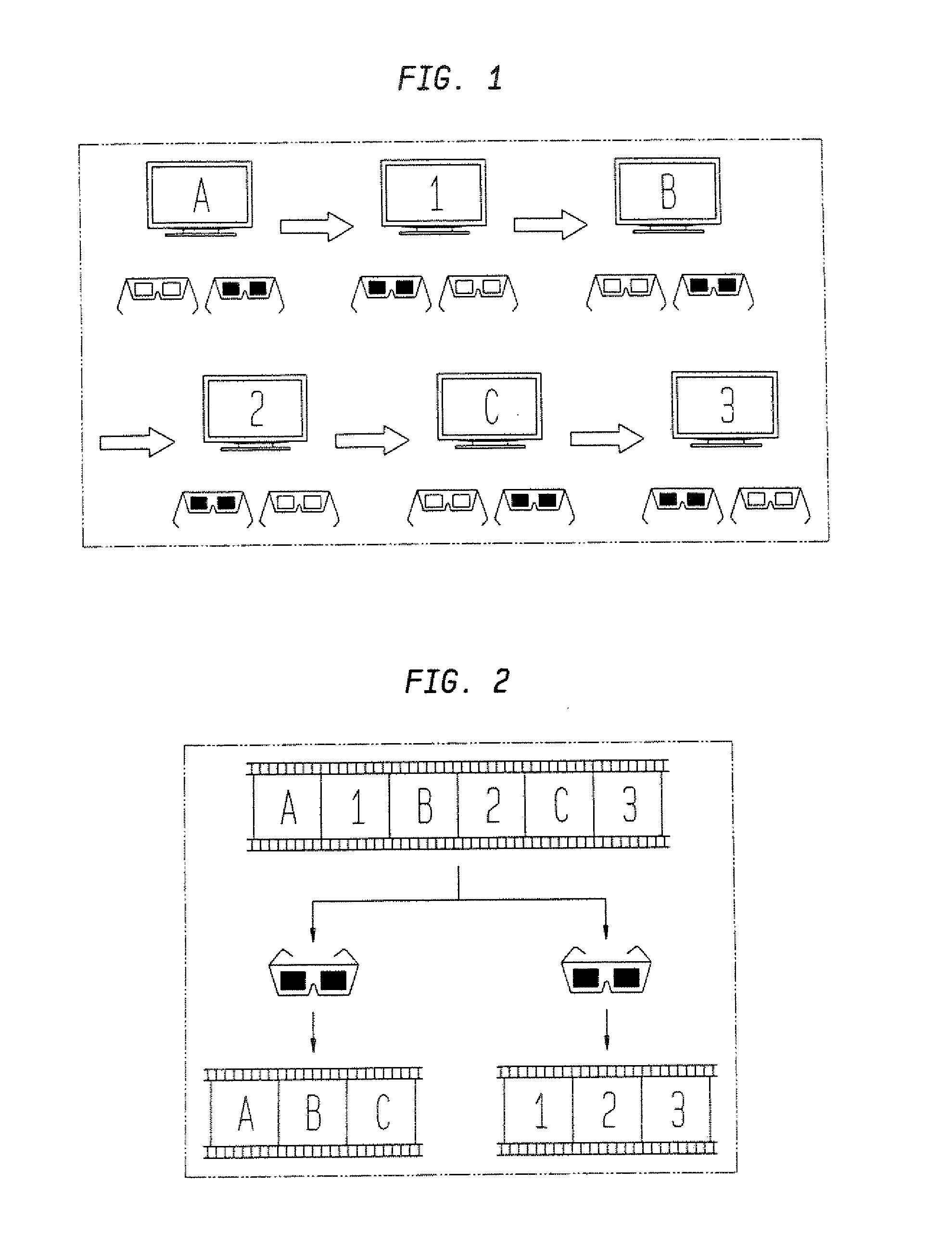
3D shutter glasses with mode switching based on orientation to display device
ActiveUS20100177174A1Reduce distractionsColor television detailsSteroscopic systemsEyewearDisplay device
A shuttered filter apparatus comprises a frame, one or more shuttered filters attached to the frame, and a tracker attached to the frame. Each shuttered filter is configured to selectively prevent a viewer from seeing through the filter in response to a signal from a controller. The tracker is configured to sense an orientation of the one or more shuttered filters relative to a video screen. The controller may use a signal from the tracker indicative of an orientation of the shutter filter(s) relative to enable shuttering when the shuttered filter apparatus is facing toward the video screen and disable shuttering when the shuttered filter apparatus is facing away from the video screen.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
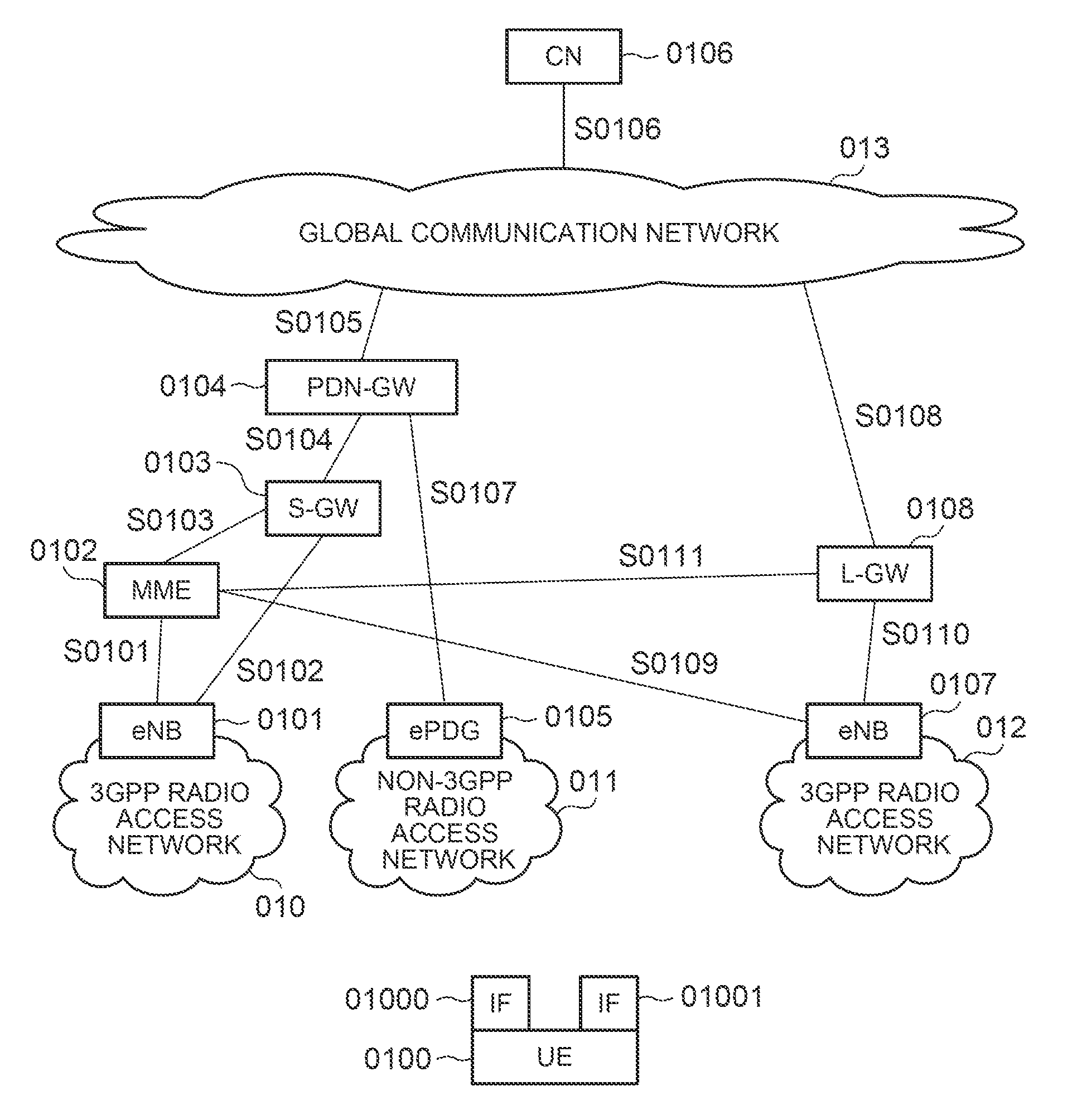
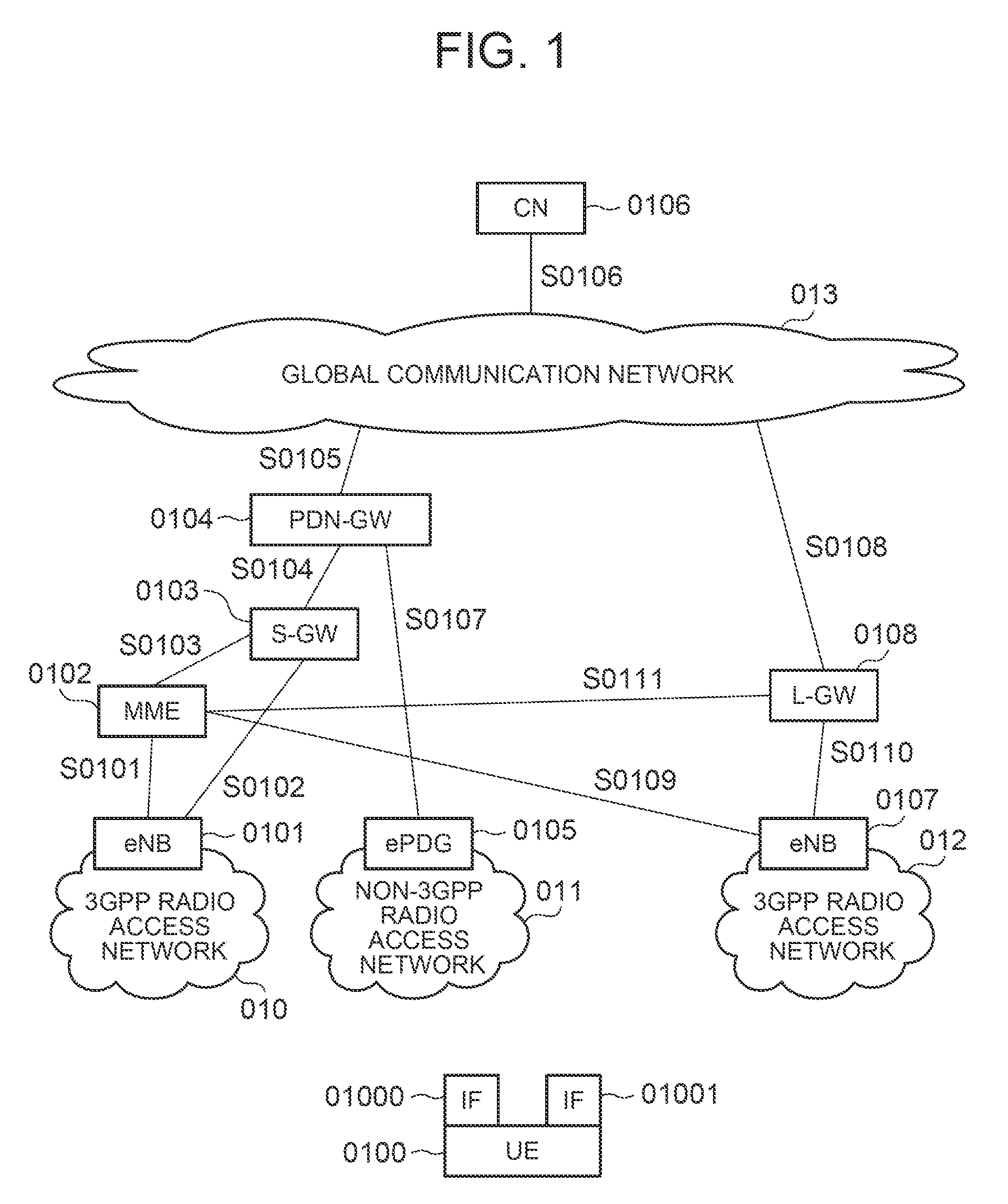
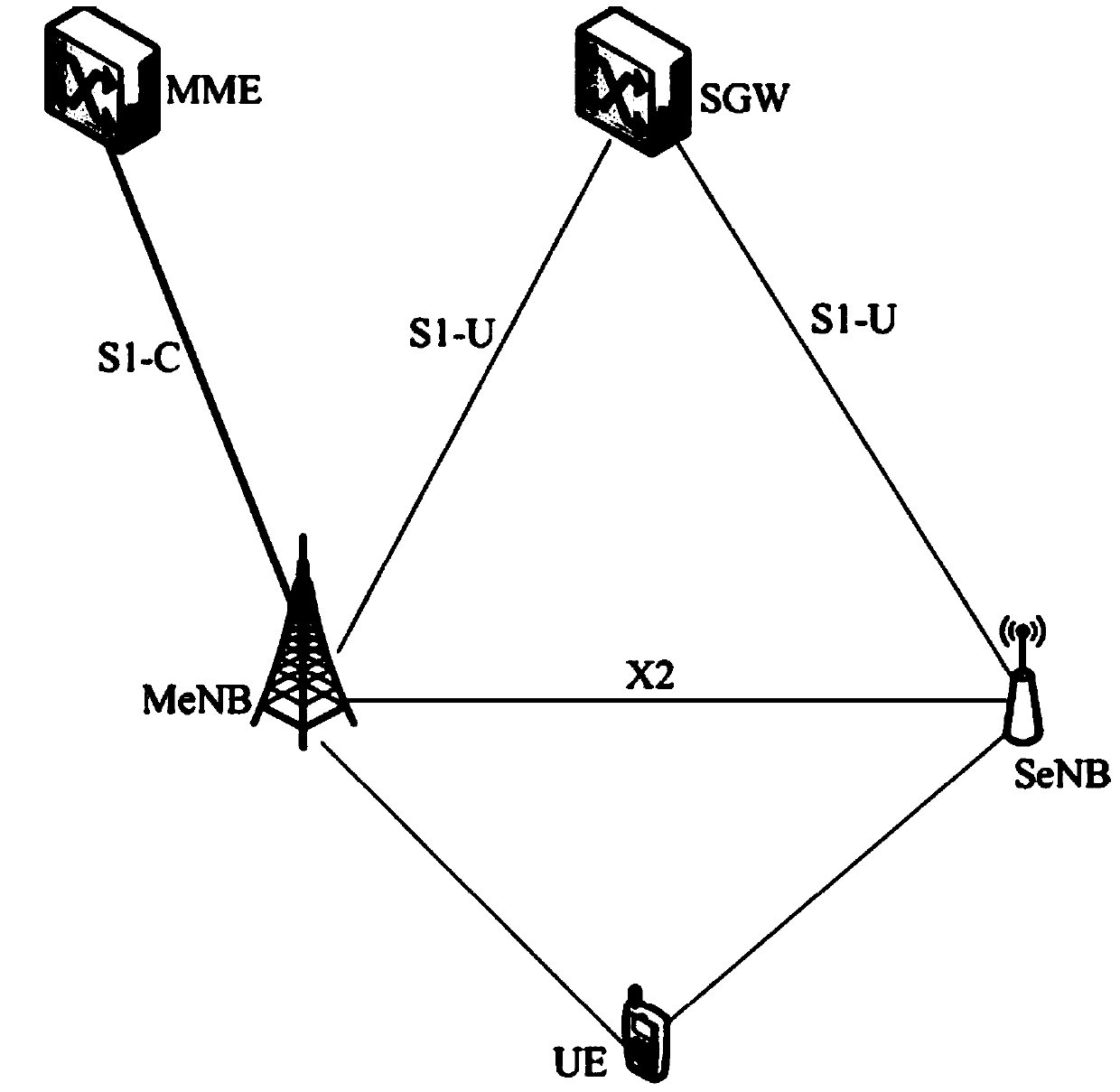
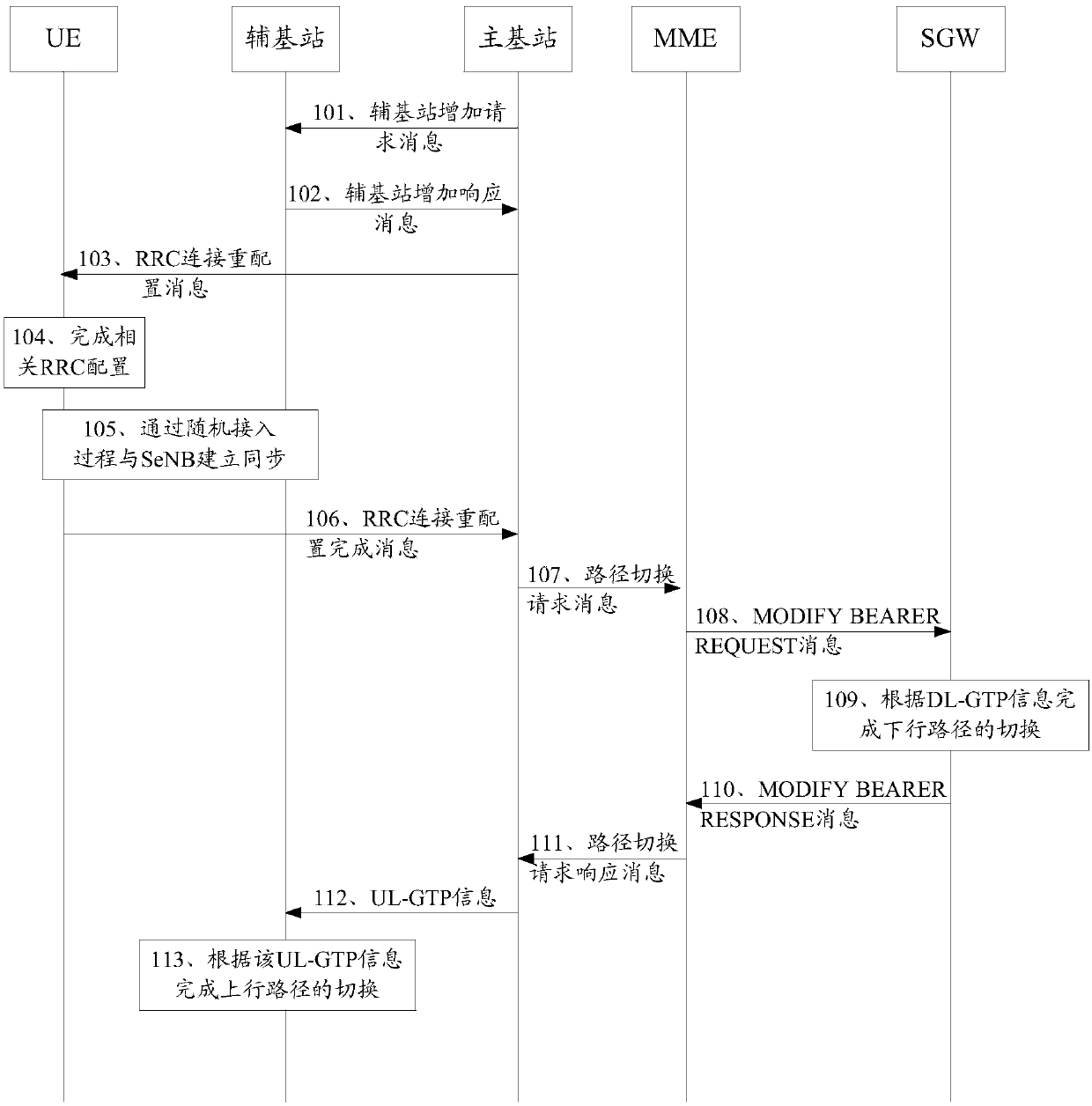
Path switching system, path switching method, and mobile terminal
ActiveUS20130028172A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork topologiesPath switchingMobile device
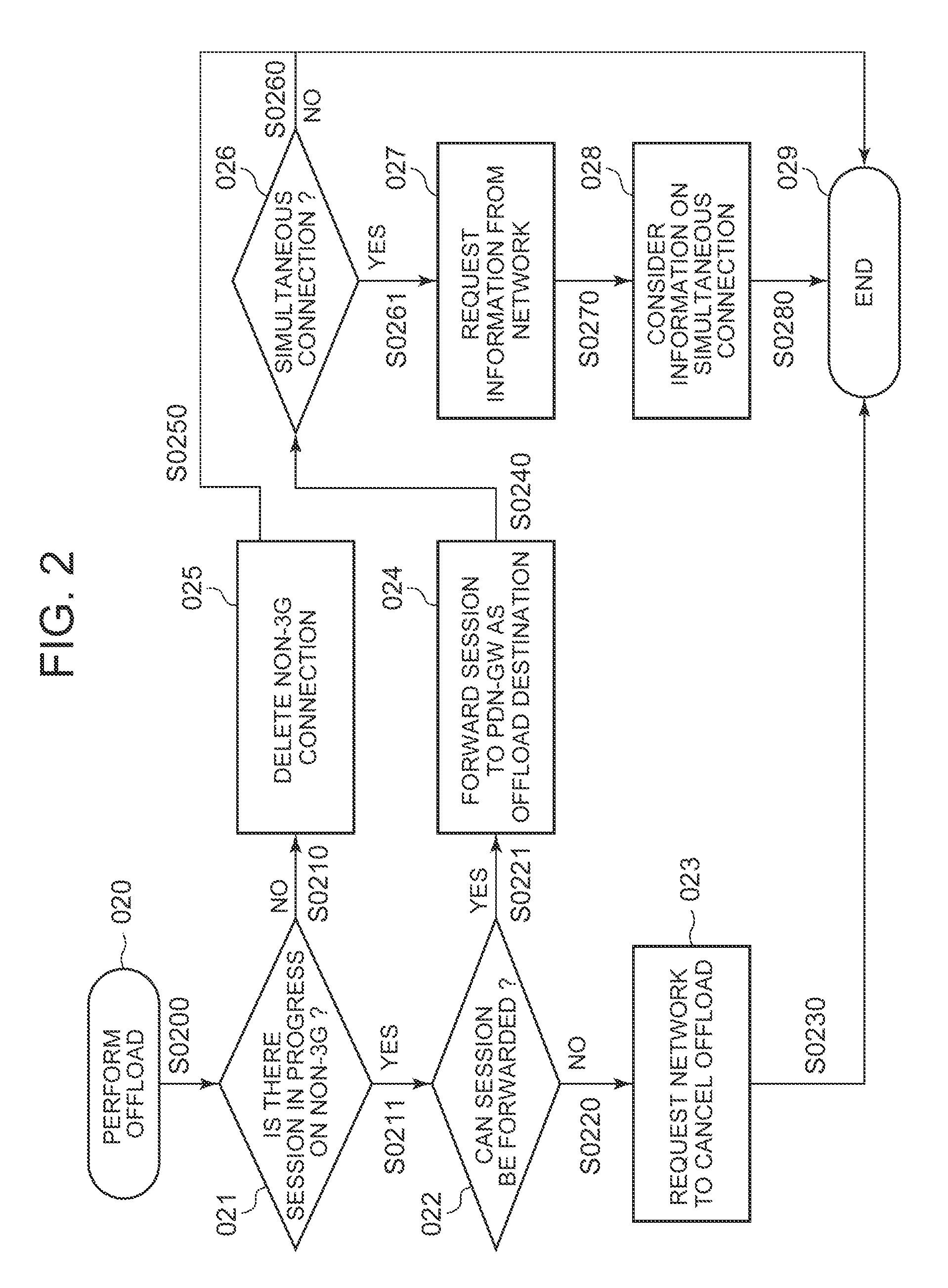
A path switching system is provided, in which when UE has been offloaded from a first PDN-GW to a second PDN-GW, if there is an additional connection of the UE to the first PDN-GW, processing related to the additional connection can be performed on the UE side. The system includes: a control unit for sending a mobile terminal a message including information indicative of having switched relay devices, which relay a packet between the mobile terminal and a communication device, from a first relay device to a second relay device; and the mobile terminal for determining whether there is an added path other than part of a path from the mobile device before movement to the communication device and capable of being managed by the control unit, established between the mobile terminal and the first relay device, and when there is the added path, performing processing on the added path.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Mixing method of movement authorities during zone switching
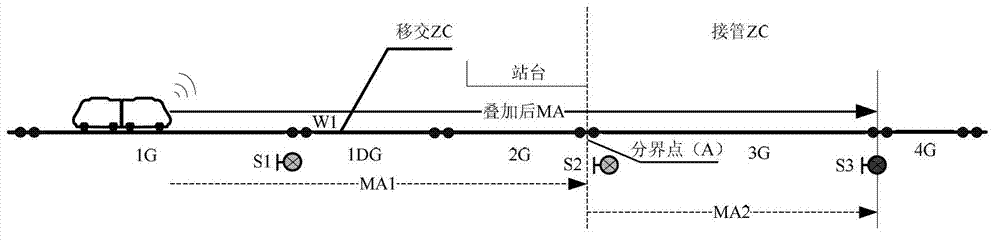
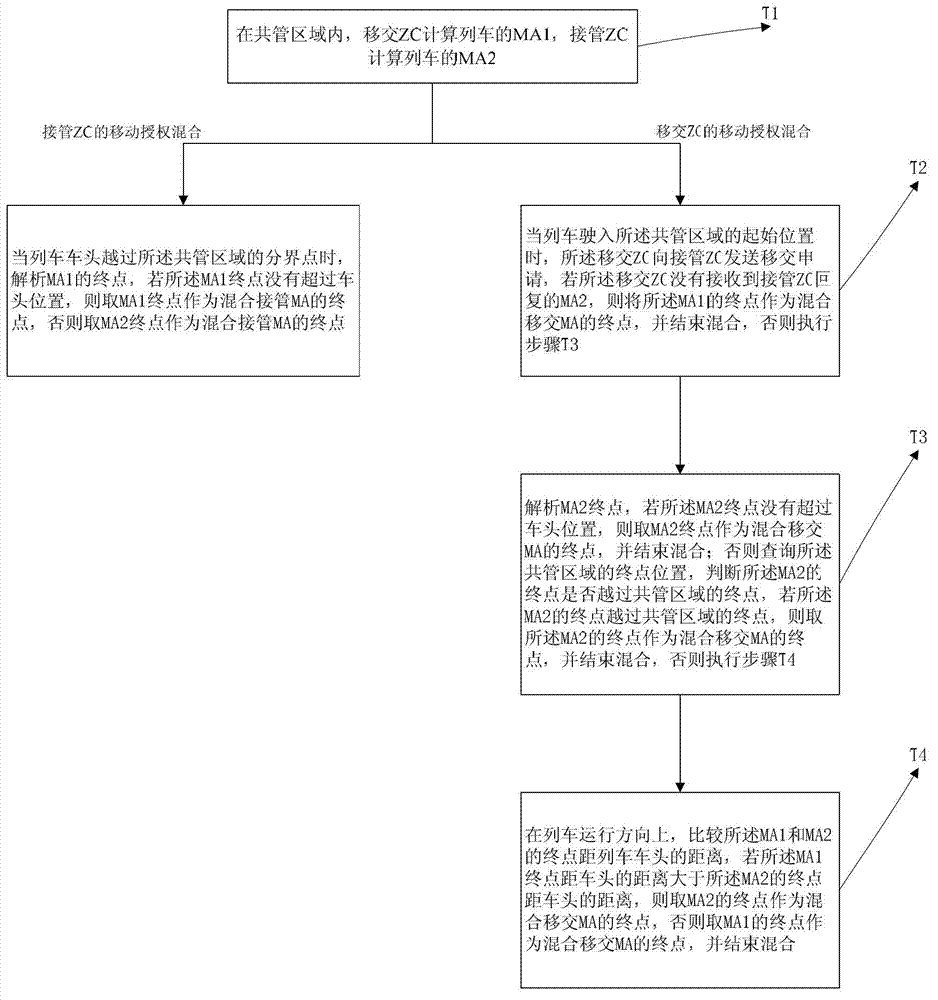
ActiveCN103029723AAvoid sudden deceleration or even emergency brakingEnsure consistencyRailway signalling and safetyState variationCo administration
The invention provides a mixing method of movement authorities during train zone switching. The mixing method comprises mixing of movement authorities of a transfer ZC (Zone Controller) and mixing of movement authorities of a takeover ZC; the movement authority mixing mode is based on a co-administration zone idea, the state of mixed MA (Movement Authority) wayside equipment is determined by combining the MA1 calculated by the transfer ZC and the MA2 calculated by the takeover ZC after the MA mixing destination is determined, so that the state change of the equipment in the co-administration area can be monitored in real time when the transfer ZC and the takeover ZC calculate corresponding mixed MAs, and therefore the response time of a system on equipment fault is prolonged; and the MA of the transfer ZC and the MA of the takeover ZC, which are generated for a train, are consistent, so that the situation that the train is suddenly decelerated, even emergently braked is avoided, and therefore the system safety is ensured.
Owner:TRAFFIC CONTROL TECH CO LTD
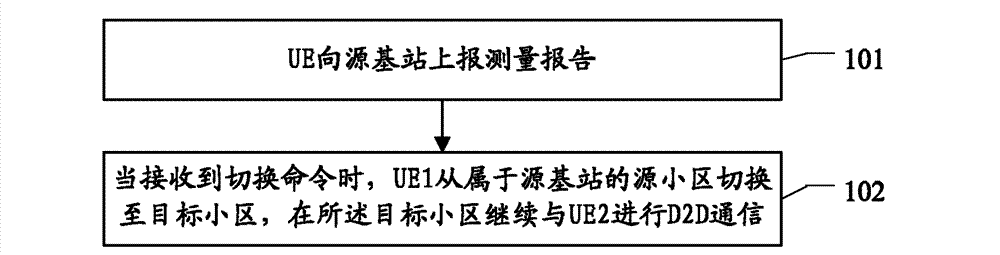
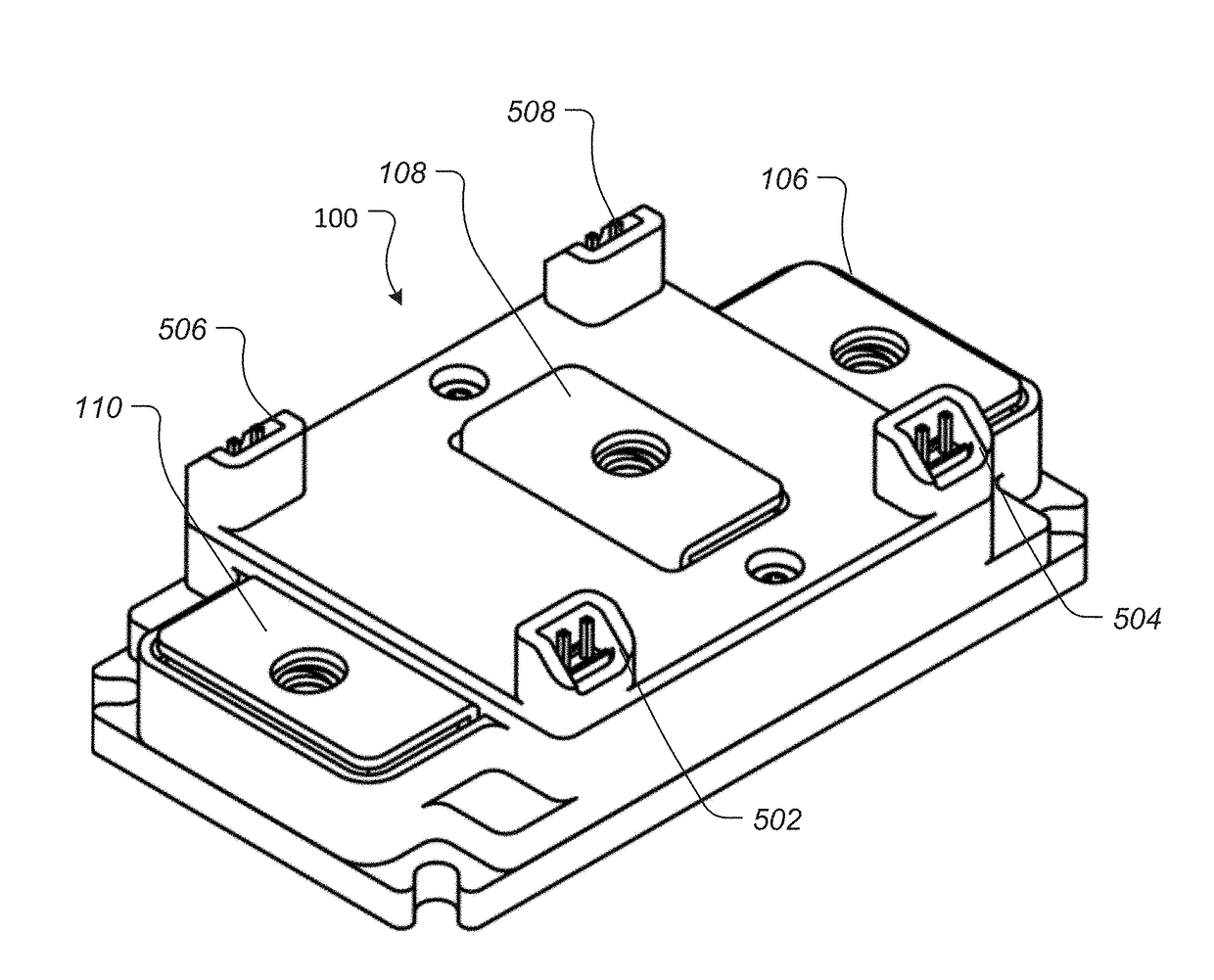
High Power Multilayer Module Having Low Inductance and Fast Switching for Paralleling Power Devices
ActiveUS20180206359A1Lower impedanceConversion constructional detailsDc-dc conversionElectricityComputer module
The disclosure is directed to a power module that includes at least one power substrate, a housing arranged on the at least one power substrate, and a first terminal electrically connected to the at least one power substrate. The first terminal includes a contact surface located above the housing at a first elevation. The power module includes a second terminal including a contact surface located above the housing at a second elevation different from the first elevation, a third terminal electrically connected to the at least one power substrate, and a plurality of power devices electrically connected to the at least one power substrate.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
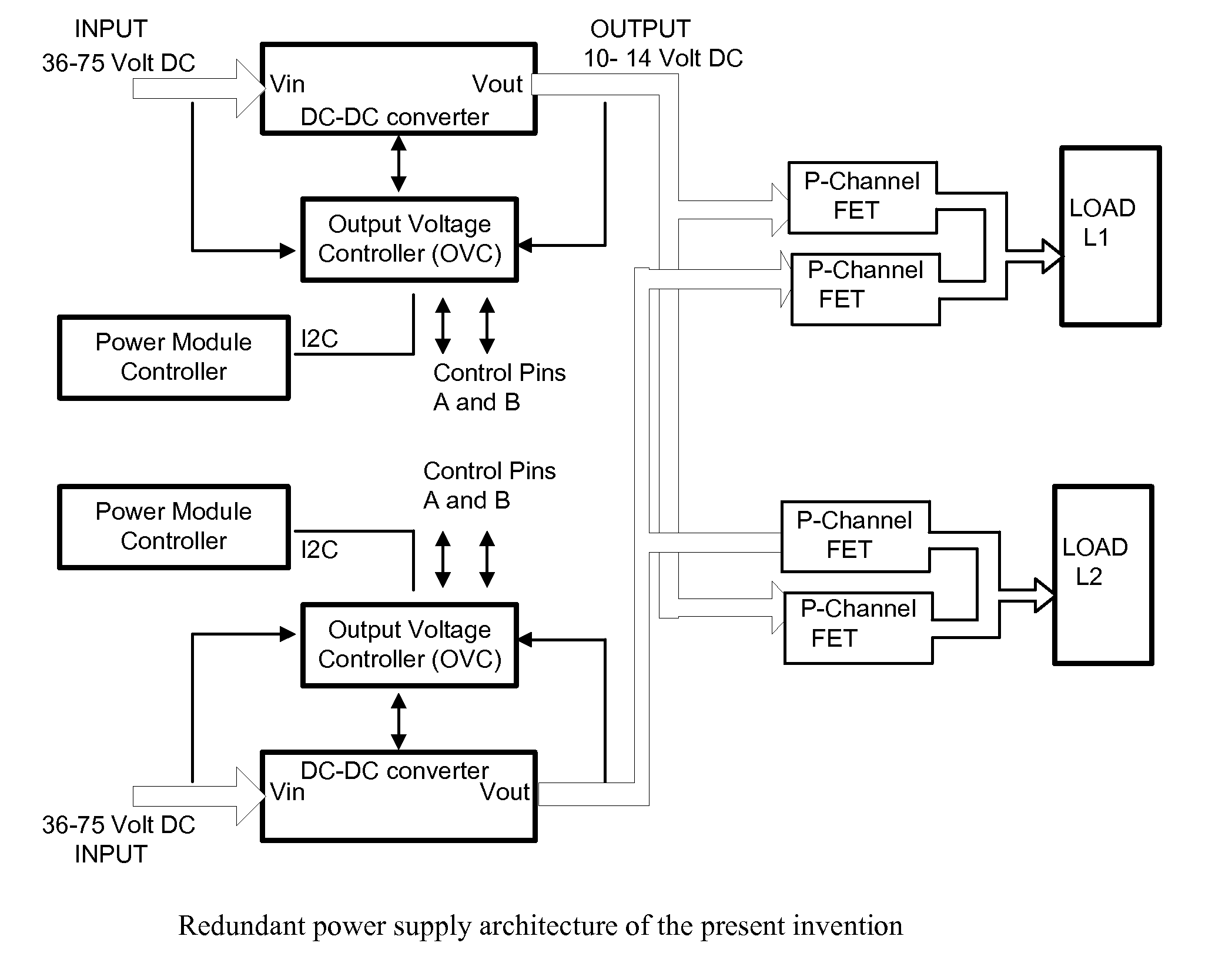
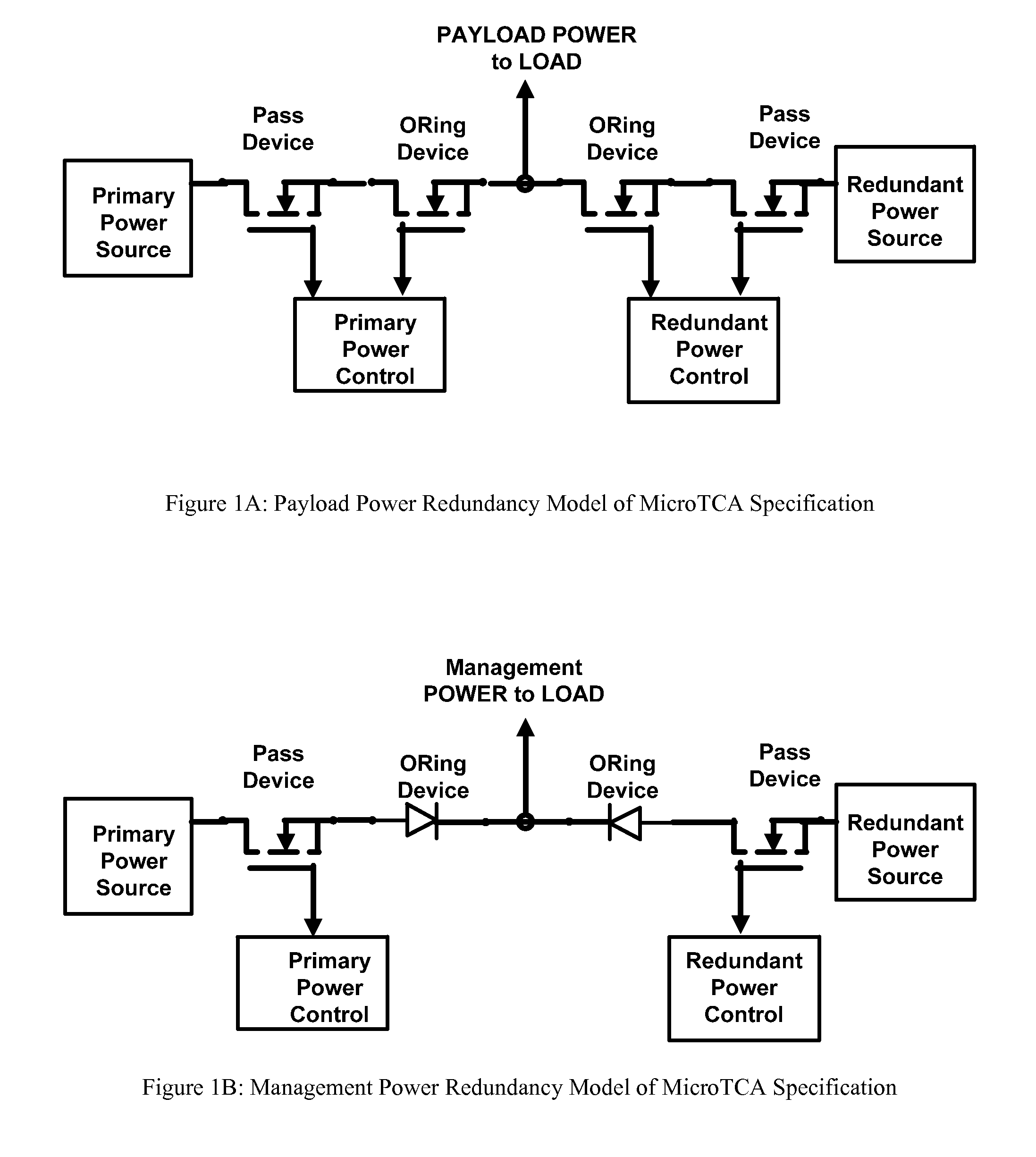
Redundant power supply architecture with voltage level range based load switching
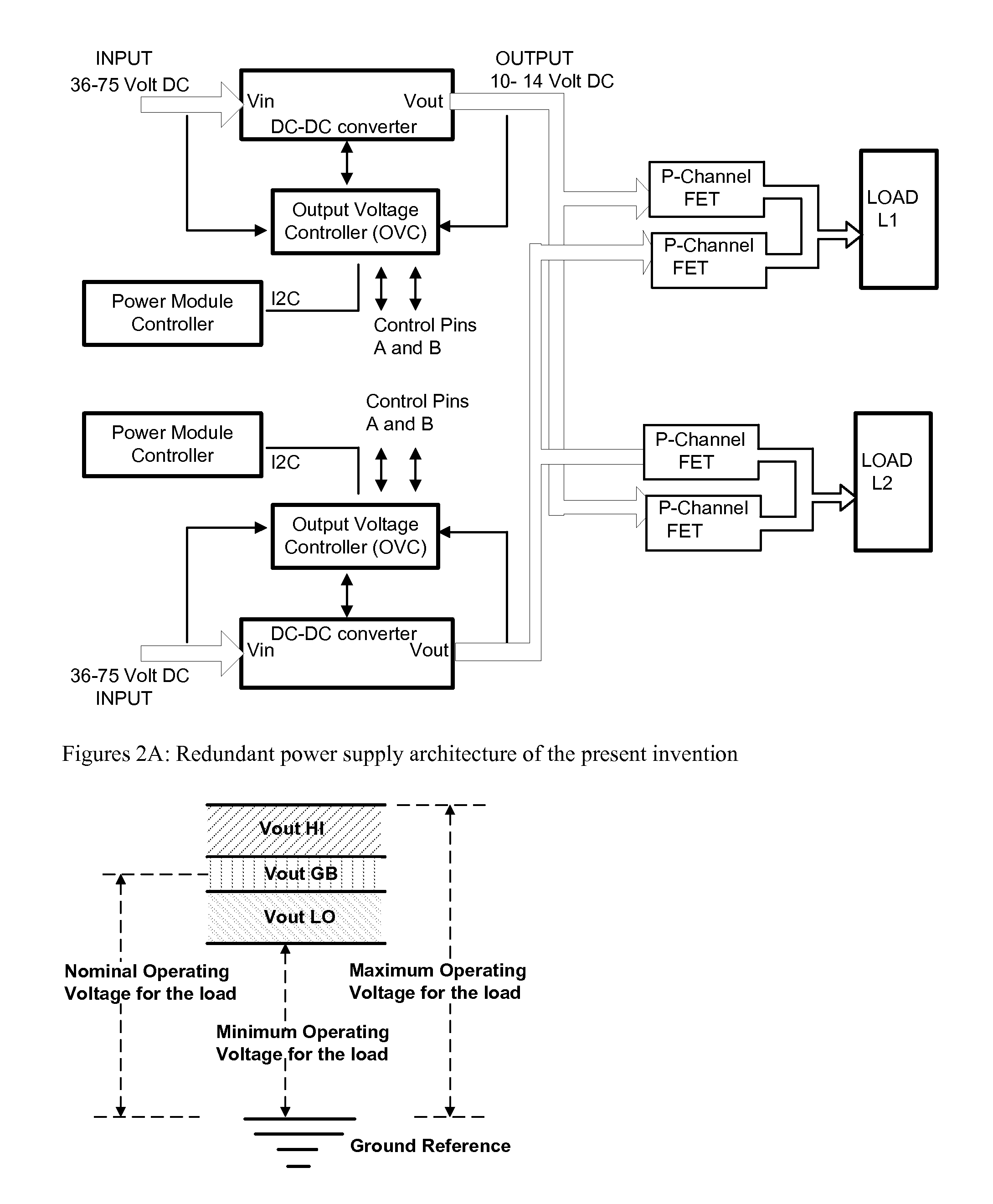
InactiveUS20080164759A1Permit useReduce the number of partsBatteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPoint of loadPotential difference
A voltage level range based redundant power supply architecture is described wherein at least two power supplies are connected to an external load and maintained in an energized state. However, only one of the power supplies sources all the current requirements of the load while the other power supply remains in standby mode. This is achieved by manually or programmatically adjusting the voltage output of a first power supply and a second power supply connected in parallel to the external load such that the first power supply always outputs a higher potential difference at the point of load than the second power supply, thereby implementing a voltage level range of outputs of the power supplies so as to guarantee that all the current requirement of the load is sourced from the first power supply. The second power supply remains energized and upon failure of the first power supply instantaneously takes over the function of the failed power supply and powers the load.
Owner:SLT LOGIC
Learning cruise control system and method used for driving style and based on mode switching
ActiveCN109624986AImprove learning efficiencyExternal condition input parametersAdaptive learningCruise control
The invention belongs to the technical field of intelligent auxiliary driving for vehicles and vehicle safety and particularly relates to a learning cruise control system and method used for a drivingstyle and based on mode switching. By means of the system and method, self-adaption cruise control is conducted through mode switching of a special driver style and self-adaption learning for the carfollowing behavior. According to the system and method, the driving style is defined to be switch strategies of a cruise control mode, an acceleration approach mode, a steady-state car following modeand a quick braking mode of a driver under different car following conditions, the driving style of the driver is learned, and the driving characteristic of the driver is further learned through a learning method based on a continuous state under each driving mode. The system is suitable for automatic driving of an L2-level vehicle, the aim is to effectively learn the driving style characteristicof the driver, and the adaptability and acceptability of the specific driver for the self-adaption cruise system under different working conditions are improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
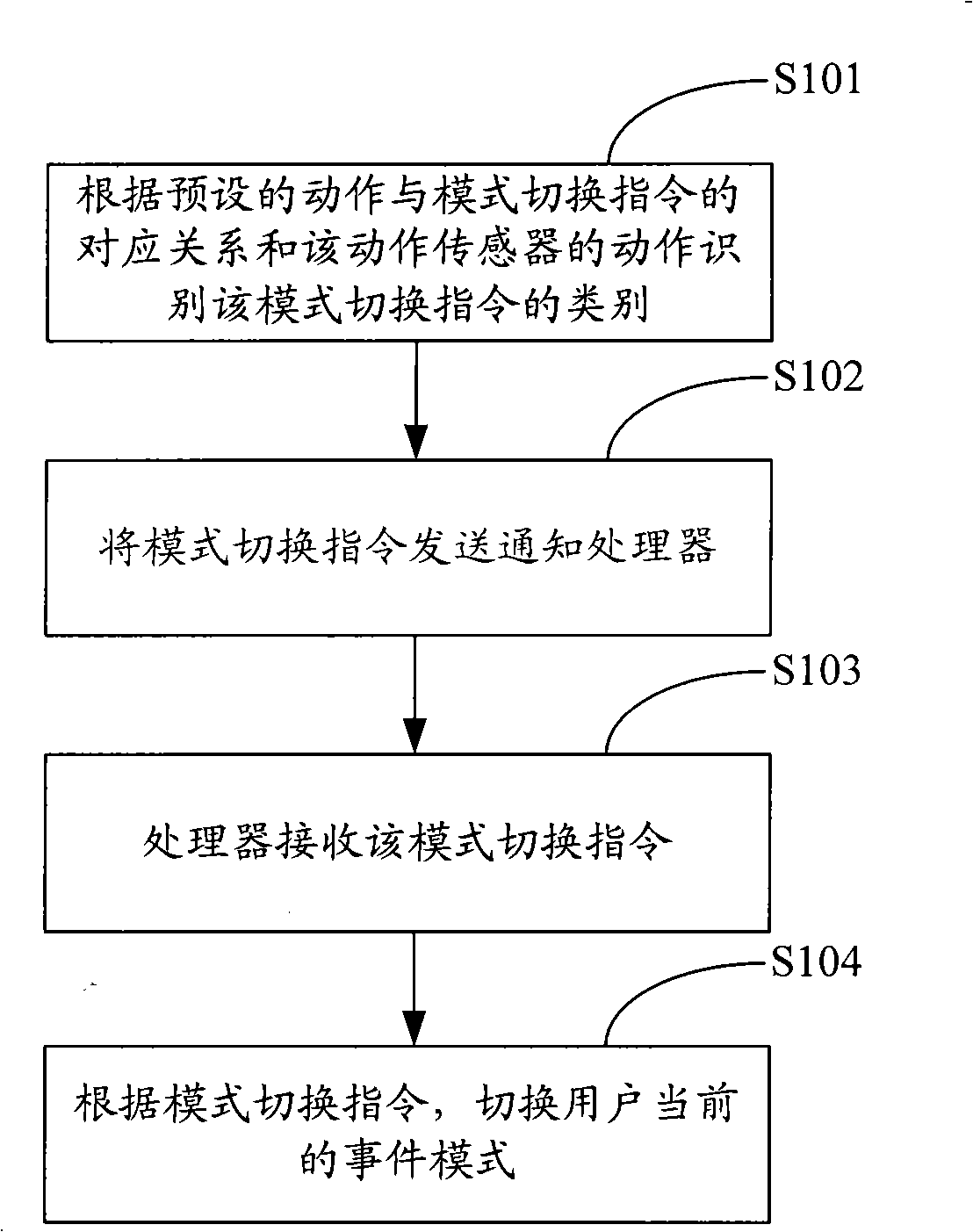
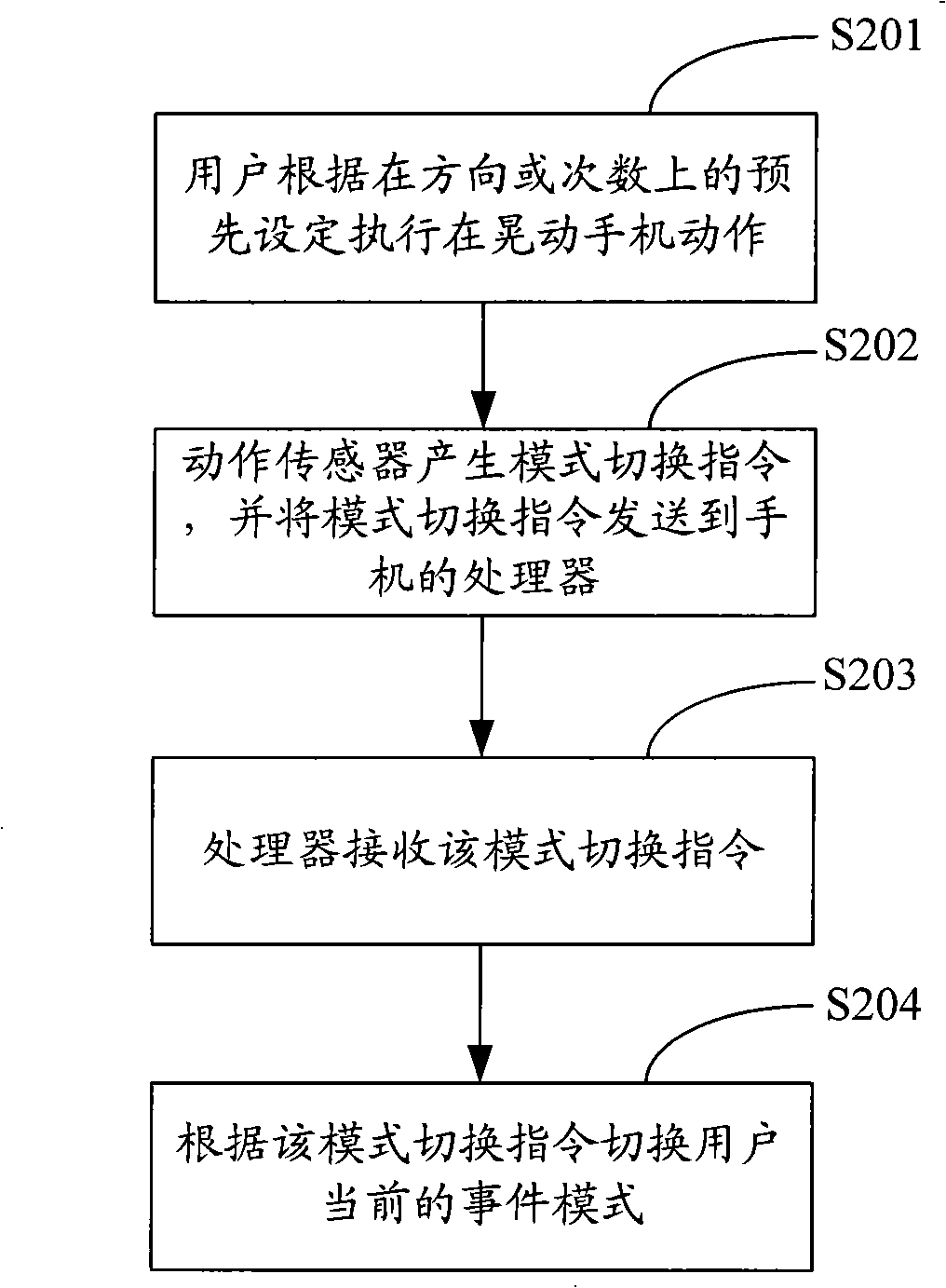
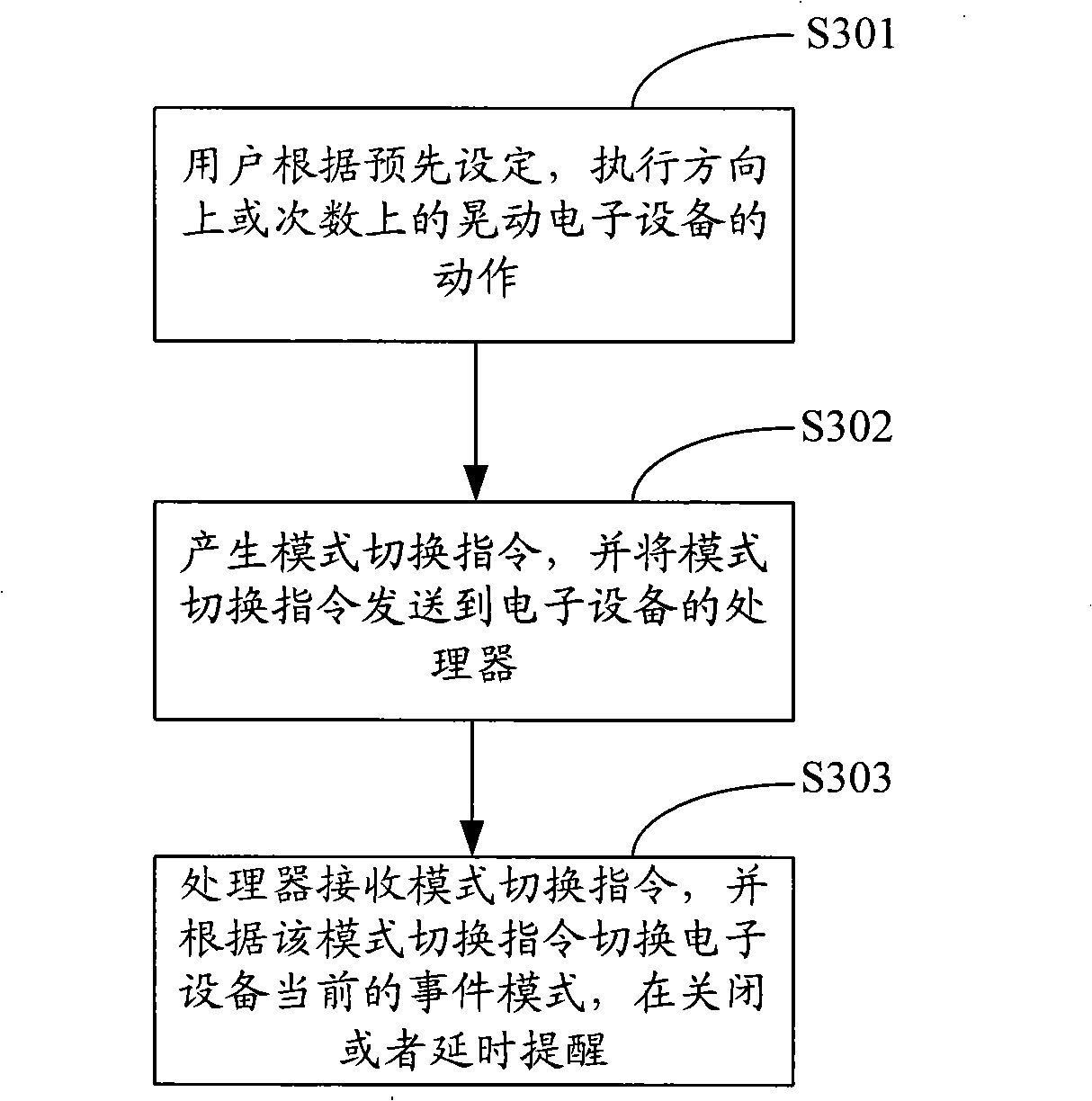
Method, system and mobile terminal for mode switching of electronic apparatus
The invention is applicable to the field of electronic technique and provides a mode switching method, a system and a mobile terminal for electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving a mode switching command generated by a motion sensor; switching the current event mode of the user according to the mode switching command. In the embodiment of the invention, the switching of the event mode of the electronic equipment is preset; when the outside incoming calls or other events come to users, the current event mode of the electronic equipment can be automatically switched by shaking the electronic equipment in certain direction or for certain times; the user does not need to immediately answer the telephone or carry out other response operation of other events, thereby bringing convenience to the user.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
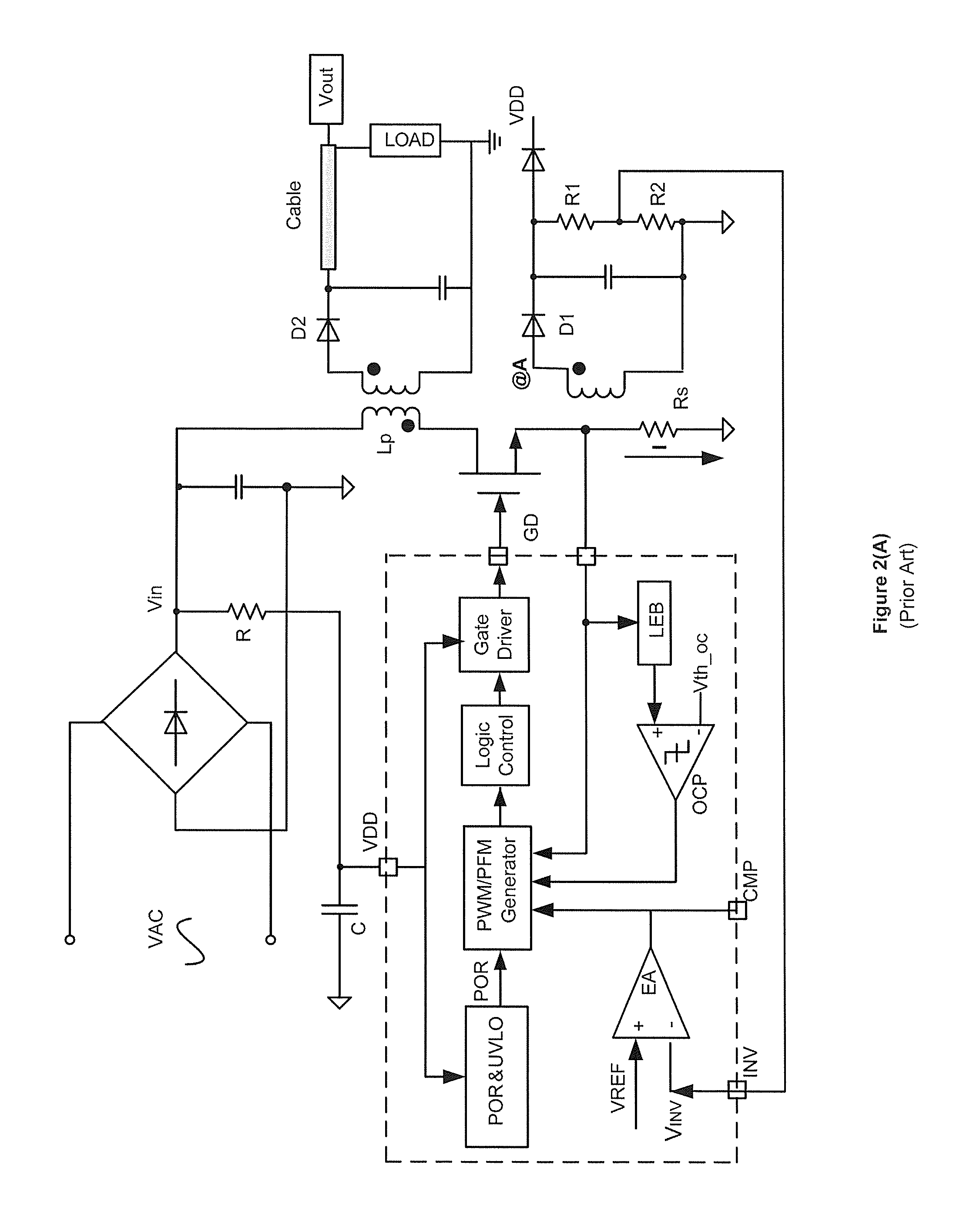
Systems and methods for primary-side regulation in off-line switching-mode flyback power conversion system
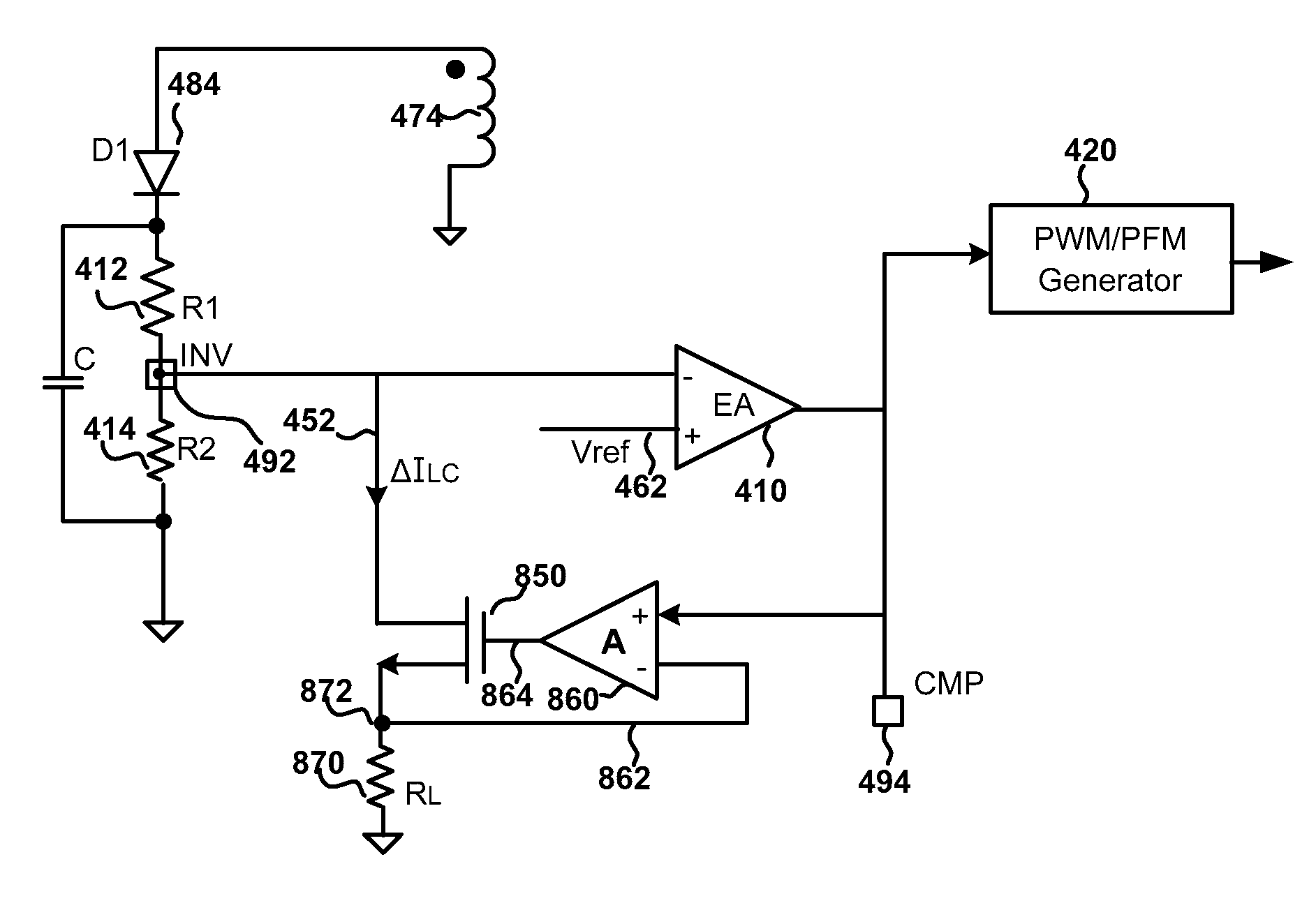
ActiveUS8305776B2Optimizing Load RegulationLow costDc network circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionEngineeringVoltage reference
Switching-mode power conversion system and method thereof. The system includes a primary winding configured to receive an input voltage, an a secondary winding coupled to the primary winding and configured to, with one or more first components, generate, at an output terminal, an output voltage and an output current. Additionally, the system includes an auxiliary winding coupled to the secondary winding and configured to, with one or more second components, generate, at a first terminal, a detected voltage. Moreover, the system includes an error amplifier configured to receive the detected voltage and a first reference voltage and generate an amplified voltage based on at least information associated with a difference between the detected voltage and the first reference voltage. Also, the system includes a compensation component configured to receive the amplified voltage and generate a second reference voltage based on at least information associated with the amplified voltage.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
Security key context distribution method, mobility management entity and base station
ActiveCN103747442AImprove reliabilityGuaranteed synchronizationNetwork topologiesConnection managementDistribution methodCarrier signal
The invention discloses a security key contextual distribution method, mobility management entity and base station, wherein, the security key contextual distribution method comprises: firstly, the mobility management entity receives a first instruction from a main base station, wherein the first instruction is used for the mobile management entity to request a path switching and indicate the path switching triggered by a inter-base station carrier aggregation; the path switching is processed according to the first instruction; the security keys context distribution method for the path switching is remained unchanged according to the first instruction, secondly, a second instruction is sent to the main base station, the security keys context distribution method is remained unchanged by indicating the main base station; or, the third instruction is sent to the main base station, a turning times of a counter of a next-hop chain of the security keys context distribution method is obtained by indicating the main base station. To be sure, the technical solution provided by the present invention can effectively improve the reliability of the path switching when the inter-base station carrier is aggregating.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Wireless communication receiver
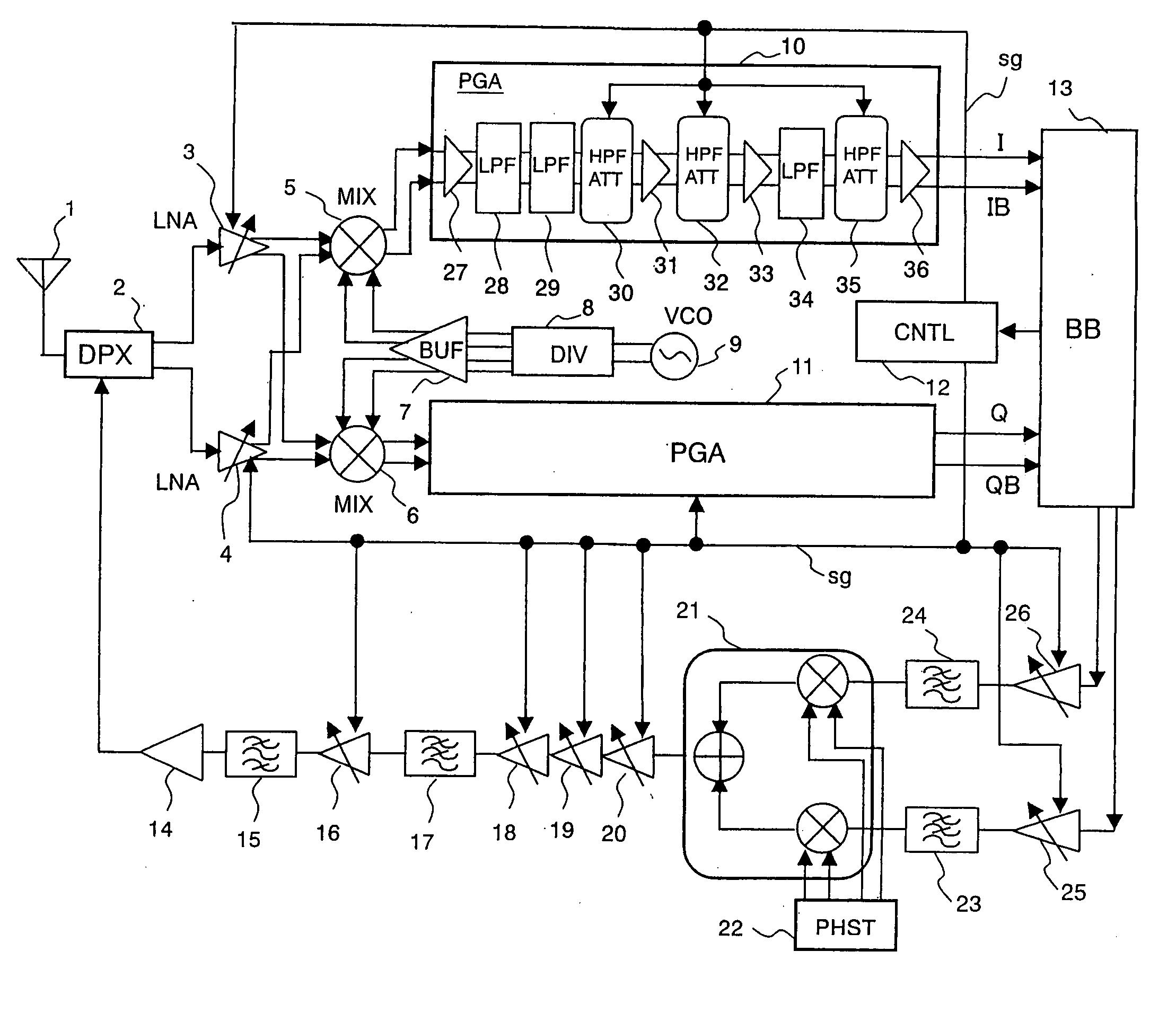
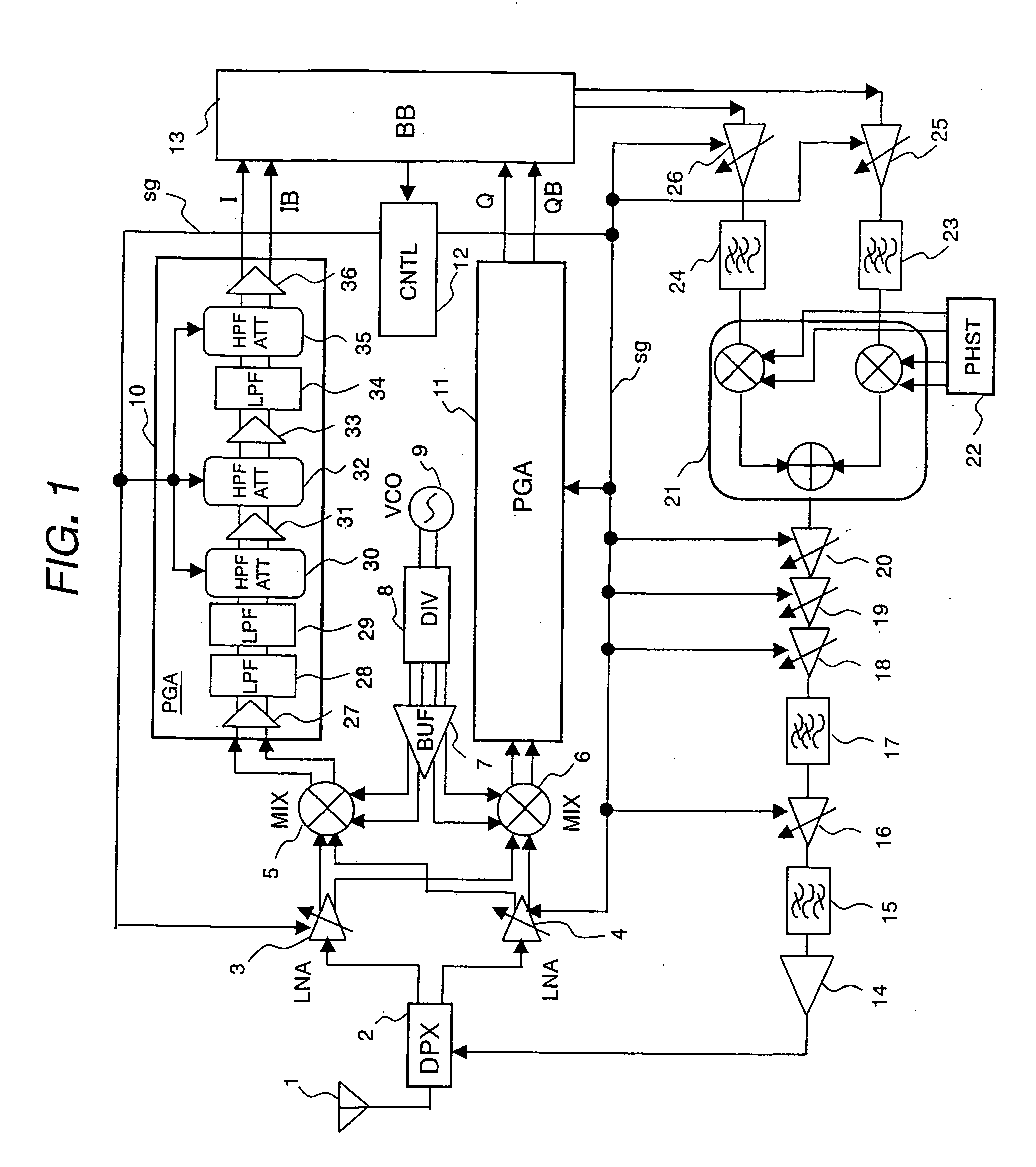
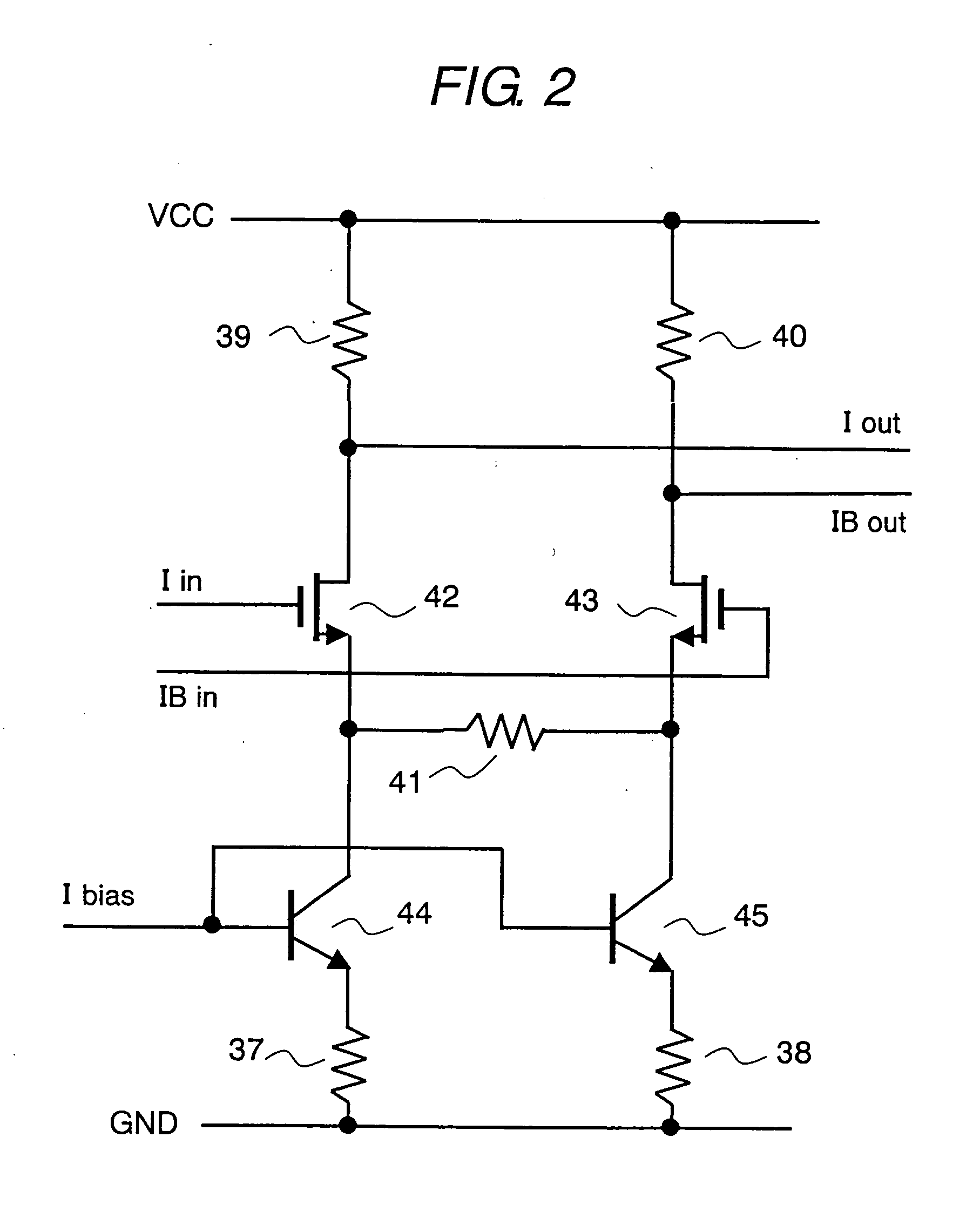
InactiveUS20060128334A1Reduce circuit areaSuppression of levelEnergy efficient ICTGain controlControl signalQ-switching
To reduce circuit area and power consumption and suppress transient response occurring at switching in PGA of a programmable gain amplifier is provided a wireless communication receiver comprising PGAs for adjusting the gain of a received signal down-converted by mixers and sending it to base-band block. Within PGAs are provided HPFATT circuits formed of capacitors arranged in series, and ladder resistors arranged in parallel, with signal lines, and a plurality of switches. HPFATT is a circuit serving as a high-pass filter and an attenuator for gain switching, wherein switches are controlled by control signal sg from a controller. Amplifiers connected to the rear stage of the HPFATT circuit are formed of MOS transistors.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
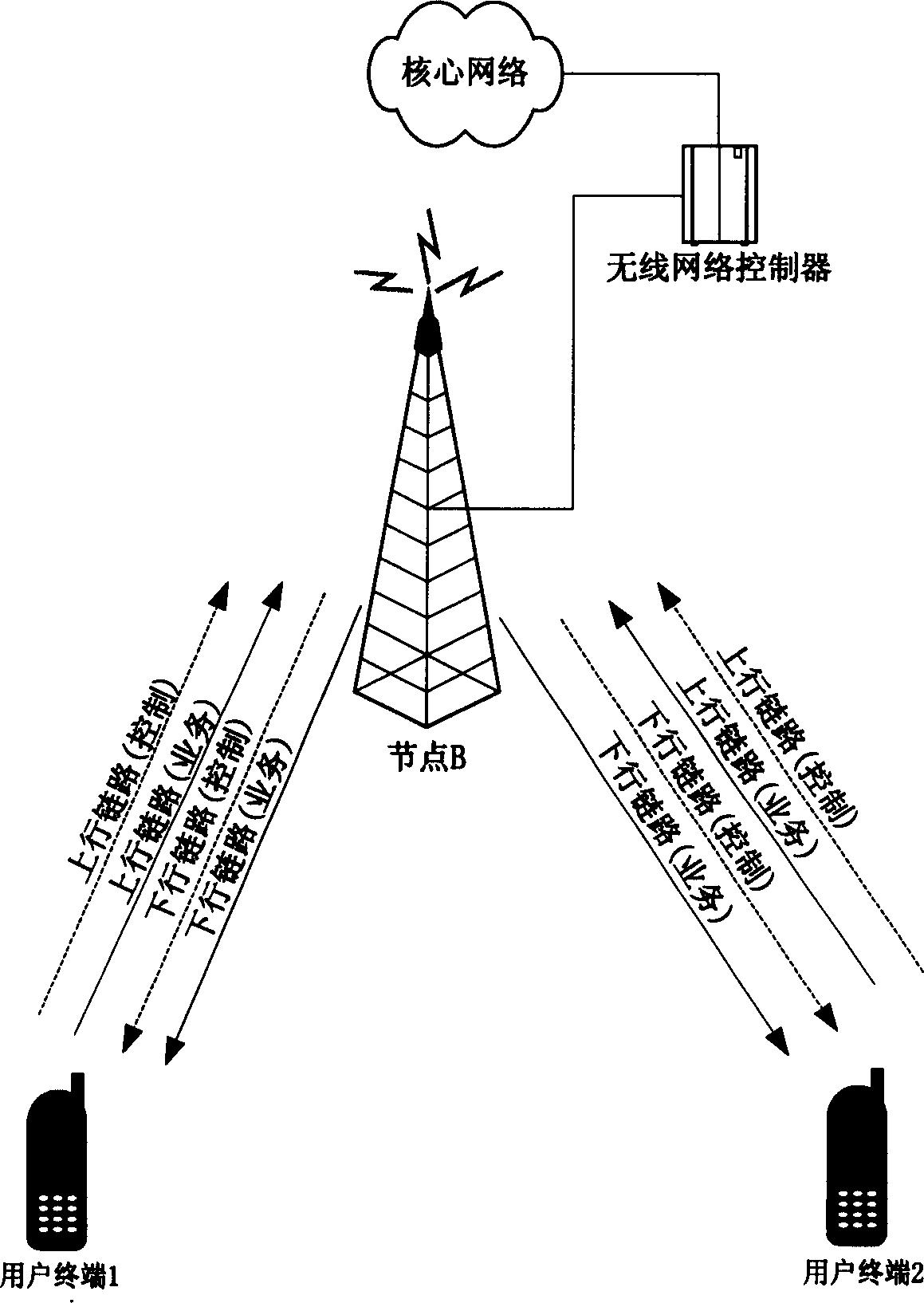
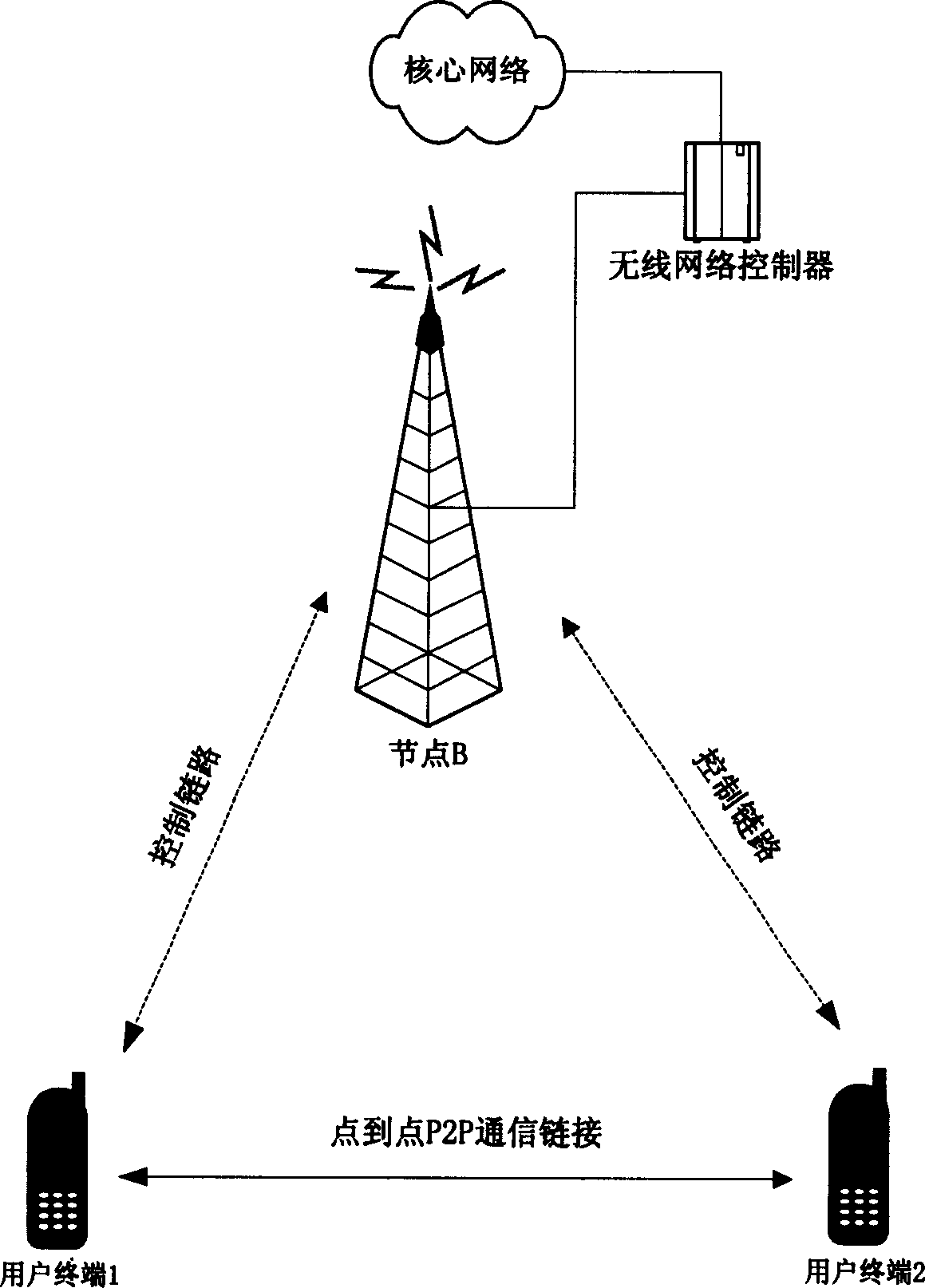
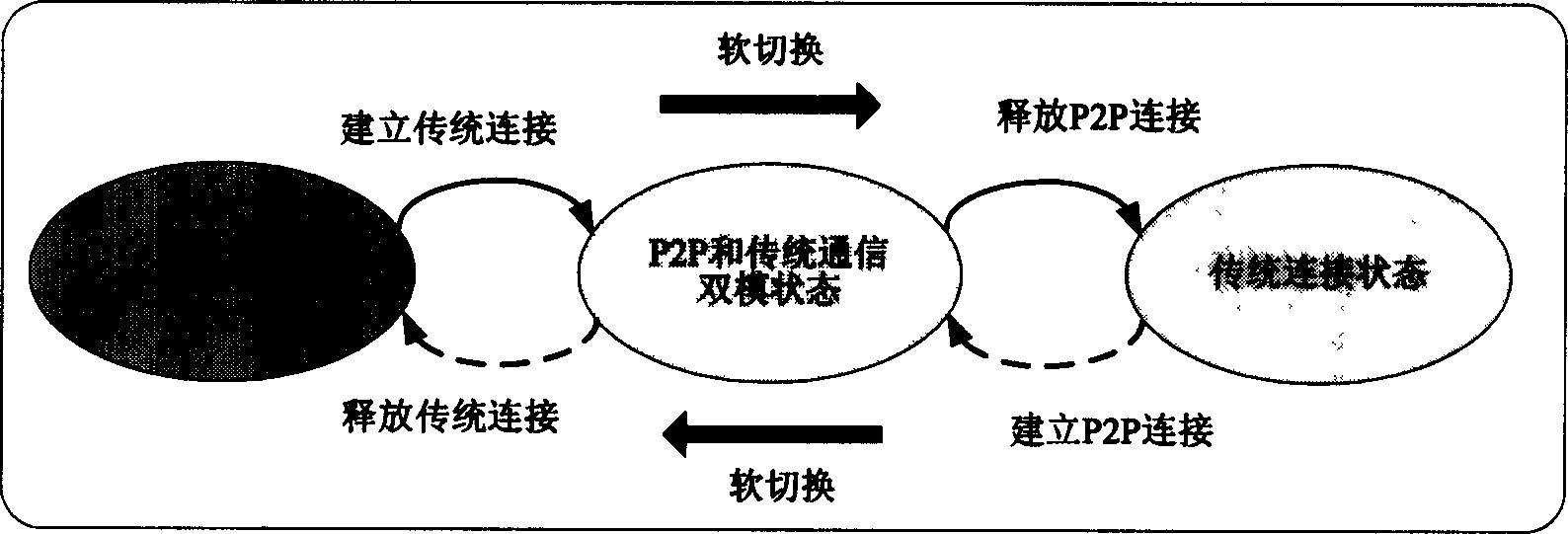
Method and apparatus for soft switching between P2P communication mode and traditional communication mode in radio communication system
InactiveCN1549613AObvious switching processSmooth transitionPower managementTransmission control/equalisingCommunication qualitySoft switching
The method is as the follows: detection is carried out for direct link which is used by user terminal to carry on P2P communication with another user termina; a request of switching in traditional communication mode is sent to a radio communication network system if direct link communication quality can not satisfies with requirements of P2P communication according to detection result; traditional communication link is established after switching in request confirmation sent from the network system is receive so that traditional communication mode is used to carry on communication with another user terminal.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com