Patents
Literature
295results about How to "Reduce additional" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
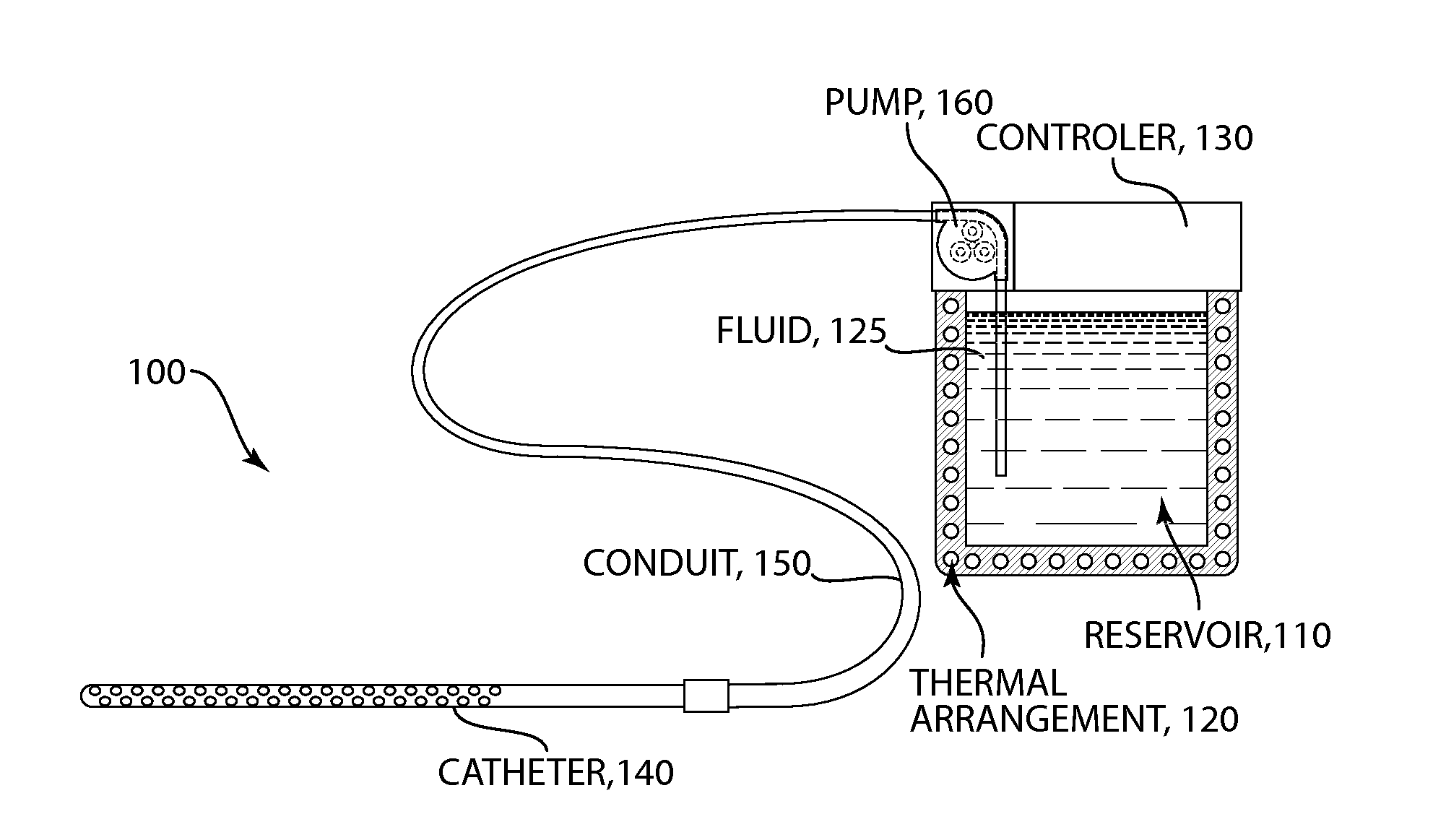
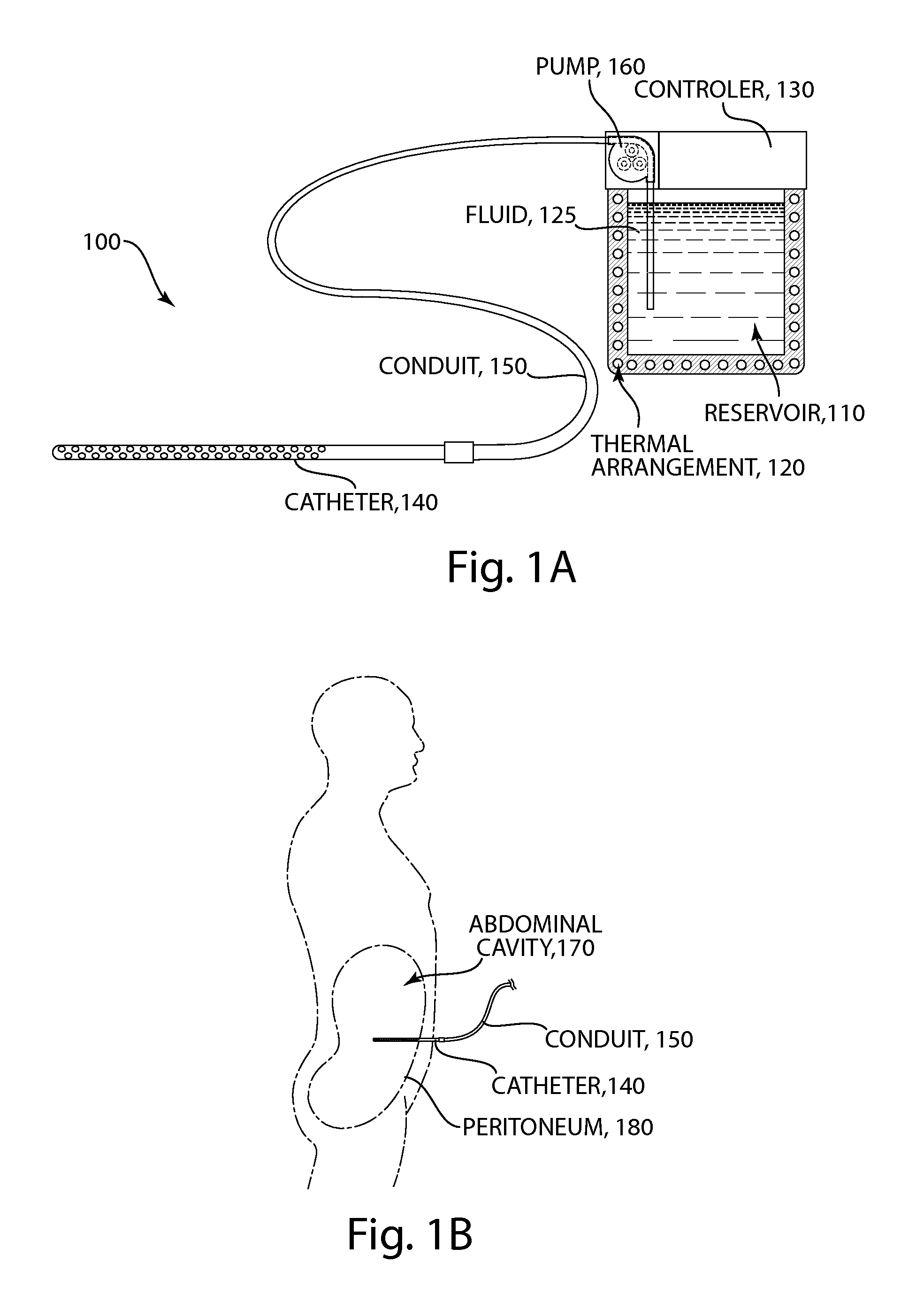
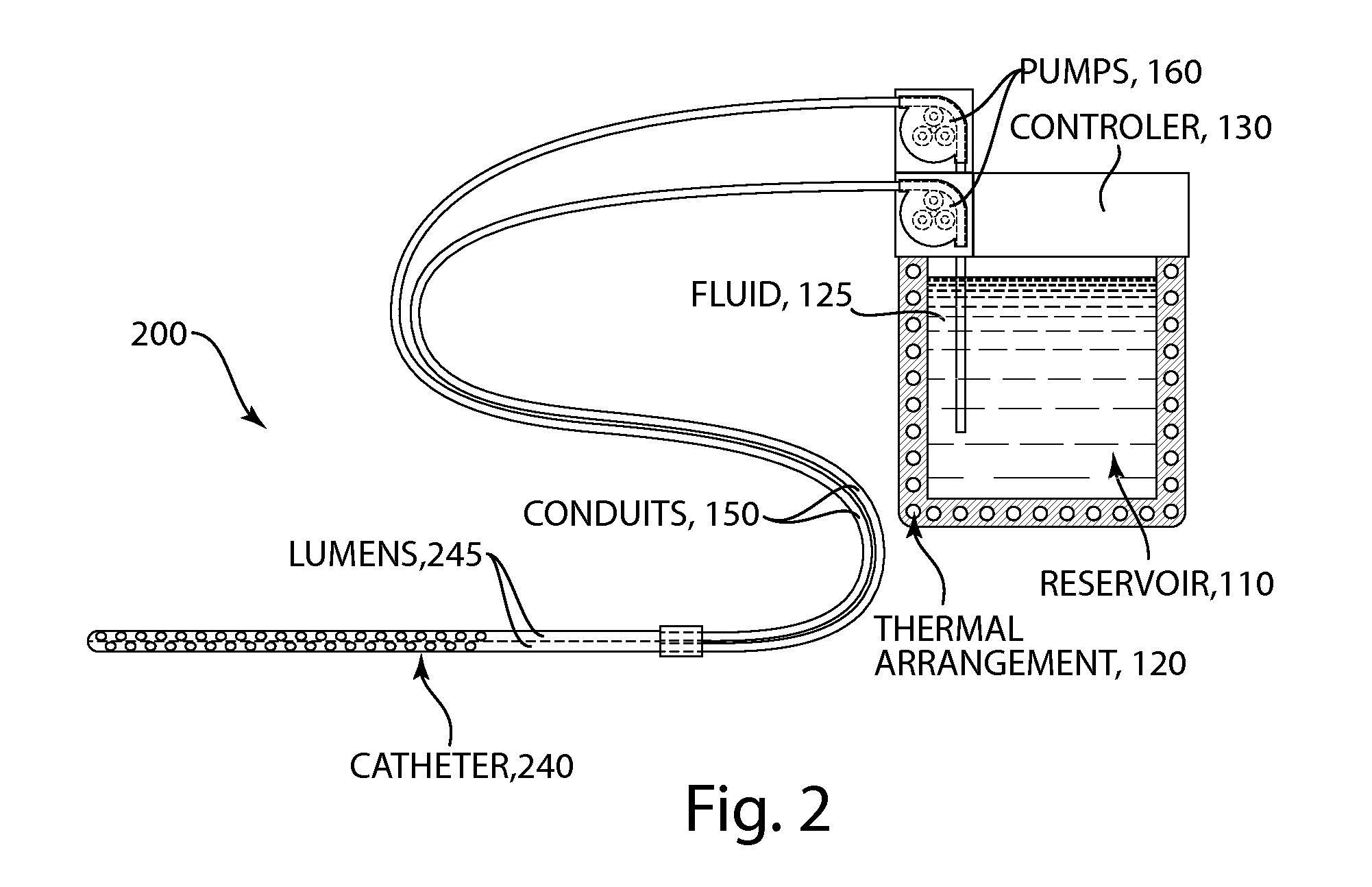
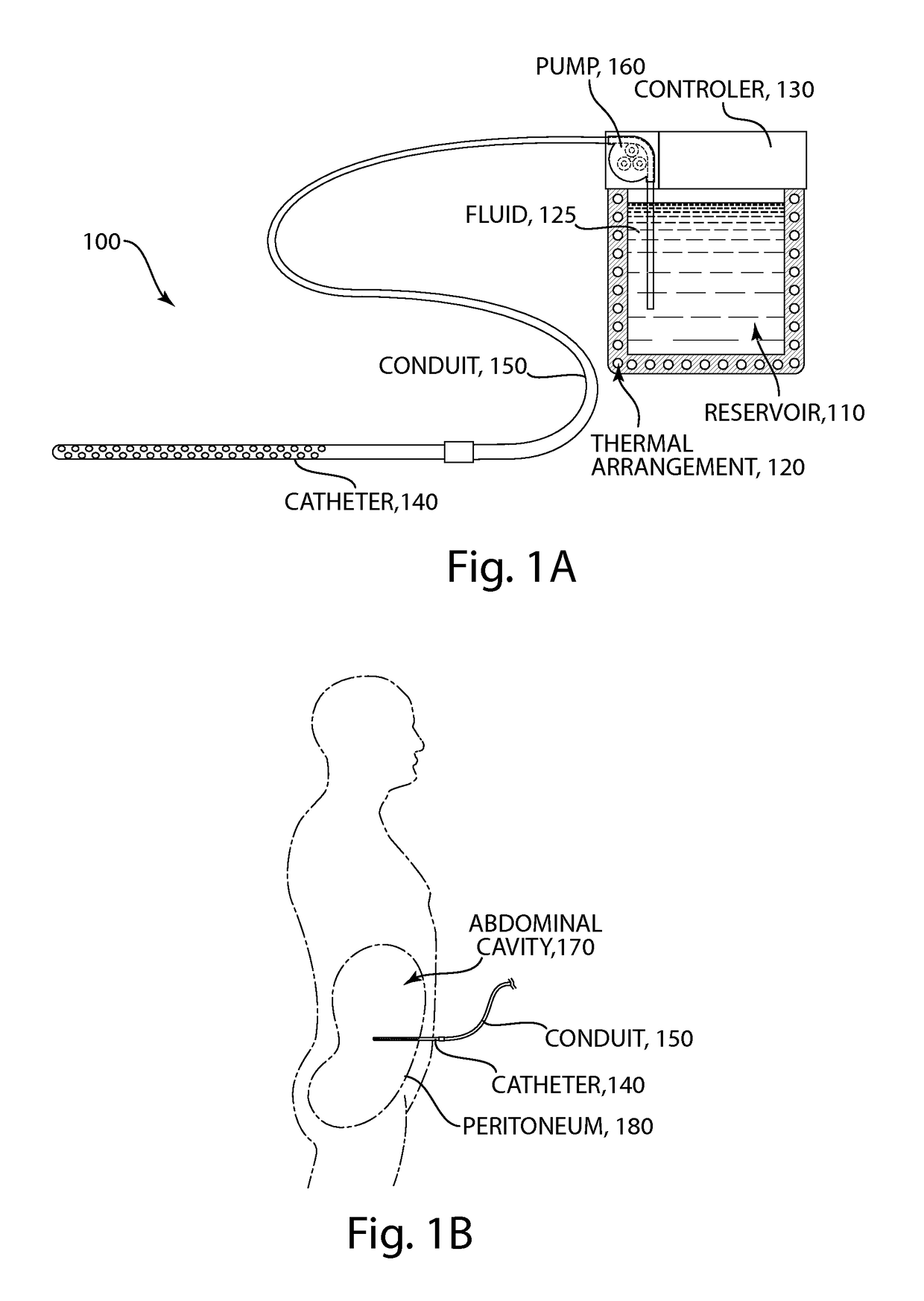
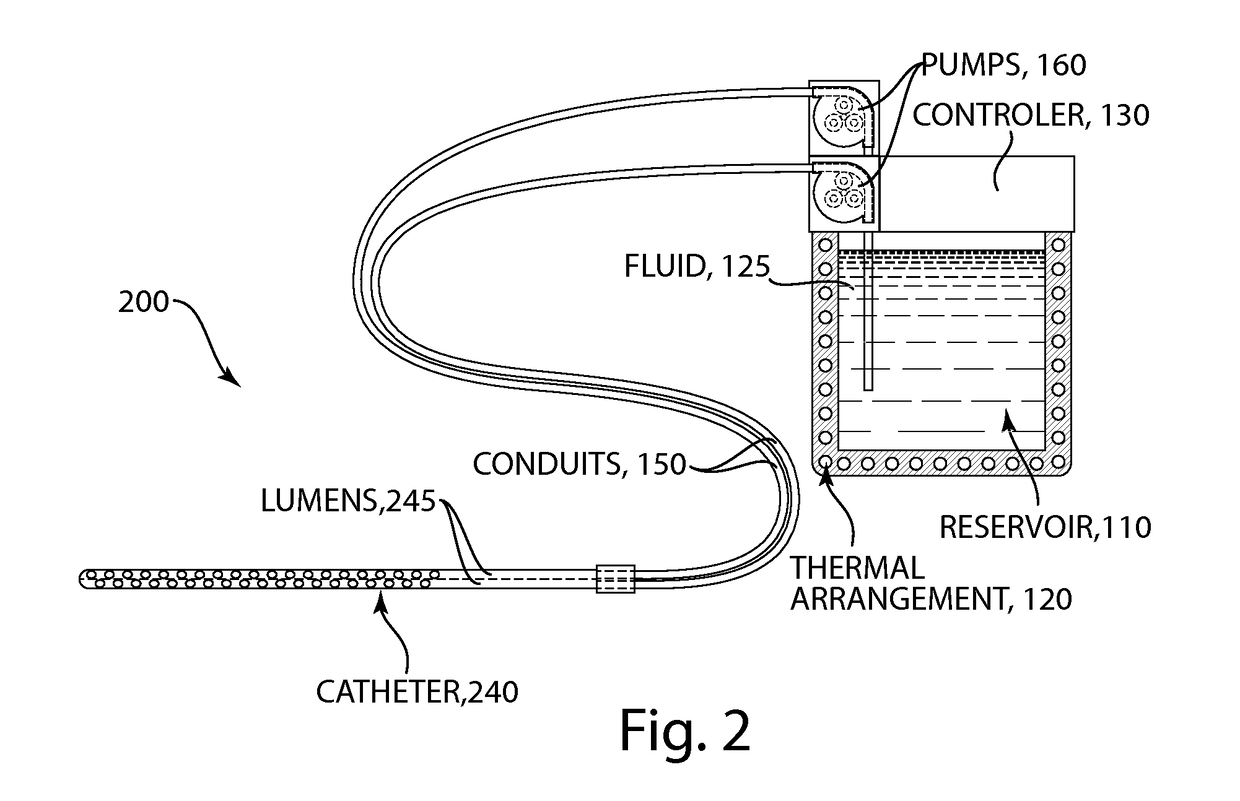
Methods and devices for selective disruption of visceral fat by controlled cooling
ActiveUS20130190744A1Reduce amountImproved health and physical appearanceSurgical instruments for coolingTherapeutic coolingNuclear medicineVisceral fat
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for use in the selective disruption of visceral fat tissue by controlled cooling.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
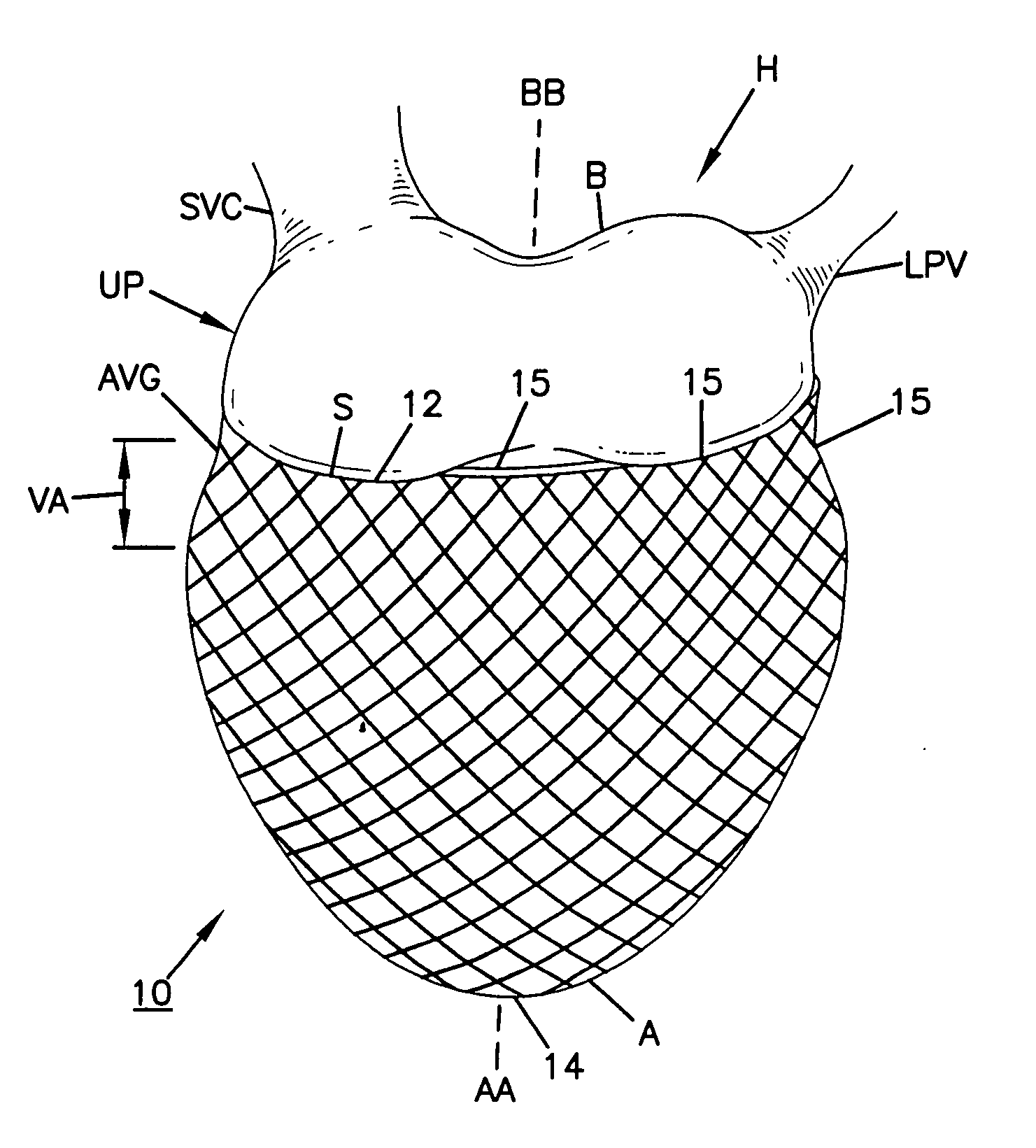
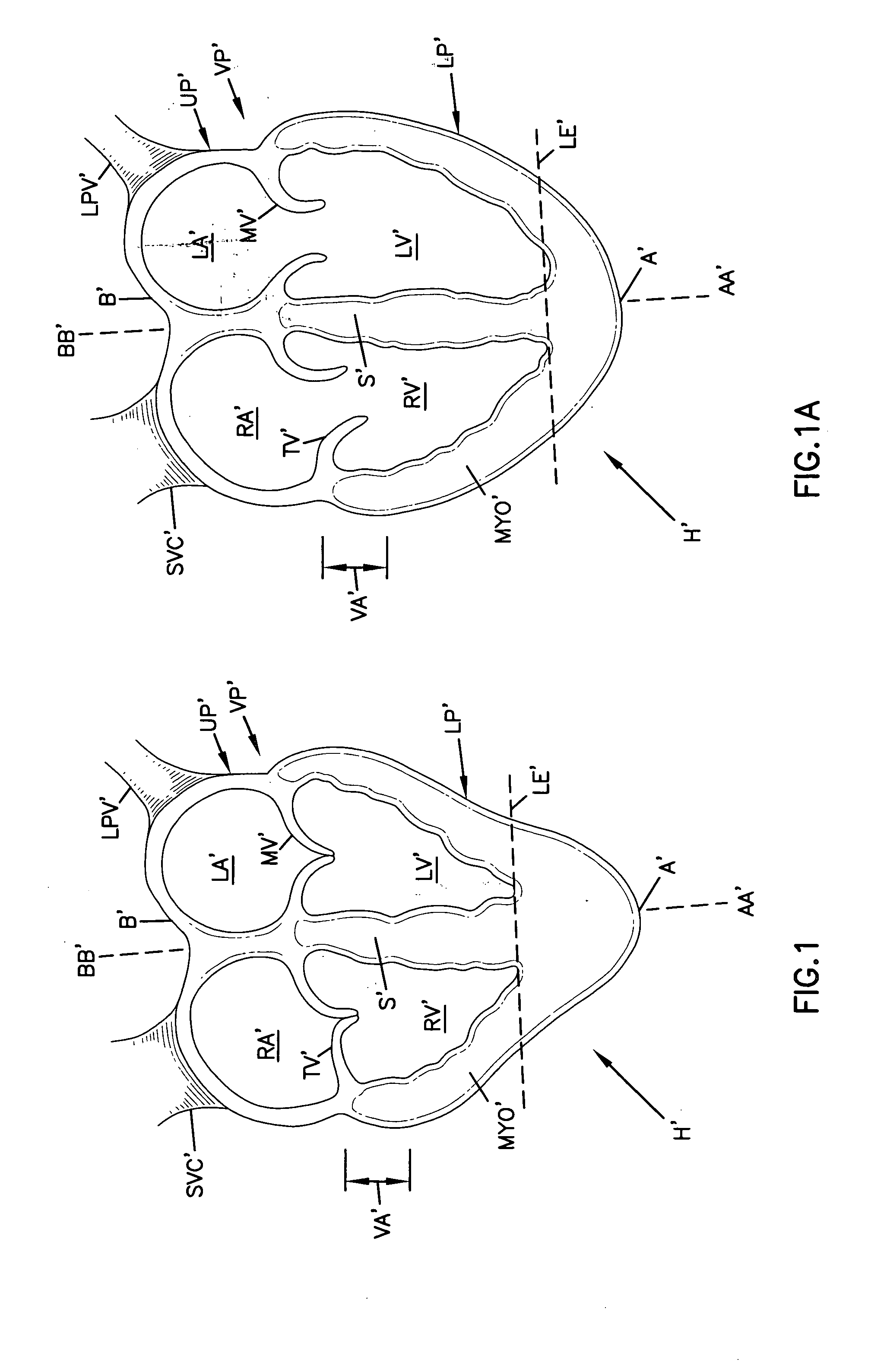
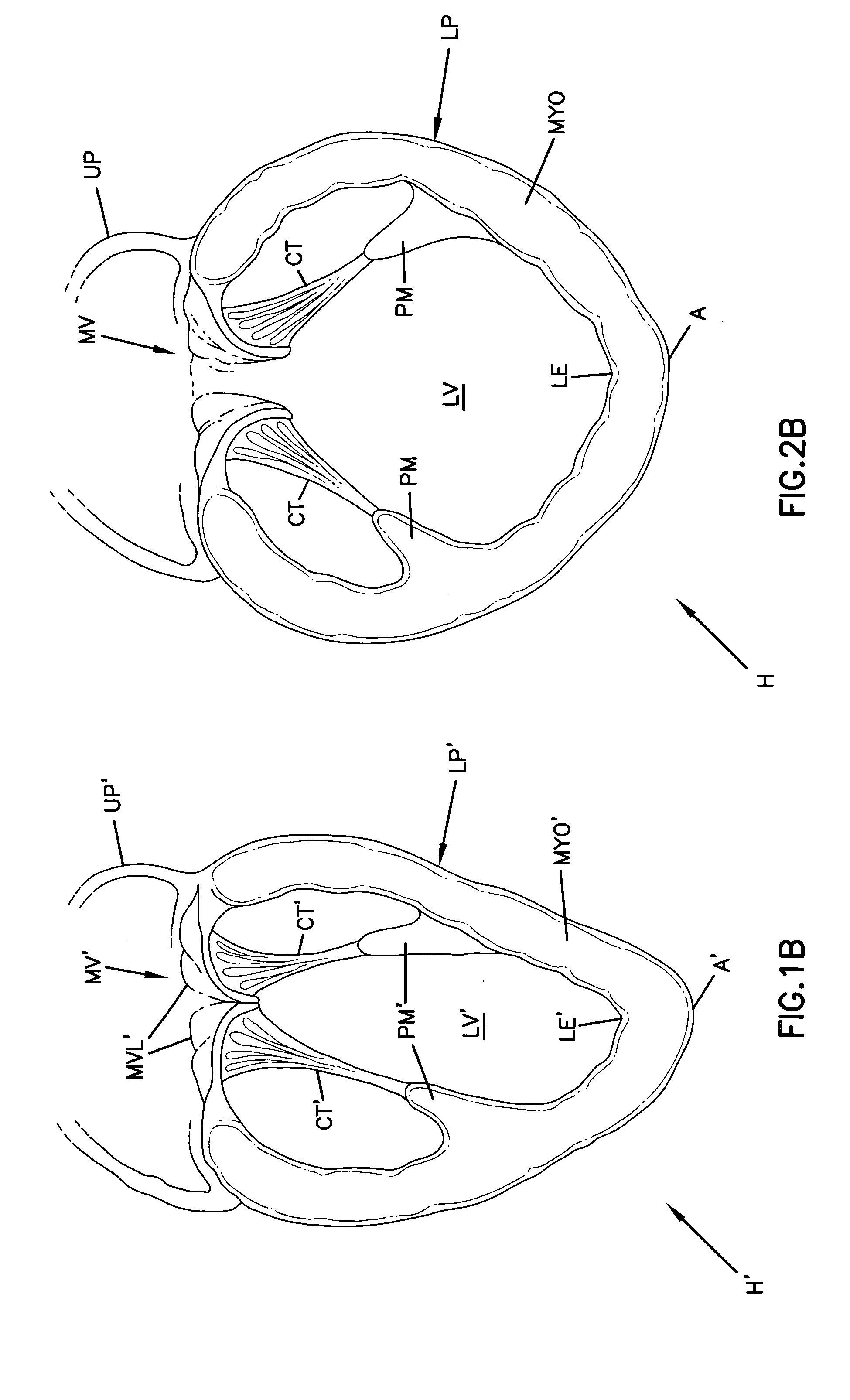
Cardiac support device
InactiveUS20050085688A1Resist dilatationReduce additionalEar treatmentHeart valvesCardiologyCardiac support
A highly compliant and elastic cardiac support device is provided. The device is constructed from a biocompatible material is applied to an external surface of a heart. The device can be used to resist dilatation of the heart, to provide acute wall support, or to enhance reduction in the size of the heart using stored potential energy, without interfering with systolic contraction.
Owner:ACORN CARDIOVASCULAR
Ferroelectric tunnel fet switch and memory
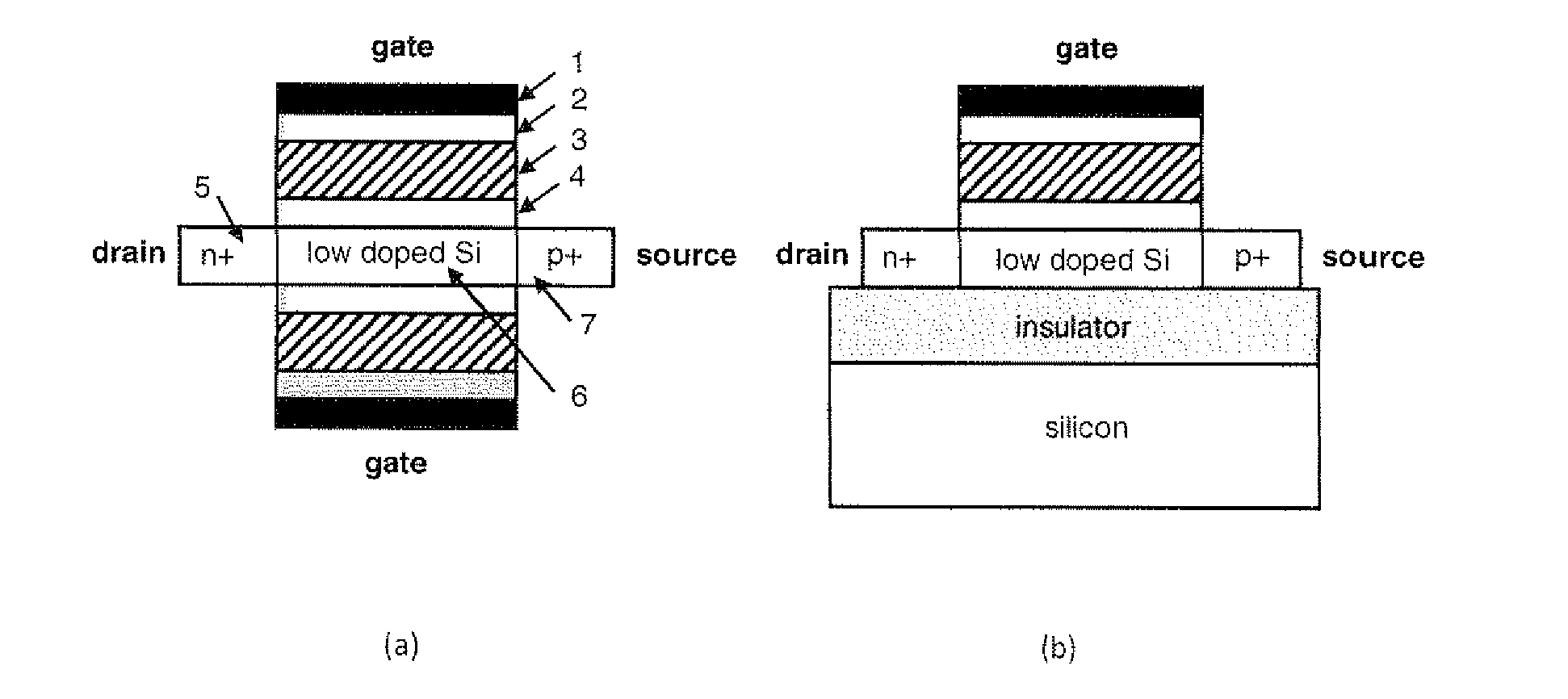
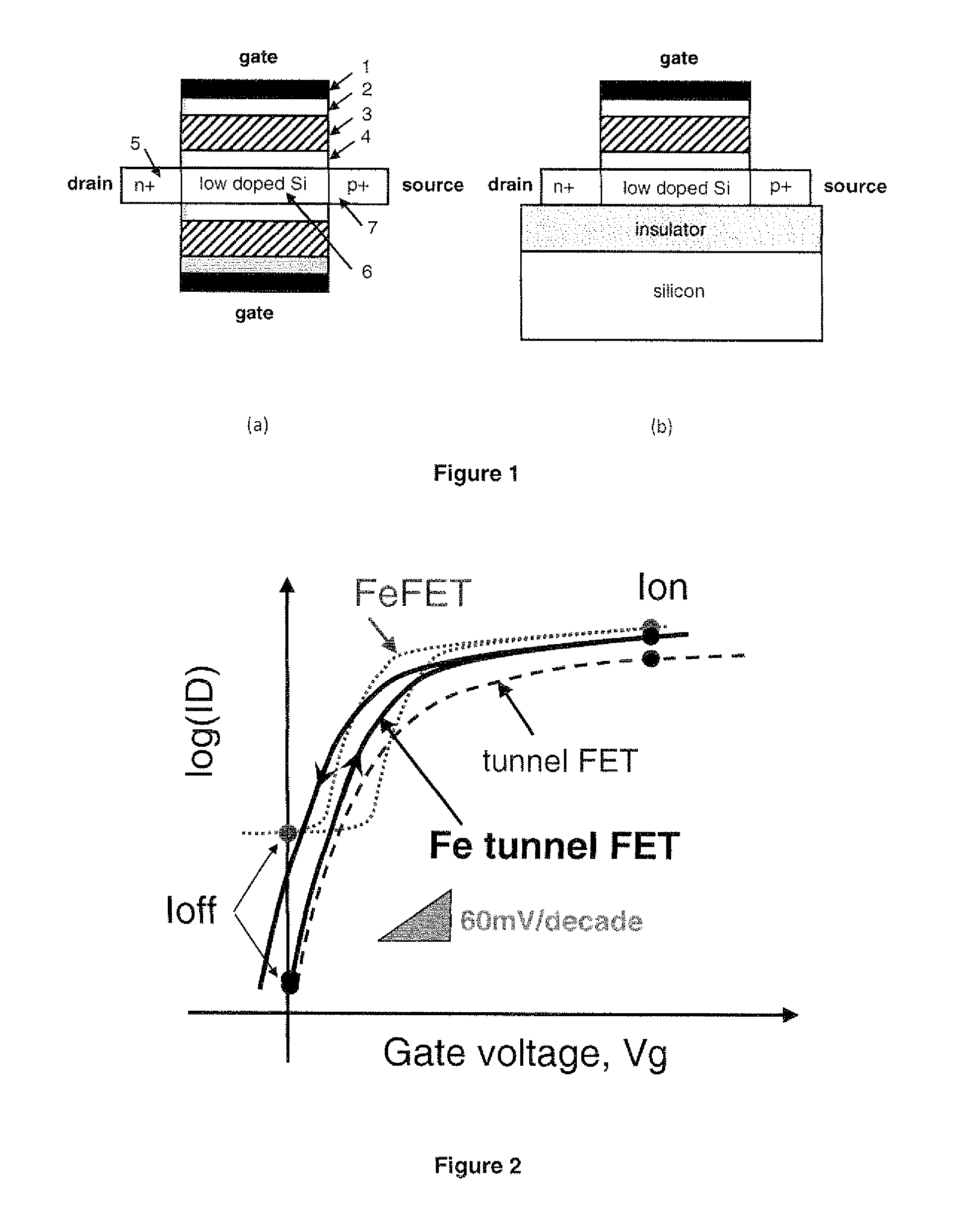
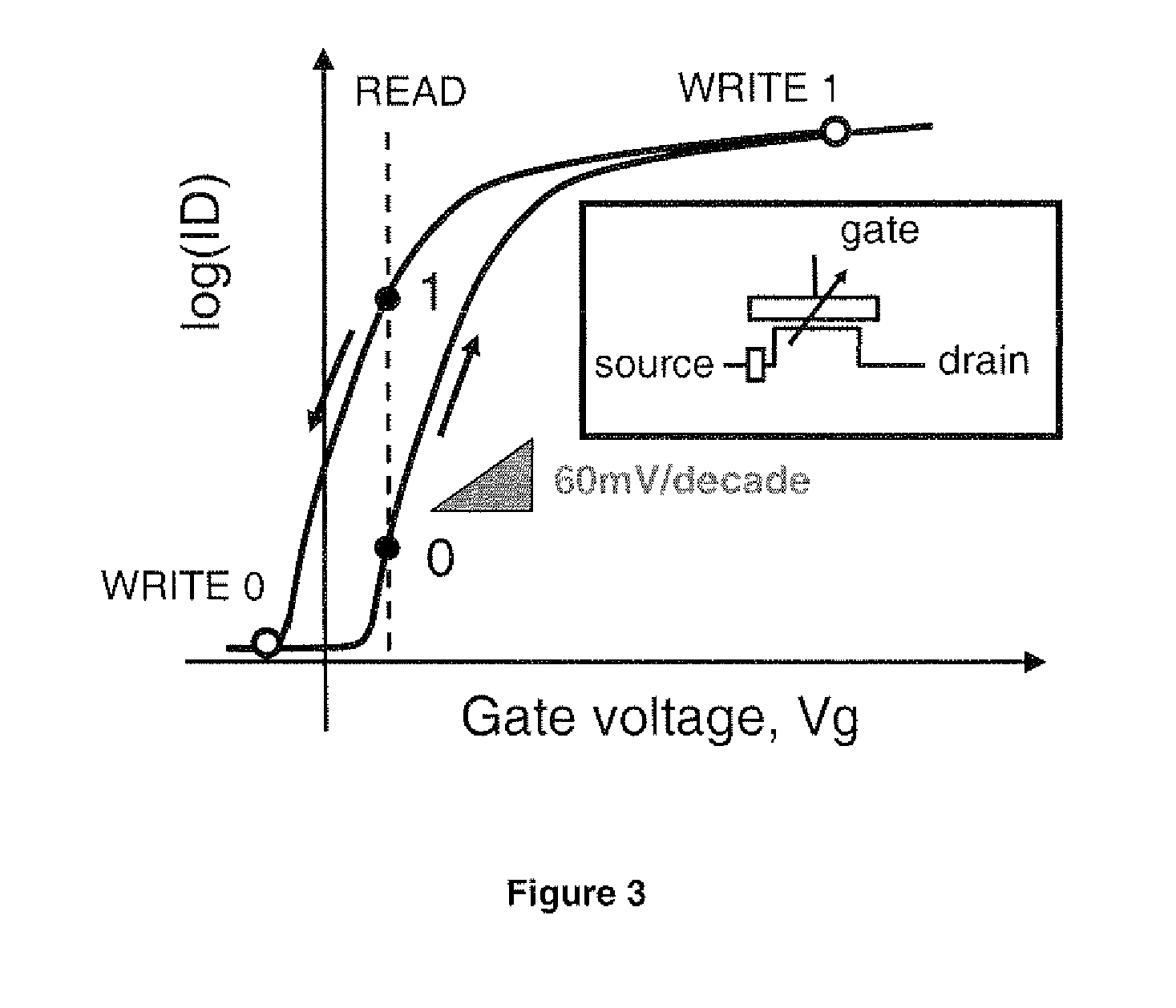
ActiveUS20100140589A1Reduce power consumptionLimited successMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceSubthreshold swing
A Ferroelectric tunnel FET switch as ultra-steep (abrupt) switch with subthreshold swing better than the MOSFET limit of 60 mV / decade at room temperature combining two key principles: ferroelectric gate stack and band-to-band tunneling in gated p-i-n junction, wherein the ferroelectric material included in the gate stack creates, due to dipole polarization with increasing gate voltage, a positive feedback in the capacitive coupling that controls the band-to-band (BTB) tunneling at the source junction of a silicon p-i-n reversed bias structure, wherein the combined effect of BTB tunneling and ferroelectric negative capacitance offers more abrupt off-on and on-off transitions in the present proposed Ferroelectric tunnel FET than for any reported tunnel FET or any reported ferroelectric FET.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
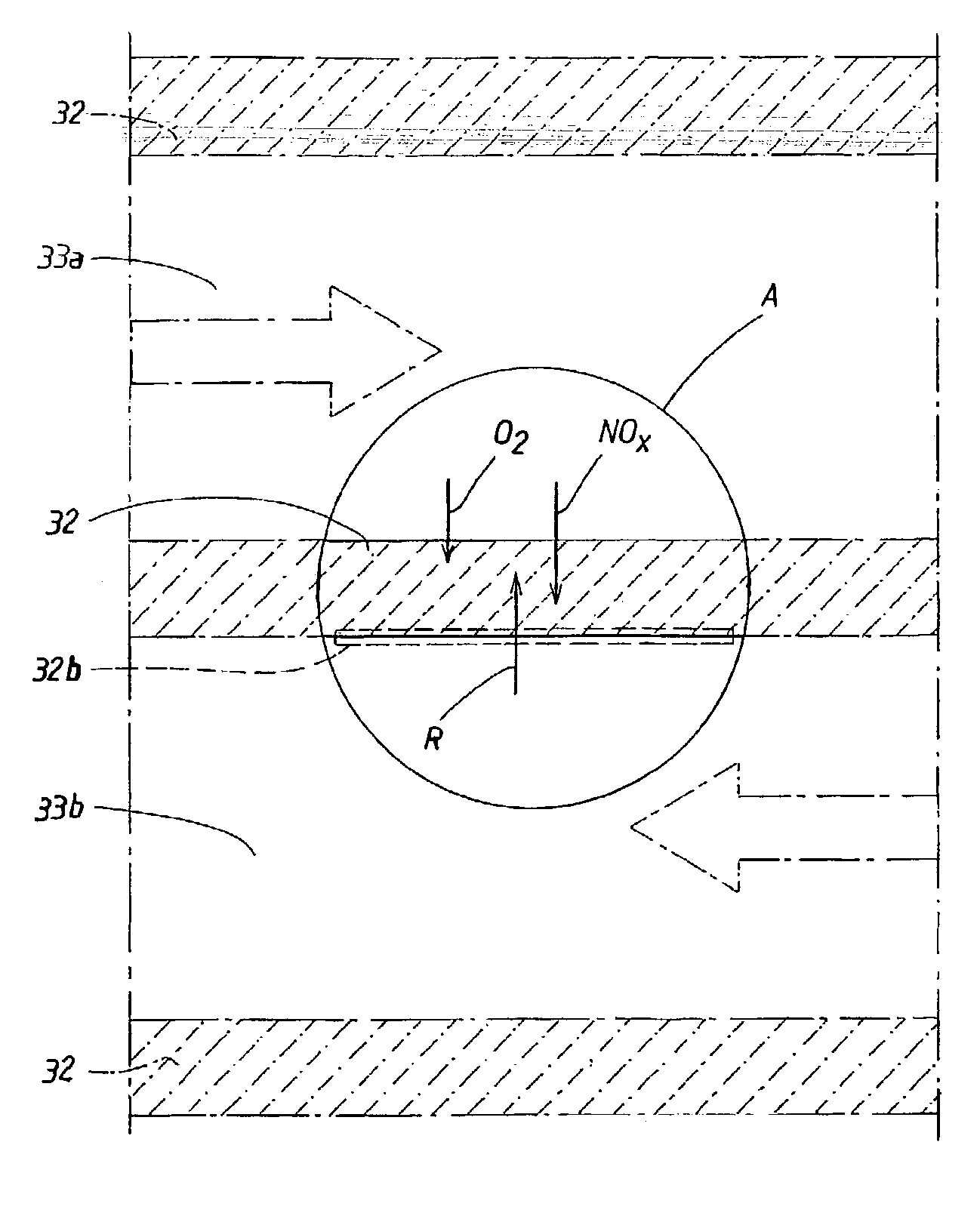
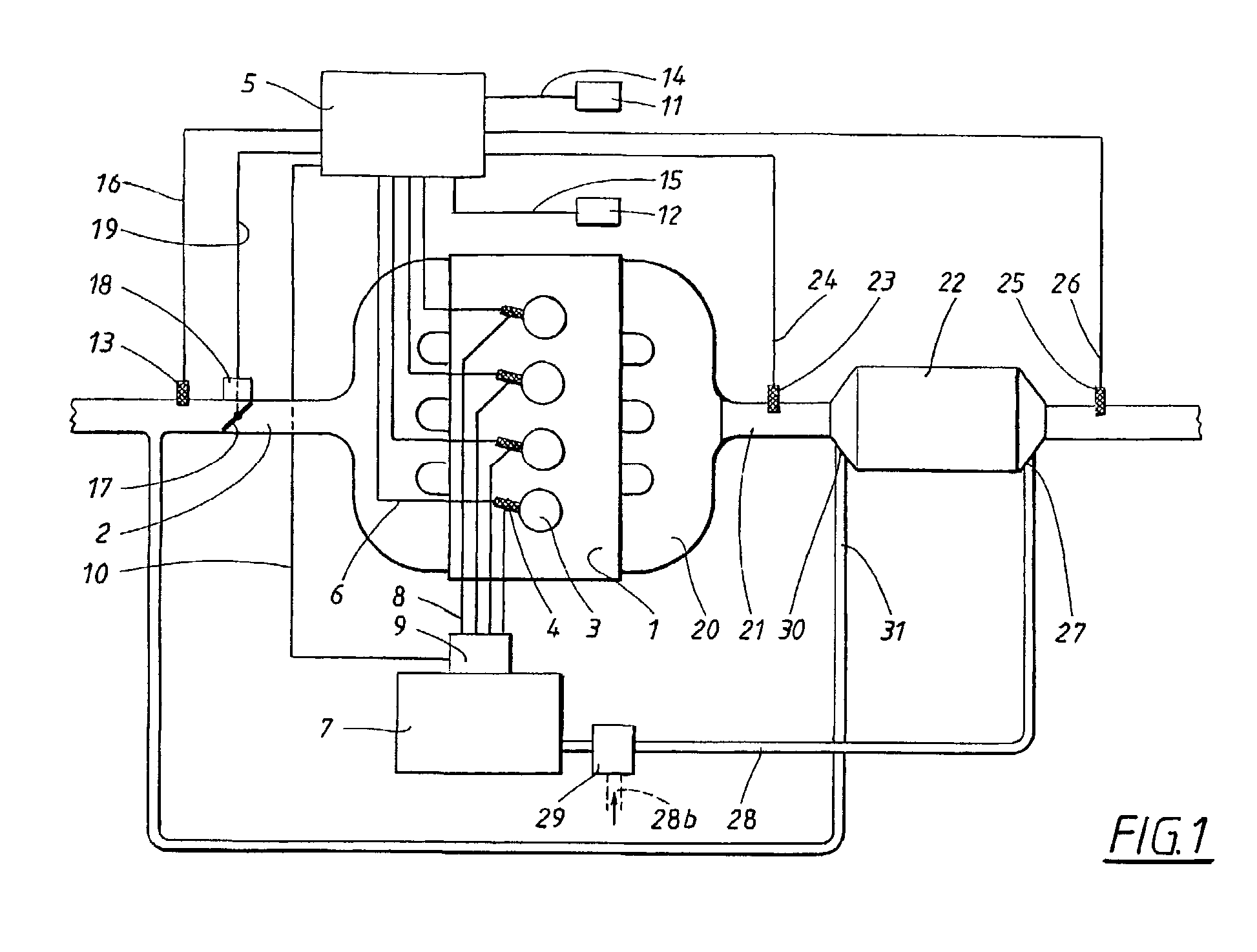
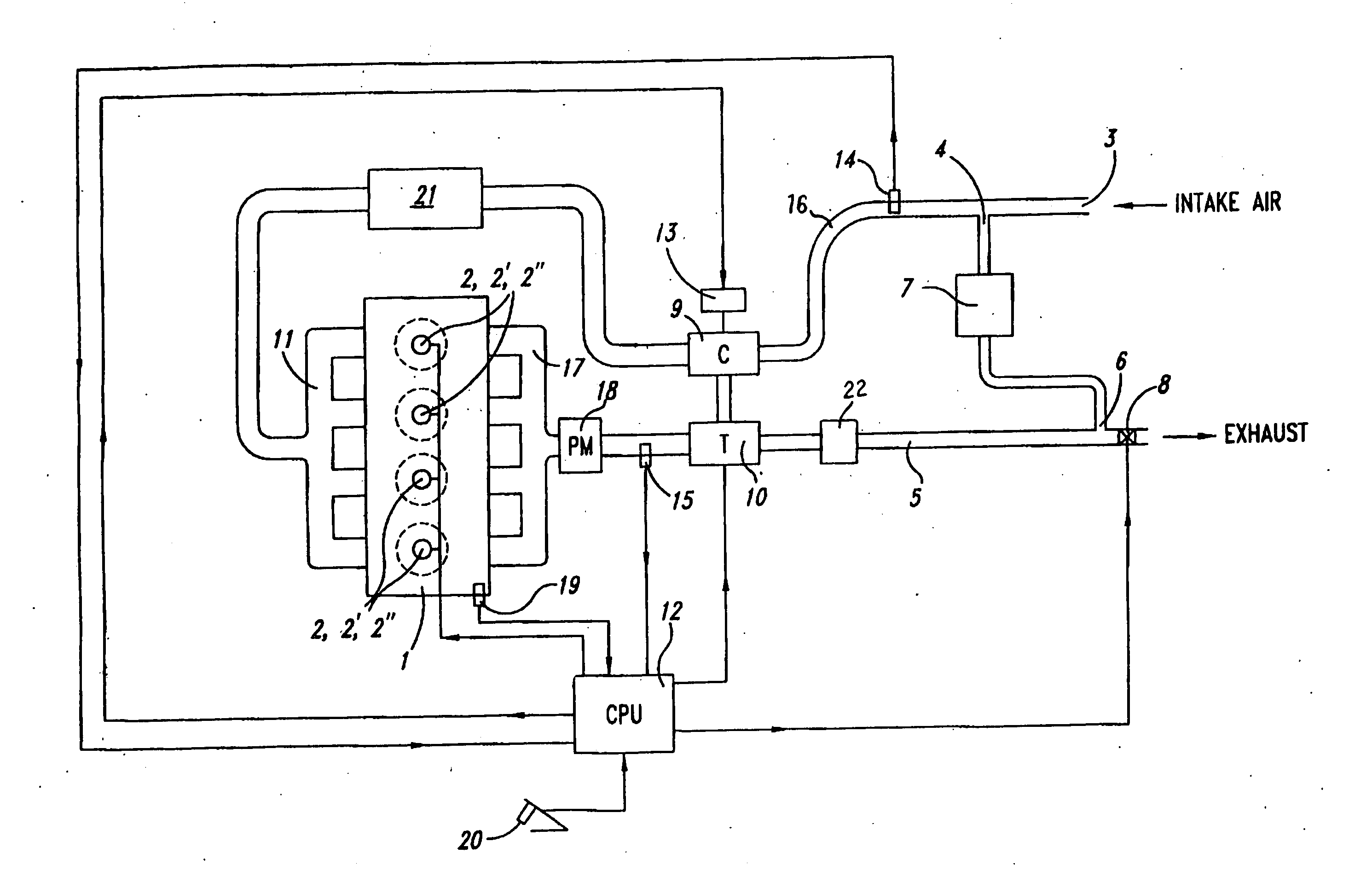
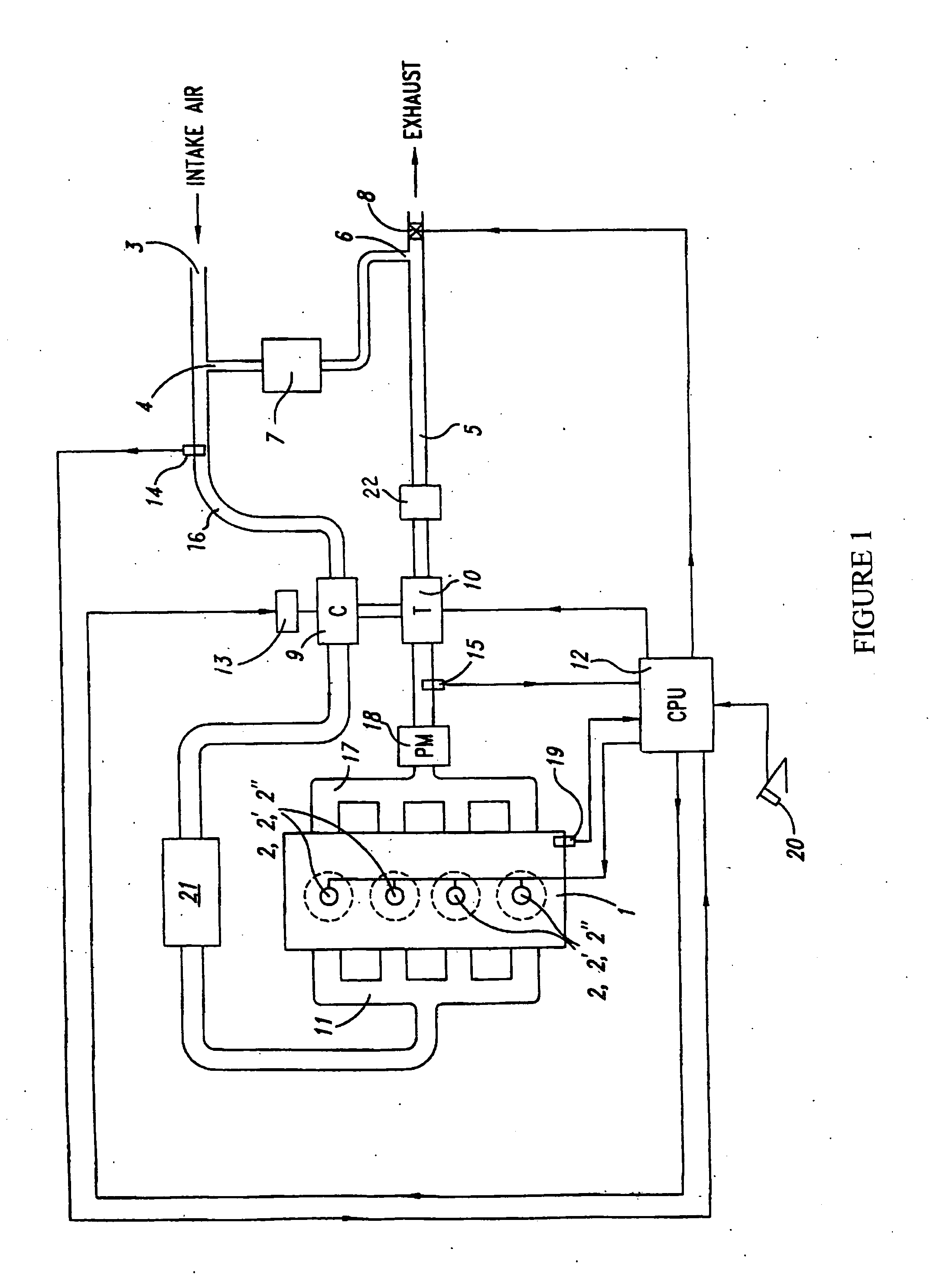
Emission control system for vehicles powered by diesel engines
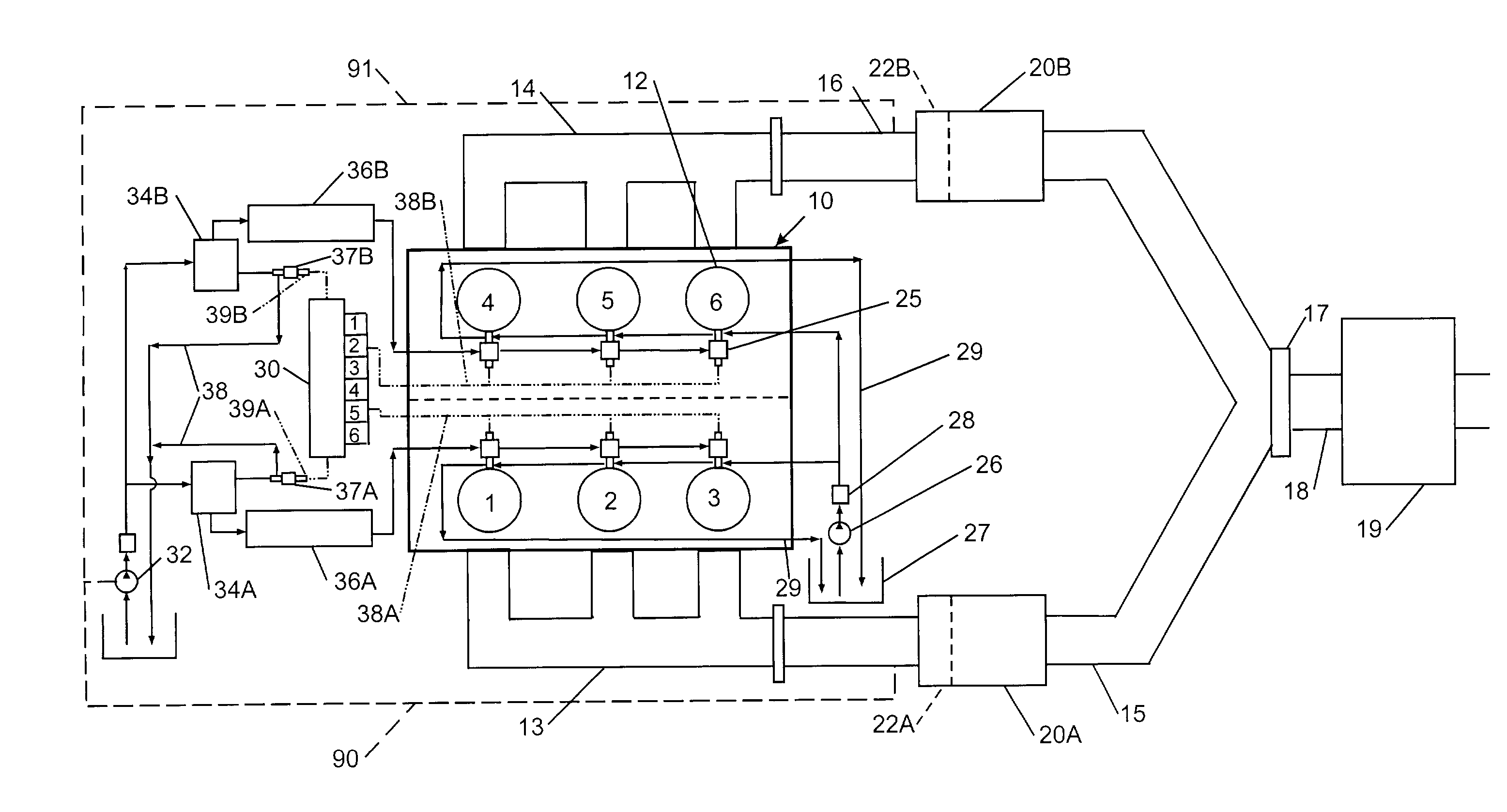
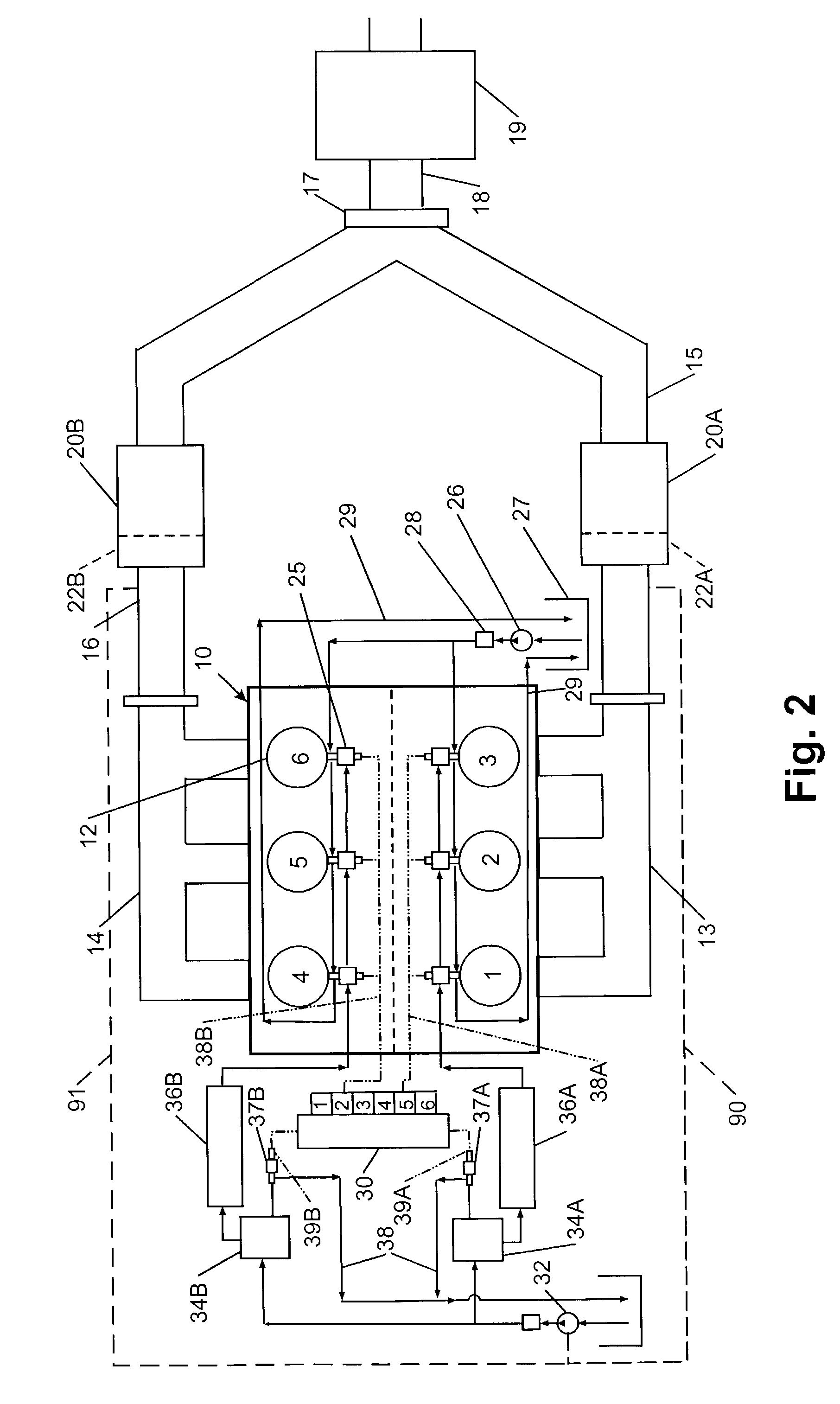
InactiveUS7055311B2Increase efficiencyStrong affinityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust gasExhaust fumes
An NOx emission system for diesel powered vehicles has a “Y” exhaust system with an NOx adsorber catalyst in each leg and an oxidation catalyst in the combined leg. One bank of cylinders sends exhaust gases to one of the “Y” legs while a second bank of cylinders send exhaust gases to the other “Y” leg. Composition of the exhaust gases in each leg is independently controlled by the engine's ECU so that exhaust gases in one leg are rich for regenerating the NOx adsorber catalyst in that leg while exhaust gas composition in the other leg is lean so that the combined gas stream is always lean and reductant slip is oxidized in the oxidation catalyst.
Owner:ENGELHARD CORP
Wireless power transmission system
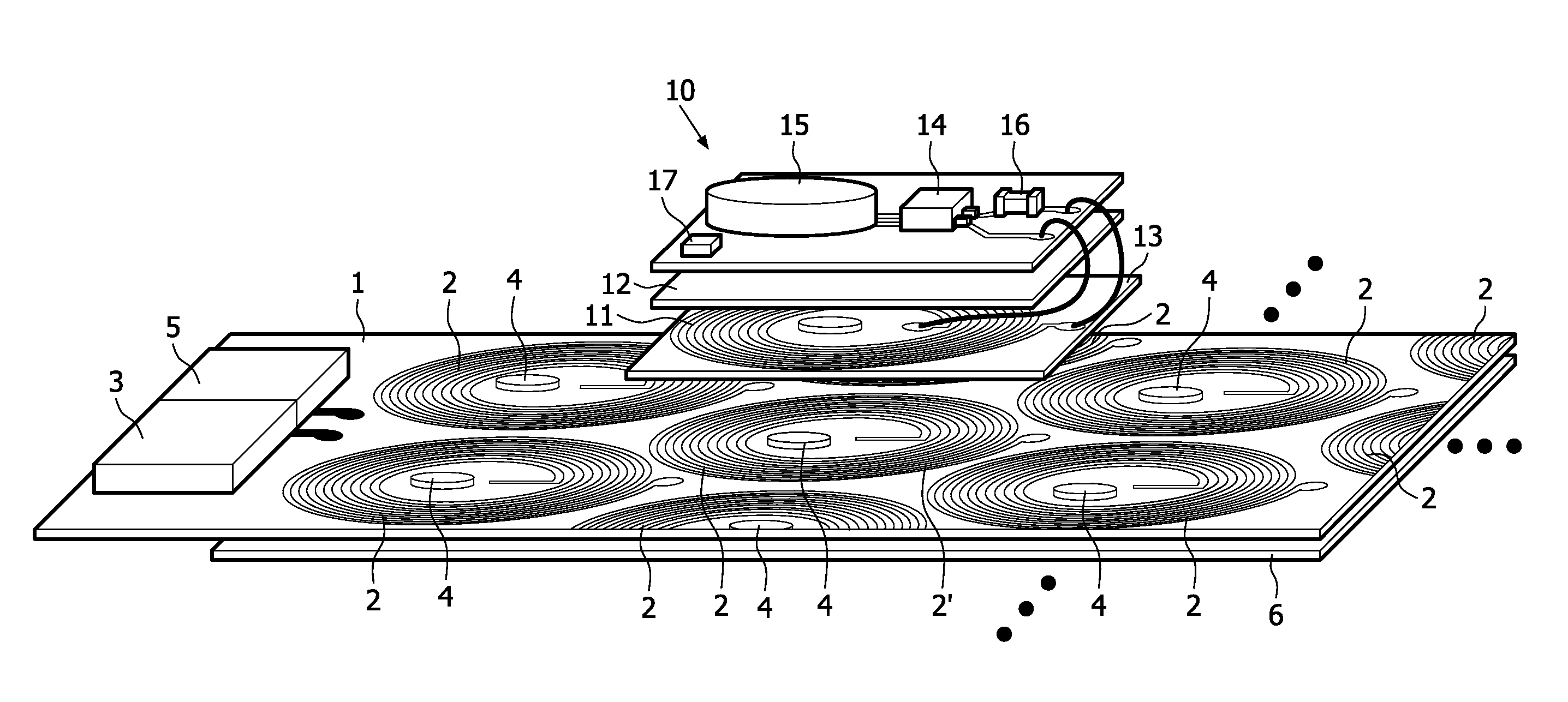
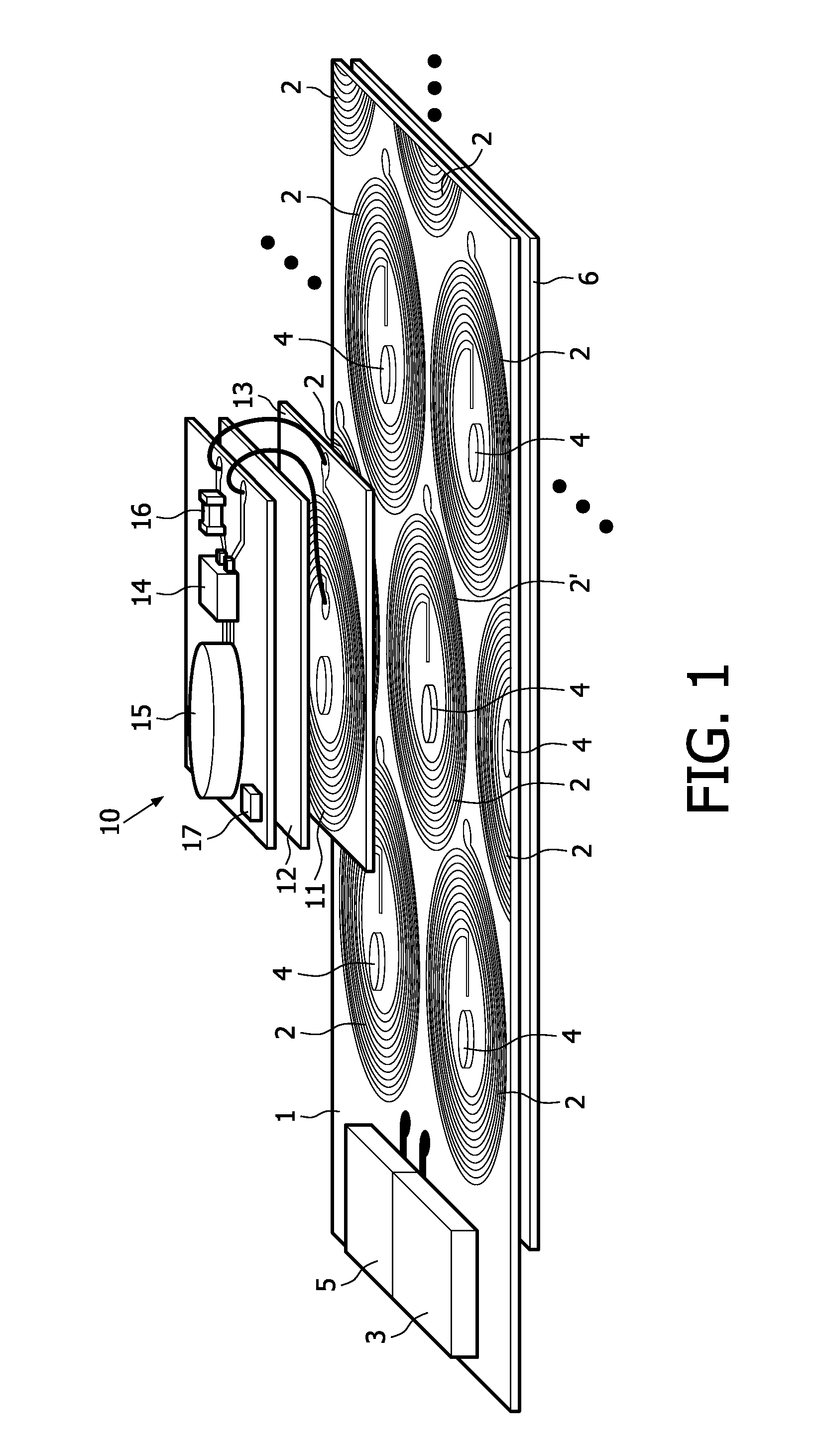
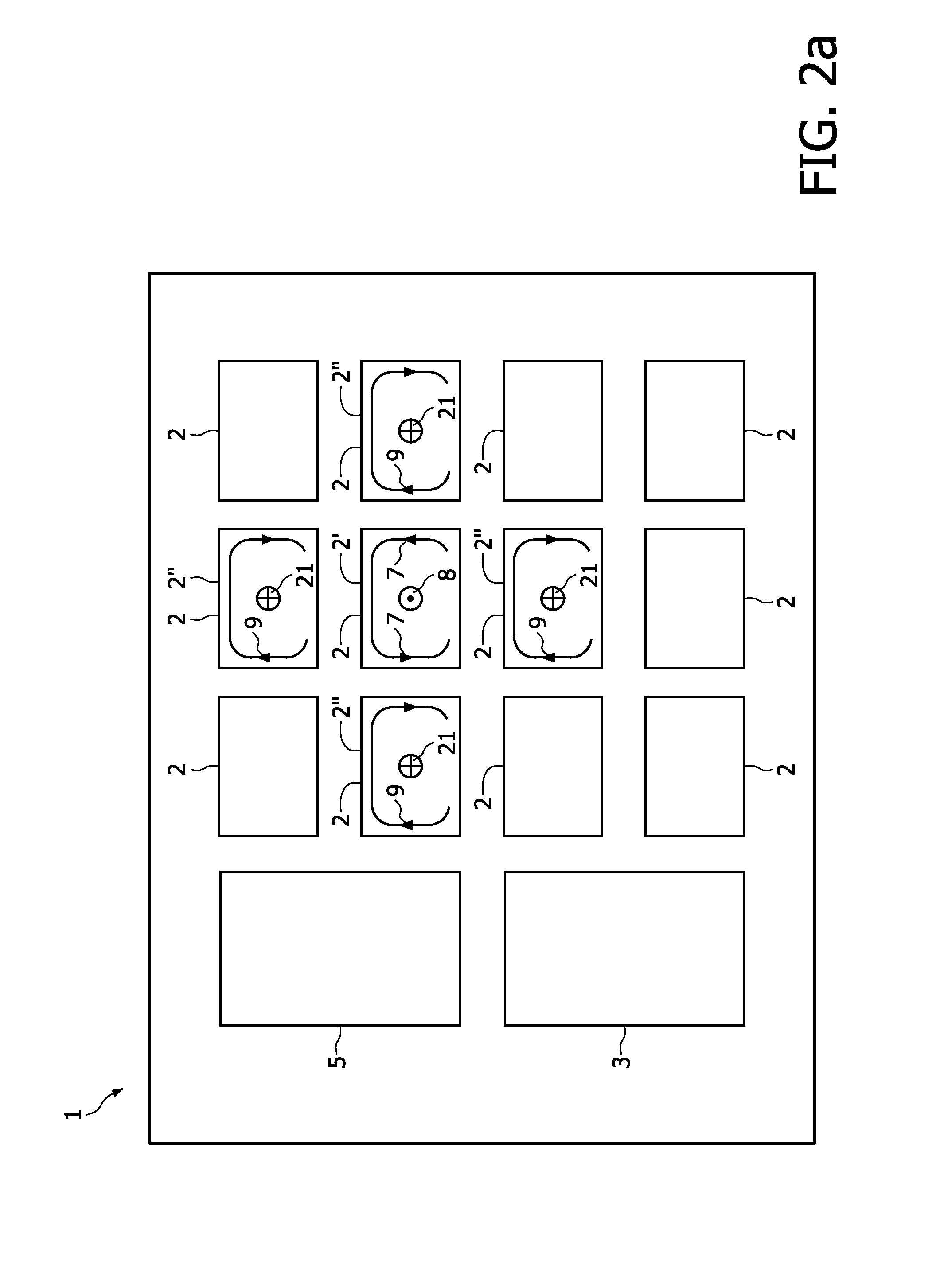
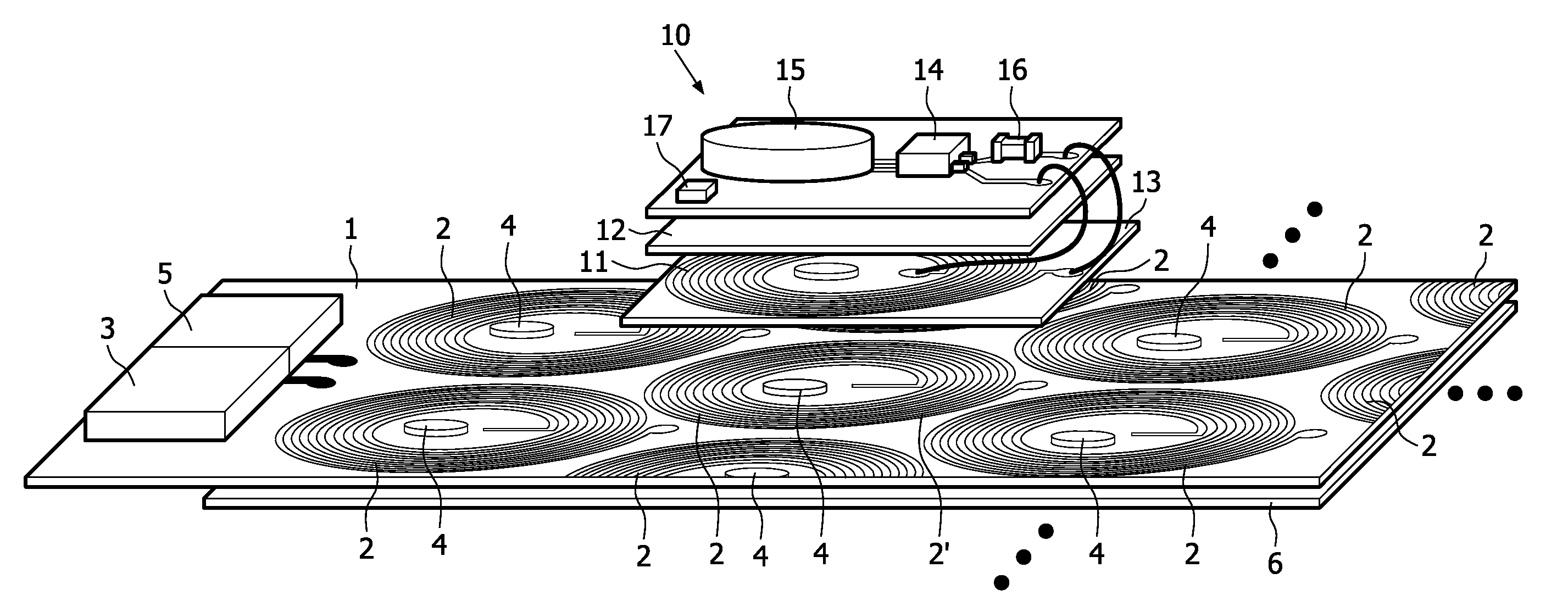
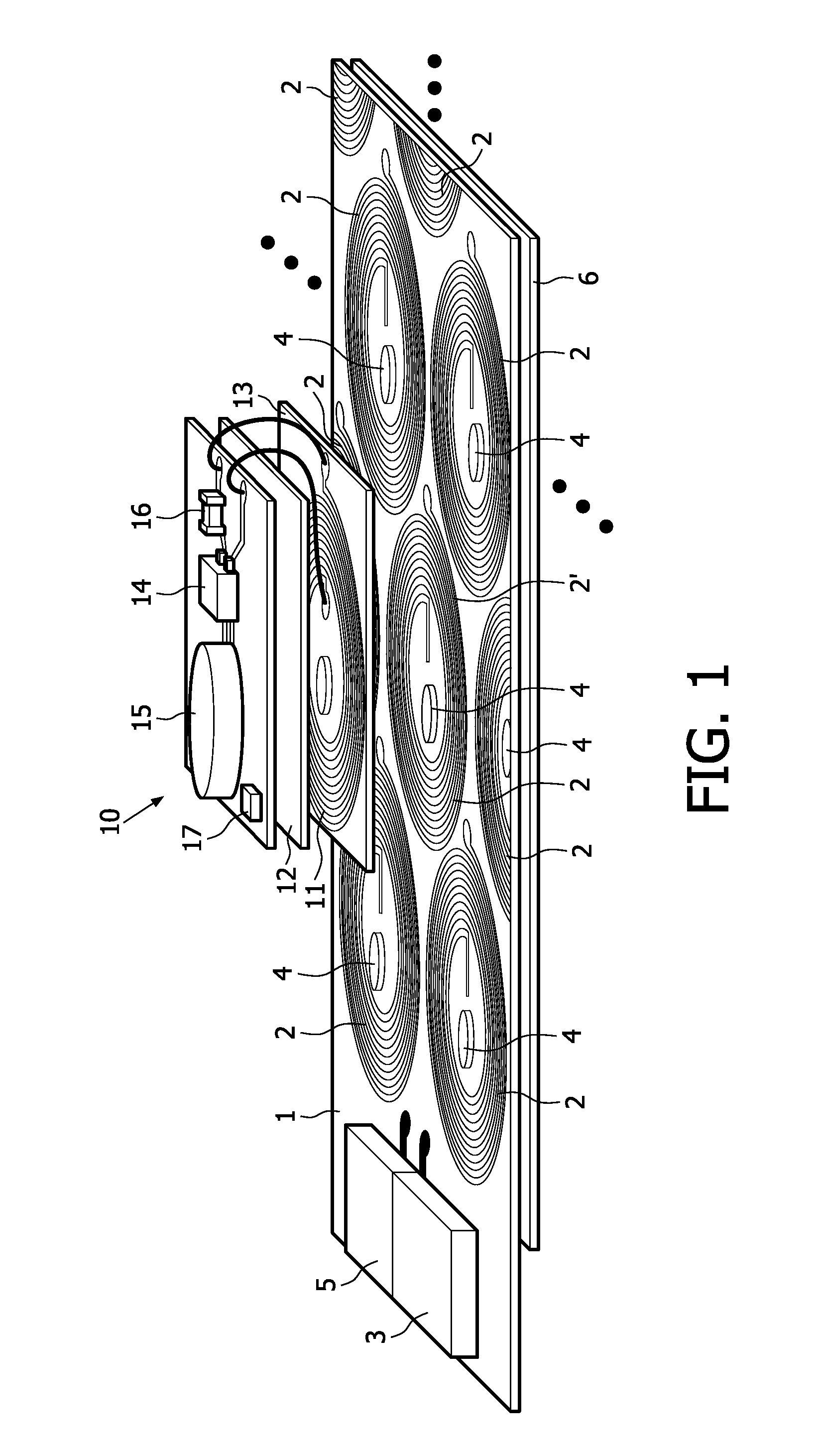
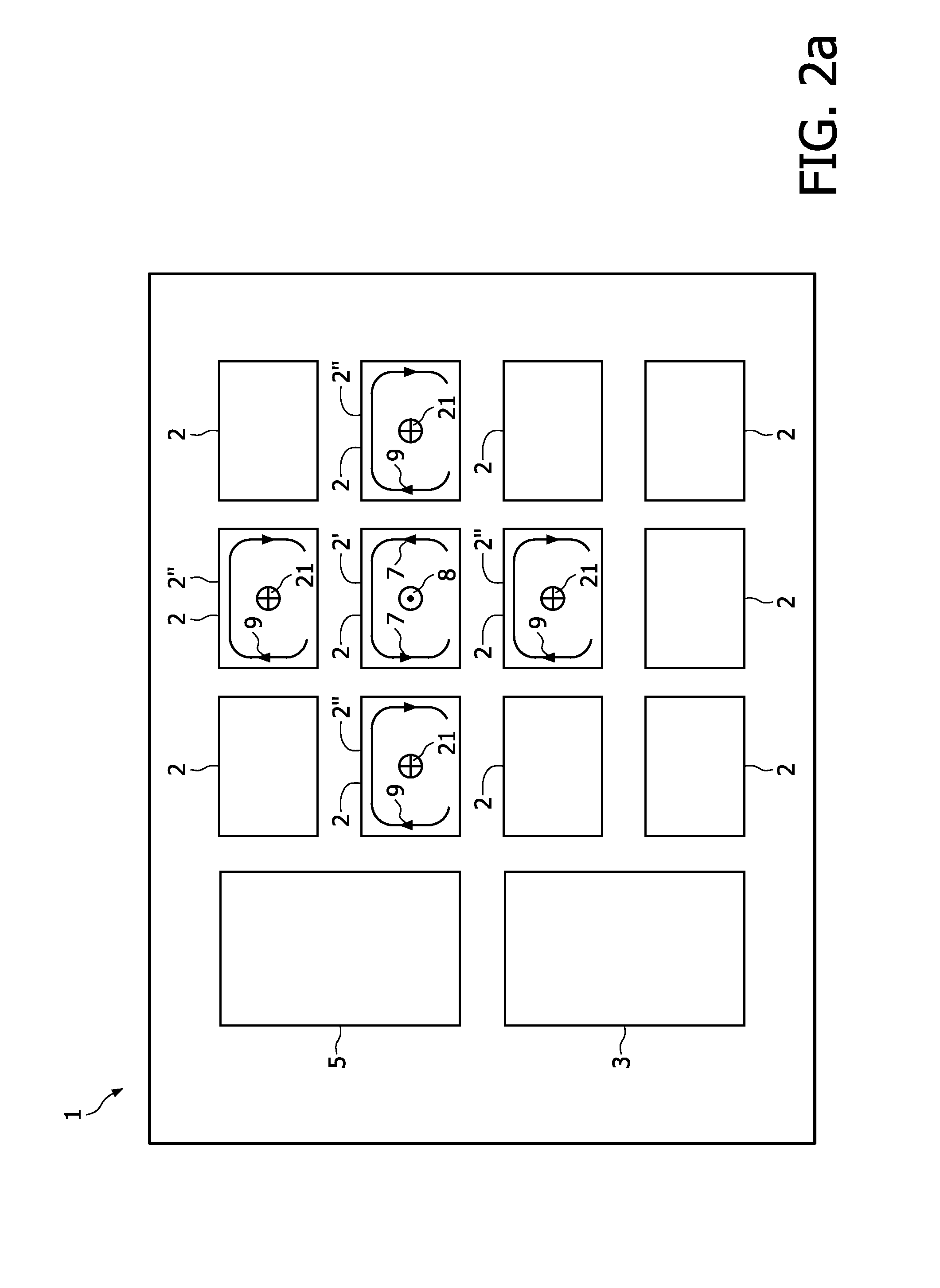
ActiveUS20110025133A1Efficient preparationEffectively cancellingNear-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemTelecommunicationsInductor
A Wireless power transmission system comprises a base unit (1) with multiple magnetic field generator circuits and a device (10), separable from said base unit (1) having a receiving inductor, adapted to receive power inductively when said device (10) is in proximity to one of said generator circuits, wherein said base unit (1) comprises a controller (3), configured to determine a transmission circuit (2′) from said generator circuits when said receiving inductor is in proximity to said transmission circuit (2′), whereupon said transmission circuit (2′) is operated to generate a first magnetic field (8), having a first phase, to induce a current in said receiving inductor and at least one of the remaining generator circuits is operated as a compensation circuit (2″, 52, 82) to generate a second magnetic field (21), having an opposite phase to said first phase.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Cardiac support device
InactiveUS20050119519A9Resist dilatationReduce additionalEar treatmentHeart valvesCardiologyCardiac support
A highly compliant and elastic cardiac support device is provided. The device is constructed from a biocompatible material is applied to an external surface of a heart. The device can be used to resist dilatation of the heart, to provide acute wall support, or to enhance reduction in the size of the heart using stored potential energy, without interfering with systolic contraction.
Owner:MARDIL
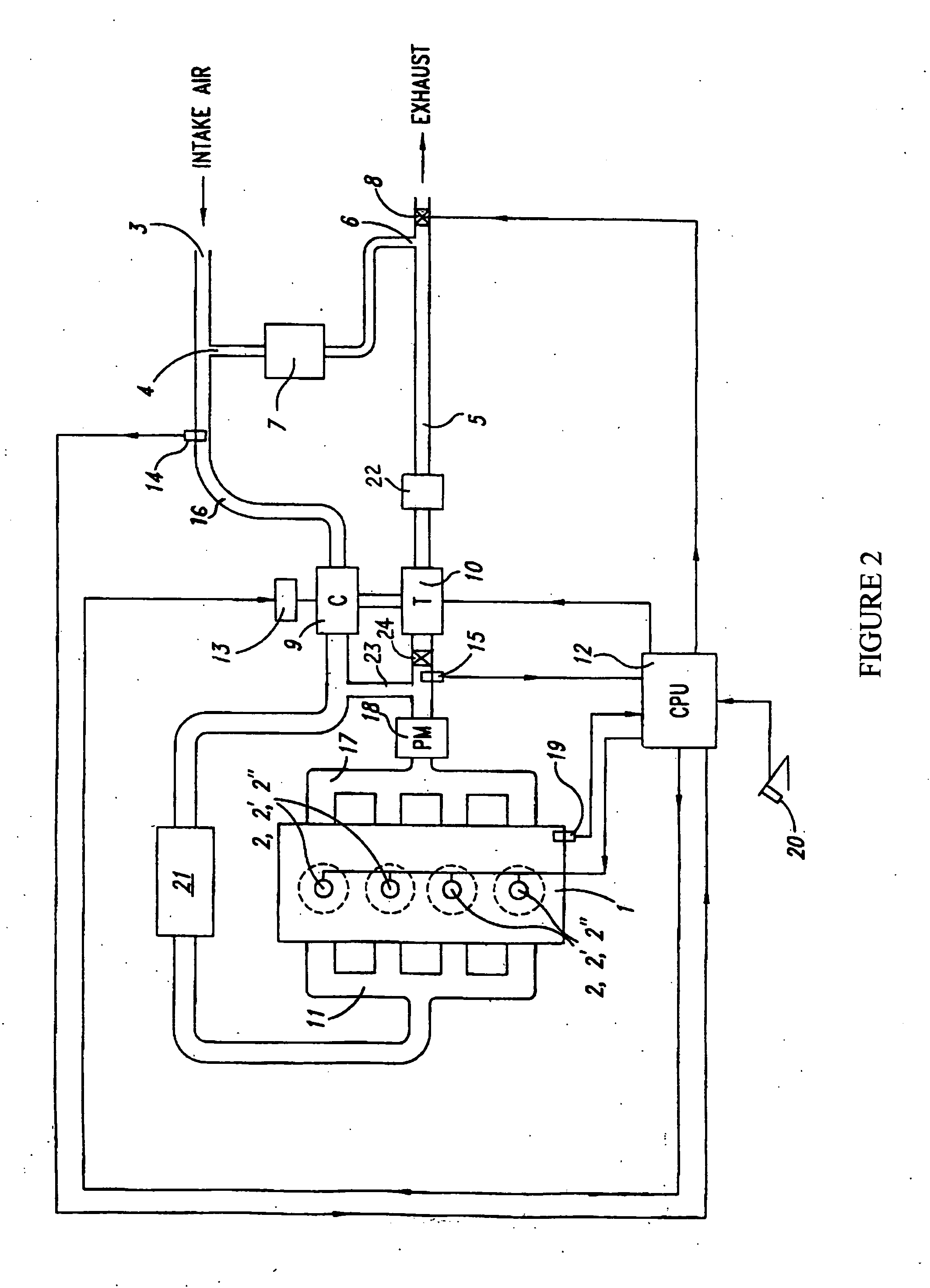
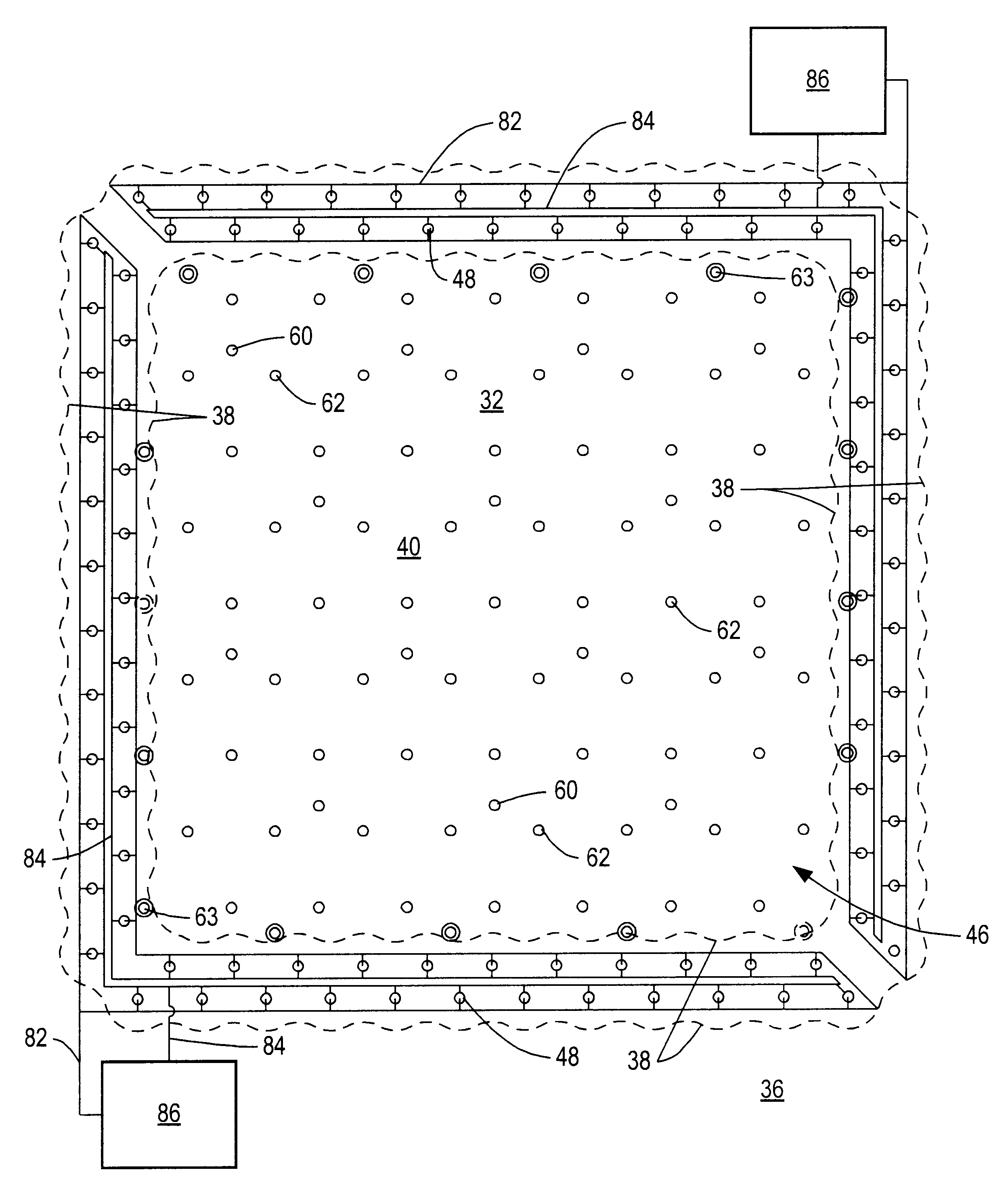
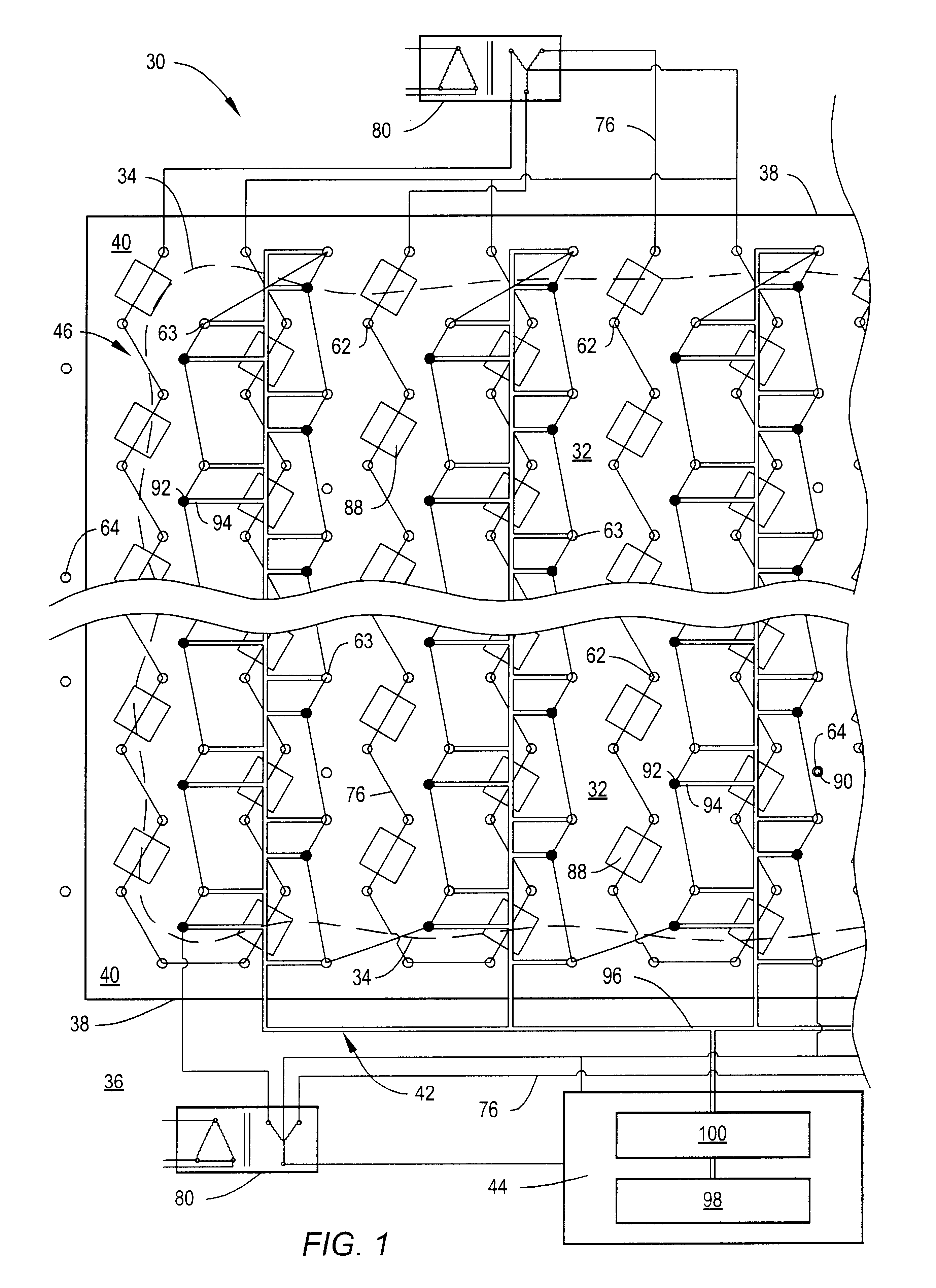
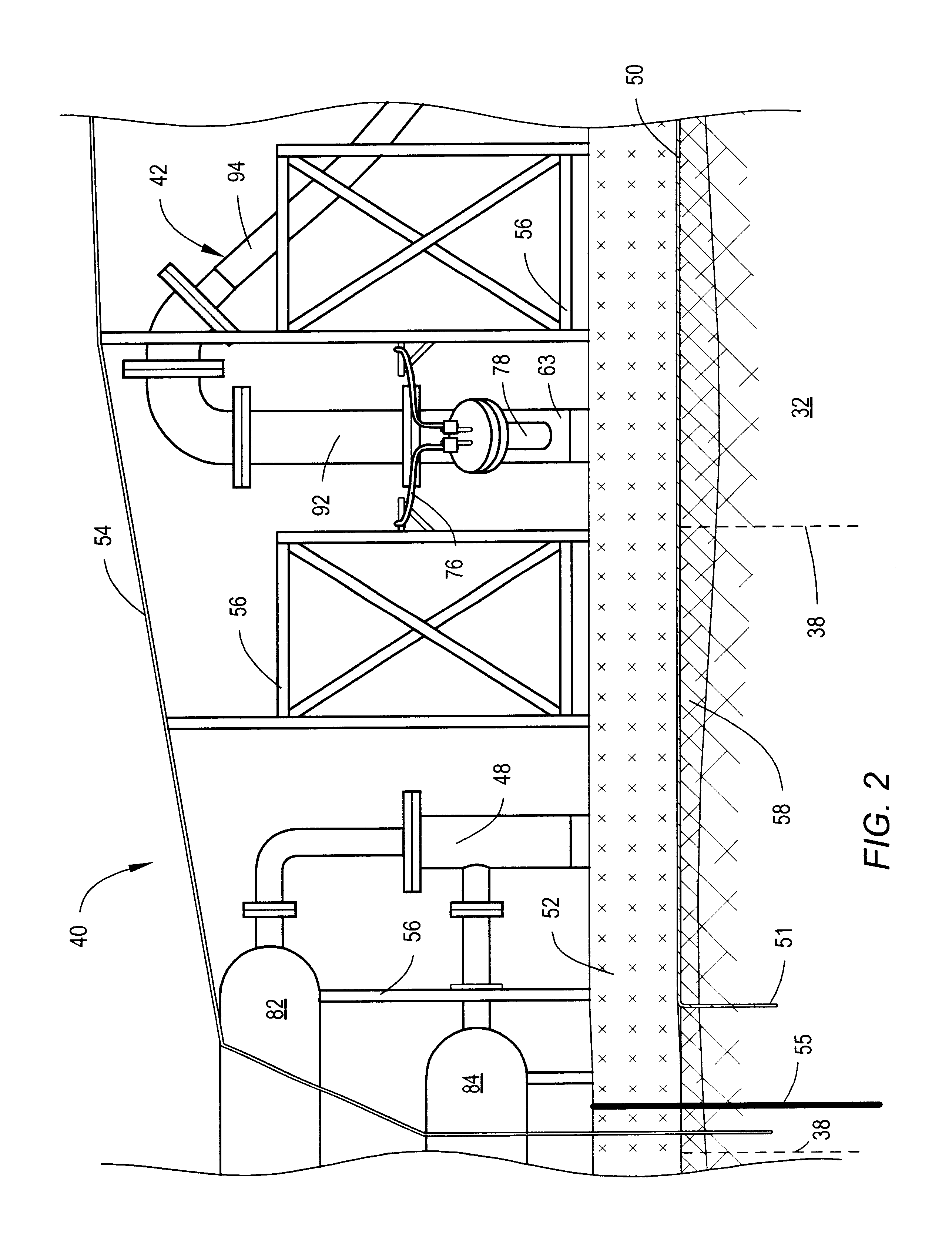
Device and method for reduction of a gas component in an exhaust gas flow of a combustion engine
InactiveUS8065870B2Reduce the amount requiredEasy dischargeCombination devicesElectrical controlCombustionProcess engineering
Method and device for reduction of a gas component in an exhaust gas flow of a combustion engine (1) that is adapted for operation by a lean air / fuel mixture. An exhaust pipe (21) is included for transport of the exhaust gas flow from the engine (1). A separation unit (22) is also included that is arranged along the exhaust pipe (21), which separation unit (22) has a wall structure (32) of a material which provides separation of the gas component from the exhaust gas flow by means of a selective passage of the gas component before other gas components in the exhaust gas flow. The method provides for a reduction and a separation unit that is intended to be utilized during such a reduction. An improved reduction of in particular NOx compounds from a so-called “lean-burn” engine is also provided.
Owner:VOLVO TECH
Wireless power transmission system
ActiveUS8810071B2Improve electromagnetic compatibilityReduces the magnetic stray fieldNear-field transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionInductor
A Wireless power transmission system comprises a base unit (1) with multiple magnetic field generator circuits and a device (10), separable from said base unit (1) having a receiving inductor, adapted to receive power inductively when said device (10) is in proximity to one of said generator circuits, wherein said base unit (1) comprises a controller (3), configured to determine a transmission circuit (2′) from said generator circuits when said receiving inductor is in proximity to said transmission circuit (2′), whereupon said transmission circuit (2′) is operated to generate a first magnetic field (8), having a first phase, to induce a current in said receiving inductor and at least one of the remaining generator circuits is operated as a compensation circuit (2″, 52, 82) to generate a second magnetic field (21), having an opposite phase to said first phase.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
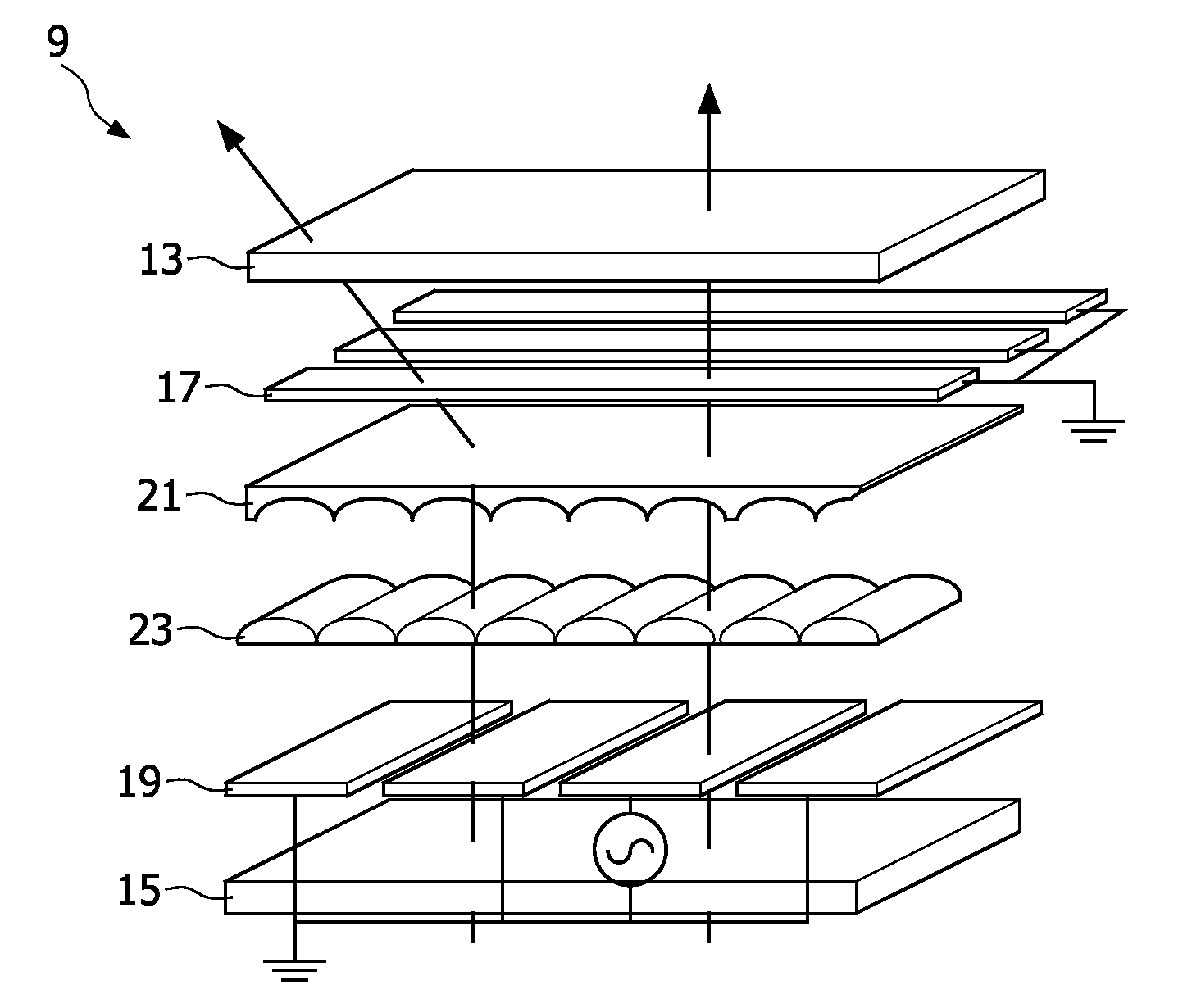
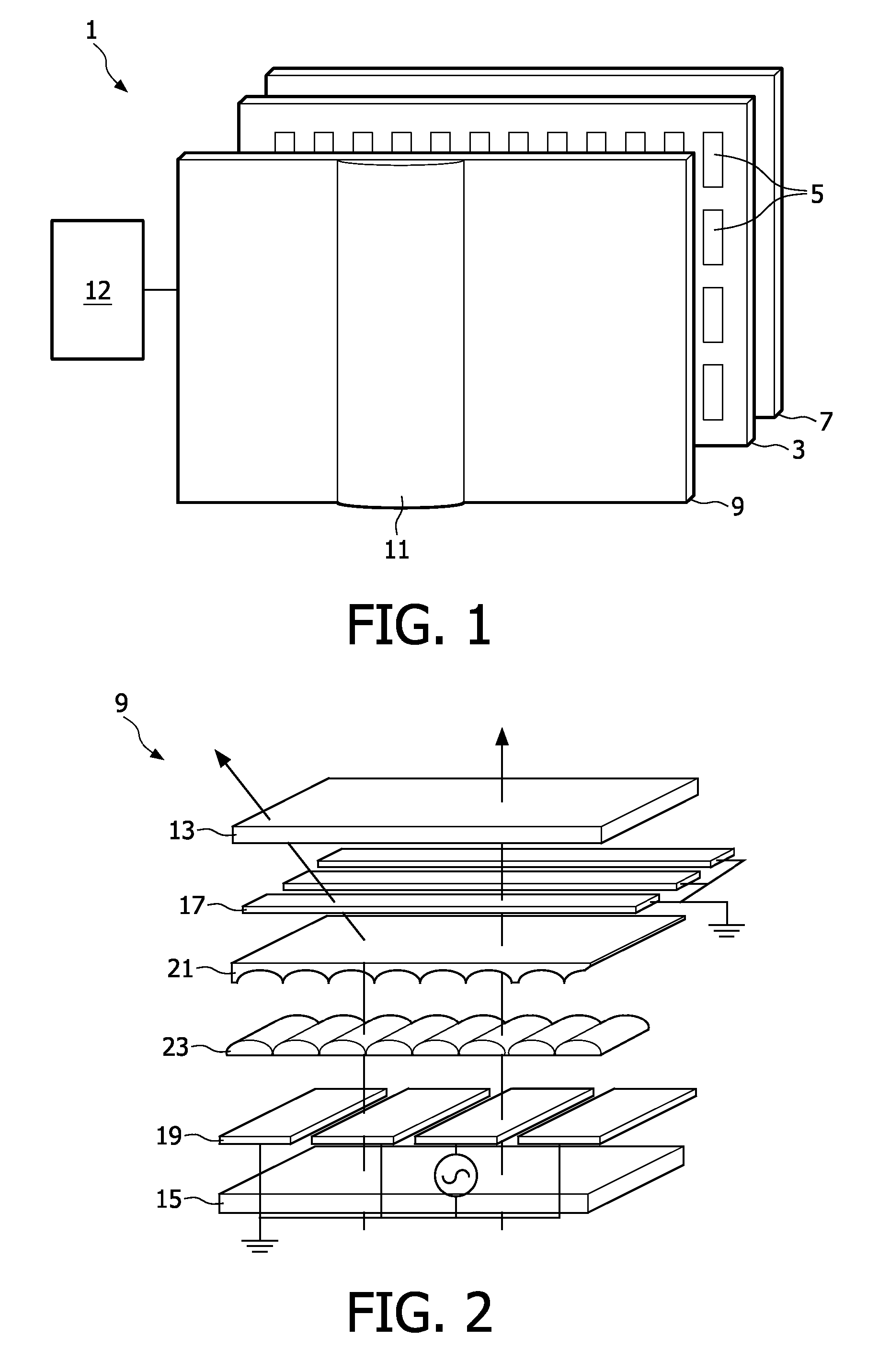
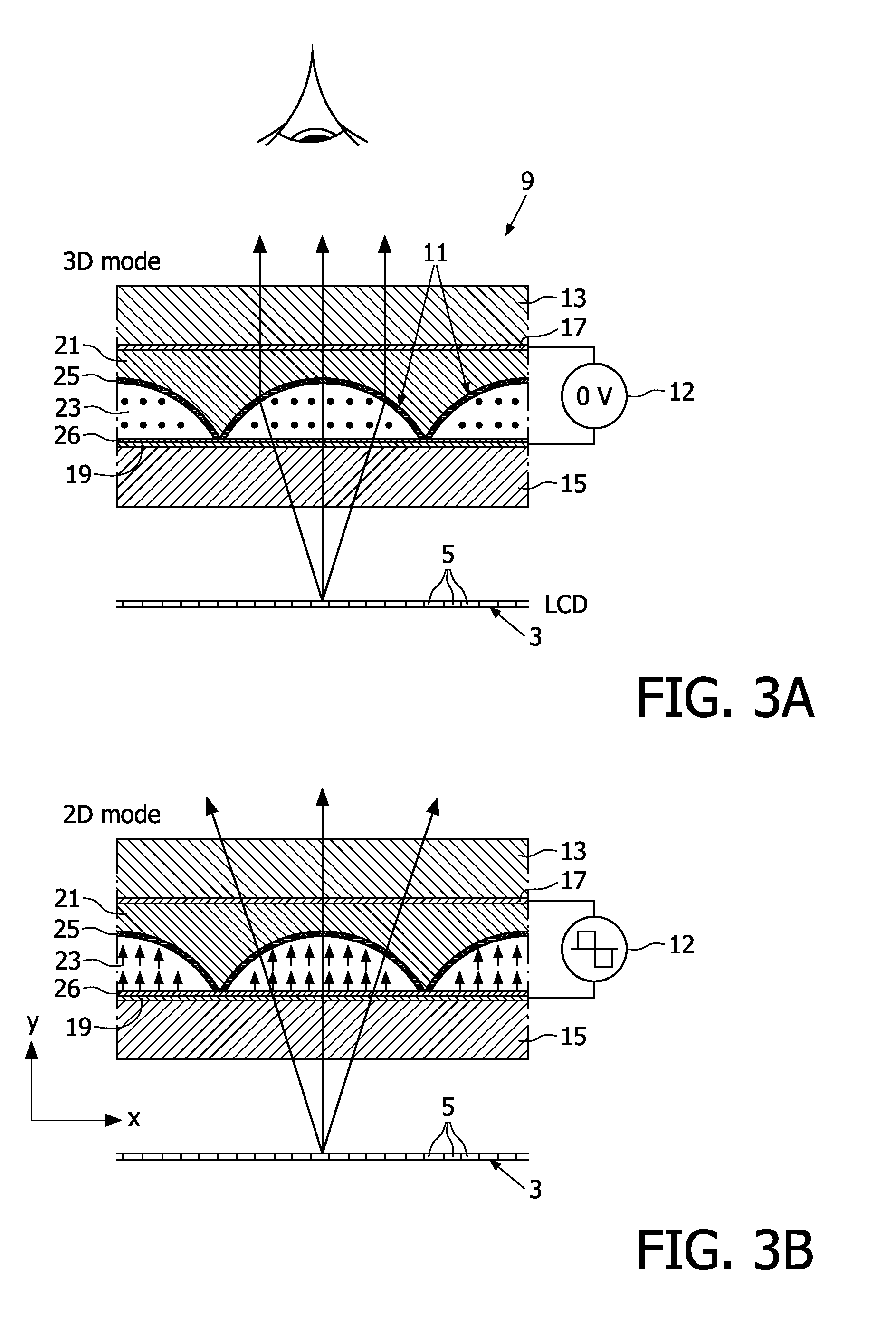
Autostereoscopic display device using controllable liquid crystal lens array for 3d/2d mode switching
ActiveUS20090033812A1Reduce additionalSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsRefractive indexDisplay device
An autostereoscopic display device has an array (9) of lenticular elements (11) overlying a display panel (3), the lenticular elements comprising electro-optic material (23) and being switchable to enable 2D and 3D viewing modes. The electro-optic material, for example liquid crystal material, is contained adjacent an optically transparent layer in the form of a lenticular body (21). A birefringent material is utilized for the lenticular body, preferably with the ordinary and extra-ordinary index of refraction substantially matching that of the electro-optic material.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
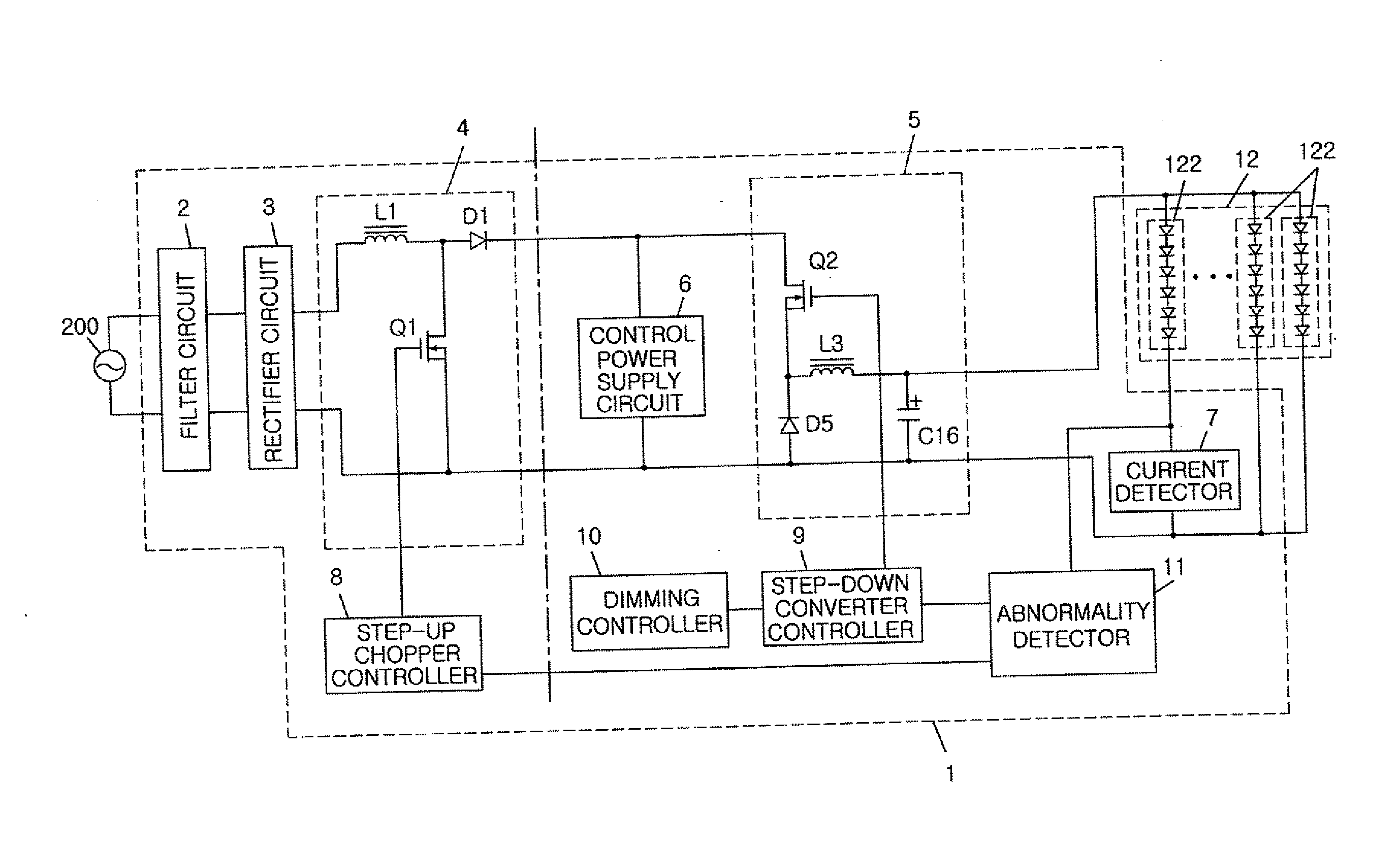
Lighting device and illumination apparatus including same
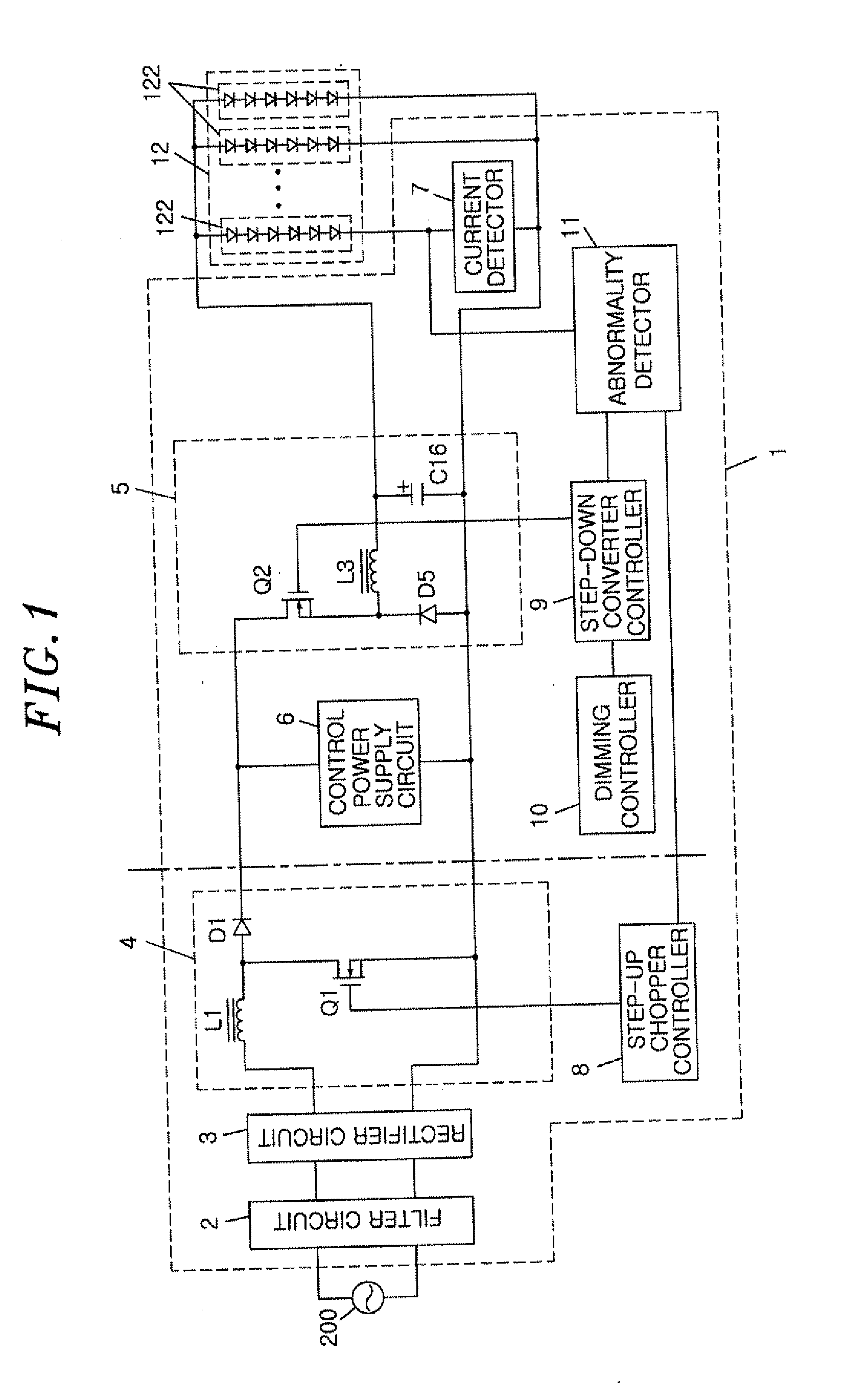
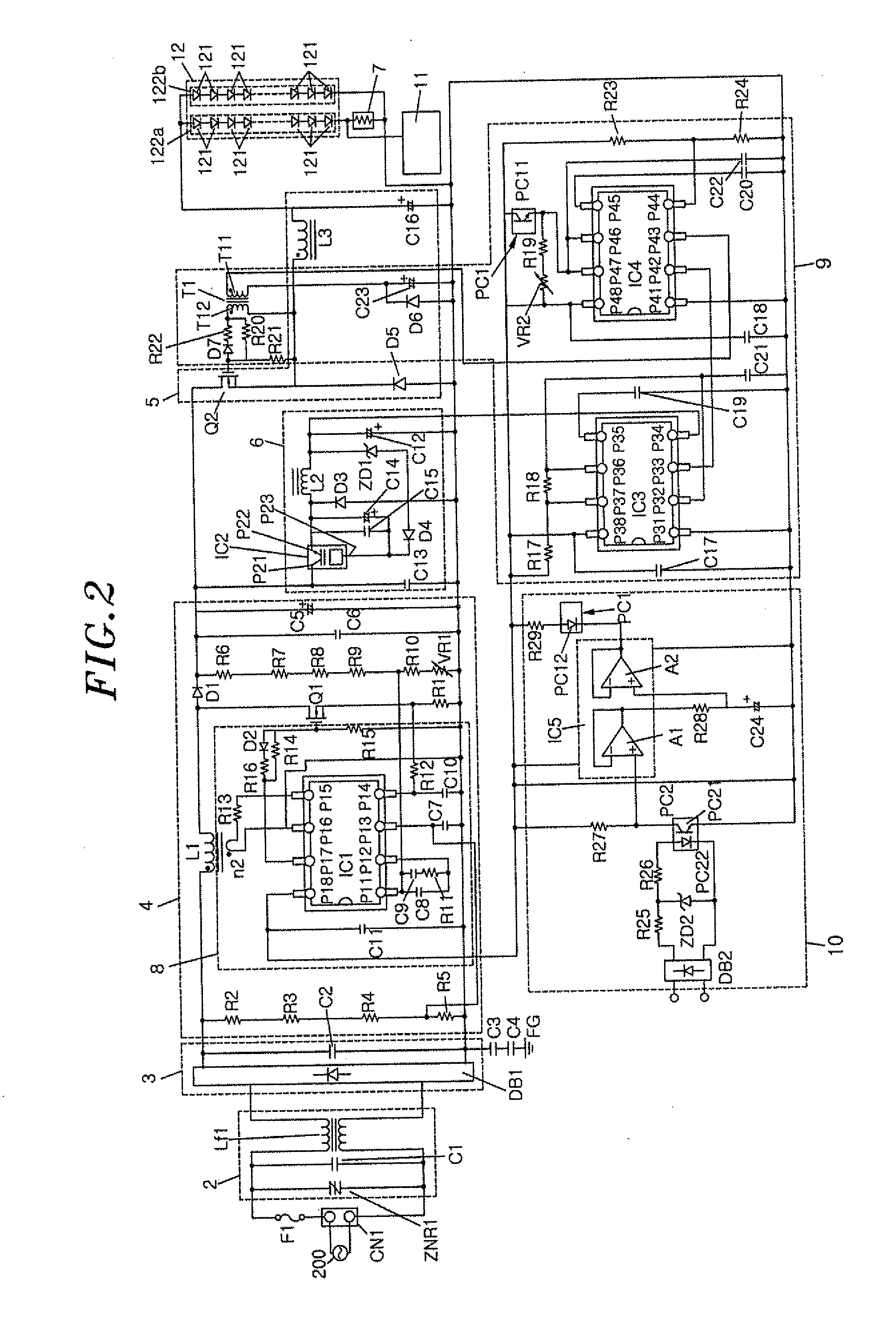
ActiveUS20120212143A1Reduce power lossSimple configurationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLower limitLight equipment
A lighting device includes a lighting unit which controls a current being supplied to a load, in which light emitting modules, each having one or more semiconductor light emitting elements connected in series, are connected in parallel, to be a constant current; a current detector which detects a current flowing through one of the light emitting modules; and an abnormality detector which compares a detected value from the current detector with an upper limit and a lower limit of a predetermined current range to detect an abnormality in the load. The abnormality detector detects the abnormality in the load if the detected value from the current detector is larger than the upper limit or smaller than the lower limit, and if the abnormality in the load is detected, the lighting unit reduces the current being supplied to the load.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
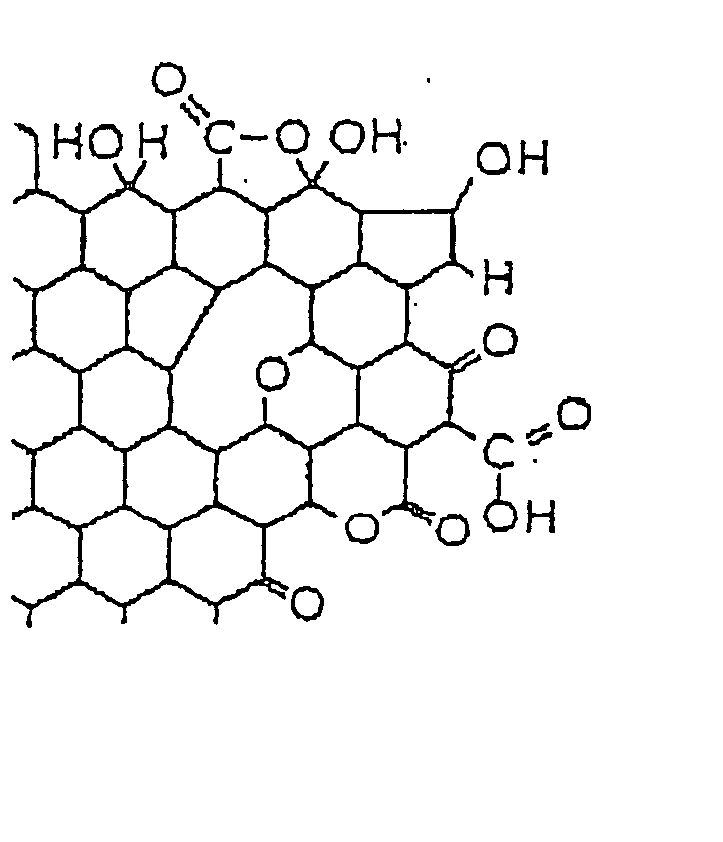
Chemicals from synthesis gas
InactiveUS20040106517A1Increase choiceReduce additionalHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesCatalystsAlkanePtru catalyst
This invention relates to an iron-based Fischer-Tropsch cataylst composition wherein the iron phase is ferrihydrite. The catalyst composition optionally includes a structural promoter which may be selected from manganese or chromium or a mixture thereof and chemical promoters selected from magnesium, zinc, copper and an alkaline or alkali metal such as potassium. The catalyst is best bound to a refractory oxide support such as silica. This catalyst composition produces significant yields of higher parafins, olefins and alcohols.
Owner:SASOL TEKHNOLODZHI PROPRIEHJTEHRI LTD
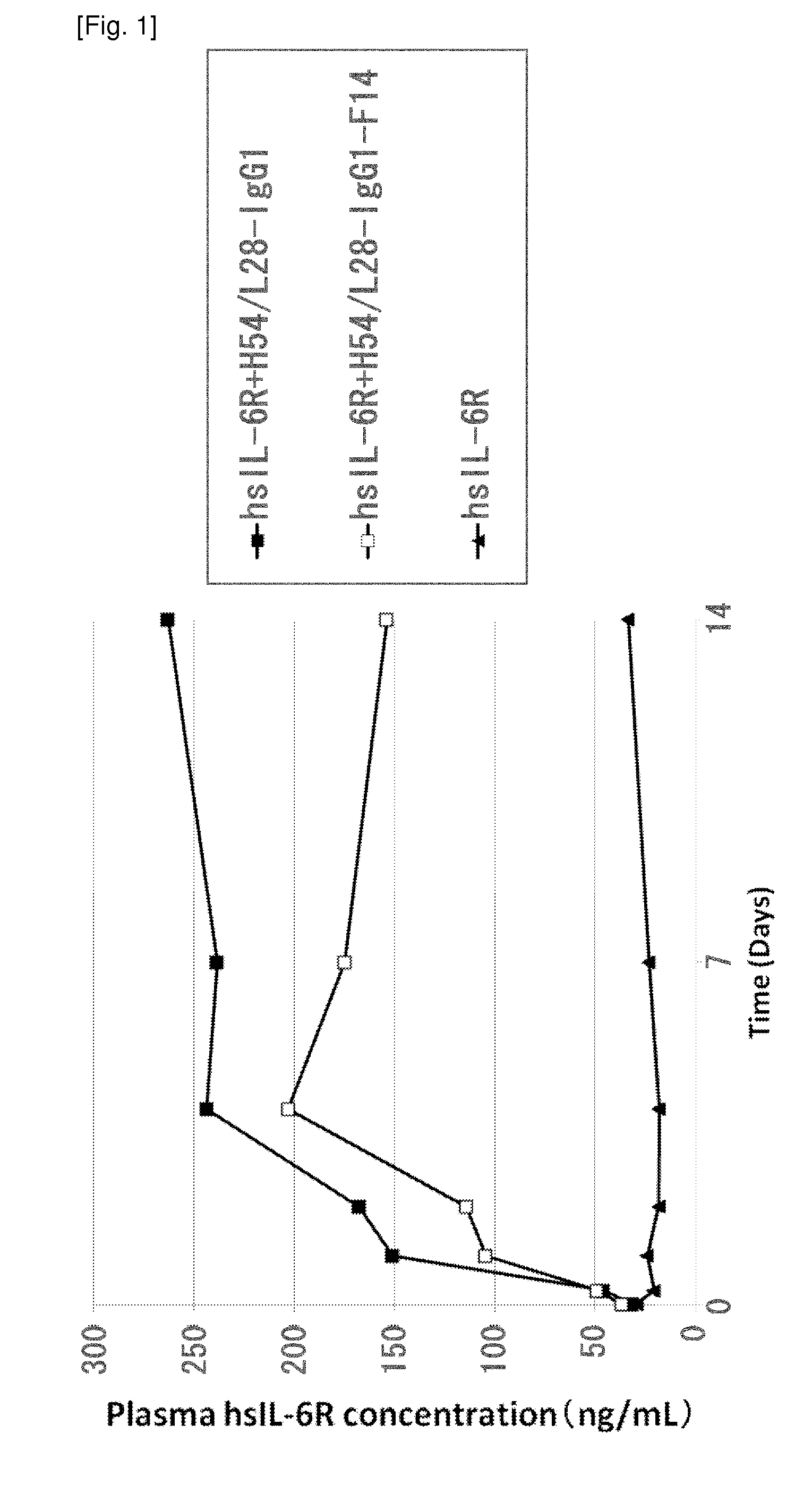
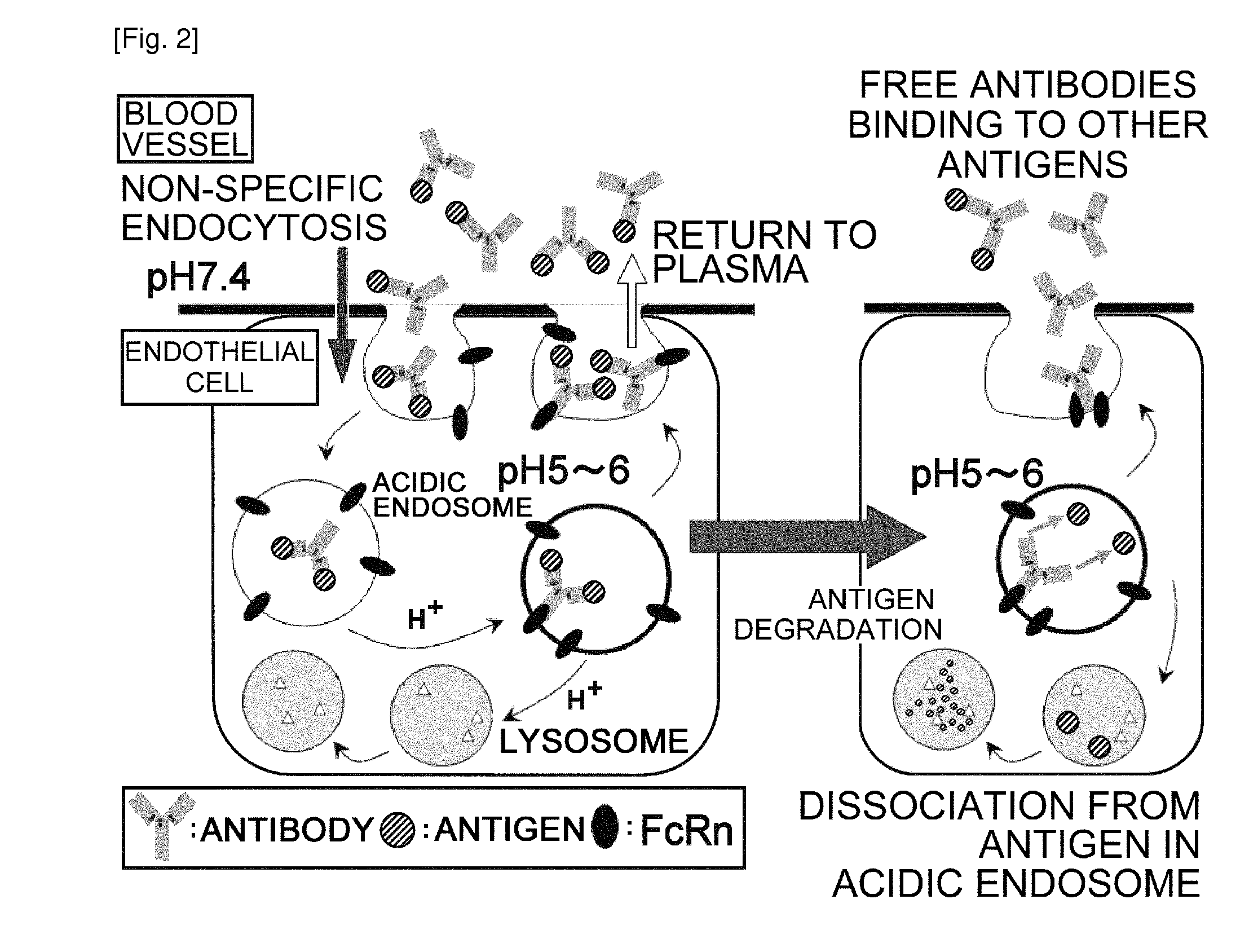
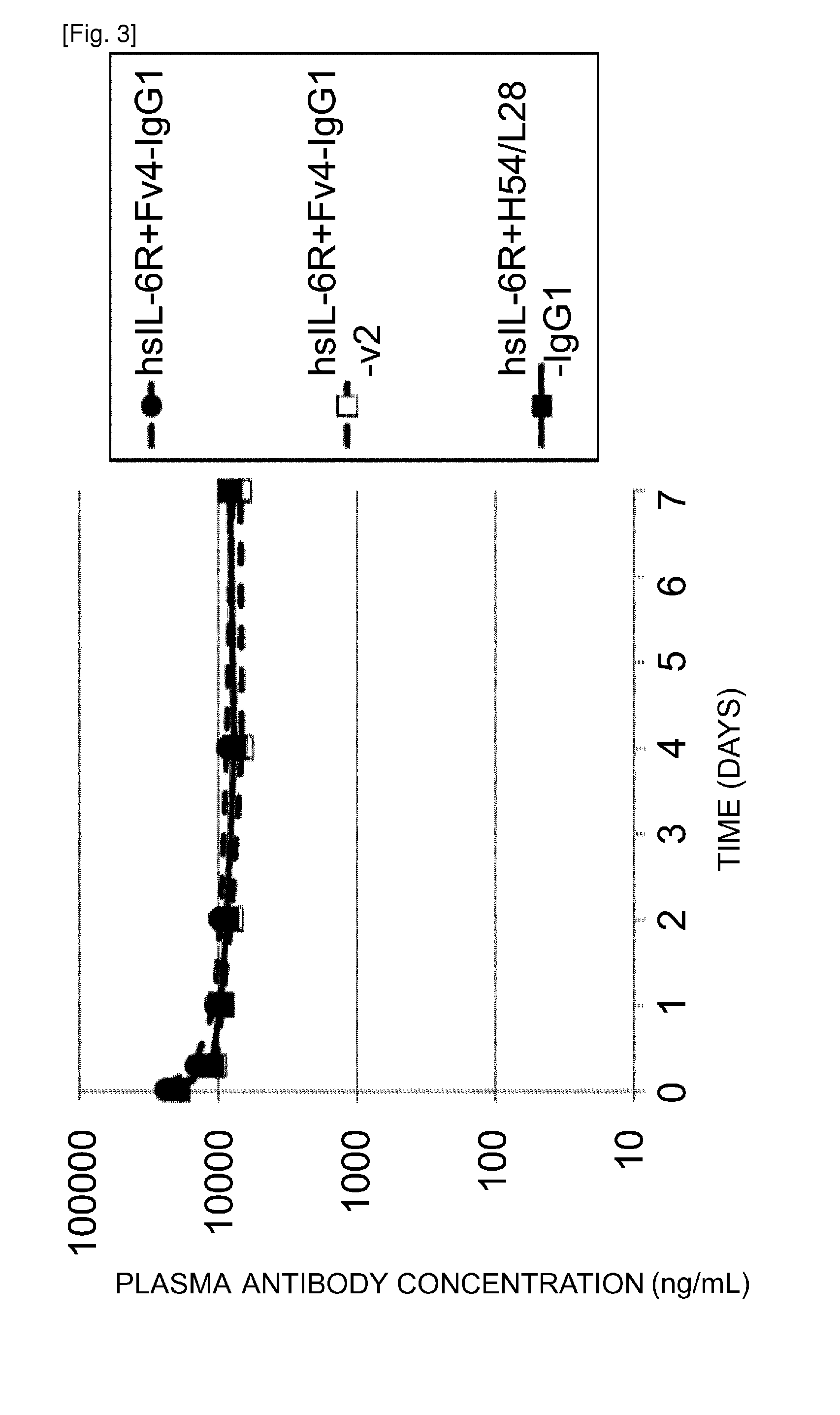
Antibodies with modified affinity to fcrn that promote antigen clearance
InactiveUS20130131319A1Increase the number ofSuperior in vivo effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen bindingAntigen uptake
An objective of the present invention is to provide methods for facilitating antigen-binding molecule-mediated antigen uptake into cells, methods for facilitating the reduction of antigen concentration in plasma, methods for increasing the number of antigens to which a single antigen-binding molecule can bind, methods for improving pharmacokinetics of antigen-binding molecules, antigen-binding molecules improved for facilitated antigen uptake into cells, antigen-binding molecules capable of facilitating the reduction of antigen concentration in plasma, antigen-binding molecules capable of repeatedly binding to antigens, antigen-binding molecules with improved pharmacokinetics, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such an antigen-binding molecule, and methods for producing those described above. The present inventors discovered that antigen uptake into cells is facilitated by an antibody having human FcRn-binding activity at the plasma pH and a lower antigen-binding activity at the early endosomal pH than at the plasma pH; such antibodies can increase the number of antigens to which a single antibody molecule can bind; the reduction of antigen in plasma can be facilitated by administering such an antibody; and antibody pharmacokinetics can be improved by using such antibodies.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Zero platinum group metal catalysts
InactiveUS20090324469A1Reduce additionalOrganic chemistryNitrogen compoundsMetal catalystNitrogen oxide
The present invention relates improving the performance of nitrogen oxide reduction by exposing rich exhaust to catalysts systems comprising a catalyst, wherein the catalyst systems are free of platinum group metals. The present invention also relates to improving reduction of carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon in exhaust by introducing air into a portion of the exhaust between a first catalyst system and a second catalyst system. The present invention also relates to improving nitrogen oxide, carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon reduction by (1) exposing rich exhaust to a first catalysts system, wherein the exhaust has an R value of greater than 1.0 and the first catalyst system comprises a catalyst and is free of platinum group metals and (2) introducing air into a portion of the exhaust in between the first catalyst system and a second catalyst system, wherein the second catalyst system is free of platinum group metals.
Owner:CATALYTIC SOLUTIONS INC
Methods and devices for selective disruption of visceral fat by controlled cooling
ActiveUS9980765B2Reduce the amount requiredGood lookingSurgical instruments for coolingTherapeutic coolingVisceral fatNuclear medicine
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for use in the selective disruption of visceral fat tissue by controlled cooling.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
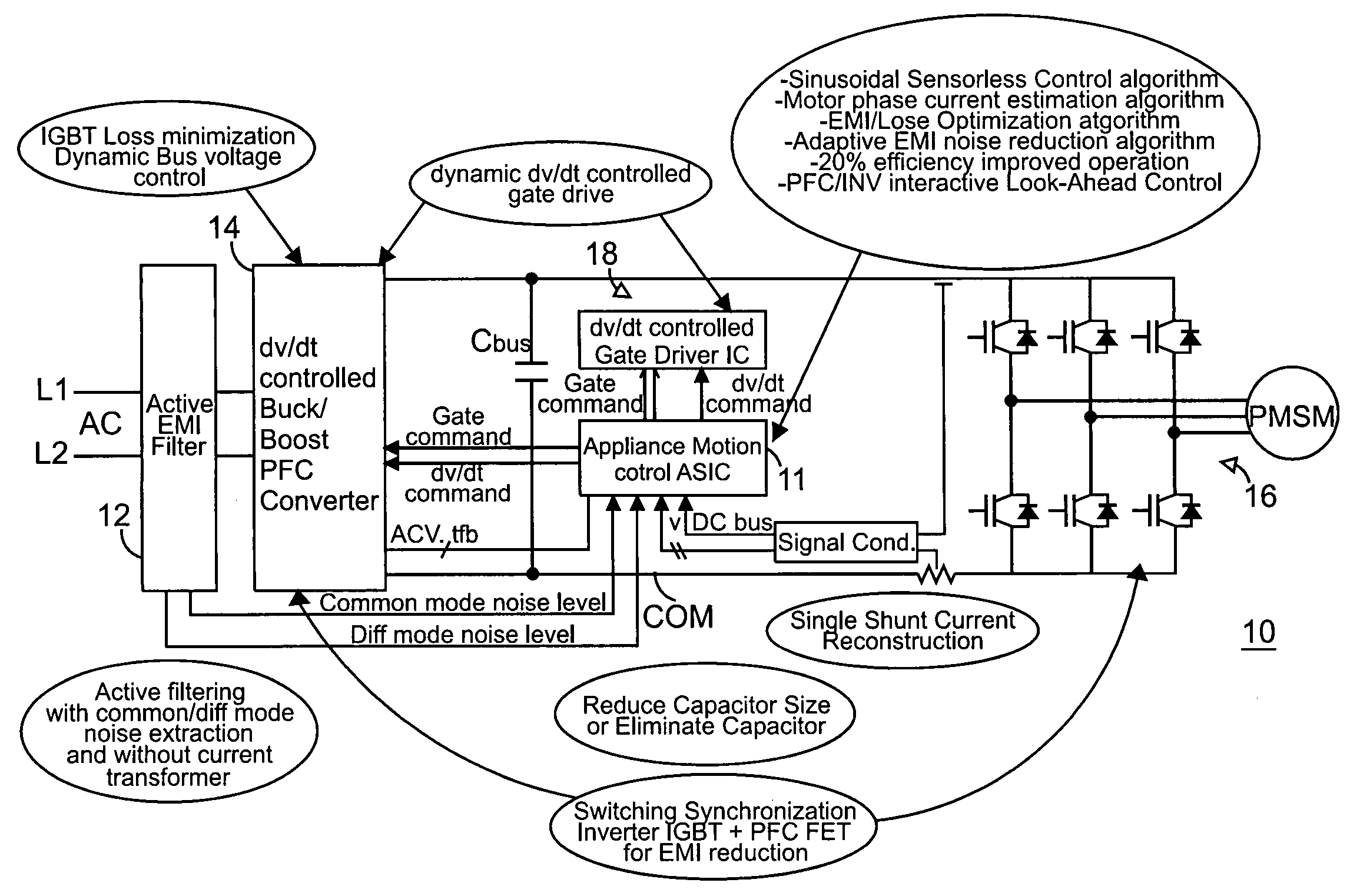
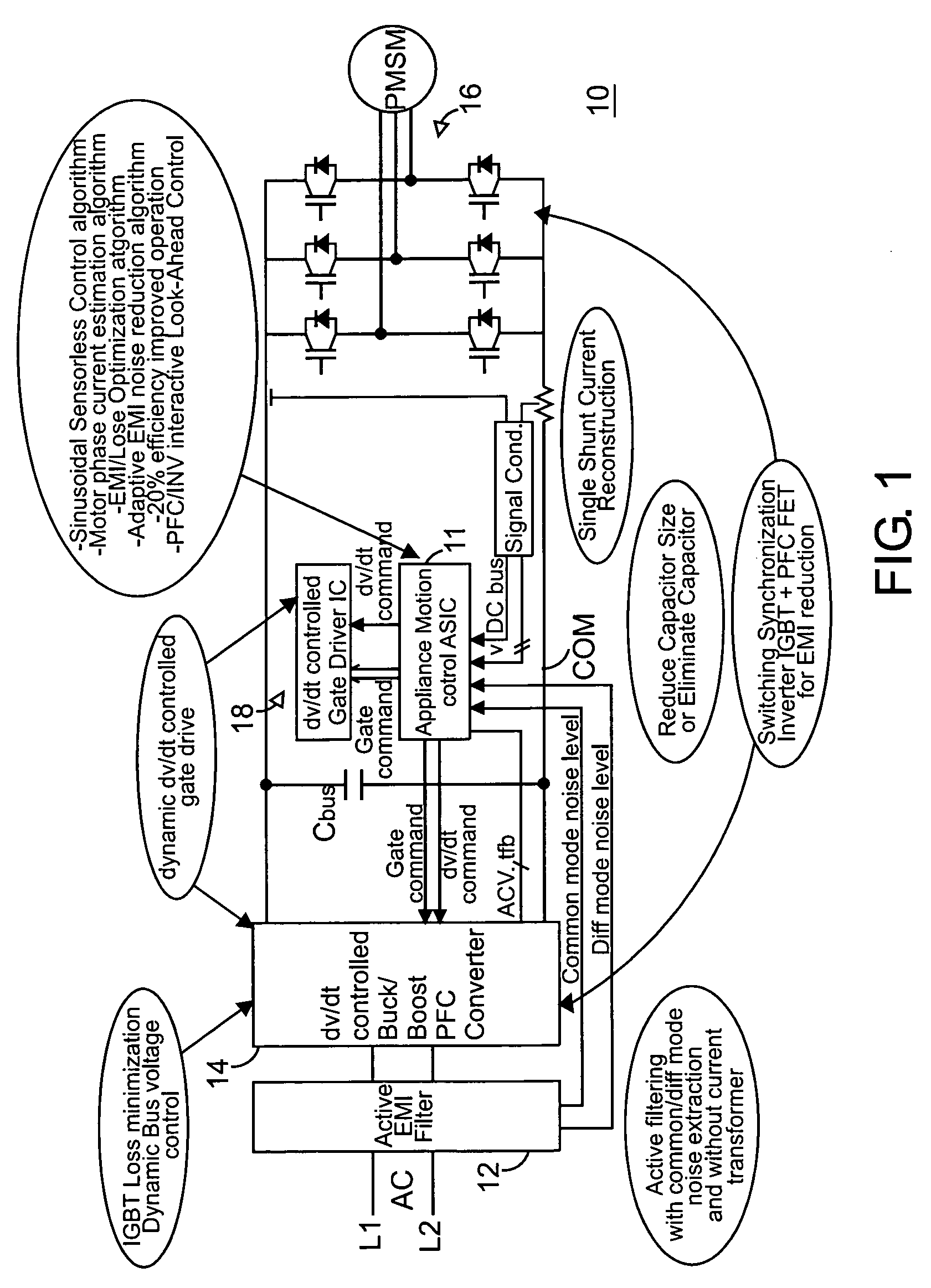
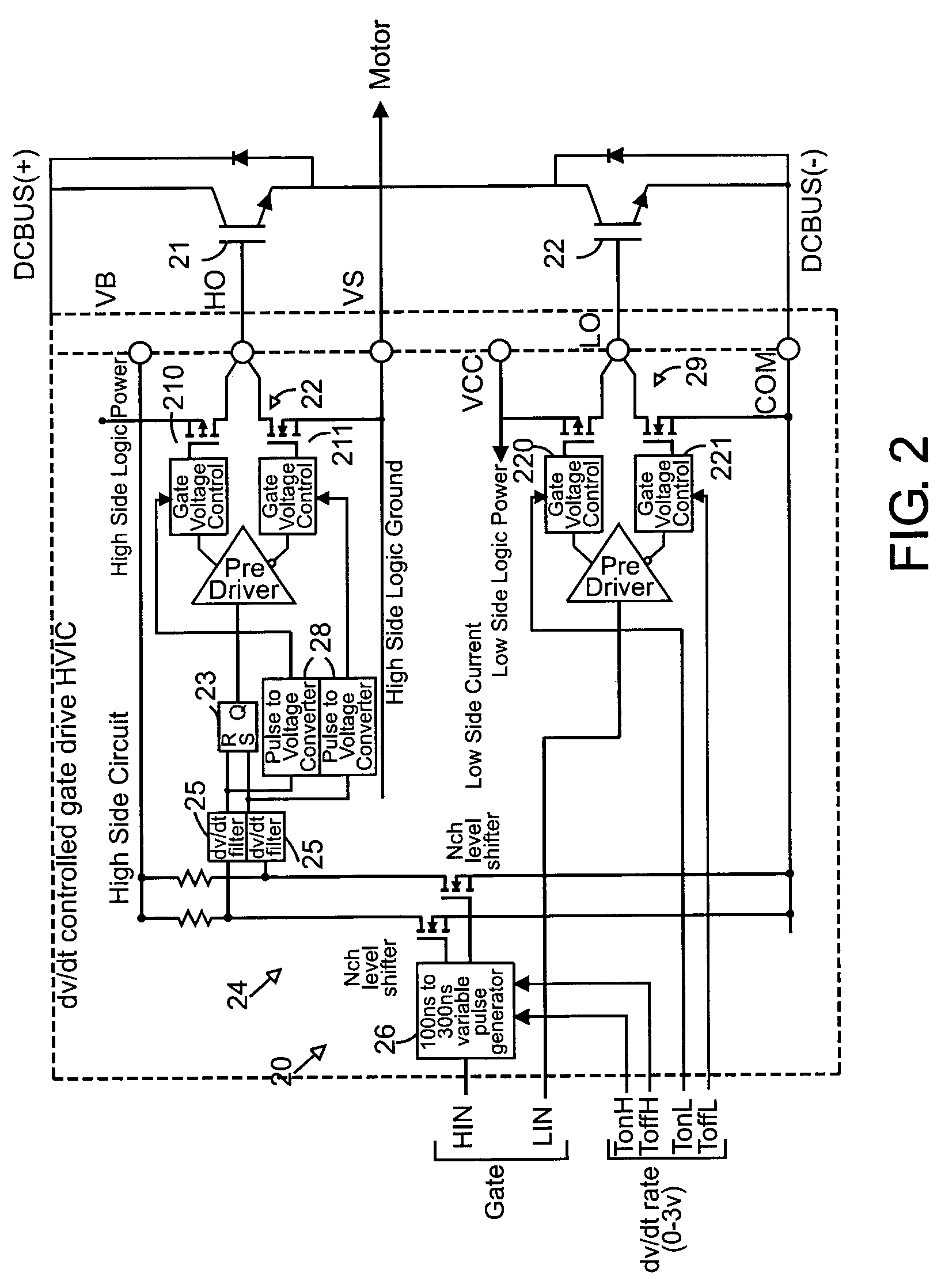
Global closed loop control system with dv/dt control and EMI/switching loss reduction
ActiveUS7061195B2Improve efficiencyReduce productionMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlLevel shiftingNoise level
A motor drive system control provides global closed loop feedback to cooperatively operate system components to adaptively reduce noise and provide noise cancellation feedback. An active EMI filter reduces differential and common mode noise on an input and provides a noise level indication to a system controller. Power switches in both a power converter and power inverter are cooperatively controlled with dynamic dv / dt control to reduce switching noise according to a profile specified by the controller. The dv / dt control is provided as an analog signal to a high voltage IC and codified as a pulse width for a level shifting circuit supplying control signals to the high voltage gate drive. A noise extraction circuit and technique obtain fast noise sampling to permit noise cancellation and adaptive noise reduction.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
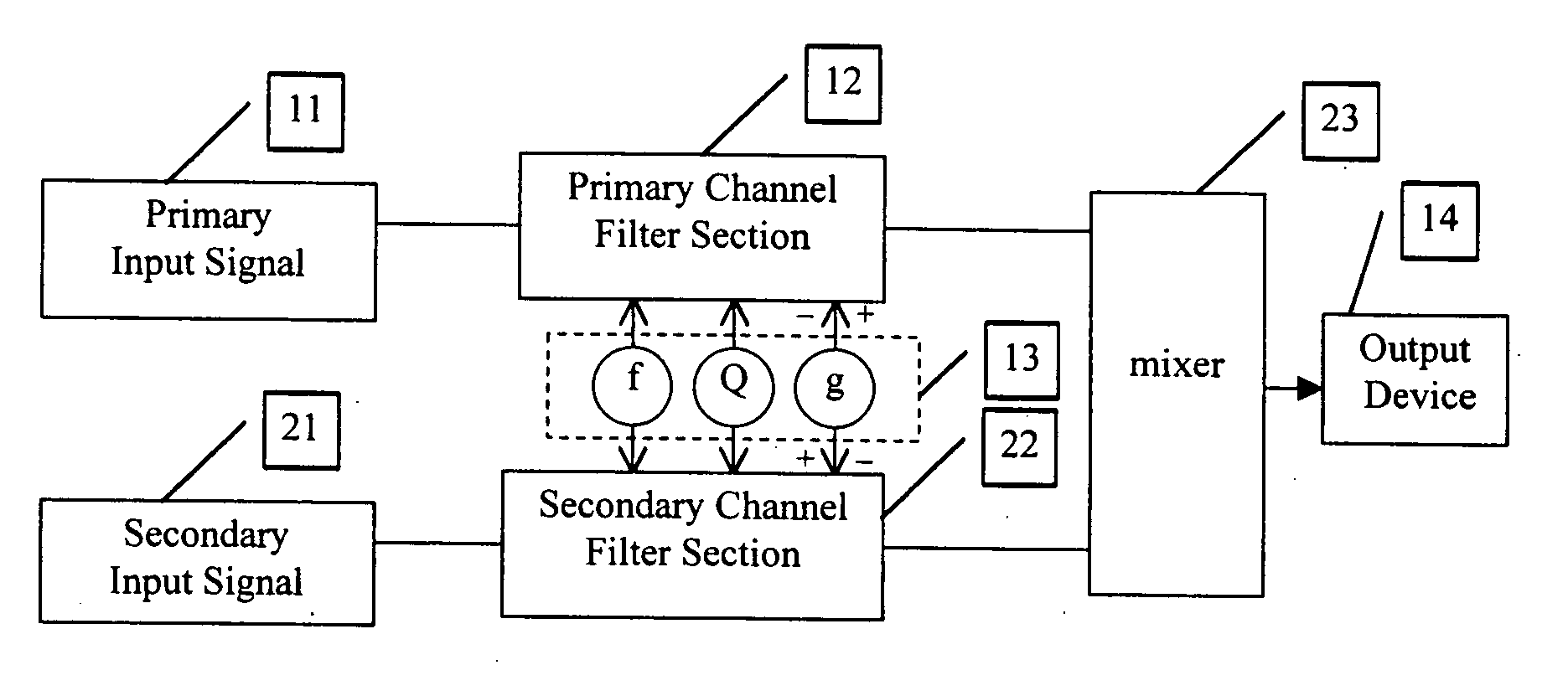
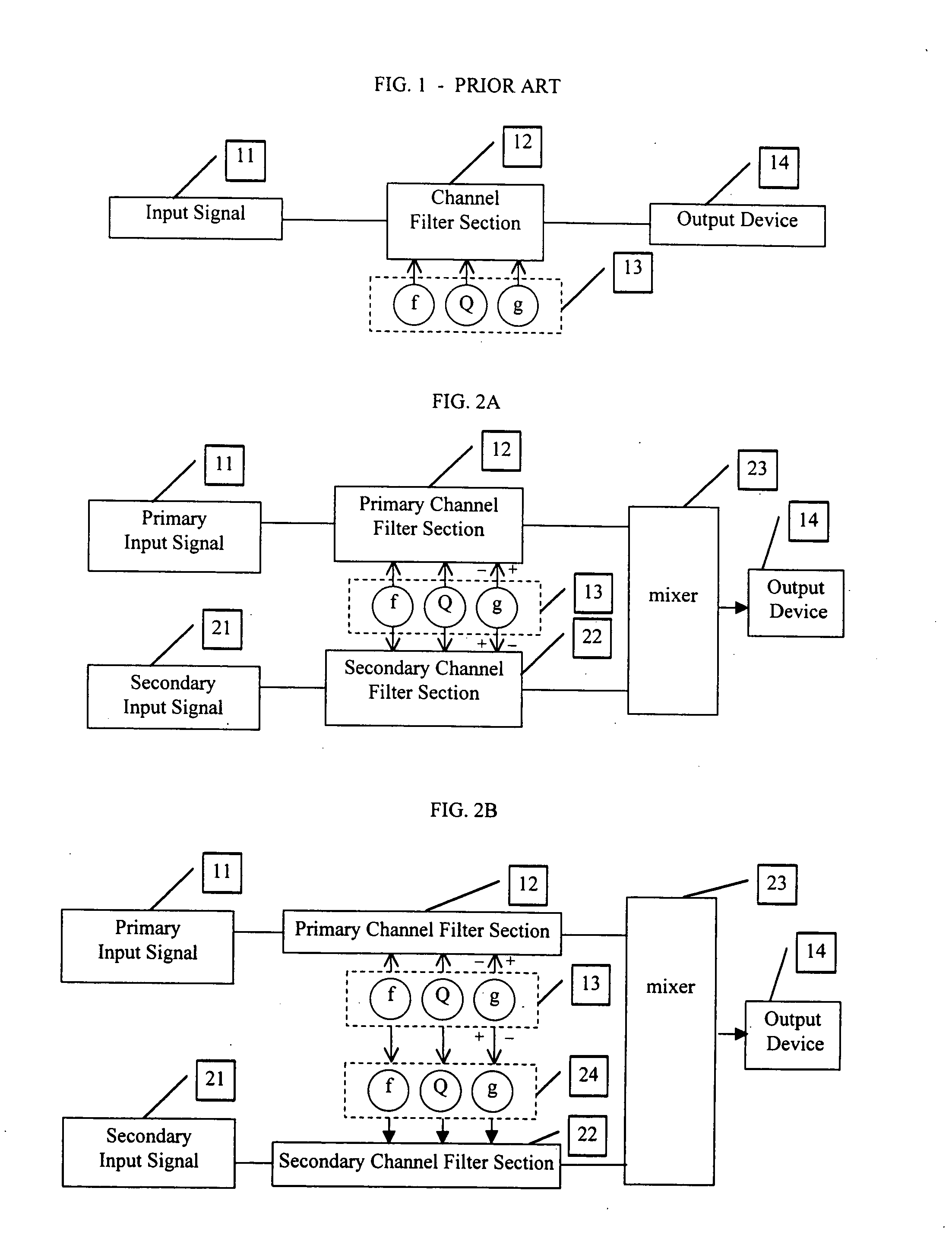
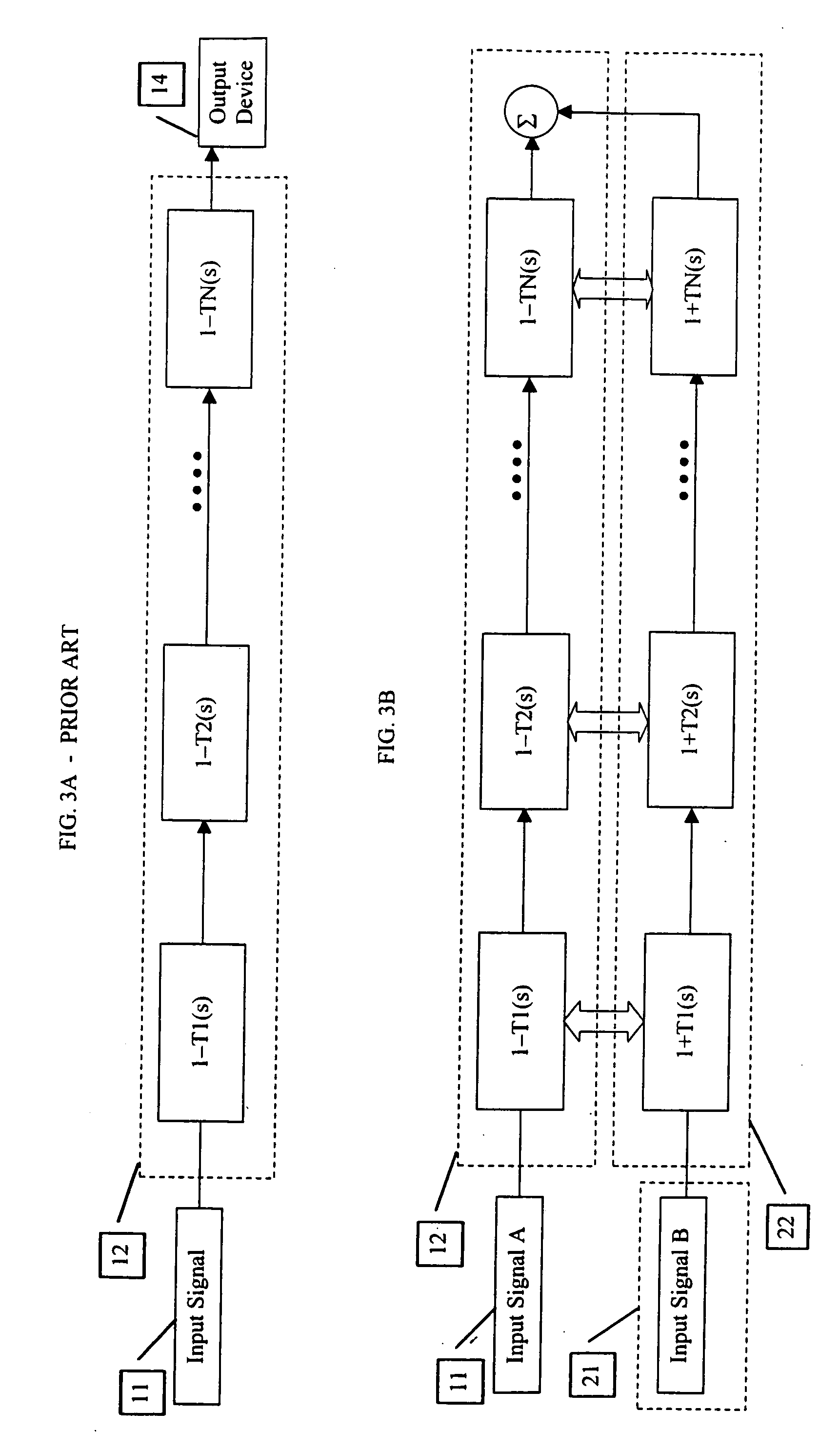
Complementary-pair equalizer
InactiveUS20060072768A1Weaken energyHigh energyTransmission noise suppressionTwo-channel systemsComplementary pairSignal processing
A method and apparatus are described which reduce the presence of an unwanted signal. According to one embodiment, a first signal is provided from a desired location that includes an unwanted signal while a second signal is provided from an alternate location (e.g., one where the unwanted signal is less of a proportion of the total signal). The first and alternate signals are provided to respective signal processors. A level for a selected frequency band of the first and alternate signals is adjusted so that an increase in one results in a decrease in the other. Doing so allows the frequency band that includes the unwanted signal to be reduced in the desired first signal and filled in with a similar frequency band from the alternate signal.
Owner:SCHWARTZ STEPHEN R +2
Laundry detergent composition for low temperature washing and disinfection
InactiveUS20130247308A1Reduce bacteria countClean supportSurface-active detergent compositionsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsAlkalinityAlcohol
The invention relates to a low temperature detergent composition of a first component for cleaning and disinfecting comprising:(a) about ≧2 wt.-% to about ≦50 wt.-% of a nonionic low alkoxylated alcohol tenside containing 1 to 2 alkylene oxide units;(b) about ≧0 wt.-% to about ≦60 wt.-% of nonionic higher alkoxylated alcohol tenside containing 3 to 40 alkylene oxide units;(c) about ≧1 wt.-% to about ≦60 wt.-% of a source of alkalinity;(d) about ≧0 wt.-% to about ≦95 wt.-% of at least one solvent; calculated on the total weight amount of the detergent composition of the first component.The invention relates further to a low temperature detergent composition for cleaning and disinfecting of a first component composition and a second component composition containing at least one bleaching agent.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Control methods for low emission internal combustion system
InactiveUS20070220864A1Reduce the formation of nitrogen oxidesImprove transient response timeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion systemEngineering
Improved transient response times are obtained while maintaining low emissions with a low pressure EGR system through methods for quickly obtaining a desired oxygen concentration for charge-air to be used for combustion. Under a first method, fuel quantity in the main combustion event is controlled in the combustion process to produce exhaust around a relatively constant target exhaust oxygen concentration value. By keeping the exhaust oxygen concentration levels at a relatively constant value, lag time in waiting for low pressure EGR valve adjustments during transients may be avoided, and the system's air handling response to meet transients may be paced solely by adjusting the mass of air to be supplied (i.e. boost response). Under a second method, a multiple-stage combustion process is utilized, in which fuel feed is controlled in a small, preliminary HCCI-type combustion event in order to produce a target oxygen concentration of charge-air to be used for the second, main combustion event. Under a third method, exhaust rebreathing is used to produce a target oxygen concentration of charge-air to be used for combustion.
Owner:US EPA OFFICE OF GENERAL COUNSEL UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE
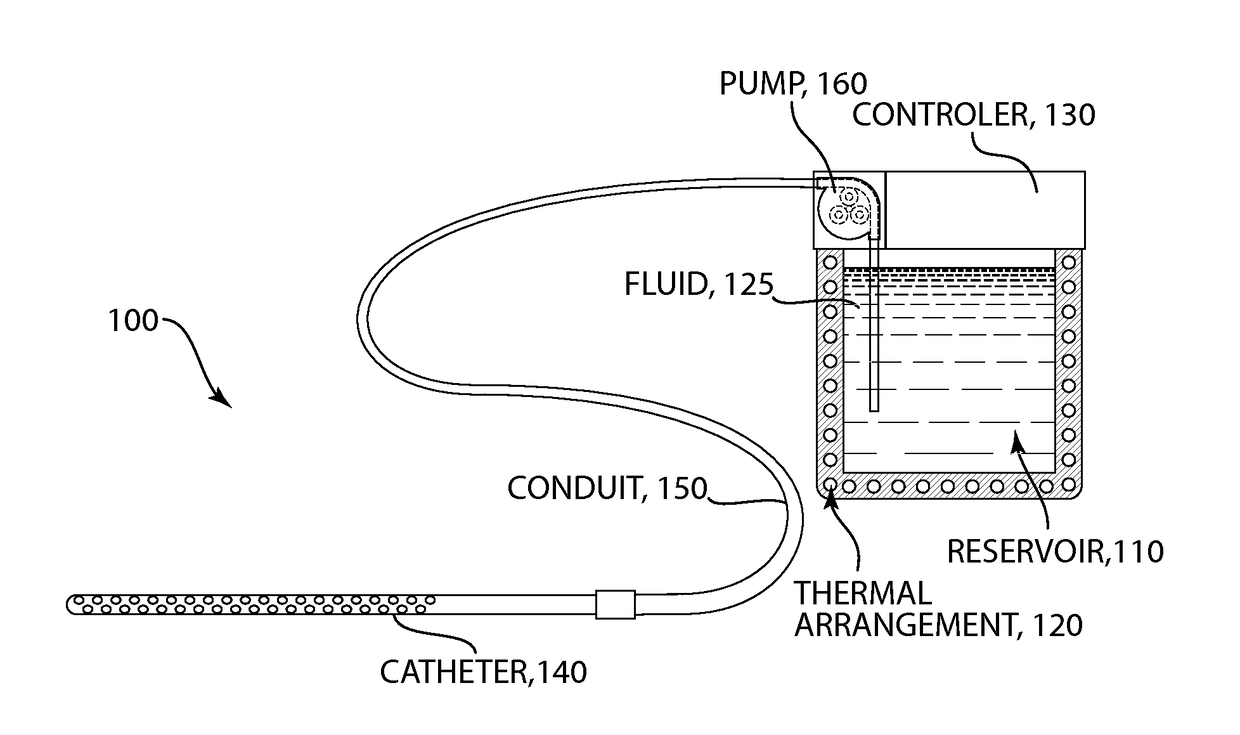
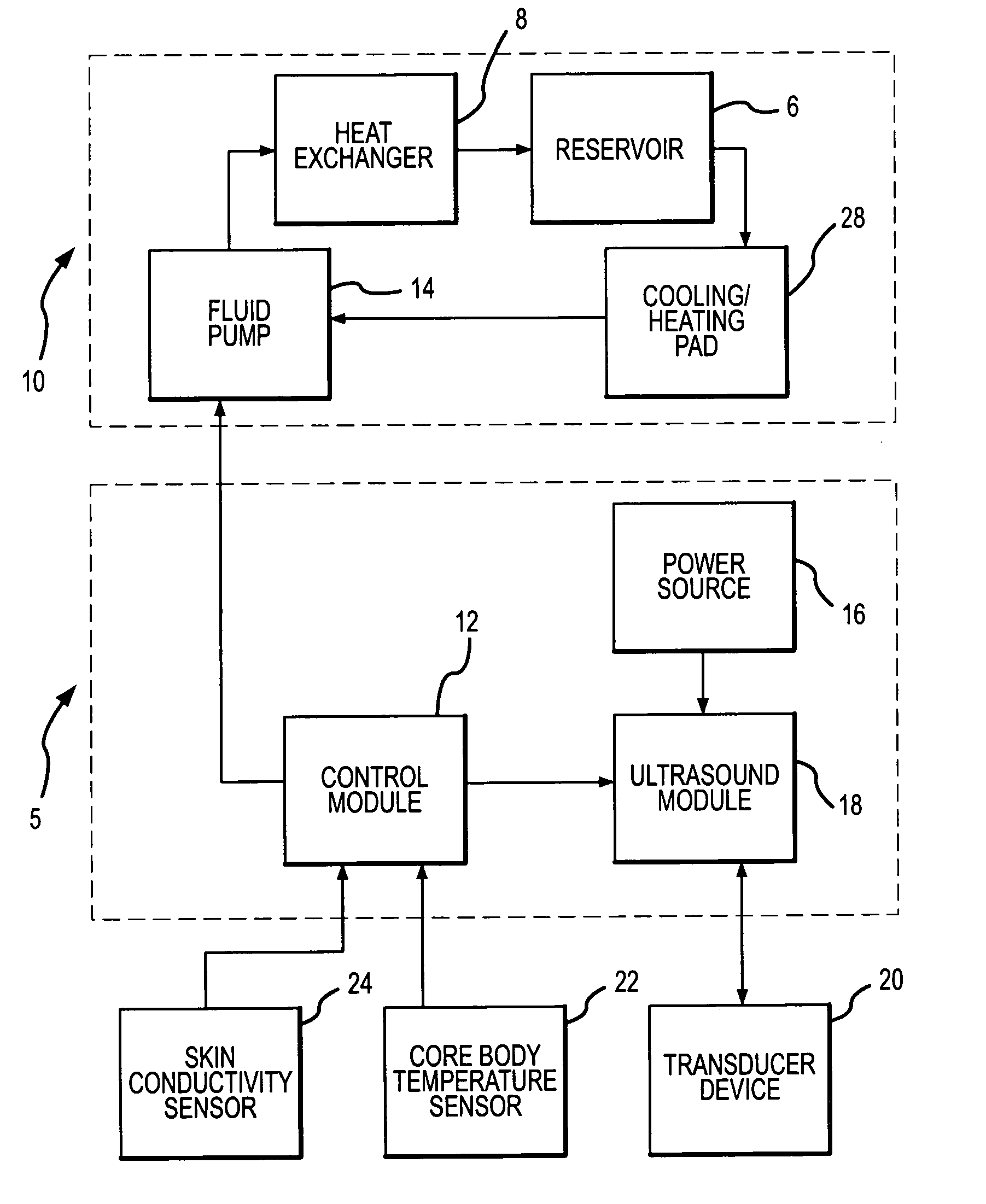
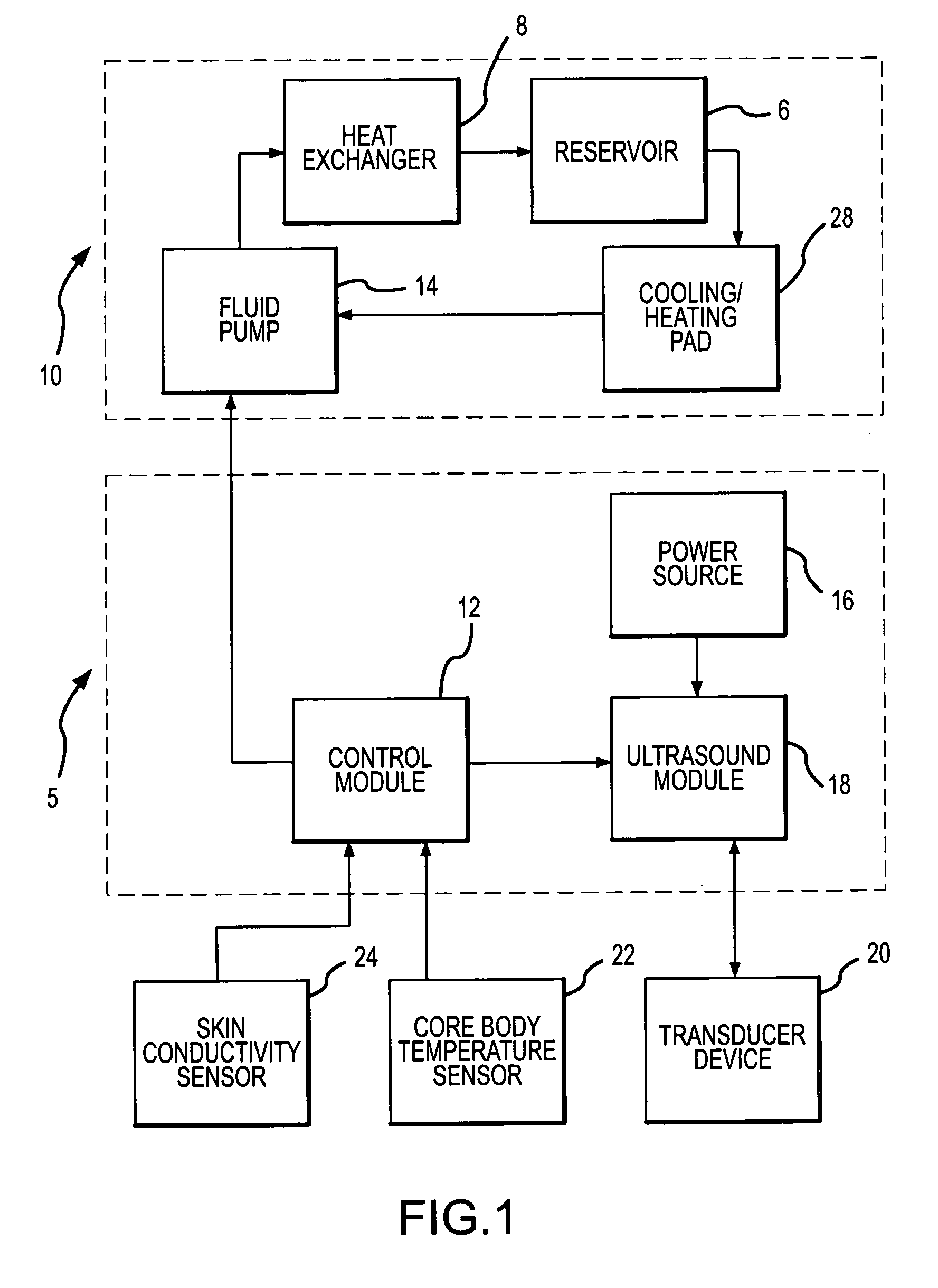
Method and apparatus for providing non-invasive ultrasound heating of the preoptic anterior hypothalamus
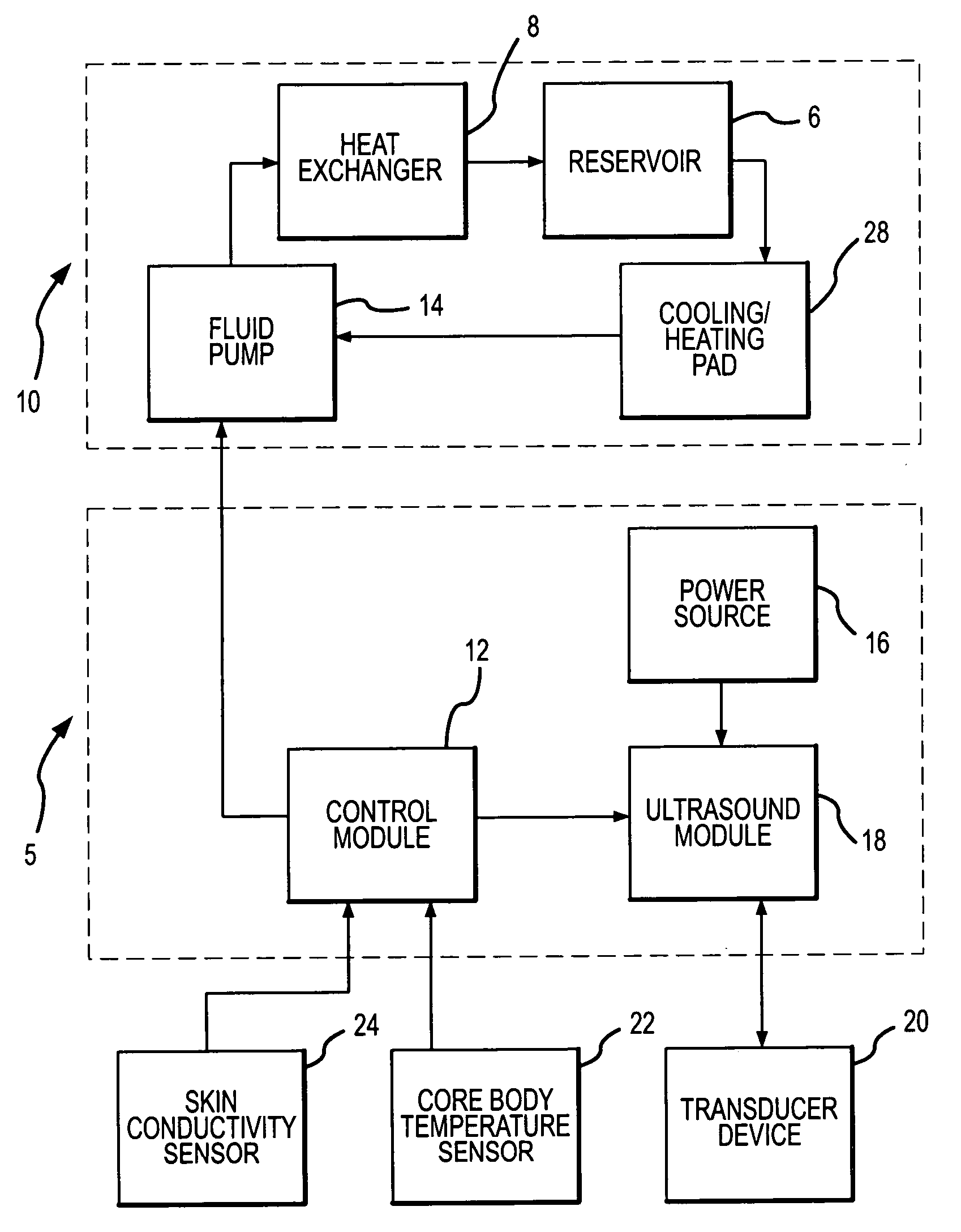
ActiveUS7044960B2Induce mild hypothermiaReduce the temperatureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyMedicineTransducer
A method and system is provided to induce mild hypothermia in a patient through controlled heating of the preoptic anterior hypothalamus (POAH) in conjunction with cooling of patient's body. The system employs an ultrasound transducer that may be positioned extracorporeally to a patient skull for emitting ultrasound energy to the POAH. The ultrasound energy heats the POAH to inhibit thermoregulatory responses of the body such that a cooling means may more effectively cool bodily tissue in order to reduce a patient's core body temperature. Feedback sensors may be positioned at various locations on the patient in order to monitor the patient's core body temperature. A control apparatus included with the system controls the amount of heat the POAH receives and the amount of cooling the body receives based on the feedback signals from the sensors.
Owner:MEDIVANCE
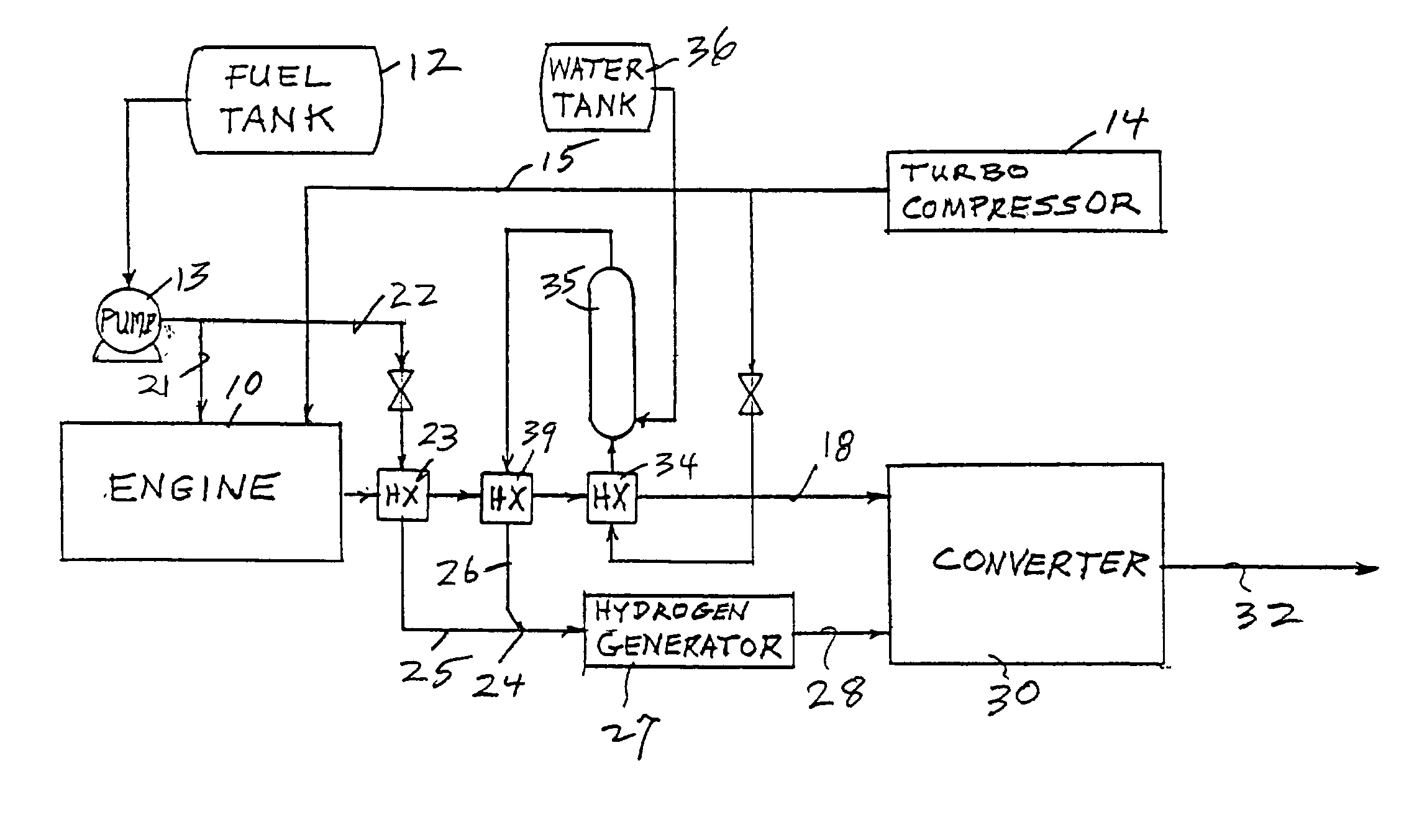
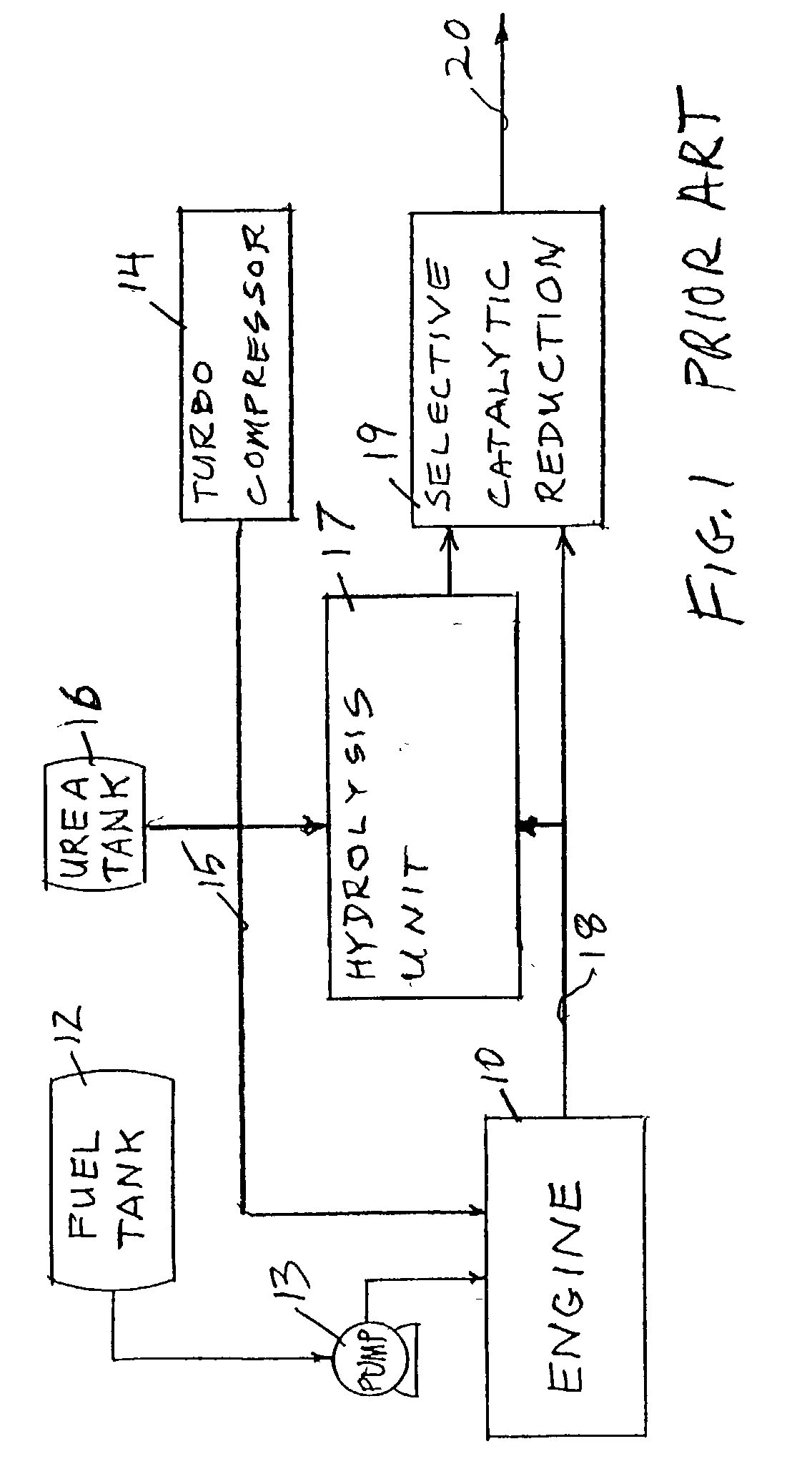
Reducing oxides of nitrogen using reformate generated from engine fuel, water and/or air
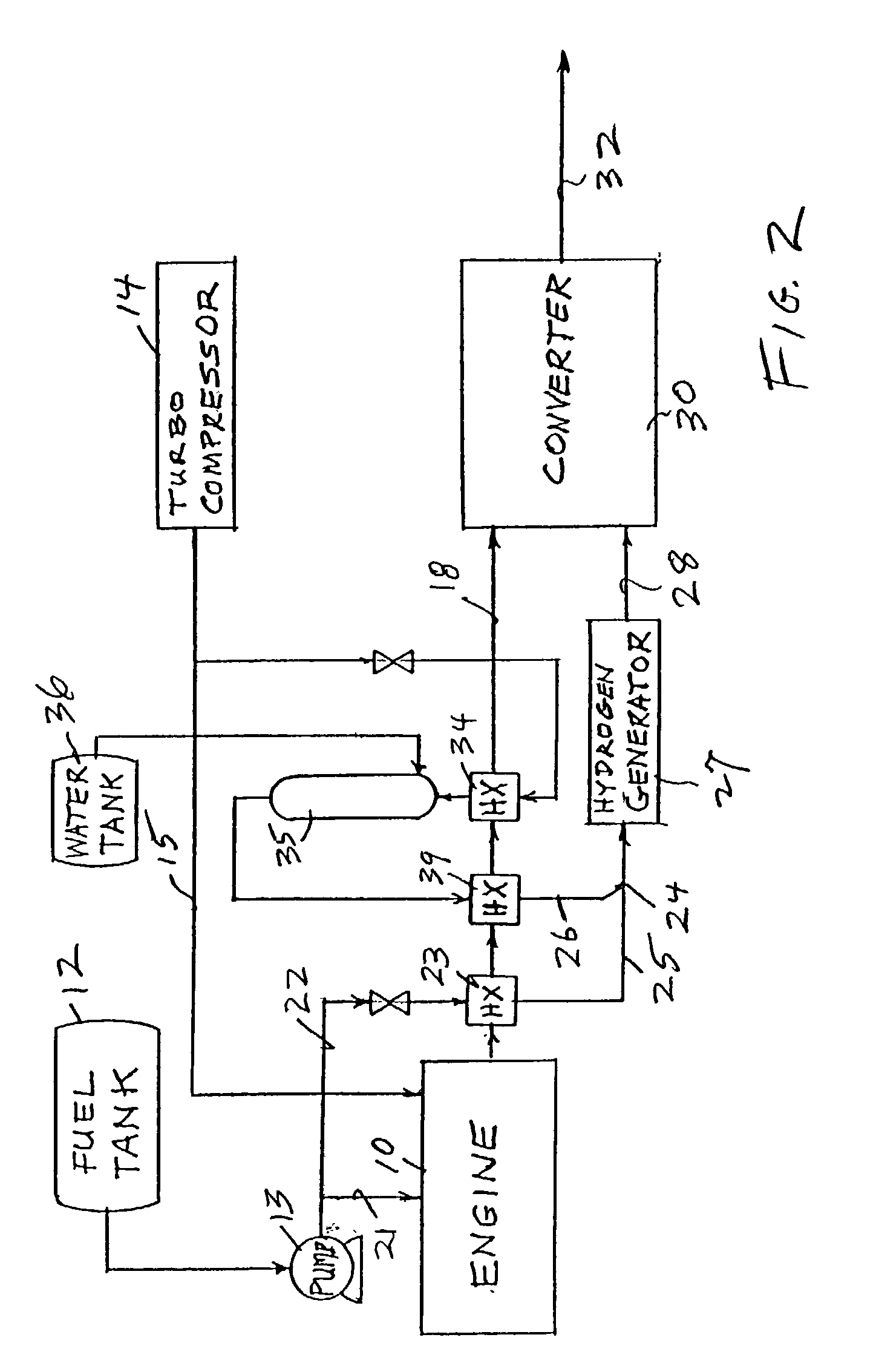
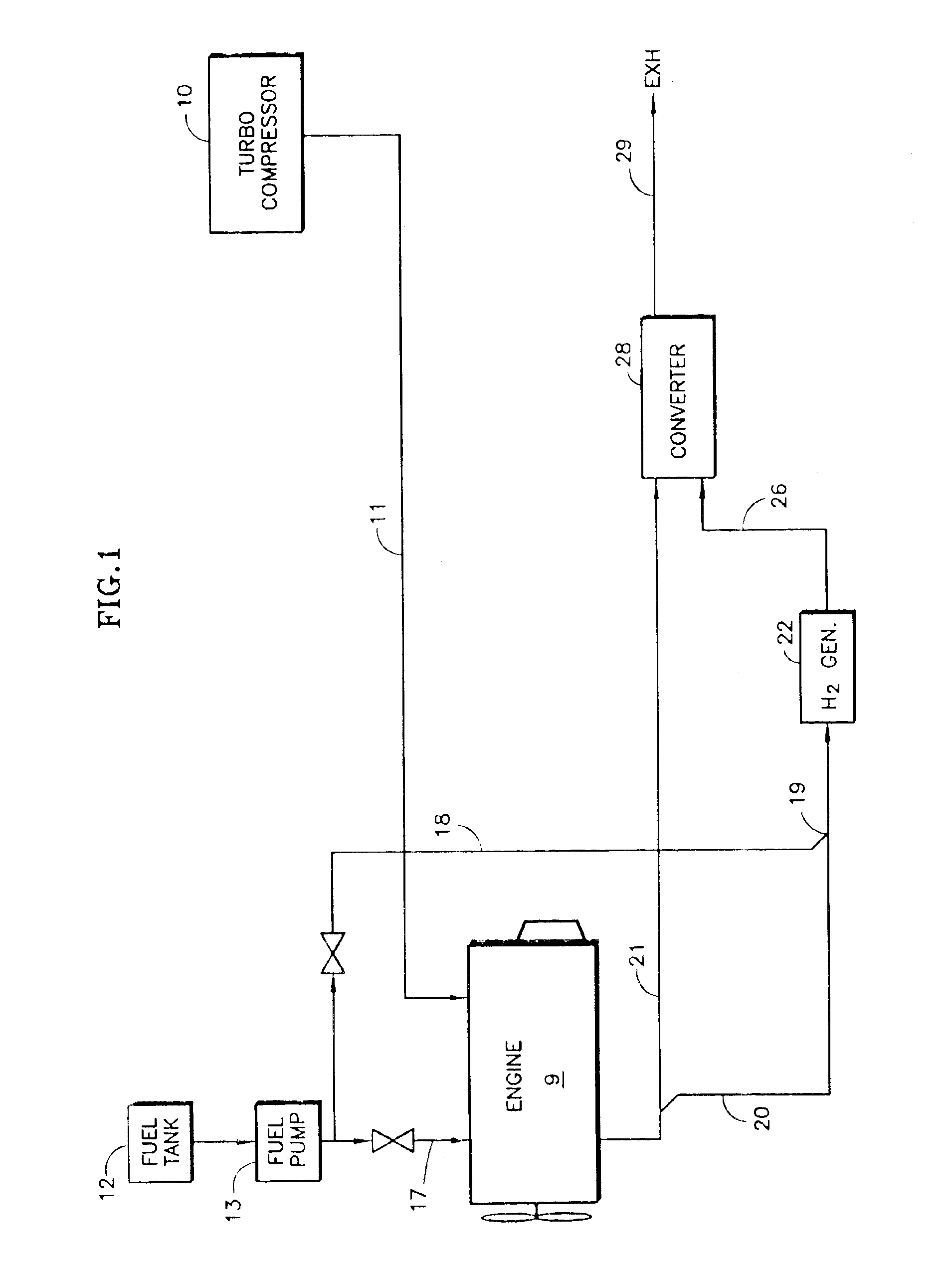
InactiveUS20030226350A1Reduce additionalSimple and low-cost hydrogen generationHydrogenInternal combustion piston enginesMethaneCatalytic converter
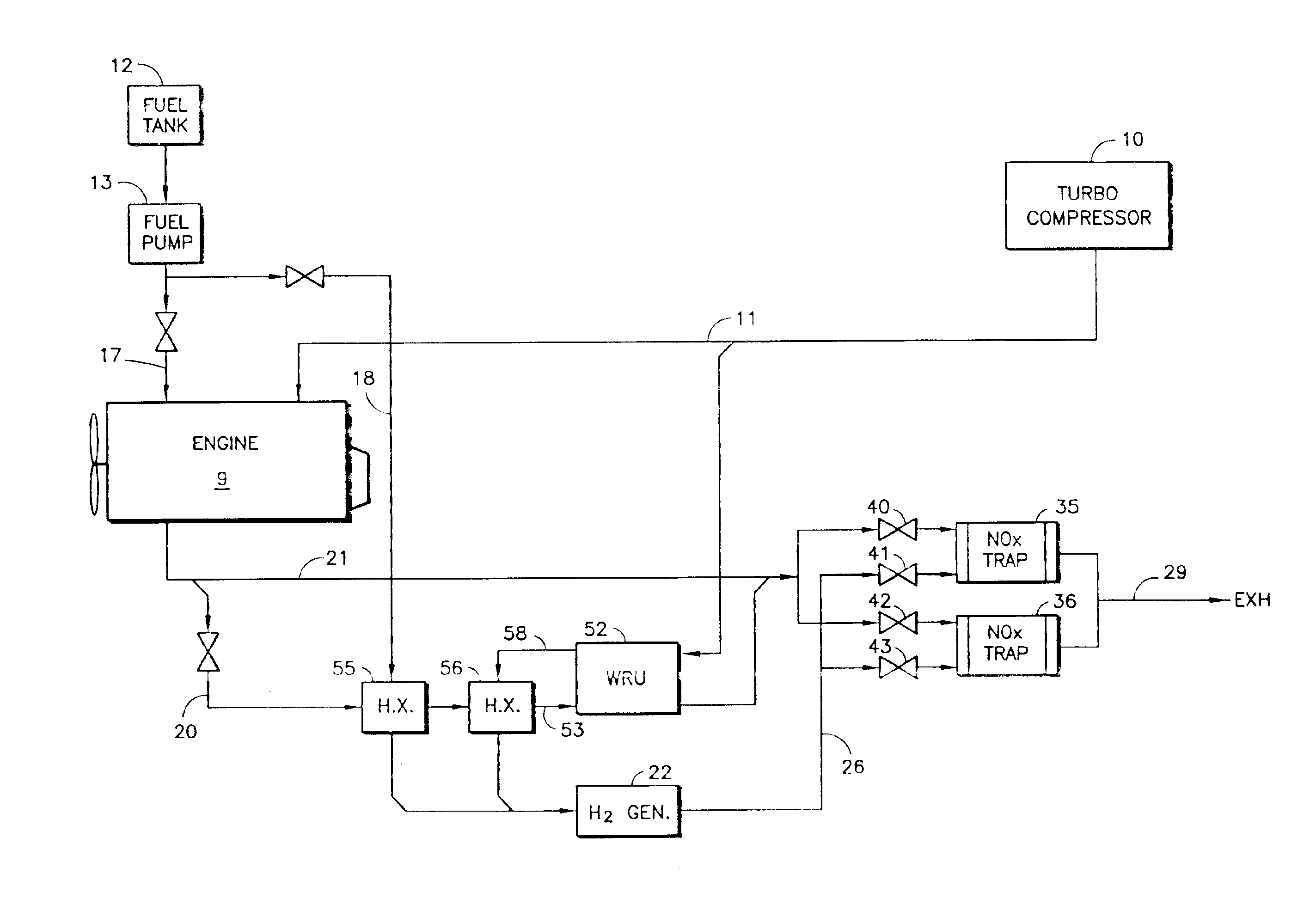
Inlet air (15) humidified in an air bubbling (or other) humidifier (35) that receives water from a tank (36) is sent to a hydrogen generator (27) along with vaporized (23) diesel fuel (22) to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide (28) for either (a) mixing with the mainstream of exhaust (18) fed to a catalytic converter (30) or (b) regenerating a pair of NOx adsorption traps (38, 39), thereby reducing oxides of nitrogen (NOx), to provide system exhaust (32) which may have less than 0.40 grams / bhp / hr of NOx and 0.28 grams / bhp / hr of non-methane hydrocarbons. In other embodiments, unhumidified air mixed with fuel feeds a homogeneous non-catalytic partial oxidizer (27) to provide the required hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Method and apparatus for providing non-invasive ultrasound heating of the preoptic anterior hypothalamus
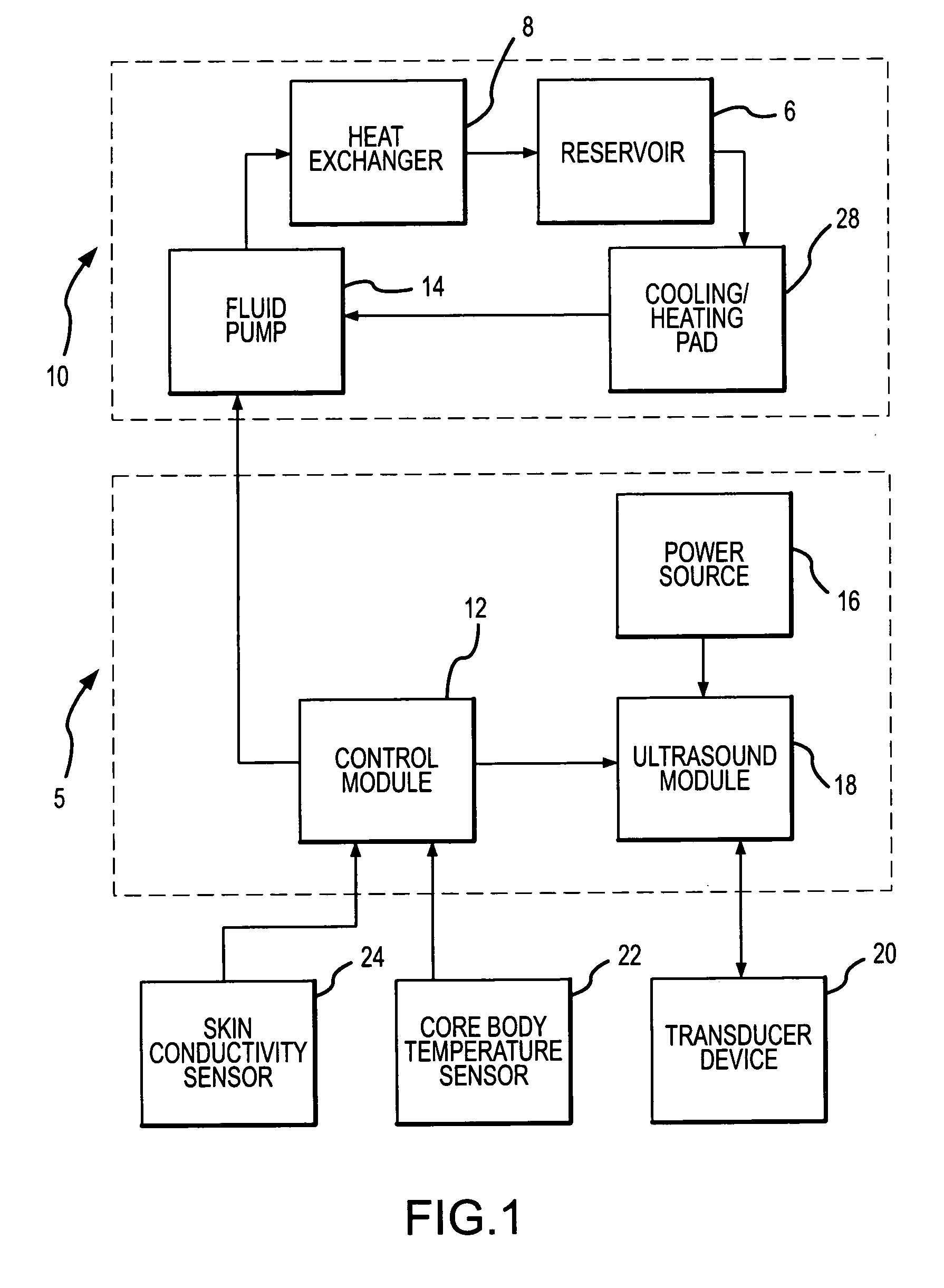
ActiveUS20050060012A1Reduction in core body temperatureEasy to useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyNon invasiveTransducer
A method and system is provided to induce mild hypothermia in a patient through controlled heating of the preoptic anterior hypothalamus (POAH) in conjunction with cooling of patient's body. The system employs an ultrasound transducer that may be positioned extracorporeally to a patient skull for emitting ultrasound energy to the POAH. The ultrasound energy heats the POAH to inhibit thermoregulatory responses of the body such that a cooling means may more effectively cool bodily tissue in order to reduce a patient's core body temperature. Feedback sensors may be positioned at various locations on the patient in order to monitor the patient's core body temperature. A control apparatus included with the system controls the amount of heat the POAH receives and the amount of cooling the body receives based on the feedback signals from the sensors.
Owner:MEDIVANCE
Method for improving lean performance of PGM catalyst systems: synergized PGM
InactiveUS8845987B1High catalytic activityReduce conversionOrganic chemistryNitrogen compoundsSpinelNitrogen oxide
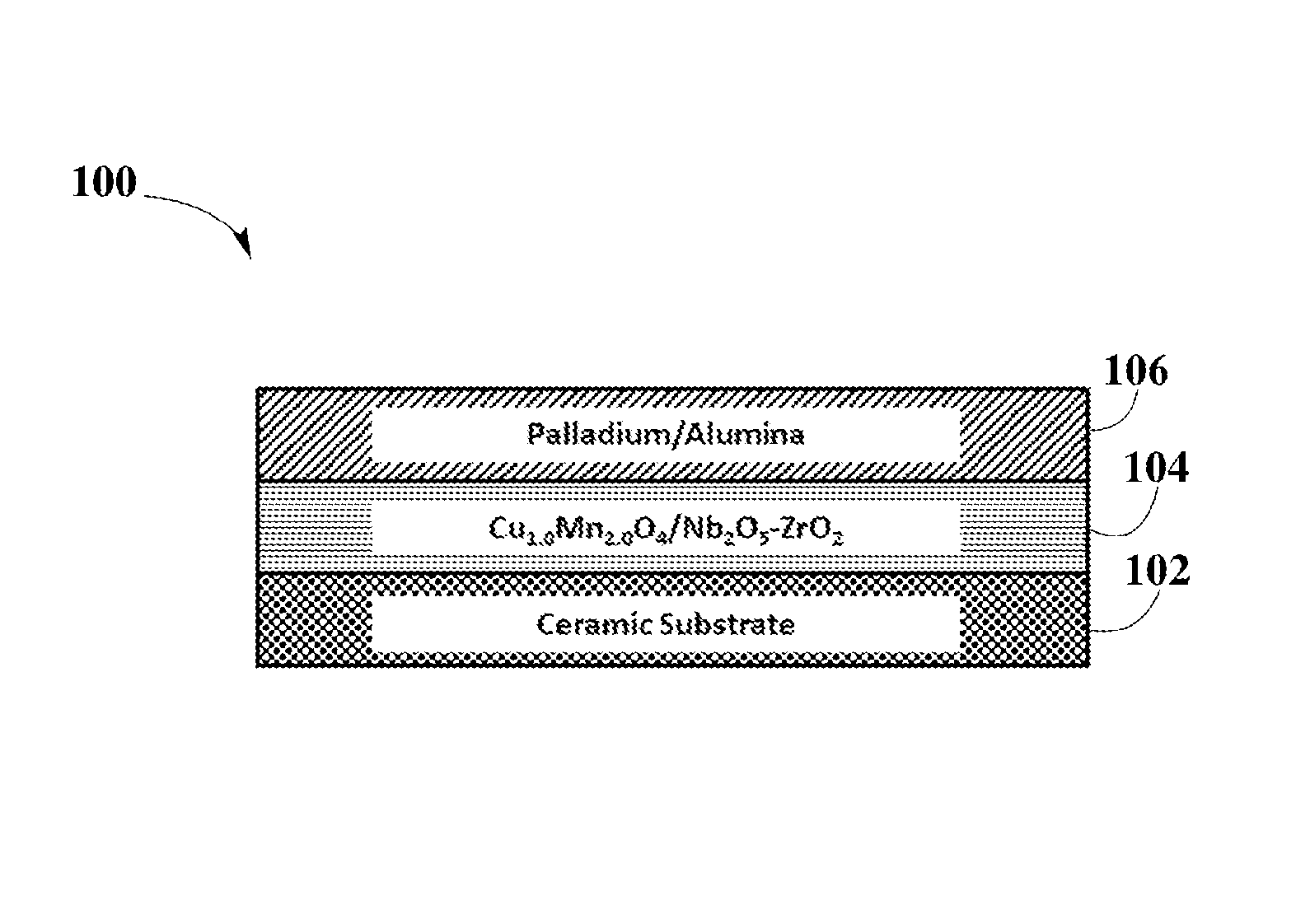
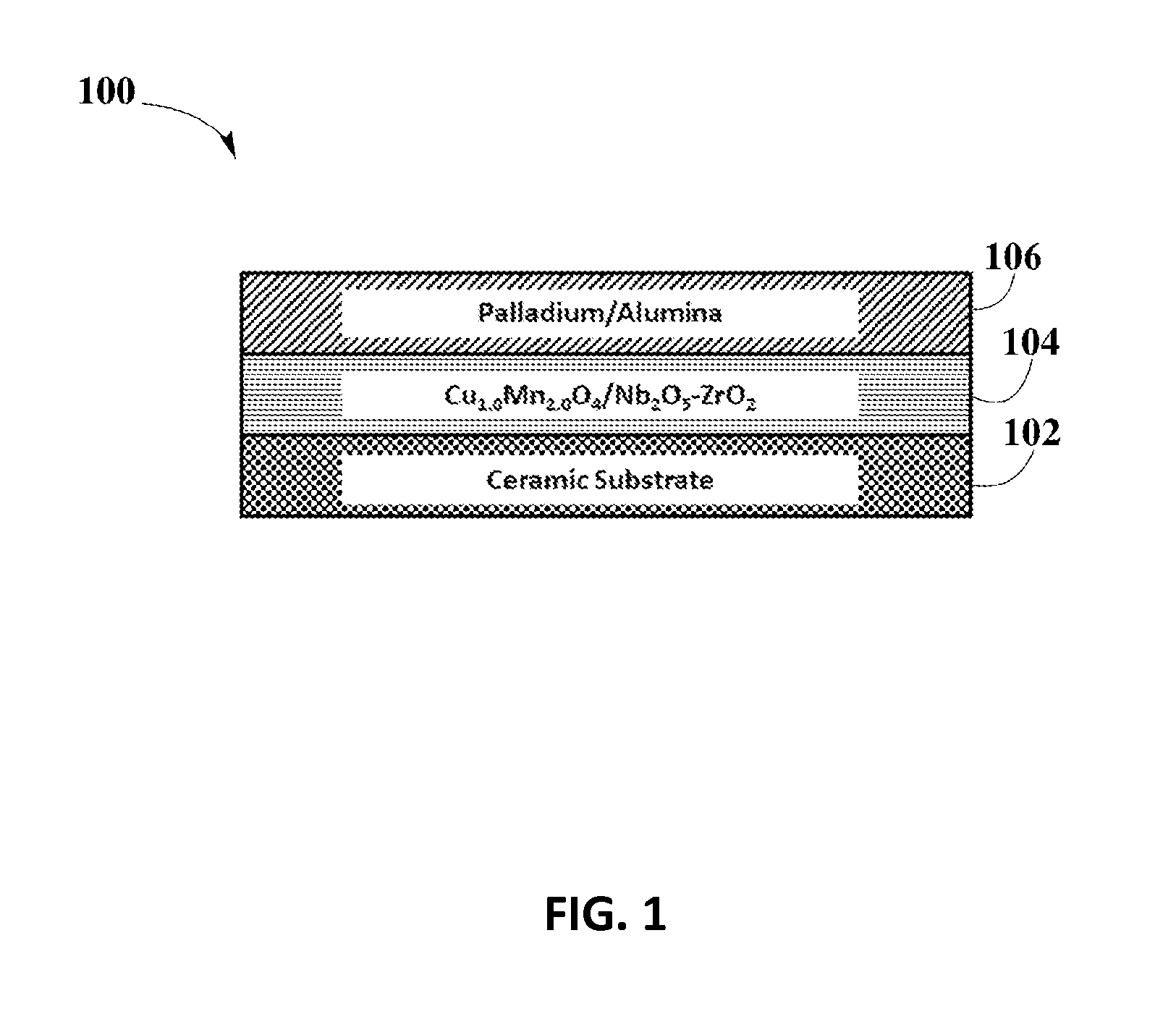
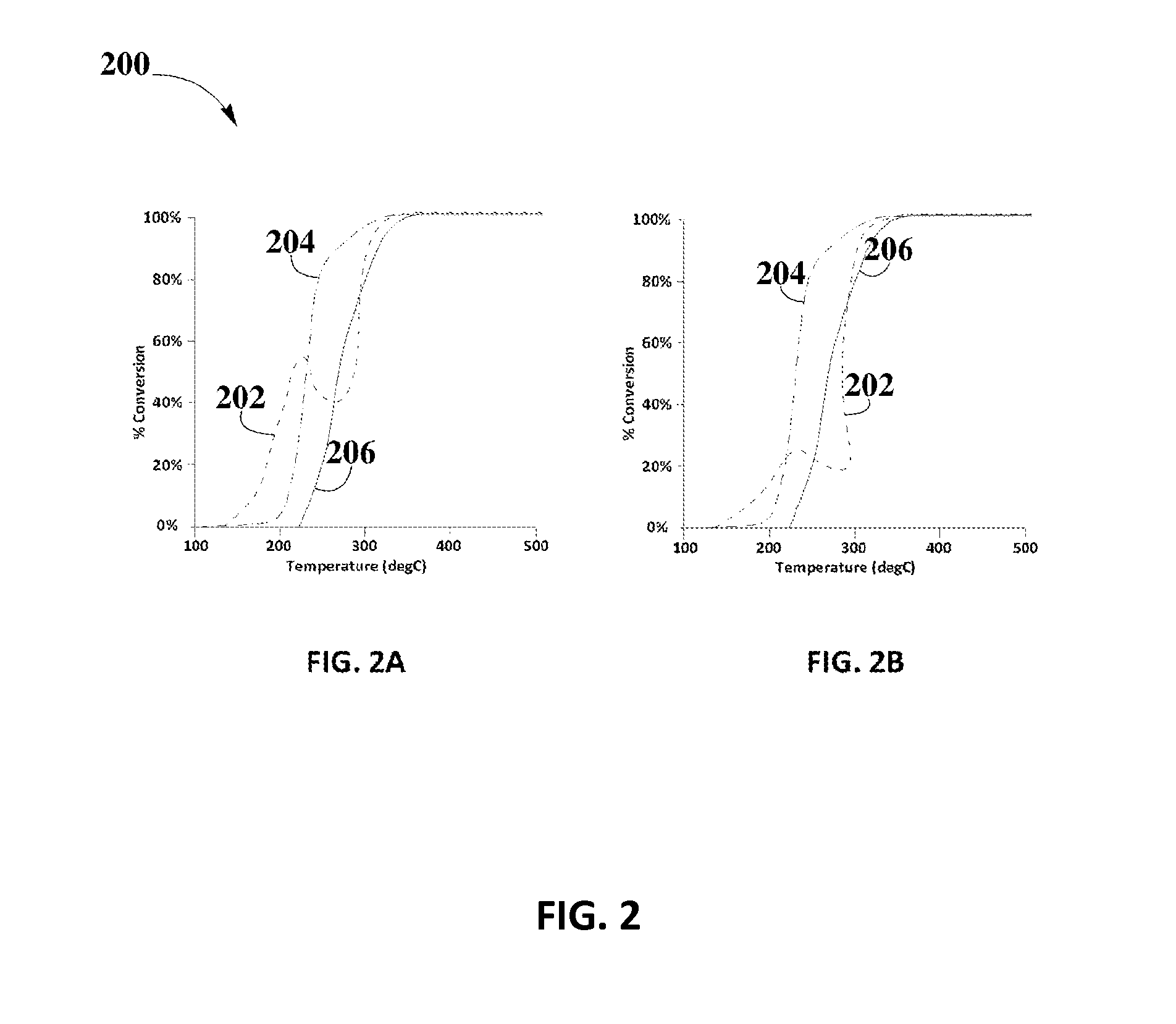
Synergized Platinum Group Metals (SPGM) catalyst system for TWC application is disclosed. Disclosed SPGM catalyst system may include a washcoat with a Cu—Mn spinel structure and an overcoat that includes PGM supported on carrier material oxides, such as alumina. SPGM catalyst system shows significant improvement in nitrogen oxide reduction performance under stoichiometric operating conditions and especially under lean operating conditions, which allows a reduced consumption of fuel. Additionally, disclosed SPGM catalyst system also enhances the reduction of carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon within catalytic converters. Furthermore, disclosed SPGM catalyst systems are found to have enhanced catalyst activity compared to commercial PGM catalyst system, showing that there is a synergistic effect among PGM catalyst and Cu—Mn spinel within the disclosed SPGM catalyst system.
Owner:CLEAN DIESEL TECHNOLOGIES
Reducing oxides of nitrogen using hydrogen generated from engine fuel and exhaust
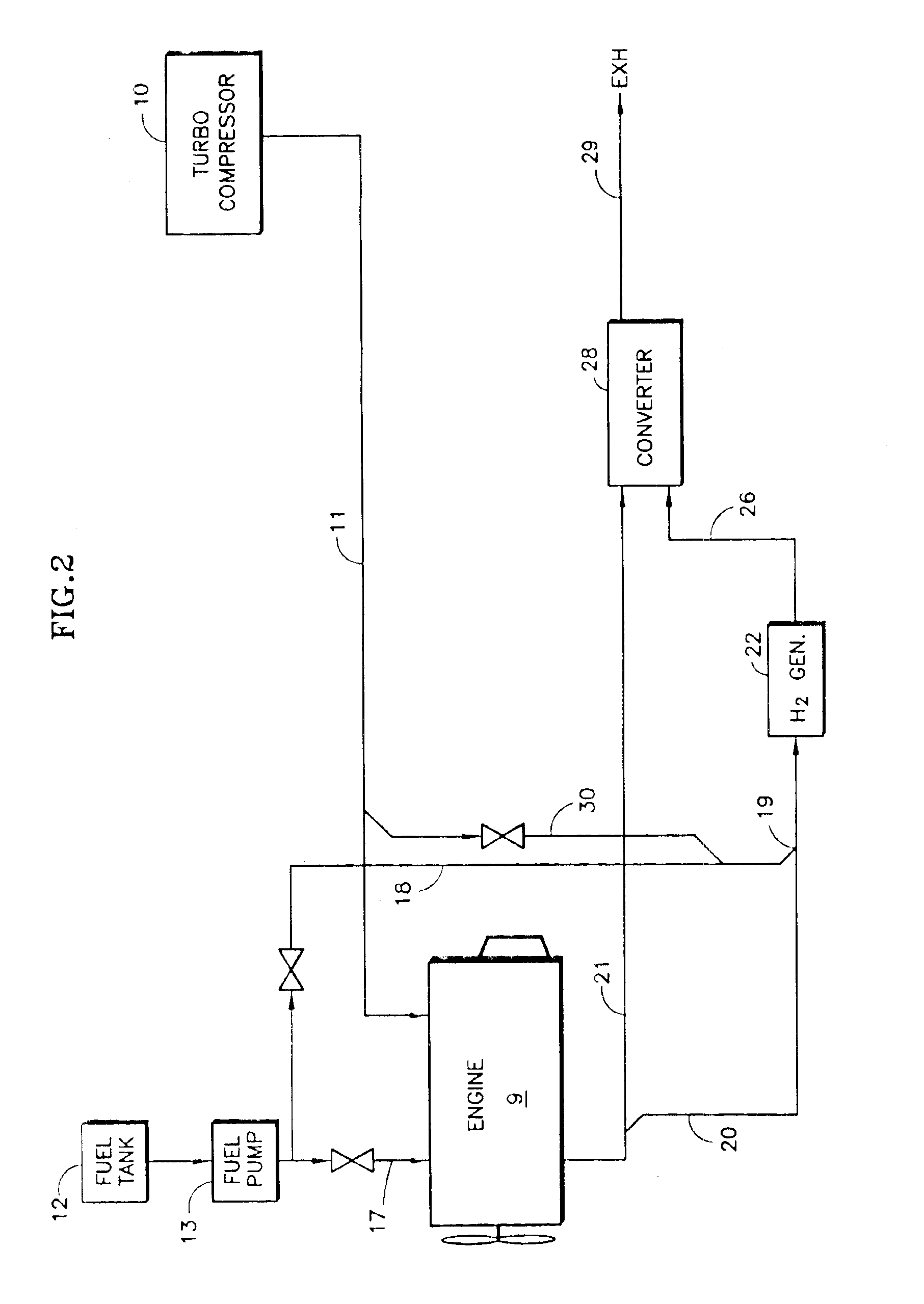
InactiveUS6895746B2Reduce additionalInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusMethaneAir bubble
Either (a) the exhaust (20) of an engine (9) and / or (b) inlet air (11) is sent to a hydrogen generator (22) along with diesel fuel (18) to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide (26) for either (c) mixing with the mainstream of exhaust fed to a catalytic converter (28) or (d) regenerating a pair of NOx adsorption traps (35, 36), thereby reducing oxides of nitrogen (NOx) to provide system exhaust (29) which may have less than 0.20 grams / bhp / hr of NOx and 0.14 grams / bhp / hr of non-methane hydrocarbons. A water recovery unit (52, 63) may extract water from either the exhaust or the effluent of the NOx traps to humidify inlet air (11) for mixture with fuel. Inlet air (11) may be humidified in an air bubbling humidifier (72) that receives water from a condenser (76) that uses inlet air to cool NOx trap effluent.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Biometric authentication system, authentication client terminal, and biometric authentication method
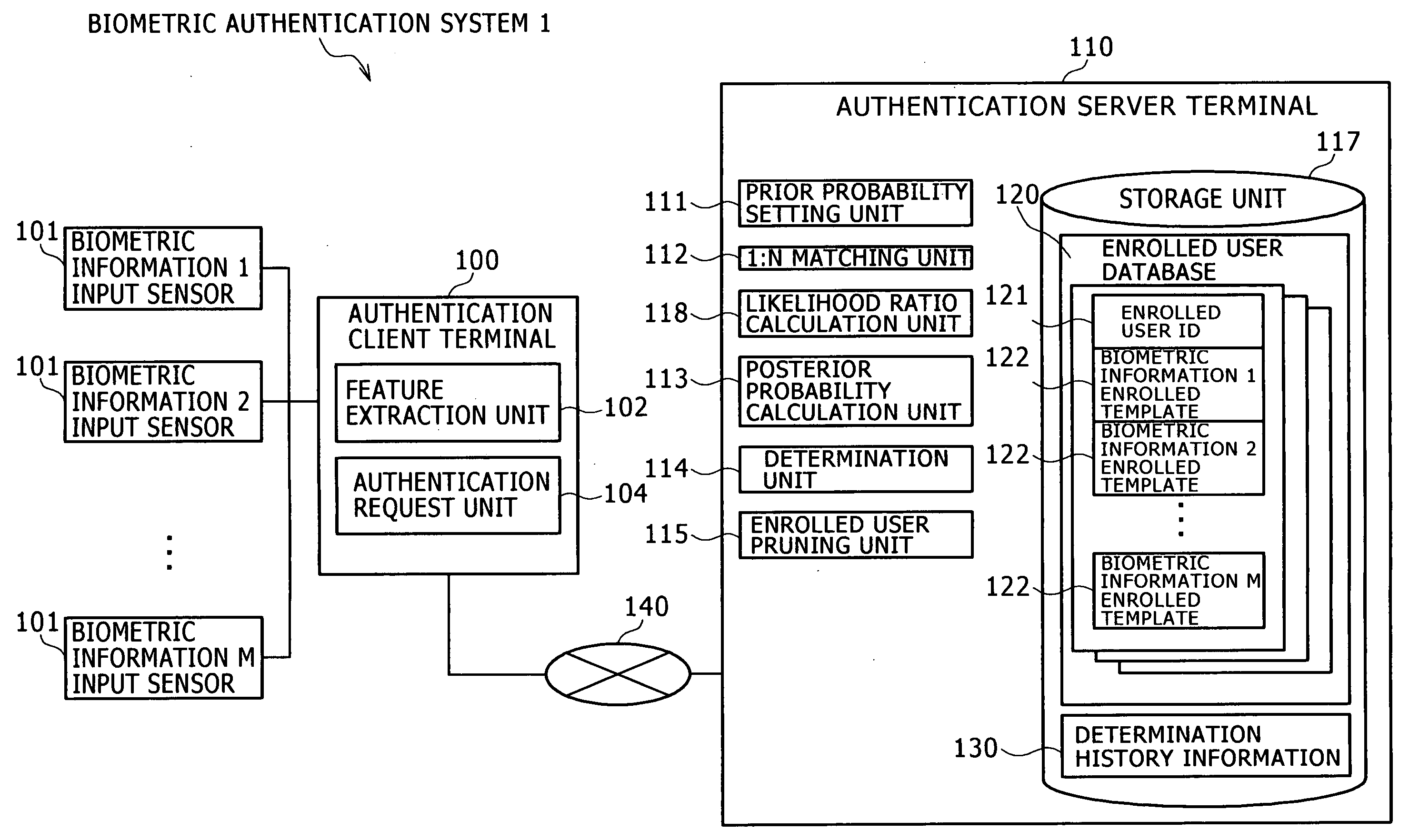
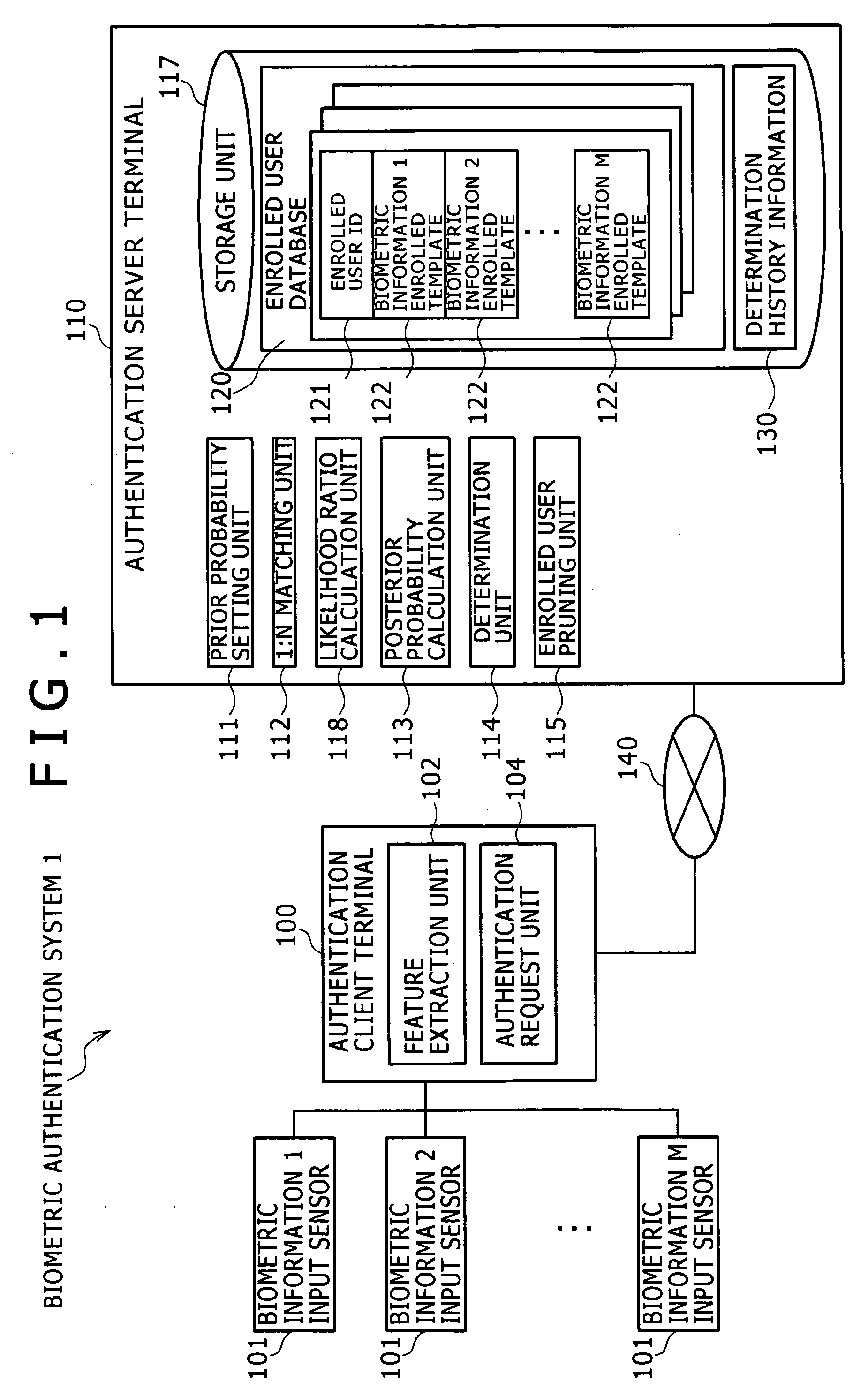
ActiveUS20090289760A1Reduce the number of inputsReduce additionalProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsBiometric dataFeature data
A biometric authentication system, authentication client terminal, and biometric authentication method are provided to reduce an expected value of the number of inputs of biometric data for authentication, while effectively preventing forgery. In a biometric authentication system, prior probabilities of enrolled users un and non-enrolled user u0 are previously set. 1:N matching is performed between feature data of a claimant v and matching feature data. The matching score is calculated for each enrolled user un. A ratio of the likelihood v=un to the likelihood v≠un is calculated for each enrolled user un using the calculated matching scores. Posterior probabilities of the enrolled users un and non-enrolled user u0 are calculated, using the likelihood ratios, and the prior probabilities of both the enrolled users un and the non-enrolled user u0. Then, determination is made by comparing each posterior probability with a first threshold.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
System and method for moving and stretching plastic tissue
InactiveUS7429265B2Minimize necrosisReduce skin problemsSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsElastomerEngineering
A system and method of moving and stretching plastic tissue using dynamic force. An elastomeric driver is adjustably attachable to one or more anchors for securing the elastomer to the plastic tissue, providing a self adjusting system that is capable of exerting relatively constant tension over a certain distance.
Owner:CANICA DESIGN
Power control of a power amplifier
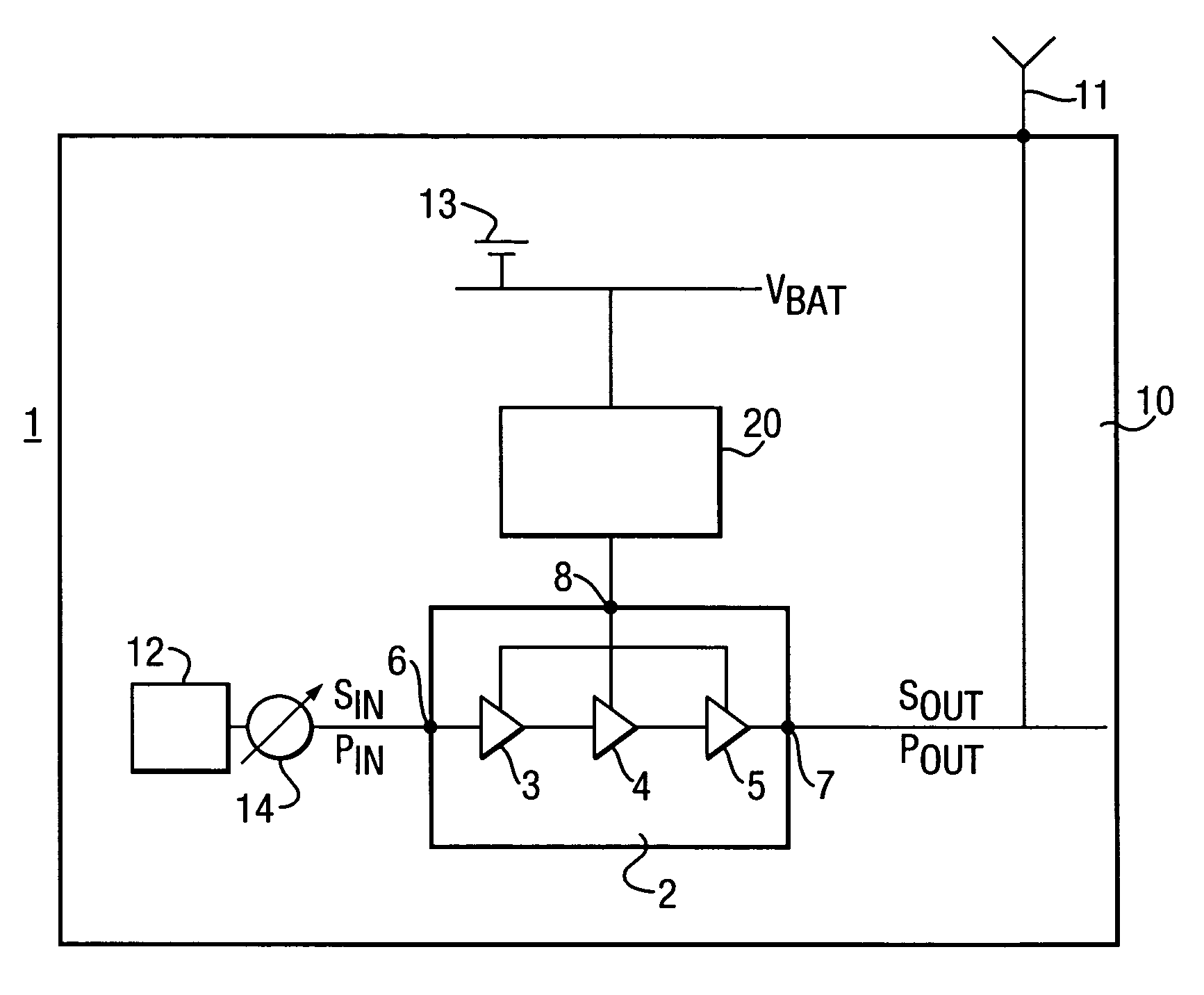
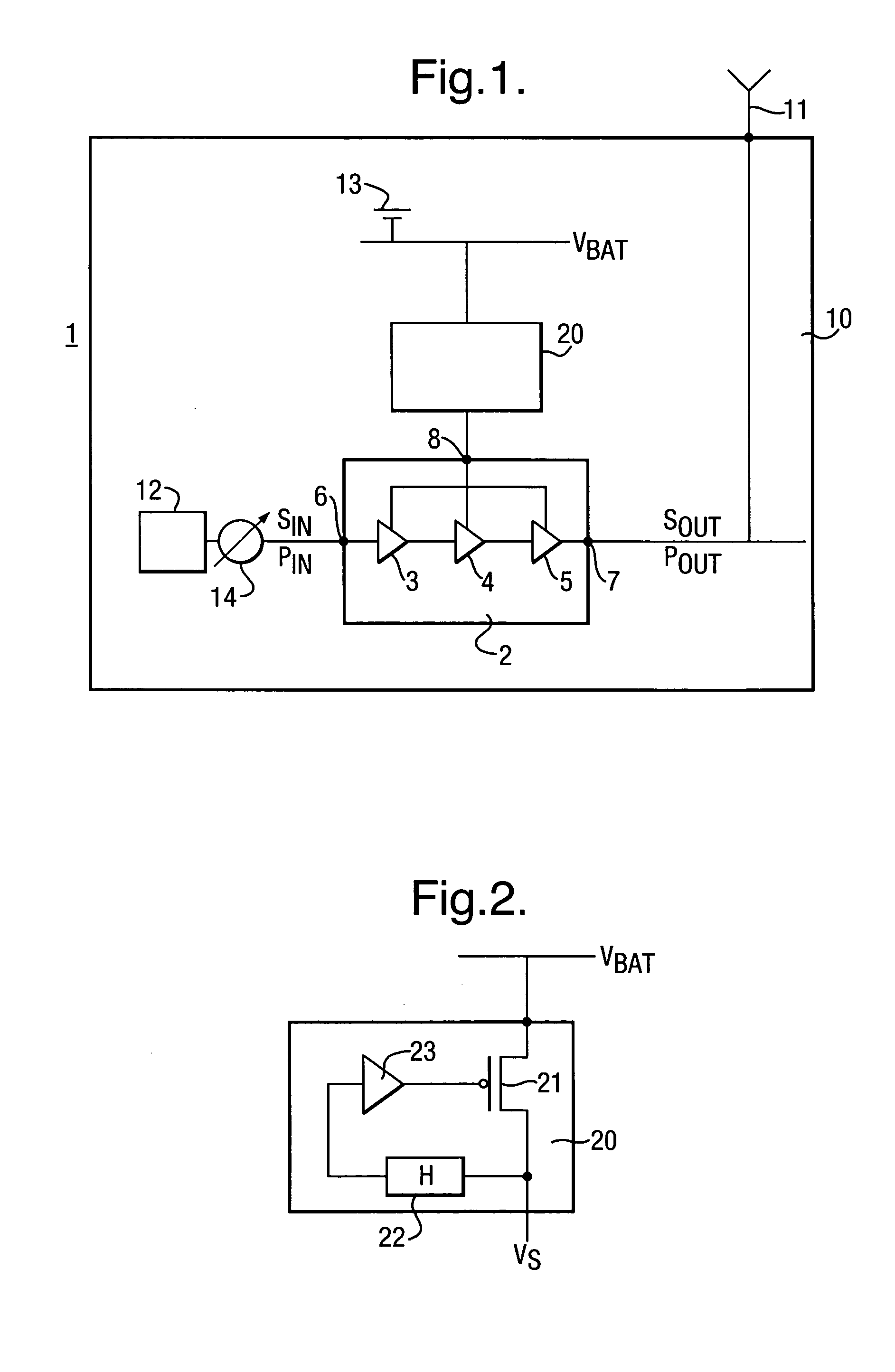
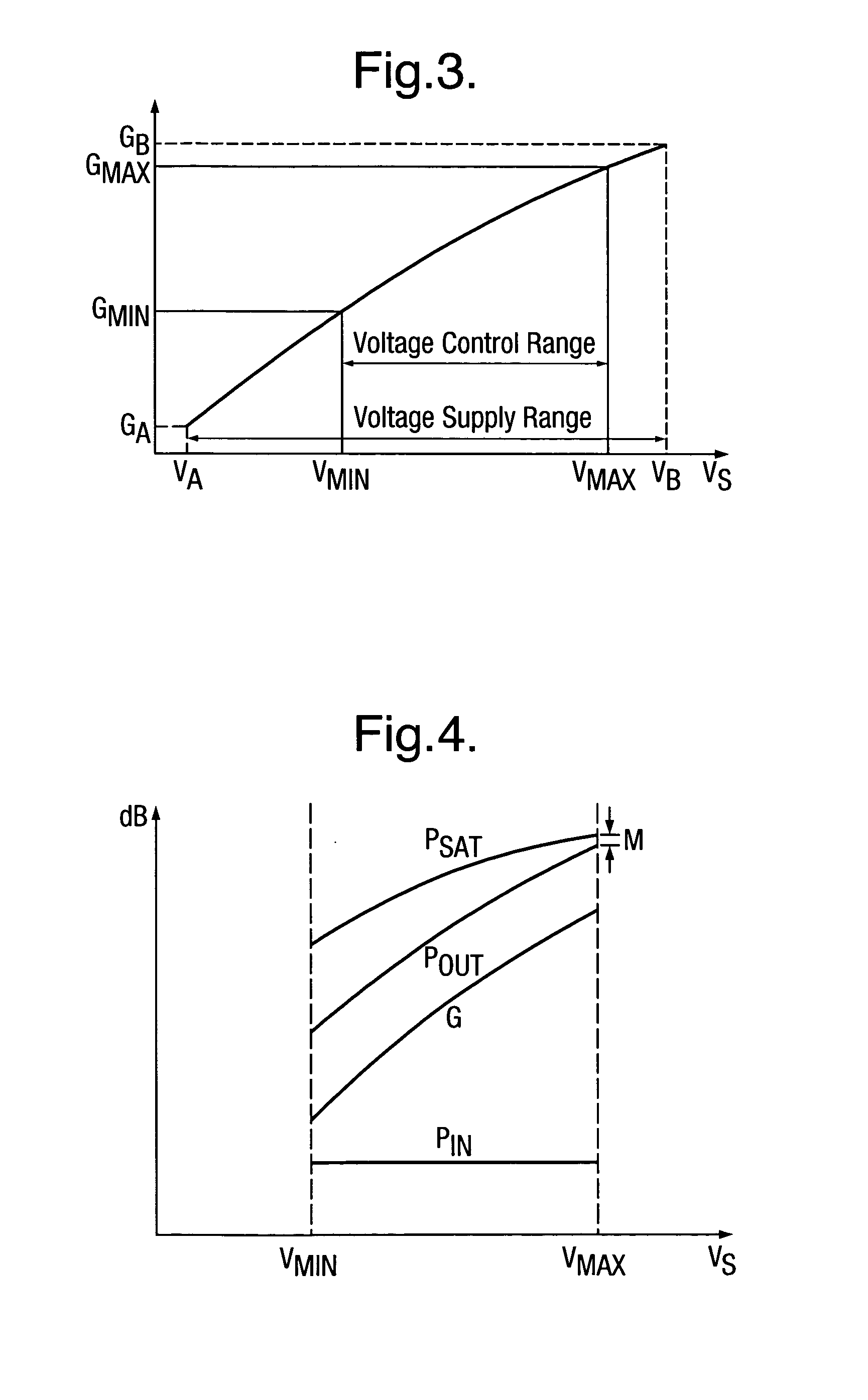
ActiveUS20060006943A1Control distortionReduce output powerGain controlPower amplifiersVariable-gain amplifierAudio power amplifier
To effect power control of a power amplifier 2 having three amplifier stages 3, 4 and 5 used to amplify input signals modulated in accordance with a variable envelope modulation scheme, there is used a power amplifier 2 having a gain which reduces as the supply voltage to the power amplifier 2 reduces, and the output power POUT of the power amplifier 2 is controlled by regulation of the supply voltage VS. Taking advantage of the reduction in gain of the power amplifier 2, it is ensured that, in respect of each respective amplifier stage 3, 4 and 5 and at each respective value of the supply voltage in the voltage control range, the output power POUT of the respective amplifier stage 3, 4 and 5 is less than the saturation output power PSAT of the respective amplifier stage 3, 4 and 5. As a result, distortion of the signal is reduced. The power control technique improves efficiency over known techniques of backing off the output power and using a variable gain amplifier stage to control the output power.
Owner:SONY EUROPE BV
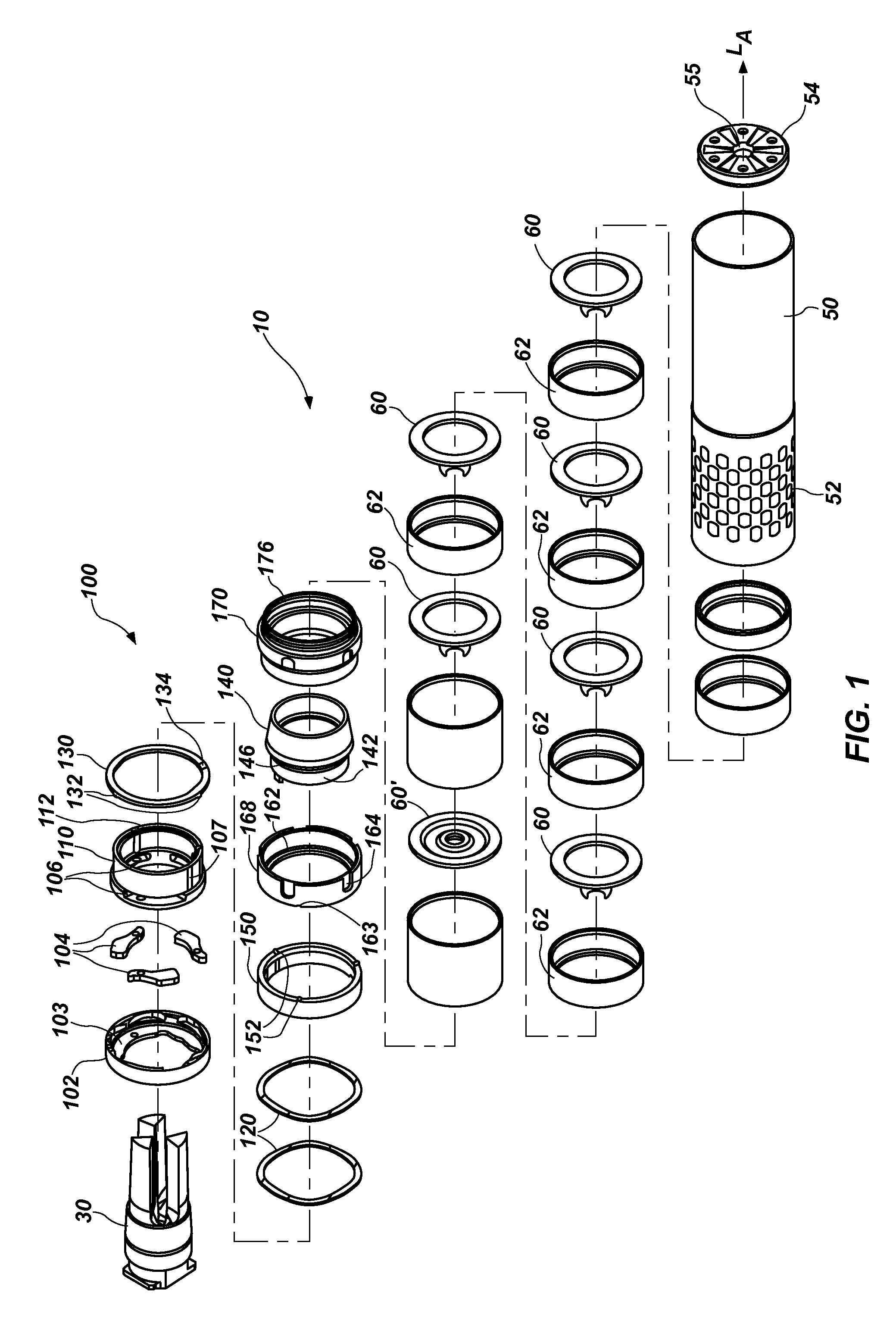
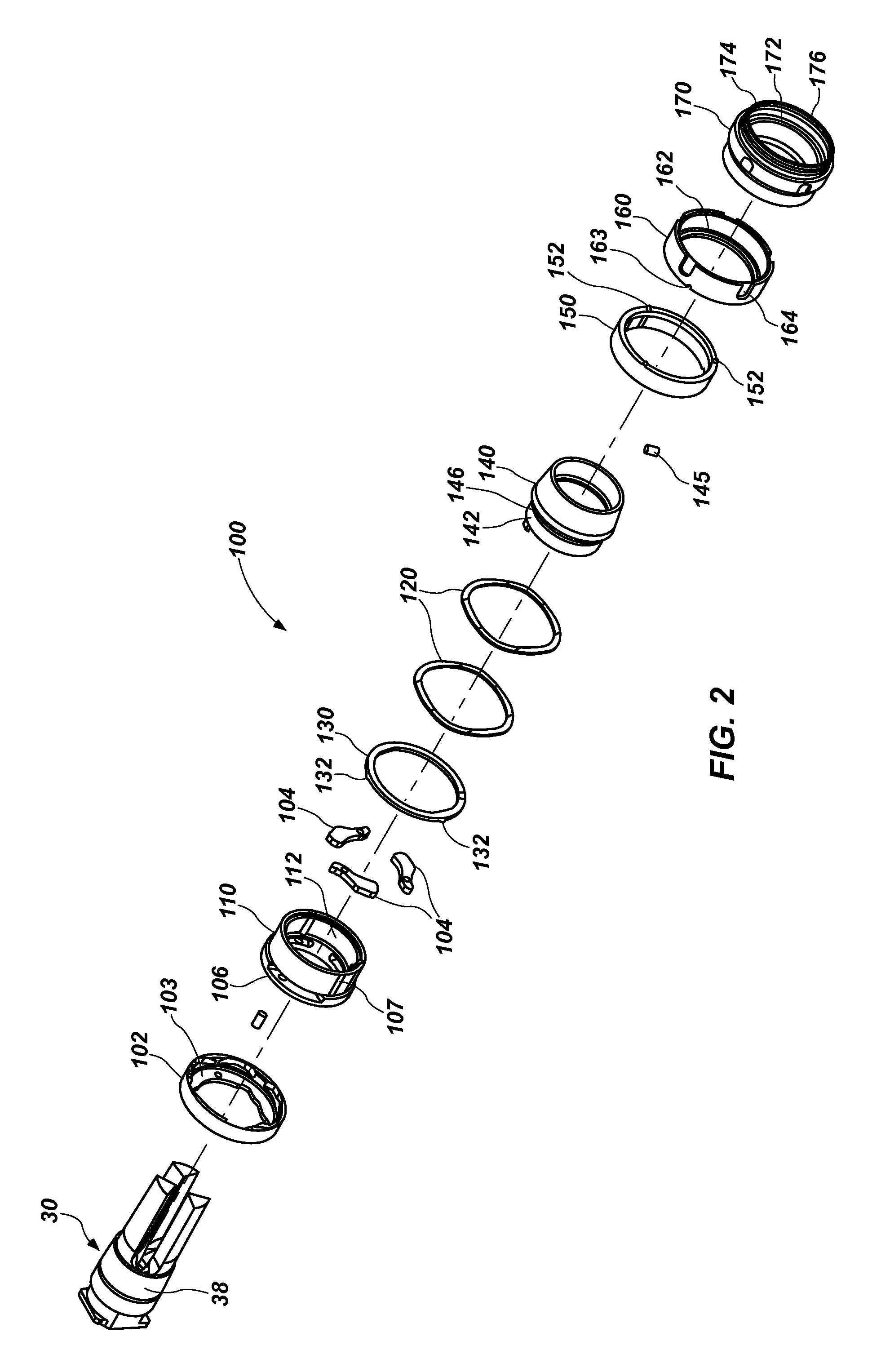
Firearm noise suppressor system
Owner:SILENCERCO LLC
Self-rechargeable alkaline battery
InactiveUS20060257734A1Improve charge retentionIncrease surface areaNon-aqueous electrolyte cellsElectrolyte/reactants regenerationManganese oxidePotassium hydroxide
Disclosed herein is a self-rechargeable alkaline battery. The battery comprises a cathode and an anode, at least one of which is constructed of a metallic plate, an electrode receptor equipped to the cathode, an electrode donor equipped to the anode, a separator provided between the electrode donor and the electrode receptor, an electrolyte comprising an aqueous potassium hydroxide solution and an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution and having at least one powdered material selected from the group consisting of aluminum oxide, manganese oxide, and silicon oxide. The battery has a self-rechargeable ability, stable output characteristics, and a remarkably increased life span.
Owner:PICO SCI CORP
Soil remediation of mercury contamination
InactiveUS6962466B2Limited effectivenessHigh densityGas treatmentDry-docksSoil remediationMercury contamination
An in situ soil remediation system may be used to remove or reduce levels of mercury contamination within soil. The soil remediation system may also remove or reduce levels of other contaminants within the soil. Mercury may be vaporized within the soil by a heating system. The vaporized mercury may be removed from the soil by a vacuum system. The vaporized mercury may pass through heated risers that elevate the vaporized mercury. After the vaporized mercury passes from the heated risers, the vaporized mercury may be allowed to cool, condense, and flow downward to a treatment facility. Removing mercury from the soil as a vapor may provide an economical, safe, and efficient way to remediate mercury contaminated soil.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
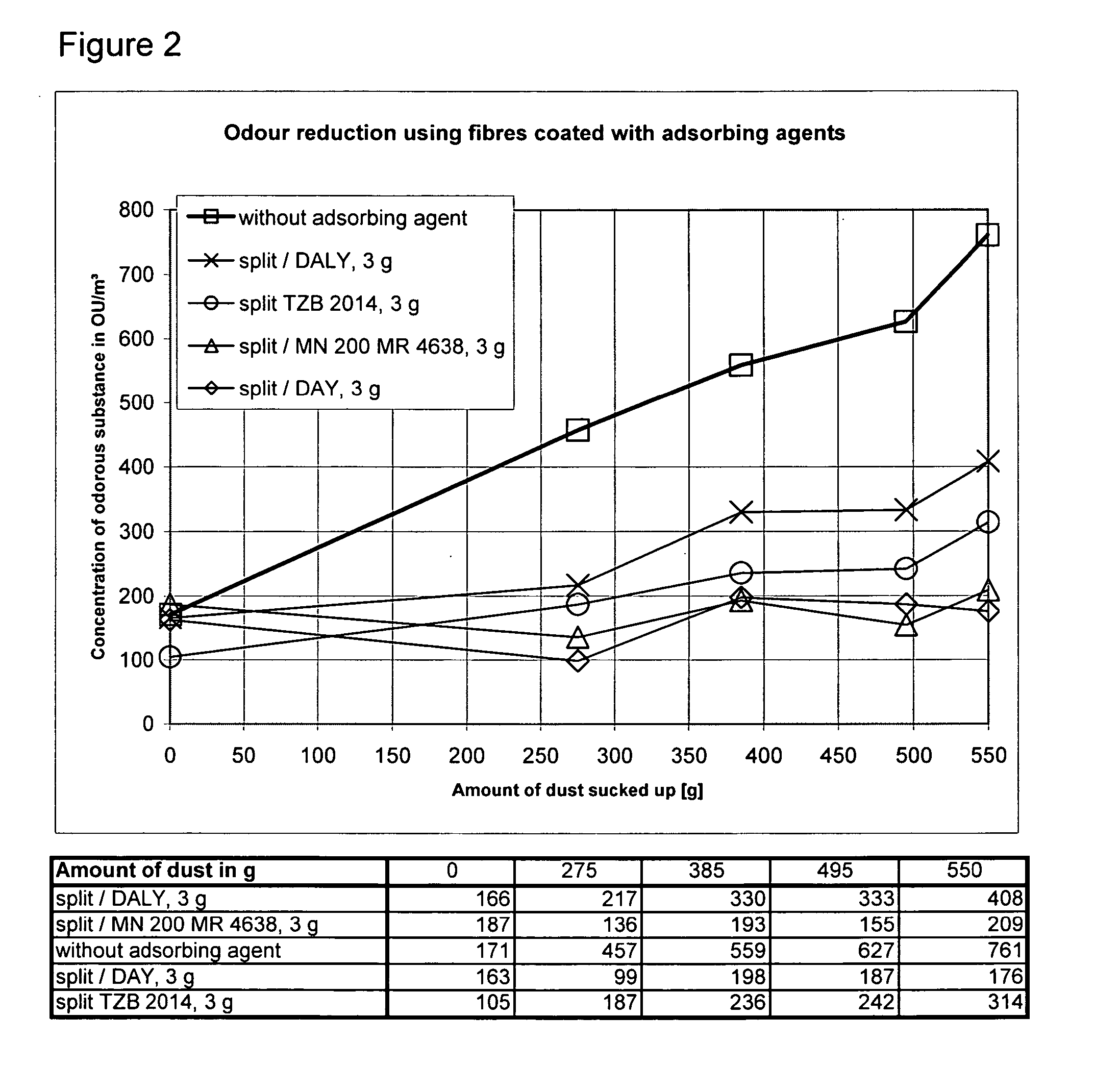
Adsorbing Agent, Dust Collection Chamber And Method For Adsorbing Odours
ActiveUS20080017036A1Good effectReduce additionalDispersed particle filtrationIsotope separationFiberSorbent
Owner:EUROLIFTERS HLDG NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com