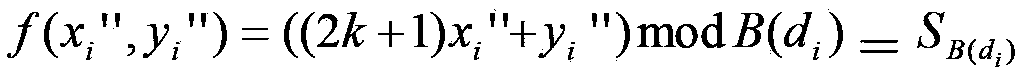Patents
Literature
151results about How to "Control distortion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
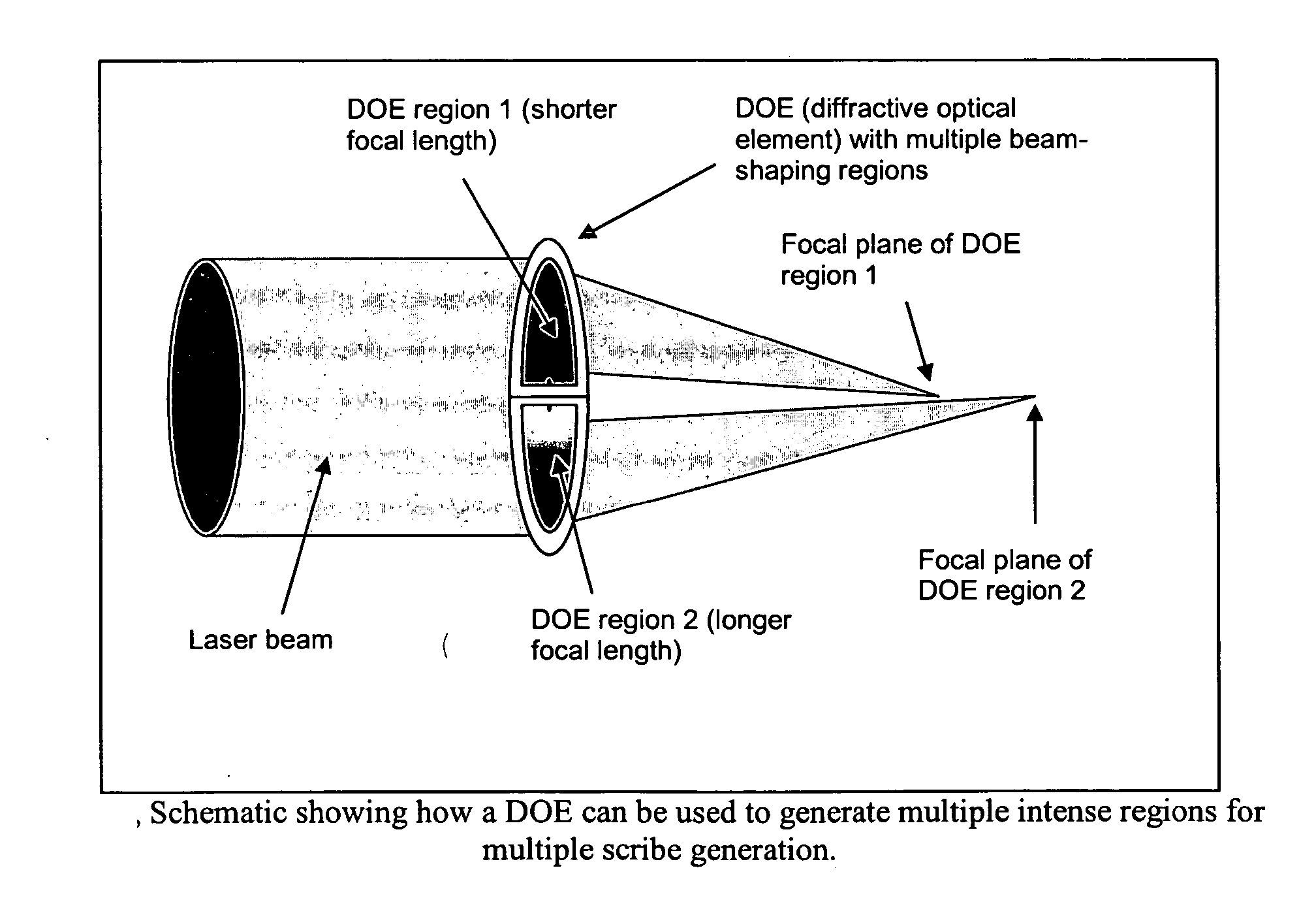
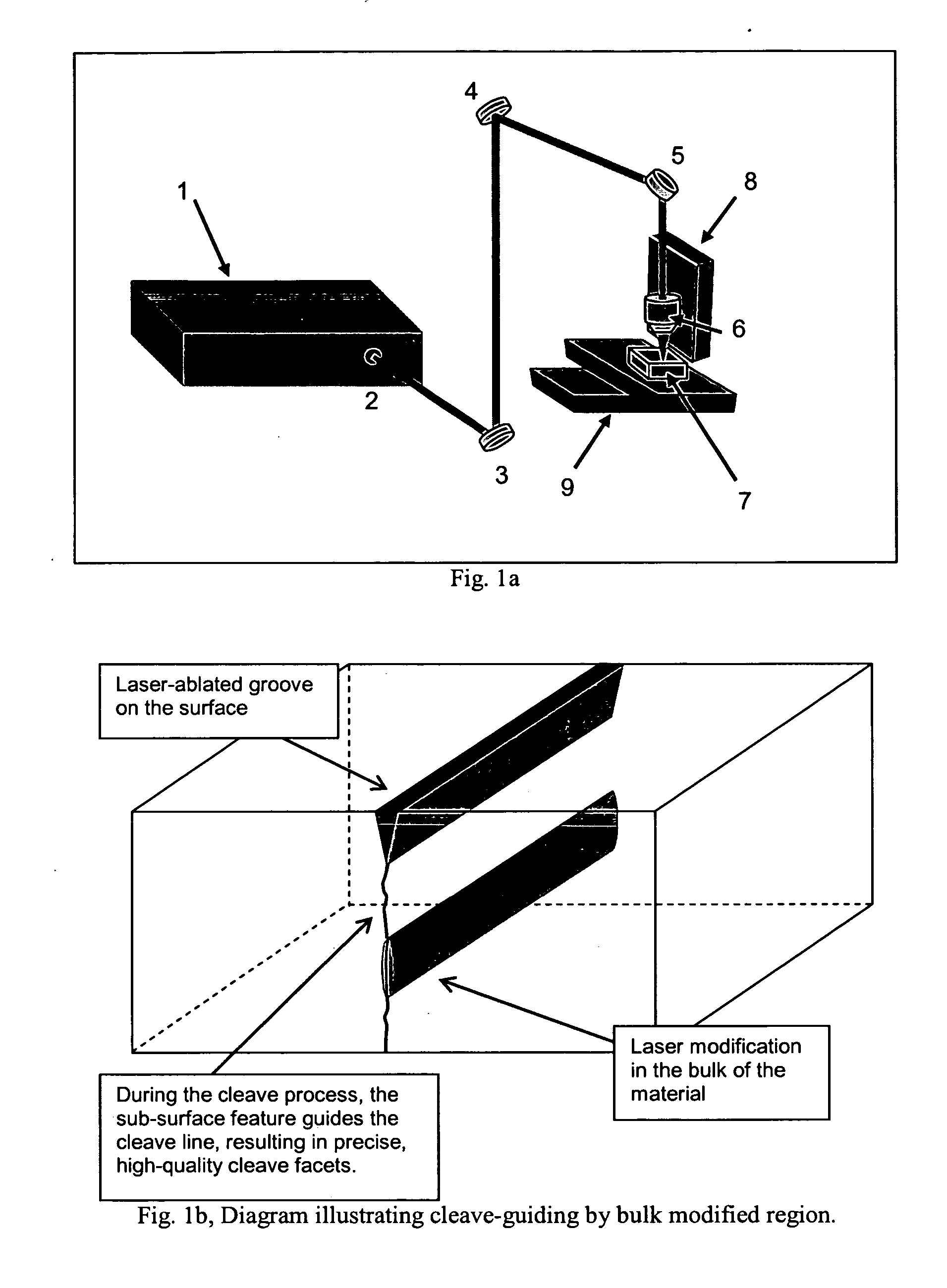
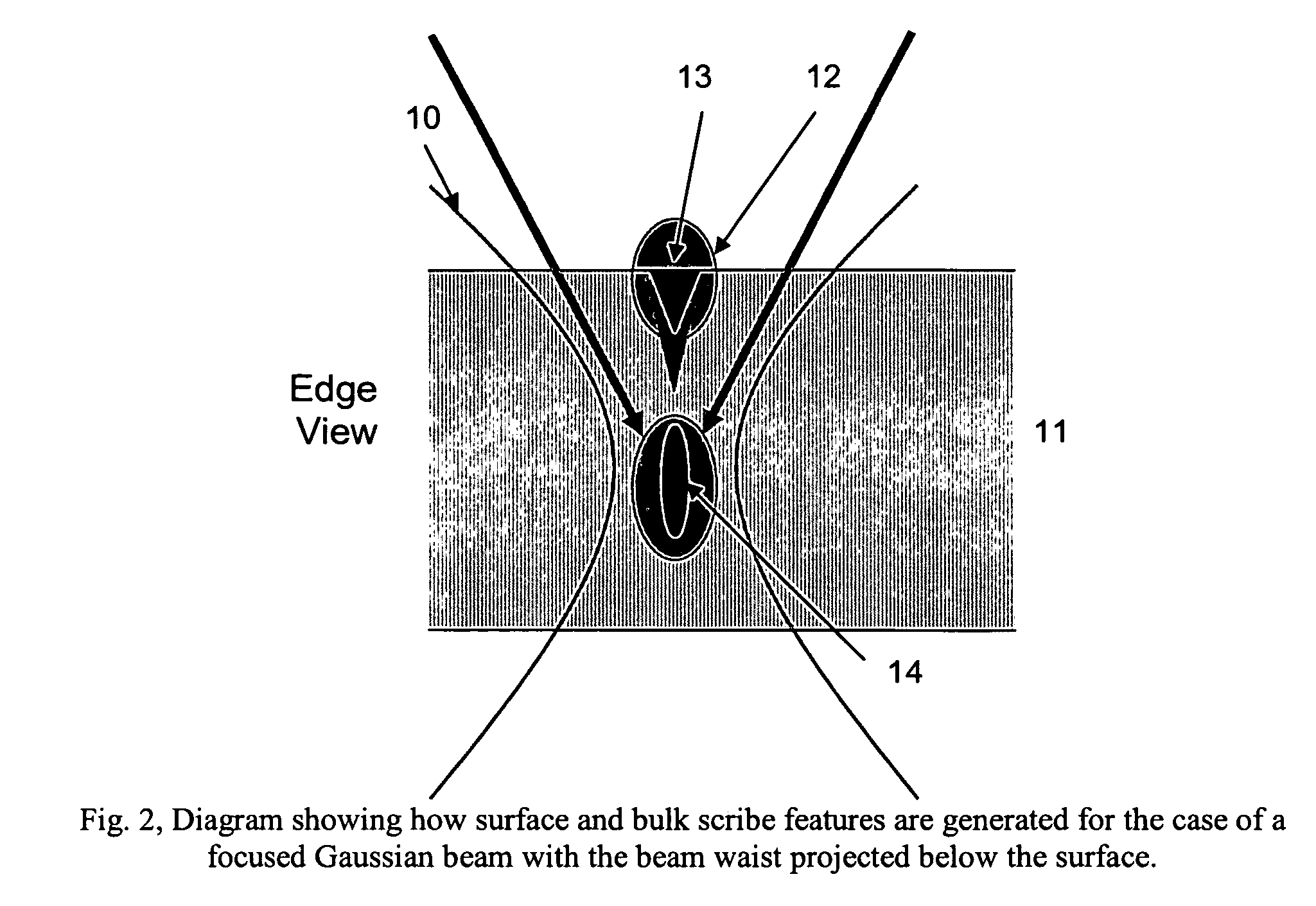
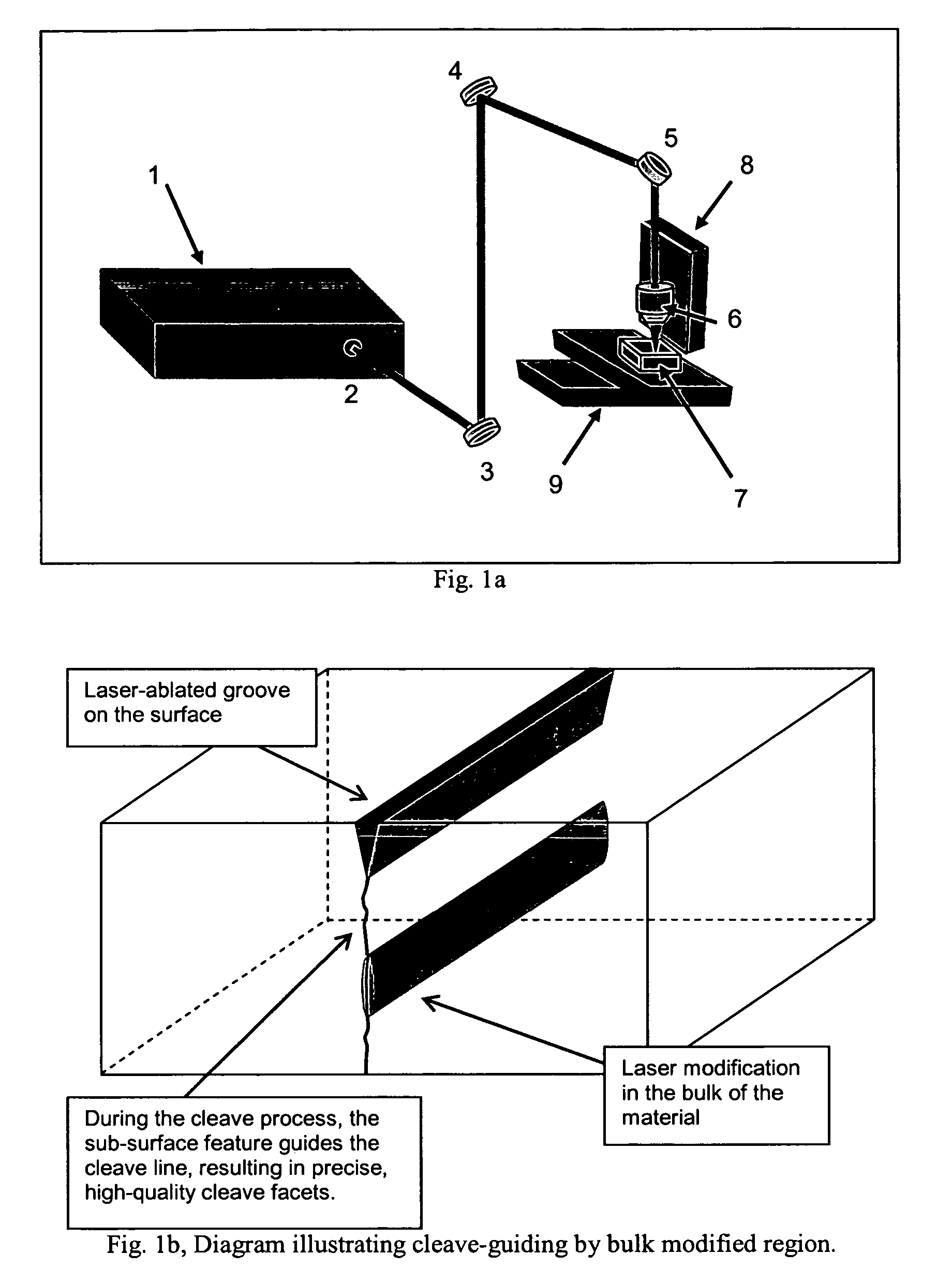
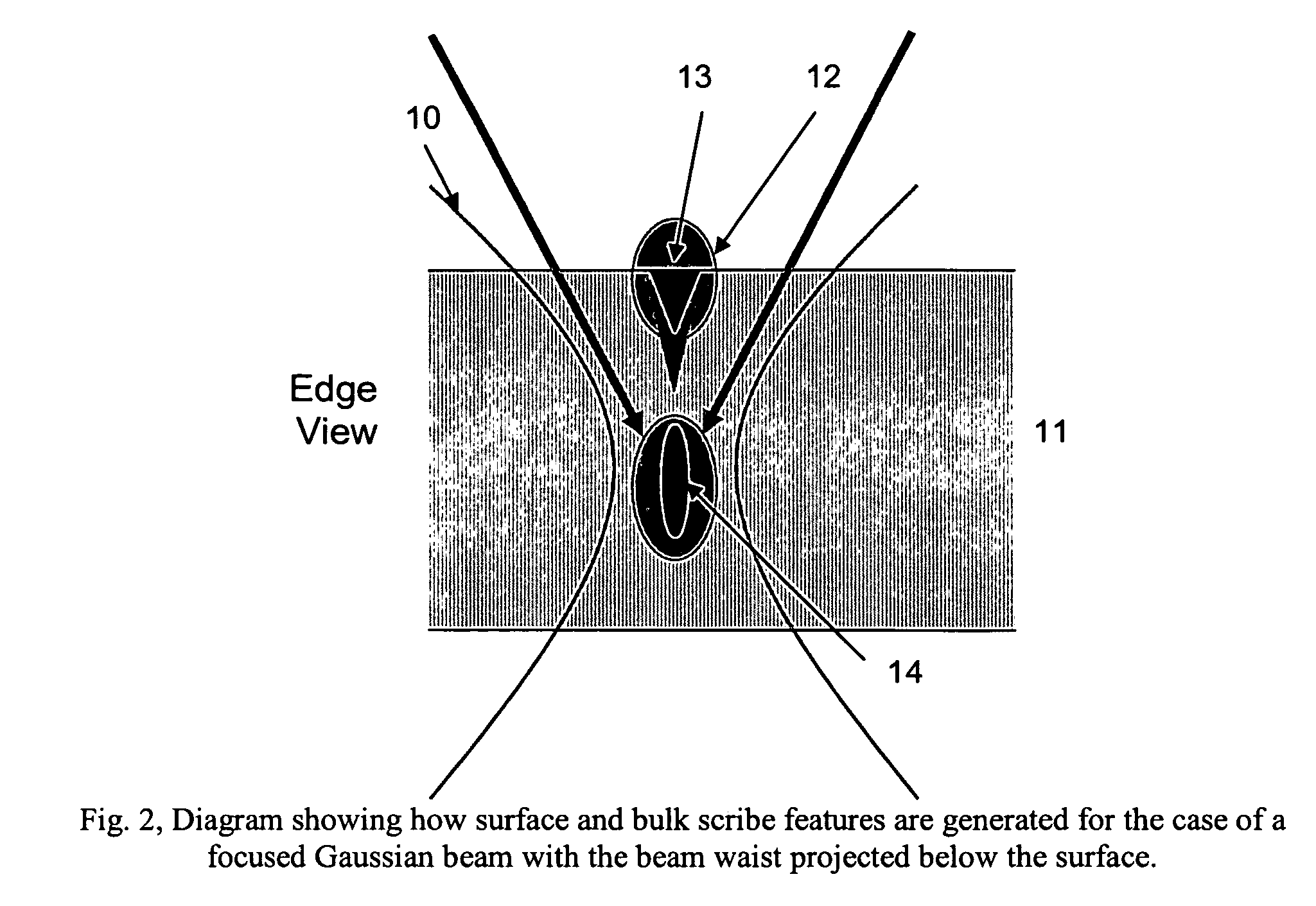
Transparent material processing with an ultrashort pulse laser
InactiveUS20070051706A1Reduce quality problemsPoor precisionFixed microstructural devicesThin material handlingHigh energyNonlinear absorption
Methods for ultrashort pulse laser processing of optically transparent materials. A method for scribing transparent materials uses ultrashort laser pulses to create multiple scribe features with a single pass of the laser beam across the material, with at least one of the scribe features being formed below the surface of the material. This enables clean breaking of transparent materials at a higher speed than conventional techniques. Slightly modifying the ultrashort pulse laser processing conditions produces sub-surface marks. When properly arranged, these marks are clearly visible with side-illumination and not clearly visible without side-illumination. In addition, a method for welding transparent materials uses ultrashort laser pulses to create a bond through localized heating. The ultrashort pulse duration causes nonlinear absorption of the laser radiation, and the high repetition rate of the laser causes pulse-to-pulse accumulation of heat within the materials. The laser is focused near the interface of the materials, generating a high energy fluence at the region to be welded. This minimizes damage to the rest of the material and enables fine weld lines.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Methods, computer program products, apparatuses, and systems to accommodate decision support and reference case management for diagnostic imaging
ActiveUS20090274384A1High resolutionLimiting problem pixelizationStill image data indexingCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionReference case
A method, apparatus, and computer program product are provided to accommodate decision support and reference case management for diagnostic imaging. An apparatus may include a processor configured to receive a request for an image from a client device. The processor may be further configured to retrieve a source image corresponding to the requested image from a memory. The processor may additionally be configured to process the source image to generate a second image having a greater resolution than the source image. The processor may also be configured to provide the second image to the client device to facilitate viewing and manipulation of the second image at the client device. Corresponding methods and computer program products are also provided.
Owner:CHANGE HEALTHCARE HLDG LLC
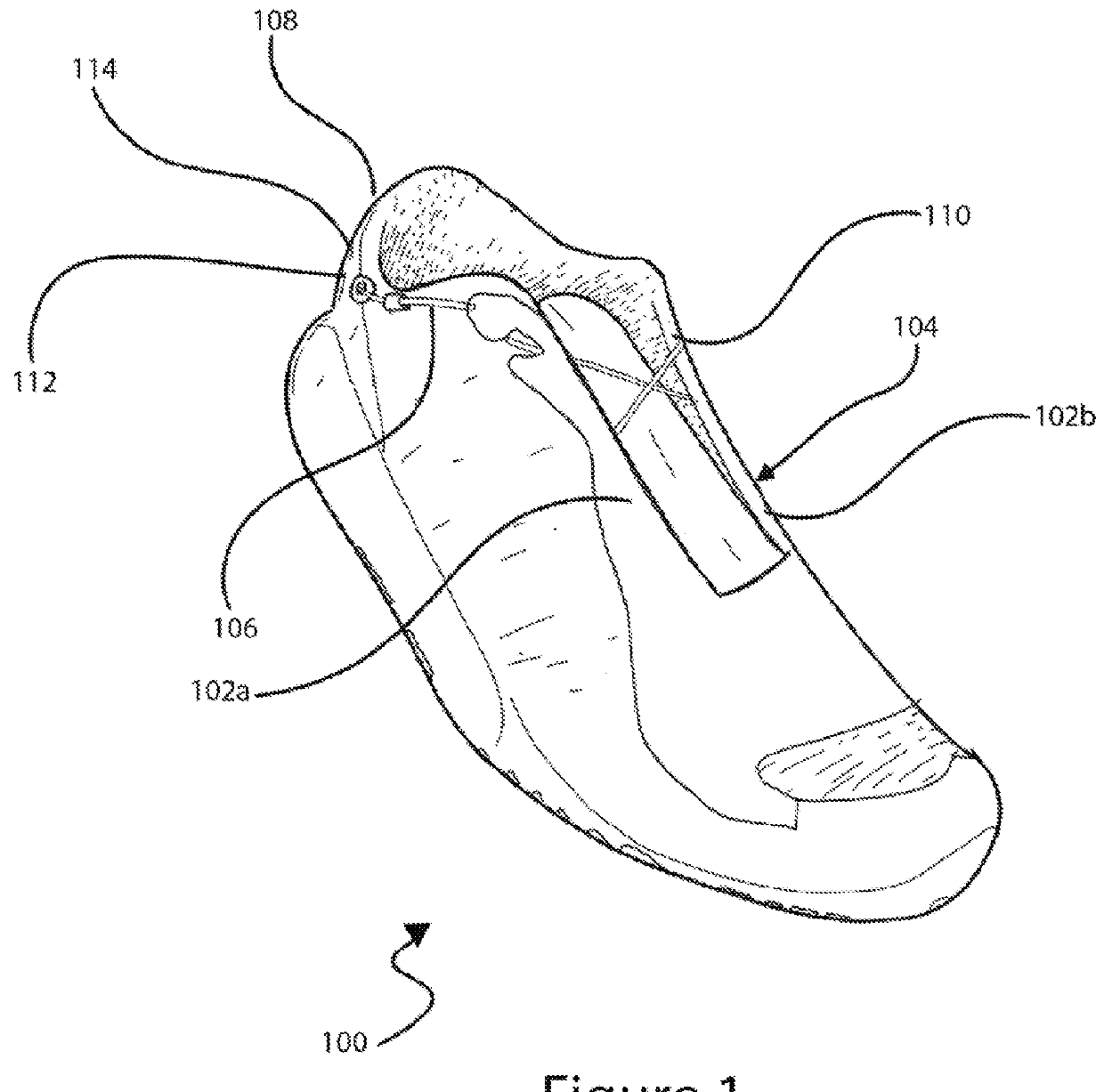
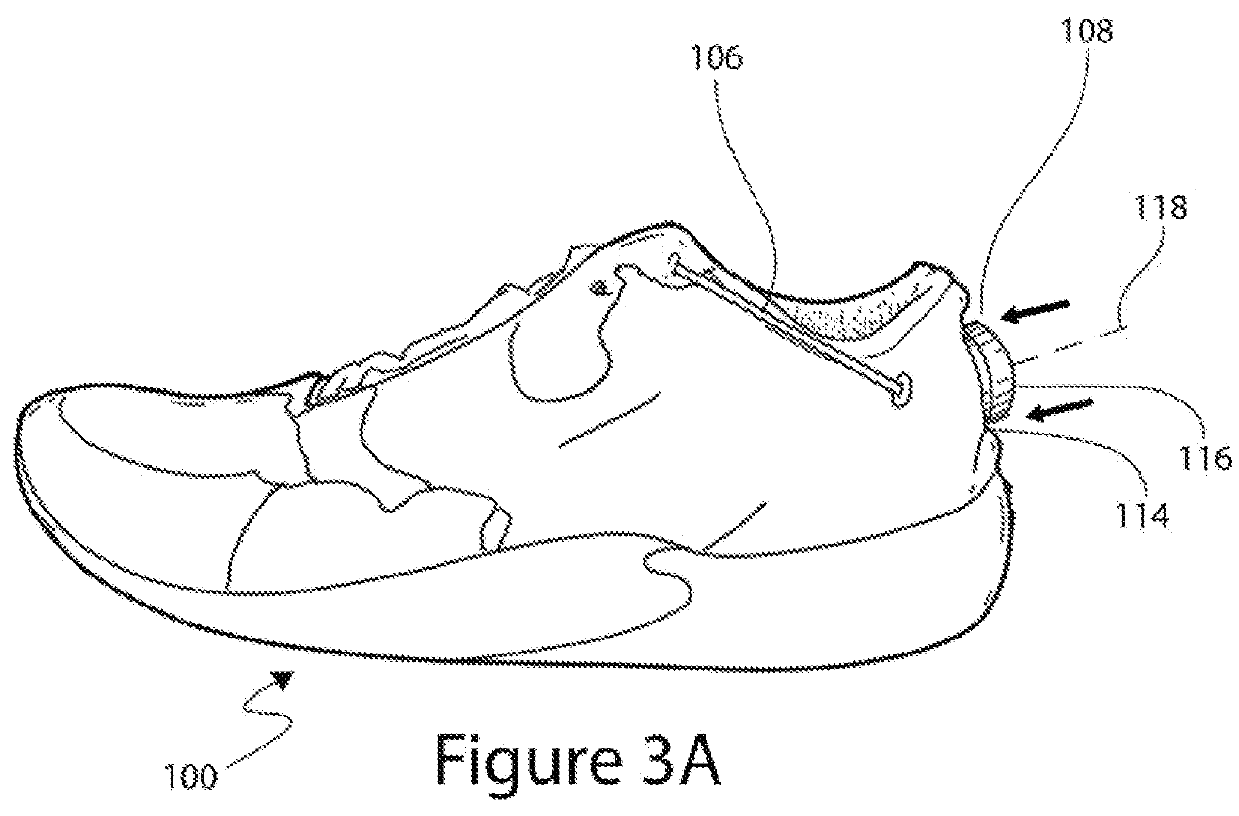
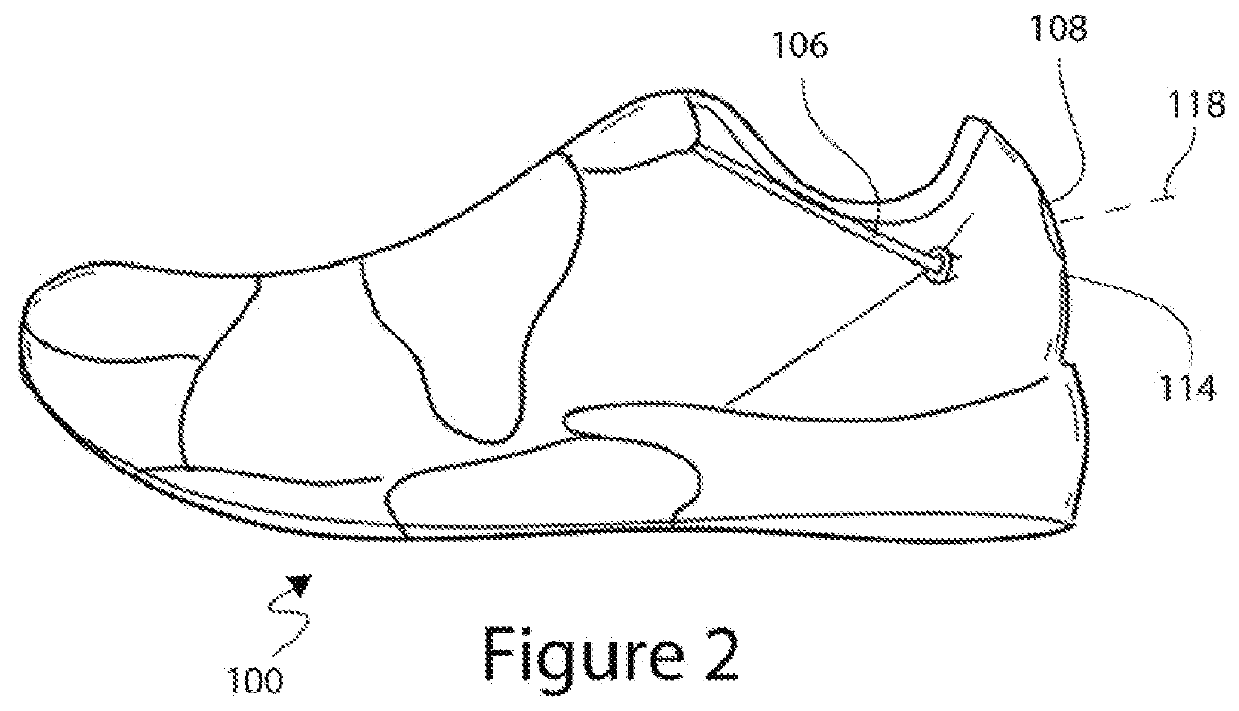
Tightening mechanisms and applications including the same
ActiveUS20130269219A1Reduce the overall heightEasy to returnMetal-working apparatusShoe lace fasteningsEngineeringMechanical engineering
This disclosure relates to articles that include a tightening mechanism, such as reel-based lace tightening mechanism, configured to tighten the article by rotation of a knob. The articles can include a concealing portion that is configured to conceal or protect at least a portion of the tightening mechanism, such as the knob. The concealing portion can be configured to prevent unintentional actuation of the tightening mechanism, such as during contact sports. The concealing portion can be configured to hide the tightening mechanism from view to improve the visual appearance of the article. The concealing portion can be collapsible such that a user can press the concealing portion down to expose the knob of the tightening mechanism.
Owner:BOA TECHNOLOGY
Fiber incorporating quantum dots as programmable dopants
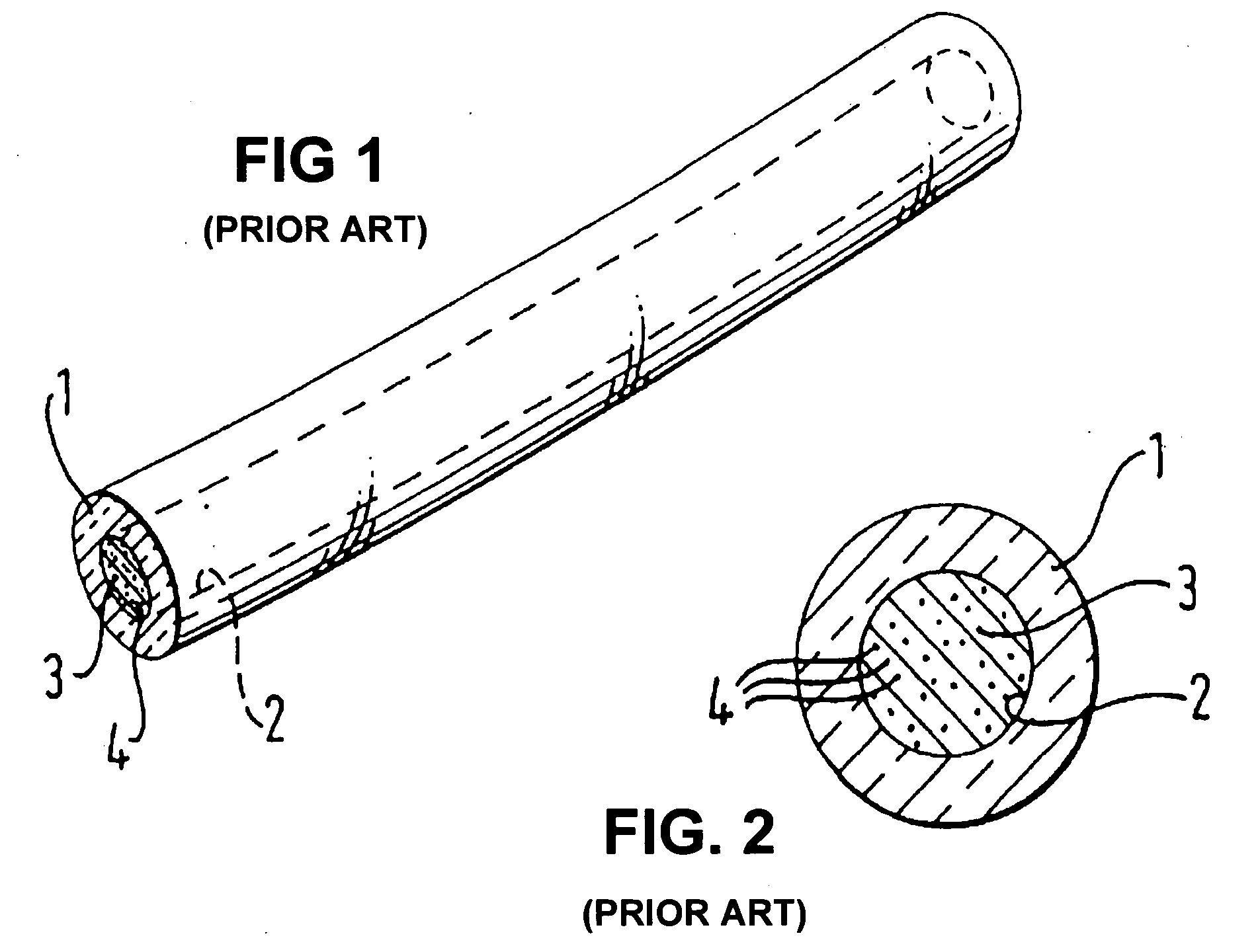
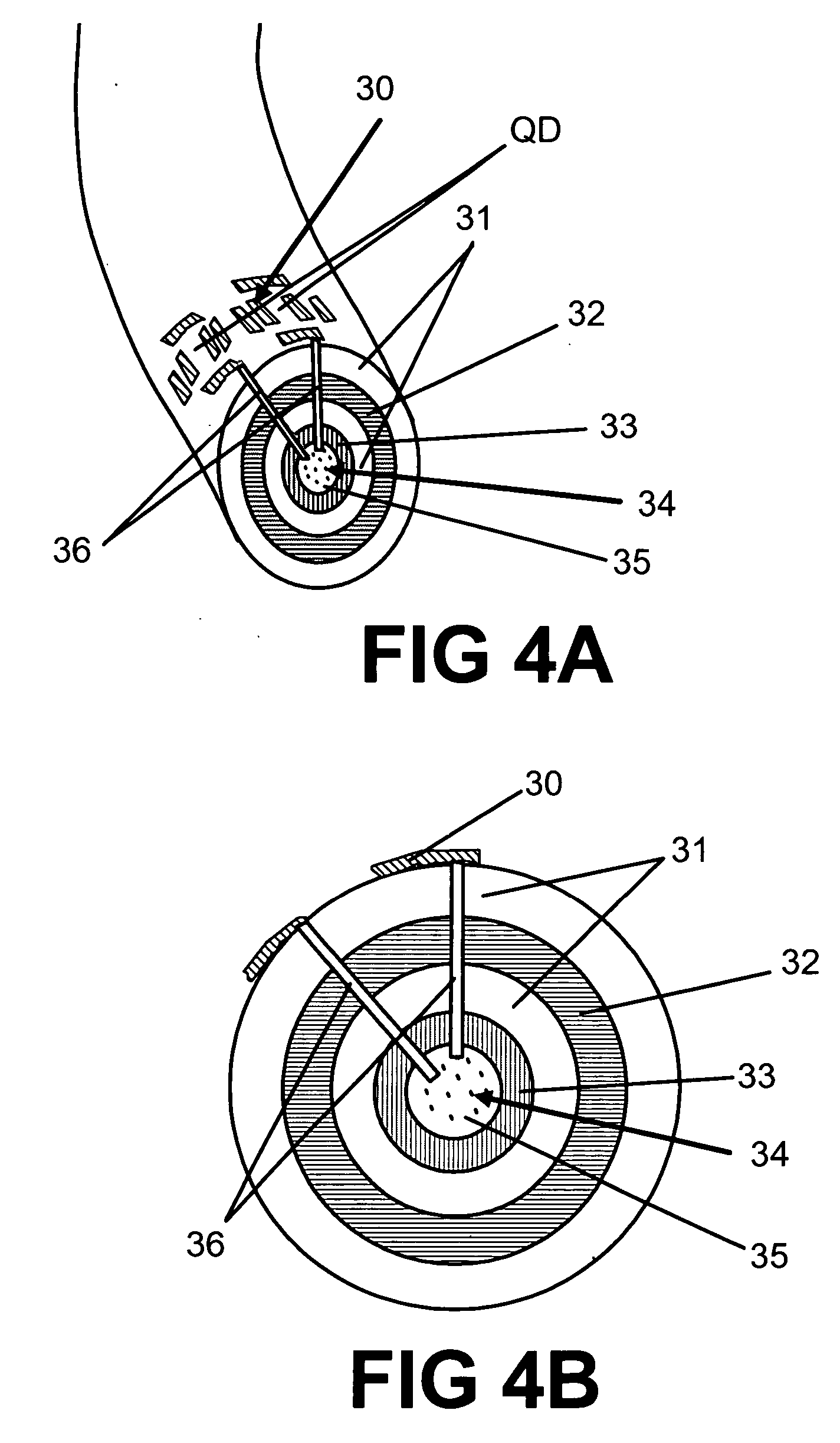
InactiveUS6978070B1Control distortionAltering their doping characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyCladded optical fibreFiberArtificial atom
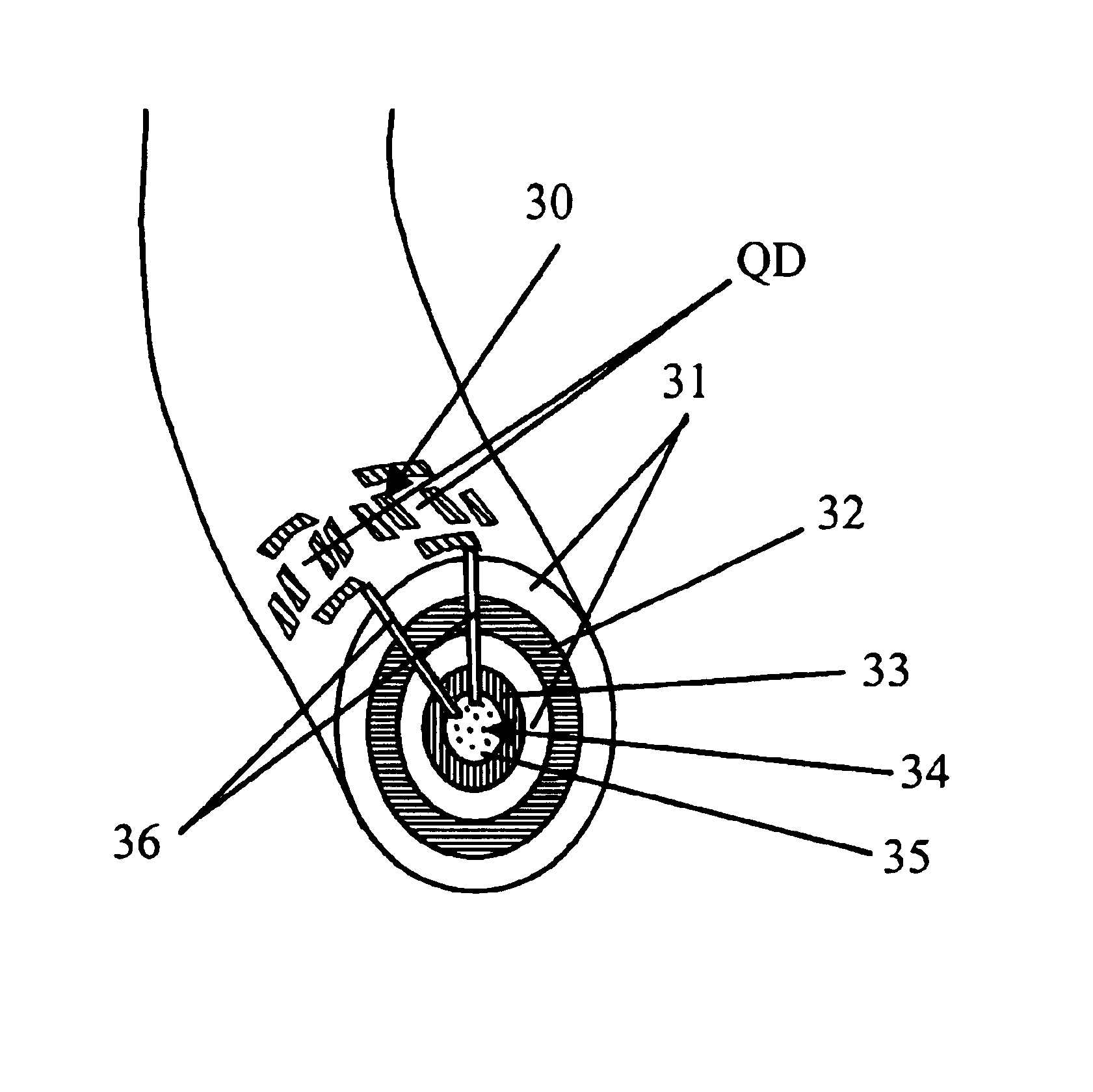
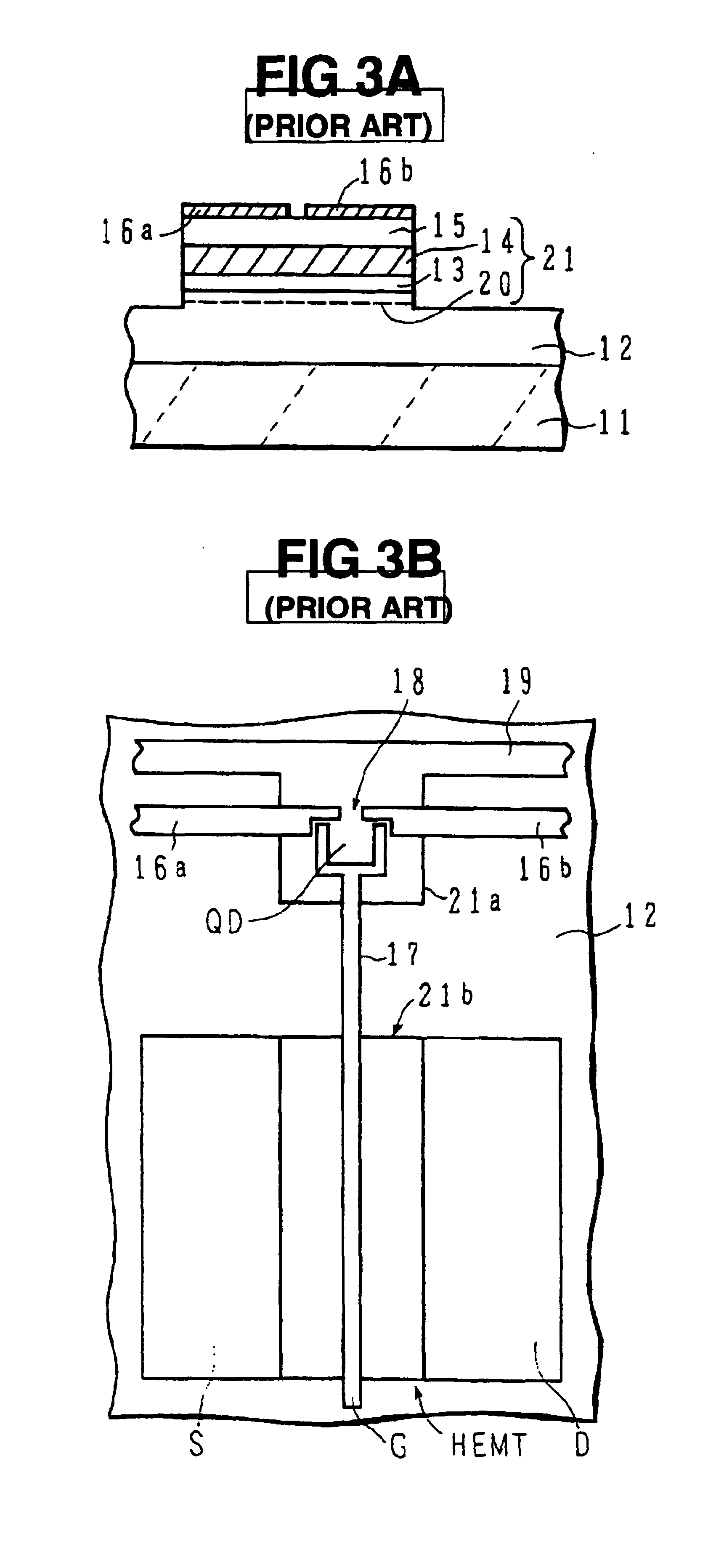
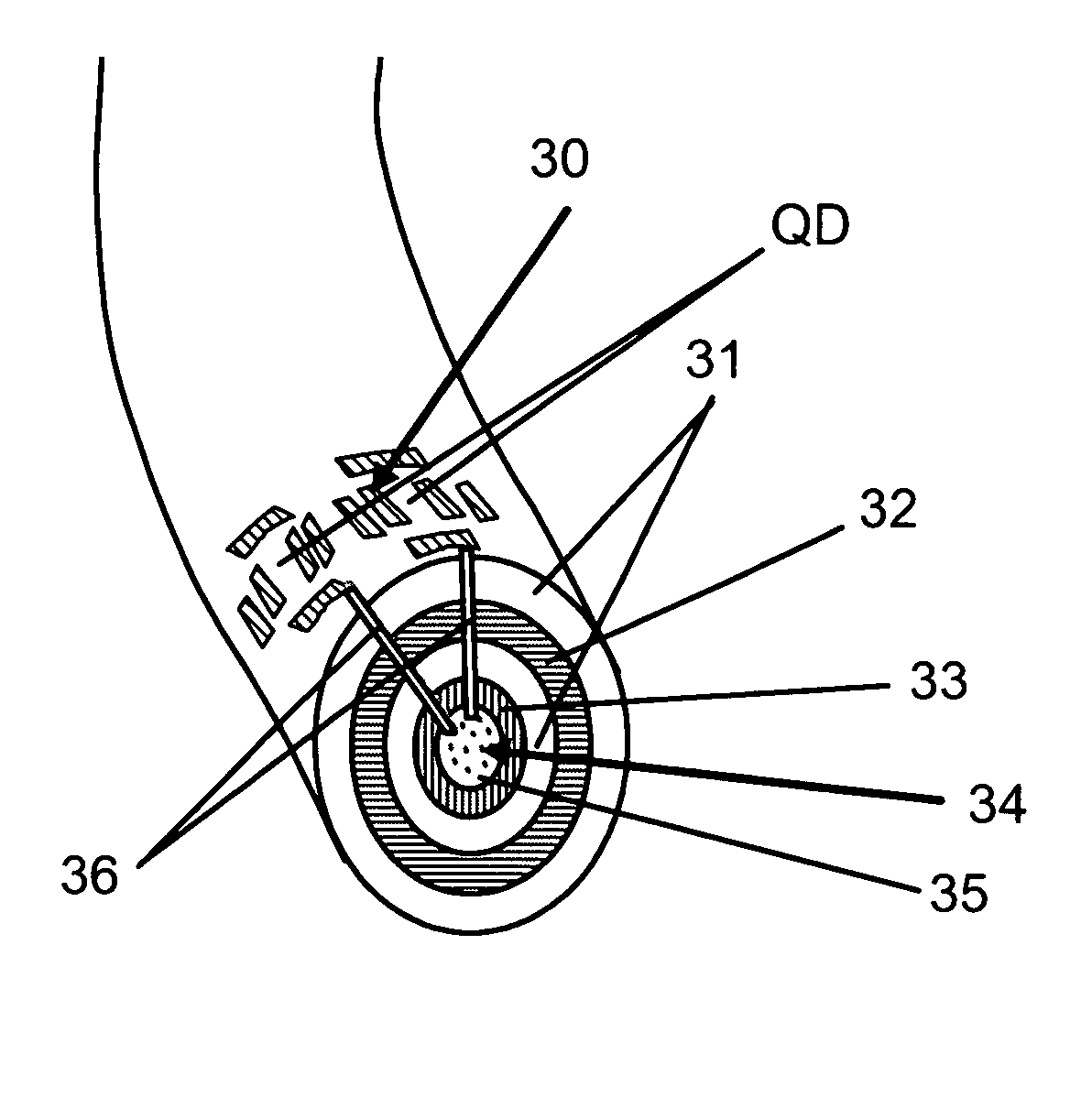
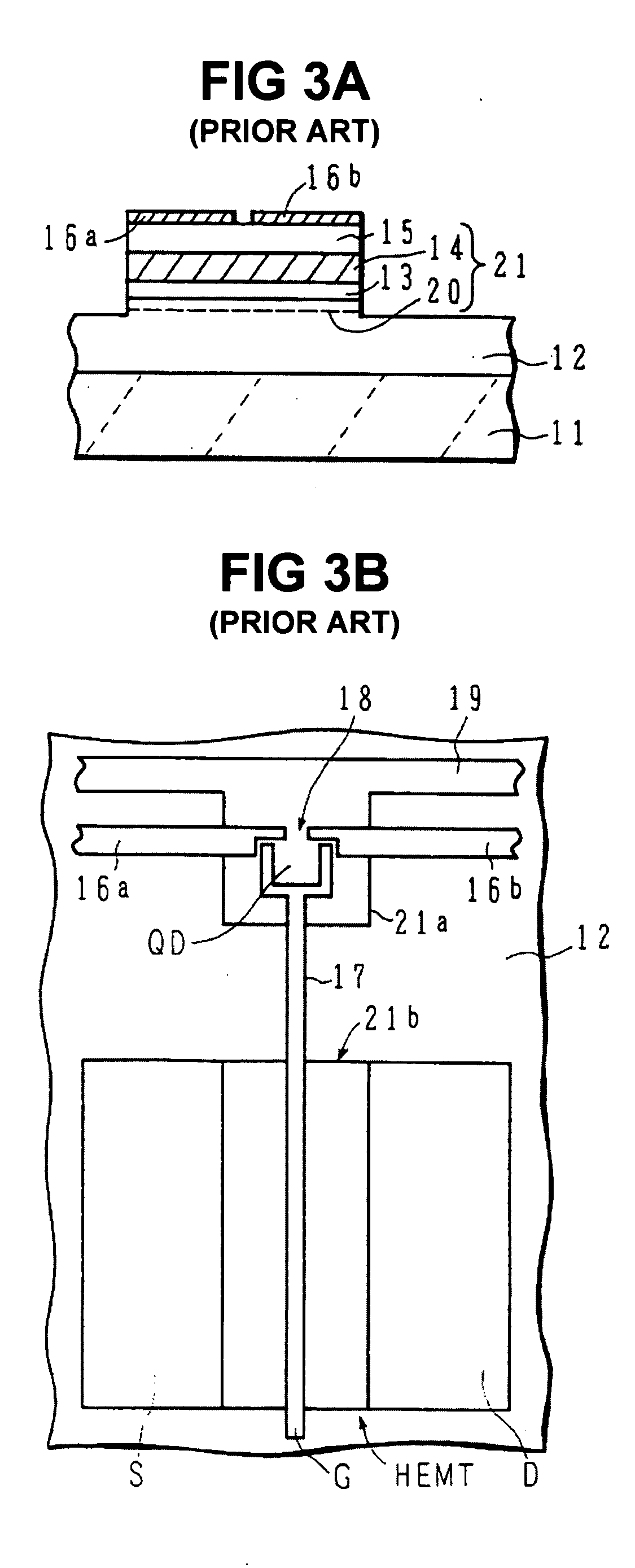
A programmable dopant fiber includes a plurality of quantum structures formed on a fiber-shaped substrate, wherein the substrate includes one or more energy-carrying control paths (34), possibly surrounded by an insulator (35), which pass energy to quantum structures. Quantum structures may include quantum dot particles (37) on the surface of the fiber or electrodes (30) on top of barrier layers (31) and transport layer (32) which form quantum dot devices (QD). The energy passing through the control paths (34) drives charge carriers into the quantum dots (QD), leading to the formation of “artificial atoms” with real-time tunable properties. These artificial atoms then serve as programmable dopants, which alter the behavior of surrounding materials. The fiber can be used as a programmable dopant inside bulk materials, as a building block for new materials with unique properties, or as a substitute for quantum dots or quantum wires in certain applications.
Owner:RAVENBRICK
Transparent material processing with an ultrashort pulse laser
InactiveUS7626138B2Reduce quality problemsPoor precisionFixed microstructural devicesThin material handlingHigh energyNonlinear absorption
Methods for ultrashort pulse laser processing of optically transparent materials. A method for scribing transparent materials uses ultrashort laser pulses to create multiple scribe features with a single pass of the laser beam across the material, with at least one of the scribe features being formed below the surface of the material. This enables clean breaking of transparent materials at a higher speed than conventional techniques. Slightly modifying the ultrashort pulse laser processing conditions produces sub-surface marks. When properly arranged, these marks are clearly visible with side-illumination and not clearly visible without side-illumination. In addition, a method for welding transparent materials uses ultrashort laser pulses to create a bond through localized heating. The ultrashort pulse duration causes nonlinear absorption of the laser radiation, and the high repetition rate of the laser causes pulse-to-pulse accumulation of heat within the materials. The laser is focused near the interface of the materials, generating a high energy fluence at the region to be welded. This minimizes damage to the rest of the material and enables fine weld lines.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
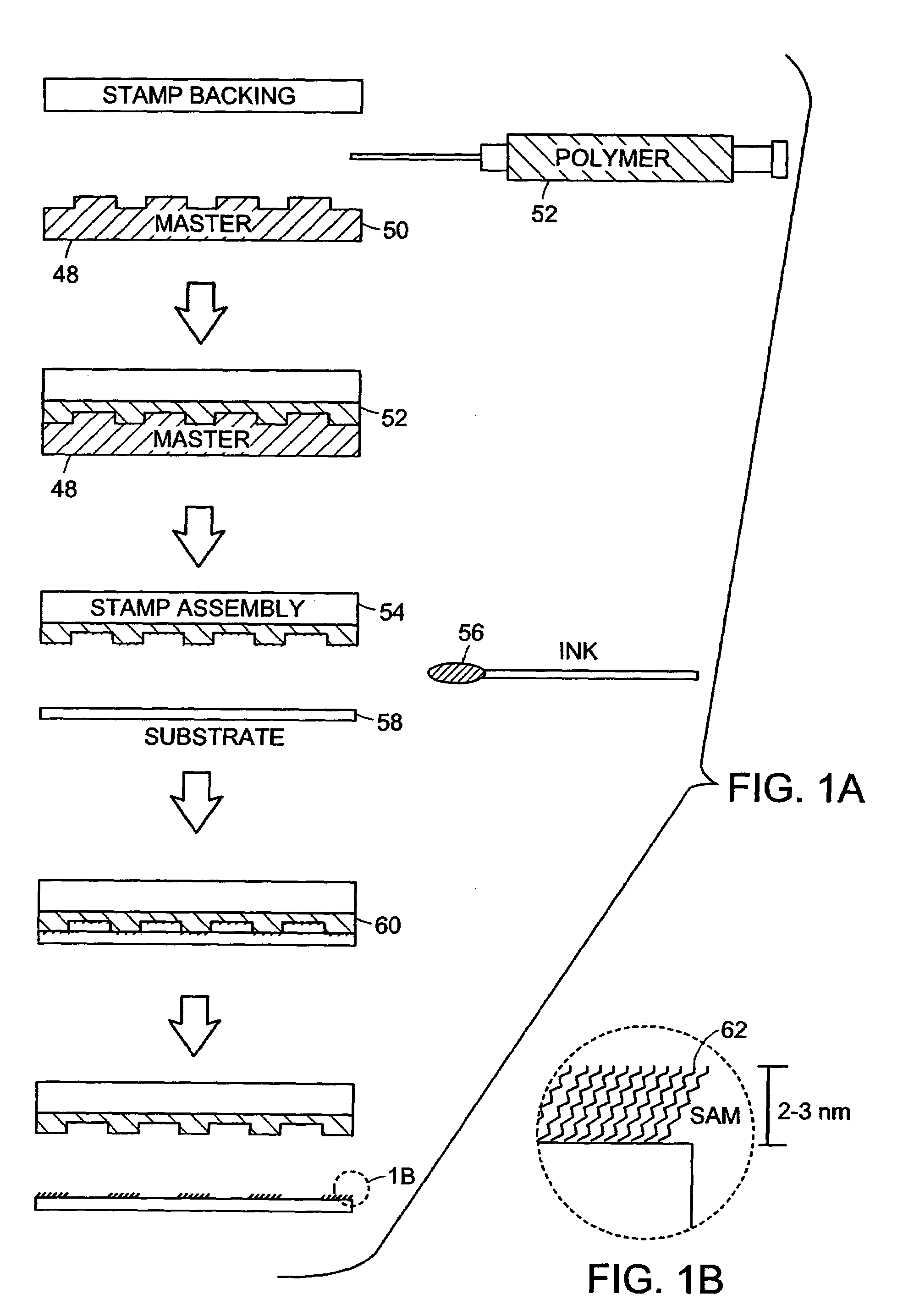
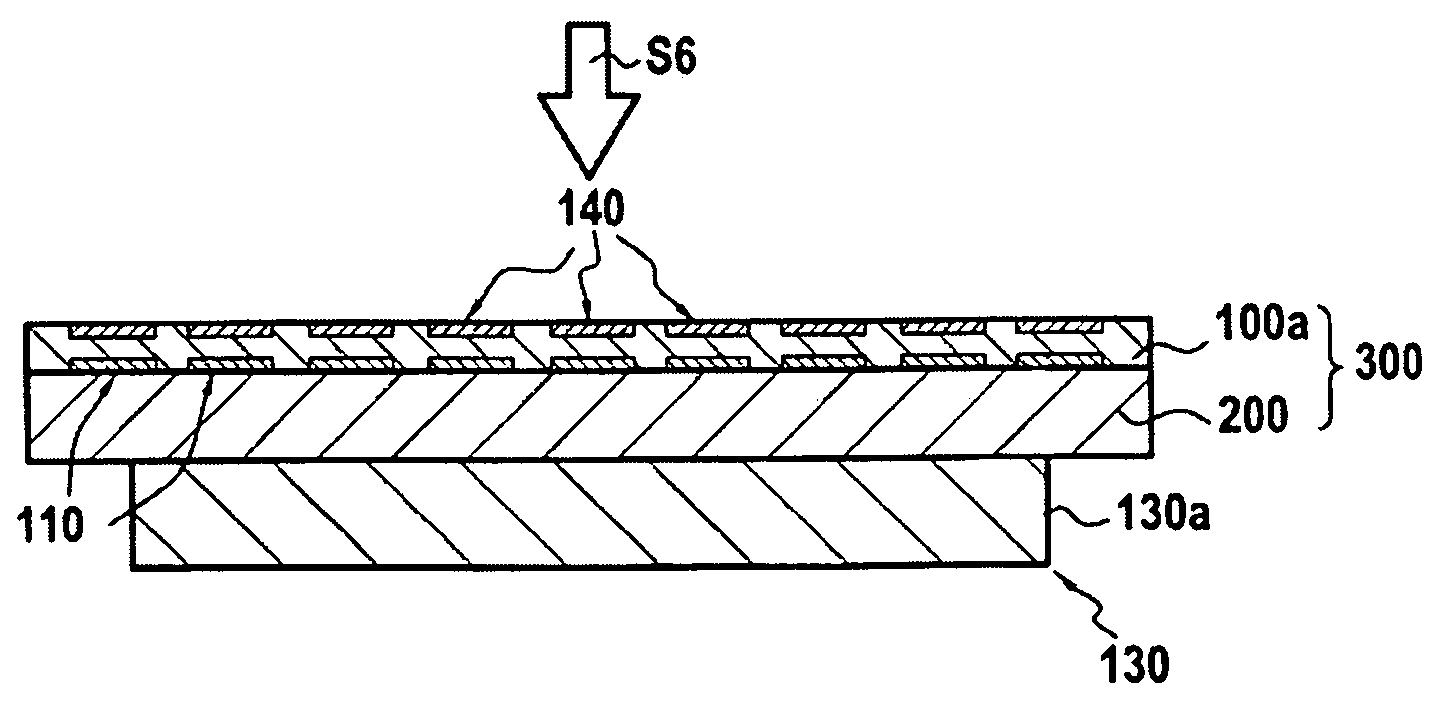
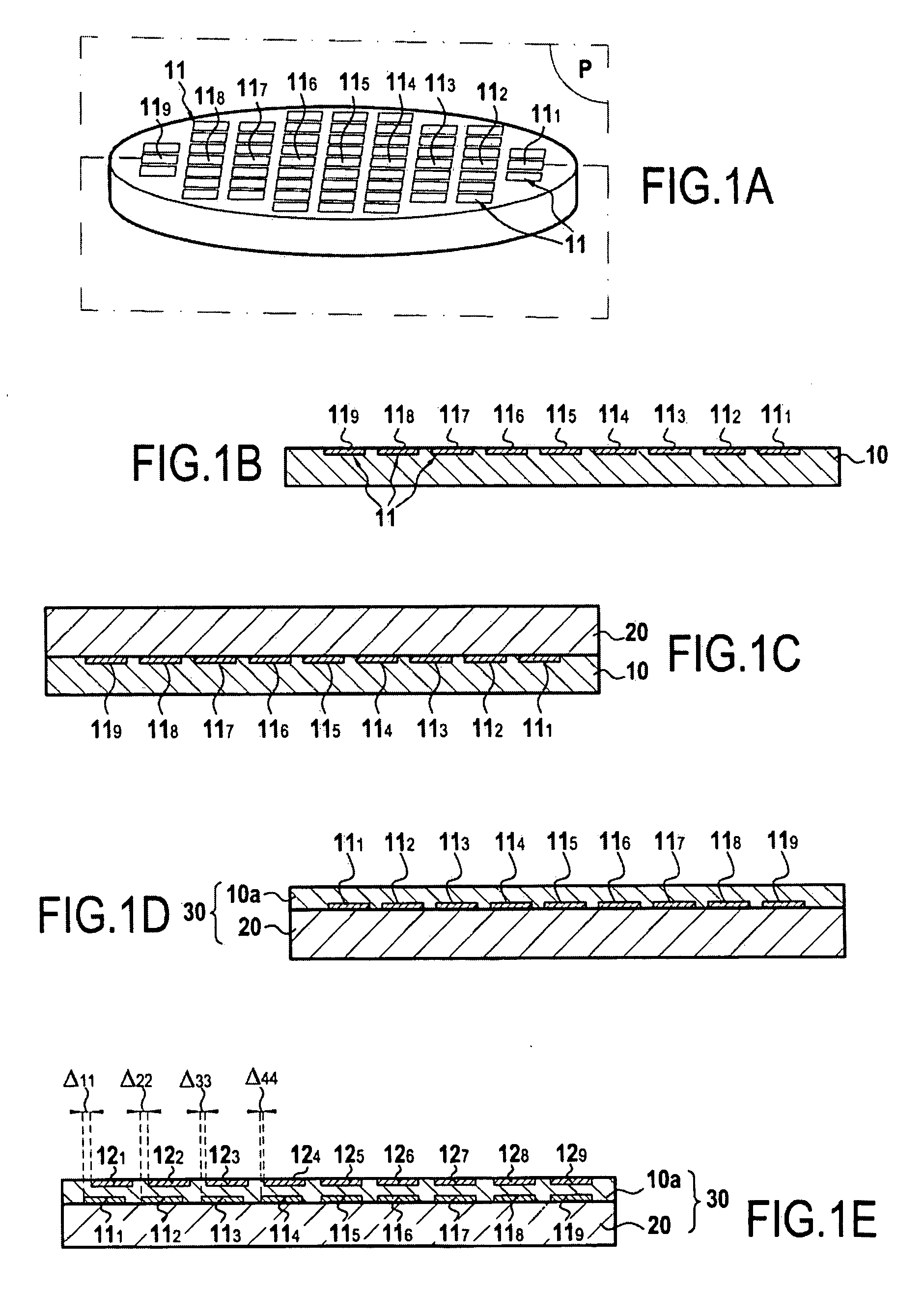
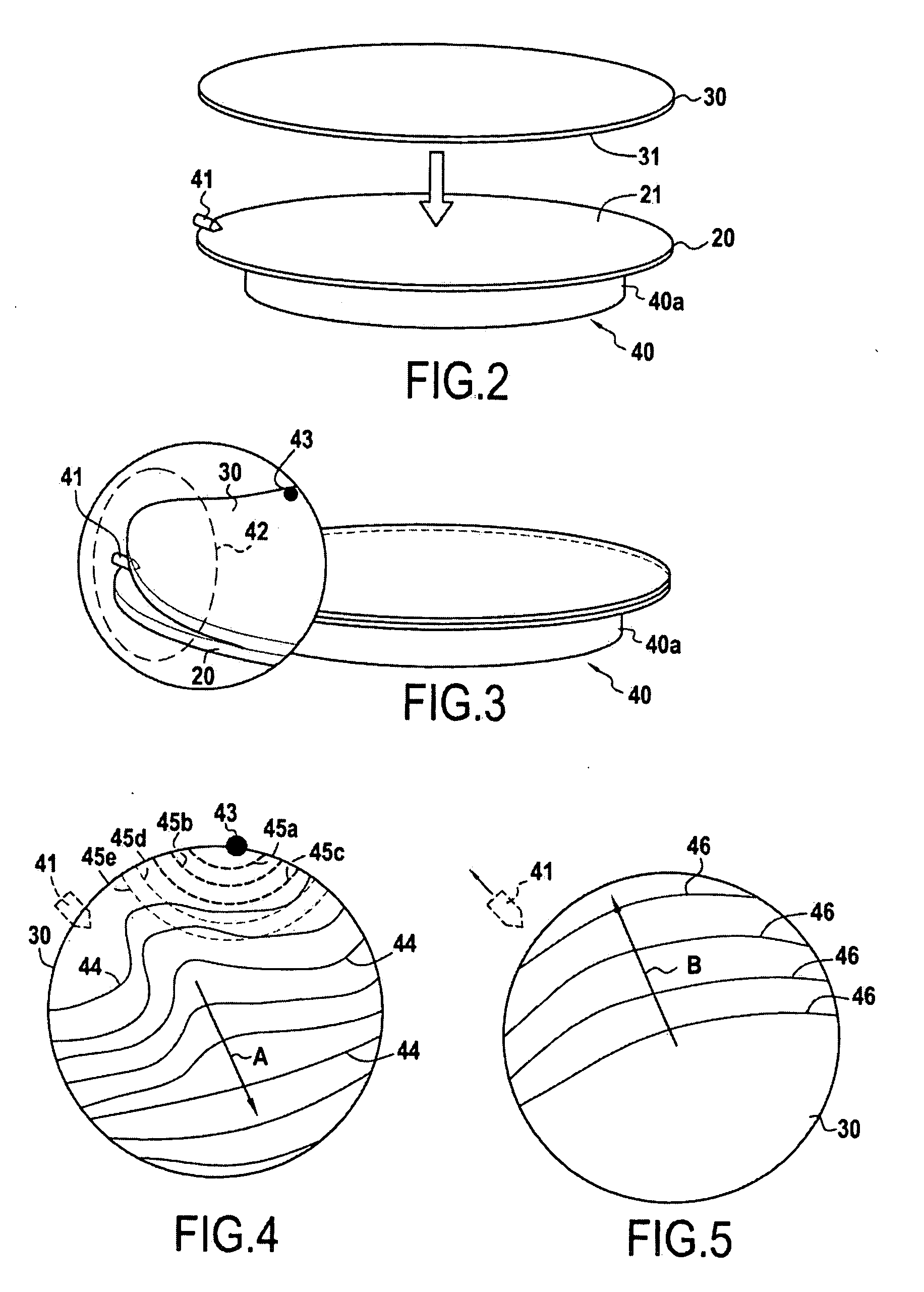
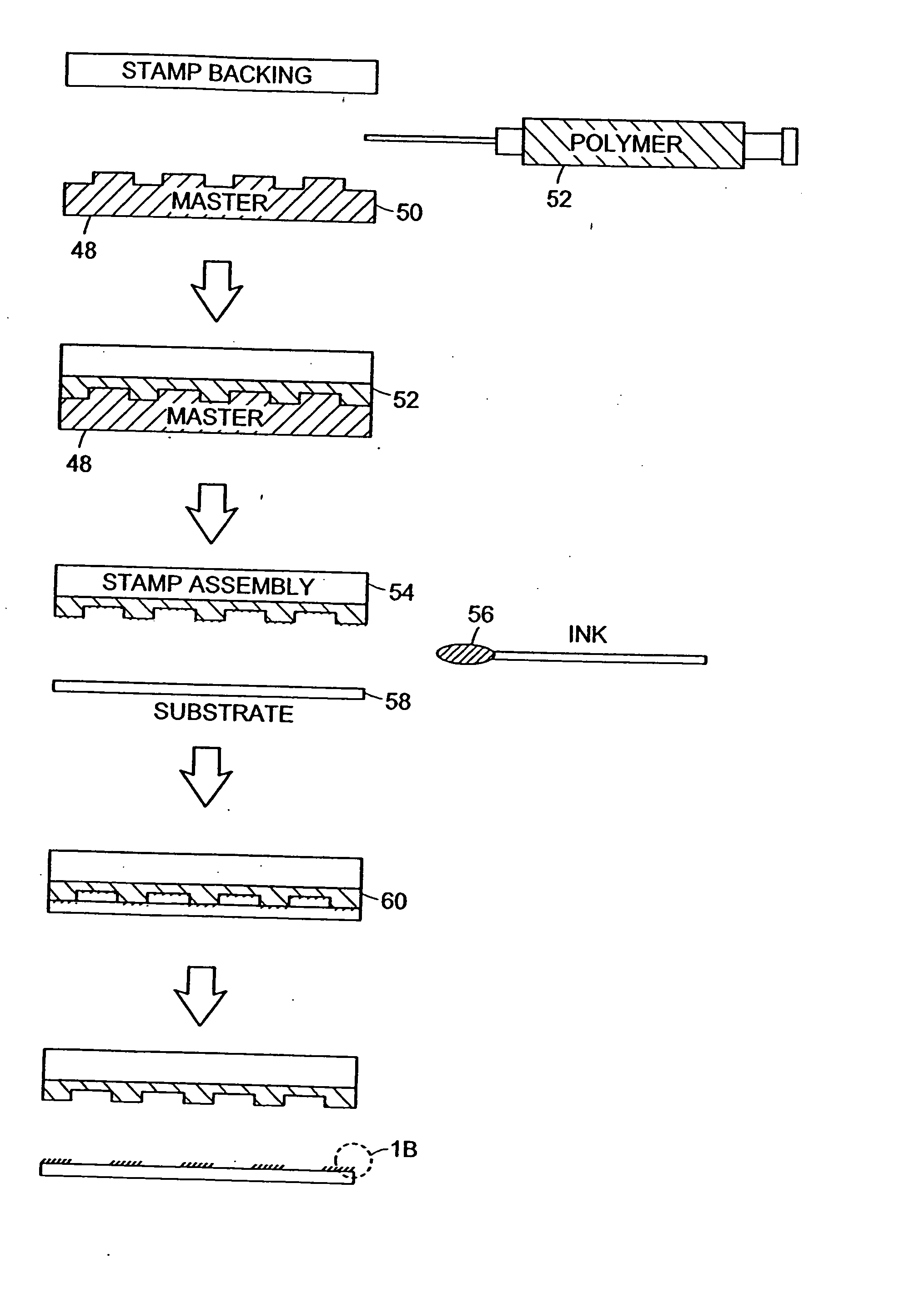
Microcontact printing
InactiveUS7117790B2Generate undesired patterning resultsControl distortionMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsMicrocontact printingEngineering
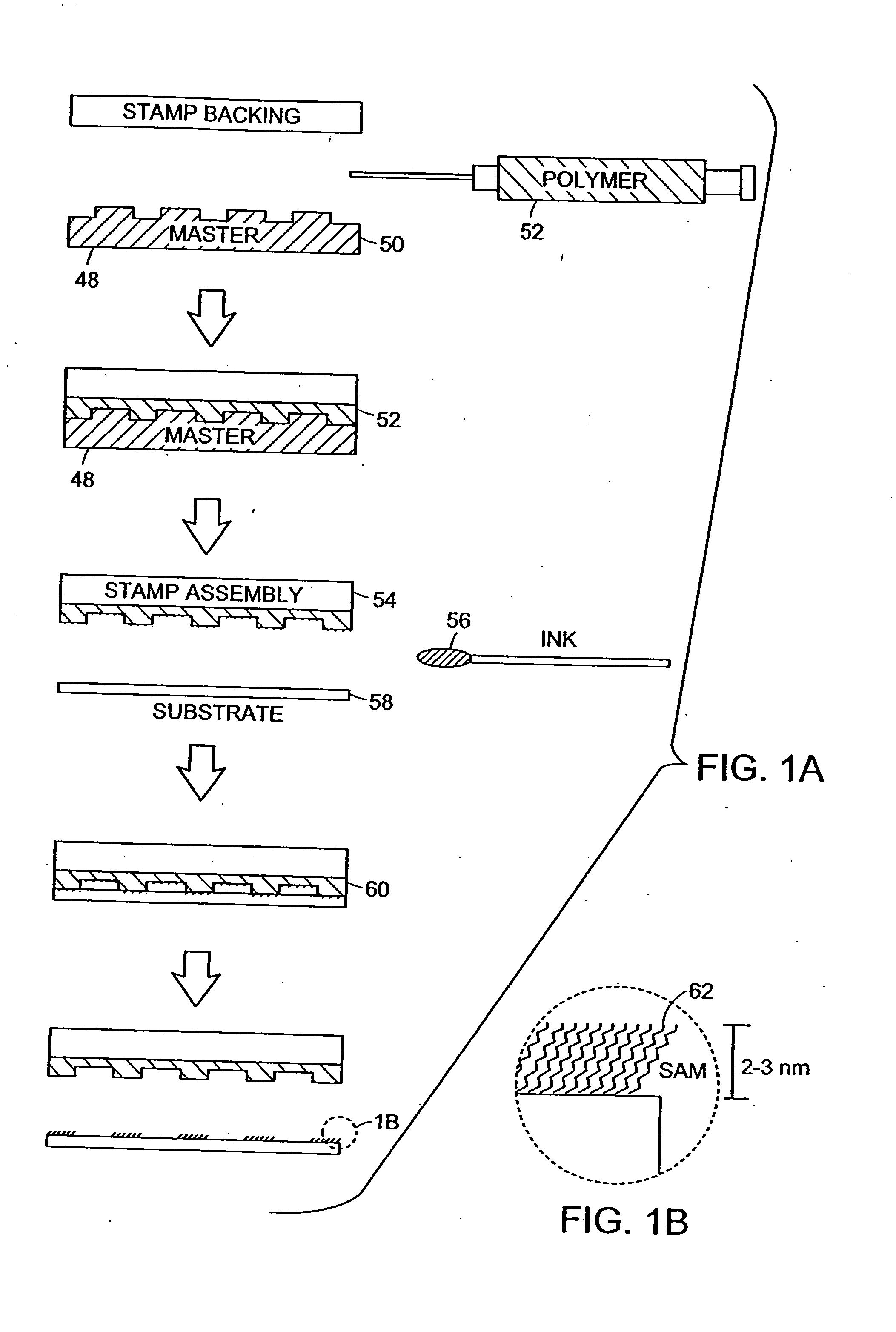
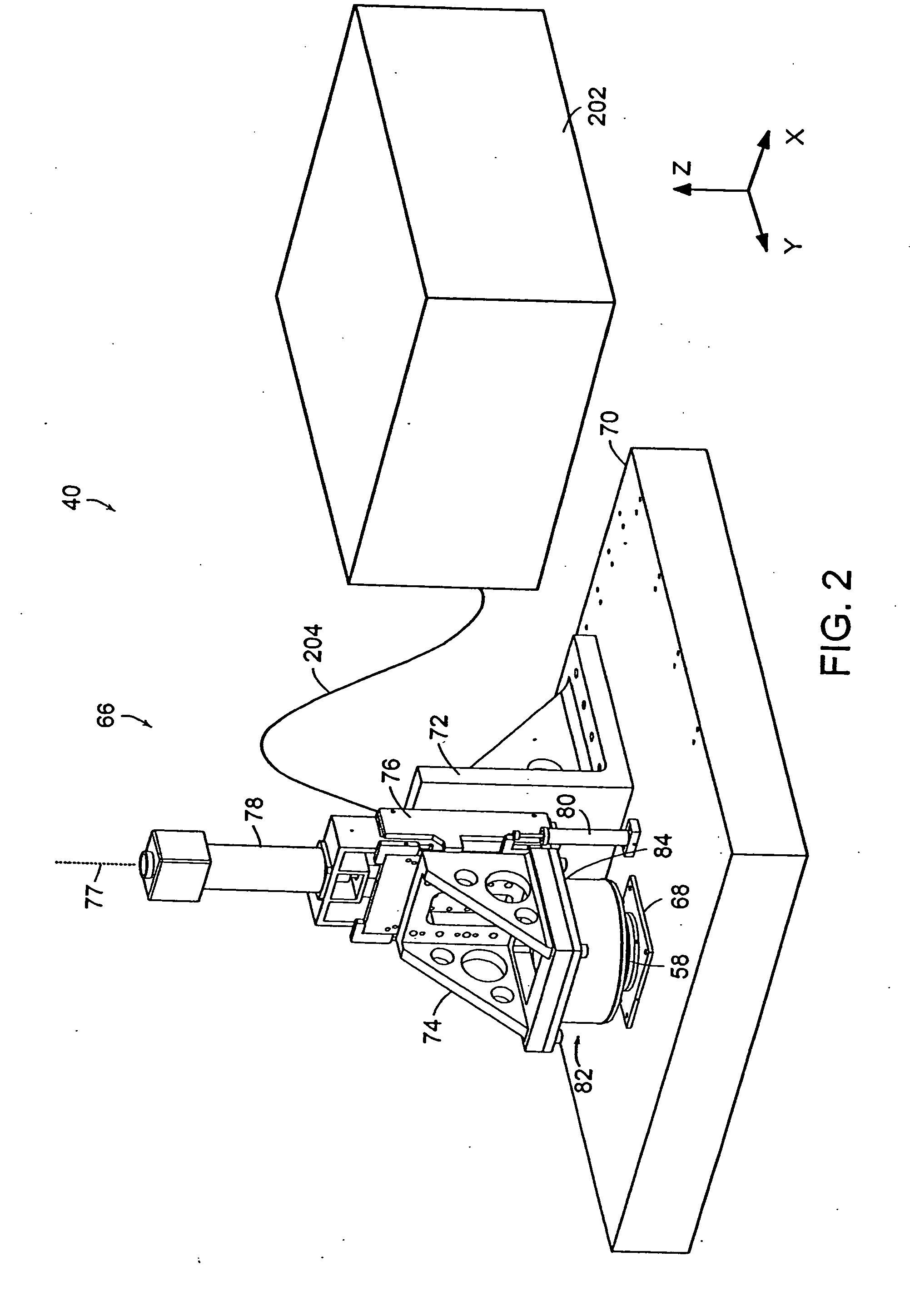
A microcontact printing tool having a print unit including a stamp head with a stamp and a wafer chuck for retaining a substrate. The stamp contained by the stamped head movable relative to the substrate by an actuator and a stage. A plurality of sensors detect the position of the stamp relative to substrate. A method of using the printing tool that includes a real-time feedback for consistent and accurate application of force during the printing of the substrate. The stamp head includes a pressure chamber carrying the stamp. The stamp backing is deflected prior to contact of the stamp with the substrate to form a minimum point and the stamp backing and the stamp is returned to a plane to create a printing propagation contact. An apparatus and method of producing the stamp on a stamp backing. The apparatus has a master backing and a stamping backing in close proximity and the stamp material drawn in through a vacuum. The stamp is separated from the master by use of a parting fluid.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
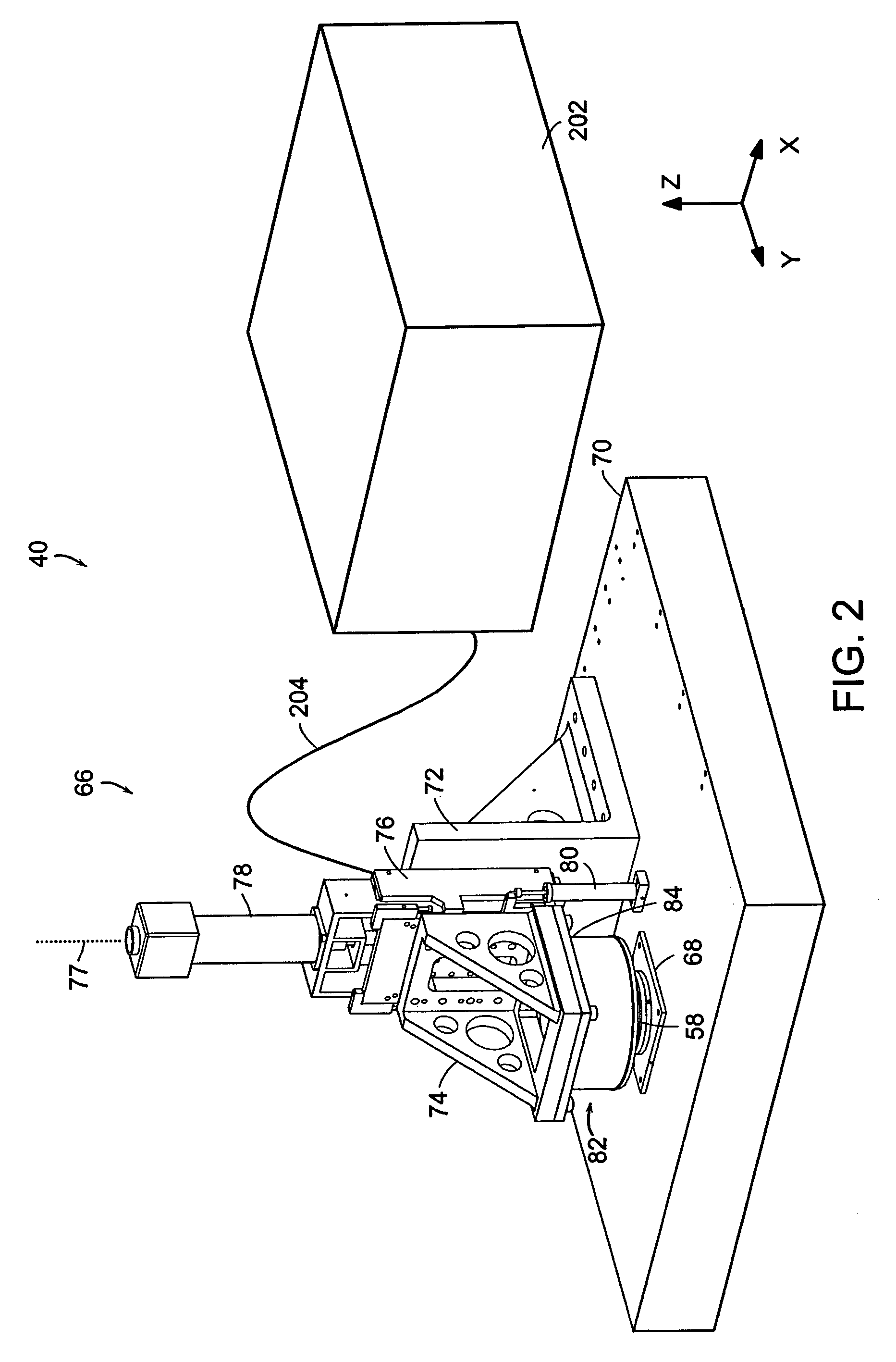
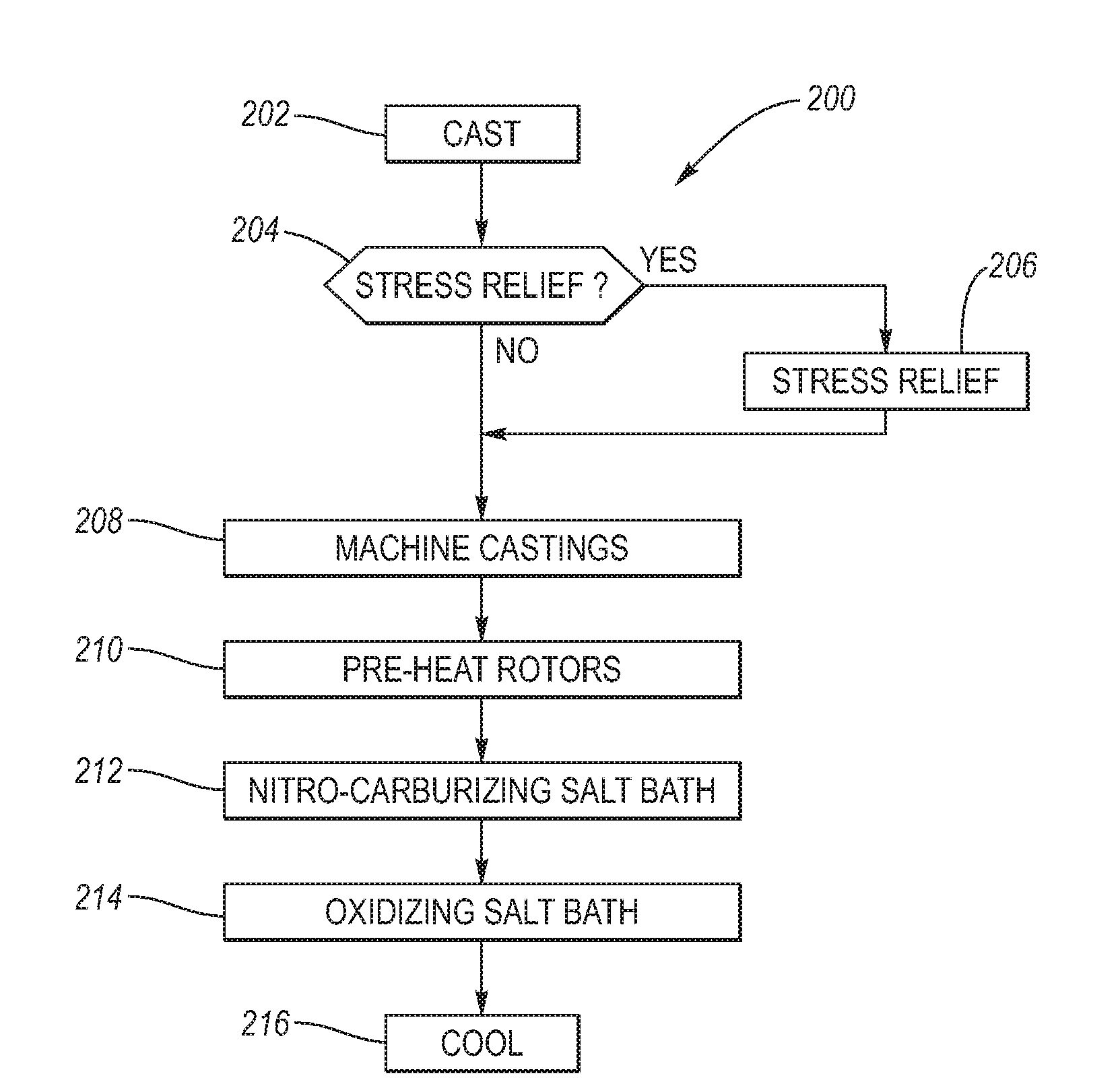
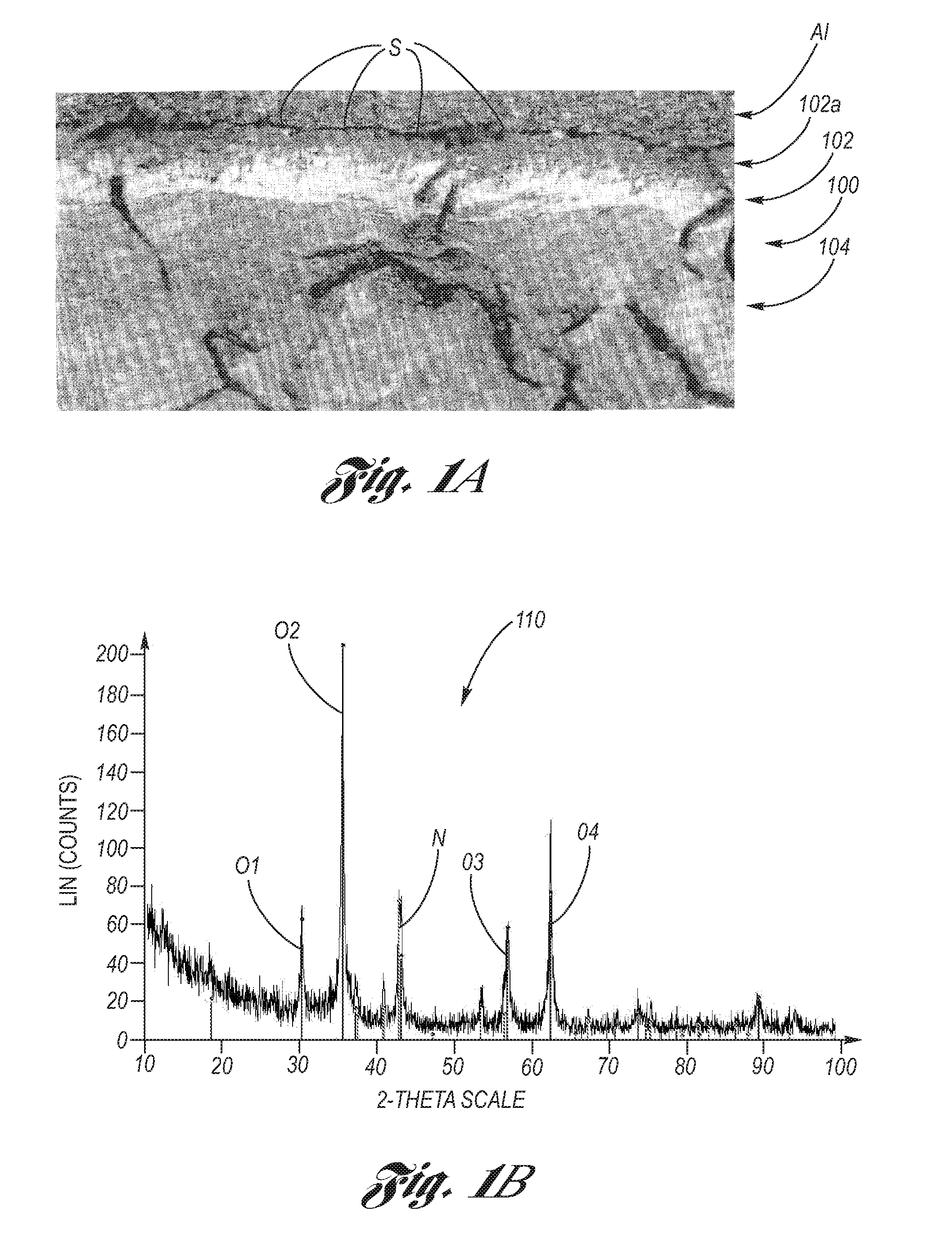
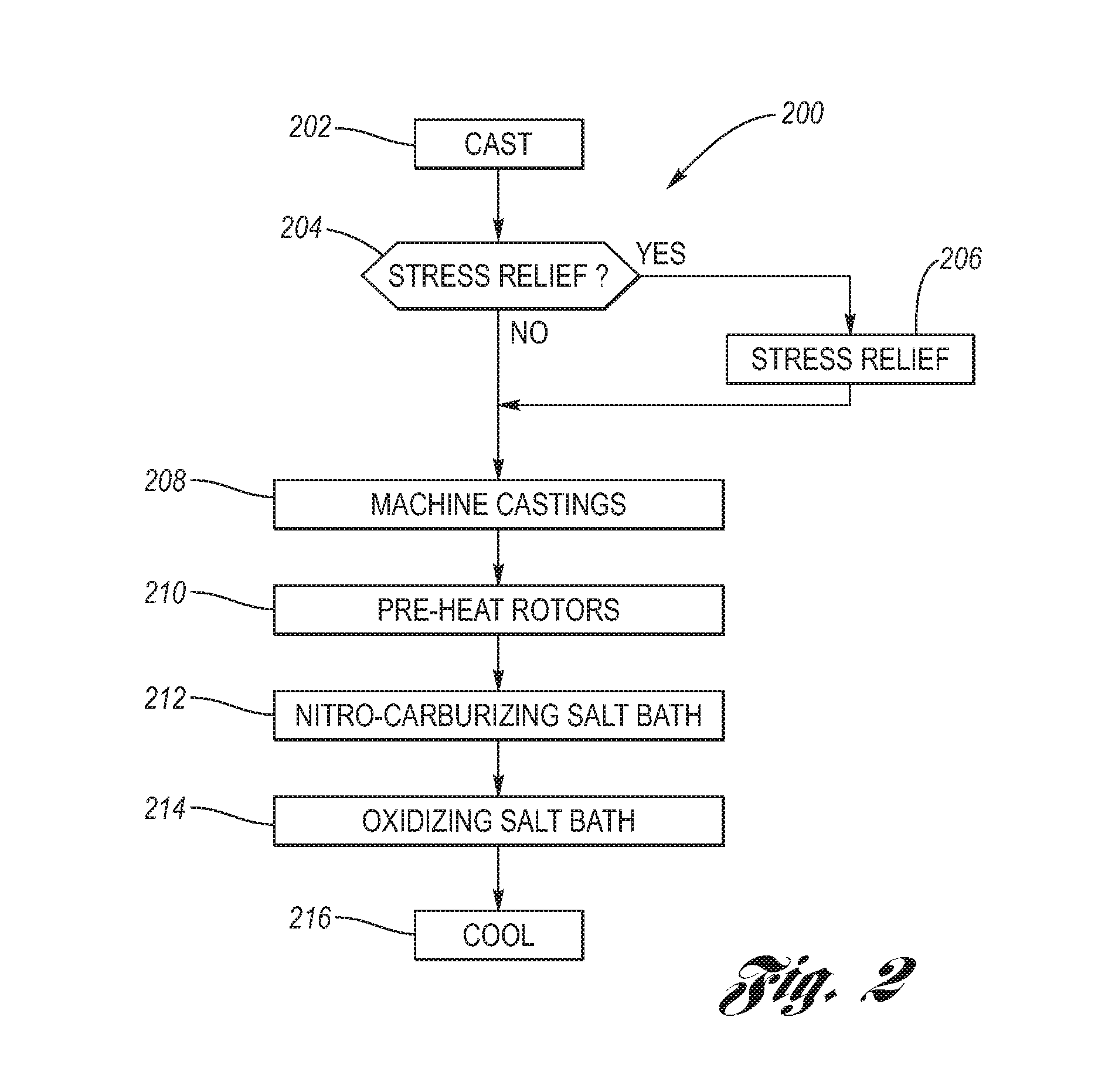
Salt Bath Ferritic Nitrocarburizing of Brake Rotors
ActiveUS20080000550A1Absence of distortionProvide resistanceBraking discsSolid state diffusion coatingRoom temperatureNitrogen
Ferritic nitrocarburized surface treatment of cast iron brake rotors providing oxidation resistance, good braking performance and absence of distortion. Machined brake rotors are pre-heated, then immersed into a high temperature molten nitrocarburizing salt bath for a first predetermined dwell time. After removing the brake rotors from the nitrocarburizing salt bath, the brake rotors are directly immersed into an oxidizing salt bath at a lower temperature than the nitrocarburizing salt bath so that the brake rotors are thermally quenched. After a predetermined second dwell time in the oxidizing salt bath, the brake rotors are removed therefrom and further cooled to room temperature, either by water application thermal quenching or slow cooling in air. A fixture provides stable holding the brake rotors with a minimum of contact during placement in the salt baths.
Owner:KOLENE +1
System and methods for x-ray backscatter reverse engineering of structures
ActiveUS7623626B2High resolutionSolve the slow scanning speedAircraft components testingMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSoft x rayImage resolution
A system and methods for x-ray backscatter reverse engineering of structures. One embodiment includes a plurality of articulated arms attached to a movable base. Another embodiment includes a single counterweighted arm attached to a movable base. The arms include x-ray detectors. At least one x-ray source, which may be mounted on the arm(s), emits x-rays, which are backscattered off the surfaces and objects of interest and captured by the detectors to generate images of hidden objects. The present system provides improved speed and resolution over prior art systems. The system has a field-of-view and effective scanning range versatile enough to work in various orientations and in environments of various sizes. In certain embodiments the system is compact and lightweight so that it can be easily transported and used within confined spaces or in environments where weight is a consideration, such as inside or underneath aircraft. The system is also pointable and adaptable.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Optical system for imaging distortions in moving reflective sheets
InactiveUS7345698B2Control distortionMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsEllipseMagnification
A method and apparatus for detecting and measuring the optical distortion in pieces of glass and other reflective sheets are disclosed. The method inspects the full length and width of large area glass sheets or multiple sheets comprising a load of glass and uses optical magnification of a reflected circular image of precise size. A plurality of circular images is projected onto the glass and reflect as ellipsoids representative of local surface contours. The major and minor axes of the reflected axis define the axis of greatest magnification and demagnification. Distortions in the glass surface are measured in lens power as localized magnification at the elliptical axis. The angle and magnitude of the minor and major axis of the reflected ellipsoids provide data to map the surface profile of the glass. The method measures distortion of random or periodic frequency and measures distortion in all axes.
Owner:LITESENTRY LLC
Variable distortion limiter using clip detect predictor
ActiveUS20060284675A1Control distortionElectric devicesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTotal harmonic distortionControl theory
A system and method for predicting and limiting distortion of an amplified signal is described. The system includes a variable total harmonic distortion (“THD”) clipping predictor, a comparator in communication with the variable THD clipping predictor and a distortion limiter in communication with the comparator. As for the method, a reference power supply value, a maximum desired total harmonic distortion value and a preamplified signal value is provided. A THD output threshold value is calculated based on the reference power supply value and the maximum desired THD value and is then compared to the preamplified signal value. Depending on if the preamplified signal value is greater than or less than the THD output threshold value, the amplitude of the preamplified signal may be increased or decreased.
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
Tightening mechanisms and applications including the same
ActiveUS9375053B2Reduce the overall heightEasy to returnMetal-working apparatusShoe lace fasteningsMechanical engineeringVisual appearance
This disclosure relates to articles that include a tightening mechanism, such as reel-based lace tightening mechanism, configured to tighten the article by rotation of a knob. The articles can include a concealing portion that is configured to conceal or protect at least a portion of the tightening mechanism, such as the knob. The concealing portion can be configured to prevent unintentional actuation of the tightening mechanism, such as during contact sports. The concealing portion can be configured to hide the tightening mechanism from view to improve the visual appearance of the article. The concealing portion can be collapsible such that a user can press the concealing portion down to expose the knob of the tightening mechanism.
Owner:BOA TECHNOLOGY
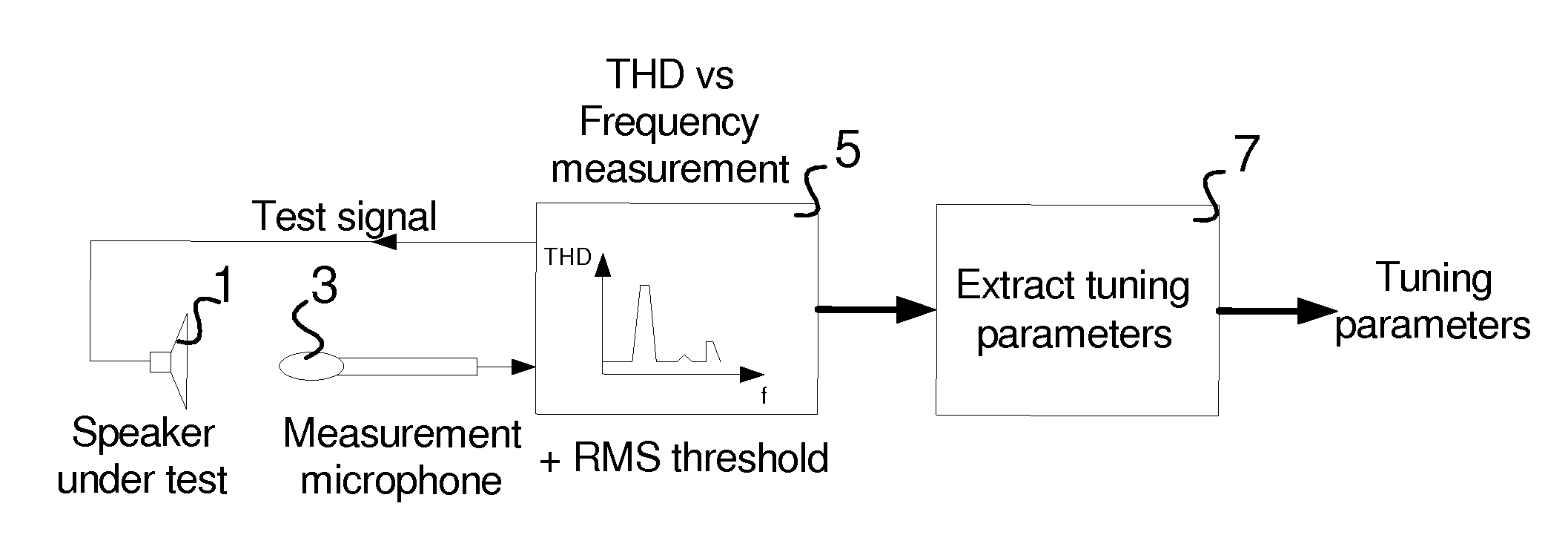
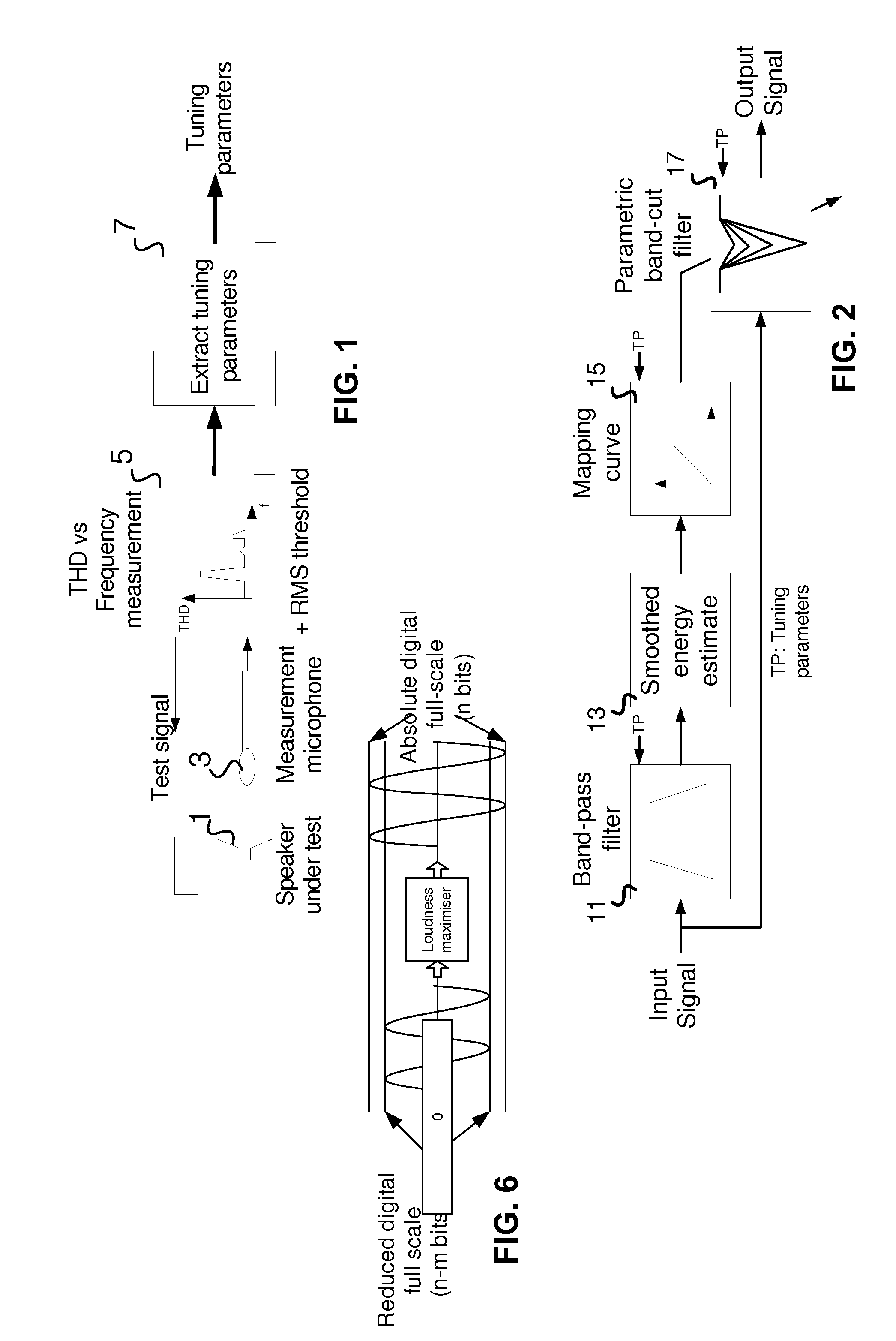
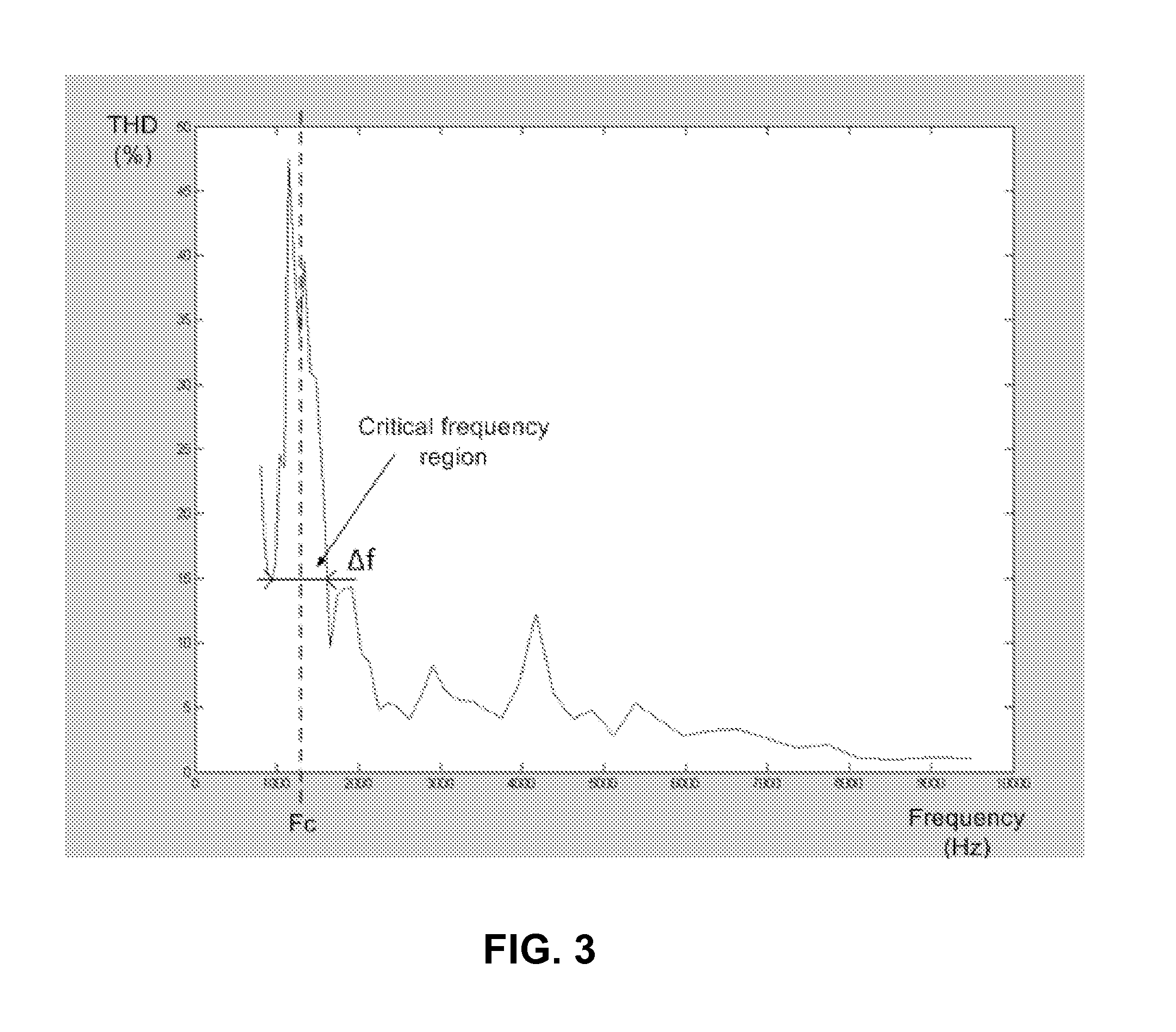
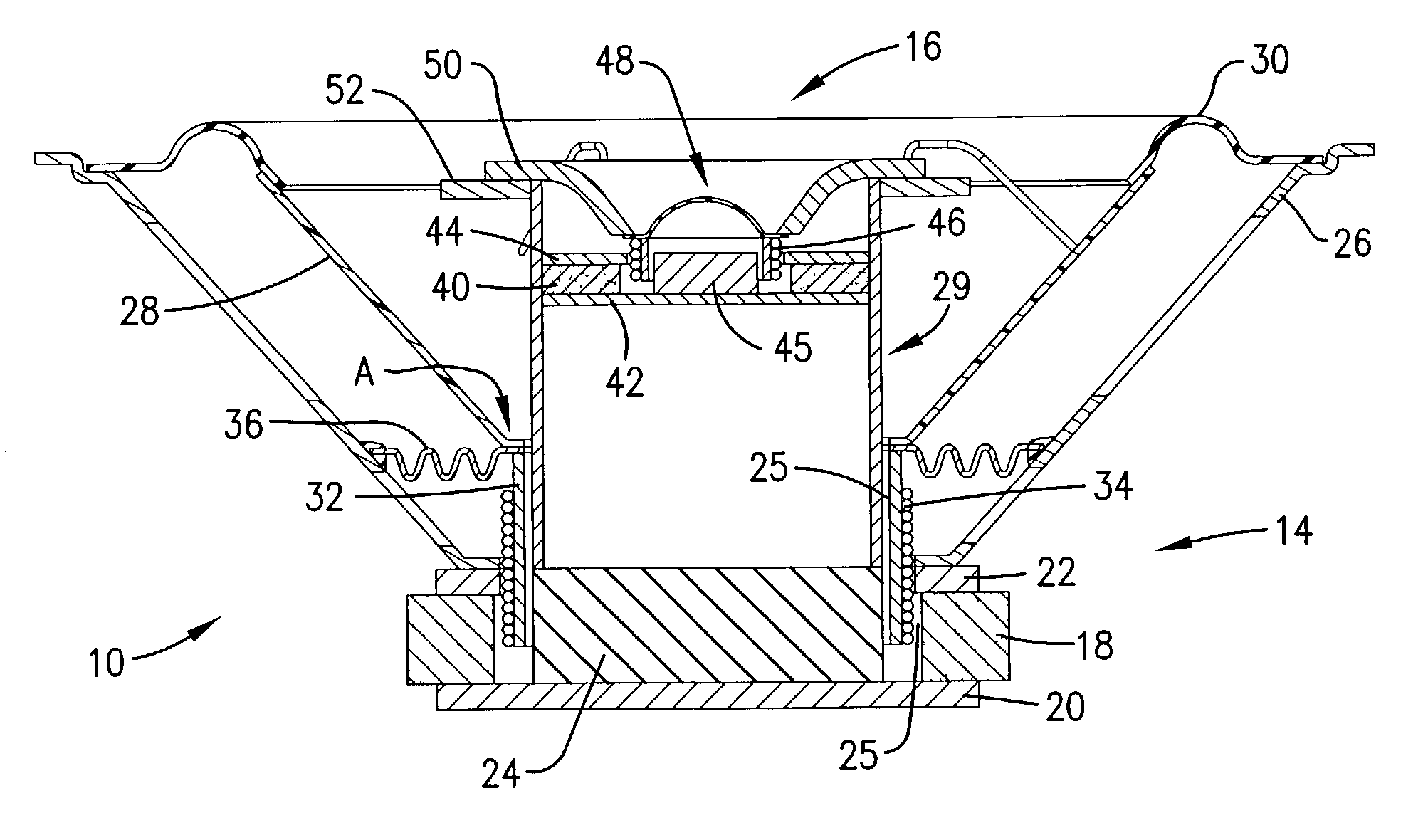
Method and system for controlling distortion in a critical frequency band of an audio signal
InactiveUS20130142360A1Increase in sizeControl distortionGain controlTransducer protection circuitsLoudspeakerAudio frequency
In some embodiments, a method and system for controlling distortion of the output of a miniature speaker by attenuating critical frequency band of the input signal to be reproduced, using tuning parameters that have been predetermined where the critical frequency band is a frequency range of the speaker's frequency response in which Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) peaks. The distortion control is performed in a manner which allows an increase in the average loudness of the speaker's output without significantly increasing distortion. The tuning parameters include a center frequency and a bandwidth of the critical frequency band, and a power threshold value. In some embodiments, the system is a loudness maximizer configured to limit distortion of a speaker's output by limiting distortion in a critical frequency band using predetermined control parameters, and limit the dynamic range of the output signal and increase its perceived overall average loudness level.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
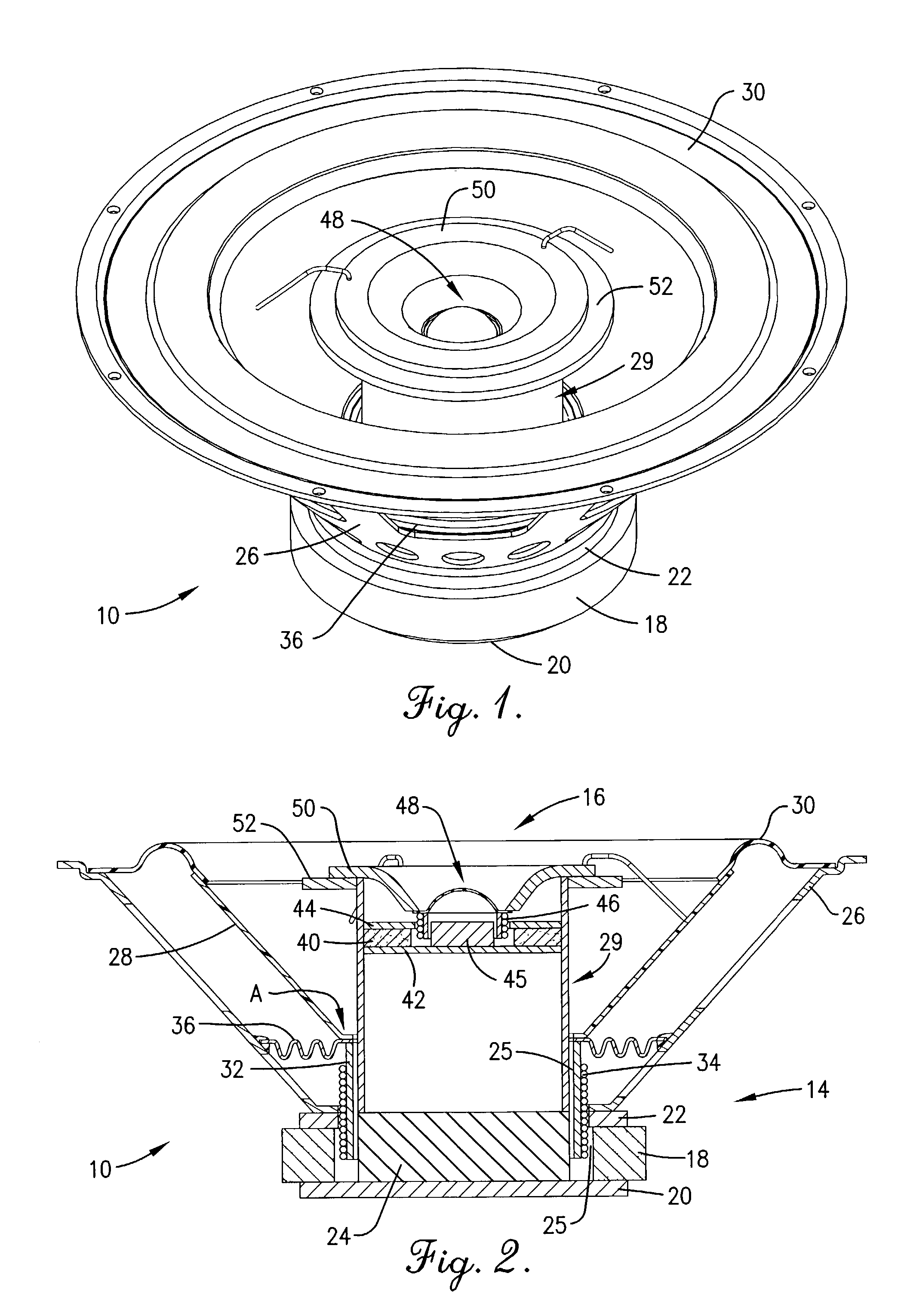
Coaxial speaker with step-down ledge to eliminate sound wave distortions and time delay
ActiveUS6963650B2Limit sound distortion soundLimit time delayFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsDeaf-aid setsTime delaysEngineering
A coaxial speaker assembly (10) with reduced sound distortion, sound time delay, and polar response distortion. The coaxial speaker assembly (10) includes a high-frequency speaker system (16) mounted coaxially with and fitting within a lower-frequency speaker system (14). A baffle (50) is secured to a diaphragm (48) of the high-frequency speaker system (16). A step-down ledge (52) is circumferentially positioned adjacent to the baffle (50) and extends outwardly therefrom. A portion of the sound waves emanating from the high-frequency diaphragm (48) are reflected off the step-down ledge (52).
Owner:MS ELECTRONICS
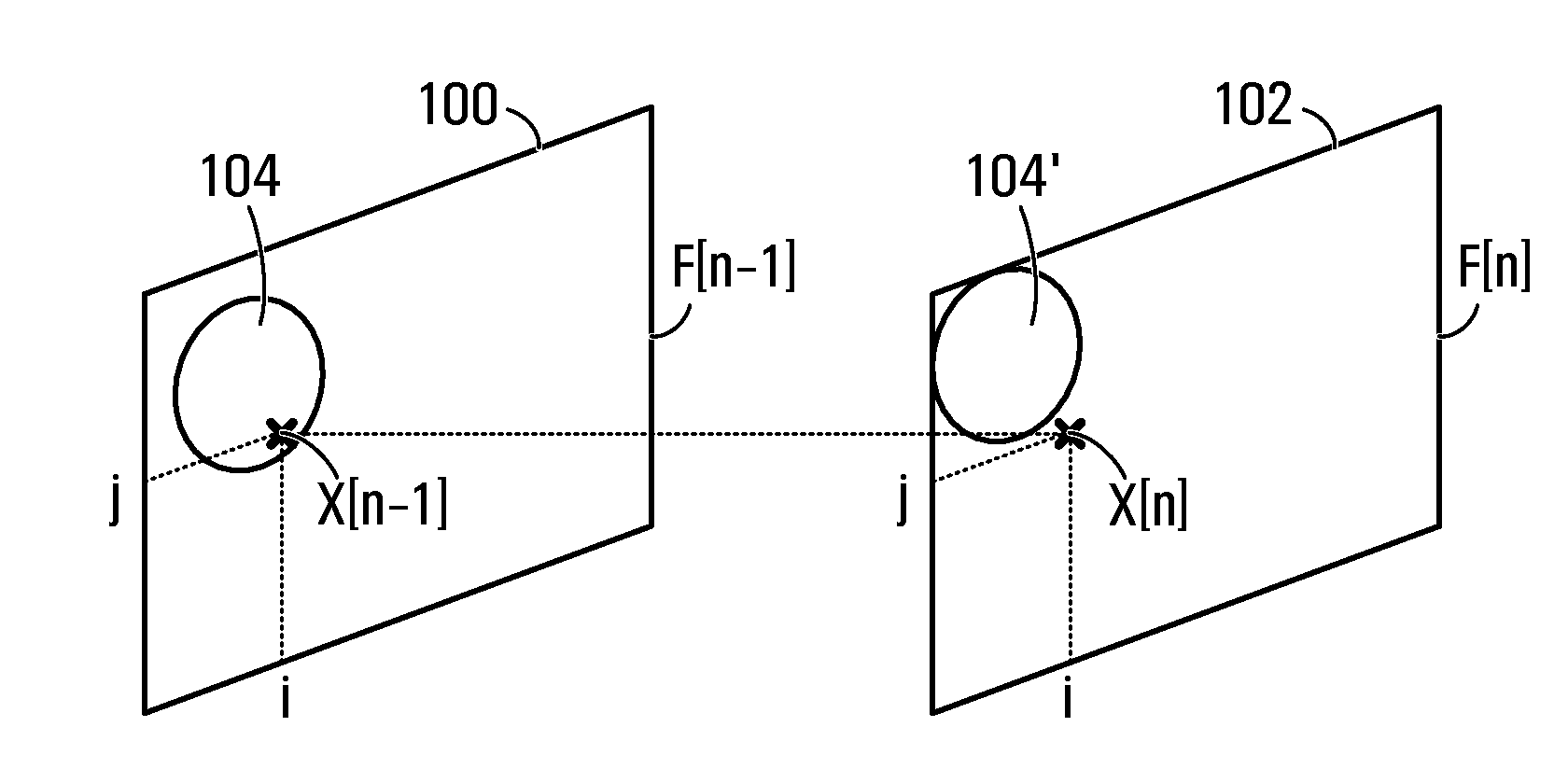
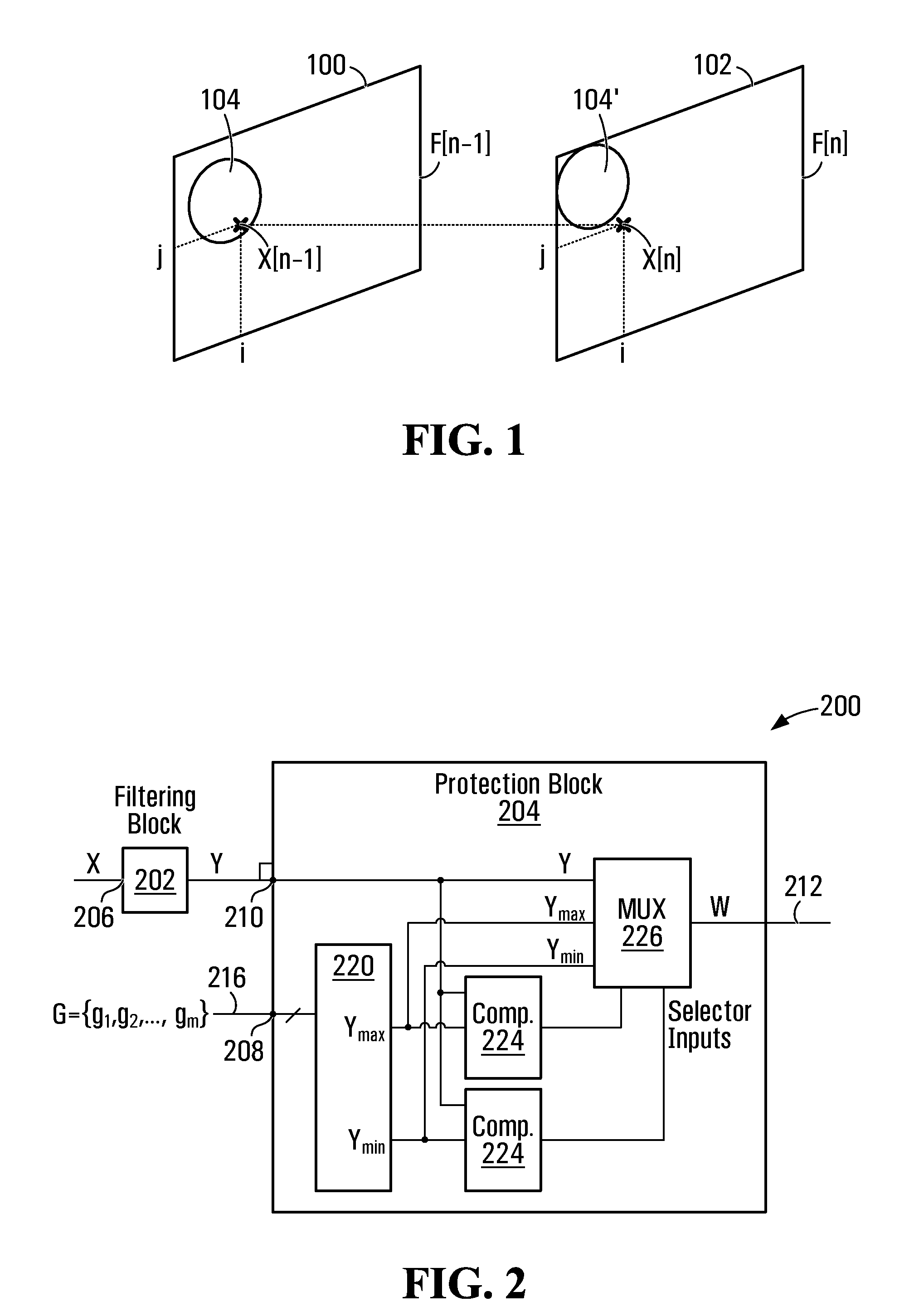
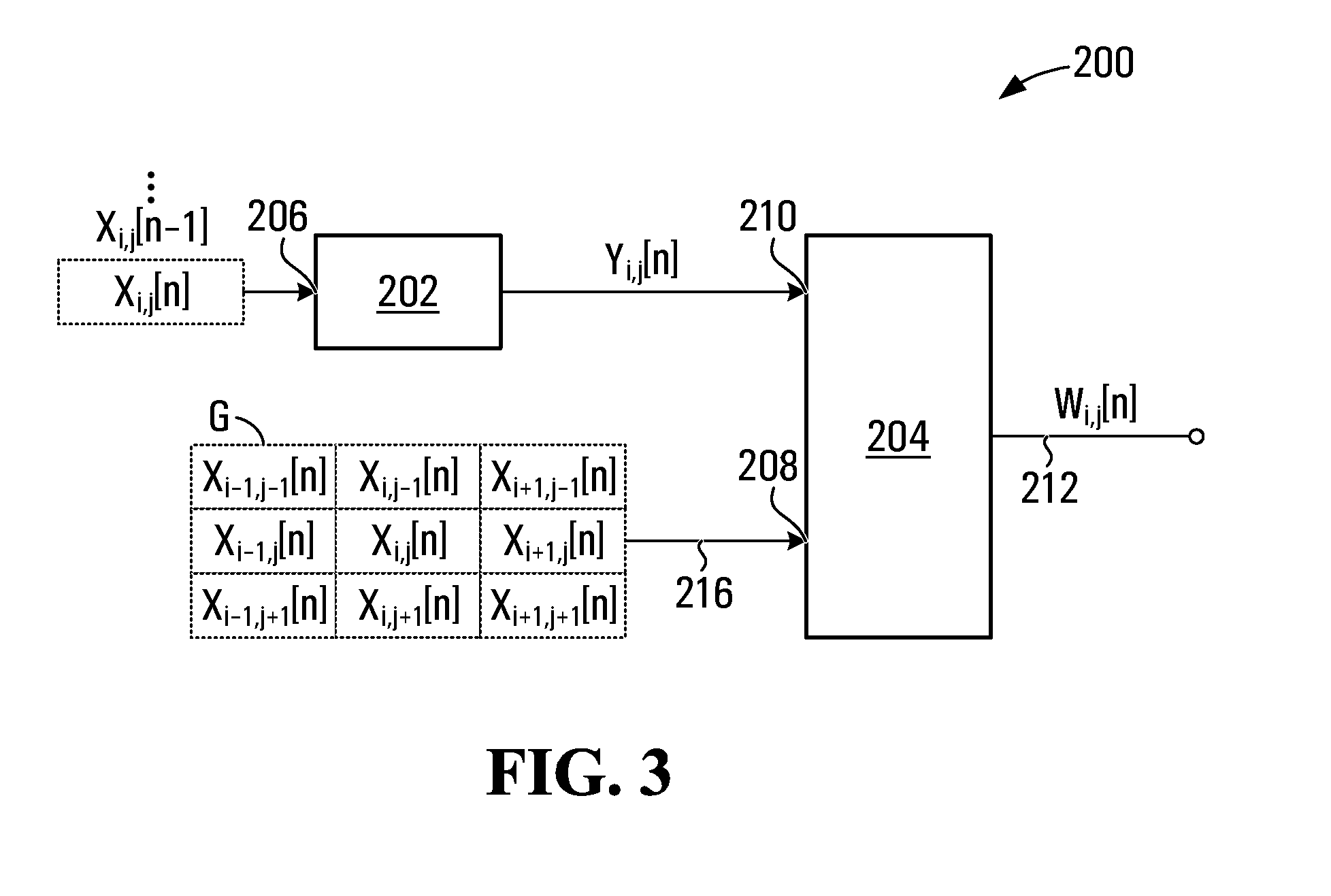
Protection filter for image and video processing
ActiveUS20100061648A1Reduce Motion ArtifactsMitigate artifact static artifactImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVideo processing
A filter includes a conventional filtering block and a protection block. The conventional filtering block receives input values and provides filtered values. The protection block receives filtered values and a group of input values proximate the current input, to ensure that the output is lies within a range computed for the current input. The range is determined by the protection block based on the group of input values proximate the current input. Any algorithm or statistical function may be applied to the group of input values to determine the range. If a filtered value provided by the conventional filtering block is outside the range, then the protection block computes and outputs a value that is within the range. The filter may be used in temporal or spatial filtering of images and video to mitigate artifacts such as motion artifacts and static artifacts.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Process for modelling a 3D scene
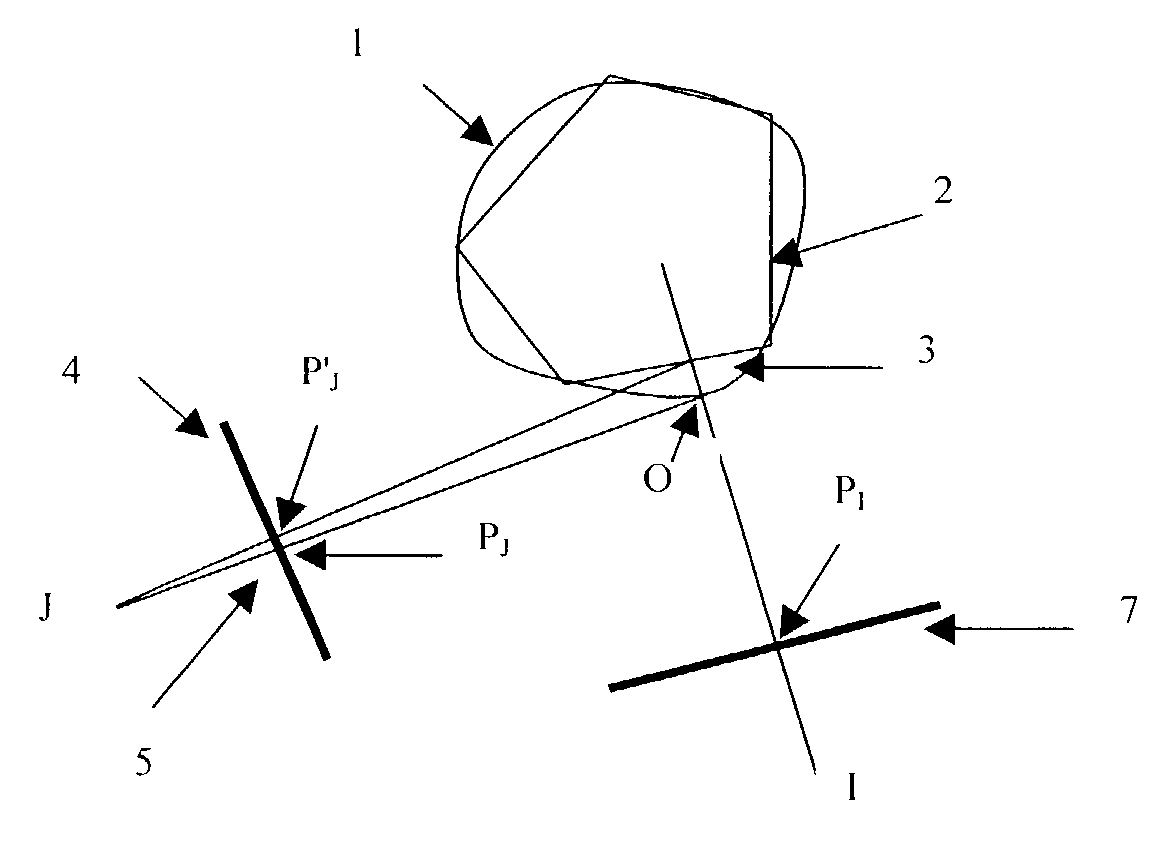
ActiveUS7113635B2Simplification of depth mapQuality lossCharacter and pattern recognitionSteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Algorithm
A process for modeling a 3D scene is provided which comprises validating the model by determining a maximum permitted distortion (5) on a 2D synthesized image (4), generated by the approximation inherent in the model (2); calculating for a point I of a reference image (7) and on a set of synthesized images (4) representing the 3D point of the scene corresponding to this point I, of the minimum (zi−Δzi1) and maximum (zi+Δzi2) depth values of the depth zi of this point I corresponding to this maximum distortion, calculating a span around the depth zi of this point I, dependant on the minimum value of the error Δzi2 and on the minimum value of the error Δzi1 among the values calculated for the synthesized images of the set.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
Fiber incorporating quantum dots as programmable dopants
InactiveUS20050157996A1Control distortionAltering their doping characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyCladded optical fibreFiberArtificial atom
A programmable dopant fiber includes a plurality of quantum structures formed on a fiber-shaped substrate, wherein the substrate includes one or more energy-carrying control paths, which pass energy to quantum structures. Quantum structures may include quantum dot particles on the surface of the fiber or electrodes on top of barrier layers and a transport layer, which form quantum dot devices. The energy passing through the control paths drives charge carriers into the quantum dots, leading to the formation of “artificial atoms” with real-time, tunable properties. These artificial atoms then serve as programmable dopants, which alter the behavior of surrounding materials. The fiber can be used as a programmable dopant inside bulk materials, as a building block for new materials with unique properties, or as a substitute for quantum dots or quantum wires in certain applications.
Owner:RAVENBRICK
Method for reducing peak-to-average power ratio of multi-carrier modulation
InactiveUS20060126748A1Limit distortionLower error rateSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsDistortionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
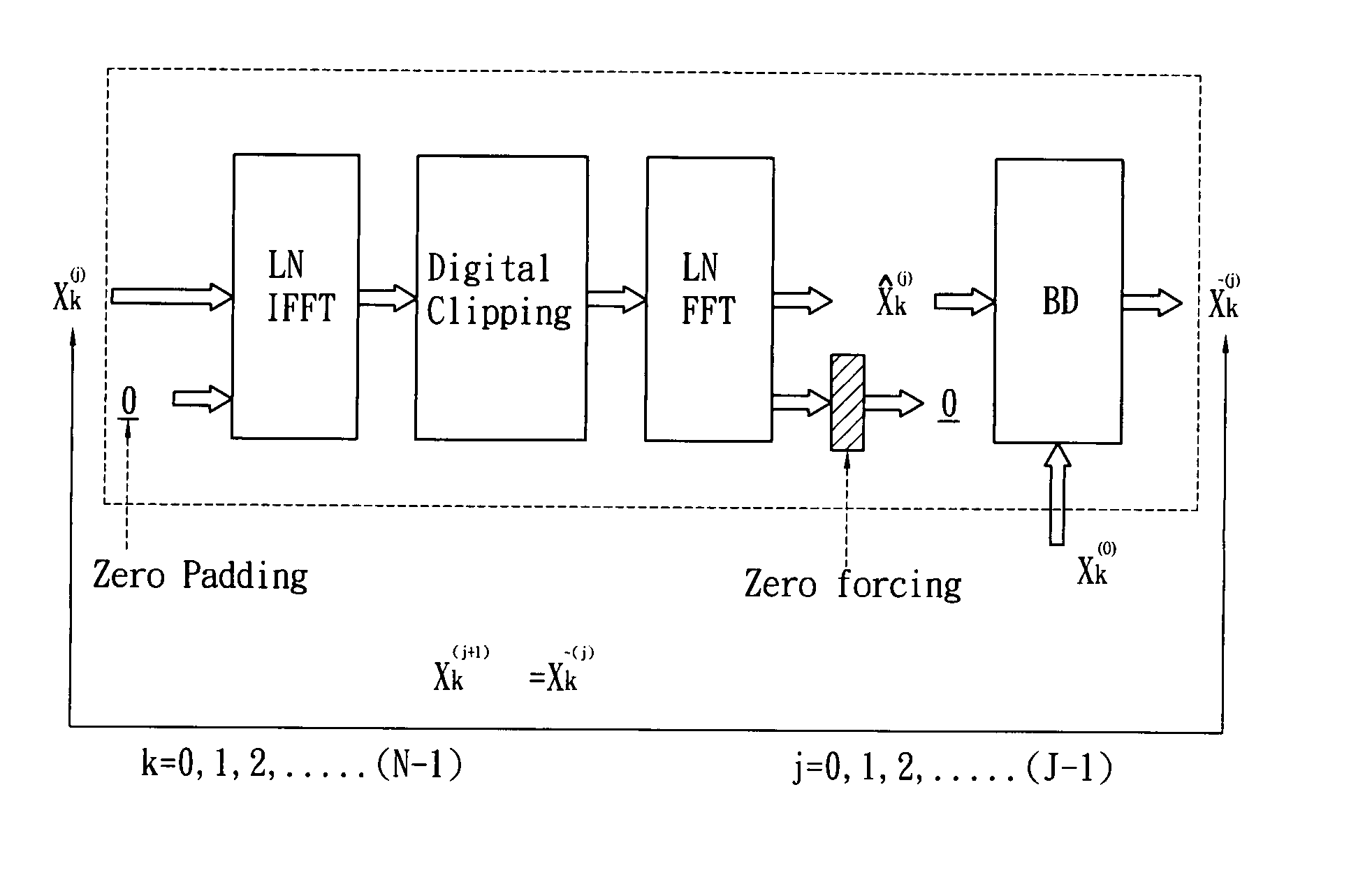
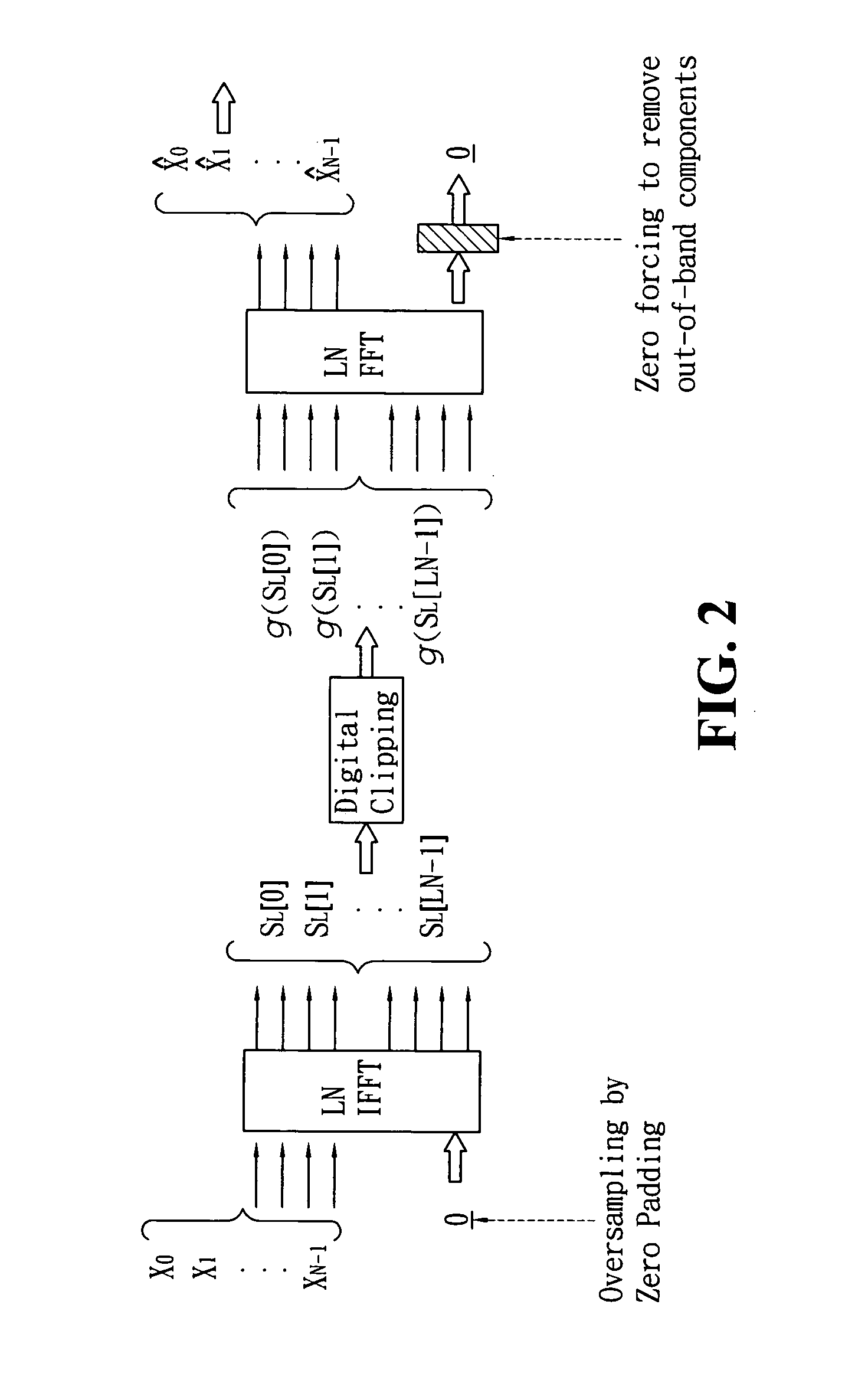
A method for reducing the peak-to-average power ratio of the time-domain signal in a communication system using multi-carrier modulation is provided herein. The present invention is based on the method of recursive clipping and filtering to reduce the peak-to-average power ratio and out-of-band spectrum, but during the recursive process, the distortion of the multi-carrier modulated signal is controlled to be bounded within a specific region. In an additive white Gaussian noise channel with high signal-to-noise ratio, the present invention could achieve significantly lower error rate and the error floor phenomenon is almost completely removed. Therefore the power amplifier could be operated at higher average output power and a smaller range of linearity.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Bi-polymer infrared optics for high-g applications
ActiveUS20130208367A1Low costSacrificing optical qualityMirrorsDirection controllersCamera lensHigh acceleration
Optical systems configured to withstand operation in high acceleration and varying temperature environments, and methods of assembling the same. In one example, an imaging optical apparatus includes a primary minor made of an unreinforced polymer, a secondary mirror made of the unreinforced polymer and optically coupled to the primary minor, a field lens optically coupled to the secondary minor, and a strut having a plurality of cross-struts and mounting features configured to mount the primary minor, the secondary mirror and the field lens. In some examples, the imaging optical apparatus further includes an outer retainer disposed behind the primary minor and coupled to the strut, and an inner retainer disposed behind the field lens and coupled to the strut, the outer and inner retainers configured to structurally support the primary minor and the field lens and to accommodate deflections of the primary minor.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Tensioner with reinstallation feature
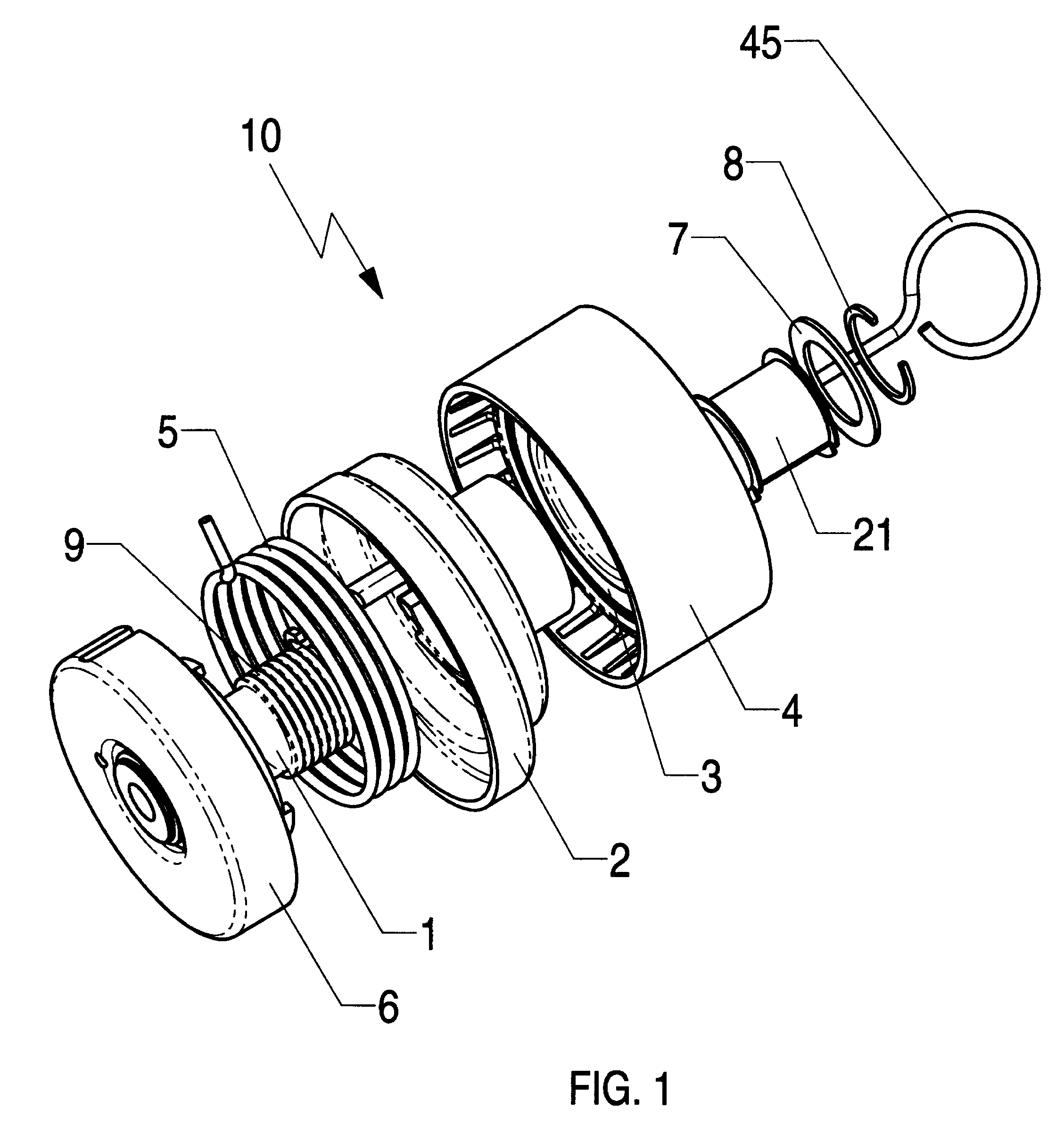
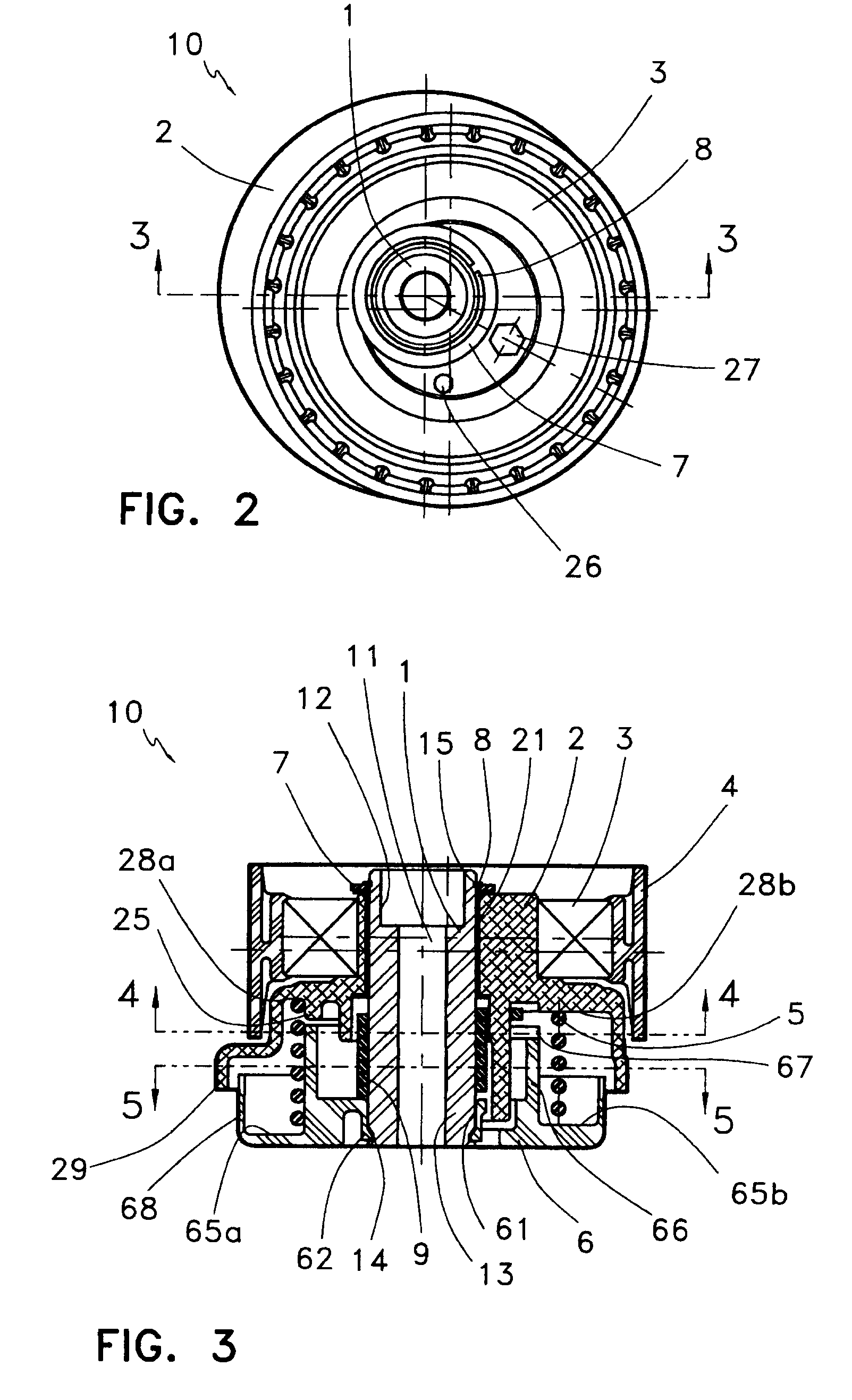
ActiveUS7874950B2Easy and reliable reinstallationAvoid excessive bending and yieldingGearingEngineeringField service
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
Tunable Pulse Width Laser
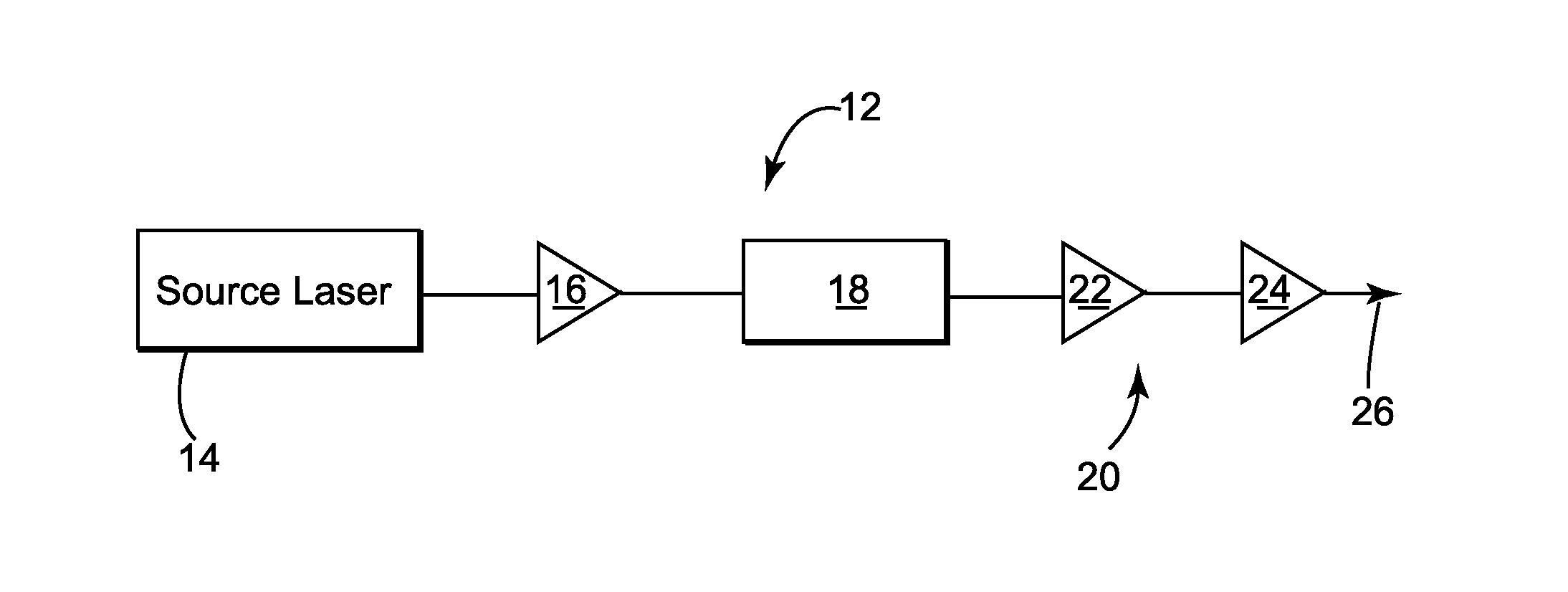
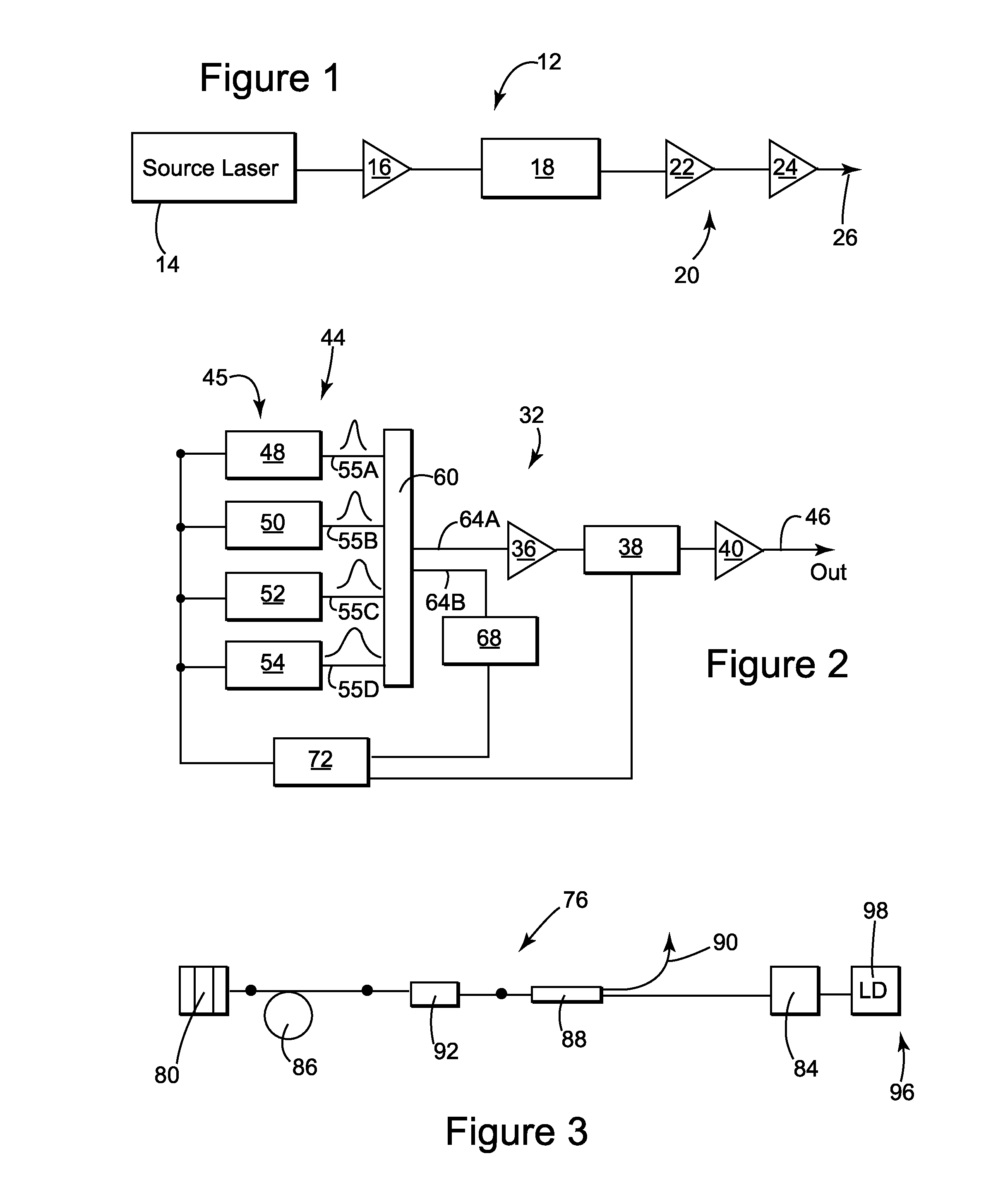
ActiveUS20130177031A1Control distortionLong durationLaser using scattering effectsSpectral bandsPulse duration
A method of tuning the time duration of laser output pulses, the method including spectrally dispersing optical pulses and further comprising providing an optical pulse having a time duration and a spectral bandwidth; spectrally dispersing (243, 245) the optical pulse so as to provide a selected change in the time duration of the pulse responsive to the spectral band-width of the pulse; outputting (226) an optical output pulse having a first time duration that is responsive to the selected change in time duration; providing another optical pulse; changing the amount of spectral bandwidth of the another optical pulse (272) to be different than that of the optical pulse or changing the amount of spectral dispersion so that spectrally dispersing the another optical pulse provides a change in time duration that is different than the selected change; and outputting (226) another optical output pulse having a second time duration that is responsive to the different change in time duration, the second time duration of the another optical output pulse being different than the first time duration of the optical output pulse.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Athermalization high-resolution prime lens
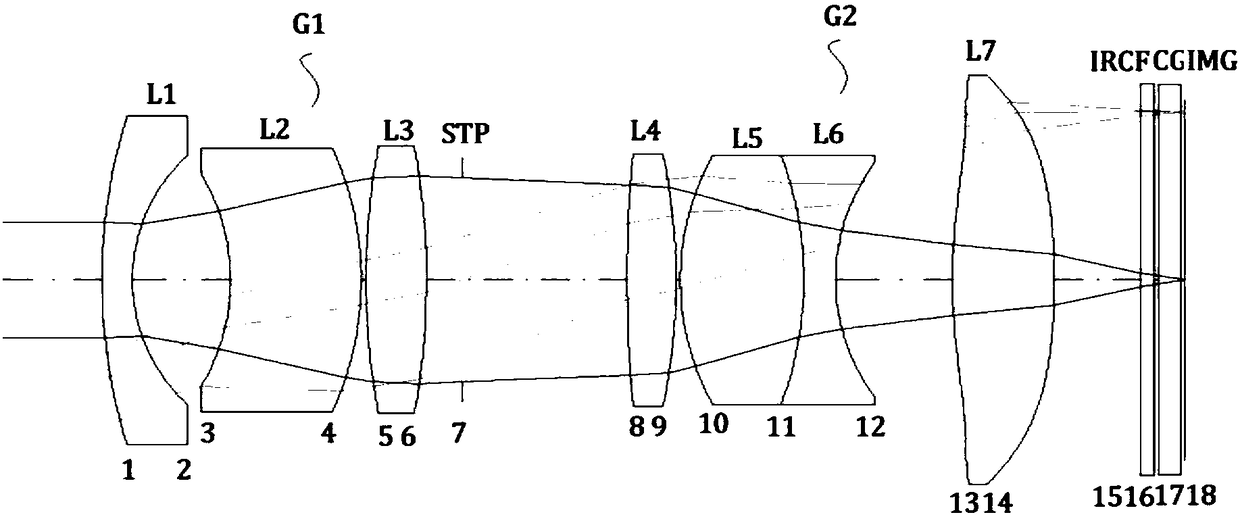
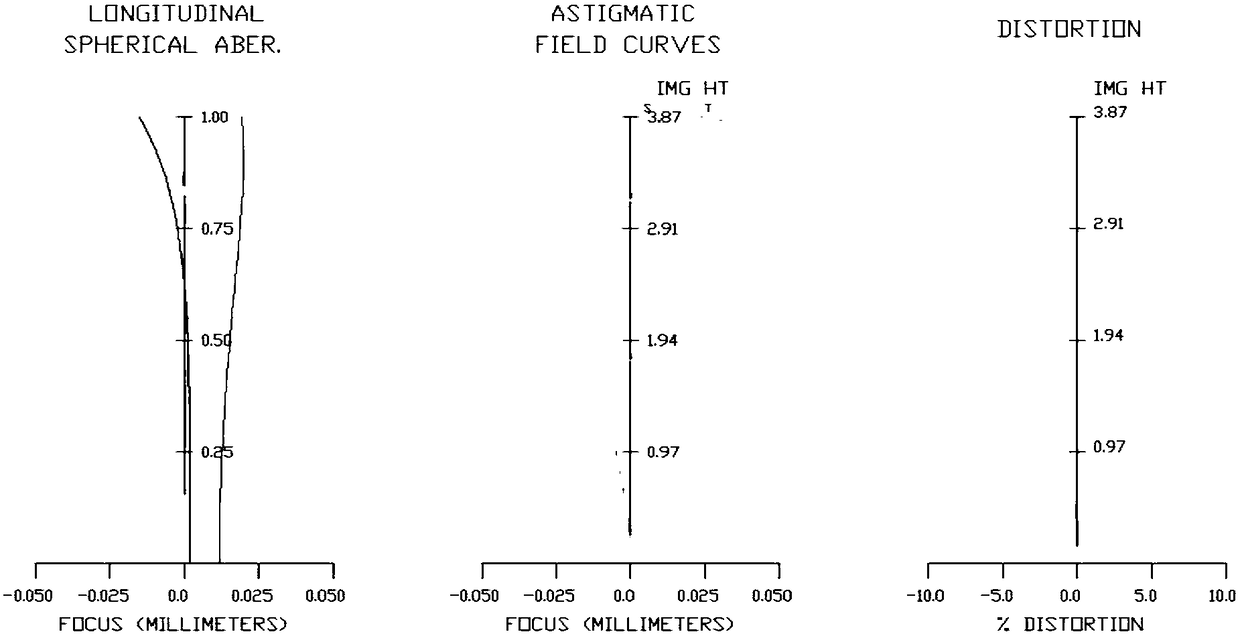
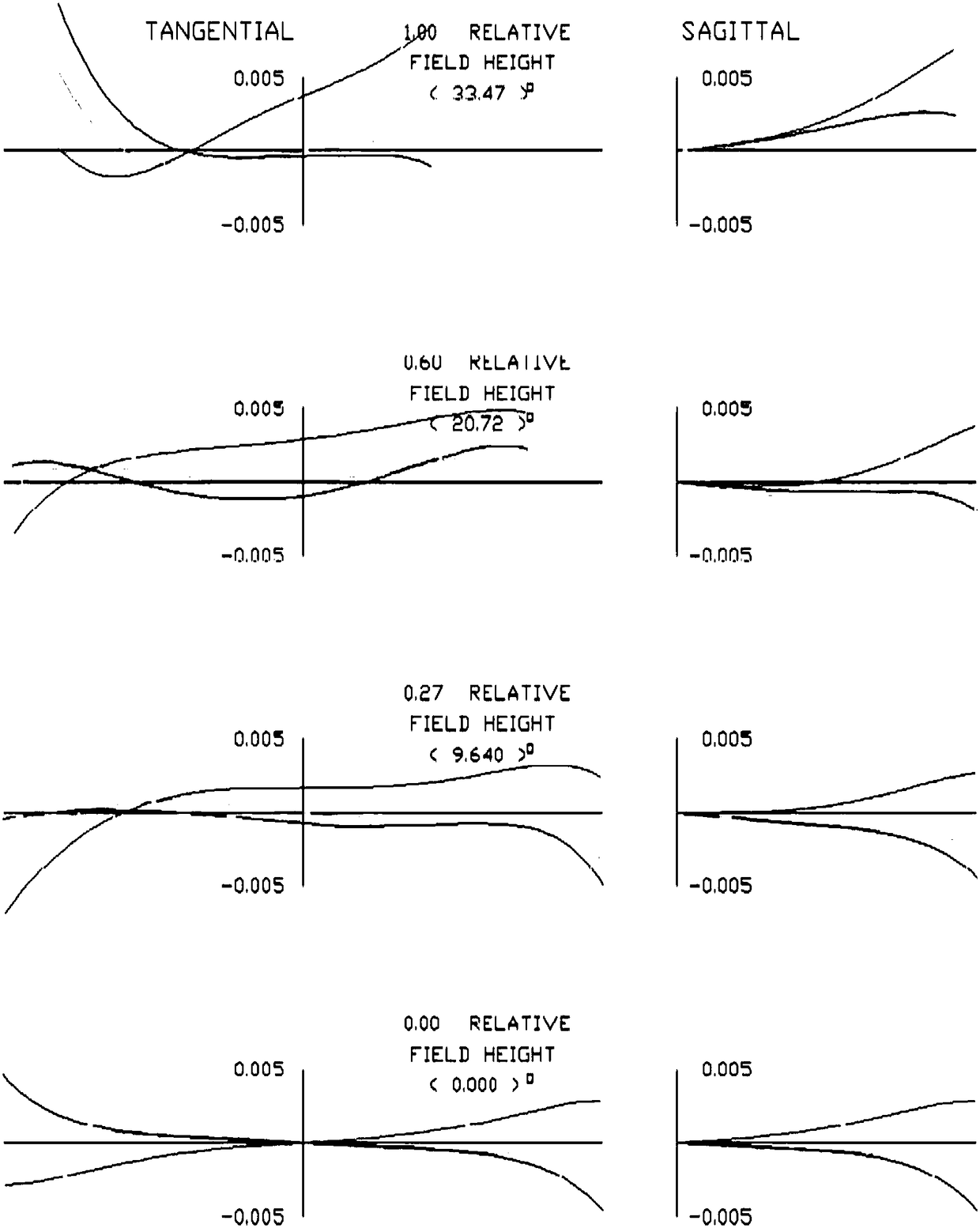
PendingCN108445611ASimple structureOvercome the defect of low image qualityOptical elementsPrime lensImaging quality
The invention discloses an athermalization high-resolution prime lens which, from the object side to the image side, sequentially comprises: a pre-group lens with negative focal power, a diaphragm, apost-group lens with positive focal power, and an imaging plane, wherein the pre-group lens sequentially comprises a first battery of lenses, a second lens with negative focal power, and a third lenswith positive focal power; the post-group lens sequentially comprises a fourth lens with positive focal power, a fifth lens with positive focal power, a sixth lens with negative focal power, and a seventh lens with positive focal power. According to the athermalization high-resolution prime lens disclosed by the invention, a small high-image-quality athermalization prime lens is designed by reasonably combining spherical surface and non-spherical surface, and has the advantages of simple structure and low cost, and overcomes the defect of low image quality of existing simple-structure lens, and perfectly controls distortion and chromatic aberration in the whole field of view.
Owner:JIAXING ZHONGRUN OPTICAL TECH
Process for assembling wafers by means of molecular adhesion
InactiveUS20090280595A1Quality improvementControl distortionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsPhysics
The invention relates to a process of bonding by molecular adhesion of two layers, such as wafers of semiconductor material, wherein propagation of a first bonding wave is initiated from a pressure point applied to at least one of the two layers, and wherein the first bonding wave step is followed by propagating a second bonding wave over an area, for example, in the vicinity of the pressure point. Propagation of the second bonding wave may be obtained through the interposing of a separation element between the two wafers and the withdrawal of the element, for example, after the beginning of the first bonding wave propagation.
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
Microcontact printing
InactiveUS20070261574A1Generate undesired patterning resultsControl distortionMaterial nanotechnologyMechanical working/deformationMicrocontact printingEngineering
A microcontact printing tool having a print unit including a stamp head with a stamp and a wafer chuck for retaining a substrate. The stamp contained by the stamped head movable relative to the substrate by an actuator and a stage. A plurality of sensors detect the position of the stamp relative to substrate. A method of using the printing tool that includes a real-time feedback for consistent and accurate application of force during the printing of the substrate. The stamp head includes a pressure chamber carrying the stamp. The stamp backing is deflected prior to contact of the stamp with the substrate to form a minimum point and the stamp backing and the stamp is returned to a plane to create a printing propagation contact. An apparatus has a master backing and a stamping backing in close proximity and the stamp material drawn in through a vacuum. The stamp is separated from the master by use of a parting fluid.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method of determining the configuration of an ophthalmic filter
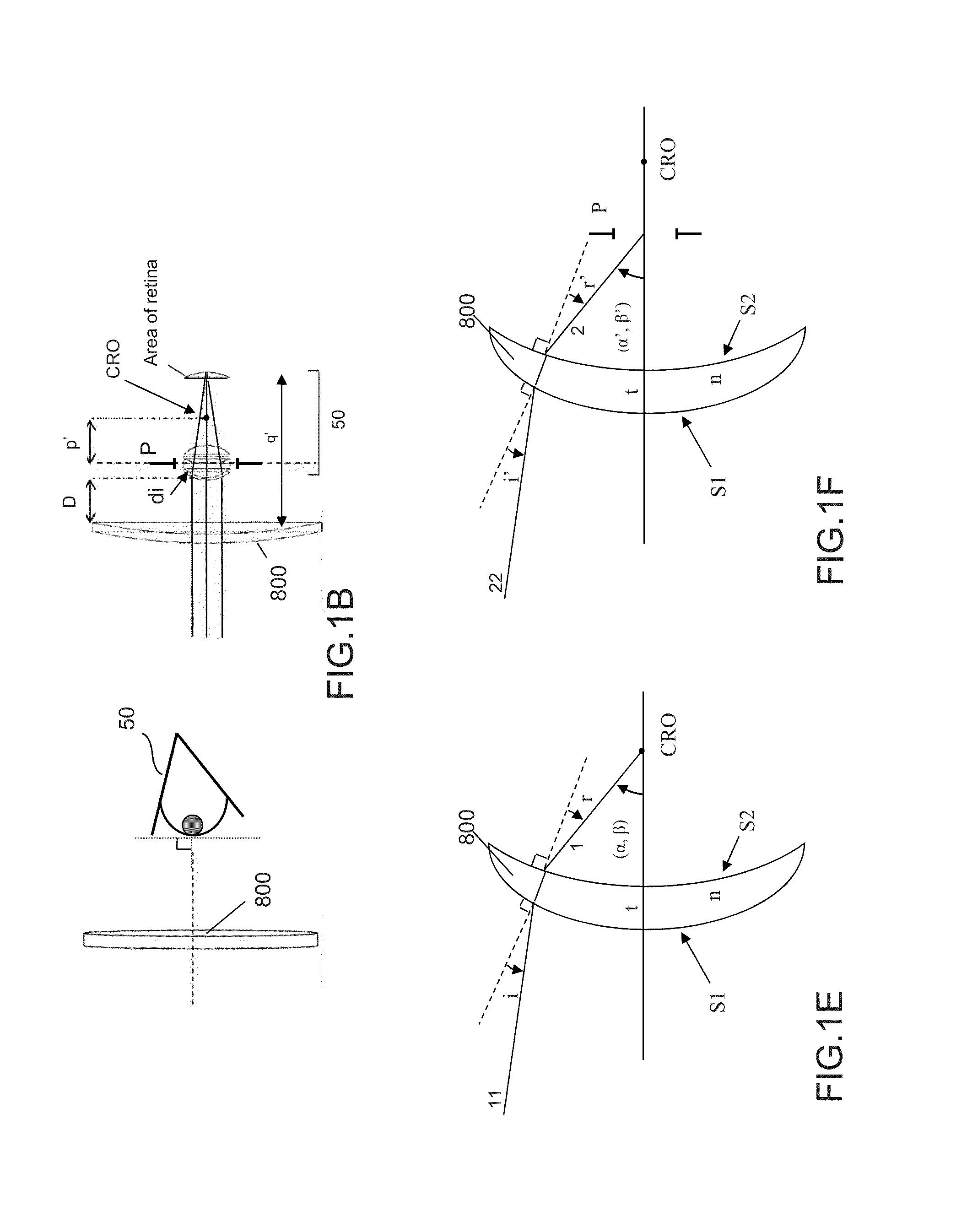
ActiveUS20140320806A1High selectivityControl distortionSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsAngle of incidenceTransmittance
Method of determining configuration of interferential filtering elements for an optical device having an optical substrate for a user, includes:providing a first set of parameters representative of at least one main line of sight of the user;determining a first selected range of angles of incidence based on the first parameters;providing a second set of parameters characterizing, for the user, a range of wavelengths to be at least partially inhibited;determining a first selected range of wavelengths of incident light to be at least partially inhibited, based on the second parameters; andconfiguring a first selective interferential filtering element and a first zone of a surface of the optical substrate based on the first selected range of angles of incidence and wavelengths such that the first selective interferential filtering elements inhibit, at a first rate of rejection, transmission of the first selected range of wavelengths of incident light.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE +1
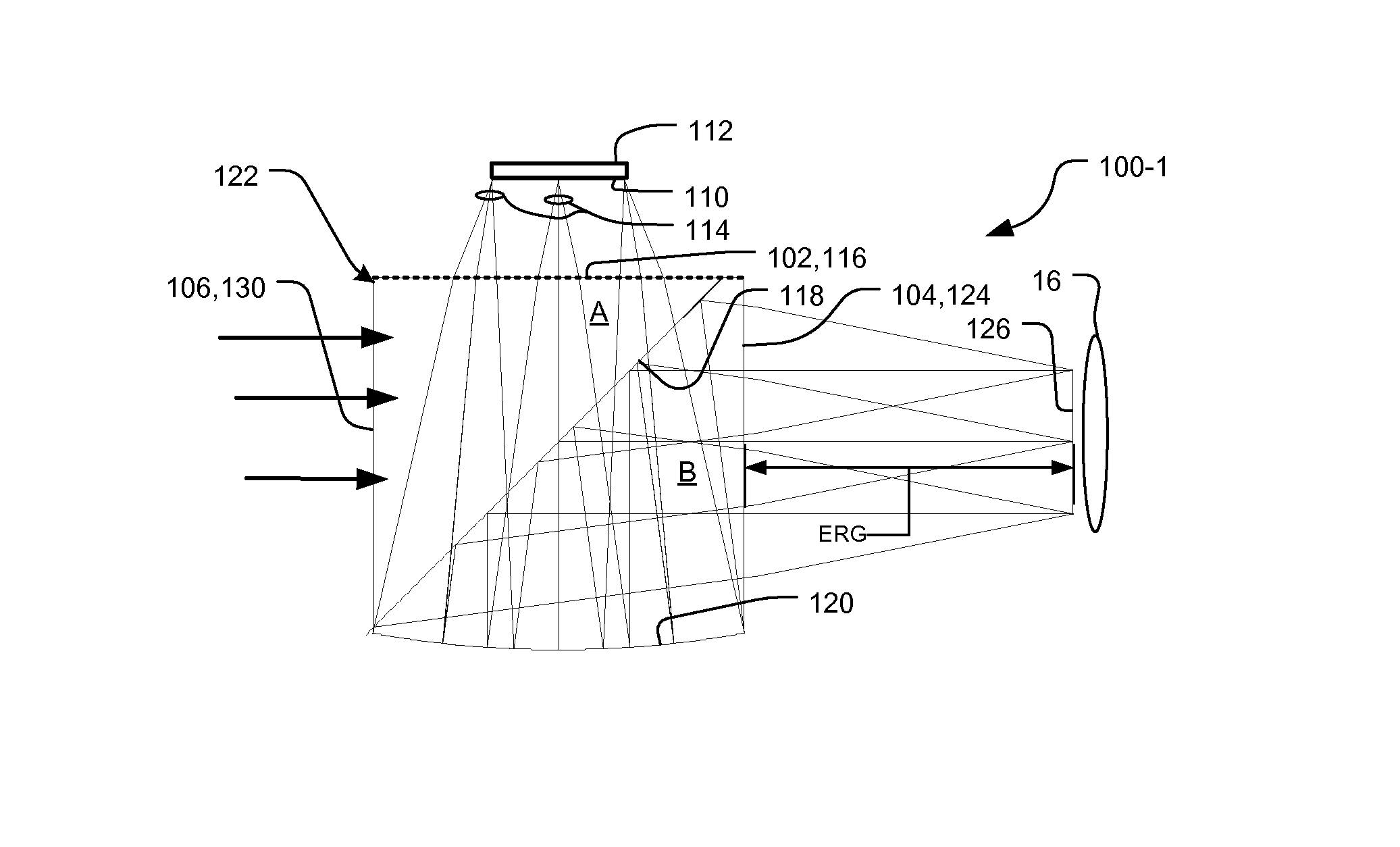
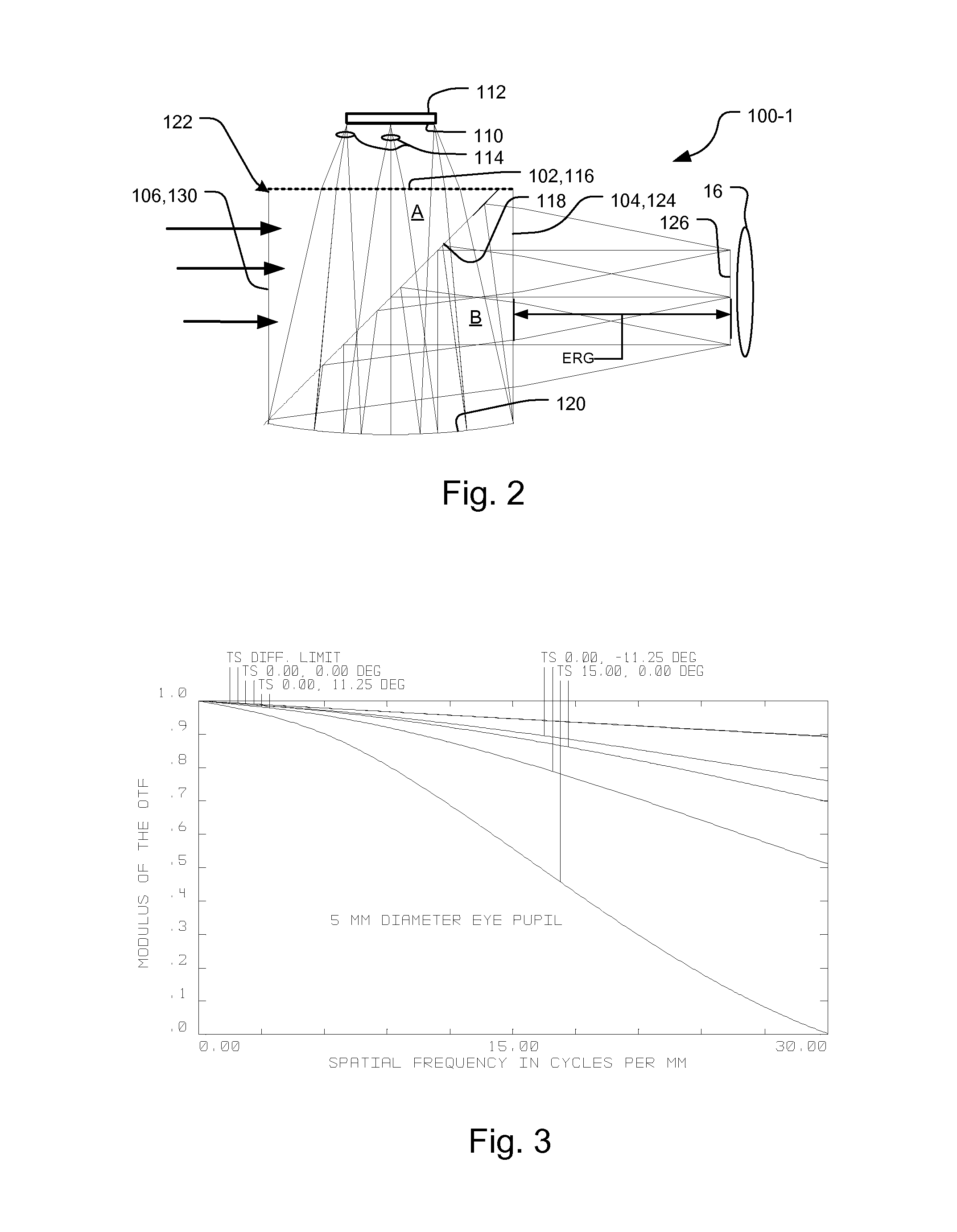
Eyepiece for head mounted display system and method of fabrication
ActiveUS7586686B1Minimizes stray lightMinimizes artifactDiffraction gratingsMagnifying glassesEyepieceImage resolution
A monolithic optical element for an eyepiece in a head mounted display system has a body, in which a first surface of the body receives light from a display device, the light passes through a second surface of the body to an eye of a user, and a reflective folding surface is located optically between the first surface and the second surface. The reflective folding surface folds an optical path between the first surface and the second surface. Finally, a diffractive optical element is provided on at least one of the first surface or the second surface. The use of the diffractive optical surface enables the eyepiece element to be constructed of a single optical substrate material, yet function over a broad color spectrum with superior resolution and minimal distortion over a large field of view.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Fiber incorporating quantum dots as programmable dopants
InactiveUS20050157997A1Control distortionAltering their doping characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyCladded optical fibreFiberArtificial atom
A programmable dopant fiber includes a plurality of quantum structures formed on a fiber-shaped substrate, wherein the substrate includes one or more energy-carrying control paths, which pass energy to quantum structures. Quantum structures may include quantum dot particles on the surface of the fiber or electrodes on top of barrier layers and a transport layer, which form quantum dot devices. The energy passing through the control paths drives charge carriers into the quantum dots, leading to the formation of “artificial atoms” with real-time, tunable properties. These artificial atoms then serve as programmable dopants, which alter the behavior of surrounding materials. The fiber can be used as a programmable dopant inside bulk materials, as a building block for new materials with unique properties, or as a substitute for quantum dots or quantum wires in certain applications.
Owner:RAVENBRICK
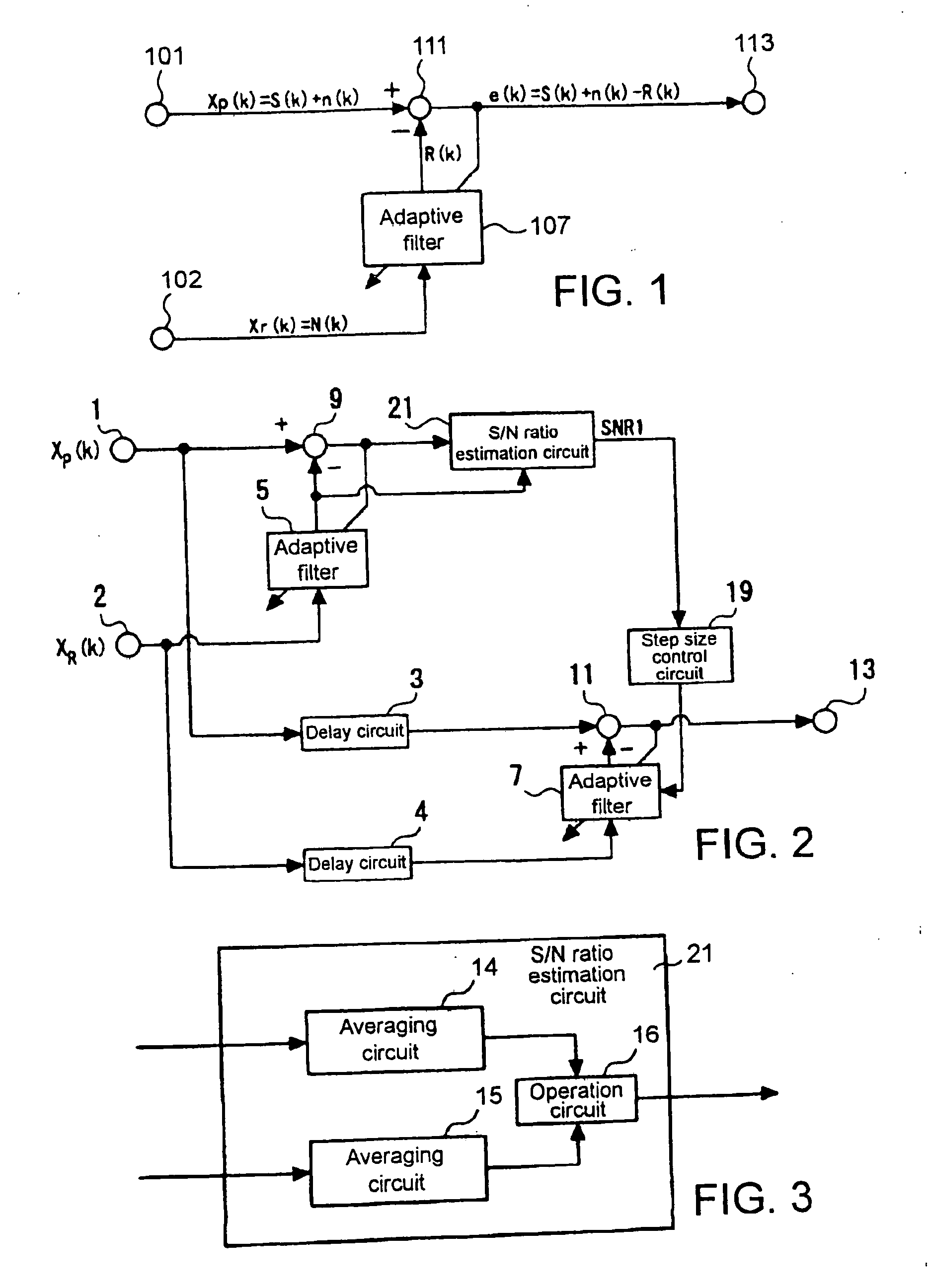
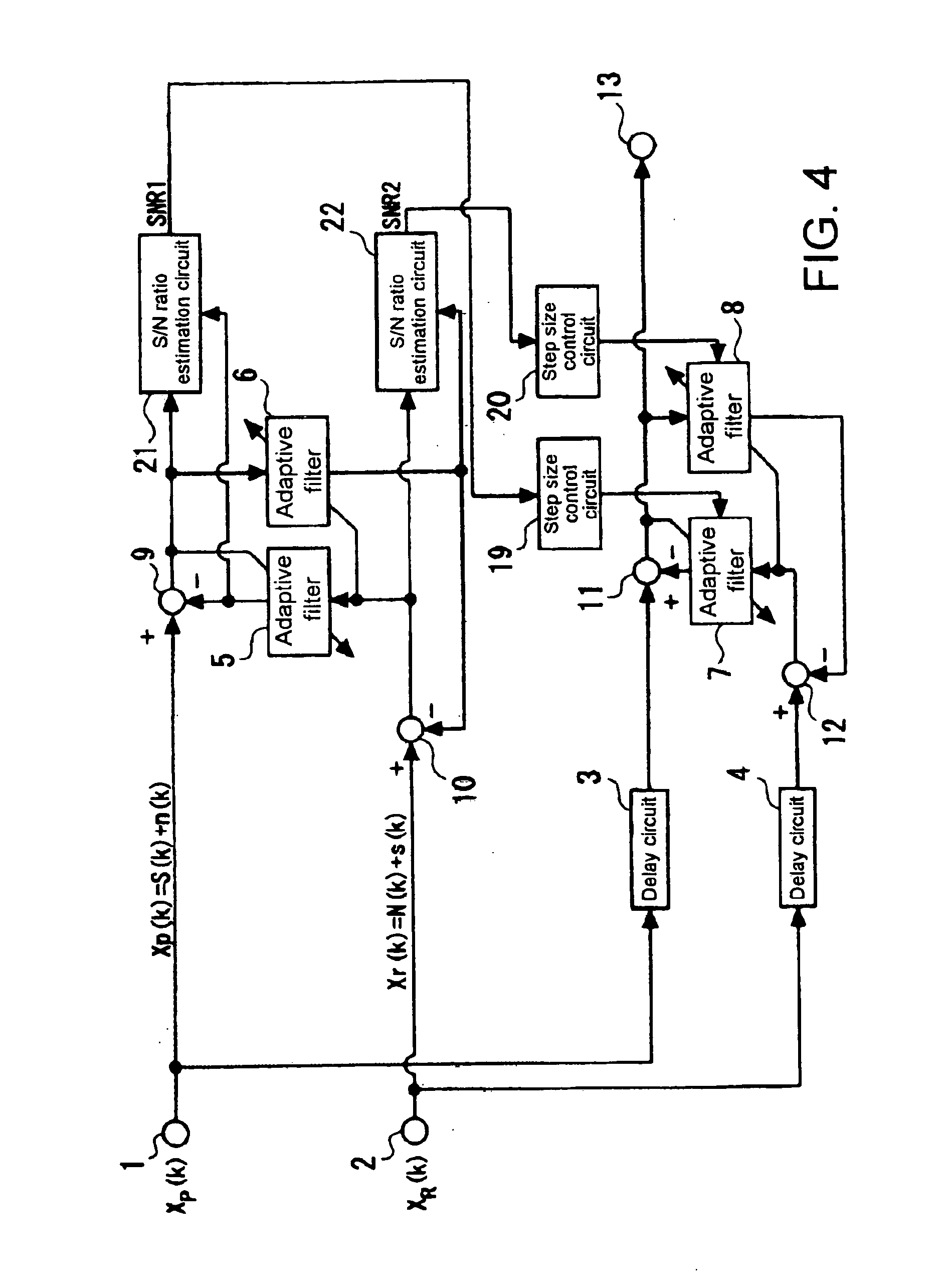
Signal processing method and apparatus
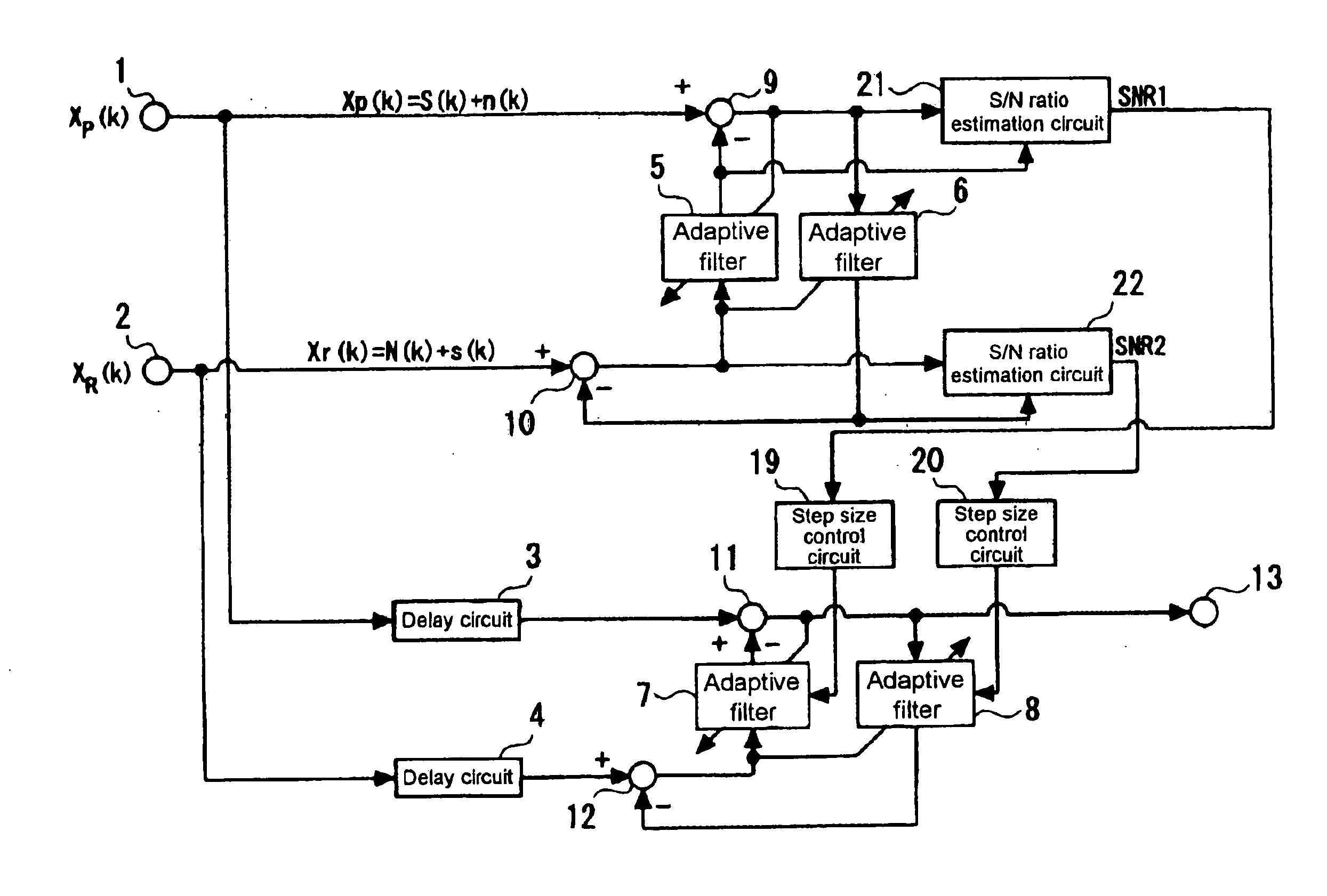
ActiveUS20070071253A1Short convergence timeLittle distortionAdaptive networkEar treatmentAdaptive filterSignal processing
A signal processor includes: a first adaptive filter that takes a first signal as input and generates a first pseudo signal; a first subtractor that subtracts the first pseudo signal from a second signal to supply a first differential signal as output; a second adaptive filter that takes the first signal as input to generate a second pseudo signal; a second subtractor that subtracts the second pseudo signal from the second signal to supply a second differential signal as output; a first step size control circuit that generates a first step size used in updating the first adaptive filter in accordance with the relation between the second pseudo signal and the second differential signal; and a second step size control circuit that generates a second step size used in updating the second adaptive filter in accordance with the relation between the first signal and the second signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
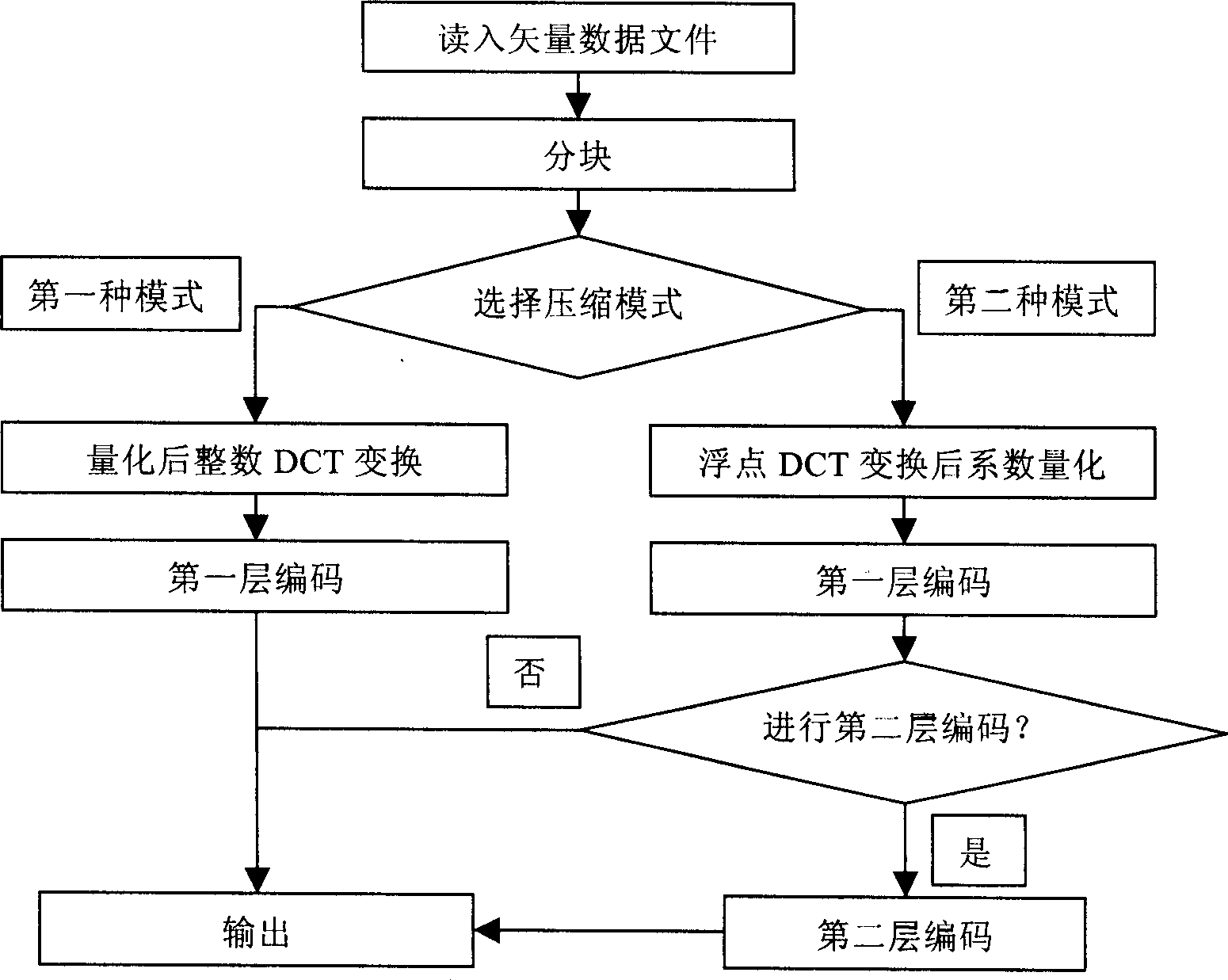
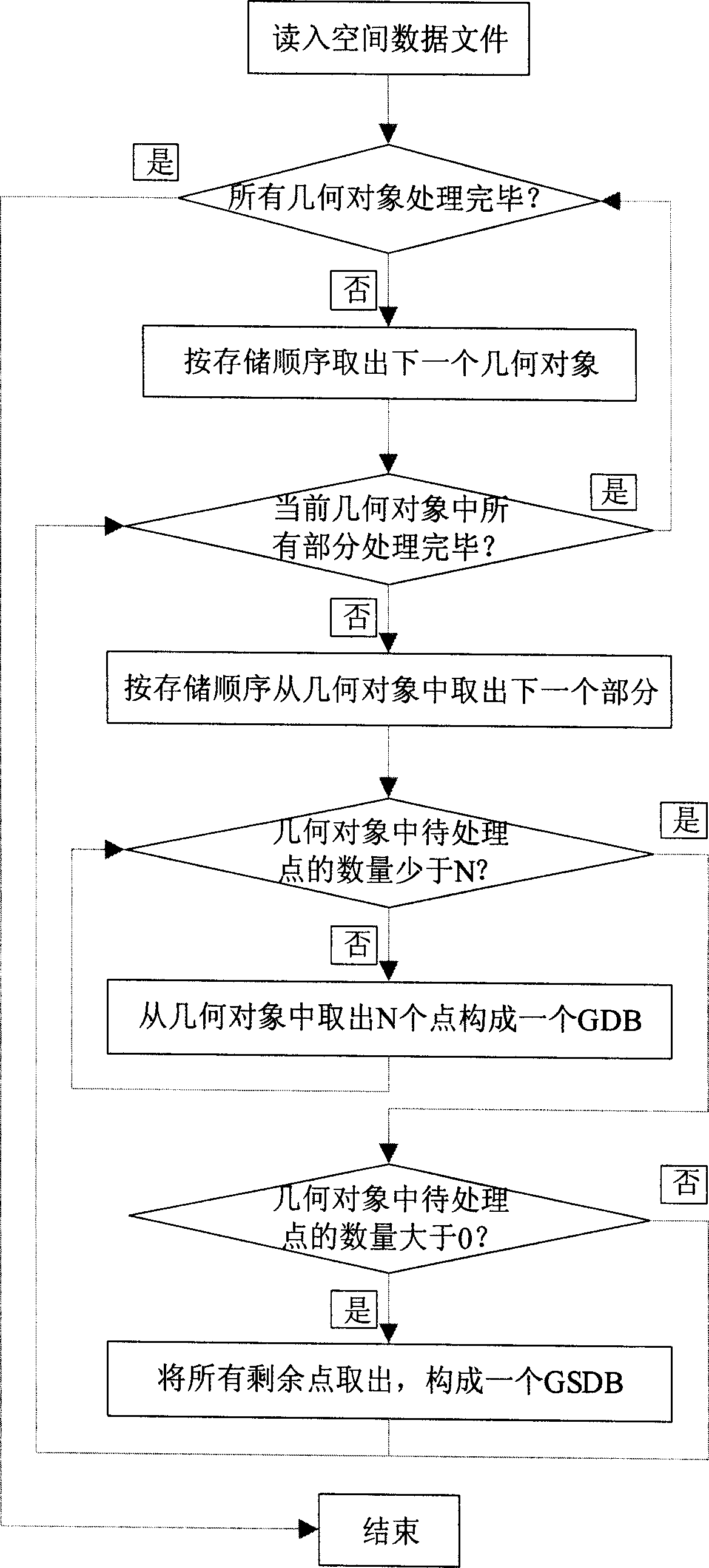
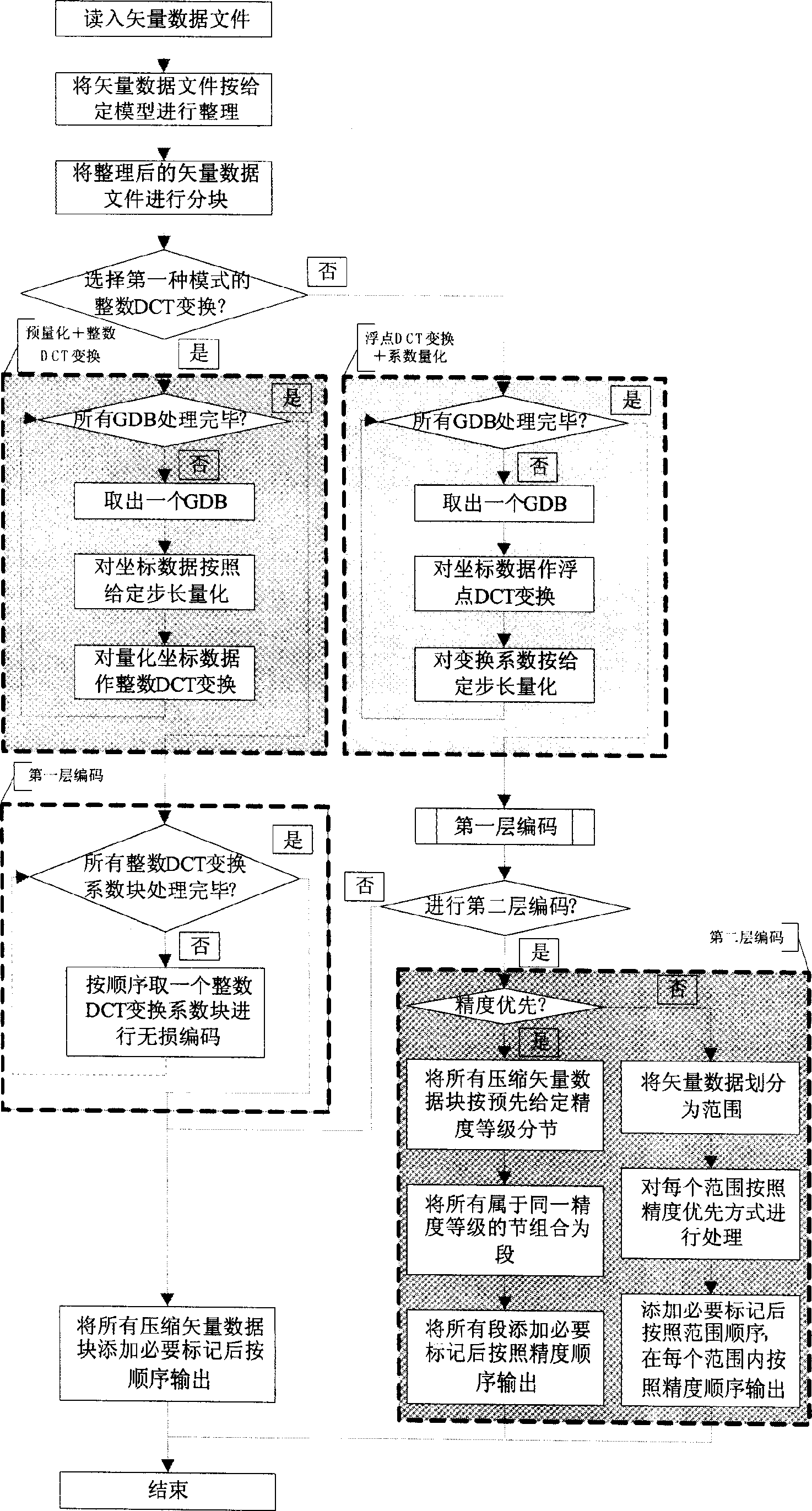
Two-dimensional vector data compression method
InactiveCN1777038AGood effectControl reconstruction errorCode conversionData compressionSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The method divides original vector data into blocks of vector data. Next, loss compression based on DCT transform is carried out for the blocks of vector data according to one of two modes. Then, entropy coding is carried out for the obtained DCT transform so as to obtain compressed blocks of vector data. Finally, all compressed blocks of vector data are organized as binary bit steam in specific format. Main effects of the invention are: compression ratio near to 20 is reached for vector data formed natural in wide range such as contour line, road network and water system etc; SNR reaches to 60dB; and maximal absolute deformation is about 10-5 order of magnitude of dynamic range of original vector data. Features are: controllable distortion generated in reconstructing error and compression process; providing technical base for asymptotic transmission of vector data flexibly and in high efficiency by combining asymptotic compression technique in space domain and in frequency domain.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
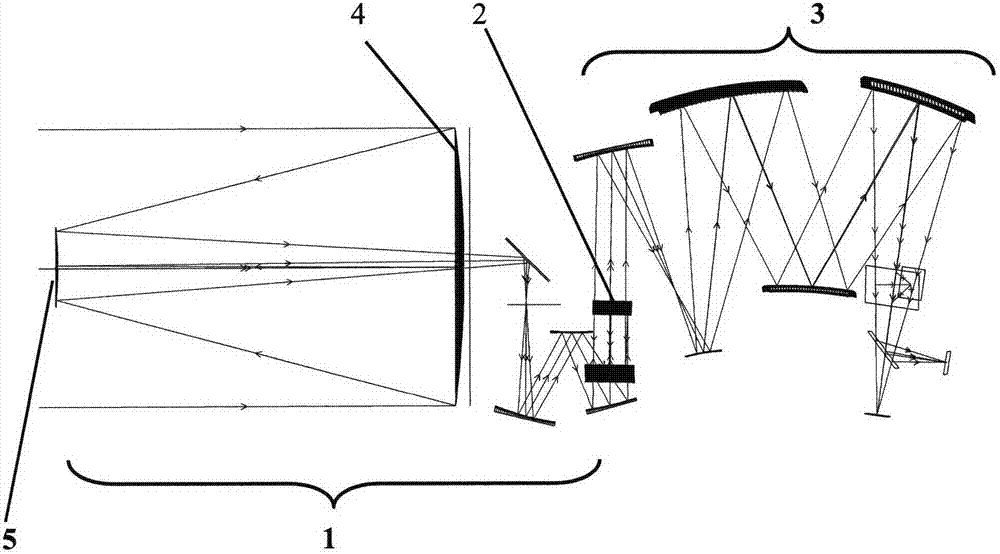
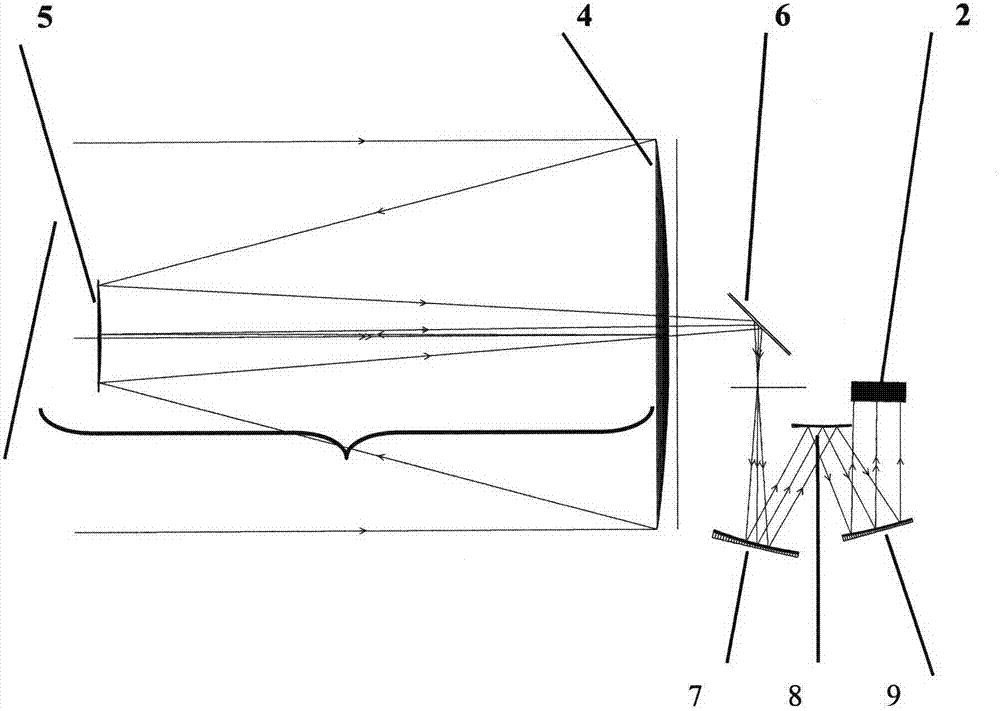
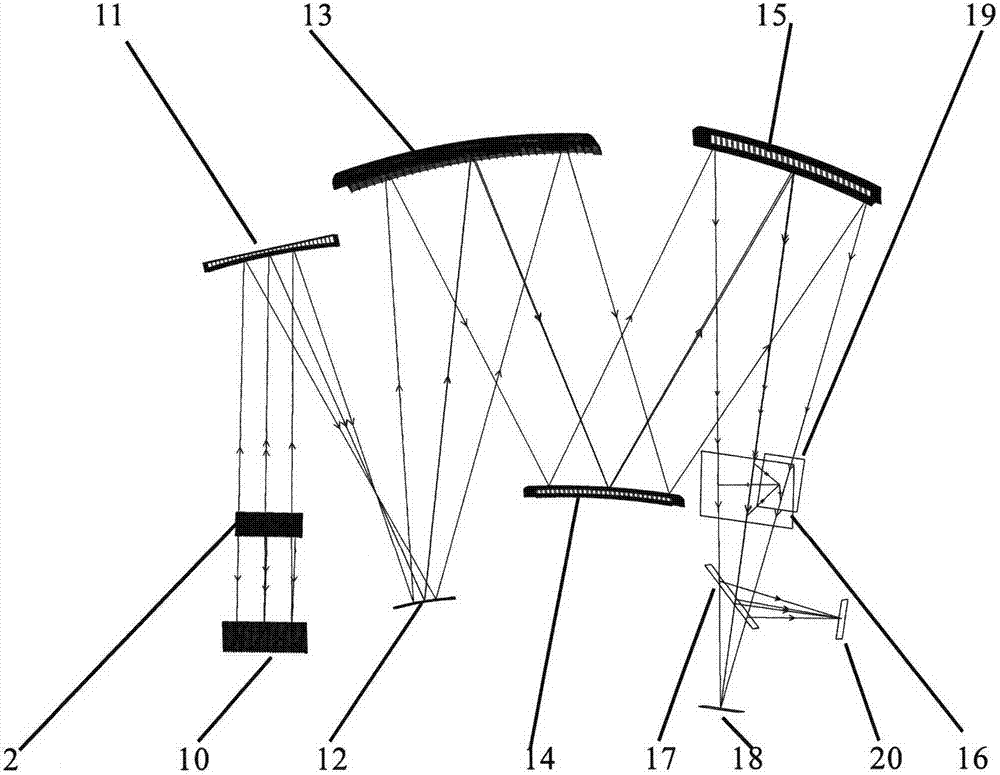
Optical system for space astronomical observation infra-red telescope
The invention discloses an optical system for a space astronomical observation infra-red telescope, which comprises a reflection-type focal-free main optical system (1), a single-axis scanning mirror (2) and a subsequent imaging optical system (3), wherein in the reflection-type focal-free main optical system (1), ray is incident into a reflexing mirror (6) via an eccentric light through hole after being successively reflected by a main mirror (4) and a secondary mirror (5), and is reflected into the single-axis scanning mirror (2) successively by the reflexing mirror (6) and a prism (7); the single-axis scanning mirror (2) ensures that the aiming line of the optical system of the space astronomical observation infra-red telescope is constant by one-dimensional linear scanning; the incident ray of the reflection-type focal-free main optical system (1) is reflected to the subsequent imaging optical system (3); the subsequent imaging optical system (3) comprises an off-axis reflection type system, a color separation filter and a focal plane; the off-axis reflection type system corrects the aberration of the reflection-type focal-free main optical system (1); and the emergent ray of the reflection-type focal-free main optical system (1) is divided into two or more than two spectral channels by the color separation filter to be imaged to a corresponding focal plane.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Image steganography method and secret information extraction method
InactiveCN103413269AIncrease embedding capacityControl distortionImage data processing detailsSteganalysisComputer vision
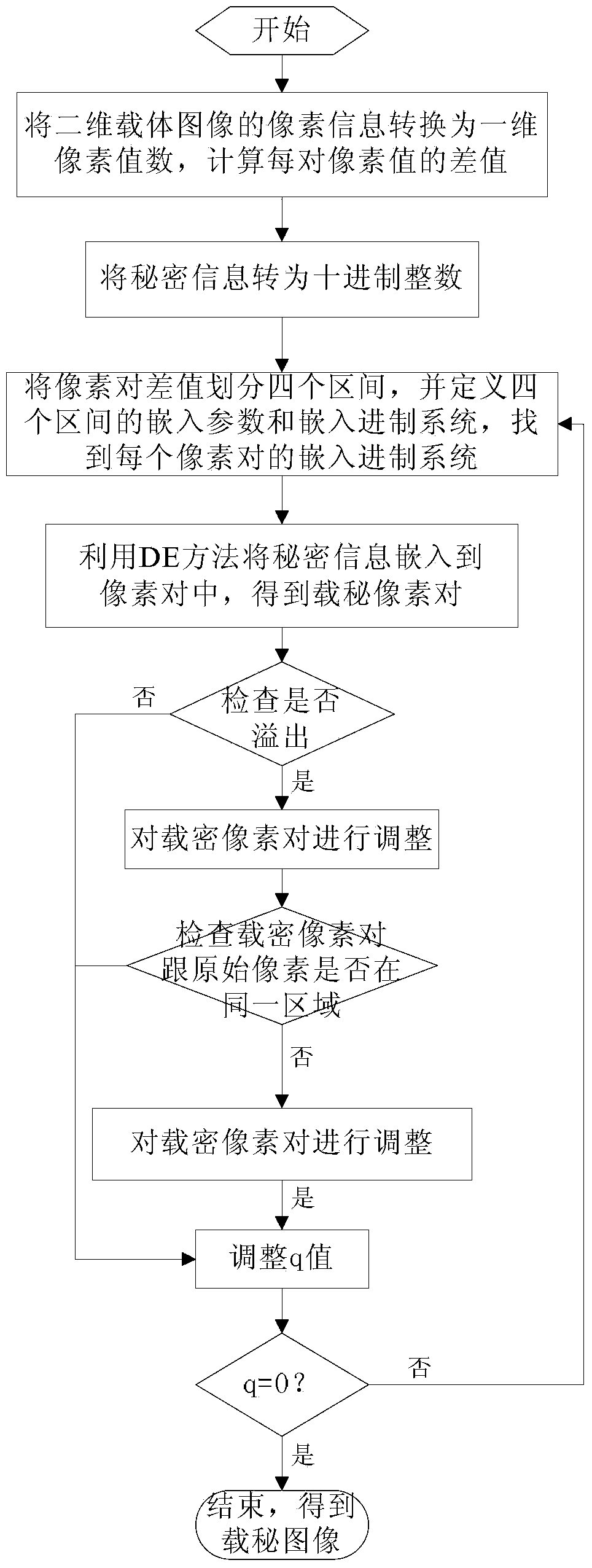
The invention relates to an image steganography method and a secret information extraction method. The image steganography method comprises the steps: (1), converting pixel information of a two-dimensional carrier image I into a set of continuous and non-overlapping one-dimensional pixel value data, and computing a difference value of each pair of pixel values, wherein the size of the two-dimensional carrier image I is N1*N2; (2), performing DES encryption on secret information S, and transferring encrypted secret information S' into a decimal integer q; (3), dividing a di value computed in the step (1) into four sections Tj; (4), obtaining SB(di) according to the equation: SB(di)=qmodB(di), and inserting SB(di) into a pixel pair (xi, yi) through a DE method; (5), detecting whether overflowing occurs or not. Compared with the prior art, the image steganography method has the advantages of being capable of improving insertion capacity of the carrier image remarkably and controlling image distortion effectively. The image steganography method has the steganalysis abilities such as the certain safety performance and resistance to RS attack, and can operate efficiently on mainstream software and hardware platforms of a mobile intelligent terminal.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com