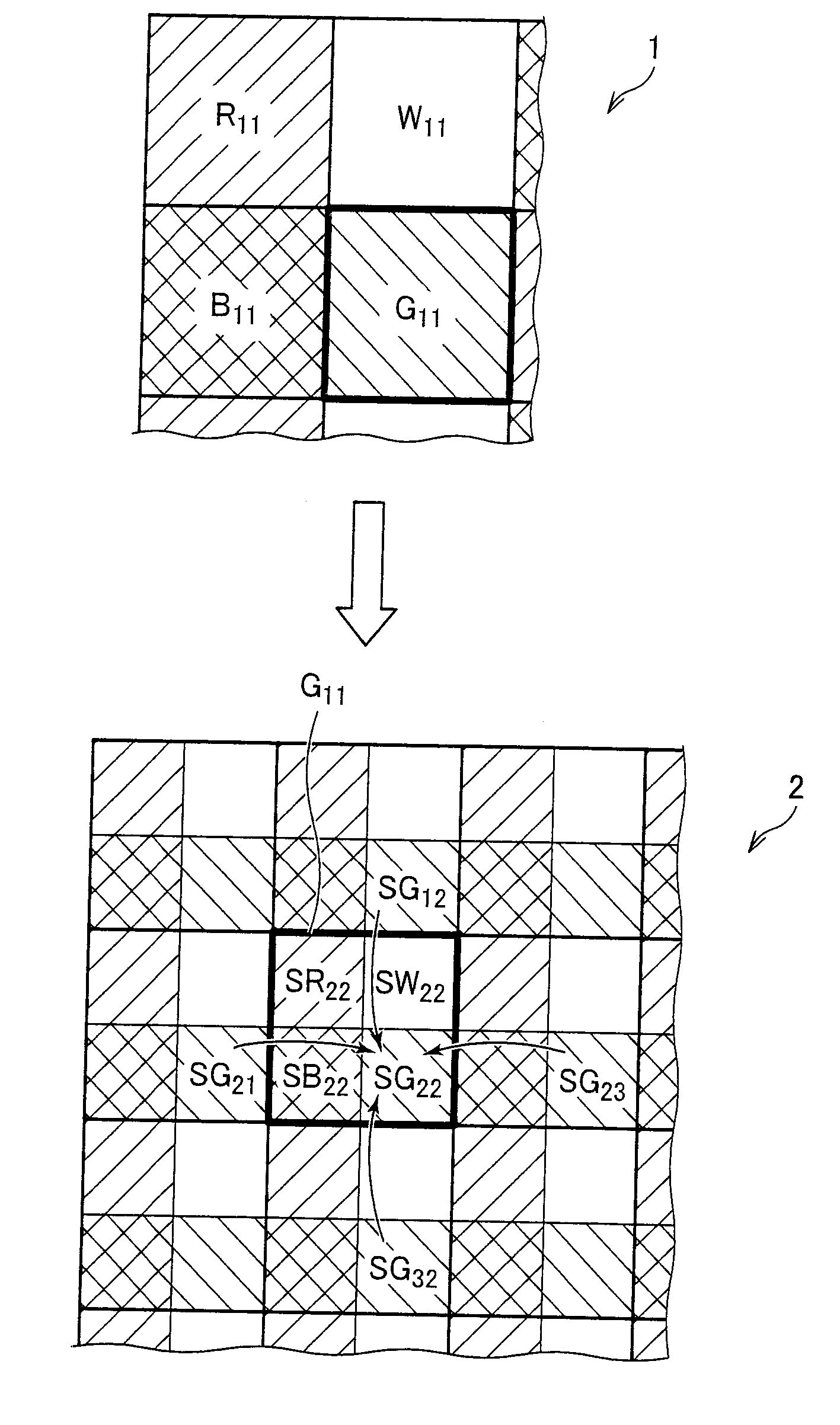
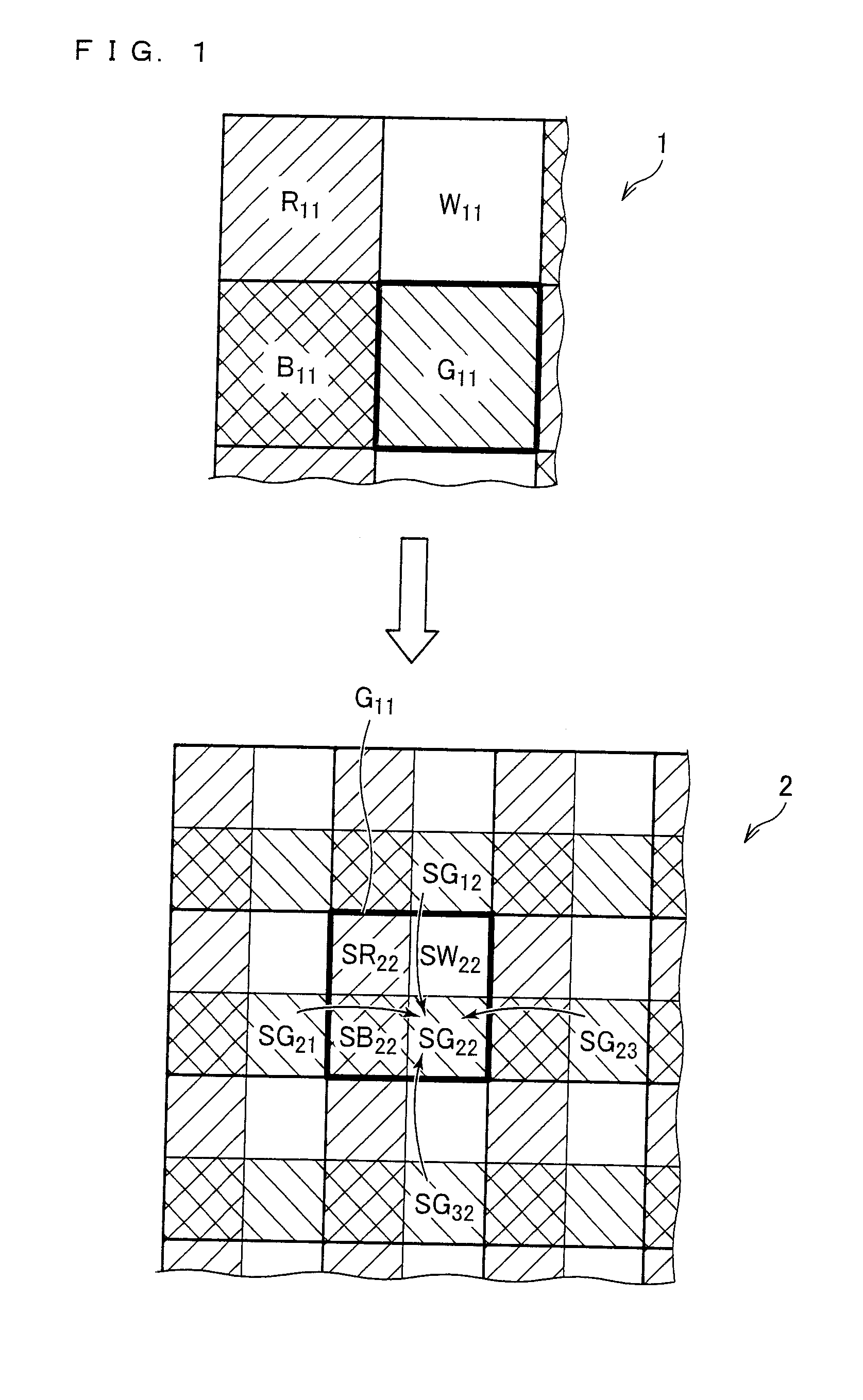
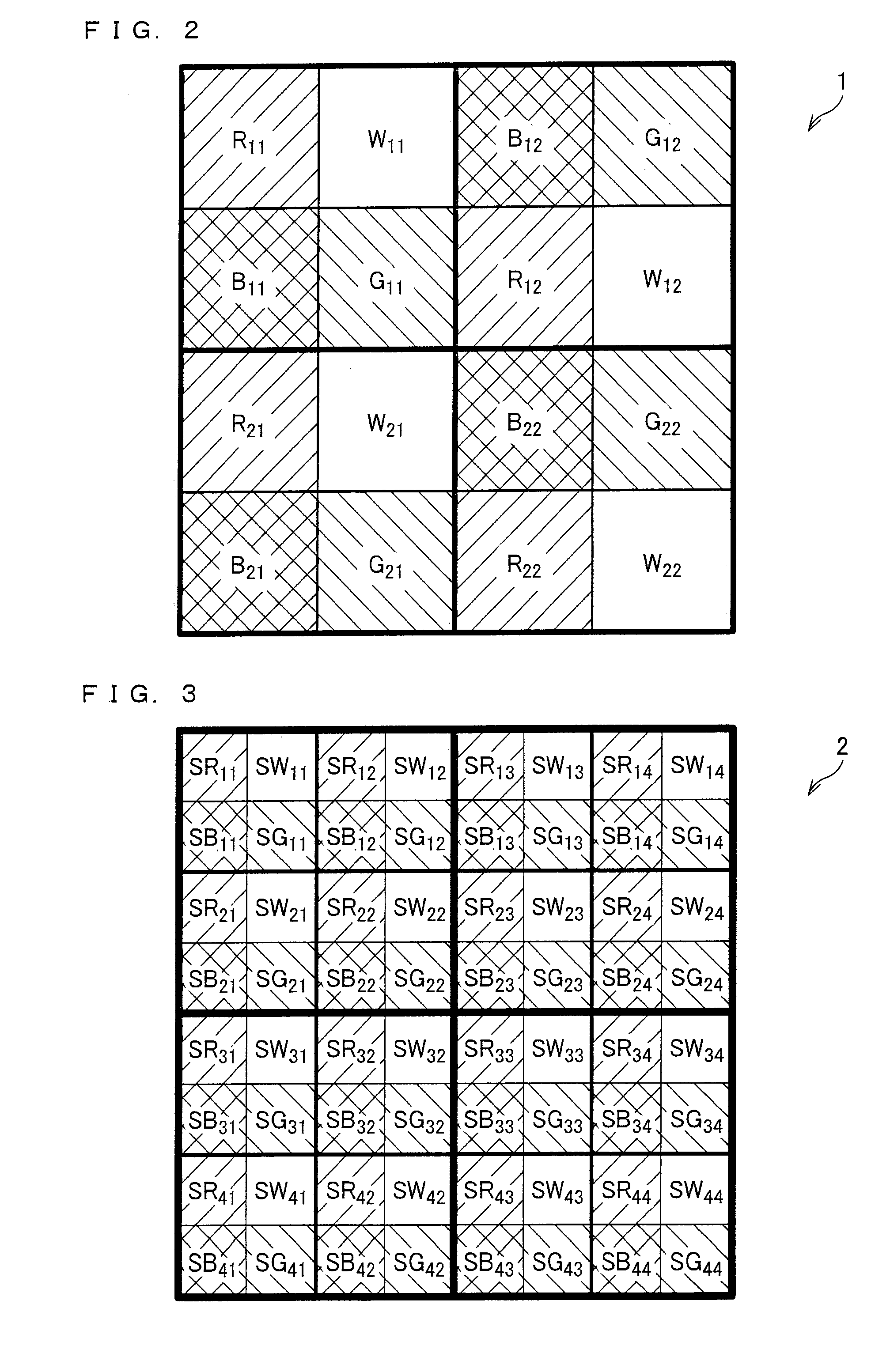
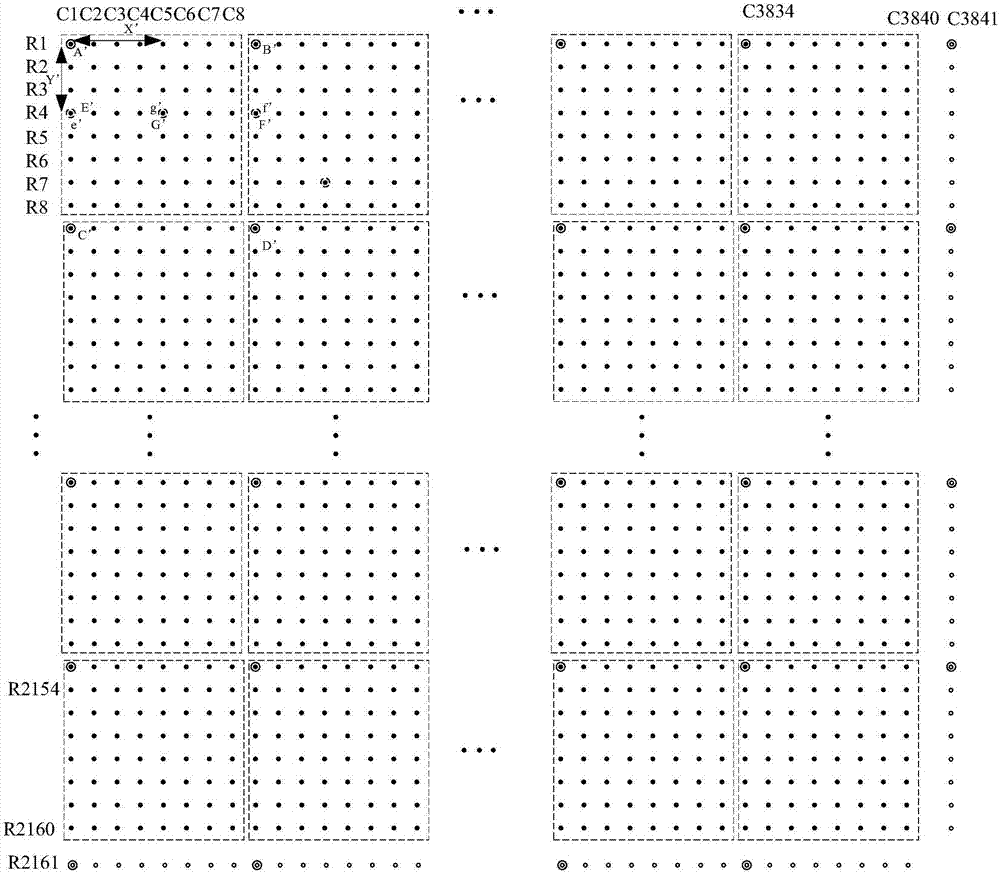
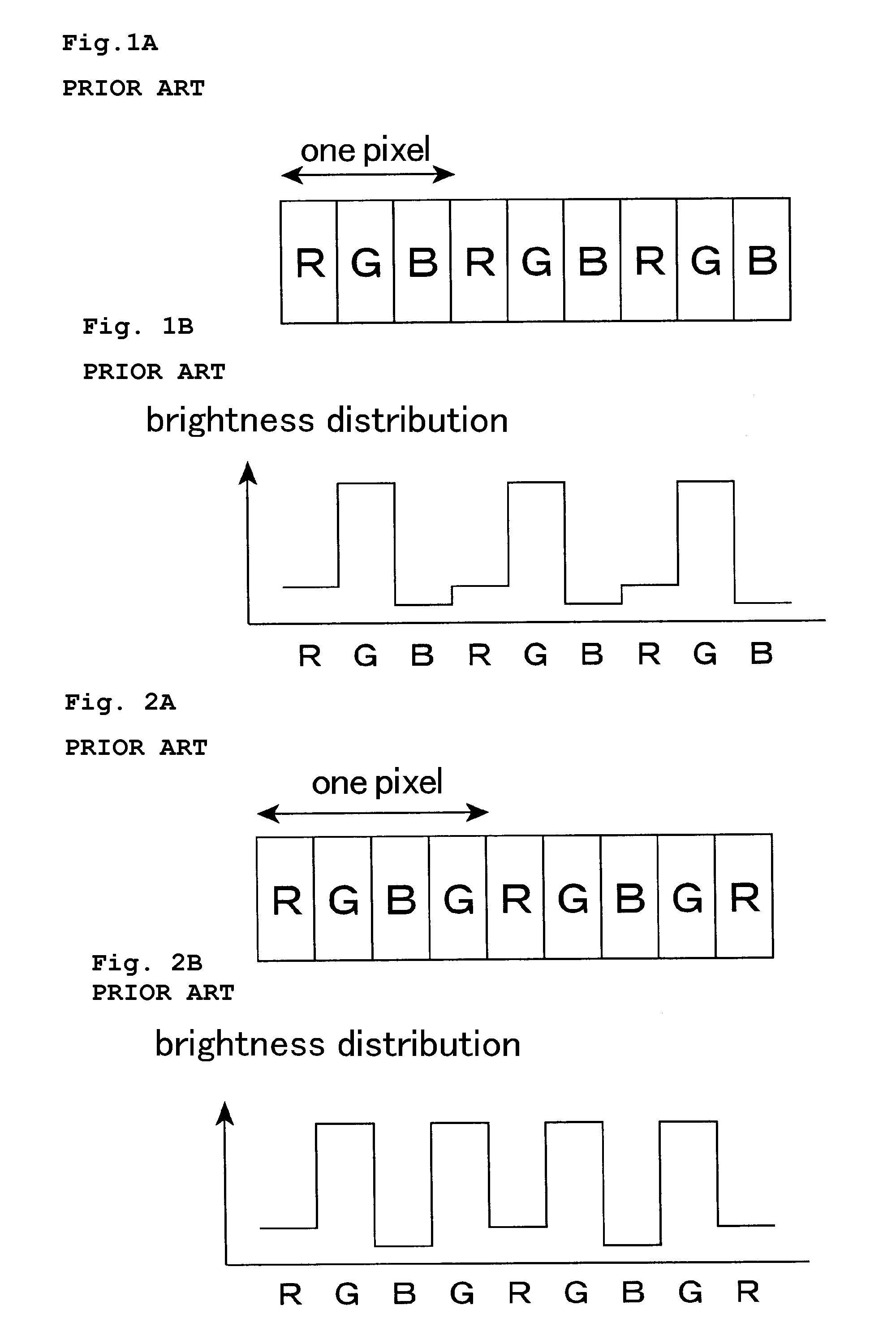
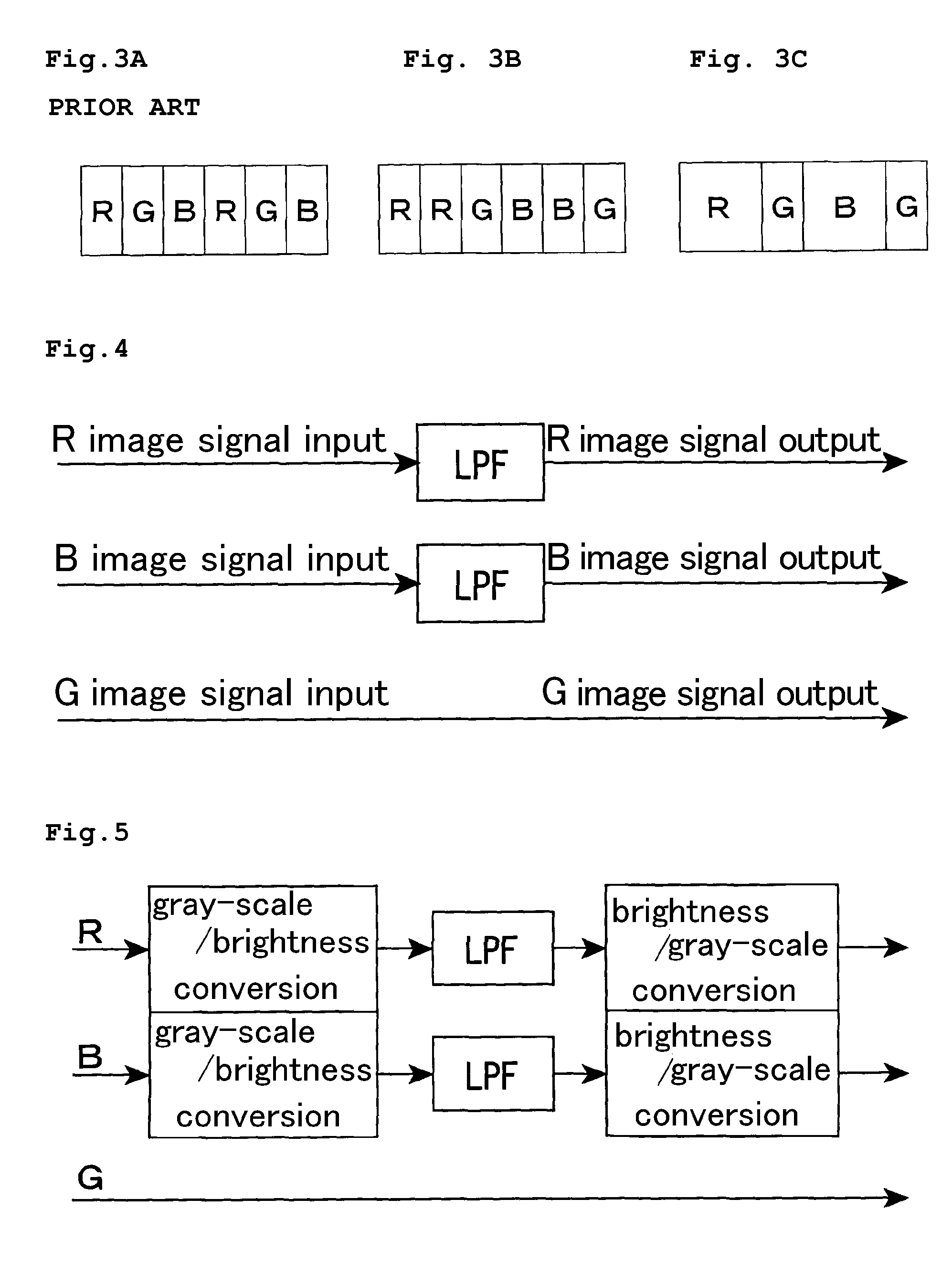
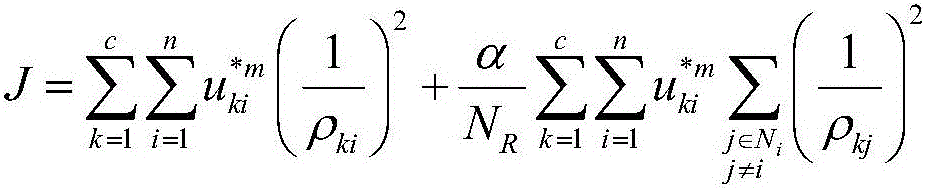Patents
Literature
1756 results about "Pixel pair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
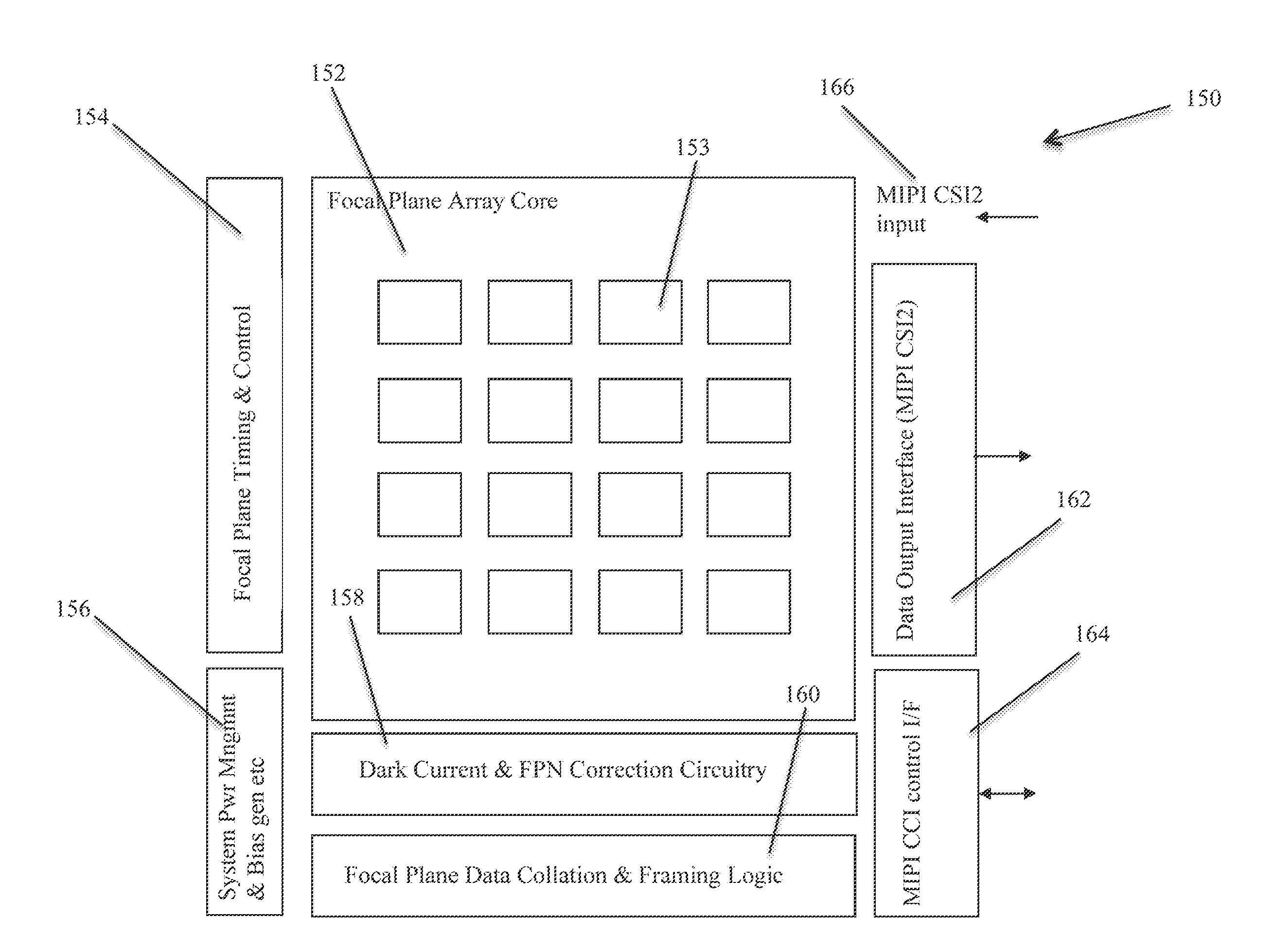
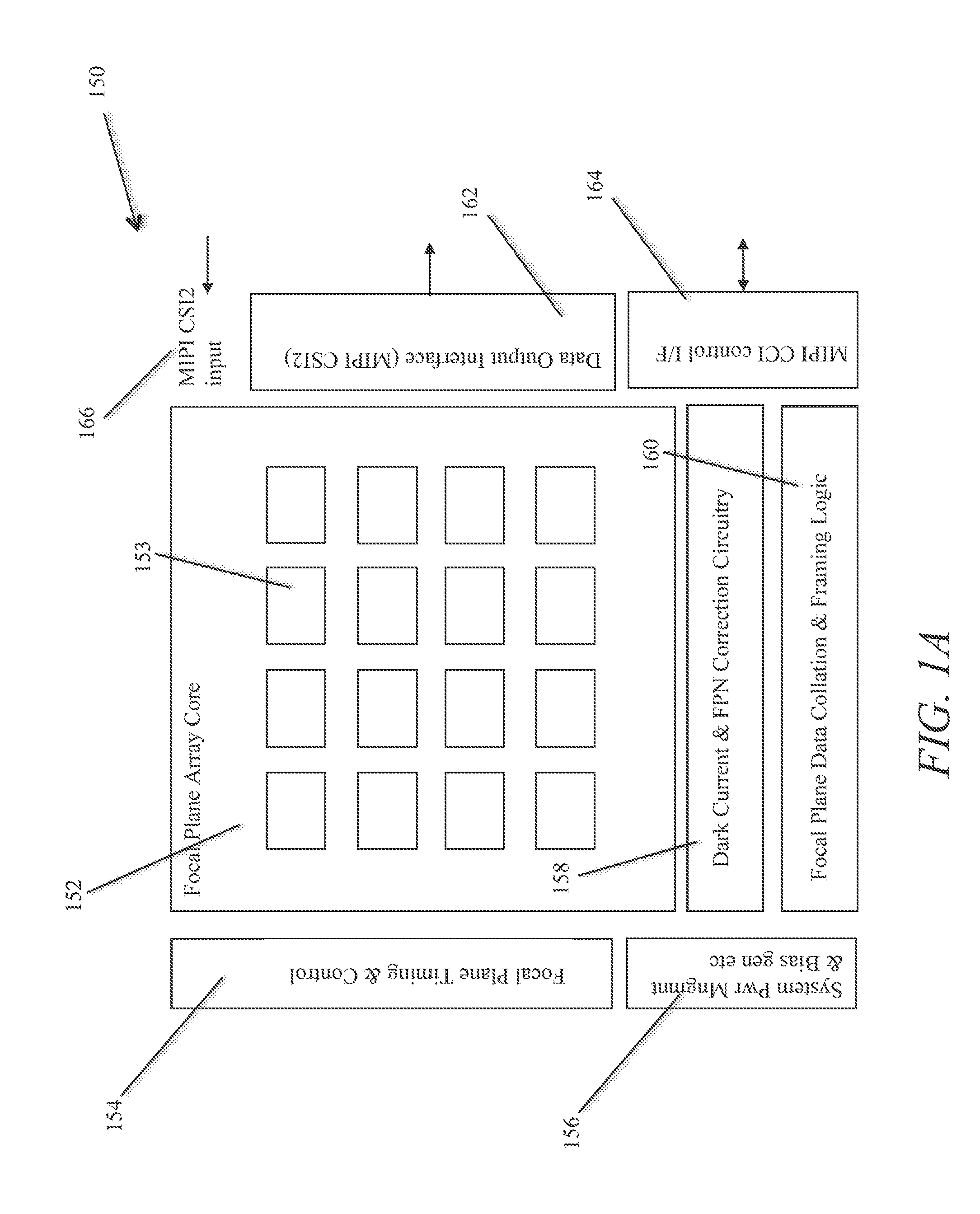
Imager array interfaces
ActiveUS20110279721A1Provide informationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer visionSampling circuits
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Image sensing apparatus, image sensing system and focus detection method
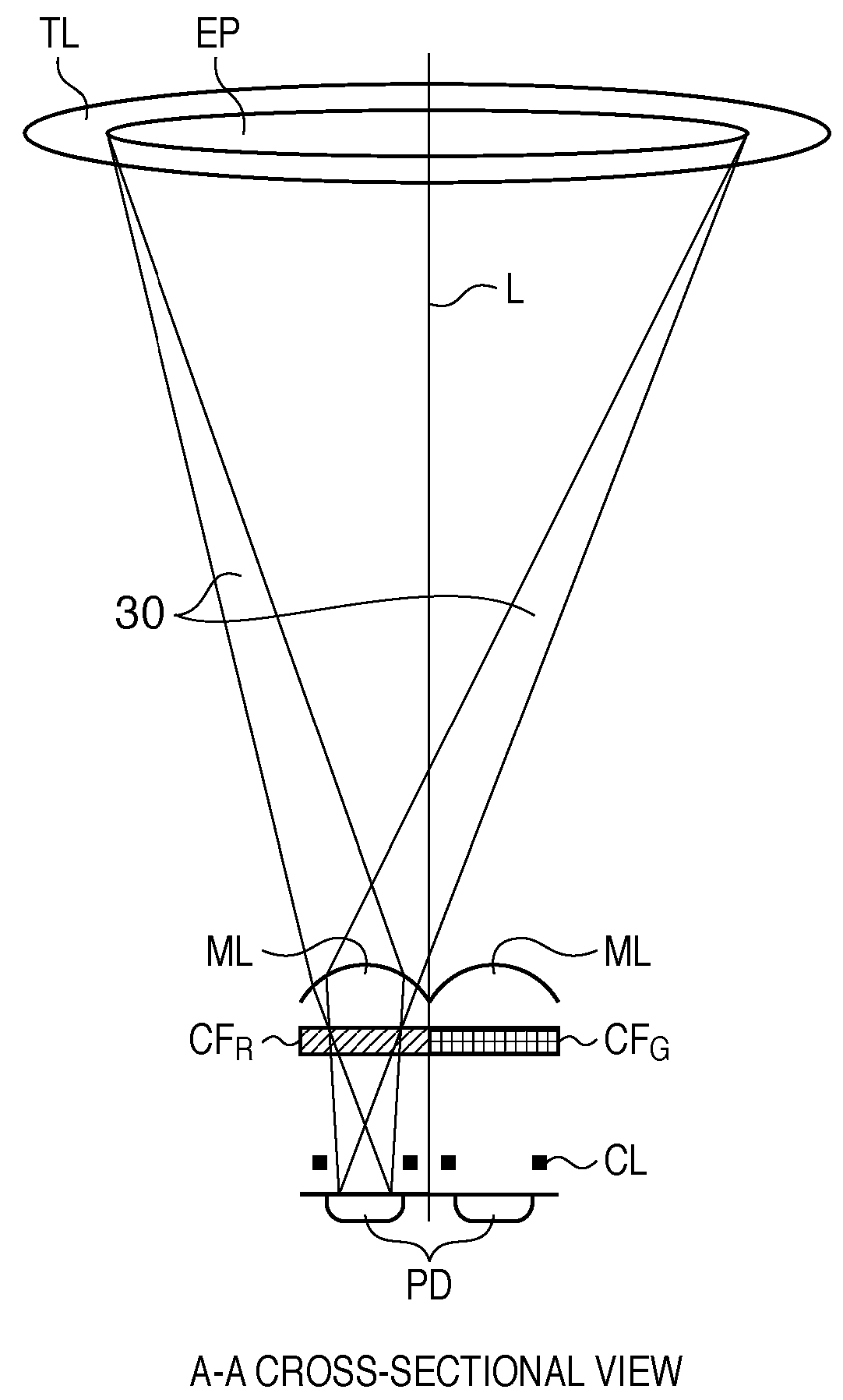
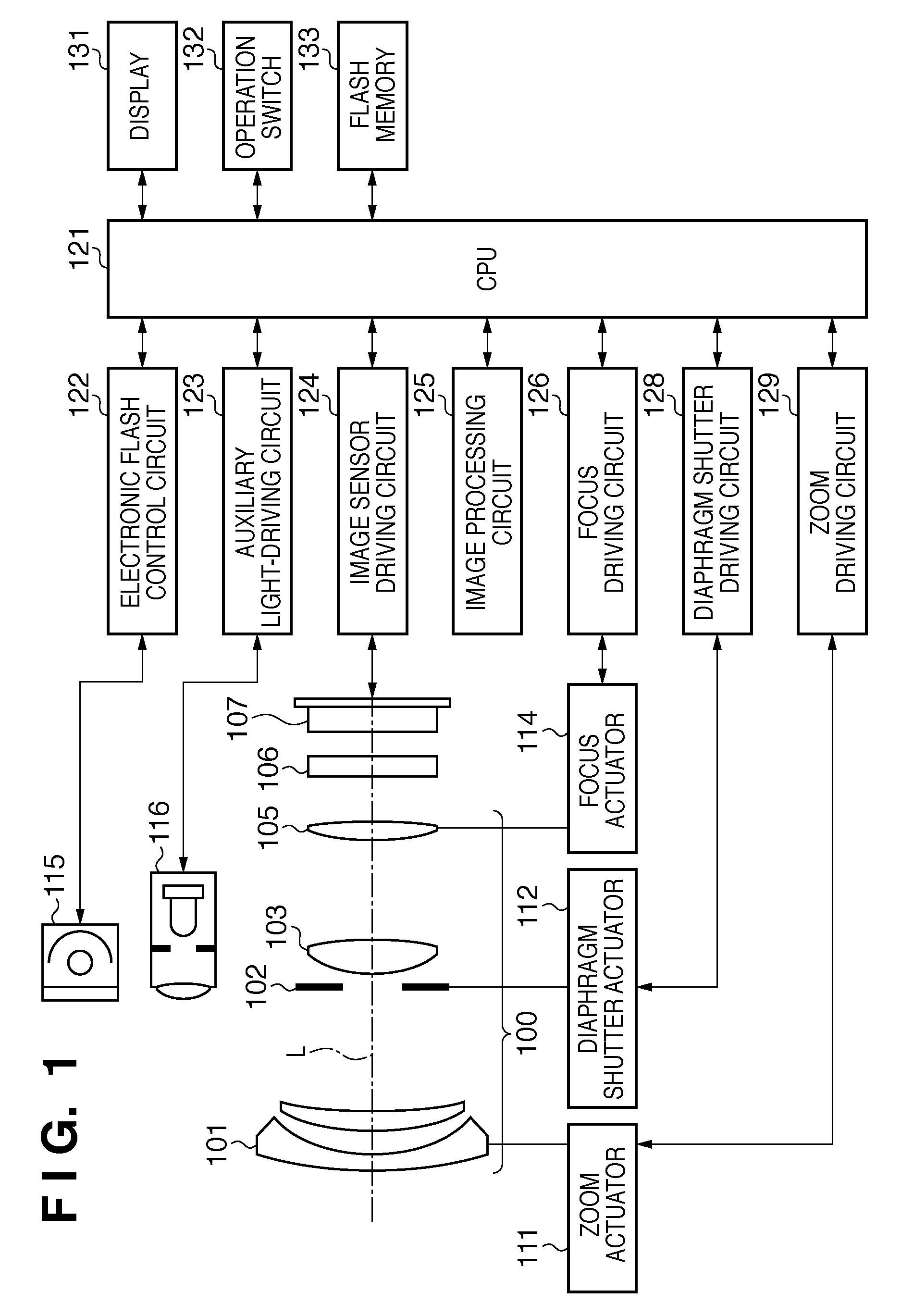
InactiveUS20100045849A1Improve accuracyMethod can be usedTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCamera lensRelative shift
An image sensing apparatus including: an image sensor including a plurality of focus detection pixel pairs that perform photoelectric conversion on each pair of light beams that have passed through different regions of a photographing lens and output an image signal pair; a flash memory that stores shift information on relative shift between an optical axis of the photographing lens and a central axis of the focus detection pixel pairs; a correction unit that corrects a signal level of the image signal pair based on the shift information and exit pupil information of the photographing lens so as to compensate for an unbalanced amount of light that enters each of the focus detection pixel pairs; and a focus detection unit that detects a focus of the photographing lens using the image signal pair corrected by the correction unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Correction of cluster defects in imagers
A method and apparatus that allows for the correction of multiple defective pixels in an imager device. In one exemplary embodiment, the method includes the steps of selecting a correction kernel for a defective pixel, determining average and difference values for pixel pairs in the correction kernel, and substituting an average value from a pixel pair for the value of the defective pixel.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Efficient optical coherence tomography (OCT) system and method for rapid imaging in three dimensions
InactiveUS20050140984A1Enhanced OCT channel sensitivityImprove accuracyScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansRapid imagingData set
An optical coherence tomography (OCT) system including a polarizing splitter disposed to direct light in an interferometer such that the OCT detector operates in a noise-optimized regime. When scanning an eye, the system detector simultaneously produces a low-frequency component representing a scanning laser ophthalmoscope-like (SLO-like) image pixel and a high frequency component representing a two-dimensional (2D) OCT en face image pixel of each point. The SLO-like image is unchanging with depth, so that the pixels in each SLO-like image may be quickly realigned with the previous SLO-like image by consulting prominent image features (e.g., vessels) should lateral eye motion shift an OCT en face image during recording. Because of the pixel-to-pixel correspondence between the simultaneous OCT and SLO-like images, the OCT image pixels may be remapped on the fly according to the corresponding SLO-like image pixel remapping to create an undistorted 3D image data set for the scanned region.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
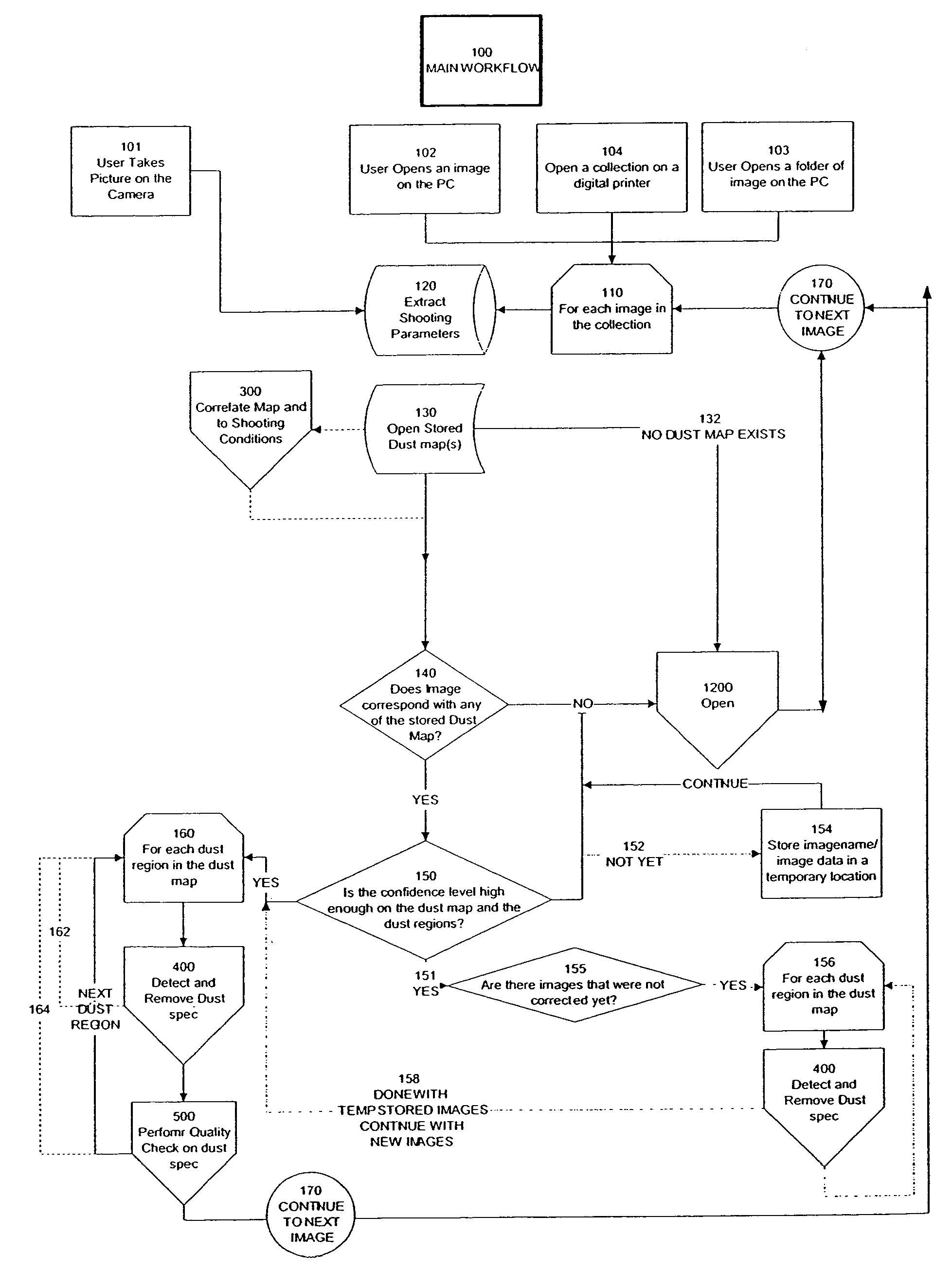
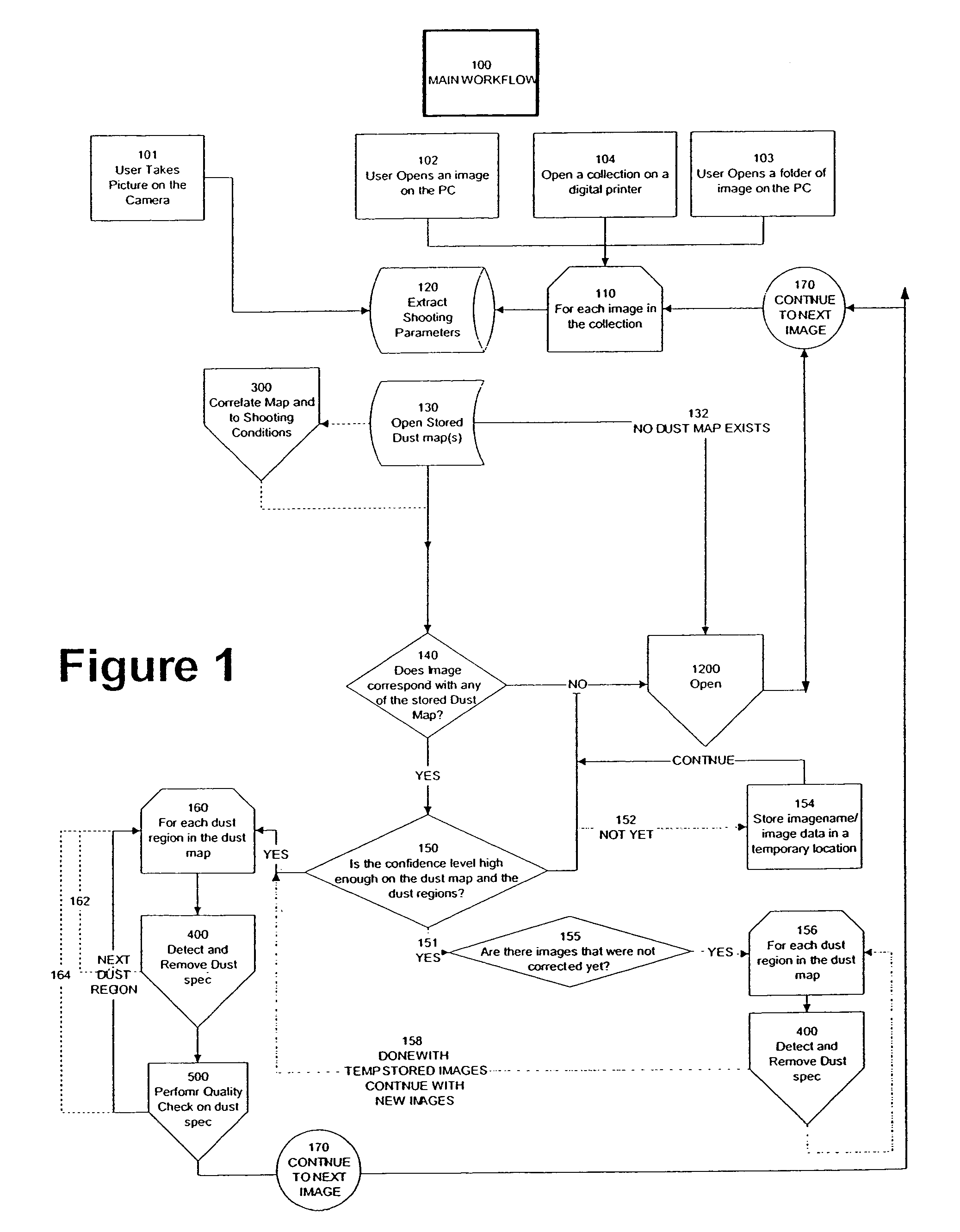
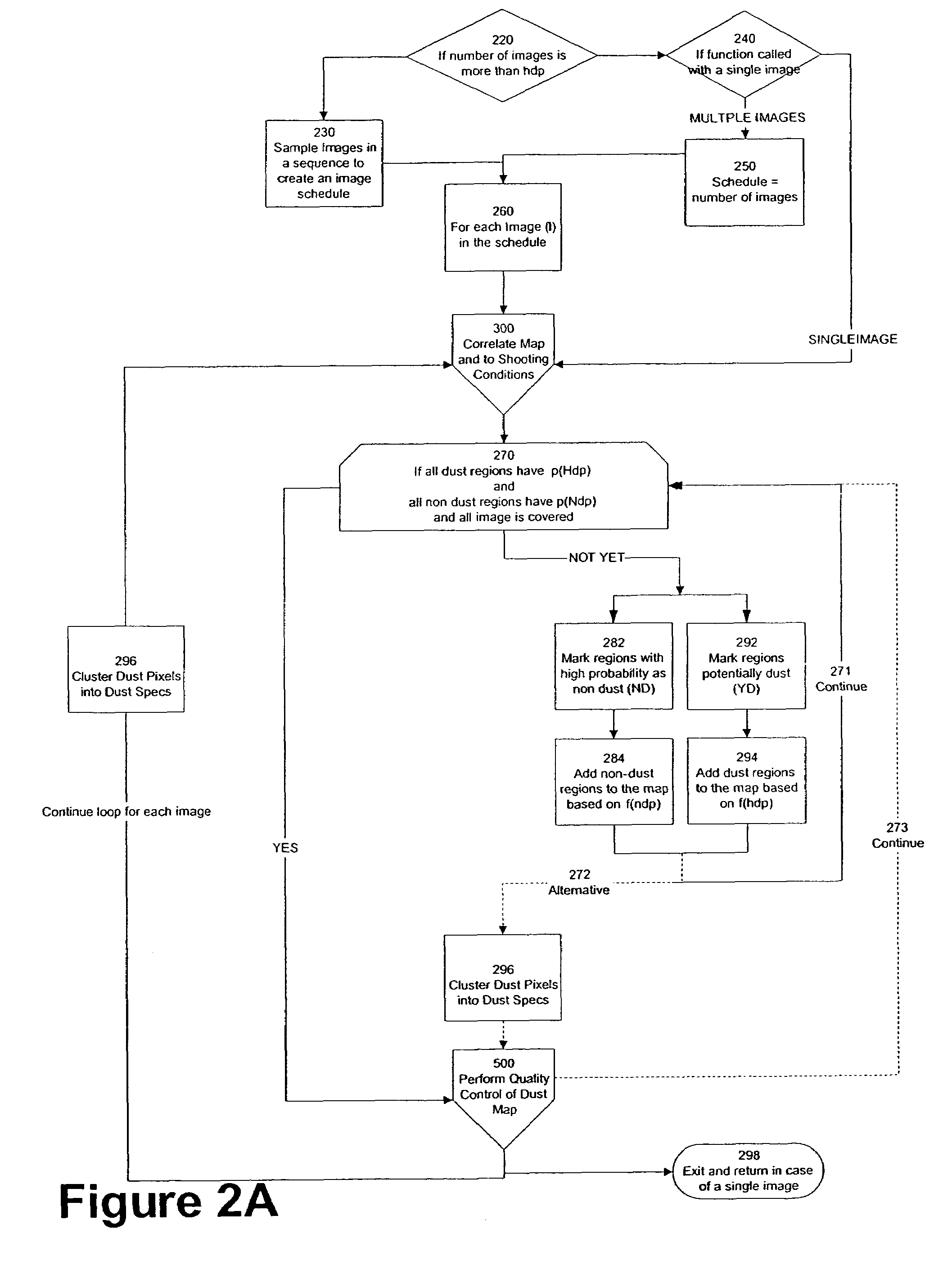
Automated statistical self-calibrating detection and removal of blemishes in digital images based on multiple occurrences of dust in images
A method automatically corrects dust artifact within images acquired by a system including a digital acquisition device including a lens assembly. Multiple original digital images are acquired with the digital acquisition device. Probabilities that certain pixels correspond to dust artifact regions within the images are determined based at least in part on a comparison of suspected dust artifact regions within two or more of the images. Probable dust artifact regions are associated with extracted parameter values relating to the lens assembly when the images were acquired. A statistical dust map is formed including mapped dust regions based on the determining and associating. Pixels corresponding to correlated dust artifact regions are corrected within further digitally-acquired images based on the associated statistical dust map.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Displaying method for the display and display
InactiveCN101009083AUniform brightness distributionImprove light and dark uniformityCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Gray level
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Driving system for active-matrix displays
ActiveUS20130201223A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriving currentActive matrix
Raw grayscale image data, representing images to be displayed in successive frames, is used to drive a display having pixels that include a drive transistor and an organic light emitting device by dividing each frame into at least first and second-frames, and supplying each pixel with a drive current that is higher in the first sub-frame than in the second sub-frame for raw grayscale values in a first preselected range, and higher in the second sub-frame than in the first sub-frame for raw grayscale values in a second preselected range. The display may be an active matrix display, such as an AMOLED display.
Owner:IGNIS INNOVATION
Display apparatus, method and program
InactiveUS20040145599A1Inhibit coloringEfficient executionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Computer vision
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and circuit for driving display device
InactiveUS20010052887A1Improve display qualityCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
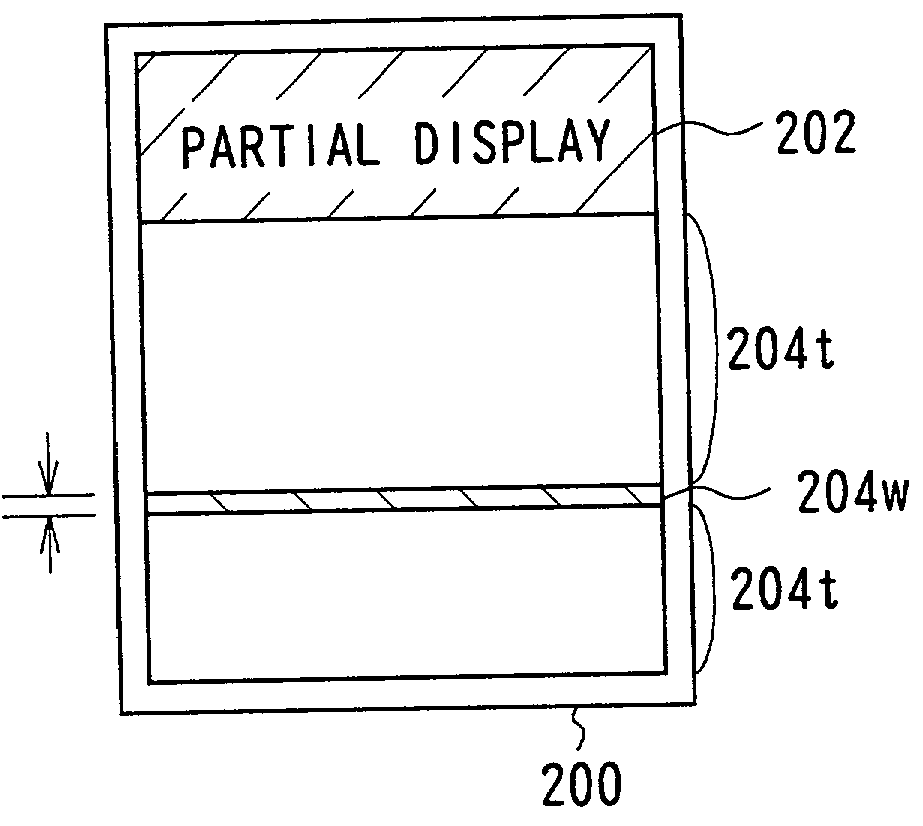
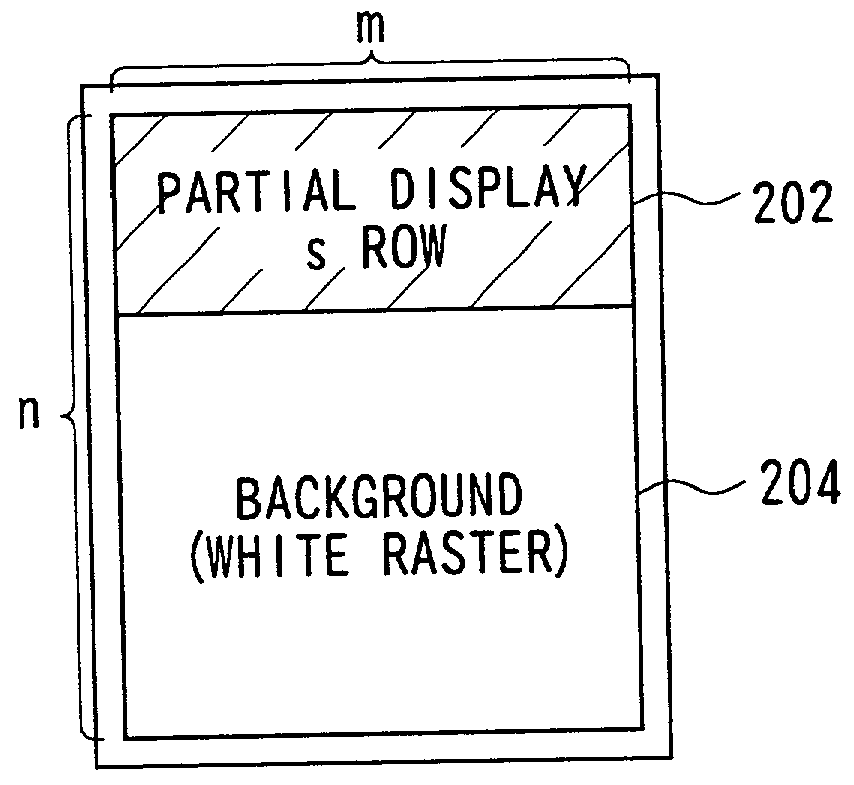
In the driving of a liquid crystal display panel with pixels in a matrix comprising n rows and m columns, when a partial display instruction is issued, respective rows in a display area (202) of s rows and m columns within the matrix are sequentially selected for one frame. Then, predetermined partial display data is written into the selected rows. Predetermined background data such as white display data is written into the background area (204) other than the partial display area (202). In the background area 204, either k rows and m columns or pixels of (the leading row ((s+1)-th row) of the background area, next to the final row in the partial display area) are selected during one frame for writing of the background display data, k rows and m columns are sequentially shifted each frame.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Display device, driving method thereof, terminal device, and display panel
ActiveUS20090096943A1Reduce the impactImprove display qualitySolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsHigh numerical apertureTerminal equipment
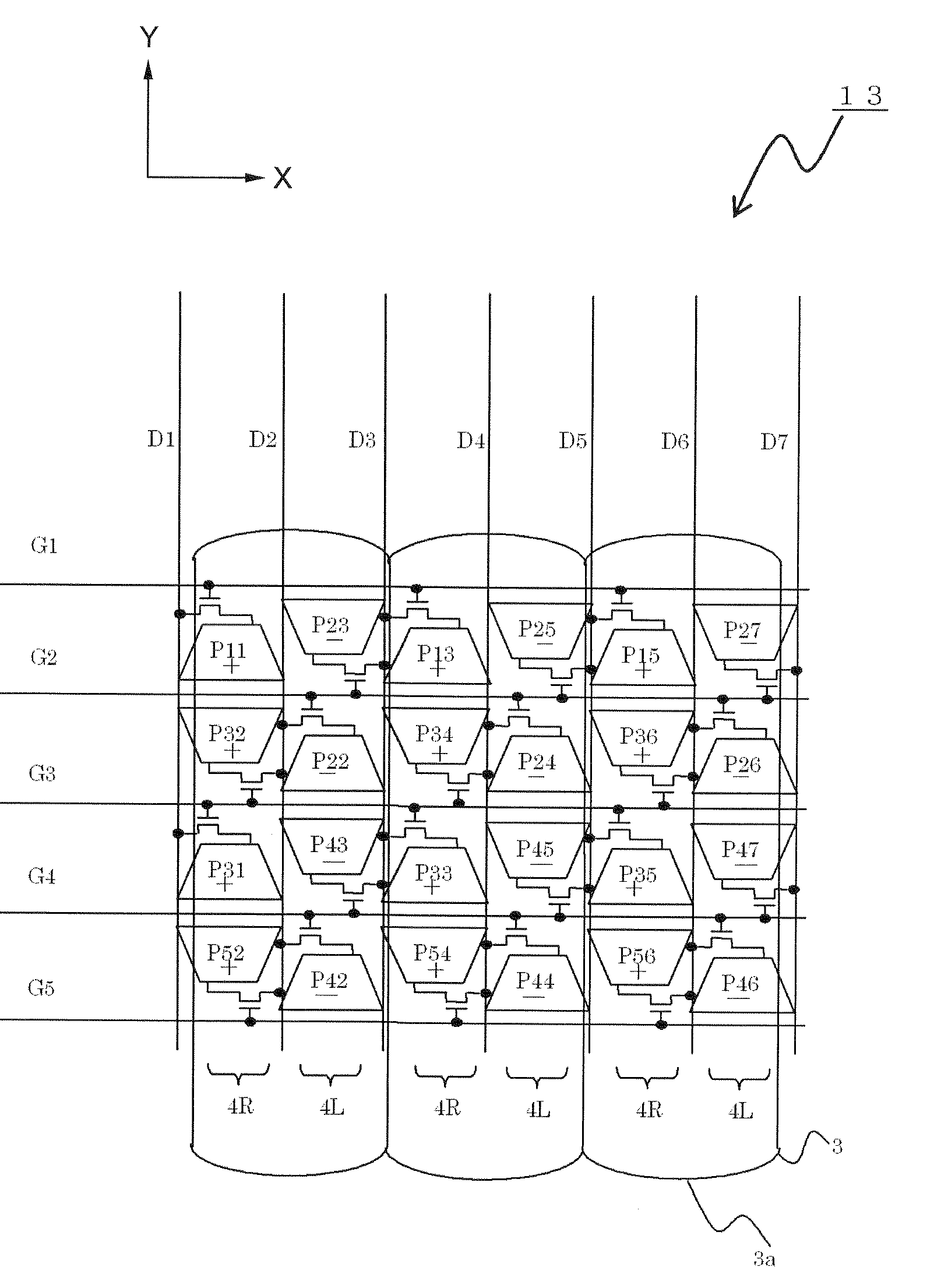
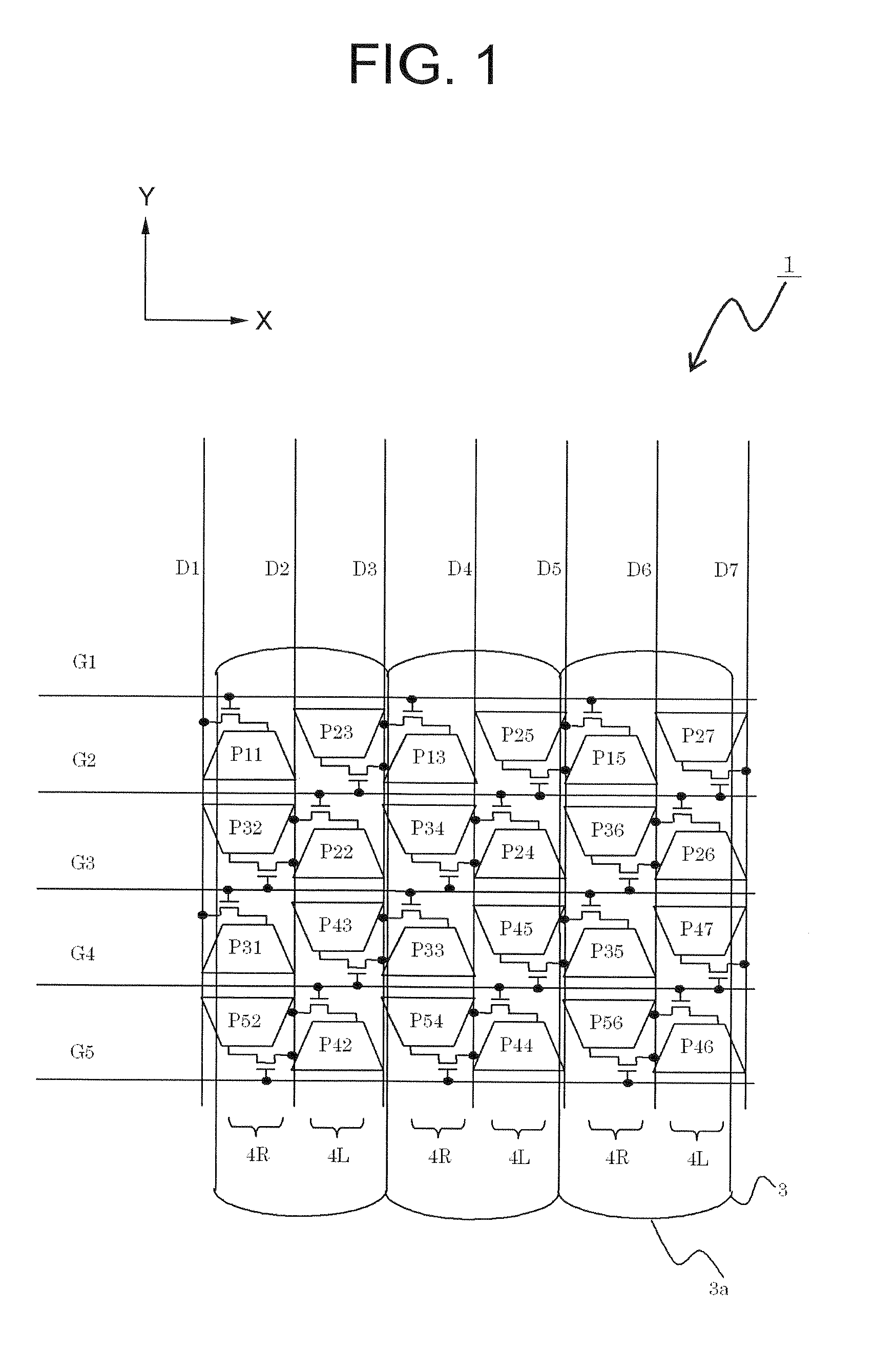
To provide a plural-viewpoint display device having an image separating optical element such as a lenticular lens or a parallax barrier, which is capable of arranging thin film transistors and wirings while achieving substantially trapezoid apertures and high numerical aperture, and to provide a driving method thereof, a terminal device, and a display panel. A neighboring pixel pair arranged with a gate line interposed therebetween is connected to the gate line placed between the pixels, each of the pixels configuring the neighboring pixel pair is connected to the data line different from each other, and each of the neighboring pixel pairs neighboring to each other in an extending direction of the gate lines is connected to the gate line different from each other.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
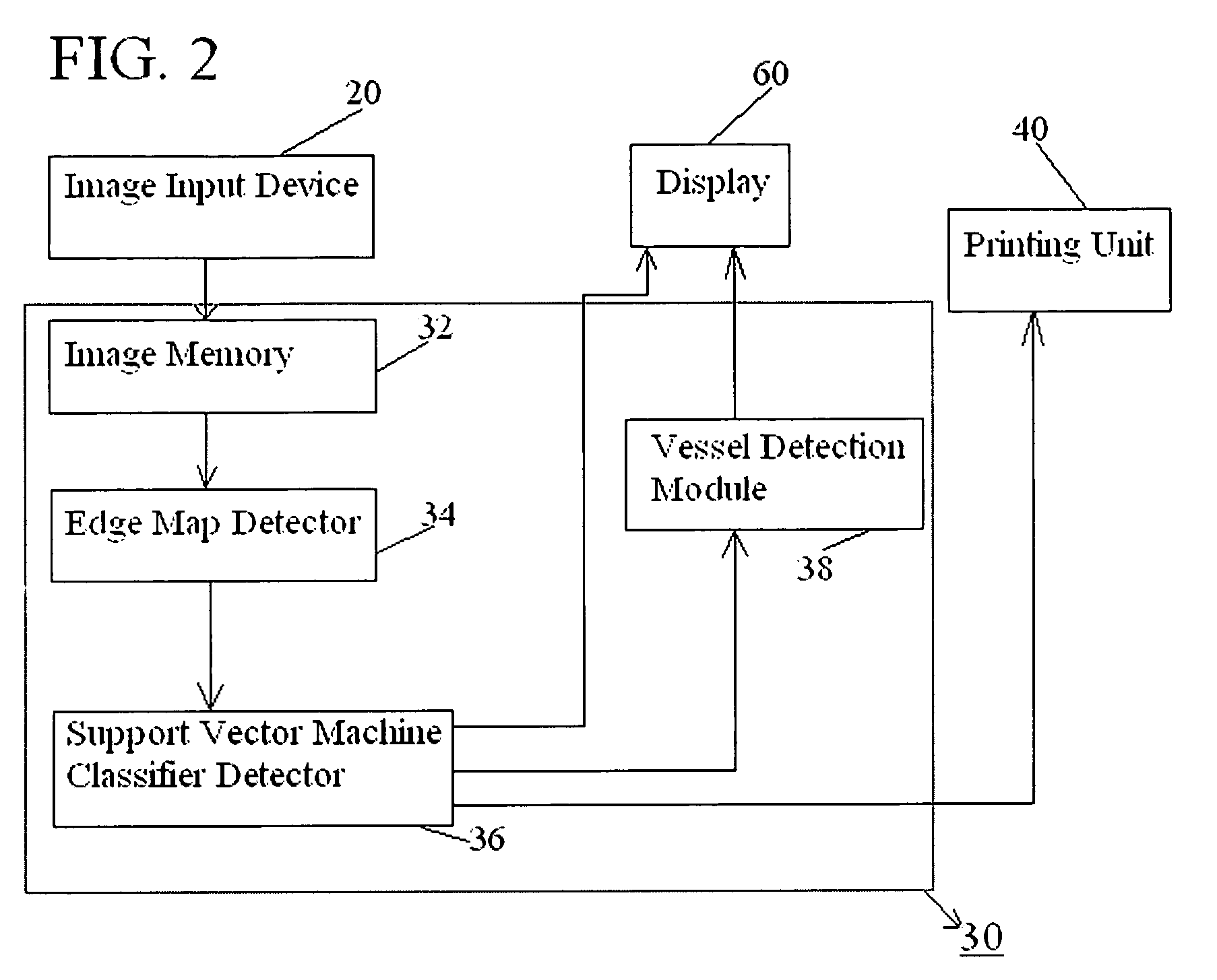
Method and apparatus for automatic and dynamic vessel detection
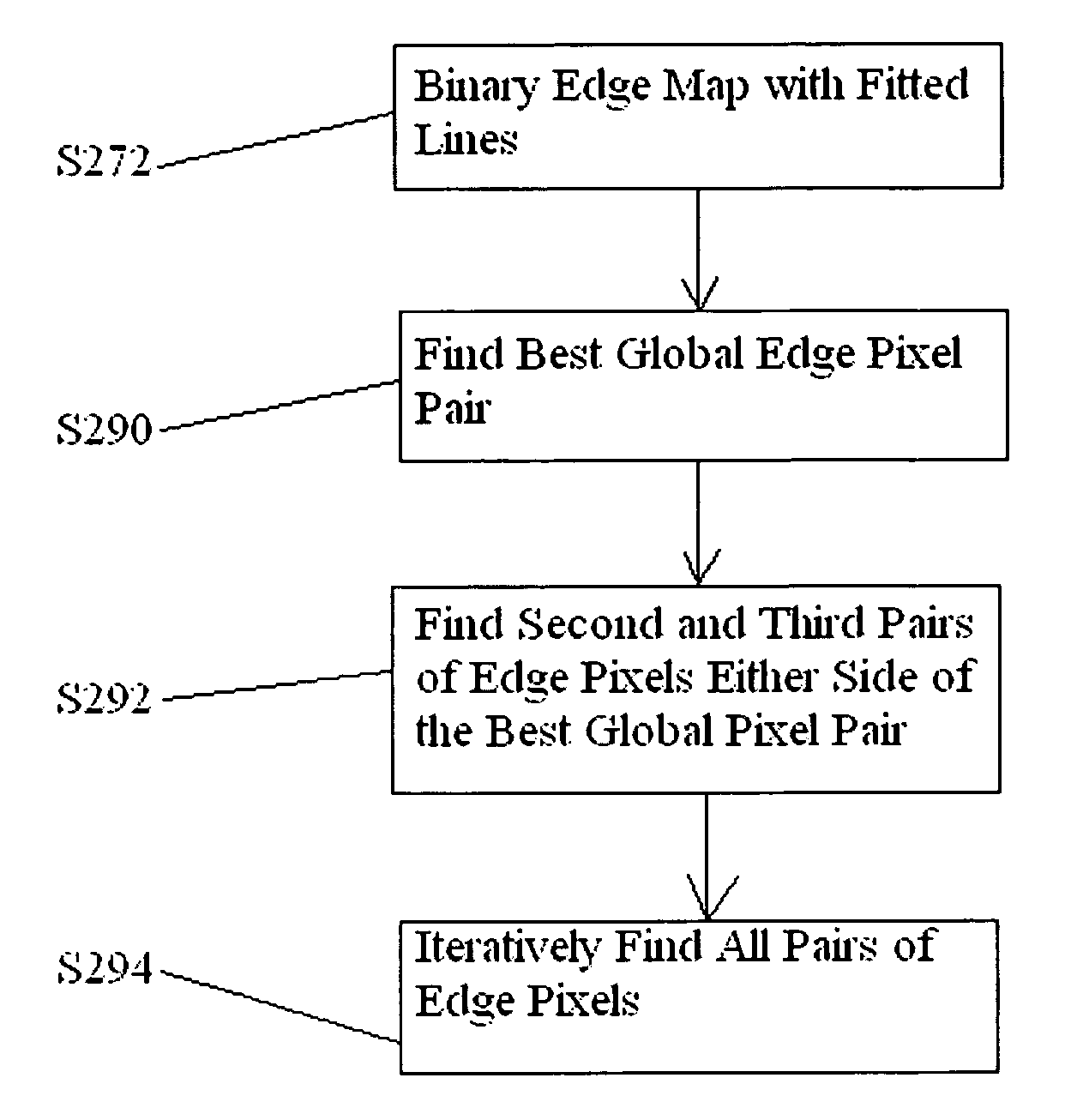
A method and an apparatus automatically detect vessels in a diagnostic image. The method according to one embodiment accesses digital image data representing a diagnostic image; detects vessel candidates in the diagnostic image by processing the diagnostic image data, the step of detecting vessel candidates including identifying edge pixel pairs of vessels in a diagnostic image by iteratively adjusting a plurality of constraints relating to a general direction and shape of a vessel for a next iteration of edge pixel pair identification in a diagnostic image; and determines whether the plurality of edge pixel pairs form a vessel using learned features.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
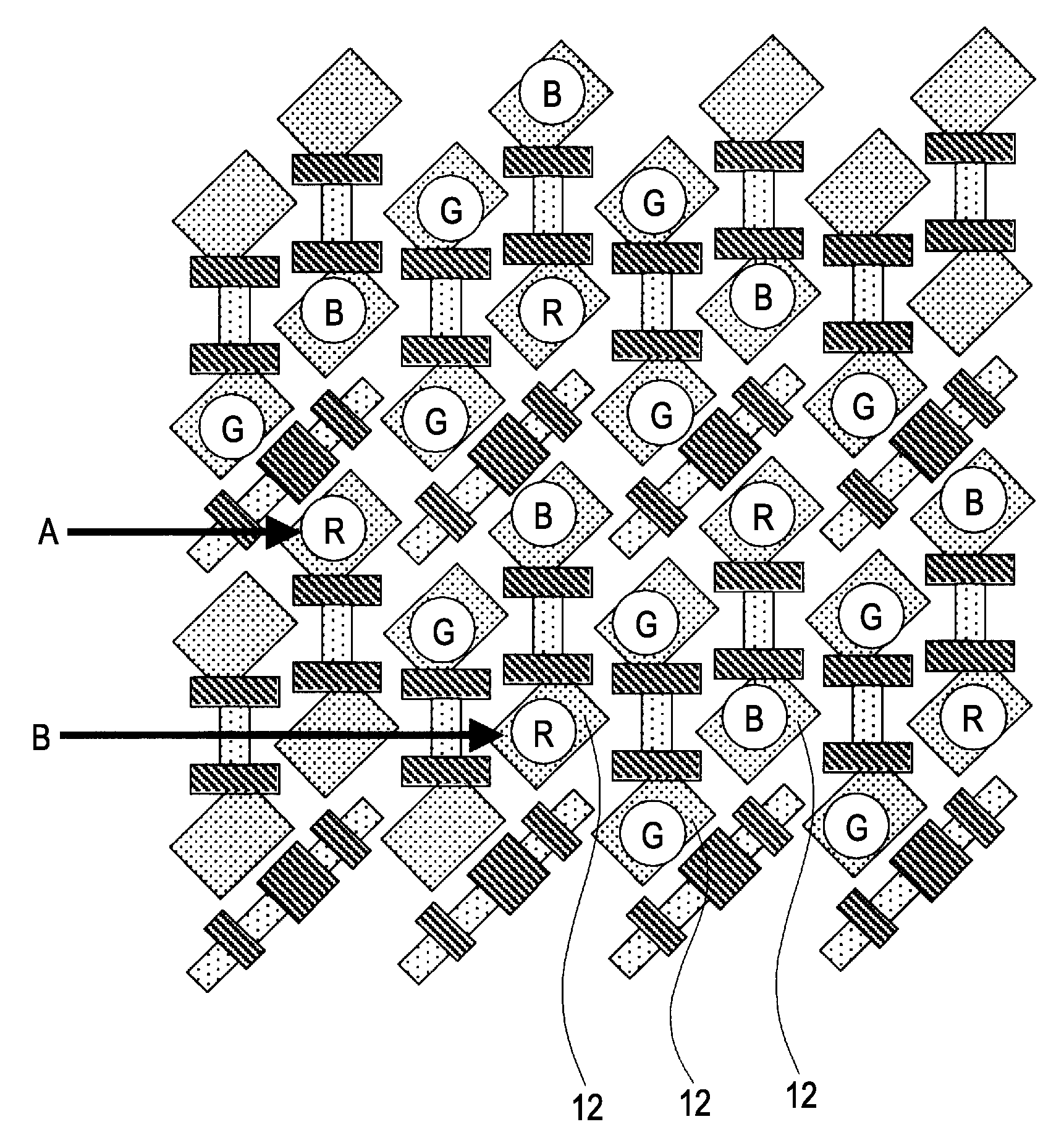
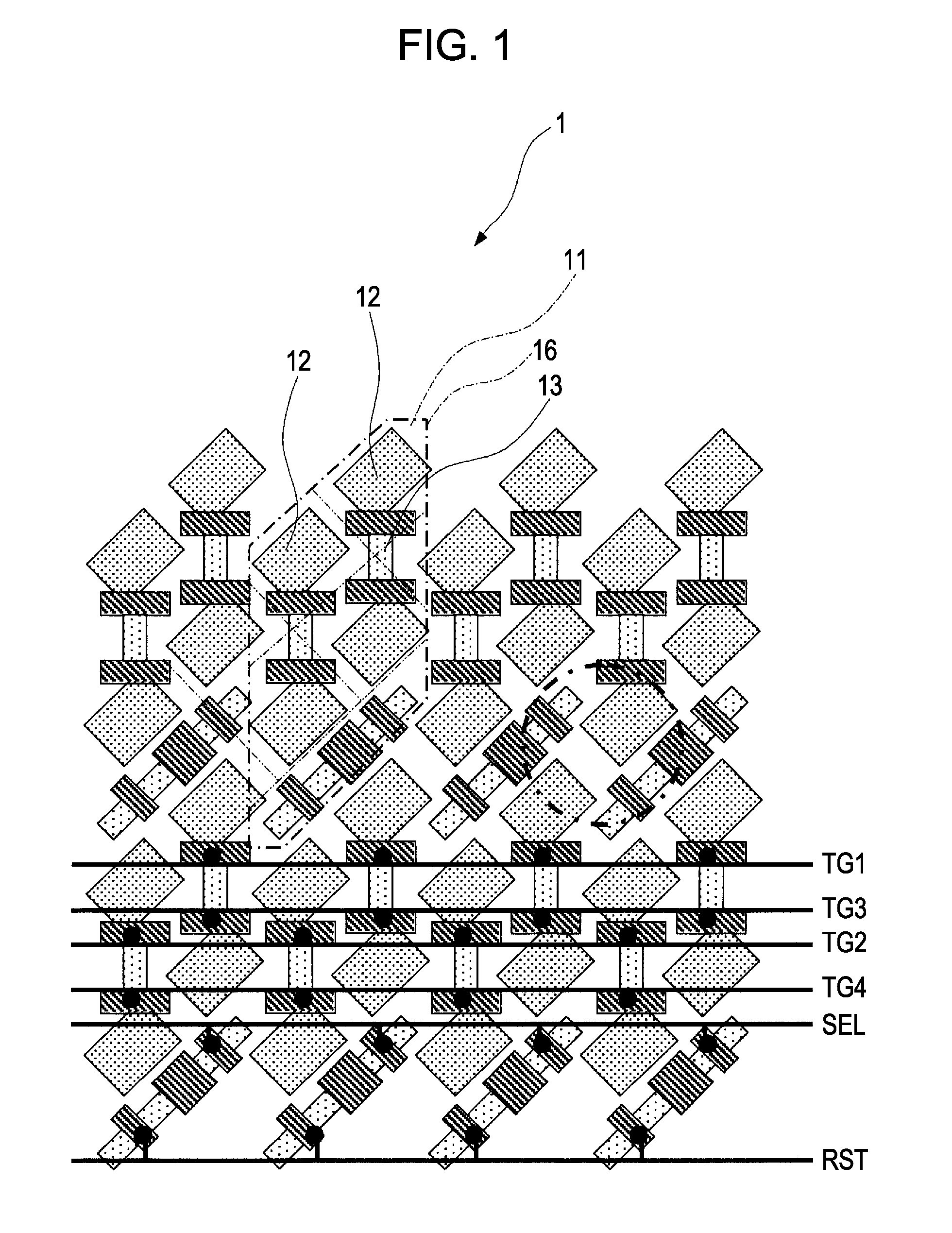
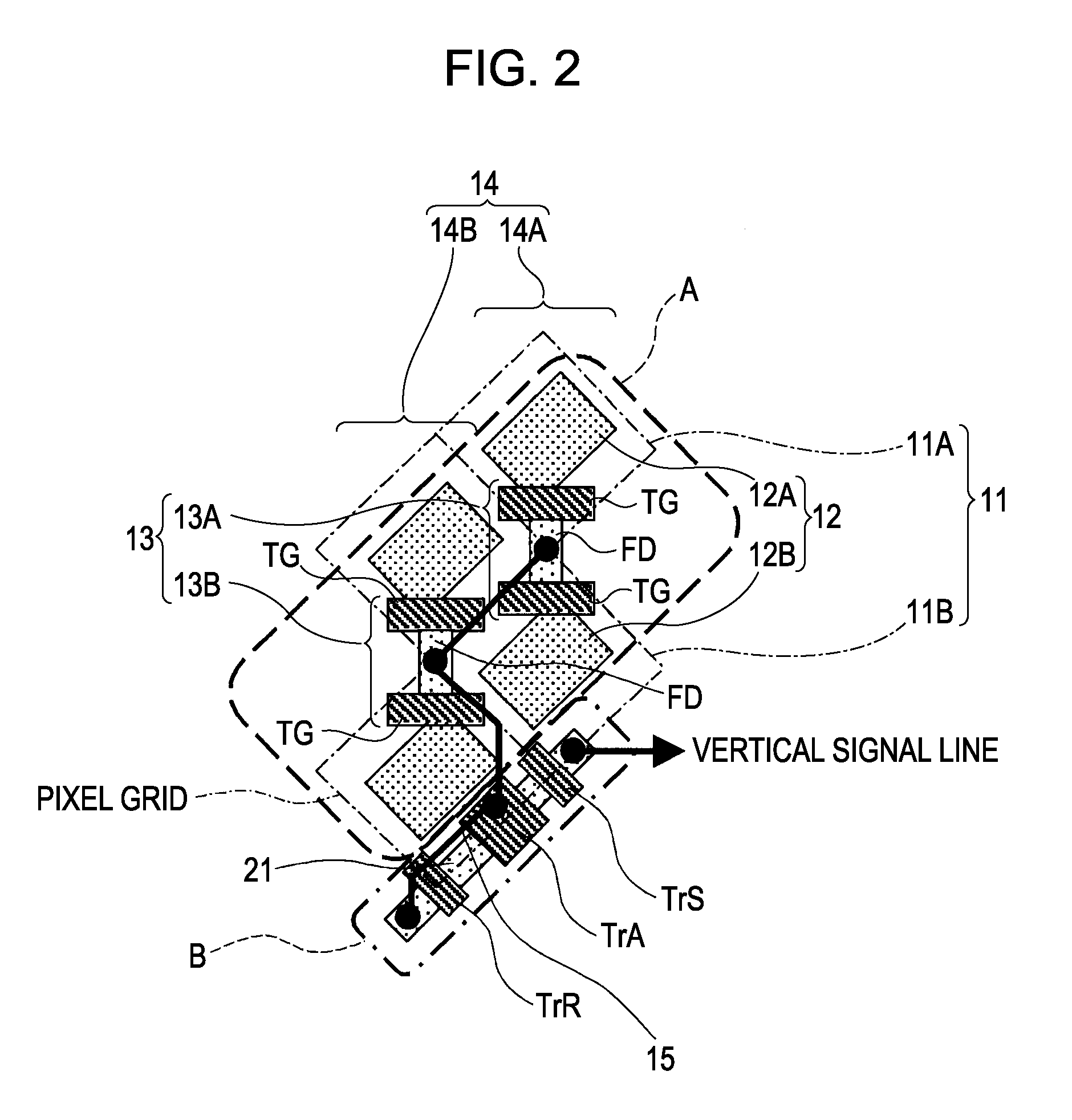
Solid-state imaging device, imaging apparatus and camera
InactiveUS20080088724A1High sensitivityMaintaining resolutionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDiagonalEngineering
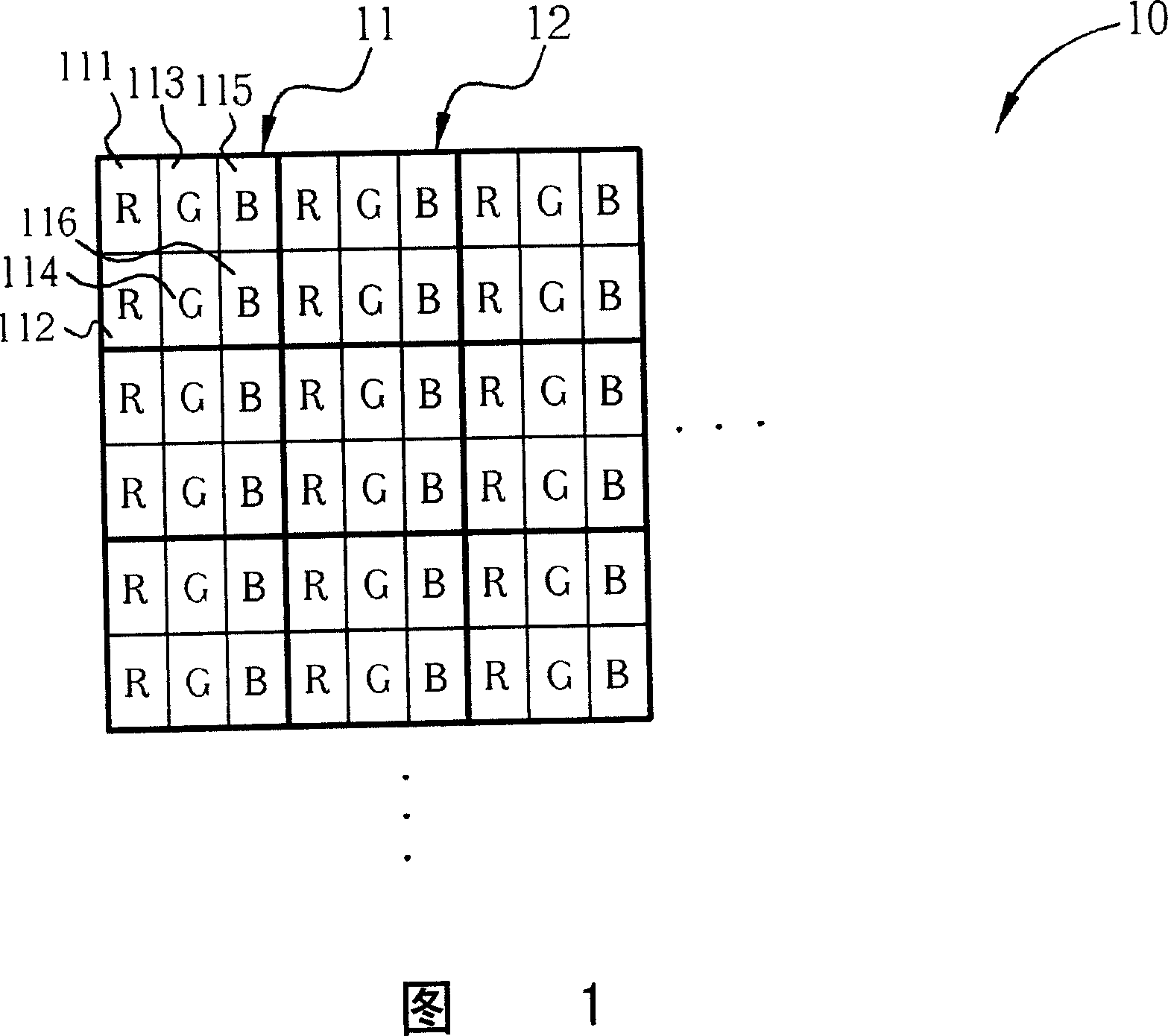
A solid-state imaging device includes: multiple pixels making up a slanted grid array inclined to a scanning direction, which include a photoelectric conversion unit configured to convert incident light quantity into an electric signal; and a charge-to-voltage conversion unit configured to convert signal charge read out from the photoelectric conversion unit disposed between two pixels adjacent to each other in the diagonal direction of the pixels of the multiple pixels into voltage; wherein the charge-to-voltage conversion unit is shared with the two pixels; and wherein a set of transistor group are disposed in a sharing block, which is configured of a pixel pair made up of the two pixels adjacent to each other in the diagonal direction, and a pixel pair adjacent to that pixel pair, including wiring to which the charge-to-voltage conversion unit of each pixel pair is connected.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image scaling
InactiveUS6825857B2Exceeding performanceFast imagingGeometric image transformationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesImage resolutionDigital filter
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Intelligent assisted driving method and system
InactiveCN107590438AStrong applicabilityLow costCharacter and pattern recognitionDistortionPerspective transformation
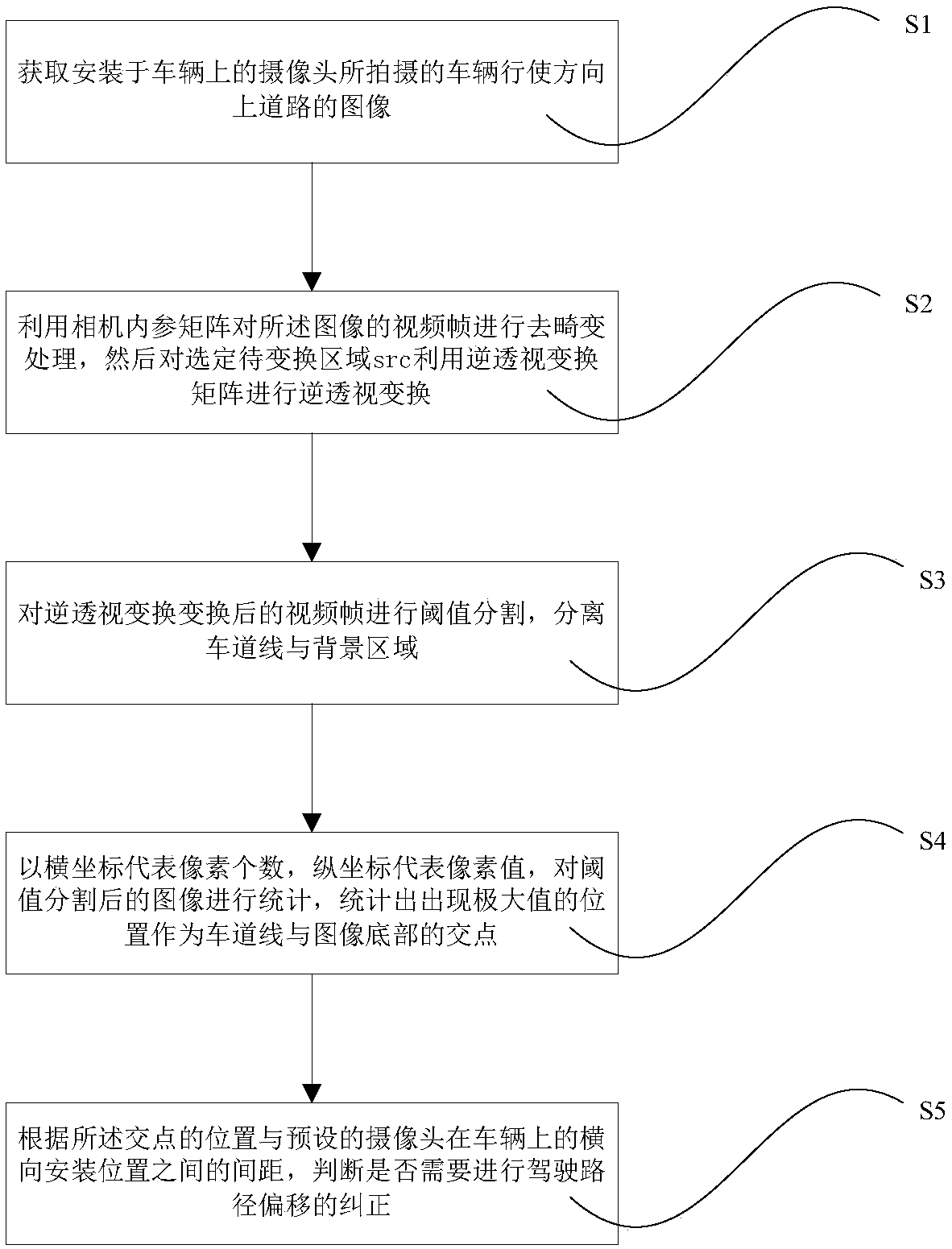
The invention relates to an intelligent assisted driving method and system. A lane line is obtained as follows: an image, shot by a camera, of a road in a vehicle driving direction is obtained; de-distortion processing is carried out on a video frame of the image by using an internal reference matrix of the camera and inverse perspective transformation is carried out on a selected to-be-transformed region src of the video frame; threshold segmentation is carried out on the video frame after inverse perspective transformation and a lane line and a background region are separated; statistics iscarried out on the lower part of the image after threshold segmentation and an intersection point of the lane line and the bottom of the image is obtained by statistics; searching is carried out by starting with the intersection point by using a sliding window, m pixels corresponding to the lane line are determined, and curve equation fitting is carried out on the m pixels to obtain a fitted laneline. With the method and system provided by the invention, the lane line is displayed in a display device inside the vehicle; and various conditions like sudden illumination changing, tree shadow shielding, and pavement blotting are detected accurately. The method and system have advantages of high applicability, low cost, high precision, good real-time performance and high stability.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Three-dimensional-information reconstructing apparatus, method and program
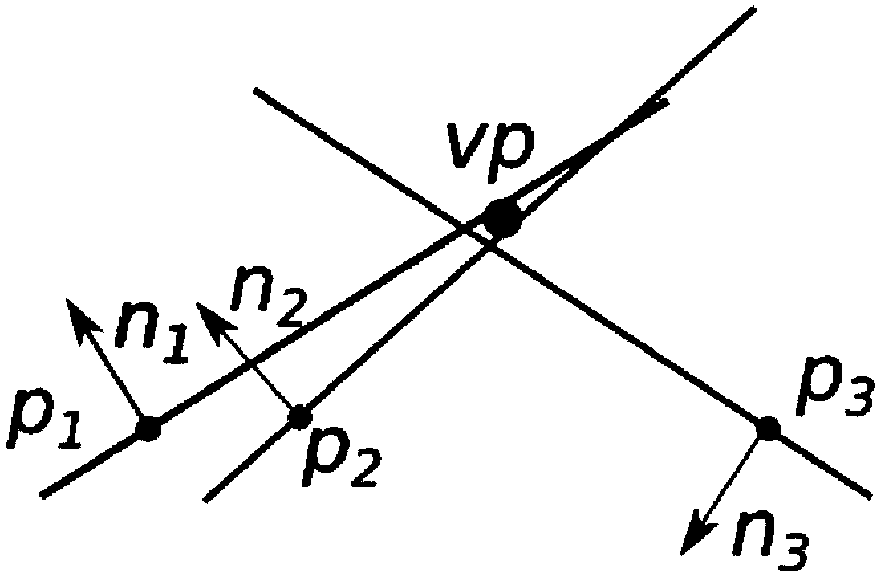
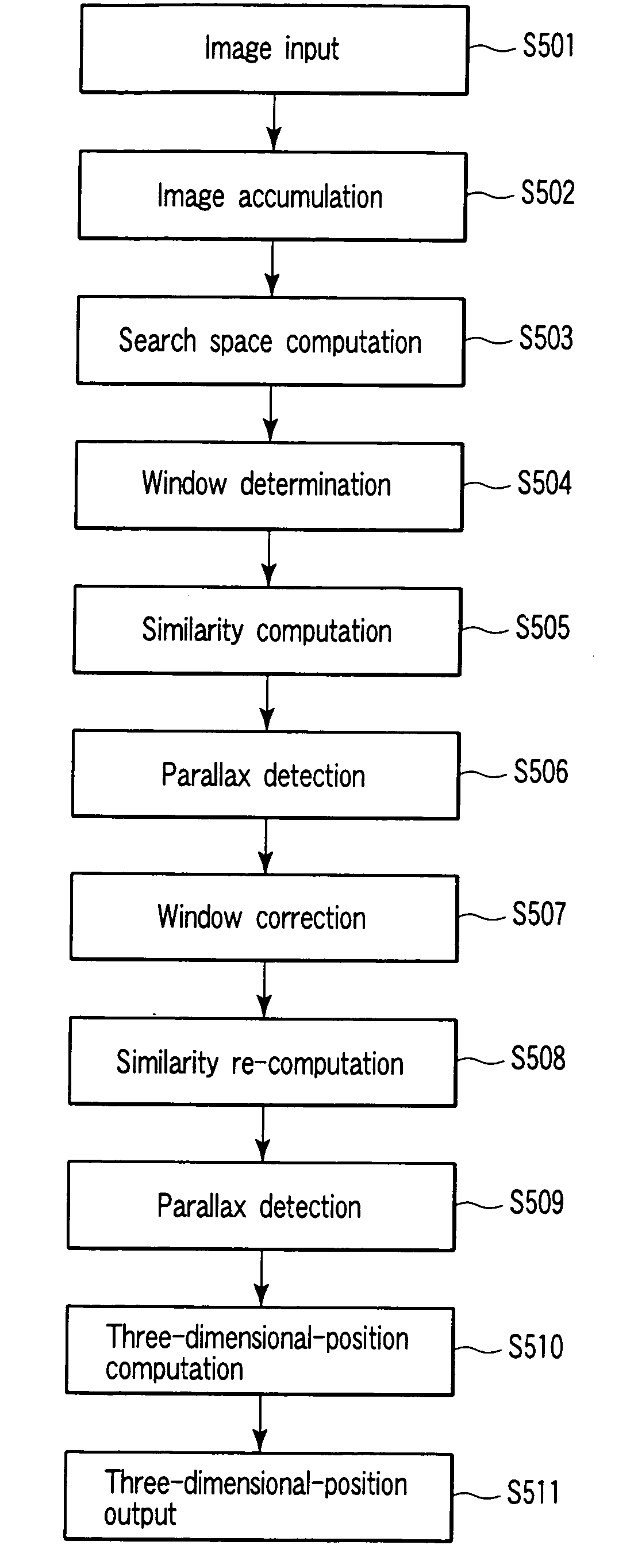
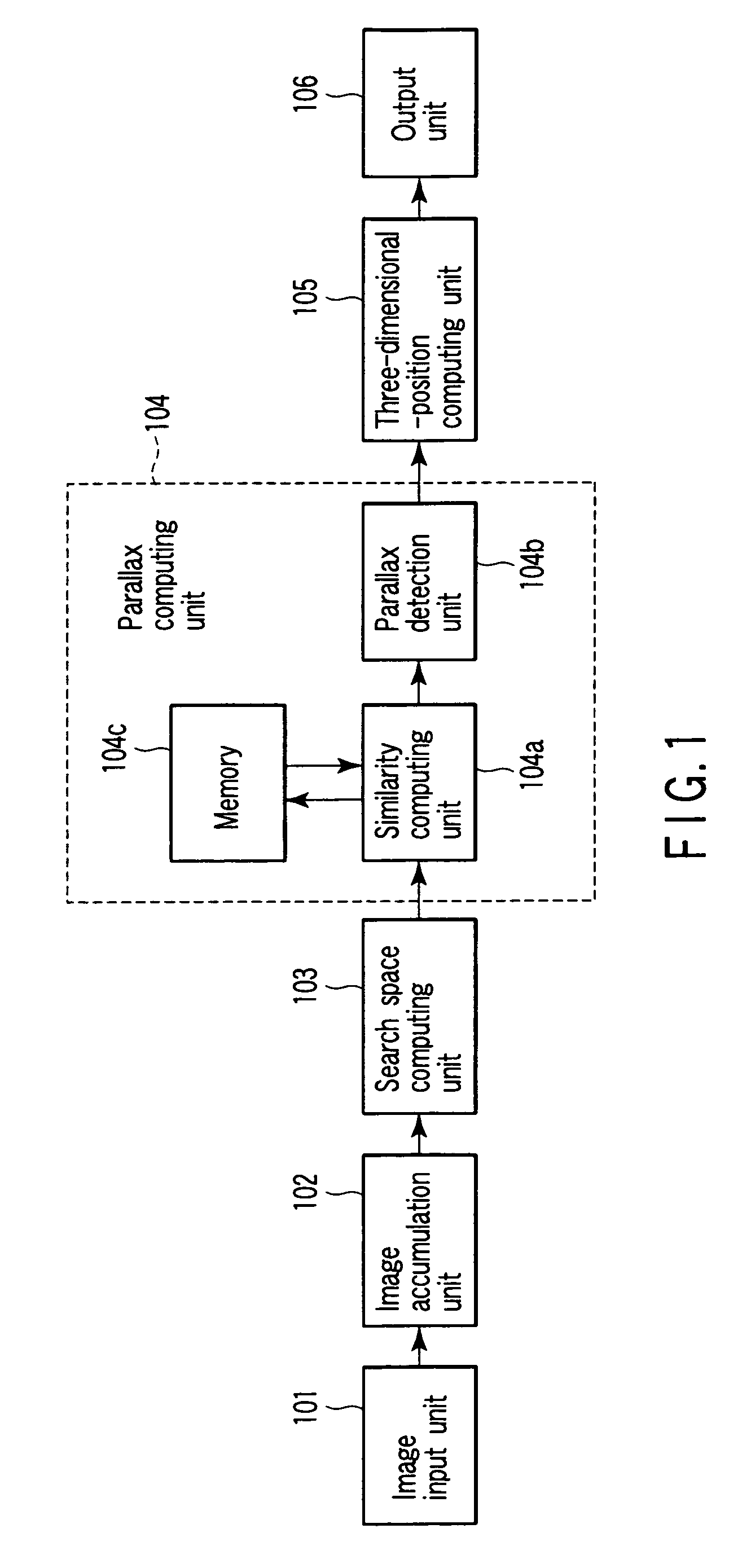
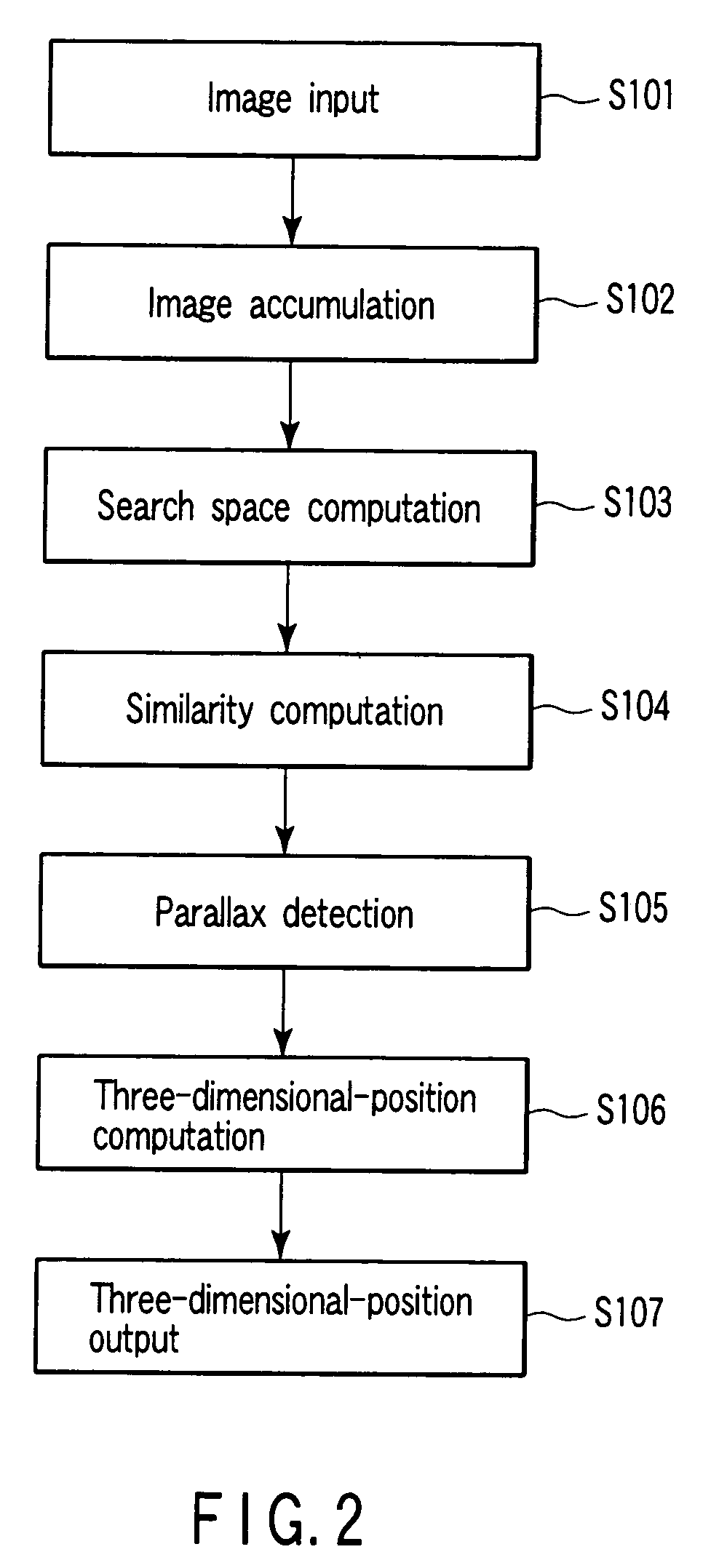
Apparatus includes unit configured to compute parallax search range in (x-y-d) three-dimensional space formed of three variables (x and y providing first point (x, y) on first image and parallax candidate d), similarity unit configured to compute degree-of-similarity C (x, y, d) between point (x, y) and second point (x′, y′) corresponding to point (x, y), using sum of products of brightness levels of corresponding pixel pairs between first window on first image and second window on second image, first window including first point (x, y) second window including second point (x′, y′) and unit configured to compute parallax D between first point (x, y) and second point (x′, y′), based on C (x, y, d), where similarity unit includes unit configured to store sum, which is used for computing C (x, y, d) between new first point on first image and new second point on second image.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Image Pickup apparatus and focus control method
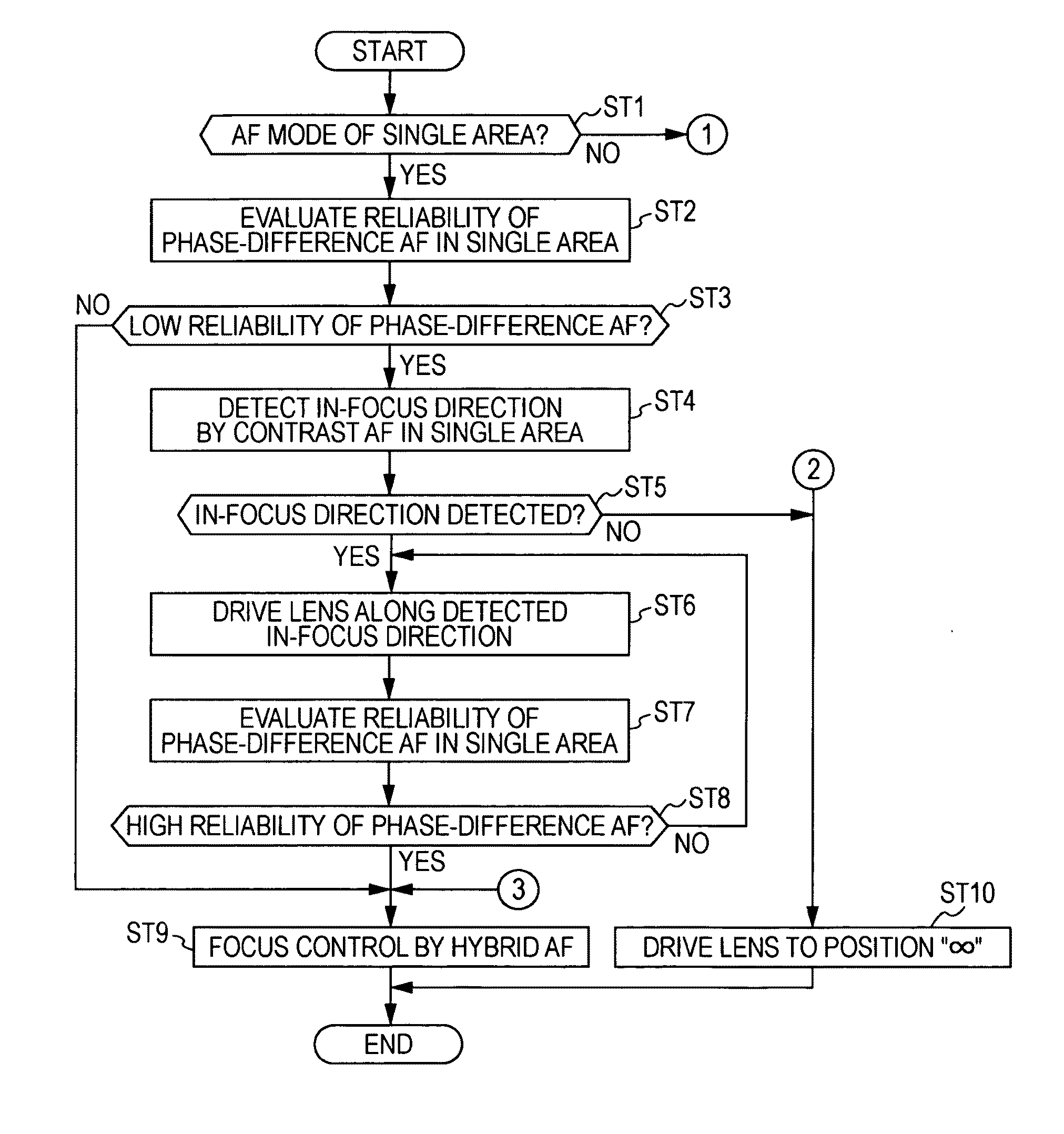
ActiveUS20100150538A1Improve detection reliabilityDetection reliability is lowProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementPhase differencePupil
An image pickup apparatus includes an imaging element having a group of AF pixel pairs that realizes a pupil-dividing function and a group of normal pixels without such a pupil-dividing function. The image pickup apparatus performs focus control for driving a focus lens toward an in-focus position detected by phase different AF based on a pixel signal generated from the group of AF pixel pairs when it is determined that the reliability of the phase difference AF is high based on the pixel signal. The image pickup apparatus performs focus control for driving a focus lens in an in-focus direction detected by contrast AF based on a pixel signal generated from the group of normal pixels when it is determined that the reliability of the phase difference AF is low.
Owner:SONY CORP
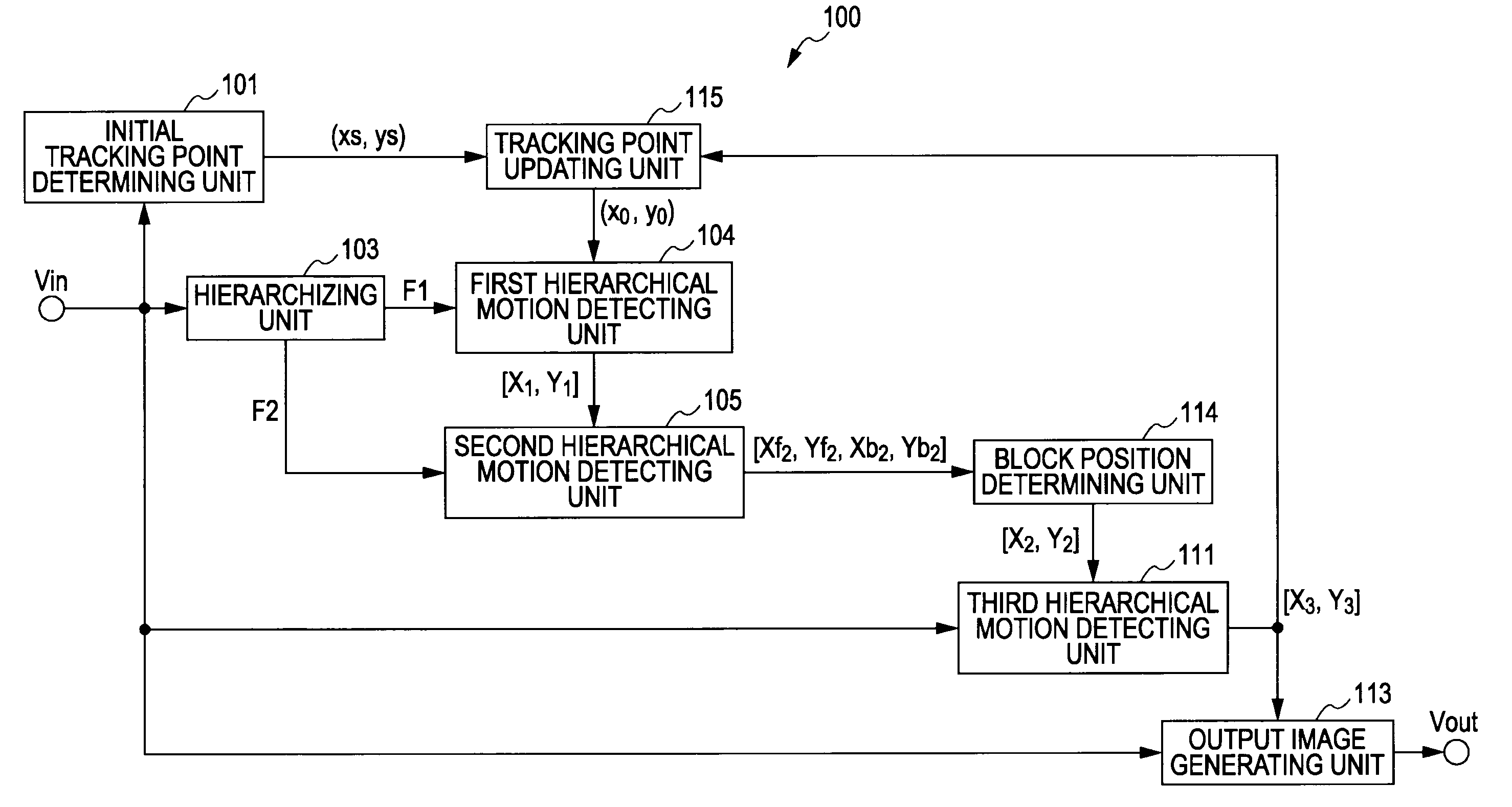
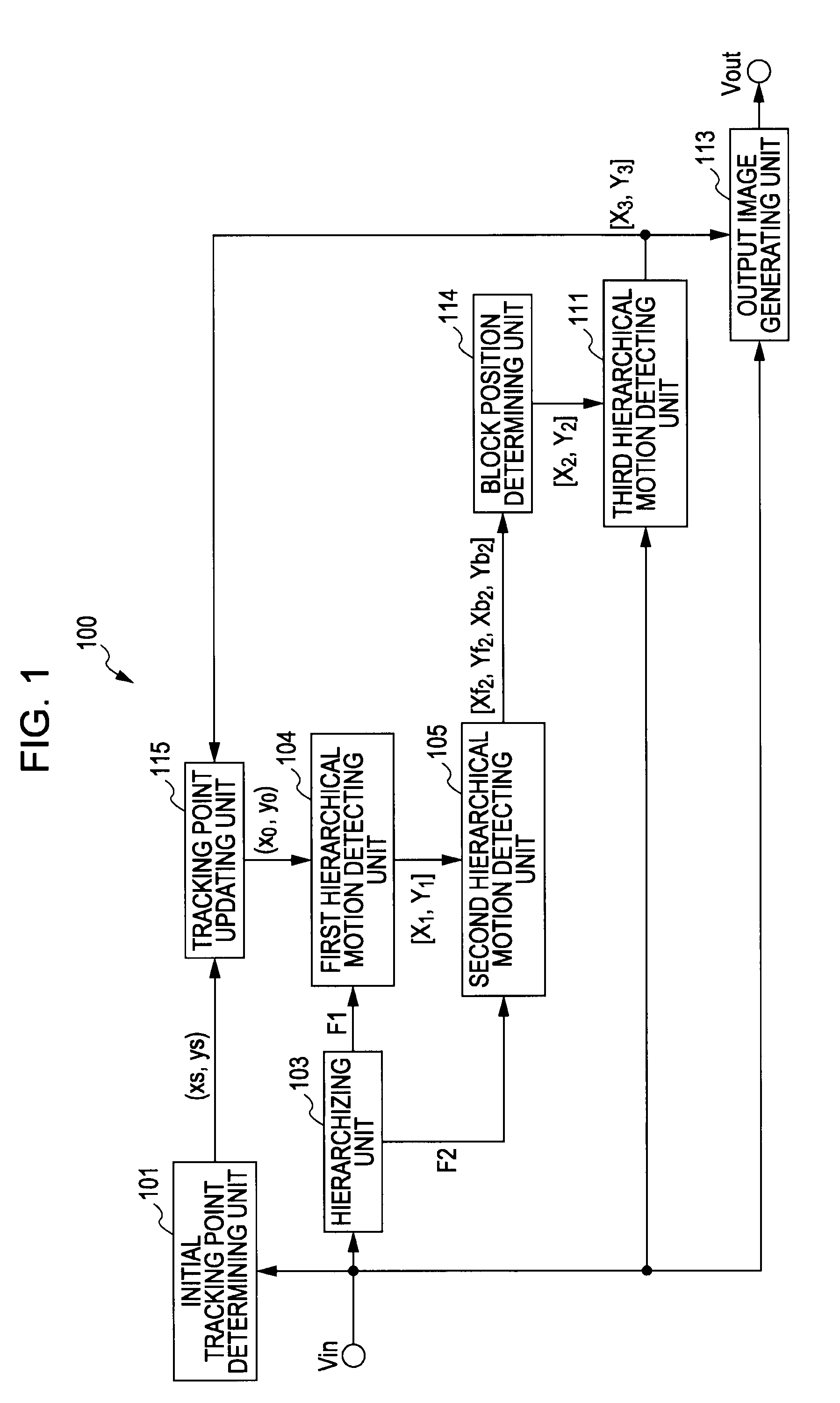
Tracking point detecting device and method, program, and recording medium
A tracking point detecting device includes: a frame decimation unit for decimation the frame interval of a moving image configured of multiple frame images continuing temporally; a first detecting unit for detecting, of two consecutive frames of the decimated moving image, a temporally-subsequent frame pixel corresponding to a predetermined pixel of a temporally-previous frame; a forward-direction detecting unit for detecting the pixel corresponding to a predetermined pixel of a temporally-previous frame of the decimated moving image, at each of the decimated frames in the same direction as time; an opposite-direction detecting unit for detecting the pixel corresponding to the detected pixel of a temporally-subsequent frame of the decimated moving image, at each of the decimated frames in the opposite direction of time; and a second detecting unit for detecting a predetermined pixel of each of the decimated frames by employing the pixel positions detected in the forward and opposite directions.
Owner:SONY CORP
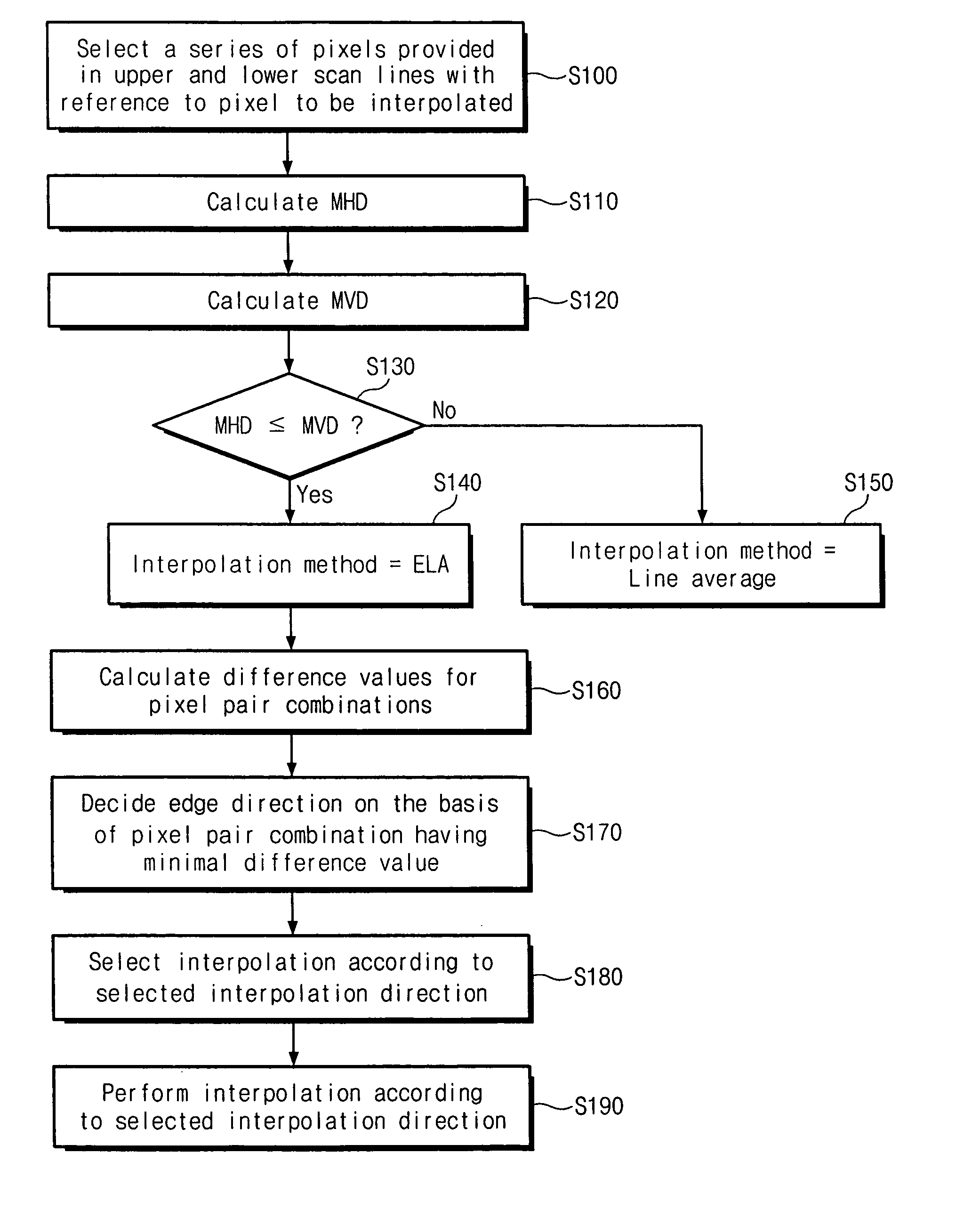
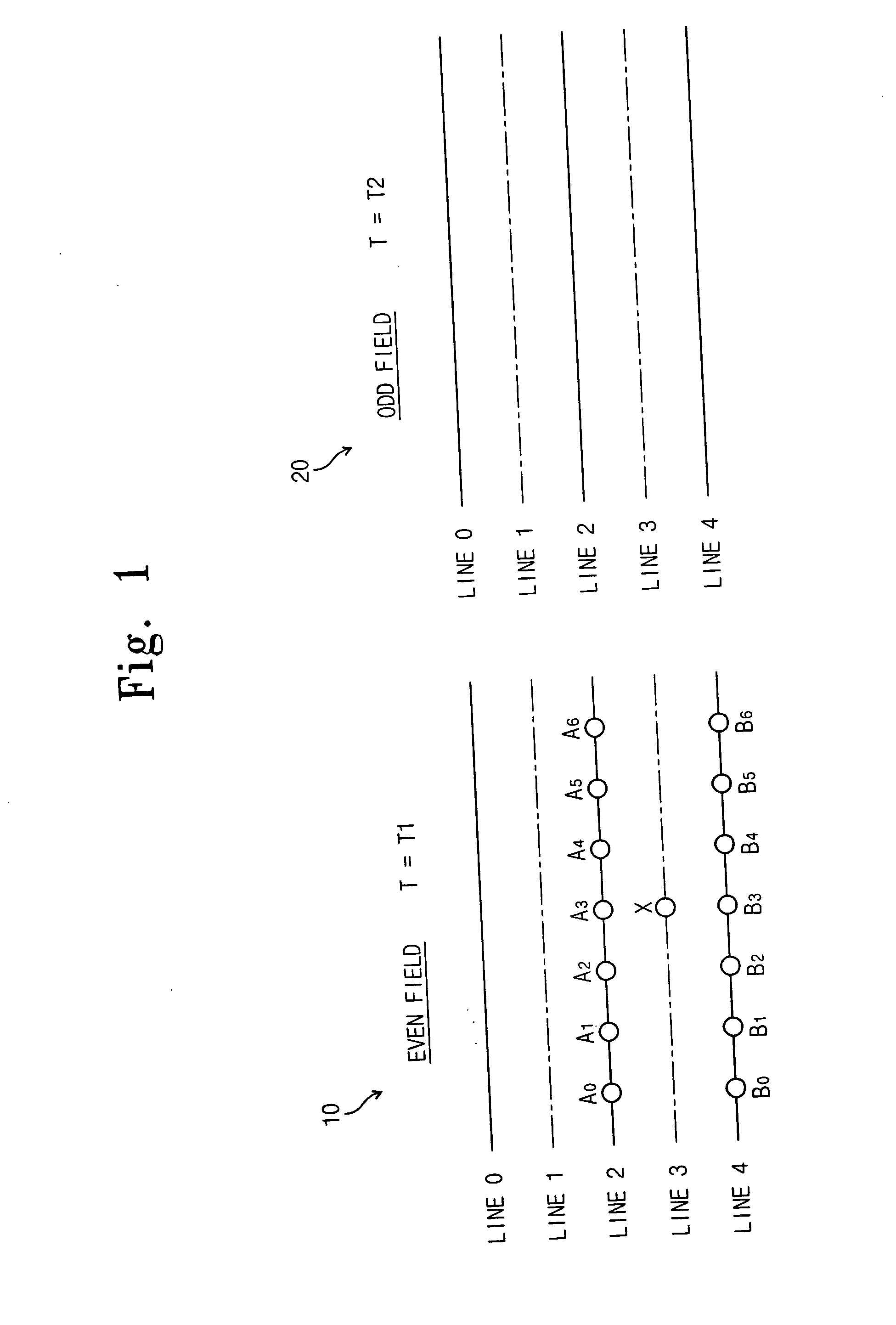
Image adaptive deinterlacing method and device based on edge
ActiveUS20050073607A1Improve picture qualityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionProgressive scan
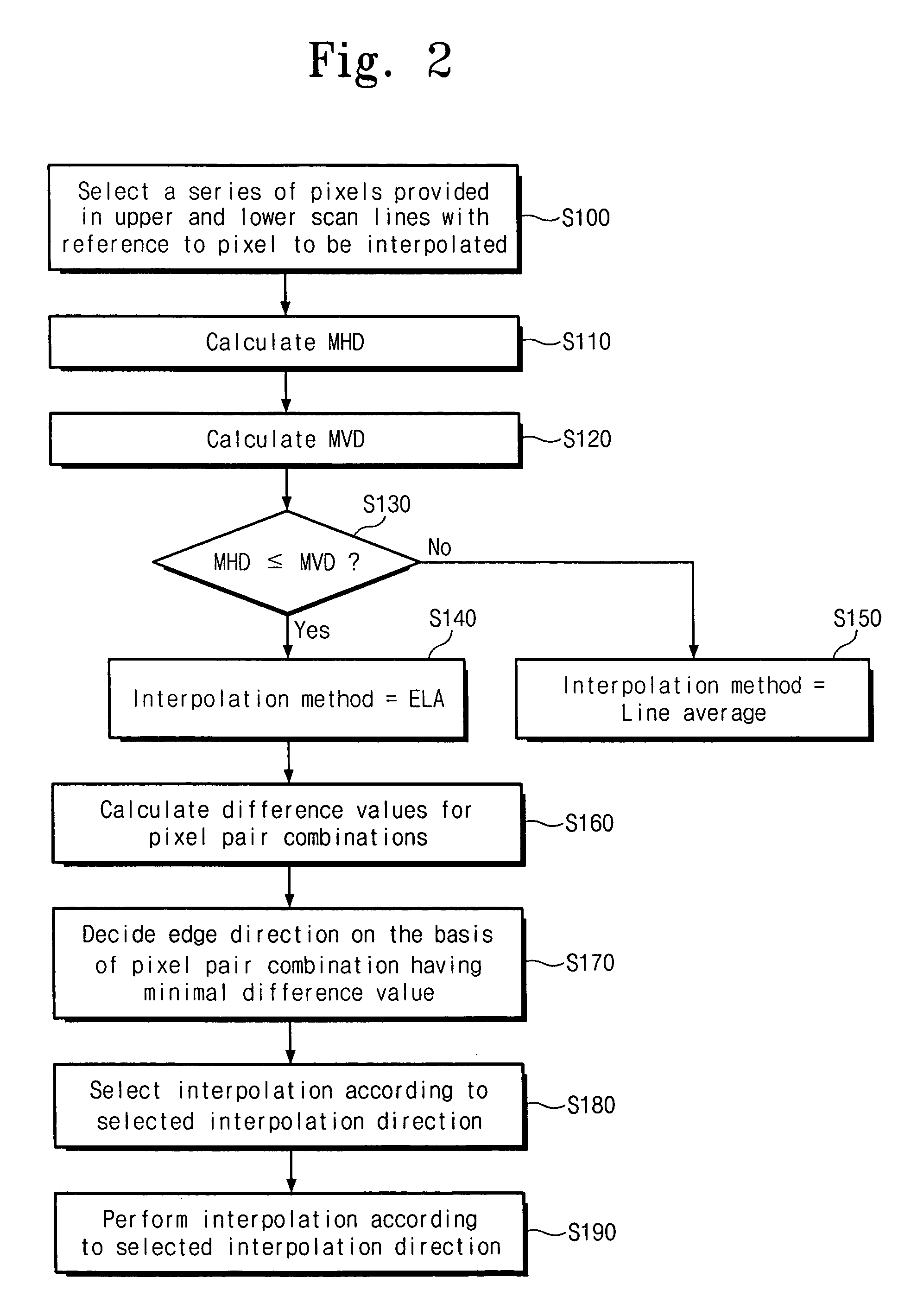
The present invention relates to a deinterlacing device and method for converting a video signal of an interlaced scan format into a video signal of a progressive scan format. The deinterlacing method including the steps of: measuring an edge gradient from a series of pixels provided in an upper scan line and a series of pixels provided in a lower scan line with reference to a pixel to be interpolated; determining an interpolation method on the basis of the measured edge gradient; calculating a difference value for each of pixel pair combinations, each of the pixel pair combinations having at least one pixel pair, the pixel pair having two pixels each one from each of the upper and lower scan lines with reference to the pixel to be interpolated, each of the pixel pair combinations having the pixel pairs that are adjacent to one another, the pixel pair combinations having different directions from one another; determining an edge direction on the basis of a direction of the pixel pair combination having the smallest difference value; and performing an interpolation for the pixel depending on the determined interpolation method and the determined edge direction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Display device, terminal device, display panel, and optical member
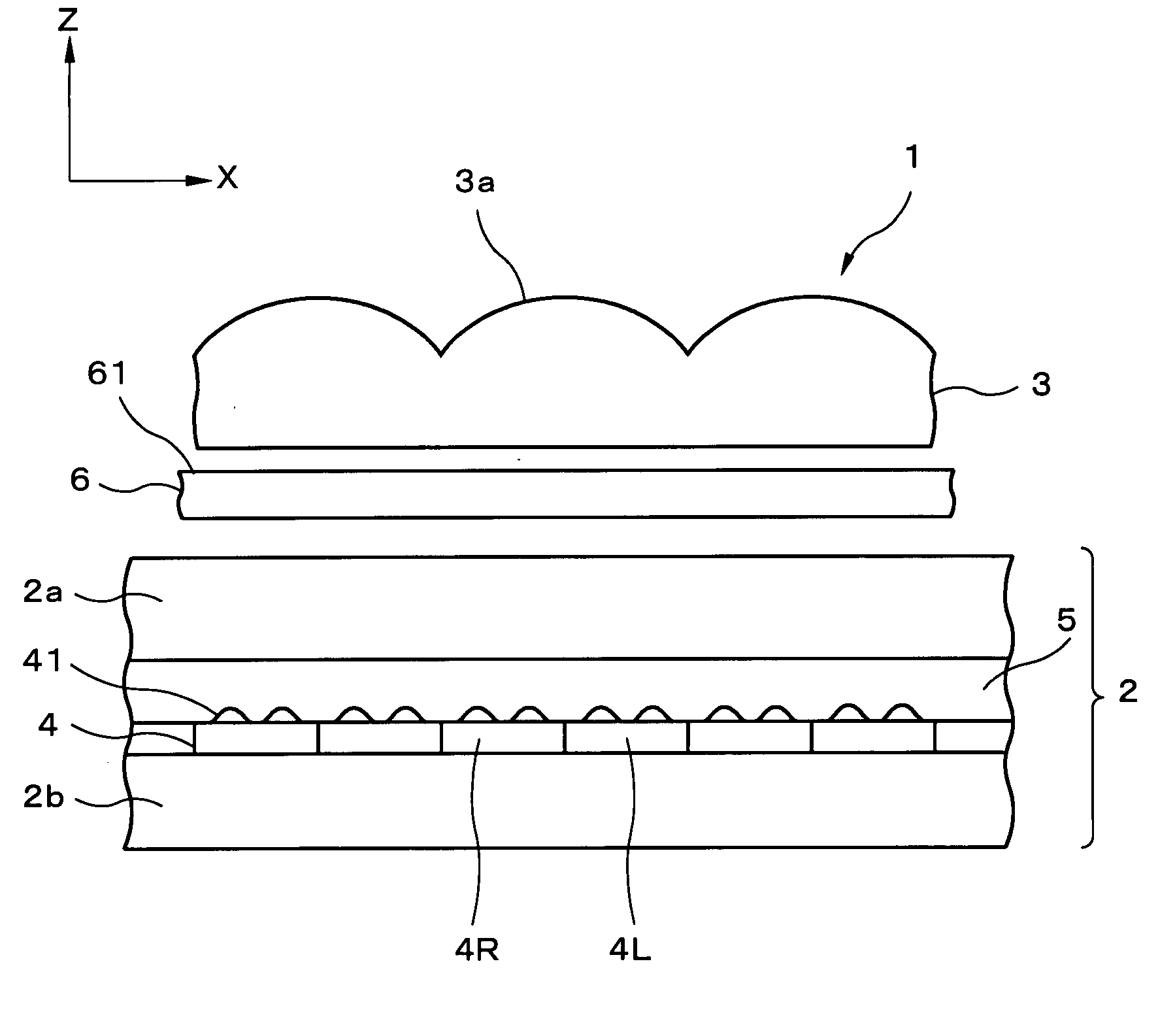
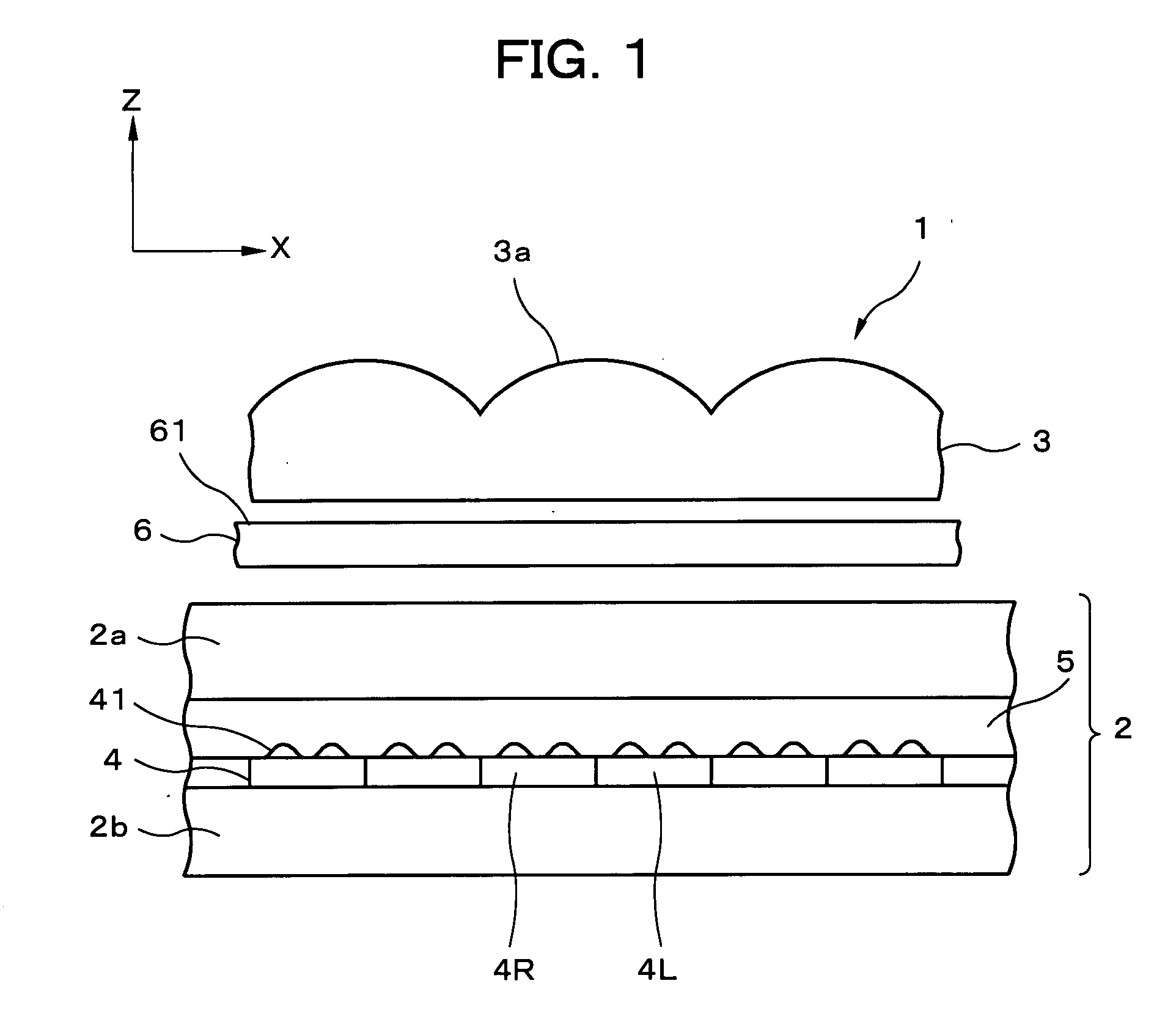
ActiveUS20080094700A1Quality improvementImprove image qualityOptical light guidesSteroscopic systemsConvex structureLiquid-crystal display
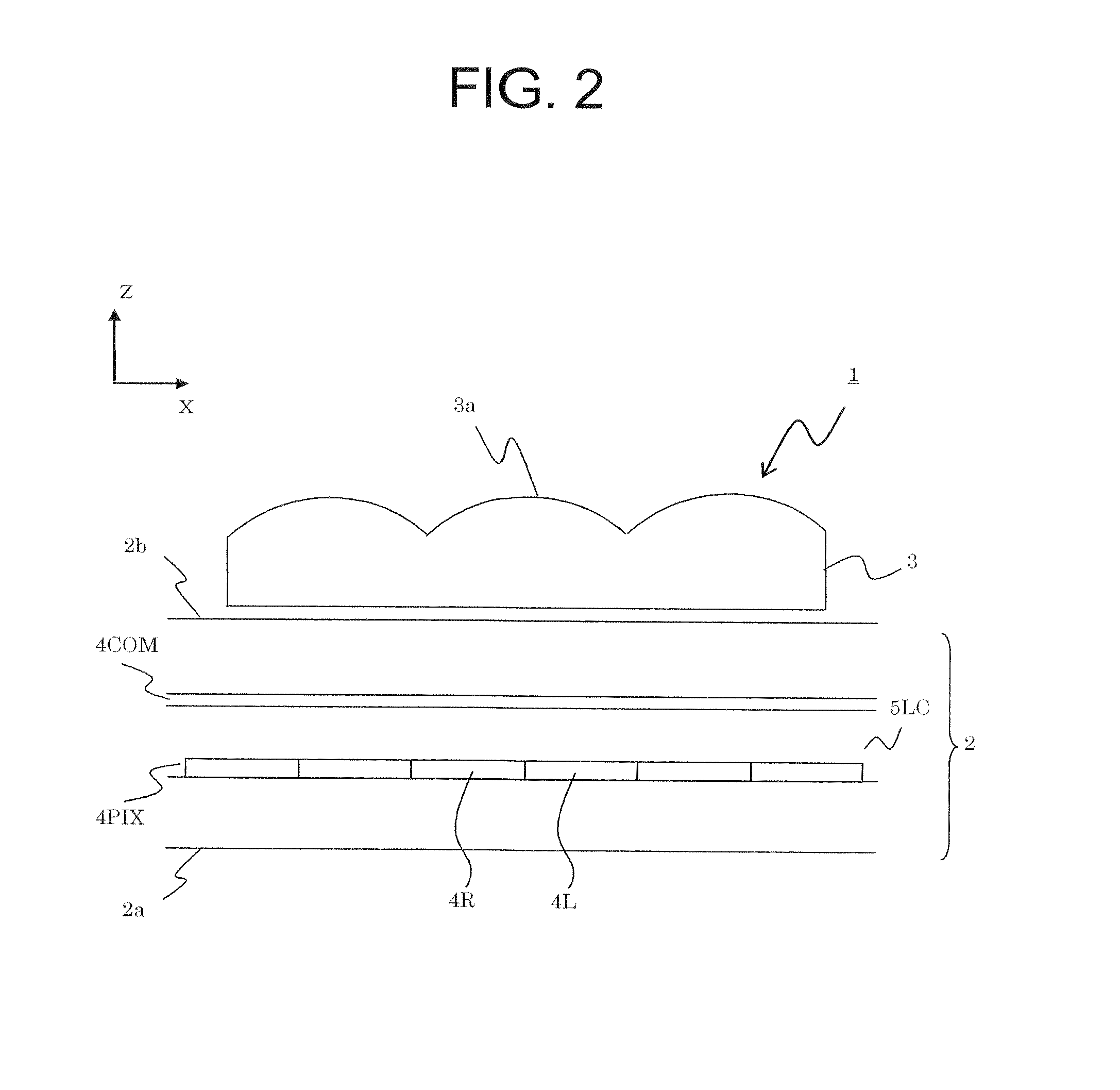
A reflective liquid crystal display panel is a display panel for three-dimensional display in which pixel pairs as display elements composed of one left-eye pixel L and one right-eye pixel R each are provided in a matrix. The lenticular lens is an optical member for image separation that is provided to separate the light from the left and right pixels, and numerous lenticular lenses form a lens array that is arranged in one dimension. An anisotropic scattering sheet as an anisotropic scattering element is provided between the lenticular lens and the reflective liquid crystal display panel. According to this configuration, a reduction in the quality of the reflective display can be minimized, and improved image quality can be achieved without changing the concavo-convex structure of the reflecting panel and the lens shape of the lenticular lens in display device that is capable of displaying different images to a plurality of viewpoints.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
Driving Device for Display Panel, Display Device Including the Driving Device, Method for Driving a Display Panel, Program, and Storage Medium
ActiveUS20080079755A1High resolutionEnhanced signalCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingColor gelDisplay device
A display panel is the one in which a pixel composed of sub-pixels of red (R), green (G), blue (B), and at least one other color has two sub-pixels at least in a vertical scanning direction, and color filters are provided respectively corresponding to the sub-pixels. There are provided: an incoming signal interpolating section which interpolate each of pixels based on incoming color signal components of red (R), green (G), and blue (B) at least in a vertical scanning direction to generate interpolated RGB signals; a luminance signal converting section which converts color signals of interpolated sub-pixels, which are obtained from the incoming signal interpolating section, into luminance signals; an another color luminance component adding section which adds a luminance signal component of at least one other color on a basis of luminance signal components of colors of red (R), green (G), and blue (B), which components are outputted from the luminance signal converting section; and a luminance reallocating section which reallocates luminance signals of peripheral interpolated sub-pixels, for a color of each of the color filters corresponding to the sub-pixels, in accordance with output from the another color luminance component adding section.
Owner:SHARP KK
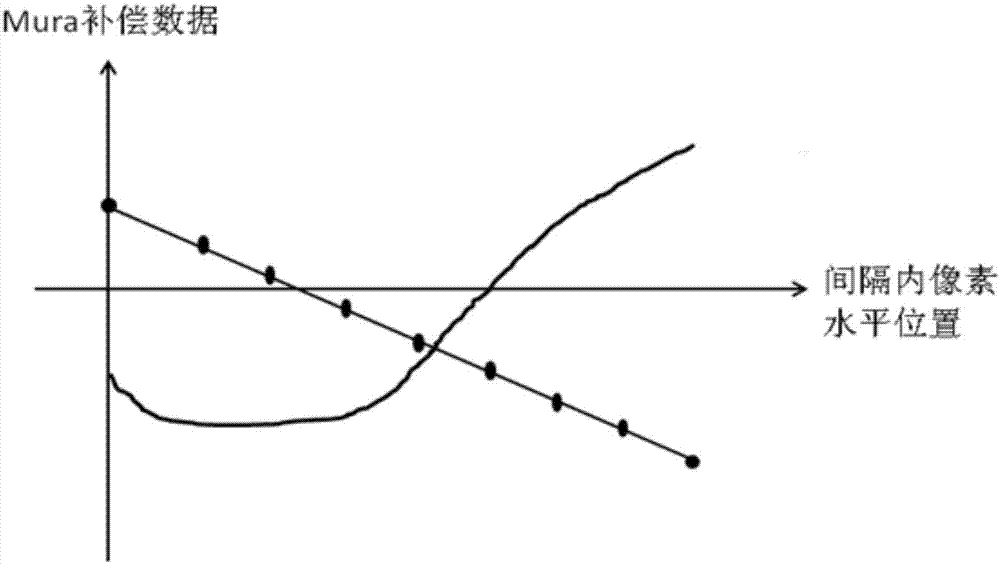
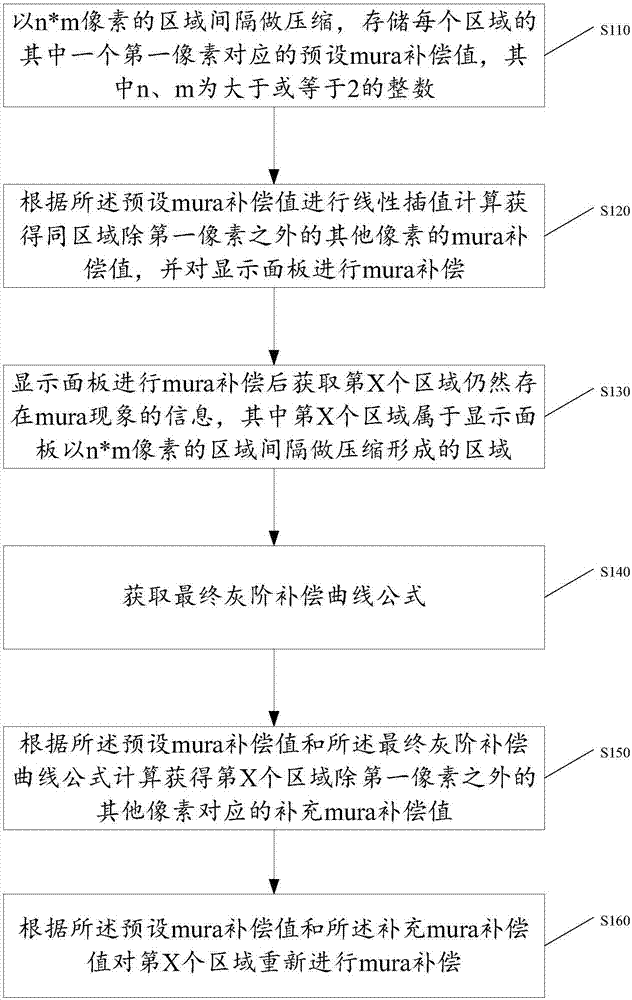
Mura phenomenon compensation method of display panel and display panel
ActiveCN106910483AImprove the display effectImprove MuraStatic indicating devicesComputer scienceBrightness perception
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
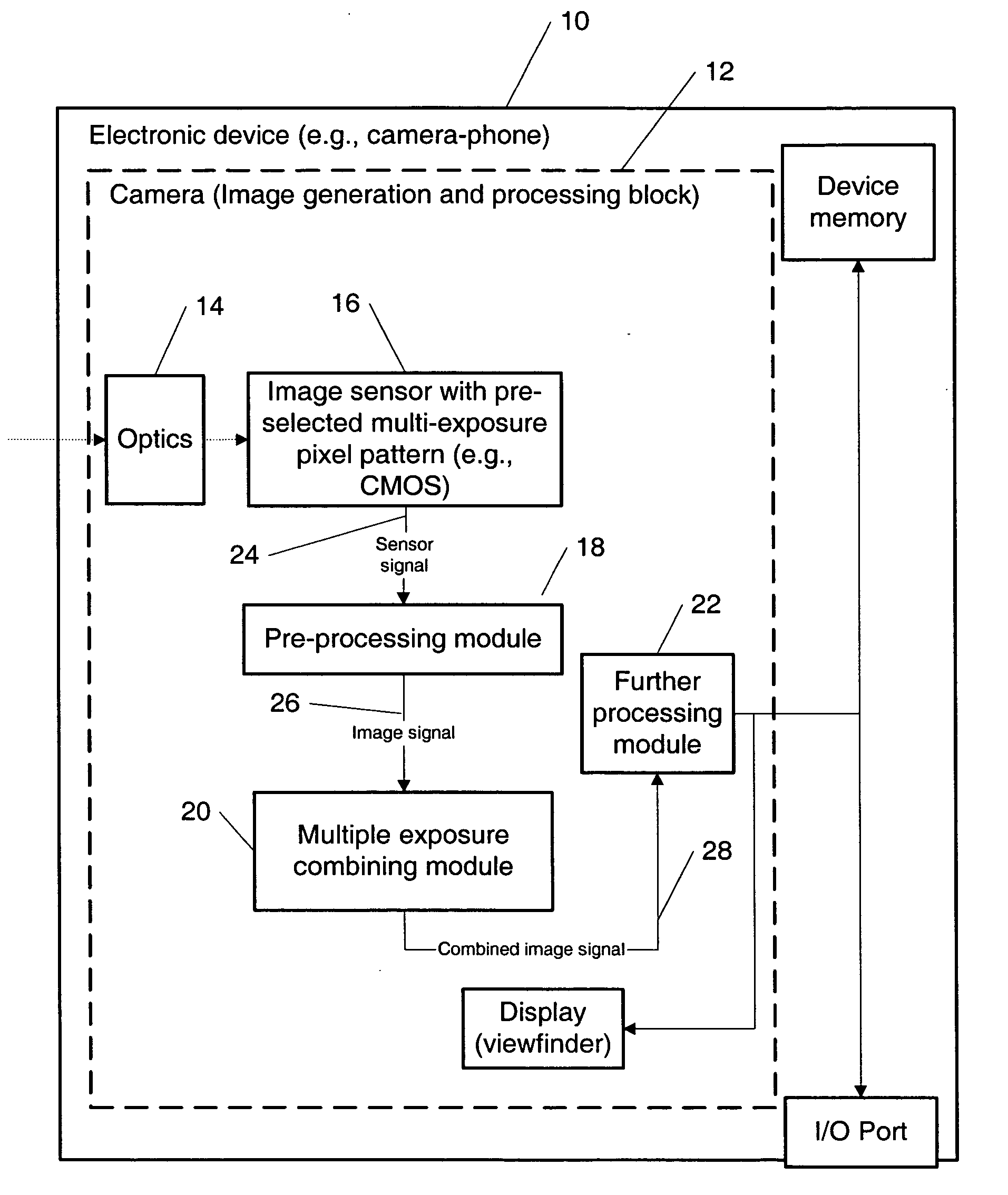
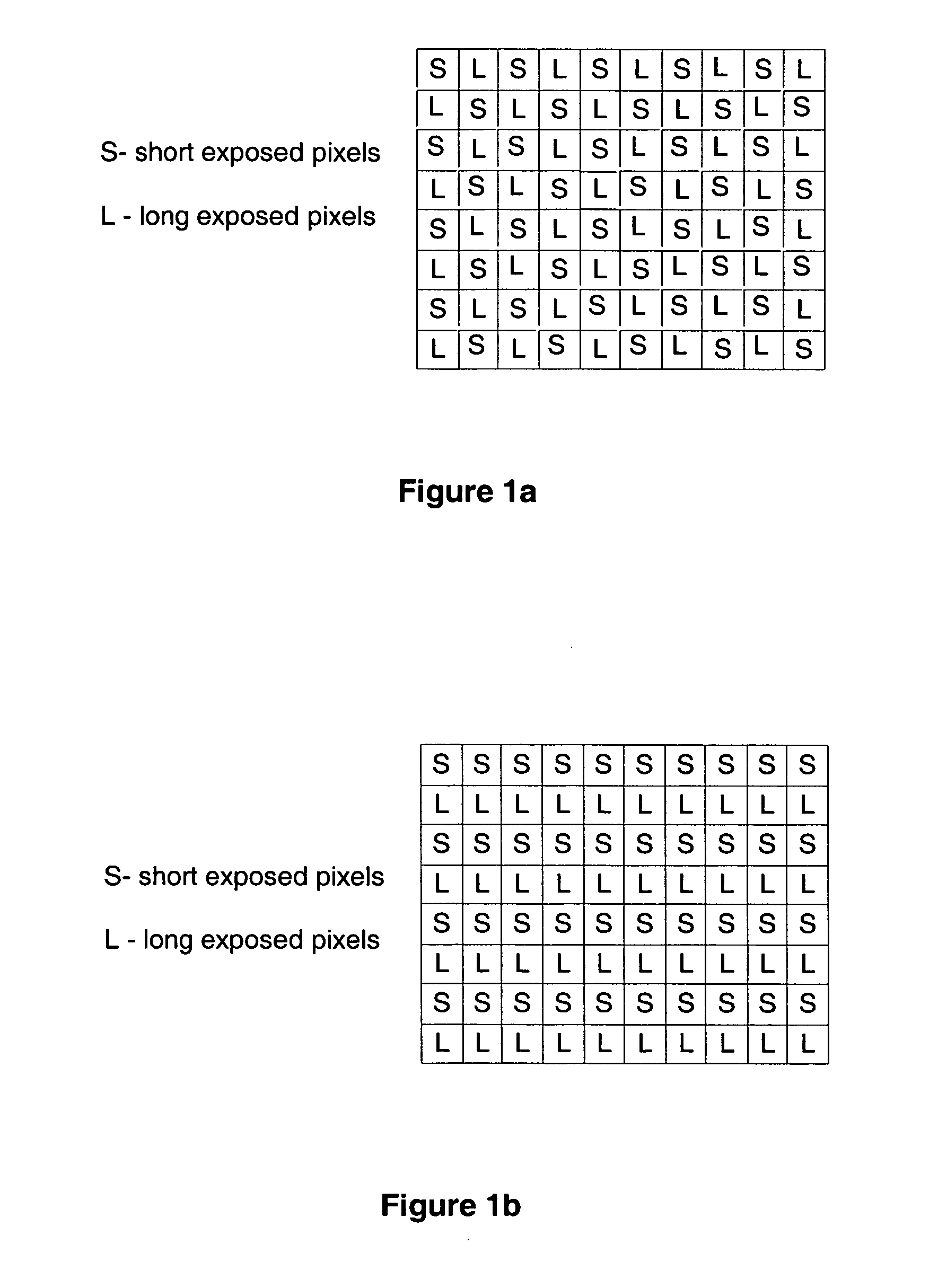
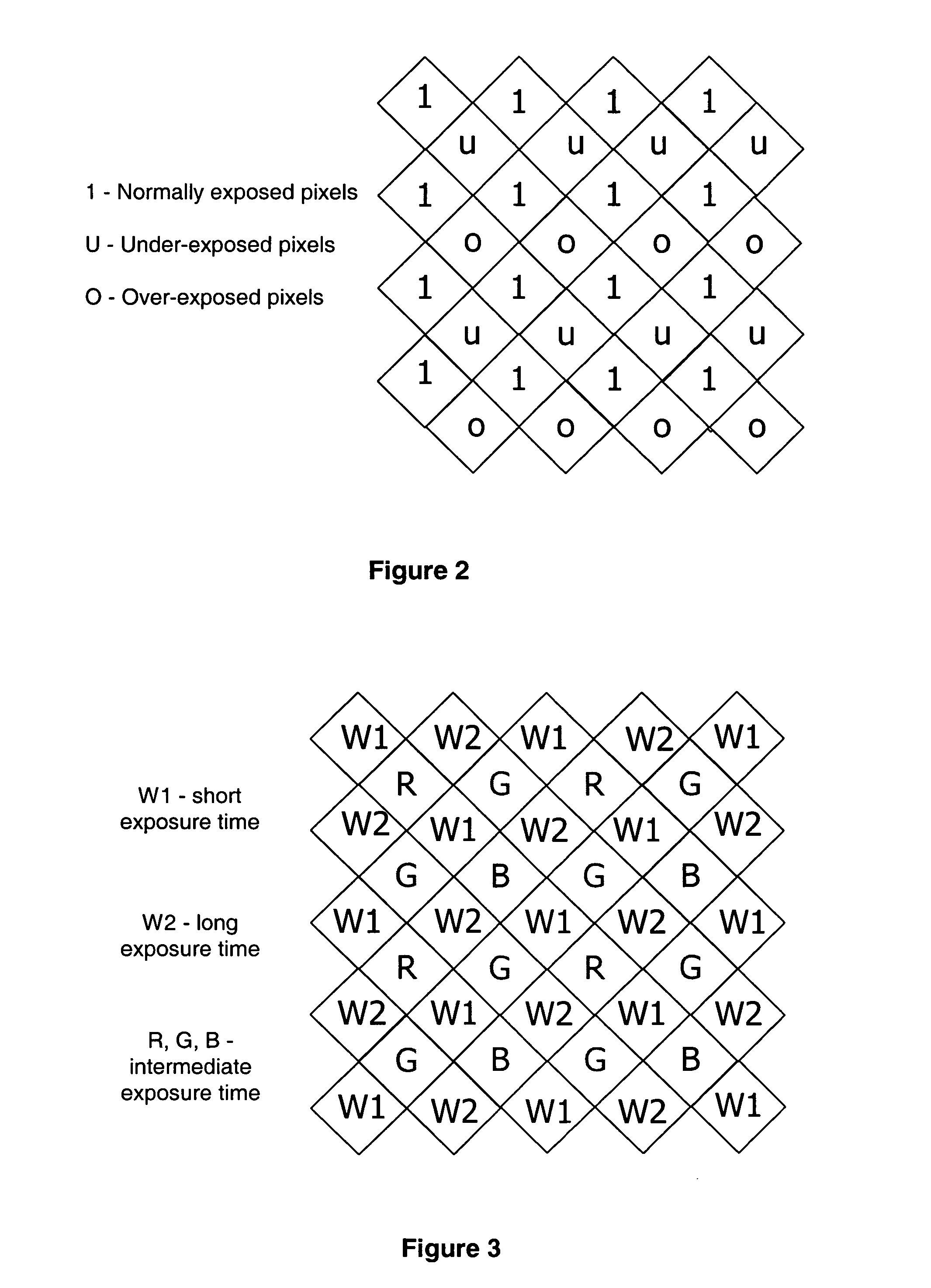
Image stabilization using multi-exposure pattern
ActiveUS20080143841A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer graphics (images)Engineering
The specification and drawings present a new method, apparatus and software product for image stabilization of an image taken with a fixed (i.e., pre-selected) multi-exposure pattern for at least one color channel by an image sensor of a camera, wherein a plurality of groups of pixels of the image sensor have different pre-selected exposure times for said at least one color channel. The camera can be a part of, e.g., an electronic device such as mobile phone or a portable electronic device.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
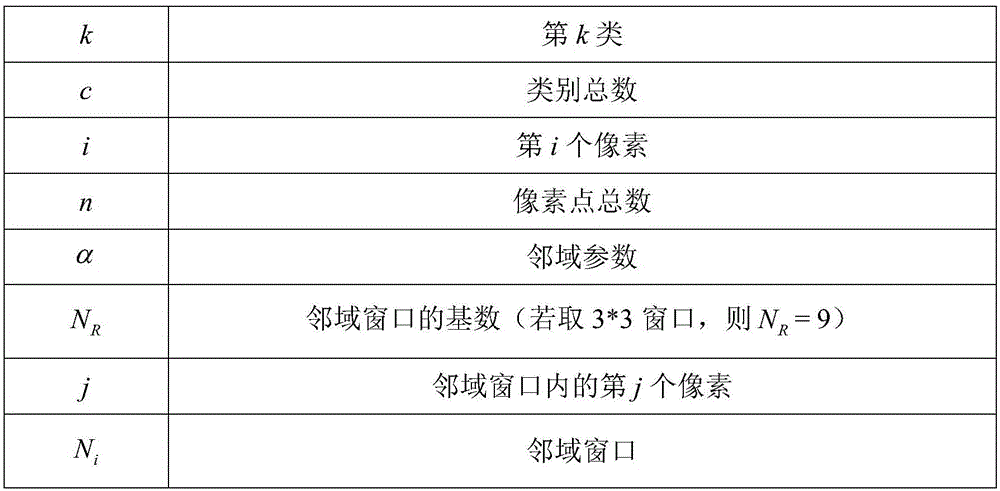
Brain MRI (magnetic resonance image) segmentation method based on improved fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm
ActiveCN106408569ADealing with uncertaintyOvercome limitationsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionCluster algorithm
The invention relates to a brain MRI (magnetic resonance image) segmentation method based on an improved fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm. The method comprises steps that 1, initial classification is carried through utilizing the fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm; 2, the clustering quantity c, a fuzzy factor m, an algorithm iteration stop threshold Epsilon, the maximum iteration times max, a neighborhood window size and other artificial setting parameters are given; 3, a similarity matrix W of two pixels is calculated; 4, similarity rhoki of pixel pair types is calculated; 5, a membership matrix U is updated; 6, if ||U(t+1)-U(t)||<Epsilon, or t=max, iteration stops, U(t+1) is outputted, otherwise t=t+1, and the process turns to the step 4; and 7, for U(t+1), the maximum membership algorithm is employed to carry out deblurring operation, and label distribution is carried out to accomplish image segmentation. Through the method, three-portion optimization including improving a clustering center mode, introducing the partial space information and utilizing the intuitionistic fuzzy set information is accomplished, effects of noise resistance enhancement and segmentation precision improvement are realized, and an actual problem of high-precision segmentation for a brain MRI is solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Graph-based segmentation integrating visible and NIR information
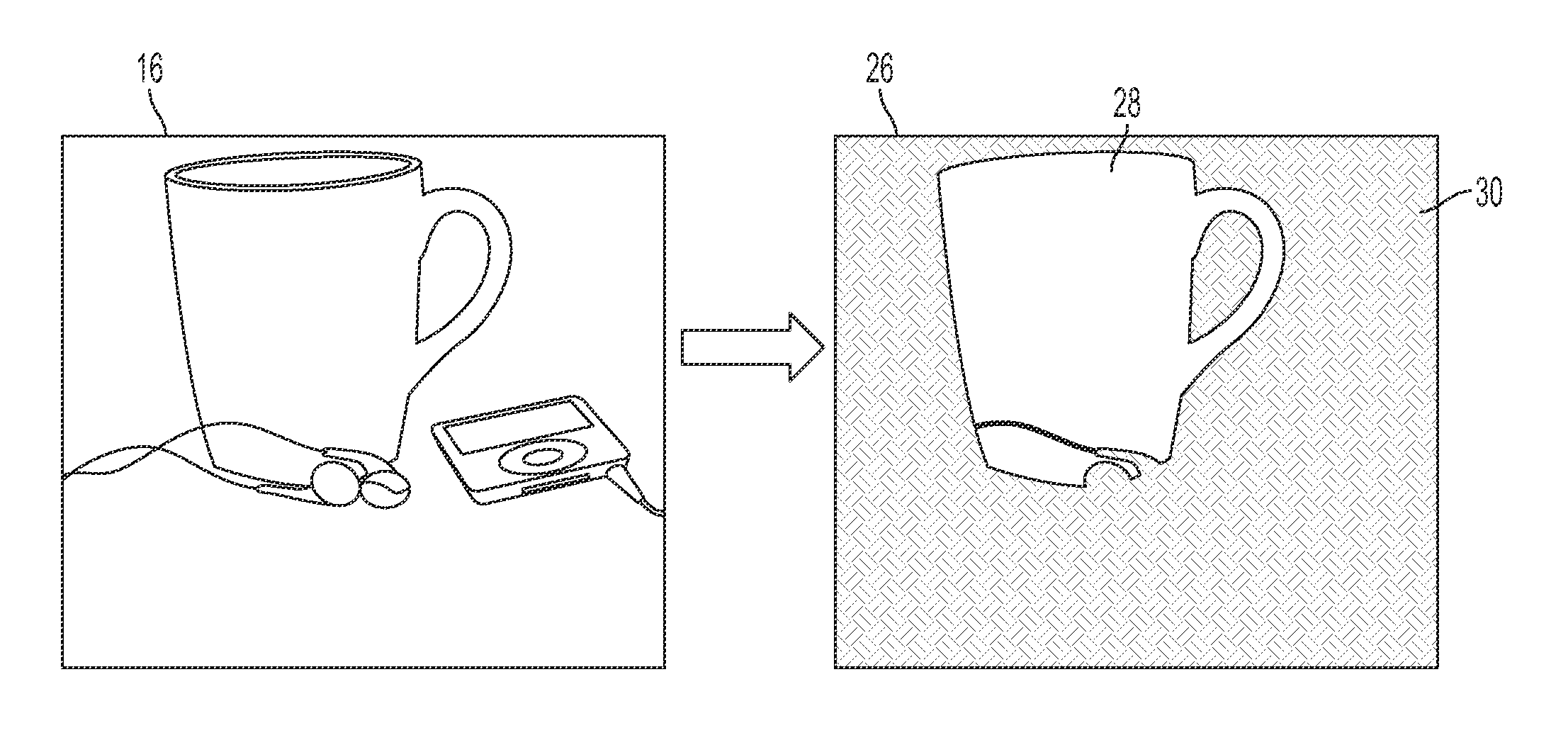
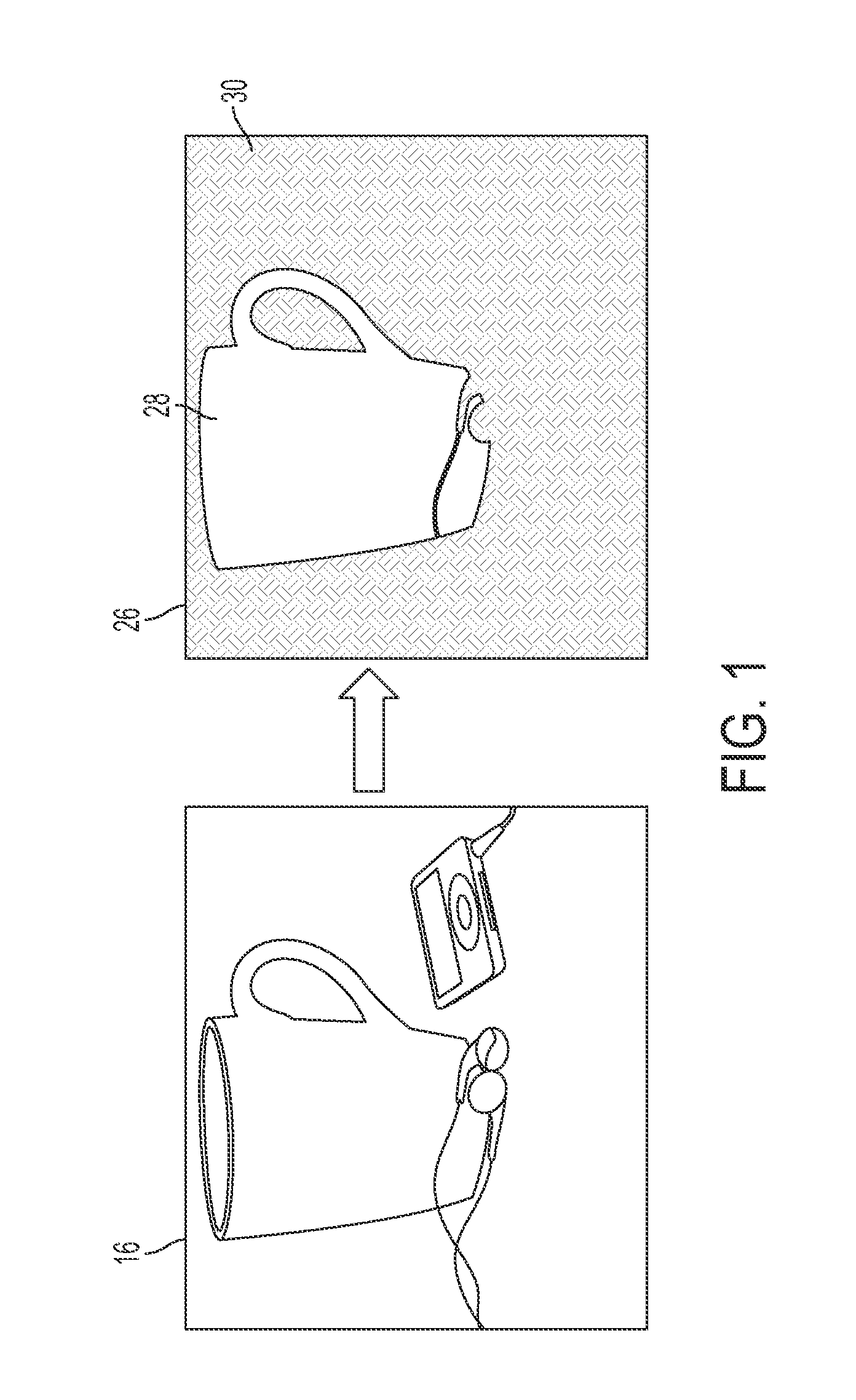
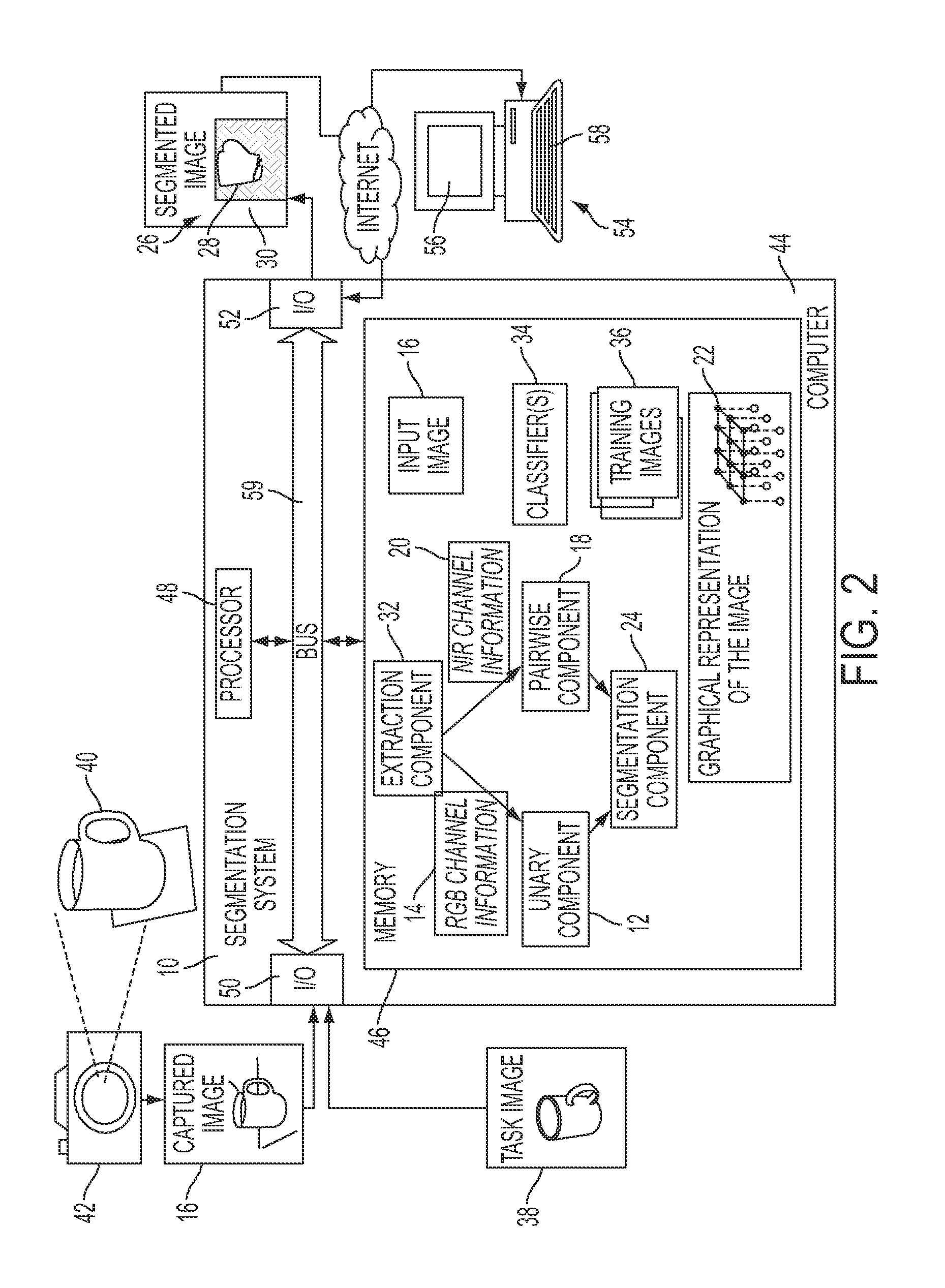
A method for segmenting an image includes extracting unary potentials for pixels of the input image. These can be based for each of a set of possible labels, on information for a first channel in the image, such as in the visible range of the spectrum. Pairwise potentials are extracted for neighboring pairs of pixels of the image. These can be based on information for a second channel in the image, such as in the infrared range of the spectrum. An objective function is optimized over pixels of the input image to identify labels for the pixels. The objective function is based on a combination of ones of the extracted unary and pairwise potentials. The image is then segmented, based on the identified pixel labels. The method and system can provide an improvement in segmentation over methods which use only the visible information.
Owner:XEROX CORP
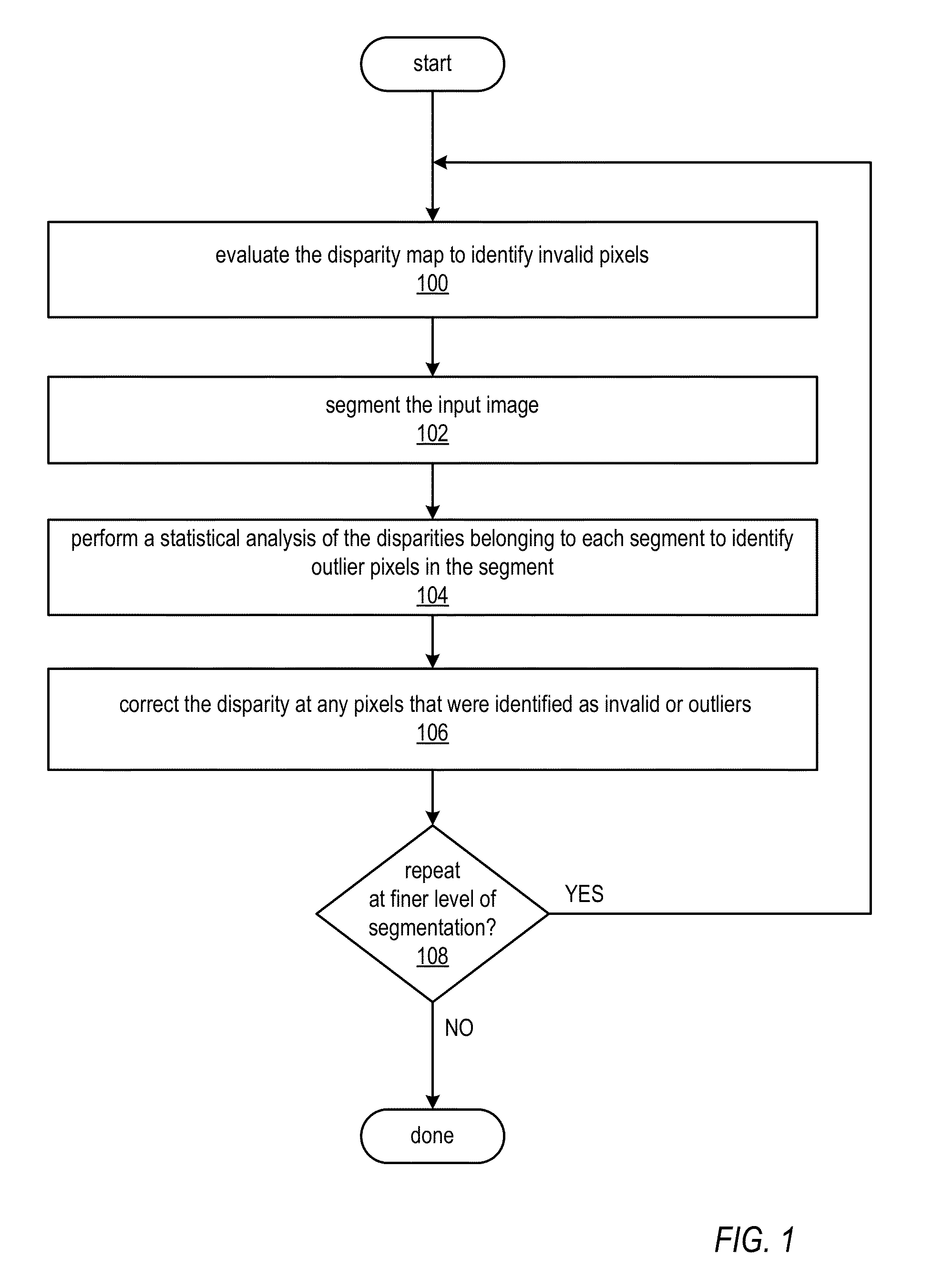
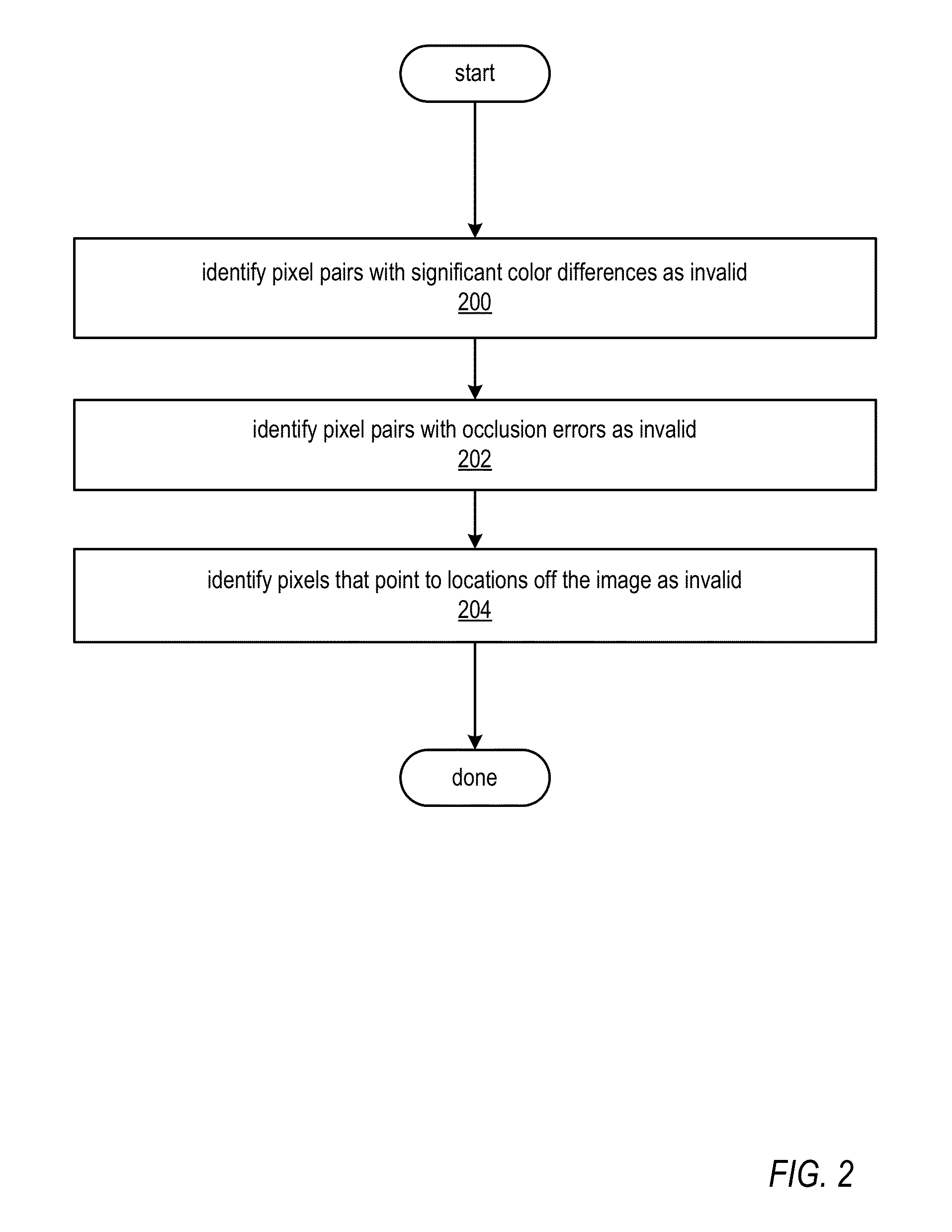
Methods and Apparatus for Correcting Disparity Maps using Statistical Analysis on Local Neighborhoods
ActiveUS20130136338A1Improve performancePromote resultsImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxStatistical analysis
Methods and apparatus for disparity map correction through statistical analysis on local neighborhoods. A disparity map correction technique may be used to correct mistakes in a disparity or depth map. The disparity map correction technique may detect and mark invalid pixel pairs in a disparity map, segment the image, and perform a statistical analysis of the disparities in each segment to identify outliers. The invalid and outlier pixels may then be corrected using other disparity values in the local neighborhood. Multiple iterations of the disparity map correction technique may be performed to further improve the output disparity map.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Correction of cluster defects in imagers
A method and apparatus that allows for the correction of multiple defective pixels in an imager device. In one exemplary embodiment, the method includes the steps of selecting a correction kernel for a defective pixel, determining average and difference values for pixel pairs in the correction kernel, and substituting an average value from a pixel pair for the value of the defective pixel.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Adaptive noise intensity video denoising method and system thereof
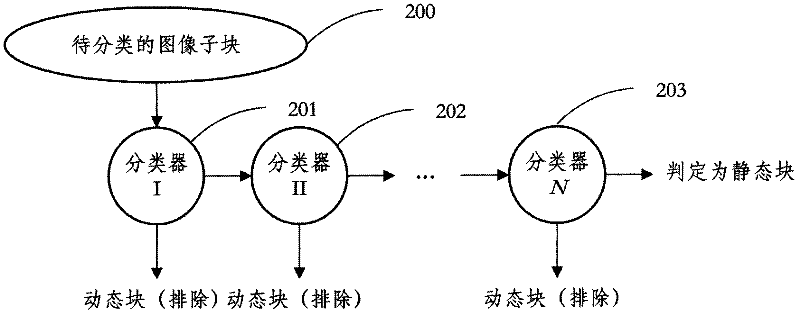
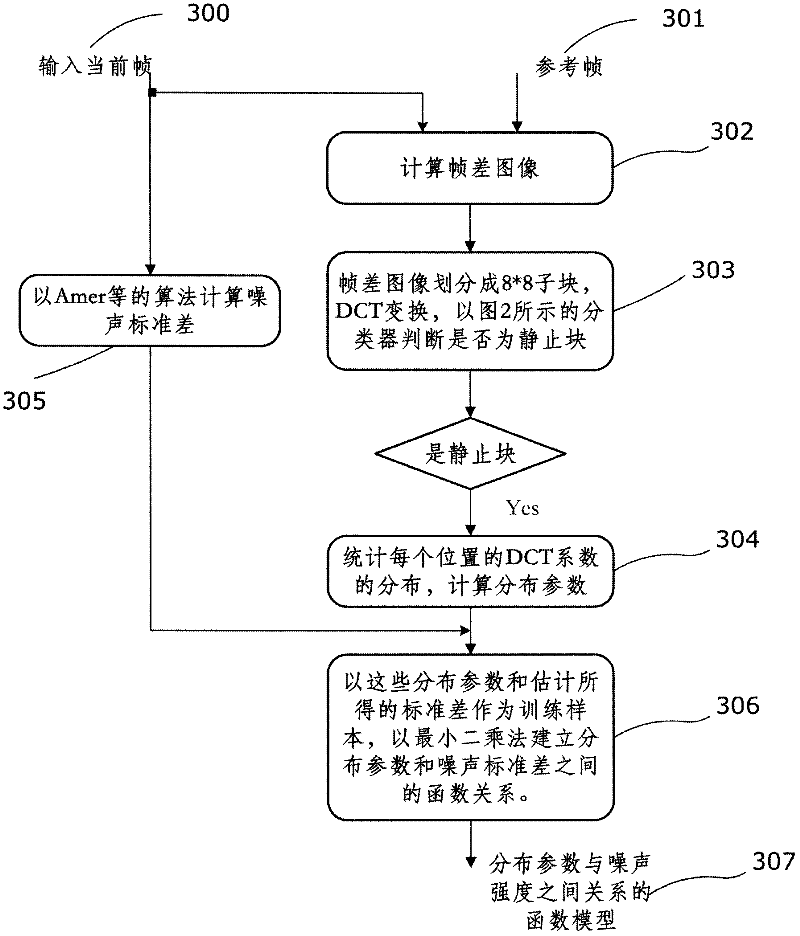
InactiveCN102368821AKeep Edges SharpImprove time and efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsPattern recognitionNoise reduction
The invention discloses an adaptive noise intensity video denoising method which is based on motion detection and is embedded in an encoder. The method comprises the following steps: (1) taking a sum of regularization frame differences in a neighborhood as an observed value, dividing input pixels into a static pixel and a dynamic pixel and using filters in different supporting domains for the two kinds of the pixels, wherein a filtering coefficient is adaptively determined according to noise intensity and an image local characteristic; (2) taking a single DCT coefficient or the sum of the several DCT coefficients as the characteristic, using AdaBoost as a tool to construct a cascade-form classifier and using the classifier to select a static block; (3) establishing a function model of connection between DCT coefficient distribution parameters of the video noise intensity and the static block and using the model to estimate the noise signal standard difference. By using noise intensity estimation embedded in the video encoder and a noise reduction technology provided in the invention, few computation costs can be used to acquire the parameters and the information needed by noise filtering. A time efficiency is good. Because a reliable clue is used to determine whether the pixels accord with a static hypothesis, the filter of the invention can effectively filter the noise and simultaneously maintain marginal sharpness of the static image. And motion blur caused by filtering in a motion area can be avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
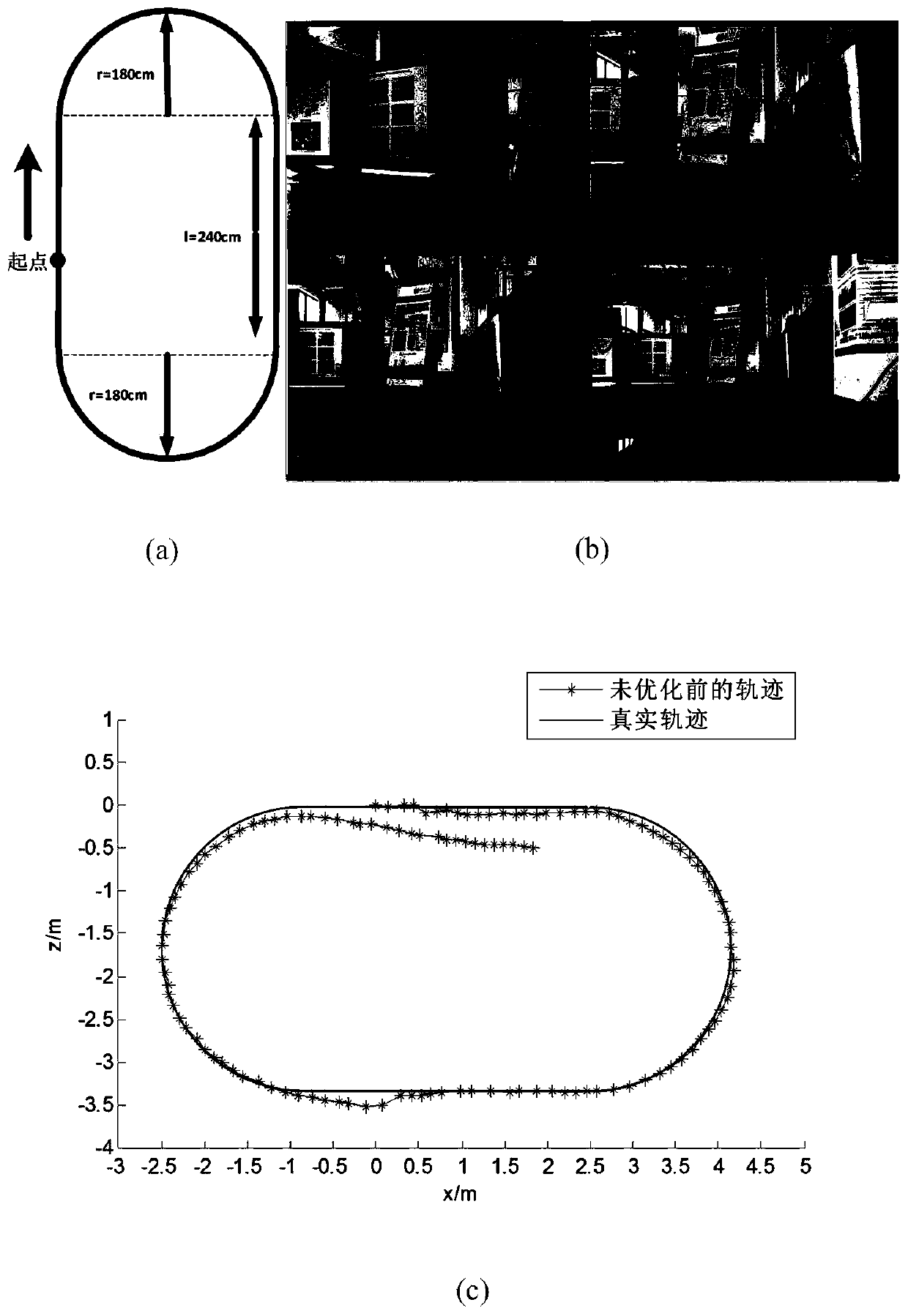
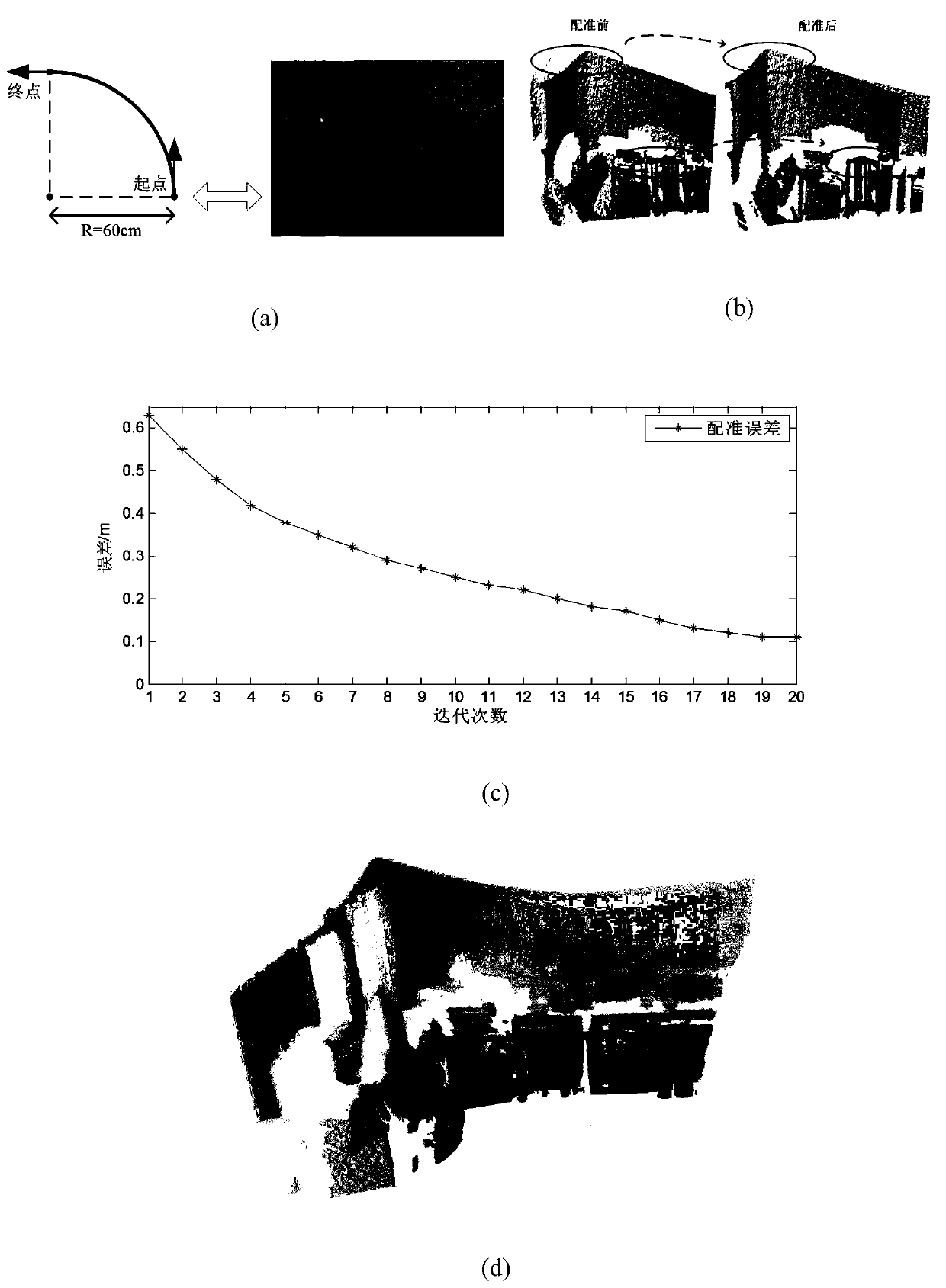
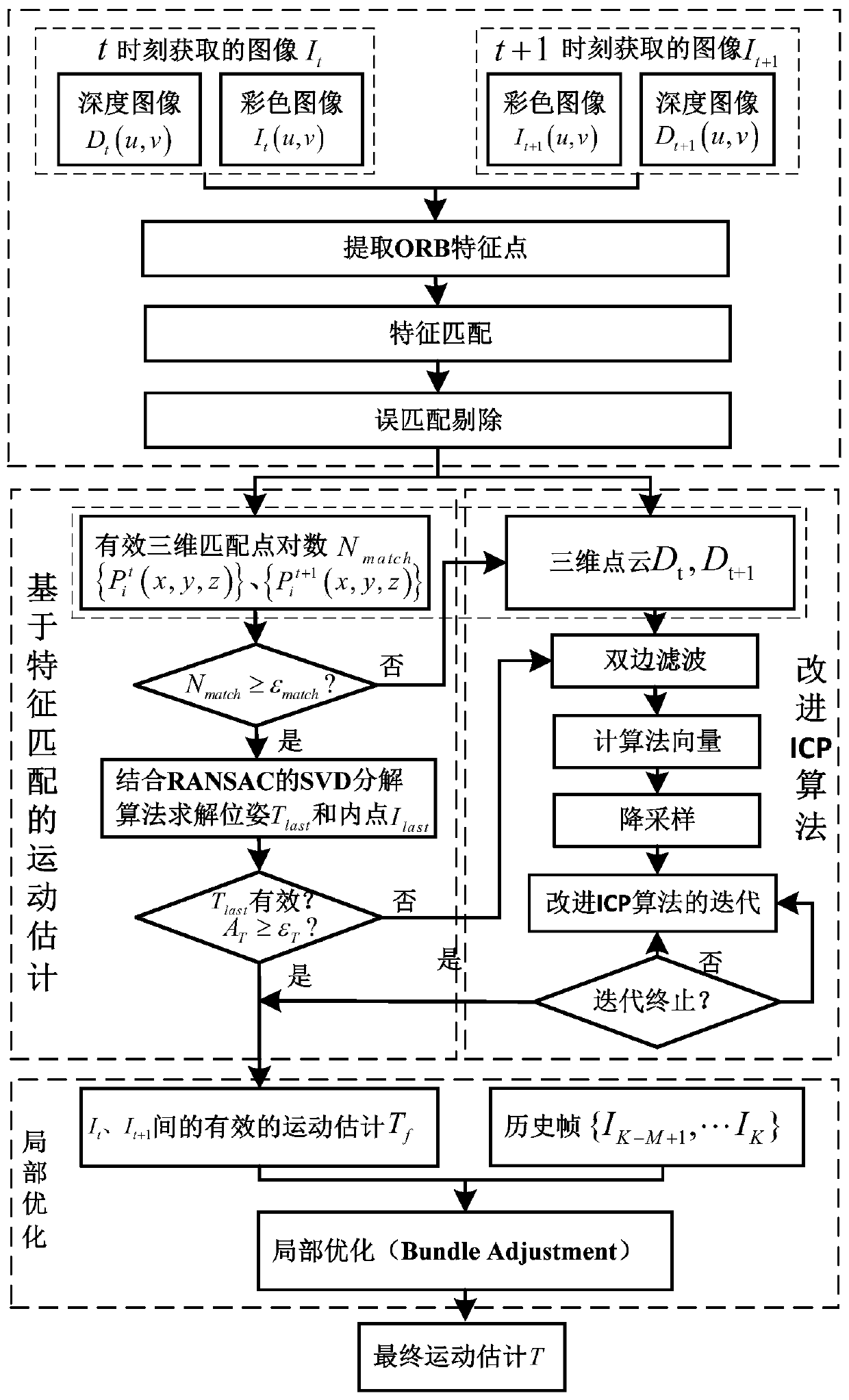
Robot scene self-adaptive pose estimation method based on RGB-D camera
PendingCN110223348ASatisfy self-positioningMeeting urgent needsImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a robot scene self-adaptive pose estimation method based on RGB-D camera. scene two-dimensional color image information of adjacent frames and space depth information corresponding to pixels of the two-dimensional color image are acquired based on a RGB-D camera; when the two-dimensional color image feature points are sufficient, ORB operators are adopted to extract features, the matching strategy provided by the invention is adopted to carry out accurate matching, and three-dimensional pose estimation is solved based on the pose estimation algorithm of the matching feature points; when the feature points are insufficient, the improved ICP algorithm provided by the invention is adopted to solve the three-dimensional pose estimation; then, a complete switching criterion is designed to fuse the two pose estimation methods; finally, pose estimation obtained through the two methods is optimized through a light beam adjustment algorithm, and finally smooth and accurate three-dimensional pose estimation is obtained. The three-dimensional pose estimation algorithm has the outstanding advantages of high robustness, high precision, small calculation amount, adaptability to different scenes and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV +1
Display device
ActiveUS20090021534A1Improve display qualityGood white balanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceComputer science
A display device has an improved white balance in white display and excellent display quality, and includes a plurality of pixels each including four sub-pixels More specifically, the display device includes a plurality of pixels each including: a sub-pixel pair of a red (R) sub-pixel and a green (G) sub-pixel; and a sub-pixel pair of a blue (B) sub-pixel and a green (G) sub-pixel, wherein in most of the pixels, a product of an aperture area per sub-pixel and a light amount per unit aperture area, in each of the red (R) sub-pixel and the blue (B) sub-pixel, is approximately two times that of the green (G) sub-pixel.
Owner:SHARP KK
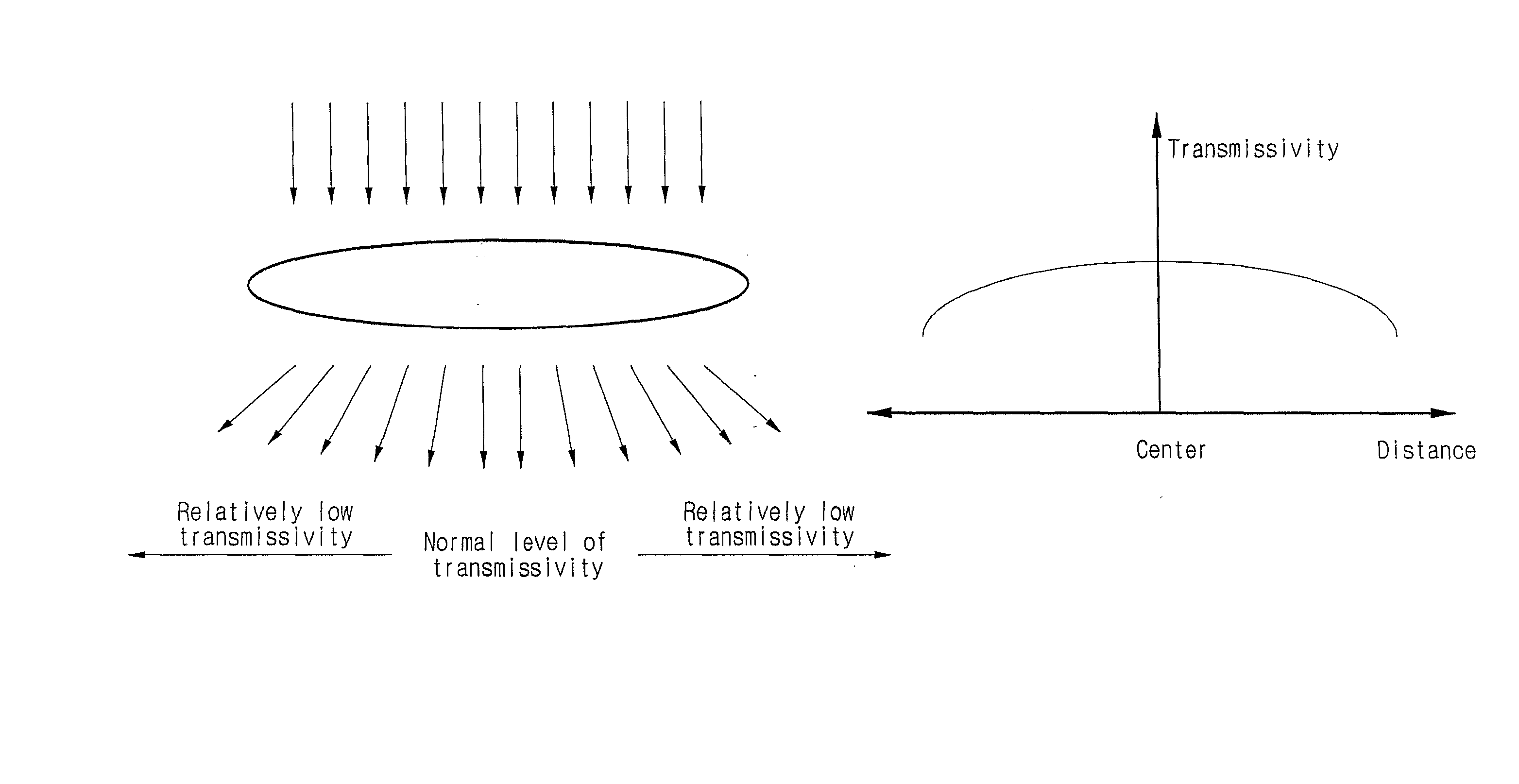
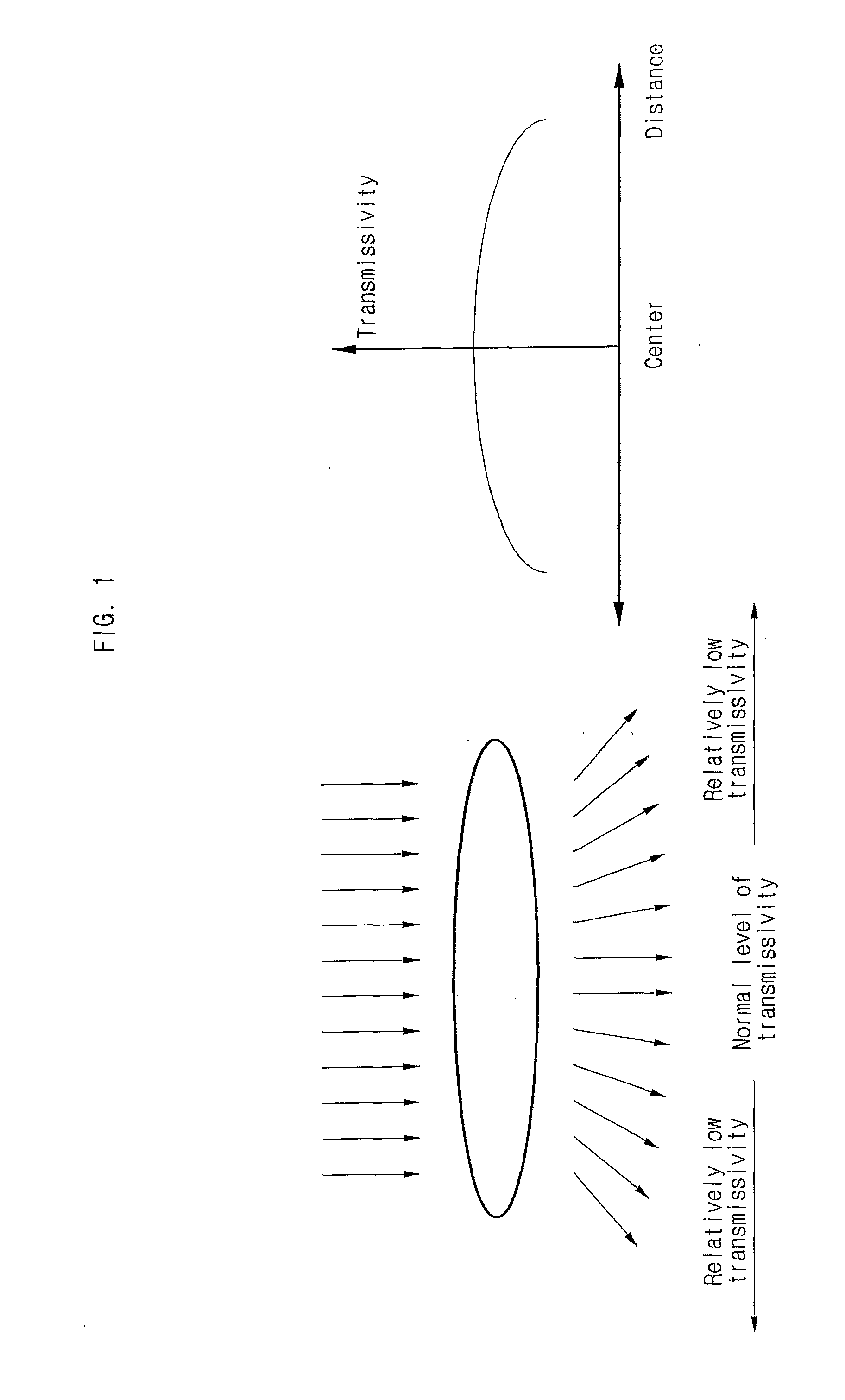
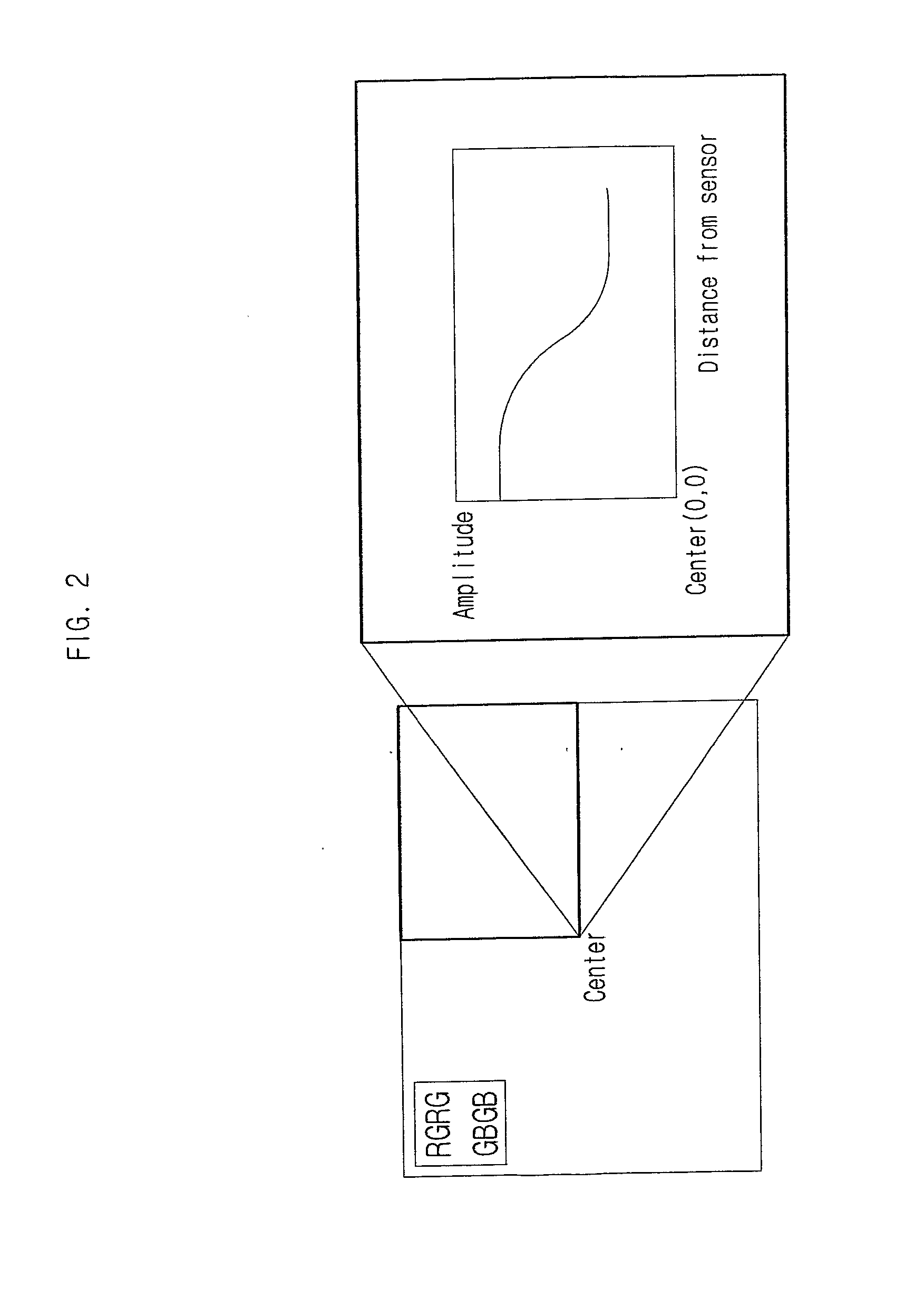
Method and Apparatus for Compensating Image Sensor Lens Shading
ActiveUS20080043117A1Reduce signal amplitudePrevent degradationTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsAnalysis dataTransmittance
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for compensating the lens shading phenomenon in image sensor. The invention first stores an inputted compensation reference value, identifies a center pixel using digital image signals received sequentially in correspondence to each pixel from a sensor, generates analysis data corresponding to each pixel, generates and stores block compensation values for blocks grouped according to the distance from the center pixel, calculates the distance from a compensation target pixel to the center pixel, calculates a compensation value corresponding to the compensation target pixel using the block compensation value corresponding to the distance, and generates for output correction pixel data by aggregating analysis data and the compensation value corresponding to the compensation target pixel. Thus, the invention allows the maintaining of colors as close as possible to the original through the respective compensation of RGB which takes into consideration the respective characteristics of the color filters and through the respective compensation of gain and level for the disparity in transmissivity according to position.
Owner:MILA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com