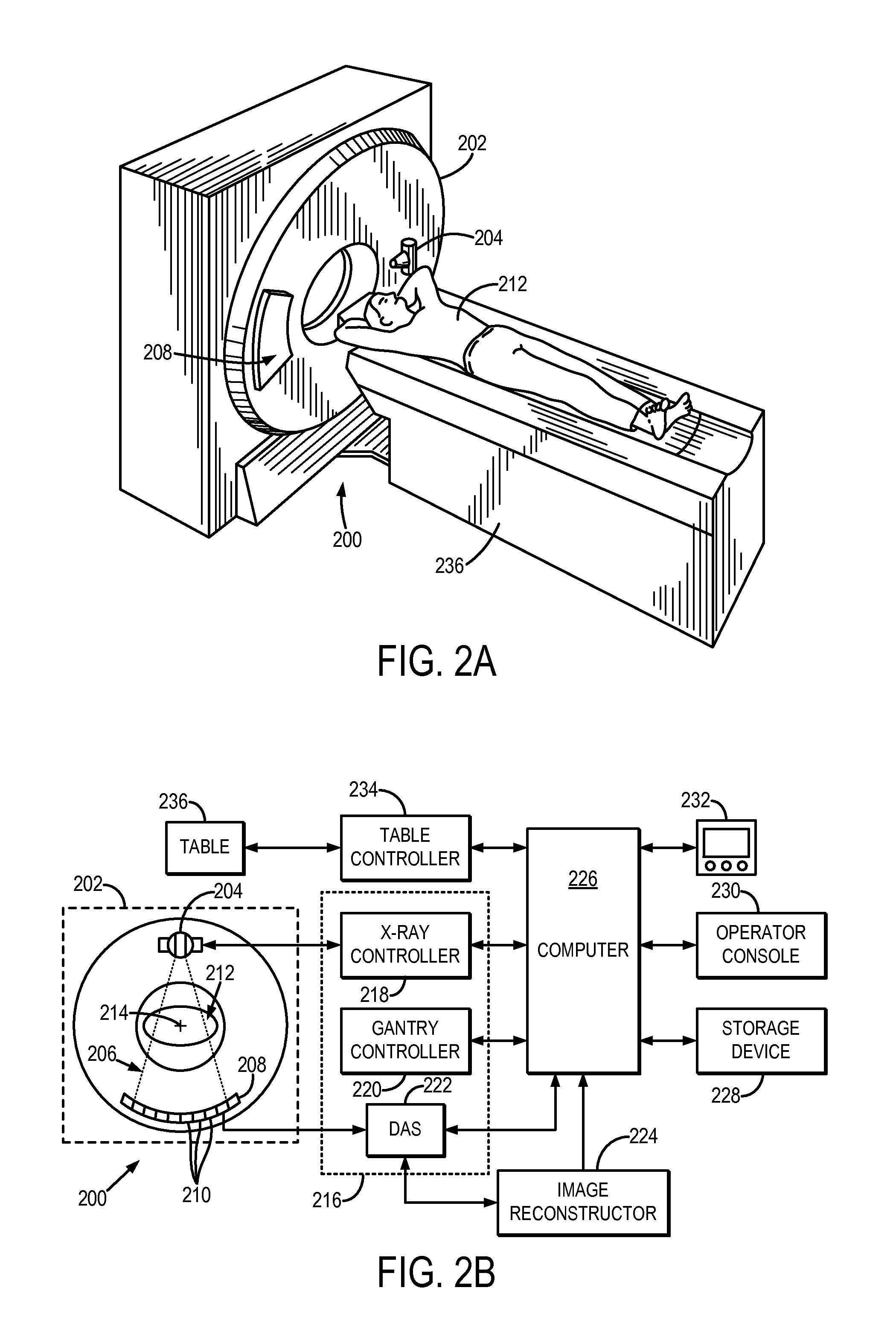
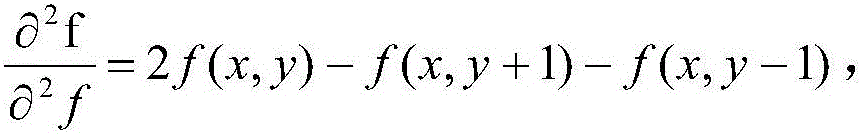Patents
Literature
33 results about "Statistical noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Statistical noise is the colloquialism for recognized amounts of unexplained variation in a sample. See errors and residuals in statistics.
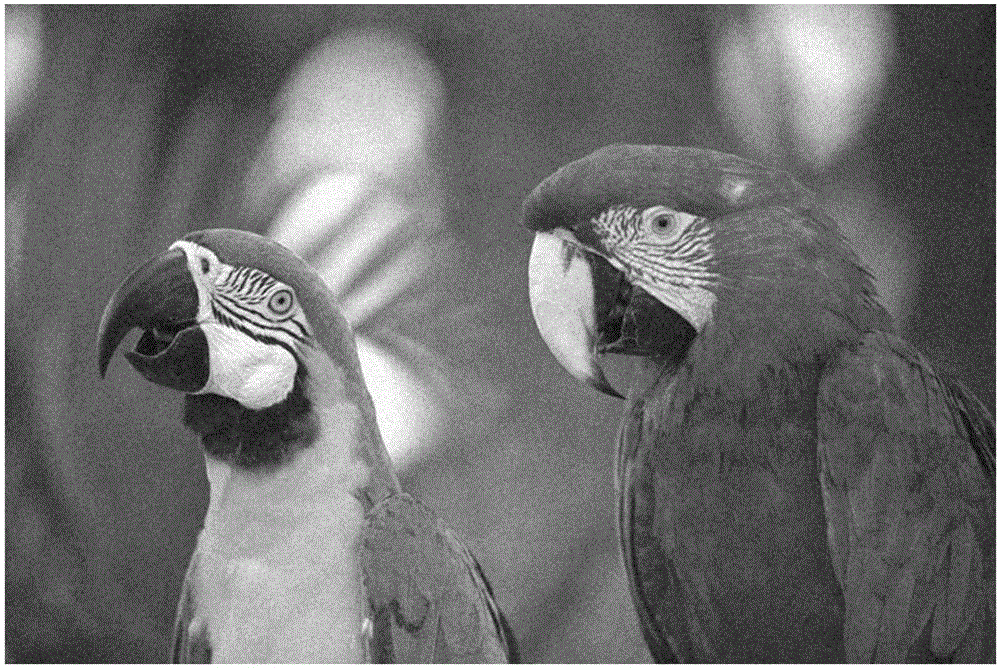
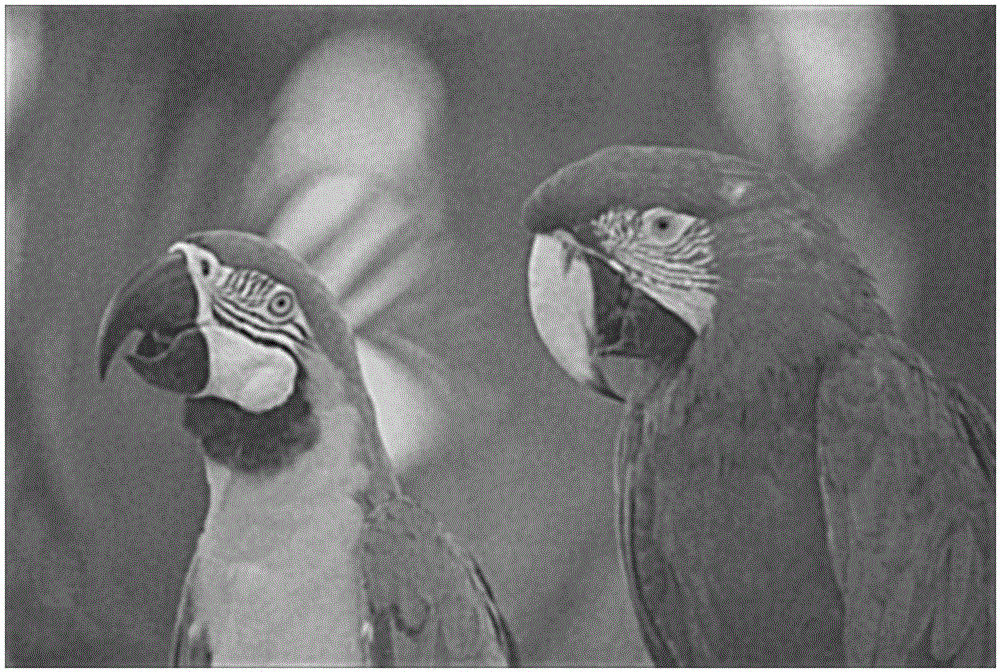
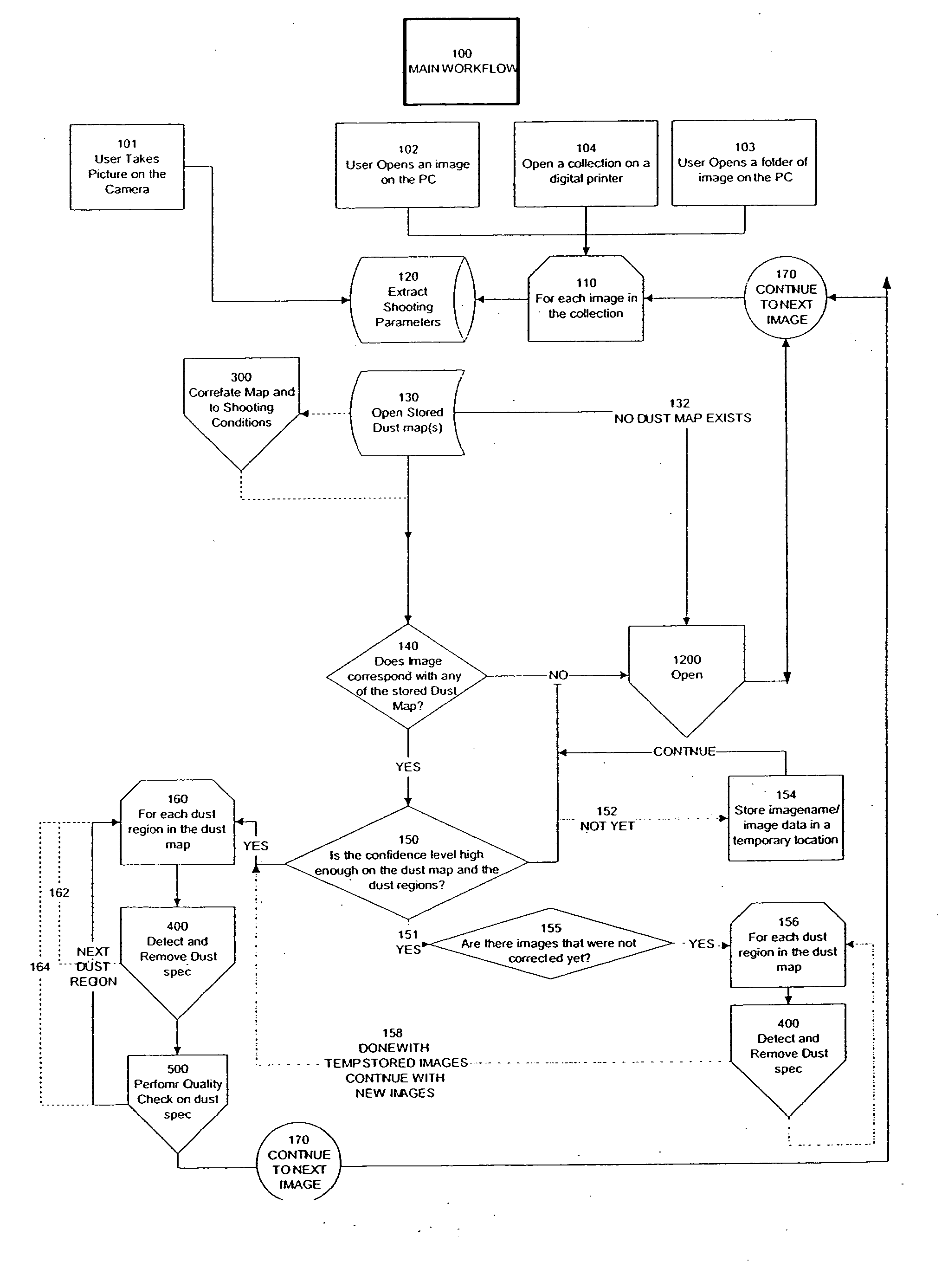
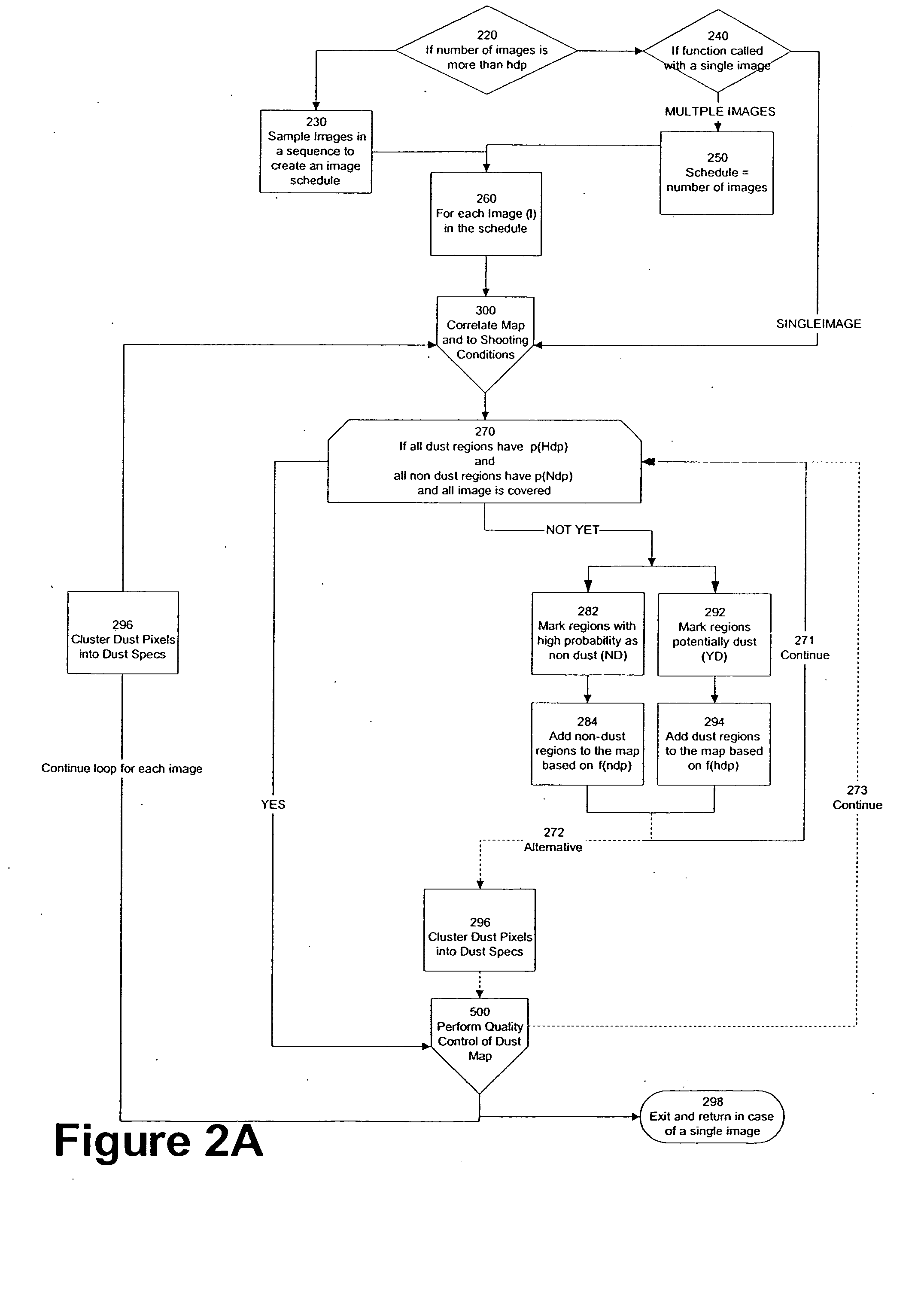
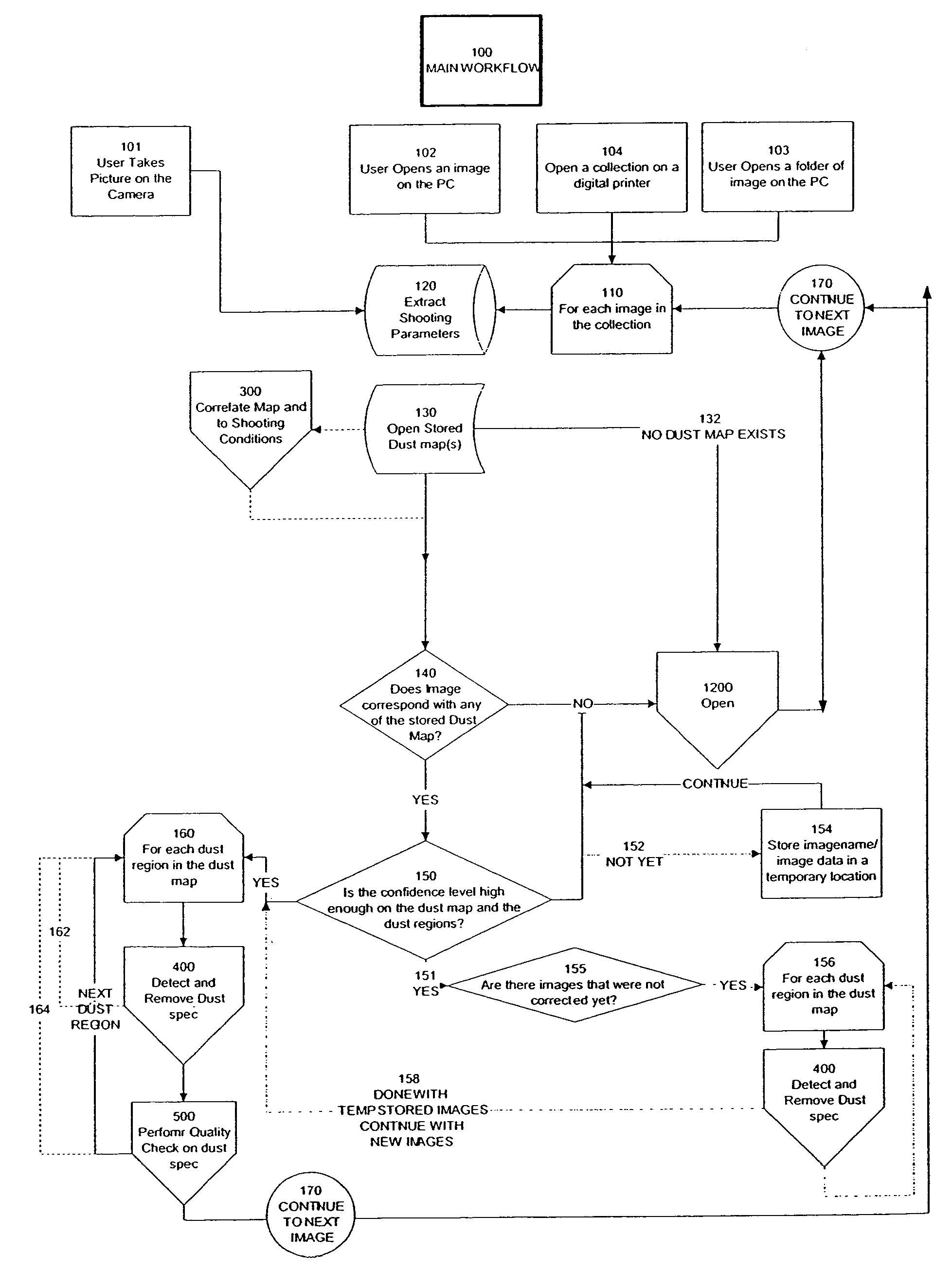
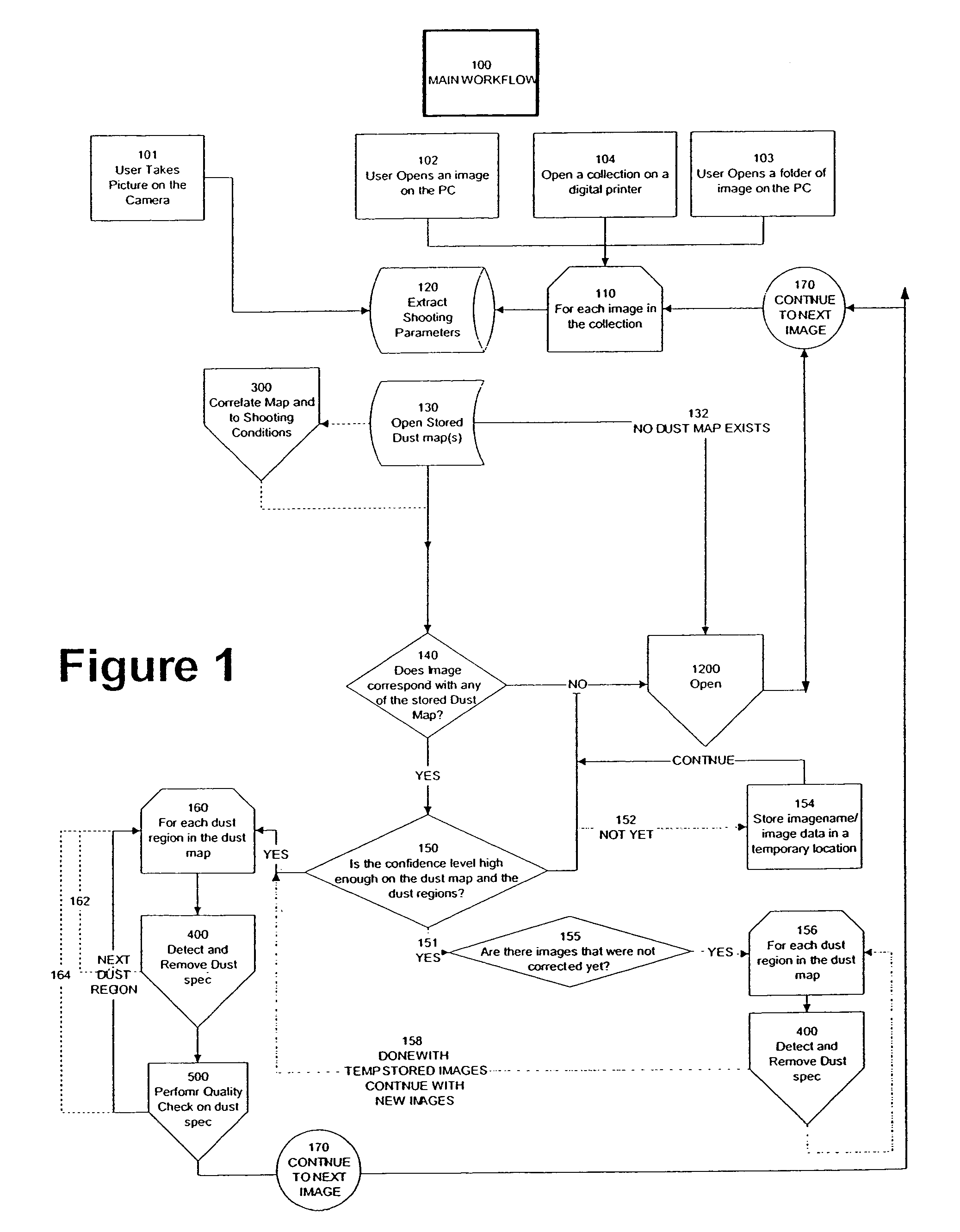
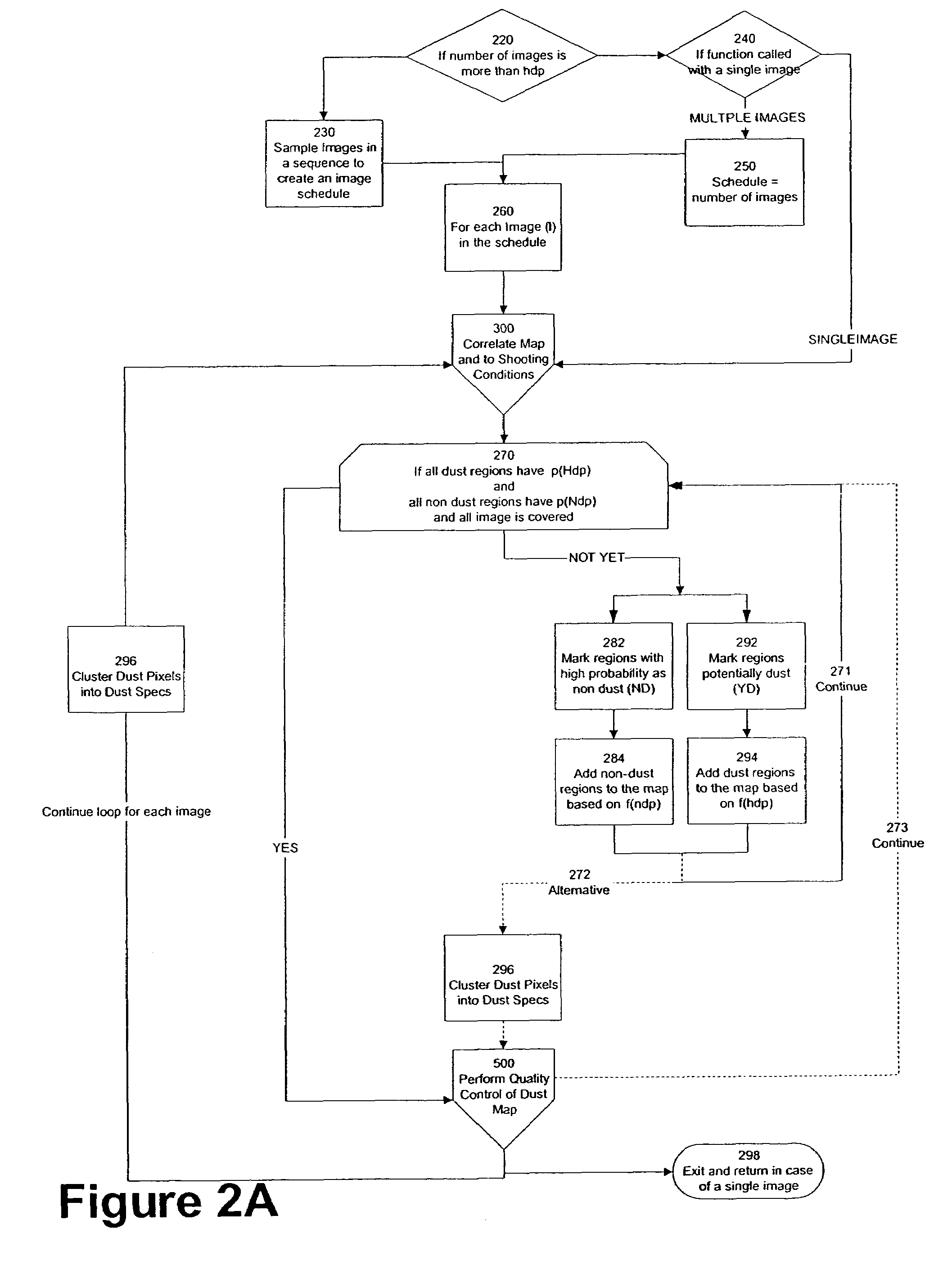
Automated statistical self-calibrating detection and removal of blemishes in digital images based on multiple occurrences of dust in images
A method automatically corrects dust artifact within images acquired by a system including a digital acquisition device including a lens assembly. Multiple original digital images are acquired with the digital acquisition device. Probabilities that certain pixels correspond to dust artifact regions within the images are determined based at least in part on a comparison of suspected dust artifact regions within two or more of the images. Probable dust artifact regions are associated with extracted parameter values relating to the lens assembly when the images were acquired. A statistical dust map is formed including mapped dust regions based on the determining and associating. Pixels corresponding to correlated dust artifact regions are corrected within further digitally-acquired images based on the associated statistical dust map.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
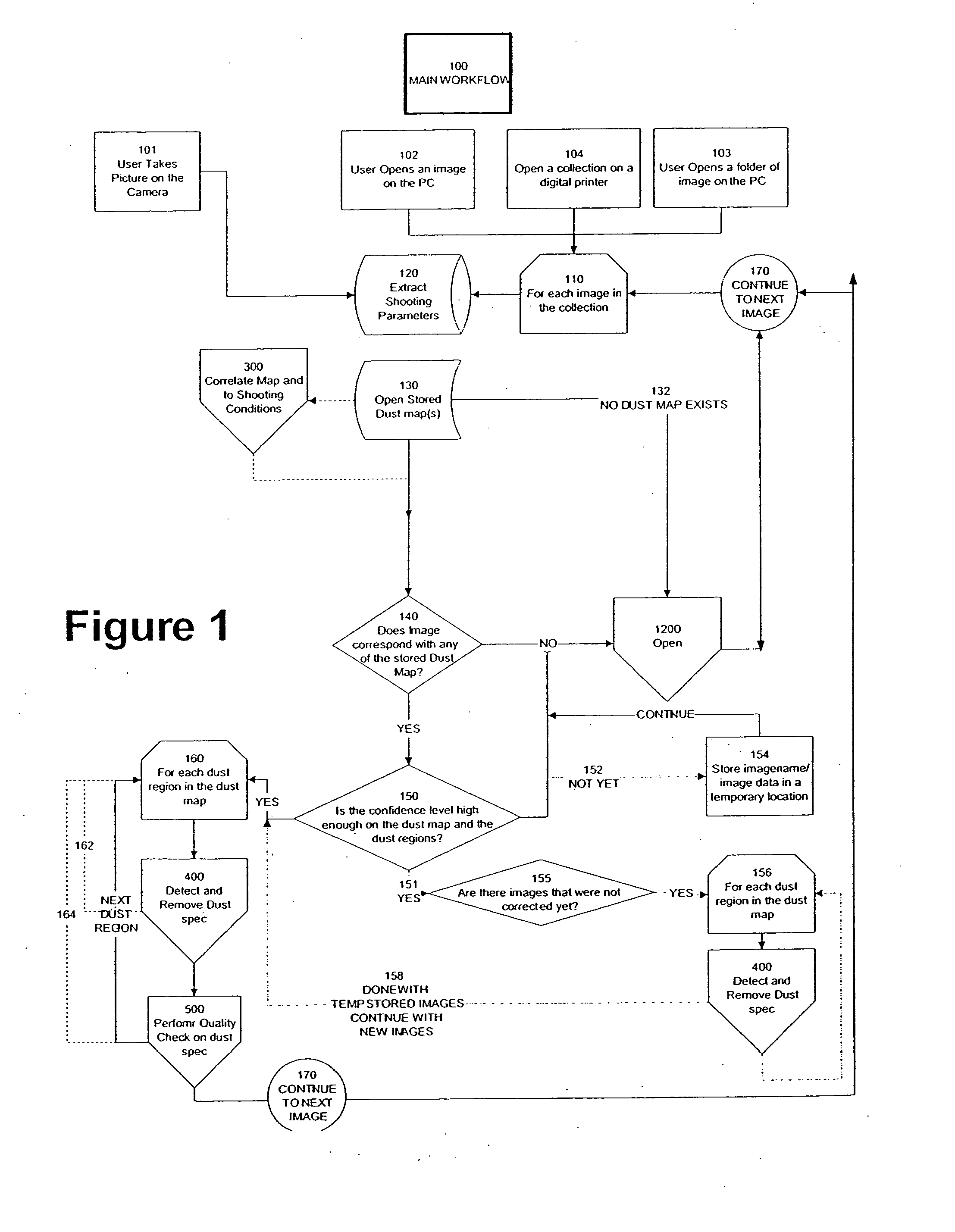
Automated statistical self-calibrating detection and removal of blemishes in digital images based on multiple occurrences of dust in images
A method automatically corrects dust artifact within images acquired by a system including a digital acquisition device including a lens assembly. Multiple original digital images are acquired with the digital acquisition device. Probabilities that certain pixels correspond to dust artifact regions within the images are determined based at least in part on a comparison of suspected dust artifact regions within two or more of the images. Probable dust artifact regions are associated with extracted parameter values relating to the lens assembly when the images were acquired. A statistical dust map is formed including mapped dust regions based on the determining and associating. Pixels corresponding to correlated dust artifact regions are corrected within further digitally-acquired images based on the associated statistical dust map.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
System and Method for Localization of Large Numbers of Fluorescent Markers in Biological Samples
ActiveUS20120193530A1Reduce respective collection solid angleExtensive collectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesFluorescenceQuantum dot
A method and system for the imaging and localization of fluorescent markers such as fluorescent proteins or quantum dots within biological samples is disclosed. The use of recombinant genetics technology to insert “reporter” genes into many species is well established. In particular, green fluorescent proteins (GFPs) and their genetically-modified variants ranging from blue to yellow, are easily spliced into many genomes at the sites of genes of interest (GoIs), where the GFPs are expressed with no apparent effect on the functioning of the proteins of interest (PoIs) coded for by the GoIs. One goal of biologists is more precise localization of PoIs within cells. The invention is a method and system for enabling more rapid and precise PoI localization using charged particle beam-induced damage to GFPs. Multiple embodiments of systems for implementing the method are presented, along with an image processing method relatively immune to high statistical noise levels.
Owner:FEI CO
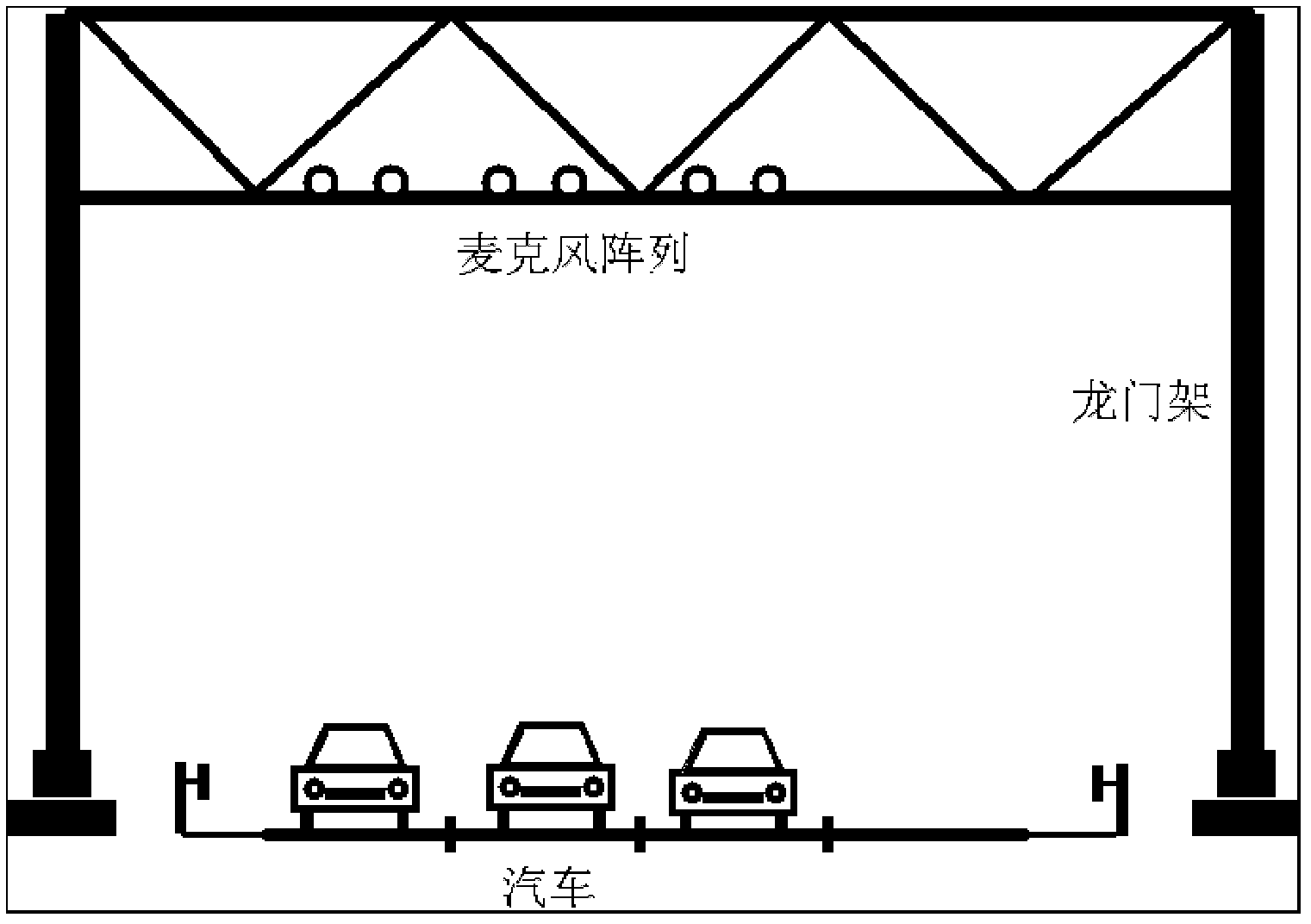
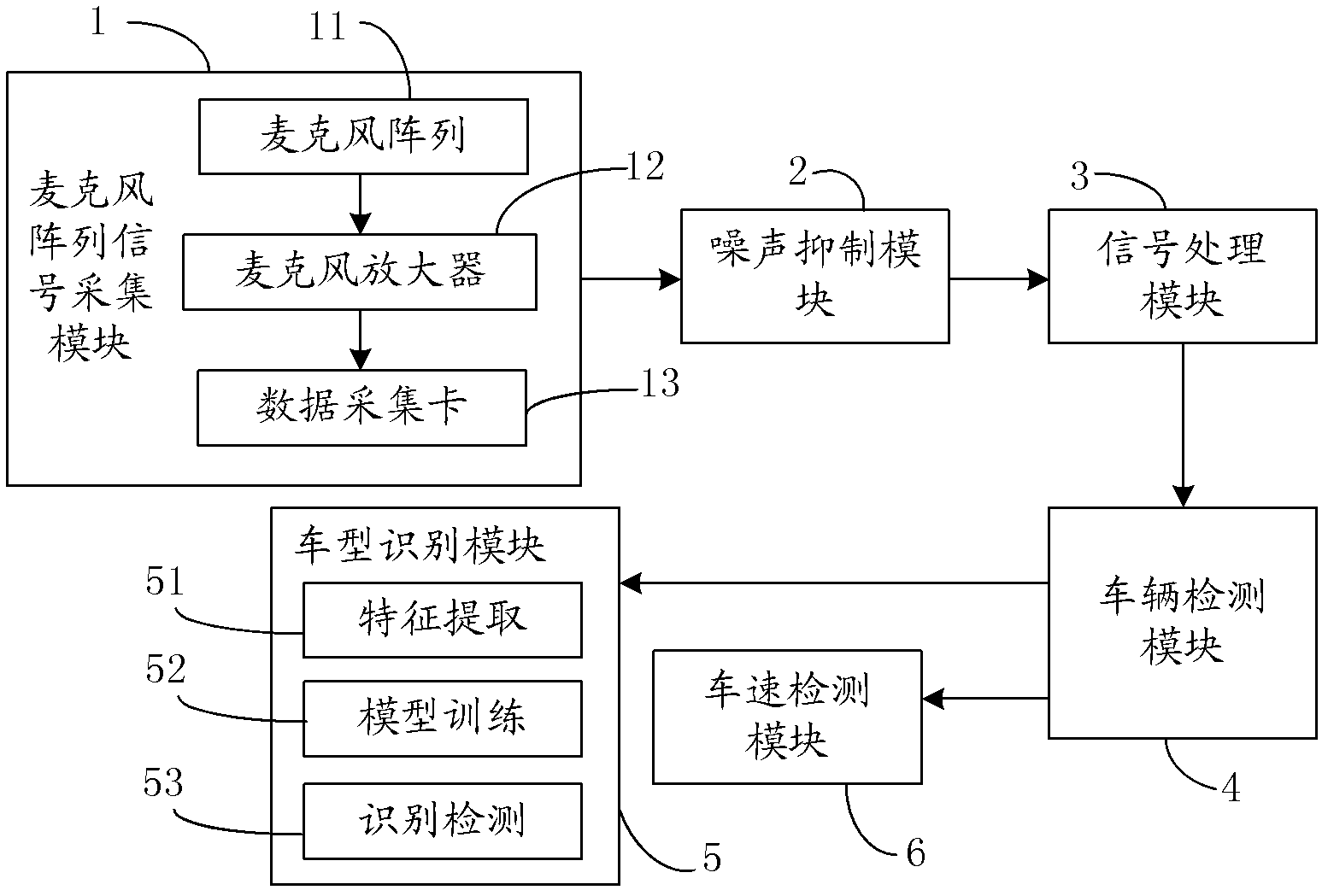
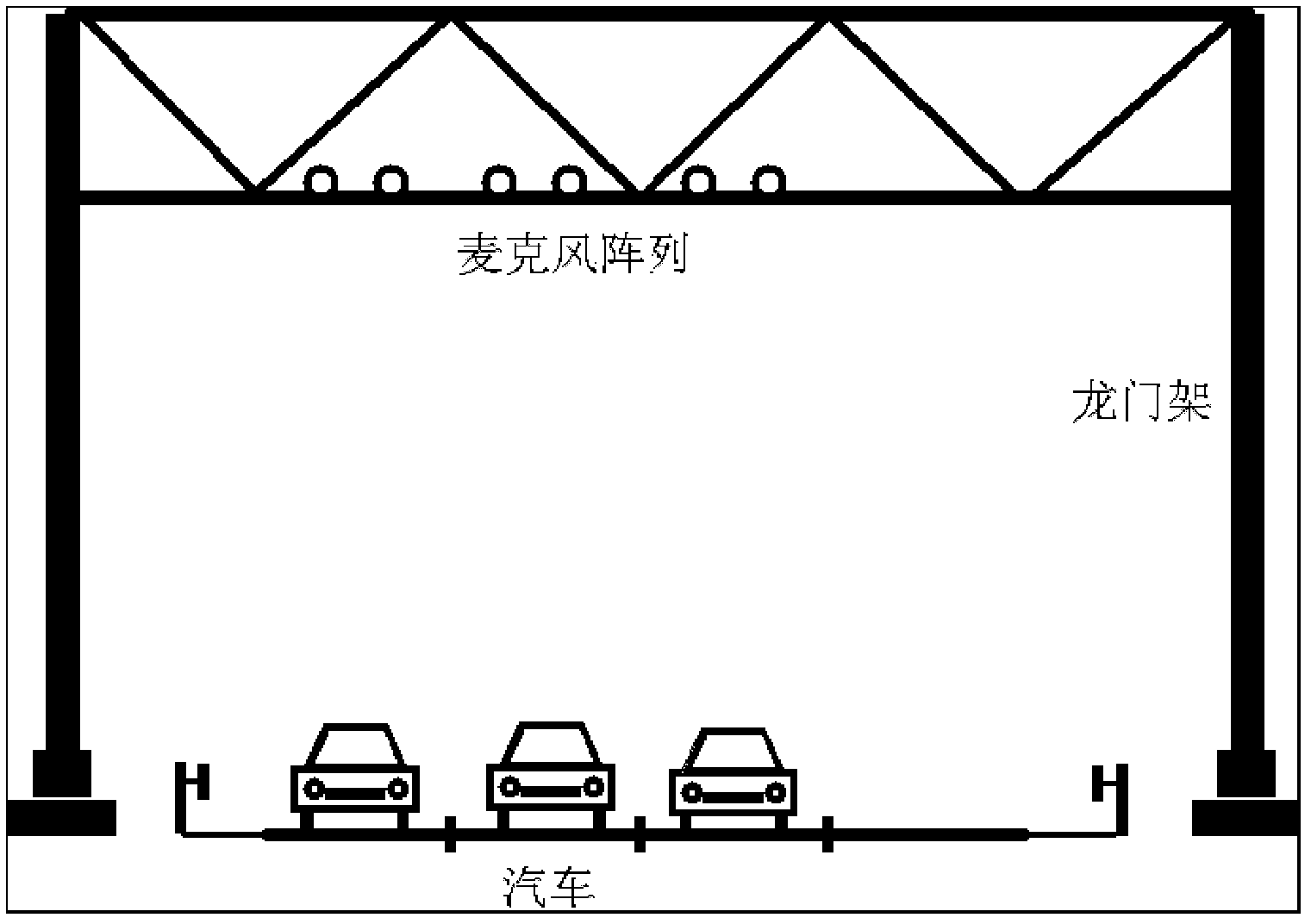
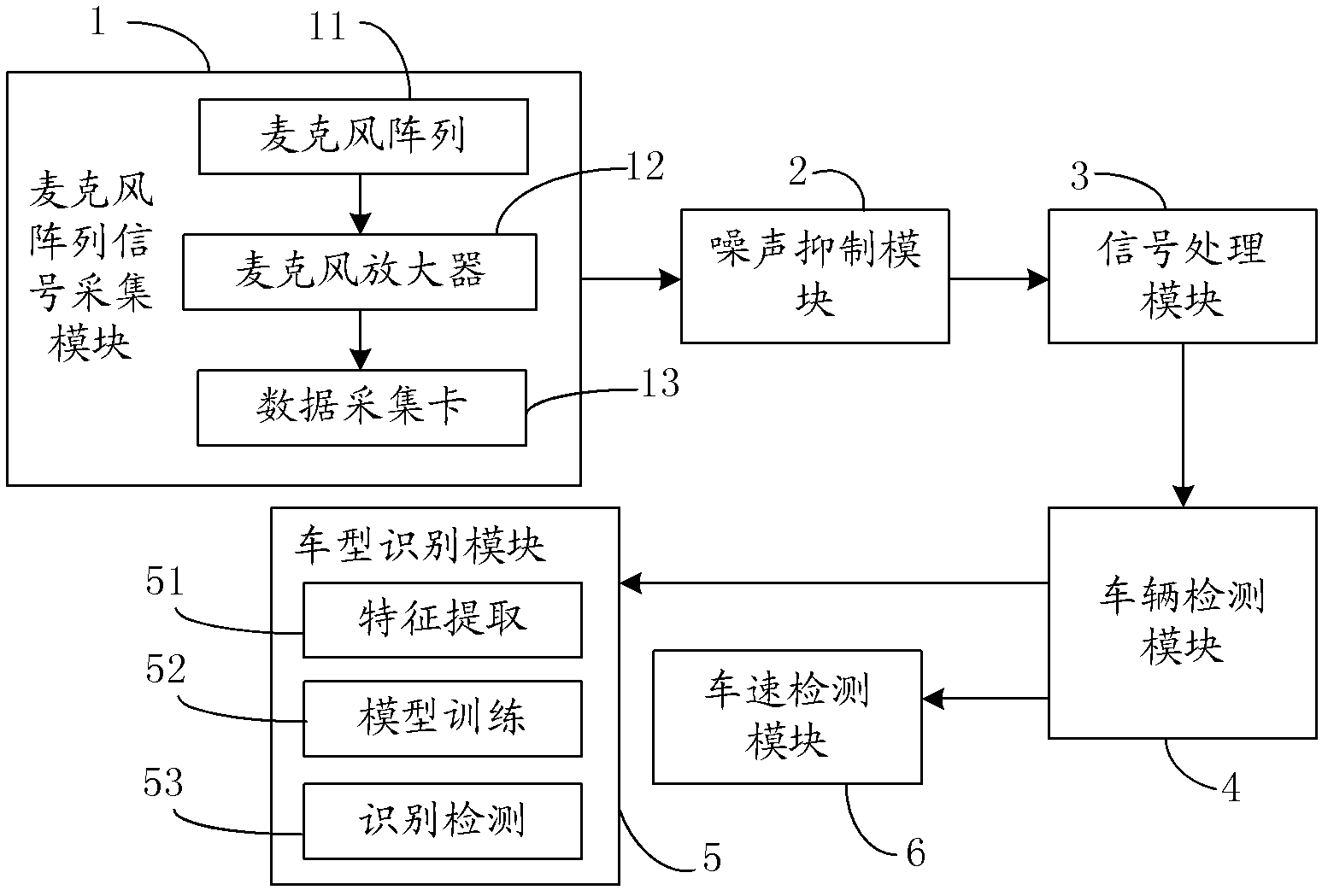
Expressway audio vehicle detection device and method thereof
ActiveCN102682765AOvercome limitationsLow costDevices using time traversedSpeech recognitionAmplitude compressionVehicle detection
The invention relates to an expressway audio vehicle detection device and a method thereof. By the aid of the detection device, a microphone array signal acquisition module acquires an audio signal on a lane, the audio signal is subjected to band-splitting filtering and framing through a signal processing module after being subjected to de-noising processing through a noise suppression module, cross-correlation processing is conducted among sub-band signals, an audio space spectrogram is obtained, a vehicle detection module tracks a track of the maximum value on the audio space spectrogram and judges whether a vehicle passes, and the vehicle type and the vehicle speed are obtained through a vehicle type recognition module and a vehicle speed recognition module if the vehicle passes. The detection method is based on the device, a minimum statistical noise estimation method of the adaptive window length is adopted, the signal which is subjected to noise suppression processing is subjected to band-splitting filtering and framing processing, then cross-correlation processing is conducted among same sub-band signals, cross-correlation results are summed after being subjected to amplitude compression and are unfolded along a timer shaft, and an audio signal space-time spectrum is obtained. The method and the device have the advantages of being low in cost, low in energy consumption,easy to construct, interference resisting, capable of working in all weather and the like.
Owner:TAIKE HIGHWAY SCI & TECH INST BEIJING CITY +1
Short-time wind speed forecasting method based on neural network
InactiveCN101788692AGood trend forecasting effectPseudo-periodicWeather condition predictionBiological neural network modelsMoving averageOriginal data
The invention discloses a short-time wind speed forecasting method based on a neural network. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) recording the moving average observing values of the wind speed, wind direction, temperature and air pressure on the same district once at the interval of 10 minutes, and ordering the observed data in a time sequence from front to back to obtain original wind speed data; (2) calculating the data of the adjacent time according to the time sequence, and generating an original wind speed added value sequence; (3) entering the original airspeed added value into a BP artificial neural network to construct a wind speed added value neural network model, calculating and counting an original wind speed added value tendency by utilizing the BP artificial neural network, training a RP artificial neural network by respectively utilizing the original wind speed added value and the original wind speed added value tendency as the original data, and obtaining a wind speed added value predicting value and a wind speed added value error tendency; (4) adding the wind speed added value predicting value into statistical noise to reduce and generate a wind speed predicting value; (5) carrying out moving filtering on the wind speed predicting value; and (6) obtaining the wind speed predicting value 4 hours in advance.
Owner:NORTHWEST CHINA GRID
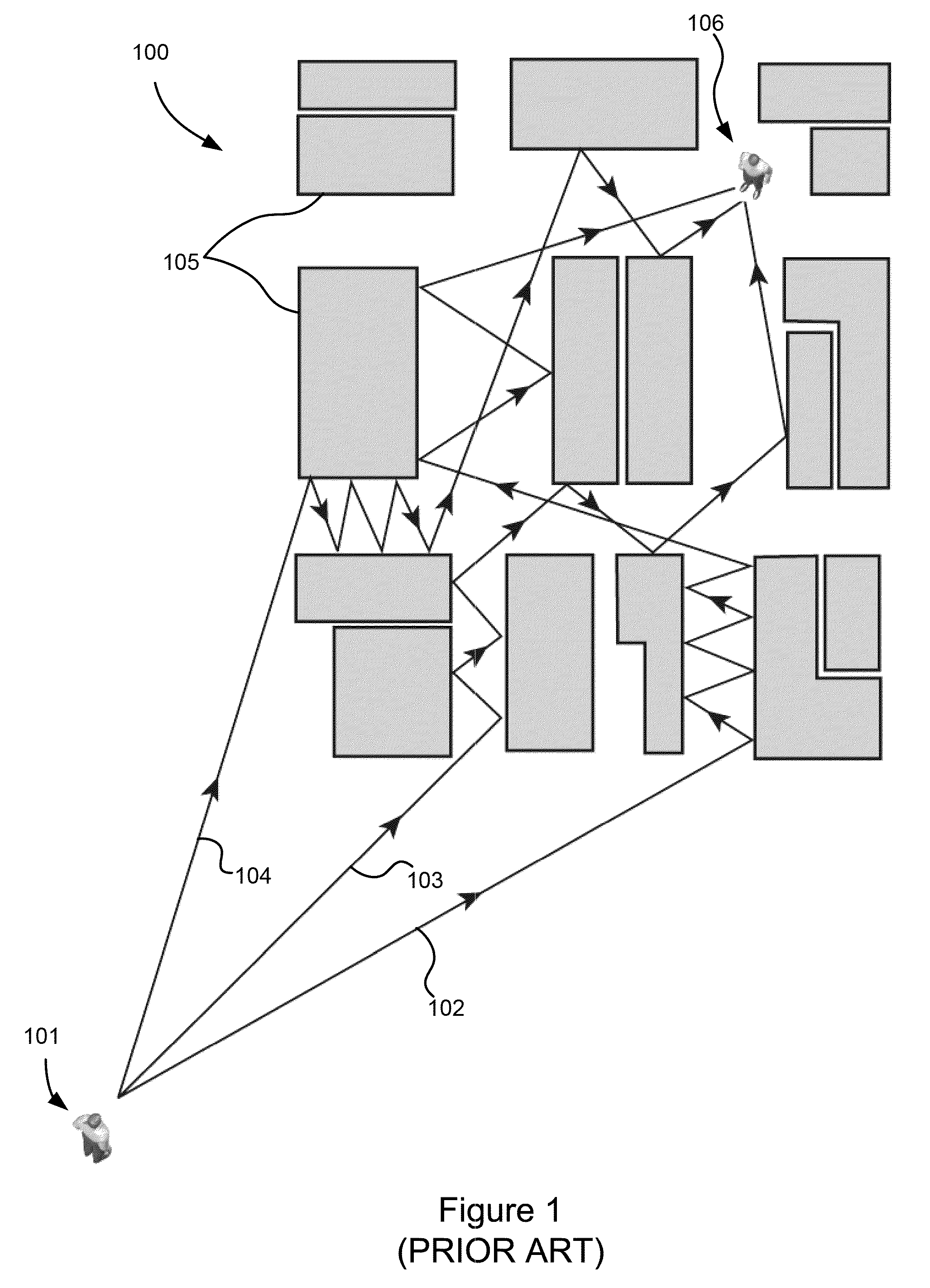
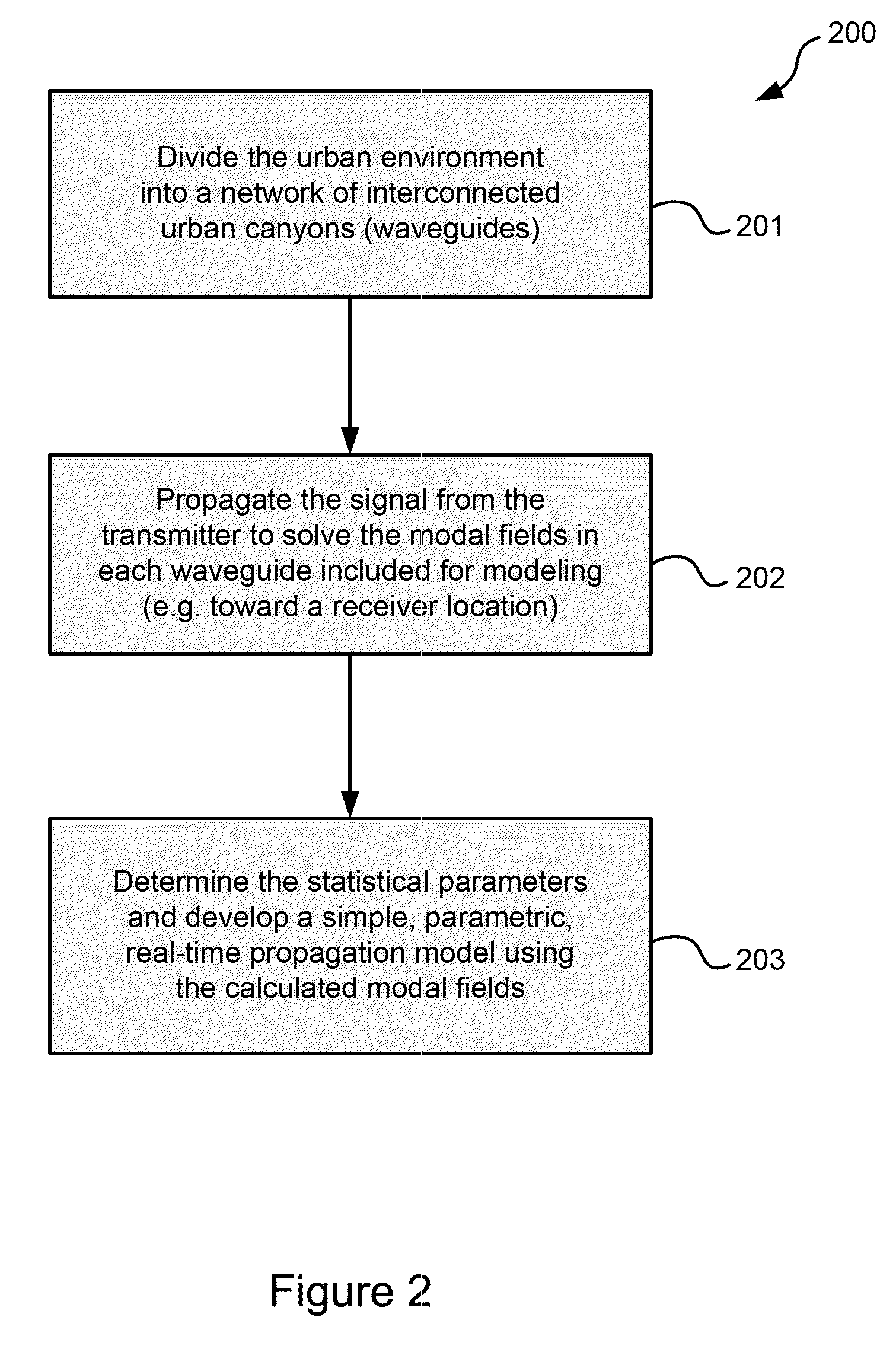
Physics-based statistical model and simulation method of RF propagation in urban environments
InactiveUS7796983B2Accurate acquisitionSimulate the realTransmission monitoringNetwork planningFrequency spectrumCanyon
A physics-based statistical model and simulation / modeling method and system of electromagnetic wave propagation (wireless communication) in urban environments. In particular, the model is a computationally efficient close-formed parametric model of RF propagation in an urban environment which is extracted from a physics-based statistical wireless channel simulation method and system. The simulation divides the complex urban environment into a network of interconnected urban canyon waveguides which can be analyzed individually; calculates spectral coefficients of modal fields in the waveguides excited by the propagation using a database of statistical impedance boundary conditions which incorporates the complexity of building walls in the propagation model; determines statistical parameters of the calculated modal fields; and determines a parametric propagation model based on the statistical parameters of the calculated modal fields from which predictions of communications capability may be made.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
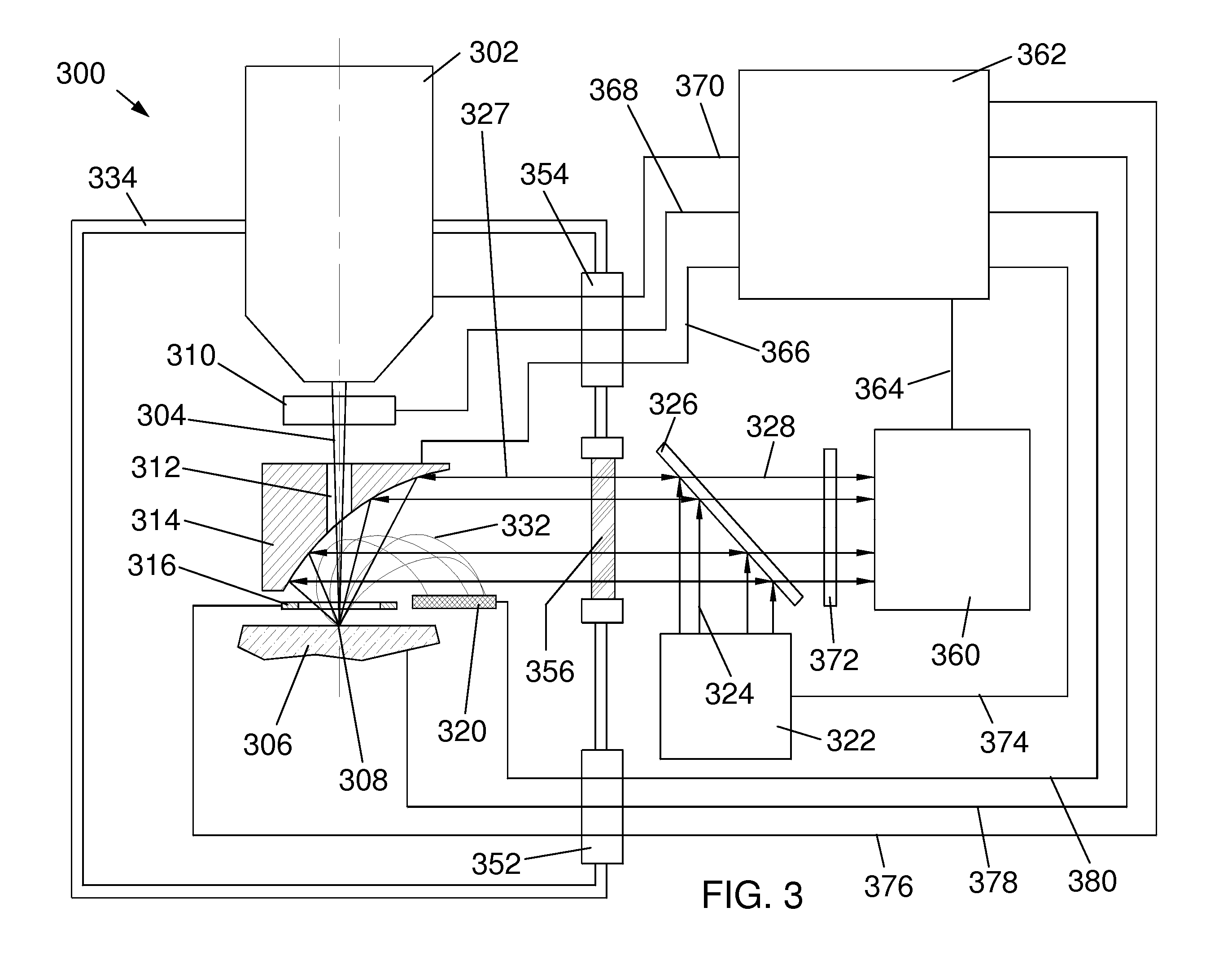
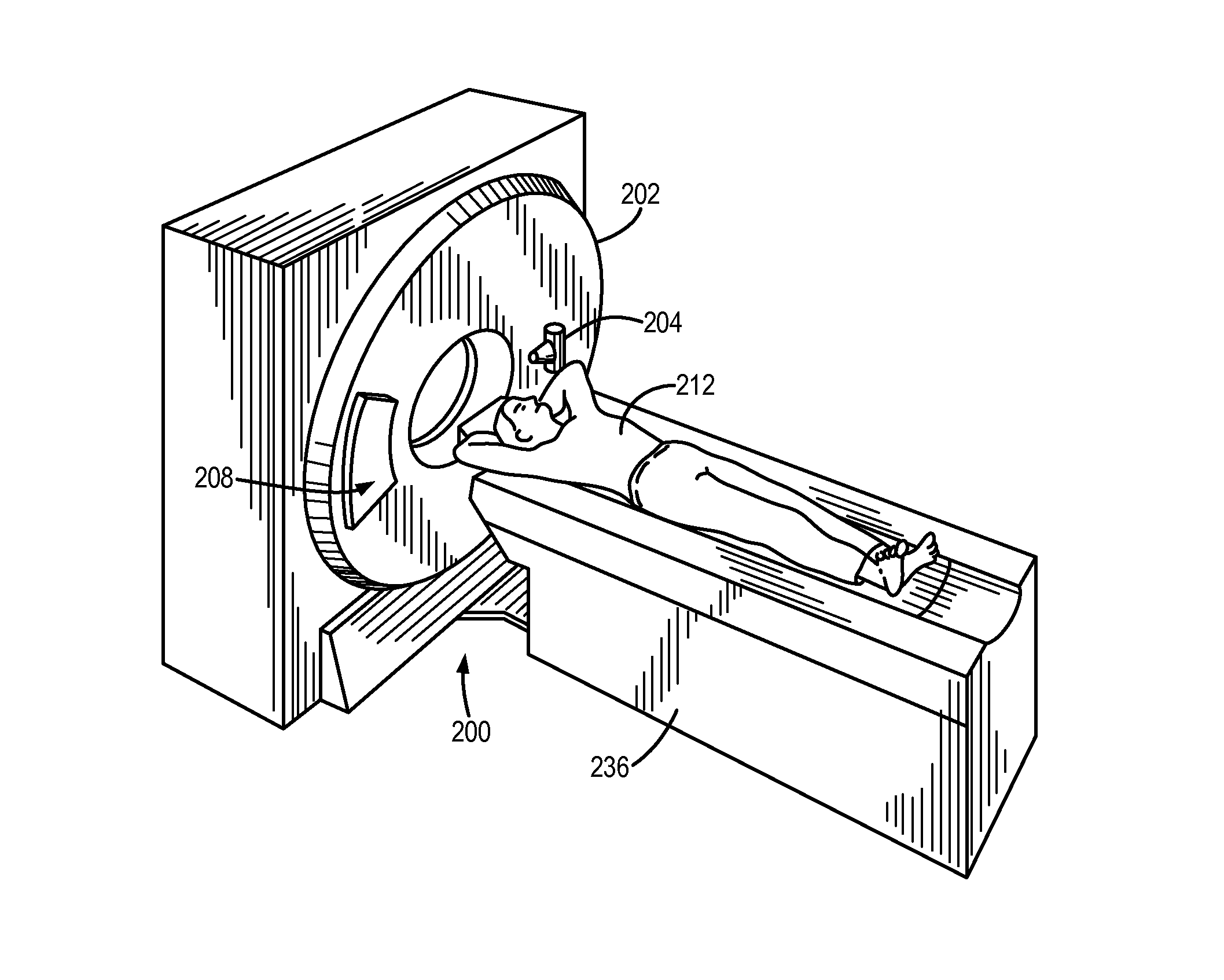
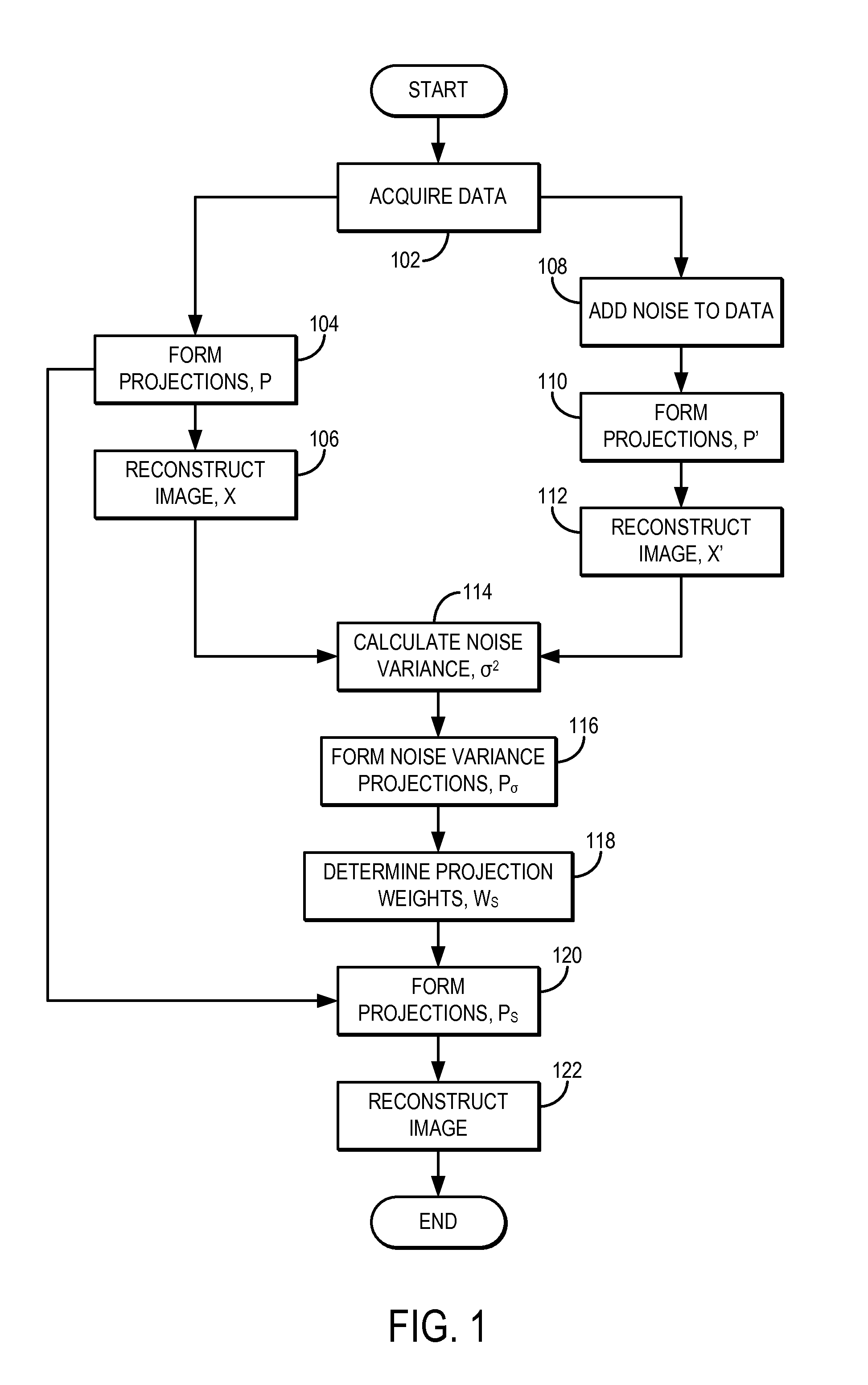
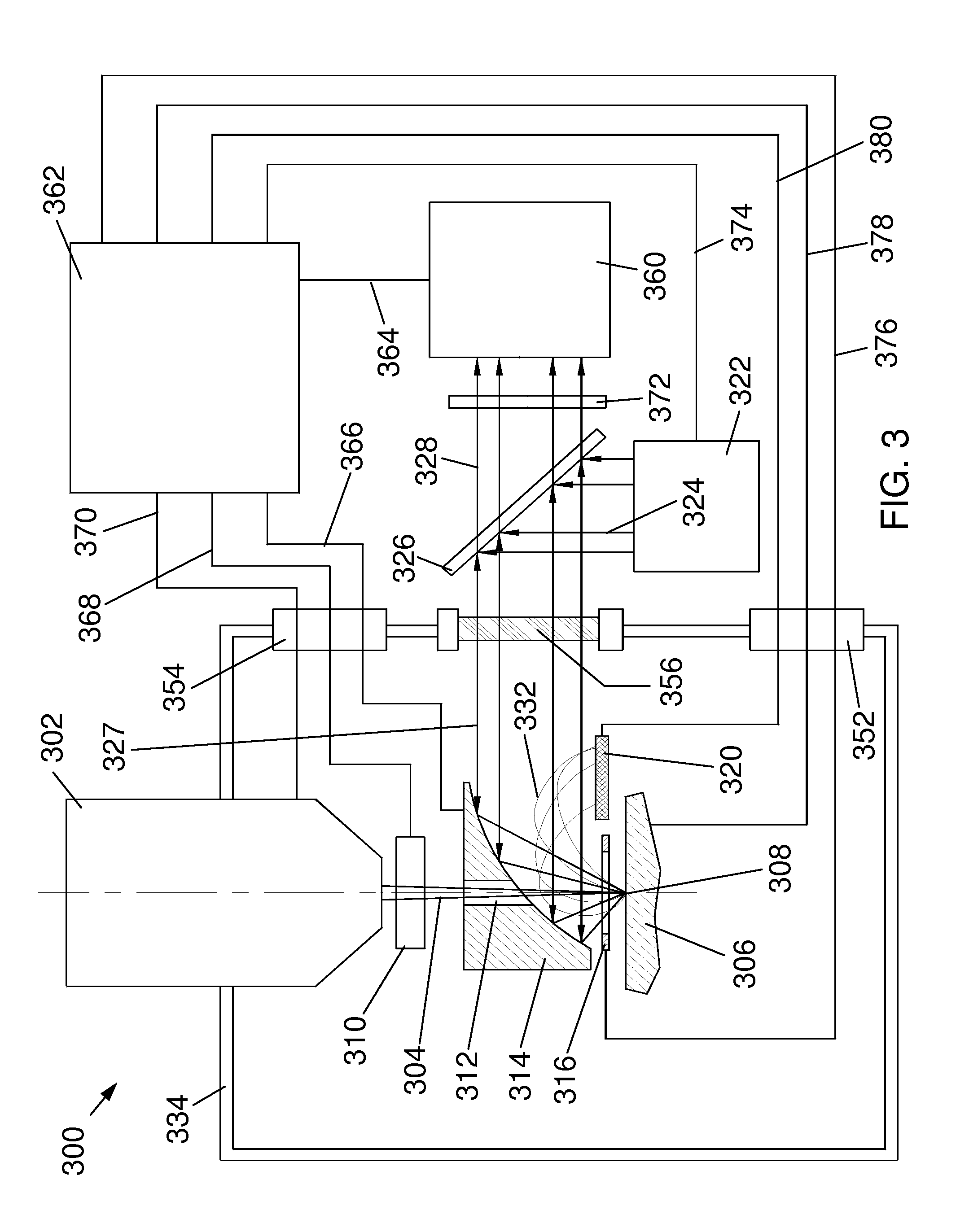
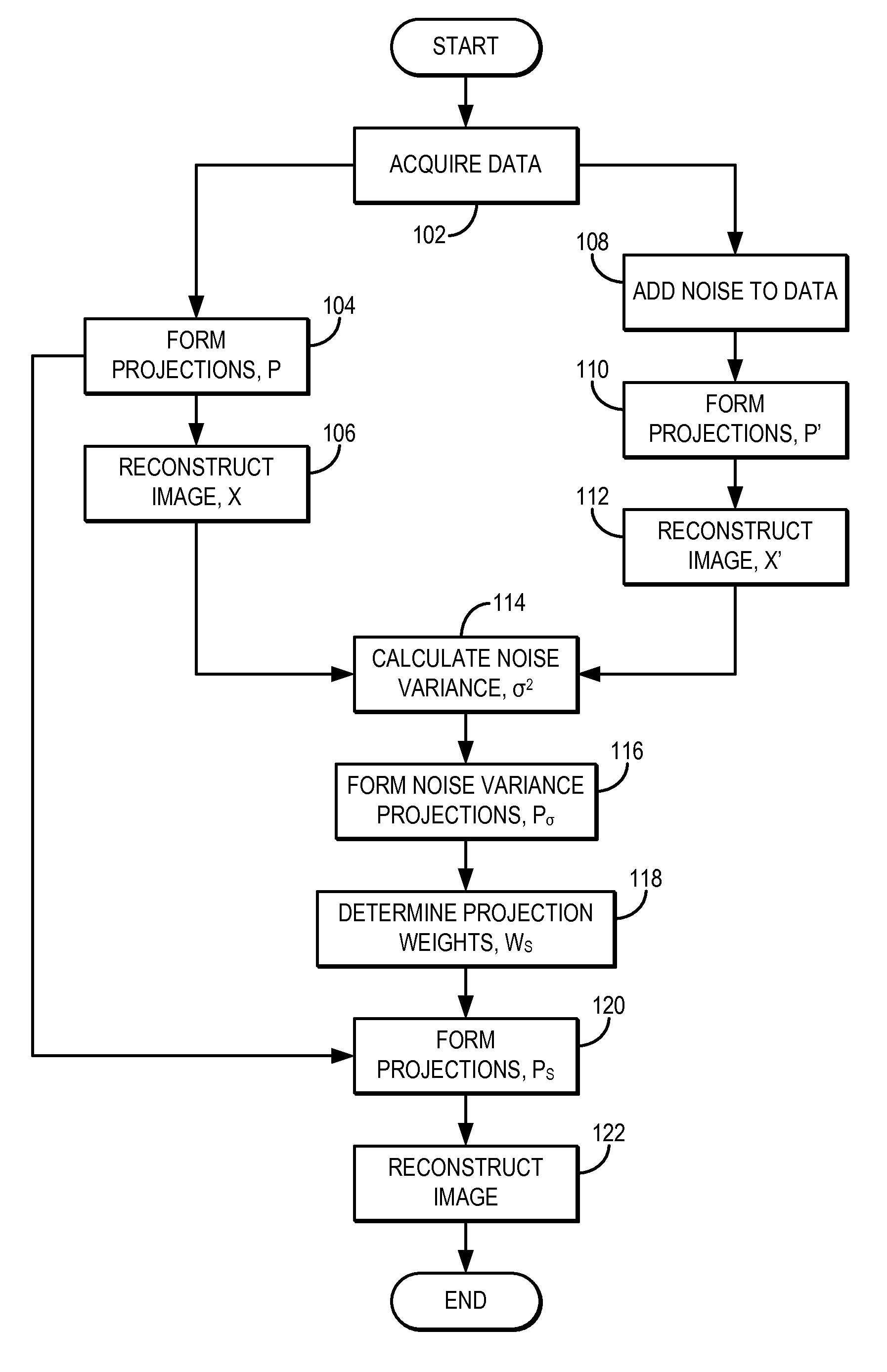
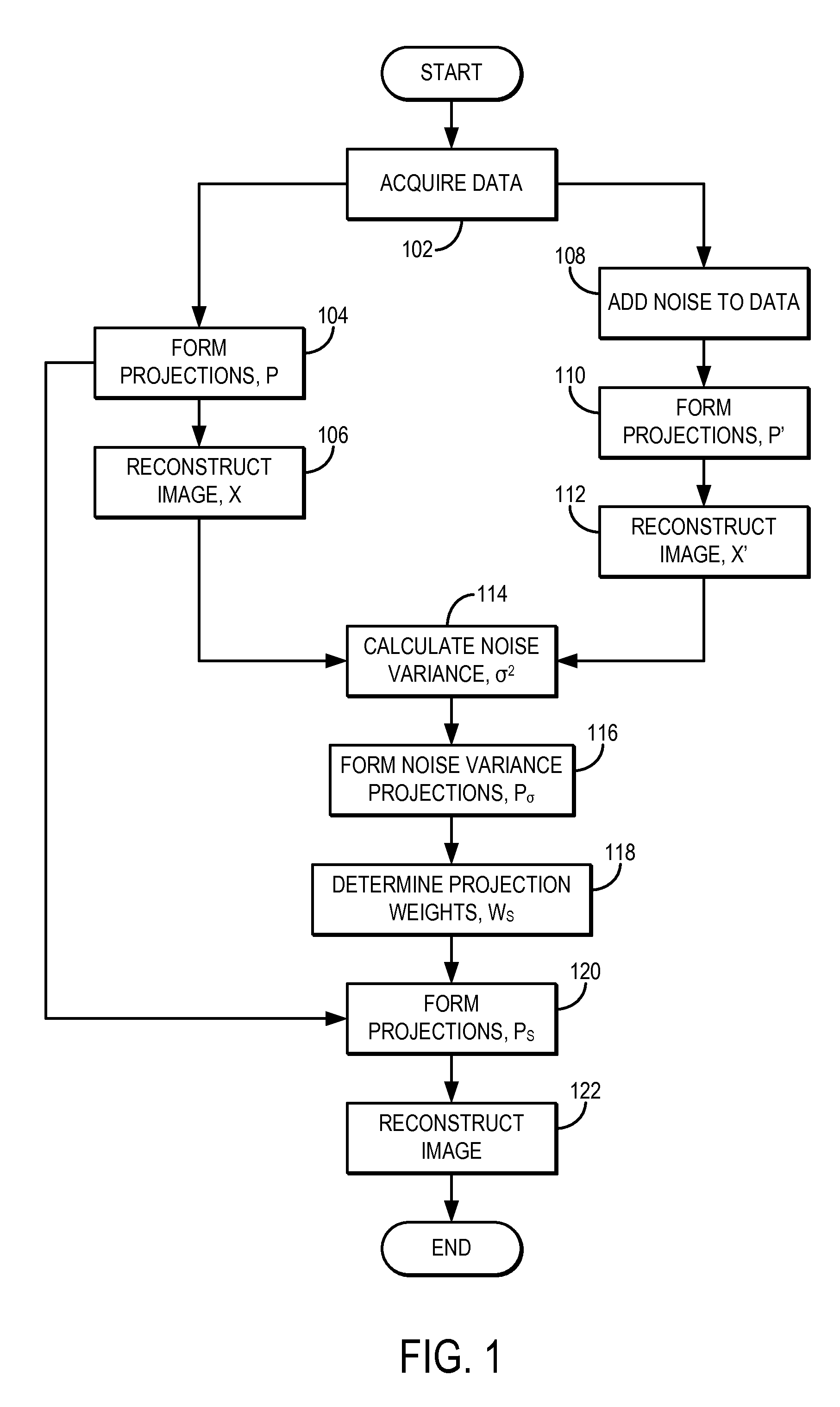
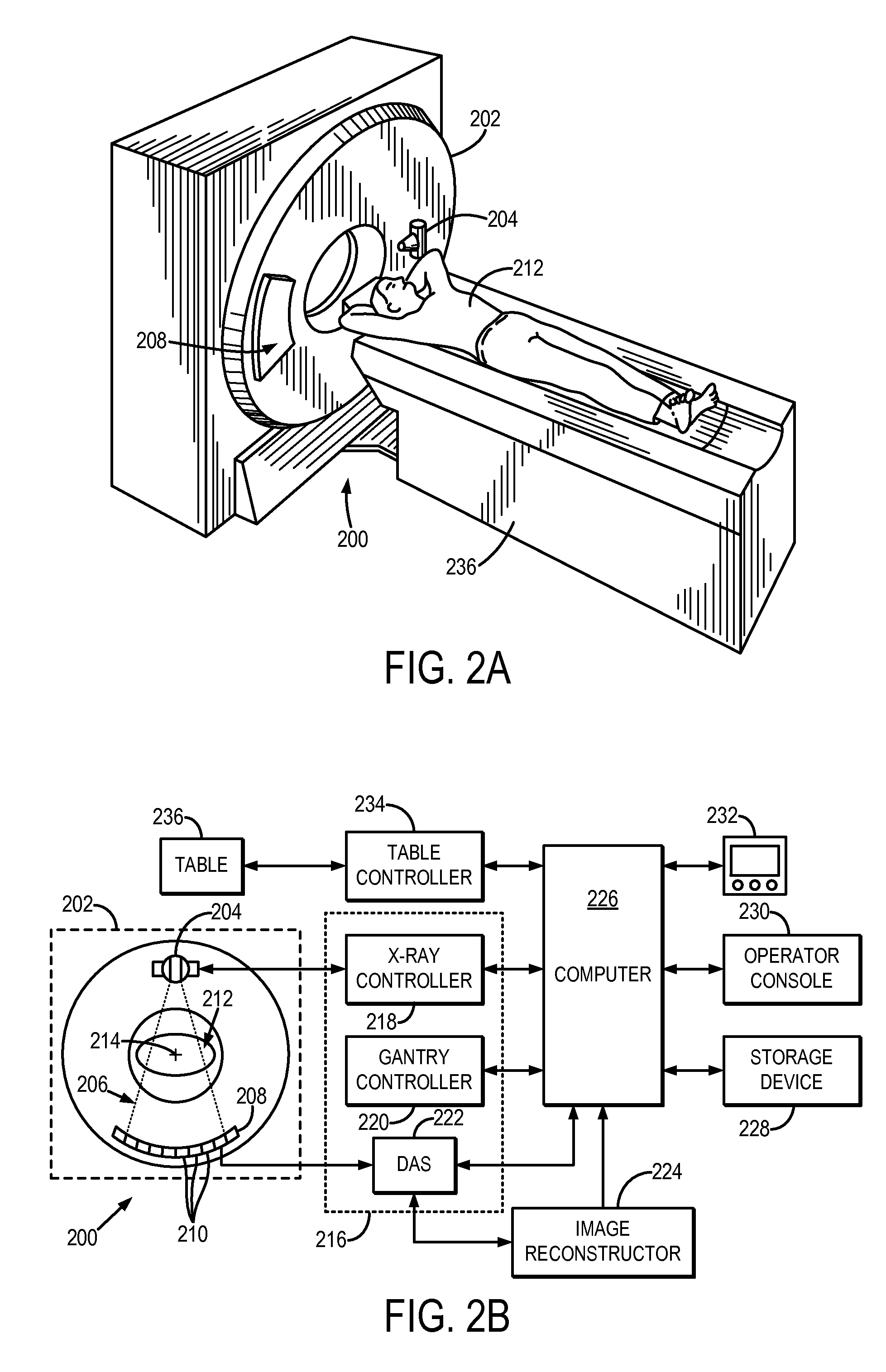
System and method for estimating a statistical noise map in x-ray imaging applications
Described here are a system and method for producing a statistical noise map that indicates the noise present in data acquired with an x-ray imaging system, such as an x-ray computed tomography system, an x-ray tomosynthesis system, a C-arm x-ray imaging system, and so on. In general, an image is reconstructed from the acquired data using, for example, any standard filtered back projection (“FBP”) image reconstruction algorithm. This image is used as a base line to estimate a noise standard distribution map. The raw projection data represents a typical measurement among many repeated measurements under the same experimental conditions; therefore, the measured projection data can be used to numerically generate an ensemble of many (e.g., twenty or more) noisy projection data sets. These noisy projection data sets are then used to reconstruct noisy images and from these noisy images and the original image, the statistical noise map can be computed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
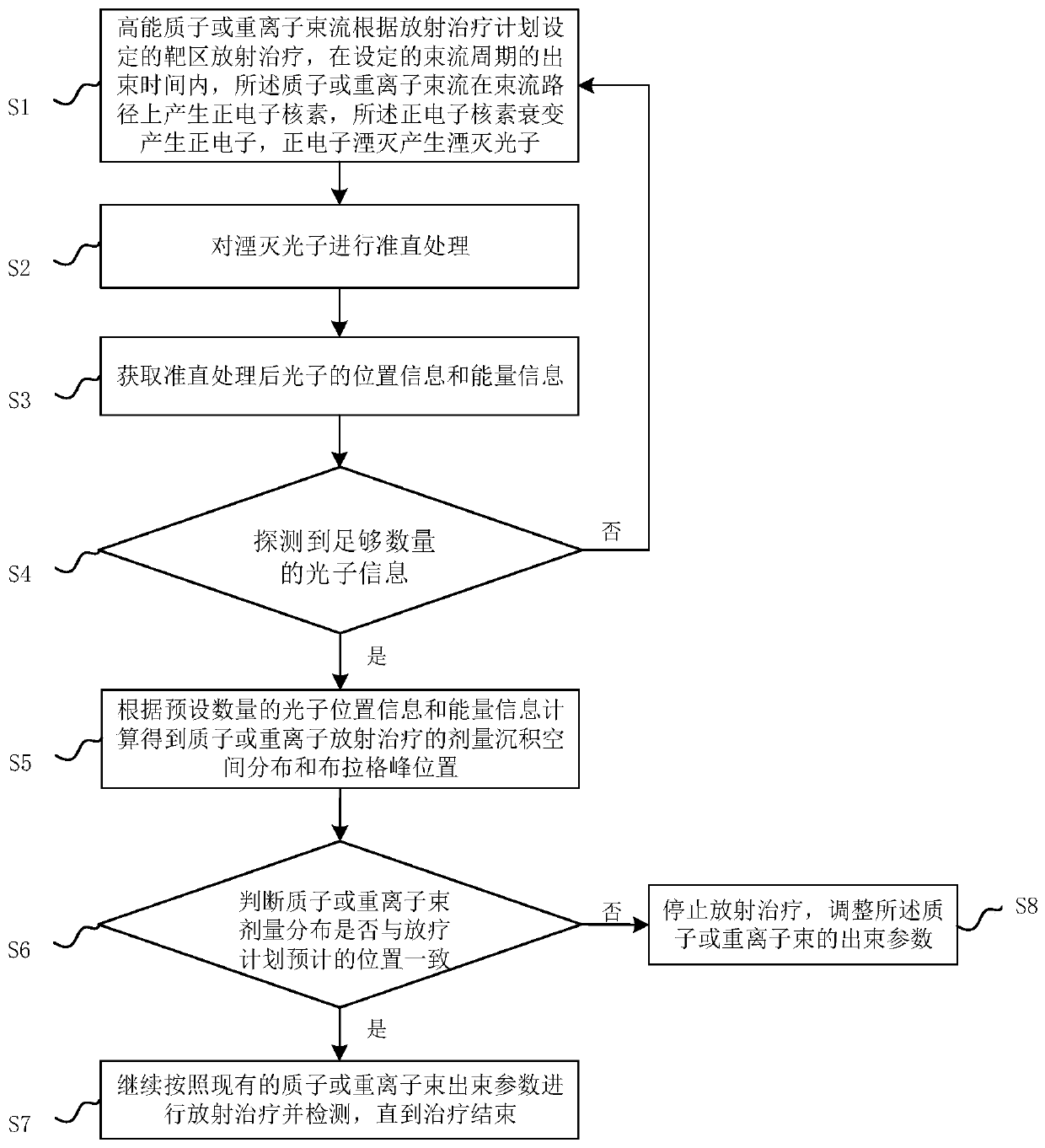
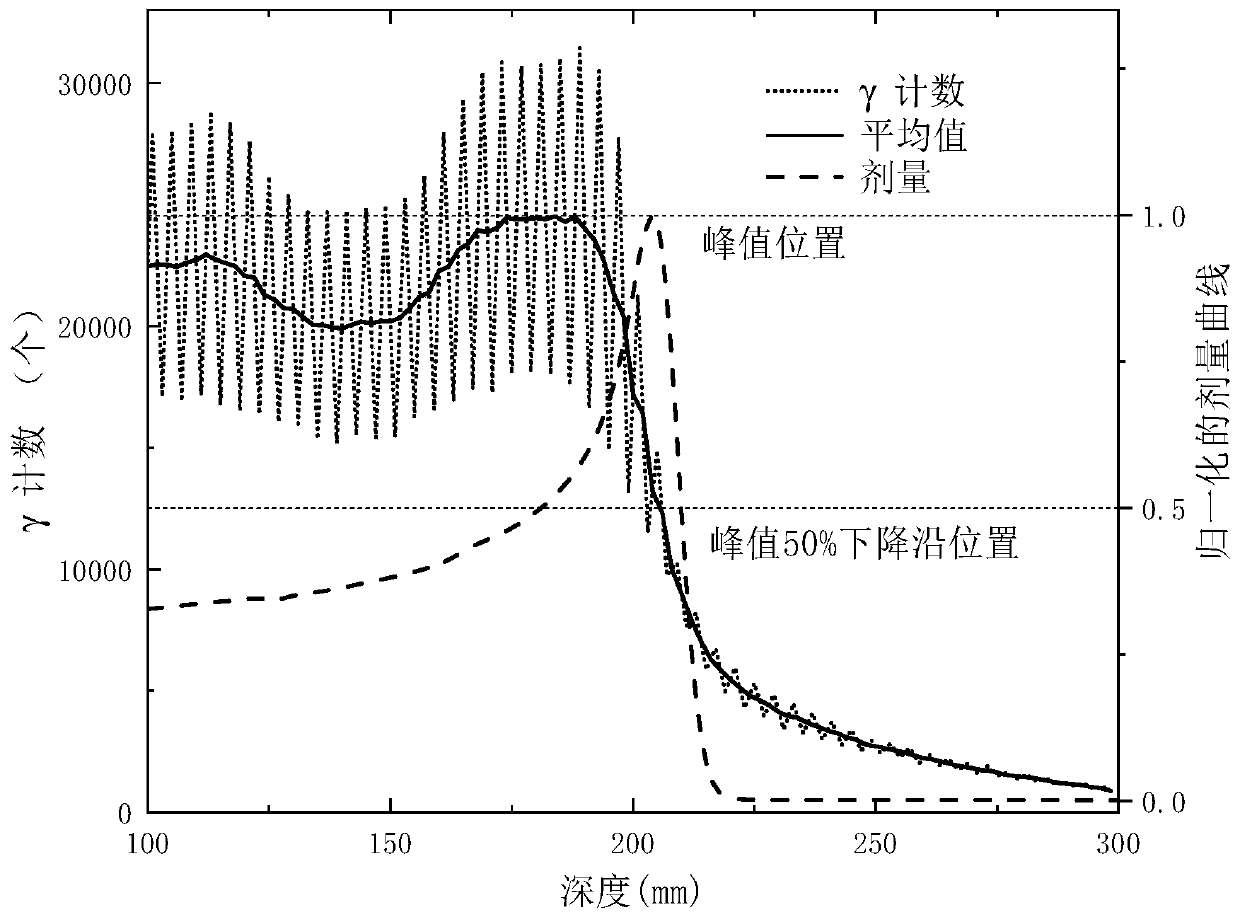
Method and system for real-time monitoring proton or heavy ion radiotherapy doses
InactiveCN110270014AHigh precisionImprove detection efficiencyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyHeavy particleHeavy Ion Radiotherapy
The invention relates to a method and a system for real-time monitoring proton or heavy ion radiotherapy heavy particle radiotherapy doses. The monitoring method utilizes distribution information of positron radionuclide produced during the high-energy proton or heavy ion radiotherapy, and measures position and energy information of annihilation photons in the intermittent time of beams according to beam cycles of protons or heavy ions to obtain dose deposition spatial distributions in the proton or heavy ion radiotherapy, thereby realizing the monitoring of dose distributions of proton or heavy ion beams. Compared with the traditional instantaneous gamma measurement method, the method has a higher detection efficiency, and the method effectively reduces statistical noise, and improves accuracy of the dose deposition of the proton or heavy ion radiotherapy; compared with the traditional positron emission tomography method, the method can realize a faster one-dimensional distribution of dose along the beam direction by carrying out a collimation treatment on the annihilation photons along the beam direction and then detecting the position and energy information of the photons, thus the method is conducive to improving monitoring efficiency.
Owner:彭浩
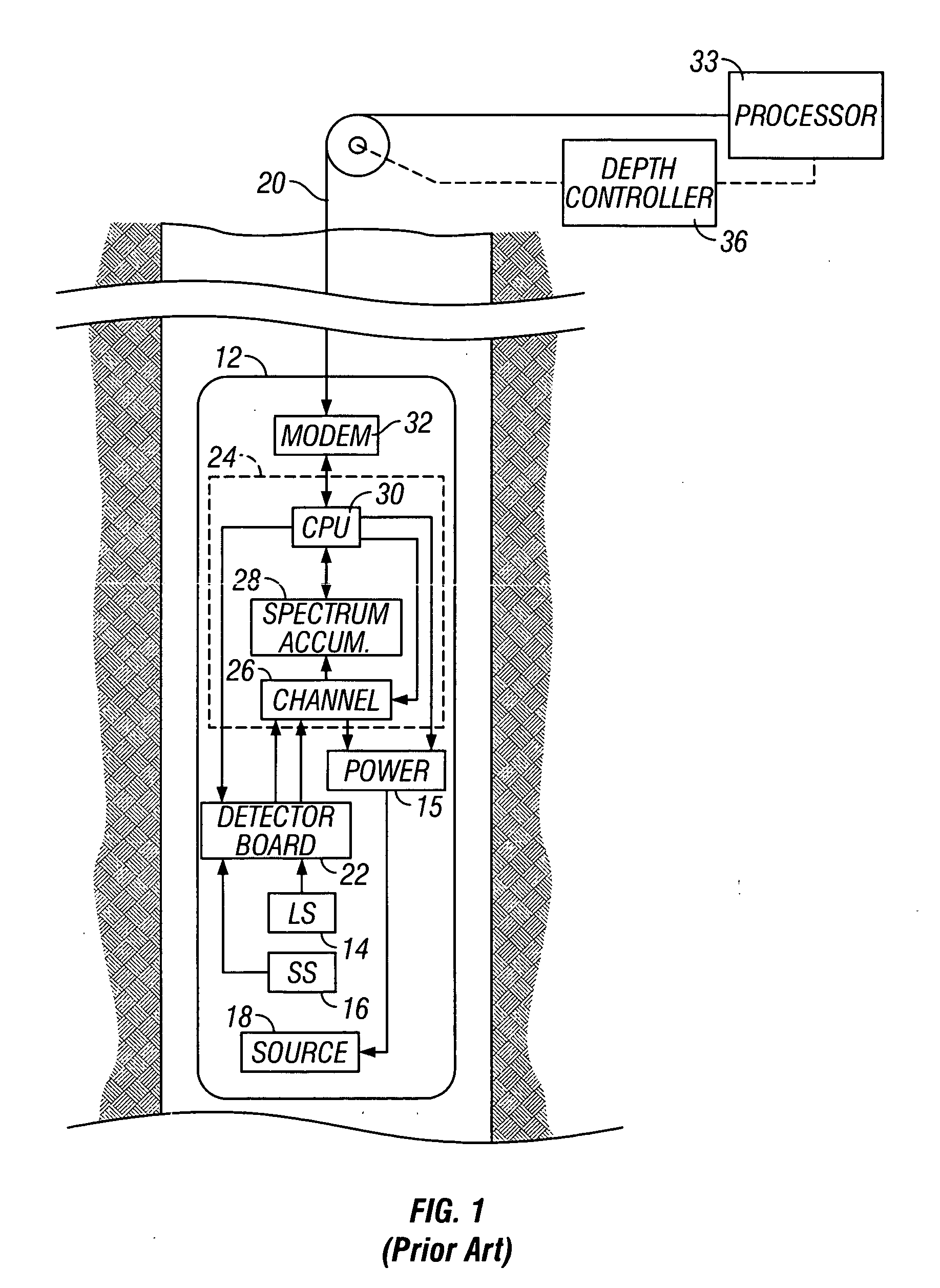
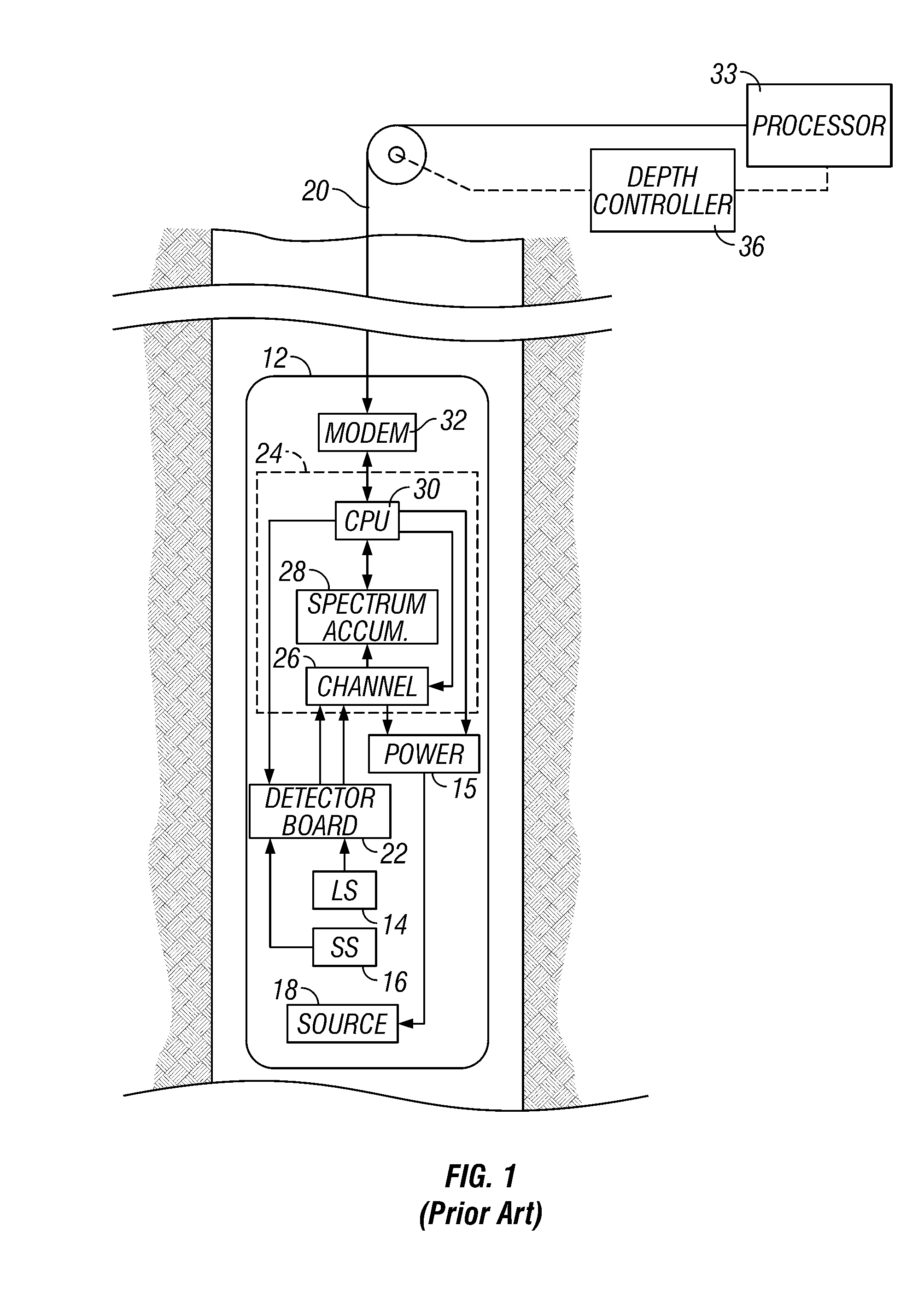
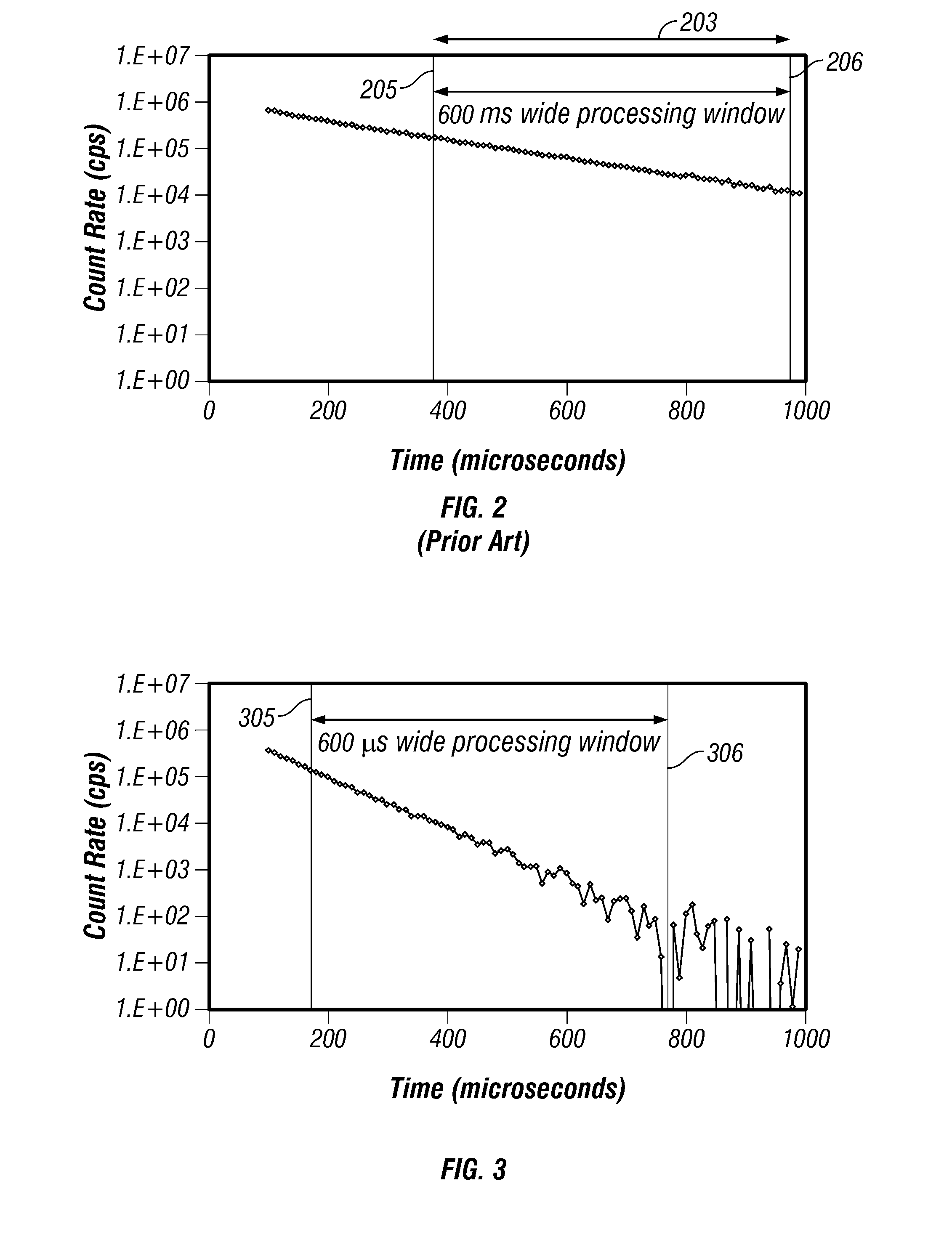
Method and apparatus for determining the thermal neutron capture cross-section of a subsurface formation from a borehole
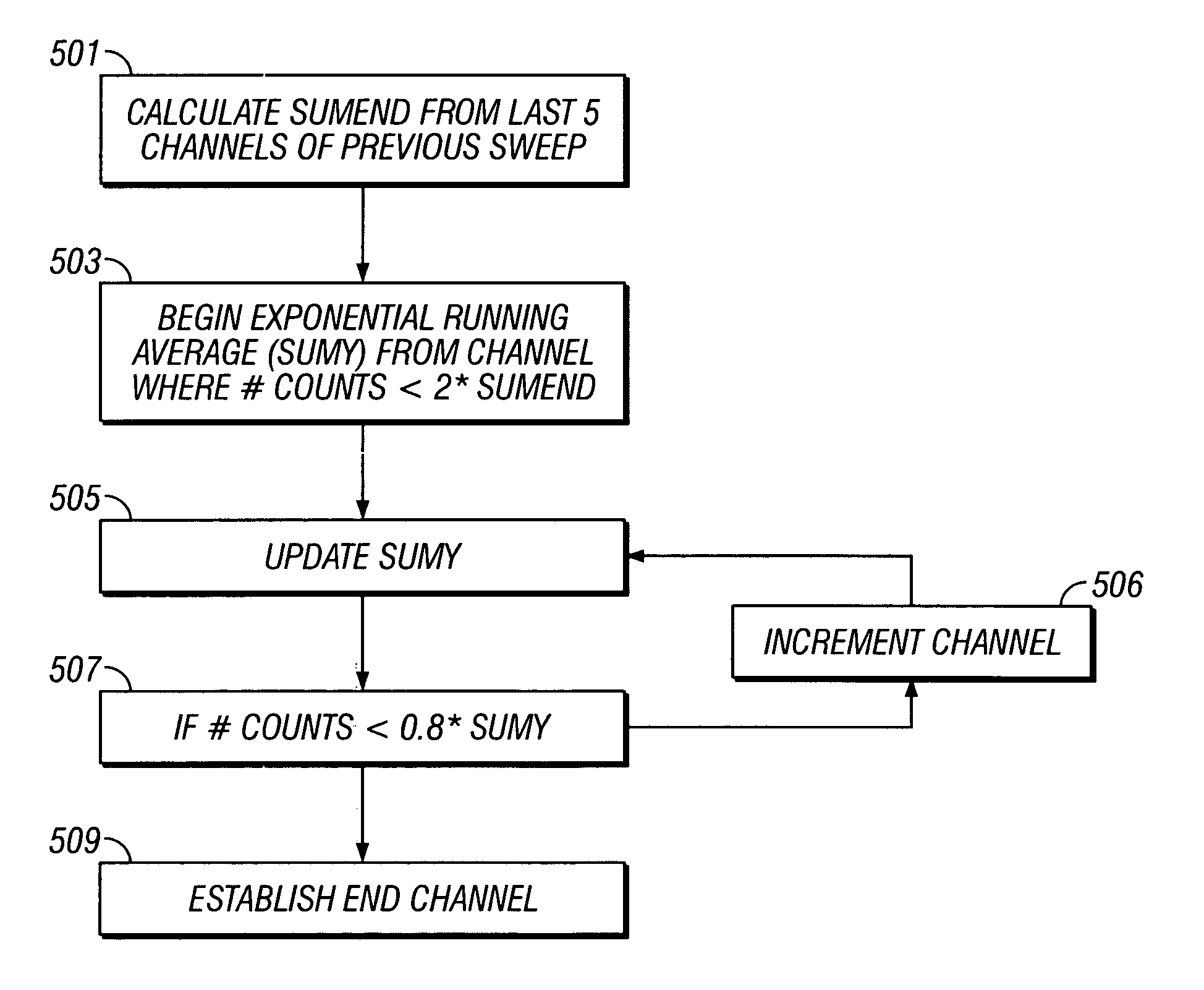
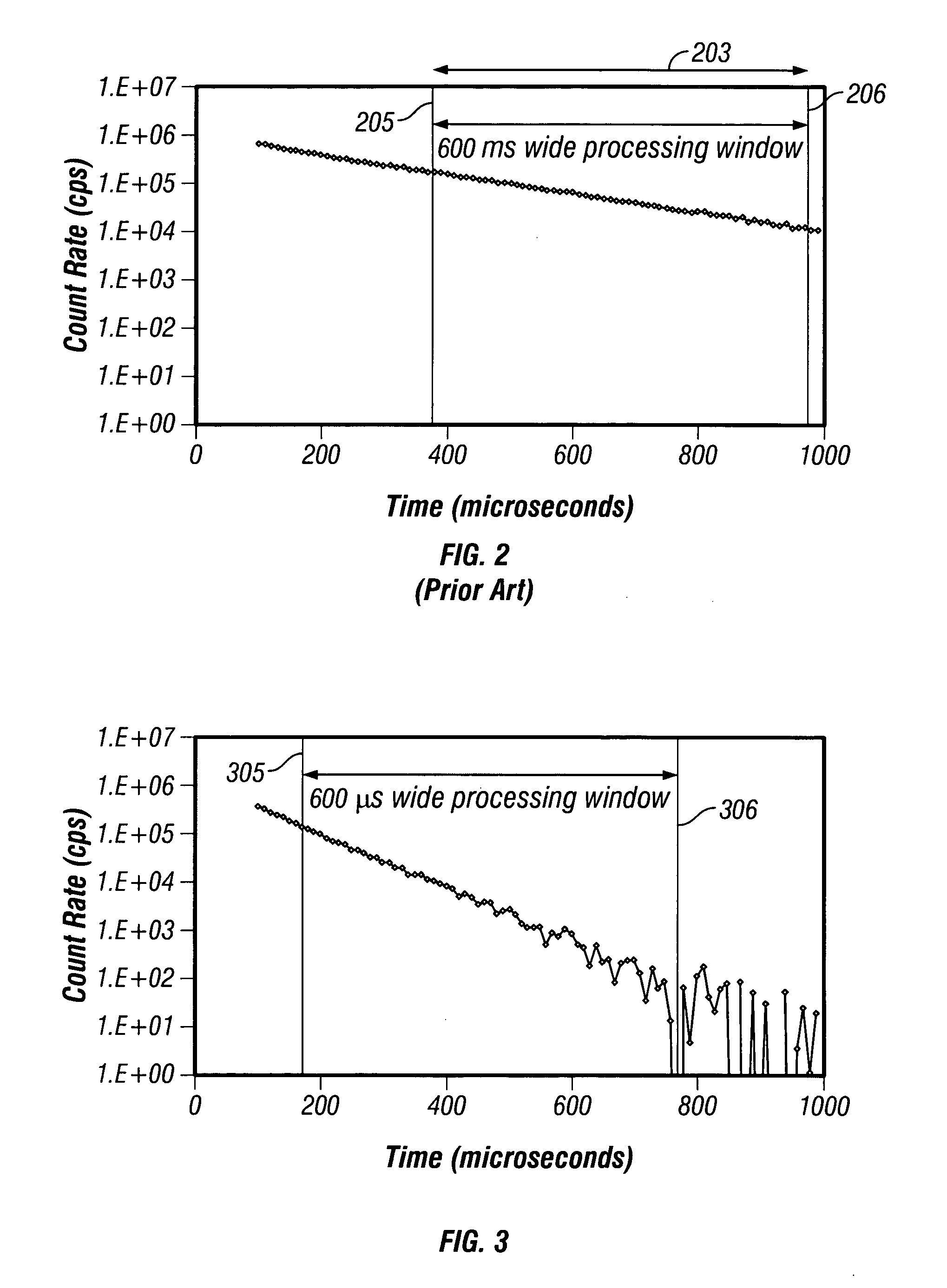
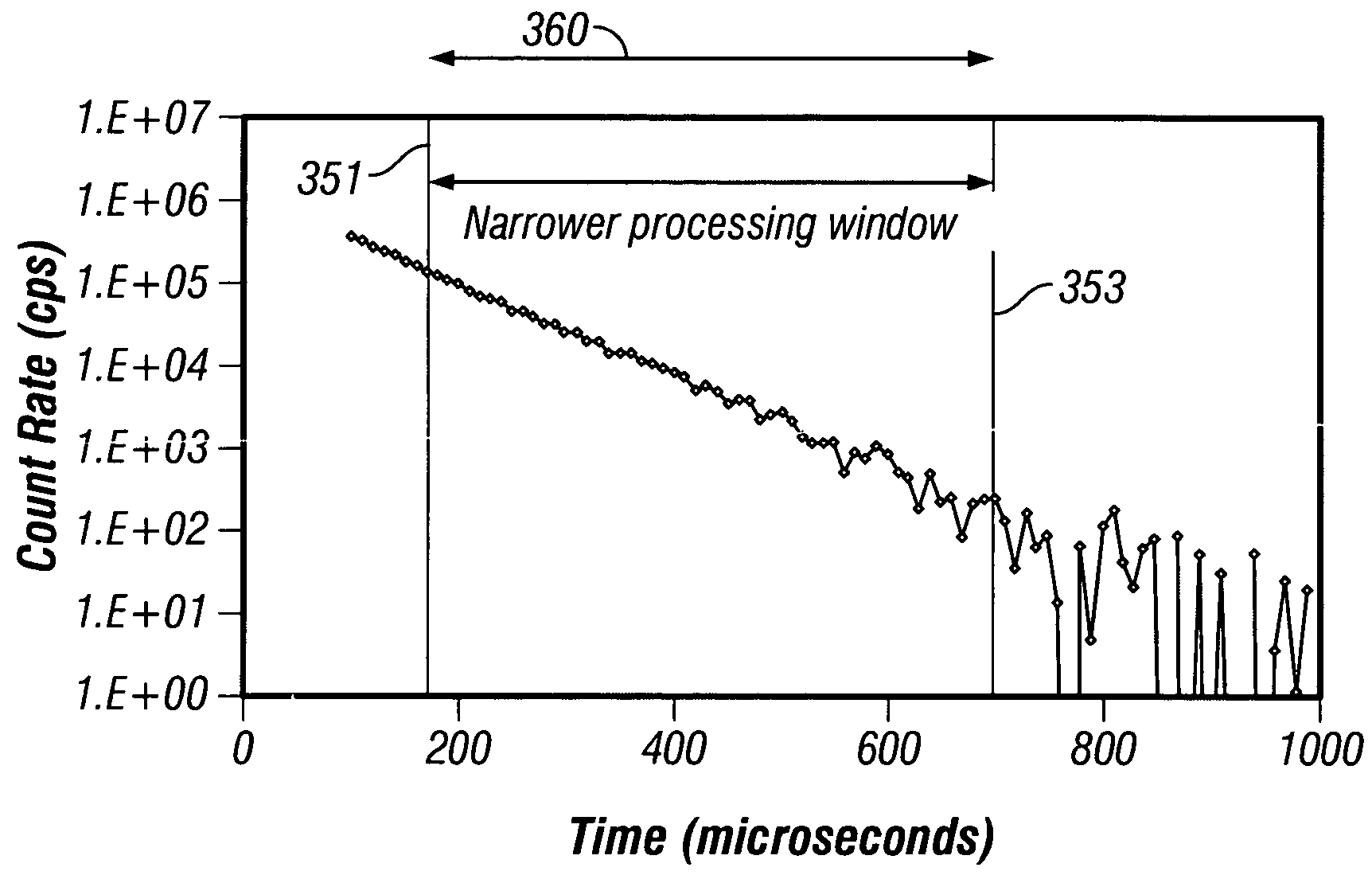
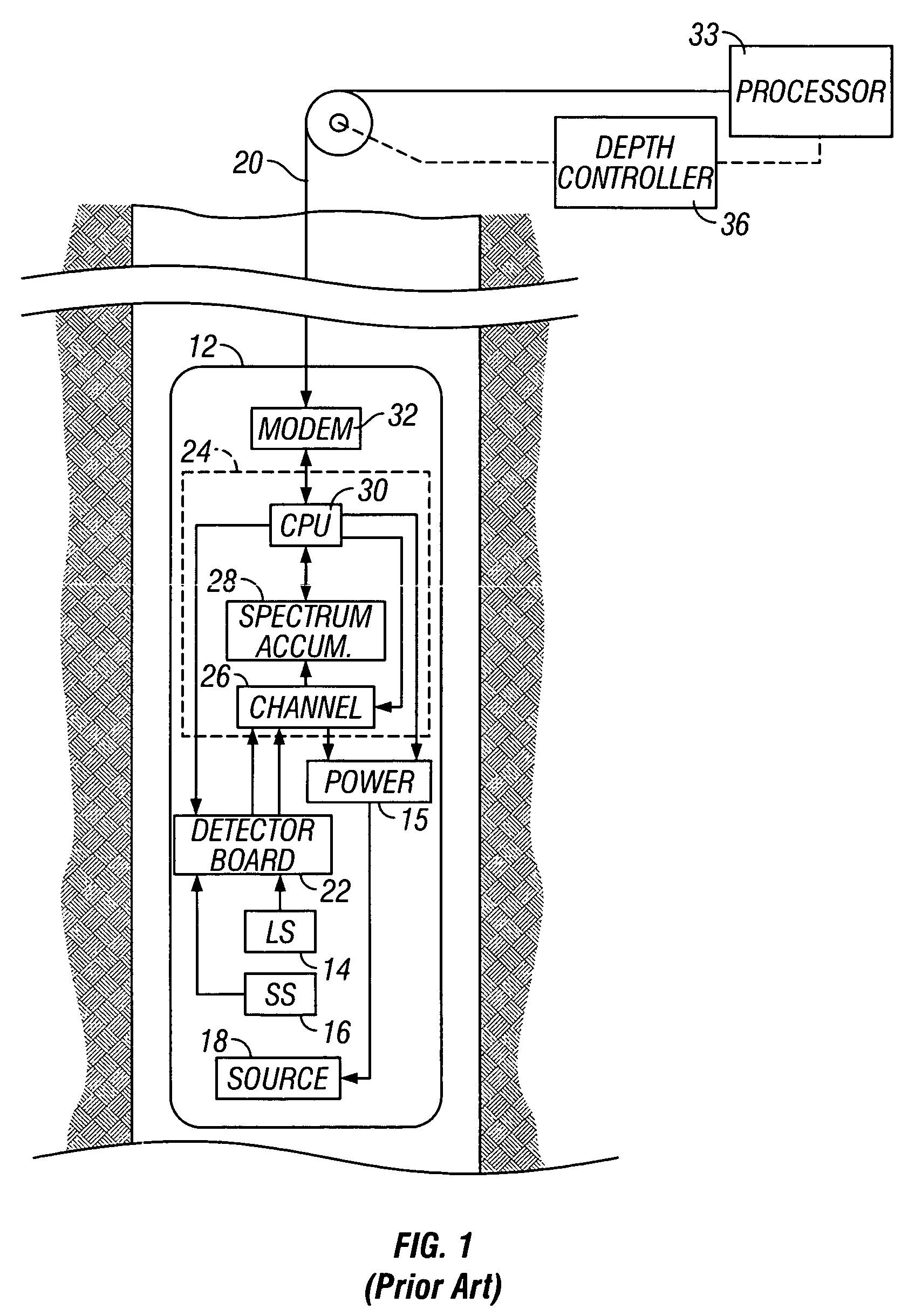
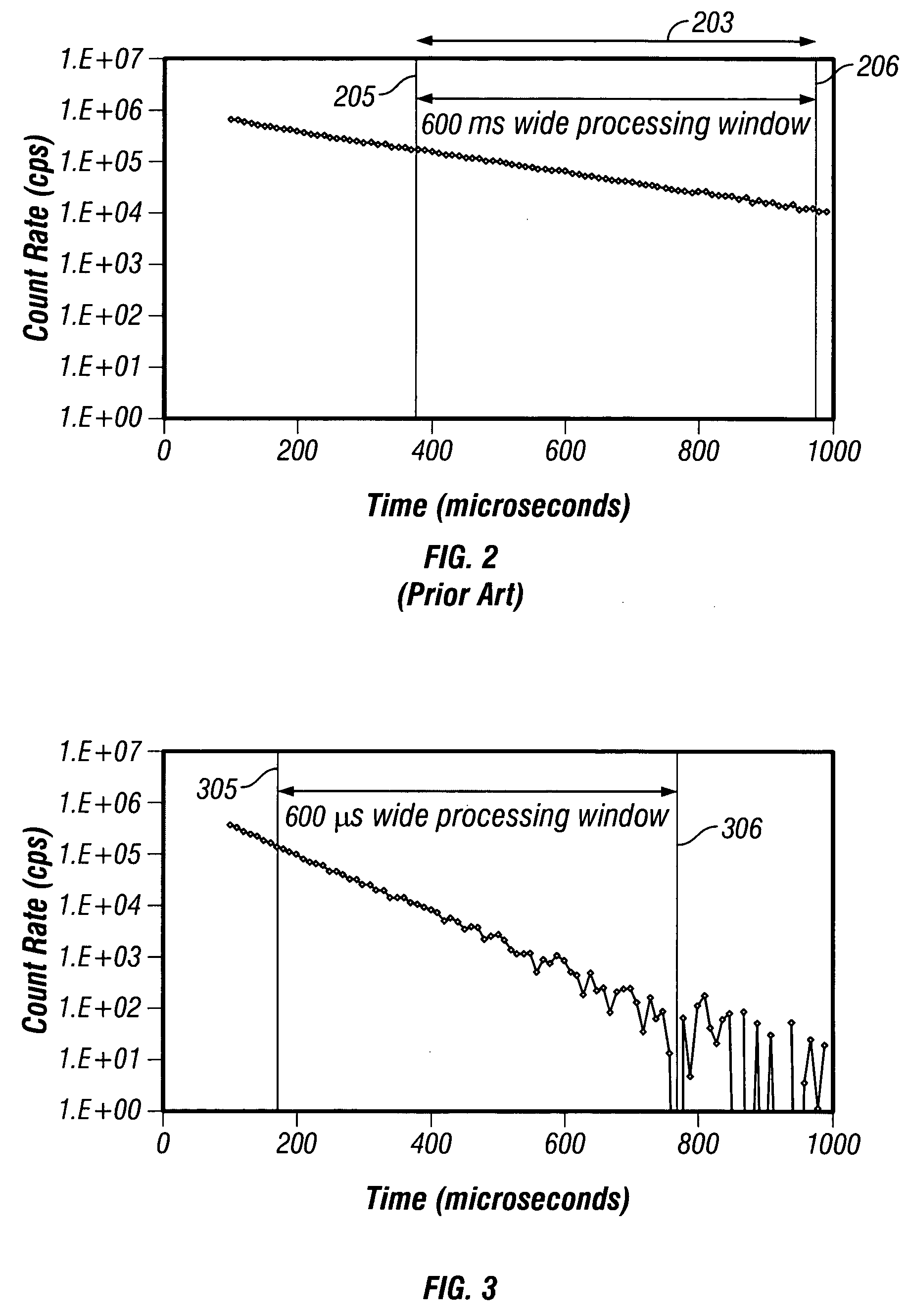
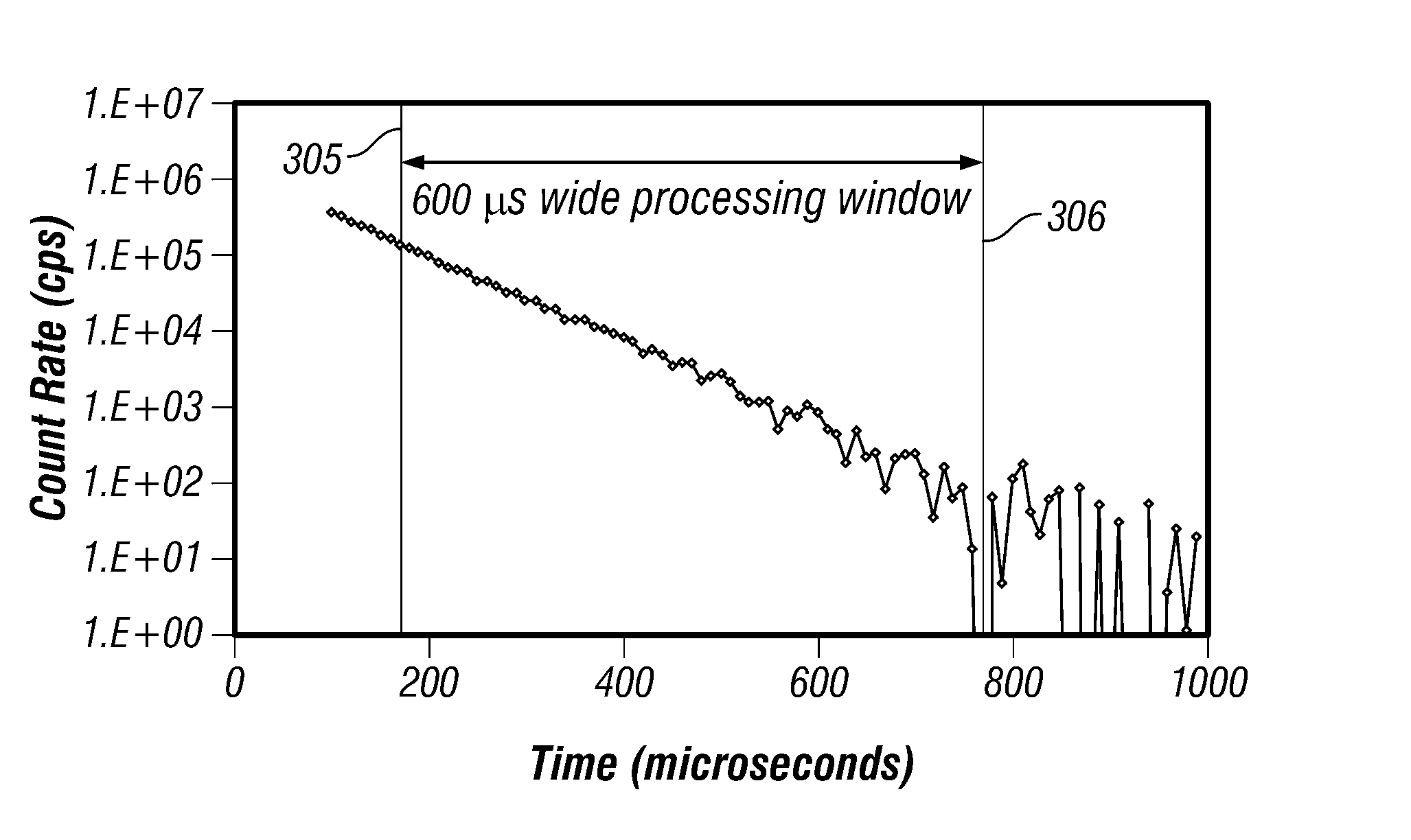
Data acquired using a pulsed nuclear source are susceptible to two sources of error. One error is due to large statistical noise towards the end of an acquisition window. Another source of error is the contamination of the early portion of the data by borehole and other effects. The beginning of the processing window is adjusted based on the signal level at the end of the processing window for the preceding pulsing of the source. The end of the processing window is derived from statistical considerations.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
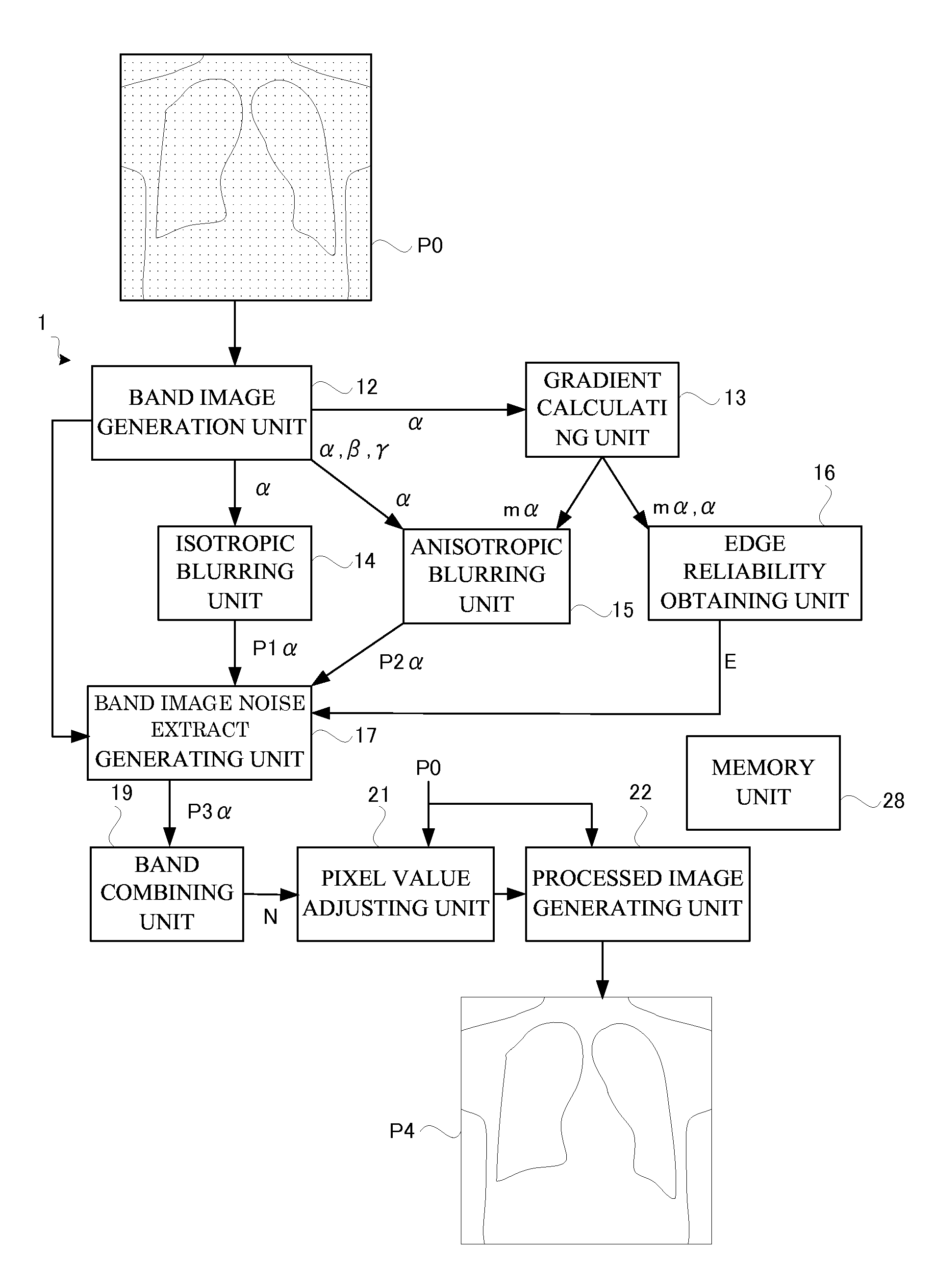
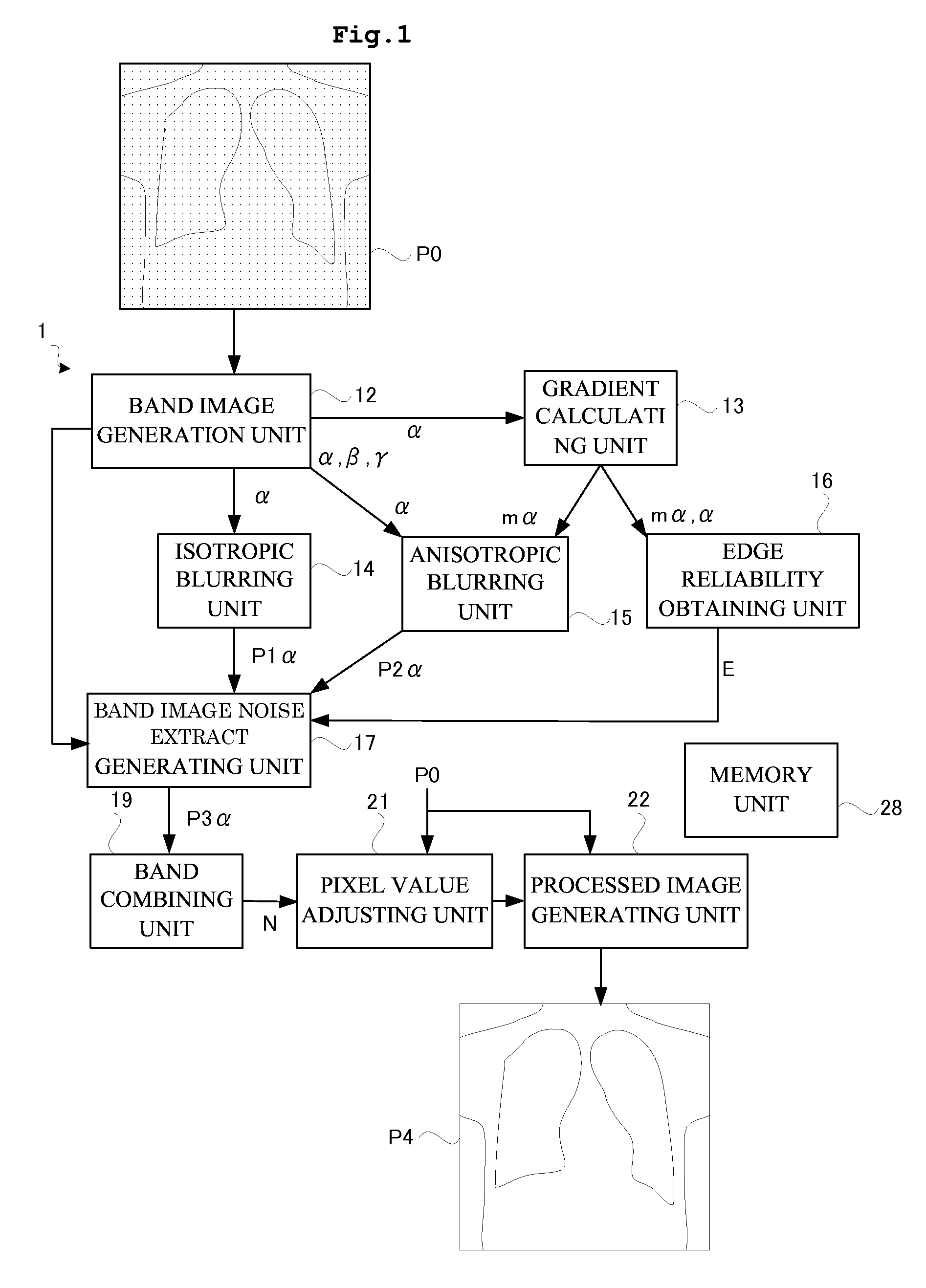
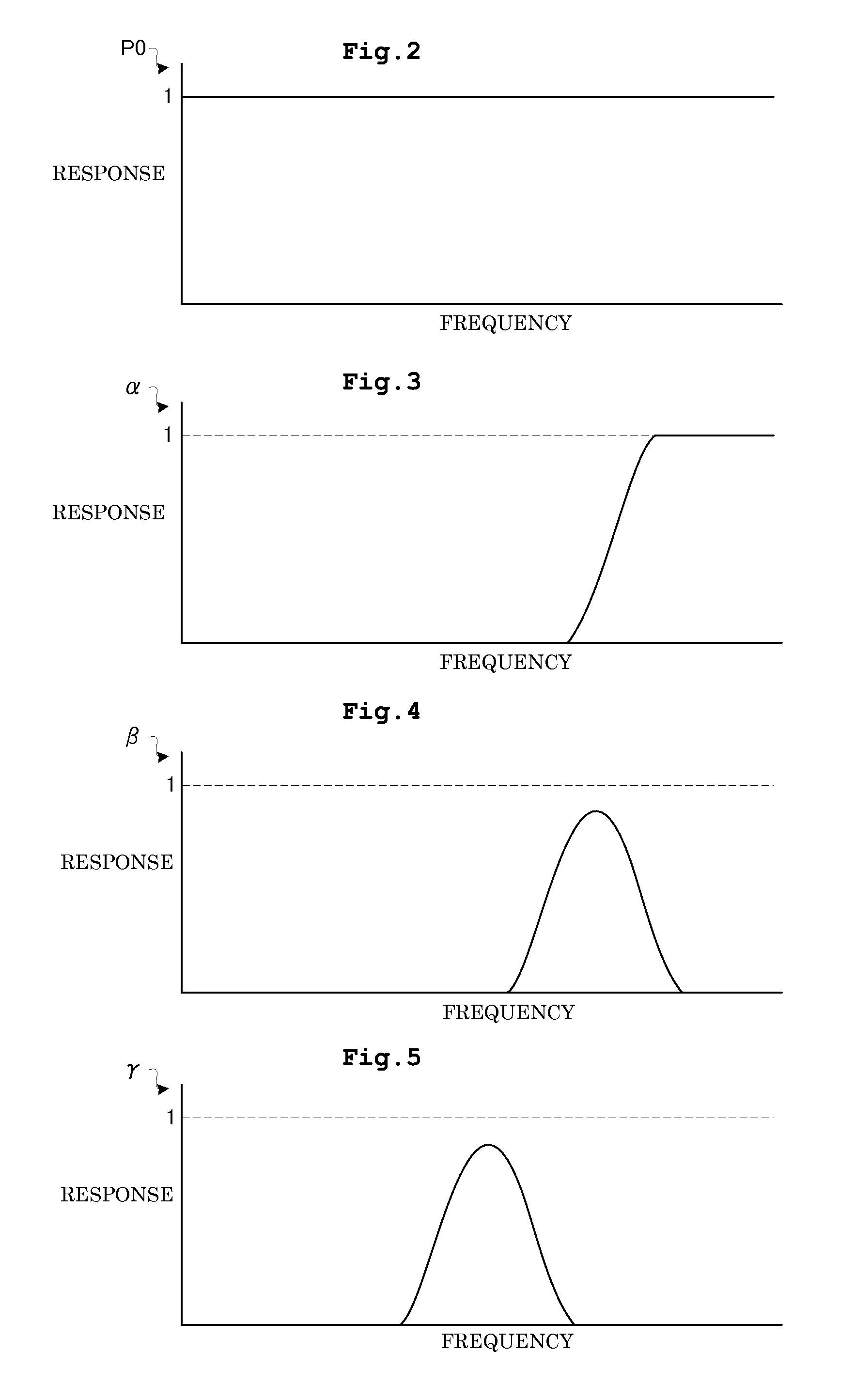
Image processing apparatus and radiographic apparatus having the same
ActiveUS20140314333A1Improve visibilityImprove processing speedImage enhancementImage analysisVisibilityImaging processing
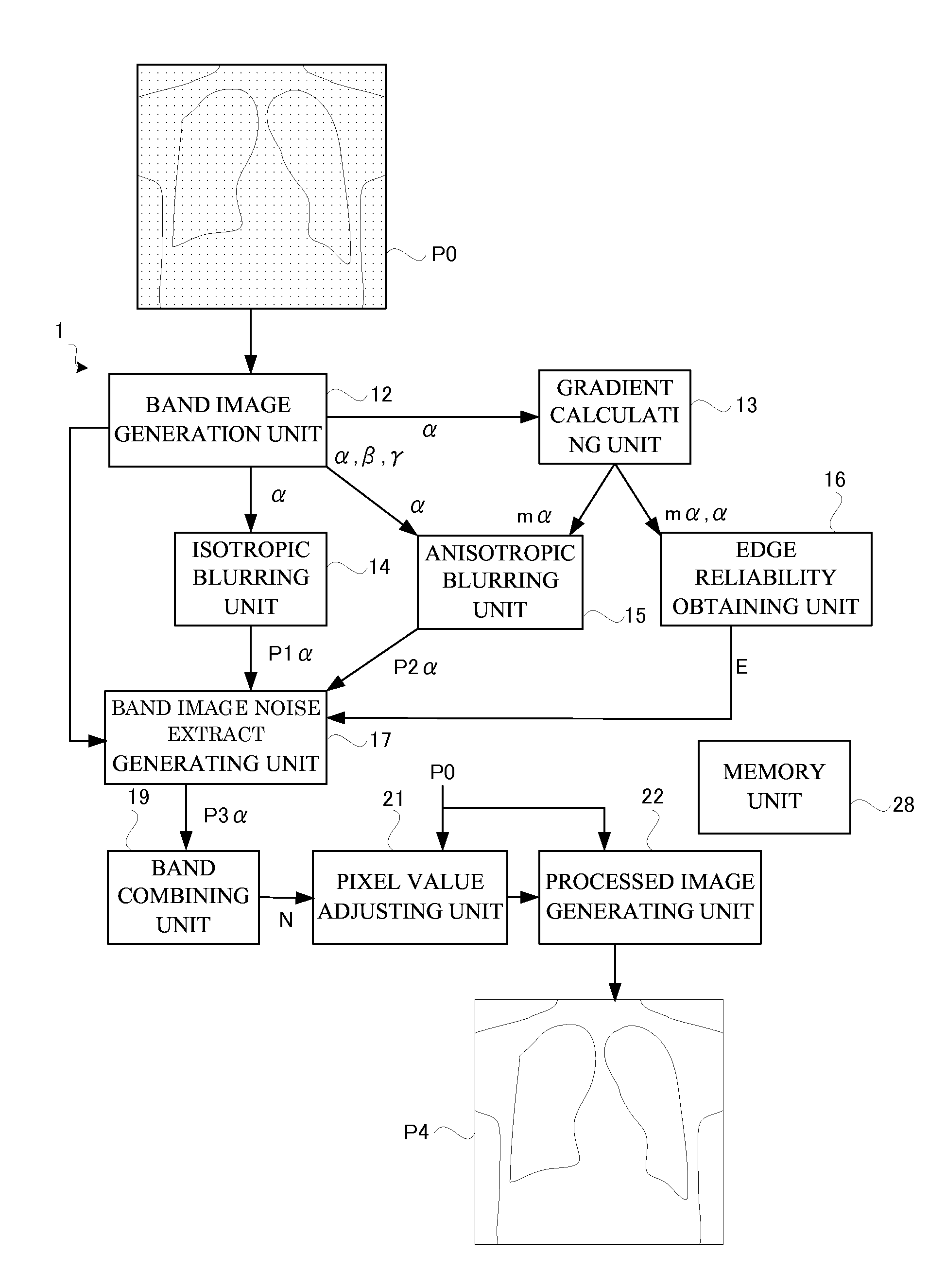
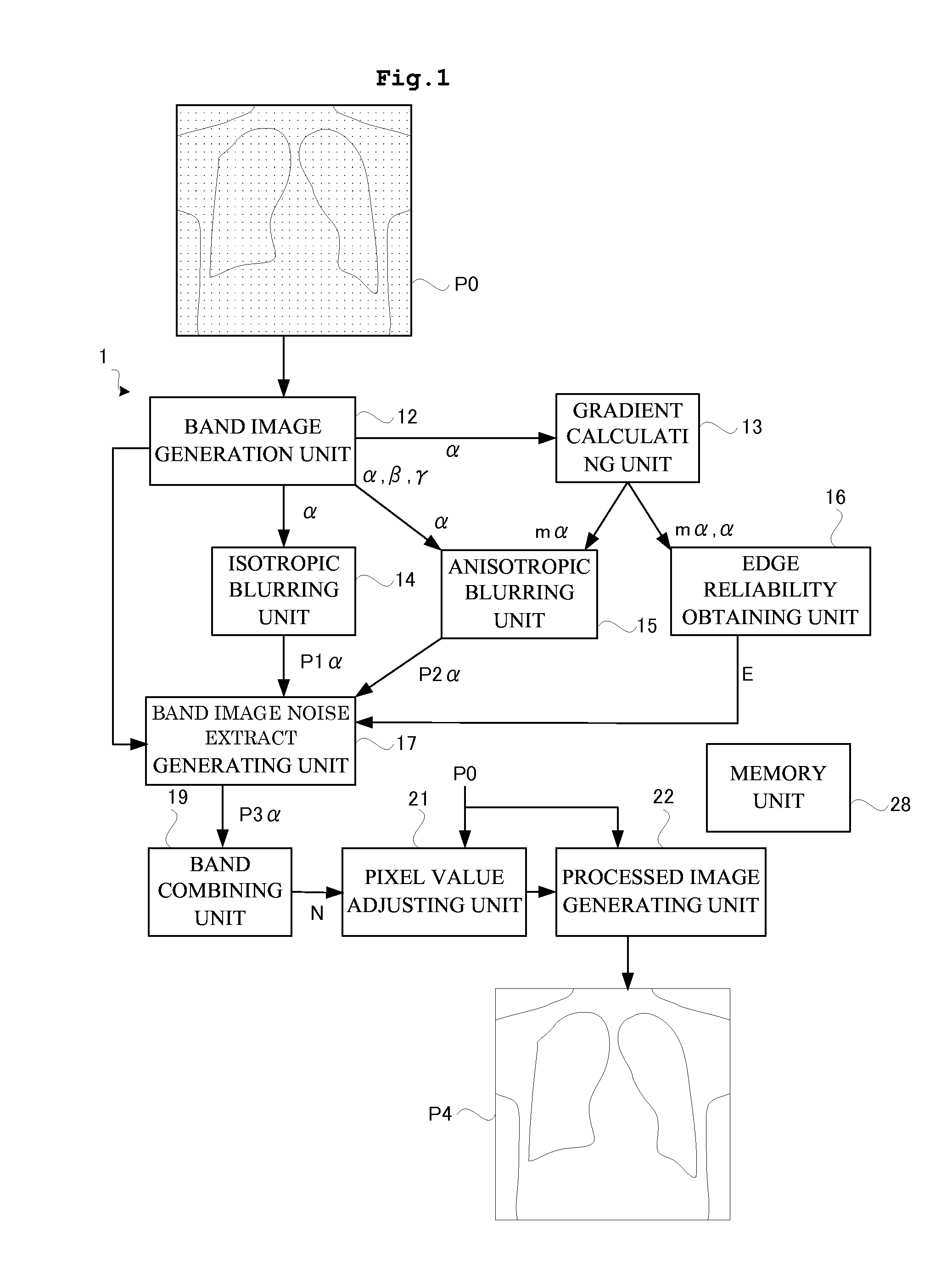
Provision can be made of a high-speed image processing apparatus that eliminates poor visibility in a dotted configuration or a superimposed portion of two streaks upon removing a false image due to statistical noise. That is, provision can be made of a high-speed image processing apparatus capable of outputting a processed image of high visibility in accordance with a shape of a configuration of a subject appearing in an original image upon removing a false image associated with the statistical noise. A band image noise extract generating unit performs image processing by superimposing a band image, an isotropic blur image, and an anisotropic blur image while changing weighting for each pixel in accordance with edge reliability. Such a construction eliminates poor visibility in the dotted configuration or the superimposed portion of two streaks upon removing the false image in the original image.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
System and method for localization of large numbers of fluorescent markers in biological samples
ActiveUS8319181B2Reduce respective collection solid angleExtensive collectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesImaging processingFluorescence
A method and system for the imaging and localization of fluorescent markers such as fluorescent proteins or quantum dots within biological samples is disclosed. The use of recombinant genetics technology to insert “reporter” genes into many species is well established. In particular, green fluorescent proteins (GFPs) and their genetically-modified variants ranging from blue to yellow, are easily spliced into many genomes at the sites of genes of interest (GoIs), where the GFPs are expressed with no apparent effect on the functioning of the proteins of interest (PoIs) coded for by the GoIs. One goal of biologists is more precise localization of PoIs within cells. The invention is a method and system for enabling more rapid and precise PoI localization using charged particle beam-induced damage to GFPs. Multiple embodiments of systems for implementing the method are presented, along with an image processing method relatively immune to high statistical noise levels.
Owner:FEI CO
Signal-to-Noise Ratio Estimation Method and Device for Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing System
InactiveCN102291349AIncrease the number of subcarriersHigh precisionMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioSynchronous frame
The invention discloses a method for estimating the signal-to-noise ratio of an OFDM system, which includes: extracting and storing time-domain data of a synchronous symbol according to system timing; performing fast Fourier transform on the time-domain data of the synchronous symbol to convert it to Transforming into frequency domain synchronization symbols; performing channel estimation on the frequency domain synchronization symbols; performing inverse fast Fourier transform on the channel estimation value of the frequency domain synchronization symbols to obtain a time domain channel impulse response; according to the time domain Statistical noise power and total power of the channel impulse response; and calculating the signal-to-noise ratio of the output signal according to the noise power and the total power. The invention also provides an OFDM system signal-to-noise ratio estimation device. The method and device for estimating the signal-to-noise ratio of the present invention use synchronous symbols in the frame structure of the OFDM system to estimate the signal-to-noise ratio, which can effectively improve the accuracy of estimating the signal-to-noise ratio of signals received by terminals in the OFDM system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
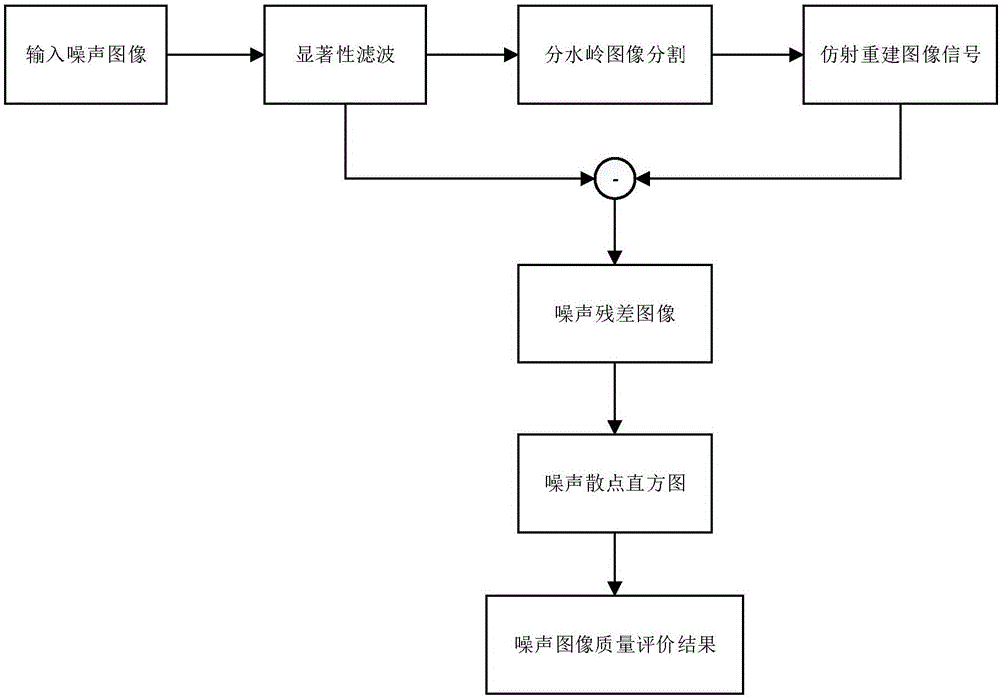
Noise image quality evaluation method combining reconstruction with noise scatter histograms
InactiveCN105139394AAccurately obtain noise image quality evaluation valueImprove consistencyImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentation algorithmImaging quality
The invention discloses a noise image quality evaluation method combining reconstruction with noise scatter histograms. The method comprises the steps: 1) performing visual significance filtering for an input noise image to be evaluated; 2) performing partitioning processing of a filtering image by using a watershed image segmentation algorithm; 3) obtaining the components of a noise image signal by using a signal affine reconstruction matrix; 4) obtaining a noise residual plot through calculation; 5) calculating the noise standard deviation value of each partitioning, and performing statistics of noise scatter histograms; and 6) obtaining a noise image evaluation value through calculation. The noise image quality evaluation method combining reconstruction with noise scatter histograms utilizes a visual sensitive comparison function to perform visual substantial characteristic filtering, and utilizes the image segmentation algorithm and an affine reconstruction optimization problem to solve the components of the image signal, and can calculate the noise residual plot and perform statistics of noise scatter histograms, and can accurately obtain the noise image evaluation value.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
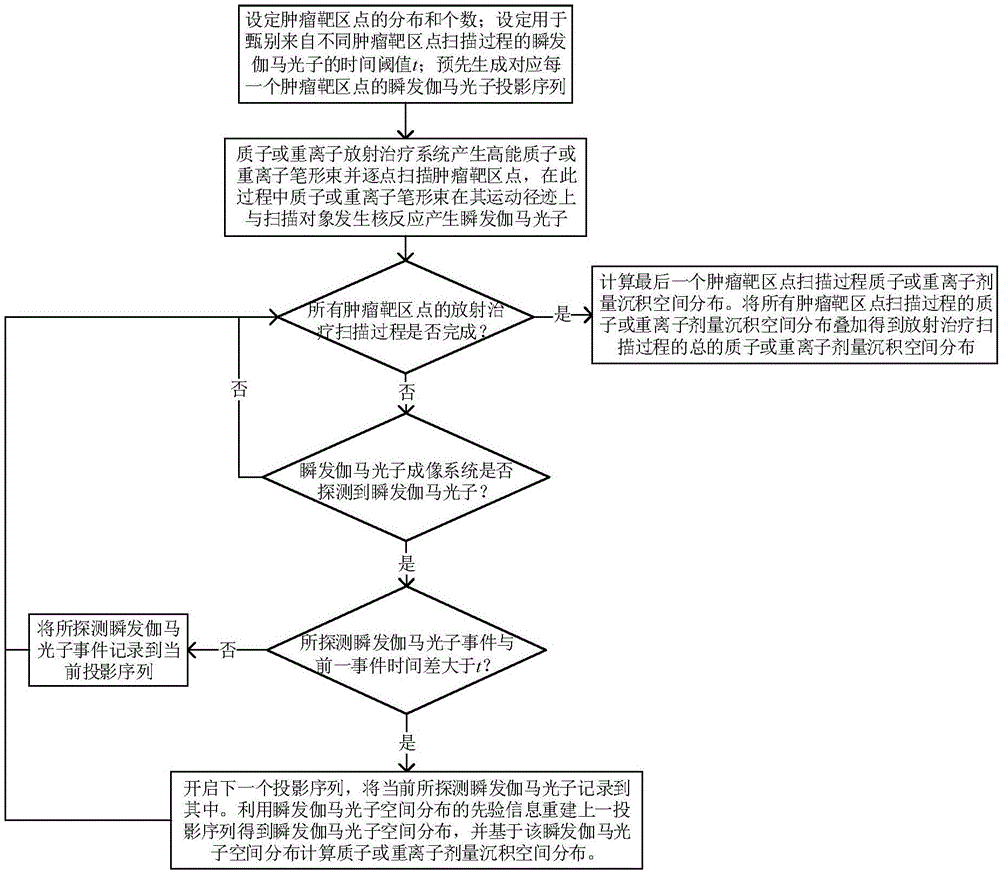
Time sequence based proton or heavy ion radiotherapy dose real-time monitoring method
InactiveCN106310543AEfficient use ofHigh precisionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTumor targetHeavy Ion Radiotherapy
The invention discloses a time sequence based proton or heavy ion radiotherapy dose real-time monitoring method, and belongs to the field of nuclear medical images. The method is based on a proton or heavy ion radiotherapy system and a prompt gamma photon imaging system, a projection sequence of prompt gamma photons generated in the spot scanning process of each rumor target region according to time sequence information of detected prompt gamma photons, rebuilding prompt gamma photon space distribution of the spot scanning process of each tumor target region according to prior information of the prompt gamma photons, and thus dose deposition space distribution of protons or heavy ions in the spot scanning process of the corresponding tumor target region is calculated, so that real-time dose monitoring for the proton or heavy ion radiotherapy process is realized. The dose monitoring method disclosed by the invention effectively utilizes the prior information of prompt gamma photon space distribution, the design of the prompt gamma photon imaging system can be simplified, influences of prompt gamma photon counting statistical noises can be reduced, and the accuracy of proton or heavy ion dose monitoring is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and device for imaging optimized angle of well earthquake reflected wave
InactiveCN101625418ATruly reflect vertical and horizontal changesReflect vertical and horizontal changesSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingImage resolutionWave shape
The invention discloses a method for imaging an optimized angle of a well earthquake reflected wave, comprising the following steps: carrying out VSP-CDP conversion of each concentrical depth point according to well data of an objective area to obtain an imaging section set; obtaining an optimized angle upper limit value according to acoustic logging data or zero VSP speed data of the objective area; and stacking and imaging sections which are smaller than the optimized angle upper limit value in the imaging section set. The method can eliminate wave shape distortion, frequency reduction, polarity inversion and statistical noise interference of a small-angle area for wide-angle reflection and can increase a reflected wave imaging resolution ratio to really reflect the vertical and horizontal variation of underground media.
Owner:中国石化集团胜利石油管理局有限公司
Expressway audio vehicle detection device and method thereof
ActiveCN102682765BSegmented signal-to-noise ratio is excellentSegmented SNR improvementDevices using time traversedSpeech recognitionAmplitude compressionVehicle detection
The invention relates to an expressway audio vehicle detection device and a method thereof. By the aid of the detection device, a microphone array signal acquisition module acquires an audio signal on a lane, the audio signal is subjected to band-splitting filtering and framing through a signal processing module after being subjected to de-noising processing through a noise suppression module, cross-correlation processing is conducted among sub-band signals, an audio space spectrogram is obtained, a vehicle detection module tracks a track of the maximum value on the audio space spectrogram and judges whether a vehicle passes, and the vehicle type and the vehicle speed are obtained through a vehicle type recognition module and a vehicle speed recognition module if the vehicle passes. The detection method is based on the device, a minimum statistical noise estimation method of the adaptive window length is adopted, the signal which is subjected to noise suppression processing is subjected to band-splitting filtering and framing processing, then cross-correlation processing is conducted among same sub-band signals, cross-correlation results are summed after being subjected to amplitude compression and are unfolded along a timer shaft, and an audio signal space-time spectrum is obtained. The method and the device have the advantages of being low in cost, low in energy consumption, easy to construct, interference resisting, capable of working in all weather and the like.
Owner:TAIKE HIGHWAY SCI & TECH INST BEIJING CITY +1
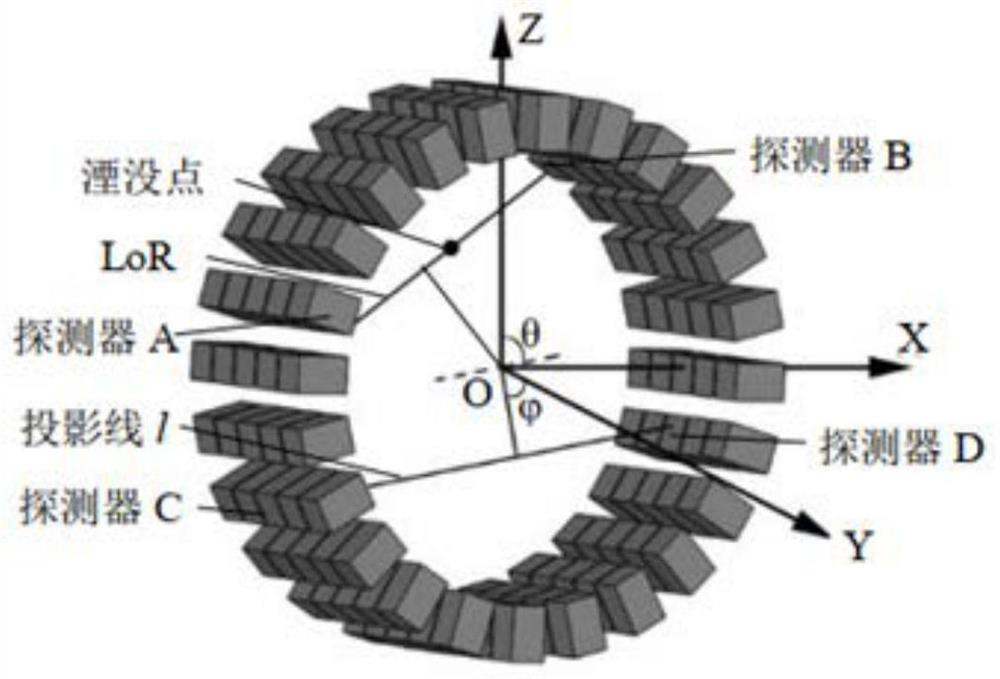
Gamma photon 3D imaging noise suppression method and application
PendingCN112419434AImprove rebuild efficiencyImprove detection resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationGamma photon3d image
The invention relates to a gamma photon 3D imaging noise suppression method and application, belongs to the technical field of industrial detection, and provides an improved OSEM algorithm of ToF datarecombination based on the mapping principle of gamma photon ToF information and positron annihilation positions, a constraint image reconstruction model of a ToF index solution is established, datarecombination is performed on LoR by taking ToF information as an index. System matrix elements are adjusted according to ToF information weight coefficients, a system matrix is compressed by sparsifying the system matrix elements, and image reconstruction efficiencyis improved. an improved OSEM algorithm of solution constraint is adopted for image reconstruction, the contribution of image pixelsto LoR is limited to be matched with the distribution probability of positron annihilation position -ToF curves of the image pixels in ToF information, the purpose of suppressing statistical noise propagation is achieved, and therefore the detection resolution is improved.
Owner:南京航空航天大学深圳研究院
Method for intelligently detecting scene video noise of transformer station
InactiveCN106530248AGreat practicabilityImprove real-time performanceImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionTransformer
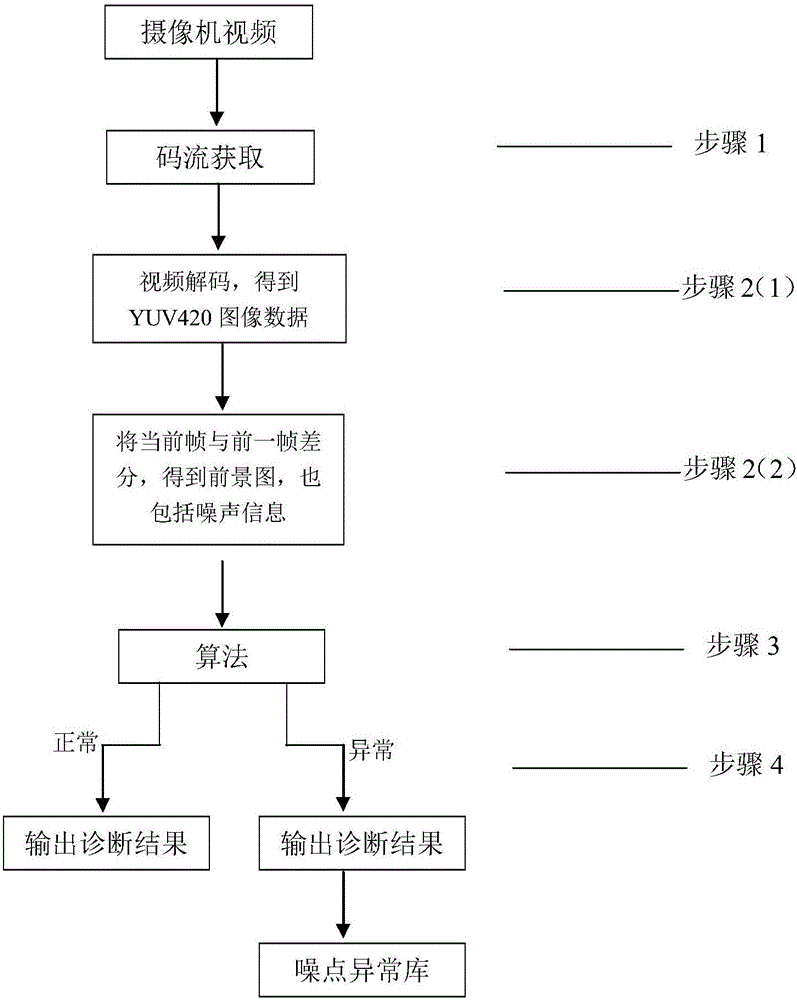
A method for intelligently detecting scene video noise of a transformer station includes the steps of S1, obtaining the original code stream of the scene video of the transformer station, and carrying out video decoding to obtain YUV420 standard Y, U, V data, S2, obtaining images of front and rear frames in the code stream, differentiating the Y, U, V data of the current frame image with those of the previous frame image to obtain a foreground image including noise information, S3, calculating a Y data Canny graph of a YUV420 image, conducting expansion processing for the Canny graph, filtering current foreground region according to the graph, conducting convolution operation by using the Laplacian operator with the operator formula being shown in the description to obtain a noise area, converting the texture information of the noise region into SIFT characteristics according to the texture information of the noise region, screening out a candidate region by using a RANSAC algorithm, calculating the noise values on the region by using noise confidence, and S4, outputting the result. The detection result is high in accuracy.
Owner:CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID COMPANY
Method and apparatus for determining the thermal neutron capture cross-section of a subsurface formation from a borehole
Data acquired using a pulsed nuclear source are susceptible to two sources of error. One error is due to large statistical noise towards the end of an acquisition window. Another source of error is the contamination of the early portion of the data by borehole and other effects. The beginning of the processing window is adjusted based on the signal level at the end of the processing window for the preceding pulsing of the source. The end of the processing window is derived from statistical considerations.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method and apparatus for determining the thermal neutron capture cross-section of a subsurface formation from a borehole
InactiveUS20080156976A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsThermal neutron captureSources of error
Data acquired using a pulsed nuclear source are susceptible to two sources of error. One error is due to large statistical noise towards the end of an acquisition window. Another source of error is the contamination of the early portion of the data by borehole and other effects. The beginning of the processing window is adjusted based on the signal level at the end of the processing window for the preceding pulsing of the source. The end of the processing window is derived from statistical considerations.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
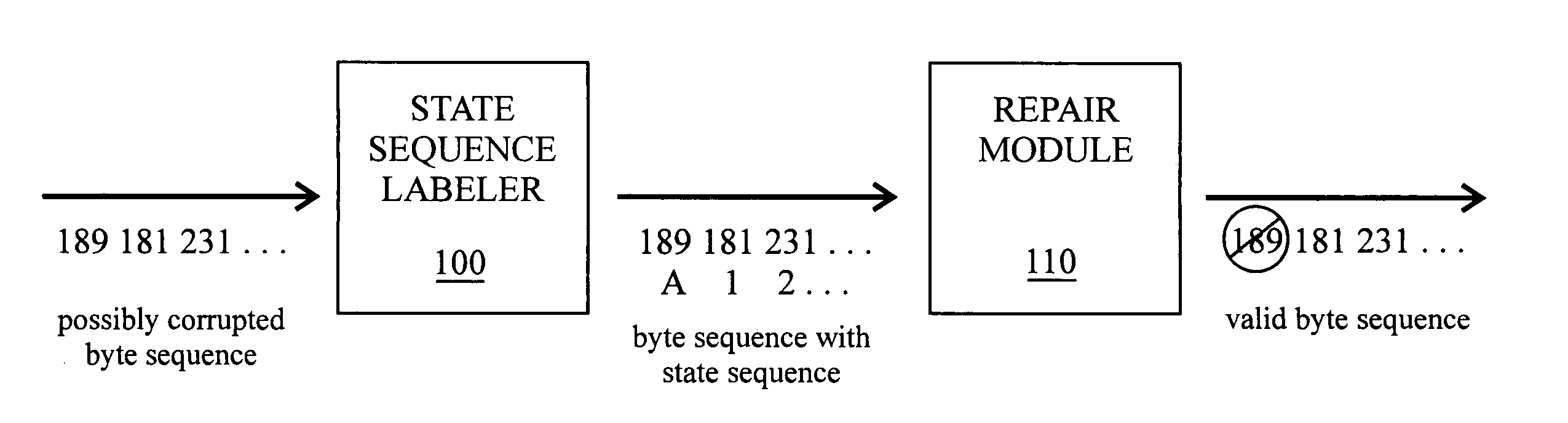
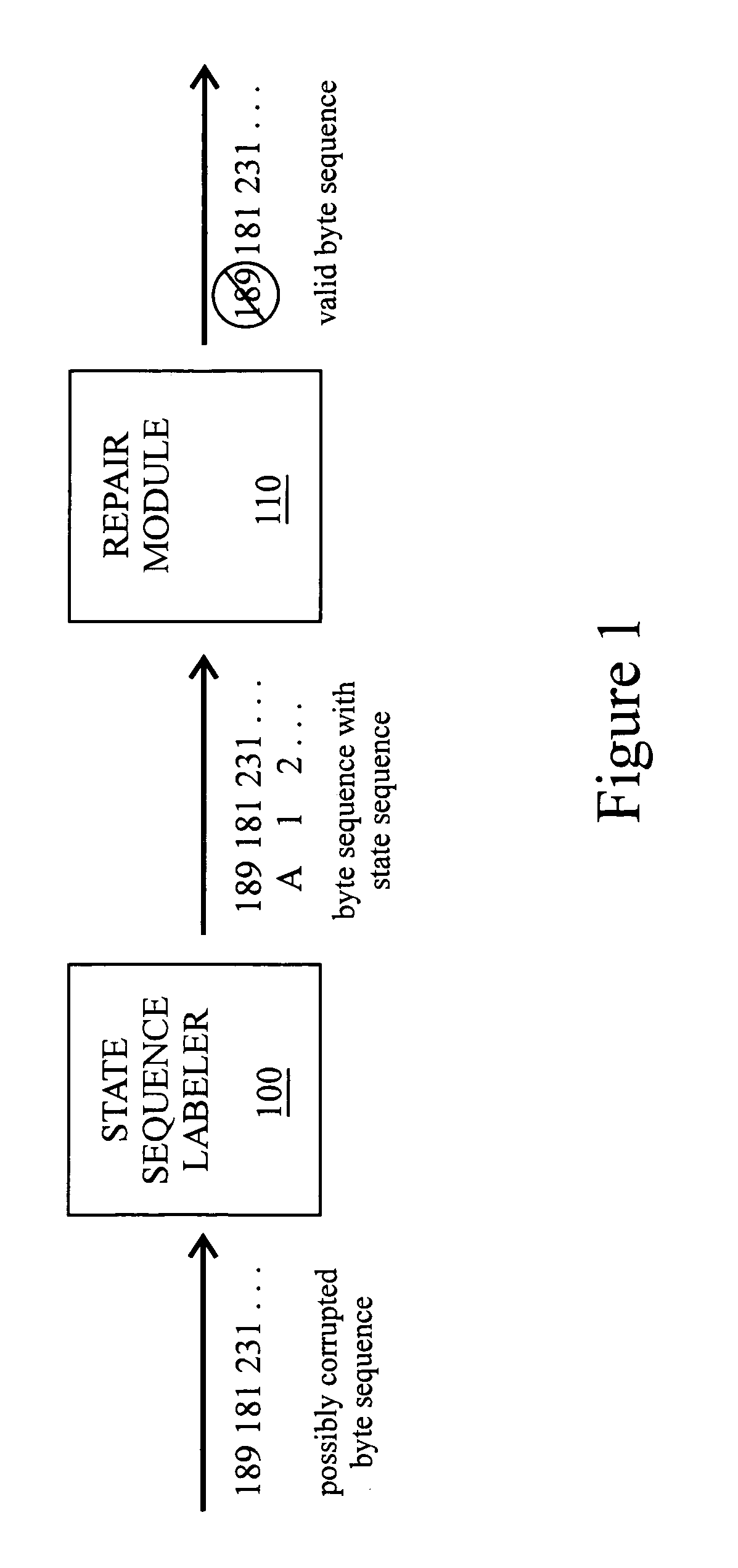
Noise removal in multibyte text encodings using statistical models
InactiveUS7013422B2Data representation error detection/correctionError preventionAlgorithmNoise removal
Disclosed is a method of validating a byte sequence having a plurality of states, the method comprising designating one or more noise states from among the plurality of states; generating a most probable state sequence for the byte sequence; utilizing said state sequence to identify all noise in the byte sequence; and localizing said noise in said noise states. Once localized, the noise may be deleted from the byte sequence.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
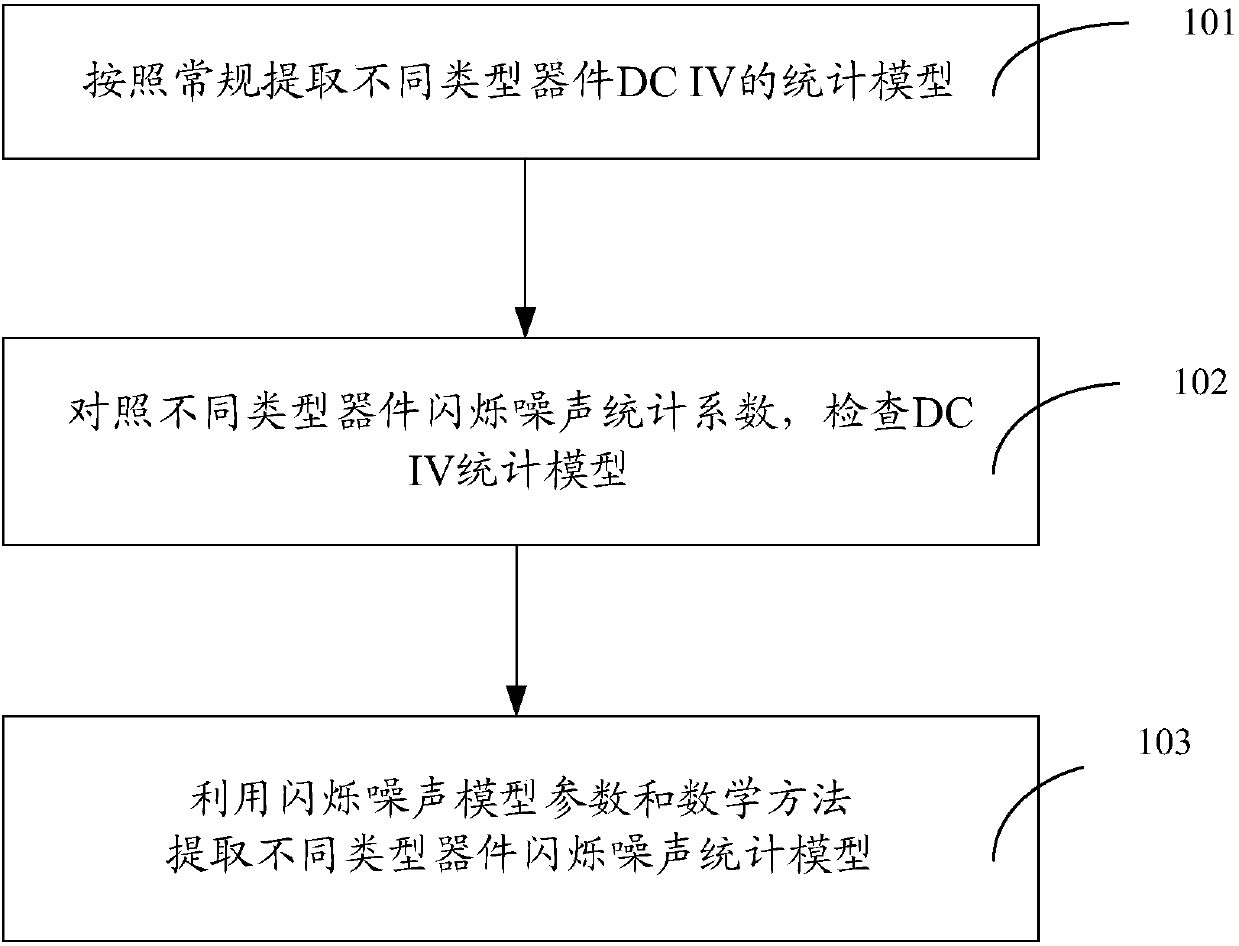
Statistical model of flicker noise and extraction method thereof
ActiveCN108021777ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsModel parametersGate oxide
The invention discloses a statistical model of flicker noise and an extraction method thereof. On the basis of an original statistical model, the correlation statistics of devices with different typesand different gate-oxide thicknesses and the influence coefficients of the flicker noise on the statistical coefficients of the devices are added, and then the statistical model parameters of the flicker noise are adjusted, so that the adjusted statistical model of the flicker noise can more accurately characterize the relationship with the flicker noise of the devices.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
System and method for estimating a statistical noise map in x-ray imaging applications
Described here are a system and method for producing a statistical noise map that indicates the noise present in data acquired with an x-ray imaging system, such as an x-ray computed tomography system, an x-ray tomosynthesis system, a C-arm x-ray imaging system, and so on. In general, an image is reconstructed from the acquired data using, for example, any standard filtered back projection (“FBP”) image reconstruction algorithm. This image is used as a base line to estimate a noise standard distribution map. The raw projection data represents a typical measurement among many repeated measurements under the same experimental conditions; therefore, the measured projection data can be used to numerically generate an ensemble of many (e.g., twenty or more) noisy projection data sets. These noisy projection data sets are then used to reconstruct noisy images and from these noisy images and the original image, the statistical noise map can be computed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Image processing apparatus and radiographic apparatus having the same
ActiveUS9183621B2Improve visibilityThick-line figure is extremely enhancedImage enhancementImage analysisVisibilityImaging processing
Provision can be made of a high-speed image processing apparatus that eliminates poor visibility in a dotted configuration or a superimposed portion of two streaks upon removing a false image due to statistical noise. That is, provision can be made of a high-speed image processing apparatus capable of outputting a processed image of high visibility in accordance with a shape of a configuration of a subject appearing in an original image upon removing a false image associated with the statistical noise. A band image noise extract generating unit performs image processing by superimposing a band image, an isotropic blur image, and an anisotropic blur image while changing weighting for each pixel in accordance with edge reliability. Such a construction eliminates poor visibility in the dotted configuration or the superimposed portion of two streaks upon removing the false image in the original image.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
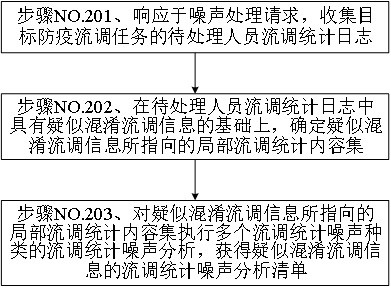
Deep learning-based epidemic prevention information processing method and epidemic prevention service system
The invention provides a deep learning-based epidemic prevention information processing method and an epidemic prevention service system, and the method comprises the steps: collecting a to-be-processed personnel traffic scheduling statistical log of a target epidemic prevention traffic scheduling task in response to a noise processing request; on the basis that suspected confusion traffic scheduling information exists in the traffic scheduling statistical log of the to-be-processed personnel, determining a local traffic scheduling statistical content set pointed by the suspected confusion traffic scheduling information; and executing flow modulation statistical noise analysis of a plurality of flow modulation statistical noise types on the local flow modulation statistical content set pointed by the suspected confusion flow modulation information to obtain a flow modulation statistical noise analysis list of the suspected confusion flow modulation information. In this way, during flow modulation statistical noise analysis, analysis results of the suspected confusion flow modulation information relative to multiple flow modulation statistical noise types can be analyzed, so that the possibility of analysis omission of individual flow modulation statistical noise of the suspected confusion flow modulation information is reduced; therefore, the accuracy and the credibility of the flow modulation statistical noise analysis of the suspected confused flow modulation information can be improved.
Owner:八爪鱼人工智能科技(常熟)有限公司
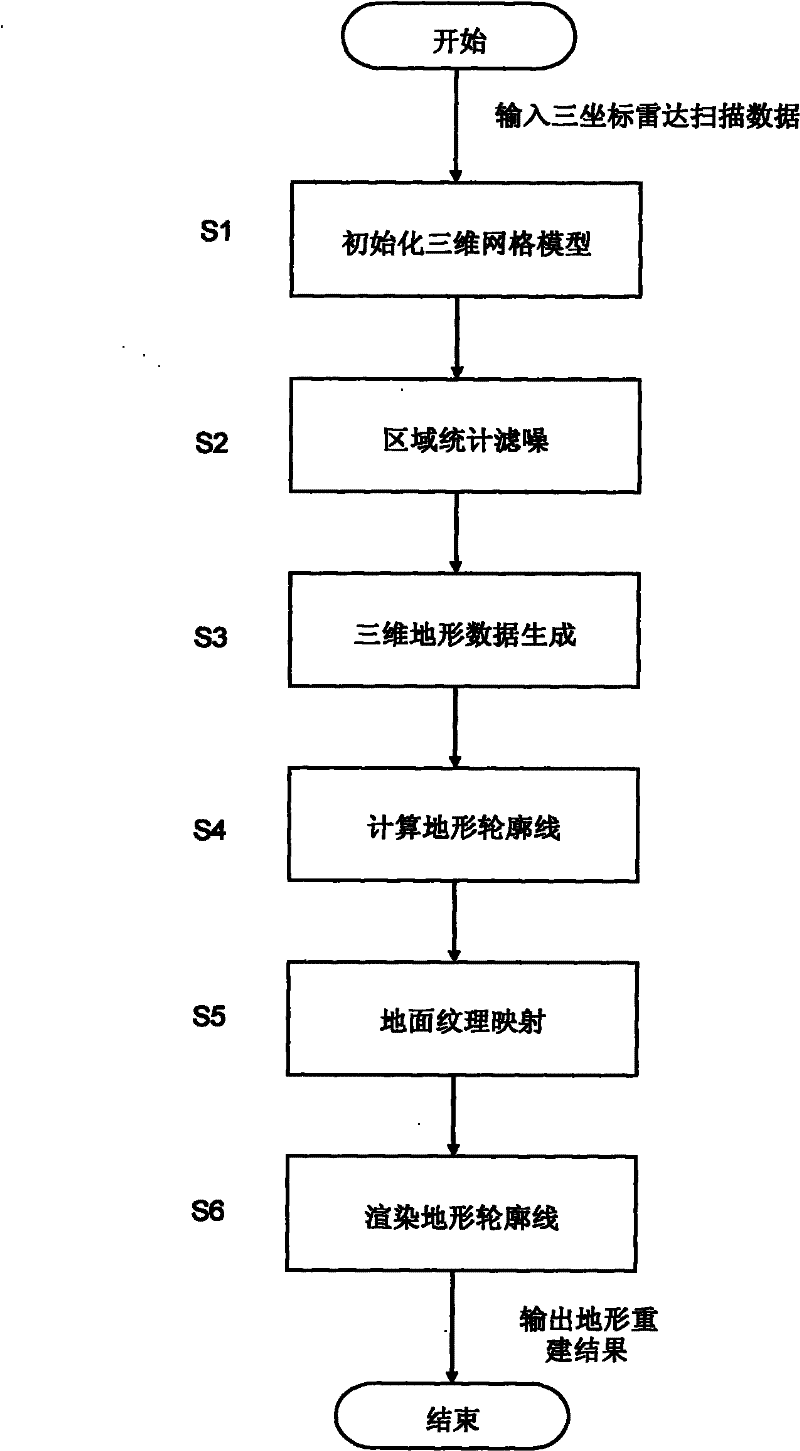
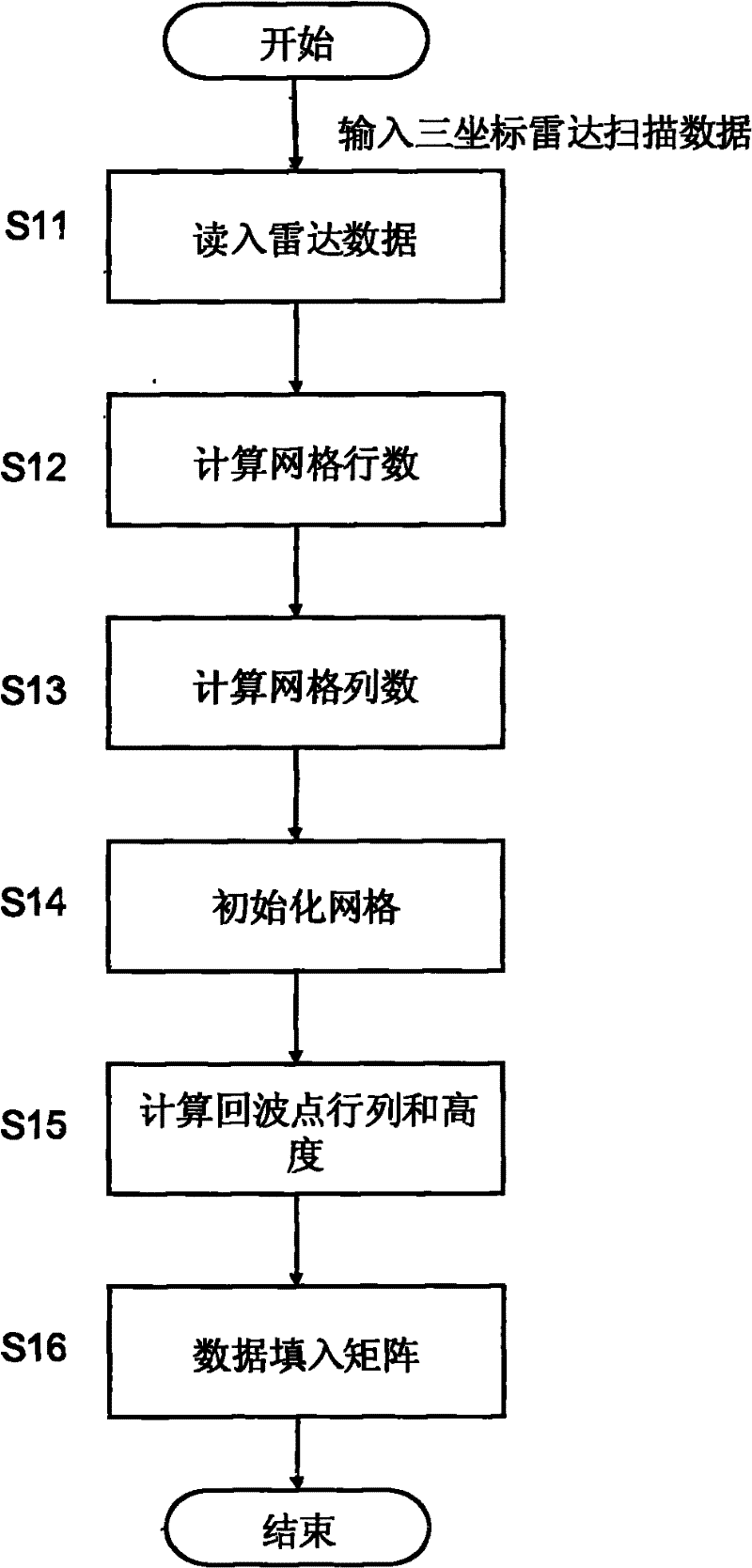
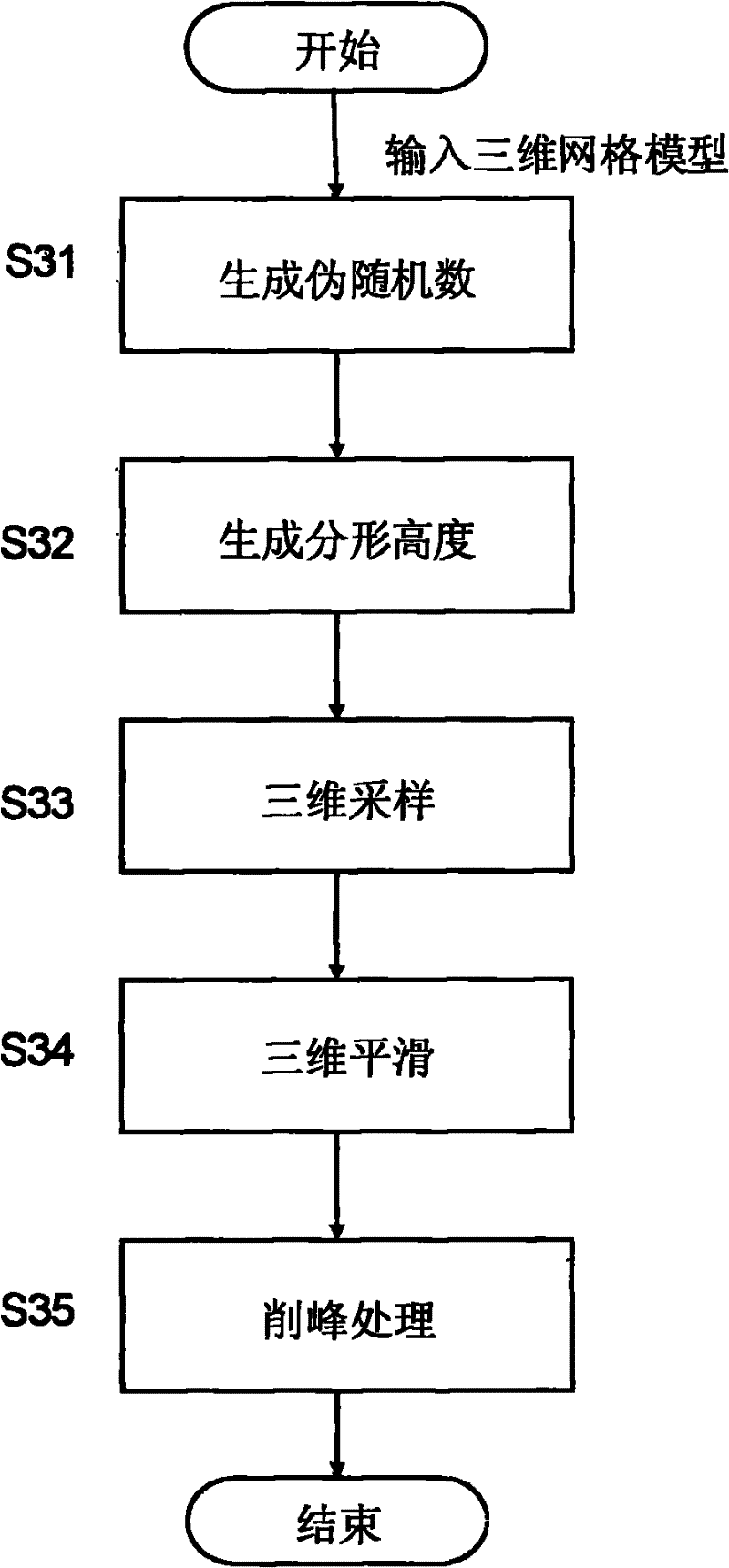
Method for reconstructing radar scanning data to generate three-dimensional visual terrain
InactiveCN101881830BRealize one-to-one correspondenceSpatial topological relationship remains unchangedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTopographic profileTerrain
The invention provides a method for reconstructing radar scanning data to generate visual three-dimensional terrain. By utilizing the method, three-dimensional terrain data obtained by the scanning of a three-dimensional radar can be reconstructed and displayed in real time. The method is implemented through the following technical scheme of: constructing a three-dimensional gridding module according to the size and resolution power of a scanning area of the three-dimensional radar, and initializing according to radar scanning data to generate a preset height surface; performing the statistical noise filtering of a region to remove the noise and dead spots of a radar system; interpolating empty data by using a constrained adaptive fractal extension method to generate the continuous and realistic three-dimensional terrain data and control the approximate shape of generated terrain to a certain degree; calculating the terrain data by utilizing a mode of six-degree of freedom voxel to form terrain contour lines in different visual angles; and completing ground texture mapping by loading mixed texture mapping with a fractal mode, and completing the rendering of the terrain contour lines by a gradient mode of luminance-height-gradient so as to generate a final three-dimensional terrain image.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
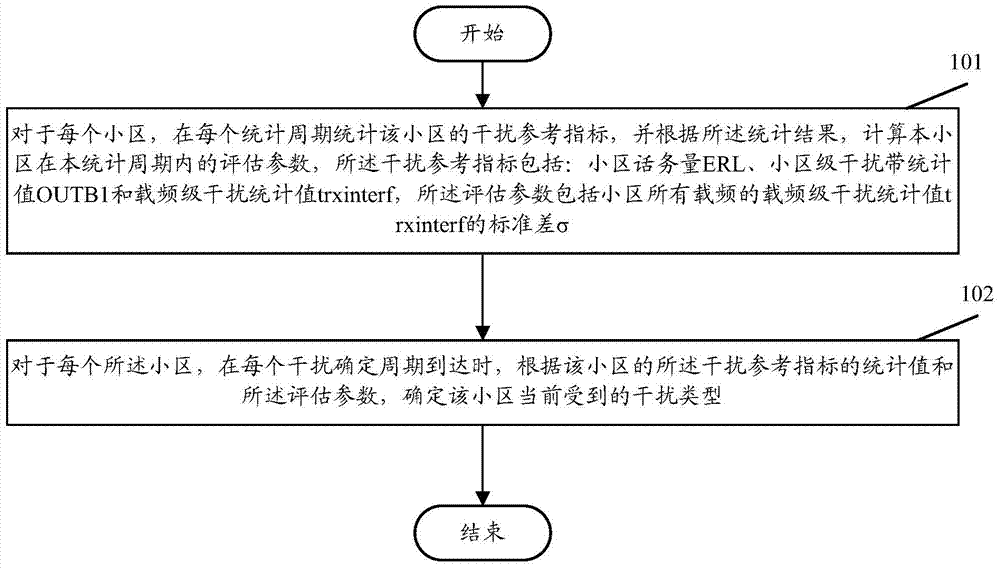
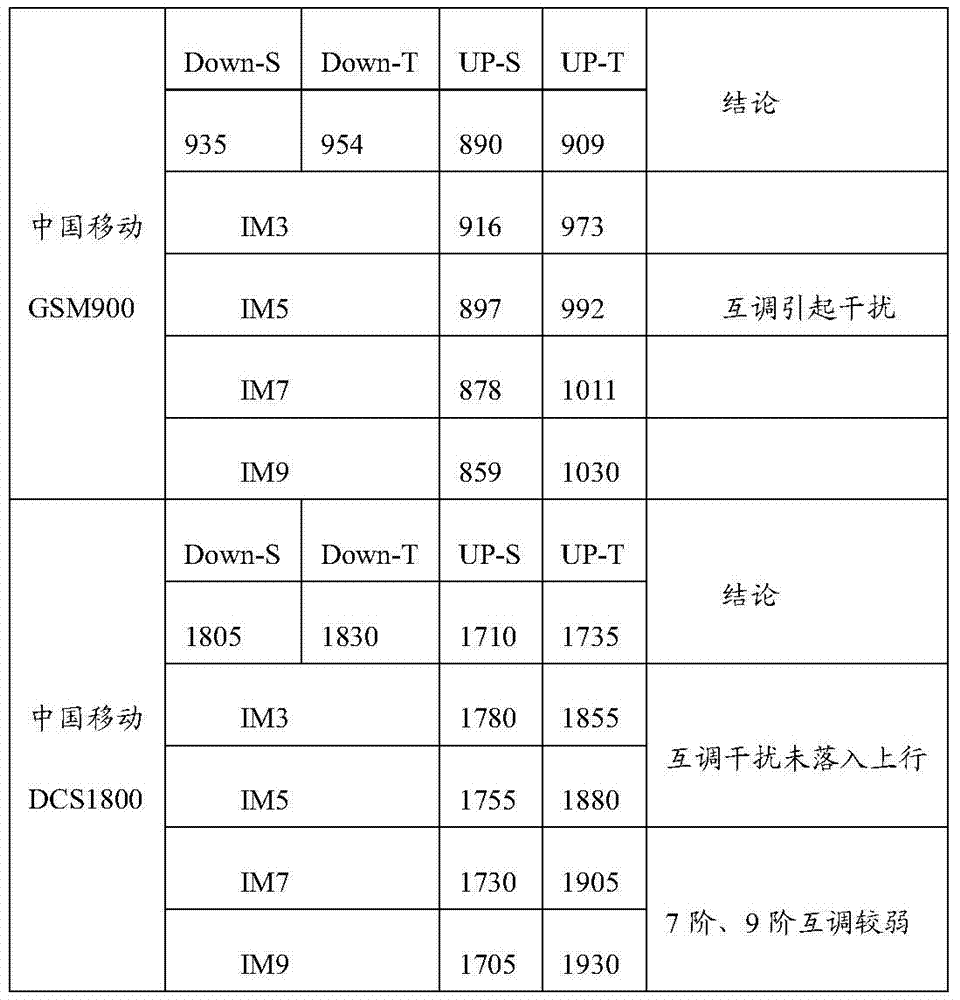
Identification method of uplink interference type
InactiveCN103957541BAchieve accurate identificationWireless communicationComputer scienceCell parameter
Owner:BEIJING GREENNET COMM TECH
Holographic positive electron concentration imaging method and system
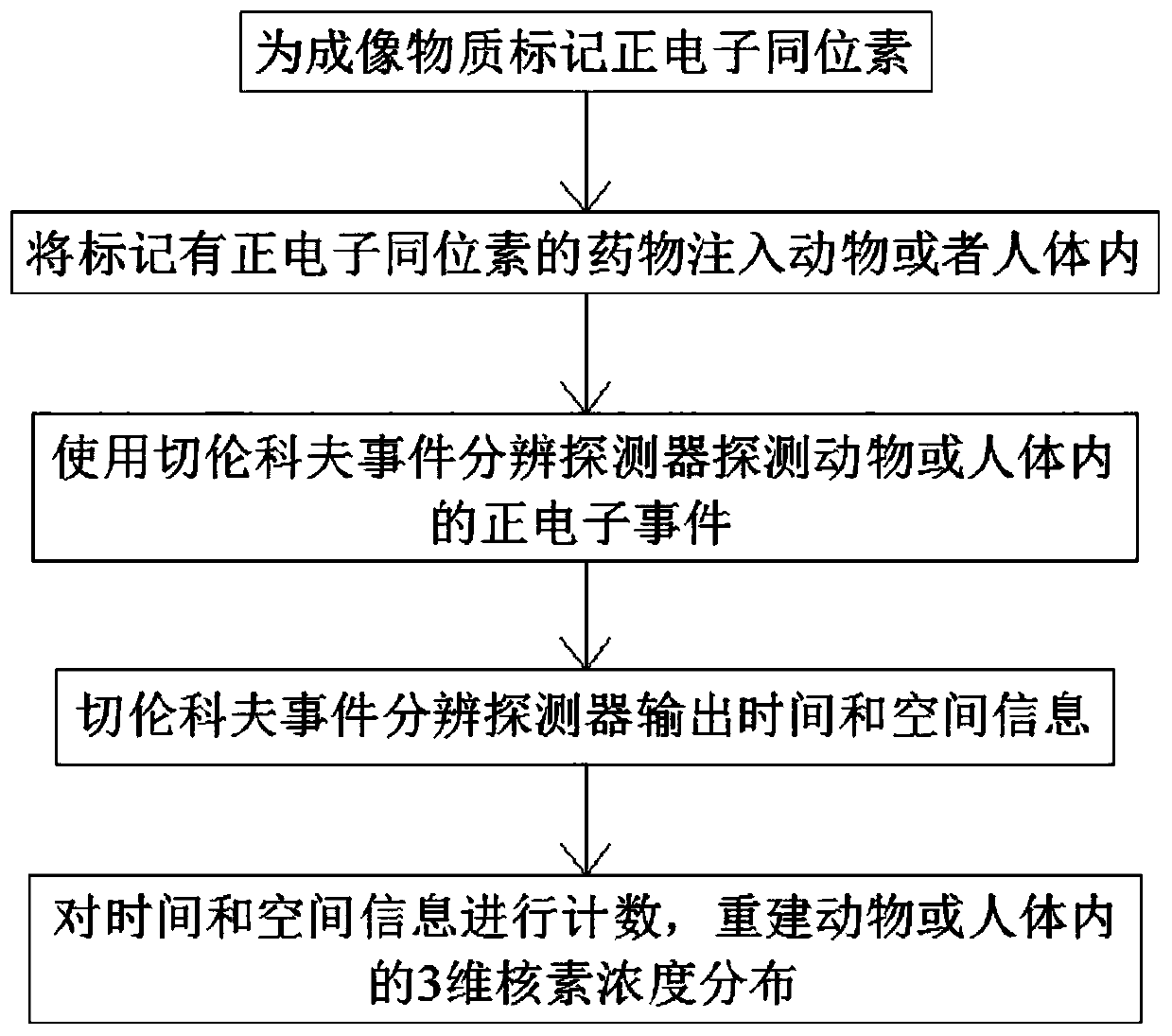
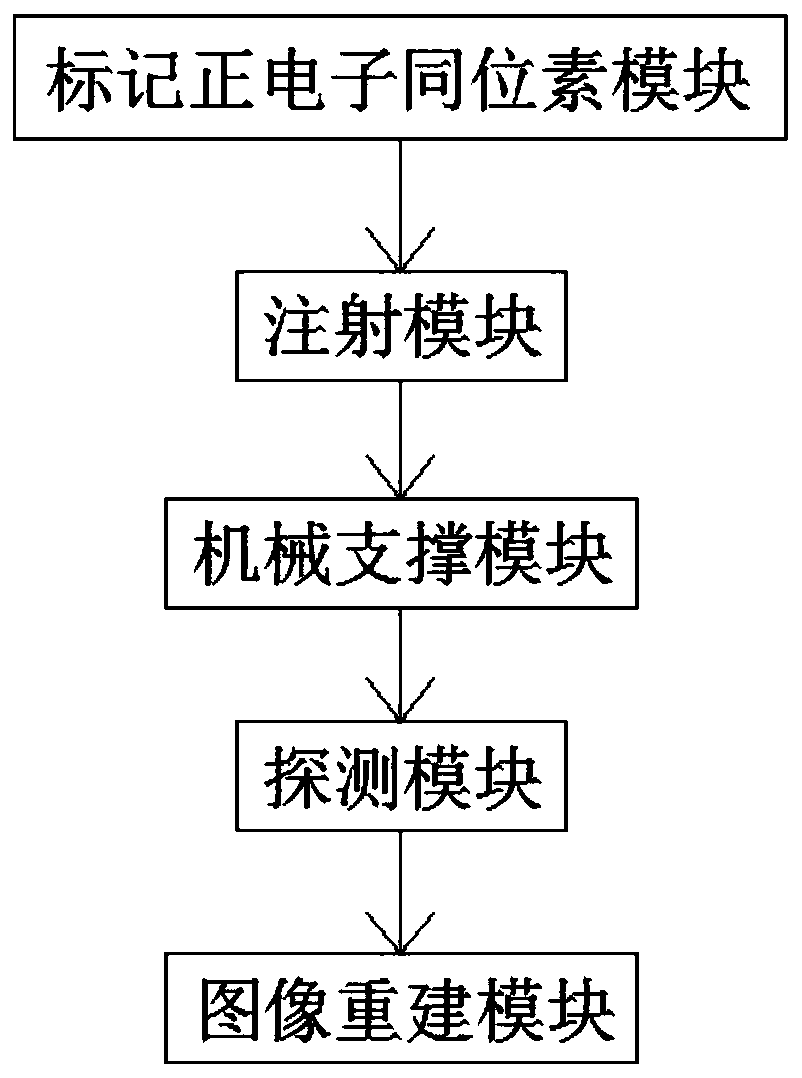
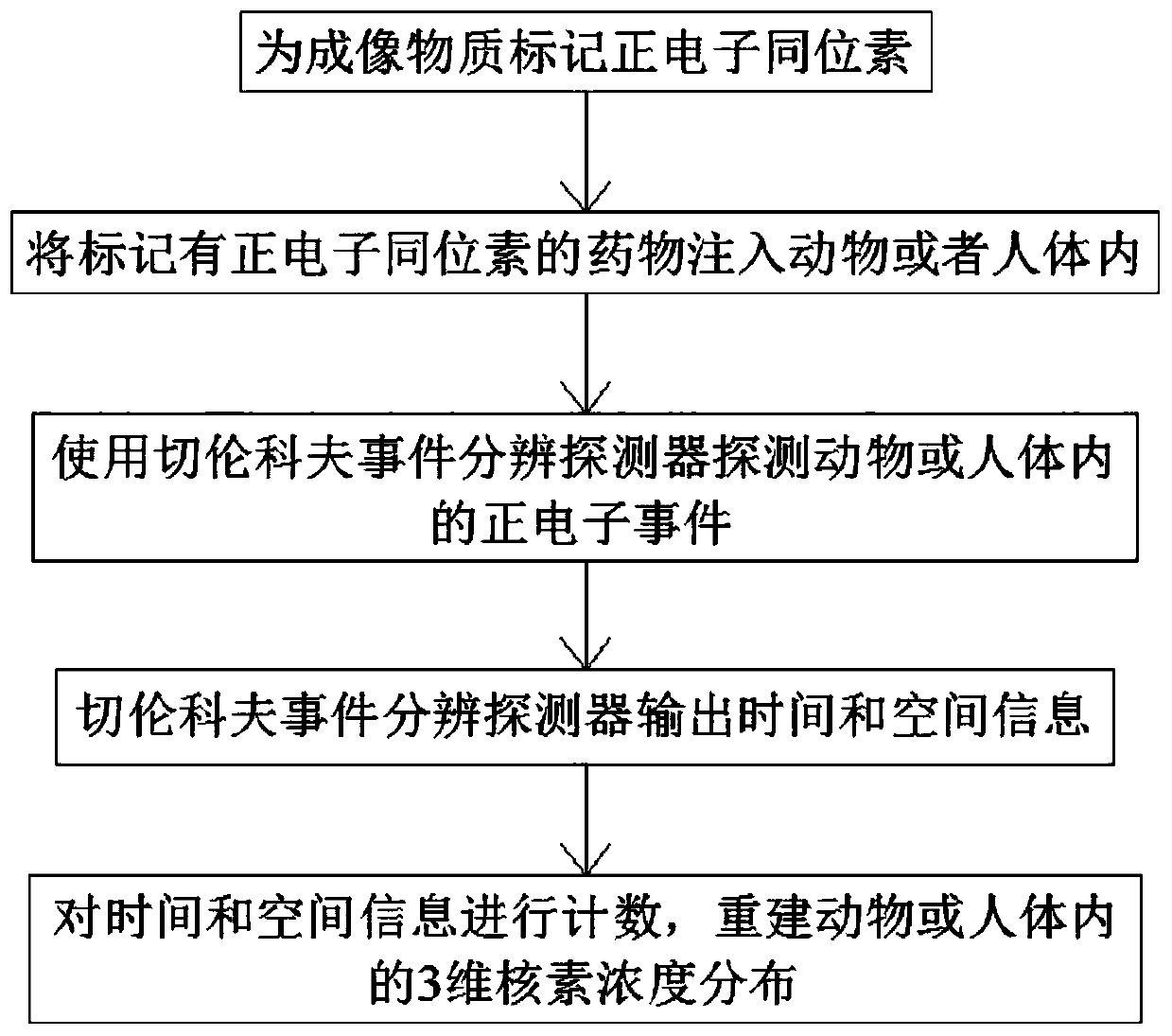
InactiveCN109998581AReduce background noiseImprove spatial resolutionComputerised tomographsTomographyImaging qualityIsotope
The invention discloses a holographic positive electron concentration imaging method. The method comprises the steps of labeling a positive electron isotope for an imaging substance; injecting a druglabeled with the positive electron isotope into an animal or the human body, so that the drug is distributed in the animal or the human body; utilizing a Cherenkov event resolution detector for detecting a positive electron event in the animal or the human body; utilizing the Cherenkov event resolution detector for outputting time and space information; counting the time and space information of the Cherenkov event resolution detector, and reconstructing three-dimensional nuclide concentration distribution in the animal or the human body. The method can effectively improve the spatial resolution and sensitivity of the gamma mode PET, is particularly suitable for clinical PET which has a very high requirement for the accuracy and precision, and is widely applied in cancers and cardiovascular diseases. The high spatial resolution and time resolution facilitate improvement of the imaging quality; the high sensitivity facilitates lowering of imaging background noise, and the problem that statistical noise influence is intensified under the high resolution is solved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Surface Classification Method Based on Background Noise Ratio of Single Photon LiDAR
ActiveCN110501716BReduce computationFast operationScene recognitionElectromagnetic wave reradiationEarth surfaceTopographic map
The invention discloses a ground surface classification method based on the background noise rate of single-photon laser radar. First, the expression of the photon reflection noise rate of the water surface is proposed according to the mirror reflection theory, and then the background is established by combining system parameters, environmental parameters and target characteristic parameters. The noise rate model provides the mathematical expressions of the land background noise rate and the water body background noise rate respectively, and finally calculates the threshold value of the surface classification noise rate. According to the significant difference between the background noise rate of land and water bodies, the statistical noise rate of the original point cloud data of lidar can be compared with the noise rate threshold to judge the surface type. This classification method does not rely on digital topographic maps or high-resolution remote sensing images used in traditional methods, and the auxiliary data used are easy to obtain, fast and efficient, and can achieve high-precision classification of surface types in coastal areas. The method is applied to MABLE original point cloud data, and the classification effect is excellent.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
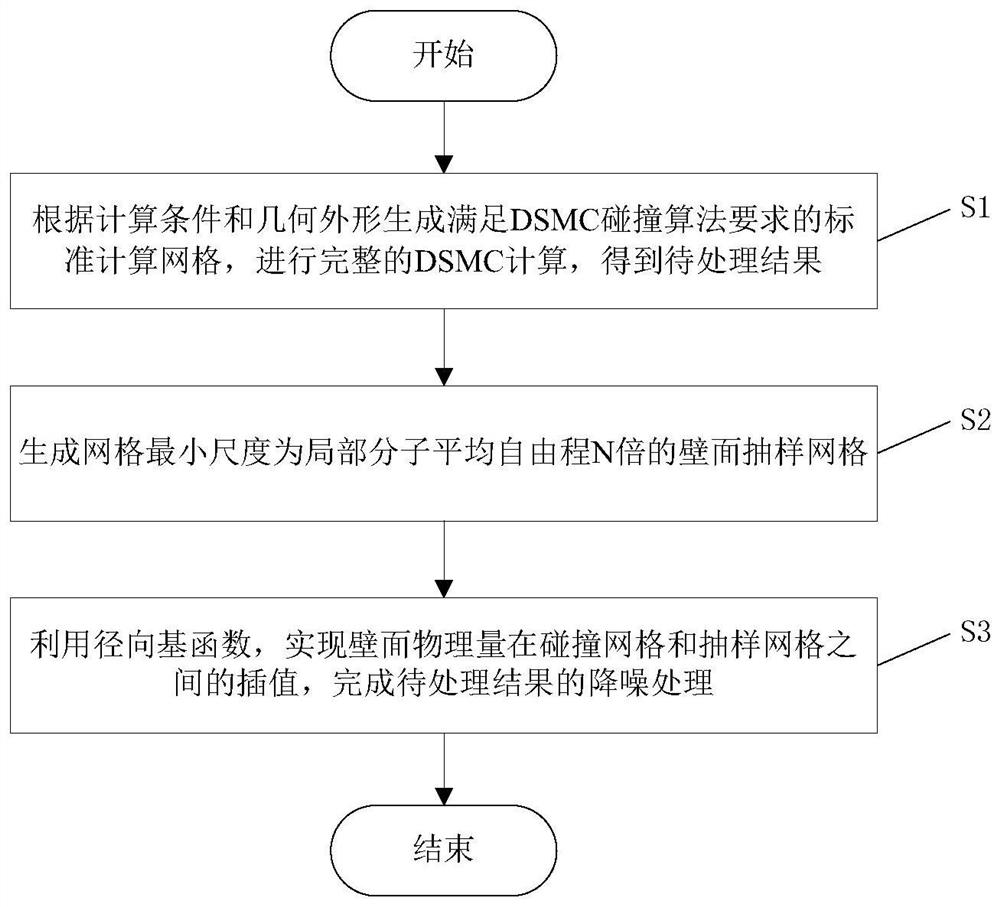
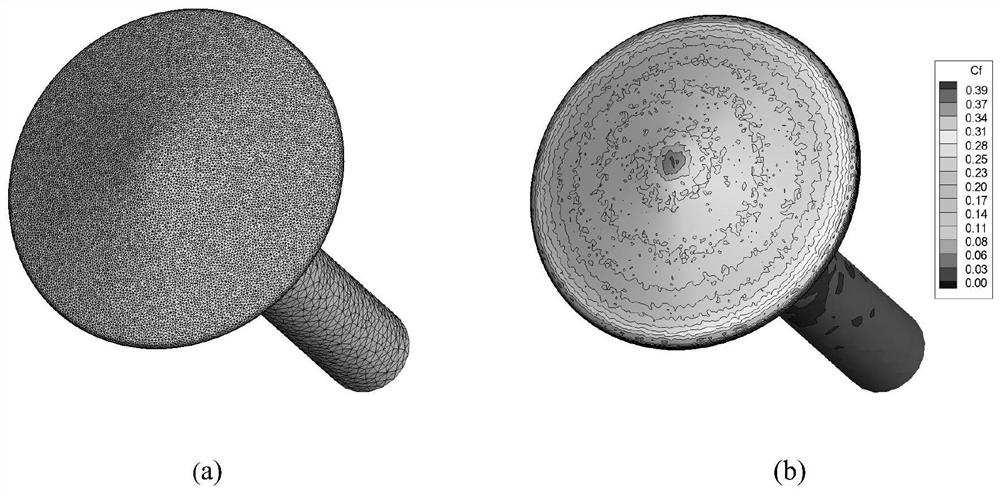
DSMC calculation result noise reduction processing method based on radial basis function
ActiveCN112560358AIncrease the number of statistical samplesIncrease the number of sampling stepsDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingComplete dataAlgorithm
The invention discloses a DSMC calculation result noise reduction processing method based on a radial basis function. According to the method, the idea that the collision grids and the sampling gridsare separated is used for reference, two sets of grids with different thicknesses are adopted, and statistical noise is reduced by increasing the number of statistical samples. A radial basis functiontool is used for completing data interpolation from physical data on an original collision grid node to a sampling grid node, the number of simulation molecules in a unit does not need to be increased or the sampling step number does not need to be increased, and the method has the advantages that a main calculation program is not affected, calculation is simple, the workload is small, and the calculation precision is high.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com