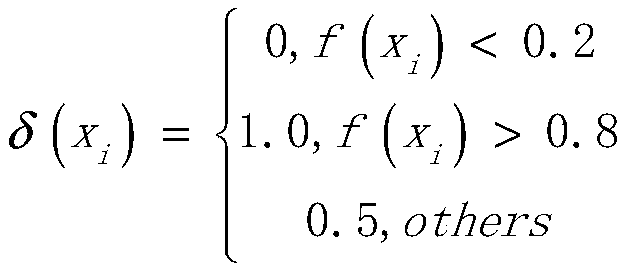Patents
Literature
87 results about "Radiotherapy dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
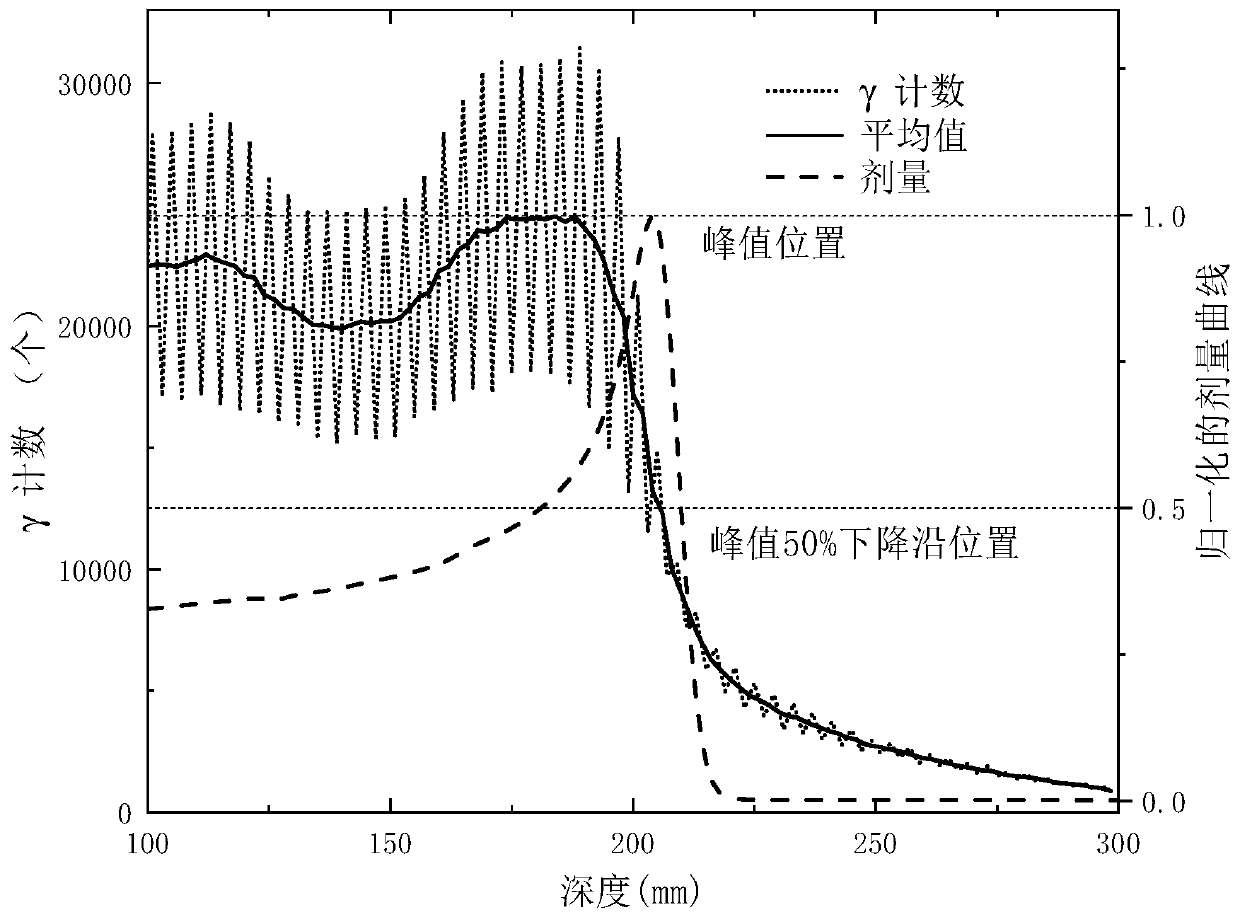
Typical dose is 180-200 cGy/day radiation is given in "fractions" as radiotherapy is cumulative. the total dose of therapy is the summation of all the separate fractions given during treatment.
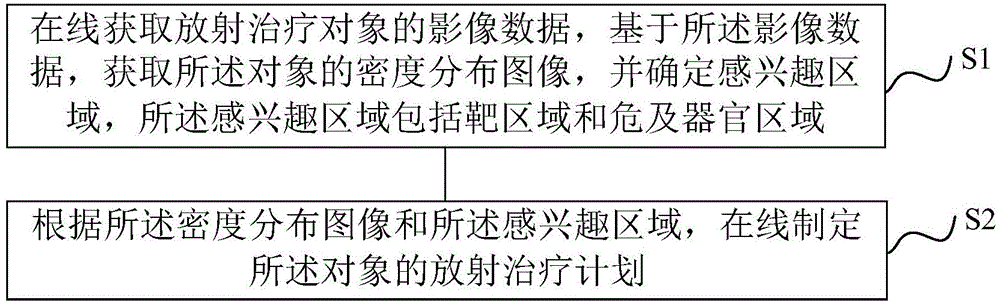
Radiotherapy planning method and device, radiotherapy dose determining method and device and radiotherapy quality guaranteeing method and device
ActiveCN104548372AHigh precisionReduce repetitive setup errorsRadiation therapyObject basedDensity distribution
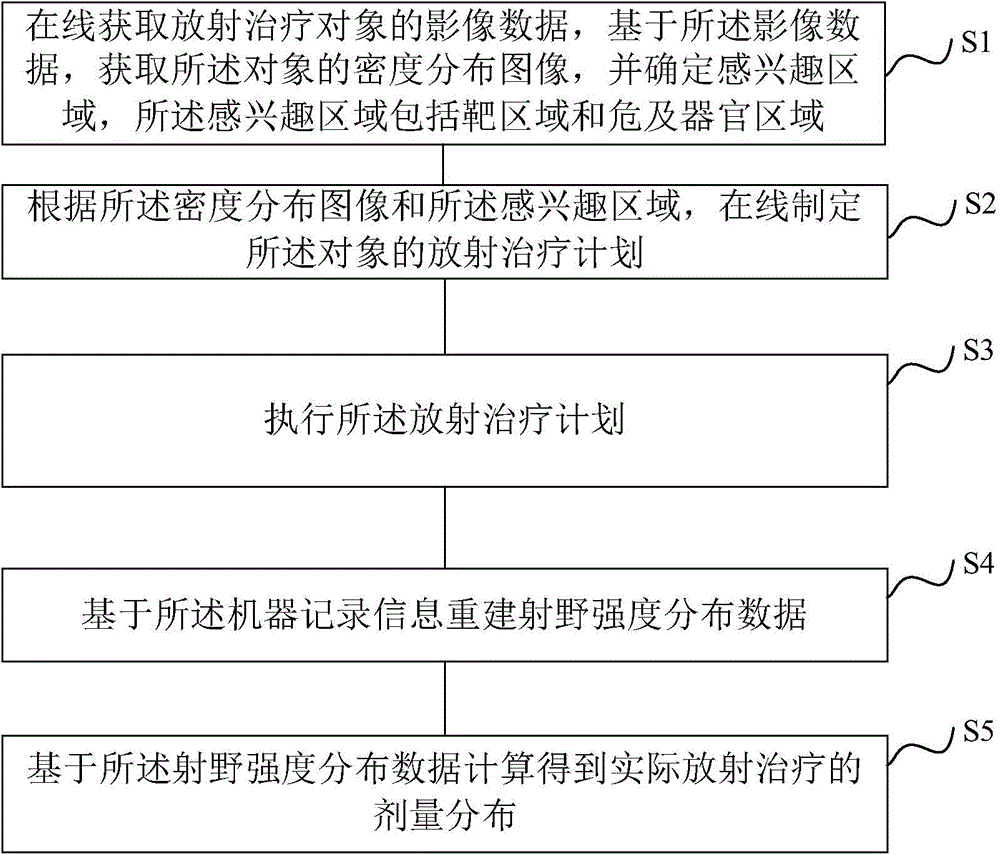
The invention discloses a radiotherapy planning method and device, a radiotherapy dose determining method and device and a radiotherapy quality guaranteeing method and device. The radiotherapy dose determining method includes the steps of online obtaining image data of a radiotherapy object, obtaining a density distribution image of the object based on the image data, determining a region of interest, and online making a radiotherapy plan of the object according to the density distribution image and the region of interest; executing the radiotherapy plan; rebuilding radiation field intensity distribution data based on information recorded by machines; carrying out calculation based on the radiation field intensity distribution data to obtain practical radiotherapy dose distribution. As the online-obtained image data are adopted, the accuracy of the image data is improved; as the radiation field intensity distribution data are rebuilt based on the information recorded by the machines, the dose distribution accuracy is higher. In the radiotherapy quality guaranteeing method, when deviation exists between the practical dose distribution result and a main plan dose, a sub-plan is modified, it is guaranteed that the use total dost is coincident with the plan dose, and the radiotherapy quality is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
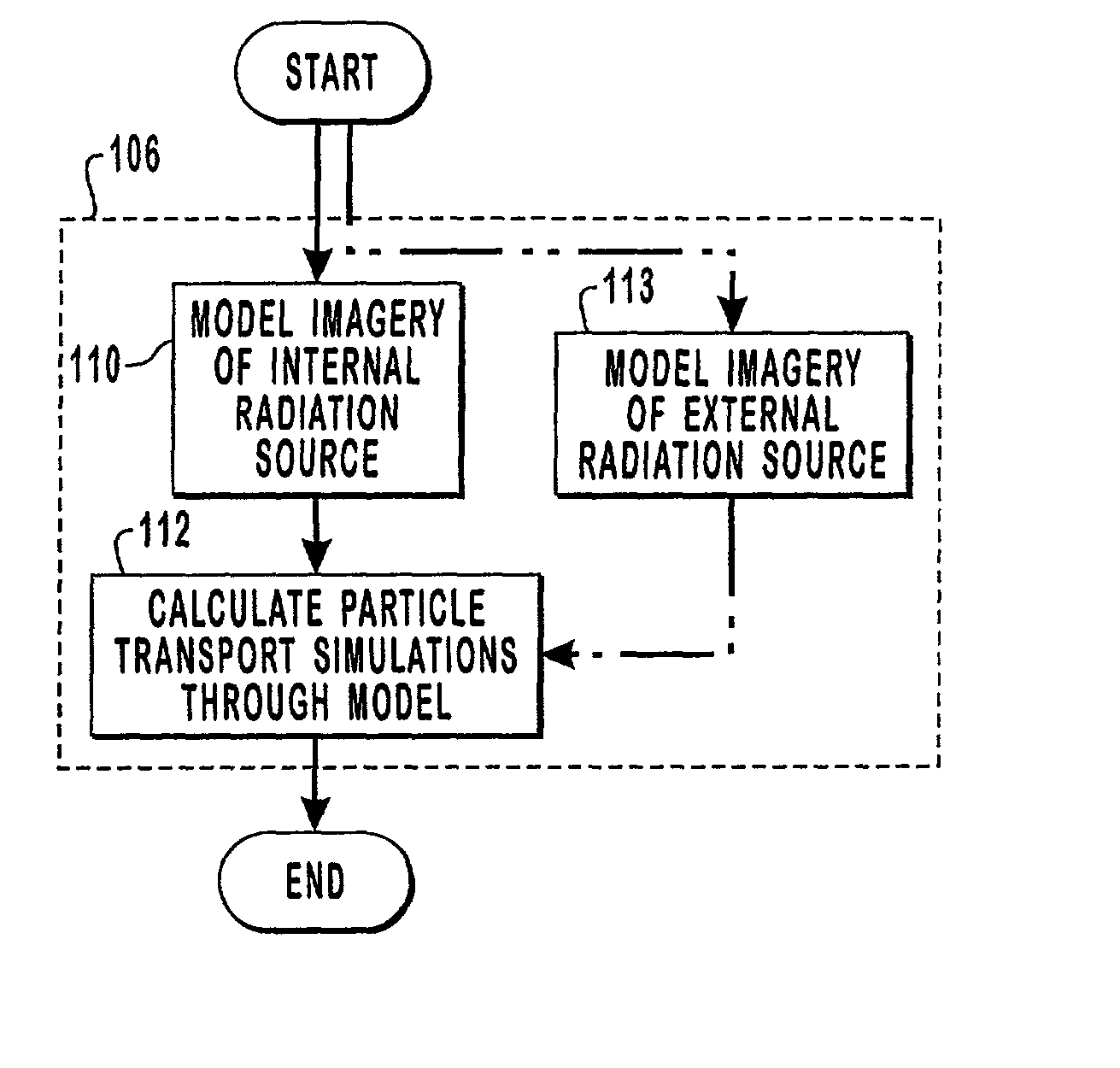
Methods and computer readable medium for improved radiotherapy dosimetry planning
InactiveUS20020046010A1Simple methodImprove calculation accuracyMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDosimetry radiationHigh energy
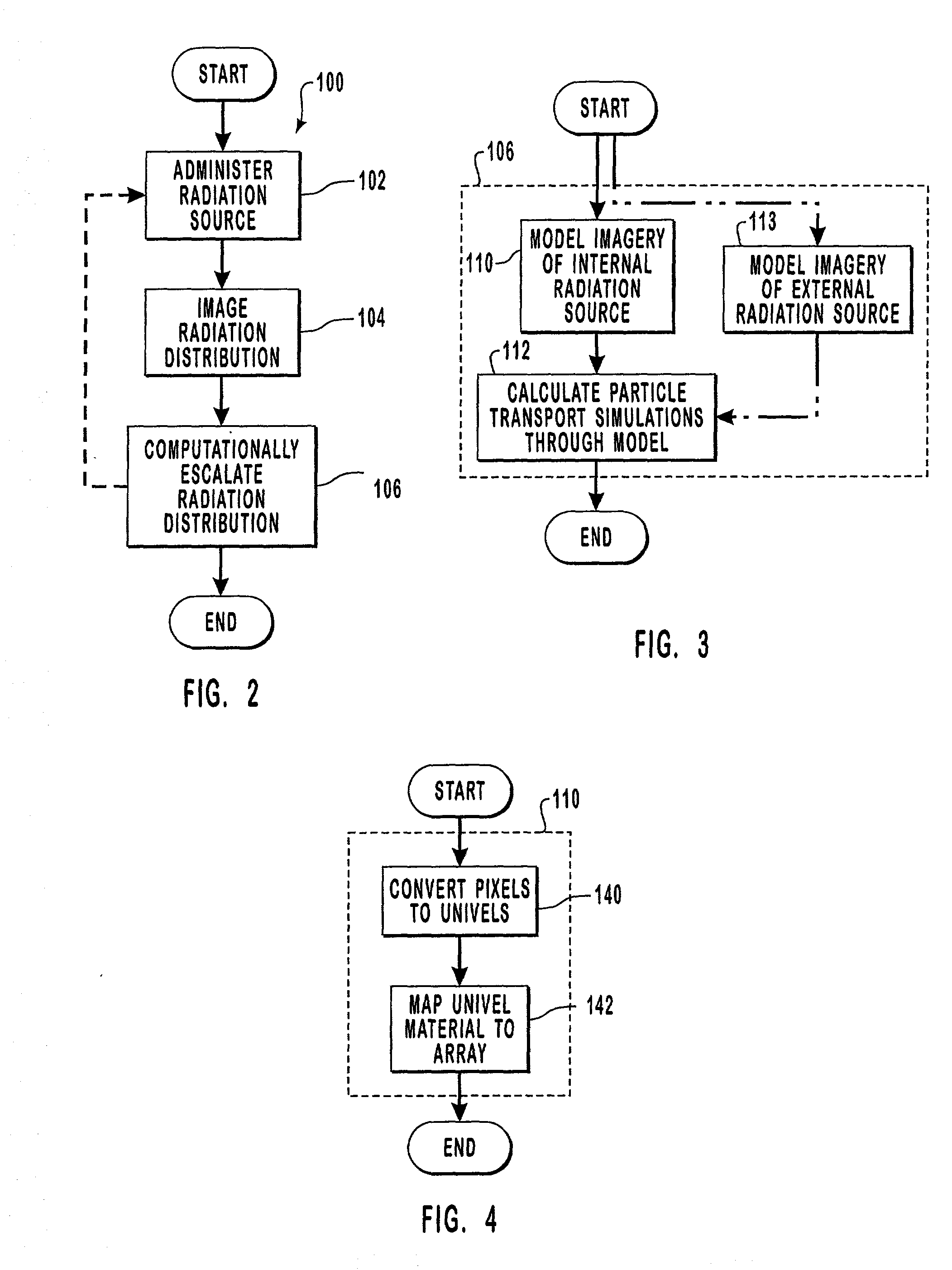
Methods and computer readable media are disclosed for ultimately developing a dosimetry plan for a treatment volume irradiated during radiation therapy with a radiation source concentrated internally within a patient or incident from an external beam. The dosimetry plan is available in near"real-time" because of the novel geometric model construction of the treatment volume which in turn allows for rapid calculations to be performed for simulated movements of particles along particle tracks therethrough. The particles are exemplary representations of alpha, beta or gamma emissions emanating from an internal radiation source during various radiotherapies, such as brachytherapy or targeted radionuclide therapy, or they are exemplary representations of high-energy photons, electrons, protons or other ionizing particles incident on the treatment volume from an external source. In a preferred embodiment, a medical image of a treatment volume irradiated during radiotherapy having a plurality of pixels of information is obtained.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
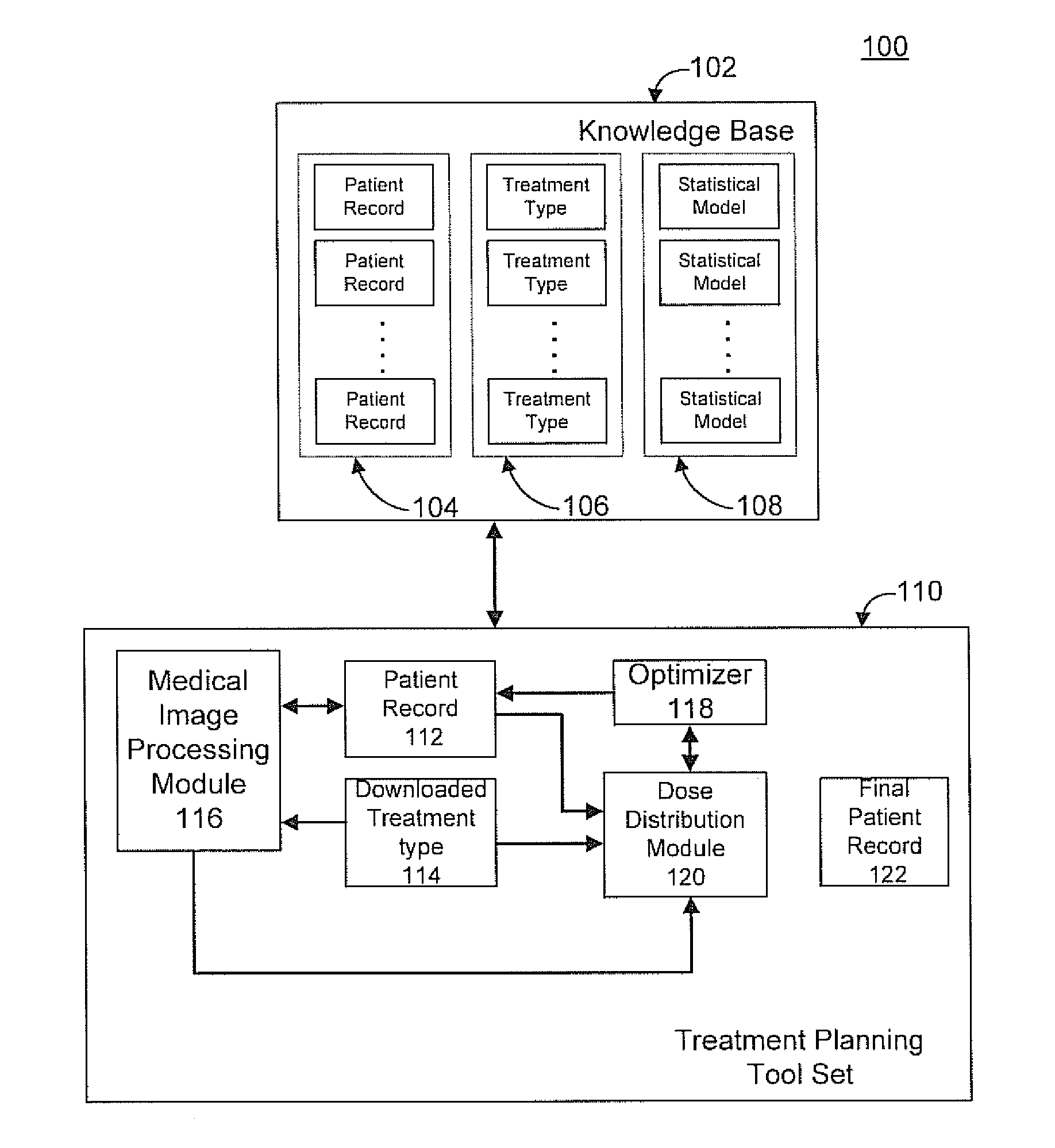
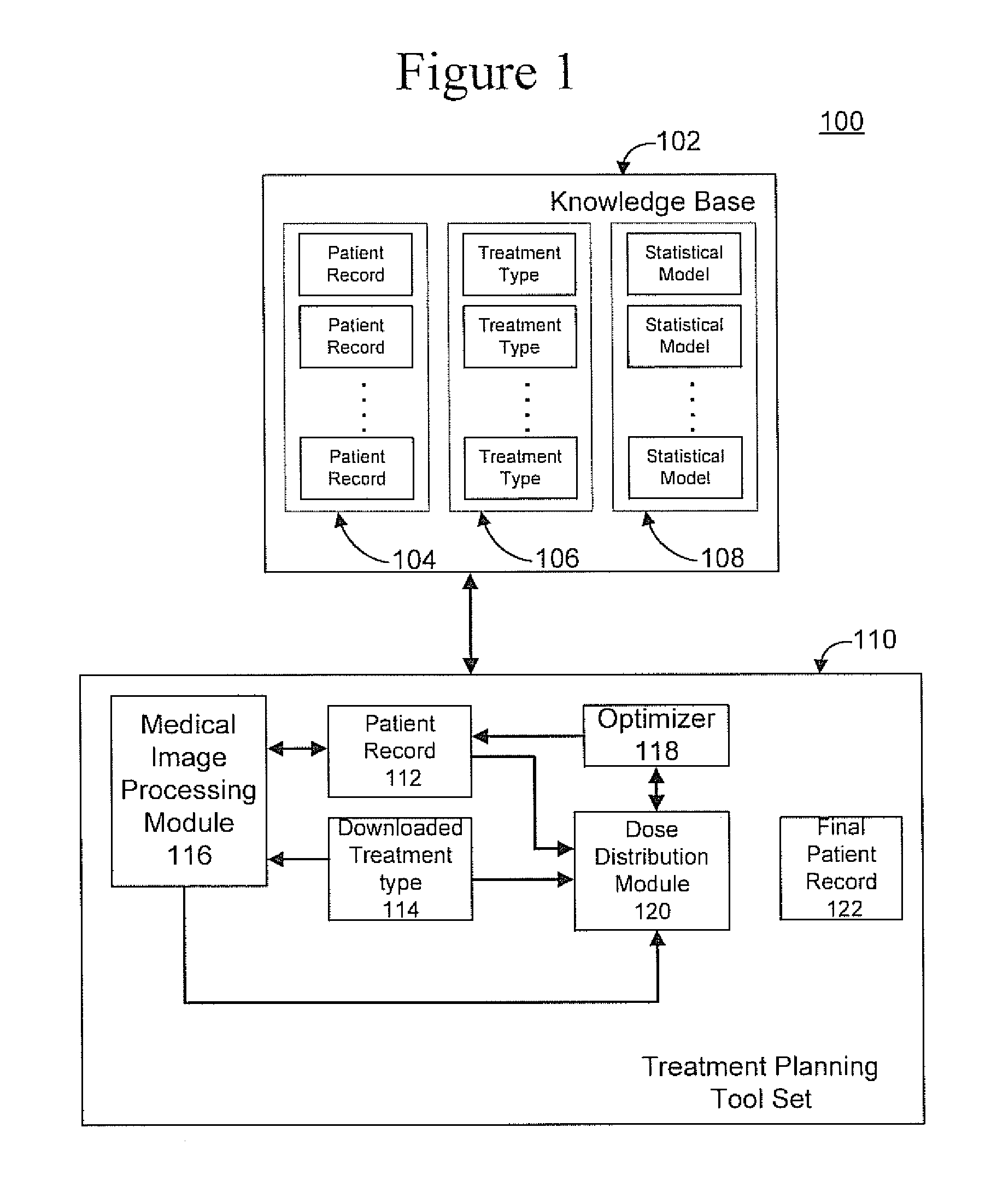
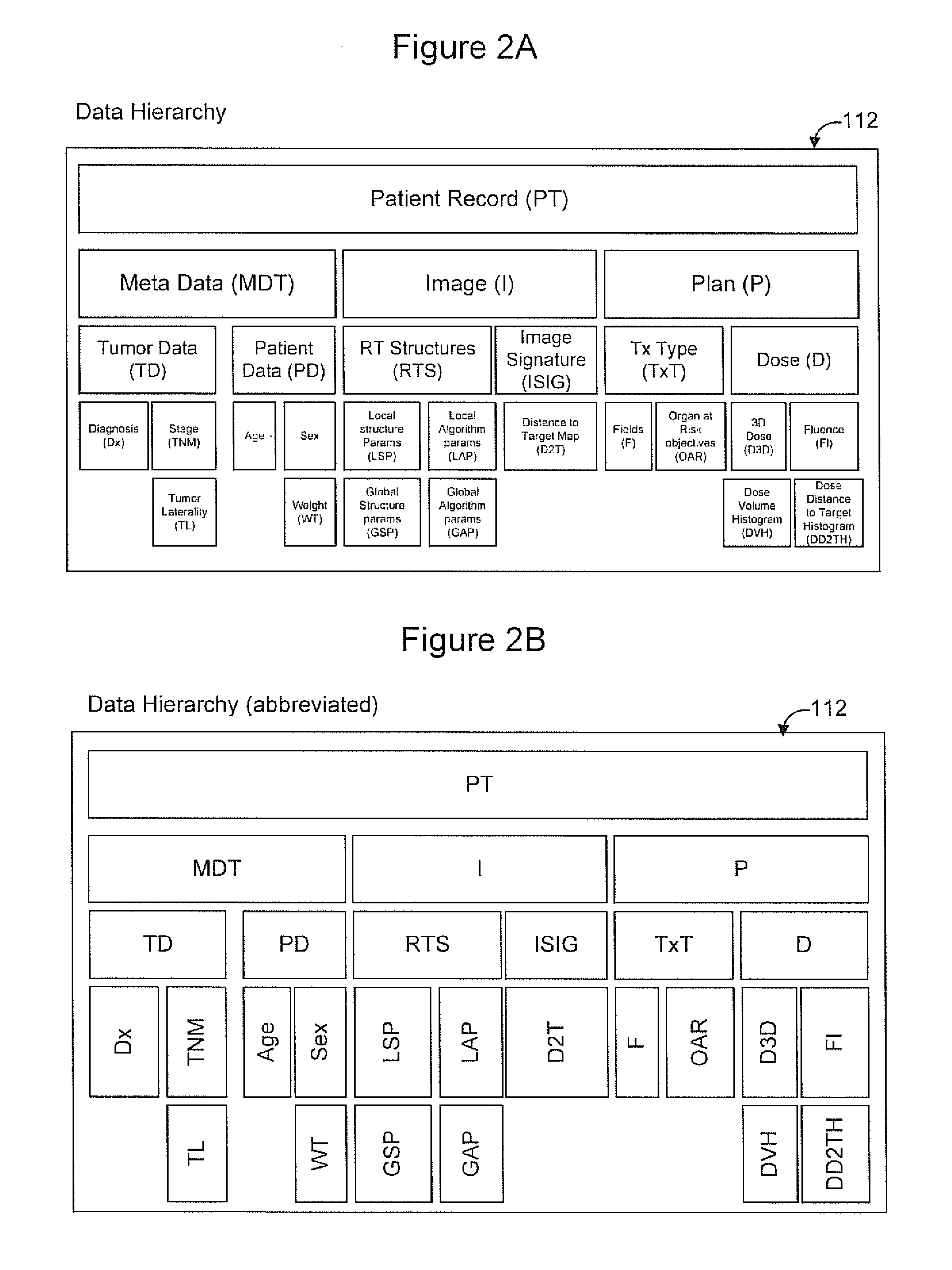
Radiation therapy treatment plan improvement through use of knowledge base
A radiation therapy dose distribution method starts with selecting a treatment type. Then an organ at risk (OAR) distance to target map is determined. The OAR distance to target map comprises distances to a target organ for portions of an OAR. The OAR distances are determined from at least one segmented patient organ image. A cohort average dose distance to target histogram is selected. A dose value to the portions of the OAR are assigned to form a first 3D dose distribution map. The dose values are from the selected cohort average dose distance to target histogram. A second 3D dose distribution map is determined based on a field arrangement determined by the treatment type and the first 3D dose distribution map. A dose distance to target histogram is calculated using the second 3D dose distribution map and the distance to target map.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
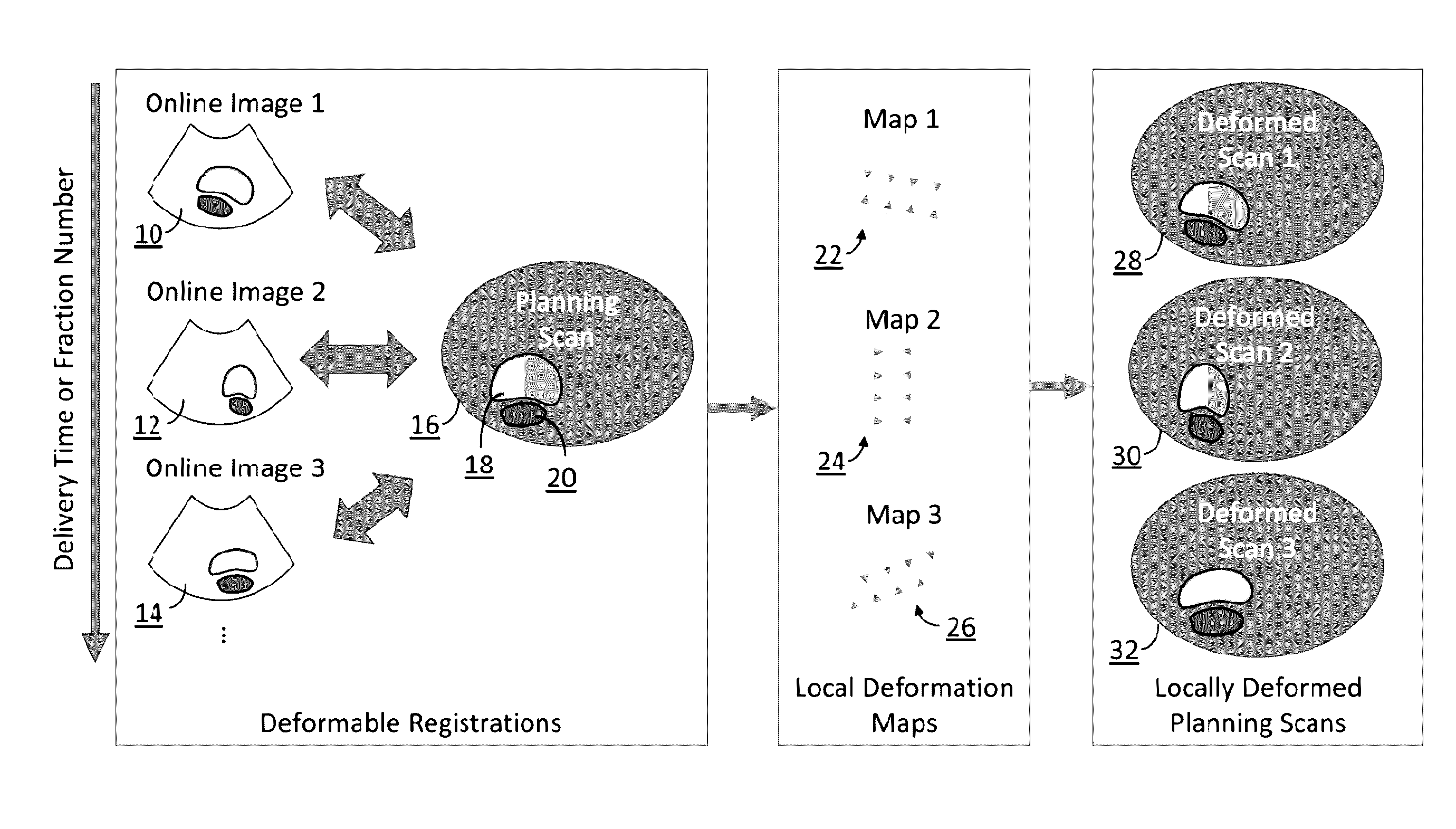
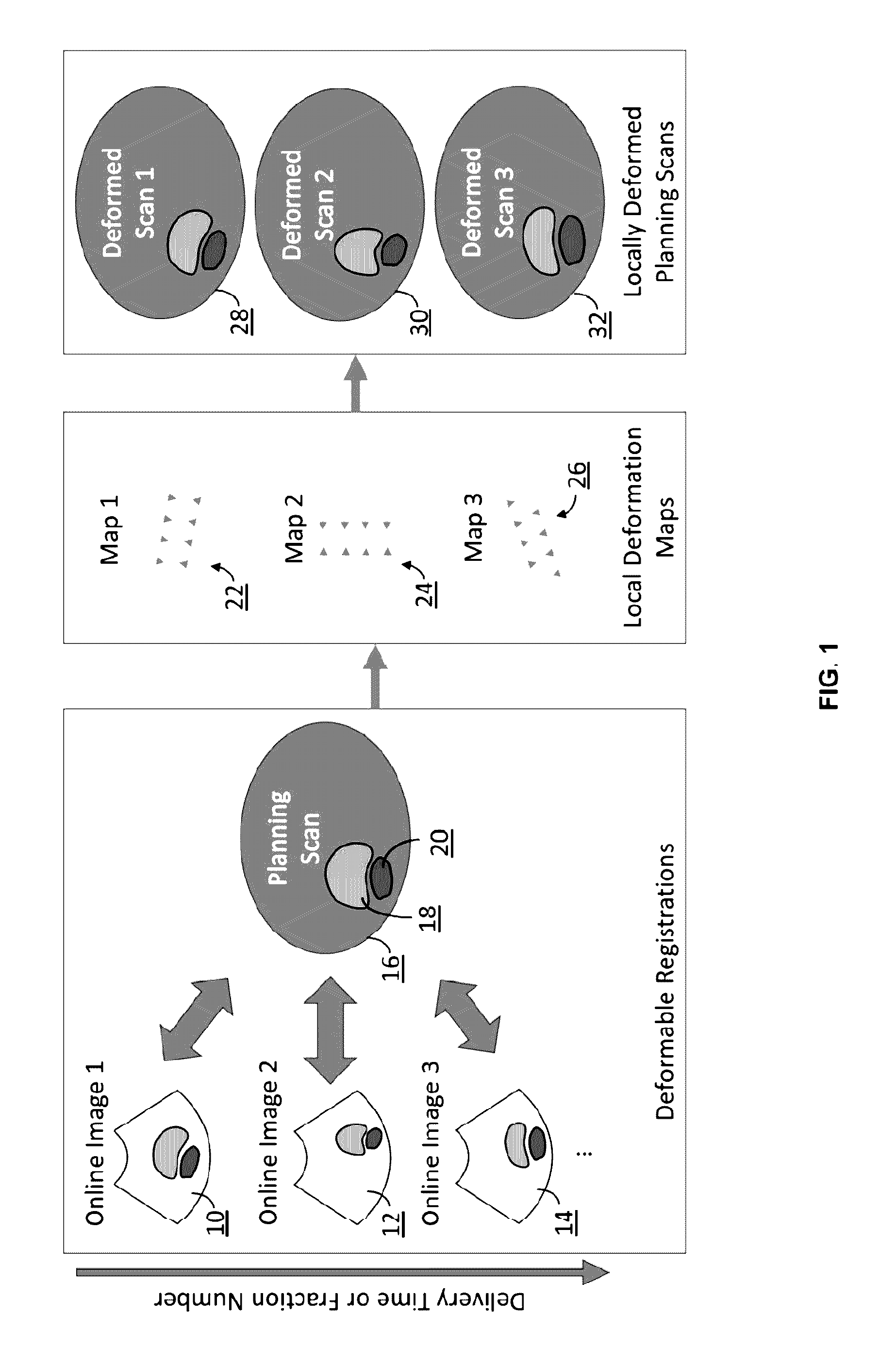
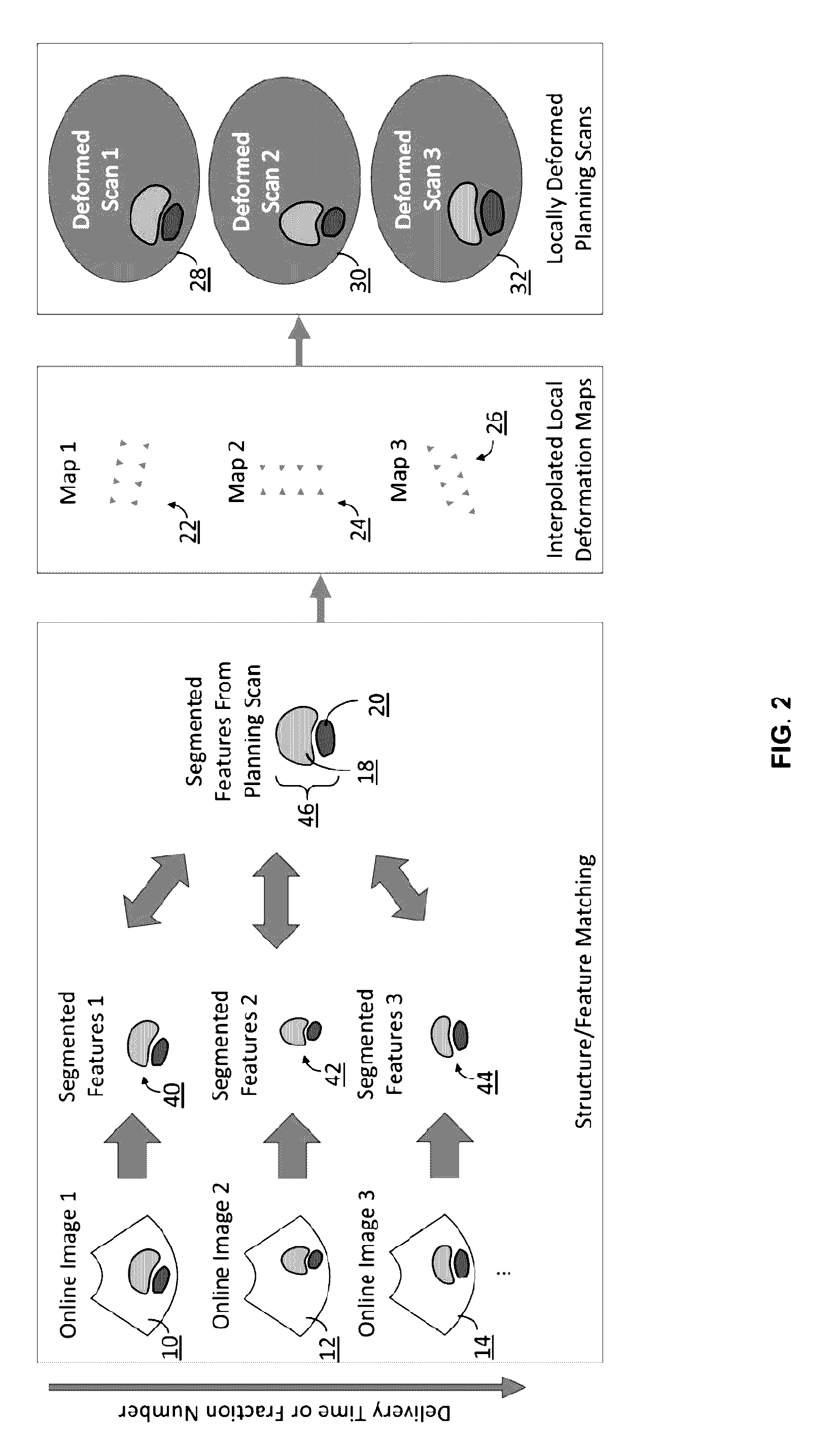
Radiotherapy dose assessment and adaption using online imaging
InactiveUS20160279444A1Improve representationUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingTreatment deliveryPlanned Dose
In external beam radiation therapy, a planning image (scan) of the patient is obtained prior to treatment as a basis for constructing a radiation delivery plan. However, since the planning scan is obtained prior to treatment (potentially days or weeks prior), it does not necessarily represent the state of the patient's anatomy as it presents at the time of treatment beam delivery. The potential mismatch between the patient's anatomy in the planning scan and anatomy at the time of treatment can result in dose discrepancies between the planned dose and the actual delivered dose. The methods herein describe the use of online images taken immediately before or during treatment delivery in order to predict, assess, and adapt to such discrepancies.
Owner:SONITRACK SYST
System and method for learning models of radiotherapy treatment plans to predict radiotherapy dose distributions
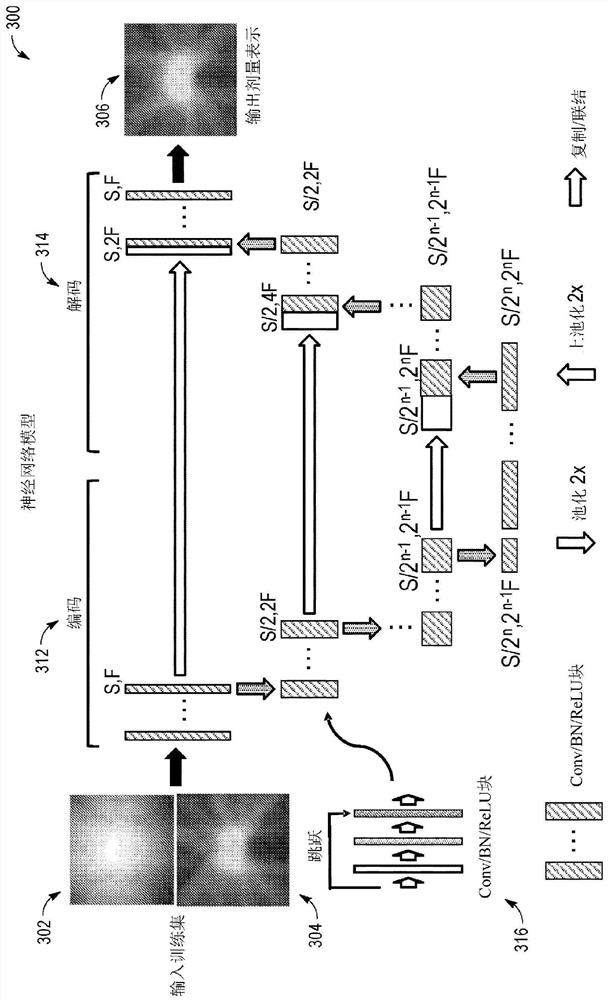
ActiveCN109843377ACutting costsLower latencyMedical automated diagnosisMedical imagesMedicineStudy methods
The present invention relates to systems and methods for developing radiotherapy treatment plans though the use of machine learning approaches and neural network components. A neural network is trained using one or more three-dimensional medical images, one or more three-dimensional anatomy maps, and one or more dose distributions to predict a fluence map or a dose map. During training the neuralnetwork receives a predicted dose distribution determined by the neural network that is compared to an expected dose distribution. Iteratively the comparison is performed until a predetermined threshold is achieved. The trained neural network is then utilized to provide a three-dimensional dose distribution.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Method and system for real-time monitoring proton or heavy ion radiotherapy doses
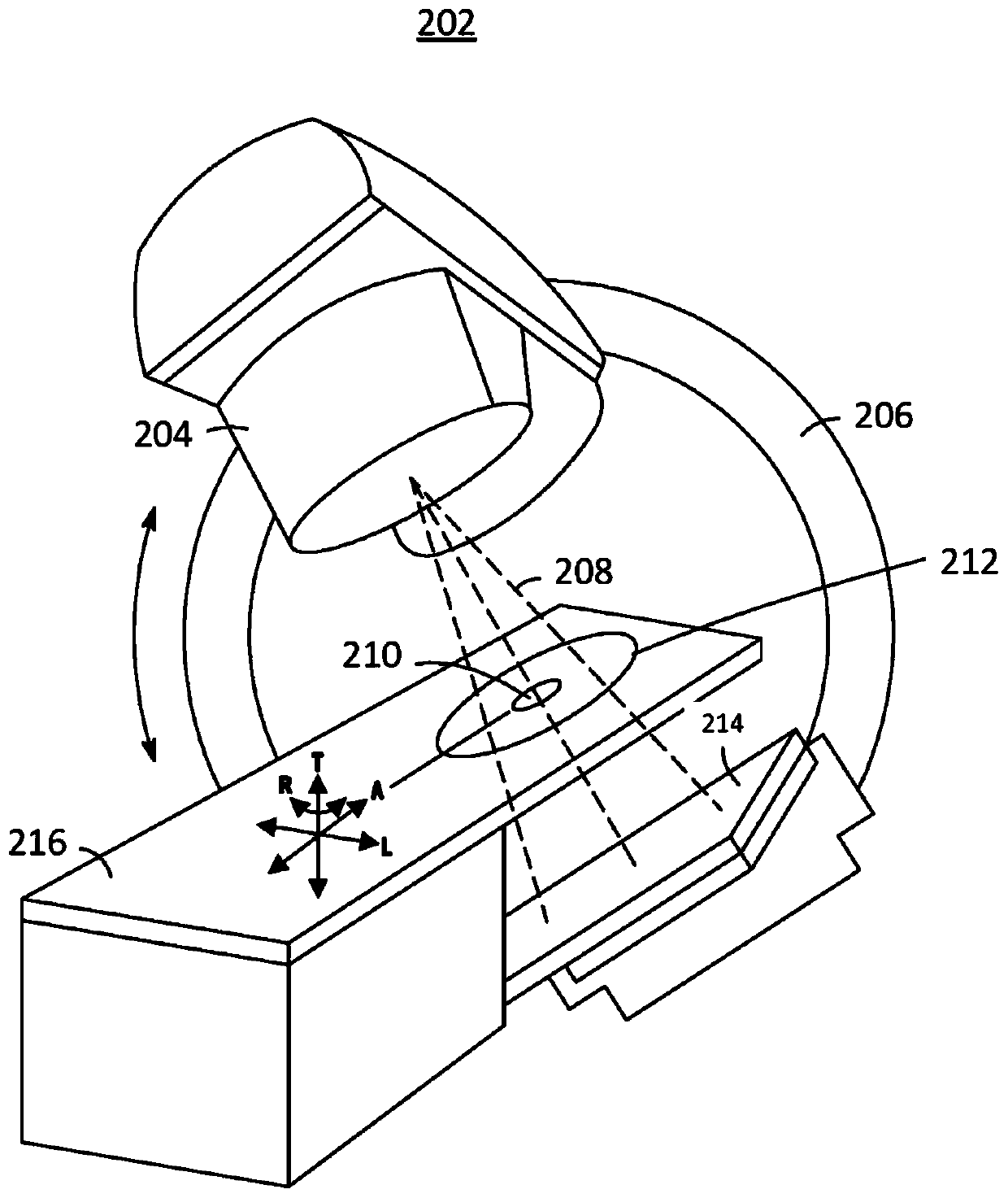
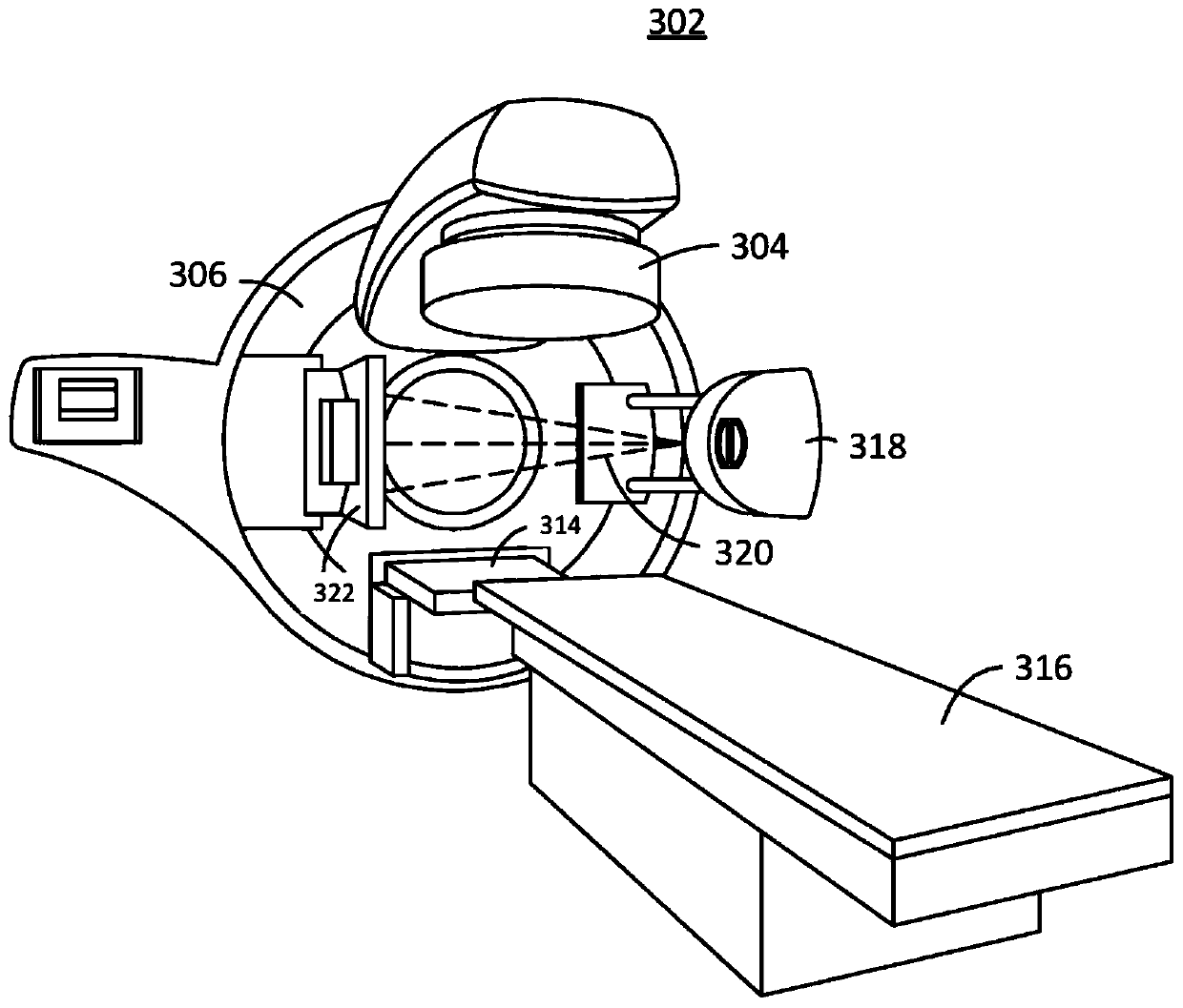
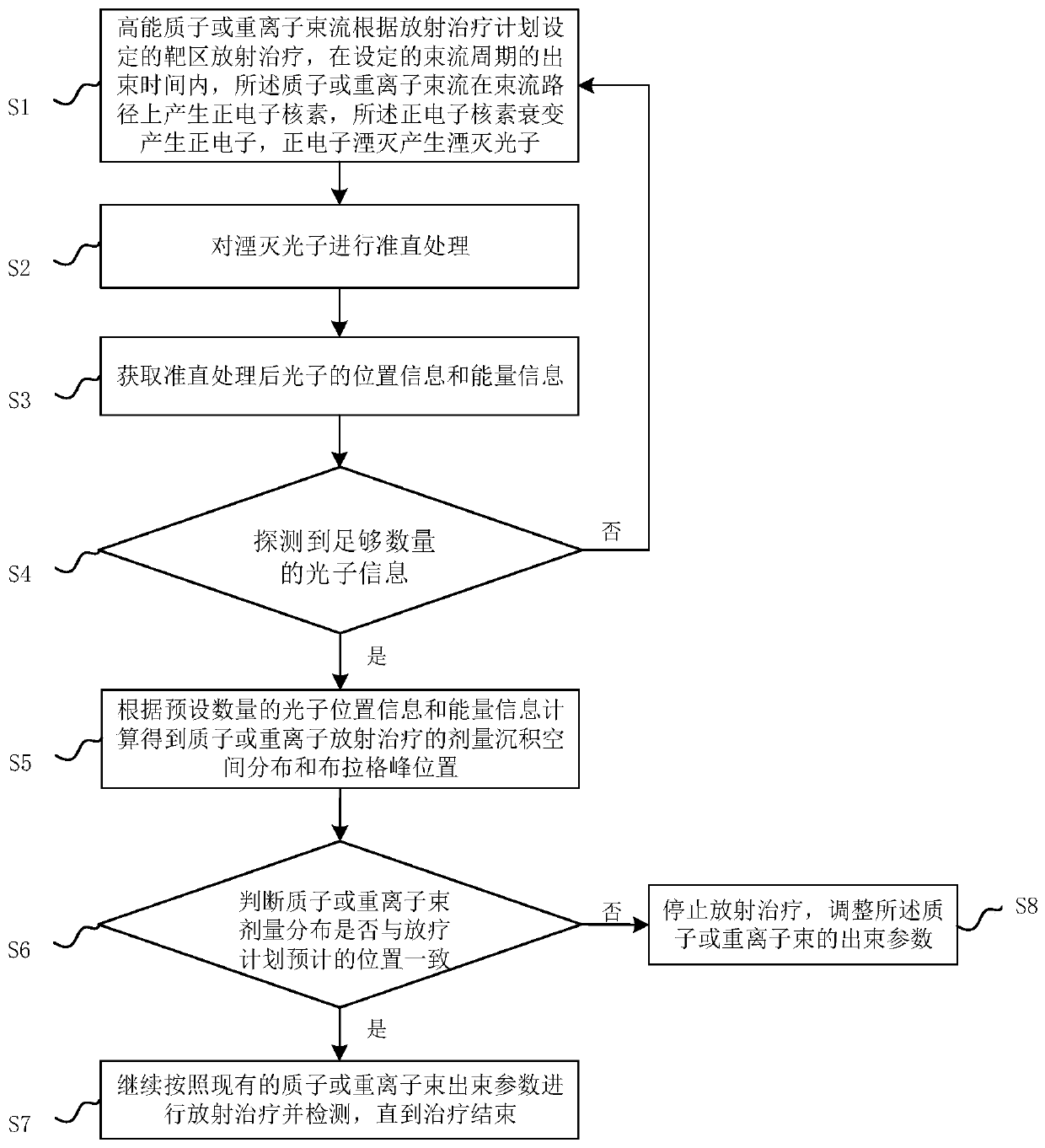
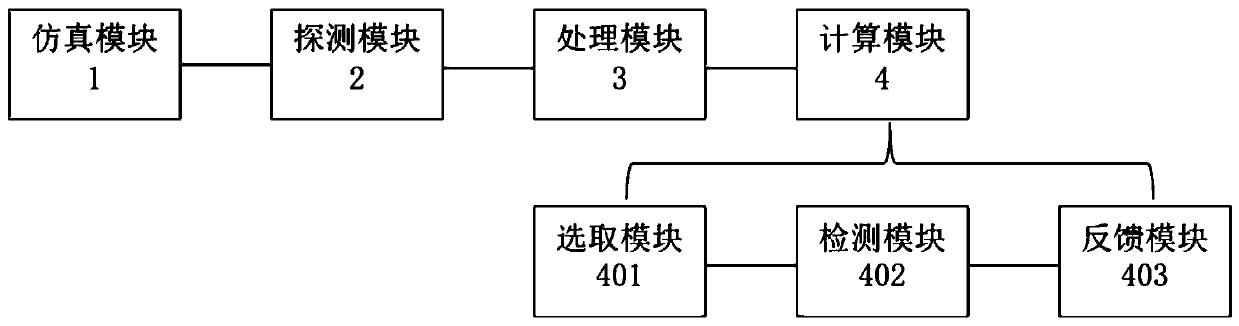
InactiveCN110270014AHigh precisionImprove detection efficiencyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyHeavy particleHeavy Ion Radiotherapy
The invention relates to a method and a system for real-time monitoring proton or heavy ion radiotherapy heavy particle radiotherapy doses. The monitoring method utilizes distribution information of positron radionuclide produced during the high-energy proton or heavy ion radiotherapy, and measures position and energy information of annihilation photons in the intermittent time of beams according to beam cycles of protons or heavy ions to obtain dose deposition spatial distributions in the proton or heavy ion radiotherapy, thereby realizing the monitoring of dose distributions of proton or heavy ion beams. Compared with the traditional instantaneous gamma measurement method, the method has a higher detection efficiency, and the method effectively reduces statistical noise, and improves accuracy of the dose deposition of the proton or heavy ion radiotherapy; compared with the traditional positron emission tomography method, the method can realize a faster one-dimensional distribution of dose along the beam direction by carrying out a collimation treatment on the annihilation photons along the beam direction and then detecting the position and energy information of the photons, thus the method is conducive to improving monitoring efficiency.
Owner:彭浩
Non-invasive tumor locating system and method
InactiveCN102697560AReal time monitoringDiagnosticsInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryAbnormal tissue growthPeristalsis
The invention relates to a non-invasive tumor locating system and a non-invasive tumor locating method. The time concept is introduced on the basis of a three-dimensional radiotherapy technology; the motion during the treatment process and the displacement error of fractionated treatment of anatomy tissue are fully considered, such as the situations at the aspects of changes of radiotherapy dose distribution and influences to the treatment plan caused by breathing peristalsis motion, daily positioning error, target region contraction and the like; and the tumor and the normal organs are monitored in real time by utilizing various kinds of advanced image devices before and during the treatment of patients, and the treatment conditions can be regulated according to the changes of the organ position, thus the radiation field follows the target region closely, and the accurate treatment is really achieved.
Owner:YITI INTELLIGENT TECH LTD SHENZHEN CITY
Method and system for calorimetry probe
InactiveUS9586060B2Calorimetric dosimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDosimetry radiationEquipment Operator
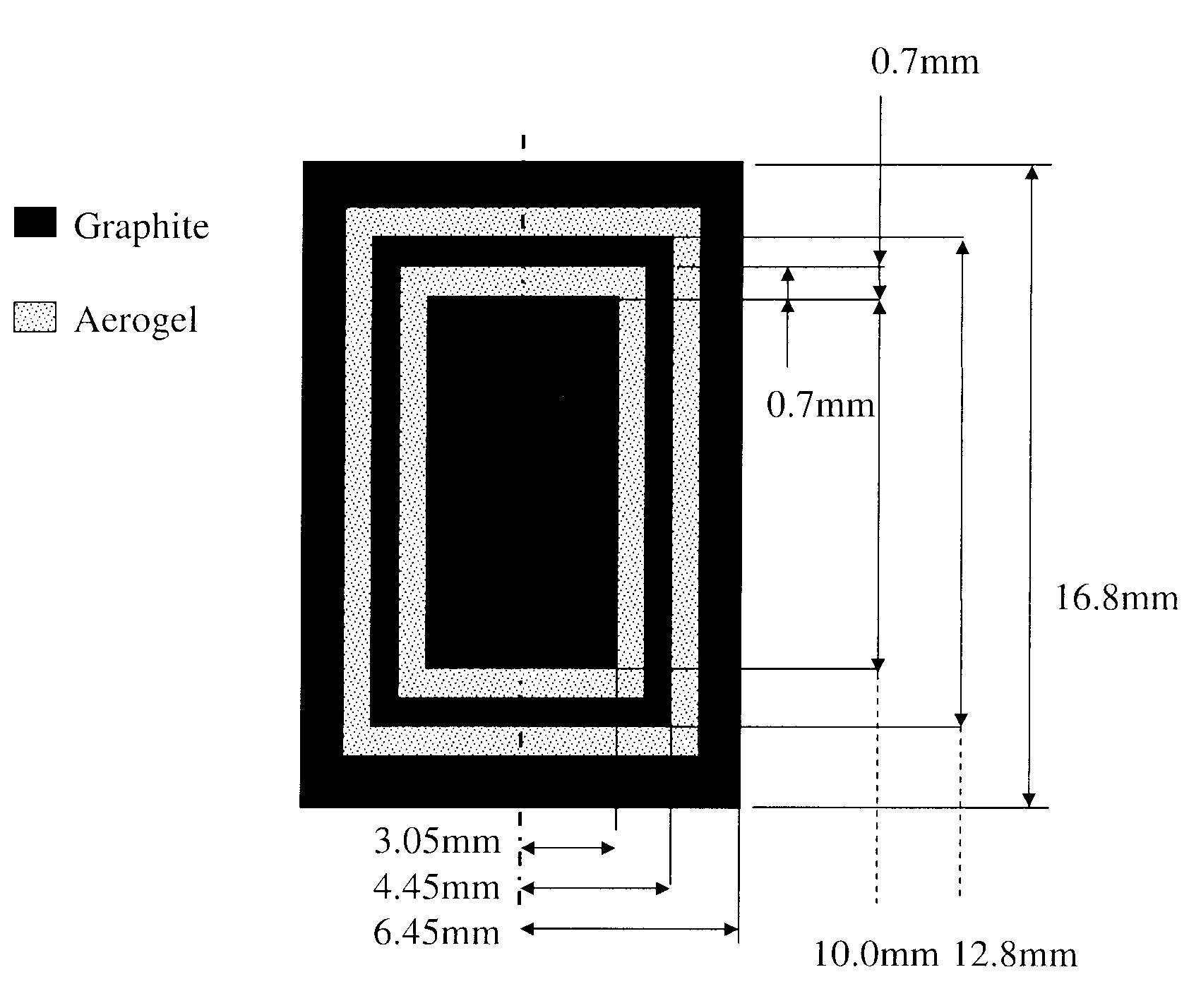
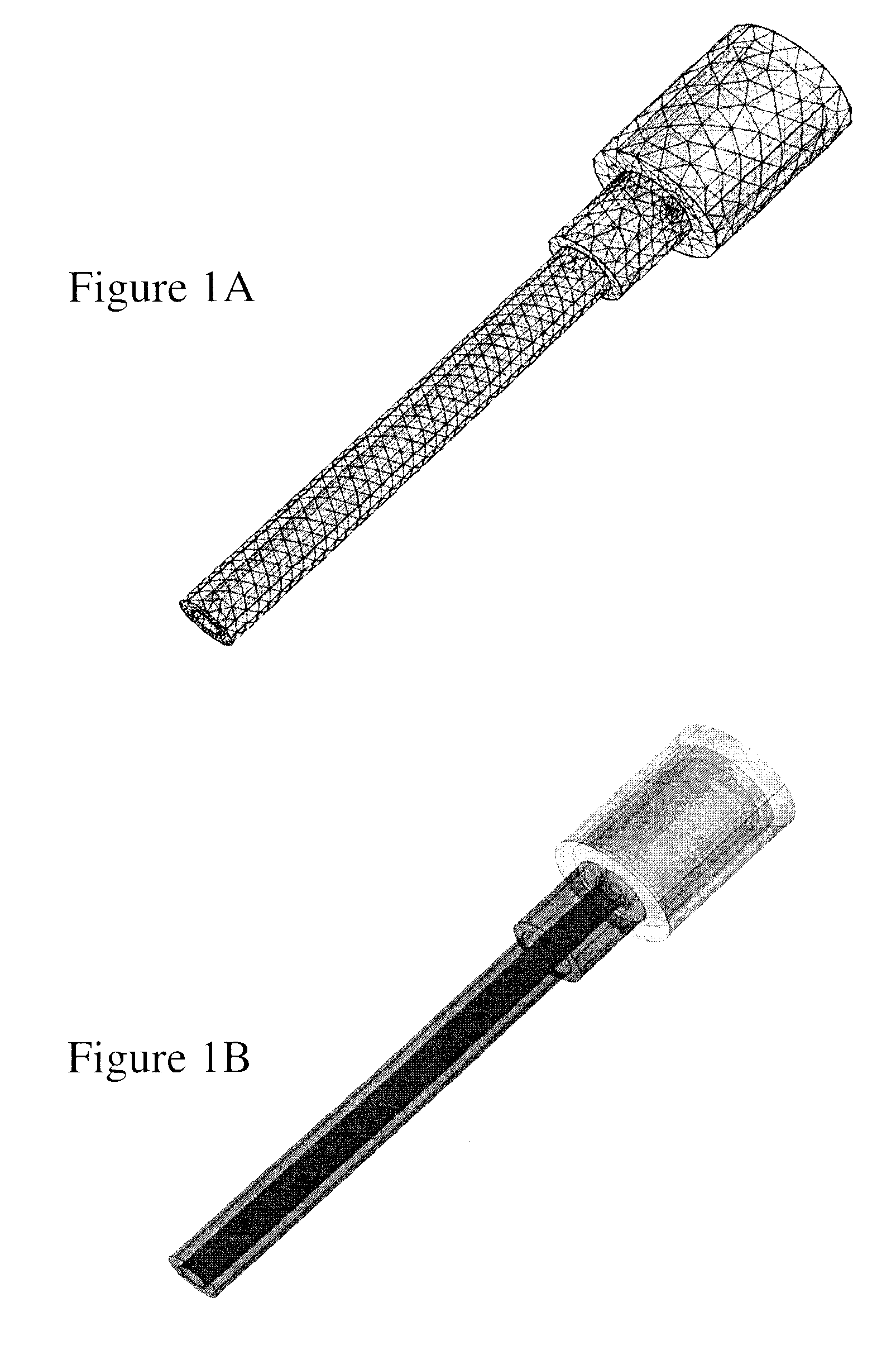
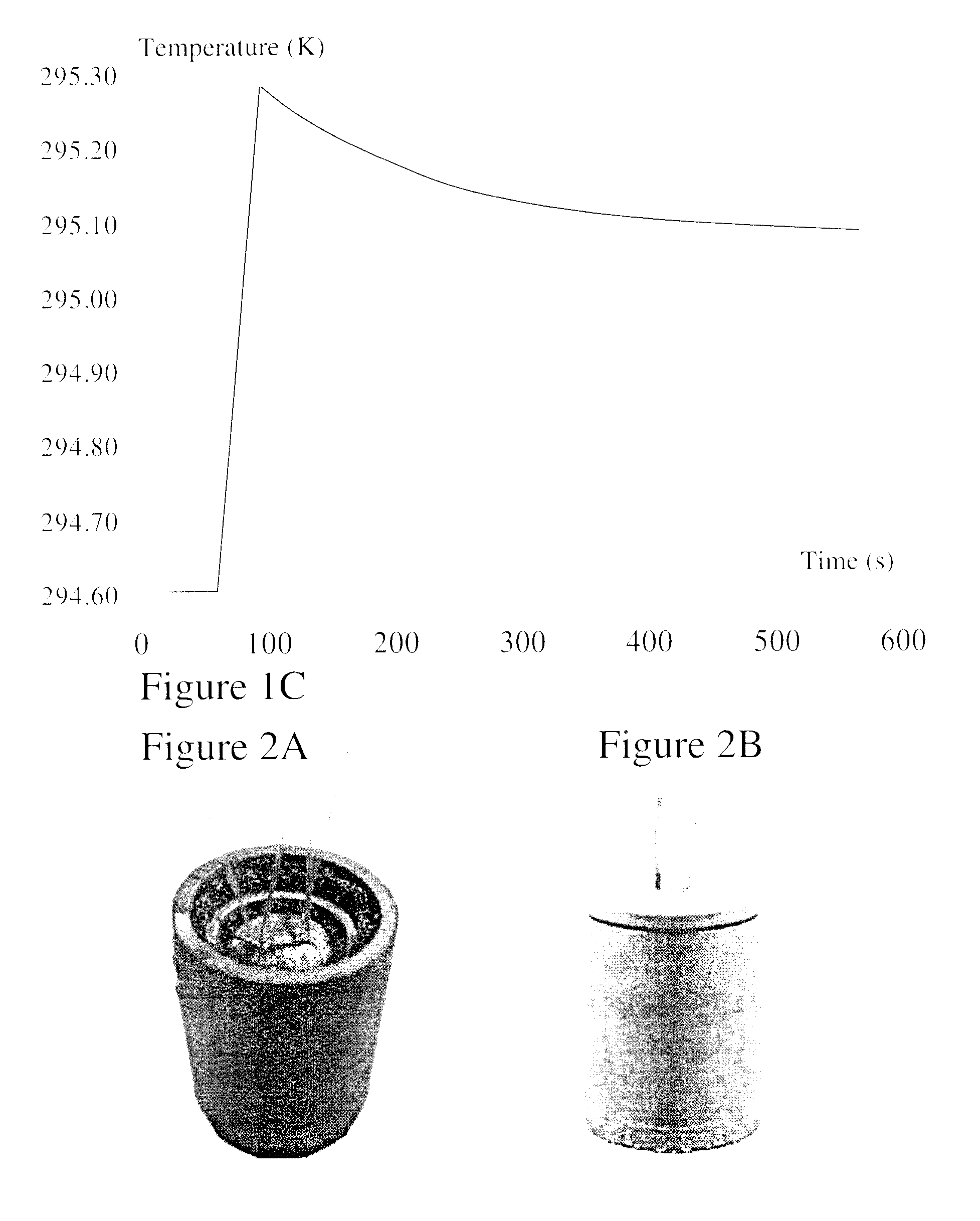
Radiotherapy is one of the most effective treatments for cancer and its success depends critically on accurate targeting and delivery of the correct radiation dose. Accurate dosimetry is therefore essential to maintain and improve patient survival rates. However, size and long wait times currently limit water and graphite based calorimeters to standards laboratories leaving field-based dosimetry to ionization chamber measurements which depend upon a reference field-specified calibration factor. It would therefore be beneficial to provide radiotherapy equipment operators a direct approach of clinical reference dosimetry wherein the dosimeter provides increased independence on dose, dose rate, radiation energy, and energy type, etc. It would be further beneficial for such novel clinical dosimeters to be compact, function as secondary standards used routinely for measurements and allow radiotherapy doses to be measured directly and in an absolute manner. According to embodiments of the invention novel compact graphite probe calorimeters are provided.
Owner:SUN NUCLEAR
Radiotherapy dose verification method, processor and system
PendingCN109147952AHigh precisionImprove accuracyMedical simulationMedical automated diagnosisProgram planningDosimeter
The invention discloses a radiotherapy dose verification method, processor and system. The method comprises the following steps: 1, obtaining an equivalent human body model based on pixel points; 2, selecting the tumor center region of the equivalent human body model as the target point so as to determine the target region and select at least one verification point; 3, collecting the actual dose of the corresponding verification point in case of radiotherapy plan irradiation by a dosimeter; 4, judging whether the dose of the current radiotherapy plan and the verification point in actual implementation is consistent or whether the difference value is within the preset threshold range; the process is ended if the judgment result is yes; or the process goes to the next step; 5, inversely simulating the error spatial distribution of the radiotherapy plan according to the spatial position of all verification points and the actual dose in case of implementation of radiotherapy plan radiation; and 6: correcting the corresponding radiotherapy plan according to the error spatial distribution of the radiotherapy plan so as to obtain the corrected target area and dose and return to the step 3.
Owner:TAISHAN MEDICAL UNIV
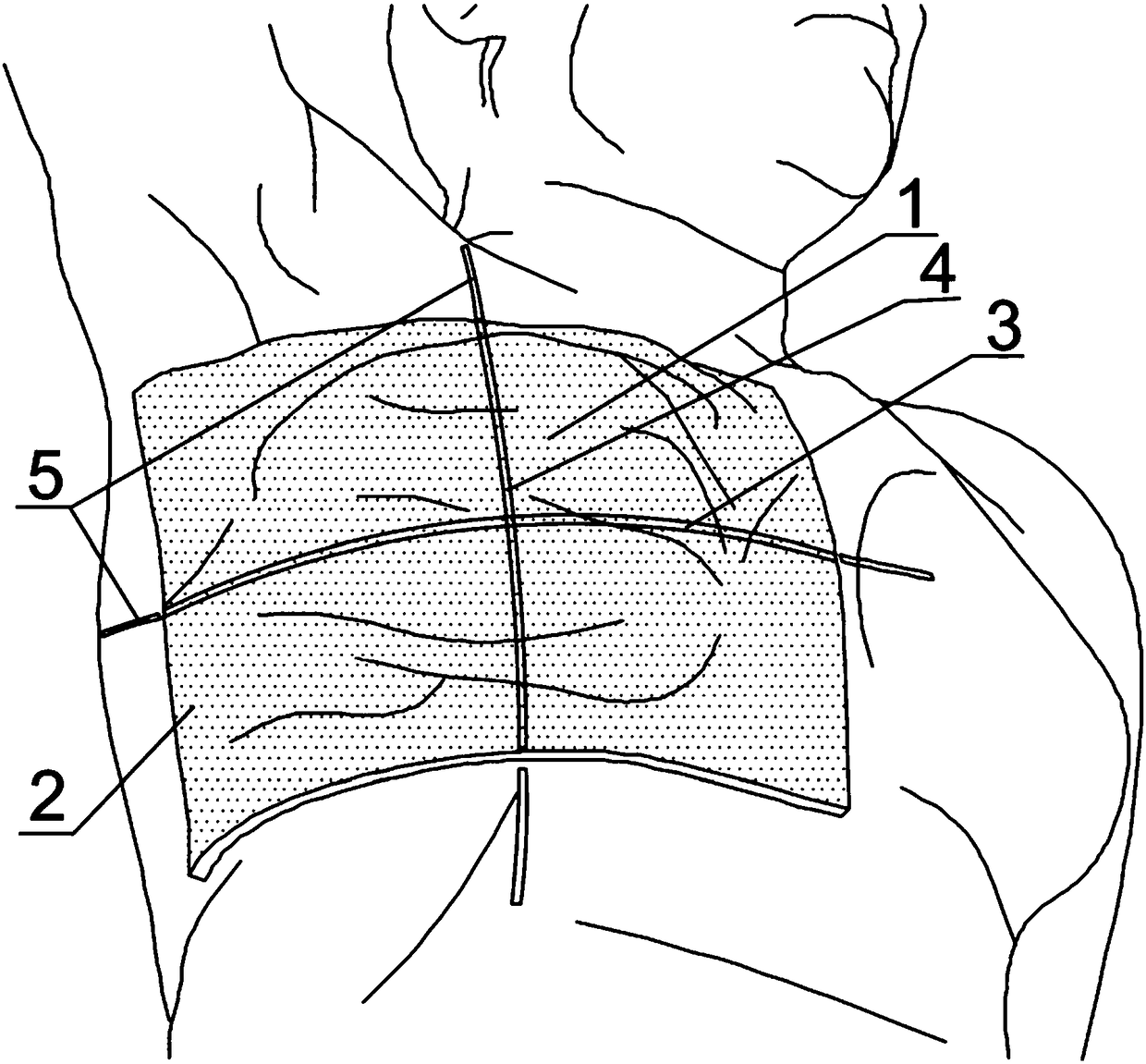
Radiotherapy target section dose regulating personalized silicone compensator and preparation method thereof
PendingCN108187242AImprove protectionSame distanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing processesSide effectCurative effect
The invention relates to a radiotherapy target section dose regulating personalized silicone compensator and a preparation method thereof. The radiotherapy target section dose regulating personalizedsilicone compensator comprises an skin expanding part, a normal tissue expanding part and positioning mark lines. According to conditions of patient's skin in the target section and normal organic contour needed to be protected, silicone comensators in different thickness are customized by the 3D printing technology, so that the compensators fit the skin better; as the compensators have differentthickness, the distances from the surfaces of the compensators in a treatment region to the deep normal tissue are the same, the radiotherapy dose of the target section near the skin can be increasedand the expose dose of the target section can also be unformized by means of dose optimization, and further, the deep normal organs can be protected better to some degrees; thus, the core of the modern precise radiotherapy is achieved, treatment effect is improved and side effect in radiotherapy to patients can also be reduced to the utmost extent. Besides, as medical silicone molding through medical silicone molds is utilized, manufacturing cost is lowered, manufacturing speed is high, and the technique is superior to the method of direct printing of silicone in terms of economical efficiencyand application and promotion.
Owner:于江平
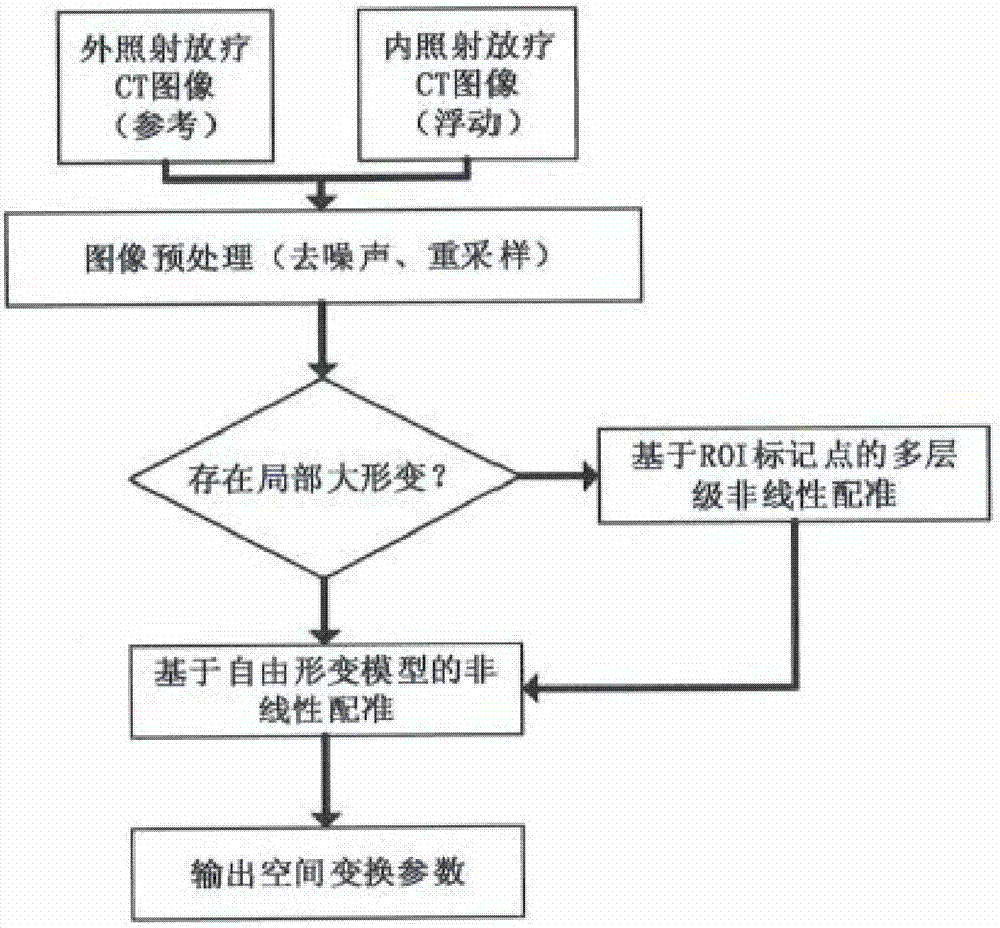
Non-linear fusion method for internal and external radiotherapy doses of a cervical cancer
ActiveCN106902477AAccurate assessmentAccurately achieve accumulationRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTumor targetExternal irradiation
The invention relates to a non-linear fusion method for internal and external radiotherapy doses of a cervical cancer. The method comprises: obtaining internal and external irradiation radiotherapy CT images and internal and external irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution of a to-be-detected cervical cancer; on the basis of non-linear image registration, mapping the internal irradiation radiotherapy CT image to the external irradiation radiotherapy CT image to obtain a transformation relationship between the internal and external irradiation radiotherapy CT images of the to-be-detected cervical cancer; according to the transformation relationship between the internal and external irradiation radiotherapy CT images, transforming internal irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution into equivalent external irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution; and carrying out fusion of the equivalent external irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution and external irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution after transformation by image fusion, rebuilding a distribution curve of internal and external radiotherapy doses, and obtaining a total practically subjected dose of a tumor target region of the to-be-detected cervical cancer and surrounding organs at risks during the comprehensive internal and external irradiation radiotherapy process. The non-linear fusion method is applied to an image-guided radiation therapy of a cervical cancer, thereby improving accuracy of radiotherapy dose evaluation.
Owner:福建省肿瘤医院 +1
Artificial intelligence guided dose prediction method and system
PendingCN111028914AImprove forecasting efficiencyImprove predictive performanceMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMedical automated diagnosisAnatomical structuresDisease
The invention discloses an artificial intelligence guided dose prediction method and system, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a medical image, stored in a preset format, of a patient; drawing the medical image to obtain a geometric anatomical structure; determining a prescription according to disease type information corresponding to the medical image, the geometric anatomical structure and a preset disease type-prescription template library; determining a radiotherapy irradiation angle according to the disease information, the geometric anatomical structure and the prescription;and inputting the disease information, the geometric anatomical structure, the prescription and the radiotherapy irradiation angle into a trained dose prediction model to obtain a radiotherapy dose result. By means of the technical scheme, full-automatic dose prediction is achieved, and the dose prediction efficiency and effect are improved.
Owner:BEIJING LINKING MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Implantation guide device for cervical cancer brachytherapy minimally invasive surgery
PendingCN108245789AAvoid the problem of inaccurate resetIncrease success rateX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyInterstitial brachytherapyLess invasive surgery
The invention discloses an implantation guide device for a cervical cancer brachytherapy minimally invasive surgery. The implantation guide device comprises a cylindrical needle passage guide post anda flat implantation protection wing, the implantation protection wing is fixedly arranged on the outer side of the tail end of the needle passage guide post, and a main guide needle passage is arranged in the needle passage guide post. Corresponding CT (computed tomography) data of a pelvic cavity and a vagina are acquired before the surgery, an interstitial implantation template is printed in a3D (three-dimensional) manner by a system and provided with a set needle passage, the interstitial implantation surgery can be more effectively and rapidly performed, so that radiotherapy dose distribution is more reasonable, the problems of poor needle inserting routes and unreasonable dose distribution due to dissection and gross tumor volume reduction inaccuracy caused by human factors are effectively avoided, and the success rate of the cervical cancer interstitial brachytherapy minimally invasive surgery is greatly increased.
Owner:北京启麟科技有限公司 +1
Radiotherapy dose distribution measurement
ActiveUS20180117361A1Easy to carryIncrease awarenessDosimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyOpaque markerVisual perception
A method for measurement of dose distribution in a radiotherapy apparatus includes providing a detector holder situated at least partially within a tank, the detector holder comprising a radio-opaque marker and a visual reference point, the marker and the reference point being separated and in a fixed spatial relationship to each other; locating the tank within a bore of the radiotherapy apparatus; rotating a gantry and monitoring the position of the detector holder with an imaging apparatus; vertically displacing the detector holder until the reference point is positioned at a desired level, and adding liquid to or removing liquid from the tank until the surface of the liquid is level with the reference point. Features of the detector holder and tank are also described.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
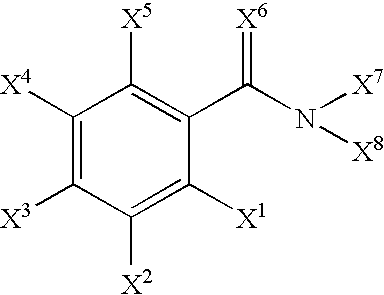
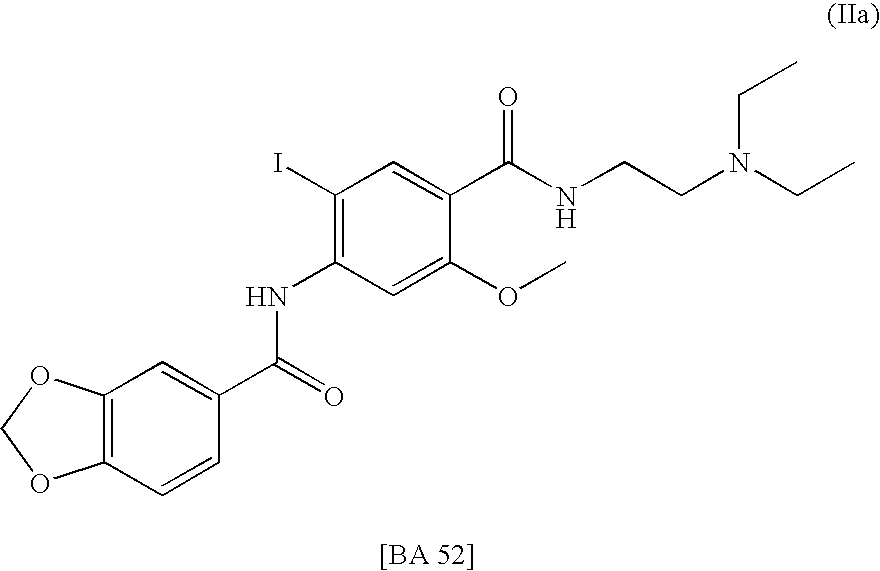
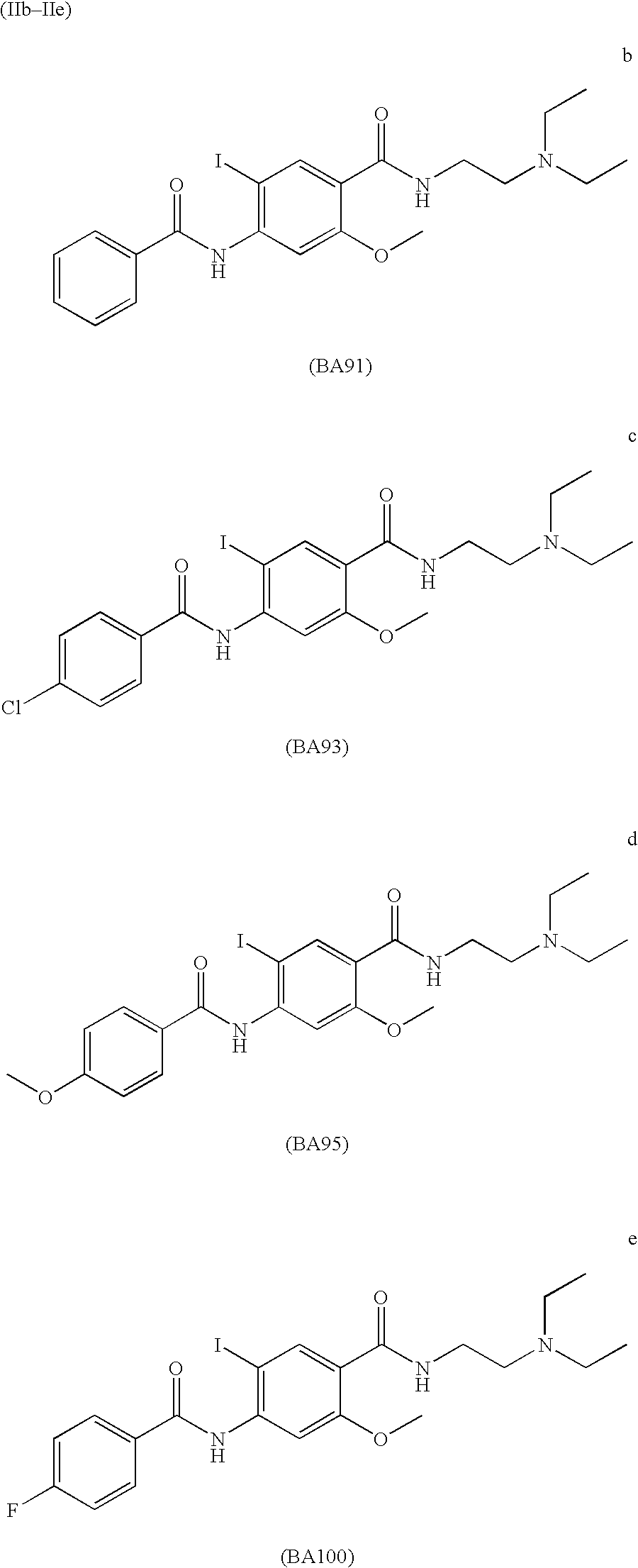
Radiohalogenated benzamide derivatives and their use in tumor diagnosis and tumor therapy
InactiveUS7427390B2Radioactive preparation carriersGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsNeoplasm diagnosisTumor therapy
This invention relates to new radiohalogenated benzamide derivatives and their use in tumor diagnosis and tumor therapy. The radiohalogenated benzamide derivatives according to the invention exhibit novel and especially advantageous properties, in particular with respect to tumor concentration and retardation, liver concentration and blood accumulation. The radiation-therapy doses to be achieved in the tumor, compared to healthy body tissue, are advantageous for the compounds according to the invention.
Owner:BAYER SCHERING PHARMA AG
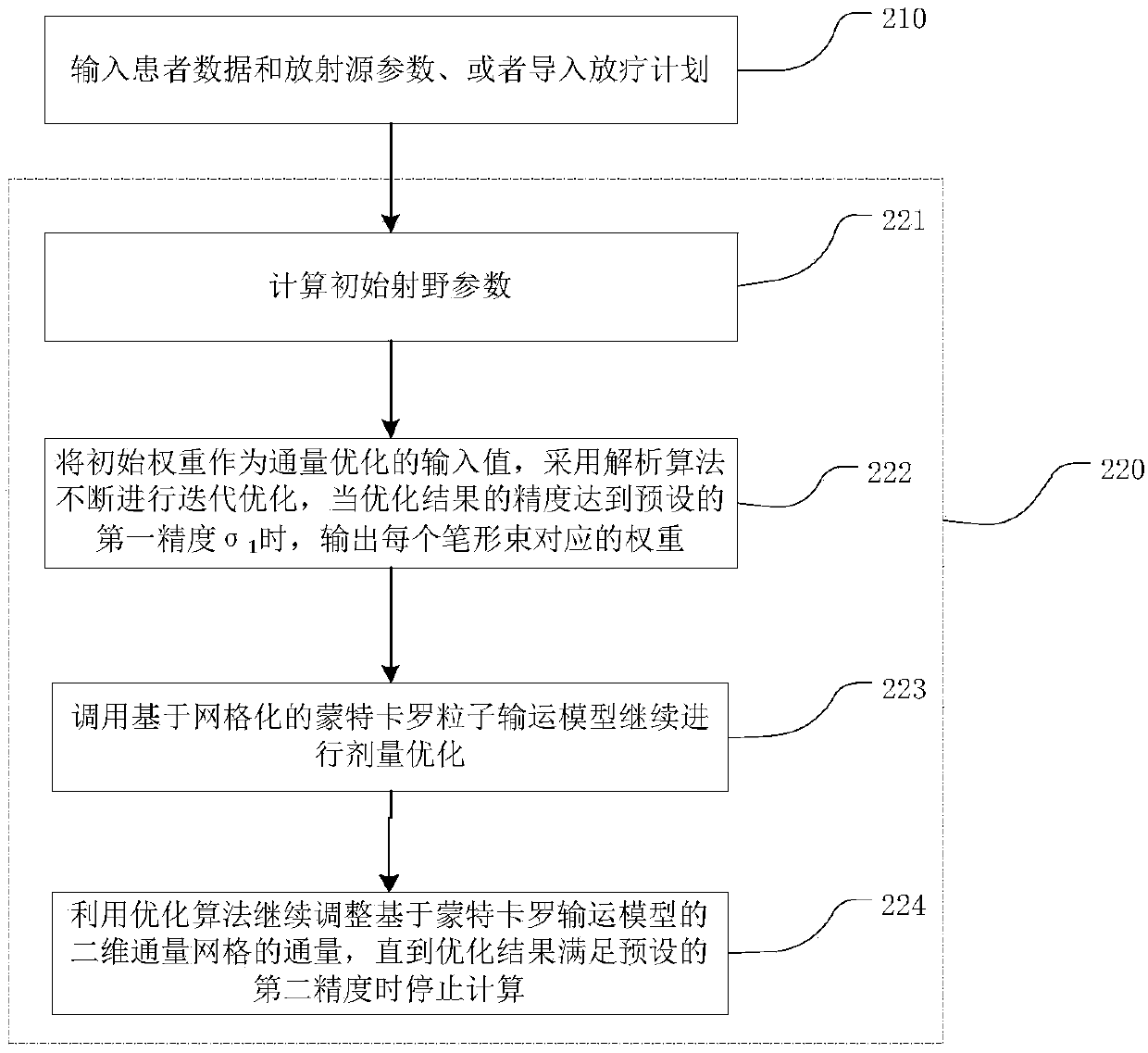
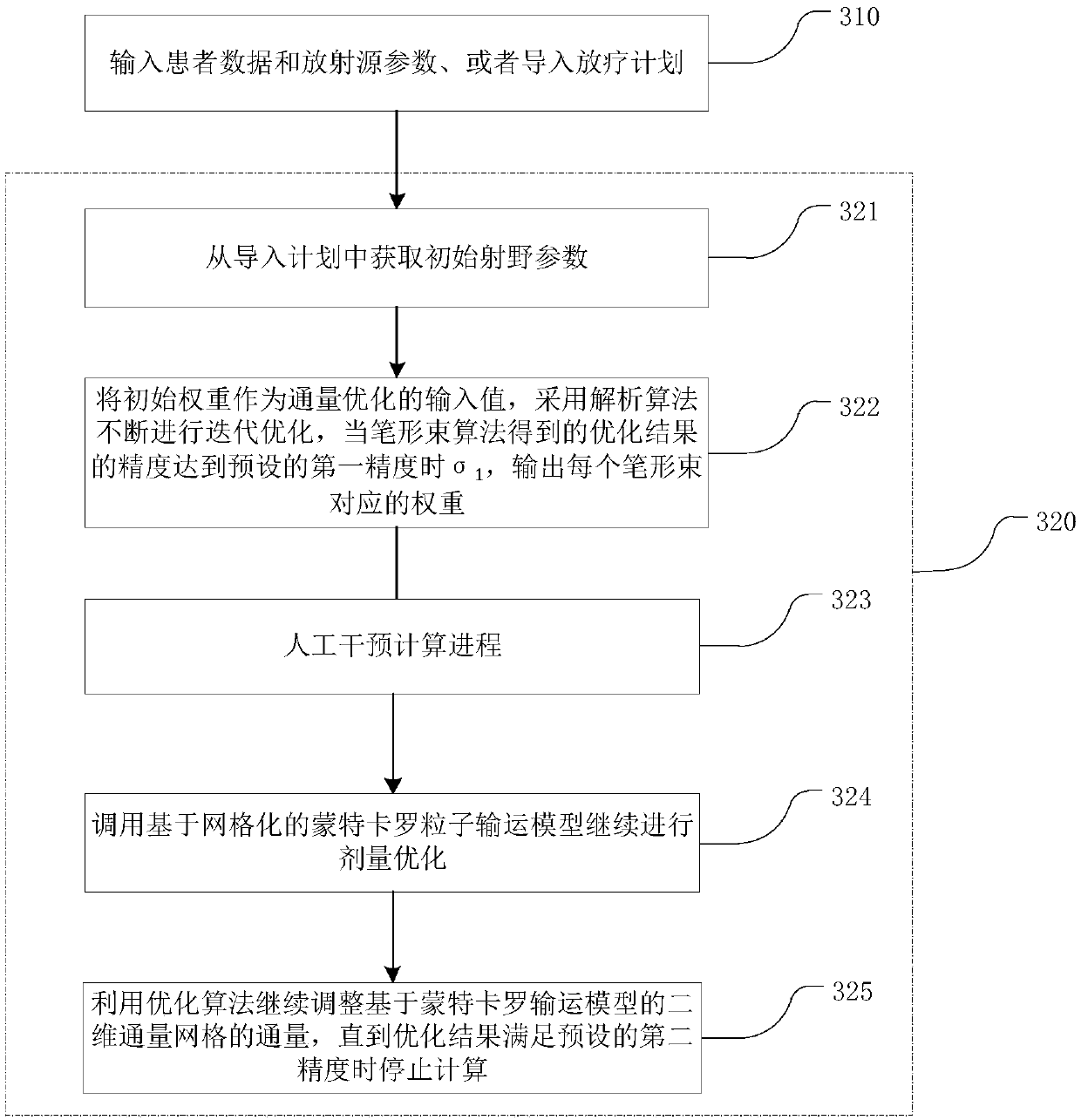
Radiotherapy reverse optimization method and device in combination with Monte Carlo, and storage medium
ActiveCN110570923ACalculation speedGuaranteed computing speedMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPatient dataRadiation field
The invention belongs to the technical field of radiotherapy dose calculation and relates to a radiotherapy reverse optimization method and device in combination with Monte Carlo, and a storage medium. The method includes the following steps: inputting patient data and radioactive source parameters, or importing a historical radiotherapy plan, wherein the imported historical radiotherapy plan includes the patient data, the radioactive source parameters, and radiation field parameters; determining, by using an analytical algorithm, the added position of the Monte Carlo algorithm, continuing tooptimize the Monte Carlo two-dimensional flux grid weights, and stopping the calculation until the second accuracy is satisfied. The method determines the added position of the Monte Carlo dose calculation by setting the accuracy threshold to be achieved by analytical calculation, so as to avoid the oscillation of a dose calculation result caused by the early added Monte Carlo dose calculation dueto a large error of an analytical algorithm calculation result and avoid meaninglessness of the addition of the Monte Carlo.
Owner:BEIJING LINKING MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Targeted nanometer photosensitizer for photodynamics deep tumor therapy and preparing method thereof
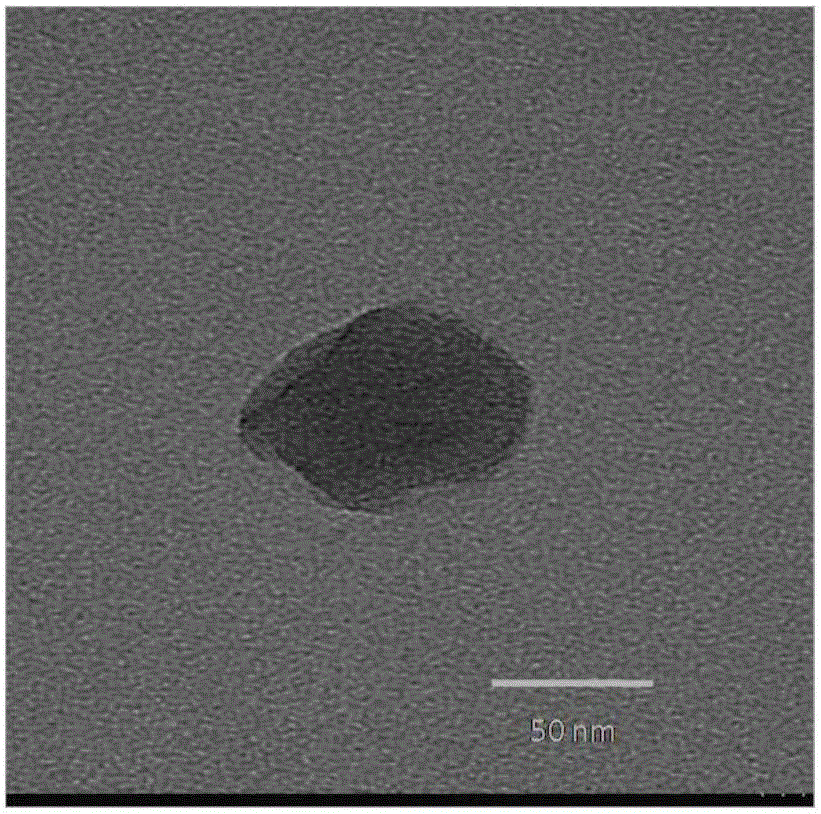
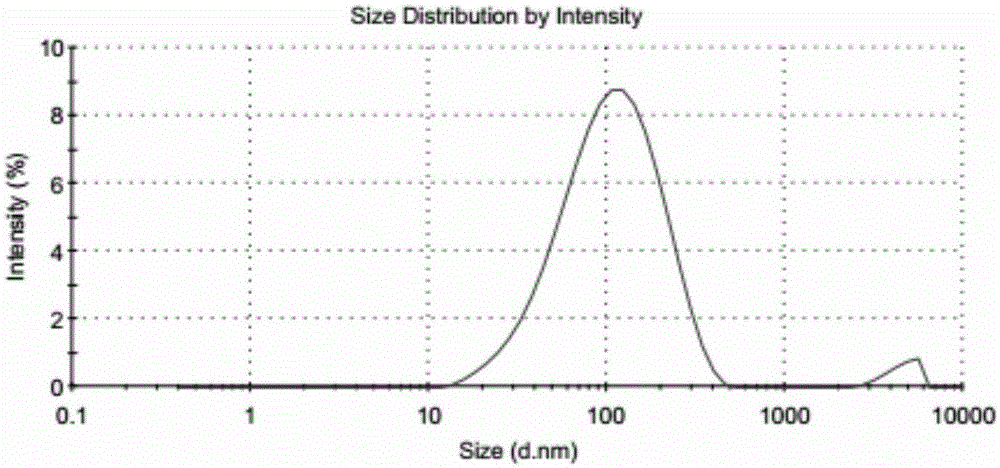
ActiveCN105233283ASolve the key technical problems of poor penetration abilityGood biocompatibilityPowder deliveryEnergy modified materialsSolubilitySide effect
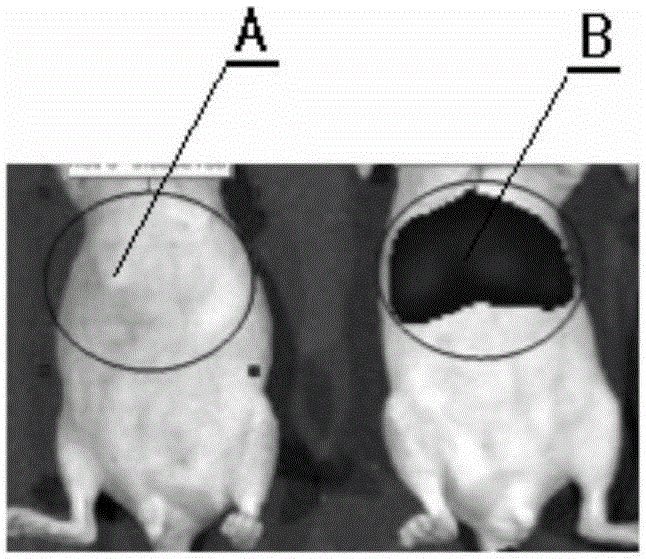
The invention relates to targeted nanometer photosensitizer for photodynamics deep tumor therapy and a preparing method thereof. According to the preparing method, protein, or polypeptide or amino acid is used for reacting with a soluble copper salt solution, and the monovalence protein chelated targeted nanometer photosensitizer or the polypeptide-copper chelated targeted nanometer photosensitizer or the amino acid-copper chelated targeted nanometer photosensitizer is obtained after reduction. Under excitation of X rays with the dosage much lower than a general radiotherapy dosage, the targeted nanometer photosensitizer can generate strong fluorescence and has a photodynamics therapy effect on tumors. The targeted nanometer photosensitizer is small in particle size, good in water solubility, small in toxic and side effect and capable of being endocytosed by deep tumor cells easily. The X rays serve as an excitation light source of the targeted nanometer photosensitizer, the therapy efficiency is high, and the problems that existing photodynamics therapy cannot be carried out on the deep tumors, and skin phototoxicity is caused can be solved. Reaction conditions of the photosensitizer are moderate, and the photosensitizer can be industrially manufactured, achieves energy conservation and environment protection, can promote the silkworm breeding and mulberry growing industrial chain to develop in the high value-added industry direction, and has good economic benefits, social benefits and ecological benefits.
Owner:广西康健奥鑫生物医药科技有限公司
Adult chest and abdomen dose verification dynamic phantom
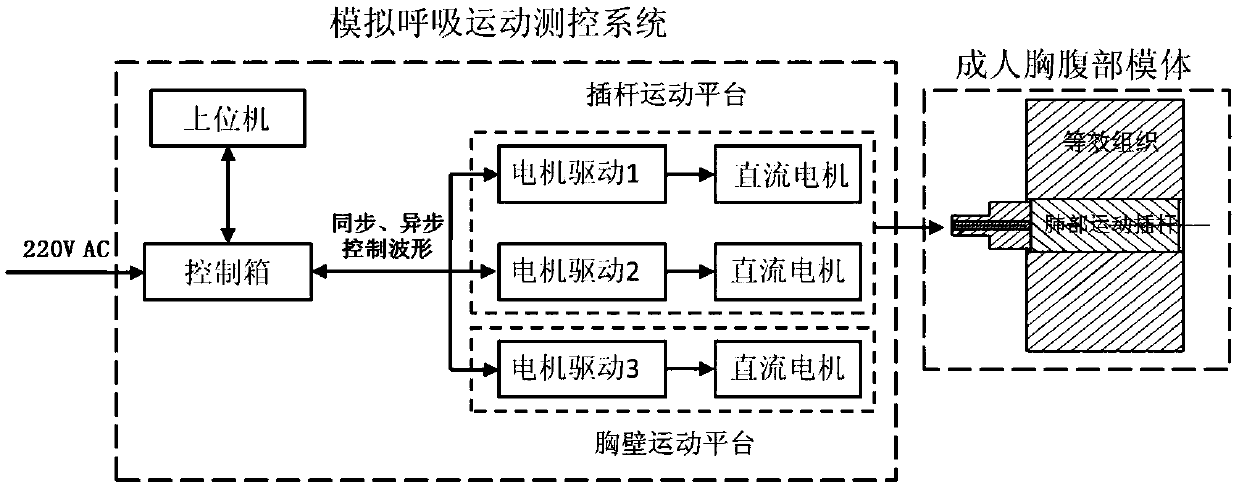
PendingCN109621229AResolve equivalenceSolve space problemsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyHuman bodyDose verification
The invention provides an adult chest and abdomen dose verification dynamic phantom. The phantom comprises a chest and abdomen phantom body and a motion measurement and control system; the chest and abdomen phantom body is made of a material equivalent to a material with human body CT values and comprises human muscle tissue, spinal bone tissue and lung tissue, the whole phantom body is formed bycombining slices, an EBT3 dosimetry development-free film can be clamped between every two slices, and the dose space distribution of the positions of interest is obtained through multiple films; lungmotion insertion rods are arranged in the lung tissue and comprise the simulated tumor insertion rod, the four-dimensional CT quality control insertion rod and the like; the motion measurement and control system comprises an insertion rod motion platform and a chest wall motion platform, a driving device is controlled by an upper computer and connected with the insertion rods, and corresponding action is generated to simulate 3D breathing motion and chest-wall up-down motion of the human body. The phantom can provide a research tool for radiotherapy dose distribution and dose verification inclinical research of motion organs.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
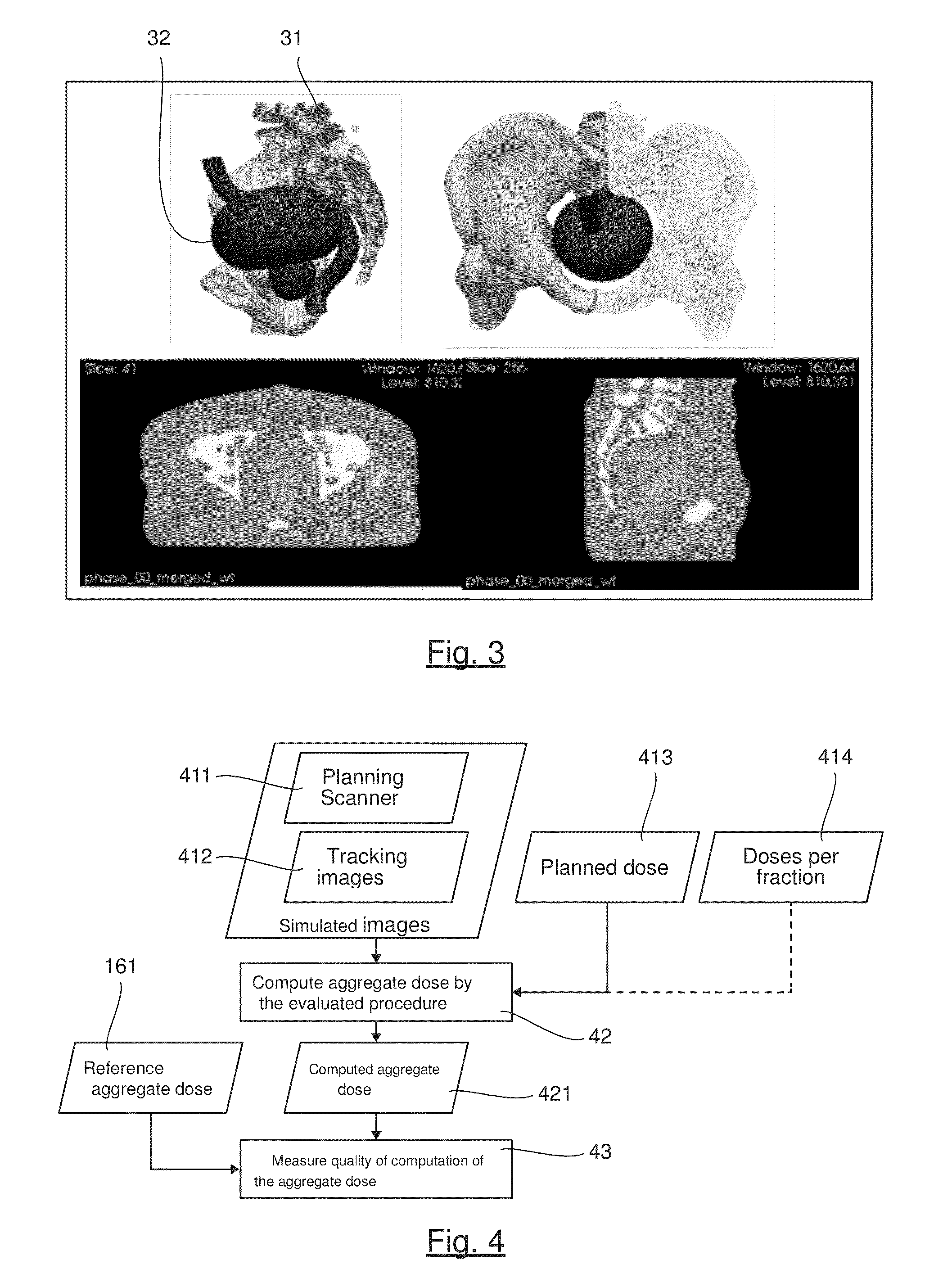
Method of Evaluating a Procedure for Determining the Aggregate Dose Received in the Course of a Radiotherapy Treatment
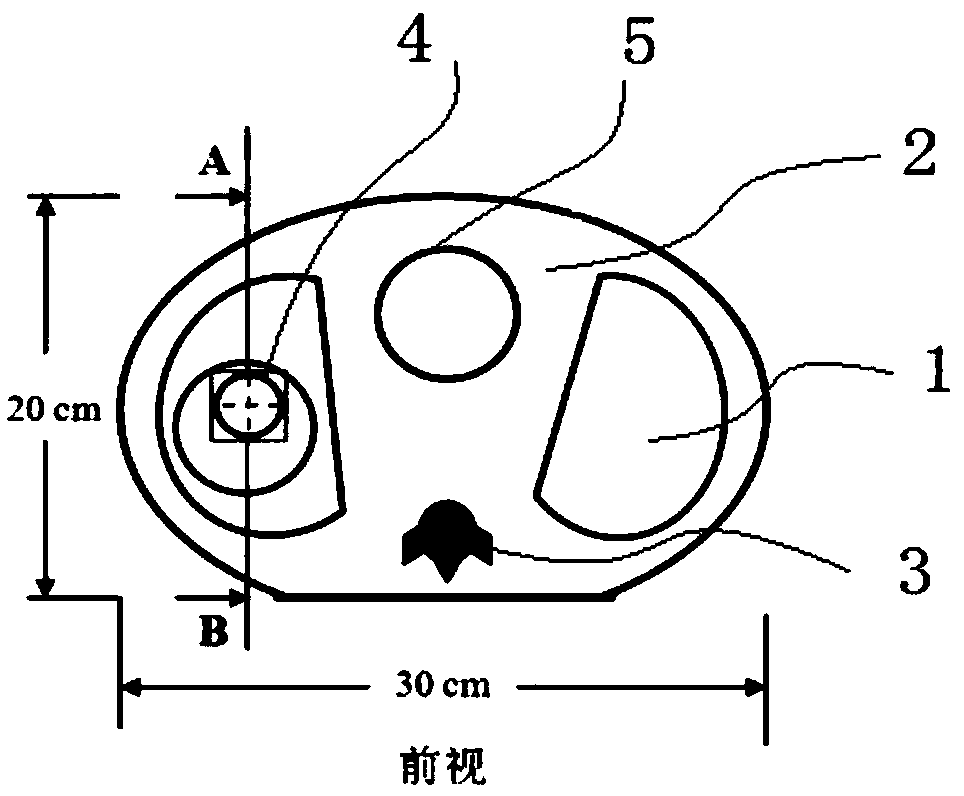
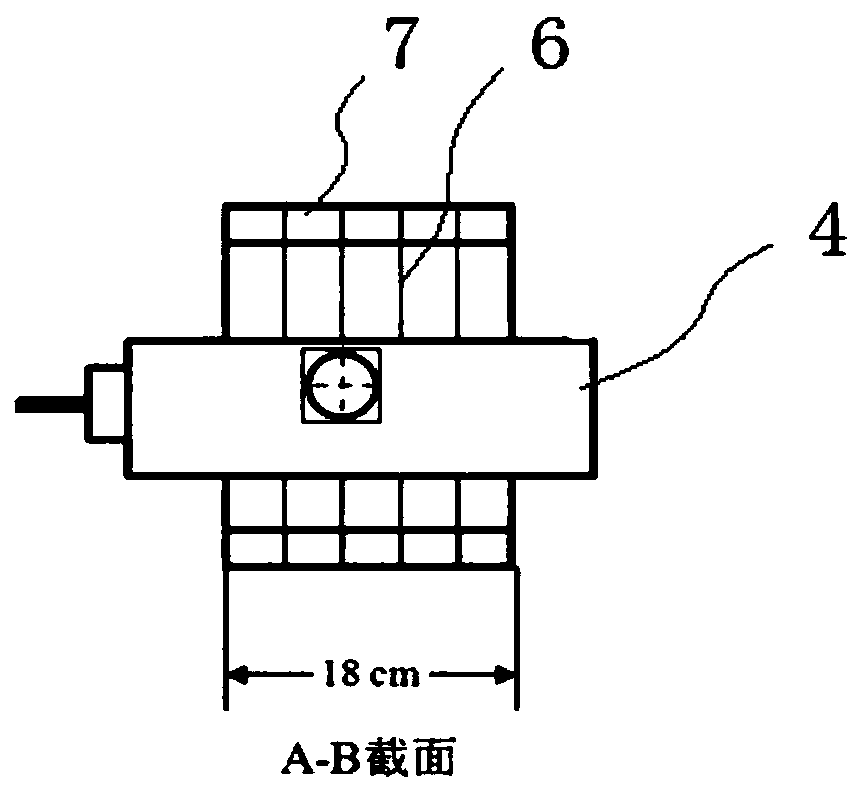
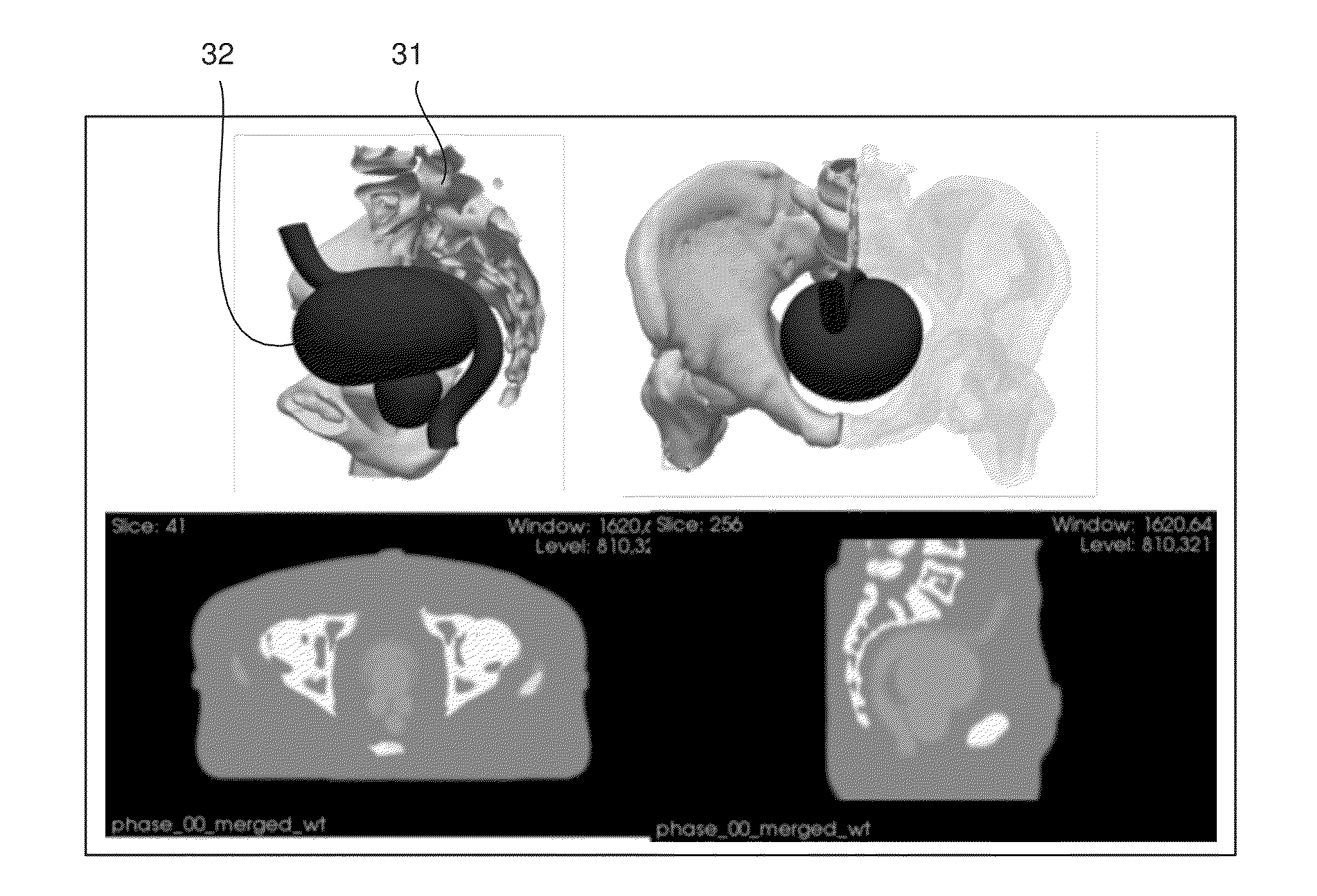
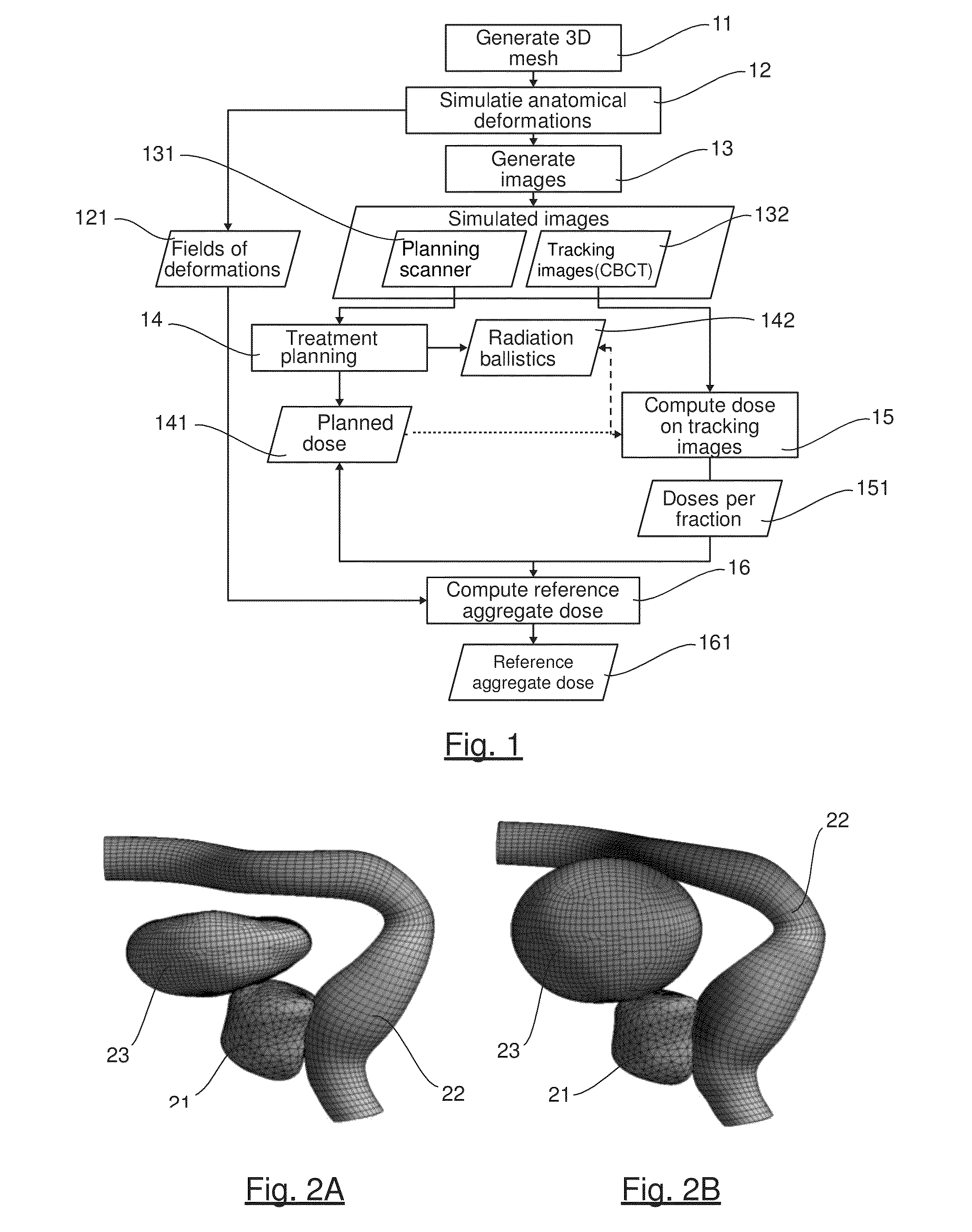
InactiveUS20150251017A1Evaluate qualityCalibration apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyReference doseRadiotherapy dose
A method is provided for evaluating a procedure for determining an aggregate radiotherapy dose received in the course of a radiotherapy treatment. The method includes: defining a deformable model of at least one organ to be treated and of at least one neighboring organ, generating a series of simulated images, interpretable by the procedure to be evaluated, with aid of the model; comparing the aggregate dose calculated by the procedure to be evaluated, applied to at least one of the simulated images, with a reference aggregate dose, so as to deliver at least one item of information representative of the quality of the procedure, the reference aggregate dose being obtained by taking into account anatomical deformations applied to the organs, so as to determine a reference dose actually received at each treatment session by the organs, as a function of their actual shape and / or actual position during this session.
Owner:UNIV DE RENNES I
Method and System for Calorimetry Probe
InactiveUS20150108356A1Address limitationsCalorimetric dosimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansDose rateDosimeter
Radiotherapy is one of the most effective treatments for cancer and its success depends critically on accurate targeting and delivery of the correct radiation dose. Accurate dosimetry is therefore essential to maintain and improve patient survival rates. However, size and long wait times currently limit water and graphite based calorimeters to standards laboratories leaving field-based dosimetry to ionization chamber measurements which depend upon a reference field-specified calibration factor. It would therefore be beneficial to provide radiotherapy equipment operators a direct approach of clinical reference dosimetry wherein the dosimeter provides increased independence on dose, dose rate, radiation energy, and energy type, etc. It would be further beneficial for such novel clinical dosimeters to be compact, function as secondary standards used routinely for measurements and allow radiotherapy doses to be measured directly and in an absolute manner. According to embodiments of the invention novel compact graphite probe calorimeters are provided.
Owner:SUN NUCLEAR
Dose optimization method and device based on Monte Carlo and storage medium
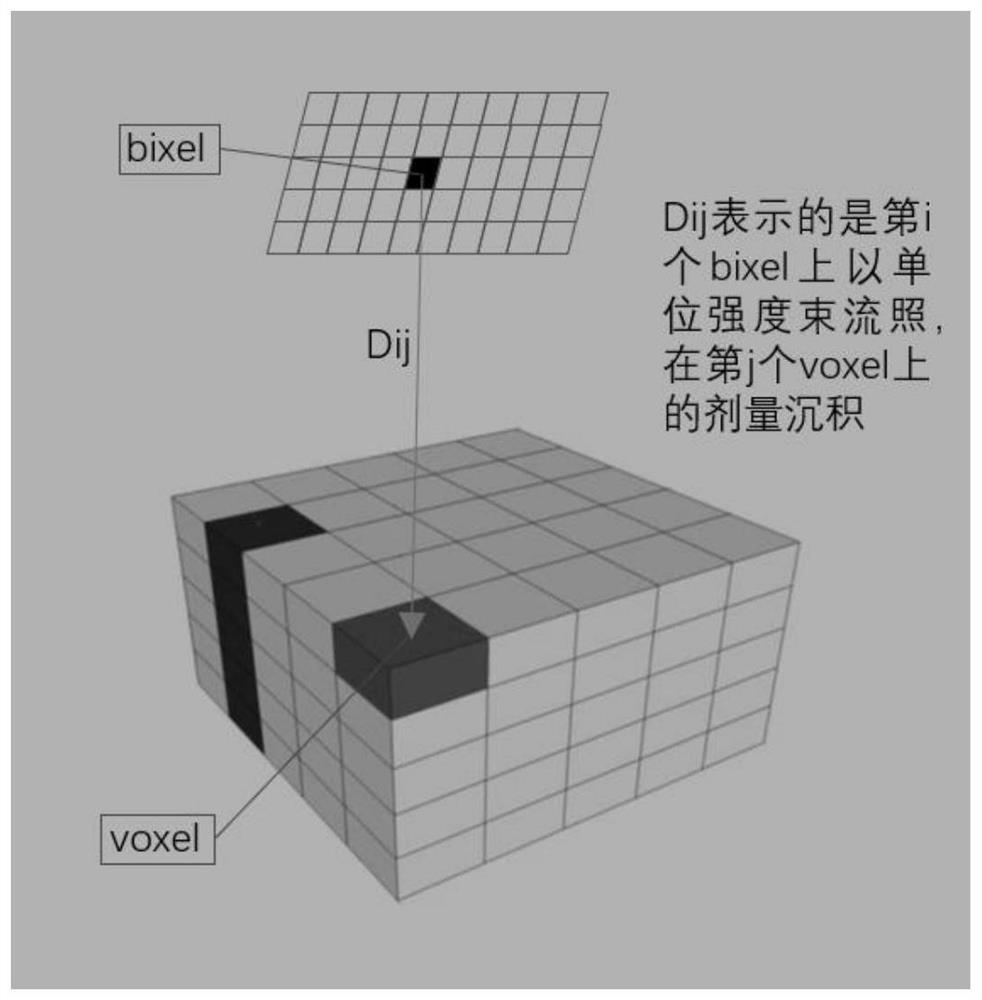
ActiveCN110556176ASolve the defect of slow calculation speedThe calculation result is accurateMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesArtificial lifeVoxelGrid based
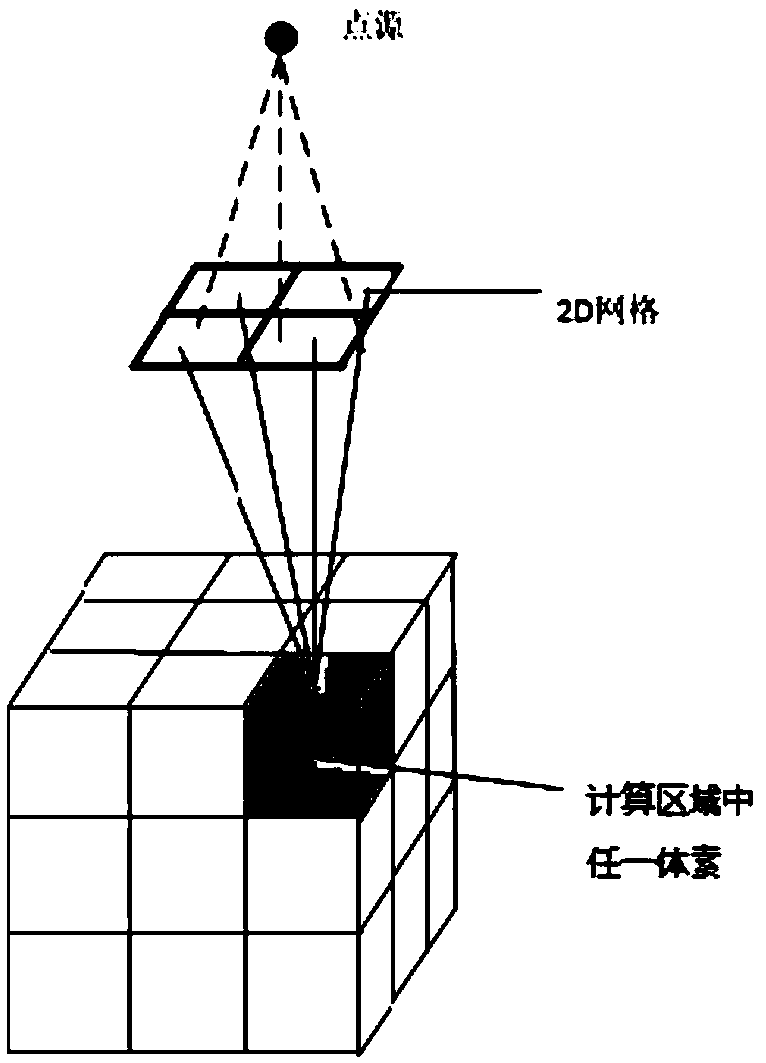
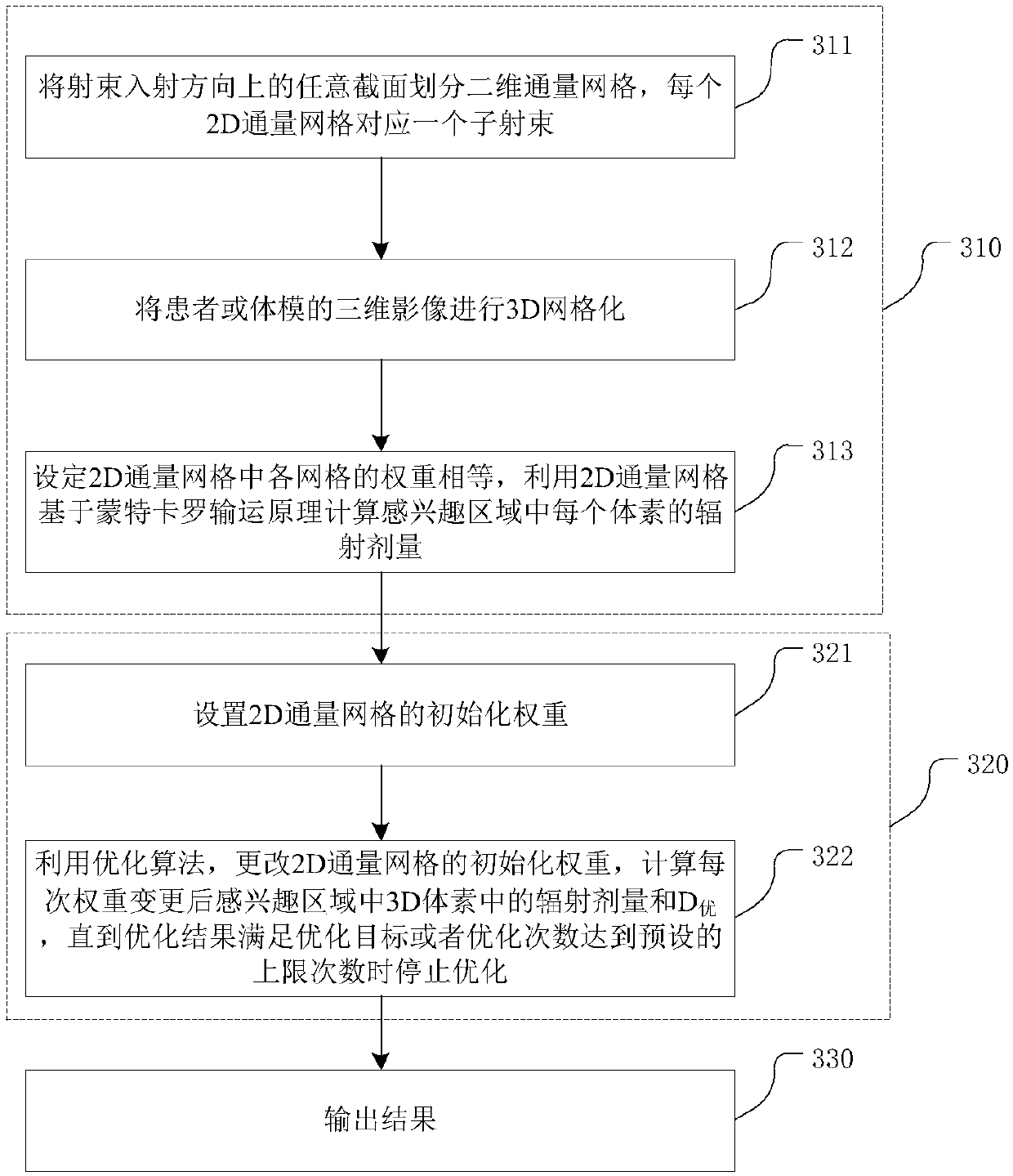
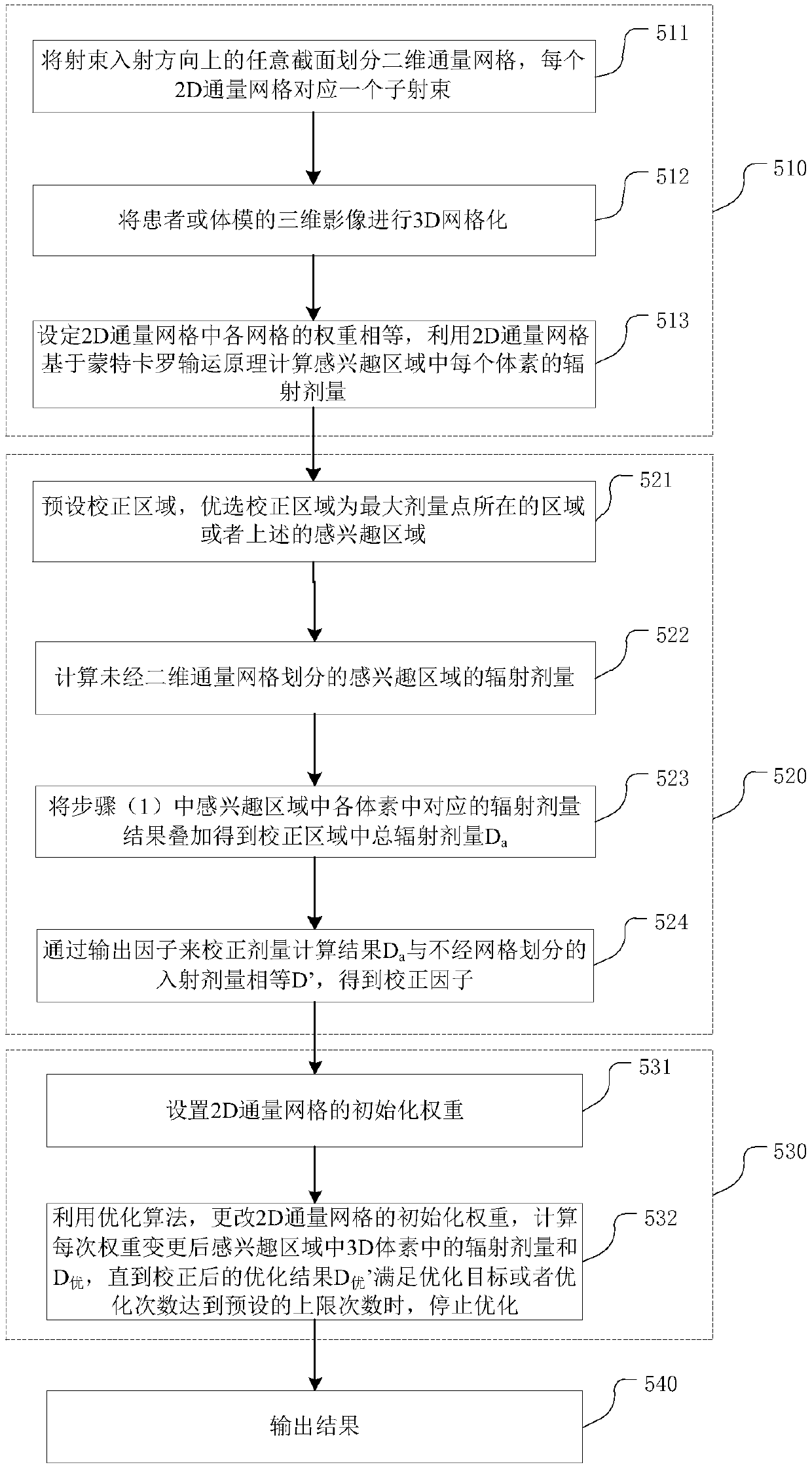
The invention belongs to the field of radiotherapy dose calculation, and relates to a dose optimization method and device based on Monte Carlo, and a storage medium. The method comprises the followingsteps: dividing any cross section in the incident direction of a beam into two-dimensional flux grids, wherein each two-dimensional flux grid is corresponding to one sub-beam; carrying out 3D gridding on the three-dimensional image of a patient or a phantom, wherein each grid is a voxel; setting the weight of each grid in the 2D flux grid to be equal, and calculating the radiation dose of each voxel in the region of interest by utilizing the 2D flux grid based on the Monte Carlo transport principle; optimizing the 2D flux grid weight by using an optimization algorithm to realize an optimization target; and outputting results. The method provided by the invention overcomes the defect of low calculation speed caused by participation of MC in each optimization in the optimization process inthe prior art; and an output factor correction step is added, so that the corrected calculation result of the radiation dose of the 3D grid is accurate, and the error is greatly reduced.
Owner:BEIJING LINKING MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
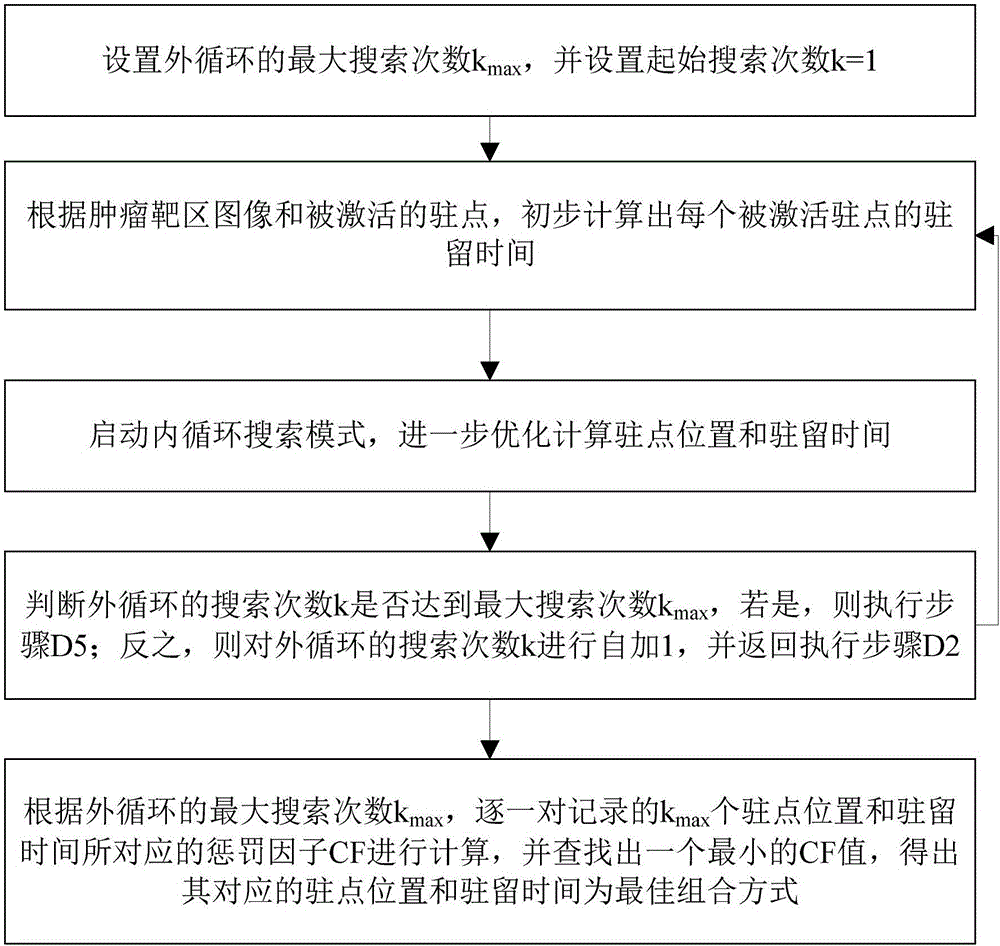
Afterloading radiotherapy dose inverse intensity-modulated optimizing calculation method and system
ActiveCN106215334ASatisfy the requirement of reverse intensity modulation optimizationOptimize gradientSpecial data processing applicationsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTumor targetAnatomical structures
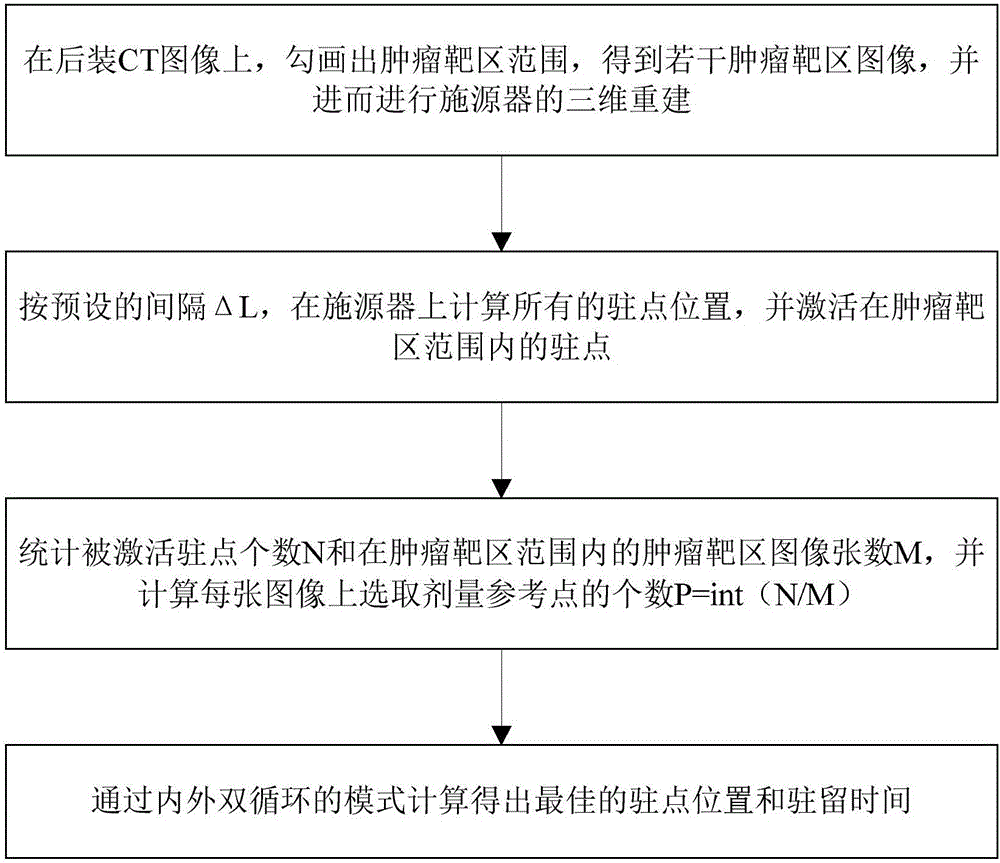
The invention discloses an afterloading radiotherapy dose inverse intensity-modulated optimizing calculation method and system. The afterloading radiotherapy dose inverse intensity-modulated optimizing calculation method comprises calculating all positions of stationary points on a source applicator and activating stationary points within a tumor target region; calculating the number of dose selection reference points in each image; and working out the optimal stationary point position and residence time through an internal-external double circulation mode. The afterloading radiotherapy dose inverse intensity-modulated optimizing calculation system comprises an image generation unit, a stationary point activation unit, a statistics unit and a circulation calculation unit. According to the invention, a customized anatomical structure is taken as the basis, the optimal combination mode of the radioactive source residence position and residence time is obtained by means of an internal-external double circulation searching mode, the customized afterloading radiotherapy dose inverse intensity-modulated optimizing demand can be satisfied, in the external circulation, a primary combination is solved by means of a relaxation method, in the internal circulation, by combining the expected dose of the tumor target region and the constraint dose which is dangerous to organs, the gradient of the stationary point position and the residence time is further optimized. The afterloading radiotherapy dose inverse intensity-modulated optimizing calculation method and system can be widely applied to afterloading radiotherapy dose calculation.
Owner:CANCER CENT OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
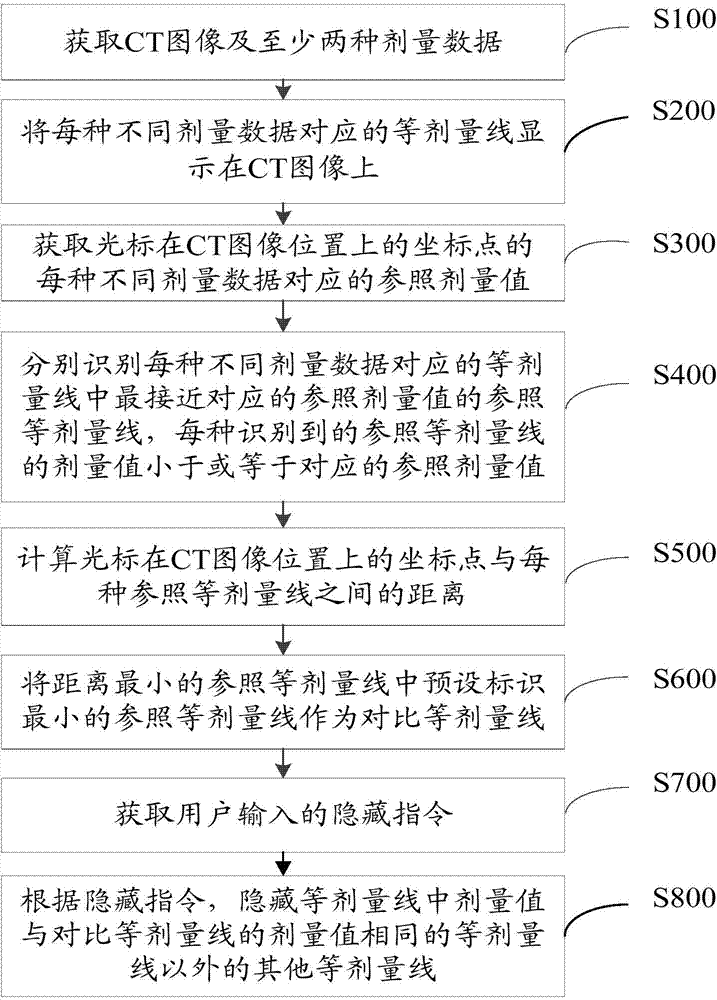
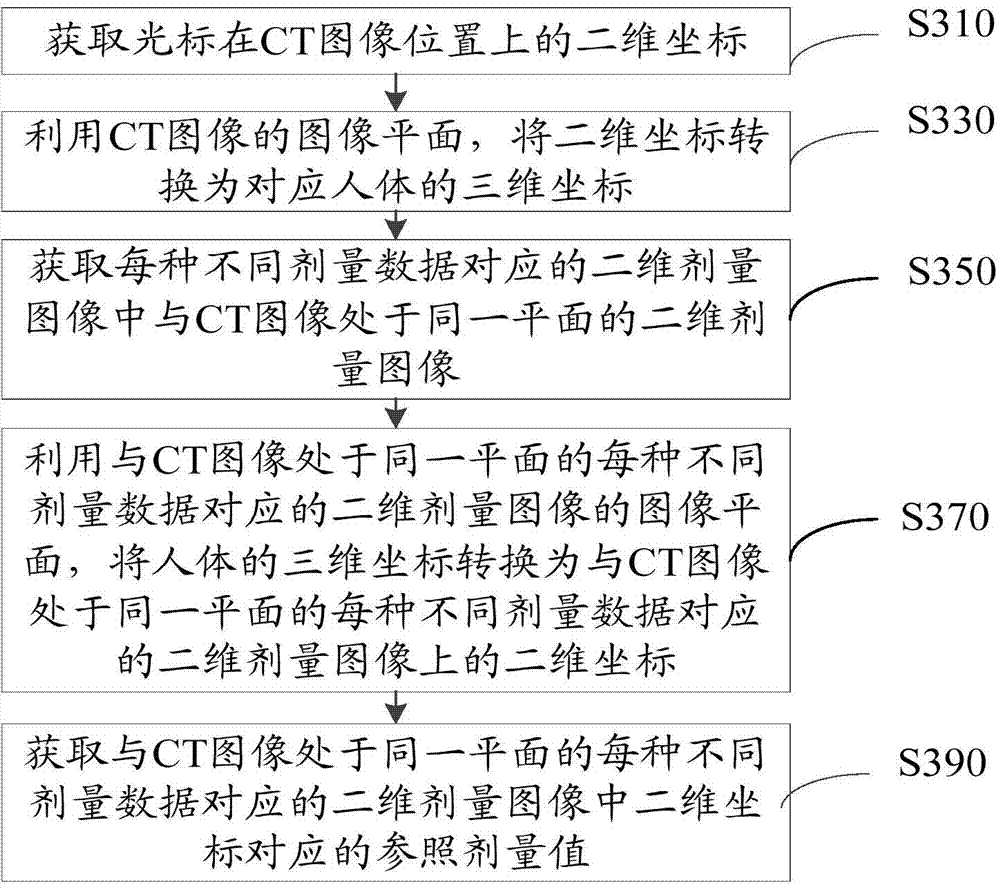
Radiotherapy dose comparing and displaying method and system
ActiveCN104759037AAchieve observationEasy to compareImage analysis3D-image renderingShortest distanceNuclear medicine
The invention discloses a radiotherapy dose comparing and displaying method and system. According to the method, by obtaining reference dose values corresponding to different dose data of all kinds of coordinates, at the CT image position, of a cursor, reference isodose lines most approximate to the corresponding reference dose values among isodose lines corresponding to the different dose data of all the kinds are recognized respectively, the distance between the reference isodose line of each kind and the coordinates, at the CT image position, of the cursor is calculated, the reference isodose line with the shortest distance is used as a comparison isodose line, and other isodose lines except the isodose lines with the dose values the same as the dose value of the comparison isodose line among the isodose lines, on a CT image, of the cursor are hidden or / and the isodose lines with the dose values the same as the dose value of the comparison isodose line among the isodose lines are highlighted. Accordingly, a doctor can observe the isodose lines with the dose values the same as the dose value of the comparison isodose line among the corresponding isodose lines at the CT image position at a glance and compare the isodose lines, and the optimal radiotherapy scheme can be obtained more accurately.
Owner:SHENZHEN YINO INTELLIGENCE TECH
Radiotherapy dose measurement method
ActiveCN106310529AIncrease success rateHigh recurrence rateX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAnatomical structuresRequirements elicitation
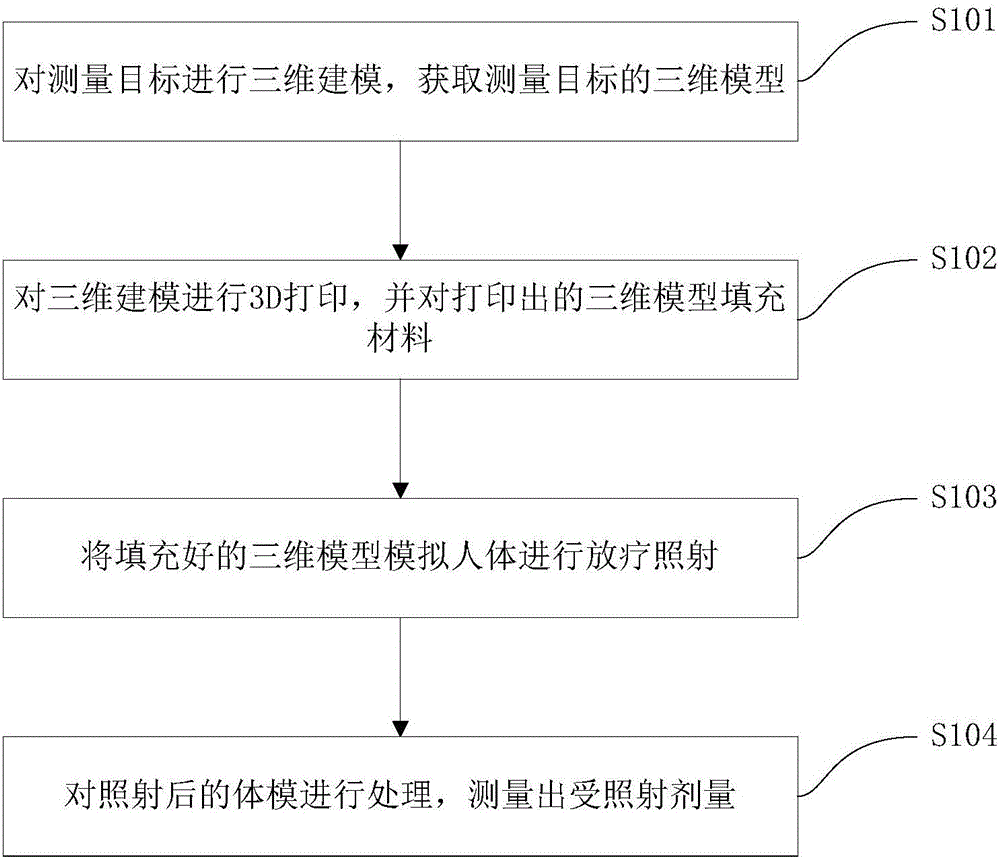
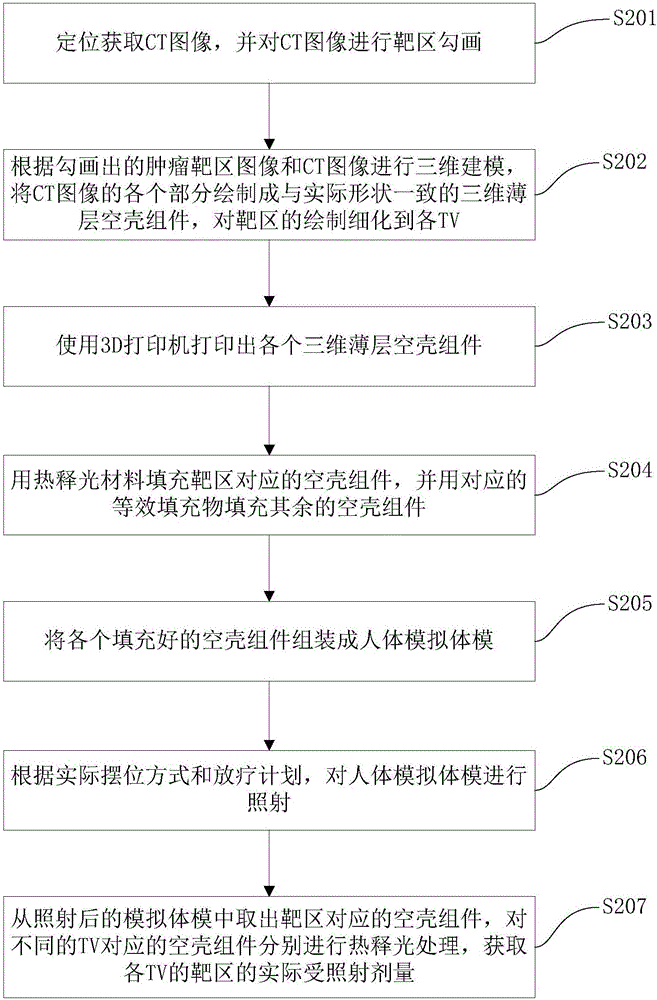
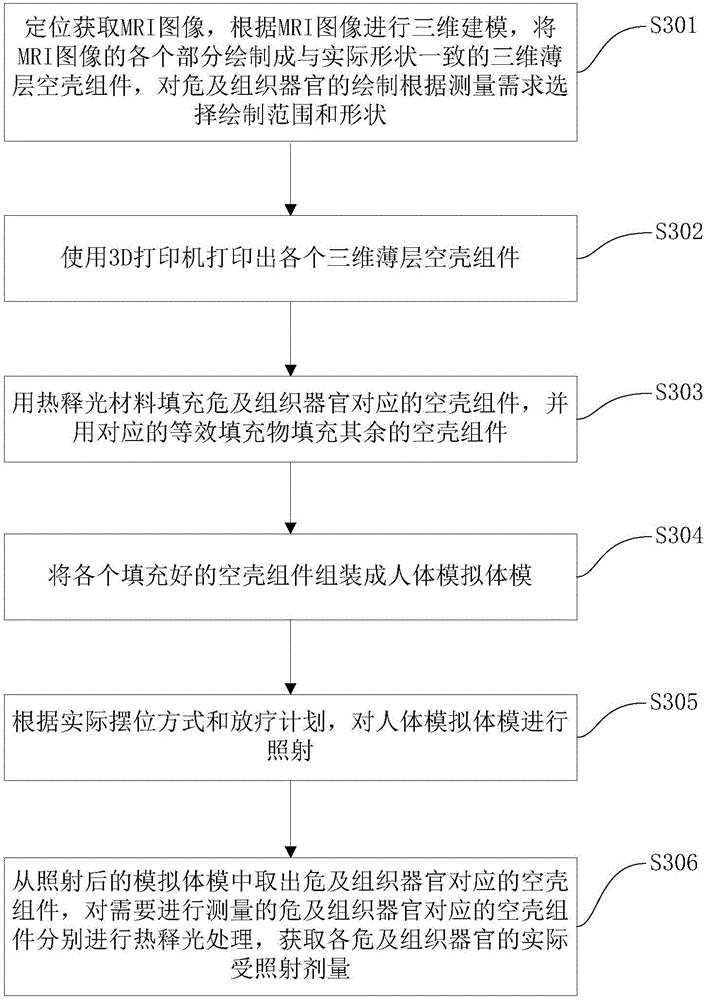
The invention discloses a radiotherapy dose measurement method, which comprises the steps of acquiring a measurement target according to requirements, performing three-dimensional modeling on the measurement target, and obtaining a three-dimensional model of the measurement target; performing 3D printing on the three-dimensional model, and filling the printed three-dimensional model with a material; performing irradiation in a mode of simulating a human body model according to the filled three-dimensional model; processing the irradiated body model, and measuring the exposure dose. The method disclosed by the invention can perform 3D personalized radiotherapy dose measurement according to requirements, so that the anatomical structure, the profile and the tumor anatomical structure of the human body are simulated to the maximum extent, and the measured exposure dose is closer to an actual value, thereby providing more valuable and more reliable experimental reference for implementation of a radiotherapy plan, and providing guarantee for ensuring the success rate of the radiotherapy plan.
Owner:朱远湖
Radiotherapy dose evaluation system and device and storage medium
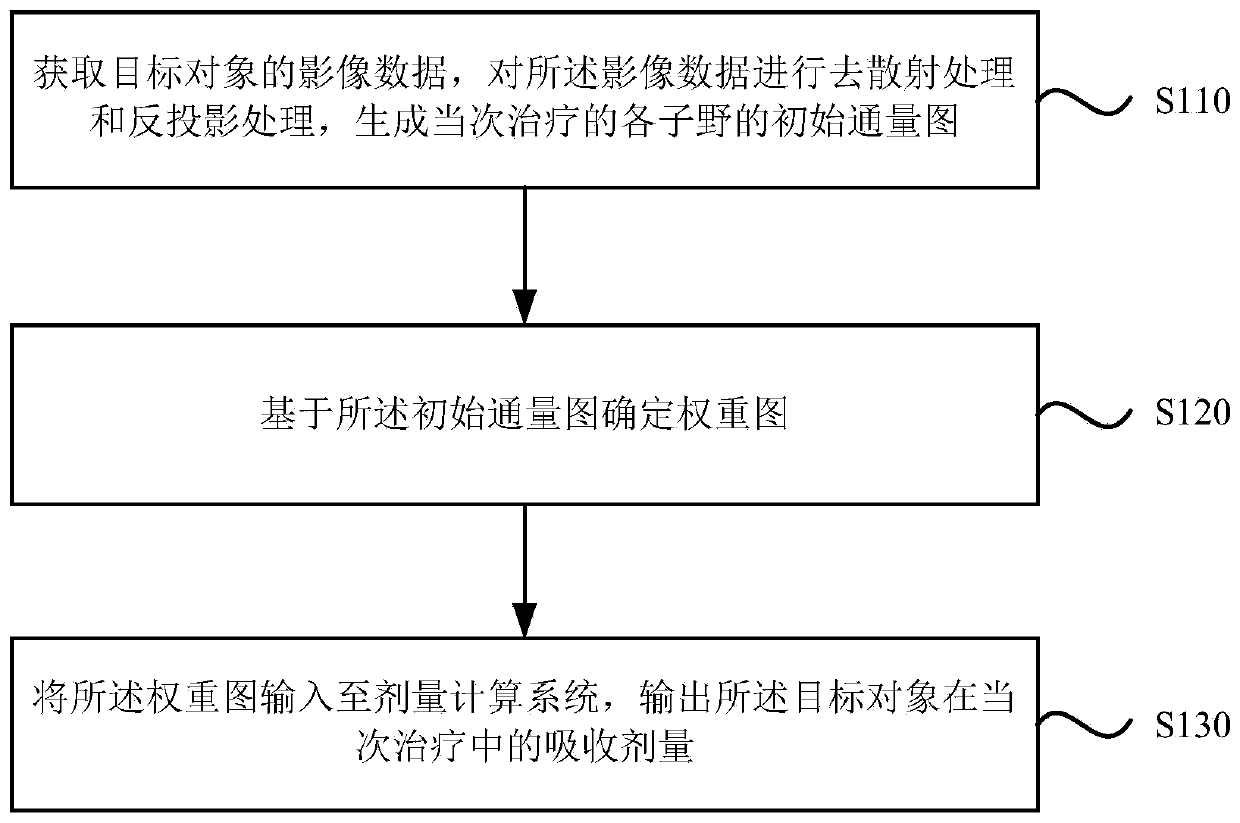
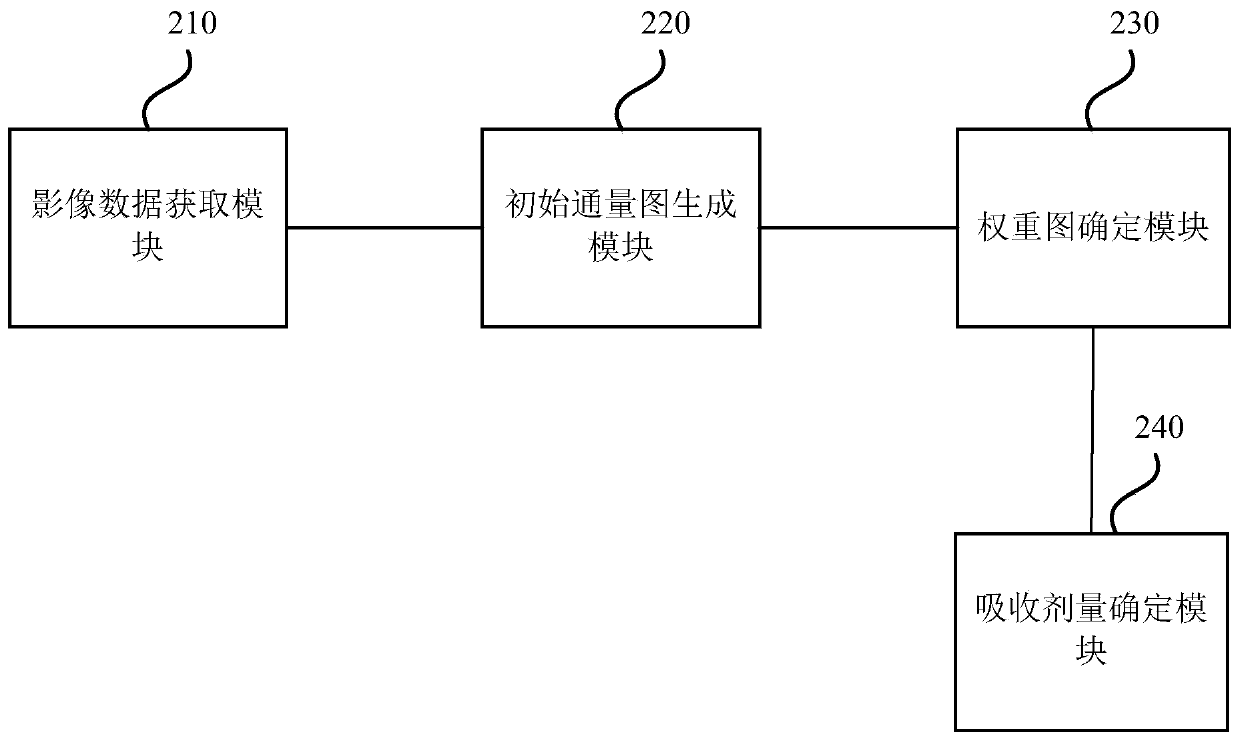
ActiveCN111001097AImprove the accuracy of useX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBack projectionHigh-LET Radiotherapy
The invention discloses a radiotherapy dose evaluation system and a device and a storage medium. The radiotherapy dose evaluation system comprises a processor, and configuration and execution steps are as follows: obtaining image data of a target object, carrying out the scattering removal treatment and back projection treatment on the image data, and generating an initial flux graph under each sub-field of the current treatment; determining a weighted graph based on the initial flux graph; and inputting the weighted graph into a dose calculation system, and outputting the absorbed dose of thetarget object in the current treatment. The radiotherapy dose evaluation system provided by the embodiment of the invention can perform high-precision evaluation on the absorbed dose of the target object in each radiotherapy process, can be used for assisting dose determination of clinical radiotherapy, and improves the use accuracy of the radiotherapy dose.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
System and method for determining three-dimensional functional liver segment based on medical image
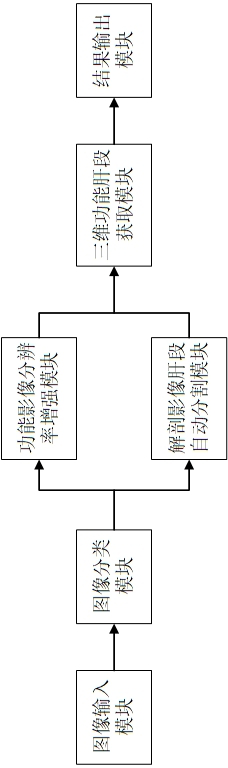
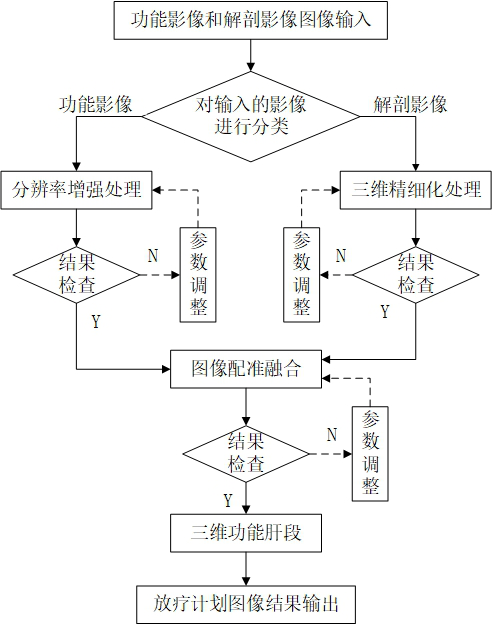
PendingCN114881914AImprove accuracyHigh-resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationAuto segmentation
The system for determining the three-dimensional functional liver segment based on the medical image comprises an image input module, an image classification module, a functional image resolution enhancement module, an anatomical image liver segment automatic segmentation module, a three-dimensional functional liver segment acquisition module and a result output module. The functional influence resolution enhancement module performs resolution enhancement processing on the functional image to obtain a high-resolution enhanced functional image, and the anatomical image liver segment automatic segmentation module performs liver segment automatic segmentation on the anatomical image to obtain a refined three-dimensional liver segment anatomical image. A functional image and an anatomical image are input, the input images are classified, resolution enhancement processing is performed on the functional image, three-dimensional refining processing and registration fusion are performed on the anatomical image to obtain a three-dimensional functional liver segment, and an image result is output and imported into a radiotherapy plan design system for radiotherapy dose calculation. According to the invention, three-dimensional functional liver segment judgment can be realized, the method is used for radiotherapy, the segmentation precision is improved, and the treatment cost of a patient is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG TUMOR HOSPITAL
Radiotherapy dose planning method and system for implanting particles into tumor, and medium
ActiveCN113181563AStable and accurate outputStable outputImage enhancementImage analysisDose optimizationSeed Implantation
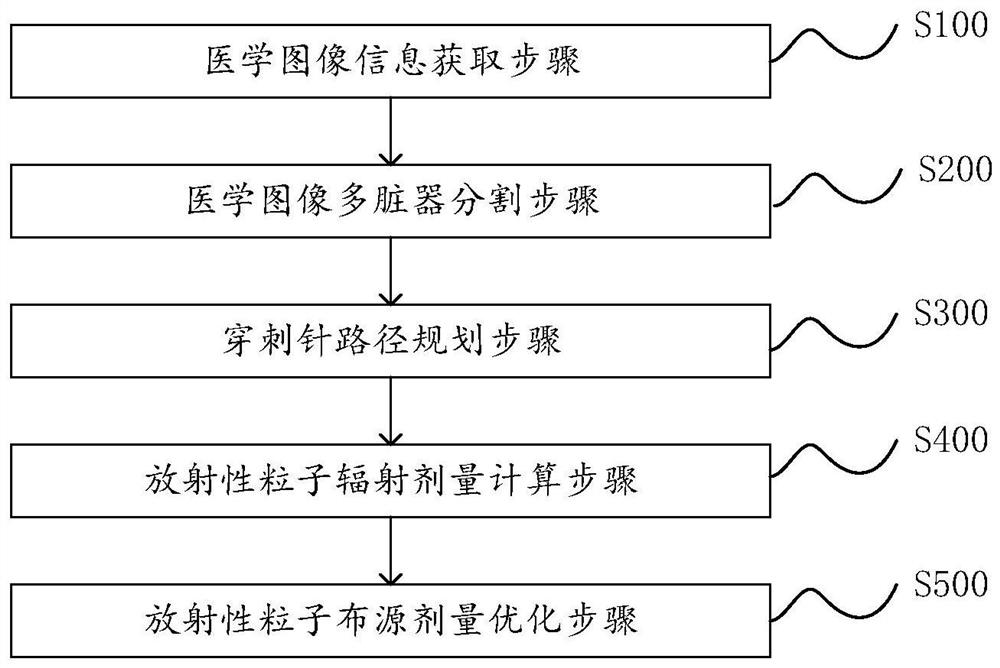
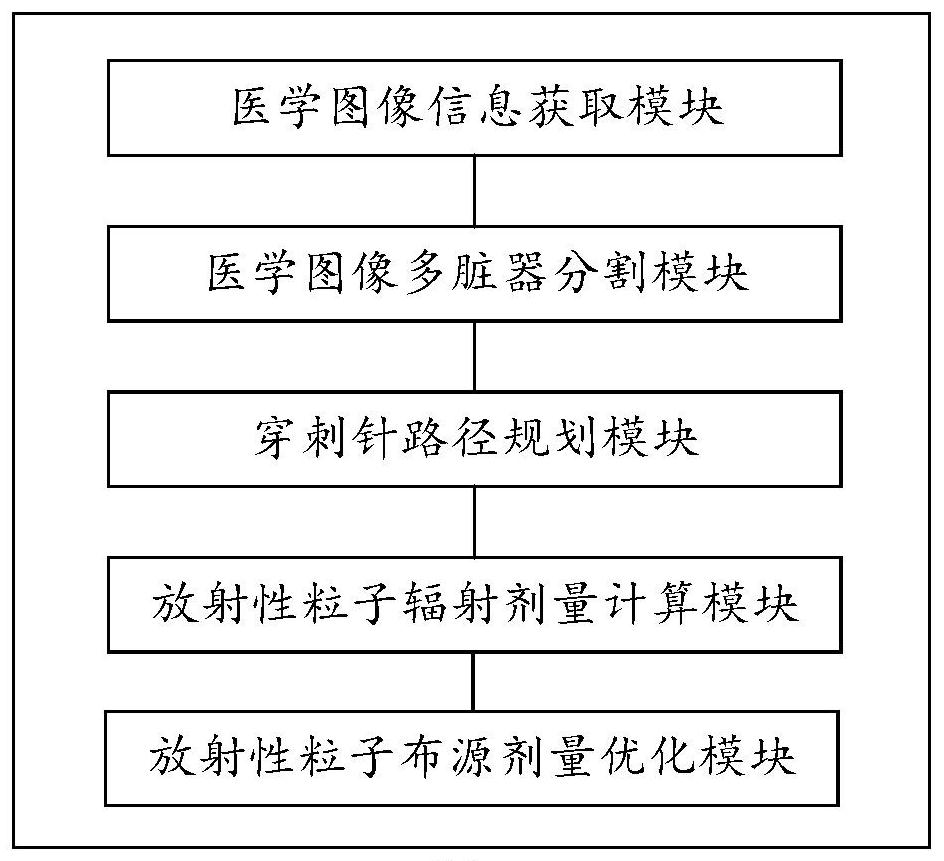
The invention discloses a radiotherapy dose planning method and system for implanting particles into a tumor, and a medium, and is used for a radiotherapy interventional surgical robot in radioactive particles. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining medical image information; a medical image multi-organ segmentation step of performing multi-organ segmentation on the medical image, including labeling one or more organs on the medical image; a puncture needle path planning step: limiting a feasible path of a puncture needle based on the marked organ and the virtual needle insertion panel; a radioactive particle radiation dose calculation step: calculating the radiation dose of the radioactive particles in the in-vivo environment; and a radioactive particle source arrangement dose optimization step: optimizing the number and spatial positions of the implanted particles according to the radiation dose of the particles and the form and volume of the tumor focus to obtain a particle source arrangement result with the accumulated radiation dose meeting the set dose. According to the invention, radiation particle dose distribution meets clinical requirements.
Owner:珠海横乐医学科技有限公司
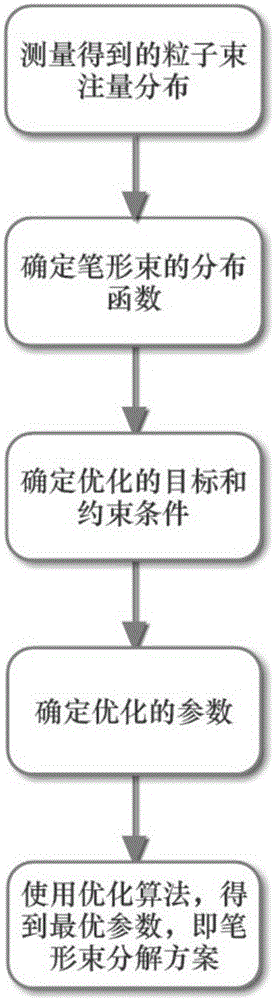
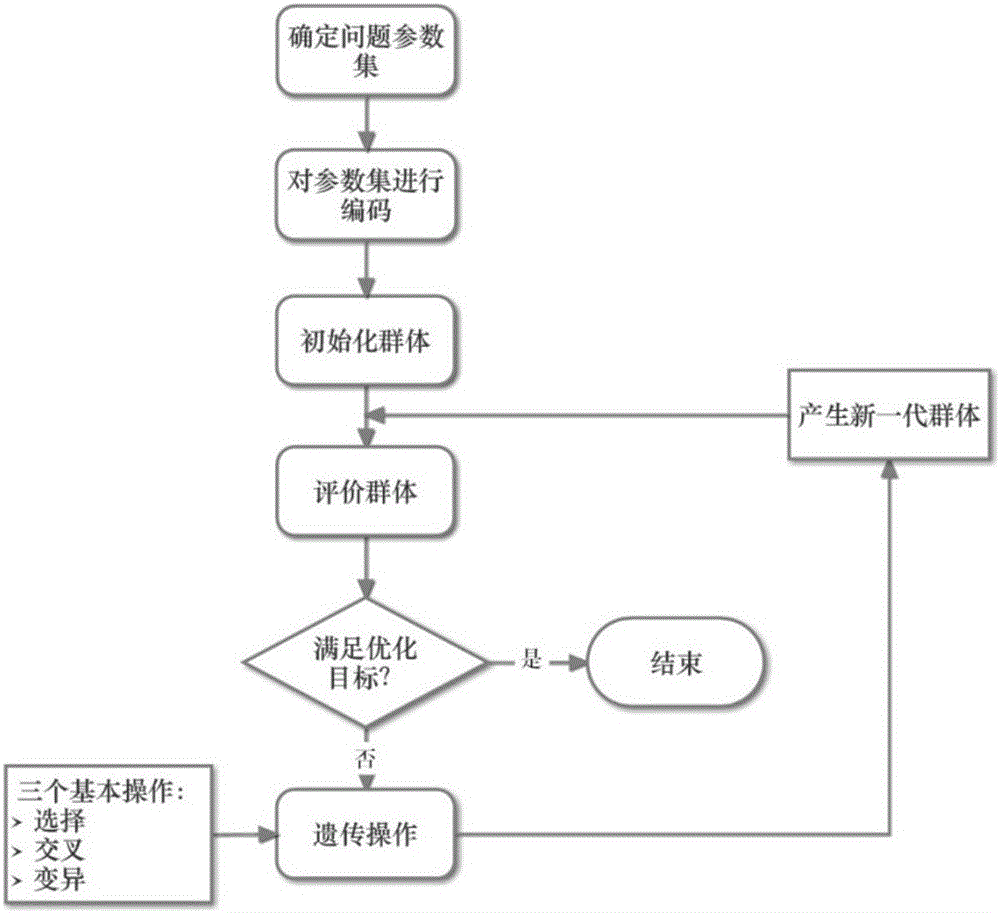
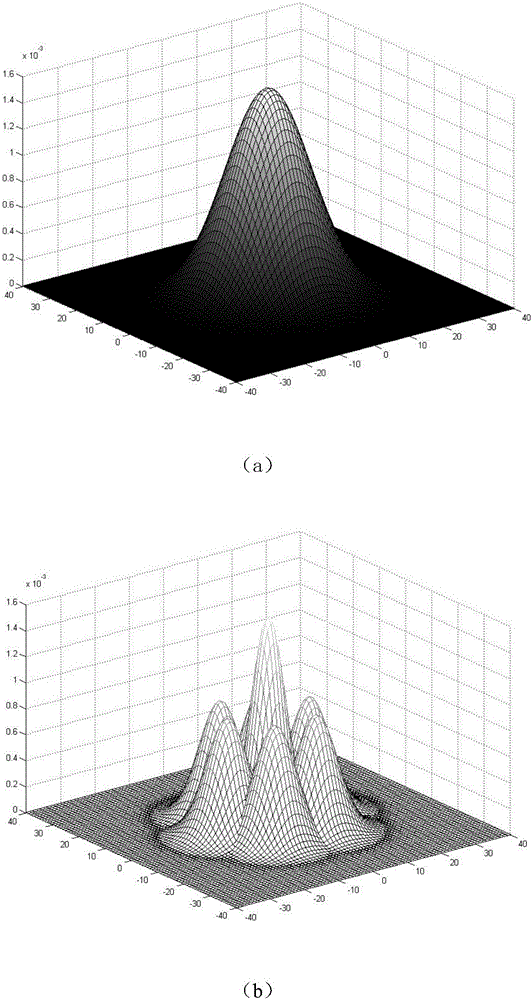
Method for decomposing particle beam fluence into pencil beams based on optimization algorithm
ActiveCN105787256AAvoid methodAvoid dependencyMedical equipmentSpecial data processing applicationsDecomposition problemDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for decomposing particle beam fluence into pencil beams based on an optimization algorithm. Particle beams are decomposed into small pencil beams based on the radiotherapy dose calculation demand of a pencil beam algorithm. The pencil beams are generally distributed in a Gaussian type. The total dose distribution is the summation of the dose distribution of each pencil beam. The method is the method by which the particle beam fluence decomposing problem in radiotherapy dose calculation of charged particles (such as proton and heavy ions) is solved, and the problem is solved by using the optimization algorithm. According to the method, the fluence distribution of the particle beams is obtained through measurement of a detector, then the particle beams are decomposed into a plurality of pencil beams based on the optimization algorithm, and the center position, size and weight of each pencil beam are obtained. The method is wide in applicability. Compared with the original distribution, the total fluence distribution after decomposition is higher in fitness; or under the same error condition, the number of the decomposed pencil beams is lower; and the radiotherapy dose calculation speed or precision of the particle beams can be greatly improved.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Radiotherapy dose optimization method and device
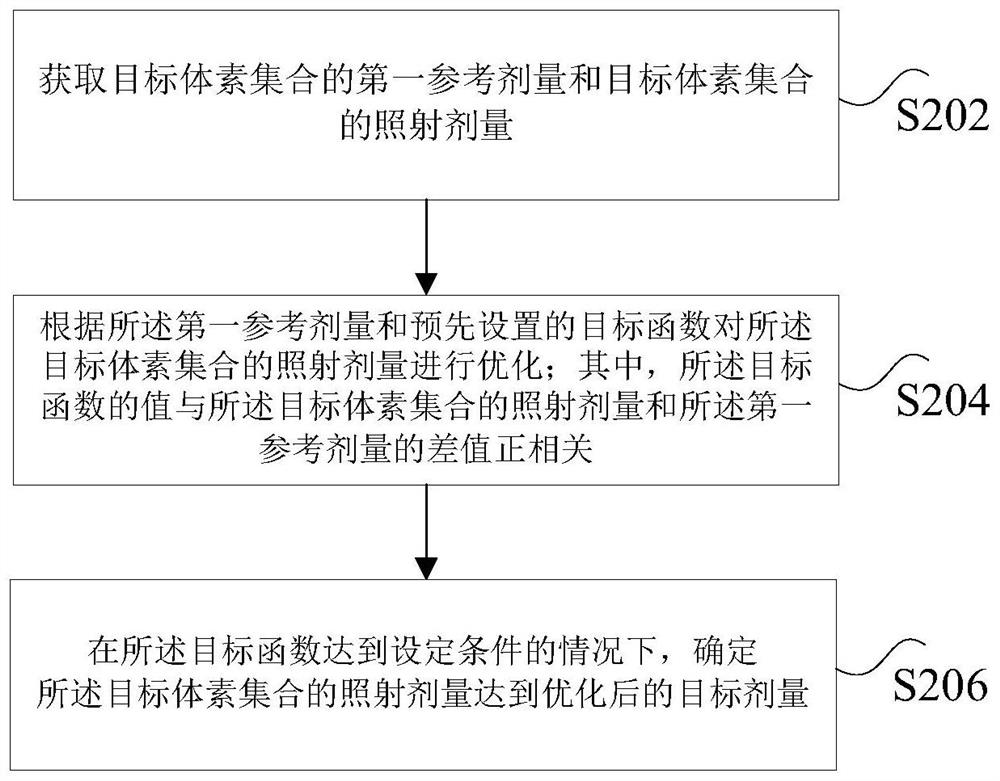
PendingCN114496161AImprove optimization efficiencySolve the technical problem of low optimization efficiencyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesHealth-index calculationVoxelRadiology
The invention discloses a radiotherapy dose optimization method and device. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a first reference dose of a target voxel set and an irradiation dose of the target voxel set; optimizing the irradiation dose of the target voxel set according to the first reference dose and a preset target function; wherein the value of the target function is in positive correlation with the difference between the irradiation dose of the target voxel set and the first reference dose; and determining that the irradiation dose of the target voxel set reaches the optimized target dose under the condition that the target function reaches a set condition. The technical problem of low radiation dose optimization efficiency caused by excessive dependence on manual debugging is solved.
Owner:MANTEIA TECH CO LTD
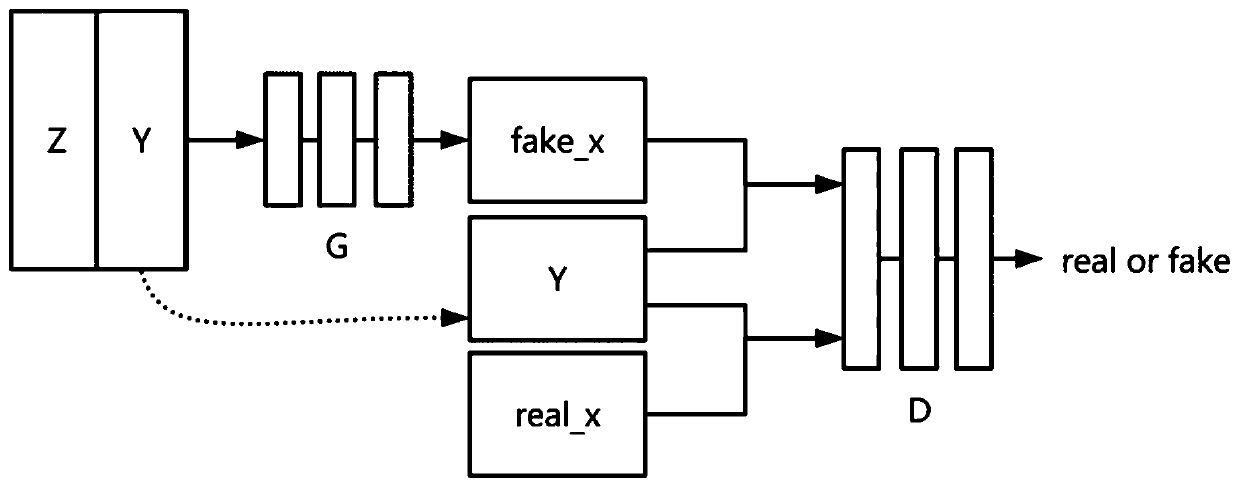
Radiotherapy treatment plan modeling using generative adversarial networks
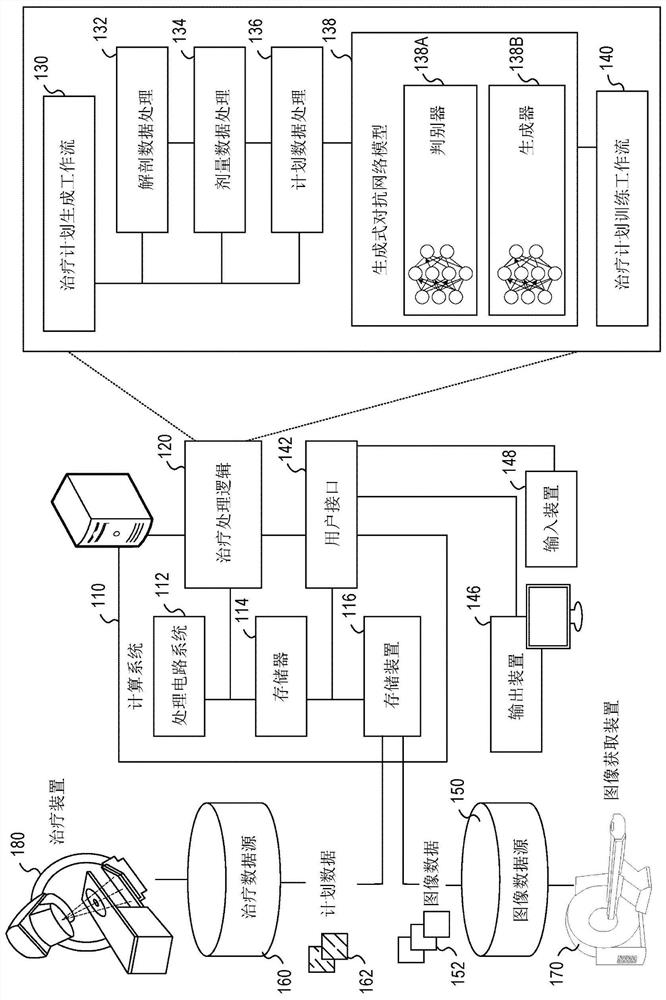
ActiveCN112041026AMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesNeural learning methodsGenerative adversarial networkRadiology
Techniques for generating radiotherapy treatment plans and establishing machine learning models for the generation and optimization of radiotherapy dose data are disclosed. An example method for generating a radiotherapy dose distribution using a generative model, trained in a generative adversarial network, includes: receiving anatomical data of a human subject that indicates a mapping of an anatomical area for radiotherapy treatment; generating radiotherapy dose data corresponding to the mapping with use of the trained generative model, as the generative model processes the anatomical data as an input and provides the dose data as output; and identifying the radiotherapy dose distribution for the radiotherapy treatment of the human subject based on the dose data. Another example method for training of the generative model includes establishing values of the generative model and a discriminative model of the generative adversarial network using adversarial training, including in a conditional generative adversarial network arrangement.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com