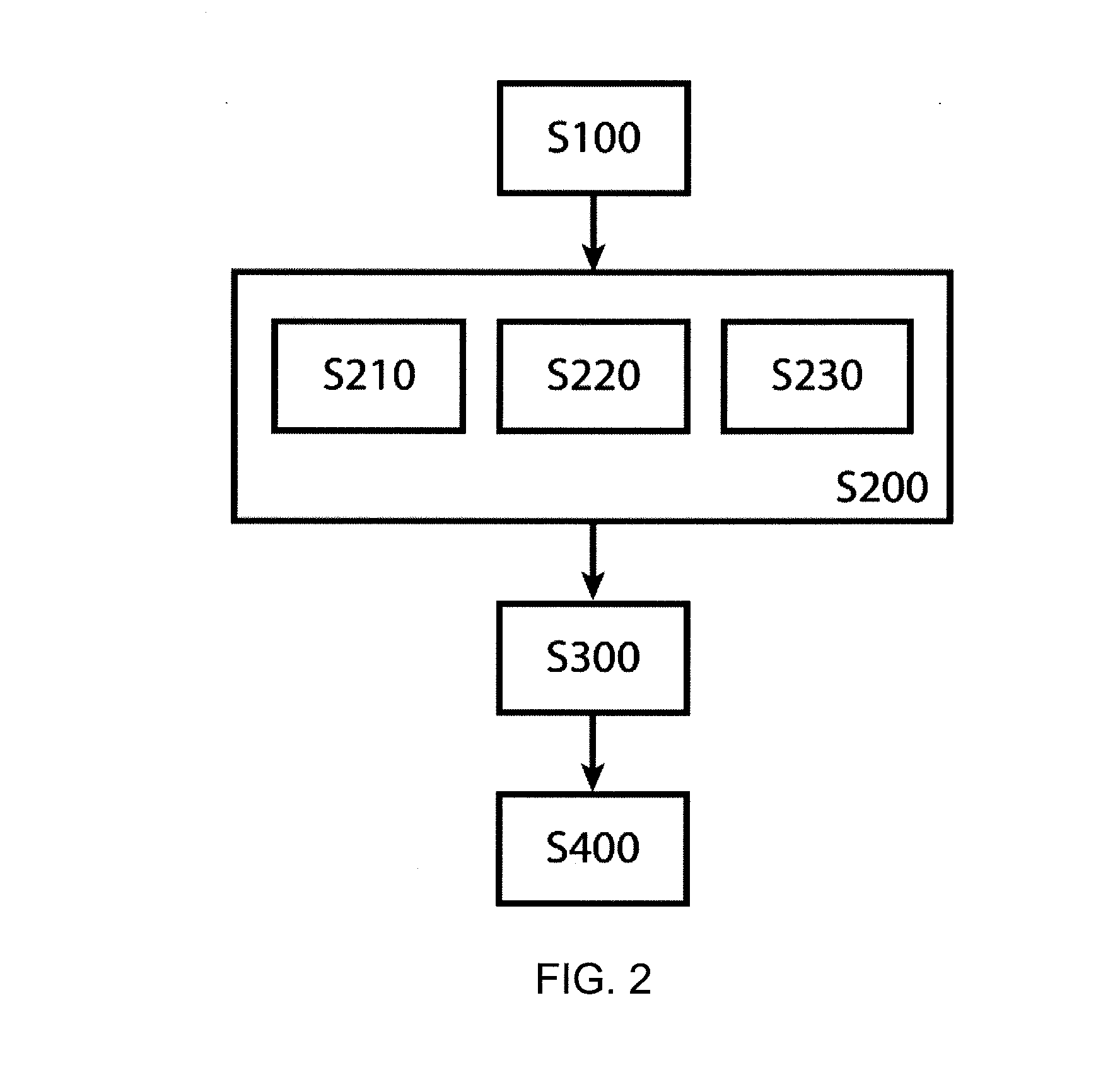
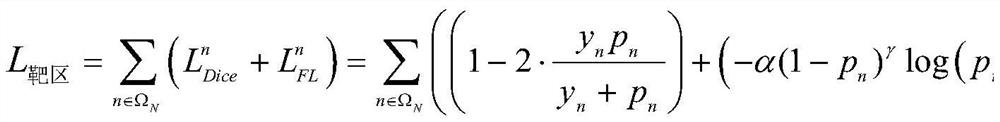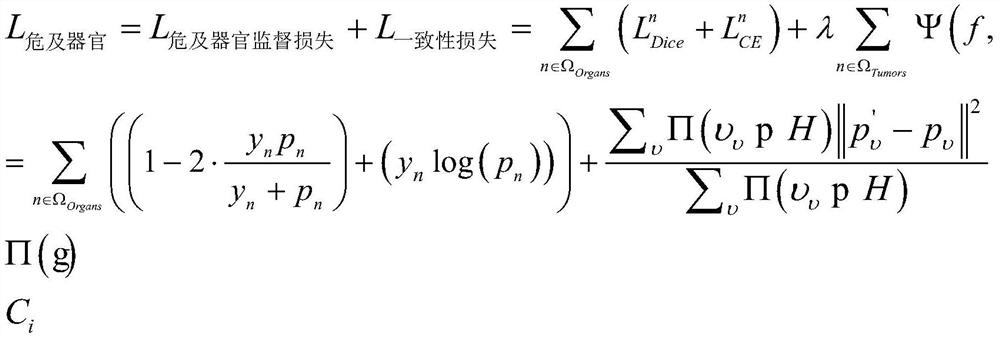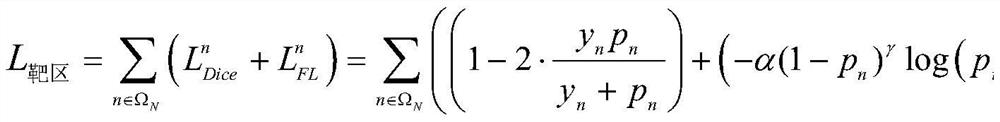Patents
Literature
103 results about "Organ at risk" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Organs at Risk. "Organs at Risk" is a descriptor in the National Library of Medicine's controlled vocabulary thesaurus, MeSH (Medical Subject Headings). Descriptors are arranged in a hierarchical structure, which enables searching at various levels of specificity. Organs which might be damaged during exposure to a toxin or to some form of therapy.
Intelligent and automatic delineation method for gross tumor volume and organs at risk
InactiveCN107403201ASmart sketchAutomatically sketchImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationMathematical Graph
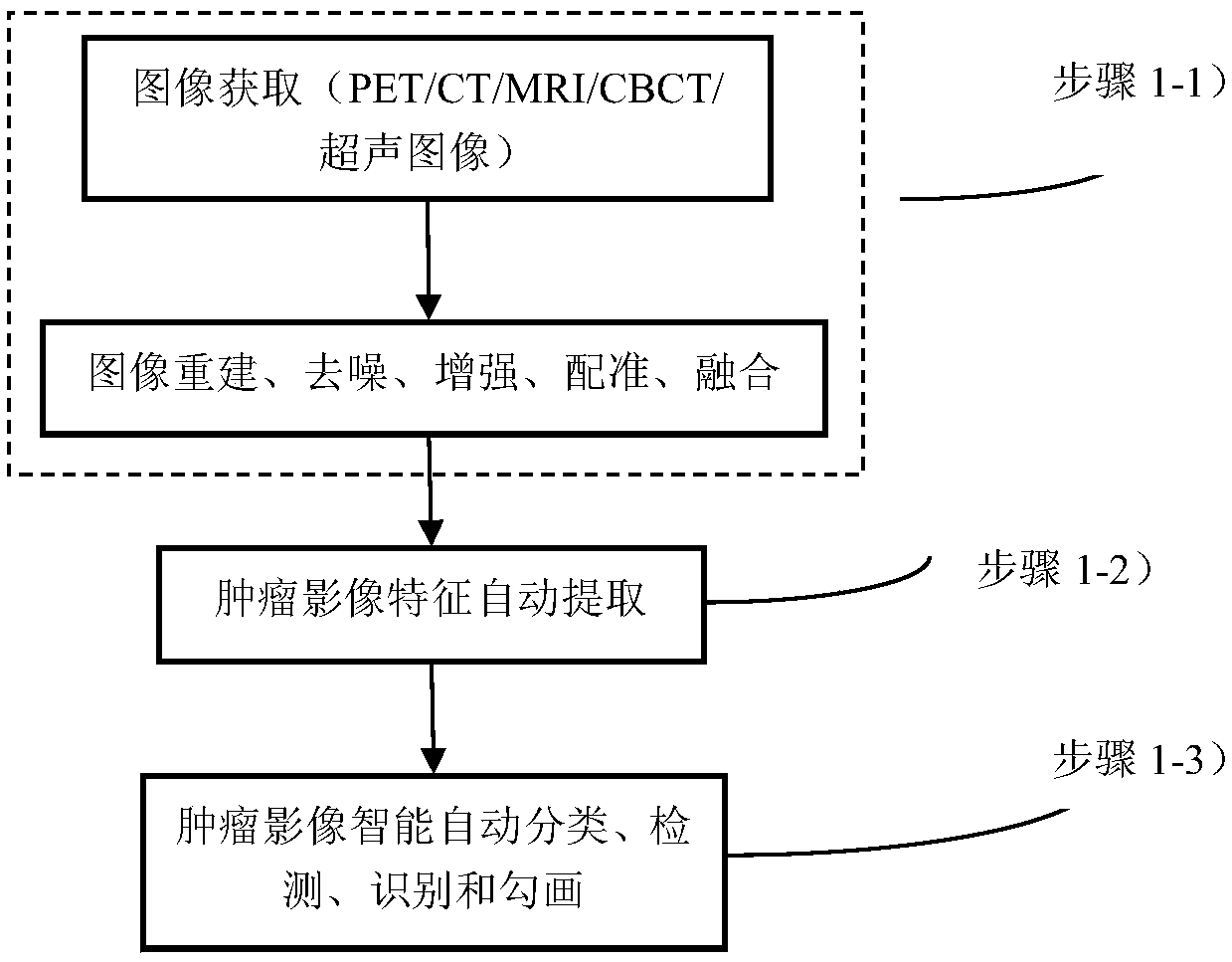
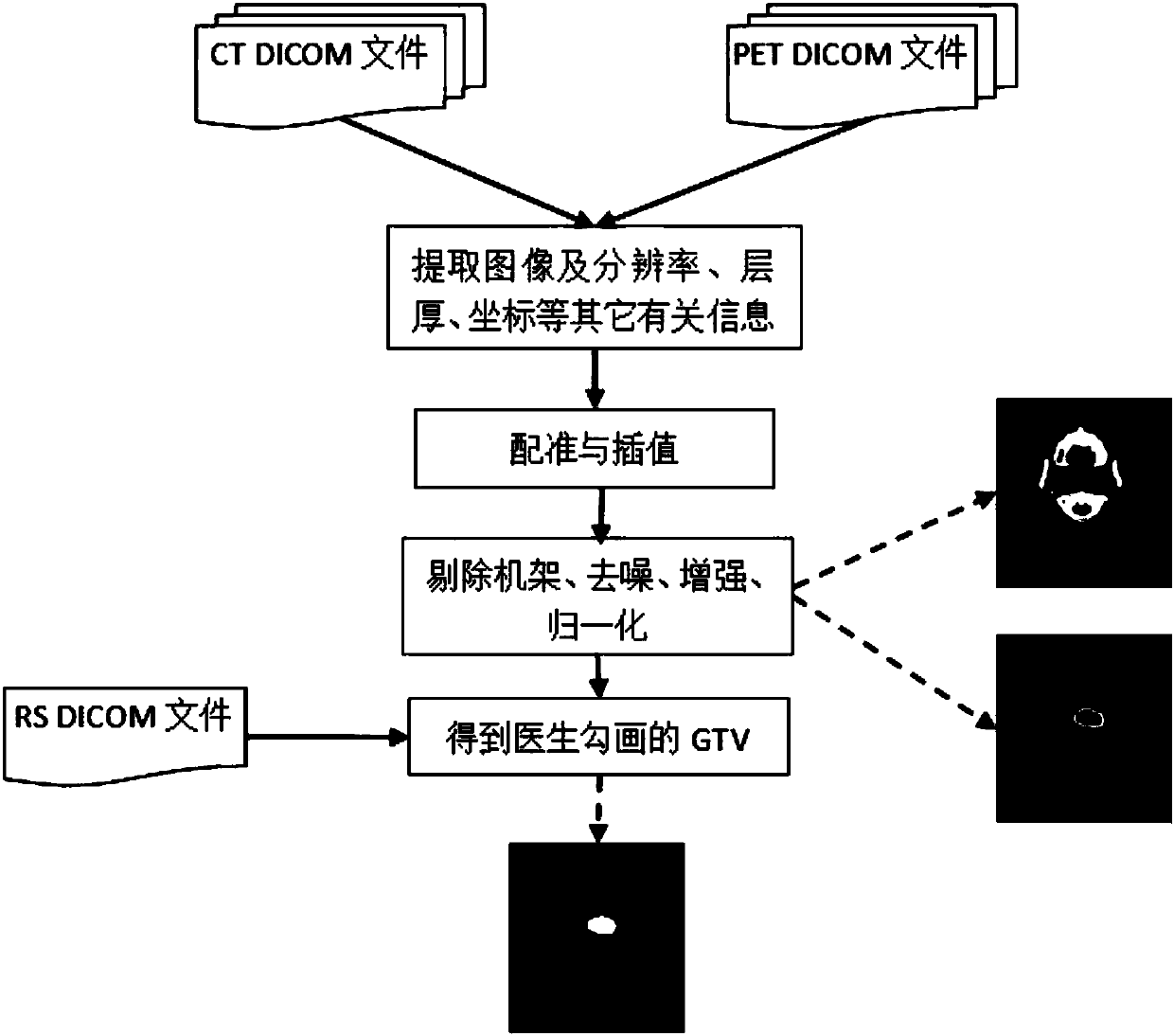
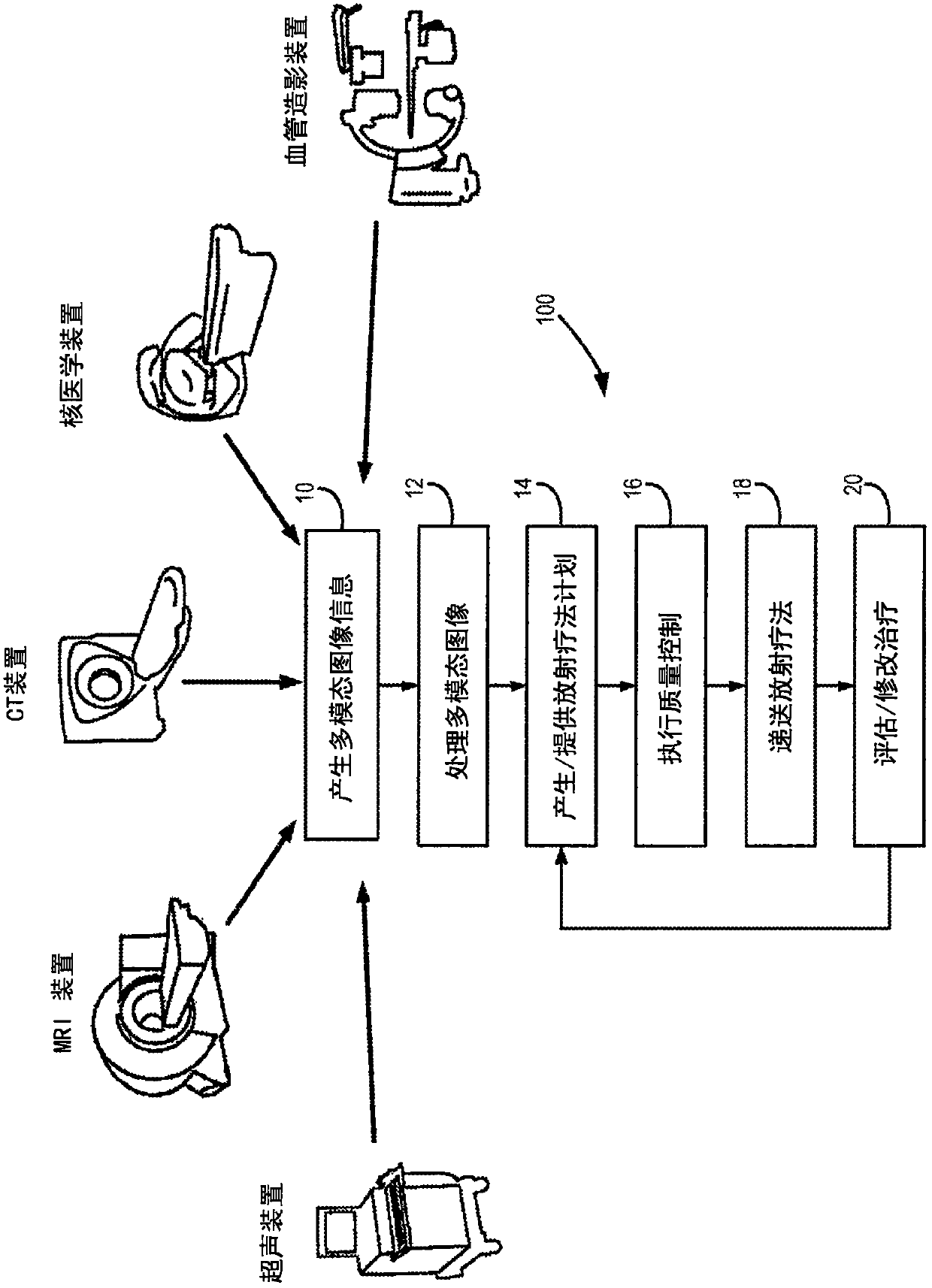
The invention relates to an intelligent and automatic delineation method for a gross tumor volume and organs at risk, which includes the following steps: (1) tumor multi-modal (mode) image reconstruction, de-noising, enhancement, registration, fusion and other preprocessing; (2) automatic extraction of tumor image features: automatically extracting one or more pieces of tumor image group (texture feature spectrum) information from CT, CBCT, MRI, PET and / or ultrasonic multi-modal (mode) tumor medical image data; and (3) intelligently and automatically delineating a gross tumor volume and organs at risk through deep learning, machine learning, artificial intelligence, regional growing, the graph theory (random walk), a geometric level set, and / or a statistical theory method. A gross tumor volume (GTV) and organs at risk (OAR) can be delineated with high precision.
Owner:强深智能医疗科技(昆山)有限公司
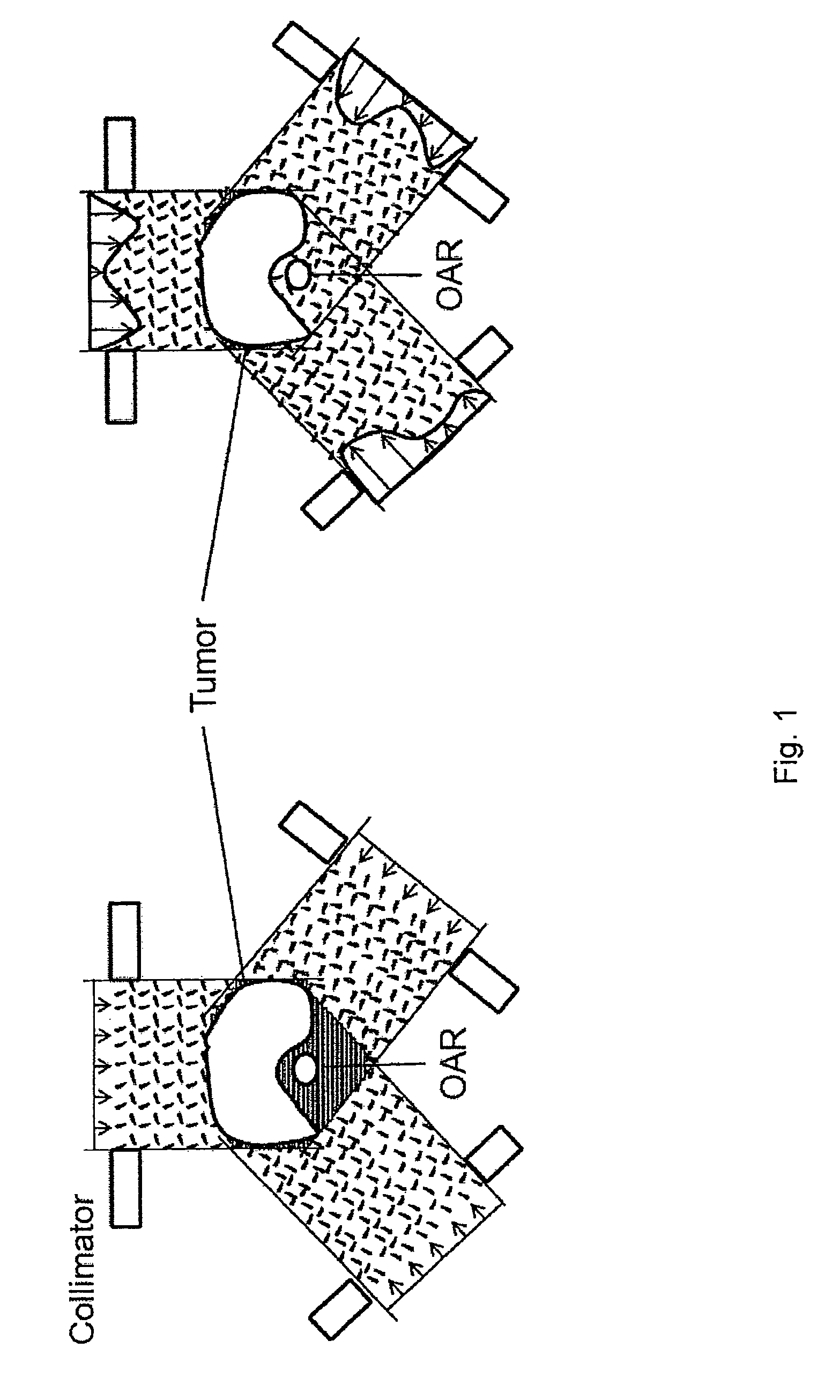
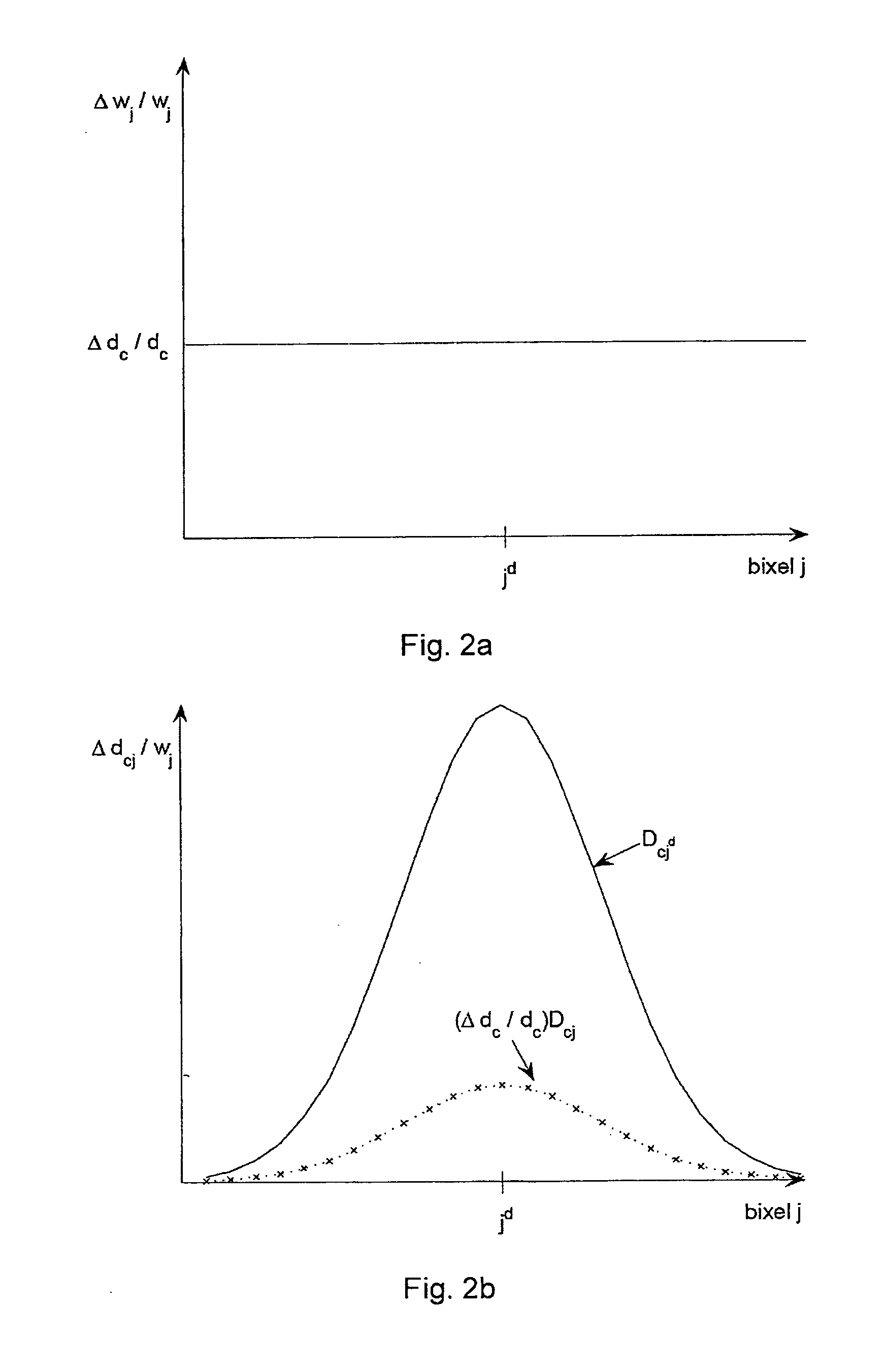
Method for assisted beam selection in radiation therapy planning
InactiveUS7027557B2Easy to mergeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPlan treatmentMulti leaf collimator
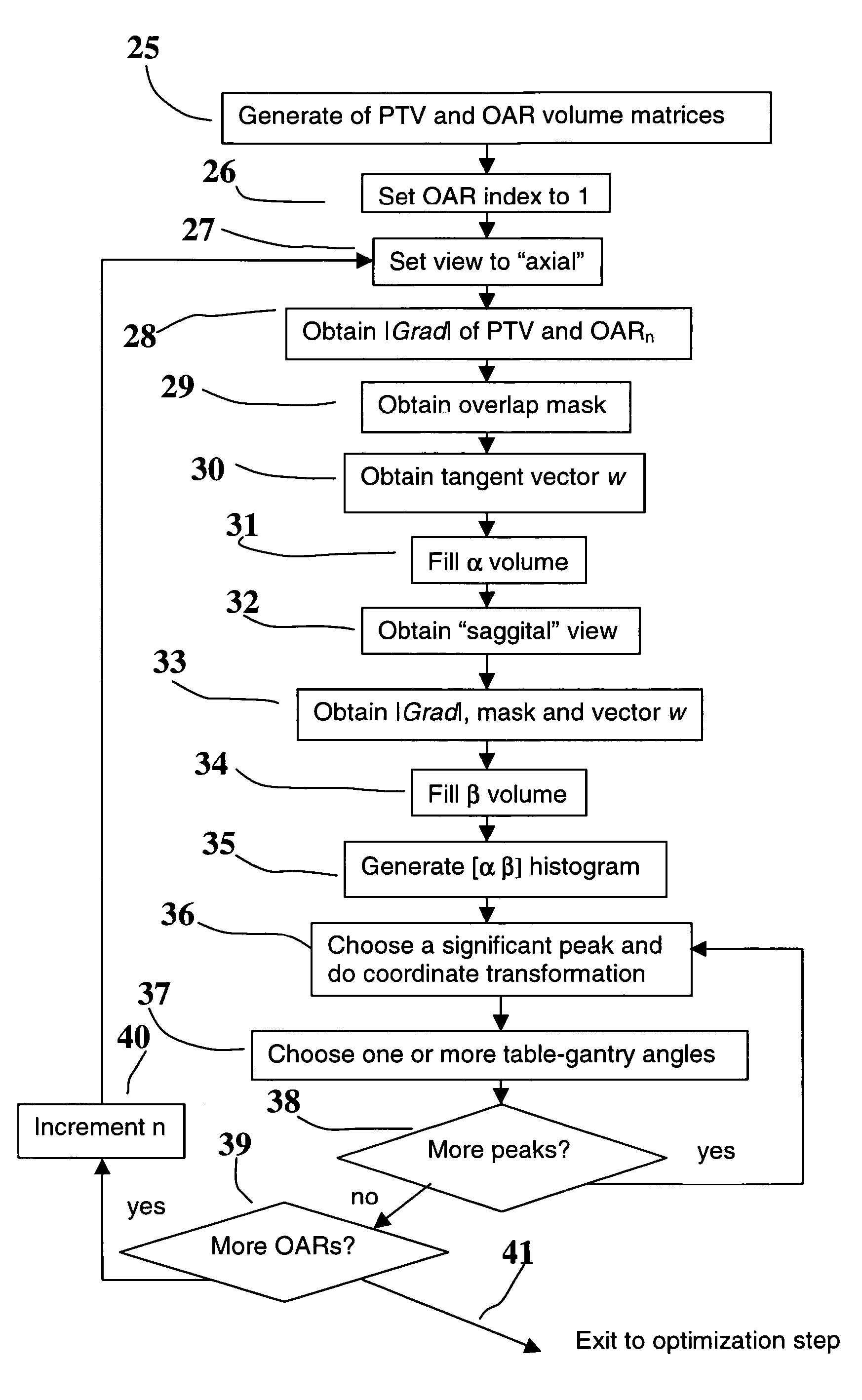
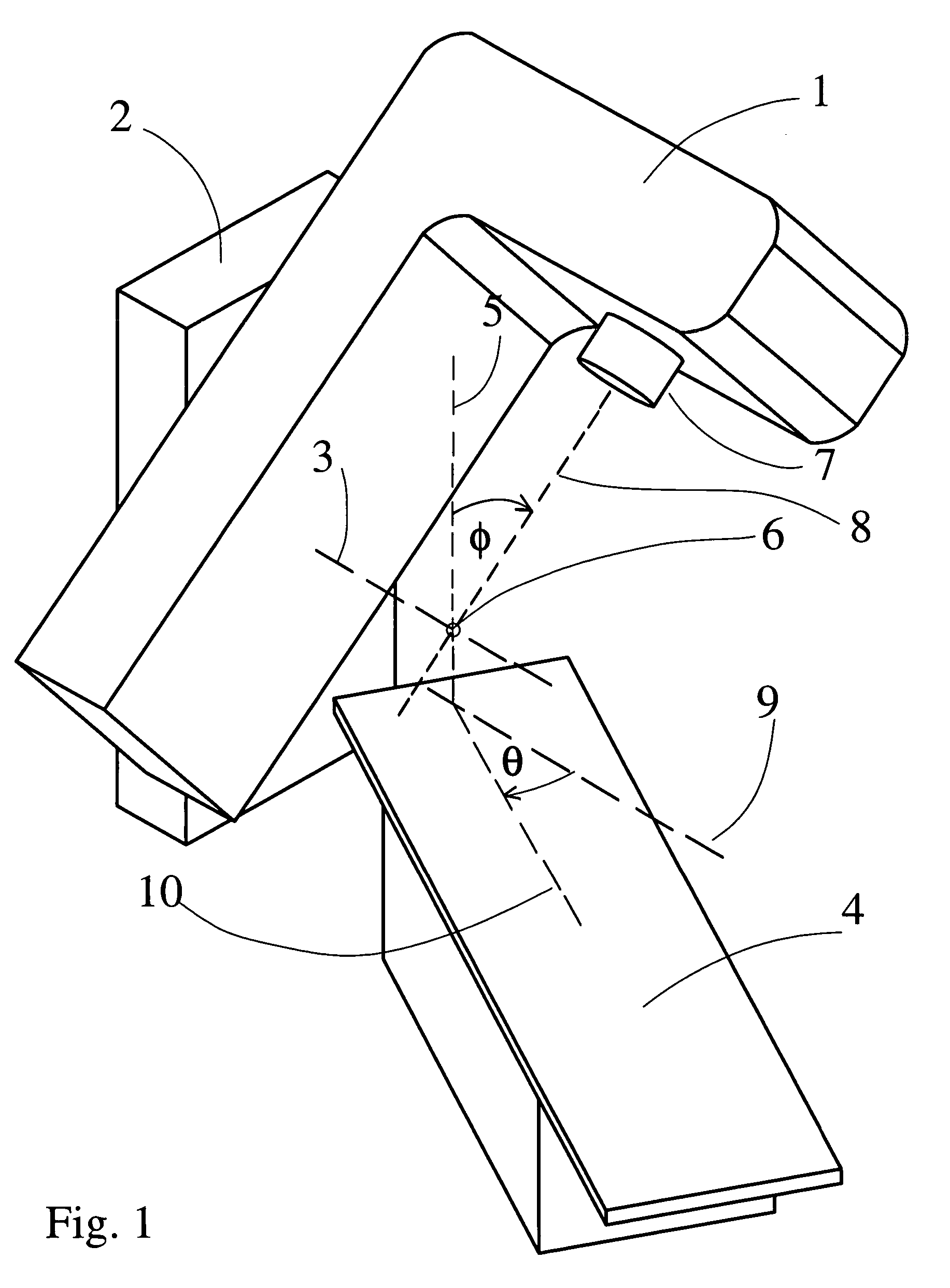
A method to assist in the selection of optimum beam orientations for radiation therapy when a planning treatment volume (PTV) is adjacent to one or more organs-at-risk (OARs). A mathematical analysis of the boundaries between the PTV and OARs allows the definition of a continuum of pairs of gantry and table angles whose beam orientations have planes that are essentially parallel to those boundaries, and can, therefore, separate the PTV from the OARs when a multi-leaf collimator is used in the therapy. The Radiation Oncologist can then select one or more pairs of gantry and table angles from the continuum as input to a beam optimization step. The selected angles can deliver highly uniform dose to the PTV, while minimizing the radiation dose to the OARs.
Owner:LLACER JORGE
Method, system and computer-readable media for treatment plan risk analysis
ActiveUS20170083682A1Risk minimizationMedical simulationMedical data miningPatient dataOrgan at risk
A method, system and computer readable medium of: providing feature data of at least one organ at risk or target volume of said patient from a database of non-transitory data stored on a data storage device of prior patients data; generating, using a data processor, a distribution of dose points of the at least one organ at risk or target volume of said patient based on said feature data; calculating, using the data processor, at least one of (i) a probability of toxicity for the at least one organ at risk or (ii) a probability of treatment failure for the at least one target volume, based on said distribution of dose points; assessing, using the data processor, a dosimetric-outcome relationship based on the calculated probability; and automatically formulating, using the data processor, a treatment plan using the dosimetric-outcome relationship to minimize the at least one treatment-related risk.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Systems and methods for specifying treatment criteria and treatment parameters for patient specific radiation therapy planning
ActiveUS20160129282A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesHealthcare resources and facilitiesProximateCombined use
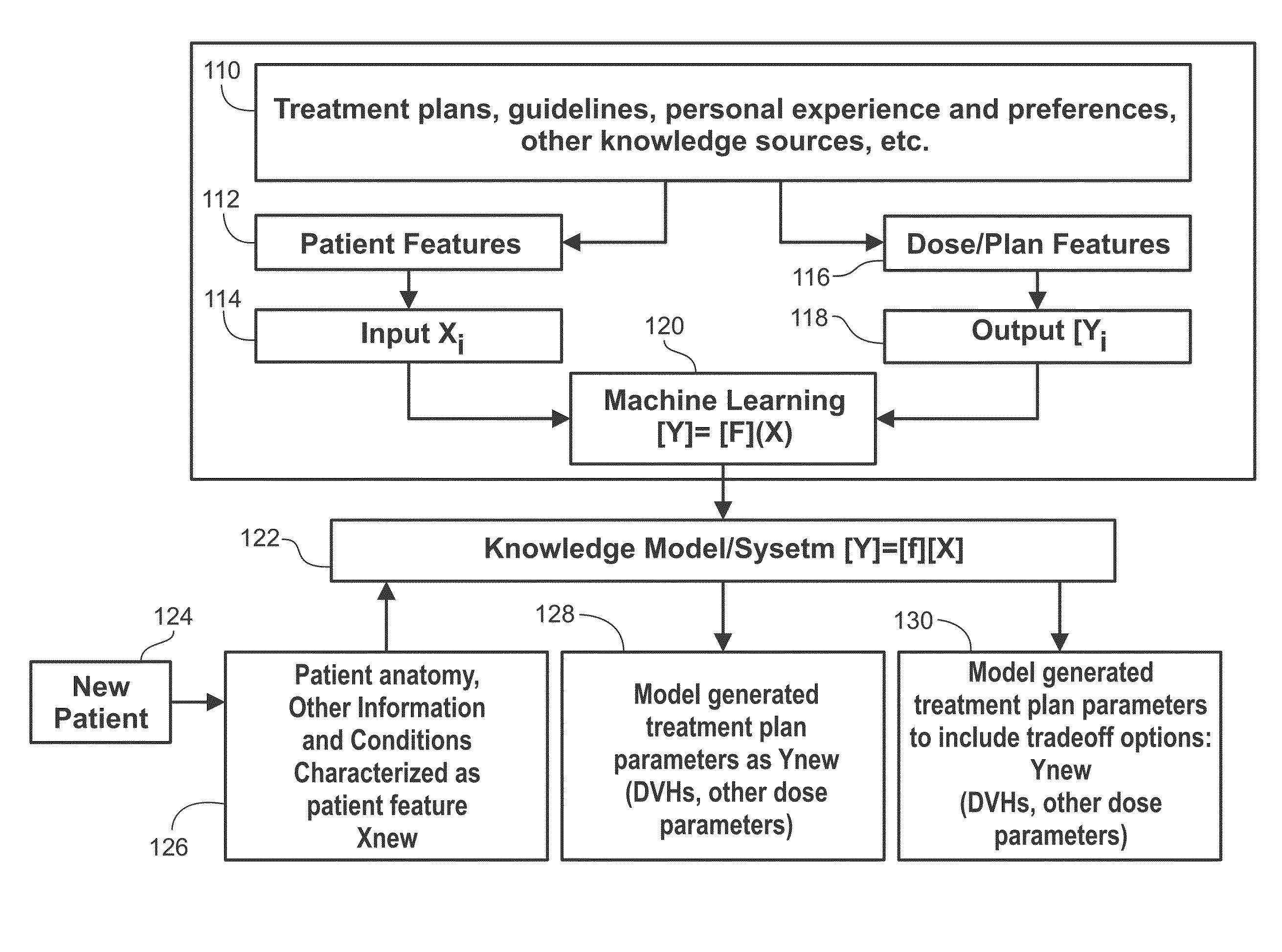
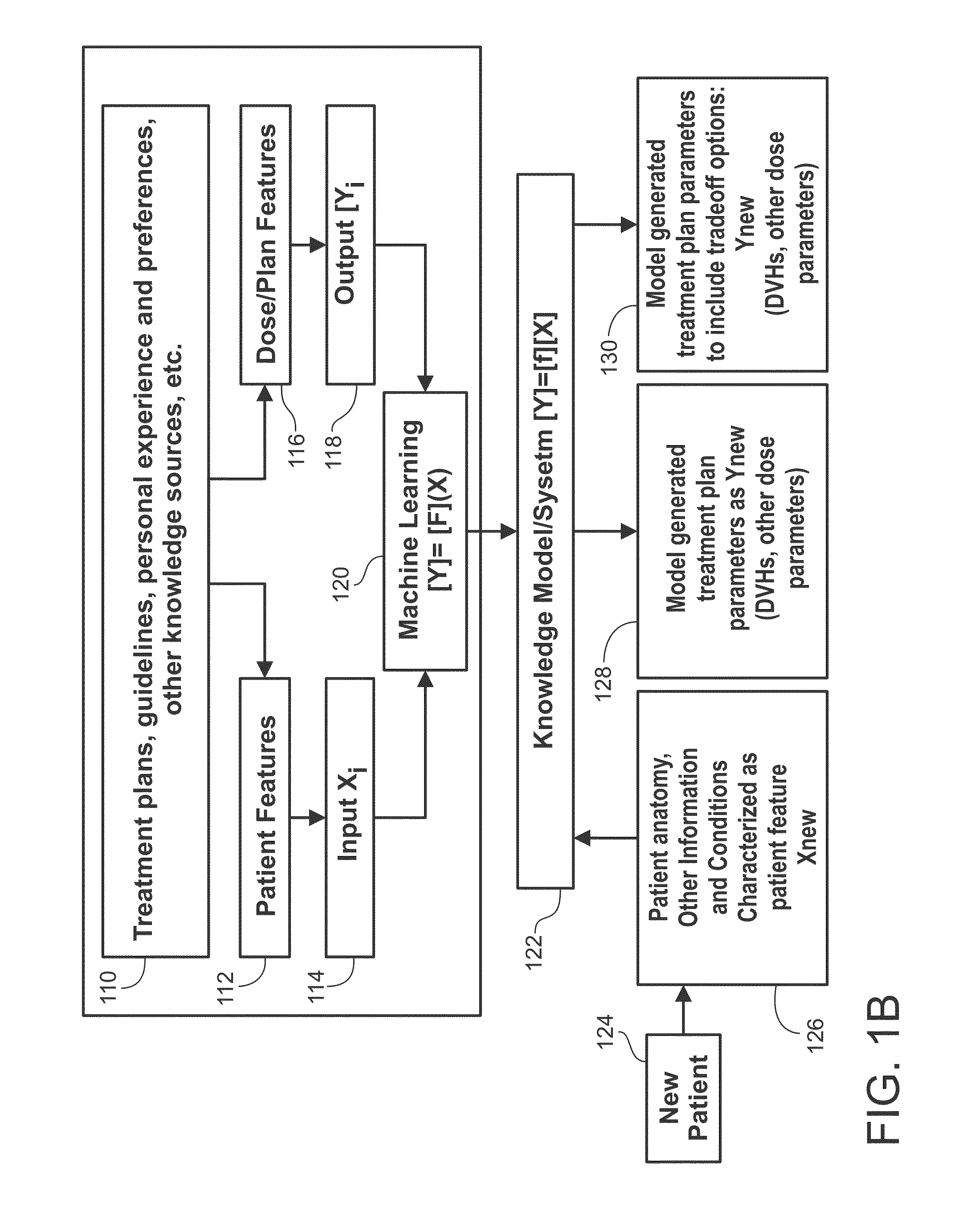
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for specifying treatment criteria and treatment planning parameters for patient specific radiation therapy planning. According to an aspect, a method includes receiving data about a patient, computing geometric characterization of one or more organs at risk proximate to a target volume of a patient or vice versa, and selecting relevant treatment knowledge and experience. The method also includes generating, based on the received data, computed geometric characterization, and available knowledge and experience, a first set of radiation treatment planning parameters that will lead to a high quality plan for the patient. Further, the method includes model-based prediction, based on the data, a second set or more of radiation treatment planning parameters that will lead to alternative achievable plans with different organ sparing objectives for treating the patient. The multiple sets for parameters can be used separately or in conjunction to generate treatment plans.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
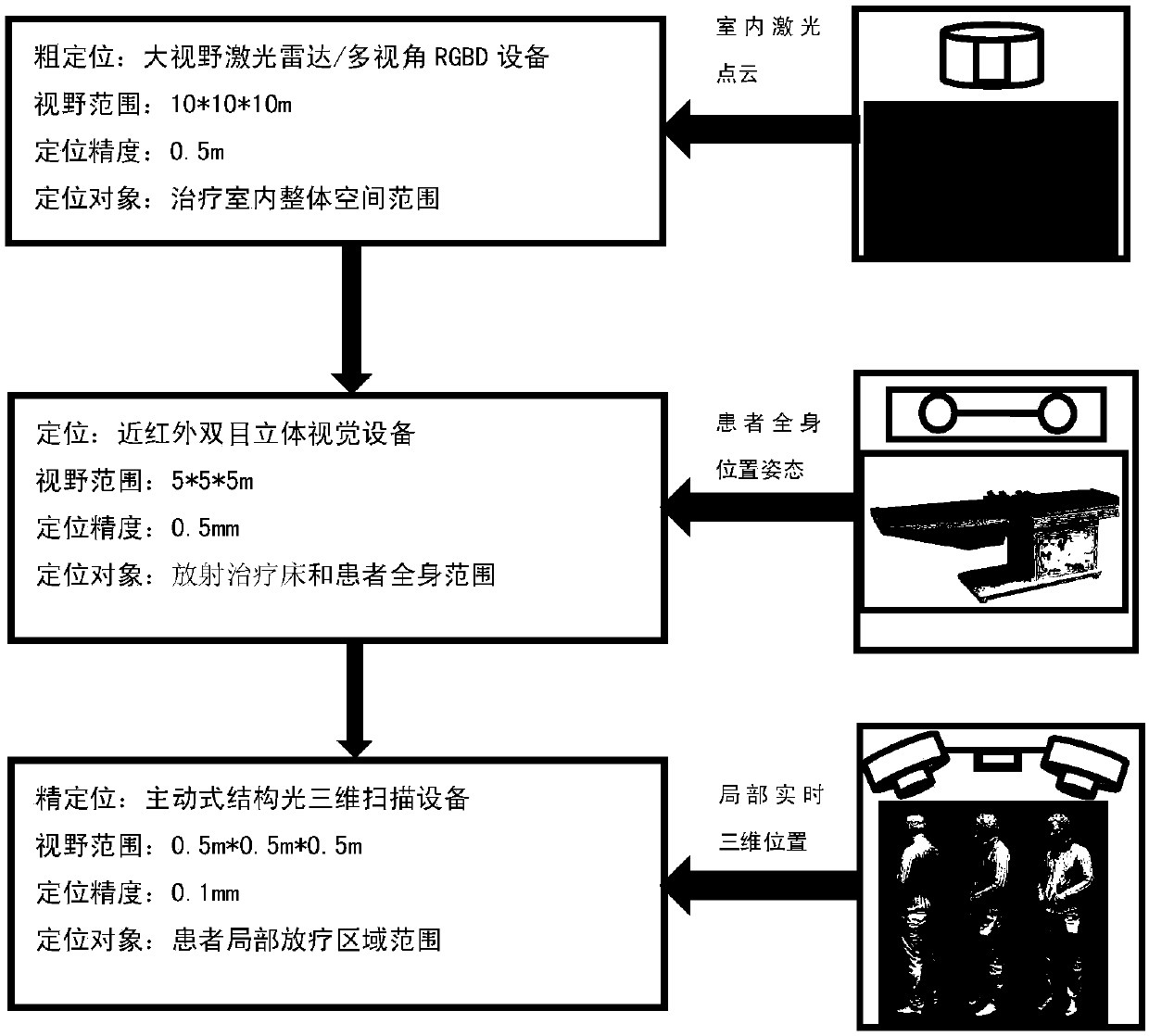
Intelligent control method of visual monitoring and visual servo of tumor radiation therapy
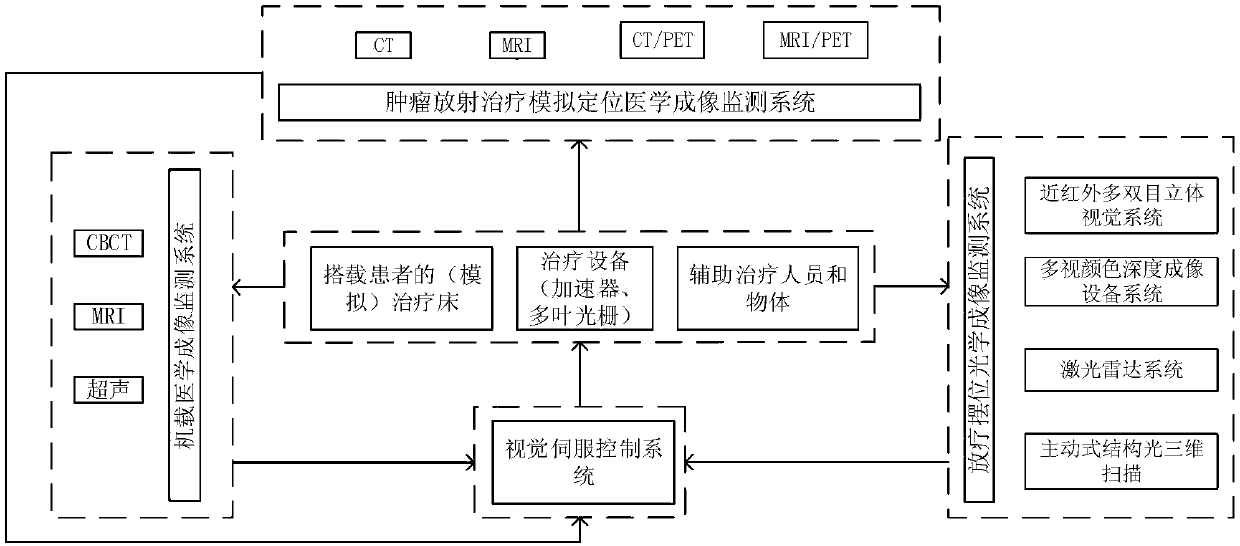
InactiveCN107358607AQuality assuranceAccurate positioningImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTherapeutic Devices
The invention relates to an intelligent control method of visual monitoring and visual servo of tumor radiation therapy. The method comprises: (1) according to multi-mode medical images and multi-vision optical images collected by a radiation-oncology-plan-stage simulation and positioning medical imaging system, a radiation-oncology-positioning-stage treatment room internal optical imaging system, and a radiation-oncology-plan-execution-stage onboard medical imaging system and the like, intelligent analysis processing is carried out to monitor, identify and localize a tumor radiotherapy target and an organ at risk, radiotherapy beds with patients, radiotherapy equipment, and the auxiliary treatment staff and objects in a treatment room during the whole radiotherapy process; and (2), on the basis of optical images and / or medical images collected at different stages of the tumor radiotherapy process as well as the quality guaranteeing requirement of the clinical radiotherapy process, a multi-stage multi-vision servo intelligent control system (algorithm) is used for carrying out intelligent, automatic, high-precision, high-robust visual servo control on the radiotherapy beds, radiotherapy equipment, the onboard medical image system, and the optical imaging system in the treatment room during the tumor radiotherapy process.
Owner:强深智能医疗科技(昆山)有限公司
Method and a system for optimizing a radiation treatment plan
A computer-based method for generating an improved radiation therapy treatment plan for a treatment volume having a target and an organ-at-risk. The method includes a step of accessing an existing radiation therapy treatment plan from a memory of a computer, a dose distribution of the existing radiation therapy treatment plan serving as a reference dose distribution; and performing machine parameter optimization on the existing radiation therapy treatment plan with the computer by pursuing an optimization goal to minimize doses to the organ-at-risk, thereby generating the improved radiation therapy treatment plan.
Owner:RAYSEARCH LAB
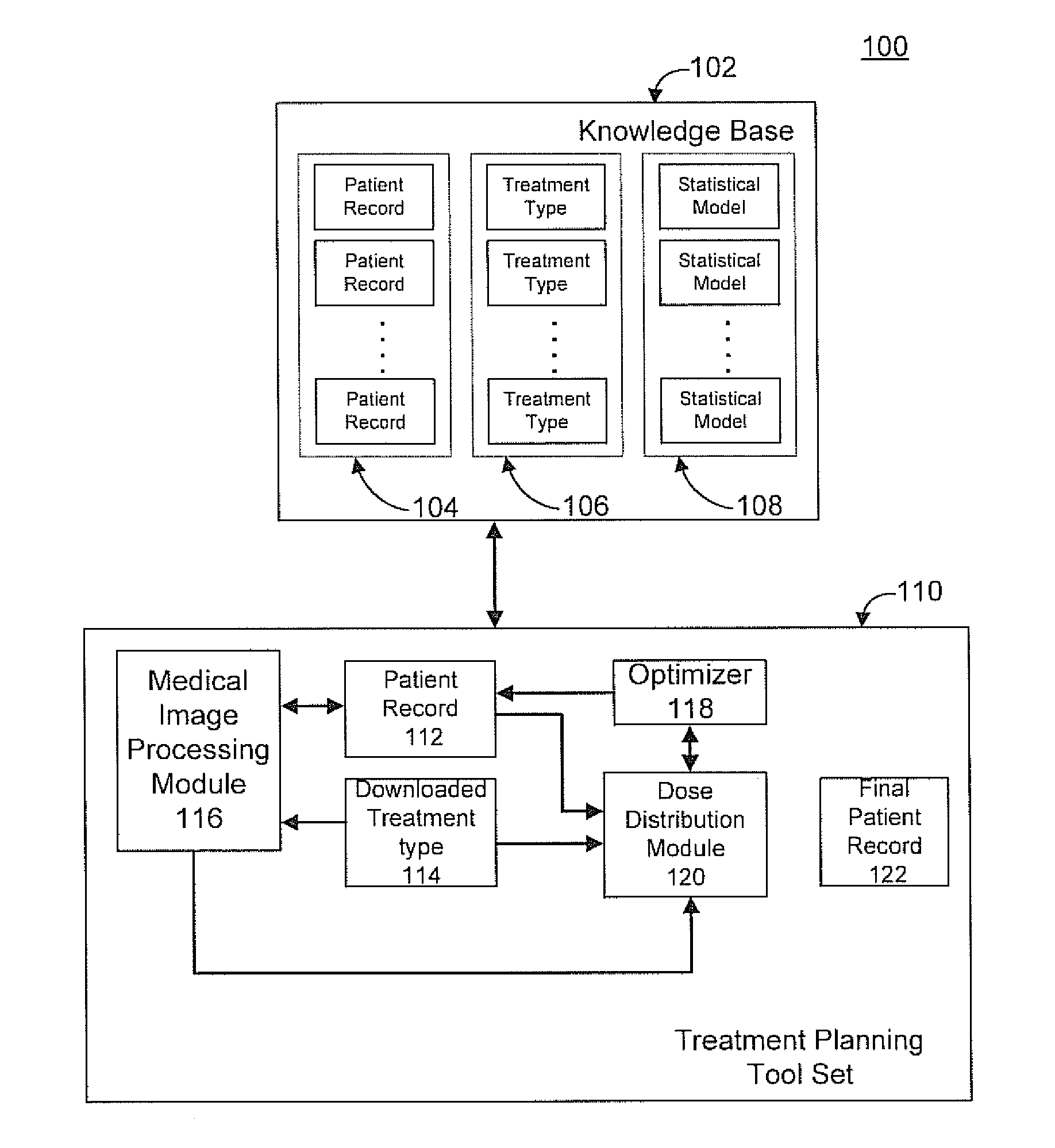
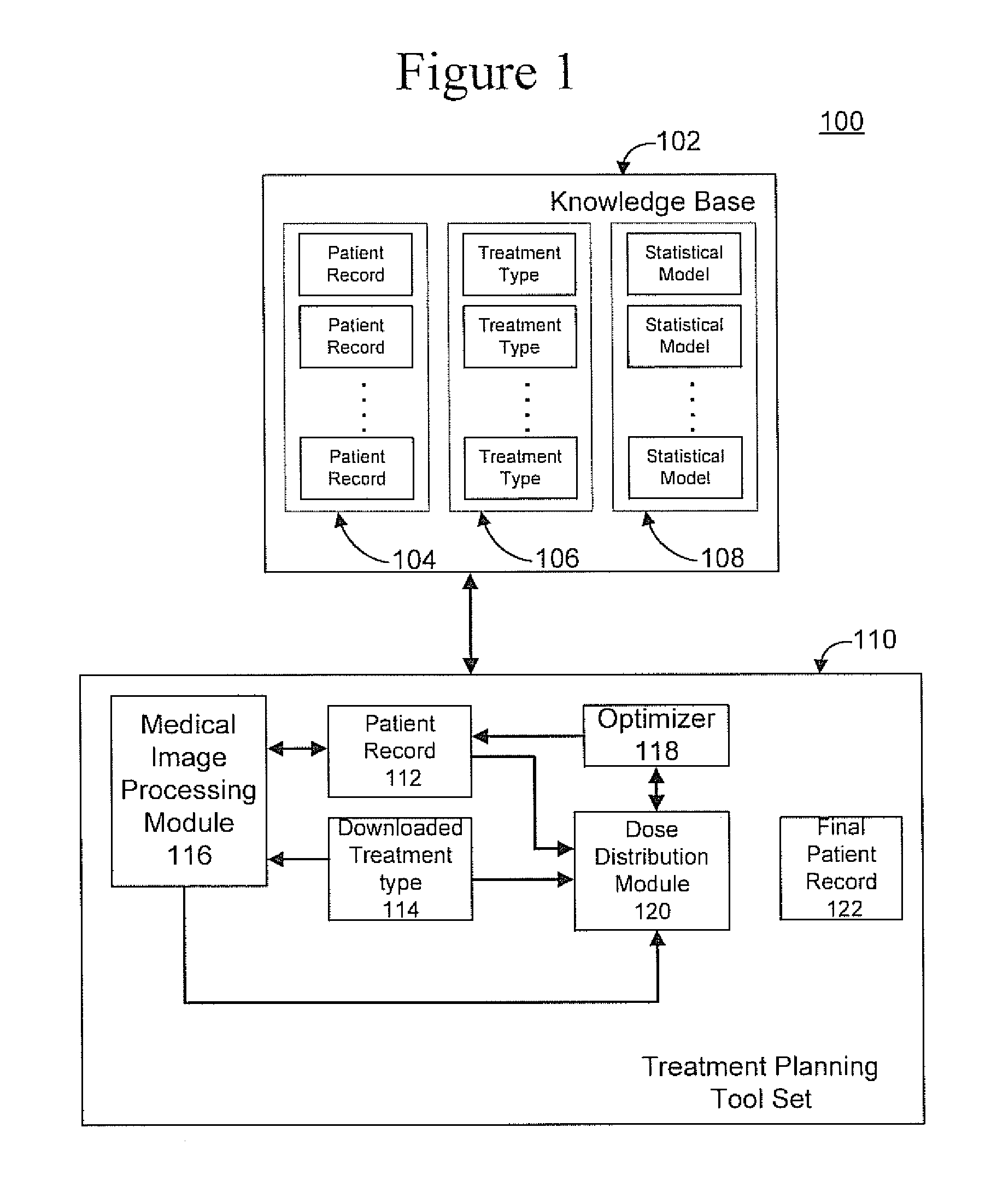
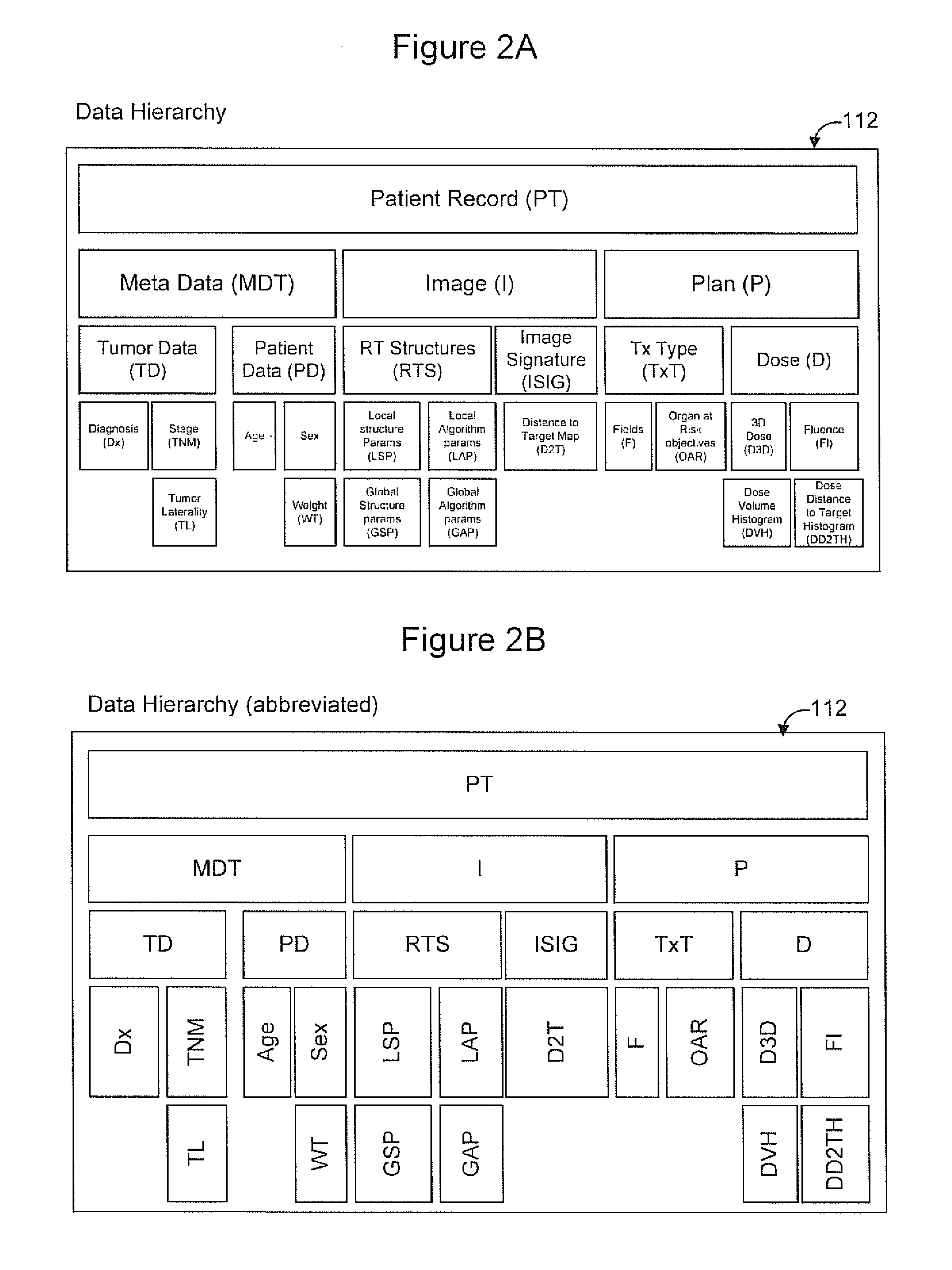
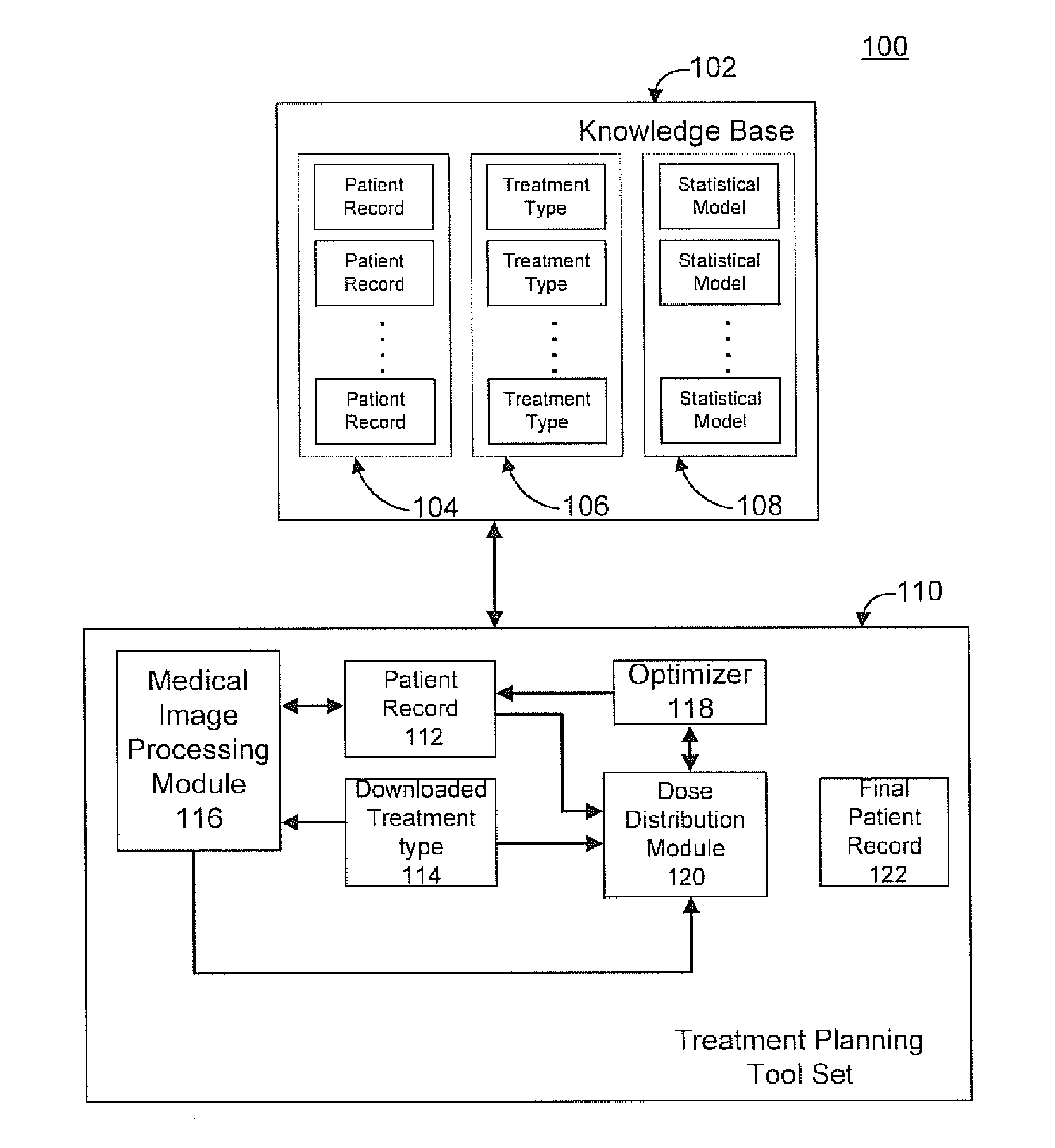
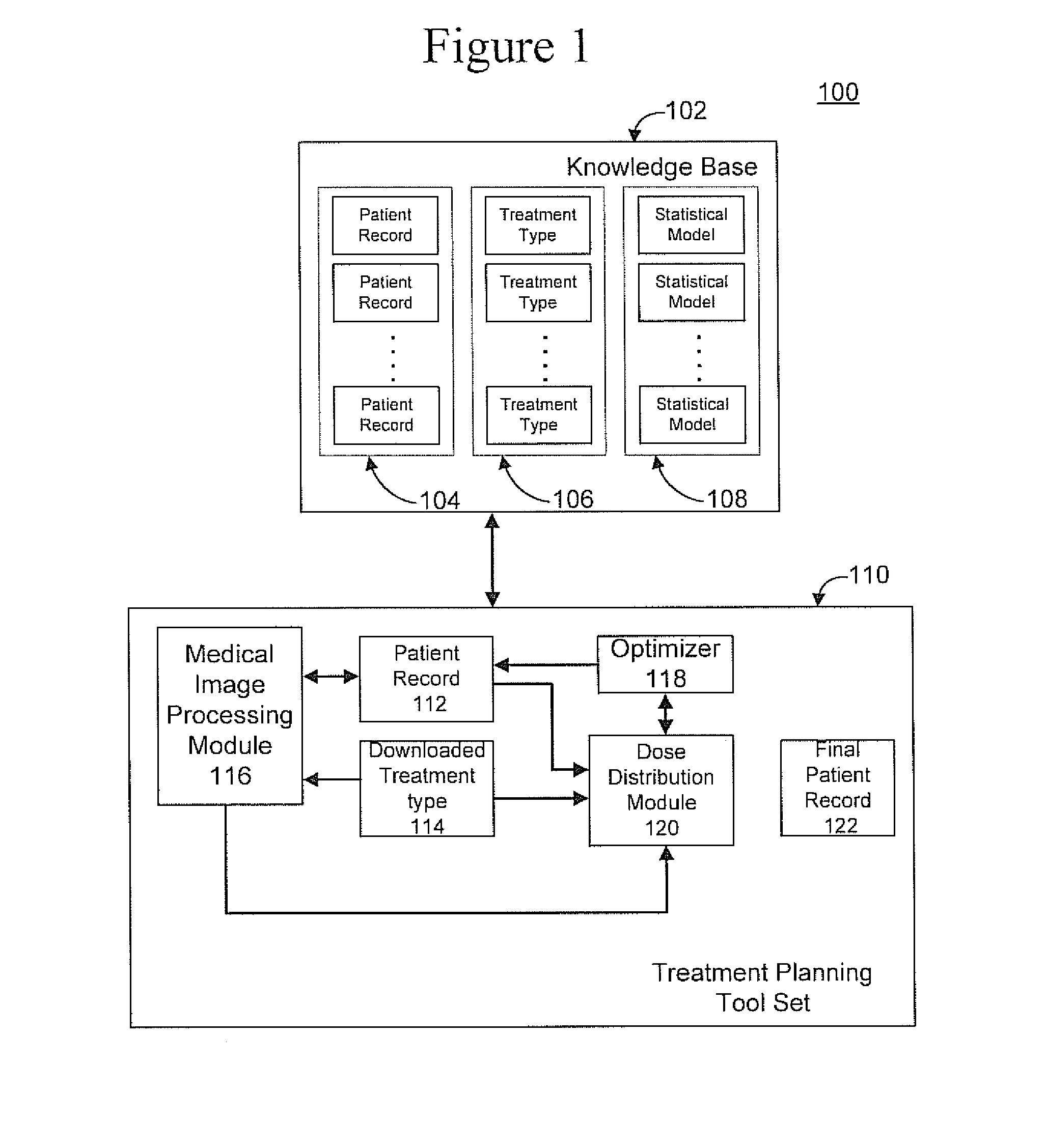
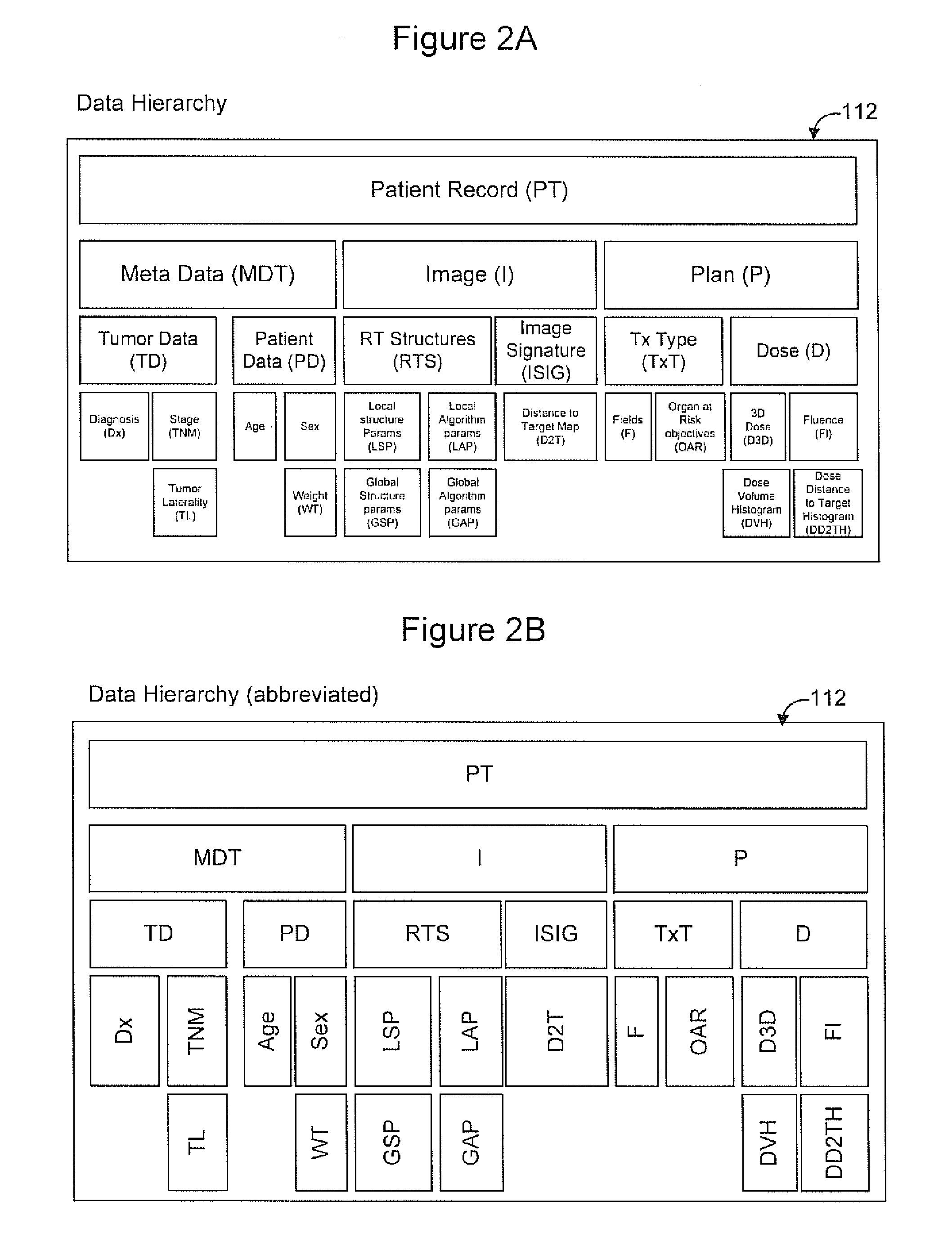
Radiation therapy treatment plan improvement through use of knowledge base
A radiation therapy dose distribution method starts with selecting a treatment type. Then an organ at risk (OAR) distance to target map is determined. The OAR distance to target map comprises distances to a target organ for portions of an OAR. The OAR distances are determined from at least one segmented patient organ image. A cohort average dose distance to target histogram is selected. A dose value to the portions of the OAR are assigned to form a first 3D dose distribution map. The dose values are from the selected cohort average dose distance to target histogram. A second 3D dose distribution map is determined based on a field arrangement determined by the treatment type and the first 3D dose distribution map. A dose distance to target histogram is calculated using the second 3D dose distribution map and the distance to target map.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
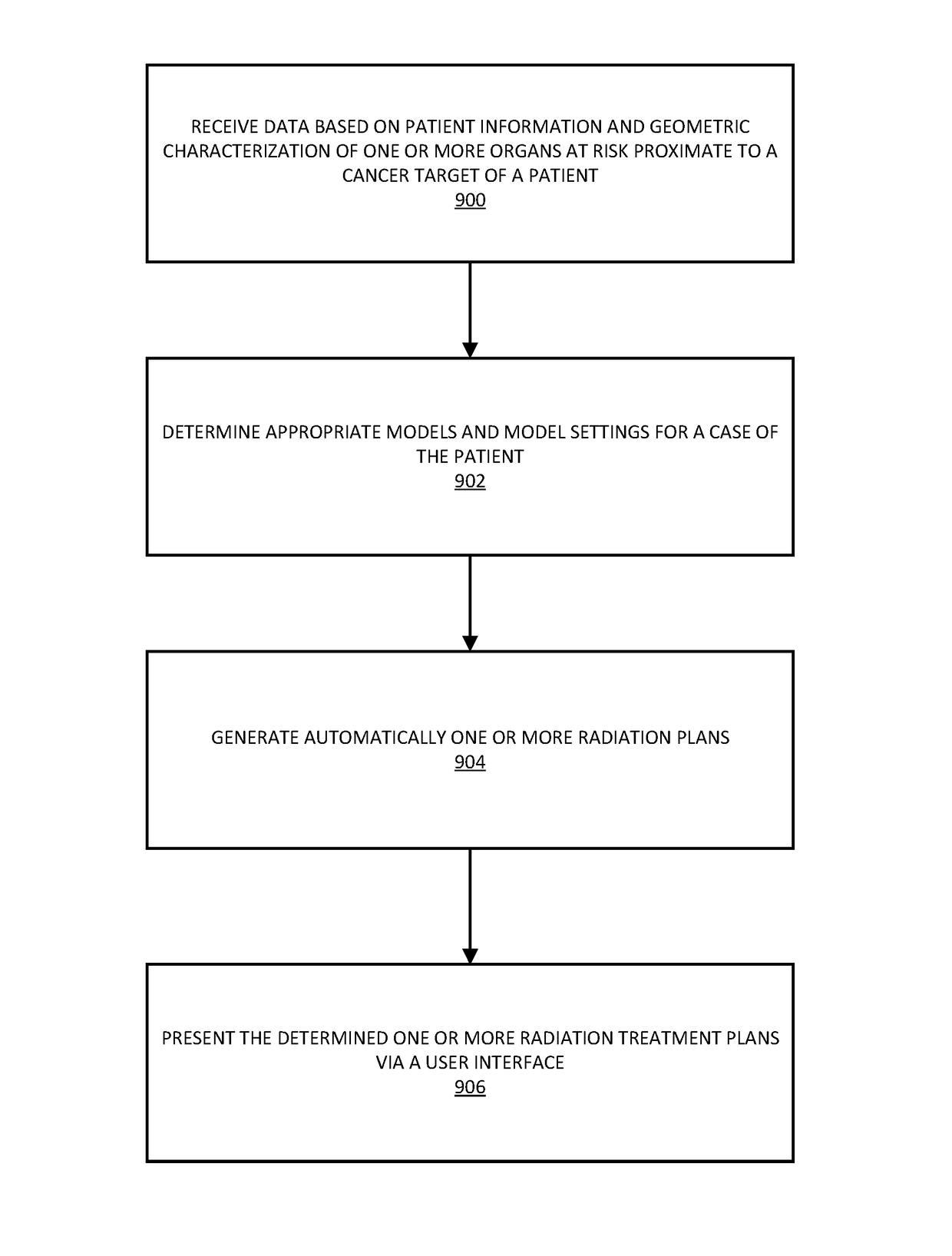
Systems and methods for automated radiation treatment planning with decision support
InactiveUS20180043182A1Medical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDecision takingOrgan at risk
Systems and methods for automated radiation treatment planning with decision support are disclosed. According to an aspect, a method includes receiving data based on patient information and geometric characterization of one or more organs at risk and a cancer target of a patient. The method also includes determining the appropriate models and model settings for the given patient case. Further, the method includes generating automatically one or more radiation treatment plans using the proper models learned from a plurality of radiation treatment plans of prior patient cases based on certain relationships, including one of a match or similarity, between the patient information and geometric characterization of the patient and the other patients. The method also includes presenting the determined one or more radiation treatment plans via a user interface.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Radiation treatment planning system and computer program product
InactiveUS20120136677A1Quality improvementConvergent stabilityData processing applicationsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesGraphicsProgram planning
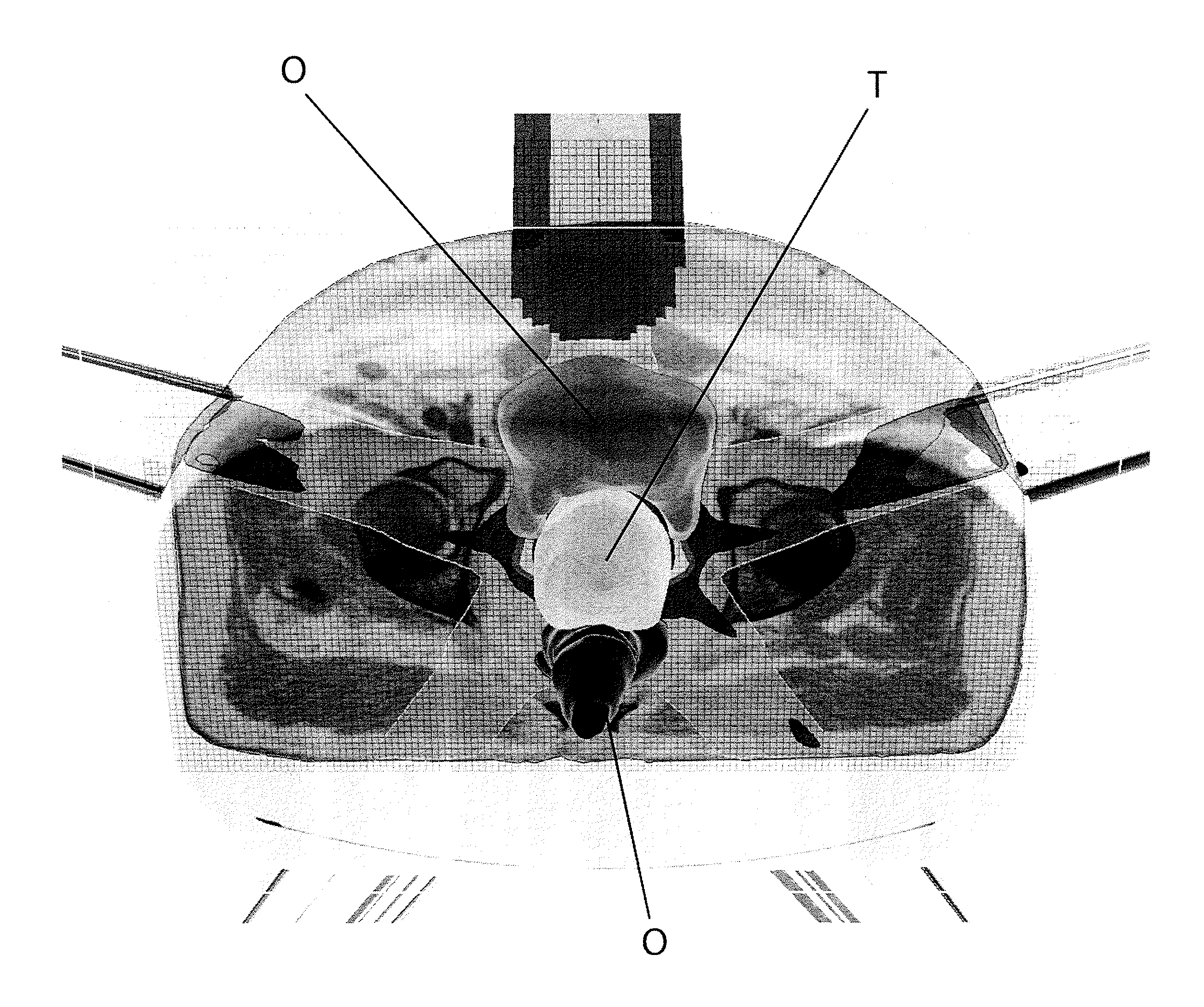
The present invention relates to a radiation treatment planning system and a corresponding computer program product. The system comprises means for graphically displaying an image representing a target area 10 to be treated with a set o therapeutic radiation beams and an adjacent structure comprising healthy tissue 14 and / or organs at risk 12, and for displaying corresponding dose values according to a preliminary treatment plan. The system further comprises means for allowing a user to interactively input a local dose variation, local dose variation means for revising the preliminary treatment plan such as to account for the local dose variation inputted by the user and dose recovery means comprising means for revising the treatment plan again such as to at least partially compensate for a change of dose in a predetermined recovery area caused by said dose variation.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
Cooling Guide Catheter And Associated Method Of Use
InactiveUS20110276115A1Minimize reperfusion injuryImprove liquidityTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingReperfusion injuryCoolant flow
A catheter apparatus configured to provide a delivery system for standard intervention devices typically used during emergency angioplasty and to provide rapid localized cooling to organs at risk of ischemic and reperfusion injury. The catheter apparatus including a catheter shaft having an inner core defining at least two coolant flow lumens adjacent to a blood conveyance lumen. Each coolant flow lumen in thermal contact with the blood conveyance lumen and thermally insulated from each other and the exterior surfaces of the catheter shaft.
Owner:MERRILL THOMAS LAD
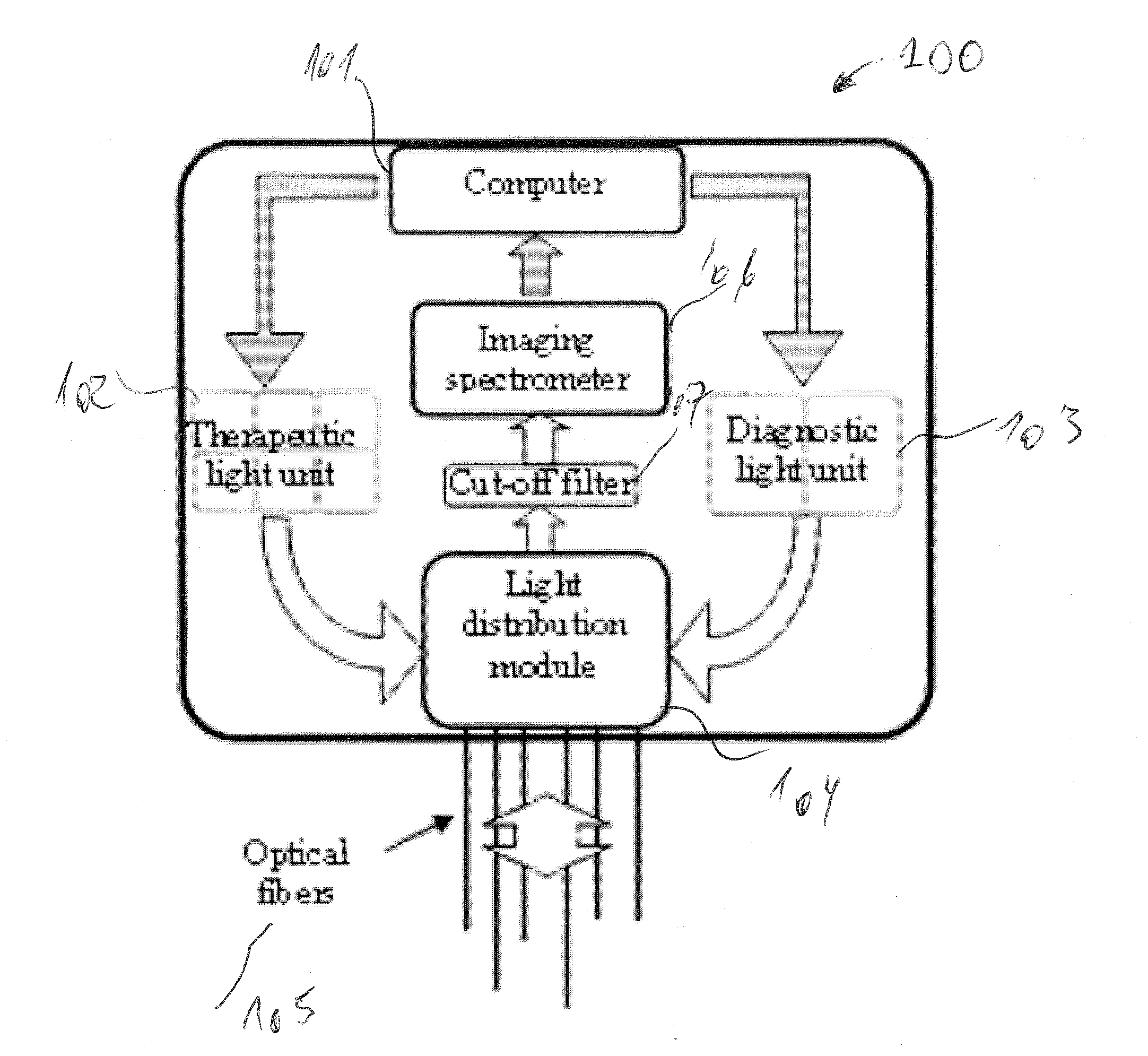
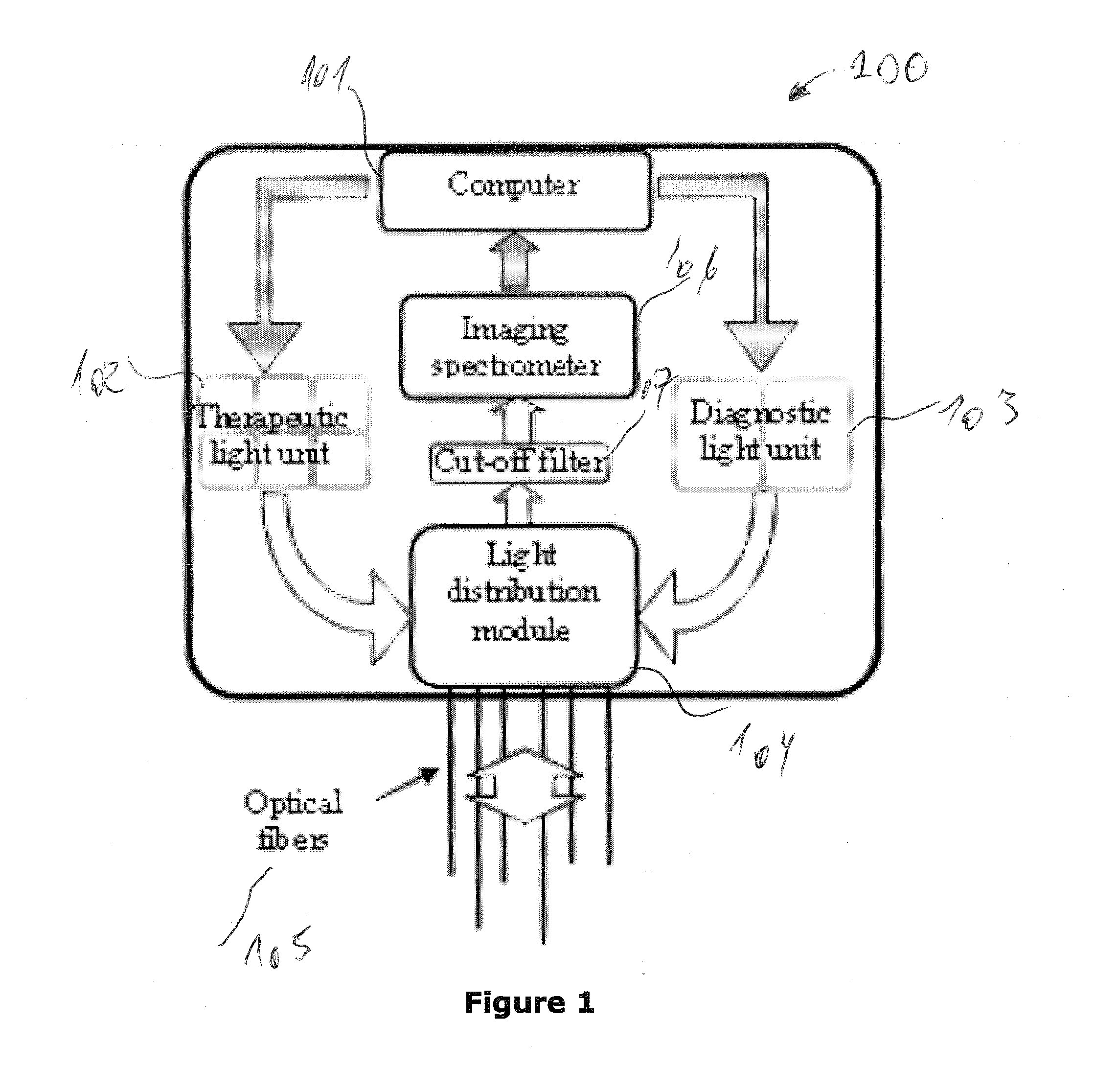
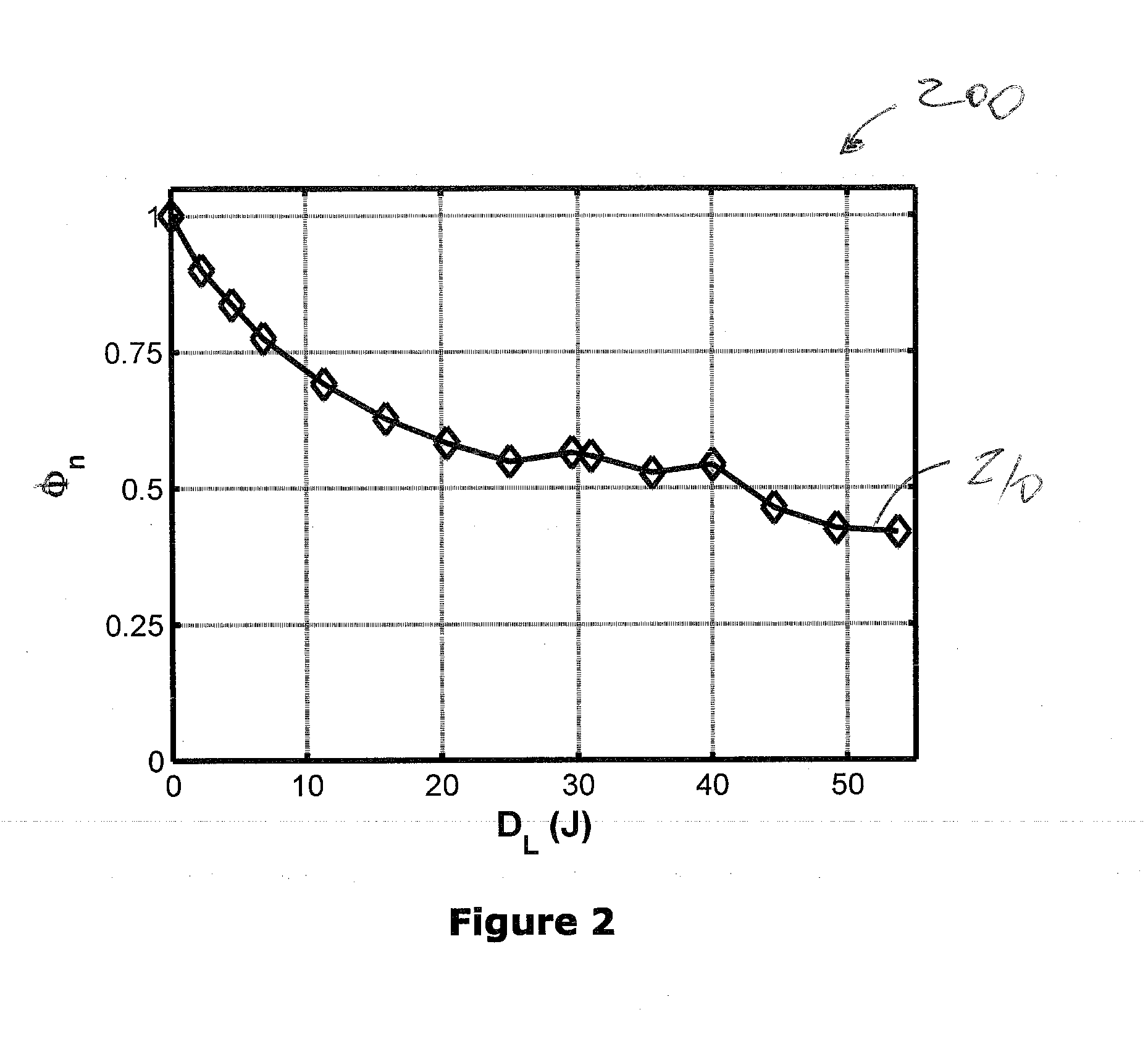
System and method for controlling and adjusting interstitial photodynamic light therapy parameters
ActiveUS20110034971A1Improve patient safetyAvoid damageDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsFiberOrgan at risk
A method and system for controlling and adjusting light in interstitial photodynamic light therapy (IPDT) in a subject is disclosed. More particularly, a method for controlling the light in interstitial tumor photodynamic light therapy is described using calculation method for determination of status of tissue during the PDT treatment. The status is used in a feedback loop to control the continued PDT treatment. Methods are disclosed that constitute pre-treatment and realtime dosimetry modules for IPDT on the whole prostate glandular tissue. The method includes reconstruction of the target geometry, optimization of source fiber positions within this geometry, monitoring of the light attenuation during the treatment procedure and updating individual fiber irradiation times to take into account any variation in tissue light transmission. A control device that is arranged to restrict delivery of therapeutic light treatment at least temporary in dependence of at least one attribute of one of photodynamic treatment parameters. In comparison to no treatment feedback, a significant undertreatment of the patient as well as damage to healthy organs at risk are avoided.
Owner:SPECTRACURE
Method for assisted beam selection in radiation therapy planning
InactiveUS20050254622A1Easy to mergeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPlan treatmentMulti leaf collimator
A method to assist in the selection of optimum beam orientations for radiation therapy when a planning treatment volume (PTV) is adjacent to one or more organs-at-risk (OARs). A mathematical analysis of the boundaries between the PTV and OARs allows the definition of a continuum of pairs of gantry and table angles whose beam orientations have planes that are essentially parallel to those boundaries, and can, therefore, separate the PTV from the OARs when a multi-leaf collimator is used in the therapy. The Radiation Oncologist can then select one or more pairs of gantry and table angles from the continuum as input to a beam optimization step. The selected angles can deliver highly uniform dose to the PTV, while minimizing the radiation dose to the OARs.
Owner:LLACER JORGE
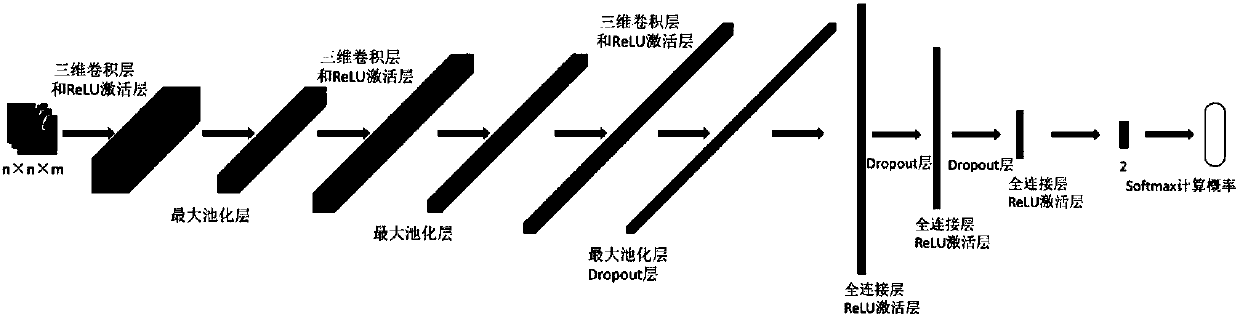
Automatic organ-at-risk sketching method and device based on neural network and storage medium
ActiveCN110310287AImprove generalization abilityImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisThree levelThree stage
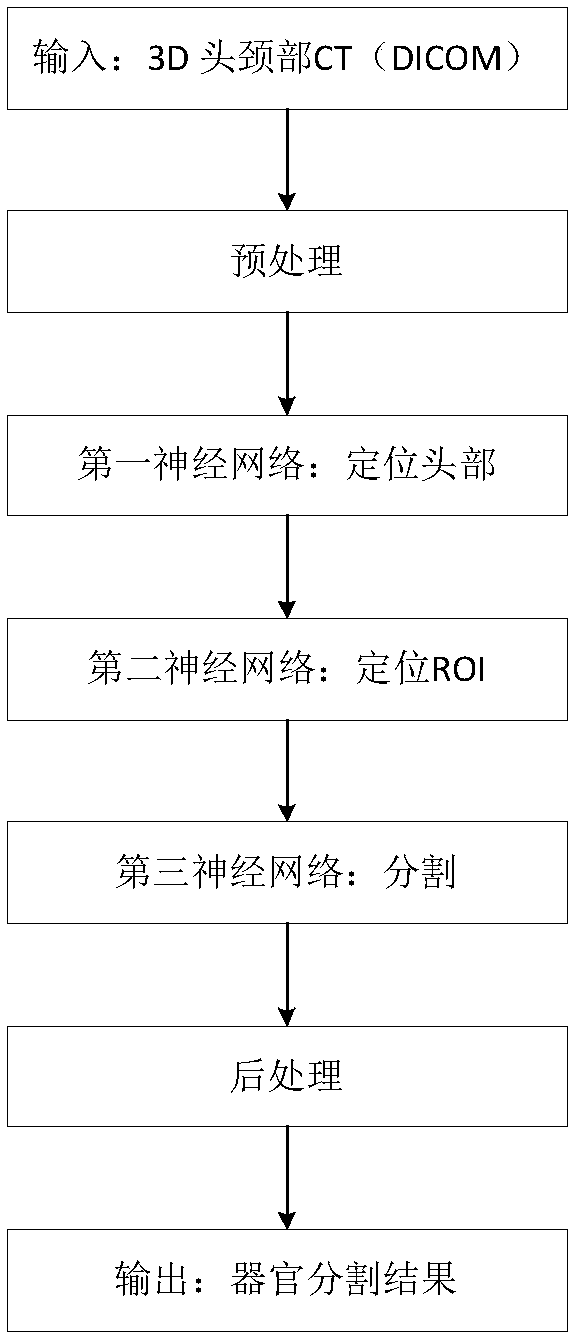
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical images, and relates to an automatic organ-at-risk sketching method and device based on a three-level convolutional neural network, and a storagemedium. The method comprises the following steps of: preprocessing the three-dimensional medical image, inputting the preprocessed three-dimensional medical image into the first-stage network, the second-stage network and the third-stage network of the trained three-stage convolutional neural network, sequentially identifying the cross section of the organ to be segmented, coarsely positioning the region of interest of the organ to be segmented, and classifying all pixel points in the region of interest; and then outputting a three-dimensional binary segmentation result; carrying out post-processing, edge extraction and edge smoothing on the binary segmentation result to obtain an automatically sketched organ. The three-level cascade convolutional neural network model is formed by cascading three convolutional neural networks, namely a first-level network, a second-level network and a third-level network. The three-level joint neural network has the advantages that priori knowledge isnot needed, the algorithm generalization ability is good, the robustness is high, the speed is high, full automation is achieved, and the segmentation accuracy is high.
Owner:BEIJING LINKING MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Adaptive replanning based on multimodality imaging
ActiveCN107072595AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementDose gradientAdaptive learning
Systems and methods directed to adaptive radiotherapy planning are provided. In some aspects, provided system and method include producing synthetic images from magnetic resonance data using relaxometry maps. The method includes applying corrections to the data and generating relaxometry maps therefrom. In other aspects, a method for adapting a radiotherapy plan is provided. The method includes determining an objective function based on dose gradients from an initial dose distribution, and generating an optimized plan based on updated images, using aperture morphing and gradient maintenance algorithms without need for organ-at-risk contouring. In yet other aspects, a method for obtaining 4D MR imaging using a temporal reshuffling of data acquired during normal breathing, a method for deformable image registration using a sequentially applied semi-physical model regularization method for multimodality images, and a method to generate 4D plans using an aperture morphing algorithm based on 4D CT or 4D MR imaging are provided.
Owner:THE MEDICAL COLLEGE OF WISCONSIN INC
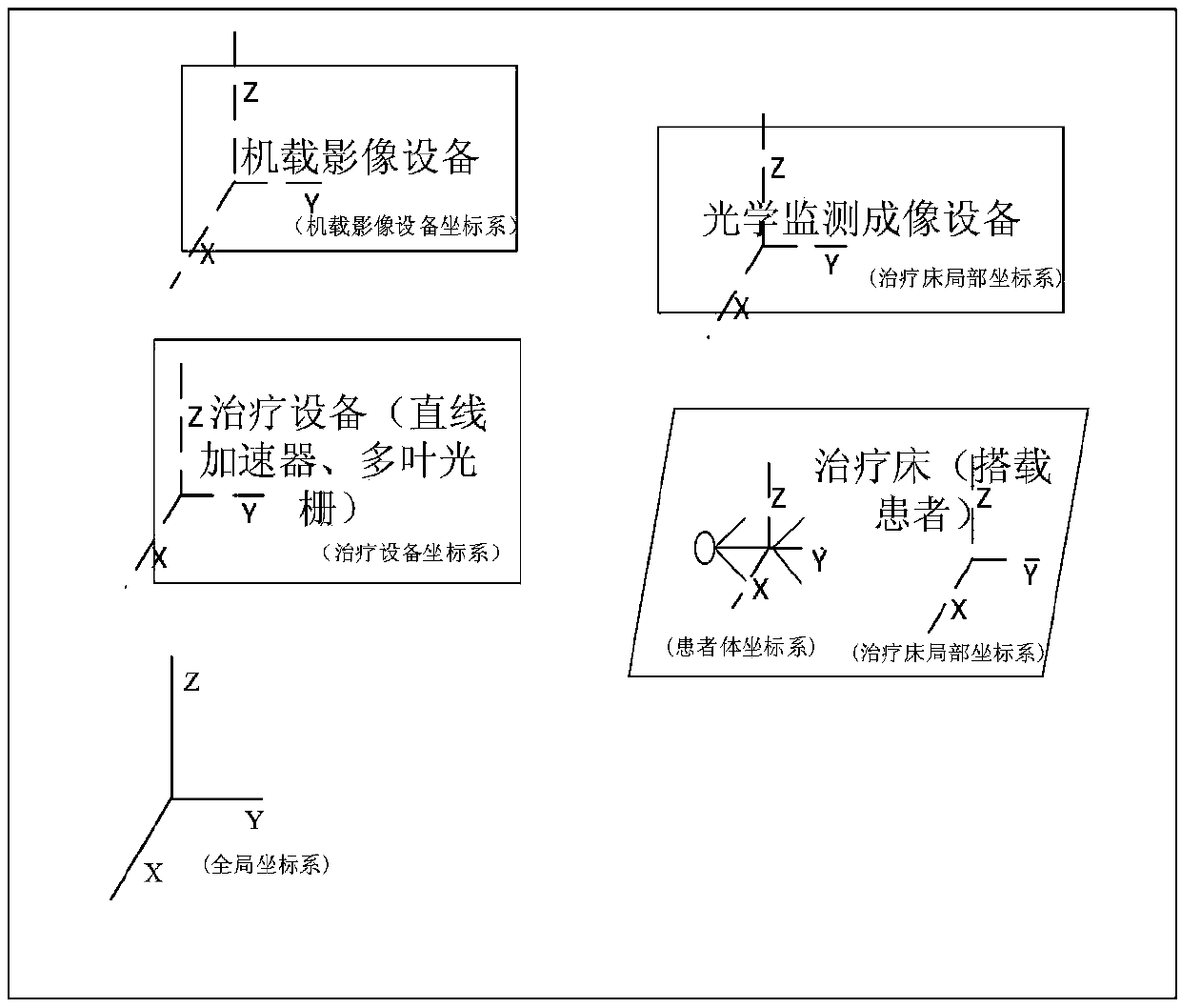
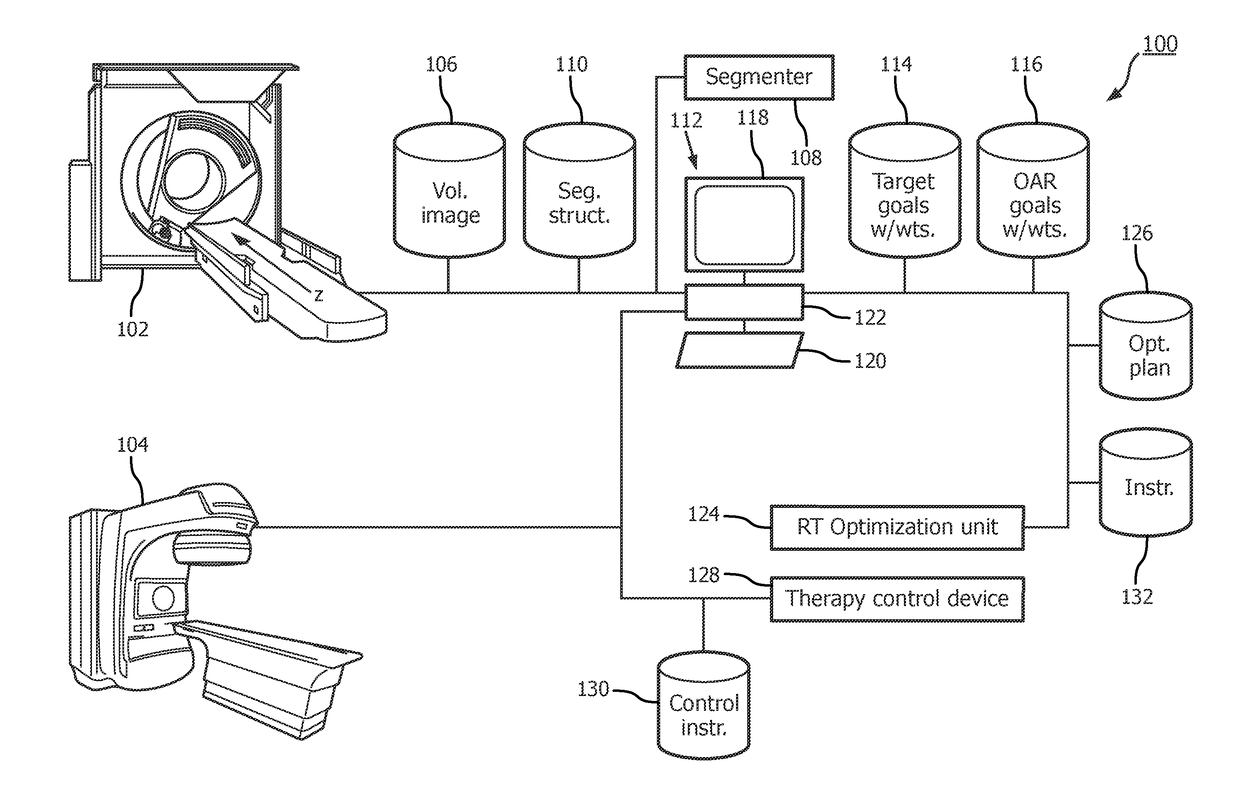
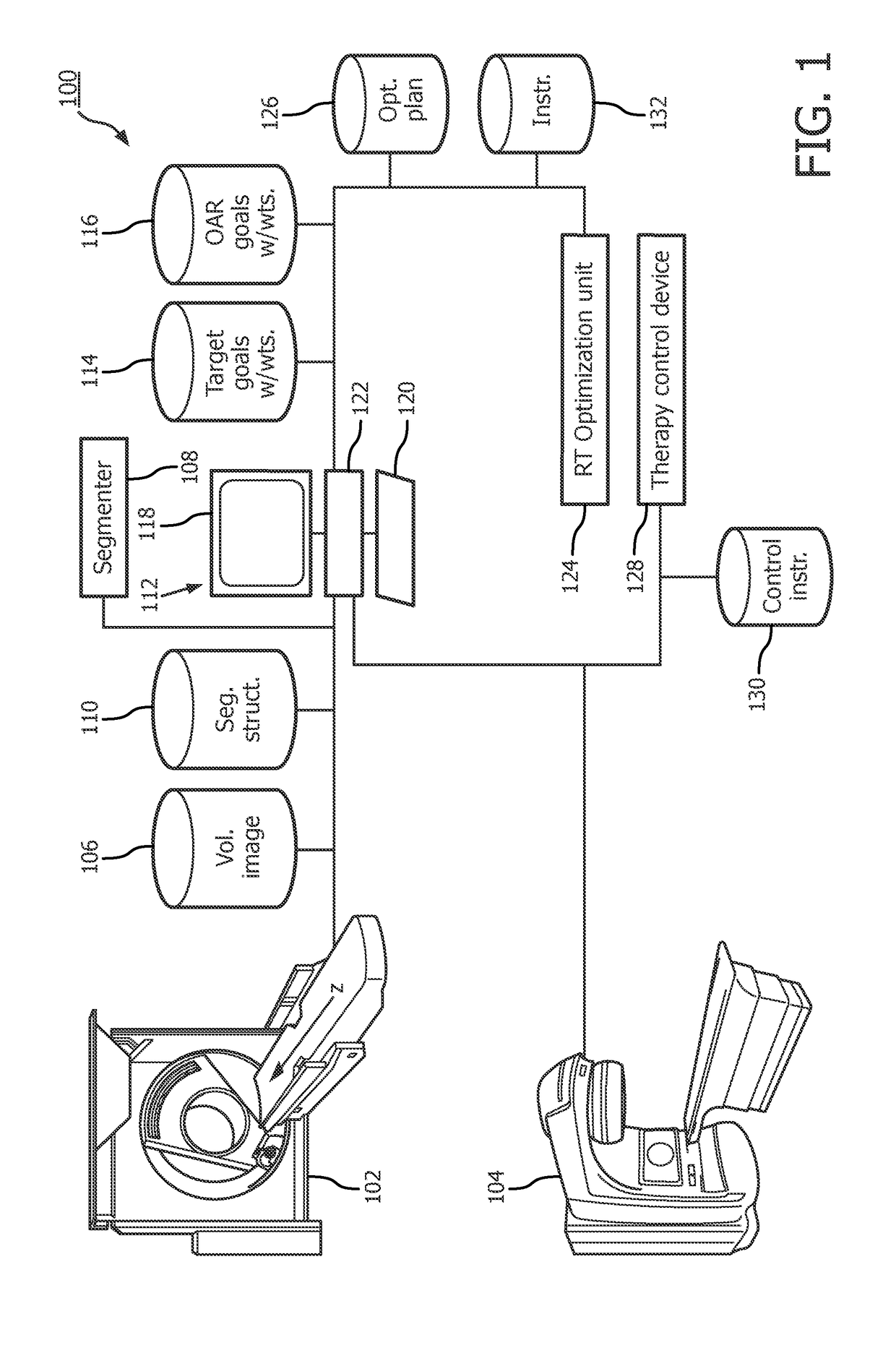
Radiation therapy interactive planning
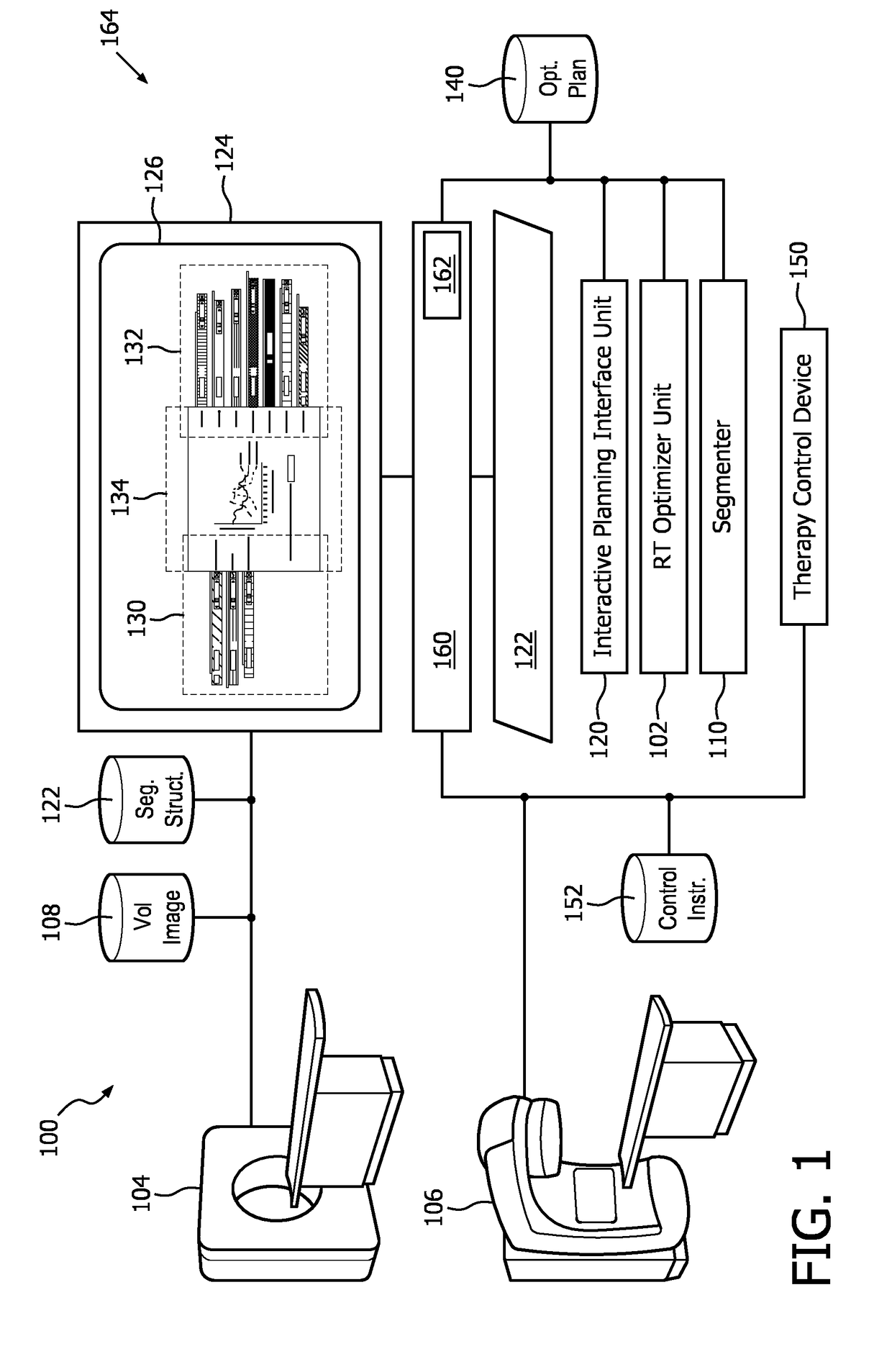
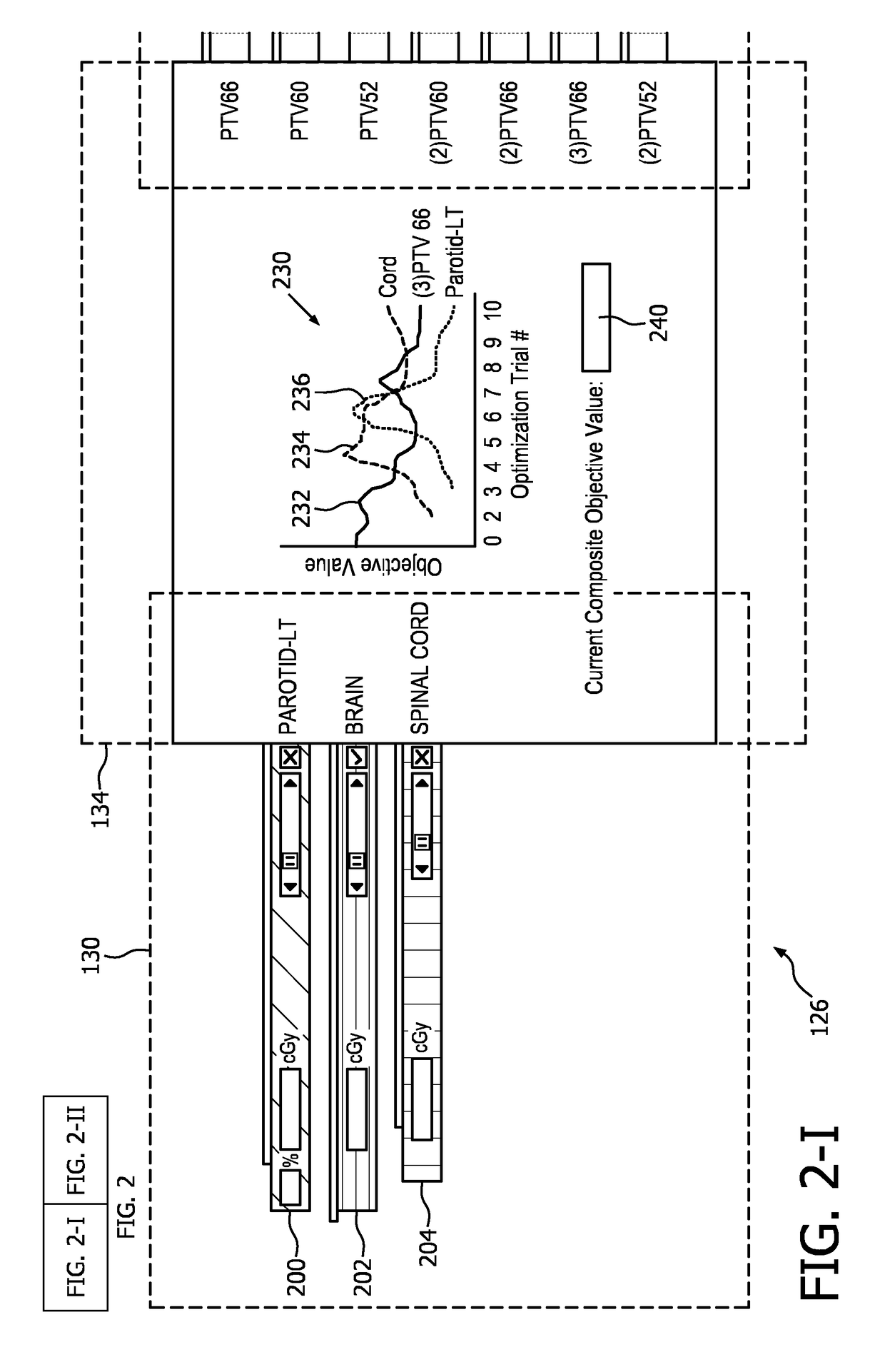
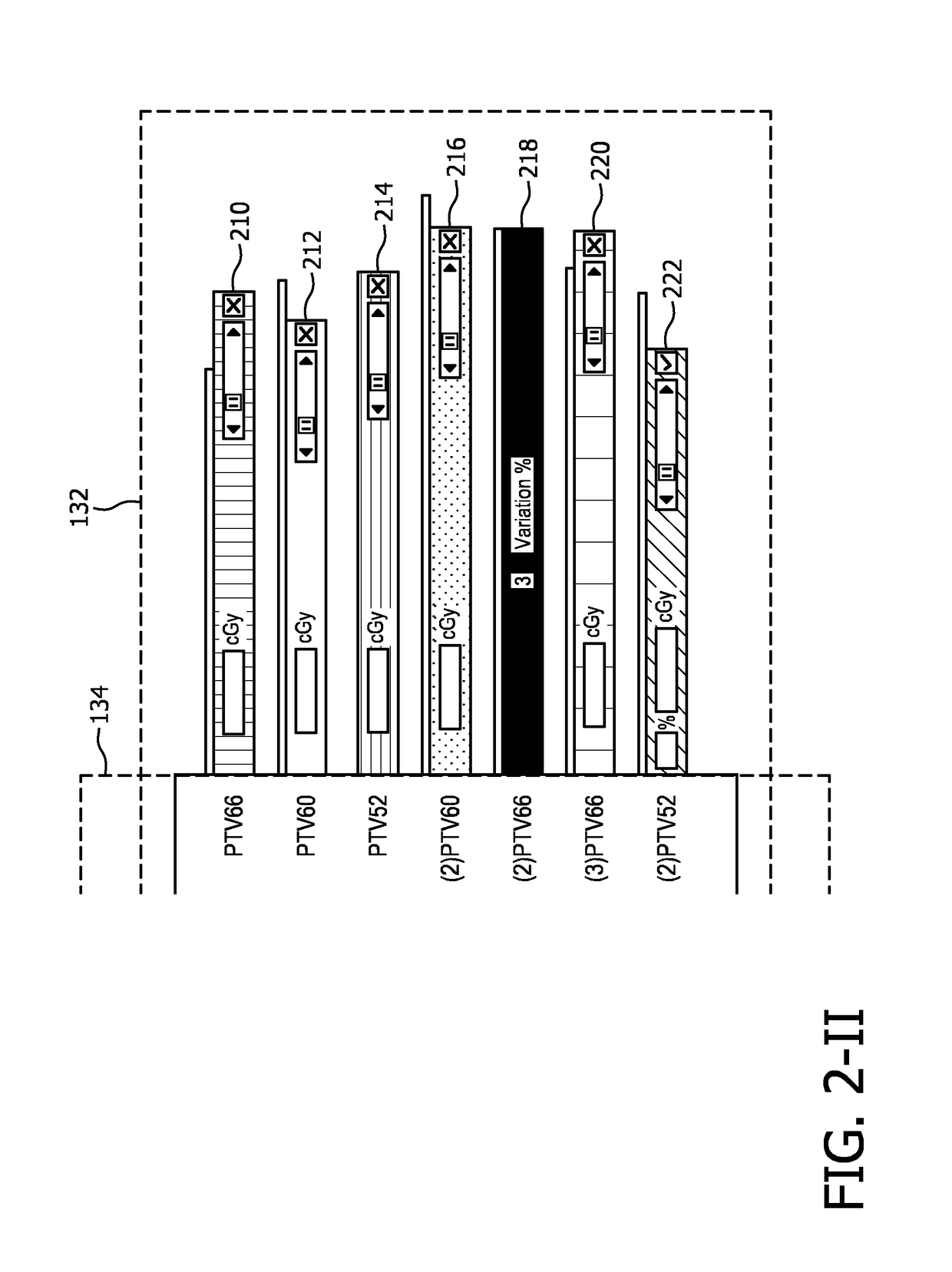
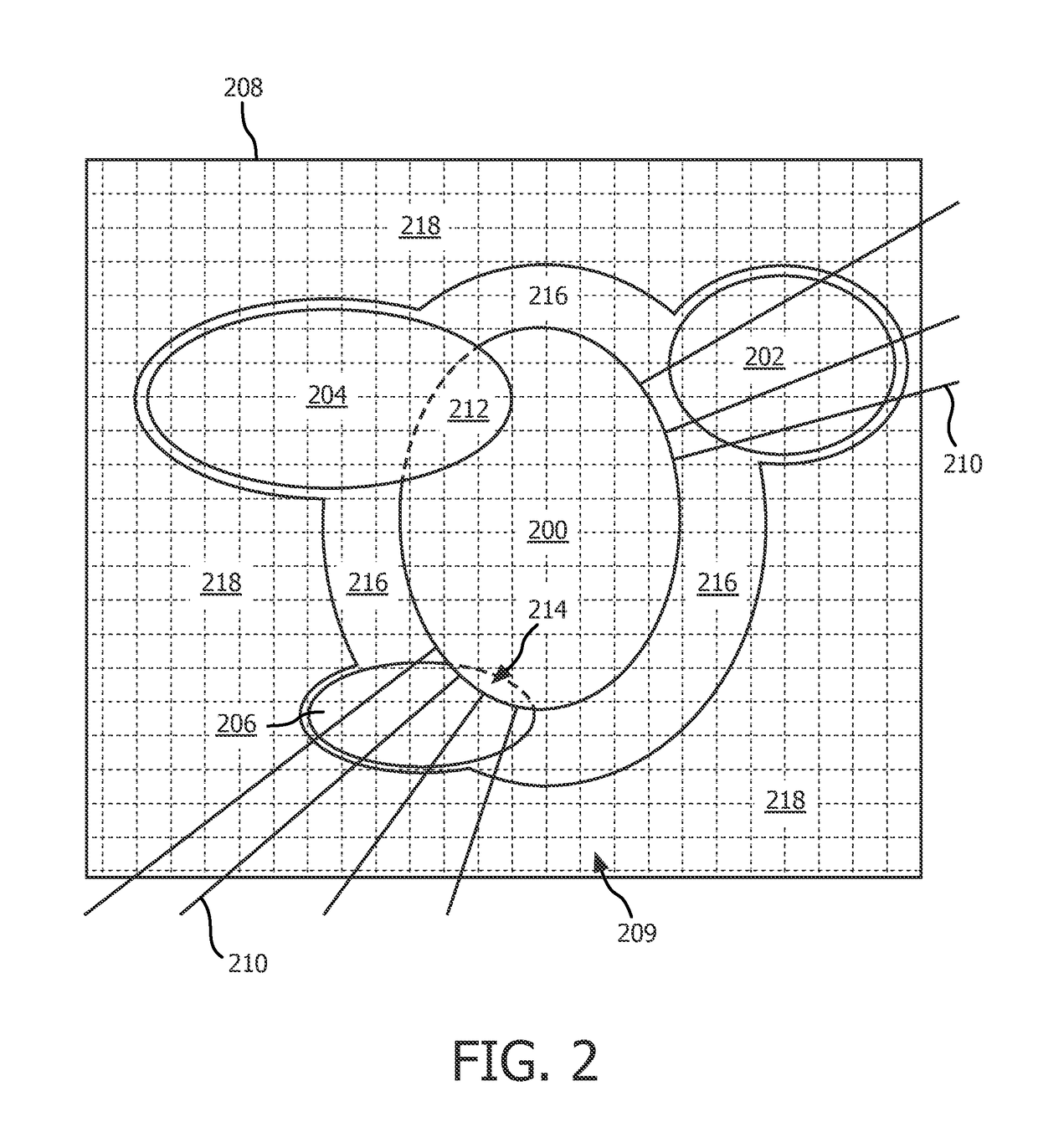
A radiation therapy system (100) includes a radiation therapy (RT) optimizer unit (102) and an interactive planning interface unit (120). The RT optimizer unit (102) receives at least one target structure and at least one organ-at-risk (OAR) structure segmented from a volumetric image (108), and generates an optimized RT plan (140) based on dose objectives (200-204, 210-222, 320), at least one dose objective of the dose objectives corresponding to each of the at least one target structure (210-222) and the at least one OAR structure (200-204). The optimized RT plan includes a planned radiation dose for each voxel of the volumetric image using external beam radiation therapy, wherein the RT optimizer unit operates iteratively. The interactive planning interface unit (120) interactively controls each of the dose objectives through controls (300) displayed on a single display (126) of a display device (124), operates the RT optimizer unit to iteratively compute the planned radiation dose according to the controls, and provide visual feedback (310, 134) on the single display according to progress of the RT optimizer unit after each trial.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Real-time adaptive dose computation radiation therapy
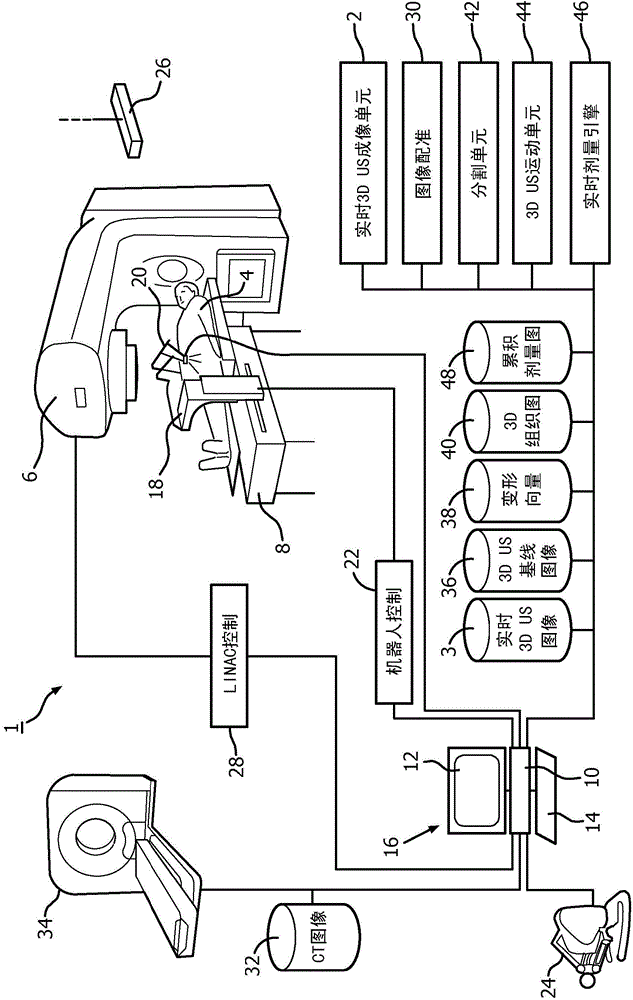
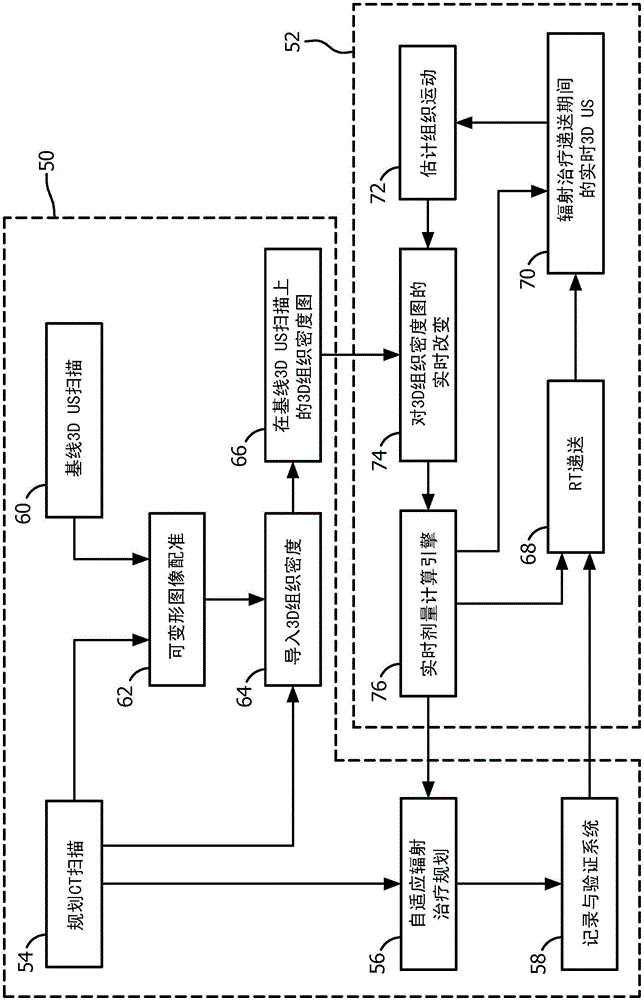
ActiveCN104884126AReal-time measurementReal-time radiation dosimetryOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsOrgan at riskRadiation therapy
A radiation therapy system (1) includes an ultrasound (US) imaging unit (2), a registration unit (30), an US motion unit (44), and a real-time dose computation engine (46). The ultrasound (US) imaging unit (2) generates a baseline and real-time US images (3) of a subject body (4) region including a target and one or more Organs At Risk (OARs). The registration unit (30) deformably registers a planning image (32) and the baseline US image (36), and maps (66) radiation absorptive properties of tissue in the planning image (32) to the baseline US image (36). The US motion unit (44) measures motion of the target volume and OARs during radiation therapy treatment based on the real-time US images. The real-time dose computation engine (46) computes a real-time radiation dose delivered to the tissues based on the tissue radiation absorptive properties mapped from the baseline or planning images to the real-time 3D US images (3).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Implementation method and equipment for 4D radiotherapy plan with respiratory compensation
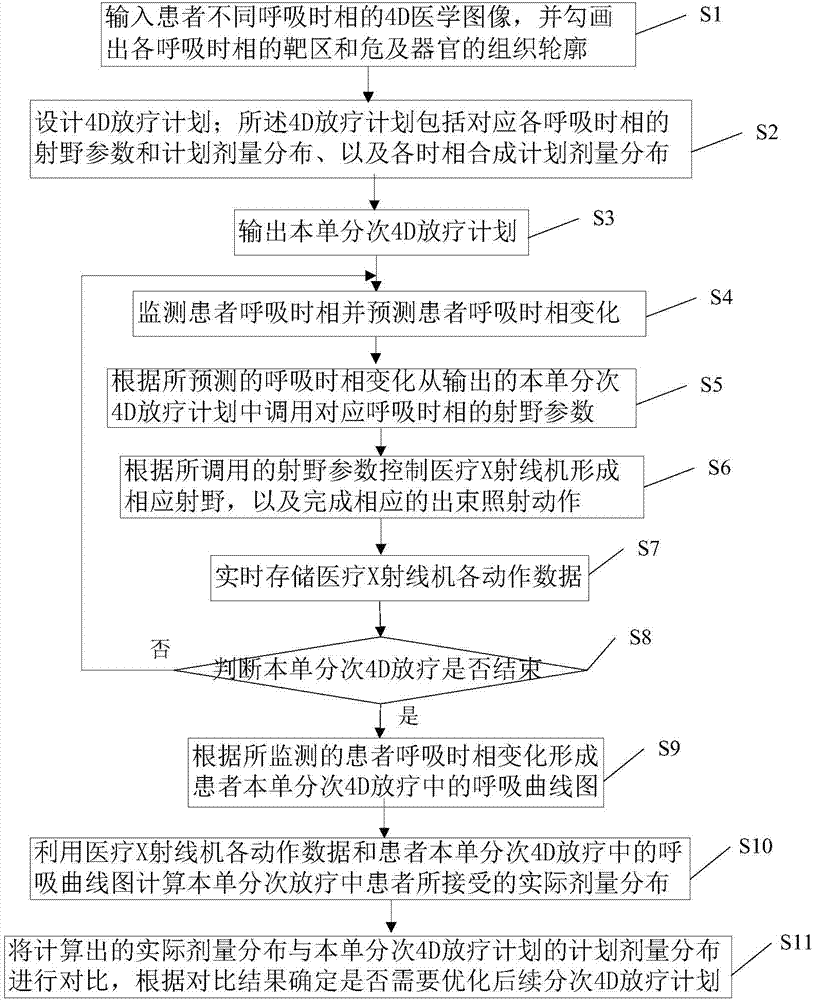
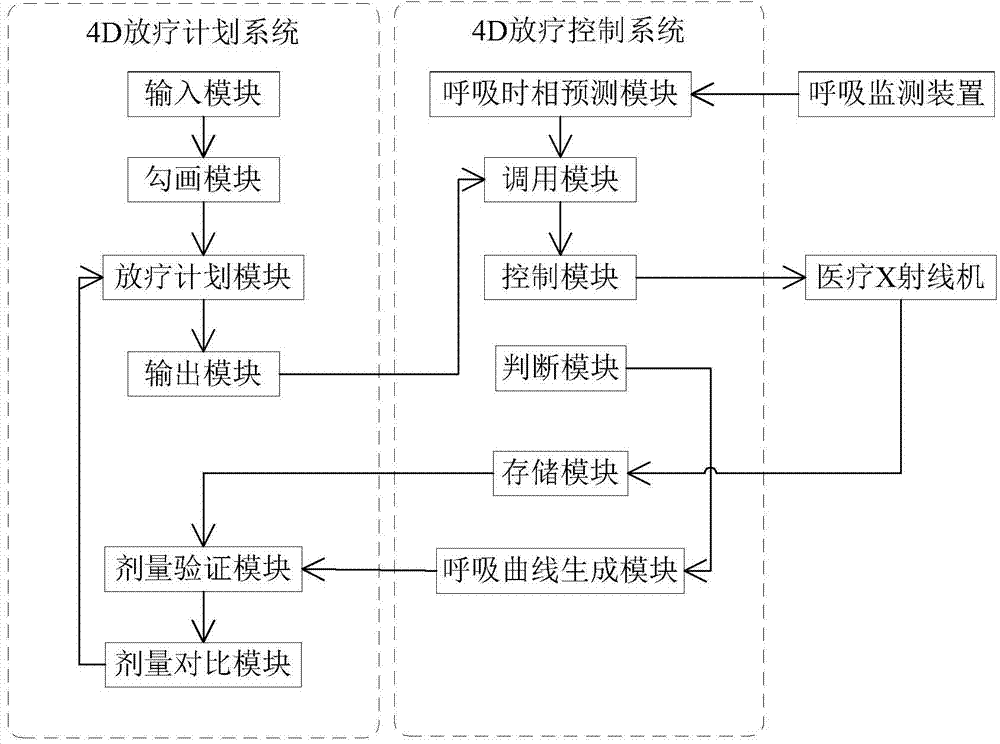
ActiveCN104225809AResolution timeSolution rangeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRespiratory compensationRespiratory phase
The invention discloses an implementation method and equipment for a 4D radiotherapy plan with respiratory compensation. The implementation method includes steps that inputting 4D medical images of different respiratory phases of a patient, and sketching a target region of each respiratory phase and a tissue outline of an organ at risk; designing the 4D radiotherapy plan; monitoring the respiratory phases of the patient and forecasting the respiratory phase change of the patient; dispatching field parameters corresponding to the respiratory phases; controlling a medical X-ray machine to form a corresponding field to finish the corresponding beam irradiation action; judging whether the 4D radiotherapy is ended, if so, forming a respiration curve diagram for the 4D radiotherapy of the patient; calculating the actual dosage distribution accepted by the patient in the radiotherapy; comparing the calculated actual dosage distribution with the planed dosage distribution of the 4D radiotherapy plane, and determining whether optimizing the subsequent 4D radiotherapy plan according to the comparative result. The implementation method and equipment for the 4D radiotherapy plan with the respiratory compensation is capable of accurately determining a four-dimensional radiotherapy target.
Owner:大连现代医疗设备科技有限公司
Radiation therapy treatment plan improvement through use of knowledge base
ActiveUS8774358B2X-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDistance to targetTherapy types
A radiation therapy dose distribution method starts with selecting a treatment type. Then an organ at risk (OAR) distance to target map is determined. The OAR distance to target map comprises distances to a target organ for portions of an OAR. The OAR distances are determined from at least one segmented patient organ image. A cohort average dose distance to target histogram is selected. A dose value to the portions of the OAR are assigned to form a first 3D dose distribution map. The dose values are from the selected cohort average dose distance to target histogram. A second 3D dose distribution map is determined based on a field arrangement determined by the treatment type and the first 3D dose distribution map. A dose distance to target histogram is calculated using the second 3D dose distribution map and the distance to target map.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
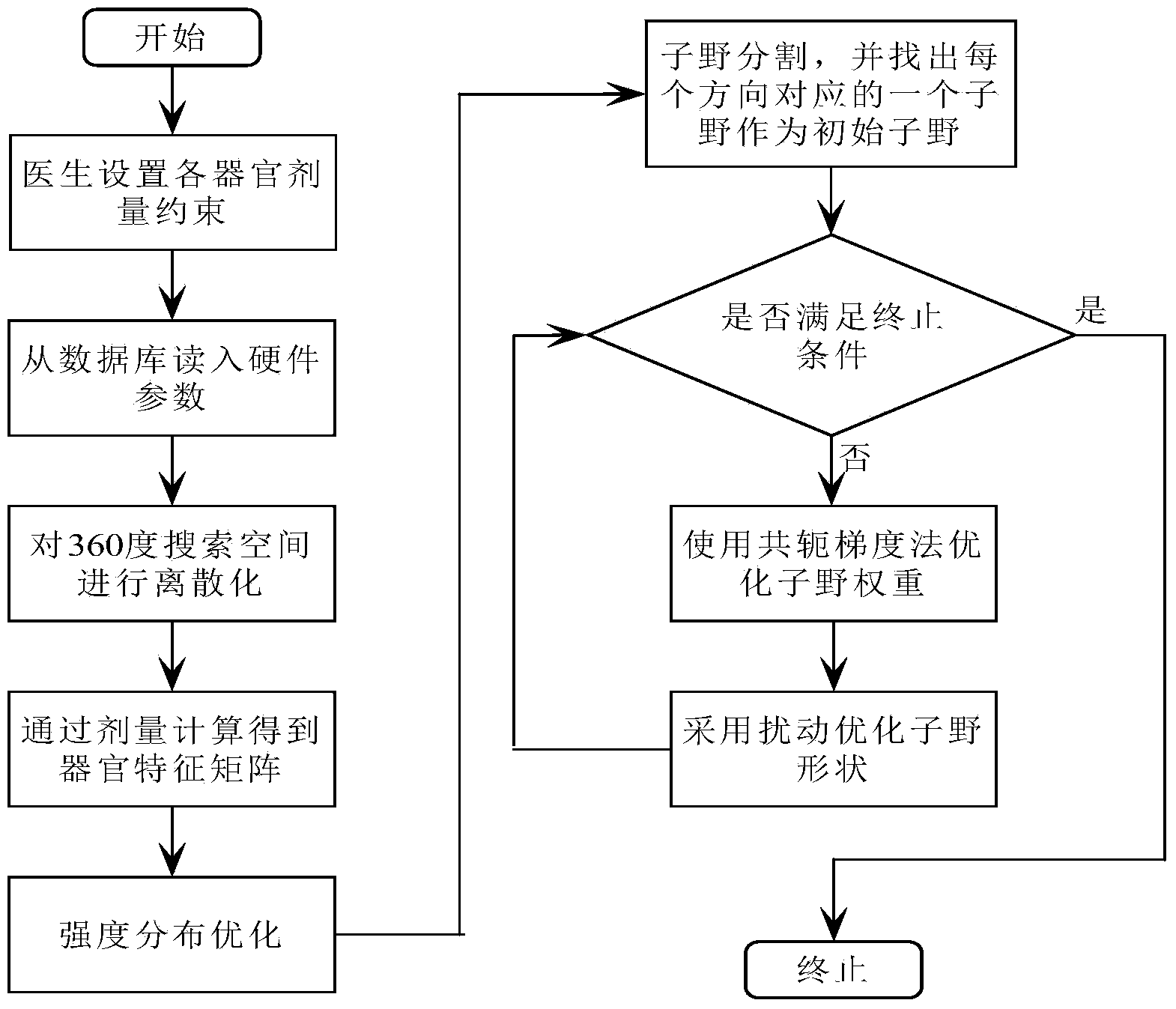
Disturbance-based intensity modulated arc therapy optimization method
ActiveCN104318122AFast optimizationMeet the requirements of computing timeSpecial data processing applicationsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMedicineMathematical model
The invention provides a disturbance-based intensity modulated arc therapy optimization method. Firstly an intensity modulated arc therapy optimization model is established according to conditions such as information on a target region and organs at risk, beam setting parameters and each organ dose (volume) constraint and hardware constraint; an initialized sub-field is obtained by using intensity distribution optimization. Then the shape of the sub-field is optimized by using disturbance, the weight of the sub-field is optimized by using a conjugate gradient method after determination of the shape, and finally the optimal solution for the intensity modulated arc therapy is optimized. According to the method, a mathematical model of an optimization problem is accurately established, the solving speed is high, the algorithm is stable and the robustness is strong.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi- objective organ-at-risk automatic segmentation method, device and system based on deep learning
InactiveCN110070546AShort timeImprove segmentation resultsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDeep belief network
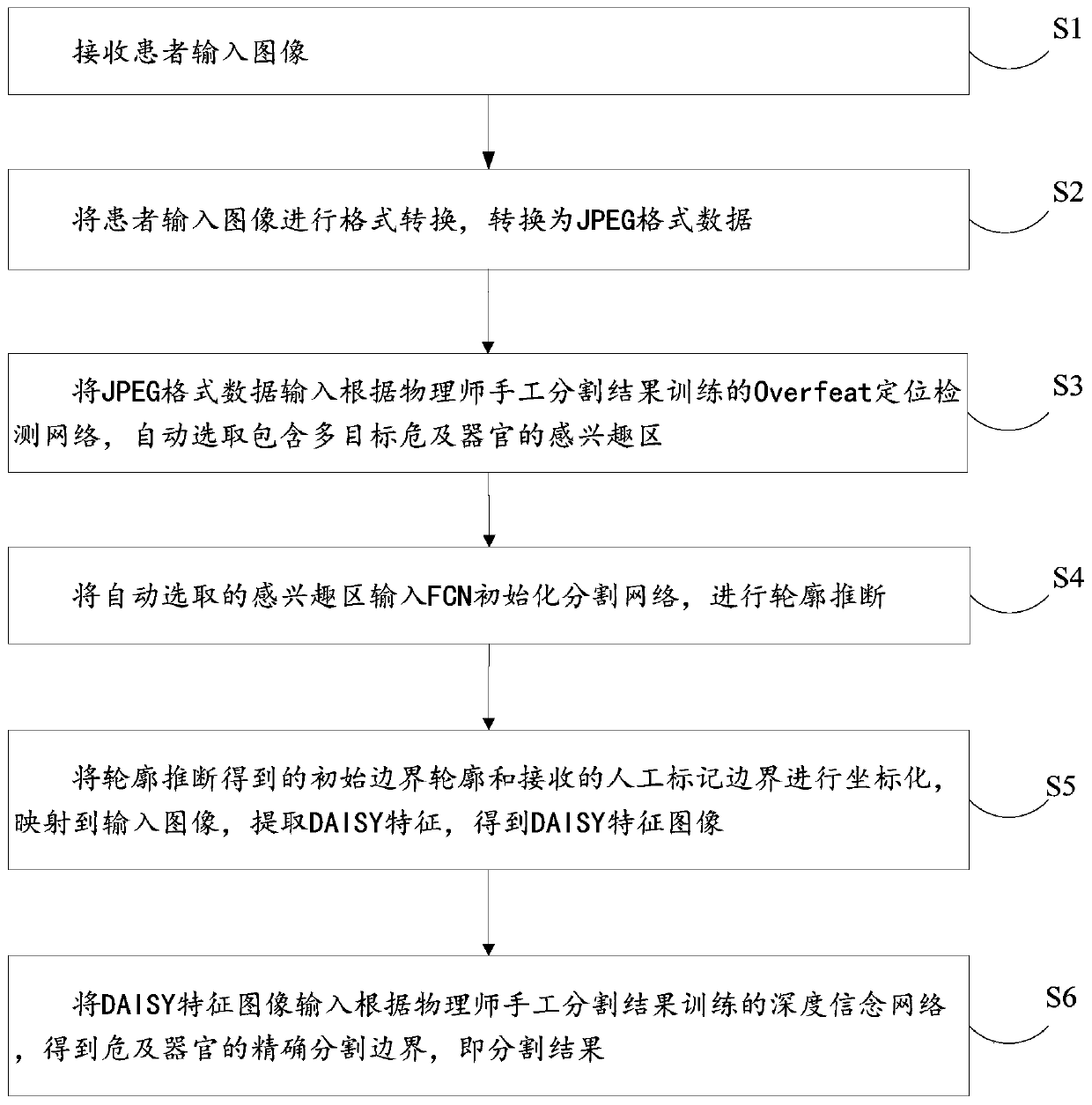
The invention discloses a multi-objective organ-at-risk automatic segmentation method, device and system based on deep learning. The method comprises the steps of receiving an input image of a patient; carrying out format conversion on the input image of the patient, and converting the input image into JPEG format data; inputting the JPEG format data into an Overfeat positioning detection networktrained according to a physician manual segmentation result, and automatically selecting a region of interest containing multi-objective organ-at-risk; inputting the automatically selected region of interest into an FCN initialization segmentation network, and carrying out contour inference; carrying out the coordinate processing of the initial boundary contour obtained through the contour inference and the received artificial mark boundary, mapping the initial boundary contour and the received artificial mark boundary to an input image, extracting a DAISY feature, and obtaining a DAISY feature image; and inputting the DAISY feature image into a deep belief network trained according to a physician manual segmentation result to obtain an accurate segmentation boundary of organ-at-risk, namely a segmentation result.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
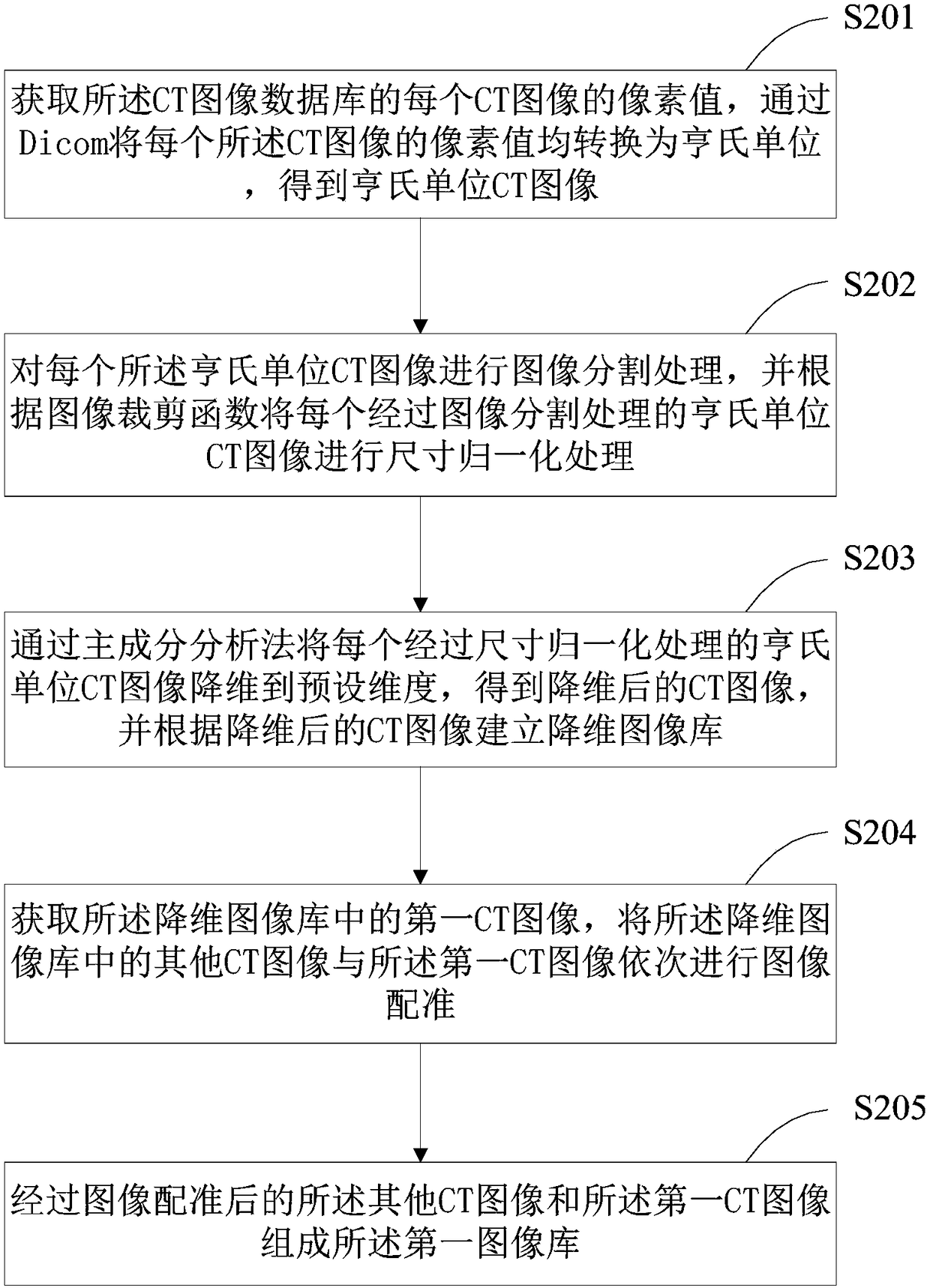
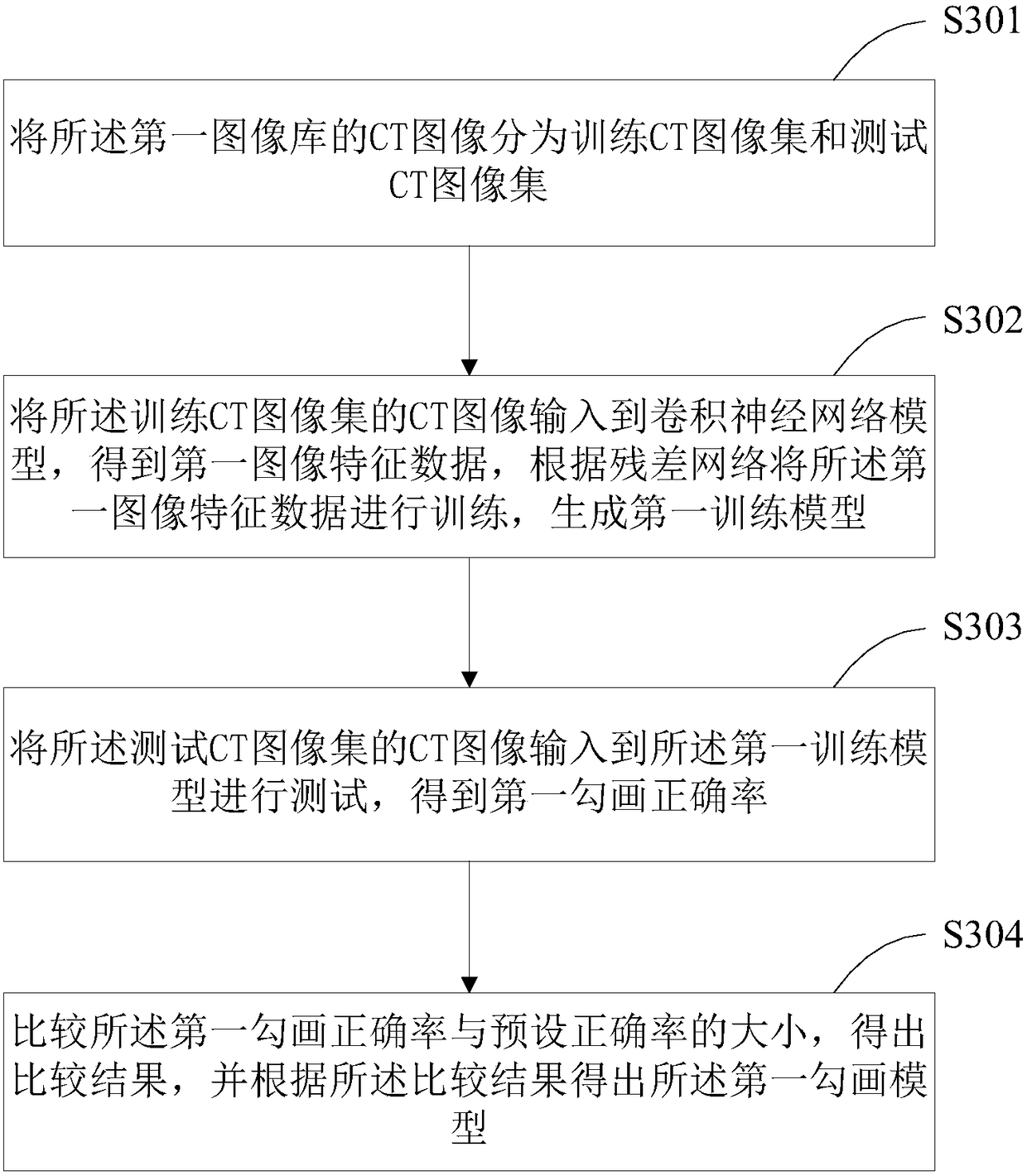
Tumor volume intelligent sketching method and device
InactiveCN108288496ARealize automatic and accurate sketchingReduce work intensityStill image data indexingMedical imagesImaging analysisCurative effect
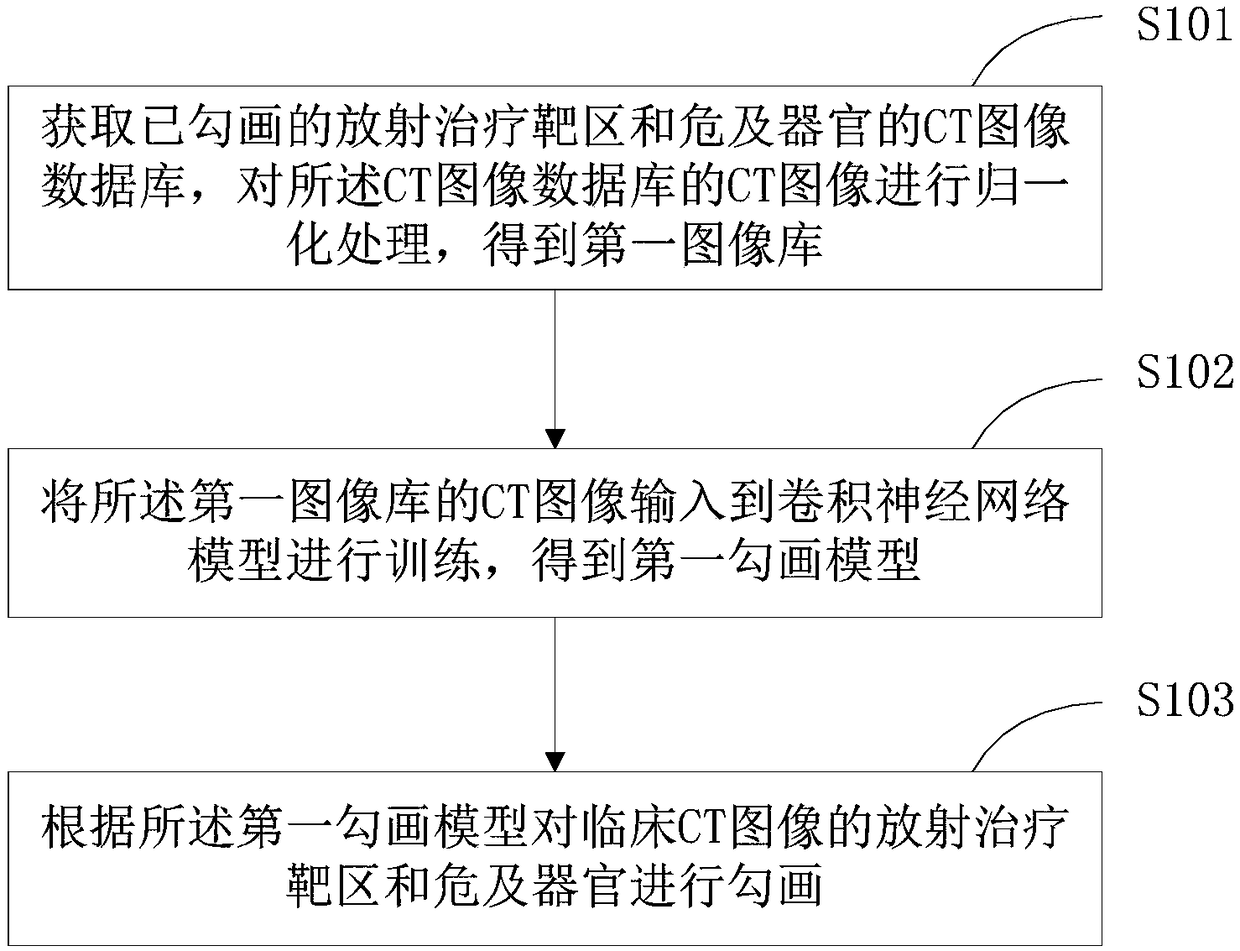
The present invention is suitable for the technical field of image analysis, and provides a tumor volume intelligent sketching method and device. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining a CT image database of a sketched tumor volume, performing normalization processing of CT images in the CT image database, and obtaining a first image library; inputting CT images in the first image library into a convolutional neural network model for training, and obtaining a first sketching model; and performing sketching of the tumor volume of a clinic CT image according to the first sketching model. The tumor volume intelligent sketching method and device can achieve automatic sketching of the tumor volume to greatly reduce the manual sketching cost, reduce the doctors' working strength, improve the accuracy of texture sketching of a radiotherapy target section and organs at risk and ensure the curative effect of the radiotherapy.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Systems and methods for specifying treatment criteria and treatment parameters for patient specific radiation therapy planning
ActiveUS10449388B2Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesHealthcare resources and facilitiesProgram planningCombined use
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for specifying treatment criteria and treatment planning parameters for patient specific radiation therapy planning. According to an aspect, a method includes receiving data about a patient, computing geometric characterization of one or more organs at risk proximate to a target volume of a patient or vice versa, and selecting relevant treatment knowledge and experience. The method also includes generating, based on the received data, computed geometric characterization, and available knowledge and experience, a first set of radiation treatment planning parameters that will lead to a high quality plan for the patient. Further, the method includes model-based prediction, based on the data, a second set or more of radiation treatment planning parameters that will lead to alternative achievable plans with different organ sparing objectives for treating the patient. The multiple sets for parameters can be used separately or in conjunction to generate treatment plans.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Method and system for automatically segmenting esophagus cancer radiotherapy target area and organs at risk
InactiveCN110211139AAvoid area searchesThe process of avoiding region consolidationImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationEsophageal cancer
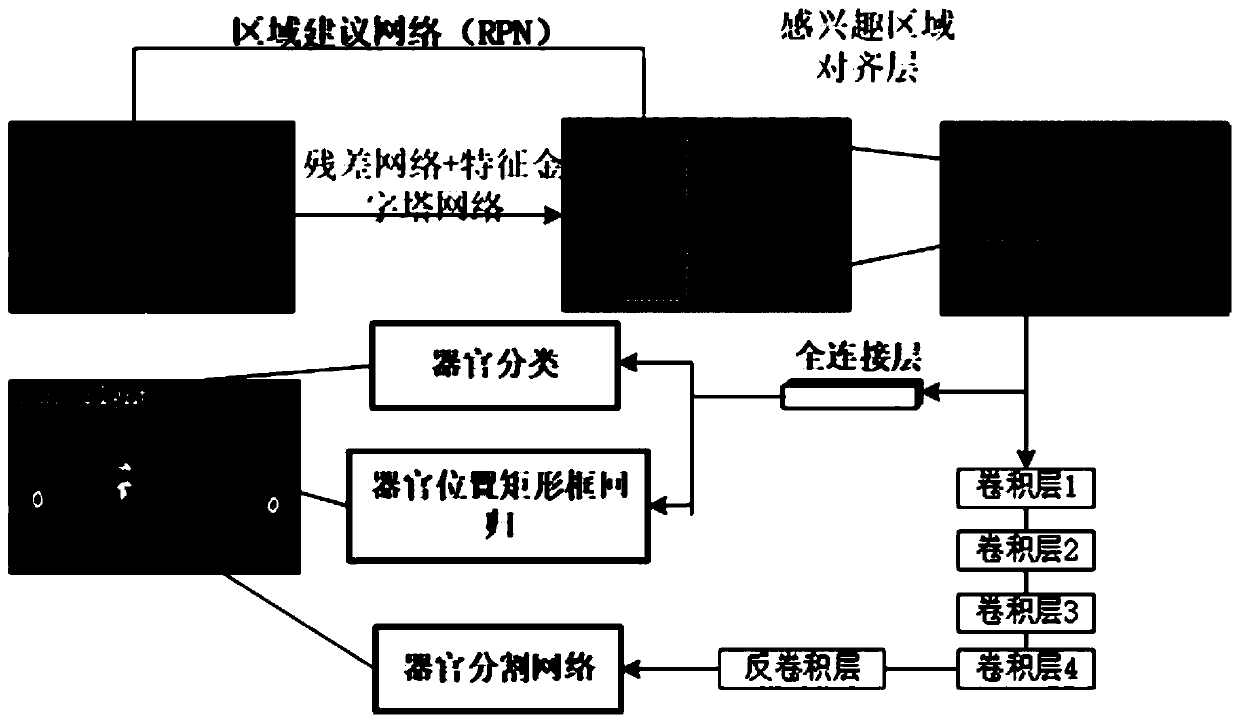
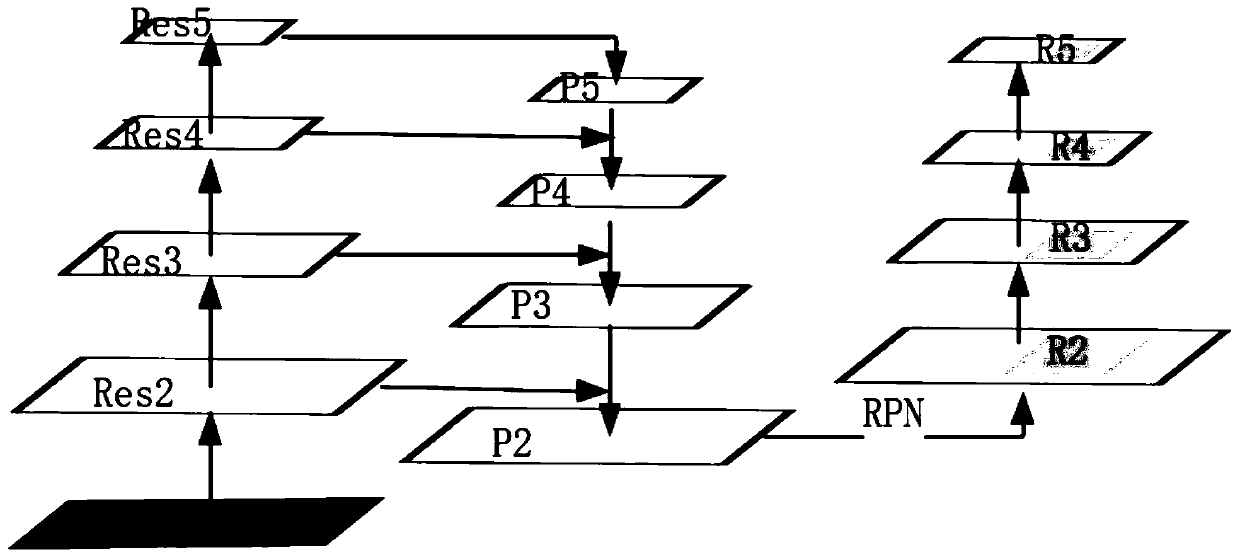
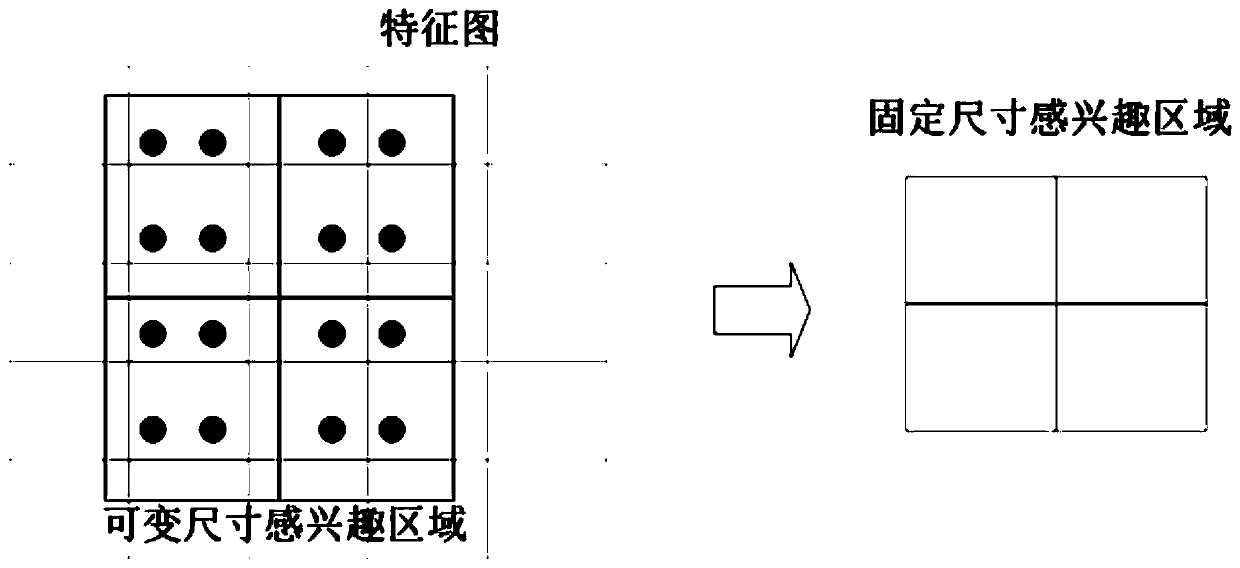
The invention discloses a method and a system for automatically segmenting an esophageal cancer radiotherapy target area and organs at risk, and relates to the field of medical image segmentation. Themethod comprises the following steps: extracting features of an input CT image through a residual network, and fusing multi-scale feature maps through a feature pyramid network; screening the regionof interest of each point in the feature map through a region suggestion network; pooling the region-of-interest screened by the region suggestion network to a fixed size in combination with the region-of-interest alignment layer; inputting a region of interest pooled to a fixed size into the full connection layer for organ classification, and performing organ position border regression; meanwhile, inputting the interest area pooled to a fixed size into the organ segmentation network. The method has the advantage that the accuracy of automatically segmenting the esophagus cancer radiotherapy target area and various organs at risk is improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Radioactive ray monitoring and treating system
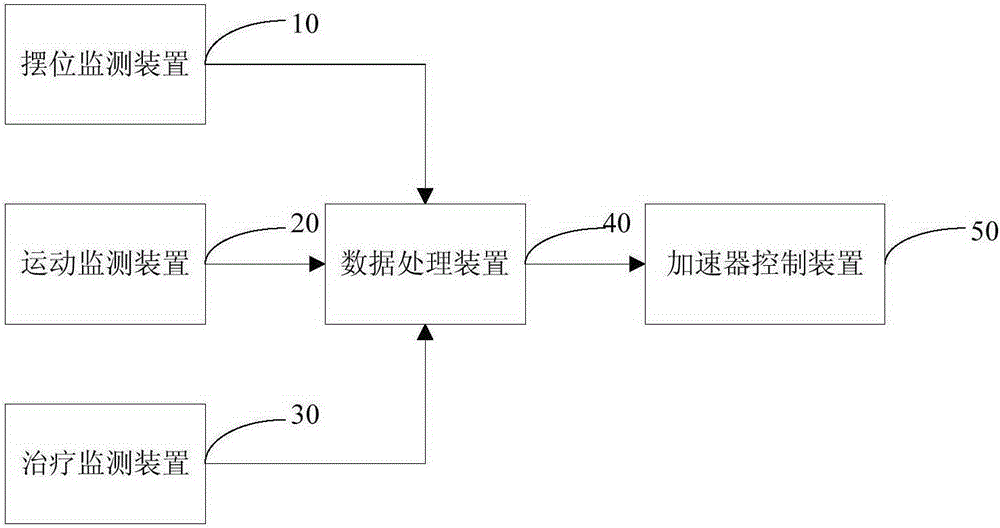
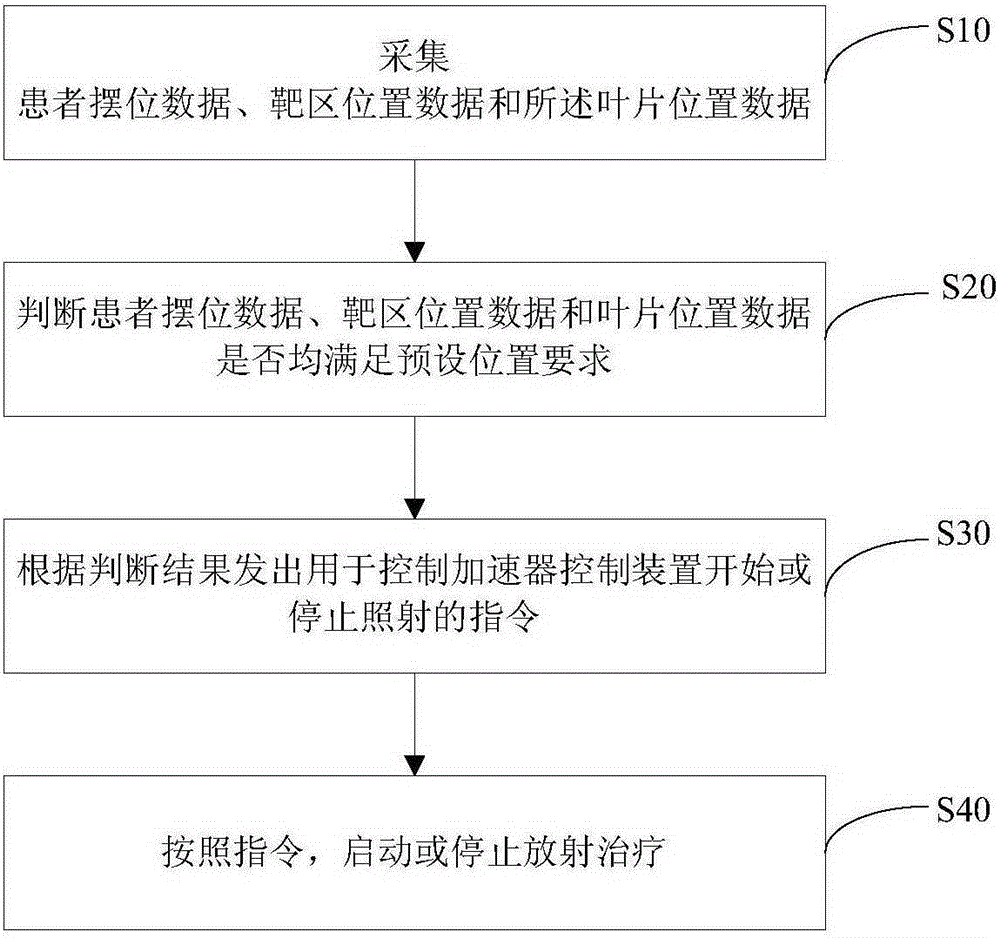
ActiveCN105342631APrecise positioningImprove real-time performanceRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyGratingMedicine
The invention discloses a radioactive ray monitoring and treating system. The radioactive ray monitoring and treating system comprises a location monitoring device, a movement monitoring device, a treating monitoring device, a data processing device and an accelerator control device. The location monitoring device is used for obtaining location data of a patient by monitoring a magnetic field of a body surface location corresponding to an area where tumors of the patient are located; the movement monitoring device is used for obtaining location data of a target area and an organ at risk by monitoring a magnetic filed of an in-vivo location corresponding to an area where the tumors and / or the organic at risk of the patient is located; the treating monitoring device is used for obtaining blade location data by monitoring a magnetic field of blade locations of a multi-blade collimator of an accelerator; the data processing device is used for judging whether the patient location data, the location data of the target area and the organ at risk and the blade location data all met preset location requirements or not and sending out an instruction used for controlling the accelerator control device to start or stop irradiation according to a judgment result; the accelerator control device is used for starting or stopping radiation treatment according to the instruction sent out by the data processing device. According to the radioactive ray monitoring and treating system, a magnetic localization mode is adopted, and the accuracy of radiation treatment is improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV FIRST HOSPITAL
Non-linear fusion method for internal and external radiotherapy doses of a cervical cancer
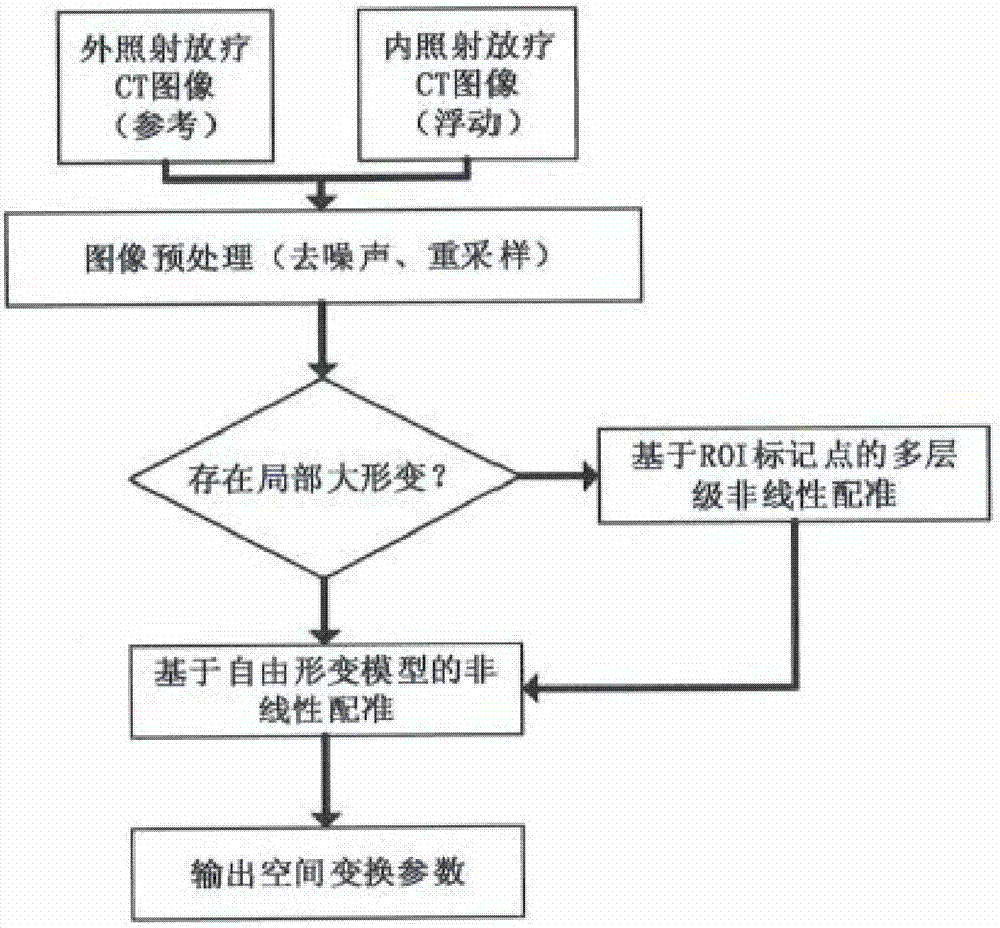
ActiveCN106902477AAccurate assessmentAccurately achieve accumulationRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTumor targetExternal irradiation
The invention relates to a non-linear fusion method for internal and external radiotherapy doses of a cervical cancer. The method comprises: obtaining internal and external irradiation radiotherapy CT images and internal and external irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution of a to-be-detected cervical cancer; on the basis of non-linear image registration, mapping the internal irradiation radiotherapy CT image to the external irradiation radiotherapy CT image to obtain a transformation relationship between the internal and external irradiation radiotherapy CT images of the to-be-detected cervical cancer; according to the transformation relationship between the internal and external irradiation radiotherapy CT images, transforming internal irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution into equivalent external irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution; and carrying out fusion of the equivalent external irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution and external irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution after transformation by image fusion, rebuilding a distribution curve of internal and external radiotherapy doses, and obtaining a total practically subjected dose of a tumor target region of the to-be-detected cervical cancer and surrounding organs at risks during the comprehensive internal and external irradiation radiotherapy process. The non-linear fusion method is applied to an image-guided radiation therapy of a cervical cancer, thereby improving accuracy of radiotherapy dose evaluation.
Owner:福建省肿瘤医院 +1
Radiation therapy optimization unit with global considerations
ActiveUS20180154177A1Reduced dosImprove conformityX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyVoxelOrgan at risk
A radiation therapy planning system (100) includes a radiation therapy optimization unit (124), which receives at least one target structure and at least one organ-at-risk (OAR) structure segmented from a volumetric image, and generates an optimized plan (126) based on at least one modified objective function. The optimized plan (126) includes a planned radiation dose for each voxel.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and a system for optimizing a radiation treatment plan based on a reference dose distribution
Owner:RAYSEARCH LAB
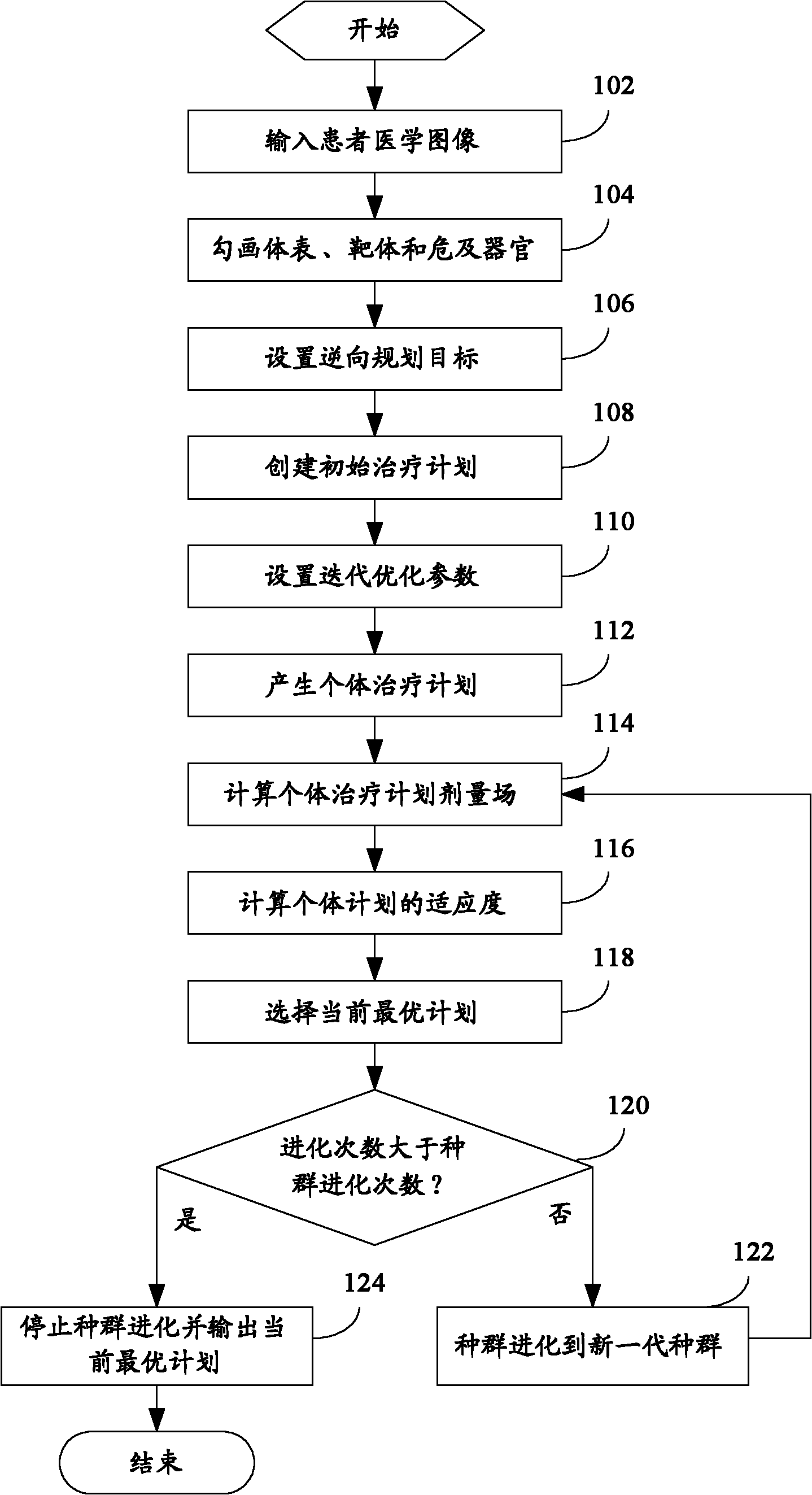
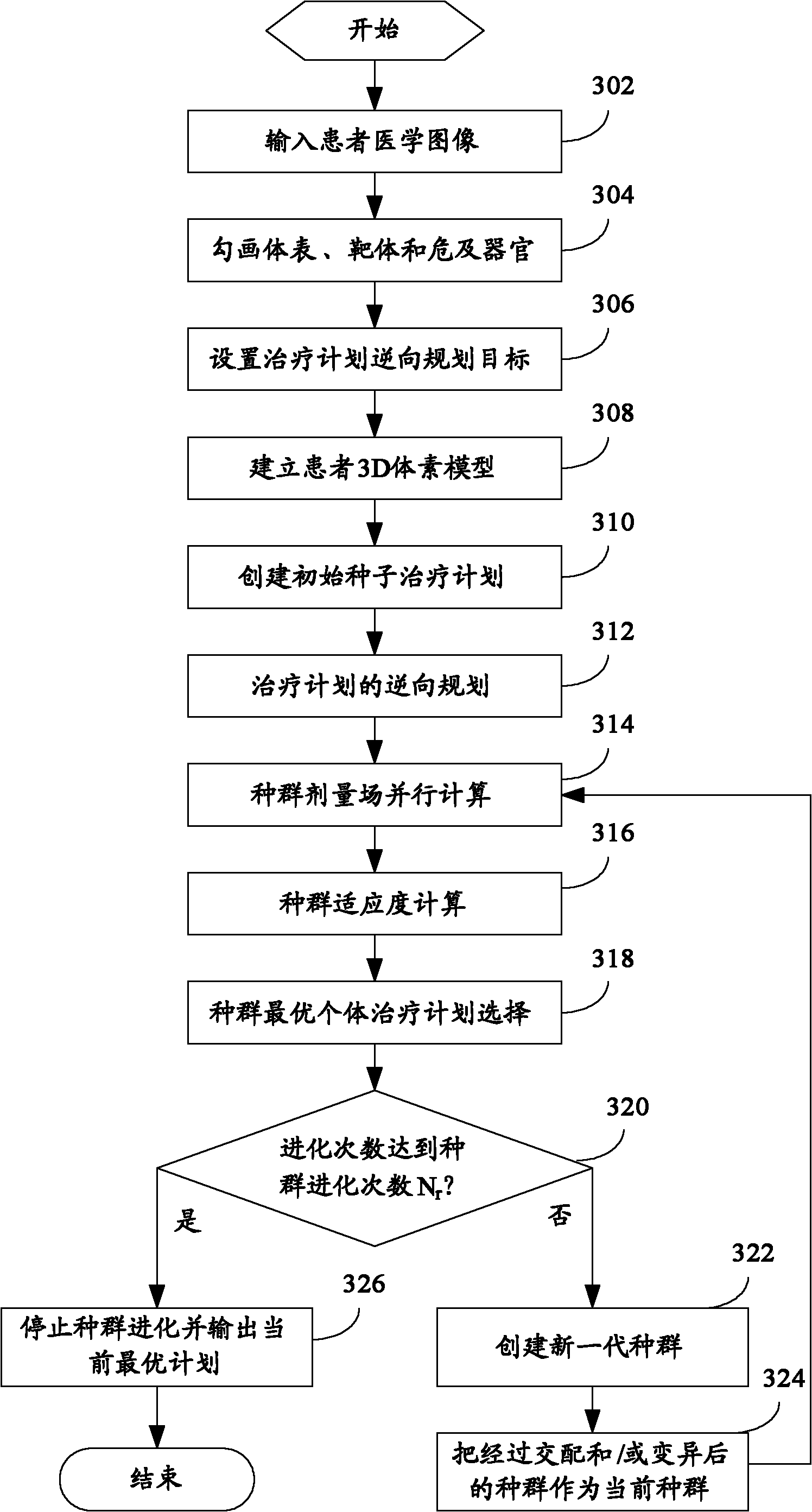
Method for reversely planning treatment plan and treatment plan system
ActiveCN102136041AImprove evolutionary efficiencyEfficient optimization processSpecial data processing applicationsInitial treatmentInitial therapy
The invention discloses a method for reversely planning a treatment plan. The method comprises the following steps of: A, inputting a medical image of a patient; B, drawing the tissue profiles of the body surface of the patient, a target body and organs at risks; C, setting a reserve planning target; D, establishing an initial treatment plan; E, setting an iterative optimization parameter; F, generating an individual treatment plan; G, computing an individual treatment plan dose field; H, computing the degree of adaptability; I, selecting a current optimal plan; J, if evolution times are greater than population evolution times, turning to a step M, or otherwise turning to a next step; K, evolving a population to a new generation of population and turning to the step G; and M, stopping population evolution and outputting a current optimal plan. The invention also discloses a treatment plan system. A method for computing the degree of adaptability is used for selecting an optimal plan, so that the evolution efficiency of the population can be increased, and an optimizing process is efficient.
Owner:SHEN ZHEN HYPER TECH SHENZHEN
Lung cancer-oriented intelligent target region and organ-at-risk segmentation method
PendingCN113793304ATo achieve common learningRich sources of dataImage enhancementImage analysisAlgorithmOncology
The invention discloses a lung cancer-oriented intelligent target region and organ-at-risk segmentation method. Dual-path segmentation is performed by adopting a common segmentation network framework of a lung cancer-oriented target region and an organ at risk; the common segmentation network framework comprises a teacher model and a student model, and the two models both adopt nnU-Net as trunks; and for the organ at risk and the target region, pre-defined auxiliary condition information is respectively given to be embedded in an up-sampling process and is connected to a corresponding decoder in a decoding process, and predicted masks are fused to obtain a final segmentation result. According to the method, the target region and the organ at risk can be accurately and efficiently segmented.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
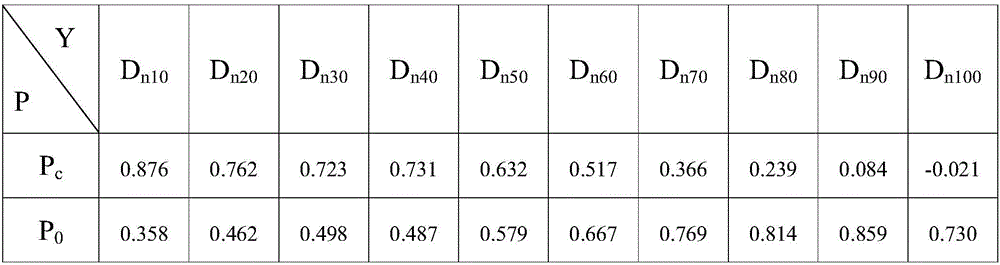
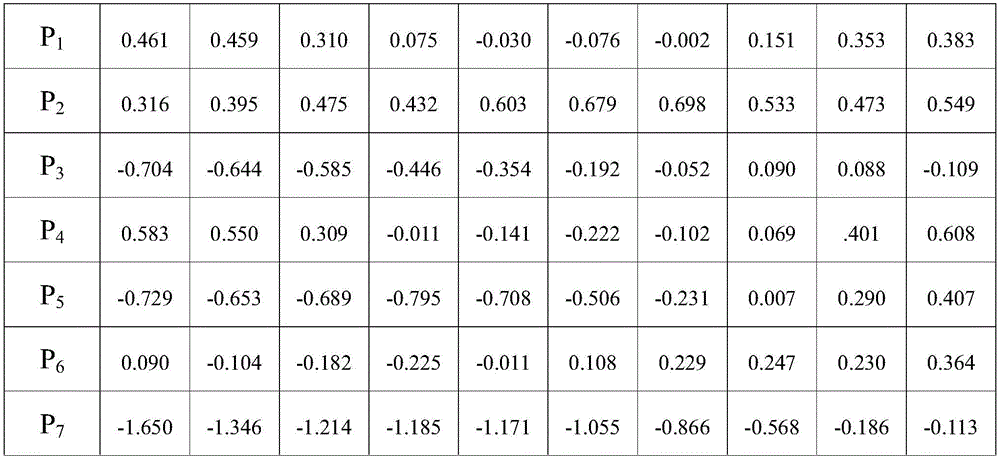
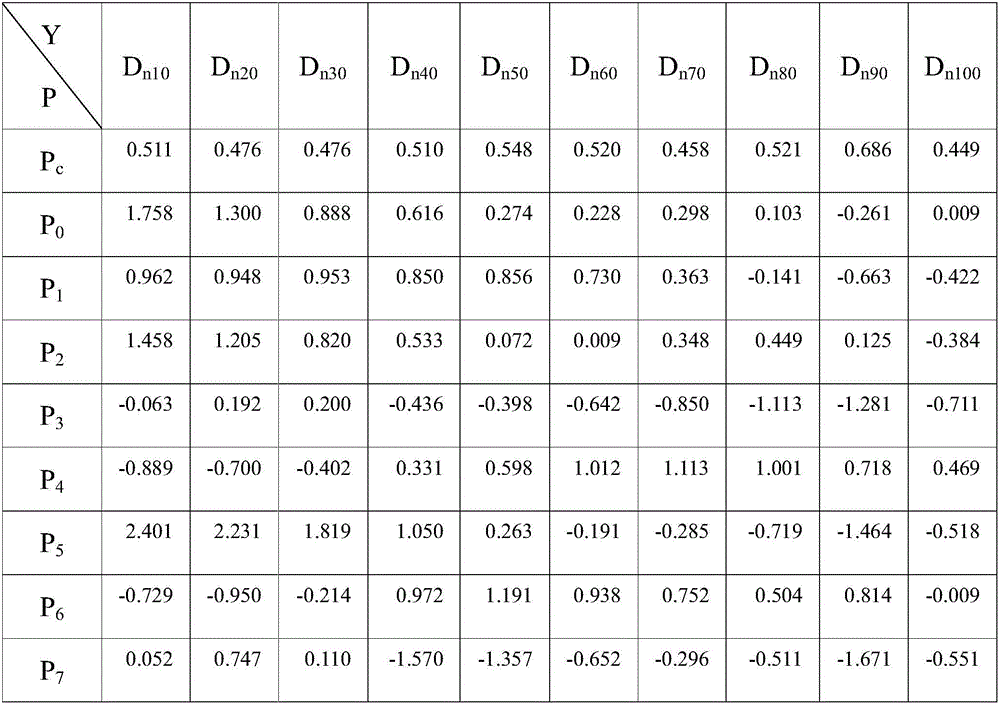
Method for constructing prediction mathematic model for organ-at-risk adsorbed dose in intensity modulated radiation therapy
ActiveCN106169028AAbsorbed dose predictionEasy to collectMedical simulationSpecial data processing applicationsExisting TreatmentRadiotherapy unit
The invention discloses a method for constructing a prediction mathematic model for organ-at-risk adsorbed dose in intensity modulated radiation therapy. The method comprises the steps of 1, dividing an organ-at-risk into n sub-organs, and obtaining the normalization volume Vn / VOAR of the n sub-organ; 2, obtaining the normalization adsorbed dose Dn10-n100 of the organ-at-risk according to an intensity modulated therapy plan; 3, obtaining the prediction mathematic model according to the normalization volume Vn / VOAR of the n sub-organ and normalization adsorbed dose Dn10-n100 of the organ-at-risk. According to the method, organ-at-risk adsorbed dose is predicted before making the intensity modulated therapy plan; the method is simple and practical, data are easy to acquire, the prediction mathematic model for organ-at-risk adsorbed dose in intensity modulated radiation therapy can be constructed by most radiotherapy units by means of the method based on an existing treatment plan system, and the method is suitable for wide application and popularization.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOUTHWEST MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com