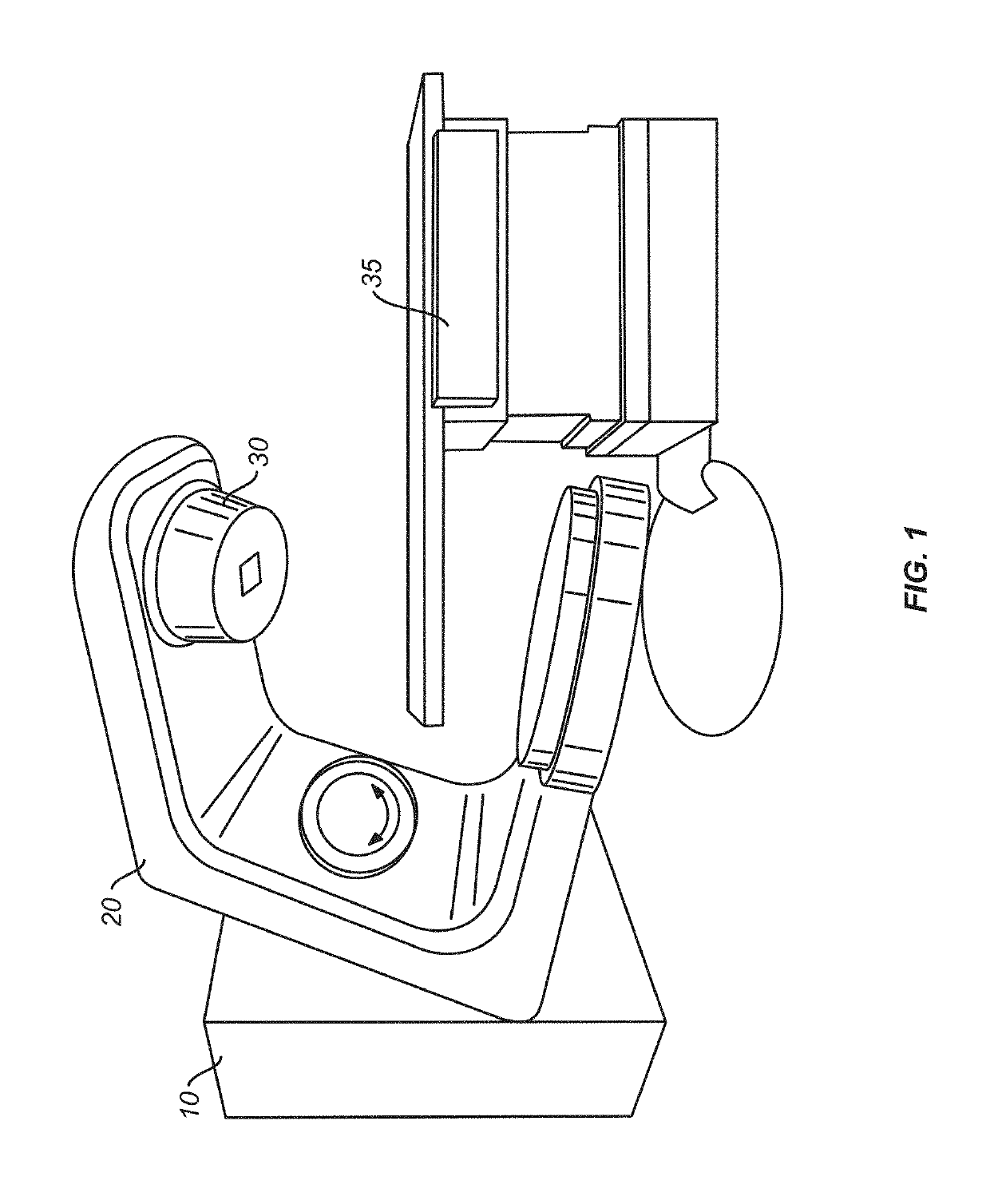
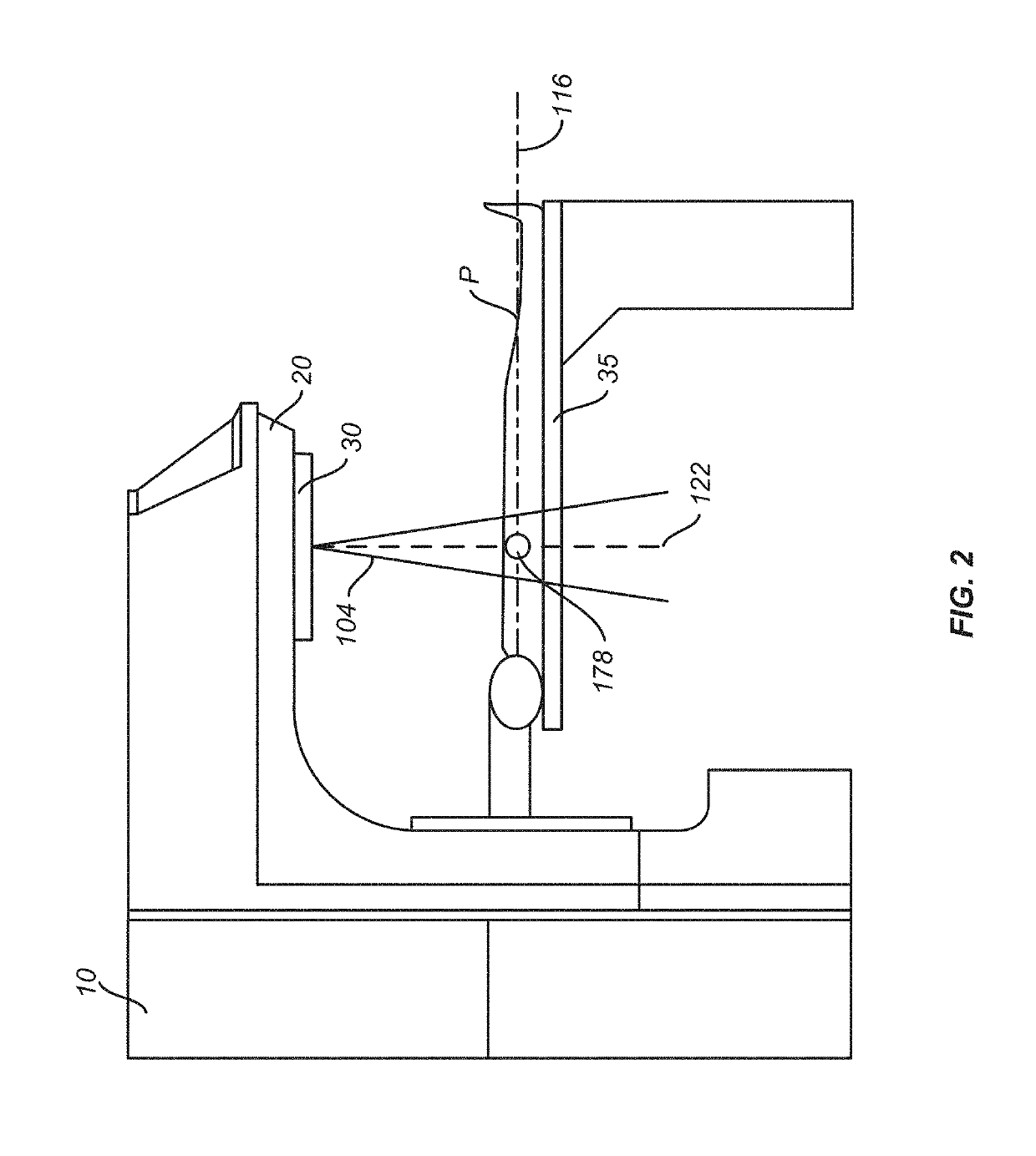
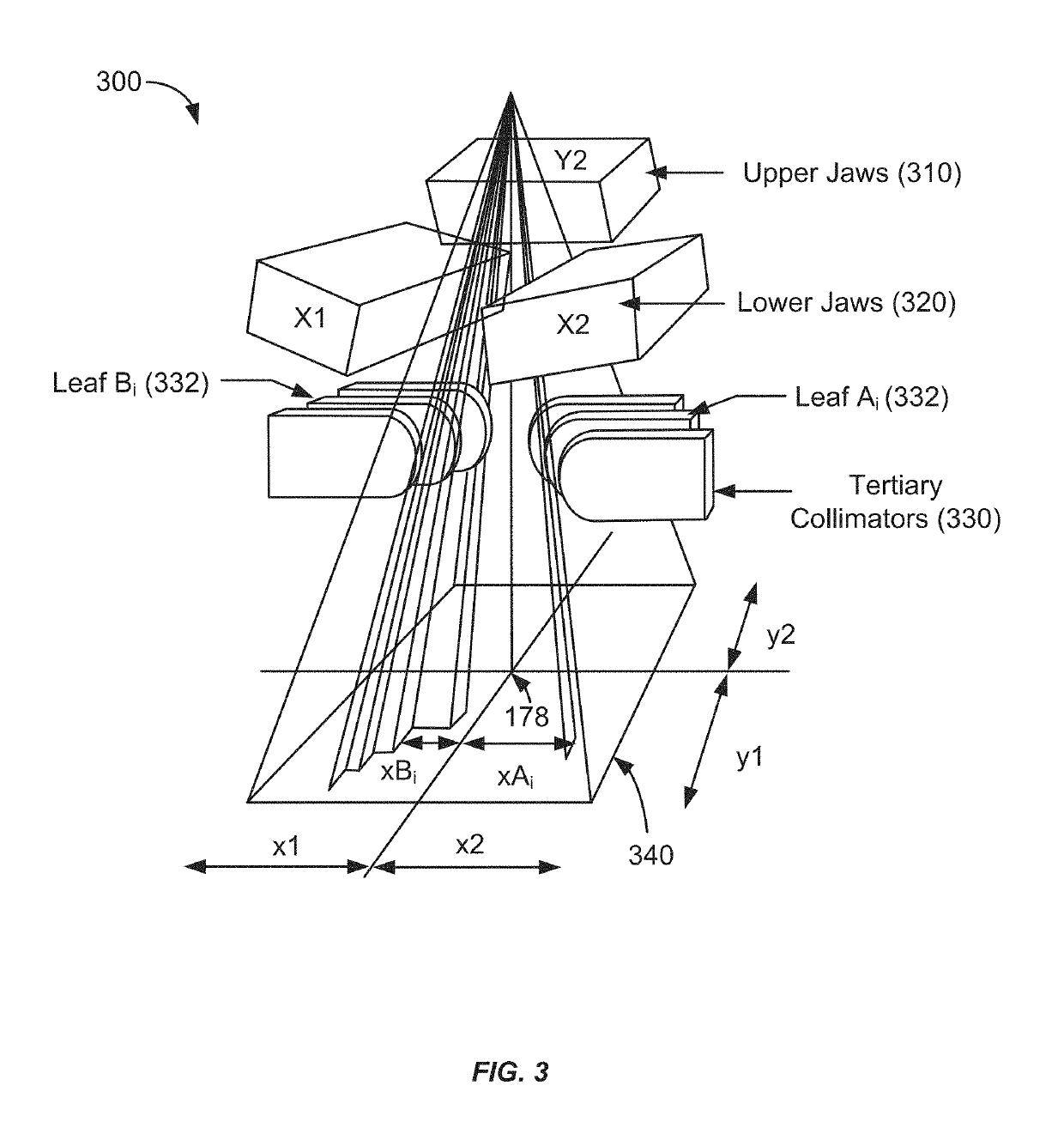
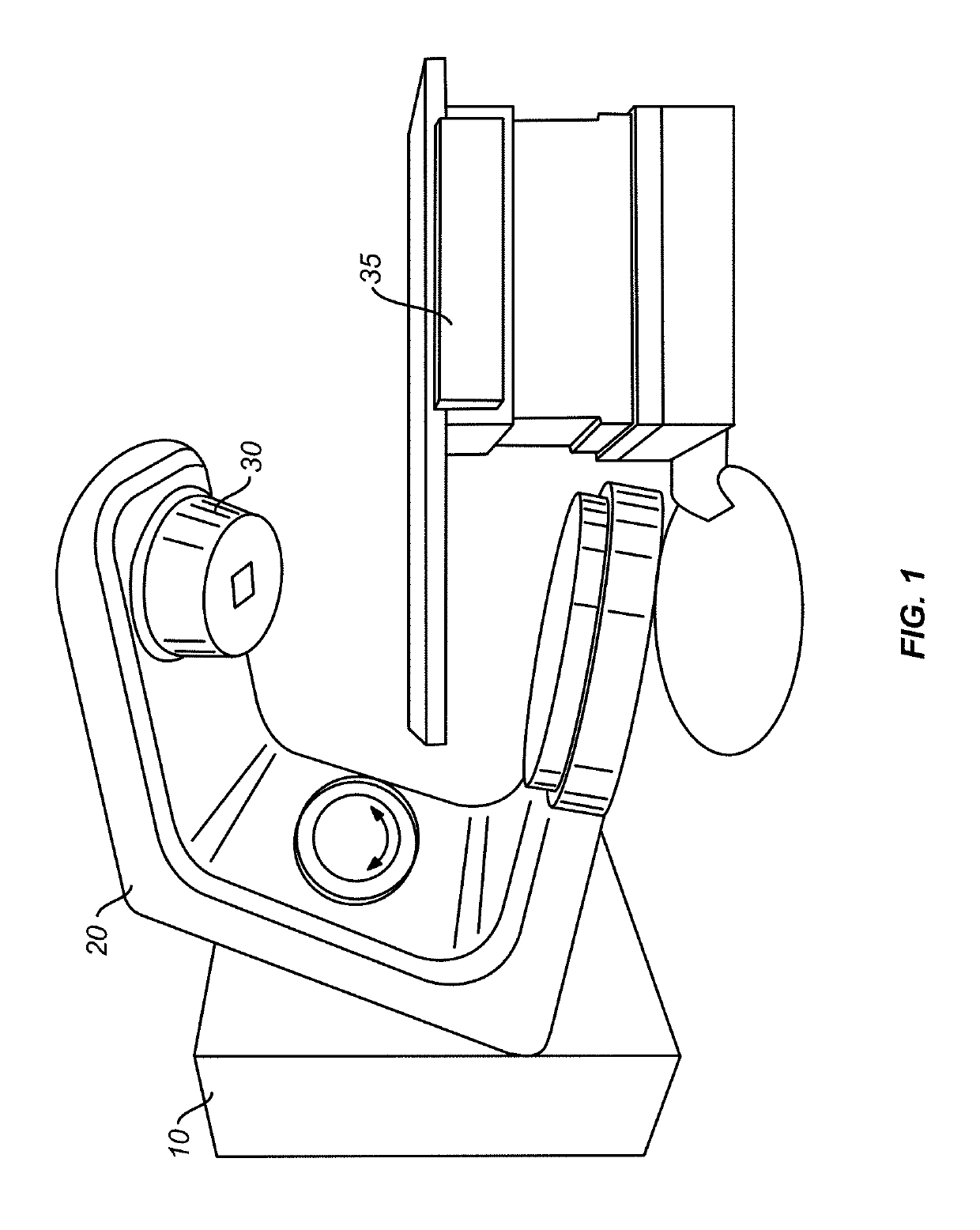
Patents
Literature
40 results about "External beam radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
External radiation (or external beam radiation) is the most common type of radiation therapy used for cancer treatment. A machine is used to aim high-energy rays (or beams) from outside the body into the tumor.
Automated treatment planning for radiation therapy
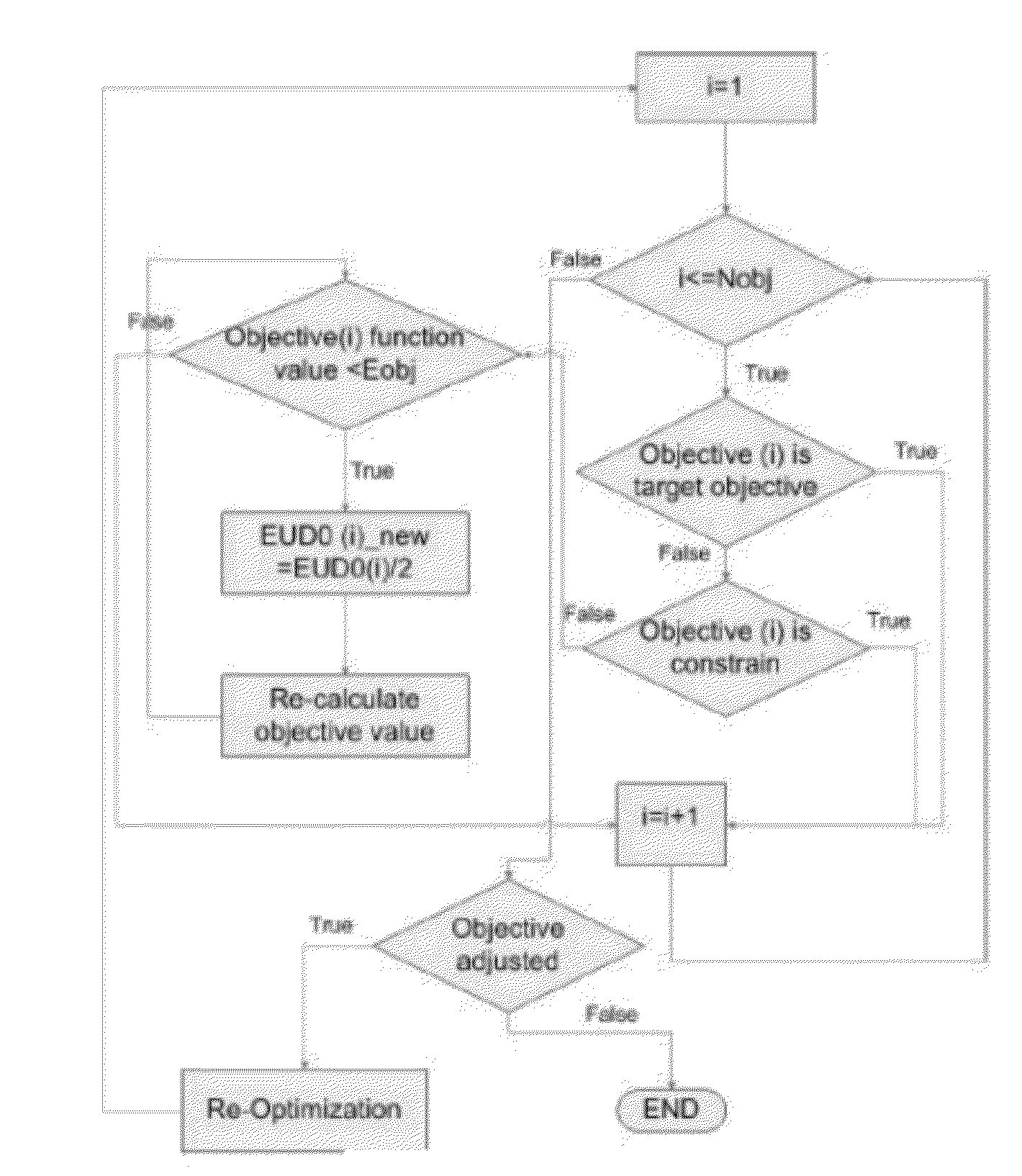
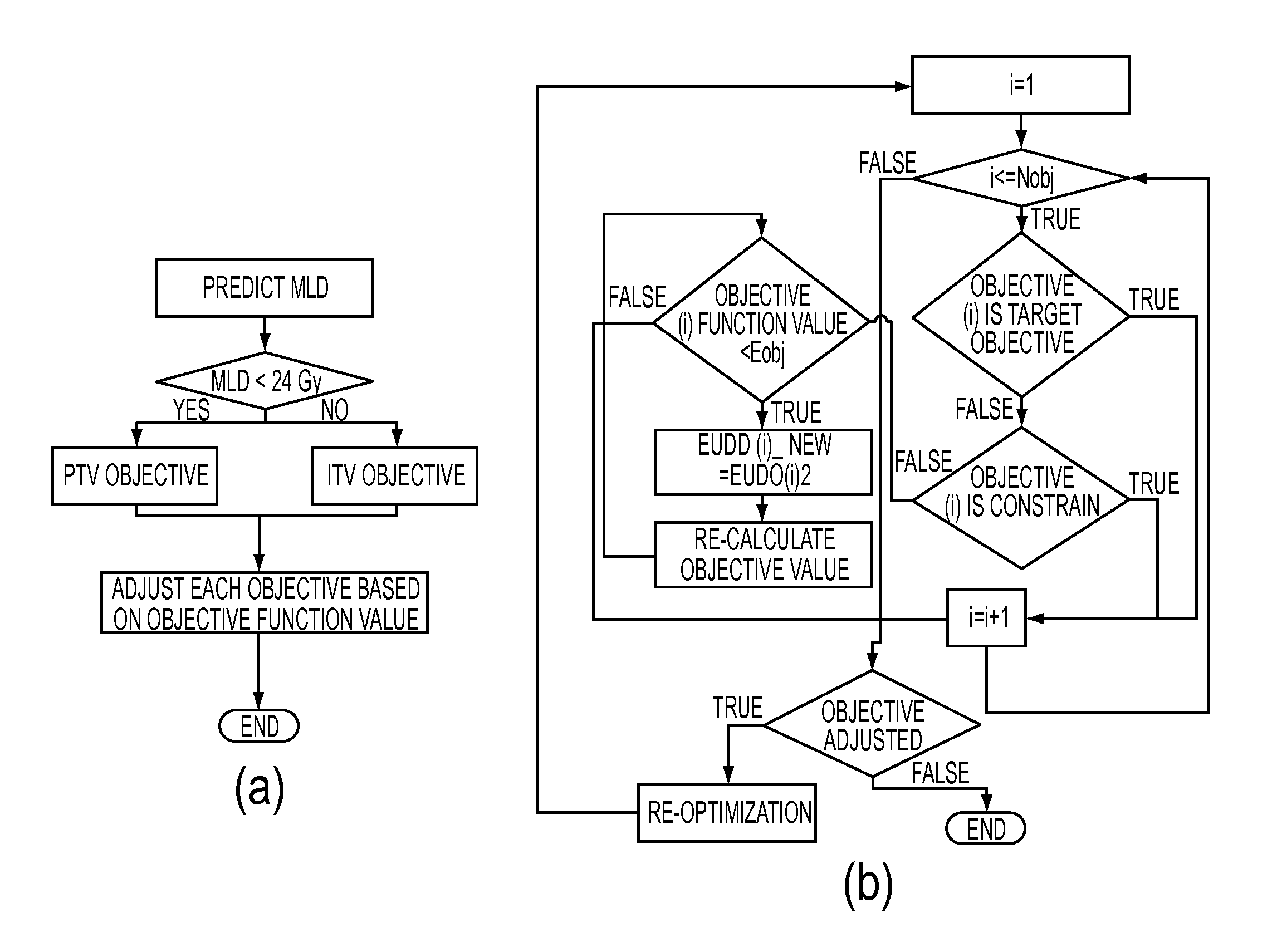
This patent generally relates to developing treatment plans for use in external beam radiation therapy, and more particularly to a method, a system and a computer readable media that contains programming for the development of external beam radiation therapy treatment plans. Embodiments of the invention include (1) automatically setting beam angles based on a beam angle automation algorithm, (2) judiciously designing planning structures and (3) automatically adjusting the objectives of the objective function based on a parameter automation algorithm.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Automated treatment planning for radiation therapy
This patent generally relates to developing treatment plans for use in external beam radiation therapy, and more particularly to a method, a system and a computer readable media that contains programming for the development of external beam radiation therapy treatment plans. Embodiments of the invention include (1) automatically setting beam angles based on a beam angle automation algorithm, (2) judiciously designing planning structures and (3) automatically adjusting the objectives of the objective function based on a parameter automation algorithm.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
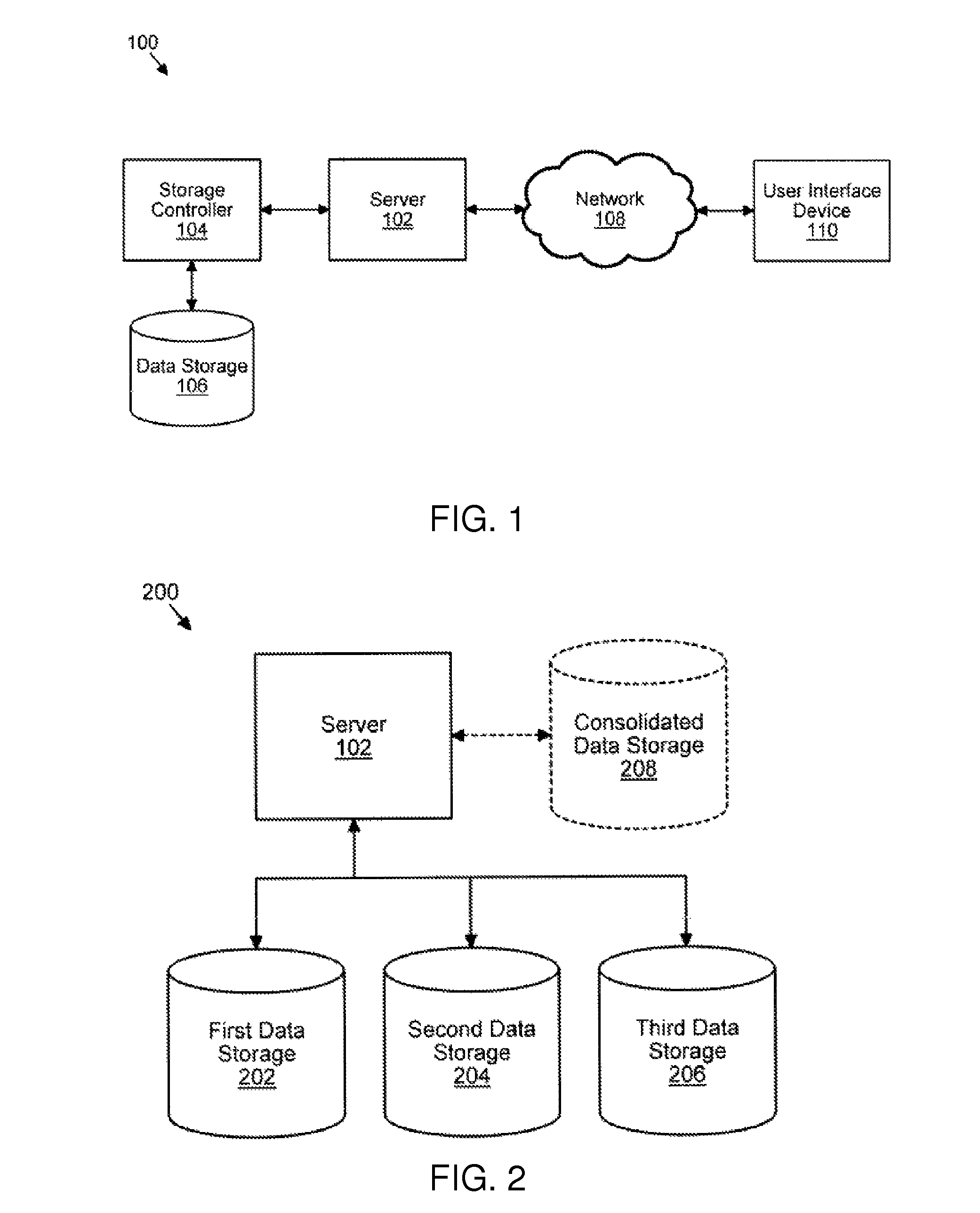
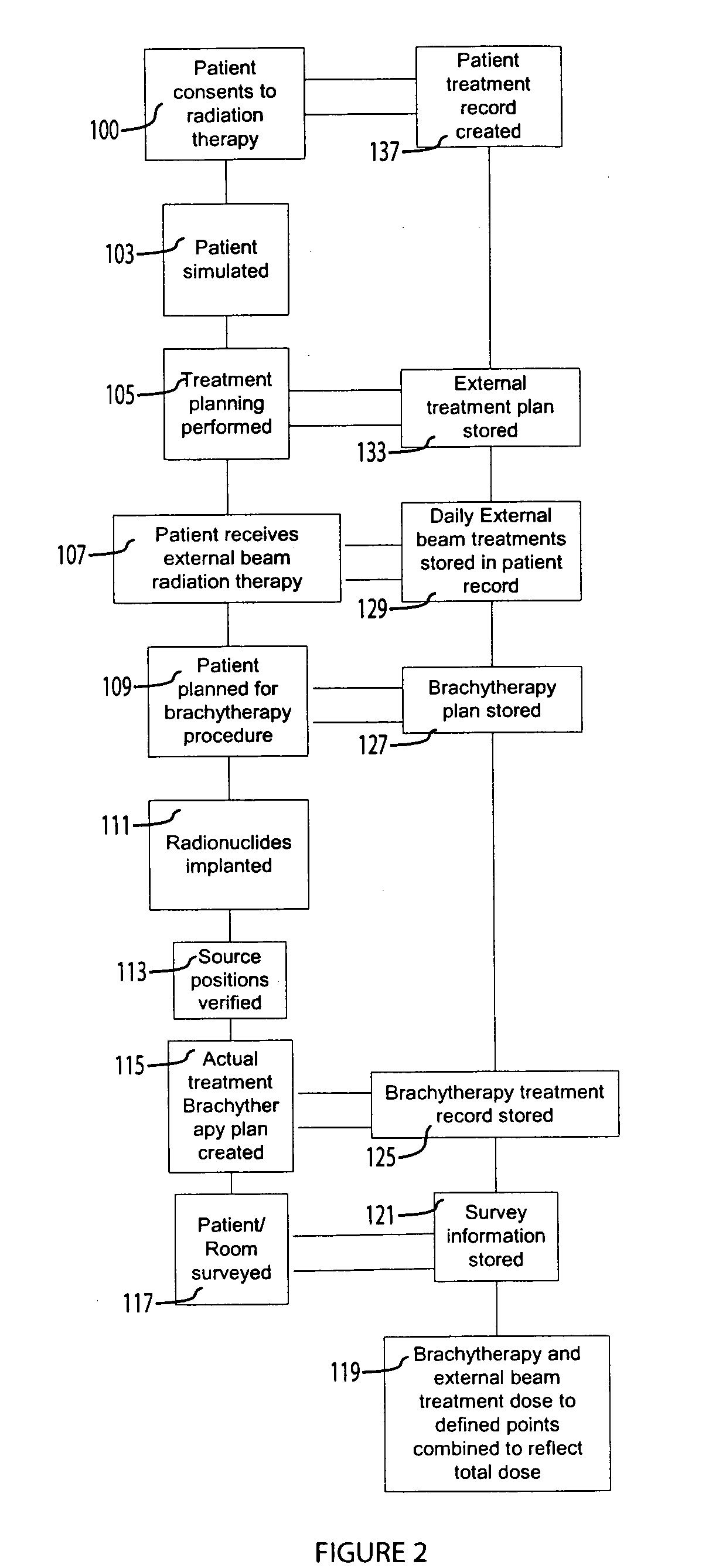
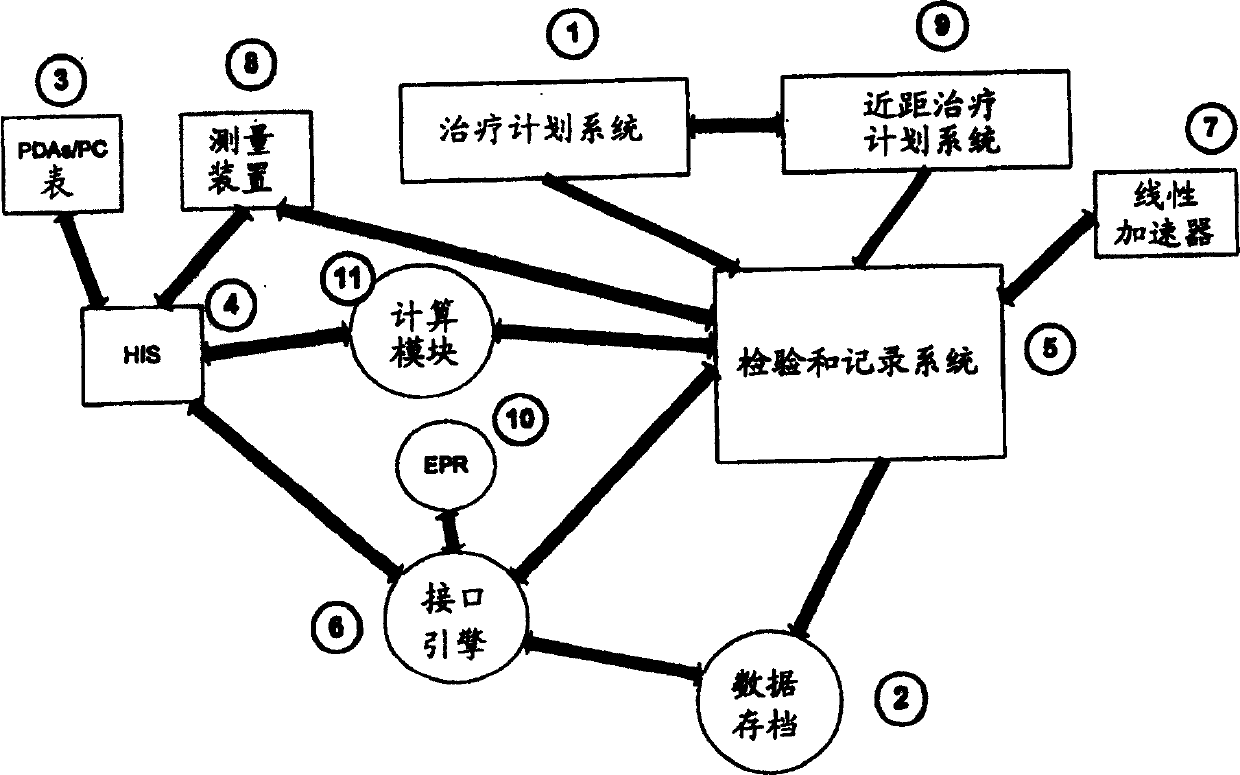
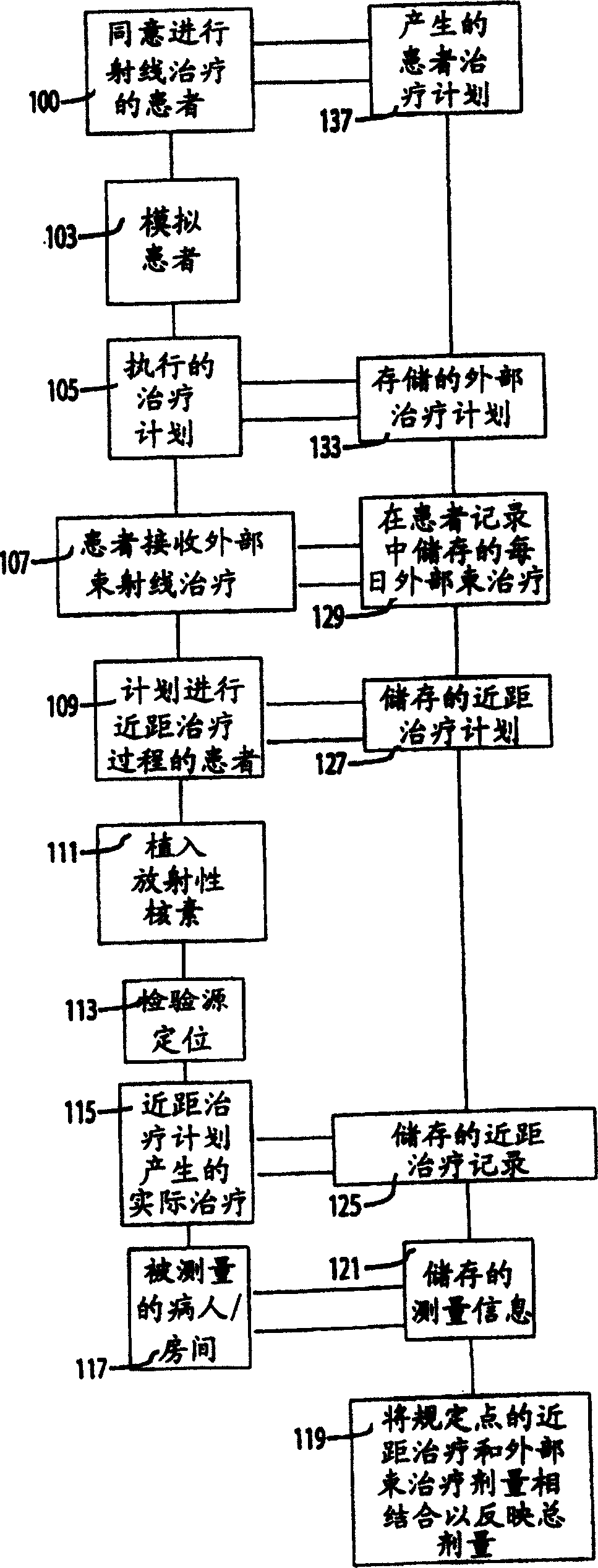
System for processing patient radiation treatment data
InactiveUS20050027196A1Convenient treatmentEasy to useRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAnatomic regionRadiation emission
A system records and documents both external beam radiation therapy and radiation from implanted sources applied to an anatomical area, in a comprehensive consolidated record of radiation treatment that also documents detected radiation emission levels from internal patient sources measured externally to the patient. A system processes data concerning patient radiation treatment. The system includes an input processor for receiving data identifying a first radiation dose received by a particular anatomical part of a patient, from a radiation source external to a patient and a second radiation dose, received by the particular anatomical part of the patient from a radiation source internal to the patient. A data processor combines data representing the first and second dose to provide a combined dose value. A storage processor stores the combined value in a record associated with the patient
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS HEALTH SERVICES CORPORAT
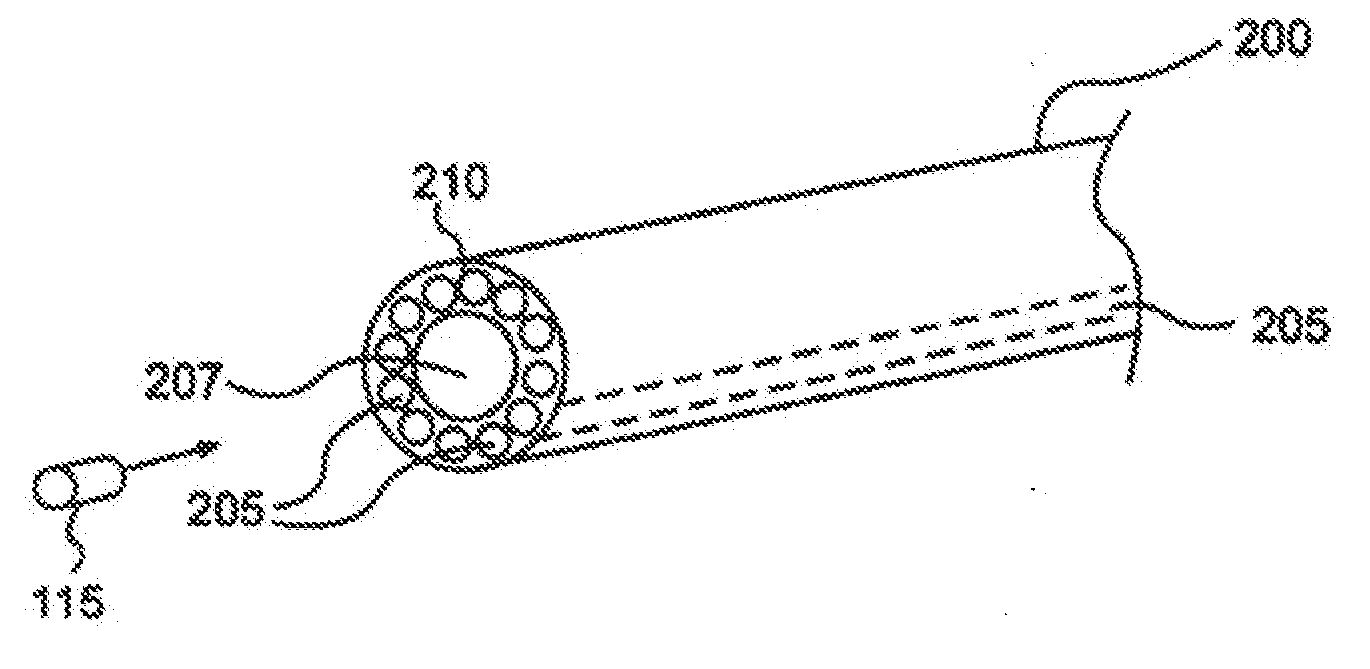
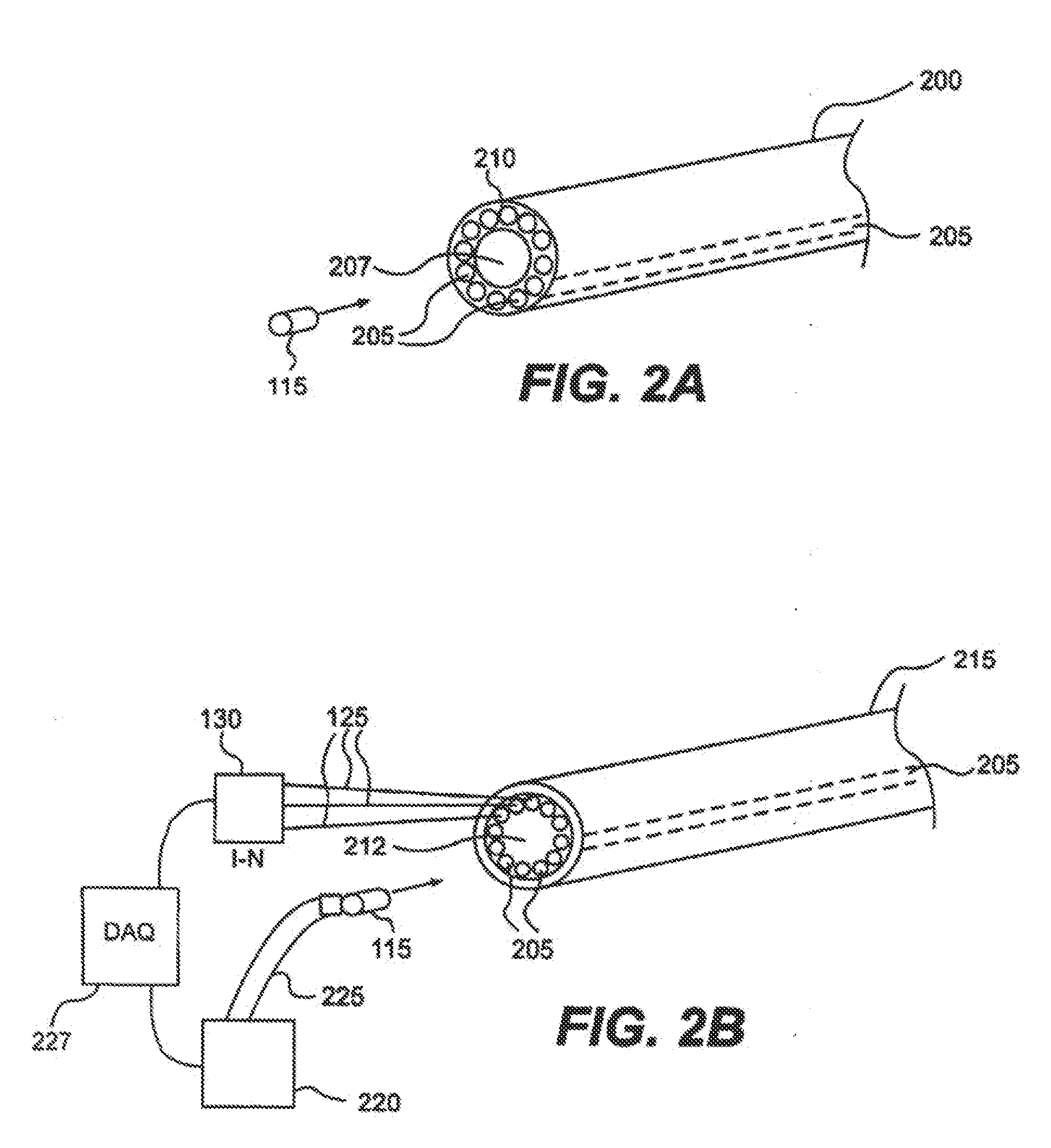
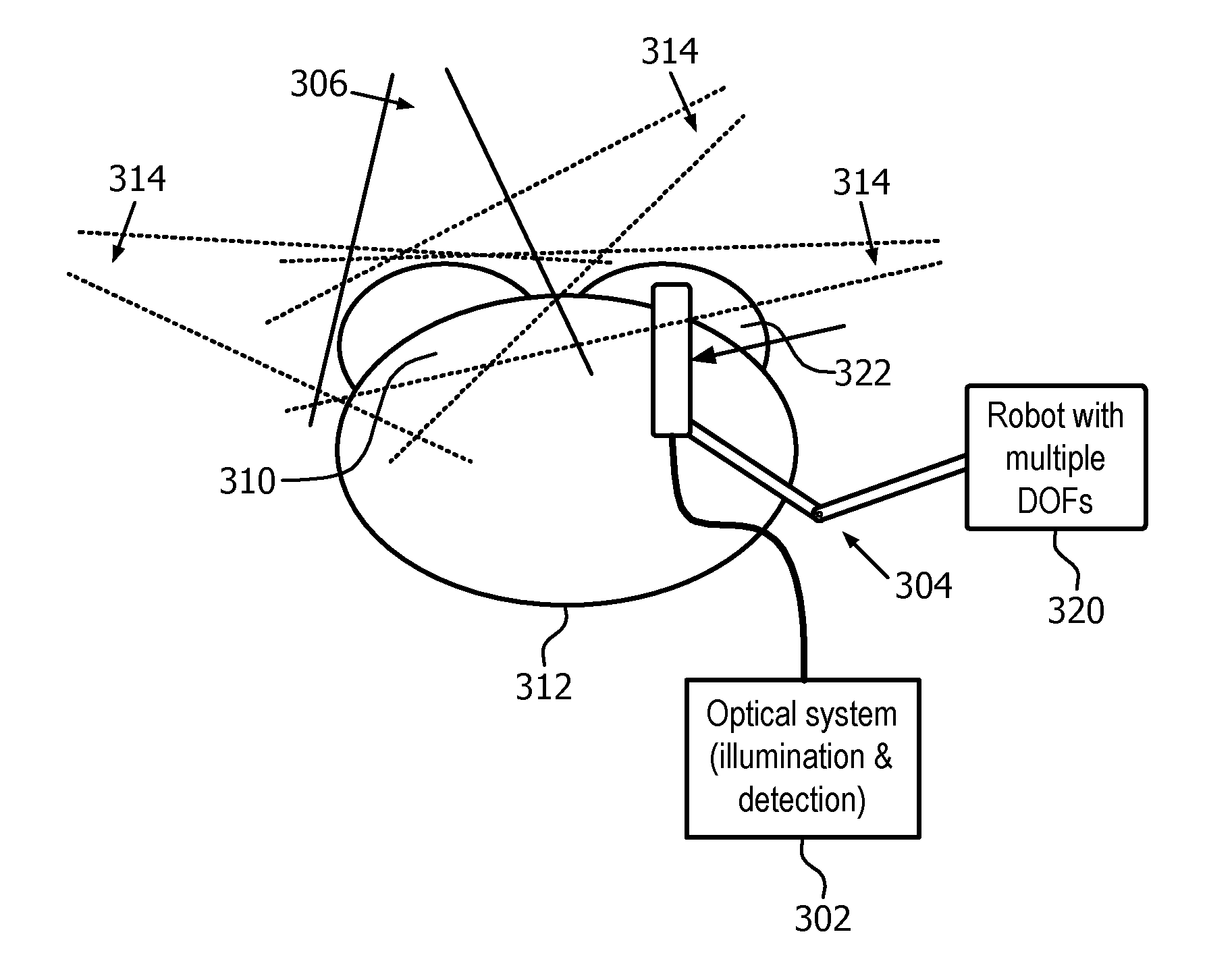
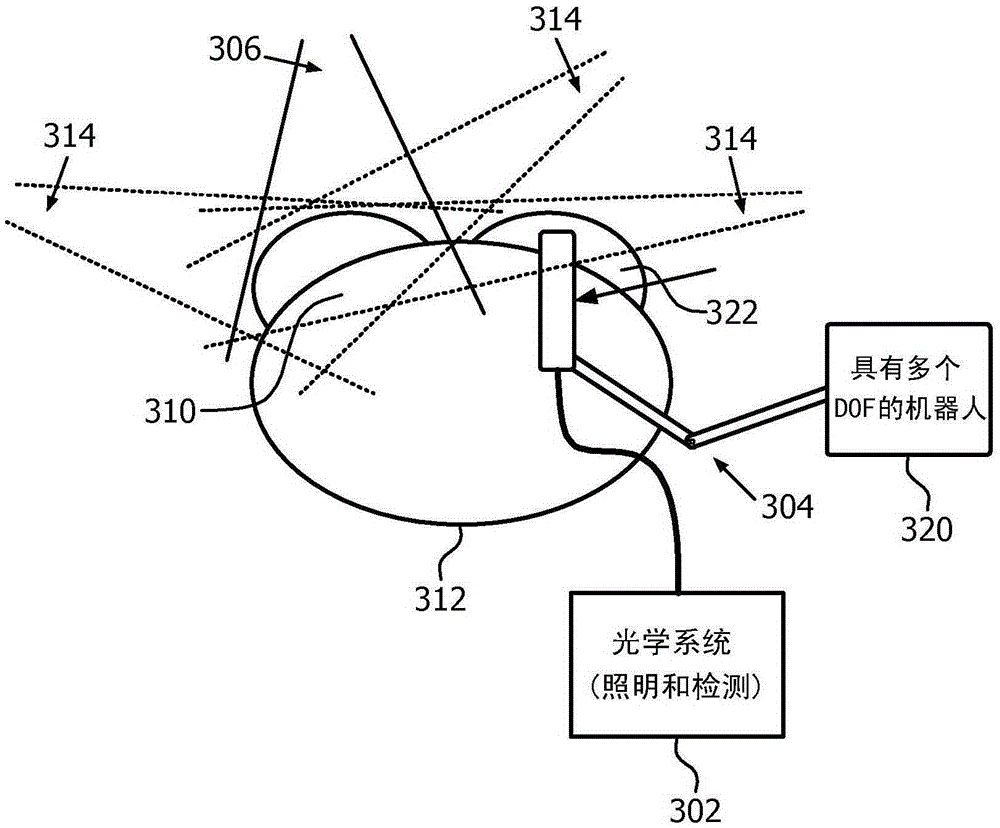
Apparatus and method for external beam radiation distribution mapping
An apparatus and method for in vivo and ex vivo control, detection and measurement of radiation in therapy, diagnostics, and related applications accomplished through scintillating fiber detection. One example includes scintillating fibers placed along a delivery guide such as a catheter for measuring applied radiation levels during radiotherapy treatments, sensing locations of a radiation source, or providing feedback of sensed radiation. Another option is to place the fibers into a positioning device such as a balloon, or otherwise in the field of the radiation delivery. The scintillating fibers provide light output levels correlating to the levels of radiation striking the fibers and comparative measurement between fibers can be used for more extensive dose mapping. Adjustments to a radiation treatment may be made as needed based on actual and measured applied dosages as determined by the fiber detectors. Characteristics of a radiation source may also be measured using scintillating materials.
Owner:HAMPTON UNIVERSITY
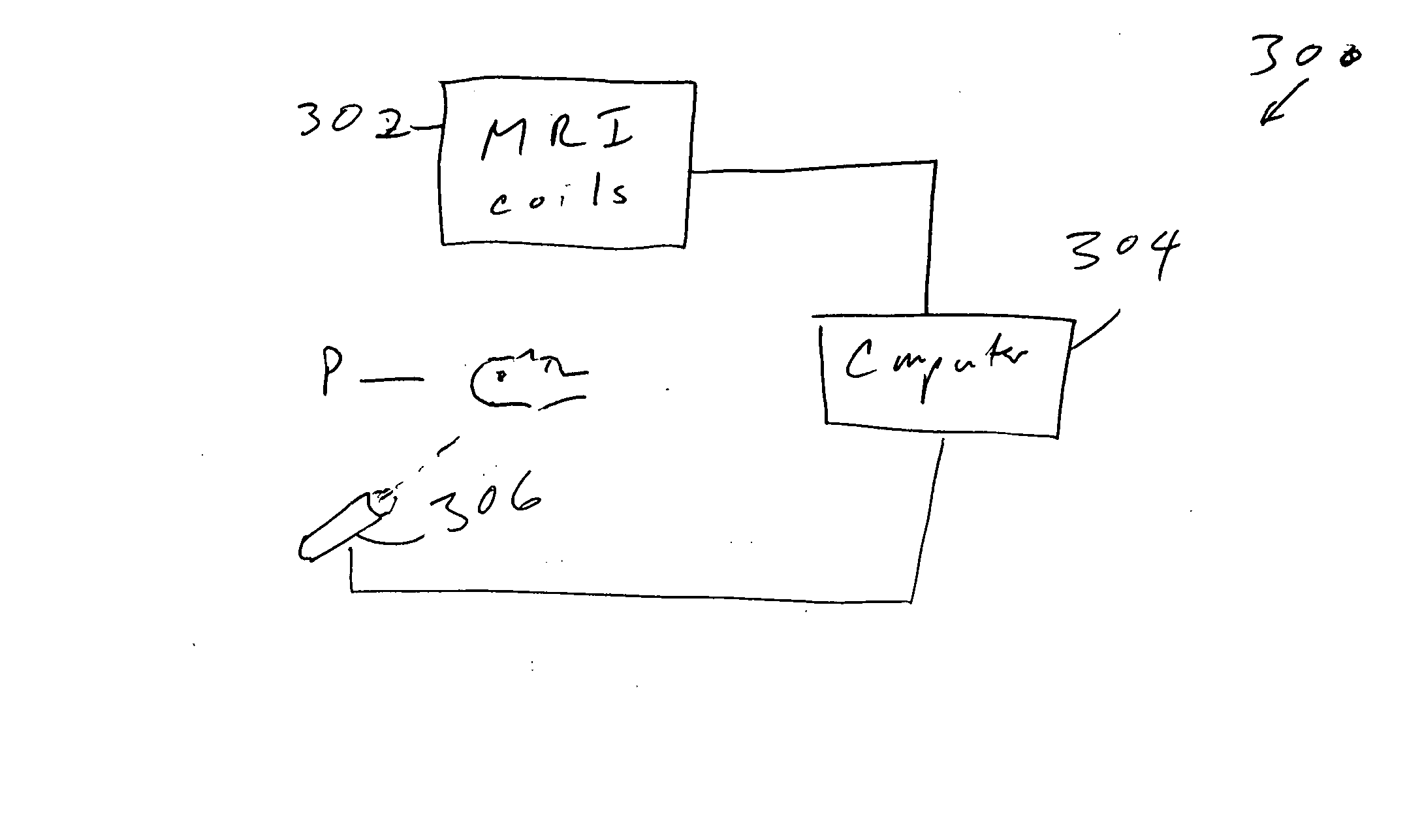
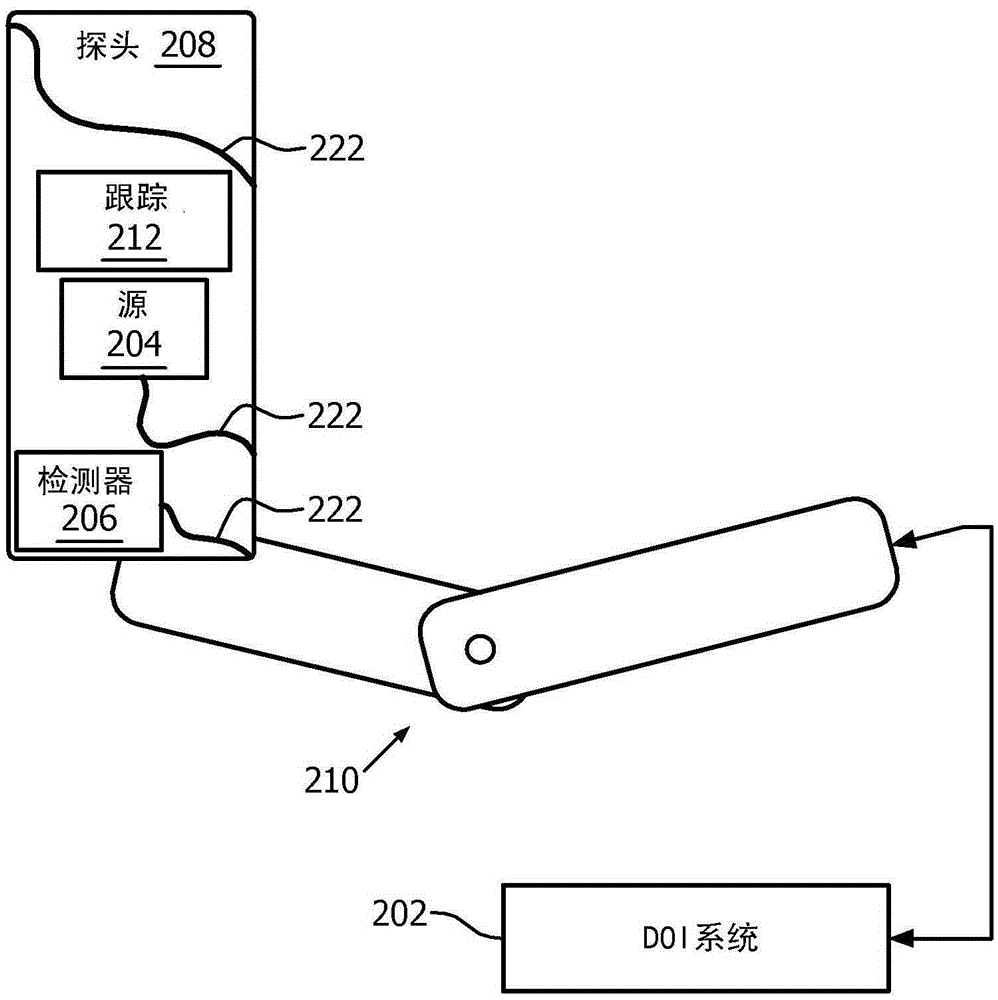
Methods, systems, and computer program products for providing dynamic data of positional localization of target implants
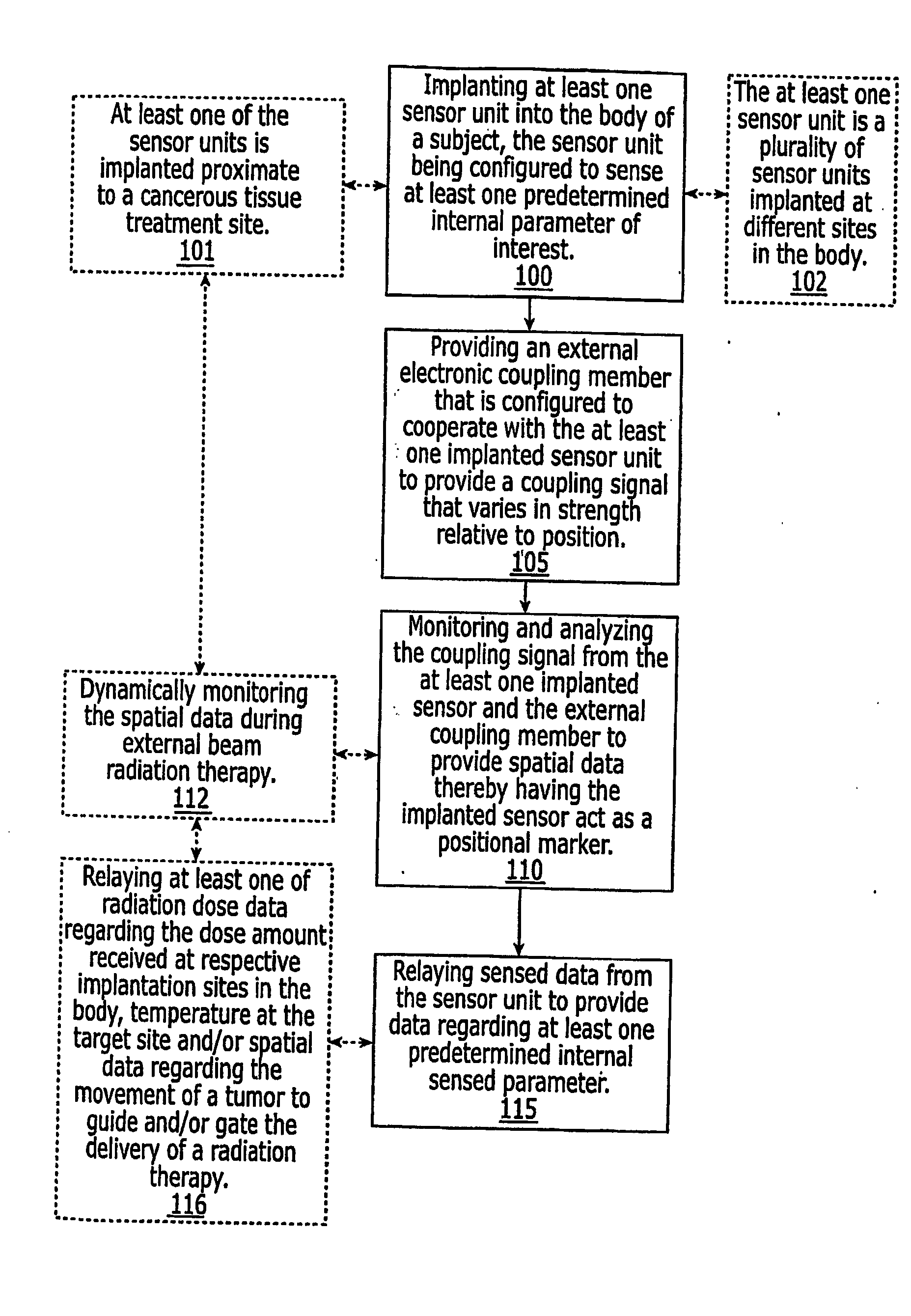
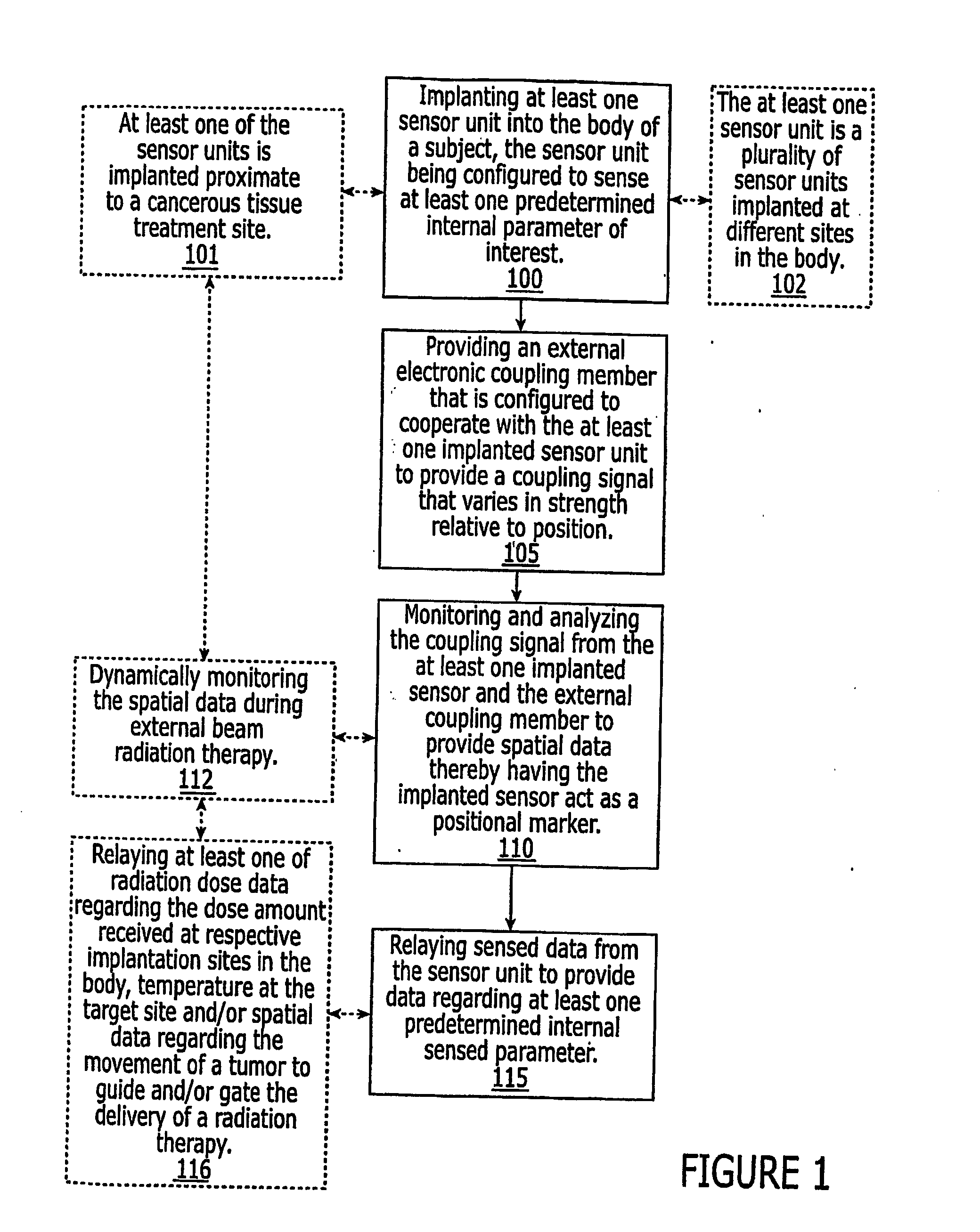
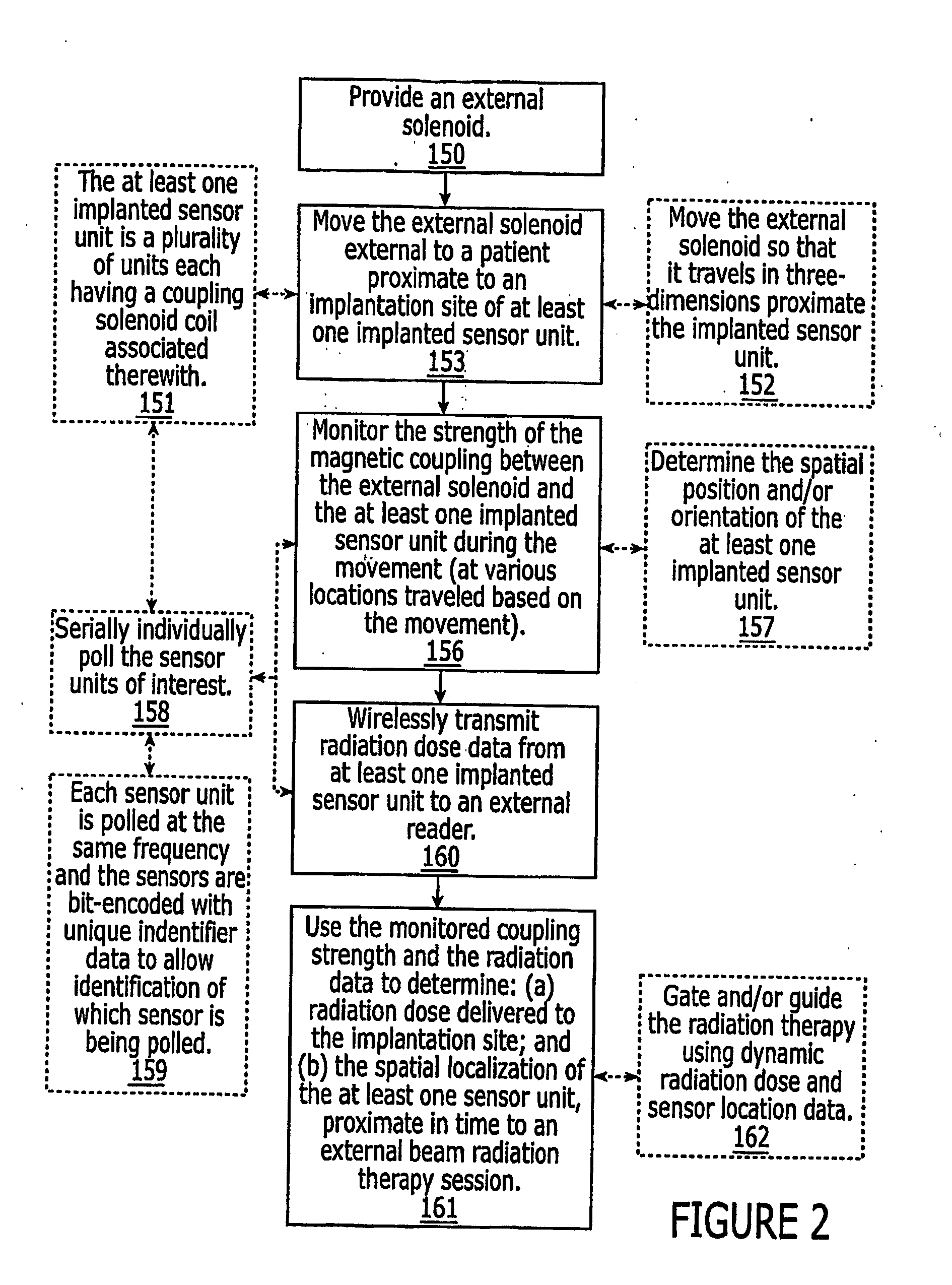
Systems for locating implanted in vivo sensors systems adapted for use with an external beam radiation therapy delivery source include: (a) an external solenoid member; (b) an articulated arm opertively associated with the external solenoid member, wherein, in operation, the articulated arm is configured to translate the solenoid; (c) a controller configured to direct the movement of the articulated arm, the controller being in communication with the power source configured to power the external solenoid; (d) at least one implantable sensors unit, wherein the at least one implantable sensor unit is configured to sense at least one predetermined parameter of interest in vivo, and wherein the at least one implantable sensor unit comprises a solenoid, and wherein, in operation, the sensor unit solenoid corporates with the external solenoid to generate a magnetic coupling signal having a signal strength that varies based on the possession of the external solenoid member relative to the implanted sensors unit; (e) a computer module in communication with the controller comprising computer programmed code that evaluates the coupling signal strength in relation to the position of the external solenoid and determines the position of the at least one sensor unit; and (f) an external reader configured to wirelessly communicate with the at least one implantable sensor unit to obtain data associated with the at least one predetermined parameter of interest.
Owner:VTQ IP HLDG
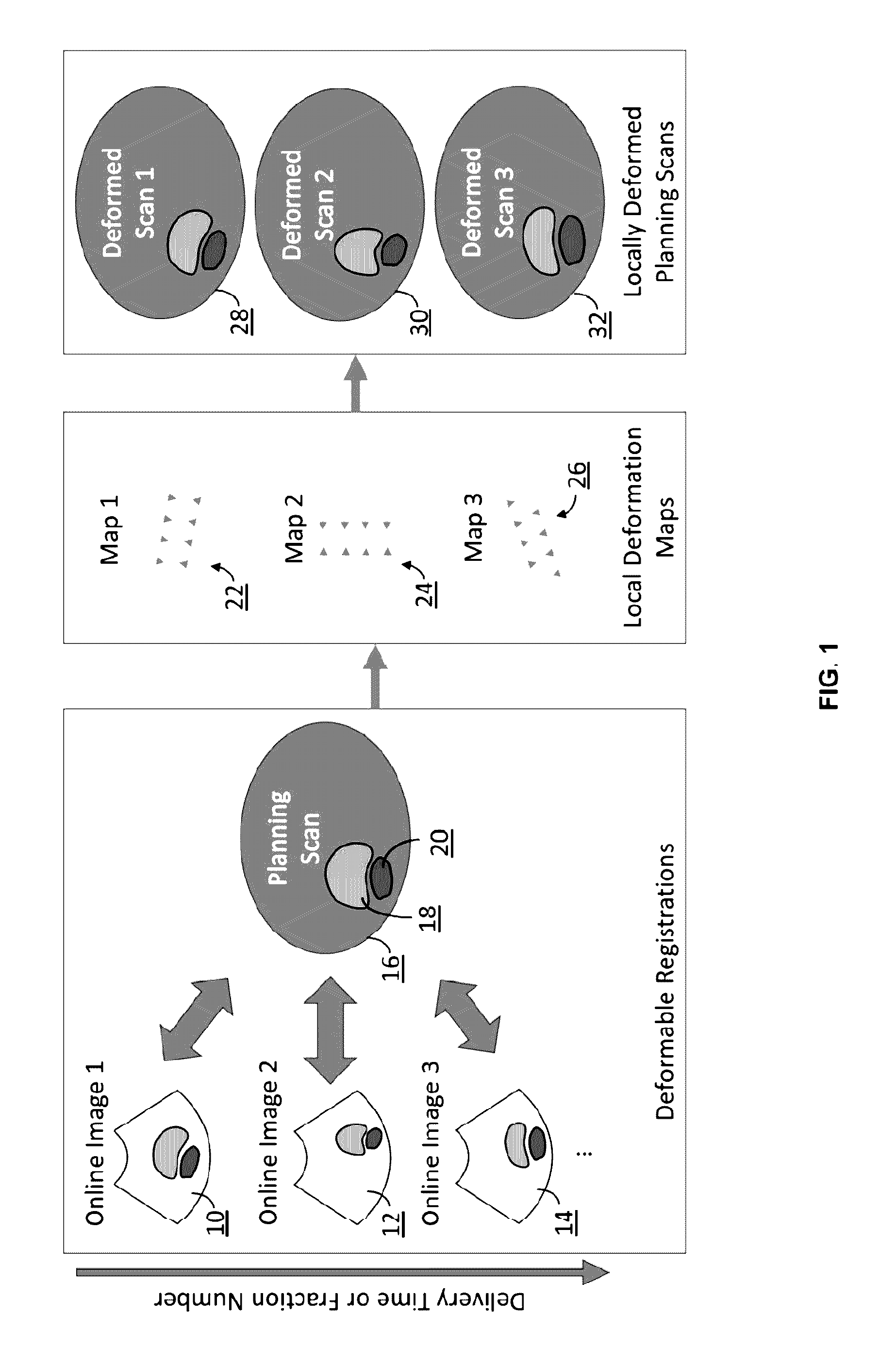
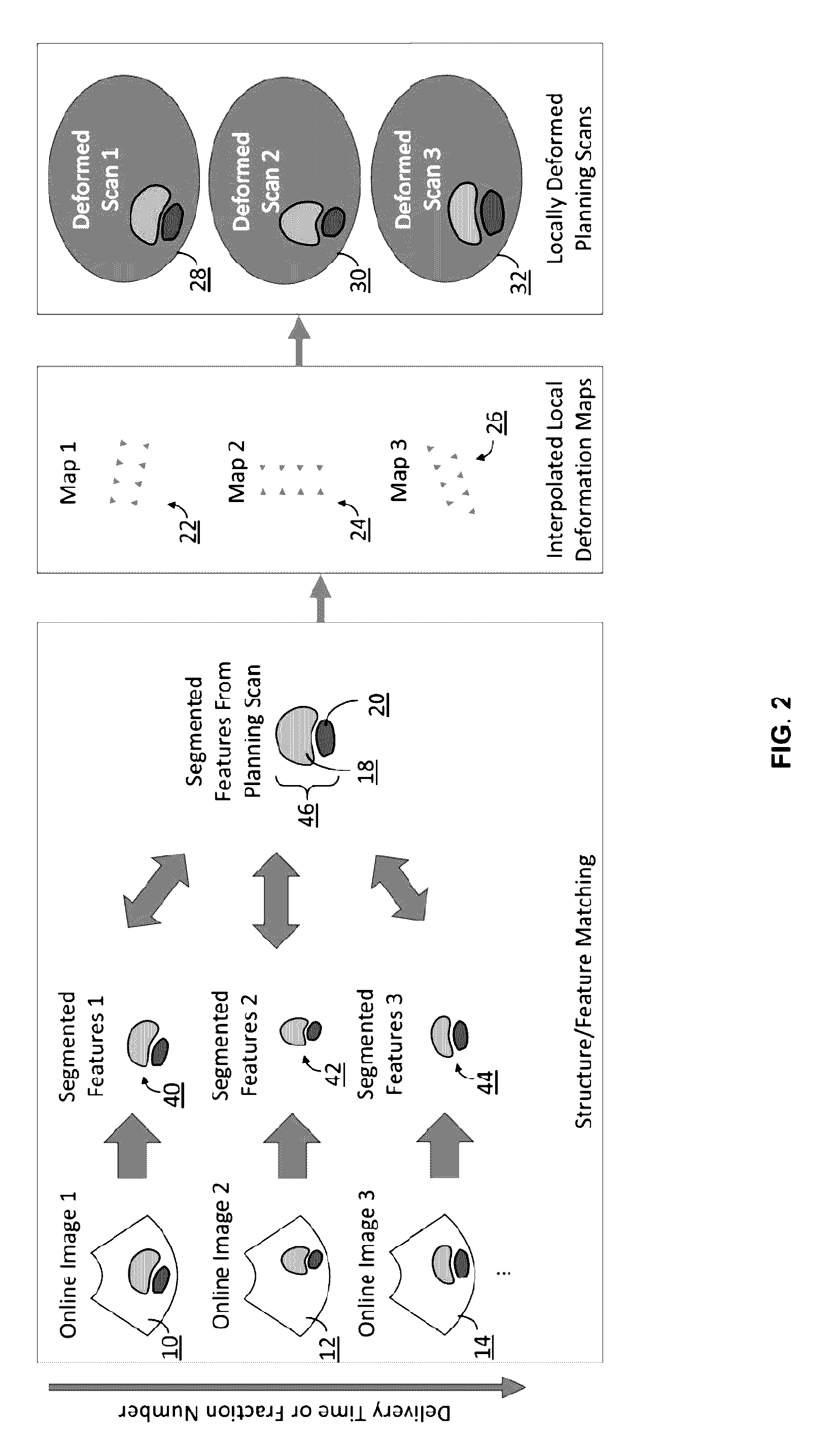
Radiotherapy dose assessment and adaption using online imaging
InactiveUS20160279444A1Improve representationUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingTreatment deliveryPlanned Dose
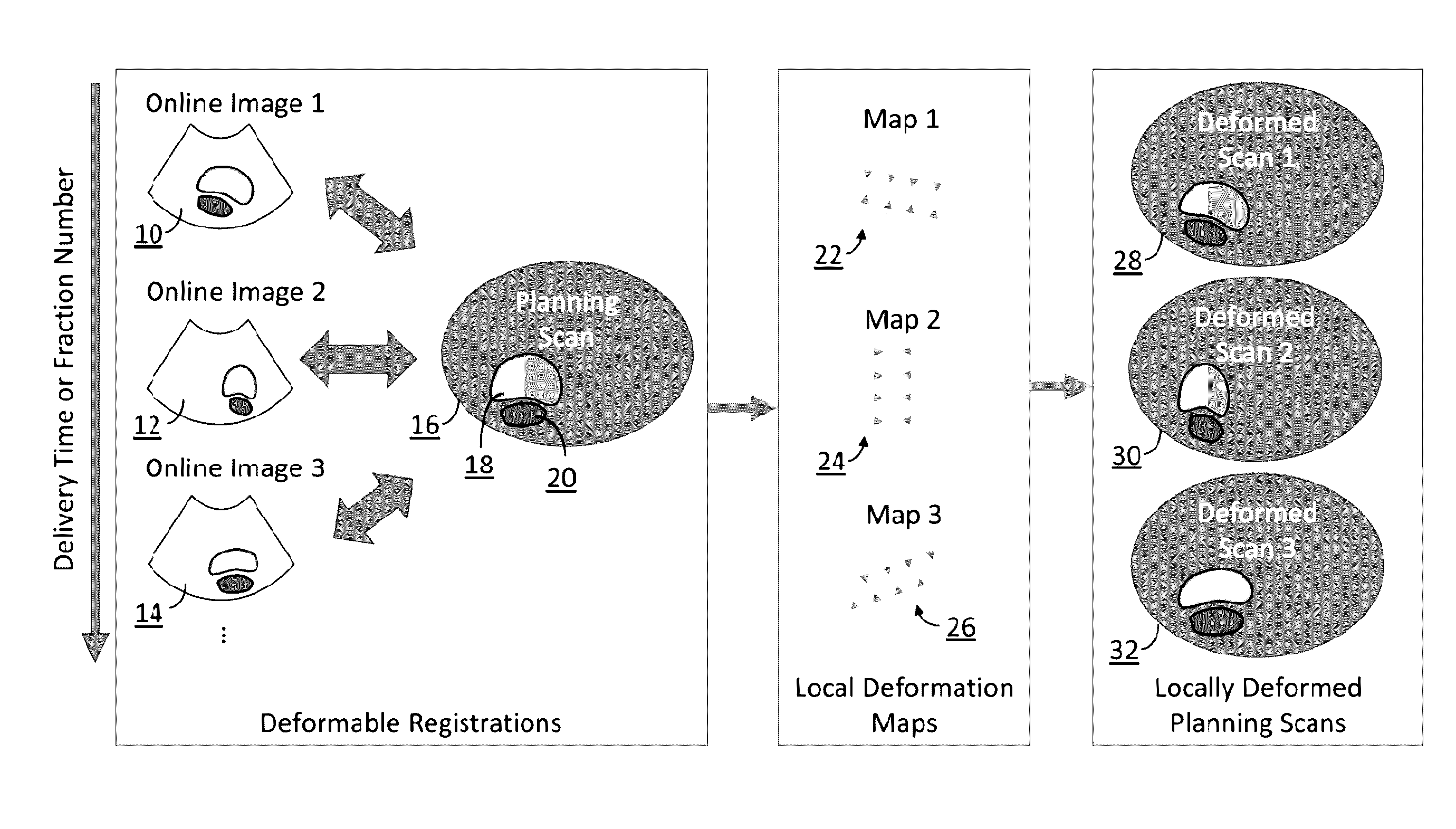
In external beam radiation therapy, a planning image (scan) of the patient is obtained prior to treatment as a basis for constructing a radiation delivery plan. However, since the planning scan is obtained prior to treatment (potentially days or weeks prior), it does not necessarily represent the state of the patient's anatomy as it presents at the time of treatment beam delivery. The potential mismatch between the patient's anatomy in the planning scan and anatomy at the time of treatment can result in dose discrepancies between the planned dose and the actual delivered dose. The methods herein describe the use of online images taken immediately before or during treatment delivery in order to predict, assess, and adapt to such discrepancies.
Owner:SONITRACK SYST
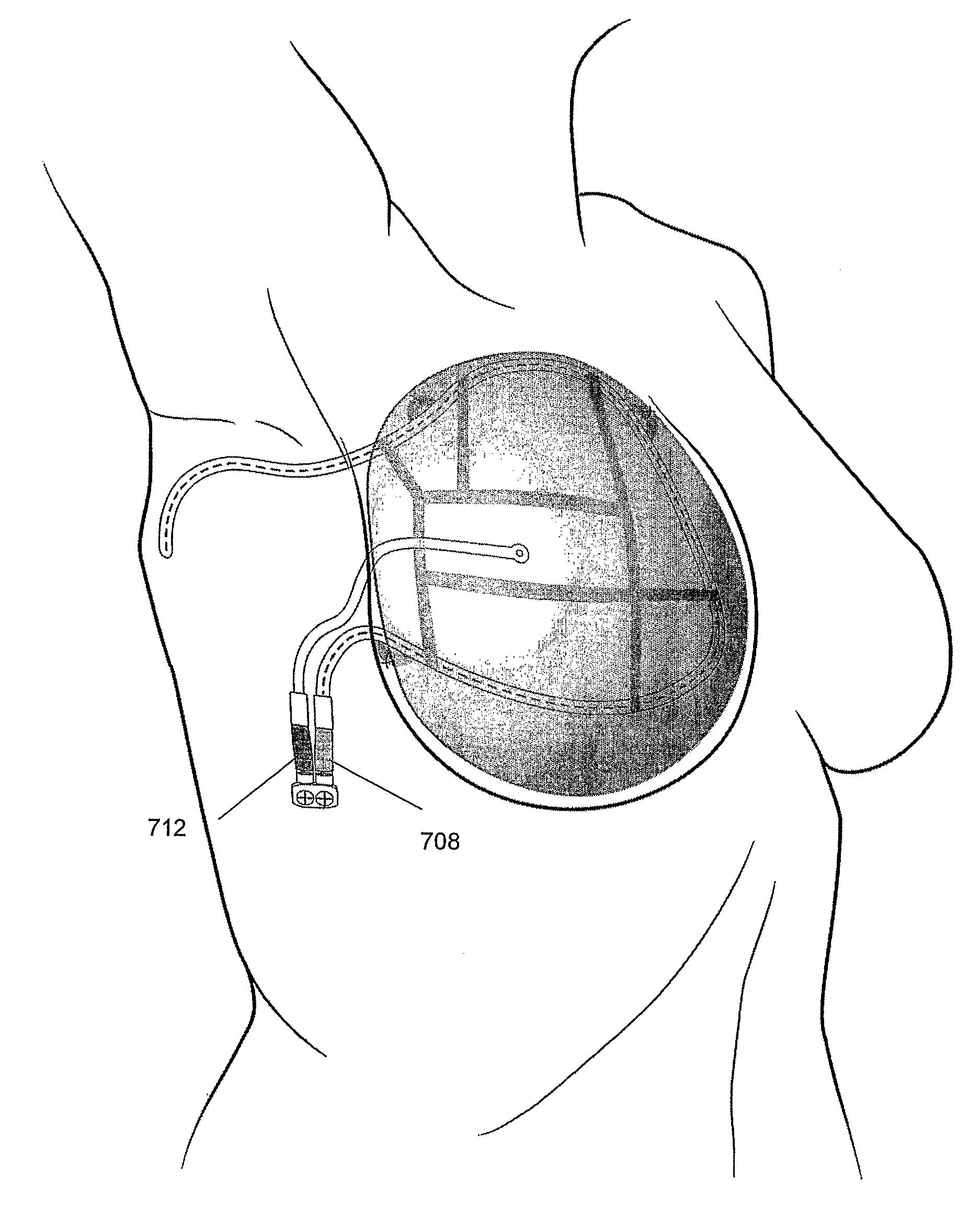
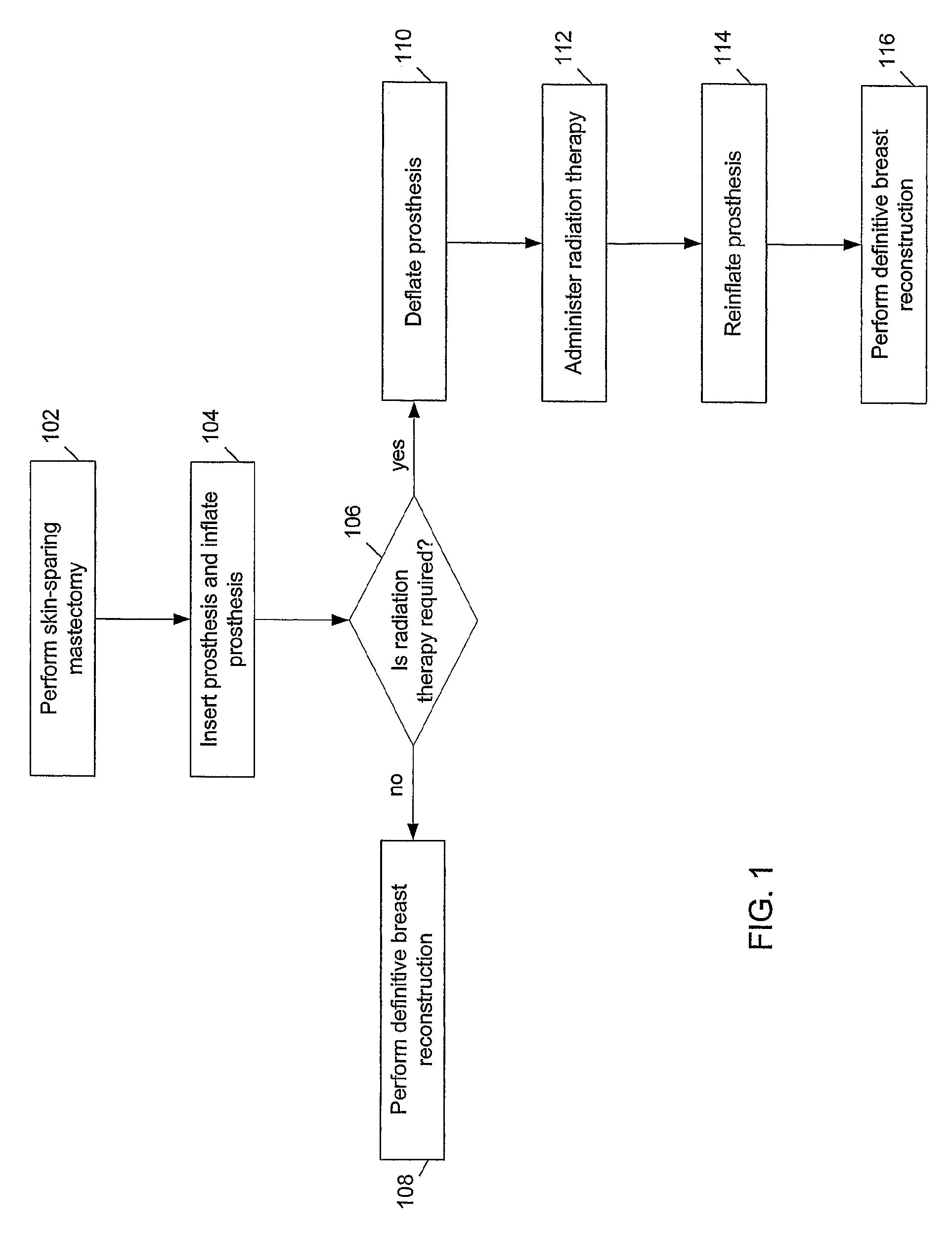
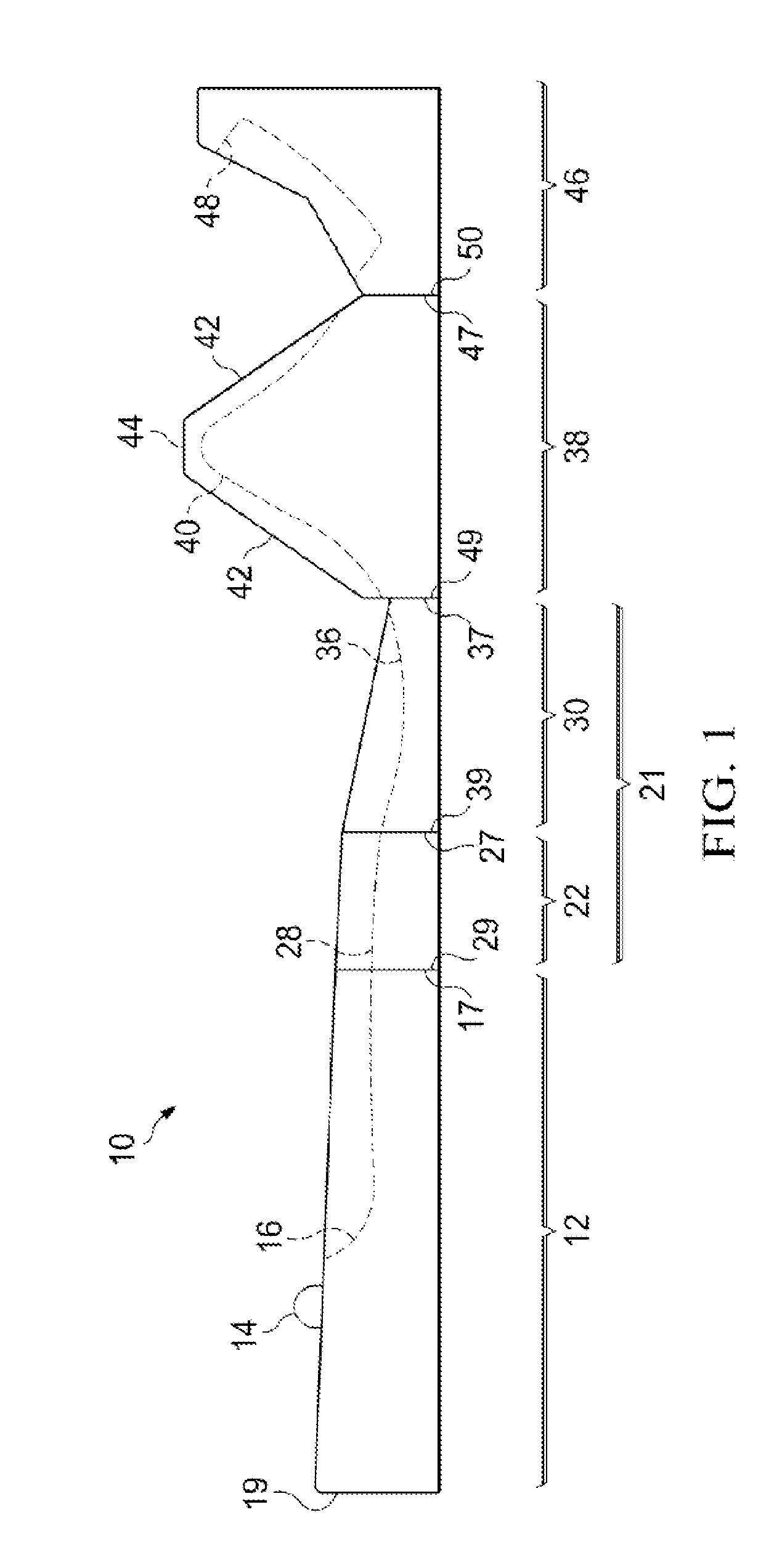
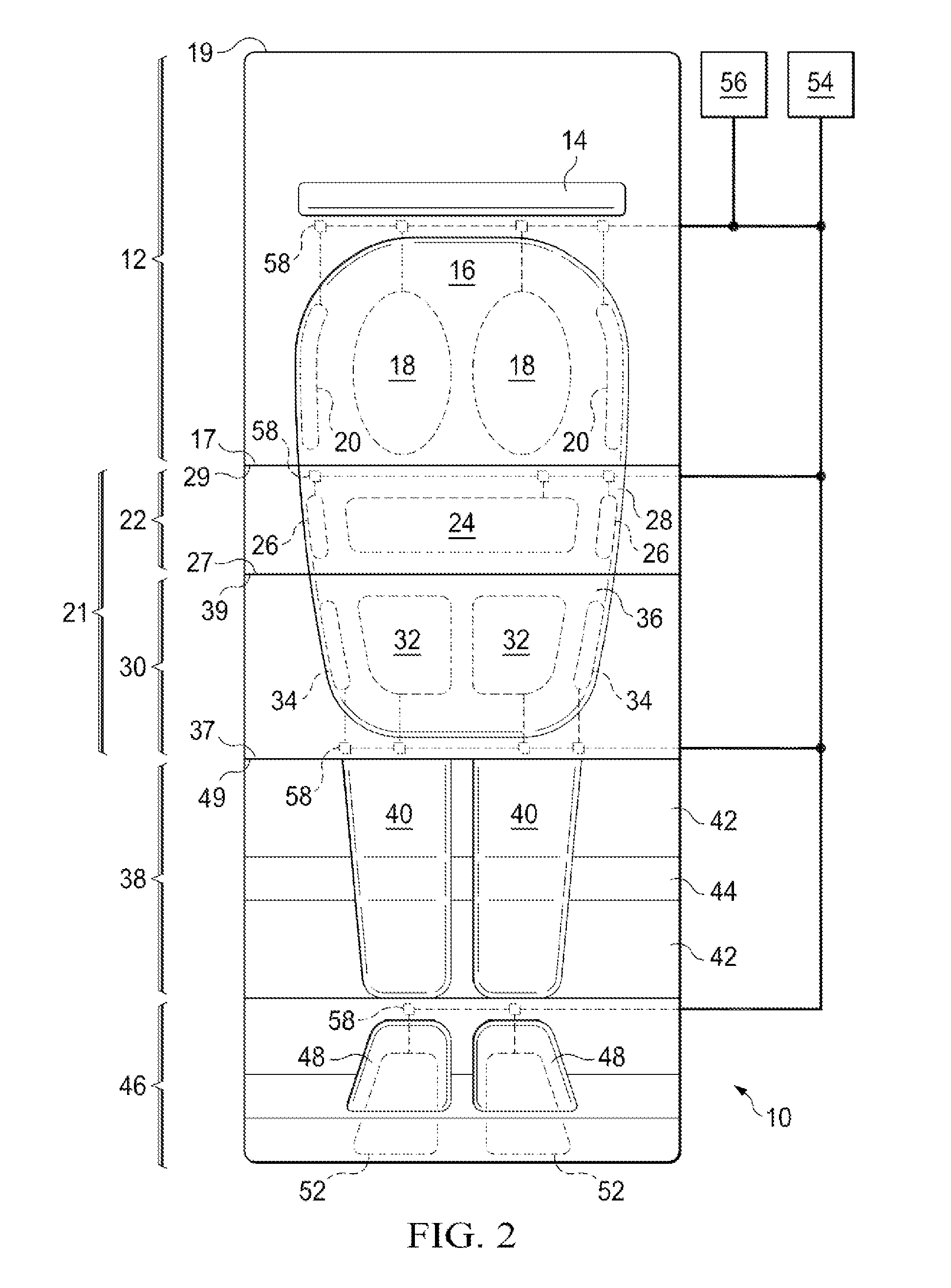
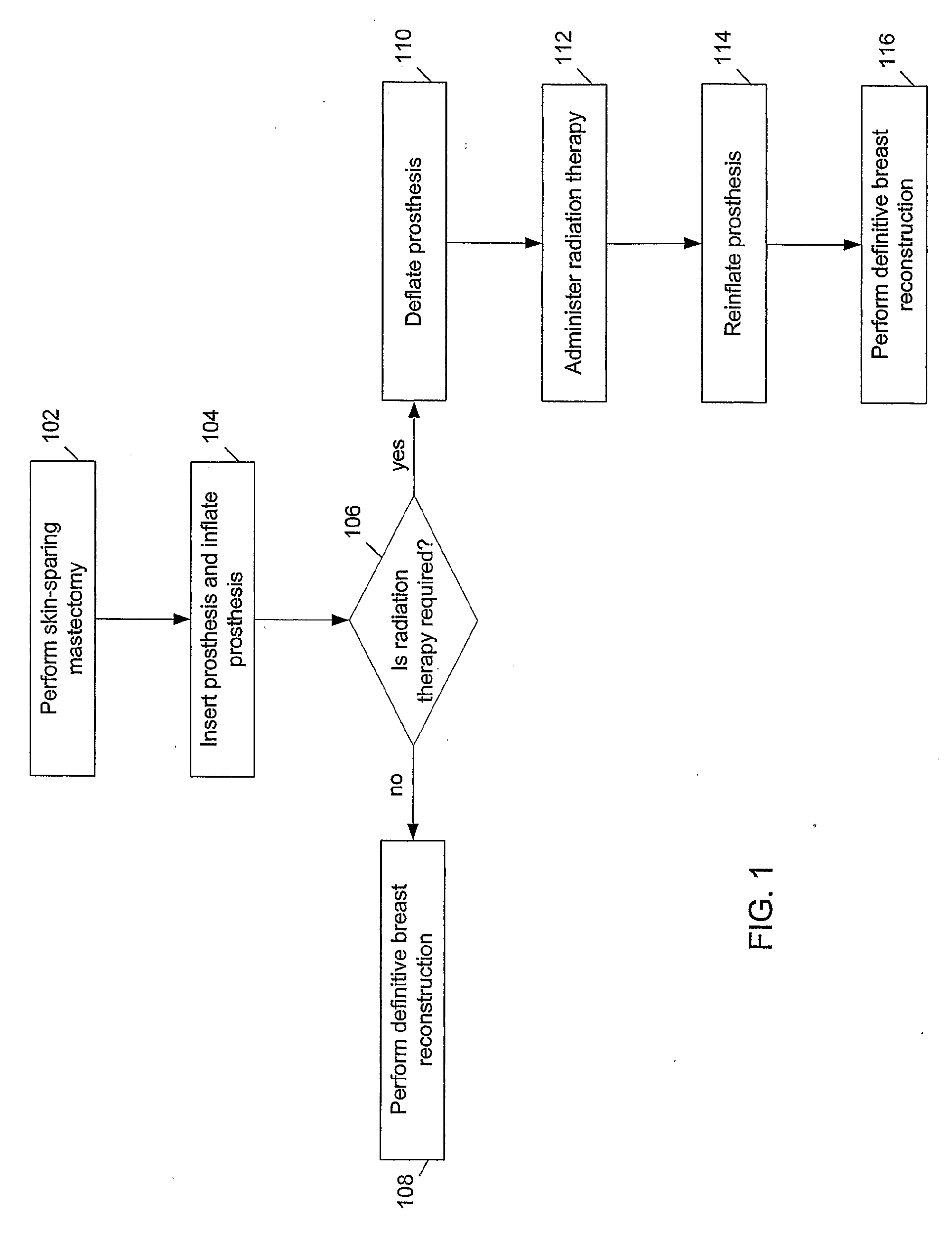
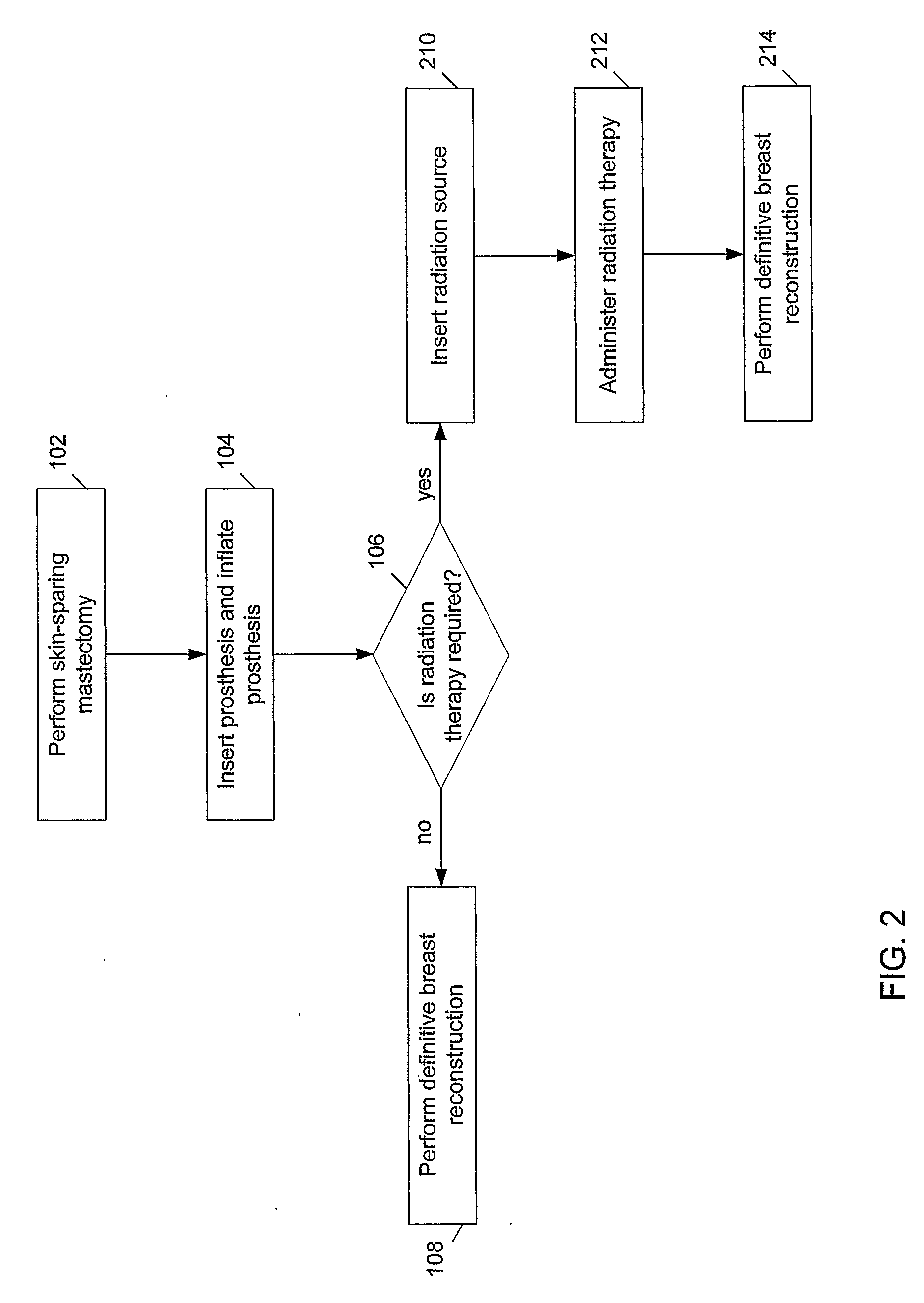
Methods and devices for breast reconstruction
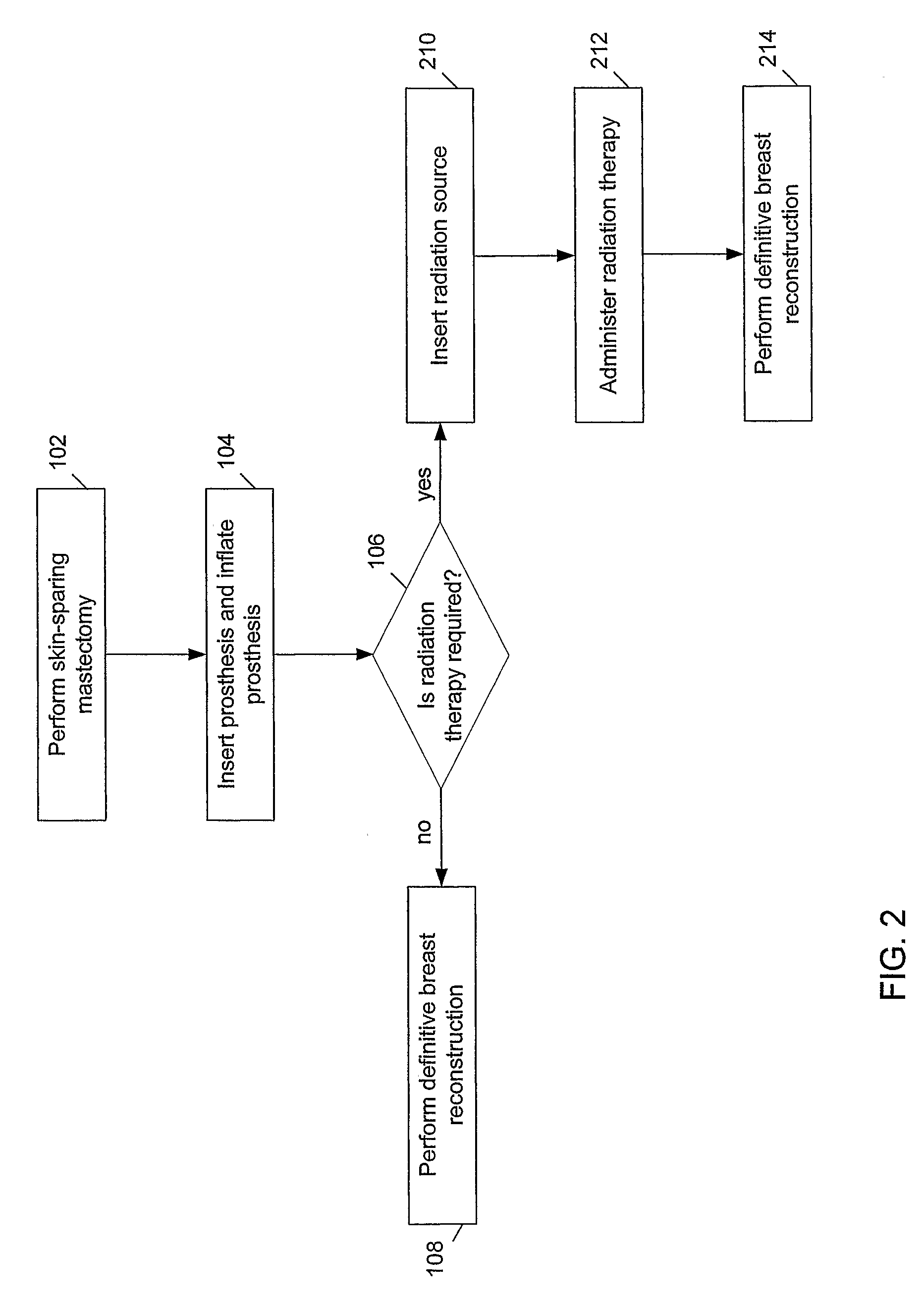
Methods for optimal breast reconstruction are disclosed. The methods include steps for performing a mastectomy that preserves a breast skin envelope. A prosthesis may be inserted into the breast and may be inflated to preserve the shape of the breast skin envelope. The prosthesis may include, a base, a balloon coupled to the base, where the balloon may be inflated to preserve the shape of the breast skin envelope. The prosthesis may also include tube coupled to port for filling the balloon to a predetermined volume. A needle-lock system, coupled to the port may be used to inject, for example, fluids into the balloon. If a patient requires post-mastectomy radiation, breast reconstruction may be delayed and the prosthesis may remain in the breast cavity during the treatment. The treatment may be external beam radiation. Alternatively, the treatment may include brachytherapy technique for treating the internal breast cavity.
Owner:KRONOWITZ STEVEN DR
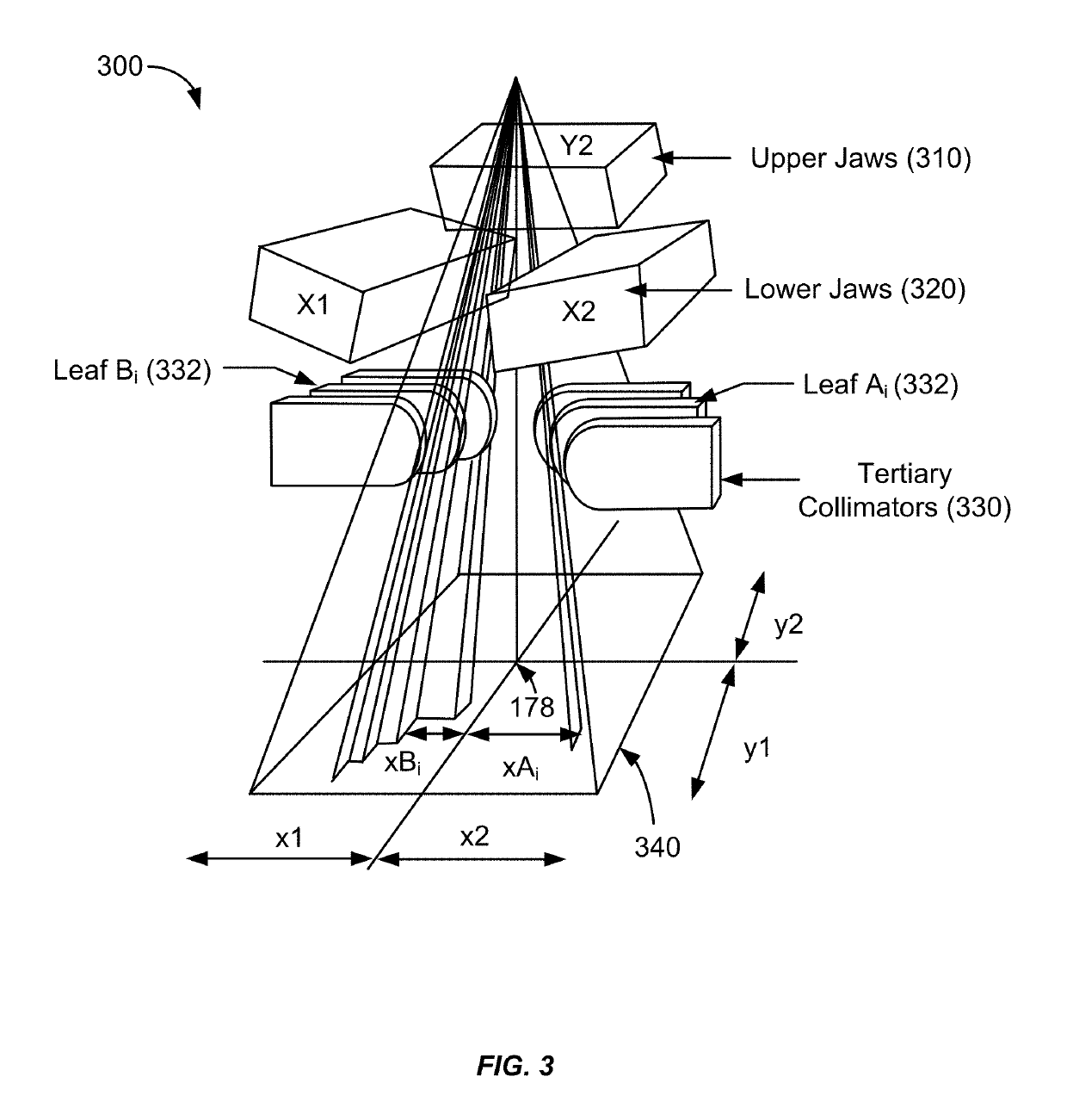
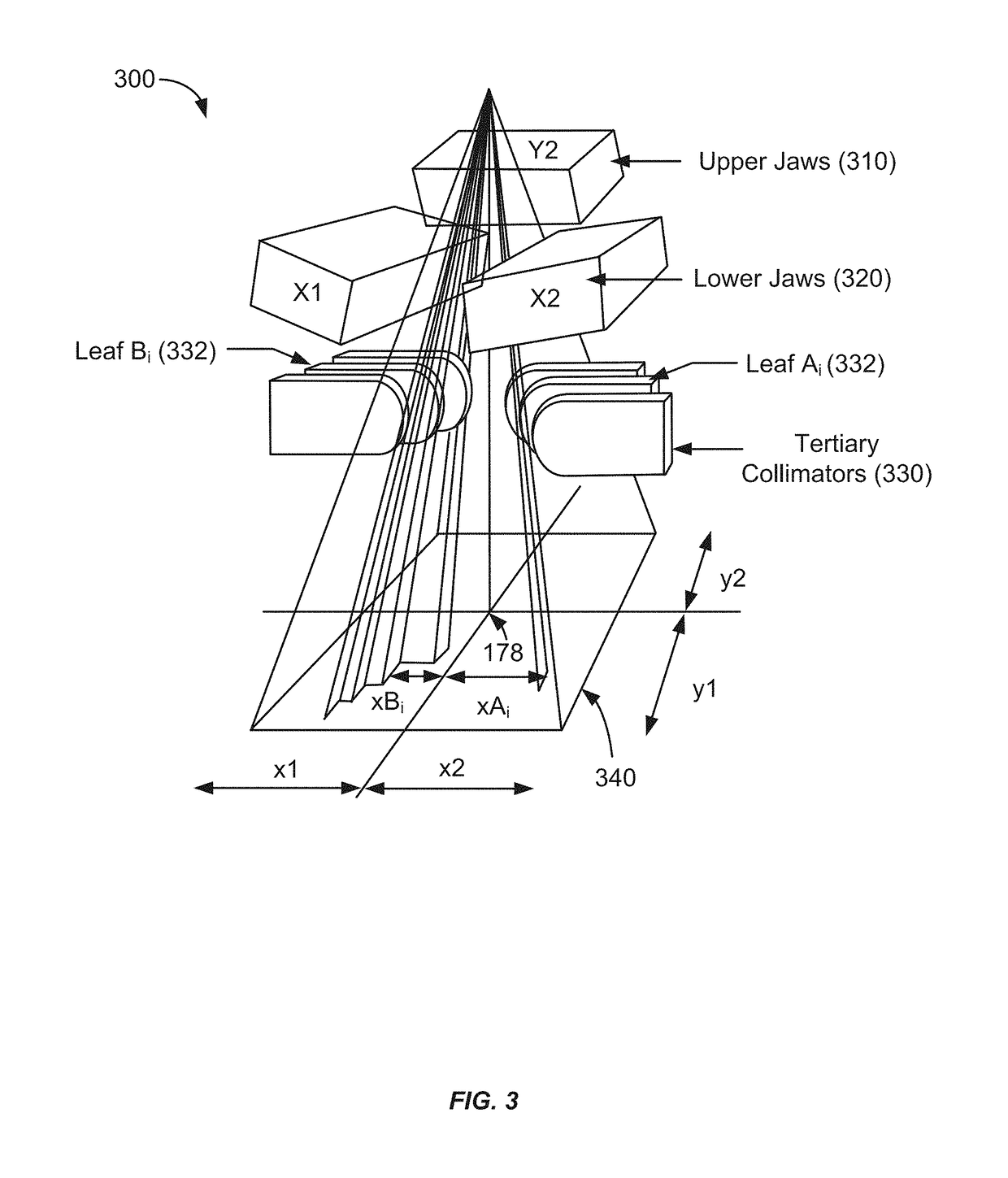
Controlling and shaping the dose distribution outside treatment targets in external-beam radiation treatments
ActiveUS20180078792A1Need for contouring control structures around each target can be reduced or eliminatedX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTreatment targetsNormal tissue
Streamlined and partially automated methods of setting normal tissue objectives in radiation treatment planning are provided. These methods may be applied to multiple-target cases as well as single-target cases. The methods can impose one or more target-specific dose falloff constraints around each target, taking into account geometric characteristics of each target such as target volume and shape. In some embodiments, methods can also take into account a planner's preferences for target dose homogeneity. In some embodiments, methods can generate additional dose falloff constraints in locations between two targets where dose bridging is likely to occur.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Optimization of radiation treatment plans for optimal treatment time in external-beam radiation treatments
An optimized radiation treatment plan may be developed in which the total monitor unit (MU) count is taken into account. A planner may specify a maximum treatment time. An optimization algorithm may convert the specified maximum treatment time to a maximum total MU count, which is then used as a constraint in the optimization process. A cost function for the optimization algorithm may include a term that penalizes any violation of the upper constraint for the MU count.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
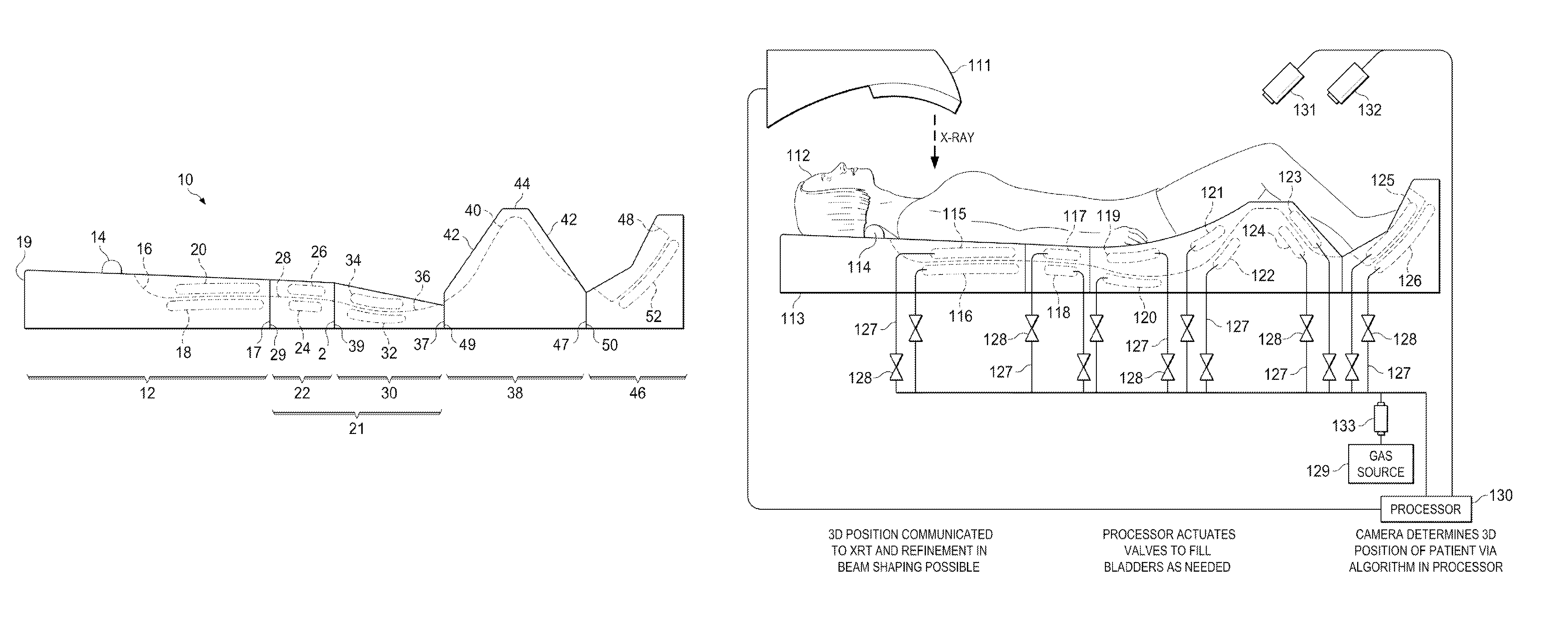
External immobilizer
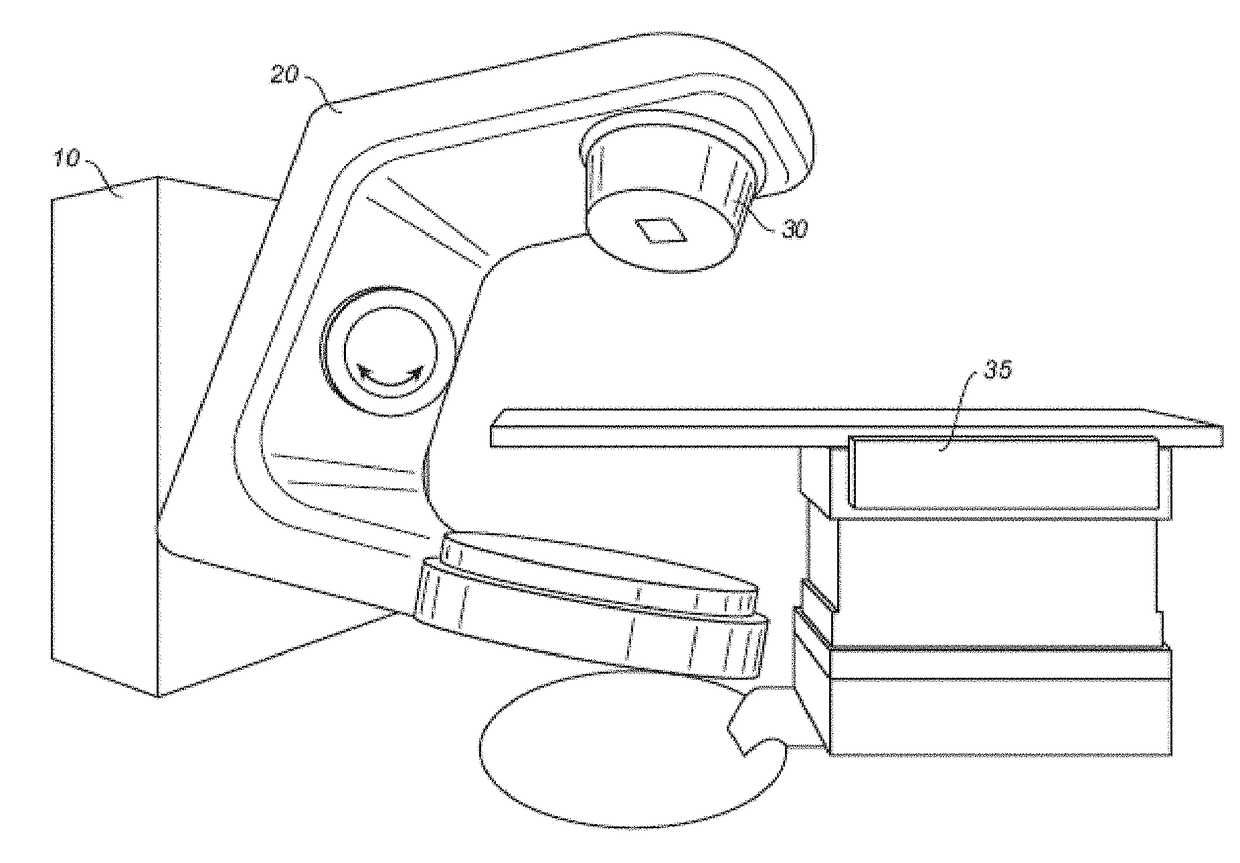
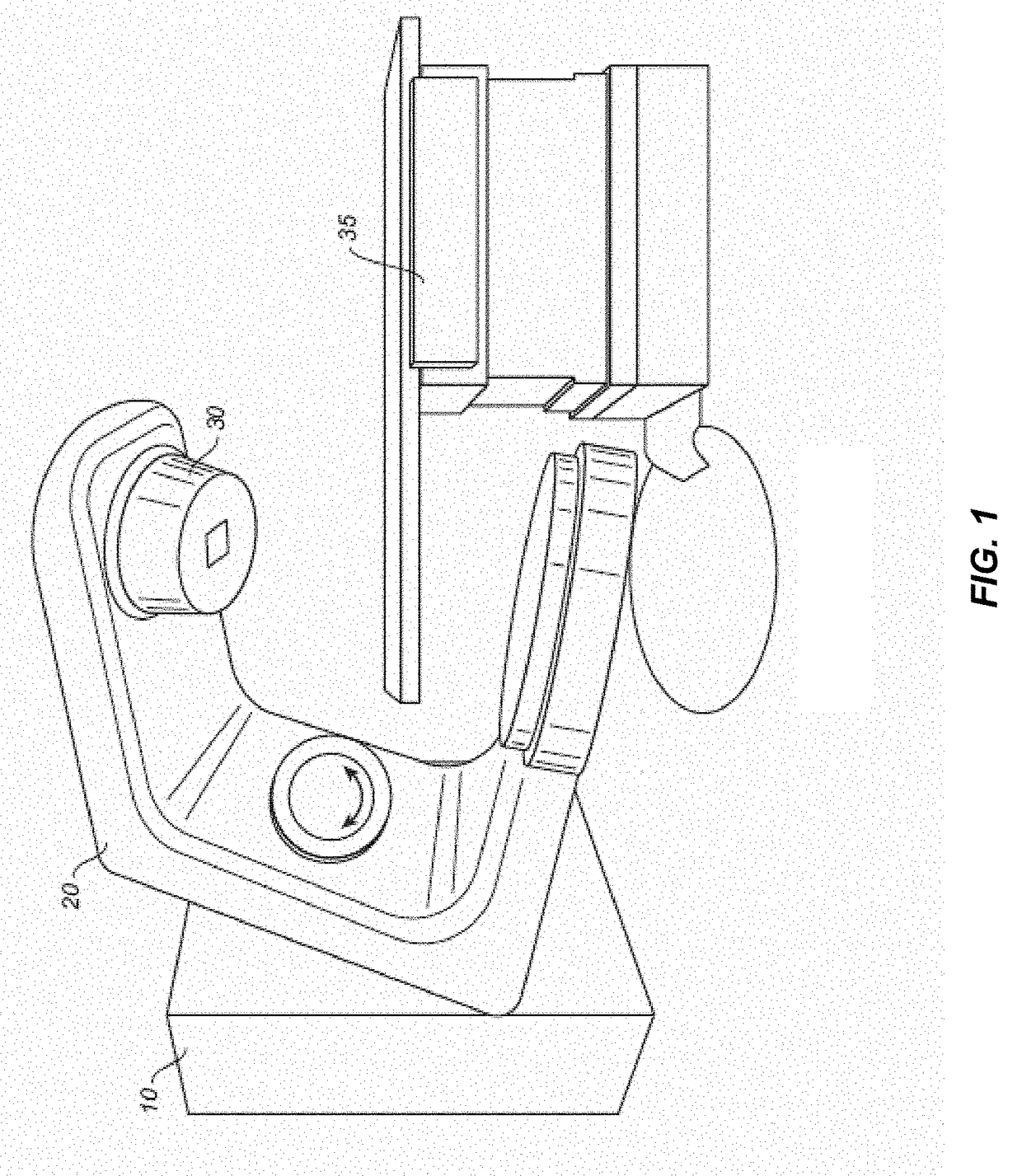
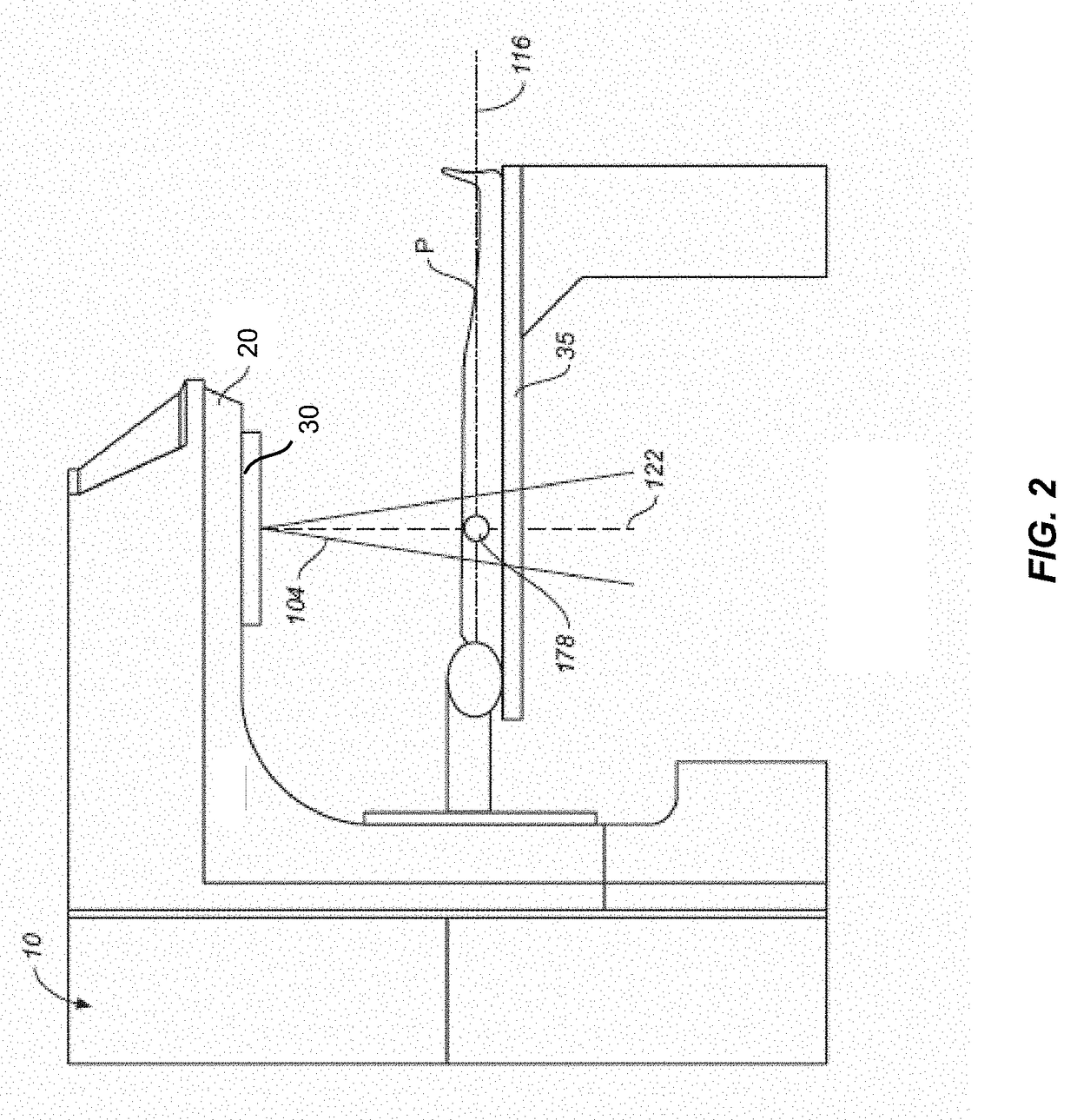
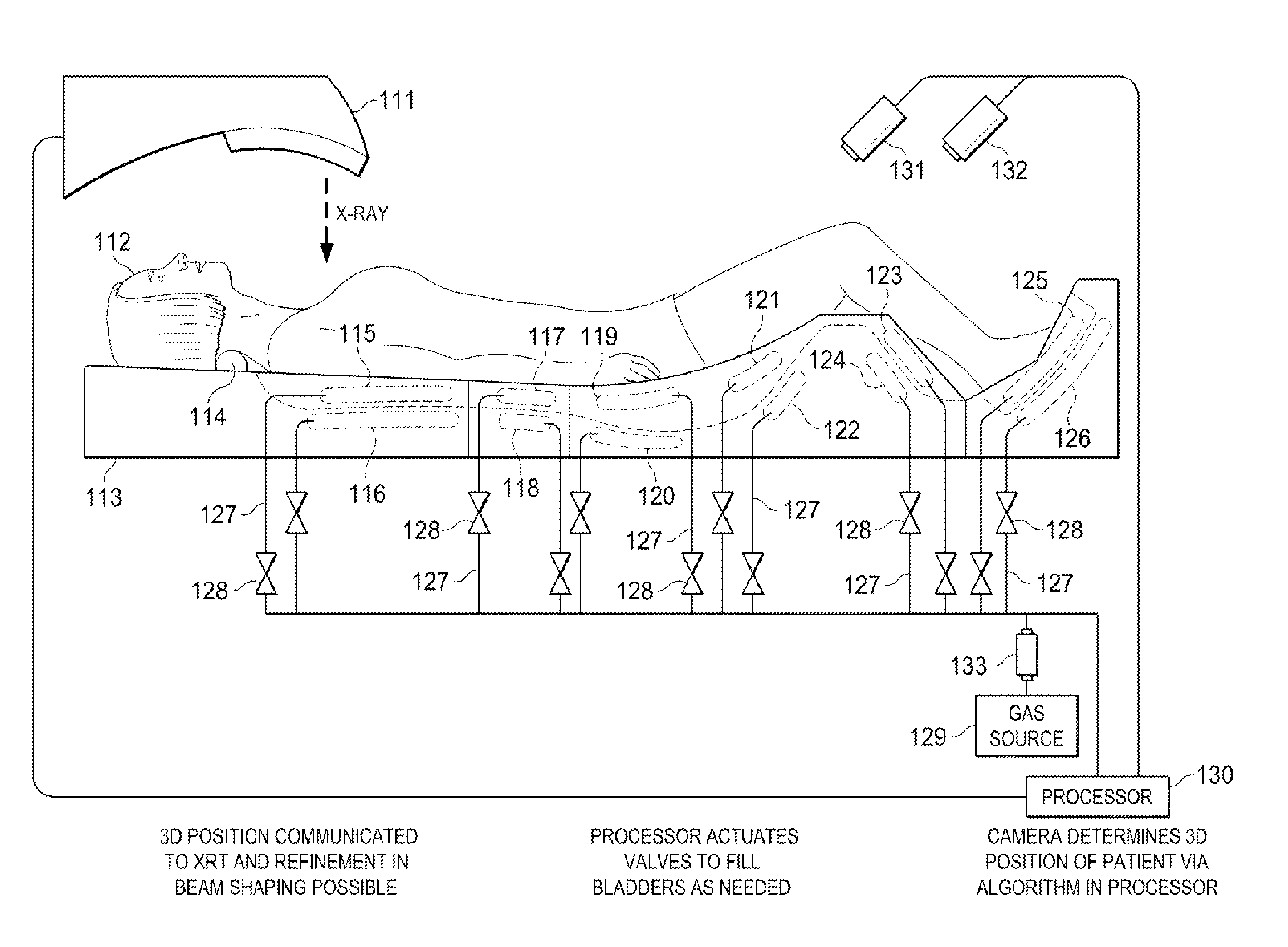
An external immobilizer for cancer treatment has a plurality of inflatable bladders that are independent finable depending on computer instruction based on patient position data provided from integrated or separate position determining means, such as external cameras or sensors, optionally with internal and / or external markers. In preferred embodiments, the immobilizer is fully integrated with an imaging means as well as the external beam radiation source, thus allowing both real time, independent anatomical compensation or correction for patient movement and fine control of beam shape and position to accurately target the tumor, even if the patient moves.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Methods and Devices for Breast Reconstruction
Methods for optimal breast reconstruction are disclosed. The methods include steps for performing a mastectomy that preserves a breast skin envelope. A prosthesis may be inserted into the breast and may be inflated to preserve the shape of the breast skin envelope. The prosthesis may include, a base, a balloon coupled to the base, where the balloon may be inflated to preserve the shape of the breast skin envelope. The prosthesis may also include tube coupled to port for filling the balloon to a predetermined volume. A needle-lock system, coupled to the port may be used to inject, for example, fluids into the balloon. If a patient requires post-mastectomy radiation, breast reconstruction may be delayed and the prosthesis may remain in the breast cavity during the treatment. The treatment may be external beam radiation. Alternatively, the treatment may include brachytherapy technique for treating the internal breast cavity.
Owner:KRONOWITZ STEVEN DR
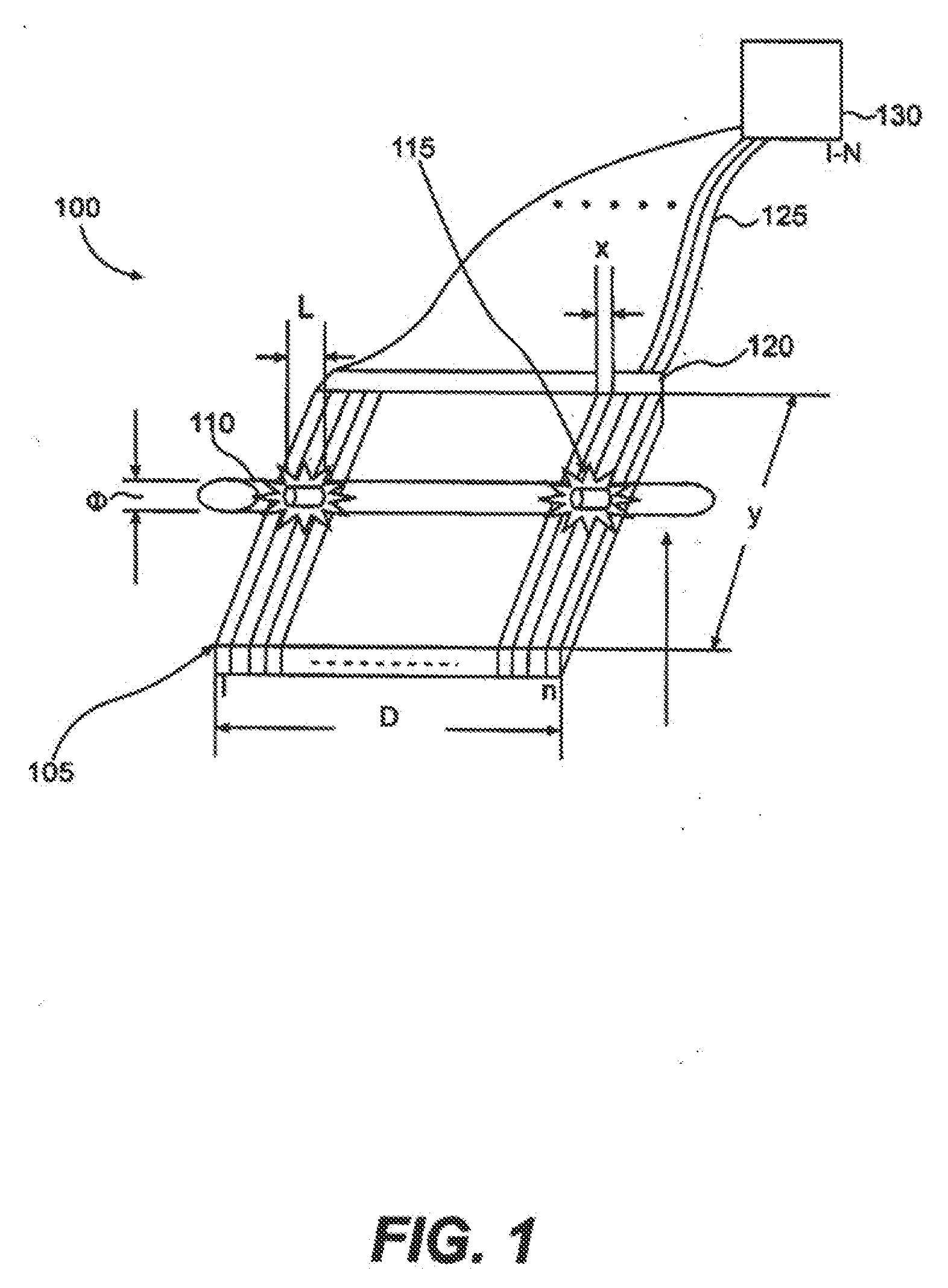
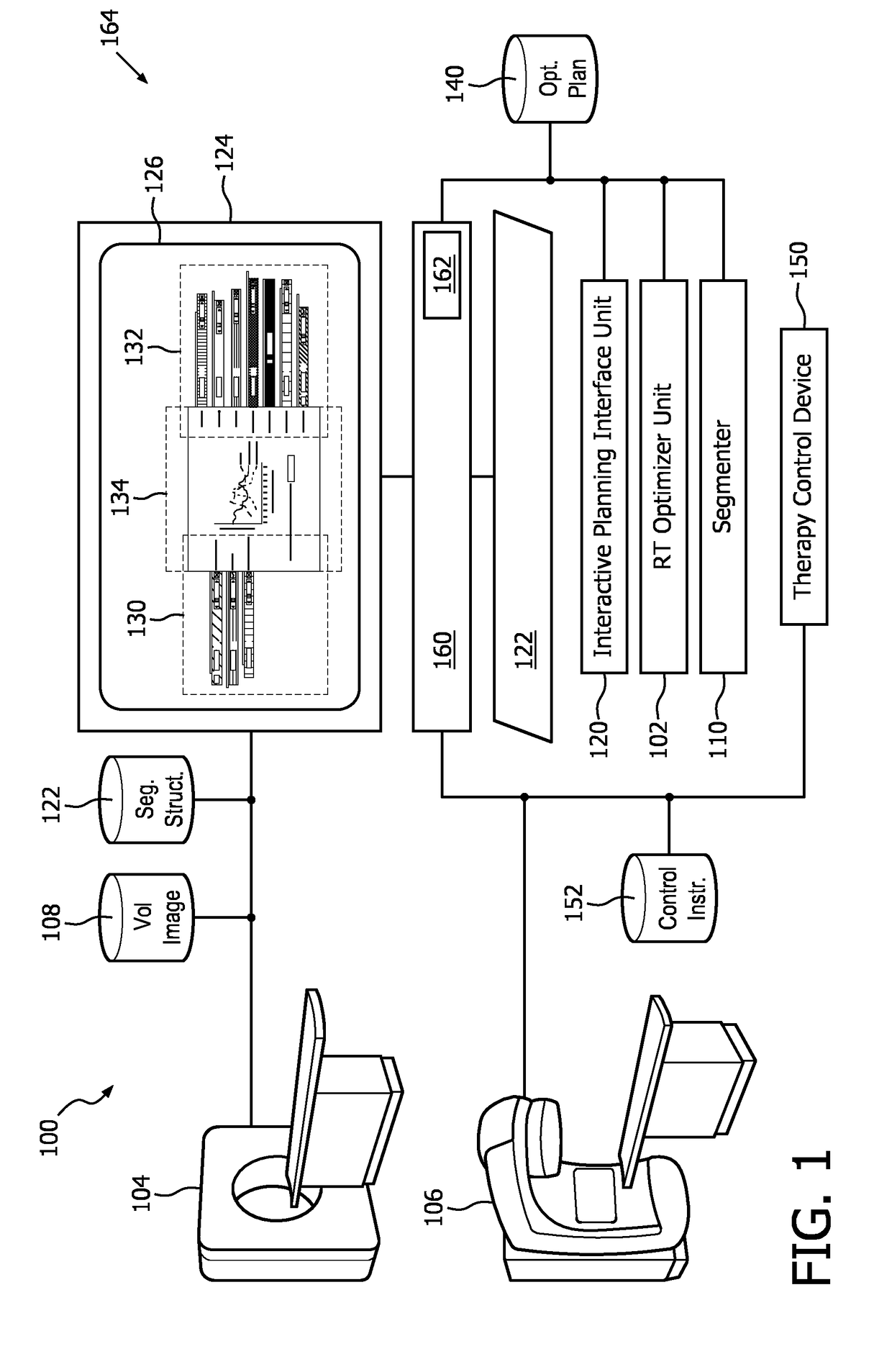
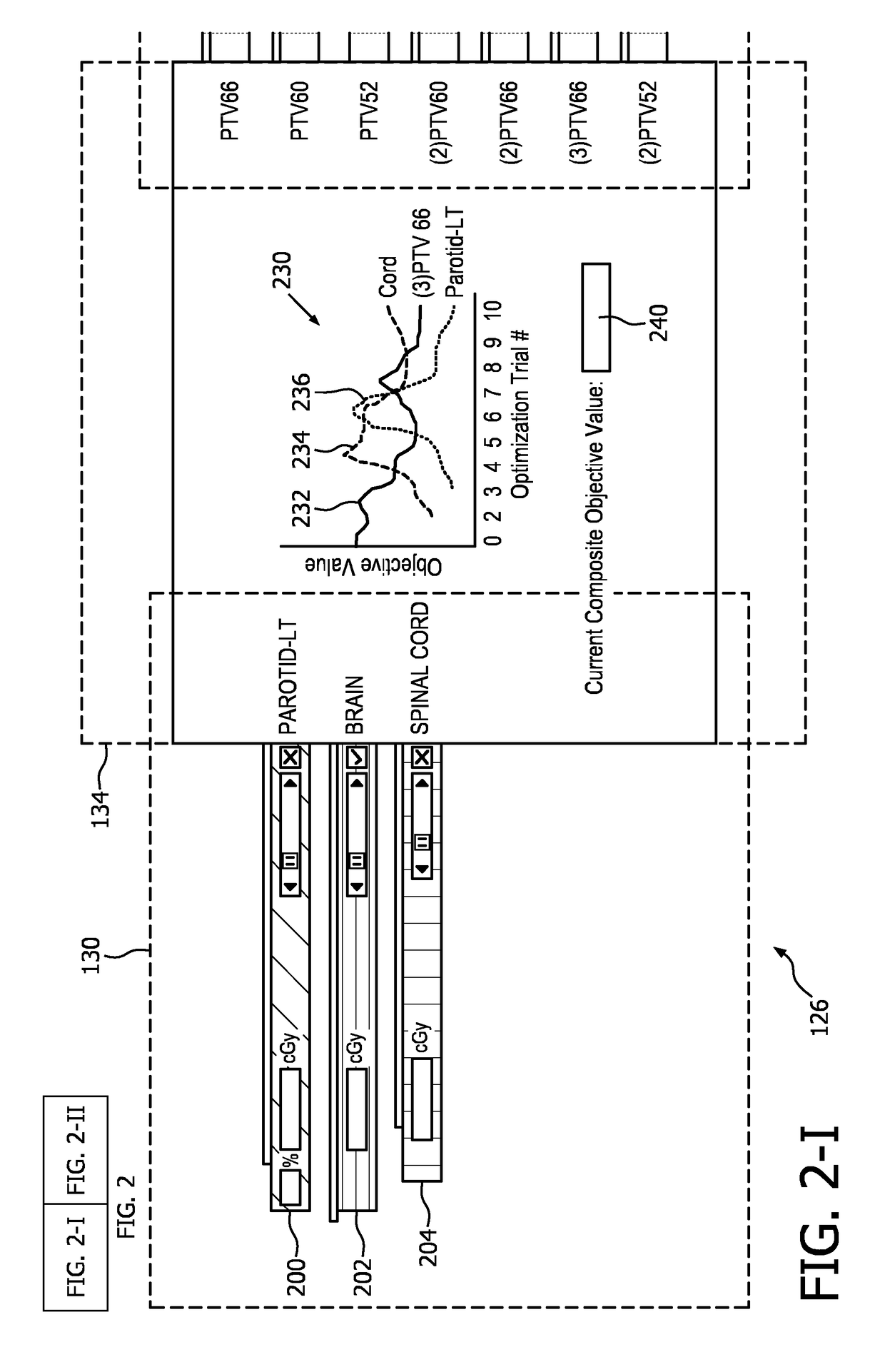
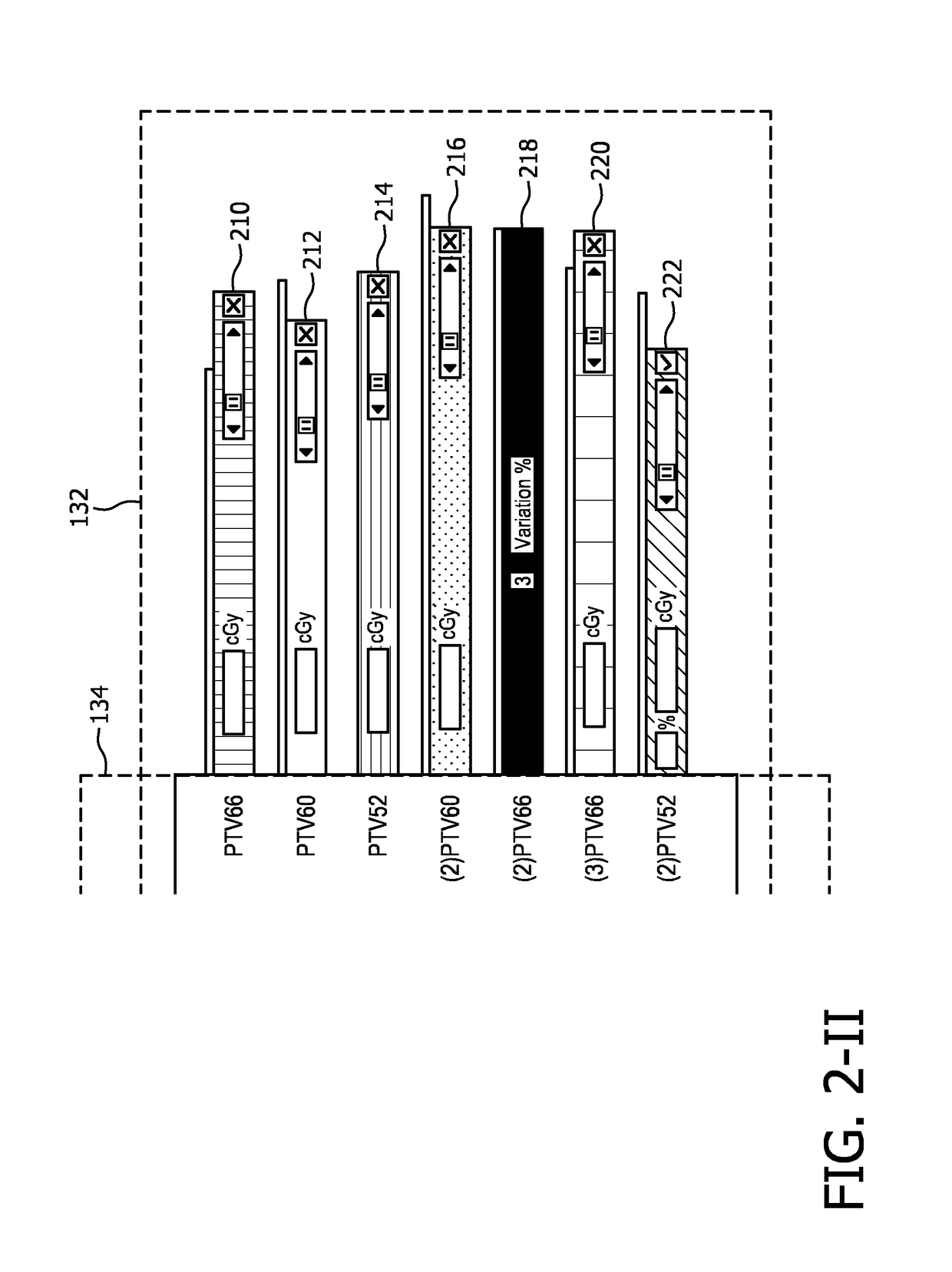
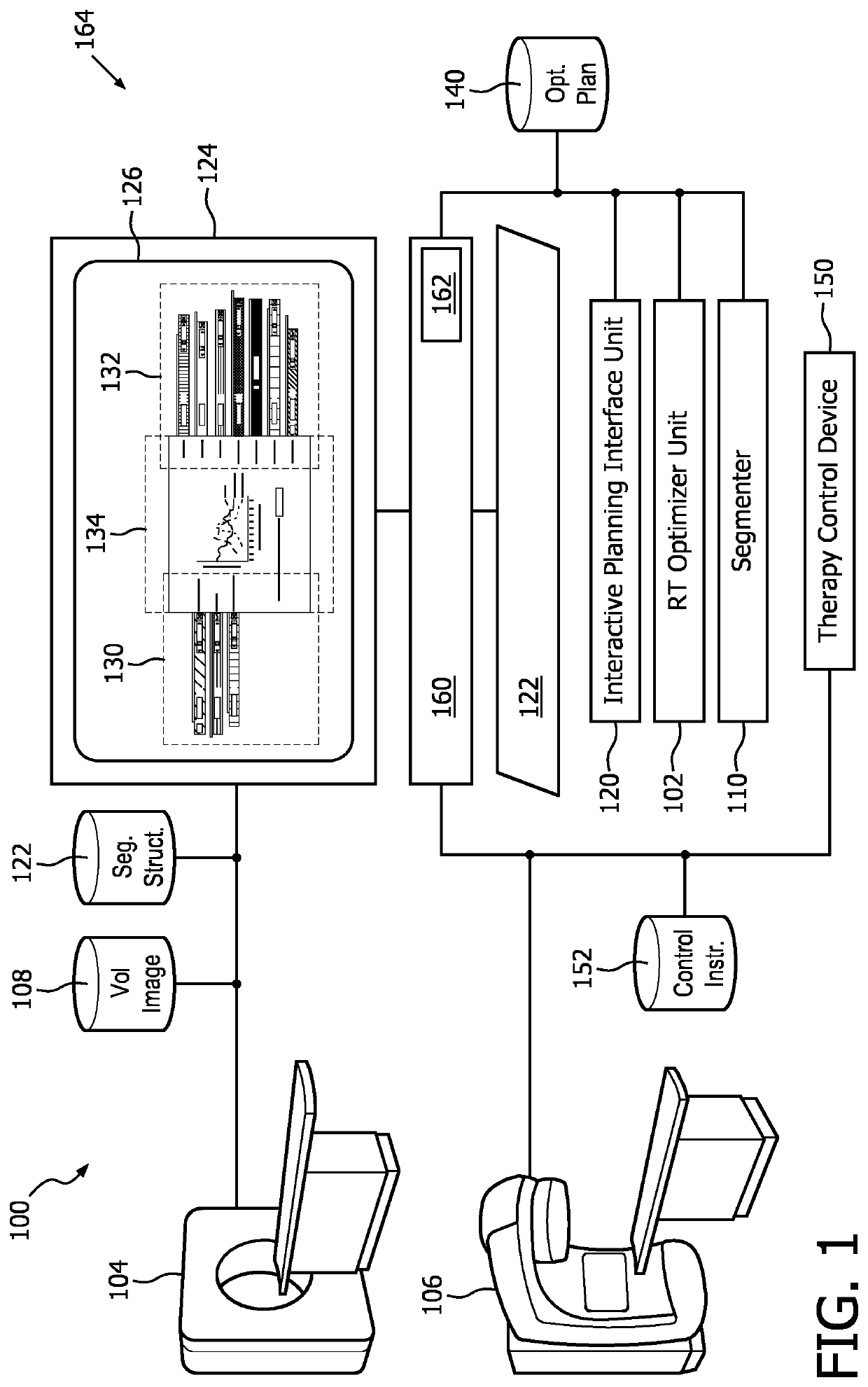
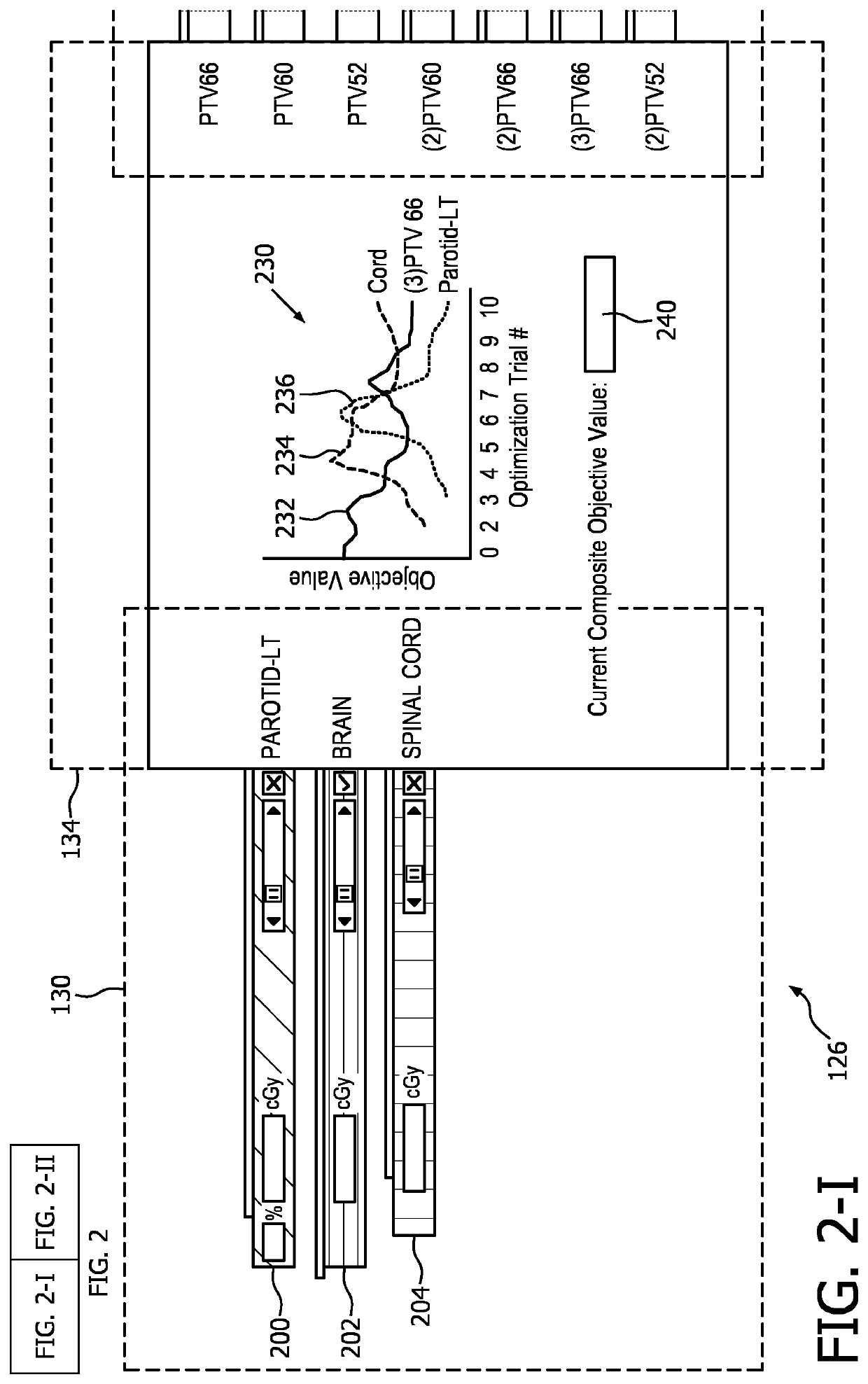
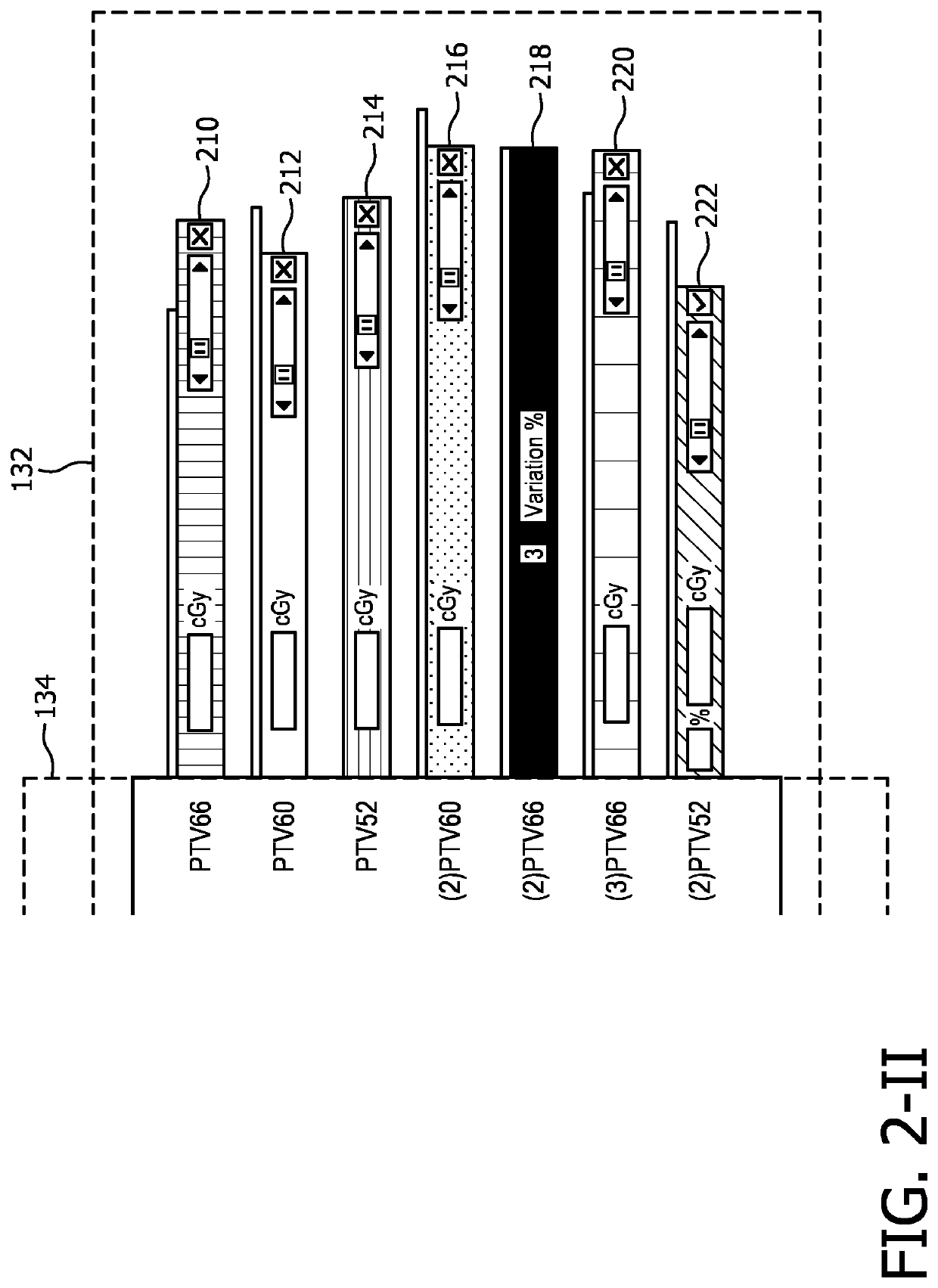
Radiation therapy interactive planning
A radiation therapy system (100) includes a radiation therapy (RT) optimizer unit (102) and an interactive planning interface unit (120). The RT optimizer unit (102) receives at least one target structure and at least one organ-at-risk (OAR) structure segmented from a volumetric image (108), and generates an optimized RT plan (140) based on dose objectives (200-204, 210-222, 320), at least one dose objective of the dose objectives corresponding to each of the at least one target structure (210-222) and the at least one OAR structure (200-204). The optimized RT plan includes a planned radiation dose for each voxel of the volumetric image using external beam radiation therapy, wherein the RT optimizer unit operates iteratively. The interactive planning interface unit (120) interactively controls each of the dose objectives through controls (300) displayed on a single display (126) of a display device (124), operates the RT optimizer unit to iteratively compute the planned radiation dose according to the controls, and provide visual feedback (310, 134) on the single display according to progress of the RT optimizer unit after each trial.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Generating time-efficient treatment field trajectories for external-beam radiation treatments
ActiveUS10272264B2X-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTreatment field
In a radiation treatment plan that includes a plurality of treatment fields of multiple treatment modalities, such as IMRT modality and dynamic treatment path modality (e.g., VMAT and conformal arc therapy), an optimized spatial point sequence may be determined that optimizes the total treatment time, which includes both the beam-on time (i.e., during the delivery of radiation dose) and the beam-off time (i.e., during transitions between consecutive treatment fields). The result is a time-ordered field trajectory that intermixes and interleaves different treatment fields. In one embodiment, a dynamic treatment path may be cut into a plurality of sections, and one or more IMRT fields may be inserted between the plurality of sections.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Optimization of radiation treatment plans for optimal treatment time in external-beam radiation treatments
An optimized radiation treatment plan may be developed in which the total monitor unit (MU) count is taken into account. A planner may specify a maximum treatment time. An optimization algorithm may convert the specified maximum treatment time to a maximum total MU count, which is then used as a constraint in the optimization process. A cost function for the optimization algorithm may include a term that penalizes any violation of the upper constraint for the MU count.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
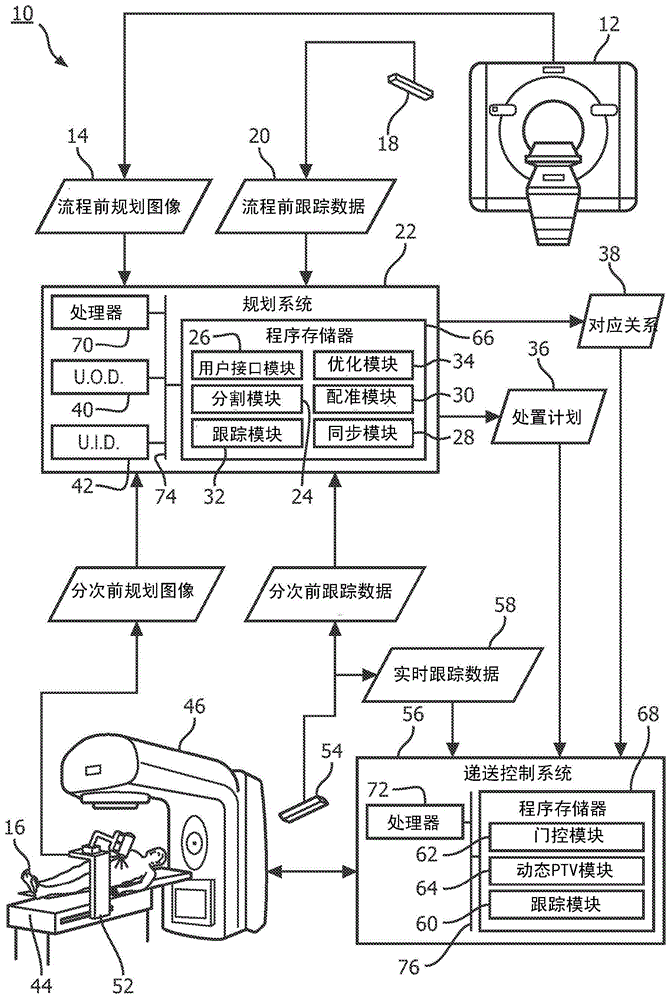
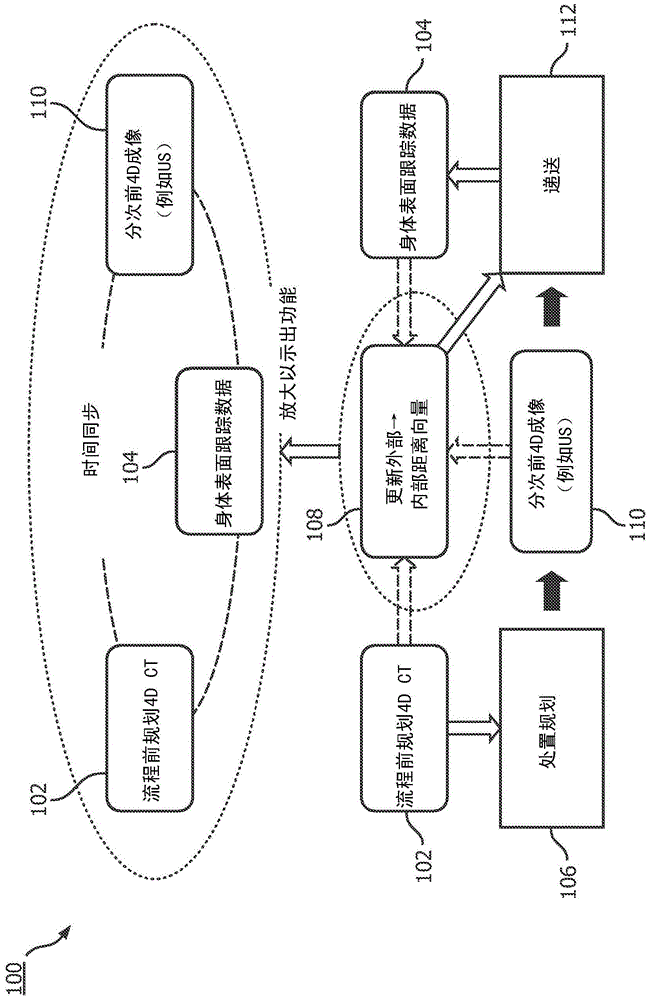
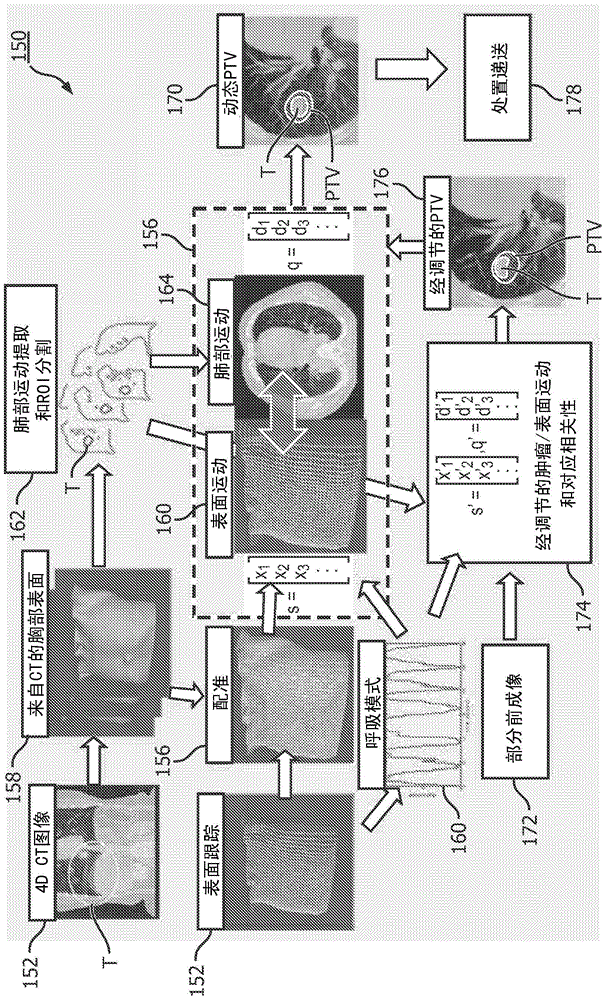
Method for improved surface tracking-based motion management and dynamic planning in adaptive external beam radiation therapy
ActiveCN105102062ASmall doseFull doseRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDynamic planningSelf adaptive
A therapy system and method treats an internal target of a patient (16). A treatment plan (36) is received to treat the internal target. The treatment plan (36) includes a plurality of treatment fractions including correspondences (38) between the internal target and an external body surface based on a pre-procedural planning image (14) and pre- procedural tracking data (20). Before selected treatment fractions of the plurality of treatment fractions, a pre-fraction planning image (50) of the target is received, tracking data (20, 52) of the external body surface of the patient (16) is received, and the correspondences (38) between the internal target and the external body surface are updated based on the received pre-fraction planning image (50) and the received tracking data (20, 52). Therapy is delivered to the patient (16) in accordance with the treatment plan (36) and using the updated correspondences (38).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
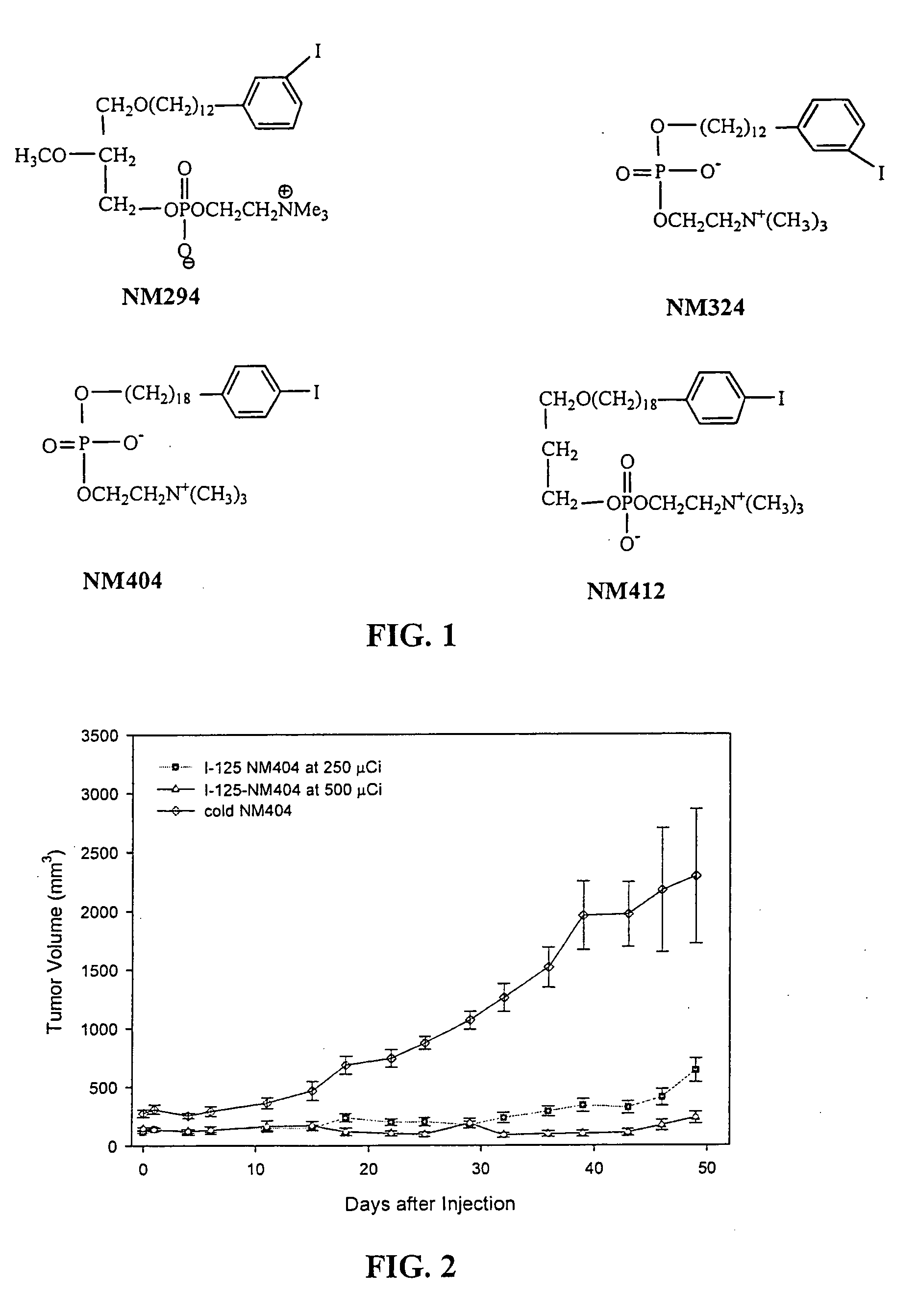
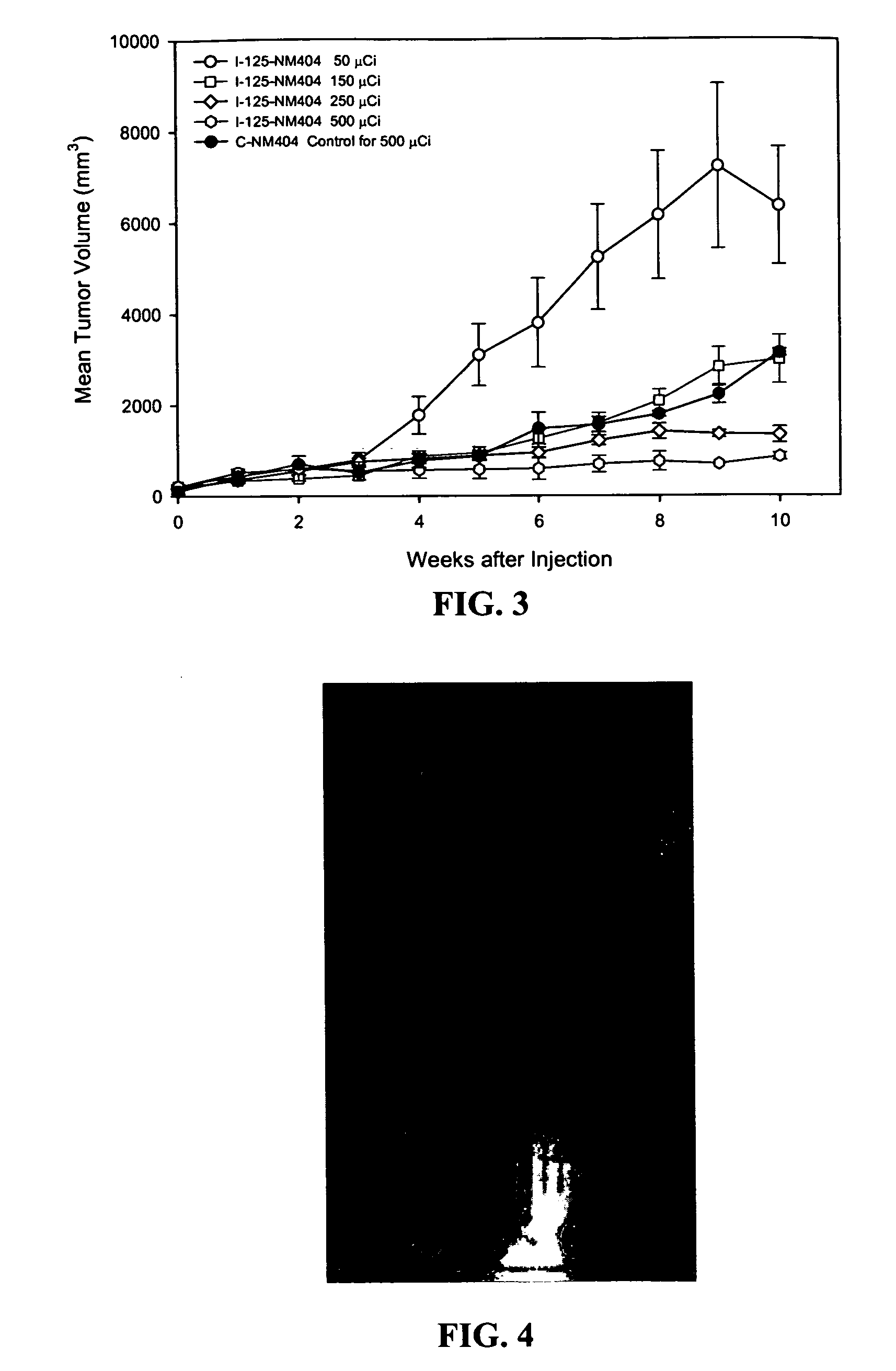
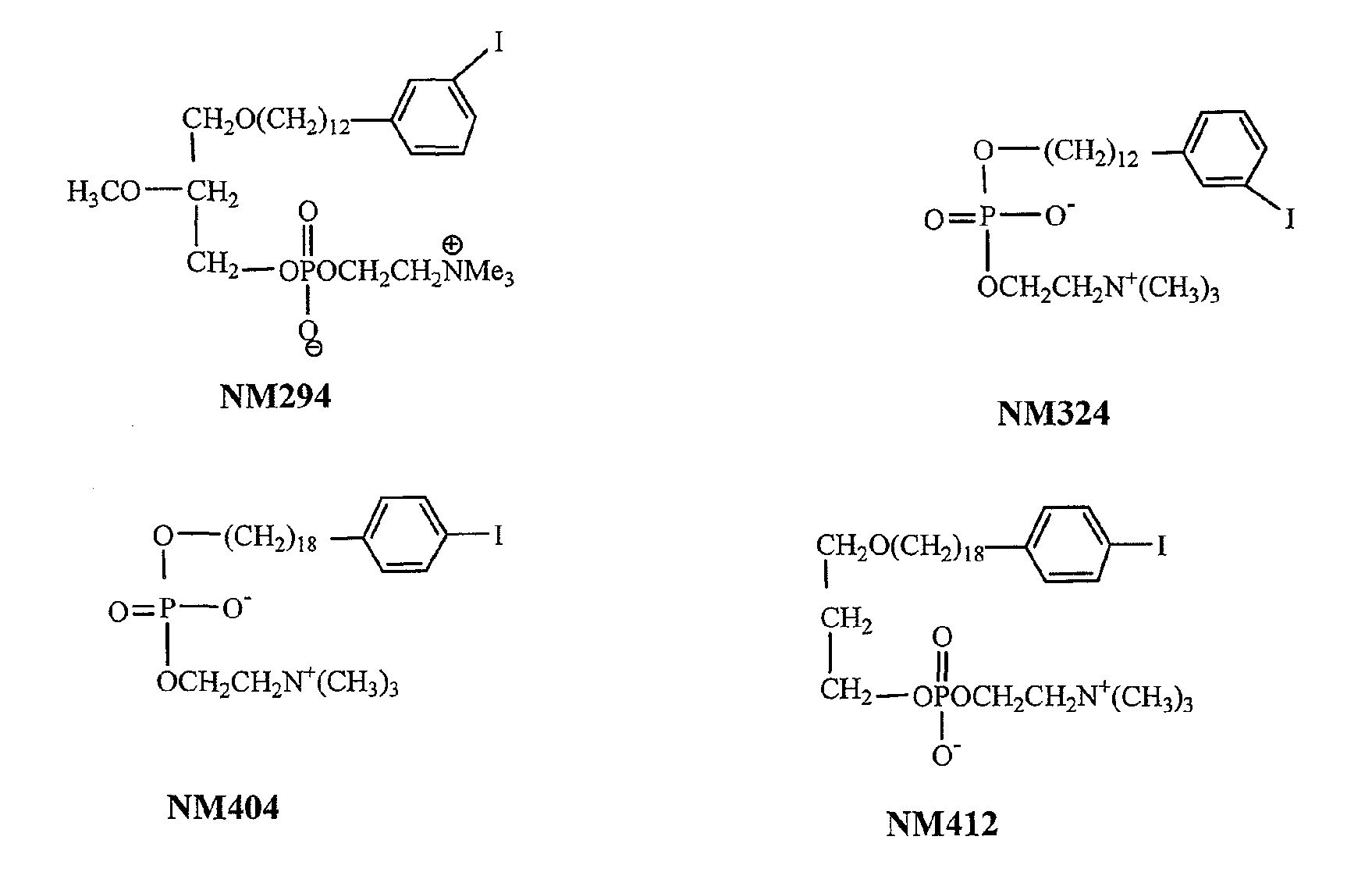
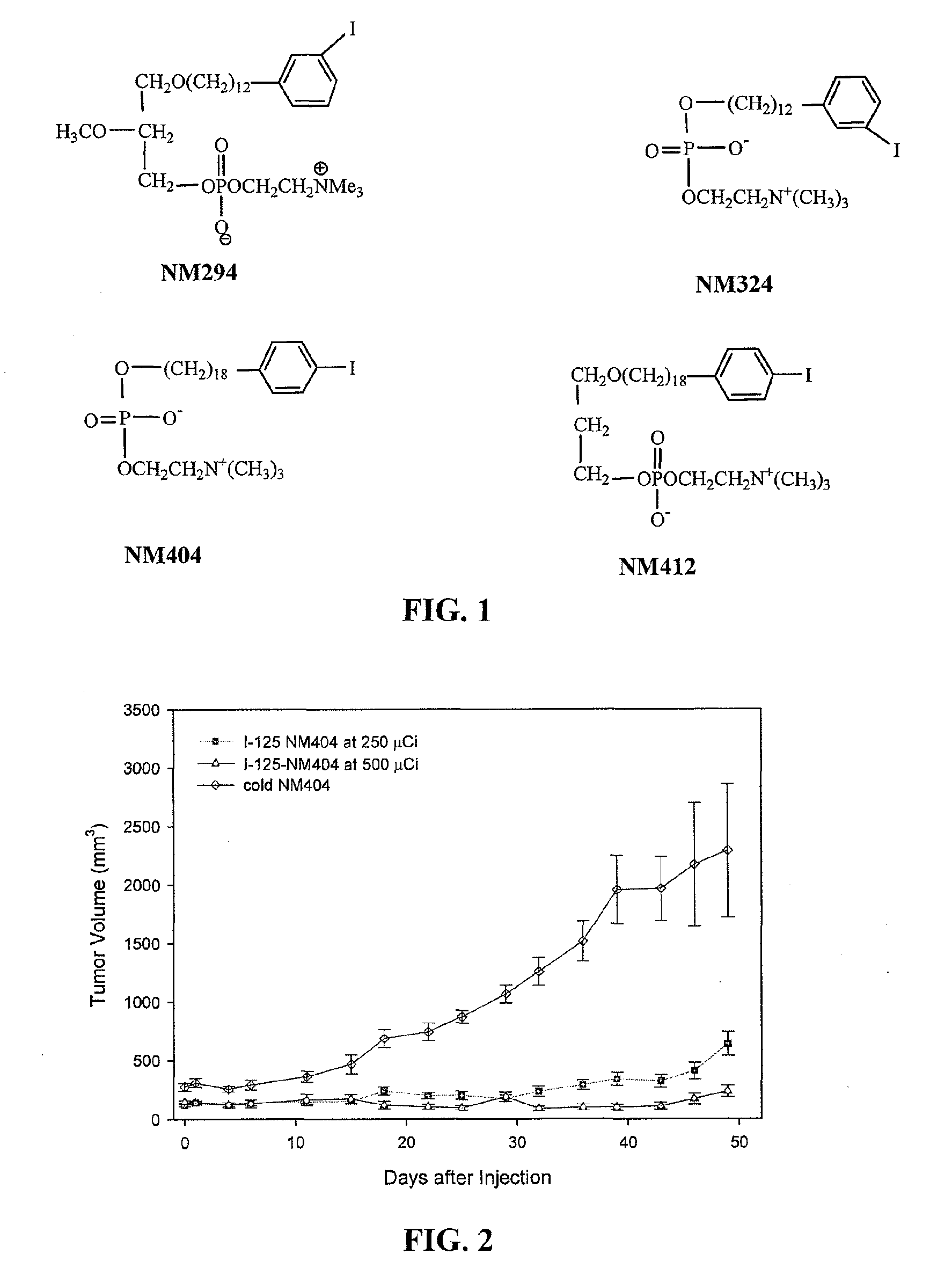
Compositions of phospholipid ether boronic acids and esters and methods for their synthesis and use
ActiveUS20090018357A1Reduce the overall heightSilicon organic compoundsBiocideCancer cellNeutron capture
The present invention discloses boronic acids and esters of phospholipid ether analogs and methods for their synthesis and use. The boronic acids and esters of phospholipid ether analogs described herein can be used in treating cancer and in particular can be used in conjunction with radiation therapy, such as external beam radiation therapy and neutron capture therapy to specifically target and kill cancer cells.
Owner:CELLECTAR
Radiation therapy interactive planning
A radiation therapy system (100) includes a radiation therapy (RT) optimizer unit (102) and an interactive planning interface unit (120). The RT optimizer unit (102) receives at least one target structure and at least one organ-at-risk (OAR) structure segmented from a volumetric image (108), and generates an optimized RT plan (140) based on dose objectives (200-204, 210-222, 320), at least one dose objective of the dose objectives corresponding to each of the at least one target structure (210-222) and the at least one OAR structure (200-204). The optimized RT plan includes a planned radiation dose for each voxel of the volumetric image using external beam radiation therapy, wherein the RT optimizer unit operates iteratively. The interactive planning interface unit (120) interactively controls each of the dose objectives through controls (300) displayed on a single display (126) of a display device (124), operates the RT optimizer unit to iteratively compute the planned radiation dose according to the controls, and provide visual feedback (310, 134) on the single display according to progress of the RT optimizer unit after each trial.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
External immobilizer
An external immobilizer for cancer treatment has a plurality of inflatable bladders that are independent finable depending on computer instruction based on patient position data provided from integrated or separate position determining means, such as external cameras or sensors, optionally with internal and / or external markers. In preferred embodiments, the immobilizer is fully integrated with an imaging means as well as the external beam radiation source, thus allowing both real time, independent anatomical compensation or correction for patient movement and fine control of beam shape and position to accurately target the tumor, even if the patient moves.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Compositions of phospholipid ether boronic acids and esters and methods for their synthesis and use
ActiveUS8022235B2Silicon organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCancer cellNeutron capture
The present invention discloses boronic acids and esters of phospholipid ether analogs and methods for their synthesis and use. The boronic acids and esters of phospholipid ether analogs described herein can be used in treating cancer and in particular can be used in conjunction with radiation therapy, such as external beam radiation therapy and neutron capture therapy to specifically target and kill cancer cells.
Owner:CELLECTAR
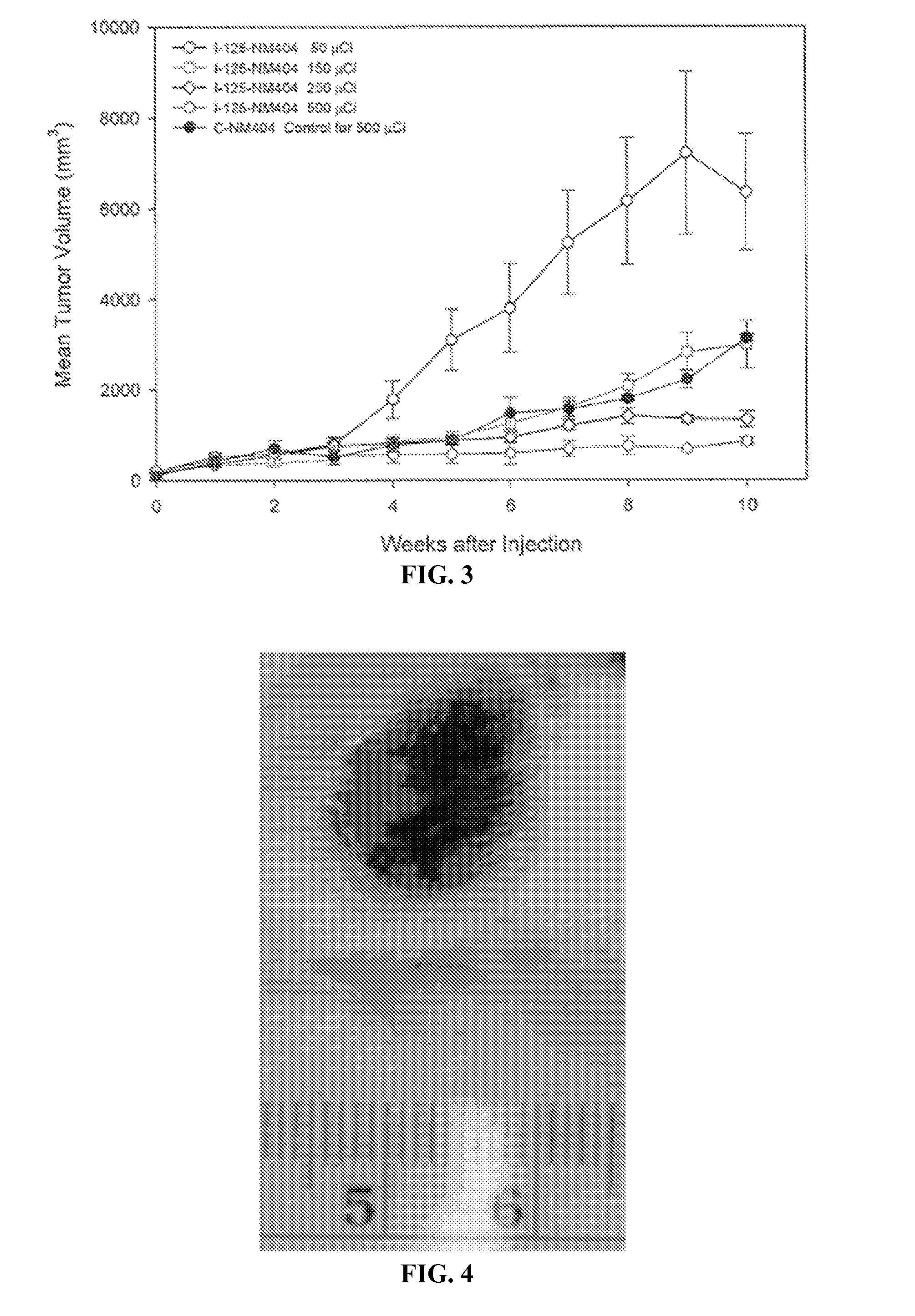
Prediction and treatment of brain tumor spread using MRI and external beam radiation
InactiveUS20080051649A1Improving cancer controlReduce marginMedical simulationMagnetic measurementsNon symmetricCancer cell
The invention is based on the realization that brain cancer cells spread preferentially along paths of elevated water diffusion, such as along nerve fiber bundles, that can be measured by magnetic resonance (MR) diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and the migration of cancer cells away from the primary tumor can be predicted using computational models that incorporate DWI information. The invention therefore applies DWI and models cell migration to develop appropriate non-symmetric margins for radiation treatment of malignant brain tumors.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Controlling and shaping the dose distribution outside treatment targets in external-beam radiation treatments
ActiveUS10143859B2Need for contouring control structures around each target can be reduced or eliminatedX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTreatment targetsNormal tissue
Streamlined and partially automated methods of setting normal tissue objectives in radiation treatment planning are provided. These methods may be applied to multiple-target cases as well as single-target cases. The methods can impose one or more target-specific dose falloff constraints around each target, taking into account geometric characteristics of each target such as target volume and shape. In some embodiments, methods can also take into account a planner's preferences for target dose homogeneity. In some embodiments, methods can generate additional dose falloff constraints in locations between two targets where dose bridging is likely to occur.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Apparatus and method for external beam radiation distribution mapping
An apparatus and method for in vivo and ex vivo control, detection and measurement of radiation in therapy, diagnostics, and related applications accomplished through scintillating fiber detection. One example includes scintillating fibers placed along a delivery guide such as a catheter for measuring applied radiation levels during radiotherapy treatments, sensing locations of a radiation source, or providing feedback of sensed radiation. Another option is to place the fibers into a positioning device such as a balloon, or otherwise in the field of the radiation delivery. The scintillating fibers provide light output levels correlating to the levels of radiation striking the fibers and comparative measurement between fibers can be used for more extensive dose mapping. Adjustments to a radiation treatment may be made as needed based on actual and measured applied dosages as determined by the fiber detectors. Characteristics of a radiation source may also be measured using scintillating materials.
Owner:HAMPTON UNIVERSITY
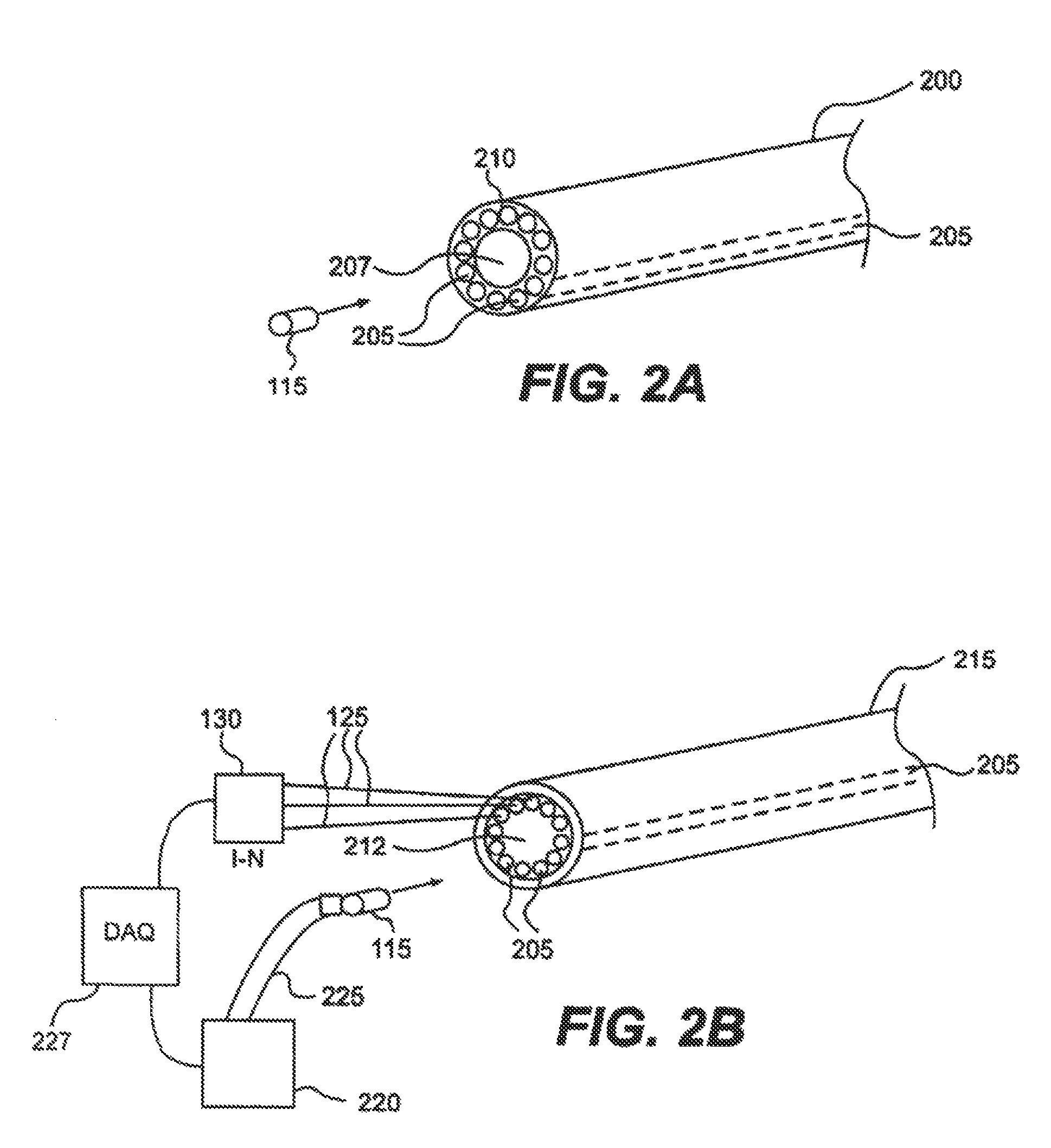
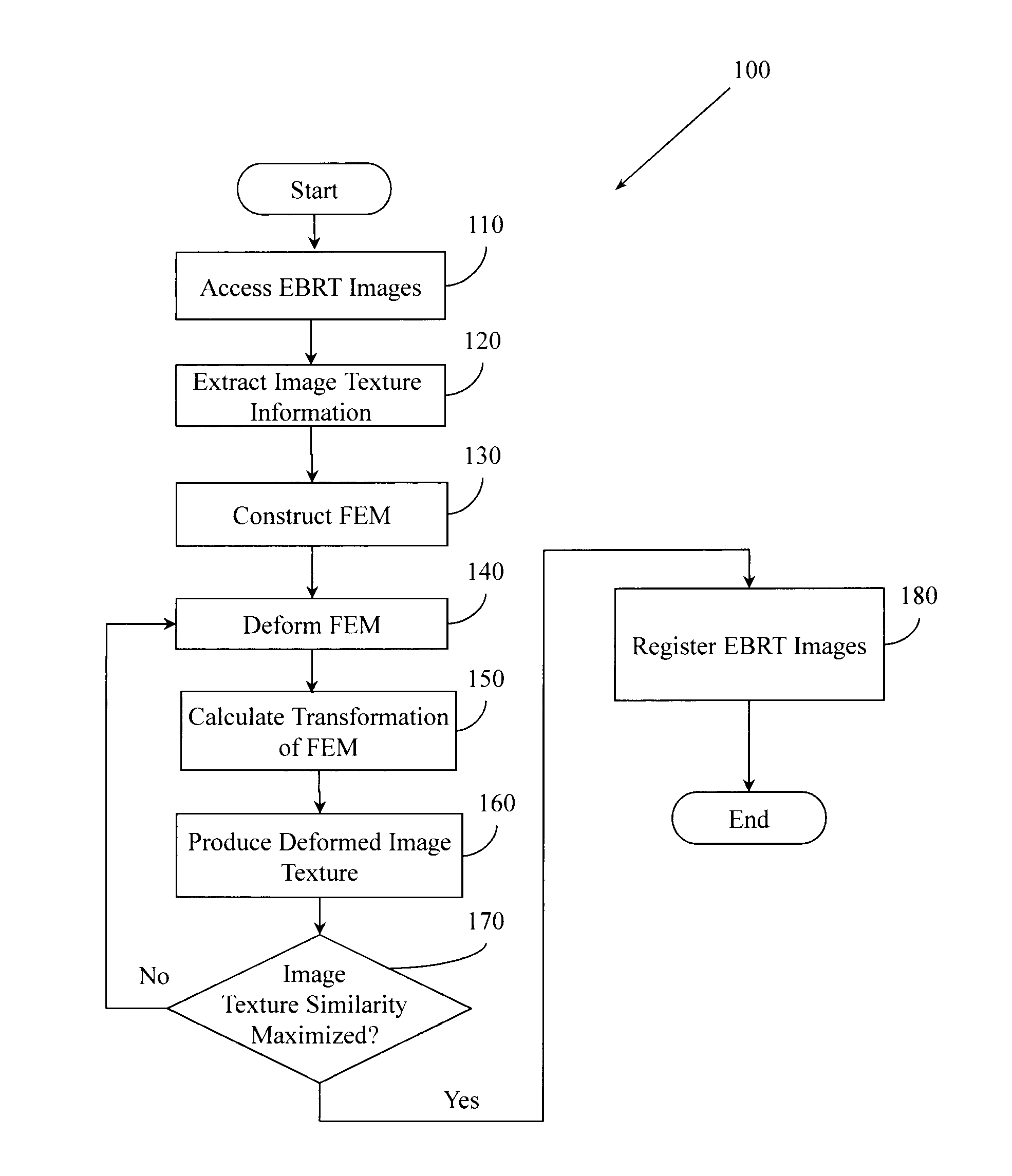
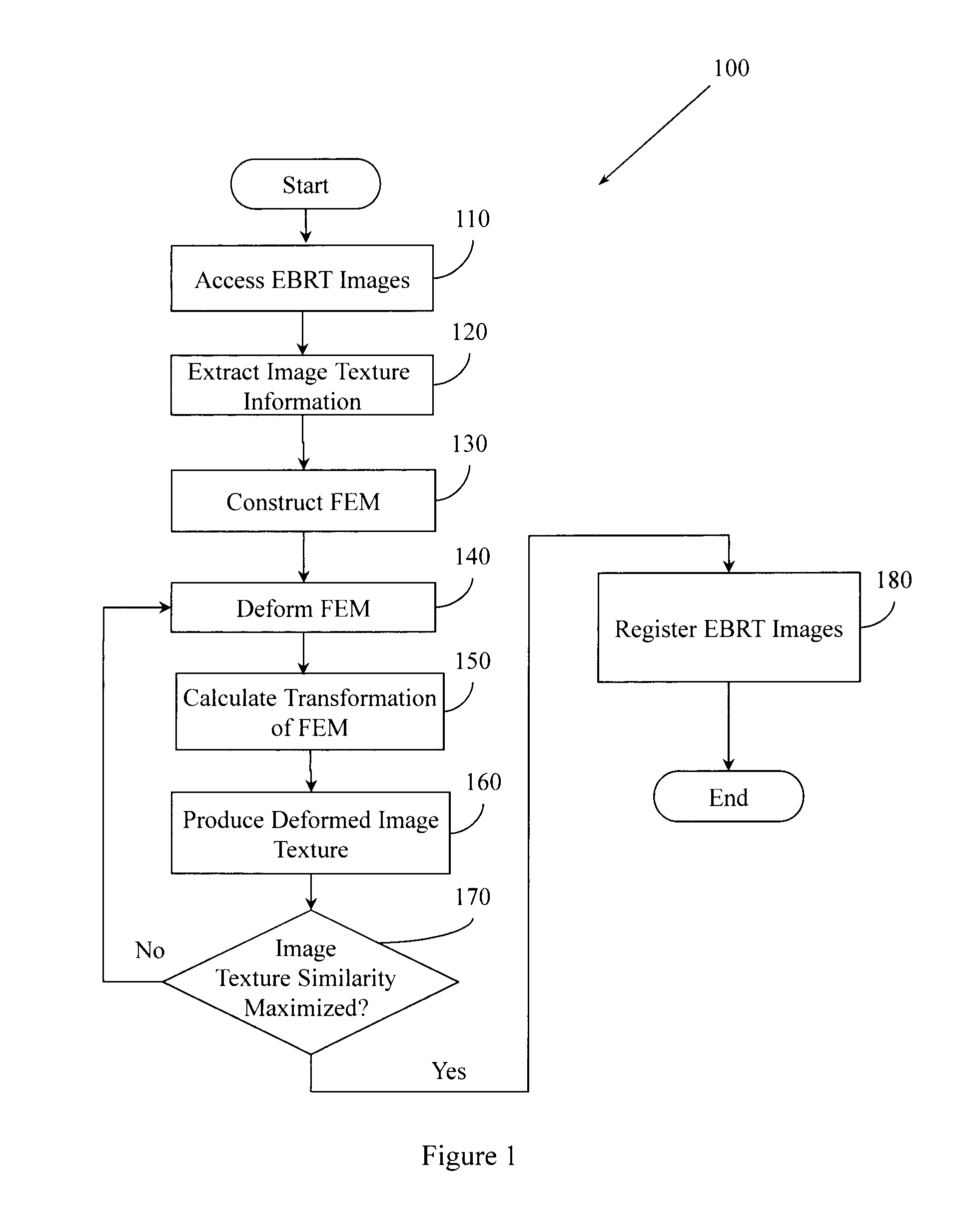
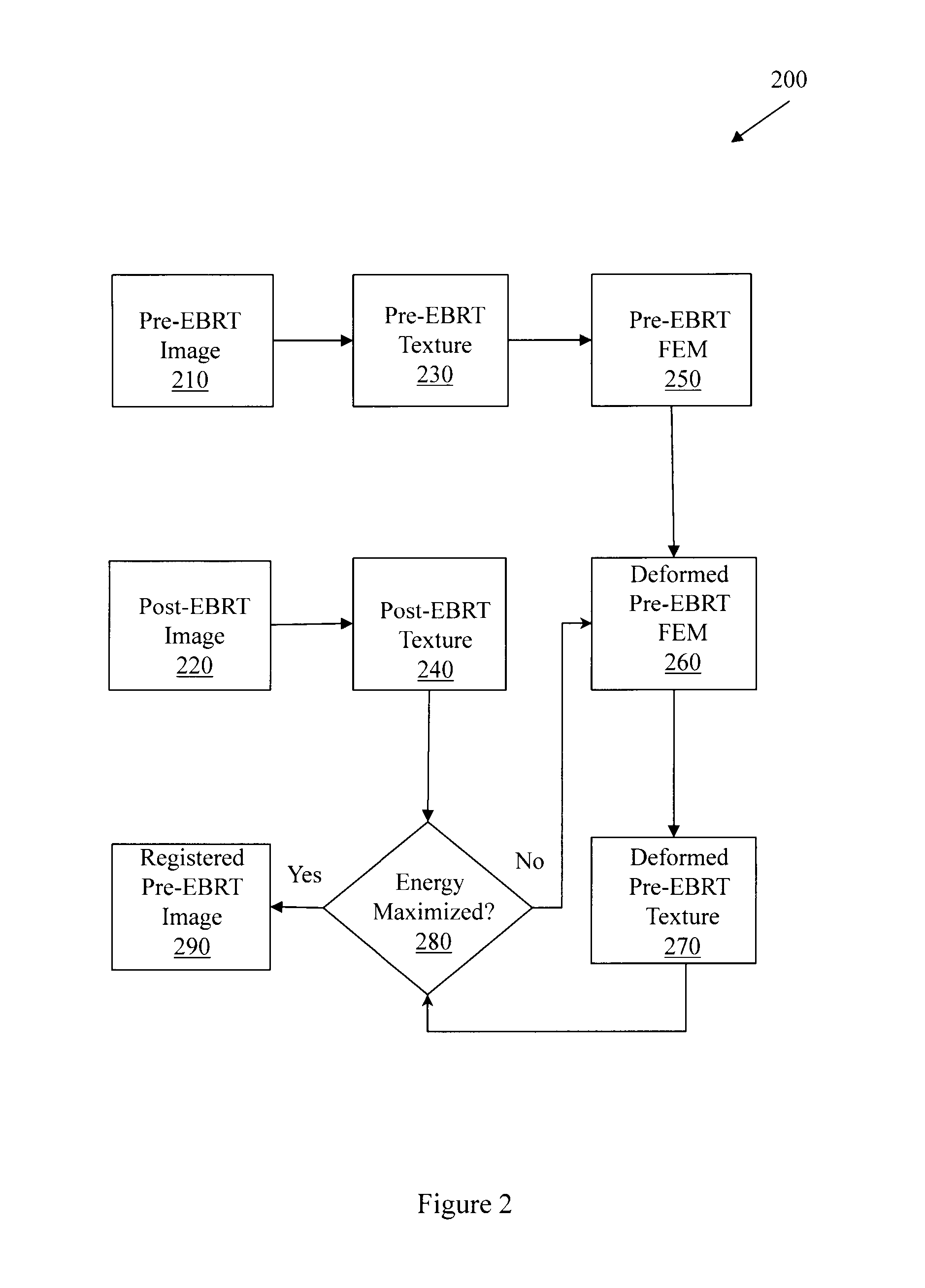
Image Similarity-Based Finite Element Model Registration
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
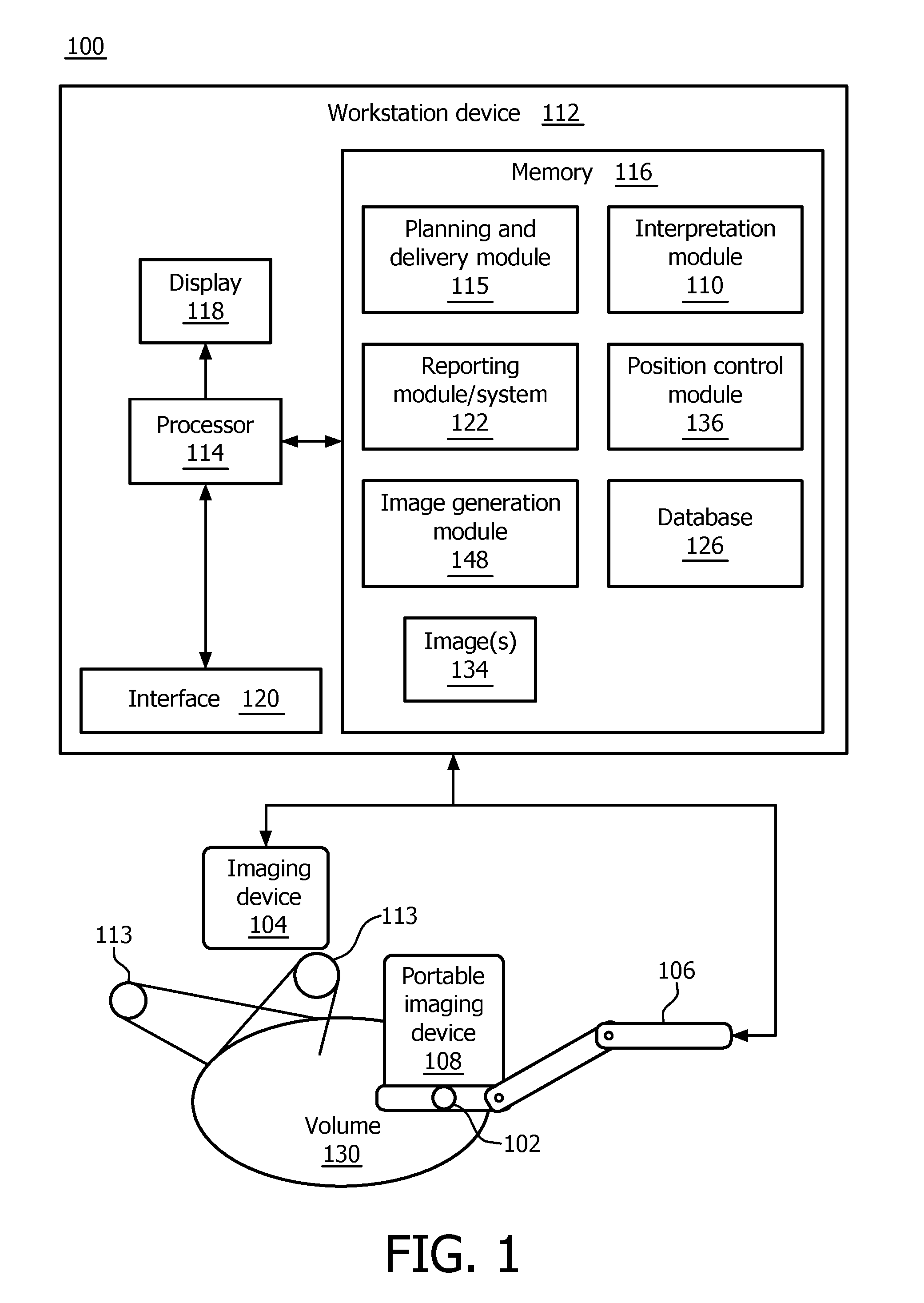
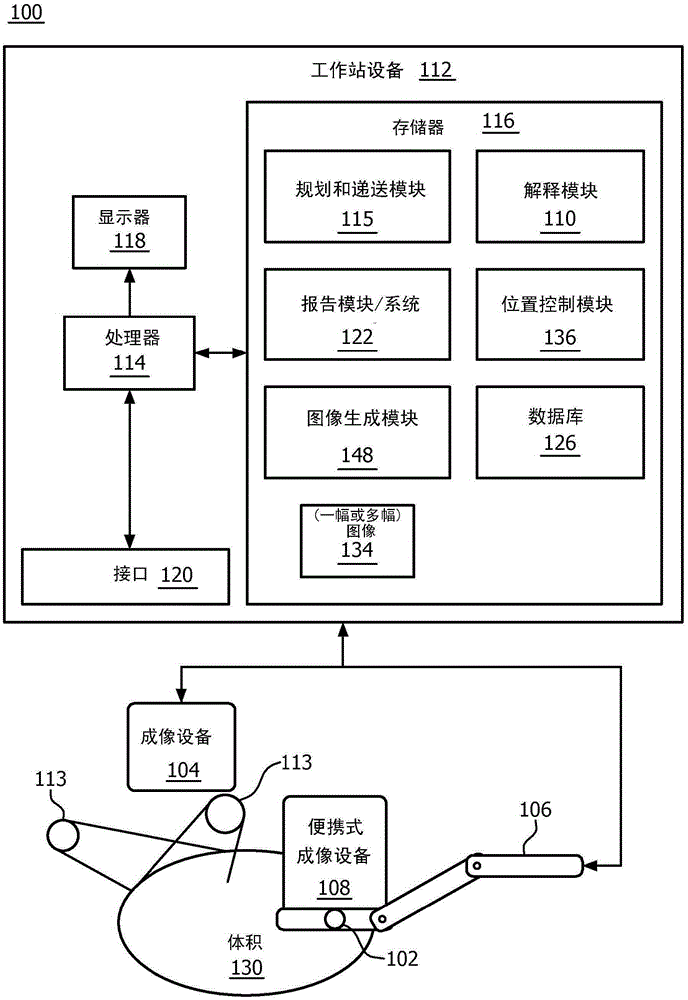
Real-time quantification of skin burns in external beam radiation therapy
ActiveUS20160136455A1X-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyExternal beam radiotherapyRegion of interest
A system for radiation therapy include an imaging device (108) configured to scan an area of interest for tissue undergoing radiation therapy to collect one or more images of the tissue. An interpretation module (110) is configured to receive the one or more images of the tissue to determine a burn status of the tissue and provide adjustments for a radiation treatment plan in accordance with the burn status.
Owner:KONINKLILJKE PHILIPS NV
Real-time quantification of skin burns in external beam radiation therapy
A system for radiation therapy includes an imaging device (108) configured to scan an area of interest for tissue undergoing radiation therapy to collect one or more images of the tissue. An interpretation module (110) is configured to receive the one or more images of the tissue to determine a burn status of the tissue and provide adjustments for a radiation treatment plan in accordance with the burn status.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS NV
System for processing patient radiation treatment data
InactiveCN1623614ASpecial data processing applicationsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyData treatmentInternal radiation
Owner:SIEMENS MED SOLUTIONS HEALTH
Repositionable Gynecological Applicator for Image-guided Radiosurgery (IGRS) and Image-guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) for Localized Treatment of Gynecological Tumors
InactiveUS20080219402A1Accurate placementError minimizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingGeometric errorAbnormal tissue growth
A method and apparatus for precisely reproducing the position of a vaginal cylinder in relation to a patient to ensure that a planned radiation dose can be delivered with high precision to the intended treatment target volumes. In order to properly define the treatment volume, a vaginal cylinder with proper diameter is inserted into the patient's vagina. This invention addresses two potential errors: one, the incorrect vaginal cylinder position in relation to the radiation beams, and second, the inconsistent positional correlation between the vaginal cylinder and the patient's body. These two geometric errors will cause dosimetric errors. The present invention provides a method and apparatus for minimizing the geometric error and dosimetric error associated with conventional external beam radiation therapy or radiosurgery used in treating gynecological tumors. First a treatment plan is carried out to determine the treatment target volume. Second, treatment delivery is carried out by using an image-guided system to locate the position of the vaginal cylinder and comparing it relative to the treatment delivery system coordinate system and the patient's coordinate system. The displacement in the position of the vaginal cylinder from the treatment plan is corrected by calculating the transformation matrix and entering the resulting value into a position adjusting assembly. The position adjusting assembly adjusts the vaginal cylinder to exactly reproduce its location relative to the patient's coordinate system. This ensures that the image-guided system locates the precise radiation delivery position and that the radiation dose is delivered precisely to the treatment target volume.
Owner:SCHWADE JAMES G M D MR
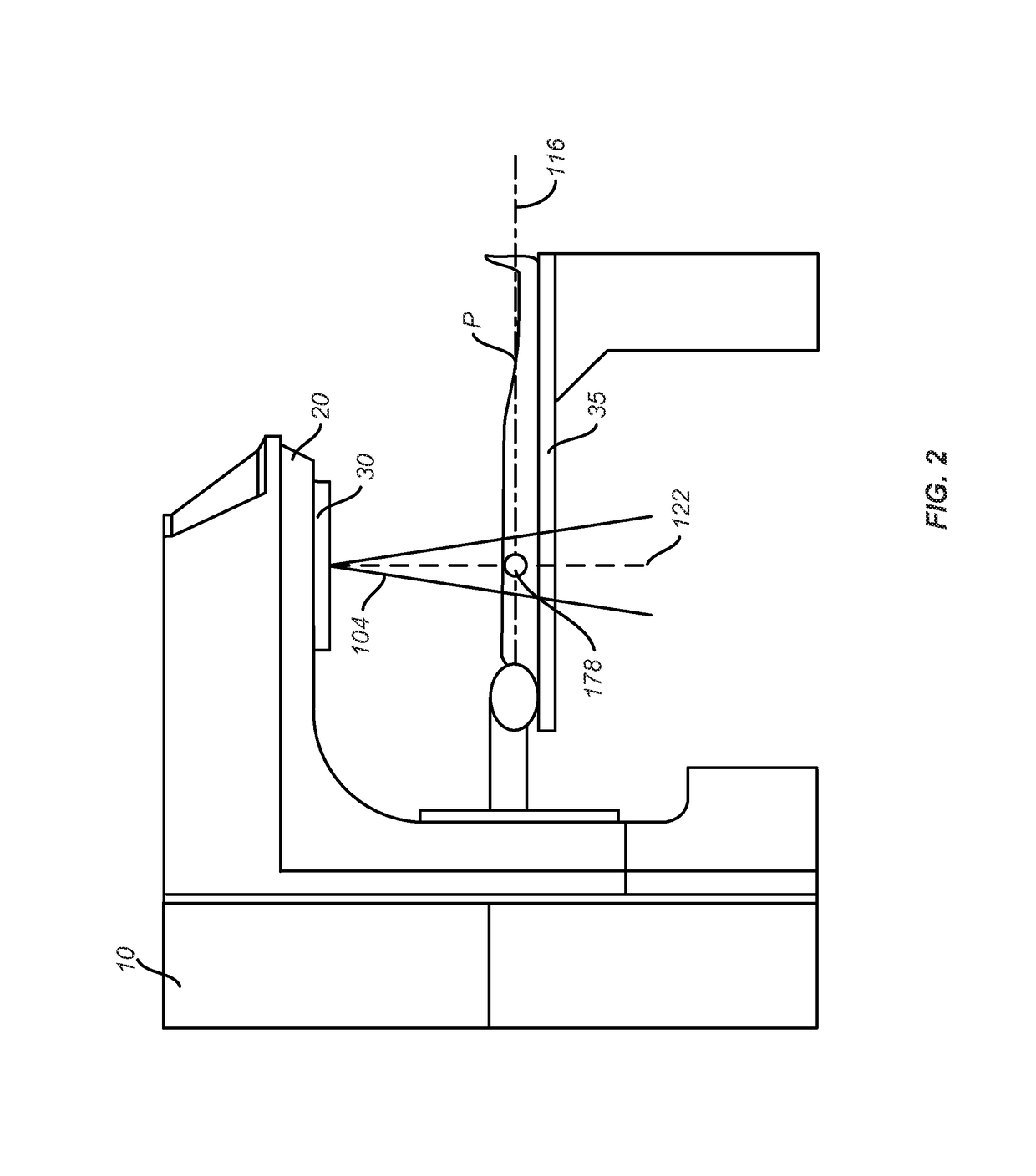
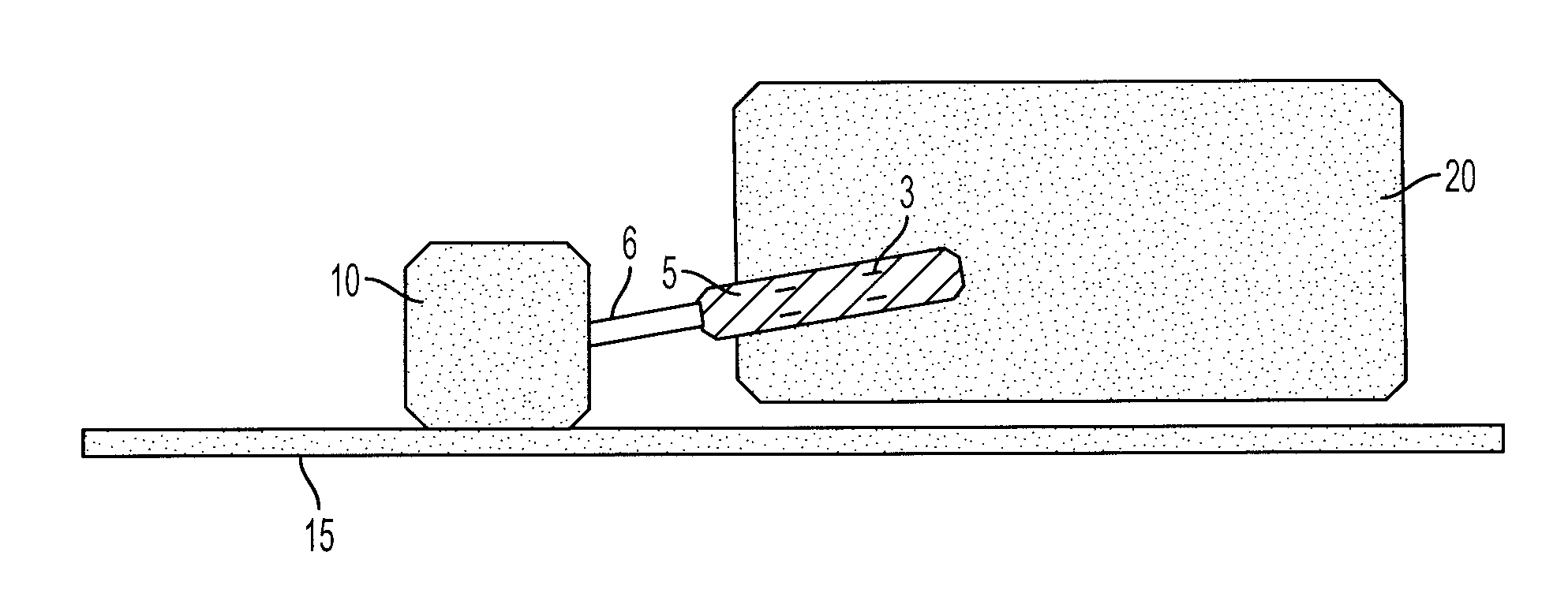
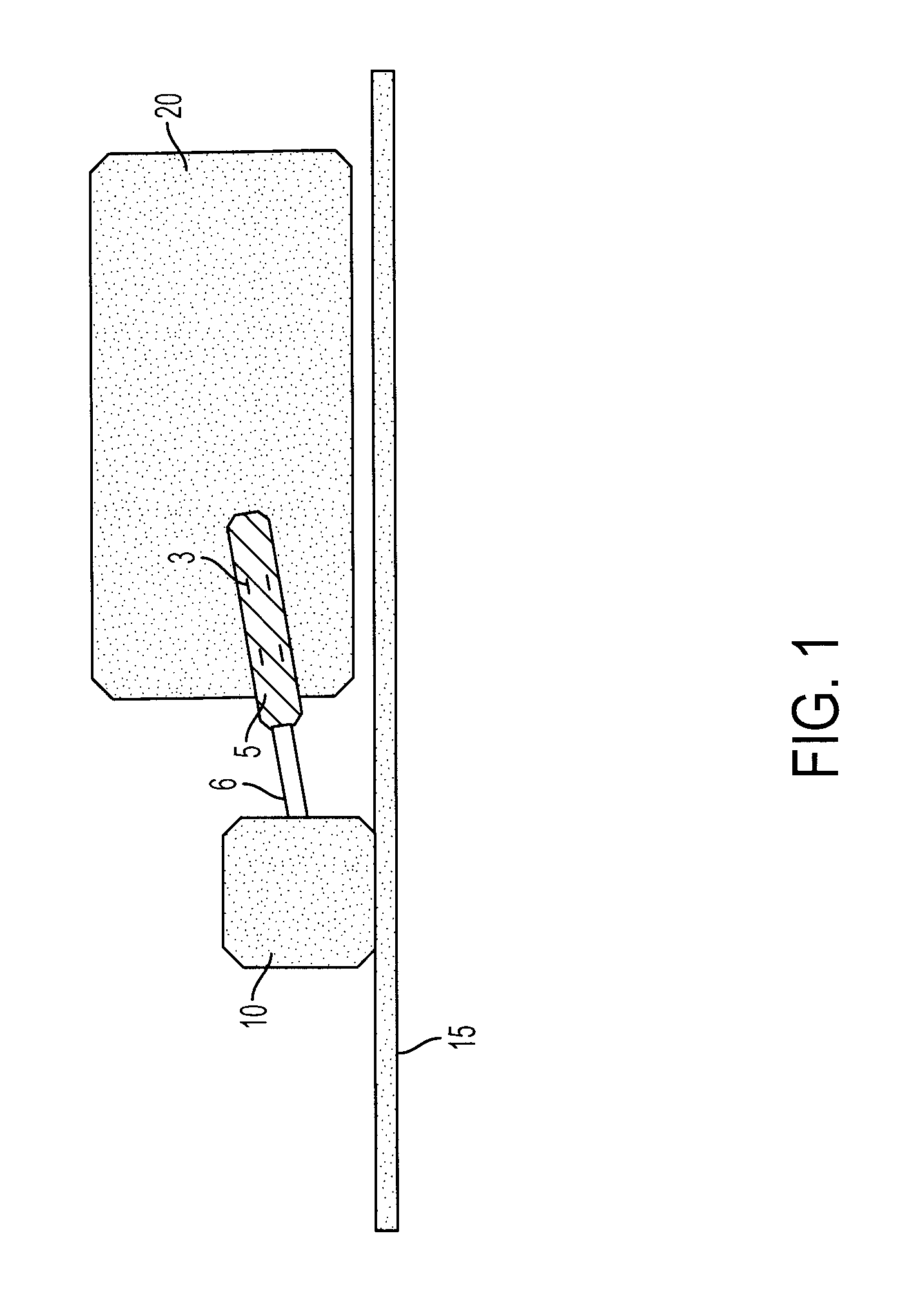
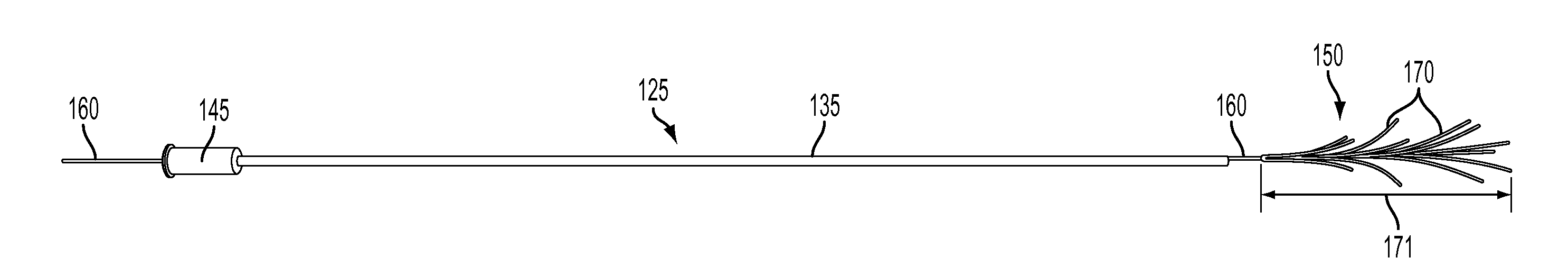
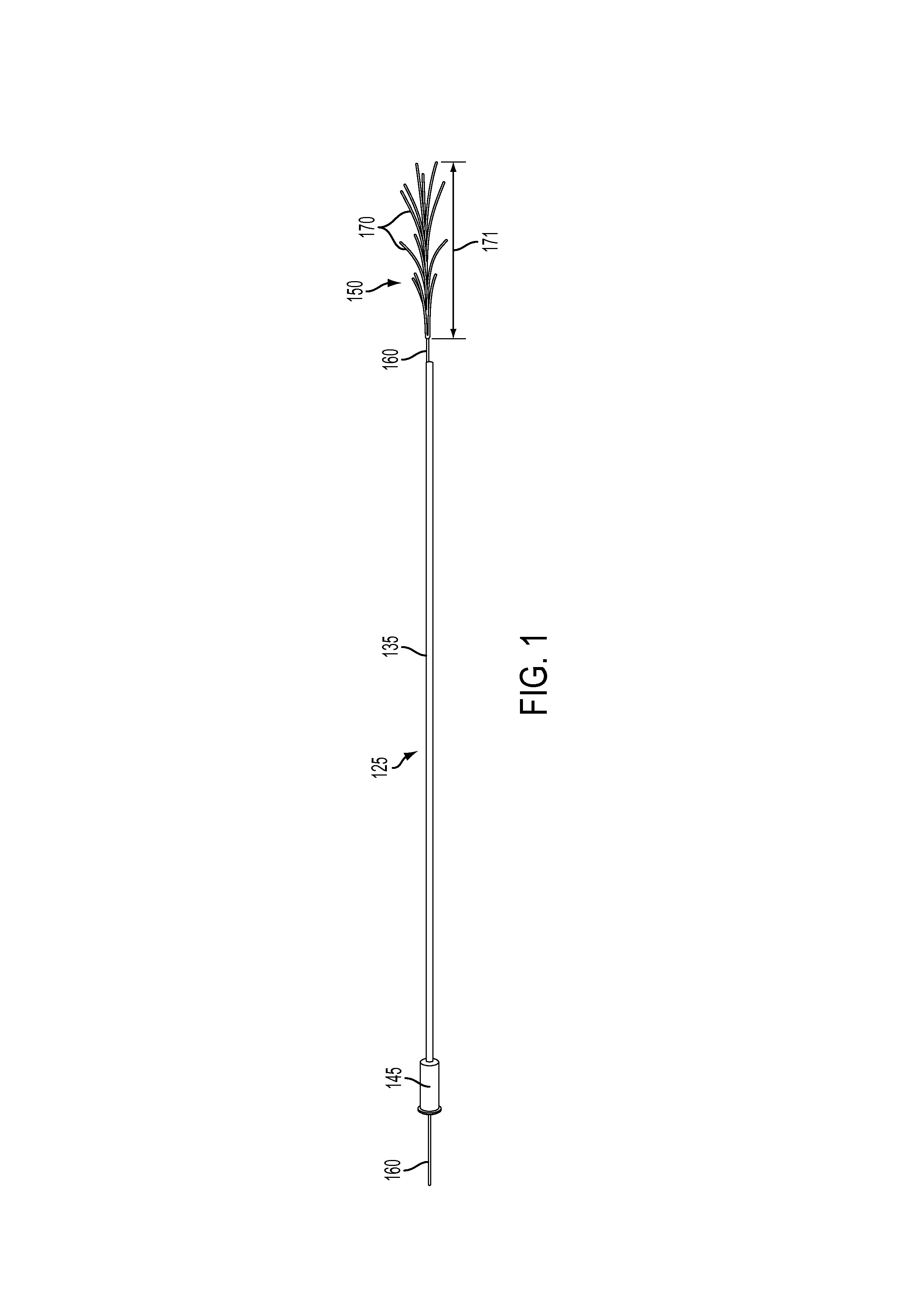
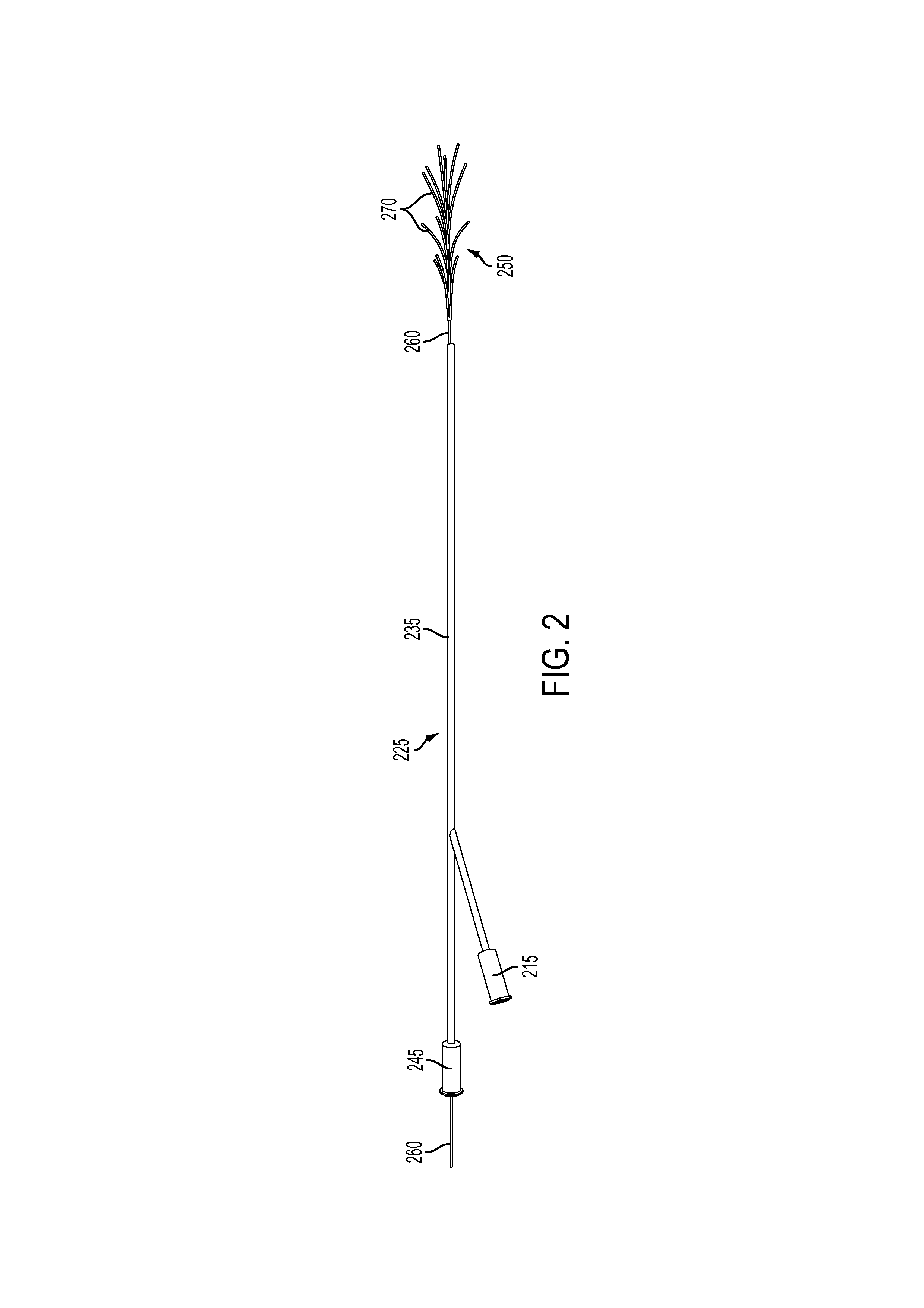
Targeting implant for external beam radiation
ActiveUS20130184577A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSuture equipmentsLight beamRadical radiotherapy
A radiation targeting system is provided. The system can include an introducer and an implant. The implant can be disposed within a cannula of the introducer and the implant can include a wire stem and multiple different wire branches each extending outwardly from a proximal portion of the wire stem. A radiation source can then be used to target the implant so that radiation therapy can be delivered to a patient. Optionally, a loader and a trocar can be included with the system.
Owner:SURGICAL RADIATION PROD
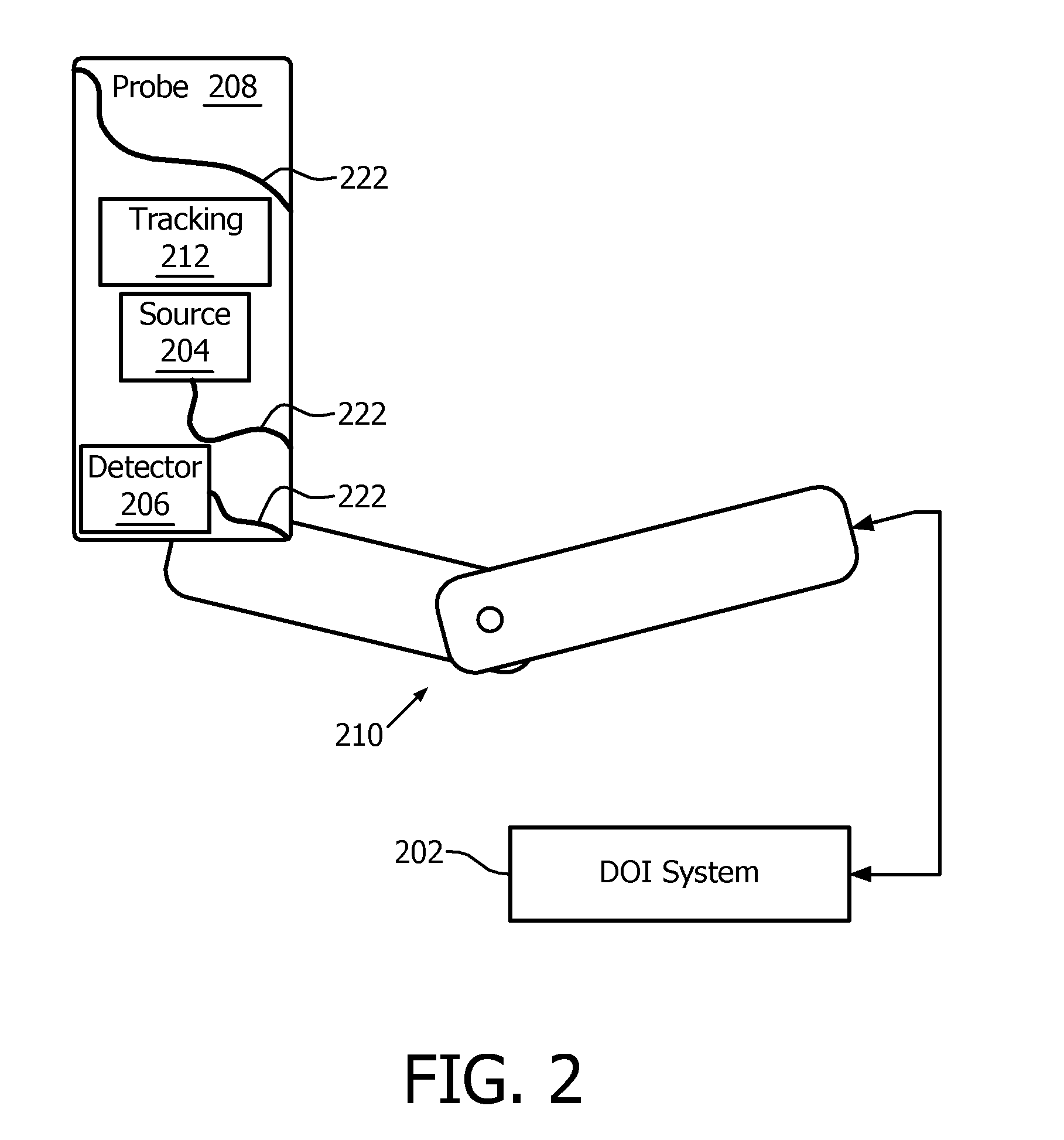
Automated detection of lung conditions for monitoring thoracic patients undertgoing external beam radiation therapy
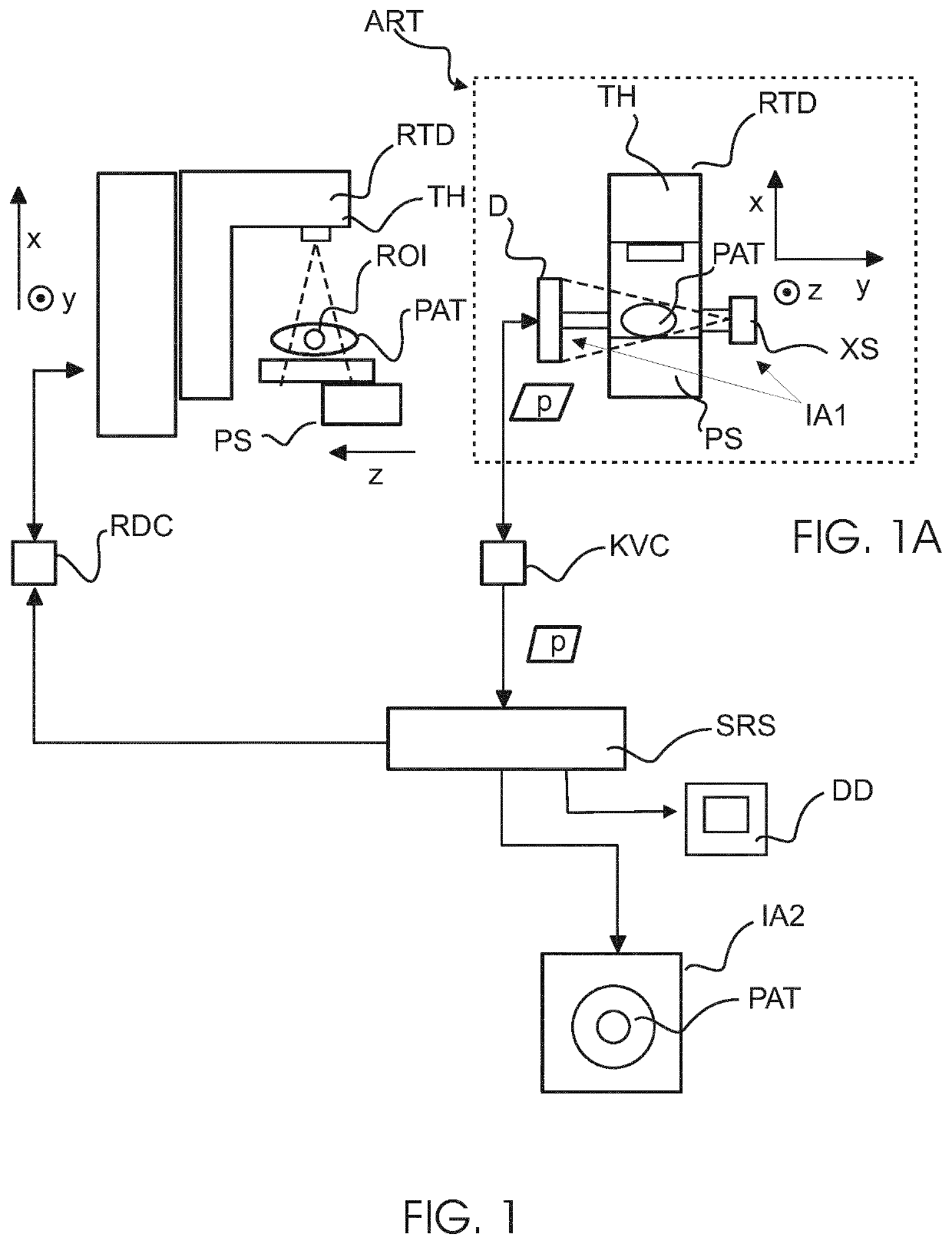
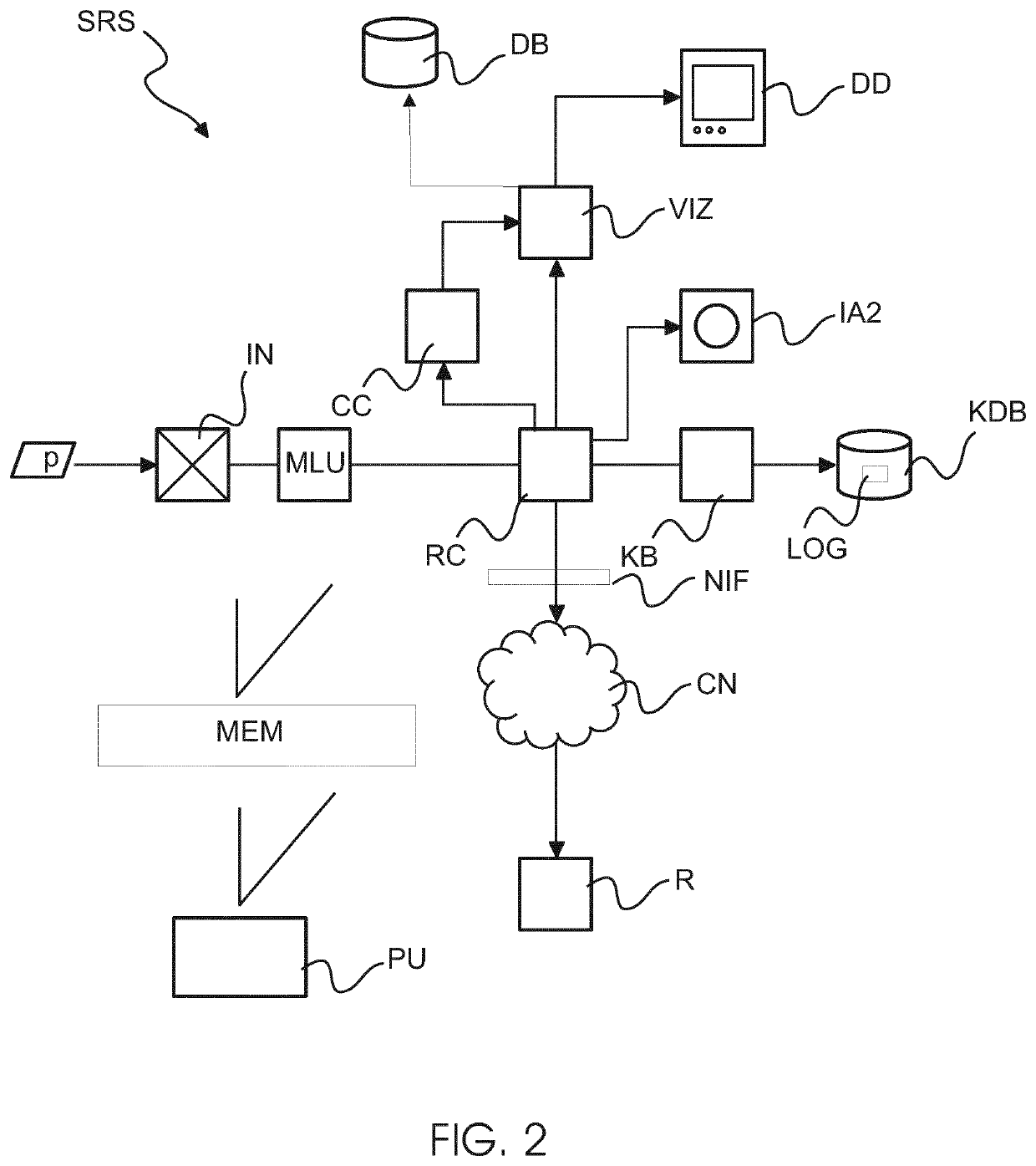
PendingUS20220076802A1Condition can be detectedSmall doseMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDiagnostic recording/measuringLearning unitComputerized system
A computerized system (SRS) for radiation therapy support. The system comprises an input interface (IN) for receiving an input image acquired by an imaging apparatus (IA1). The input image represents a region of interest (ROI) internal of a patient (PAT) and acquired before delivery of a dose fraction by a radiation therapy delivery apparatus (RTD). A pre-trained machine learning unit (MLU) of the system is configured to process the input image to detect a medical condition. A communication component (RC) of the system is configured to provide, based on the detected medical condition, an indication for one or more clinical actions to be performed in relation to the patient.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Stent based method and apparatus for directing external beam radiation therapy
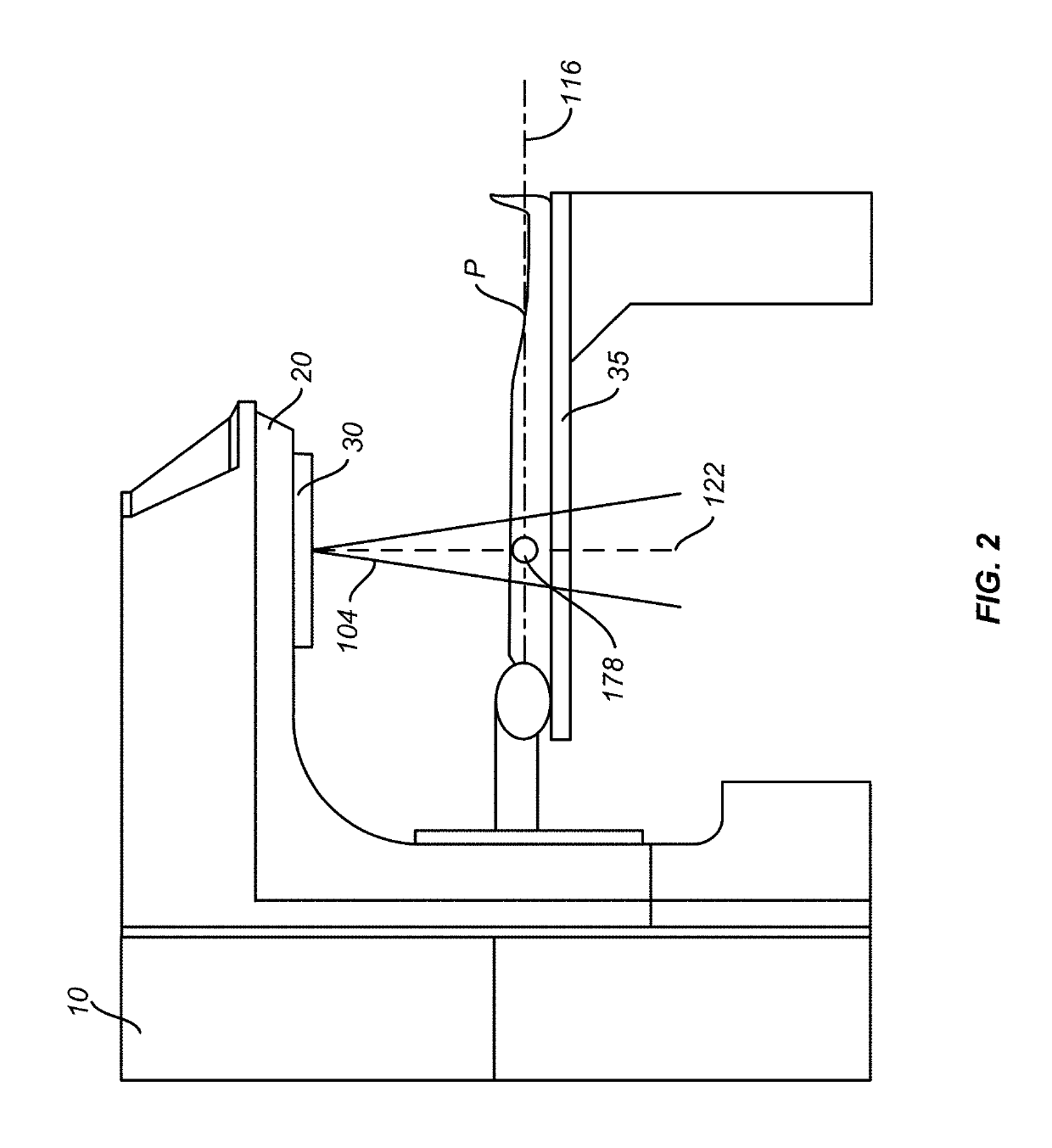
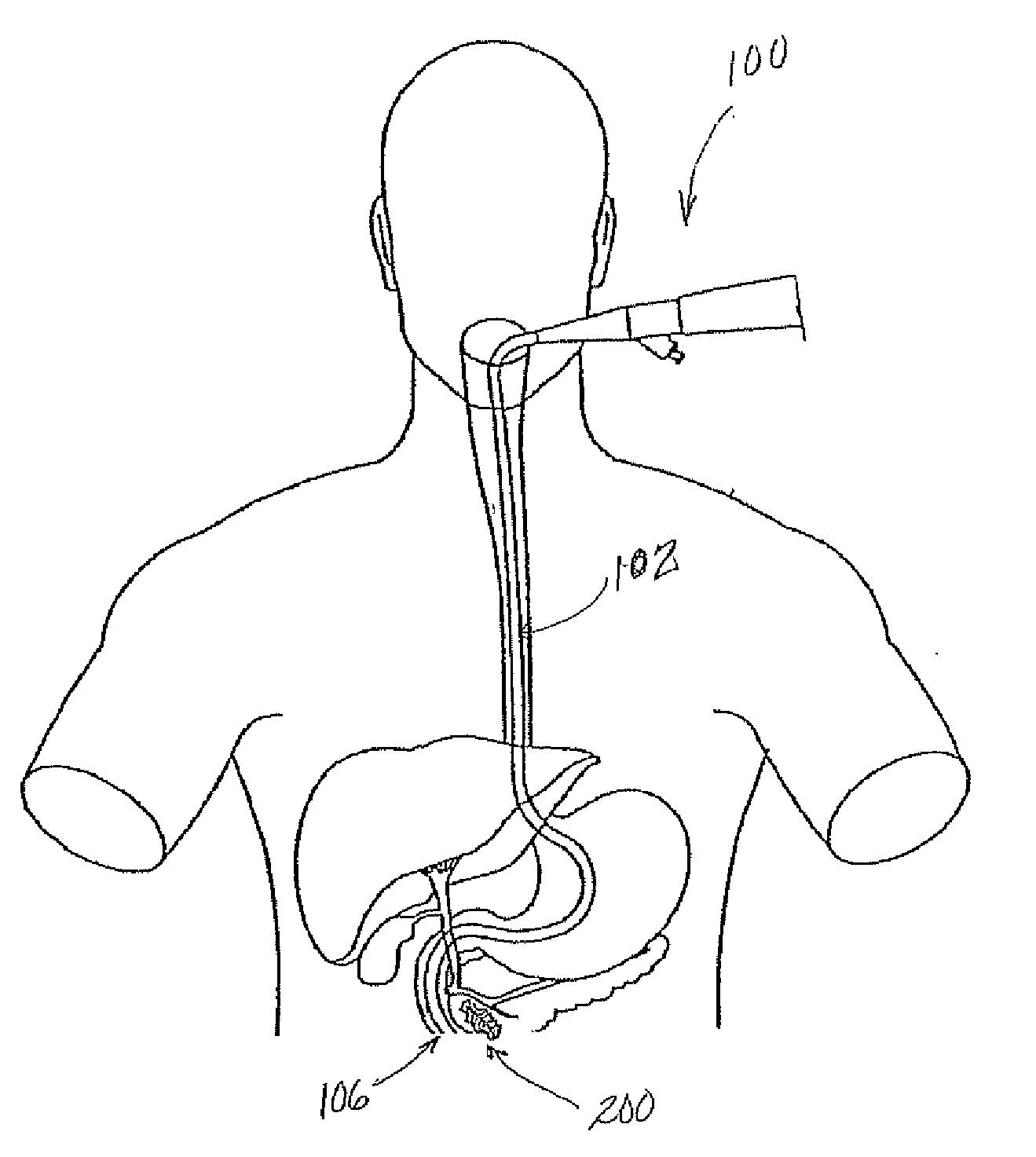
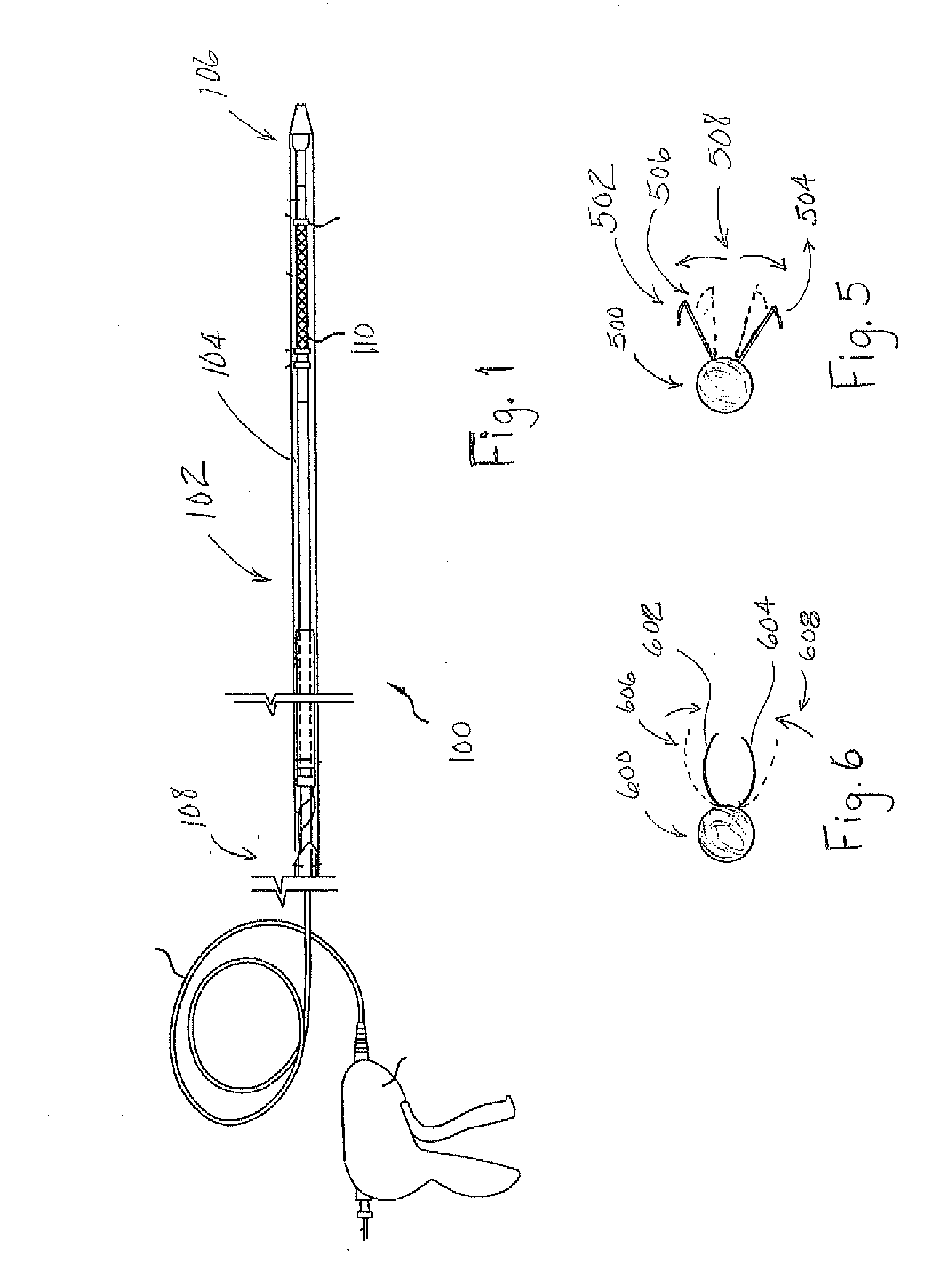
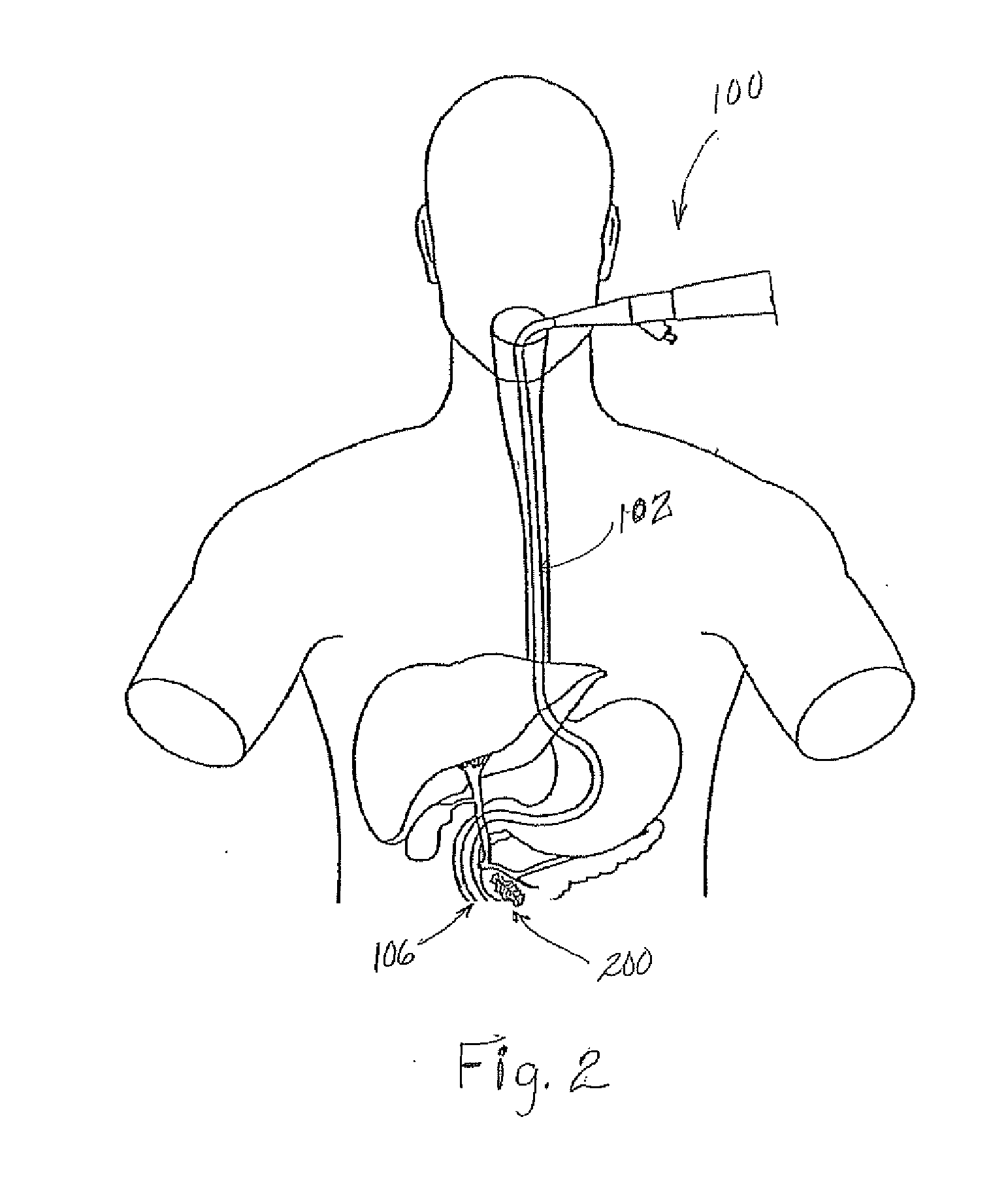
A stent based apparatus and method for directing external beam radiation comprising a series of devices and a system of implanting these devices within a patient to direct therapeutic radiation given to the patient. Each of the devices can deliver a tiny gold fiducial (or fiducial constructed of another material capable of acting as a target to direct external beam therapeutic radiation) to a target area in the vicinity of a cancer or other lesion that is considered an appropriate target for external beam radiation therapy, using, for example, the beam radiation system referred to as the Cyberknife radiation delivery system. The current system and devices envision placement of gold fiducials through hollow organs in the body (for example, the gastrointestinal tract, the ureter, blood vessels, bile duct, or the cerebro spinal fluid space). This implantation method can utilize conventional endoscopy or angiography.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com