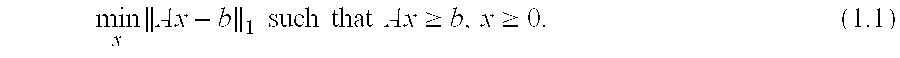Patents
Literature
104 results about "Target dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
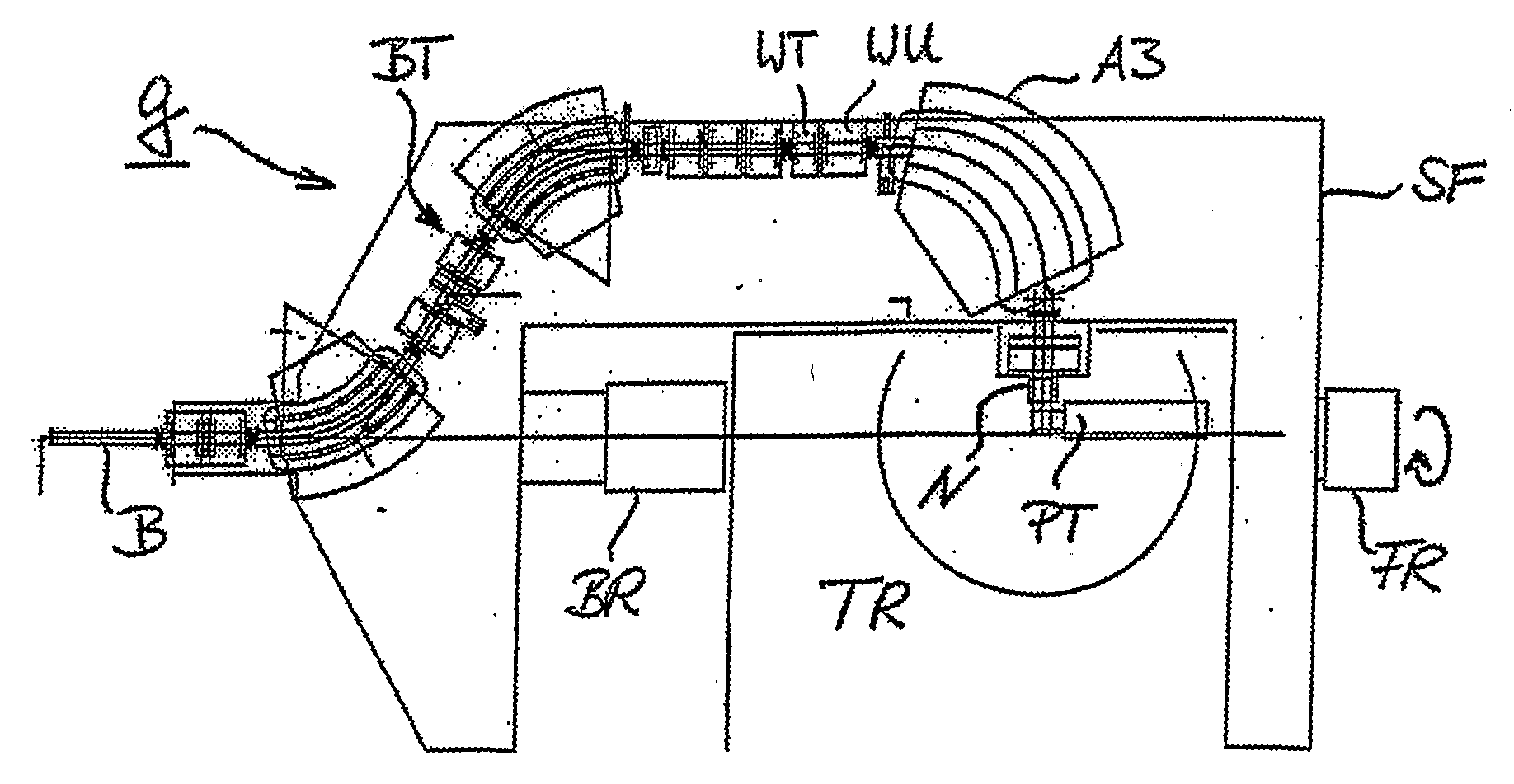
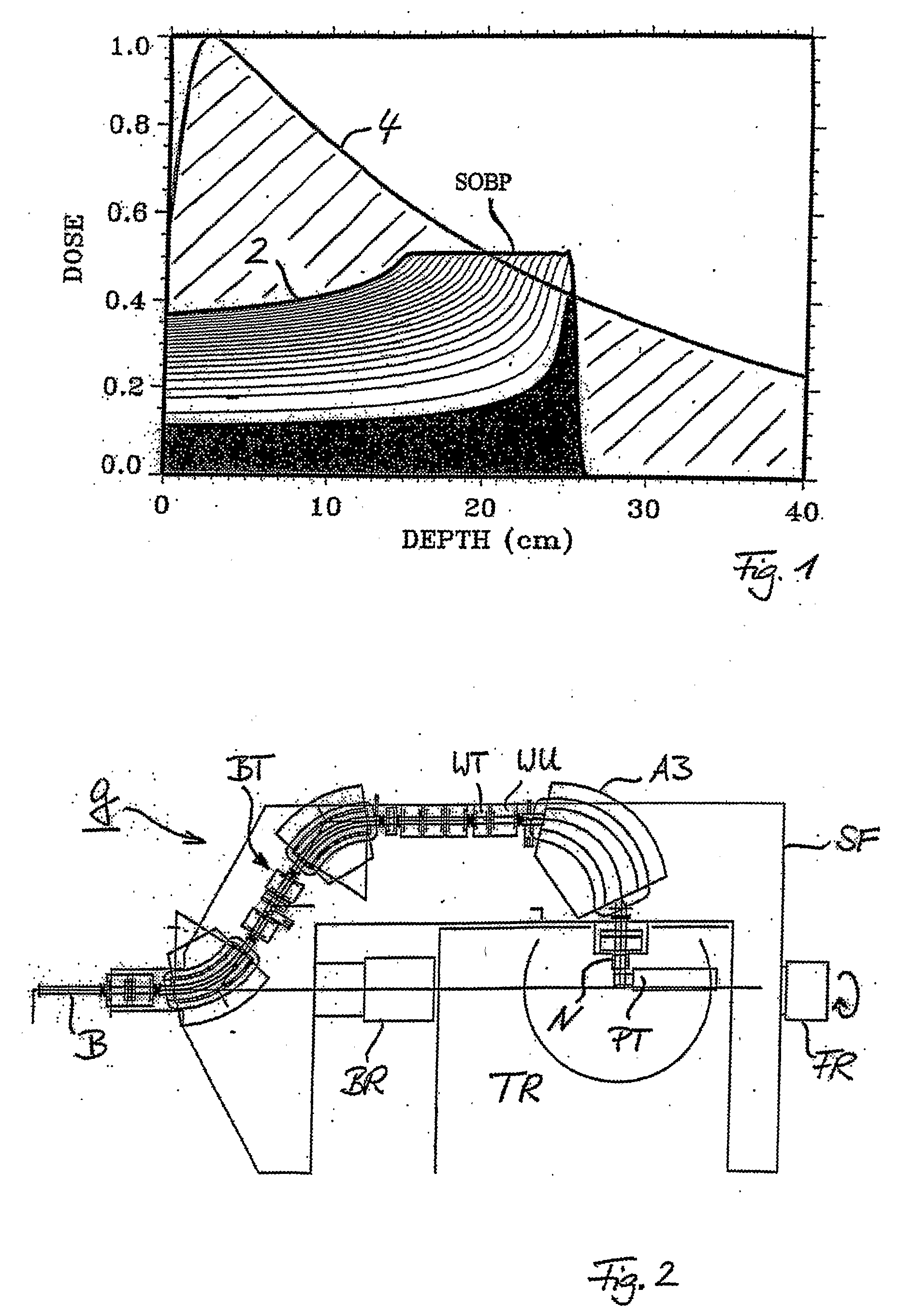
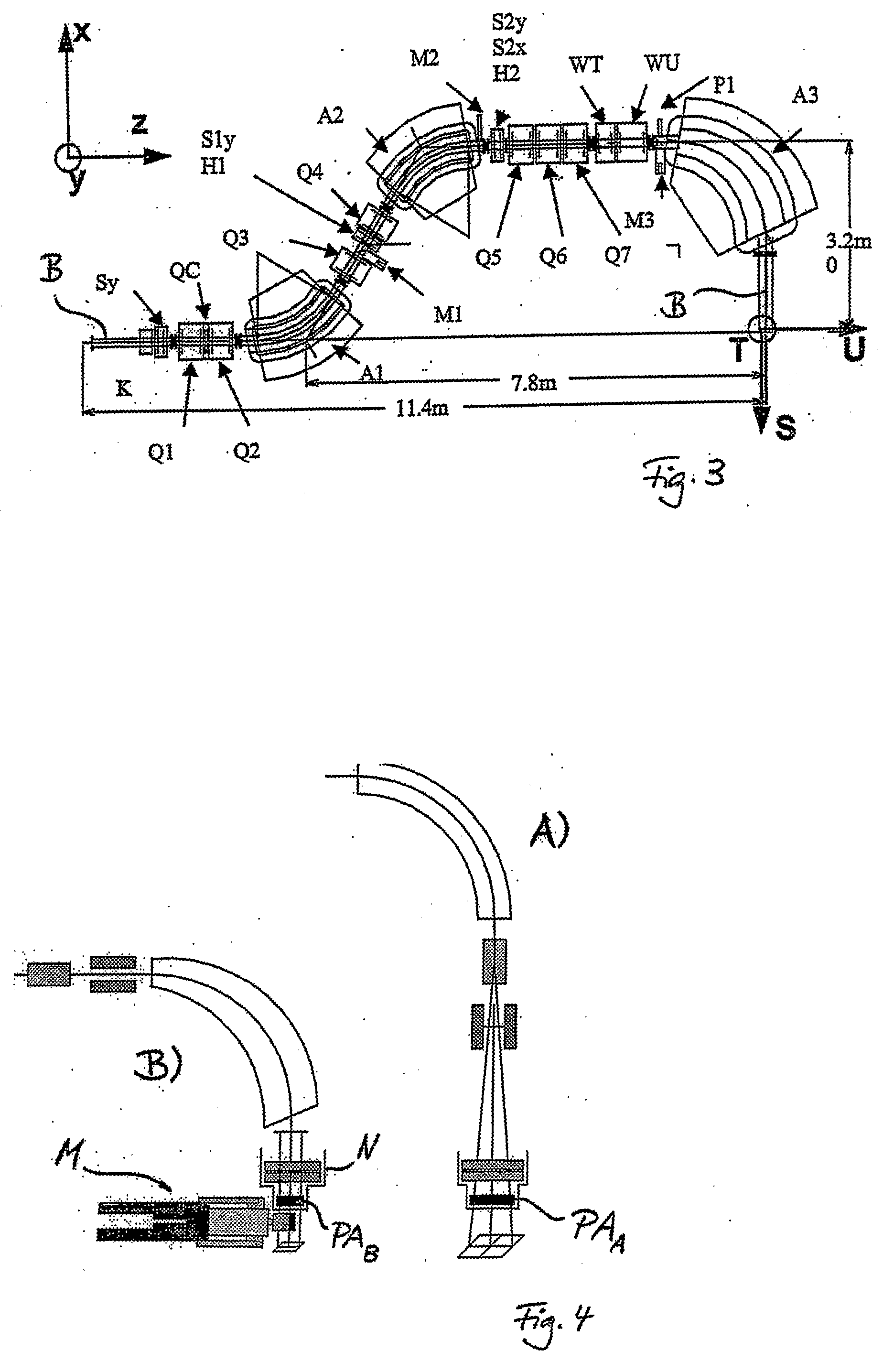
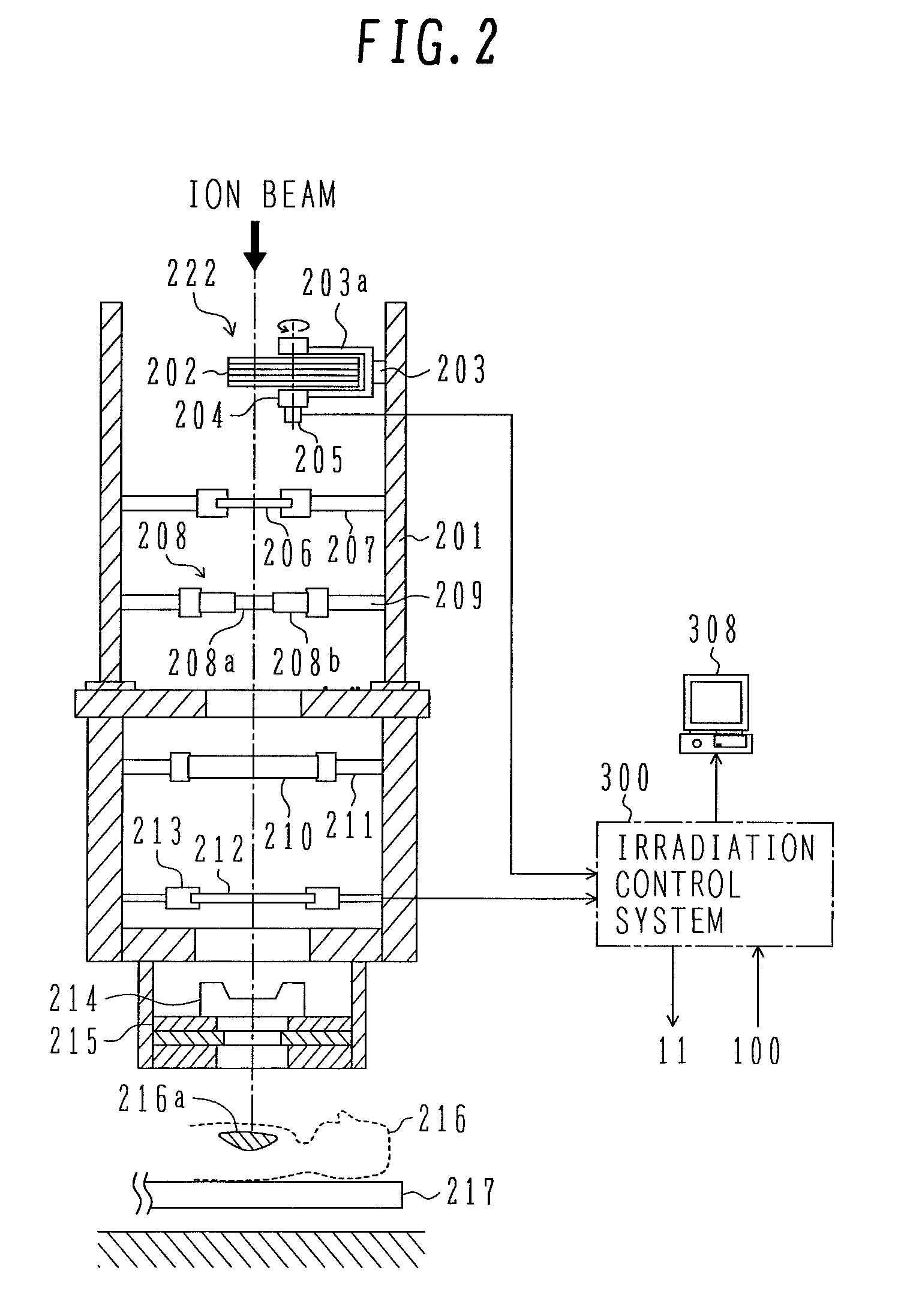
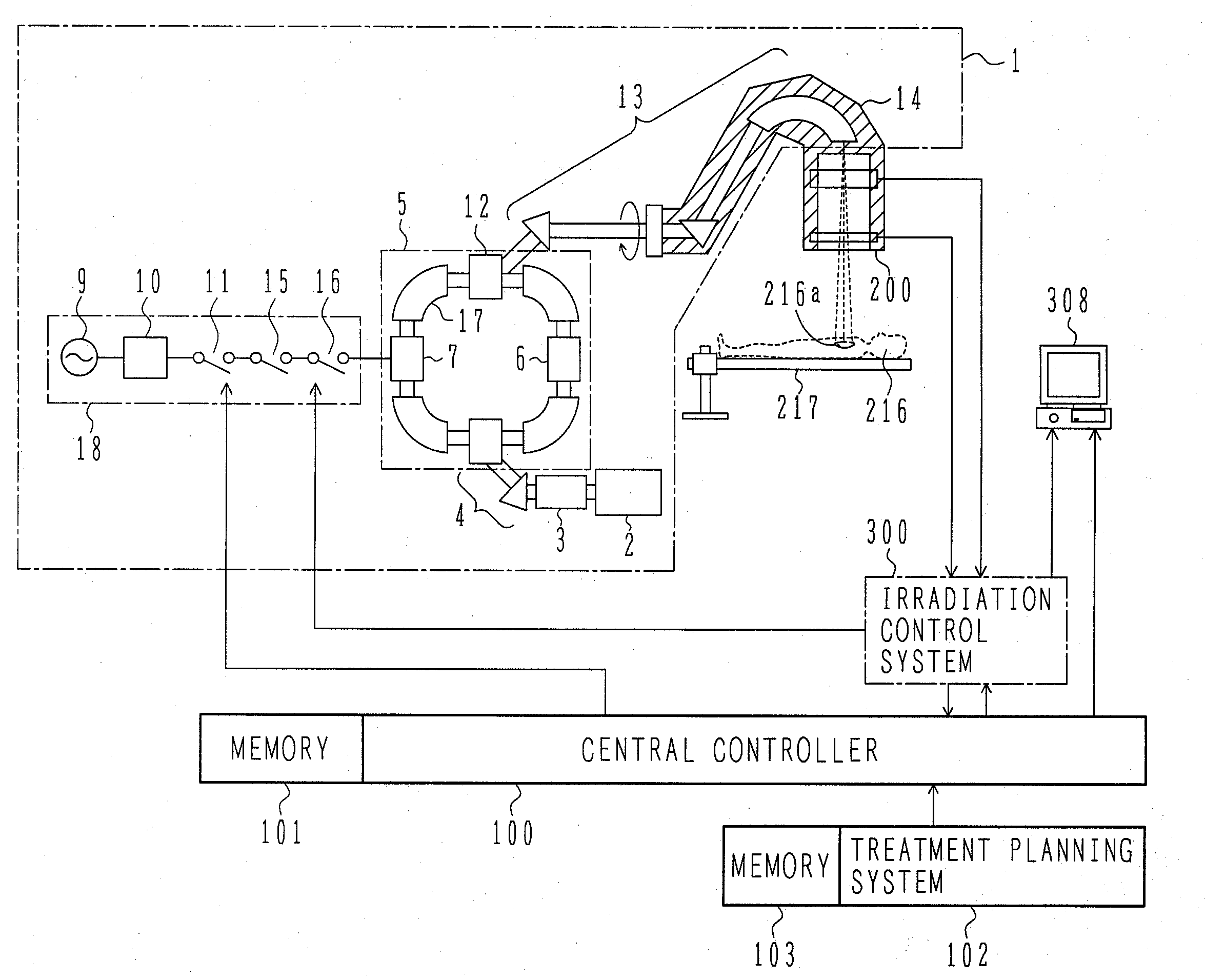
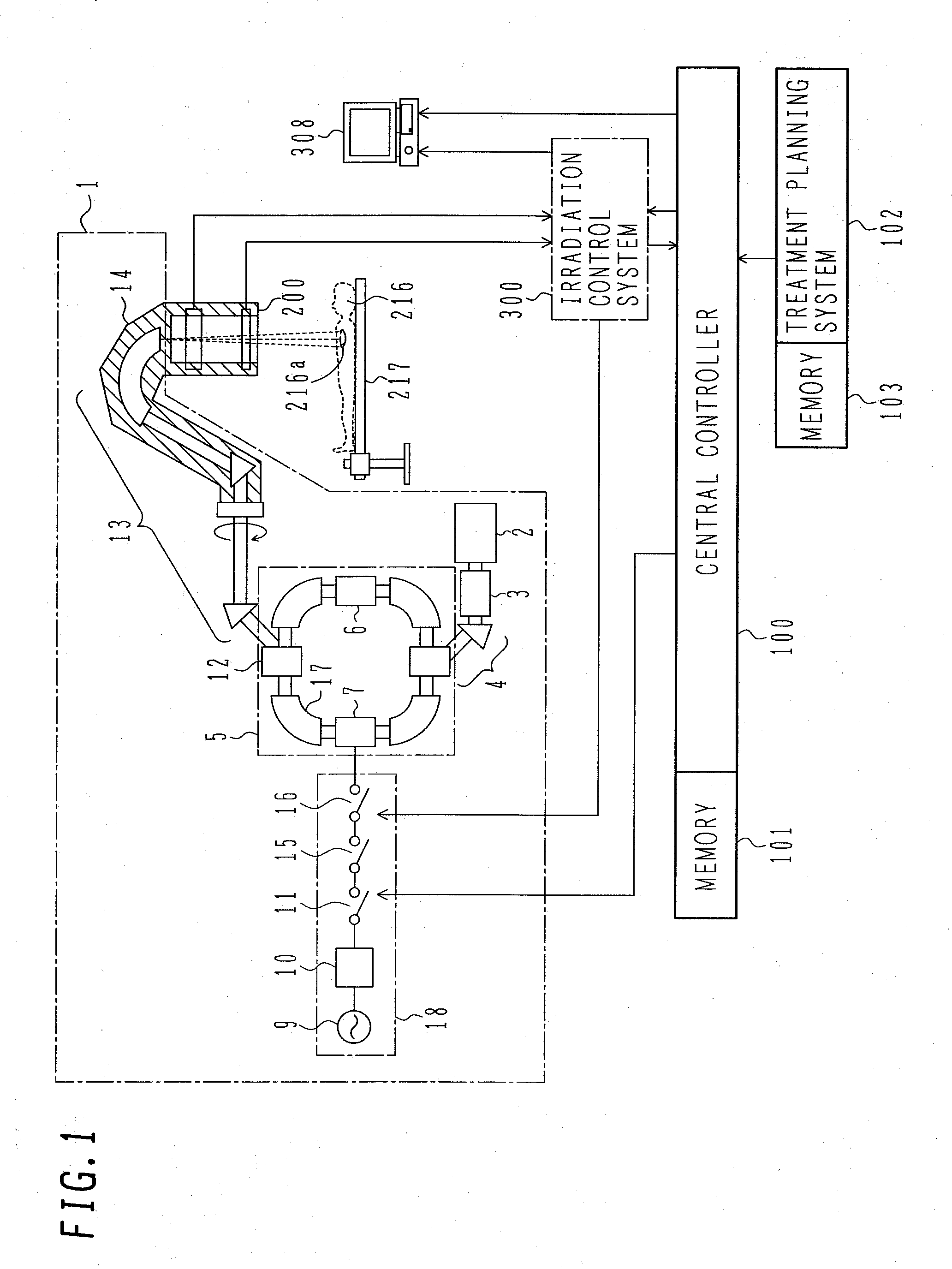
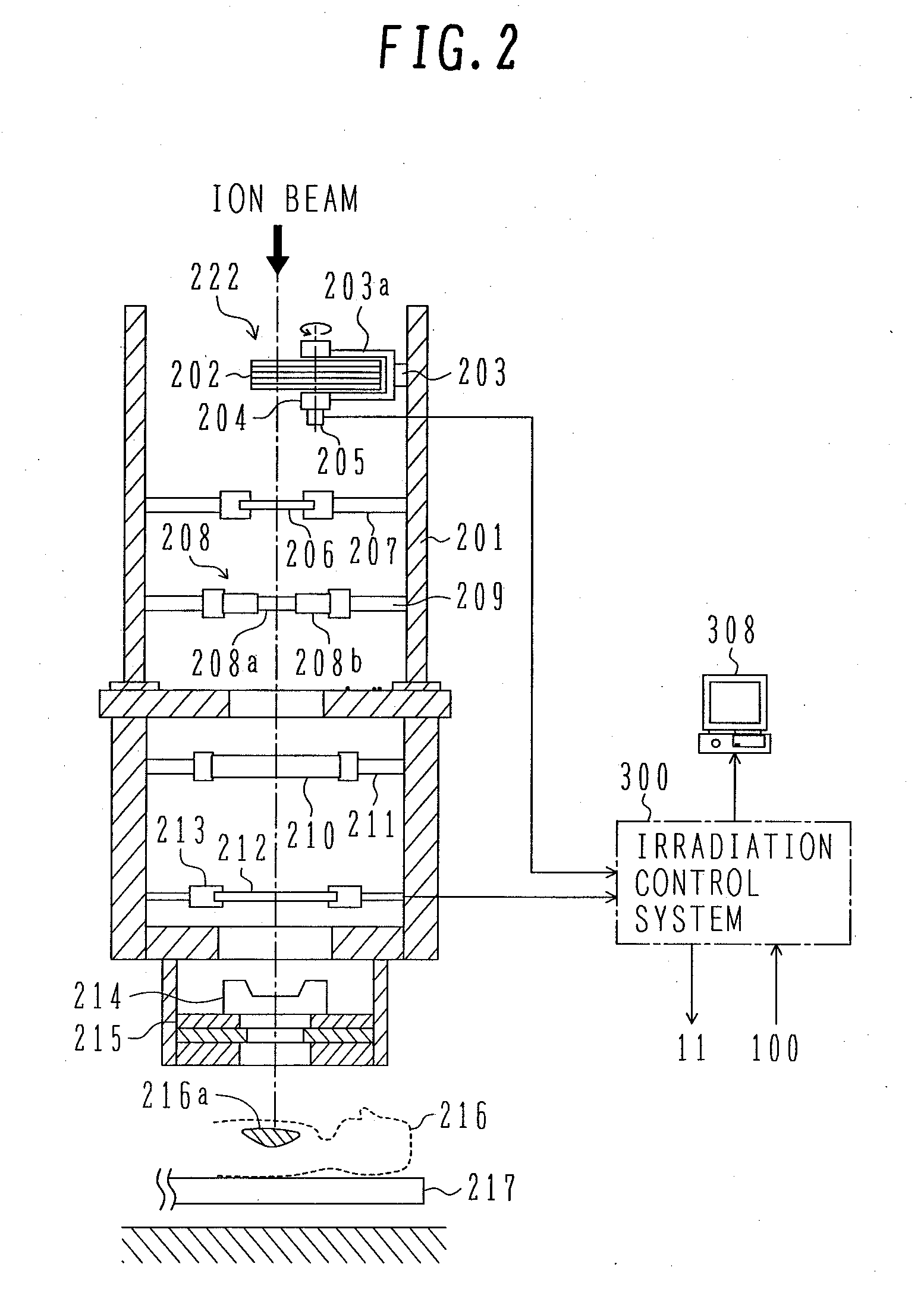
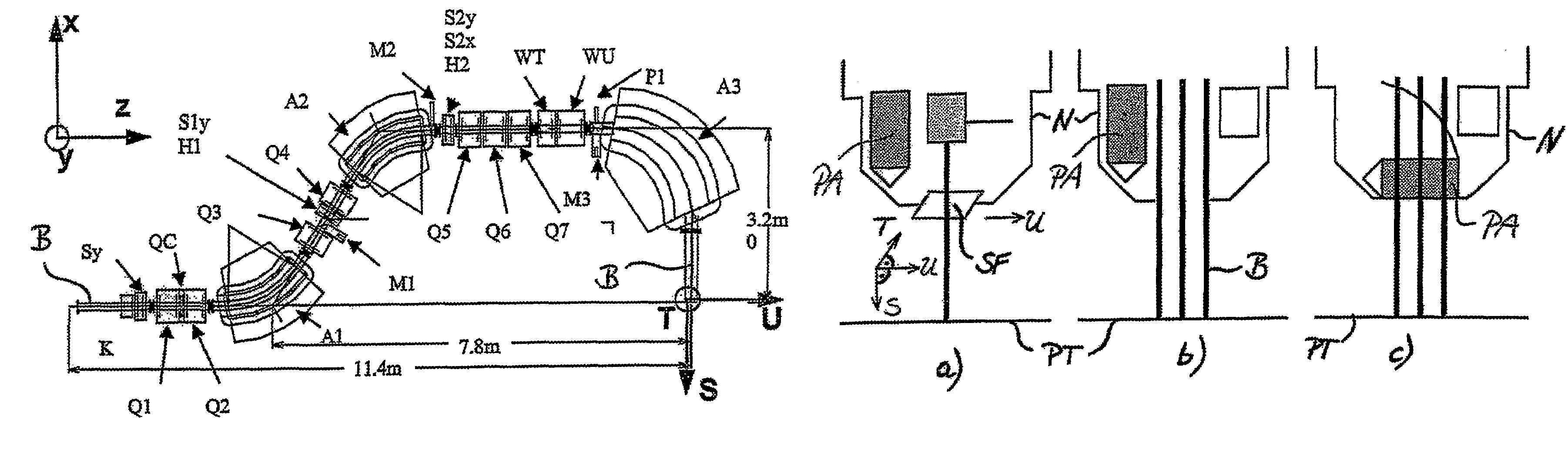
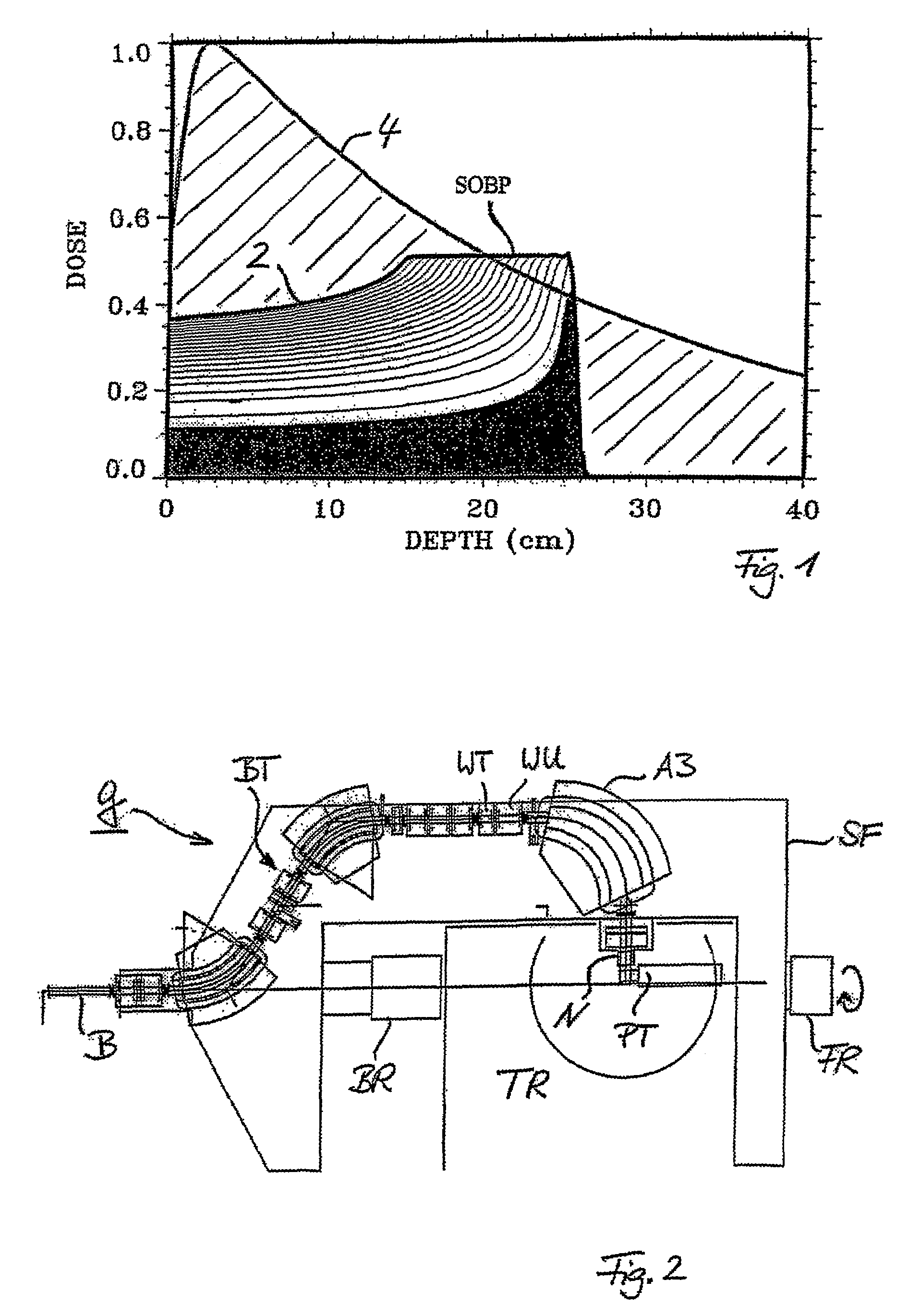
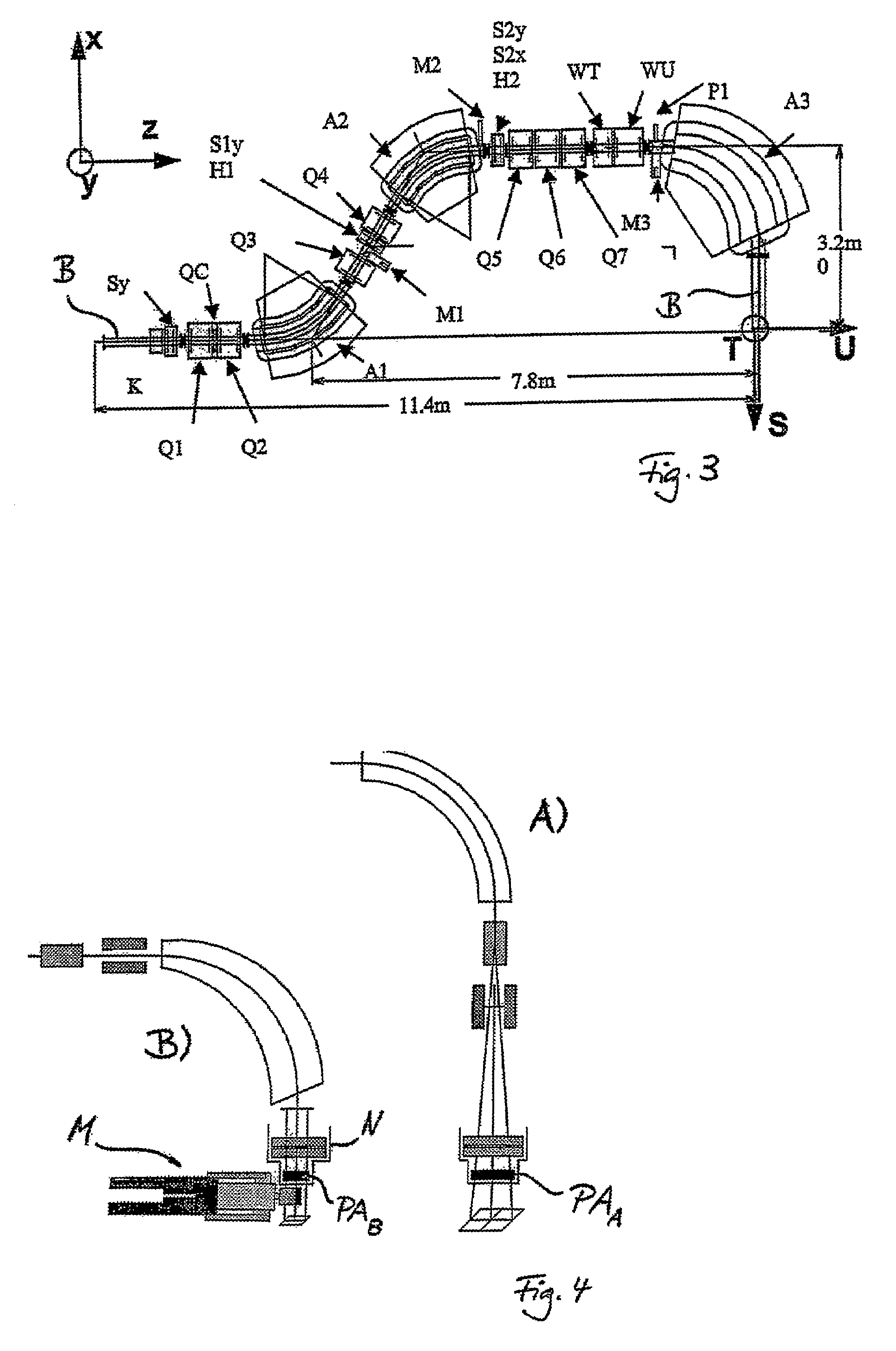
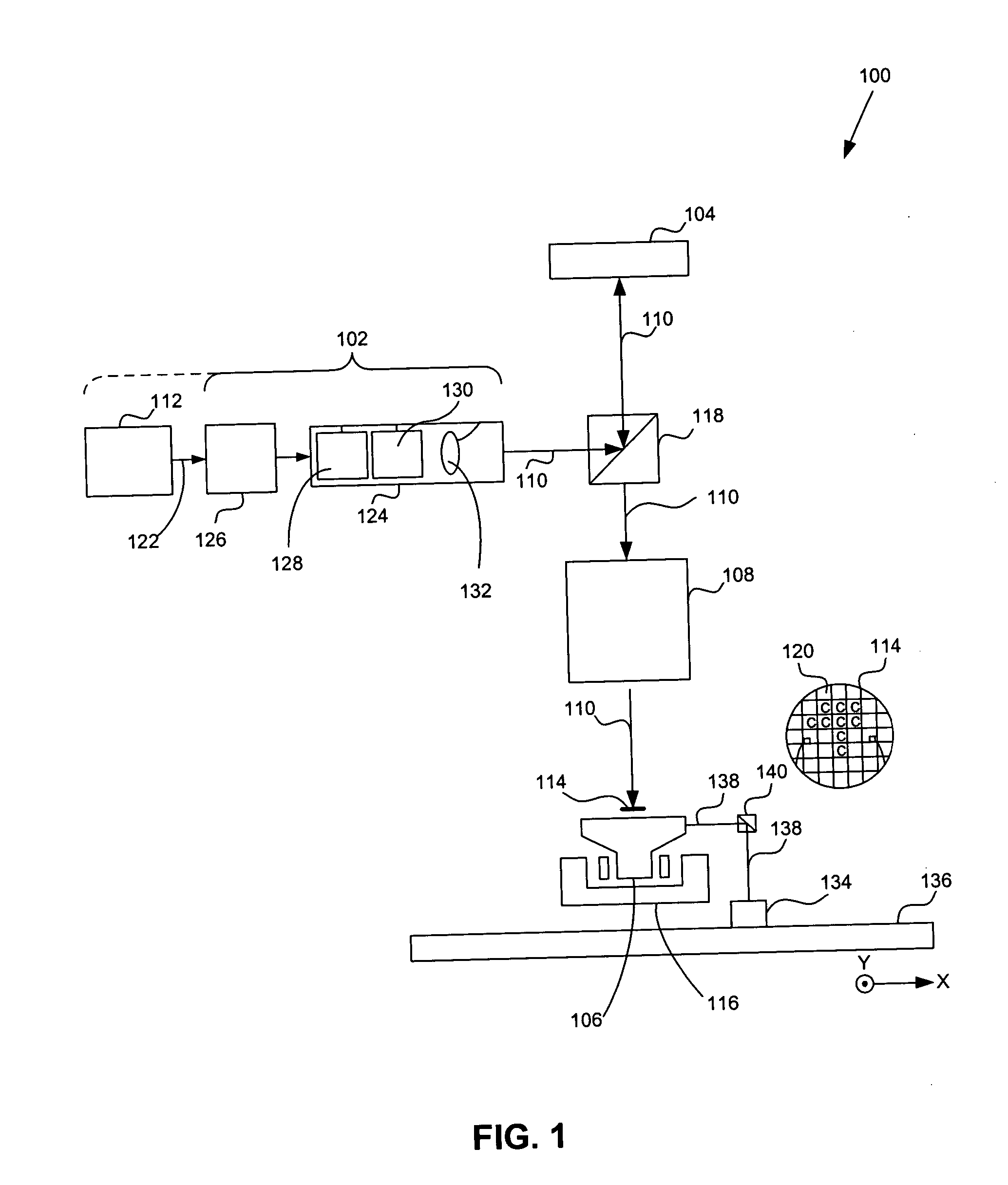
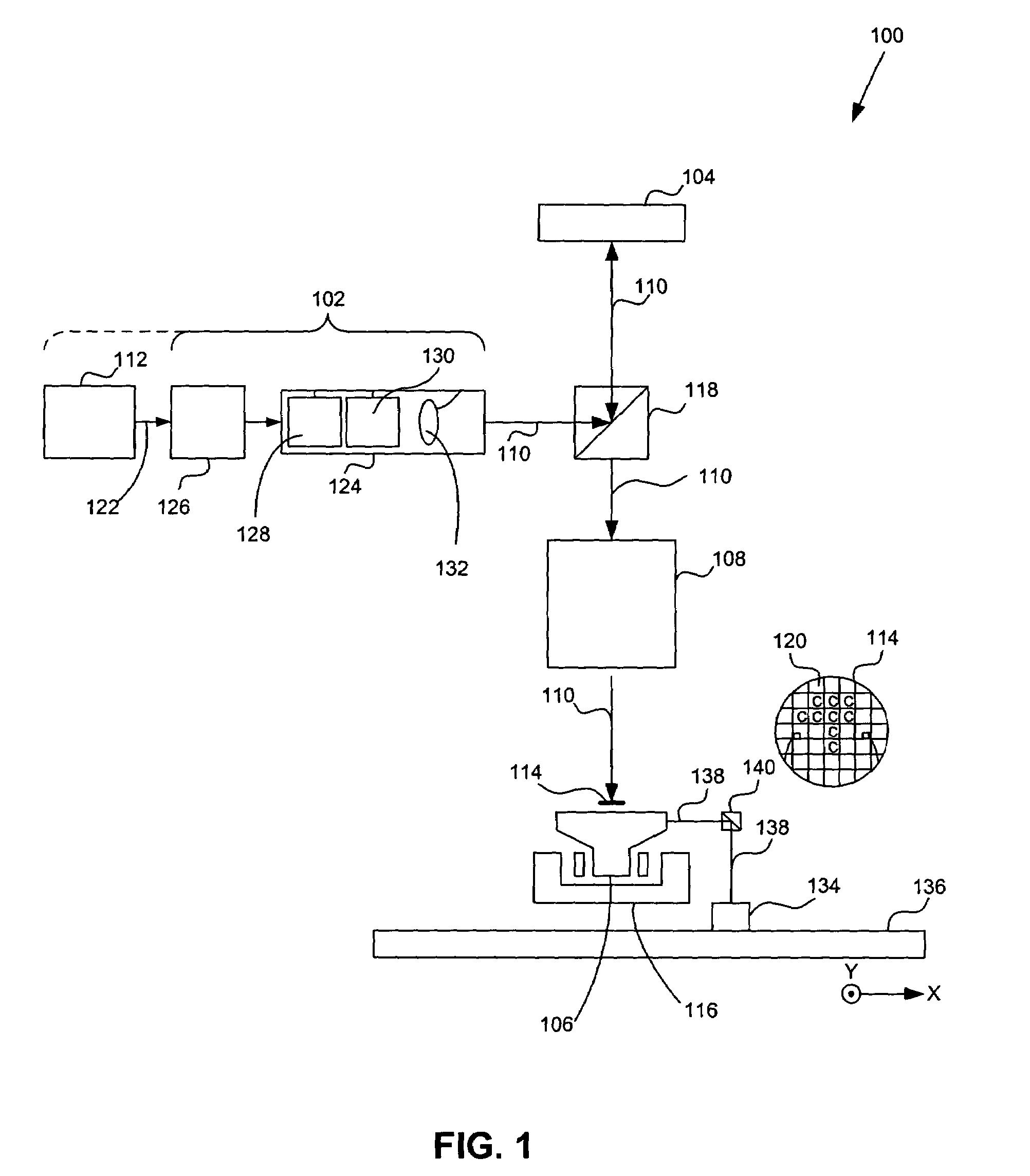
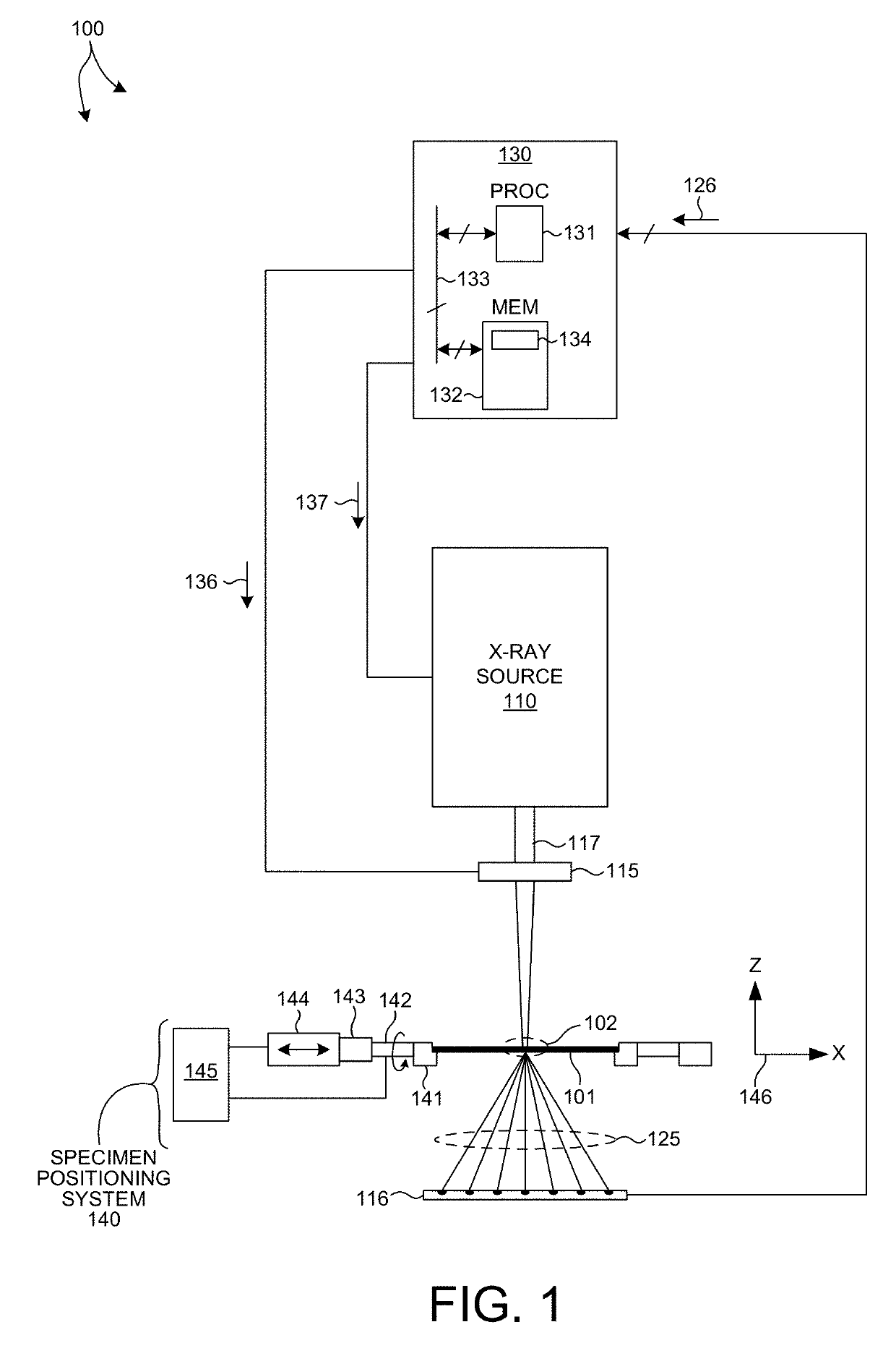
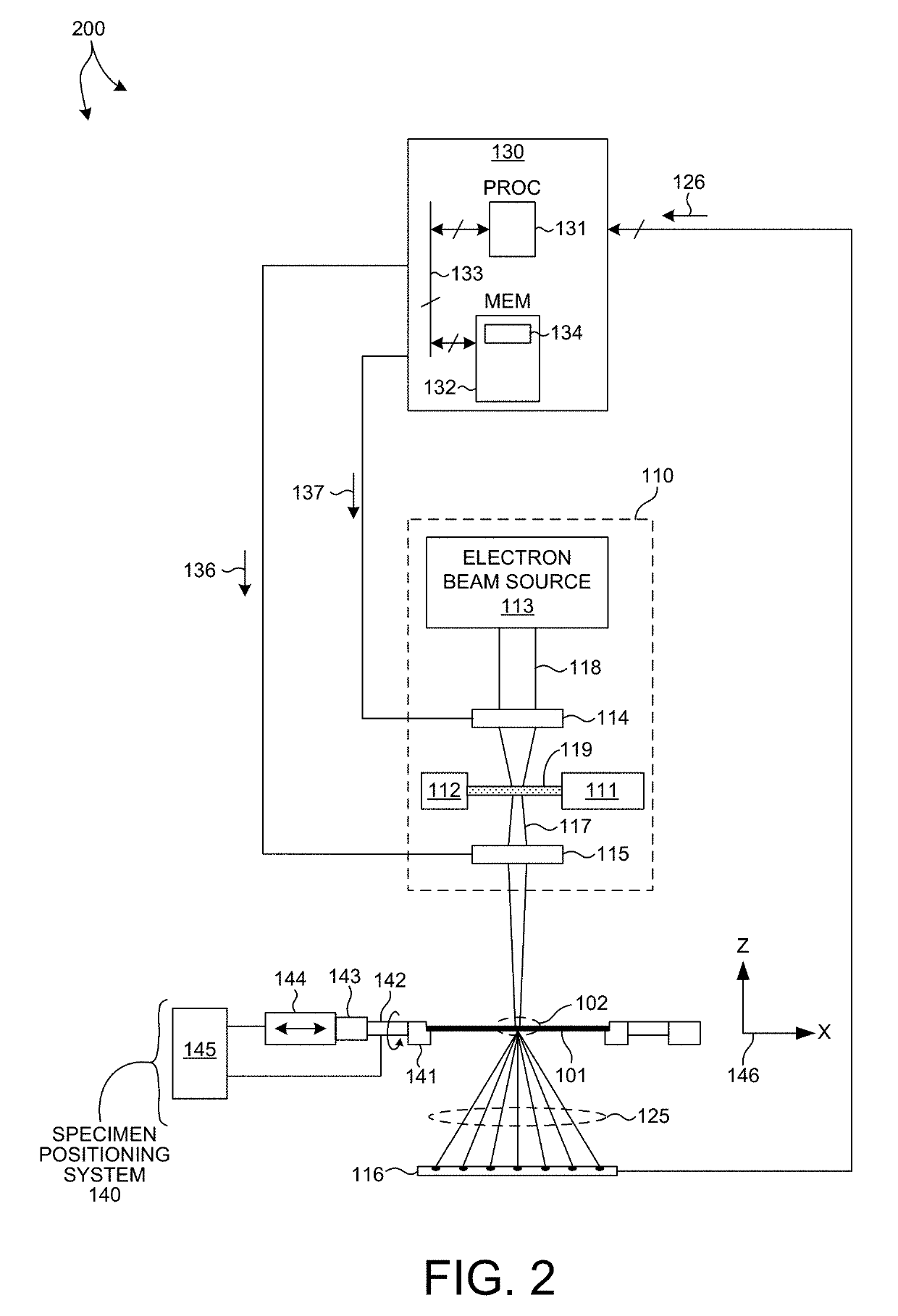
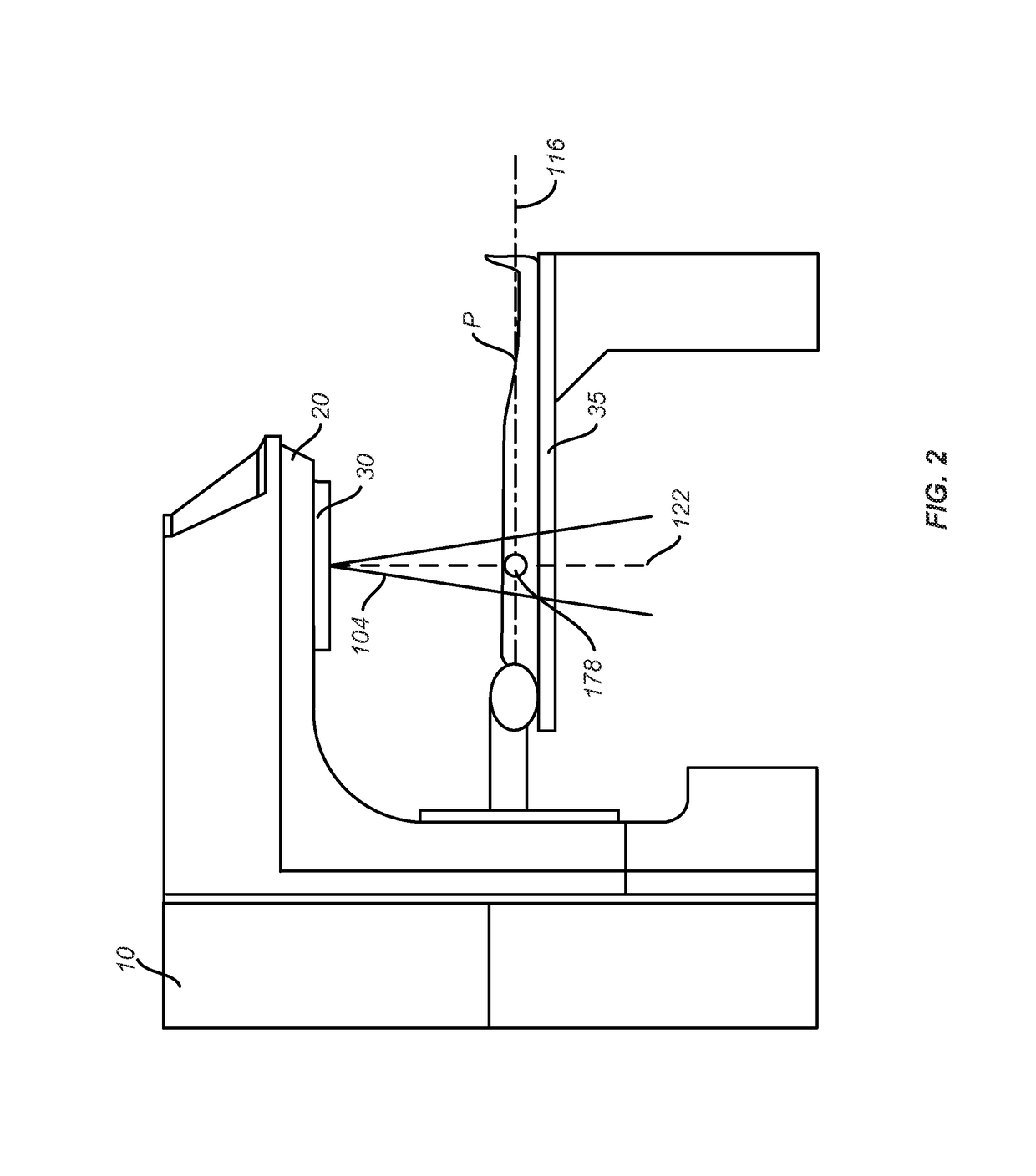
System for the Delivery of Proton Therapy
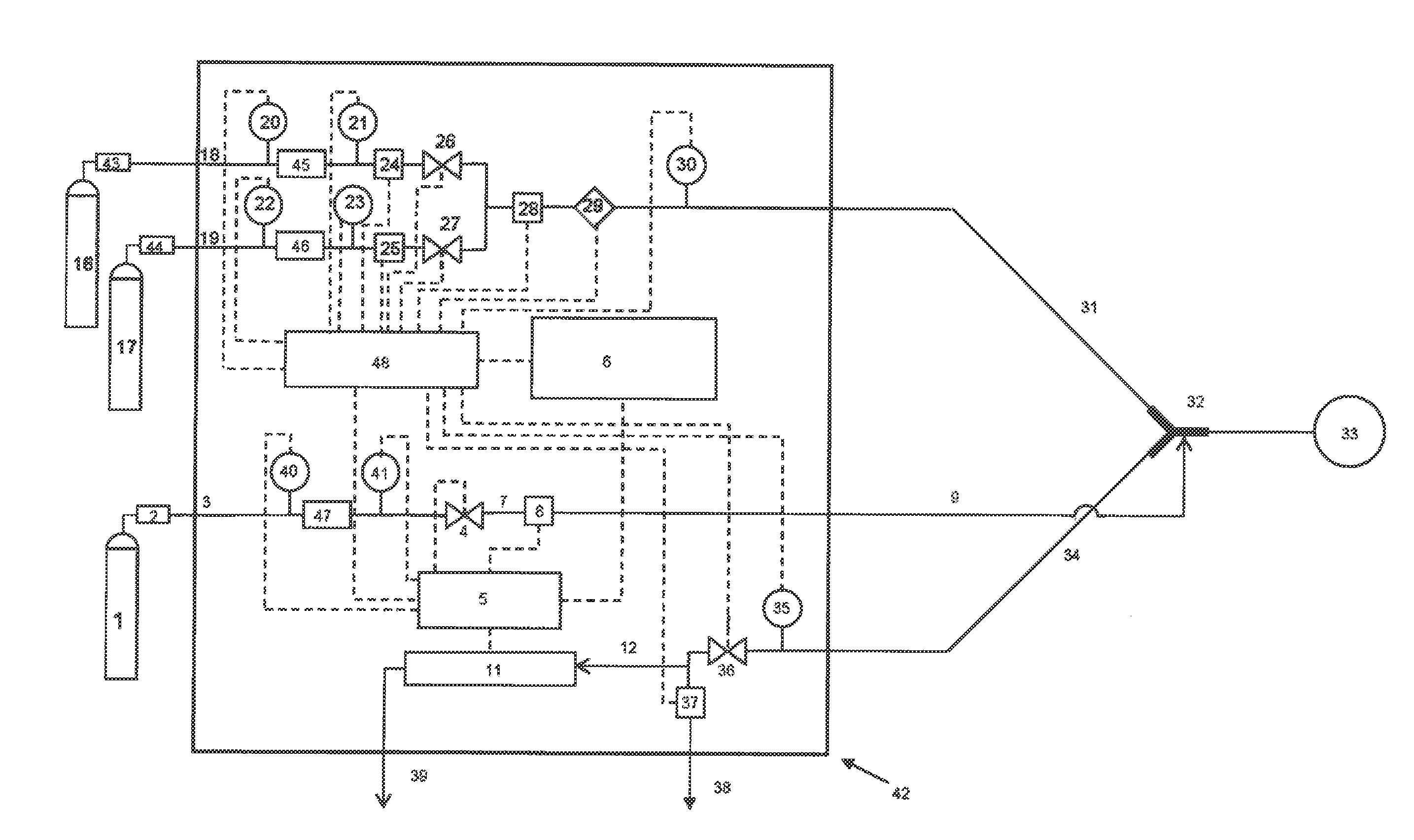
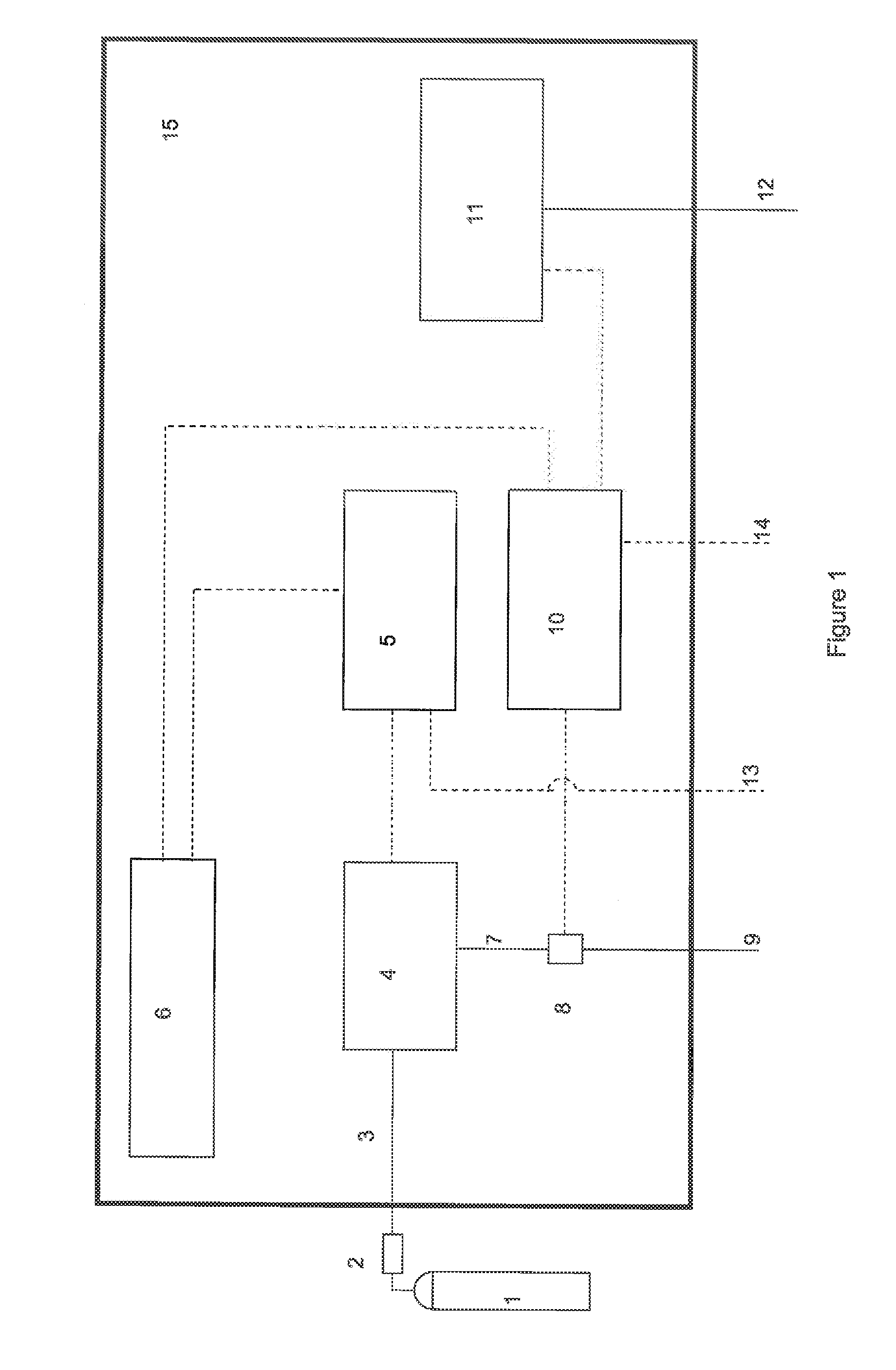
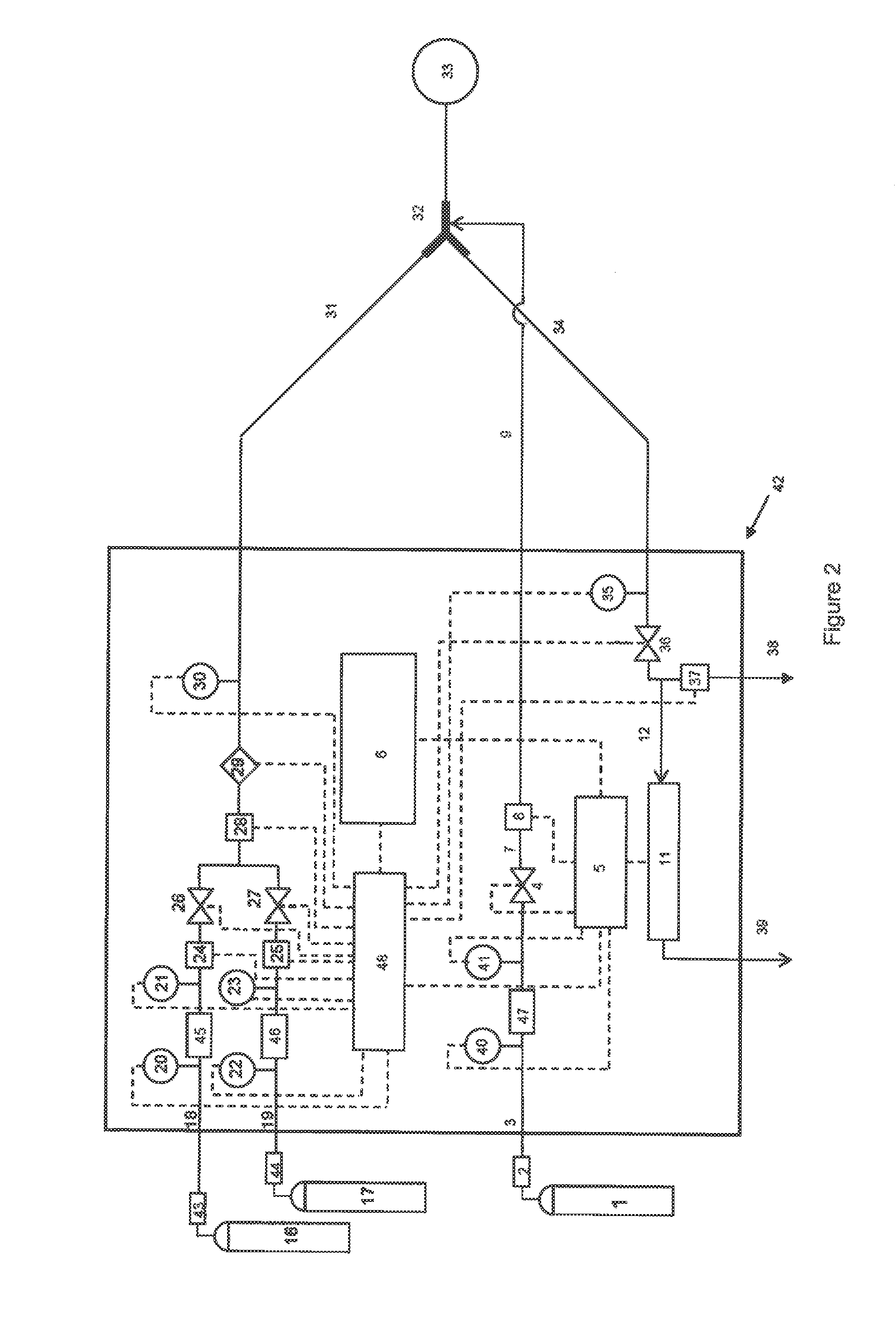
InactiveUS20080023644A1Improve consistencyIncrease rangeThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersProtonIntensity modulation
A process for an intensity-modulated proton therapy of a predetermined volume within an object includes discretising the predetermined volume into a number of iso-energy layers each corresponding to a determined energy of the proton beam. A final target dose distribution is determined for each iso-energy layer. The final target dose distribution or at least a predetermined part of this final target dose distribution is applied by parallel beam scanning by controlling the respective beam sweepers, thereby scanning one iso-energy layer after the other using an intensity-modulated proton beam while scanning a predetermined iso-energy layer.
Owner:PAUL SCHERRER INSTITUT
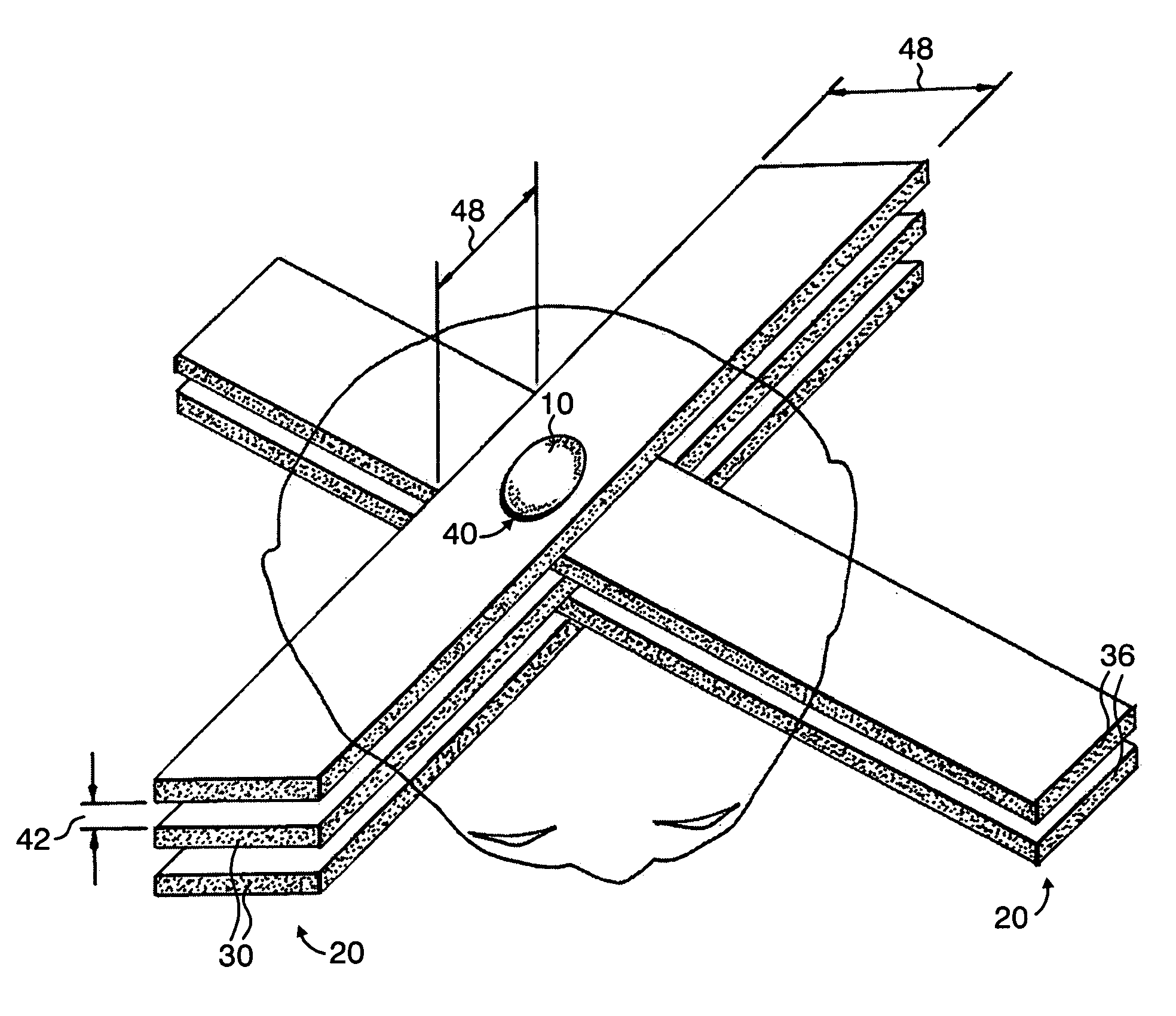
Methods for implementing microbeam radiation therapy
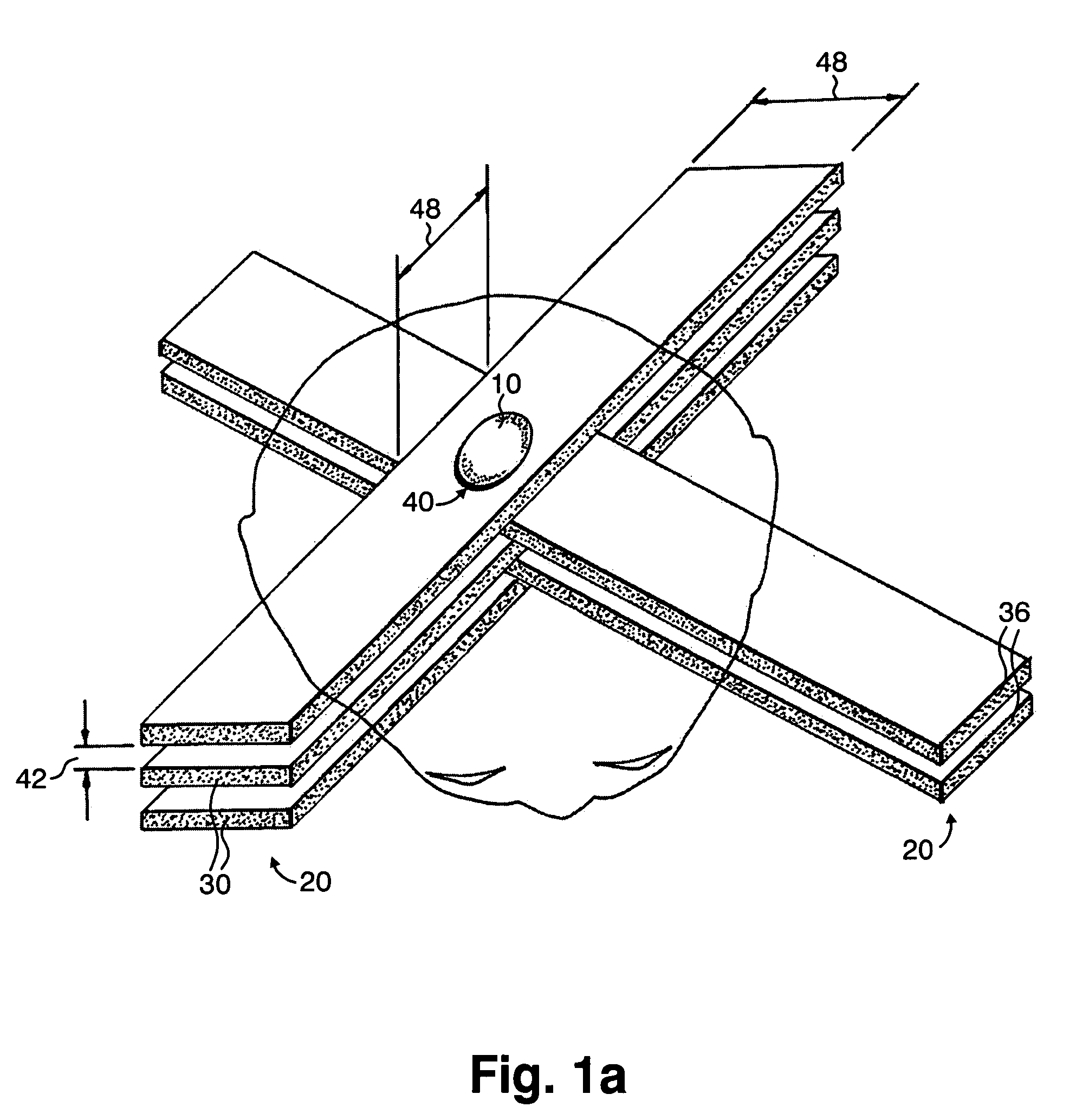
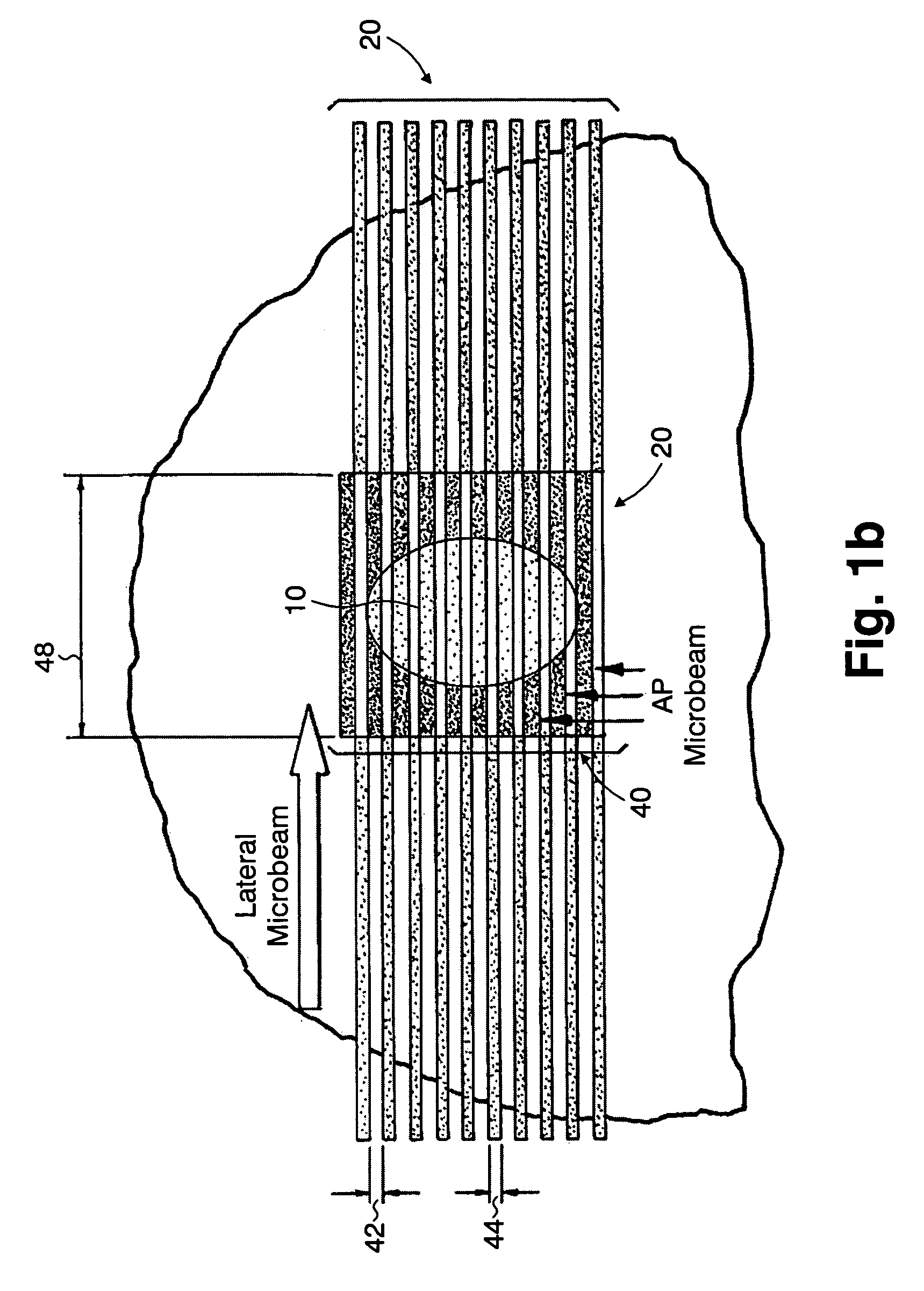
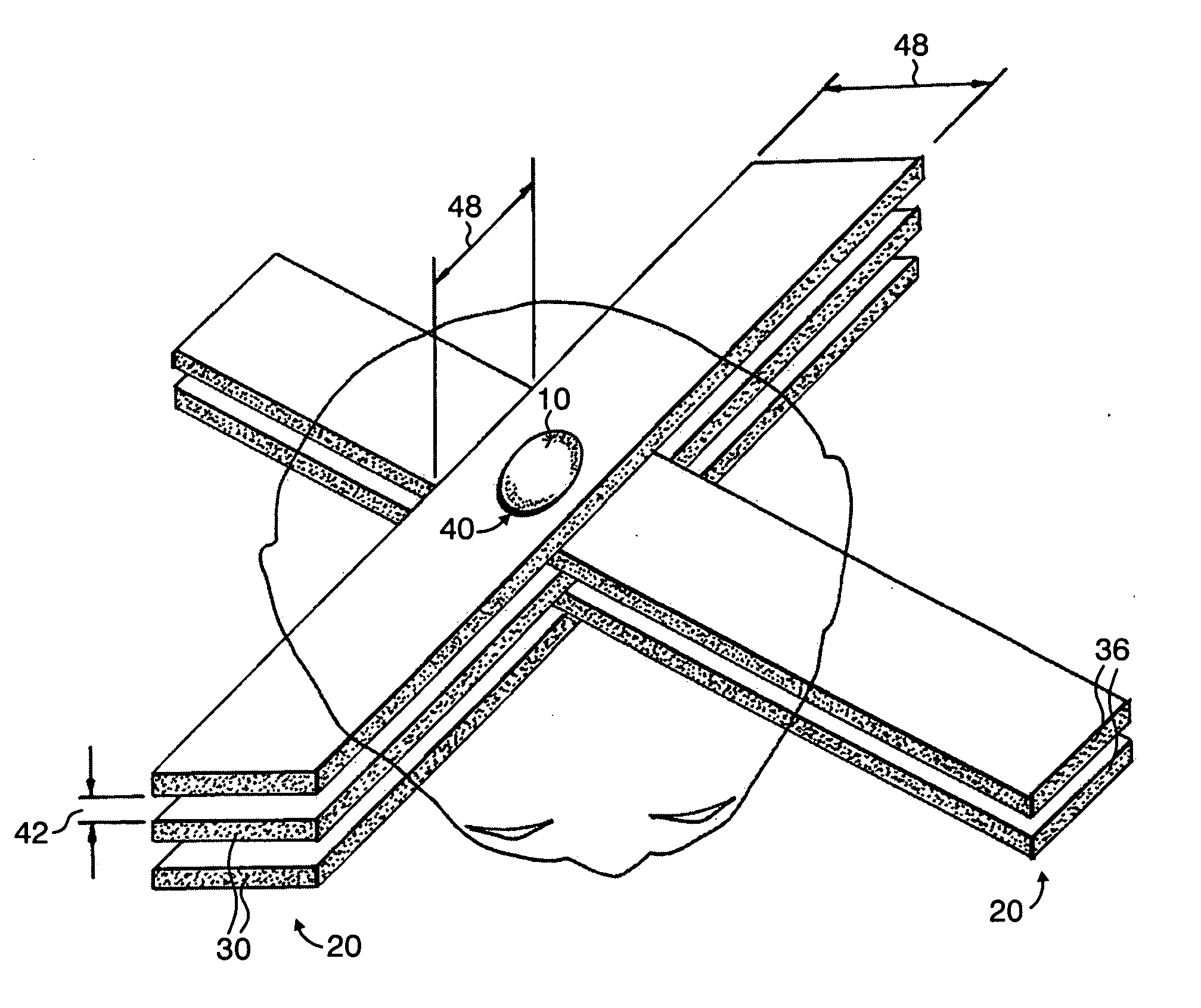
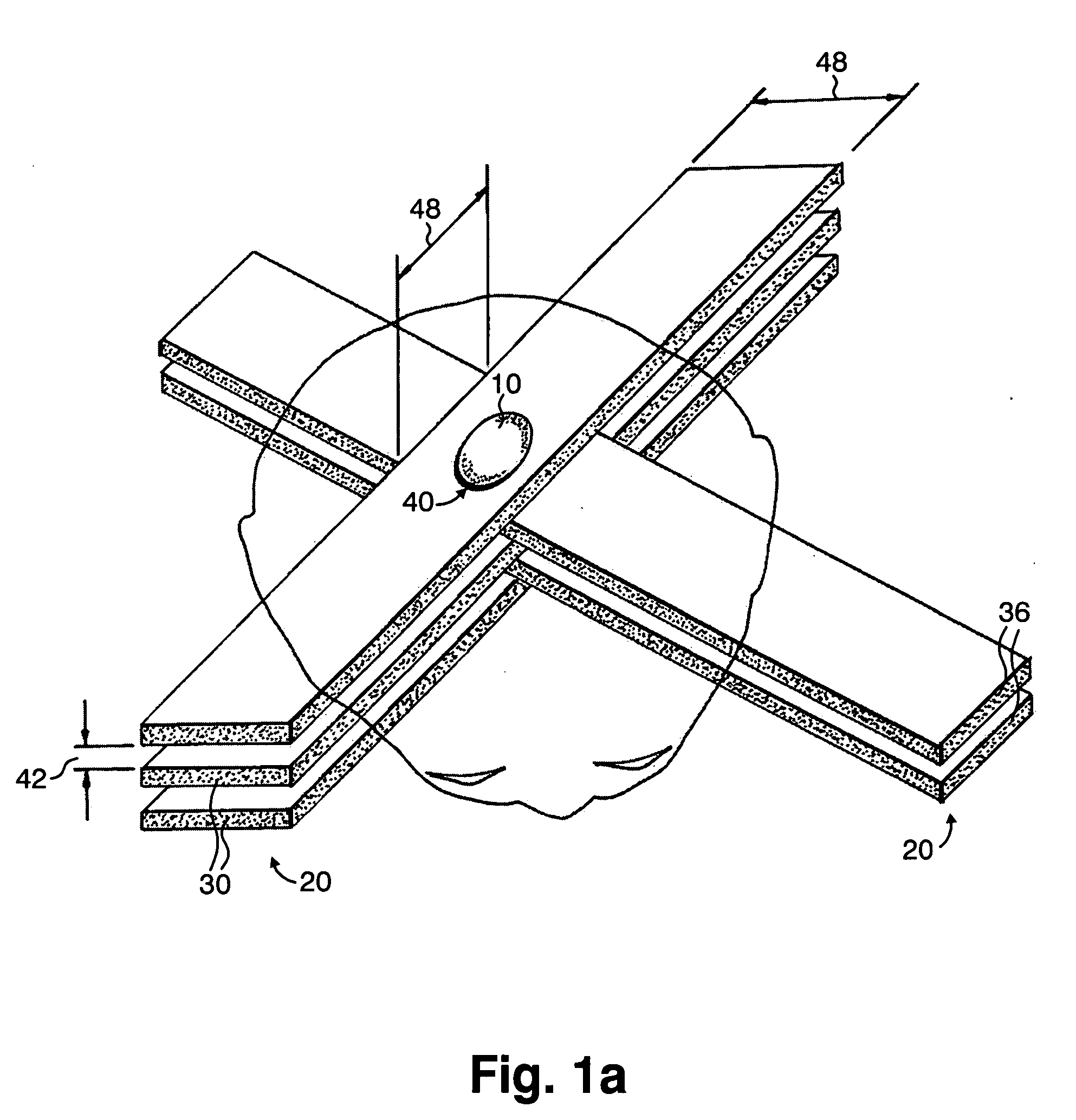
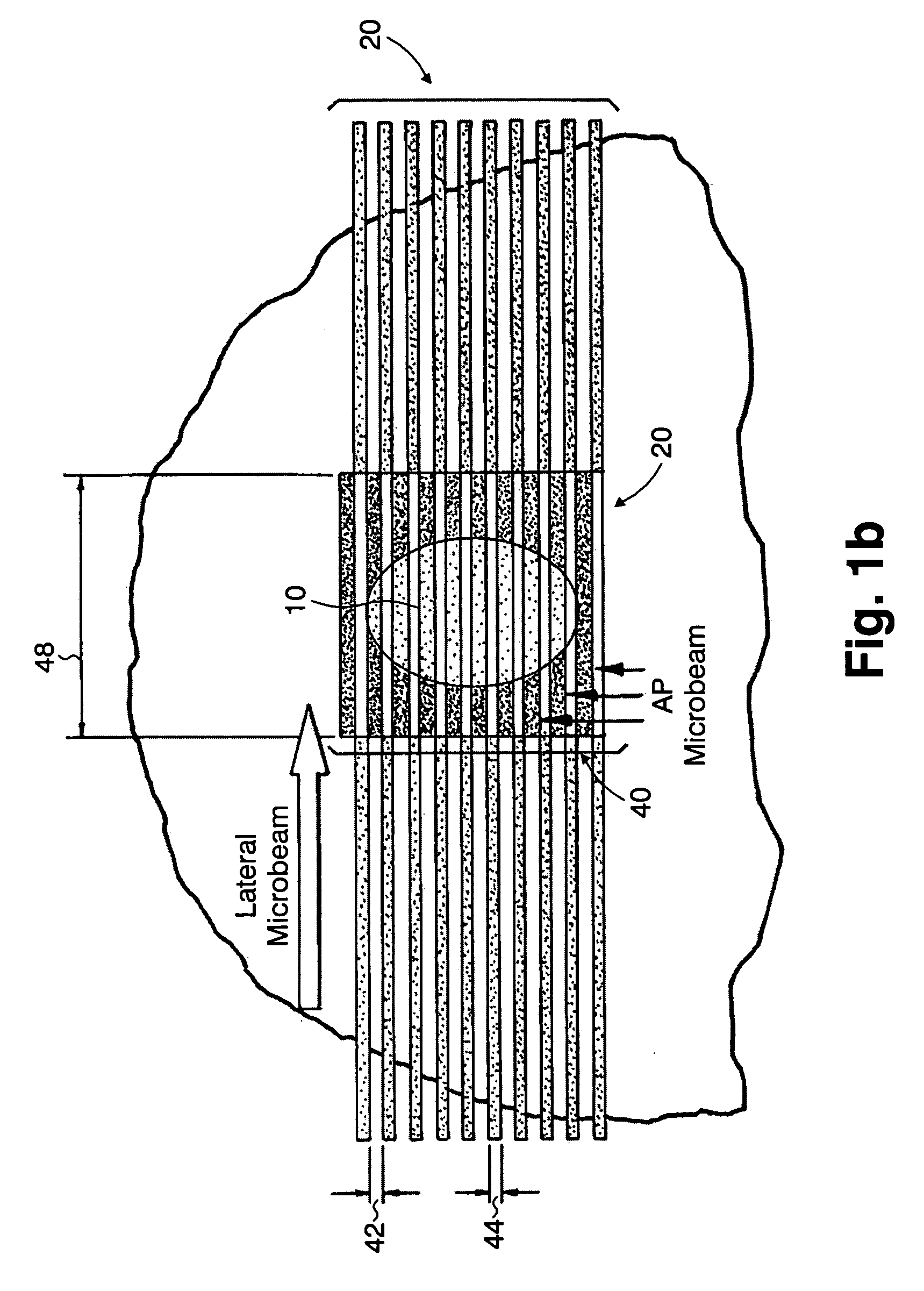
InactiveUS7194063B2Reduce harmEasily damagedIrradiation devicesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyLight beamGadolinium
A method of performing radiation therapy includes delivering a therapeutic dose such as X-ray only to a target (e.g., tumor) with continuous broad beam (or in-effect continuous) using arrays of parallel planes of radiation (microbeams / microplanar beams). Microbeams spare normal tissues, and when interlaced at a tumor, form a broad-beam for tumor ablation. Bidirectional interlaced microbeam radiation therapy (BIMRT) uses two orthogonal arrays with inter-beam spacing equal to beam thickness. Multidirectional interlaced MRT (MIMRT) includes irradiations of arrays from several angles, which interleave at the target. Contrast agents, such as tungsten and gold, are administered to preferentially increase the target dose relative to the dose in normal tissue. Lighter elements, such as iodine and gadolinium, are used as scattering agents in conjunction with non-interleaving geometries of array(s) (e.g., unidirectional or cross-fired (intersecting) to generate a broad beam effect only within the target by preferentially increasing the valley dose within the tumor.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Charged particle beam irradiation system and charged particle beam extraction method
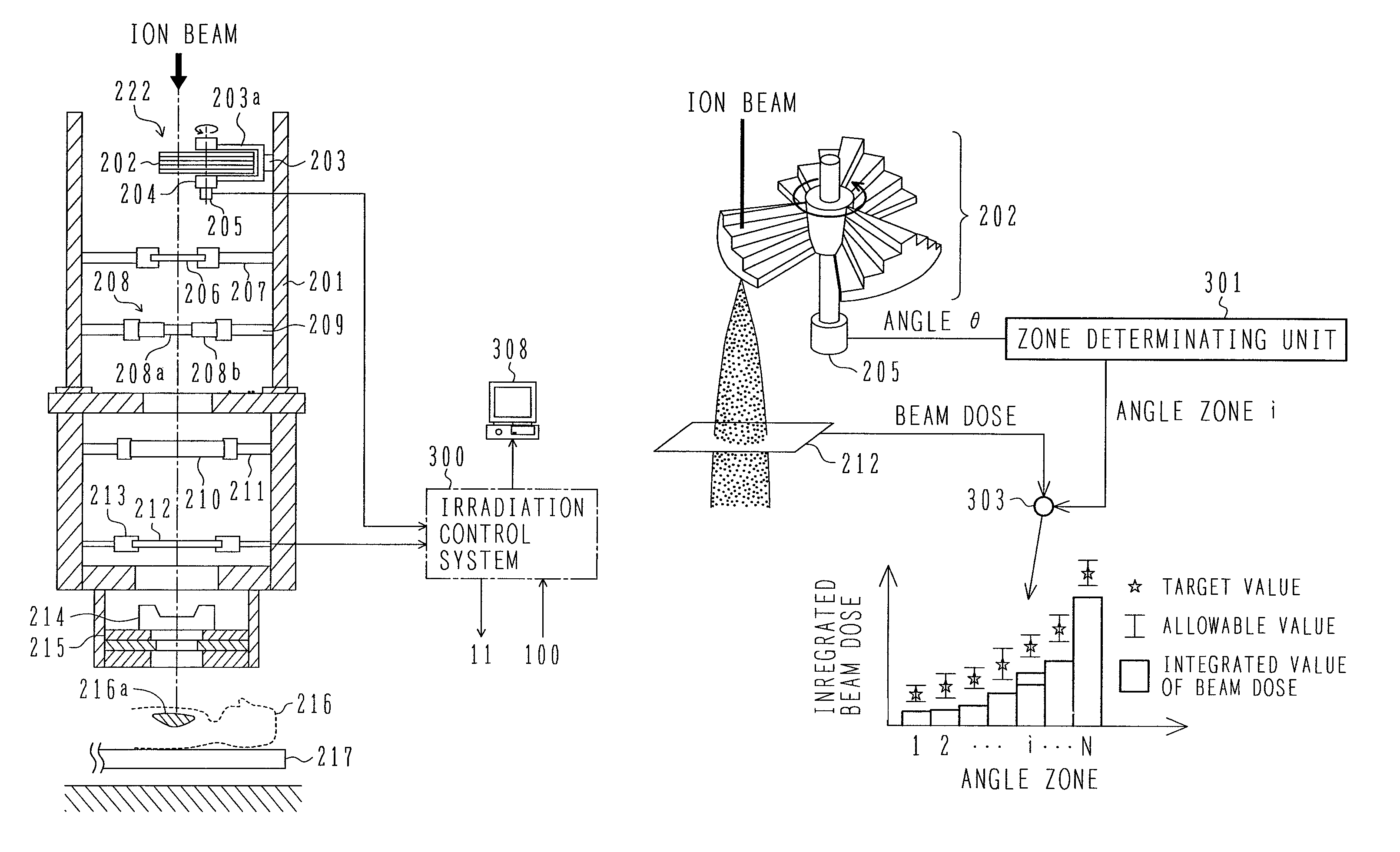
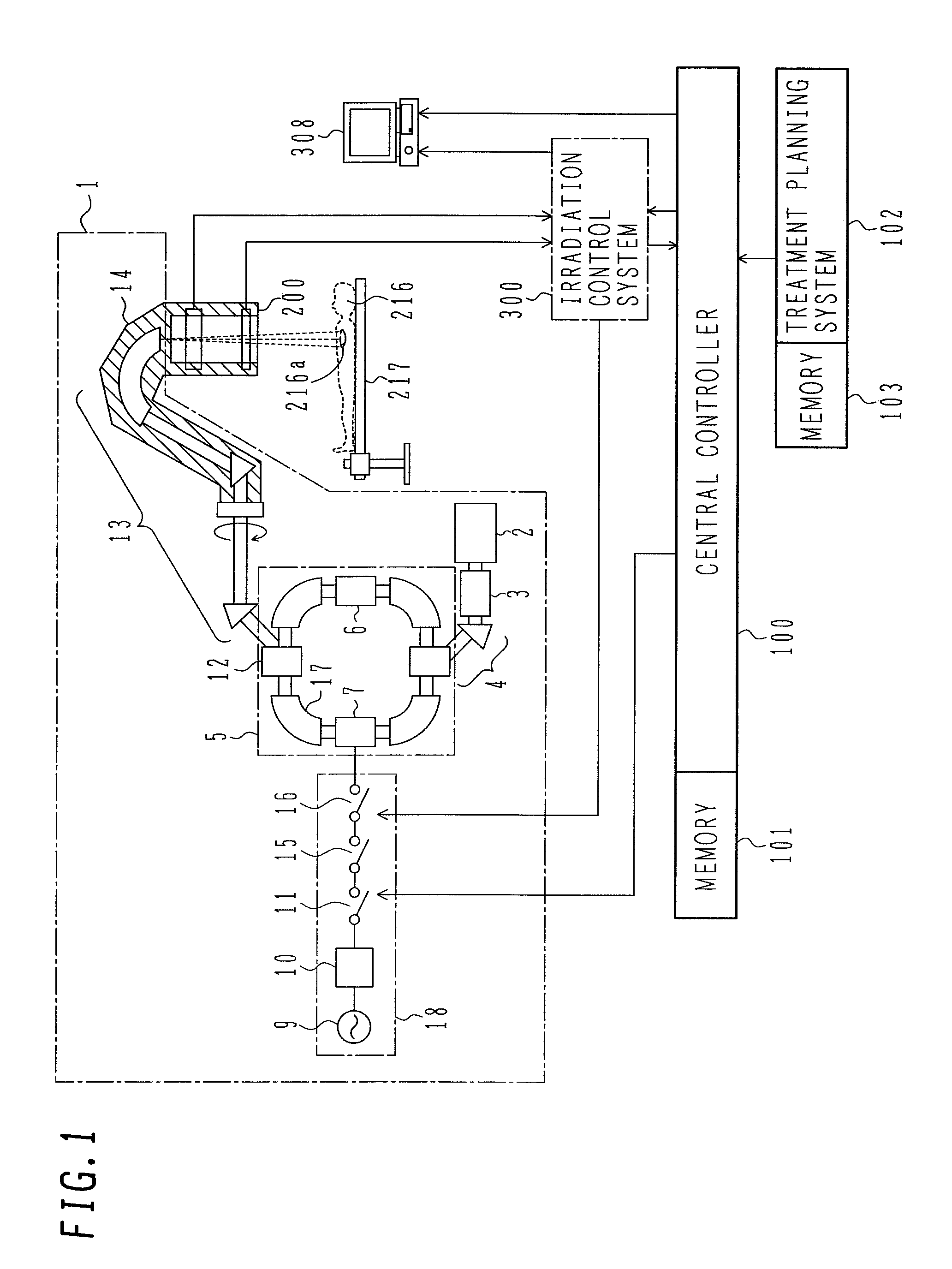
InactiveUS7825388B2Reduce probabilityEasy to adjustElectrotherapyRadiation/particle handlingParticle beamIon beam
A charged particle beam irradiation system and a charged particle beam extraction method which can prevent erroneous irradiation of a charged particle beam in the direction of advance of the charged particle beam. The system and method are featured in stopping supply of an ion beam to one or more of a plurality of angle zones in each of which a target dose is attained, the angle zones being formed by dividing an RMW in a rotating direction thereof, and in allowing the supply of the ion beam to one or more other angle zones in each of which a target dose is not yet attained. The invention can easily adjust beam doses at various positions in an affected part of the patient body in the direction of advance of the ion beam, and can greatly reduce the probability of erroneous irradiation that the beam dose becomes excessive or deficient at the various positions within the affected part of the patient body in the direction of advance of the ion beam.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Charged particle beam irradiation system and charged particle beam extraction method
InactiveUS20080067405A1Reduce probabilityEasy to adjustThermometer detailsElectrotherapyParticle beamIon beam
A charged particle beam irradiation system and a charged particle beam extraction method which can prevent erroneous irradiation of a charged particle beam in the direction of advance of the charged particle beam. The system and method are featured in stopping supply of an ion beam to one or more of a plurality of angle zones in each of which a target dose is attained, the angle zones being formed by dividing an RMW in a rotating direction thereof, and in allowing the supply of the ion beam to one or more other angle zones in each of which a target dose is not yet attained. The invention can easily adjust beam doses at various positions in an affected part of the patient body in the direction of advance of the ion beam, and can greatly reduce the probability of erroneous irradiation that the beam dose becomes excessive or deficient at the various positions within the affected part of the patient body in the direction of advance of the ion beam.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Methods for implementing microbeam radiation therapy
InactiveUS20060176997A1Enhance in-beam absorptionEnhance therapeutic doseX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIrradiation devicesAbnormal tissue growthOrthogonal array
A method of performing radiation therapy includes delivering a therapeutic dose such as X-ray only to a target (e.g., tumor) with continuous broad beam (or in-effect continuous) using arrays of parallel planes of radiation (microbeams / microplanar beams). Microbeams spare normal tissues, and when interlaced at a tumor, form a broad-beam for tumor ablation. Bidirectional interlaced microbeam radiation therapy (BIMRT) uses two orthogonal arrays with inter-beam spacing equal to beam thickness. Multidirectional interlaced MRT (MIMRT) includes irradiations of arrays from several angles, which interleave at the target. Contrast agents, such as tungsten and gold, are administered to preferentially increase the target dose relative to the dose in normal tissue. Lighter elements, such as iodine and gadolinium, are used as scattering agents in conjunction with non-interleaving geometries of array(s) (e.g., unidirectional or cross-fired (intersecting) to generate a broad beam effect only within the target by preferentially increasing the valley dose within the tumor.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
System for the delivery of proton therapy
InactiveUS7560715B2Avoid the broadening of the beam due MCSIncrease rangeThermometer detailsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsProtonLight beam
A process for an intensity-modulated proton therapy of a predetermined volume within an object includes discretising the predetermined volume into a number of iso-energy layers each corresponding to a determined energy of the proton beam. A final target dose distribution is determined for each iso-energy layer. The final target dose distribution or at least a predetermined part of this final target dose distribution is applied by parallel beam scanning by controlling the respective beam sweepers, thereby scanning one iso-energy layer after the other using an intensity-modulated proton beam while scanning a predetermined iso-energy layer.
Owner:PAUL SCHERRER INSTITUT
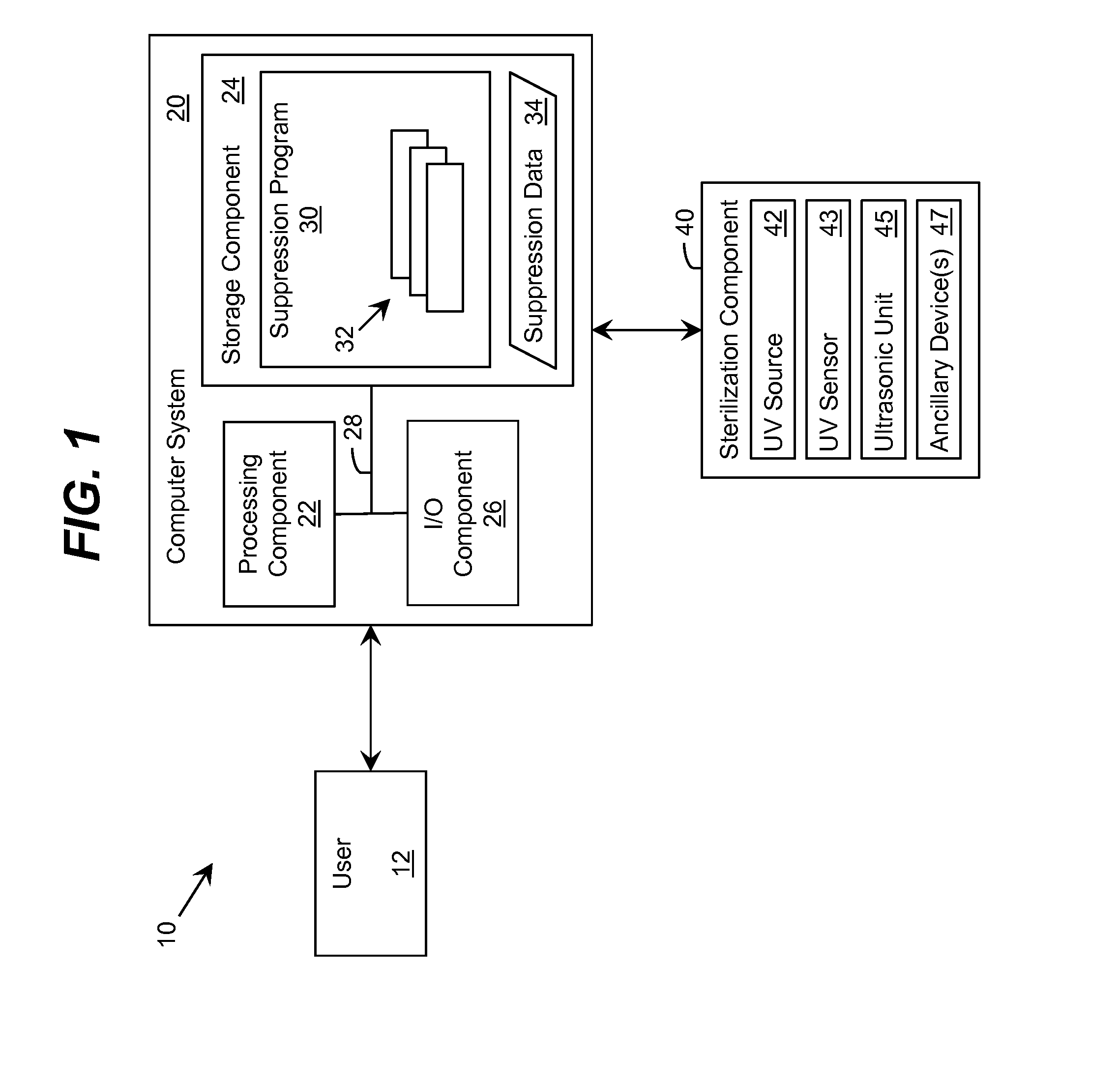
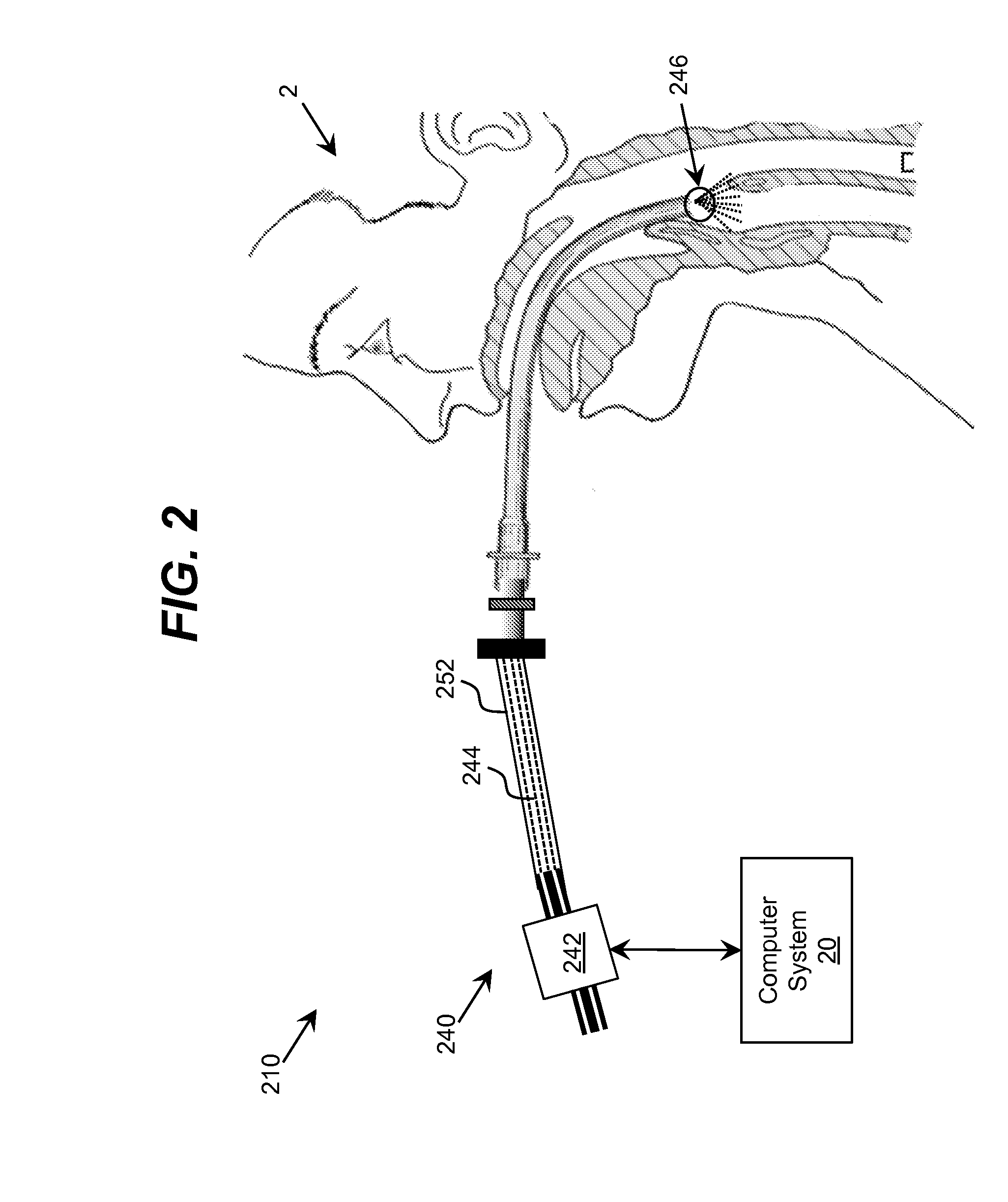
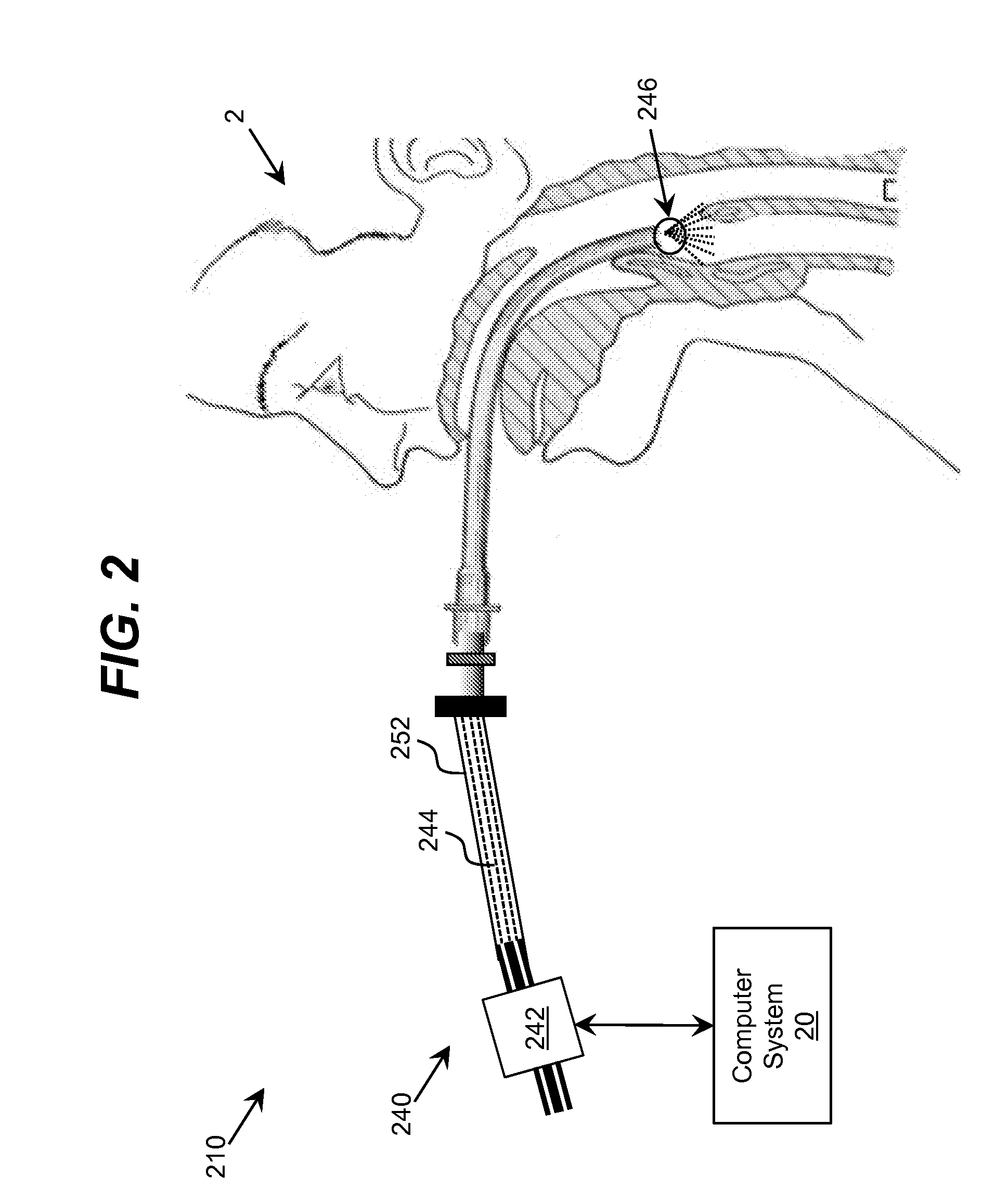
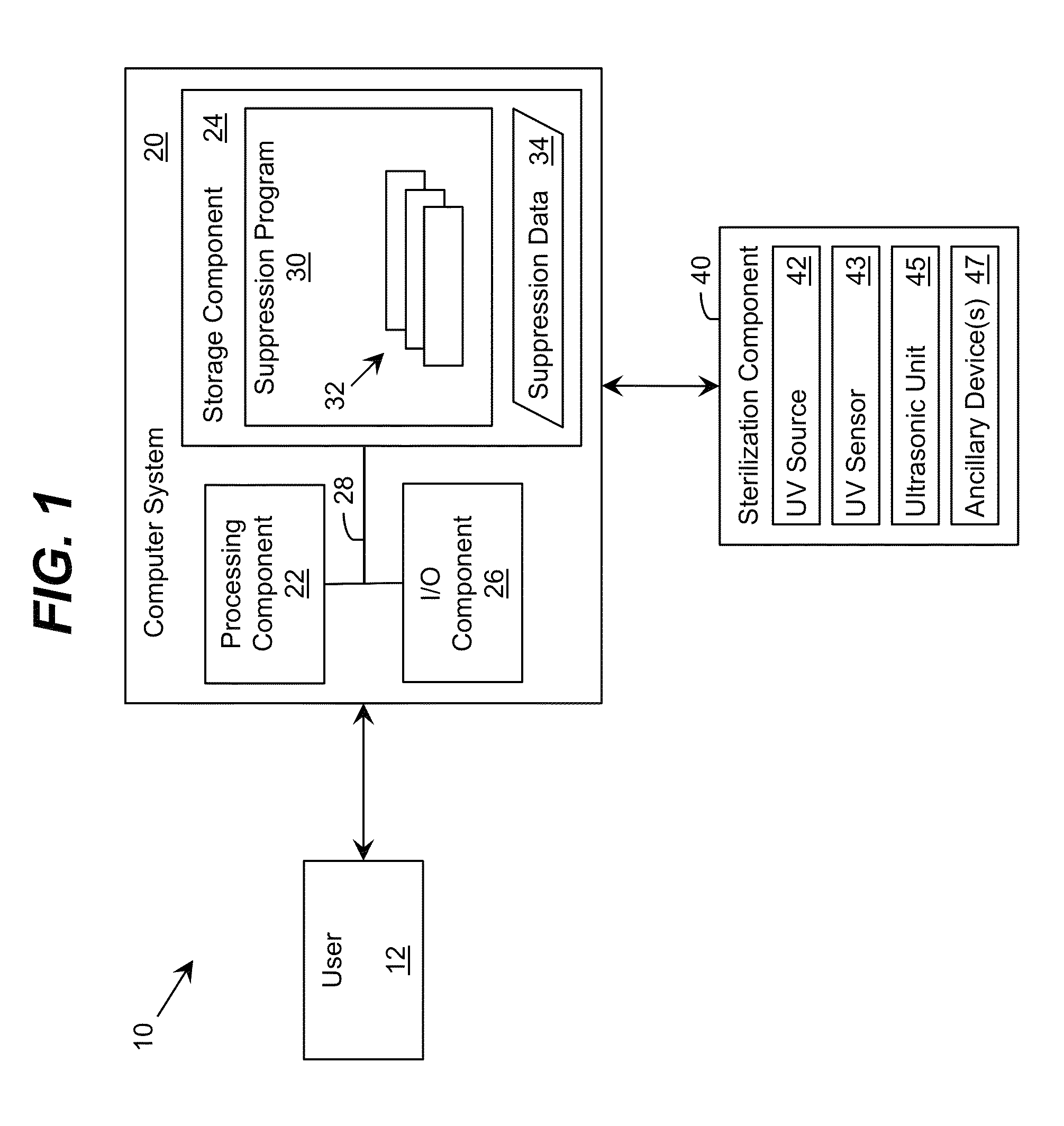
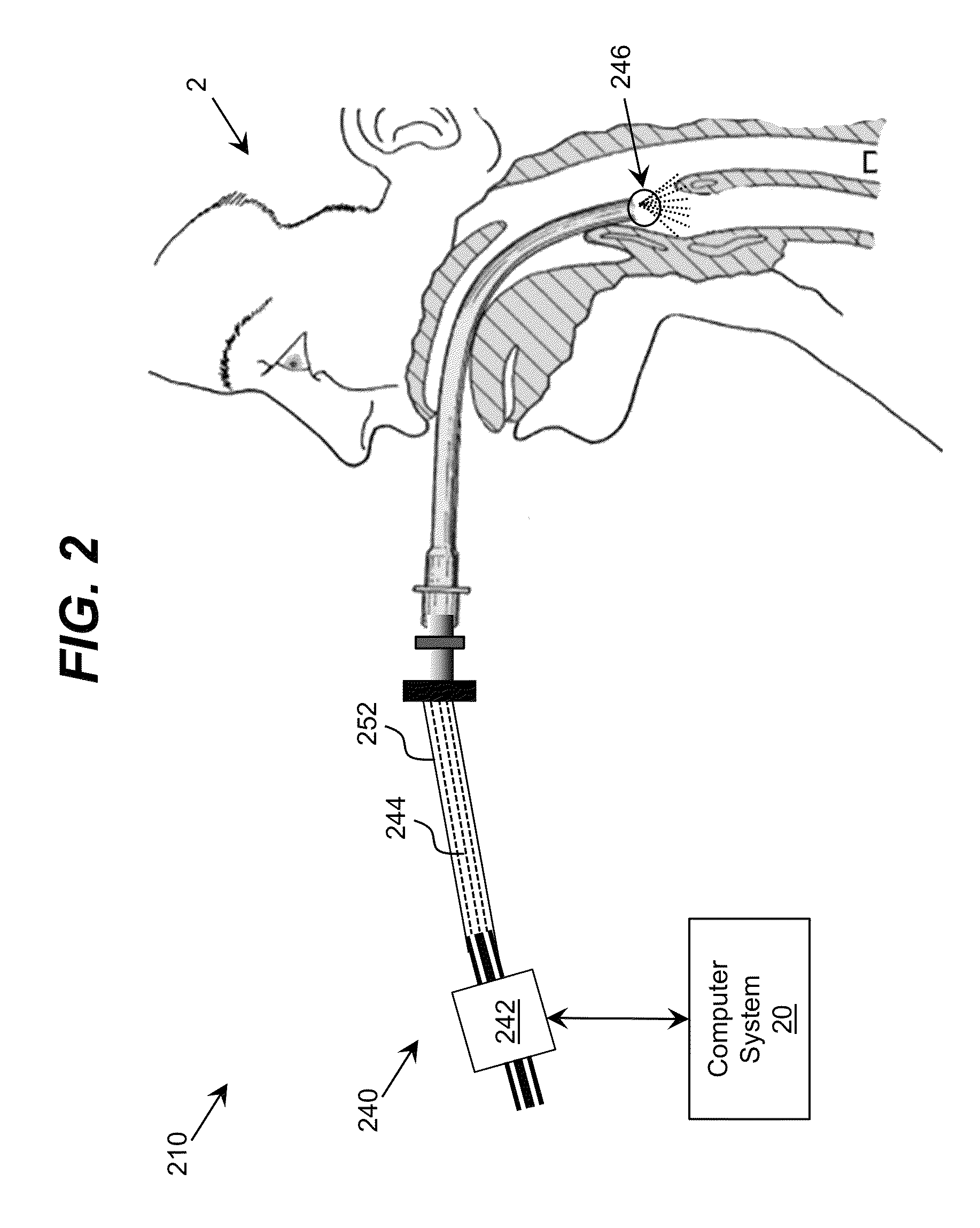
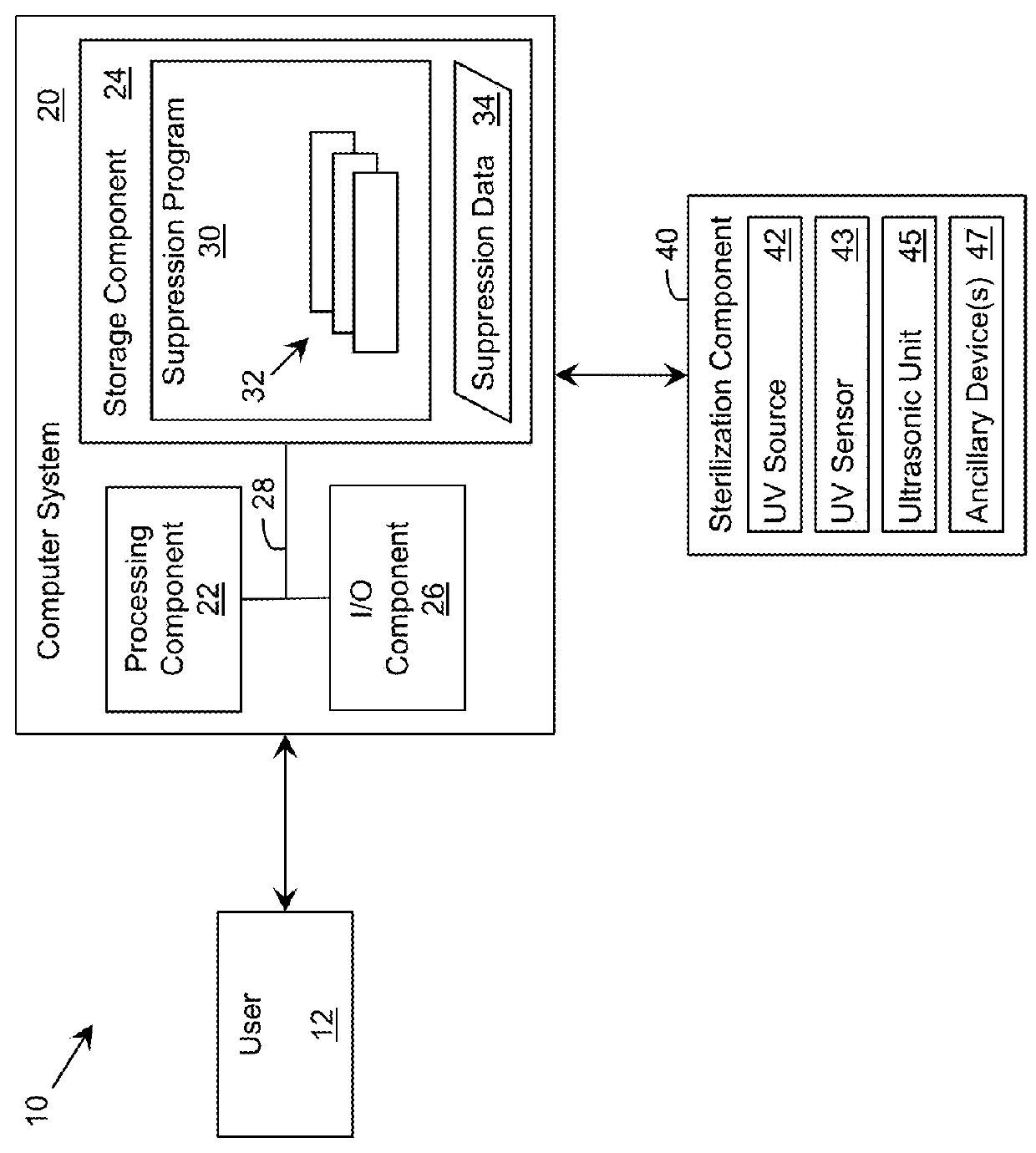
Ultraviolet-Based Sterilization
ActiveUS20130270445A1Scattering properties measurementsLight therapyTarget surfaceUltraviolet radiation
A system for sterilizing at least one surface of an object is provided. The system includes a set of ultraviolet radiation sources and a set of wave guiding structures configured to direct ultraviolet radiation having a set of target attributes to a desired location on at least one surface of the object. The set of wave guiding structures can include at least one ultraviolet reflective surface having an ultraviolet reflection coefficient of at least thirty percent. Furthermore, the system can include a computer system for operating the ultraviolet radiation sources to deliver a target dose of ultraviolet radiation to the at least one target surface of the object.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Ultraviolet-Based Sterilization
ActiveUS20150297767A1Material analysis by optical meansLight therapyTarget surfaceUltraviolet radiation
A system for sterilizing at least one surface of an object is provided. The system includes a set of ultraviolet radiation sources and a set of wave guiding structures configured to direct ultraviolet radiation having a set of target attributes to a desired location on at least one surface of the object. The set of wave guiding structures can include at least one ultraviolet reflective surface having an ultraviolet reflection coefficient of at least thirty percent. Furthermore, the system can include a computer system for operating the ultraviolet radiation sources to deliver a target dose of ultraviolet radiation to the at least one target surface of the object.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Ultraviolet-based sterilization
ActiveUS9061082B2Scattering properties measurementsLavatory sanitoryTarget surfaceUltraviolet radiation
A system for sterilizing at least one surface of an object is provided. The system includes a set of ultraviolet radiation sources and a set of wave guiding structures configured to direct ultraviolet radiation having a set of target attributes to a desired location on at least one surface of the object. The set of wave guiding structures can include at least one ultraviolet reflective surface having an ultraviolet reflection coefficient of at least thirty percent. Furthermore, the system can include a computer system for operating the ultraviolet radiation sources to deliver a target dose of ultraviolet radiation to the at least one target surface of the object.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
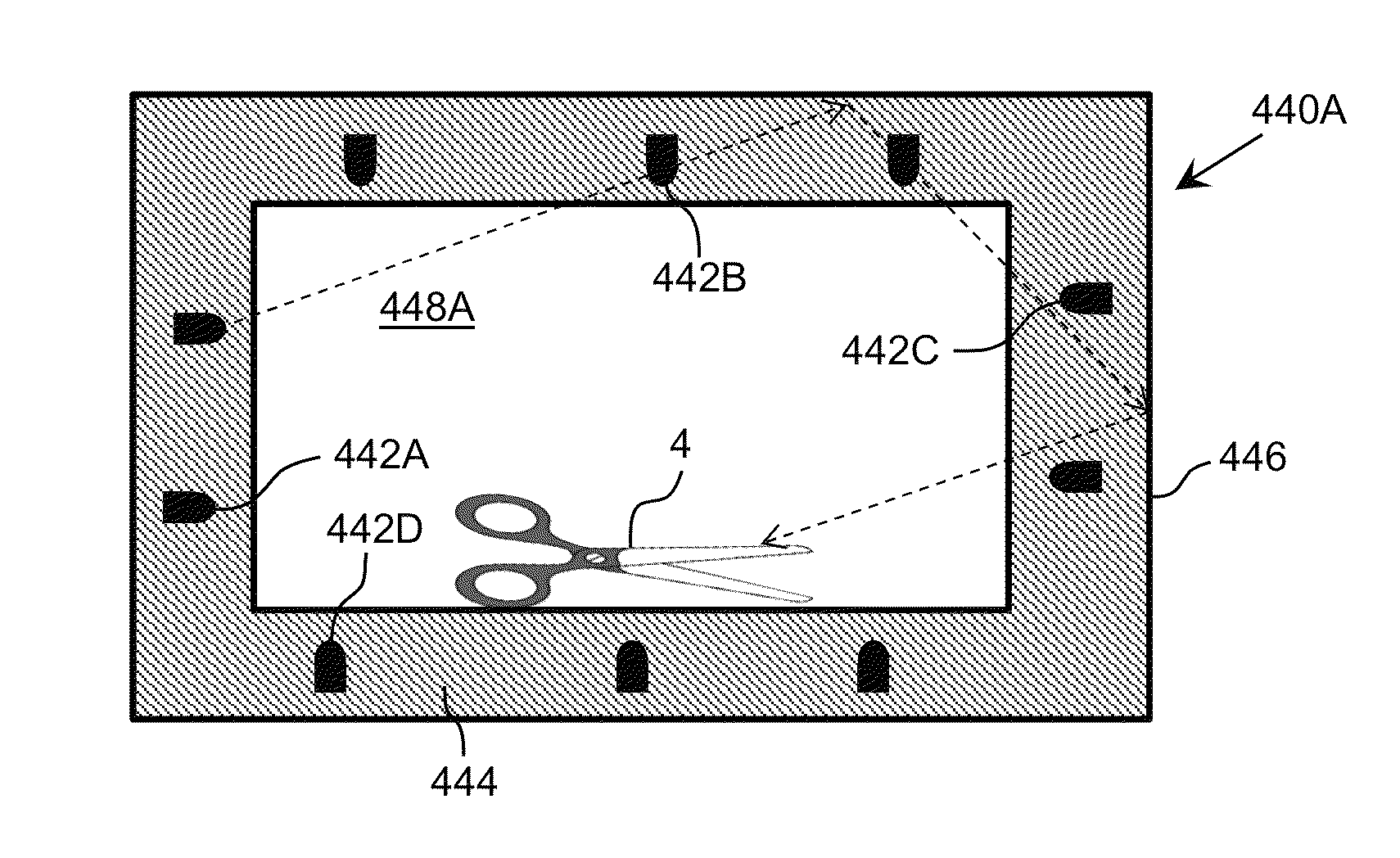
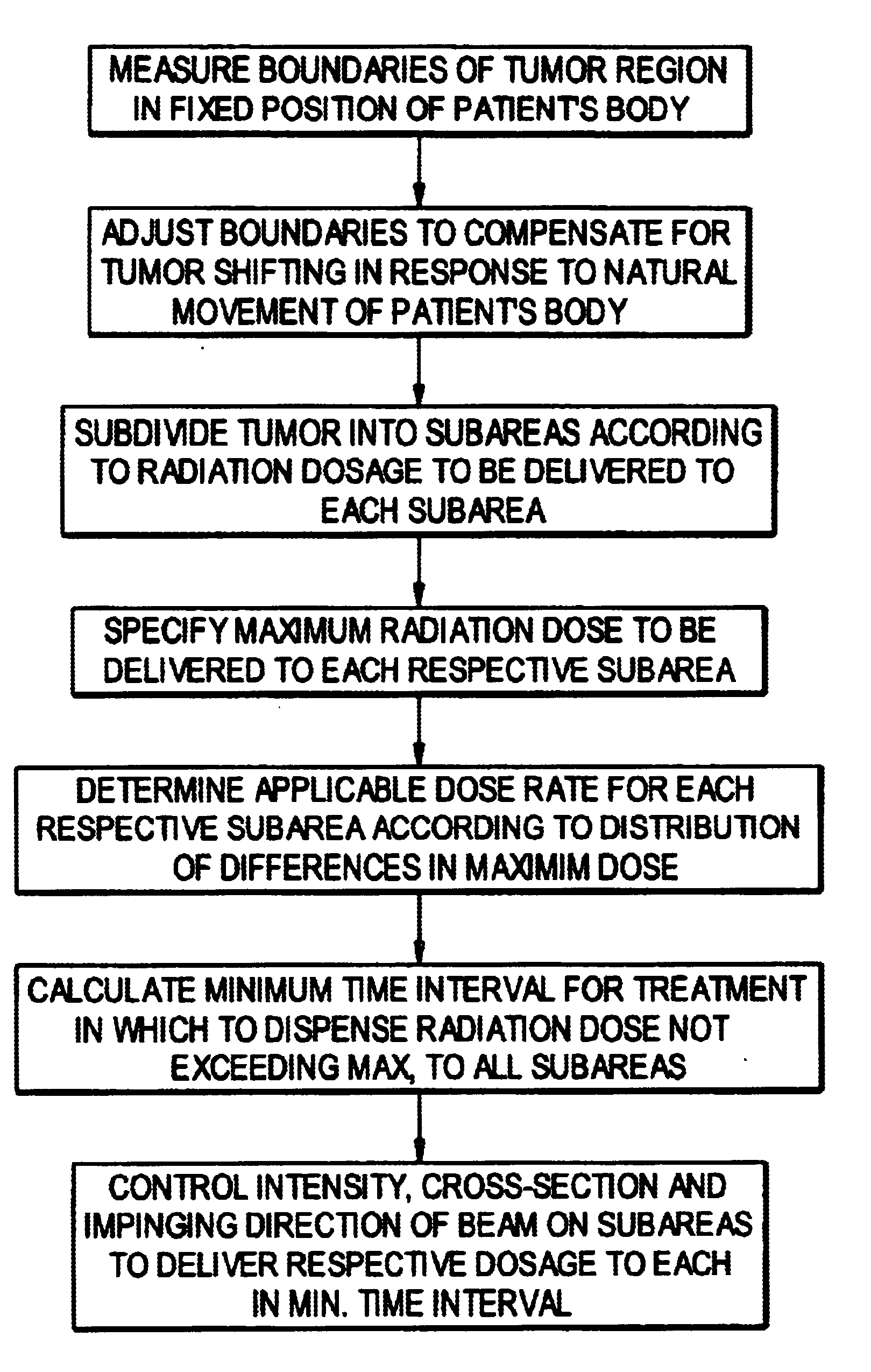
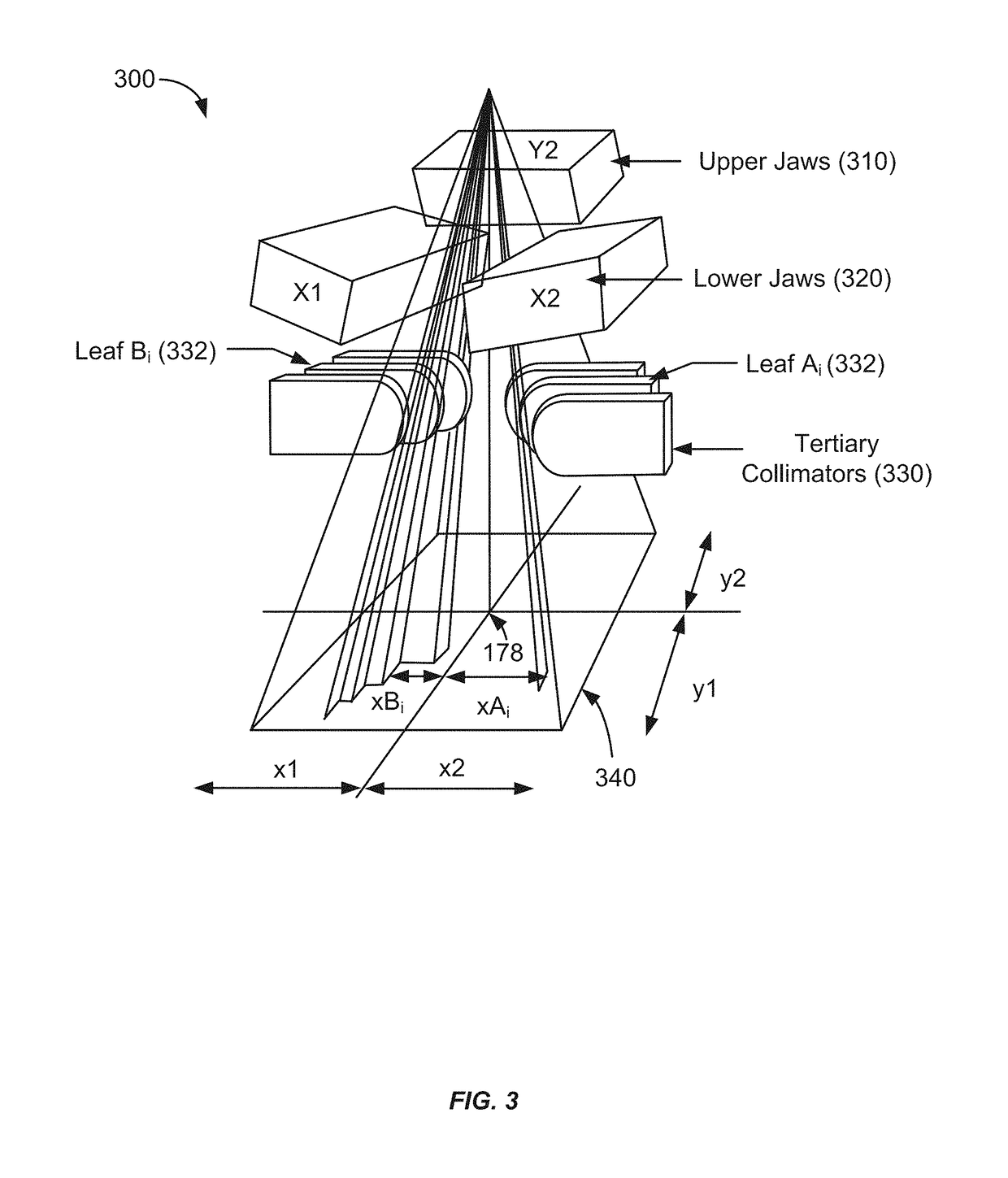
Method to control delivery of radiation therapy
InactiveUS7096055B1Rapid and accurate calculationReduce in quantitySurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringMulti leaf collimatorLight beam
A method is disclosed for controlling the delivery of radiation therapy to a tumor of a patient from one or more beams of ionizing radiation, to conform to a prescribed dosage of radiation for each of predetermined plural respectively shaped portions of the tumor according to the shape and other characteristics of the tumor. A radiation beam is selectively generated from different directions with respect to travel of the beam along a plurality of spatial paths including oscillating and arcuate movements. Parameters of the beam are calculated from conditions of distribution of a target dose, and the cross-section of the beam is adjusted so as to deliver the prescribed dosage of radiation to each of the respectively shaped portions of the tumor on which the beam impinges. The cross-section of the beam is constantly adjusted according to a predetermined area of the tumor which is to receive radiation therapy, and adjusted cross-sections of the beam are moved along selected individual ones of the spatial paths at least one time. Also, movements of the beam along individual spatial paths are split according to the plural portions of the tumor which are to receive different radiation doses. Travel of the beam is controlled along the selected individual paths so as to deliver radiation therapy within the prescribed dosage to each of the plural portions of the tumor in a minimum amount of time. In one embodiment, a micro multi-leaf collimator is placed between the beam and the tumor, and the collimator leaves are adjusted to change the cross-section of the beam impinging on a specified portion of the tumor according to the shape of the specified portion.
Owner:SCHWEIKARD ACHIM
Ultraviolet-Based Sterilization
A system for sterilizing at least one surface of an object is provided. The system includes a set of ultraviolet radiation sources and a set of wave guiding structures configured to direct ultraviolet radiation having a set of target attributes to a desired location on at least one surface of the object. The set of wave guiding structures can include at least one ultraviolet reflective surface having an ultraviolet reflection coefficient of at least thirty percent. Furthermore, the system can include a computer system for operating the ultraviolet radiation sources to deliver a target dose of ultraviolet radiation to the at least one target surface of the object.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Low silicone glass prefillable syringe
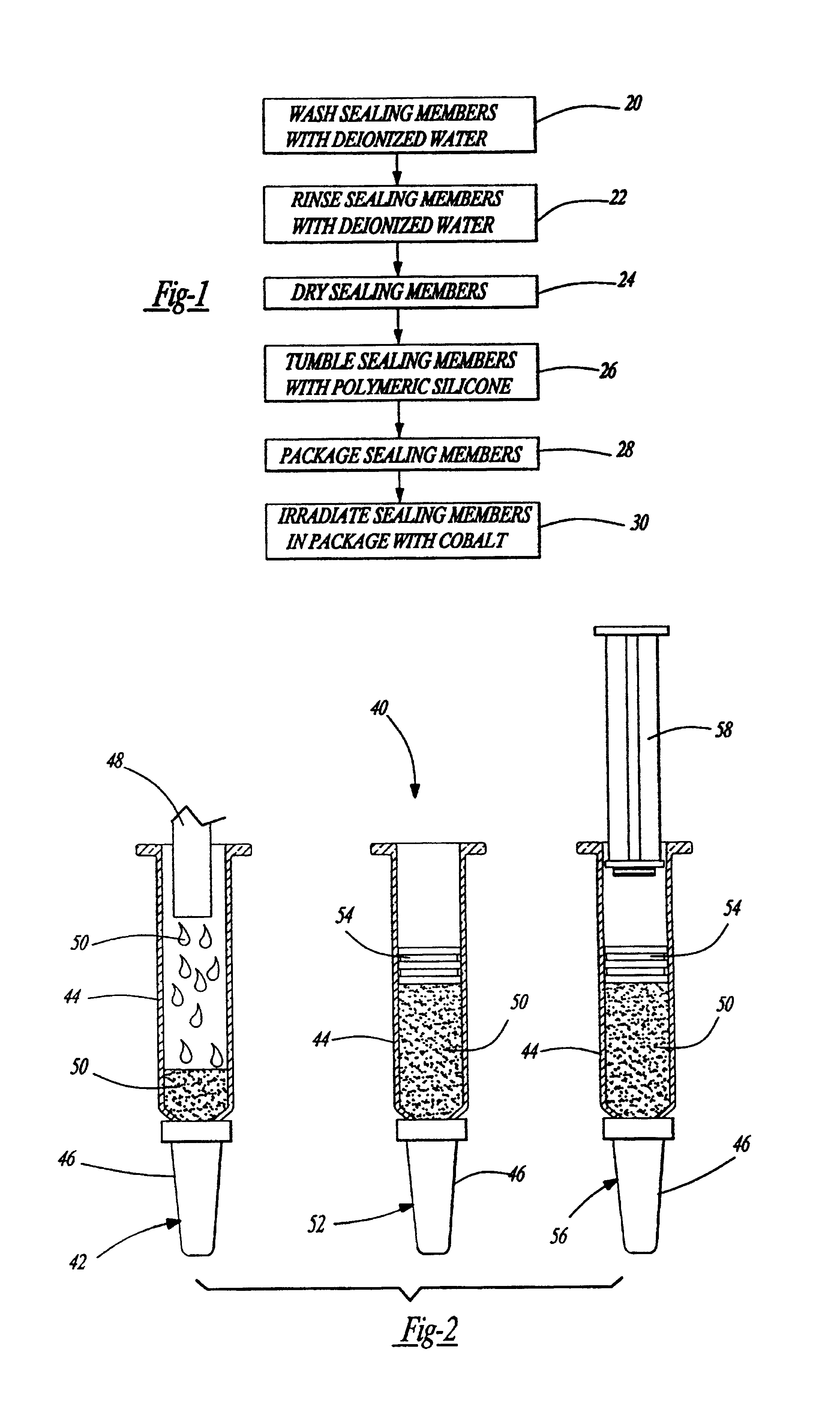
A method for lubricating a sealing member in a drug delivery device includes the steps of washing and rinsing the sealing members in hot deionized water following by drying the sealing members. The dried sealing members are tumbled with polymeric silicone and then irradiated at a target dose between 2.5 and 4.0 Mrads. The irradiated sealing members are then utilized in a variety of drug delivery devices including syringes, pre-filed syringes, drug cartridges, and needleless injector ampules.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Controlling and shaping the dose distribution outside treatment targets in external-beam radiation treatments
ActiveUS20180078792A1Need for contouring control structures around each target can be reduced or eliminatedX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTreatment targetsNormal tissue
Streamlined and partially automated methods of setting normal tissue objectives in radiation treatment planning are provided. These methods may be applied to multiple-target cases as well as single-target cases. The methods can impose one or more target-specific dose falloff constraints around each target, taking into account geometric characteristics of each target such as target volume and shape. In some embodiments, methods can also take into account a planner's preferences for target dose homogeneity. In some embodiments, methods can generate additional dose falloff constraints in locations between two targets where dose bridging is likely to occur.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
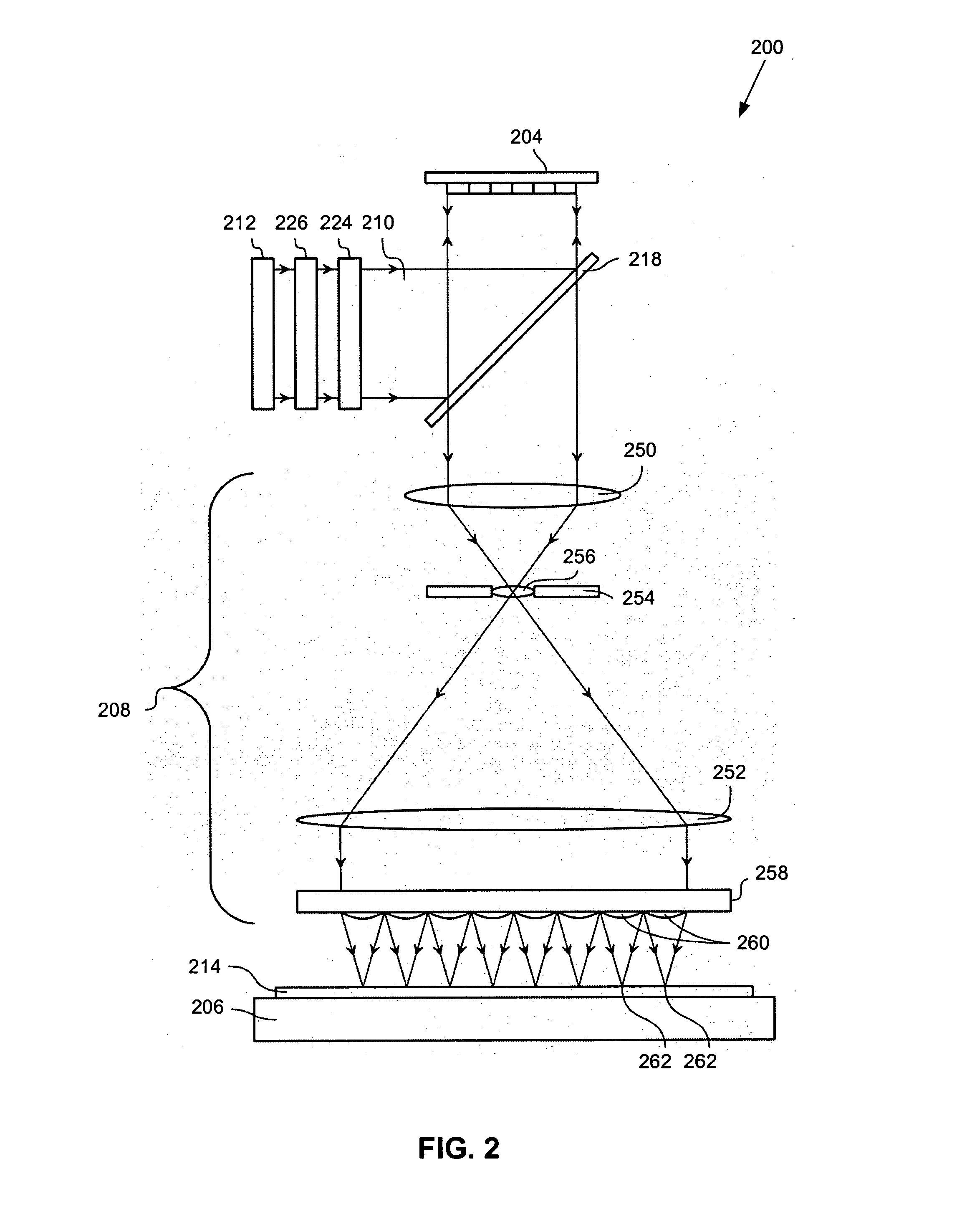
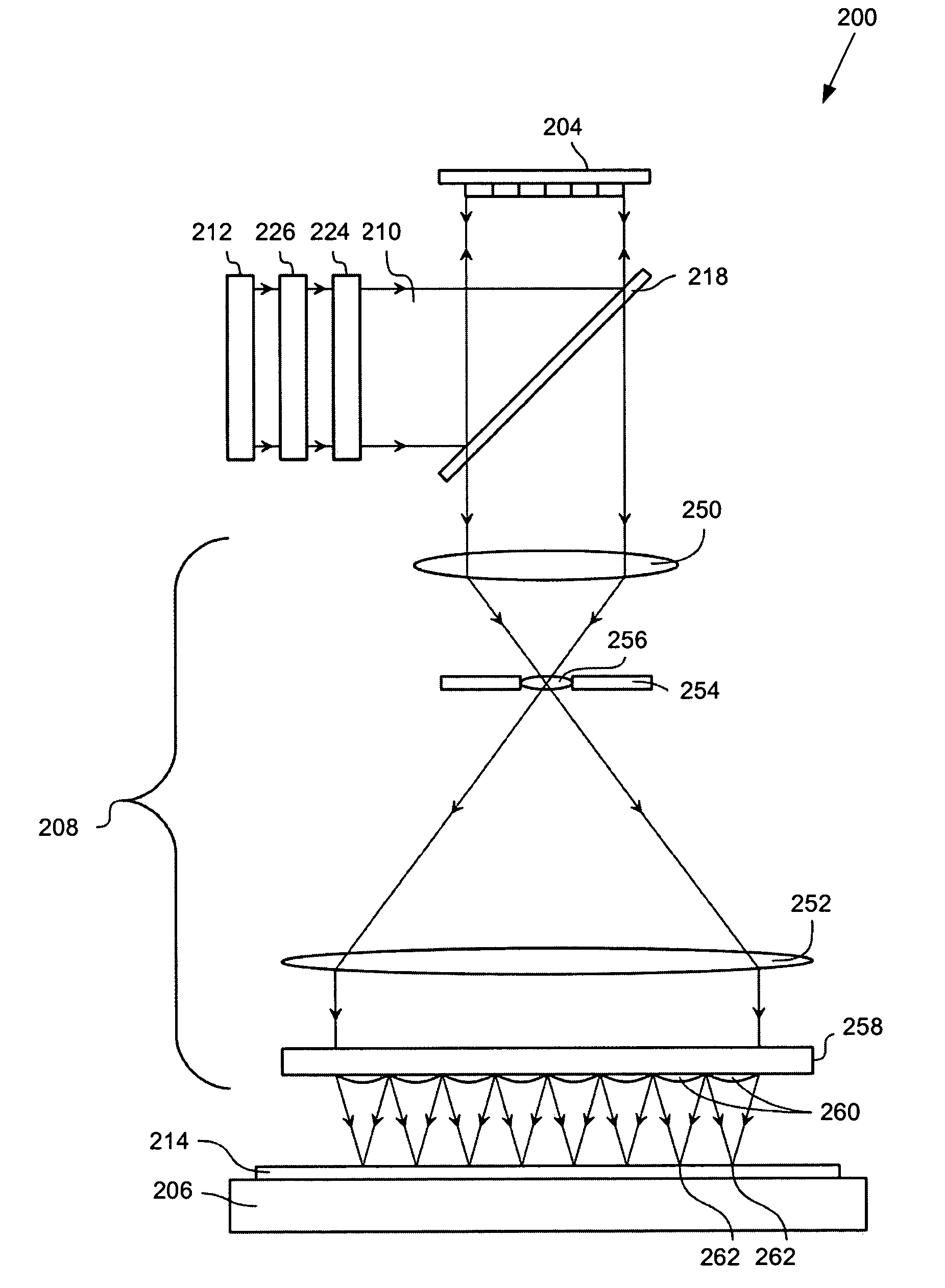
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method utilizing data filtering
An apparatus and method are used to form patterns on a substrate. The comprise a projection system, a patterning device, a low-pass filter, and a data manipulation device. The projection system projects a beam of radiation onto the substrate as an array of sub-beams of radiation. The patterning device modulates the sub-beams of radiation to substantially produce a requested dose pattern on the substrate. The low-pass filter operates on pattern data derived from the requested dose pattern in order to form a frequency-clipped target dose pattern that comprises only spatial frequency components below a selected threshold frequency. The data manipulation device produces a control signal comprising spot exposure intensities to be produced by the patterning device, based on a direct algebraic least-squares fit of the spot exposure intensities to the frequency-clipped target dose pattern. In various examples, filters for pattern sharpening, image log slope control, and / or CD biasing can also be used.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method utilizing data filtering
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method for using heated substrates for process chemistry control
ActiveUS10249498B2Facilitated DiffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess chemistryOperating variables
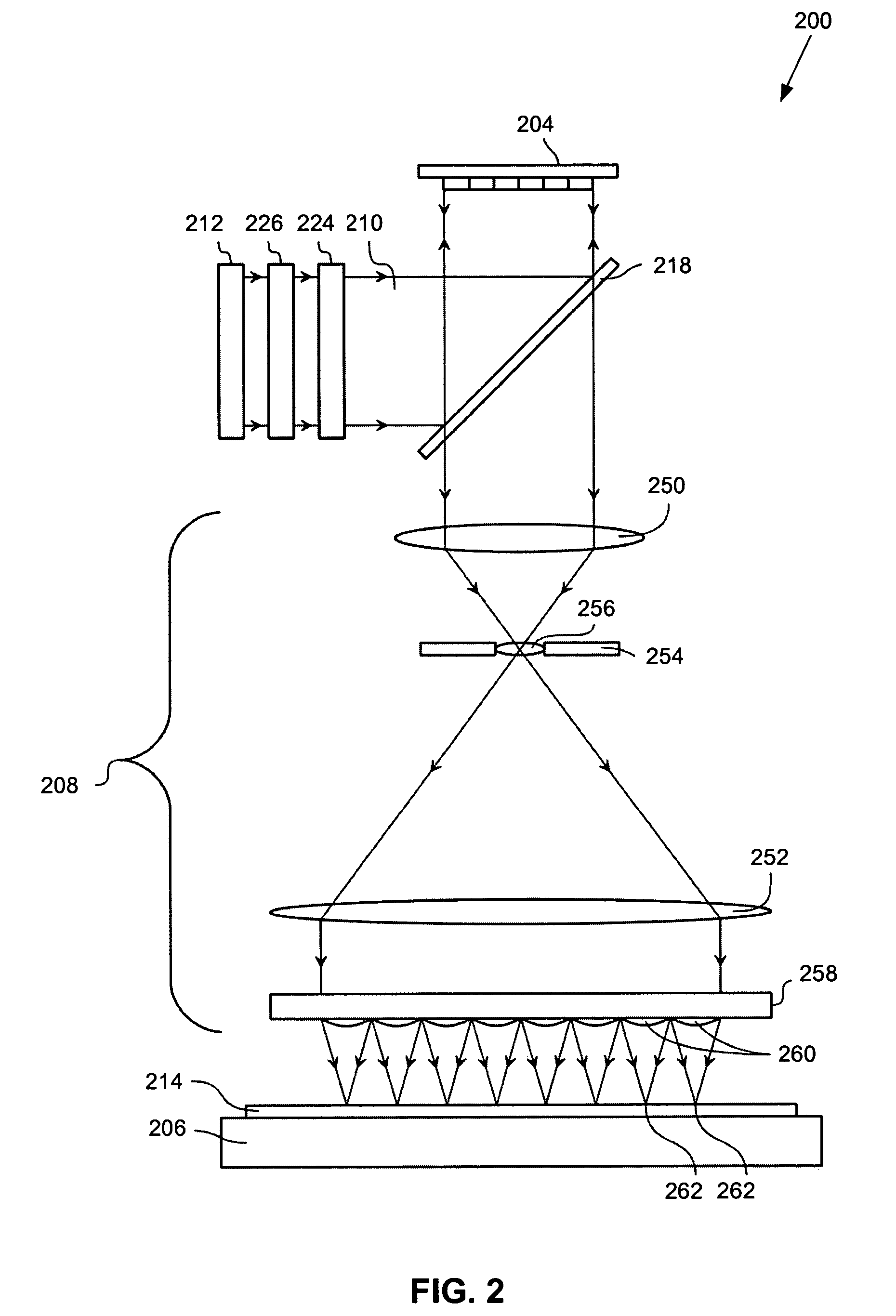
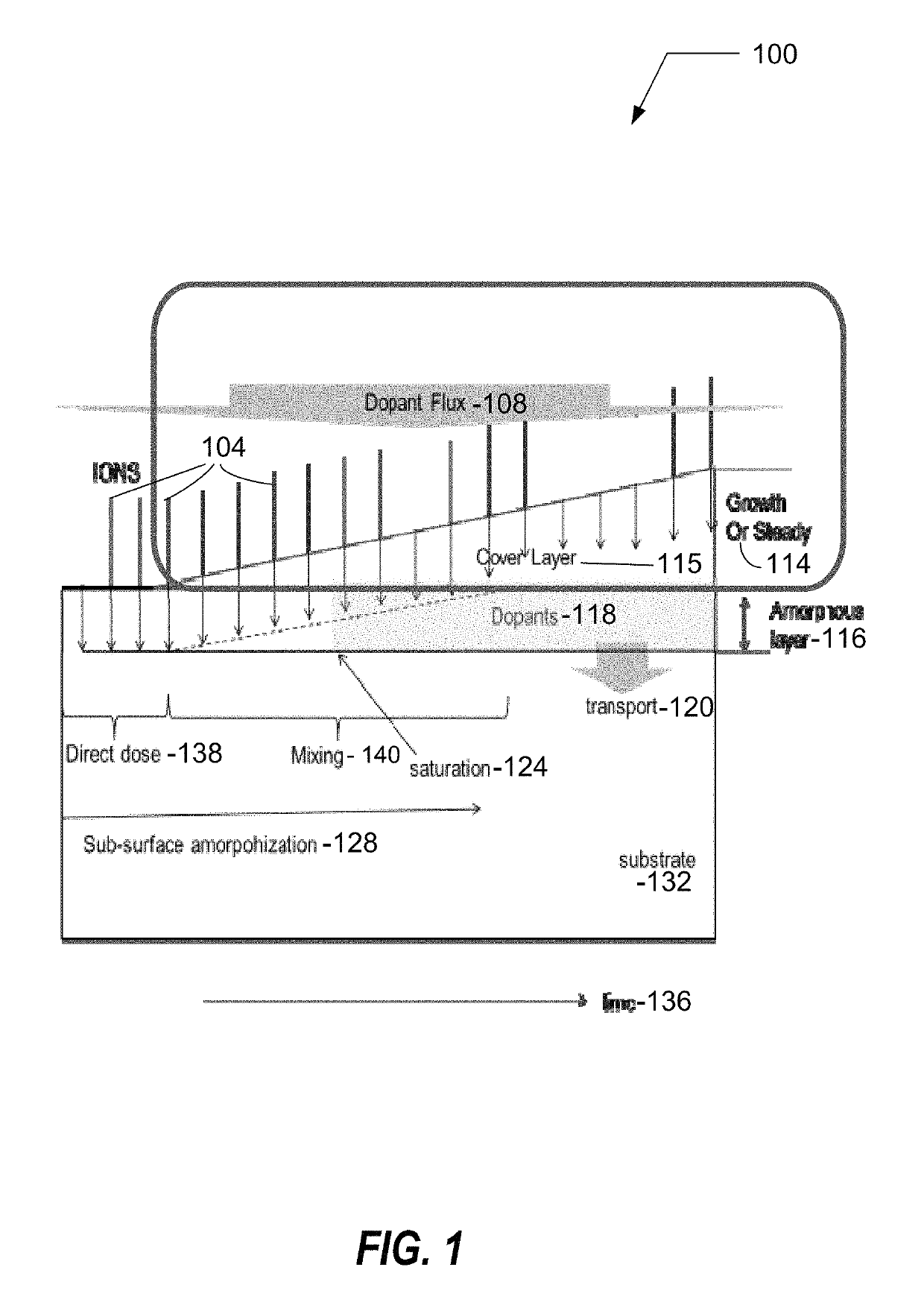
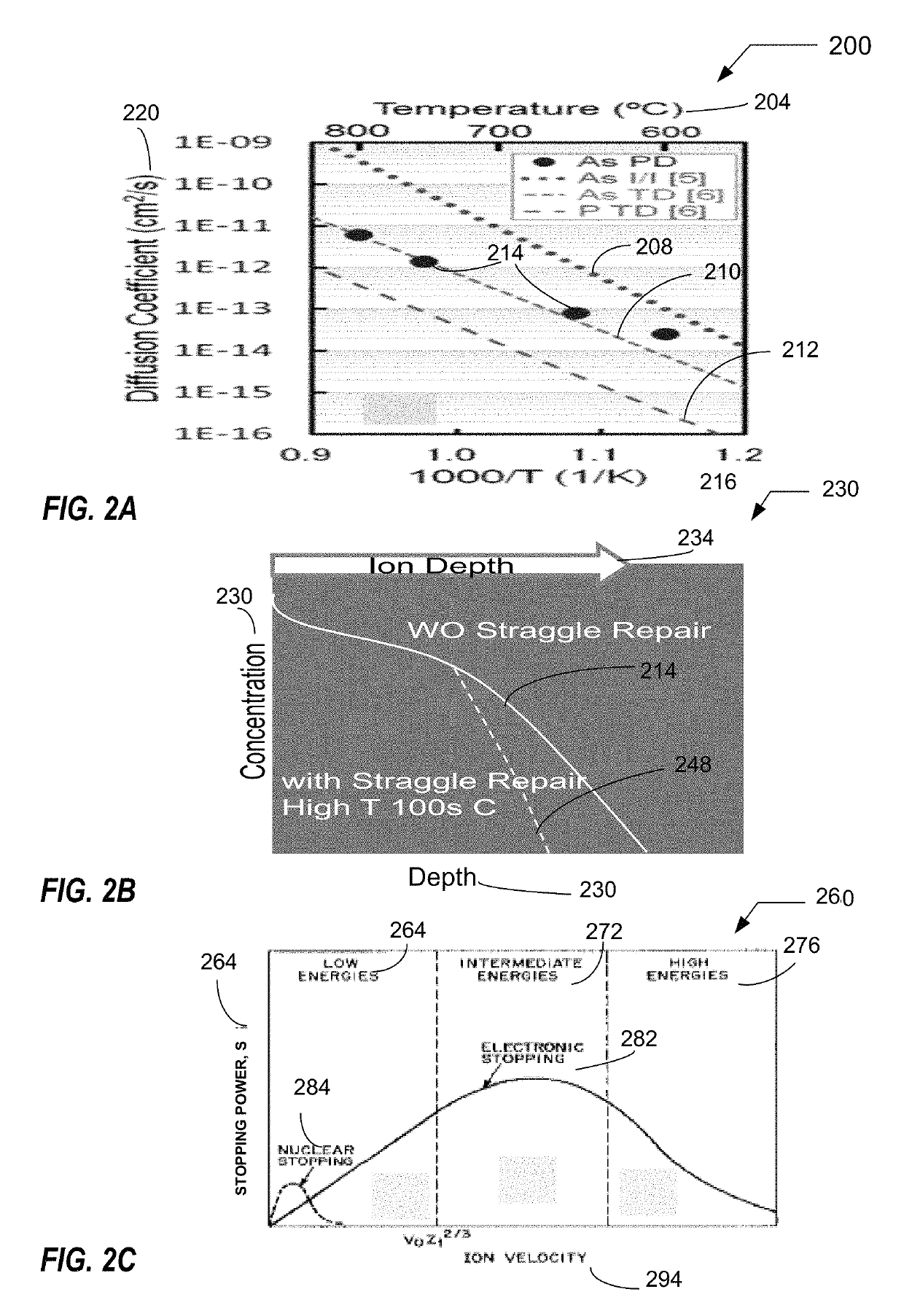
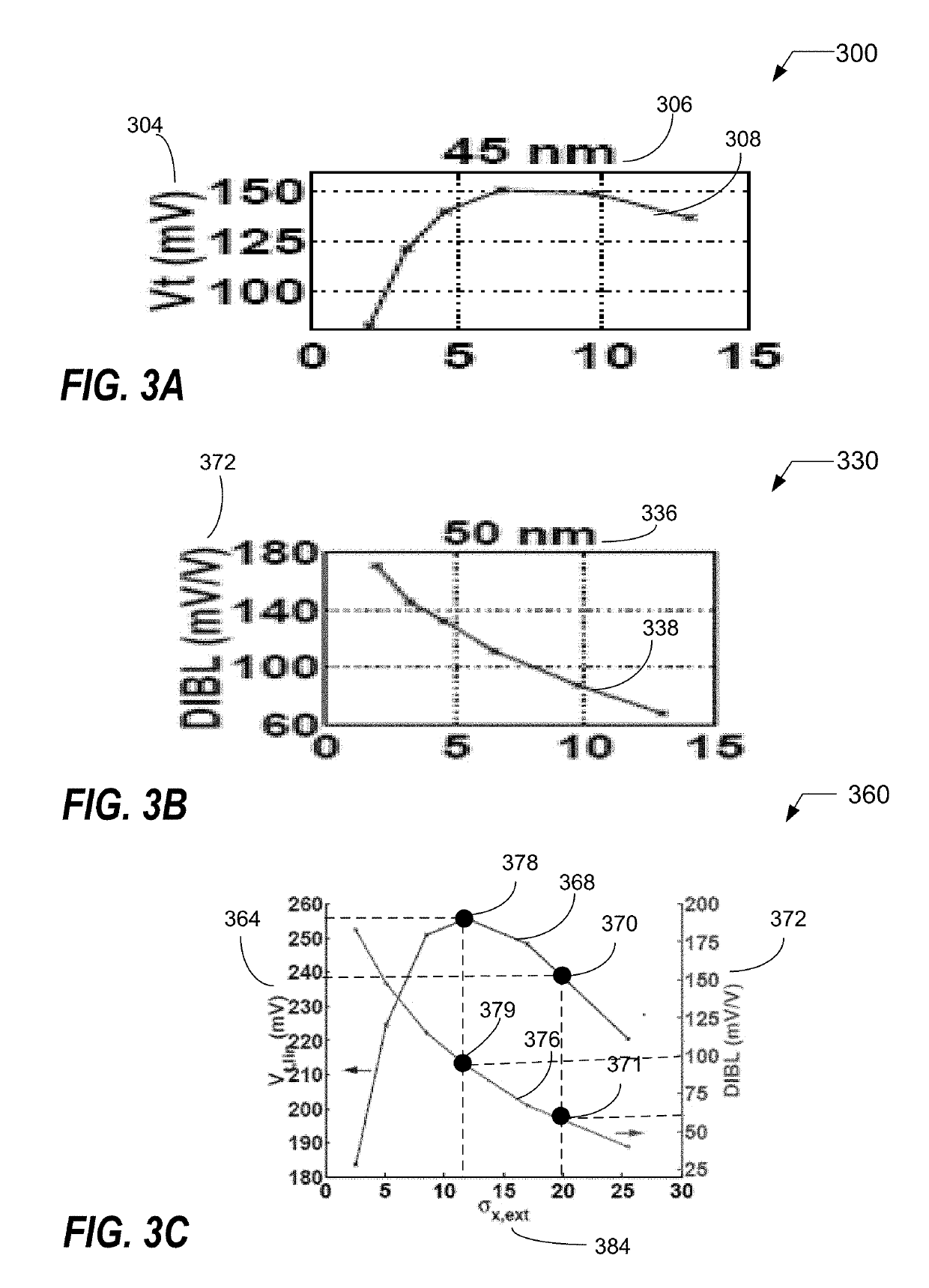
A method of controlling doping of a substrate, the method comprising: providing the substrate in a process chamber of a doping system; performing a doping process to impart a target dose on a surface of the substrate using a abruptness depth control technique; and controlling selected operating variables of plasma doping in order to meet doping objectives.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Radiation therapy treatment planning using regression
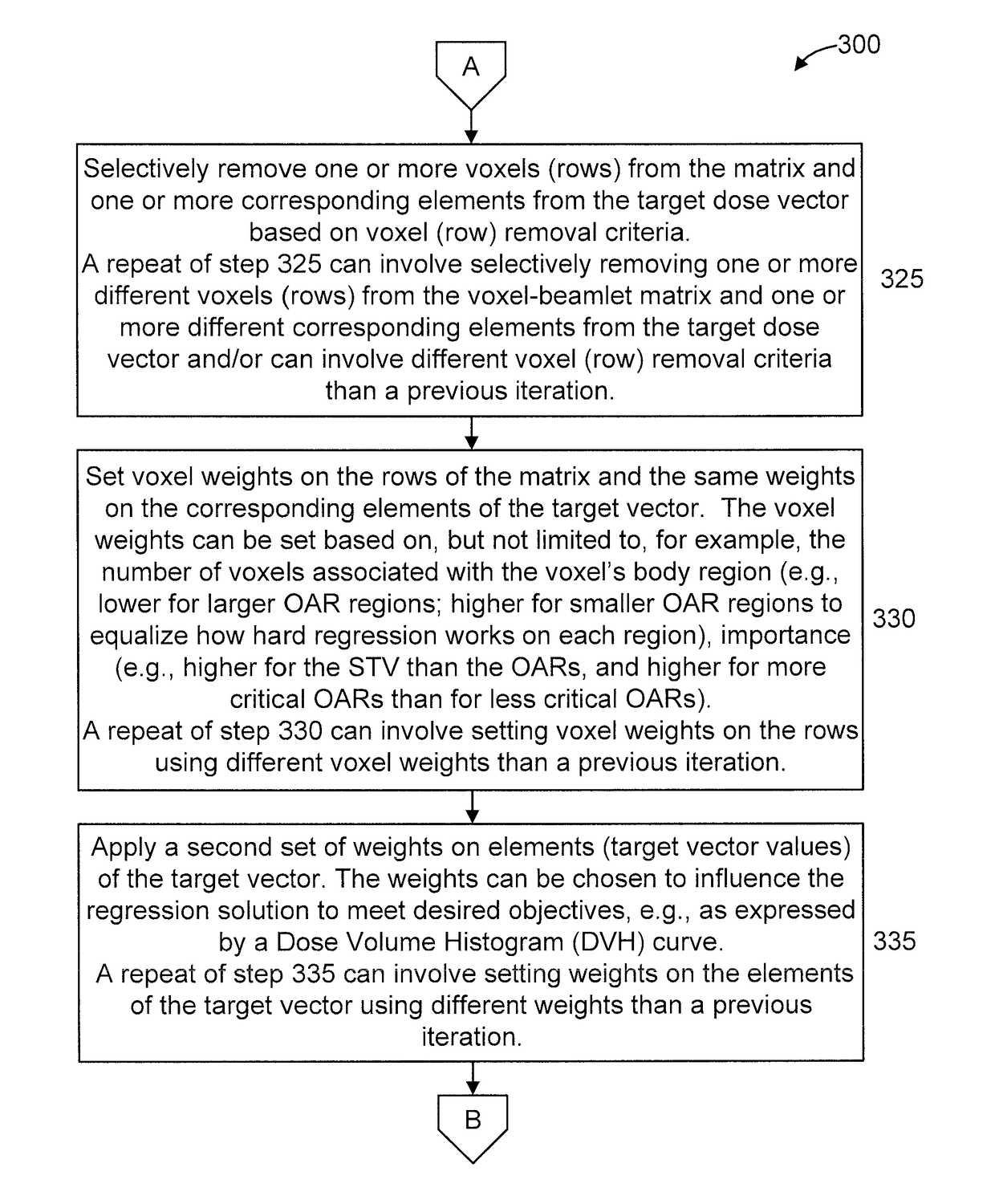
A method and system are provided. The method includes splitting, by a processor based on radiation beamlet contributions to neighboring voxels, at least one row in a voxel-beamlet matrix and corresponding elements of a target dose vector prior to, and in preparation for, a regression operation. The voxel-beamlet matrix has a row for each of a plurality of voxels in a three-dimensional patient volume and a column for each of a plurality of radiation beamlets. The target dose vector represents a desired energy amount for each of the plurality of voxels in the three-dimensional patient volume. The target dose vector corresponds voxel-by-voxel to rows in the voxel-beamlet matrix. The method further includes performing, by the processor, the regression operation on the voxel-beamlet matrix and target dose vector to obtain beamlet weights. The method also includes determining an actual radiation dosing scheme for a given patient based on the beamlet weights.
Owner:IBM CORP
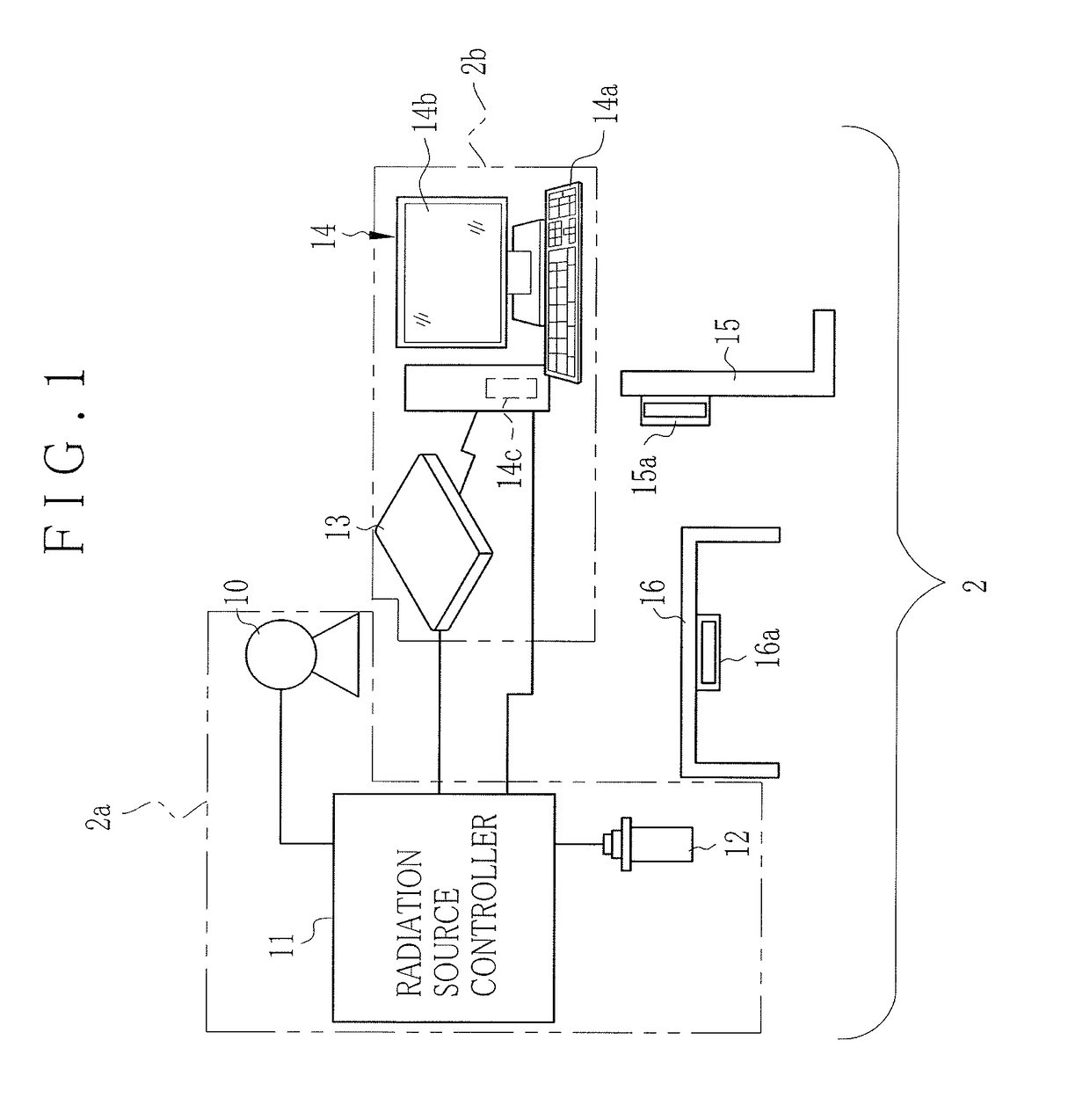
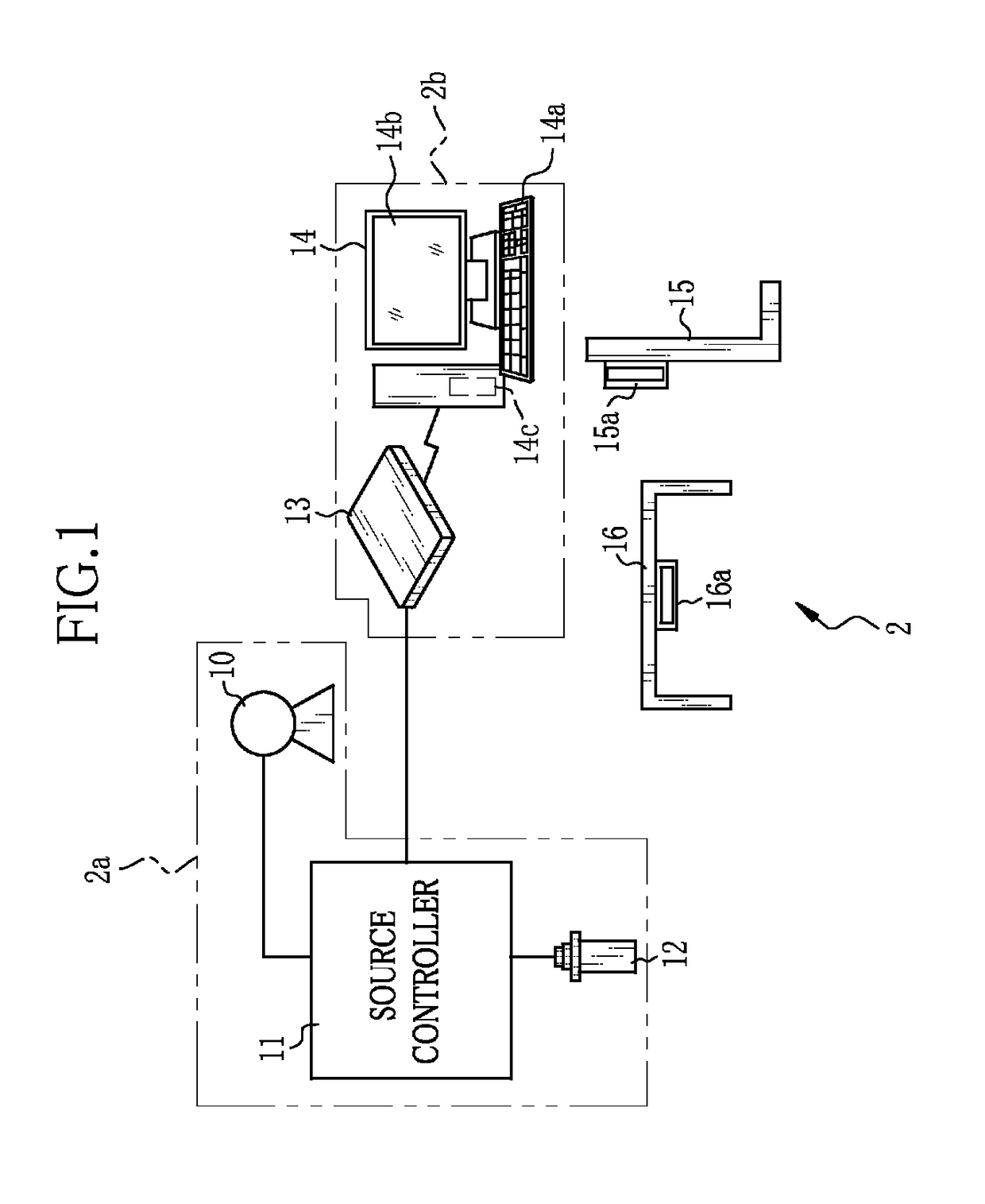
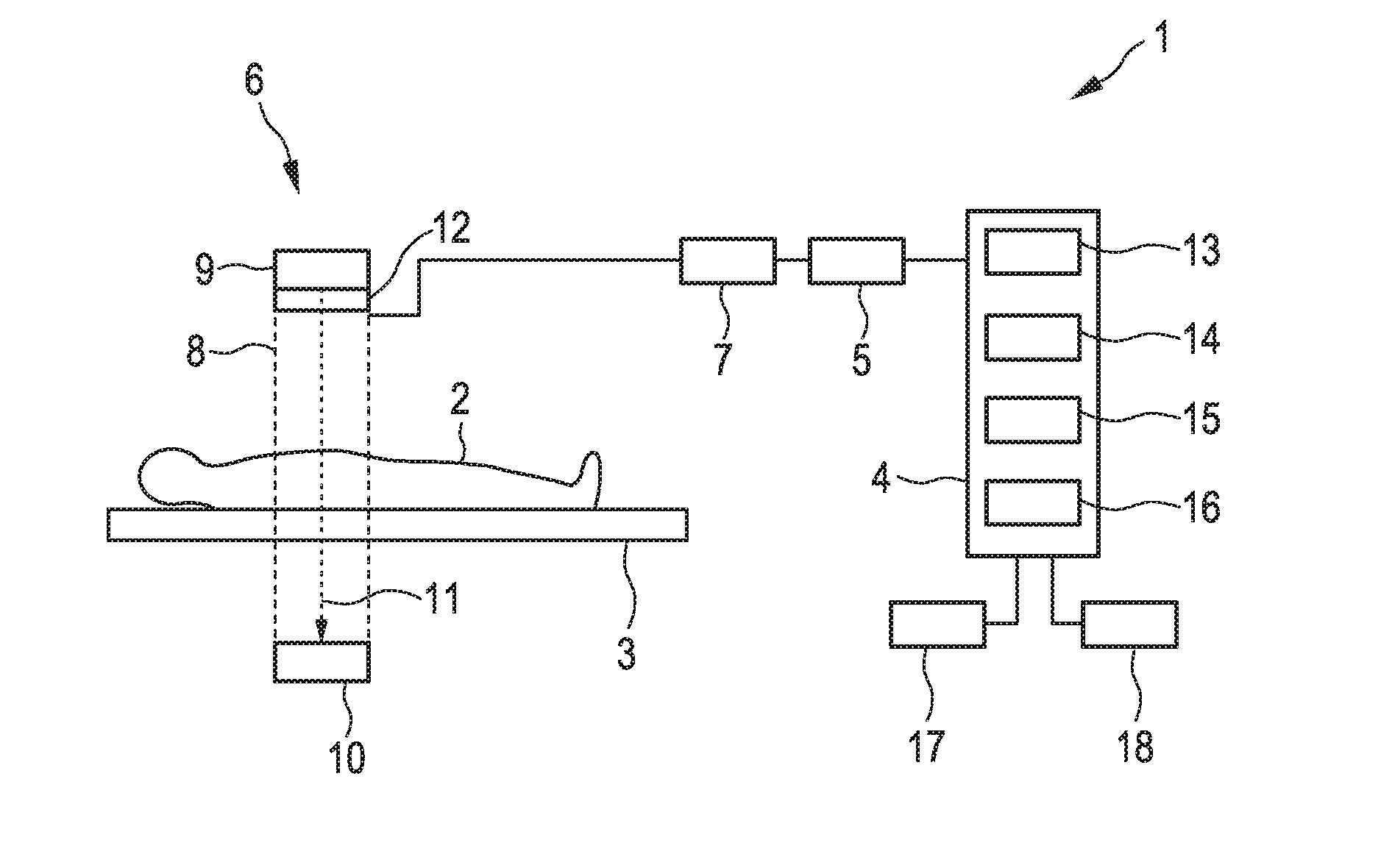
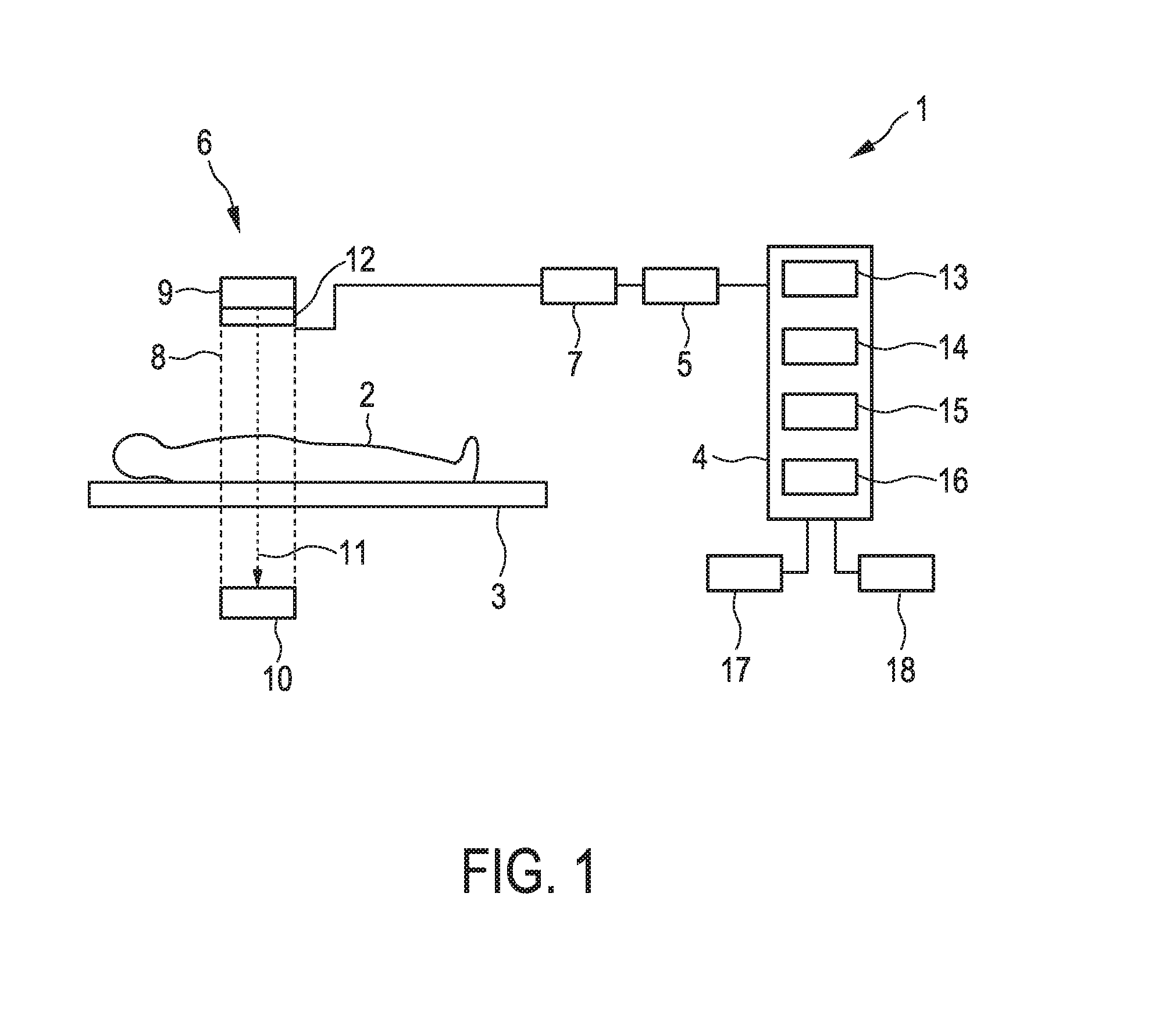
Radiographic imaging apparatus, method and system
ActiveUS10022102B2Television system detailsRadiation diagnostic device controlStart timeAcquisition time
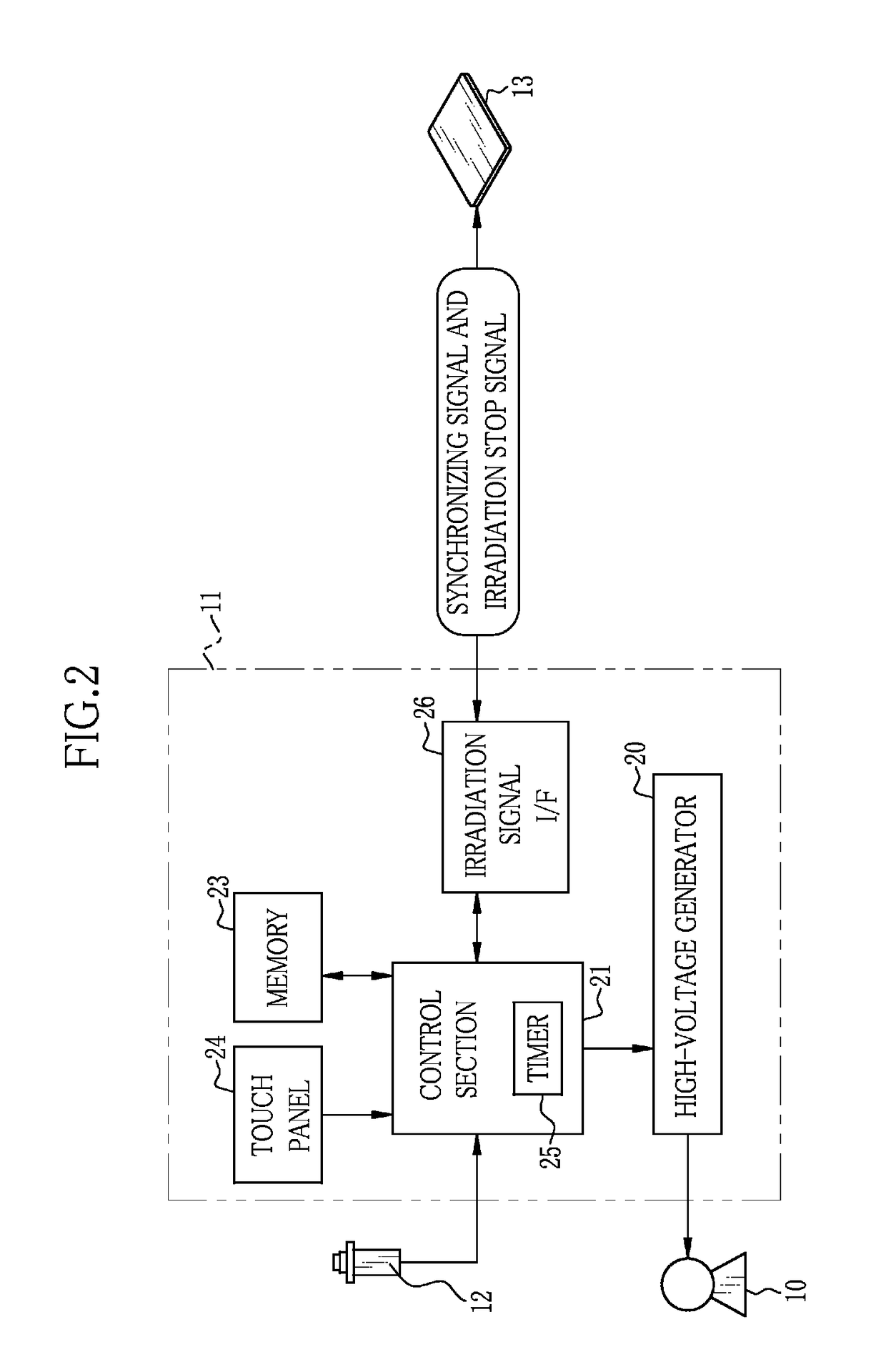
In an X-ray imaging apparatus, a detection panel has monitor pixels for monitoring X-rays. A signal processor samples a dose signal of a dose per unit time of X-rays according to an output of the monitor pixels. A start detector checks whether irradiation of X-rays is started according to a result of comparison between the dose signal and a start threshold. An AEC device acquires cumulative dose from a start time of the start of irradiation of X-rays until acquisition time after a predetermined time according to the dose signal. According to the cumulative dose, a predicted time point of a reach of the cumulative dose to a target dose is estimated. A stop signal is transmitted to a radiation source controller at the predicted time point, to stop the irradiation of X-rays.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
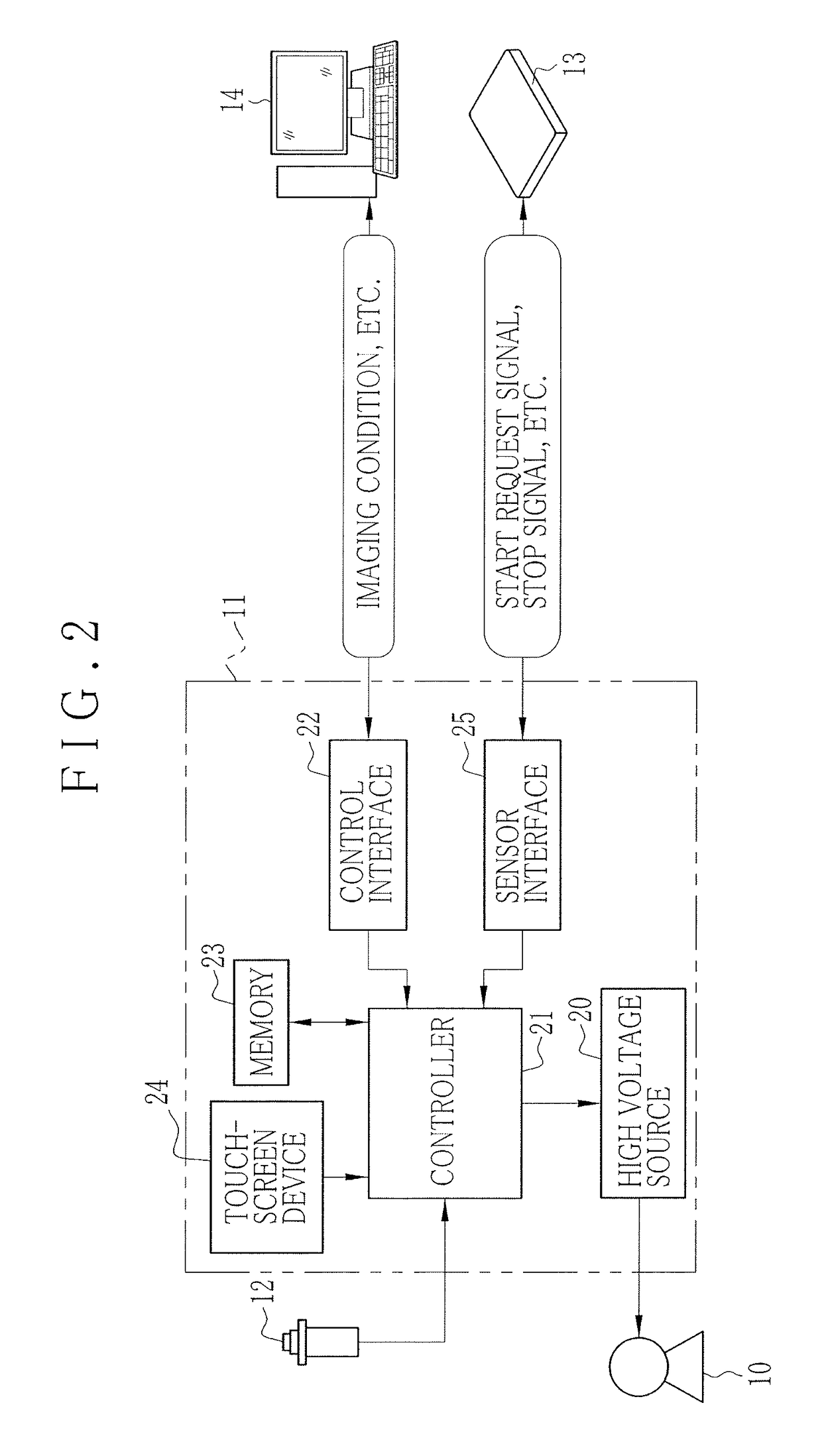
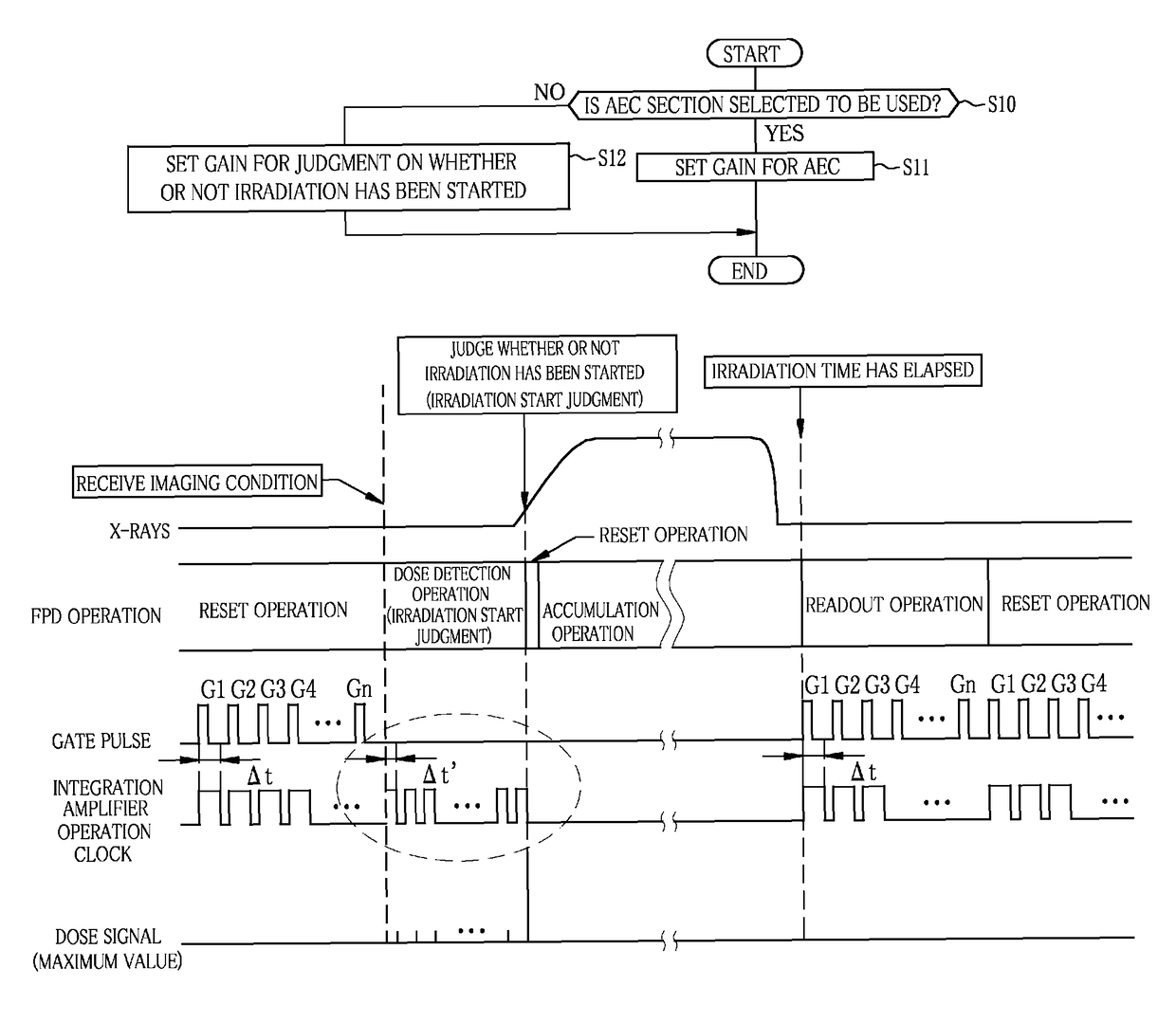
Radiation image detecting device
InactiveUS9848845B2Accurate judgmentTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSoft x rayAudio power amplifier
A sensor panel of an electronic cassette includes detection pixels each for outputting a dose signal corresponding to a dose of X-rays, an irradiation start judging section for judging whether or not X-ray irradiation has been started based on the dose signal, and an AEC section for judging whether or not an accumulated dose of X-rays has reached a target dose based on the dose signal. A gain setting section sets a gain of an integration amplifier in the case of using the irradiation start judging section lower than that in the case of using the AEC section.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Pet tracer for imaging of neuroendocrine tumors
ActiveUS10159759B2Enhance the imageX-ray constrast preparationsRadioactive preparation carriersNeuroendocrine tumorsPet tracer
There is provided a radiolabelled peptide-based compound for diagnostic imaging using positron emission tomography (PET). The compound may thus be used for diagnosis of malignant diseases. The compound is particularly useful for imaging of somatostatin overexpression in tumors, wherein the compound is capable of being imaged by PET when administered with a target dose in the range of 150-350 MBq, such as 150-250 MBq, preferable in the range of 191-210 MBq.
Owner:SOMSCAN APS
Methods And Systems For Real Time Measurement Control
ActiveUS20190293578A1Minimizes combinationMinimize sumMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementRobustificationSemiconductor structure
Methods and systems for improving a measurement recipe describing a sequence of measurements employed to characterize semiconductor structures are described herein. A measurement recipe is repeatedly updated before a queue of measurements defined by the previous measurement recipe is fully executed. In some examples, an improved measurement recipe identifies a minimum set of measurement options that increases wafer throughput while meeting measurement uncertainty requirements. In some examples, measurement recipe optimization is controlled to trade off measurement robustness and measurement time. This enables flexibility in the case of outliers and process excursions. In some examples, measurement recipe optimization is controlled to minimize any combination of measurement uncertainty, measurement time, move time, and target dose. In some examples, a measurement recipe is updated while measurement data is being collected. In some examples, a measurement recipe is updated at a site while data is collected at another site.
Owner:KLA CORP
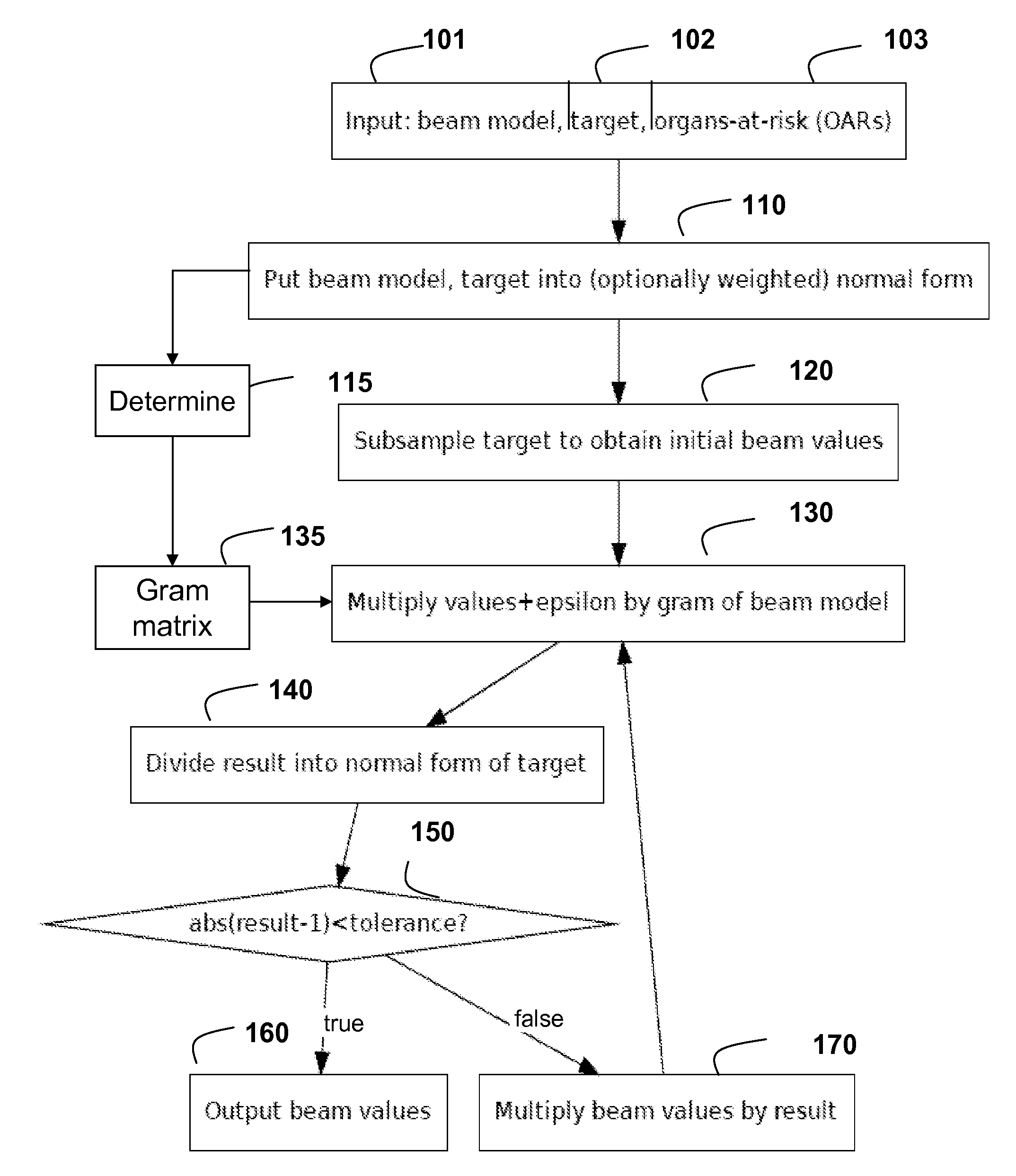
Method for Optimization Radiotherapy Particle Beams
ActiveUS20110291028A1Electric discharge tubesChemical conversion by chemical reactionGramParticle beam
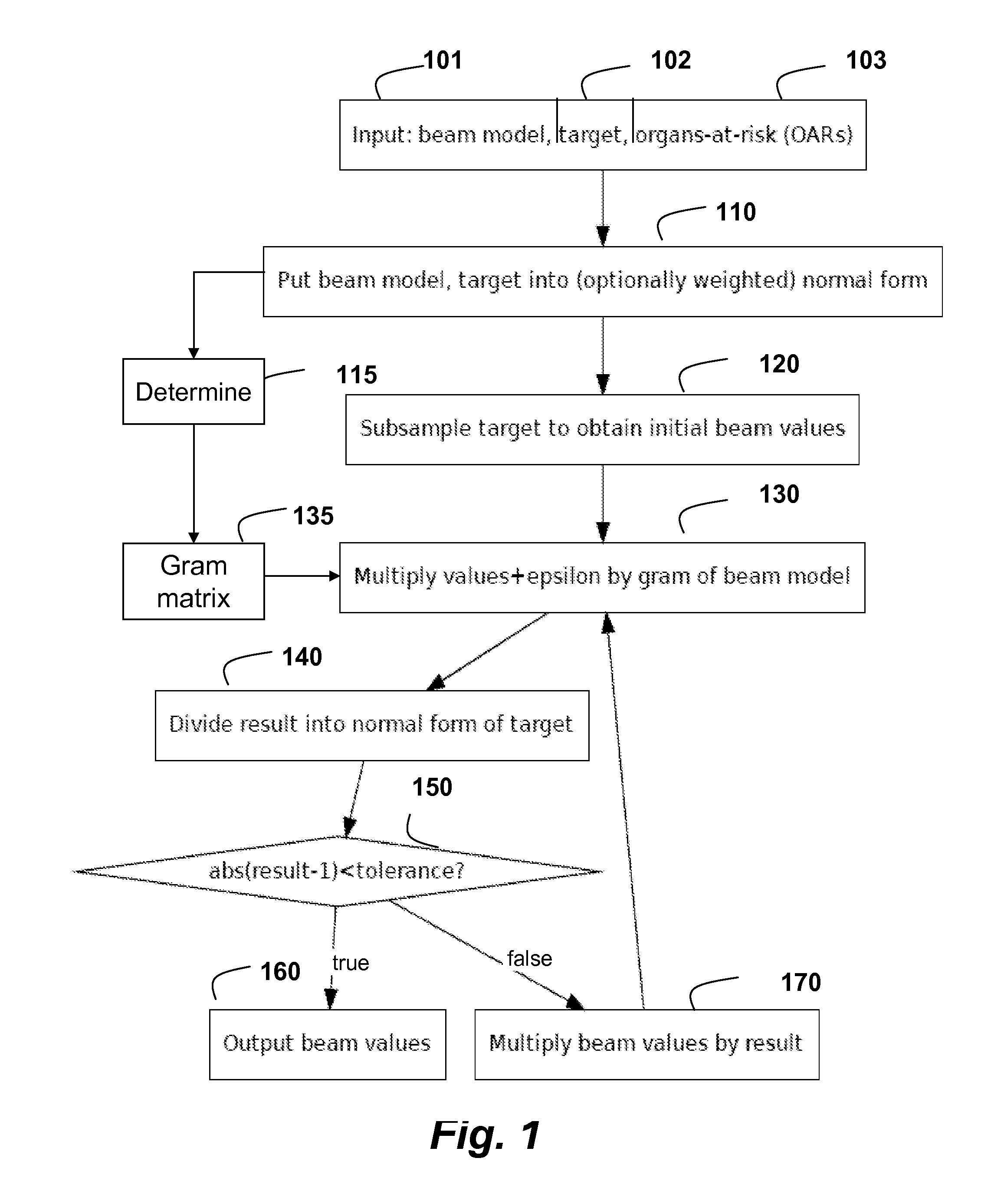
Radiation doses are optimized by providing a model of the set of beams and a target dose in normalized forms. A Gram matrix is determined from the model. The target dose is subsampled to determine initial intensity values for the set of beams. Then, the following steps are iterated until convergence. A very small positive value, 0<ε<<1, is added to each intensity value to ensure the intensity value is greater than zero. Each intensity value is multiplied by the Gram matrix to determine a product, which is divided element-wise into the normalized target dose to determine corresponding ratios. If the ratios are all close to 1, within a numerical error tolerance, the intensity values of the set of beam are output. Otherwise, the intensity values are multiplied by the ratios before a next iteration.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method for Using Heated Substrates for Process Chemistry Control
ActiveUS20160372327A1Facilitated DiffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess chemistryOperating variables
A method of controlling doping of a substrate, the method comprising: providing the substrate in a process chamber of a doping system; performing a doping process to impart a target dose on a surface of the substrate using a abruptness depth control technique; and controlling selected operating variables of plasma doping in order to meet doping objectives.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Dosimetric therapeutic gas delivery method for rapid dosimetry adjustment and optimization
The disclosure describes a technique for monitoring patient utilization of inhaled Nitric Oxide as well as waste exhaust of Nitric Oxide in gases exhaled from patient lungs. By monitoring the real dose provided to a patient, actual compliance with therapeutic target doses may be monitored to improve patient safety and therapeutic benefit from inhaled Nitric Oxide. Simultaneously, unnecessary waste of inhaled Nitric Oxide may be avoided thereby increasing the cost effectiveness of Nitric Oxide therapy. The minimization of Nitric Oxide waste has the further benefit of reducing environmental Nitrogen Dioxide levels in e.g. a NICU environment thereby mitigating medical personnel's Nitrogen Dioxide exposure.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC +1
Dosimetric therapeutic gas delivery system for rapid dose monitoring and control
The disclosure describes a technique for monitoring patient utilization of inhaled Nitric Oxide as well as waste exhaust of Nitric Oxide in gases exhaled from patient lungs. By monitoring the real dose provided to a patient, actual compliance with therapeutic target doses may be monitored to improve patient safety and therapeutic benefit from inhaled Nitric Oxide. Simultaneously, unnecessary waste of inhaled Nitric Oxide may be avoided thereby increasing the cost effectiveness of Nitric Oxide therapy. The minimization of Nitric Oxide waste has the further benefit of reducing environmental Nitric Oxide and Nitrogen Dioxide levels in e.g. a NICU environment thereby mitigating medical personnel's Nitric Oxide and Nitrogen Dioxide exposure.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC +1
Controlling and shaping the dose distribution outside treatment targets in external-beam radiation treatments
ActiveUS10143859B2Need for contouring control structures around each target can be reduced or eliminatedX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTreatment targetsNormal tissue
Streamlined and partially automated methods of setting normal tissue objectives in radiation treatment planning are provided. These methods may be applied to multiple-target cases as well as single-target cases. The methods can impose one or more target-specific dose falloff constraints around each target, taking into account geometric characteristics of each target such as target volume and shape. In some embodiments, methods can also take into account a planner's preferences for target dose homogeneity. In some embodiments, methods can generate additional dose falloff constraints in locations between two targets where dose bridging is likely to occur.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Apparatus for determining a number of beams in imrt
InactiveUS20160008630A1Optimize the numberQuality improvementX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyLight beamBiomedical engineering
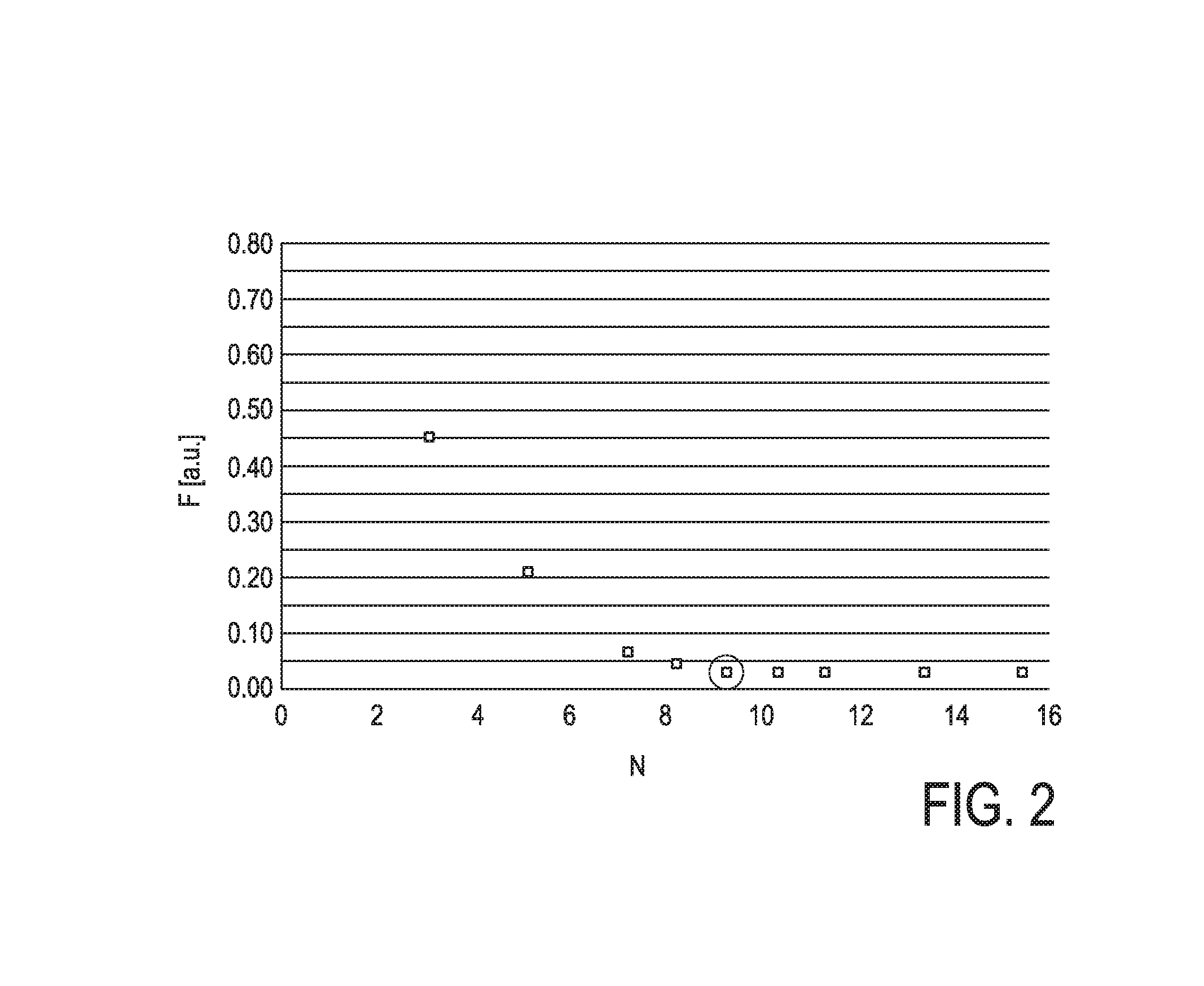
The invention relates to an apparatus for determining a number of beams in IMRT. An objective function providing unit (13) provides an objective function of an IMRT procedure, wherein the objective function depends on a target dose to be applied during the IMRT procedure. A sensitivity determination unit (14) determines the sensitivity of the objective function with respect to changes of the target dose, and a beam number determination unit (15) determines the number of beams depending on the determined sensitivity. It has been found that the sensitivity of the objective function with respect to changes of the target dose is an accurate measure for reliably determining an optimized number of beams in IMRT, which allows for generating a high quality treatment plan and which in turn leads to an improved IMRT procedure.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Radiotherapy planning system, determining device and storage medium
InactiveCN109453473ASolve the actual exposure doseAddressing discrepancies in target dosesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTumor targetProgram planning
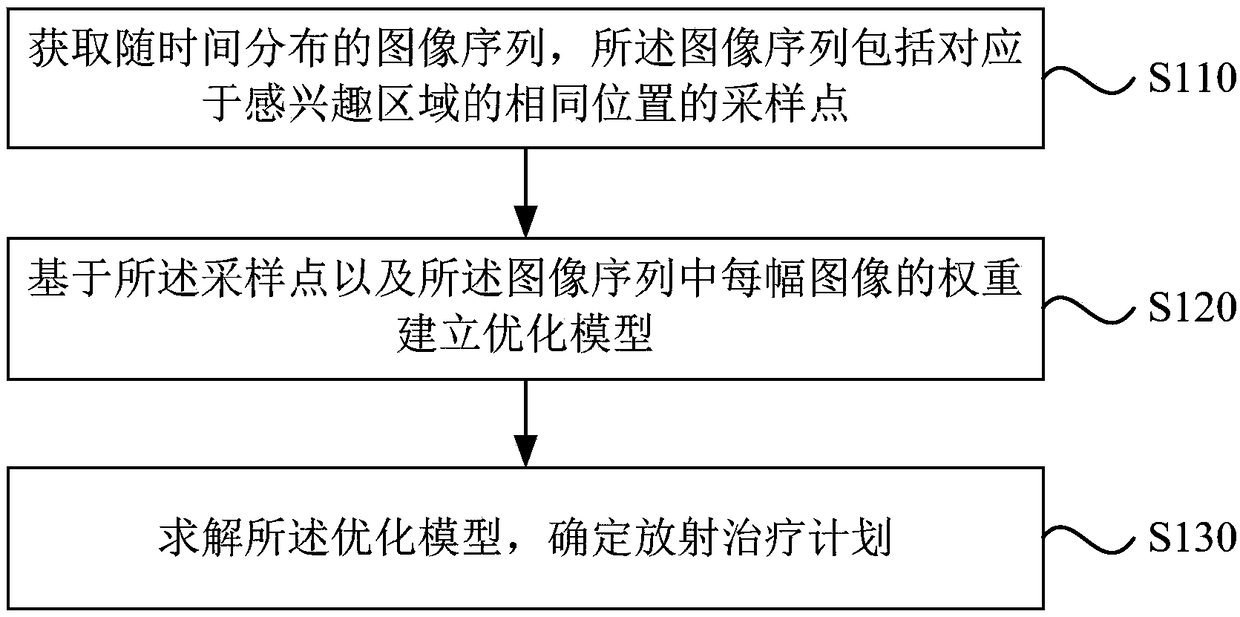
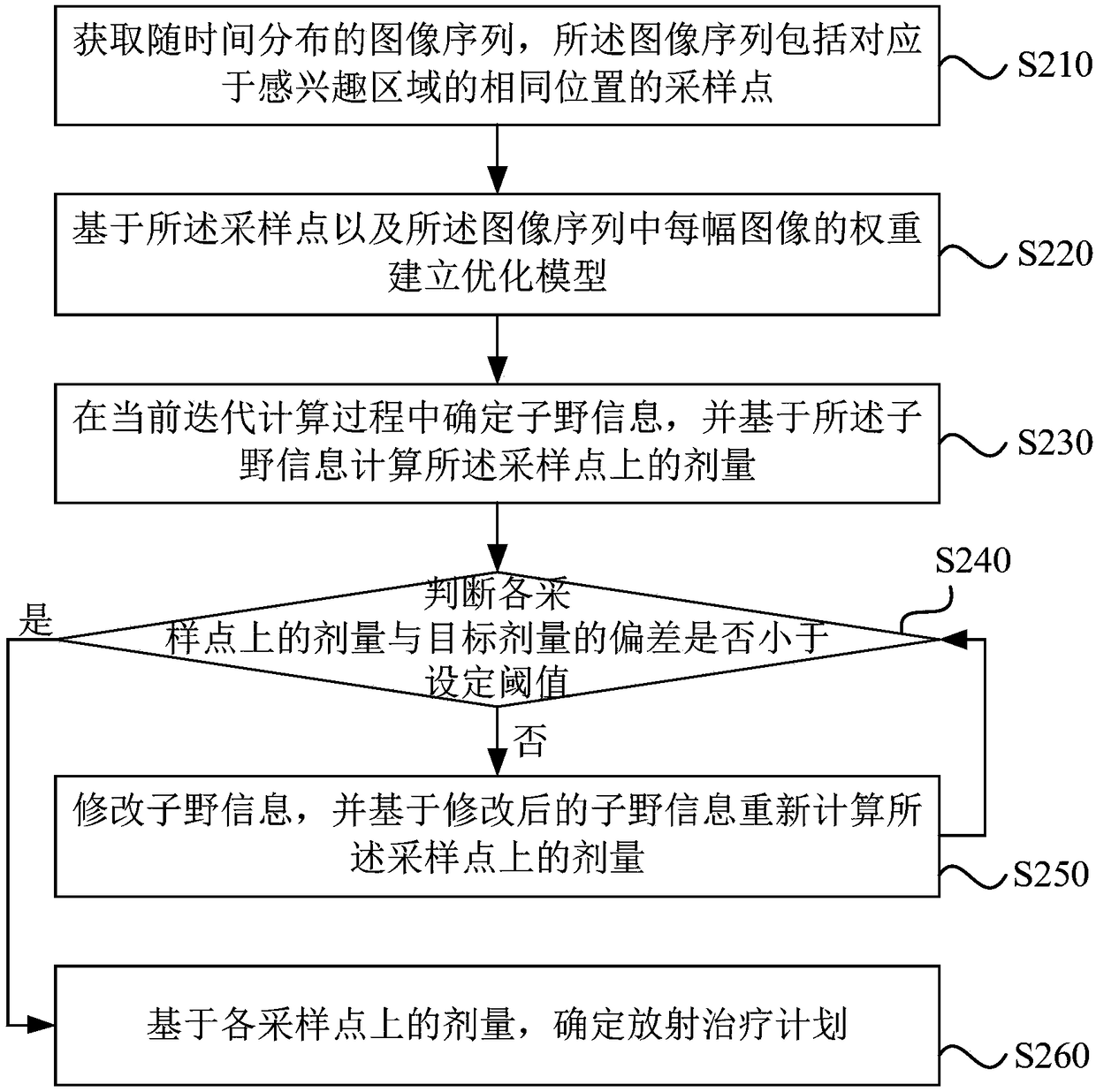
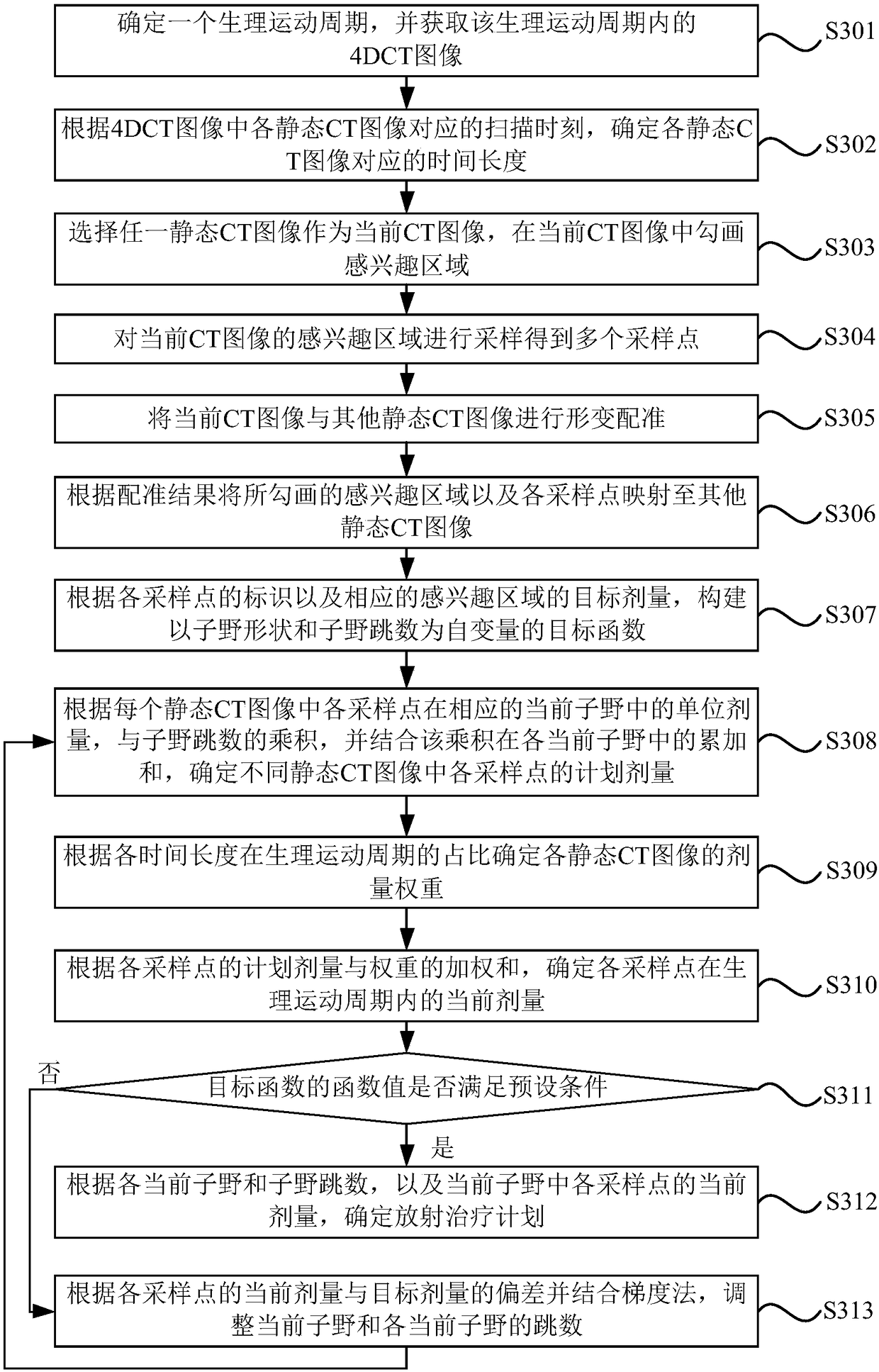
The invention discloses a radiotherapy planning system, a determining device and a storage medium. The system includes one or more processors, and a storage device for storing one or more programs; the one or more programs are executed by one or more processors, and the one or more processors perform the following steps: acquiring image sequences distributed with time, wherein the image sequencesincluding sample points corresponding to the same location of an interest region; establishing an optimization model based on the sampling points and the weight of each image in the image sequences; and solving the optimization model to determine the radiation therapy plan. The above technical scheme solves the problem that in the prior art, a tumor target area generates periodic movements due tobreathing, heartbeat, and the like, so that the actual exposure dose of the target area and surrounding endangered organs is different from the target dose, the system provides a more precise radiotherapy plan for the movement target area, facilitates more precise treatment, effectively protects the surrounding endangered organs of the target area, and is suitable for use with most existing radiotherapy equipment that implements radiotherapy plans.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
EUV lpp source with improved dose control by tracking dose over specified window
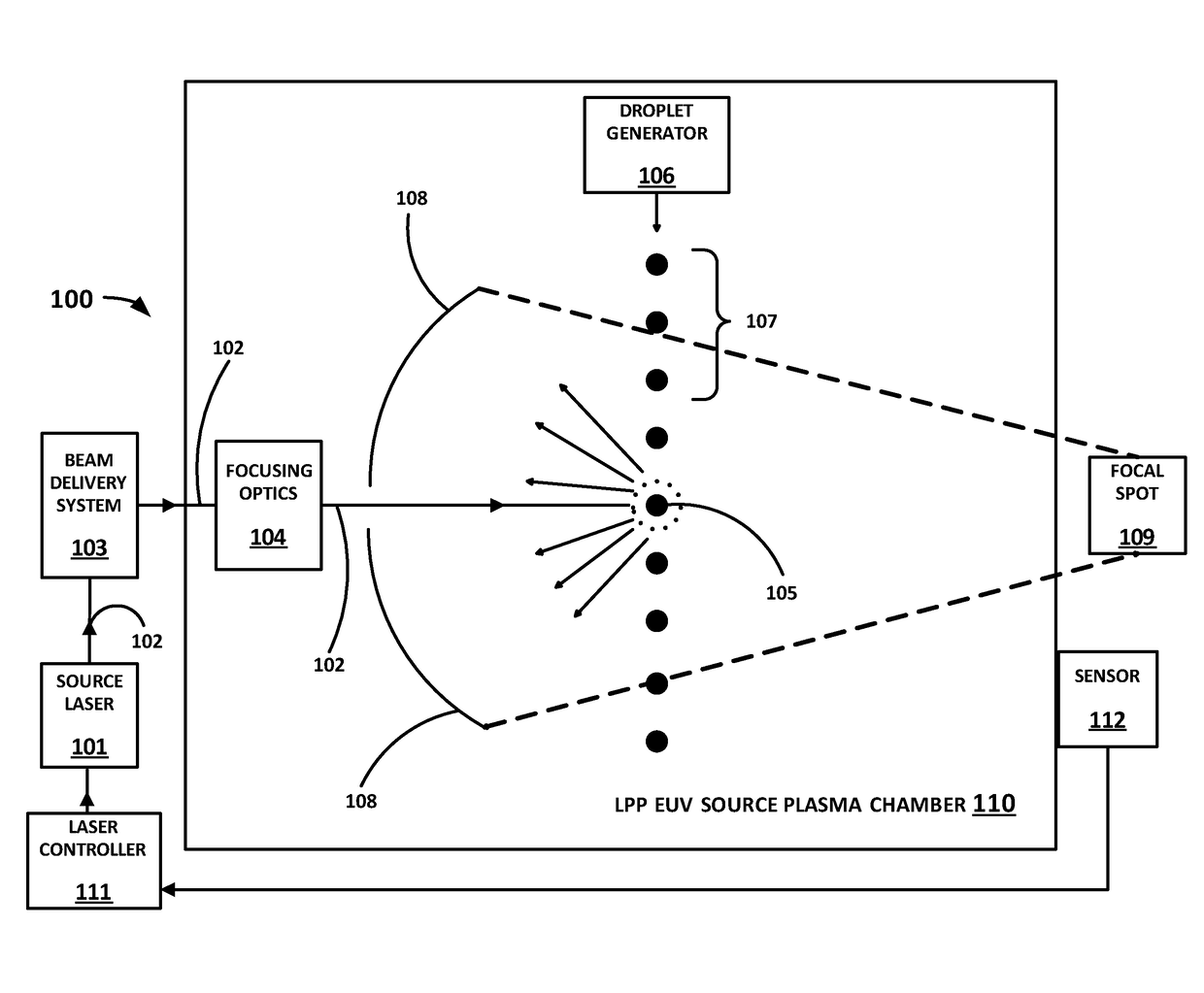
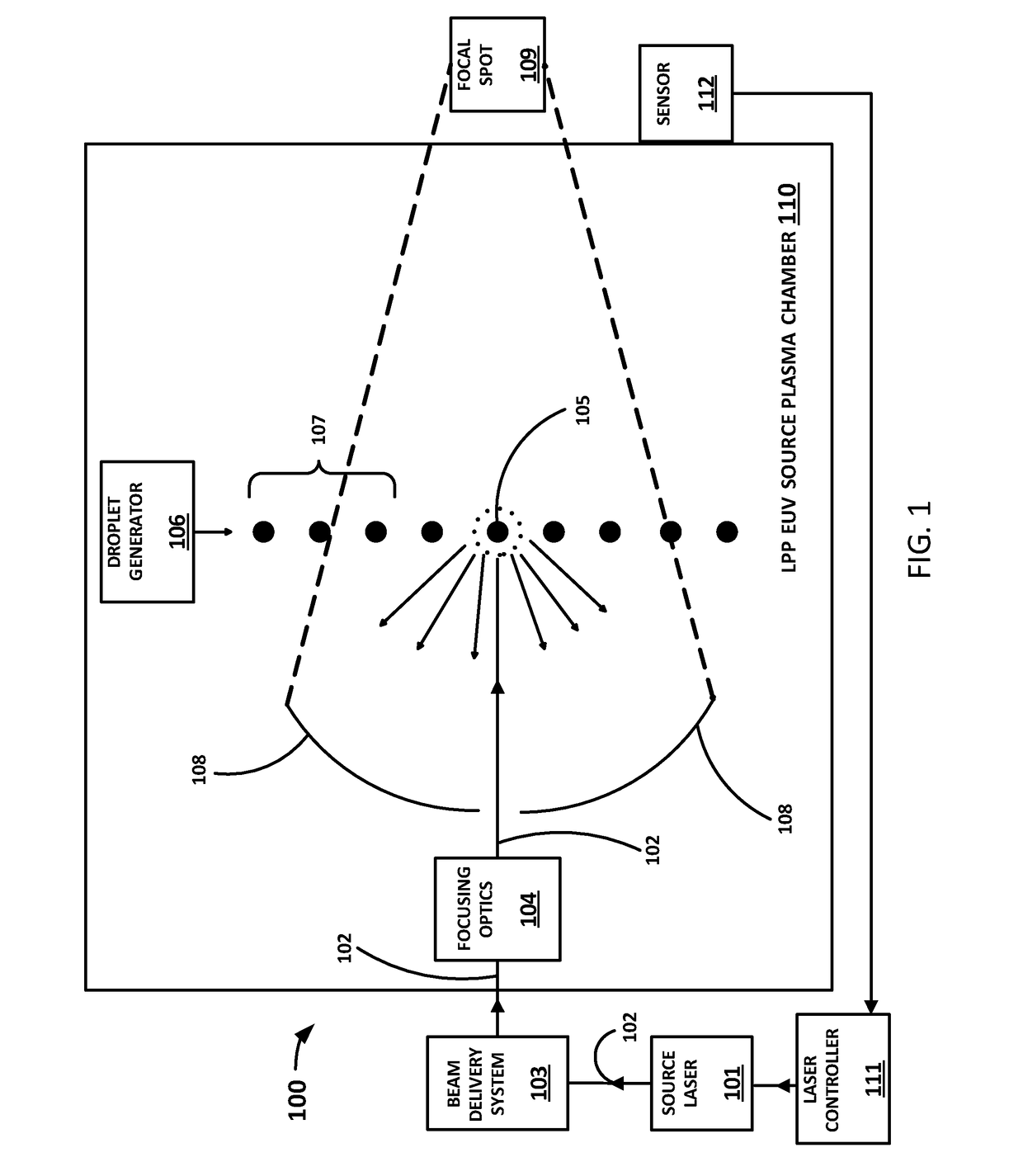
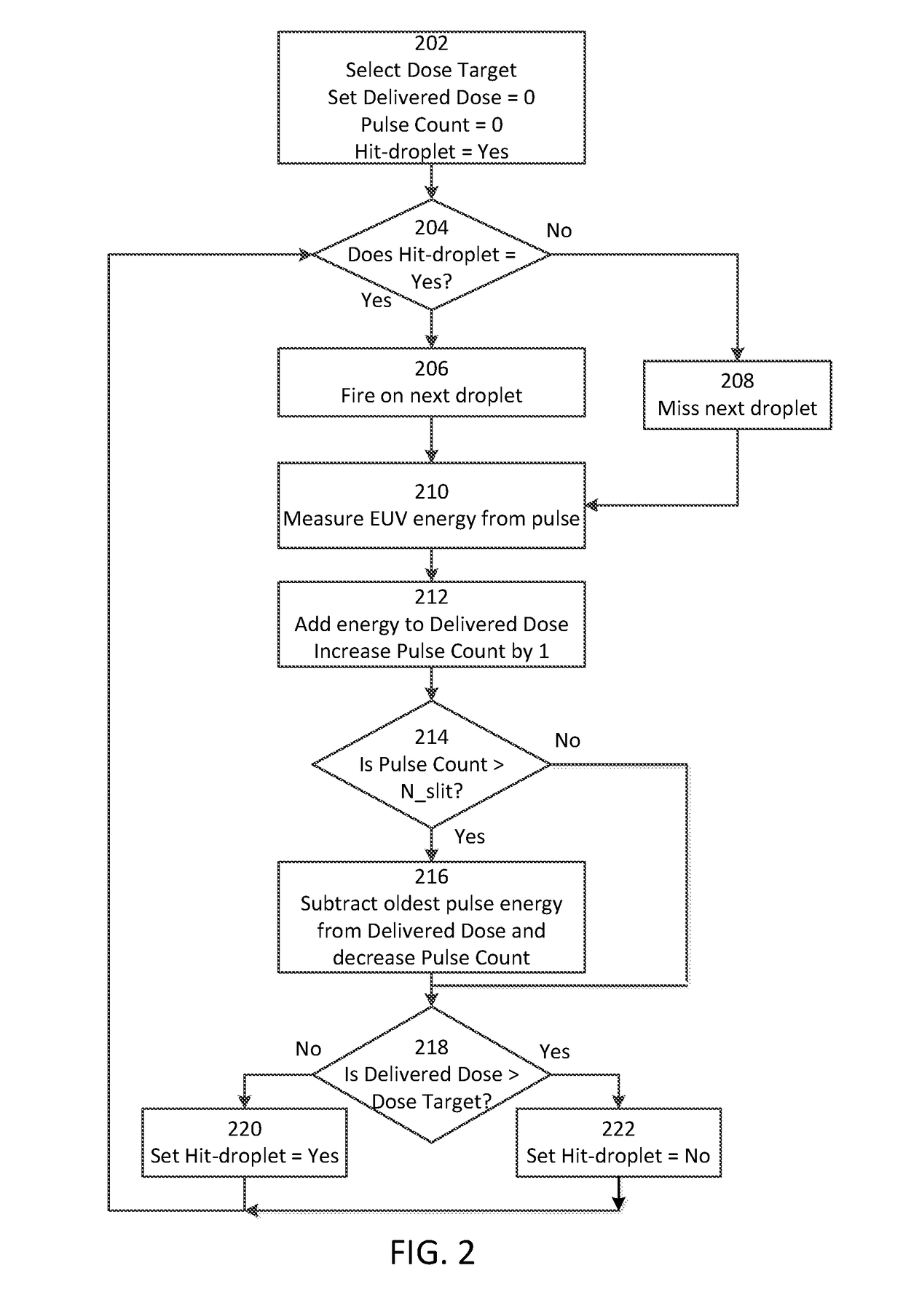
ActiveUS20170181258A1Improving control of doseEasy to controlX-ray tube with very high currentX-ray apparatusSide effectOptoelectronics
A method and apparatus for controlling a dose of extreme ultraviolet (EUV) radiation generated by a laser produced plasma (LPP) EUV light source. In one embodiment, a running total of the EUV energy generated over a predetermined number of laser pulses is measured; once that number of pulses is exceeded, the energy from the pulse immediately preceding the most recent predetermined number of pulses is dropped from the running total, so that the running total is from the most recent predetermined number of pulses. If the running total of the EUV energy exceeds a target dose, the next pulse is caused to not hit a droplet. This avoids the unwanted side effects of various prior art solutions, such as needing to miss many droplets in a row, or requiring the laser pulses to be shortened or reduced in power as in other prior art solutions.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method and device for constructing radiation field map, and robot
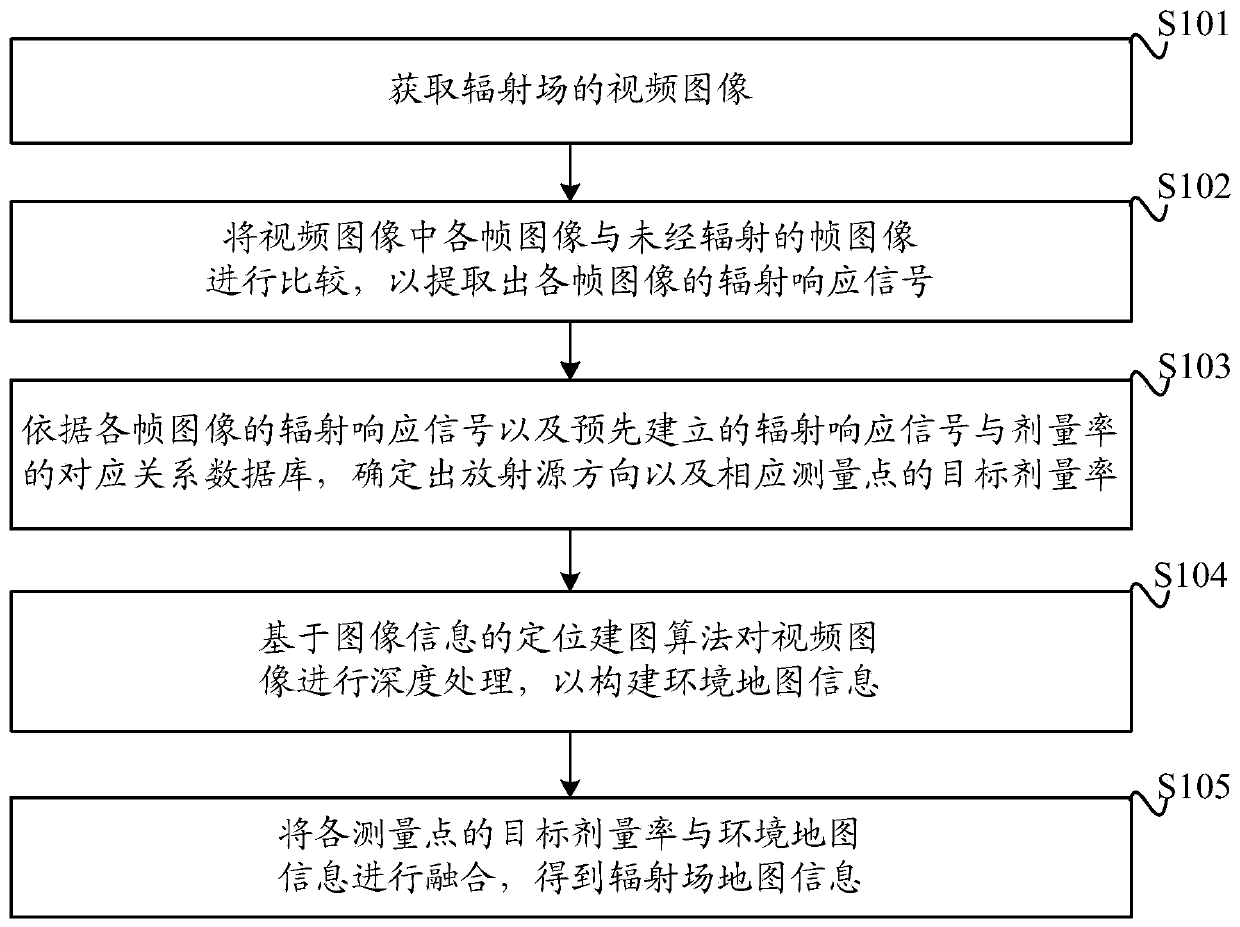
ActiveCN110231642AIncrease flexibilityDosimetersCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurement pointRelational database
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and device for constructing a radiation field map, and a robot. A processor is used for comparing each frame image in an obtained video image with anunradiated frame image to extract a radiation response signal of each frame image. The radiation source direction and the target dosage rate of a corresponding measuring point are determined according to the radiation response signal of each frame image and a pre-established corresponding relation database of the radiation response signal and the dose rate. The processor is used for performing deep processing on the video image based on a positioning mapping algorithm of the image information to construct the environmental map information. The target dose rate of each measuring point is fusedwith the environmental map information to obtain radiation field map information. Two-way processing of visible light and ionizing radiation information are carried out on the collected video image through the processor, two processing results are fused, and the construction of the radiation field map can be realized. The technical solution is applicable to an unknown radiation field environmentwith uncertain radioactive levels and complicated conditions.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com