Patents
Literature
48 results about "Cumulative dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cumulative dose is the total dose resulting from repeated exposures of ionizing radiation to an occupationally exposed worker to the same portion of the body, or to the whole body, over a period of time.
Area sterilizer and method of disinfection
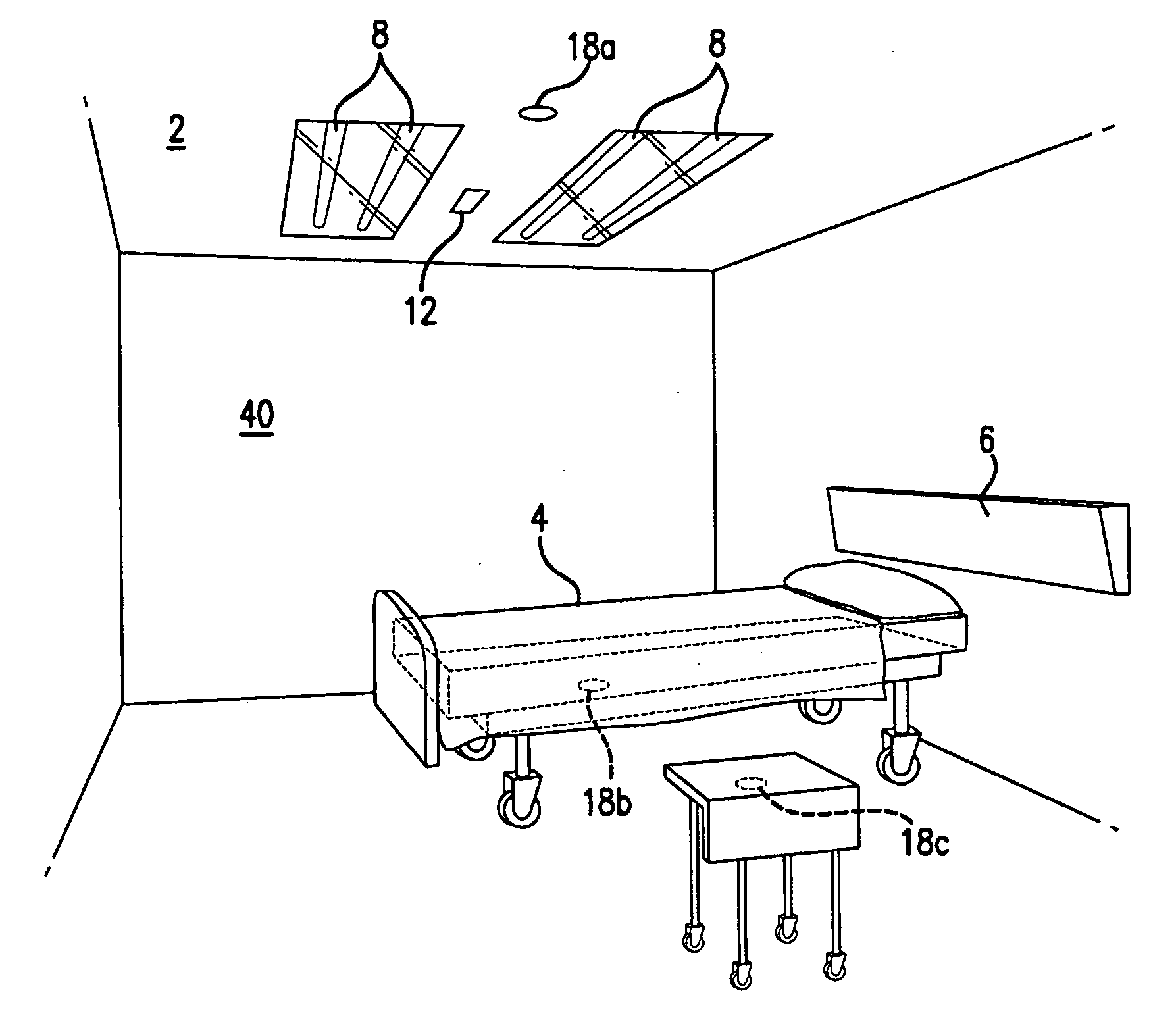
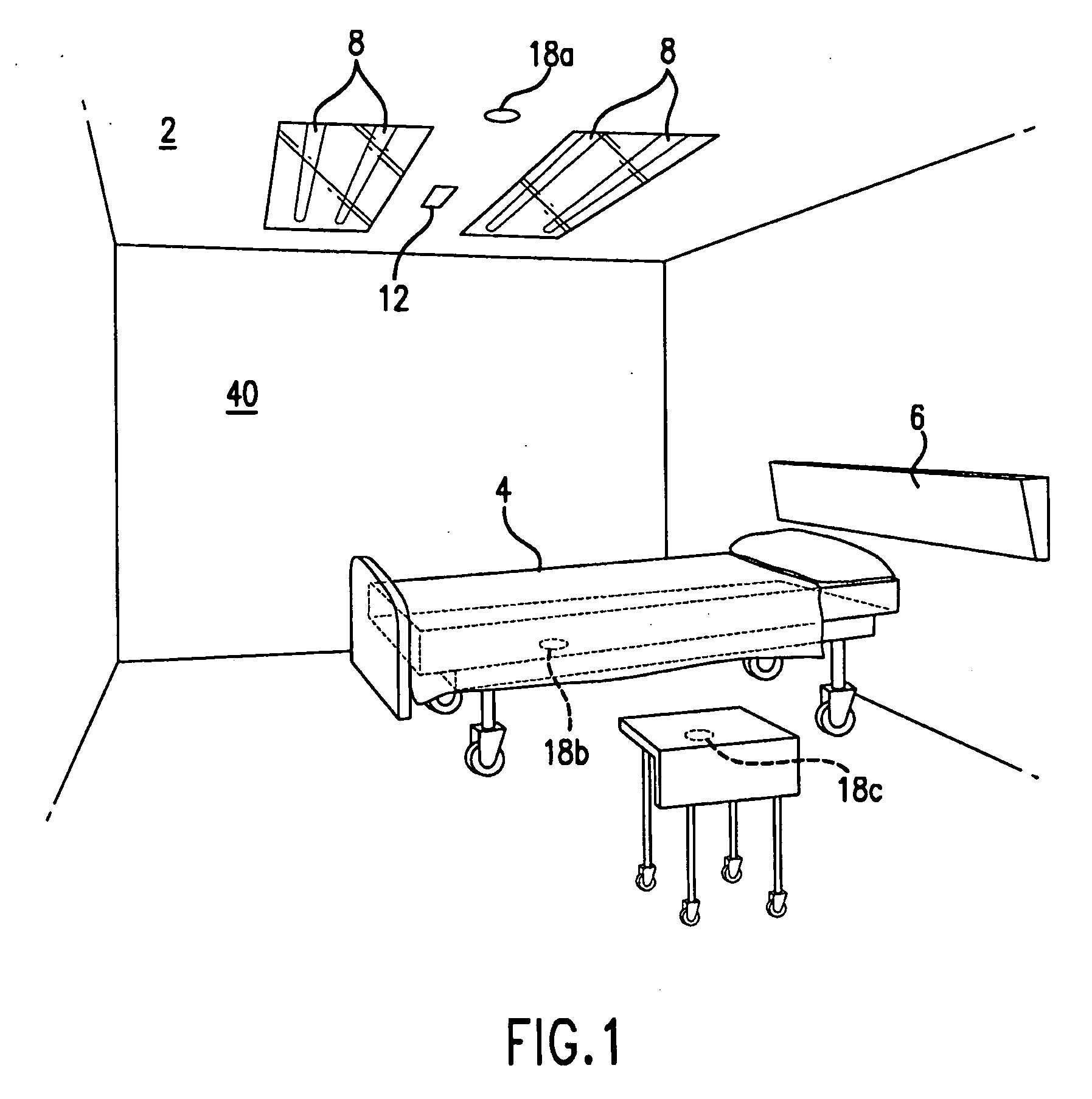
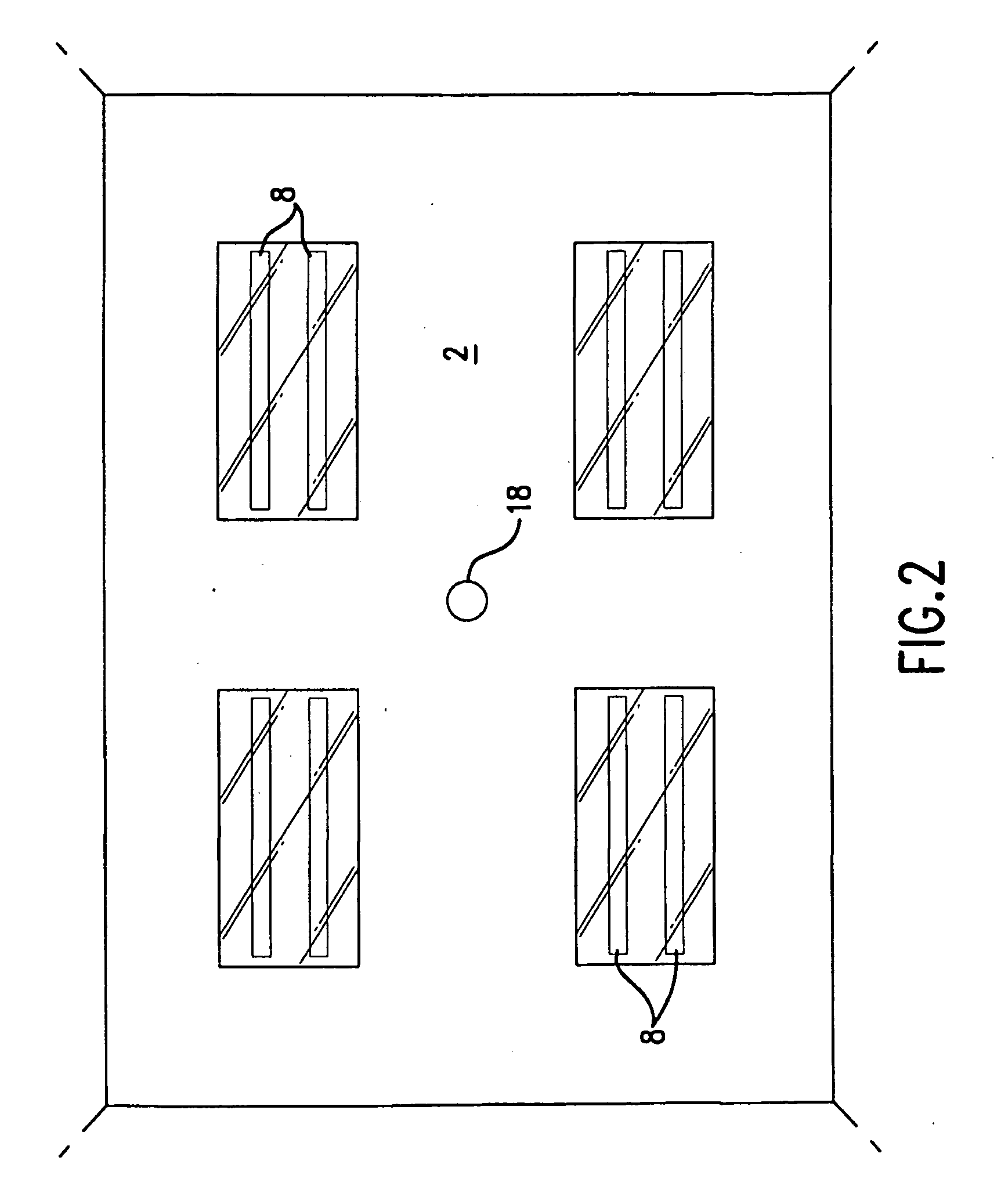
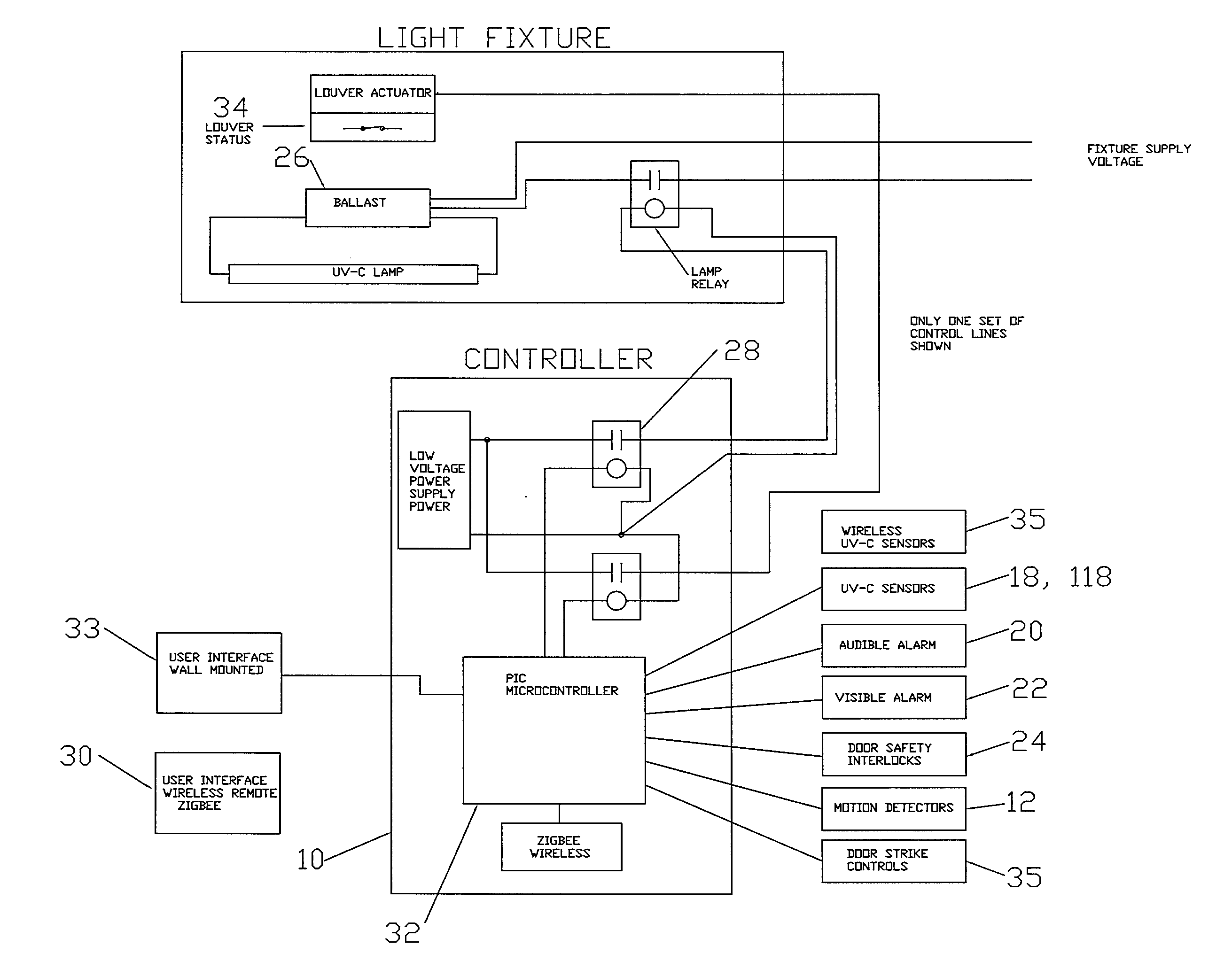
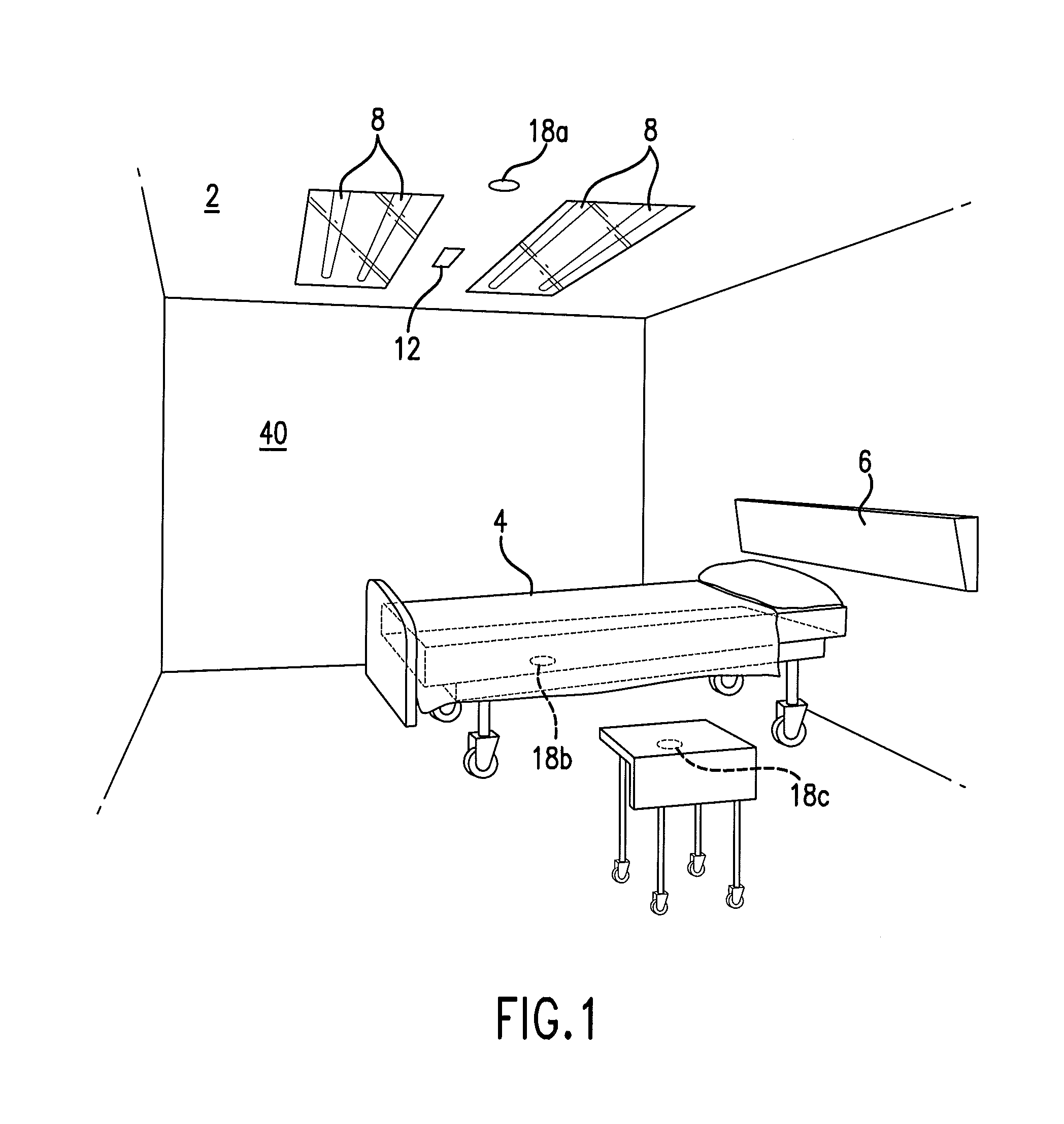
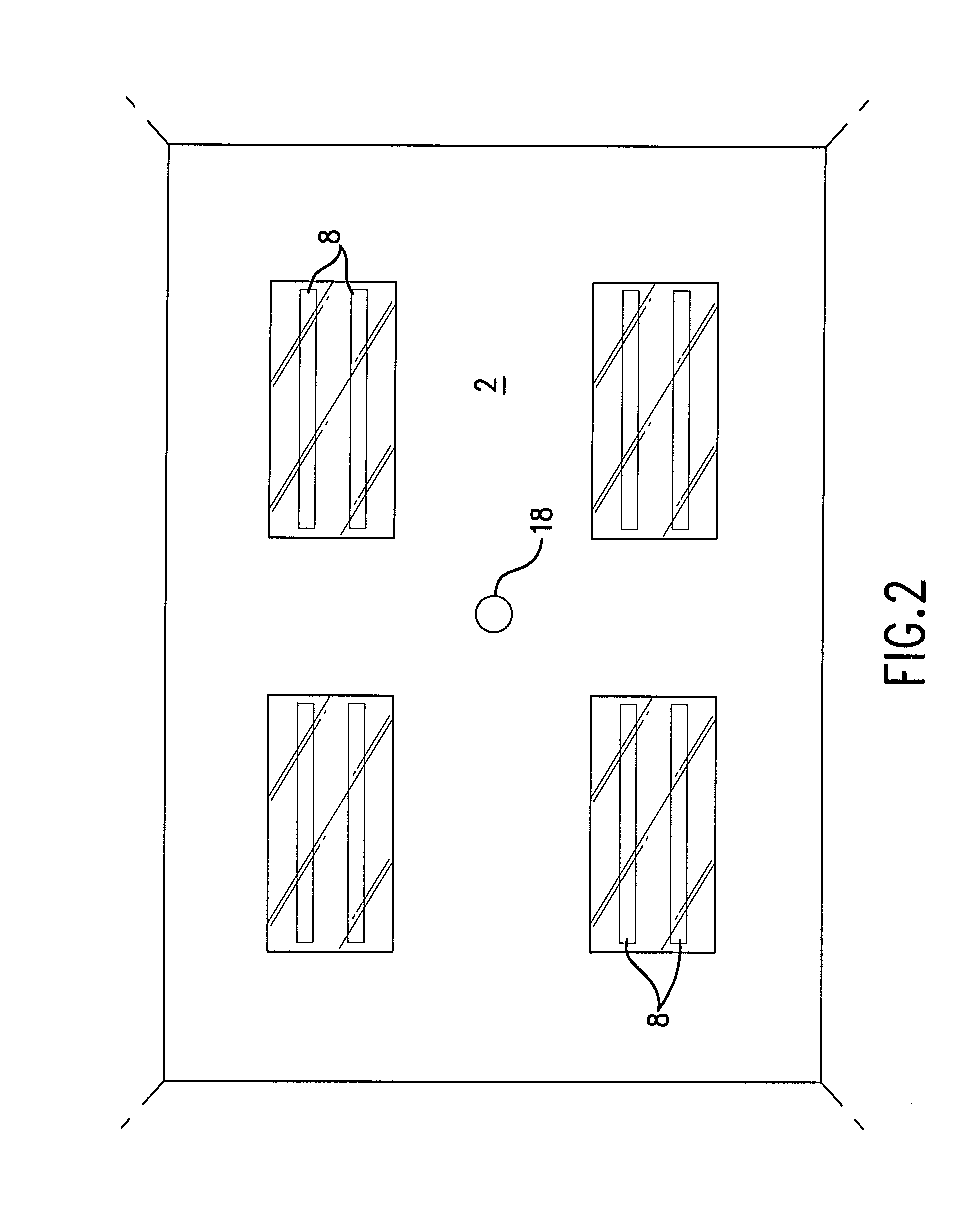
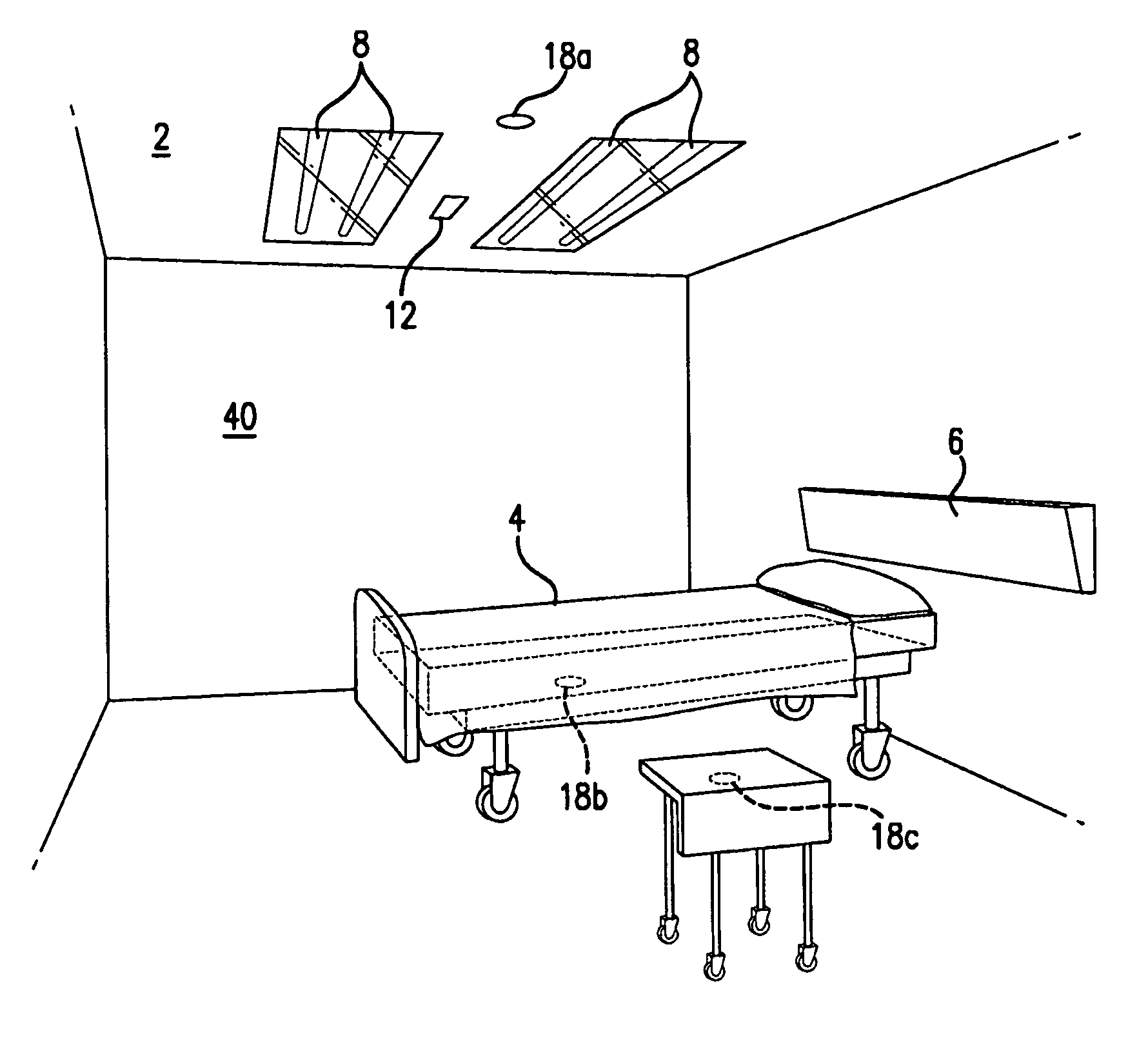
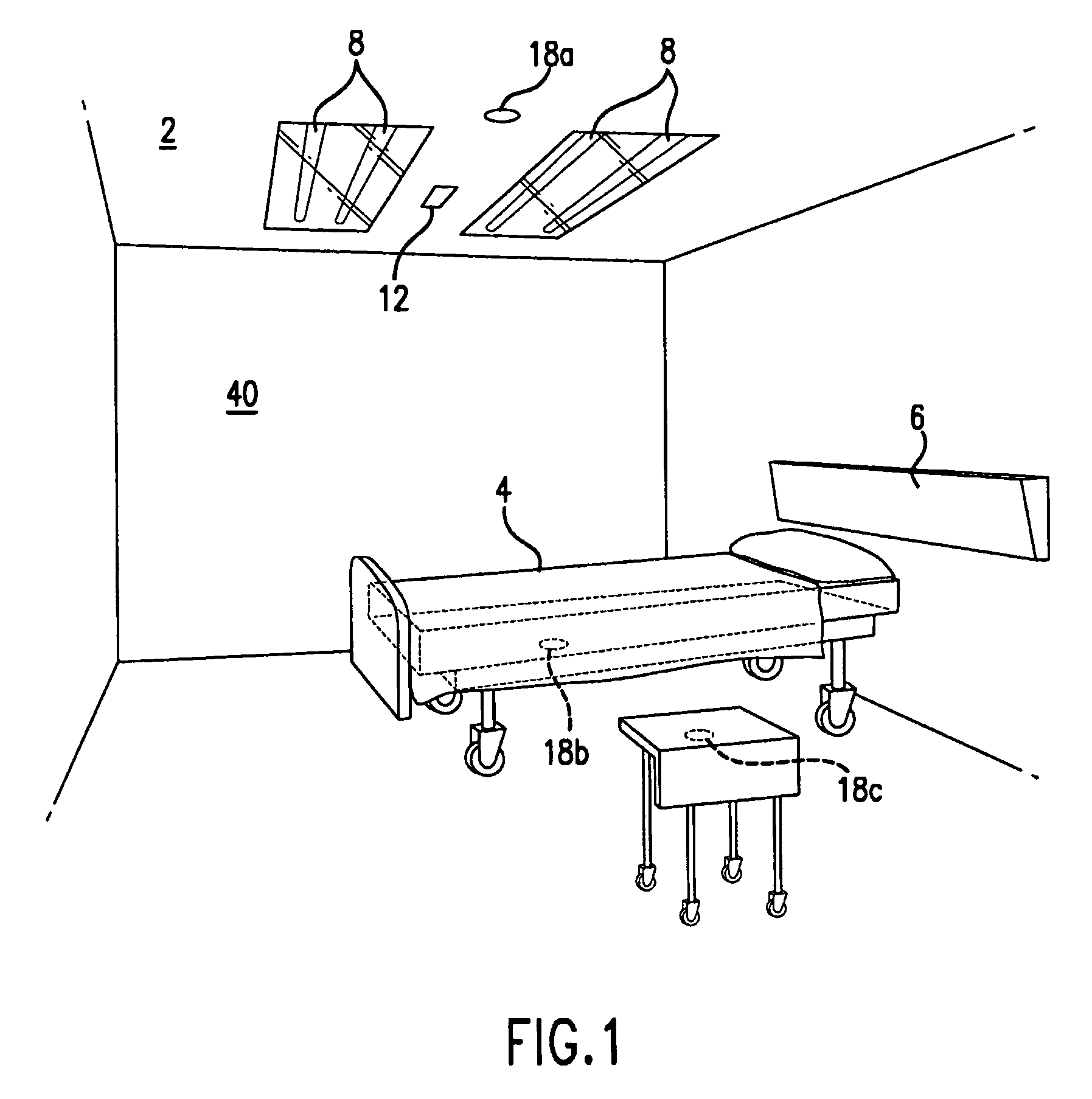
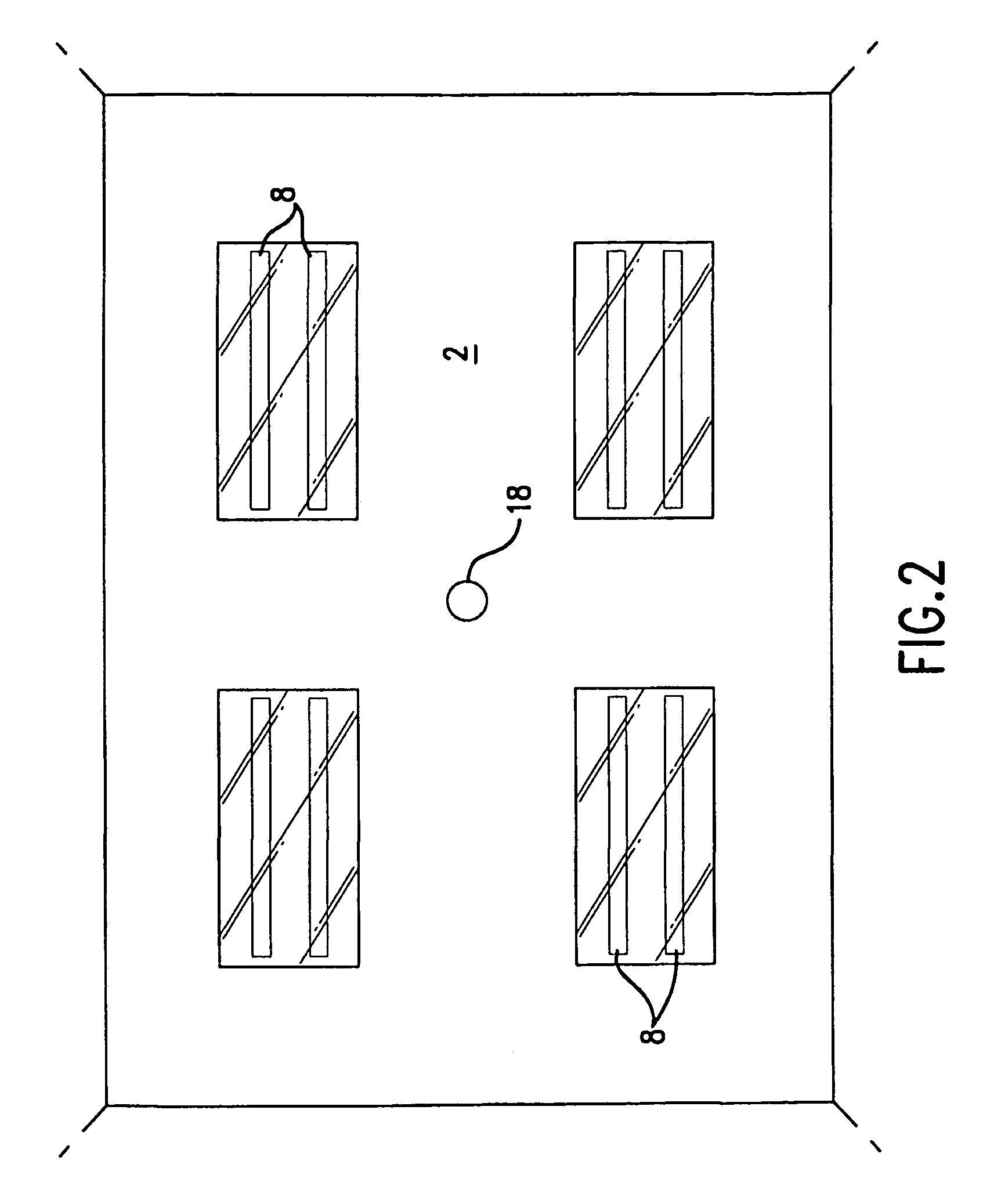
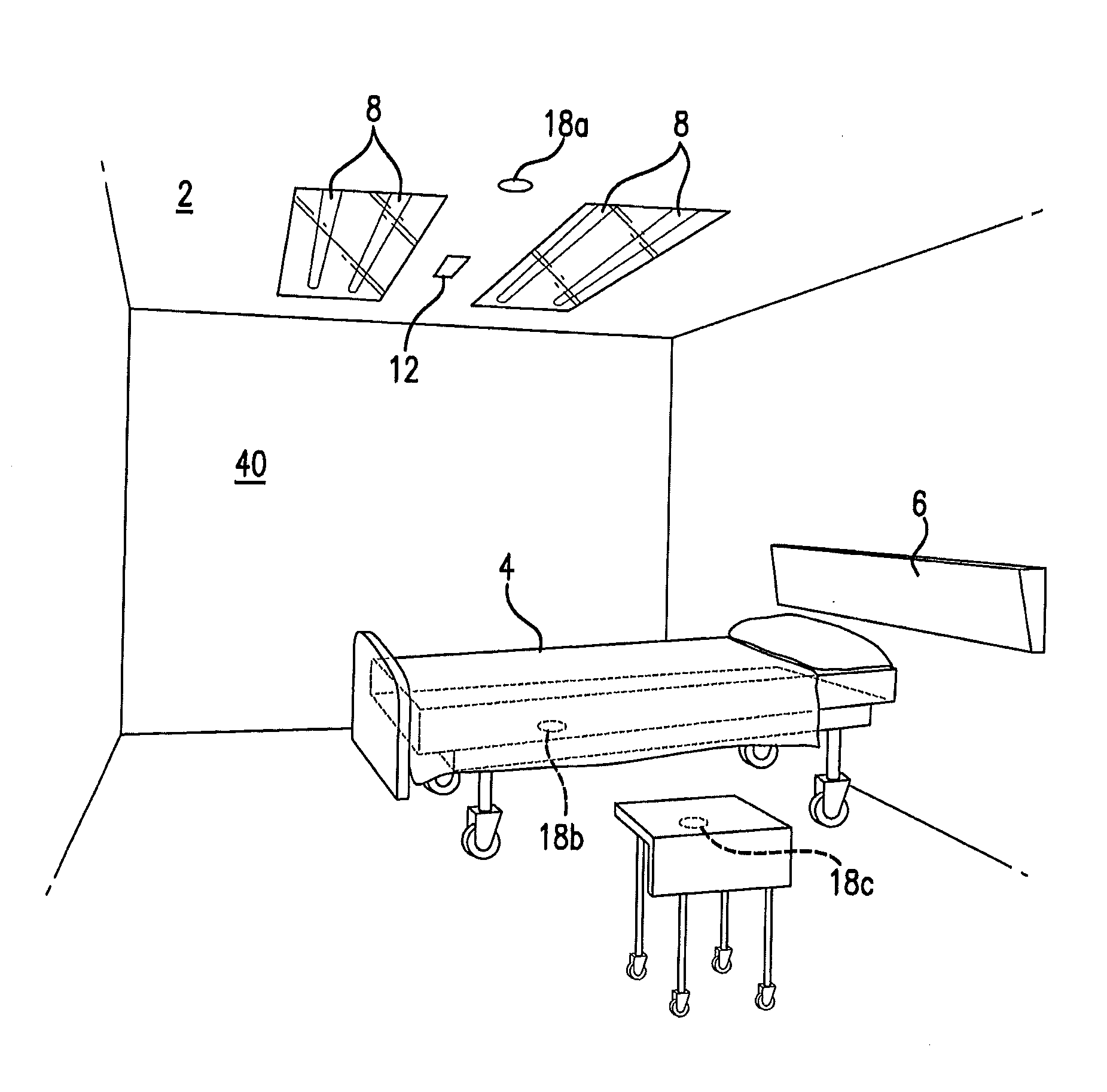
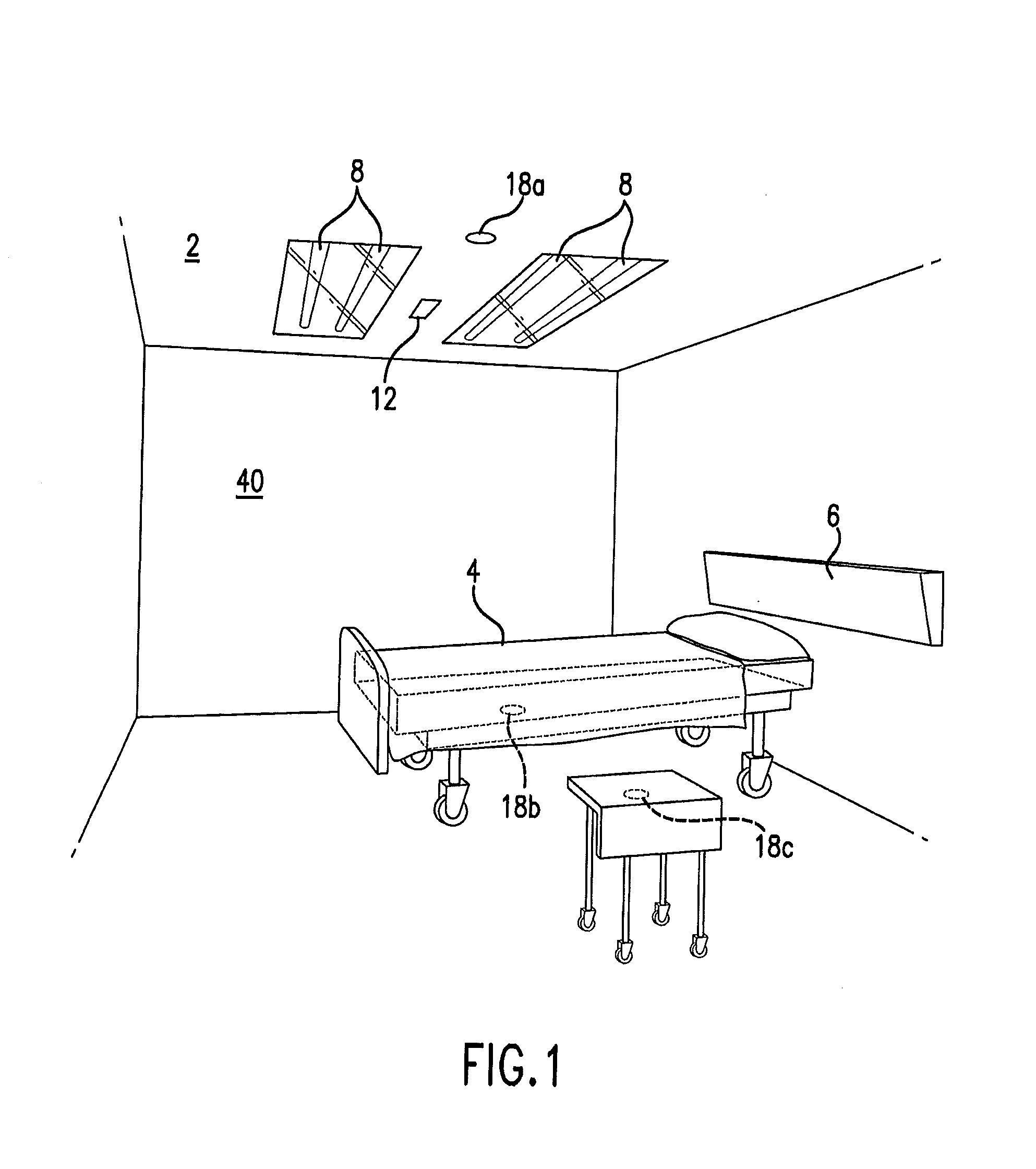
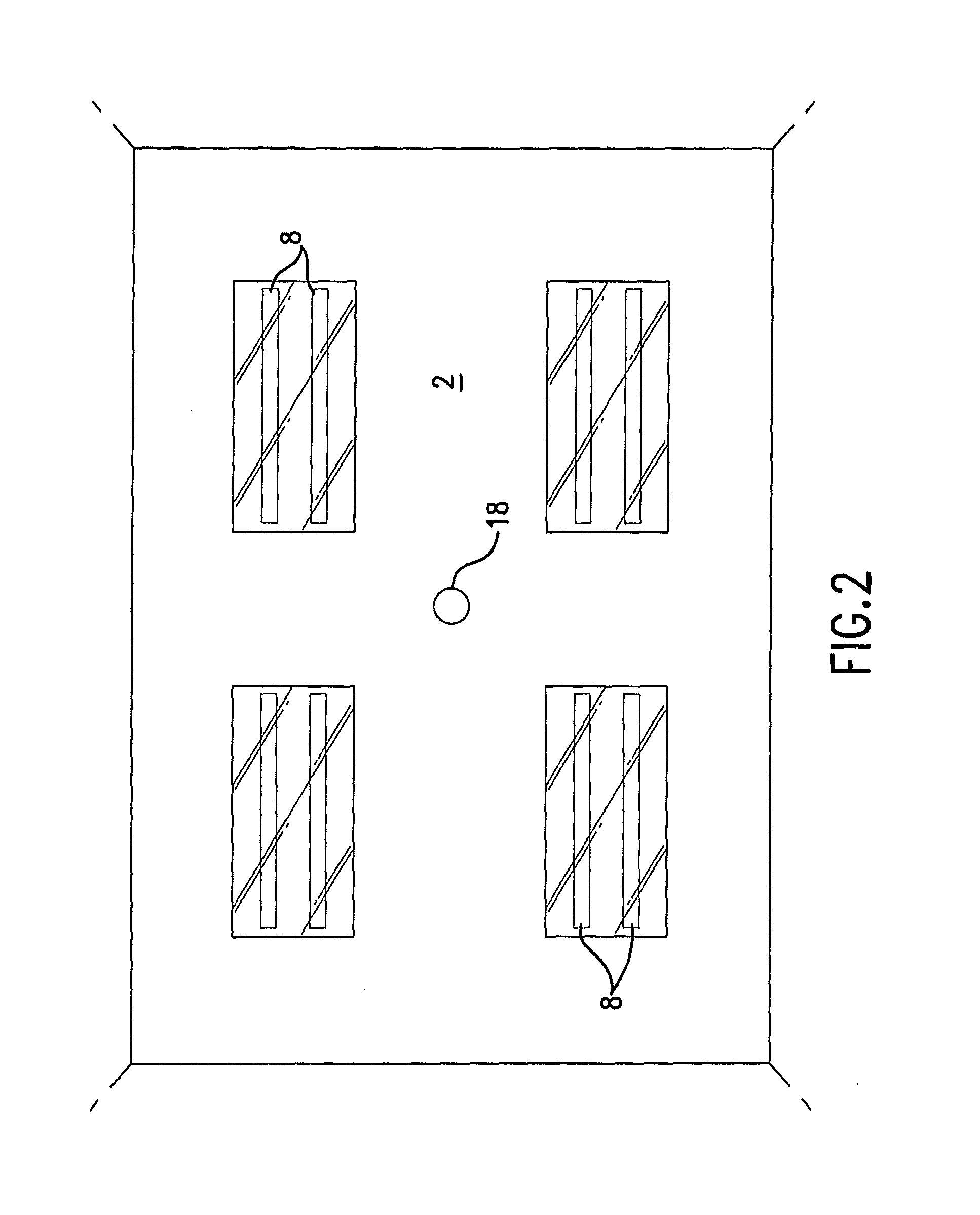
An ultraviolet area sterilizer or disinfector is incorporated into a building structure where concern exists regarding the presence of pathogenic bacteria on environmental surfaces. Ultraviolet C (UV-C) generators generate UV-C that is directed to architectural partitions of an enclosed area. The architectural partitions reflect UV-C to kill pathogens in the enclosed area. The device transmits a calculated dose of UV-C from a fixture mounted to an architectural partition in the enclosed area. Once an effective cumulative dose of UV-C has been reflected to radiation sensors, as measured by the sensors, the device shuts down.
Owner:UVAS
Disinfection device and method
InactiveUS20120126134A1Electrical apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansUv c radiationUltraviolet
An ultraviolet area sterilizer or disinfector is incorporated into a building structure where concern exists regarding the presence of pathogenic bacteria on environmental surfaces. Ultraviolet C (UV-C) generators generate UV-C that is directed to architectural partitions of an enclosed area. The architectural partitions reflect UV-C to kill pathogens in the enclosed area. The device transmits a calculated dose of UV-C from a fixture mounted to an architectural partition in the enclosed area. Once an effective cumulative dose of UV-C has been reflected to radiation sensors, as measured by the sensors, the device shuts down. The device allocates power to specific UV-C emitters so as to direct UV-C radiation more uniformly throughout the area, as measured by the sensors.
Owner:DEAL JEFFERY L +1
Area sterilizer and method of disinfection
An ultraviolet area sterilizer or disinfector is incorporated into a building structure where concern exists regarding the presence of pathogenic bacteria on environmental surfaces. Ultraviolet C (UV-C) generators generate UV-C that is directed to architectural partitions of an enclosed area. The architectural partitions reflect UV-C to kill pathogens in the enclosed area. The device transmits a calculated dose of UV-C from a fixture mounted to an architectural partition in the enclosed area. Once an effective cumulative dose of UV-C has been reflected to radiation sensors, as measured by the sensors, the device shuts down.
Owner:UVAS
Disinfection device and method
ActiveUS20130234041A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesUv c radiationUltraviolet
Owner:UVAS
Disinfection device and method
ActiveUS8859994B2Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry for measuring UV lightUv c radiationUltraviolet
An ultraviolet area sterilizer or disinfector is incorporated into a building structure where concern exists regarding the presence of pathogenic bacteria on environmental surfaces. Ultraviolet C (UV-C) generators generate UV-C that is directed to architectural partitions of an enclosed area. The architectural partitions reflect UV-C to kill pathogens in the enclosed area. The device transmits a calculated dose of UV-C from a fixture mounted to an architectural partition in the enclosed area. Once an effective cumulative dose of UV-C has been reflected to radiation sensors, as measured by the sensors, the device shuts down. The device may allocate power to specific UV-C emitters so as to direct UV-C radiation more uniformly throughout the area, as measured by the sensors.
Owner:UVAS
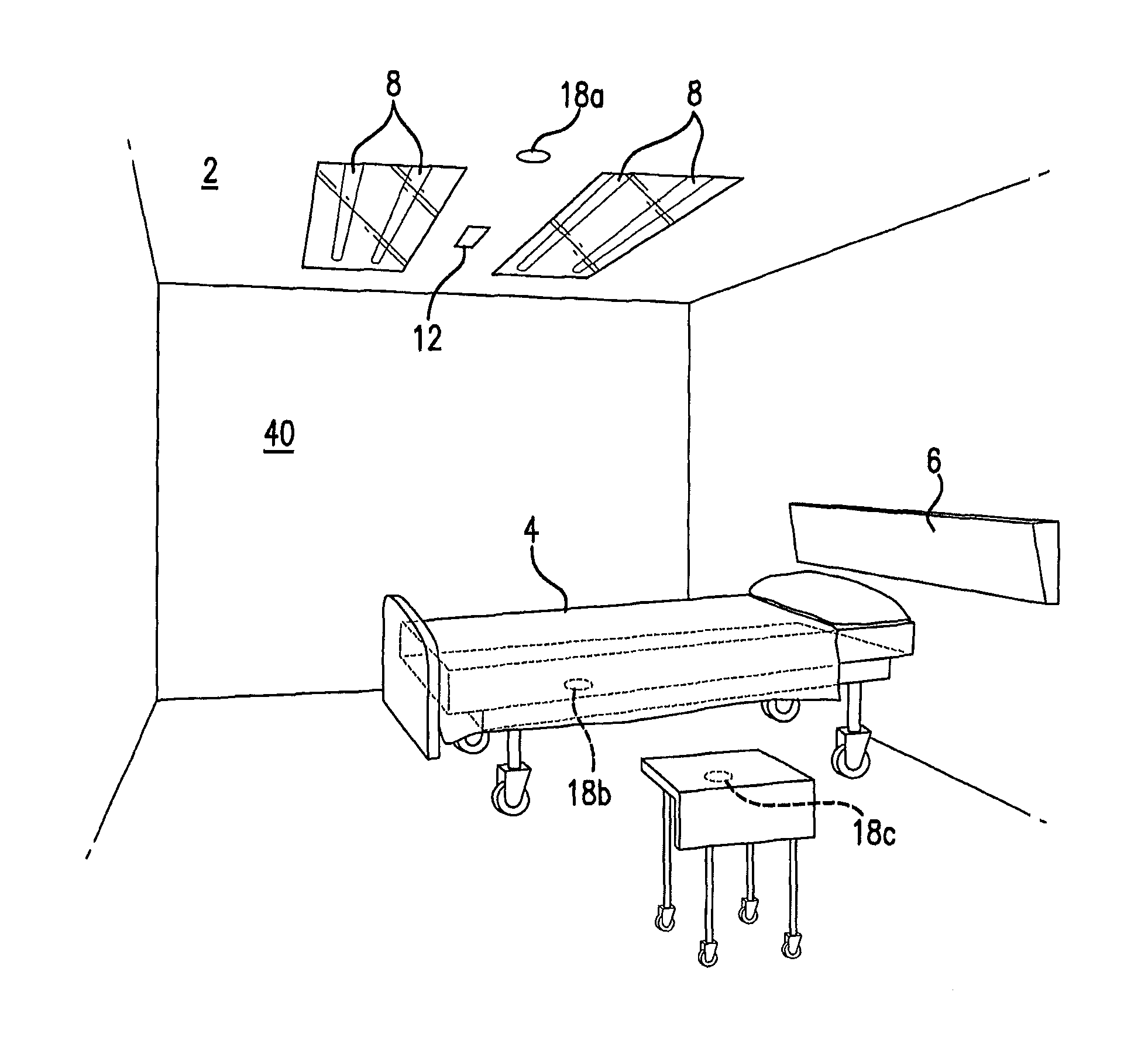
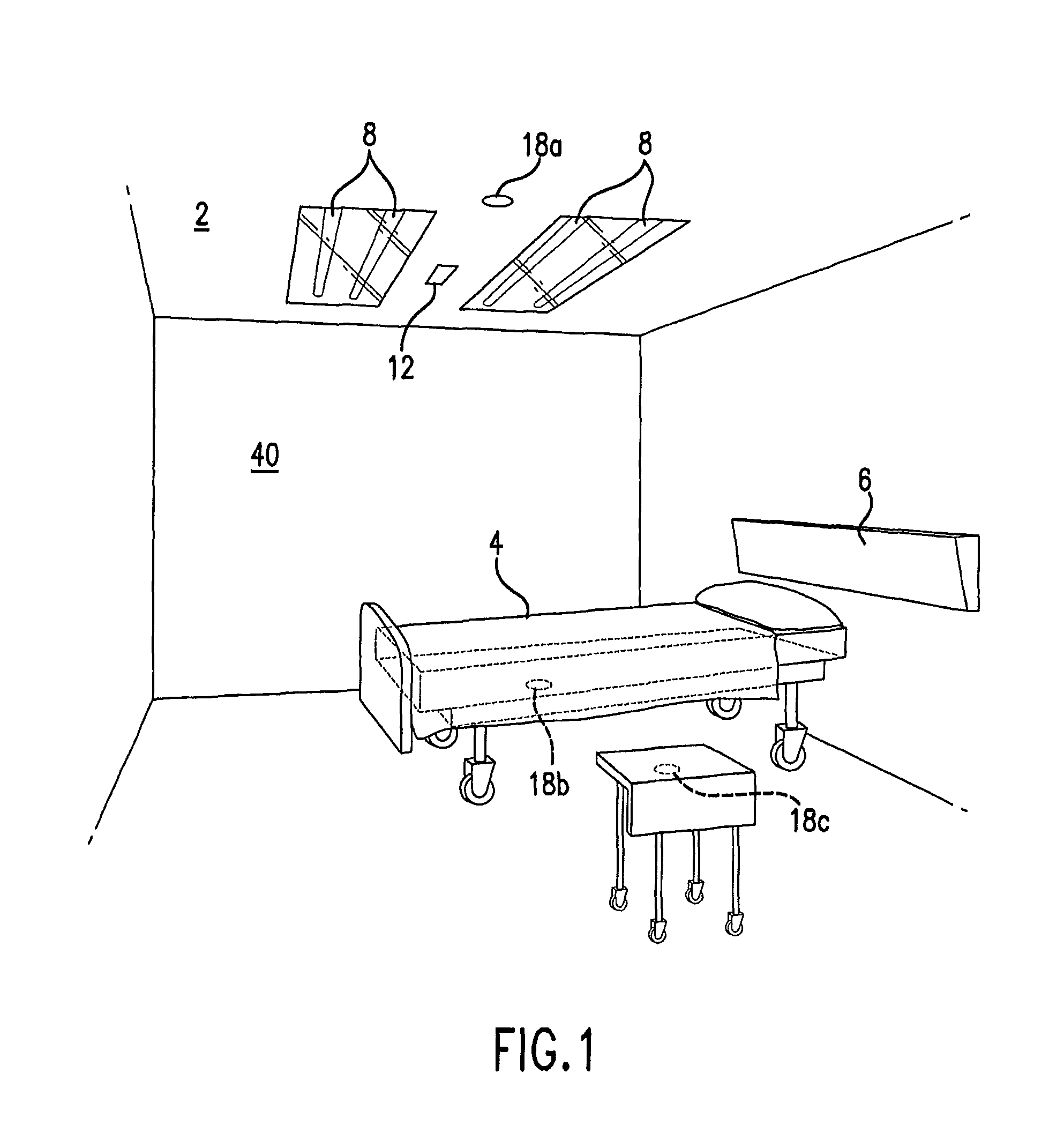
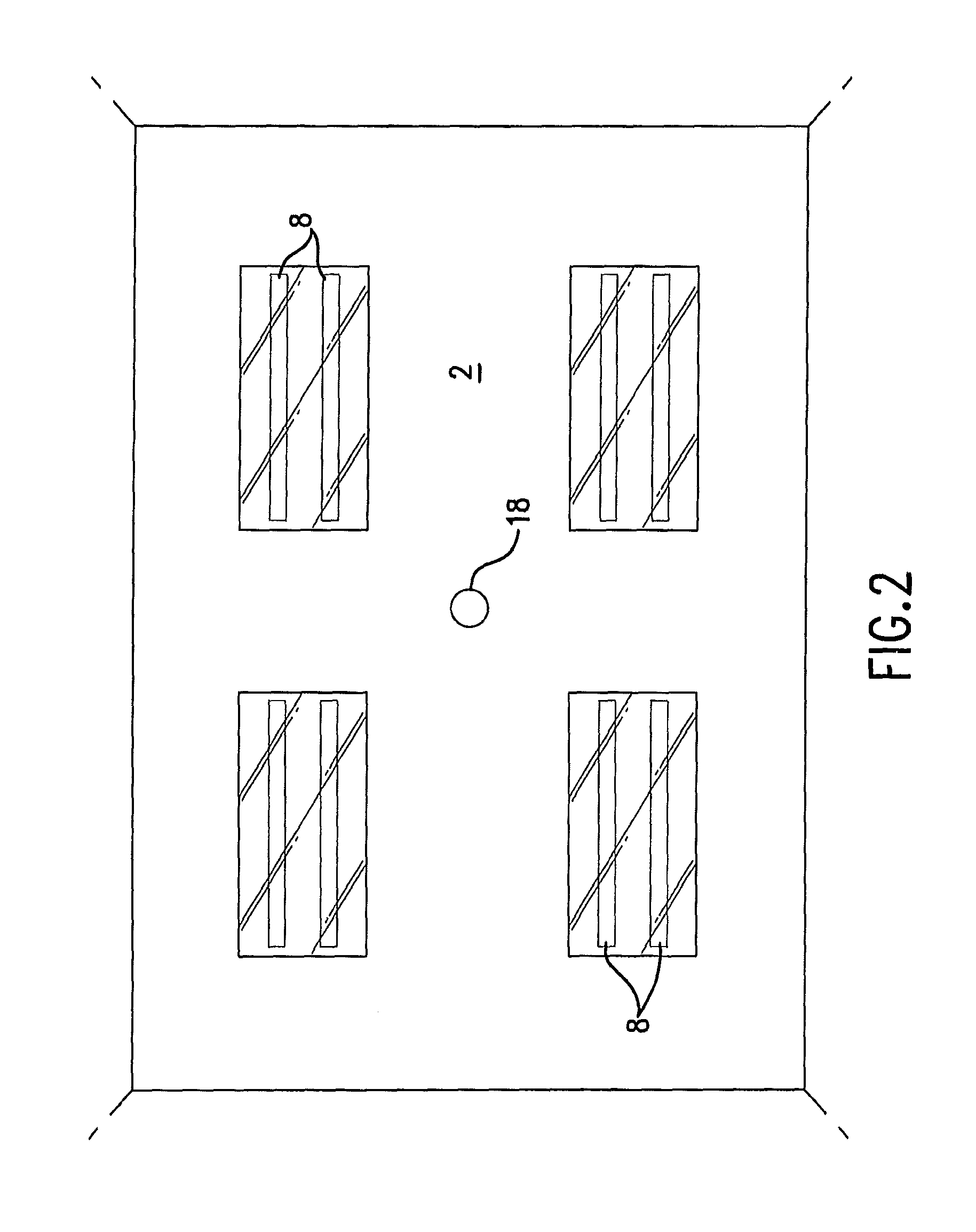
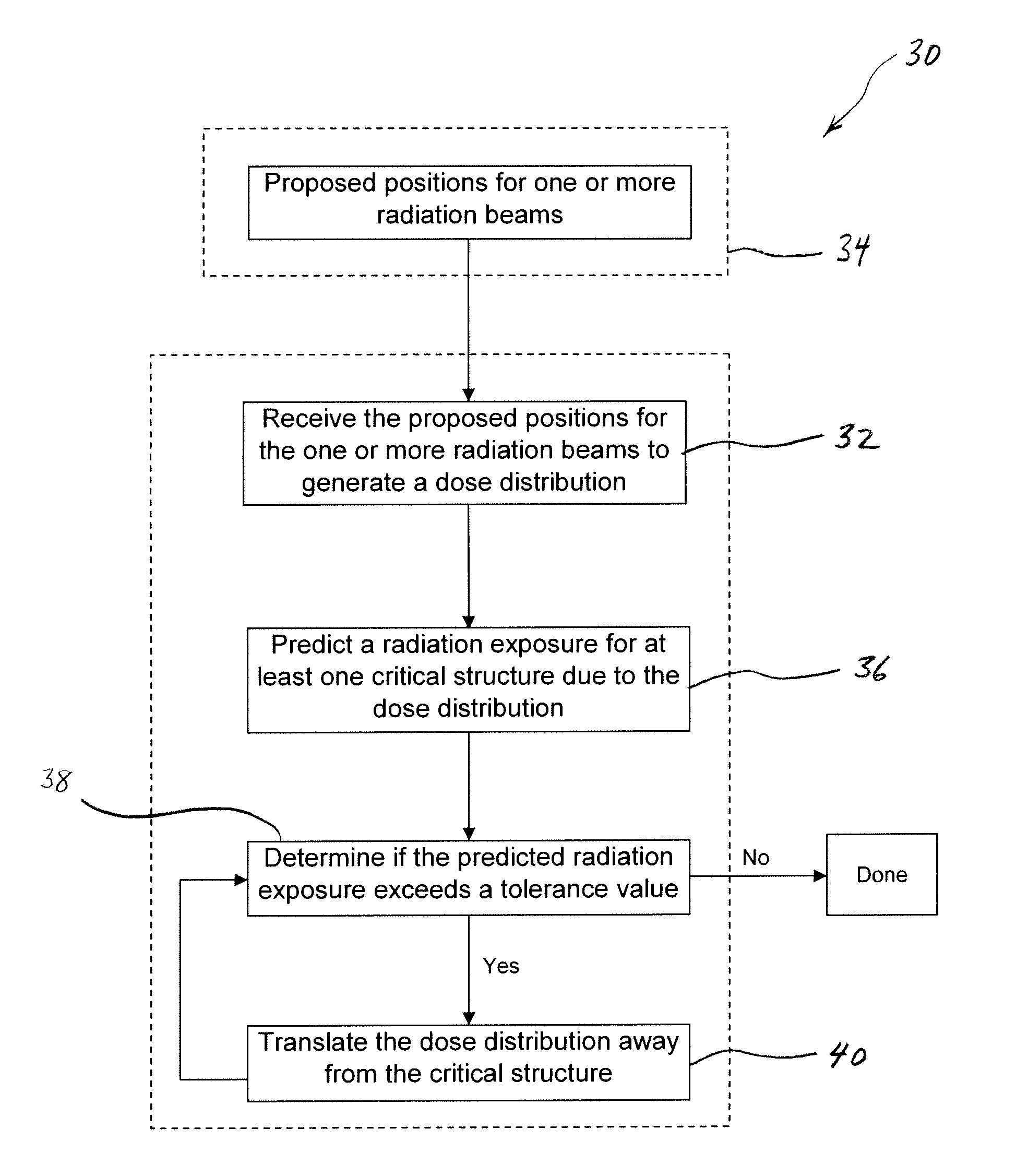
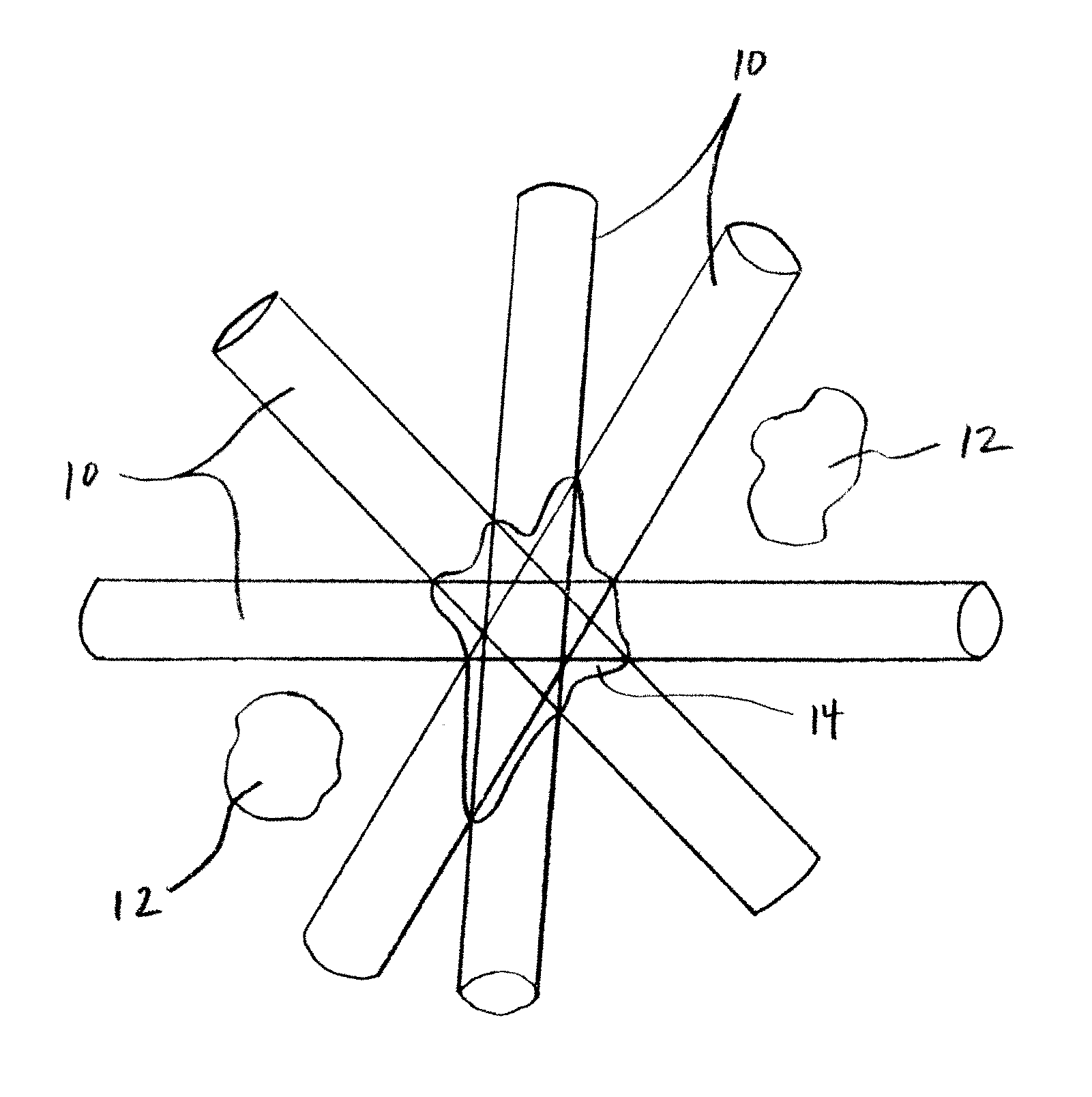
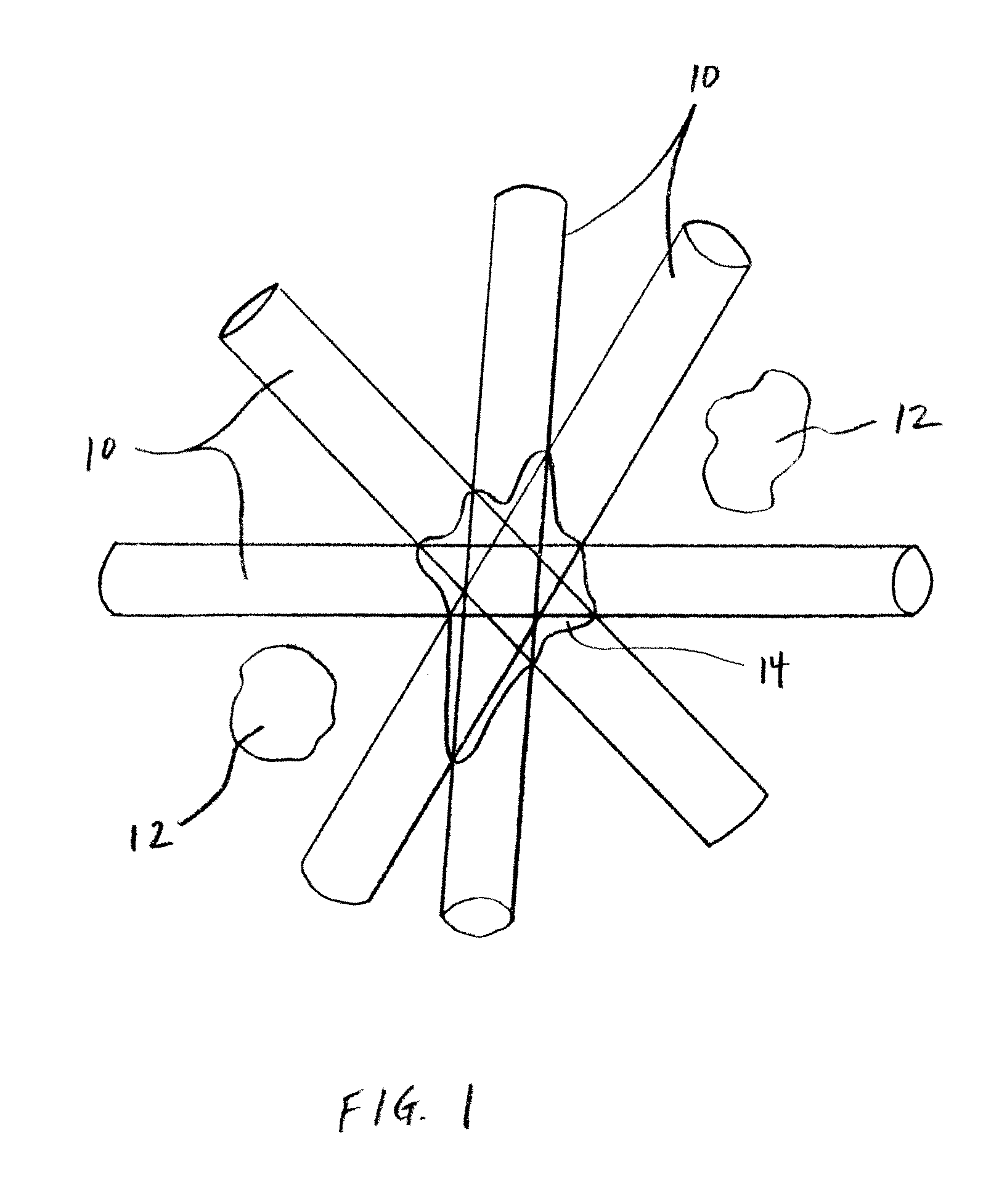
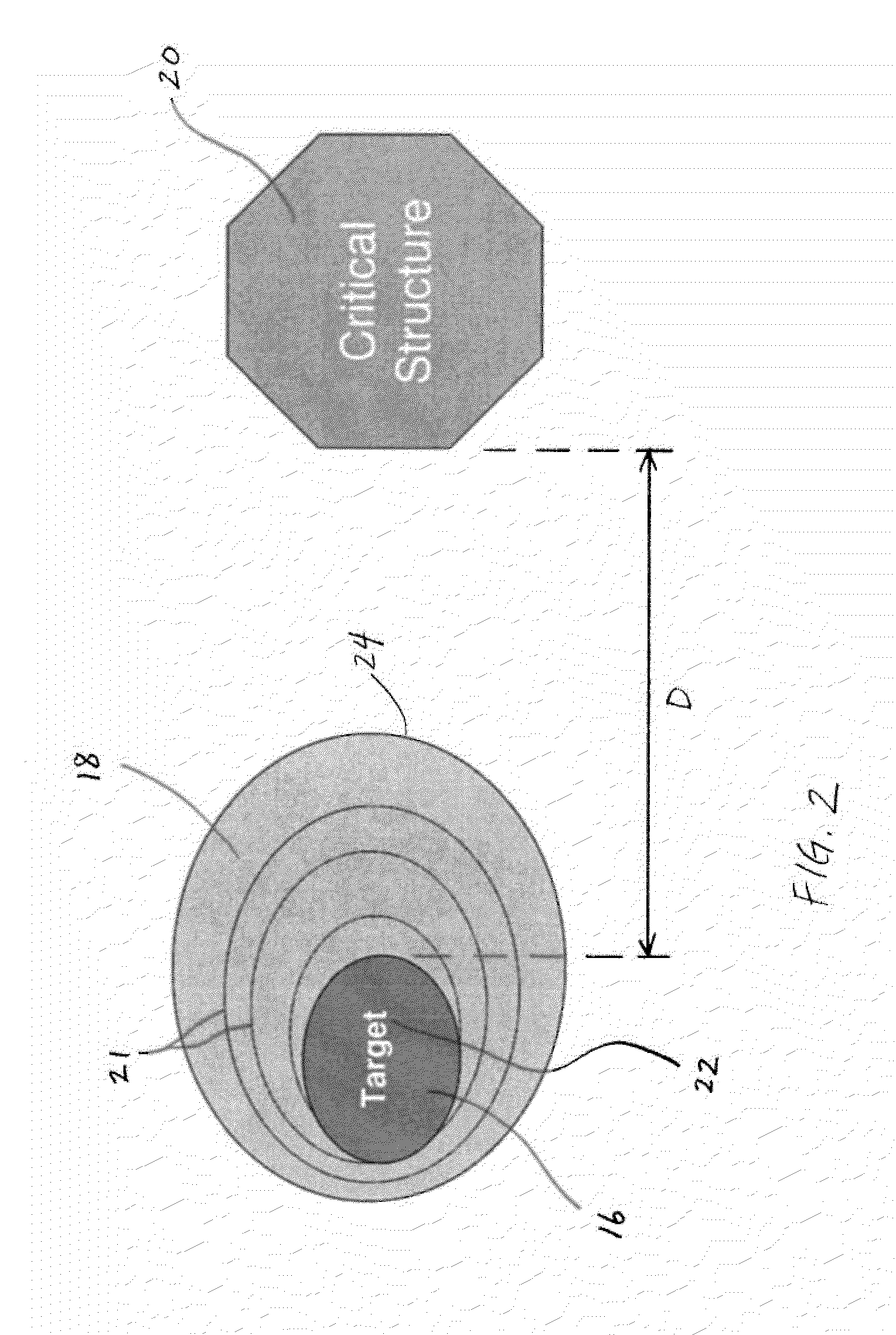
Methods and Systems for Protecting Critical Structures During Radiation Treatment
ActiveUS20120326057A1Simple processExpensive and and intensive processMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCritical structureRadiation beam
Methods and systems are provided for protecting a critical structure during the administration of radiation treatment to a patient. A register receives proposed positions for one or more radiation beams with respect to a critical structure. A processor predicts a cumulative dose volume for the critical structure based on the dose distribution, and determines if the cumulative dose volume exceeds a tolerance value. If the cumulative dose volume exceeds the tolerance value, the dose distribution may be translated at least in part based on a relationship between the cumulative dose volume and the dose distribution position.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
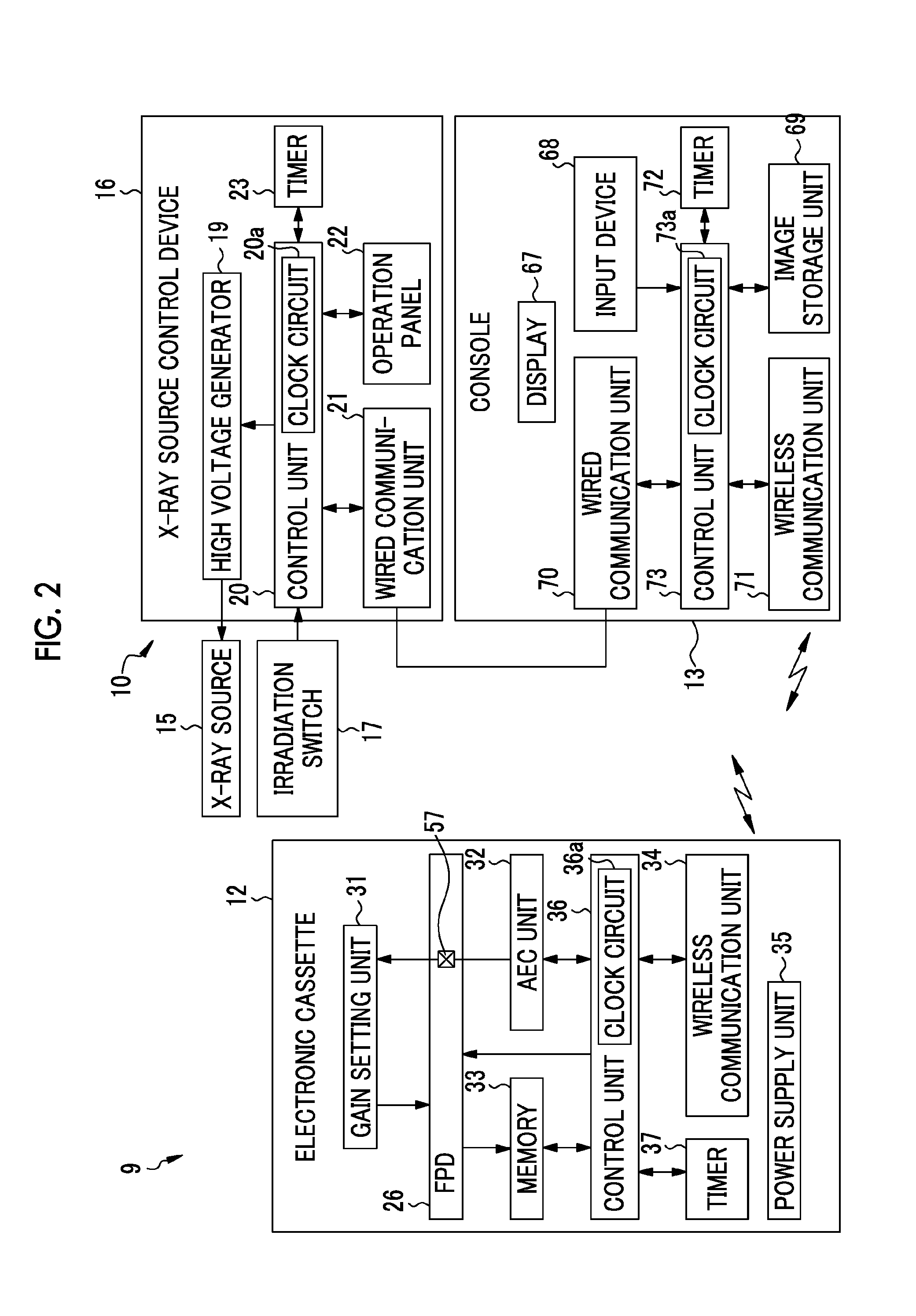
Radiographic device, radiographic system, control method and recording medium for radiographic device
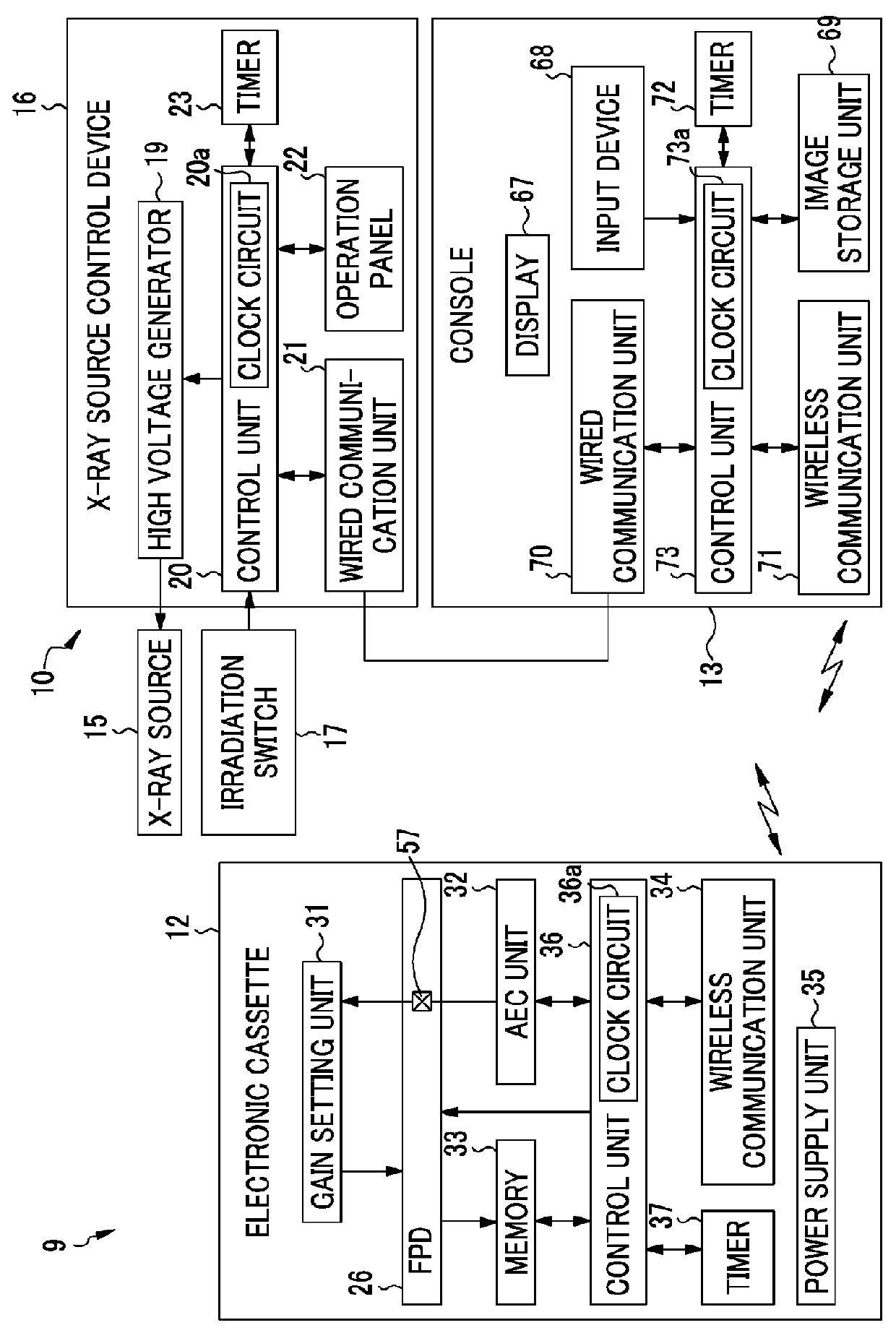
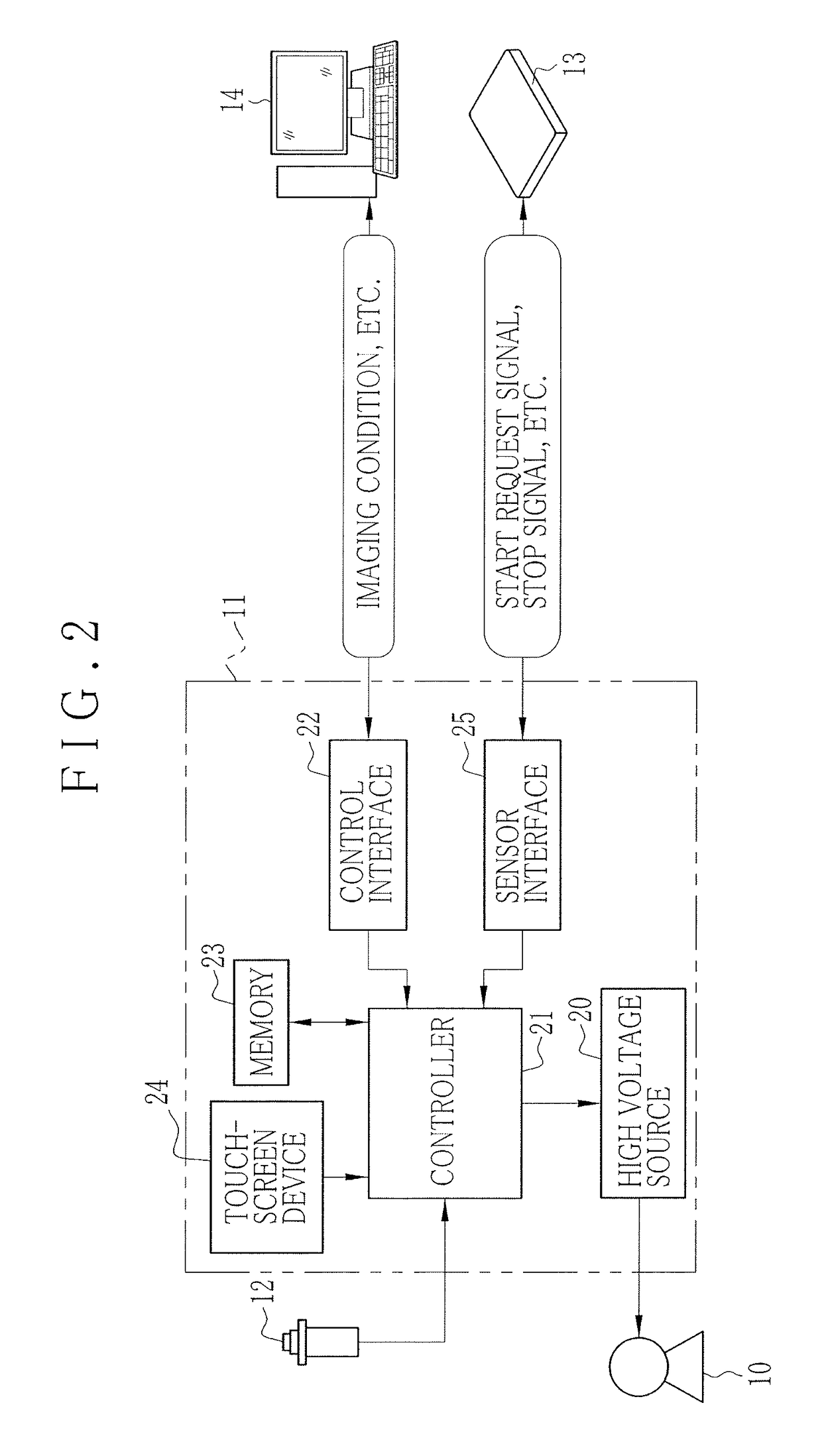
ActiveUS20130148784A1Reduce doseStopping irradiationRadiation diagnosis data transmissionX-ray apparatusX-rayStop time
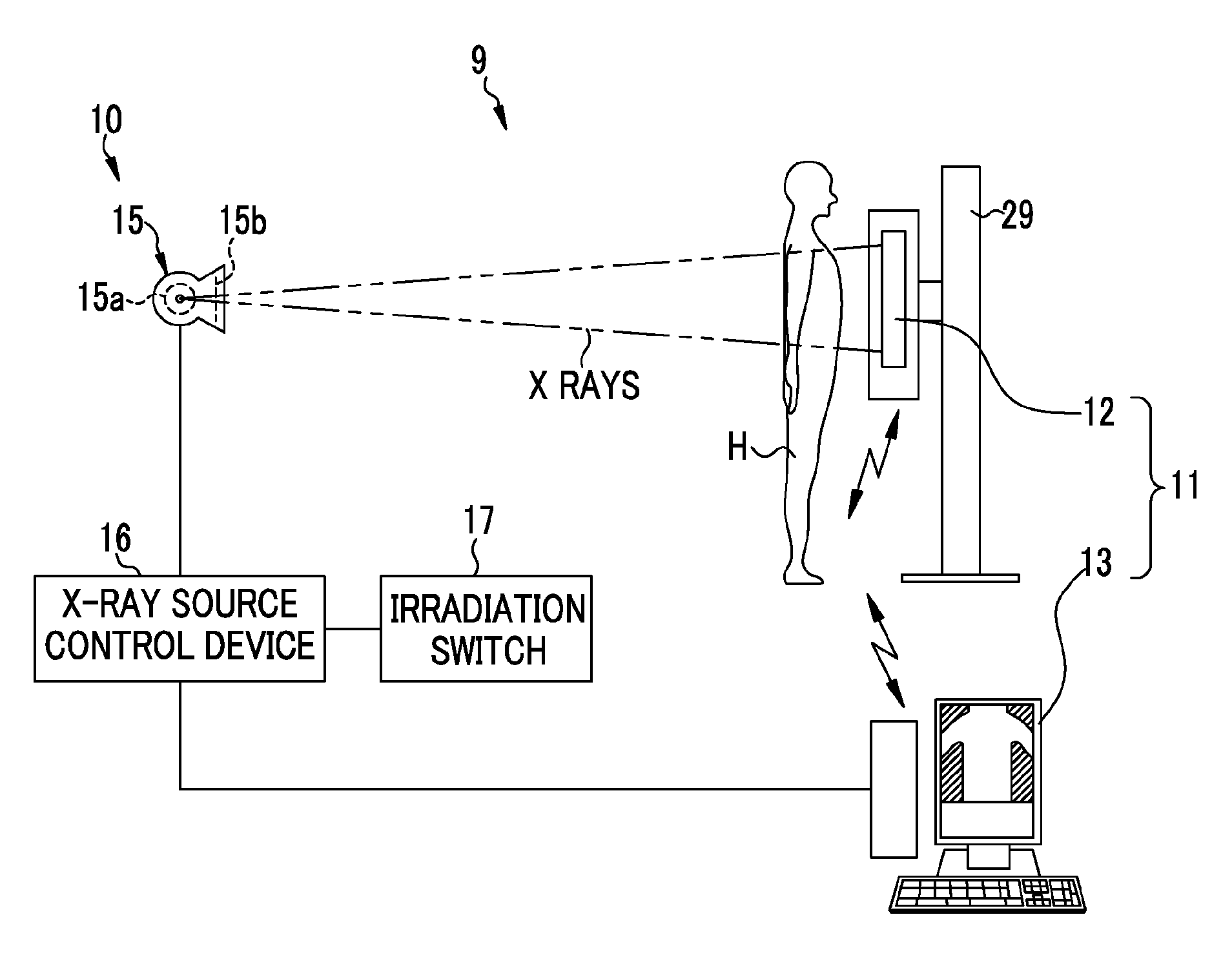
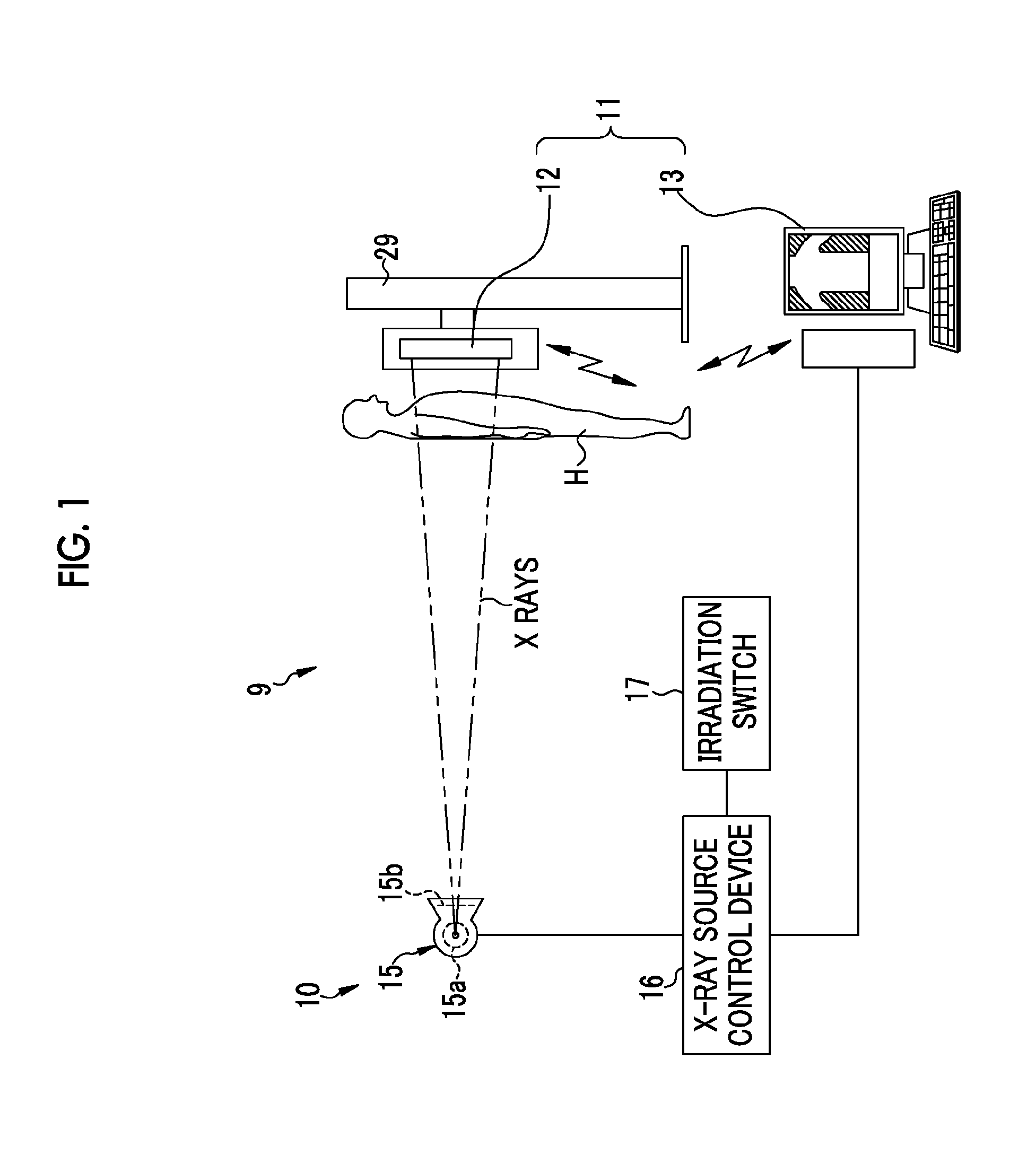
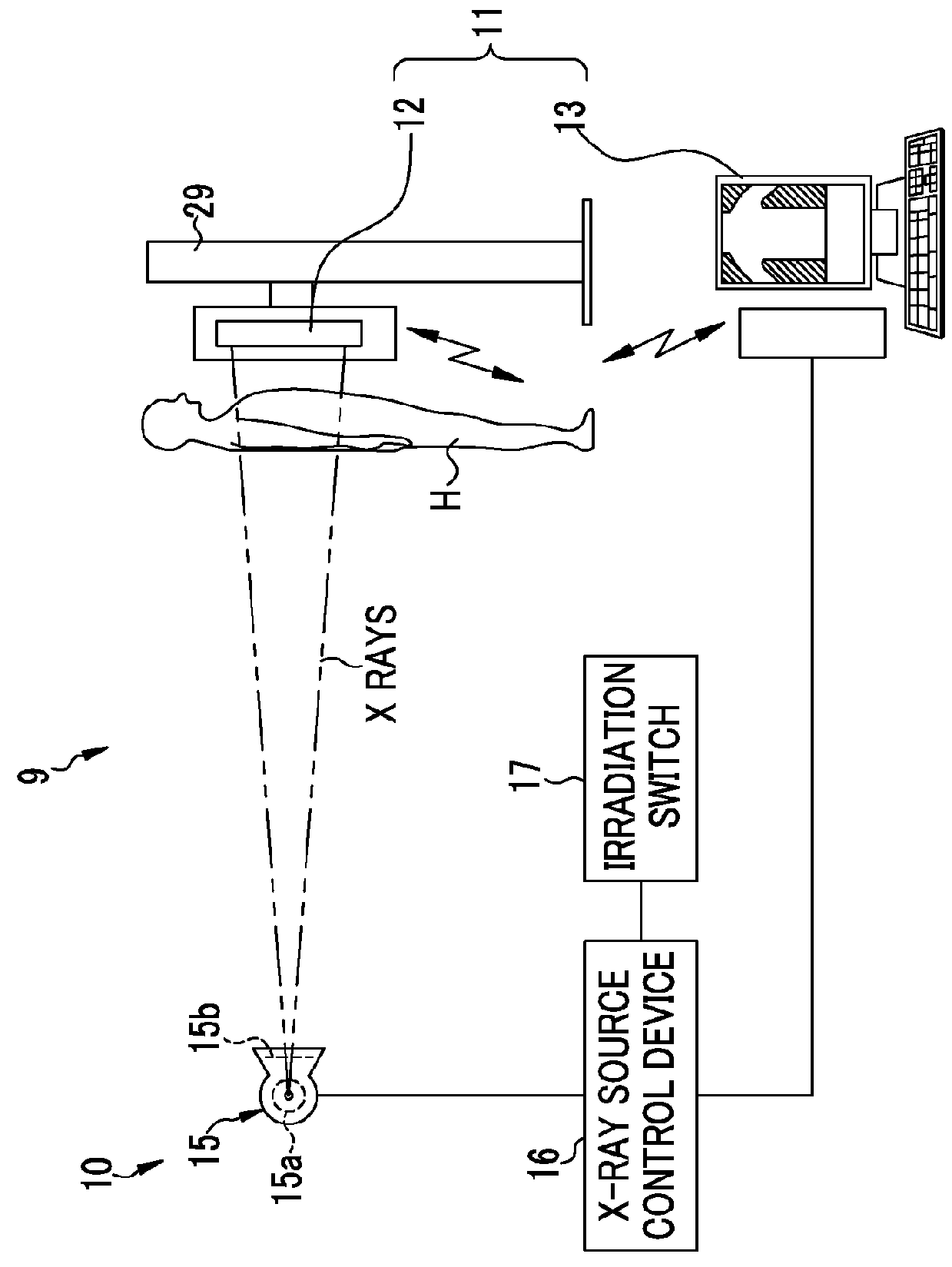
An AEC unit of an electronic cassette sets a dose target value and a short-circuited pixel used for AEC based on a radiographing condition. When a control unit of the electronic cassette detects start of irradiation of X rays, the AEC unit starts integration of a cumulative dose of X rays which are incident to a target region based on a dose detection signal output by the short-circuited pixel. The AEC unit predicts a stop timing at the time point t1, waits until the time point t2 which is a predetermined time earlier than a scheduled stop time, and sends a stop timing notification to an X-ray generation device at the time point t2. When the stop timing notification is received, a X-ray source control device immediately inputs an irradiation stop command so as to stop an operation of an X-ray source.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
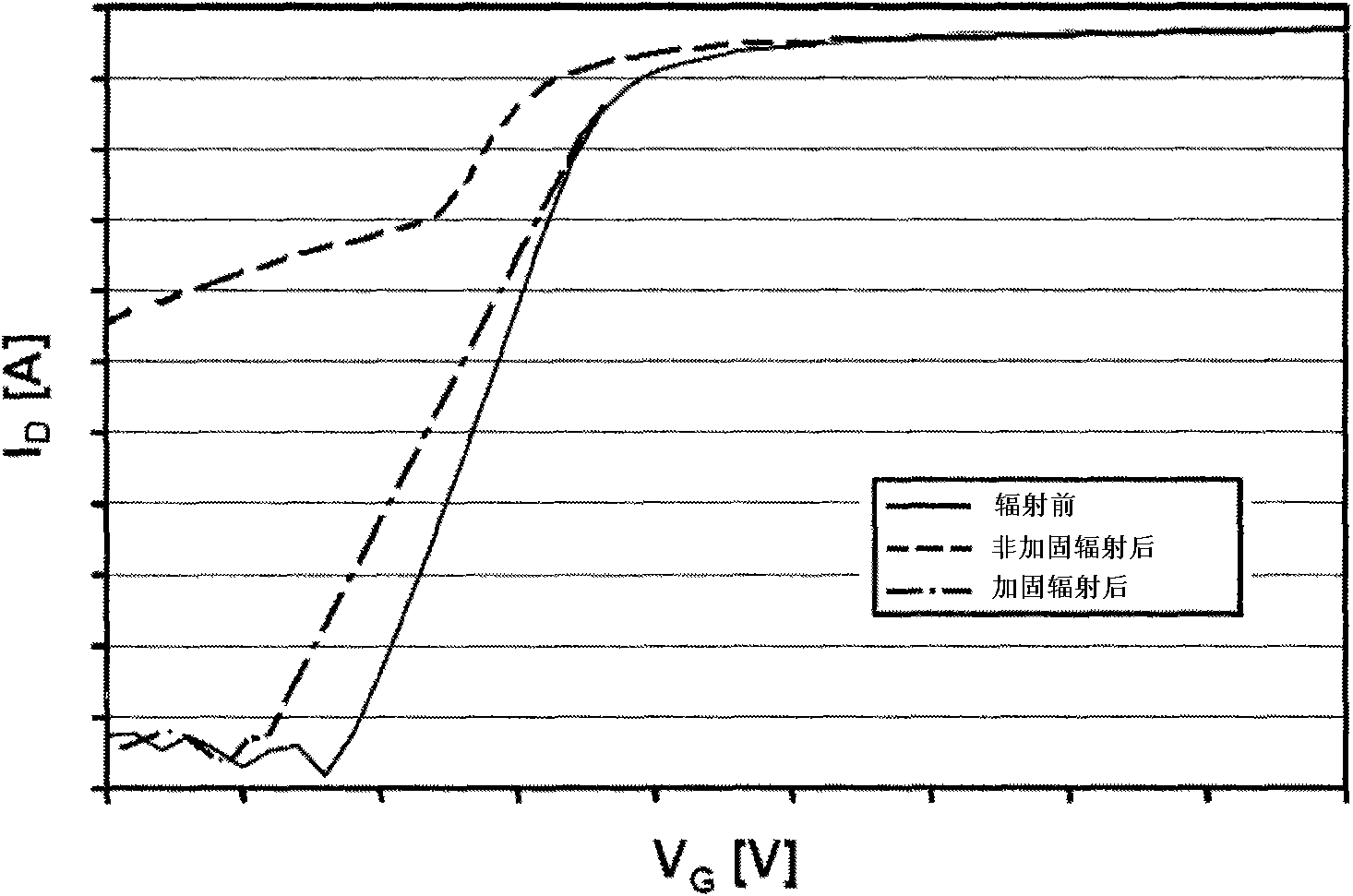
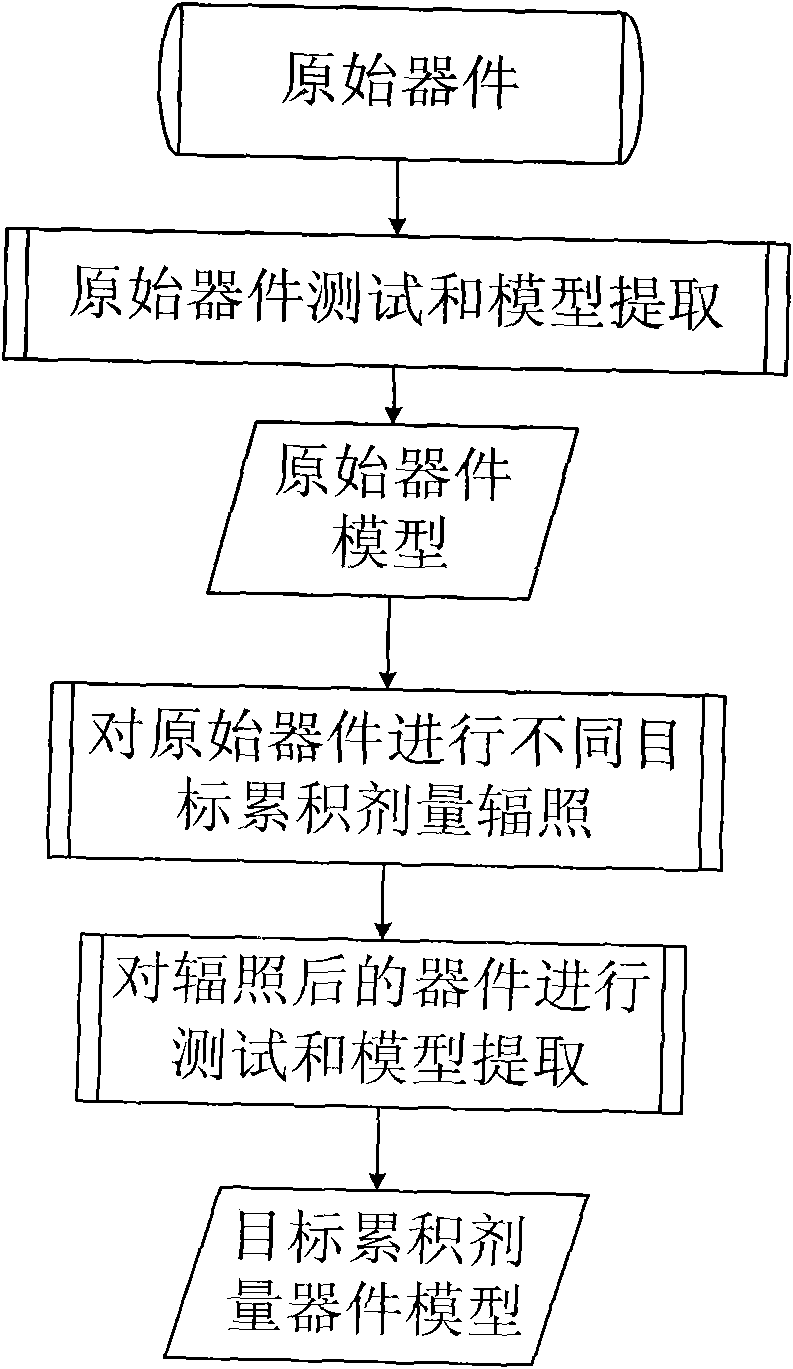
A device modeling method in relation to total dose radiation
InactiveCN101551831ASolve modeling problemsHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsModel extractionComputational physics
A device modeling method in relation to total dose radiation, wherein firstly, an original electronic device is designed and undergoes testing and model extraction to obtain the model of the original device, secondly, the obtained original device undergoes radiation at different target cumulative doses and model extraction to obtain the device model after radiation at all target cumulative doses, and lastly, the obtained original device model and the device model that has received radiation at all target cumulative doses jointly constitute the device model in relation to total dose radiation. Through testing and parameter extraction of the original device and the device that has received radiation at all target cumulative doses, the present invention provides a method for accurate modeling of hardened devices and unhardened devices. Meanwhile it adds radiation dose as a variable into the realization method of device model so that the performance of the circuit that has received radiation at different doses can be accurately predicted through simulation, thus raising the design efficiency and success rate of the circuits.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
Radiation detector and radiological image radiographing apparatus
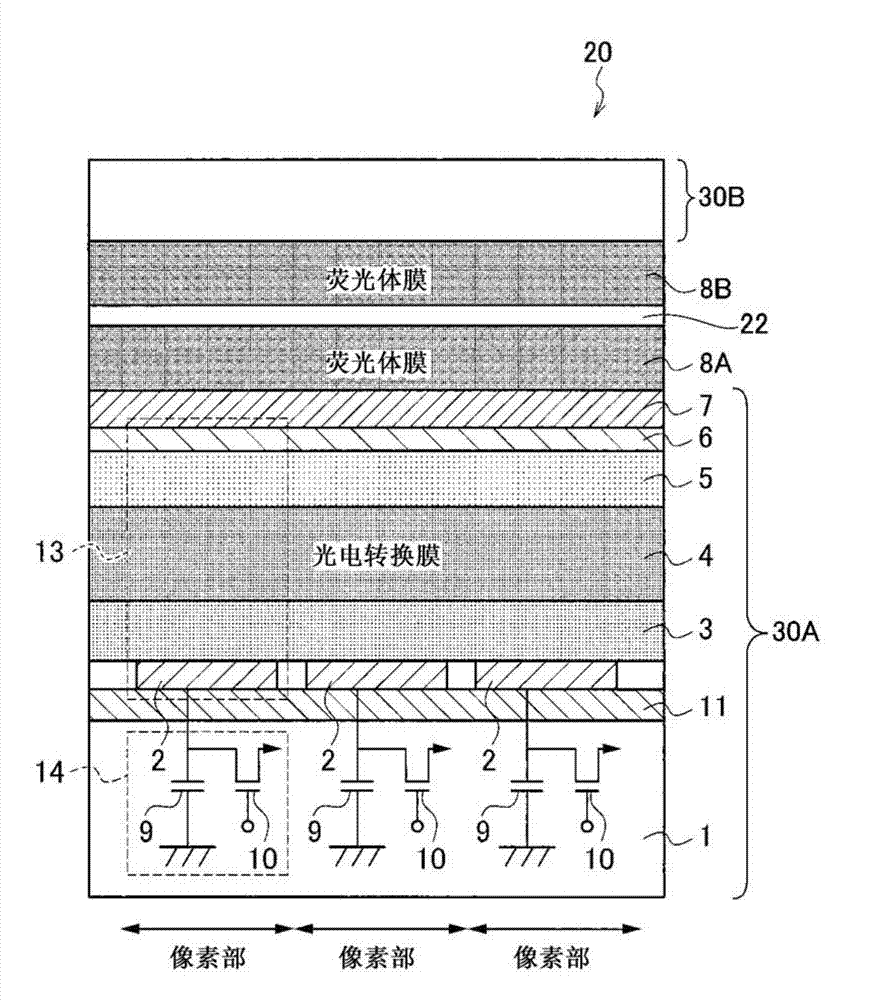
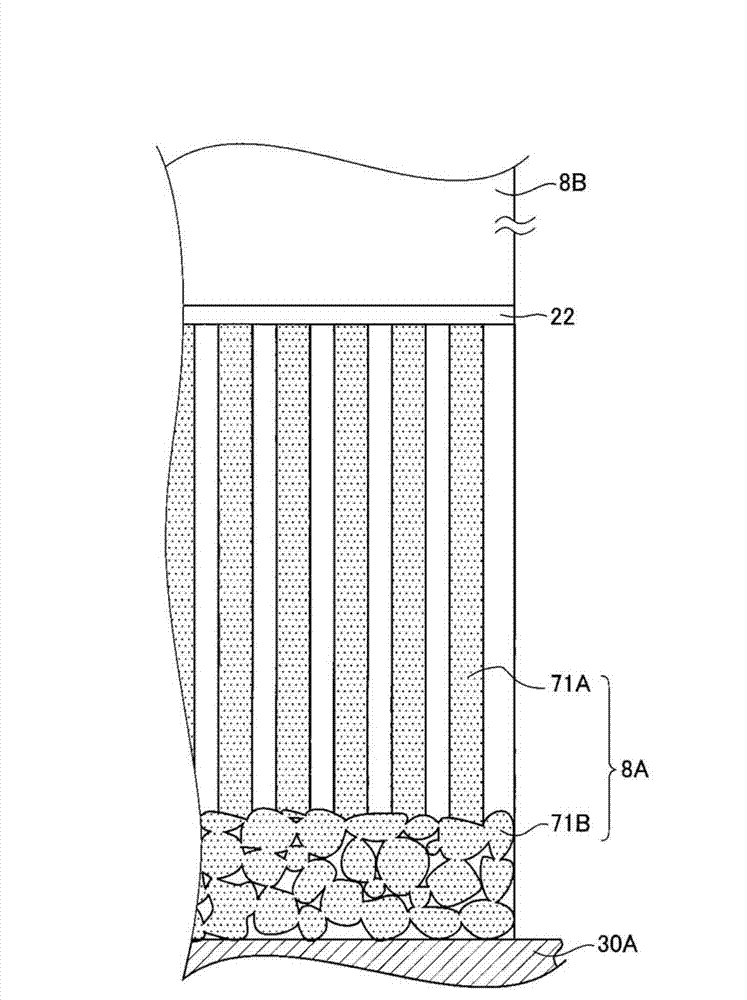
InactiveUS20130048865A1Suppressing deterioration of sensitivityQuality improvementSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhosphorFluorescence
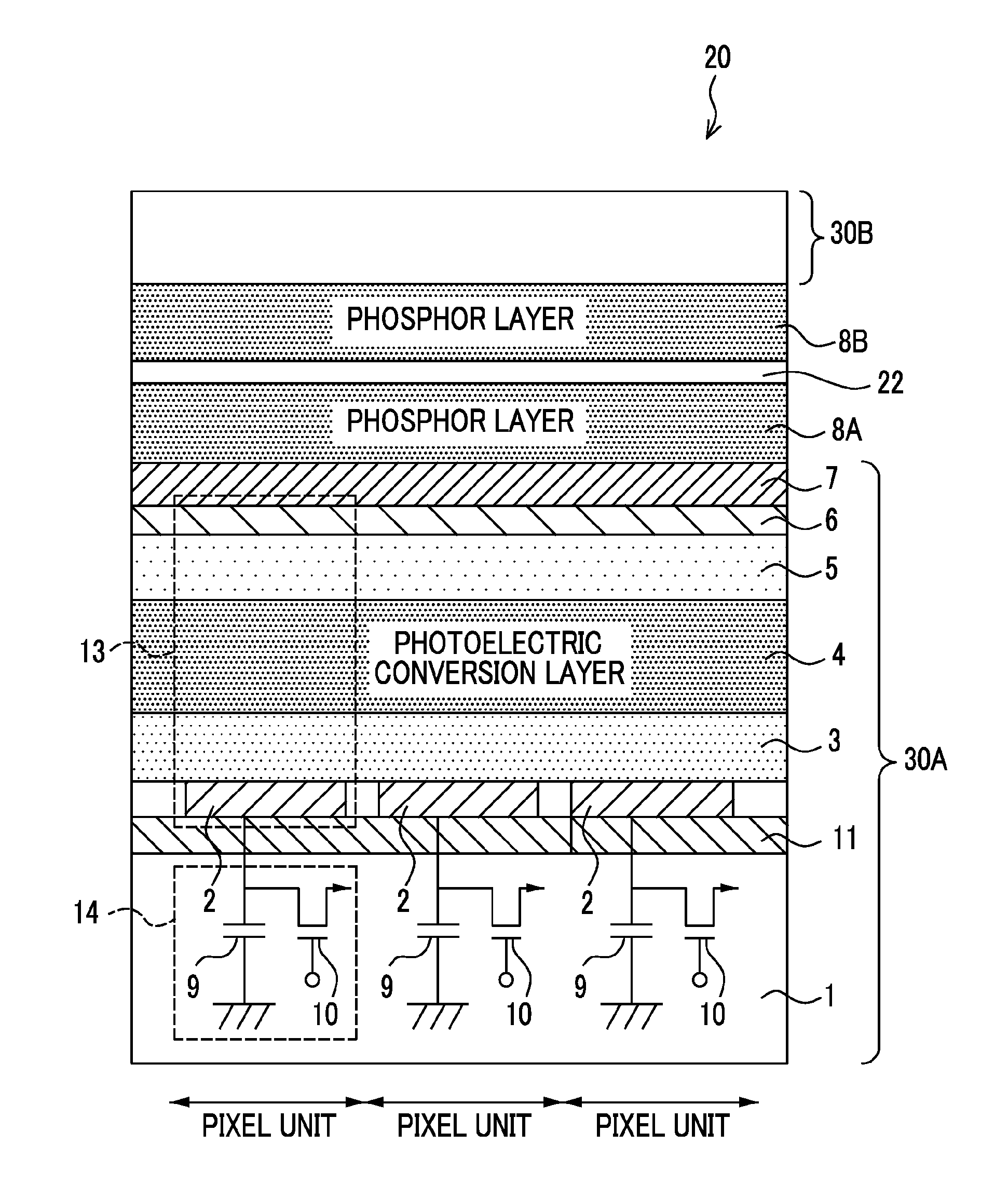
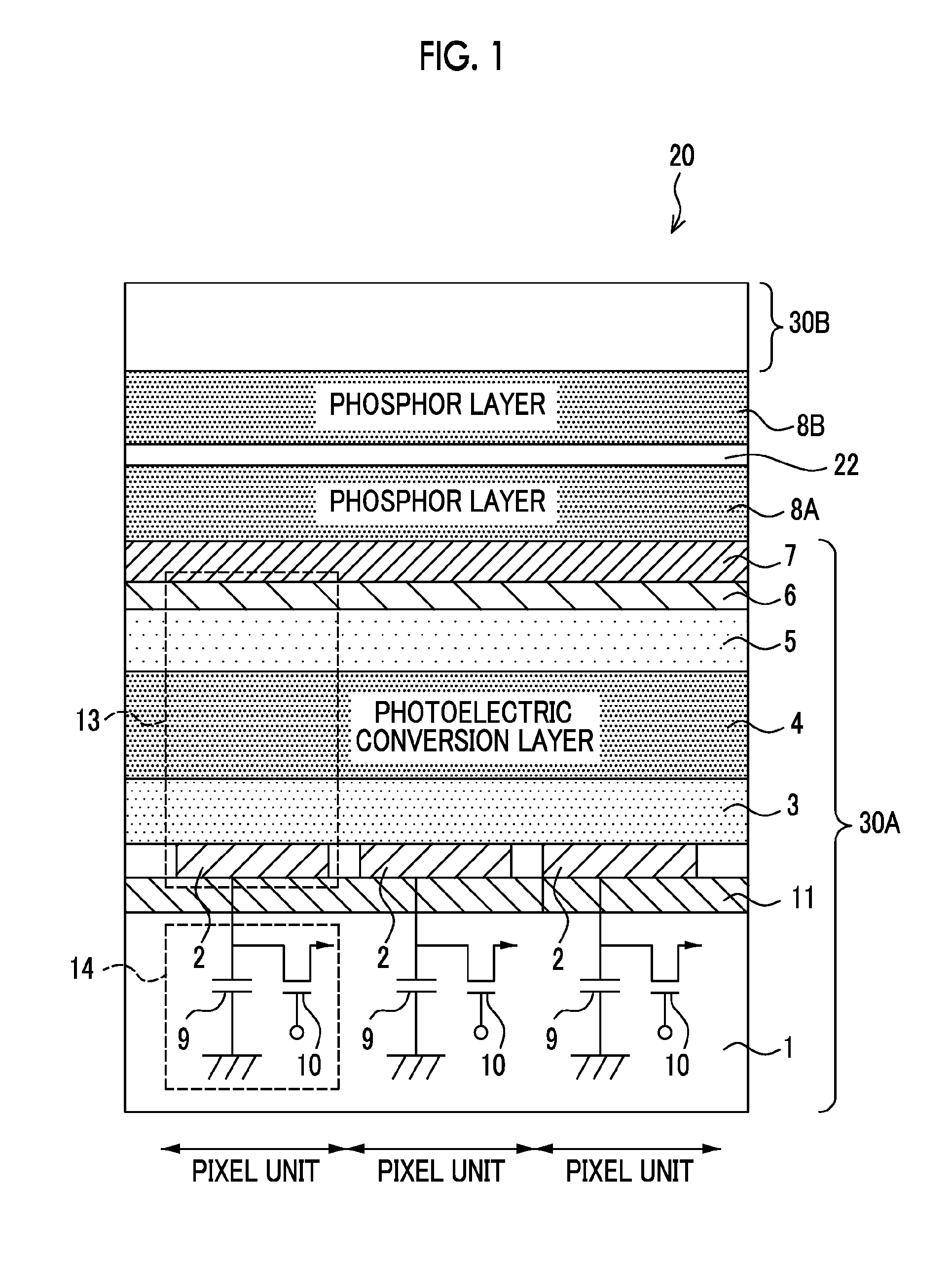
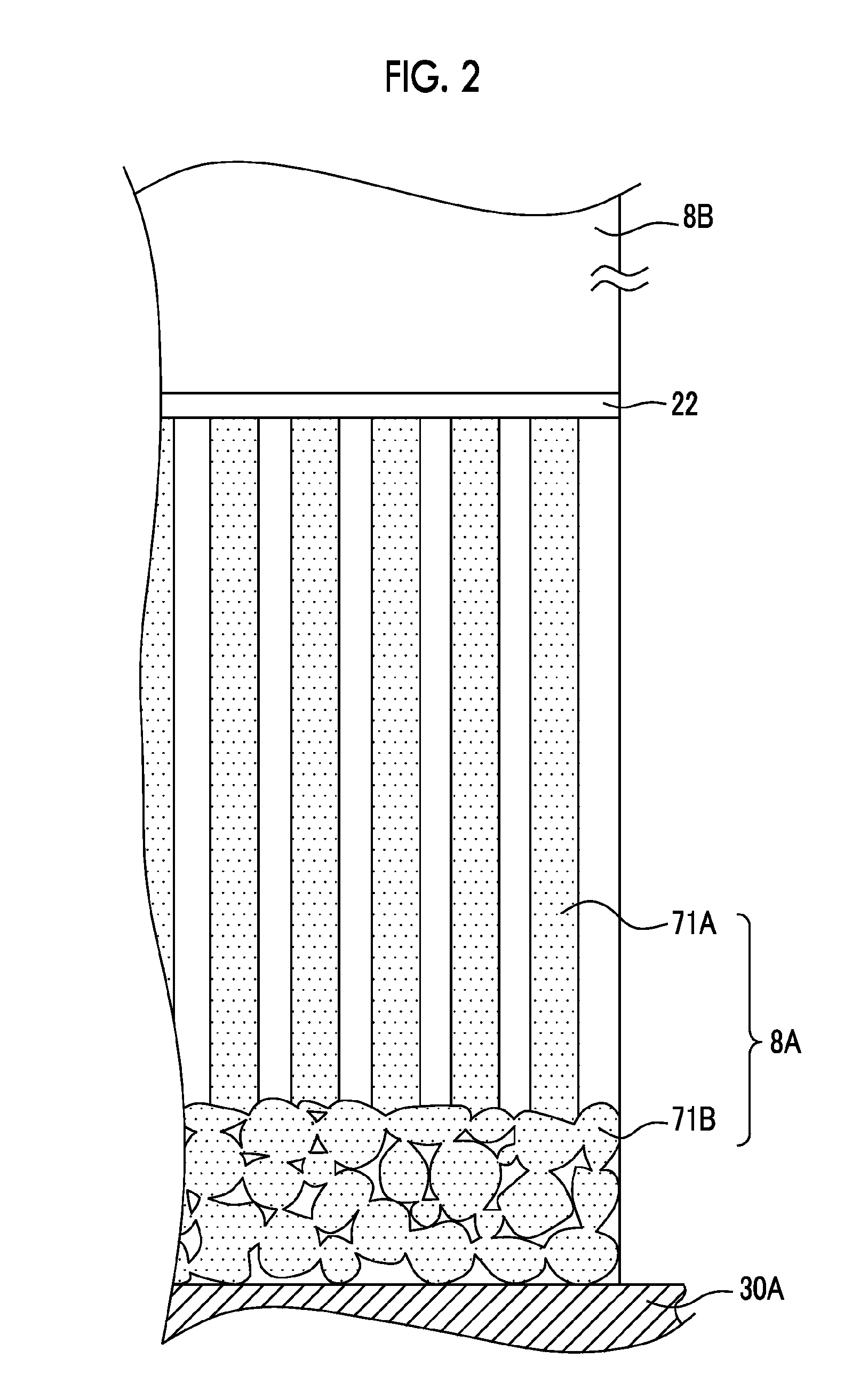
There are provided a radiation detector and a radiological image radiographing apparatus capable of improving the quality of an obtained radiological image while suppressing the deterioration of the sensitivity of a phosphor layer according to the cumulative dose of radiation. In the radiation detector, a second scintillator which absorbs lower radiation energy than radiation energy absorbed by a first scintillator and whose deterioration of sensitivity according to the cumulative dose of radiation is larger than that of the first scintillator is provided at the downstream side of the first scintillator in the emission direction of the radiation. In addition, two substrates of a first substrate, which mainly acquires electric charges corresponding to light generated by the first scintillator, and a second substrate, which mainly acquires electric charges corresponding to light generated by the second scintillator, are provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Radiographic imaging device and method with stop timing based on dosage detection
ActiveUS9232620B2Reduce doseStopping irradiationRadiation diagnosis data transmissionX-ray apparatusX-rayStop time
An AEC unit of an electronic cassette sets a dose target value and a short-circuited pixel used for AEC based on a radiographing condition. When a control unit of the electronic cassette detects start of irradiation of X rays, the AEC unit starts integration of a cumulative dose of X rays which are incident to a target region based on a dose detection signal output by the short-circuited pixel. The AEC unit predicts a stop timing at the time point t1, waits until the time point t2 which is a predetermined time earlier than a scheduled stop time, and sends a stop timing notification to an X-ray generation device at the time point t2. When the stop timing notification is received, a X-ray source control device immediately inputs an irradiation stop command so as to stop an operation of an X-ray source.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Radiographic imaging apparatus, method and system
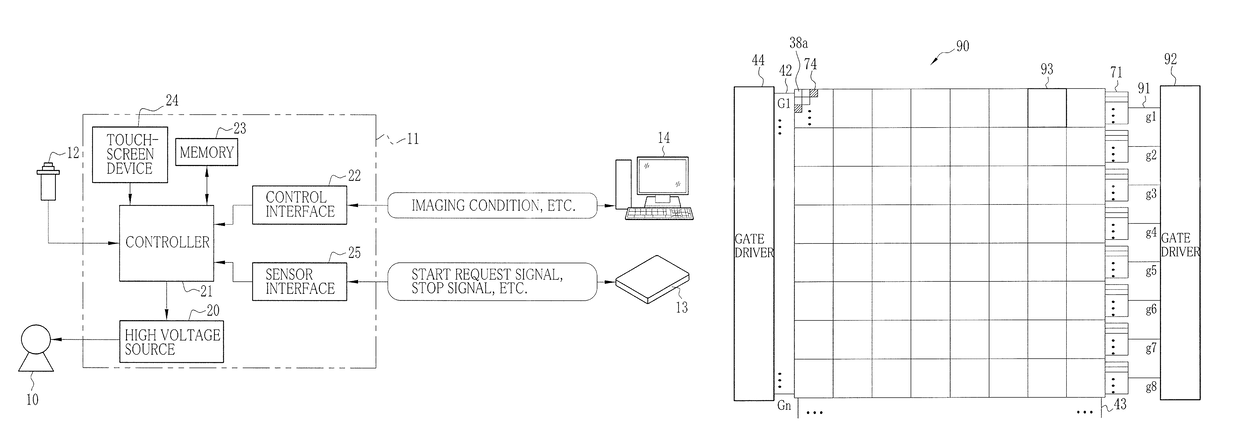
ActiveUS10022102B2Television system detailsRadiation diagnostic device controlStart timeAcquisition time
In an X-ray imaging apparatus, a detection panel has monitor pixels for monitoring X-rays. A signal processor samples a dose signal of a dose per unit time of X-rays according to an output of the monitor pixels. A start detector checks whether irradiation of X-rays is started according to a result of comparison between the dose signal and a start threshold. An AEC device acquires cumulative dose from a start time of the start of irradiation of X-rays until acquisition time after a predetermined time according to the dose signal. According to the cumulative dose, a predicted time point of a reach of the cumulative dose to a target dose is estimated. A stop signal is transmitted to a radiation source controller at the predicted time point, to stop the irradiation of X-rays.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
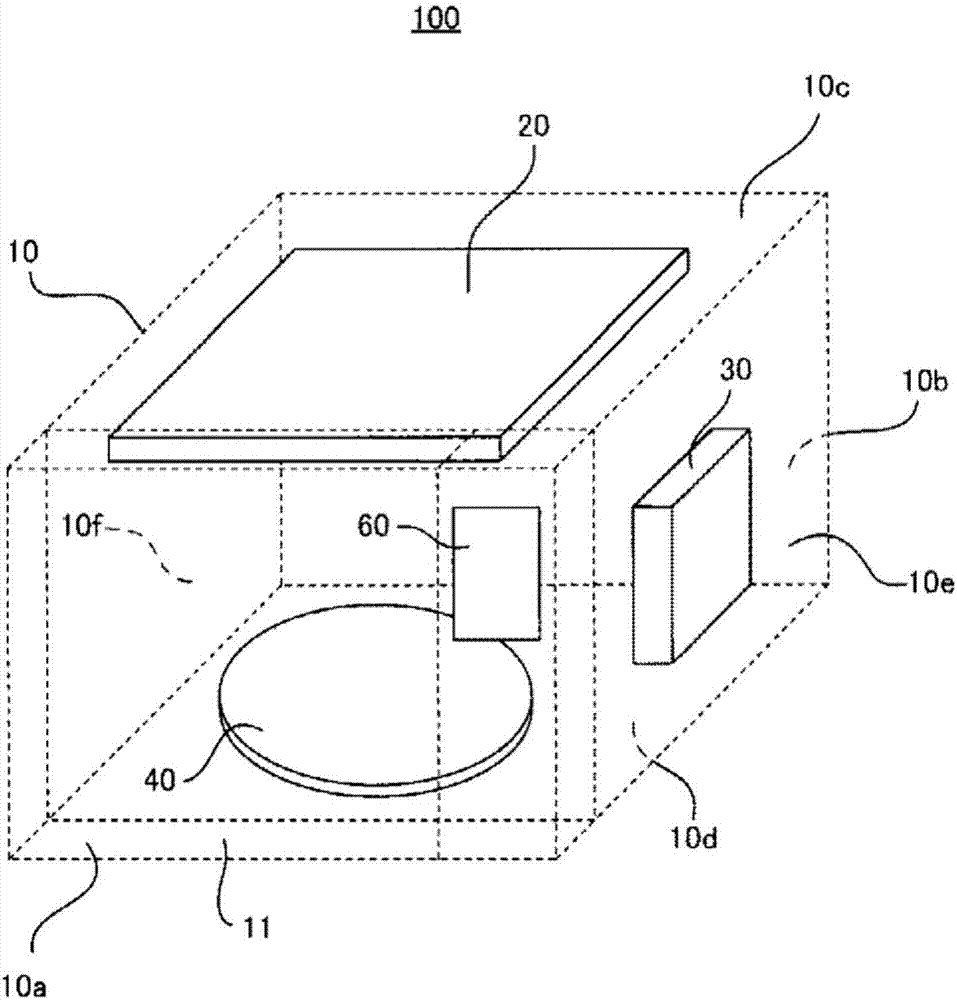
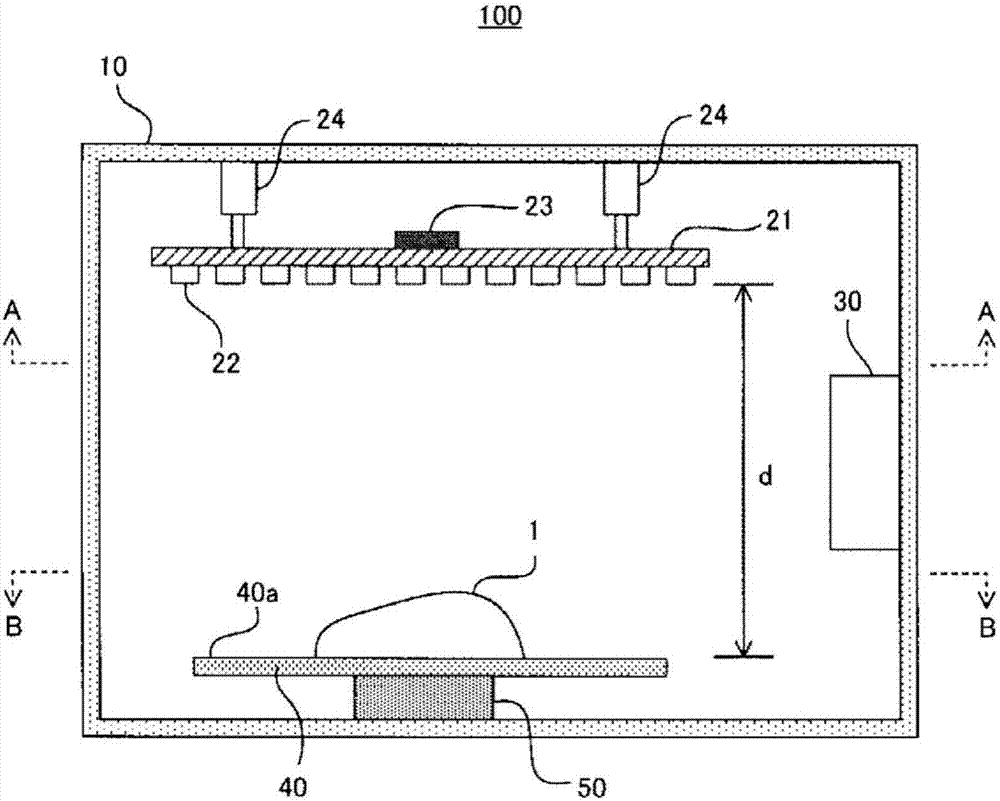
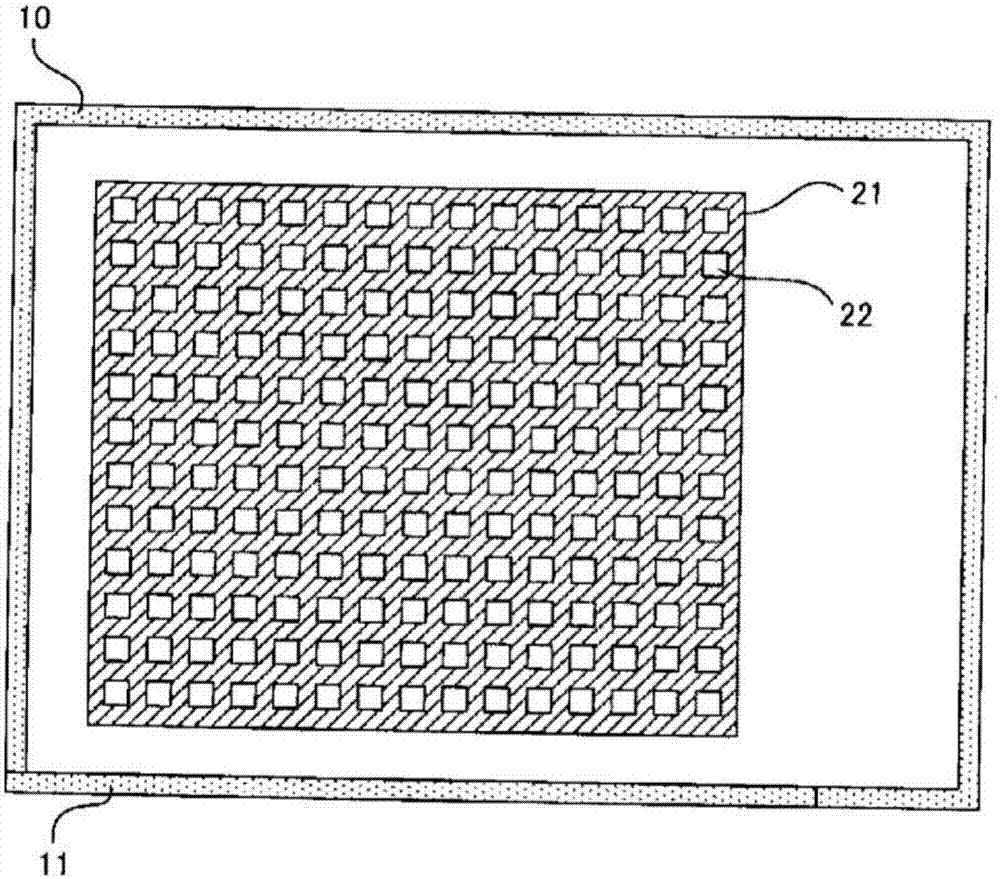
Ultraviolet sterilization device
InactiveCN107405415AReliable sterilizationPhotometrySemiconductor devicesUltraviolet lightsUltraviolet light emitting diodes
This ultraviolet sterilization device comprises: a deep-ultraviolet light source that has at least one deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diode and applies deep-ultraviolet light to an object to be sterilized; and a control means. The control means controls at least one selected from (1) an irradiation time t (unit: second) which is defined as the duration of application of deep-ultraviolet light to the object to be sterilized, (2) the distance d (unit: cm) between the object to be sterilized and the deep-ultraviolet light source, and (3) the light output P (unit: mW) of the deep-ultraviolet light source so that the cumulative dose I (unit: mJ / cm2) of deep-ultraviolet light to be applied to the object to be sterilized within the irradiation time is a predetermined value I0.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
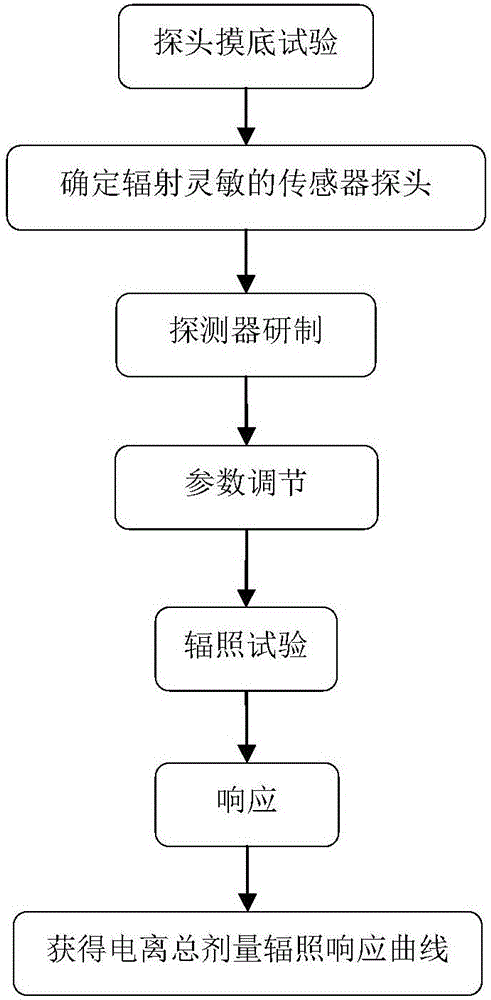
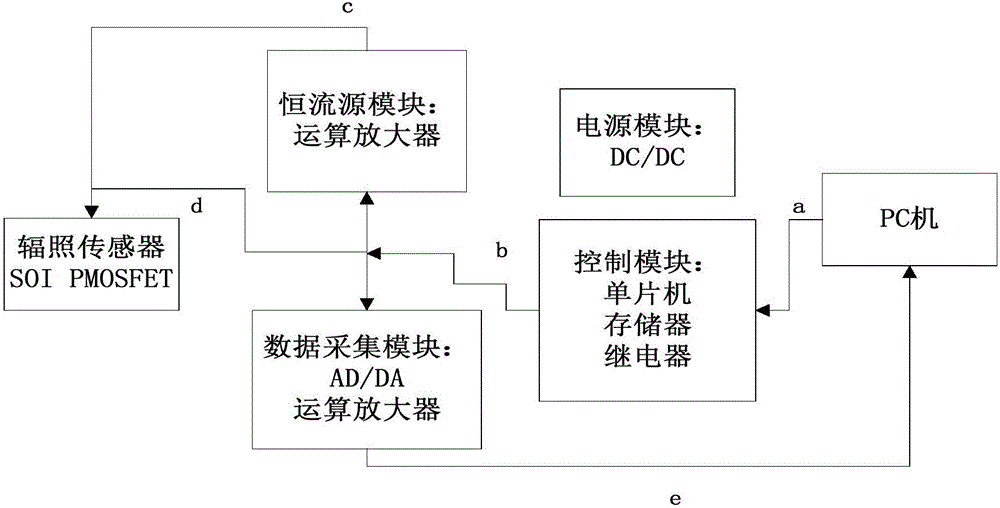
System and method of ionization total dose detection based on SOI structure
ActiveCN106802427ARealize localizationHigh sensitivityProgramme controlComputer controlDosimeterEngineering
The present invention relates to the radiation environment detection technology field, and relates to the system and method of ionization total dose detection based on an SOI (Silicon-On-Insulator) structure. The detection system comprises a probe module, a constant flow source module, a data collection module and a control module. The input end of the control module is connected with a PC, the output end of the control module is connected with the constant flow source module, the data collection module and the probe module; the constant flow source module is connected with the probe module; the input end of the data collection module is connected with the probe module, and the output end of the data collection module is connected with the PC; and the probe module comprises a radiation sensor of the SOI structure. The system and method of the ionization total dose detection based on the SOI structure realizes the sensor nationalization of a satellite PMOS dosimeter, improves the sensitivity, and can be used for the test for lower dosage accumulation; and the detector is portable, flexible and easily used based on the structure, and is suitable for the space environment monitoring, the semiconductor device ionization effect assessment and the life prediction.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
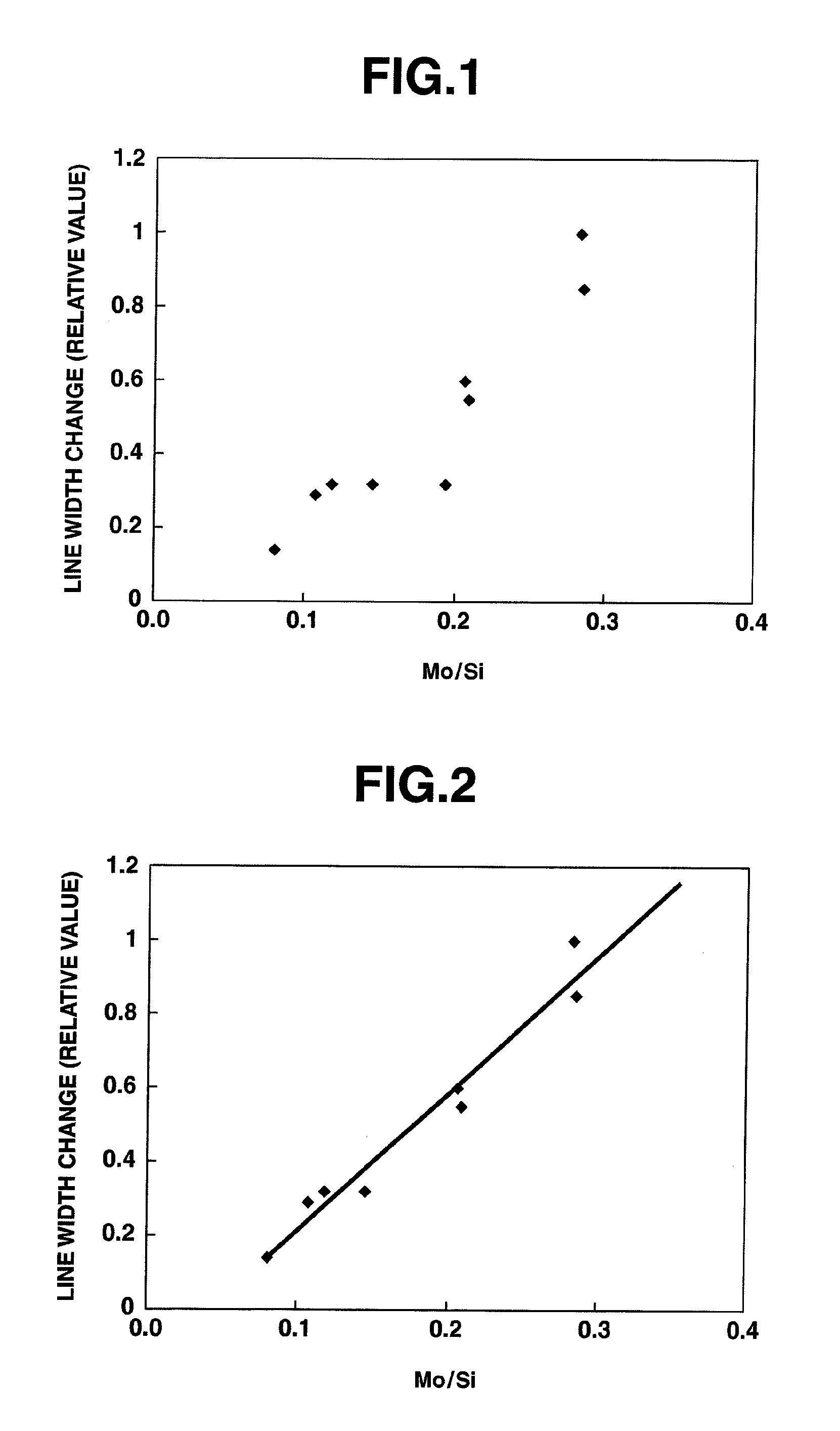
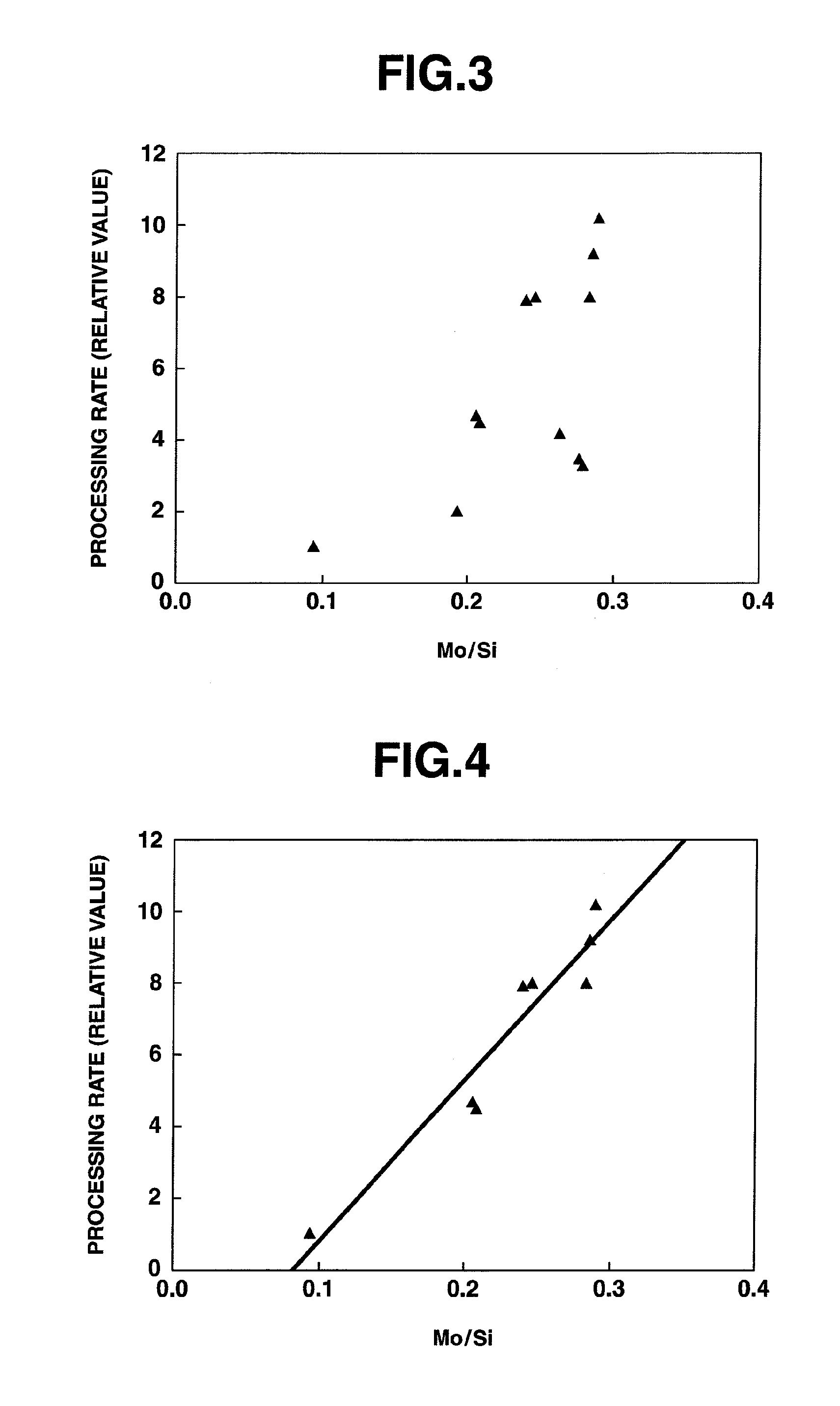
Light pattern exposure method, halftone phase shift mask, and halftone phase shift mask blank
ActiveUS20130130159A1Inhibits pattern size variation degradationSufficient etching selectivity ratioPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentResistPhase shifted
A light pattern exposure method is by irradiating ArF excimer laser light to a resist film through a halftone phase shift mask. The mask includes a transparent substrate and a pattern of halftone phase shift film of a material comprising a transition metal, silicon, nitrogen and oxygen and having an atomic ratio (Met / Si) of 0.18-0.25, a nitrogen content of 25-50 atom %, and an oxygen content of 5-20 atom %. The mask may be irradiated with ArF excimer laser light in a cumulative dose of at least 10 kJ / cm2.
Owner:TOPPAN PHOTOMASK CO LTD +1
Radiation detector and radiological image radiographing apparatus
InactiveCN102956659ASuppresses deterioration of sensitivityImprove qualitySolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesPhosphorFluorescence
There are provided a radiation detector and a radiological image radiographing apparatus capable of improving the quality of an obtained radiological image while suppressing the deterioration of the sensitivity of a phosphor layer according to the cumulative dose of radiation. In the radiation detector, a second scintillator which absorbs lower radiation energy than radiation energy absorbed by a first scintillator and whose deterioration of sensitivity according to the cumulative dose of radiation is larger than that of the first scintillator is provided at the downstream side of the first scintillator in the emission direction of the radiation. In addition, two substrates of a first substrate, which mainly acquires electric charges corresponding to light generated by the first scintillator, and a second substrate, which mainly acquires electric charges corresponding to light generated by the second scintillator, are provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
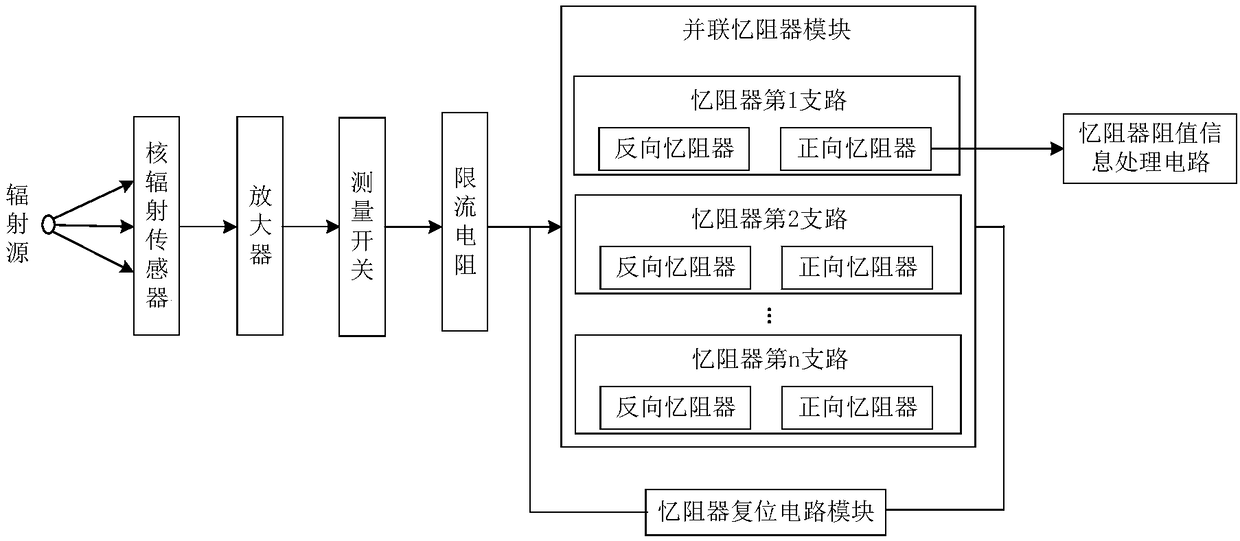
Measuring system for nuclear radiation cumulative dose based on memristor
ActiveCN109343097ARealize measurementReduce power consumptionDosimetersInformation processingNuclear radiation
The invention discloses a measuring system for nuclear radiation cumulative dose based on a memristor. The measuring system comprises a nuclear radiation sensor, an amplifier, a measuring switch S1, acurrent limiting resistor, a parallel memristor module, an information processing circuit for a resistance value of the memristor and a reset circuit module of the memristor. The nuclear radiation sensor is connected to the parallel memristor module through the amplifier, the measuring switch S1 and the current limiting resistor. The information processing circuit for the resistance value of thememristor is connected to the parallel memristor module. The reset circuit module of the memristor is connected in parallel with the parallel memristor module. The parallel memristor module comprisesn reverse series memristor branches connected in parallel, each of the reverse series memristor branches comprises a forward memristor and a reverse memristor connected in series, wherein n is a natural number greater than or equal to 2 and less than or equal to 8.
Owner:西安翱翔新材料科技有限公司
Light pattern exposure method, photomask, and photomask blank
ActiveUS20130130160A1Inhibits pattern size variation degradationSufficient etching selectivity ratioPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentResistNitrogen
A light pattern exposure method is by irradiating ArF excimer laser light to a resist film through a photomask. The photomask includes a transparent substrate and a pattern of optical film of a material comprising a transition metal, silicon, nitrogen and oxygen, with contents thereof falling in a specific range. The photomask may be irradiated with ArF excimer laser light in a cumulative dose of at least 10 kJ / cm2.
Owner:TOPPAN PHOTOMASK CO LTD +1
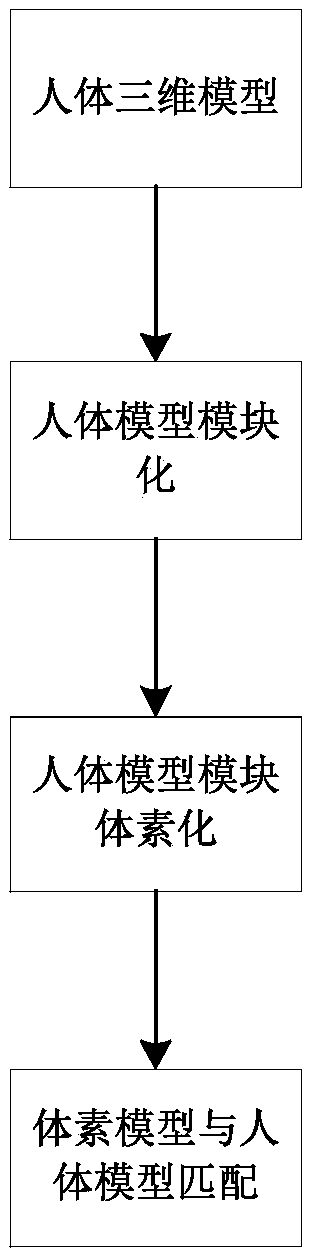
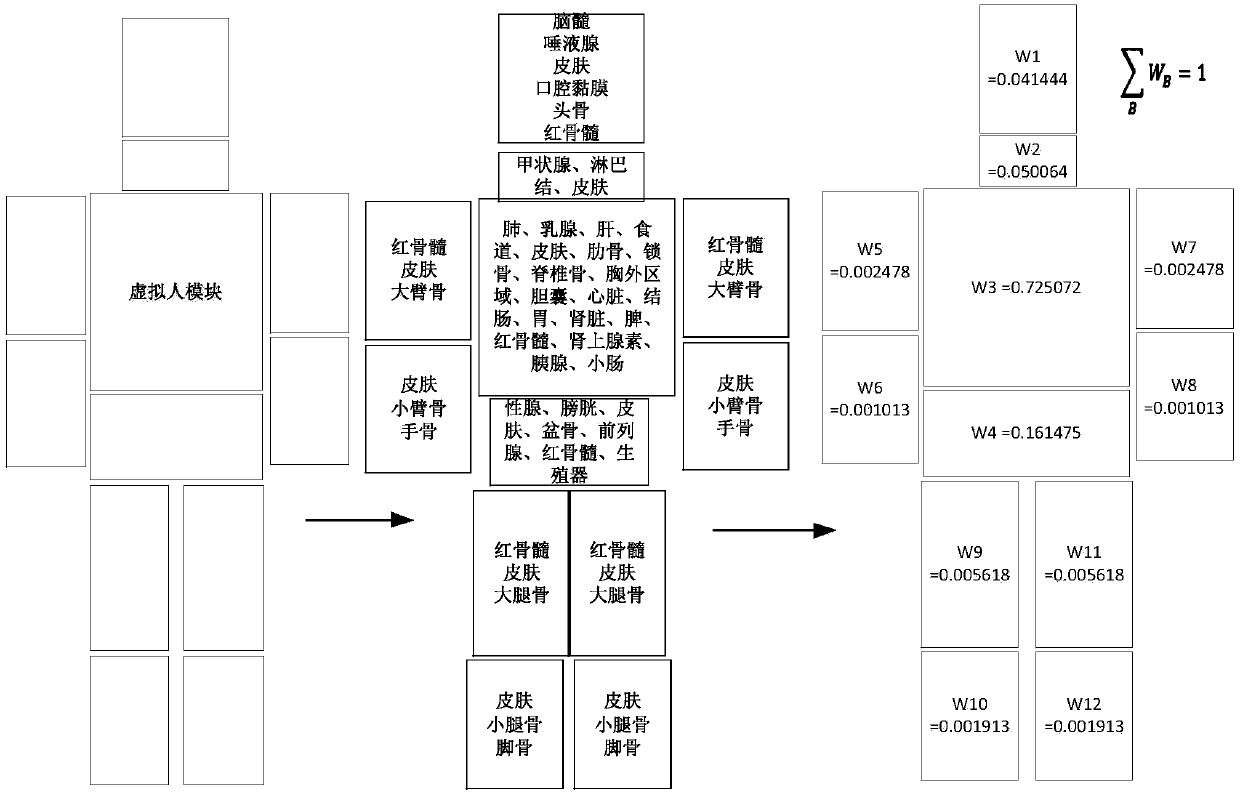
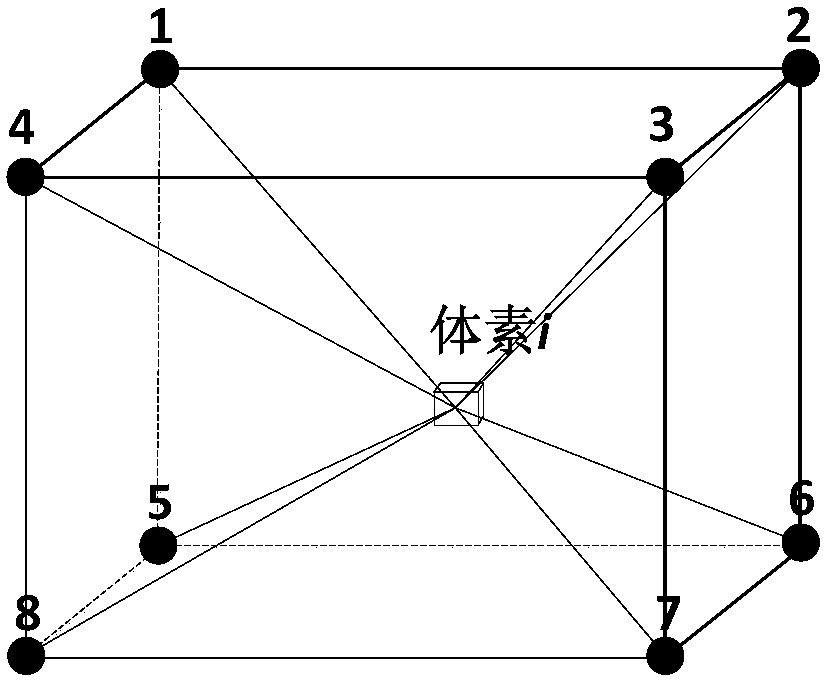
Voxel-based body external irradiation dose simulation method
ActiveCN107832545AImplement voxelizationSimple stepsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNuclear radiationVoxel
The invention provides a voxel-based body external irradiation dose simulation method. According to the method, 3dsMax software is used to establish a virtual human model with a skeleton animation; dose distribution data in a virtual nuclear radiation field is initialized; according to a body structure and a skeleton structure of a virtual human, a body voxel model is established; body modules areallocated, and weights of all the modules and a body effective dose calculation formula are defined; an interpolation method is utilized to calculate an instant exposure dose rate and an accumulateddose of the virtual human; a body exposure dose is calculated based on the skeleton animation; and all the modules perform parallel calculation. Through the method, voxelization is not directly performed on a three-dimensional model of the virtual human, the steps are easier and more convenient, the voxel model can move along with human skeletons, and real-time dose evaluation is realized.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
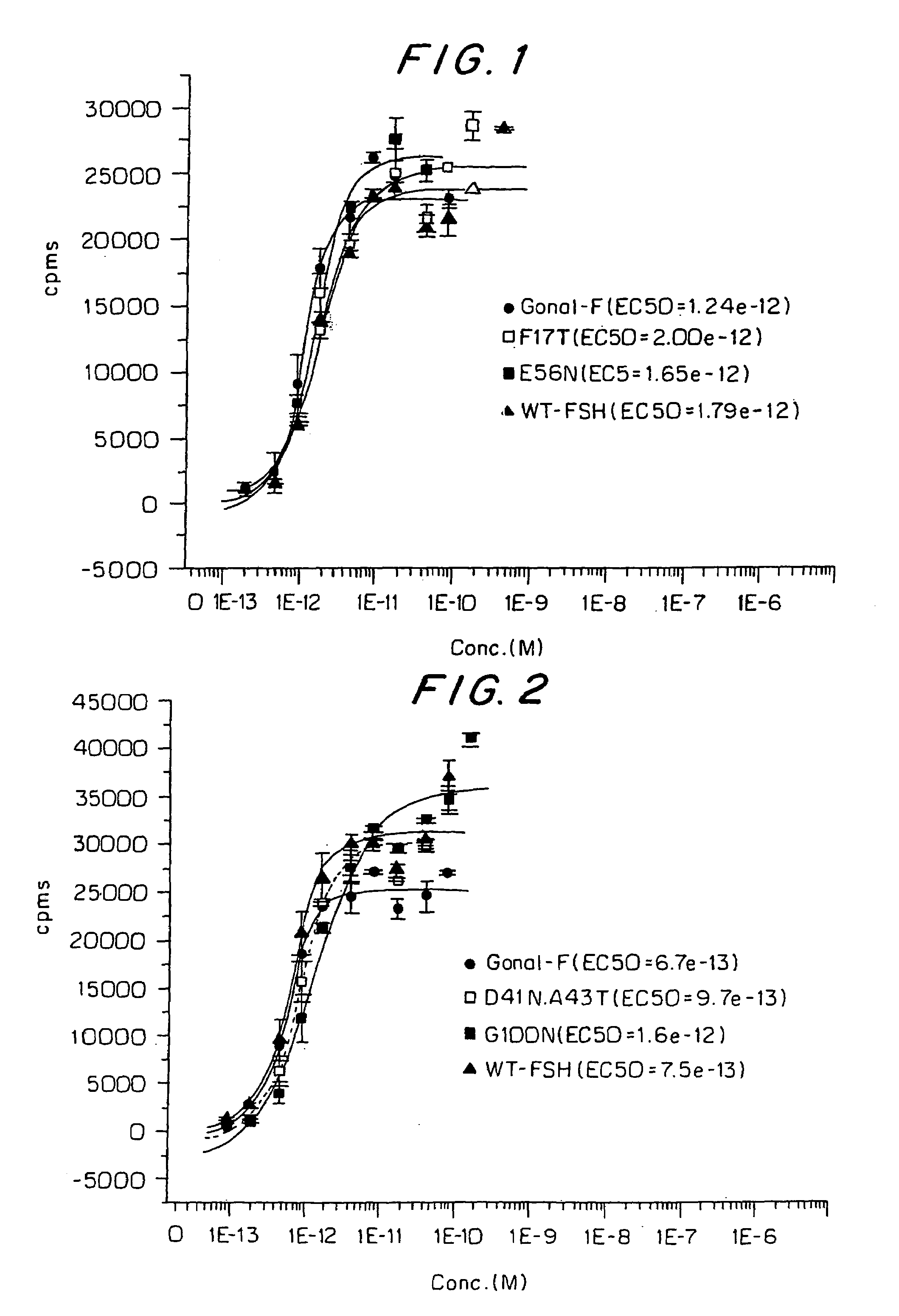
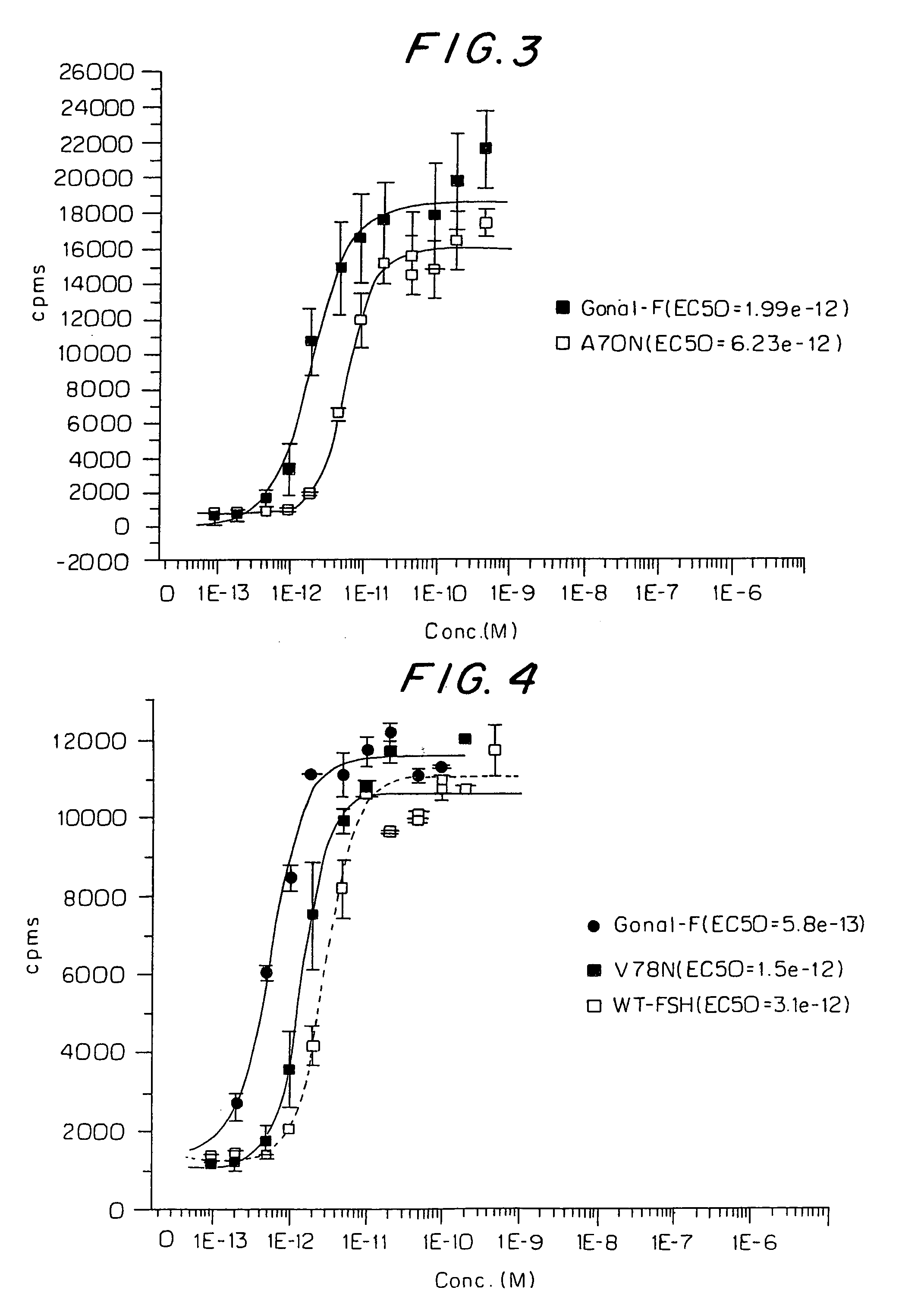
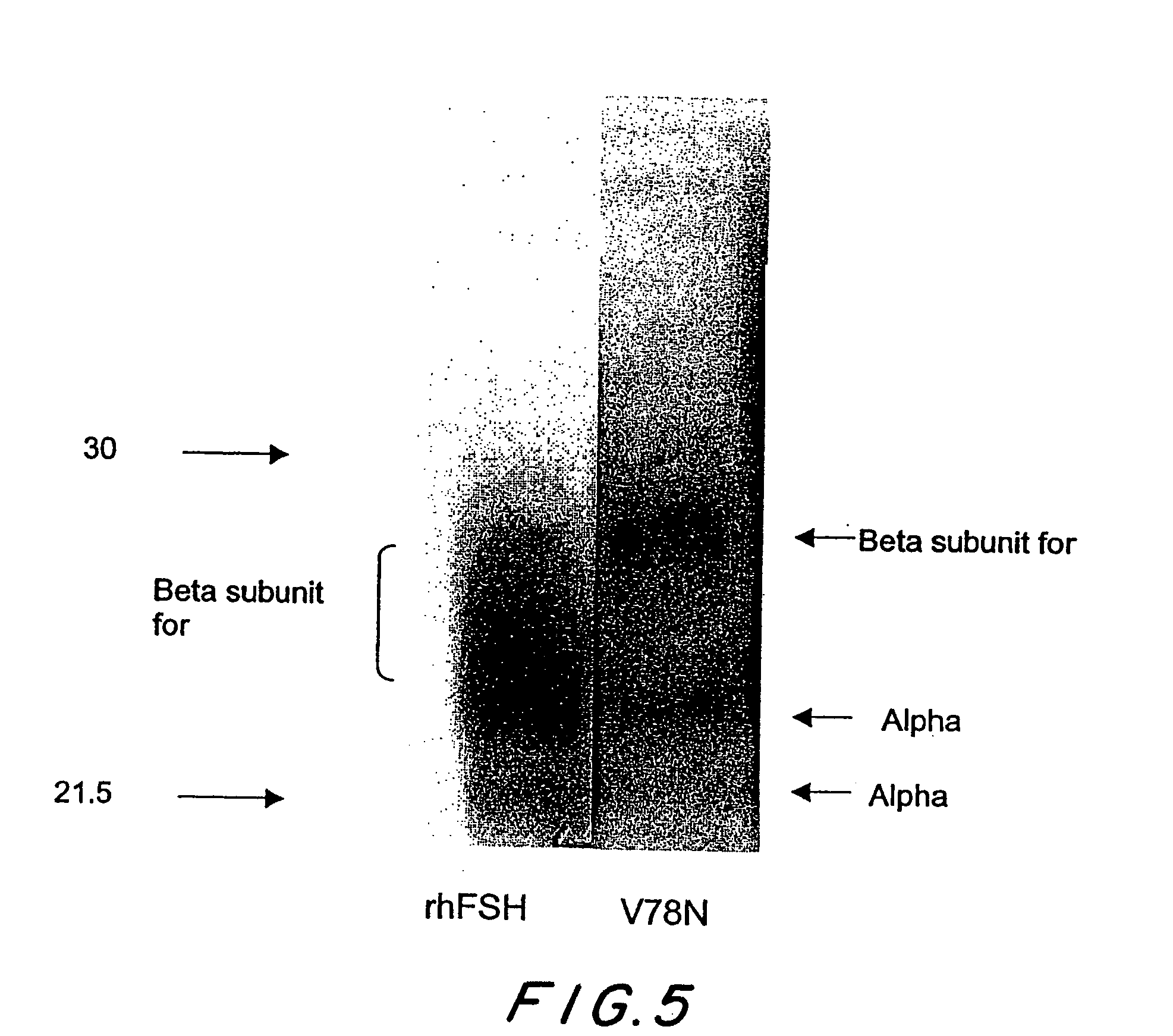
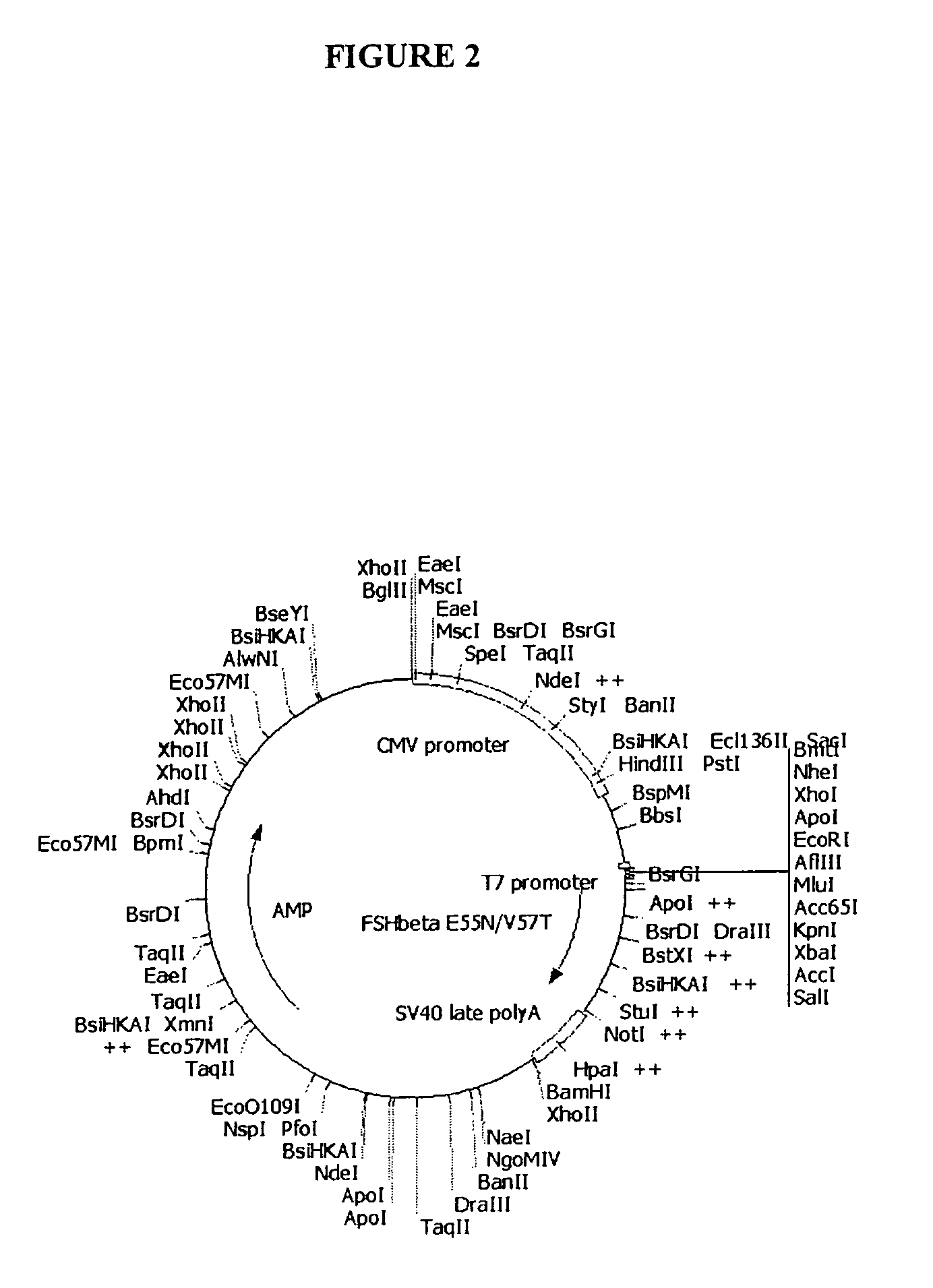
Mutant glycoproteins
InactiveUS7317095B2Increased glycosylationLong half-livesPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsHalf-lifeHuman patient
The inventors have designed novel FSH mutants with increased glycosylation and longer half-lives for use in inducing folliculogenesis in human patients. The use of a FSH mutant preparation of the invention permits the use of lower cumulative doses of FSH to achieve the same or better clinical result.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
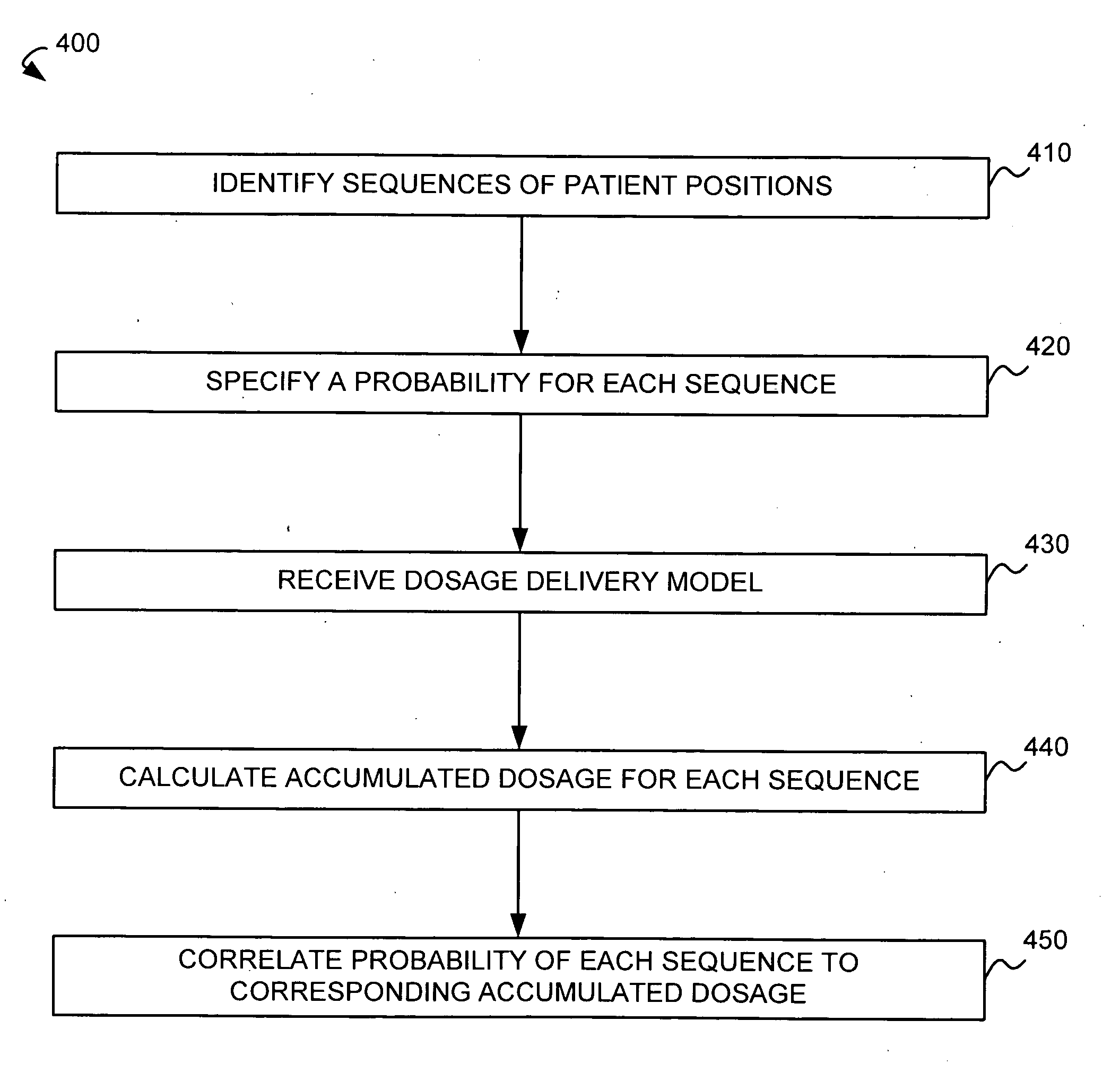
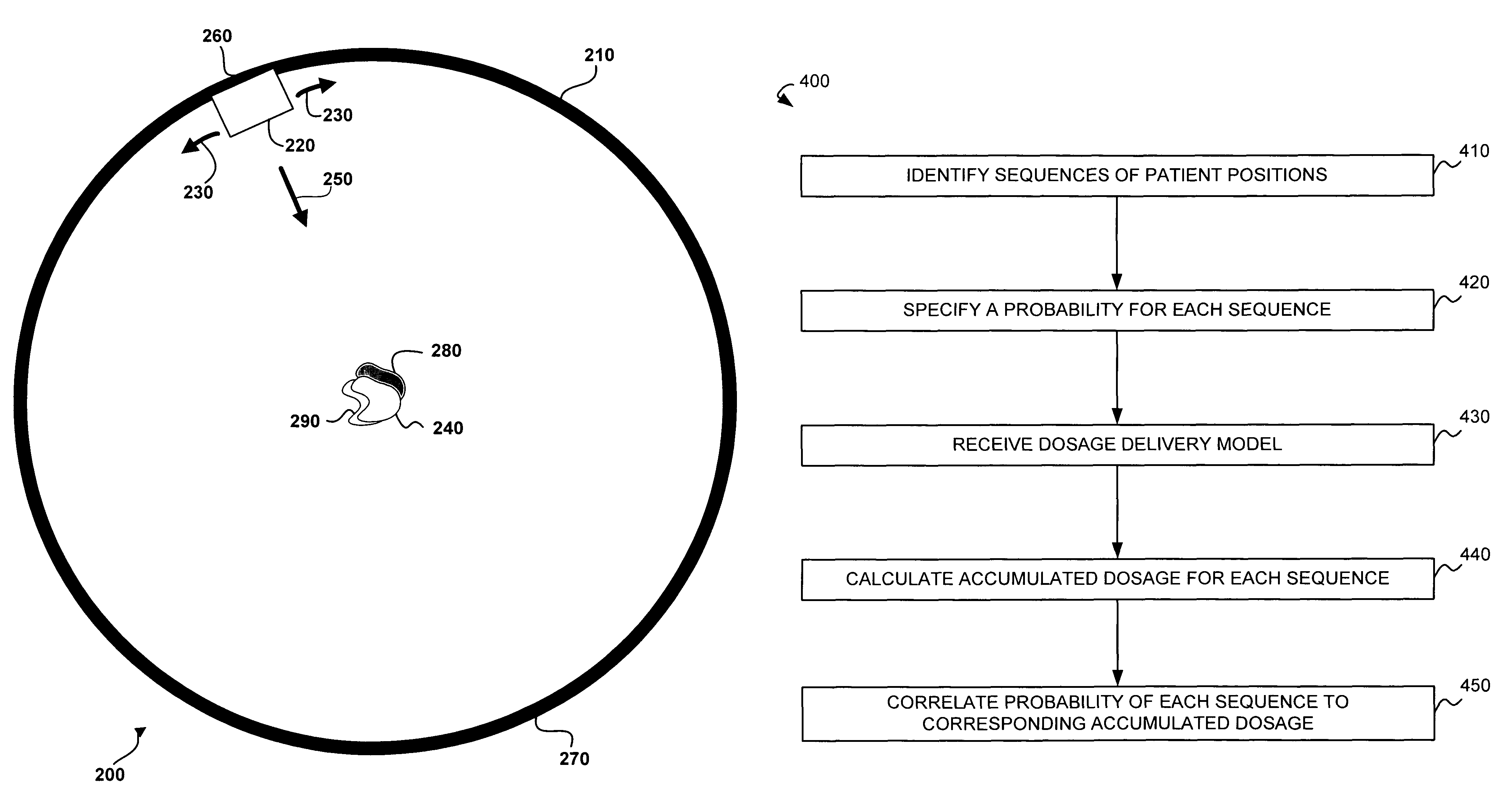
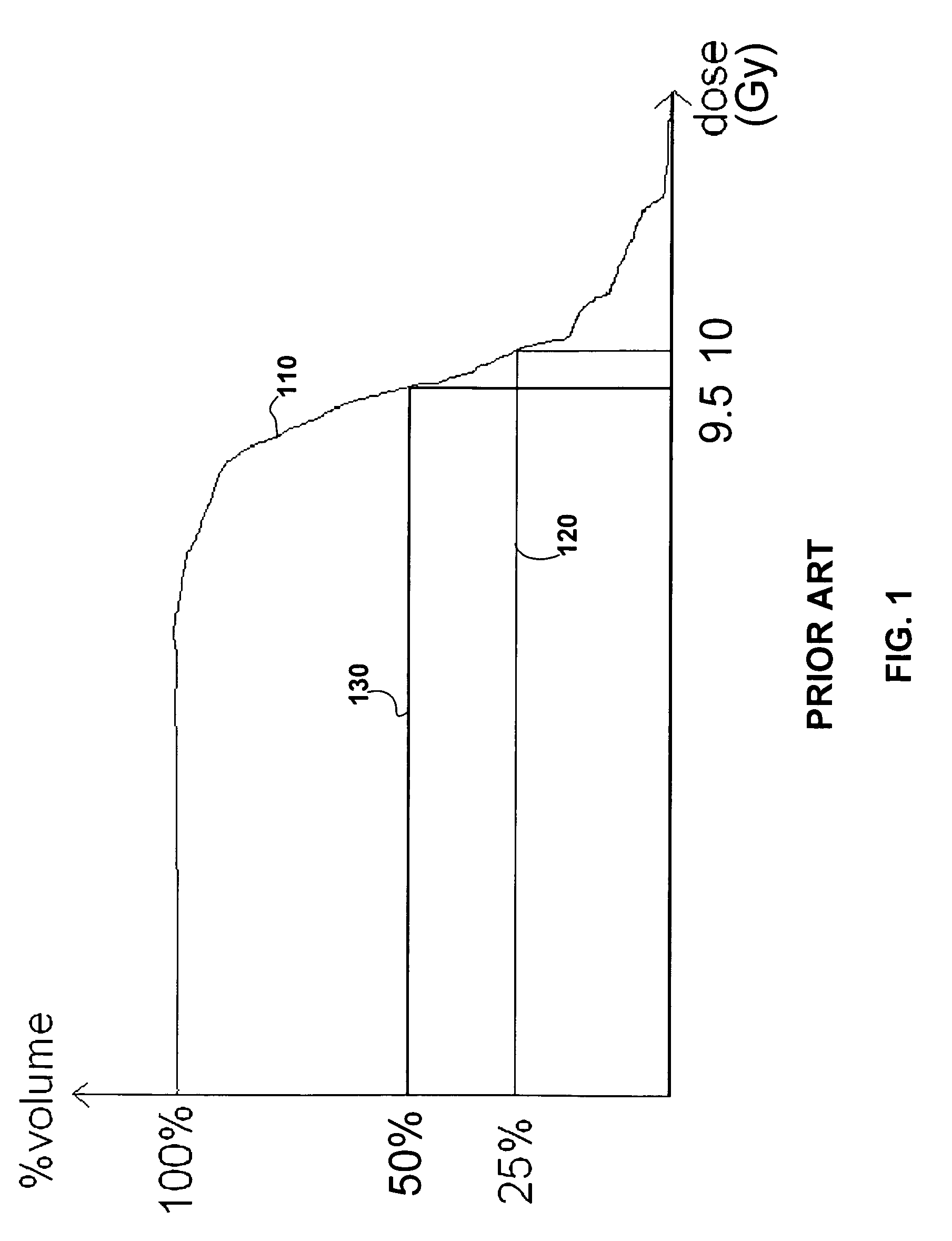
Calculation of probable accumulated dosages based on patient movement
A stochastic patient movement model and a dosage delivery plan are used to determine probabilities of dosages received by a target volume during a radiation treatment. The stochastic patient movement model is created by identifying possible sequences of patient positions during the treatment with probabilities specified for each. The dosage delivery plan specifies dosage levels and radiation locations over time. Accumulated dosages are calculated for each sequence of patient positions and the dosage delivery plan. The specified probability for each sequence is then correlated to the accumulated dosage for that sequence.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Combination formulation
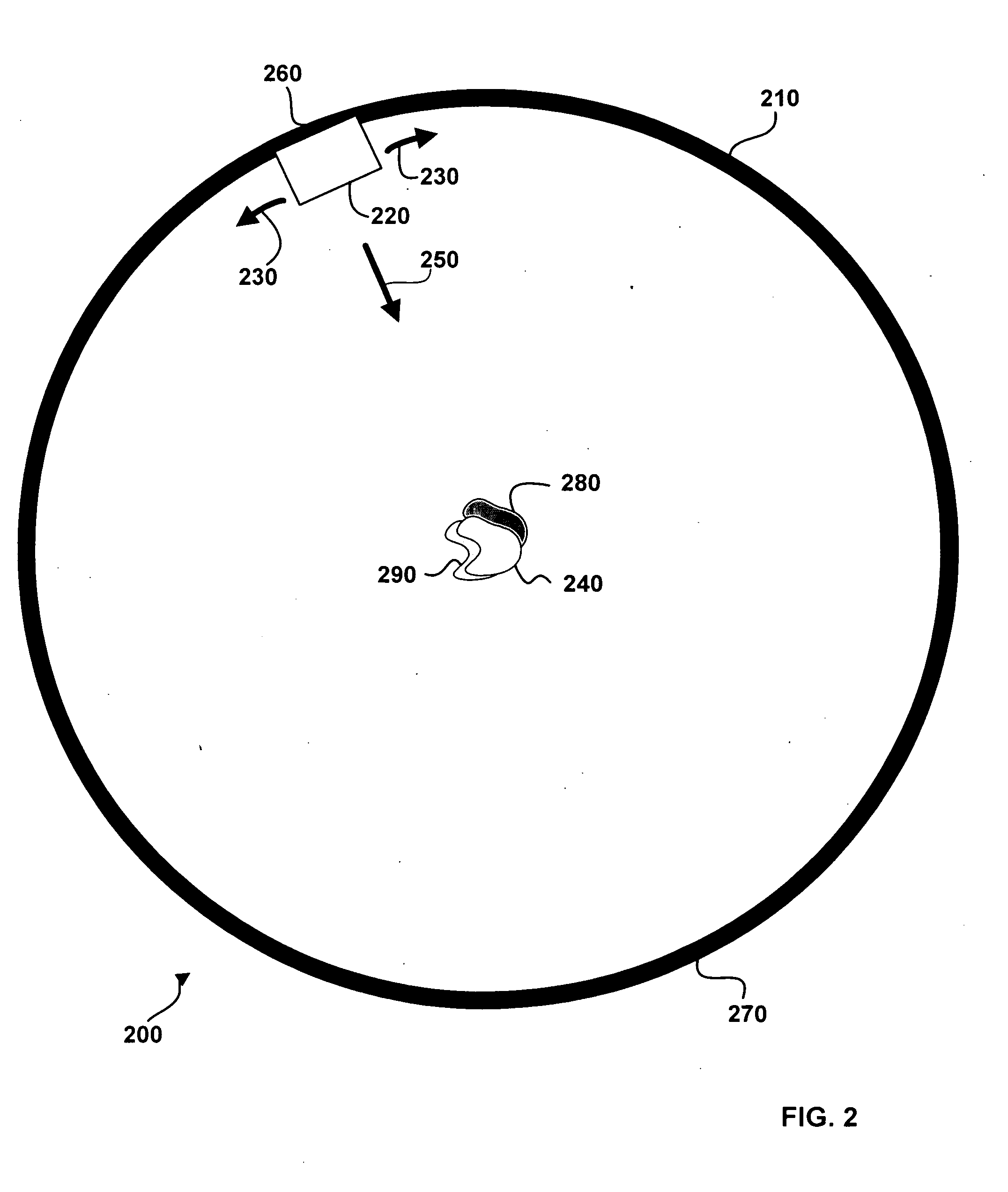
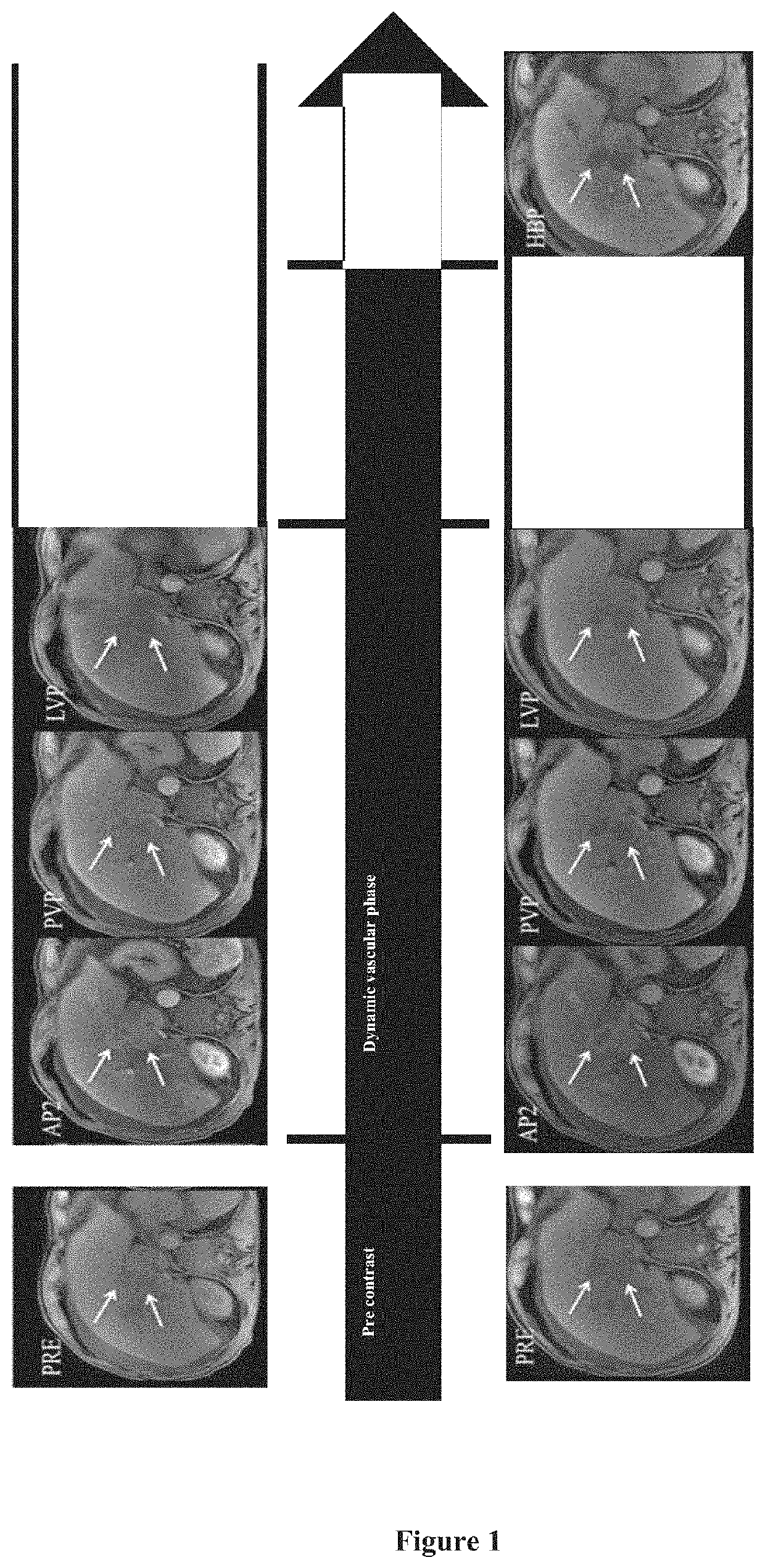
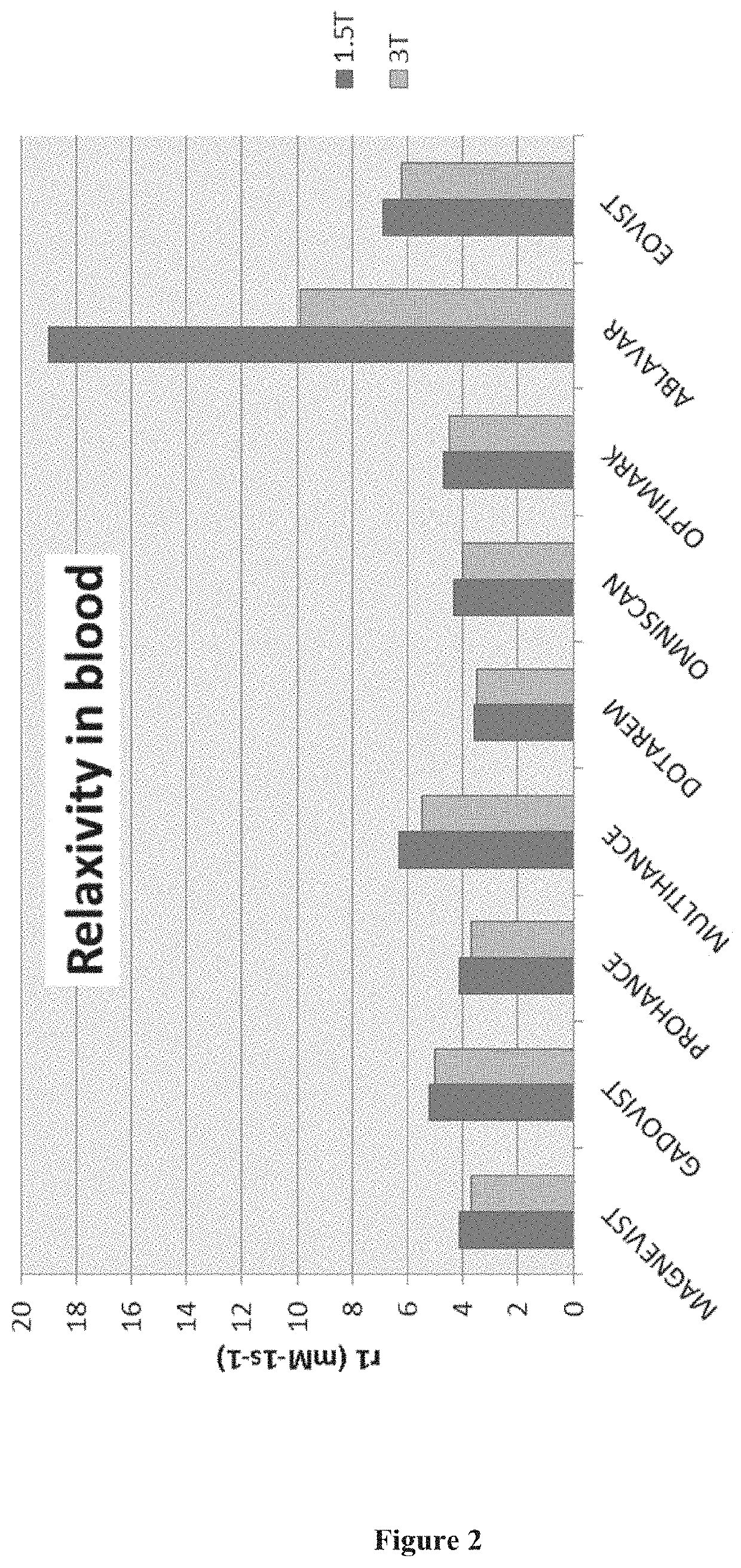
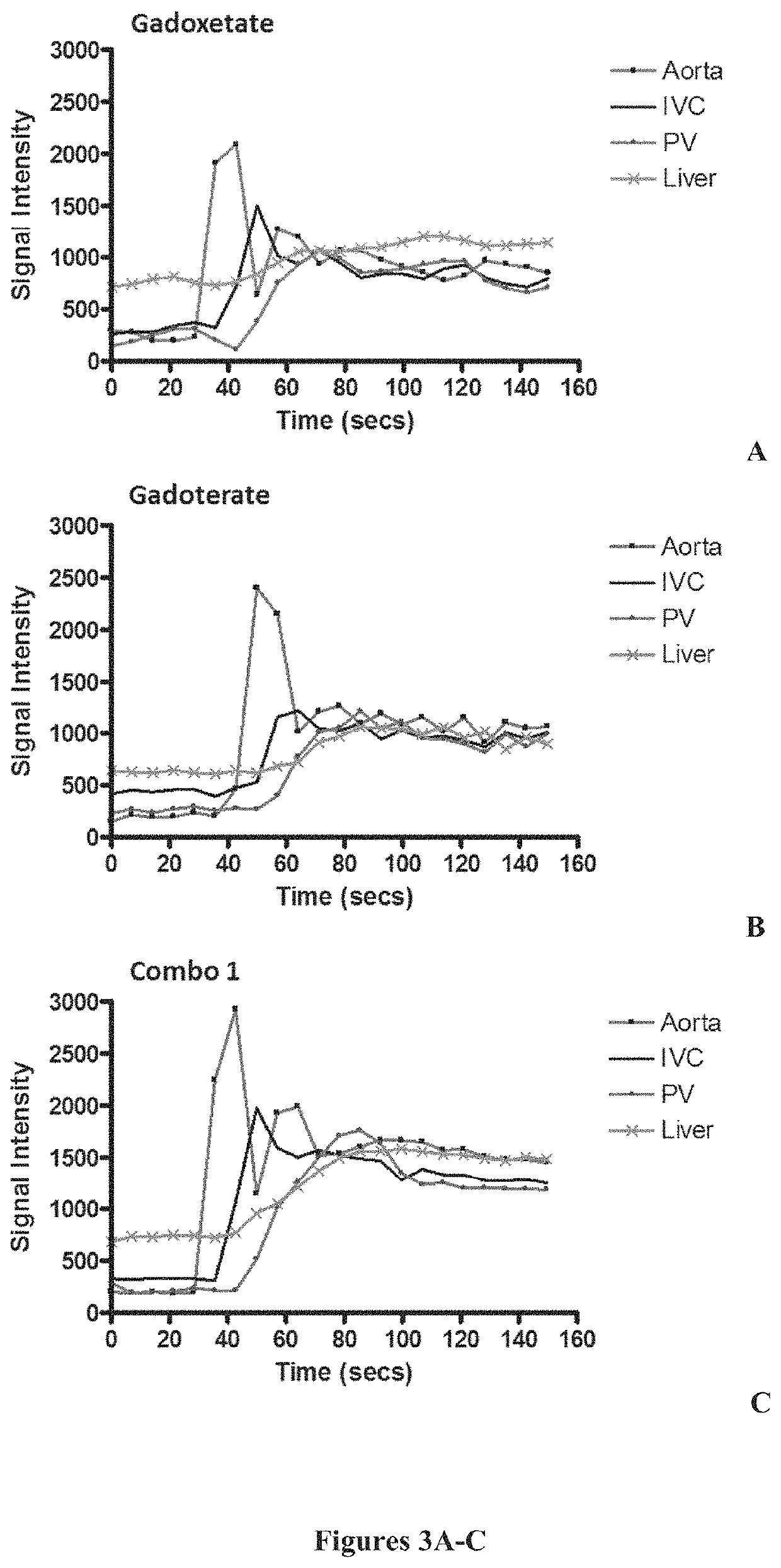
ActiveUS11110185B2For accurate visualizationImprovement in sustained vascular enhancementIn-vivo testing preparationsPatient comfortIn vivo
The present invention relates to in vivo imaging and in particular to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Provided by the present invention is a pharmaceutical formulation suitable for use in an MRI procedure and which offers advantages over known such formulations. A particular dose of the pharmaceutical formulation of the invention is also envisioned as well as the use of said dose in a method of in vivo imaging. This present invention provides for simultaneous administration of a liver specific agent and a second MR contrast agent that is capable of better / further enhancing the dynamic vascular phase in a patient. The method of the invention has the advantage of simplicity and patient comfort, compared to sequential injections. Furthermore, the method of the invention provides the advantage that it can enable a lower cumulative dose of contrast agents.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE AS
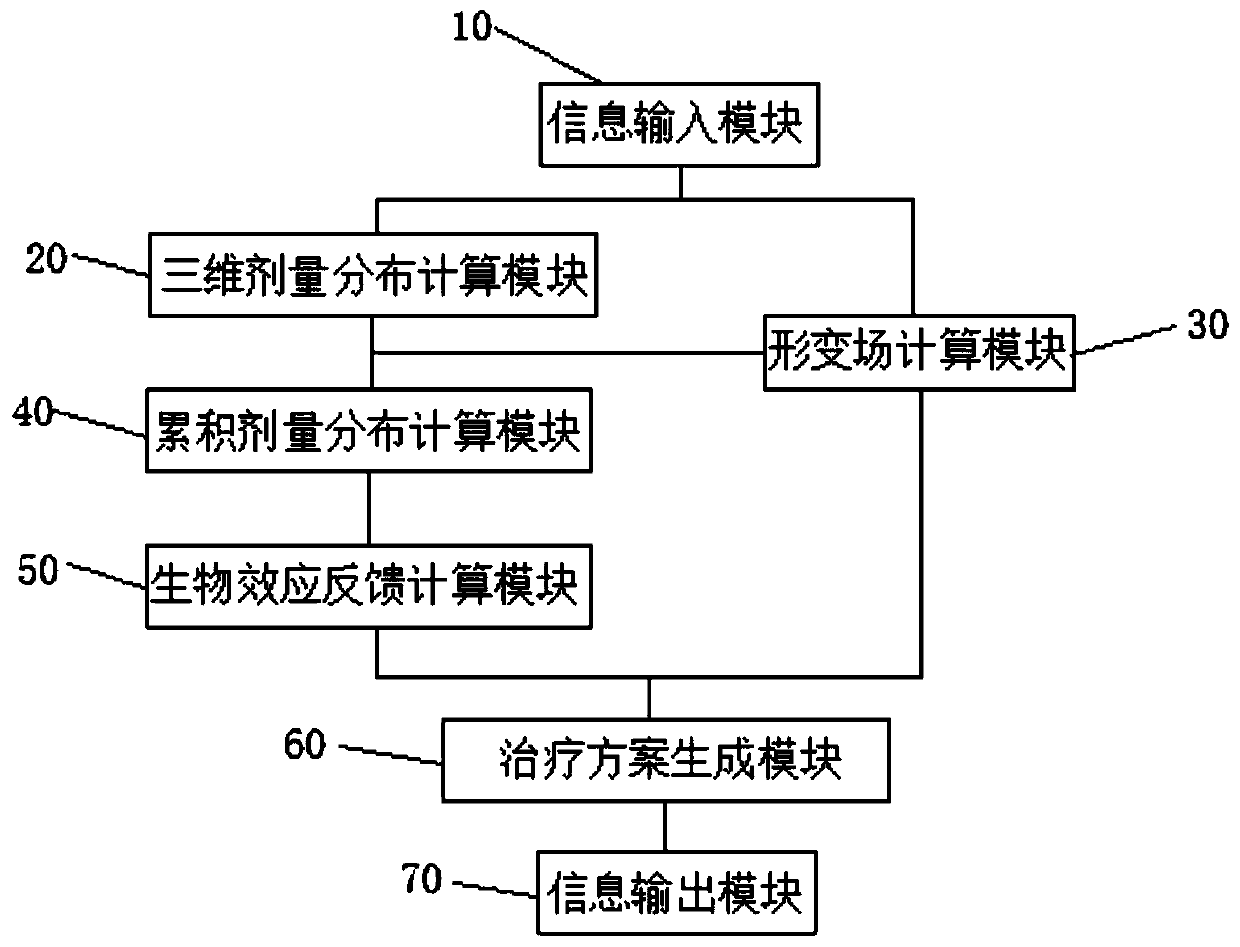
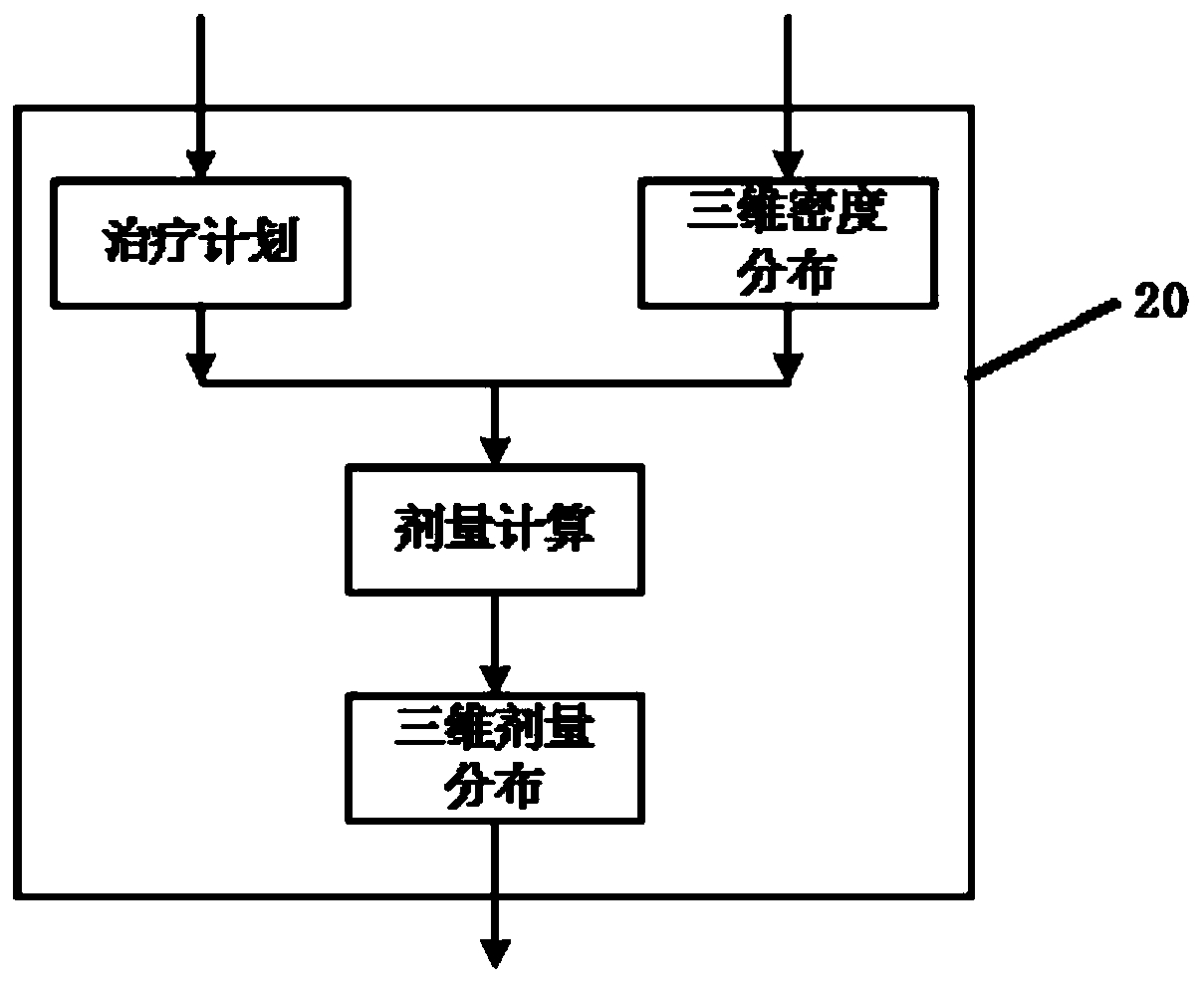
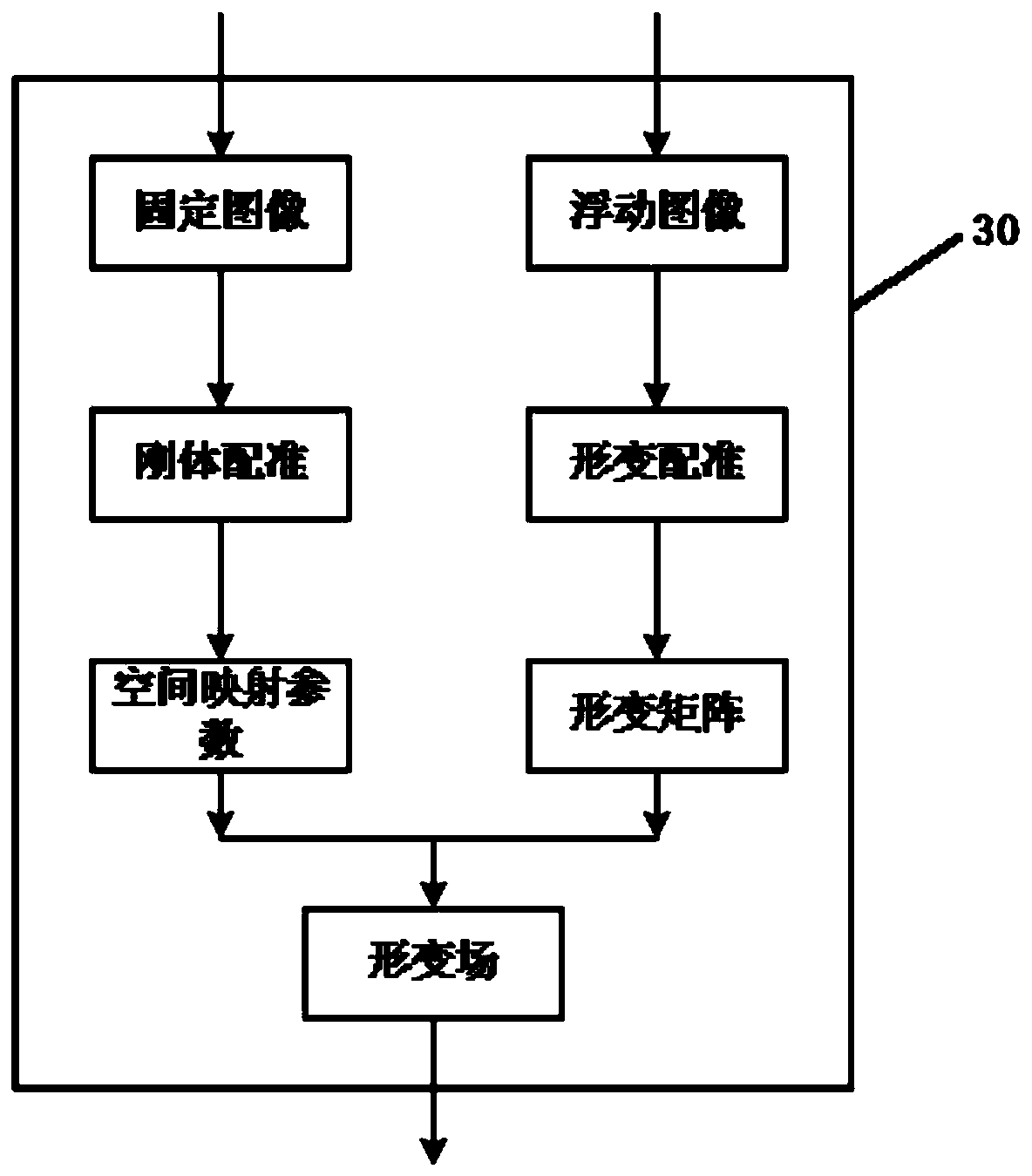
Biological effect-guided self-adaptive radiotherapy system
The invention discloses a biological effect-guided self-adaptive radiotherapy system. The system comprises an information input module, a three-dimensional dose distribution calculation module, a deformation field calculation module, a cumulative dose distribution calculation module, a biological effect feedback calculation module, a treatment plan generation module and an information output module; the information input module isused for inputting required data information,the three-dimensional dose distribution calculation module is used for calculating three-dimensional dose distribution completing fractionated irradiation and calculating the dose distribution of the current fractionated irradiation, the deformation field calculation module is used for calculating a deformation field, the cumulative dose distribution calculation module is used for calculating cumulativedose distribution completing fractionated irradiation, the biological effect feedback calculation module is used for constructing the total dose model,calculatingtotal dose distribution and calculating the biological effect feedback of each organ in a patient, the treatment plan generation module is used for generating a current fractionated irradiation plan, and the information output module is used for outputting the current fractionated irradiationplan. Accordingly, the biological effect feedback is utilized for guiding the fractionated irradiationplan optimizing process, and on the condition that fractionated irradiation has irradiation errors, the influence of repair and multiplication of cells amongfractionated irradiation on the radiotherapy quality is comprehensively considered.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
FSH beta mutants that are glycosilated at residues N55 and T57
A novel FSH mutant with increased glycosylation and longer half-lifes for use in inducing folliculogenesis in human patients is described. The FSH mutant permits the use of lower cumulative doses of FSH to achieve the same or better clinical result.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
Calculation of probable accumulated dosages based on patient movement
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Method for modifying printing and dyeing paste
InactiveCN103113485AFavorable viscosity valueOptimal radiation doseDyeing processTextile printerTamarind seed
The invention discloses a method for modifying a printing and dyeing paste. The printing and dyeing paste is a natural paste; and the natural paste is irradiated with an electron beam generated by an electron accelerator. The natural paste is guar gum or tamarind seed gum, and the cumulative dose of the irradiation is 5-70kGy. According to the invention, the electron accelerator is utilized to irradiate and degrade the printing and dyeing paste for textile-natural paste, so that the viscosity of the paste is lowered to the viscosity number beneficial to textile printing and dyeing, and the optimal irradiation dose of the viscosity number can be obtained. The invention is simple to operate, and has the advantages of high processing efficiency and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI SINOTEX HIGH ENERGY TECH
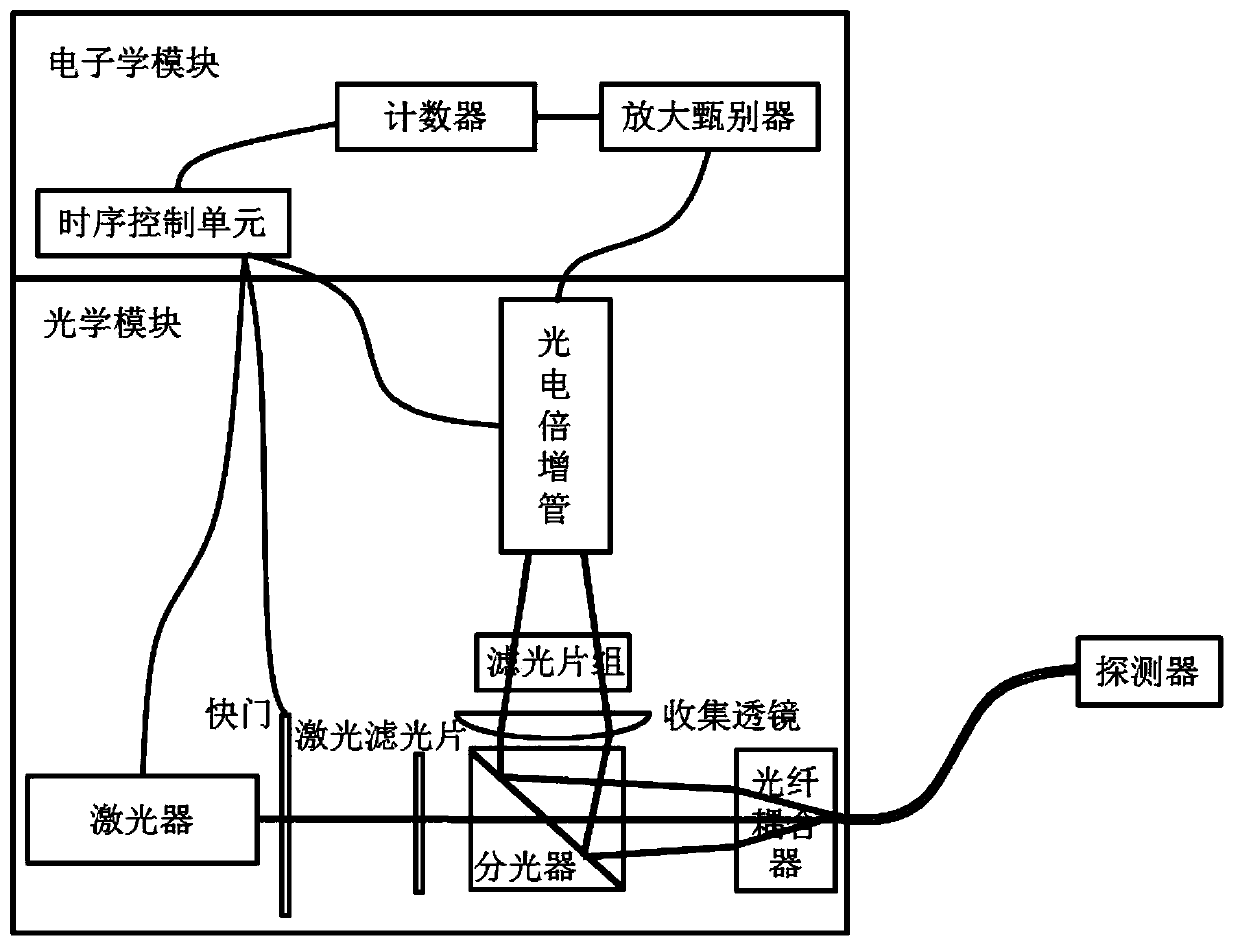
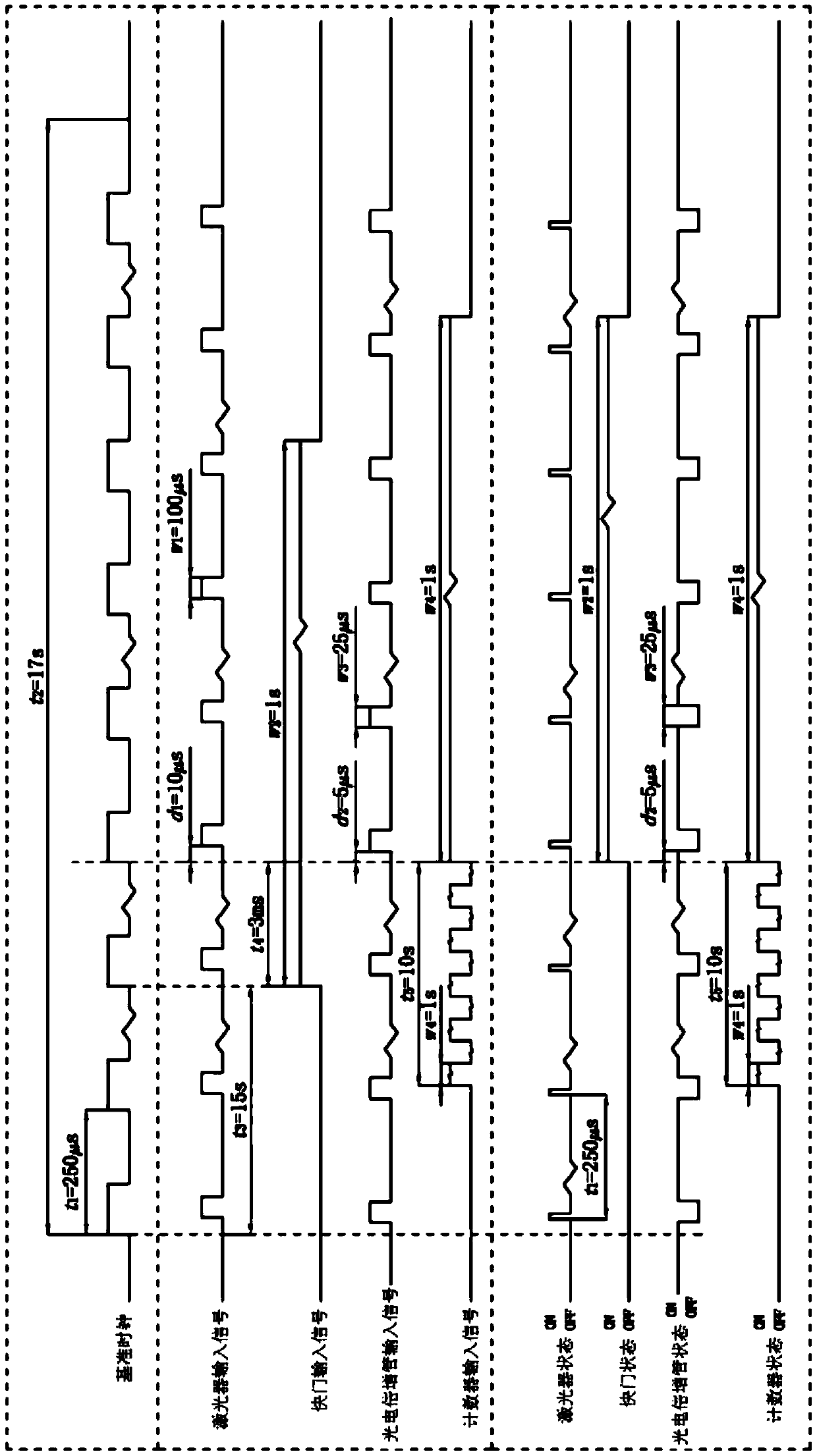
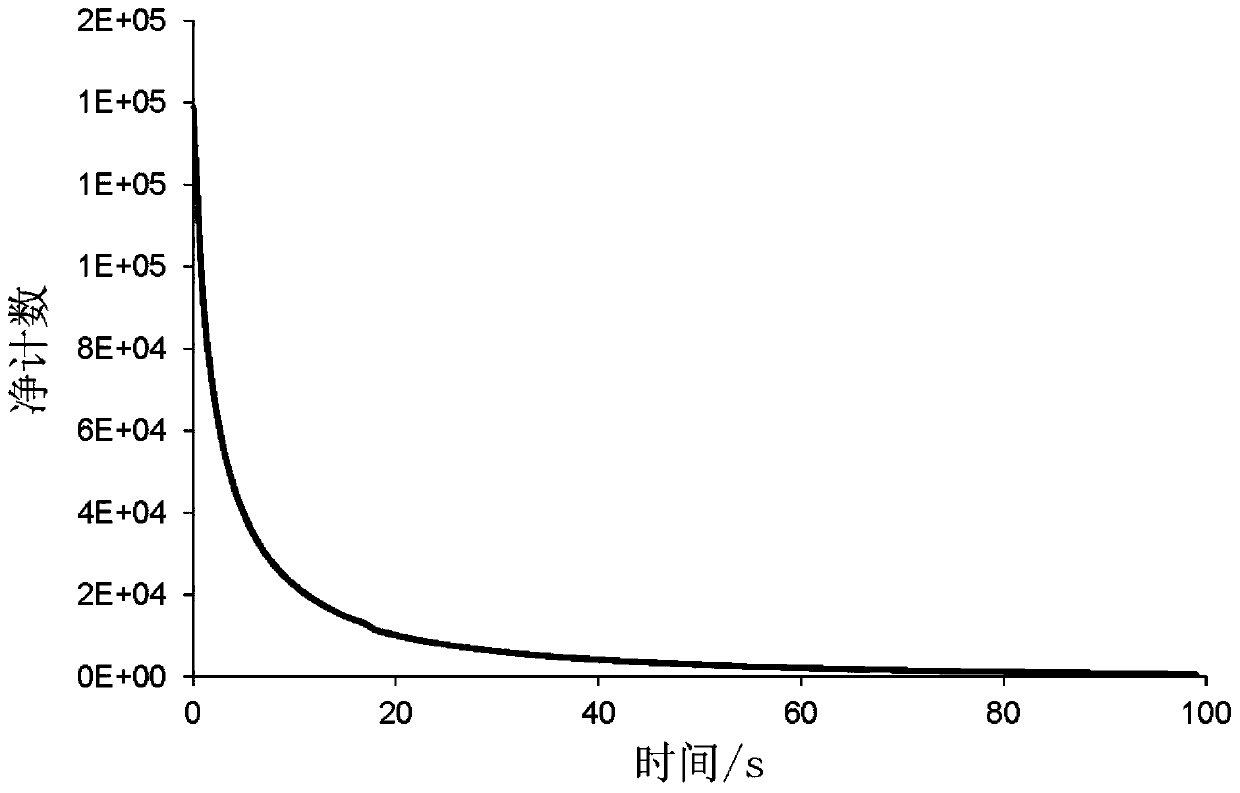
Time sequence control logic and signal processing algorithm suitable for pulsed optically stimulated luminescence technique-based quasi-real-time dose rate measuring devices
ActiveCN110376937APrecise timing controlAccurately give quasi-real-time dose rateProgramme controlComputer controlMeasurement deviceDose rate
The invention relates to the technical field of nuclear radiation detection and provides time sequence control logic and signal processing algorithm suitable for pulsed optically stimulated luminescence technique-based quasi-real-time dose rate measuring devices. The time sequence control logic provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that a same reference clock is adopted as a reference to generate input pulse signals of a laser, a shutter, a photomultiplier and a counter; and the precise time sequence control of the laser, the shutter, the photomultiplier and the counter can be realized by each pulse signal through setting the number of skipped reference pulses and the relative time delay relative to the reference clock. The signal processing algorithm provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that various dynamic and static backgrounds are considered; the relationship between cumulative dose and count value is given by linear fitting results of experimental data; the cumulative dose loss caused by each dose rate measurement is compensated; and therefore, the quasi-real-time dose rate can be accurately given.
Owner:NO 719 RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
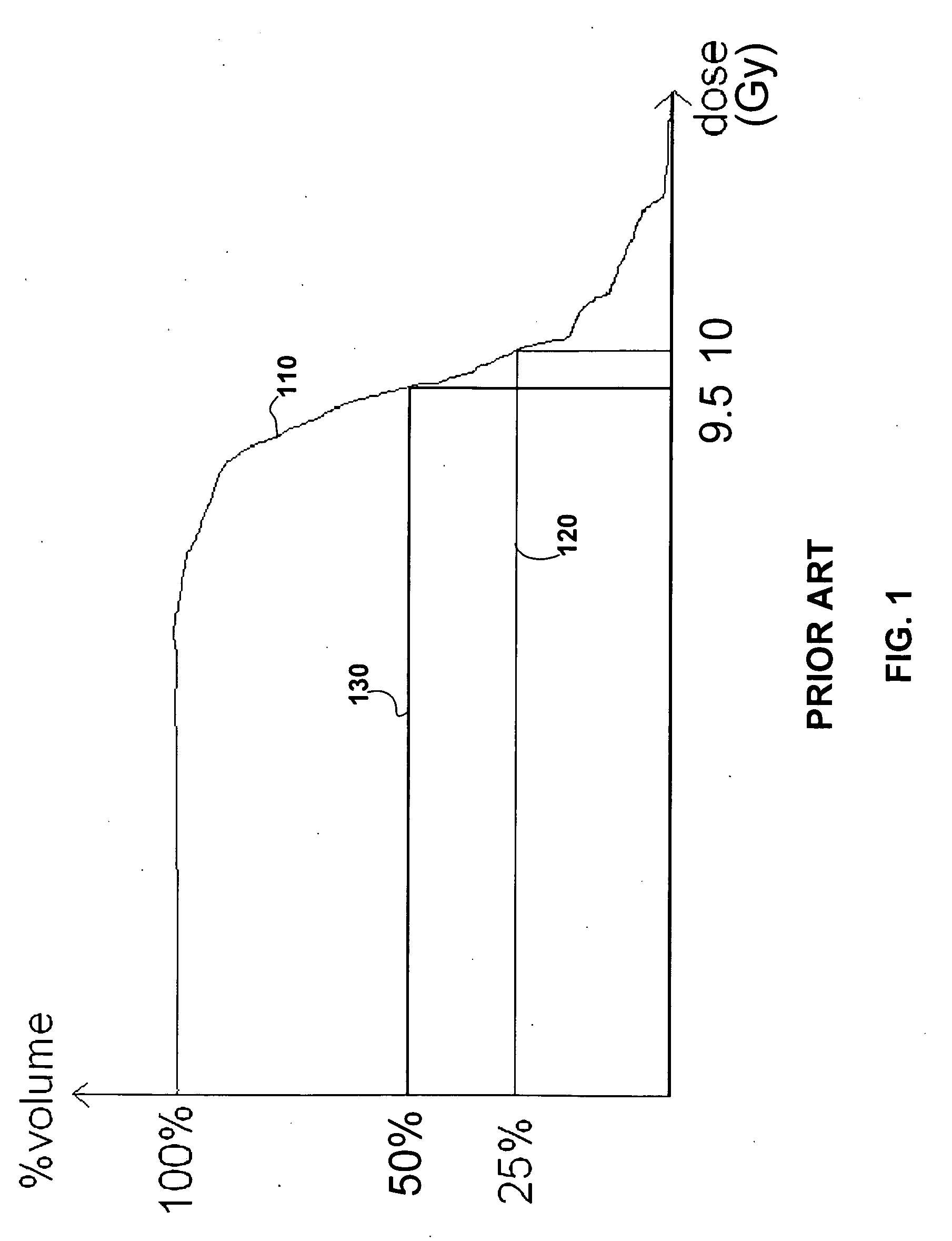
Methods and systems for protecting critical structures during radiation treatment
ActiveUS8421038B2Simple processExpensive and and intensive processMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCritical structureRadiation treatment planning
Methods and systems are provided for protecting a critical structure during the administration of radiation treatment to a patient. A register receives proposed positions for one or more radiation beams with respect to a critical structure. A processor predicts a cumulative dose volume for the critical structure based on the dose distribution, and determines if the cumulative dose volume exceeds a tolerance value. If the cumulative dose volume exceeds the tolerance value, the dose distribution may be translated at least in part based on a relationship between the cumulative dose volume and the dose distribution position.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
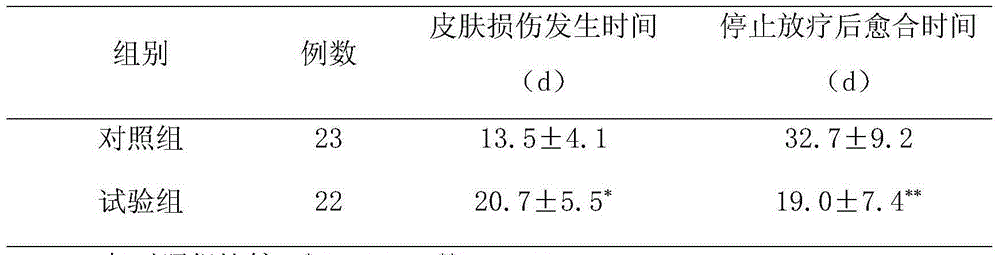
Pharmaceutical composition for prevention of rectal carcinoma radioactive skin damage and application thereof
InactiveCN104998179AAvoid lossPromote growthDermatological disorderAntineoplastic agentsTolerabilityRadiation therapy
The invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition for prevention of rectal carcinoma radioactive skin damage and an application thereof; the pharmaceutical composition is prepared from an active component and auxiliary materials; the active component is prepared by water extraction and alcohol precipitation of the following traditional Chinese medicine raw materials in parts by weight: 13-20 parts of potentilla fulgens wall, 12-18 parts of tribulus terrestris, 12-18 parts of mandarin orange seed, 13-20 parts of abelmoschus crinitus wall, 21-30 parts of herba lycopi, 21-30 parts of white atractylodes rhizome, 6-12 parts of fructus amomi, and 10-20 parts of herba hyperici. The pharmaceutical composition not only can delay the generation of radioactive skin damage, ensure smooth performing of radiation therapy and improve tolerability of patient skins on the cumulative dose of radiation, but also can promote healing of radioactive skin damage wound surfaces.
Owner:江琴
Irradiation-resistant camera
InactiveCN110121019AStrong radiation resistanceImprove clarityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsInformation processingRadiation resistant
The invention discloses an irradiation-resistant camera which is composed of an external protection assembly and an internal function assembly. The external protection assembly is composed of an outercylinder assembly, an upper cover assembly and a lower cover assembly. The internal function assembly is composed of a lens assembly, a filtering assembly, an image information acquisition device, ashielding plate, an image information processing device, a left supporting plate, a right supporting plate and a heat dissipation plate. The irradiation-resistant camera has high irradiation resistance, and the cumulative dose can reach 103 Gy; high definition can still be ensured in a strong irradiation environment; the guiding device is arranged, so that the imaging positive direction of the radiation-resistant camera can be quickly determined; all the modules are reasonable in structural layout, and the radiation resistance of the camera is high.
Owner:北京中天星控科技开发有限公司
A special silicone sealant for internal structure of nuclear power plant and its sealing structure
ActiveCN104830269BImprove adhesionImprove flexibilityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesRelative displacementNuclear engineering
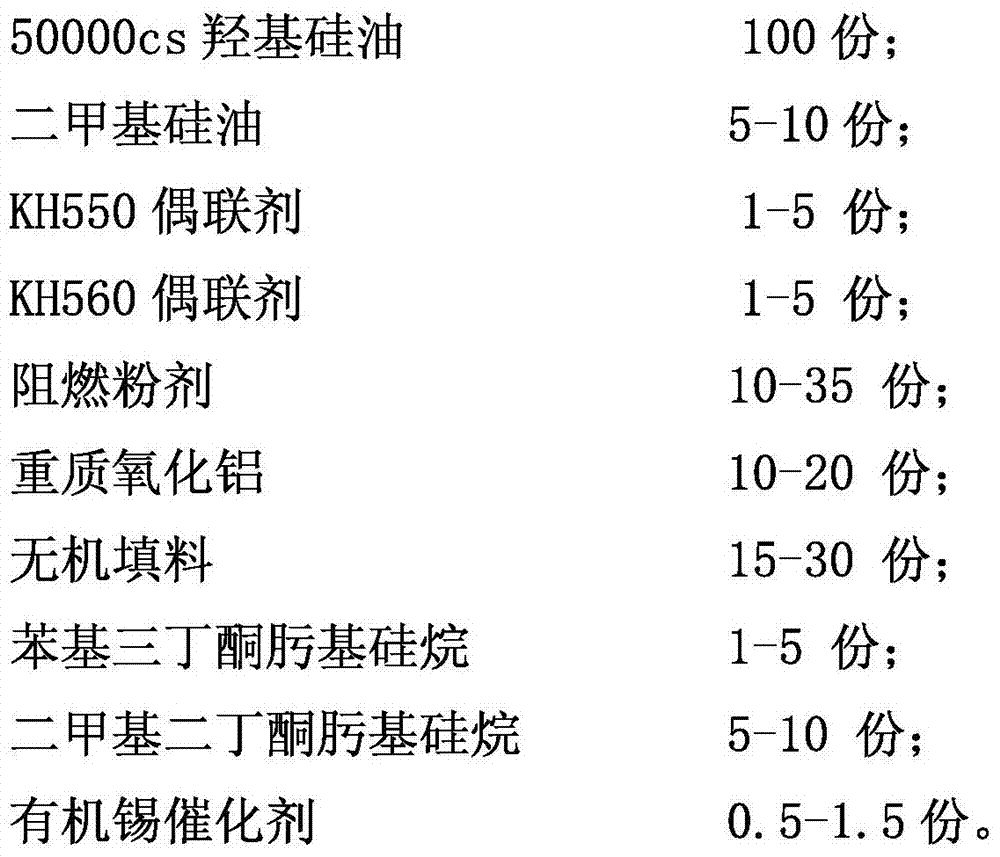
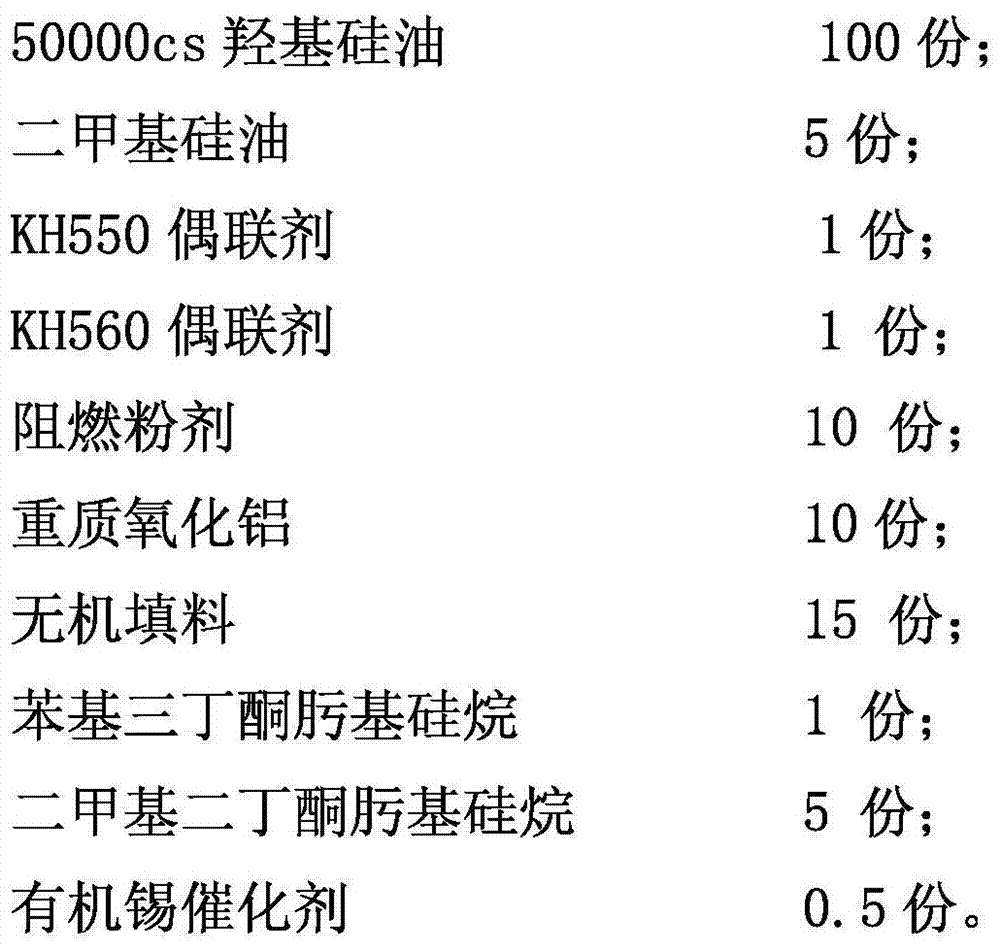
The invention relates to a special silicone sealant for the internal structure of a nuclear power plant, which comprises the following components in mass-number ratio: 100 parts of 50000cs hydroxyl silicone oil; 5-10 parts of dimethyl silicone oil; 1-5 parts of KH550 coupling agent ; 1-5 parts of KH560 coupling agent; 10-35 parts of flame retardant powder; 10-20 parts of heavy alumina; 15-30 parts of inorganic filler; 5-10 parts of dibutylketoxime silane; 0.5-1.5 parts of organotin catalyst. An internal sealing structure of a nuclear power plant includes a CV steel plate and a concrete wall, and silicone sealant. A depression is provided at the joint between the concrete wall and the CV steel plate, and the silicone sealant is provided in the depression. The beneficial effect of the present invention is: after the cumulative radiation dose and LOCA test of the 60-year lifetime of the nuclear power plant, there is no pulverization and degradation, and still has good bonding performance and flexibility; the pressure of 66psig (455kPa) inside the simulated CV Under this condition, a relative displacement of lin (25.4mm) occurs between the CV and the concrete, which can ensure good watertight and airtight performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI NUCLEAR ENG RES & DESIGN INST CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com