Patents
Literature
198 results about "Radiation treatment planning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
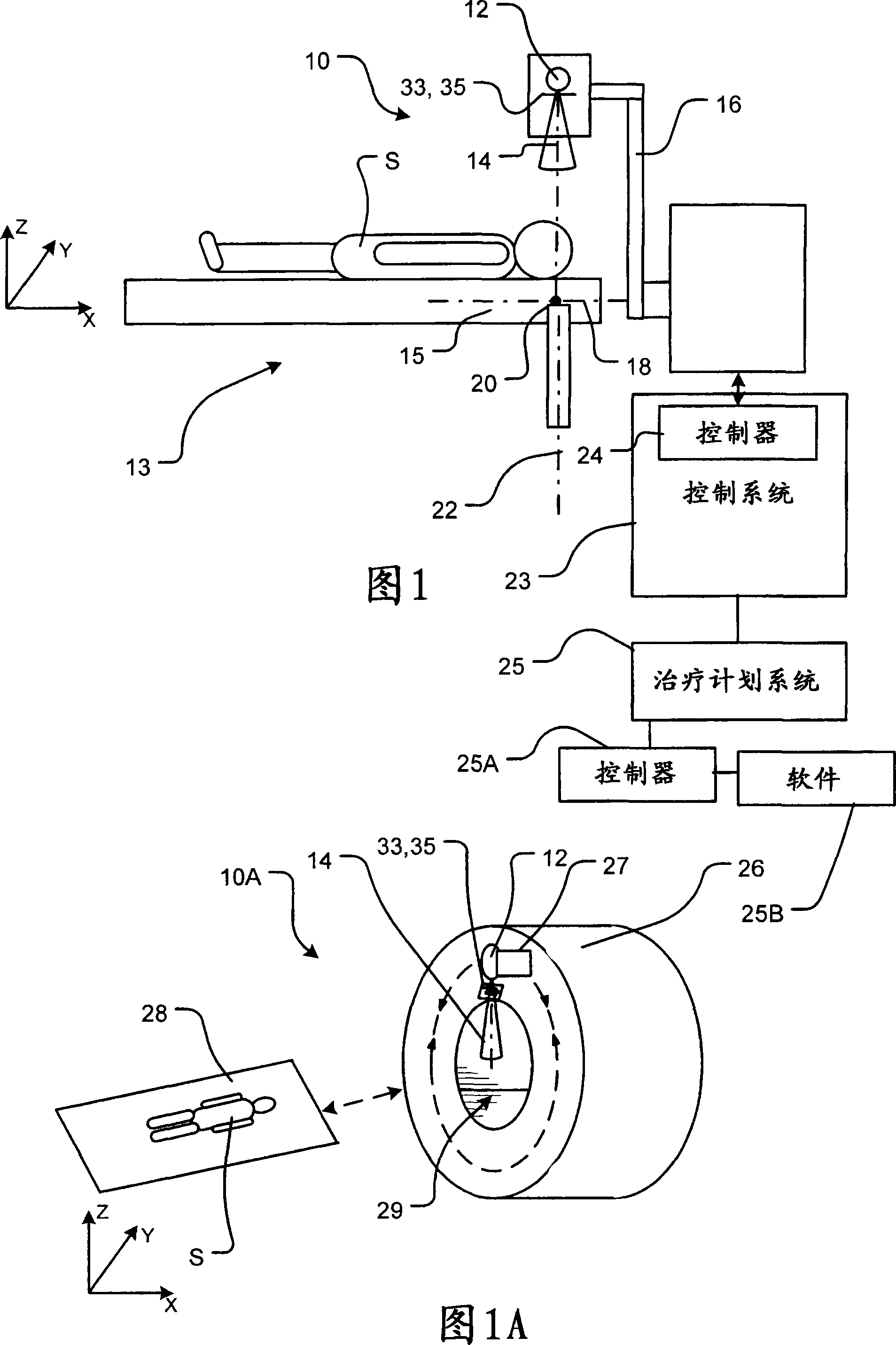
In radiotherapy, radiation treatment planning is the process in which a team consisting of radiation oncologists, radiation therapist, medical physicists and medical dosimetrists plan the appropriate external beam radiotherapy or internal brachytherapy treatment technique for a patient with cancer.
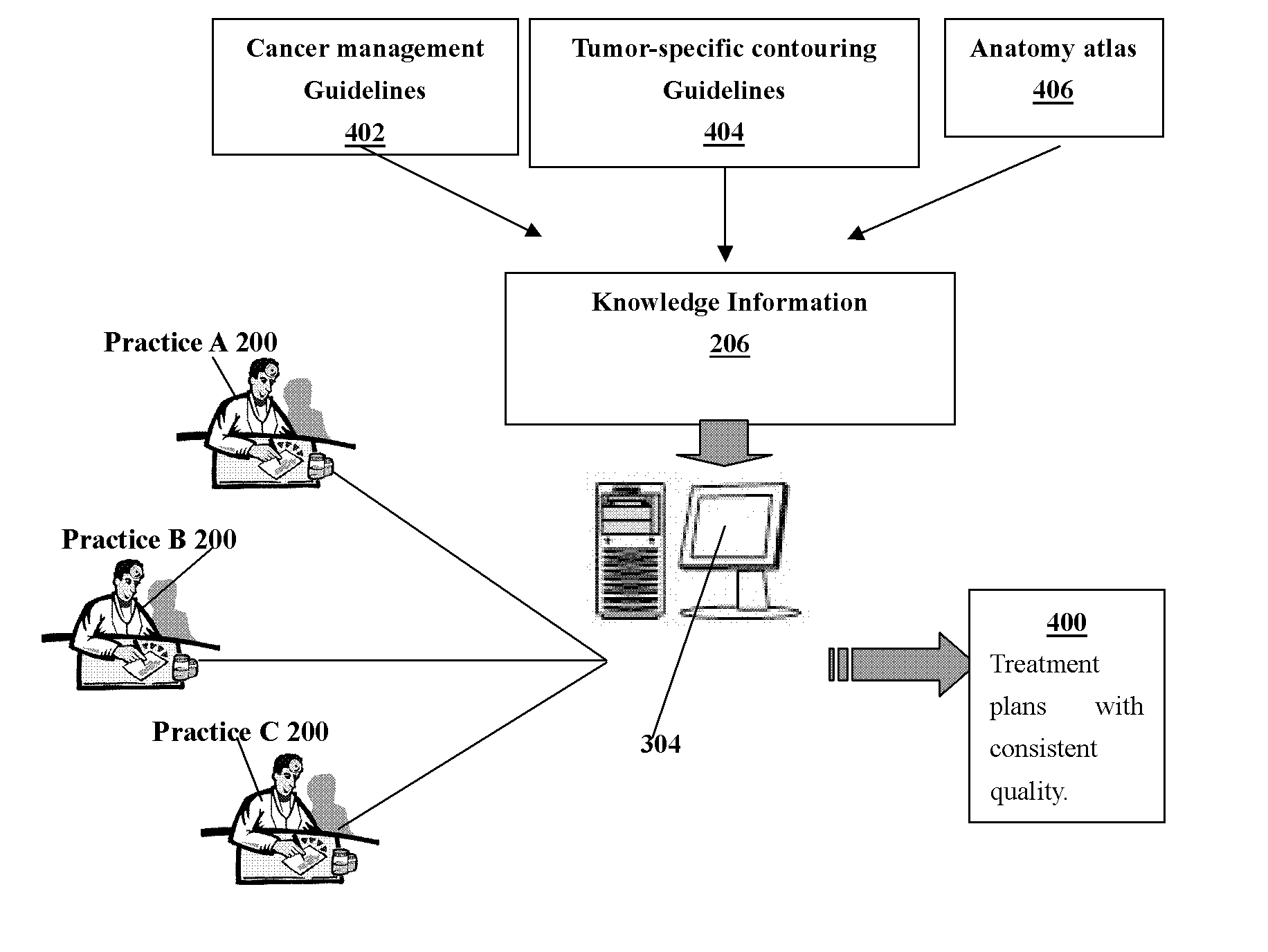
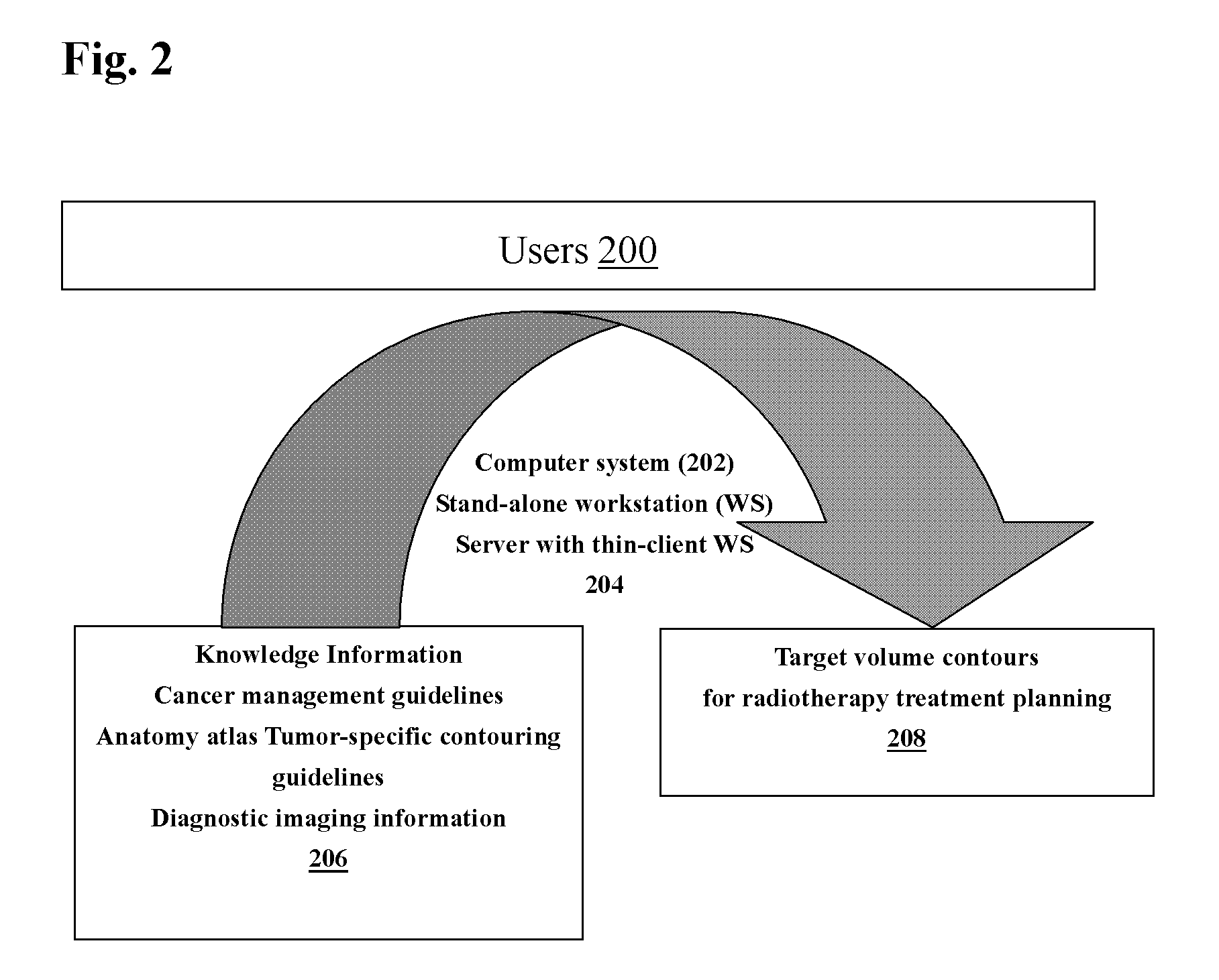
Reducing variation in radiation treatment therapy planning
InactiveUS7995813B2Shorten the timeConvenient treatmentSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionProgram planningGeolocation
A method and apparatus are disclosed that reduces variation in radiation therapy treatment planning among plurality of users within the same or different geographic locations. The system includes a method and an apparatus that provide users with the knowledge information and utilizing the knowledge information to contour target volumes for radiation treatment planning. The mode of operation includes utilizing a stand-alone workstation or a server computer connected to the plurality of thin client workstations.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
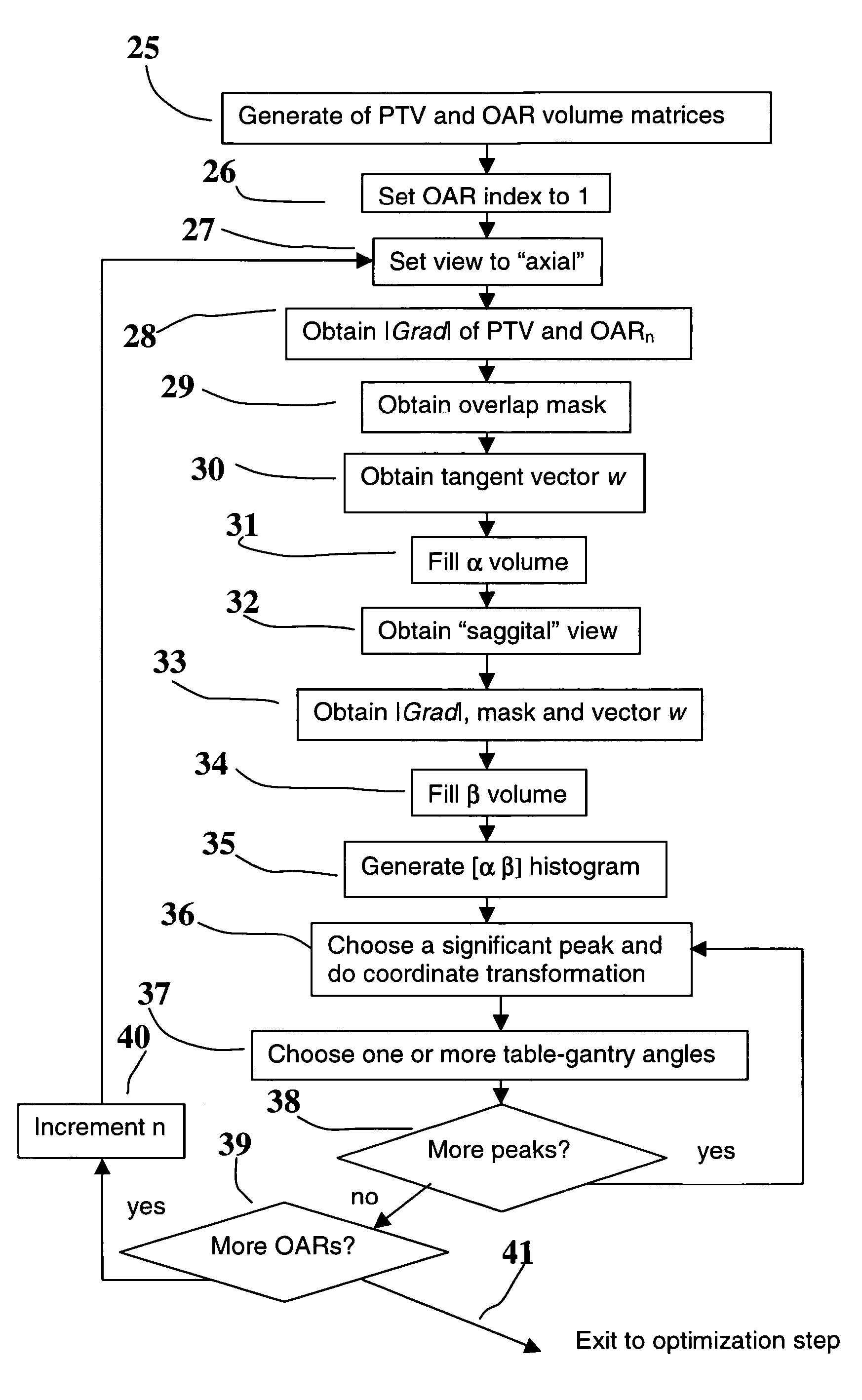
Method for assisted beam selection in radiation therapy planning
InactiveUS7027557B2Easy to mergeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPlan treatmentMulti leaf collimator
A method to assist in the selection of optimum beam orientations for radiation therapy when a planning treatment volume (PTV) is adjacent to one or more organs-at-risk (OARs). A mathematical analysis of the boundaries between the PTV and OARs allows the definition of a continuum of pairs of gantry and table angles whose beam orientations have planes that are essentially parallel to those boundaries, and can, therefore, separate the PTV from the OARs when a multi-leaf collimator is used in the therapy. The Radiation Oncologist can then select one or more pairs of gantry and table angles from the continuum as input to a beam optimization step. The selected angles can deliver highly uniform dose to the PTV, while minimizing the radiation dose to the OARs.
Owner:LLACER JORGE
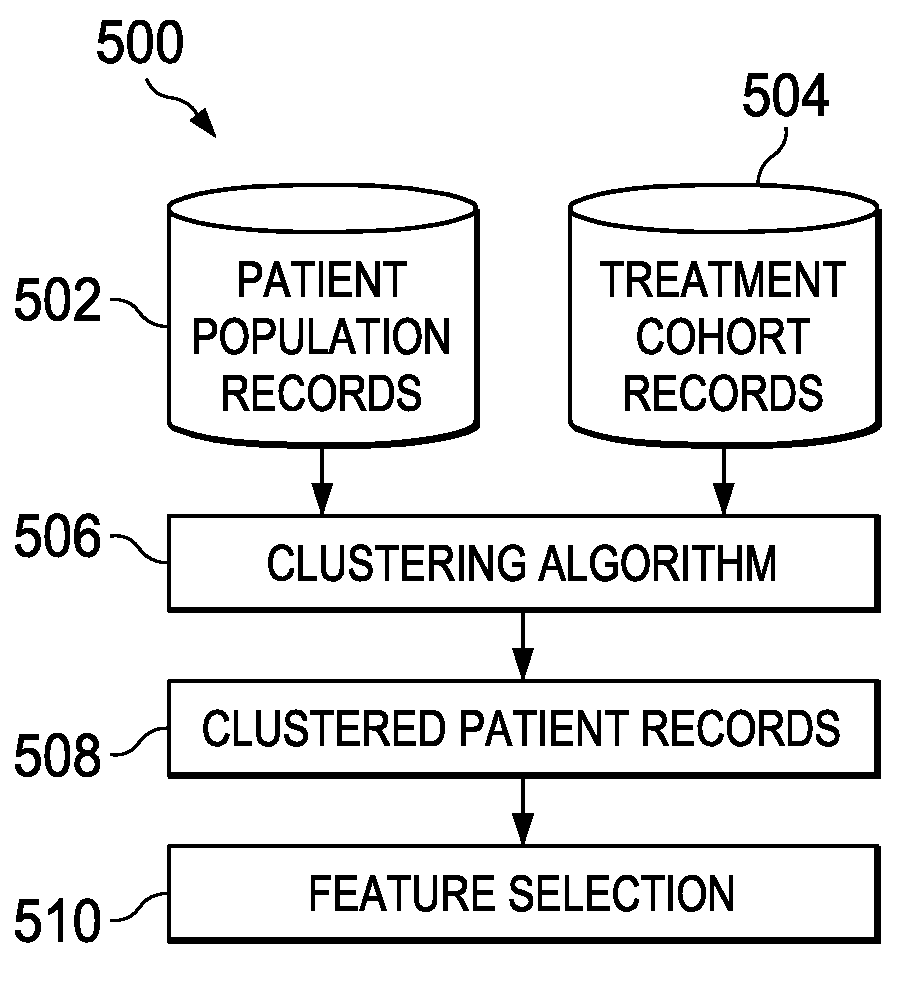
System and method for optimizing medical treatment planning and support in difficult situations subject to multiple constraints and uncertainties
InactiveUS20090299766A1Minimize the differenceData processing applicationsMedical automated diagnosisRadiation treatment planningMedical treatment
A computer implemented method for managing a condition of a patient during a chaotic event. A datum regarding a first patient is received. A first set of relationships is established. The first set of relationships comprises at least one relationship of the datum to at least one additional datum existing in a database. Based on the first set of relationships, cohorts to which the first patient belongs are established. Ones of the plurality of cohorts contain first data regarding the first patient and second data regarding a set of additional information. The set of additional information is related to the first data. The second data further regards a constraint imposed by a chaotic event. The plurality of cohorts is clustered according to at least one parameter. A cluster of cohorts is formed. Which of at least two cohorts in the cluster are closest to each other is determined.
Owner:IBM CORP
Automatic Generation of Patient-Specific Radiation Therapy Planning Parameters
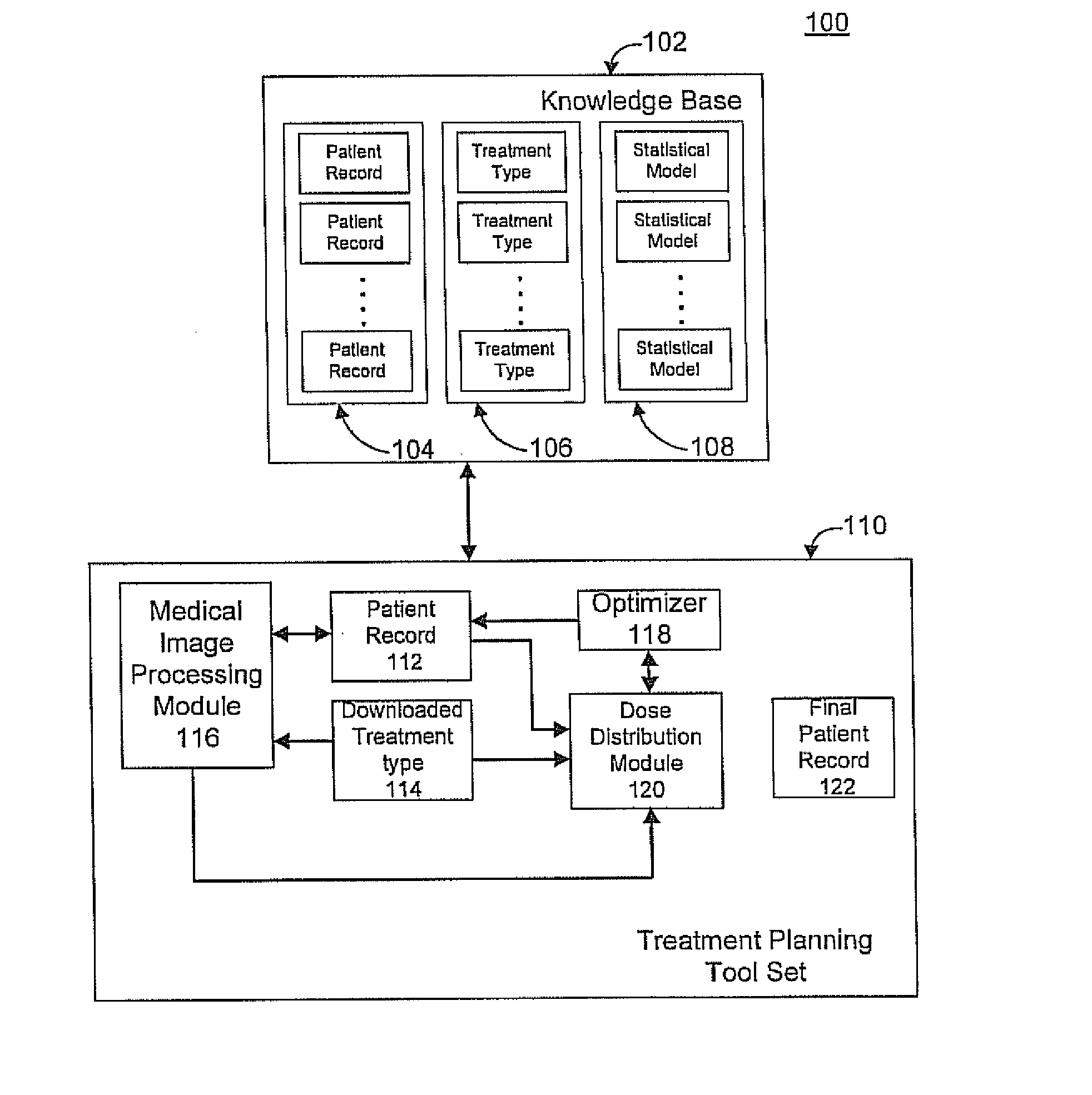
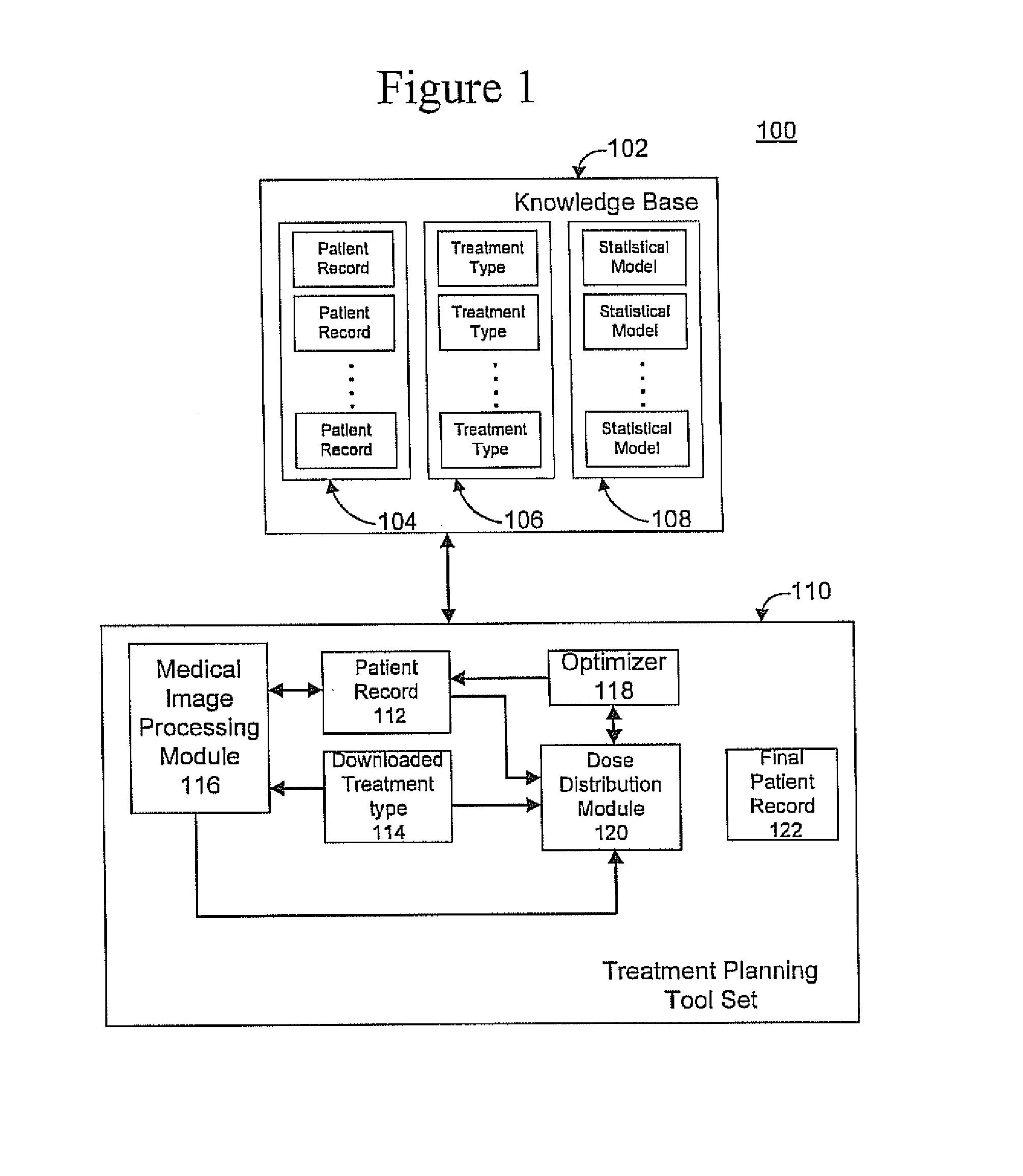
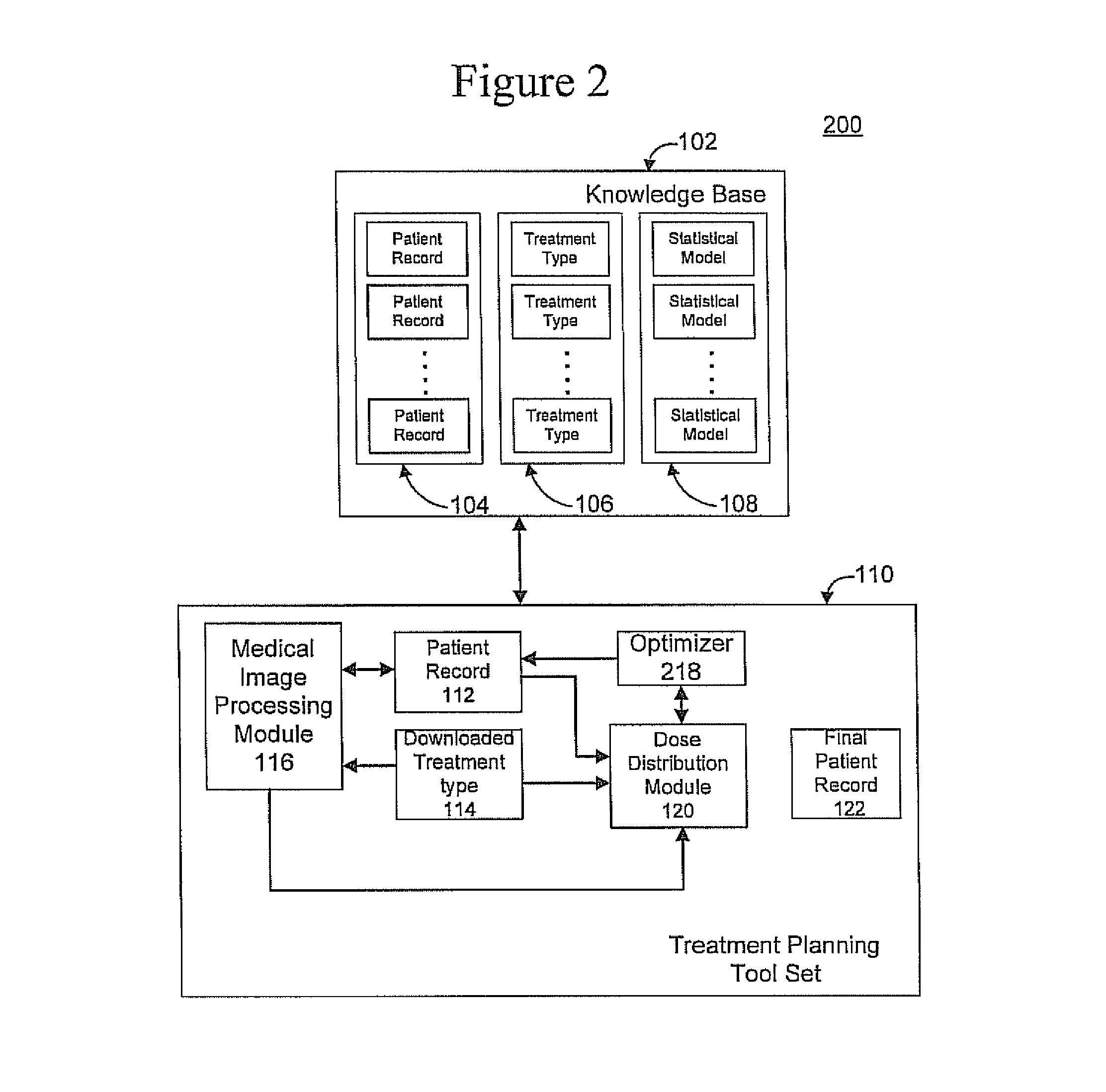
An apparatus and method for automatically generating radiation treatment planning parameters are disclosed. In accordance with the illustrative embodiment, a database is constructed that stores: (i) patient data and past treatment plans by expert human planners for these patients, and (ii) optimal treatment plans that are generated using multi-objective optimization and Pareto front search and that represent the best tradeoff opportunities of the patient case, and a predictive model (e.g., a neural network, a decision tree, a support vector machine [SVM], etc.) is then trained via a learning algorithm on a plurality of input / output mappings derived from the contents of the database. During training, the predictive model is trained to identify and infer patterns in the treatment plan data through a process of generalization. Once trained, the predictive model can then be used to automatically generate radiation treatment planning parameters for new patients.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
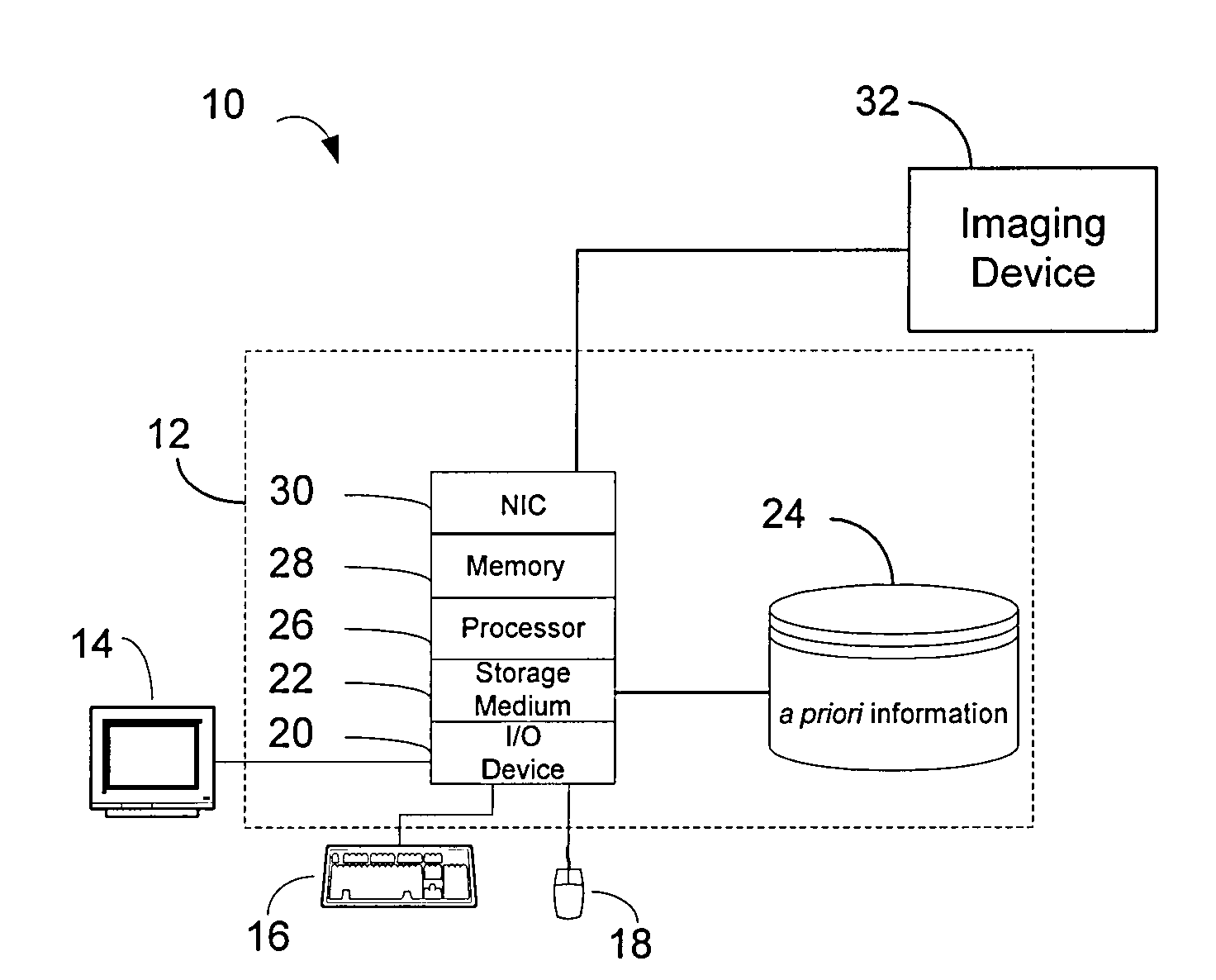
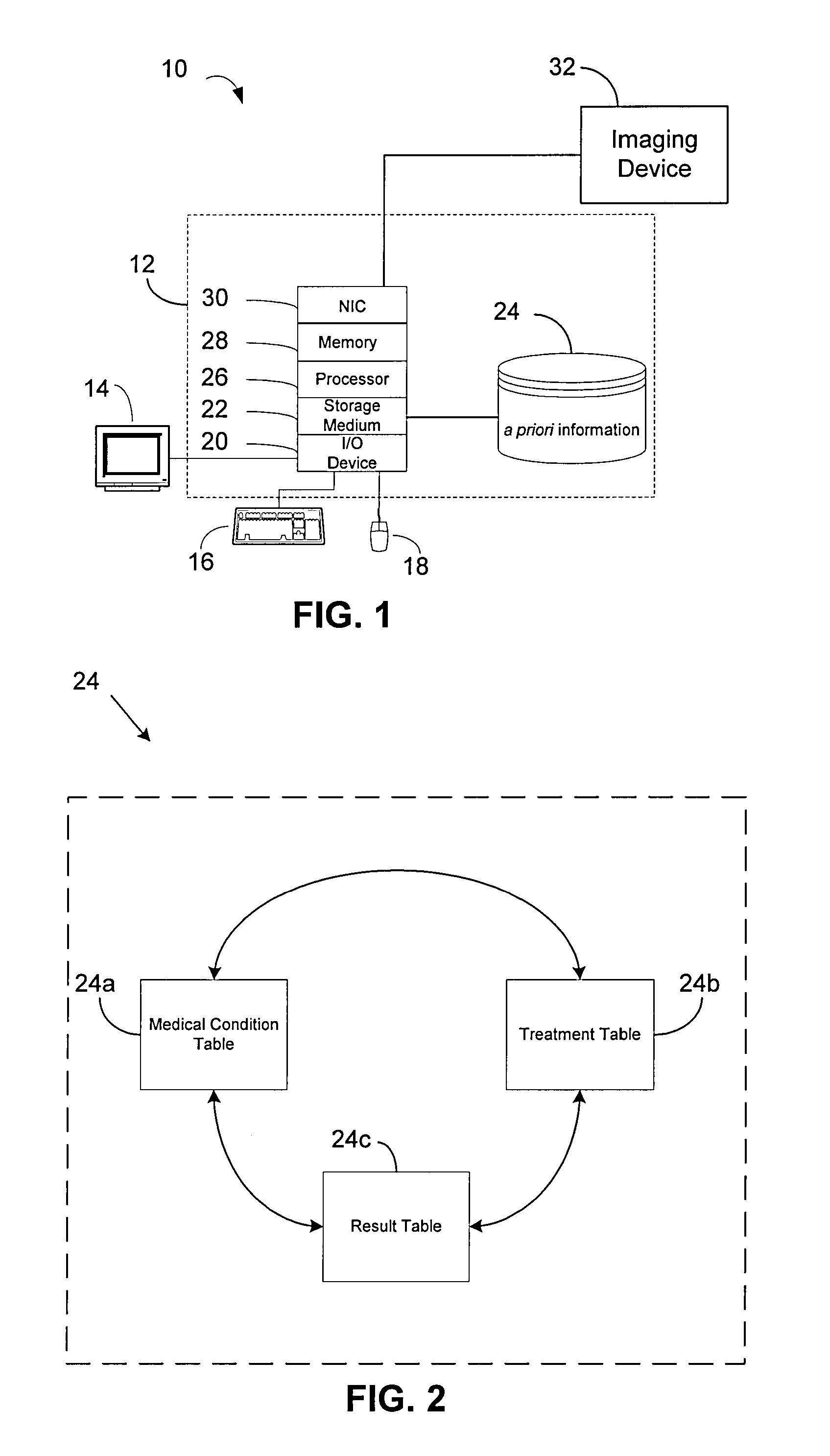
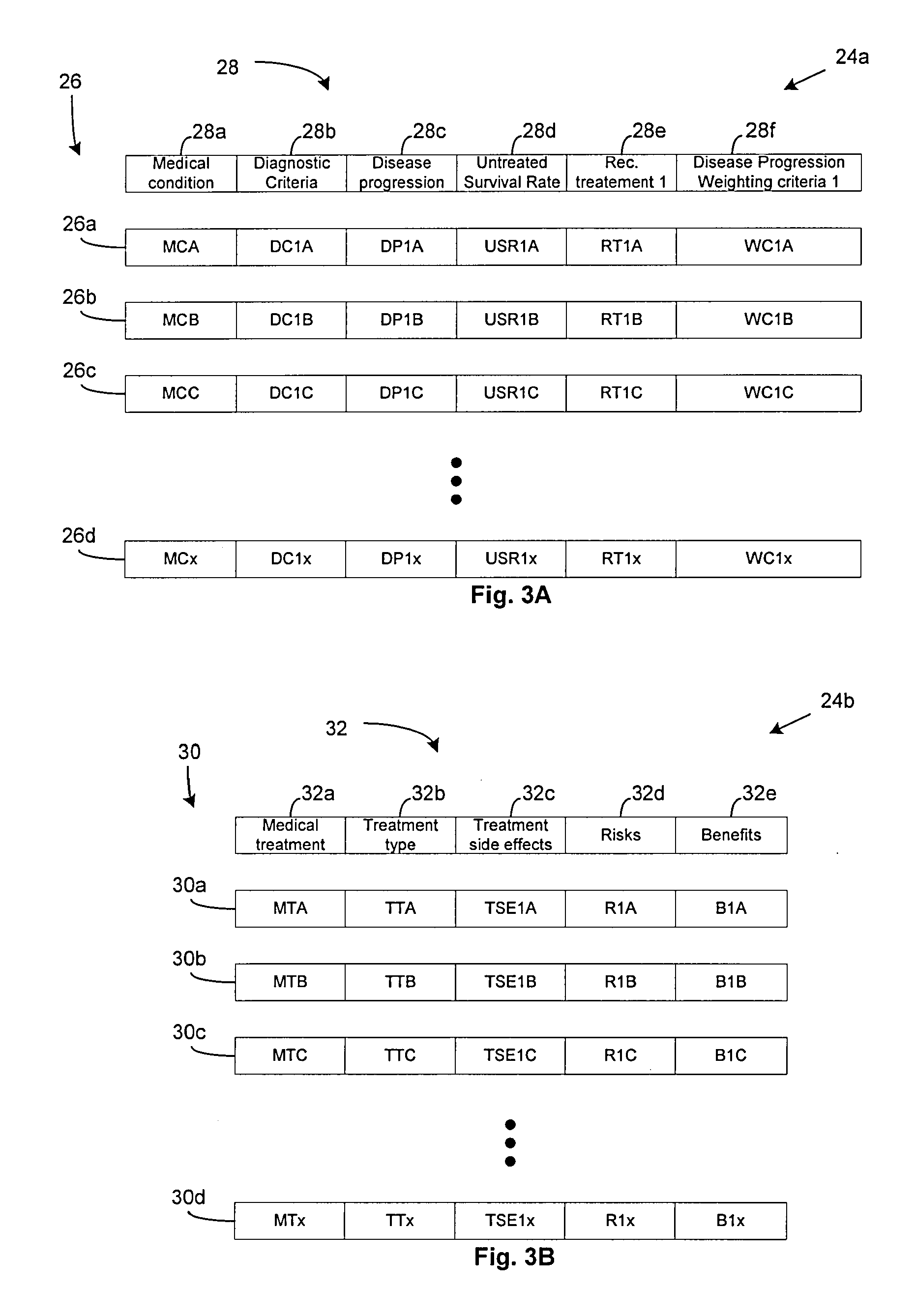
Integrated treatment planning system
A medical treatment planning system includes a computer including a processor and memory, data stored in the memory, said data including a priori of information relating to medical conditions, medical treatments and treatment results, and treatment planning logic stored in the memory and executable by the processor. The treatment planning logic includes logic that obtains pre-treatment patient data describing the patient's medical condition, logic that analyzes the pre-treatment patient data relative to the a priori of information and, based on the analysis, formulates a first treatment plan for treating the patient, and logic that outputs the first treatment plan for evaluation by medical personnel.
Owner:BRAINLAB
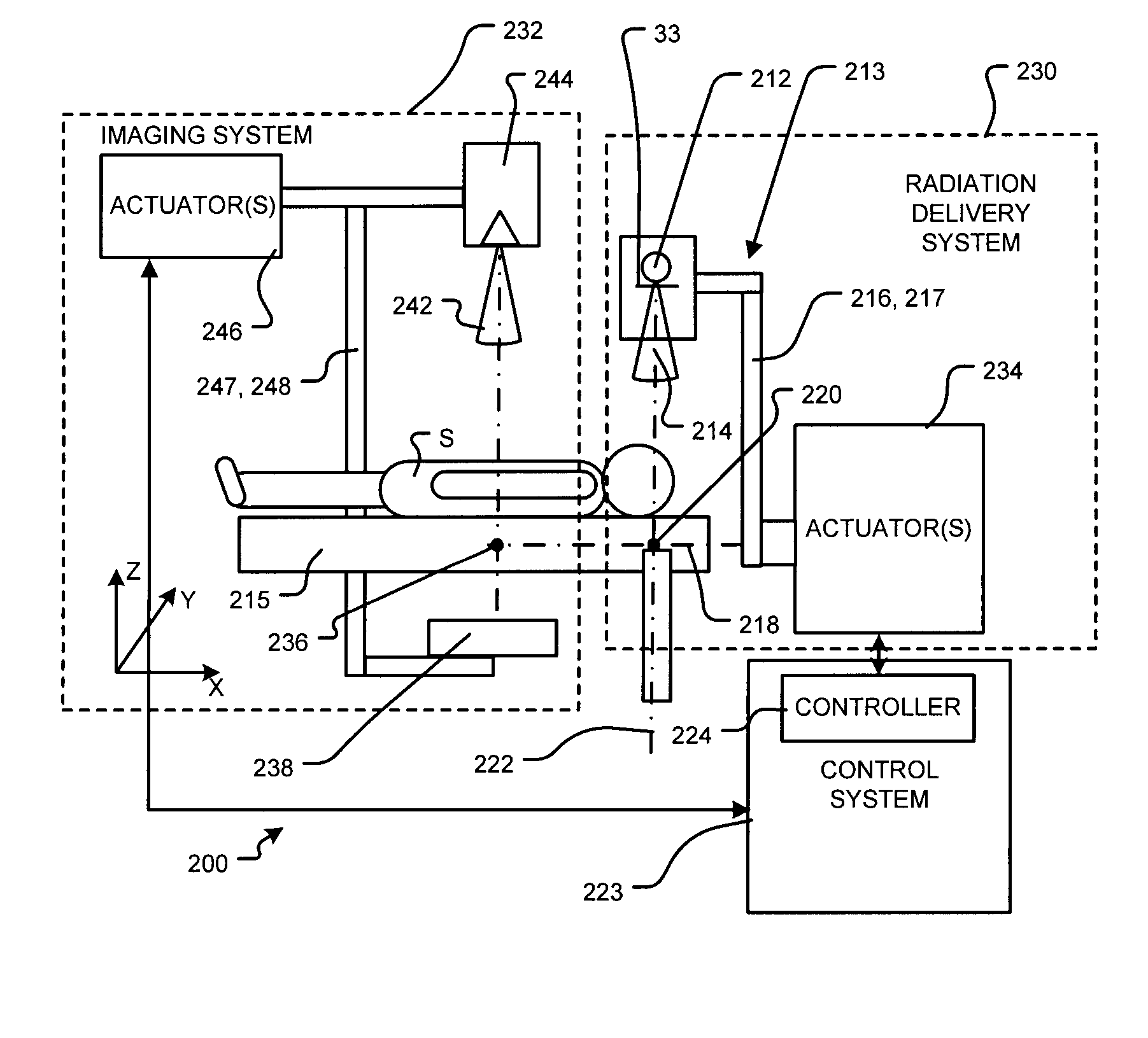
Systems and methods for optimization of on-line adaptive radiation therapy
ActiveUS20100020931A1Sterographic imagingX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiation treatment planningTherapy planning
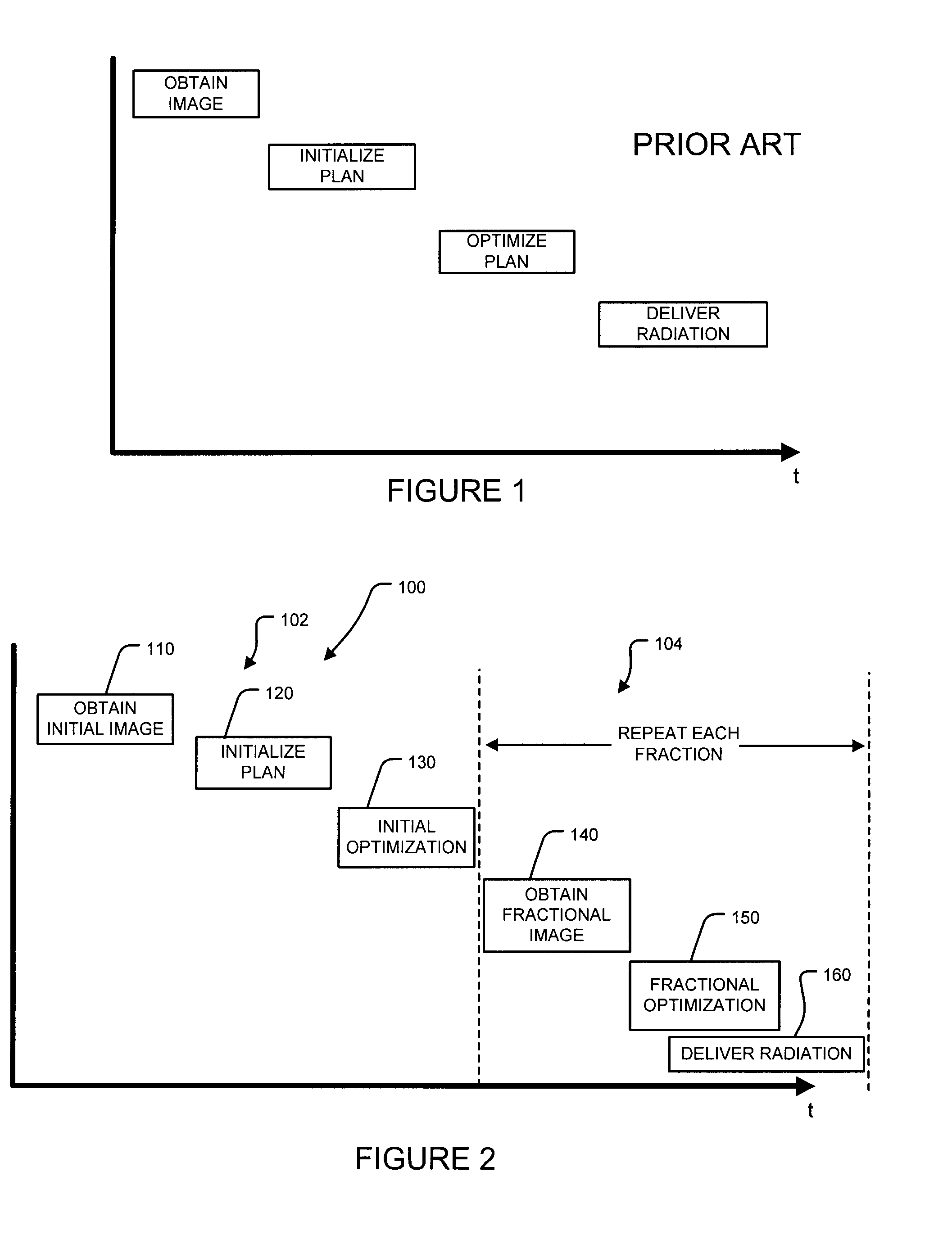
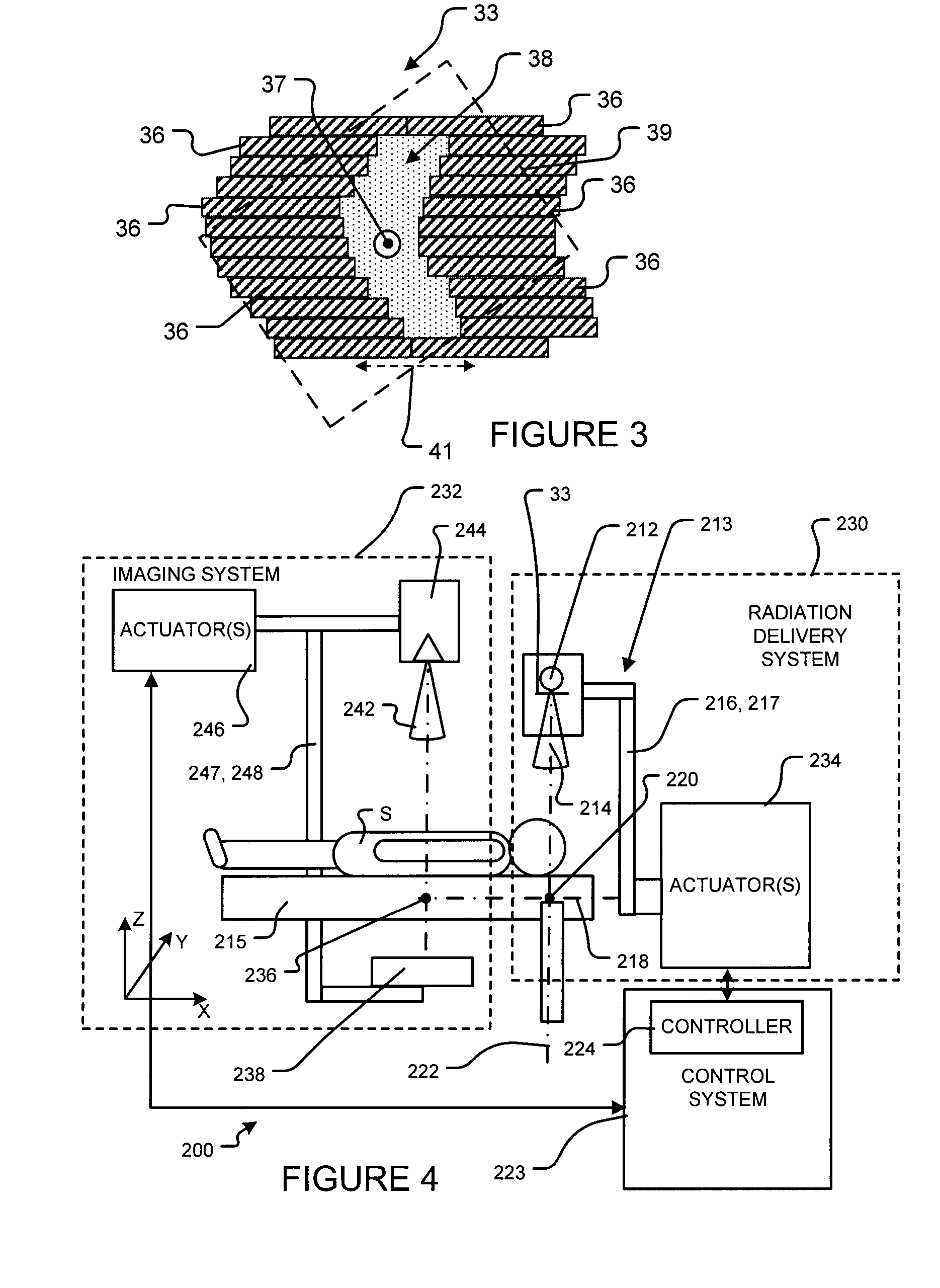
Methods and systems are disclosed for radiation treatment of a subject involving one or more fractional treatments. A fractional treatment comprises: obtaining fractional image data pertaining to a region of interest of the subject; performing a fractional optimization of a radiation treatment plan to determine optimized values of one or more radiation delivery variables based at least in part on the fractional image data; and delivering a fraction of the radiation treatment plan to the region of interest using the optimized values of the one or more radiation delivery variables as one or more corresponding parameters of the radiation treatment plan. A portion of performing the fractional optimization overlaps temporally with a portion of at least one of: obtaining the fractional image data and delivering the fraction of the radiation treatment plan.
Owner:BRITISH COLUMBIA CANCER AGENCY BRANCH
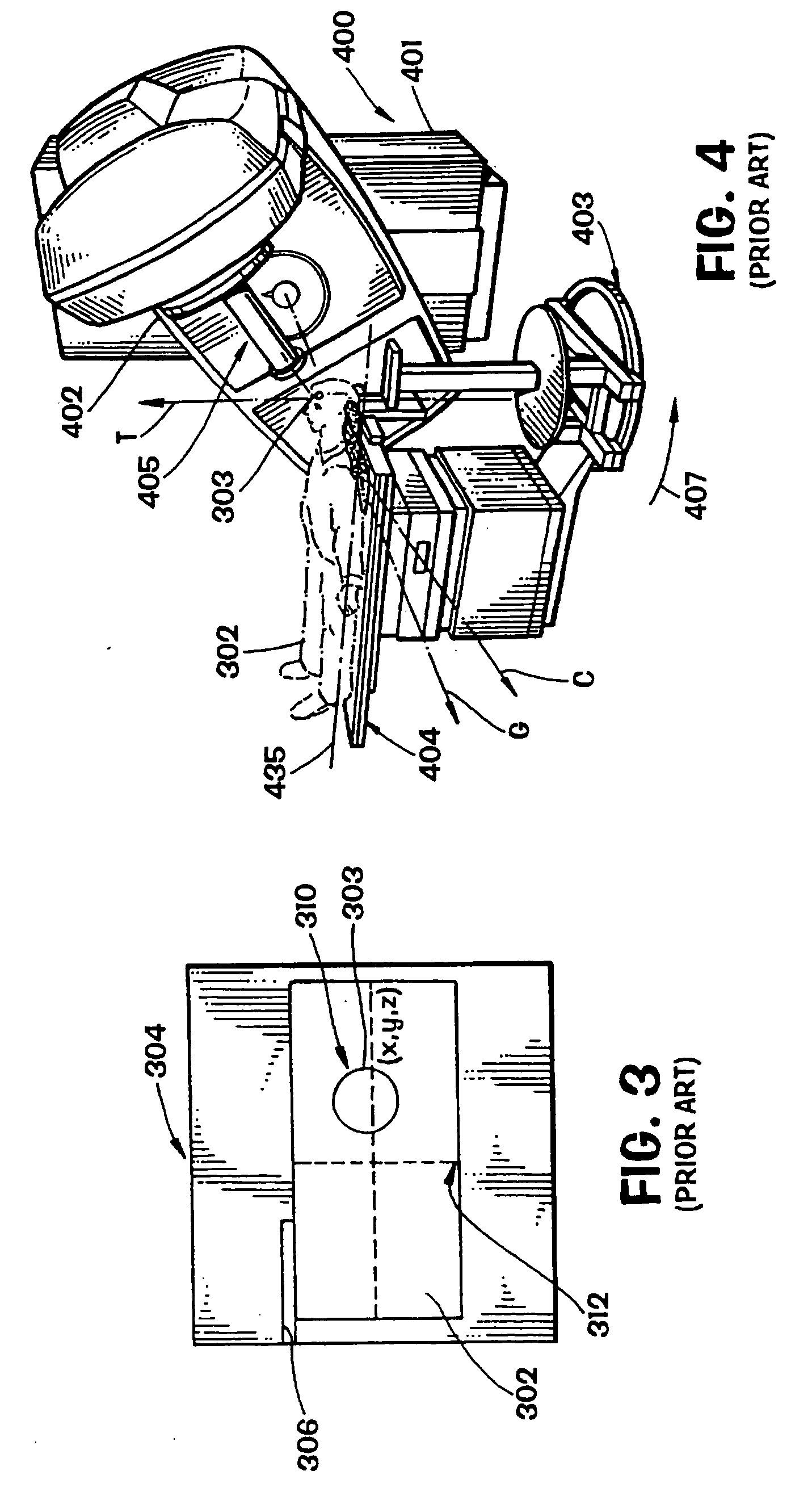
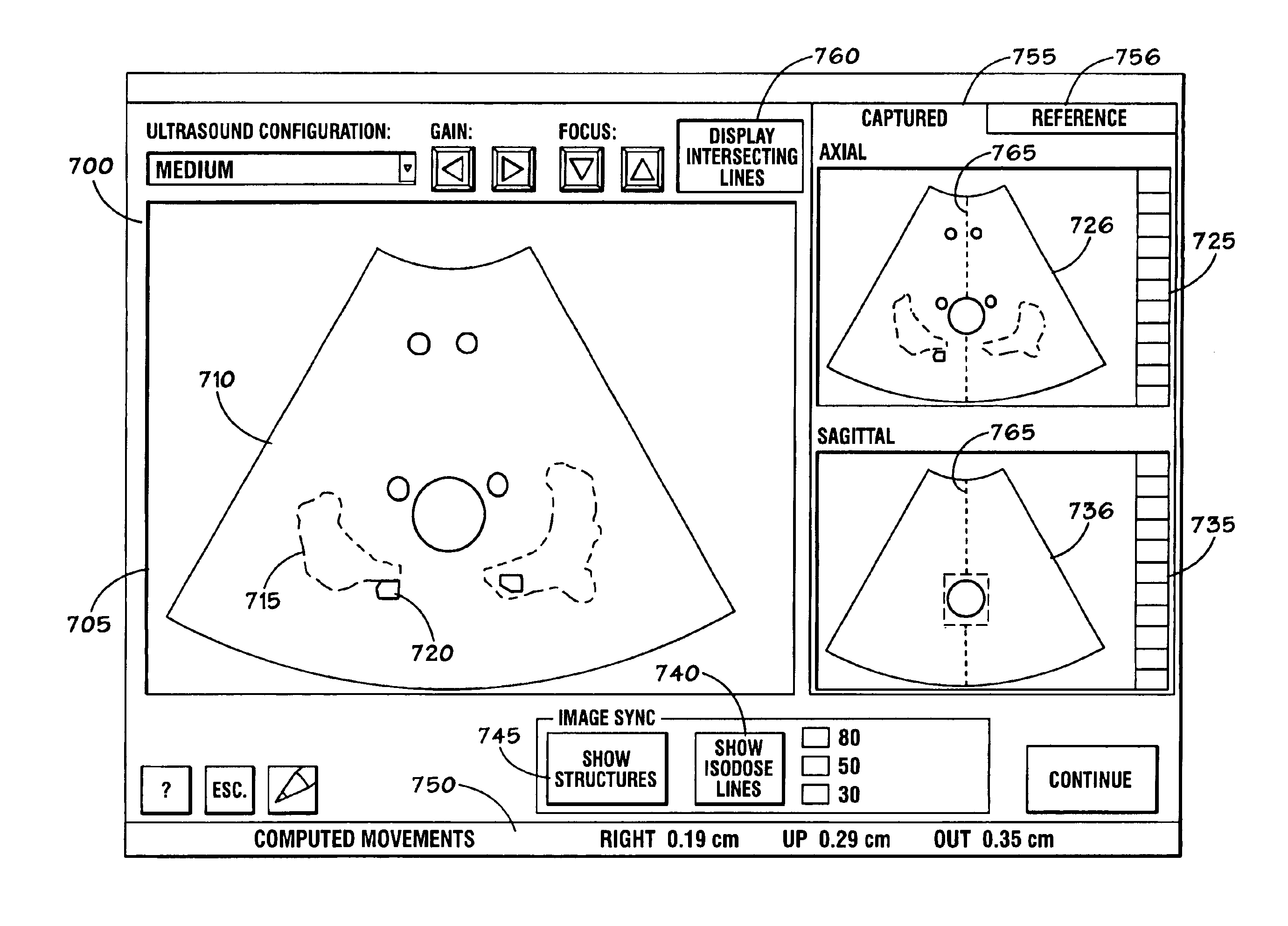
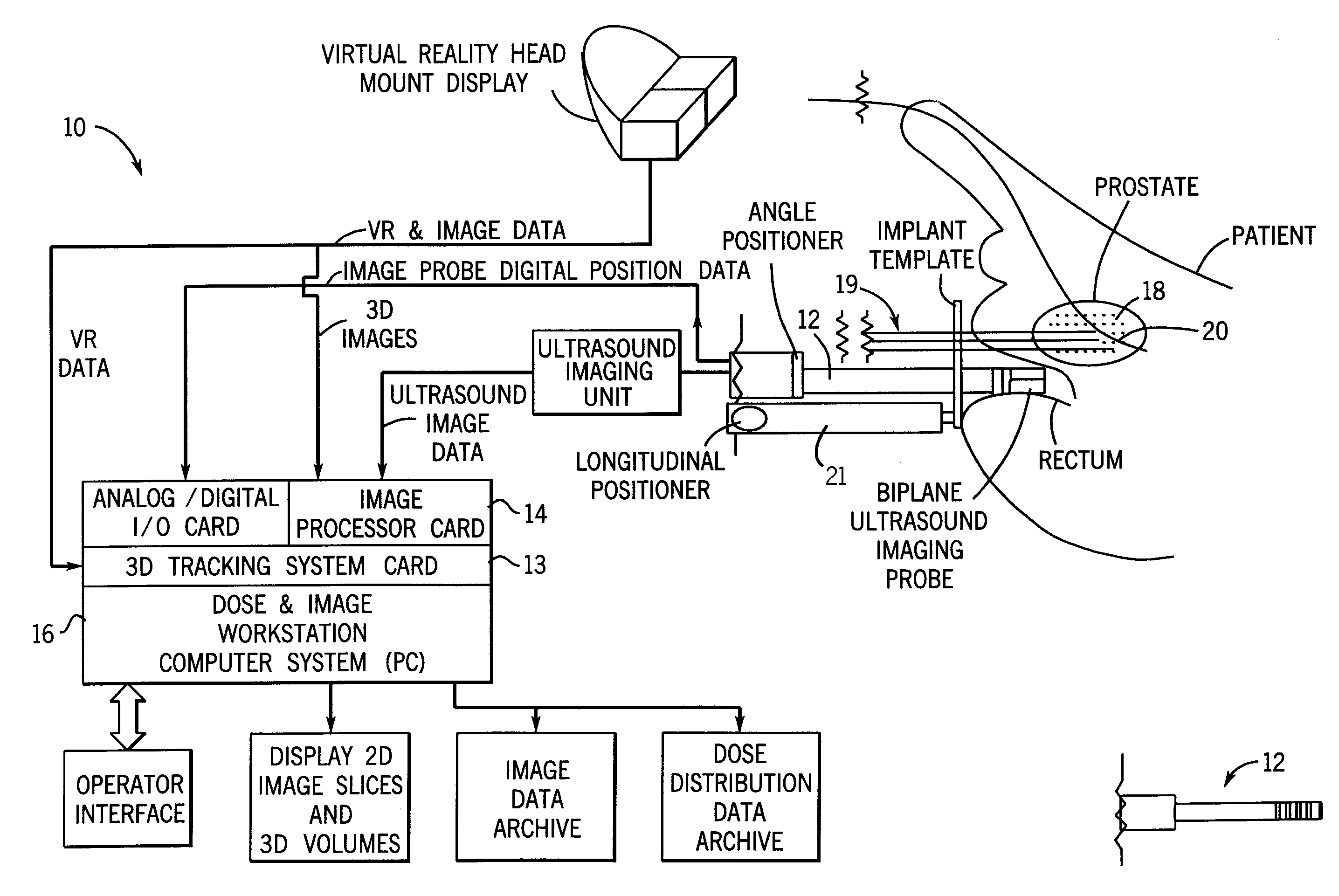
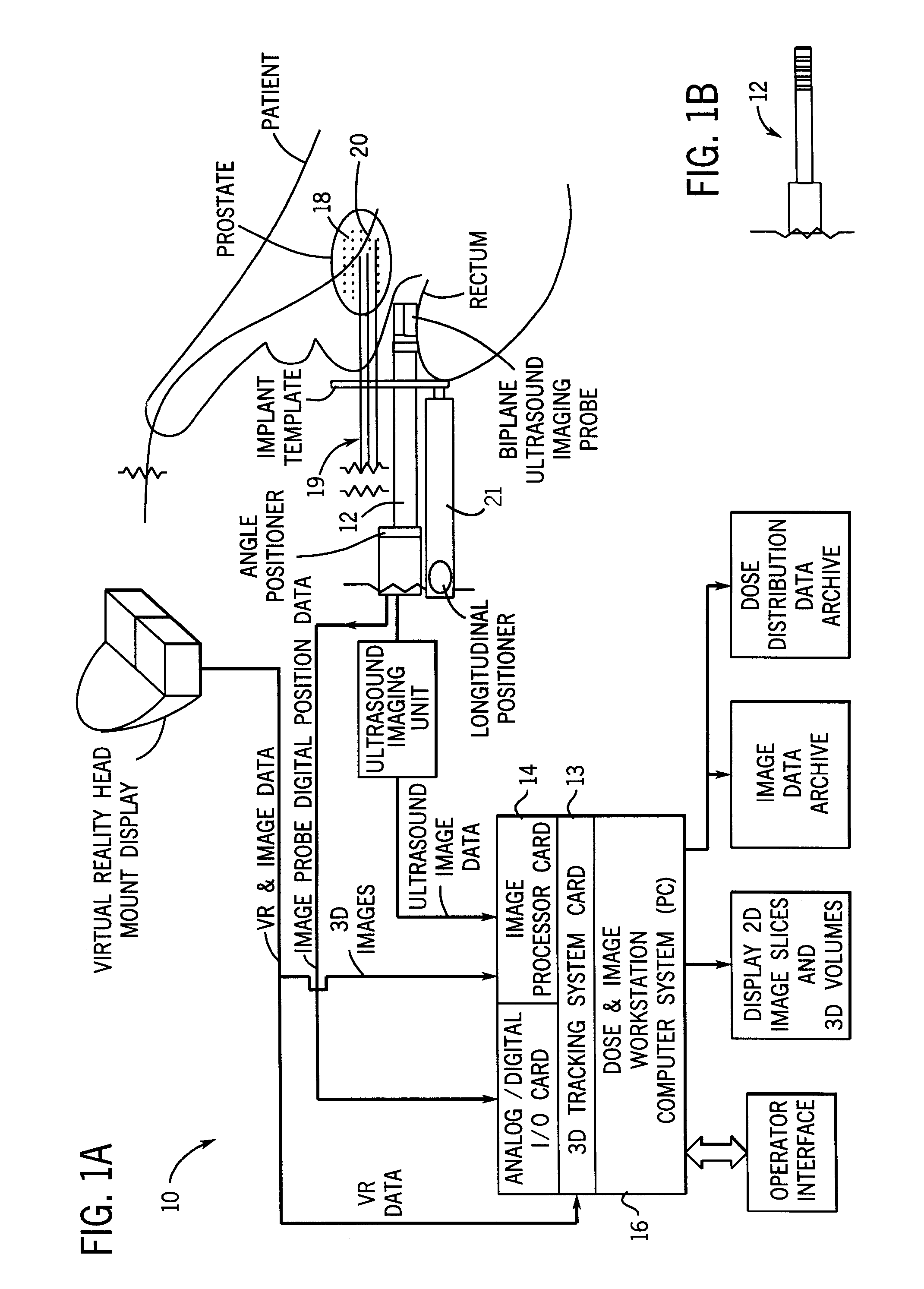
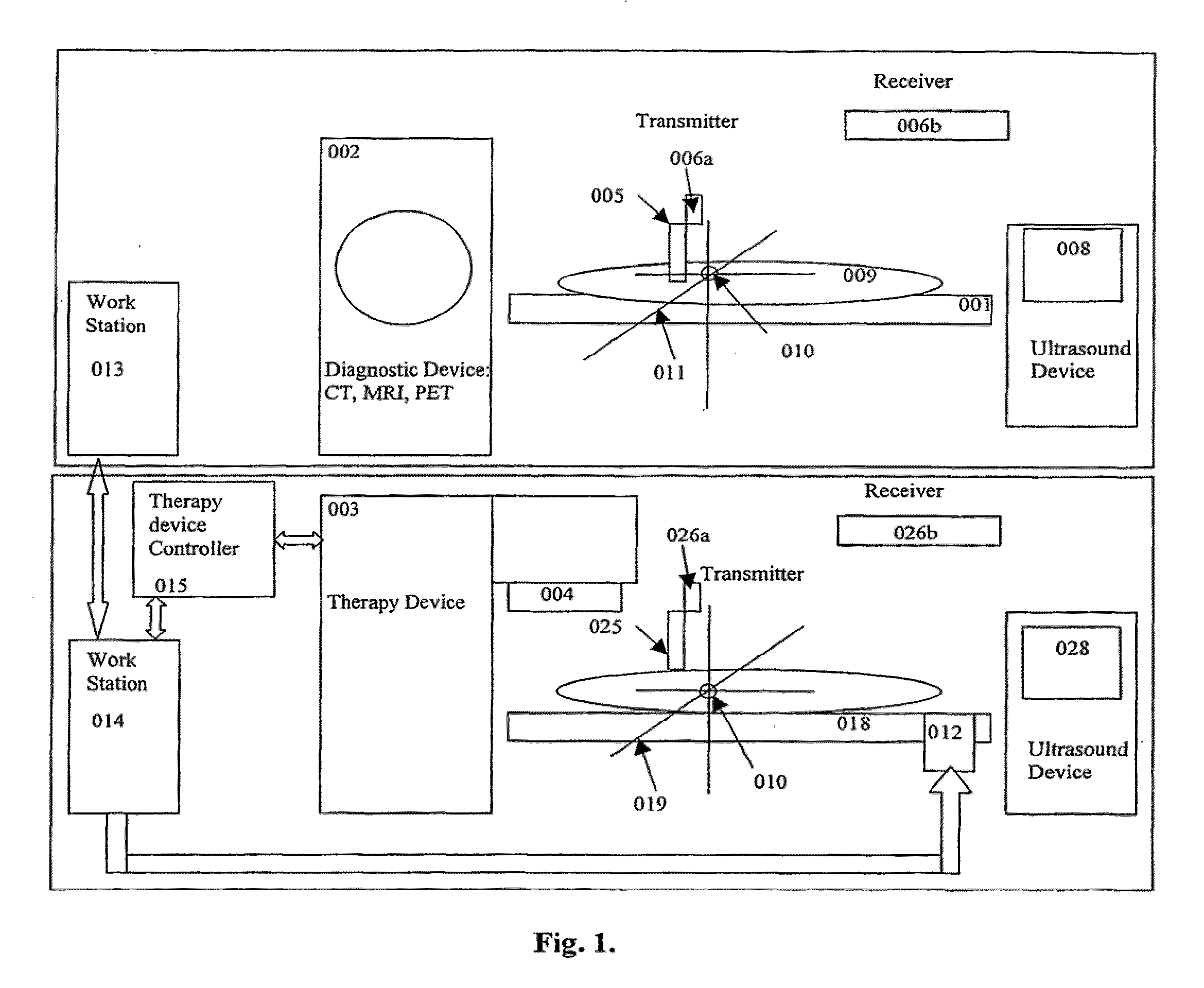
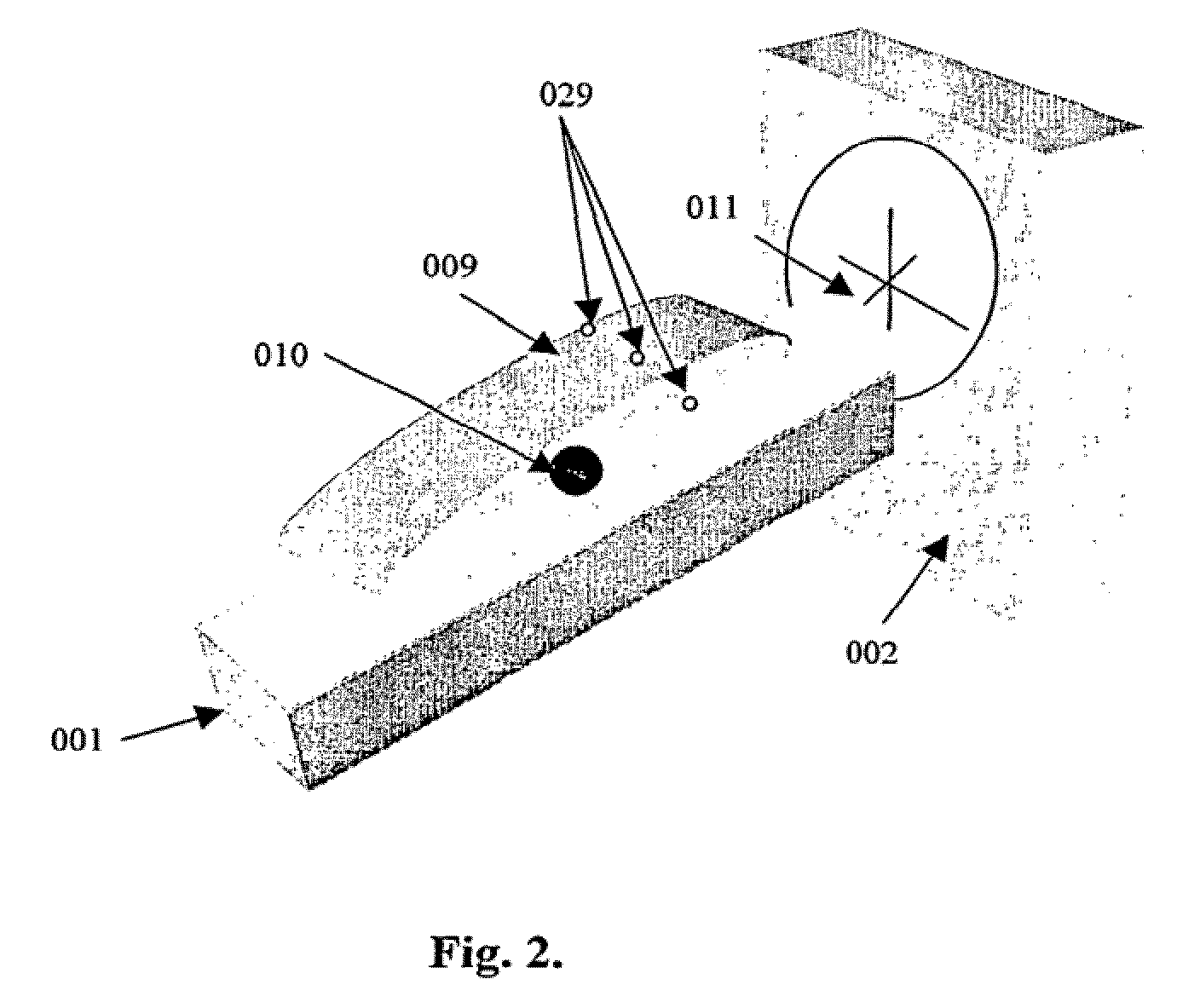
Method and apparatus for target position verification
ActiveUS20050020917A1Avoid problemsOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsRadiation therapyUltrasound probe
A system and method for aligning the position of a target within a body of a patient to a predetermined position used in the development of a radiation treatment plan can include an ultrasound probe used for generating live ultrasound images, a position sensing system for indicating the position of the ultrasound probe with respect to the radiation therapy device, and a computer system. The computer system is used to display the live ultrasound images of a target in association with representations of the radiation treatment plan, to align the displayed representations of the radiation treatment plan with the displayed live ultrasound images, to capture and store at least two two-dimensional ultrasound images of the target overlaid with the aligned representations of the treatment plan data, and to determine the difference between the location of the target in the ultrasound images and the location of the target in the representations of the radiation treatment plan.
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
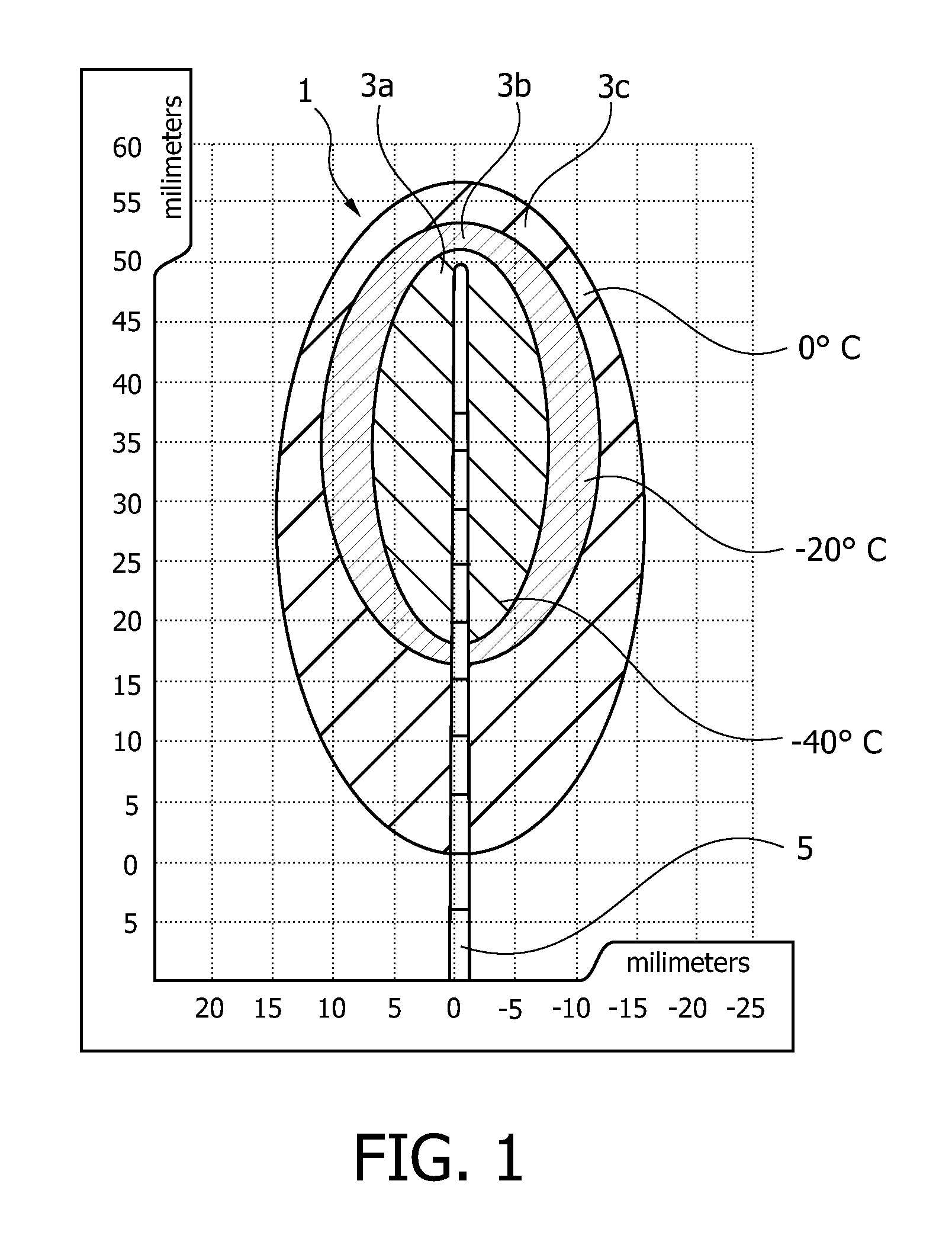
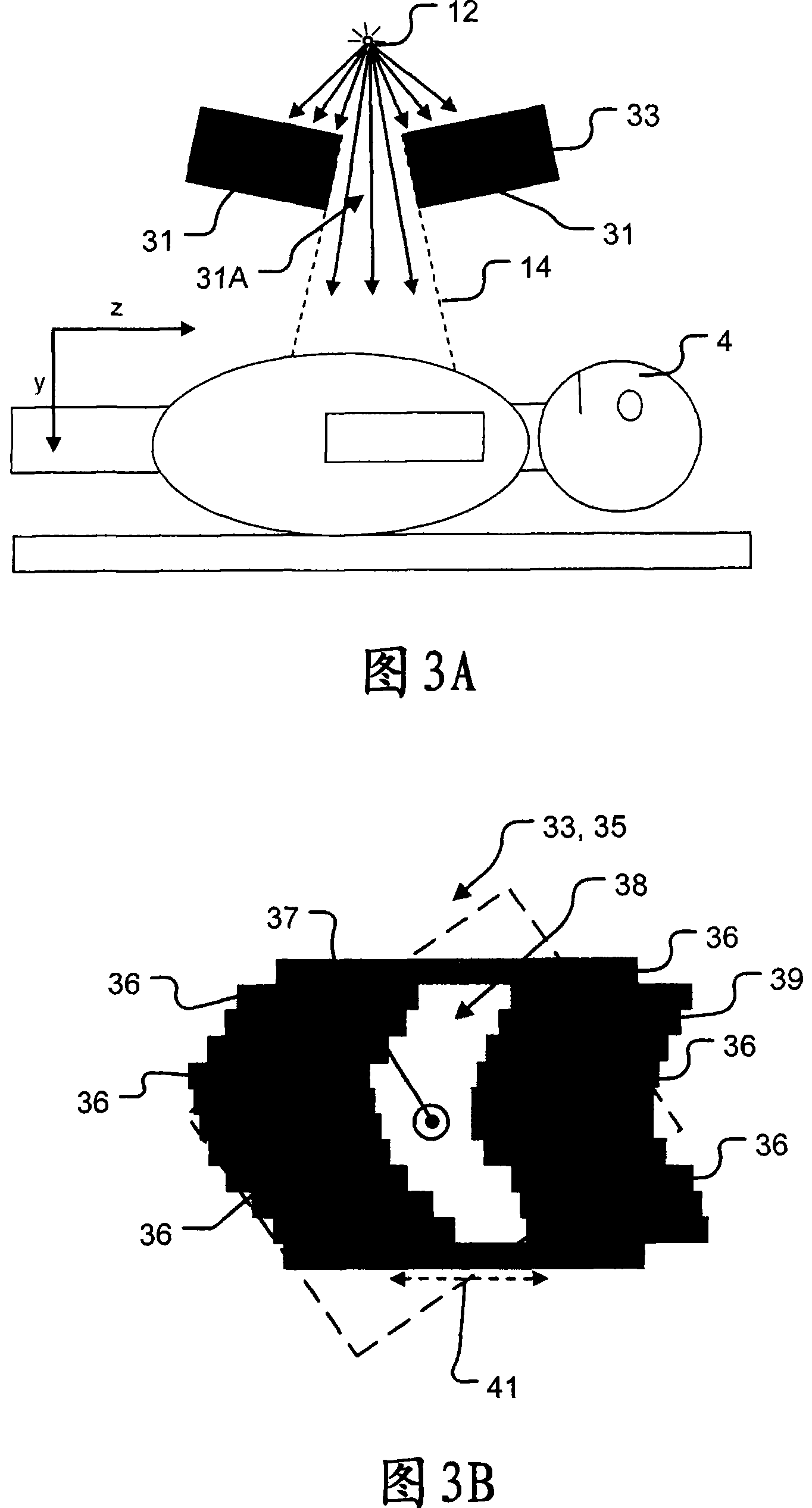
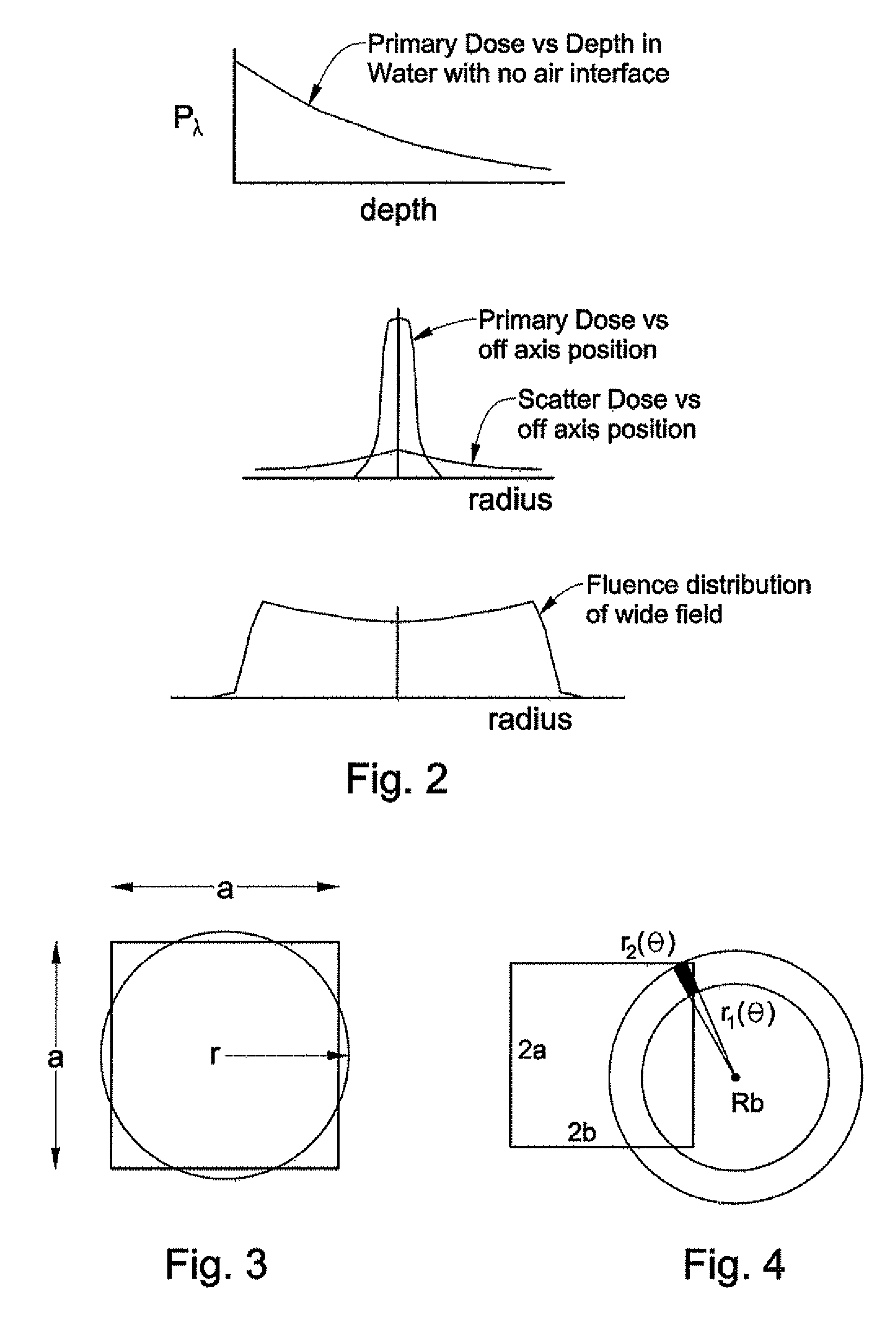
Phantom for evaluating nondosimetric functions in a multi-leaf collimated radiation treatment planning system
InactiveUS20050013406A1Enhance the imageInstrumentsRadiation diagnosticsEngineeringRadiation treatment planning
A phantom for evaluating nondosimetric functions in radiation therapy installation having a patient couch and a gantry with a head thereon for generating a multi-leaf collimated beam, wherein the beam is directed toward the couch at an orientation dictated by relative orientations of the couch and gantry. The phantom comprises a base adapted for disposition on the couch, and a component mounted to the base for rotation in accordance with the relative orientations of the couch and gantry. The component incorporates a plurality of known geometrical structures corresponding in shape to the multi-leaf collimated beam. Upon imaging the component, nondosimetric functions may be evaluated by comparing the known geometrical structures with images of the structures and identifying discrepancies therebetween.
Owner:CANCER CARE ONTARIO
Method and apparatus for target position verification
ActiveUS6961405B2Avoid problemsOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryComputerized systemRadiation treatment planning
A system and method for aligning the position of a target within a body of a patient to a predetermined position used in the development of a radiation treatment plan can include an ultrasound probe used for generating live ultrasound images, a position sensing system for indicating the position of the ultrasound probe with respect to the radiation therapy device, and a computer system. The computer system is used to display the live ultrasound images of a target in association with representations of the radiation treatment plan, to align the displayed representations of the radiation treatment plan with the displayed live ultrasound images, to capture and store at least two two-dimensional ultrasound images of the target overlaid with the aligned representations of the treatment plan data, and to determine the difference between the location of the target in the ultrasound images and the location of the target in the representations of the radiation treatment plan.
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
Automatic treatment planning
Orthodontic and / or dental treatment planning methods and apparatuses. In particular, described herein are methods of generating a plurality of potential treatment plan variations for the concurrent and interactive review of the treatment plan variations. Each variation may be optimized to best address the user's treatment goals, as well as approximating as closely as possible an ideal or target final position. Also described herein are orthodontic and / or dental treatment planning methods and apparatuses that allow a user to form, modify, and select a treatment plan from a plurality of different treatment plans, in real time.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
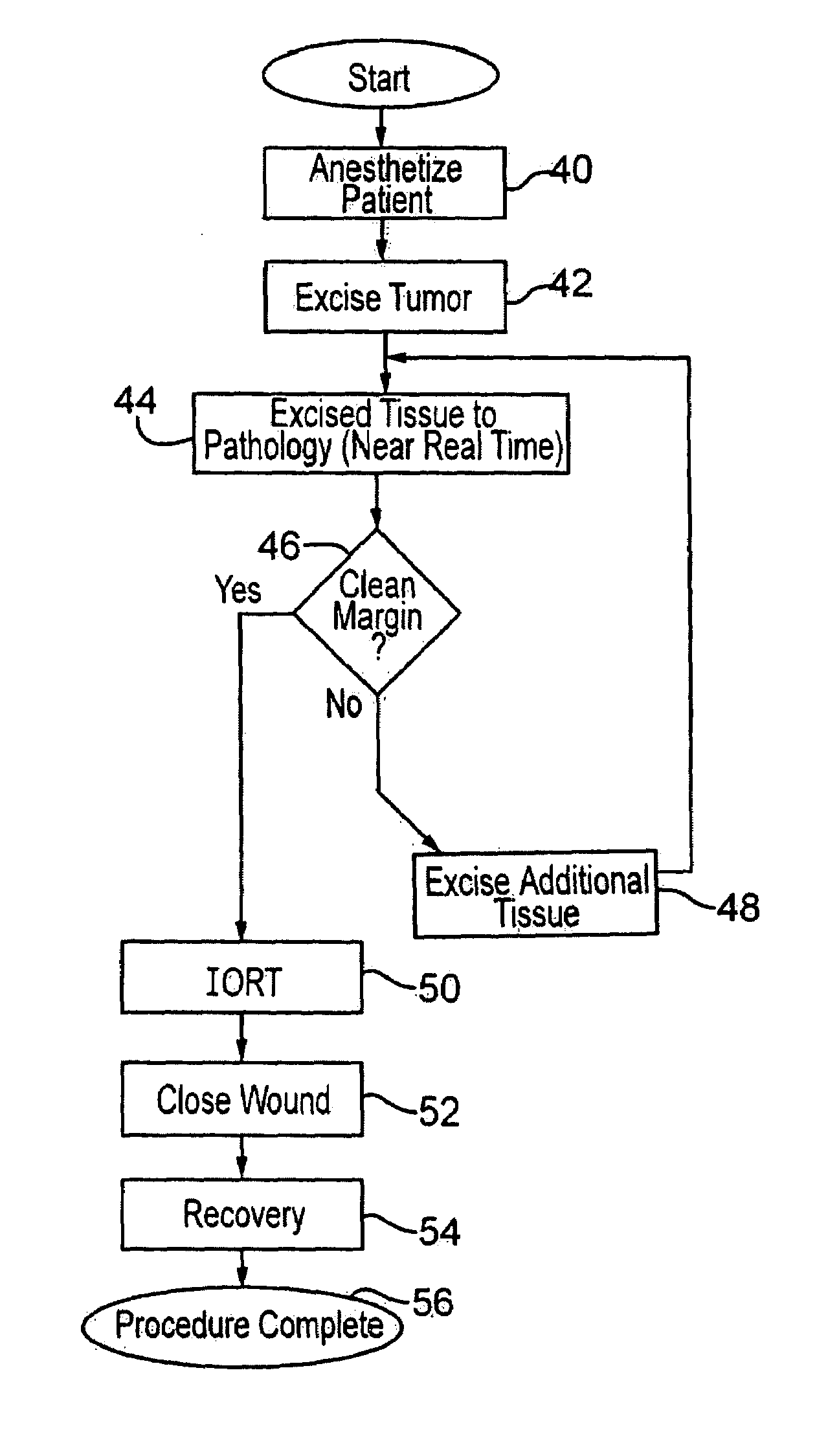
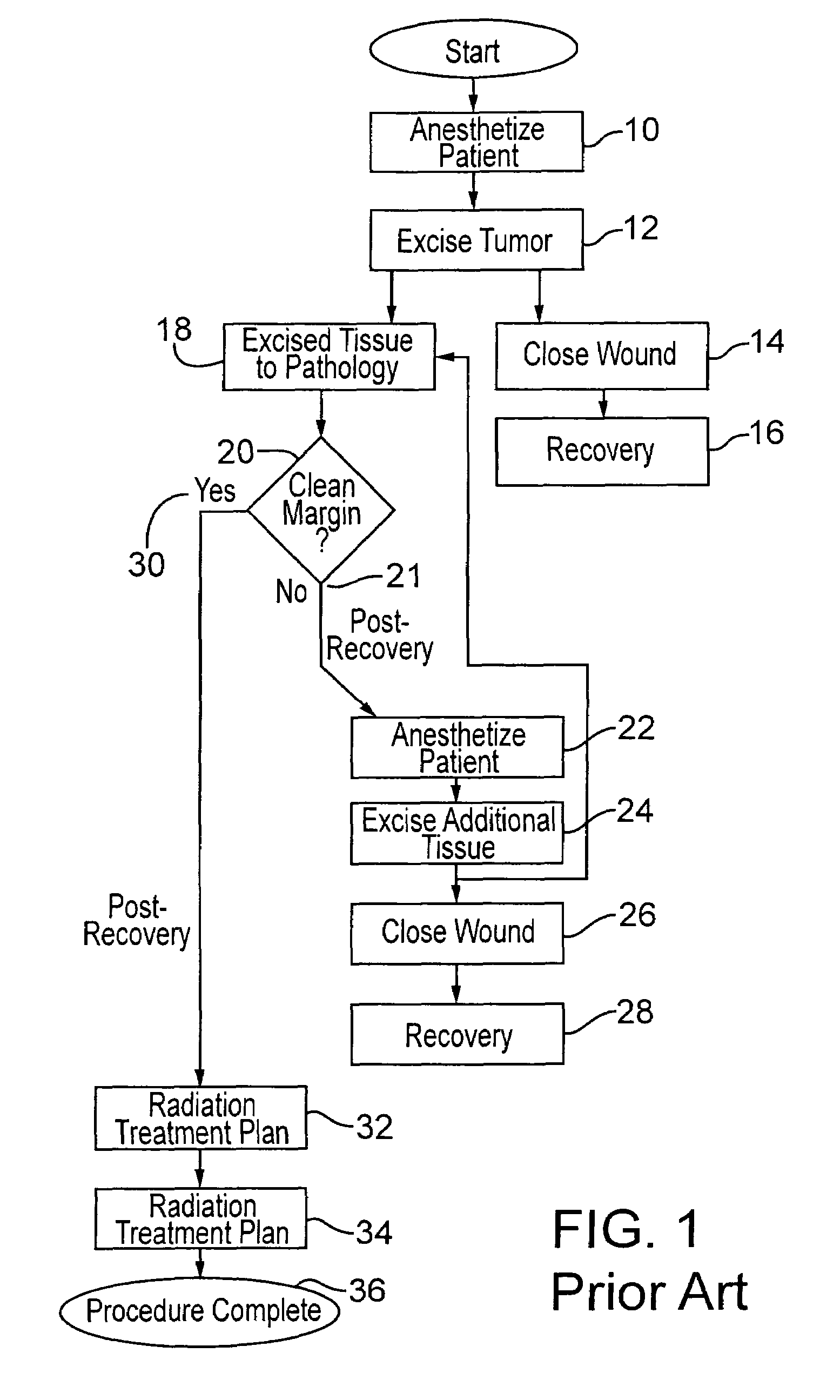
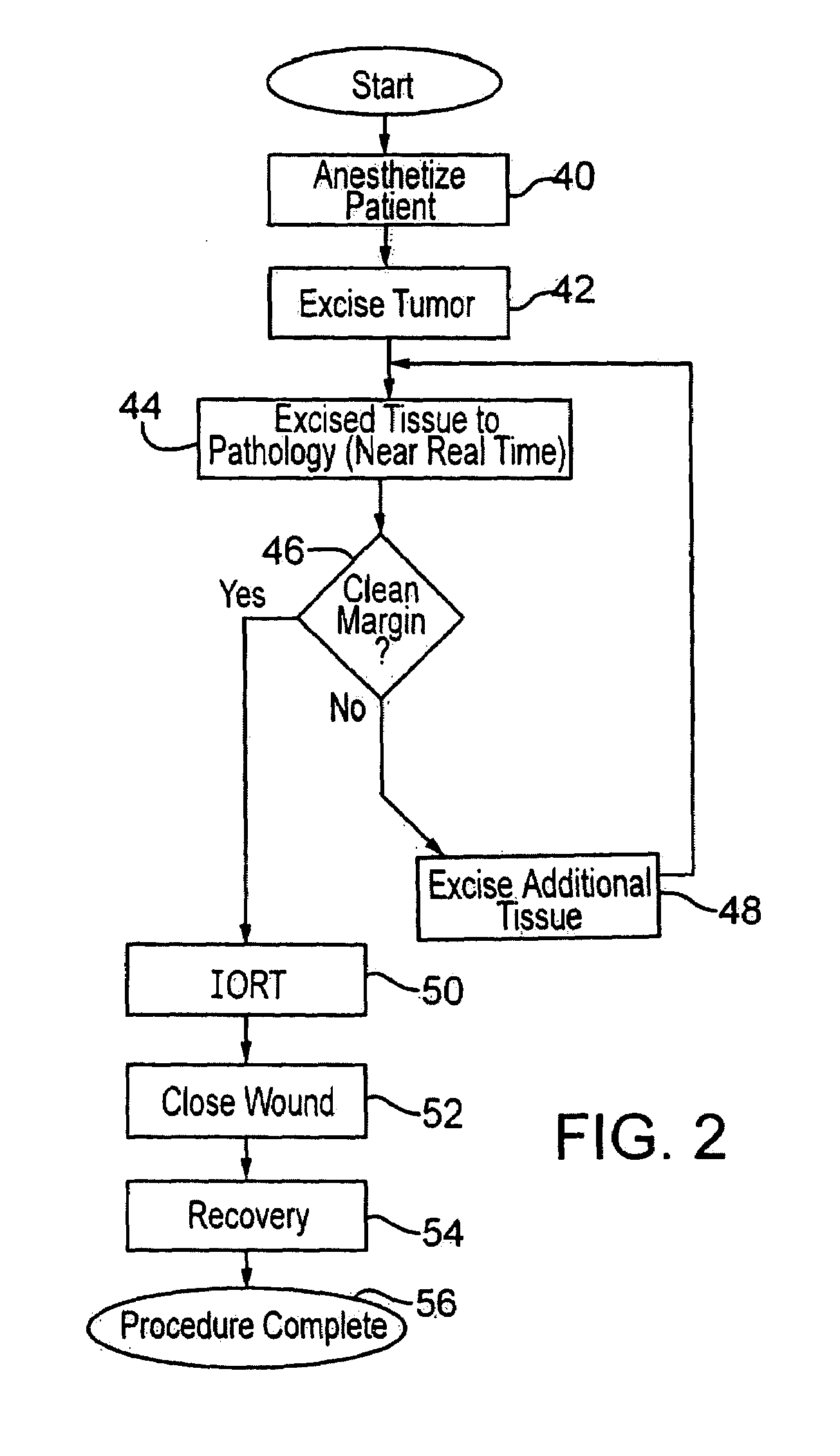
Method for radiation treatment
InactiveUS7322929B2Reduce penetration depthEnsure correct executionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTumor removalRadical radiotherapy
Breast cancer patients are treated intraoperatively with radiation shortly after excision of a tumor. Pathology of the tissue is determined with a nearly instantaneous method, further excision is performed if needed, and the patient, still anesthetized and preferably unmoved, is then treated with radiation therapy. In a preferred embodiment an applicator is inserted into the excision cavity, the cavity is three-dimensionally mapped using radiation sources and a sensor, a radiation treatment plan is developed using a radiation prescription and the determined shape and location of the cavity, and the treatment plan is executed, all while the patient remains under anesthesia.
Owner:XOFT INC
Radiation treatment planning and delivery for moving targets in the heart
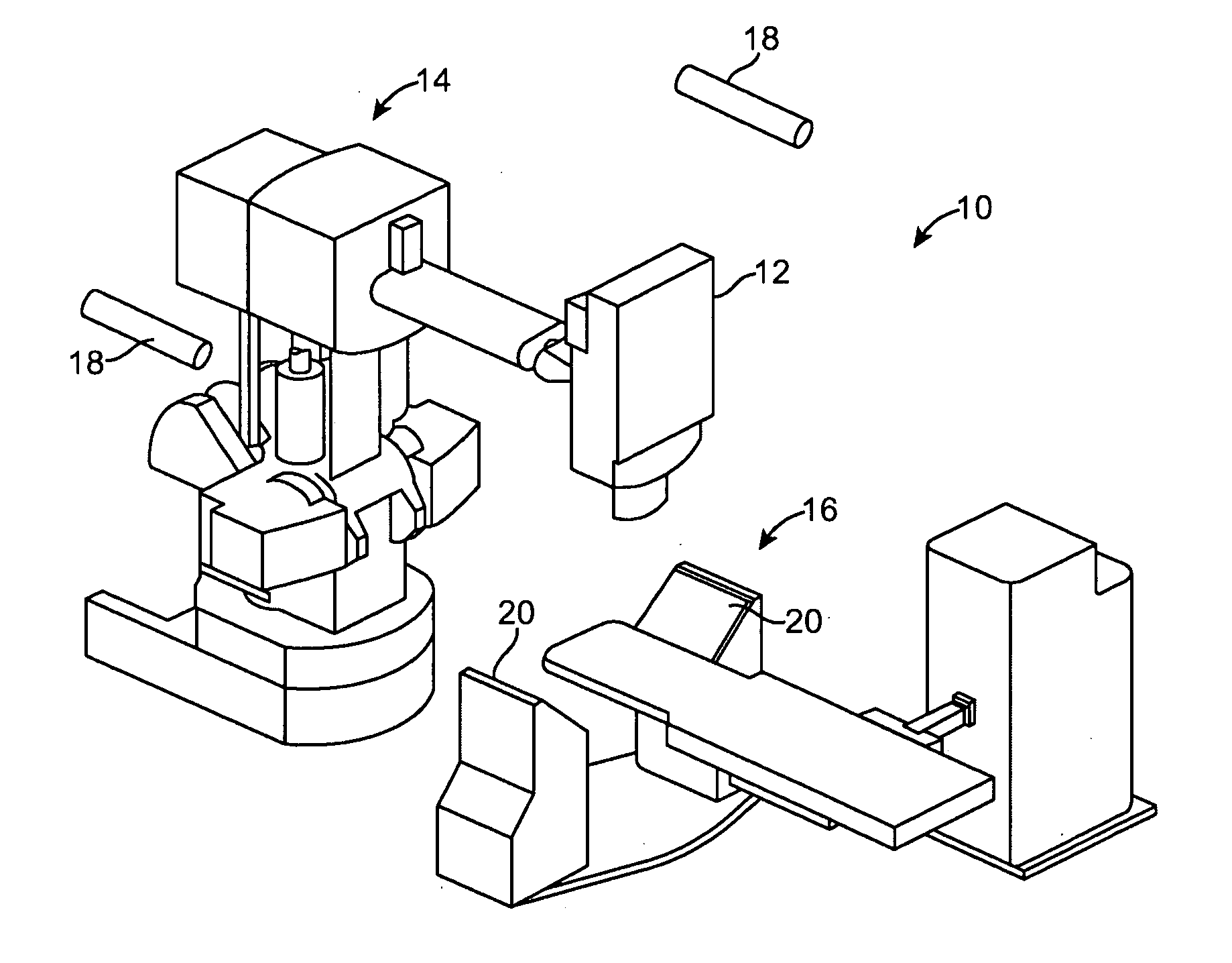
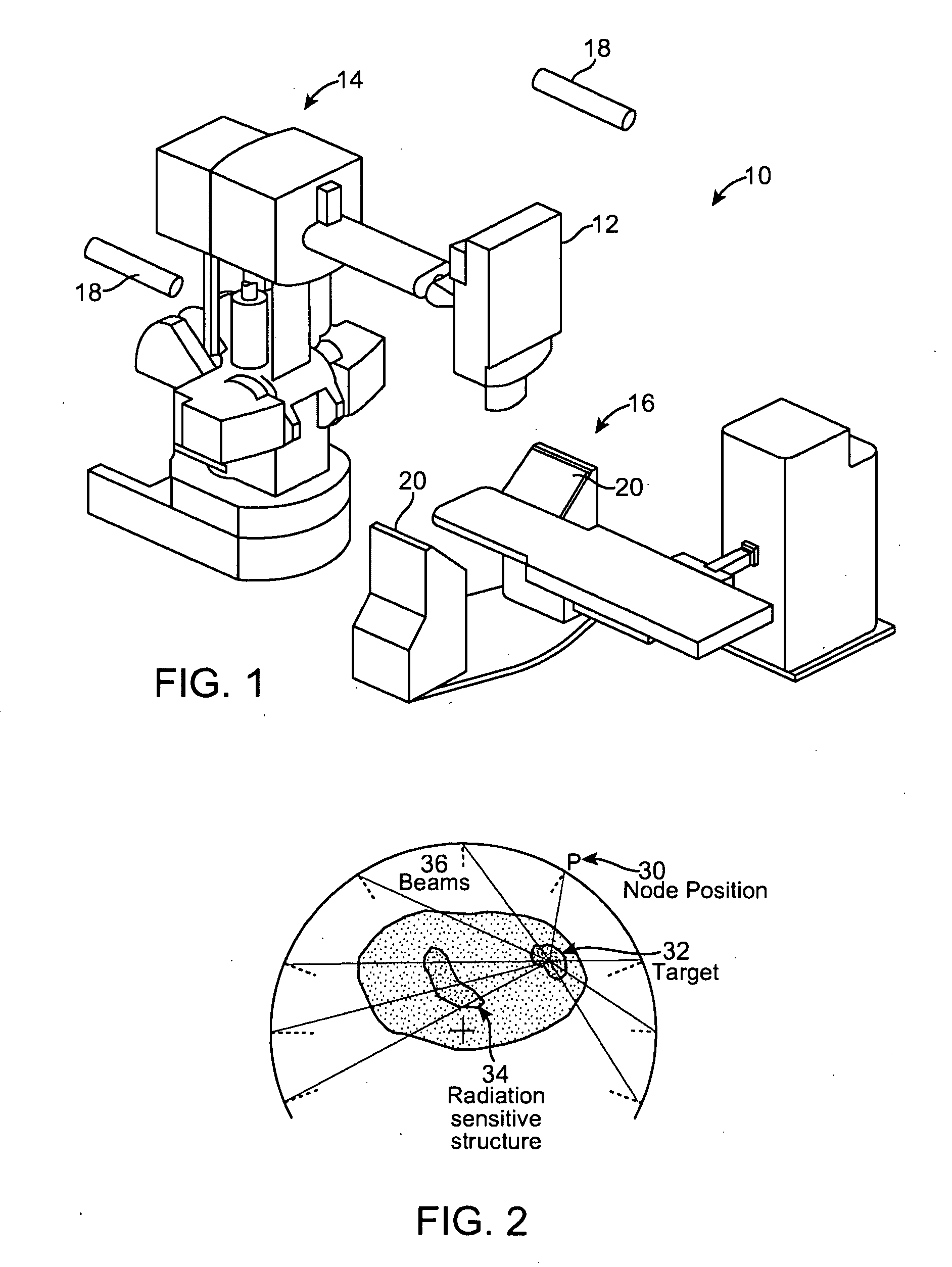
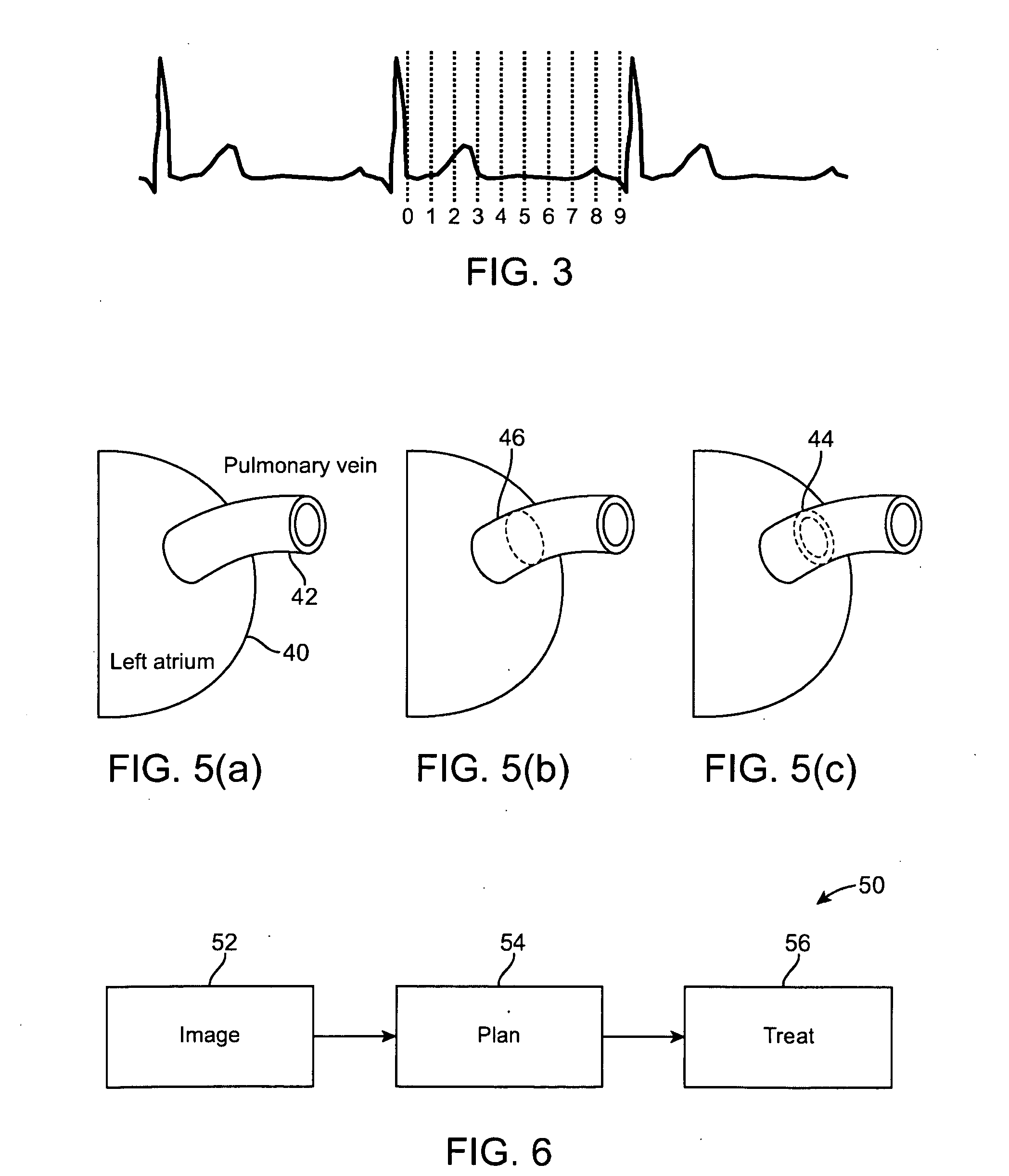
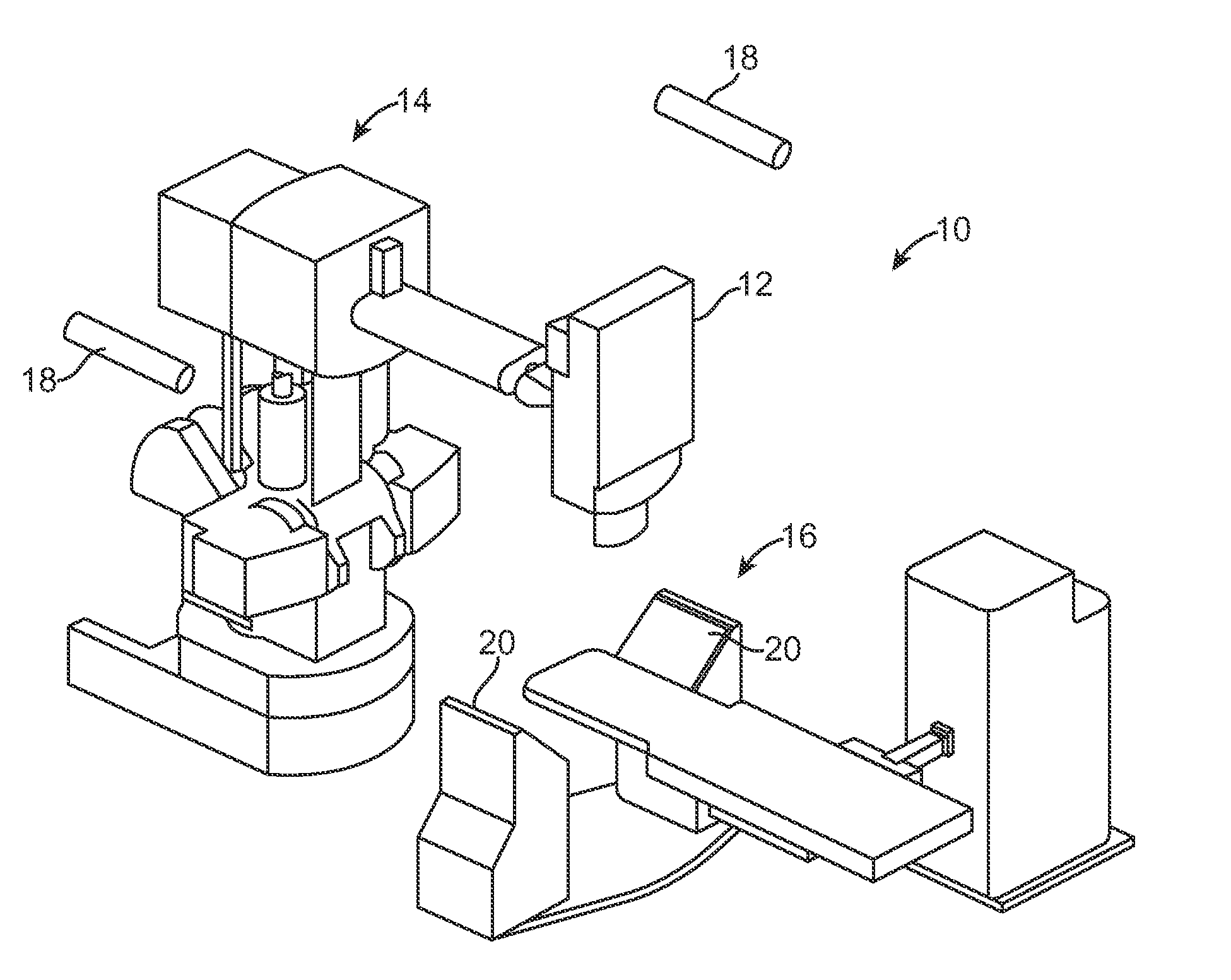
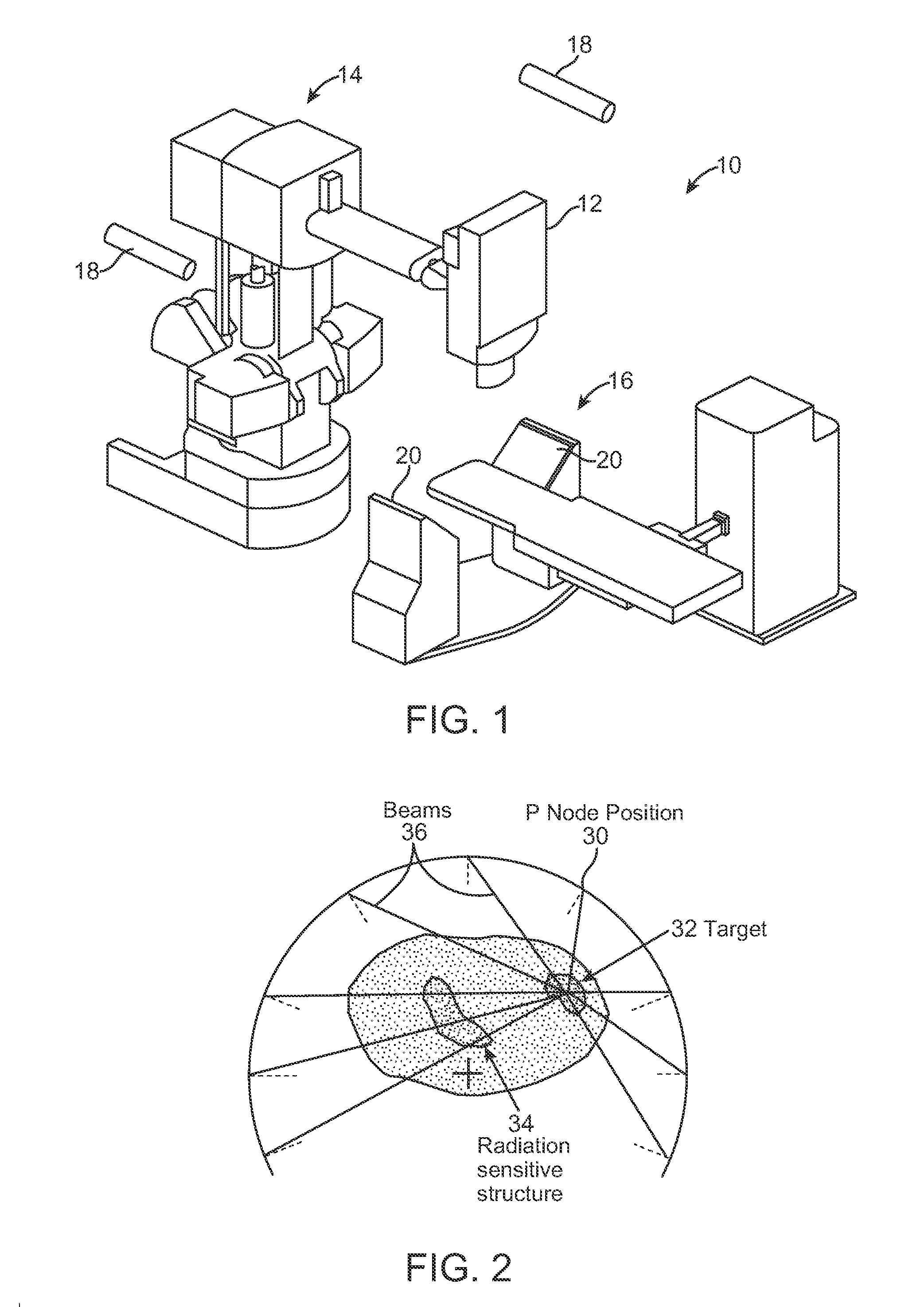
InactiveUS20080317204A1Improved radiosurgical treatment of tissueReduce arrhythmiaElectrocardiographyTomographyRadiation treatment planningTarget tissue
Method and systems are disclosed for radiating a moving target inside a heart. The method includes acquiring sequential volumetric representations of an area of the heart and defining a target tissue region and / or a radiation sensitive structure region in 3D for a first of the representations. The target tissue region and / or radiation sensitive structure region are identified for another of the representations by an analysis of the area of the heart from the first representation and the other representation. Radiation beams to the target tissue region are fired in response to the identified target tissue region and / or radiation sensitive structure region from the other representation.
Owner:CYBERHEART
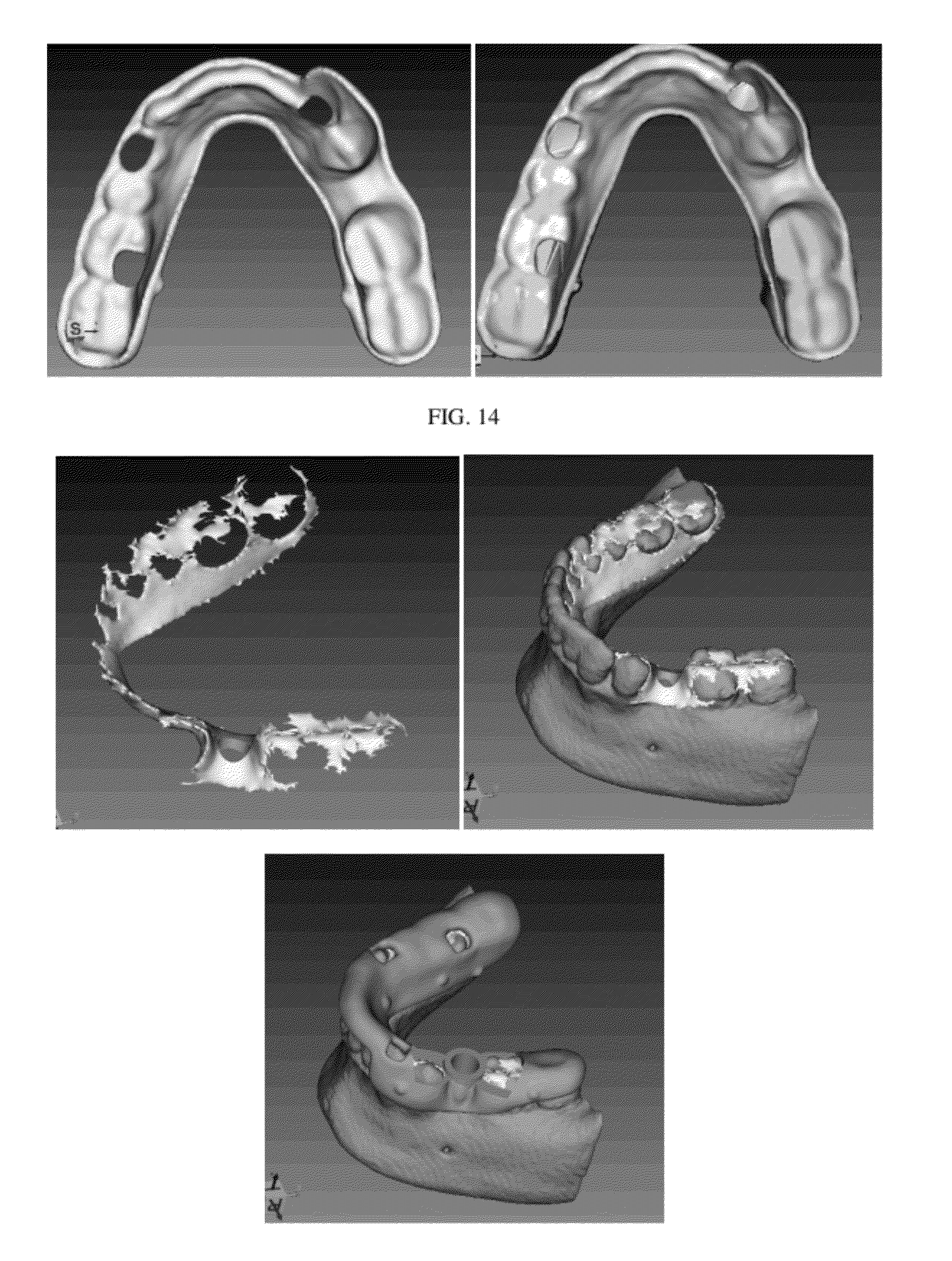
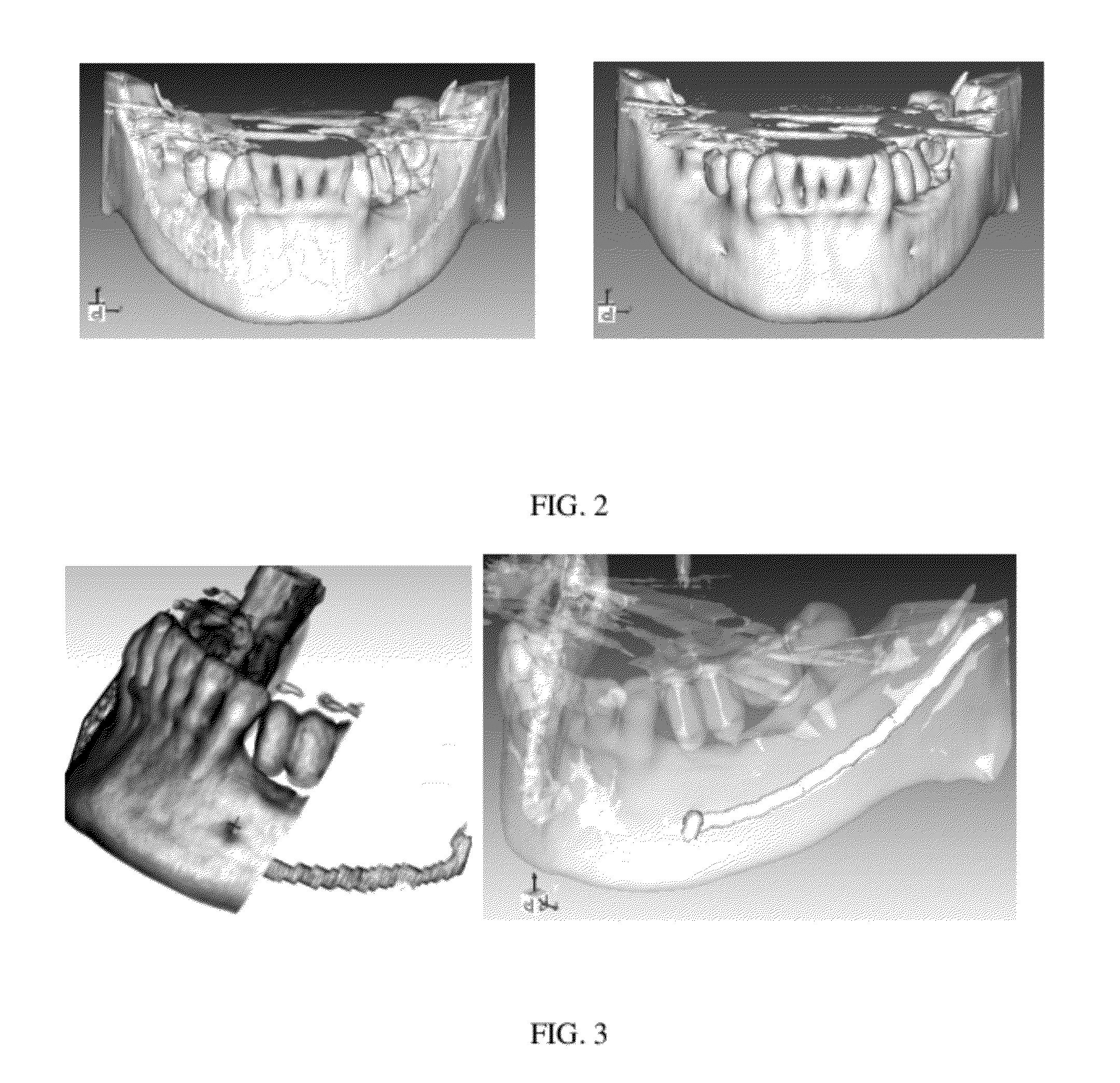
Hybrid method for dental implant treatment planning
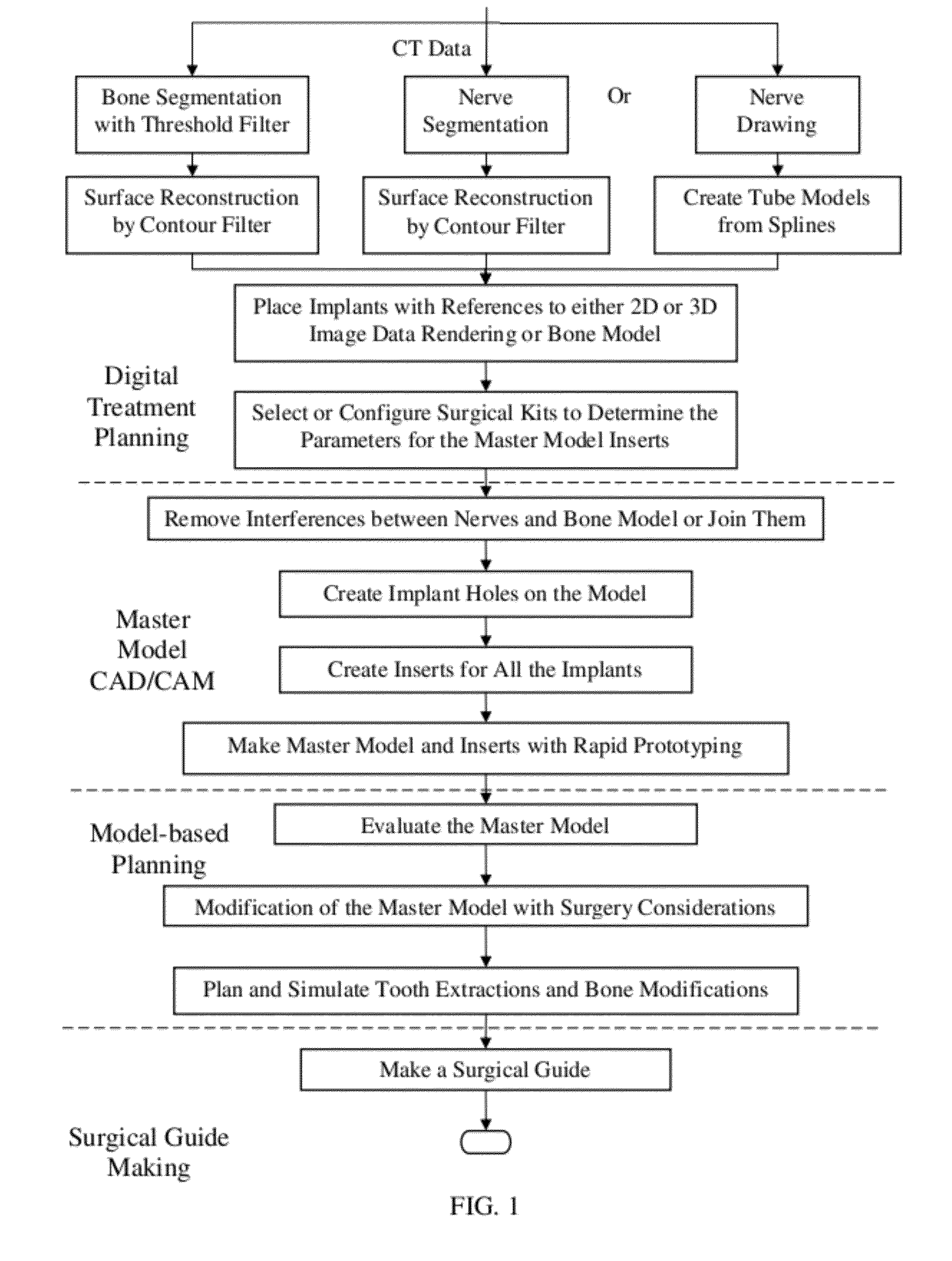
InactiveUS20120046914A1Fast technologyDental implantsAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical operationAnatomical structures
A hybrid method for dental implant treatment planning and a corresponding approach to make a surgical guide. After digital treatment planning is performed with CT scan data, a master model is created, which embodies the patient anatomy and entire treatment plan. Jaw bone, tooth surfaces, soft tissues and nerves are all contained by the master model. The plan details including implant sizes and positions, surgical guide drill options, as well as the choice of a surgical kit, are all conveyed by the master model. Meanwhile, models of specially designed “implant inserts (or replicas)” are also generated, which have one end that fits into the implant holes on the master model and another end to make the surgical guide. The master model and inserts are manufactured with rapid prototyping technology. A surgical guide is later on made from them with conventional lab processes. A main characteristic of this approach is that the master model and the inserts are the physical embodiment of a virtual treatment plan. With them, the surgeons can continue the treatment planning for operations like tooth extractions and bone modifications before making the surgical guides. Therefore the treatment planning workflow is a combination of digital treatment planning and a physical model based planning, in other words, a hybrid approach. A differentiator in this invention is the generation of a closed solid model of the soft tissue, as part of the master model, from the scan data. This approach can be applied to create both bone-borne and tissue-borne surgical guides with low cost process, which is a big advantage over other approaches.
Owner:GAO FEI
Producing a radiation treatment plan
ActiveUS7920675B2Improve the level ofLose weightX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPlan treatmentVolumetric Mass Density
The present embodiments relate to producing a radiation treatment plan. In one embodiment, the method may include specifying a dataset in which an object requiring to be irradiated is represented; determining a target volume requiring to be irradiated within the object; ascertaining a metric identifying a density heterogeneity for a region that will be struck by the planned treatment beam; and determining as a function of the ascertained metric a safety margin for the target volume requiring to be irradiated.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST PARTICLE THERAPY GMBH & CO KG
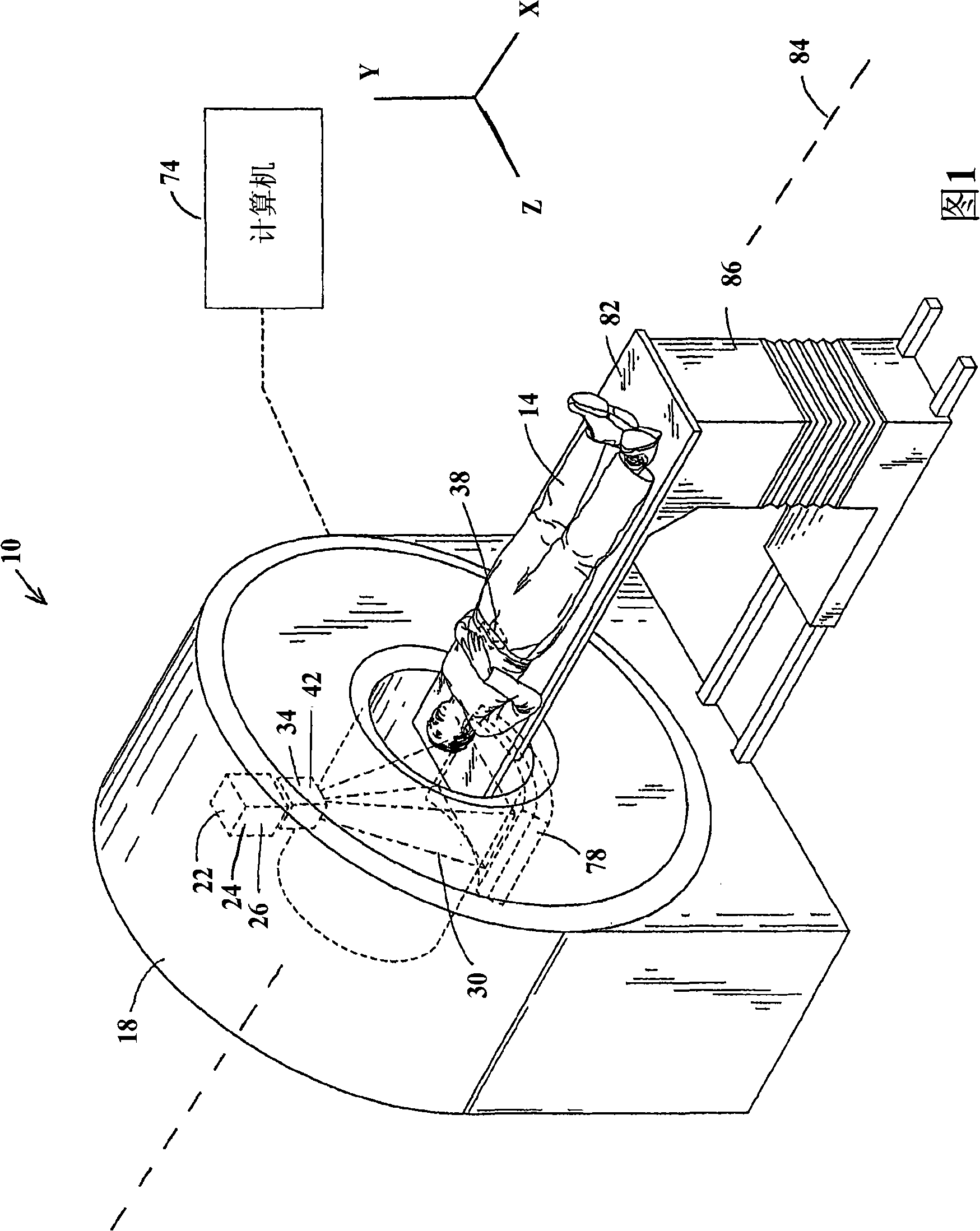
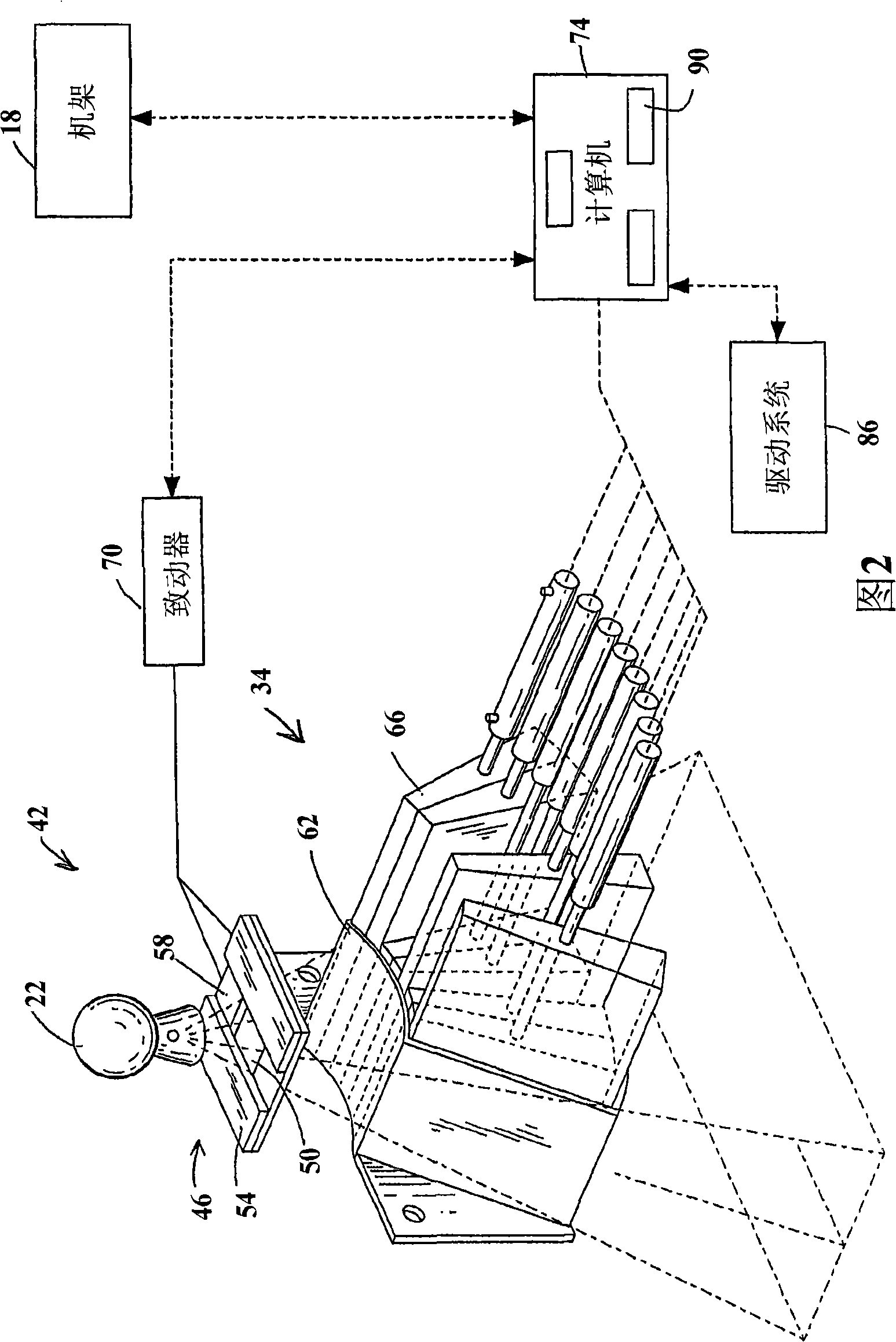
Real time brachytherapy spatial registration and visualization system
A method and system for monitoring loading of radiation into an insertion device for use in a radiation therapy treatment to determine whether the treatment will be in agreement with a radiation therapy plan. In a preferred embodiment, optical sensors and radiation sensors are used to monitor loading of radioactive seeds and spacers into a needle as part of a prostate brachytherapy treatment.
Owner:IMPAC MEDICAL SYST
Ablation treatment planning and device
ActiveUS20120237105A1Risk minimizationAvoid damageImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionTumour tissueMulti-planar Reformatting
An ablation treatment planning and, optionally, guiding method usable for e.g. tumour tissue ablation with a cryoablation needle which cools down an adjacent tumour tissue to thereby generate an ablation volume is proposed. In order to be able to plan an ablation treatment, a 3D image data set of a region of interest may be acquired by e.g. X-ray imaging using e.g. a C-arm system. Then, 3D model data of the ablation volume are introduced into the 3D image data set for example by tagging image pixels using a stencil buffer and possibly by culling specific inside areas and / or outside areas of the ablation volume. Finally, a 2D image to be visualized to a physician and comprising a projection of the region of interest and the ablation volume is drawn wherein an MPR (multi planar reformatting) plane in which the 2D image is drawn is used as a clipping plane. With such graphical approach, an ablation volume having any arbitrary shape such as for example an ellipsoid shape may be visualized within a 3D image space by drawing 2D images in any desired MPR plane such that also oblique orientations of the ablation volume can be represented. In a subsequent guiding procedure, an ablation needle may be guided to a location and in an orientation as previously planned.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and system for adapting a radiation therapy treatment plan based on a biological model
InactiveCN101267858AMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesRadical radiotherapyRadiation treatment planning
The invention provides a method and system for adapting a radiation therapy treatment plan based on a biological model. The method includes the acts of preparing a treatment plan for a patient, acquiring images of the patient, performing deformable registration of the images, acquiring data relating to a radiation dose delivered to the patient, applying a biological model relating the radiation dose delivered and a patient effect, and adapting the radiation therapy treatment plan based on the deformable registration and the biological model.
Owner:TOMOTHERAPY INC
Benchmark system for radiation therapy planning
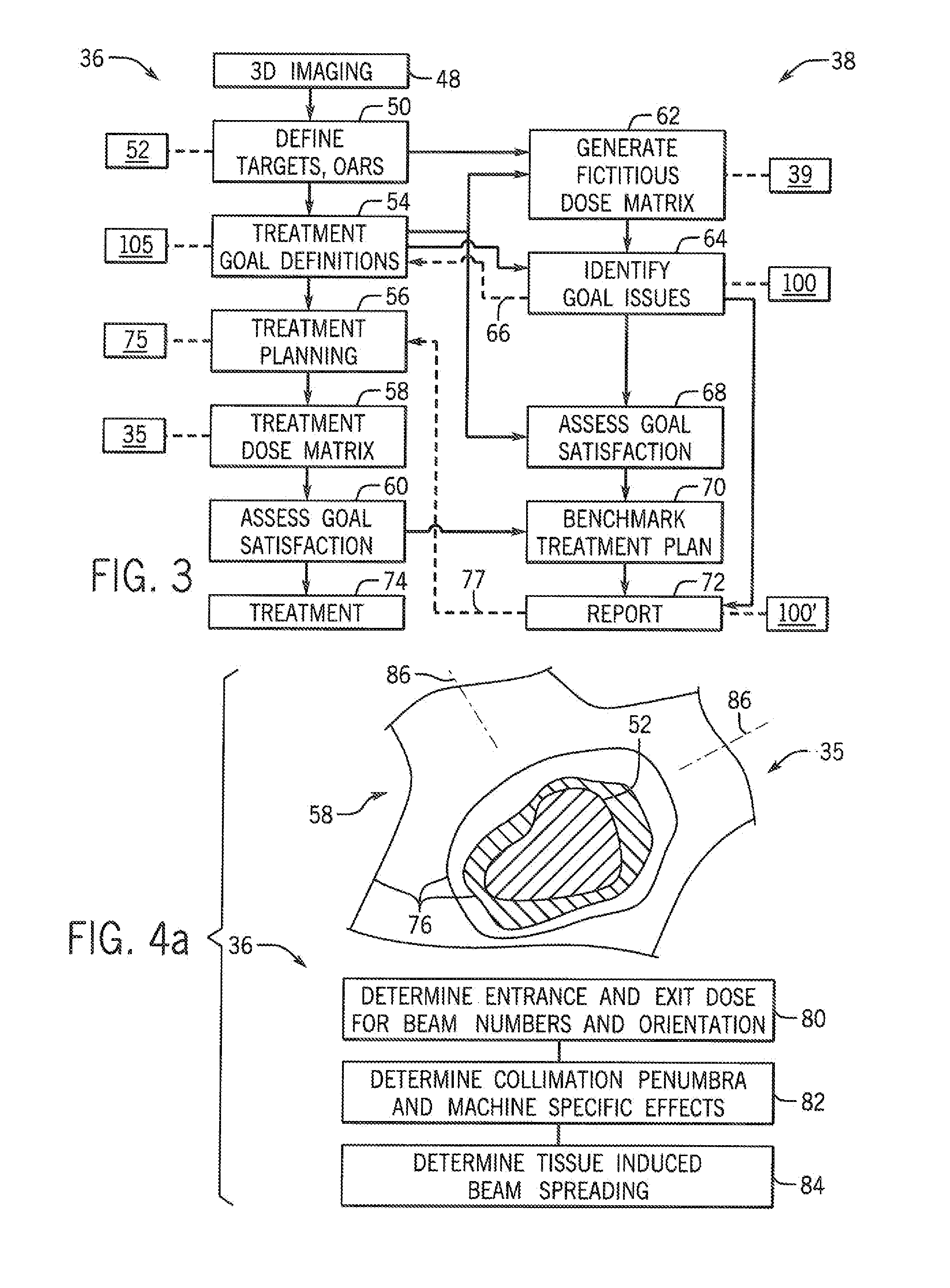
ActiveUS20150087879A1Reduce impactSimple modelRadiation diagnostics testing/calibrationRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsRadiation treatment planningBaseline system
A system for evaluating radiation treatment planning generates a fictitious treatment dose matrix with a quality of dose placement beyond that achievable with physically realizable radiation therapy machines. Such a fictitious treatment dose matrix provides an objective measure that is readily tailored to different clinical situations, and although unattainable, thereby provides a benchmark allowing evaluation of radiation plan goals and the radiation plans between different multiple clinical situations and individuals.
Owner:SUN NUCLEAR
System and method for automatic generation of initial radiation treatment plans
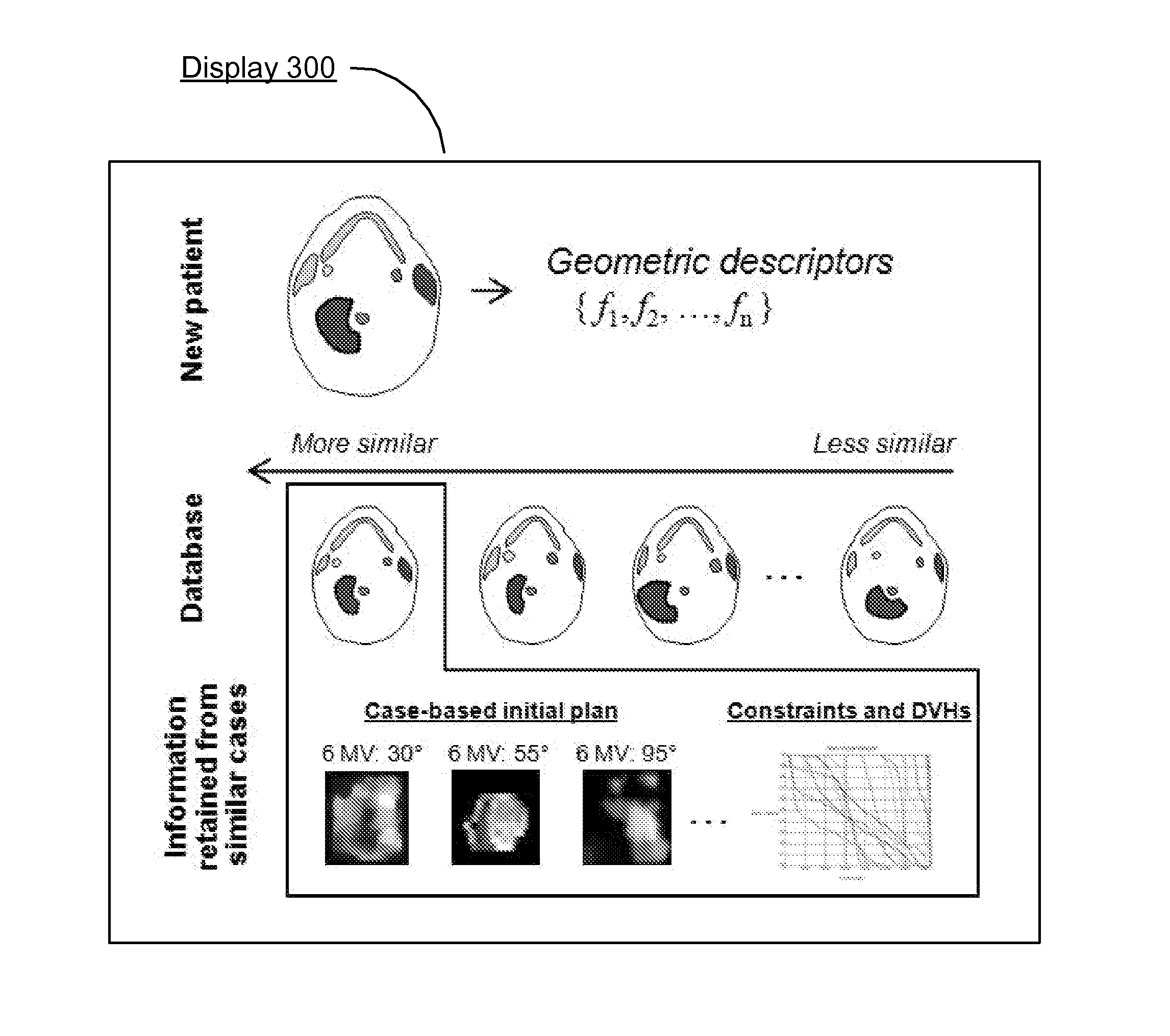
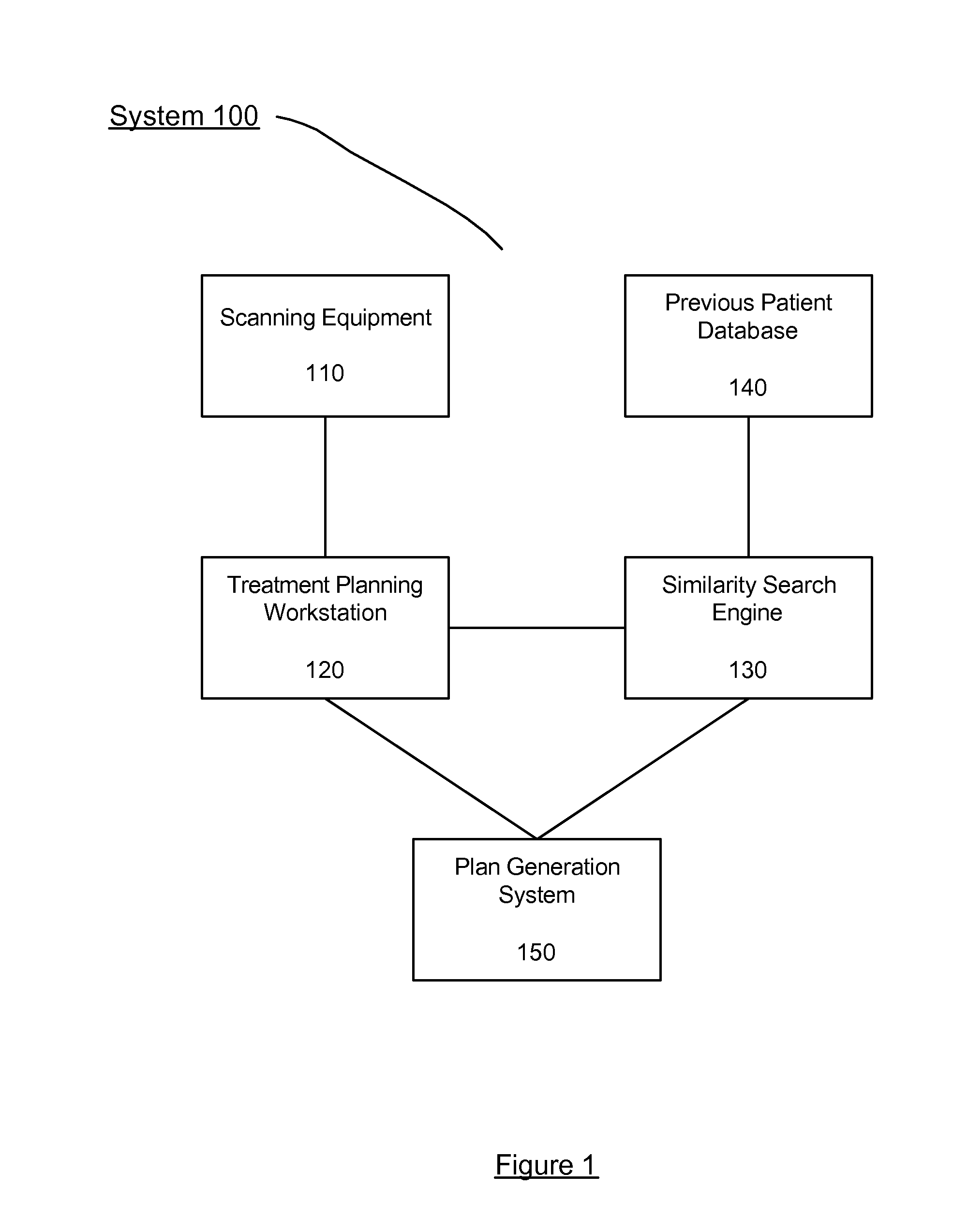
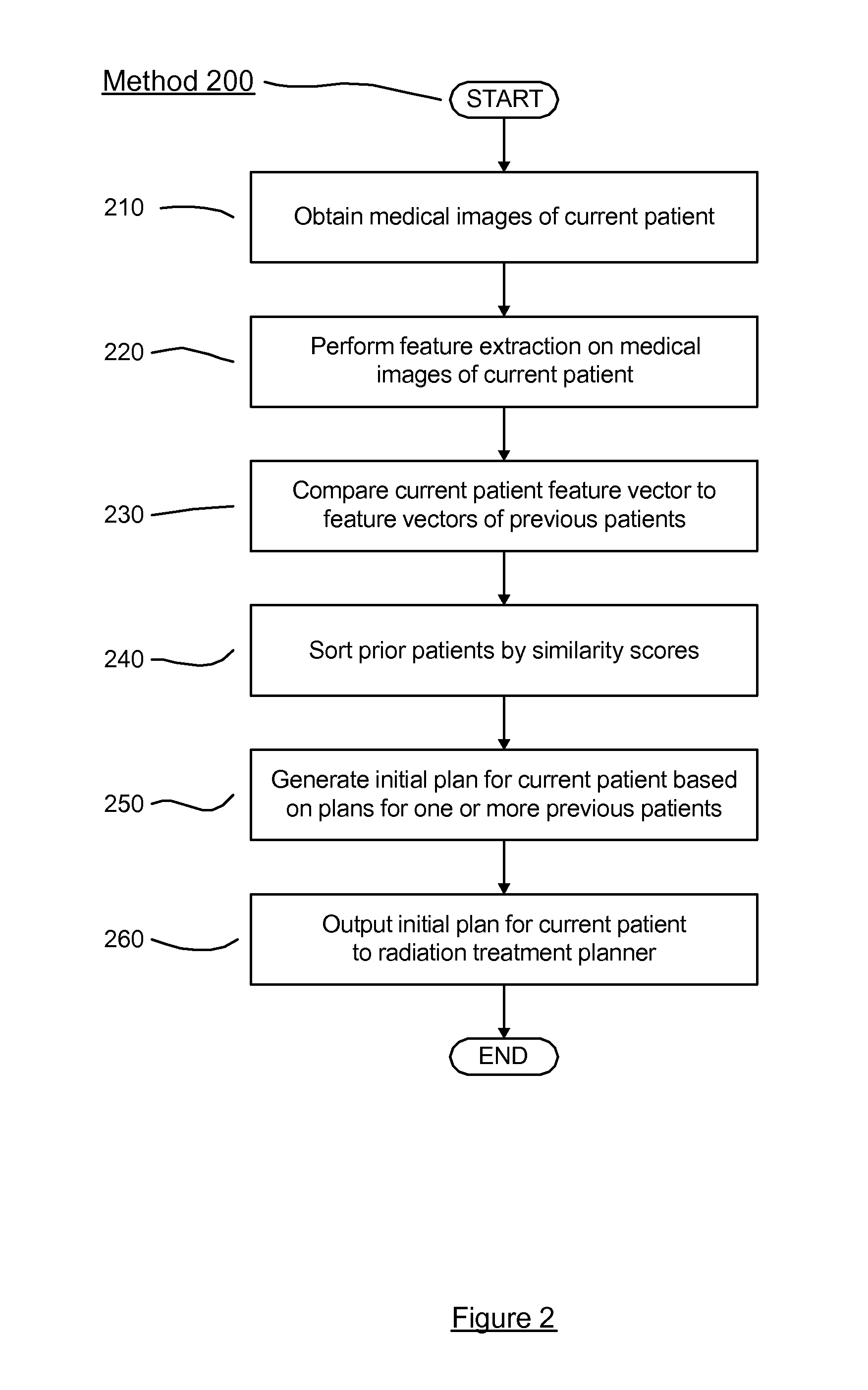
ActiveUS20130272593A1Image enhancementMedical data miningGeometric similarityRadiation treatment planning
A non-transitory computer-readable storage medium storing a set of instructions executable by a processor. The set of instructions is operable to receive a current patient medical image of a current patient, compare the current patient medical image to a plurality of previous patient medical images, each of the previous patient medical images corresponding to a previous patient, select one of the previous patients based on a geometric similarity between the previous patient medical image of the selected one of the previous patients and the current patient medical image, and determine an initial radiation treatment plan based on a radiation treatment plan of the selected one of the previous patients.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Radiotherapeutic treatment plan adaptation
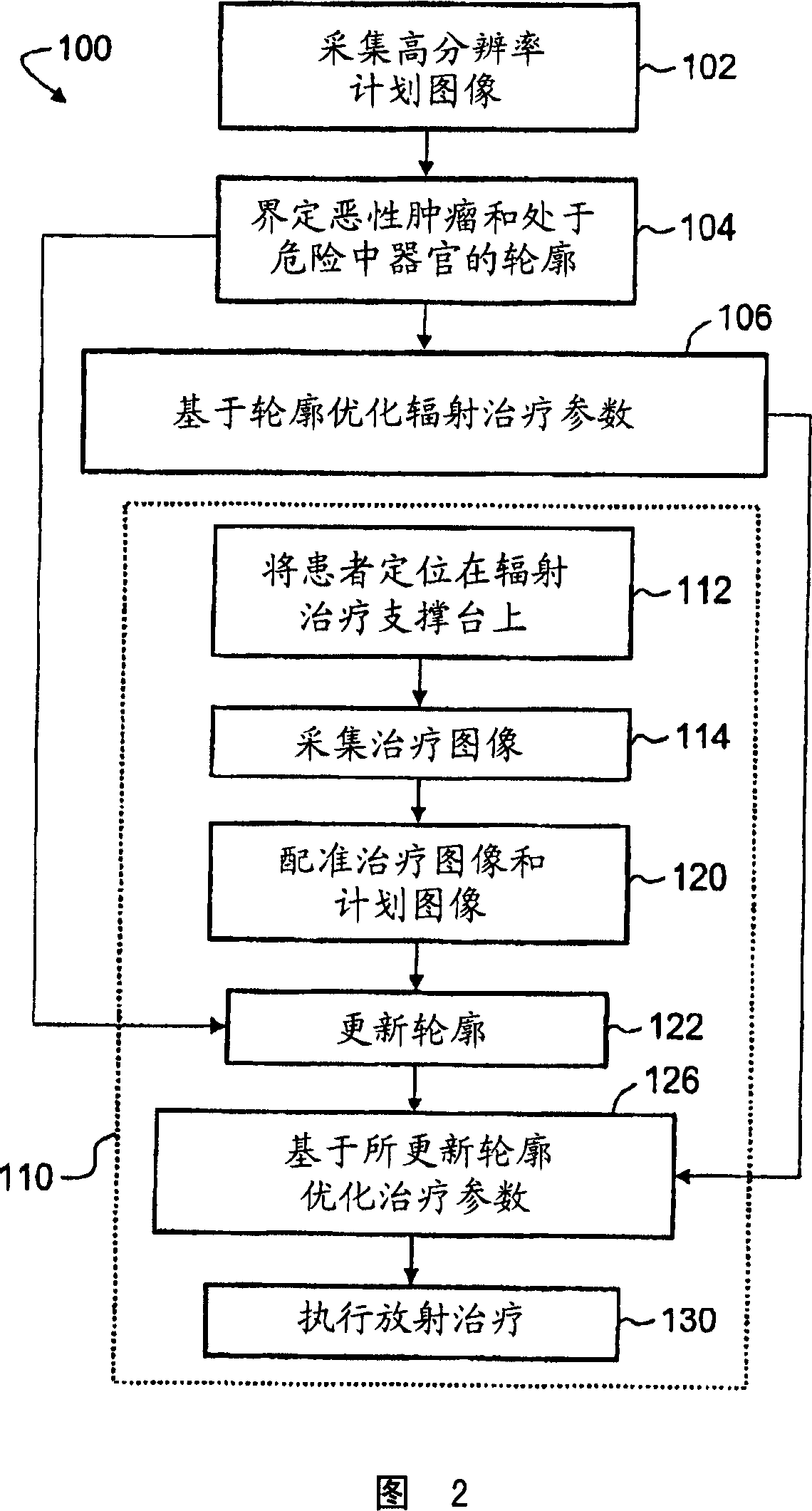
ActiveCN101005874AReduce indirect radiation damageImprove accuracyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesCharacter and pattern recognitionRadiation treatment planningTreatment plan
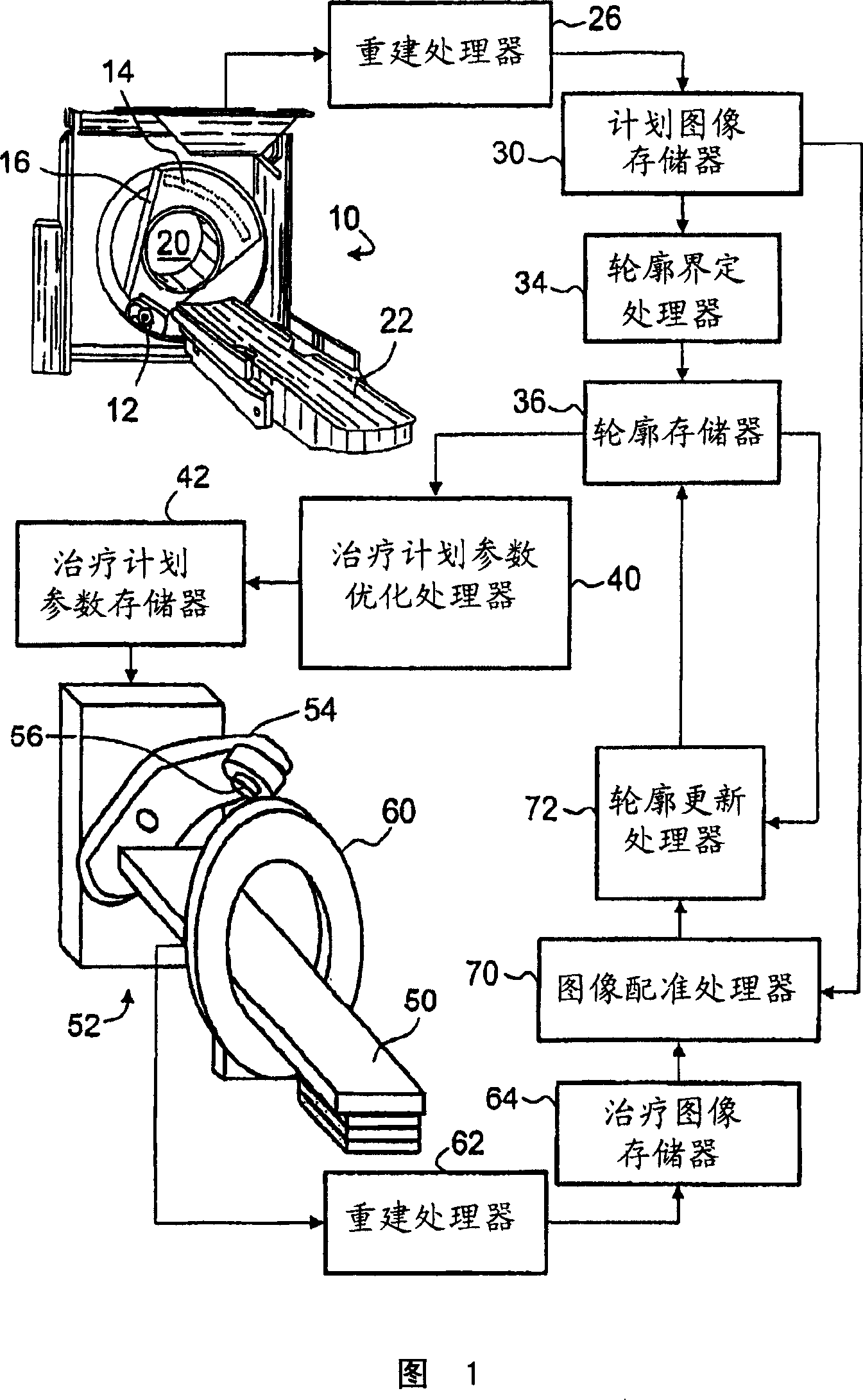
In a radiation therapy method, one or more planning images are acquired (102) of a subject. Features of at least malignant tissue are contoured in the one or more planning images to produce one or more initial feature contours. One or more treatment images of the subject are acquired (114). The one or more initial feature contours are updated (122) based on the one or more treatment images. Radiation treatment parameters are optimized (126) based upon the updated one or more feature contours. Radiation treatment of the subject is performed (130) using the optimized parameters.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Semantic radiation treatment plan optimization guidance
InactiveUS20130085343A1Easy to optimizeImproving treatment plan optimizationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAlternative treatmentTherapy types
A method for radiation therapy treatment plan optimization, comprising generating a first radiation therapy treatment plan for a patient using a selected treatment type from a database and optimizing the first radiation therapy treatment plan. A selection of metrics from the first radiation therapy treatment plan are identified and compared to metrics from aggregated prior patient records selected from the database. At least one parameter is identified that affects the ability of the first radiation therapy treatment plan to meet an identified metric. The at least one parameter for the identified metric is compared to at least one parameter for a competing metric and at least one alternative treatment step for the treatment plan is determined that will change the identified at least one parameter to improve the identified metric.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
Methods and apparatus for the planning and delivery of radiation treatments
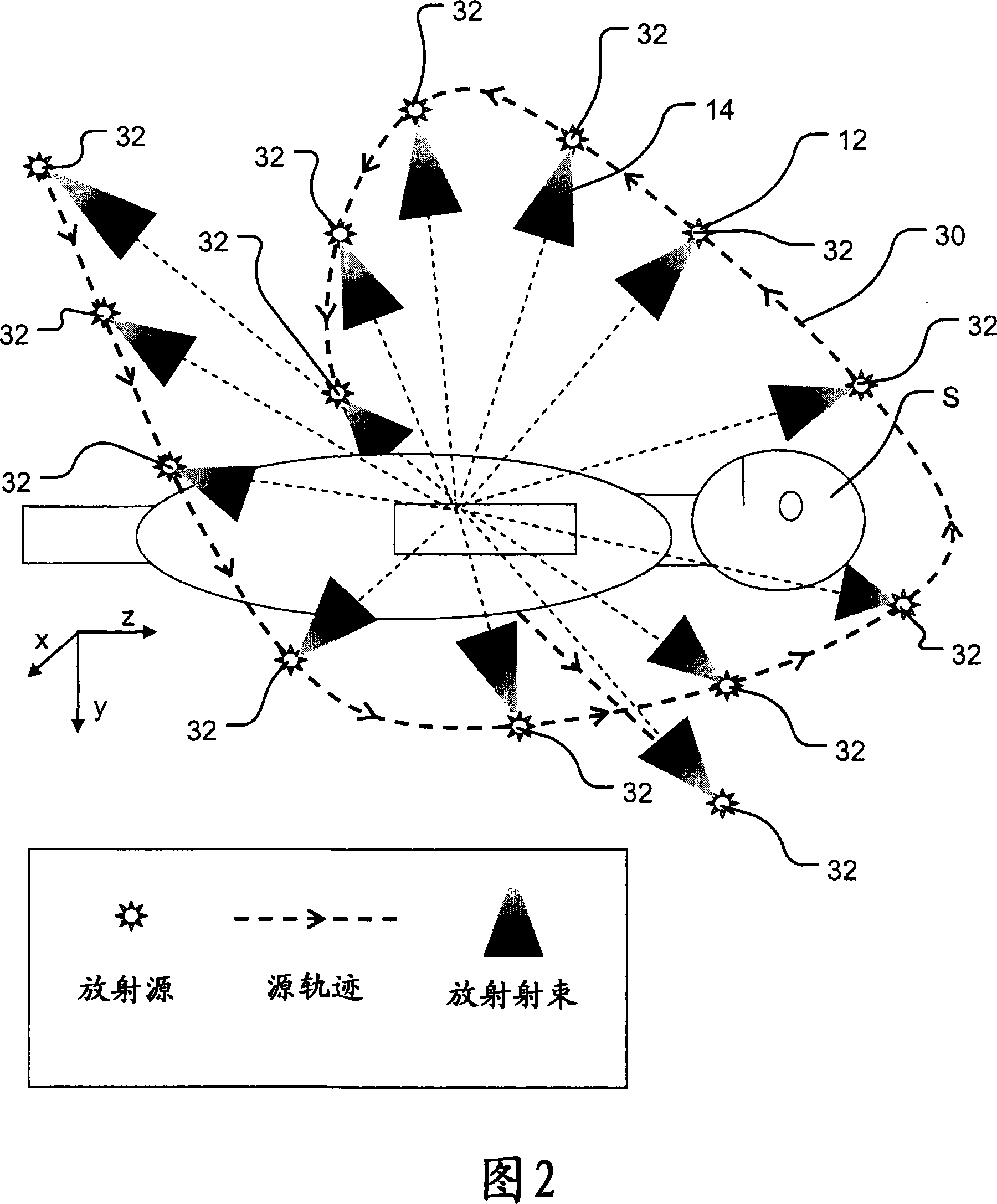
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for planning and delivering radiation therapy, characterized by moving a radiation source along a trajectory relative to the recipient while delivering radiation to the recipient. In some embodiments, the radioactive source moves continuously along the trajectory, and in some embodiments, the radioactive source moves intermittently. Some embodiments include optimizing a radiation delivery plan to meet optimization objectives while satisfying several constraints. For each of a number of control points along the trajectory, the radiation delivery plan may include: a set of motion axis parameters, a set of beam shape parameters, and a beam intensity.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
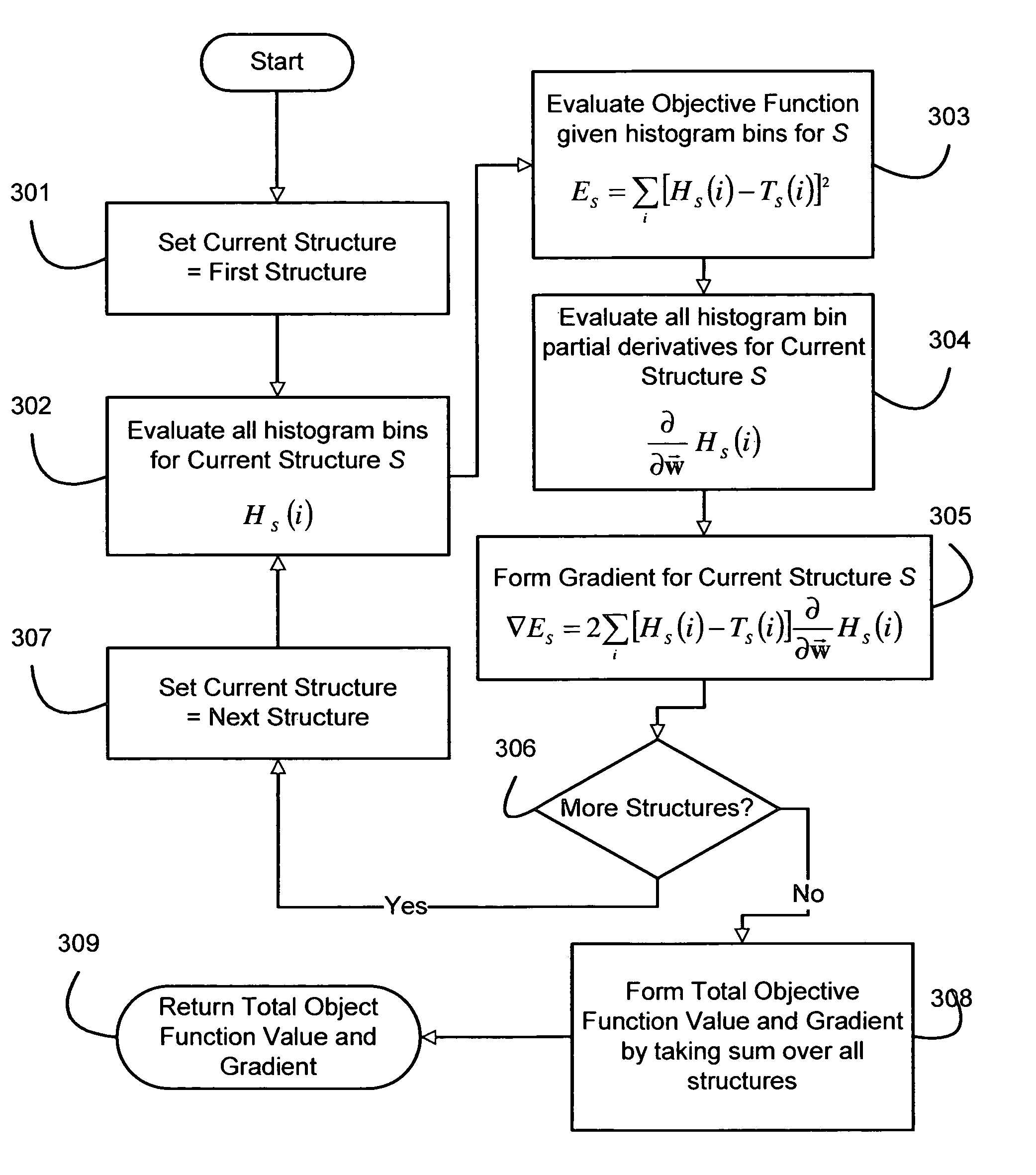
Information theoretic inverse planning technique for radiation treatment
InactiveUS7369645B2Effective evaluationShorten the timeX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyImaging processingRadiation treatment planning
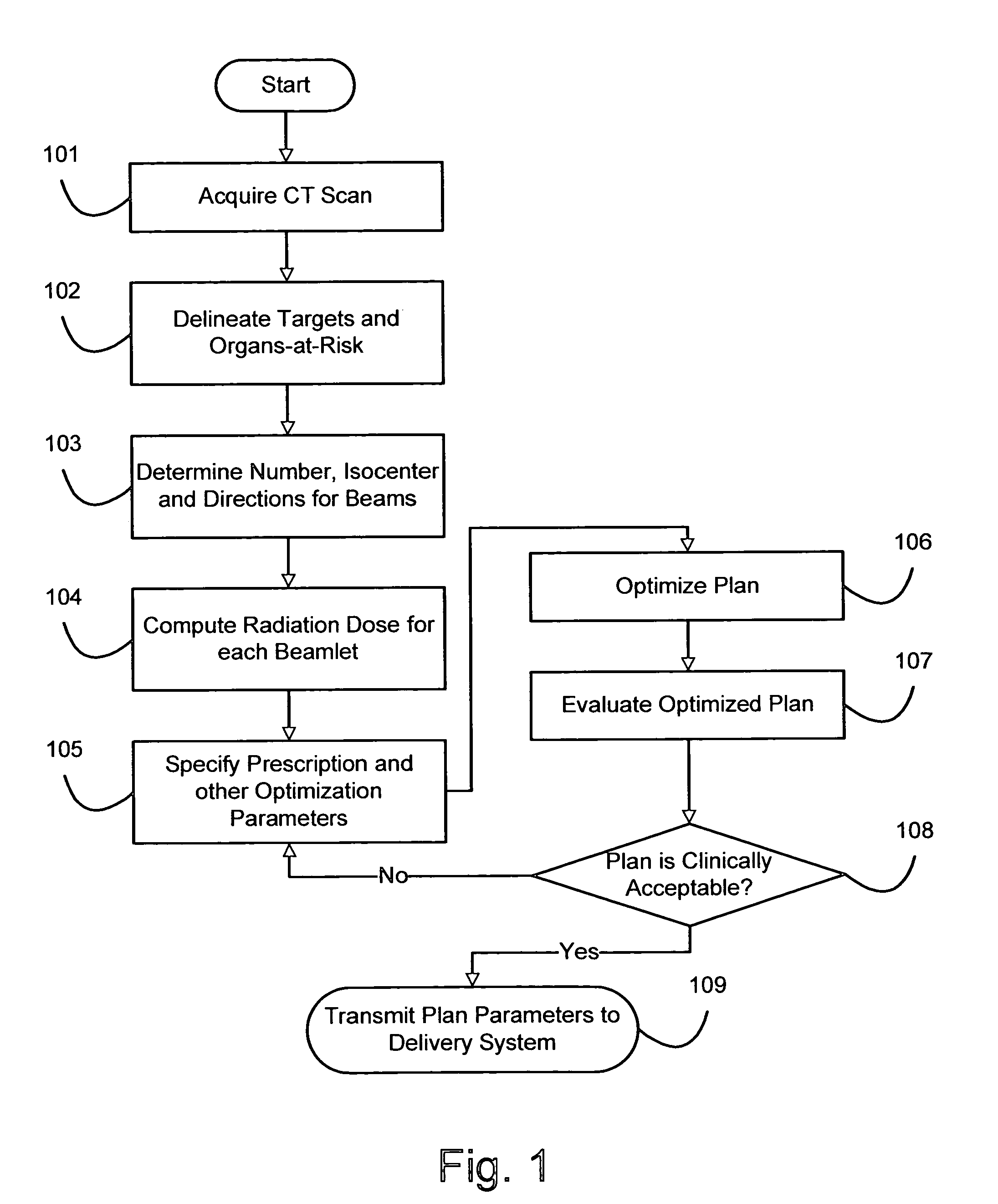
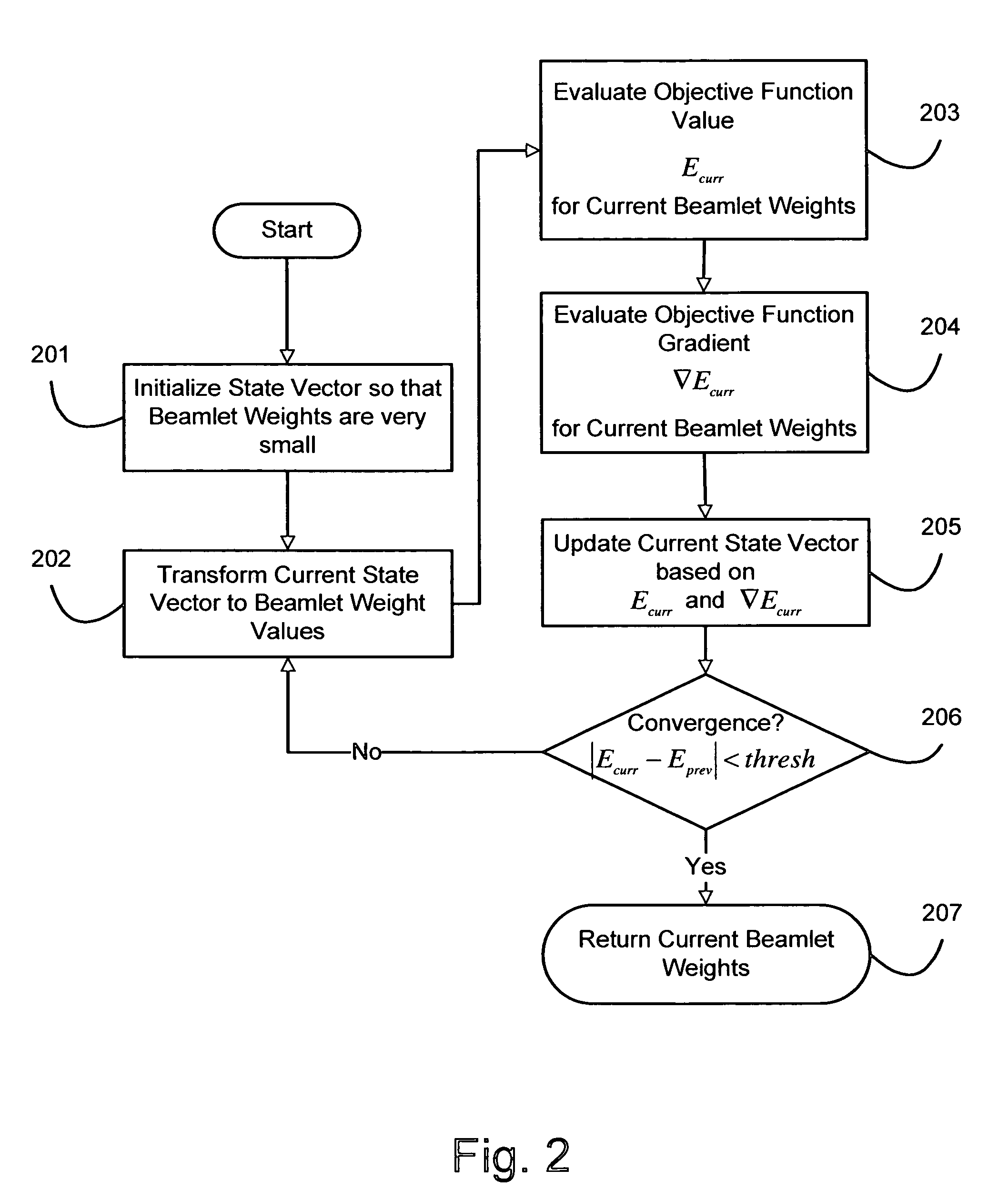
A method for fast inverse planning of IMRT treatment plans is disclosed. The method relies on a computationally efficient algorithm for evaluating the gradient of a general class of objective functions, and also on the efficient optimization that is realized due to the directional conjugacy of the objective functions. Several types of clinically relevant objective functions that belong to this class are described. The computational evaluation relies on operations that are commonly used for signal- and image-processing, and so can benefit from a number of well-known acceleration techniques.
Owner:LANE DEREK GRAHAM
System for enhancing intensity modulated radiation therapy, program product, and related methods
ActiveUS7519150B2Improve accuracyCost efficientX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIrradiation devicesComputation complexityHigh energy
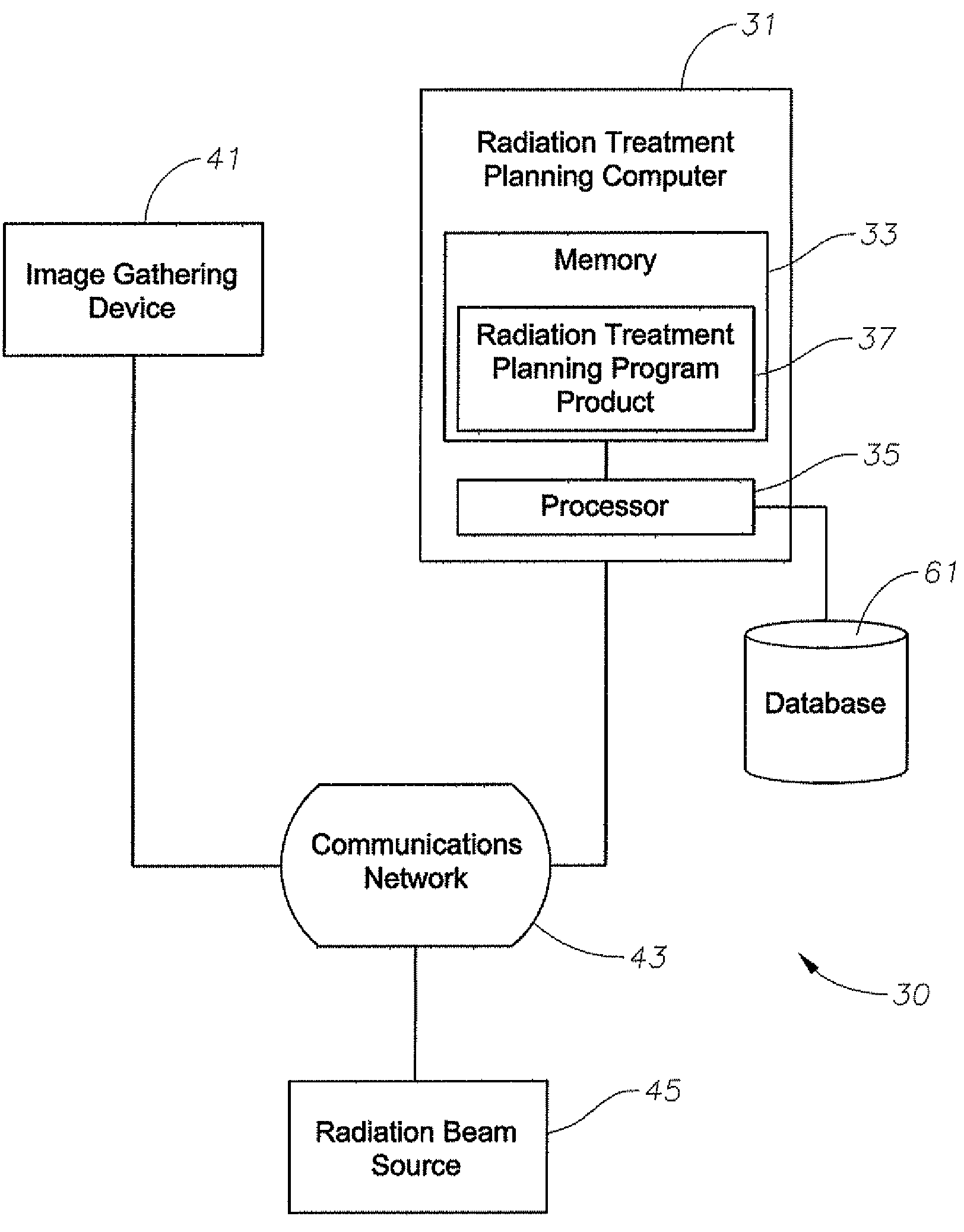
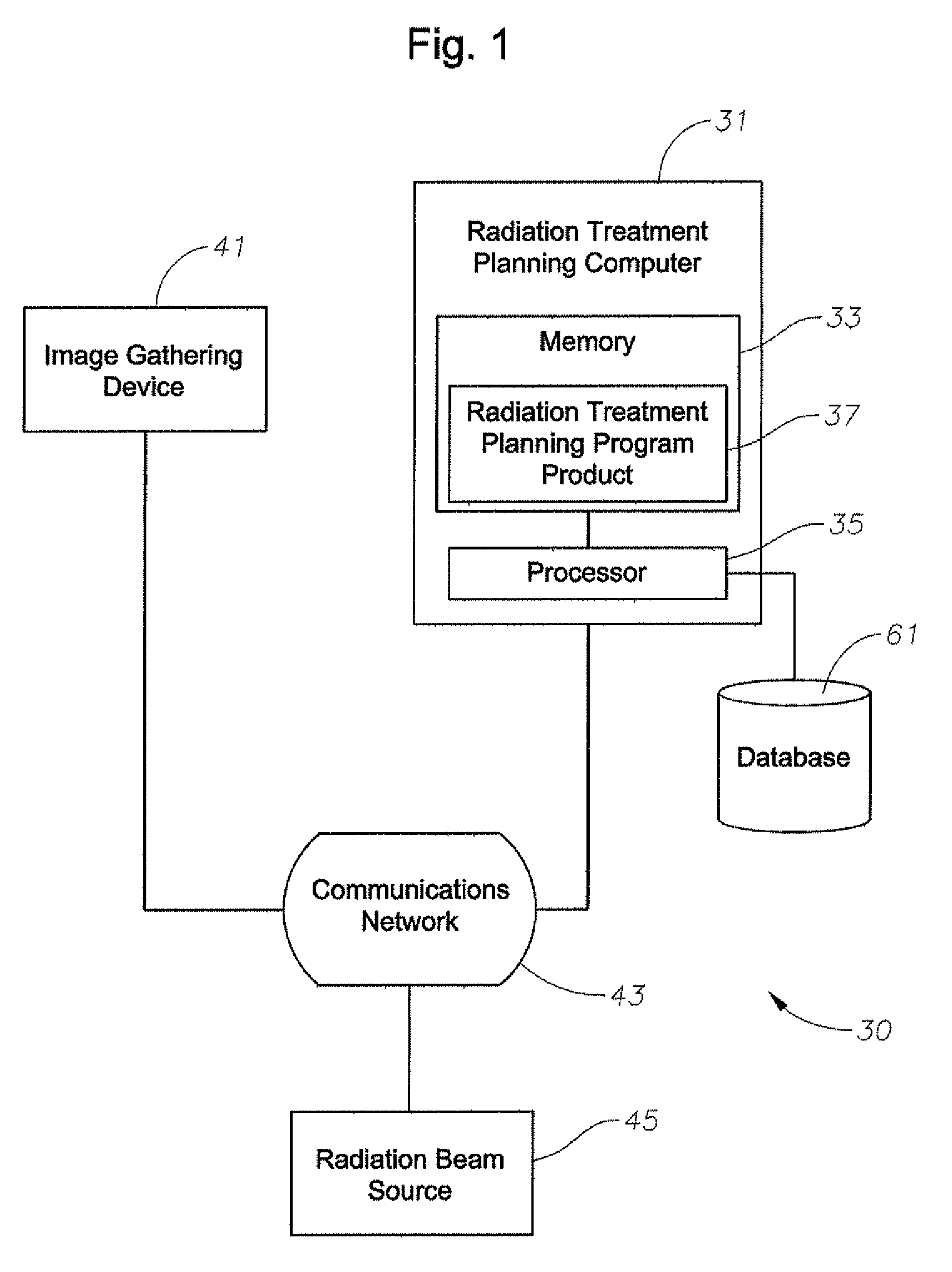
A system to provide enhanced computational efficiency in determining dose in a media of varying density from a high-energy radiation-beam for radiation treatment, program product, and related methods are provided. The system can include a radiation treatment planning computer and radiation treatment planning program product adapted to enhance optimization of a radiation treatment plan for delivering radiation to a complex medium defining a patient volume. The program product provides functions including those for predetermining a delivery machine-dependent representation of radiation dose for different electron densities selected over a representative range, predetermining a depth-dependent representation of central axis properties of a pencil beam passing through a complex medium, and determining with constant time computational complexity, radiation dose for each of a plurality of points of interest in a heterogeneous medium having a complex spatial distribution of heterogeneous electron densities by applying the predetermined machine-dependent and depth-dependent representations.
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
Phantom for evaluating nondosimetric functions in a multi-leaf collimated radiation treatment planning system
A phantom for evaluating nondosimetric functions in radiation therapy installation having a patient couch and a gantry with a head thereon for generating a multi-leaf collimated beam, wherein the beam is directed toward the couch at an orientation dictated by relative orientations of the couch and gantry. The phantom comprises a base adapted for disposition on the couch, and a component mounted to the base for rotation in accordance with the relative orientations of the couch and gantry. The component incorporates a plurality of known geometrical structures corresponding in shape to the multi-leaf collimated beam. Upon imaging the component, nondosimetric functions may be evaluated by comparing the known geometrical structures with images of the structures and identifying discrepancies therebetween.
Owner:CANCER CARE ONTARIO
Accurate stereotactic radiosurgery treatment device
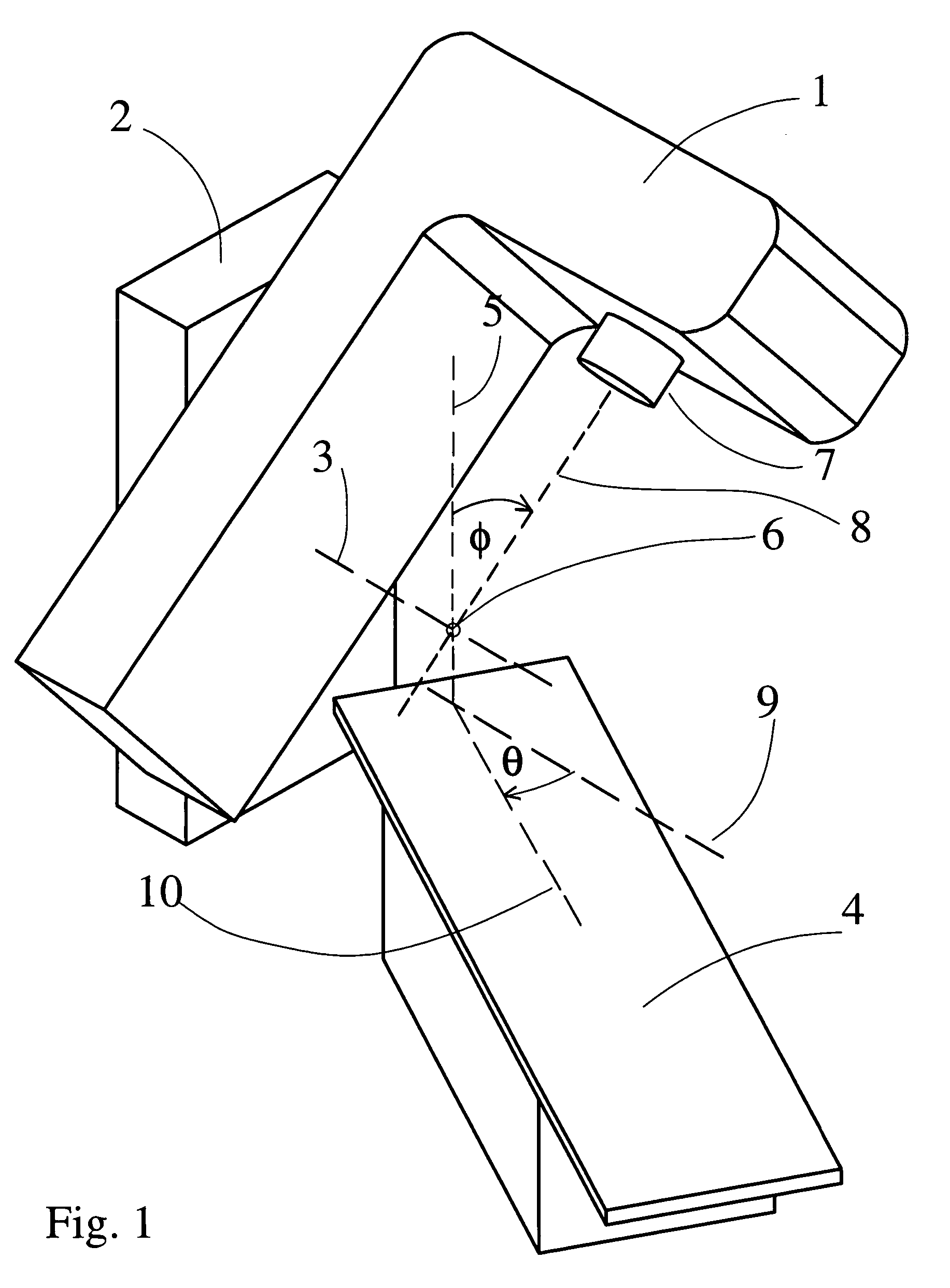
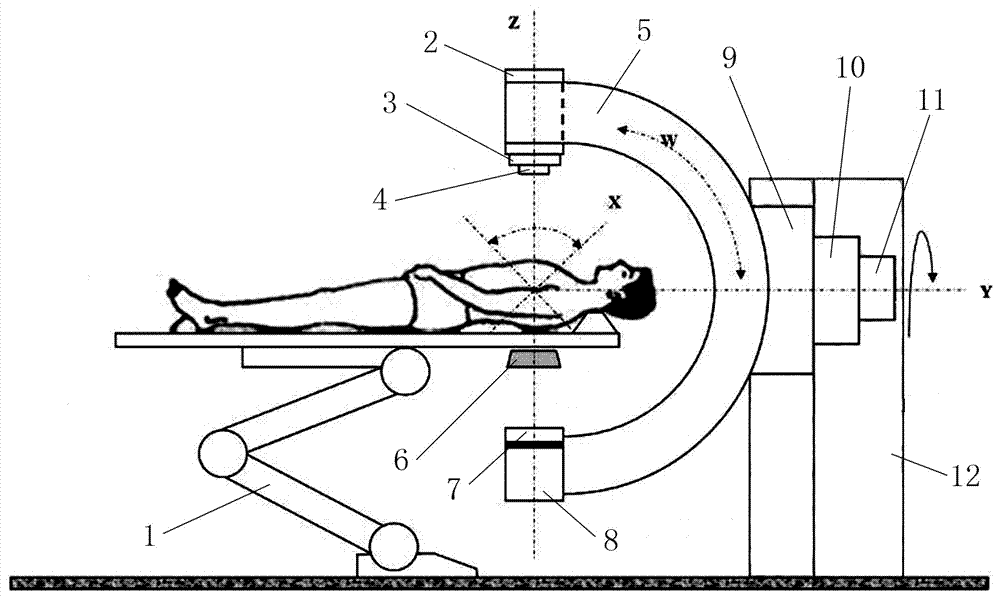
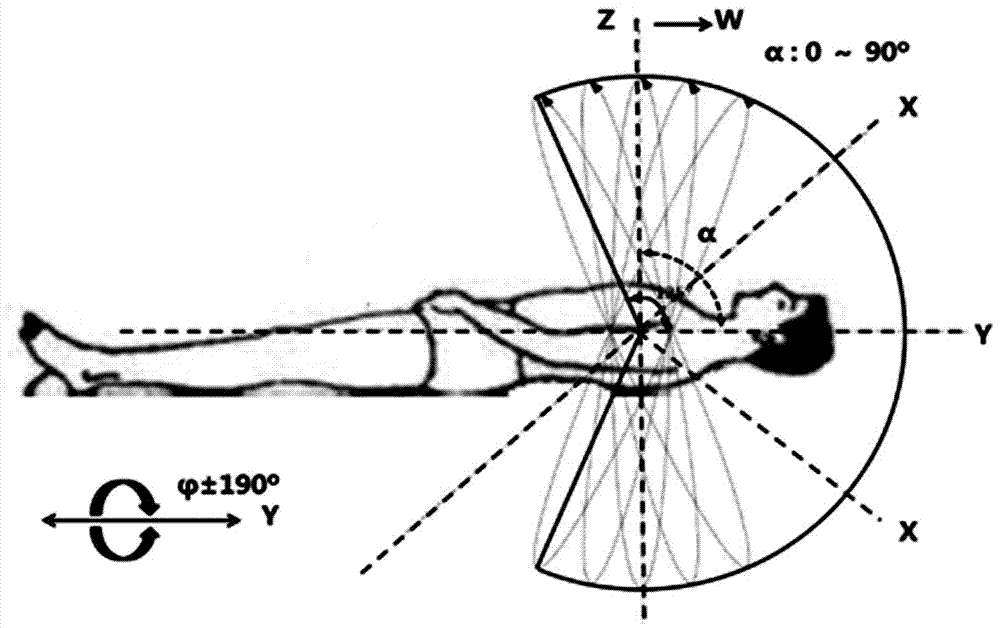
InactiveCN107362464AMechanical balance counterweight problem solvingReduce shielding requirementsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiosurgeryEngineering
The invention provides an accurate stereotactic radiosurgery treatment device which belongs to the field of a medical device. The accurate stereotactic radiosurgery treatment device is composed of a radiation device system, a six-dimensional robot treatment bed 1 and a treatment planning system. The radiation device system is composed of a frame 12 and a C-shaped machine arm 5. The frame 12 is provided with a rotating shaft 10. The rotating shaft 10 is connected with a guiderail 9 and controls rotation of the guiderail 9. The C-shaped machine arm 5 is mounted on the guiderail 9 and performs arc-shaped motion along the guiderail 9. One end of the C-shaped machine arm 5 is provided with a radiation source 2. The bottom end of the radiation source 2 is provided with a small machine head 3. The bottom end of the small machine head 3 is provided with a collimator. The other end of the C-shaped machine arm 5 is provided with a telescopic electronic portal imaging device 7 and a movable shielding protecting counterweight 8. A target organ positioning and detecting device 6 is mounted at the side part or the lower part of the six-dimensional robot treatment bed 1. The radiation treatment head of the accurate stereotactic radiosurgery treatment device can perform 90-degree (or + / -45-degree) rotation around an X axis so that rays can be transmitted in a 4pi non-coplanar track.
Owner:吴大可
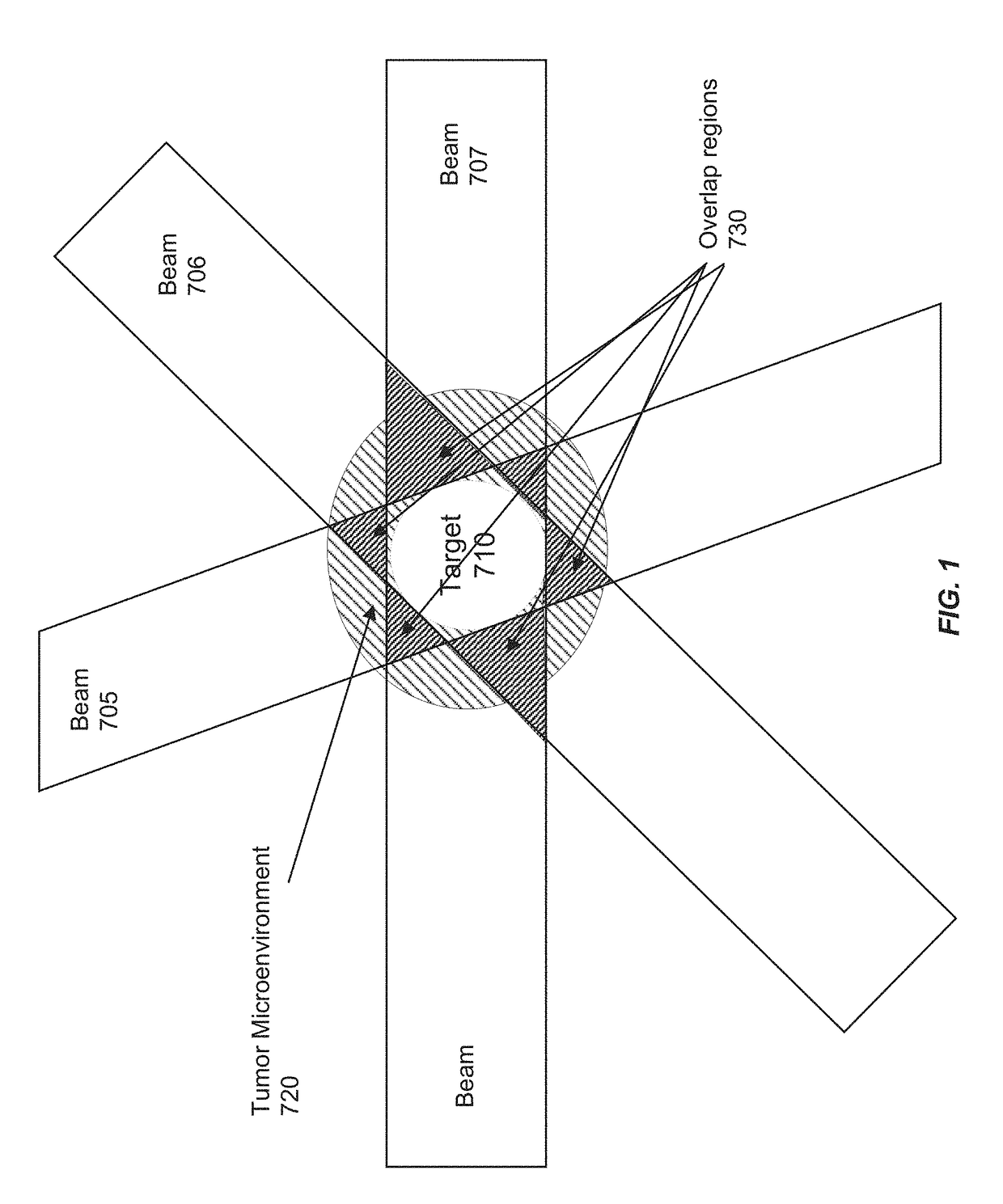
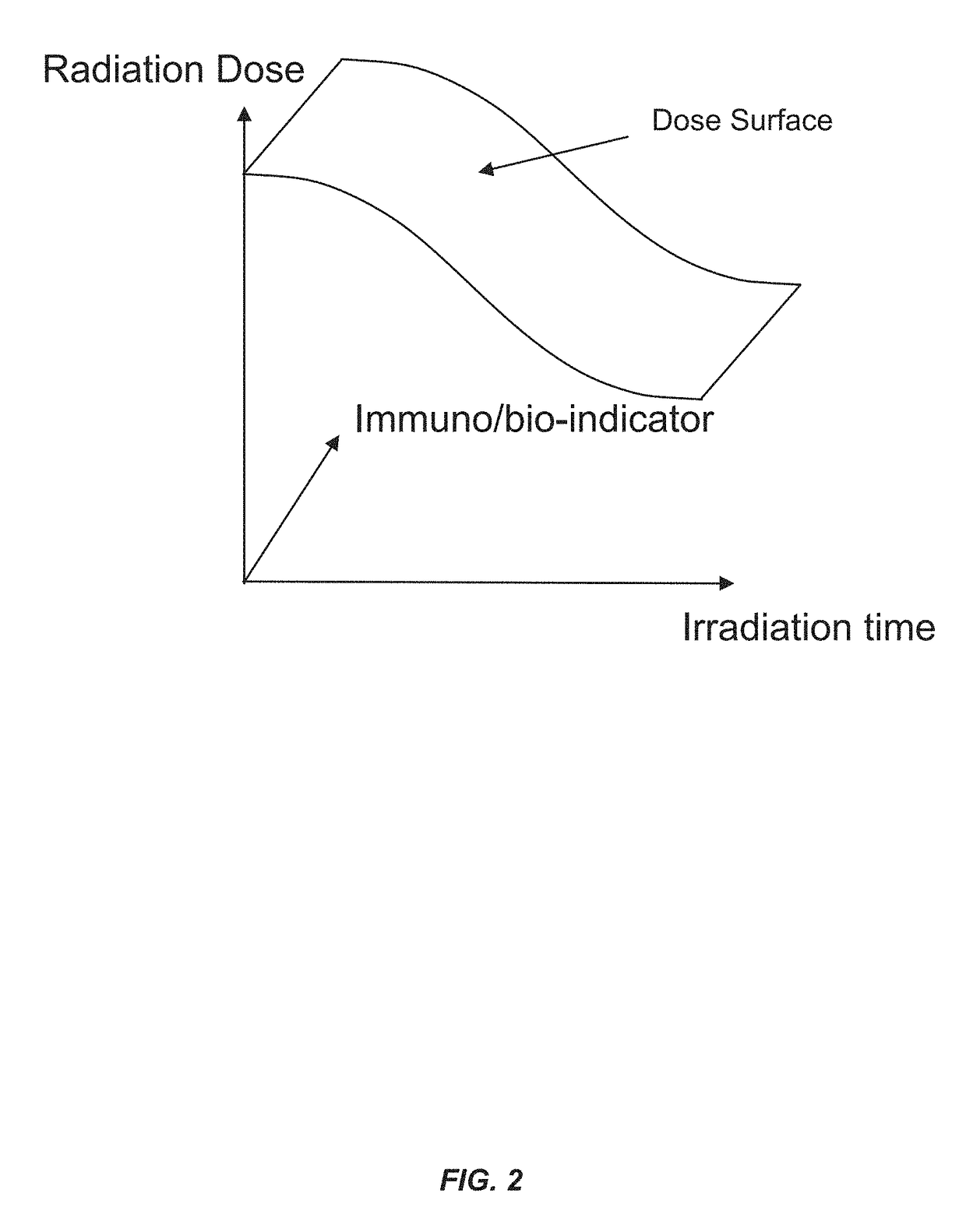
Methods of use of ultra-high dose rate radiation and therapeutic agent
ActiveUS20190022411A1Improve therapeutic windowDecreasing normal tissue side effectOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryDose rateHigh doses
Methods for treating tumors by administering FLASH radiation and a therapeutic agent to a patient with cancer are disclosed. The methods provide the dual benefits of anti-tumor efficacy plus normal tissue protection when combining therapeutic agents with FLASH radiation to treat cancer patients. The methods described herein also allow for the classification of patients into groups for receiving optimized radiation treatment in combination with a therapeutic agent based on patient-specific biomarker signatures. Also provided are radiation treatment planning methods and systems incorporating FLASH radiation and therapeutic agents.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
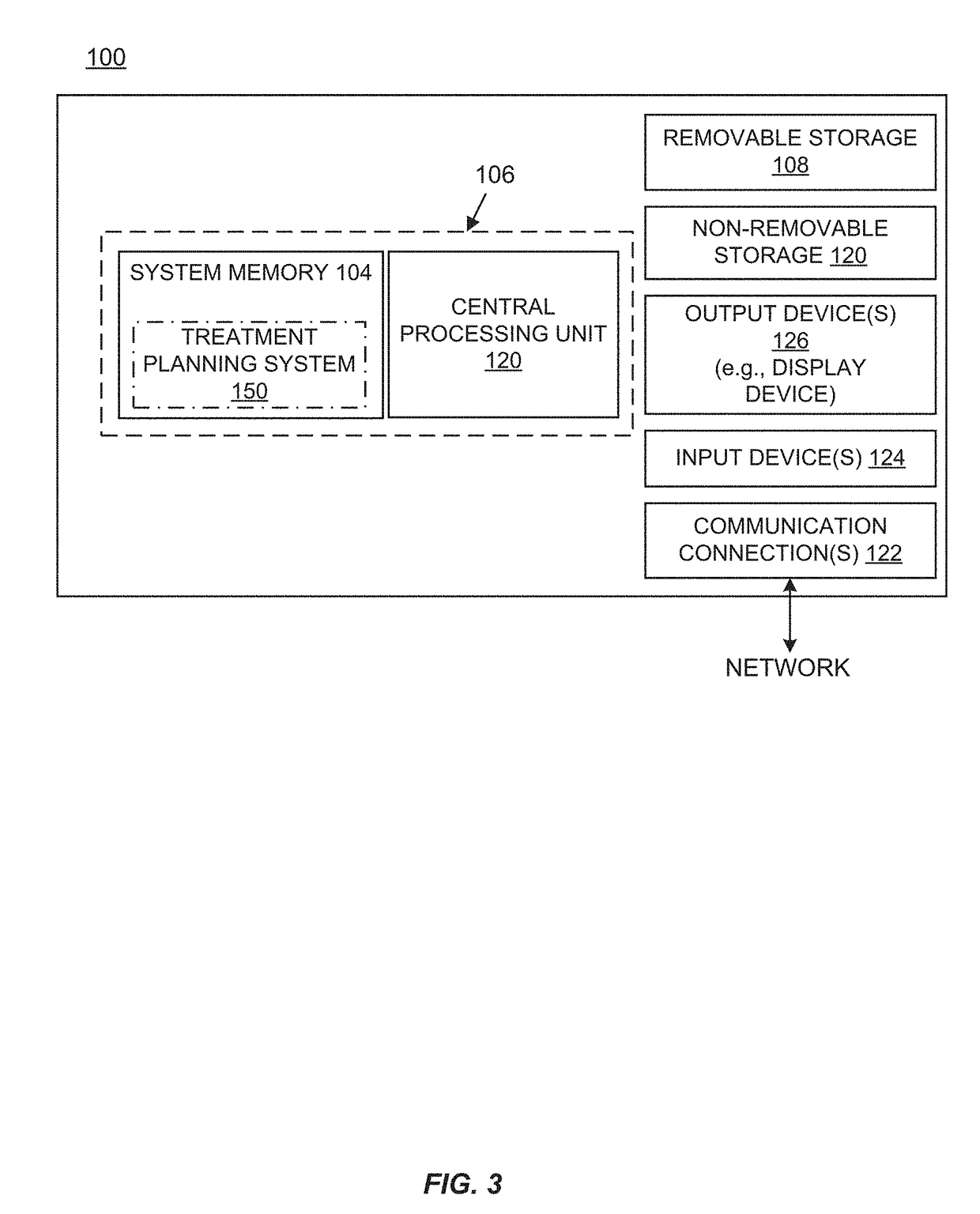
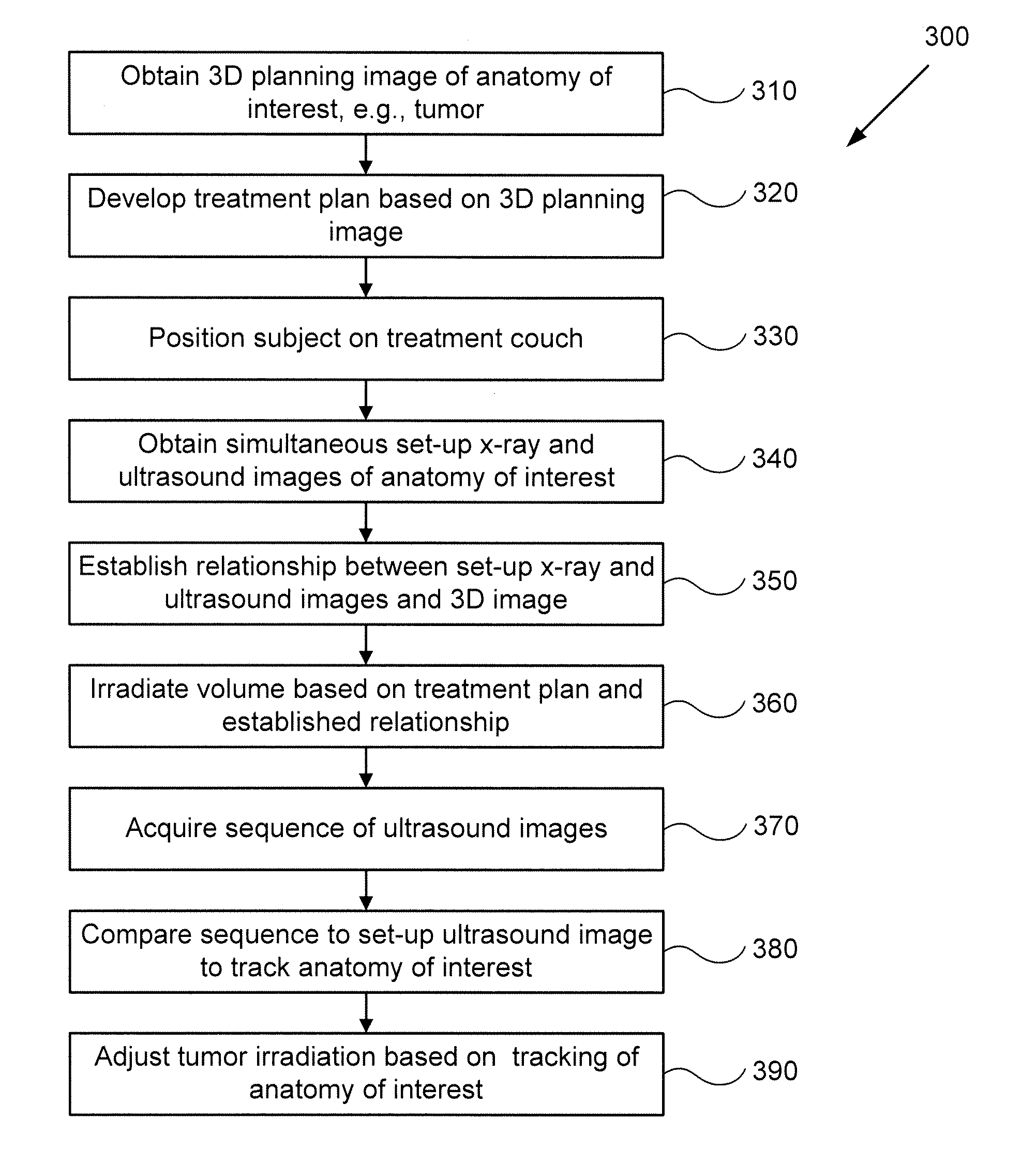
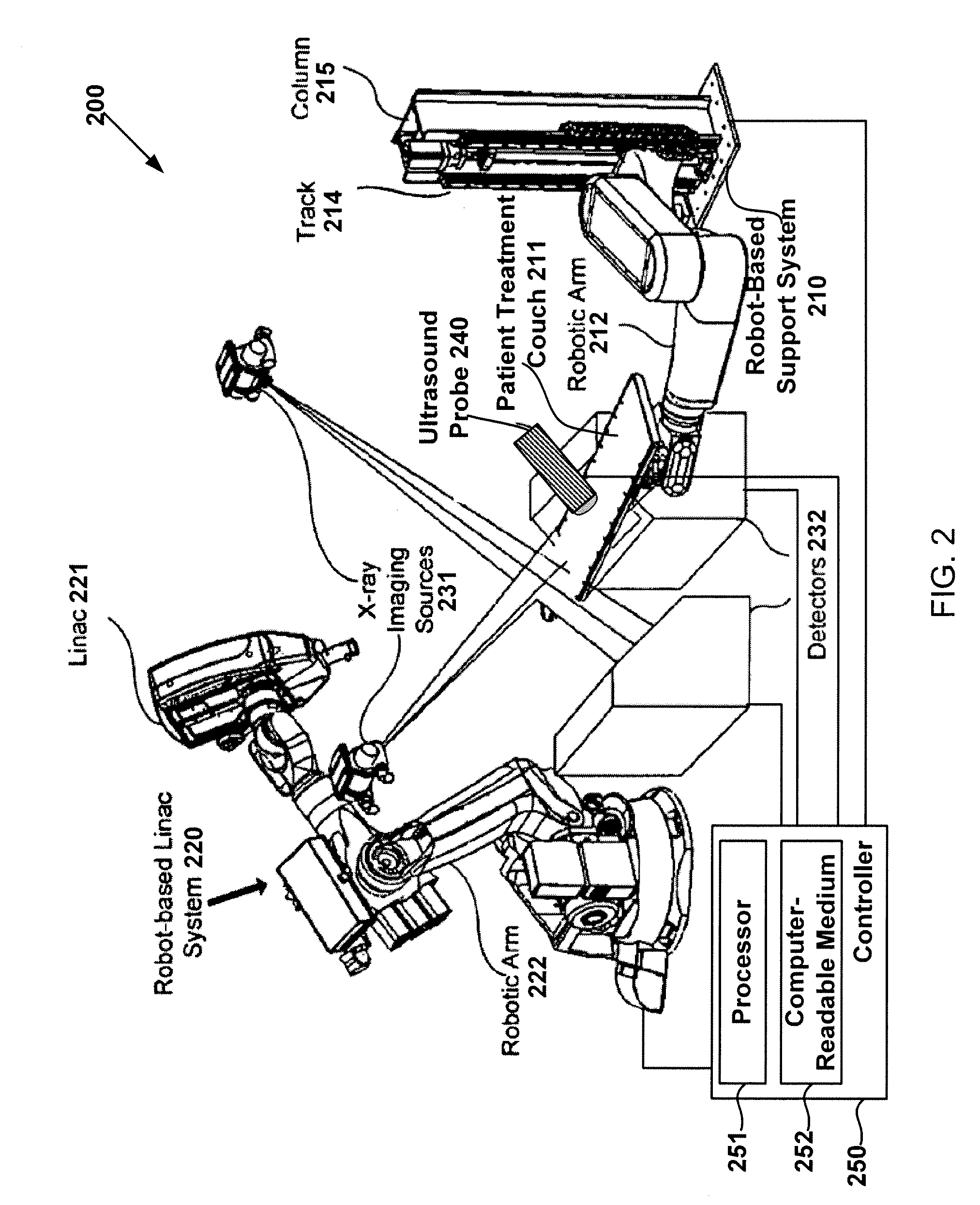
Systems and methods for real-time tumor tracking during radiation treatment using ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS9108048B2Satisfy safety performance requirementsSoft imageSurgeryDiagnostic markersUltrasound imaging3d image
Systems and methods for tracking a target volume, e.g., tumor, in real-time during radiation treatment are provided. Under one aspect, a system includes an ultrasound probe, an x-ray imager, a processor, and a computer-readable medium that stores a 3D image of the tumor in a first reference frame and instructions for causing the processor to: instruct the x-ray imager and ultrasound probe to substantially simultaneously obtain inherently registered x-ray and set-up ultrasound images of the tumor in a second reference frame; establish a transformation between the first and second reference frames by registering the 3D image and the x-ray image; instruct the ultrasound probe to obtain an intrafraction ultrasound image of the tumor; registering the intrafraction ultrasound image with the set-up ultrasound image; and track target volume motion based on the registered intrafraction ultrasound image.
Owner:ACCURAY
Radiation Treatment Planning and Delivery for Moving Targets in the Heart
ActiveUS20090257557A1Improved radiosurgical treatment of tissueReduce arrhythmiaX-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiation treatment planningTarget tissue
Method and systems are disclosed for radiating a moving target inside a heart. The method includes acquiring sequential volumetric representations of an area of the heart and defining a target tissue region and / or a radiation sensitive structure region in 3D for a first of the representations. The target tissue region and / or radiation sensitive structure region are identified for another of the representations by an analysis of the area of the heart from the first representation and the other representation. Radiation beams to the target tissue region are fired in response to the identified target tissue region and / or radiation sensitive structure region from the other representation.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
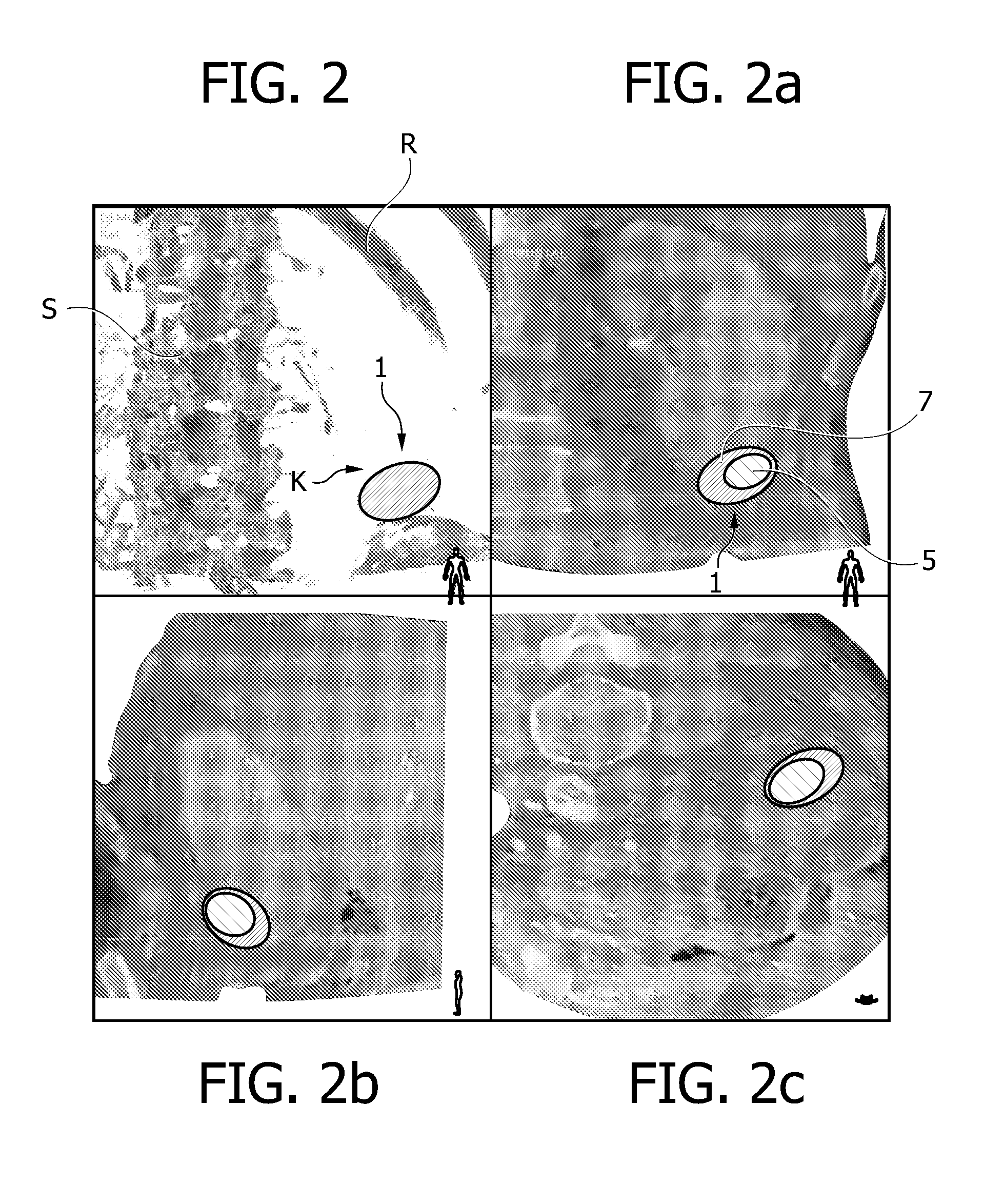
Methods and Systems for Lesion Localization, Definition and Verification
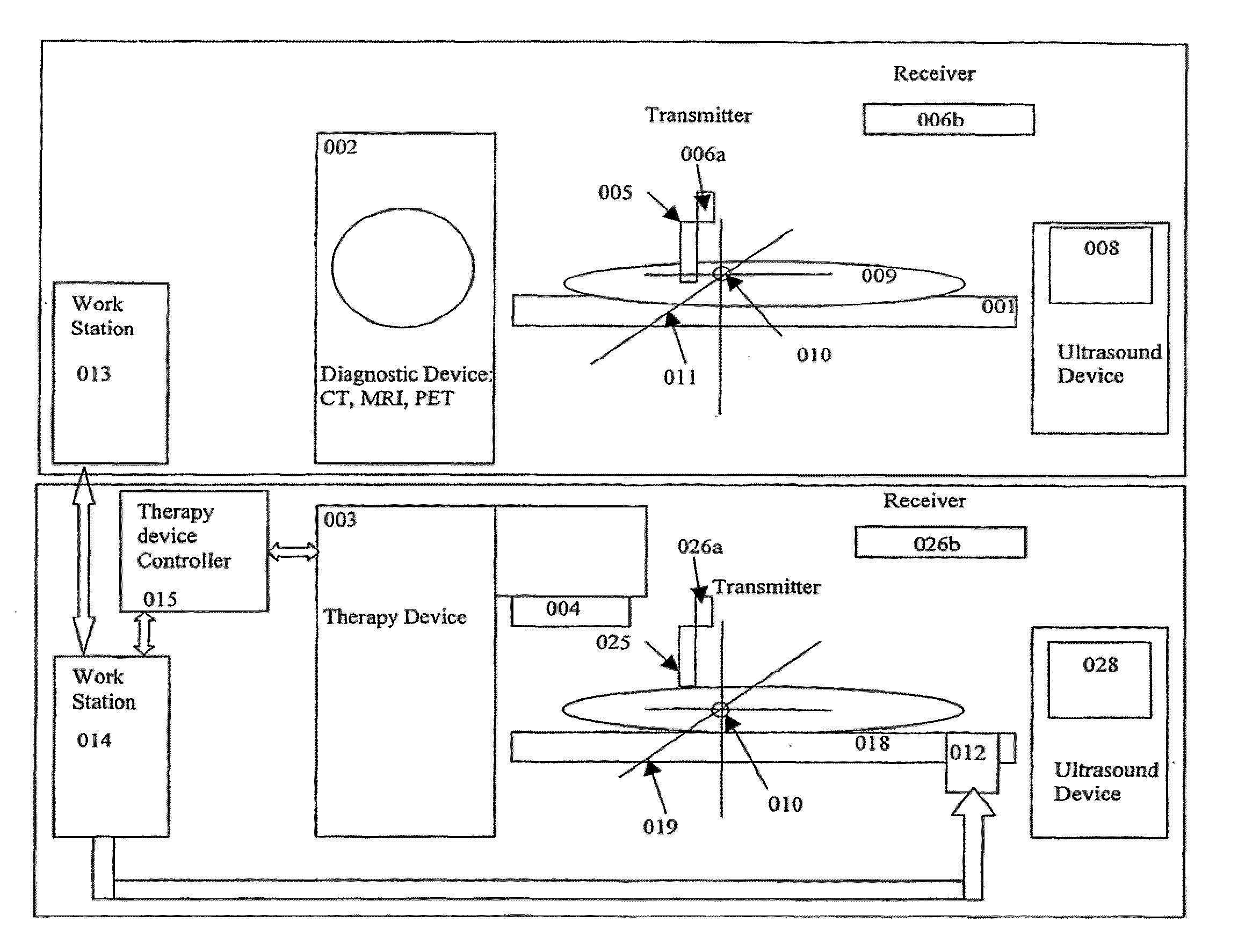
InactiveUS20090275830A1Accurate imagingCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsUltrasound imagingSonification
A method and apparatus for lesion or organ definition for the purpose of radiation treatment planning localization and treatment position verification. The apparatus uses a combination of an ultrasound imaging system and a diagnostic imaging system to acquire localization ultrasound images referenced in the coordinate space of the diagnostic imaging system through the use of position sensing system. The method compares the location of the lesion in the localization ultrasound images with the position of the lesion in ultrasound images taken while the patient lies on the treatment table of a therapy treatment unit, suggests corrective measures to place the lesion in its intended treatment position and executes the correction upon confirmation from qualified personnel.
Owner:FALCO TONY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com