Patents
Literature
38 results about "Portal imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Edge-on SAR scintillator devices and systems for enhanced spect, pet, and compton gamma cameras
InactiveUS20090134334A1Improved SAR resolutionReduce photodetector readout noiseSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh energyX-ray
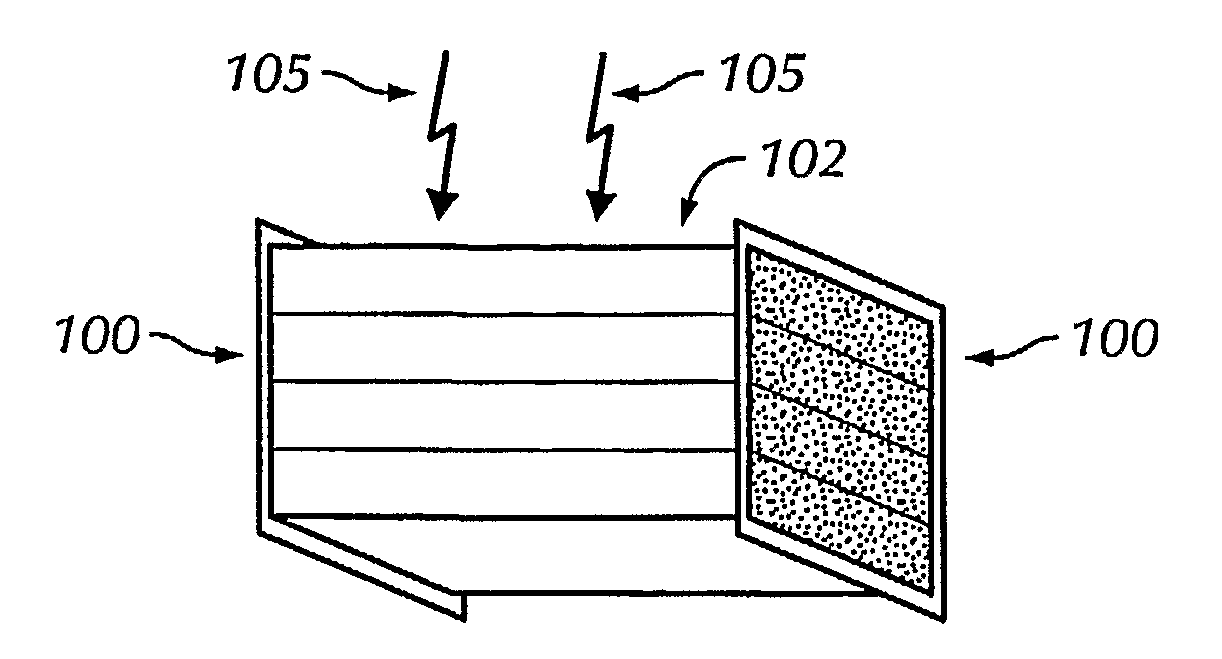
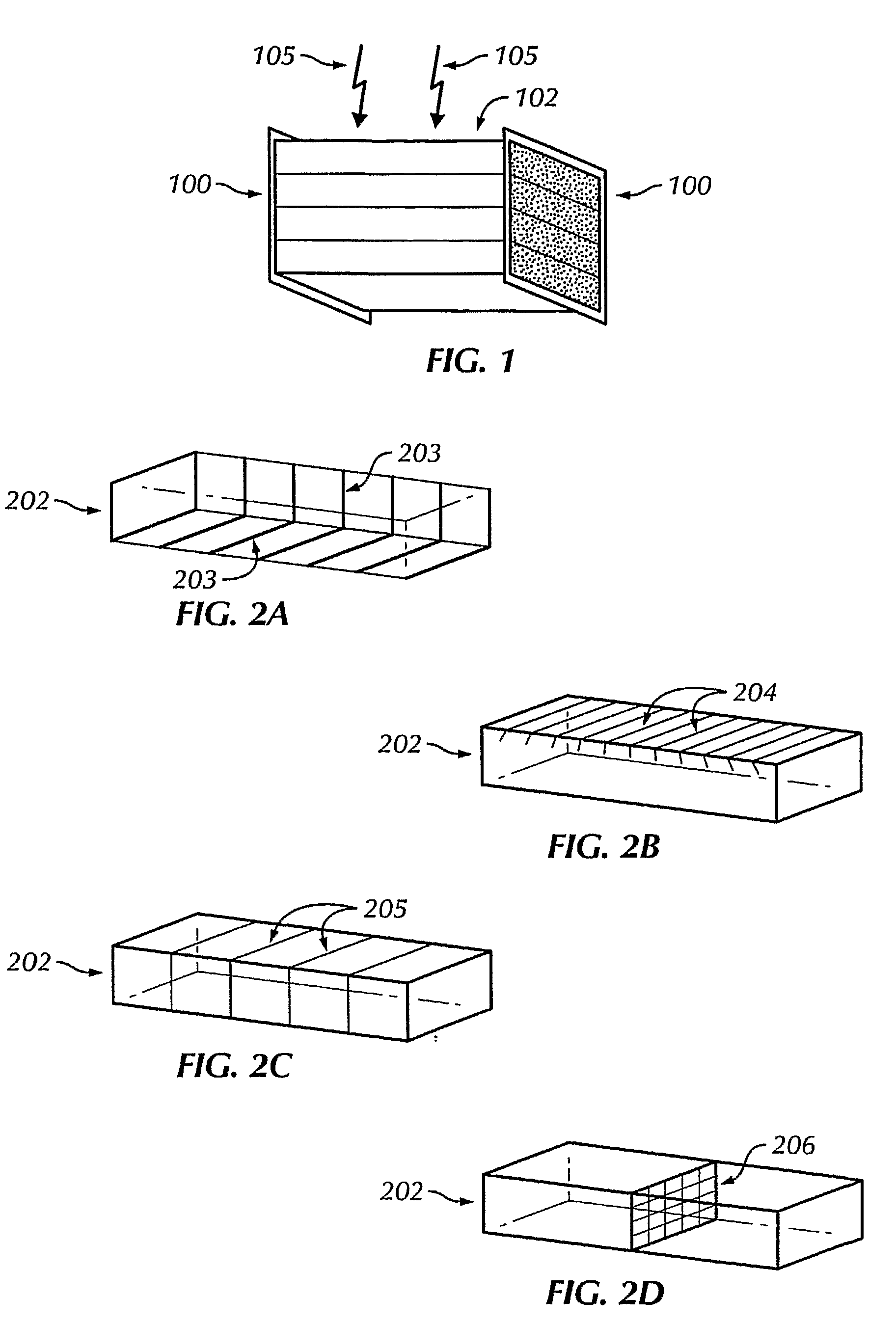
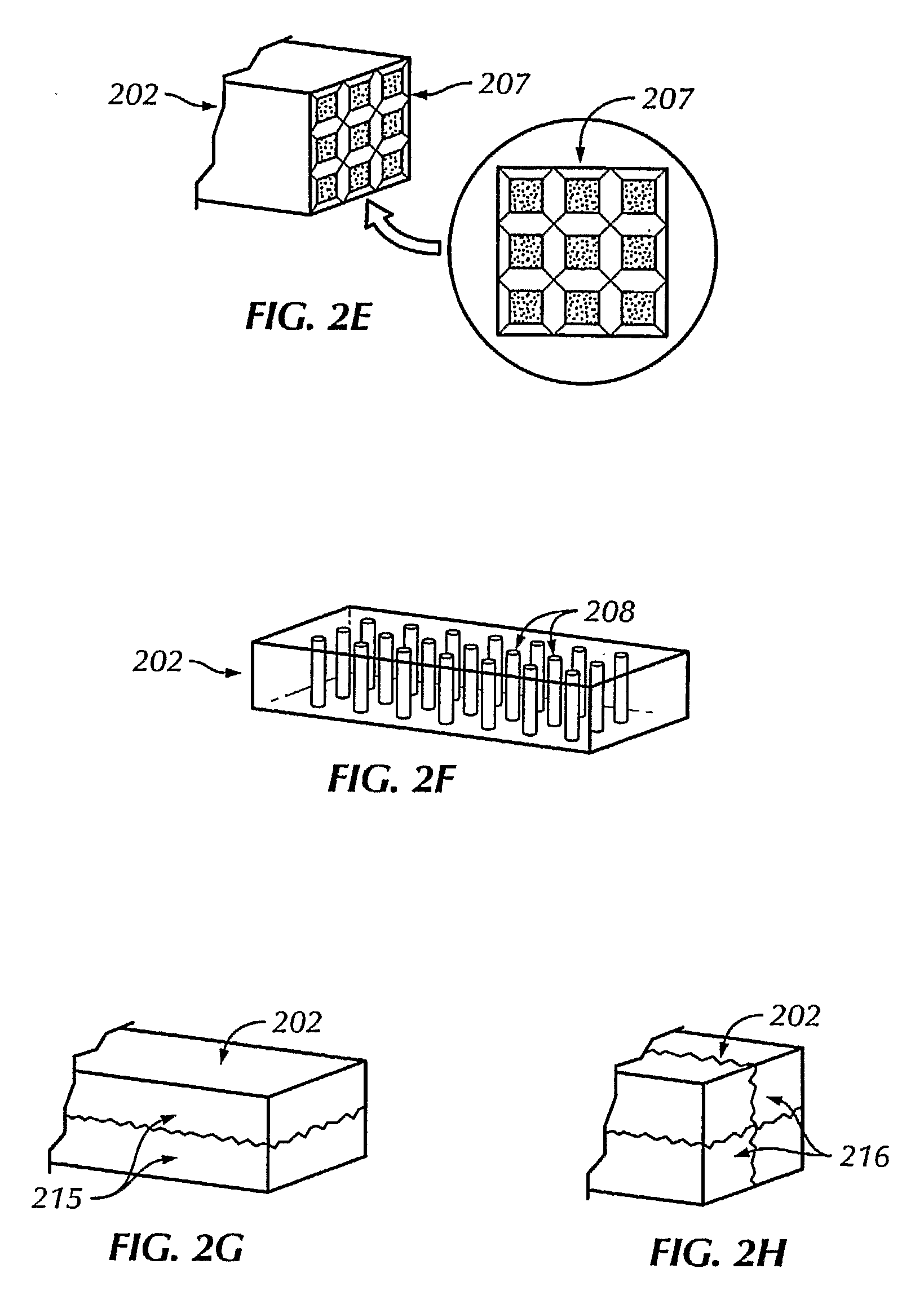
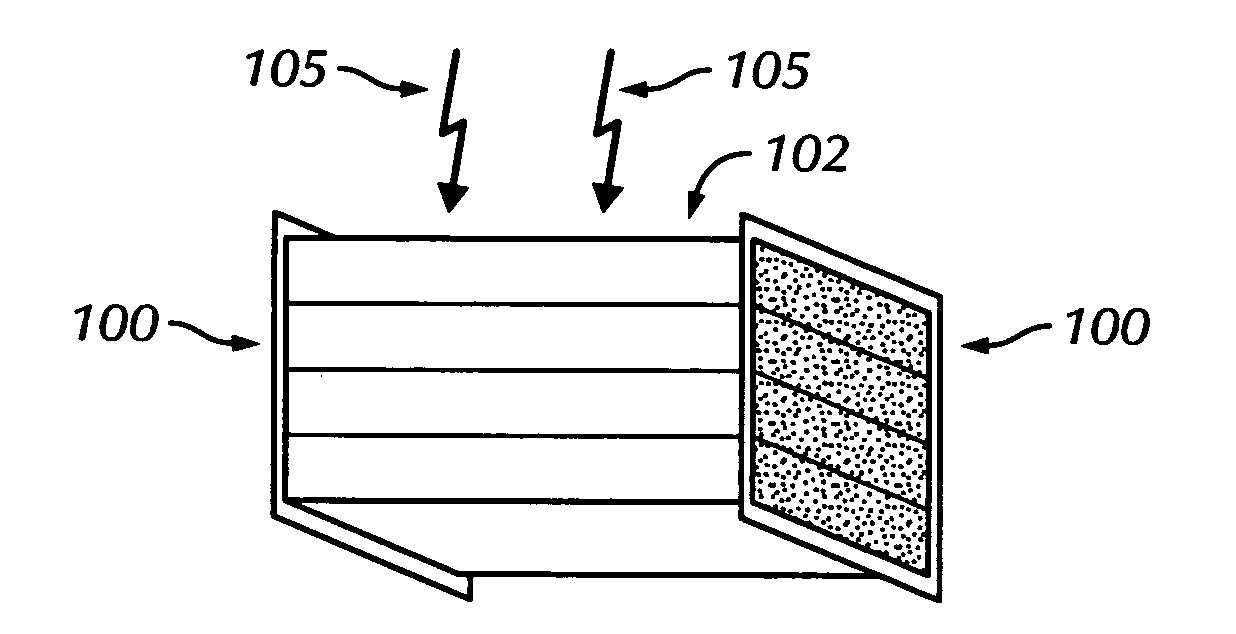
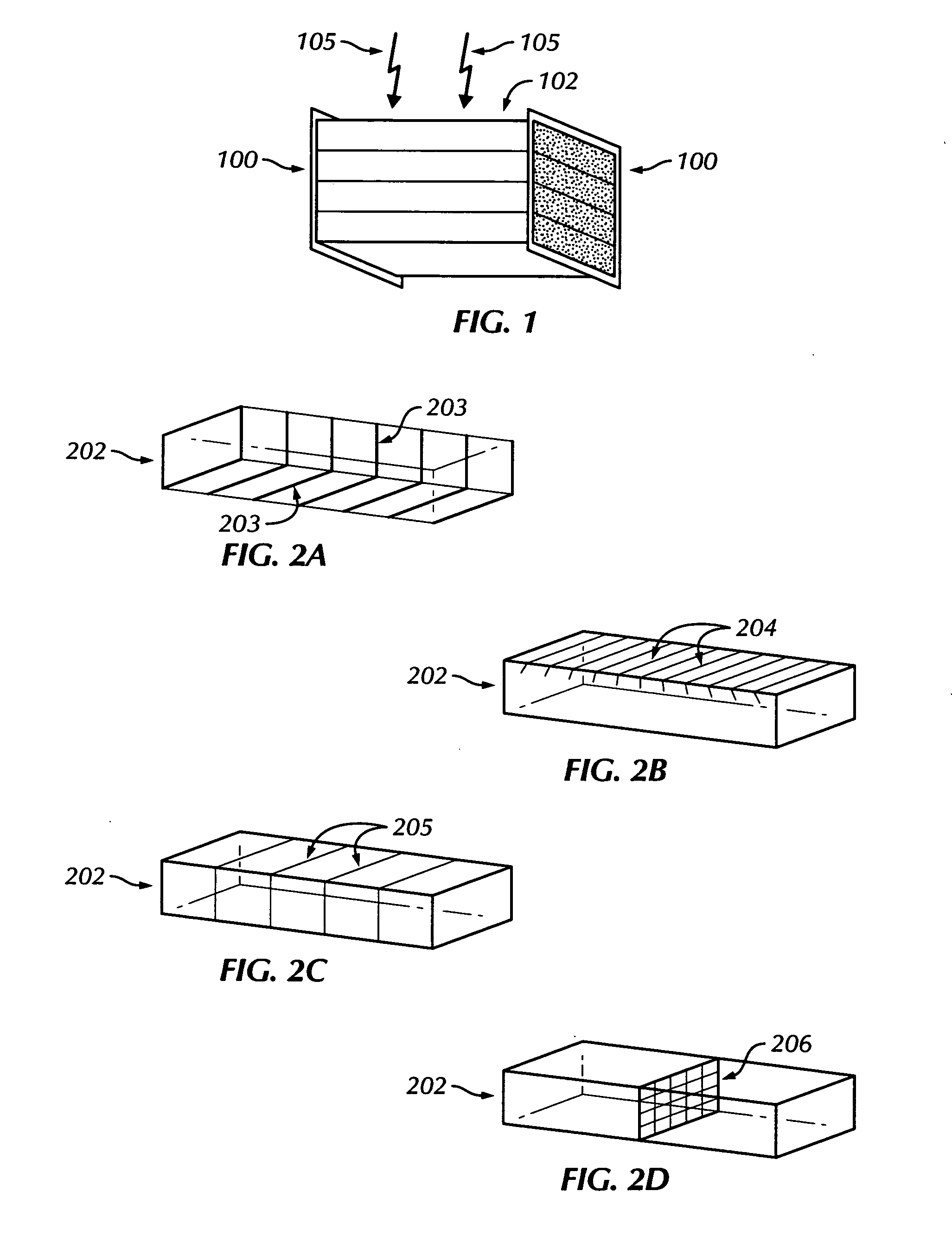
The invention provides methods and apparatus for detecting radiation including x-ray, gamma ray, and particle radiation for nuclear medicine, radiopaphic imaging, material composition analysis, high energy physics, container inspection, mine detection and astronomy. The invention provides detection systems employing one or more detector modules (102) comprising edge-on scintillator detectors (101) with sub-aperture resolution (SAR) capability employed, e.g., in nuclear medicine, such as radiation therapy portal imaging, nuclear remediation, mine detection, container inspection, and high energy physics and astronomy. The invention also provides edge-on imaging probe detectors for use in nuclear medicine, such as radiation therapy portal imaging, or for use in nuclear remediation, mine detection, container inspection, and high energy physics and astronomy.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
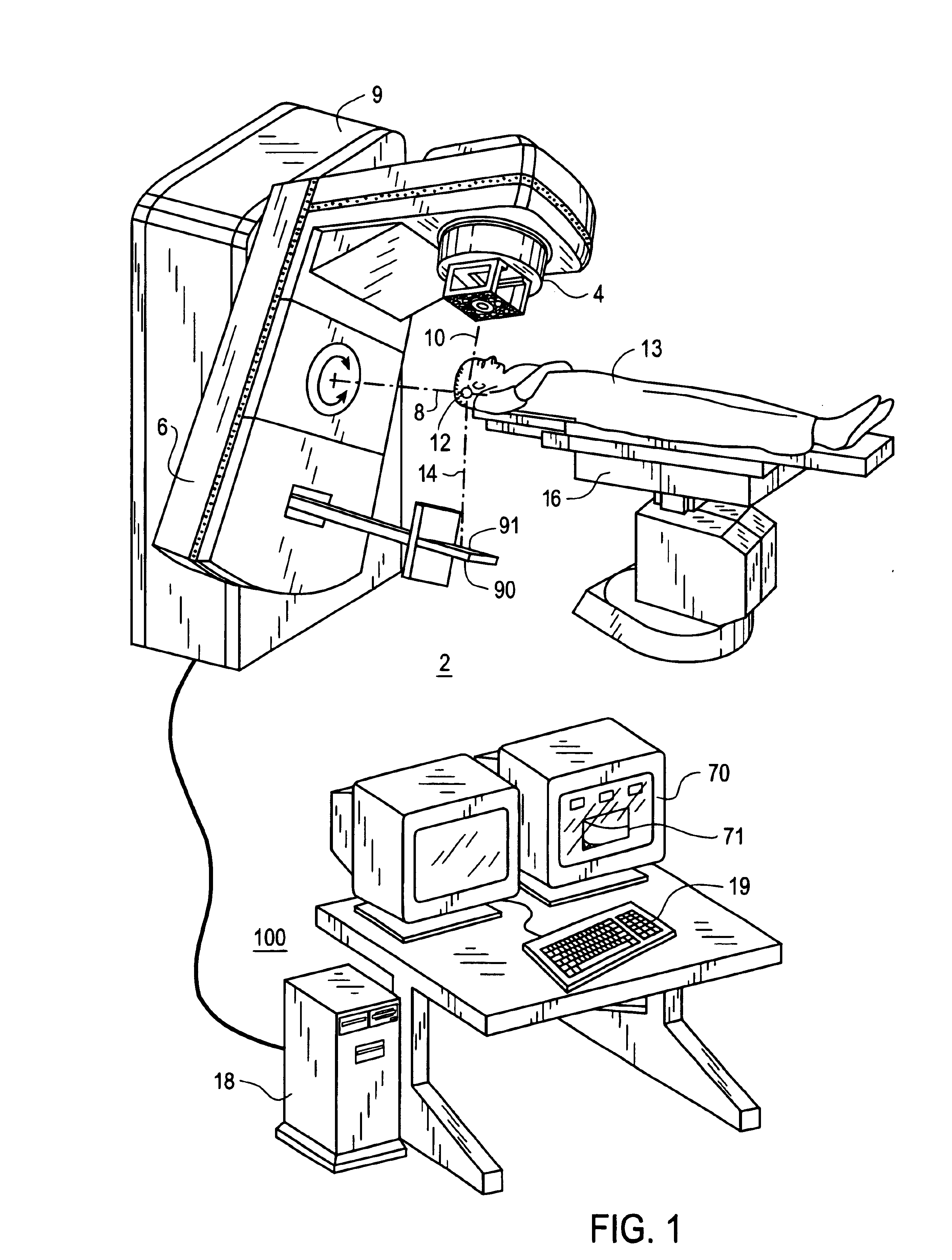
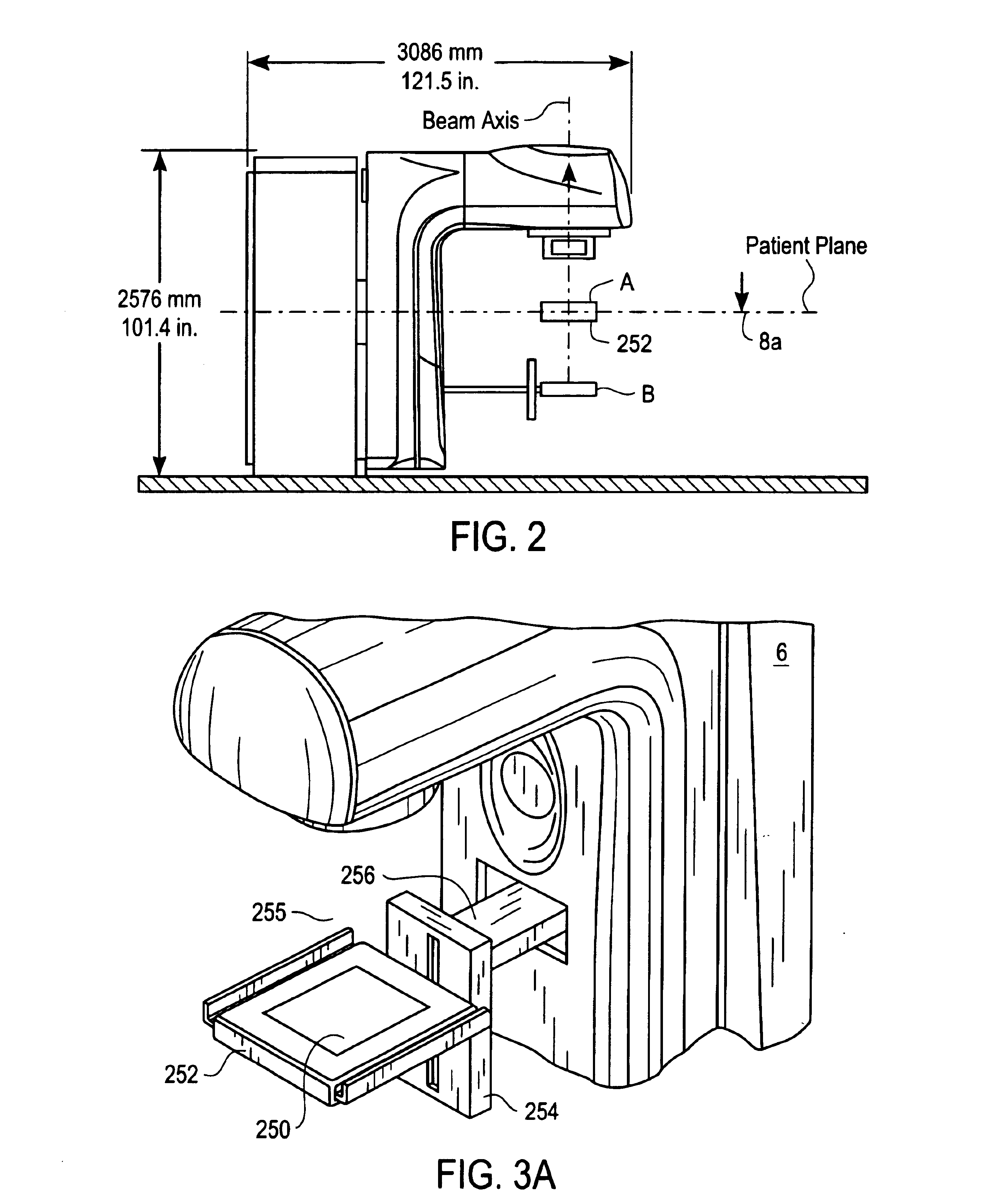
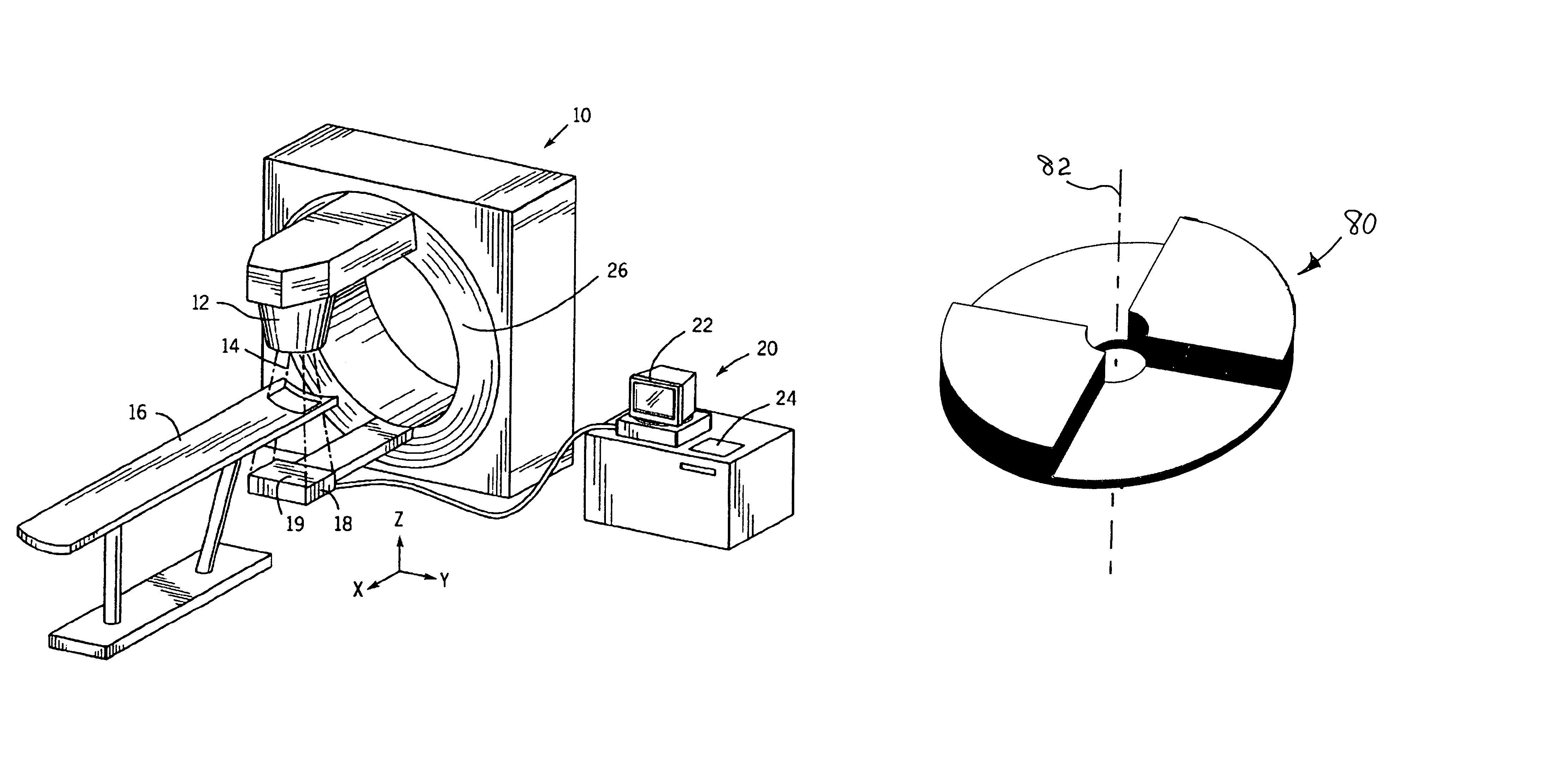
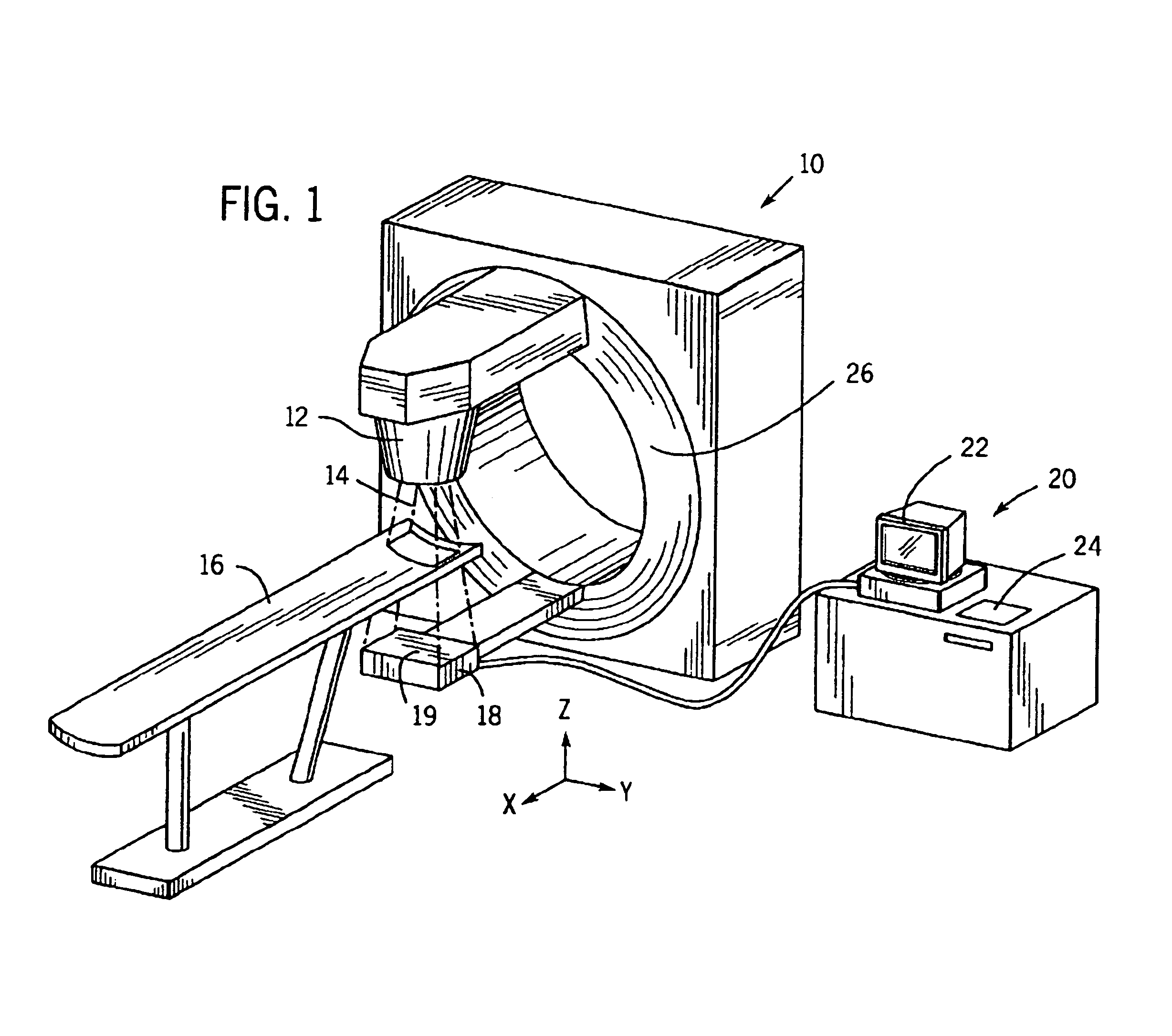
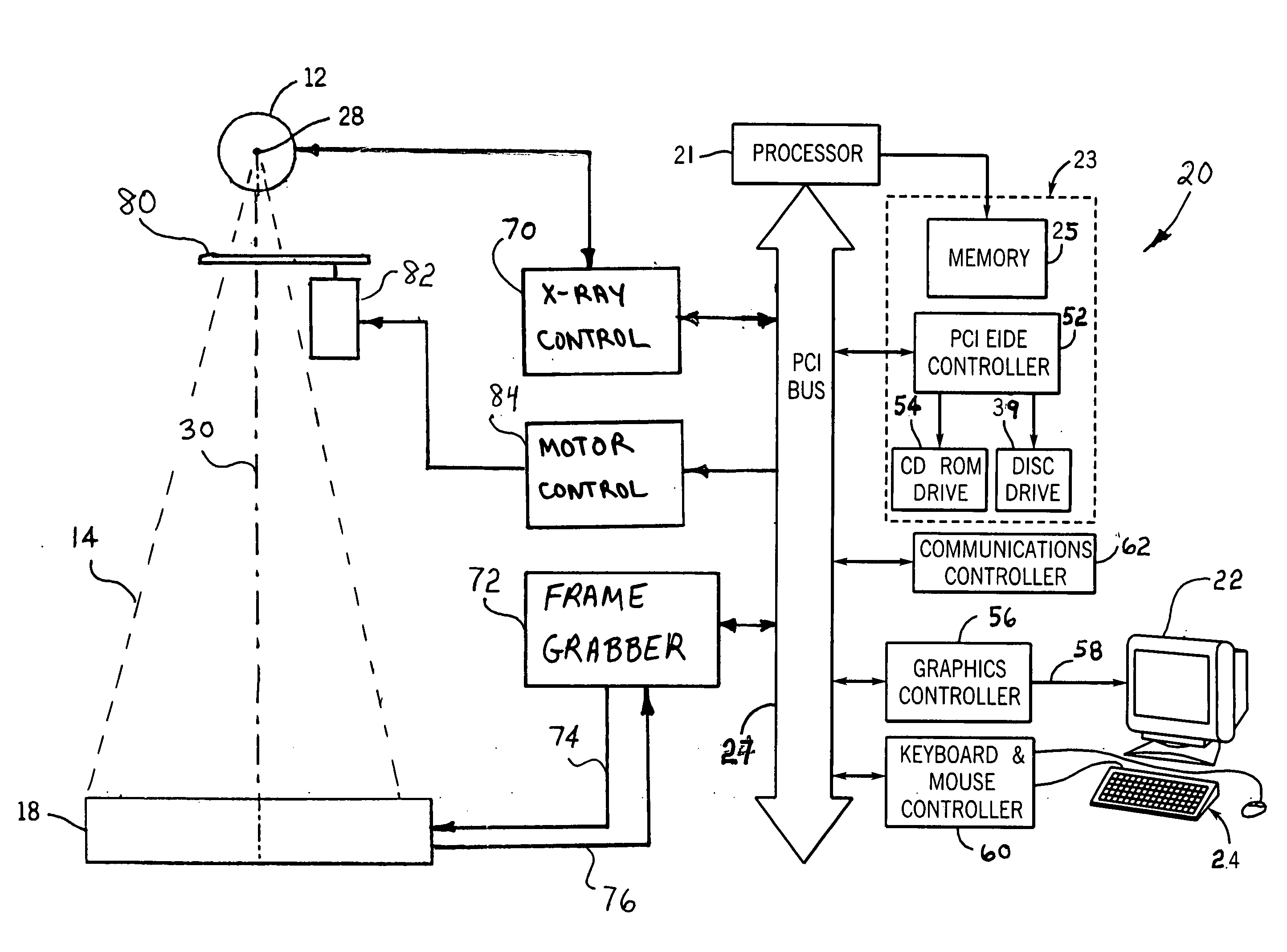
System and method for positioning an electric portal imaging device
InactiveUS6839404B2Precise positioningSufficient clearanceRadiation beam directing meansX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyEngineeringImaging equipment
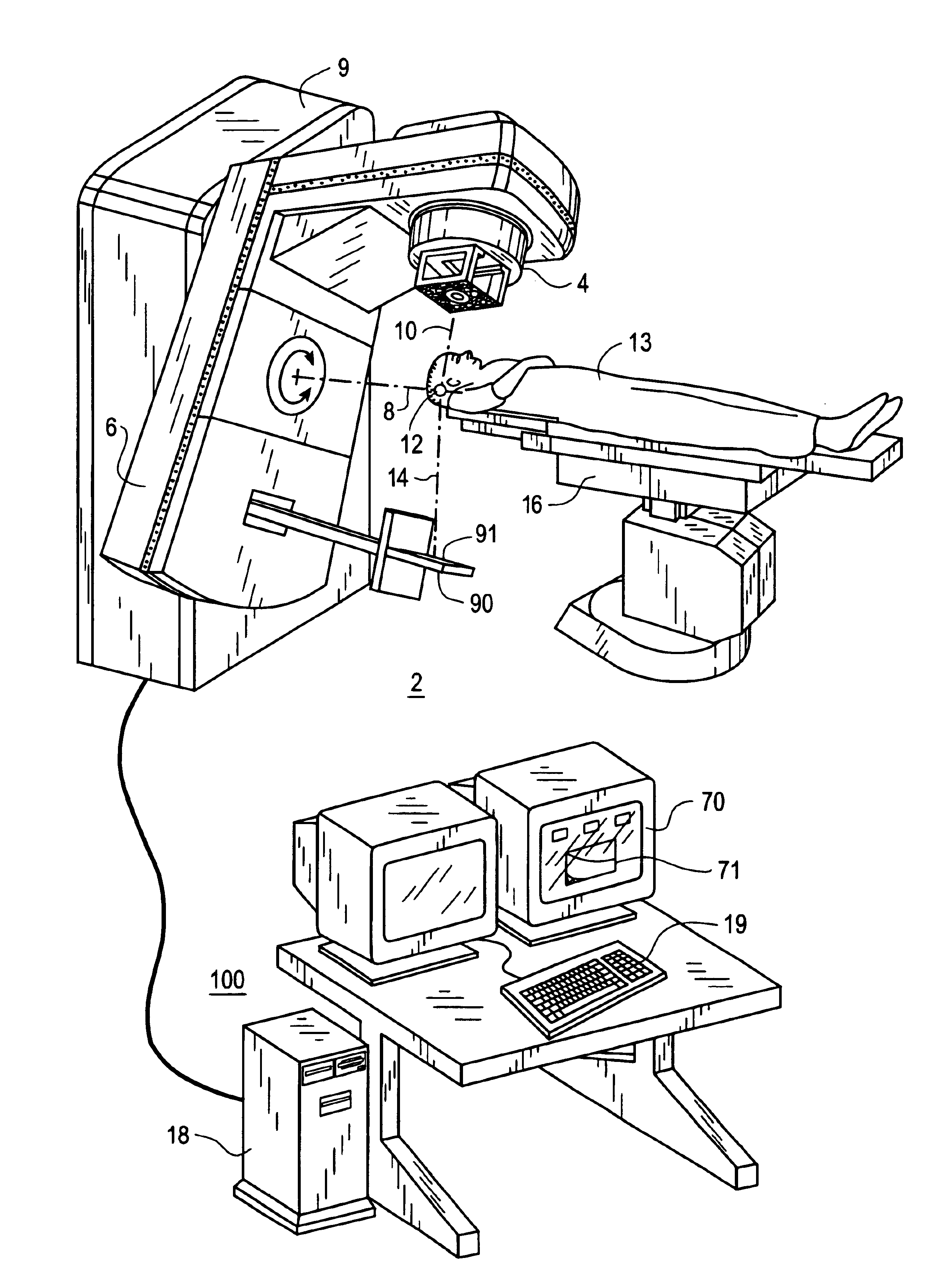
A portal imaging device positioning apparatus includes a portal imaging device positioner (255) attachable to a support (256). The portal imaging device positioner (255) is adapted to vertically adjust an imaging panel (250) in a treatment or dosimetry mode to receive radiation through a body in the patient plane (8a), and adjust the panel in a physics mode to receive radiation at the patient plane (8a).
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Edge-on SAR scintillator devices and systems for enhanced SPECT, PET, and compton gamma cameras
InactiveUS7635848B2Space minimizationHigh resolutionSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh energyX-ray
The invention provides methods and apparatus for detecting radiation including x-ray, gamma ray, and particle radiation for nuclear medicine, radiographic imaging, material composition analysis, high energy physics, container inspection, mine detection and astronomy. The invention provides detection systems employing one or more detector modules (102) comprising edge-on scintillator detectors (101) with sub-aperture resolution (SAR) capability employed, e.g., in nuclear medicine, such as radiation therapy portal imaging, nuclear remediation, mine detection, container inspection, and high energy physics and astronomy. The invention also provides edge-on imaging probe detectors for use in nuclear medicine, such as radiation therapy portal imaging, or for use in nuclear remediation, mine detection, container inspection, and high energy physics and astronomy.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
High quantum efficiency x-ray detector for portal imaging
ActiveUS7030386B2Increasing probability of absorptionSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansMicro structureHigh energy
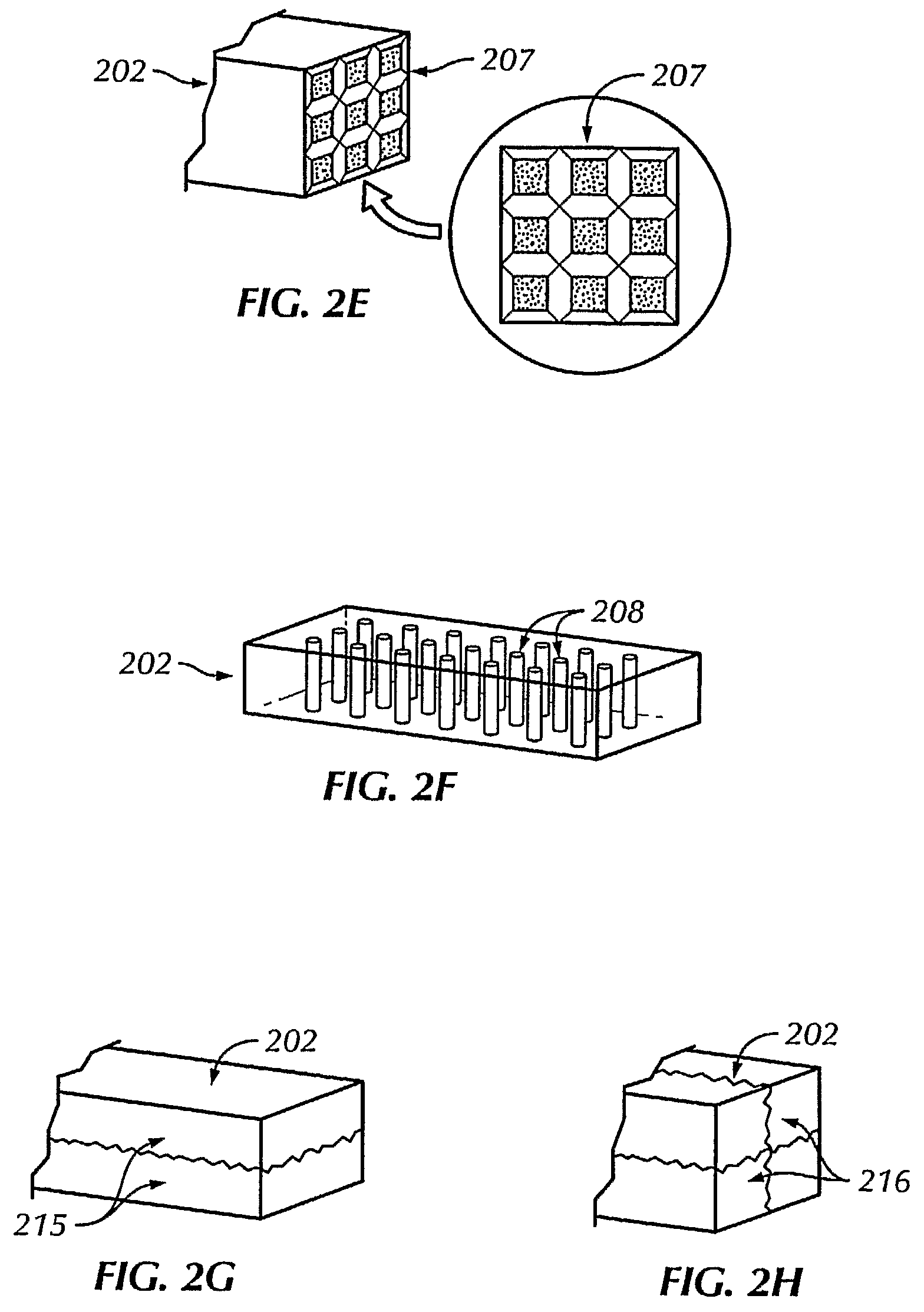
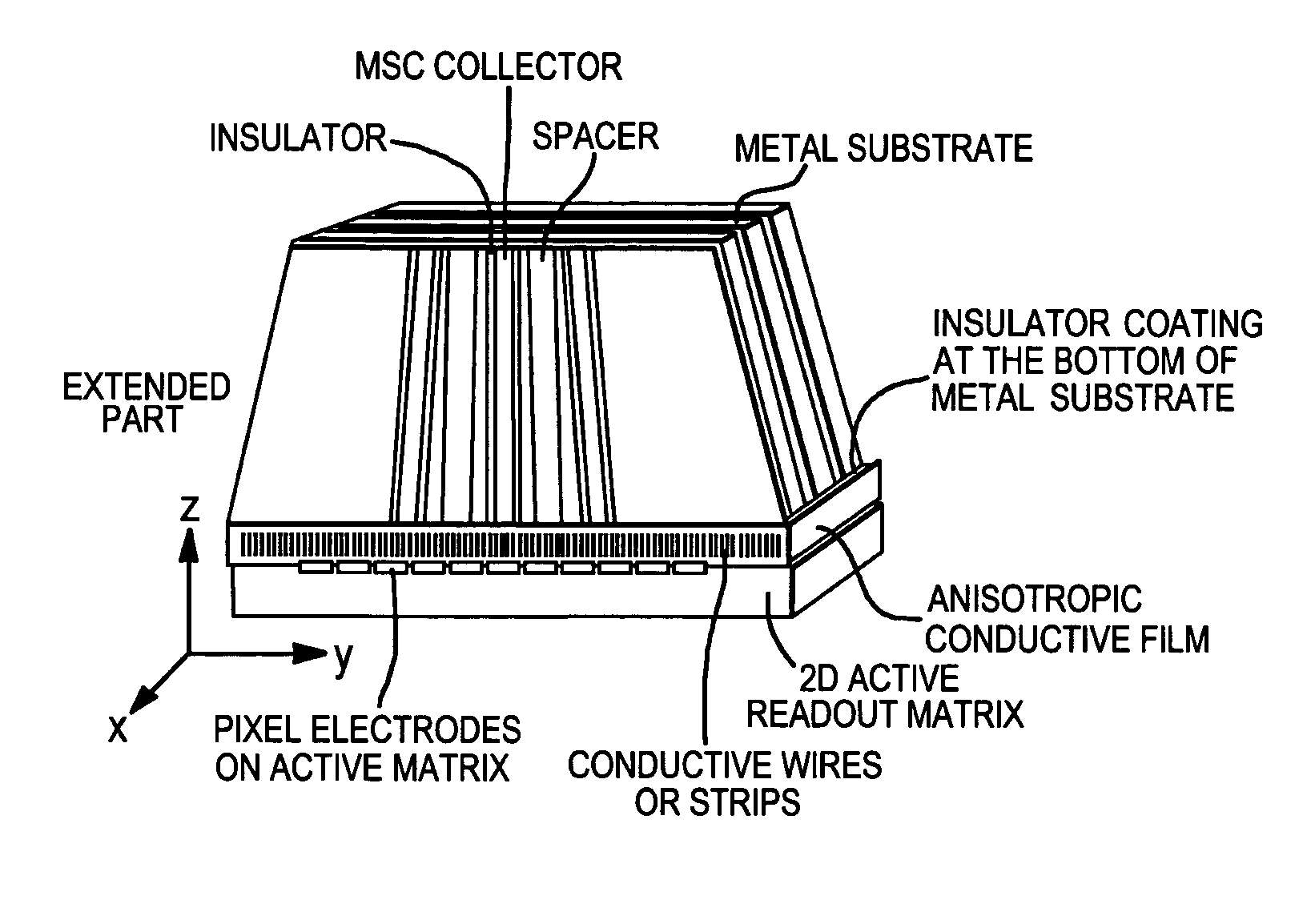
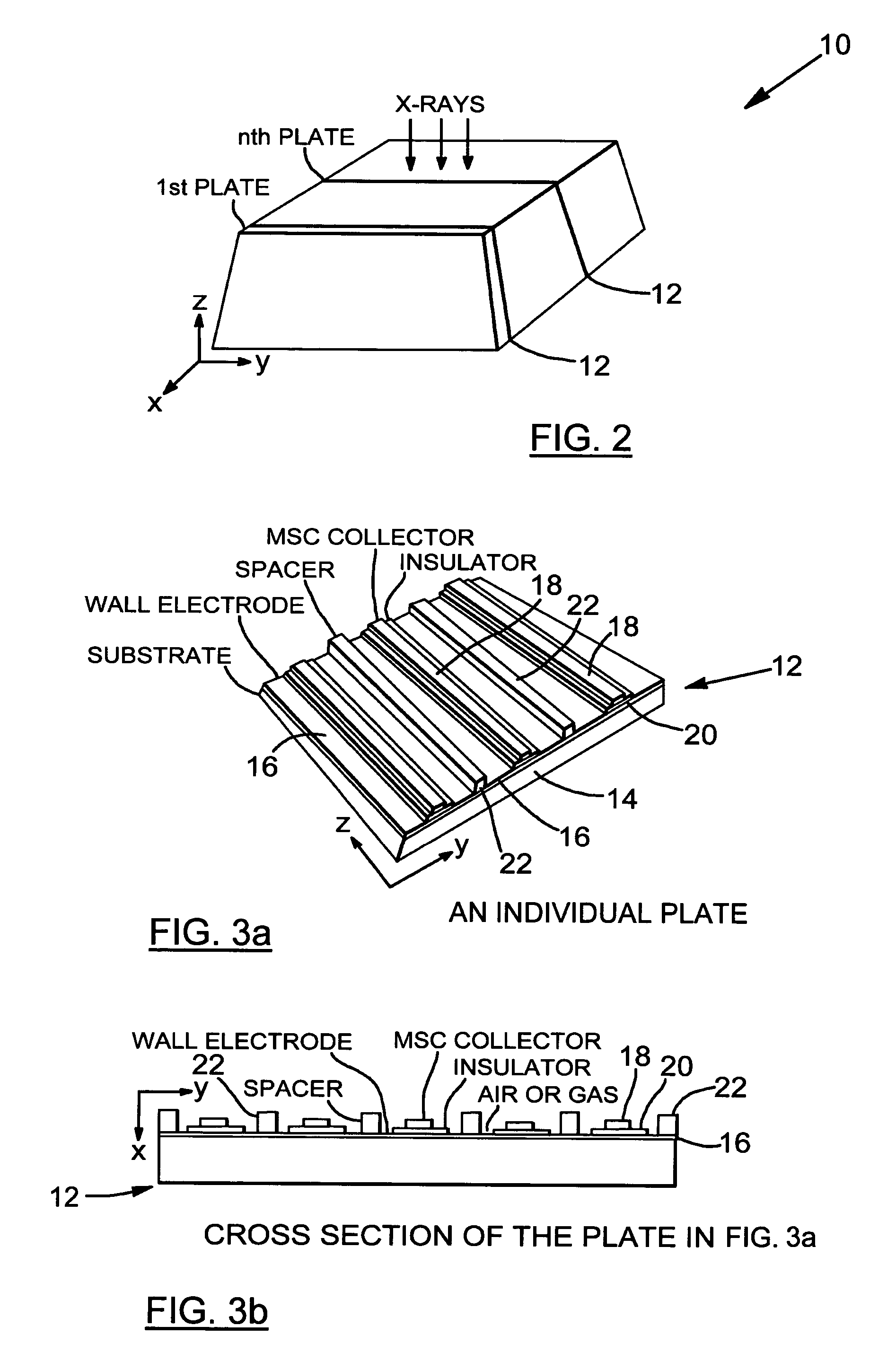
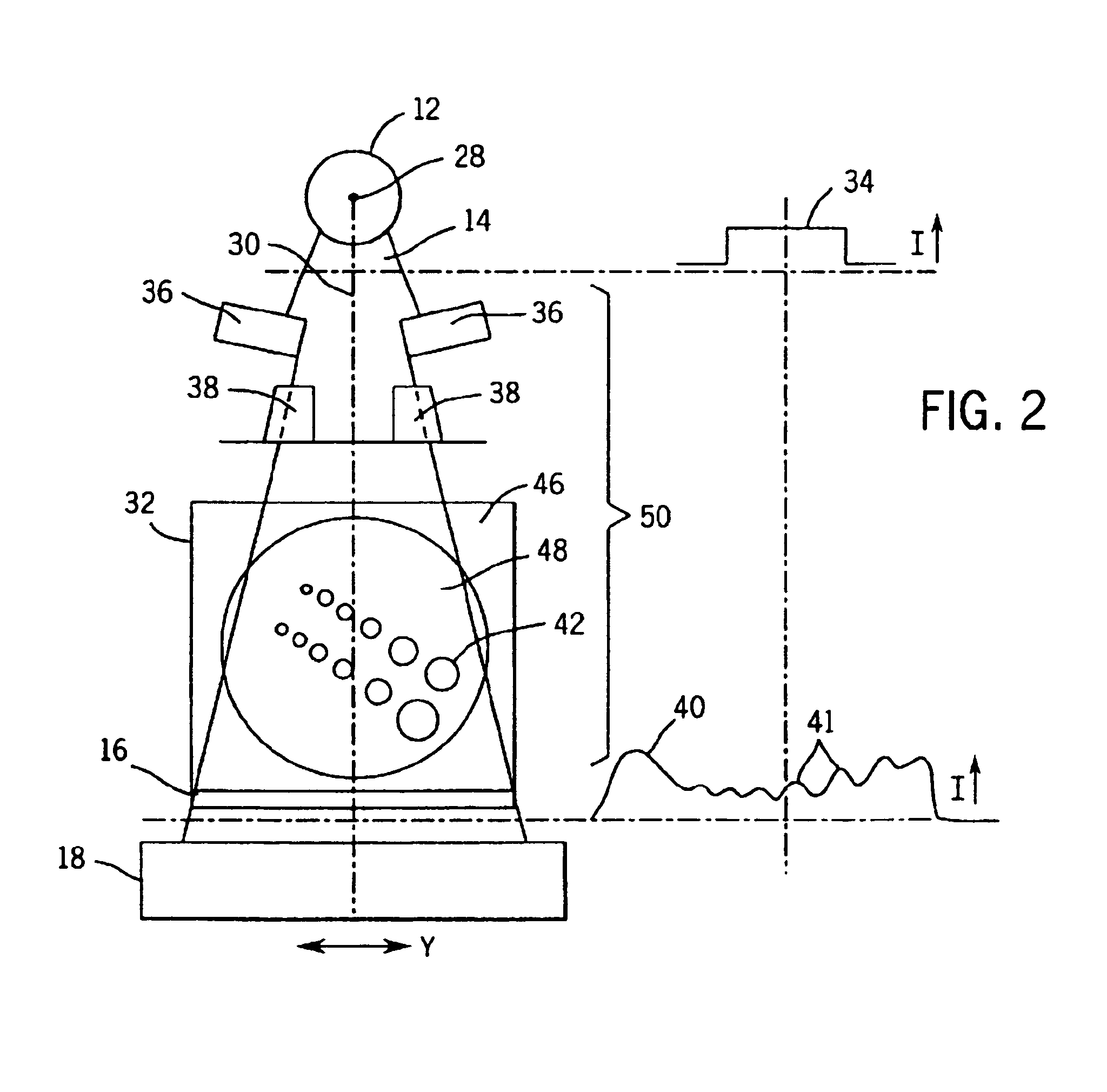
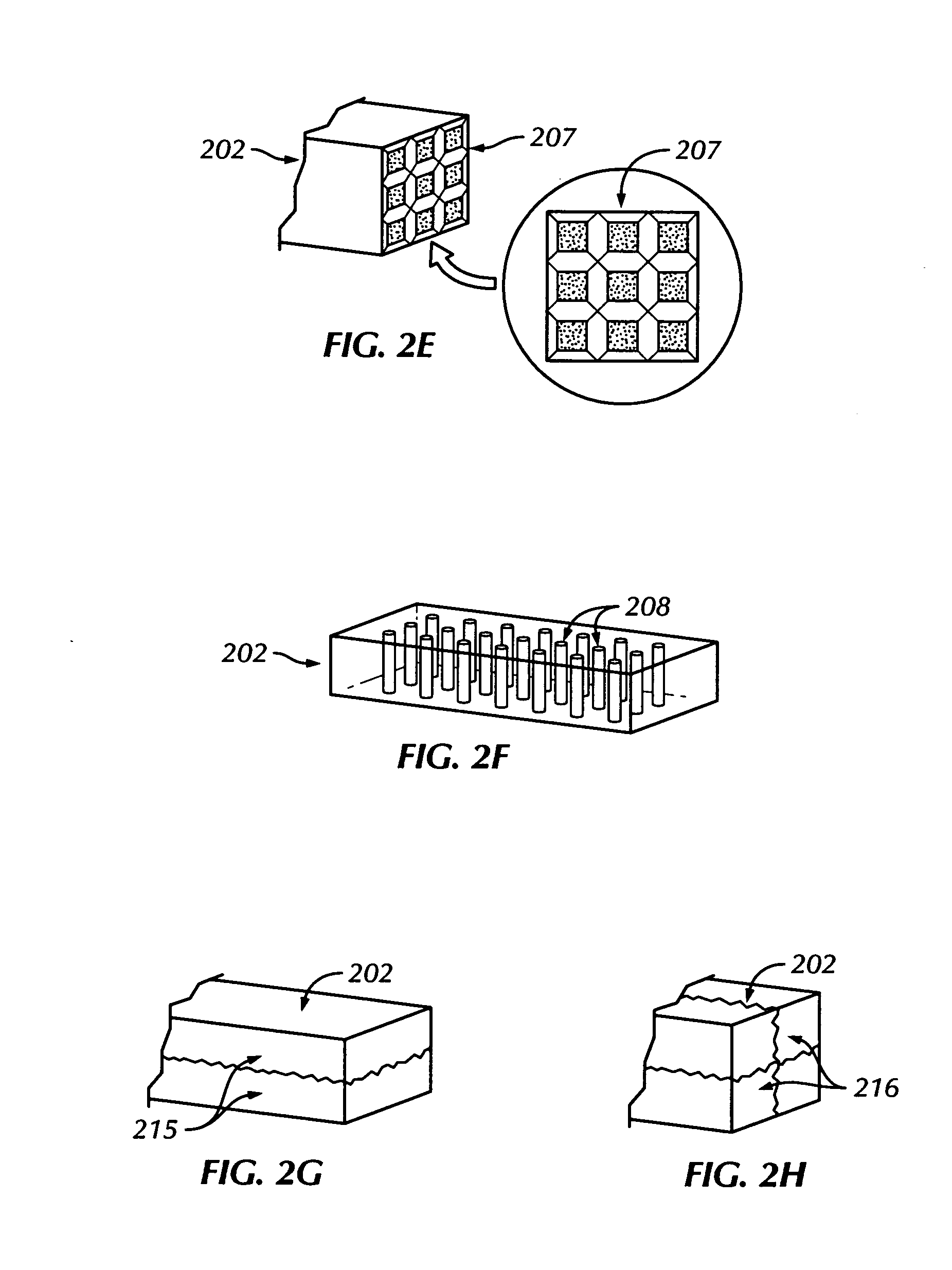
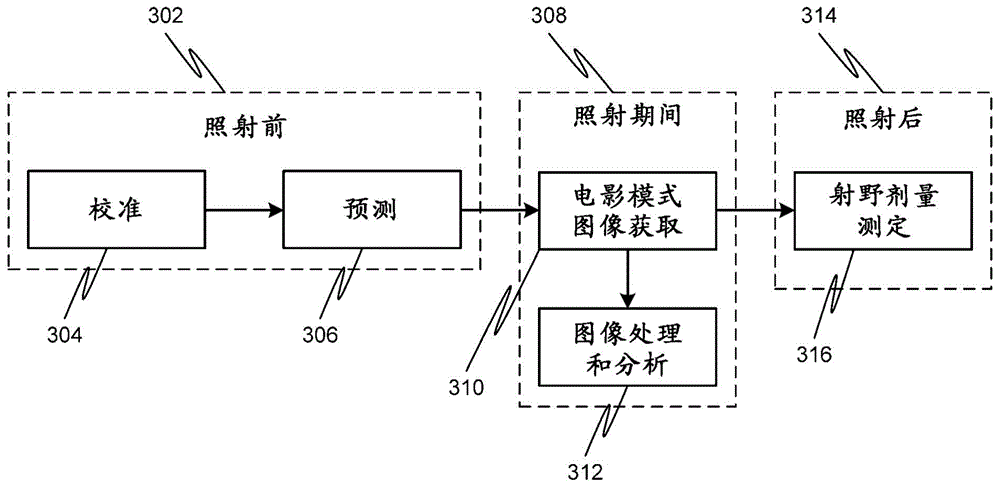
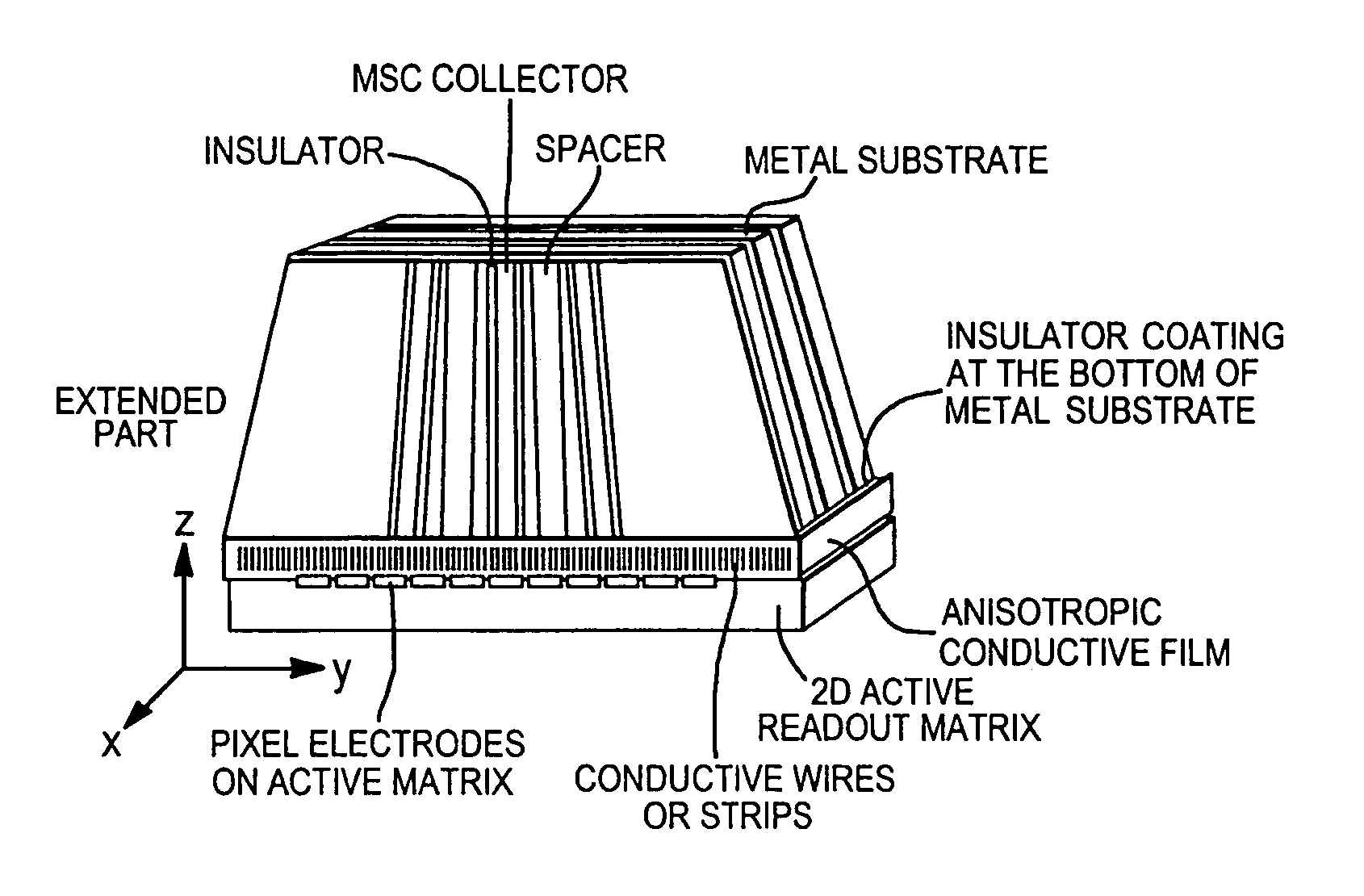
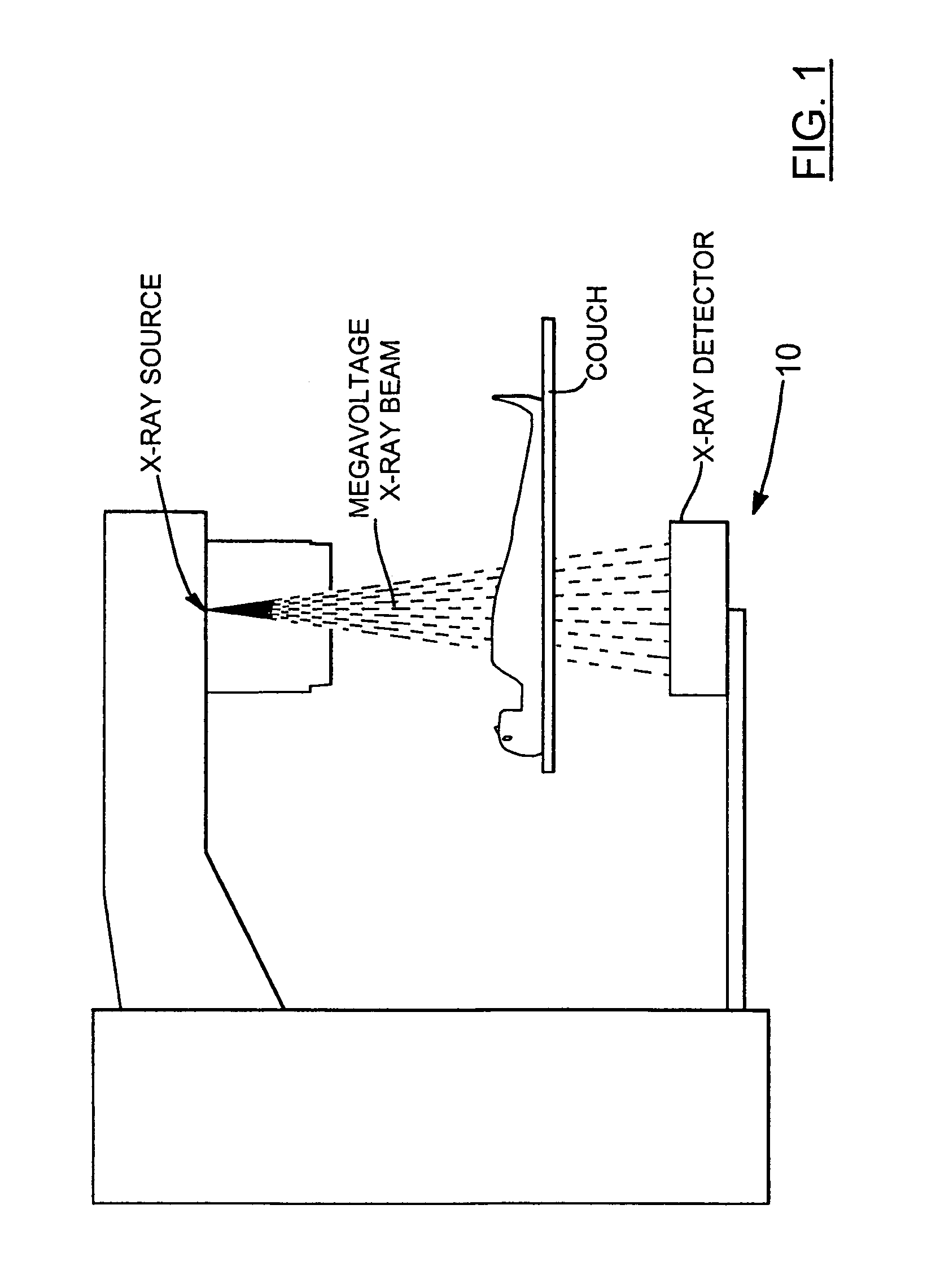
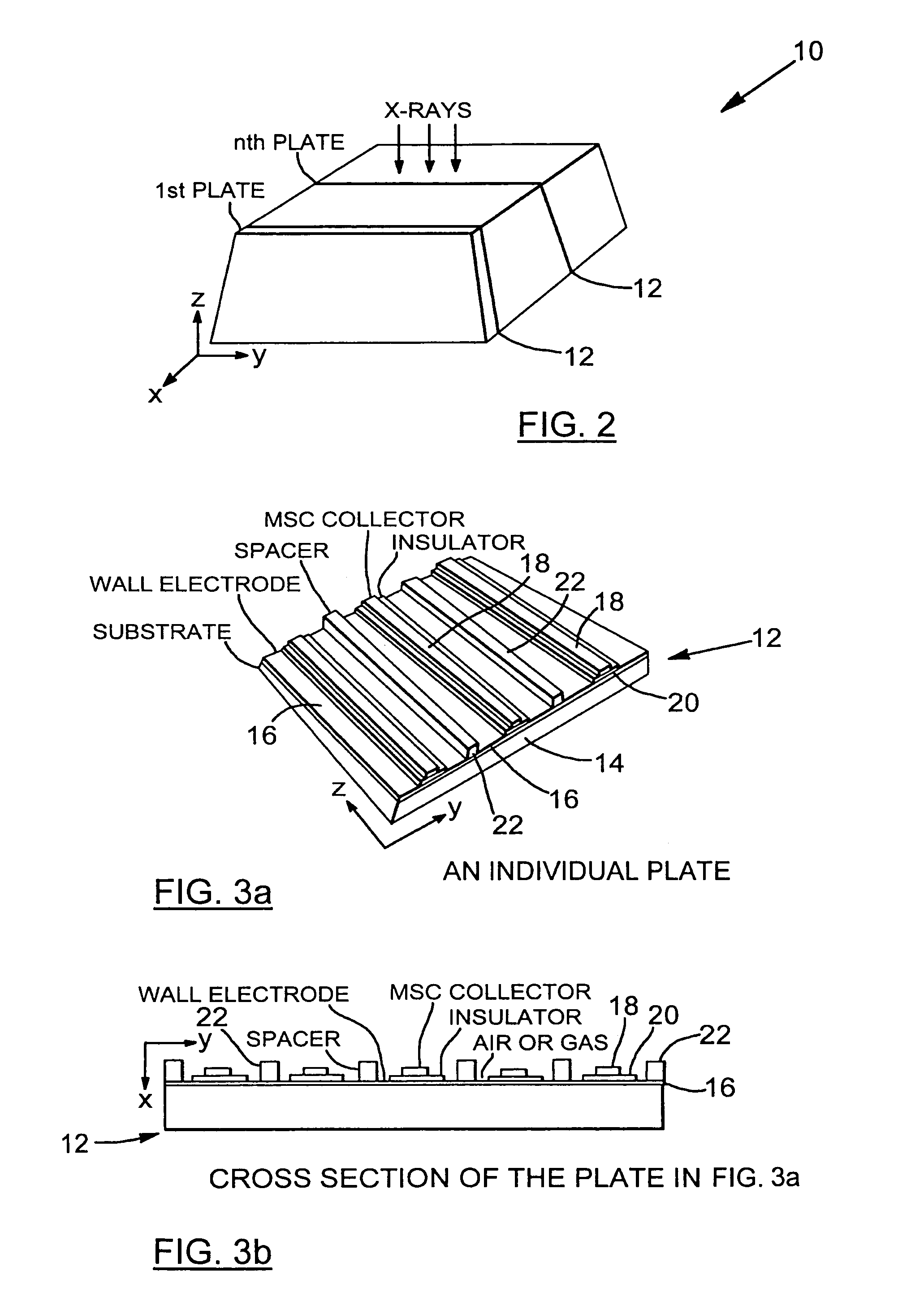
The present invention provides a practical design of a megavoltage x-ray detector with both high quantum efficiency (QE) and high resolution. The x-ray detector disclosed herein has a QE that can be an order of magnitude higher than that of current flat panel systems and yet has a spatial resolution equivalent to that of current flat panel systems used for portal imaging. The x-ray detector includes a large number of micro-structured electrically conducting plates, packed together with thin spacers placed between neighboring plates with the micro-structured plates oriented to be parallel to the incident x-rays in operation. Each plate includes an electrically conductive substrate with a first planar surface, elongate electrically conductive strip electrodes separated from each other with strip spacers placed in between and sitting on an insulating layer interposed between the first planar surface of the electrically conductive substrate and the strip electrodes. A power supply applies a bias voltage between each electrically conductive substrate and the electrically conductive strip electrodes, whereby x-rays absorbed in the conductive substrate generates high energy electrons which produce ions in an ionization medium located in spaces between the conductive substrate and the electrically conductive strips. A detector detects an electrical current generated in the electrically conductive strip electrodes and a 2D active readout matrix is coupled to the detector.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK & WOMENS COLLEGE HEALTH SCI CENT +1
Method for collecting spatial population distribution in real time on basis of mobile phone big data and realizing large passenger flow early warning
InactiveCN105488120ALow costIncrease frequencyData processing applicationsLocation information based serviceHuman population distributionMobile communication network
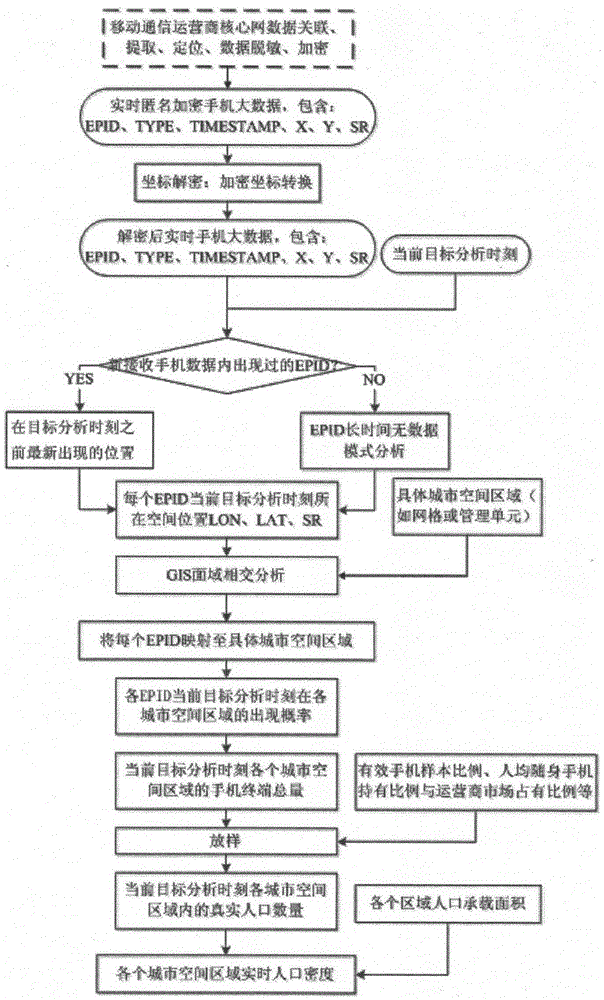
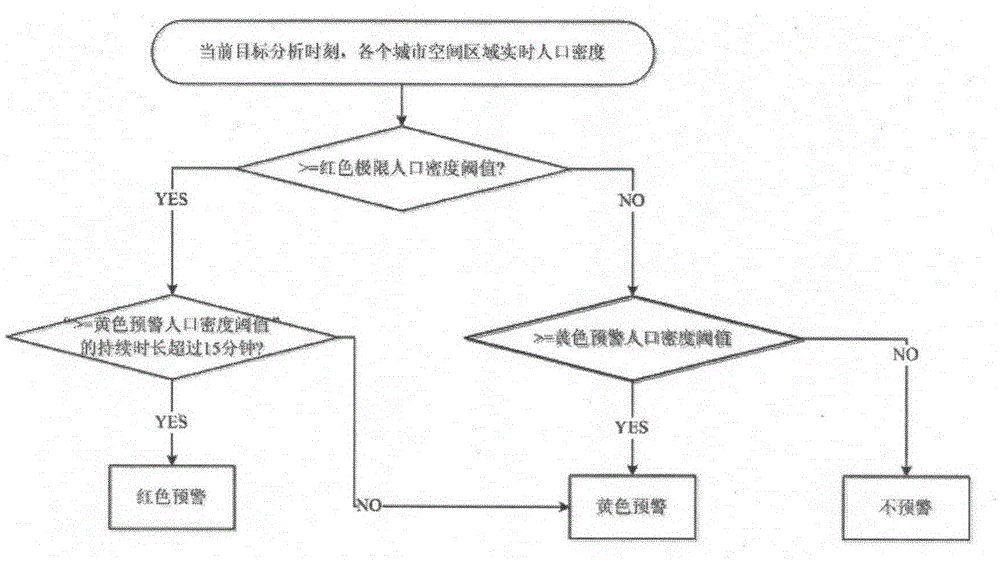
The invention aims at providing a method for collecting spatial population distribution in real time on the basis of mobile phone big data and realizing large passenger flow early warning. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of obtaining real-time mobile phone big data from a mobile phone communication operator at each statistics moment; dividing a target region into different space regions; at the current statistics moment, mapping the latest space position of each EPID (Electronic Portal Imaging Device) obtained in the first step to each space region of the target region; and obtaining the real population size (the distribution condition of the total population in the whole target region) in each space region at the current statistics moment. The method has the advantages that the sufficient relying on the existing mobile phone big data resources is realized; the continuous encrypted position information of the existing mass anonymous mobile phone users in the mobile communication network is used; the low-cost high-frequency and automatic implementation can be realized; and the popularization distribution data in a large-range urban space range can be continuously obtained in a fast deploying way.
Owner:上海川昱信息科技有限公司
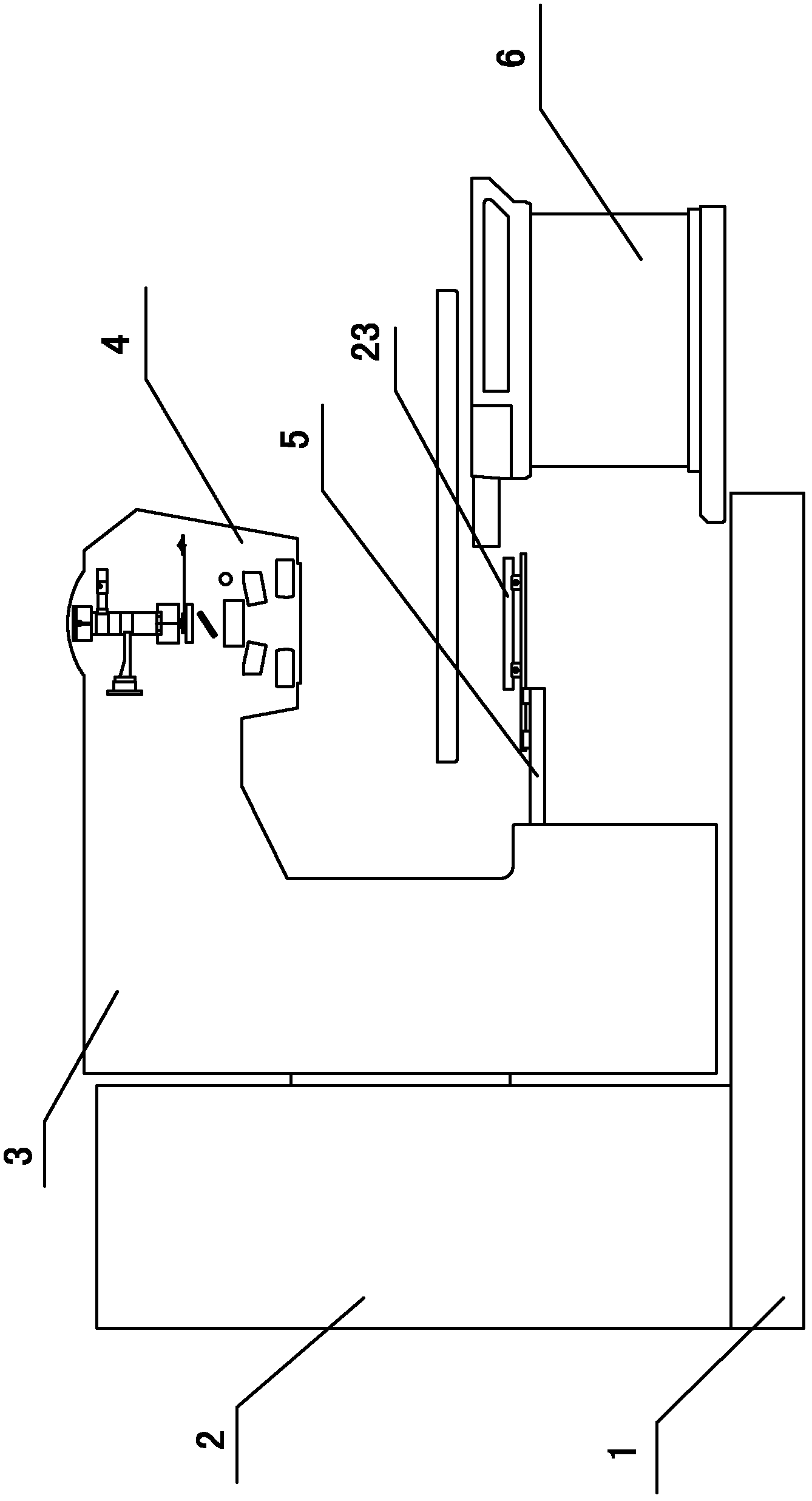
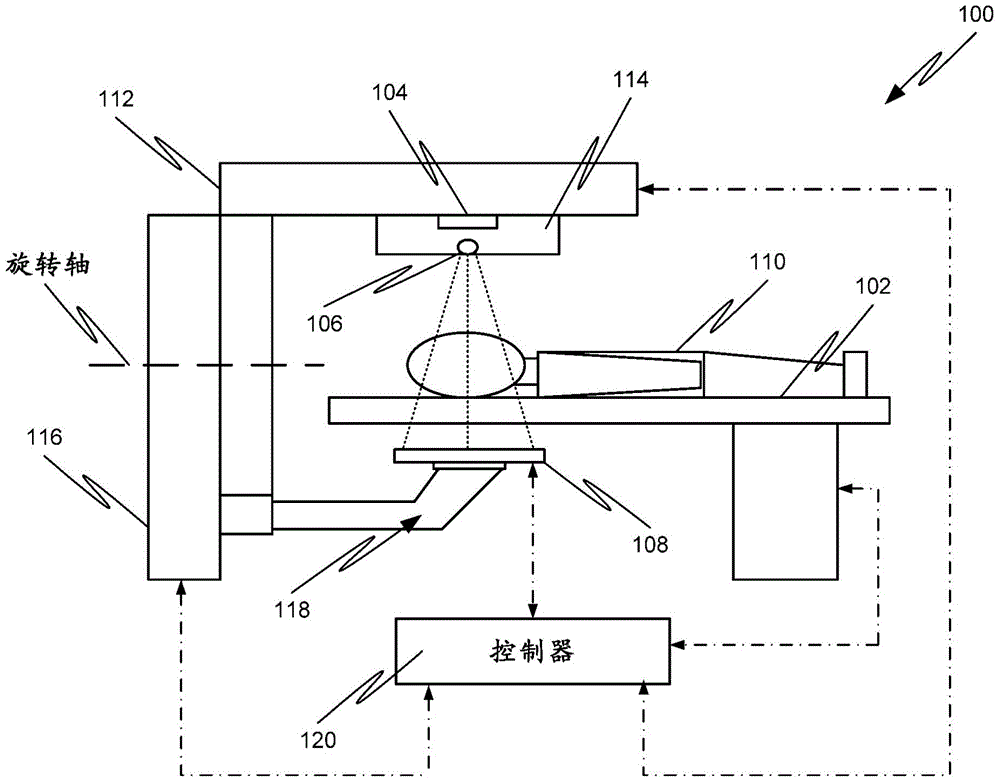
Accurate stereotactic radiosurgery treatment device
InactiveCN107362464AMechanical balance counterweight problem solvingReduce shielding requirementsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiosurgeryEngineering
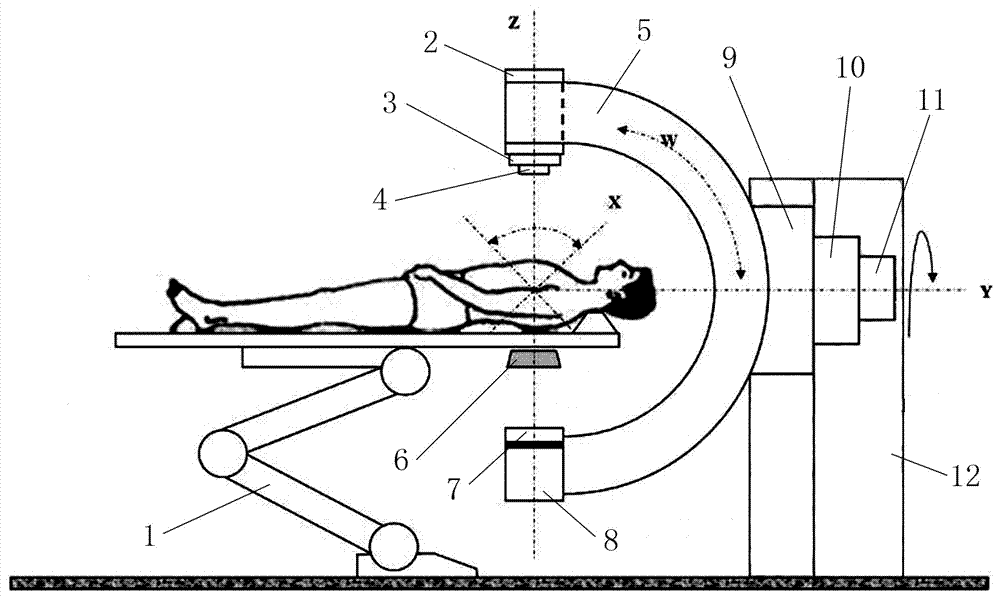
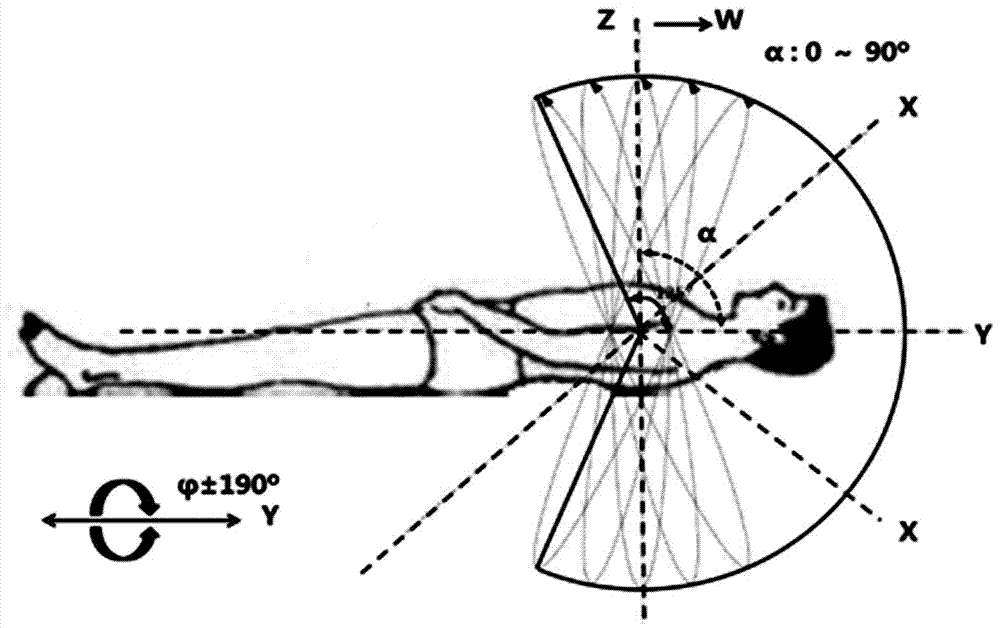
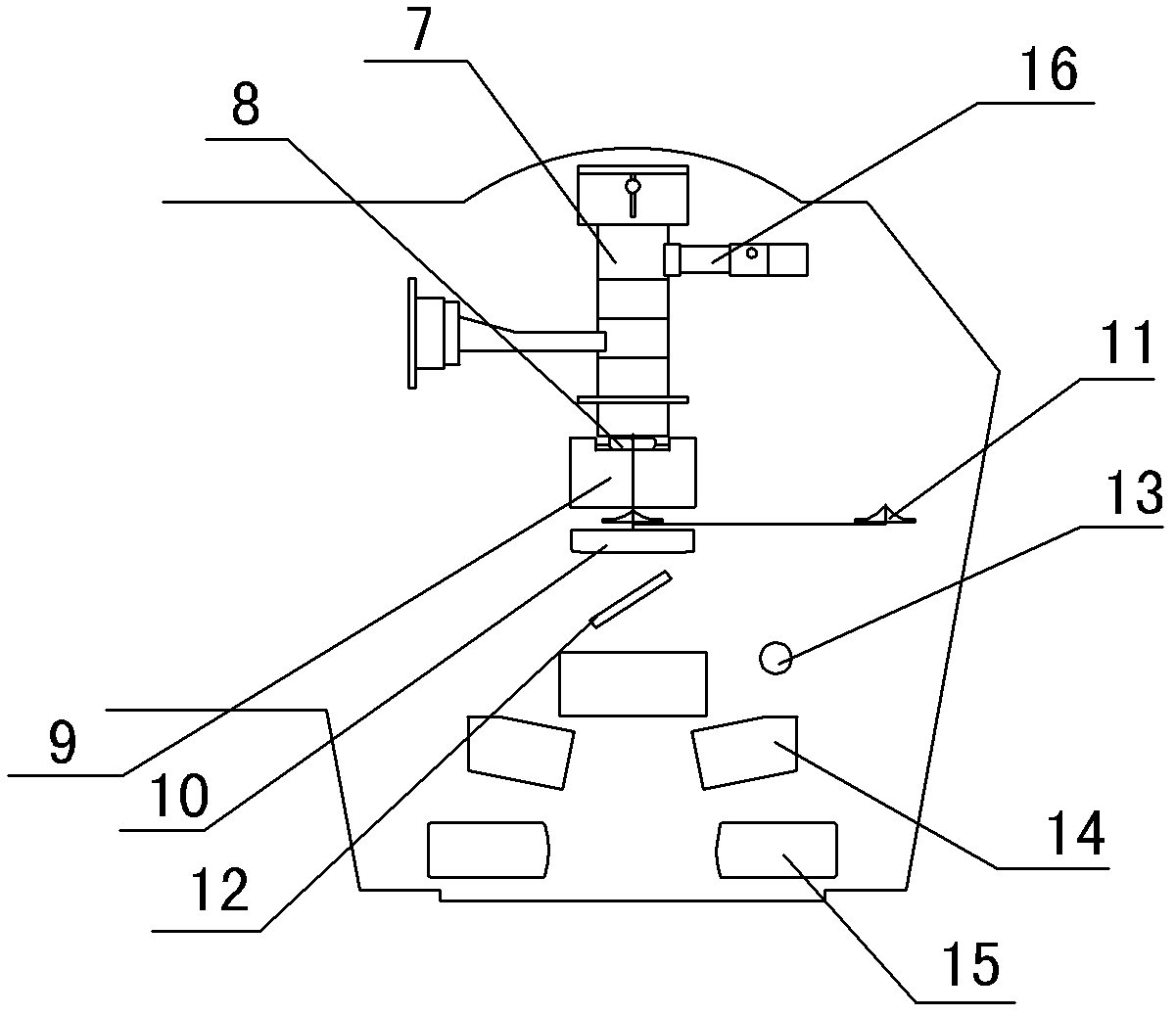
The invention provides an accurate stereotactic radiosurgery treatment device which belongs to the field of a medical device. The accurate stereotactic radiosurgery treatment device is composed of a radiation device system, a six-dimensional robot treatment bed 1 and a treatment planning system. The radiation device system is composed of a frame 12 and a C-shaped machine arm 5. The frame 12 is provided with a rotating shaft 10. The rotating shaft 10 is connected with a guiderail 9 and controls rotation of the guiderail 9. The C-shaped machine arm 5 is mounted on the guiderail 9 and performs arc-shaped motion along the guiderail 9. One end of the C-shaped machine arm 5 is provided with a radiation source 2. The bottom end of the radiation source 2 is provided with a small machine head 3. The bottom end of the small machine head 3 is provided with a collimator. The other end of the C-shaped machine arm 5 is provided with a telescopic electronic portal imaging device 7 and a movable shielding protecting counterweight 8. A target organ positioning and detecting device 6 is mounted at the side part or the lower part of the six-dimensional robot treatment bed 1. The radiation treatment head of the accurate stereotactic radiosurgery treatment device can perform 90-degree (or + / -45-degree) rotation around an X axis so that rays can be transmitted in a 4pi non-coplanar track.
Owner:吴大可
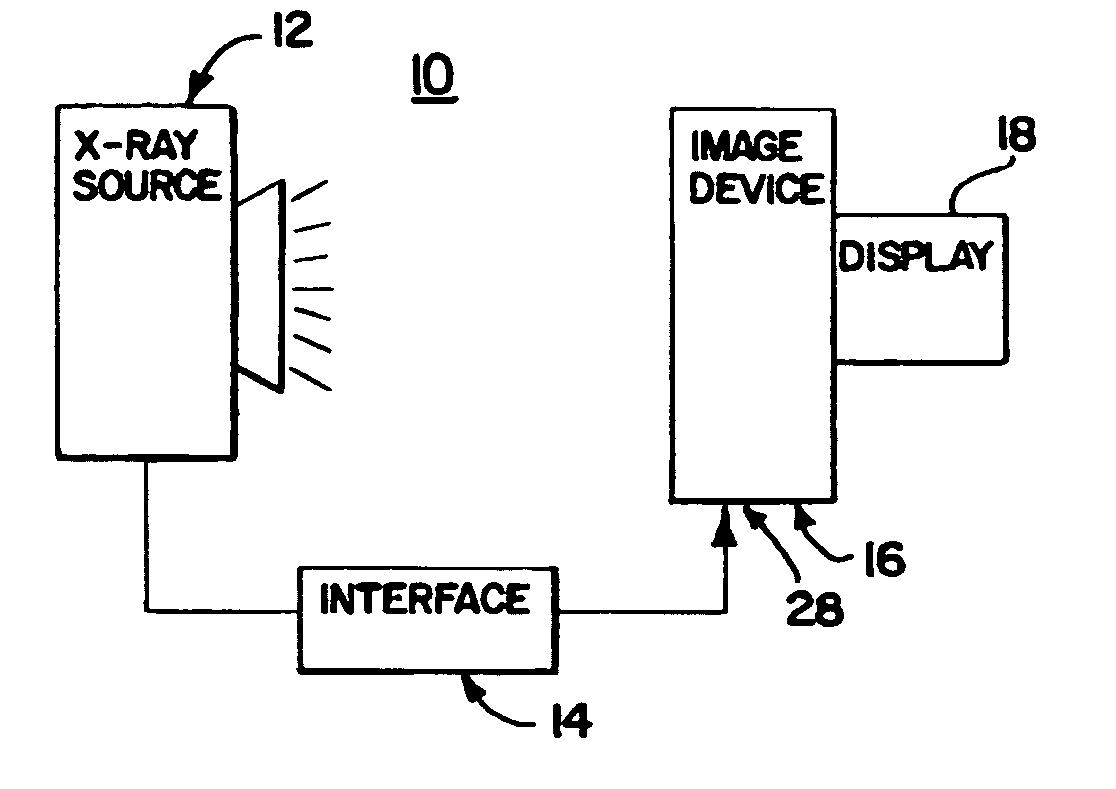
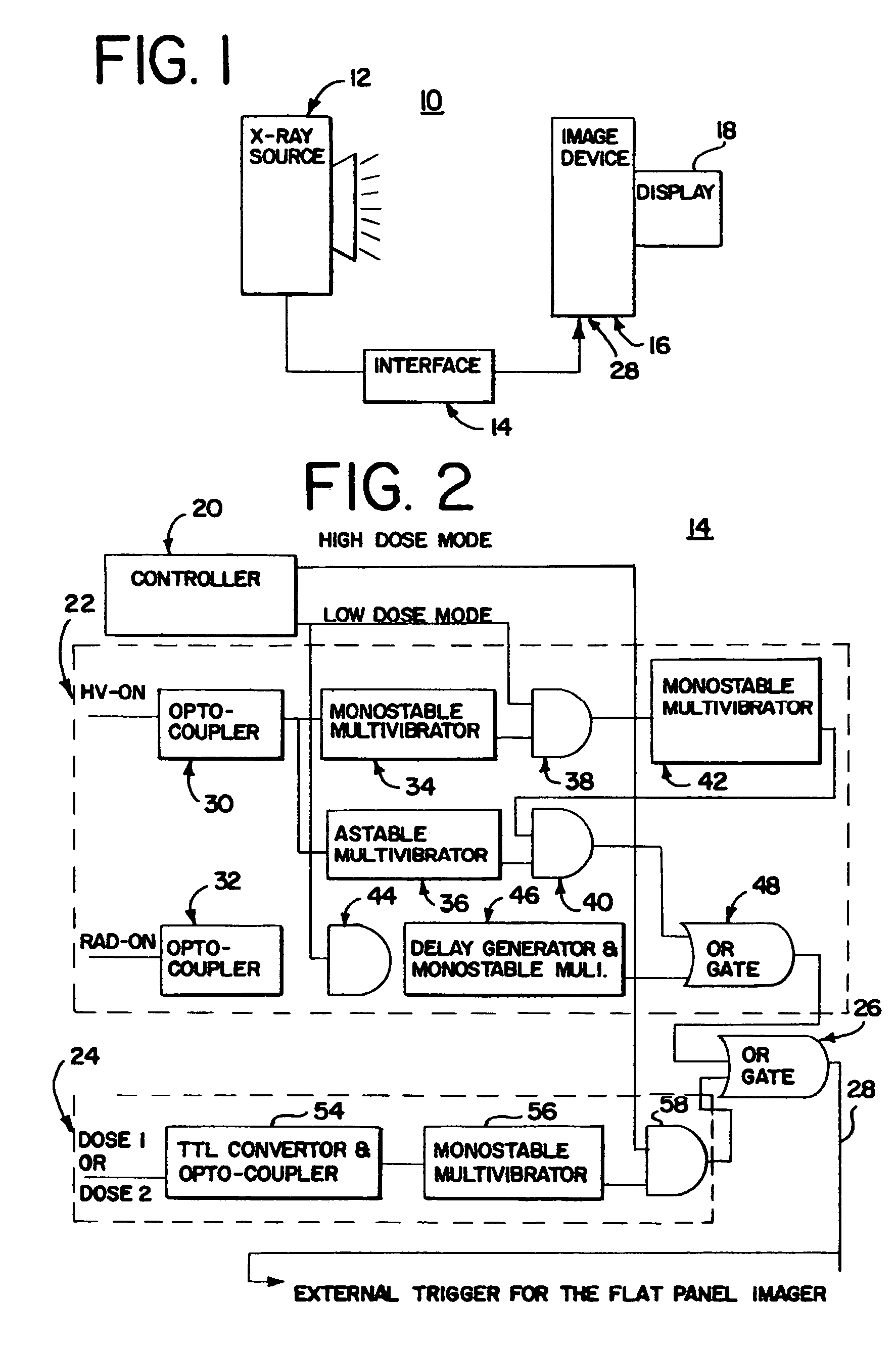
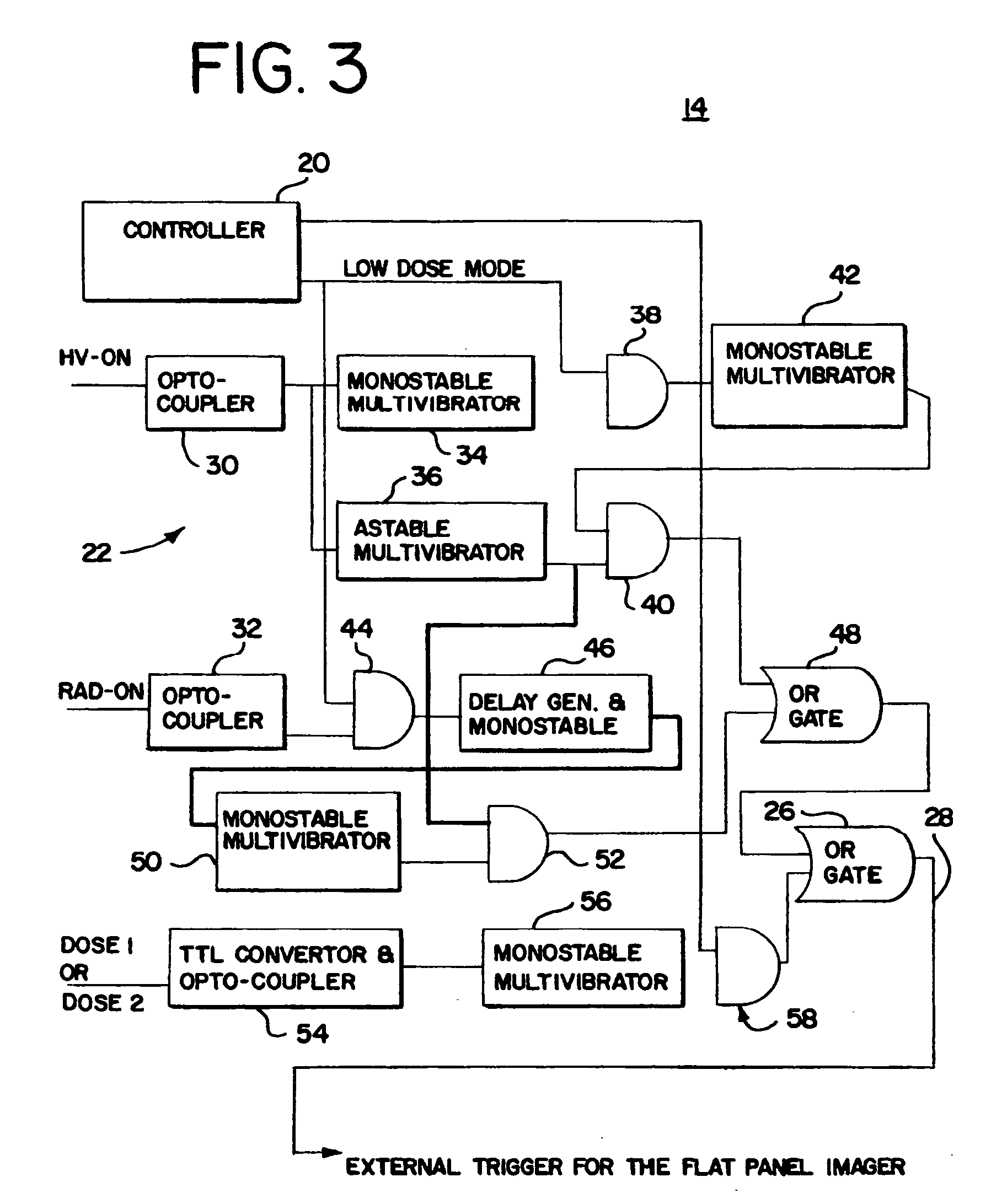
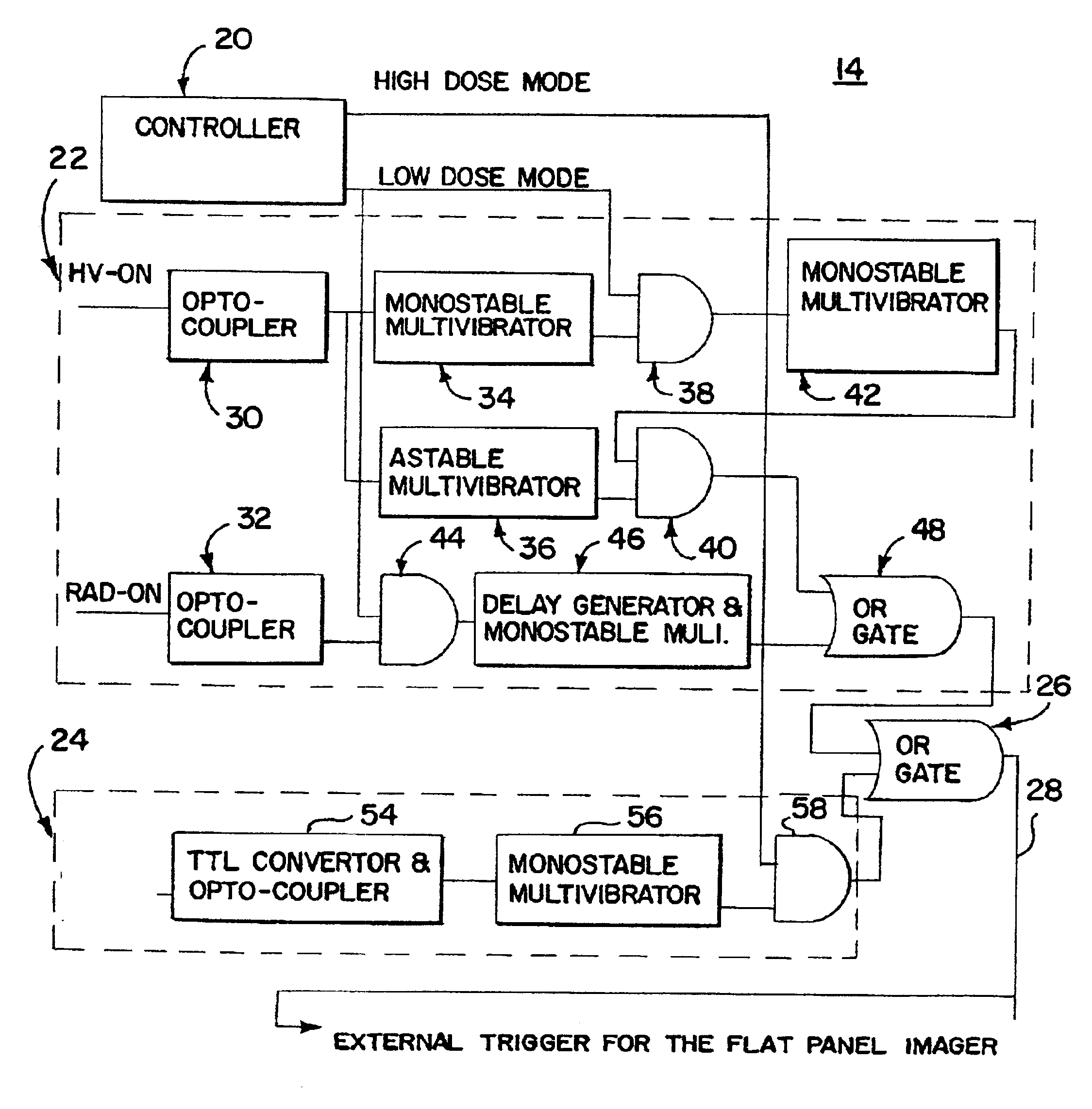
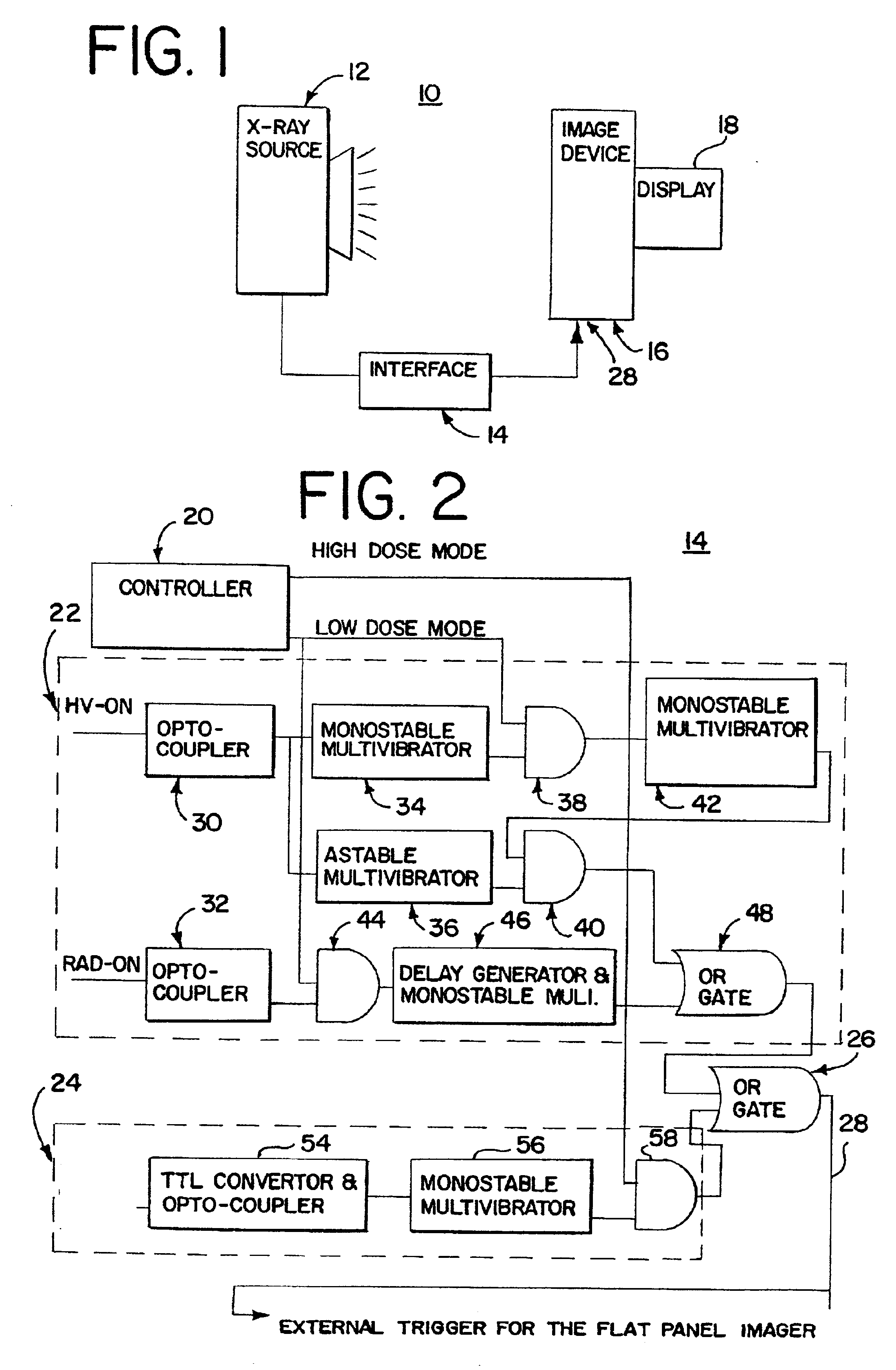
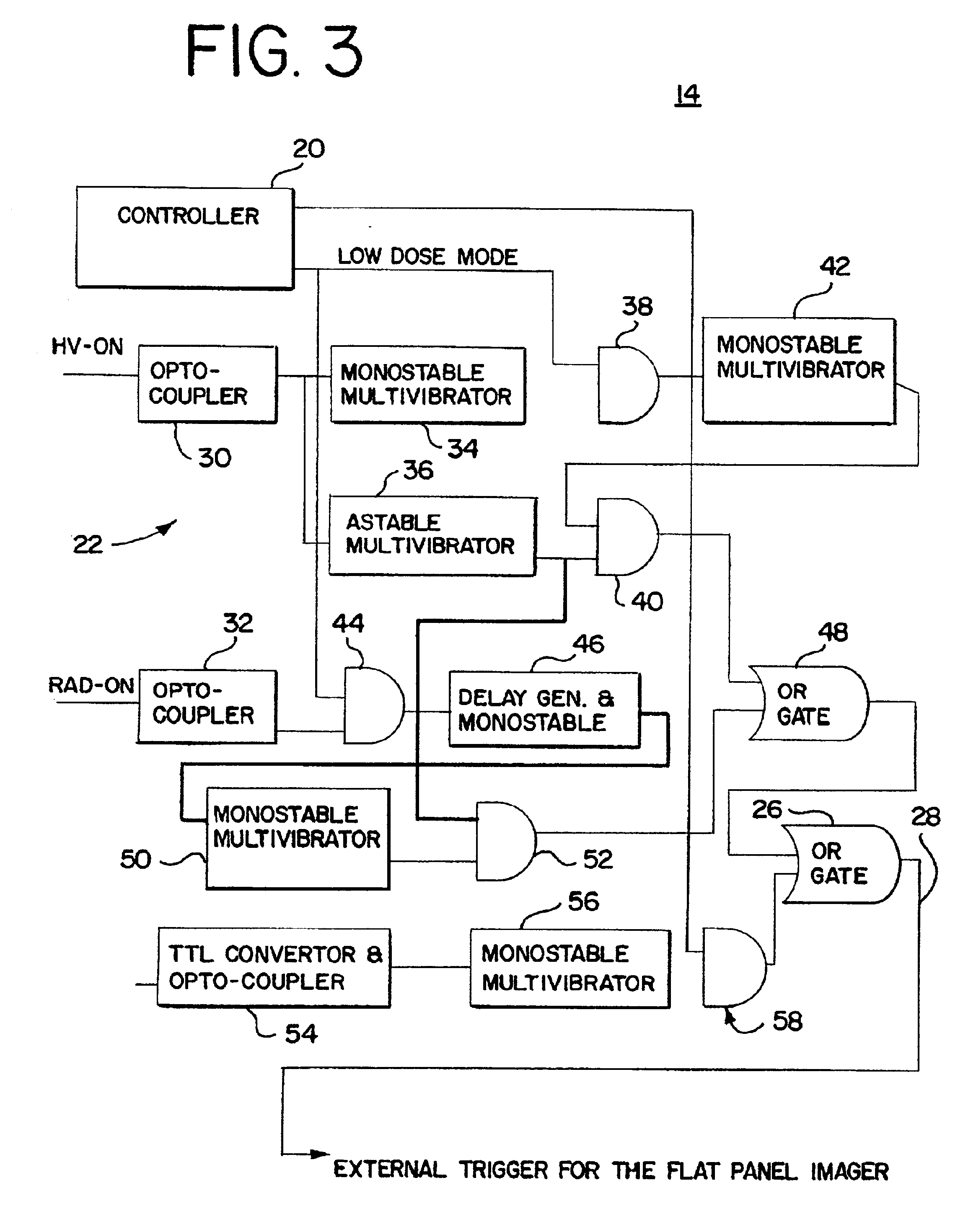
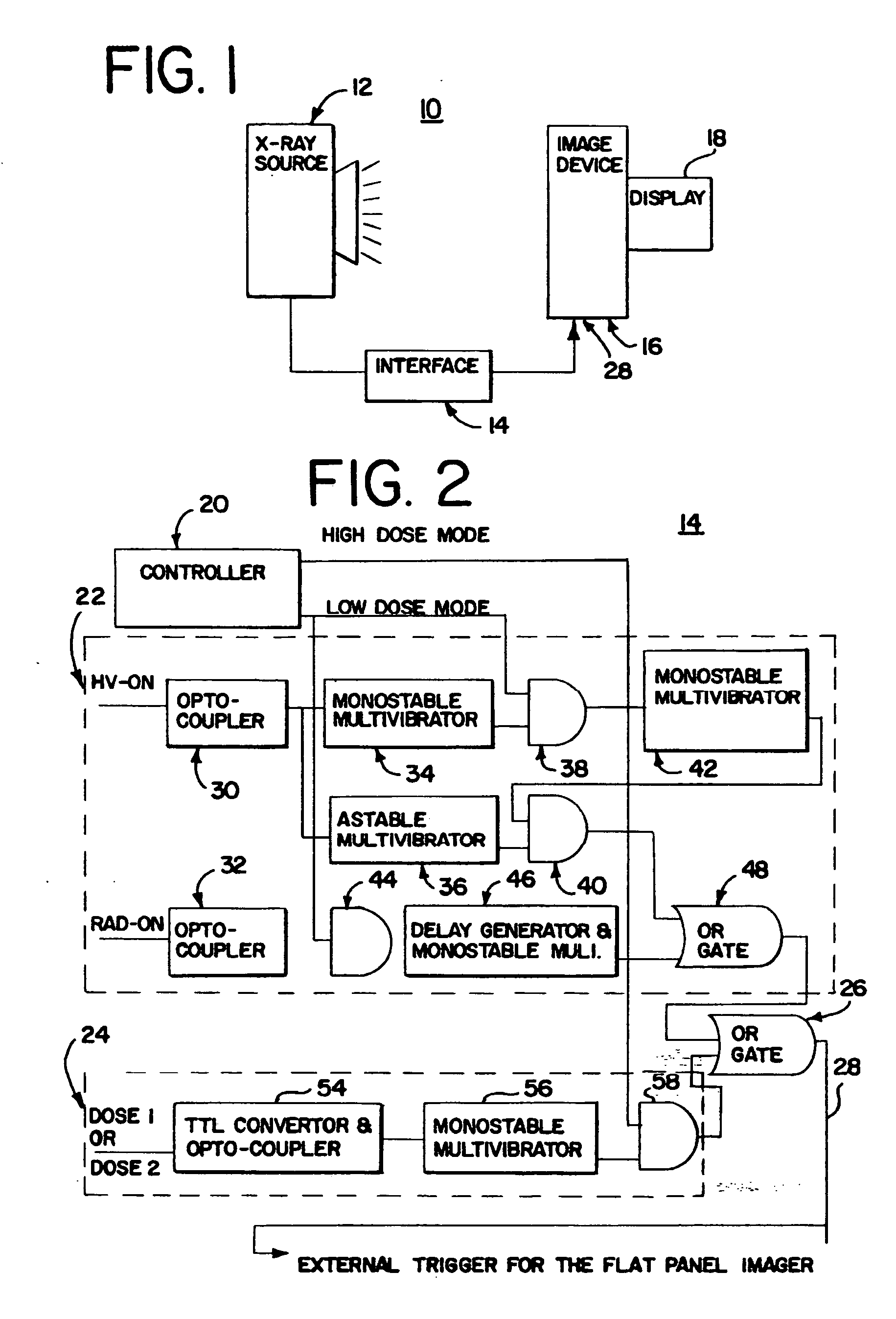
X-ray therapy electronic portal imaging system and method for artifact reduction
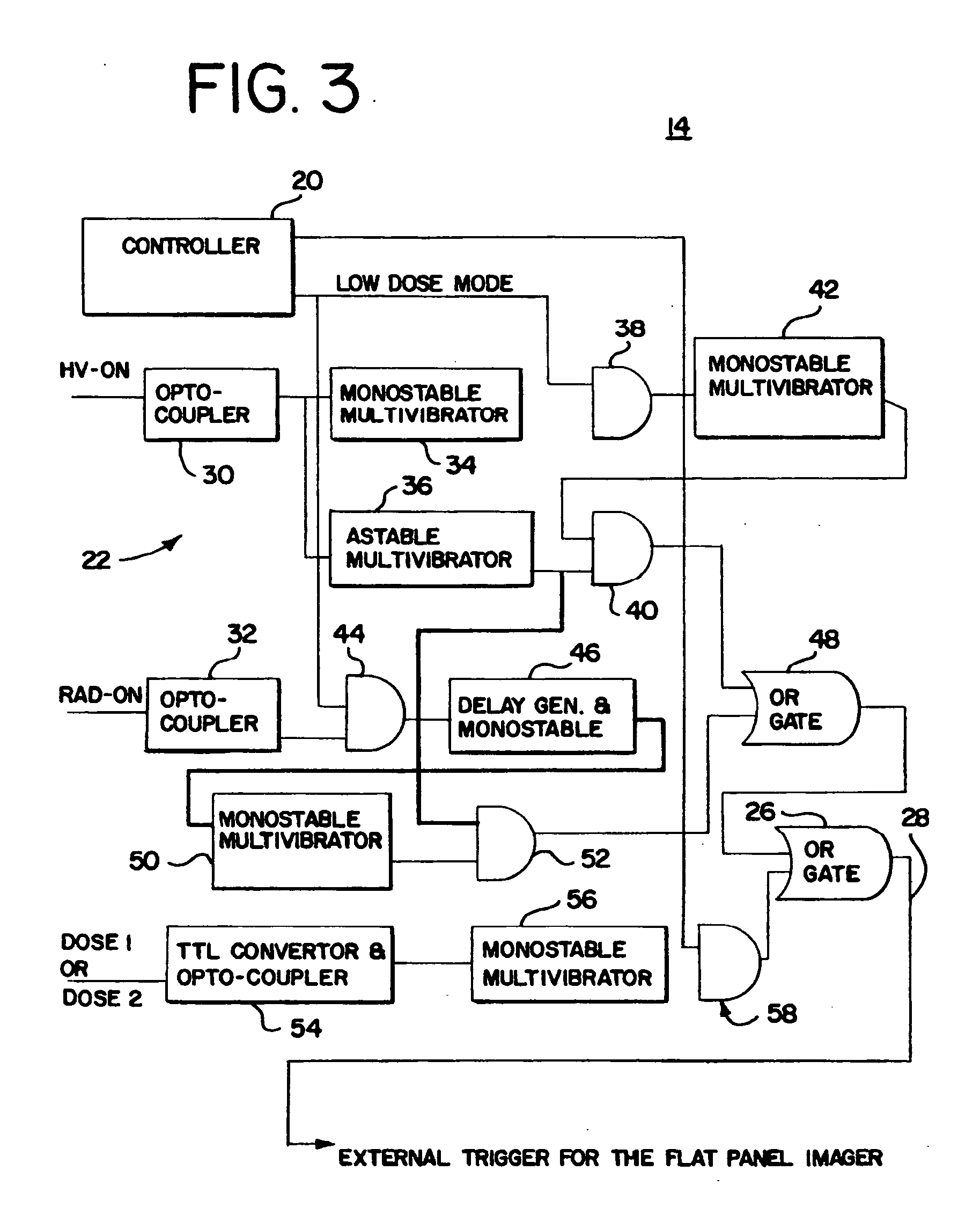
InactiveUS7027558B2Reduce variationReduce removalTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayPulse rate
X-ray therapy EPI artifact reduction and control of imaging is provided. Scanning of images is synchronized with the pulse rate of the x-rays. The scanning period is longer than the pulse rate period, so artifacts are generated within the resulting images. Due to the synchronization, the pulse variation artifacts are aligned across multiple images. The synchronization and resulting alignment of linear artifacts allows for gain correction as a function of lines within the image. Such gain correction reduces or removes non-linearities associated with pulse rate variation.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Same-source double-energy medical electron linear accelerator for image guided radiation therapy (IGRT)
InactiveCN102256434ARadial imaging is clearElectron beam energy reductionLinear acceleratorsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyX-rayImage-guided radiation therapy
The invention relates to a medical apparatus for tumor radiation therapy, in particular to a same-source double-energy medical electron linear accelerator for image guided radiation therapy (IGRT). The same-source double-energy medical electron linear accelerator for the IGRT is characterized in that: an accelerating tube is vertically arranged and is connected with a moving target below the accelerating tube; an energy switch is arranged on the accelerating tube; an X-ray heavy metal target and a low atomic number target are arranged on the moving target; and the X-ray heavy metal target and the low atomic number target are connected with a driving mechanism of the moving target. The same-source double-energy medical electron linear accelerator for the IGRT has the advantages that: energy of an electron beam generated by the accelerating tube is reduced by the energy switch; by using the characteristic that the electron beam impacts the low atomic number target to generate more low-energy beams, X rays with clear portal imaging are obtained; and the same-source double-energy medical electron linear accelerator for the IGRT has the characteristics of easy mode conversion, same source, stable beam, clear image, economy, reliability, simpleness and convenience in clinical use and the like.
Owner:SHINVA MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
Systems, methods, and devices for radiation beam alignment and radiation beam measurements using electronic portal imaging devices
ActiveCN107041997AEliminate dependenciesLow costTomographyDiaphragms for radiation diagnosticsMeasurement deviceSystems approaches
Systems and methods for using electronic portal imaging devices (EPIDs) as absolute radiation beam measuring devices and as radiation beam alignment devices without implementation of elaborate and complex calibration procedures.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
X-ray therapy electronic portal imaging system and method for artifact reduction
InactiveUS7076023B2Reduce variationReduce removalTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSoft x rayX-ray
X-ray therapy EPI artifact reduction and control of imaging is provided. Scanning of images is synchronized with the pulse rate of the x-rays. The scanning period is longer than the pulse rate period, so artifacts are generated within the resulting images. Due to the synchronization, the pulse variation artifacts are aligned across multiple images. The synchronization and resulting alignment of linear artifacts allows for gain correction as a function of lines within the image. Such gain correction reduces or removes non-linearities associated with pulse rate variation.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
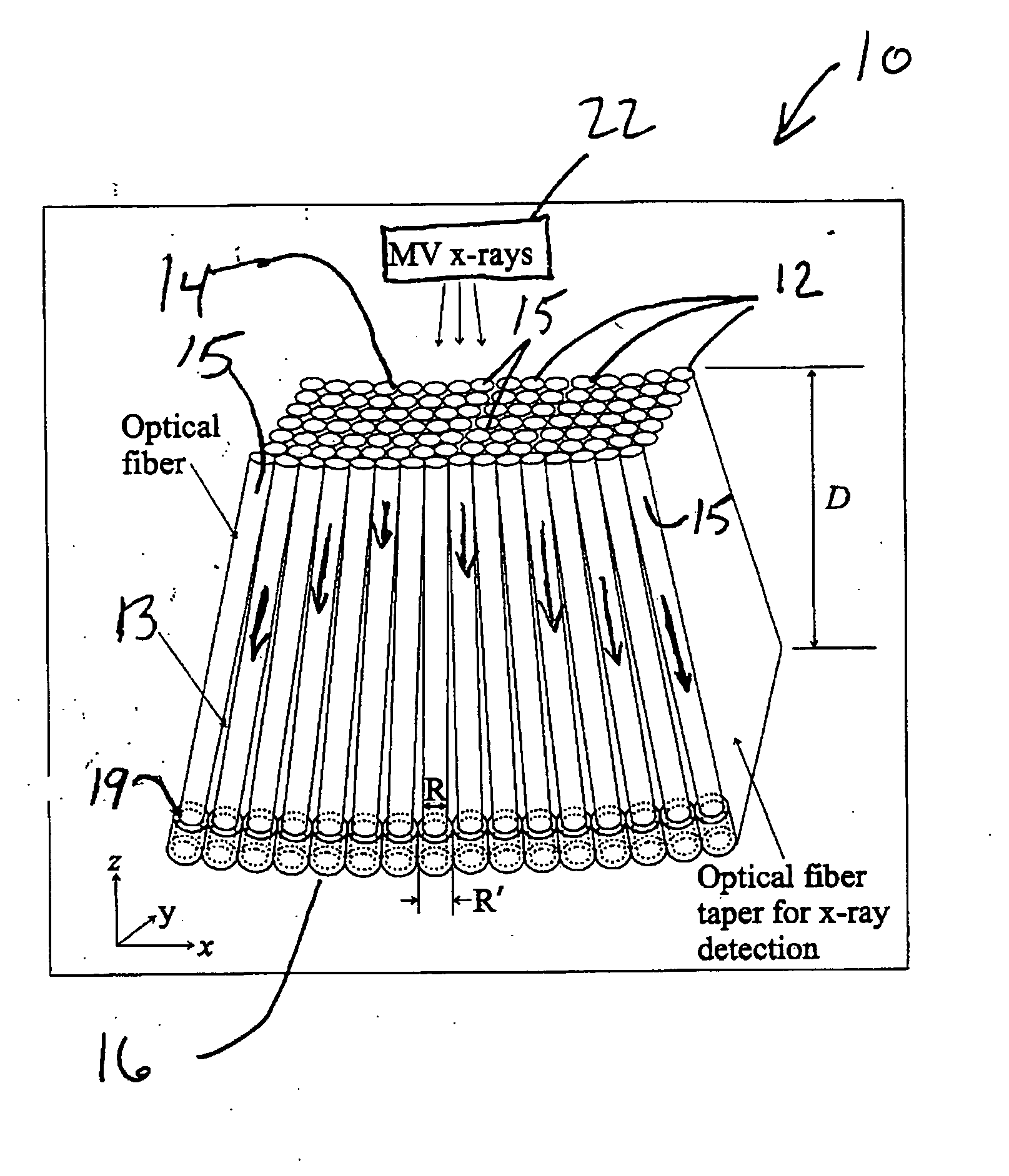
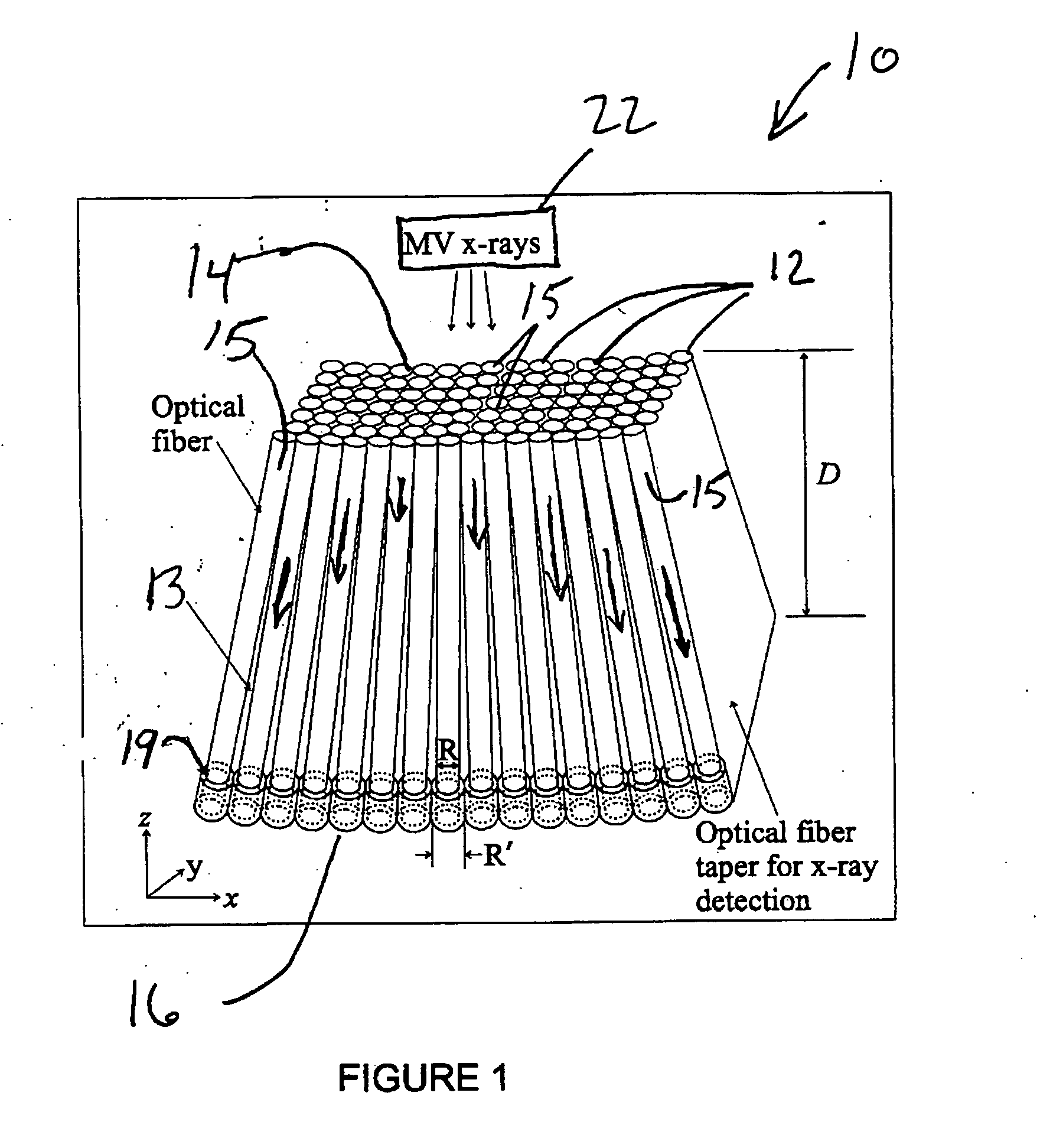
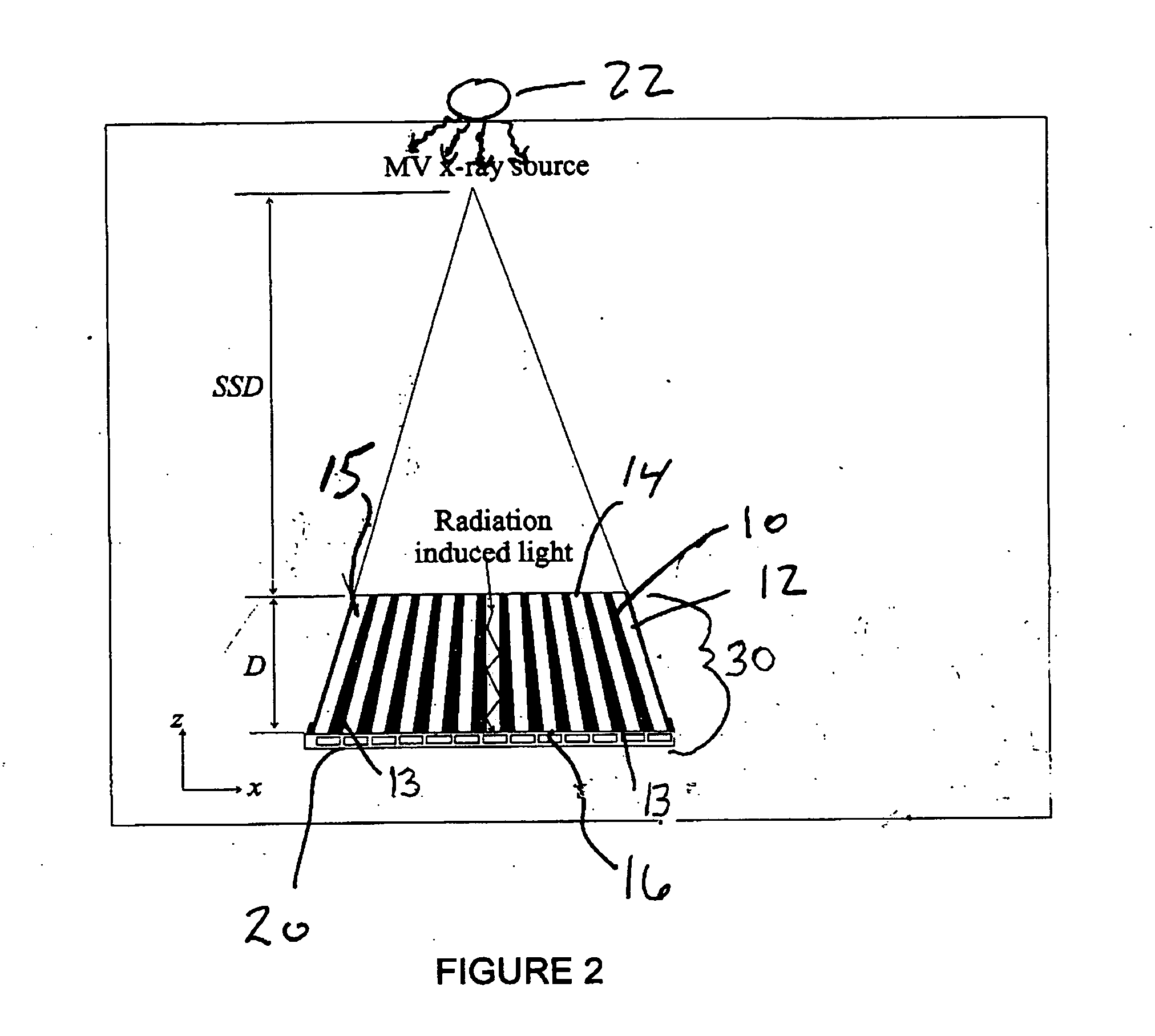
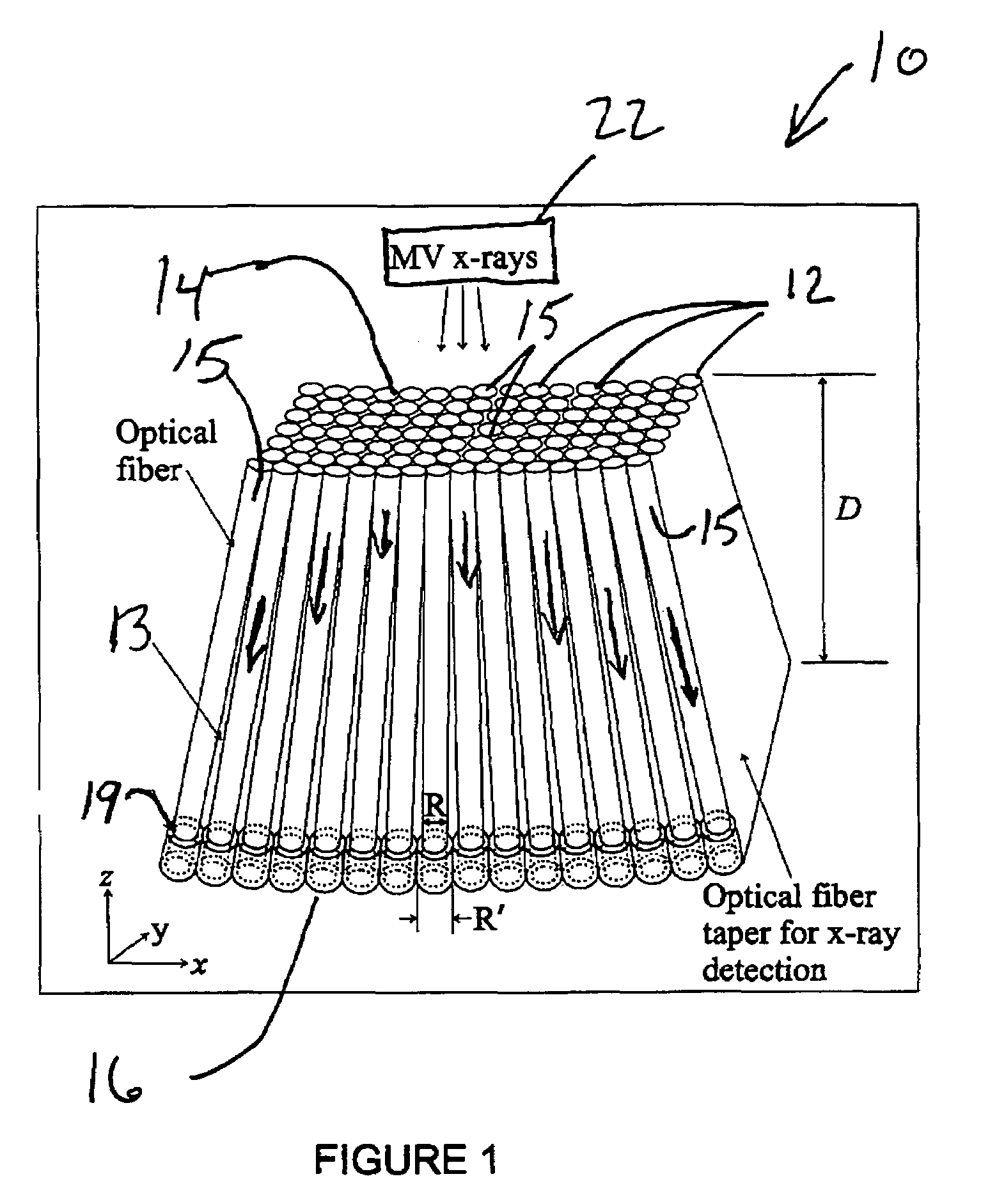
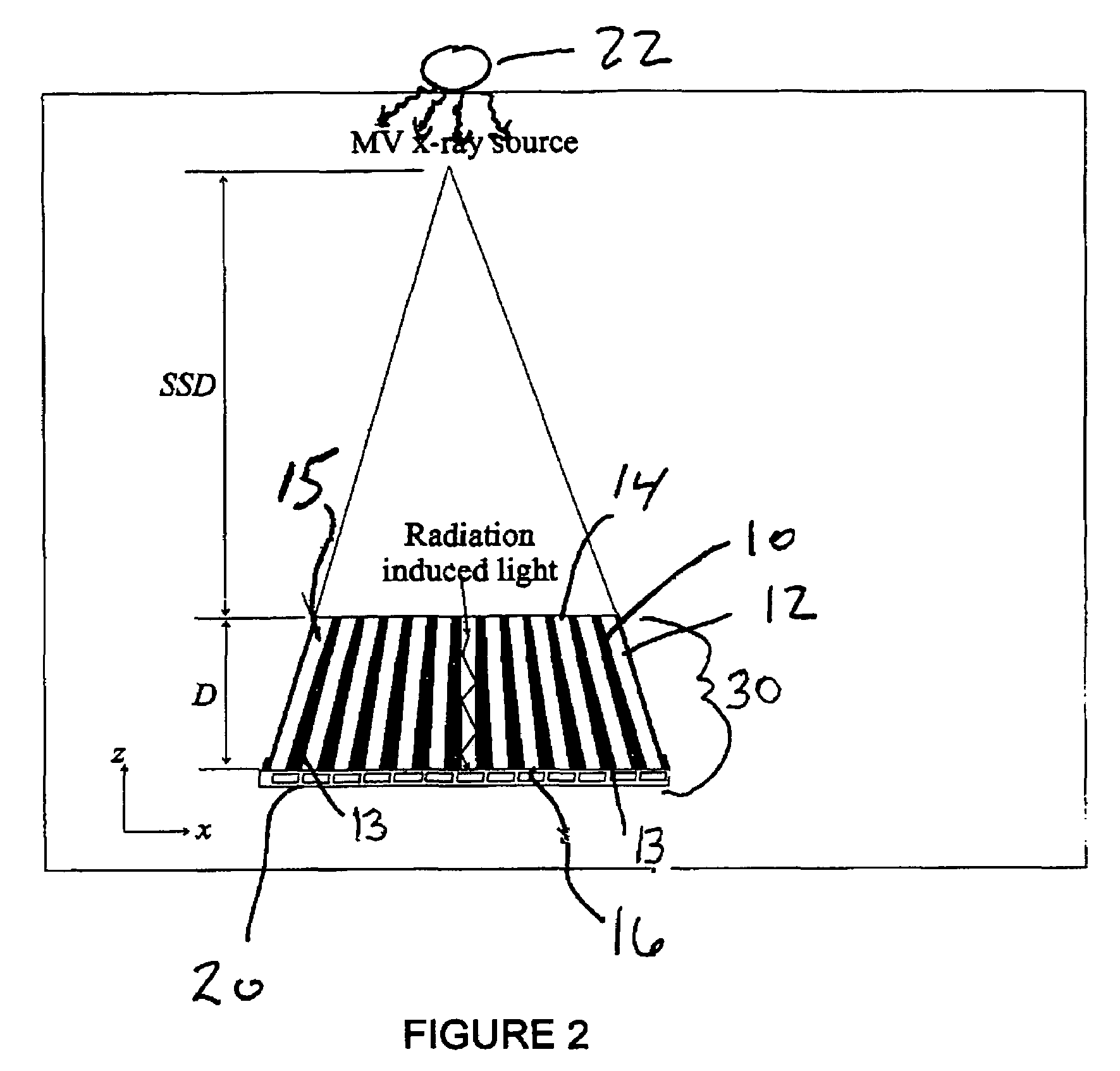
Cerenkov x-ray detector for portal imaging
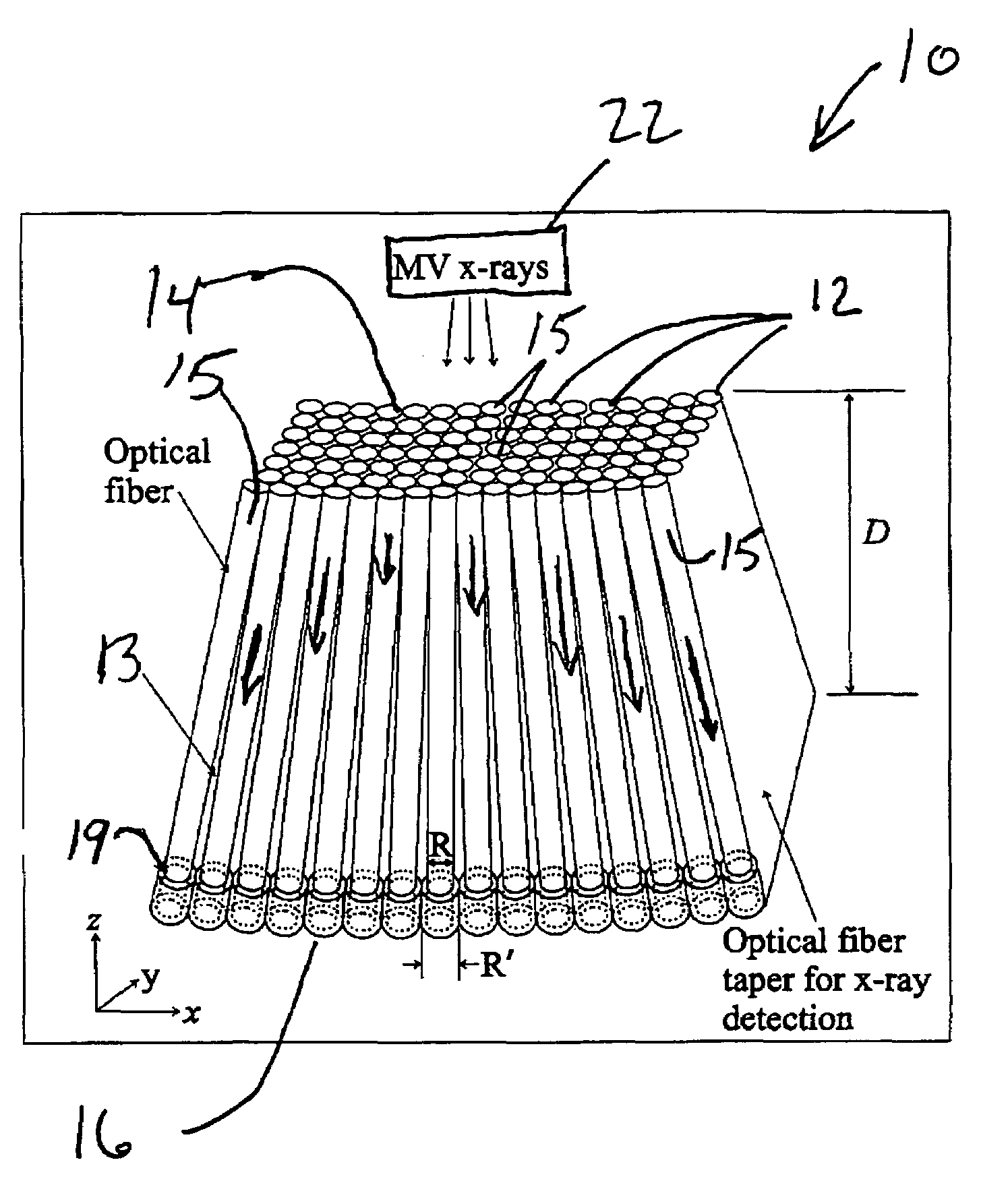
The present invention provides a practical design of a megavoltage x-ray detector with both high quantum efficiency (QE) and high resolution. The x-ray detector includes an optical-fiber taper (OFT) made from a large number of optical fibers, each of which is aligned with the incident x-rays from an x-ray source hitting a top surface of the optical fiber taper. The optical-fiber taper is a matrix of optical fibers with the core material made of, e.g., silica and coated with a cladding glass or polymer such that light created within the core of each optical fiber will be guided to the bottom ends of the fiber with the ends of the fibers at the bottom being optically coupled to and optical image read-out device. Each optical fiber in the optical fiber taper is fully aligned with the incident x-ray source so that x-rays entering the top of the fiber travel directly towards the bottom of the same fiber. This alignment (or focusing) of the optical-fiber taper towards the x-ray source can be achieved by an extra coating at the bottoms of the optical fibers so they have a larger diameter than the other top ends of the fibers.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
Systems, methods, and devices for radiation beam asymmetry measurements using electronic portal imaging devices
ActiveUS20180250531A1Eliminate beam asymmetryX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionImaging equipmentPortal imaging
Systems and methods for determining beam asymmetry in a radiation treatment system using electronic portal imaging devices (EPIDs) without implementation of elaborate and complex EPID calibration procedures. The beam asymmetry is determined based on radiation scattered from different points in the radiation beam and measured with the same region of interest ROI of the EPID.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHINEERS INT AG
Portal imaging using modulated treatment beam
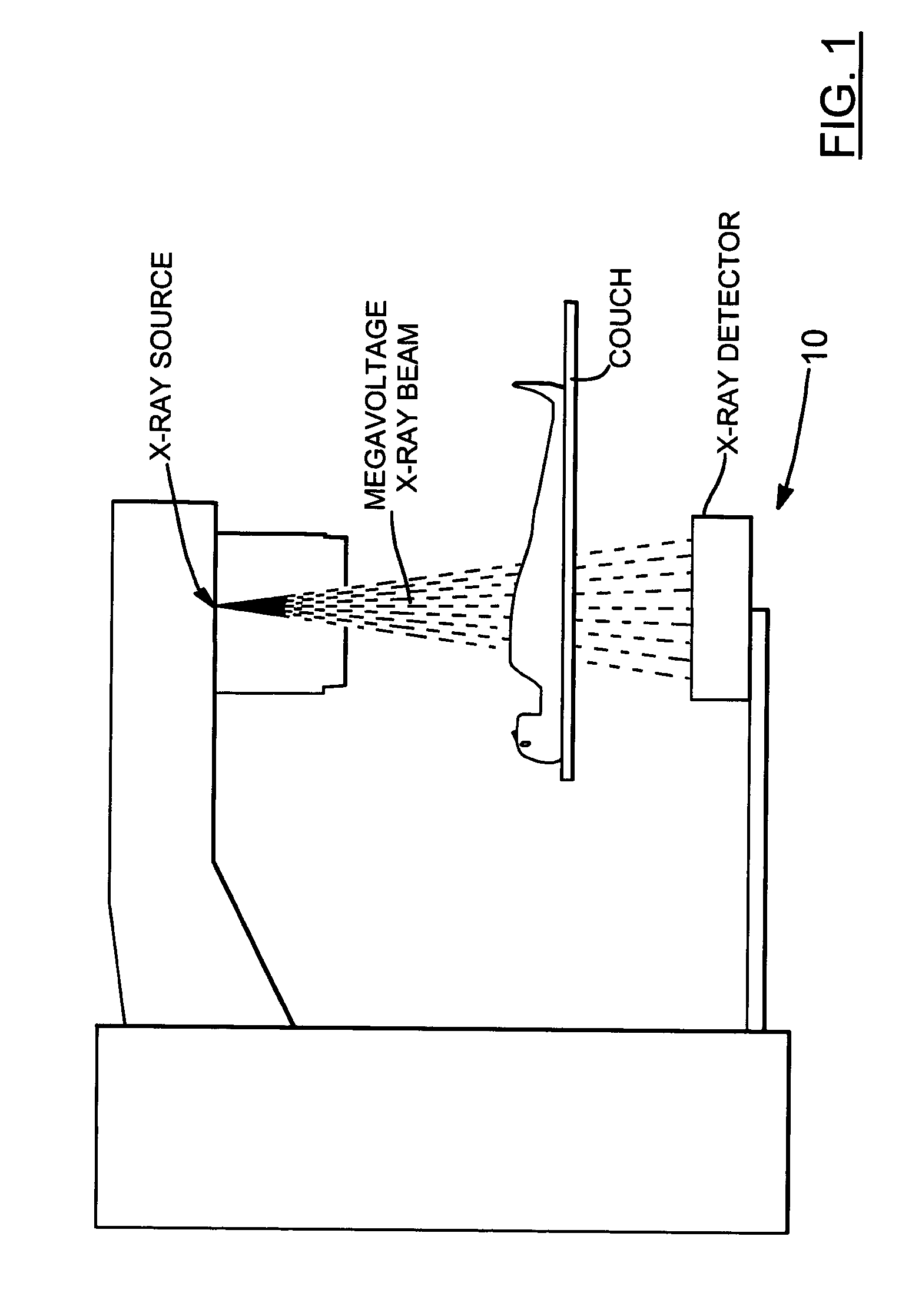
A radiation therapy system produces a treatment beam that is detected by an electronic portal imaging device (EPID) after it passes through the subject being treated. A chopper wheel modulates low energy components of the beam while leaving the higher energy components substantially unmodulated. Modulated components in the image signals produced by the EPID are detected and used to produce portal images.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Computer radiographic oncology portal imaging
Image storage assemblies comprise thin metal screens adjacent phosphor storage screens. The thin metal screen is from about 0.01 to about 0.75 mm in thickness when composed of copper and from about 0.05 to about 0.4 mm when composed of lead. These image storage assemblies can be used in portal imaging whereby imaging radiation is directed through the thin metal screens before the phosphor storage screens. Stimulating radiation can then be directed to the phosphor storage screen before it reaches the thin metal screen.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Cerenkov x-ray detector for portal imaging
The present invention provides a practical design of a megavoltage x-ray detector with both high quantum efficiency (QE) and high resolution. The x-ray detector includes an optical-fiber taper (OFT) made from a large number of optical fibers, each of which is aligned with the incident x-rays from an x-ray source hitting a top surface of the optical fiber taper. The optical-fiber taper is a matrix of optical fibers with the core material made of, e.g., silica and coated with a cladding glass or polymer such that light created within the core of each optical fiber will be guided to the bottom ends of the fiber with the ends of the fibers at the bottom being optically coupled to and optical image read-out device. Each optical fiber in the optical fiber taper is fully aligned with the incident x-ray source so that x-rays entering the top of the fiber travel directly towards the bottom of the same fiber. This alignment (or focusing) of the optical-fiber taper towards the x-ray source can be achieved by an extra coating at the bottoms of the optical fibers so they have a larger diameter than the other top ends of the fibers.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
X-ray therapy electronic portal imaging system and method for artifact reduction
InactiveUS20050094768A1Reduced pulse rate artifact variationReduces and removes non-linearitiesTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiologyNuclear medicine
X-ray therapy EPI artifact reduction and control of imaging is provided. Scanning of images is synchronized with the pulse rate of the x-rays. The scanning period is longer than the pulse rate period, so artifacts are generated within the resulting images. Due to the synchronization, the pulse variation artifacts are aligned across multiple images. The synchronization and resulting alignment of linear artifacts allows for gain correction as a function of lines within the image. Such gain correction reduces or removes non-linearities associated with pulse rate variation.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Portal imaging using modulated treatment beam
ActiveUS20070237304A1Quality improvementHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray apparatusHigh energyTherapy Object
A radiation therapy system produces a treatment beam that is detected by an electronic portal imaging device (EPID) after it passes through the subject being treated. A chopper wheel modulates low energy components of the beam while leaving the higher energy components substantially unmodulated. Modulated components in the image signals produced by the EPID are detected and used to produce portal images.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Edge-on SAR scintillator devices and systems for enhanced SPECT, PET, and Compton gamma cameras
InactiveUS20100090117A1Space minimizationHigh resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementMedical radiographyHigh energy
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
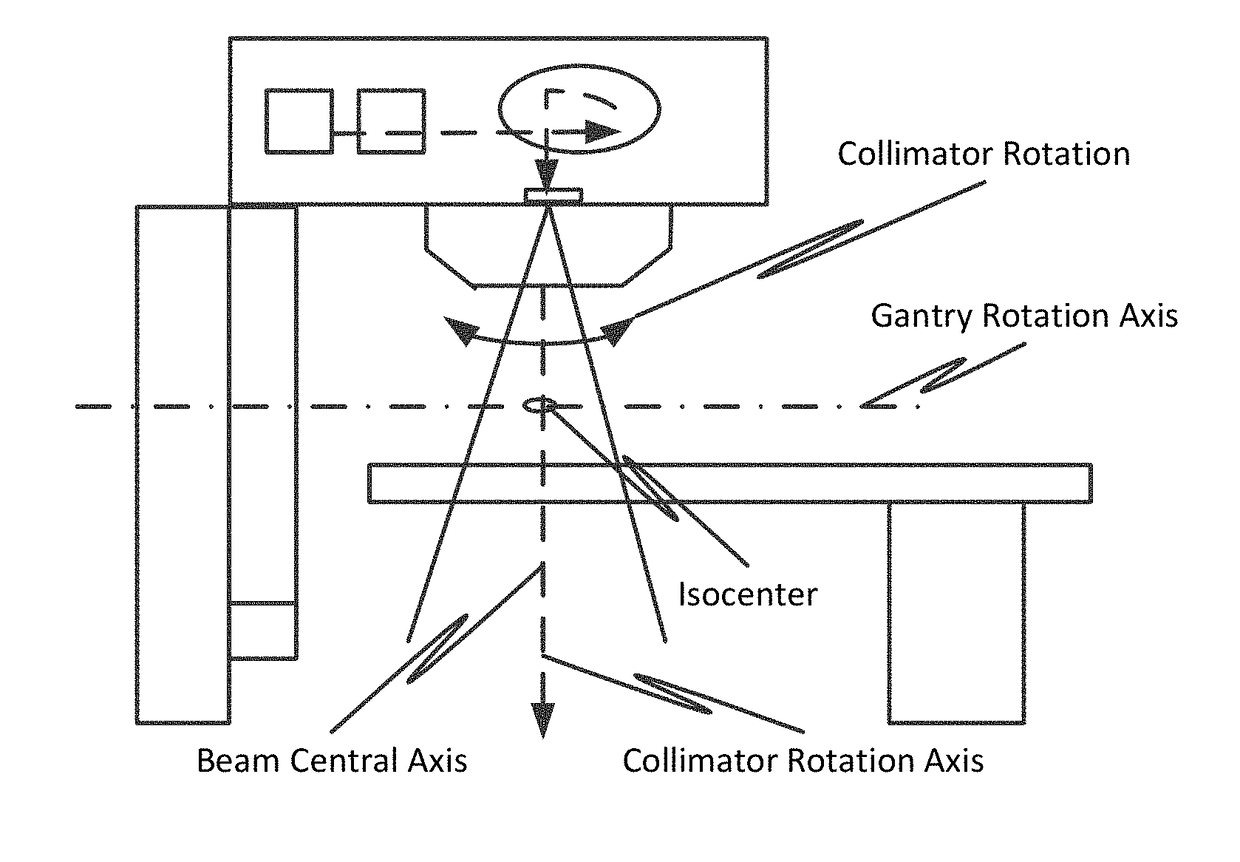
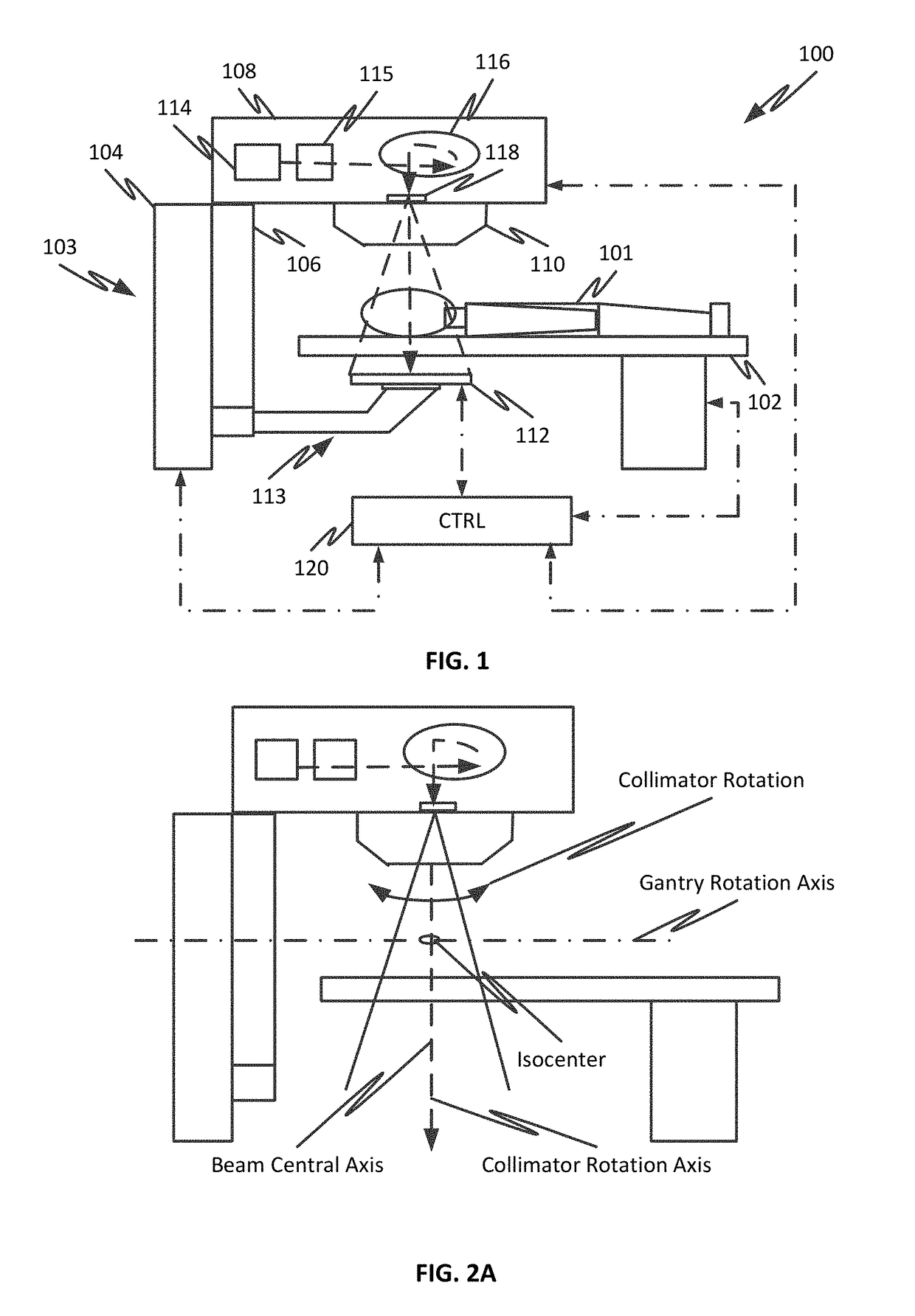
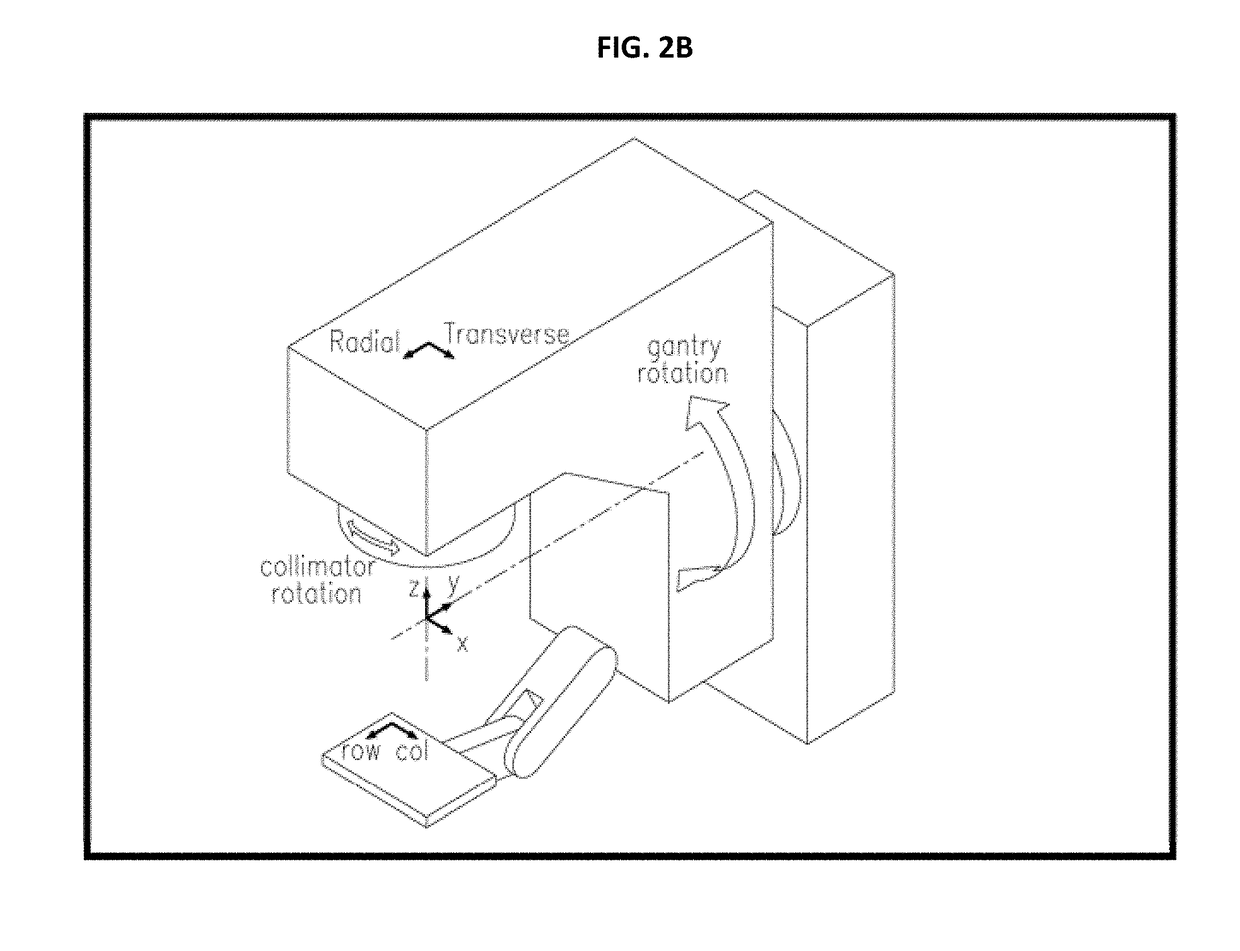
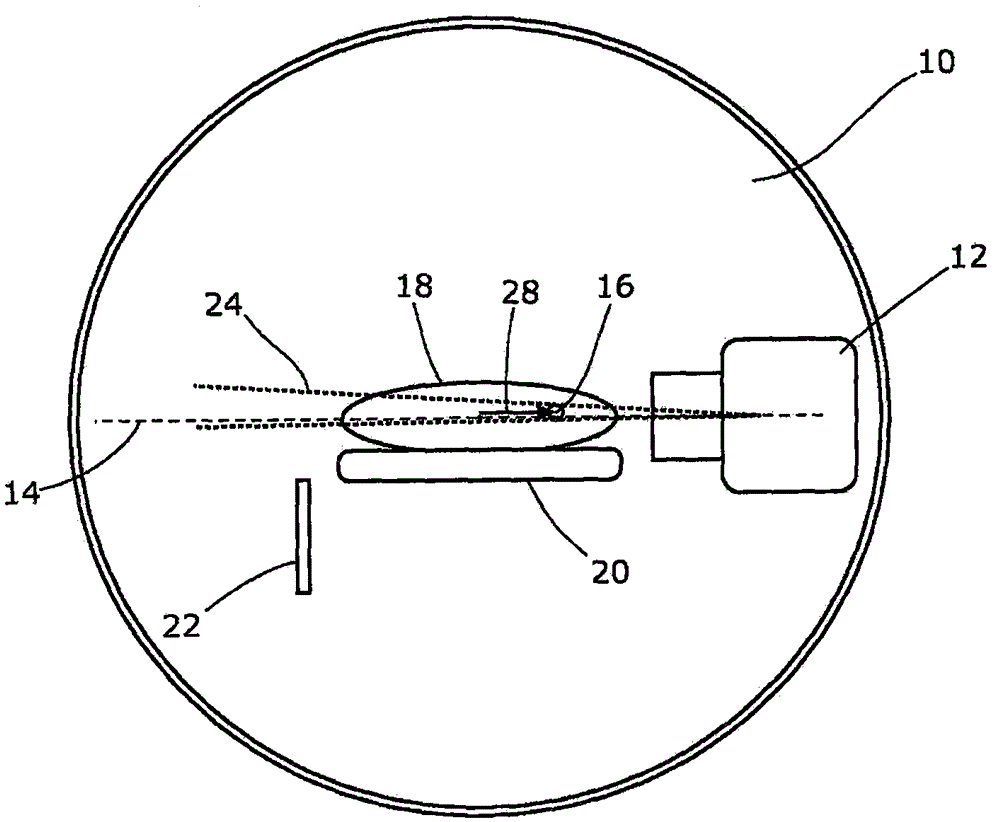
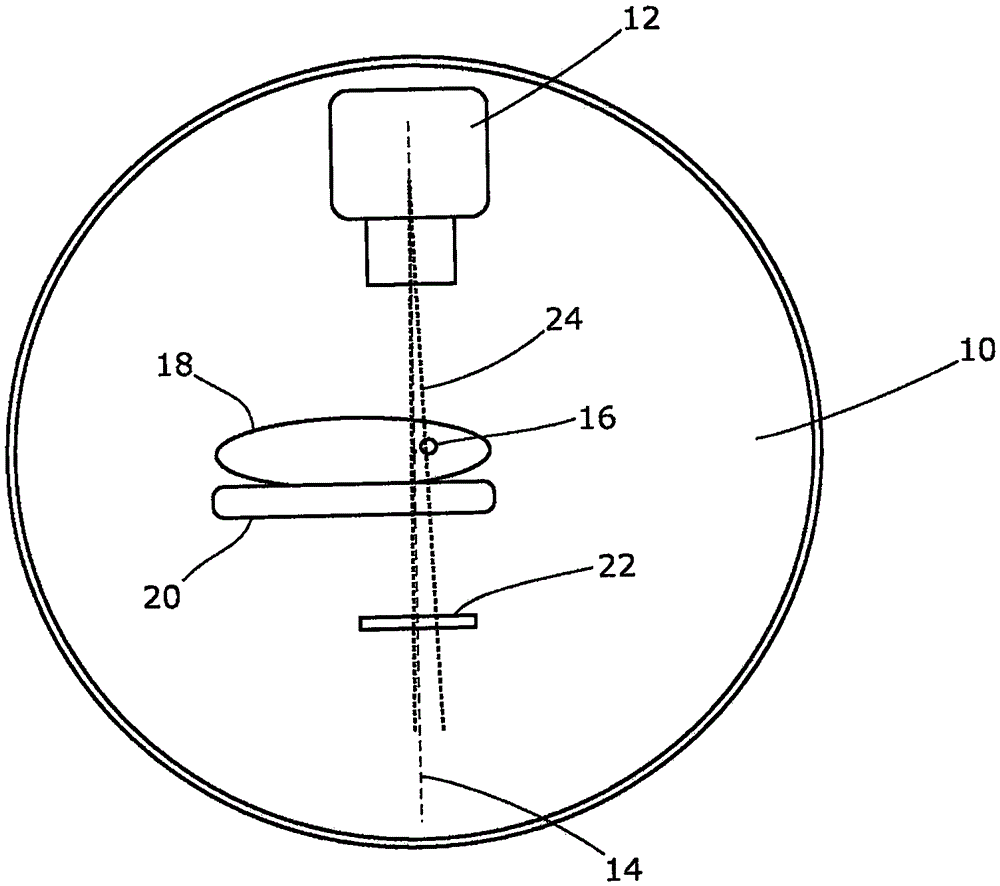
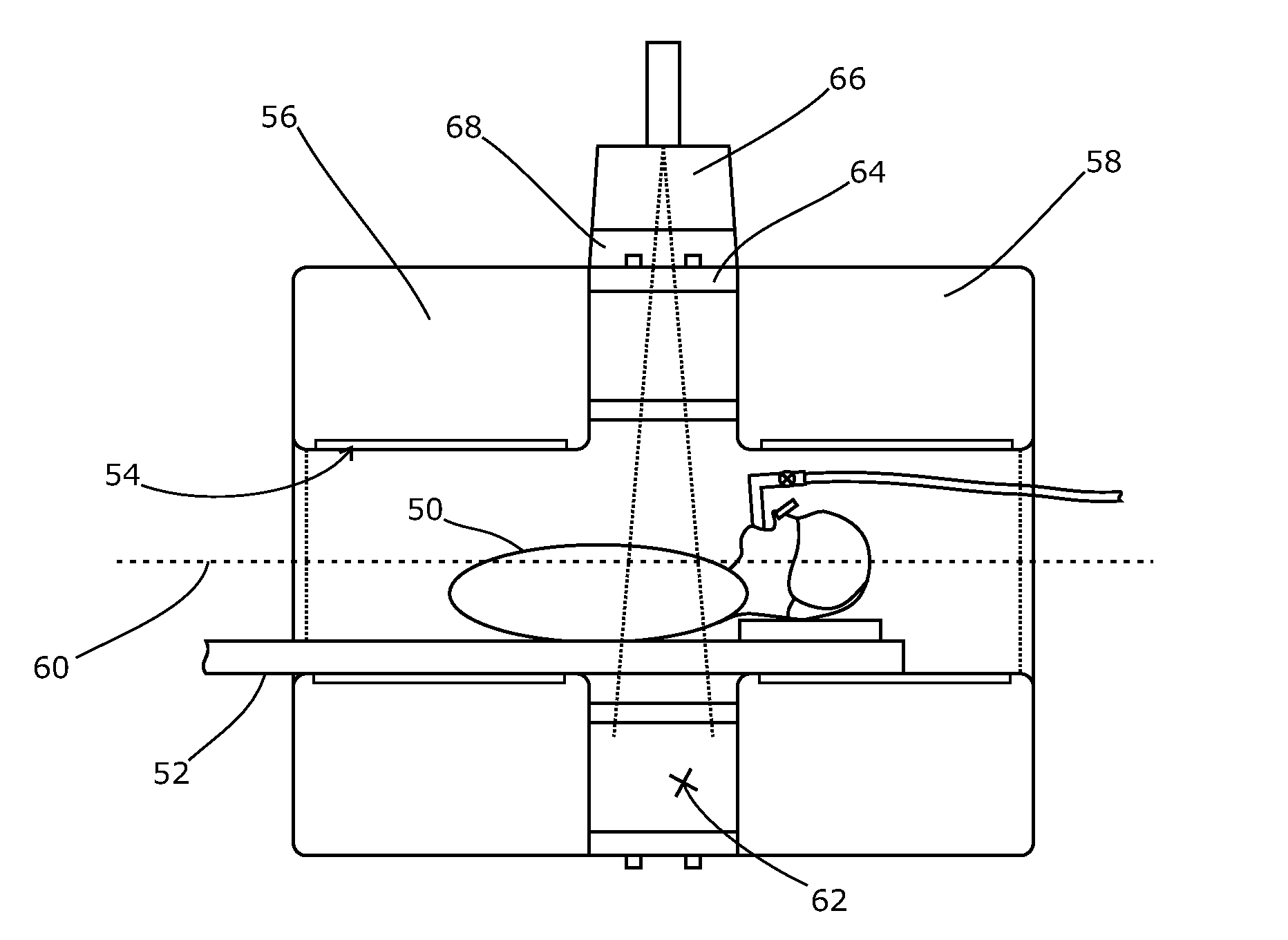
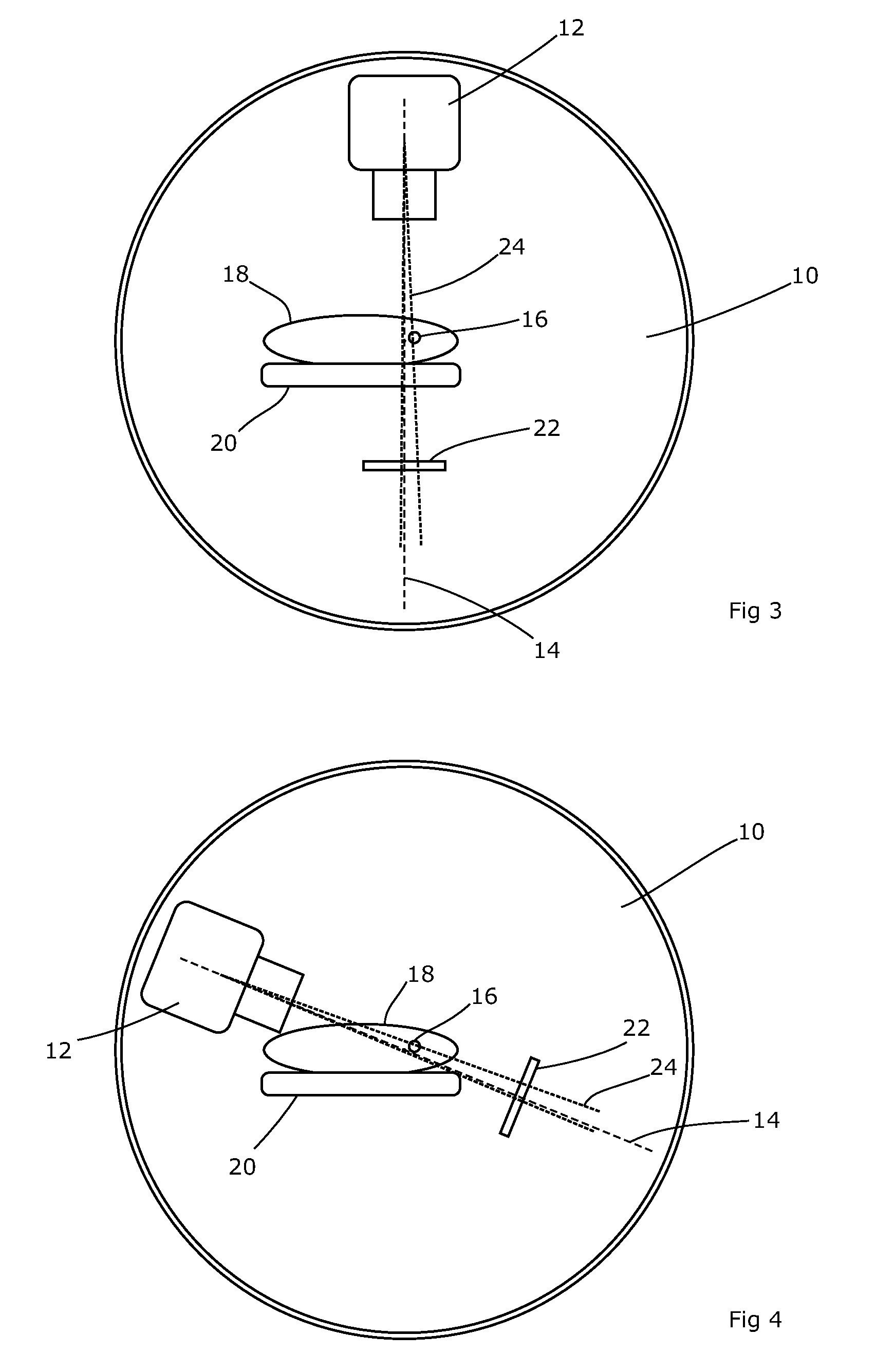
Portal imaging during radiotherapy
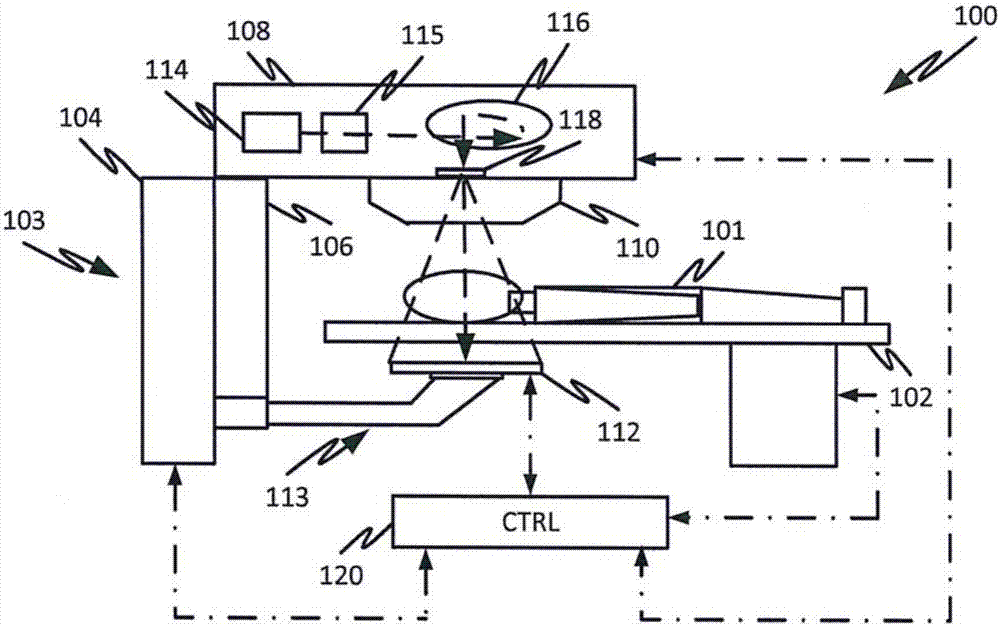
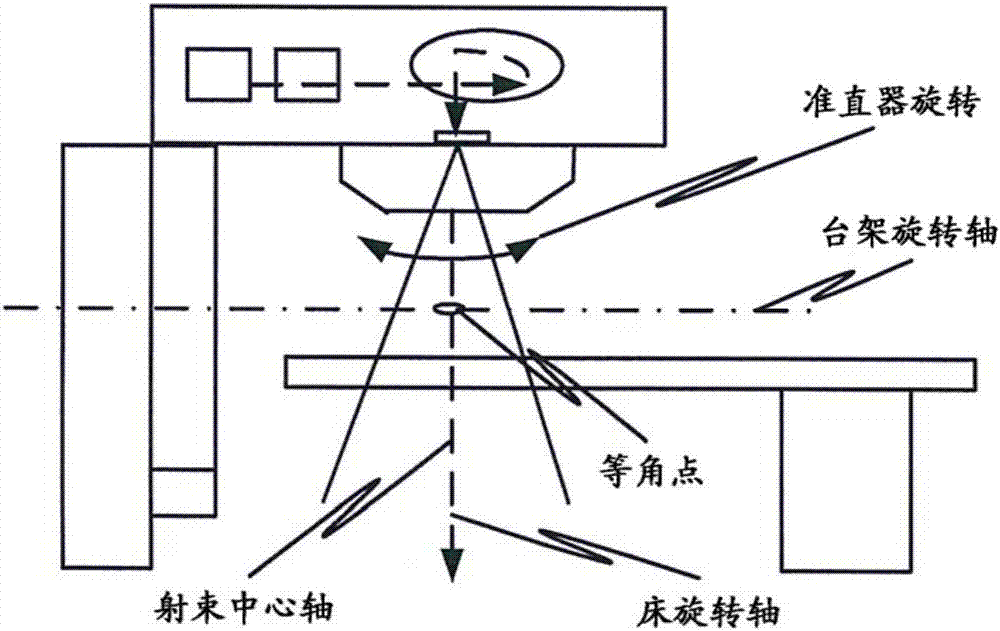
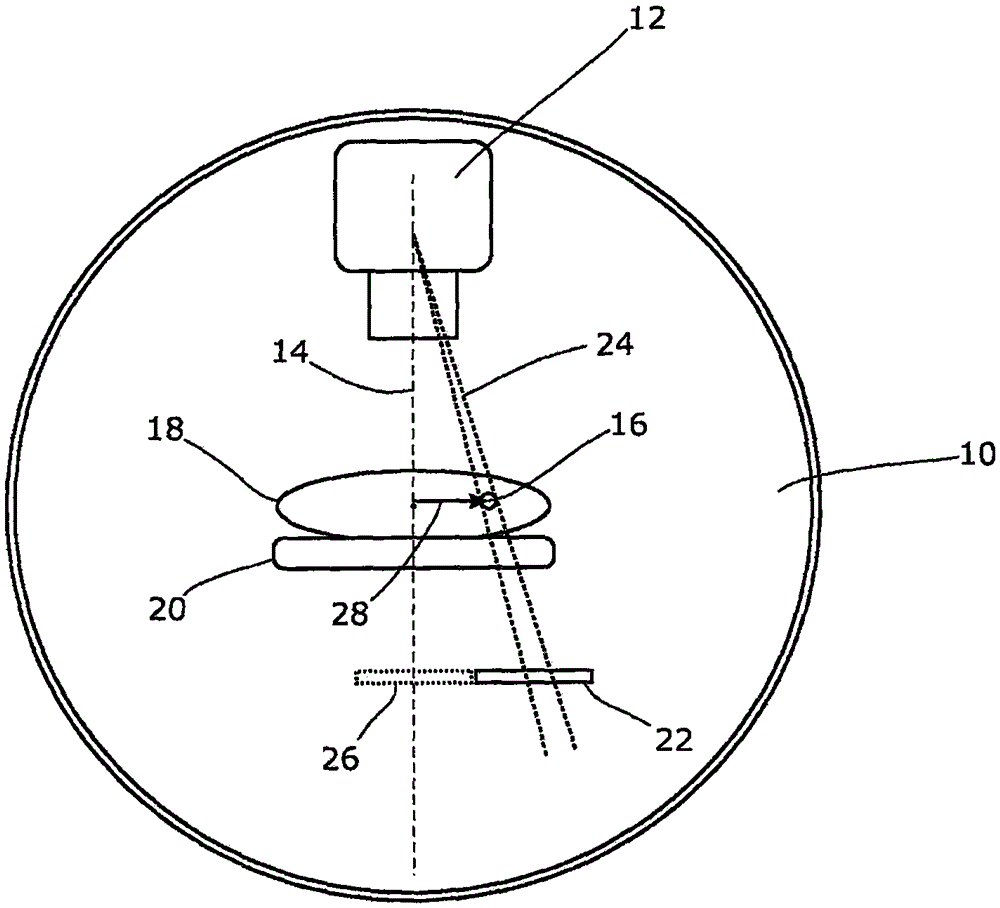
A radiotherapy apparatus comprises: a source for producing a beam of ionising radiation along an axis, the beam covering a maximum aperture of the source; a collimator for collimating the beam to produce a collimated beam covering a sub-part of the maximum aperture; a patient support positioned in the path of the beam; a rotatable gantry, on which the source is mounted, for rotating the source around the patient support thereby to deliver the beam from a range of directions; an imaging device located opposite the source and with the patient support between the source and the imaging device, and mounted on the gantry via a drive member allowing translational motion of the imaging device in at least one direction perpendicular to the axis; and a control unit adapted to control the drive member to move the imaging device within the maximum aperture and maintain coincidence between the imaging device and the sub-part of the maximum aperture. Accordingly, the EPID can be moved during the treatment in order to maintain the collimated field of the radiation beam within the bounds of the EPID. This ensures that the image is valid and prevents damage to the EPID as a result of exposure of more sensitive (or less shielded) parts to the beam.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
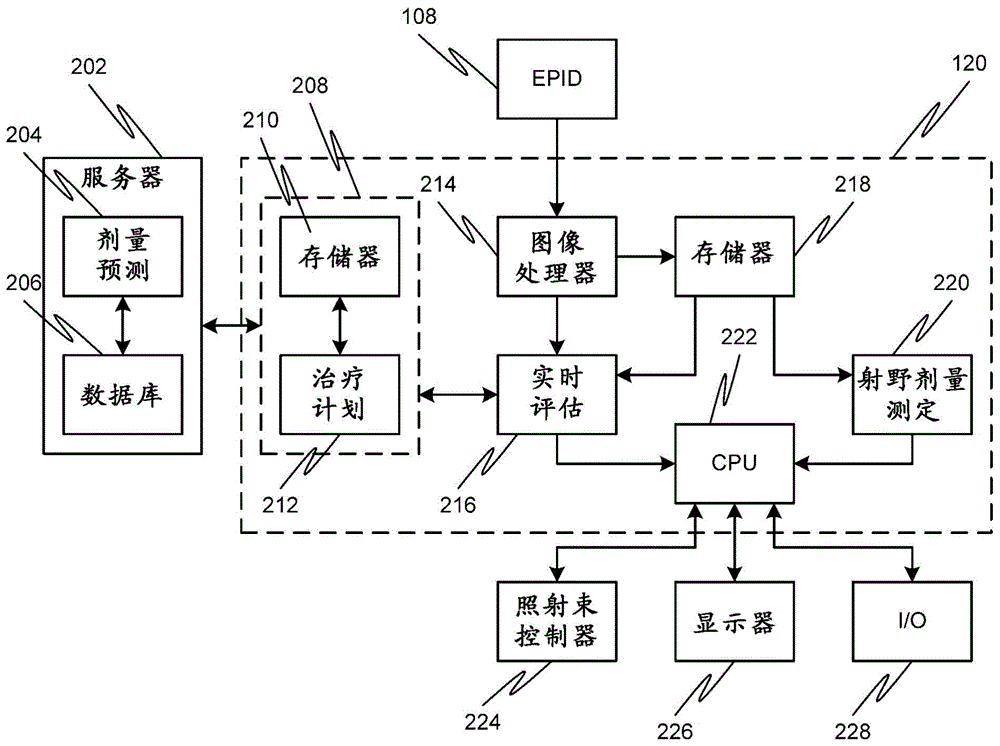
Systems, methods, and devices for real-time treatment verification using electronic portal imaging device
InactiveCN104825178ARadiation diagnostic image/data processingRadiation detection arrangementsNon complianceTreatment verification
A radiation dose received by a patient 110 from a radiation therapy system 100 can be verified by acquiring a cine stream of image frames from an electronic portal imaging device (EPID) 108 that is arranged to detect radiation exiting the patient during irradiation. The cine stream of EPID image frames can be processed in real-time to form exit images providing dose measurements at the EPID (e.g., absolute dose as dose-to-water values), which can be representative of the characteristics of the radiation received by the patient. Compliance with predetermined characteristics for the field can be determined during treatment by periodically comparing the dose measurements with the predetermined characteristics, which can include a predicted total dose in the field after full treatment and / or a complete irradiation area outline (CIAO). The system operator can be alerted or the irradiation automatically stopped when non-compliance is detected.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
High quantum efficiency x-ray detector for portal imaging
InactiveUS7205548B2Increasing probability of absorptionElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesMicro structureHigh energy
The present invention provides a practical design of a megavoltage x-ray detector with both high quantum efficiency (QE) and high resolution. The x-ray detector disclosed herein has a QE that can be an order of magnitude higher than that of current flat panel systems and yet has a spatial resolution equivalent to that of current flat panel systems used for portal imaging. The x-ray detector includes a large number of micro-structured electrically conducting plates, packed together with thin spacers placed between neighboring plates with the micro-structured plates oriented to be parallel to the incident x-rays in operation. Each plate includes an electrically conductive substrate with a first planar surface, elongate electrically conductive strip electrodes separated from each other with strip spacers placed in between and sitting on an insulating layer interposed between the first planar surface of the electrically conductive substrate and the strip electrodes. A power supply applies a bias voltage between each electrically conductive substrate and the electrically conductive strip electrodes, whereby x-rays absorbed in the conductive substrate generates high energy electrons which produce ions in an ionization medium located in spaces between the conductive substrate and the electrically conductive strips. A detector detects an electrical current generated in the electrically conductive strip electrodes and a 2D active readout matrix is coupled to the detector.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
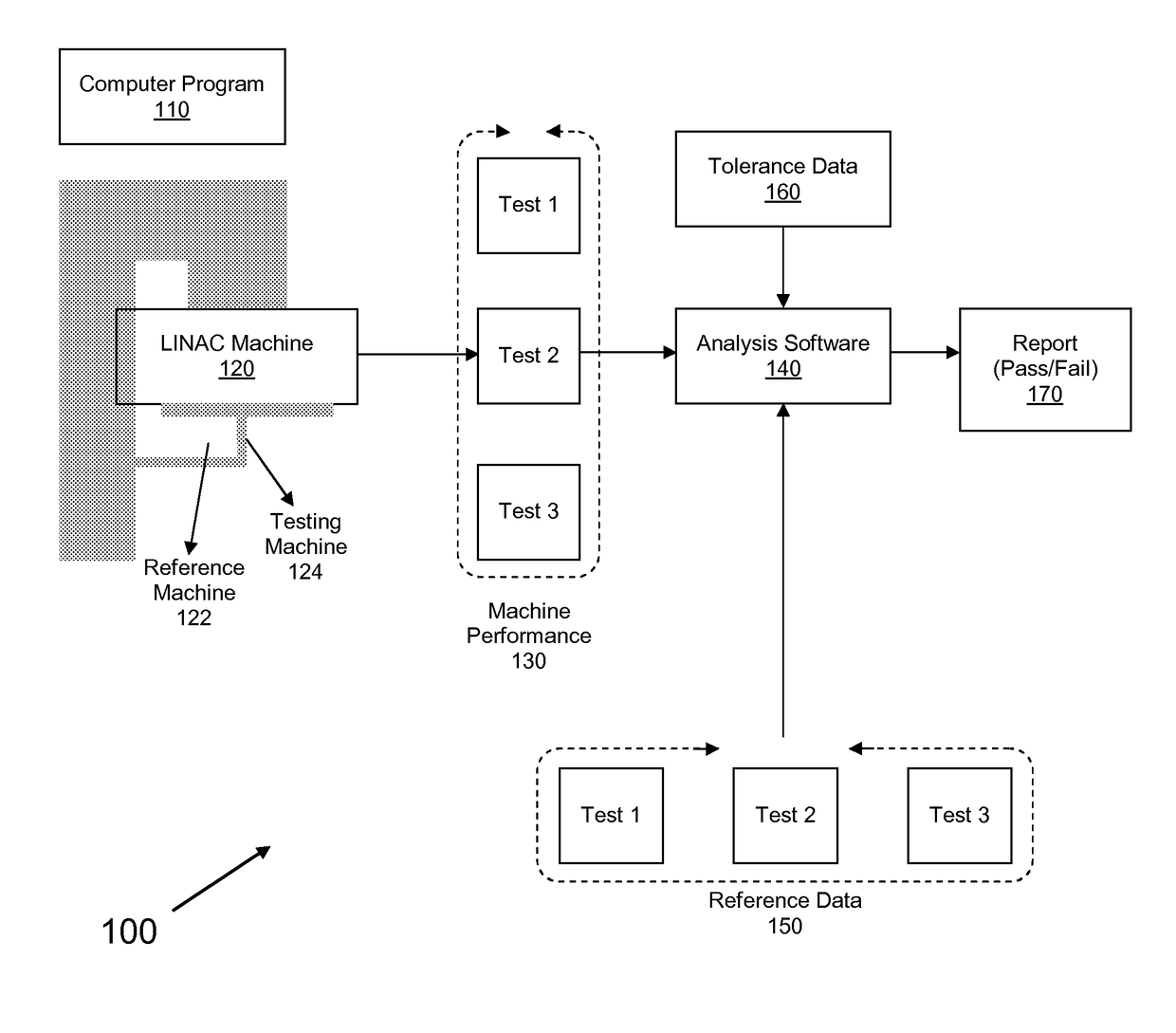
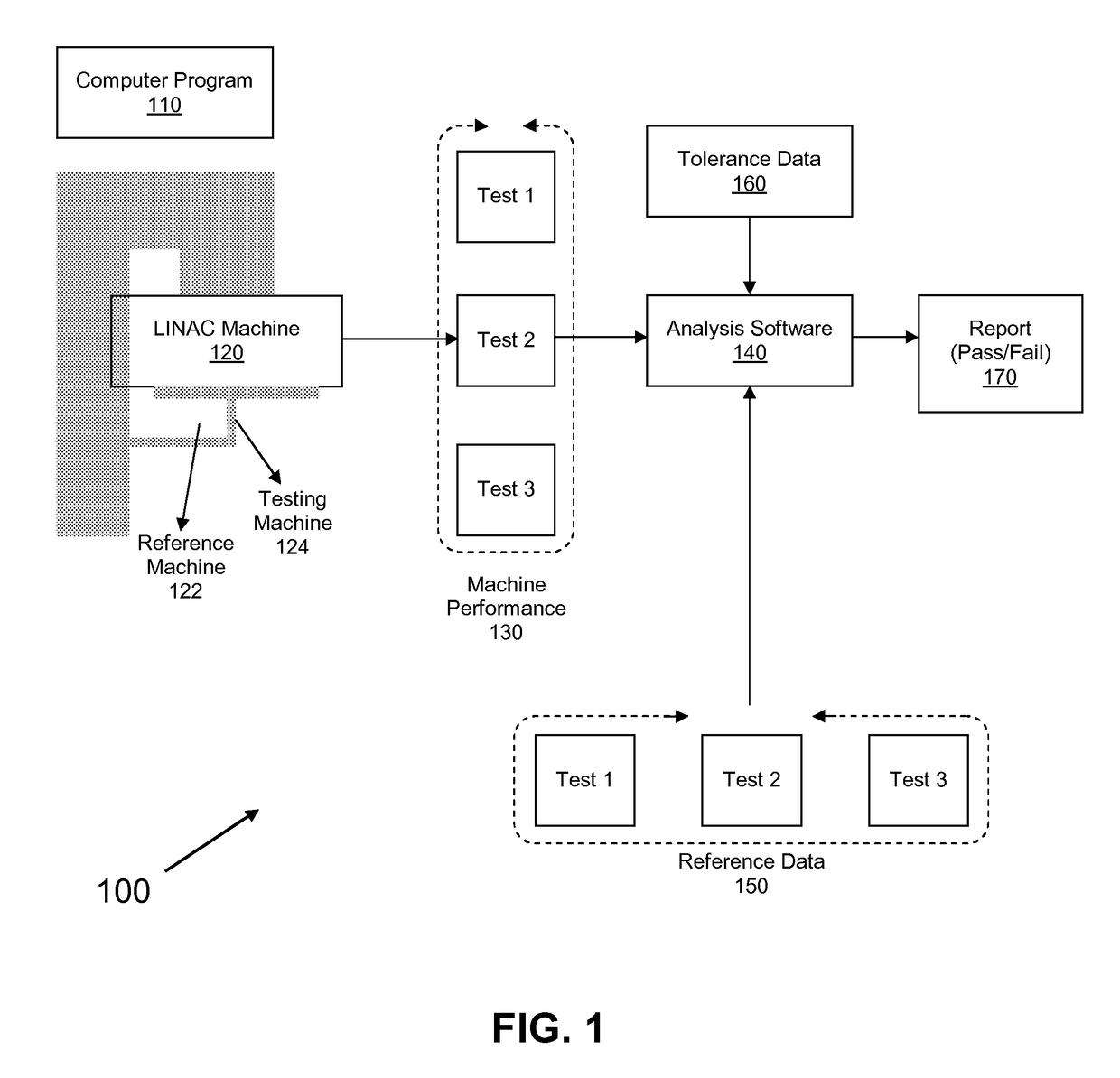
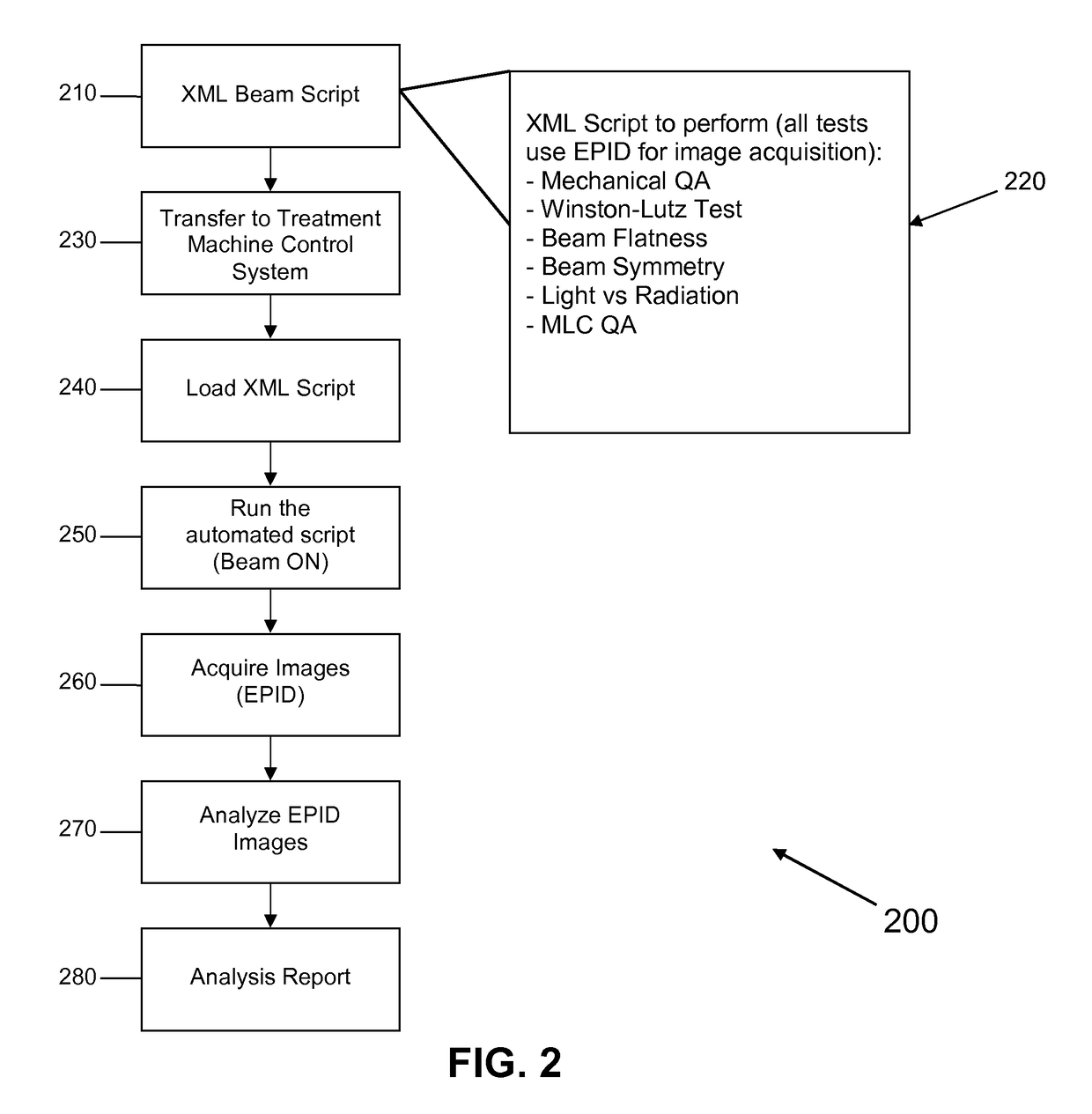
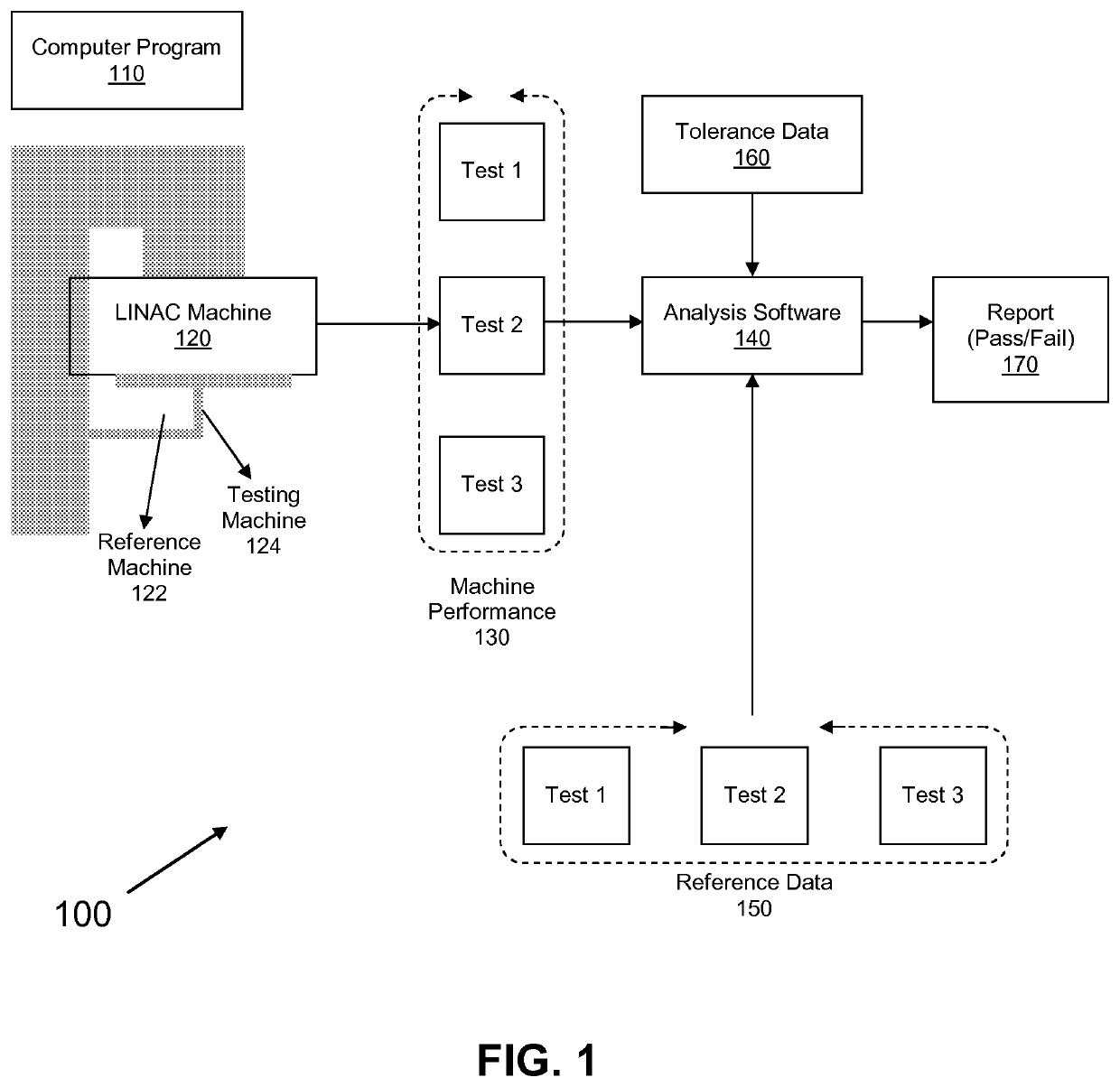
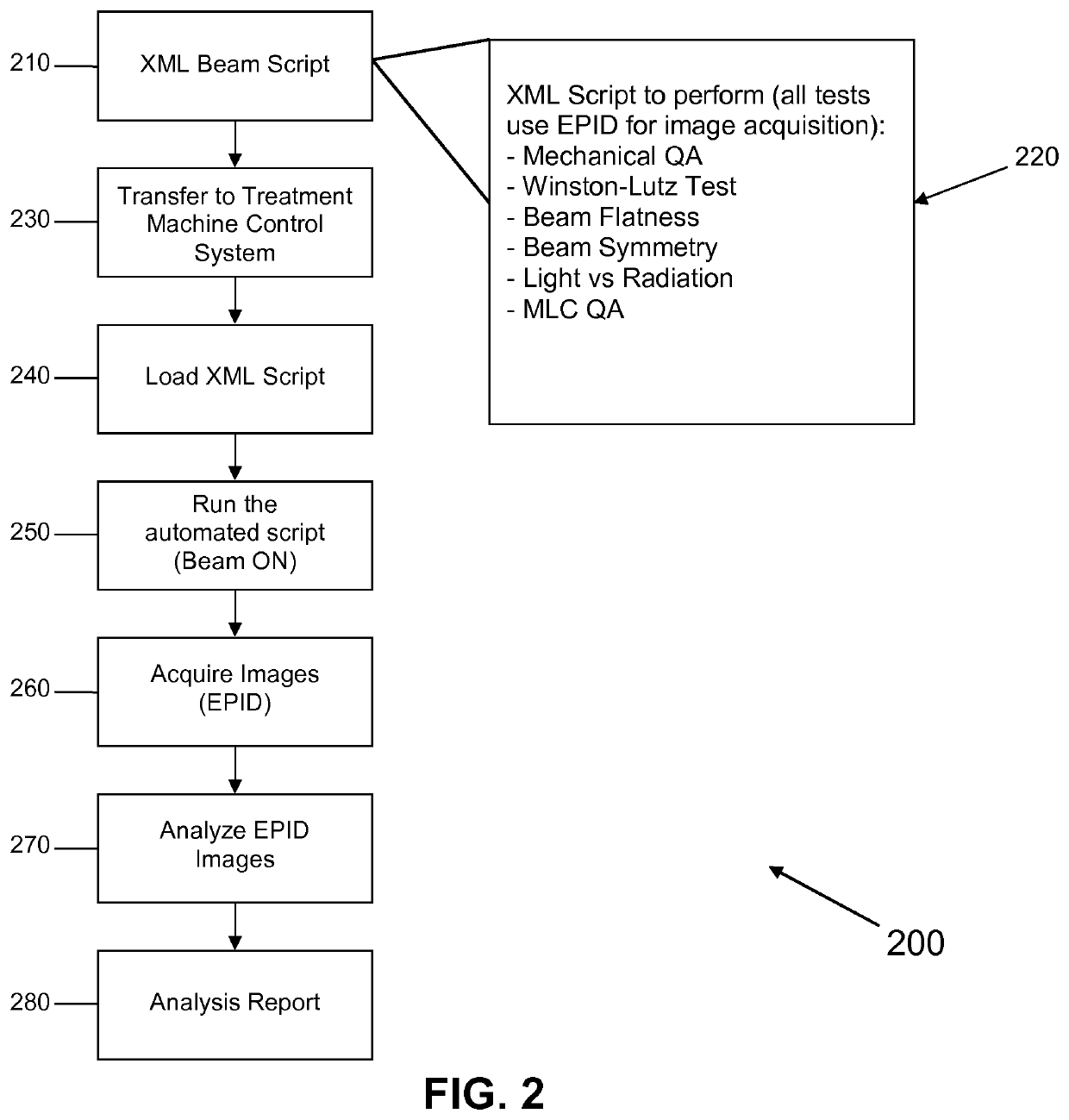
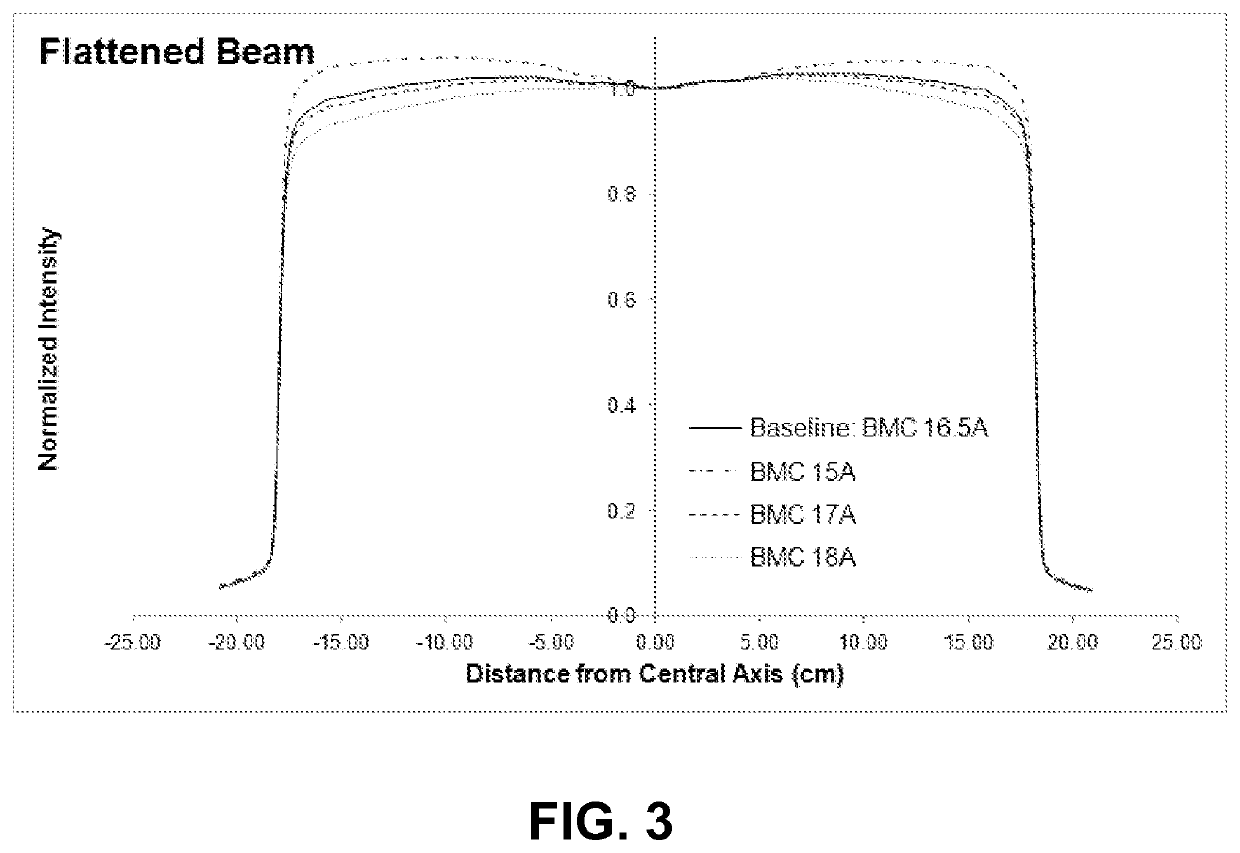
Acceptance, commissioning, and ongoing benchmarking of a linear accelerator (LINAC) using an electronic portal imaging device (EPID)
ActiveUS20170199971A1Local control/monitoringMedical equipmentLinear particle acceleratorBaseline testing
The present invention is a method or system for acceptance testing and commissioning of a LINAC and treatment planning system (TPS). For a LINAC commissioning, the present invention collects reference data from a fully calibrated LINAC and compares the reference data with machine performance data collected from a testing LINAC. The compared results are analyzed to assess accuracy of the testing LINAC. For a TPS commissioning, the present invention collects standard reference data from standard treatment plans and standard input data and compares the standard reference data with results from standard tests that are performed by a testing treatment plan system. The compares results are analyzed to assess accuracy of the testing treatment plan system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Acceptance, commissioning, and ongoing benchmarking of a linear accelerator (LINAC) using an electronic portal imaging device (EPID)
ActiveUS10553313B2Medical equipmentX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBaseline testingImaging equipment
The present invention is a method or system for acceptance testing and commissioning of a LINAC and treatment planning system (TPS). For a LINAC commissioning, the present invention collects reference data from a fully calibrated LINAC and compares the reference data with machine performance data collected from a testing LINAC. The compared results are analyzed to assess accuracy of the testing LINAC. For a TPS commissioning, the present invention collects standard reference data from standard treatment plans and standard input data and compares the standard reference data with results from standard tests that are performed by a testing treatment plan system. The compares results are analyzed to assess accuracy of the testing treatment plan system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Portal imaging during radiotherapy
ActiveUS20160074673A1Avoid damageTomographyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyLight beamPortal imaging
A radiotherapy apparatus comprises a source for producing a beam of ionising radiation along an axis, the beam covering a maximum aperture of the source, a collimator for collimating the beam to produce a collimated beam covering a sub-part of the maximum aperture, a patient support positioned in the path of the beam, a rotatable gantry, on which the source is mounted, for rotating the source around the patient support thereby to deliver the beam from a range of directions, an imaging device located opposite the source and with the patient support between the source and the imaging device, and mounted on the gantry via a drive member allowing translational motion of the imaging device in at least one direction perpendicular to the axis, and a control unit adapted to control the drive member to move the imaging device within the maximum aperture and maintain coincidence between the imaging device and the sub-part of the maximum aperture. Accordingly, the EPID can be moved during the treatment in order to maintain the collimated field of the radiation beam within the bounds of the EPID. This ensures that the image is valid and prevents damage to the EPID as a result of exposure of more sensitive (or less shielded) parts to the beam.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
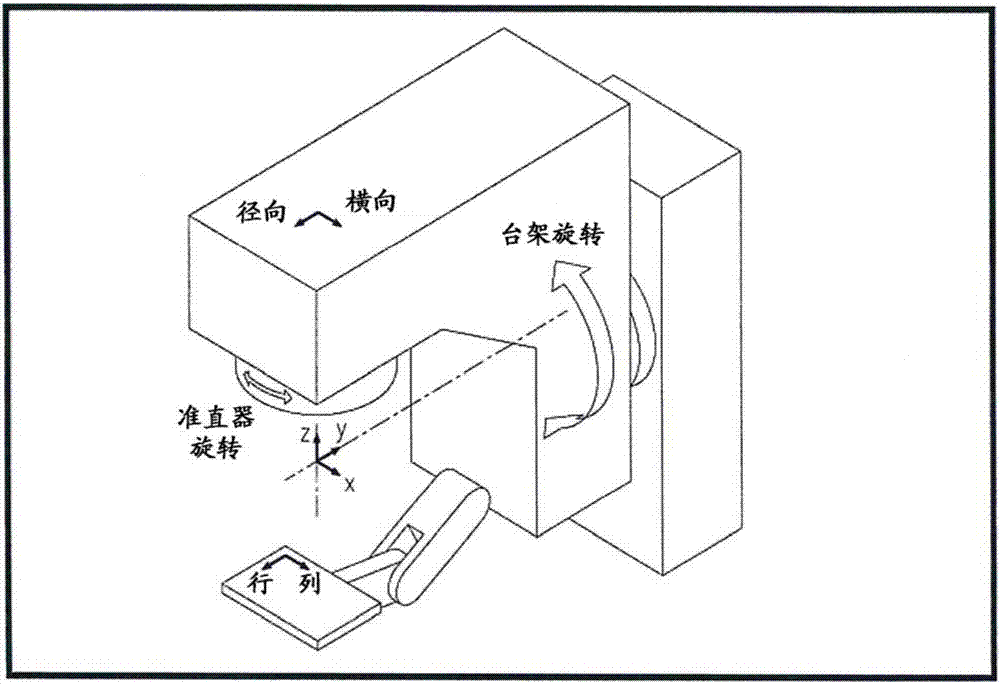
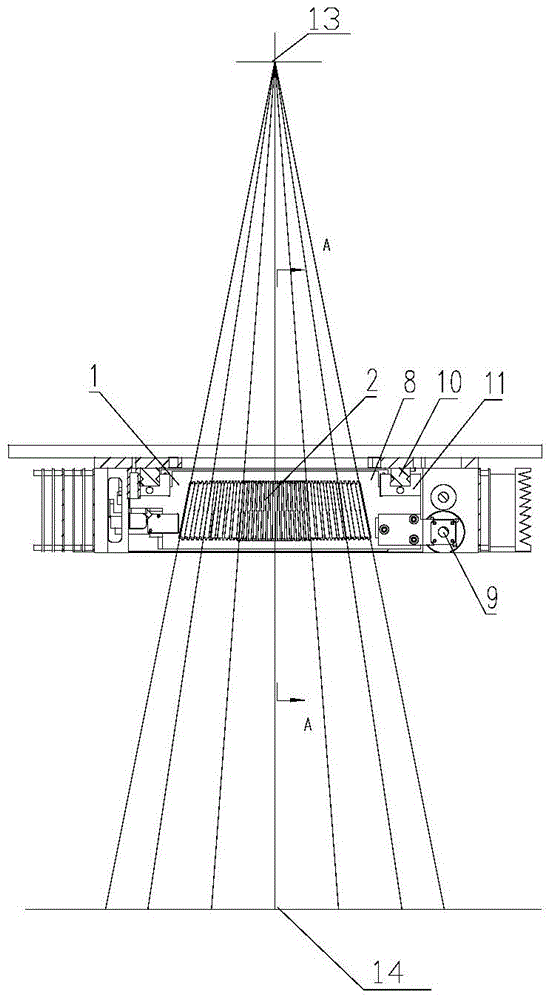
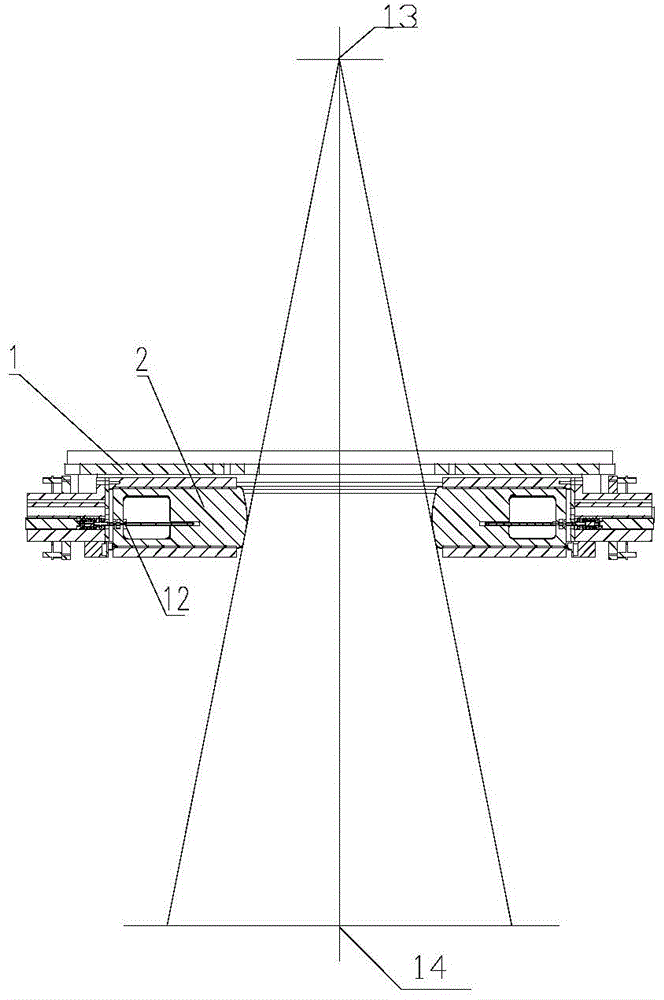
Novel high-resolution portal imaging system
ActiveCN104027892AGuaranteed accuracyImprove performanceX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyEngineeringPortal imaging
The invention relates to a novel high-resolution portal imaging system, belongs to the field of medical instruments, and is applied to tumor radiotherapy. The novel high-resolution portal imaging system comprises a multi-blade collimator comprising multiple blades which are installed in a box body. The box body is installed on a slide block of a linear guide rail and can move along the linear guide rail. Each blade can move along blade guide grooves of the box body. The box body moves in a dragging way via a leading screw transmission mechanism. The blades move in the dragging way via leading screw nuts. A required portal shape is formed by positions of the multiple blades and the box body via positioning and controlling, and dimension of a dose calculation matrix unit of the portal imaging system is 2.5mm*2.5mm. The novel high-resolution portal imaging system is characterized in that the blades comprise a group of intermediate blades, a second group of blades and a third group of blades. The second group of blades are arranged at the two sides of the group of intermediate blades. The third group of blades are arranged at the two sides of the second group of blades. The novel high-resolution portal imaging system has characteristics of being high in performance, low in cost and high in practicality.
Owner:SHINVA MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
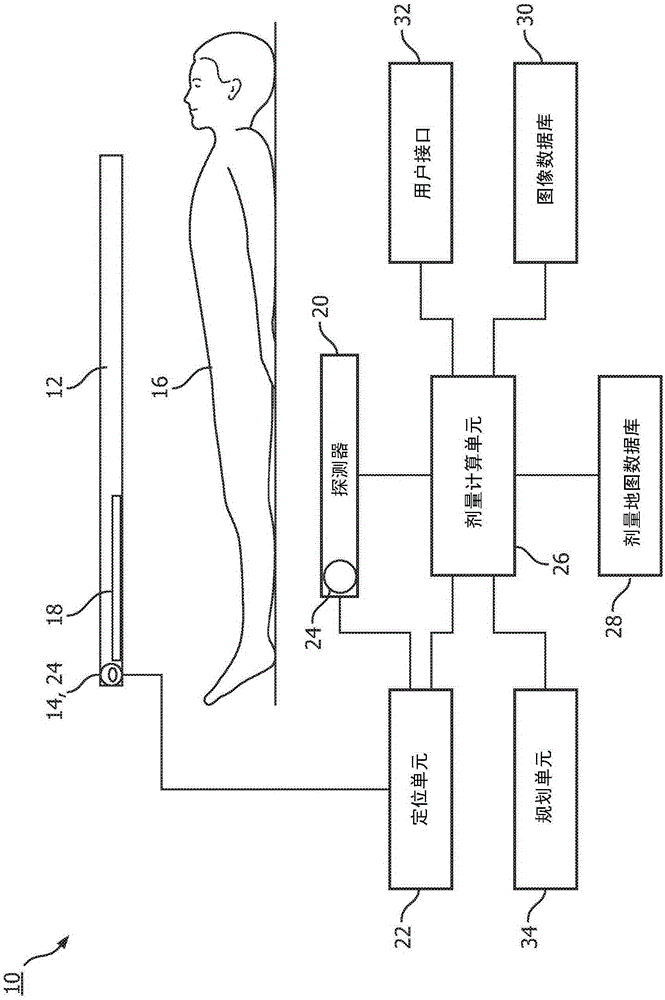
Portal imaging for brachytherapy
InactiveCN105407966AComputer-aided surgeryX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBrachytherapyTherapy planning
A system for interventional brachytherapy for generating data to be used directly for therapy and / or for therapy planning includes a radiation source which irradiates tissue of a patient and one or more radiation detectors which detect radiation delivered to the patient and generate radiation dosage data indicative thereof. One or more position sensors determine the position of the radiation source and a localization unit, in communication with the one or more position sensors, generates position data indicative of the position of the radiation source. An image database stores one or more anatomical images of the patient. A dose calculation unit which co-registers the one or more anatomical images with the positional and radiation dosage data and generates dose monitoring data based on the co-registration
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
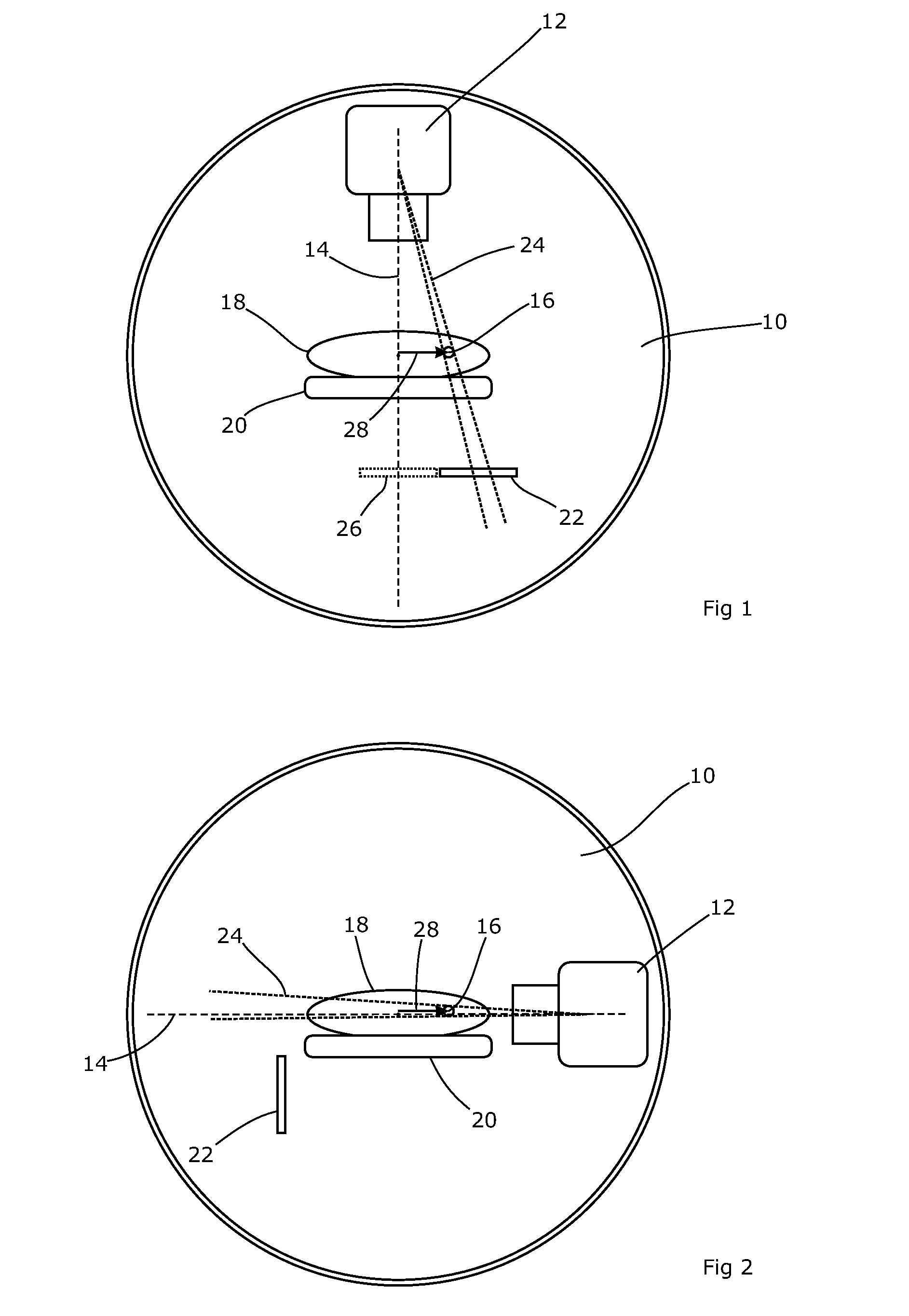
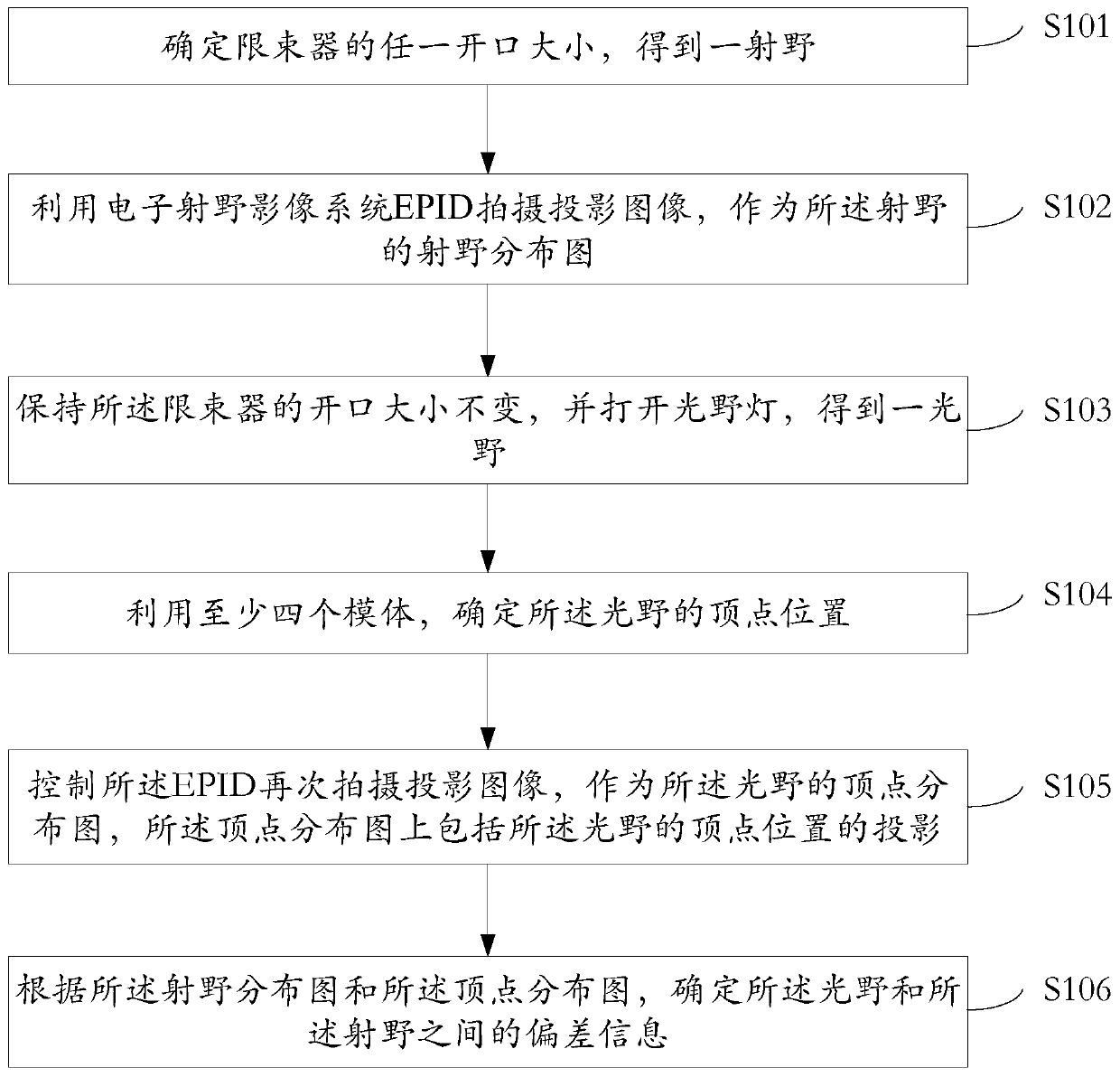
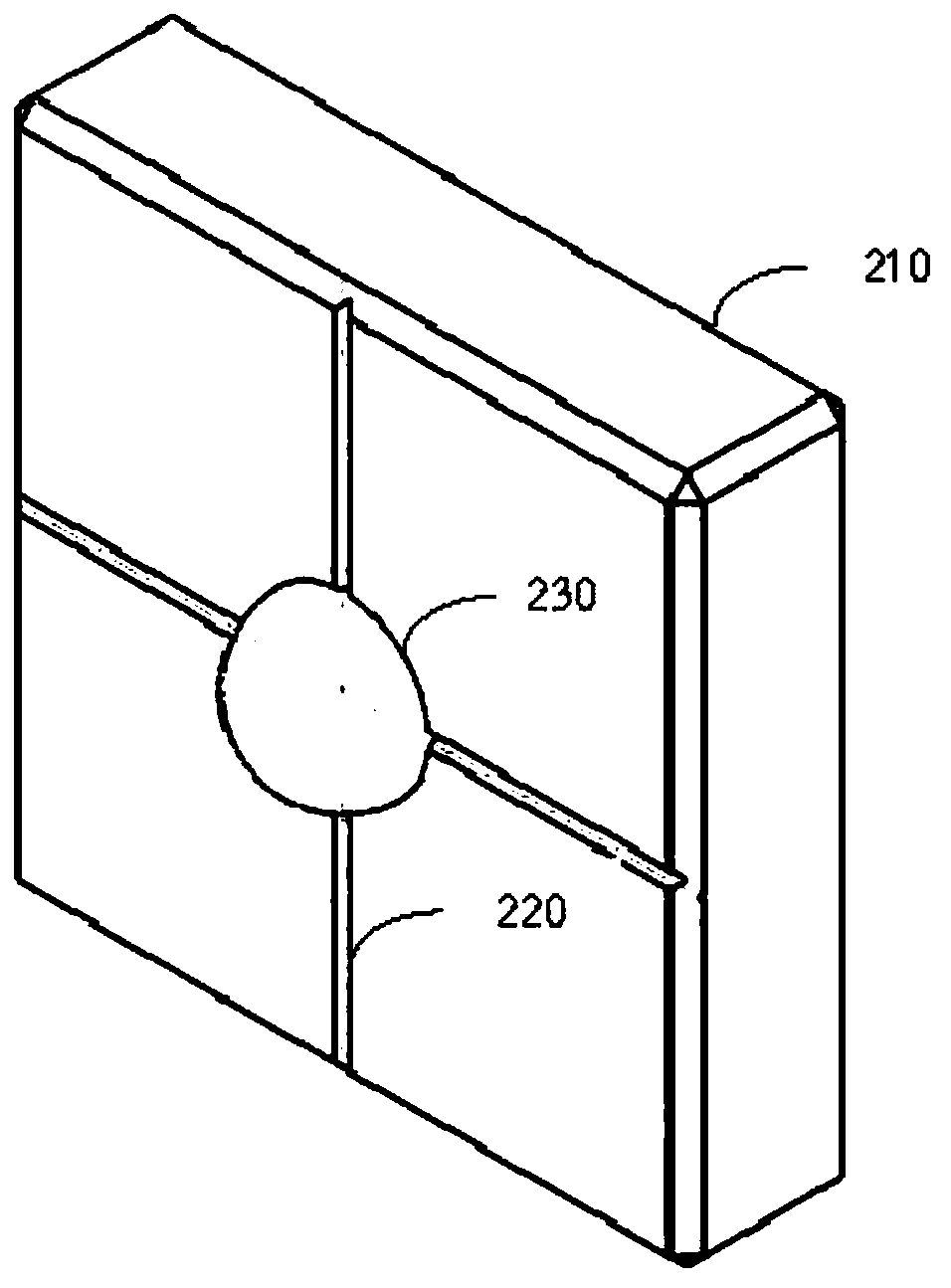
A light field consistency detection phantom, method, device and equipment
ActiveCN107693959BSolve the lack of flexibilityX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyProjection imageRadiation field
Methods and devices for detecting consistency between an invisible radiation field and a visible light field are provided. In an example, the method includes: an invisible radiation field is obtained by controlling a size of an opening of a beam limiting device; a first projection image is captured by an Electron Portal Imaging Device (EPID) as a distribution map of the invisible radiation field; a visible light field is obtained by turning on a light field lamp without changing the size of the opening of the beam limiting device; a phantom is positioned at each of vertices of the visible light field; a second projection image is captured by the EPID as a vertex distribution map of the visible light field; and deviation information between the invisible radiation field and the visible light field is determined according to the distribution map of the invisible radiation field and the vertex distribution map of the visible light field.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
Method, apparatus and radiotherapy equipment for verifying radiation therapy dose
ActiveCN109464756BVerify rationalityCalculation speedX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyEnergy fluenceNuclear medicine
The present invention provides a device for verifying radiotherapy dose, comprising: a memory for storing instructions executable by a processor; a processor for executing the instructions to implement the following method: acquiring the measurement detected by the electronic portal imaging device An image, the measurement image characterizes the dose distribution of the radiotherapy beam on the electronic portal imaging device; uses a dose algorithm to calculate the energy fluence distribution map of the beam on the electronic portal imaging device; according to the energy fluence distribution map and The energy response curve of the electronic portal imaging device calculates a predicted image, the predicted image characterizes the dose distribution of the virtual beam on the electronic portal imaging device; and compares the predicted image with the measurement image. The invention can quickly and accurately predict the dose distribution generated by the radiotherapy plan, thereby efficiently verifying the rationality of the radiotherapy plan.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
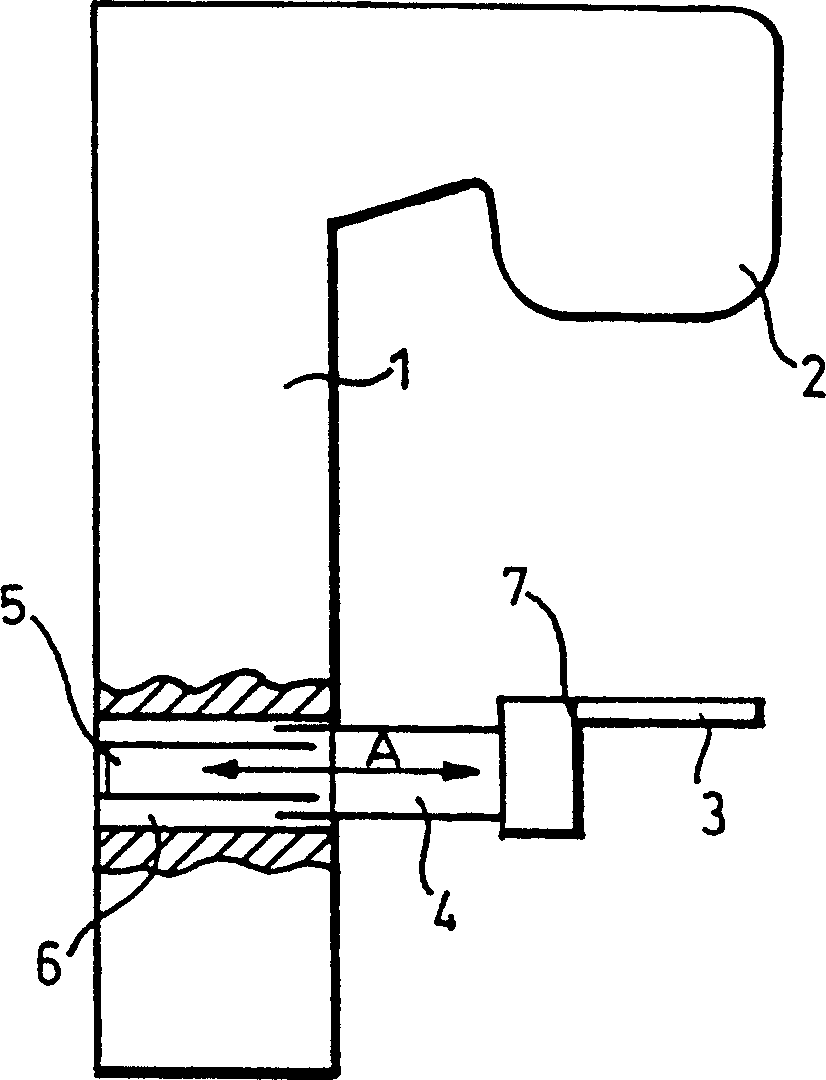
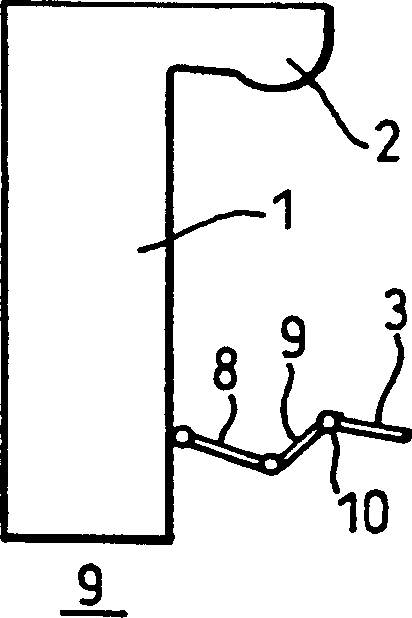
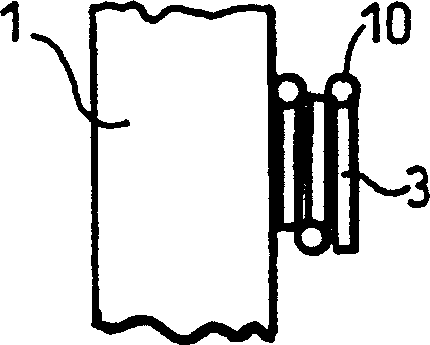
Portal imaging device
InactiveCN1196444CAvoid disadvantagesRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySurface mountingDistal portion
A surface mountable device for positioning an imaging device relative to a gantry of a radiation therapy device. The device includes: a mounting device for mounting the device on a stand surface; an extendable telescopic arm pivotally connected to the mounting device; and a holder for holding an imaging device, the A retainer is attached to the distal portion of the extendable telescopic arm. The device is mechanically simple and relatively cheap to manufacture. When assembled to a radiotherapy device, the device provides an accurate and lightweight device for positioning and stowing the imaging device.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
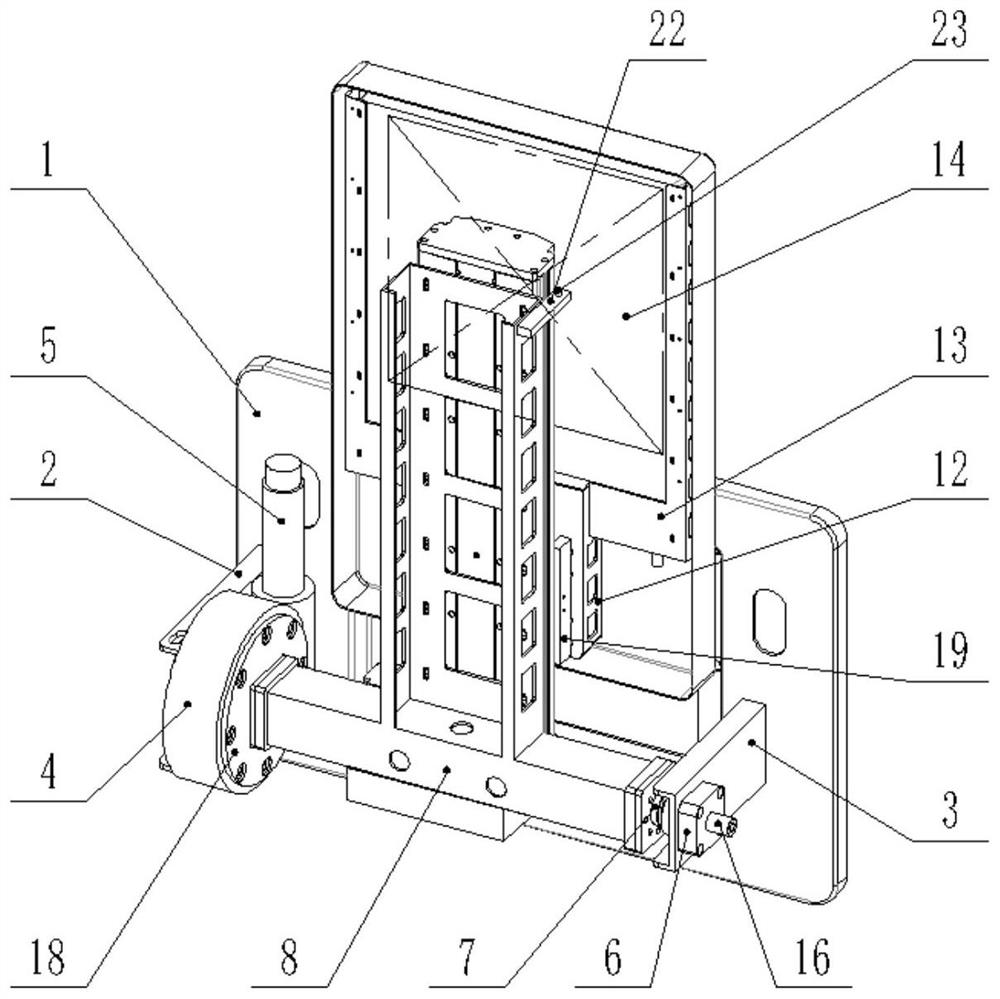
A positioning device for an electronic portal image system for a medical accelerator
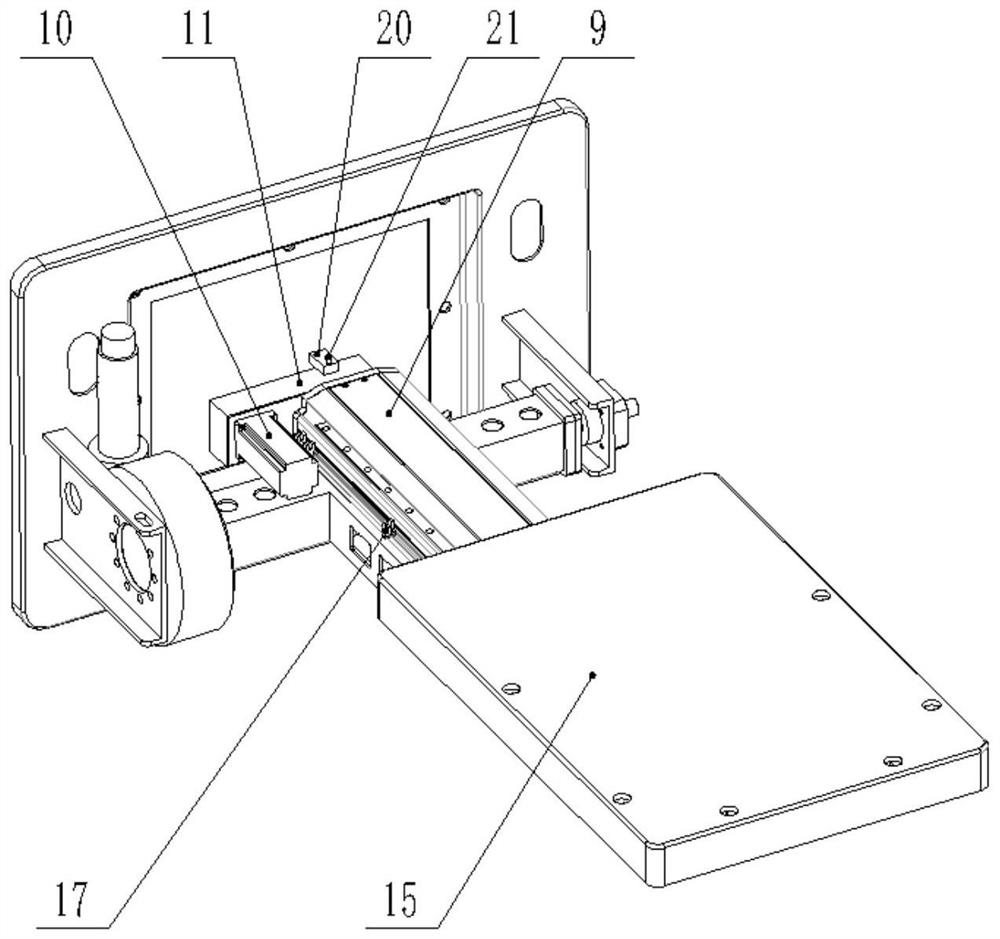
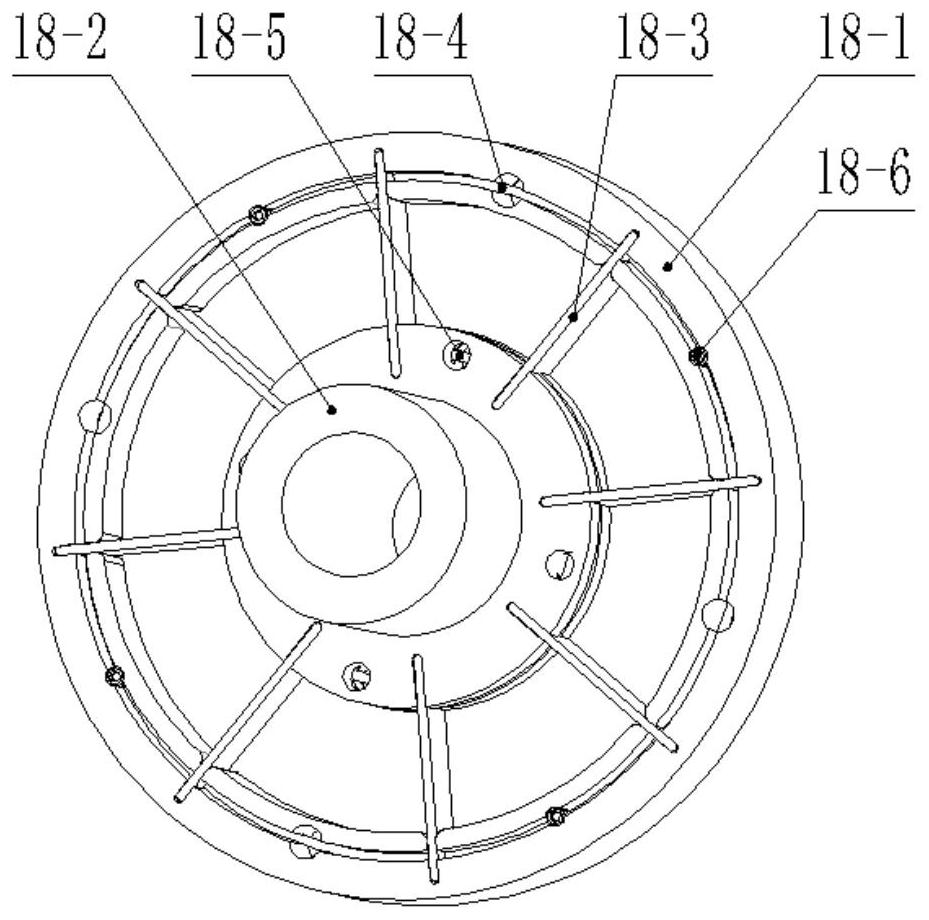
ActiveCN109954228BCorner positioning is reliableNo hysteresisX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyLinear motionControl theory
Owner:江苏海明医疗器械有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com