Patents
Literature
57 results about "Image-guided radiation therapy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
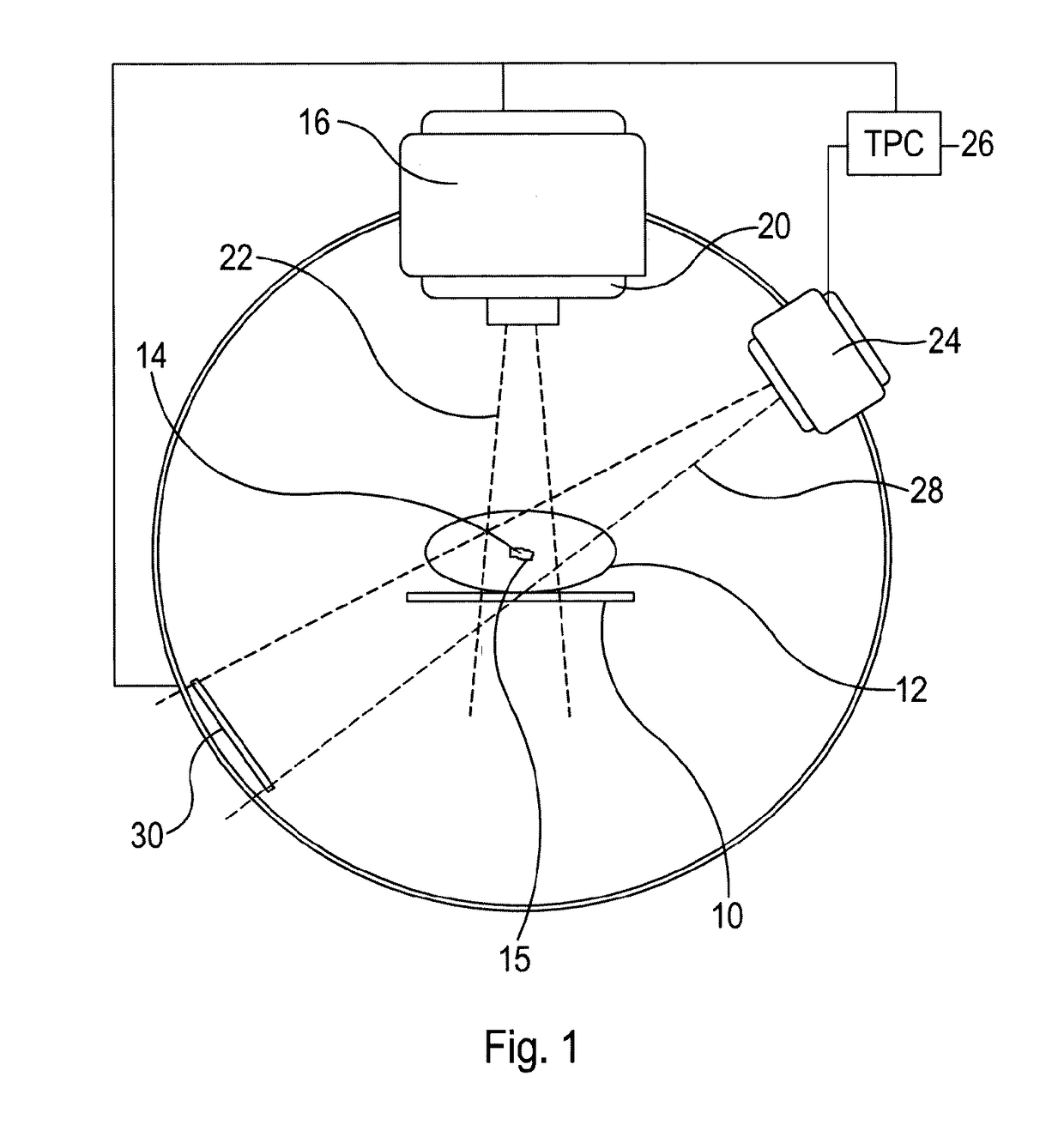
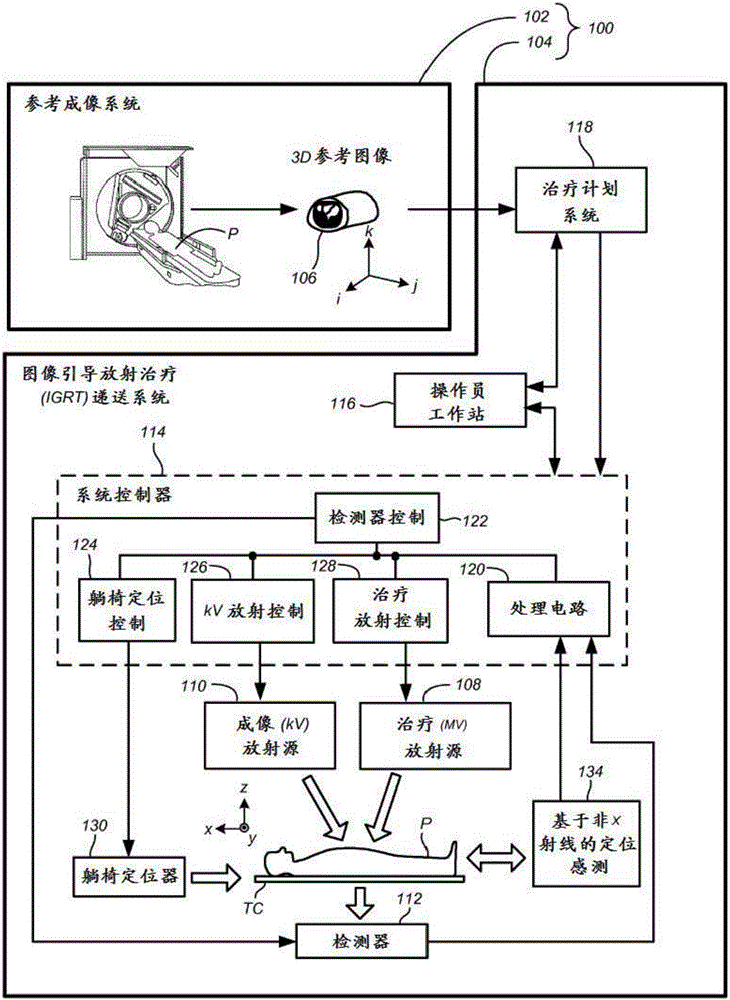
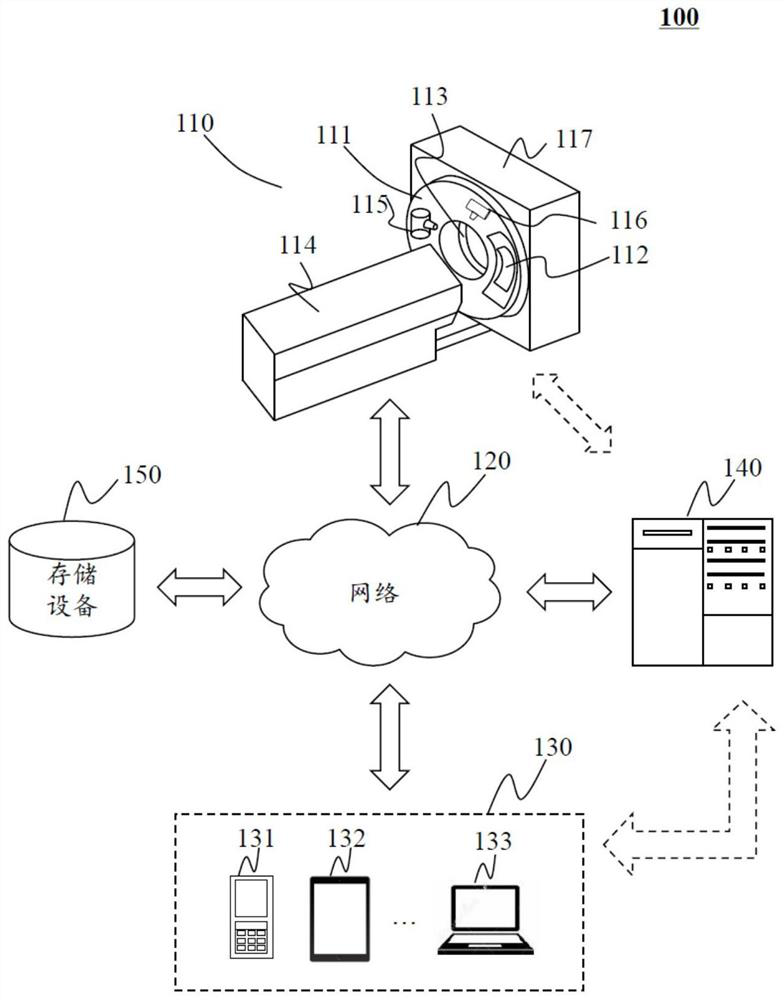
Image-guided radiation therapy is the process of frequent two and three-dimensional imaging, during a course of radiation treatment, used to direct radiation therapy utilizing the imaging coordinates of the actual radiation treatment plan. The patient is localized in the treatment room in the same position as planned from the reference imaging dataset. An example of IGRT would include localization of a cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) dataset with the planning computed tomography (CT) dataset from planning. IGRT would also include matching planar kilovoltage (kV) radiographs or megavoltage (MV) images with digital reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) from the planning CT. These two methods comprise the bulk of IGRT strategies currently employed circa 2013.
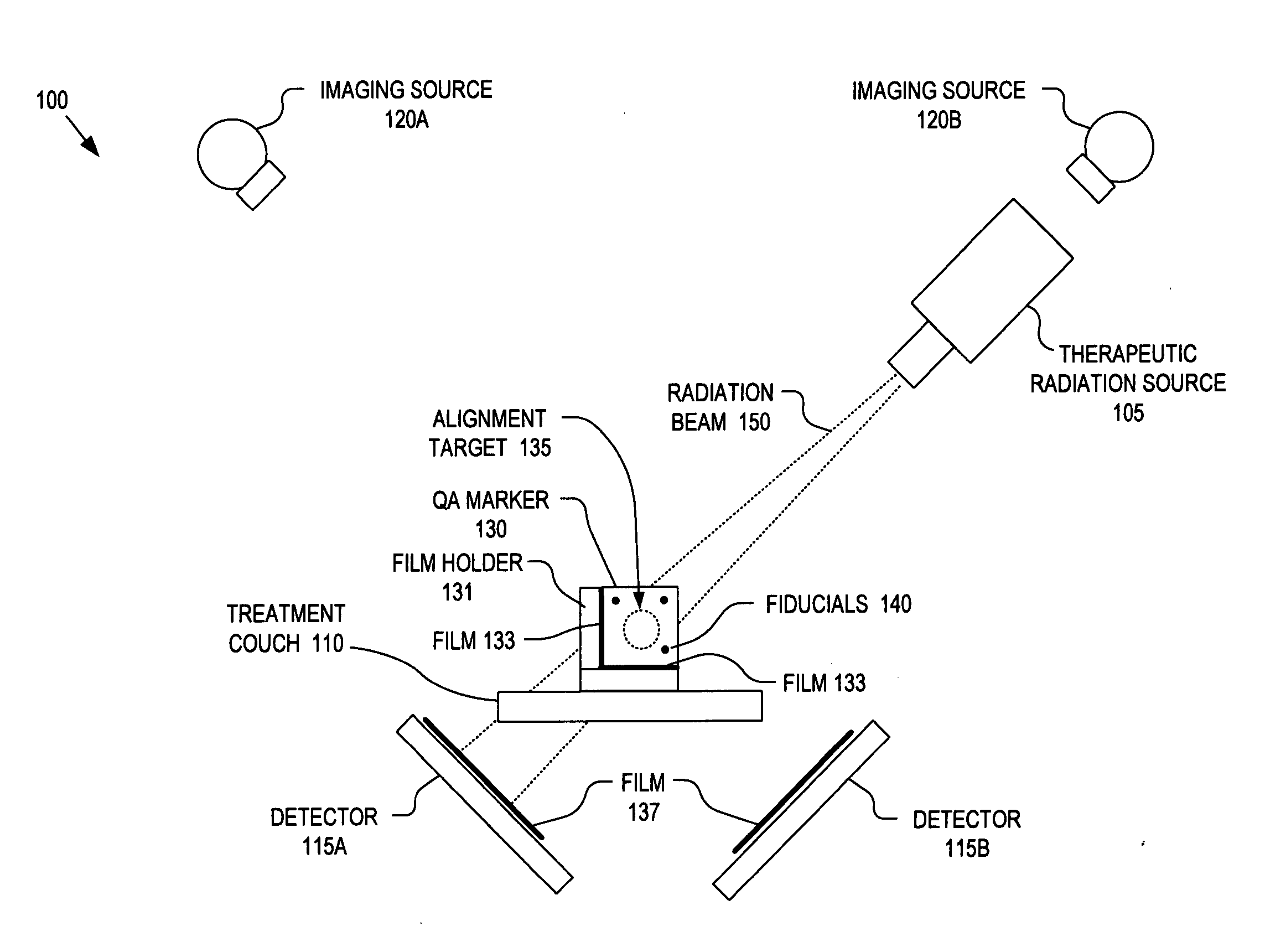
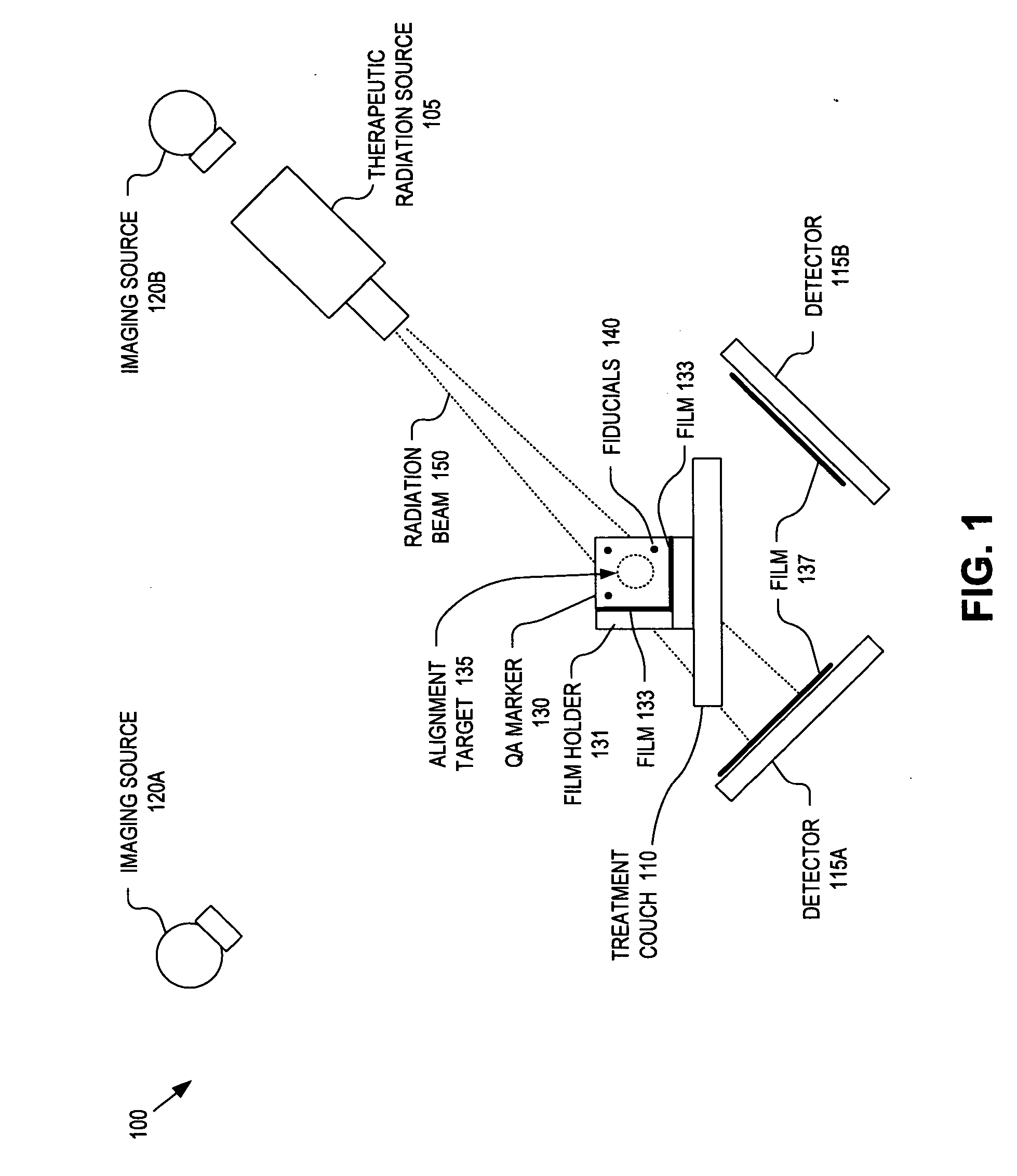
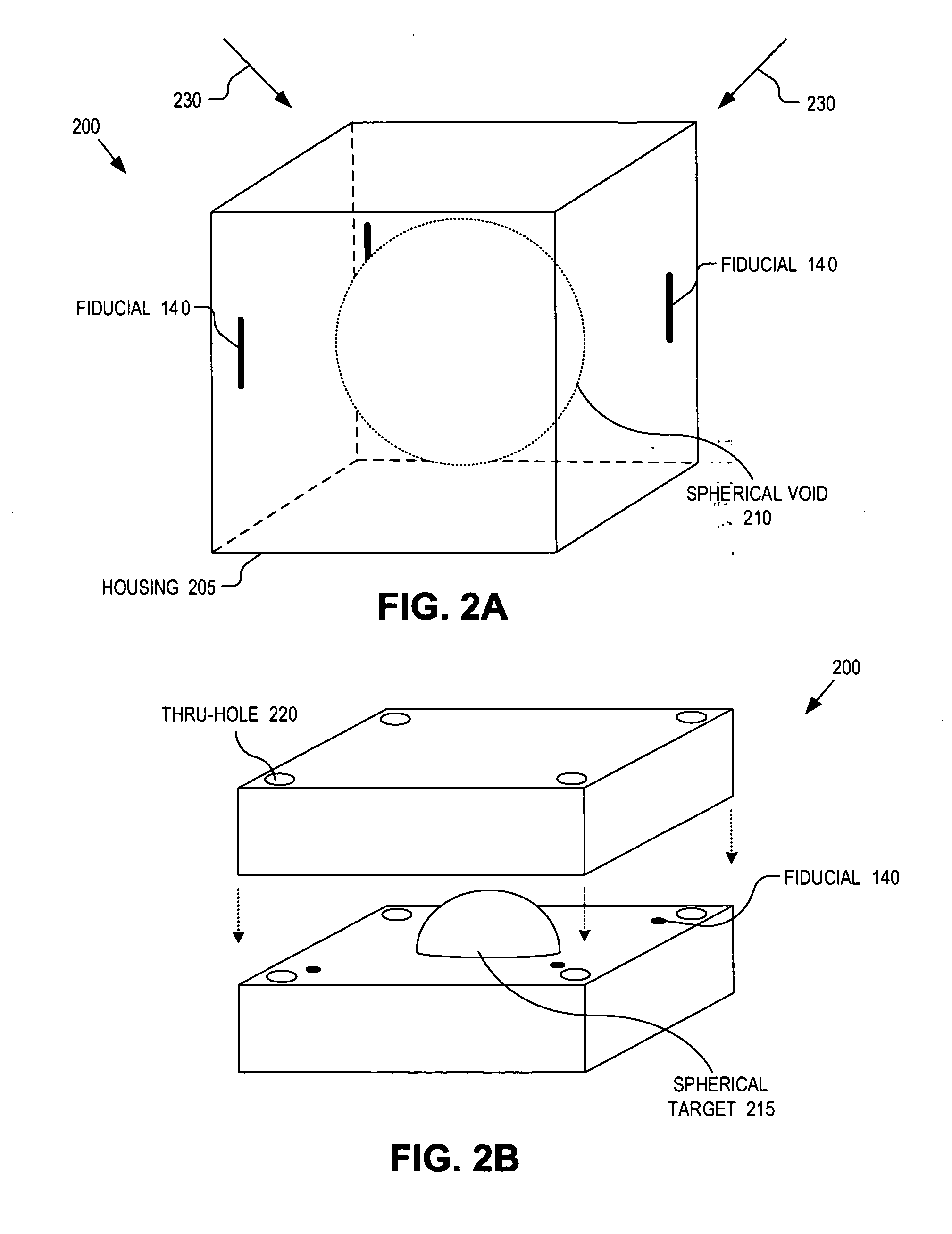
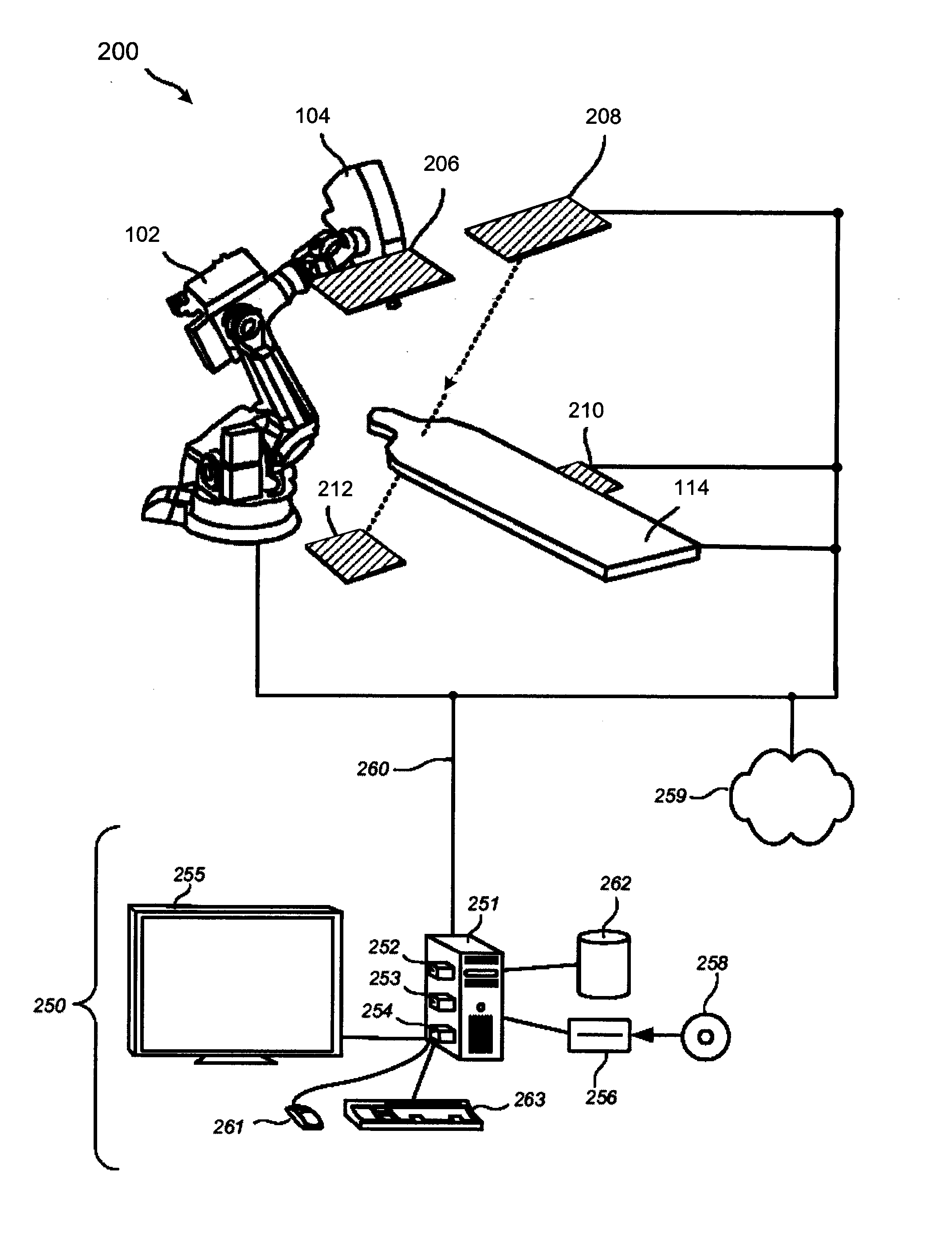
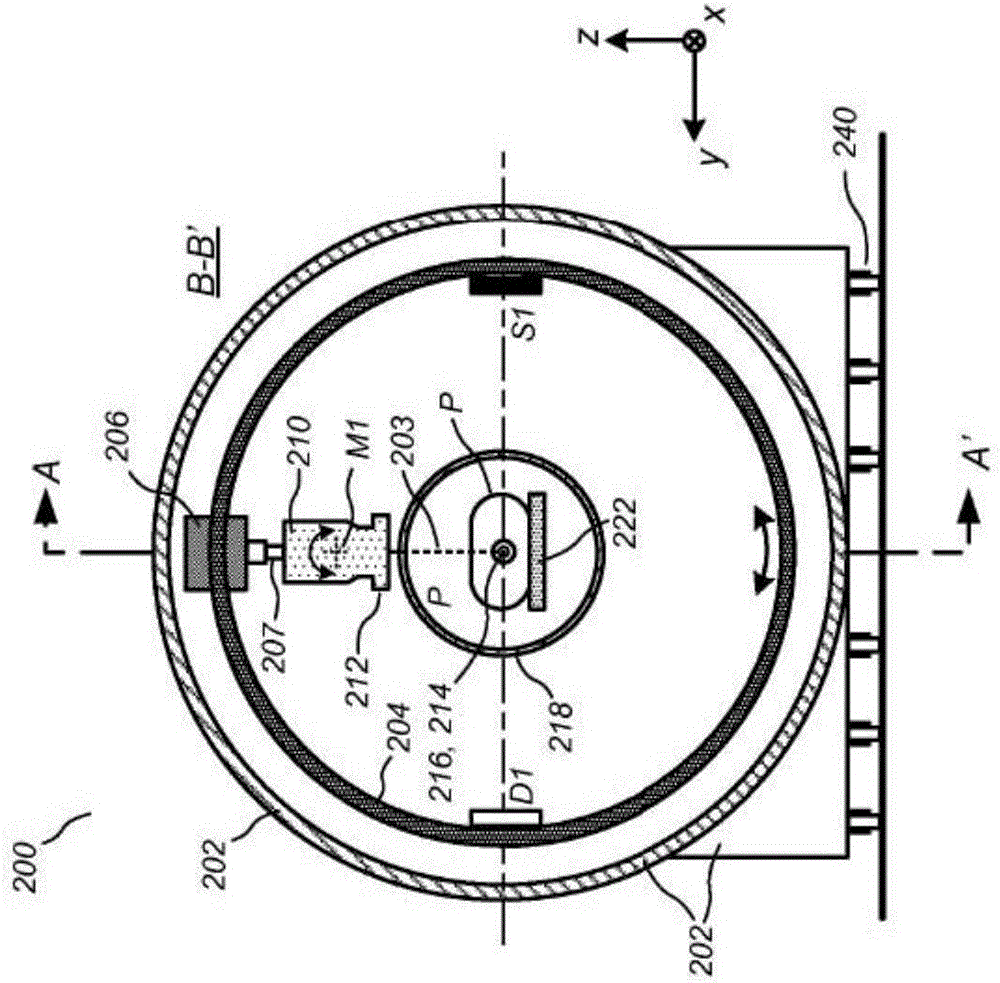
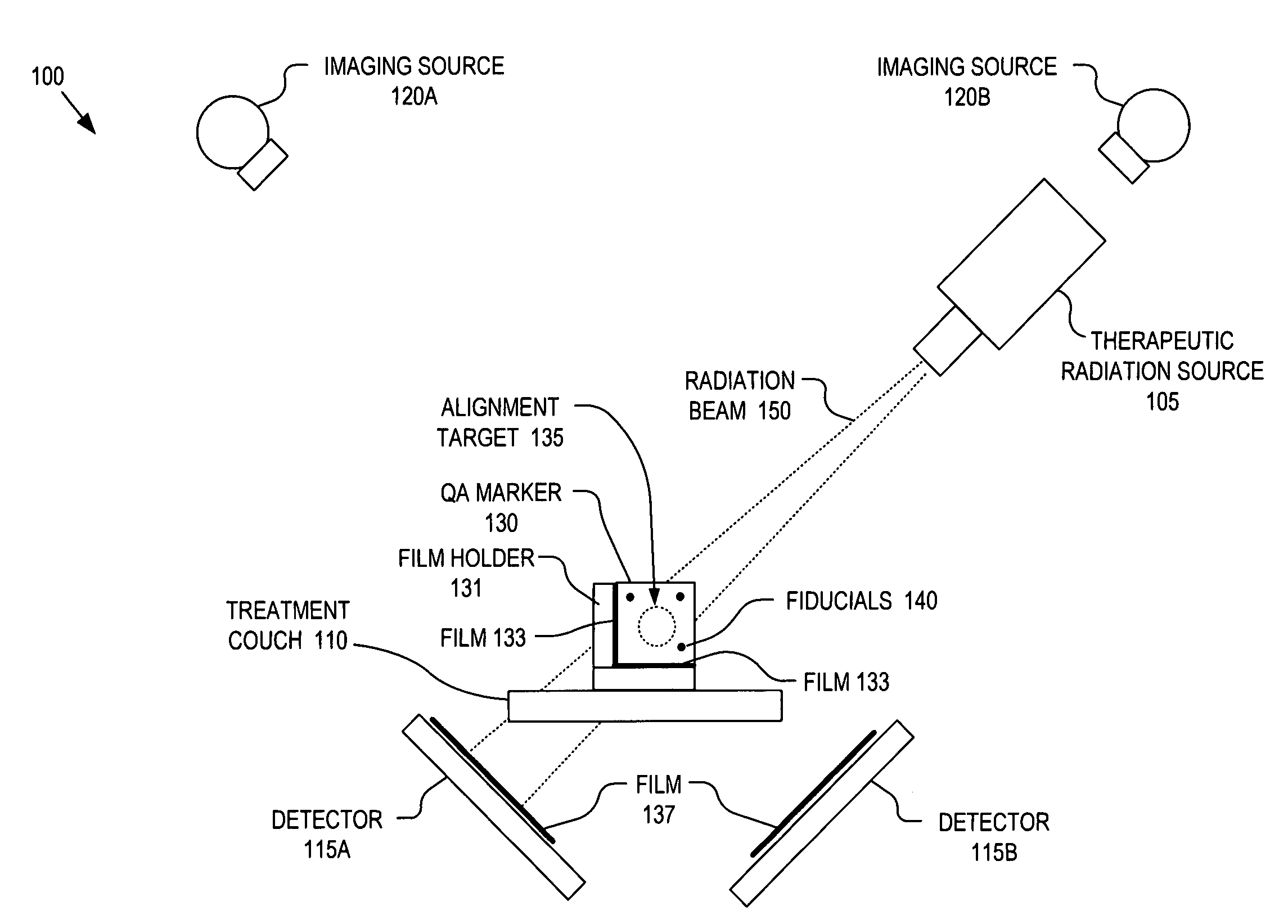
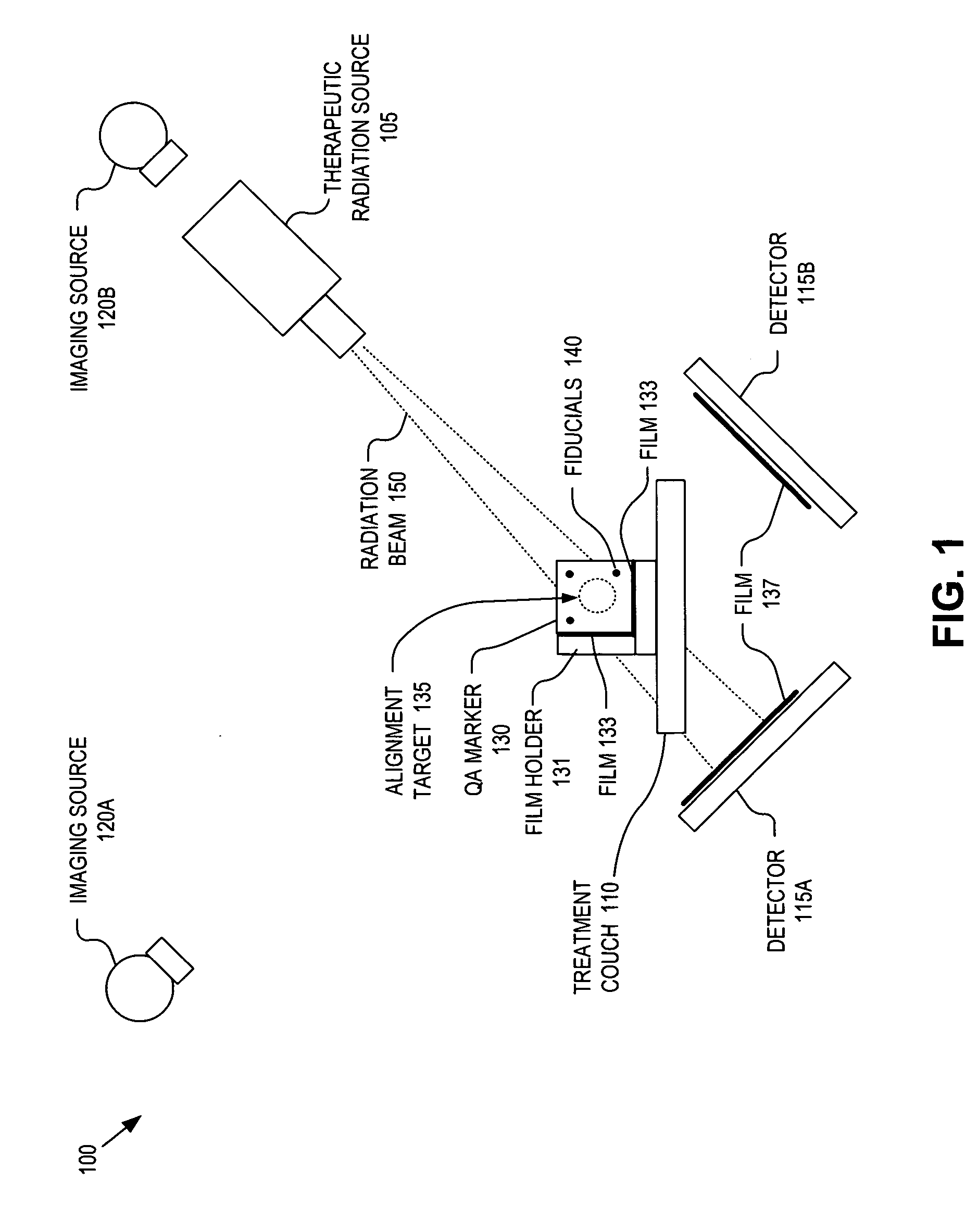
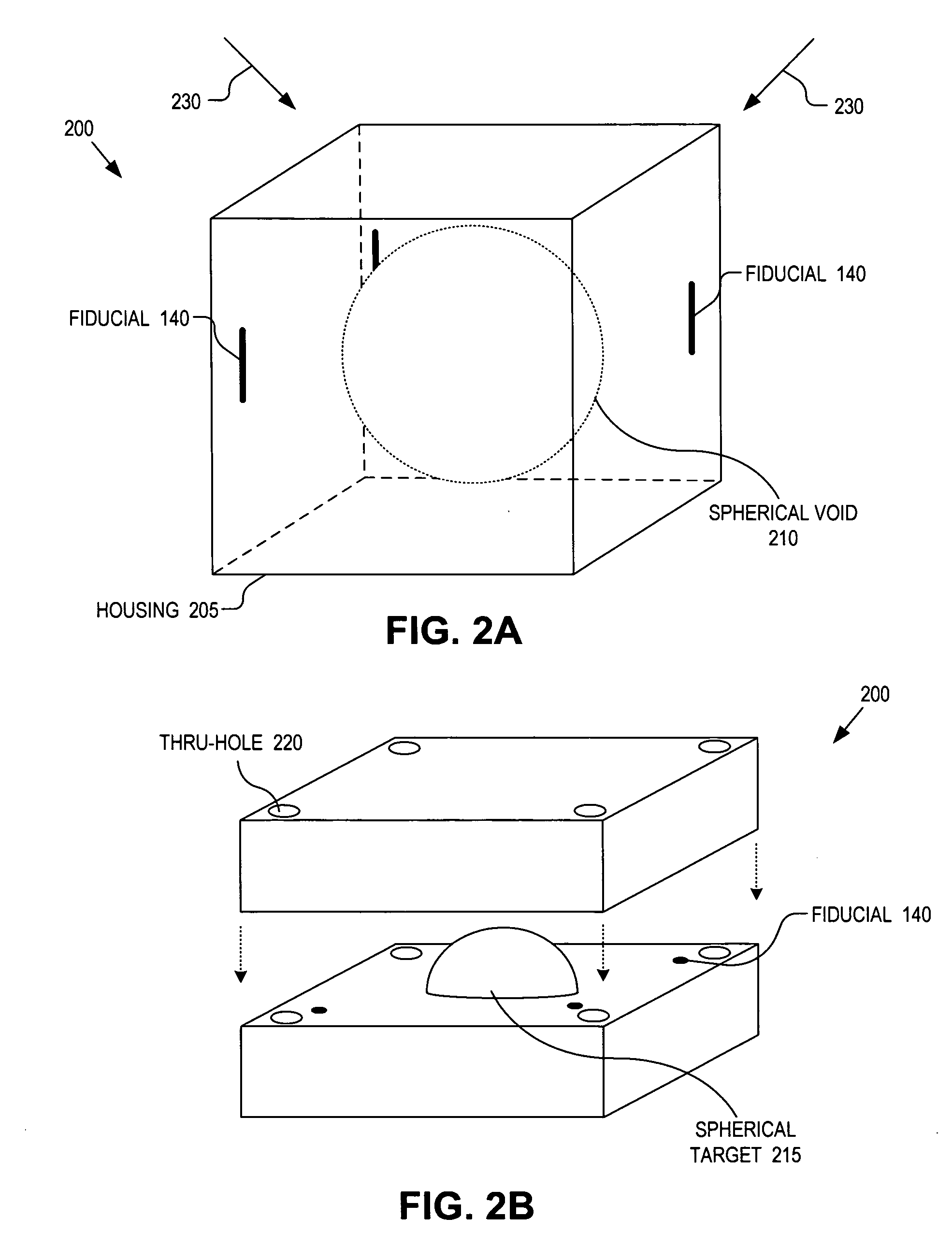
Integrated quality assurance for an image guided radiation treatment delivery system
ActiveUS20070071176A1Calibration apparatusRadiation beam directing meansQuality assuranceImage-guided radiation therapy
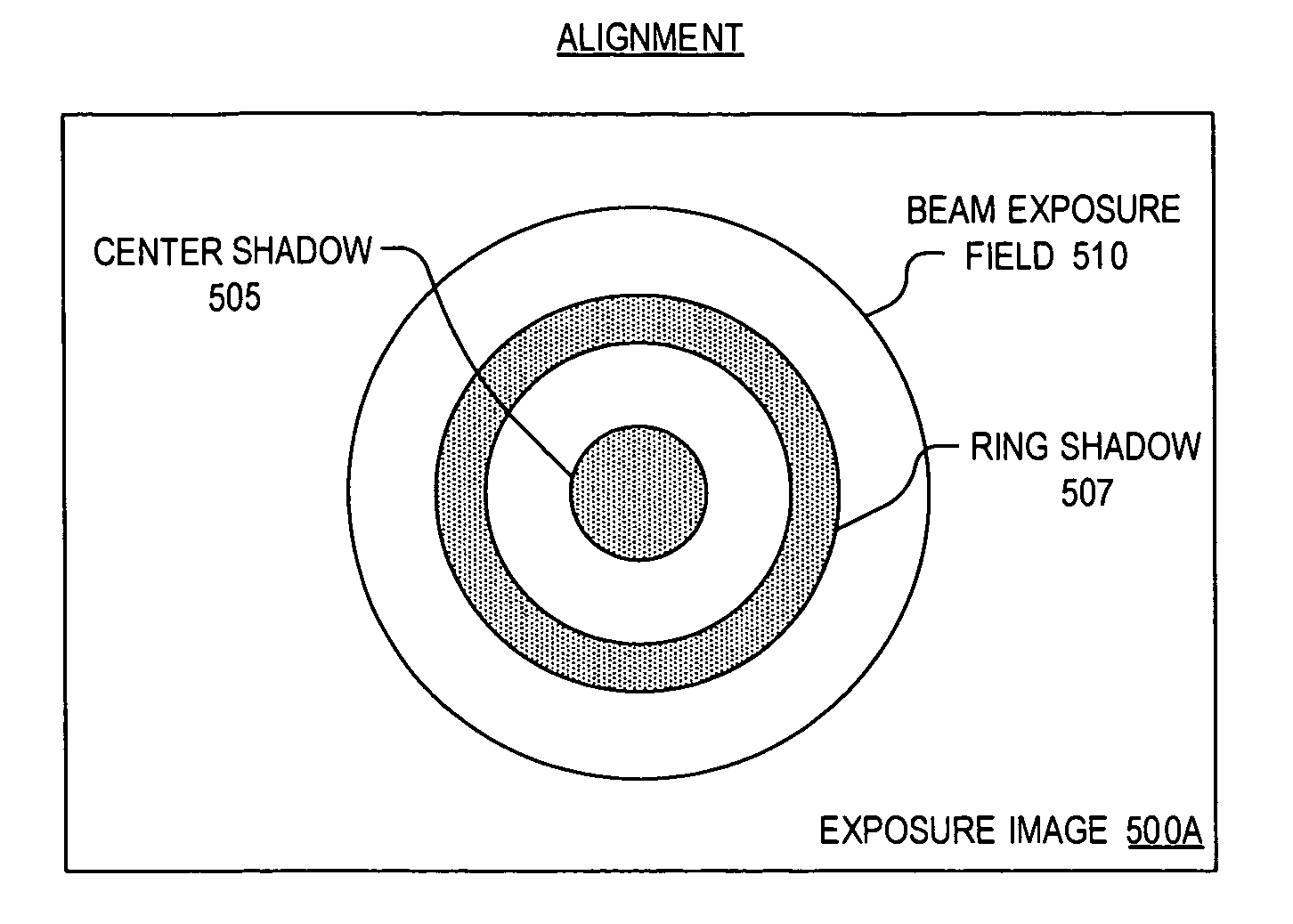
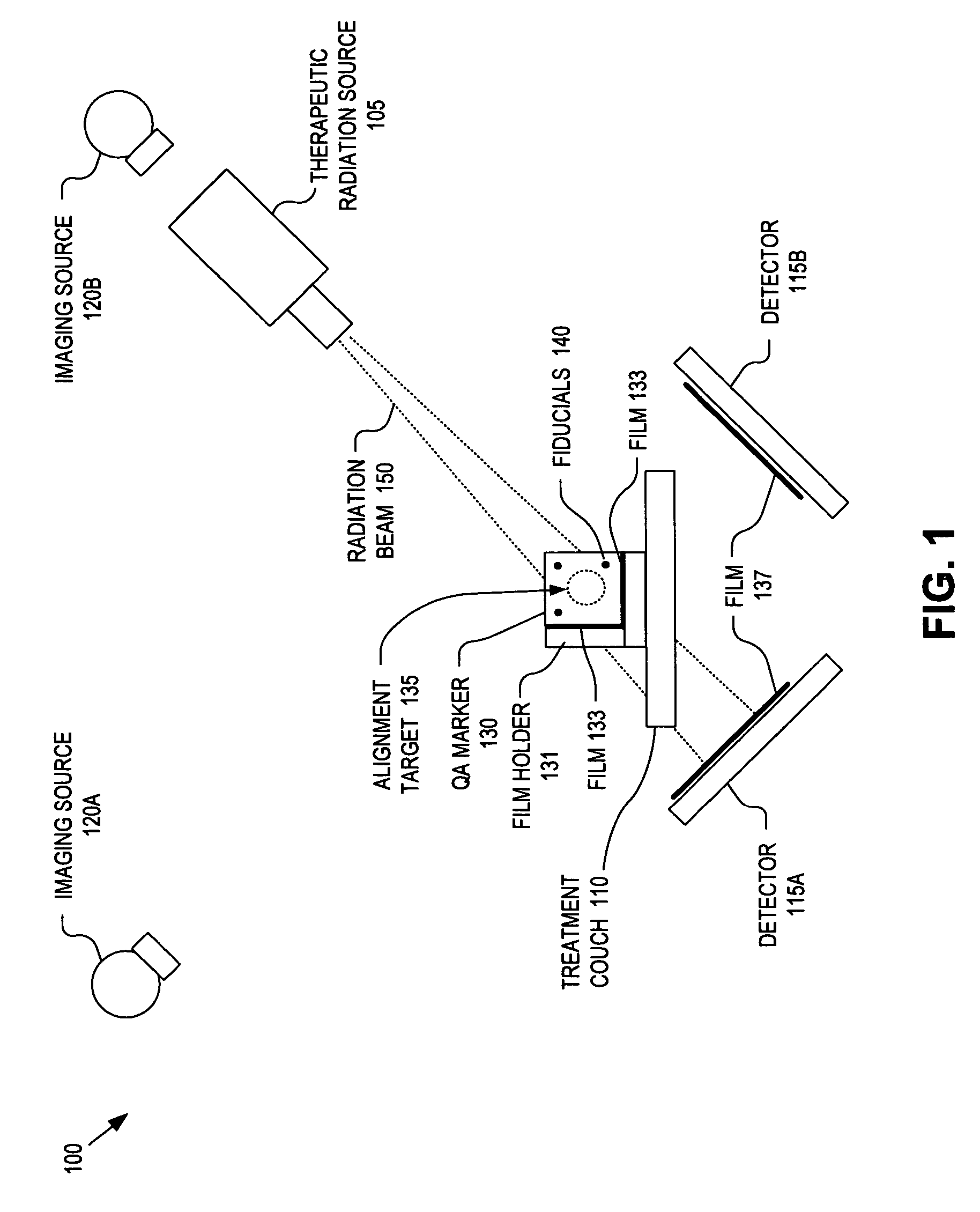
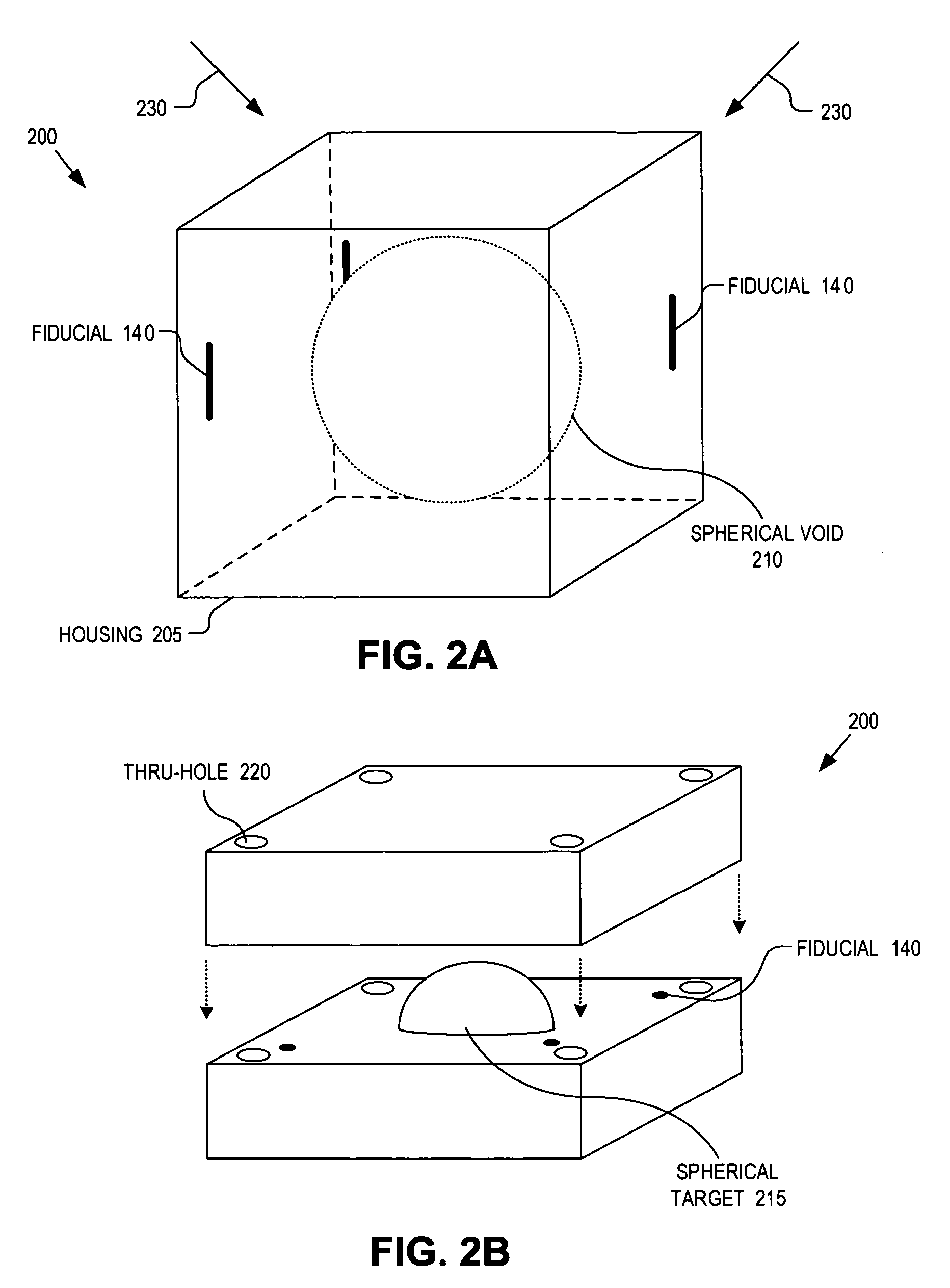
A method and apparatus for quality assurance of an image guided radiation treatment delivery system. A quality assurance (“QA”) marker is positioned at a preset position under guidance of an imaging guidance system of a radiation treatment delivery system. A radiation beam is emitted from a radiation source of the radiation treatment delivery system at the QA marker. An exposure image of the QA marker due to the radiation beam is generated. The exposure image is then analyzed to determine whether the radiation treatment delivery system is aligned.
Owner:ACCURAY
Apparatus for generating multi-energy x-ray images and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20130101082A1Improve tumor visibilityImproved Healing AccuracyRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisSoft x rayTreatment delivery
Apparatus for generating multi-energy x-ray images and systems and methods for processing and using multi-energy x-ray images are provided for treating a target, e.g., a tumor, for image-guided radiation therapy. An image-guided radiation therapy system is provided including a treatment delivery system, a multi-energy imaging system, and a system processor. The treatment delivery system includes a radiation source configured to generate treatment radiation beams. The multi-energy imaging system is configured to generate a first set of image data of the patient using imaging radiation at a first energy level and a second set of image data of the patient using imaging radiation at a second energy level. The system processor is configured to process the first and second sets of image data to generate an enhanced image of the patient and to direct the treatment delivery system based on information obtained from the enhanced image.
Owner:ACCURAY
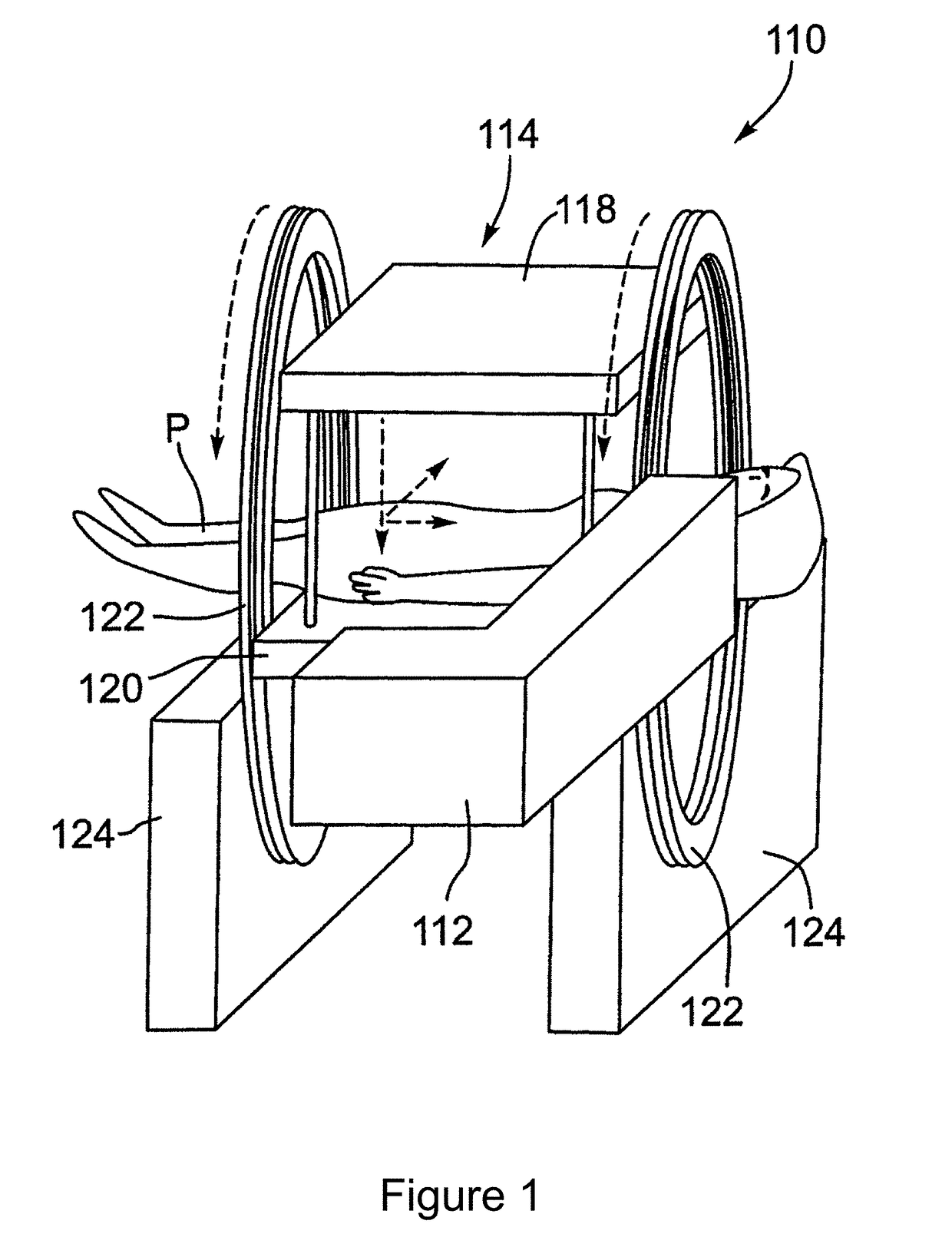
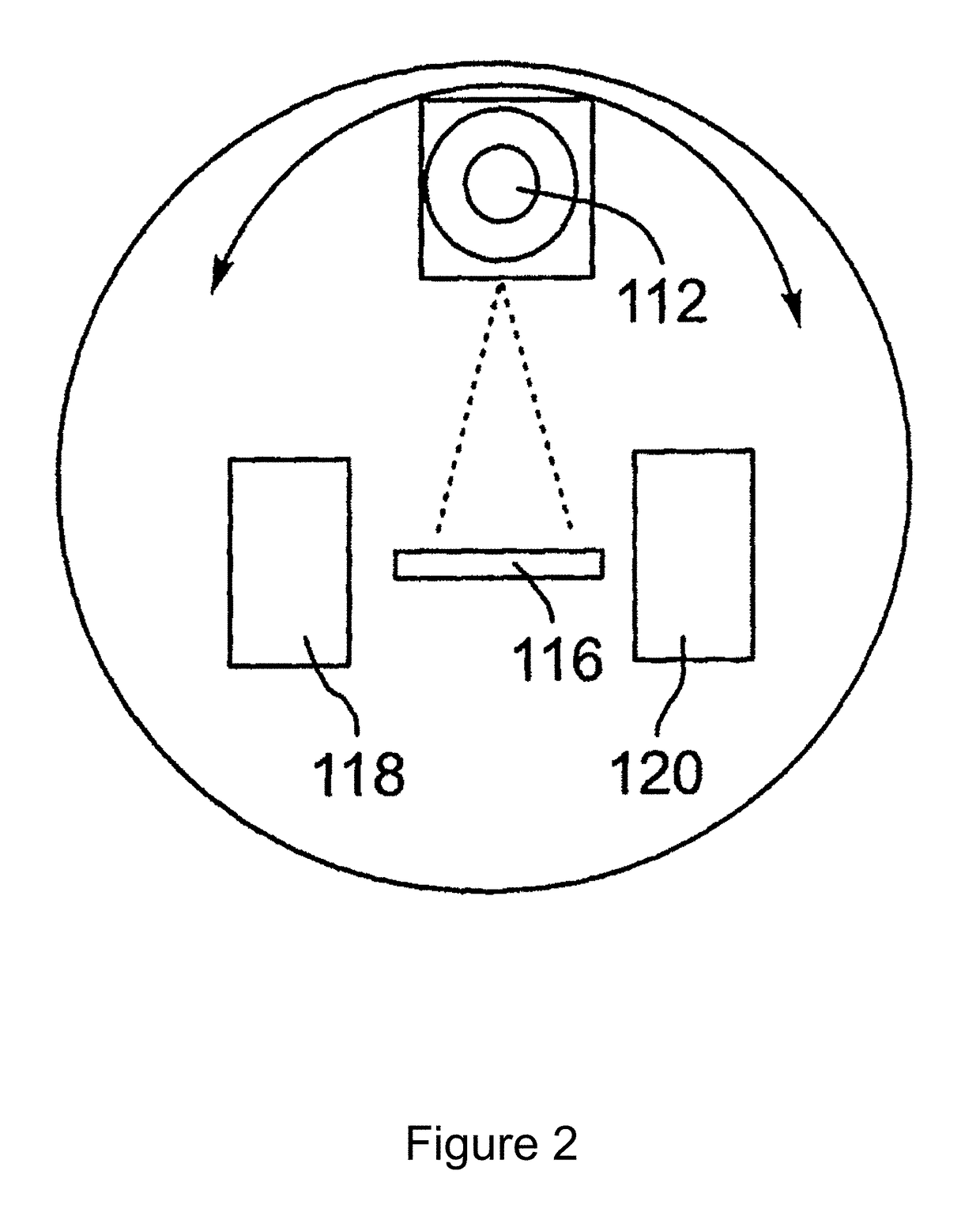
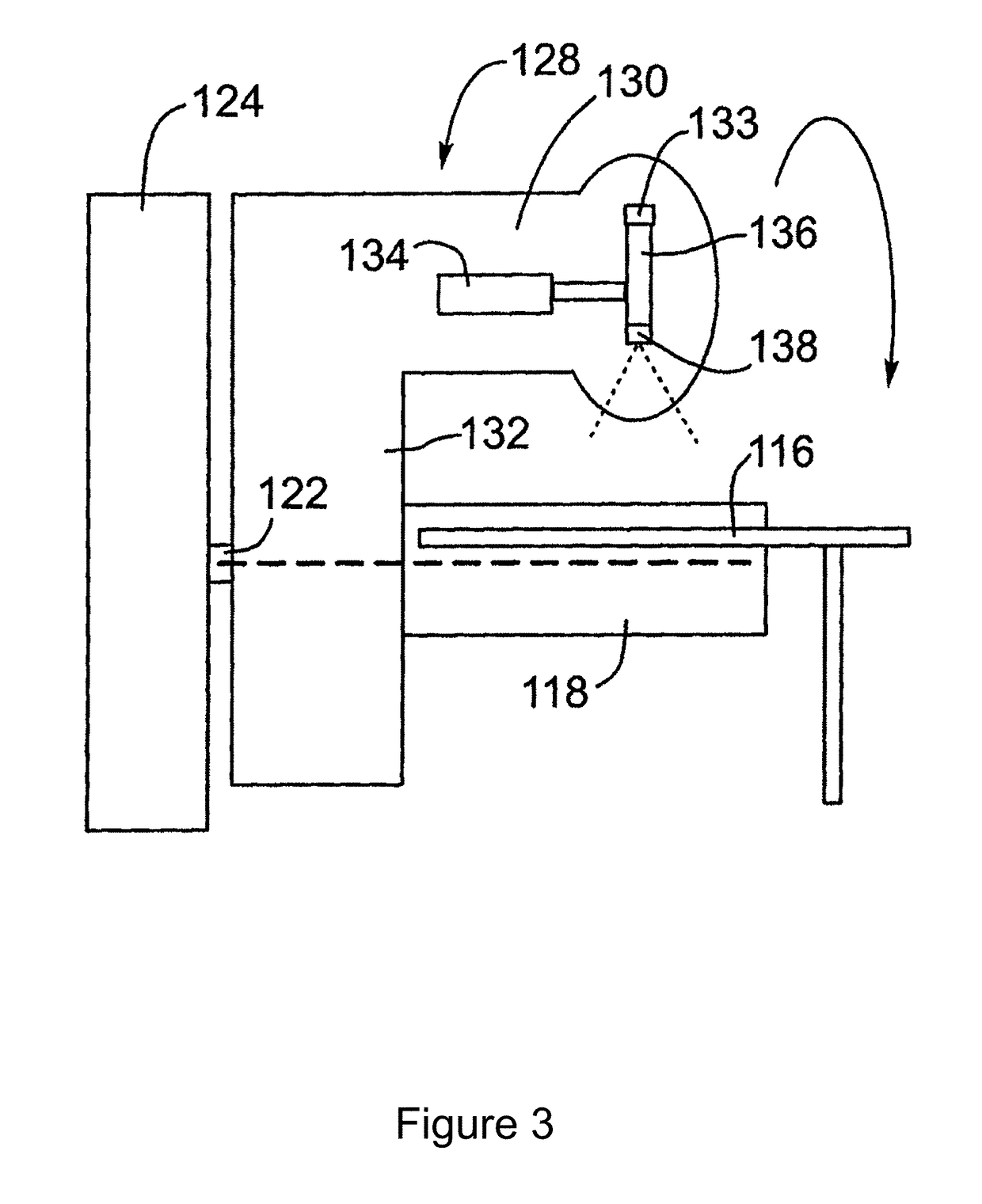
Image guided radiation therapy
ActiveUS20100329414A1Improve accuracyIncrease heightMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingImage-guided radiation therapyNuclear medicine
Radiation therapy of a lesion in a part of a patient is carried out by maintaining the patient on a patient support table in fixed position using an immobilization device while the table is rotated between a magnetic resonance imaging system, a CT imaging system for generating a 360 degree scanned image of the patient at the location of the lesion and the radiation therapy system for generating a beam of radiation for treatment of the lesion and for scanning the beam 360 degrees around the lesion. The MR image locates the lesion and the CT system is used to calculate the treatment. Registration between the MR image, the CT image and the radiation treatment is provided by the fixed position of the part of the patient on the table which is held fixed using an immobilization system suitable for the part concerned which may include a molded head mask where the head is involved.
Owner:DEERFIELD IMAGING INC
Image-guided radiation therapy equipment
ActiveCN101961530ADo real-time trackingQuick Scan TherapyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySoft x rayCt scanners
The invention discloses image-guided radiation therapy equipment, which comprises a radiation therapy equipment body and a treatment table, wherein the radiation therapy equipment body further comprises a slip ring frame structure, a radiation therapy device and a computed tomography (CT) scanner; the CT scanner and the radiation therapy device are both arranged on the slip ring frame structure; the radiation therapy device comprises a ray source body; and the CT scanner comprises an X-ray tube and an X-ray detector which are arranged to be in front of and behind the ray source body by 90 degrees respectively. The image-guided radiation therapy equipment provided by the invention can realize the real-time positioning of focal points of rays and gross target volumes to realize real-time tracking, extract two-dimensional images and display in real time the variations of lesion target volumes.
Owner:MASEP MEDICAL SCI & TECH DEV SHENZHEN
Integrated quality assurance for in image guided radiation treatment delivery system
ActiveUS7356120B2Calibration apparatusRadiation beam directing meansQuality assuranceImage-guided radiation therapy
A method and apparatus for quality assurance of an image guided radiation treatment delivery system. A quality assurance (“QA”) marker is positioned at a preset position under guidance of an imaging guidance system of a radiation treatment delivery system. A radiation beam is emitted from a radiation source of the radiation treatment delivery system at the QA marker. An exposure image of the QA marker due to the radiation beam is generated. The exposure image is then analyzed to determine whether the radiation treatment delivery system is aligned.
Owner:ACCURAY
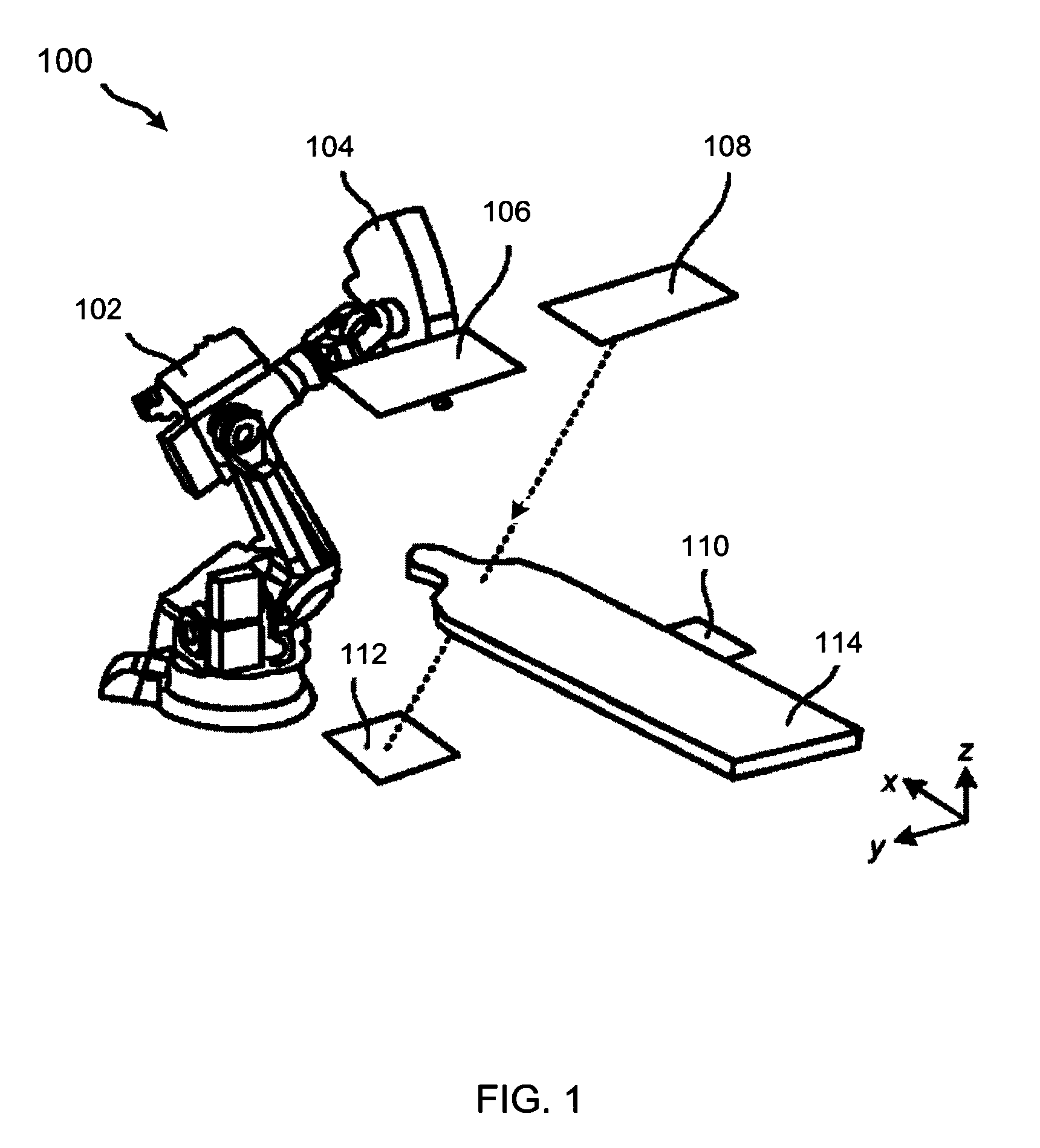
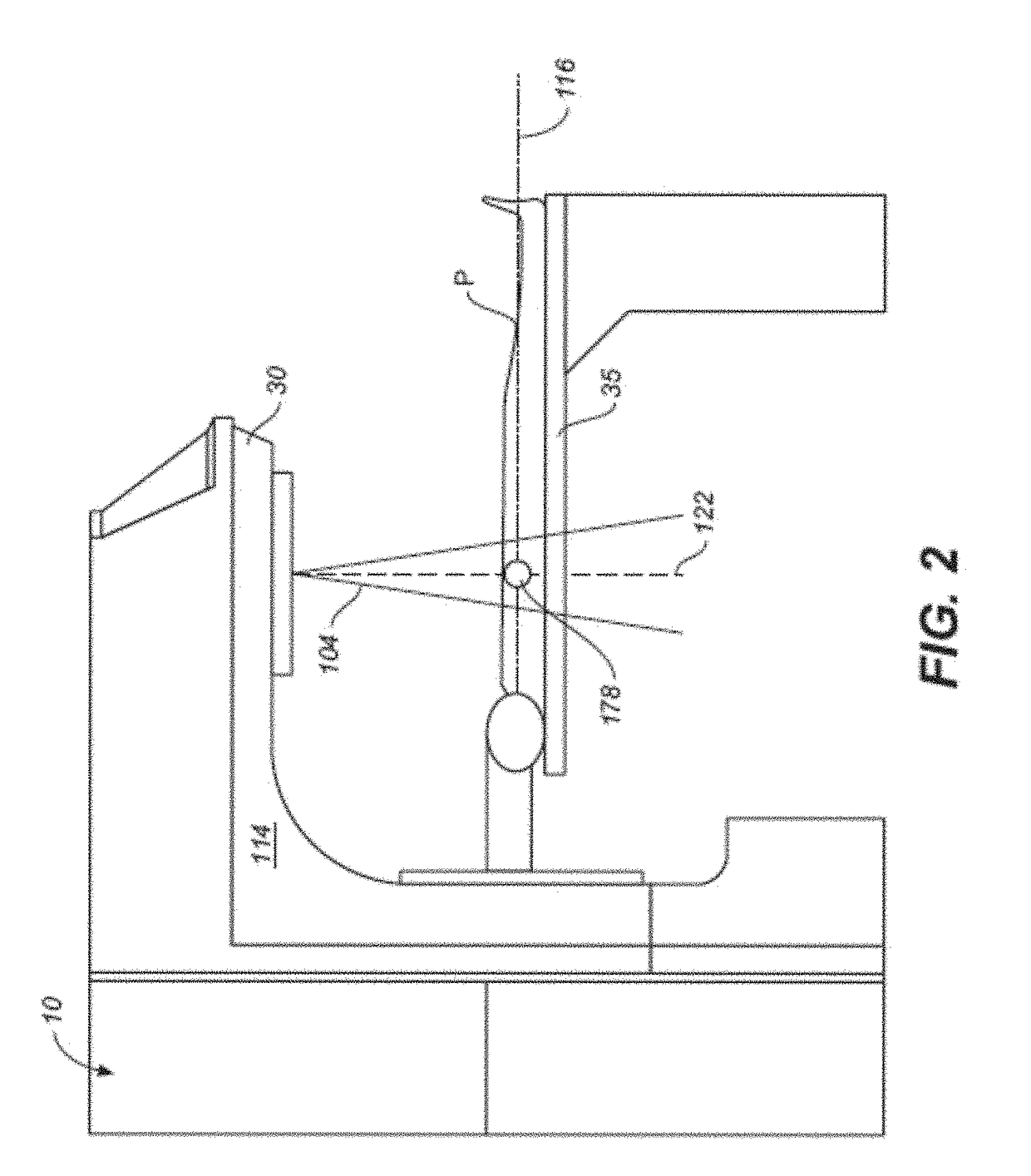
Radiation treatment delivery system with ring gantry
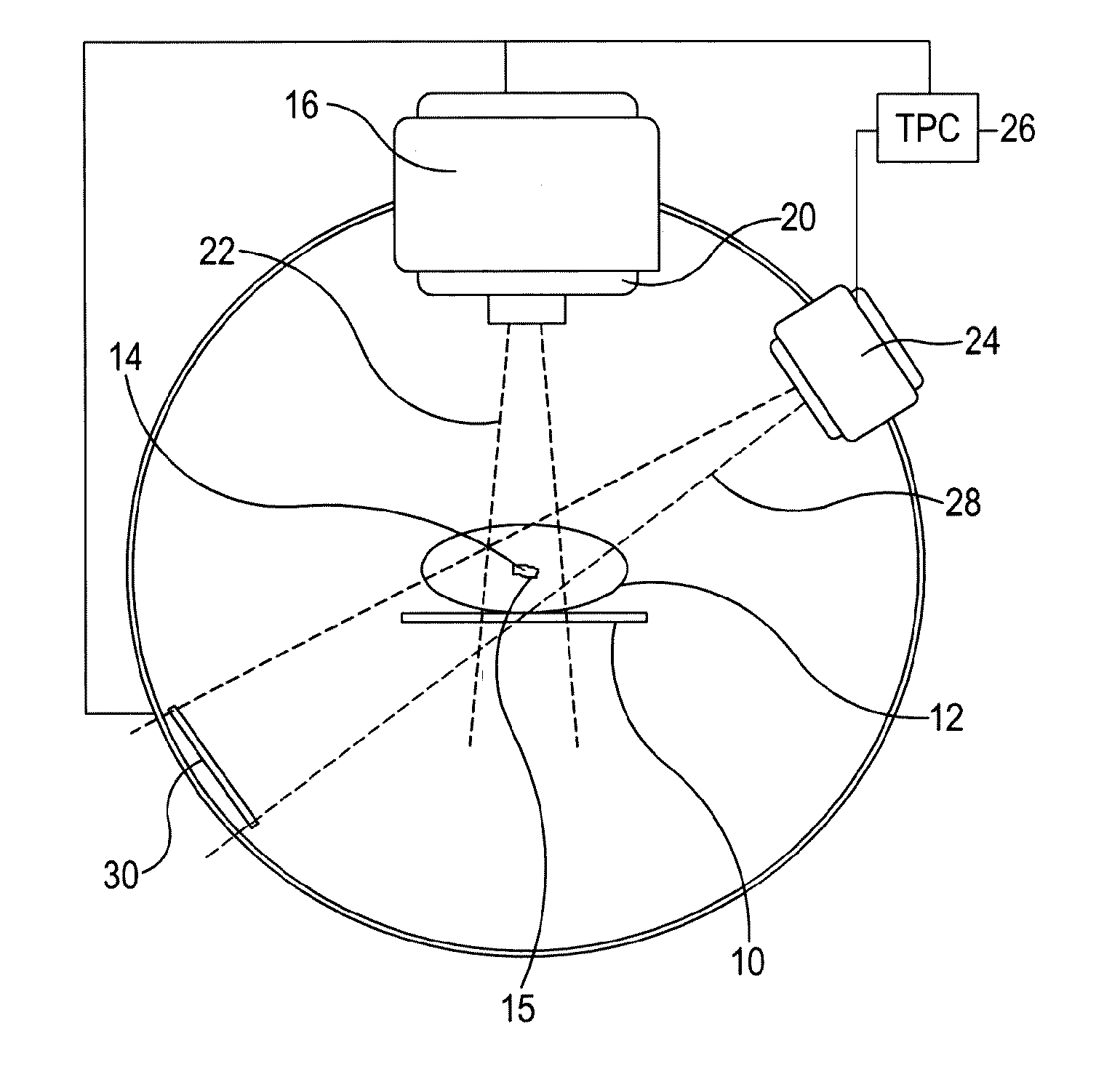
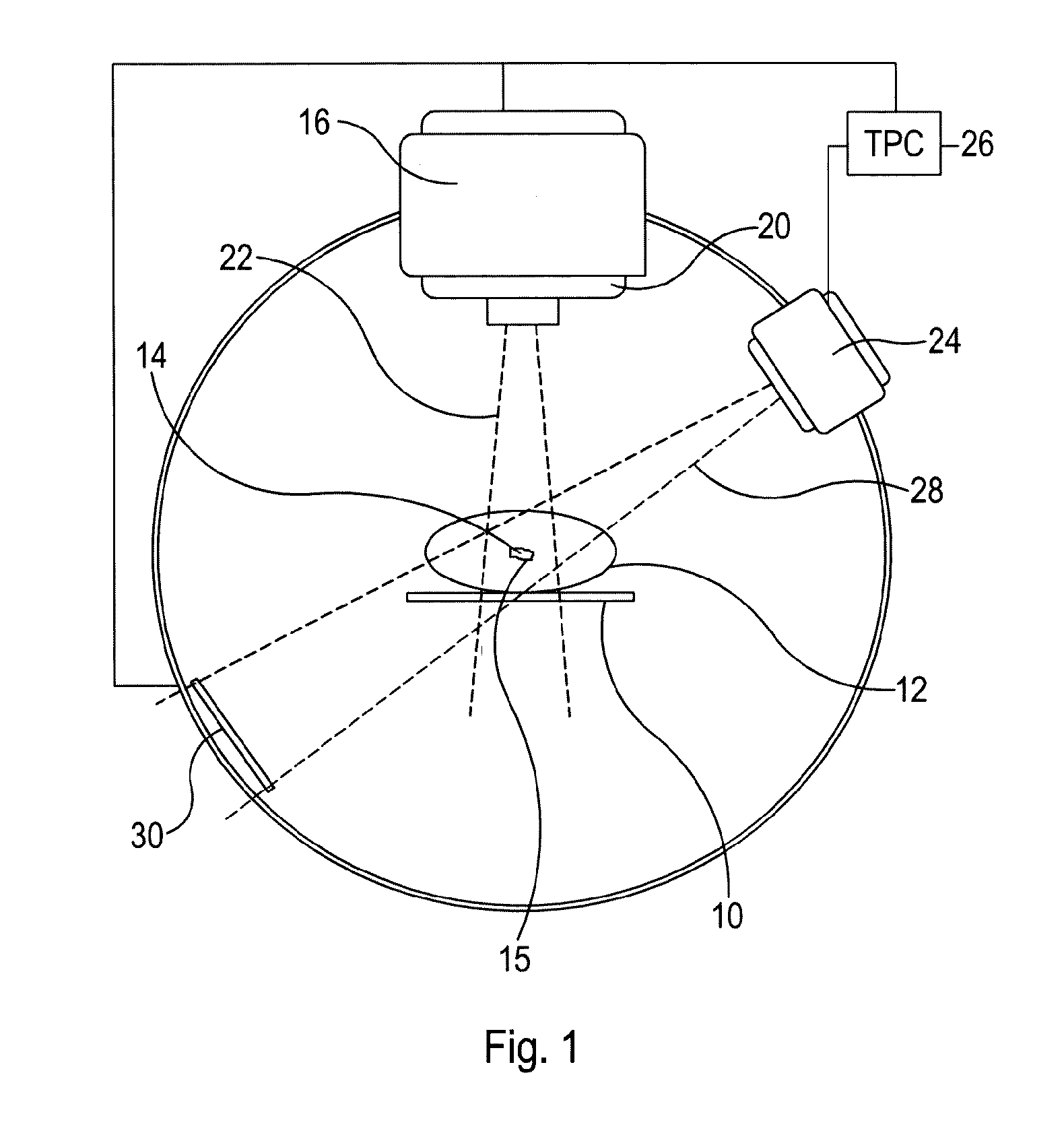
Systems, methods, and related computer program products for image-guided radiation treatment (IGRT) are described. For one preferred embodiment, an IGRT apparatus is provided comprising a ring gantry having a central opening and a radiation treatment head coupled to the ring gantry that is rotatable around the central opening in at least a 180 degree arc. For one preferred embodiment, the apparatus further comprises a gantry translation mechanism configured to translate the ring gantry in a direction of a longitudinal axis extending through the central opening. Noncoplanar radiation treatment delivery can thereby be achieved without requiring movement of the patient. For another preferred embodiment, an independently translatable 3D imaging device distinct from the ring gantry is provided for further achieving at least one of pre-treatment imaging and setup imaging of the target tissue volume without requiring movement of the patient.
Owner:爱可瑞公司
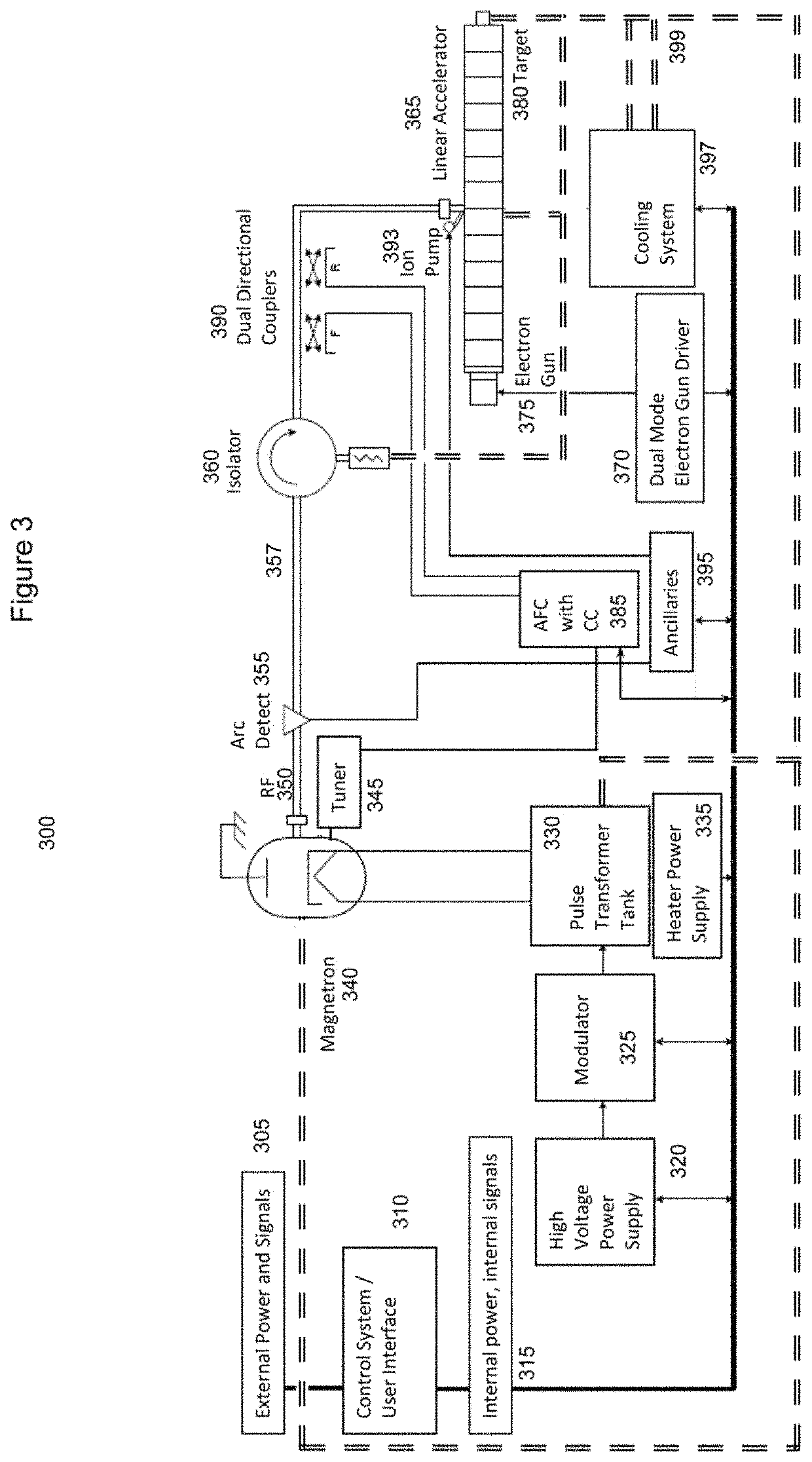
Same-source double-energy medical electron linear accelerator for image guided radiation therapy (IGRT)
InactiveCN102256434ARadial imaging is clearElectron beam energy reductionLinear acceleratorsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyX-rayImage-guided radiation therapy
The invention relates to a medical apparatus for tumor radiation therapy, in particular to a same-source double-energy medical electron linear accelerator for image guided radiation therapy (IGRT). The same-source double-energy medical electron linear accelerator for the IGRT is characterized in that: an accelerating tube is vertically arranged and is connected with a moving target below the accelerating tube; an energy switch is arranged on the accelerating tube; an X-ray heavy metal target and a low atomic number target are arranged on the moving target; and the X-ray heavy metal target and the low atomic number target are connected with a driving mechanism of the moving target. The same-source double-energy medical electron linear accelerator for the IGRT has the advantages that: energy of an electron beam generated by the accelerating tube is reduced by the energy switch; by using the characteristic that the electron beam impacts the low atomic number target to generate more low-energy beams, X rays with clear portal imaging are obtained; and the same-source double-energy medical electron linear accelerator for the IGRT has the characteristics of easy mode conversion, same source, stable beam, clear image, economy, reliability, simpleness and convenience in clinical use and the like.
Owner:SHINVA MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
Simulation device for human body pleuroperitoneal cavity movement caused by breathing
ActiveCN105286998AReduce the amplitudeEasy to get synchronouslyComputer-aided planning/modellingDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyImage-guided radiation therapy
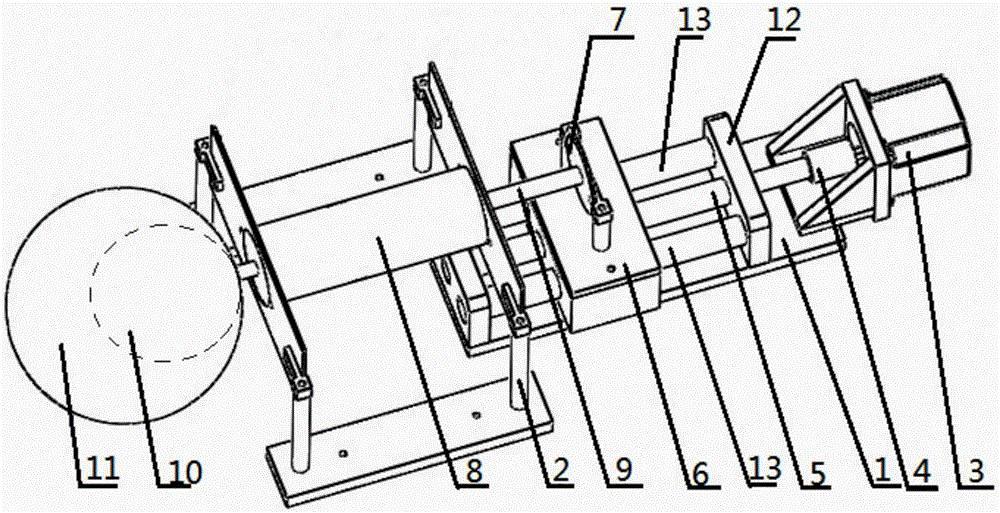
The invention discloses a simulation device for human body pleuroperitoneal cavity movement caused by breathing. The simulation device comprises a workbench, a base, a support, a drive motor, lead screw, a slide block, a push plate, a needle cylinder body, a needle cylinder piston and a push rod, wherein the base and the support are sequentially arranged on the workbench, the drive motor is arranged on the base, the lead screw is connected with the output end of the drive motor through a coupling, the slide block is arranged on the lead screw and can move leftwards and rightwards along with rotation of the lead screw, and the push plate is perpendicularly arranged at the top of the slide block; the needle cylinder body is arranged on the support, a needle cylinder piston is arranged in the needle cylinder body, and the push rod is connected with the exterior of the needle cylinder piston; the push rod is fixedly connected with the push plate, meanwhile a needle nozzle of the needle cylinder body is provided with a balloon for in-vivo simulation, and the outer side of the balloon for in-vivo simulation is sleeved with balloon for body surface simulation. The simulation device has the advantages that relevance three-dimensional movement of the chest wall body surface and in-vivo tumor generated when a human body breathes is represented, an accurate movement model is provided for breathing tracking and positioning research of tumor radiotherapy, and the accurate positioning function of breathing motion compensation on the image-guided radiation therapy.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
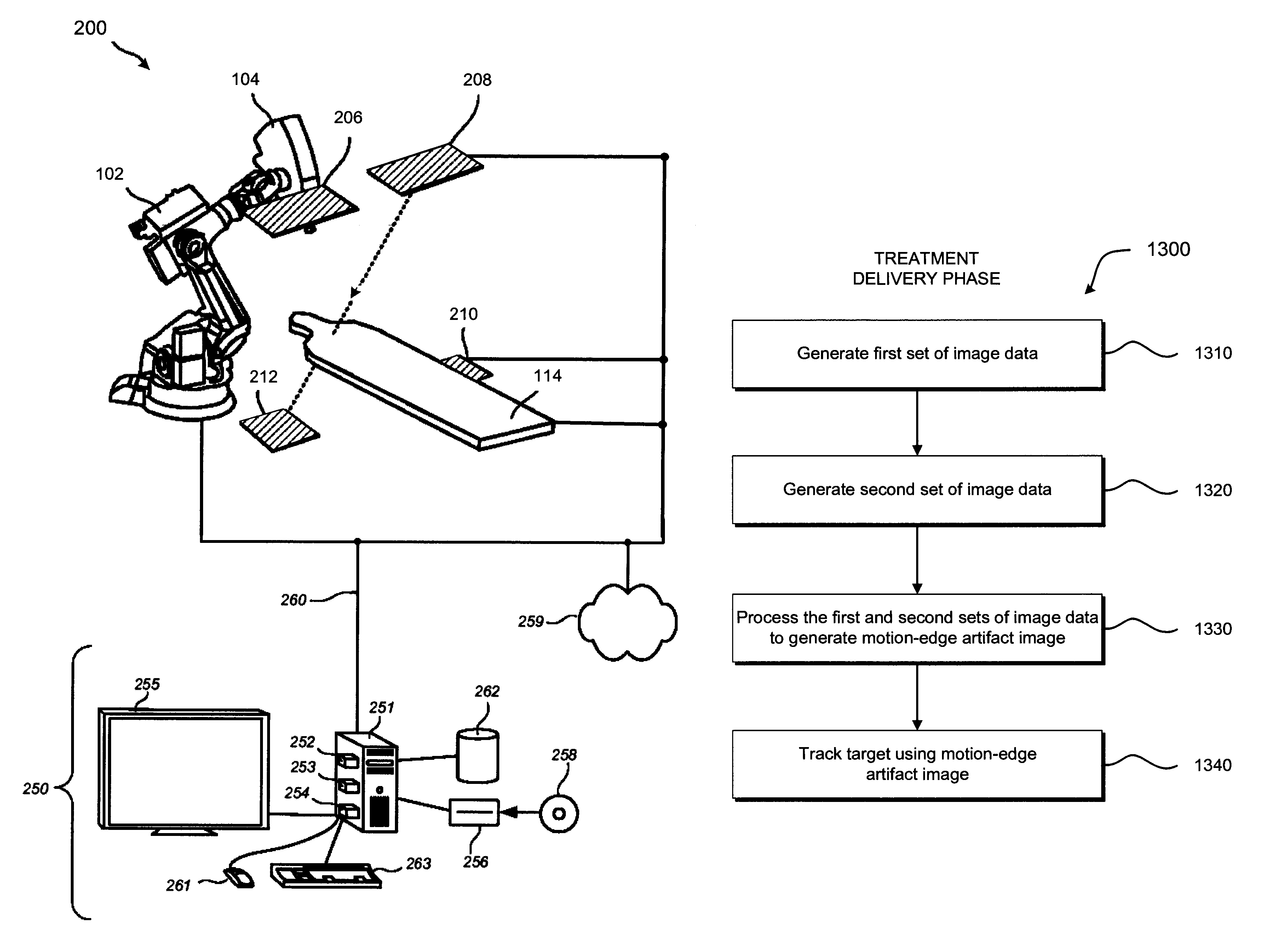
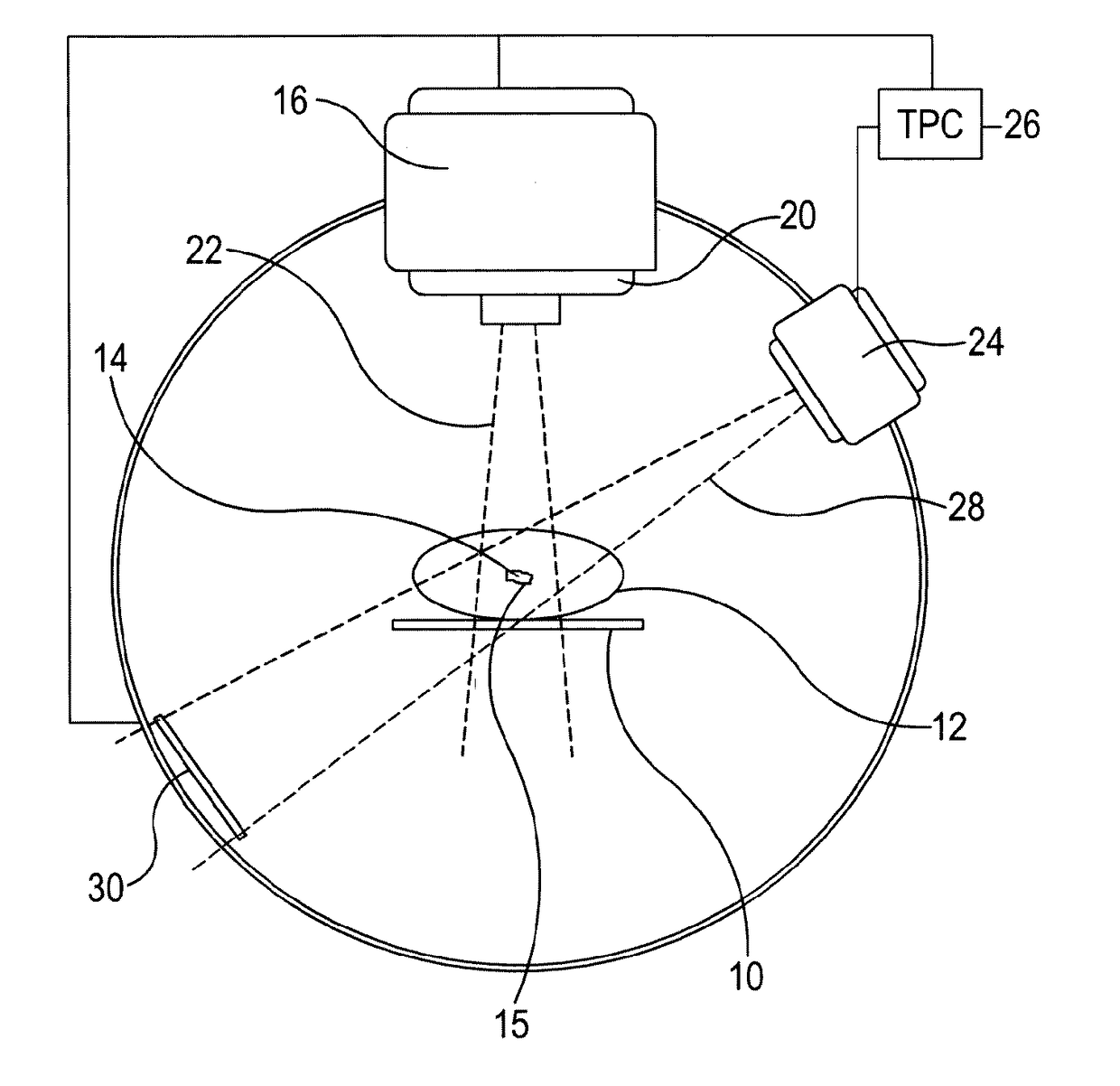
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy
ActiveUS20170028221A1Determine efficiencyImprove accuracyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBeam angleLight beam
The disclosed systems and methods for Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT), utilises an iterative approach which adjusts a treatment plan based on inter- or intra-fraction images to improve the accuracy of the radiation delivered during the overall treatment. The prescribed dose of radiotherapeutic radiation is mapped onto the patient's anatomy using an image acquired of the region, which is to be the target for radiotherapeutic radiation. Following beam-angle-optimisation, fluence optimisation and segmentation, the efficiency of delivery of each segment is determined using an objective function, and the segments ranked according to their efficiency. The plan proceeds with the choice of the most efficient segment (or segments) to be delivered first. When this radiation has been delivered, having been tracked to establish its distribution, this delivered distribution can be subtracted from the original prescribed dose and the process repeated so that the delivered radiation gradually converges on the original prescribed dose.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
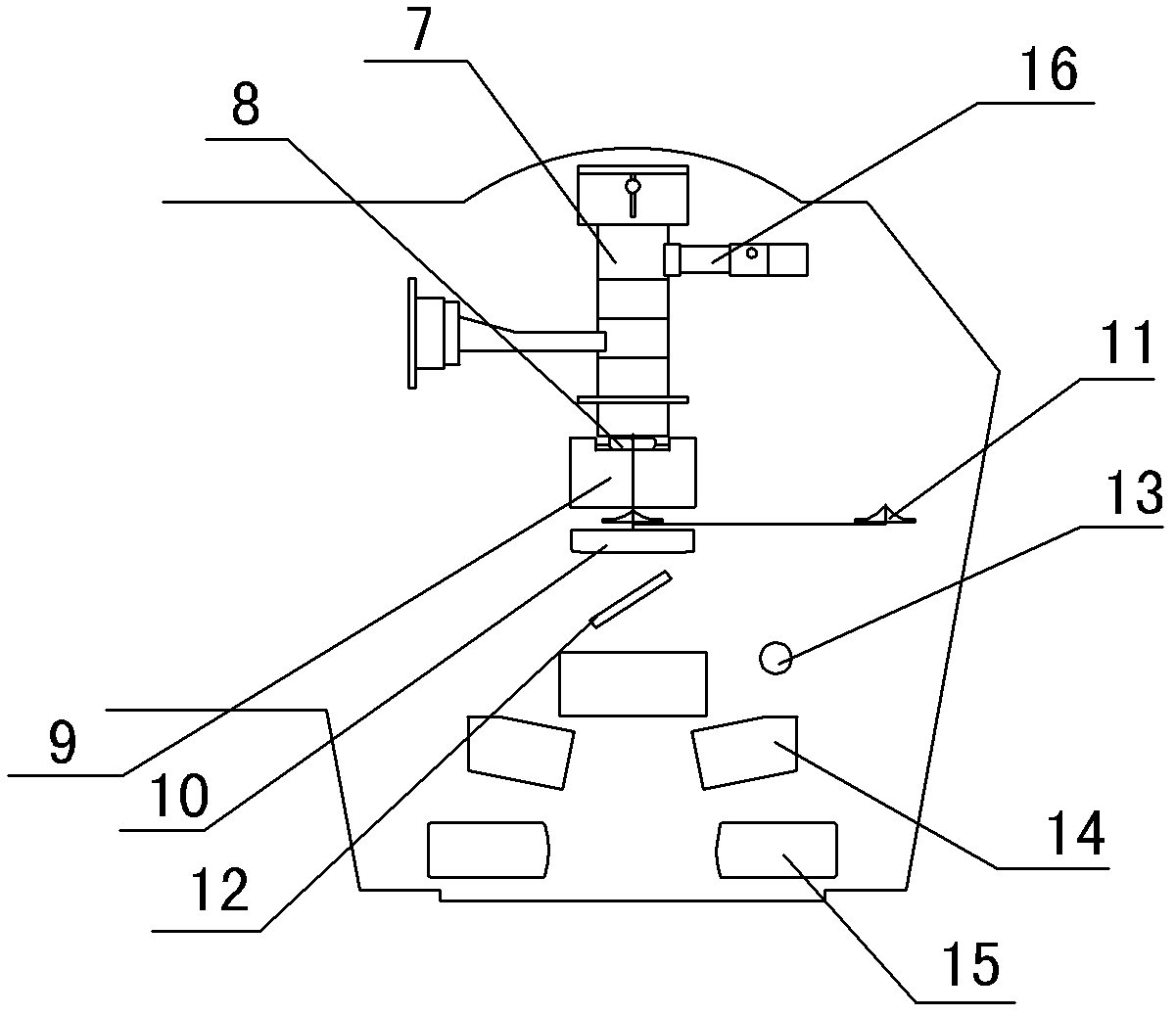
Simulated positioning device and simulated positioning method for intra-operative image guided radiation therapy
ActiveCN105879244AMeeting the needs of intraoperative image-guided radiotherapyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyImage-guided radiation therapyImaging equipment
The invention discloses a simulated positioning device and a simulated positioning method for intra-operative image guided radiation therapy. The simulated positioning device comprises a multifunctional light limiting cylinder, and the multifunctional light limiting cylinder is composed of a material which imaging equipment can penetrate to image a body part of a patient about to receive radiation treatment. The multifunctional light limiting cylinder is provided with a positioning mark which is composed of a material different from that of the multifunctional light limiting cylinder so the positioning mark can be distinguished from other areas in display in an image formed by the imaging equipment, and the distinct display of the positioning mark is for positioning the body part about to receive radiation treatment. Therefore, the simulated positioning device disclosed by an embodiment of the invention can cooperate with the imaging equipment to image a body part of a patient about to receive radiation treatment, no unnecessary barrier is produced, and the need of intra-operative image guided radiation therapy is well satisfied.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
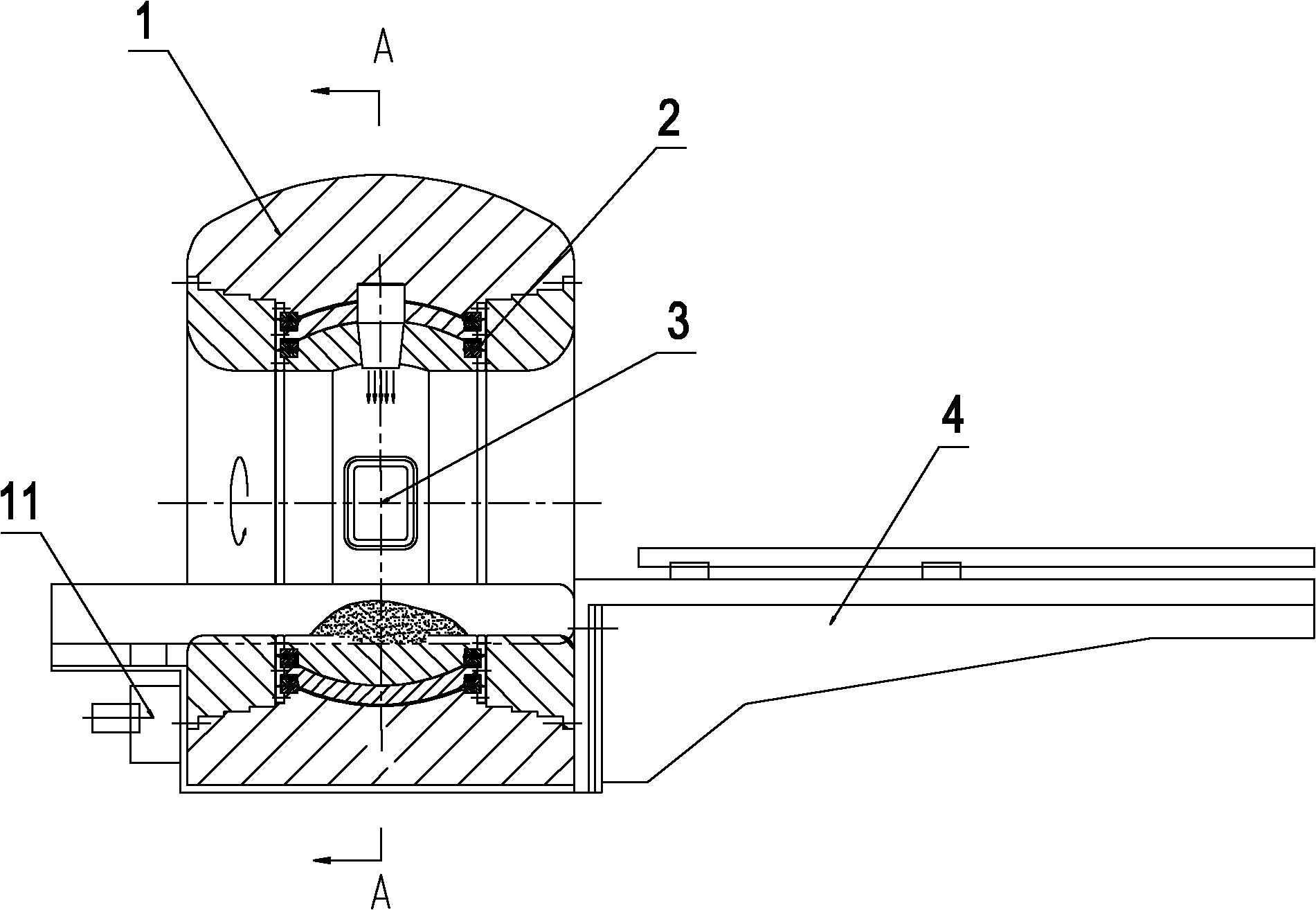
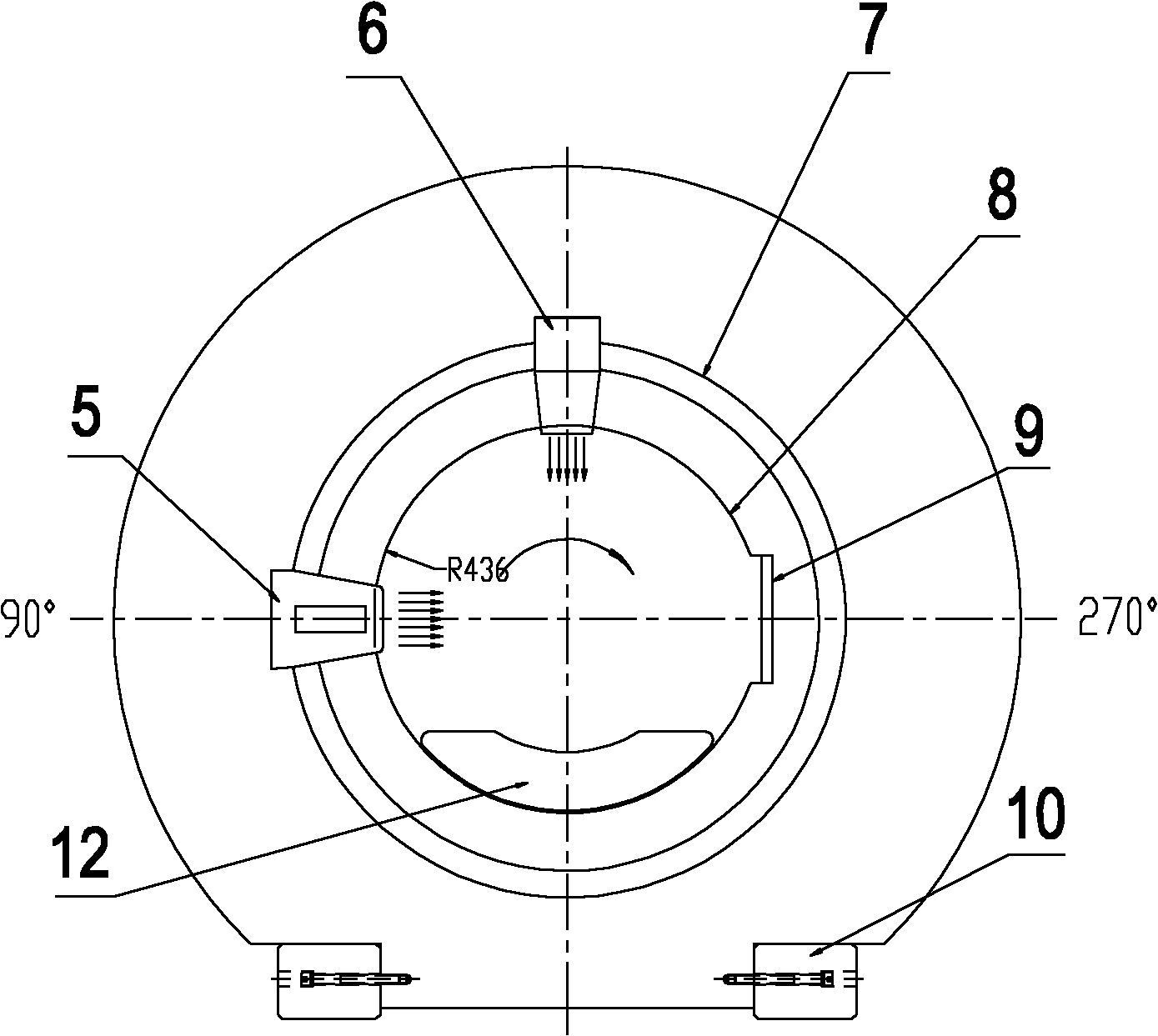
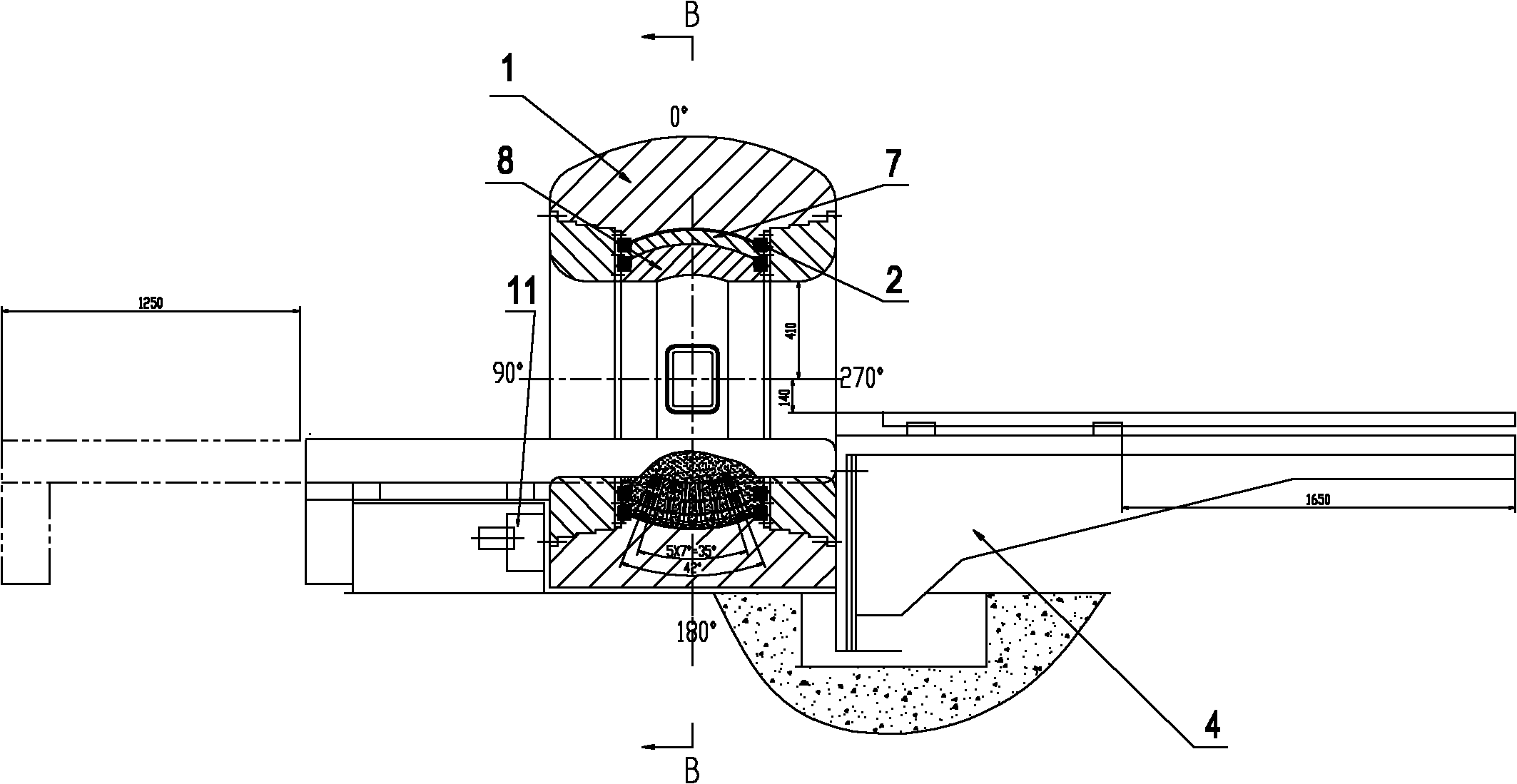
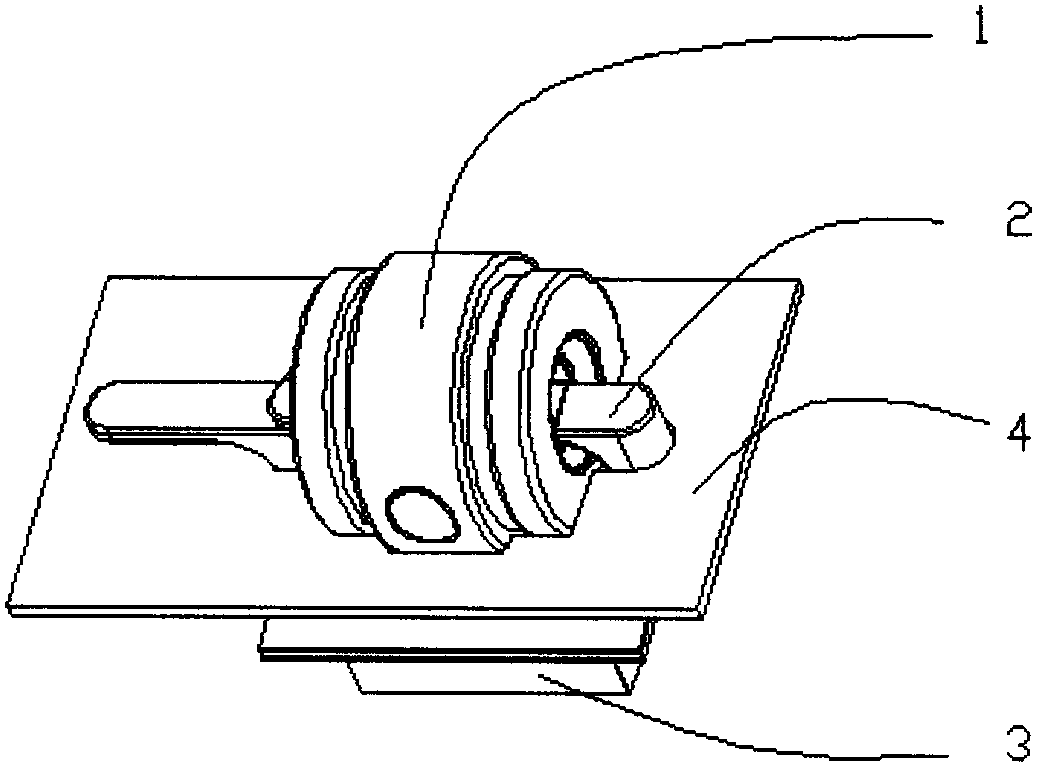
Image-guided radiation treatment equipment
ActiveCN102698374ARealize image trackingRealize real-time monitoringX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTherapeutic DevicesEngineering
The invention provides image-guided radiation treatment equipment. The image-guided radiation therapy equipment comprises an installation base, a treatment couch which is fixedly arranged on the installation base and a treatment equipment main body, wherein the treatment equipment main body comprises a shield body roller, a source body roller and a collimation body roller component which are coaxially sleeved together and can rotate relative to one another, wherein the source body roller is provided with a detachable radioactive source component; the collimation body roller component is provided with a collimator; rays emitted from the radioactive source component emit into the treatment equipment main body after the beam limiting of the collimator; the treatment equipment main body surrounds the whole circumference of the treatment couch at 360 degrees; an image guide device is fixedly arranged on the source body roller and can rotate along with the source body roller, so that the image tracking of a patient in a 360-degree range and the real-time monitoring in a treatment process are realized, and a target spot follows up; and therefore, the aim of image-guided precise radioactive treatment is fulfilled.
Owner:WUHAN CYBERMED SYST CO LTD
Apparatus for generating multi-energy x-ray images and methods of using the same
ActiveUS9415240B2Improve imaging clarityImprove dynamic rangeRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisTreatment deliveryX-ray
Apparatus for generating multi-energy x-ray images and systems and methods for processing and using multi-energy x-ray images are provided for treating a target, e.g., a tumor, for image-guided radiation therapy. An image-guided radiation therapy system is provided including a treatment delivery system, a multi-energy imaging system, and a system processor. The treatment delivery system includes a radiation source configured to generate treatment radiation beams. The multi-energy imaging system is configured to generate a first set of image data of the patient using imaging radiation at a first energy level and a second set of image data of the patient using imaging radiation at a second energy level. The system processor is configured to process the first and second sets of image data to generate an enhanced image of the patient and to direct the treatment delivery system based on information obtained from the enhanced image.
Owner:ACCURAY
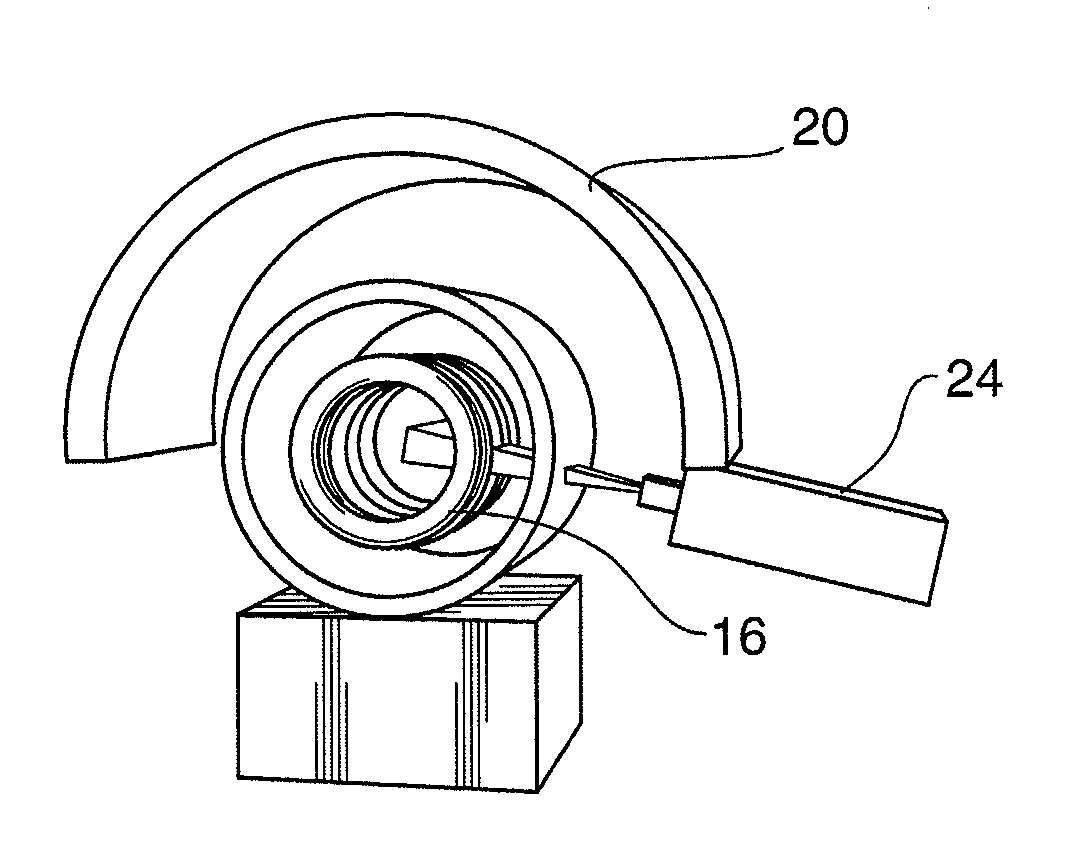
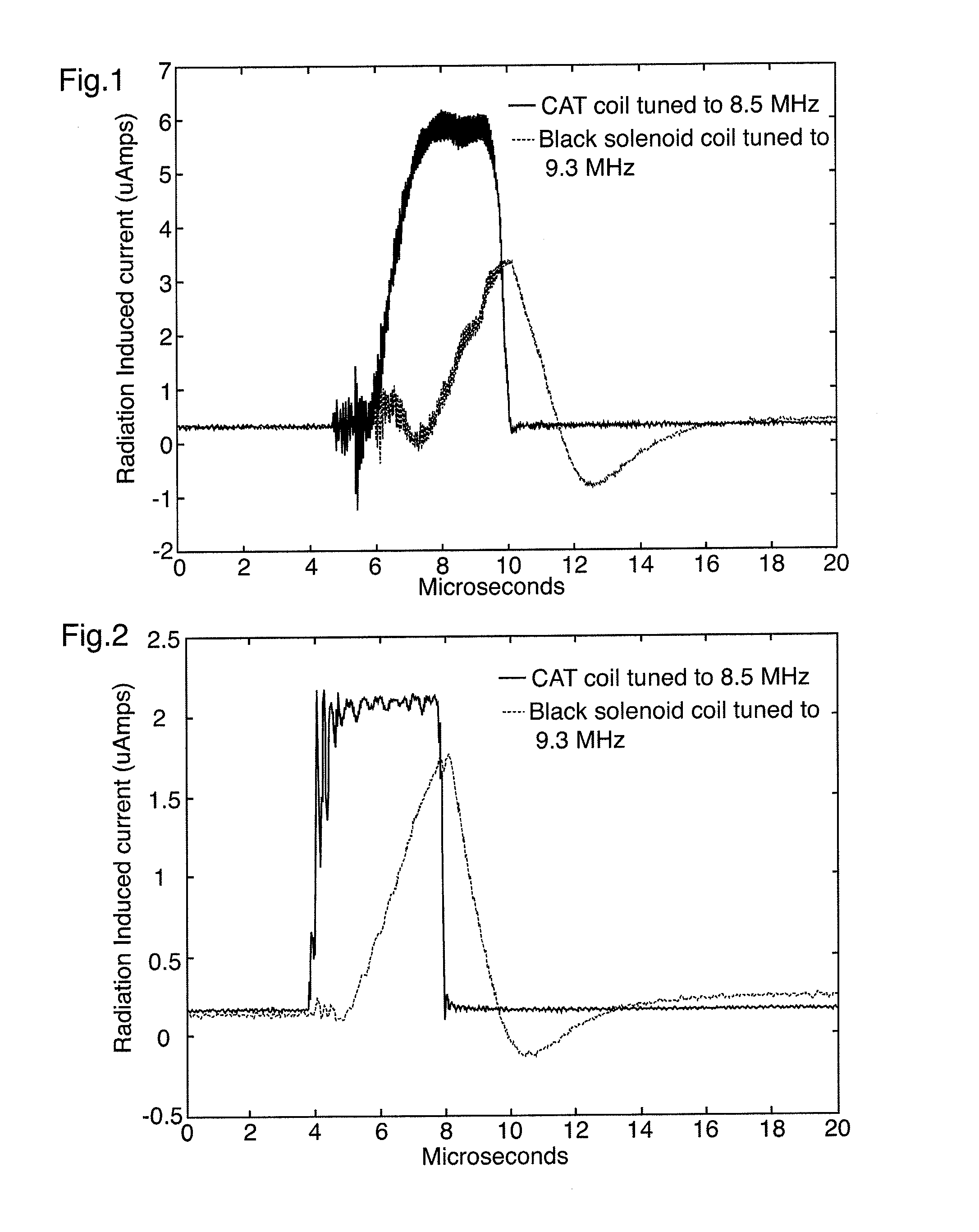
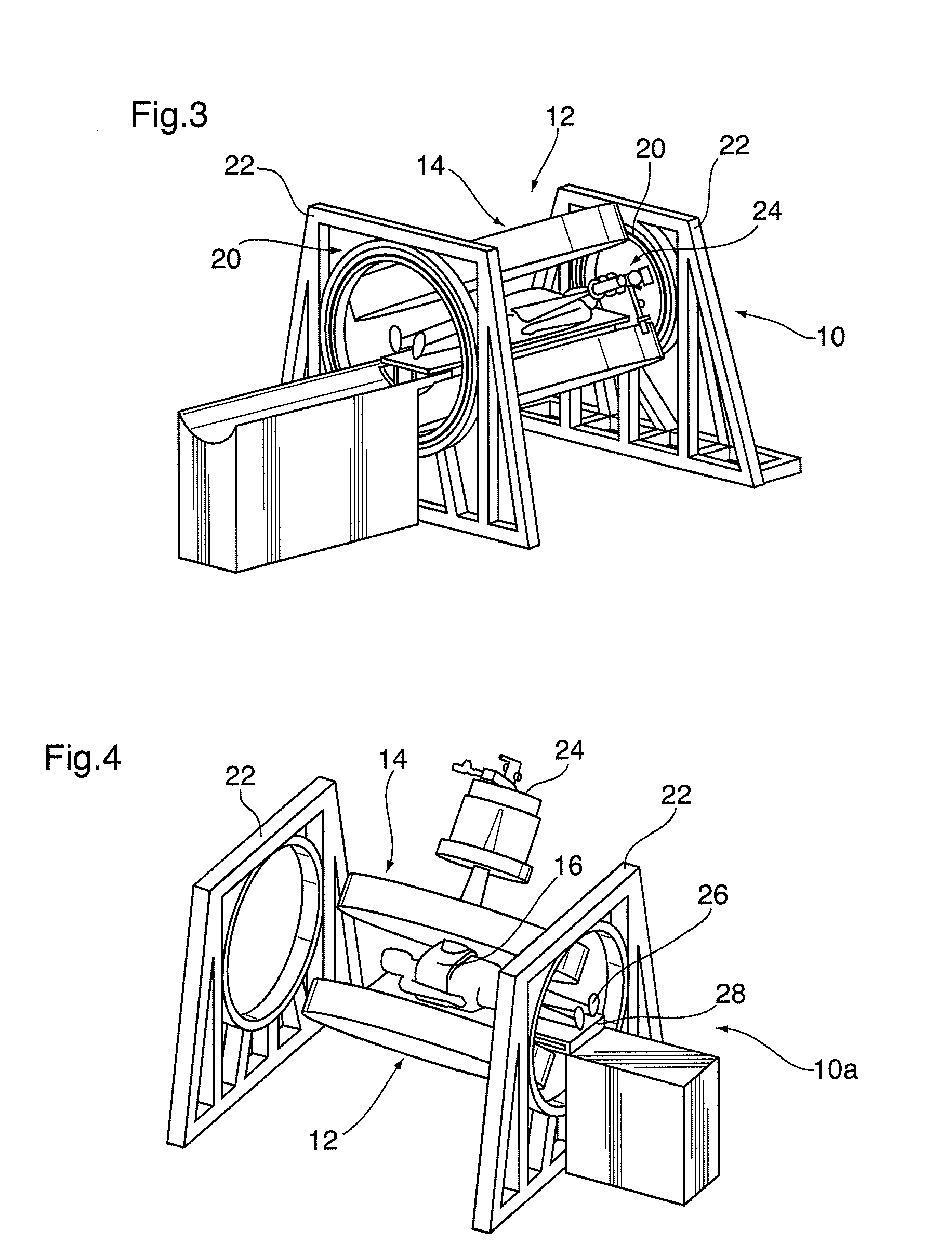
Image guided radiation therapy system and shielded radio frequency detector coil for use therein
InactiveUS20120150016A1Total current dropReduce the amount of noiseMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityImage-guided radiation therapy
A radiation therapy system includes a radiation source capable of generating a beam of radiation; a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus comprising at least one radiofrequency detector coil; and an electrically grounded dielectric material between the radiation source and the radiofrequency detector coil for shielding the at least one radiofrequency detector coil from the beam of radiation. Also disclosed is a radiofrequency detector coil for a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus sheathed at least in part by a dielectric material that is adapted to be electrically grounded.
Owner:ALBERTA HEALTH SERVICES
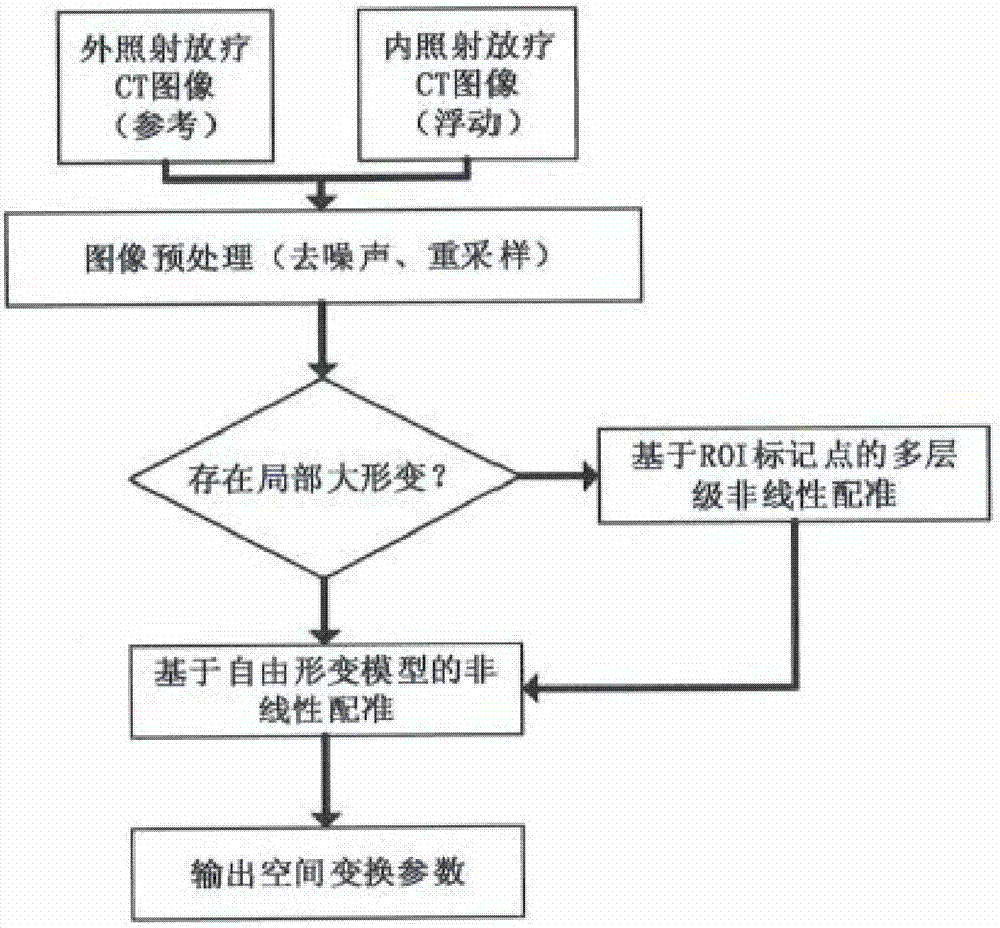
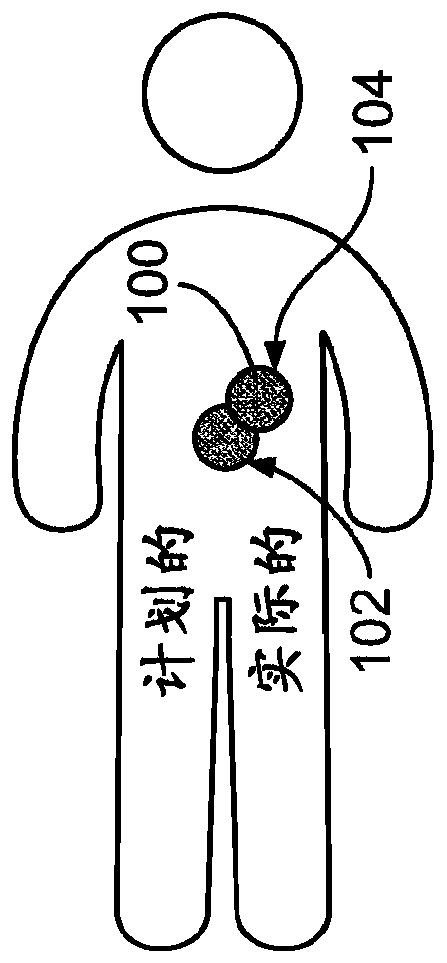
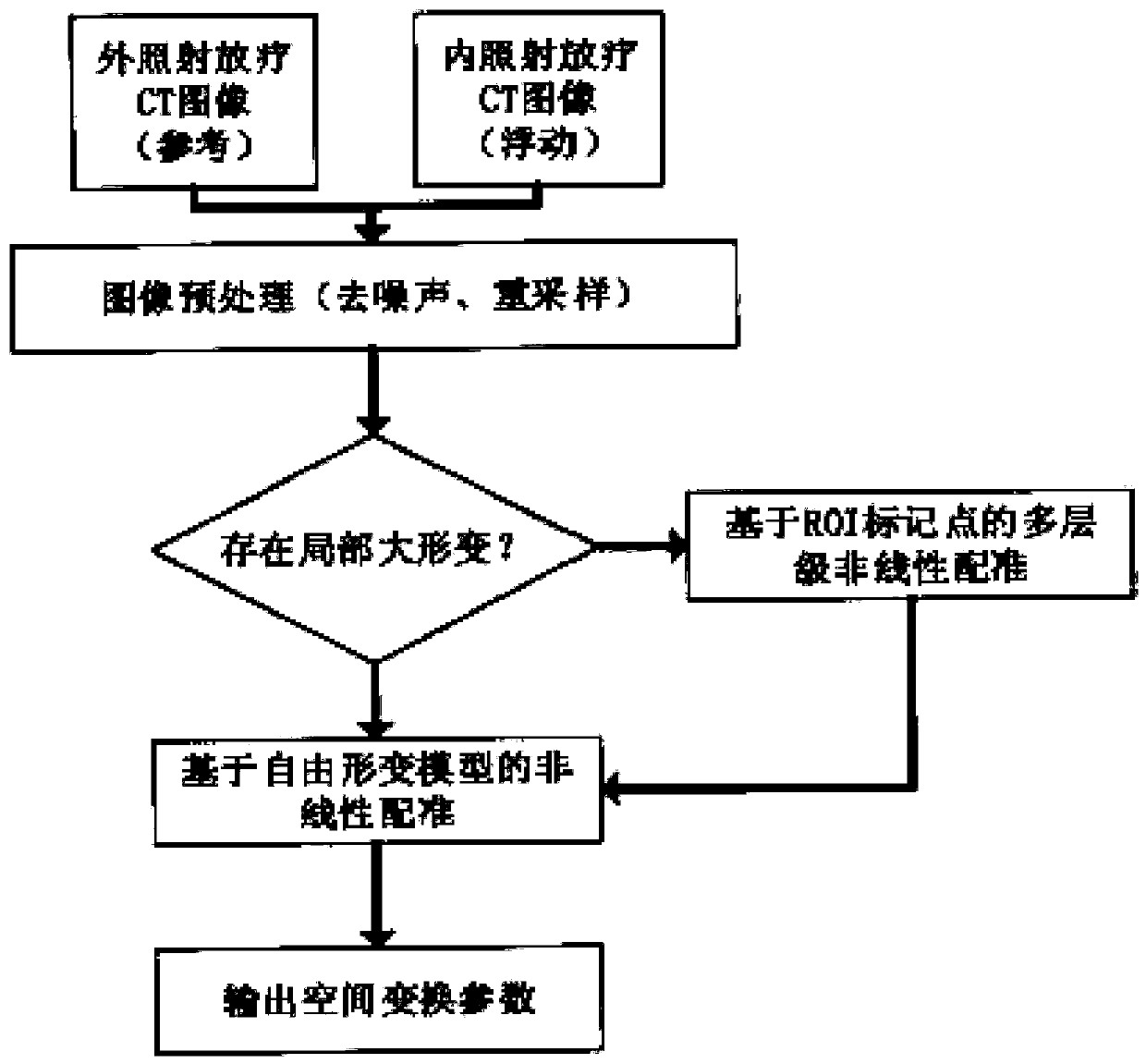
Non-linear fusion method for internal and external radiotherapy doses of a cervical cancer
ActiveCN106902477AAccurate assessmentAccurately achieve accumulationRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTumor targetExternal irradiation
The invention relates to a non-linear fusion method for internal and external radiotherapy doses of a cervical cancer. The method comprises: obtaining internal and external irradiation radiotherapy CT images and internal and external irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution of a to-be-detected cervical cancer; on the basis of non-linear image registration, mapping the internal irradiation radiotherapy CT image to the external irradiation radiotherapy CT image to obtain a transformation relationship between the internal and external irradiation radiotherapy CT images of the to-be-detected cervical cancer; according to the transformation relationship between the internal and external irradiation radiotherapy CT images, transforming internal irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution into equivalent external irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution; and carrying out fusion of the equivalent external irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution and external irradiation radiotherapy dose distribution after transformation by image fusion, rebuilding a distribution curve of internal and external radiotherapy doses, and obtaining a total practically subjected dose of a tumor target region of the to-be-detected cervical cancer and surrounding organs at risks during the comprehensive internal and external irradiation radiotherapy process. The non-linear fusion method is applied to an image-guided radiation therapy of a cervical cancer, thereby improving accuracy of radiotherapy dose evaluation.
Owner:福建省肿瘤医院 +1
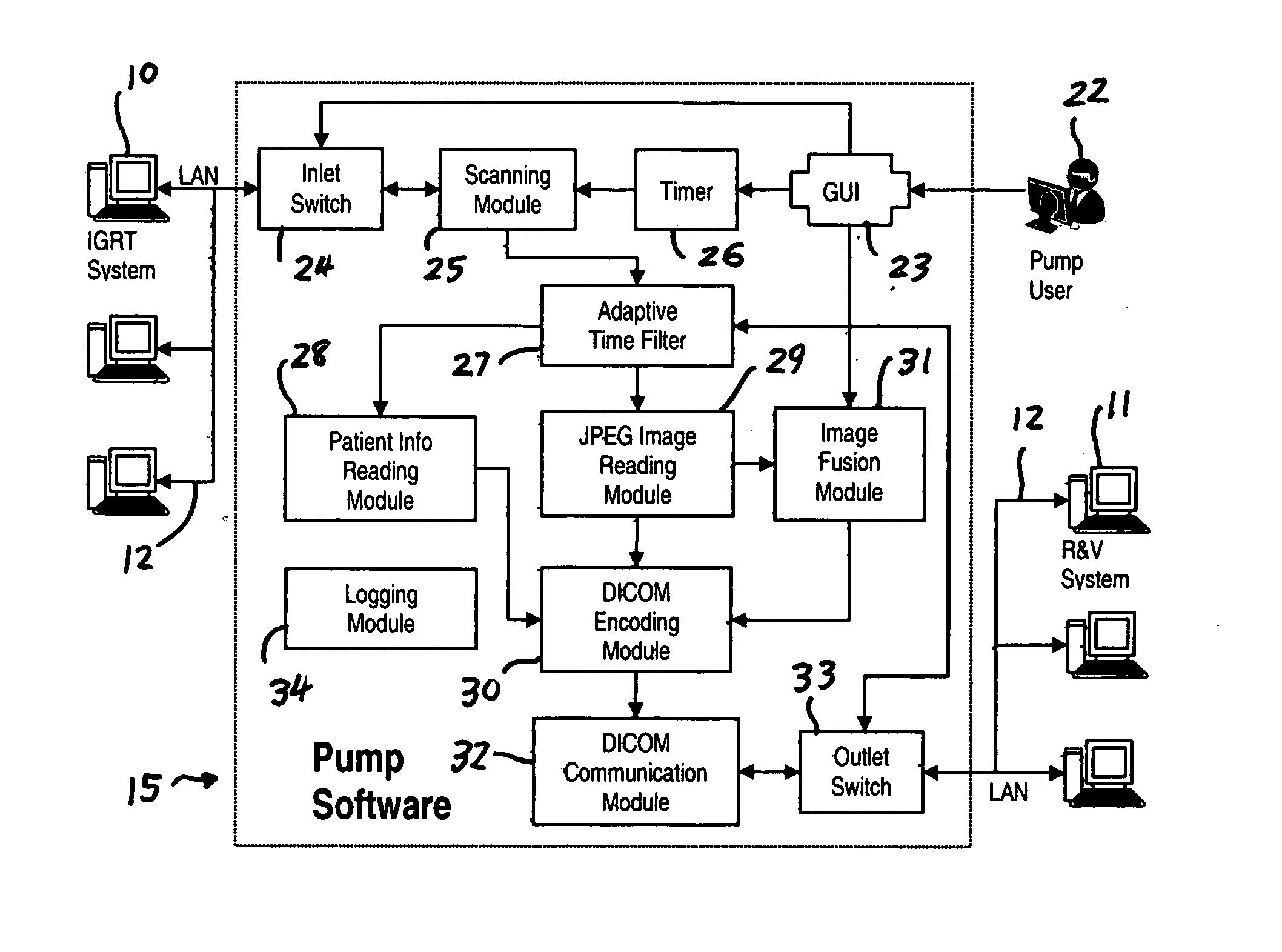
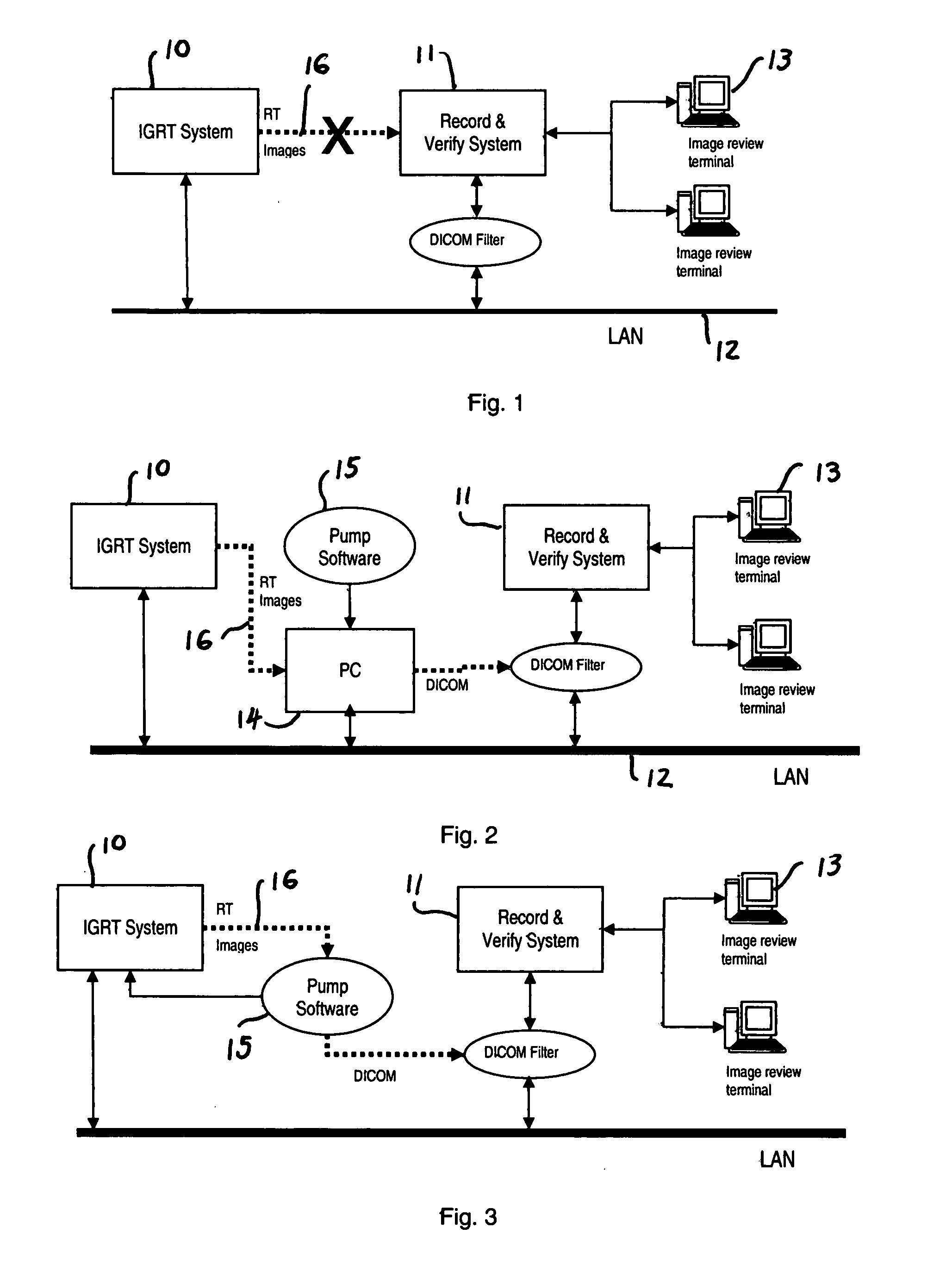
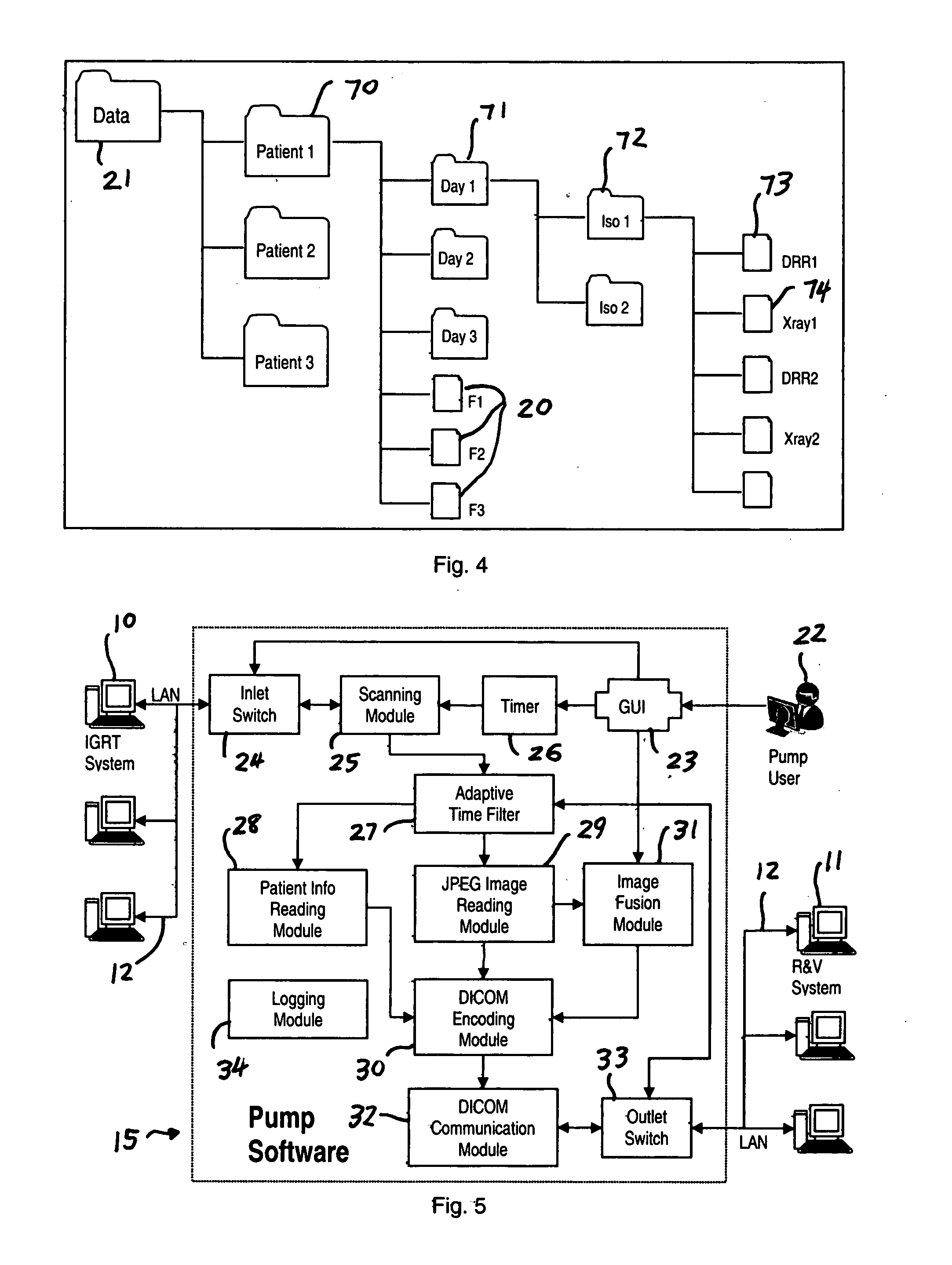
Method and system for image pumping
InactiveUS20090080721A1Quantitative estimation of image registration accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionMedical imagesDICOMImage-guided radiation therapy
A method and system to “pump” radiation therapy (RT) images and associated patient information on an Image Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) system to a Record and Verify (R&V) system via a standard DICOM connection to allow remote image viewing. Targeted image files in IGRT systems are searched for and transferred automatically. The user identifies the “inlet,” i.e. the source from which the image files are searched, and the “outlet,” i.e., the DICOM server to which the “pumped” imaged are directed. The images can be sent in their original form or fused. The “input” source is scanned periodically at a user-determined time interval. In order not to send the same image multiple time, a time filter skips images generated before a user-selected time and date.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
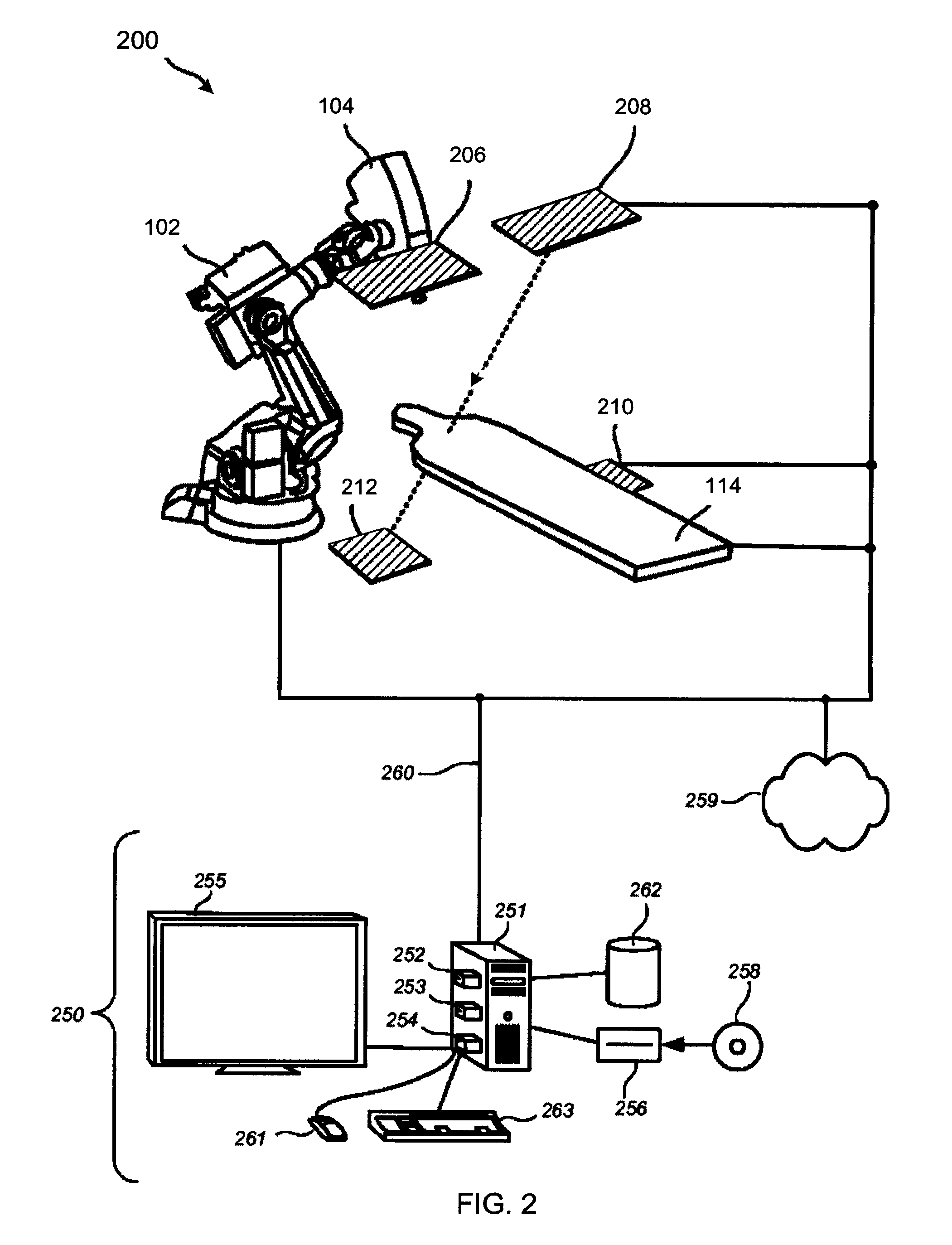
Image guided radiation therapy system
A magnetic resonance (MR)-radiotherapy (RT) hybrid system for treating a patient is disclosed. The MR-RT hybrid system includes a radiation source for supplying a radiation beam to treat the patient and an MR imaging (MRI) apparatus for generating a divergent gradient field shaped to match a divergent geometry of the radiation beam of the radiation source.
Owner:ALBERTA HEALTH SERVICES
Image-guided radiation therapy
ActiveUS9919166B2Improve accuracyEfficient deliveryX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIrradiation devicesLight beamImage-guided radiation therapy
The disclosed systems and methods for Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT), utilizes an iterative approach which adjusts a treatment plan based on inter- or intra-fraction images to improve the accuracy of the radiation delivered during the overall treatment. The prescribed dose of radiotherapeutic radiation is mapped onto the patient's anatomy using an image acquired of the region, which is to be the target for radiotherapeutic radiation. Following beam-angle-optimization, fluence optimization and segmentation, the efficiency of delivery of each segment is determined using an objective function, and the segments ranked according to their efficiency. The plan proceeds with the choice of the most efficient segment (or segments) to be delivered first. When this radiation has been delivered, having been tracked to establish its distribution, this delivered distribution can be subtracted from the original prescribed dose and the process repeated so that the delivered radiation gradually converges on the original prescribed dose.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
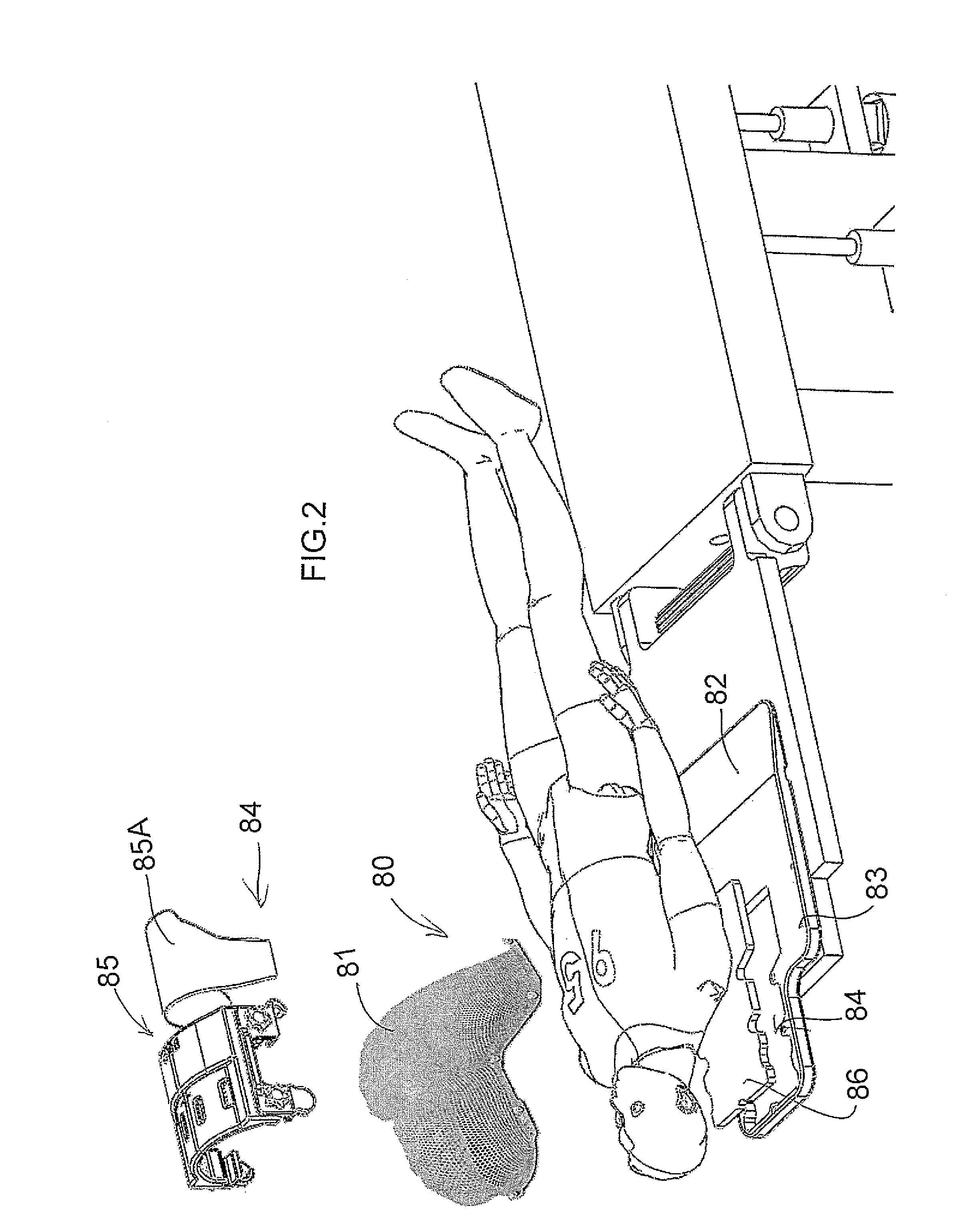
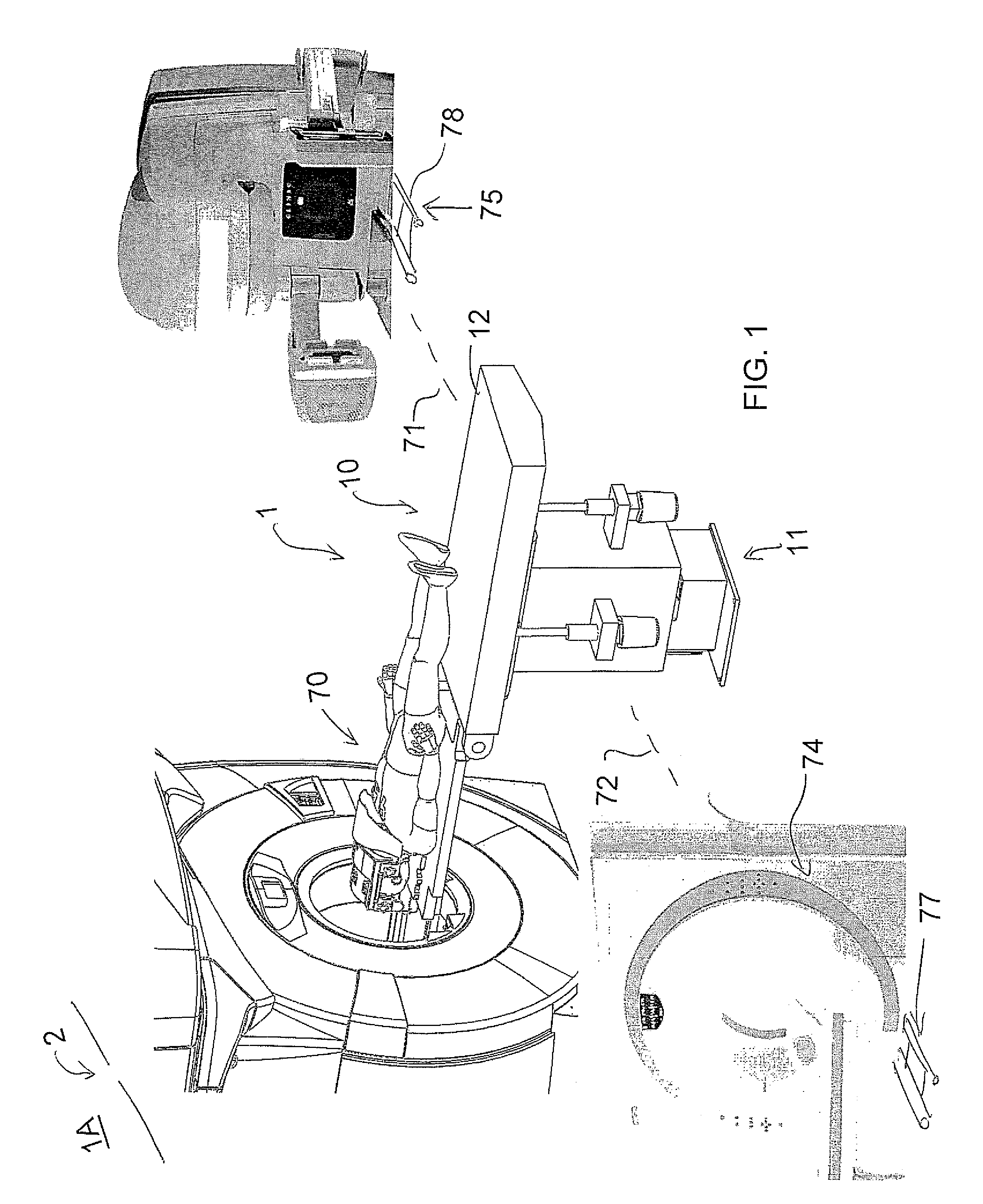
Radiation Treatment Device and method for performing image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) on a body part of a patient
ActiveCN105816195APatient positioning for diagnosticsComputerised tomographsImage-guided radiation therapyPerformed Imaging
The invention describes a radiation treatment device and a method for performing an image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) on a body part of a patient. The radiation treatment device includes a ring gantry having a central opening; a radiation treatment head coupled to the ring gantry that is rotatable around the central opening in at least a 180 degree arc; and a gantry translation mechanism configured to translate the ring gantry in a direction of a longitudinal axis extending through the central opening.
Owner:ACRE CORP
Integrated quality assurance for an image guided radiation treatment delivery system
ActiveUS20080144776A1Calibration apparatusRadiation beam directing meansQuality assuranceImage-guided radiation therapy
A method and apparatus for quality assurance of an image guided radiation treatment delivery system. A quality assurance (“QA”) marker is positioned at a preset position under guidance of an imaging guidance system of a radiation treatment delivery system. A radiation beam is emitted from a radiation source of the radiation treatment delivery system at the QA marker. An exposure image of the QA marker due to the radiation beam is generated. The exposure image is then analyzed to determine whether the radiation treatment delivery system is aligned.
Owner:ACCURAY
Iterative image reconstruction in image-guided radiation therapy
ActiveCN108882897AReconstruction from projectionComputerised tomographsComputed tomographyProjection image
Reconstruction of projection images of a CBCT scan is performed by generating simulated projection data, comparing the simulated projection data to the projection images of the CBCT scan, determininga residual volume based on the comparison, and using the residual volume to determine an accurate reconstructed volume. The reconstructed volume can be used to segment a tumor (and potentially one ormore organs) and align the tumor to a planning volume (e.g., from a CT scan) to identify changes, such as shape of the tumor and proximity of the tumor to an organ. These changes can be used to updatea radiation therapy procedure, such as by altering a radiation treatment plan and fine-tuning a patient position.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
Image guided radiation therapy
ActiveUS8295430B2Reduce the numberAvoiding damaging healthy tissueMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic measurementsImage-guided radiation therapyScanning beam
Owner:DEERFIELD IMAGING INC
Iterative image reconstruction in image-guided radiation therapy
ActiveUS20180229056A1Accurate volumeReconstruction from projectionComputerised tomographsImage-guided radiation therapyTherapy planning
Reconstruction of projection images of a CBCT scan is performed by generating simulated projection data, comparing the simulated projection data to the projection images of the CBCT scan, determining a residual volume based on the comparison, and using the residual volume to determine an accurate reconstructed volume. The reconstructed volume can be used to segment a tumor (and potentially one or more organs) and align the tumor to a planning volume (e.g., from a CT scan) to identify changes, such as shape of the tumor and proximity of the tumor to an organ. These changes can be used to update a radiation therapy procedure, such as by altering a radiation treatment plan and fine-tuning a patient position.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
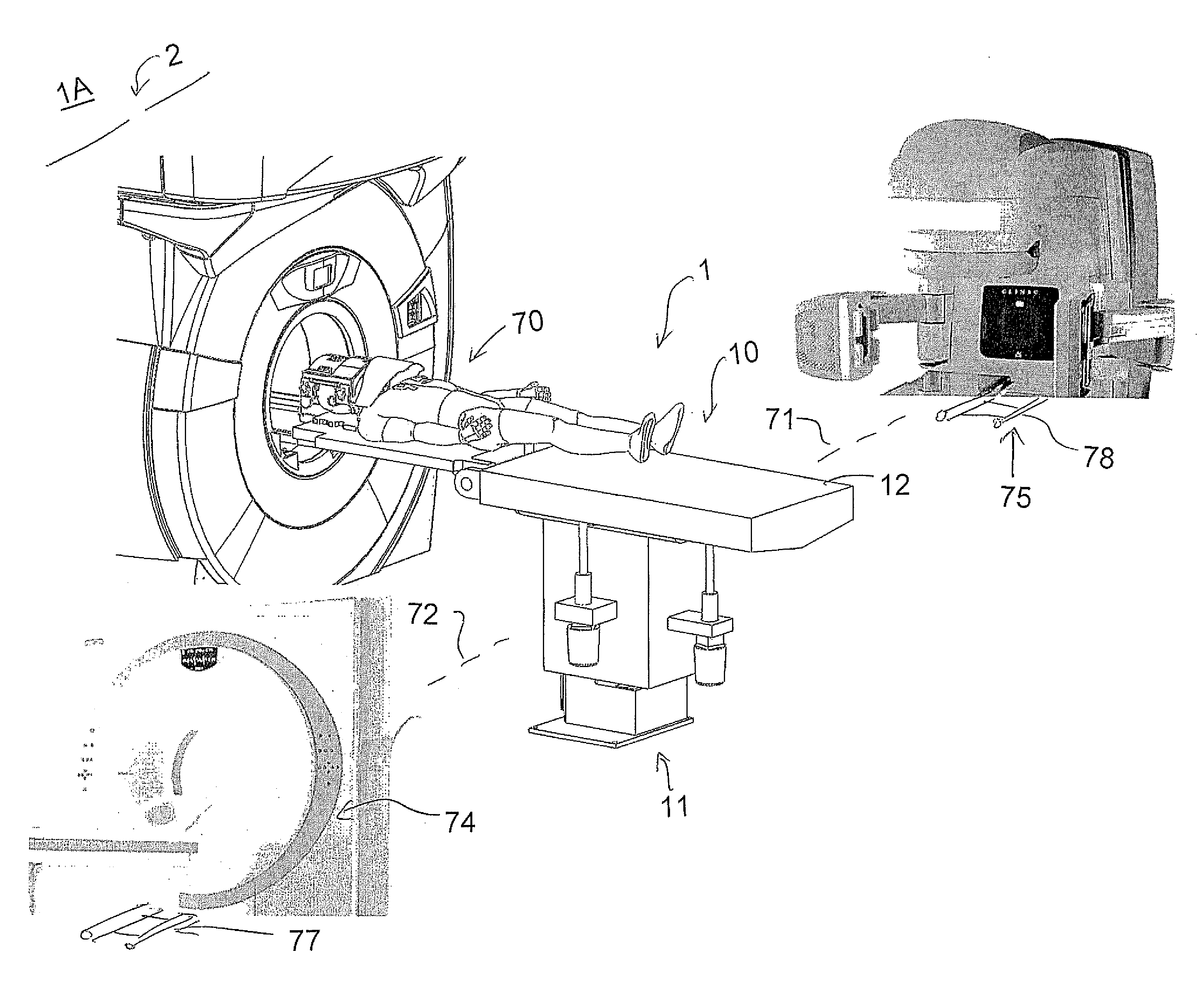
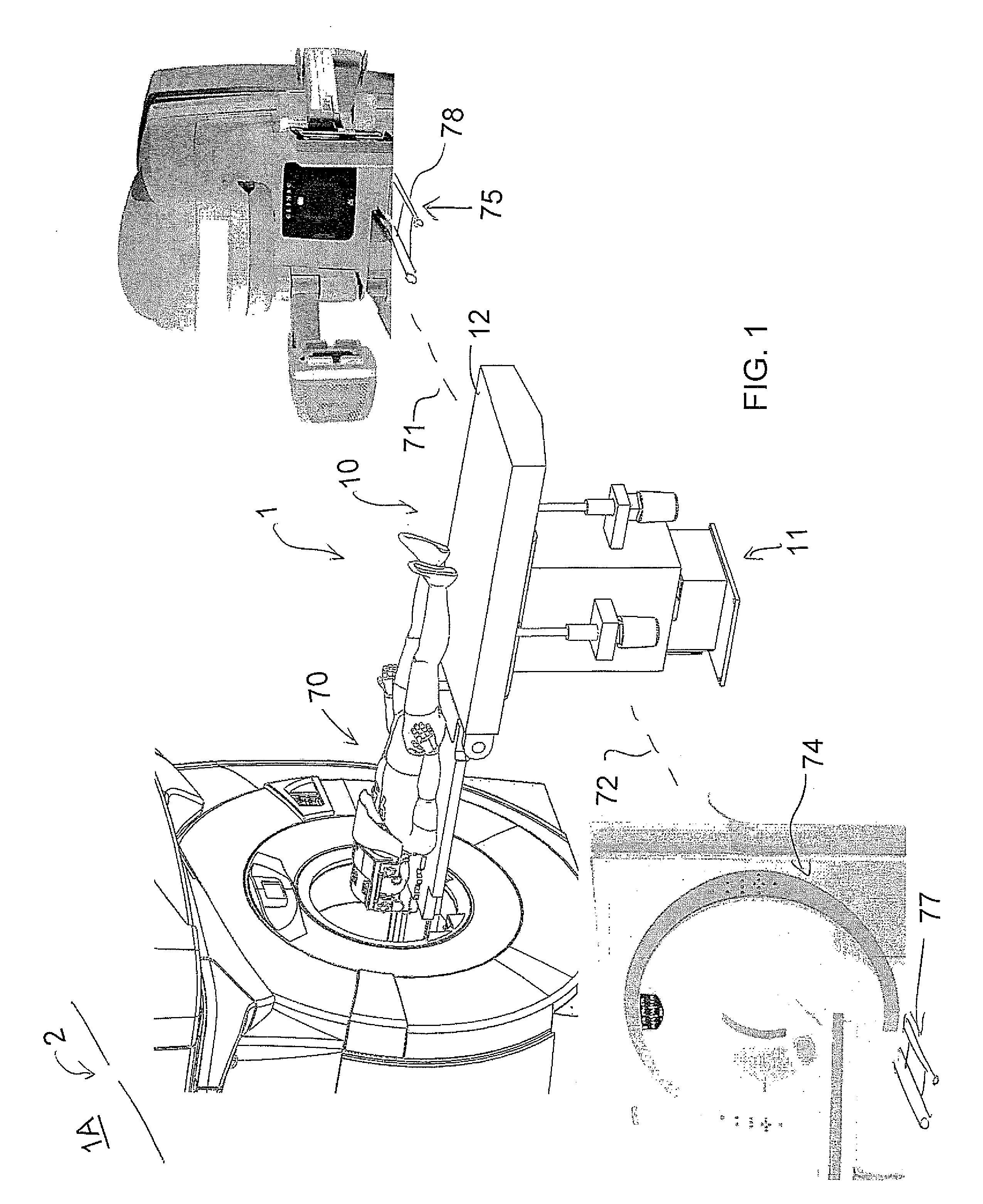
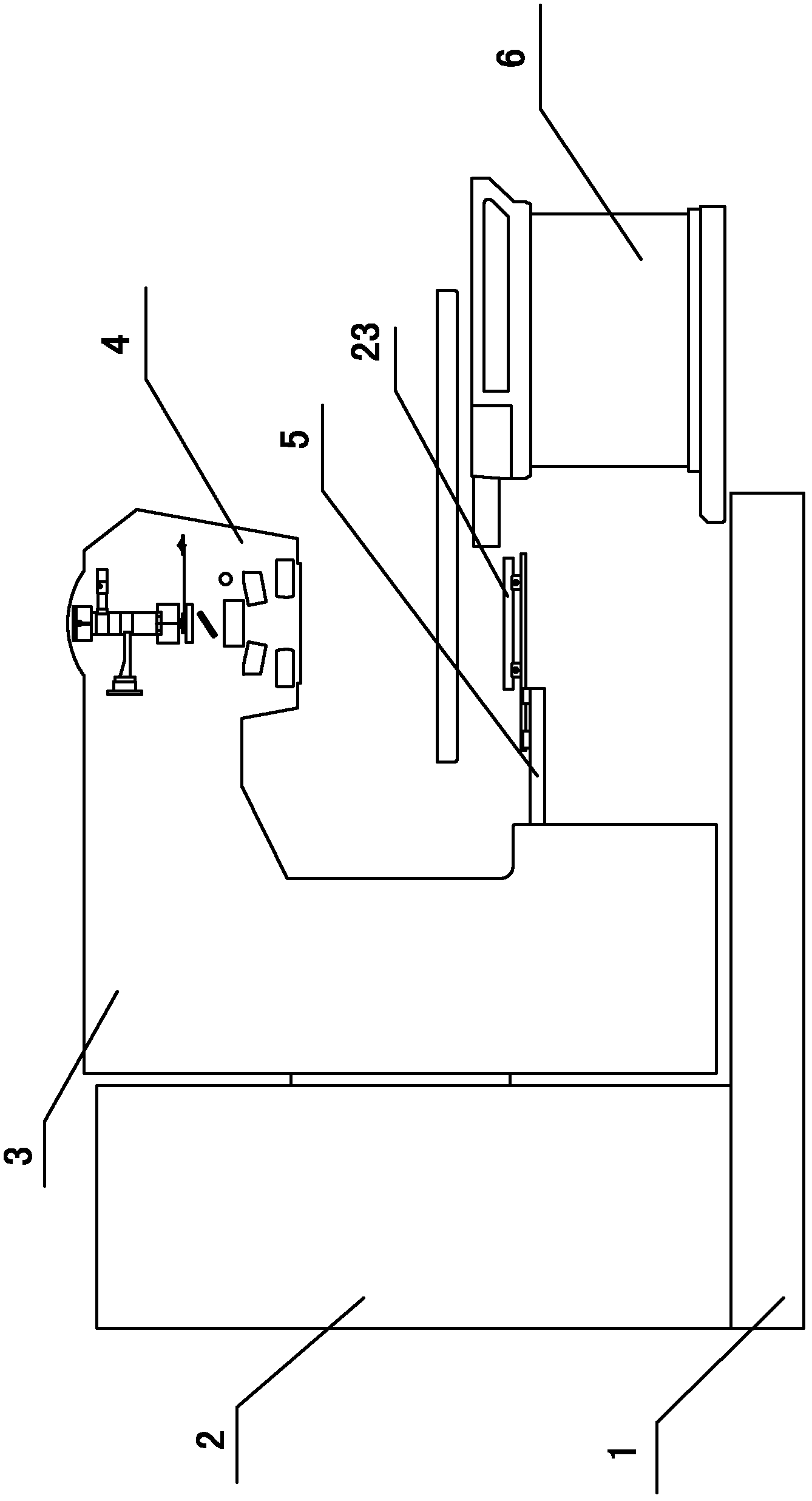
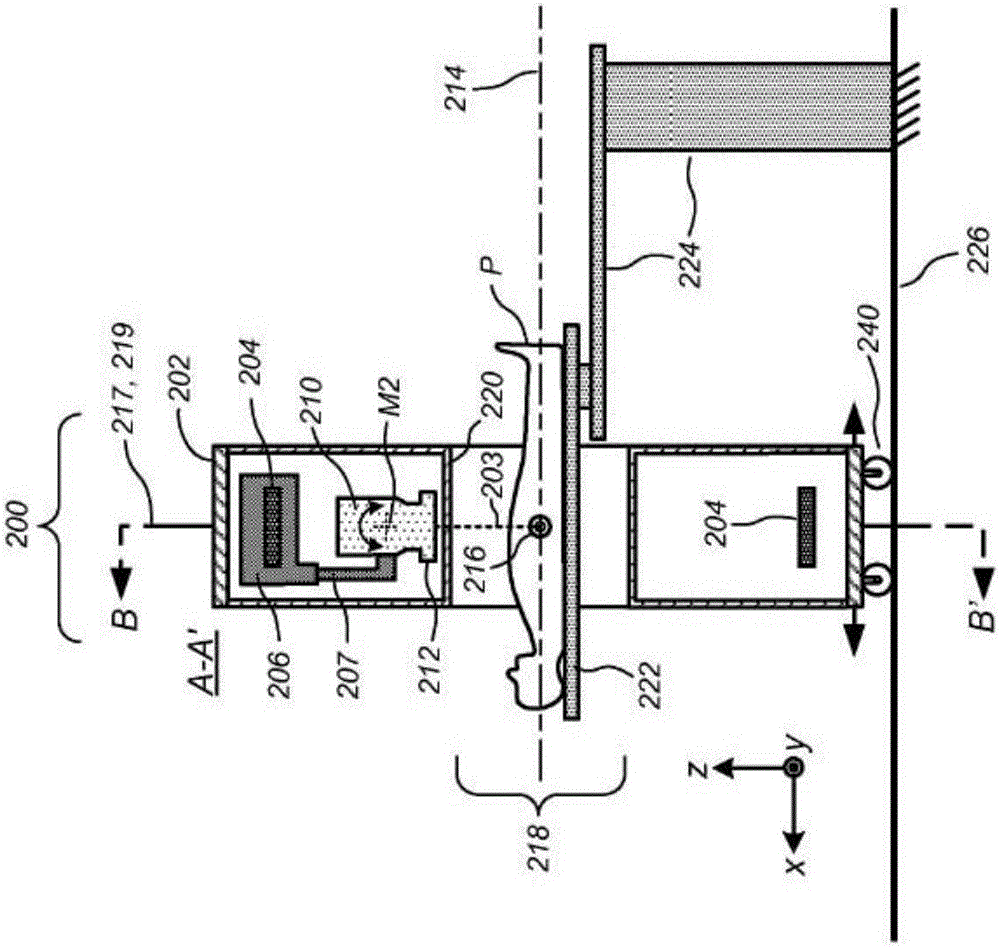
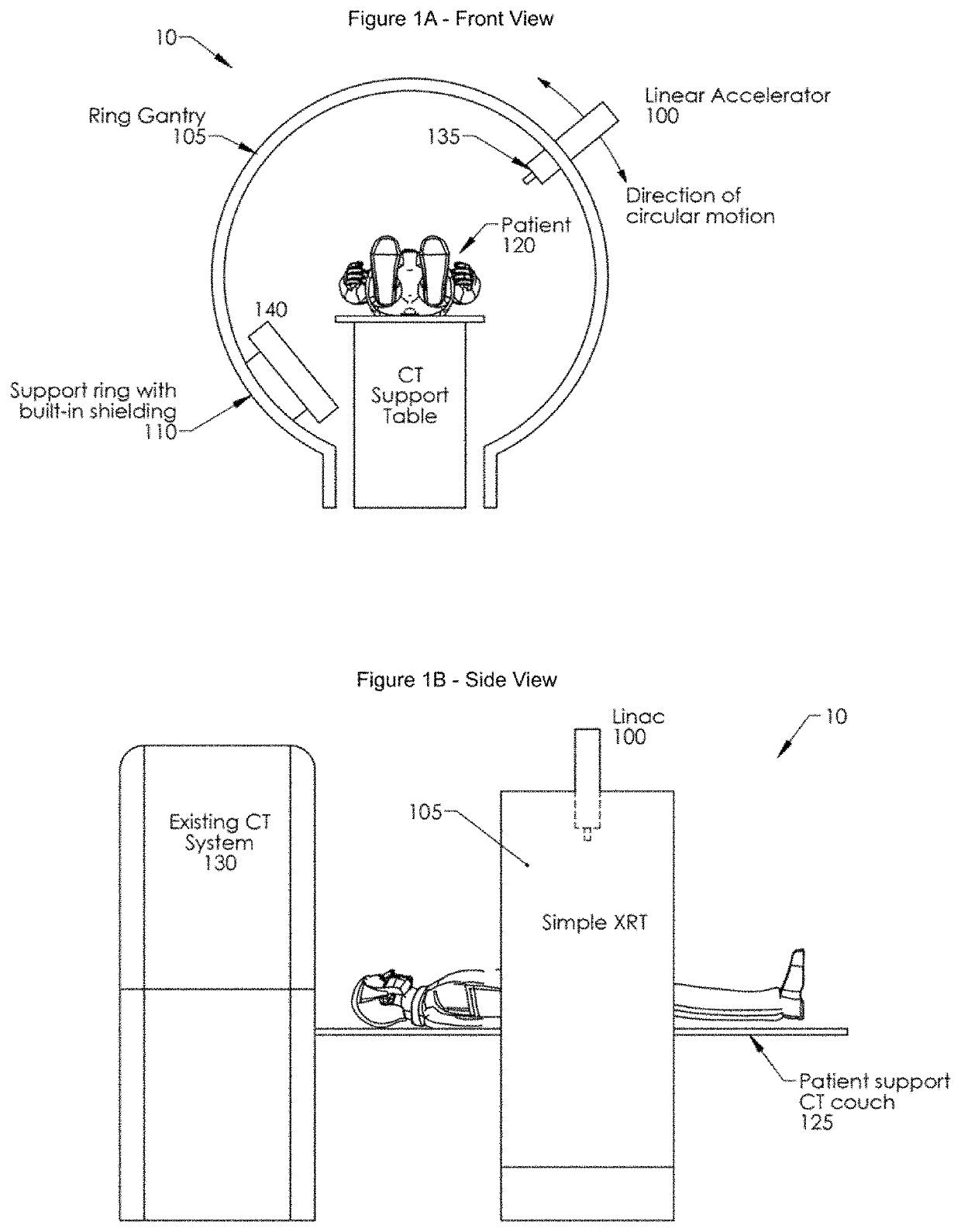
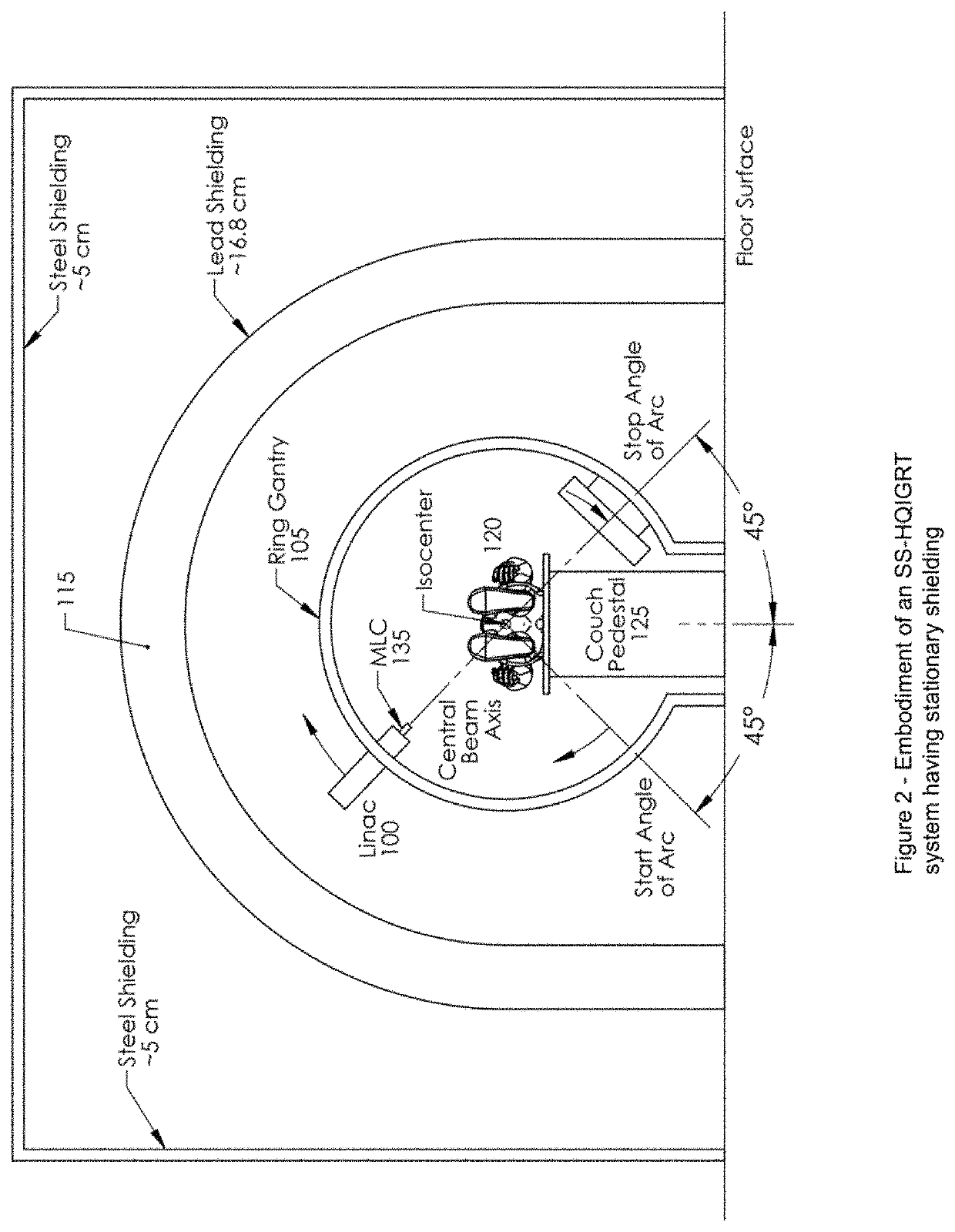
Self-shielded image guided radiation oncology system
ActiveUS10737122B2Eliminate needImprove image qualityRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsPatient positioning for diagnosticsCt scannersRadiology
An image-guided radiotherapy system adapted to be juxtaposed adjacent a CT scanner comprises a frame having an orifice adapted to permit passage therethrough of a couch on which a patient is positioned, together with a gantry assembly rotatably mounted on the frame in which the gantry assembly comprises a shielding cylinder having an orifice therethrough in alignment with the orifice in the frame. The shielding cylinder has affixed thereto a linac-based treatment head configured to provide radiotherapy, and a beamstop positioned angularly opposite the treatment head to absorb radiation from the treatment head. The shielding cylinder provides sufficient shielding of radiation scattered from the patient and the remainder of the system to not require a conventional vault. In some embodiments an arch may be used instead of a cylinder.
Owner:ETM ELECTROMATIC
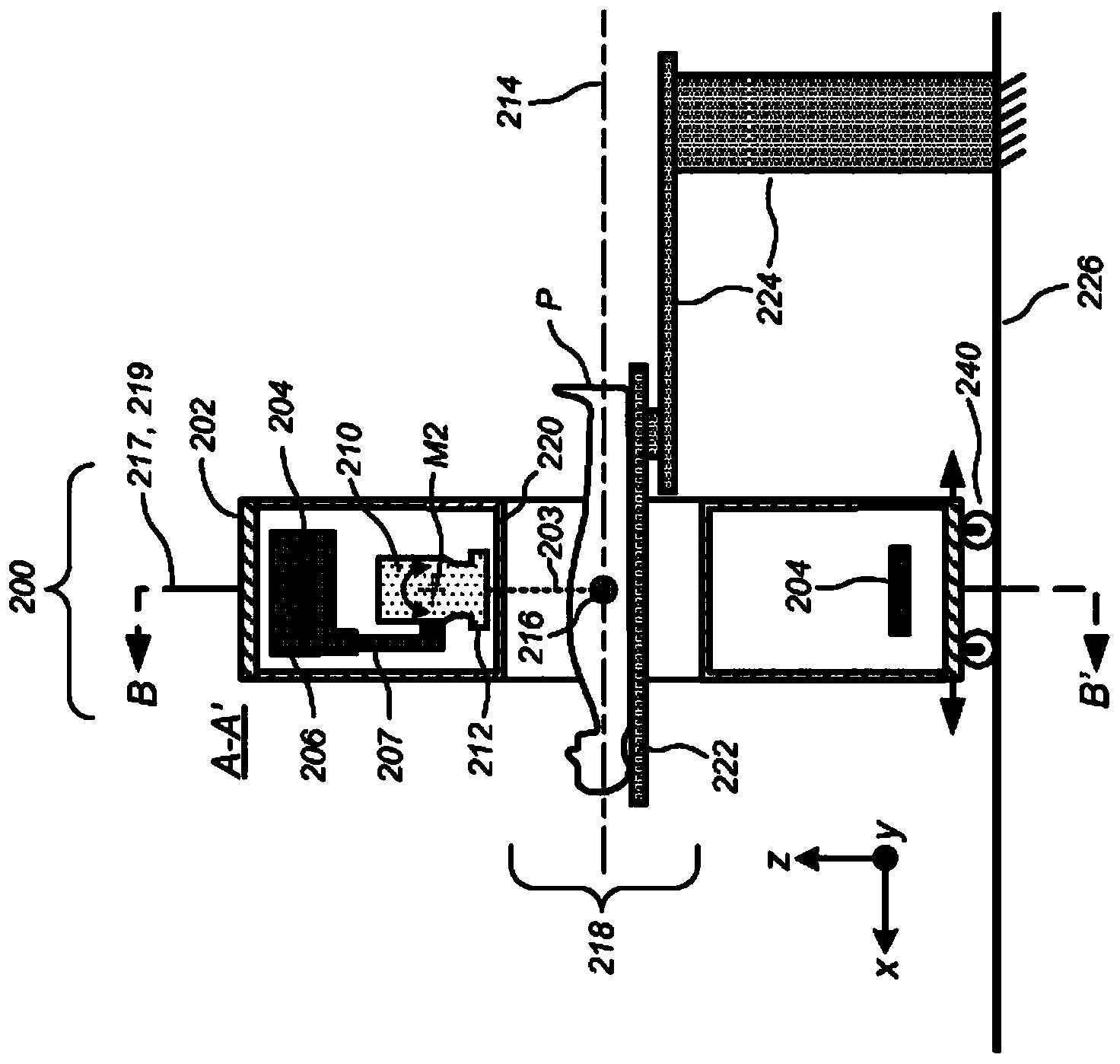
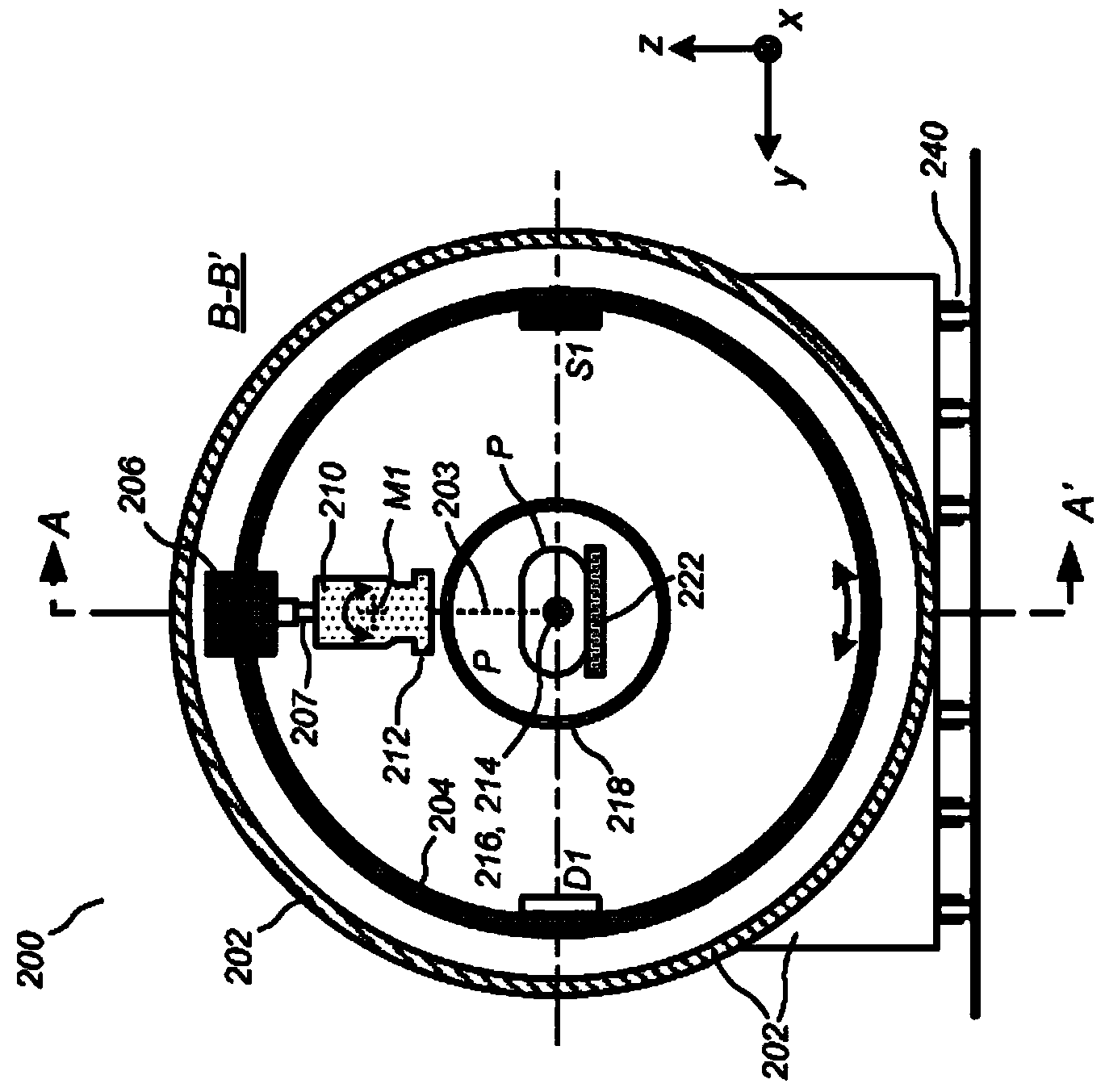
Repositionable Gynecological Applicator for Image-guided Radiosurgery (IGRS) and Image-guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) for Localized Treatment of Gynecological Tumors
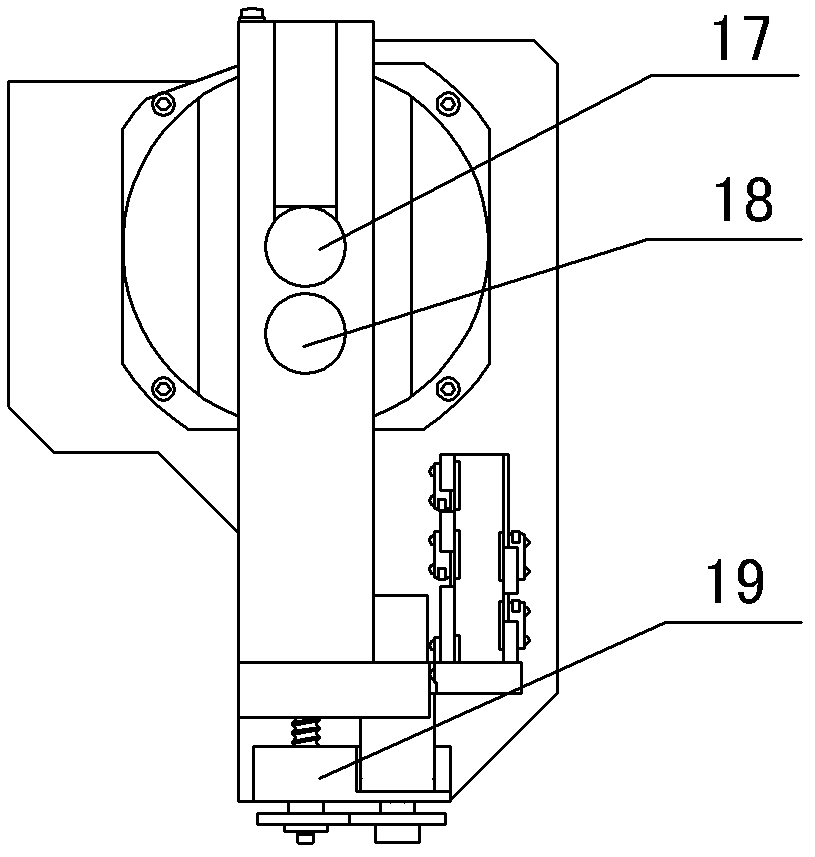
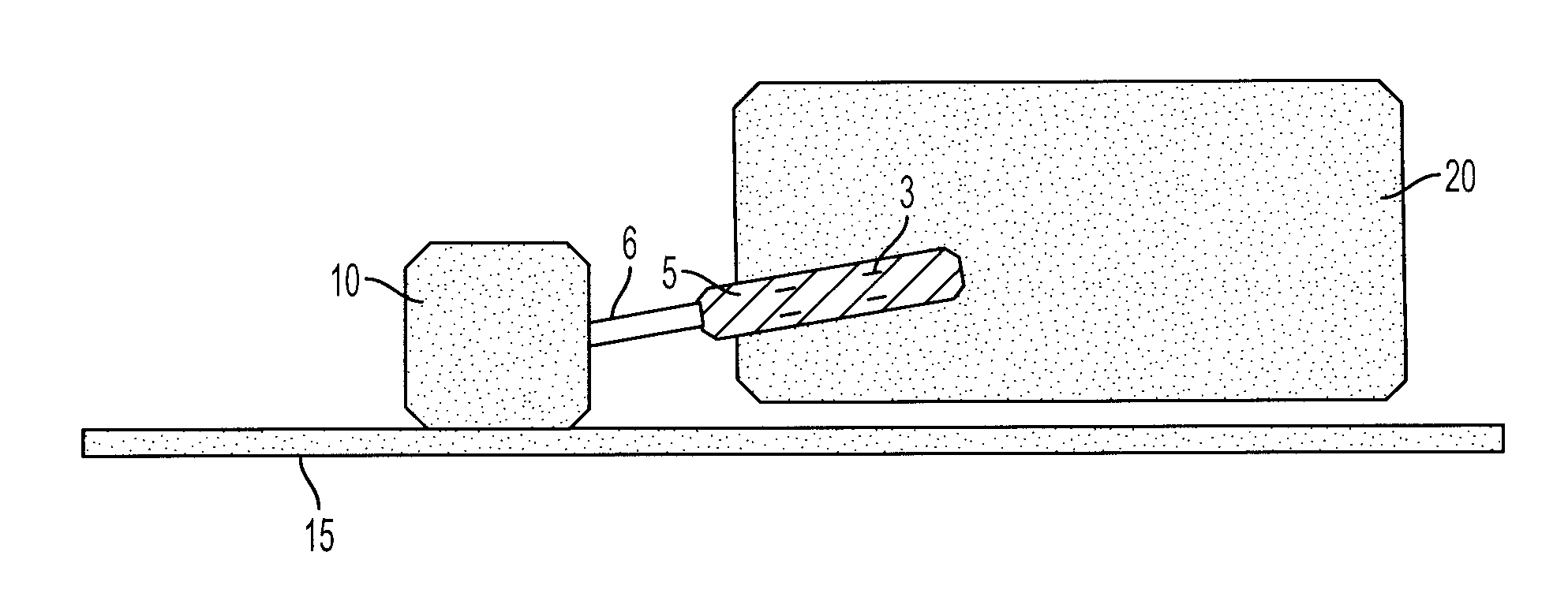
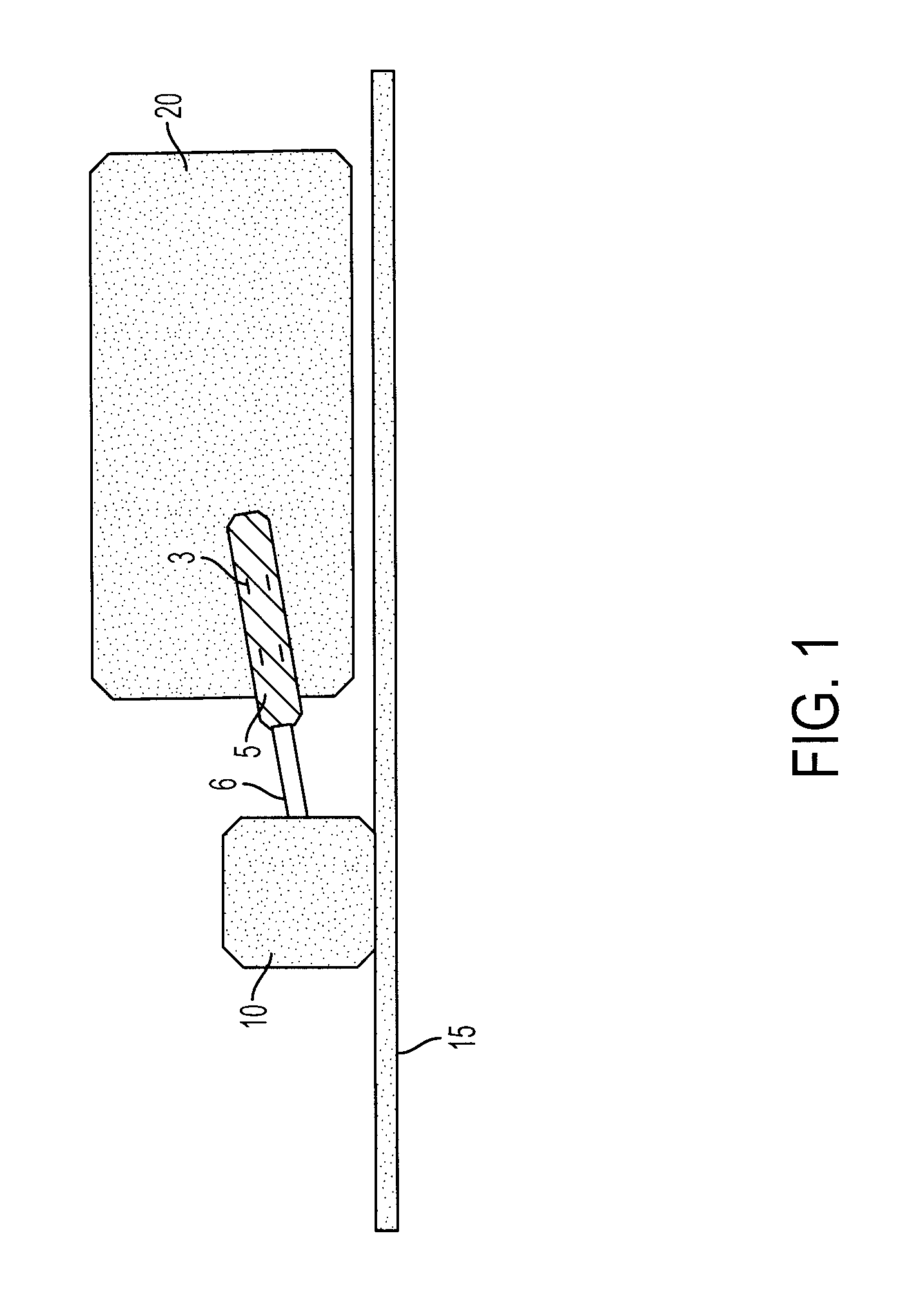
InactiveUS20080219402A1Accurate placementError minimizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingGeometric errorAbnormal tissue growth
A method and apparatus for precisely reproducing the position of a vaginal cylinder in relation to a patient to ensure that a planned radiation dose can be delivered with high precision to the intended treatment target volumes. In order to properly define the treatment volume, a vaginal cylinder with proper diameter is inserted into the patient's vagina. This invention addresses two potential errors: one, the incorrect vaginal cylinder position in relation to the radiation beams, and second, the inconsistent positional correlation between the vaginal cylinder and the patient's body. These two geometric errors will cause dosimetric errors. The present invention provides a method and apparatus for minimizing the geometric error and dosimetric error associated with conventional external beam radiation therapy or radiosurgery used in treating gynecological tumors. First a treatment plan is carried out to determine the treatment target volume. Second, treatment delivery is carried out by using an image-guided system to locate the position of the vaginal cylinder and comparing it relative to the treatment delivery system coordinate system and the patient's coordinate system. The displacement in the position of the vaginal cylinder from the treatment plan is corrected by calculating the transformation matrix and entering the resulting value into a position adjusting assembly. The position adjusting assembly adjusts the vaginal cylinder to exactly reproduce its location relative to the patient's coordinate system. This ensures that the image-guided system locates the precise radiation delivery position and that the radiation dose is delivered precisely to the treatment target volume.
Owner:SCHWADE JAMES G M D MR
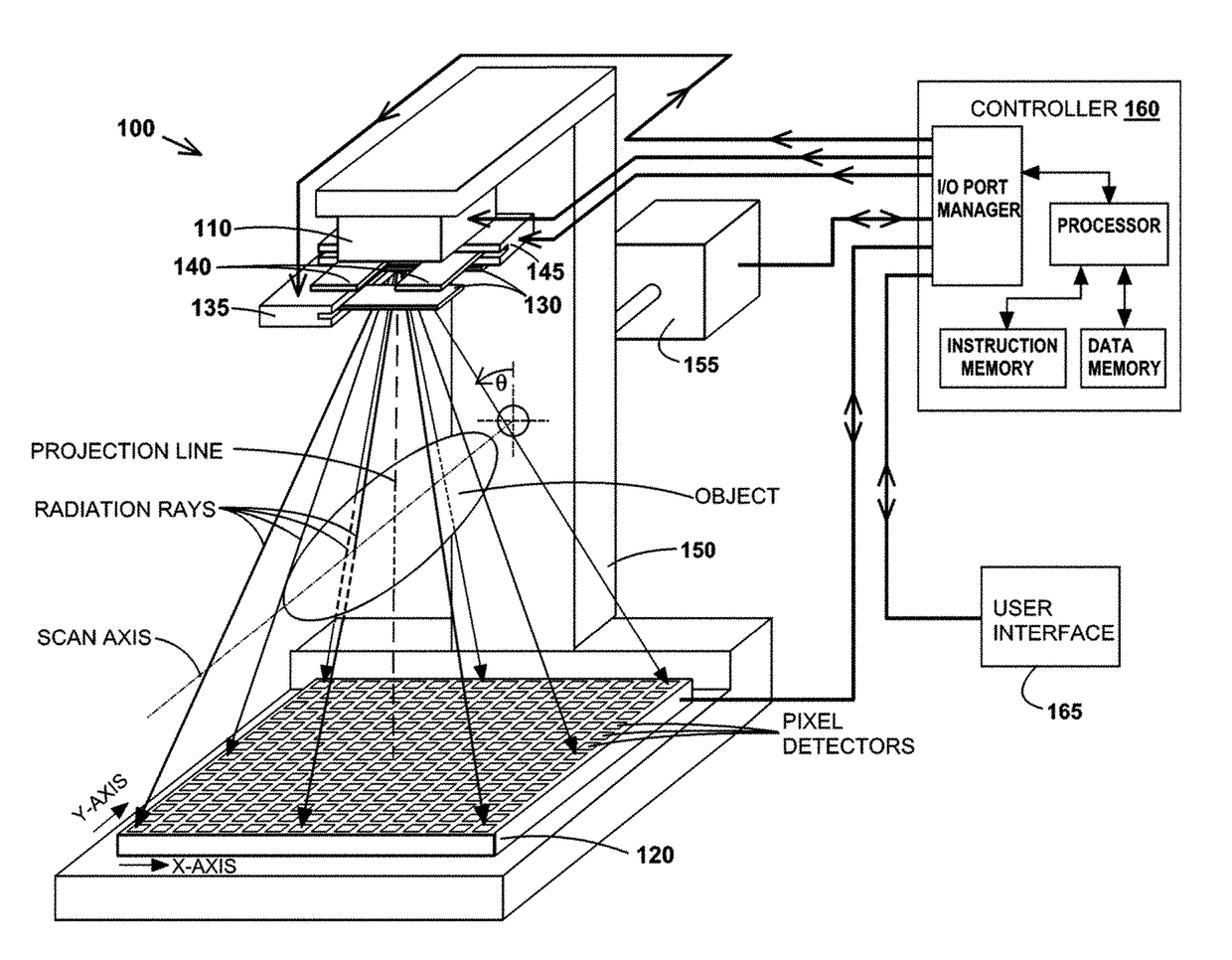
Systems and methods for intrafractional ct imaging in image-guided radiotherapy
A radiation system may include a treatment assembly including a first radiation source, a second radiation source, and a first radiation detector. The first radiation source may be configured to deliver a treatment beam covering a treatment region of the radiation system, and the treatment region may be located in a bore of the radiation system. The second radiation source may be configured to deliver a first imaging beam covering a first imaging region of the radiation system, and may be mounted rotatably on a first side of the treatment assembly. The first radiation detector may be configured to detect at least a portion of the first imaging beam, and may be mounted rotatably on a second side of the treatment assembly. The treatment assembly, the second radiation source, and the first radiation detector may be positioned such that the treatment region is addressable for the radiation system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
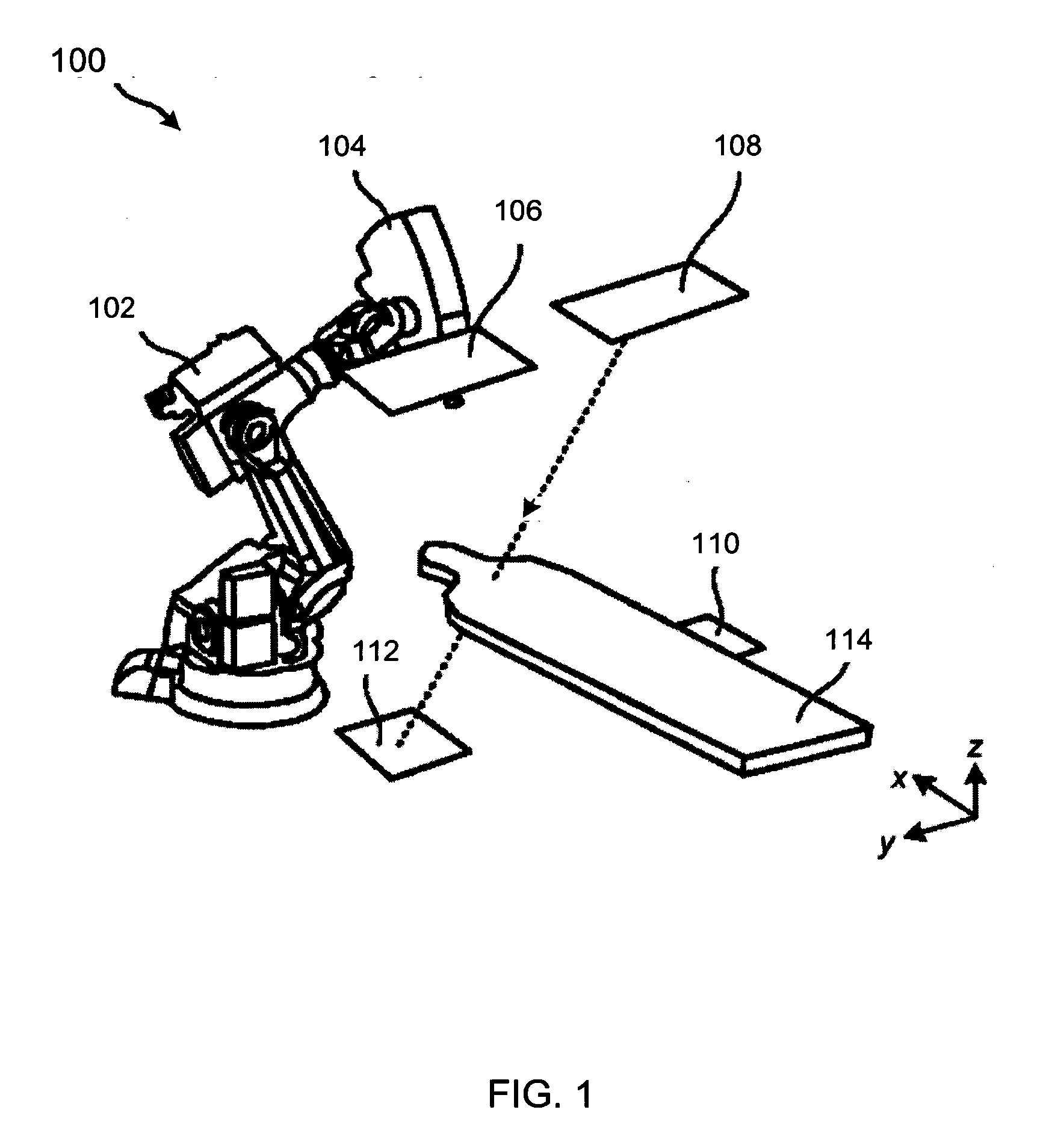
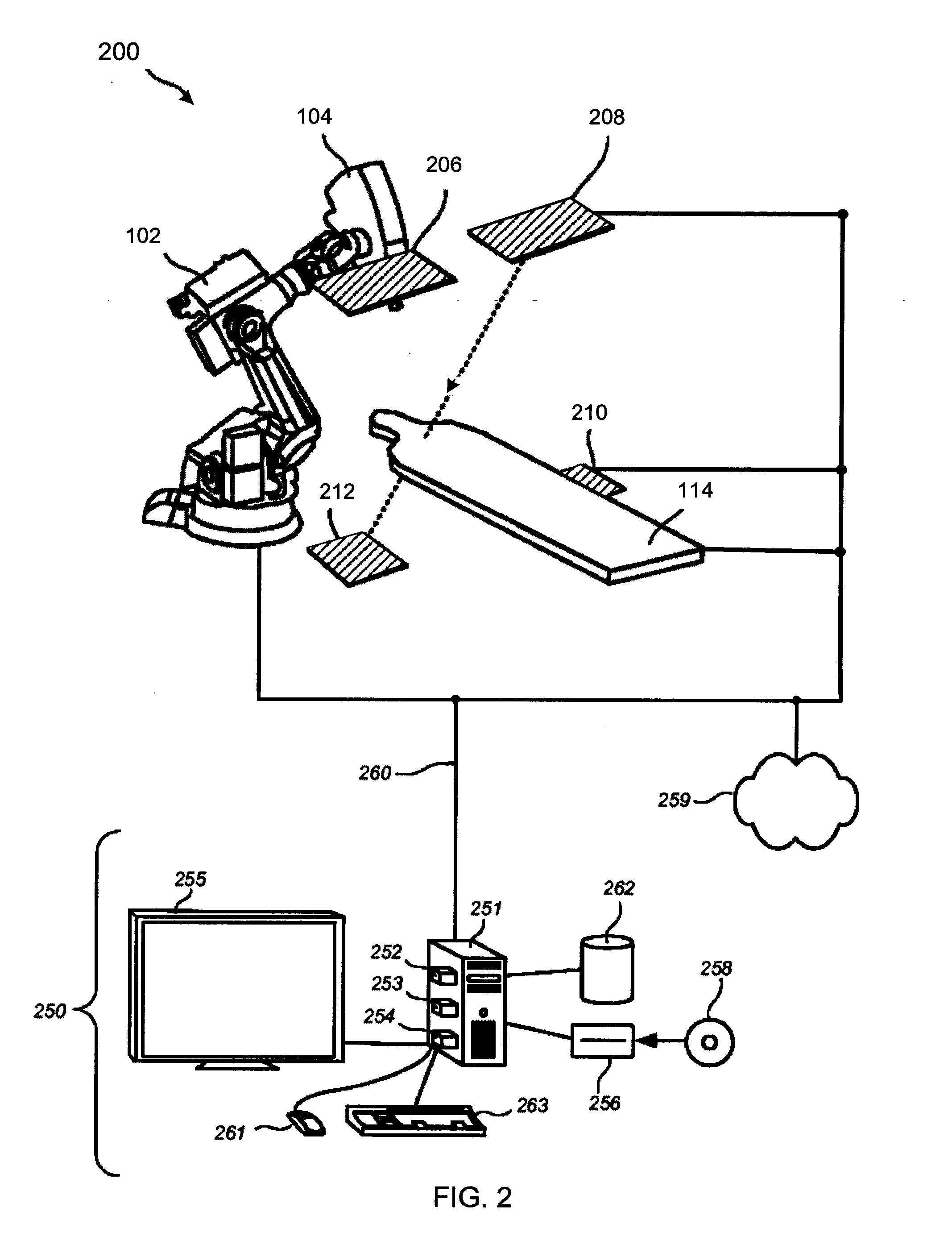
Systems and methods for image-guided radiotherapy using dual robot architecture
PendingCN110719798AAvoid collisionTomographyRadiation beam directing meansImage-guided radiation therapyDirect radiation
A system for coordinating radiation therapy and imaging processes includes a radiation therapy system an radiation source mounted on a robotically-controlled system to move the radiation source abouta subject to direct radiation to a target area in the subject according to a treatment plan. The system also includes an imaging system configured to acquire imaging data from a subject. The imaging system and the radiation therapy system are independently movable. The system also includes a coordination system configured to coordinate operation of the imaging system to acquire the imaging data from the subject during movement of the radiation source about the subject according to the treatment plan to avoid collisions of the radiation therapy system with the imaging system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method for CT imaging in image-guided radiotherapy
A system and method for image-guided radiotherapy is provided. The system may include a treatment assembly and an imaging assembly. The treatment assembly may include a first radiation source configured to deliver a treatment beam. The treatment assembly may have a treatment region relating to an object. The imaging assembly may include a second radiation source and a radiation detector. The second radiation source may be configured to deliver an imaging beam, and the radiation detector may be configured to detect at least a portion of the imaging beam. The imaging assembly may have an imagingregion relating to the object. The first radiation source may be rotatable in a first plane, and the second radiation source may be rotatable in a second plane different from the first plane, such that the treatment region and the imaging region at least partially overlap.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
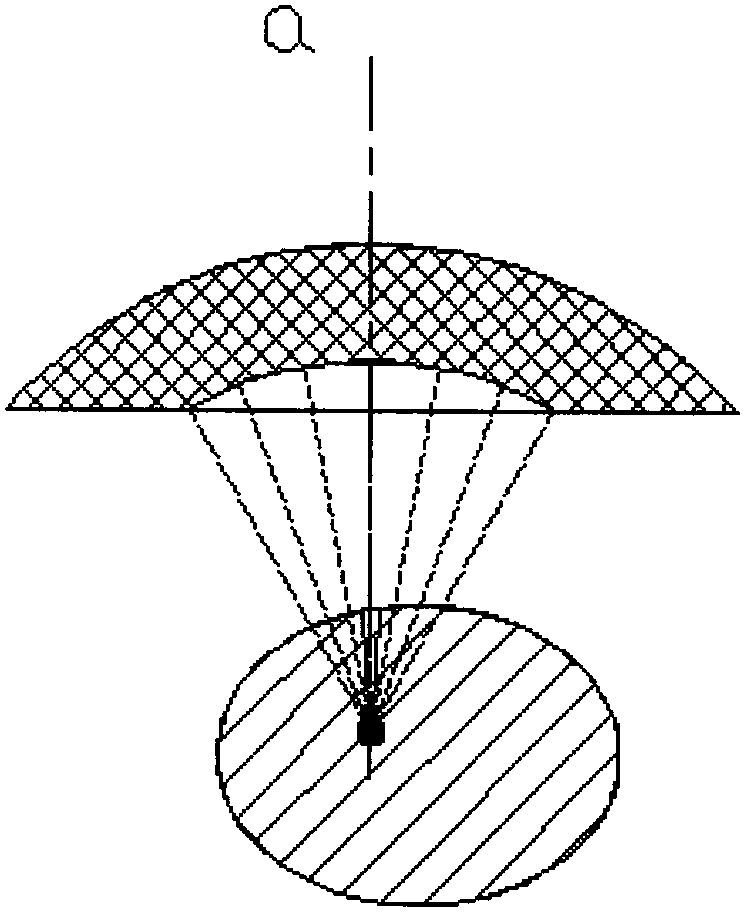
Three dimensional localization and tracking for adaptive radiation therapy
The present disclosure relates to systems, methods, and computer-readable storage media for segmenting a medical image. Embodiments of the present disclosure may locate and track a moving, three-dimensional (3D) target in a patient undergoing image-guided radiation therapy. For example, an adaptive filter model for a region of interest in the patient may be received, wherein the adaptive filter model is based on the target to be tracked. An image acquisition device may obtain a two-dimensional (2D) slice of a region of interest in the patient. A processor may then apply the adaptive filter model to the 2D slice, wherein the adaptive filter model includes an offset value. The processor may also determine a location of the target in the 2D slice based on the adaptive filter model. The processor may also estimate a potential location of the target based on the offset value. The processor may then repeat one or more of the above steps to track the moving target during image-guided radiation therapy of the patient.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Methods for real-time image guided radiation therapy
ActiveCN110997063AComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringRadiologyImage-guided radiation therapy
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for guiding the delivery of therapeutic radiation using incomplete or partial images acquired during a treatment session. A partial image does not have enoughinformation to determine the location of a target region due to, for example, poor or low contrast and / or low SNR. The radiation fluence calculation methods described herein do not require knowledge or calculation of the target location, and yet may help to provide real-time image guided radiation therapy using arbitrarily low SNR images.
Owner:REFLEXION MEDICAL INC
A nonlinear fusion method of internal and external radiotherapy doses for cervical cancer
ActiveCN106902477BAccurate assessmentAccurately achieve accumulationRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTumor targetExternal irradiation
Owner:福建省肿瘤医院 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com