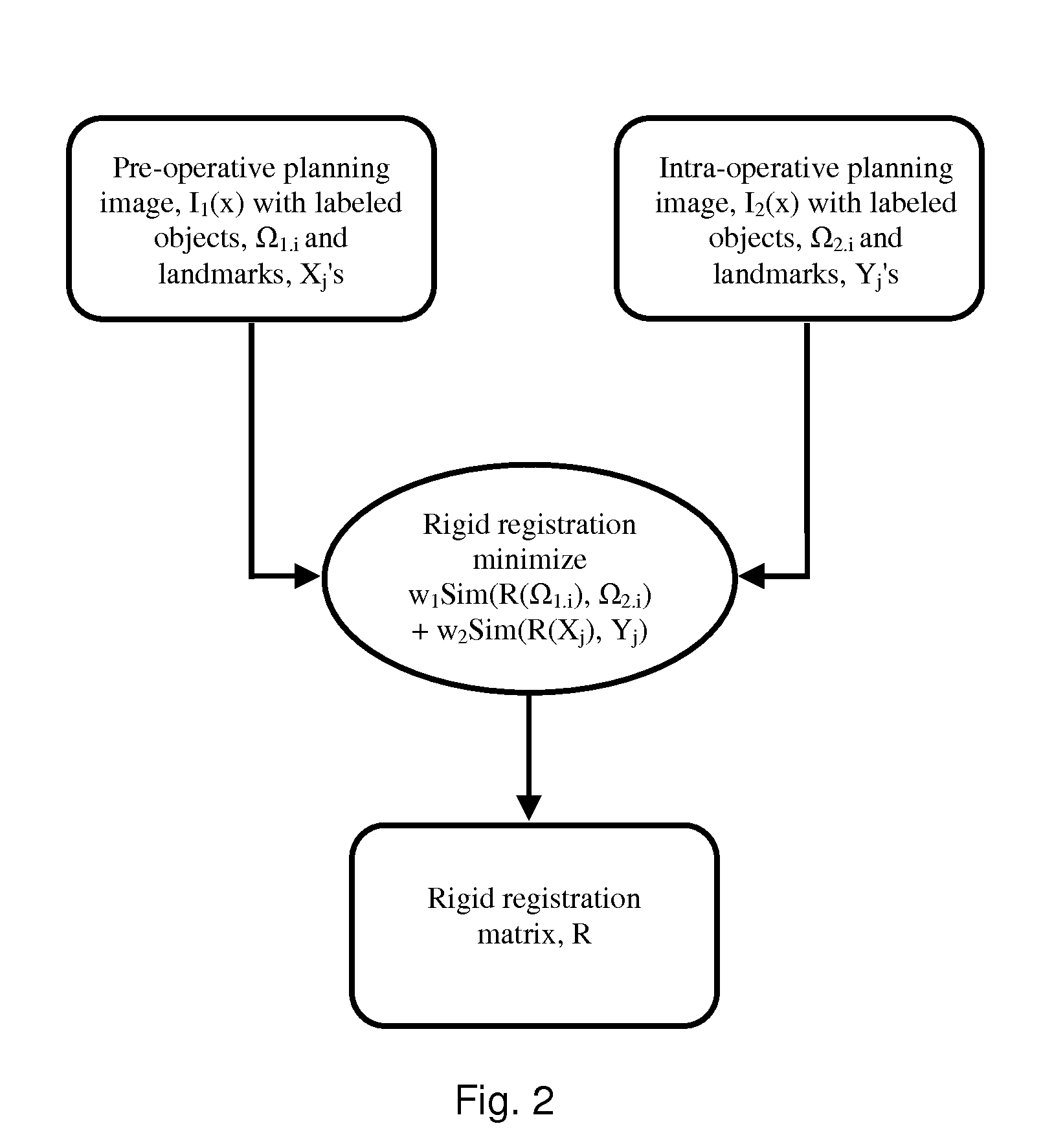
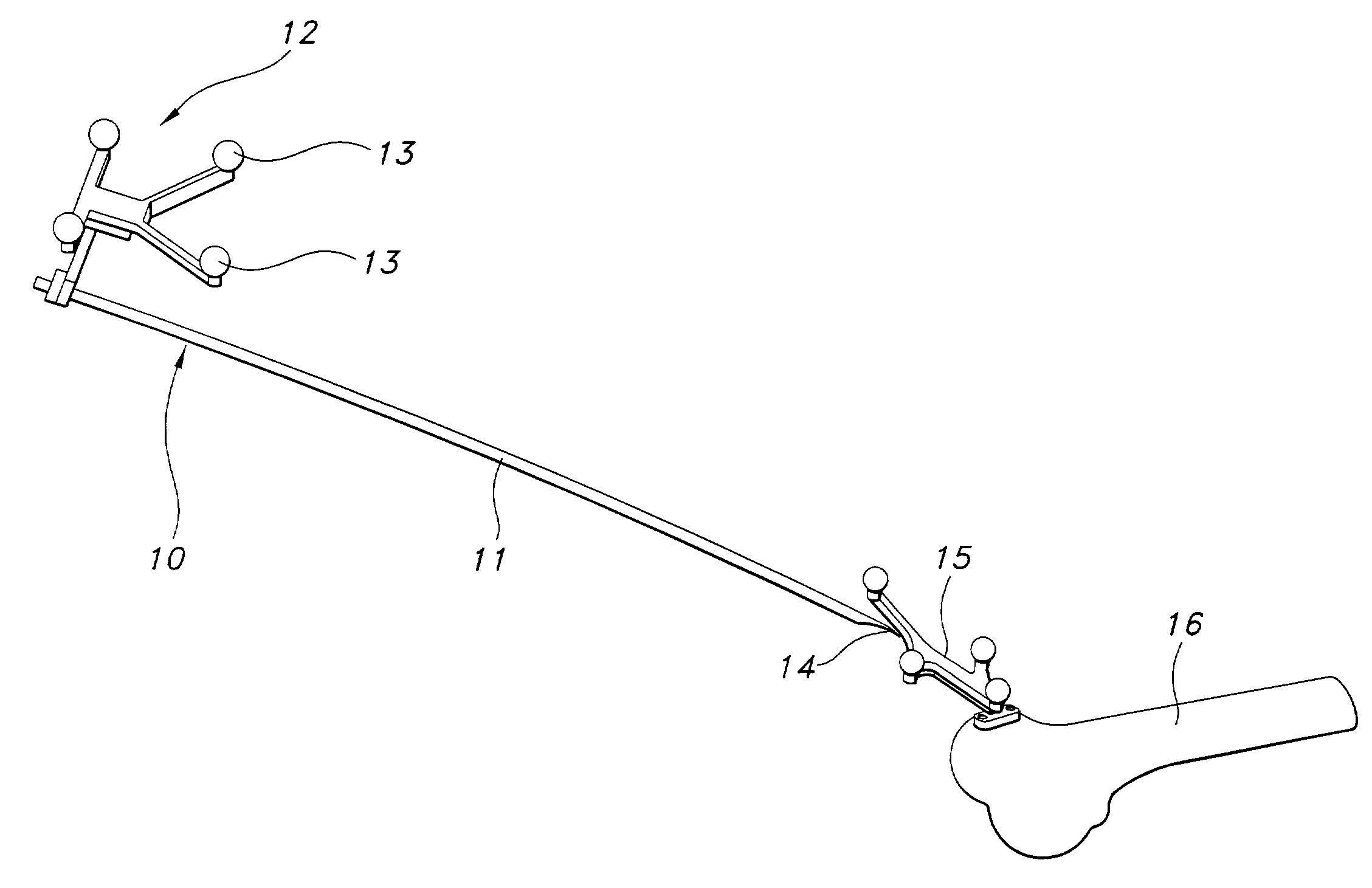
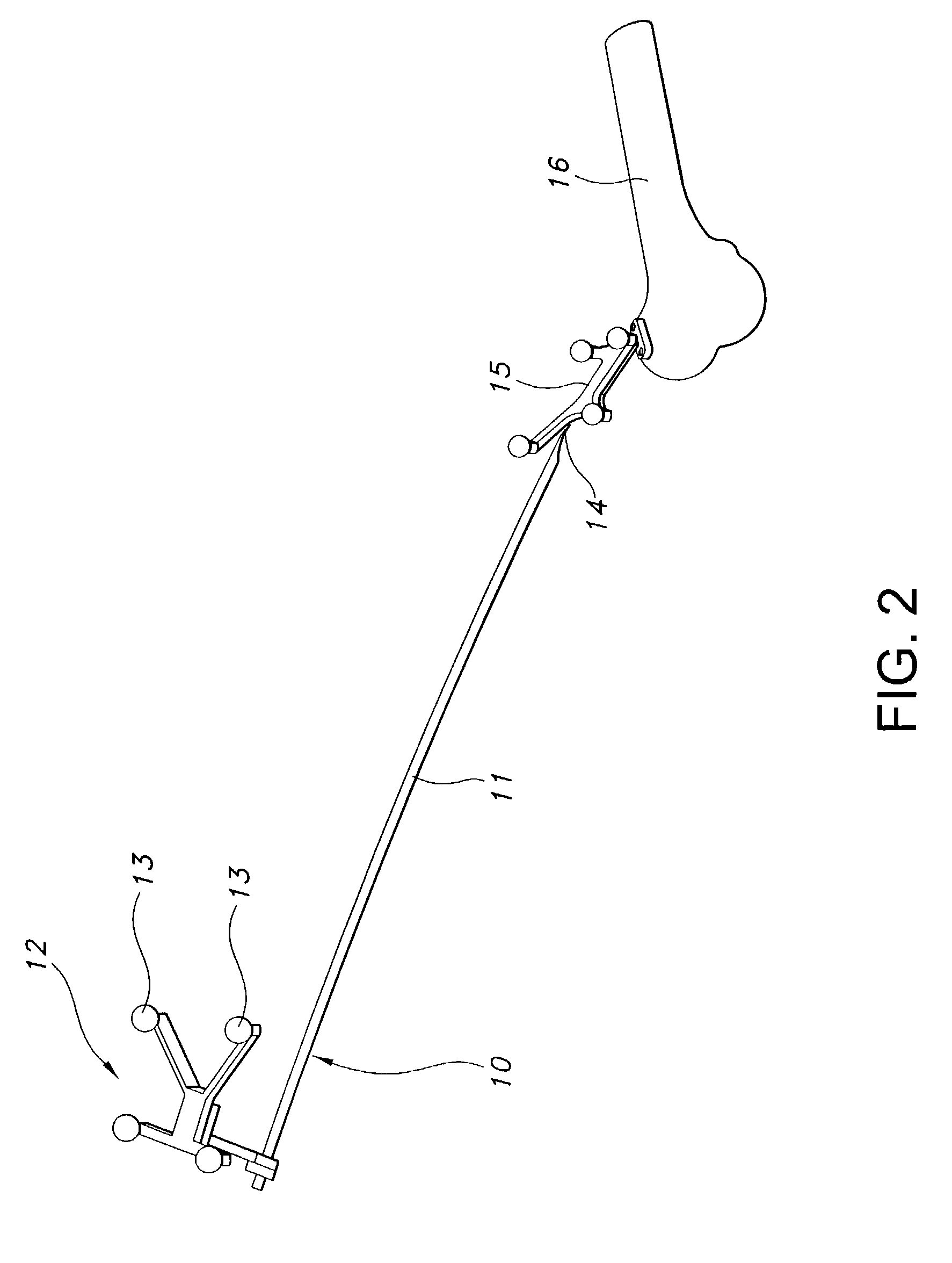
Patents
Literature
315 results about "Imaging guidance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
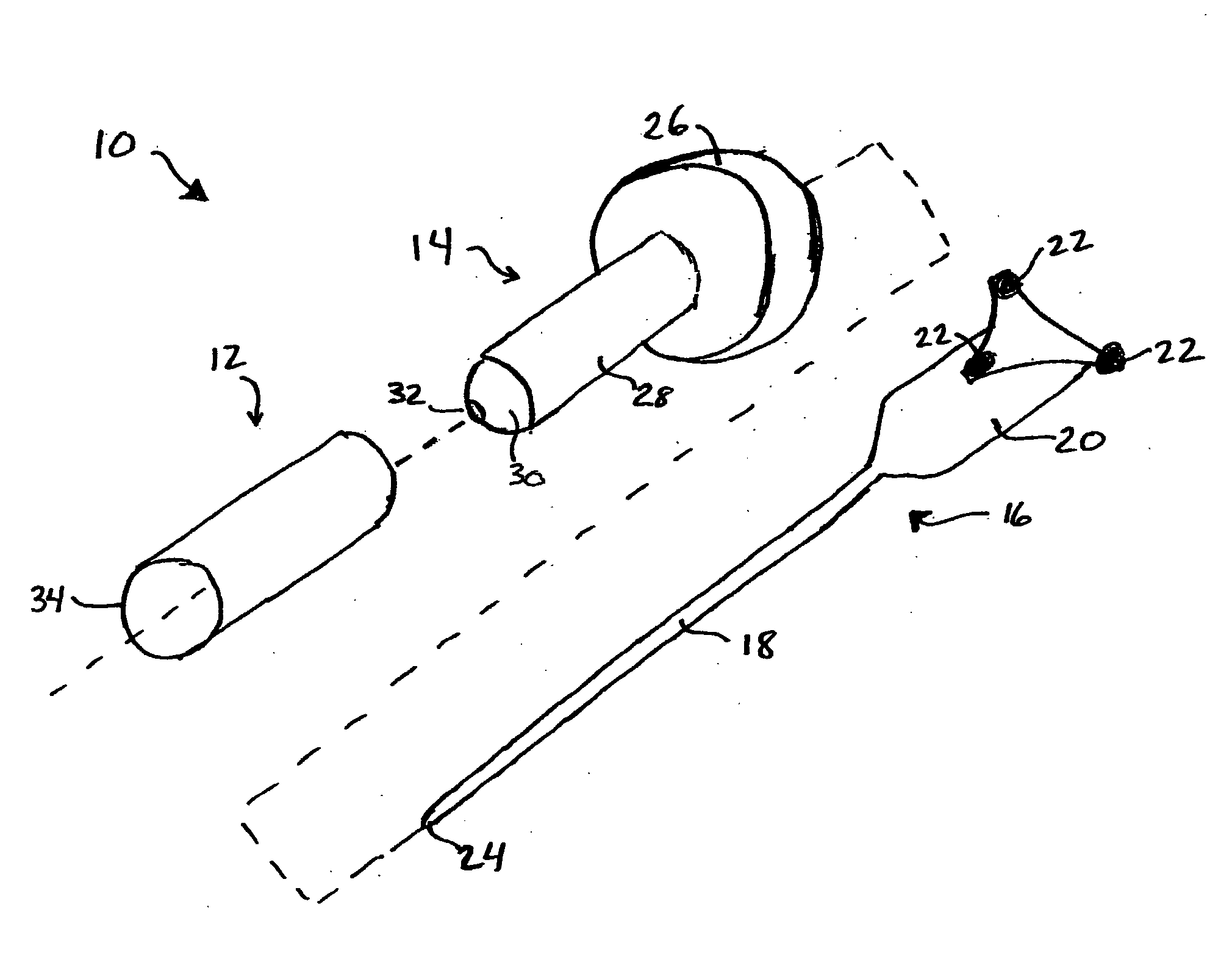
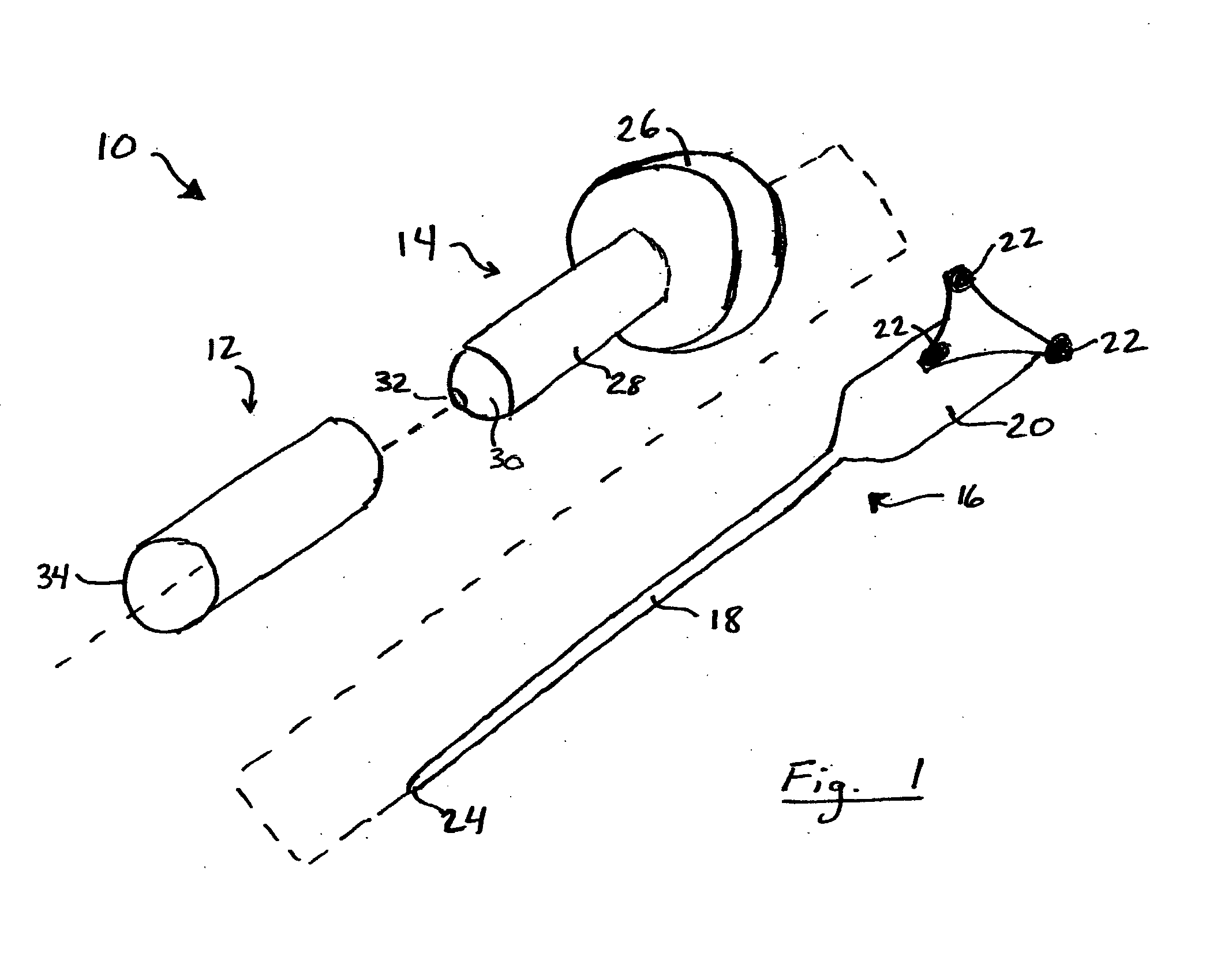
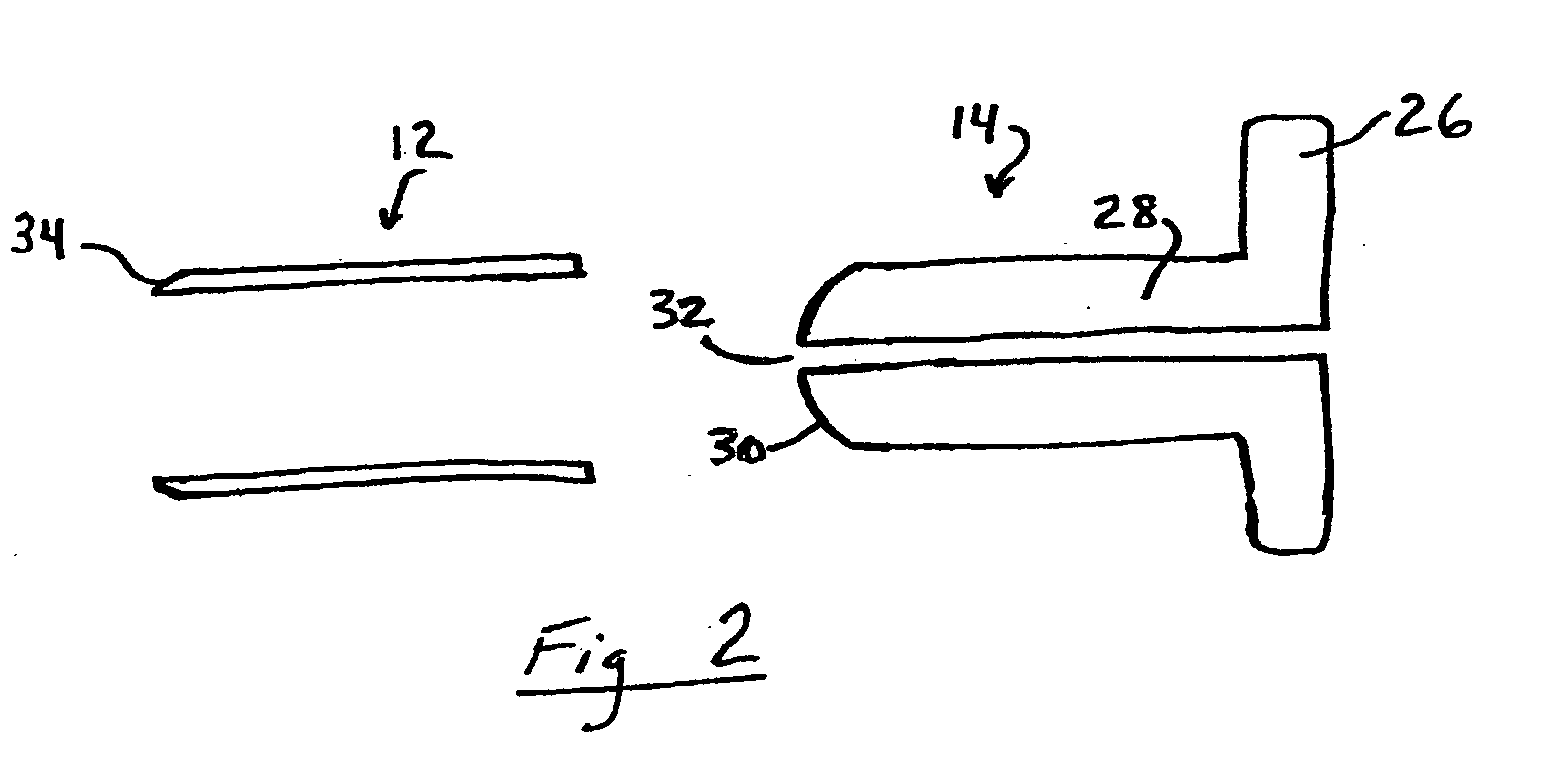
Surgical apparatus and method
InactiveUS6264086B1Minimizing chanceGood removal effectSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleSurgical incision
Owner:MCGUCKIN JR JAMES F
Surgical apparatus and method
InactiveUS7235089B1Reduce morbidityReduce mortalitySuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleSurgical incision
Surgical method and apparatus for resectioning tissue, preferably lumenal tissue, with a remaining portion of an organ being anastomized with staples or other fastening devices, preferably endolumenally. The apparatus may be inserted via a naturally occurring body orifice or a surgical incision and then advanced using either endoscopic or radiological imaging guidance to an area where surgery is to be performed. Under endoscopic or diagnostic imaging guidance the apparatus is positioned so tissue to be resected is manipulated into an inner cavity of the apparatus. The apparatus then cuts the diseased tissue after stapling and retains the diseased tissue within the apparatus. The rent resulting in a border of healthy tissue is anastomosed with surgical staples.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP
Percutaneous cardiac valve repair with adjustable artificial chordae
InactiveUS20070118151A1Reduction of mitral valve regurgitationEasy to operateSuture equipmentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass time
The invention includes a novel method and system to achieve leaflet coaptation in a cardiac valve percutaneously by creation of neochordae to prolapsing valve segments. This technique is especially useful in cases of ruptured chordae, but may be utilized in any segment of prolapsing leaflet. The technique described herein has the additional advantage of being adjustable in the beating heart. This allows tailoring of leaflet coaptation height under various loading conditions using image-guidance, such as echocardiography. This offers an additional distinct advantage over conventional open-surgery placement of artificial chordae. In traditional open surgical valve repair, chord length must be estimated in the arrested heart and may or may not be correct once the patient is weaned from cardiopulmonary bypass. The technique described below also allows for placement of multiple artificial chordae, as dictated by the patient's pathophysiology.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Methods and apparatus for treating disorders of the ear, nose and throat
InactiveUS20060063973A1Improve visualizationEasy accessBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesAnatomical structuresDisease
Methods and apparatus for treating disorders of the ear, nose, throat or paranasal sinuses, including methods and apparatus for dilating ostia, passageways and other anatomical structures, endoscopic methods and apparatus for endoscopic visualization of structures within the ear, nose, throat or paranasal sinuses, navigation devices for use in conjunction with image guidance or navigation system and hand held devices having pistol type grips and other handpieces.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
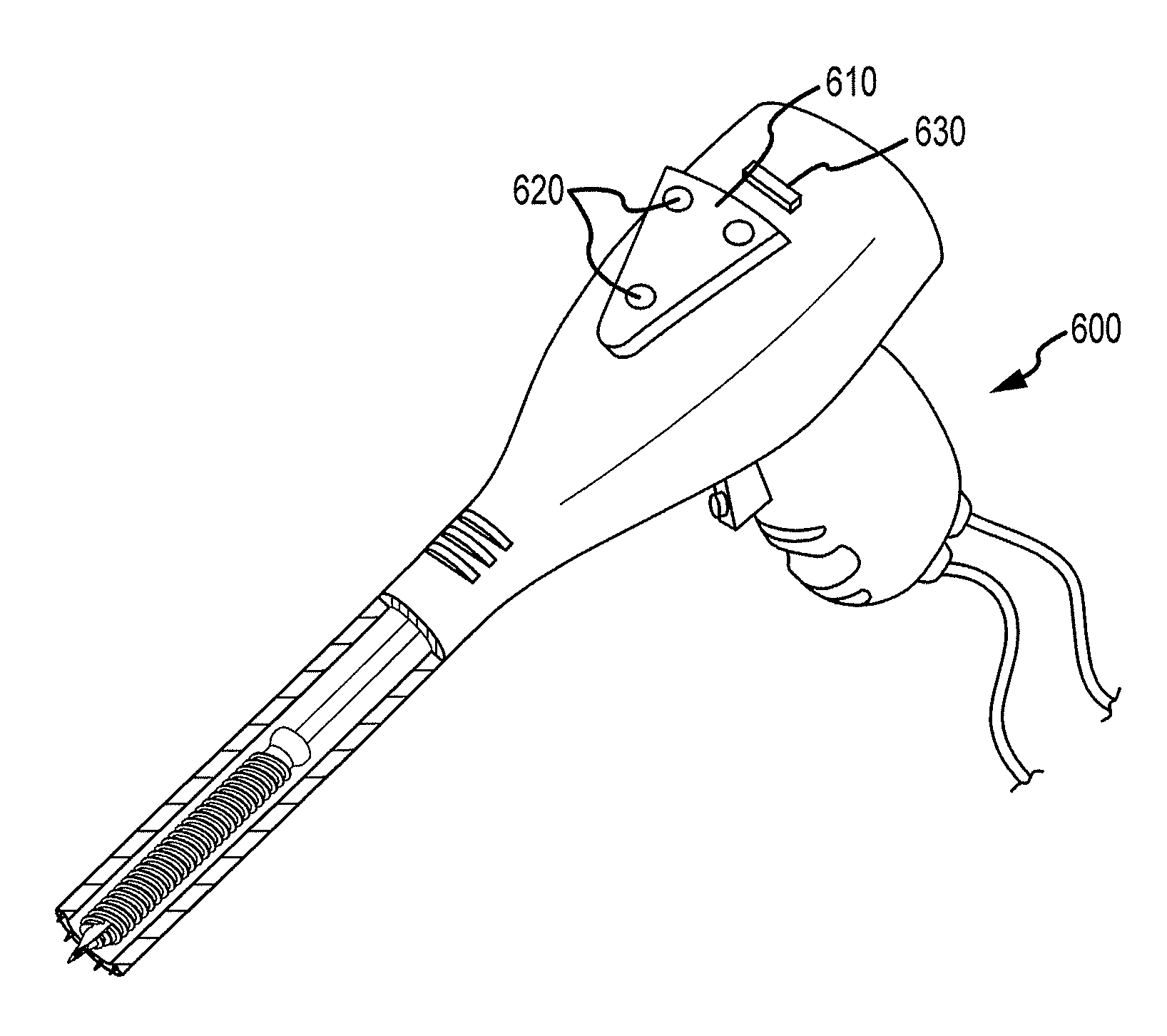
Image-guided minimal-step placement of screw into bone
ActiveUS8366719B2Procedure is time-consumeImprove accuracyInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsScrew placementMonitoring system
The present disclosure describes a device and methods for safely and accurately placing screws into bones with a powered driving device. By employing multiple layers of fail-safe features and image-guidance systems, the powered driving device provides safe, accurate, and efficient screw placement. That is, the powered driving device may continuously monitor a screw advancement and placement and may automatically shutdown when improper placement is detected. Monitoring placement may be conducted by a microcurrent-monitoring system, by an image-guidance system, or by any other appropriate sensory system. Additionally, upon detecting that screw insertion is complete, the powered driving device may be automatically shutdown. As screw placement is continuously simulated by image-guidance in real time, multiple redundant verification steps are eliminated, providing highly accurate screw placement while decreasing clinician error, device contamination, and surgical time, the decreased surgical time associated with decreased patient-recovery time and associated medical costs.
Owner:INTEGRATED SPINAL CONCEPTS
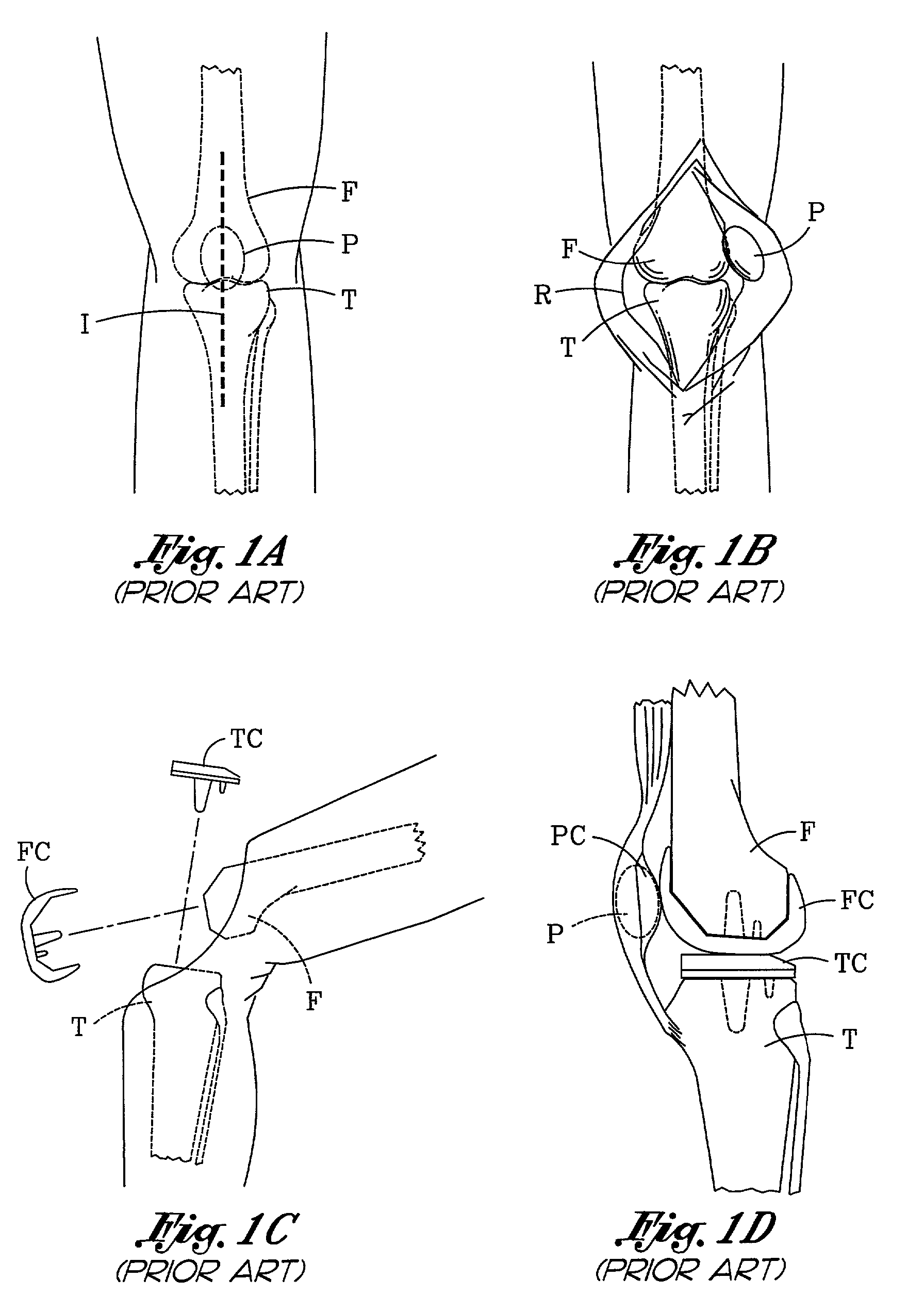
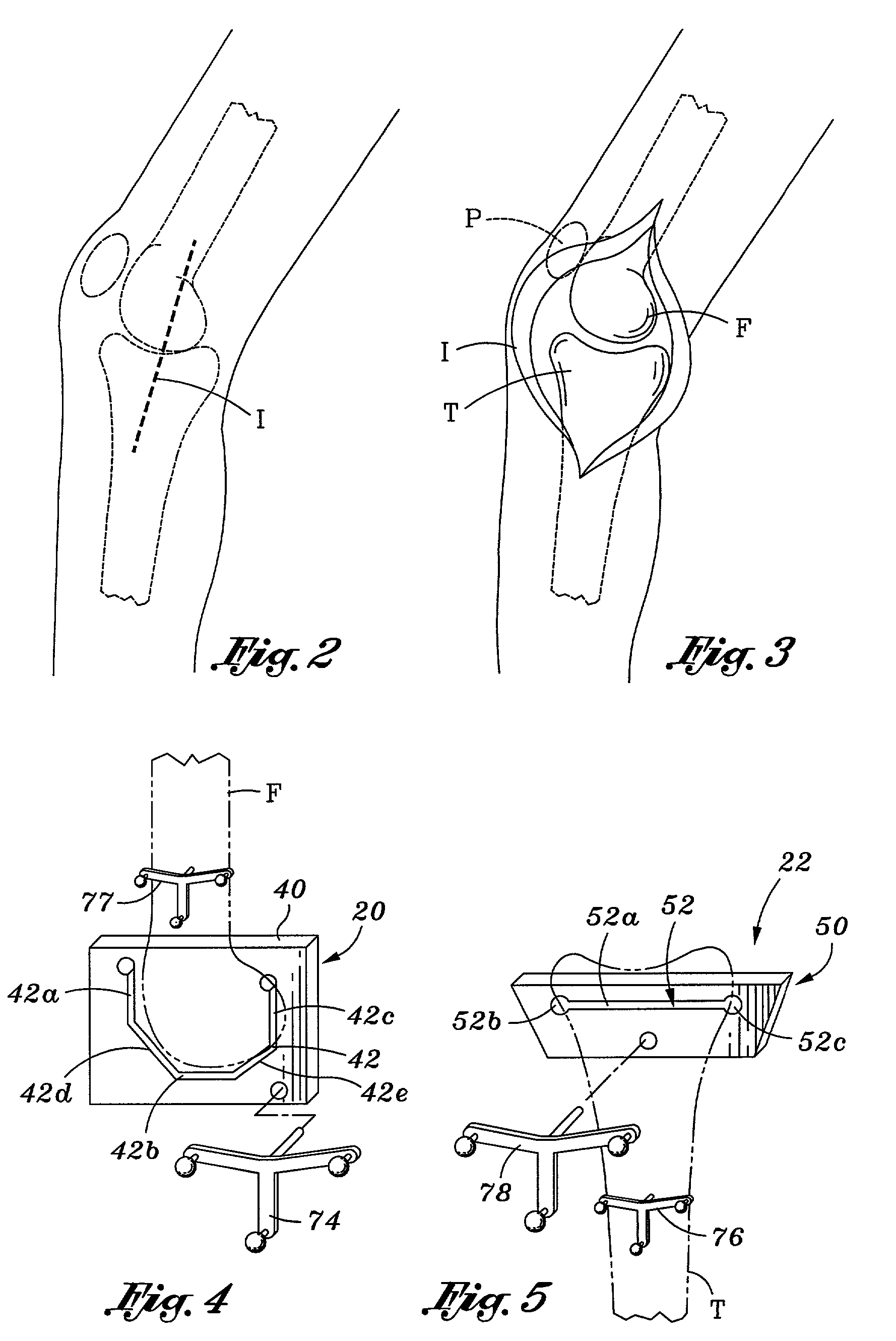
Method and apparatus for minimally invasive knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS7048741B2Minimized overall profileLength minimizationDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsKnee replacementImage guidance
The invention is a method for performing a minimally invasive knee arthroplasty and components for this procedure. The method involves creating an incision along the medial or lateral aspect of a patient's knee, exposing the knee joint, resecting the distal end of the femur, the proximal end of the tibia and the posterior patella through the medial or lateral incision, and connecting a femoral, tibial and patellar knee replacement component through the incision. Components include specialized femoral, tibial and patellar cutting guides for use in resecting the femur, tibia and patella through the medial or lateral incision. In one embodiment, the method is performed with the aid of an image guidance system. In another embodiment, the method is performed with instruments which align the components, such as the cutting guides, without the use of an image guidance system.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
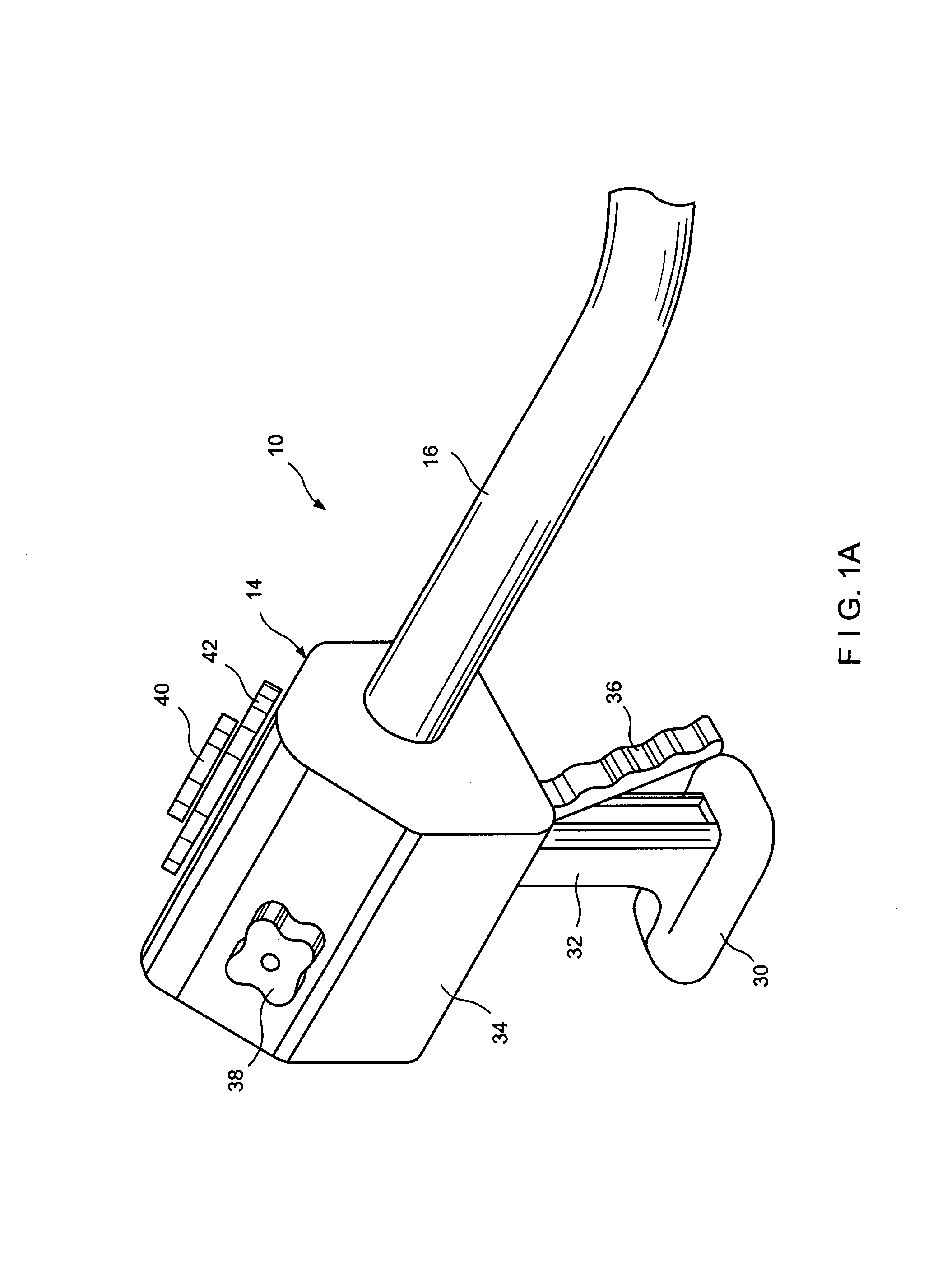
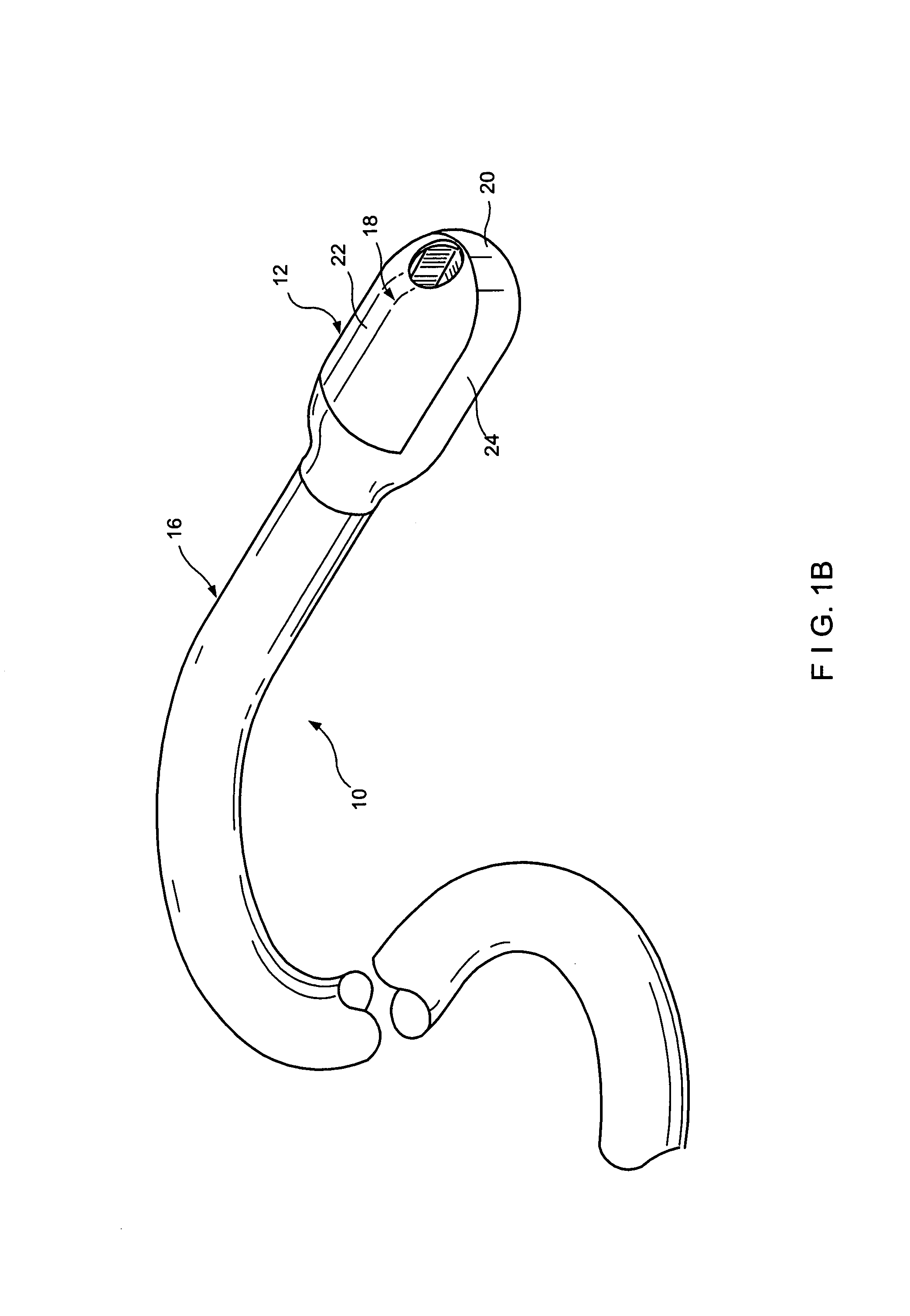
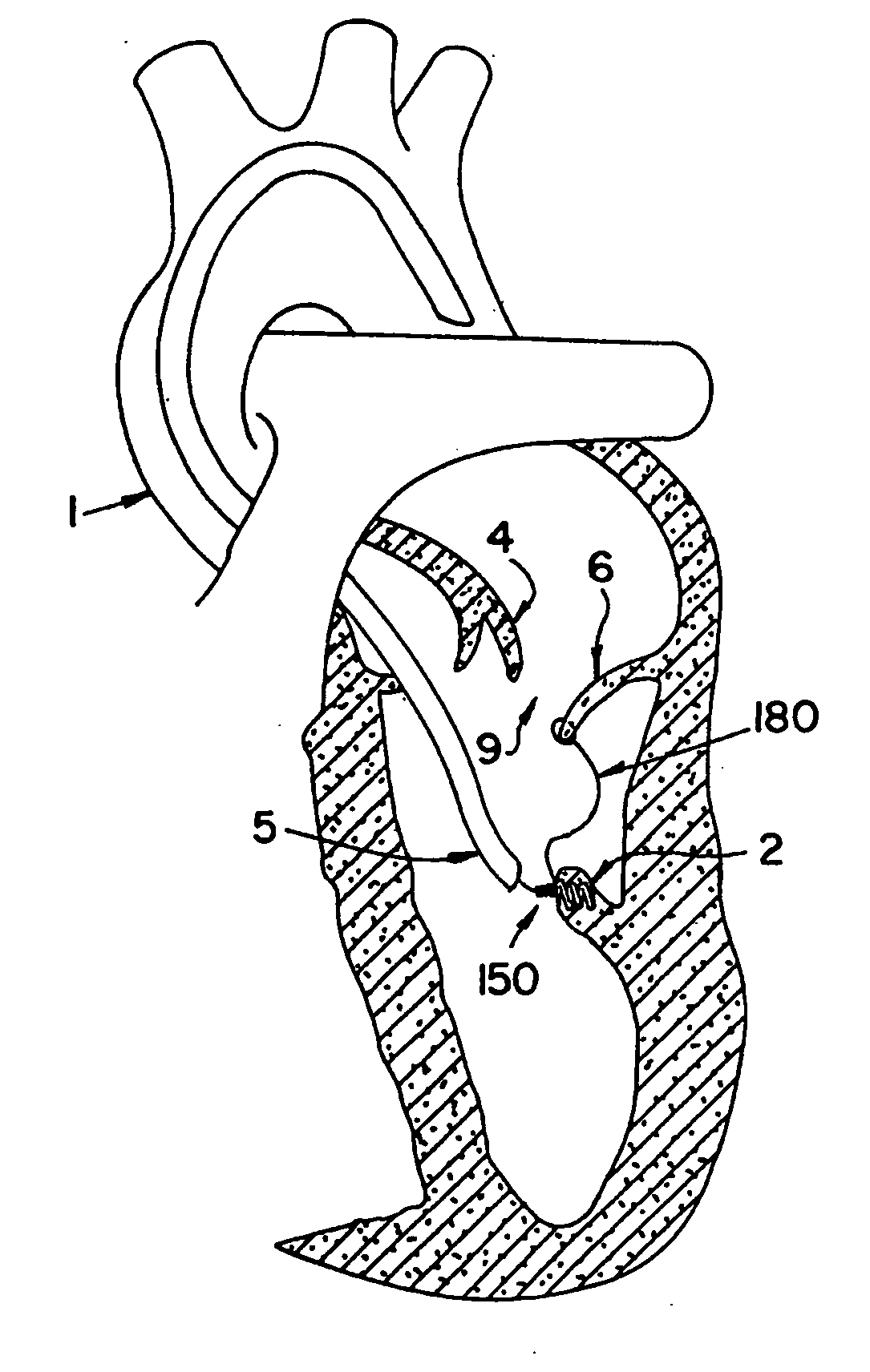
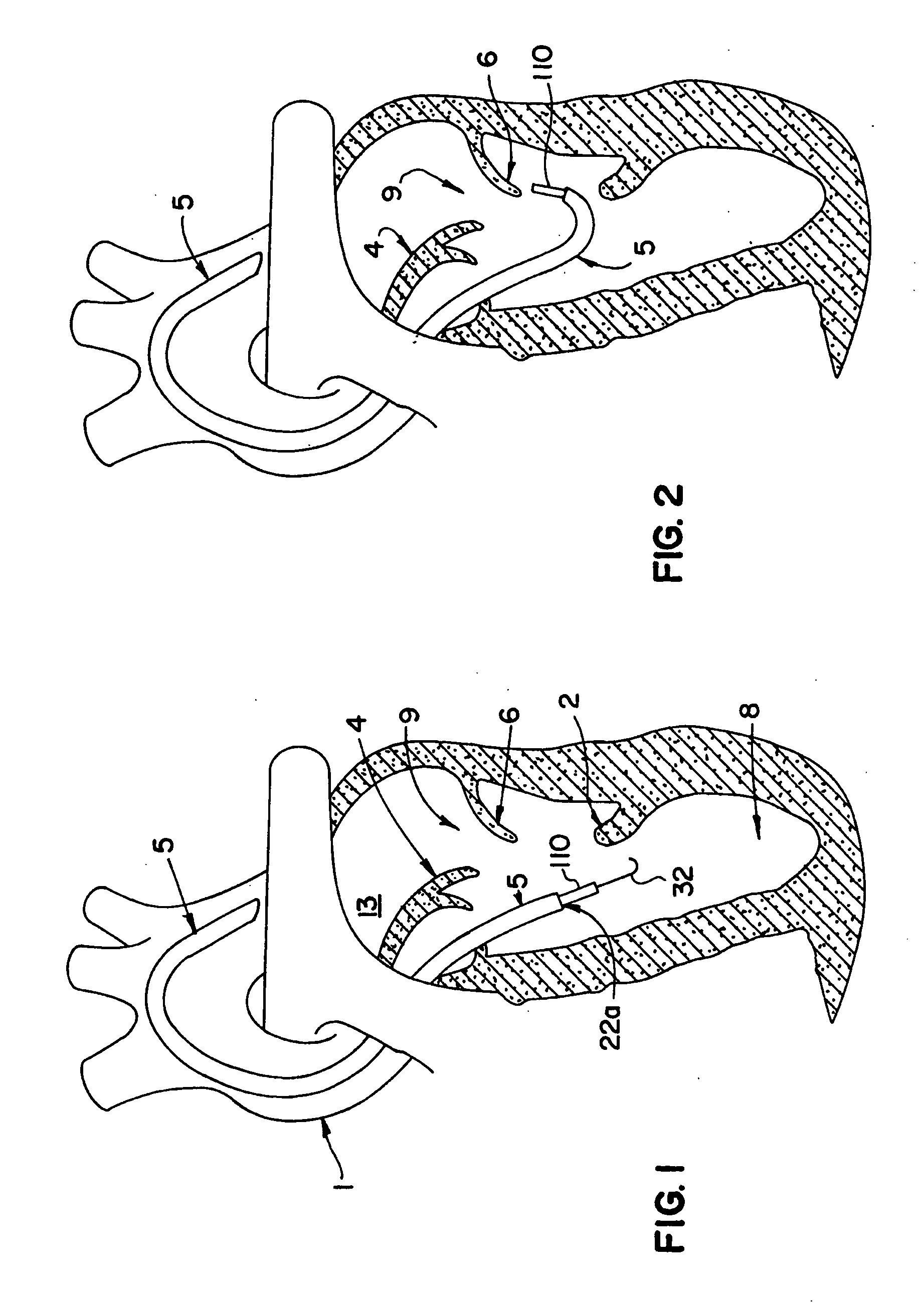
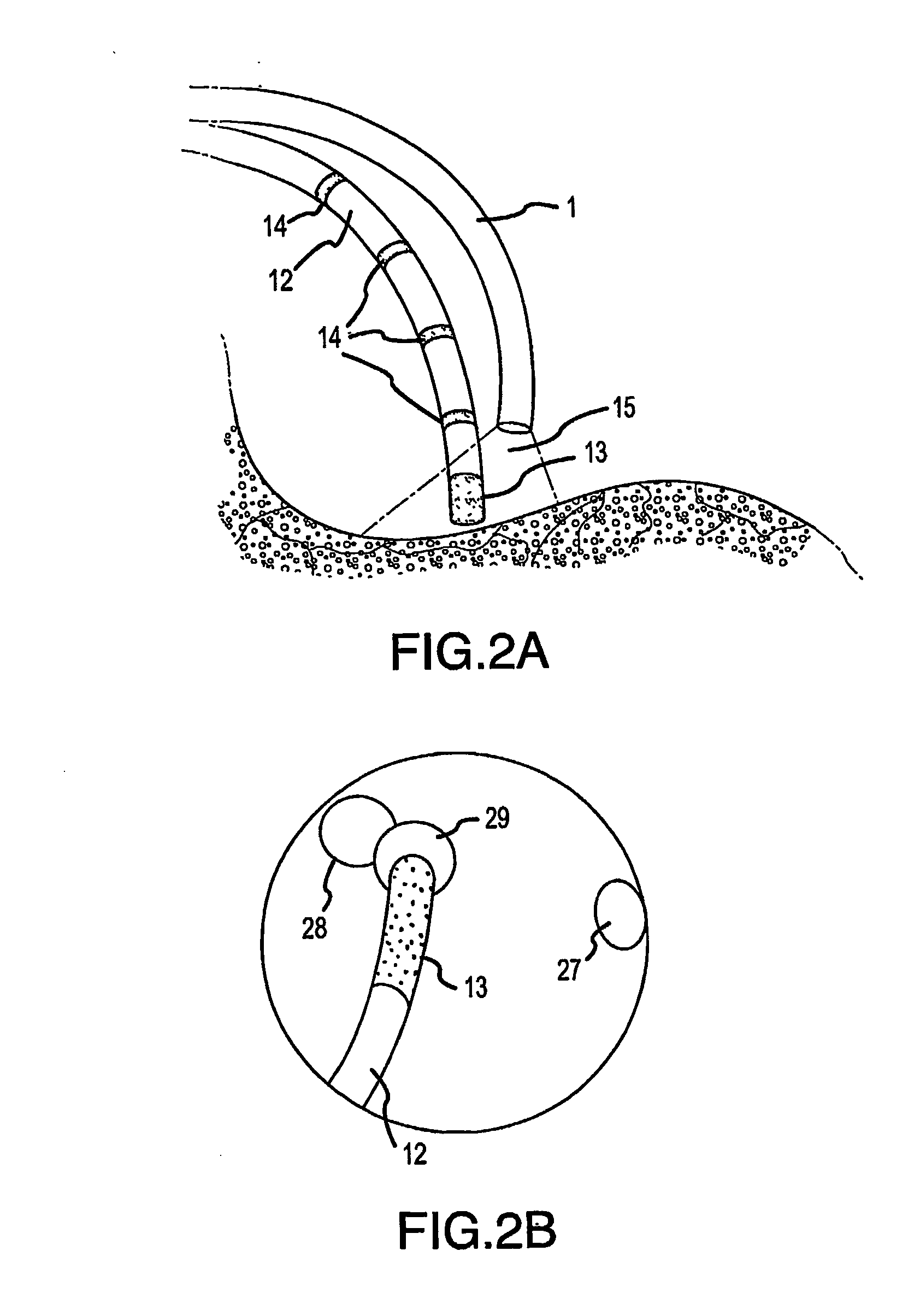
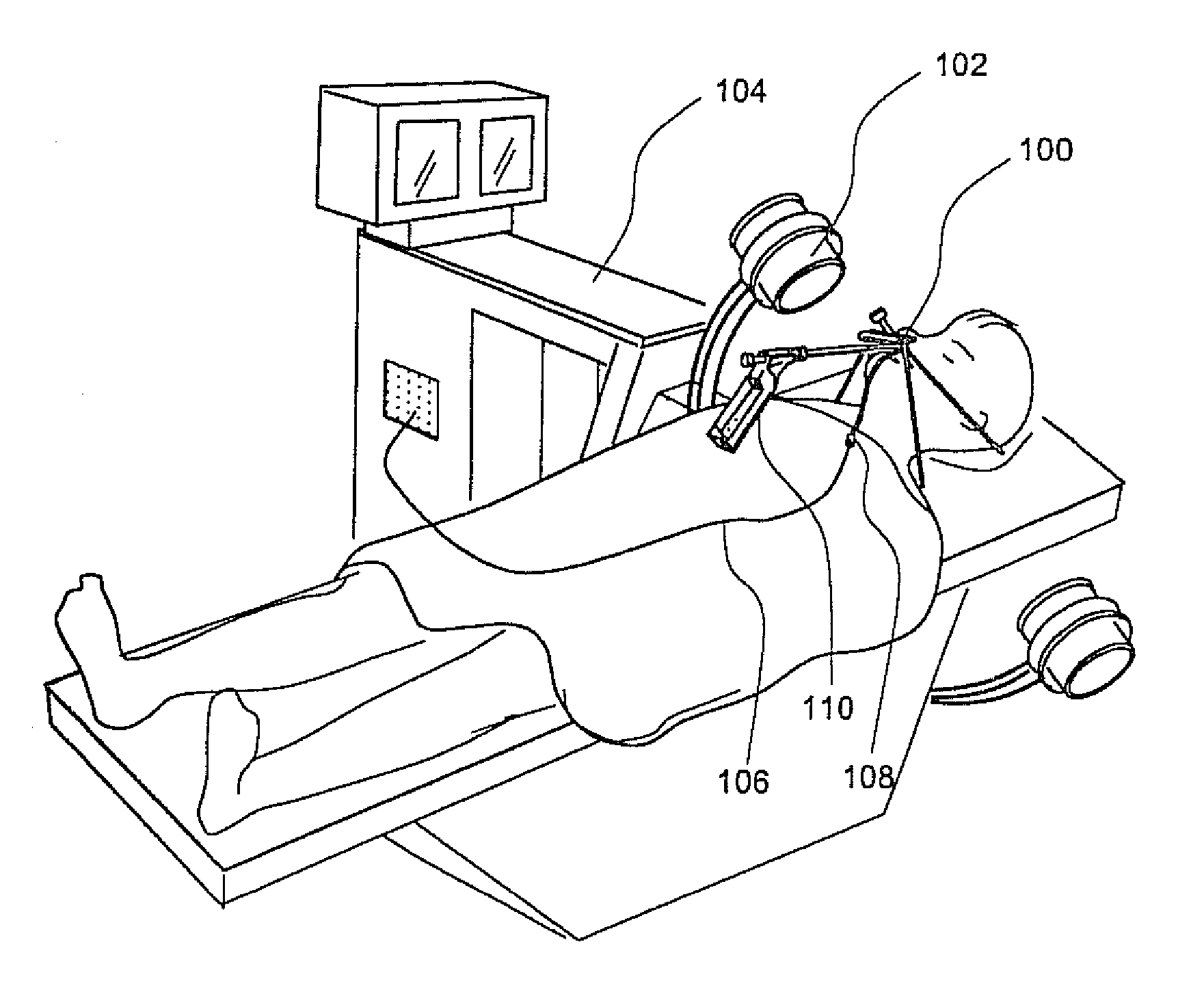
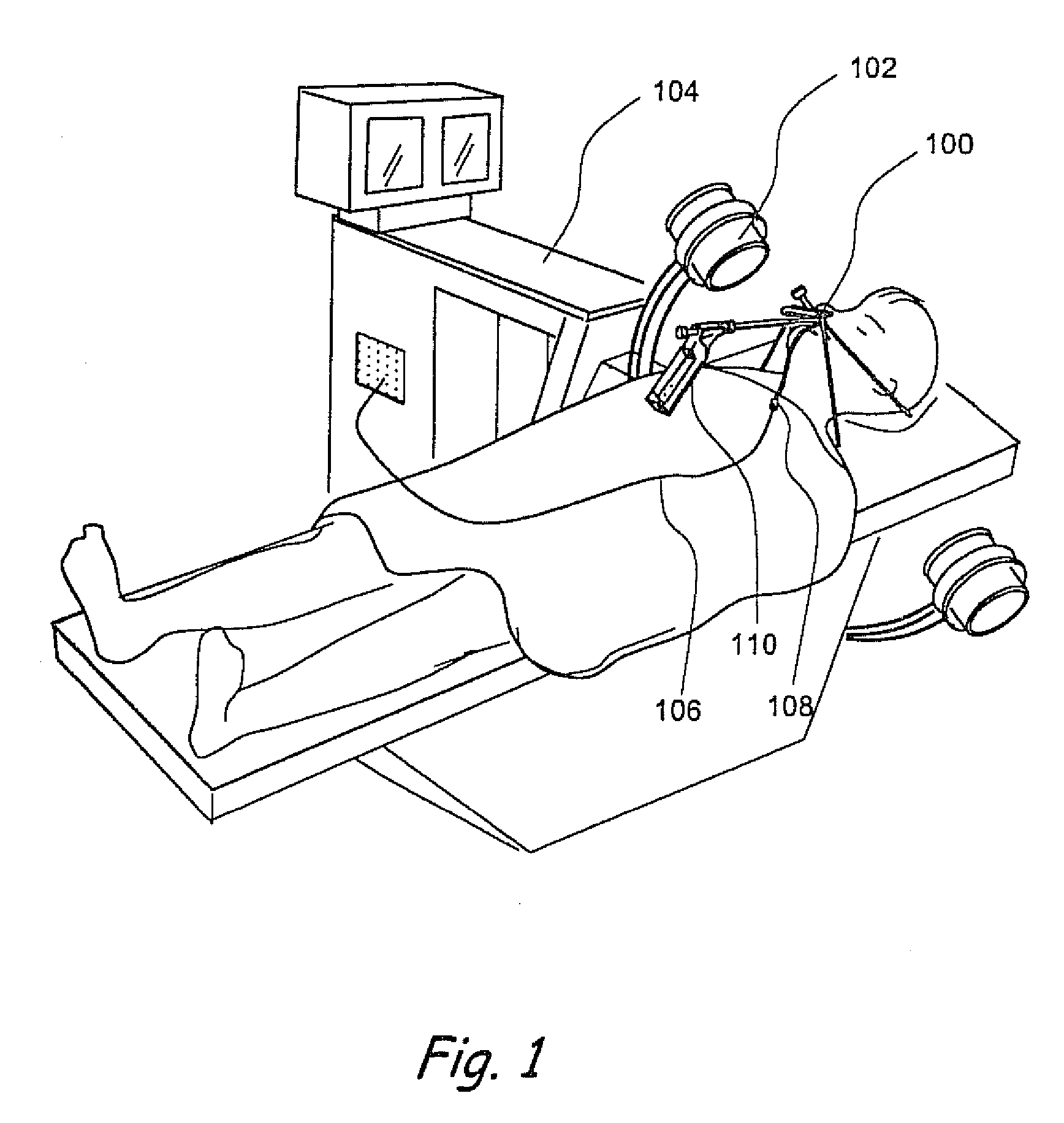
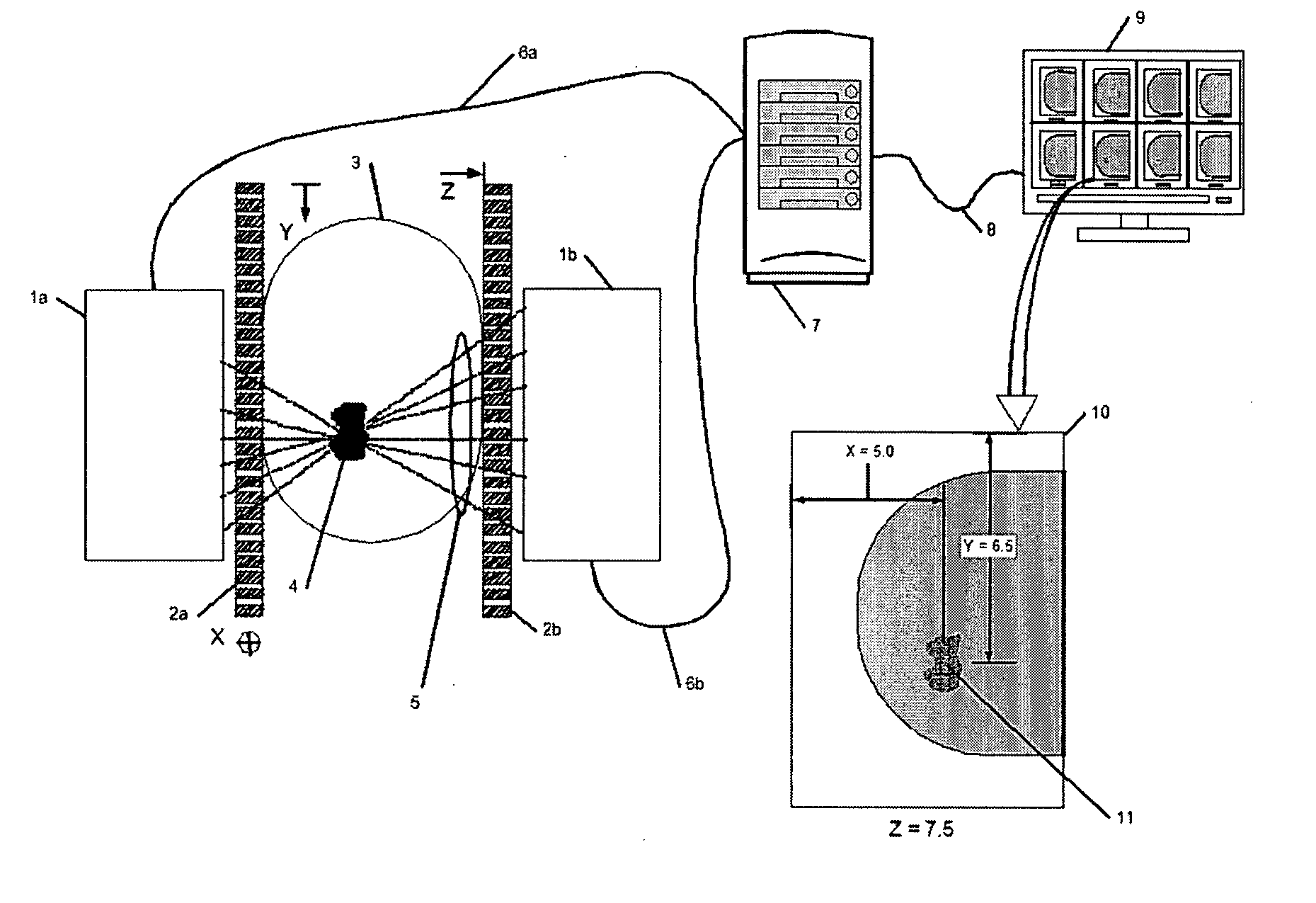
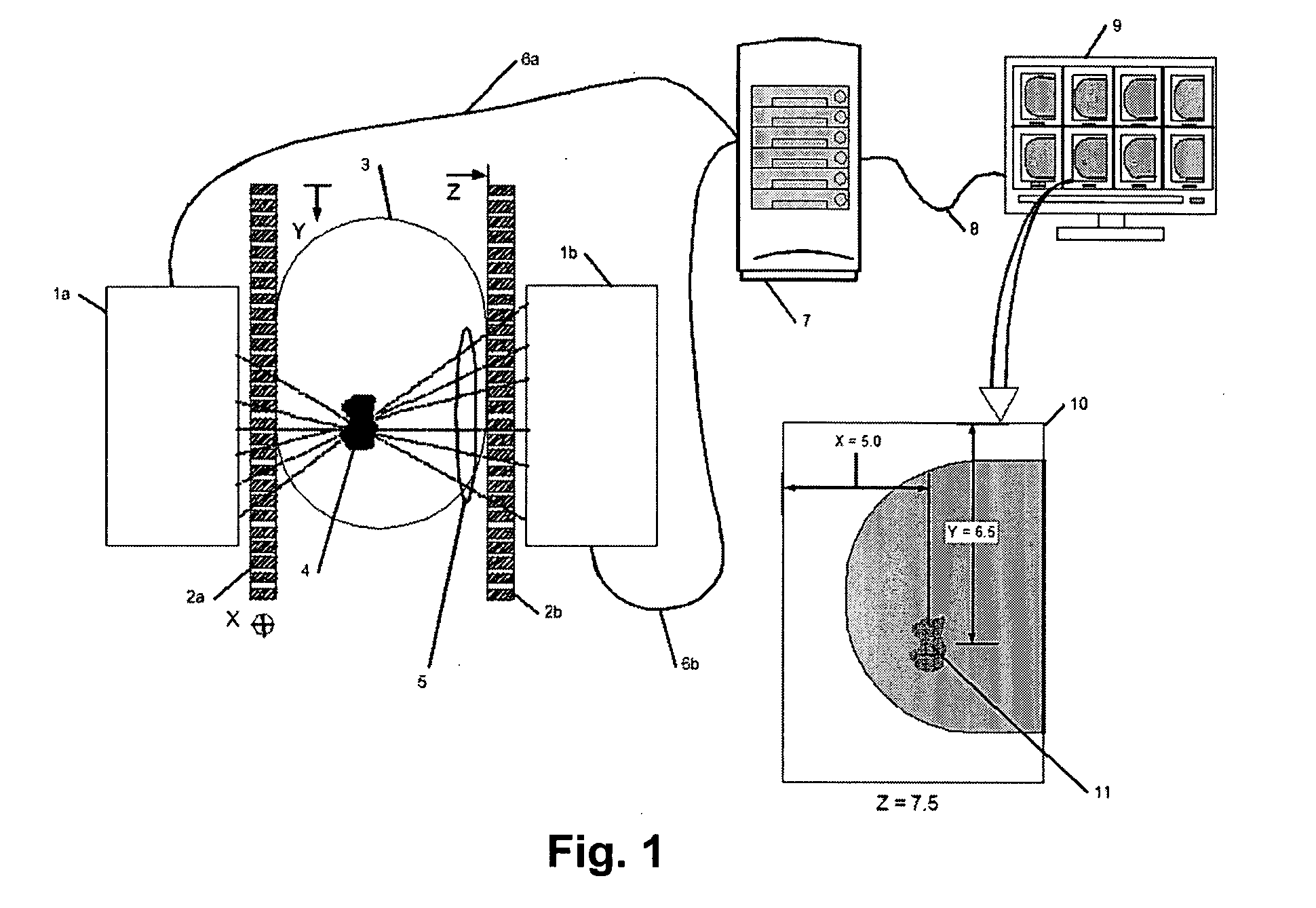
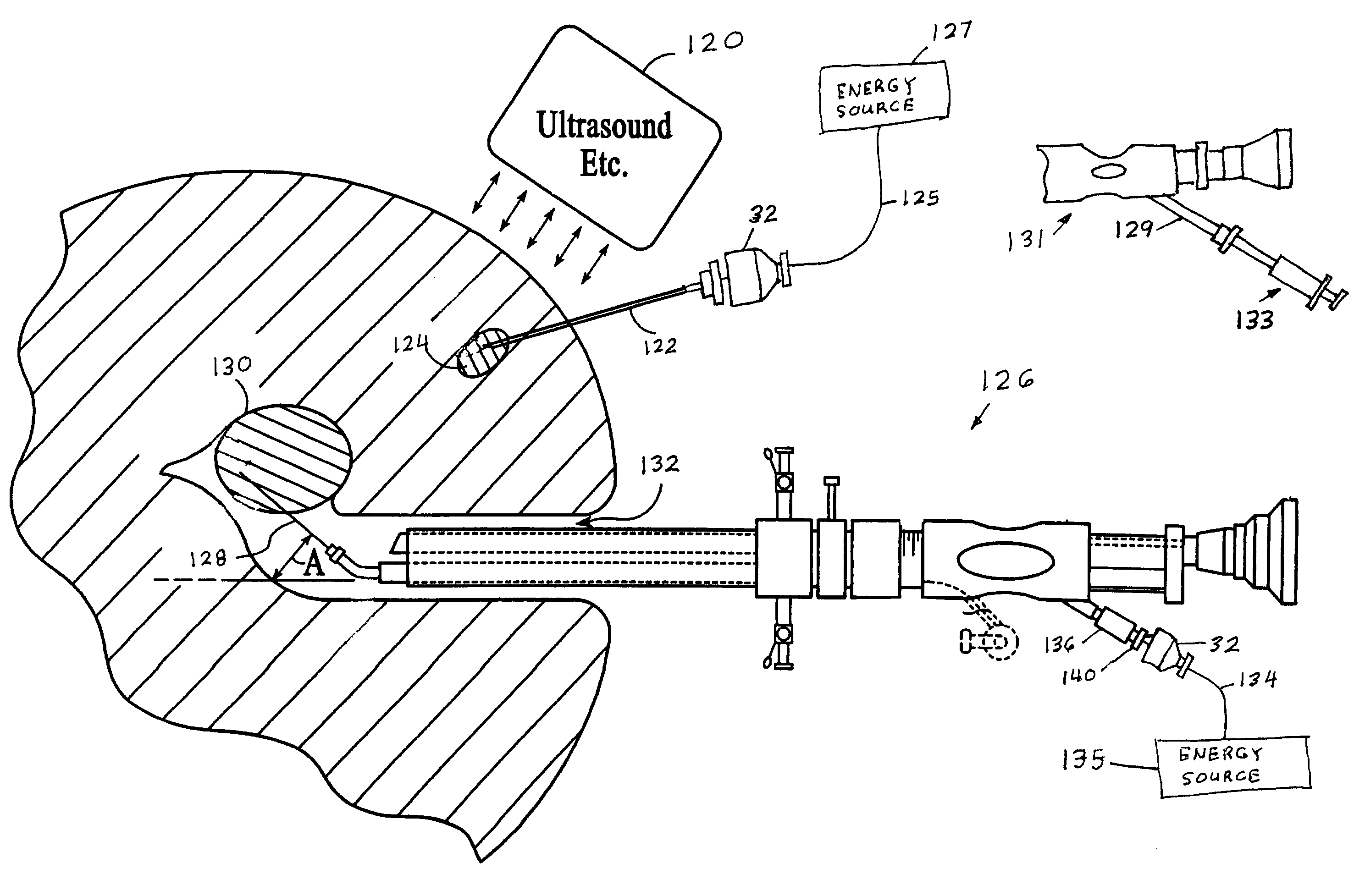
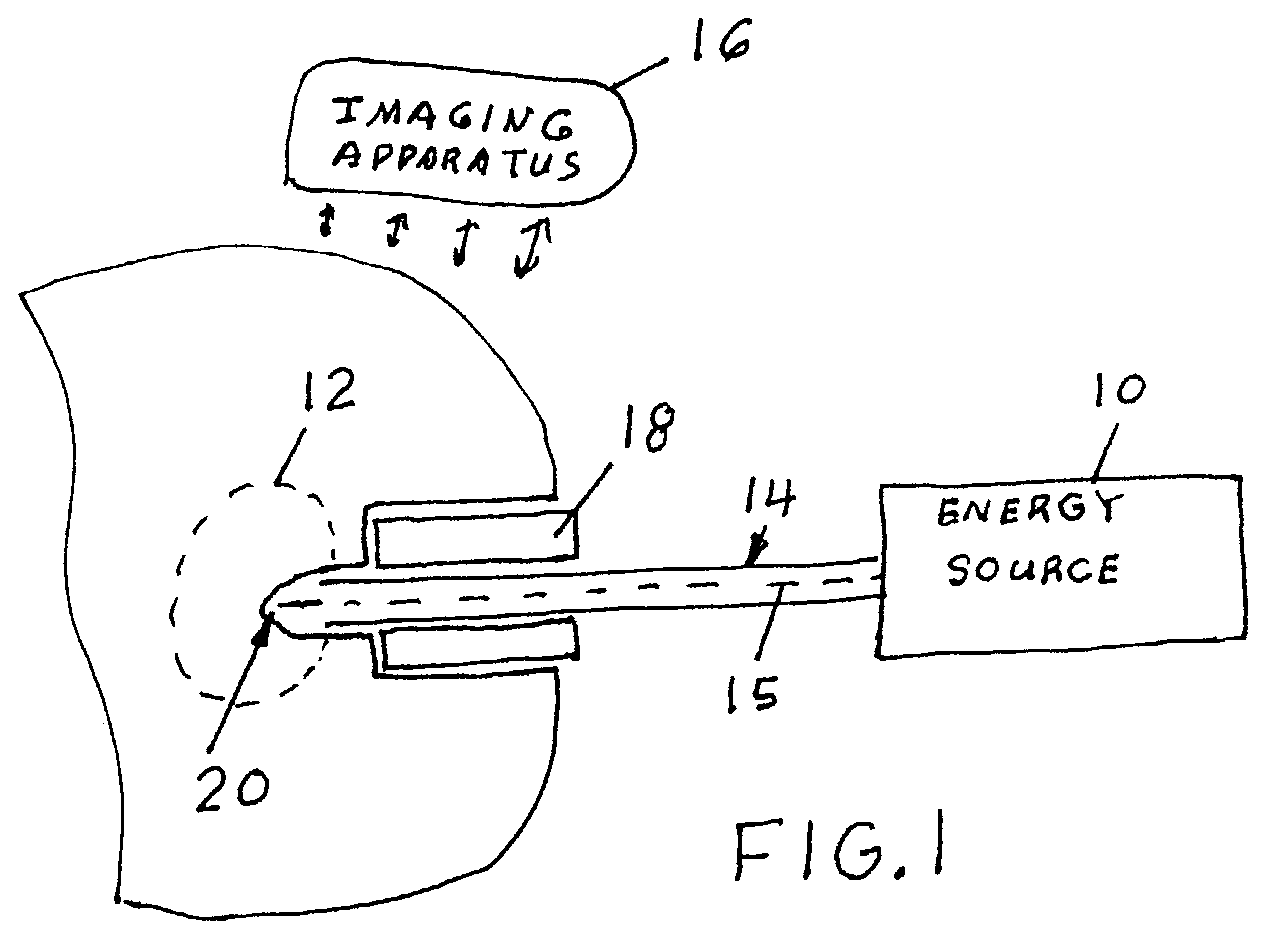
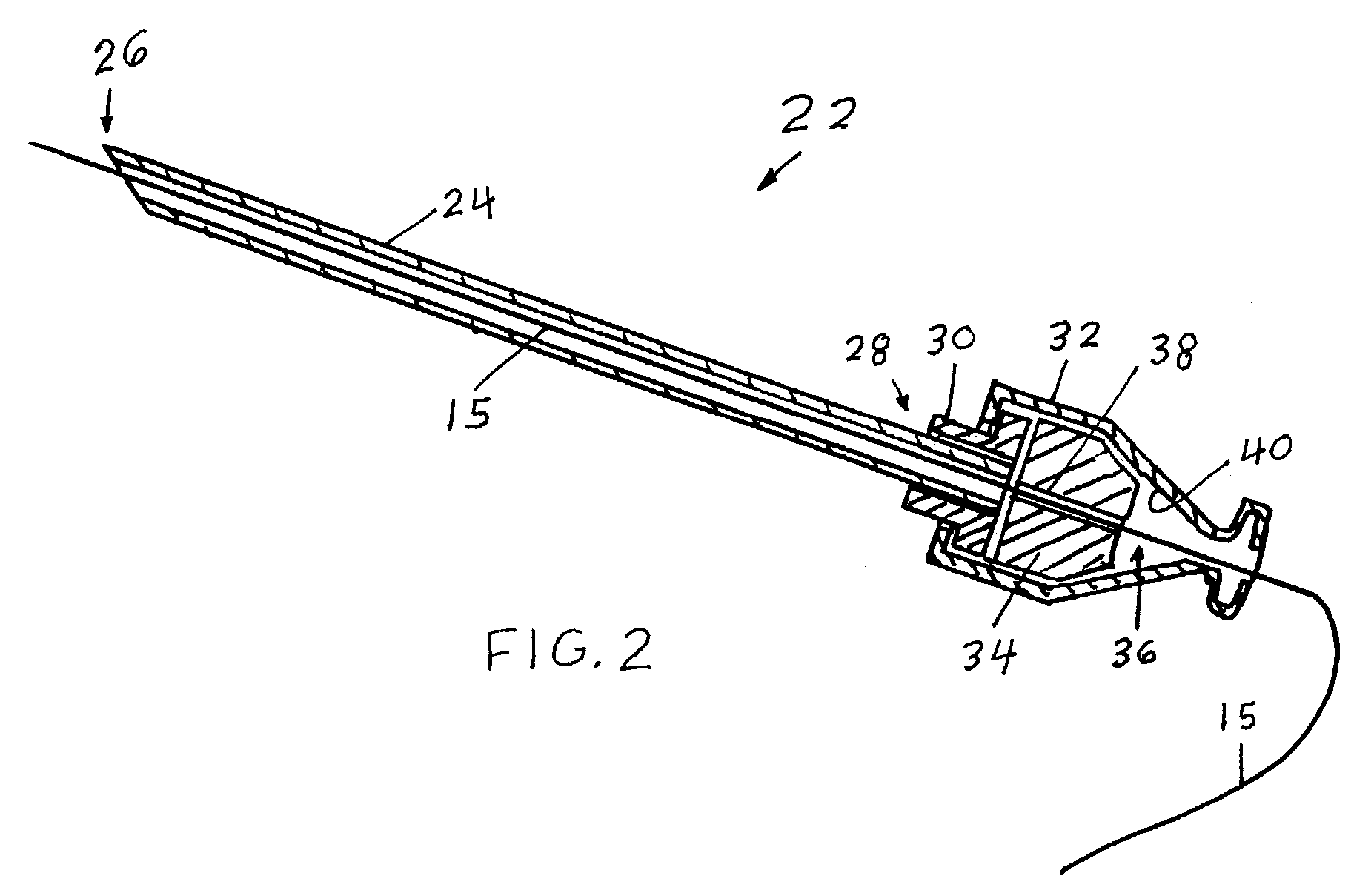
Direct, real-time imaging guidance of cardiac catheterization
Devices (1) and methods for accomplishing tasks within a body using infrared imaging are disclosed which, in connection with other known components, are useful in ablation, stitching and other operations, identification of sizes and composition of objects, and the creation of maps by taking multiple images at different positions or times.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Methods and Apparatus for Treating Disorders of the Ear Nose and Throat
ActiveUS20080097154A1Facilitate precise handling positioningUnwanted movementBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesDiseaseAnatomical structures
Methods and apparatus for treating disorders of the ear, nose, throat or paranasal sinuses, including methods and apparatus for dilating ostia, passageways and other anatomical structures, endoscopic methods and apparatus for endoscopic visualization of structures within the ear, nose, throat or paranasal sinuses, navigation devices for use in conjunction with image guidance or navigation system and hand held devices having pistol type grips and other handpieces.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Methods and Apparatus for Treating Disorders of the Ear Nose and Throat
ActiveUS20080103521A1Facilitate precise handling positioningUnwanted movementBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesDiseaseAnatomical structures
Methods and apparatus for treating disorders of the ear, nose, throat or paranasal sinuses, including methods and apparatus for dilating ostia, passageways and other anatomical structures, endoscopic methods and apparatus for endoscopic visualization of structures within the ear, nose, throat or paranasal sinuses, navigation devices for use in conjunction with image guidance or navigation system and hand held devices having pistol type grips and other handpieces.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Methods and apparatuses for image guided medical procedures
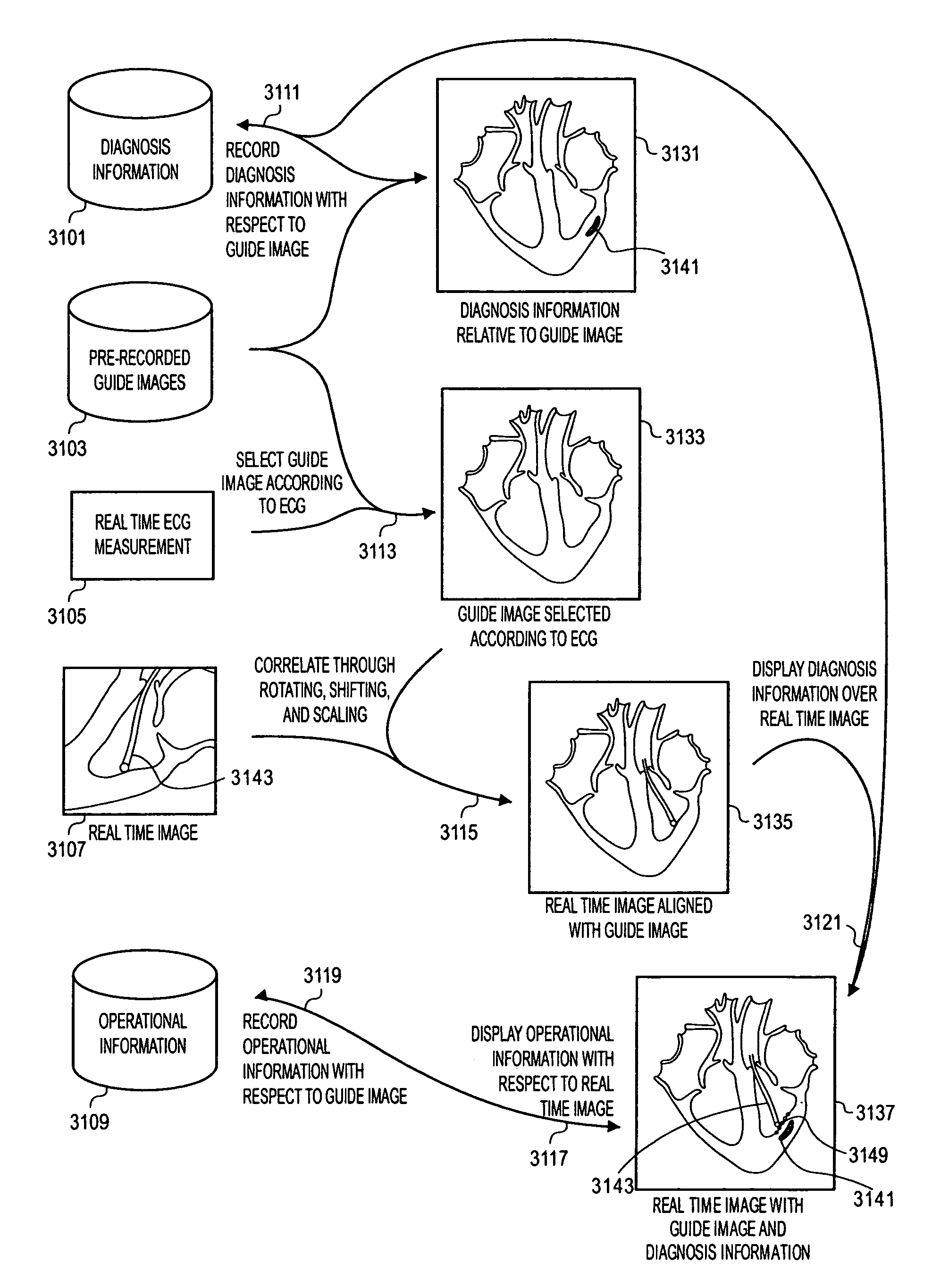
ActiveUS8303505B2Uncertainty errorLocation uncertaintyMedical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTime informationImaging data
Methods and apparatuses for the image guidance and documentation of medical procedures. One embodiment includes combining small field of view images into a recorded image of with a large field of view and aligning the small field of view real time image with the recorded image through correlation of imaging data. A location and orientation determination system may be used to track the imaging system and provide a starting set of image alignment parameters and / or provide change updates to a set of image alignment parameters, which is then further improved through correlating imaging data. The recorded image may be selected according to real time measurement of a cardiac parameter during an image guided cardiac procedure. Image manipulations planned based on the recorded image can be stored and applied to the real time information. The position of the medical device may be determined and recorded through manipulating a cursor in a 3-D image space shown in two non-parallel views.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
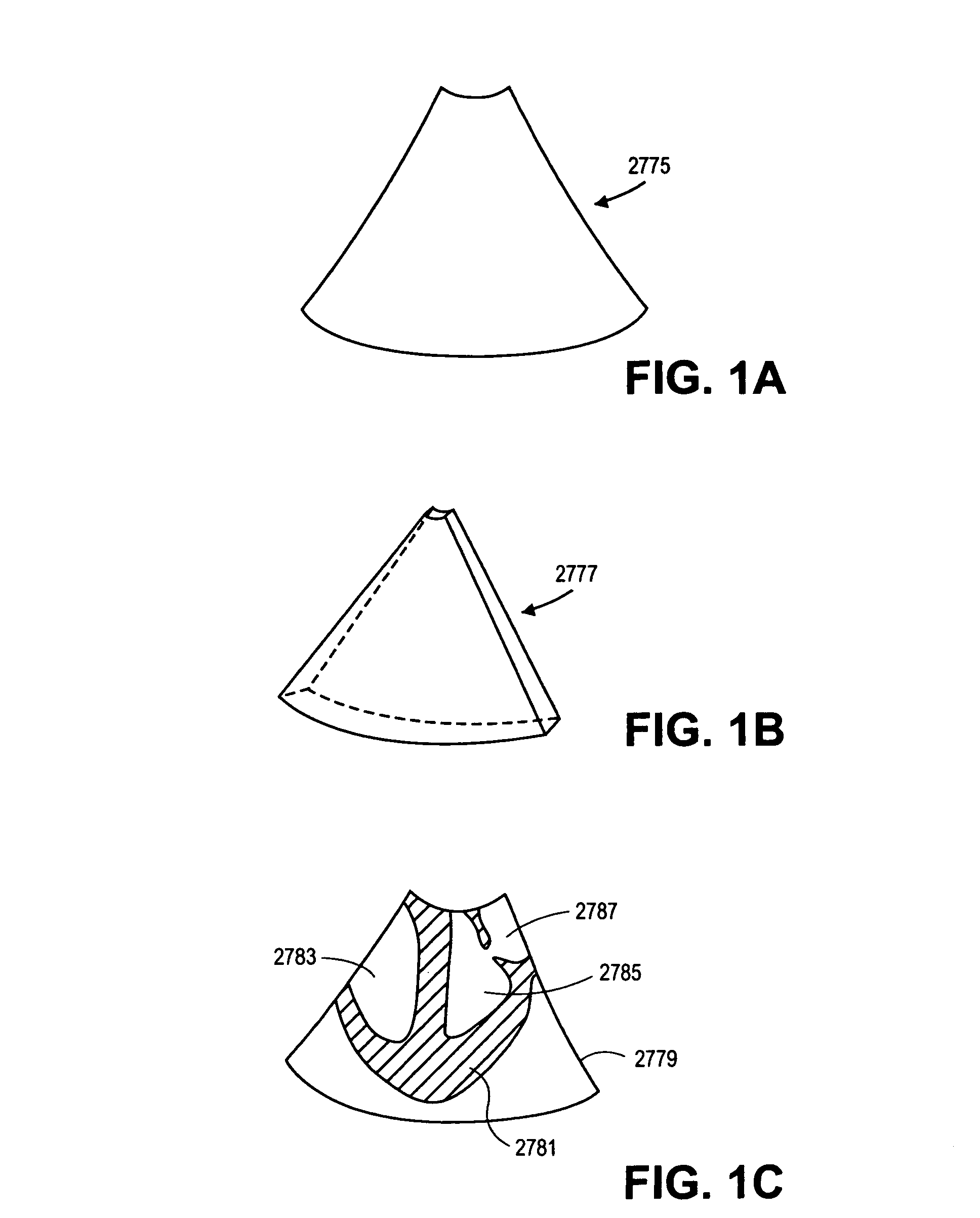
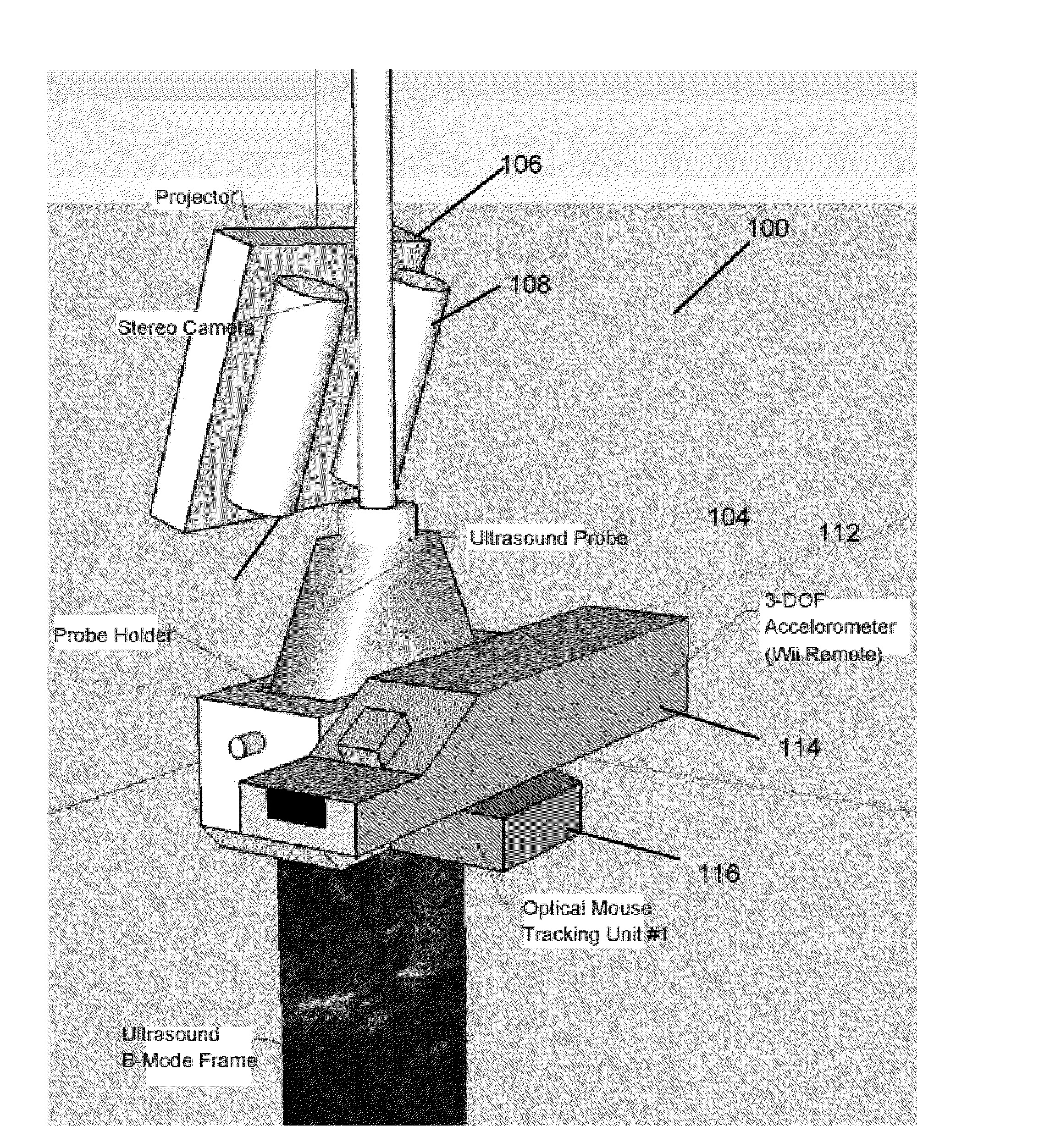
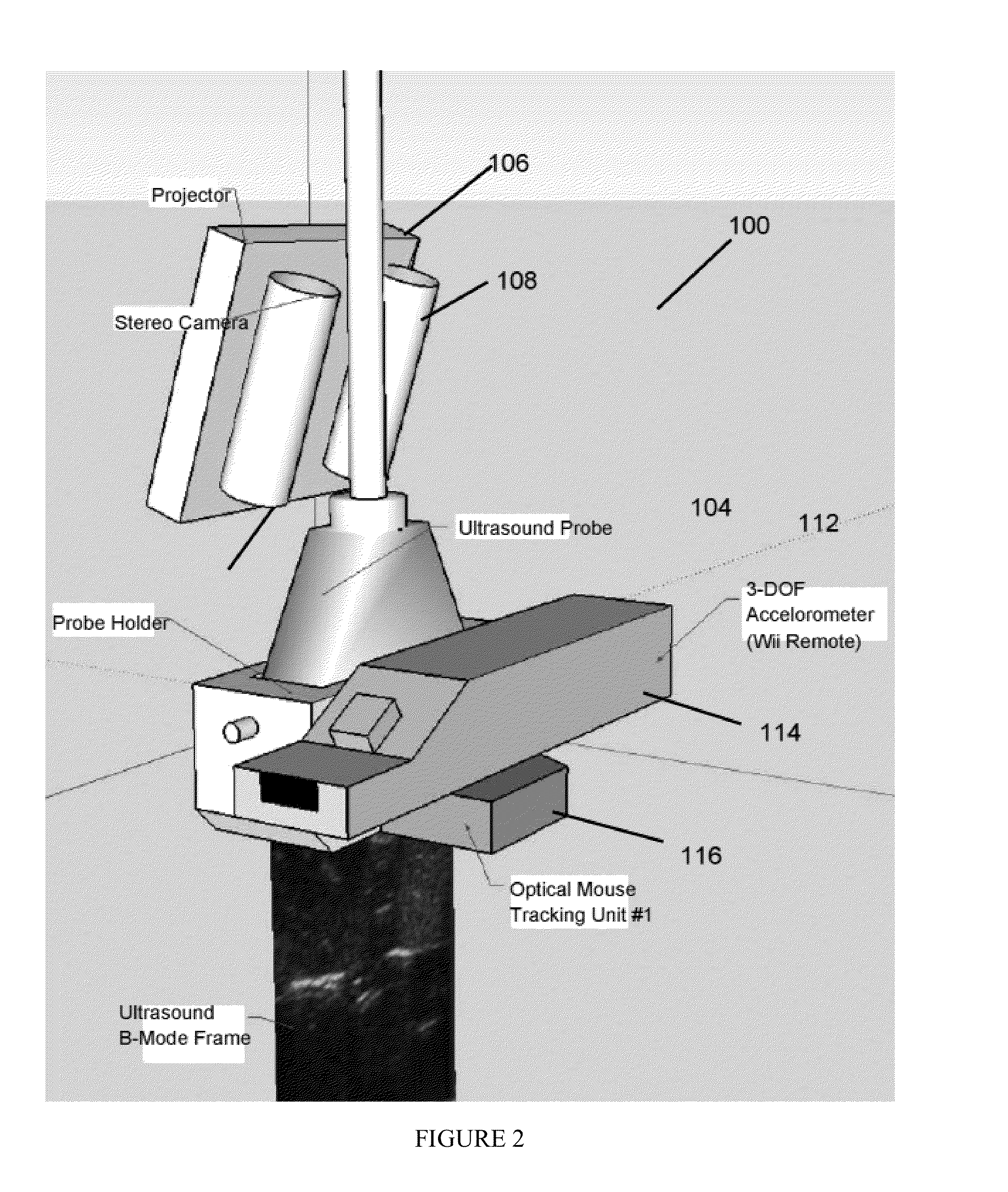
Interventional In-Situ Image-Guidance by Fusing Ultrasound and Video
InactiveUS20130218024A1Easy alignmentSurgical drapesComputerised tomographsImage guidanceSensor system
An augmentation device for an imaging system has a bracket structured to be attachable to an imaging component, and a projector attached to the bracket. The projector is arranged and configured to project an image onto a surface in conjunction with imaging by the imaging system. A system for image-guided surgery has an imaging system, and a projector configured to project an image or pattern onto a region of interest during imaging by the imaging system. A capsule imaging device has an imaging system, and a local sensor system. The local sensor system provides information to reconstruct positions of the capsule endoscope free from external monitoring equipment.
Owner:CLEAR GUIDE MEDICAL
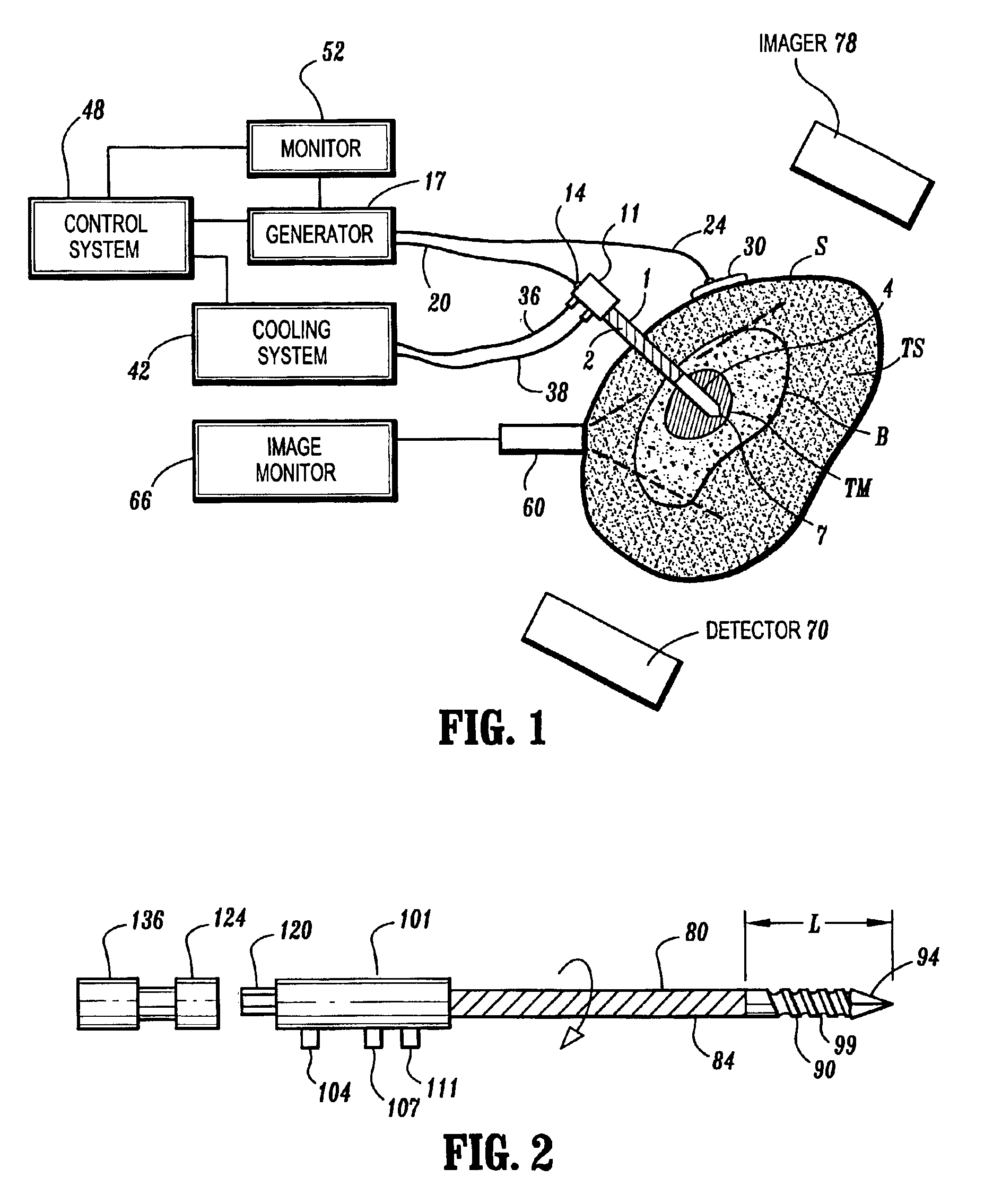
Ablation treatment of bone metastases
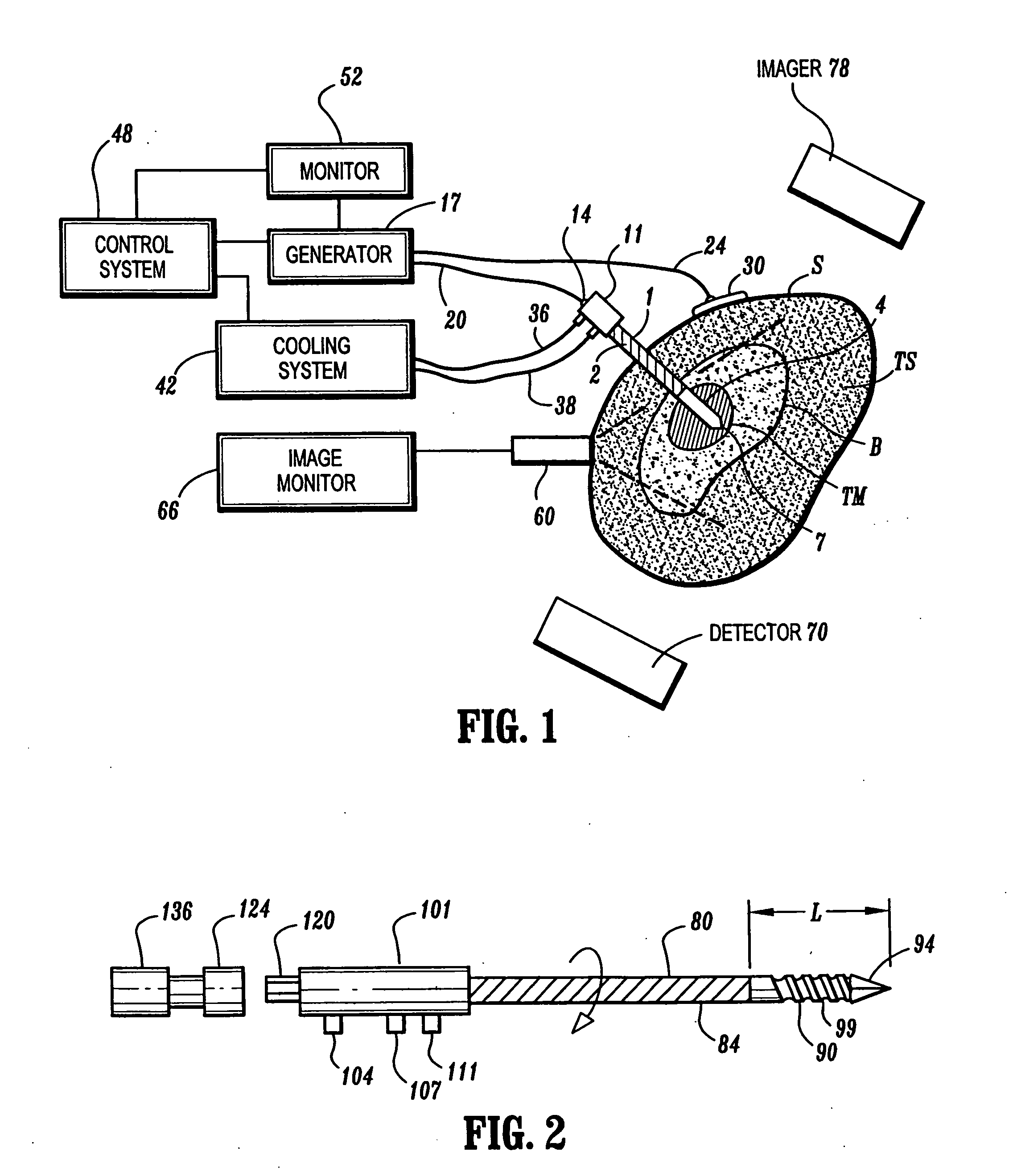
InactiveUS6881214B2Easily toleratedReduce the dependency of the patientDiagnosticsSurgical needlesElectrode placementHigh frequency power
Ablative treatment of metastatic bone tumors and relief of pain associated with metastatic bone tumors is achieved by heat ablation of the bone tumor or tissue near the bone tumor by an ablation probe. In one form the probe is an electrode coupled to a high frequency power supply to provide ablative heating of tissue proximate to an electrode that is placed in or near the bone tumor. Cooling of the electrode by fluid circulation from a cooling apparatus outside the patient's body may be used to enlarge the region of high frequency heating around the electrode. Image guidance of the electrode placement may be monitored by an imaging device. Tracking of the electrode by an image-guided navigator helps in placement of the electrode with respect to the configuration of the bone and bone metastasis. A set of tools accommodates biopsy and various shapes of electrodes according to clinical requirements. Several forms of electrodes, energy delivery and cooling apparatus and methods accommodate the specific objectives.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Automatic registration of images for image guided surgery
InactiveUS20110098553A1Robust recognitionSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringImage guidanceComputer science
Automatic registration of an MR image is carried out in an image guidance system by placing MR visible markers at known positions relative to markers visible in a camera tracking system. The markers are carried on a common fixture which is attached to a head clamp together with a reference marker which is used when the markers are covered or removed. The tracking system includes a camera with a detection array for detecting visible light a processor arranged to analyze the output from the array. Each object to be detected carries a single marker with a pattern of contrasted areas of light and dark intersecting at a specific single feature point thereon with an array around the specific location to allow the processor is able to detect an angle of rotation of the pattern and to distinguish each marker from the other markers.
Owner:IMRIS
Ablation treatment of bone metastases
InactiveUS20050192564A1Easily toleratedReduce the dependency of the patientDiagnosticsSurgical needlesElectrode placementAbnormal tissue growth
Ablative treatment of metastatic bone tumors and relief of pain associated with metastatic bone tumors is achieved by heat ablation of the bone tumor or tissue near the bone tumor by an ablation probe. In one form the probe is an electrode coupled to a high frequency power supply to provide ablative heating of tissue proximate to an electrode that is placed in or near the bone tumor. Cooling of the electrode by fluid circulation from a cooling apparatus outside the patient's body may be used to enlarge the region of high frequency heating around the electrode. Image guidance of the electrode placement may be monitored by an imaging device. Tracking of the electrode by an image-guided navigator helps in placement of the electrode with respect to the configuration of the bone and bone metastasis. A set of tools accommodates biopsy and various shapes of electrodes according to clinical requirements. Several forms of electrodes, energy delivery and cooling apparatus and methods accommodate the specific objectives.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
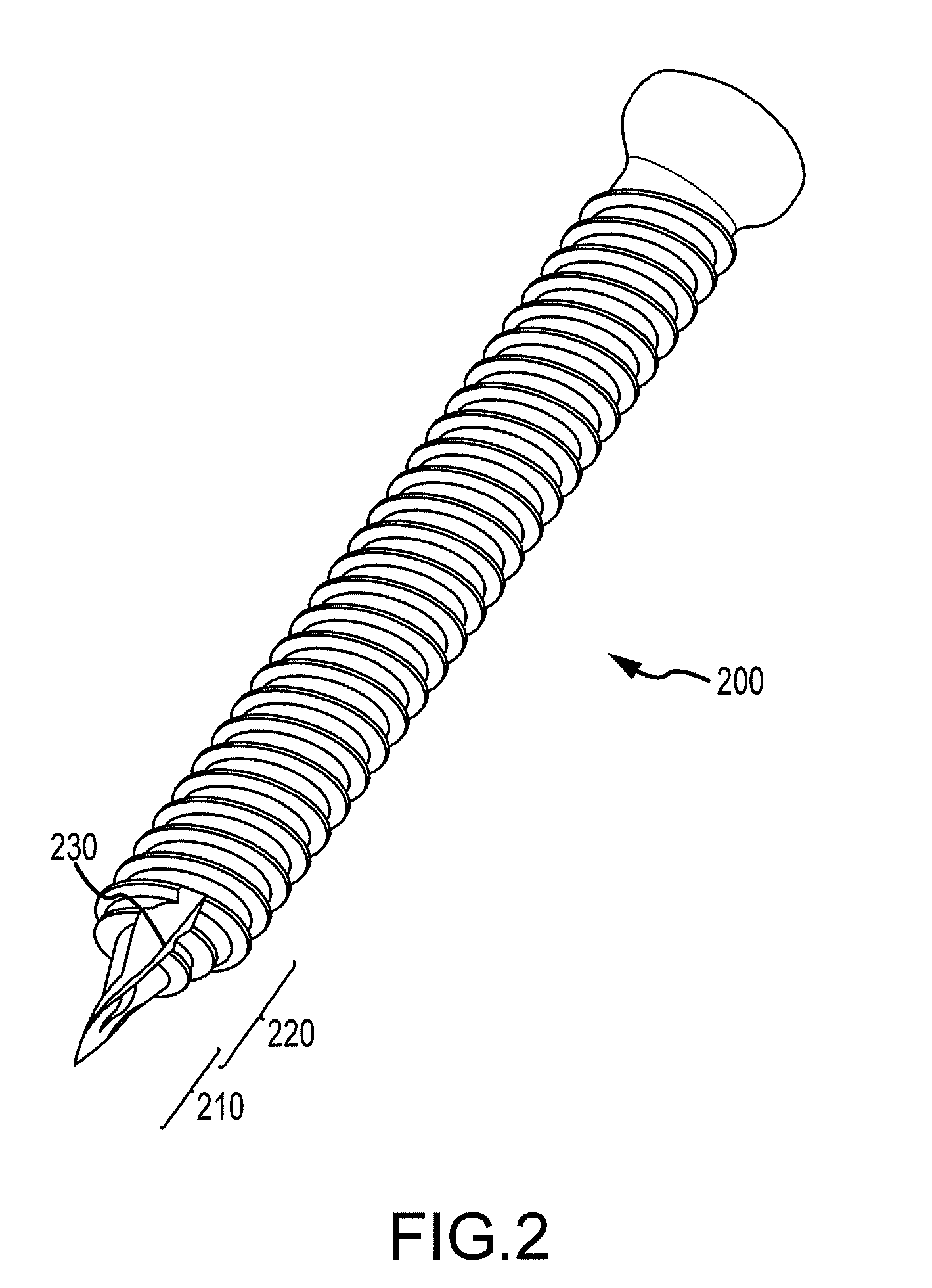
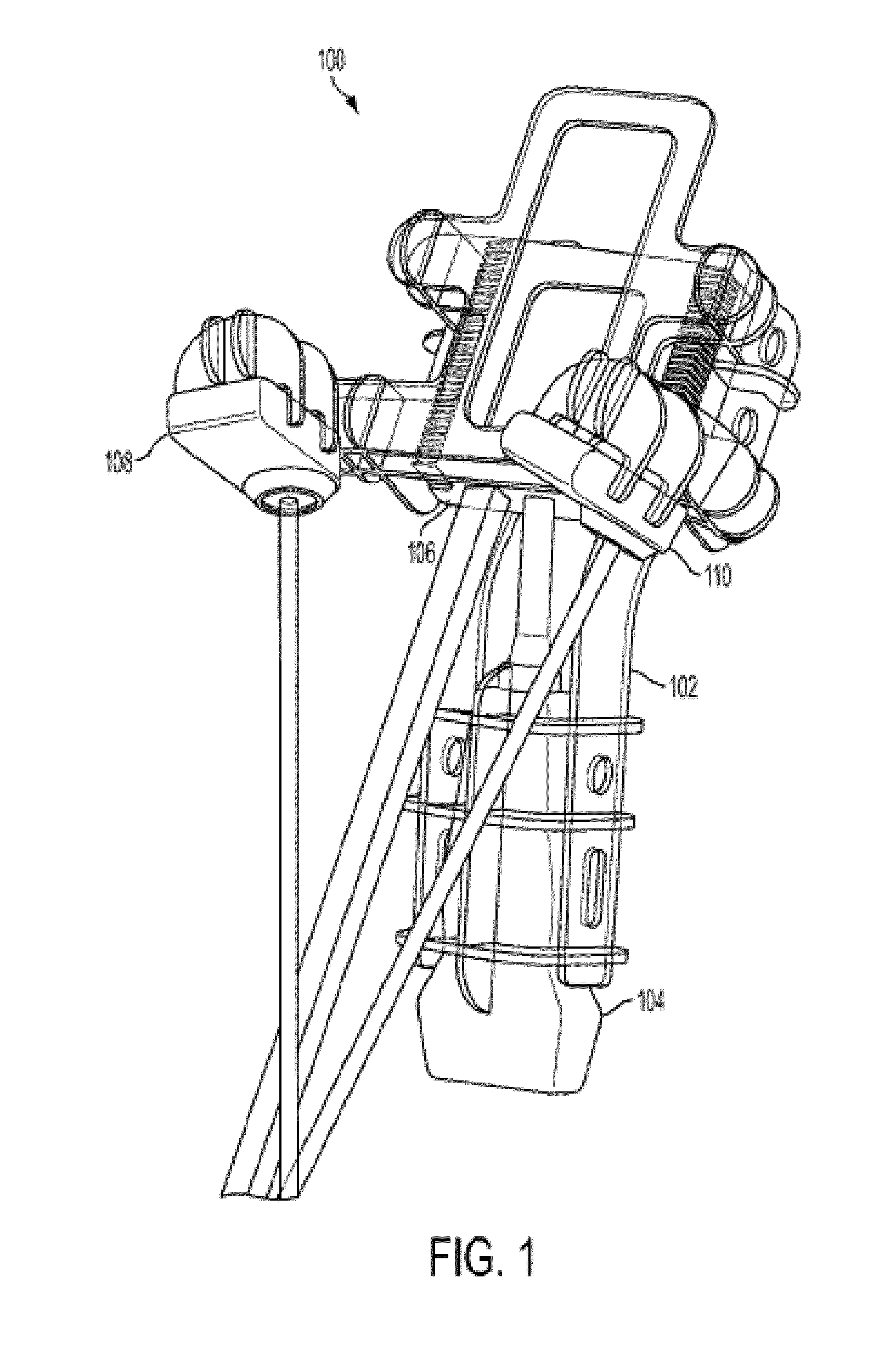
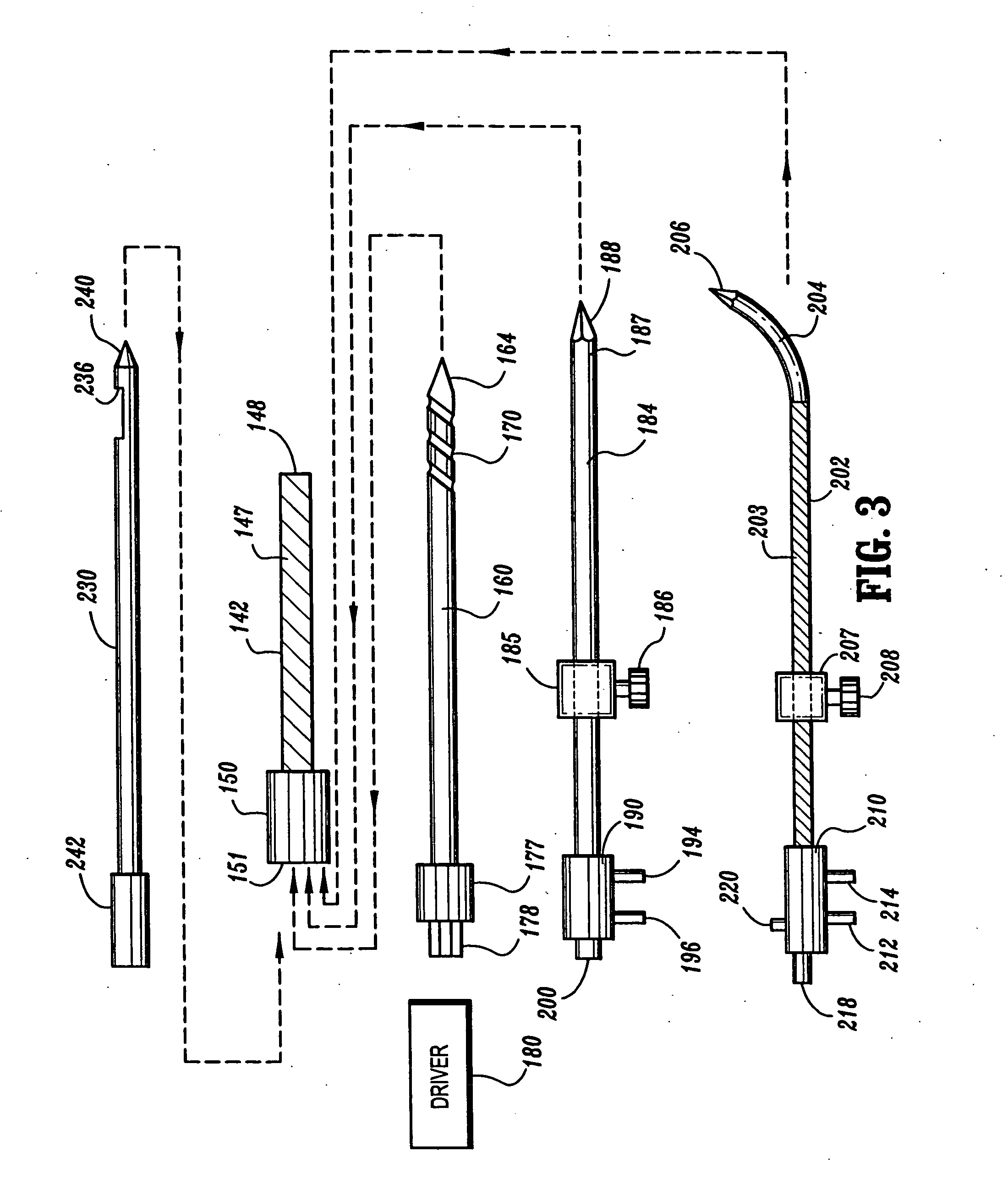
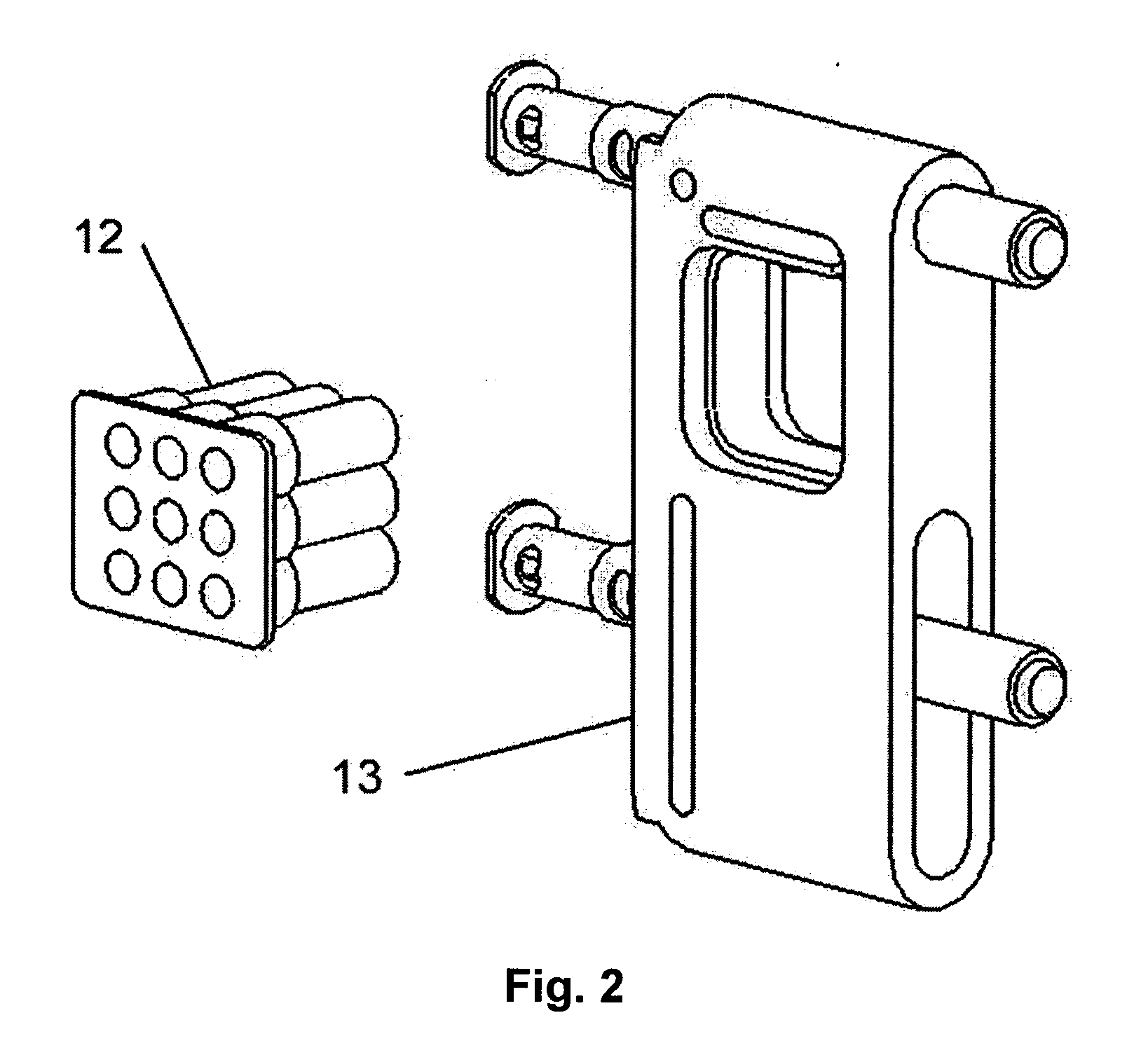
Minimally invasive pedicle screw and guide support
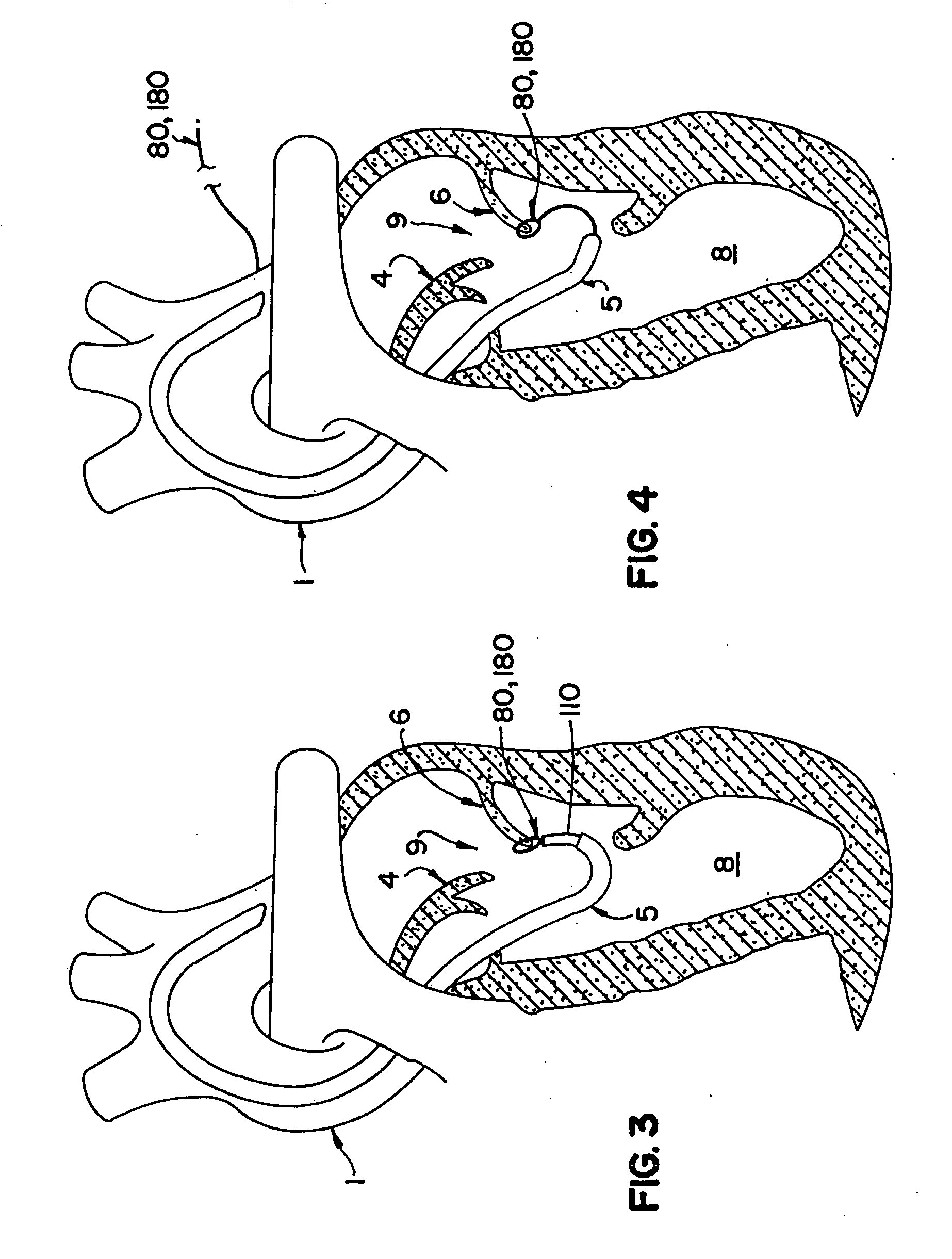
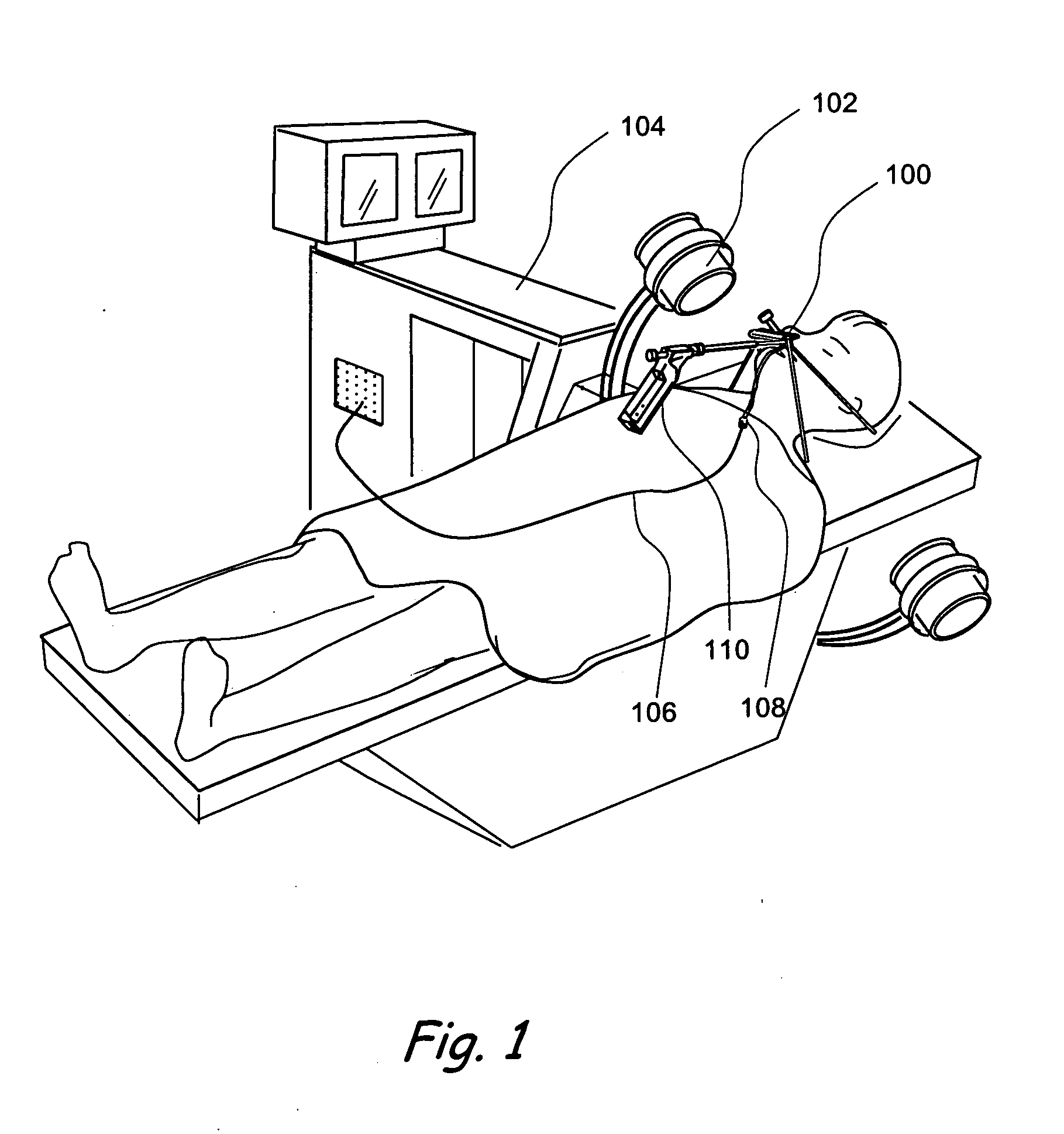
A minimally invasive orthopedic bone attachment system comprising a pedicle screw and guide support sleeve for insertion of the screw. The pedicle screw is a self-boring, self-tapping integral screw having a distal sharply pointed end for guiding the insertion of the screw as well as forming a borehole for the self-tapping threads of the screw. The proximal end of the screw provides a cylindrical extension which can include a recess for receiving a rotational drive tool or wrench. The length of the threads and the type of threads provided in the screw are designed for the type of orthopedic surgery that is intended. A relatively thin hollow support sleeve including an internal threaded section in the distal end is provided to match the threads and the length of the threaded portion of the pedicle screw. The proximal end of the sleeve includes a central passageway having an internal diameter that can receive the extension portion of the screw and also guide and receive a drive device for the screw. A retainer clip associated with circumferential slots spacedly indexed along the longitudinal surface of the drive device can be used to limit the depth of the screw upon insertion as well as to lock the drive device as an assembly with the screw and sleeve to form the attachment system. A small diameter passageway can be provided along the longitudinal axis of the assembly extending from the proximal end of the drive device through the screw to exit through the pointed distal end of the screw. A thin rigid rod having a point at the distal end is slidably positioned within the narrow passageway. The proximal end of the road includes a cap. A flange surface on the under portion of the cap limits the travel of the rod through the assembly. The length of the rod is determined so that it equals the length of the assembly plus an additional dimension corresponding to the anticipated installed depth of the screw. Prior to insertion of the screw, the rod is driven into the bone through the assembly. The location of the rod is ascertained by an image guidance system to determine the correct final projected location of the screw upon installation.
Owner:WONG DAVID A
Method, apparatus, and system for image guided bone cutting
ActiveUS7641660B2Accurate placementImprove accuracyDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsImage guidanceBiomedical engineering
A system for cutting a bone at a desired location may include an image guided drill cylinder configured to receive either a drill bit to create a bore at a target location on the bone or a pin for insertion into the target location, and a cutting block having a plurality of adjustable guides, each defining a cutting path to guide a cutting instrument, a mounting location configured to attach to the bone at the target location, and a plurality of adjustors for adjusting the position of the guides relative to the target location. The system may further include a tracking instrument for providing image guidance of the adjustments to the positions of the guides.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
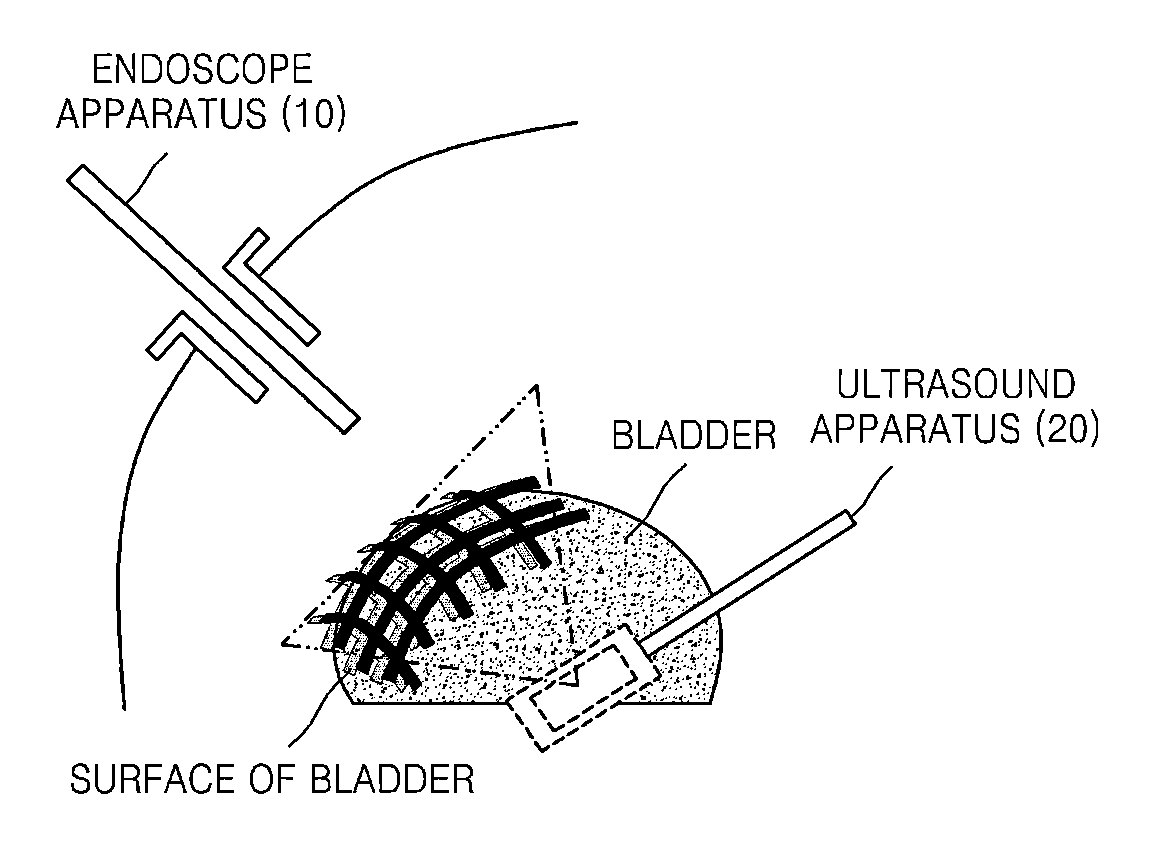
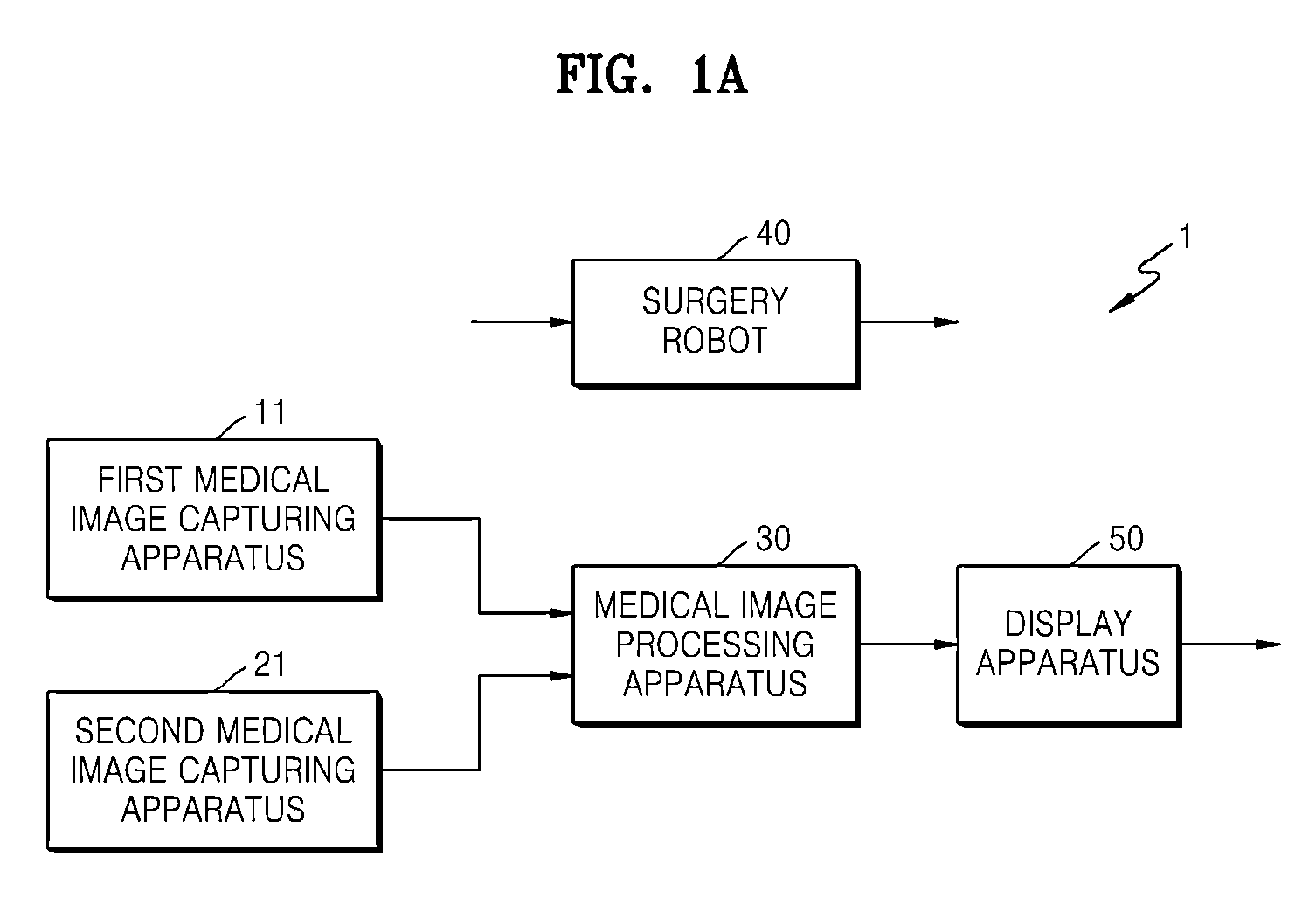
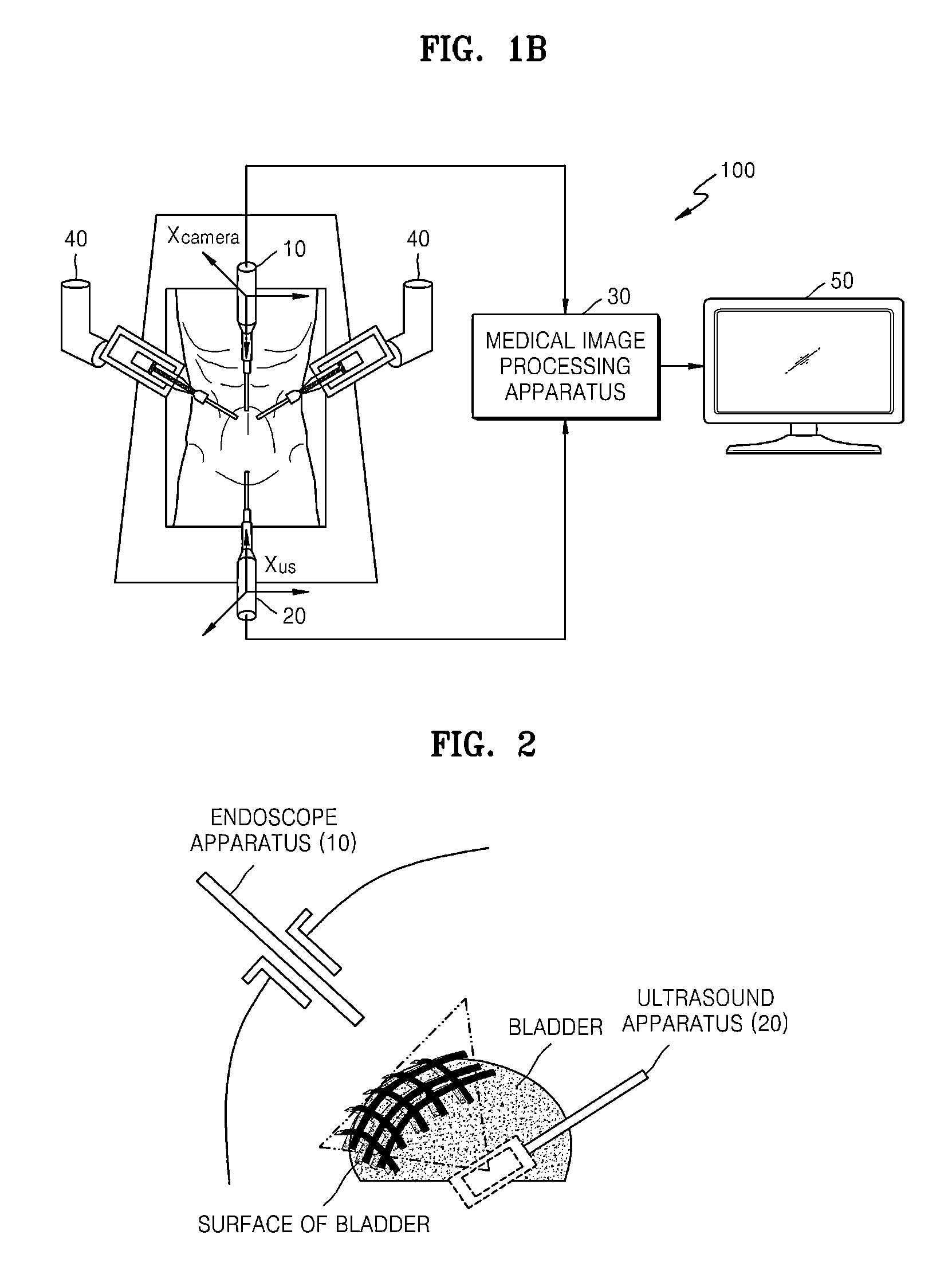
Method and apparatus for processing medical image, and robotic surgery system using image guidance
InactiveUS20130035583A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsImage guidanceImage capture
A synthesis image in which medical images captured using different medical image capturing apparatuses are registered is generated by mapping the medical images to each other. The synthesis image may be used for image guidance while a diagnosis or a robotic surgery of a patient is being performed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
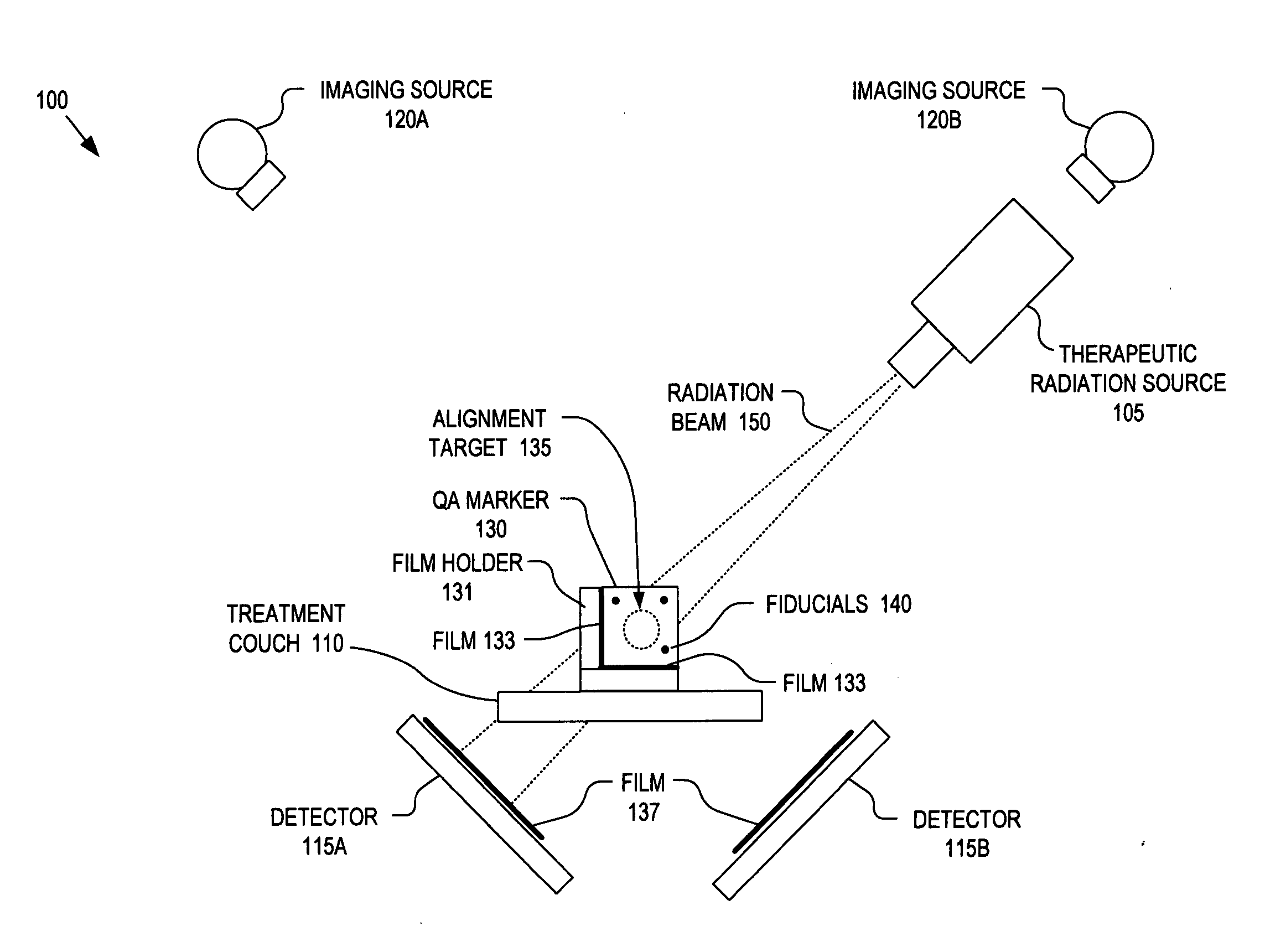
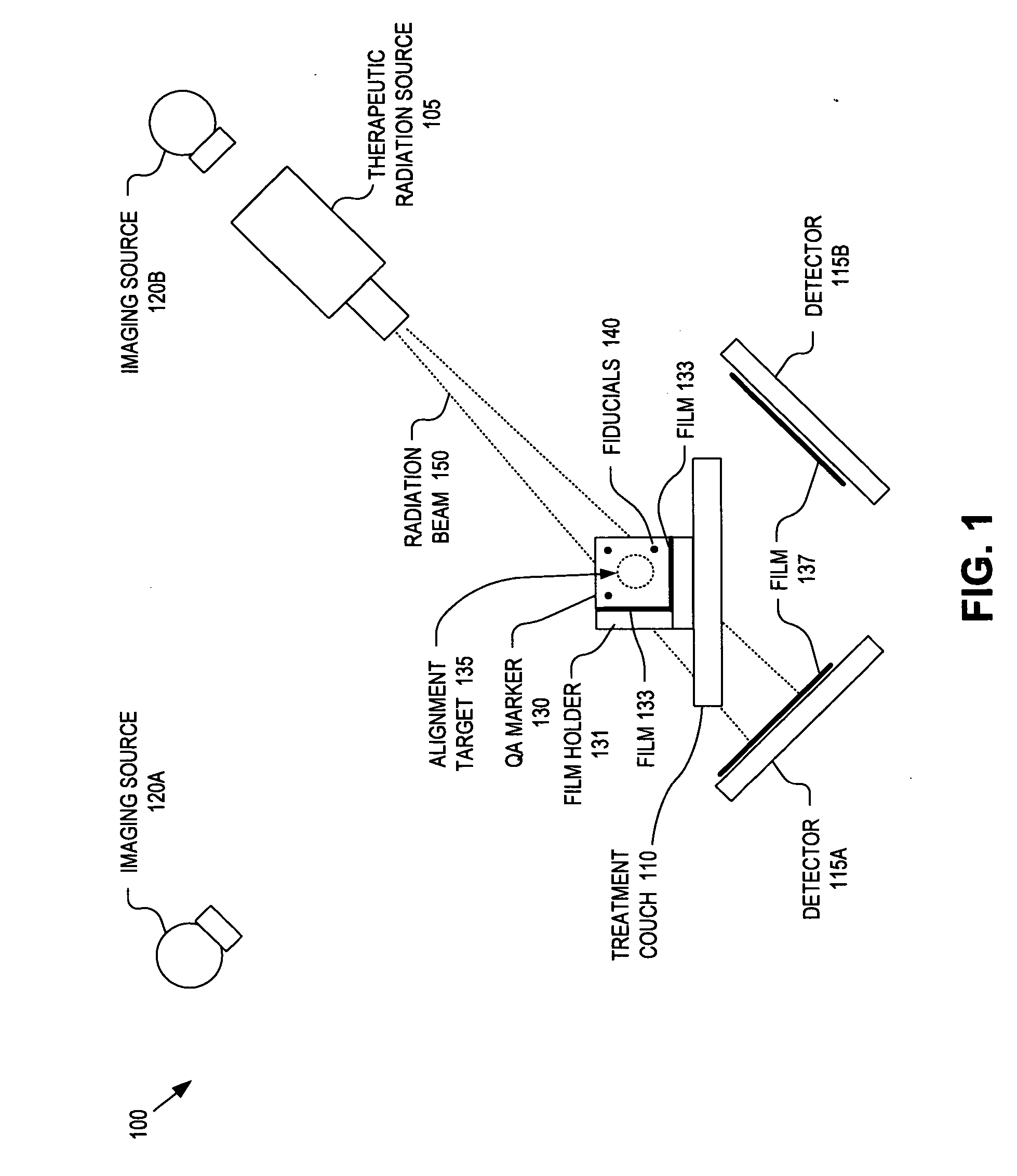
Integrated quality assurance for an image guided radiation treatment delivery system
ActiveUS20070071176A1Calibration apparatusRadiation beam directing meansQuality assuranceImage-guided radiation therapy
A method and apparatus for quality assurance of an image guided radiation treatment delivery system. A quality assurance (“QA”) marker is positioned at a preset position under guidance of an imaging guidance system of a radiation treatment delivery system. A radiation beam is emitted from a radiation source of the radiation treatment delivery system at the QA marker. An exposure image of the QA marker due to the radiation beam is generated. The exposure image is then analyzed to determine whether the radiation treatment delivery system is aligned.
Owner:ACCURAY
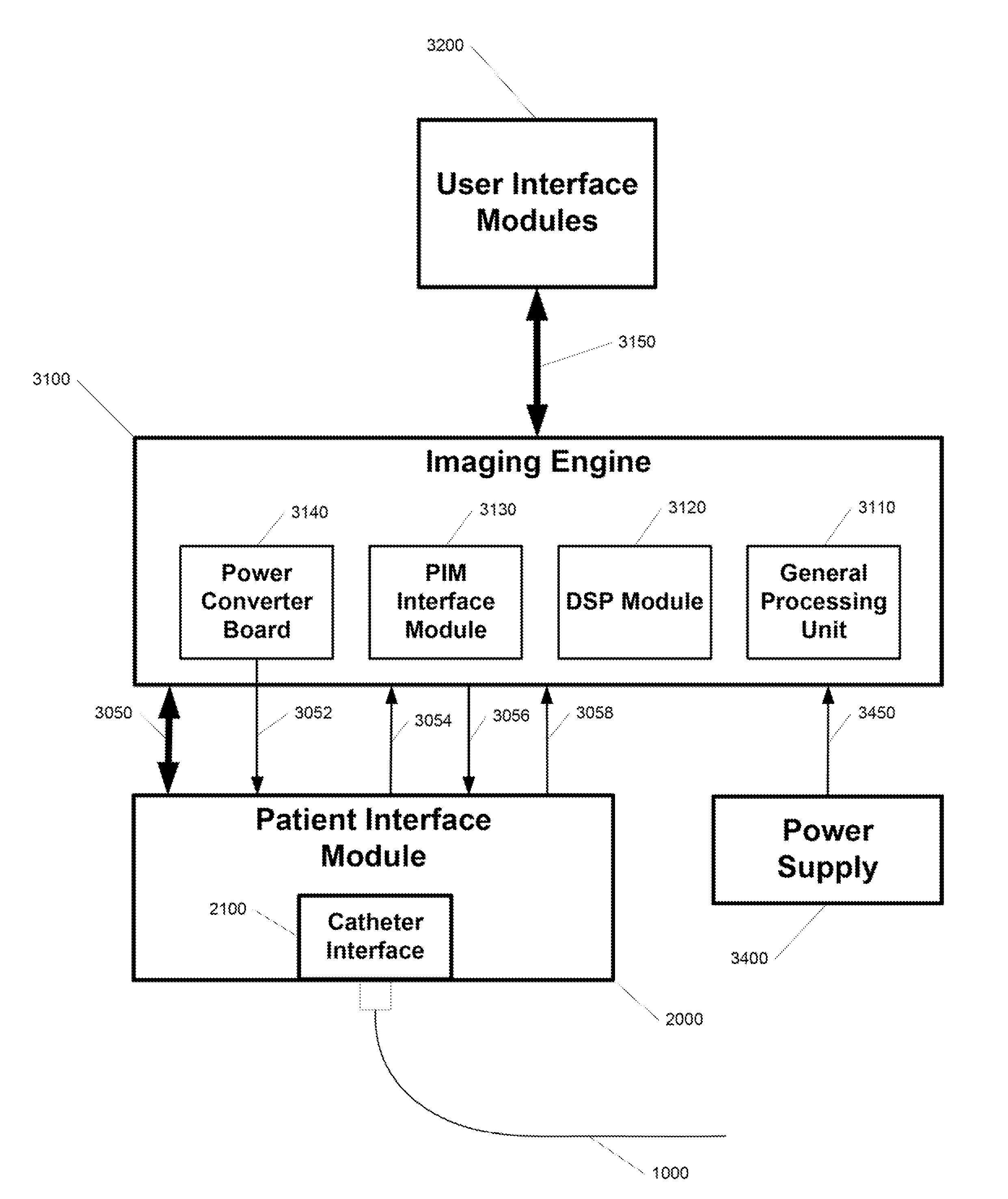
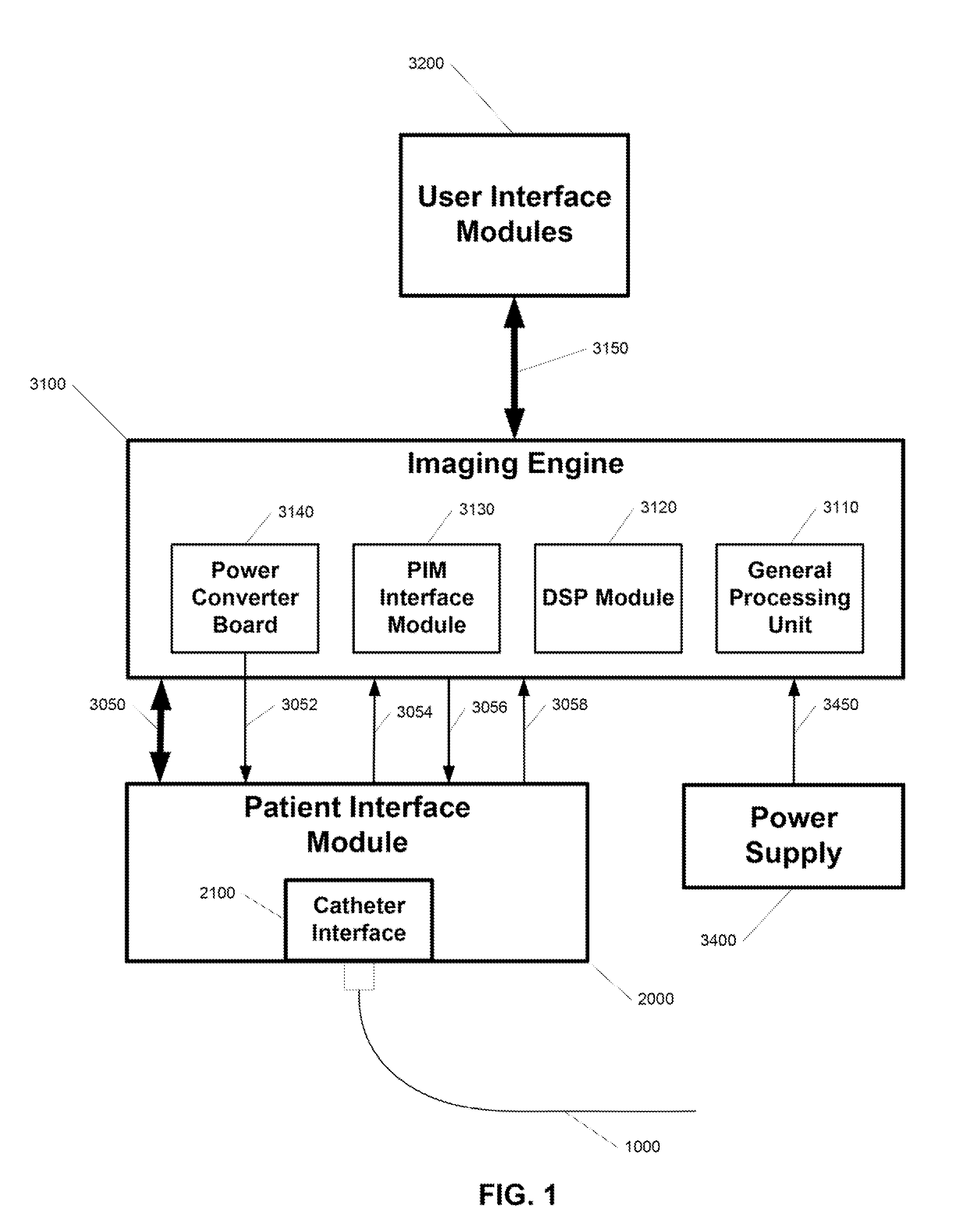
System and catheter for image guidance and methods thereof
ActiveUS20100152590A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOesophagoscopesControl systemUltrasonic imaging
A catheter-based imaging system comprises a catheter having a telescoping proximal end, a distal end having a distal sheath and a distal lumen, a working lumen, and an ultrasonic imaging core. The ultrasonic imaging core is arranged for rotation and linear translation. The system further includes a patient interface module including a catheter interface, a rotational motion control system that imparts controlled rotation to the ultrasonic imaging core, a linear translation control system that imparts controlled linear translation to the ultrasonic imaging core, and an ultrasonic energy generator and receiver coupled to the ultrasonic imaging core. The system further comprises an image generator coupled to the ultrasonic energy receiver that generates an image.
Owner:ACIST MEDICAL SYST
Apparatus and Methods for Performing Brain Surgery
InactiveUS20080109026A1Easy to installAssisting understandingCannulasInfusion syringesLess invasive surgeryMedicine
Less invasive surgical techniques for performing brain surgery are disclosed in which a dilating obturator and cannula assembly is inserted into brain tissue until the obturator tip and cannula are adjacent the target tissue. The obturator is removed and surgery is performed through the cannula. In preferred embodiments the obturator and cannula are placed using image guidance techniques and systems to coordinate placement with pre-operative surgical planning. A stylet with associated image guidance may he inserted prior to insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly to guide insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly. Surgery preferable is performed using an endoscope partially inserted into the cannula with an image of the target tissue projected onto a monitor.
Owner:NICO CORP
Apparatus and methods for performing brain surgery
ActiveUS20090048622A1Many of techniqueEasy to installCannulasSurgical needlesLess invasive surgeryLess invasive
Less invasive surgical techniques for performing brain surgery are disclosed in which a dilating obturator and cannula assembly is inserted into brain tissue until the obturator tip and cannula are adjacent to the target tissue. The obturator is removed and surgery is performed through the cannula. In preferred embodiments the obturator and cannula are placed using image guidance techniques and systems to coordinate placement with pre-operative surgical planning. A stylet with associated image guidance may be inserted prior to insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly to guide insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly. Surgery preferably is performed using an endoscope partially inserted into the cannula with an image of the target tissue projected onto a monitor. Dilating obturator structures having a rounded or semi-spherical tip and / or an optical window for visualizing brain tissue during expansion are contemplated.
Owner:VYCOR MEDICAL INC
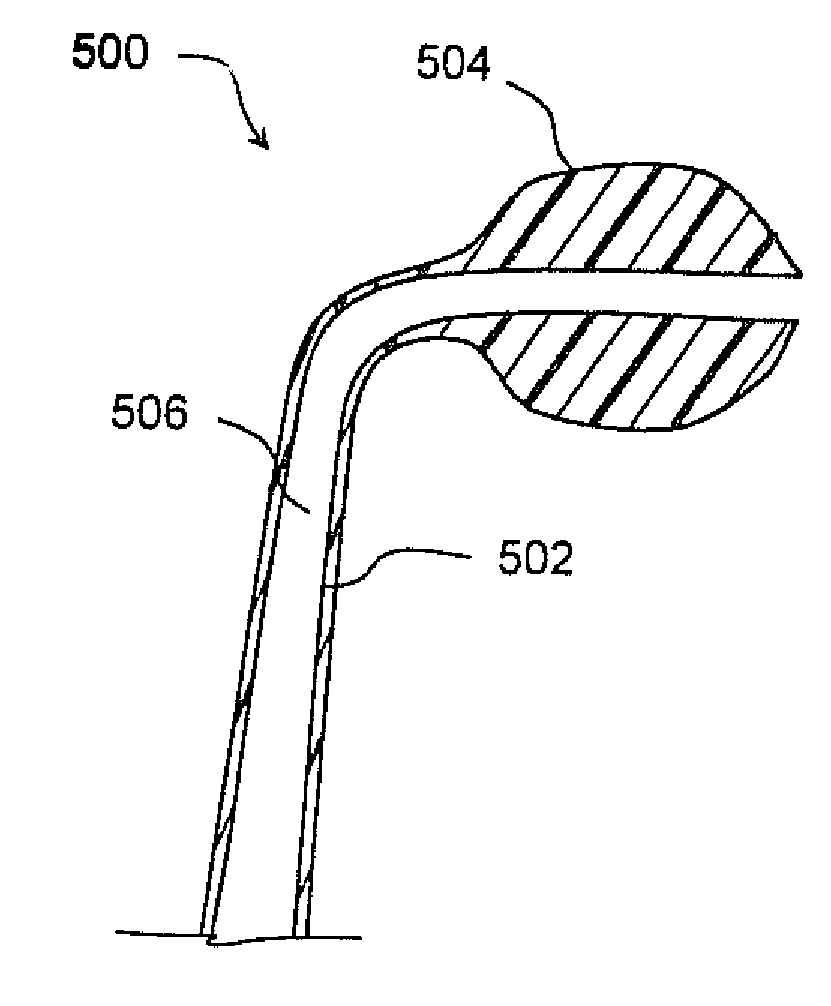
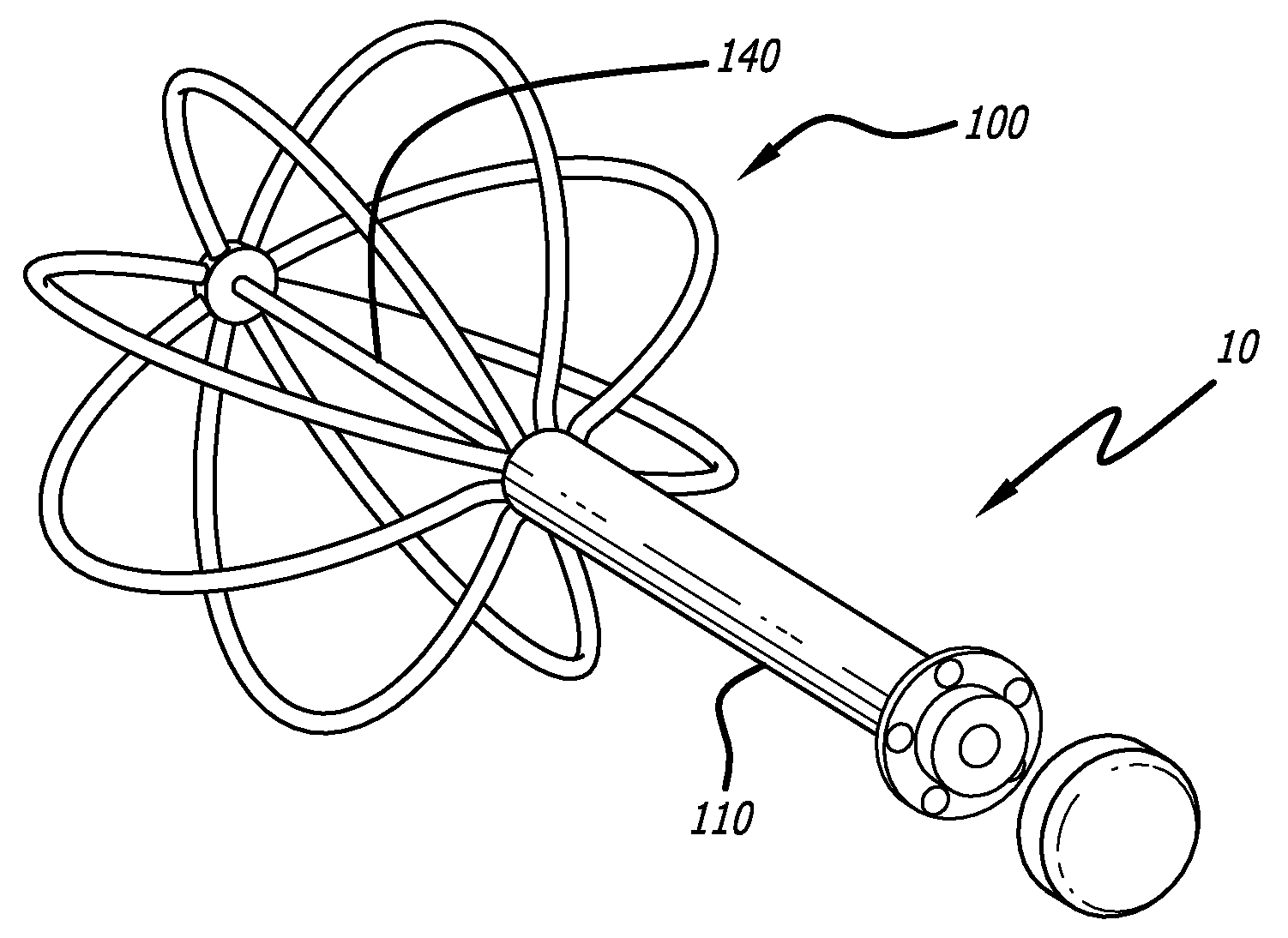
Brachytherapy apparatus for asymmetrical body cavities
InactiveUS20070270627A1Reduce in quantityOptimize treatment planX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPartial Breast IrradiationAbdominal trocar
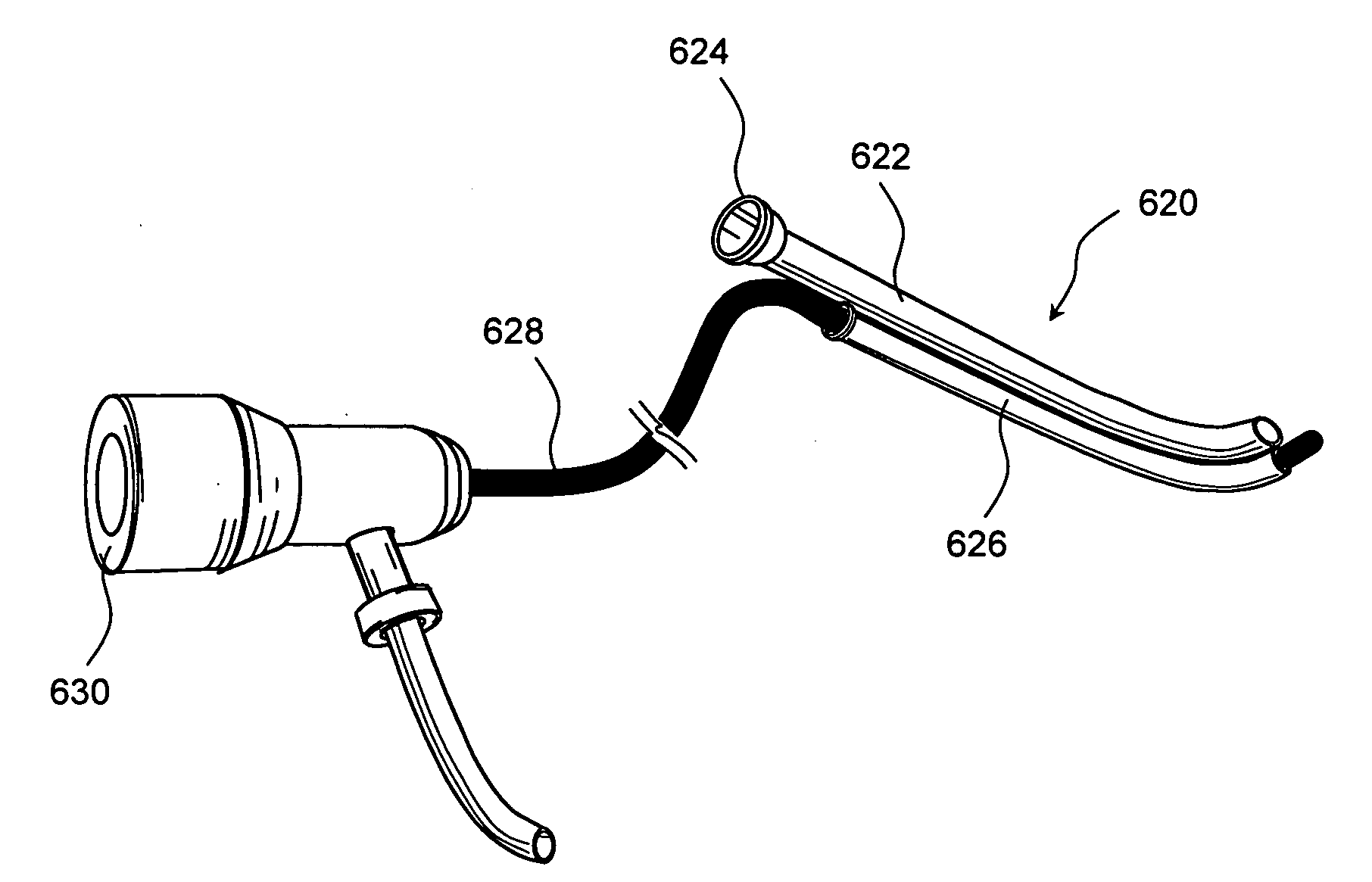
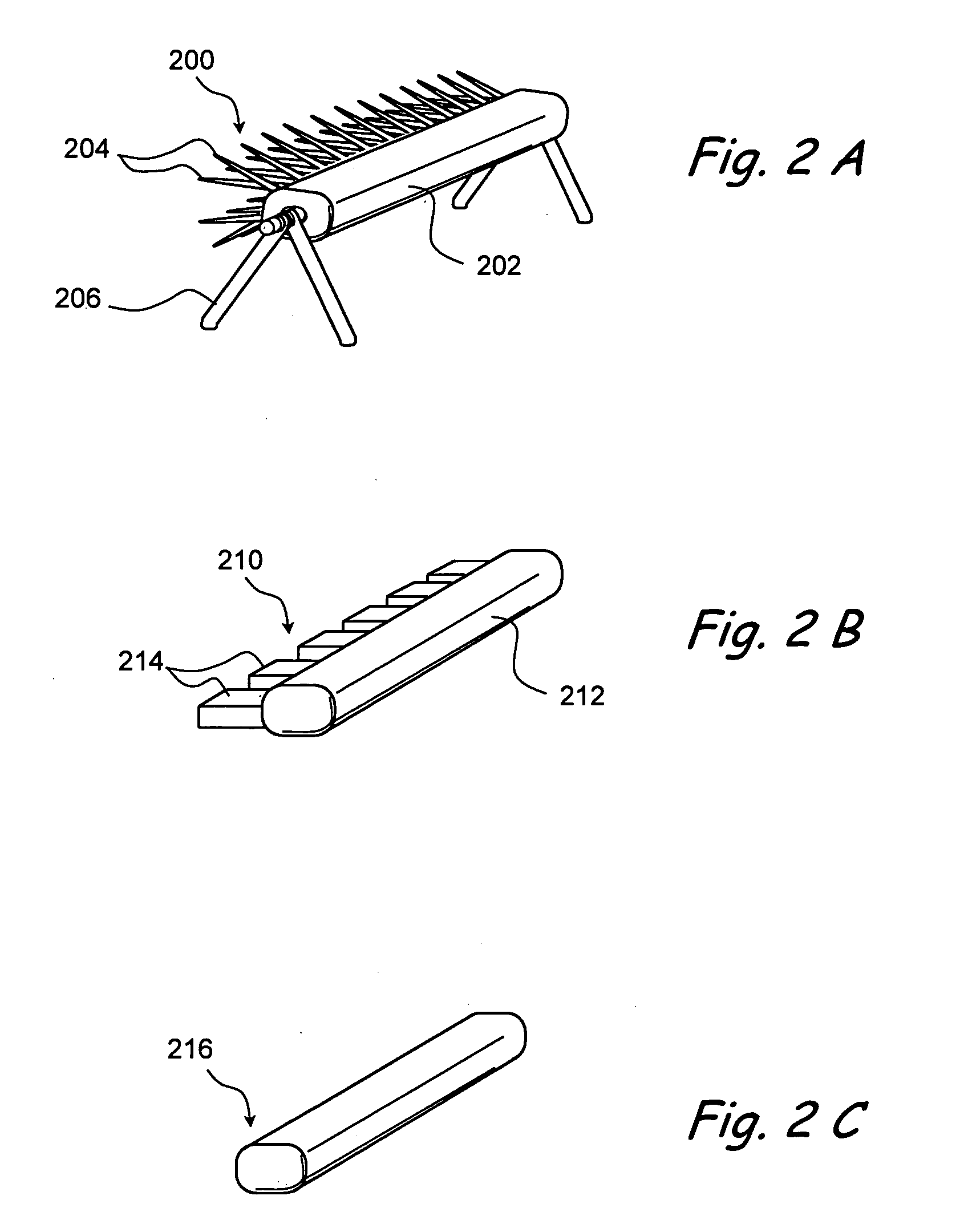
The present disclosure provides a brachytherapy apparatus, system and method that delivers partial breast irradiation treatment for post-lumpectomy patients via introduction of a catheter-like device through a trocar. The apparatus may be introduced post-surgically with local anesthesia under image guidance into the previous excision site and into a cavity by a surgeon. The brachytherapy apparatus includes one or more thin-walled tubes, each of said thin-walled tubes being configured to contain one or more radioactive sources, at least one radiation source configured to deliver a prescribed dose of radiation, a whisk adjuster configured to permit adjustment of each of the one or more thin-walled tubes so that the tubes substantially conform to a size of the body cavity; and an expansion element configured to expand outwardly said one or more thin-walled tubes within the cavity so that the thin-walled tubes substantially conform to a shape and / or size of the body cavity.
Owner:PORTOLA MEDICAL
System and method for image guided medical procedures
InactiveUS20140073907A1Correction can be minimizedEasy to useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySoft tissue deformation
A system and method combines information from a plurality of medical imaging modalities, such as PET, CT, MRI, MRSI, Ultrasound, Echo Cardiograms, Photoacoustic Imaging and Elastography for a medical image guided procedure, such that a pre-procedure image using one of these imaging modalities, is fused with an intra-procedure imaging modality used for real time image guidance for a medical procedure for any soft tissue organ or gland such as prostate, skin, heart, lung, kidney, liver, bladder, ovaries, and thyroid, wherein the soft tissue deformation and changes between the two imaging instances are modeled and accounted for automatically.
Owner:CONVERGENT LIFE SCI
Image-guided fracture reduction
InactiveUS7237556B2Internal osteosythesisSurgical navigation systemsFracture reductionImage guidance
Embodiments of the present invention include products and methods for reducing fractures with the aid of image guidance. In one embodiment, products and methods are directed to reduction for the placement of an intramedullary nail.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Tissue interventions using nuclear-emission image guidance
InactiveUS20070167749A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRadioactive agentPosition dependent
A method and apparatus for marking a lesion in a body part is provided. The method includes the steps of obtaining a first nuclear-emission image of the body part; determining a position of the lesion from the first image; percutaneously introducing a cannula to the determined position; inserting a wire into the cannula, the wire including radioactive material; retracting the cannula while holding the wire in place; and obtaining a second nuclear-emission image of the body part. The second image includes data relating to a position of the lesion and data relating to a position of the wire.
Owner:COMPANIA MEXICANA DE RADIOLOGIA CGR S A DE
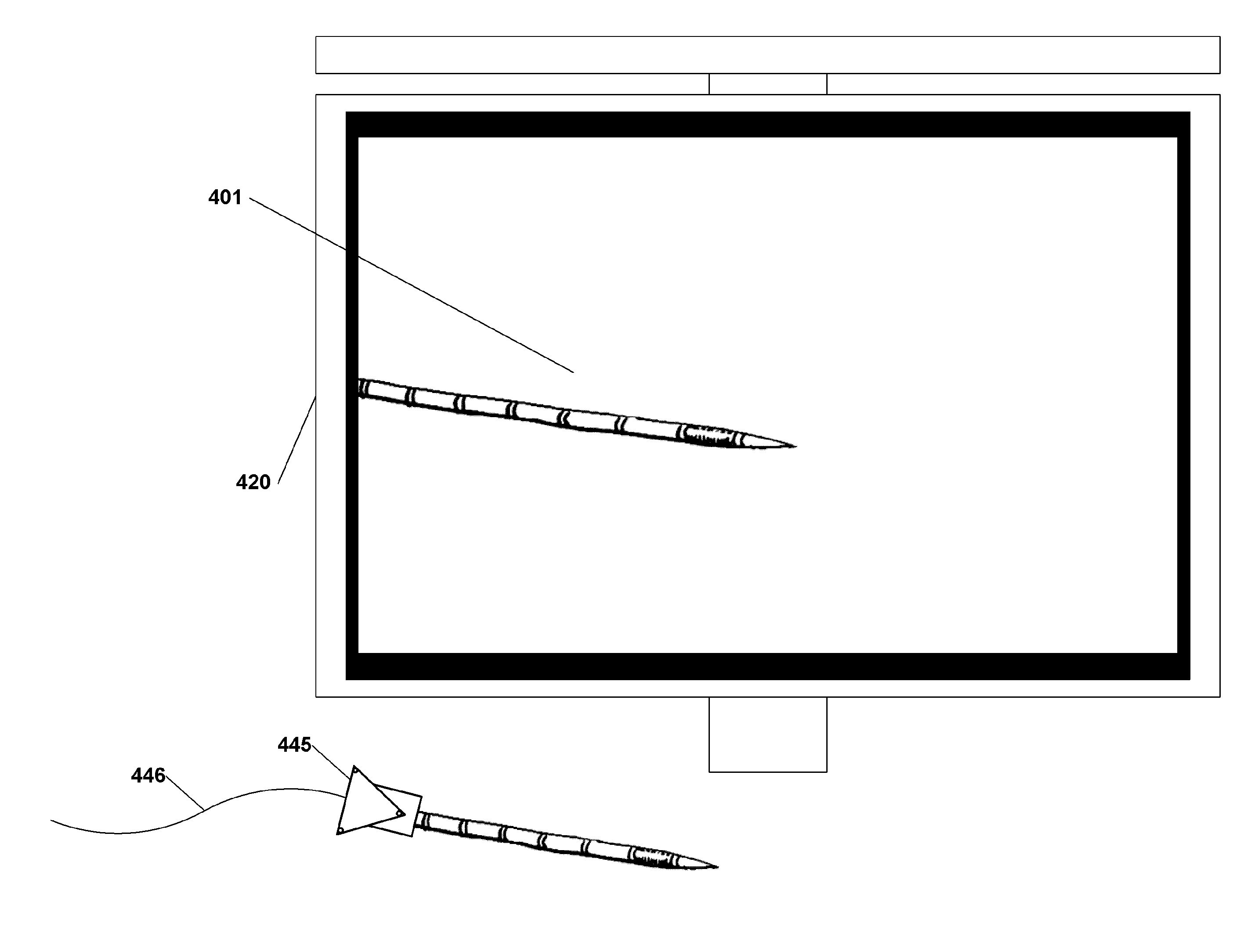
Systems, methods, apparatuses, and computer-readable media for image guided surgery
Presented herein are methods, systems, devices, and computer-readable media for image guided surgery. The systems herein allow a physician to use multiple instruments for a surgery and simultaneously provide image-guidance data for those instruments. Various embodiments disclosed herein provide information to physicians about procedures they are performing, the devices (such as ablation needles, ultrasound wands or probes, scalpels, cauterizers, etc.) they are using during the procedure, the relative emplacements or poses of these devices, prediction information for those devices, and other information. Some embodiments provide useful information about 3D data sets. Additionally, some embodiments provide for quickly calibratable surgical instruments or attachments for surgical instruments.
Owner:INNEROPTIC TECH
Image Guided Navigation System
An image guidance system for tracking a surgical instrument within the oral cavity. The image guidance system includes a plurality of cameras adapted to be located within the oral cavity to provide intraoral images of optically visible patterns within oral cavity. A processing system receives and processes the intraoral images to recognize patterns and triangulate the locations and orientations of each camera. The processing system uses a reference dataset which defines a reference coordinate system based on alignment to a portion of the oral anatomy. The processing system determines the location and orientation of the tracked instrument based on the reference dataset. In an embodiment, the system includes an oral fixture that is removably attachable to teeth in a patient and is configured to hold one of the cameras.
Owner:X NAV TECH
System and method for fused image based navigation with late marker placement
ActiveUS9436993B1Enhance the imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementImaging processingHand held
Systems and methods for image guidance, which may include an image processing unit, cameras, and handheld real-time imaging components or handheld displays, wherein the cameras observe visual features on patients, tools, or other components, and wherein said features allow camera or object positions to be determined relative to secondary image data or a reference position, and wherein the image processing unit is configured to dynamically register observations with secondary image data, and to compute enhanced images based on combinations of one or more of secondary image data, positioning data, and real-time imaging data.
Owner:CLEAR GUIDE MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for tissue treatment with laser and electromagnetic radiation
InactiveUS7549424B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsElectromagnetic radiationLength wave
A method and apparatus wherein an application of energy is limited to a specific diseased portion of body tissue (target tissue) for the purpose of localizing the treatment to the target tissue and avoiding an adverse effect on surrounding tissue. In one embodiment, access to the target tissue is provided by inserting an energy transmission device through a needle for delivery of the energy into the target tissue. Guidance of the needle is alternatively enhanced through use of an image guidance device. Alternatively, in addition the localized treatment is further controlled by use of an energy-concentrating / enhancement agent and / or photosensitizing / photoselective agent, chromophore dye and viscous substance to cause selective interaction with a specific wavelength of an energy source. The treatment can be further controlled and localized by improving the accuracy and positioning of the delivery device into the target tissue using imaging guidance.
Owner:PRO SURG
Image Guidance System for Deep Brain Stimulation
InactiveUS20090220136A1High precisionData thereby acquiredSurgical systems user interfaceCharacter and pattern recognitionImage guidanceMr images
This invention provides computerized image guidance systems for deep brain stimulation (DBS) surgery and related methods that improve accuracy of positioning of electrodes in the brains of subjects. Image guidance systems in accordance with the present invention incorporate advanced features such as capability of displaying, in any desired plane of view, a digitized three-dimensional neuroanatomical brain map that can be form fitted to a patient's medical images, such as brain MR images, and capability of displaying on the patient's medical images both the contours of anatomic structures from a digitized brain map, and digitized electrode recording data obtained intra-operatively.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com