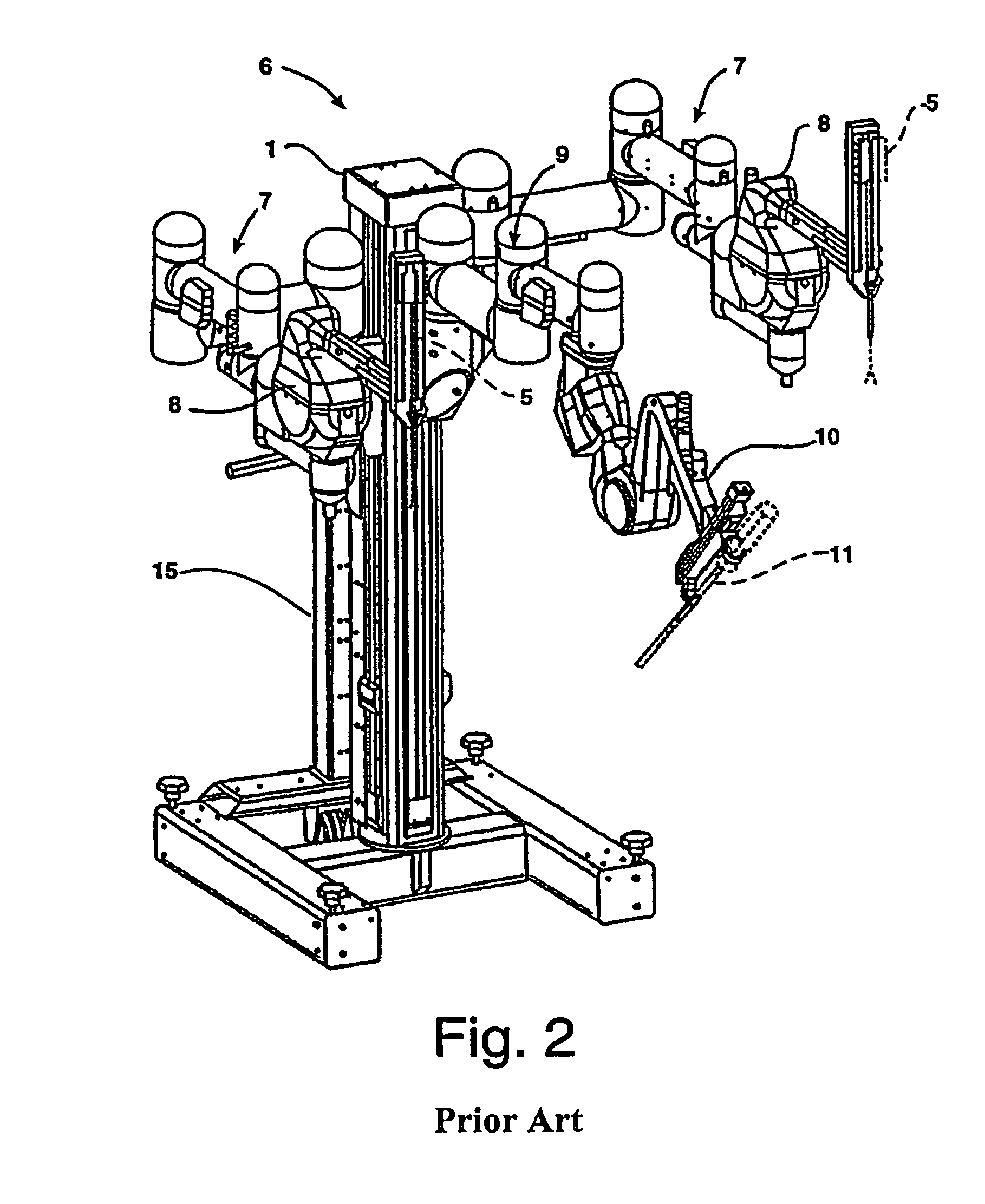
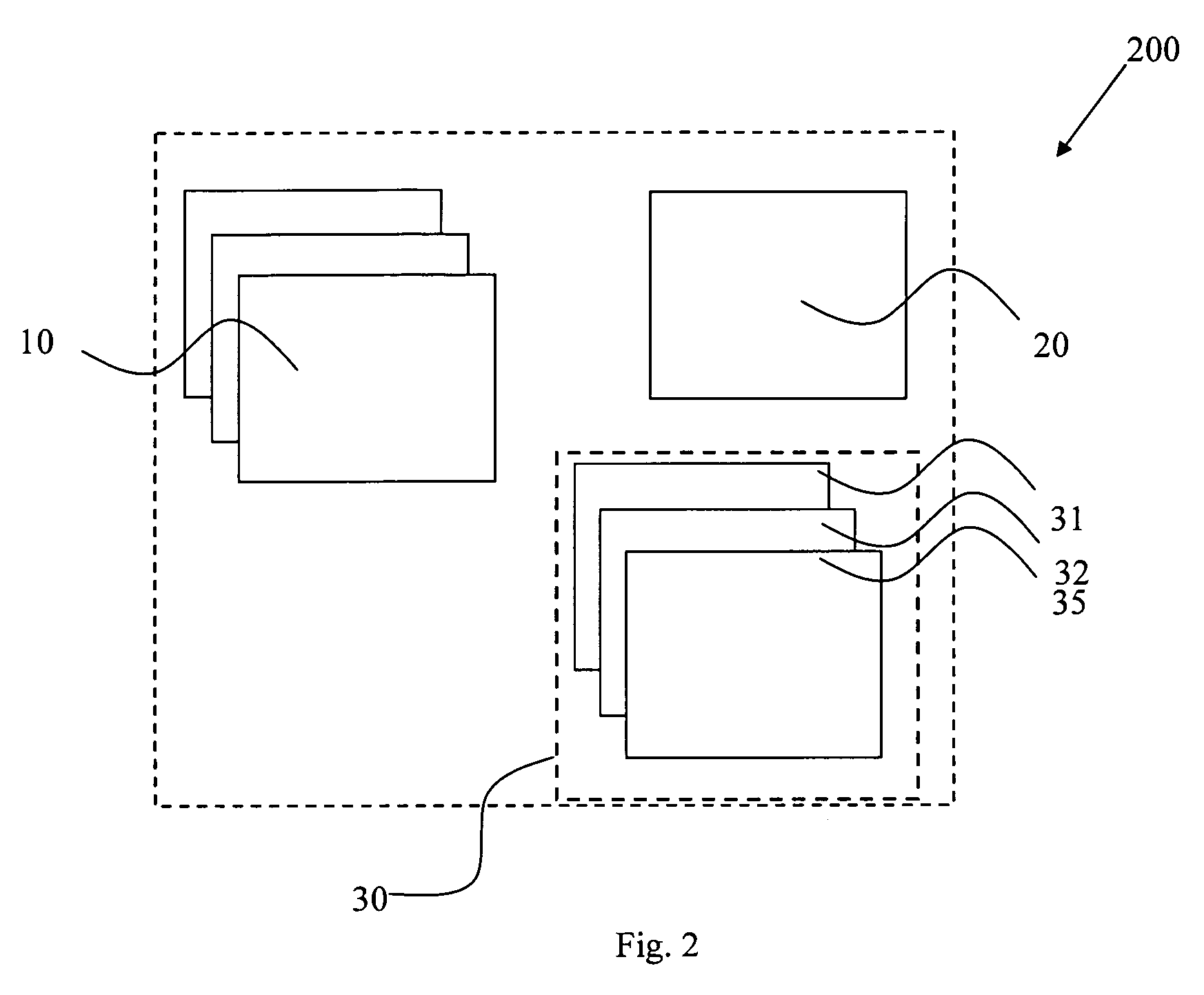
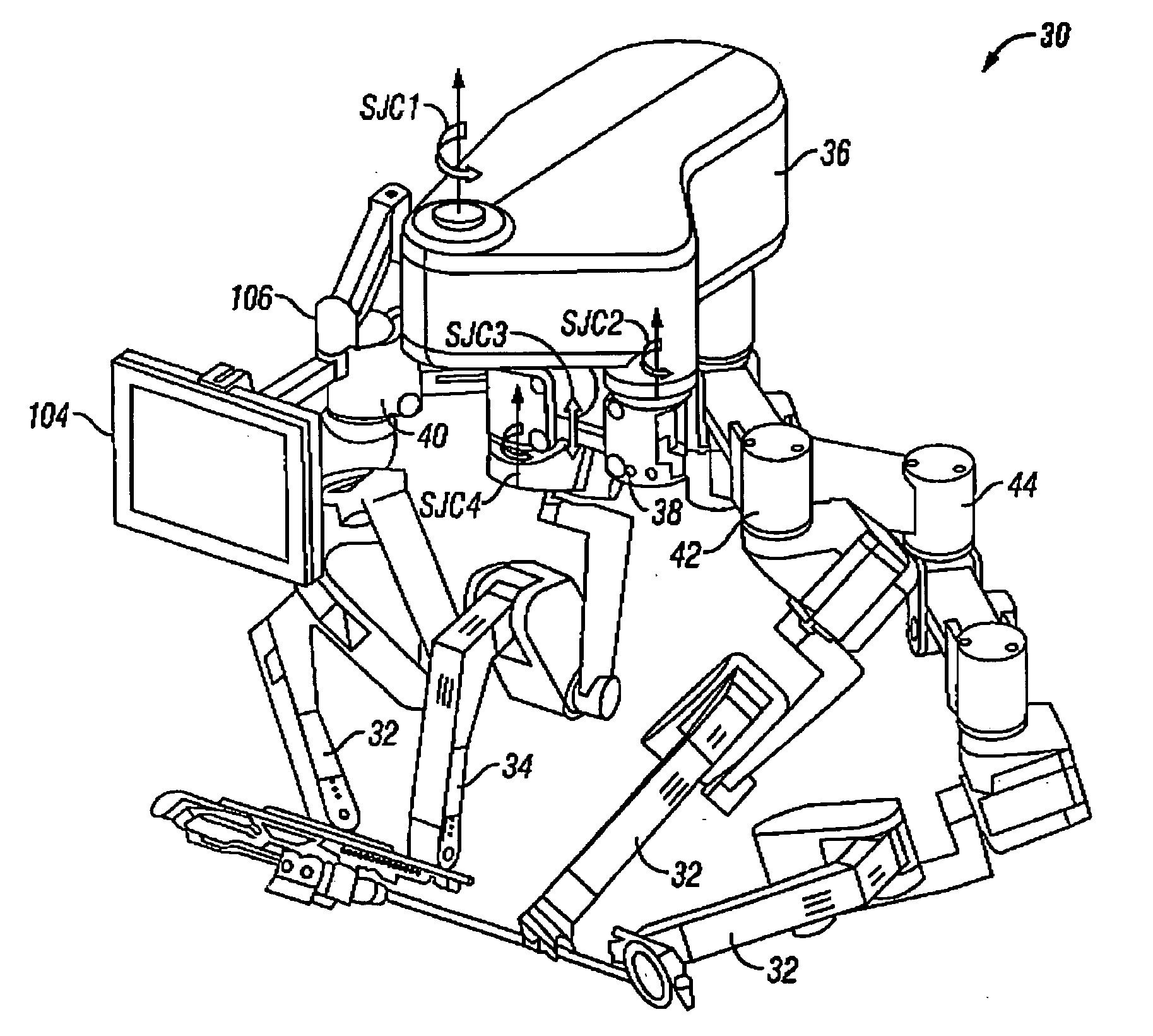
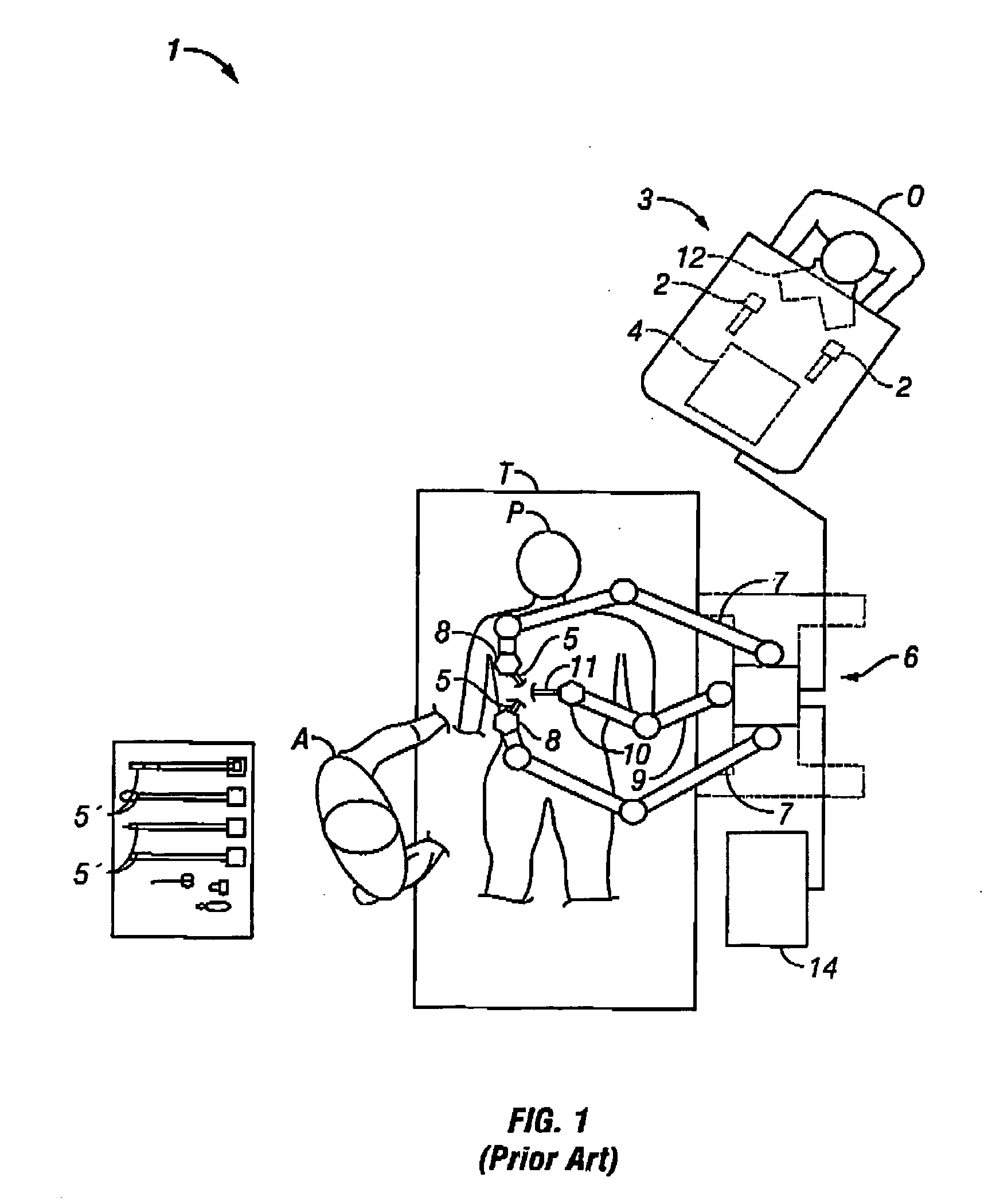
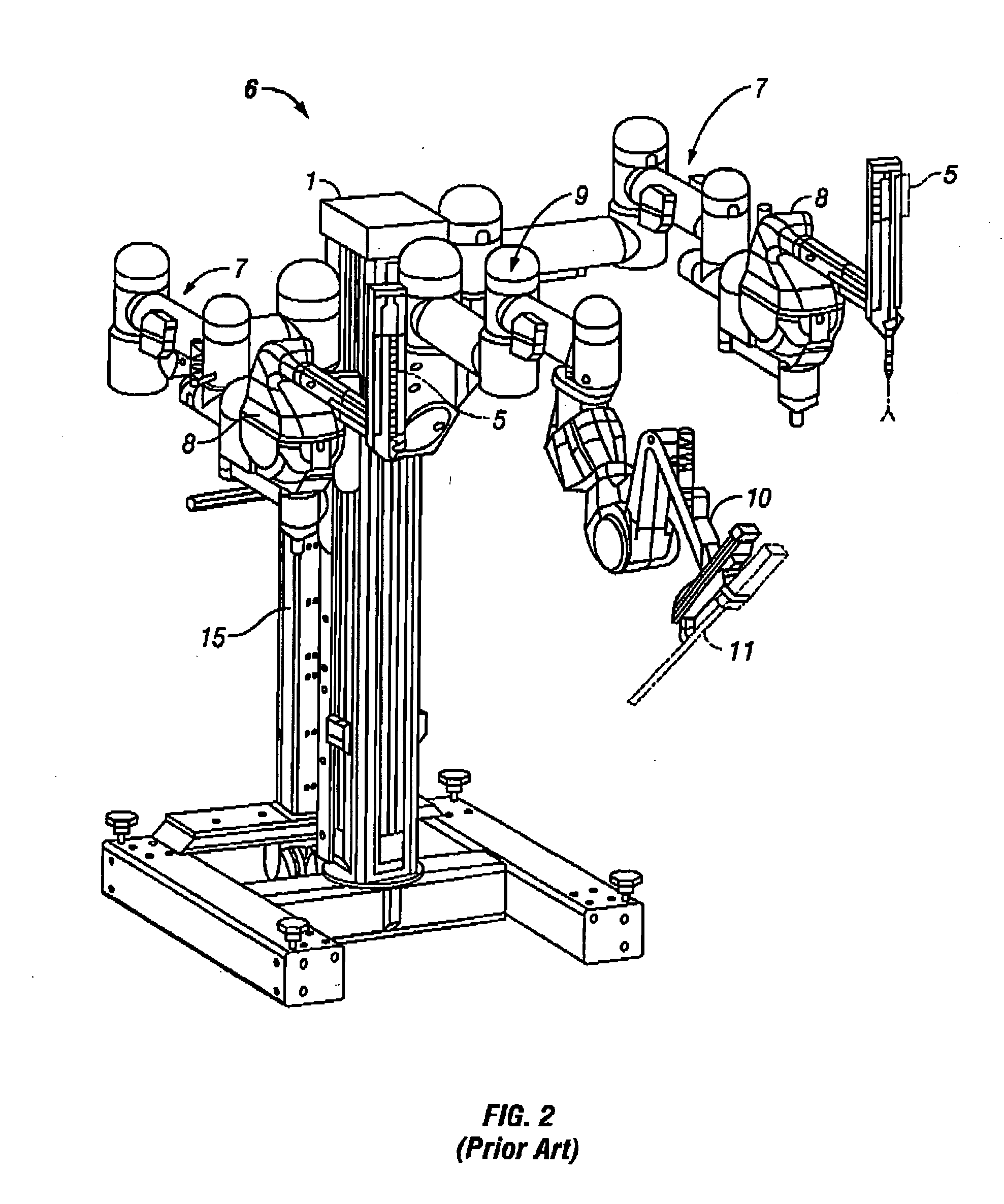
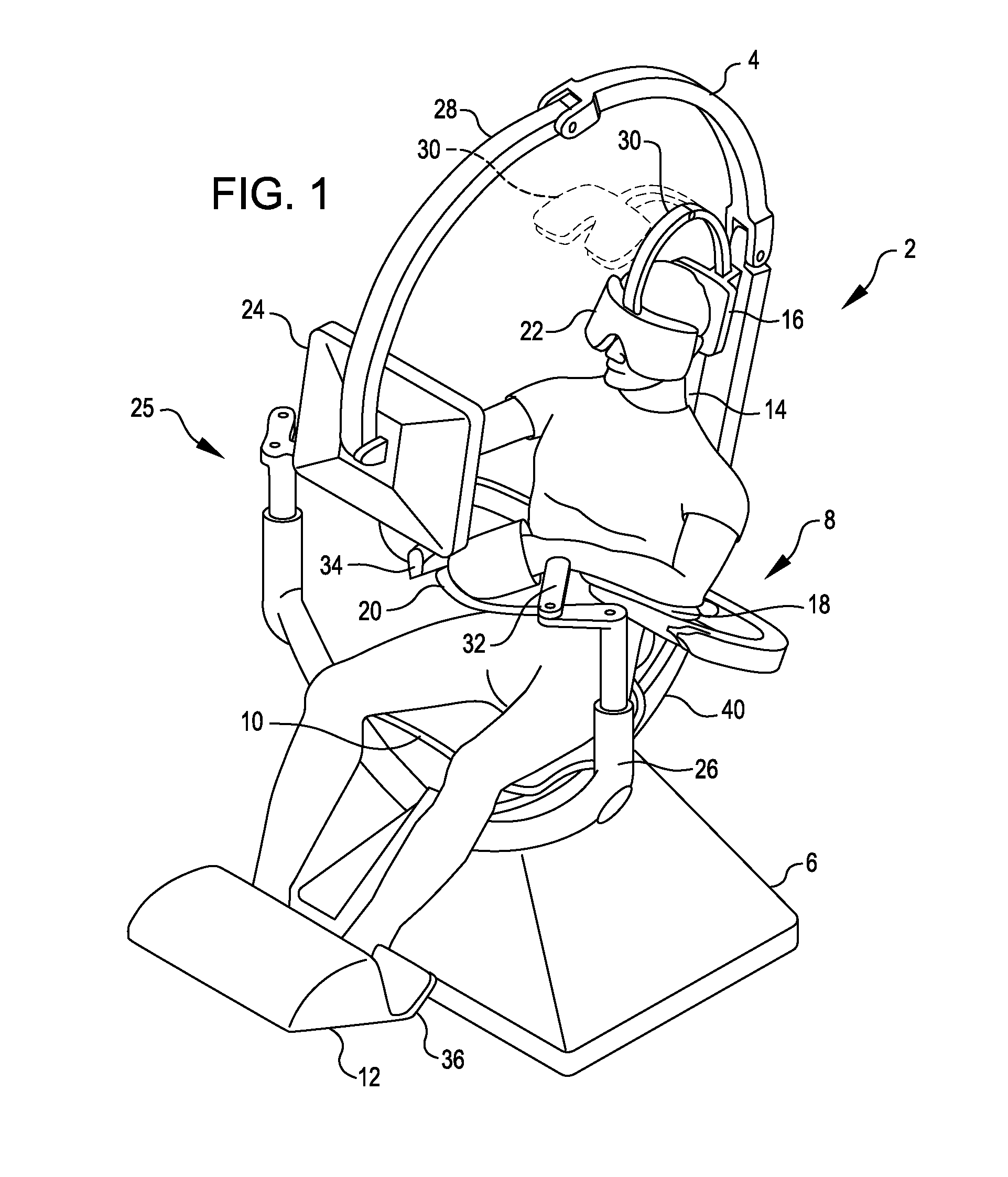
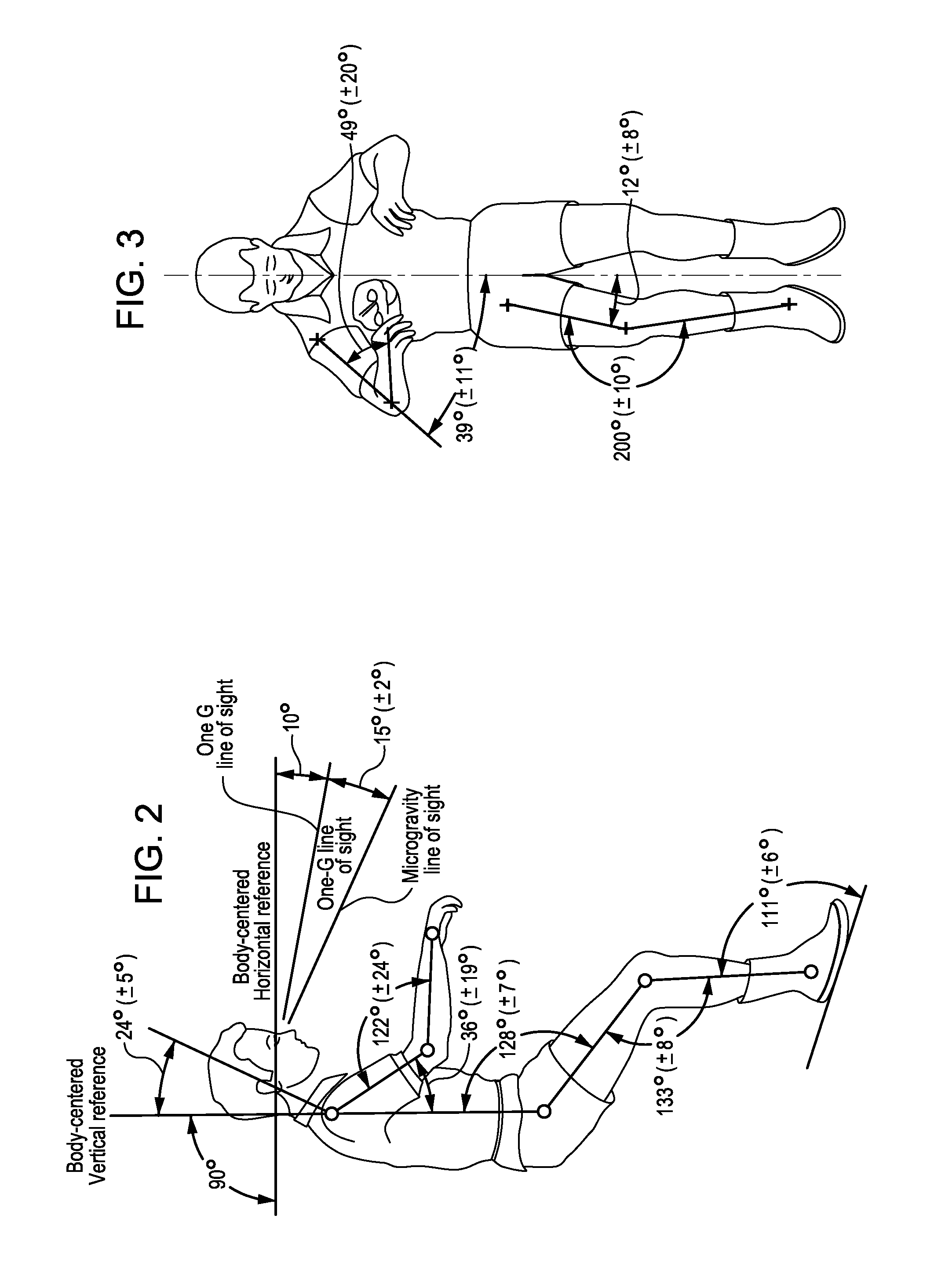
Patents
Literature
411 results about "Robotic surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
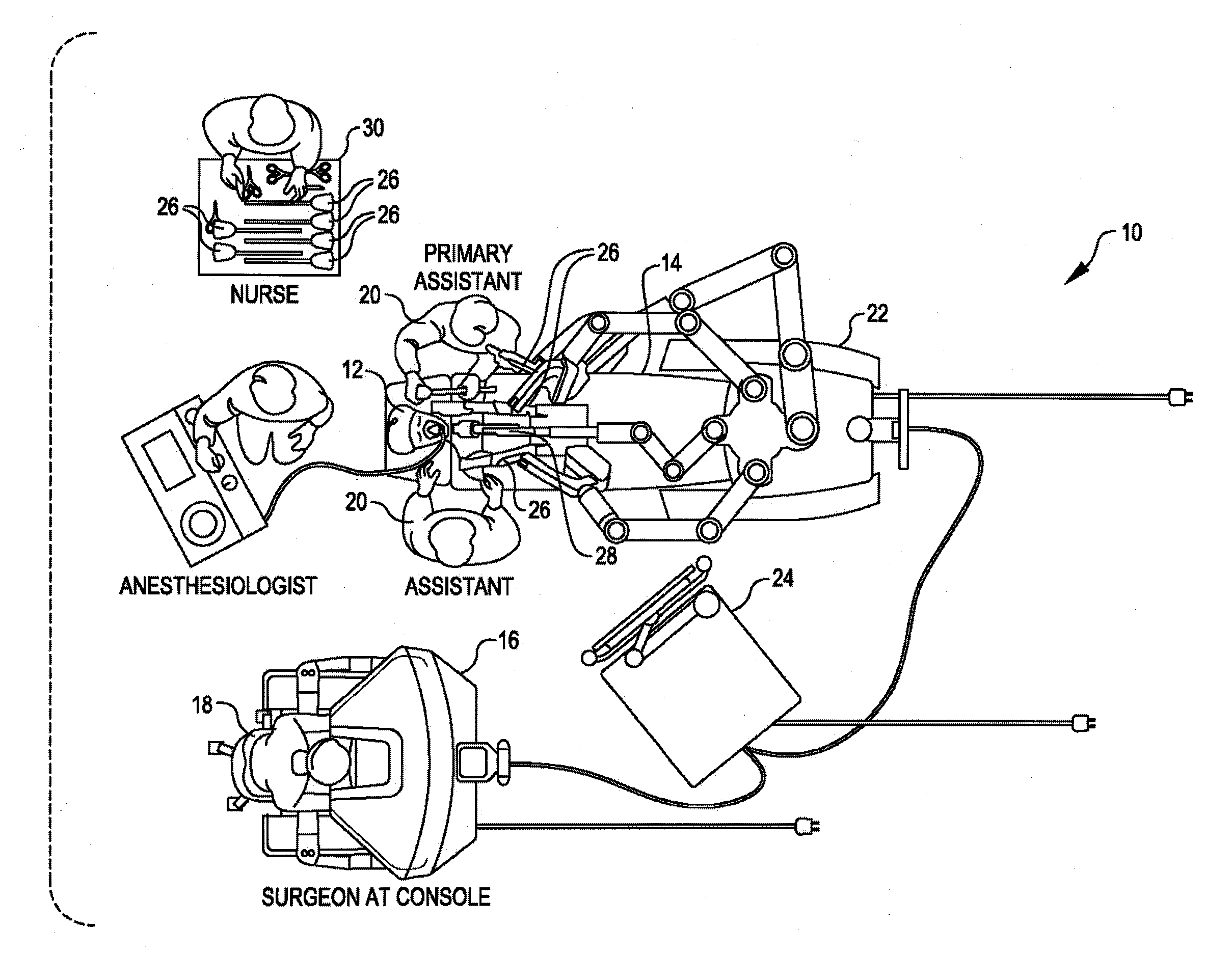
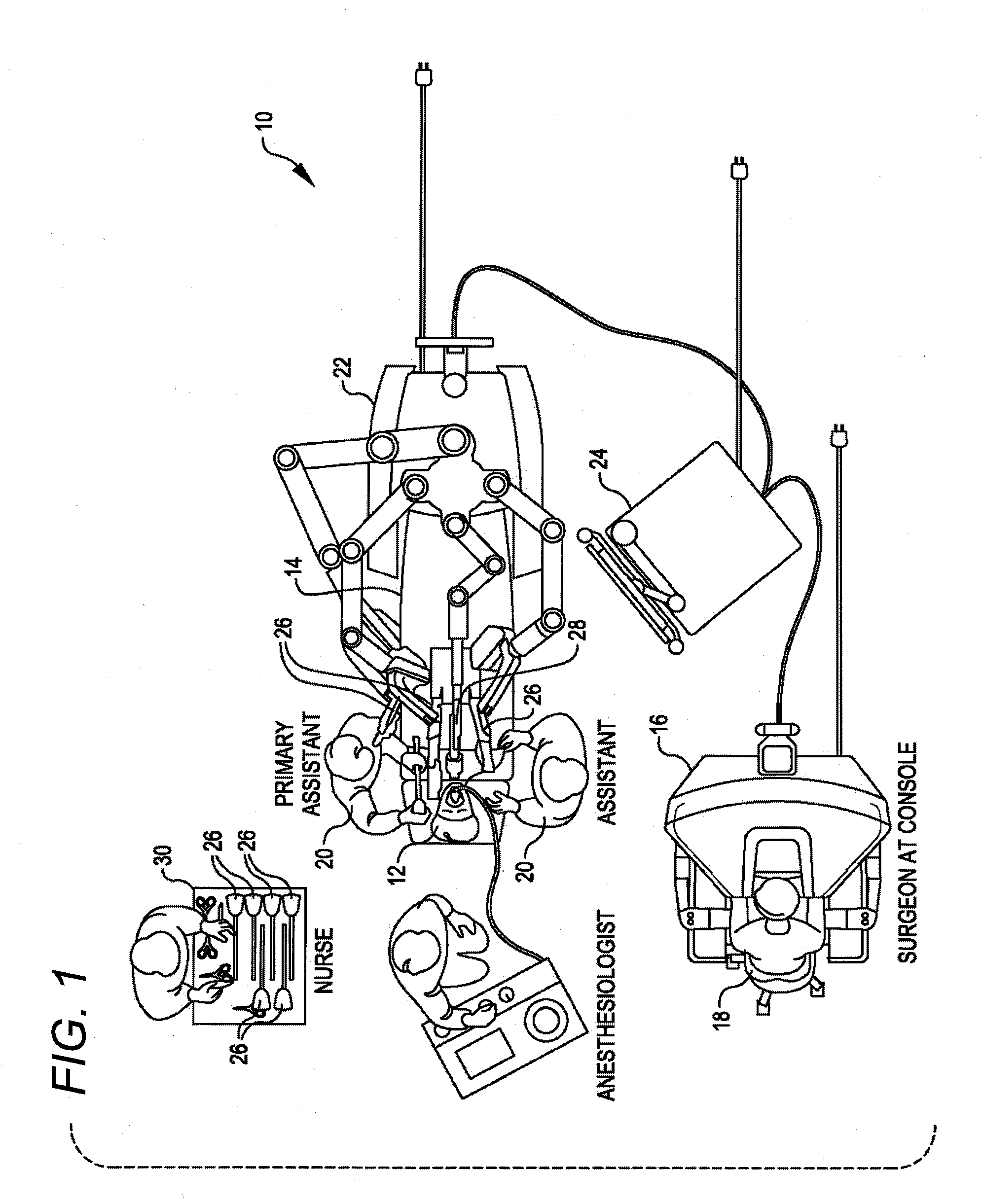
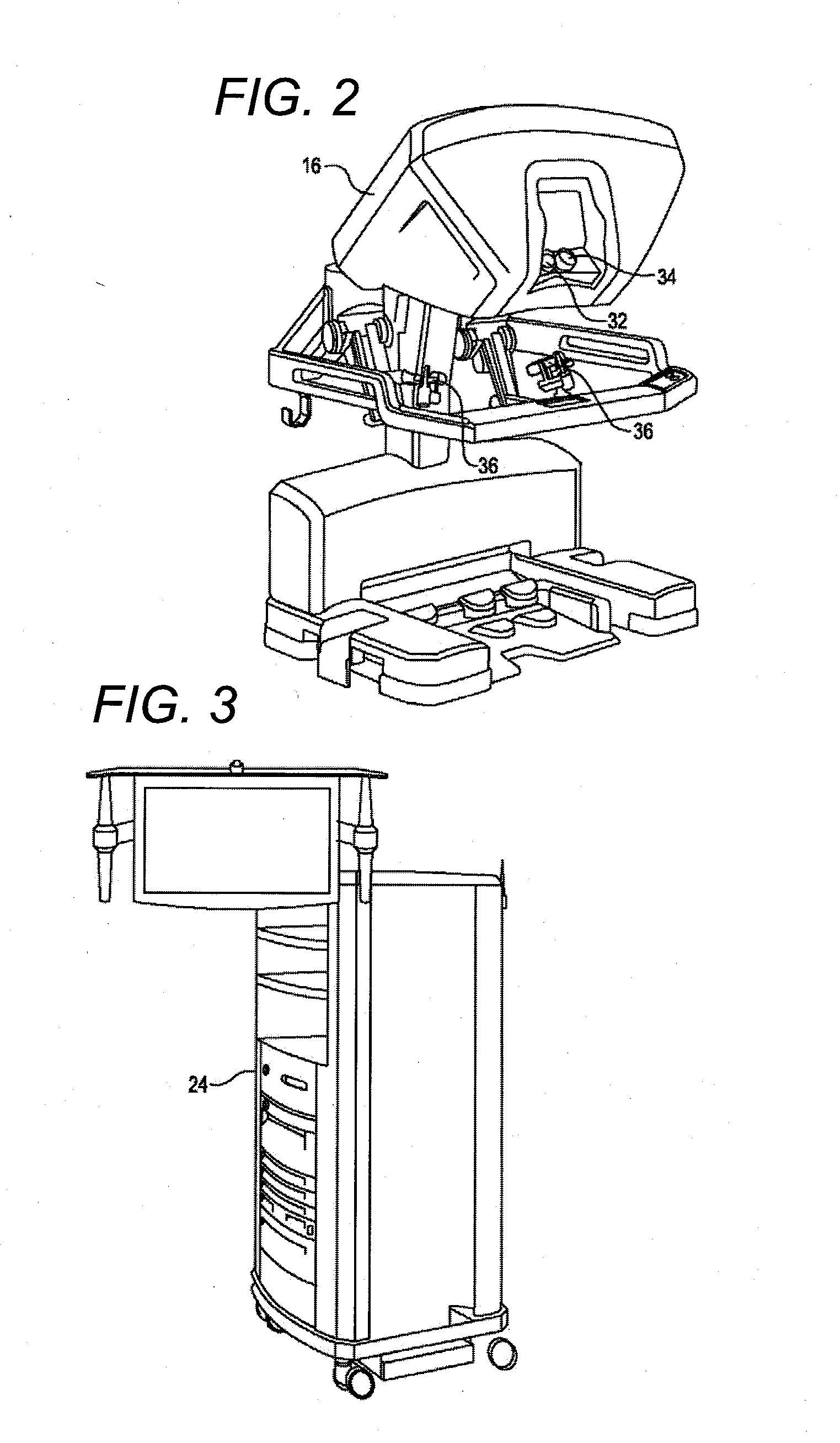
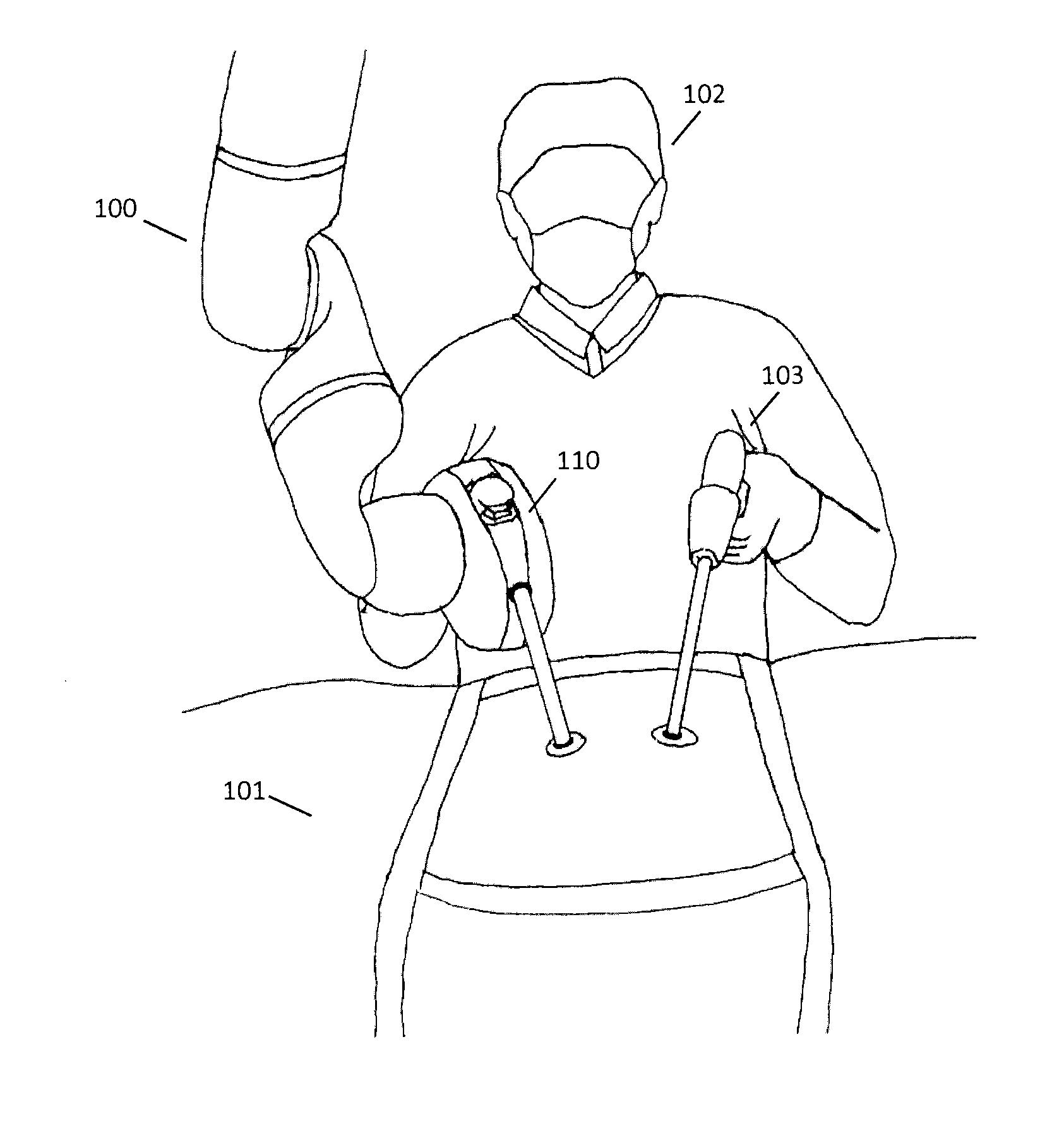
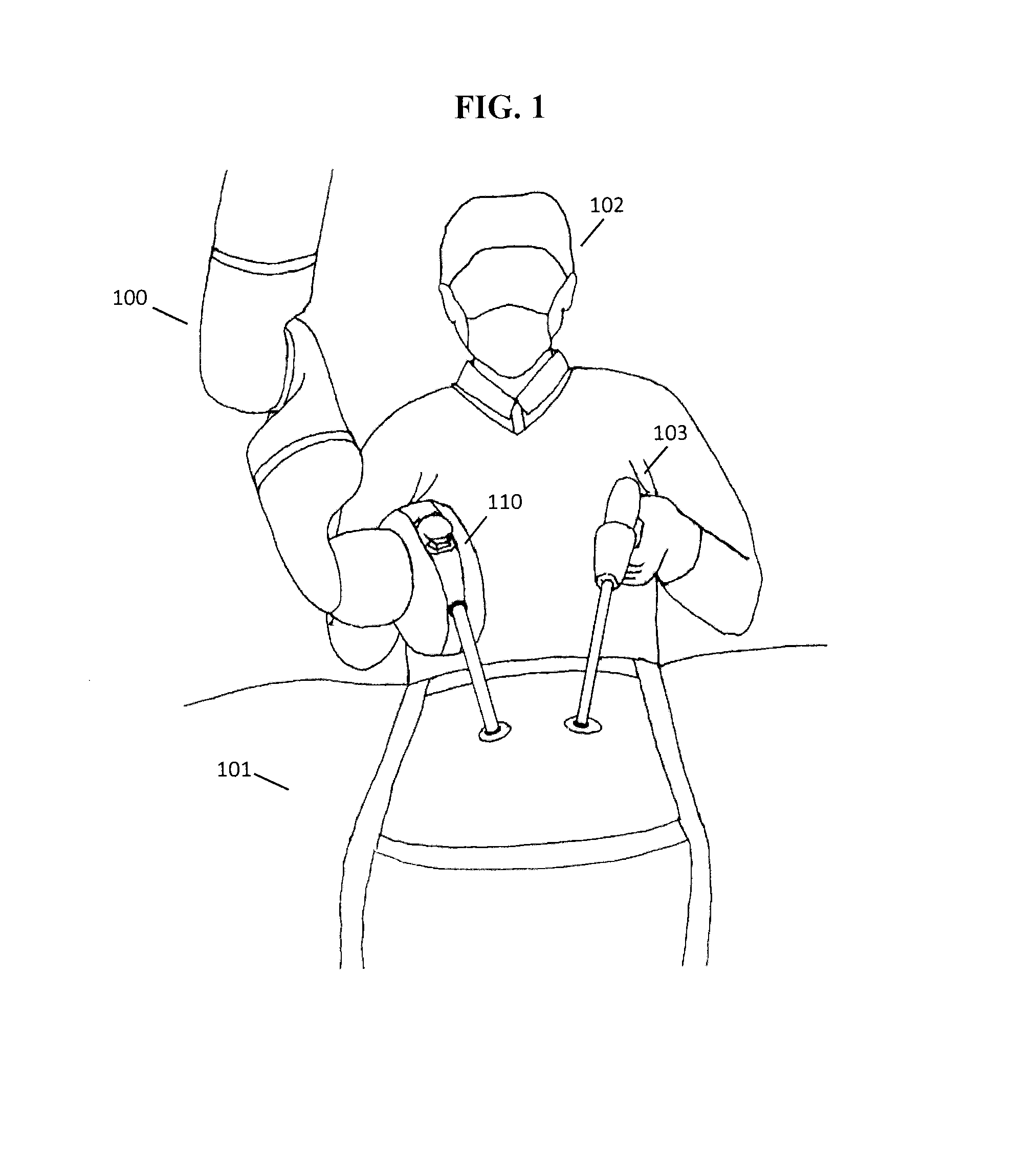
Robotic surgery are types of surgical procedures that are done using robotic systems. Robotically-assisted surgery was developed to try to overcome the limitations of pre-existing minimally-invasive surgical procedures and to enhance the capabilities of surgeons performing open surgery.
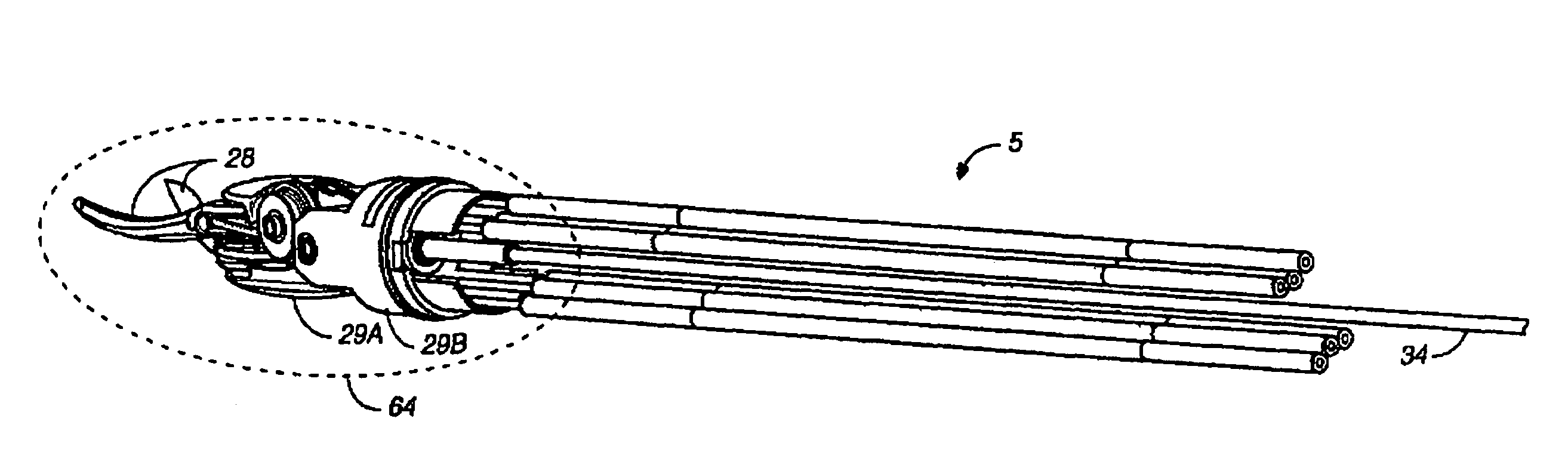
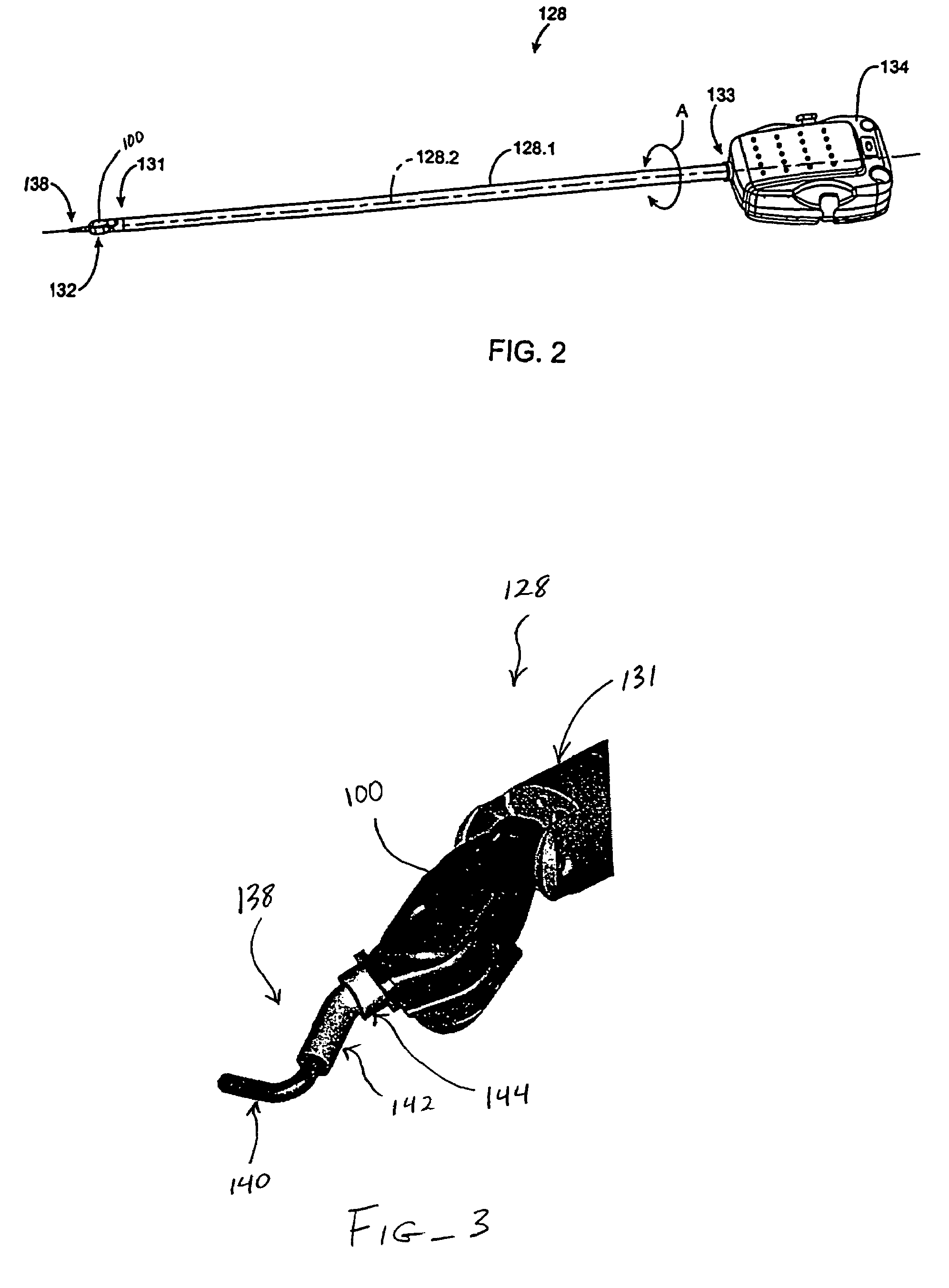
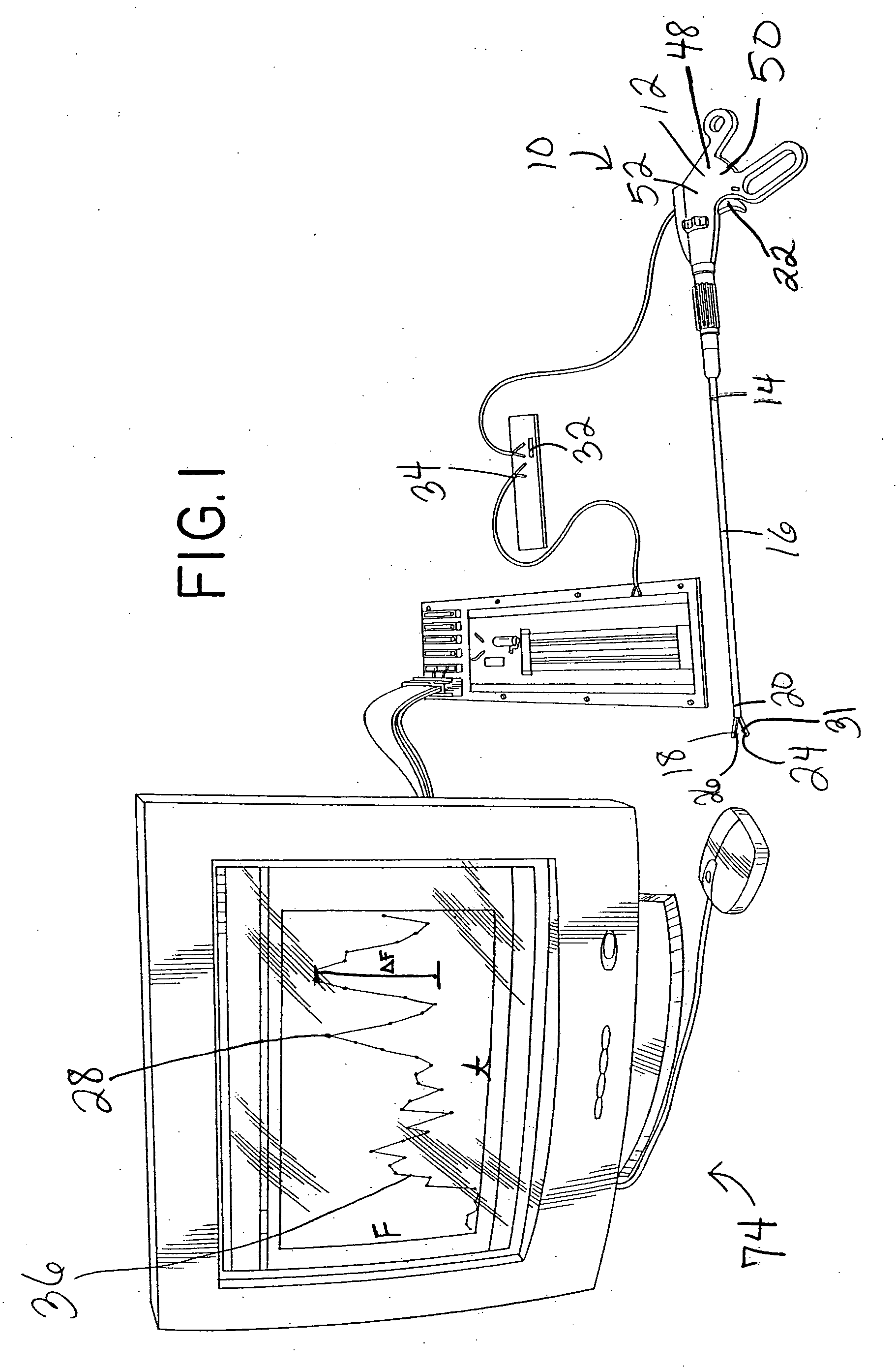
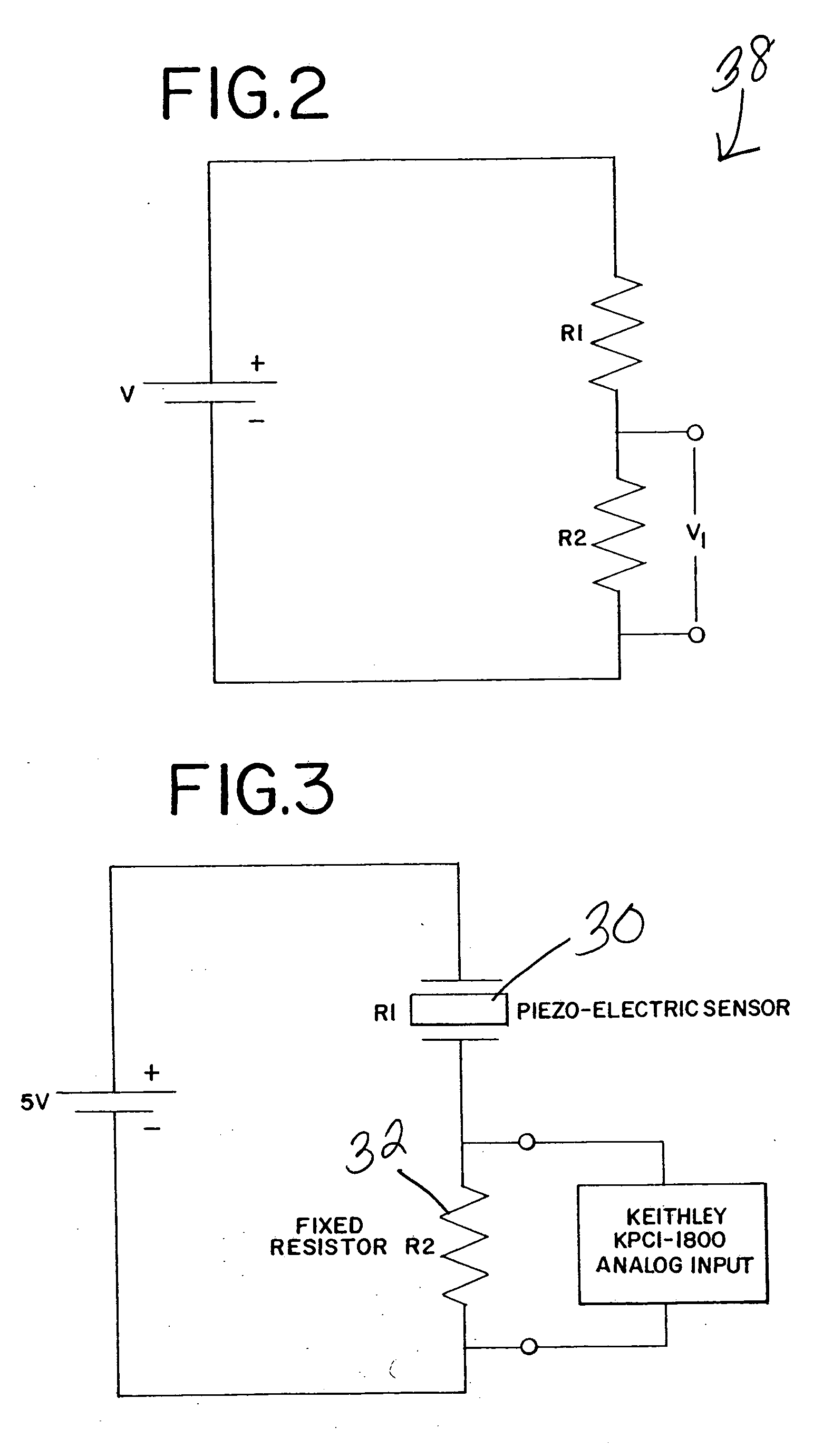
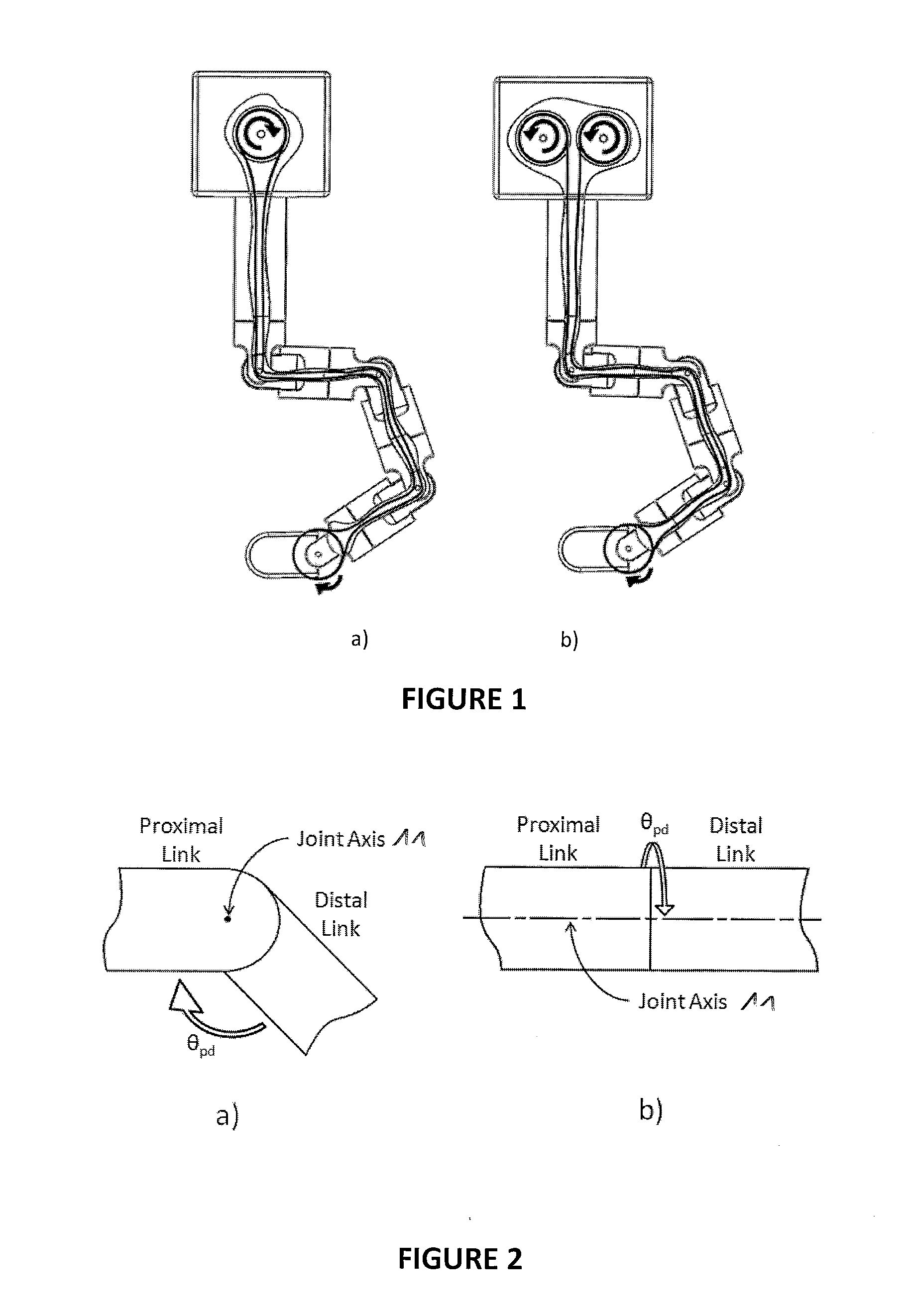
Robotic tool with wristed monopolar electrosurgical end effectors
ActiveUS7824401B2Avoid conductionSmall outer diameterDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingElectrical conductorBlood coagulations
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Surgical robotic tools, data architecture, and use
Robotic surgical tools, systems, and methods for preparing for and performing robotic surgery include a memory mounted on the tool. The memory can perform a number of functions when the tool is loaded on the tool manipulator: first, the memory can provide a signal verifying that the tool is compatible with that particular robotic system. Secondly, the tool memory may identify the tool-type to the robotic system so that the robotic system can reconfigure its programming. Thirdly, the memory of the tool may indicate tool-specific information, including measured calibration offsets indicating misalignment of the tool drive system, tool life data, or the like. This information may be stored in a read only memory (ROM), or in a nonvolatile memory which can be written to only a single time. The invention further provides improved engagement structures for coupling robotic surgical tools with manipulator structures.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Gentle touch surgical instrument and method of using same
A surgical grasper is provided. The grasper comprises a handle, two jaws operably connected to the handle, which jaws can be actuated by the handle, and a sensor. A surgical grasper for use in robotic surgery is also provided. The grasper comprises a shaft, two jaws at a distal end of the shaft, which jaws can be actuated in response to a robot command, and a sensor. A method for measuring an amount of force being applied by a jaw of a grasper is also provided. The method comprises the steps of: providing a grasper comprising a handle and two jaws operably connected to the handle, which jaws can be actuated by the handle; providing a sensor on the grasper; and, providing for measuring an amount of force being applied to the sensor. A method for measuring an amount of force being applied by a jaw of a grasper for use in robotic surgery is also provided. The method comprises the steps of: providing a grasper for use in robotic surgery, the grasper comprising a shaft and two jaws at a distal end of the shaft, which jaws can be actuated responsive to a robot command; providing a sensor; and, providing for measuring an amount of force being applied to the sensor. A surgical feedback system is also provided. The surgical feedback system comprises a surgical grasper capable of taking a force measurement and a data concentrator coupled to the grasper via a wired or wireless interface using a first data transmission protocol with internal storage. A method for obtaining surgical feedback is also provided. The method comprises the steps of: providing a surgical grasper capable of taking a force measurement; and, providing a data concentrator coupled to the grasper via a wired or wireless interface using a first data transmission protocol with internal storage.
Owner:TELESURGIX
Tool grip calibration for robotic surgery
ActiveUS7386365B2Limited tool lifeStringent manufacturing toleranceProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsEngineeringActuator
Telerobotic, telesurgical, and surgical robotic devices, systems, and methods selectively calibrate end effector jaws by bringing the jaw elements into engagement with each other. Commanded torque signals may bring the end effector elements into engagement while monitoring the resulting position of a drive system, optionally using a second derivative of the torque / position relationship so as to identify an end effector engagement position. Calibration can allow the end effector engagement position to correspond to a nominal closed position of an input handle by compensating for wear on the end effector, the end effector drive system, then manipulator, the manipulator drive system, the manipulator / end effector interfacing, and manufacturing tolerances.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
In vivo accessories for minimally invasive robotic surgery
InactiveUS7125403B2Reduce downtimeReduce needSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSurgical siteEngineering
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Grip force control in a robotic surgical instrument
ActiveUS9913694B2Minimally invasivePrevent movementDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsGrip forceEngineering
Surgical assemblies, instruments, and related methods are disclosed that control tissue gripping force. A surgical assembly includes an end effector including a jaw operable to grip a patient tissue and a spring assembly. The spring assembly includes an output link drivingly coupled with the jaw, an input link drivingly coupled to an articulation source, and a spring coupled with the input and output links to transfer an articulation force from the input link to the output link. The spring is preloaded to inhibit relative movement between the input link and the output link while the transferred articulation force is below a predetermined level and so as to allow relative movement between the input link and the output link when the transferred articulation force is above the predetermined level.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
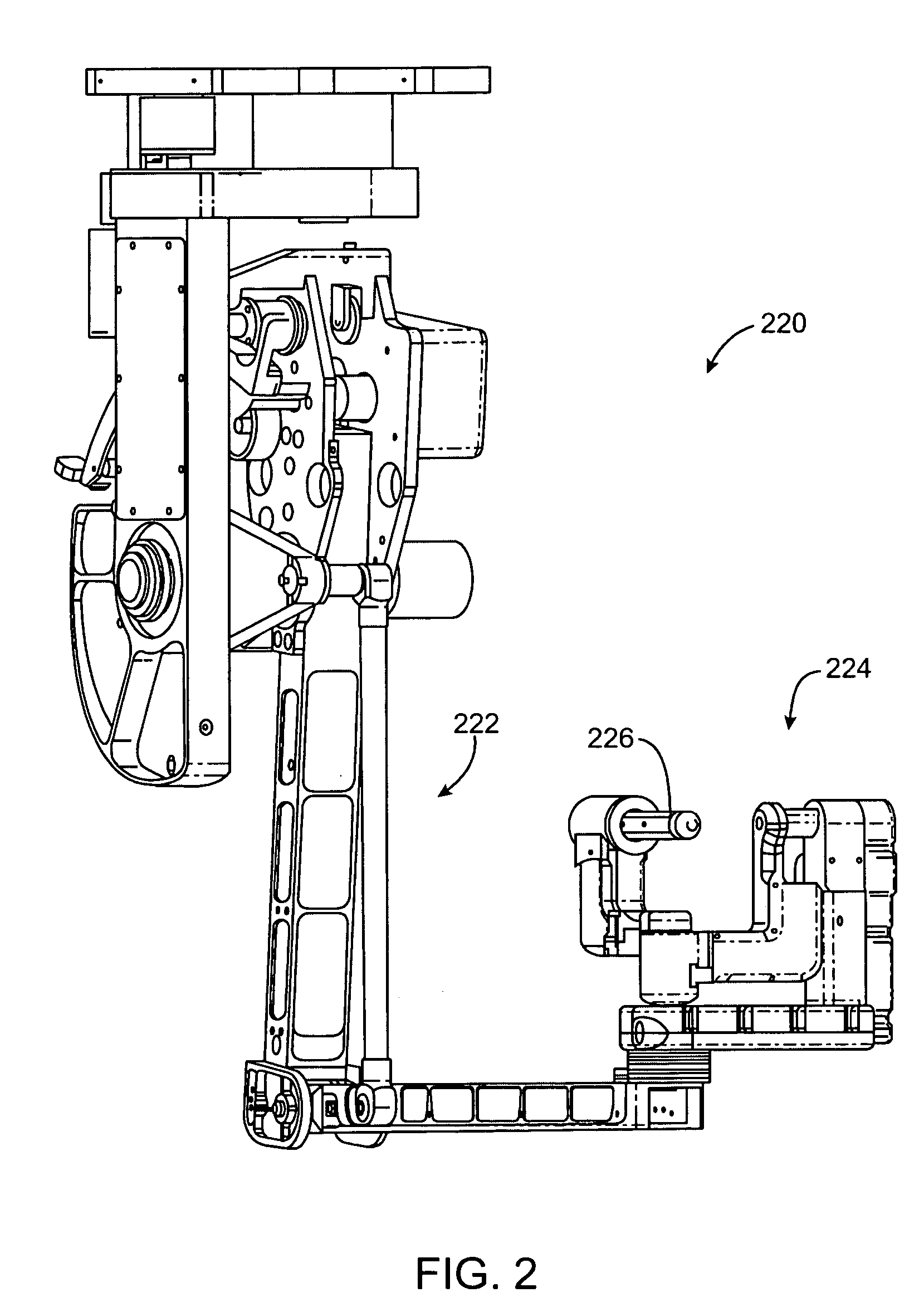
Offset remote center manipulator for robotic surgery
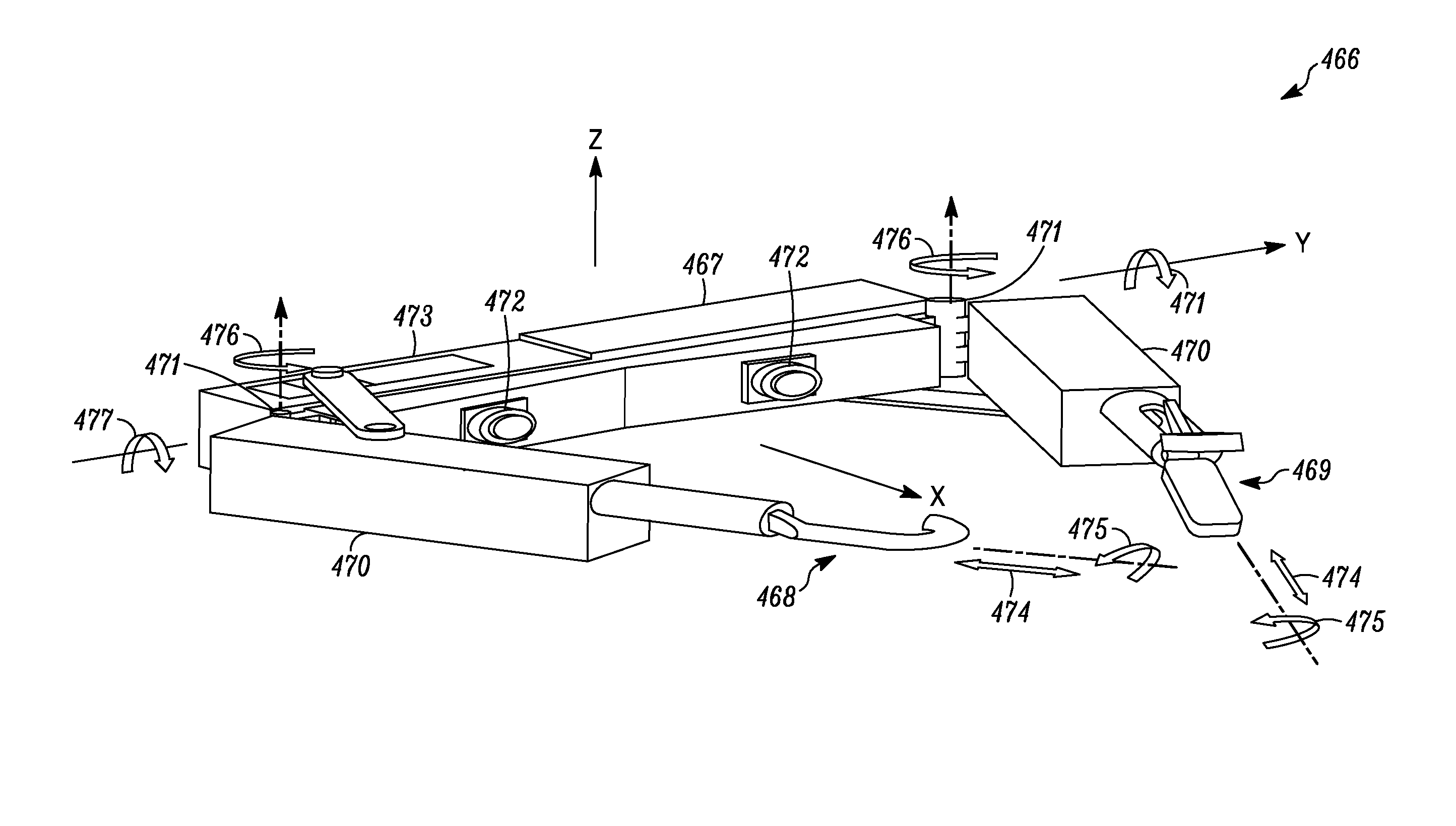
ActiveUS7594912B2Increase rangeReduces overall complexity and size and physical weightMechanical apparatusDiagnosticsEngineeringManipulator
Medical, surgical, and / or robotic devices and systems often including offset remote center parallelogram manipulator linkage assemblies which constrains a position of a surgical instrument during minimally invasive robotic surgery are disclosed. The improved remote center manipulator linkage assembly advantageously enhances the range of instrument motion while at the same time reduces the overall complexity, size, and physical weight of the robotic surgical system.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
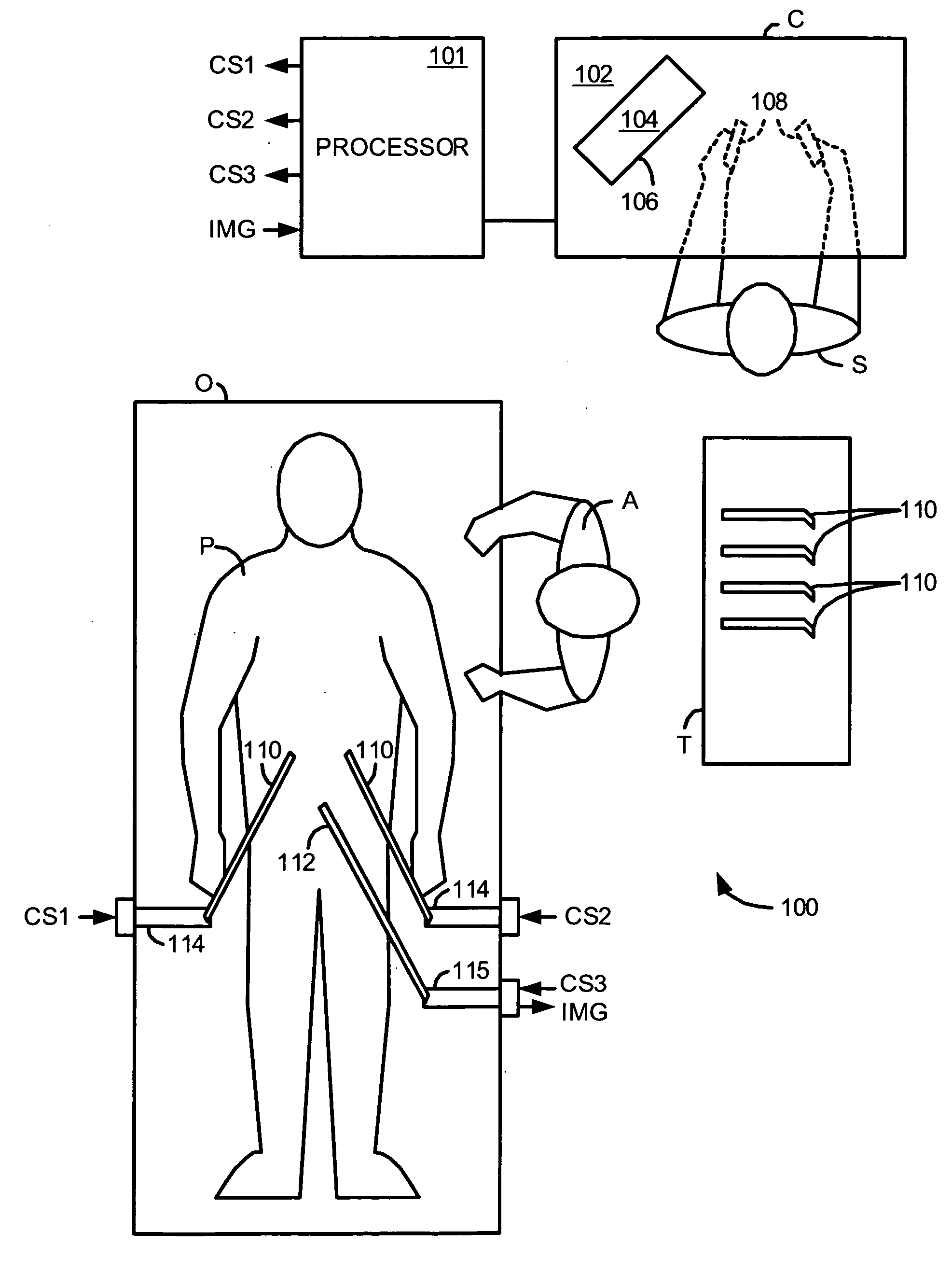
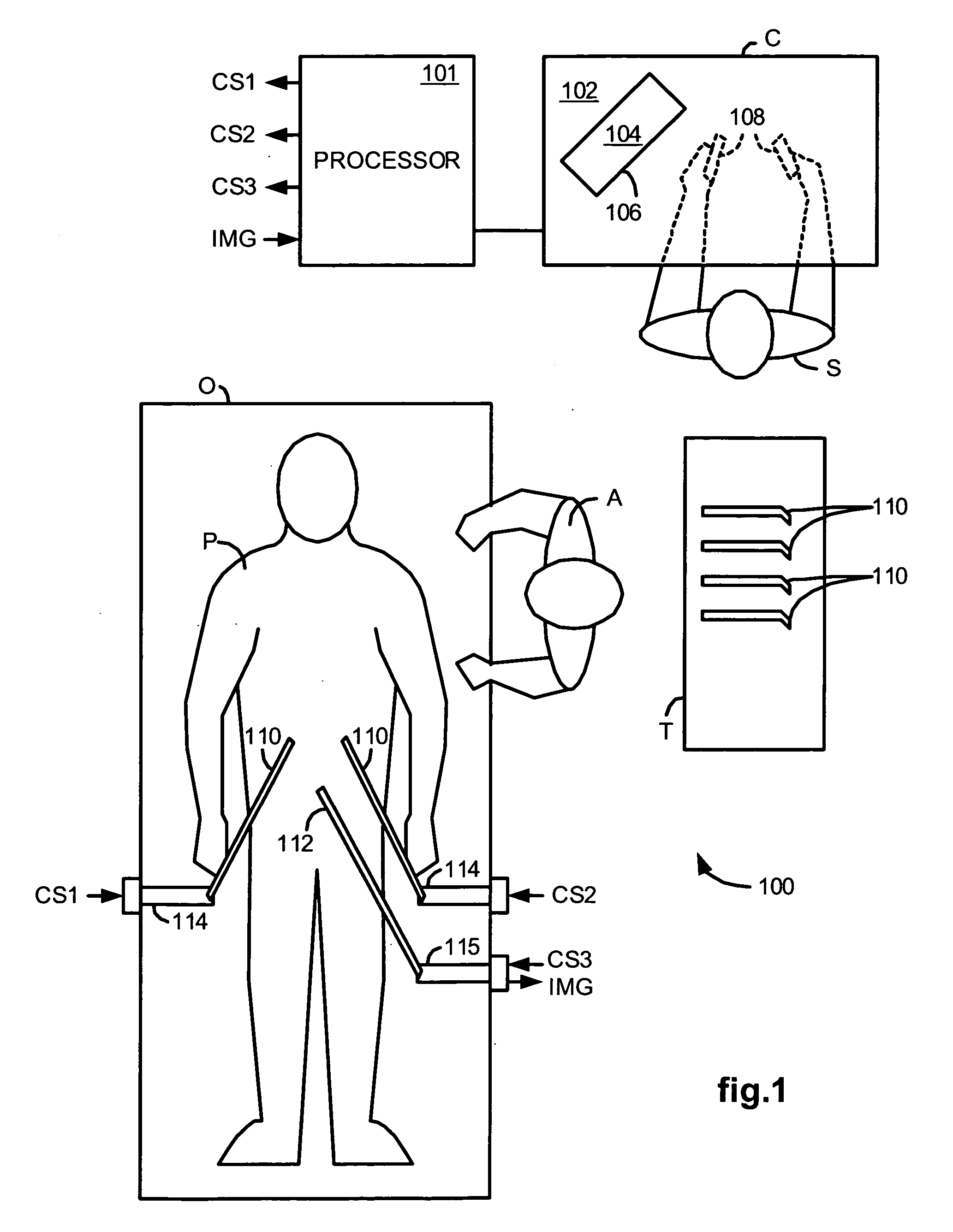
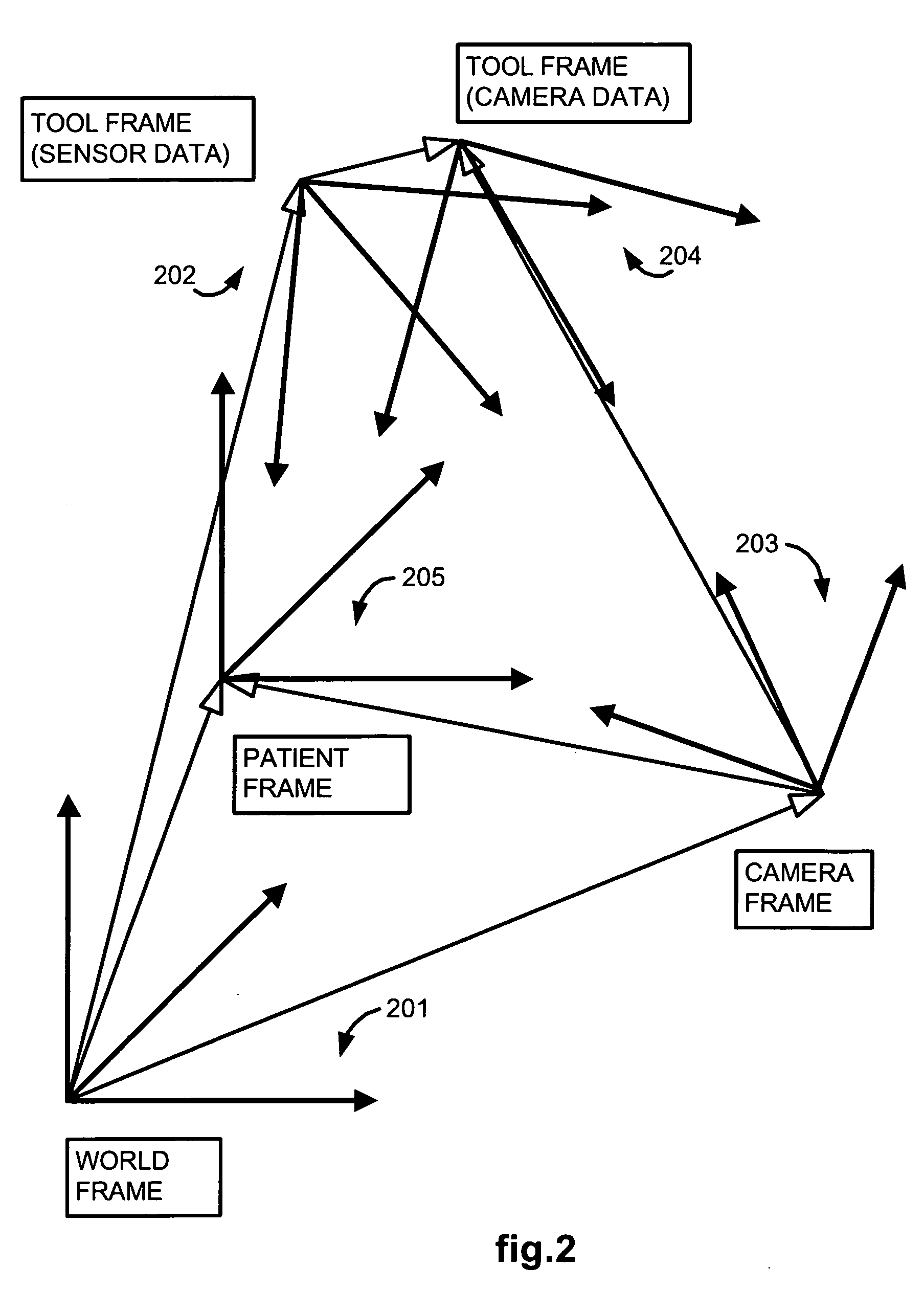
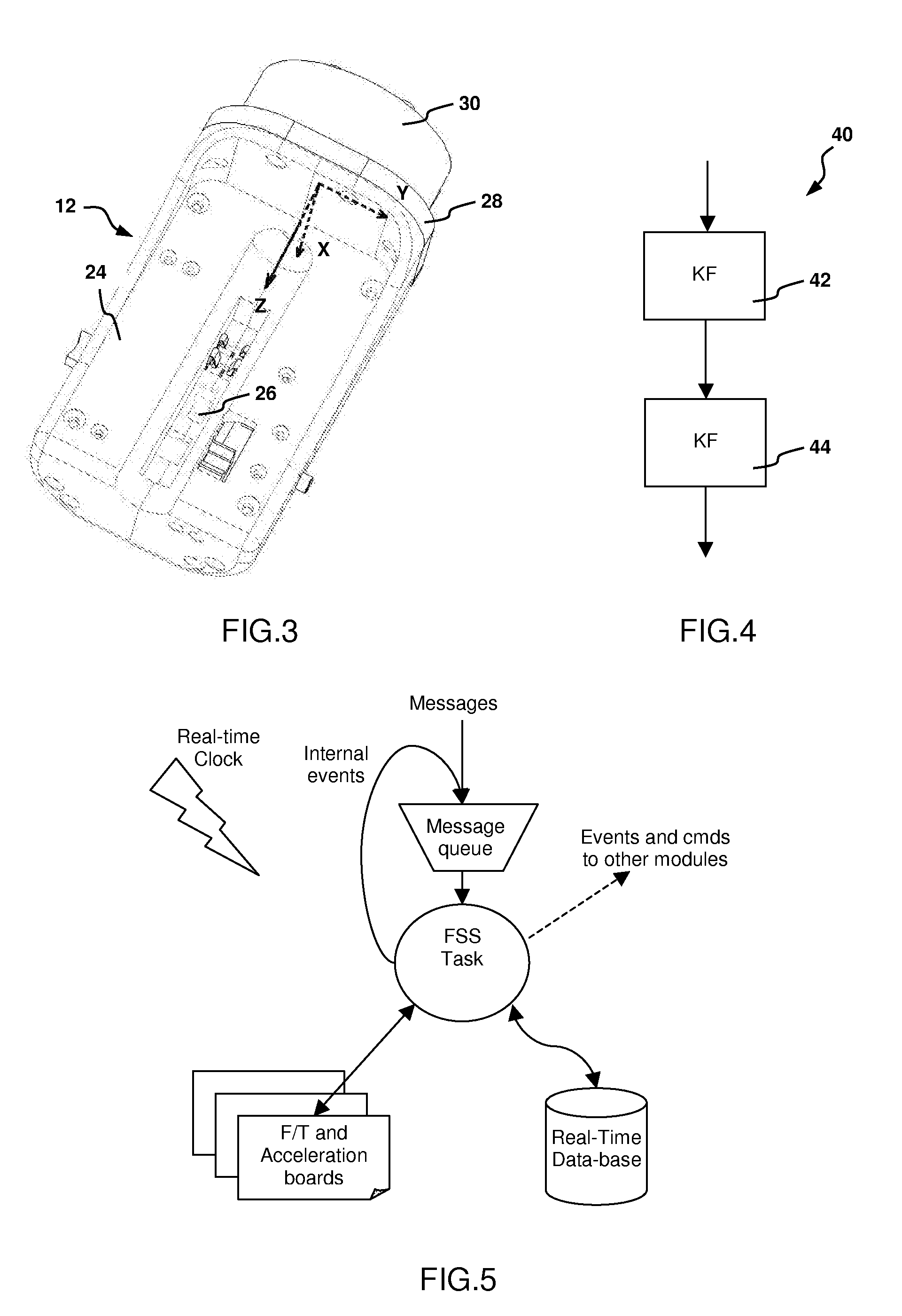
Methods and system for performing 3-D tool tracking by fusion of sensor and/or camera derived data during minimally invasive robotic surgery
ActiveUS20060258938A1Easy to distinguishFacilitate communicationSurgical navigation systemsLaproscopesTriangulationExternal camera
Methods and system perform tool tracking during minimally invasive robotic surgery. Tool states are determined using triangulation techniques or a Bayesian filter from either or both non-endoscopically derived and endoscopically derived tool state information, or from either or both non-visually derived and visually derived tool state information. The non-endoscopically derived tool state information is derived from sensor data provided either by sensors associated with a mechanism for manipulating the tool, or sensors capable of detecting identifiable signals emanating or reflecting from the tool and indicative of its position, or external cameras viewing an end of the tool extending out of the body. The endoscopically derived tool state information is derived from image data provided by an endoscope inserted in the body so as to view the tool.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Robotic visualization and collision avoidance
Methods and devices are provided for robotic surgery, and in particular for controlling various motions of a tool based on visual indicators. In general, a surgical tool can include an elongate shaft and an end effector coupled to a distal end of the elongate shaft and including first and second jaws. The tool can have at least one visual indicator disposed thereon and configured to indicate a size, position, or speed of movement of the tool or components of the tool.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Grip strength with tactile feedback for robotic surgery
InactiveUS6879880B2Enhanced telepresenceImprove grip strengthProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsSurgical robotEngineering
Surgical robots and other telepresence systems have enhanced grip actuation for manipulating tissues and objects with small sizes. A master / slave system is used in which an error signal or gain is artificially altered when grip members are near a closed configuration.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Electro-surgical instrument with replaceable end-effectors and inhibited surface conduction
ActiveUS7367973B2Avoid conductionInhibit currentDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingElectricityActive electrode
Improved robotic surgery end-effectors include at least one insulation material for inhibiting surface conduction of electrical current in a proximal direction, from a distal active electrode toward the proximal end of the end-effector and toward the rest of the surgical instrument itself. Some embodiments include two layers of insulation to further prevent proximally-directed current. By inhibiting proximal current flow, the end-effectors prevent unwanted patient burns as well as electricity-related wear and tear in and around the area where the end-effector is coupled with the rest of the surgical instrument. In various embodiments, such end-effectors are preferably removably coupleable with a robotic surgical instrument.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
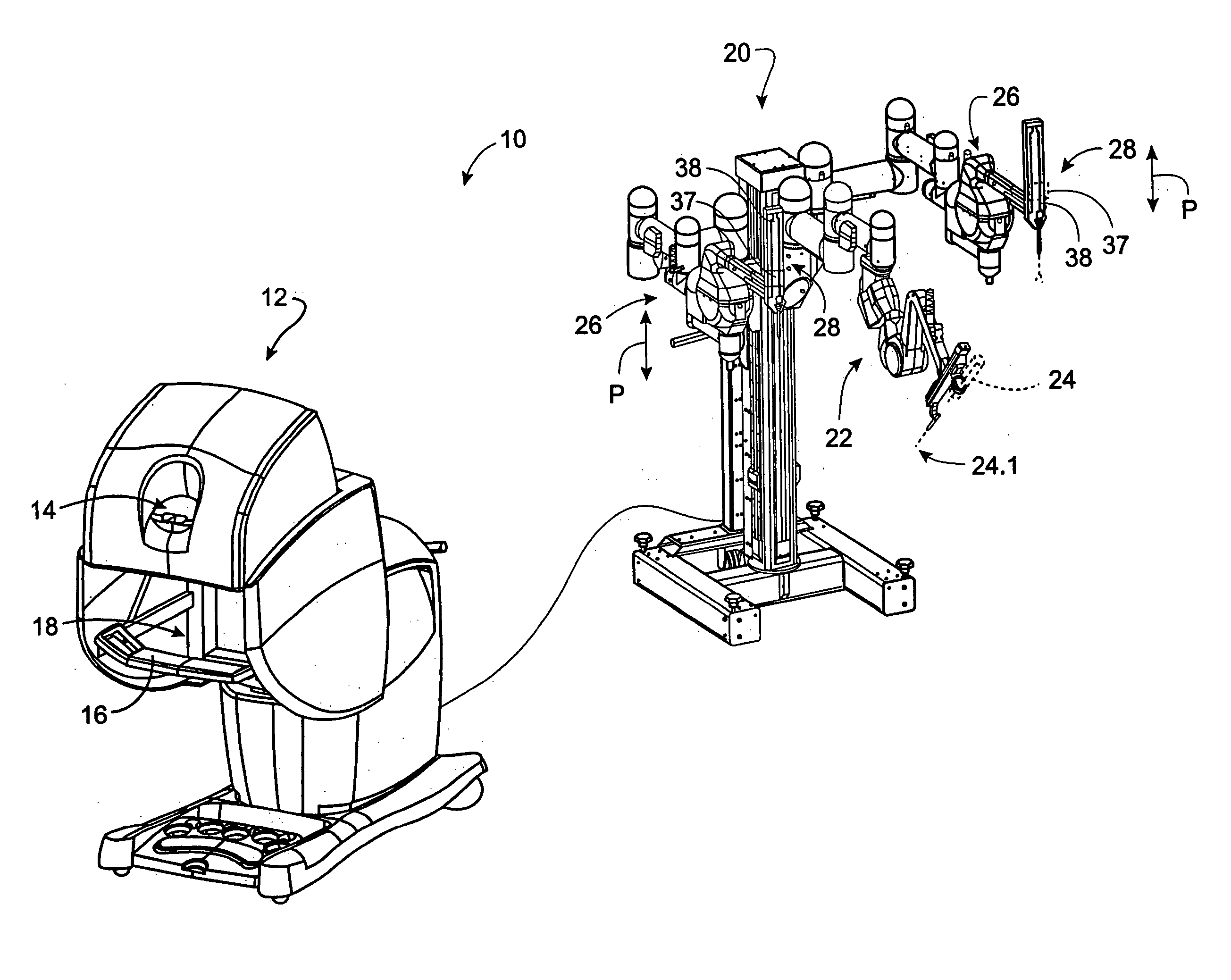
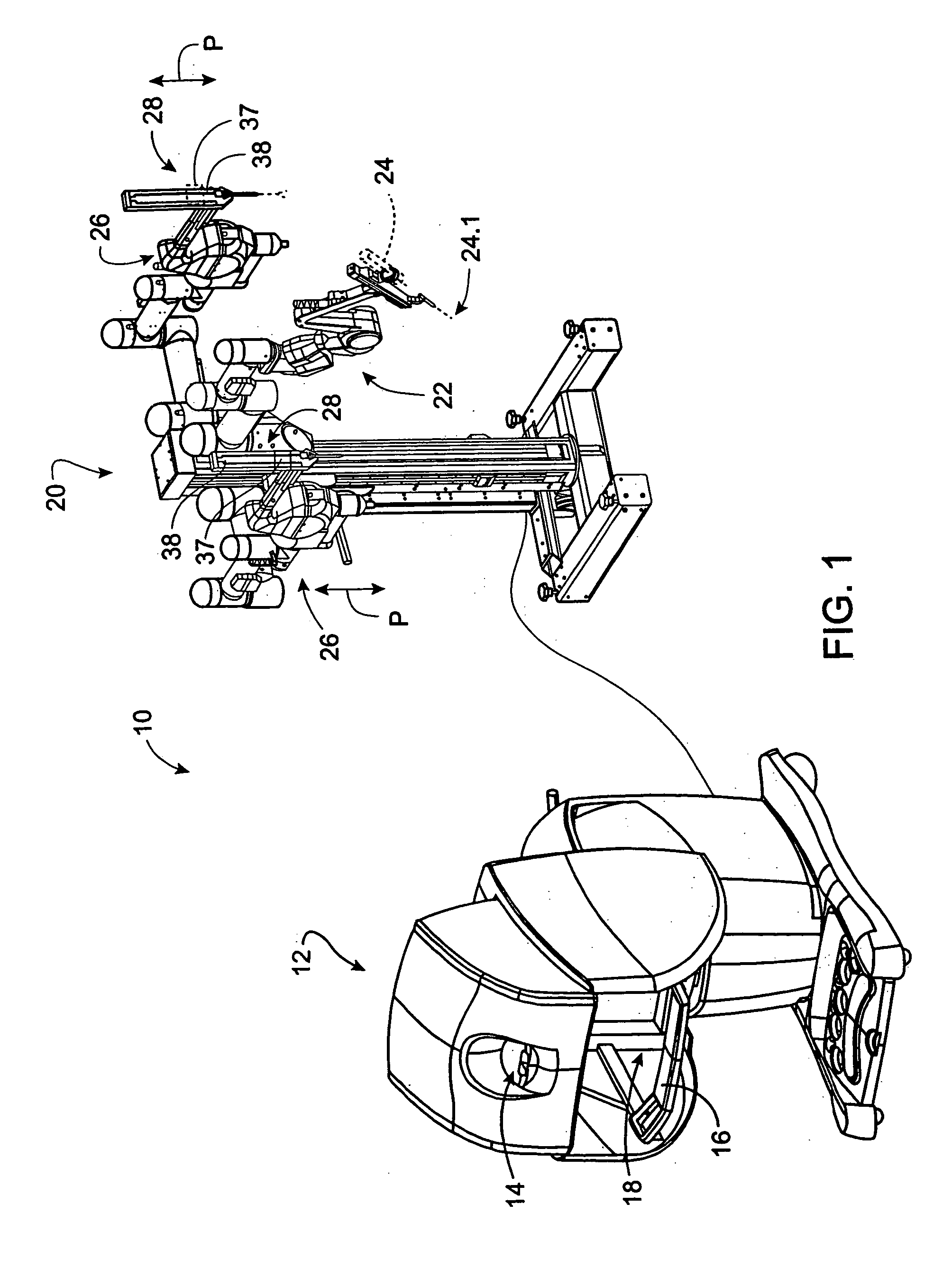
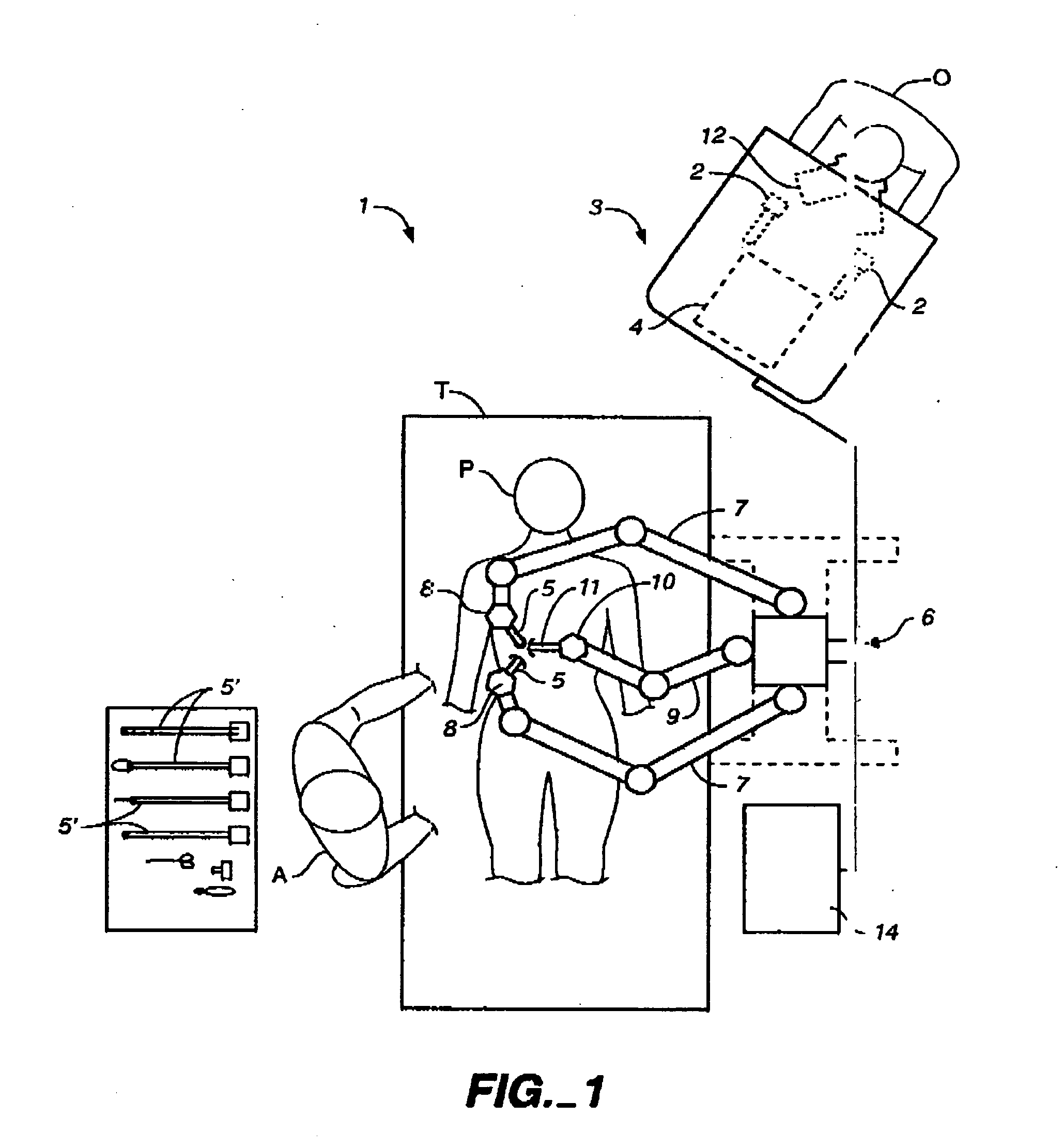
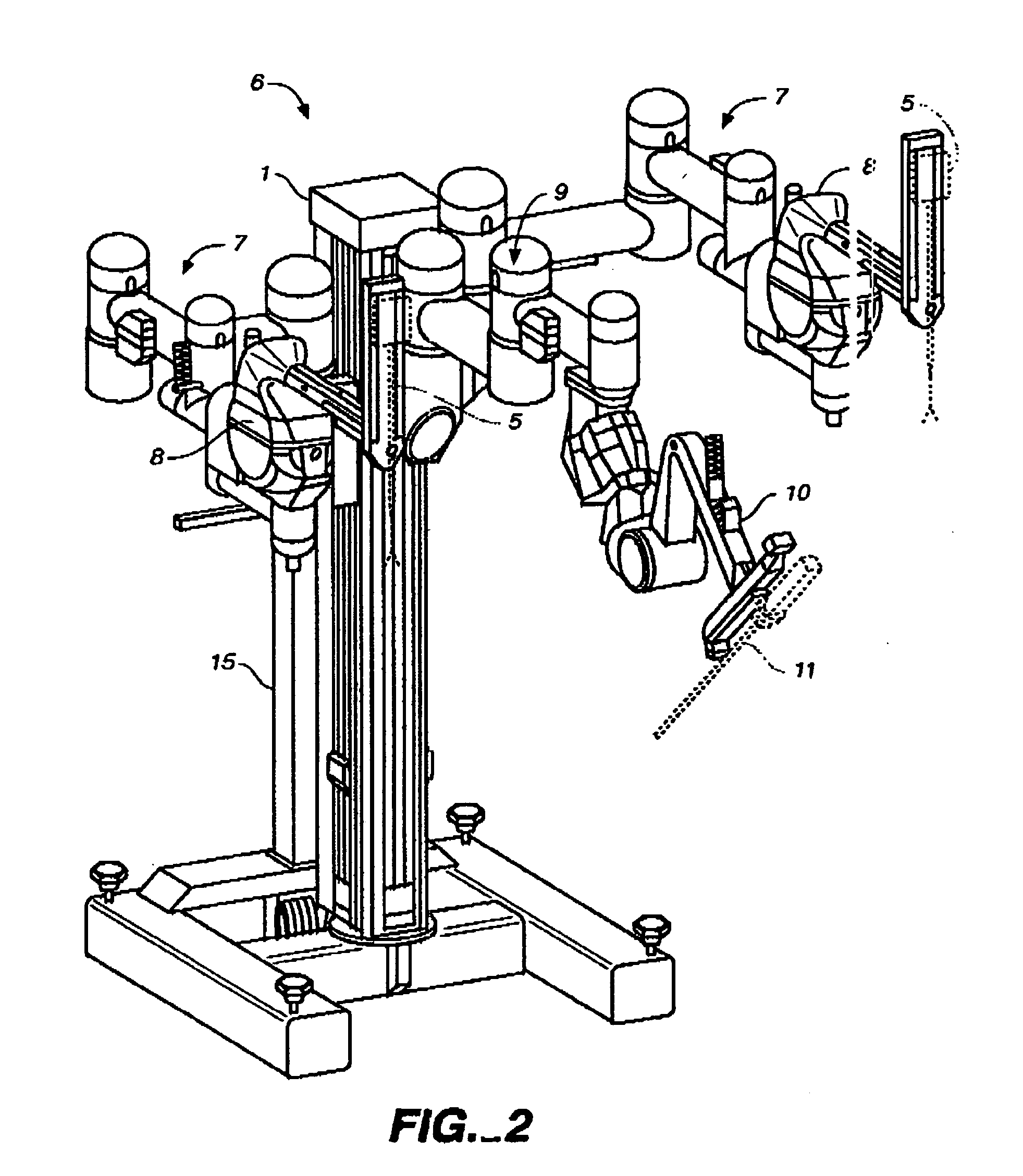
Modular manipulator support for robotic surgery
InactiveUS7763015B2Simple structureReduce complexityDiagnosticsRobotSurgical instrumentationModularity
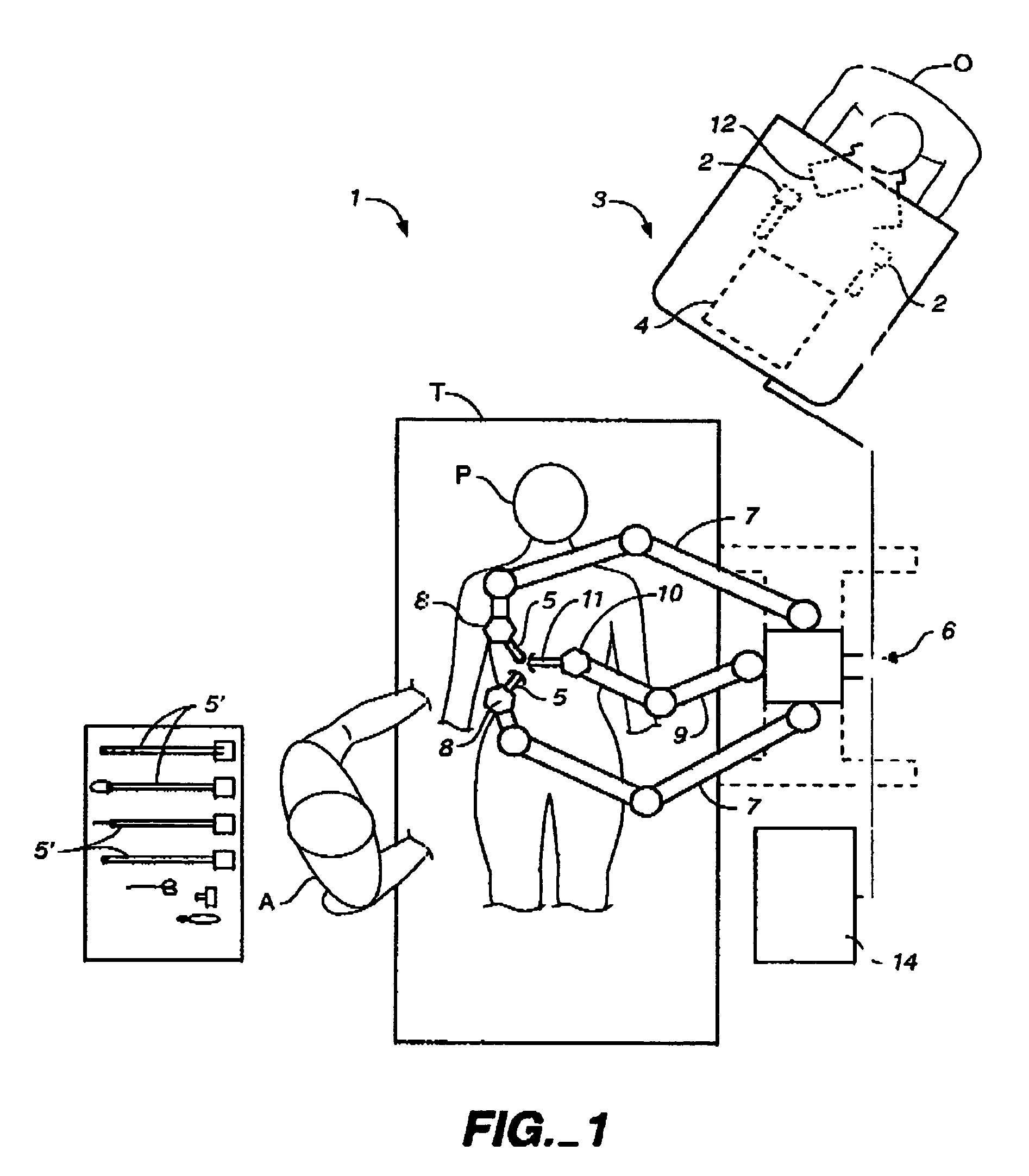
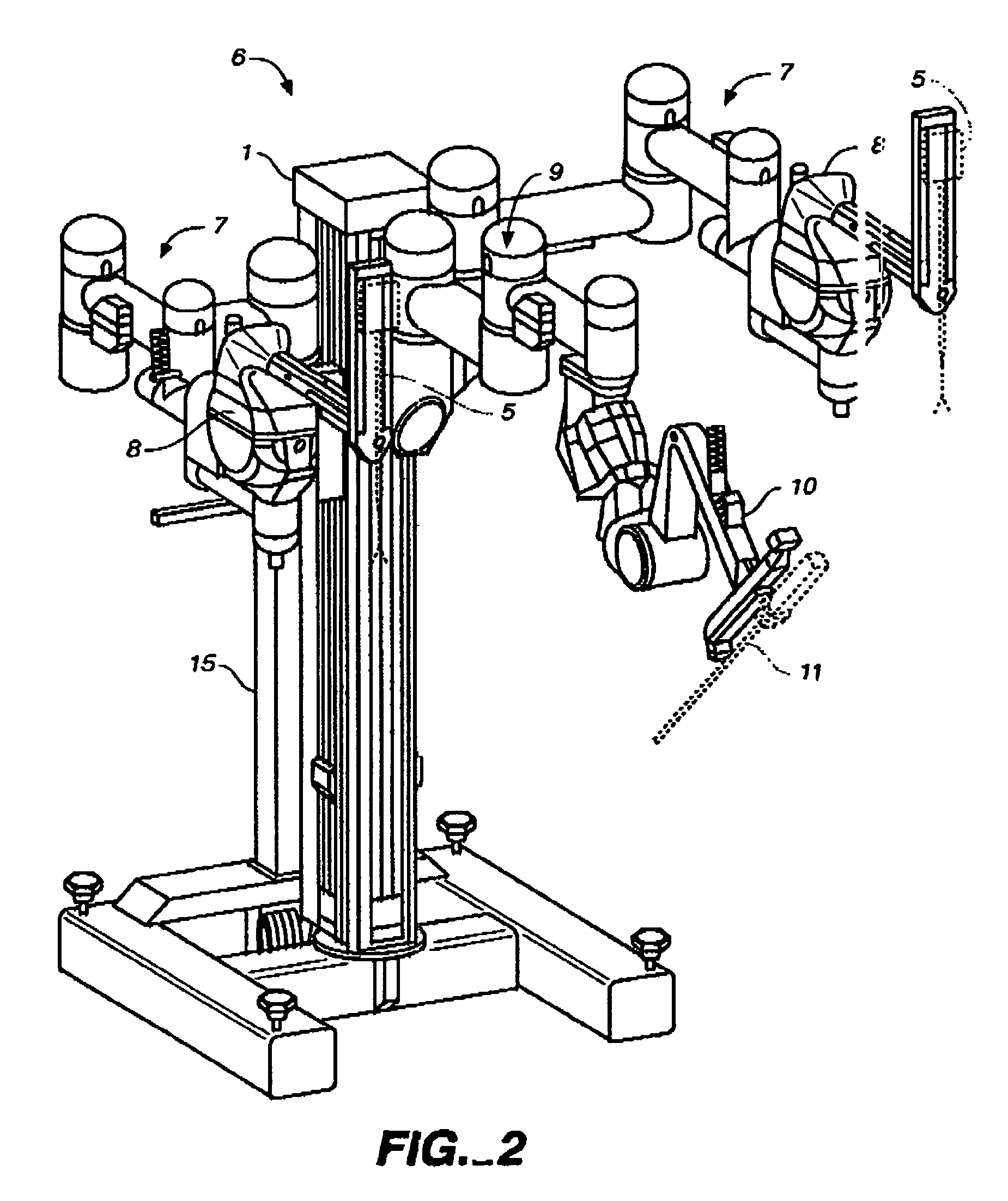
A robotic surgery system comprises a mounting base, a plurality of surgical instruments, and an articulate support assembly. Each instrument is insertable into a patient through an associated minimally invasive aperture to a desired internal surgical site. The articulate support assembly movably supports the instruments relative to the base. The support generally comprises an orienting platform, a platform linkage movably supporting the orienting platform relative to the base, and a plurality of manipulators mounted to the orienting platform, wherein each manipulator movably supports an associated instrument.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
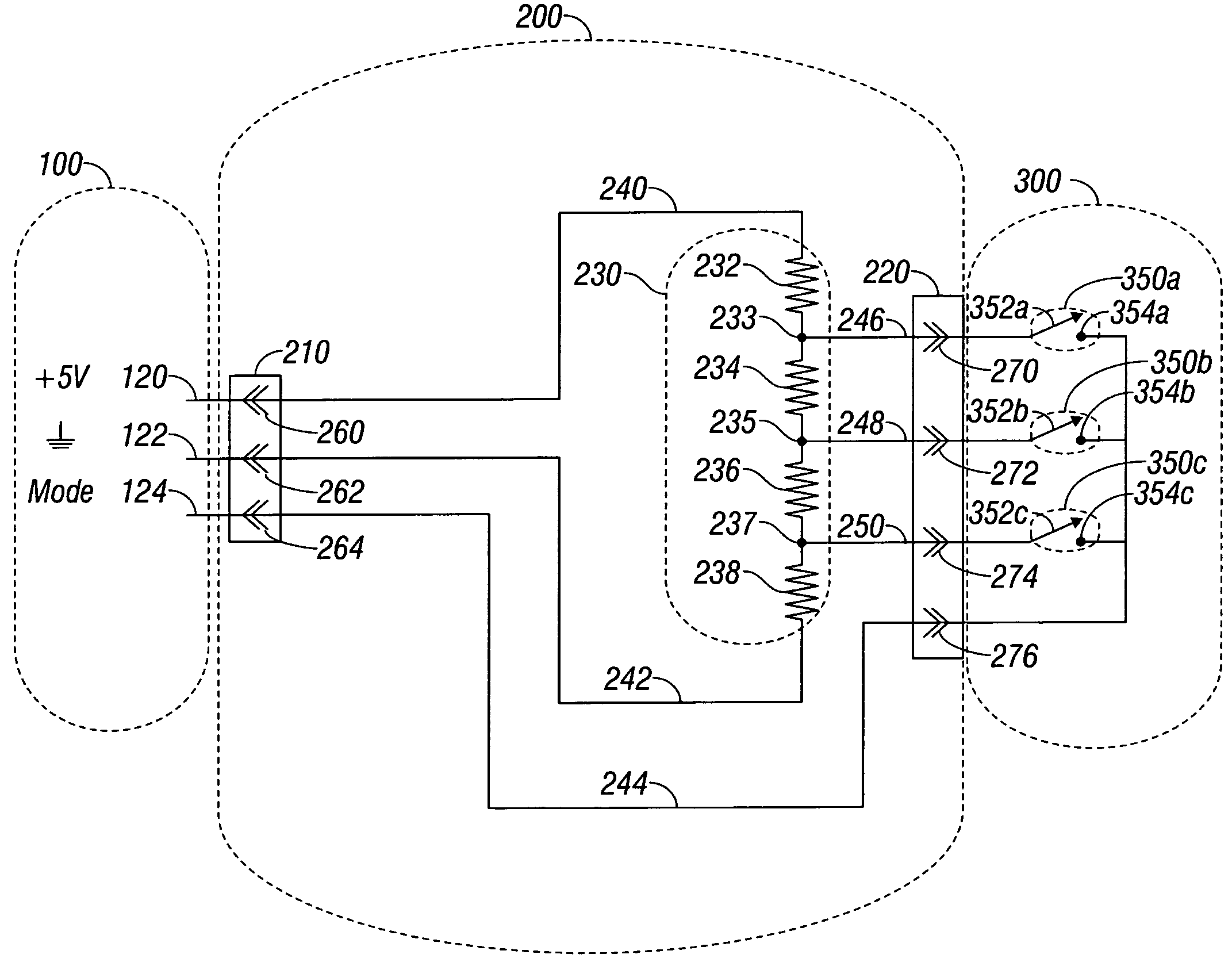
Connection cable and method for activating a voltage-controlled generator
ActiveUS7834484B2Batteries circuit arrangementsIncorrect coupling preventionSurgical operationElectrosurgery
A connection cable is disclosed for controlling a voltage-controlled generator such as an electrosurgery generator from a controlling device such as a robotic surgery system. The cable includes a first connector adapted to connect to a voltage-controlled generator and a second connector adapted to connect to a controlling device. Within the cable is a voltage divider interdisposed between the first connector and the second connector. The voltage divider is configured to divide a reference voltage provided by the voltage-controlled generator into at least one control voltage which is selectable by the controlling device. The cable additionally includes a plurality of electrical wires which operatively connect the first connector, the second connector and the voltage divider. During robotic electrosurgery, said operating parameters can be actuated by a surgeon operating at the robotic surgical system console, which causes a corresponding control voltage to be switched to a control voltage input on an electrosurgery generator, which, in turn, generates a corresponding electrosurgical signal in response thereto.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Gentle touch surgical instrument and method of using same
A surgical grasper is provided. The grasper comprises a handle, two jaws operably connected to the handle, which jaws can be actuated by the handle, and a sensor. A surgical grasper for use in robotic surgery is also provided. The grasper comprises a shaft, two jaws at a distal end of the shaft, which jaws can be actuated in response to a robot command, and a sensor. A method for measuring an amount of force being applied by a jaw of a grasper is also provided. The method comprises the steps of: providing a grasper comprising a handle and two jaws operably connected to the handle, which jaws can be actuated by the handle; providing a sensor on the grasper; and, providing for measuring an amount of force being applied to the sensor. A method for measuring an amount of force being applied by a jaw of a grasper for use in robotic surgery is also provided. The method comprises the steps of: providing a grasper for use in robotic surgery, the grasper comprising a shaft and two jaws at a distal end of the shaft, which jaws can be actuated responsive to a robot command; providing a sensor; and, providing for measuring an amount of force being applied to the sensor.
Owner:TELESURGIX
Robotic surgical tool with ultrasound cauterizing and cutting instrument
InactiveUS20050021018A1Enhancing robotic surgeryPrecise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSurgical siteActuator
A surgical instrument for enhancing robotic surgery generally includes an elongate shaft with an ultrasound probe, an end effector at the distal end of the shaft, and a base at the proximal end of the shaft. The end effector includes an ultrasound probe tip and the surgical instrument is generally configured for convenient positioning of the probe tip within a surgical site by a robotic surgical system. Ultrasound energy delivered by the probe tip may be used to cut, cauterize, or achieve various other desired effects on tissue at a surgical site. In various embodiments, the end effector also includes a gripper, for gripping tissue in cooperation with the ultrasound probe tip. The base is generally configured to removably couple the surgical instrument to a robotic surgical system and to transmit forces from the surgical system to the end effector, through the elongate shaft. A method for enhancing robotic surgery generally includes coupling the surgical instrument to a robotic surgical system, positioning the probe tip in contact with tissue at a surgical site, and delivering ultrasound energy to the tissue.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL
Methods and apparatus for surgical planning
ActiveUS7607440B2Easy to planPrecise positioningProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSurgical siteEngineering
Methods and apparatus for enhancing surgical planning provide enhanced planning of entry port placement and / or robot position for laparoscopic, robotic, and other minimally invasive surgery. Various embodiments may be used in robotic surgery systems to identify advantageous entry ports for multiple robotic surgical tools into a patient to access a surgical site. Generally, data such as imaging data is processed and used to create a model of a surgical site, which can then be used to select advantageous entry port sites for two or more surgical tools based on multiple criteria. Advantageous robot positioning may also be determined, based on the entry port locations and other factors. Validation and simulation may then be provided to ensure feasibility of the selected port placements and / or robot positions. Such methods, apparatus, and systems may also be used in non-surgical contexts, such as for robotic port placement in munitions diffusion or hazardous waste handling.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC +1
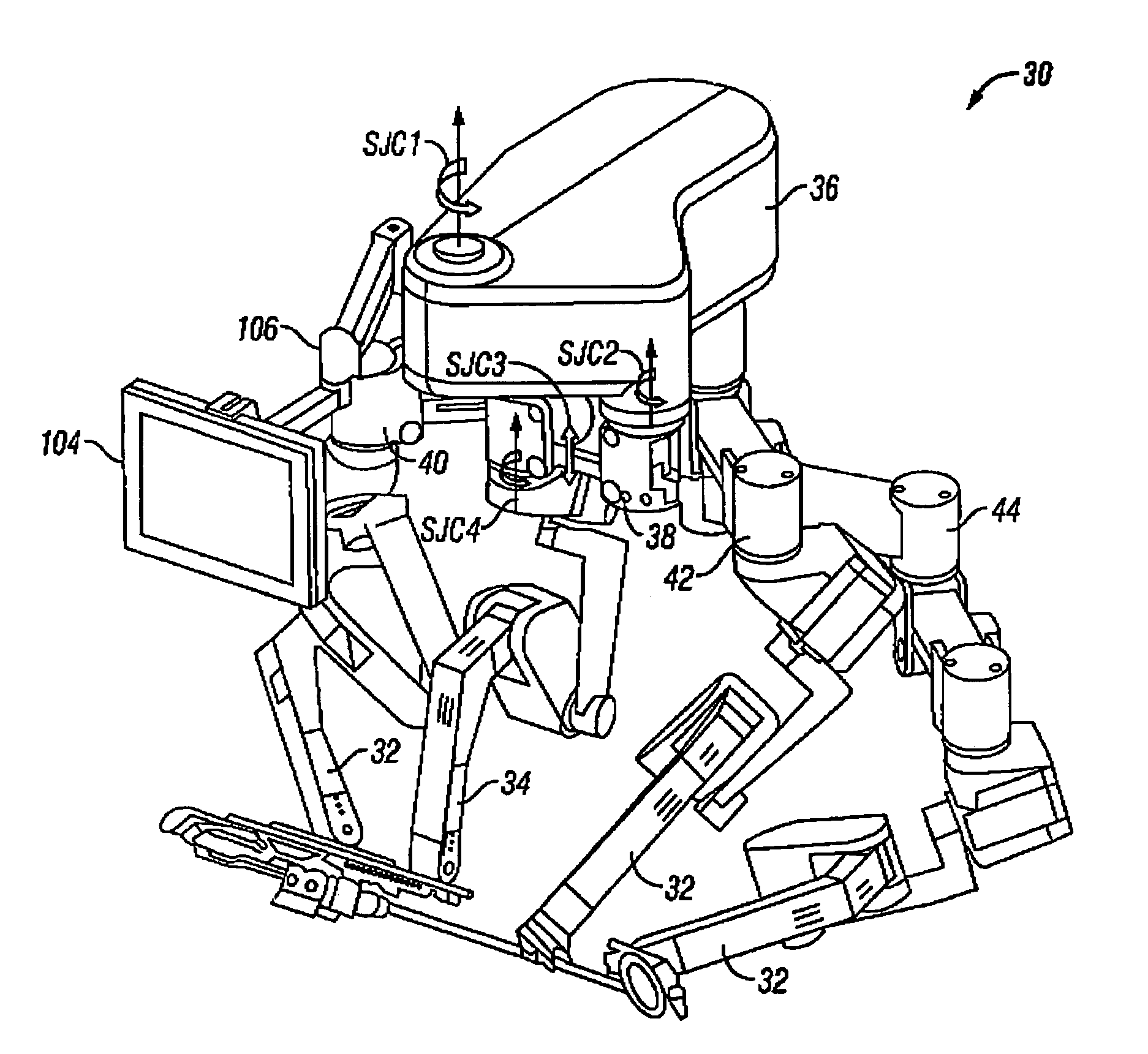
Multi-port surgical robotic system architecture
ActiveUS20130325033A1Improve mobilityEasy and fast setupPortable framesDiagnosticsRobotic systemsEngineering
A robotic surgery system includes an orienting platform, a support linkage movably supporting the orienting platform, a plurality of surgical instrument manipulators, and a plurality of set-up linkages. Each of the manipulators includes an instrument holder and is operable to rotate the instrument holder around a remote center of manipulation (RC). At least one of the manipulators includes a reorientation mechanism that when actuated moves the attached manipulator through a motion that maintains the associated RC in a fixed position.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Hybrid control surgical robotic system
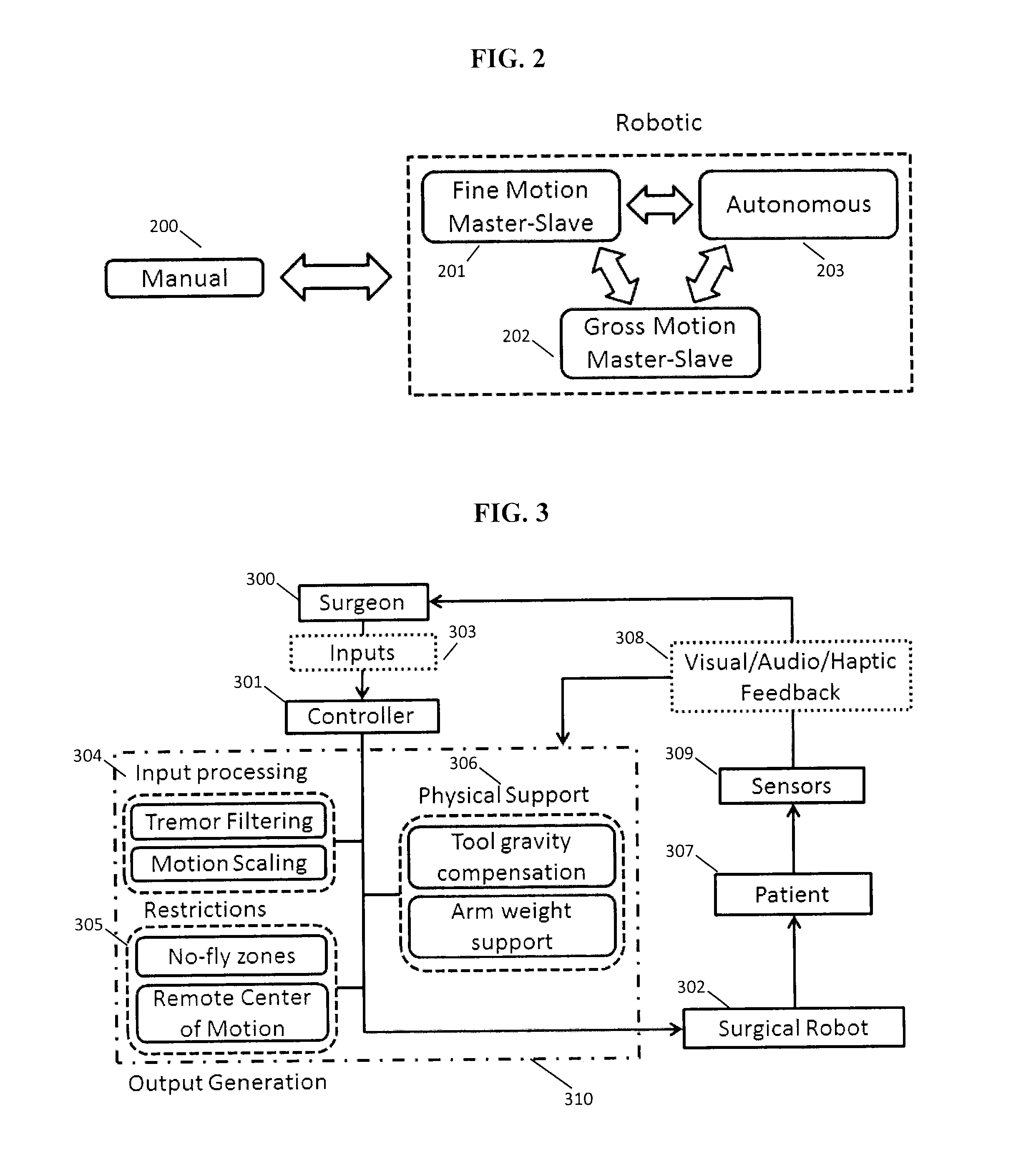
ActiveUS20140222023A1Control and awarenessImprove safety and efficiencyDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingArm exerciseHand tremor
The present disclosure describes a method and system for performing robot-assisted surgical procedures. The system includes a robotic arm system assembly, an end effector assembly, and a hybrid control mechanism for robotic surgery. The robotic arm is a lightweight, bedside robot with a large range of motion, which can be easily manipulated to position endoscope and surgical instruments. The control console is mounted at the distal end of the robotic arm to enable robotic arm to follow operators arm movement, provide physical support, filter out hand tremor, and constrain motion. A universal adapter is also described as an interface to connect traditional laparoscopic tools to the robotic arm.
Owner:CHILDRENS NAT MEDICAL CENT
Tool memory-based software upgrades for robotic surgery
Robotic devices, systems, and methods for use in robotic surgery and other robotic applications, and / or medical instrument devices, systems, and methods includes both a reusable processor and a limited-use robotic tool or medical treatment probe. A memory the limited-use component includes machine readable code with data and / or programming instructions to be implemented by the processor. Programming of the processor can be updated by shipping of new data once downloaded by the processor from a component, subsequent components can take advantage of the updated processor without repeated downloading.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
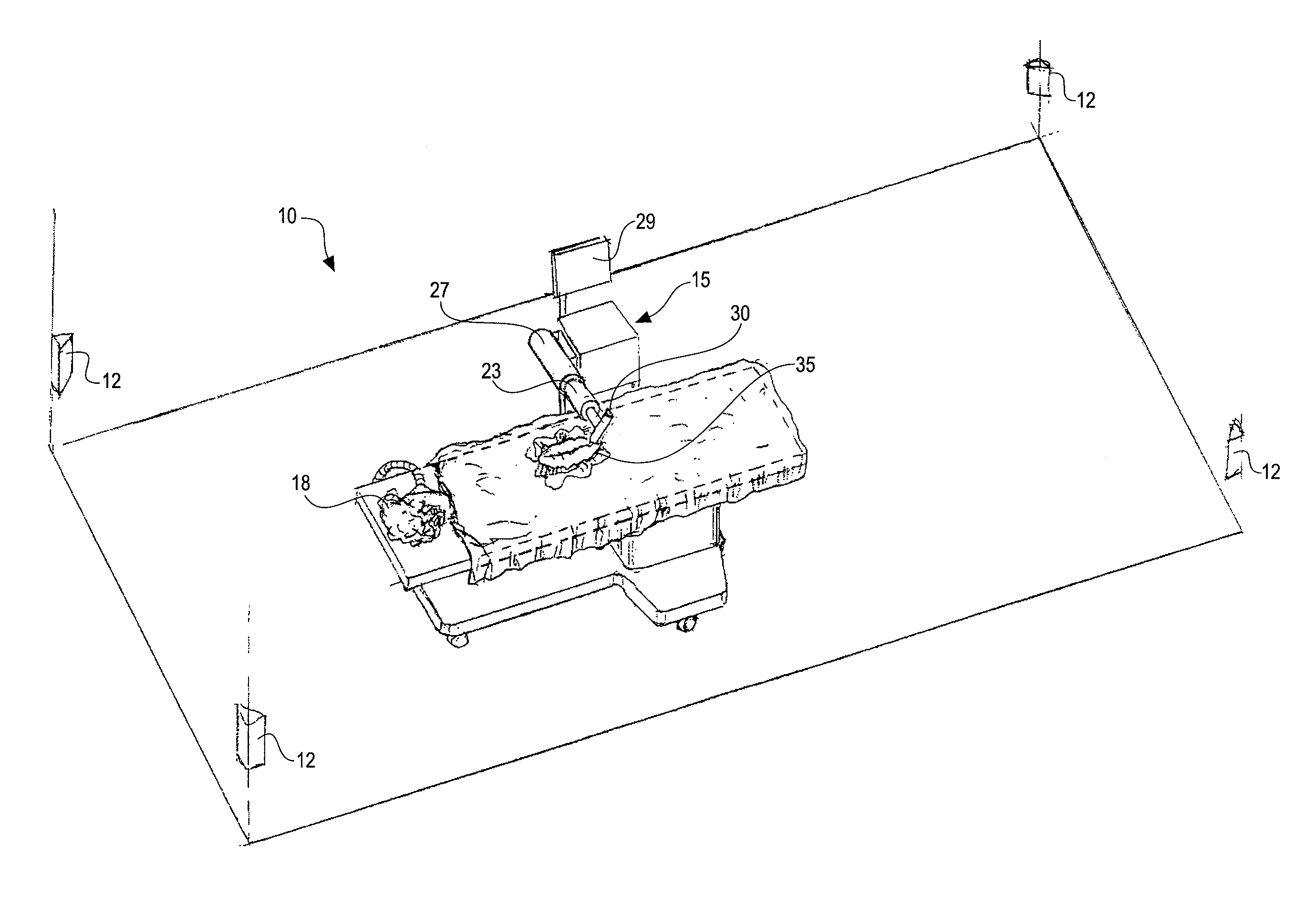
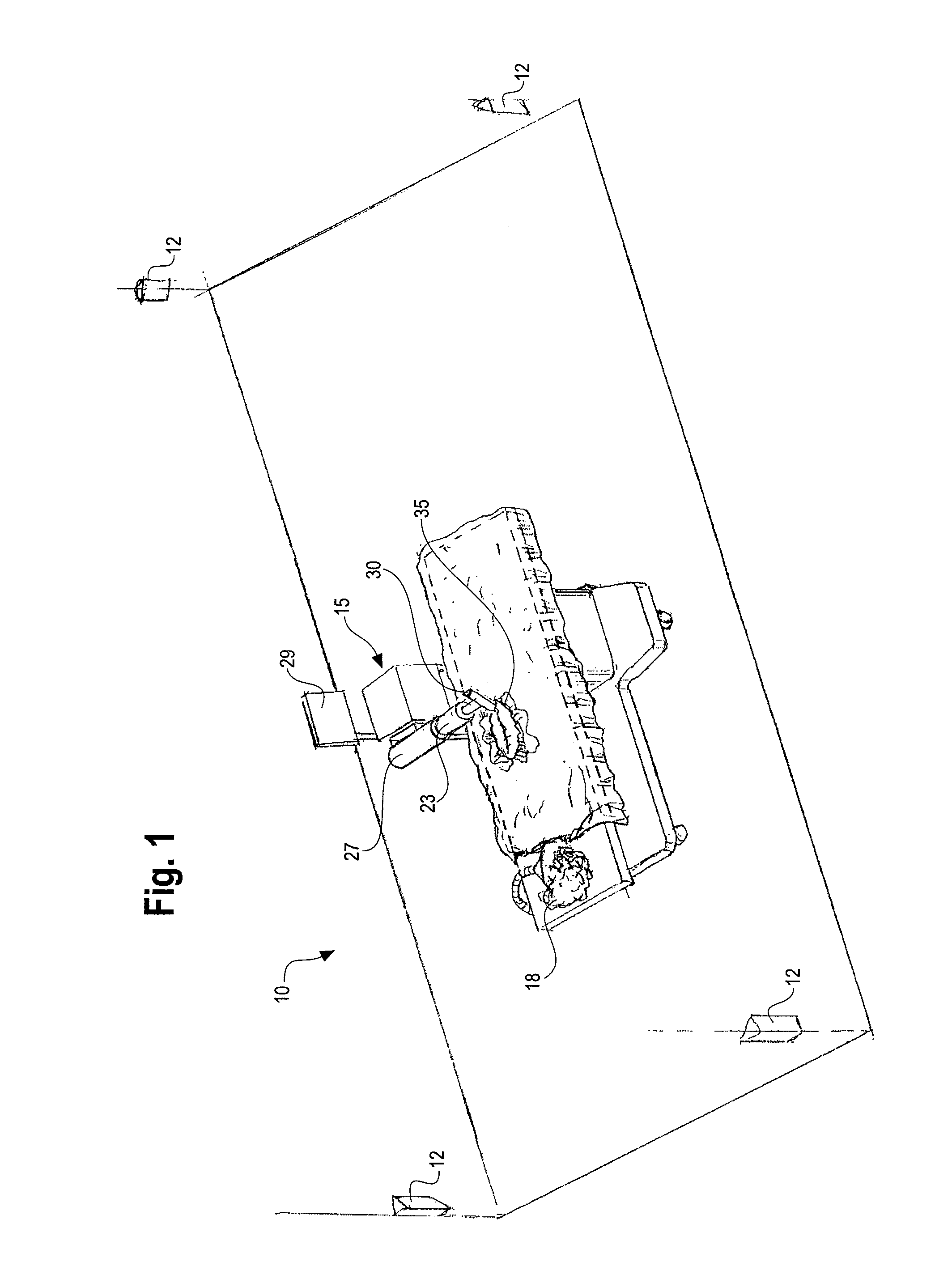
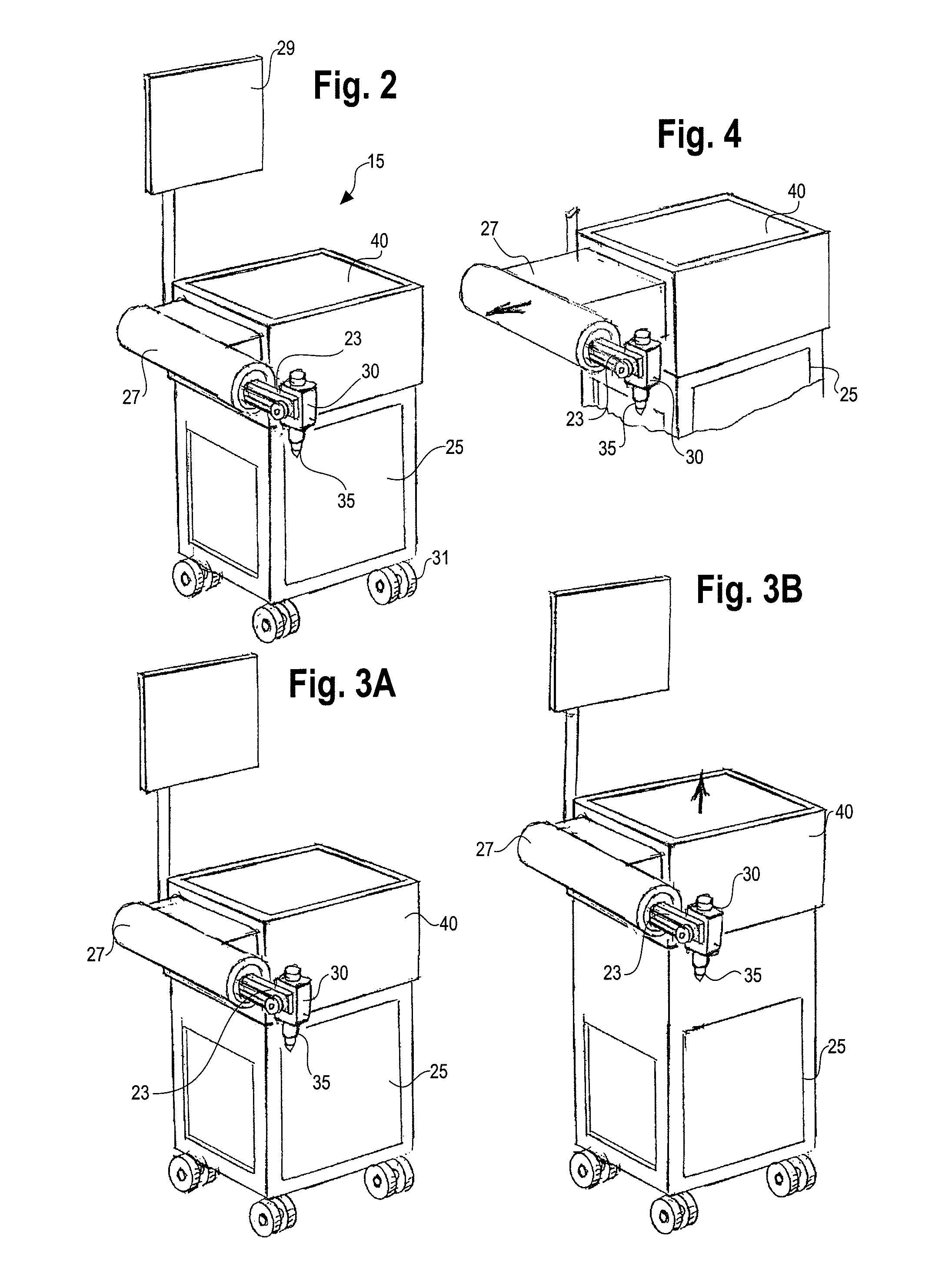
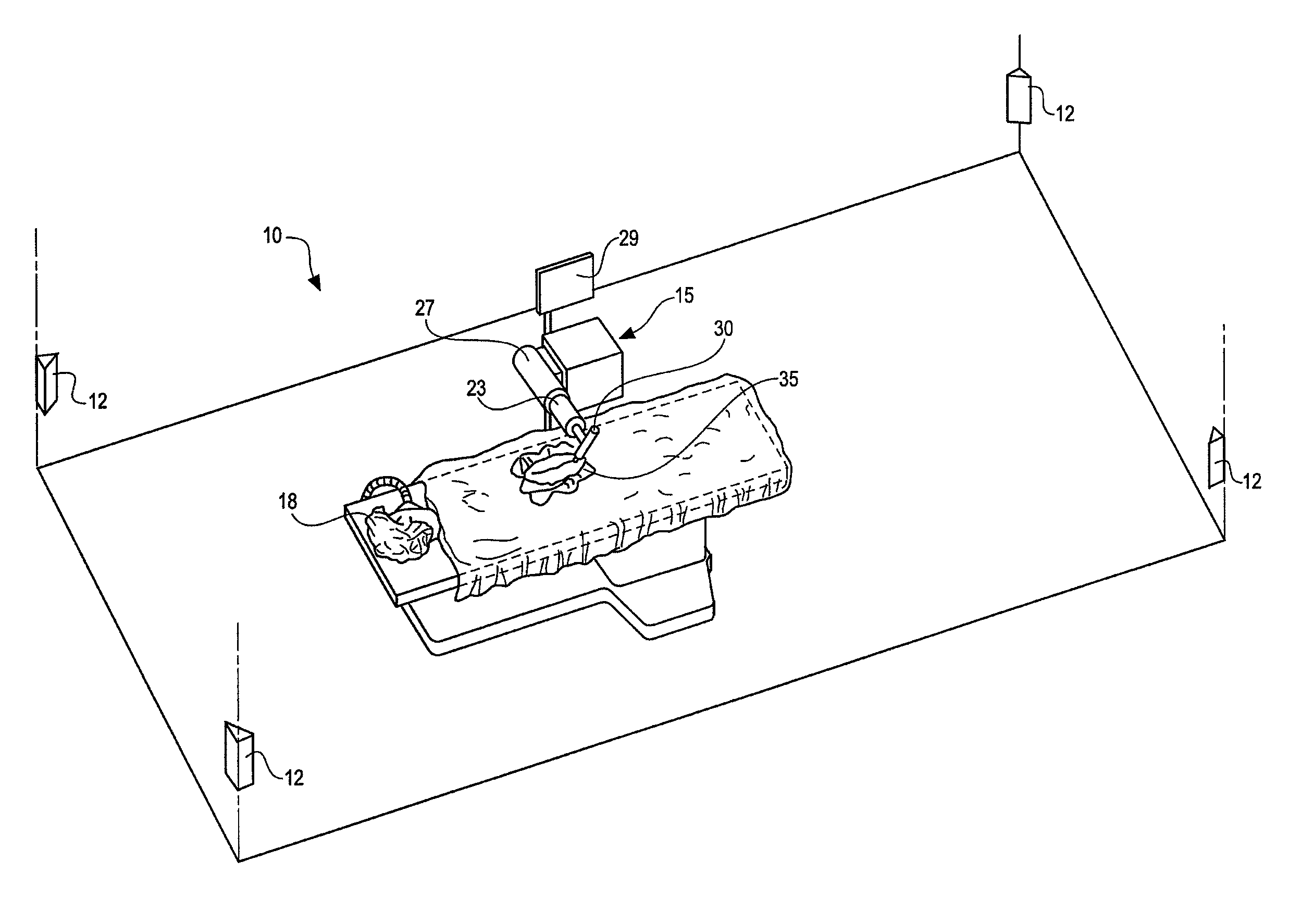
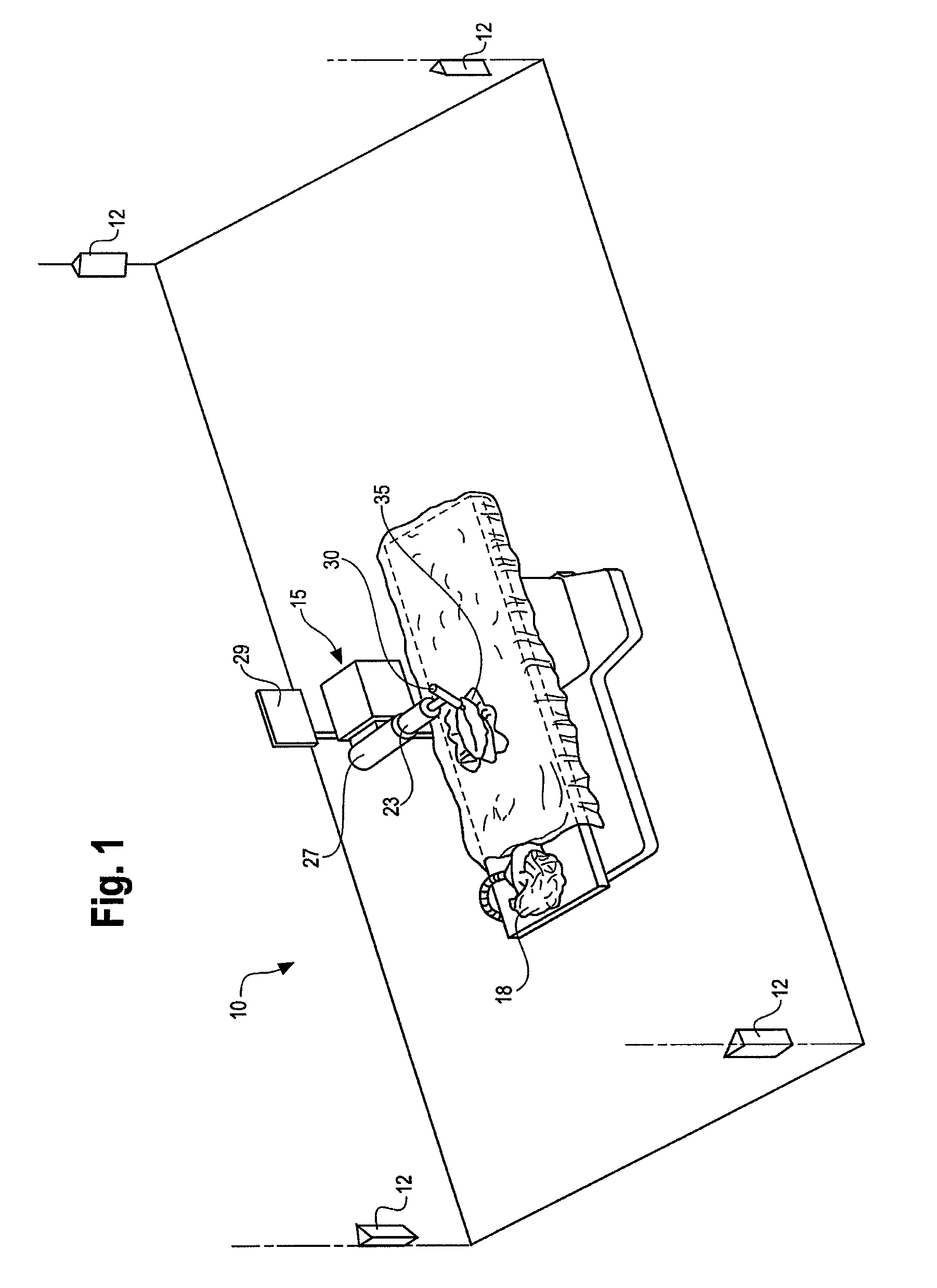
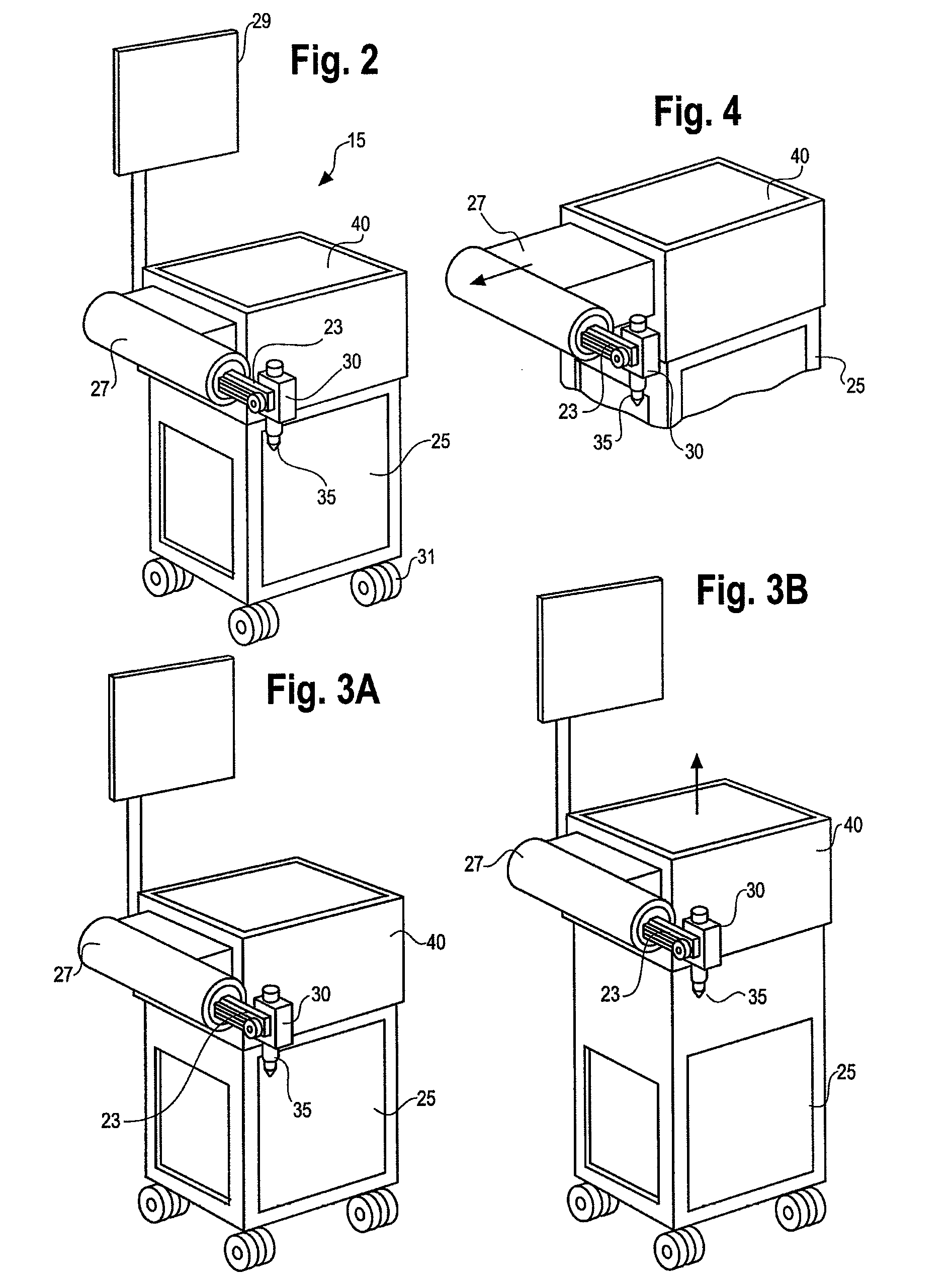
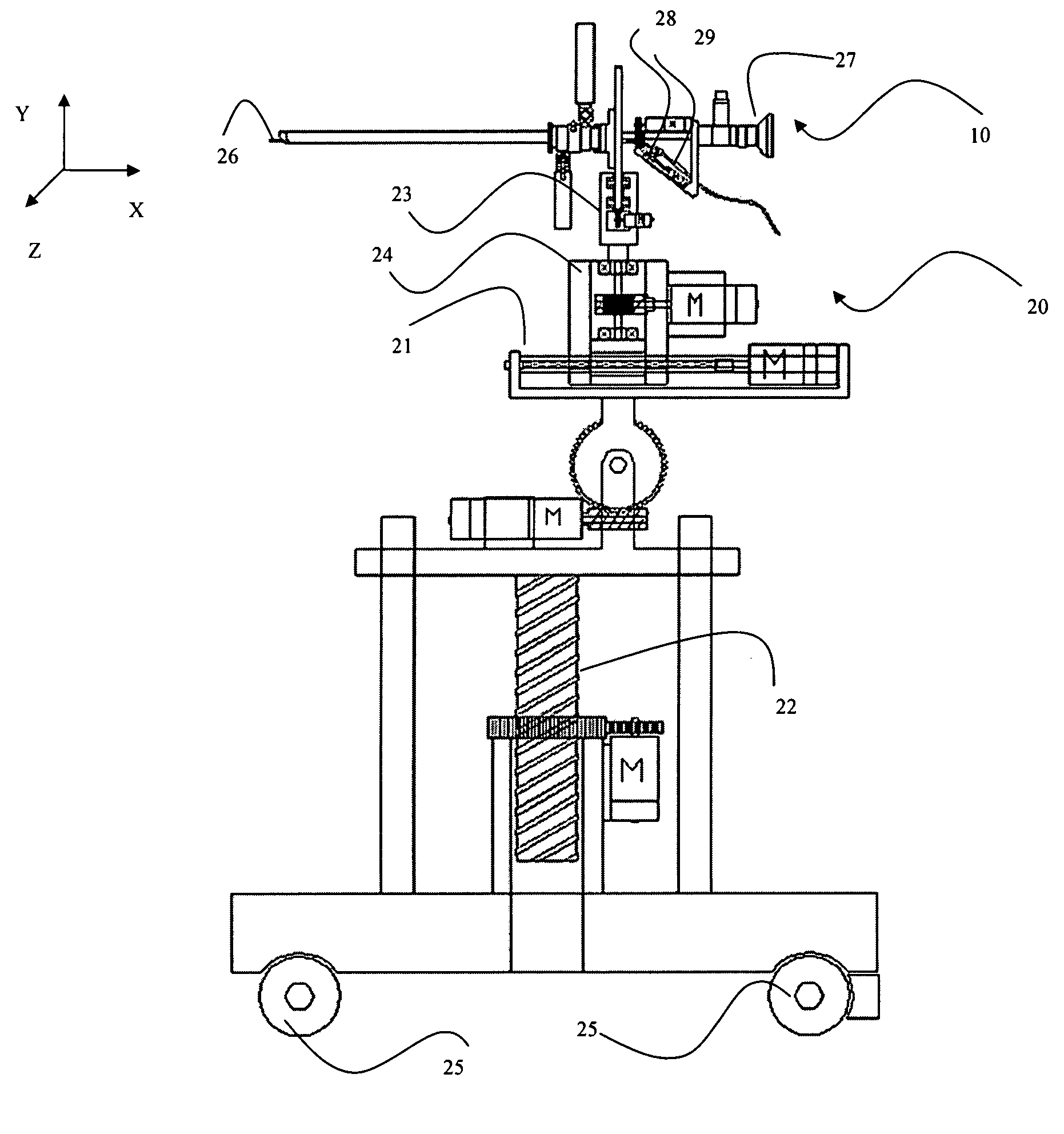
Method and system for performing invasive medical procedures using a surgical robot
ActiveUS8219178B2Degree of precisionInternal osteosythesisSurgical needlesGuidance systemSurgical robot
A method and system for performing invasive procedures includes a surgical robot which is controlled by a guidance system that uses time of flight calculations from RF transmitters embedded in the robot, surgical instrument, and patient anatomy. Sensors around the room detect RF transmissions emitted by the RF transmitters and drive the robot according to a preprogrammed trajectory entered into the guidance system.
Owner:CATHOLIC HEALTHCARE WEST ST JOSEPHS HOSPITAL +1
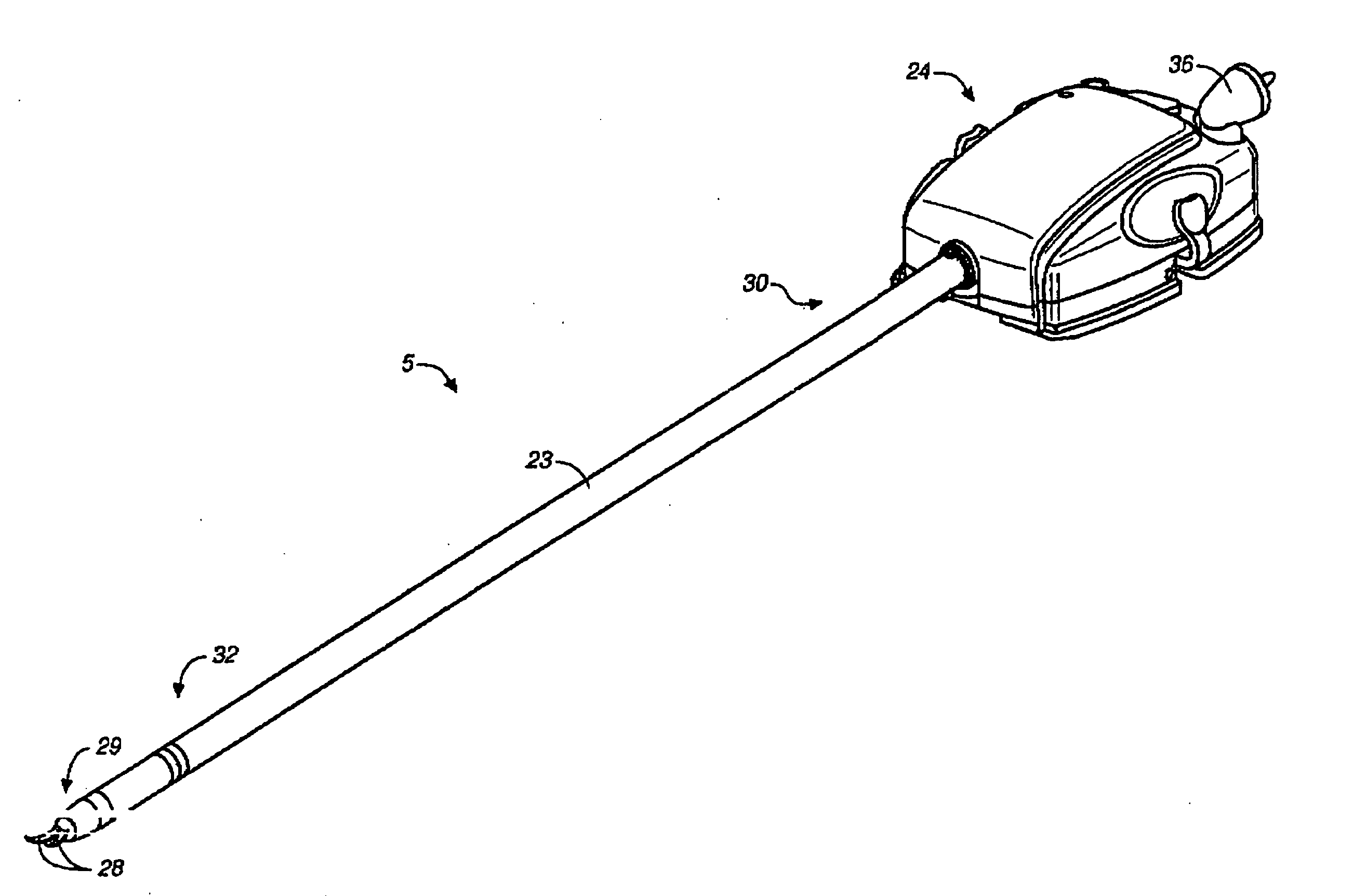
Robotic tool with wristed monopolar electrosurgical end effectors
ActiveUS20060079884A1Improve mobilityKeep the lengthDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsElectrical conductorEngineering
A surgical instrument for use with a robotic surgical system is described. The instrument includes an elongate shaft having a proximal end and a distal end. An electrically live wrist member is disposed at the distal end of the shaft. An electrocautery end effector is mounted to the wrist member. An interface is disposed at the proximal end of the shaft. The interface is removably connectable to the robotic surgical system. A conductor extends from the interface to the end effector so as to deliver electrical energy to tissue engaged by the end effector. A tip cover is disposed over the wrist member so that electrical current can only be conducted to tissues through the exposed end effector (e.g., to promote blood coagulation during usage) and not to other parts of the patient's body.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
System and method for robotic surgical intervention
ActiveUS20110077504A1Low costEfficient executionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEngineeringMedical procedure
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
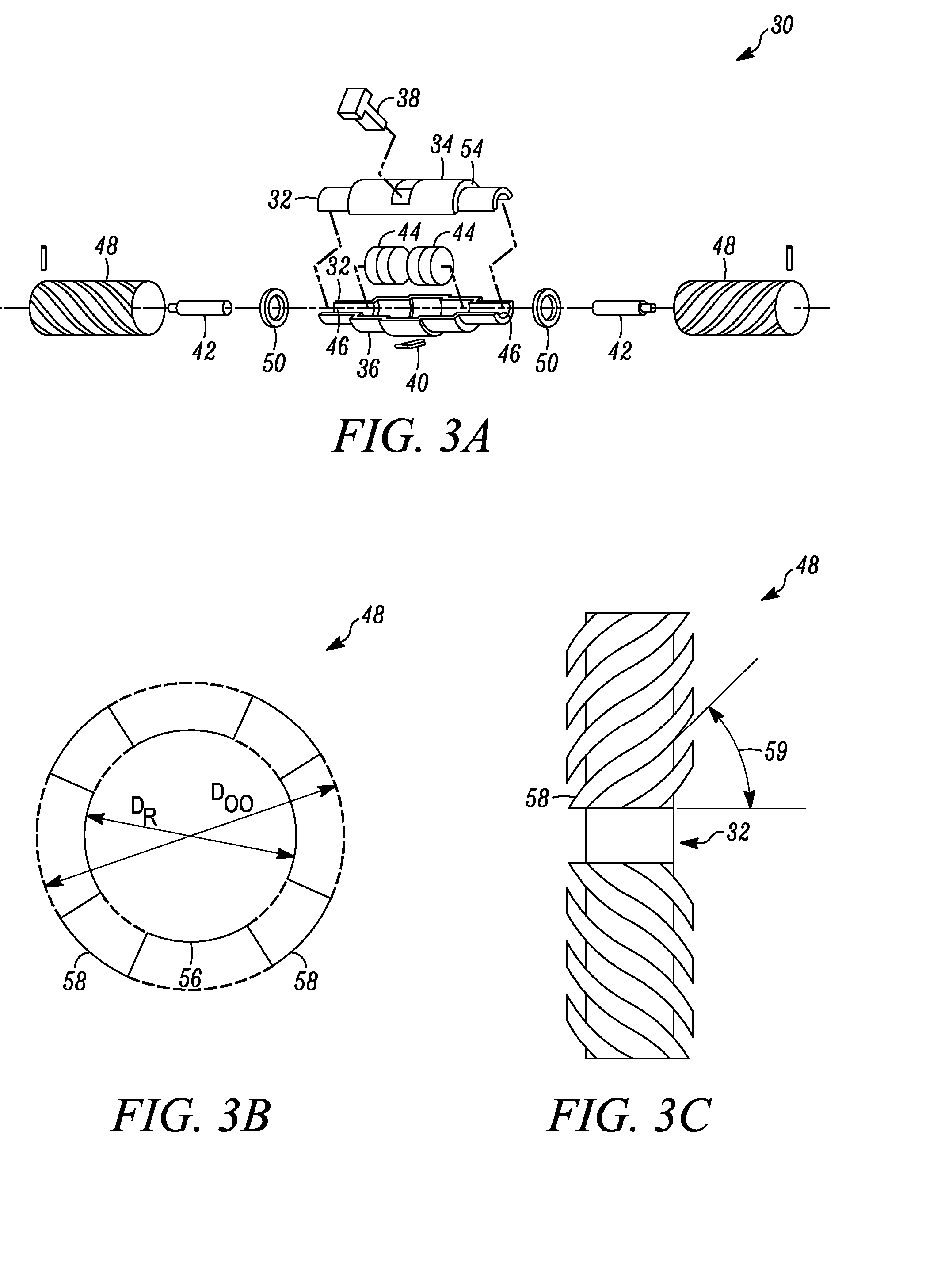
Force estimation for a minimally invasive robotic surgery system
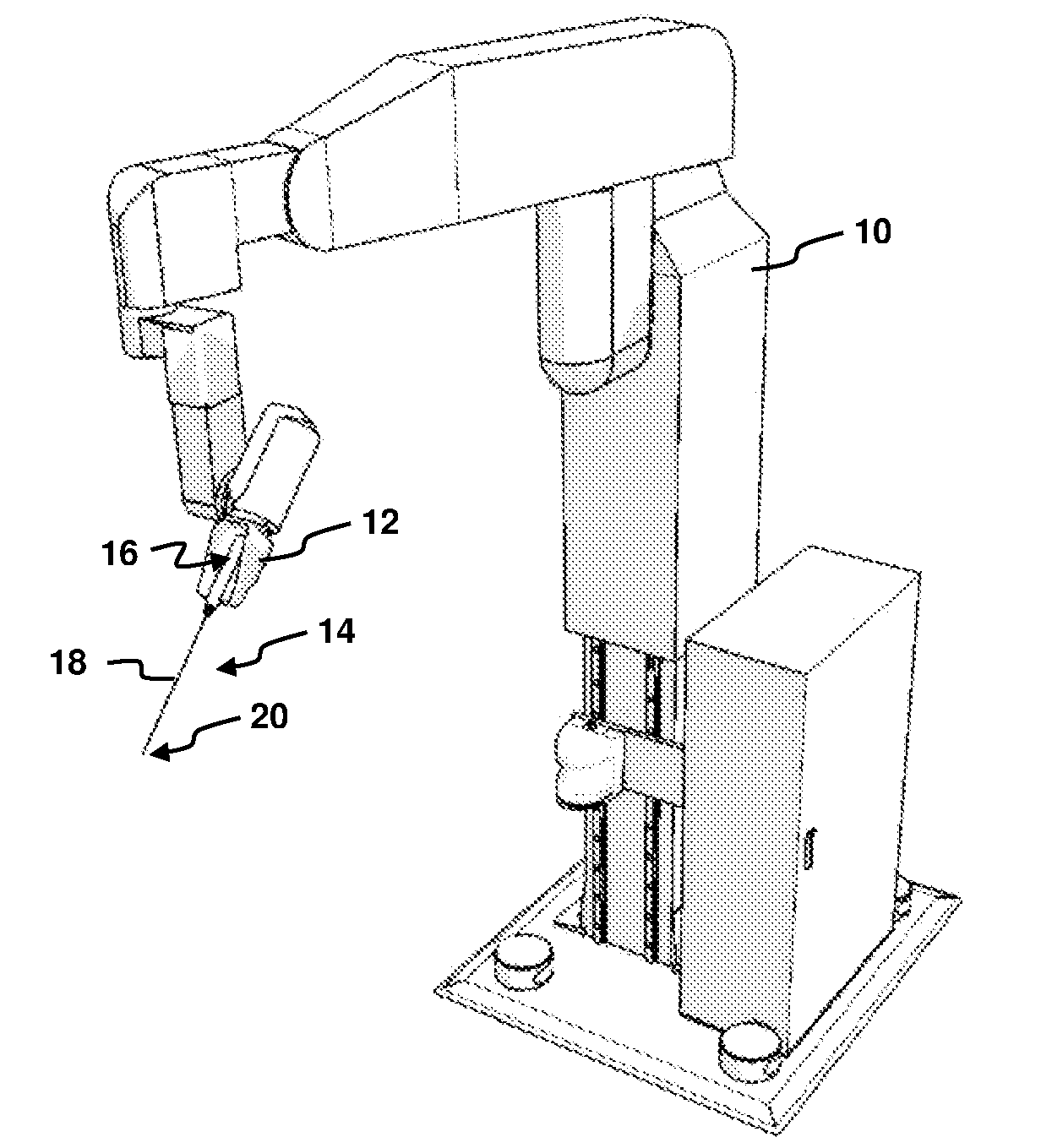
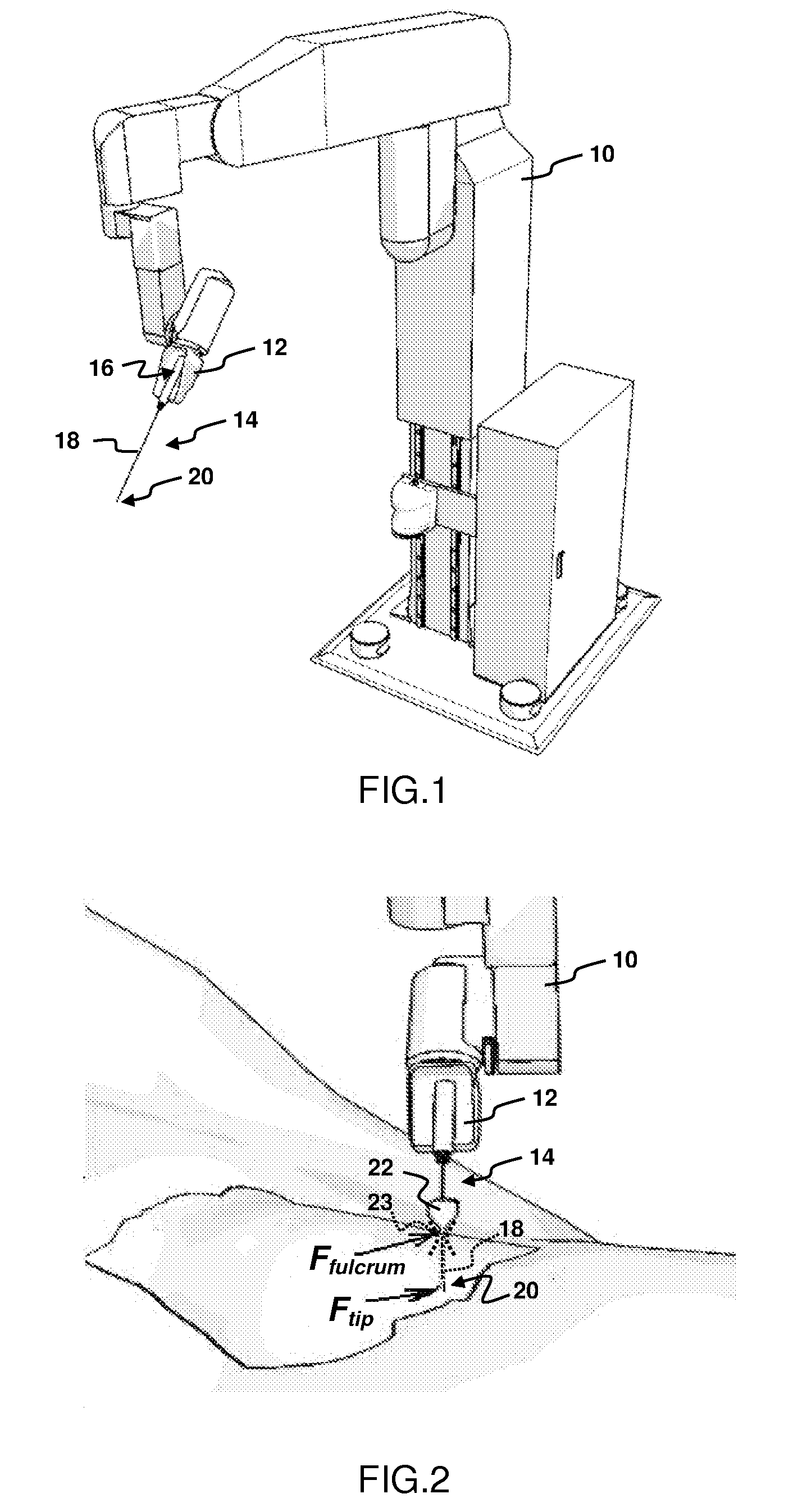
ActiveUS20100094312A1Efficient and cost-effectiveAvoid the needProgramme-controlled manipulatorAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDegrees of freedomEngineering
A method of force estimation for a minimally invasive medical system comprising a robot manipulator (10). The manipulator has an effector unit (12) equipped with a 6-degrees-of-freedom (DOF) force / torque sensor and is configured to hold a minimally invasive instrument (14) having a first end (16) mounted to the effector unit and a second end (20) located beyond an external fulcrum (23) that limits the instrument in motion, usually to 4 DOF. The method comprising the steps: —determining a position of the instrument relative to the fulcrum; —measuring by means of the 6-DOF force / torque sensor a force and a torque exerted onto the effector unit by the first end of the instrument; and —calculating by means of the principle of superposition an estimate of a force exerted onto the second end of the instrument based on the determined position, the measured force and the measured torque.
Owner:EURATOM
Method and system for performing invasive medical procedures using a surgical robot
ActiveUS8219177B2Degree of precisionSurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsGuidance systemSurgical robot
A method and system for performing invasive procedures includes a surgical robot which is controlled by a guidance system that uses time of flight calculations from RF transmitters embedded in the robot, surgical instrument, and patient anatomy. Sensors around the room detect RF transmissions emitted by the RF transmitters and drive the robot according to a preprogrammed trajectory entered into the guidance system.
Owner:CATHOLIC HEALTHCARE WEST ST JOSEPHS HOSPITAL +1
Magnetically coupleable robotic surgical devices and related methods
The present invention relates to magnetically coupleable robotic surgical devices. More specifically, the present invention relates to robotic surgical devices that can be inserted into a patient's body and can be positioned within the patient's body using an external magnet.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
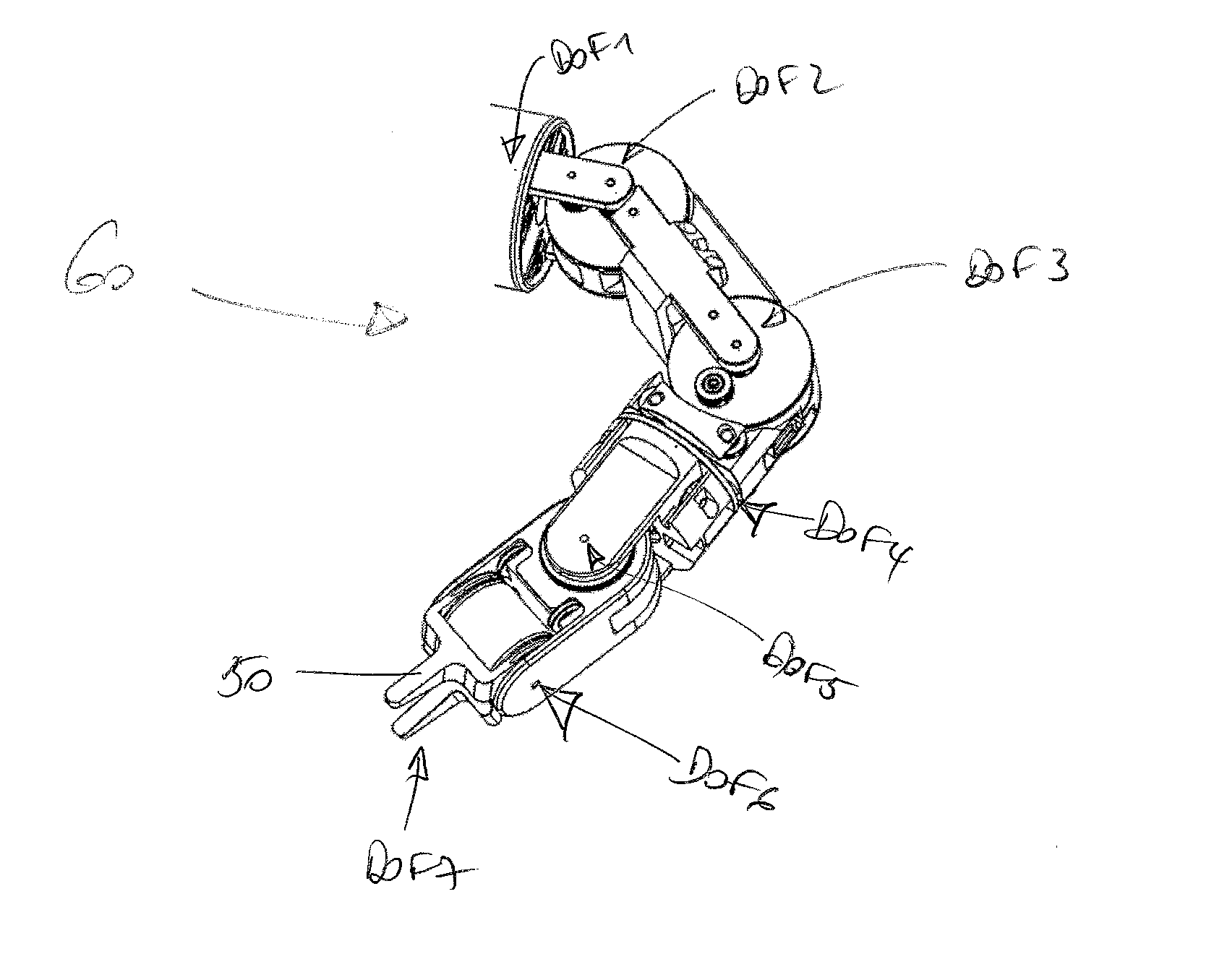
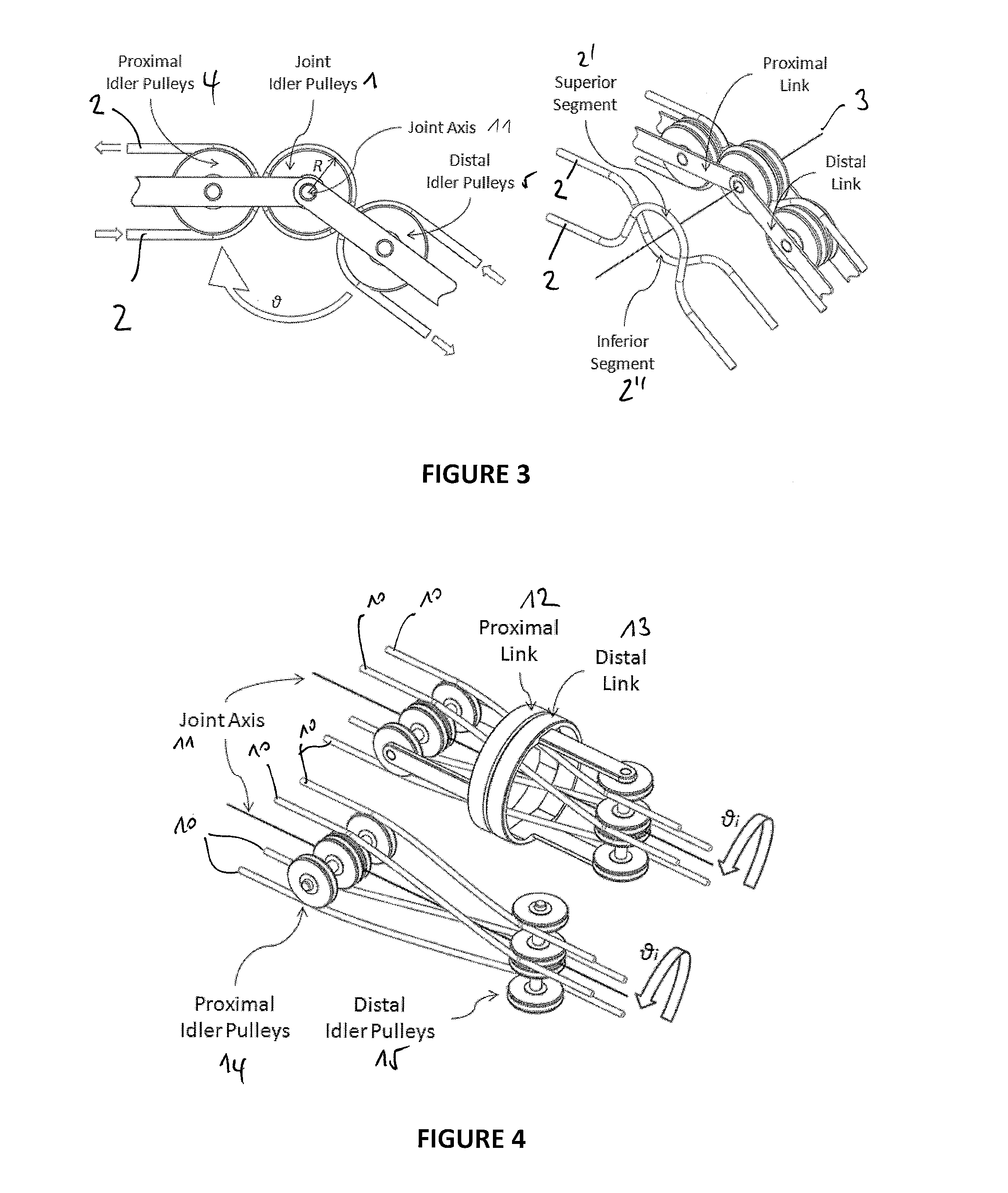
Mechanical manipulator for surgical instruments
ActiveUS20130304084A1Solve the lack of stiffnessSolve the lack of precisionDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsConventional laparoscopyEngineering
A novel mechanical system, based on a new cable driven mechanical transmission, able to provide sufficient dexterity, stiffness, speed, precision and payload capacity to actuate multi-DOF micro-manipulators. Besides the possibility of being used in several articulated surgical instruments and robotic systems for surgery or other applications involving remote manipulation, it enables the design of a novel fully mechanical surgical instrument, which offer the advantages of conventional laparoscopy (low cost, tactile feedback, high payload capacity) combined with the advantages of single port surgery (single incision, scarless surgery, navigation through several quadrants of the abdominal cavity) and robotic surgery (greater degrees of freedom, short learning curve, high stiffness, high precision, increased intuition). The unique design of the proposed system provides an intuitive user interface to achieve such enhanced manoeuvrability, allowing each joint of a teleoperated slave system to be driven by controlling the position of a mechanically connected master unit.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Robotic surgical system
InactiveUS20090228019A1Quicker procedureDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsSurgical operationEngineering
It is an object of the present invention to provide an automated, a semi-automated, a surgeon-guided quasi-automated and / or a fully surgeon's controlled surgical system surgical system useful for performing a fully automated medical procedure within a body cavity such that faultless and quick medical procedure is obtained. Each of the surgical systems comprises: (a) at least one effecter for performing the medical procedure; (b) at least one maneuverable platform reversibly coupled with the effecter; the platform provides the effecter with a scheduled set of independent displacements selected from a group consisting of up to six (degrees of freedom) DOFs, namely linear movement along the X,Y,Z-coordinates, and radial movement around the X,Y,Z coordinates, such that the time-resolved spatial position of the effecter is defined by the up to six coordinates (three-dimensional spatial position, 3DSP); and (c) sensing and processing means.
Owner:GROSS YOSEF +4
Modular manipulator support for robotic surgery
InactiveUS20060167440A1Simple structureReduce complexityDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsSurgical siteModularity
A robotic surgery system comprises a mounting base, a plurality of surgical instruments, and an articulate support assembly. Each instrument is insertable into a patient through an associated minimally invasive aperture to a desired internal surgical site. The articulate support assembly movably supports the instruments relative to the base. The support generally comprises an orienting platform, a platform linkage movably supporting the orienting platform relative to the base, and a plurality of manipulators mounted to the orienting platform, wherein each manipulator movably supports an associated instrument.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
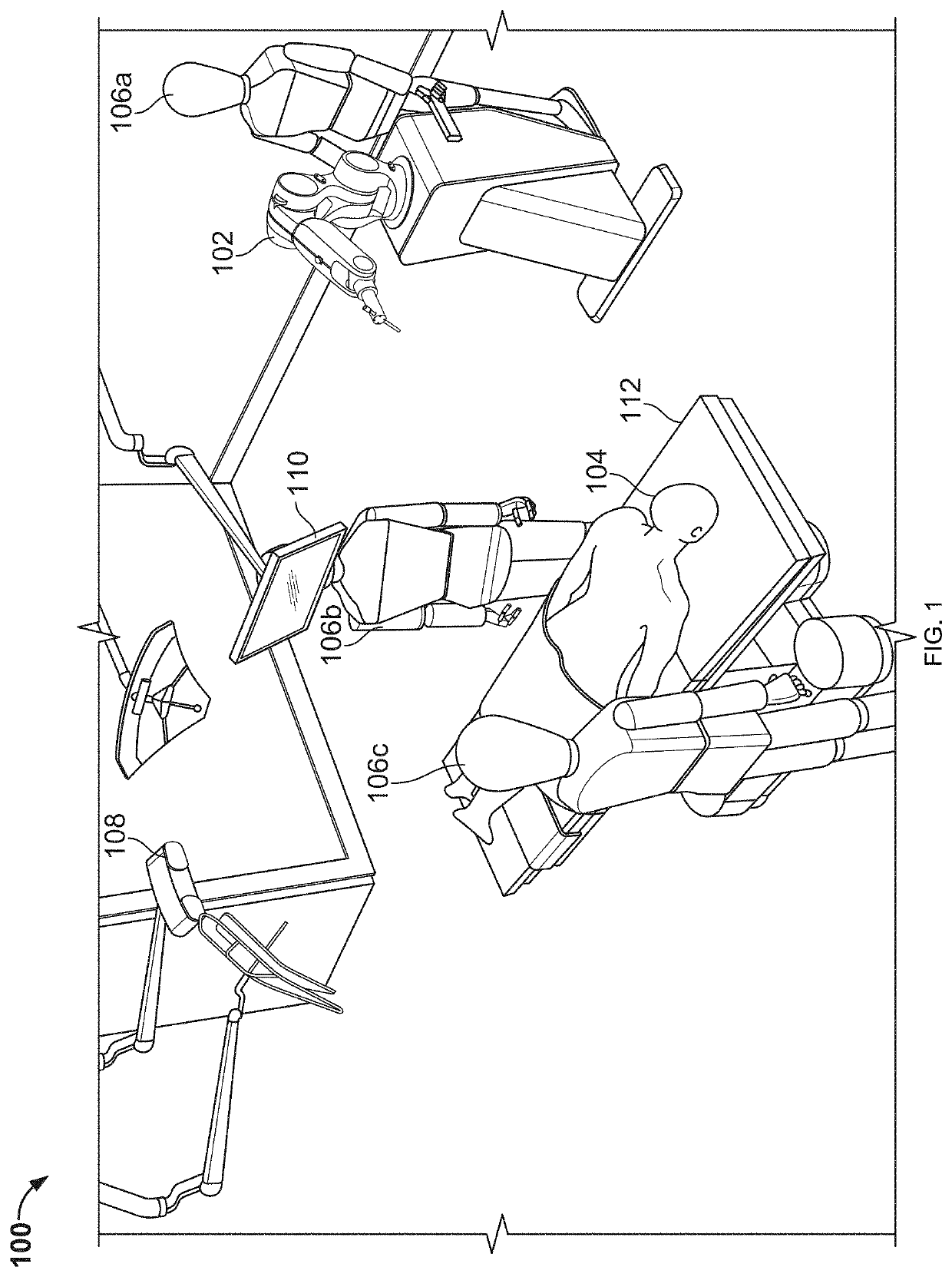
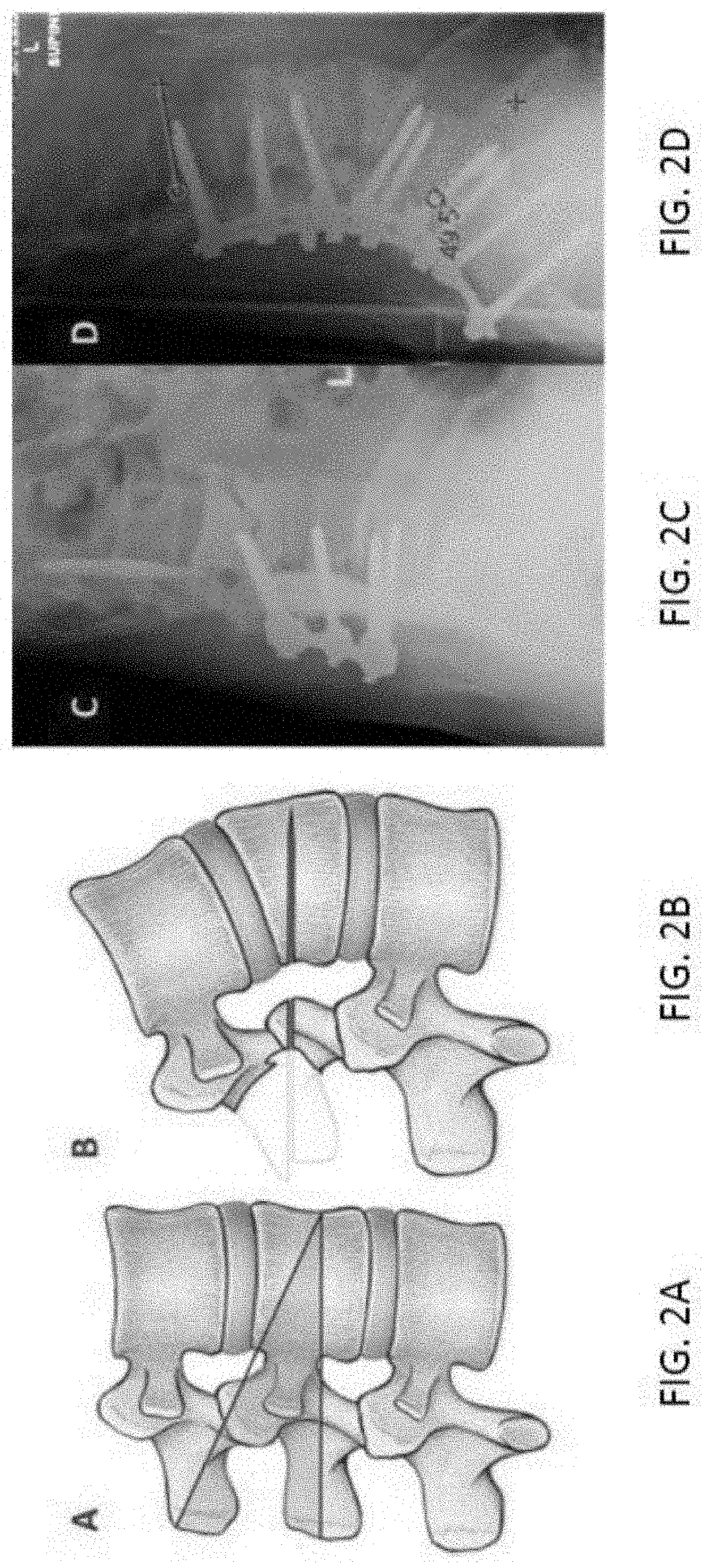
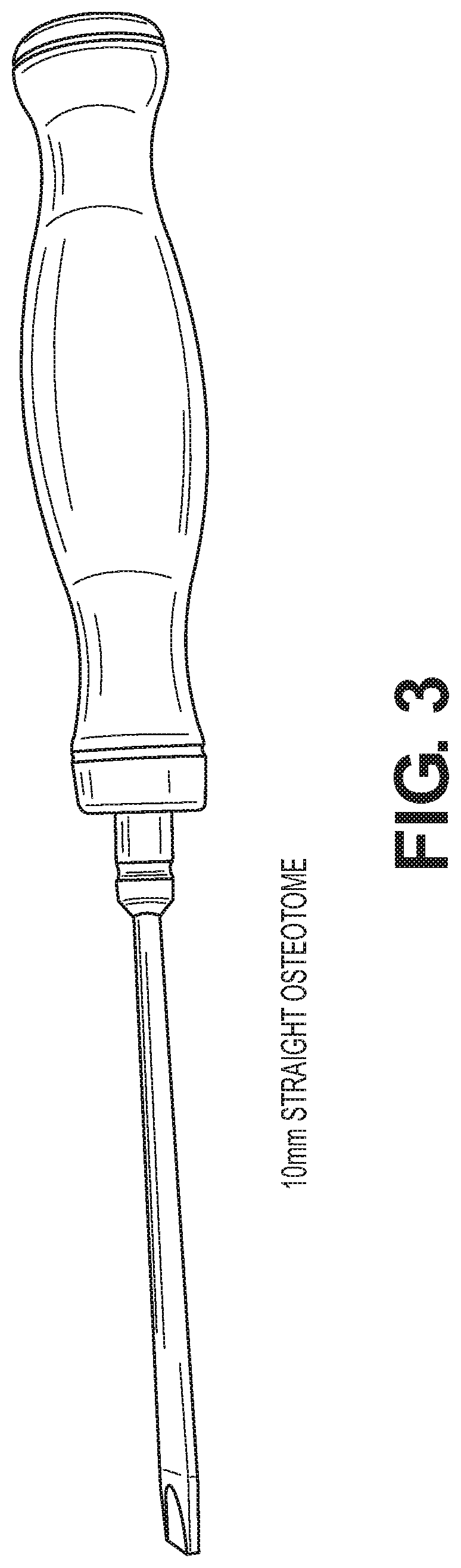
Robotic surgical systems and methods
ActiveUS10687905B2Avoid damageMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSurgical instrument detailsSurgical operationBone structure
The disclosed technology relates to robotic surgical systems for improving surgical procedures. In certain embodiments, the disclosed technology relates to robotic surgical systems for use in osteotomy procedures in which bone is cut to shorten, lengthen, or change alignment of a bone structure. The osteotome, an instrument for removing parts of the vertabra, is guided by the surgical instrument guide which is held by the robot. In certain embodiments, the robot moves only in the “locked” plane (one of the two which create the wedge—i.e., the portion of the bone resected during the osteotomy). In certain embodiments, the robot shall prevent the osteotome (or other surgical instrument) from getting too deep / beyond the tip of the wedge. In certain embodiments, the robotic surgical system is integrated with neuromonitoring to prevent damage to the nervous system.
Owner:KB MEDICAL SA
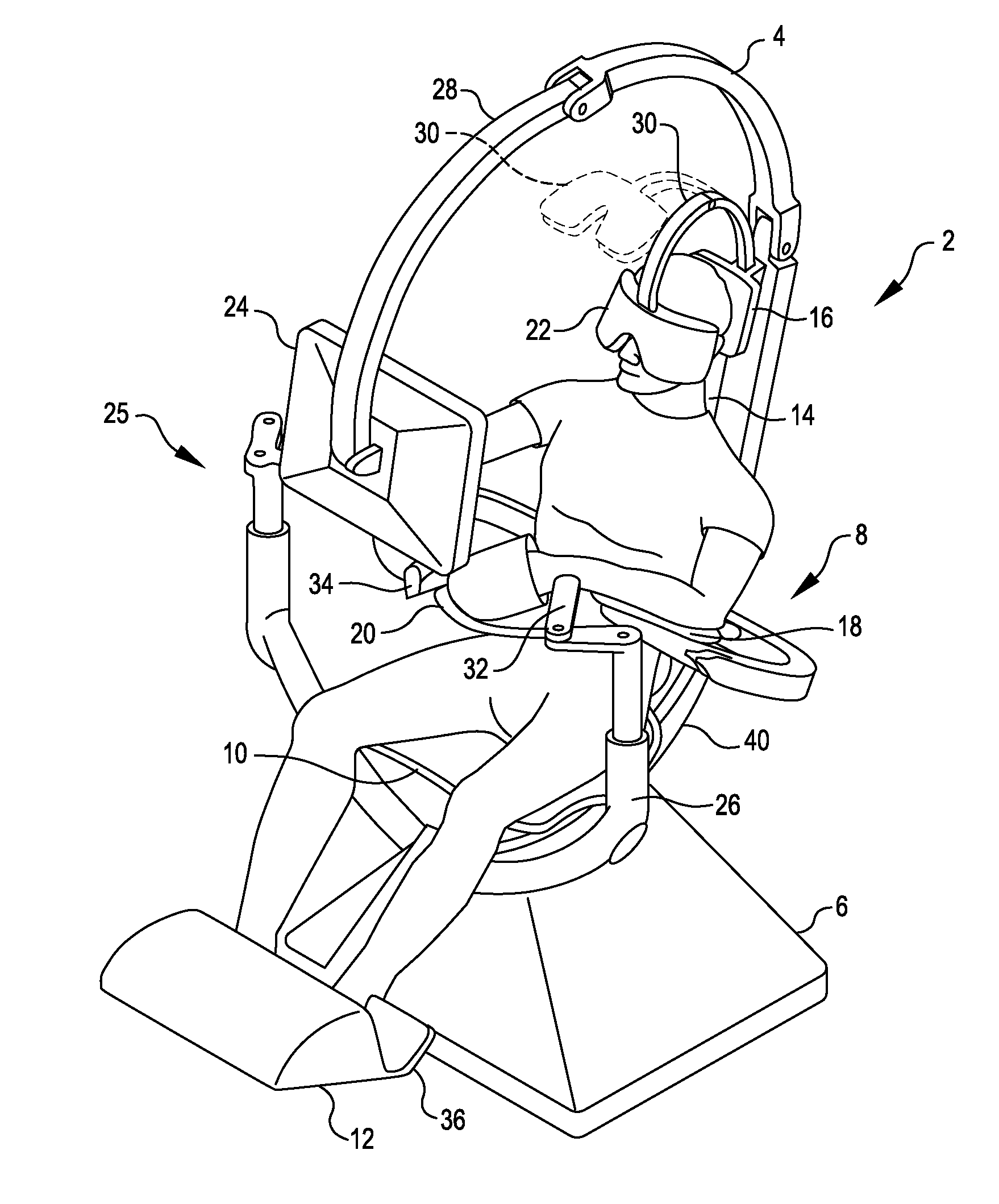
Surgical Cockpit Comprising Multisensory and Multimodal Interfaces for Robotic Surgery and Methods Related Thereto
InactiveUS20110238079A1Accurately respondEnhanced Situational AwarenessMedical communicationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesRemote surgeryCommunications system
Local surgical cockpits comprising local surgical consoles that can communicate with any desired remote surgical module (surgical robot), for example via a shared Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP / IP) or other unified open source communication protocol or other suitable communication system. The systems and methods, etc., herein can also comprise a modular approach wherein multiple surgical consoles can network supporting collaborative surgery regardless of the physical location of the surgeons relative to each other and / or relative to the surgical site. Thus, for example, an operator operating a local surgical cockpit can teleoperate using a remote surgical module on a patient in the same room as the surgeon, or surgeons located in multiple safe locations can telemanipulate remote multiple surgical robots on a patient in or close to a war zone.
Owner:SPI SURGICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com