Patents
Literature
3988results about "Robot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
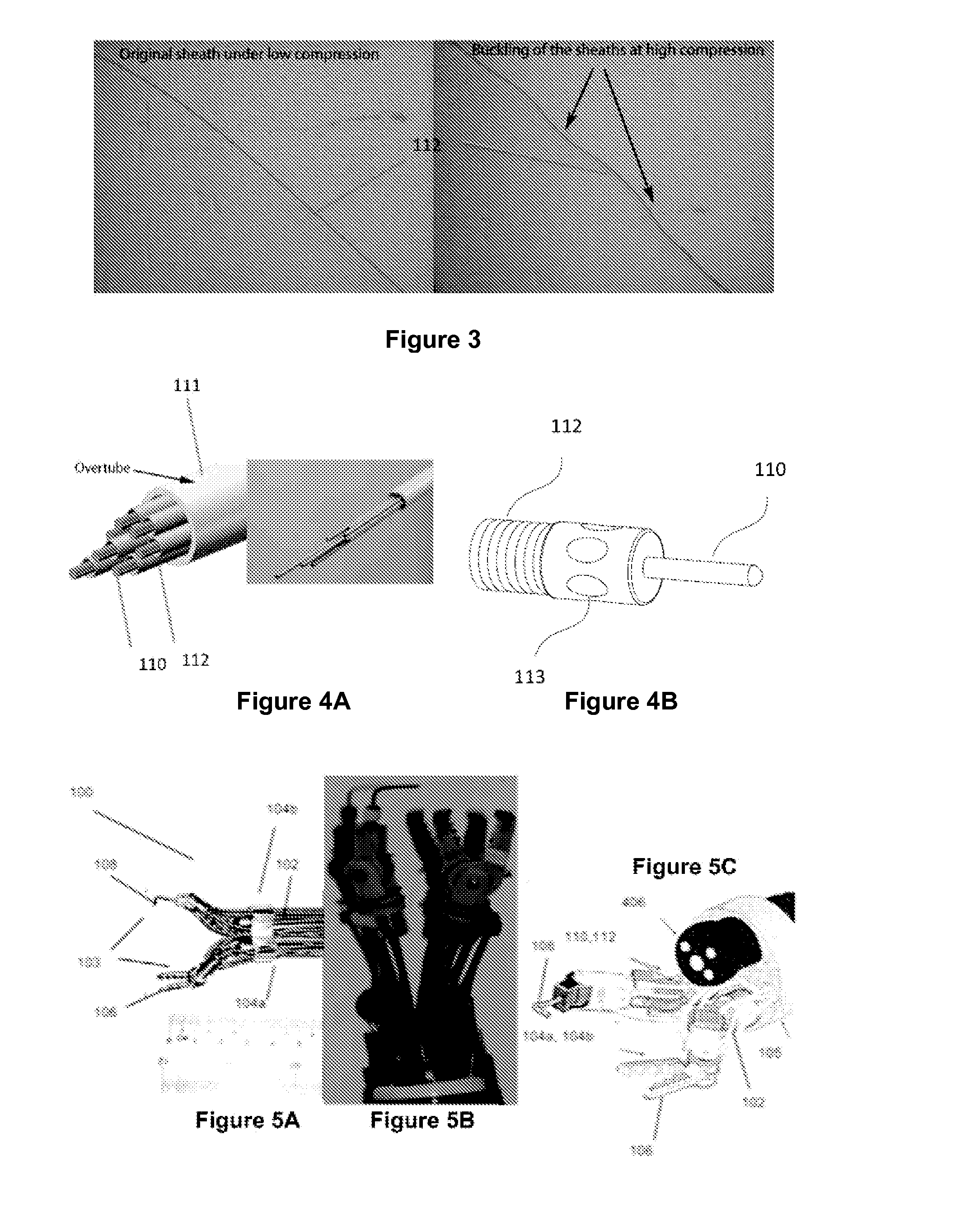
Surgical robotic tools, data architecture, and use
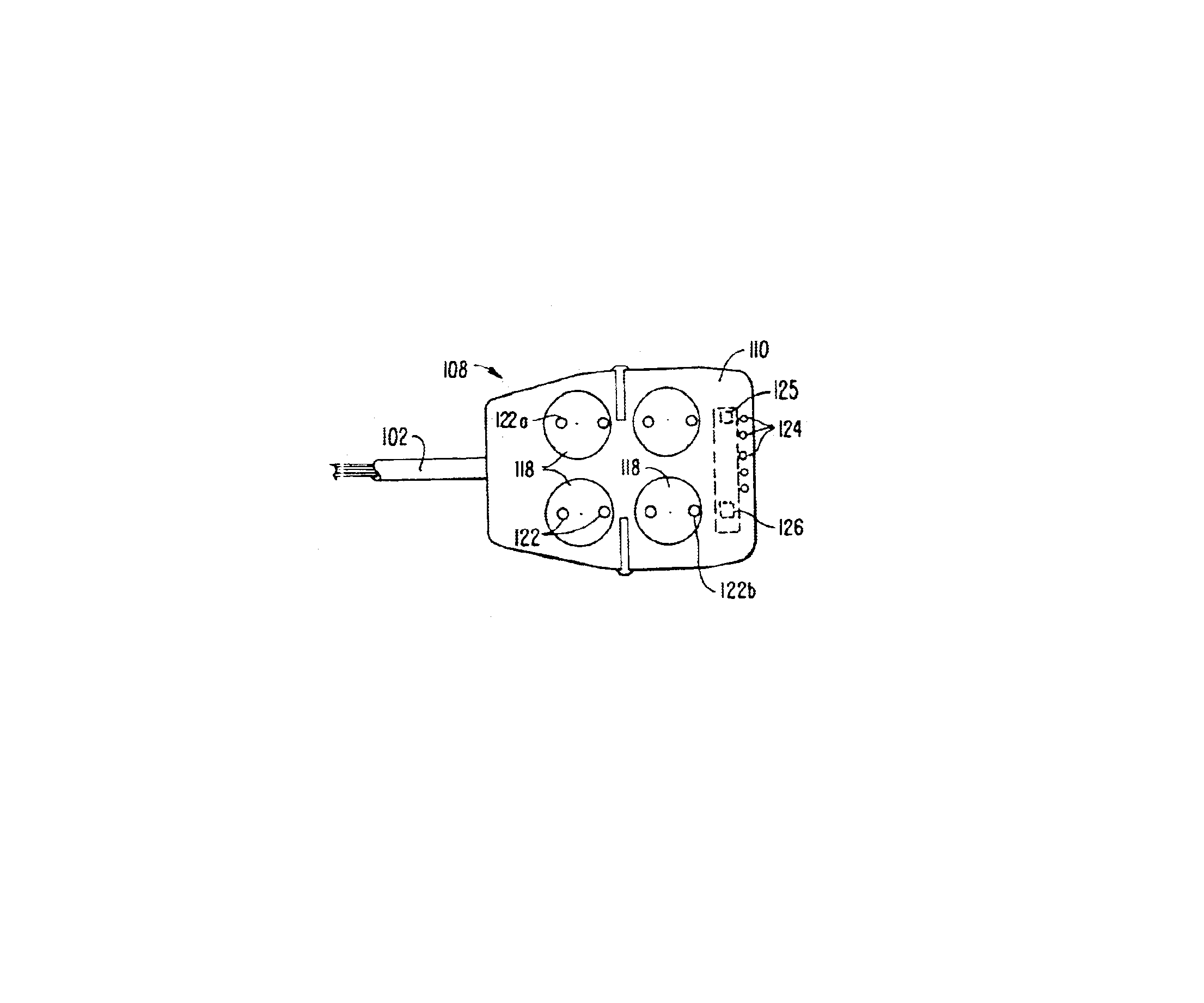
Robotic surgical tools, systems, and methods for preparing for and performing robotic surgery include a memory mounted on the tool. The memory can perform a number of functions when the tool is loaded on the tool manipulator: first, the memory can provide a signal verifying that the tool is compatible with that particular robotic system. Secondly, the tool memory may identify the tool-type to the robotic system so that the robotic system can reconfigure its programming. Thirdly, the memory of the tool may indicate tool-specific information, including measured calibration offsets indicating misalignment of the tool drive system, tool life data, or the like. This information may be stored in a read only memory (ROM), or in a nonvolatile memory which can be written to only a single time. The invention further provides improved engagement structures for coupling robotic surgical tools with manipulator structures.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Tool grip calibration for robotic surgery
ActiveUS7386365B2Limited tool lifeStringent manufacturing toleranceProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsEngineeringActuator
Telerobotic, telesurgical, and surgical robotic devices, systems, and methods selectively calibrate end effector jaws by bringing the jaw elements into engagement with each other. Commanded torque signals may bring the end effector elements into engagement while monitoring the resulting position of a drive system, optionally using a second derivative of the torque / position relationship so as to identify an end effector engagement position. Calibration can allow the end effector engagement position to correspond to a nominal closed position of an input handle by compensating for wear on the end effector, the end effector drive system, then manipulator, the manipulator drive system, the manipulator / end effector interfacing, and manufacturing tolerances.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
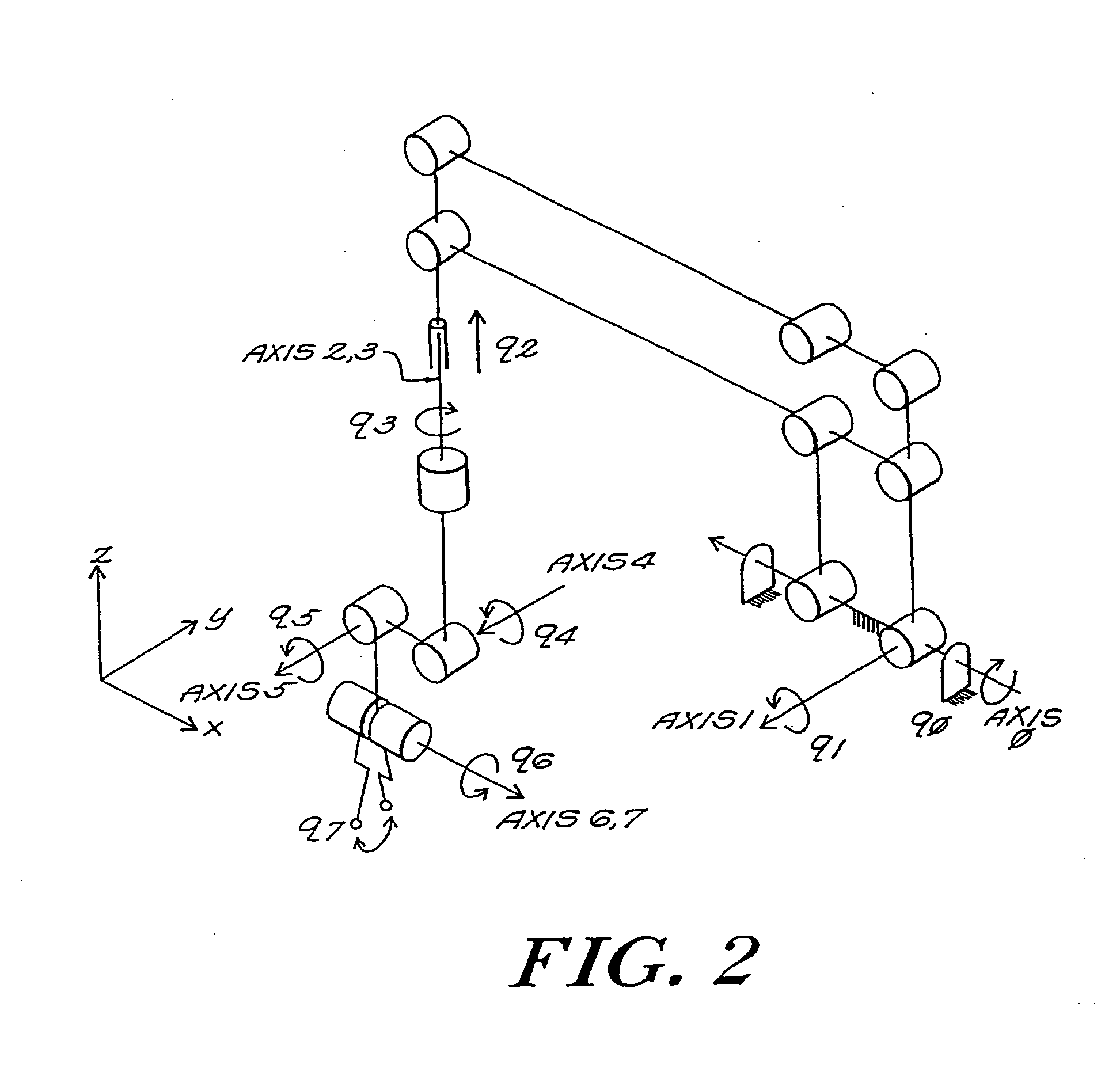
Robotic apparatus
InactiveUS20090012534A1Minimize cost functionProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsRobot end effectorEngineering
A robotic apparatus has eight actuators (M0-M7) and a linkage (LINK 0-LINK 5) that actuates an end effector. Three serial macro freedoms have large ranges of motion and inertias. Four serial micro freedoms have small ranges of motion and inertias. Translation of the end effector in an y direction is actuated by at least one micro joint and at least one macro joint. The apparatus can be part of a master and slave combination, providing force feedback without any explicit force sensors. The slave is controlled with an Inverse Jacobian controller, and the mater with a Jacobian Transpose controller. A slave having more degrees of freedom (DOFs) than the master can be controlled. A removable effector unit actuates its DOFs with cables. Beating heart surgery can be accomplished by commanding the slave to move with a beating heart and cancelling out any such motion in the motions perceived by the master.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
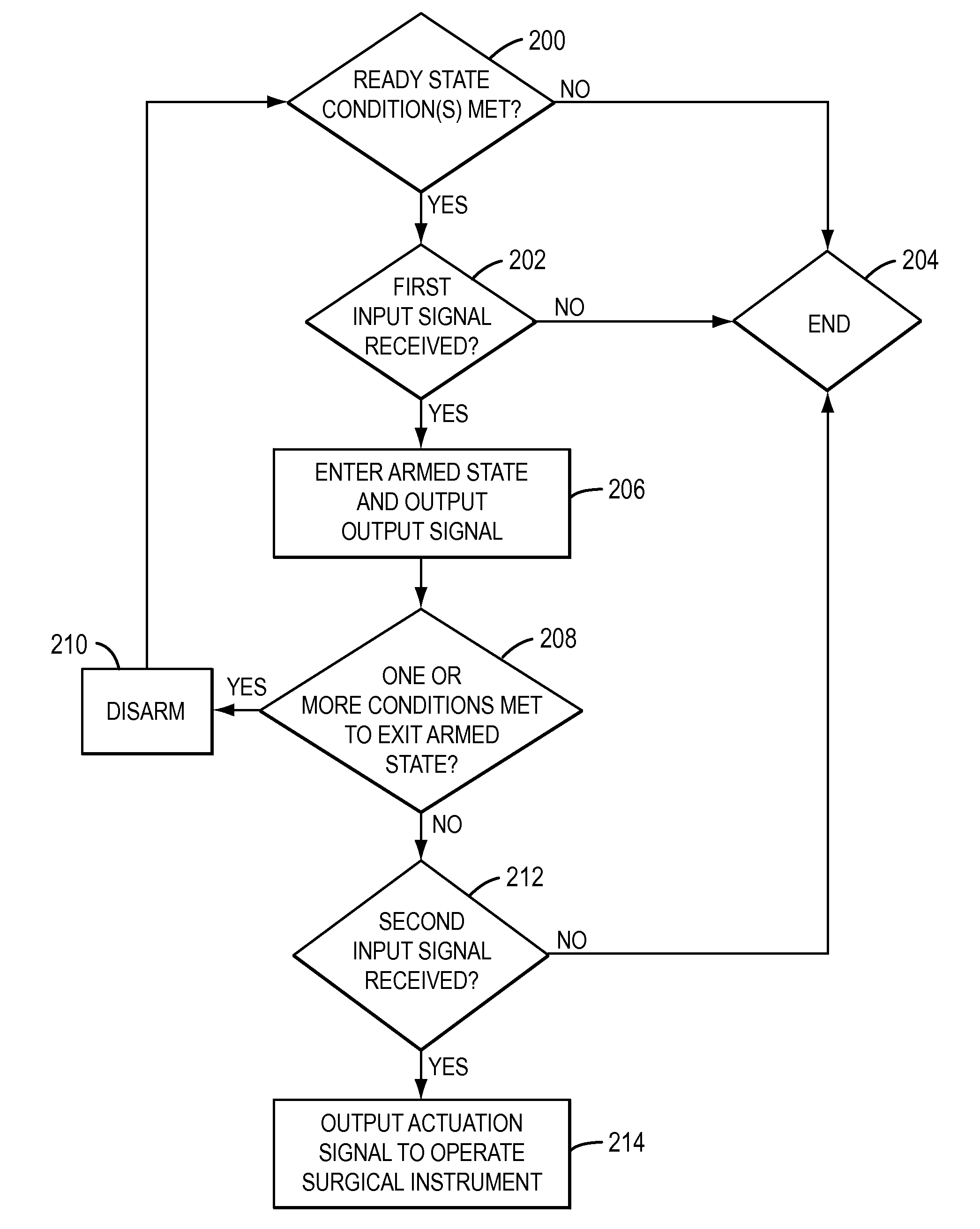
Positive control of robotic surgical instrument end effector
A method of controlling an operation of a robotically-controlled surgical instrument can include receiving a first input signal at a controller indicative of a user's readiness to actuate the surgical instrument to perform a surgical procedure, outputting an output signal from the controller to provide feedback to the user in response to the received first input signal, receiving a second input signal at the controller confirming the user's readiness to actuate the surgical instrument, outputting an actuation signal from the controller in response to receiving the second input signal, and actuating the surgical instrument to perform the surgical procedure based on the actuation signal.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
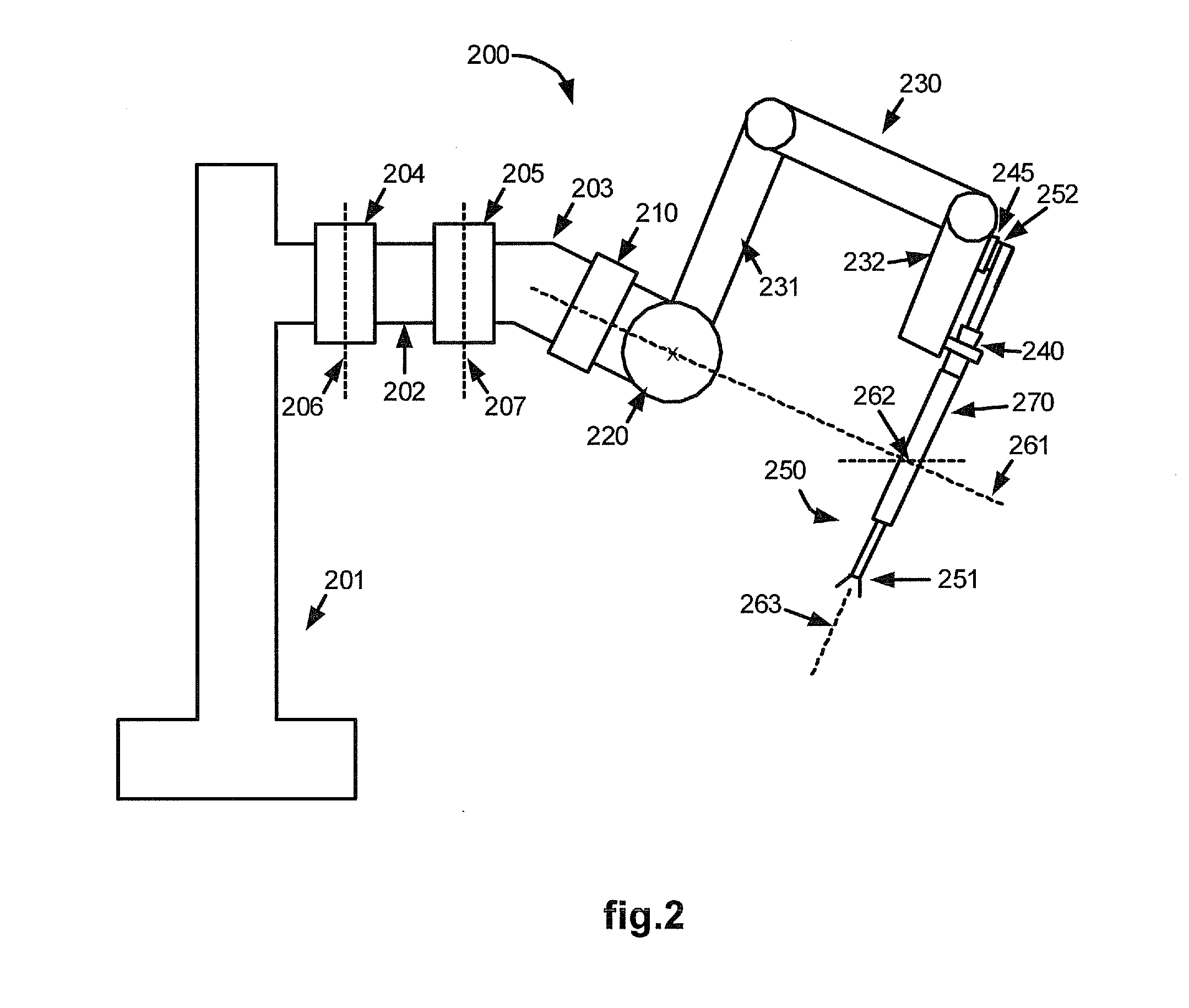
Surgical tool with a two degree of freedom wrist
ActiveUS8852174B2Amount of maneuverabilityShorten the lengthYielding couplingDiagnosticsDrive shaftAngular degrees
Surgical tools having a two degree-of-freedom wrist, wrist articulation by linked tension members, mechanisms for transmitting torque through an angle, and minimally invasive surgical tools incorporating these features are disclosed. An elongate intermediate wrist member is pivotally coupled with a distal end of an instrument shaft so as to rotate about a first axis transverse to the shaft, and an end effector body is pivotally coupled with the intermediate member so as to rotate about a second axis that is transverse to the first axis. Linked tension members interact with attachment features to articulate the wrist. A torque-transmitting mechanism includes a coupling member, coupling pins, a drive shaft, and a driven shaft. The drive shaft is coupled with the driven shaft so as to control the relative orientations of the drive shaft, the coupling member, and the driven shaft.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
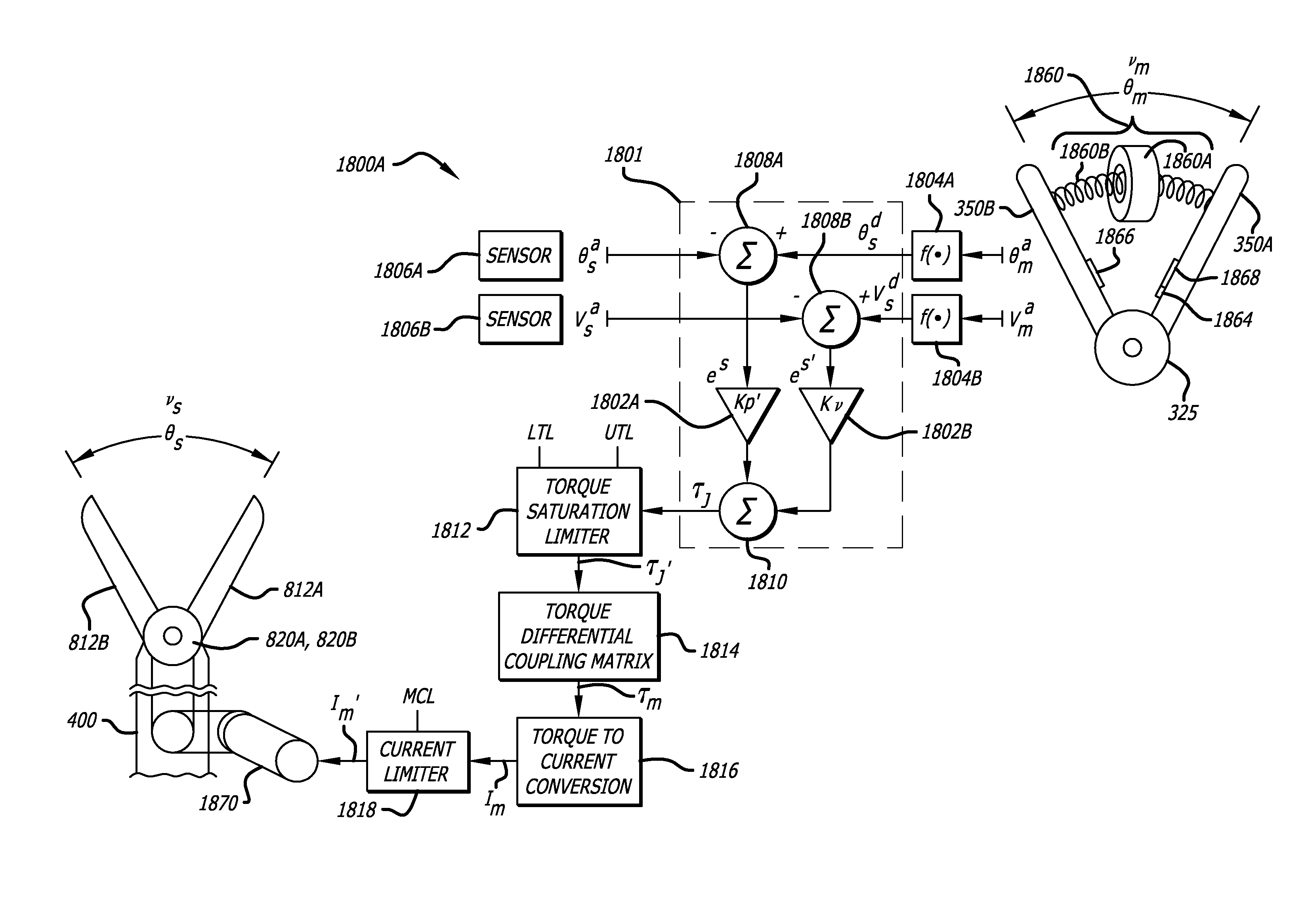
Maximum torque driving of robotic surgical tools in robotic surgical systems
ActiveUS9002518B2Programme-controlled manipulatorMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMaximum torqueMotor drive
In one embodiment of the invention, a control system for a robotic surgical instrument is provided including a torque saturation limiter, a torque to current converter coupled to the torque saturation limiter, and a motor coupled to the torque to current converter. The torque saturation limiter receives a desired torque signal for one or more end effectors and limits the desired torque to a range between an upper torque limit and a lower torque limit generating a bounded torque signal. The torque to current converter transforms a torque signal into a current signal. The motor drives an end effector of one or more end effectors to the bounded torque signal in response to the first current signal.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
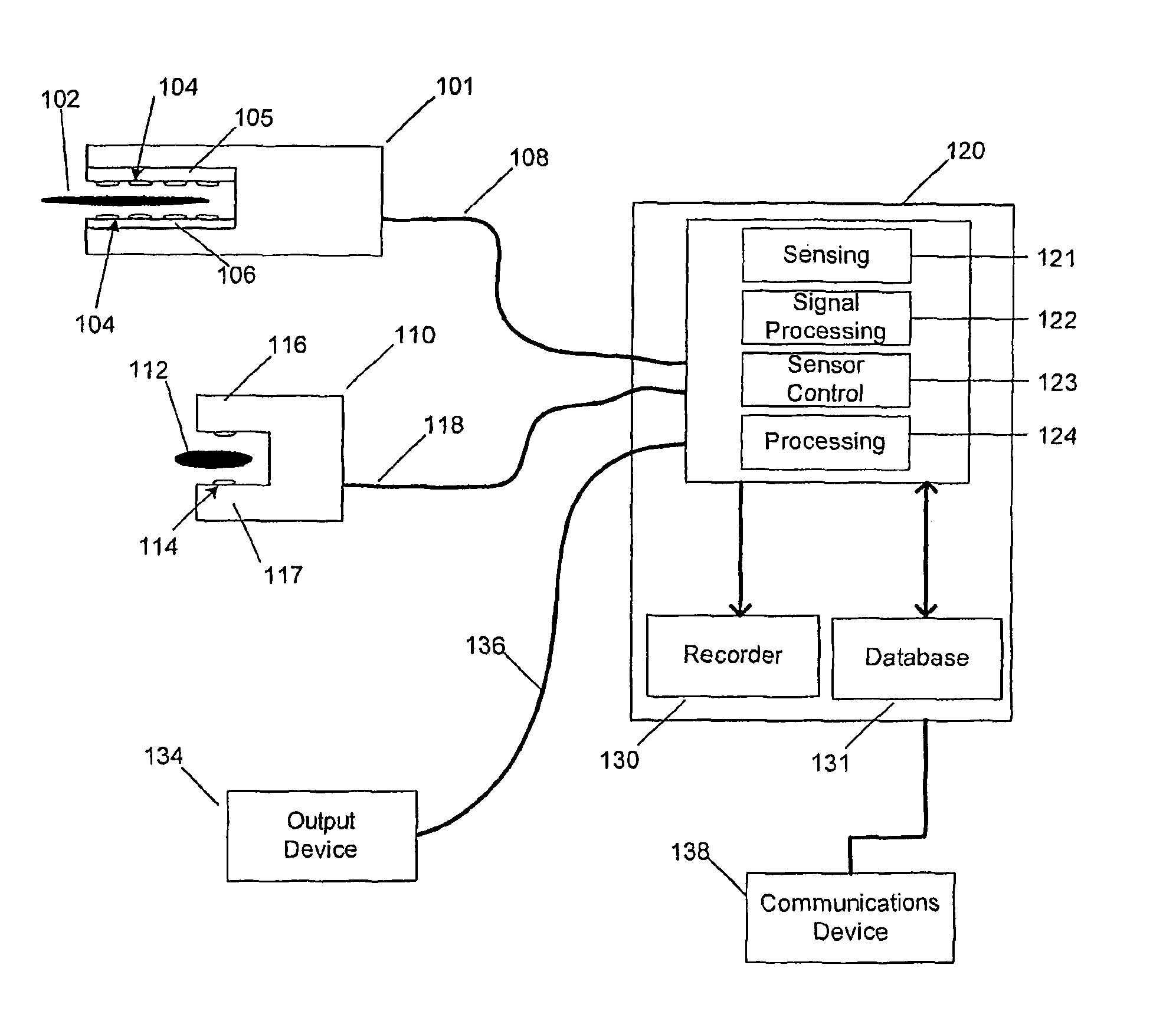
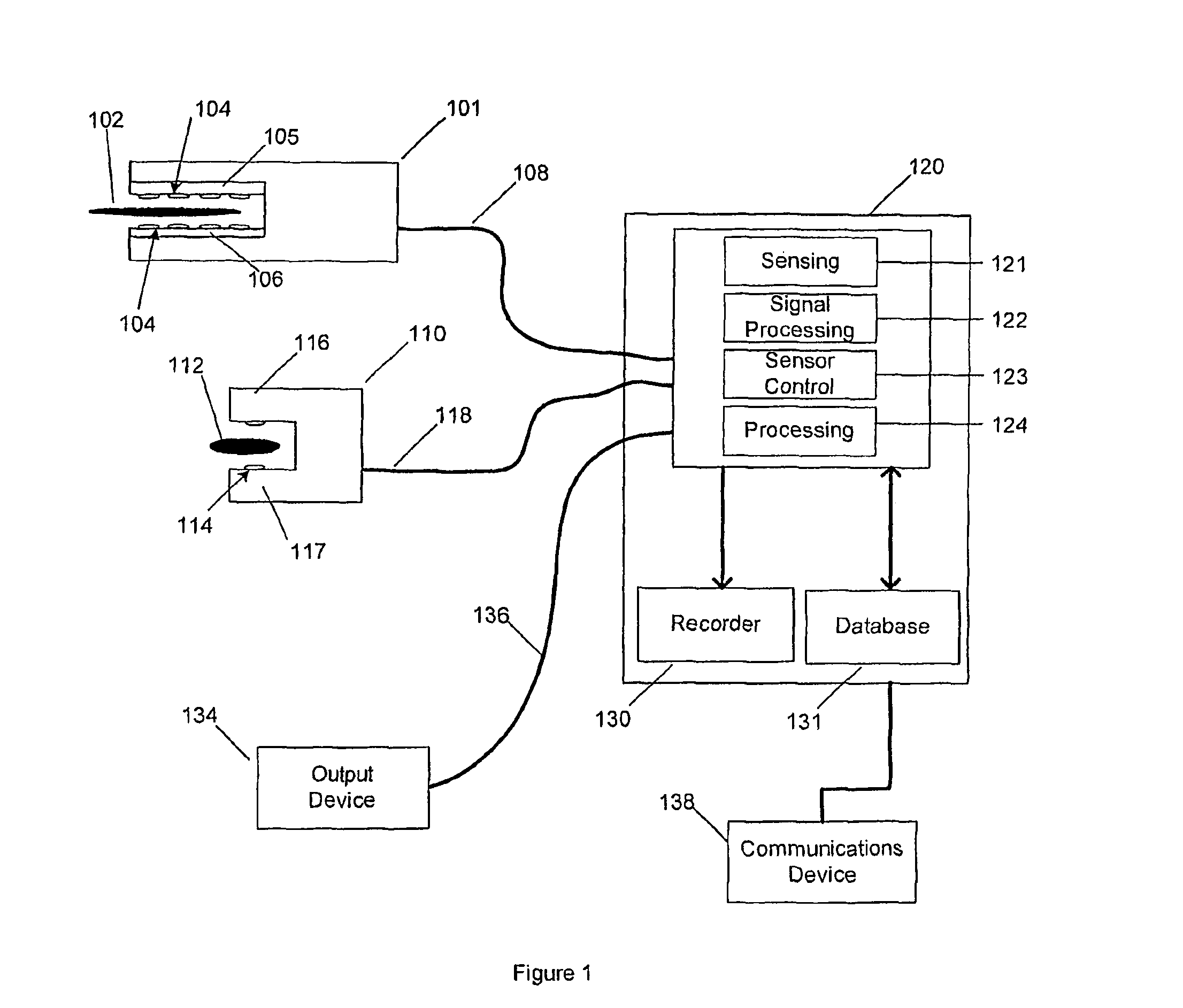
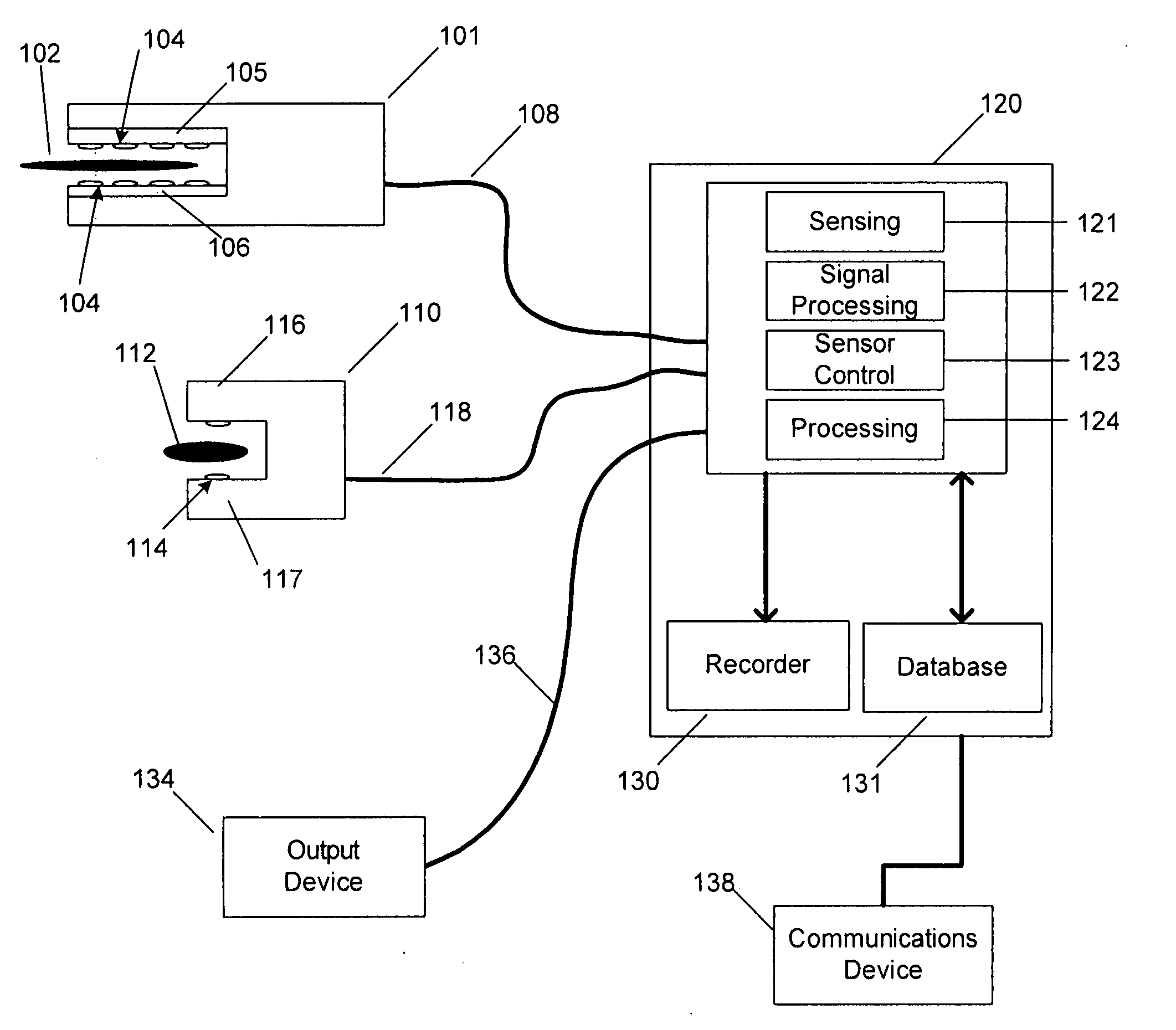
Surgical instruments with sensors for detecting tissue properties, and system using such instruments
ActiveUS9204830B2Avoiding and detecting failurePredict successDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterData setPatient state
A system is provided that furnishes expert procedural guidance based upon patient-specific data gained from surgical instruments incorporating sensors on the instrument's working surface, one or more reference sensors placed about the patient, sensors implanted before, during or after the procedure, the patient's personal medical history, and patient status monitoring equipment. Embodiments include a system having a surgical instrument with a sensor for generating a signal indicative of a property of a subject tissue of the patient, which signal is converted into a current dataset and stored. A processor compares the current dataset with other previously stored datasets, and uses the comparison to assess a physical condition of the subject tissue and / or to guide a procedure being performed on the tissue.
Owner:SURGISENSE CORP
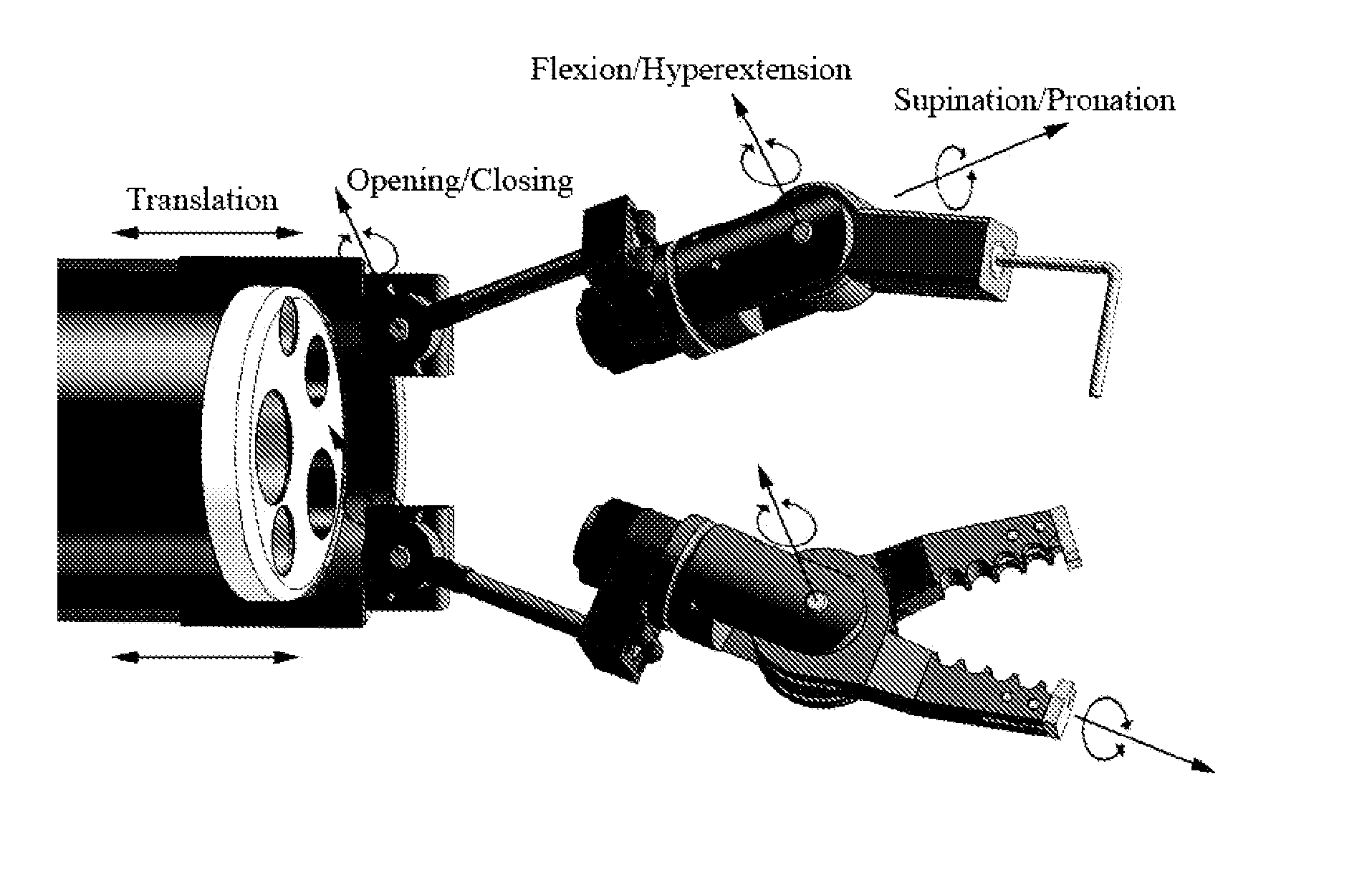
Hand-actuated device for remote manipulation of a grasping tool
The invention provides an articulating mechanism useful, for example, for remote manipulation of various surgical instruments and diagnostic tools within, or to, regions of the body. Movement of segments at the proximal end of the mechanism results in a corresponding, relative movement of segments at the distal end of the mechanism. The proximal and distal segments are connected by a set of cables in such a fashion that each proximal segment forms a discrete pair with a distal segment. This configuration allows each segment pair to move independently of one another and also permits the articulating mechanism to undergo complex movements and adopt complex configurations. The articulating mechanisms may also be combined in such a way to remotely mimic finger movements for manipulation of an object or body tissue.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Maximum torque driving of robotic surgical tools in robotic surgical systems
ActiveUS20080046122A1Improve the level ofProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesLower limitMaximum torque
In one embodiment of the invention, a control system for a robotic surgical instrument is provided including a torque saturation limiter, a torque to current converter coupled to the torque saturation limiter, and a motor coupled to the torque to current converter. The torque saturation limiter receives a desired torque signal for one or more end effectors and limits the desired torque to a range between an upper torque limit and a lower torque limit generating a bounded torque signal. The torque to current converter transforms a torque signal into a current signal. The motor drives an end effector of one or more end effectors to the bounded torque signal in response to the first current signal.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
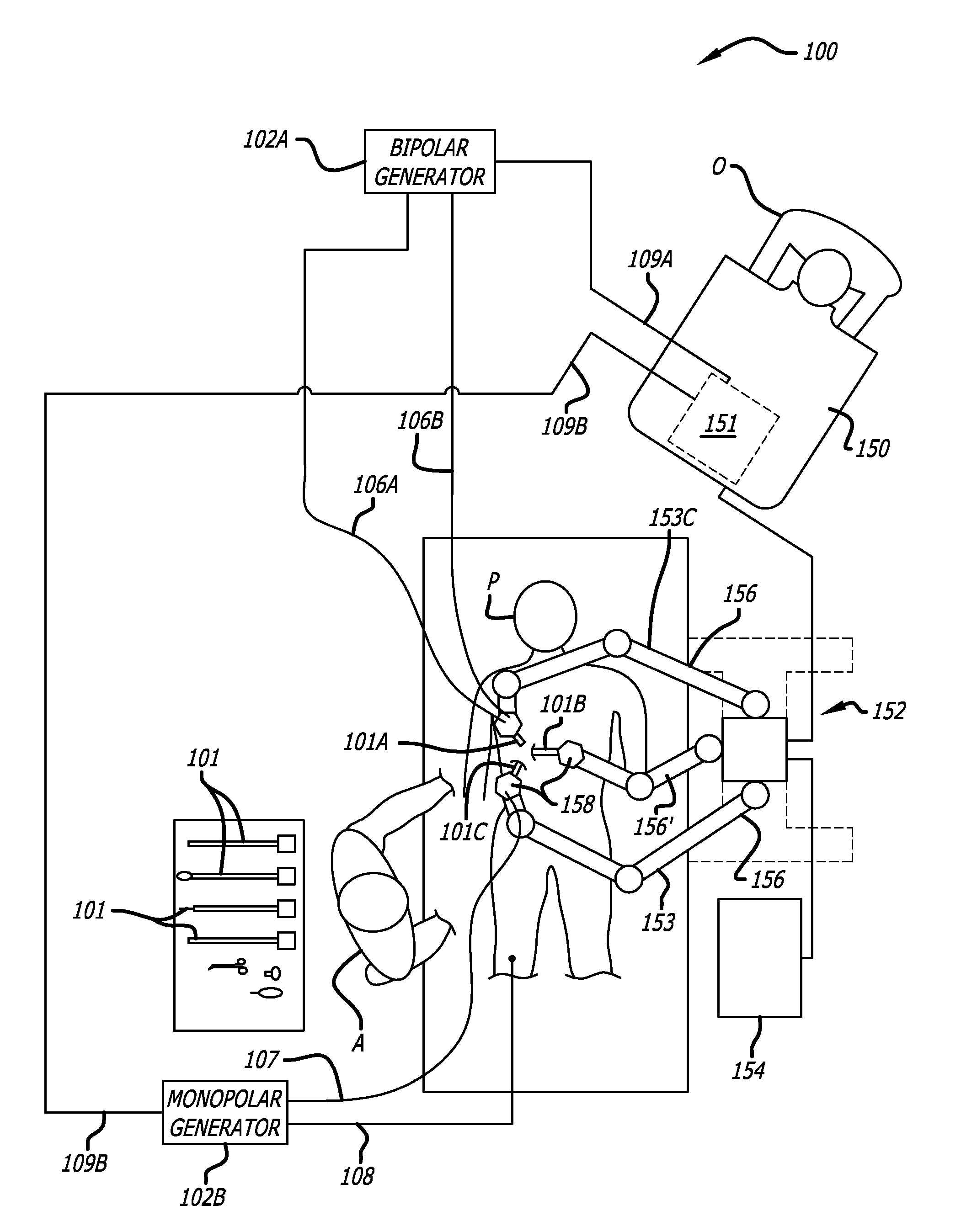
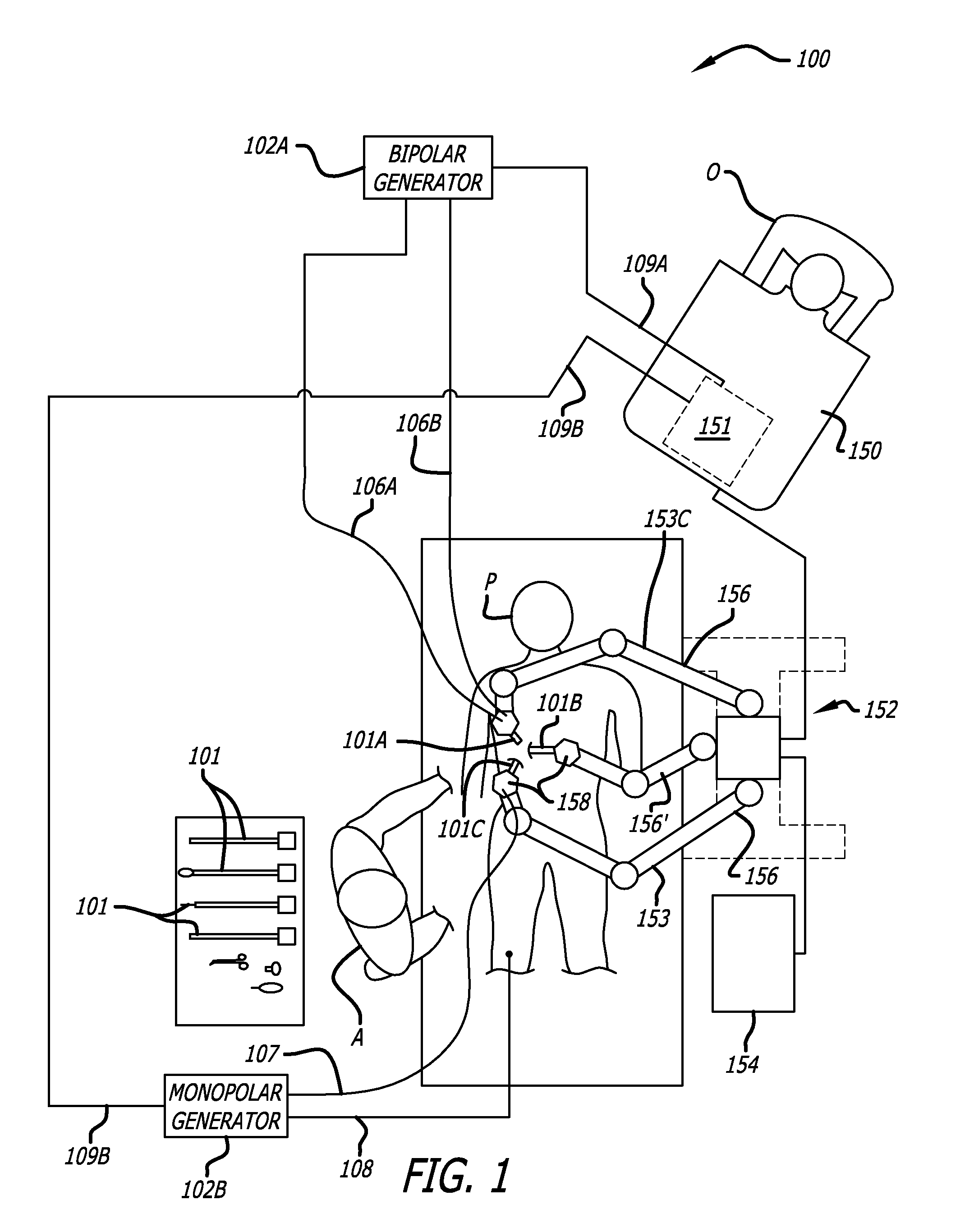
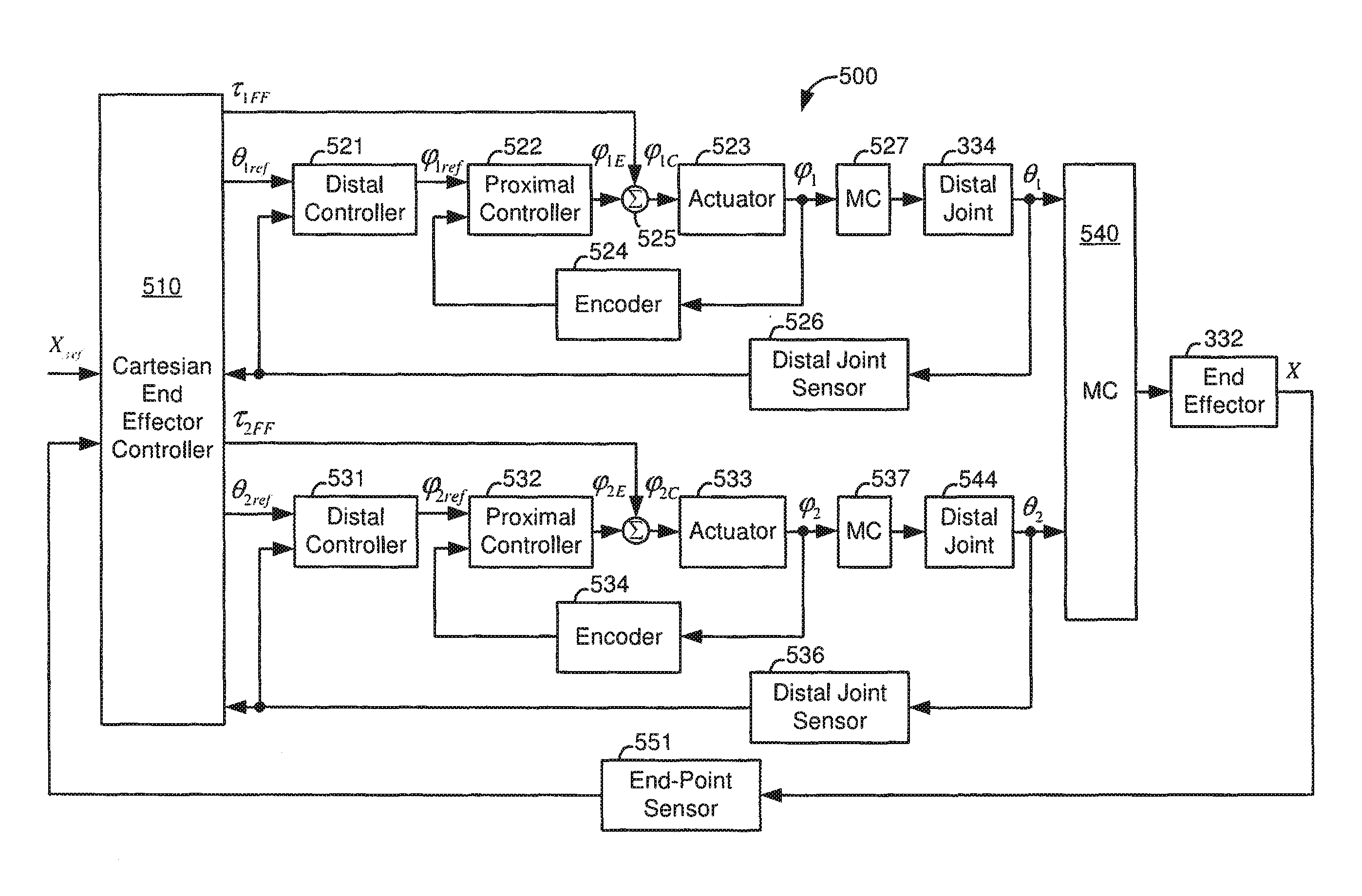
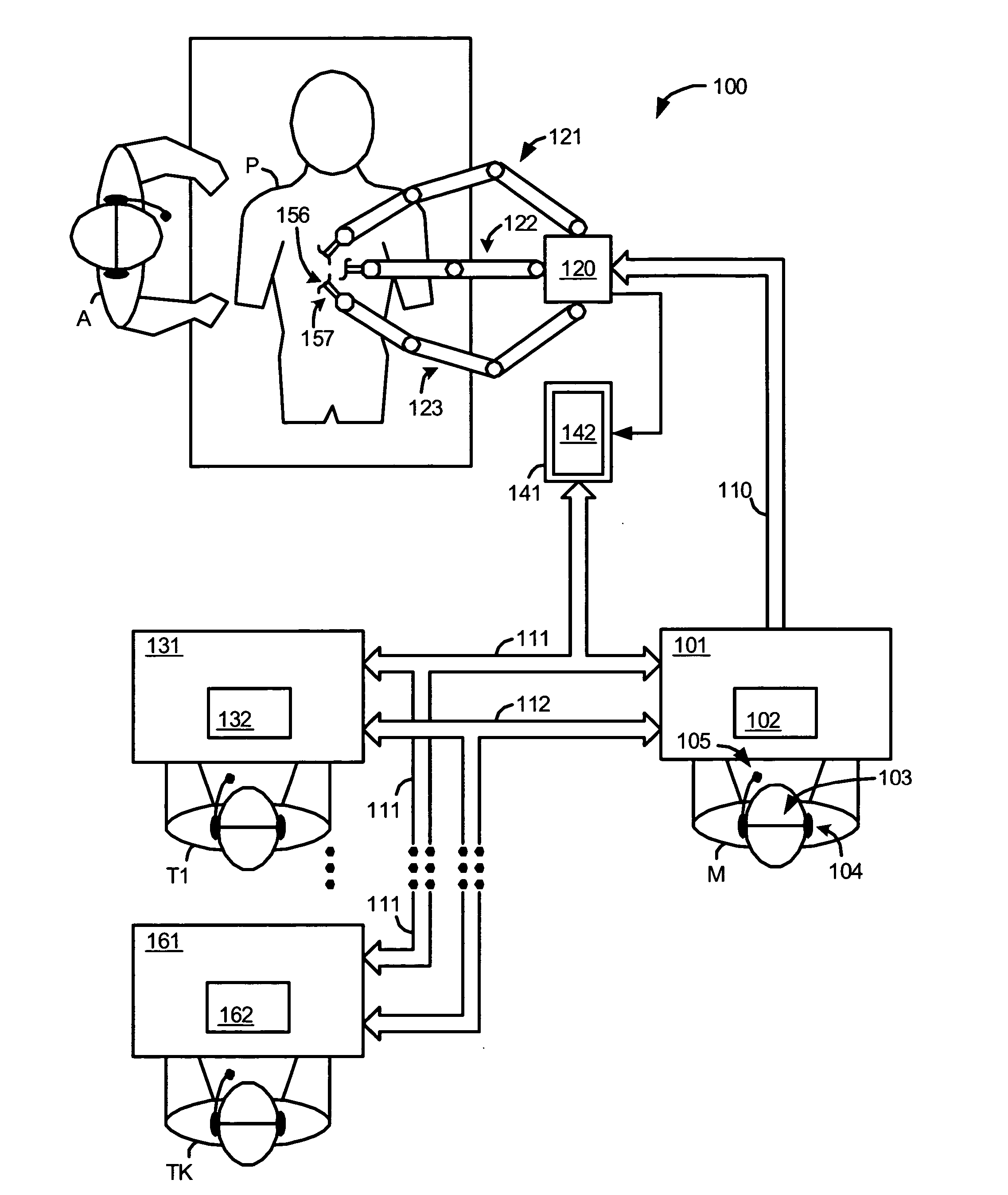
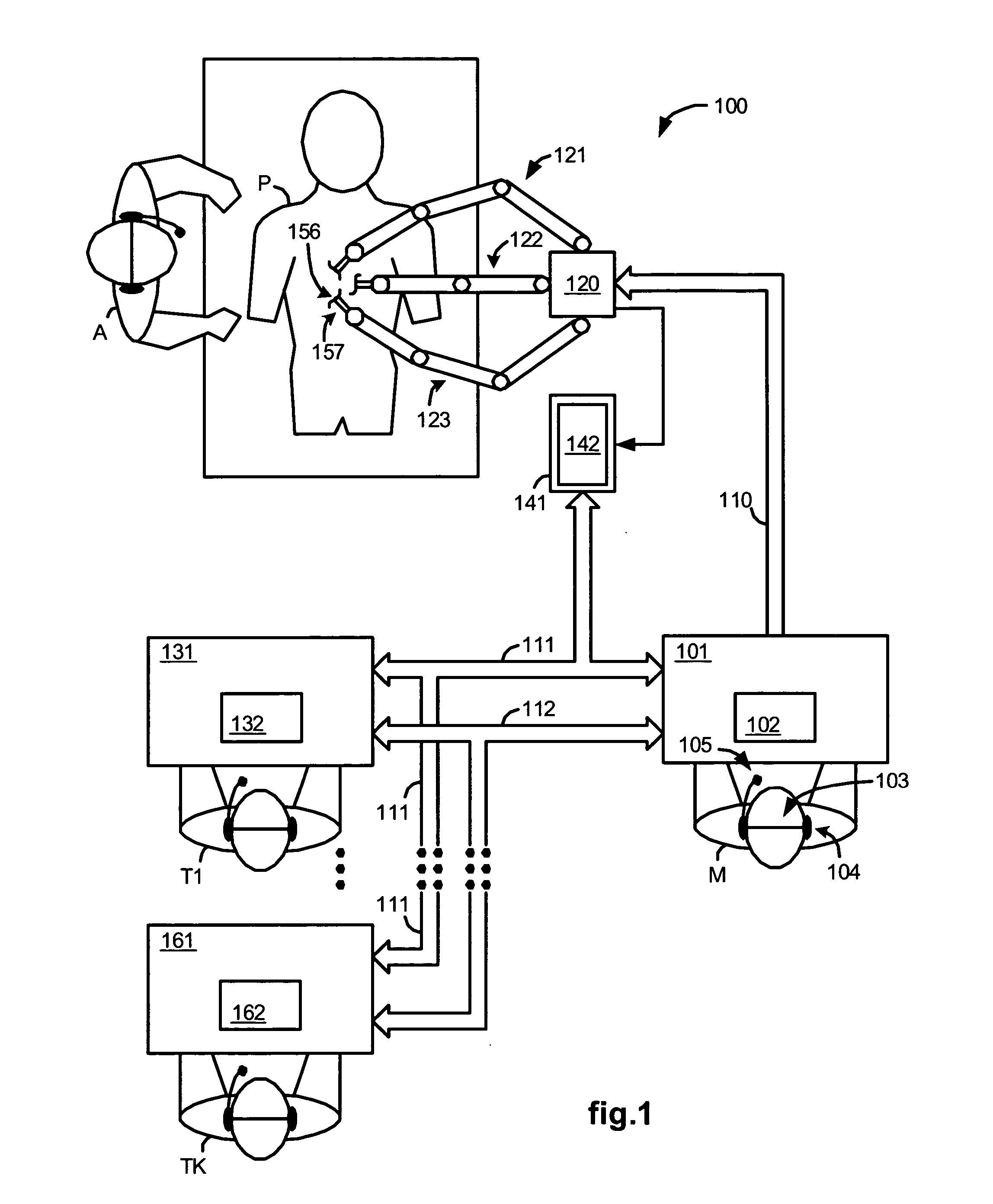
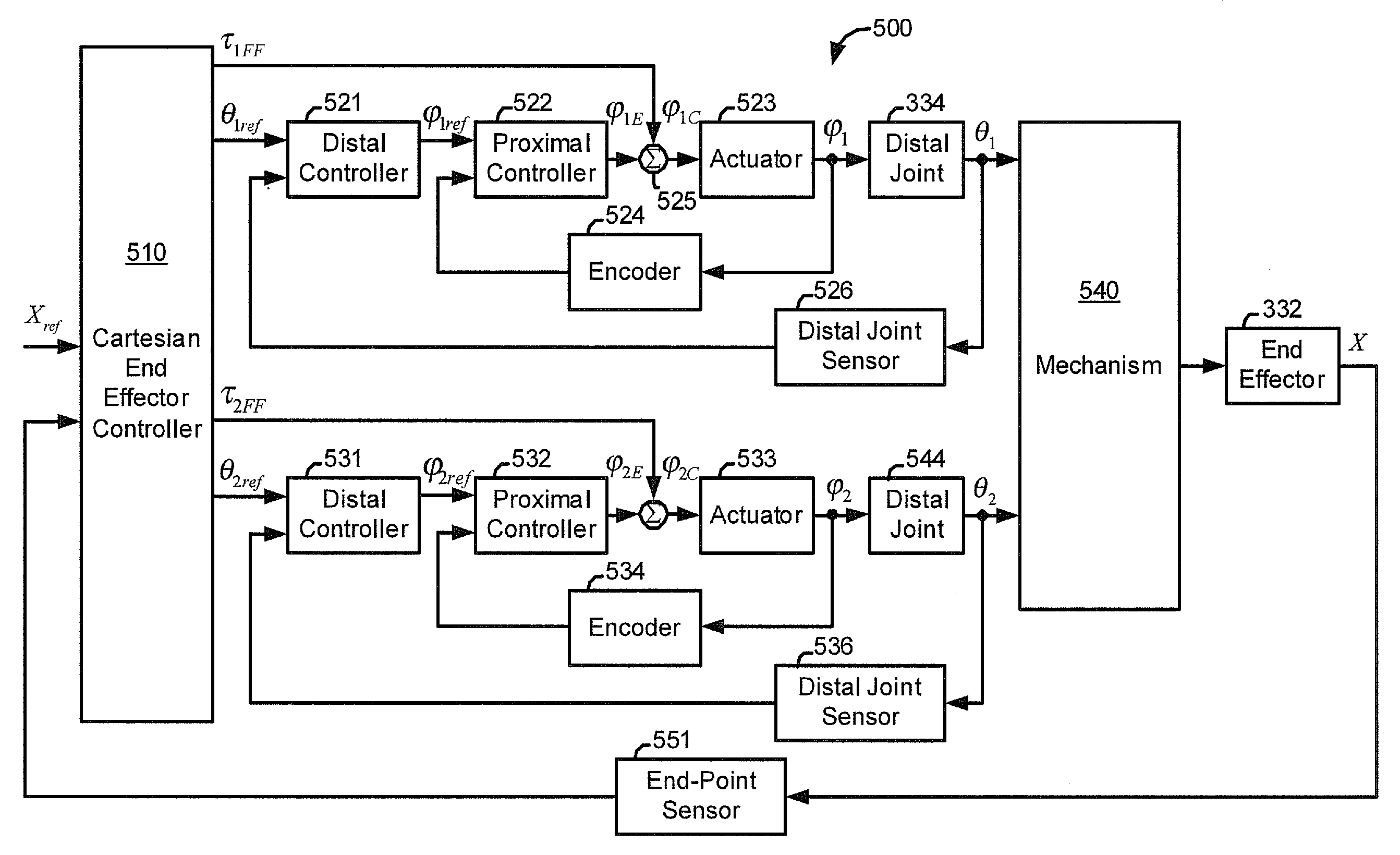
Control system configured to compensate for non-ideal actuator-to-joint linkage characteristics in a medical robotic system
A medical robotic system having non-ideal actuator-to-joint linkage characteristics, includes a control system including a proximal control loop with actuator sensor feedback to control dynamic response of an actuator coupled to a distal joint which in turn, is coupled to an end effector to provide a degree of freedom movement of the end effector, a distal control loop with distal joint sensor feedback and feedforward to the actuator to ensure steady-state convergence of the distal joint position, and an end effector control loop with end-point sensor feedback to control the end effector position to reach a commanded end effector position.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
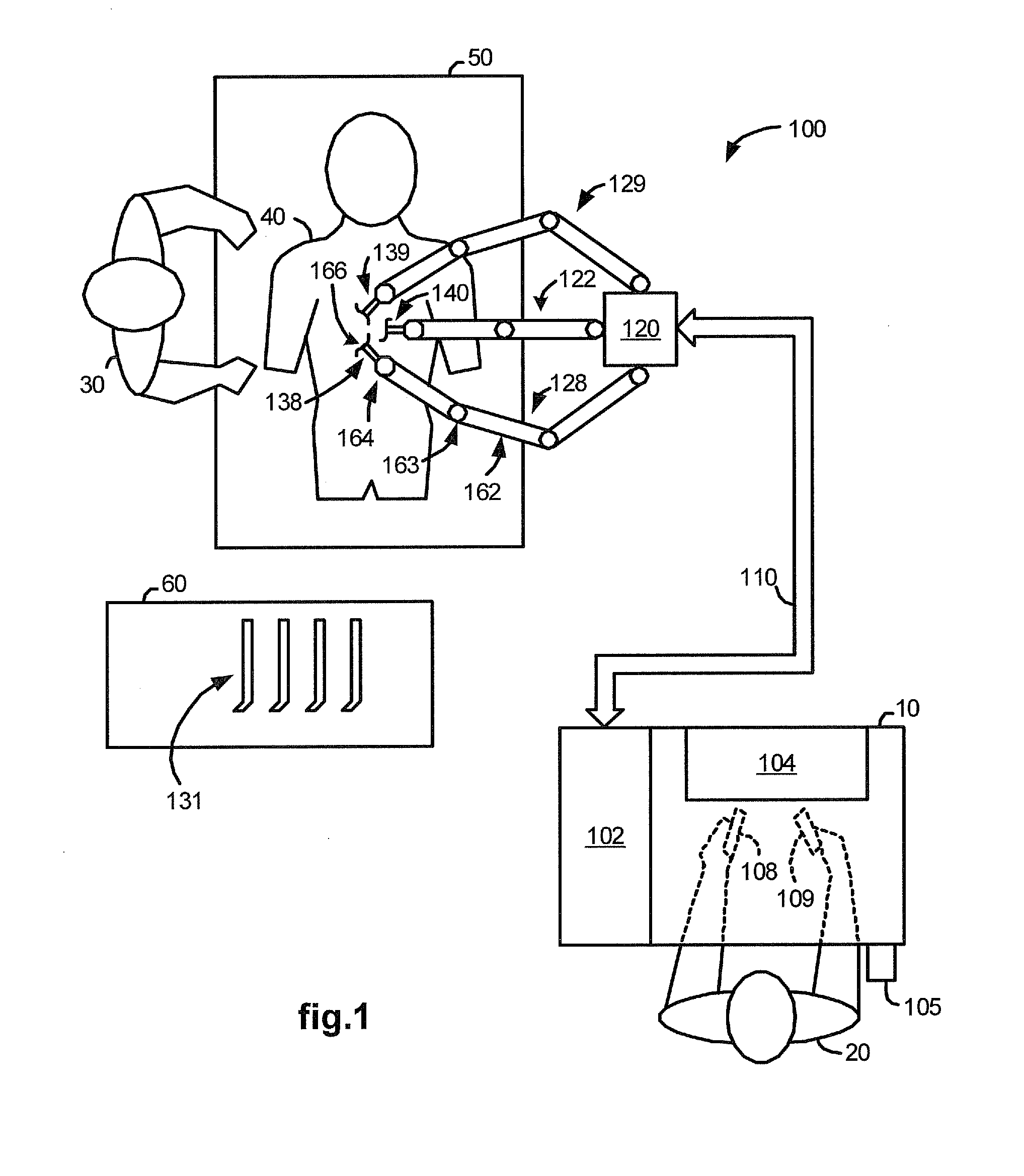
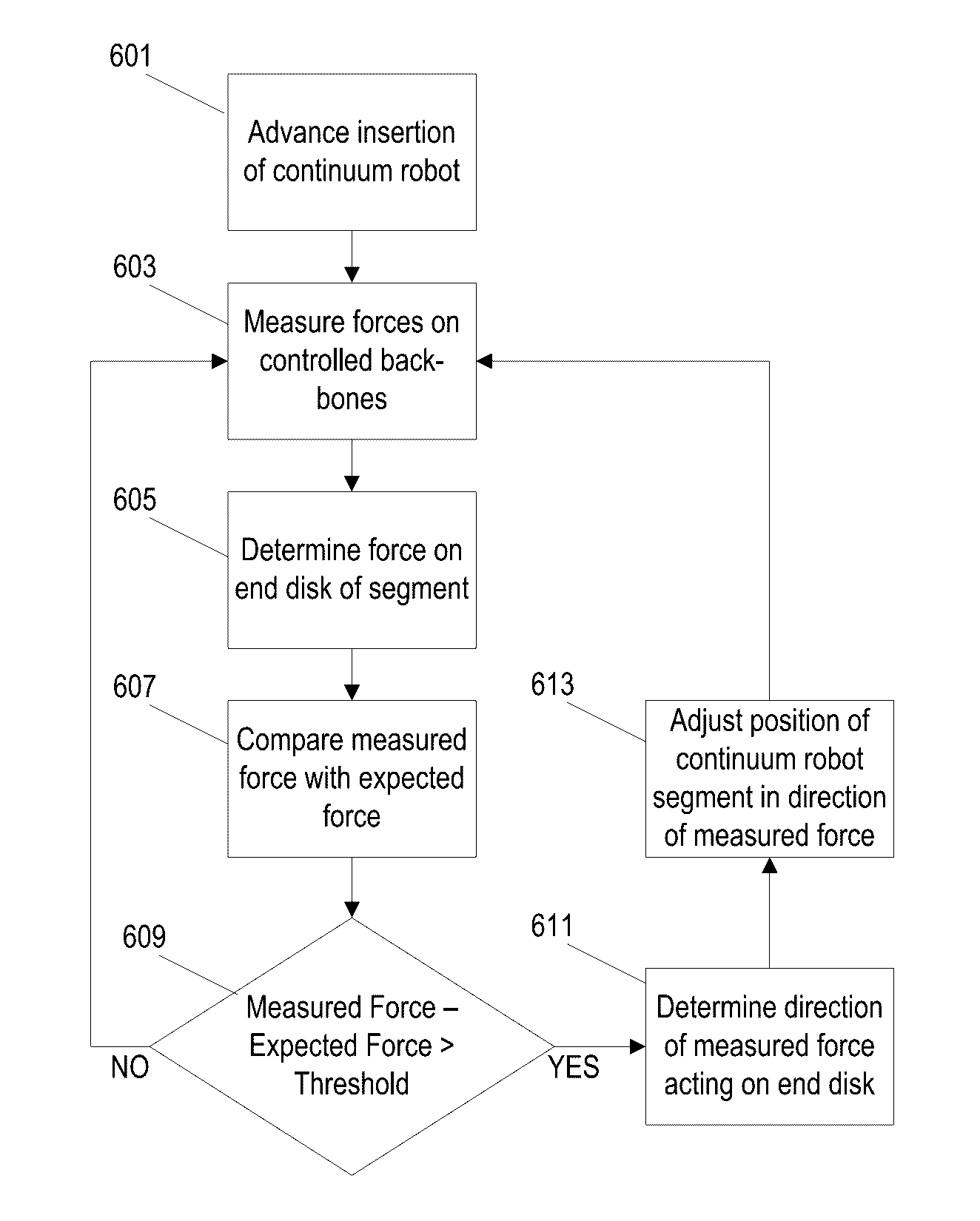
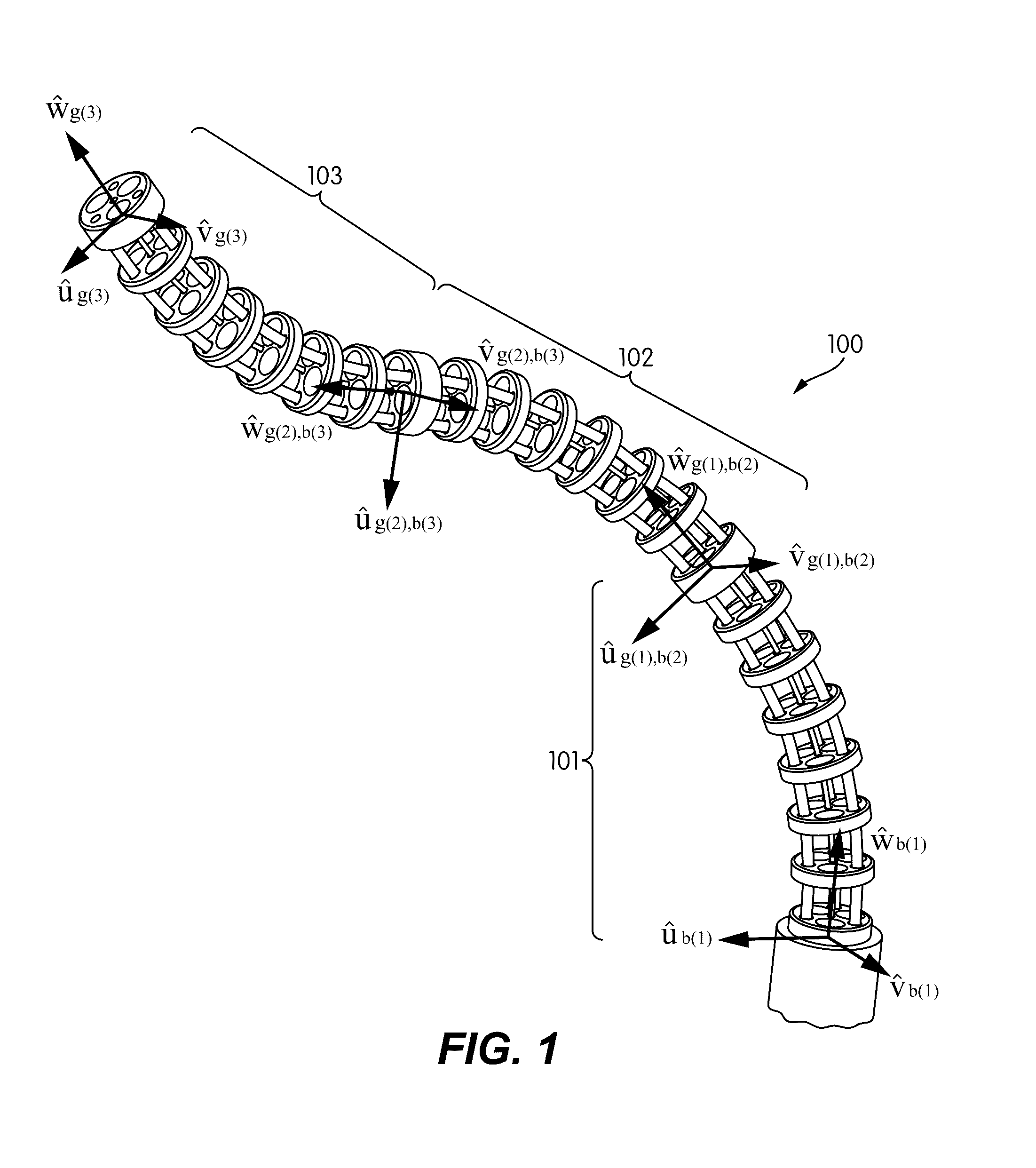
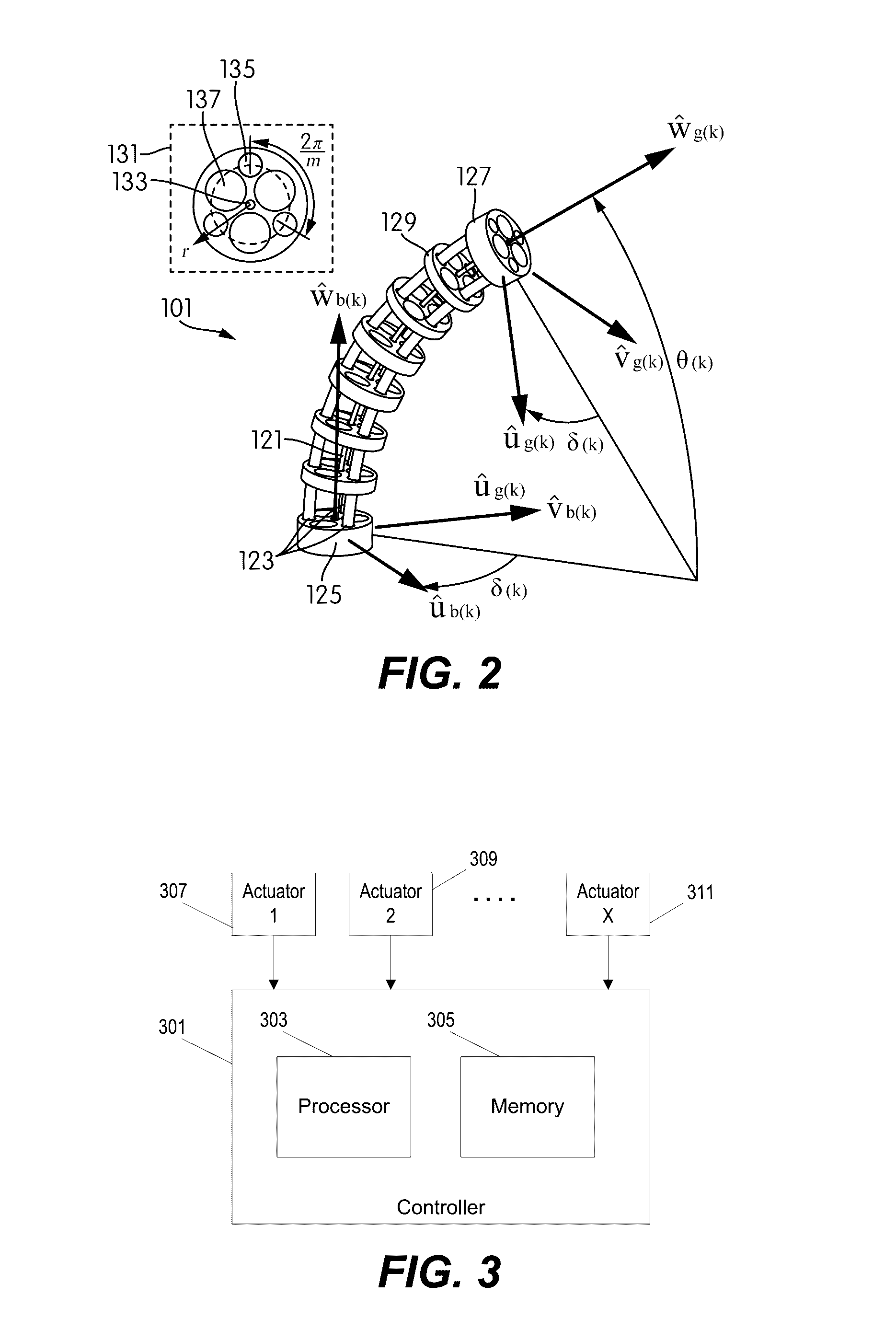
Systems and methods for safe compliant insertion and hybrid force/motion telemanipulation of continuum robots
ActiveUS9539726B2Easy to operateImprove stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsEngineeringManipulator
Methods and systems are described for controlling movement of a continuum robot that includes a plurality of independently controlled segments along the length of the continuum robot. The continuum robot is inserted into a cavity of unknown dimensions or shape. A plurality of forces acting upon the continuum robot by the surrounding cavity are estimated. A positioning command indicating a desired movement of the distal end of the continuum robot is received from a manipulator control. The desired movement is augmented based, at least in part, on the estimated plurality of forces acting on the continuum robot such that movement is restricted to within safe boundaries of the surrounding cavity. The positioning of the continuum robot is then adjusted based on the augmented desired movement.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Companion robot for personal interaction
ActiveUS20070192910A1Improving presence scoreEnhanced presenceProgramme-controlled manipulatorLocal control/monitoringThird partyTeleconference
A mobile robot guest for interacting with a human resident performs a room-traversing search procedure prior to interacting with the resident, and may verbally query whether the resident being sought is present. Upon finding the resident, the mobile robot may facilitate a teleconferencing session with a remote third party, or interact with the resident in a number of ways. For example, the robot may carry on a dialogue with the resident, reinforce compliance with medication or other schedules, etc. In addition, the robot incorporates safety features for preventing collisions with the resident; and the robot may audibly announce and / or visibly indicate its presence in order to avoid becoming a dangerous obstacle. Furthermore, the mobile robot behaves in accordance with an integral privacy policy, such that any sensor recording or transmission must be approved by the resident.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
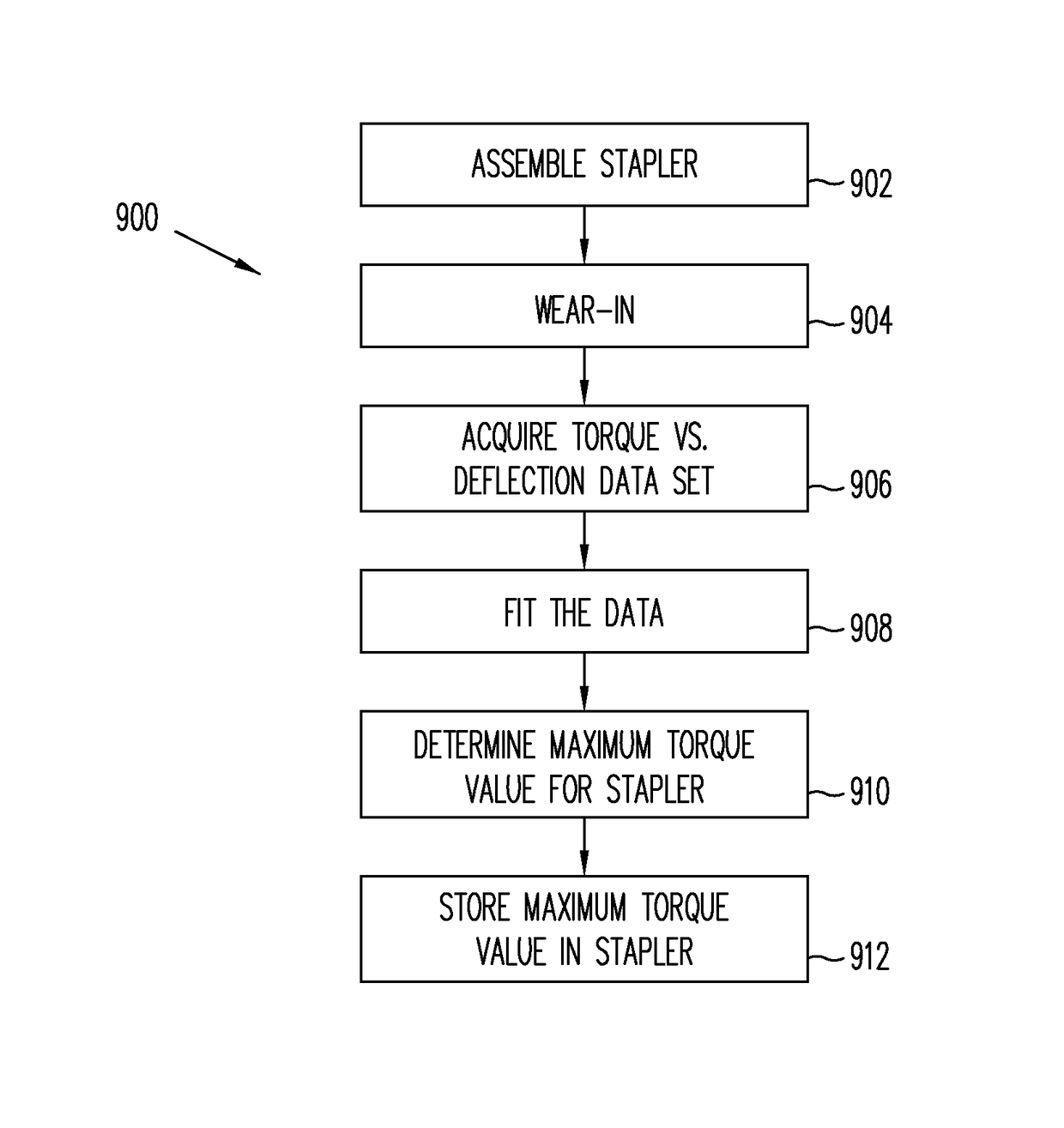
Torque compensation
ActiveUS9675354B2Programme-controlled manipulatorSurgical furnitureOperating temperatureIndustrial engineering
Embodiments of a clamping system are disclosed. In some embodiments, a system used with a motor assembly and a clamping device is presented, the system adjusting torque limits in the motor assembly according to conditions, for example operating temperature of the motor assembly and aging of the clamping device and the motor assembly. The clamping device can be, for example, a stapler or a vessel sealer.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Surgical instruments with sensors for detecting tissue properties, and system using such instruments
ActiveUS20090054908A1Avoiding and detecting failurePredict successDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterData setPatient status
A system is provided that furnishes expert procedural guidance based upon patient-specific data gained from surgical instruments incorporating sensors on the instrument's working surface, one or more reference sensors placed about the patient, sensors implanted before, during or after the procedure, the patient's personal medical history, and patient status monitoring equipment. Embodiments include a system having a surgical instrument with a sensor for generating a signal indicative of a property of a subject tissue of the patient, which signal is converted into a current dataset and stored. A processor compares the current dataset with other previously stored datasets, and uses the comparison to assess a physical condition of the subject tissue and / or to guide a procedure being performed on the tissue.
Owner:SURGISENSE CORP
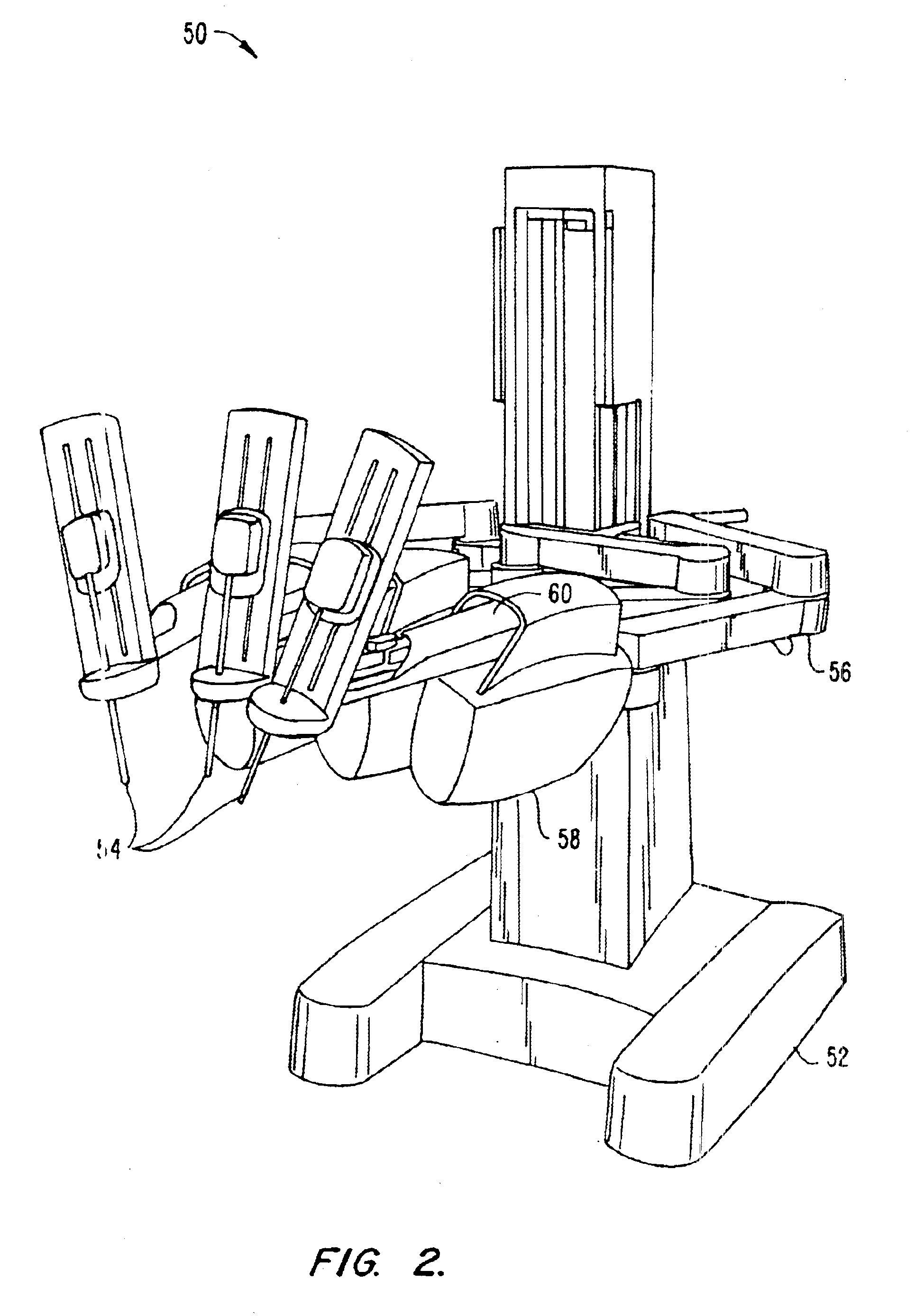
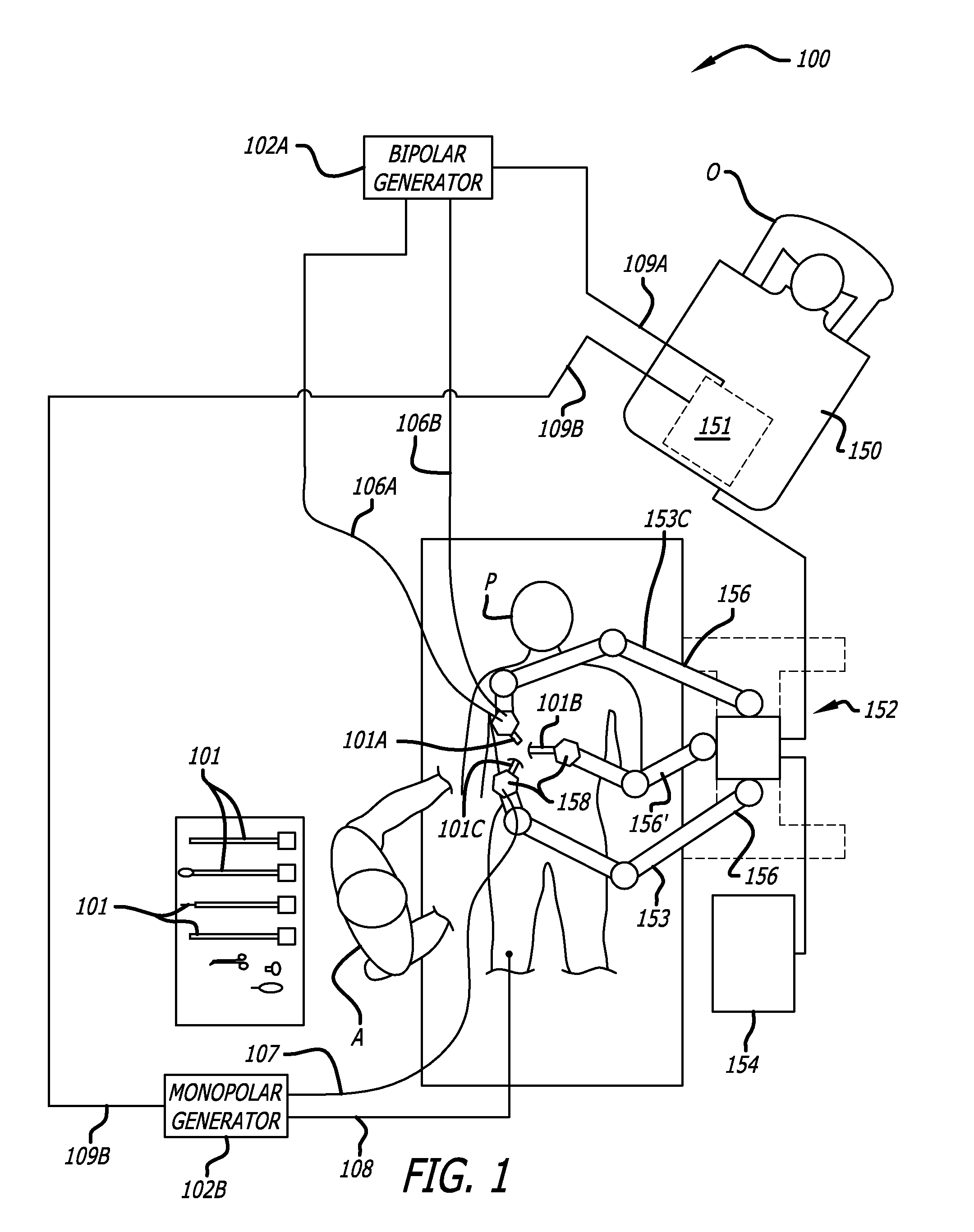
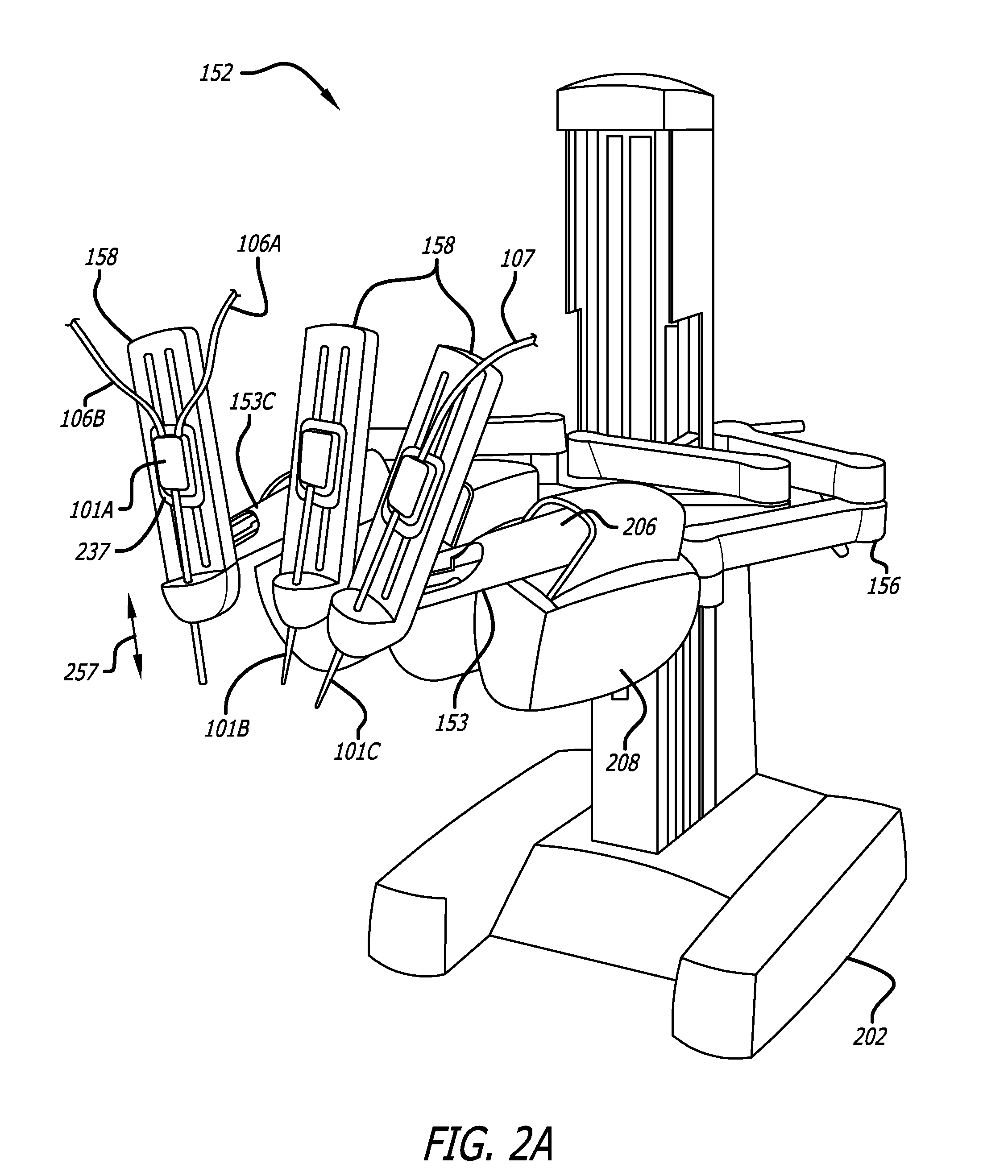
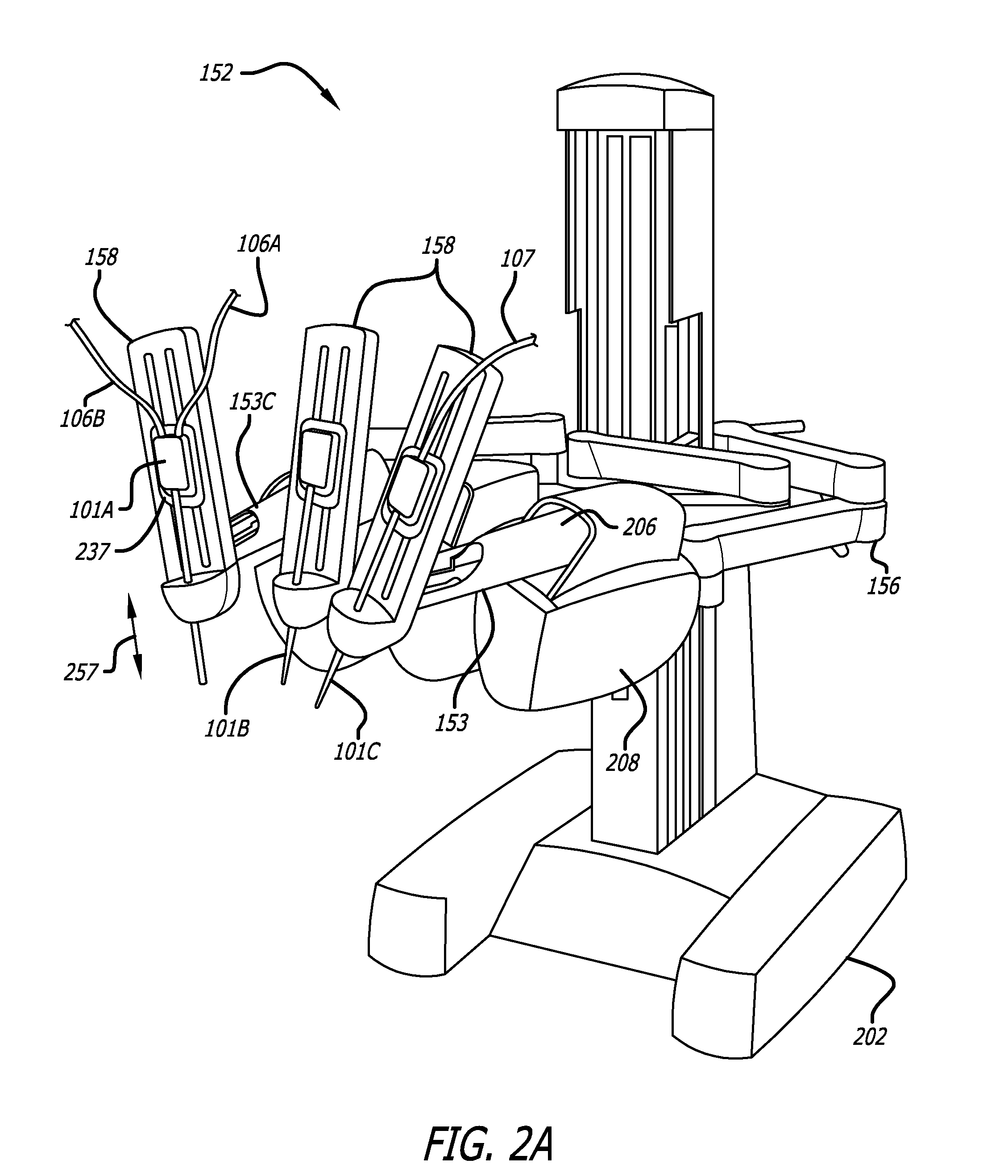
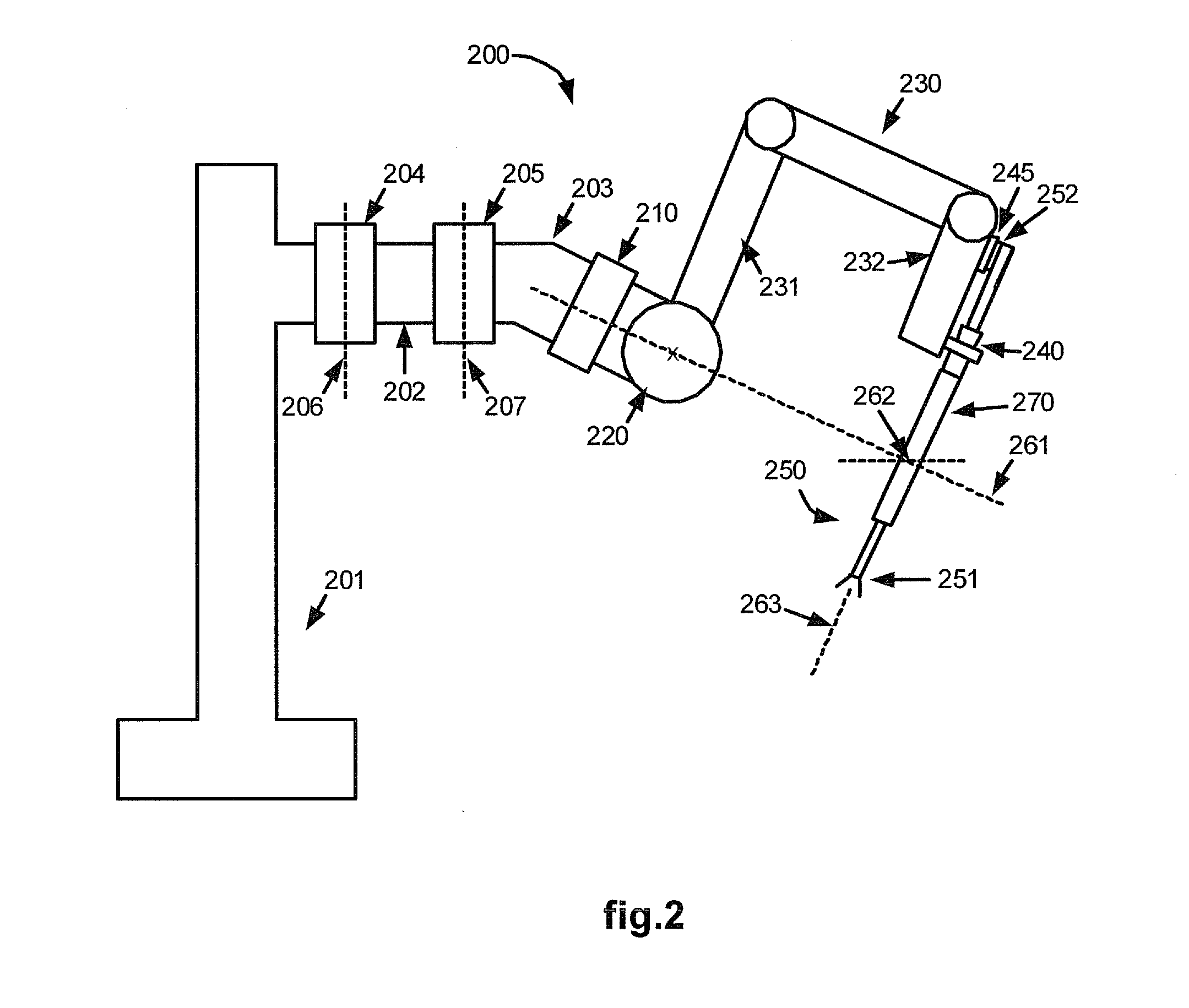
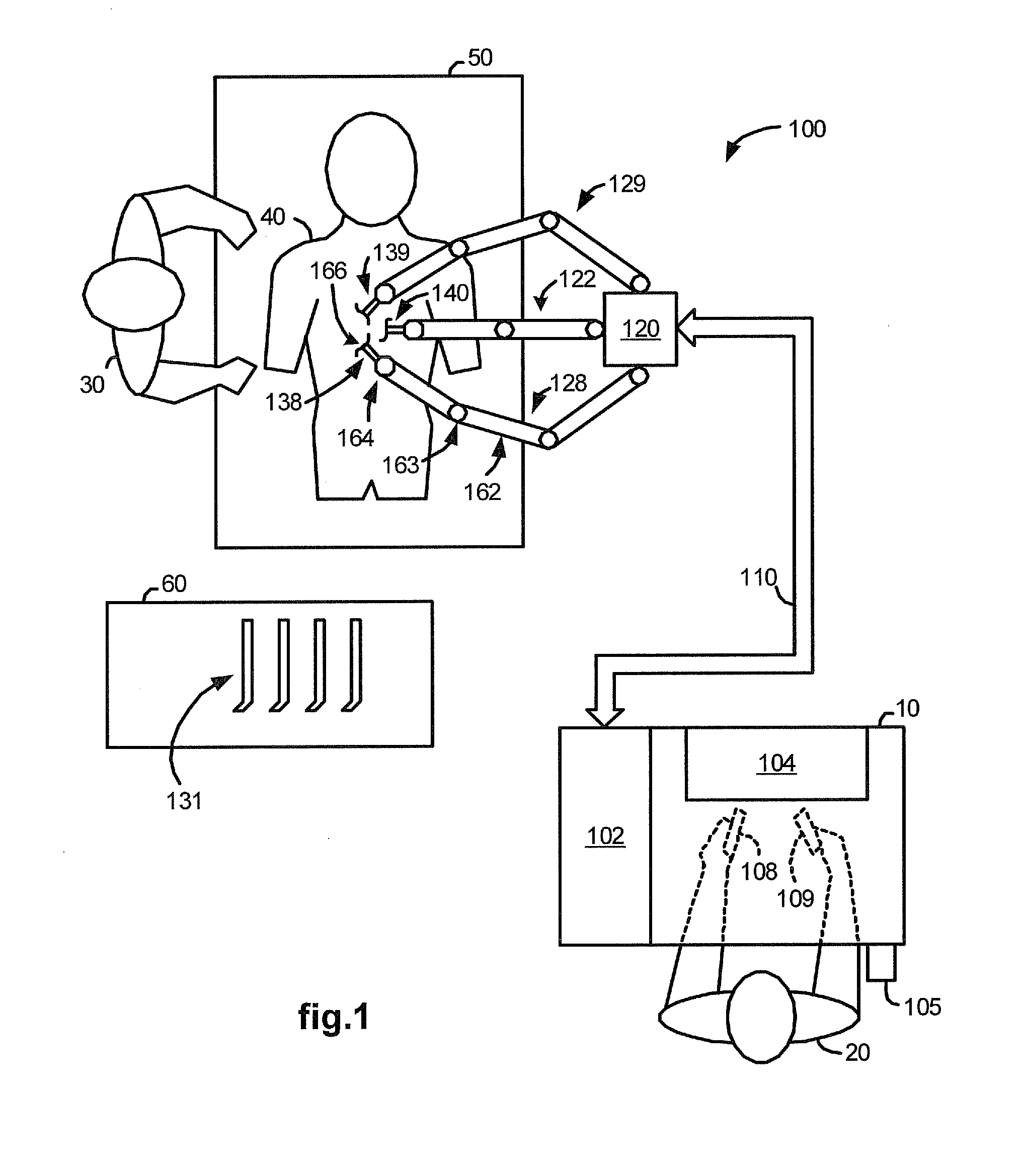
Offset remote center manipulator for robotic surgery
ActiveUS7594912B2Increase rangeReduces overall complexity and size and physical weightMechanical apparatusDiagnosticsEngineeringManipulator
Medical, surgical, and / or robotic devices and systems often including offset remote center parallelogram manipulator linkage assemblies which constrains a position of a surgical instrument during minimally invasive robotic surgery are disclosed. The improved remote center manipulator linkage assembly advantageously enhances the range of instrument motion while at the same time reduces the overall complexity, size, and physical weight of the robotic surgical system.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
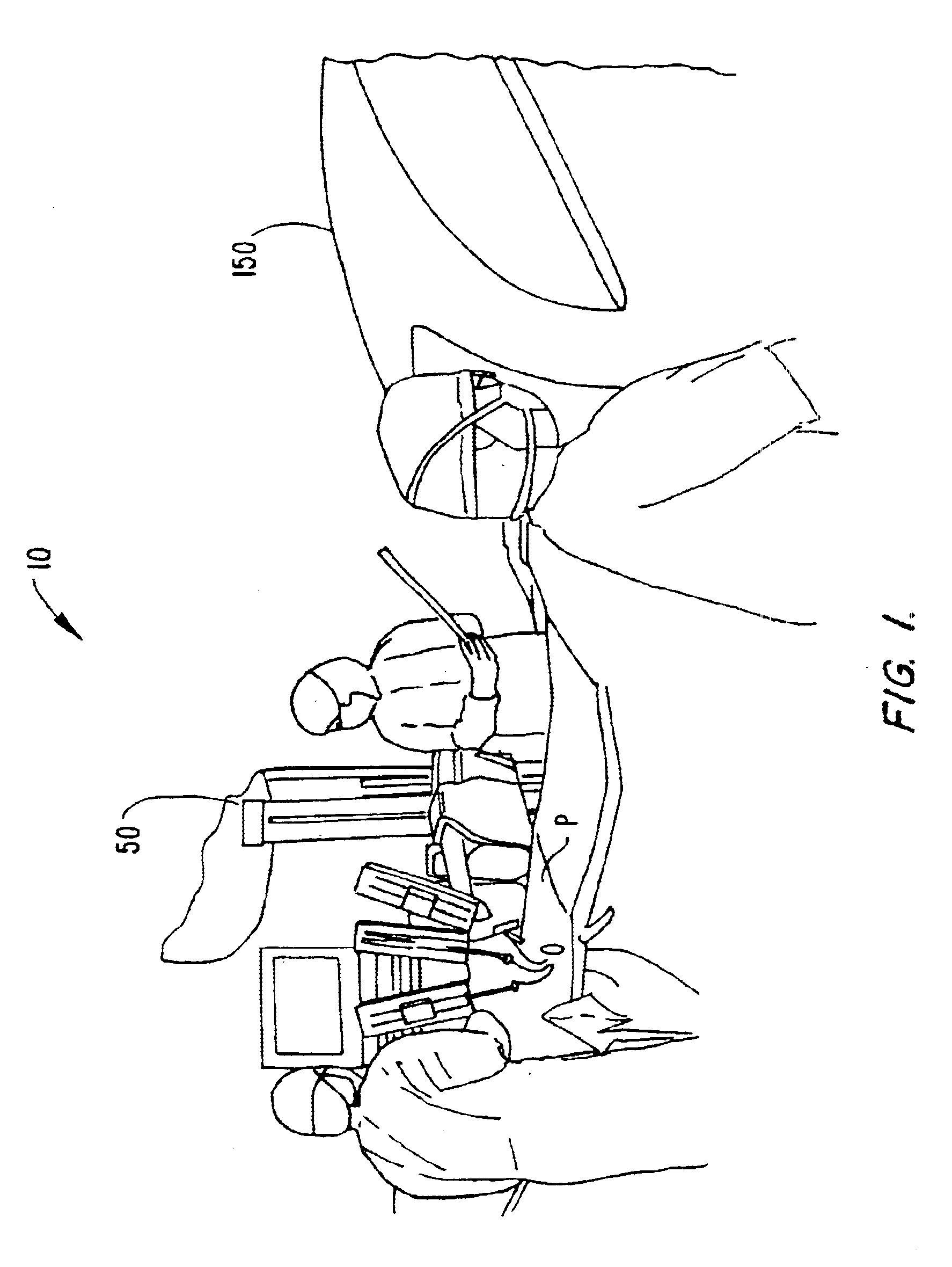
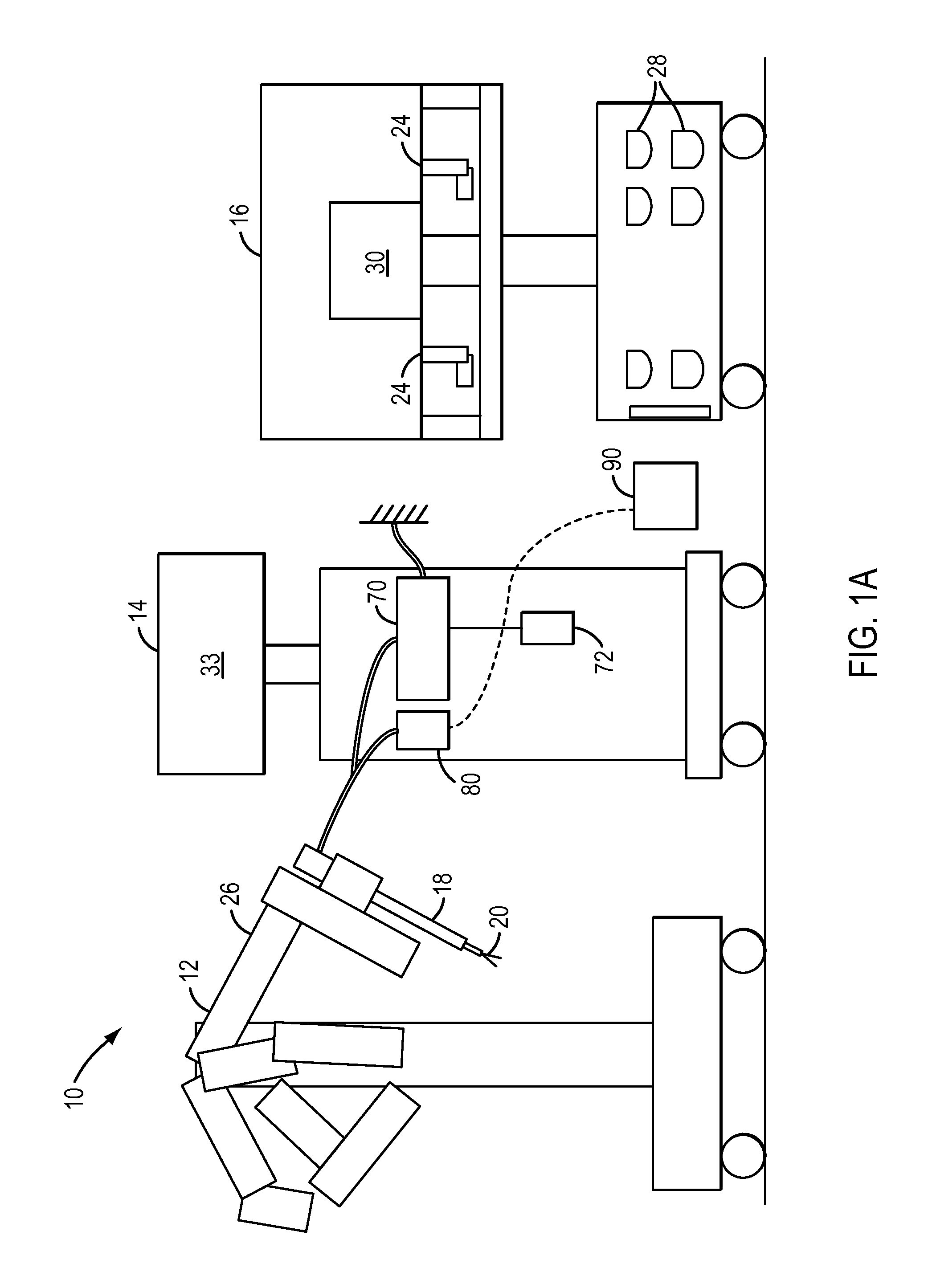
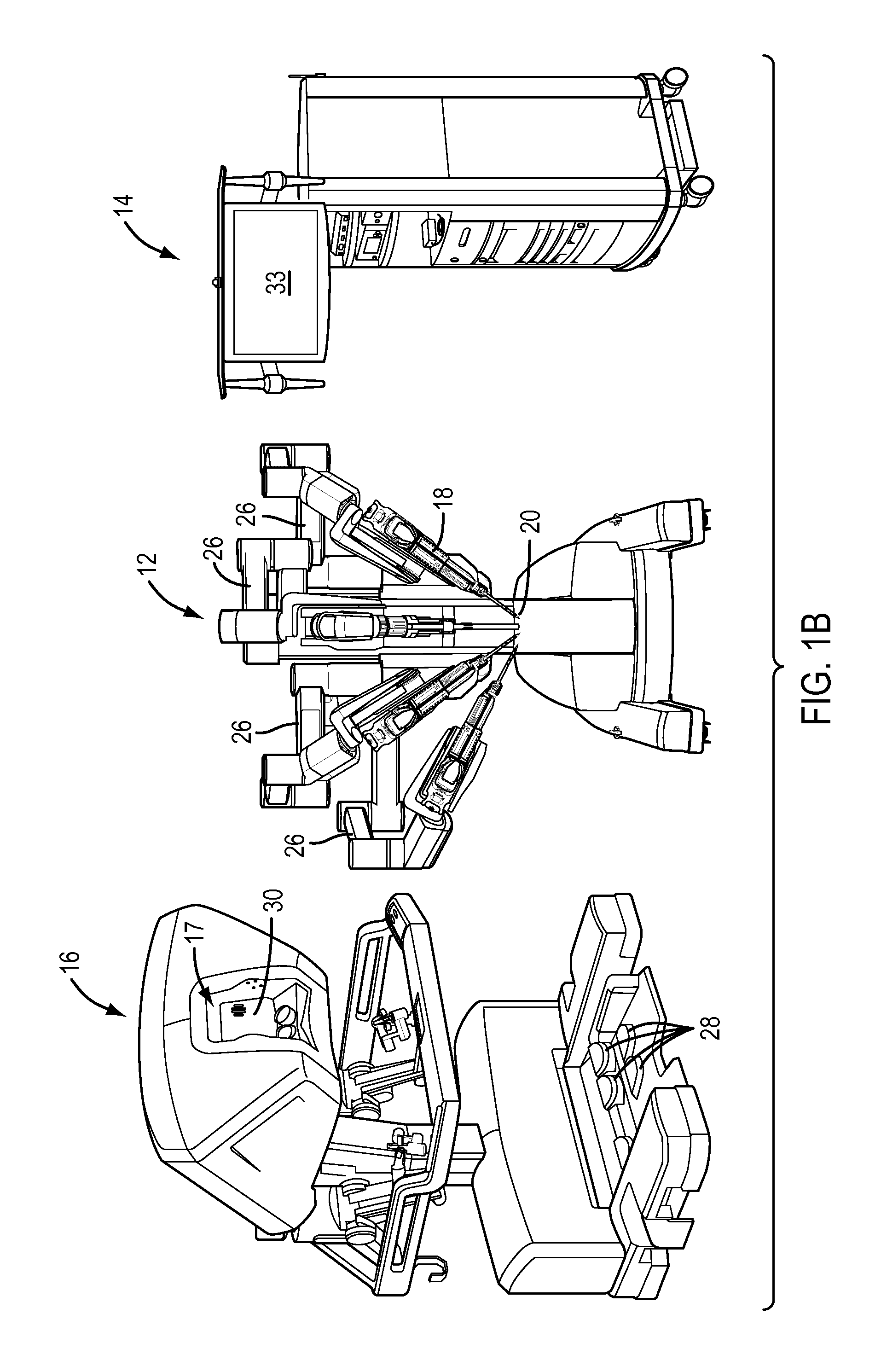
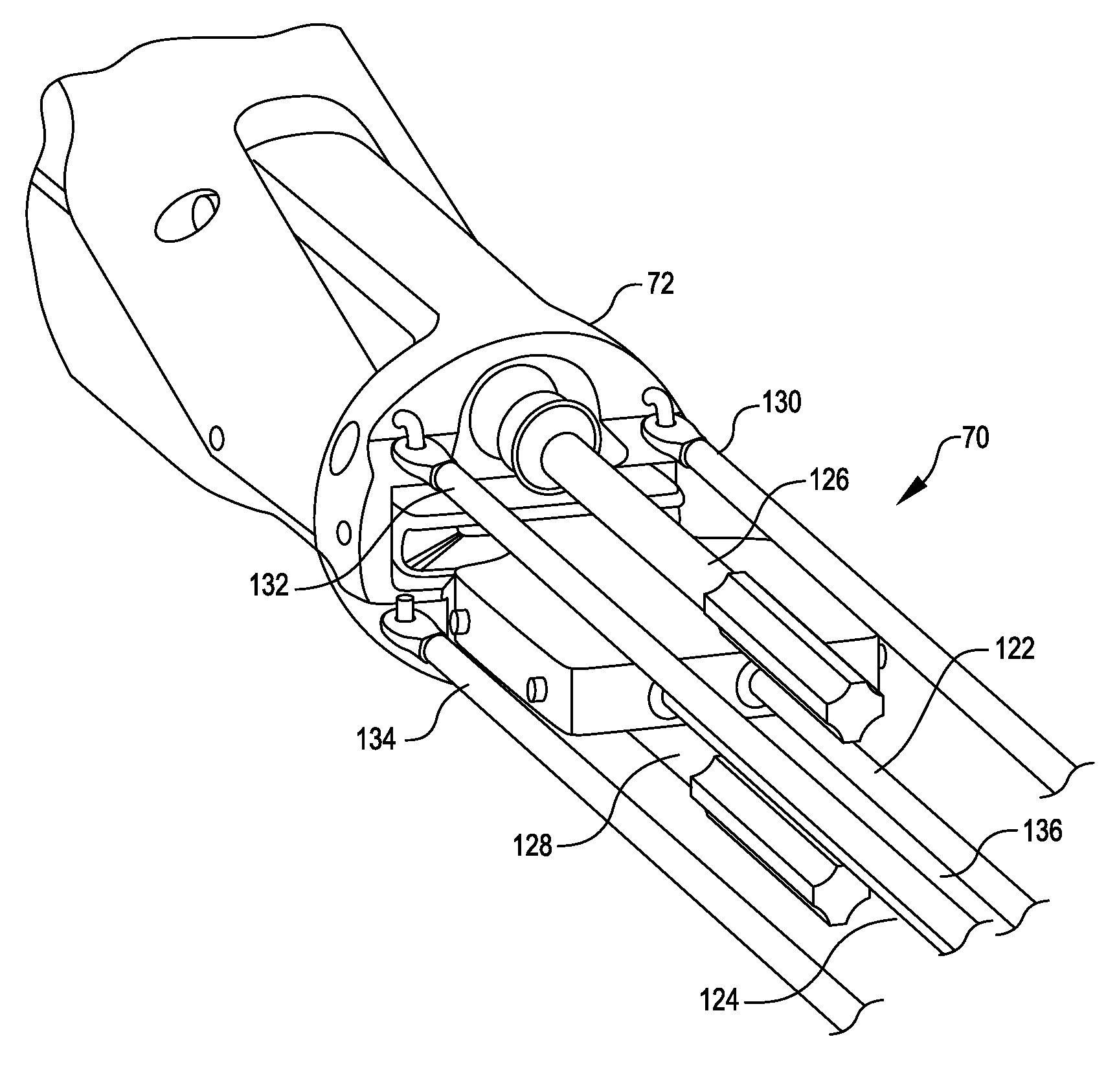
Patient-side surgeon interface for a minimally invasive, teleoperated surgical instrument
A patient-side surgeon interface provides enhanced capabilities in using a minimally invasive, teleoperated surgical system. The patient-side surgeon interface has components within the sterile surgical field of the surgery. The components allow a surgeon to control teleoperated slave surgical instruments from within the sterile surgical field. The patient-side surgeon interface permits a surgeon to be in the sterile surgical field adjacent a patient undergoing surgery. Controlling minimally invasive slave surgical instruments from within the sterile surgical field permits minimally invasive surgery combined with direct visualization by the surgeon. The proximity to the patient allows the surgeon to control a teleoperated slave surgical instrument in tandem with controlling manually controlled instruments such as a laparoscopic instrument. Also, the surgeon, from within the sterile surgical field, can use the patient-side surgeon interface to control at least one proxy visual in proctoring another surgeon.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
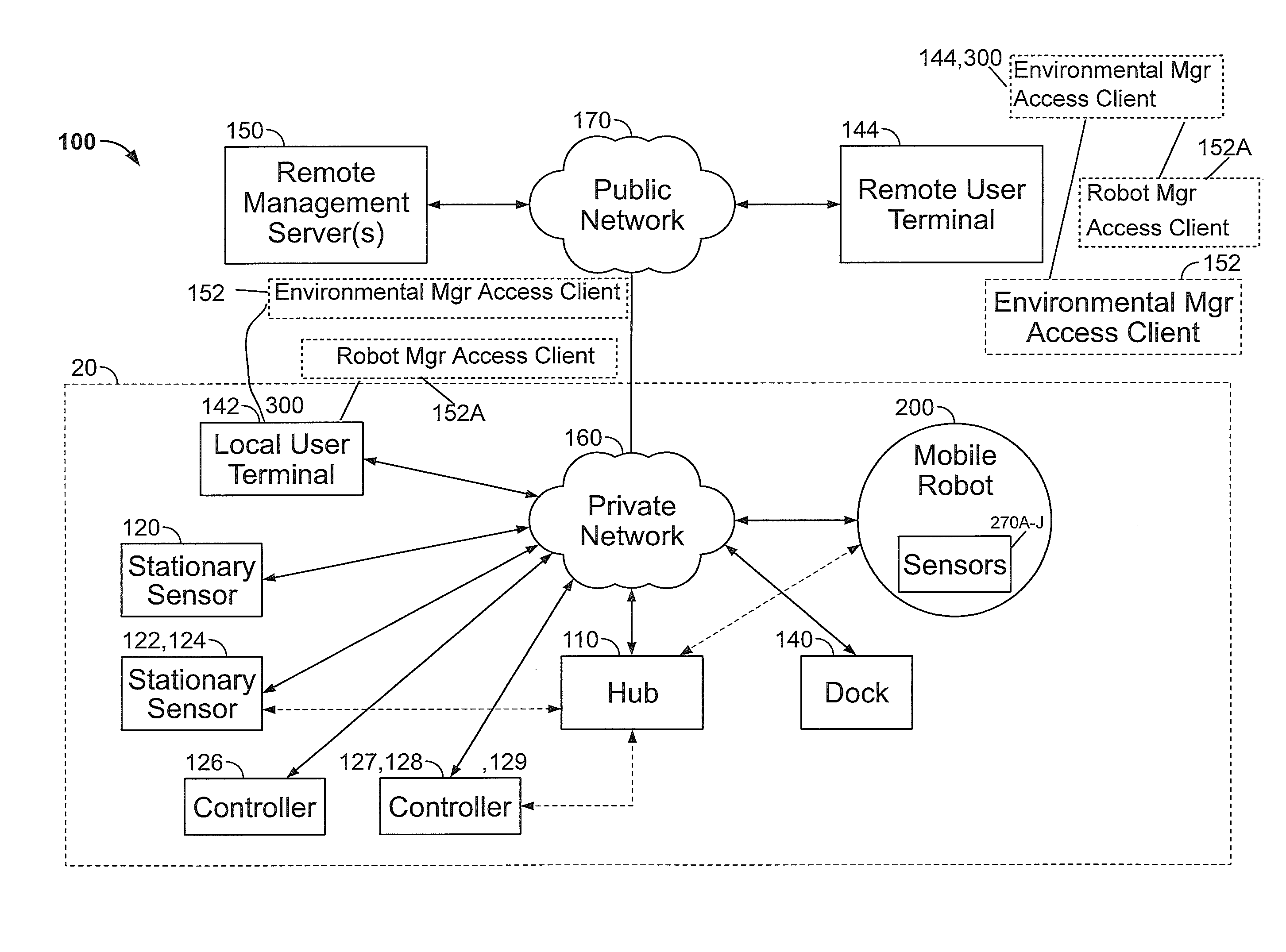
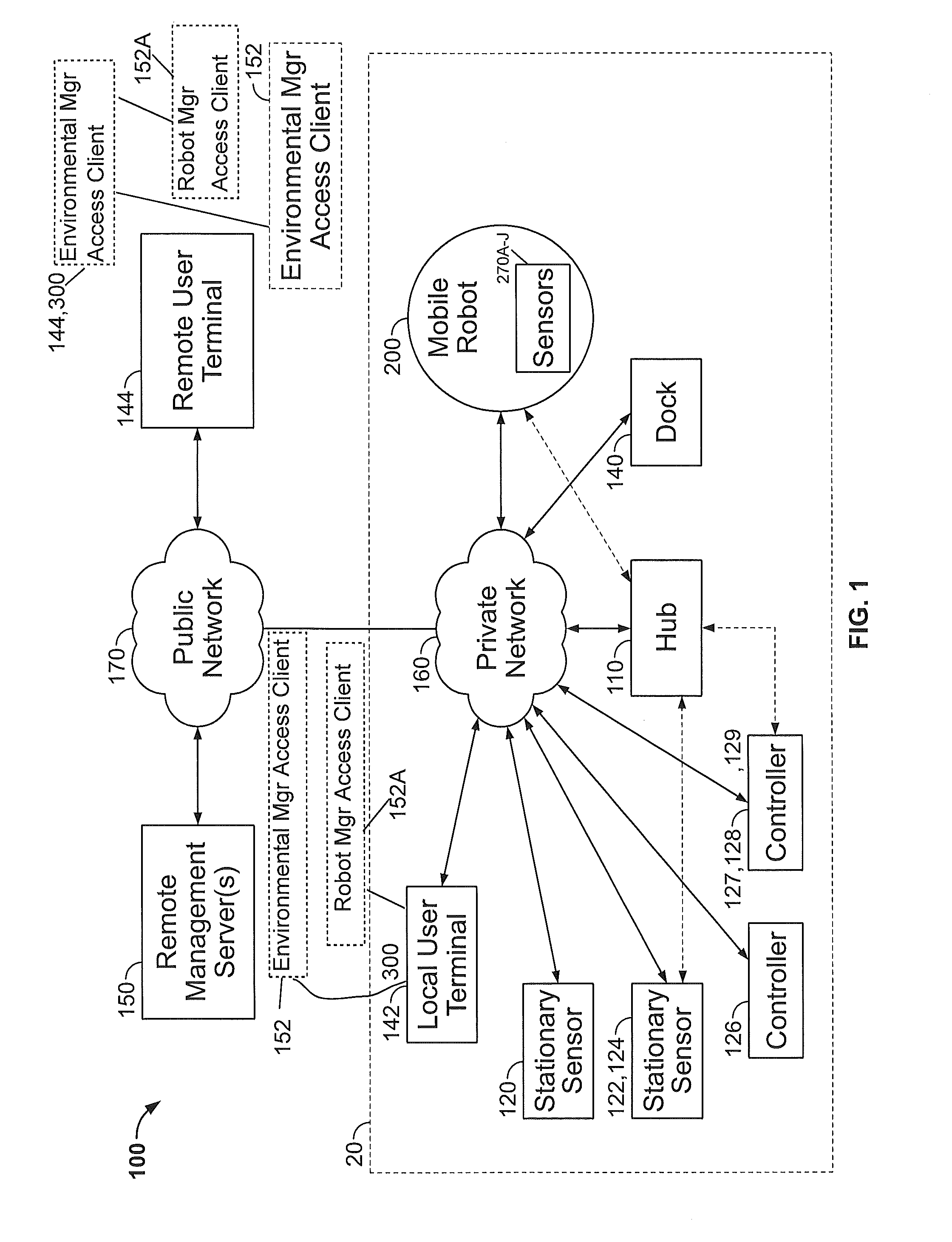
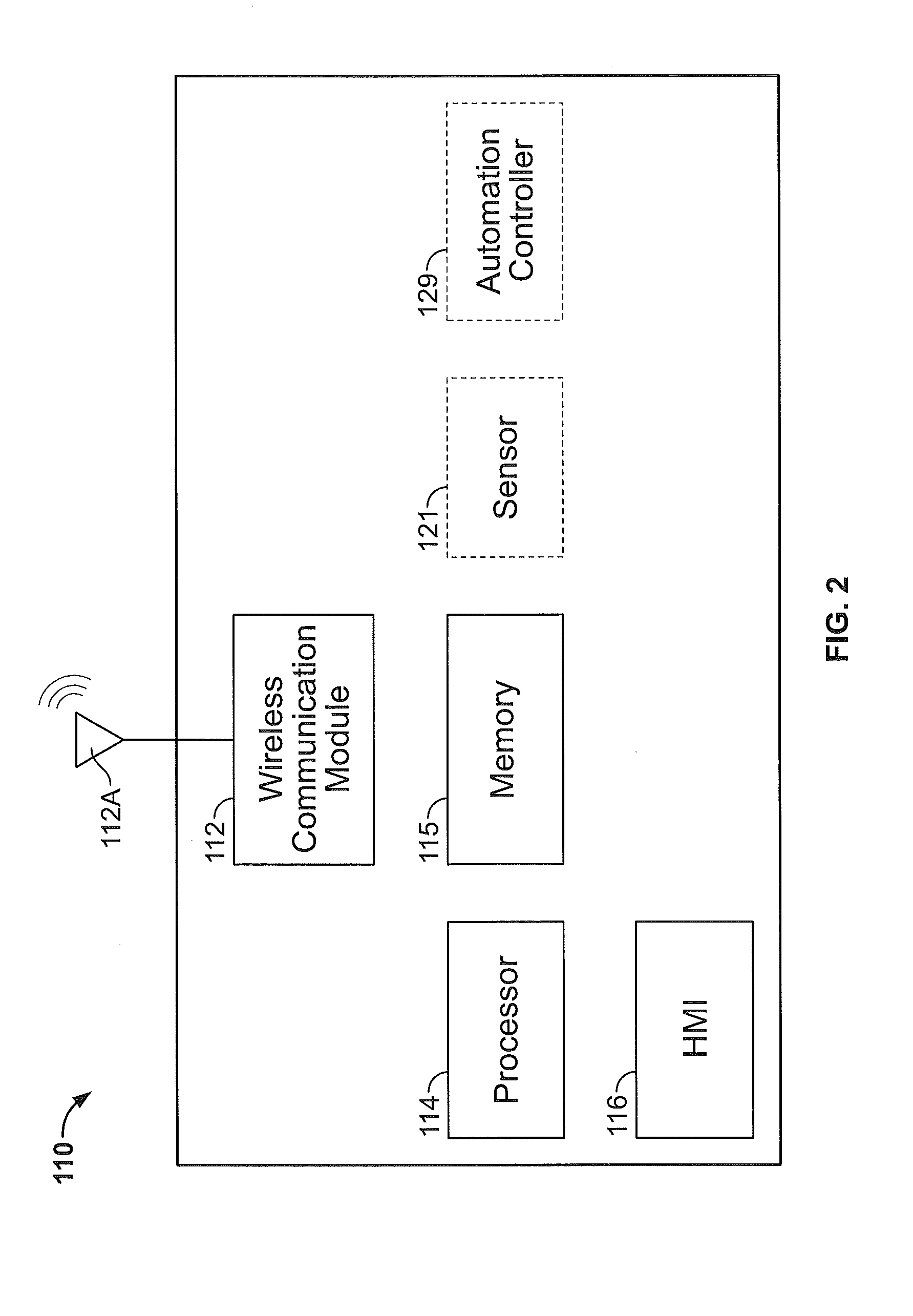
Mobile Robot Providing Environmental Mapping for Household Environmental Control
ActiveUS20140207282A1Improve reliabilityConfidenceProgramme-controlled manipulatorNear-field transmissionActuatorAction status
A mobile robot includes a processor connected to a memory and a wireless network circuit, for executing routines stored in the memory and commands generated by the routines and received via the wireless network circuit. The processor drives the mobile robot to a multiplicity of accessible two dimensional locations within a household, and commands an end effector, including at least one motorized actuator, to perform mechanical work in the household. A plurality of routines include a first routine which monitors a wireless local network and detects a presence of a network entity on the wireless local network, a second routine which receives a signal from a sensor detecting an action state of one of the network entities, the action state changeable between waiting and active, and a third routine which commands the end effector to change state of performing mechanical work based on the presence and on the action state.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
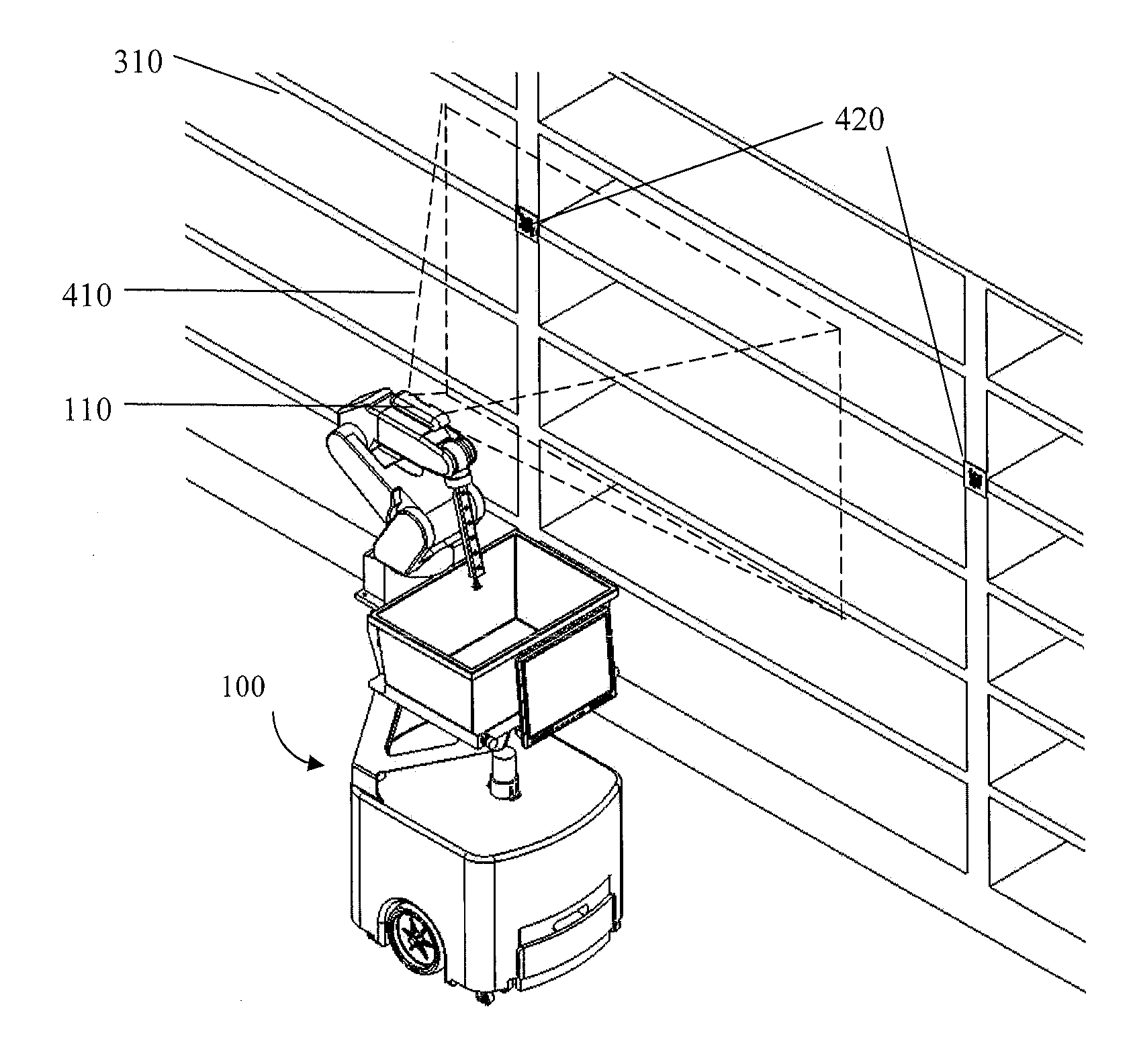
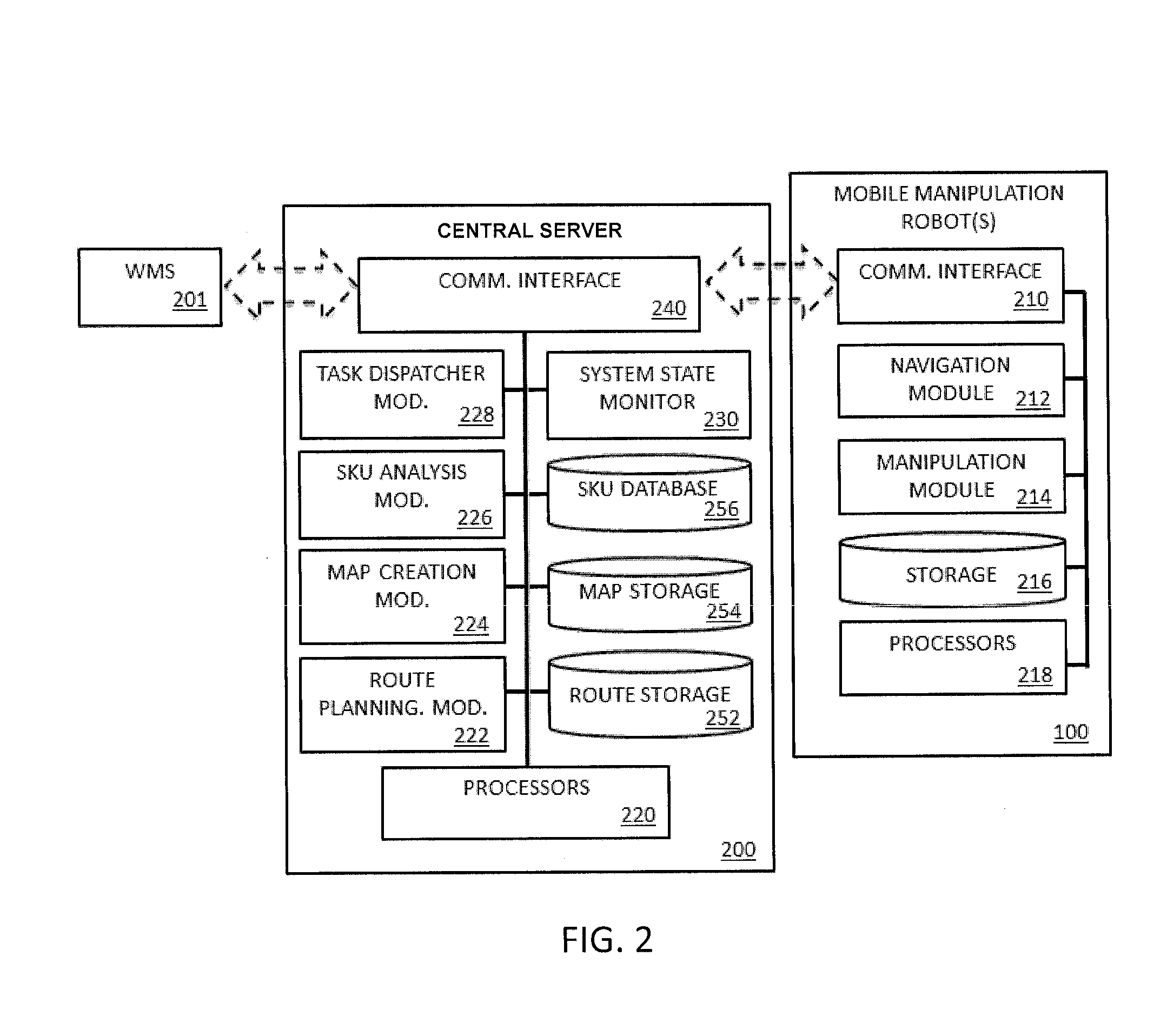
System and method for piece-picking or put-away with a mobile manipulation robot
ActiveUS20150032252A1Overcomes shortcomingReduce complexity and costProgramme-controlled manipulatorAutonomous decision making processLogistics managementPosition dependent
A method and system for piece-picking or piece put-away within a logistics facility. The system includes a central server and at least one mobile manipulation robot. The central server is configured to communicate with the robots to send and receive piece-picking data which includes a unique identification for each piece to be picked, a location within the logistics facility of the pieces to be picked, and a route for the robot to take within the logistics facility. The robots can then autonomously navigate and position themselves within the logistics facility by recognition of landmarks by at least one of a plurality of sensors. The sensors also provide signals related to detection, identification, and location of a piece to be picked or put-away, and processors on the robots analyze the sensor information to generate movements of a unique articulated arm and end effector on the robot to pick or put-away the piece.
Owner:IAM ROBOTICS
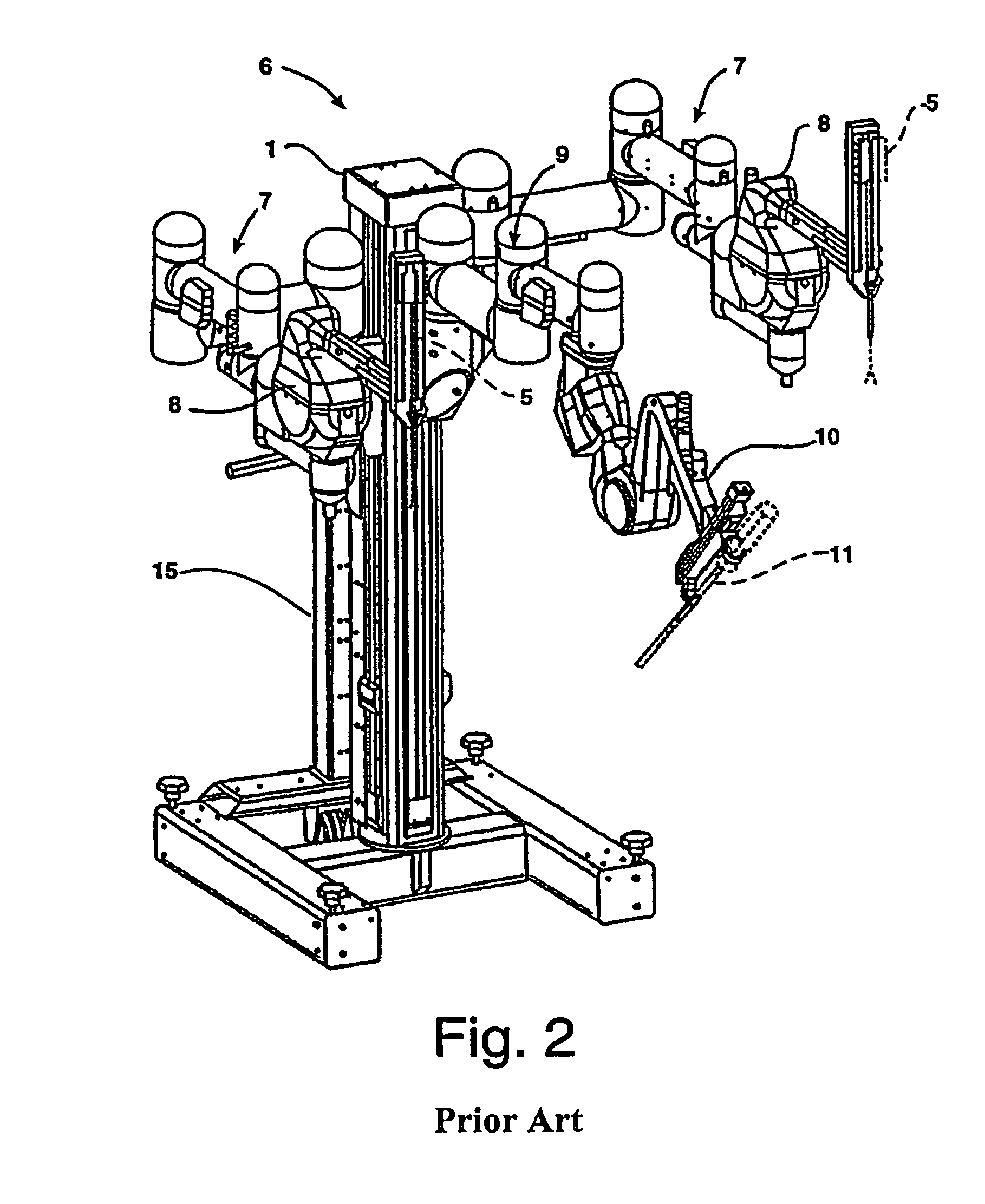
Modular manipulator support for robotic surgery
InactiveUS7763015B2Simple structureReduce complexityDiagnosticsRobotSurgical instrumentationModularity
A robotic surgery system comprises a mounting base, a plurality of surgical instruments, and an articulate support assembly. Each instrument is insertable into a patient through an associated minimally invasive aperture to a desired internal surgical site. The articulate support assembly movably supports the instruments relative to the base. The support generally comprises an orienting platform, a platform linkage movably supporting the orienting platform relative to the base, and a plurality of manipulators mounted to the orienting platform, wherein each manipulator movably supports an associated instrument.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Clamping device and workpiece conveying robot
InactiveUS8764085B2High positionalImprove retentionGripping headsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SINFONIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
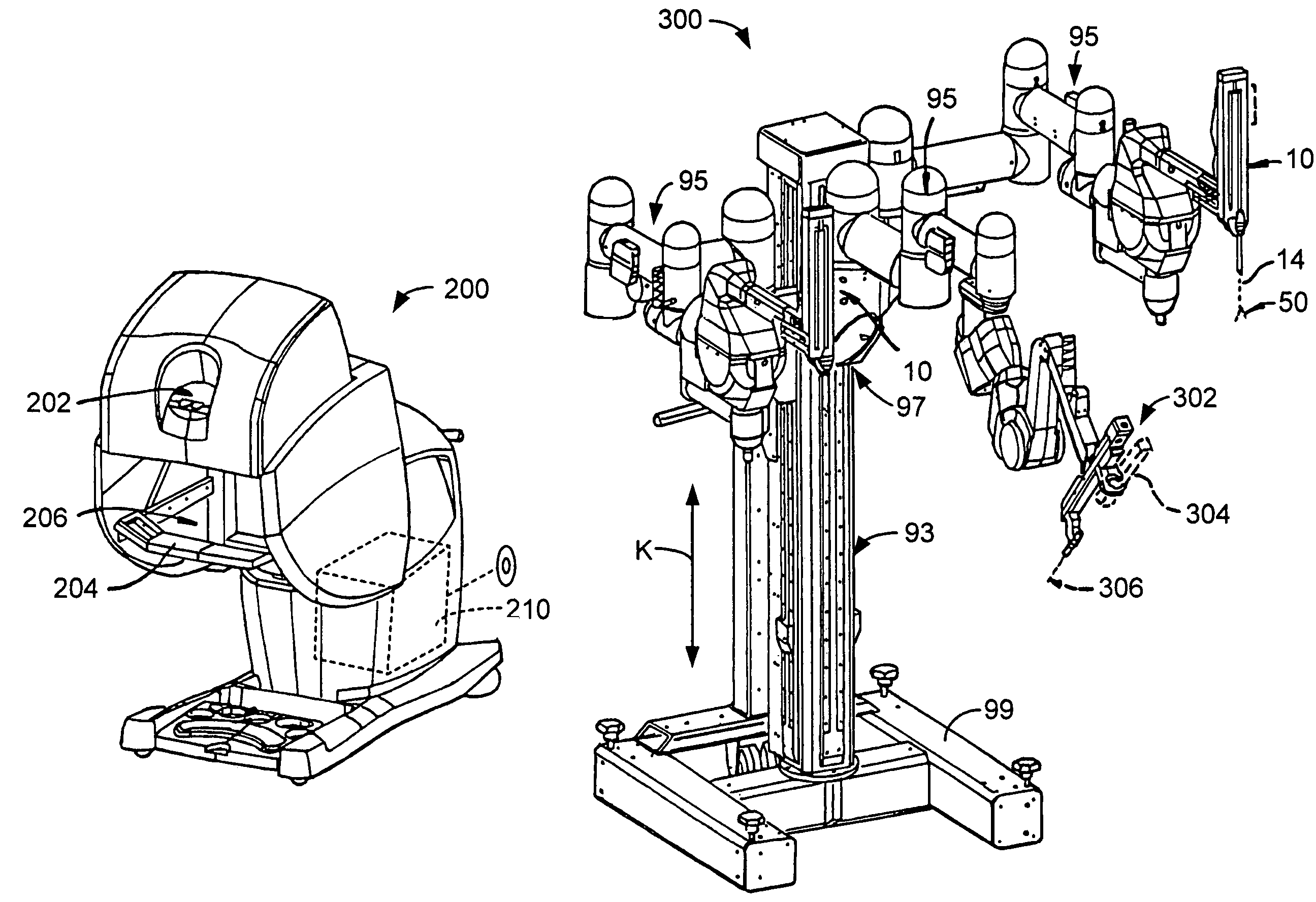
Multi-user medical robotic system for collaboration or training in minimally invasive surgical procedures
ActiveUS20060178559A1Promote collaborationMinimally invasiveMedical communicationProgramme controlLess invasive surgeryRobotic systems
A multi-user medical robotic system for collaboration or training in minimally invasive surgical procedures includes first and second master input devices, a first slave robotic mechanism, and at least one processor configured to generate a first slave command for the first slave robotic mechanism by switchably using one or both of a first command indicative of manipulation of the first master input device by a first user and a second command indicative of manipulation of the second master input device by a second user. To facilitate the collaboration or training, both first and second users communicate with each other through an audio system and see the minimally invasive surgery site on first and second displays respectively viewable by the first and second users.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Control system configured to compensate for non-ideal actuator-to-joint linkage characteristics in a medical robotic system
A medical robotic system having non-ideal actuator-to-joint linkage characteristics, includes a control system including a proximal control loop with actuator sensor feedback to control dynamic response of an actuator coupled to a distal joint which in turn, is coupled to an end effector to provide a degree of freedom movement of the end effector, a distal control loop with distal joint sensor feedback and feedforward to the actuator to ensure steady-state convergence of the distal joint position, and an end effector control loop with end-point sensor feedback to control the end effector position to reach a commanded end effector position.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Single-and dual-chamber module-attachable wafer-handling chamber
ActiveUS20140174354A1Increased Design FreedomLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBiochemical engineeringProcess module
A single- and dual-chamber module-attachable wafer-handling chamber includes: a wafer-handling main chamber equipped with a wafer-handling robot therein, and adaptors for connecting process modules to the wafer-handling main chamber. The adaptors are detachably attached to the sides of the wafer-handling main chamber, respectively, and the process modules are detachably attached to the adaptors, respectively, so that the process modules can be attached to the wafer-handling main chamber, regardless of whether the process modules are of a single-chamber type or dual-chamber type.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Robot arm
ActiveUS20130084156A1Precise positioningPollution suppressionProgramme-controlled manipulatorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical medicine and rehabilitationWafering
The robot arm of the present application is a robot arm that transports semiconductor wafers. The robot arm includes a hand, a lower arm link, and an upper arm link. The hand is connected to the lower arm link via a first joint. The upper arm link is connected to the lower arm link via a second joint. In the robot arm of the present application, the lower arm link is capable of being separated at a location between the first joint and the second joint.
Owner:NABLESCO CORP
Single-and dual-chamber module-attachable wafer-handling chamber
ActiveUS9640416B2Increased Design FreedomSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRobotProcess moduleBiochemical engineering
A single- and dual-chamber module-attachable wafer-handling chamber includes: a wafer-handling main chamber equipped with a wafer-handling robot therein, and adaptors for connecting process modules to the wafer-handling main chamber. The adaptors are detachably attached to the sides of the wafer-handling main chamber, respectively, and the process modules are detachably attached to the adaptors, respectively, so that the process modules can be attached to the wafer-handling main chamber, regardless of whether the process modules are of a single-chamber type or dual-chamber type.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
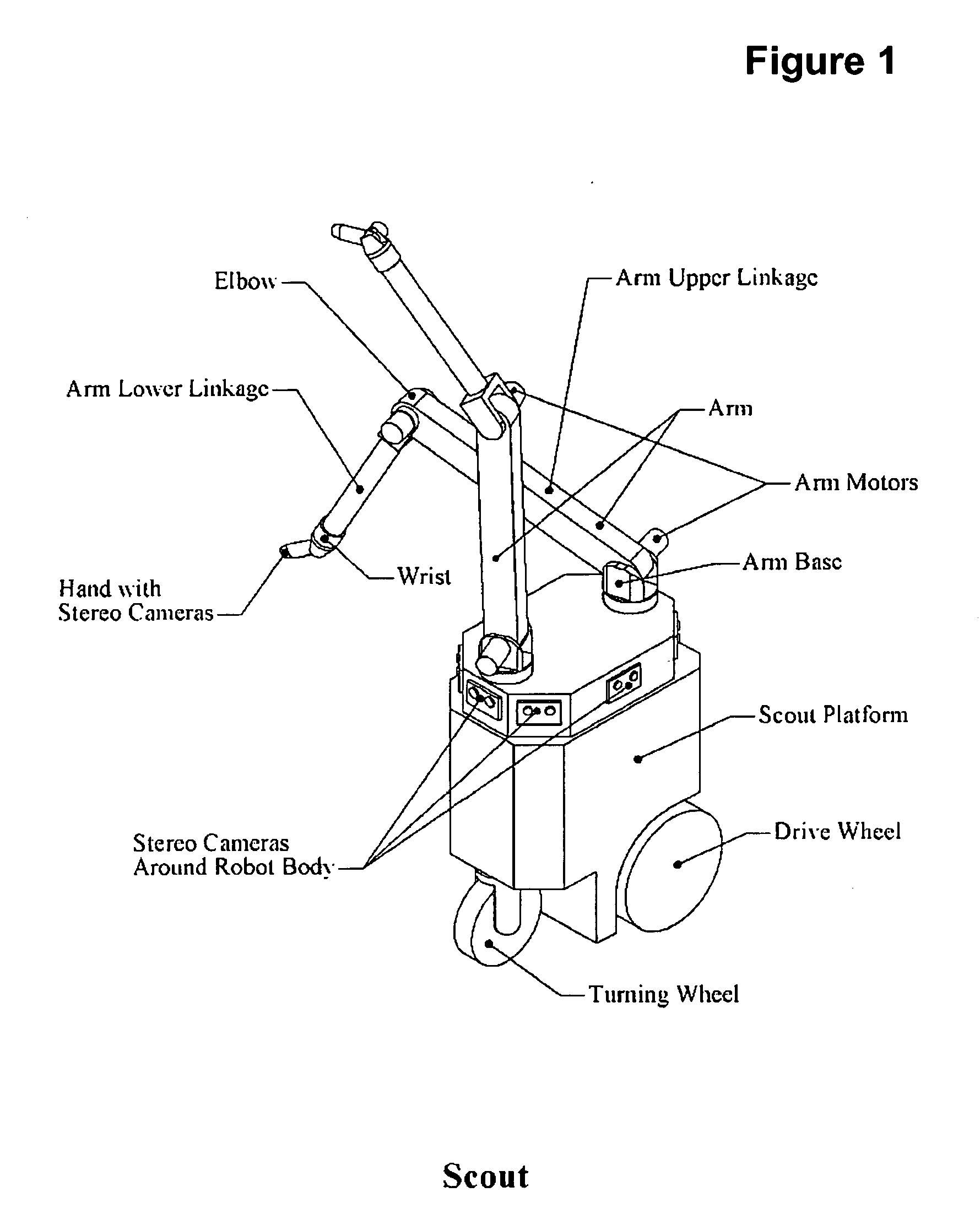
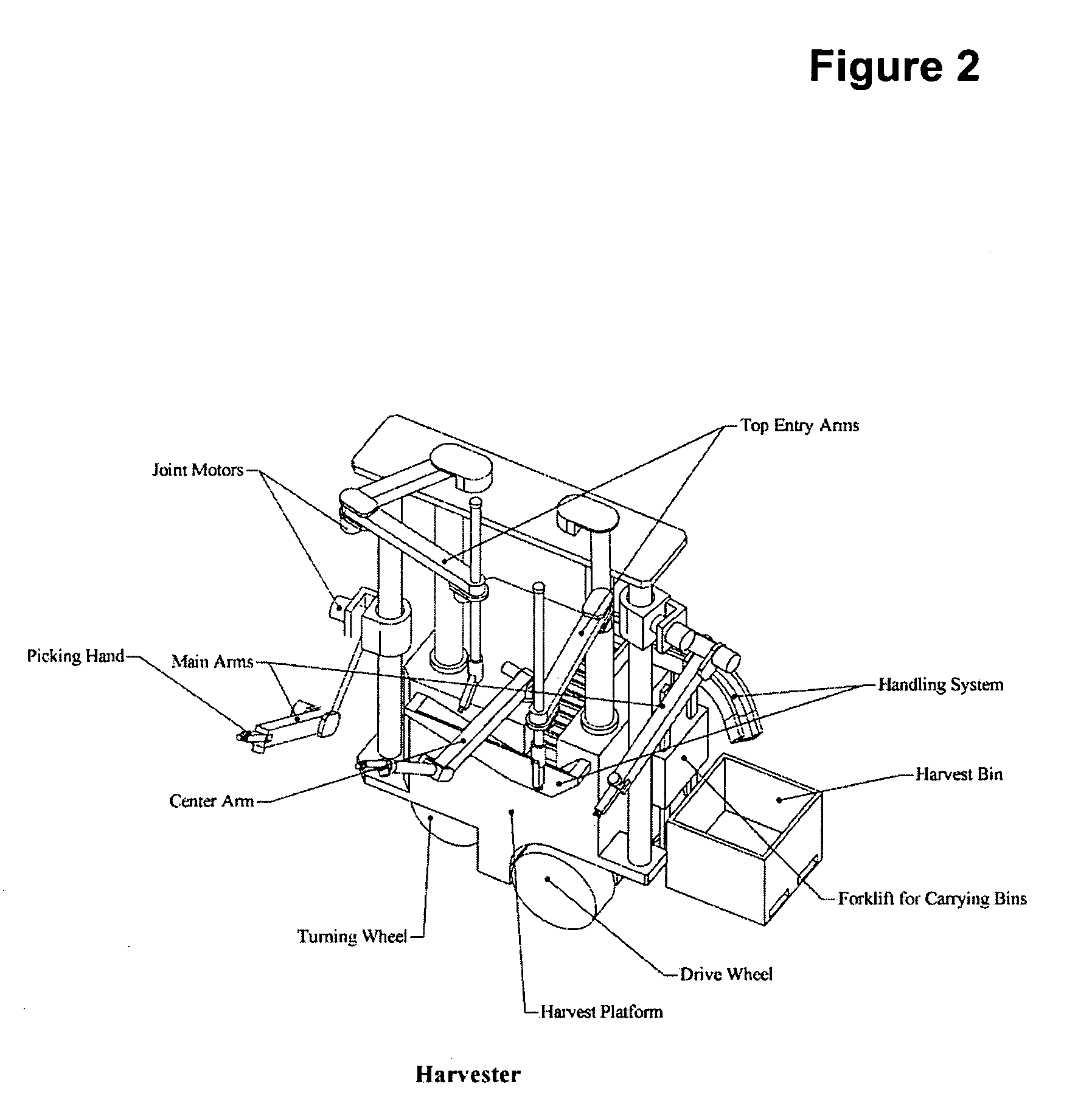
Agricultural robot system and method
InactiveUS20060213167A1Maximize efficiencyMaximizing cost-effectivenessAnalogue computers for trafficMowersMachine visionAction plan
An agricultural robot system and method of harvesting, pruning, culling, weeding, measuring and managing of agricultural crops. Uses autonomous and semi-autonomous robot(s) comprising machine-vision using cameras that identify and locate the fruit on each tree, points on a vine to prune, etc., or may be utilized in measuring agricultural parameters or aid in managing agricultural resources. The cameras may be coupled with an arm or other implement to allow views from inside the plant when performing the desired agricultural function. A robot moves through a field first to “map” the plant locations, number and size of fruit and approximate positions of fruit or map the cordons and canes of grape vines. Once the map is complete, a robot or server can create an action plan that a robot may implement. An action plan may comprise operations and data specifying the agricultural function to perform.
Owner:VISION ROBOTICS
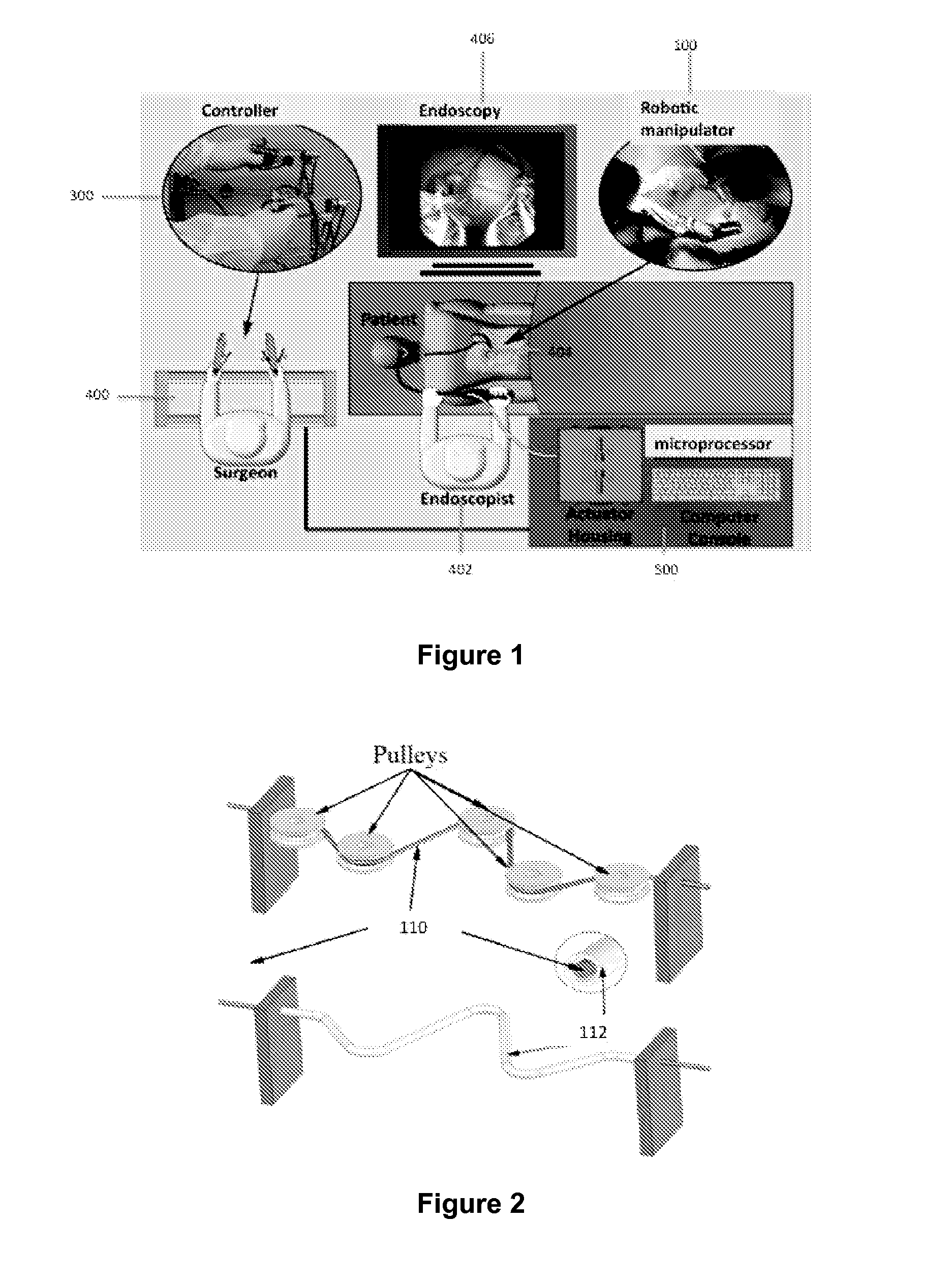
Robotic system for flexible endoscopy
InactiveUS8882660B2Intricate and precise surgical interventionRemove scarsEndoscopesSurgical instruments for heatingFlexible endoscopyRobotic systems
A robotic manipulator controller and system for use in flexible endoscopy, the manipulator comprising a flexible member configured to be coupled to an endoscope, and an arm connected to and movable by the flexible member, wherein the flexible member has a first end connected to the arm and a second end connectable to the controller to allow a physical movement of the arm to be controllable by a physical movement of the controller.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
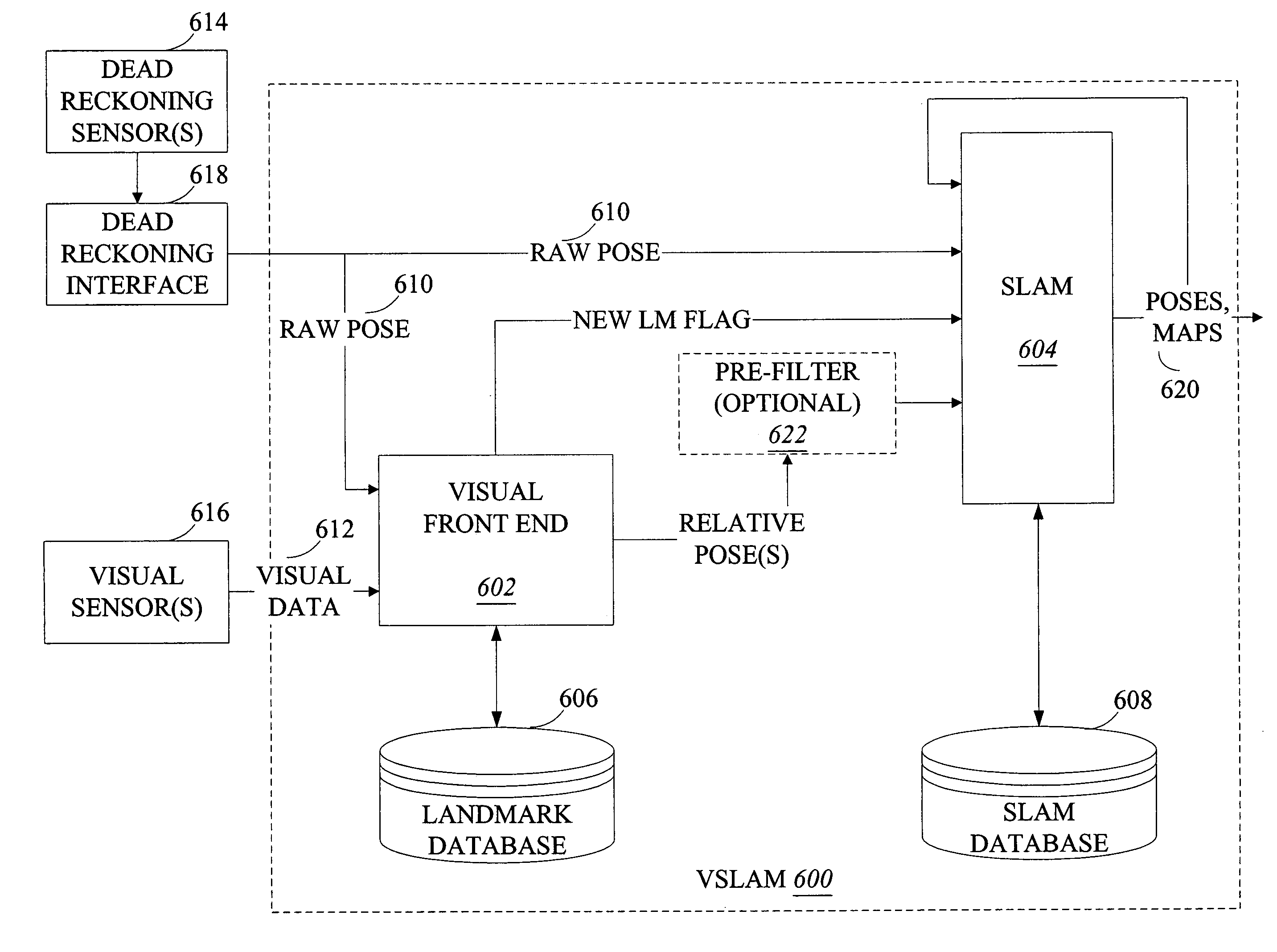
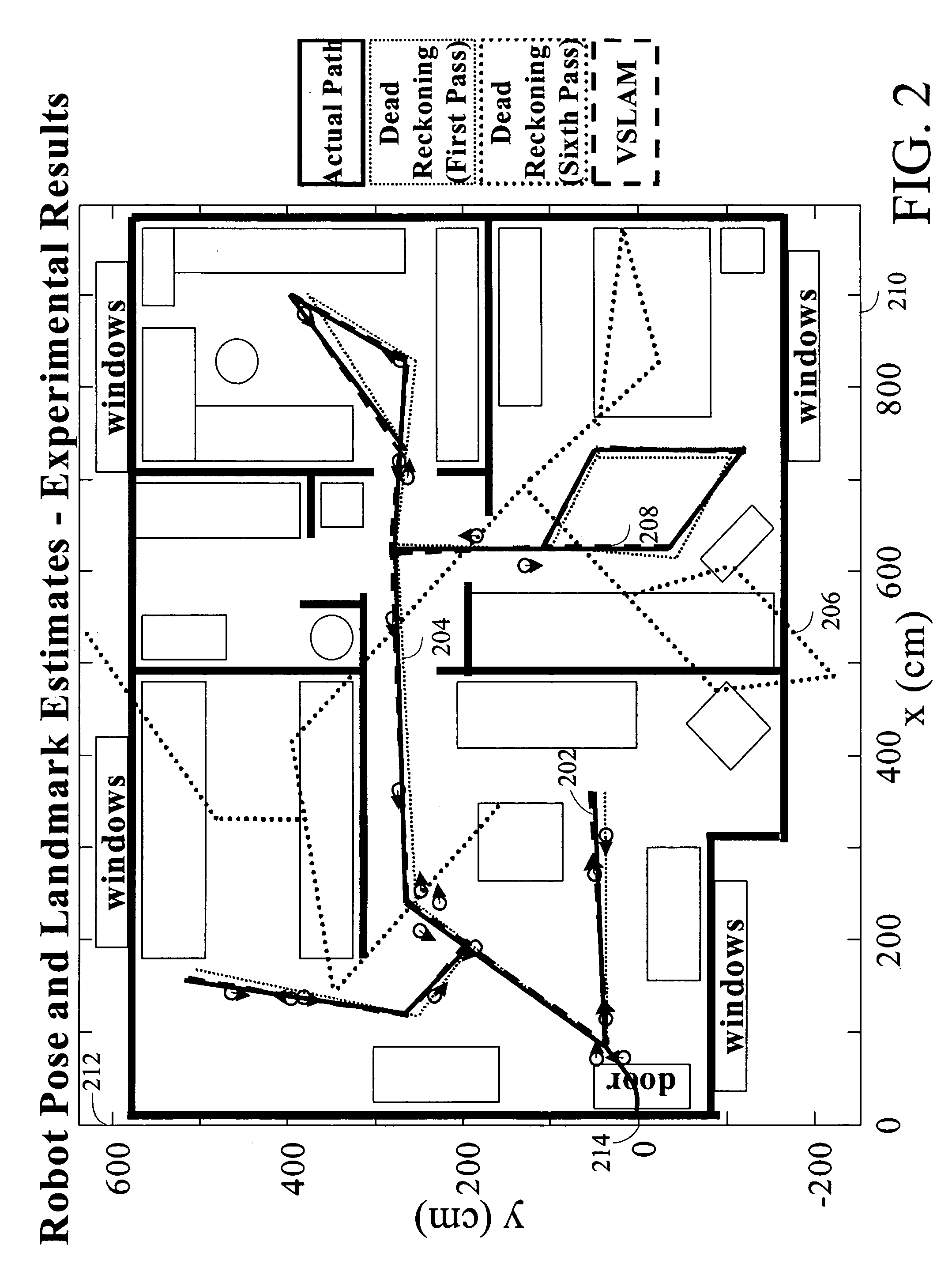
Systems and methods for incrementally updating a pose of a mobile device calculated by visual simultaneous localization and mapping techniques
The invention is related to methods and apparatus that use a visual sensor and dead reckoning sensors to process Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). These techniques can be used in robot navigation. Advantageously, such visual techniques can be used to autonomously generate and update a map. Unlike with laser rangefinders, the visual techniques are economically practical in a wide range of applications and can be used in relatively dynamic environments, such as environments in which people move. One embodiment further advantageously uses multiple particles to maintain multiple hypotheses with respect to localization and mapping. Further advantageously, one embodiment maintains the particles in a relatively computationally-efficient manner, thereby permitting the SLAM processes to be performed in software using relatively inexpensive microprocessor-based computer system.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Multi-user medical robotic system for collaboration or training in minimally invasive surgical procedures
ActiveUS8527094B2Promote collaborationMinimally invasiveMedical communicationProgramme controlLess invasive surgeryRobotic systems
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Patient-side surgeon interface for a minimally invasive, teleoperated surgical instrument
A patient-side surgeon interface provides enhanced capabilities in using a minimally invasive, teleoperated surgical system. The patient-side surgeon interface has components within the sterile surgical field of the surgery. The components allow a surgeon to control teleoperated slave surgical instruments from within the sterile surgical field. The patient-side surgeon interface permits a surgeon to be in the sterile surgical field adjacent a patient undergoing surgery. Controlling minimally invasive slave surgical instruments from within the sterile surgical field permits minimally invasive surgery combined with direct visualization by the surgeon. The proximity to the patient allows the surgeon to control a teleoperated slave surgical instrument in tandem with controlling manually controlled instruments such as a laparoscopic instrument. Also, the surgeon, from within the sterile surgical field, can use the patient-side surgeon interface to control at least one proxy visual in proctoring another surgeon.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com