Patents
Literature
276 results about "Search procedure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Systems and methods for interacting with advanced displays provided by an interactive media guidance application
InactiveUS20100153885A1Television system detailsVideo data queryingInteractive televisionApplication software
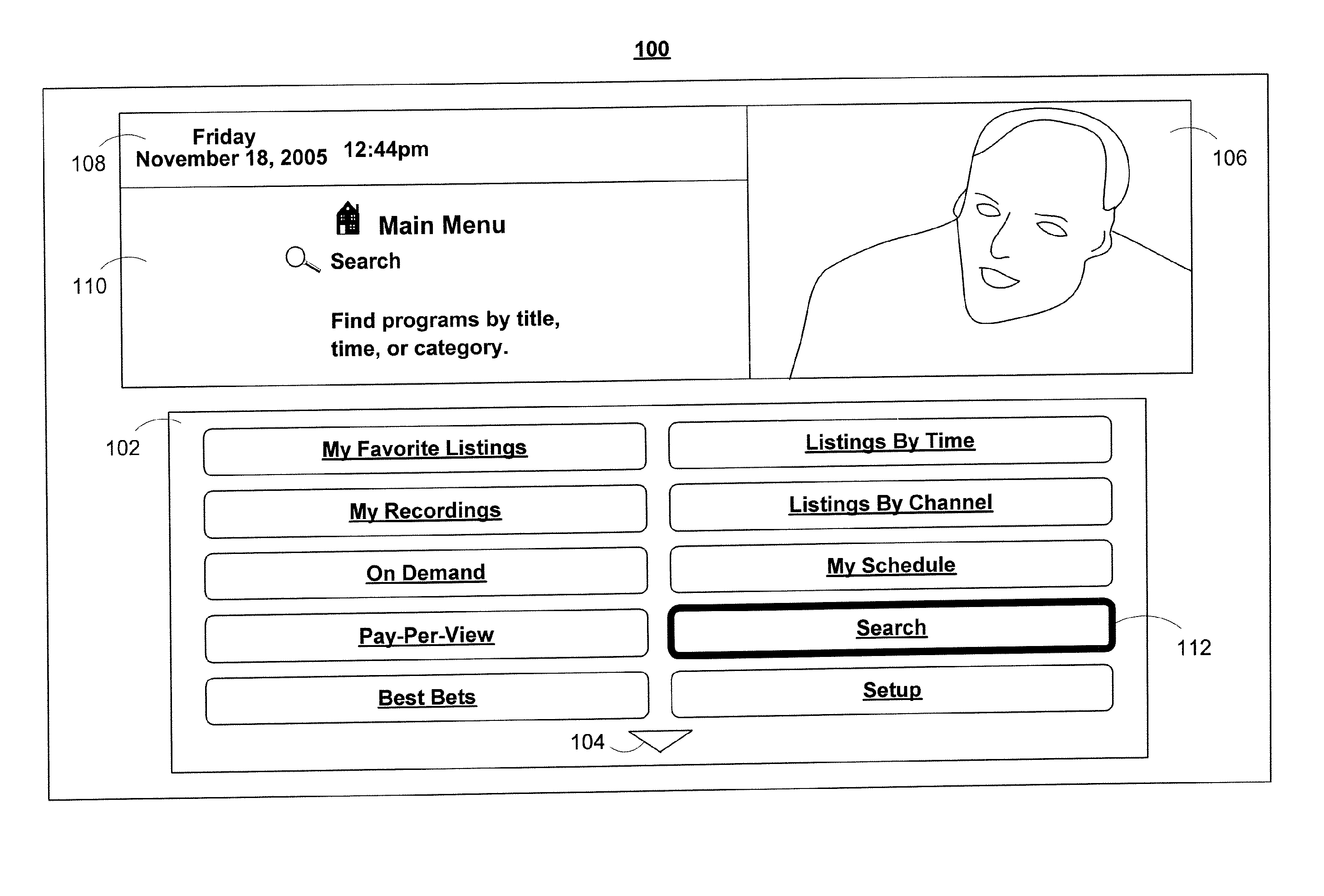
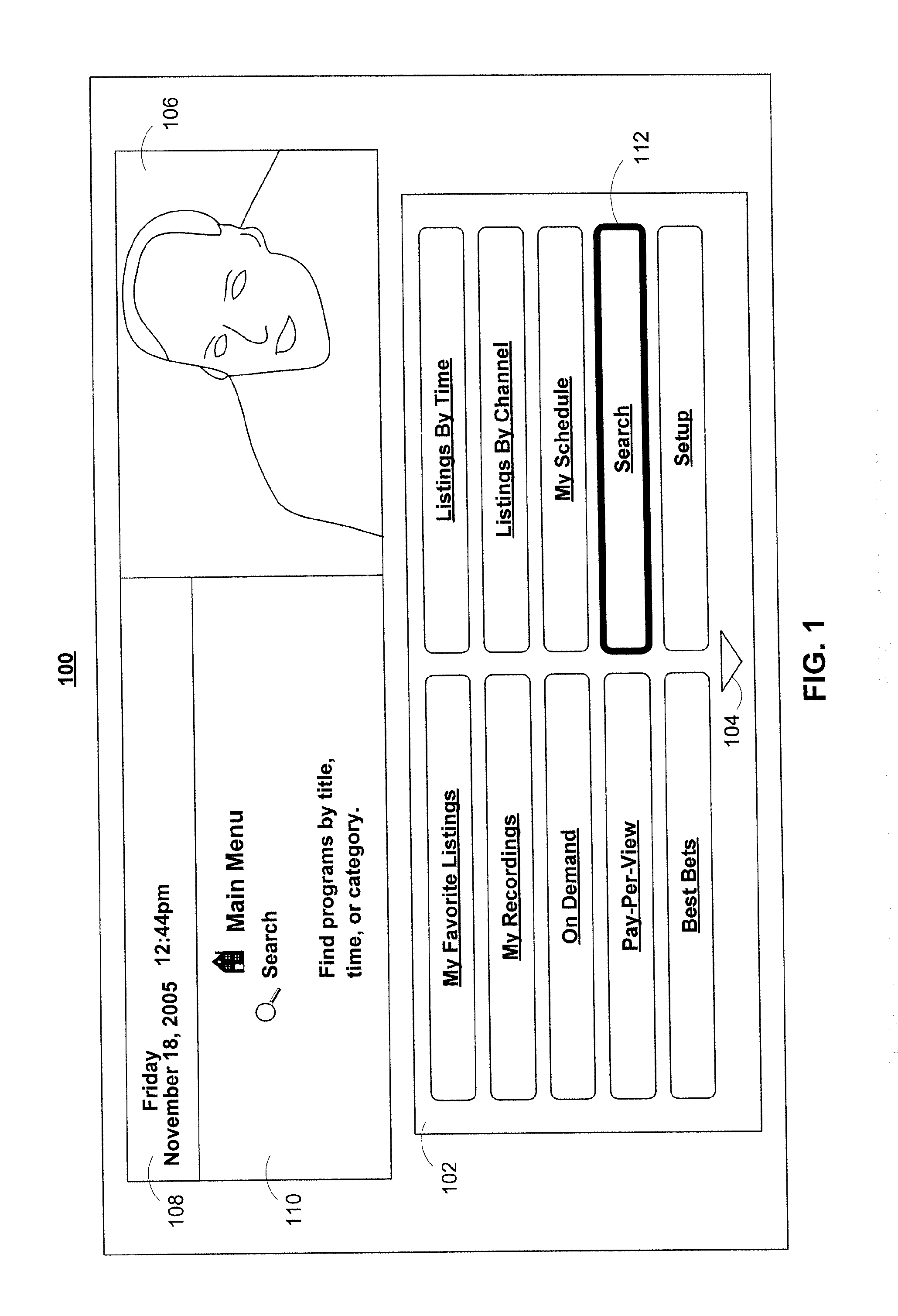
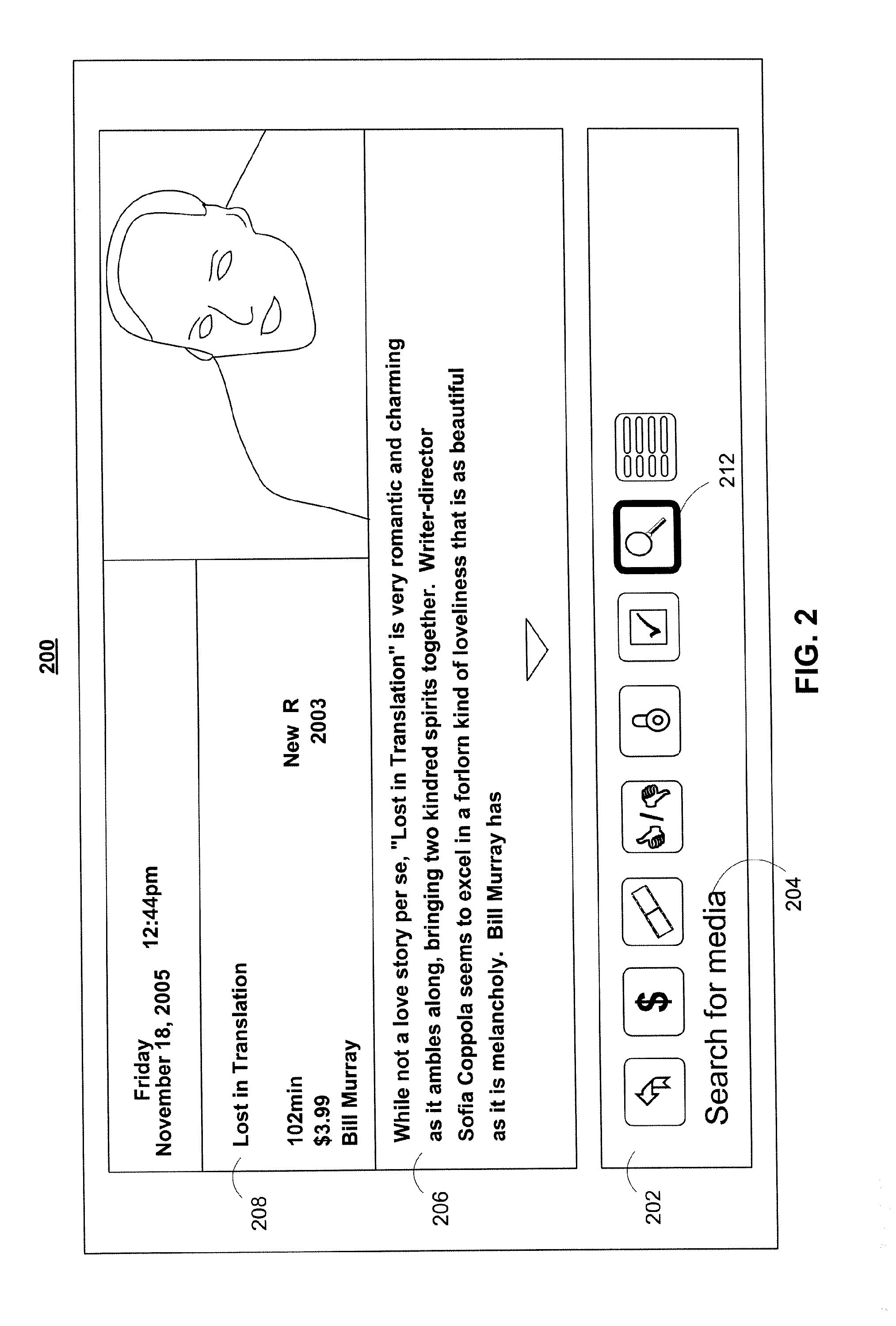
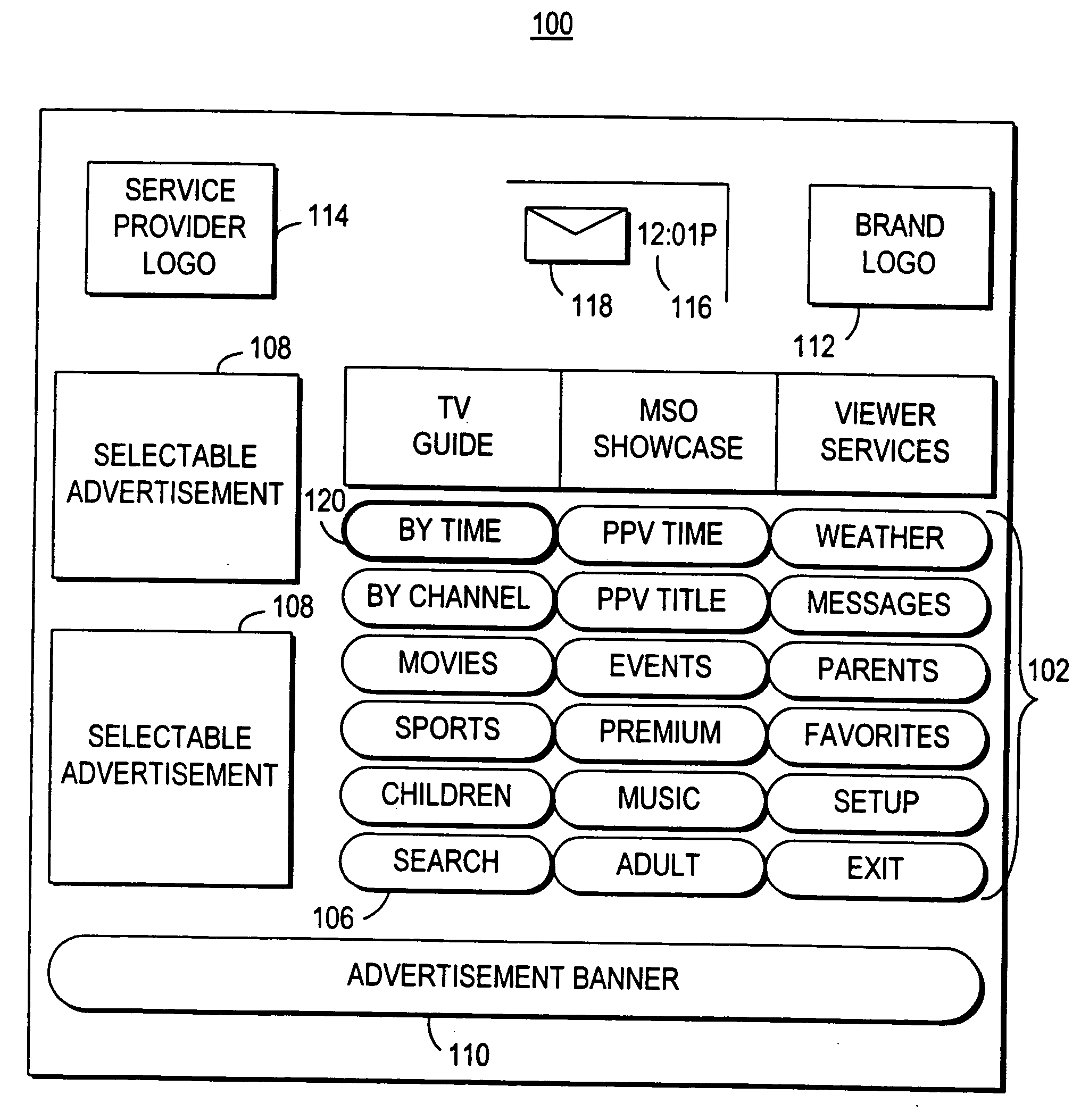
An interactive television application is used to provide search results to a user. The user is provided with an opportunity to indicate a desire to search for programs. In response, the interactive television application generates search criteria and searches for programs. The search results that are displayed to the user include mosaic listings associated with programs that match the search criteria. In some embodiments, the interactive television application displays the mosaic listings in a manner that accentuates the different levels of relevance of the search results to the search criteria.
Owner:ALL MEDIA GUIDE +10
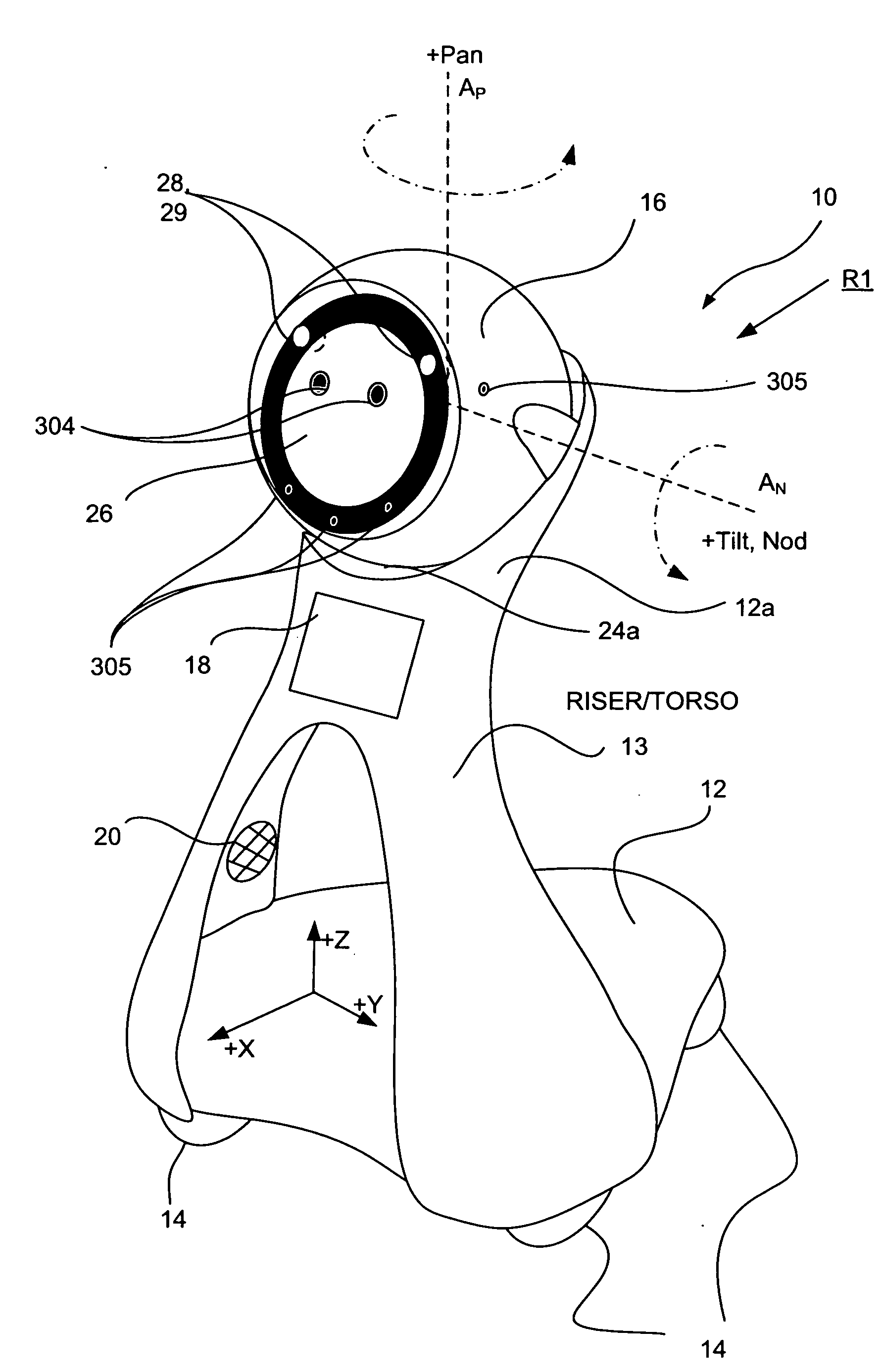
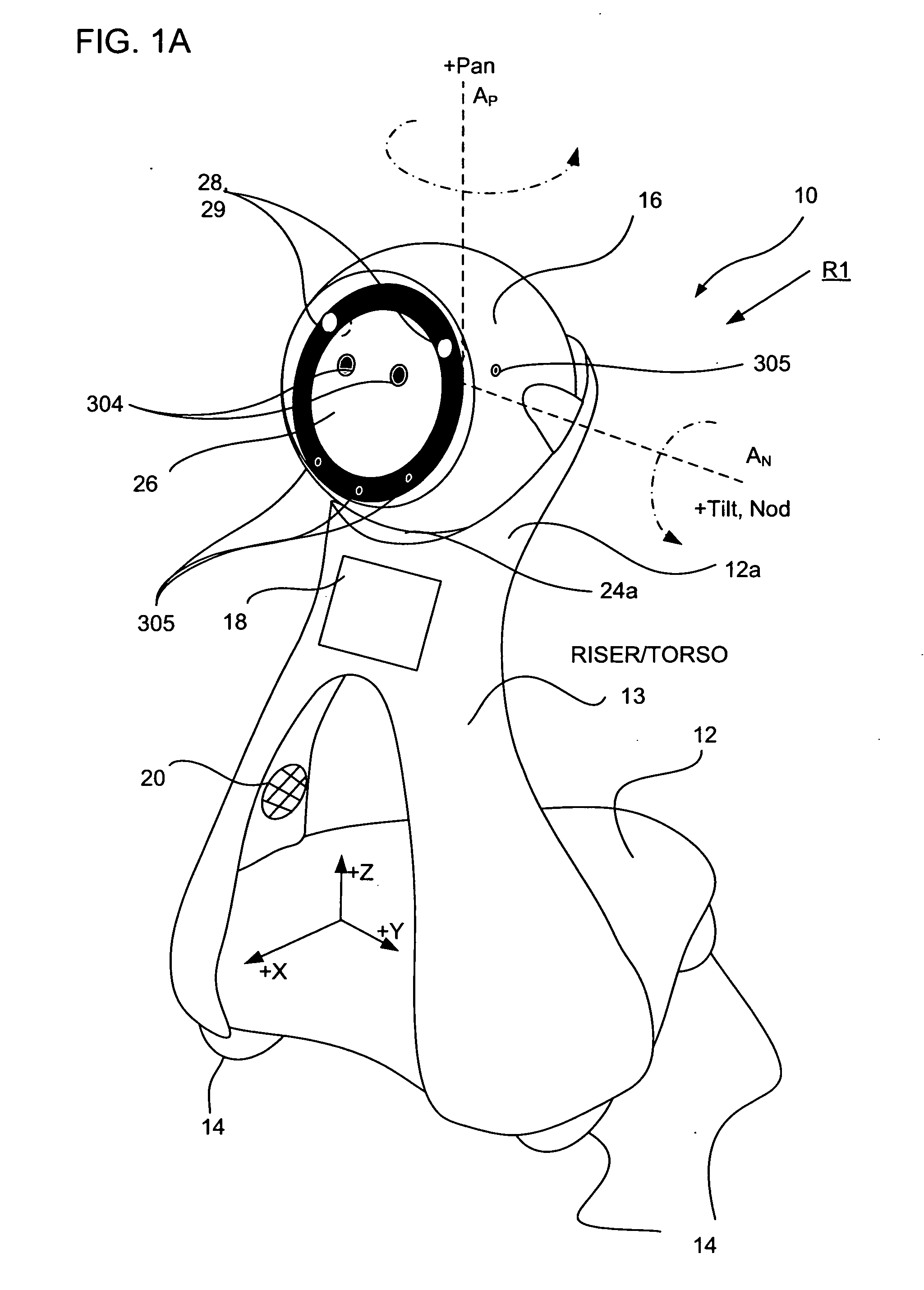
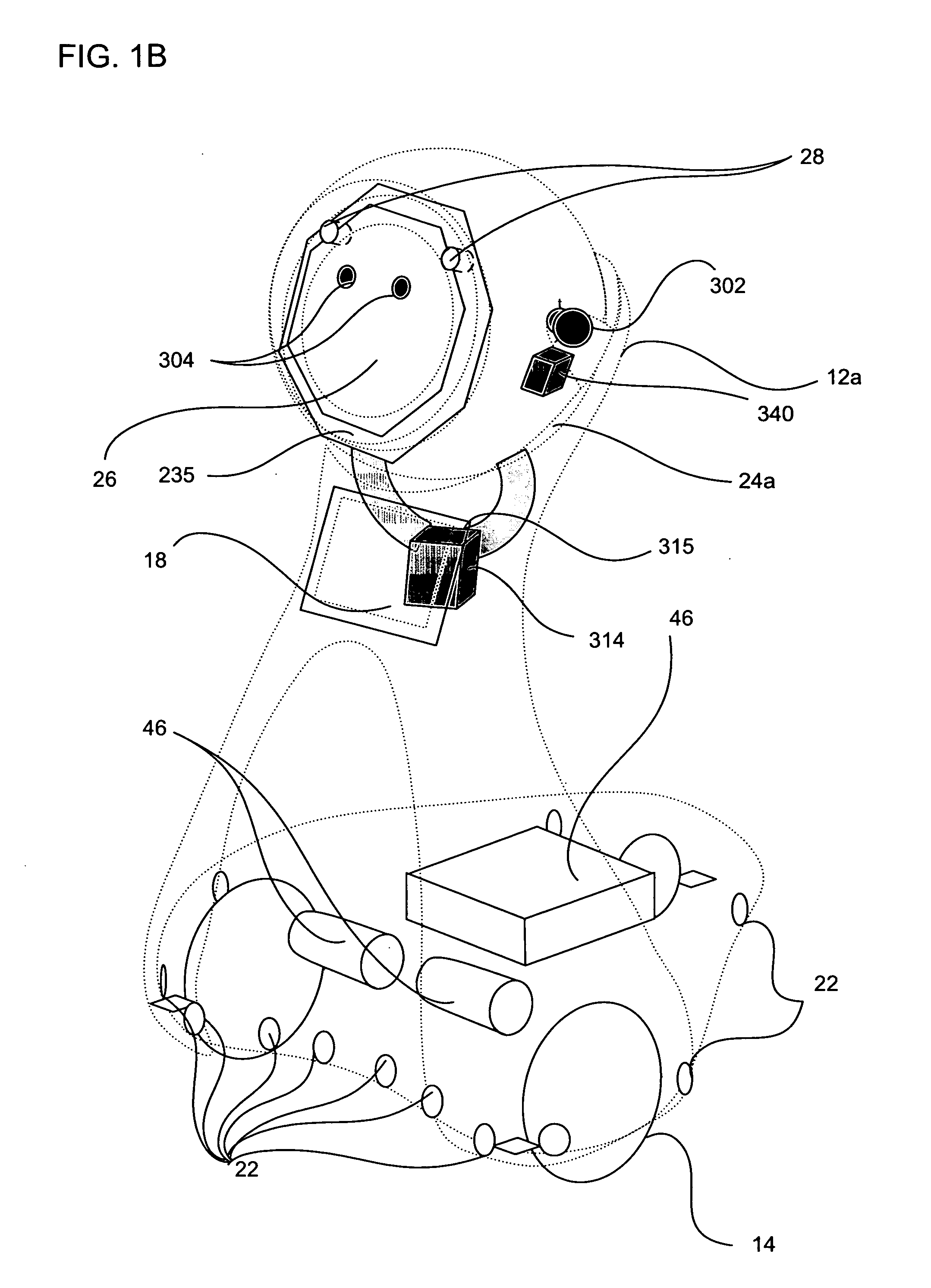
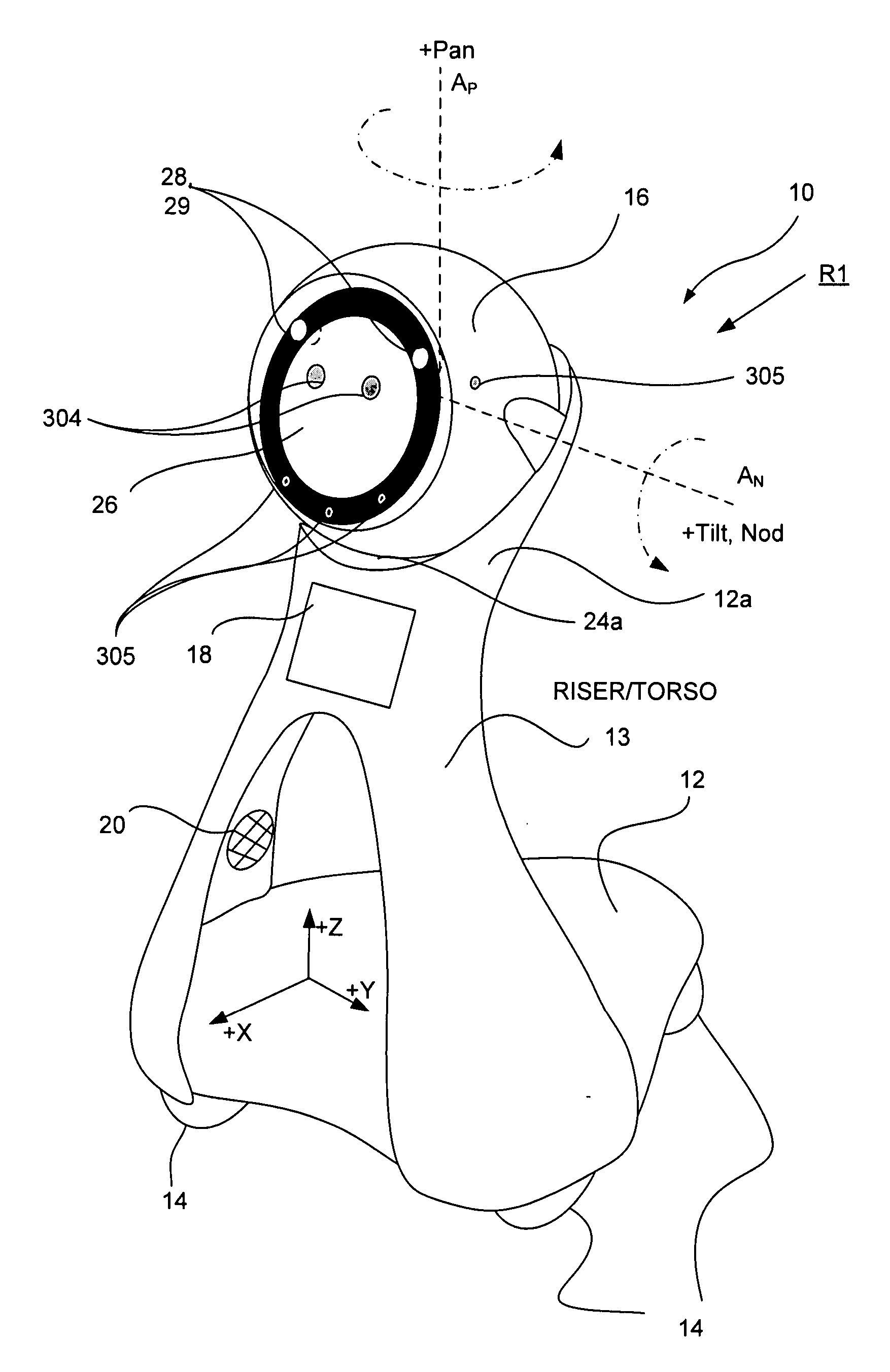
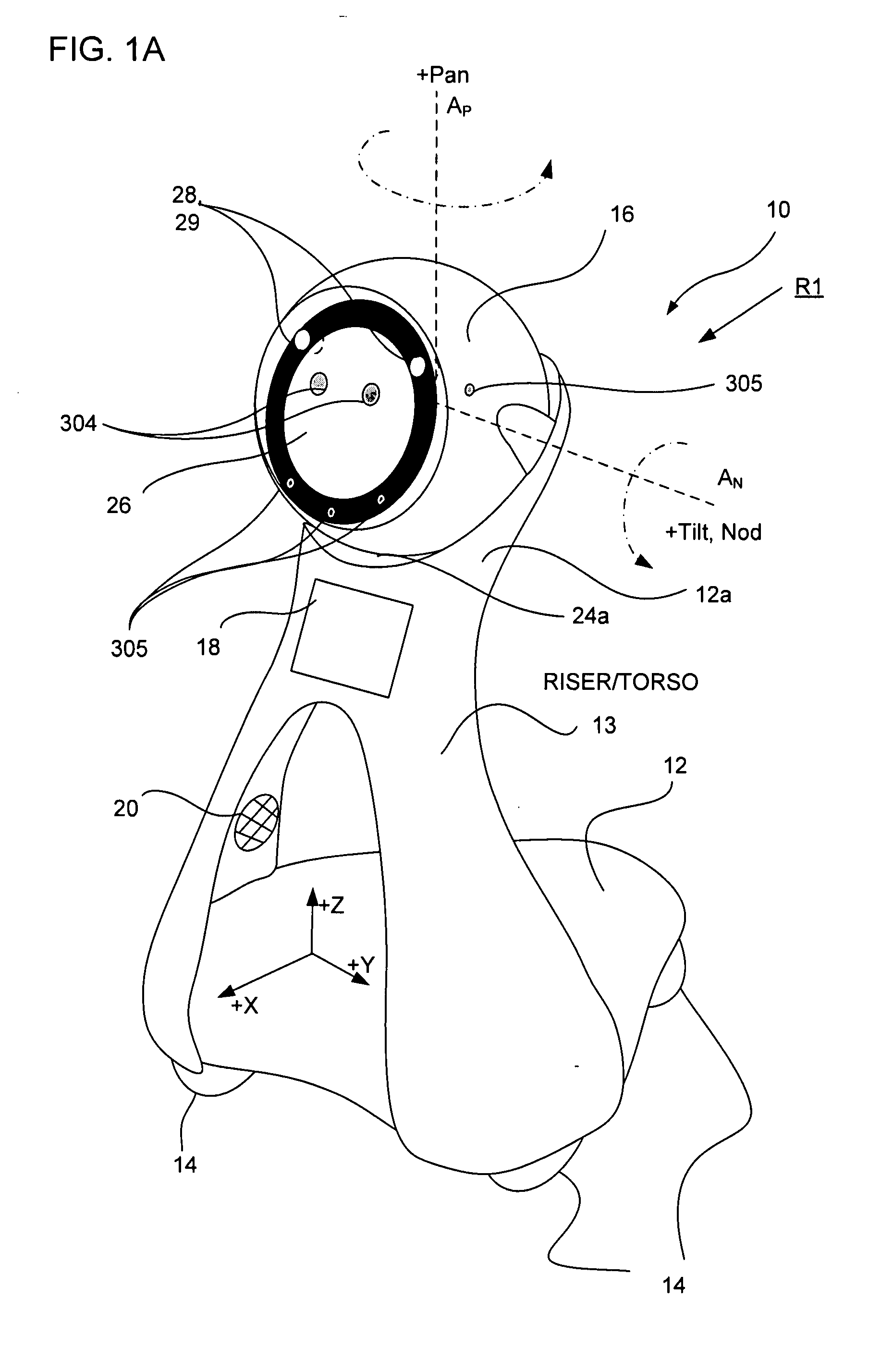
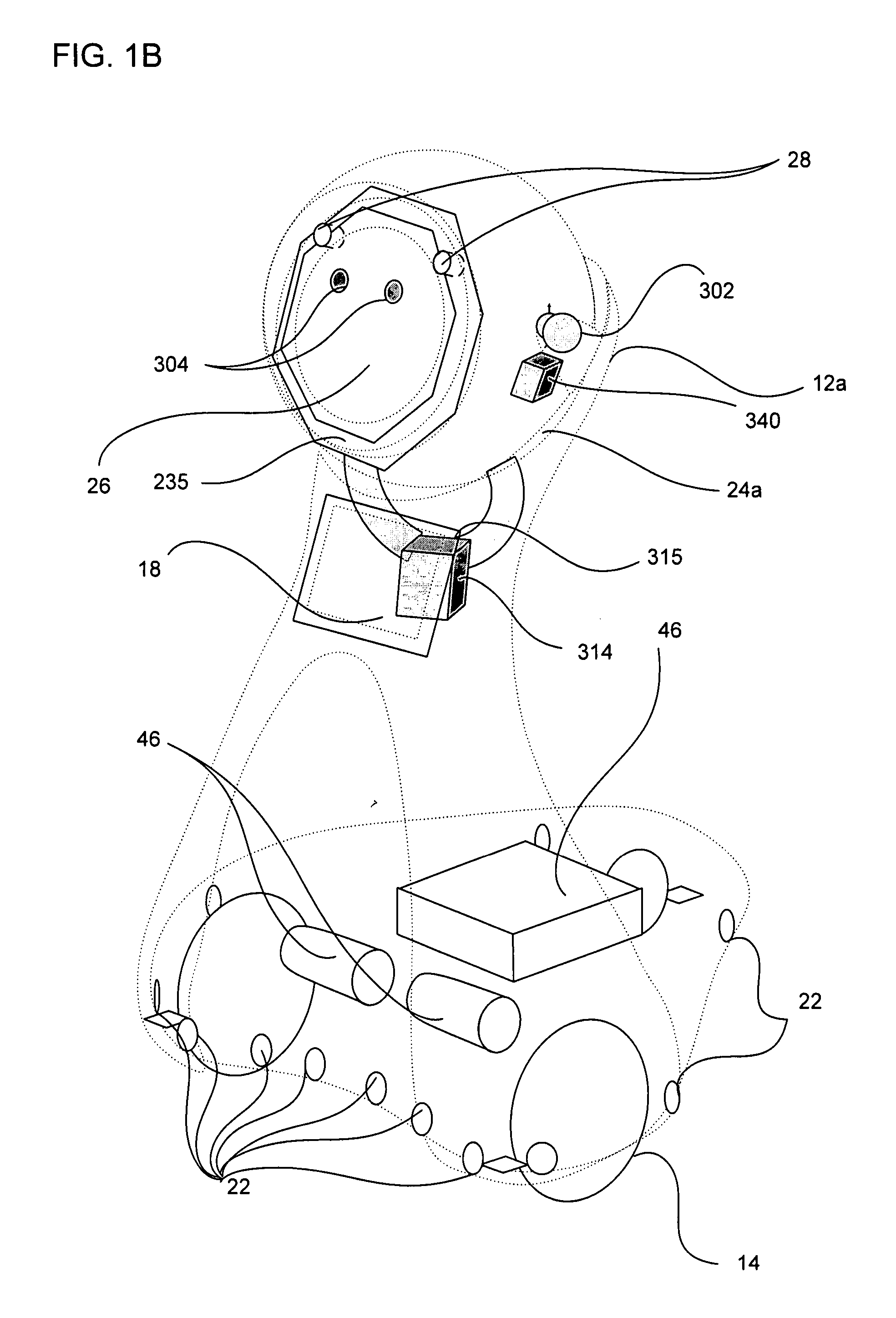
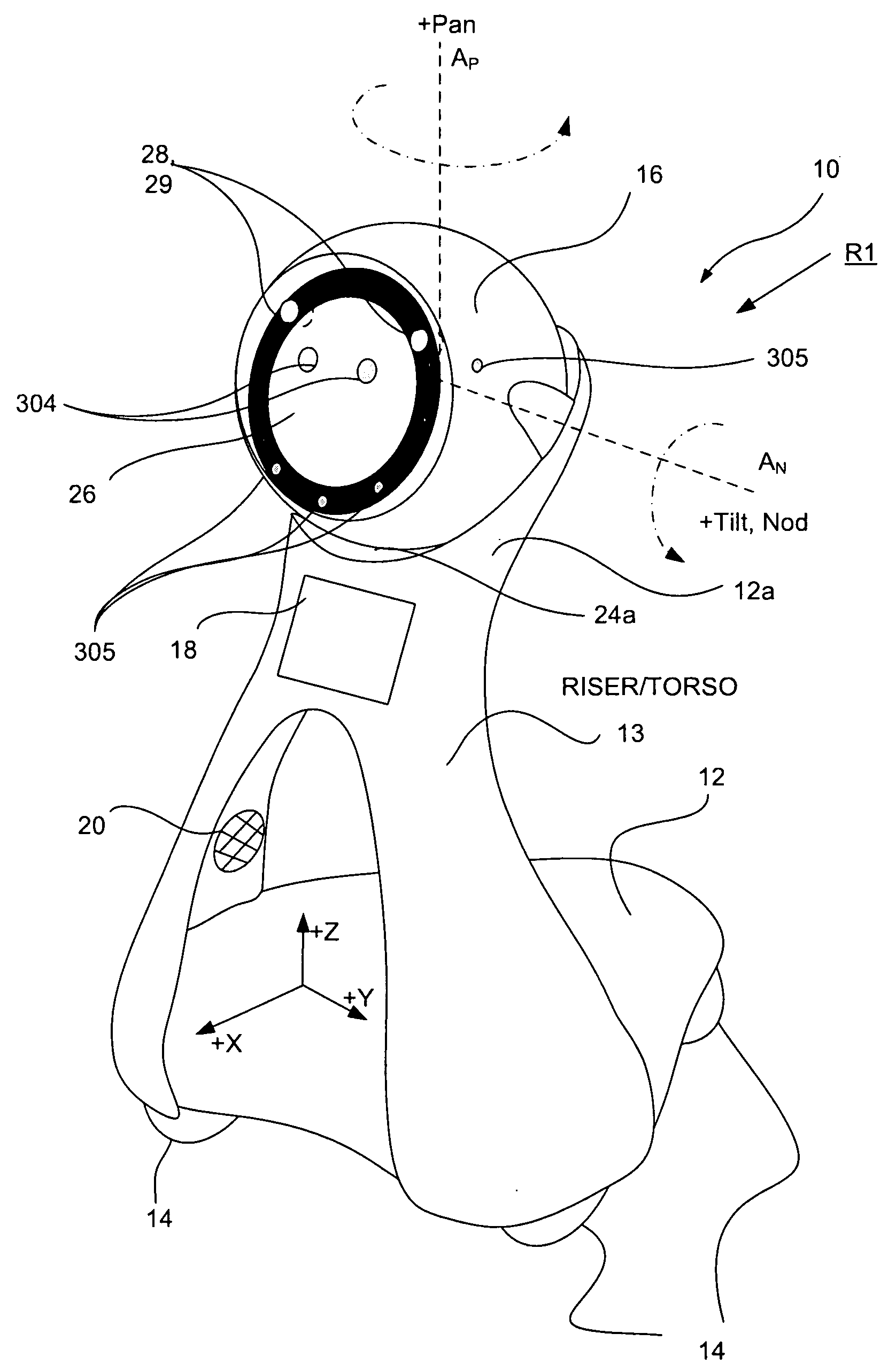
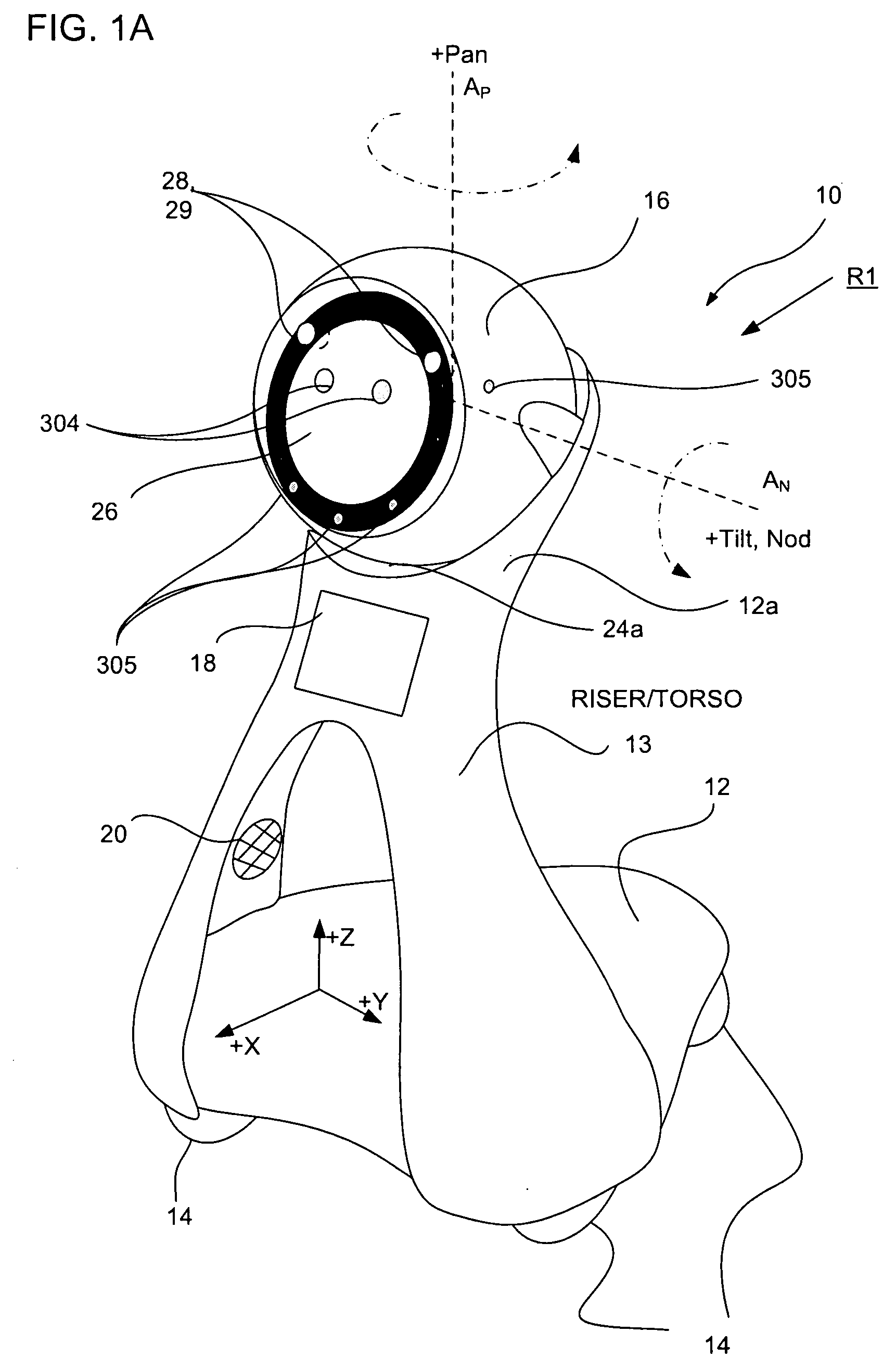
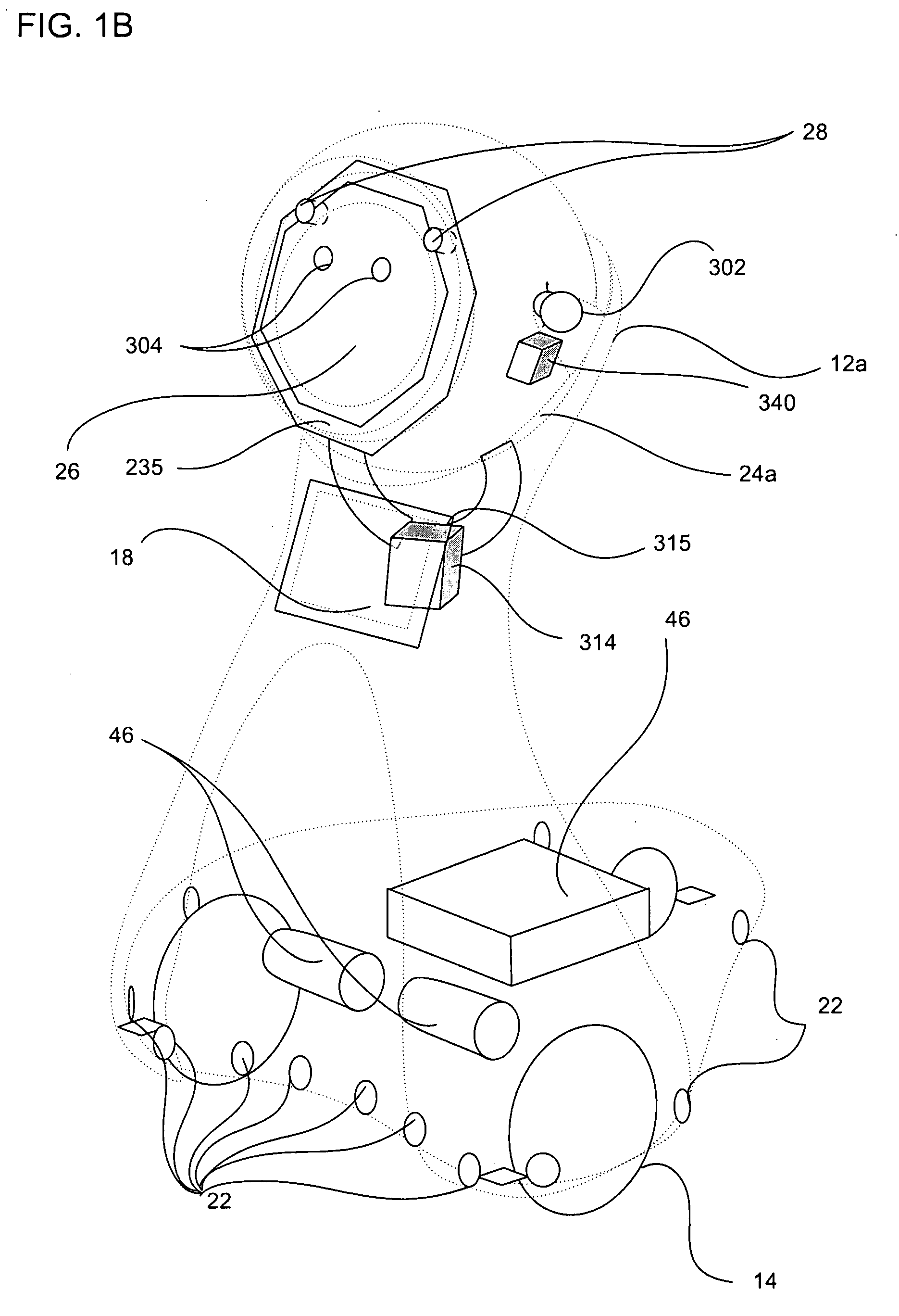
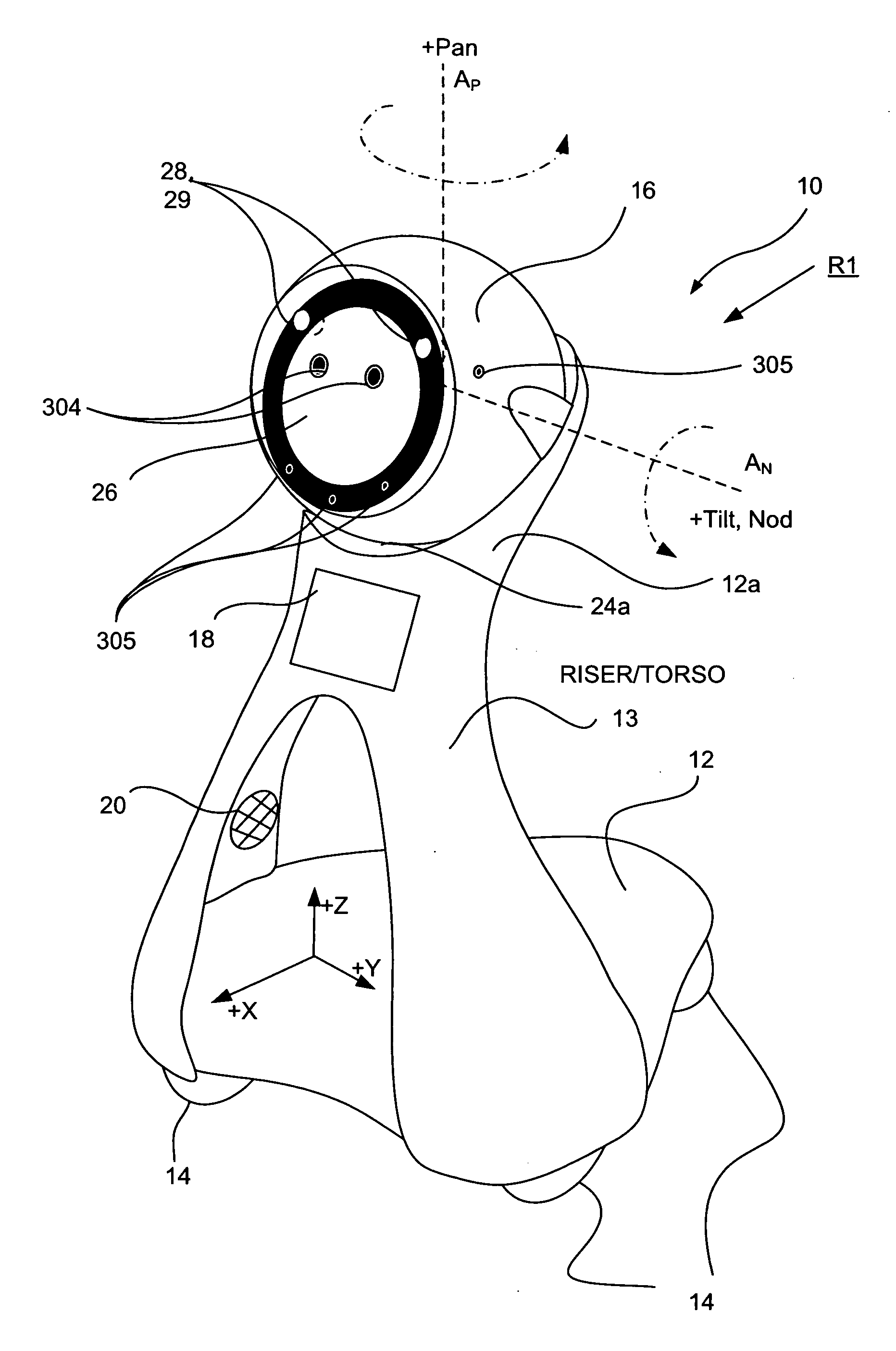
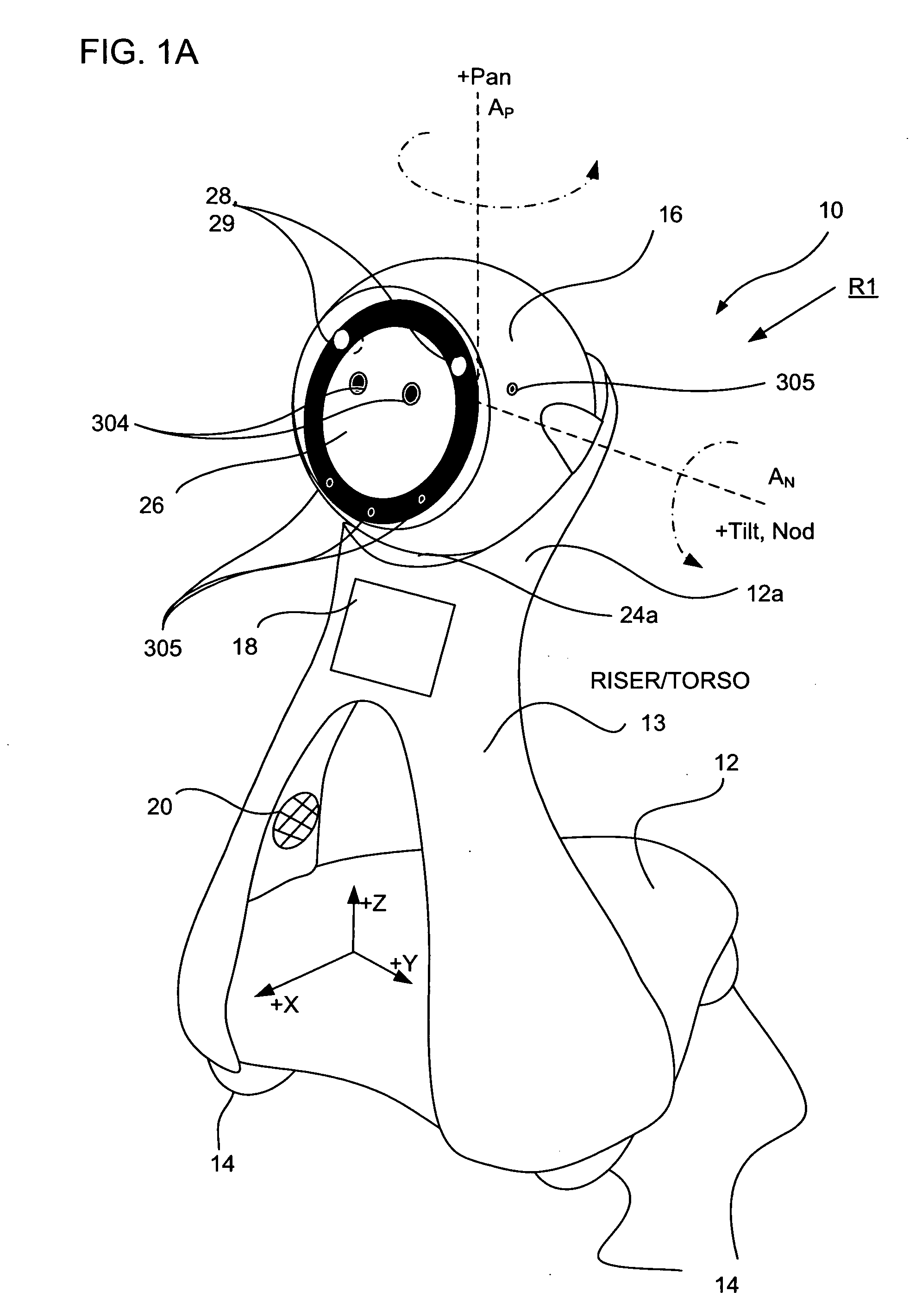
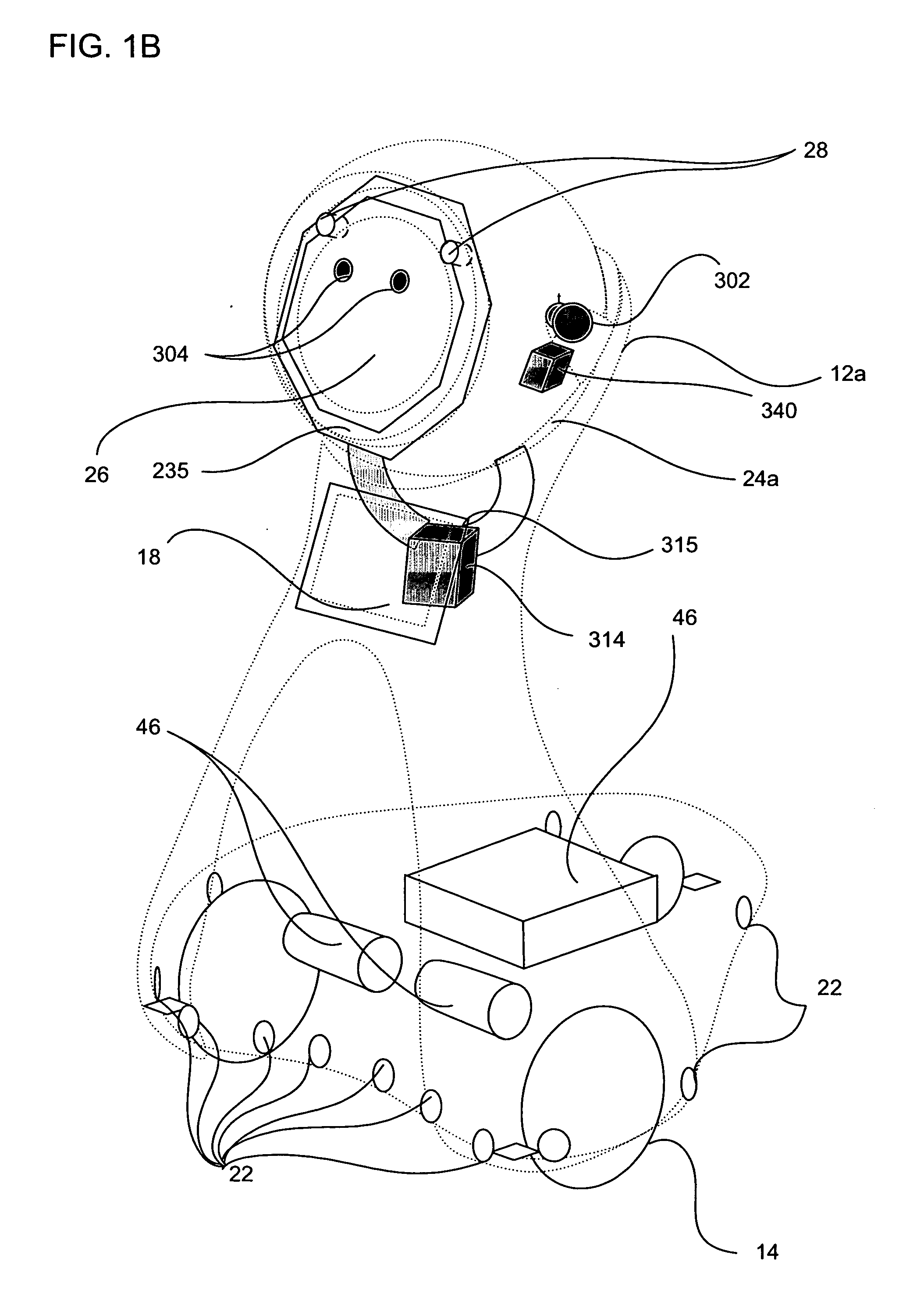
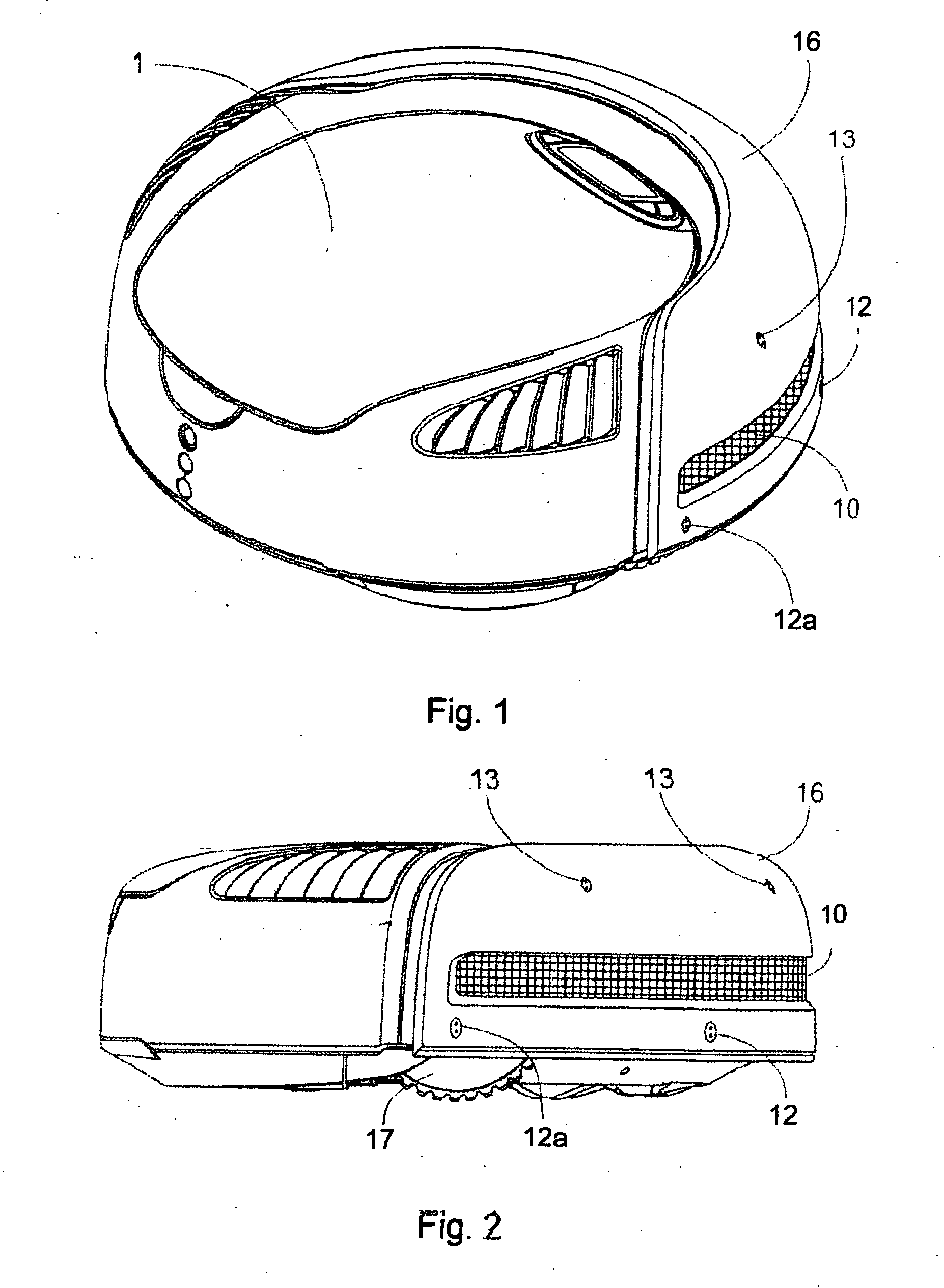
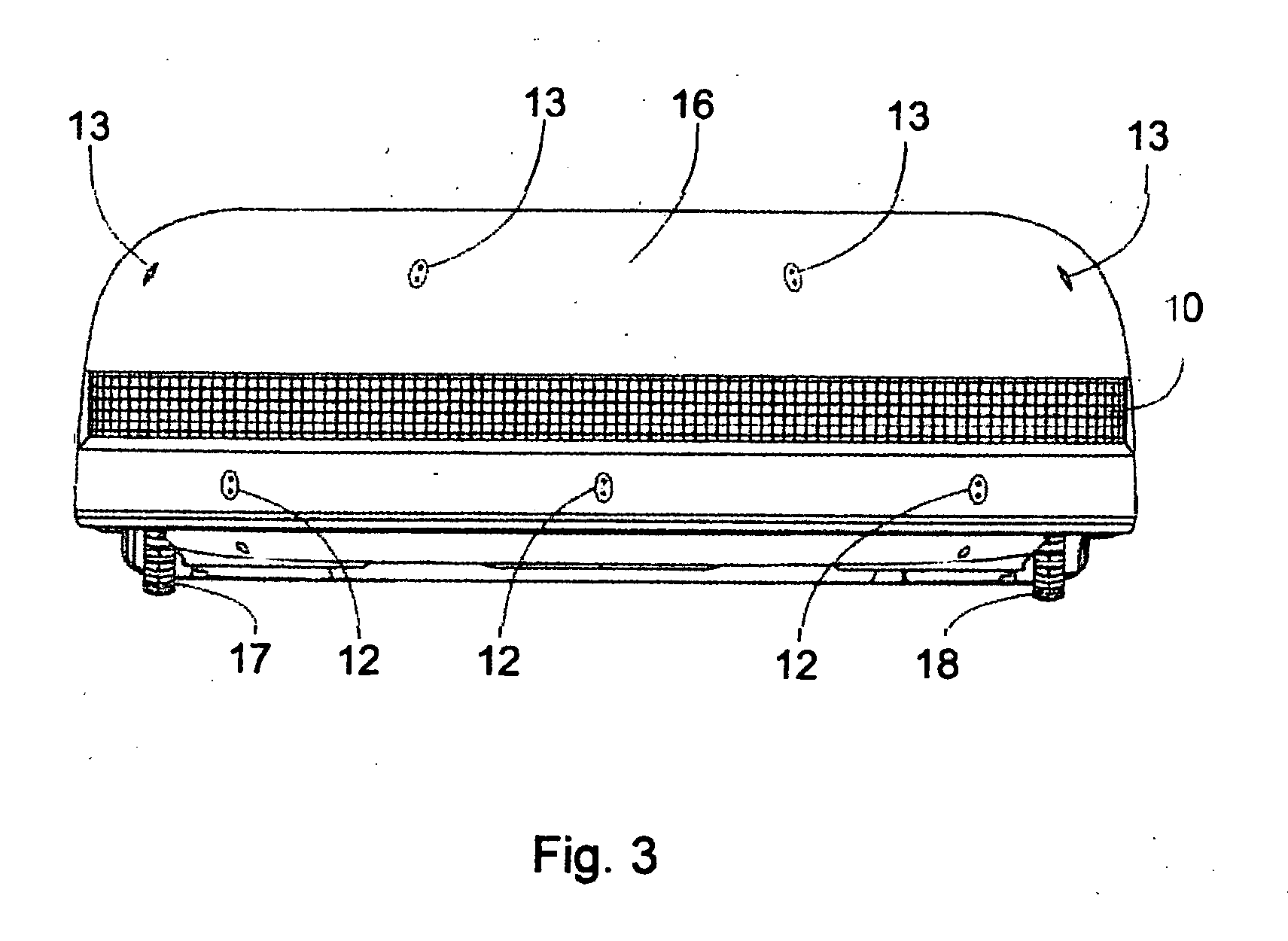
Companion robot for personal interaction
ActiveUS20070192910A1Improving presence scoreEnhanced presenceProgramme-controlled manipulatorLocal control/monitoringThird partyTeleconference
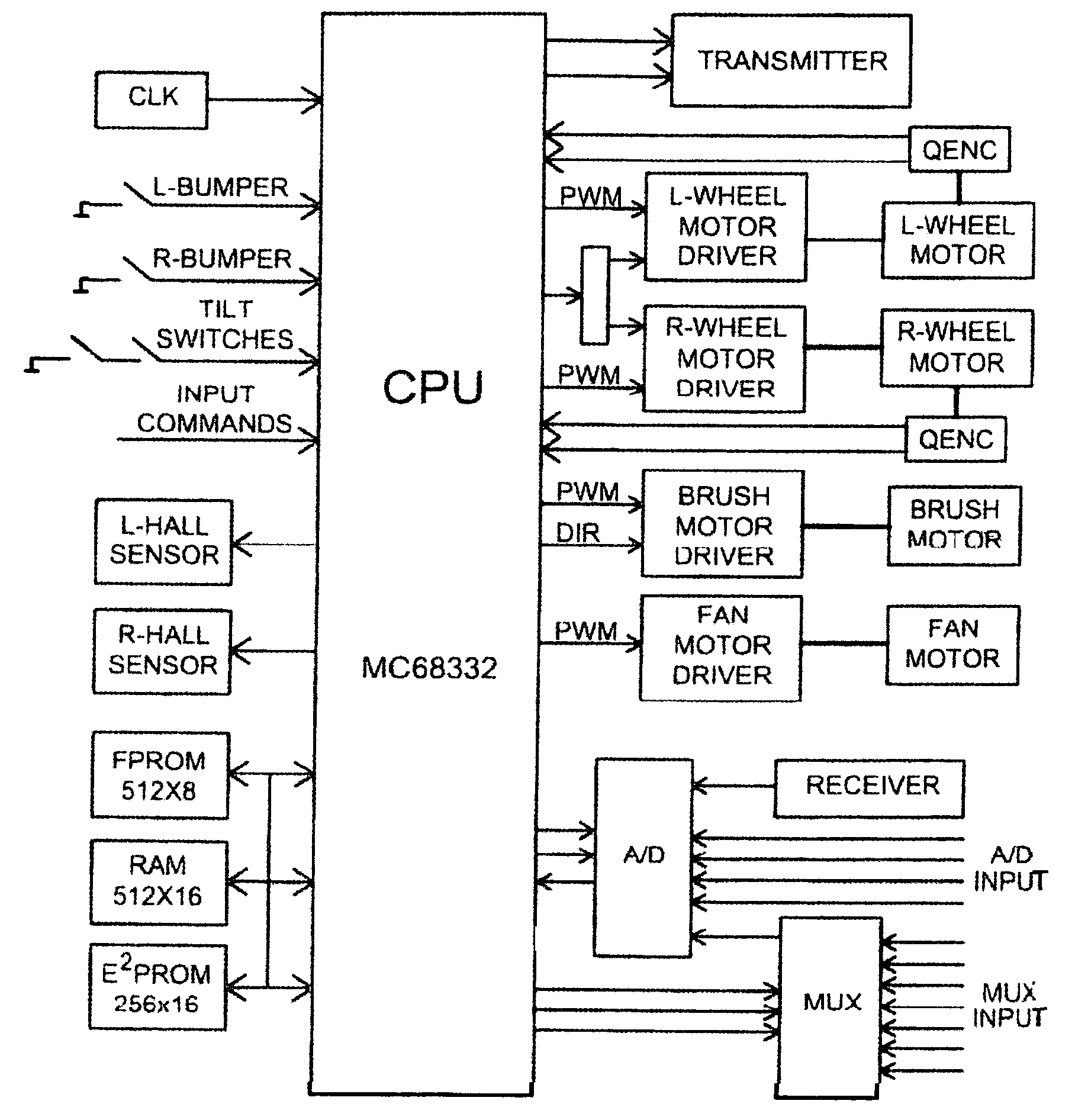
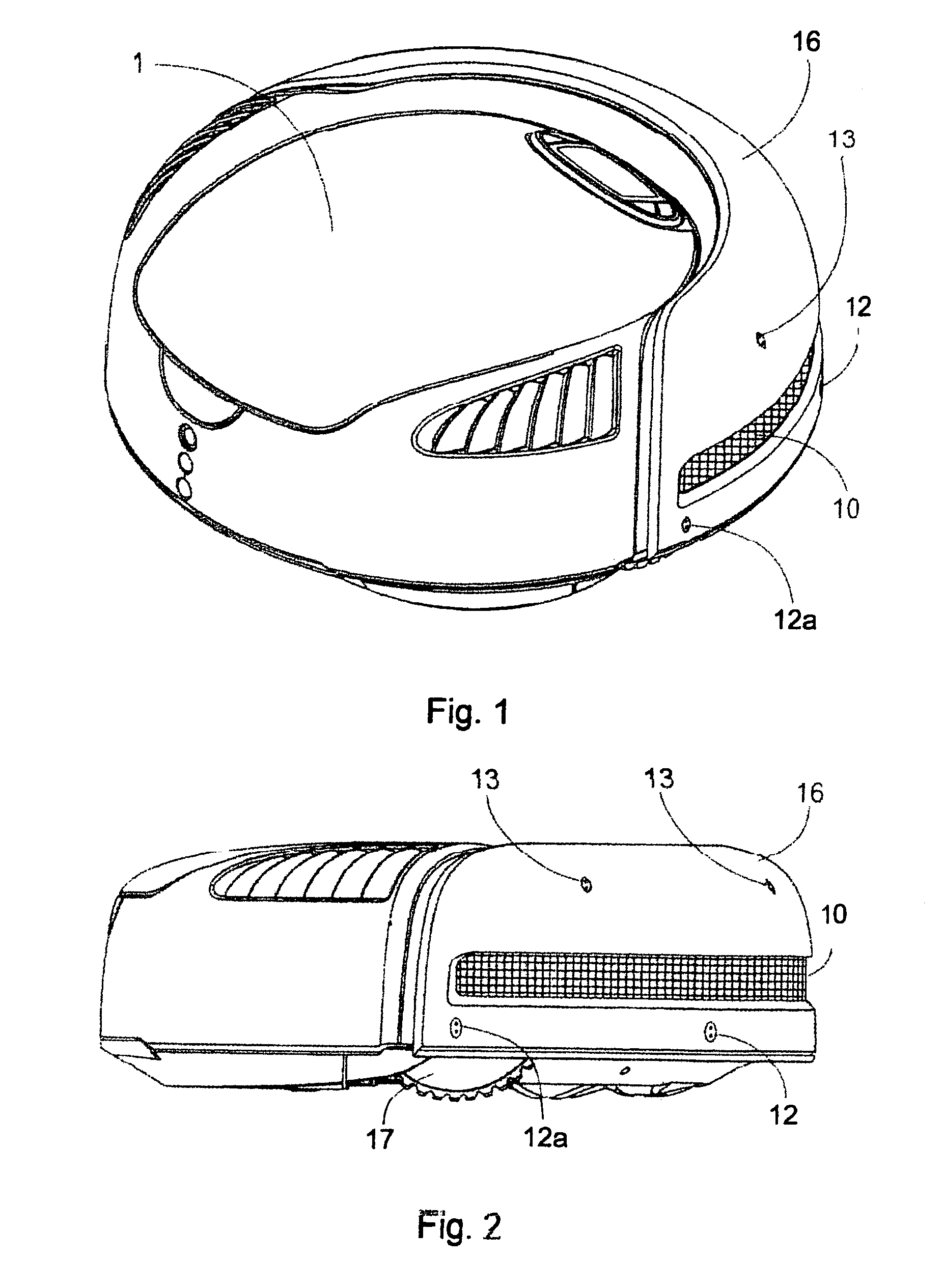
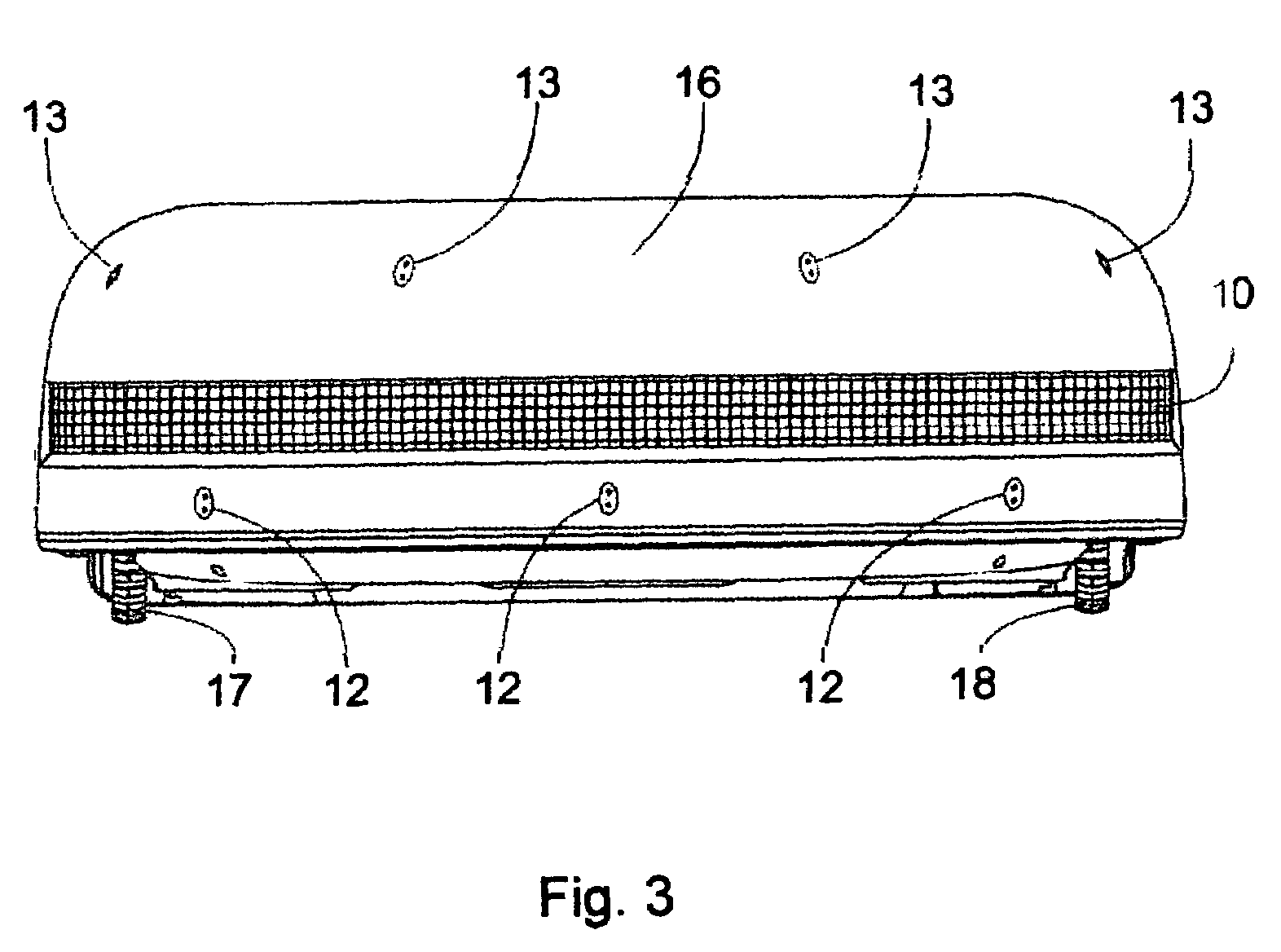
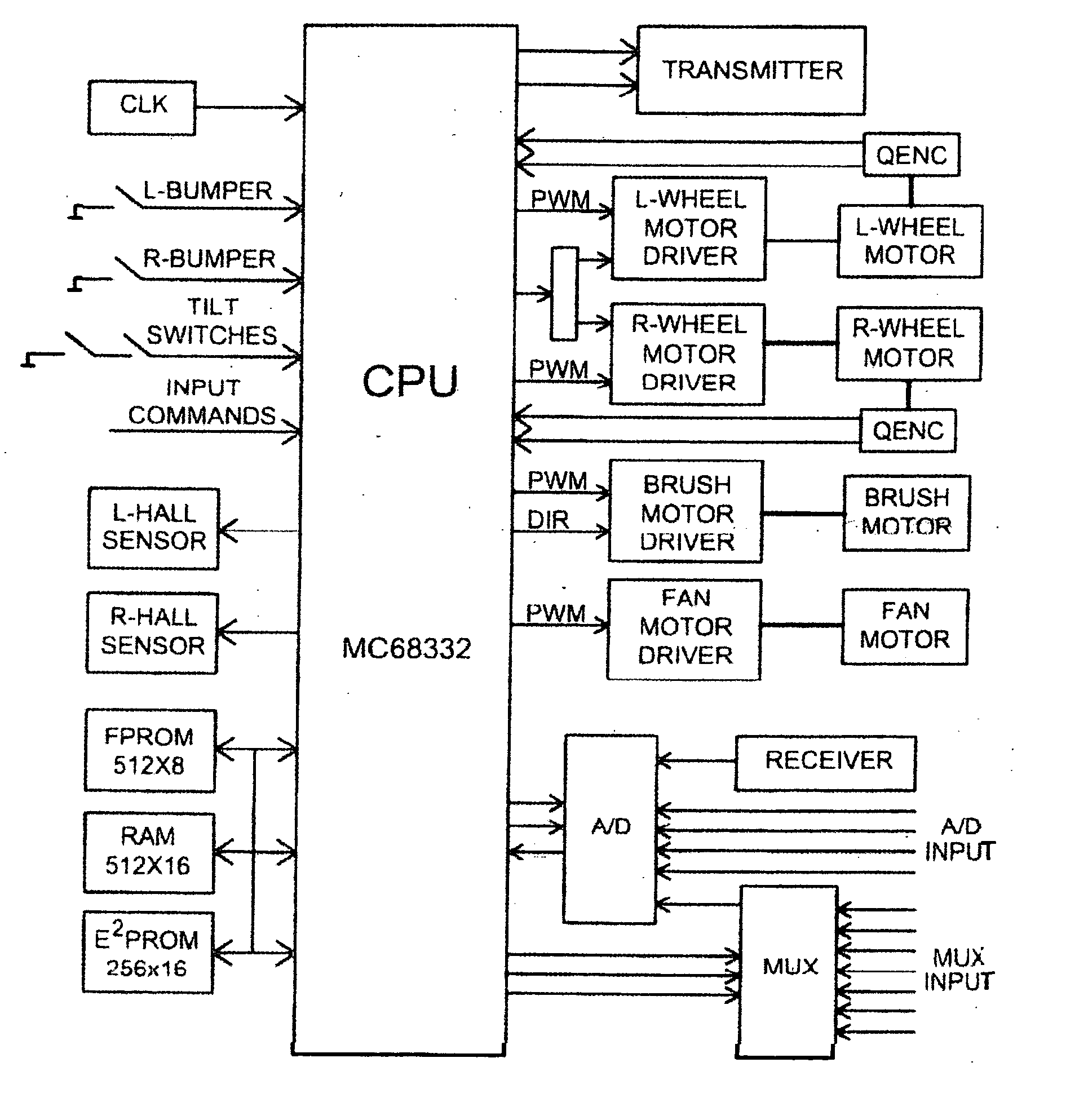
A mobile robot guest for interacting with a human resident performs a room-traversing search procedure prior to interacting with the resident, and may verbally query whether the resident being sought is present. Upon finding the resident, the mobile robot may facilitate a teleconferencing session with a remote third party, or interact with the resident in a number of ways. For example, the robot may carry on a dialogue with the resident, reinforce compliance with medication or other schedules, etc. In addition, the robot incorporates safety features for preventing collisions with the resident; and the robot may audibly announce and / or visibly indicate its presence in order to avoid becoming a dangerous obstacle. Furthermore, the mobile robot behaves in accordance with an integral privacy policy, such that any sensor recording or transmission must be approved by the resident.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Companion robot for personal interaction
ActiveUS20070199108A1Enhanced presenceProgramme-controlled manipulatorLocal control/monitoringThird partyTeleconference
A mobile robot guest for interacting with a human resident performs a room-traversing search procedure prior to interacting with the resident, and may verbally query whether the resident being sought is present. Upon finding the resident, the mobile robot may facilitate a teleconferencing session with a remote third party, or interact with the resident in a number of ways. For example, the robot may carry on a dialogue with the resident, reinforce compliance with medication or other schedules, etc. In addition, the robot incorporates safety features for preventing collisions with the resident; and the robot may audibly announce and / or visibly indicate its presence in order to avoid becoming a dangerous obstacle. Furthermore, the mobile robot behaves in accordance with an integral privacy policy, such that any sensor recording or transmission must be approved by the resident.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Companion robot for personal interaction
ActiveUS20090177323A1Enhanced presenceProgramme-controlled manipulatorDrug and medicationsThird partyRoomba
A mobile robot guest for interacting with a human resident performs a room-traversing search procedure prior to interacting with the resident, and may verbally query whether the resident being sought is present. Upon finding the resident, the mobile robot may facilitate a teleconferencing session with a remote third party, or interact with the resident in a number of ways. For example, the robot may carry on a dialogue with the resident, reinforce compliance with medication or other schedules, etc. In addition, the robot incorporates safety features for preventing collisions with the resident; and the robot may audibly announce and / or visibly indicate its presence in order to avoid becoming a dangerous obstacle. Furthermore, the mobile robot behaves in accordance with an integral privacy policy, such that any sensor recording or transmission must be approved by the resident.
Owner:AVA ROBOTICS INC
Efficient navigation of autonomous carriers
InactiveUS7206677B2Effective strategyMinimize energy consumptionSuction cleanersSpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexityEngineering
According to the invention, autonomous carriers or vehicles are efficiently navigated over a field of operation. The carriers are equipped to execute a selected procedure at more than one desired location on the field, and the navigation system of the invention directs the carrier to the location that is preferentially accessible to it, based on a defined criterion. After the carrier has executed the selected procedure at the location which is preferentially accessible to it, the navigation system directs the carrier to the location which is preferentially accessible to the carrier from the carrier's new position. This procedure is repeated until all the locations at which the procedure is to be executed have been reached. The task of determining a navigation route to a location that can be preferentially accessed is based on an efficient, structured search procedure of low computational complexity.
Owner:AB ELECTROLUX
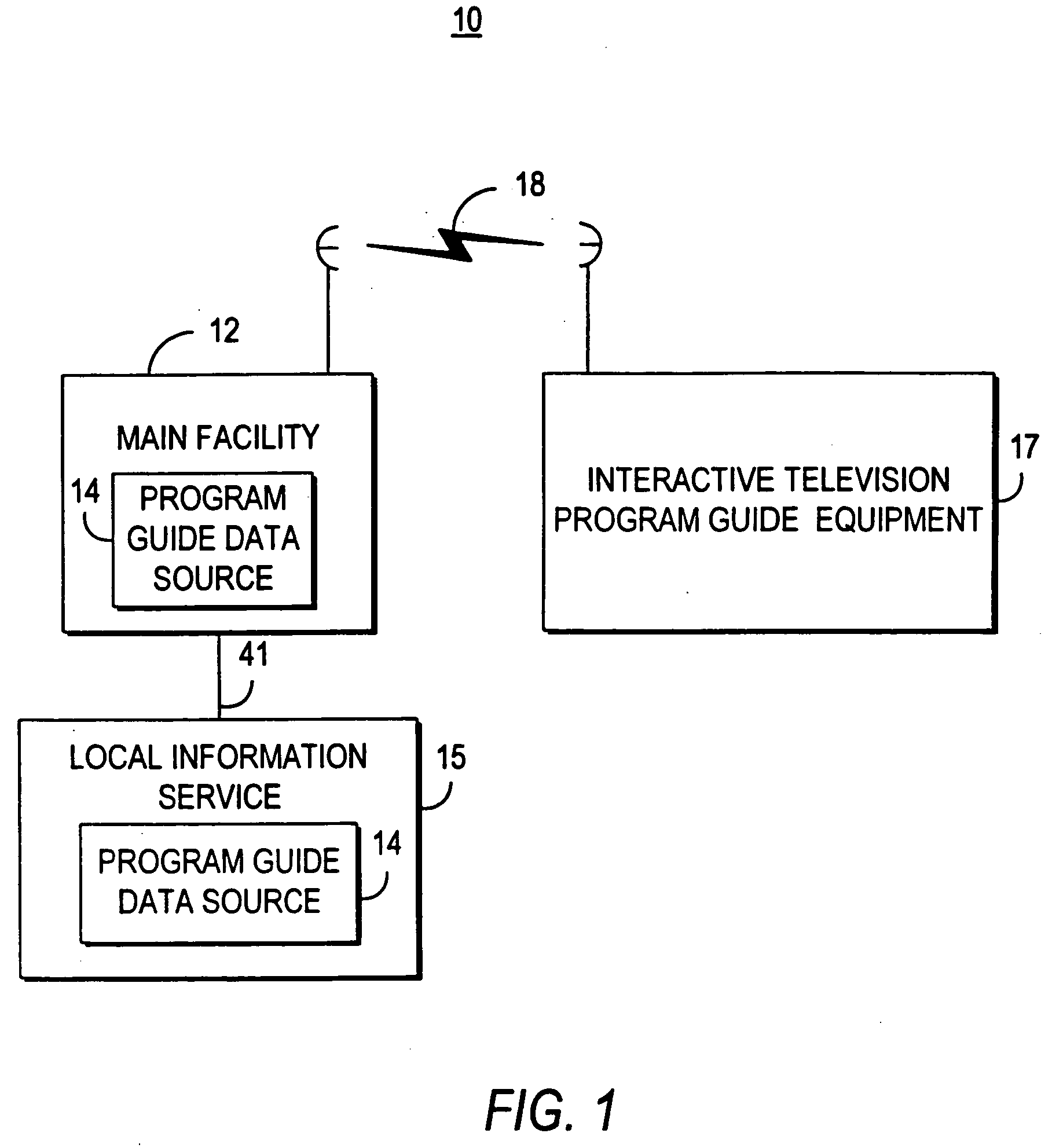
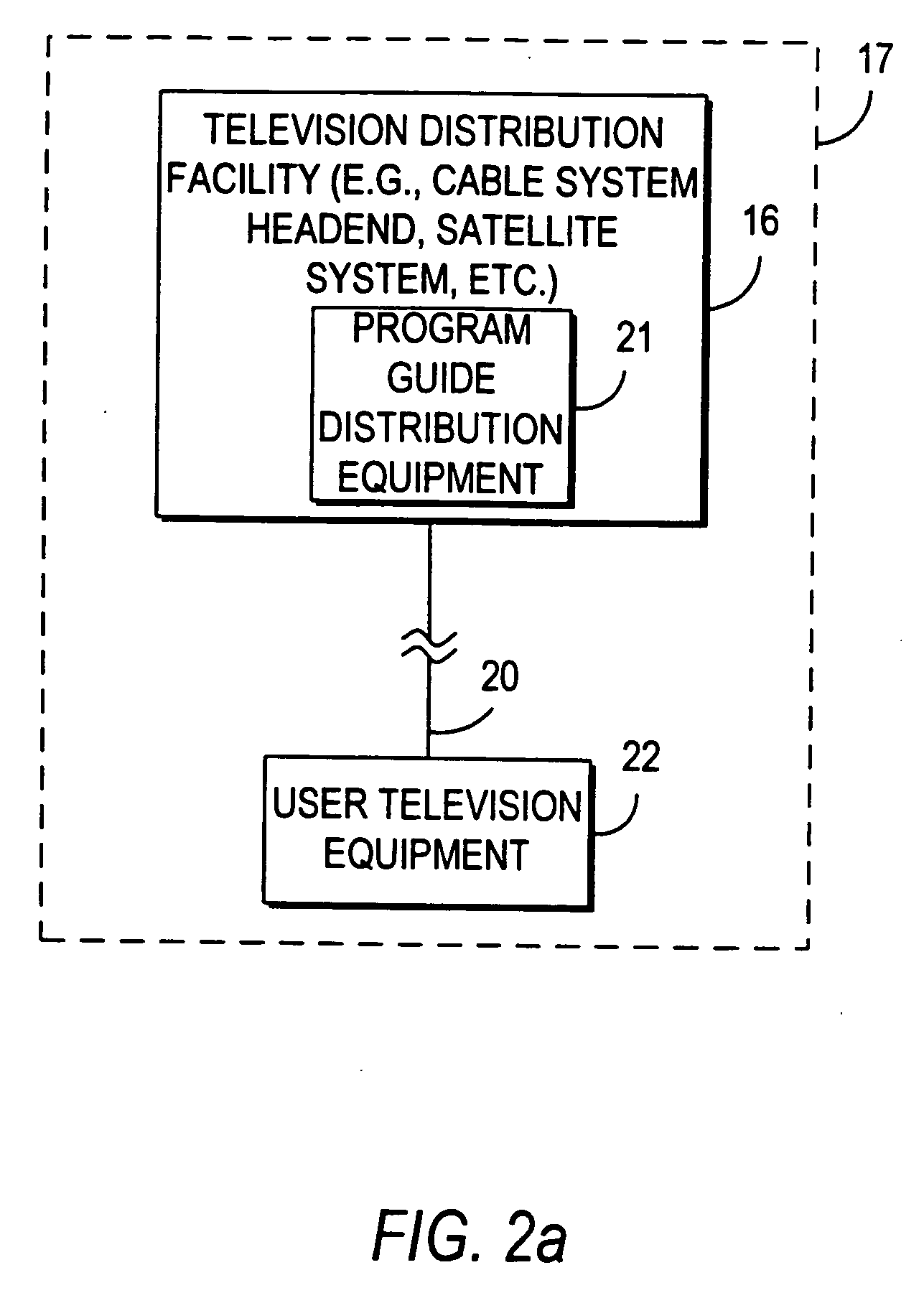
Interactive program guide system and method
InactiveUS20050204387A1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsInteractive televisionSearch procedure
An interactive television program guide system and method is provided. Time separators are displayed within lists of program listings to allow users to more easily view the program listings. On-screen arrows have their display characteristics changed according to user actions. Similar program listings are displayed only once when using search program listings. Users are provided with an opportunity to view channel information before setting channels as favorites. Information from local information services is provided in program guide display screens that are configurable by a main facility. Users are provided with an opportunity to centrally lock and unlock programs, and to bypass locks when desired.
Owner:KNUDSON EDWARD B +7
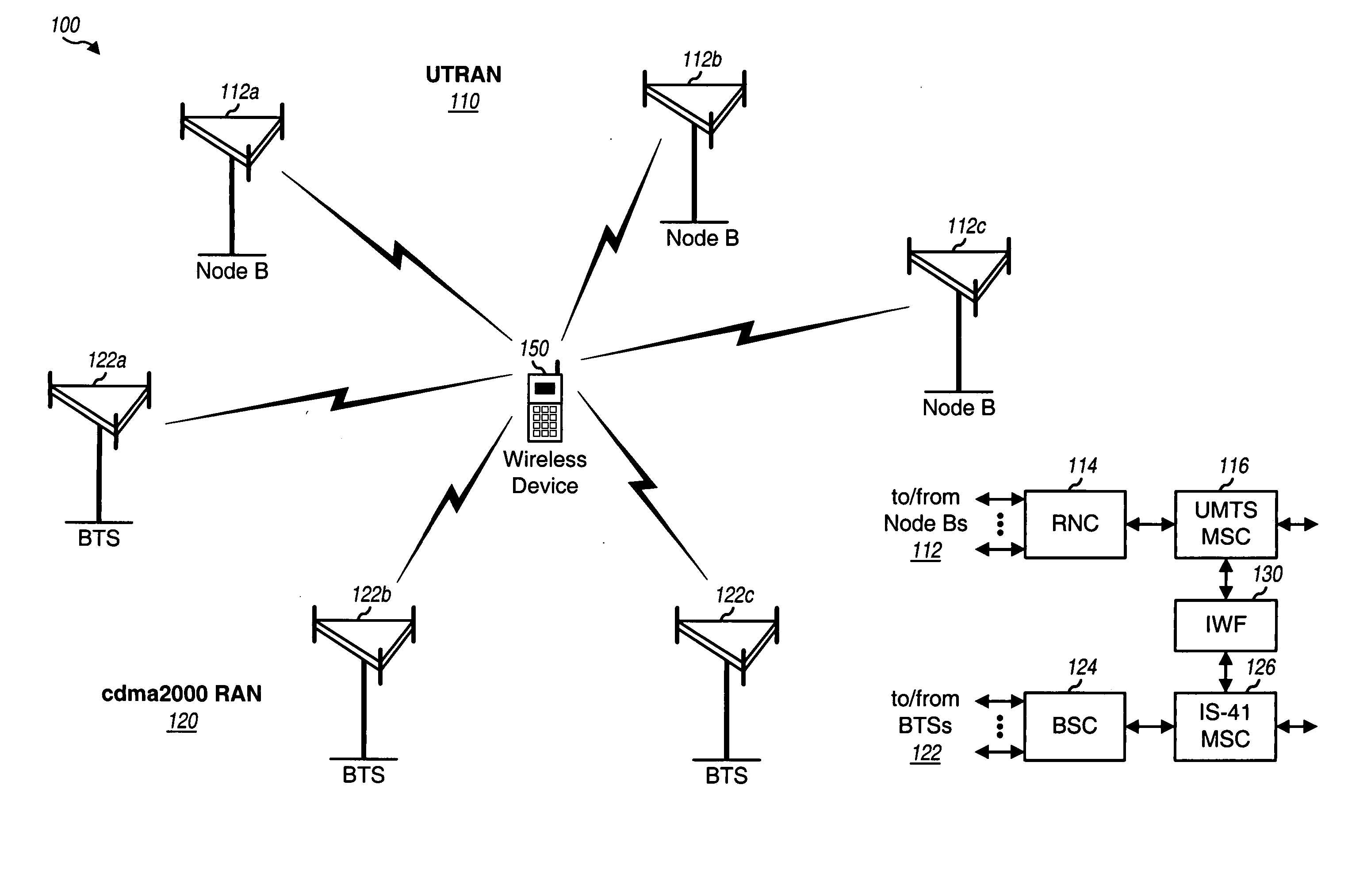
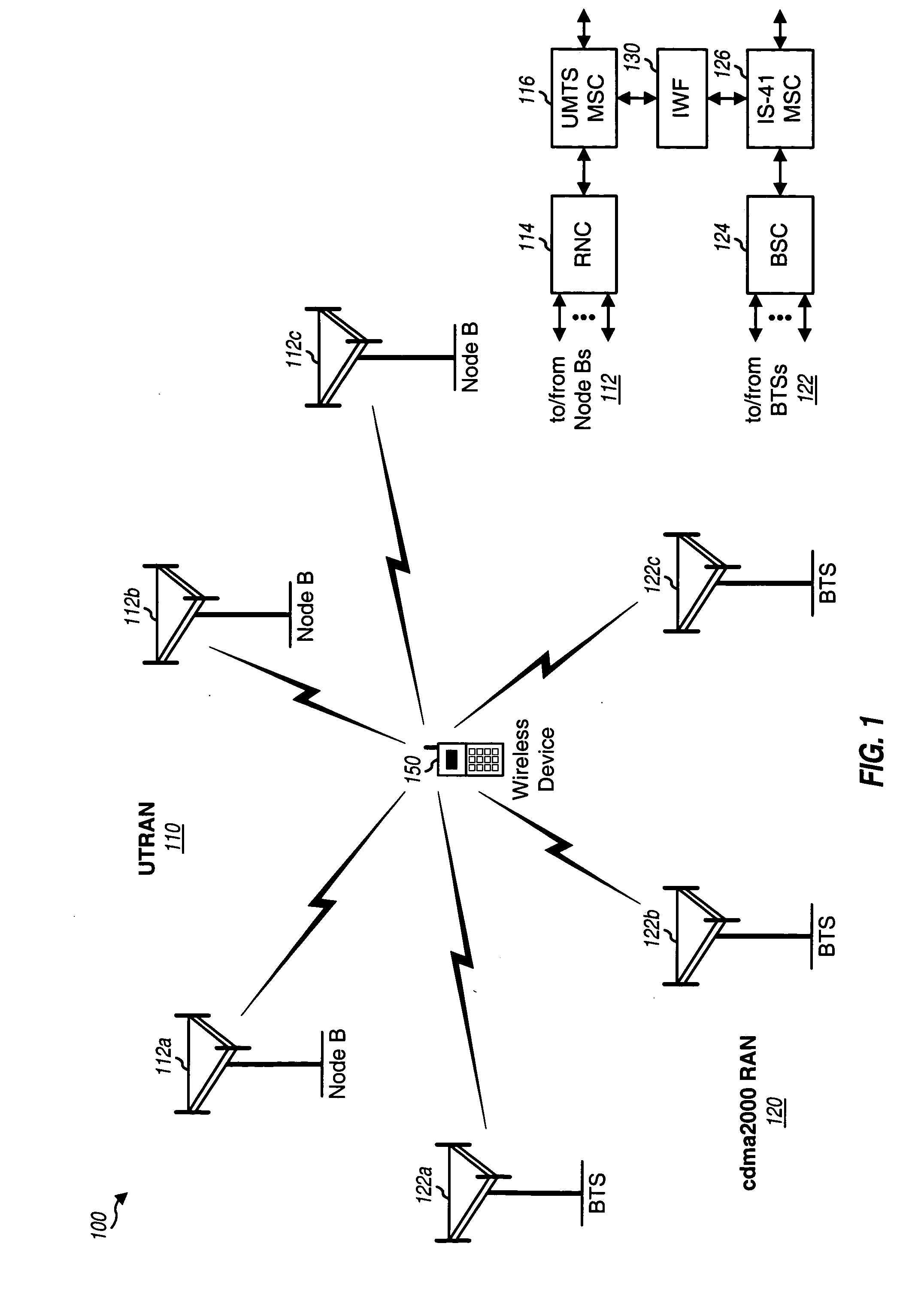
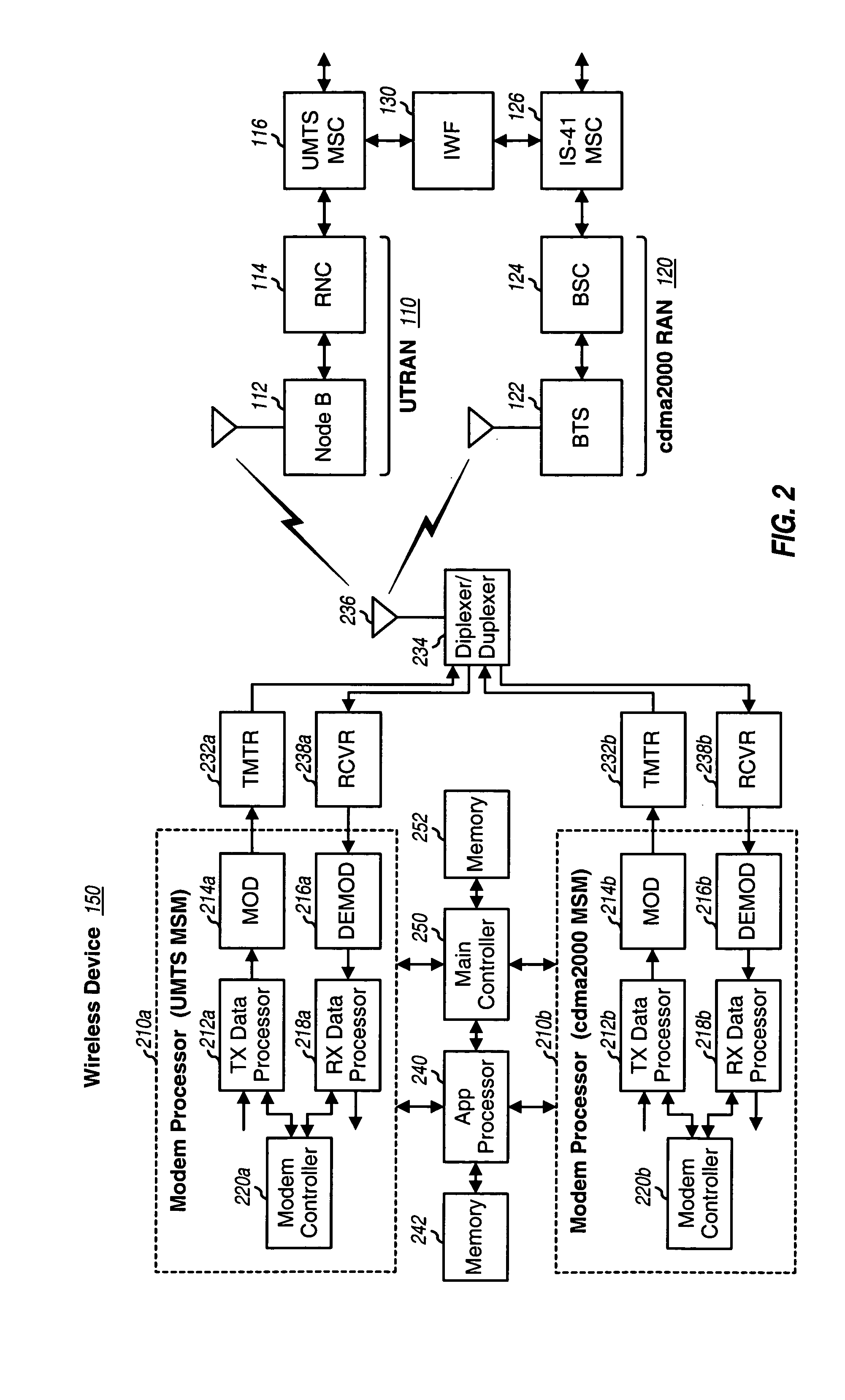
Inter-system handoff between wireless communication networks of different radio access technologies
Various schemes for performing inter-system handoff, e.g., from a UTRAN to a cdma2000 radio access network (RAN) are described. For a MAHHO scheme, the UTRAN uses measurements obtained by a multi-RAT device to determine suitable cdma2000 cell(s) for handover. The measurements are obtained by a candidate frequency search procedure, and the handover is accomplished by a handoff execution procedure. For a MDHHO scheme, the UTRAN relies on location information for the multi-RAT device to select suitable cdma2000 cell(s) for handover. For a CRHHO scheme, a new call is established on the cdma2000 RAN and the pending call on the UTRAN is released in a manner such that the handover appears seamless to the multi-RAT device. The multi-RAT device includes two modem processors that perform processing for the UTRAN and cdma2000 RAN and an application processor that controls the modem processors.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Companion robot for personal interaction
ActiveUS20070198128A1Enhanced presenceProgramme-controlled manipulatorLocal control/monitoringThird partyTeleconference
A mobile robot guest for interacting with a human resident performs a room-traversing search procedure prior to interacting with the resident, and may verbally query whether the resident being sought is present. Upon finding the resident, the mobile robot may facilitate a teleconferencing session with a remote third party, or interact with the resident in a number of ways. For example, the robot may carry on a dialogue with the resident, reinforce compliance with medication or other schedules, etc. In addition, the robot incorporates safety features for preventing collisions with the resident; and the robot may audibly announce and / or visibly indicate its presence in order to avoid becoming a dangerous obstacle. Furthermore, the mobile robot behaves in accordance with an integral privacy policy, such that any sensor recording or transmission must be approved by the resident.
Owner:AVA ROBOTICS INC
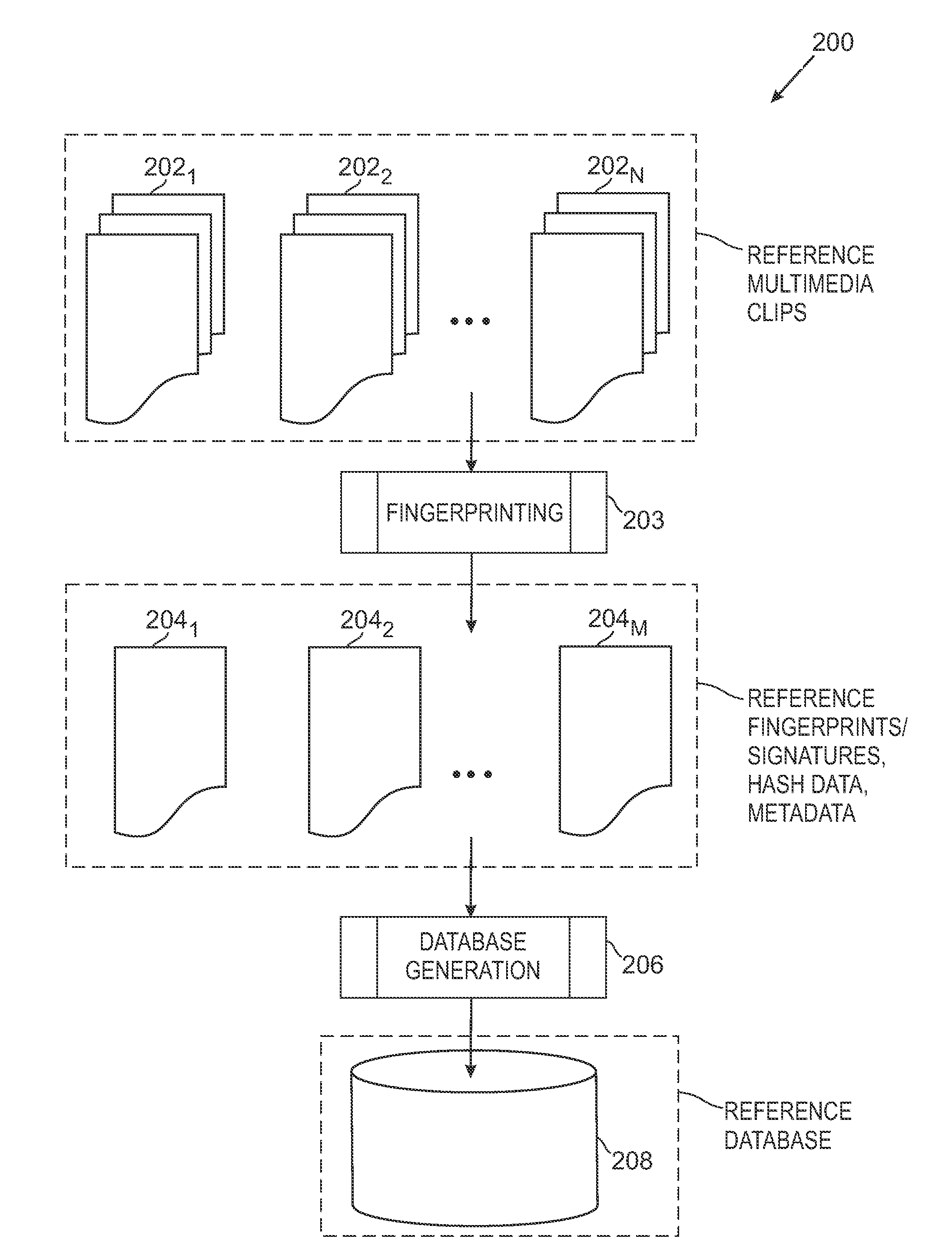
Media Fingerprinting and Identification System
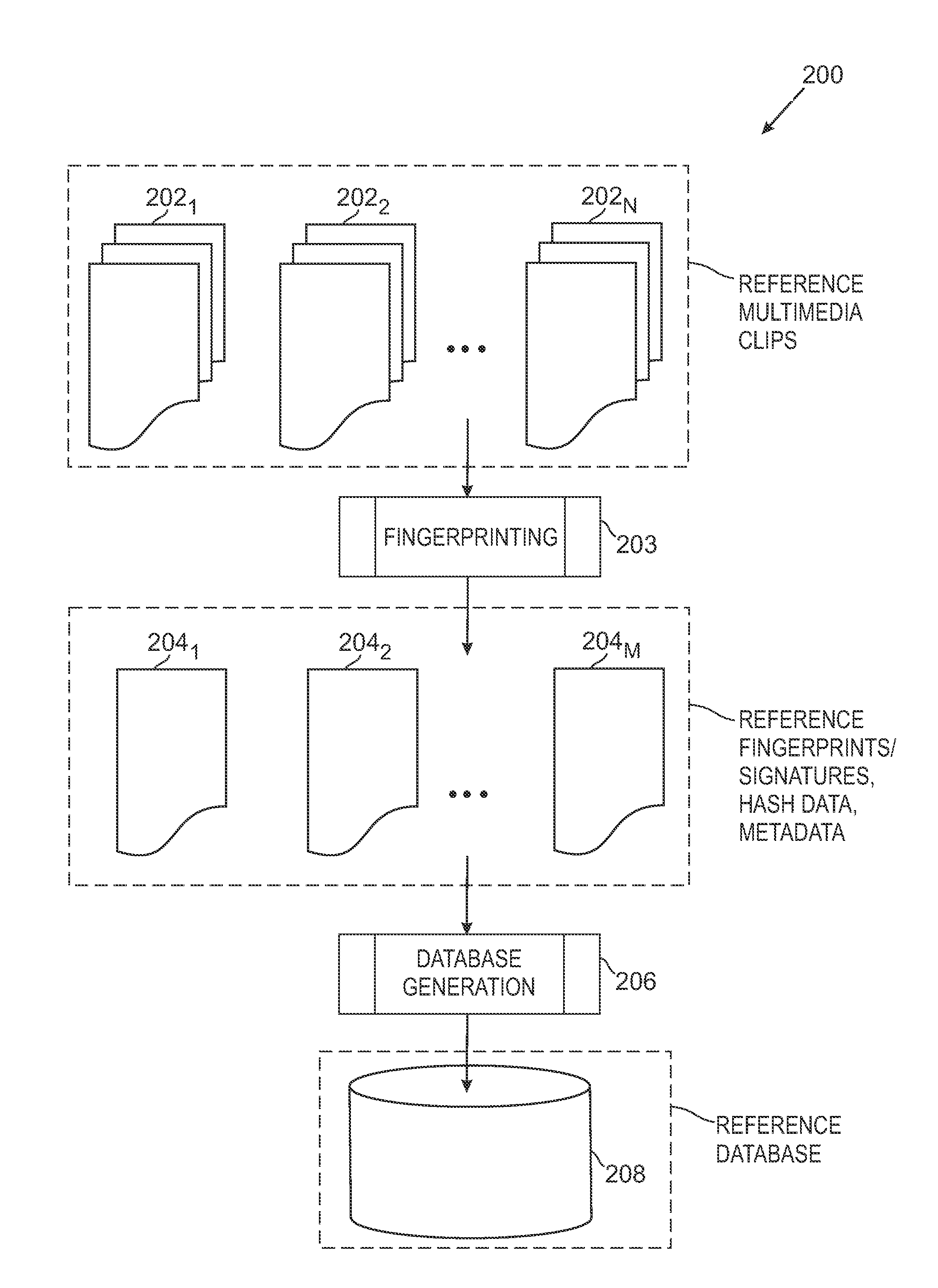
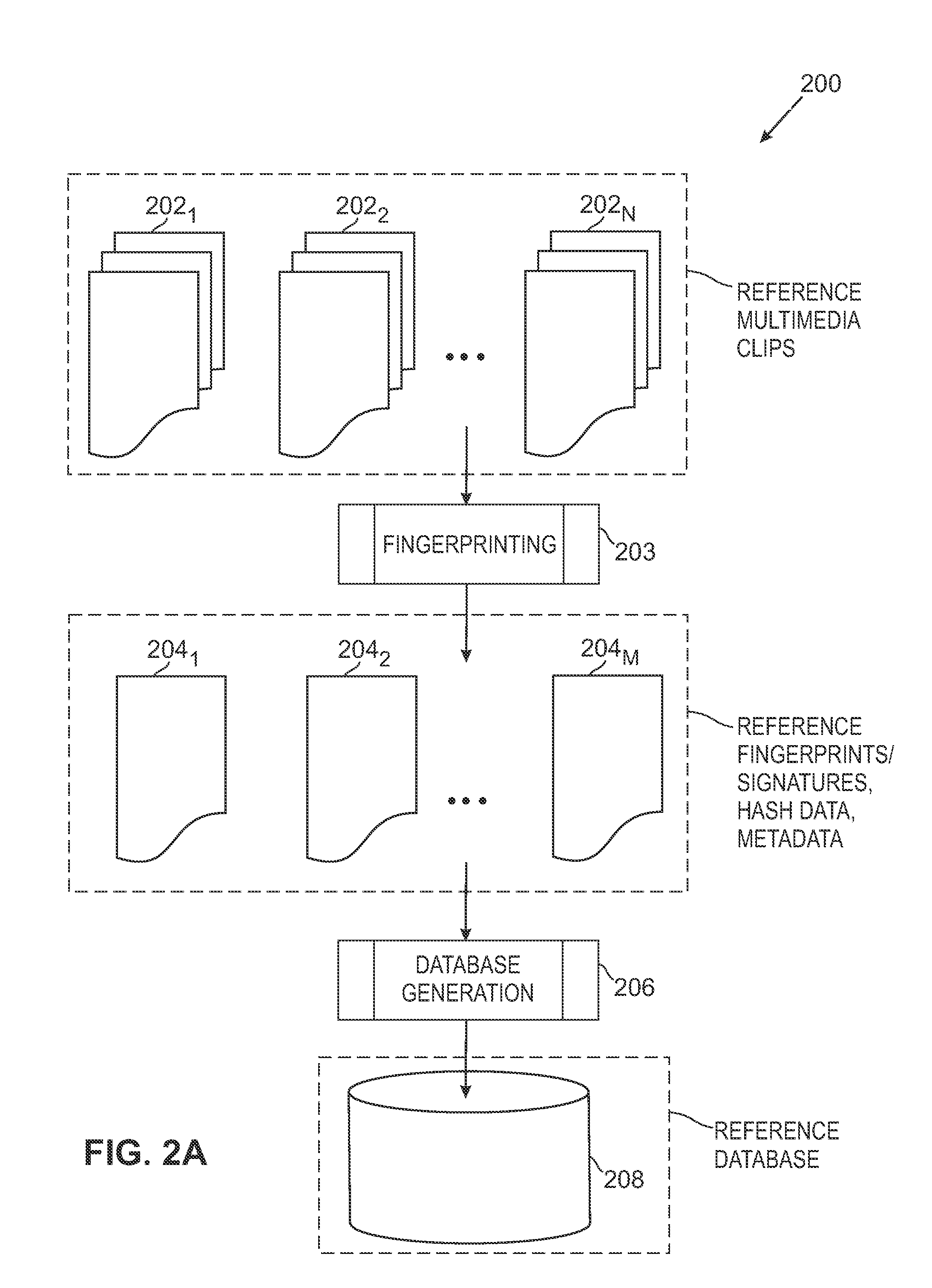
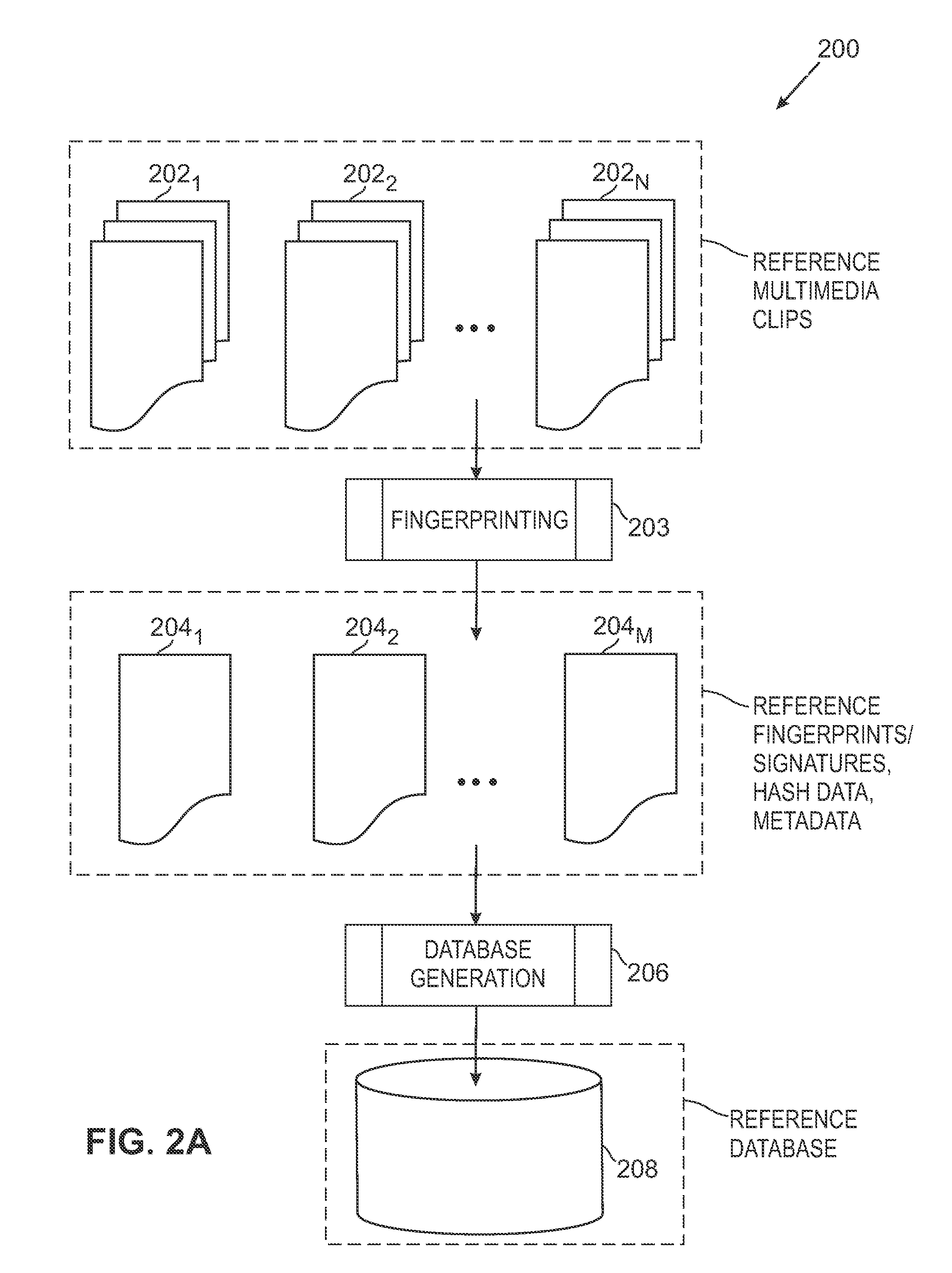
ActiveUS20100318515A1Highly accurate in findingMany typesMultimedia data indexingData processing applicationsReference databaseNumerical descriptors
The overall architecture and details of a scalable video fingerprinting and identification system that is robust with respect to many classes of video distortions is described. In this system, a fingerprint for a piece of multimedia content is composed of a number of compact signatures, along with traversal hash signatures and associated metadata. Numerical descriptors are generated for features found in a multimedia clip, signatures are generated from these descriptors, and a reference signature database is constructed from these signatures. Query signatures are also generated for a query multimedia clip. These query signatures are searched against the reference database using a fast similarity search procedure, to produce a candidate list of matching signatures. This candidate list is further analyzed to find the most likely reference matches. Signature correlation is performed between the likely reference matches and the query clip to improve detection accuracy.
Owner:ROKU INCORPORATED
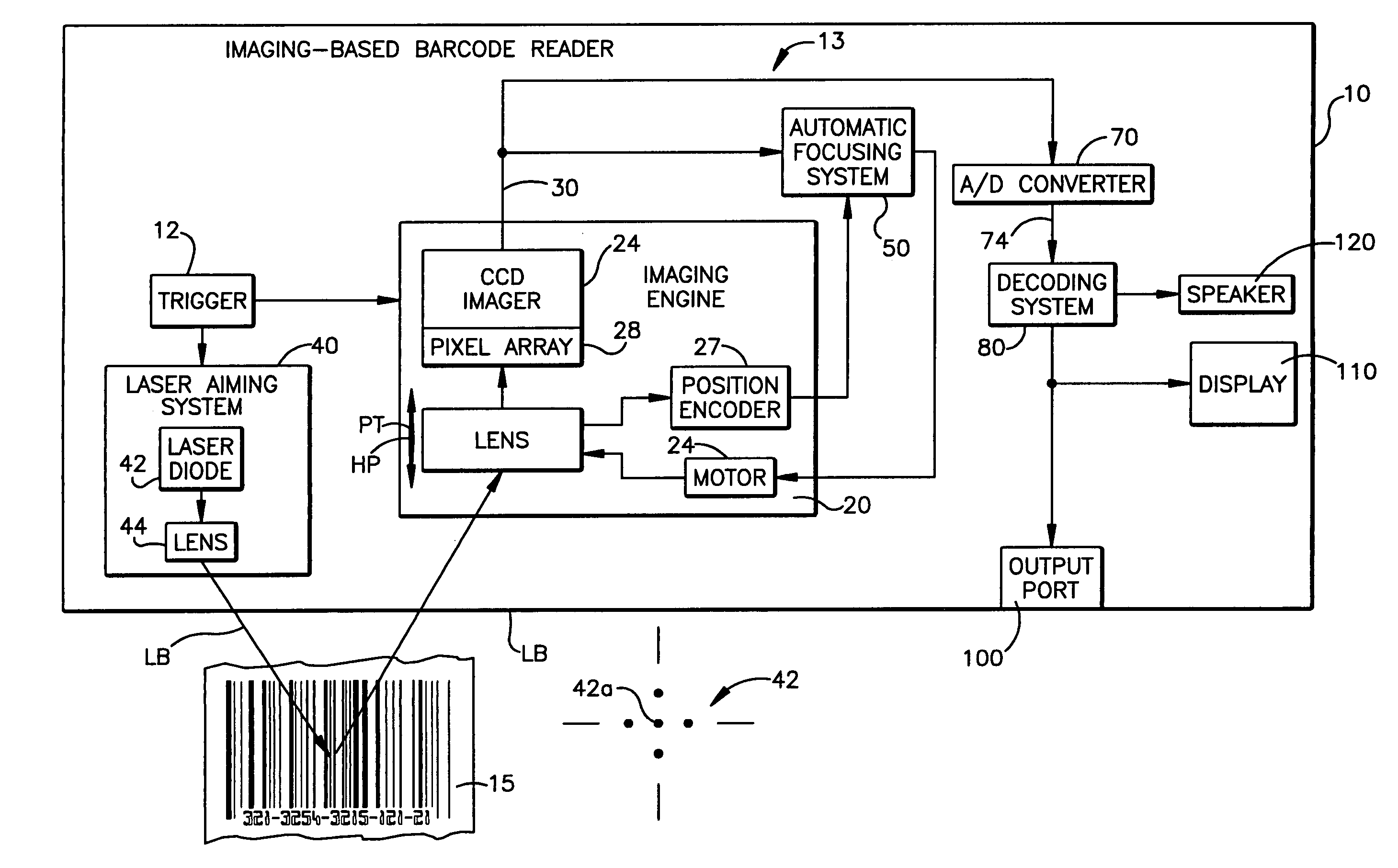
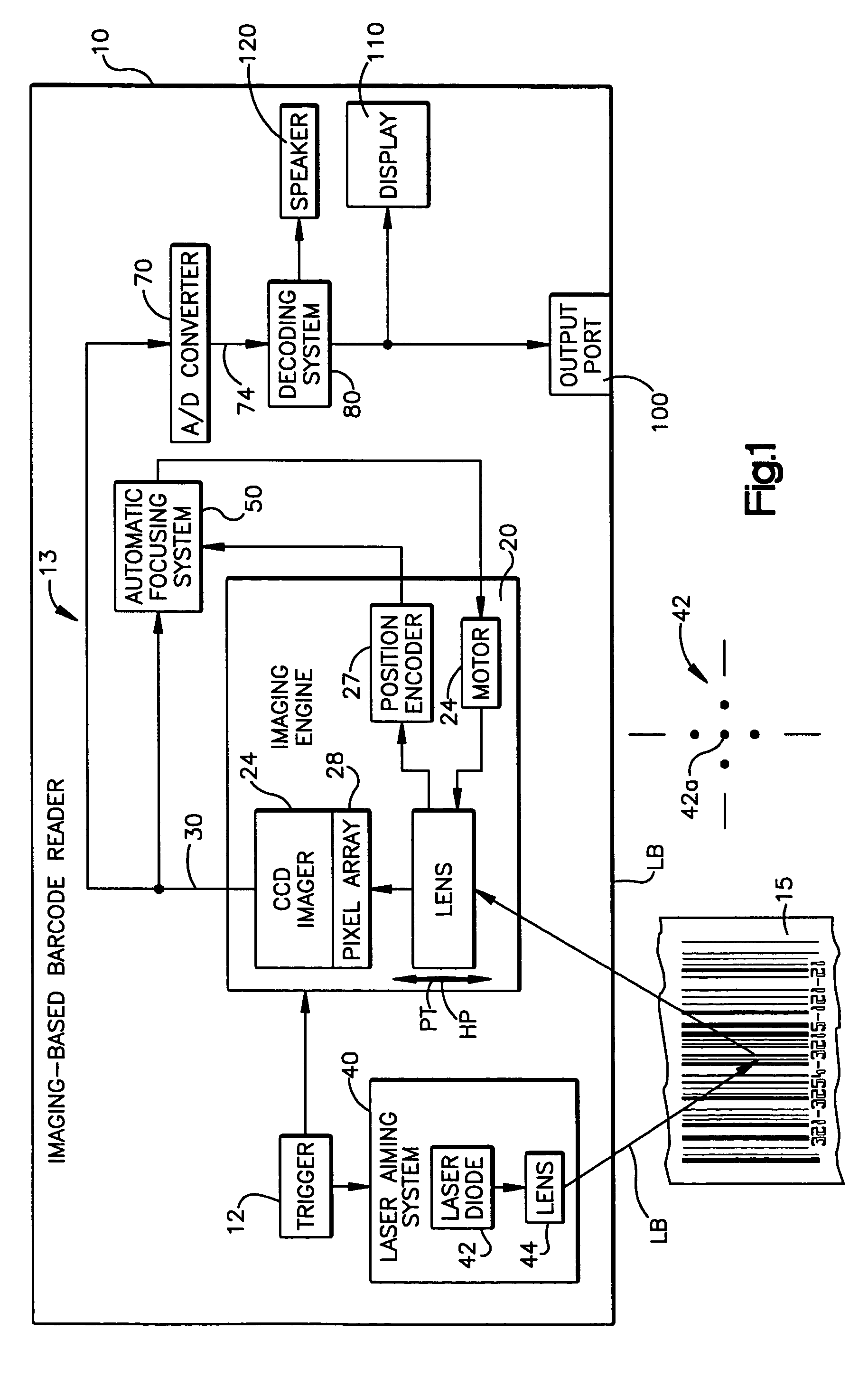
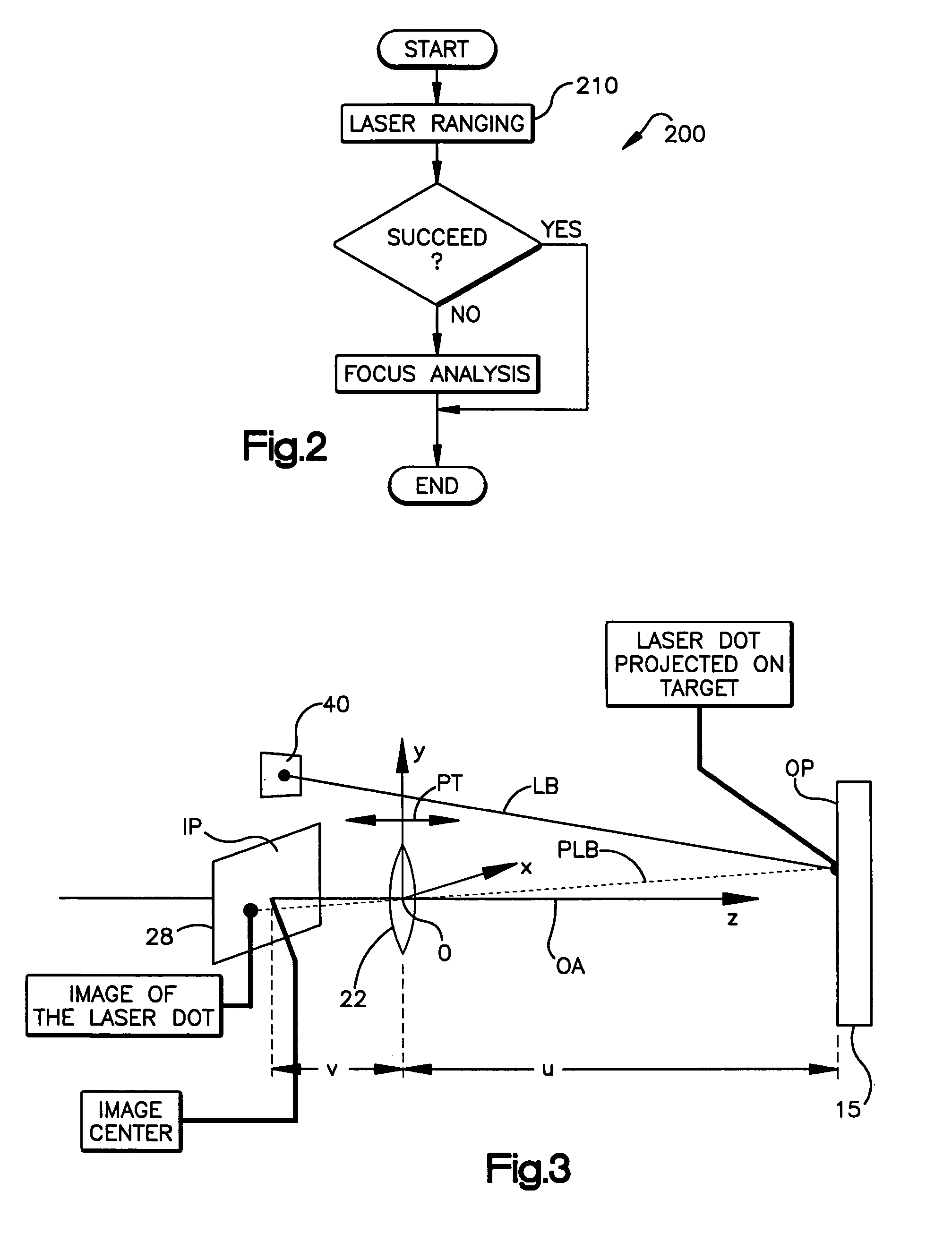
Automatic focusing system for imaging-based bar code reader
An automatic focusing system for an imaging-based bar code reader. The automatic focusing system employs a two step process for moving a lens of an imaging system along its path of travel such that a sharp image of a target bar code is projected or focused onto an imaging system pixel array. The first step is laser ranging which utilizes a laser beam for range finding. Laser ranging determines a distance between the imaging system pixel array and the target bar code. Given the determined distance, the automatic focusing system moves the lens to a suitable position for imaging the target bar code. If ambient conditions prevent laser ranging from properly working, the second step is focus analysis. Focus analysis involves moving the lens in accordance with a search routine and analyzing image frames of the target object to find a suitable focus position.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Media fingerprinting and identification system
ActiveUS8195689B2Multimedia data indexingData processing applicationsReference databaseNumerical descriptors
The overall architecture and details of a scalable video fingerprinting and identification system that is robust with respect to many classes of video distortions is described. In this system, a fingerprint for a piece of multimedia content is composed of a number of compact signatures, along with traversal hash signatures and associated metadata. Numerical descriptors are generated for features found in a multimedia clip, signatures are generated from these descriptors, and a reference signature database is constructed from these signatures. Query signatures are also generated for a query multimedia clip. These query signatures are searched against the reference database using a fast similarity search procedure, to produce a candidate list of matching signatures. This candidate list is further analyzed to find the most likely reference matches. Signature correlation is performed between the likely reference matches and the query clip to improve detection accuracy.
Owner:ROKU INCORPORATED
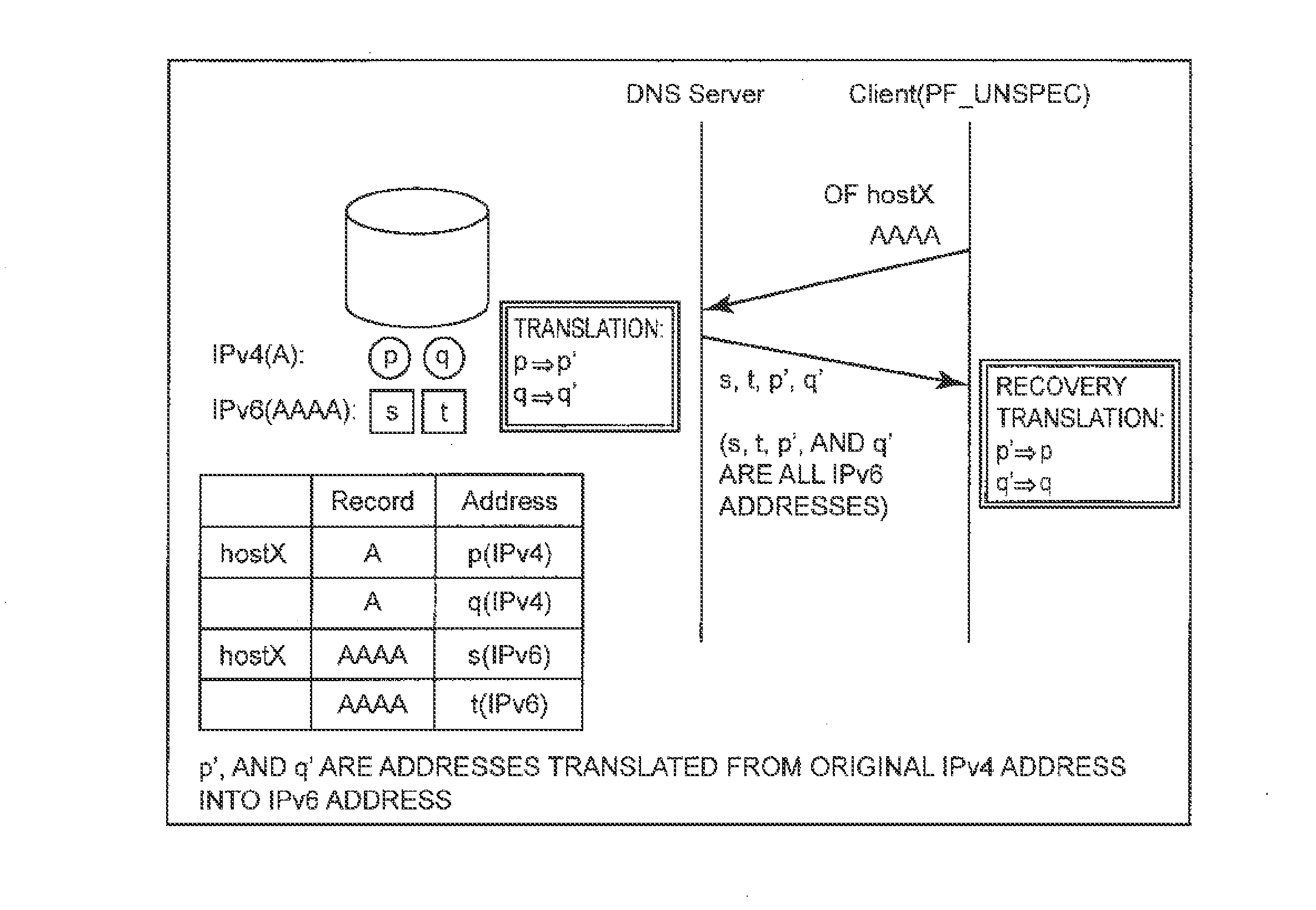
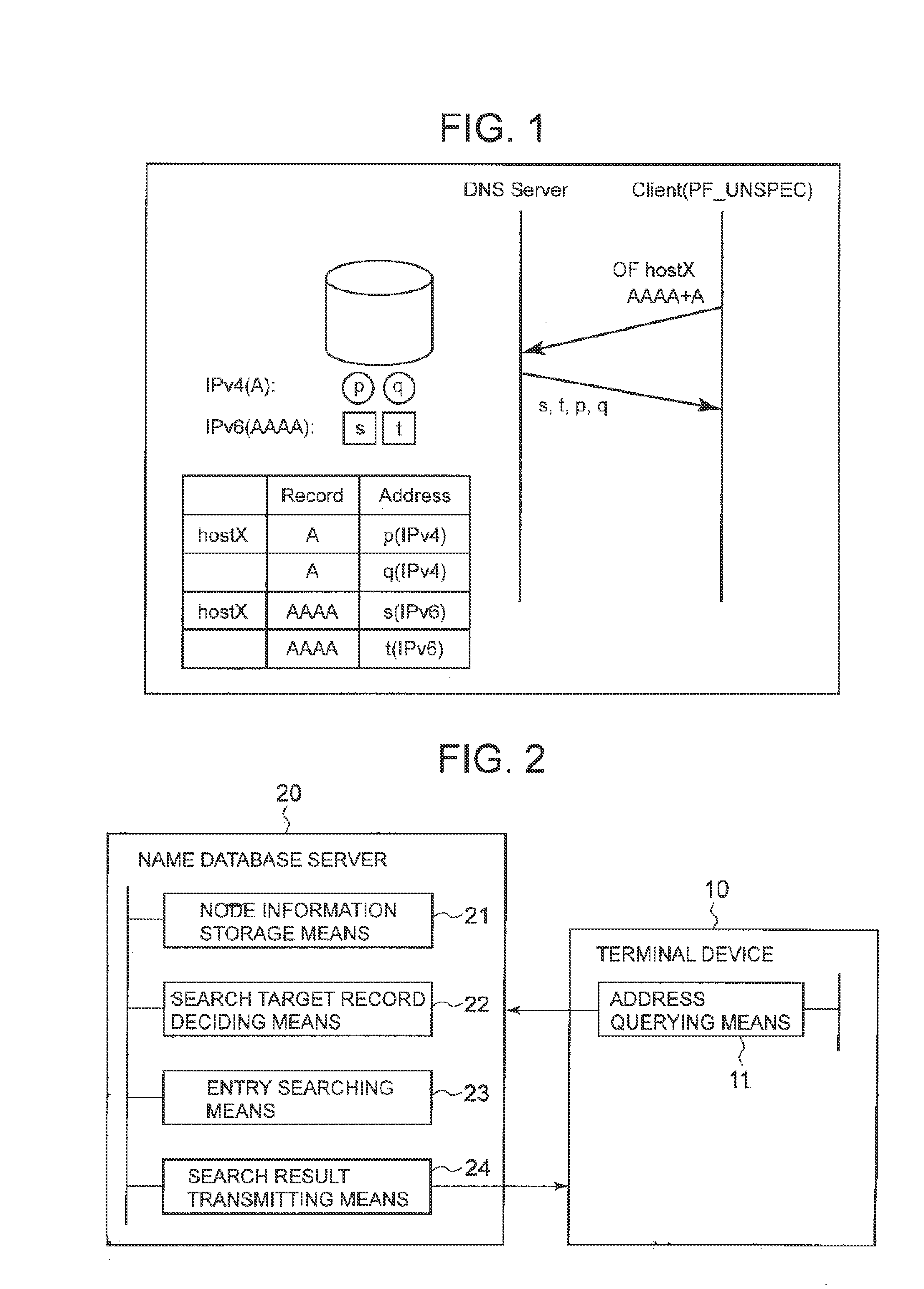
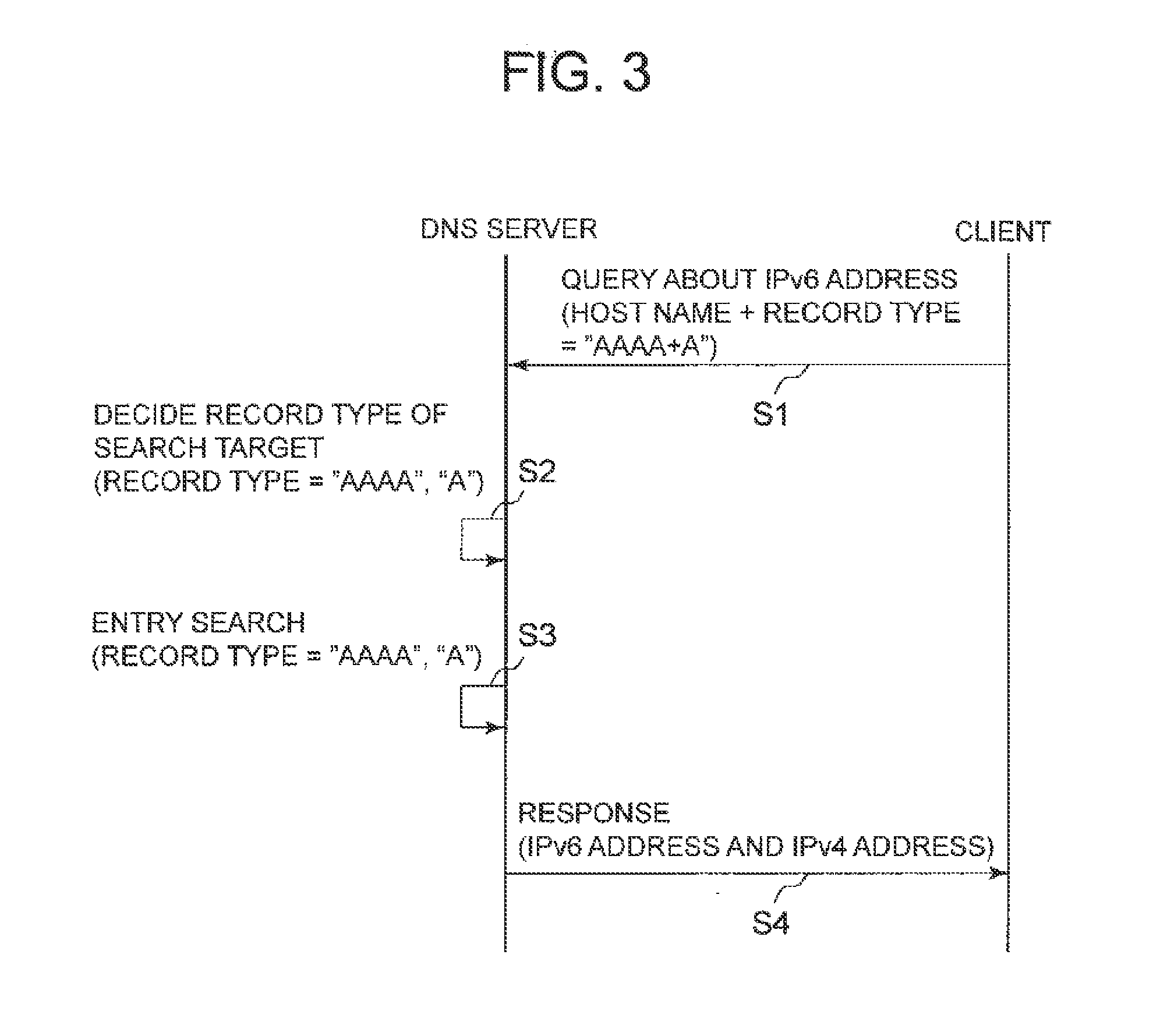
Name database server, name resolution system, entry search method and entry search program
ActiveUS20130191412A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDatabase serverTerminal equipment
A node information storage means stores an entry of node information in which at least an address and a record type are associated with a host name. A search target record deciding means decides a record type of an entry of a search target from a received virtual record type based on a search rule that is a rule specifying a record type of a search target according to a virtual record type. An entry searching means searches the node information storage means, and specifies an entry that corresponds to the entry specifying information received from the terminal device and has the record type decided by the search target record deciding means. A search result transmitting means transmits node information included in the entry specified by the entry searching means to the terminal device.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and apparatus for indexing, searching and displaying data
InactiveUS20060242564A1Simplifies research taskEasy to demonstrateData processing applicationsWeb data indexingSpatial OrientationsGraphics
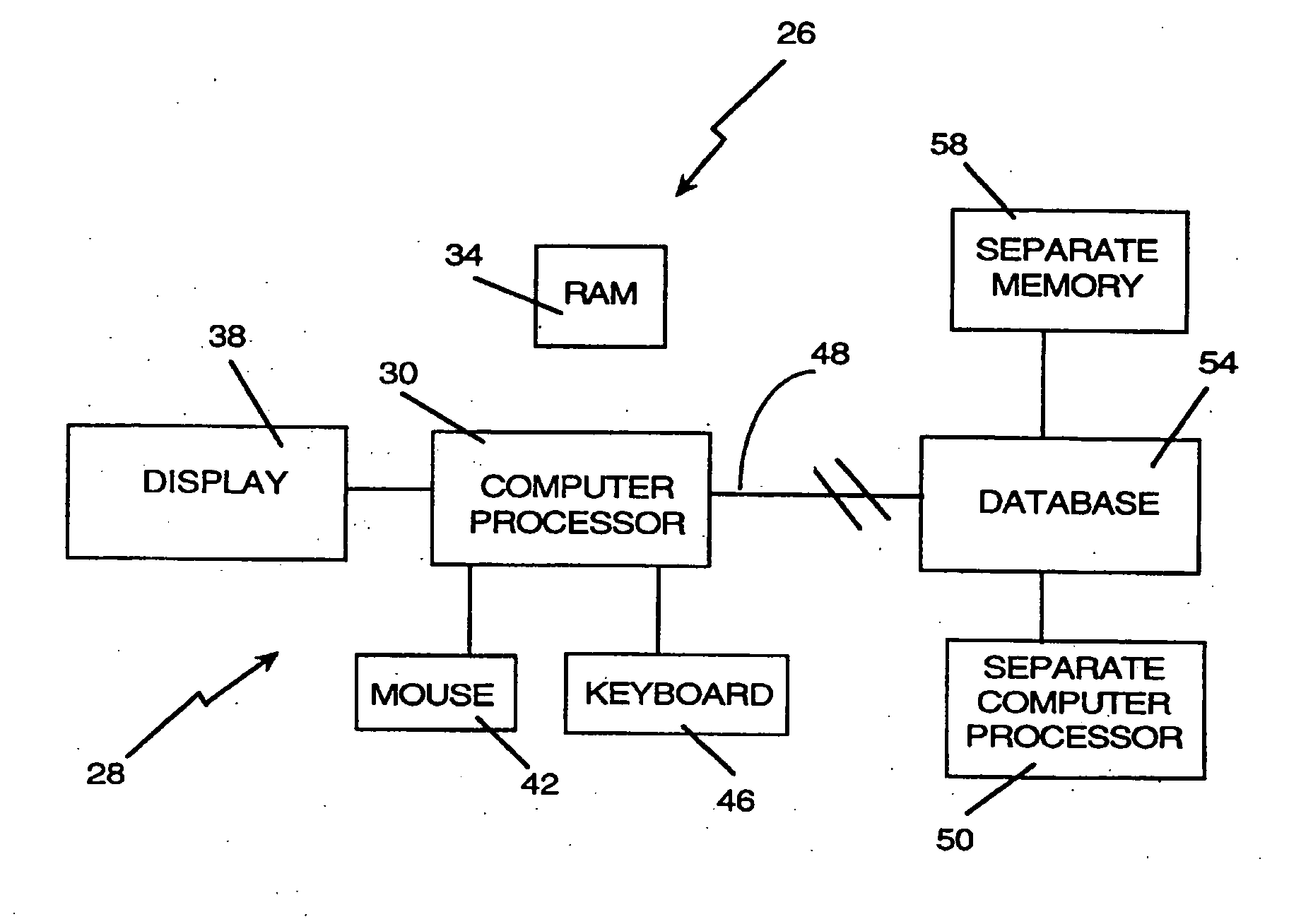
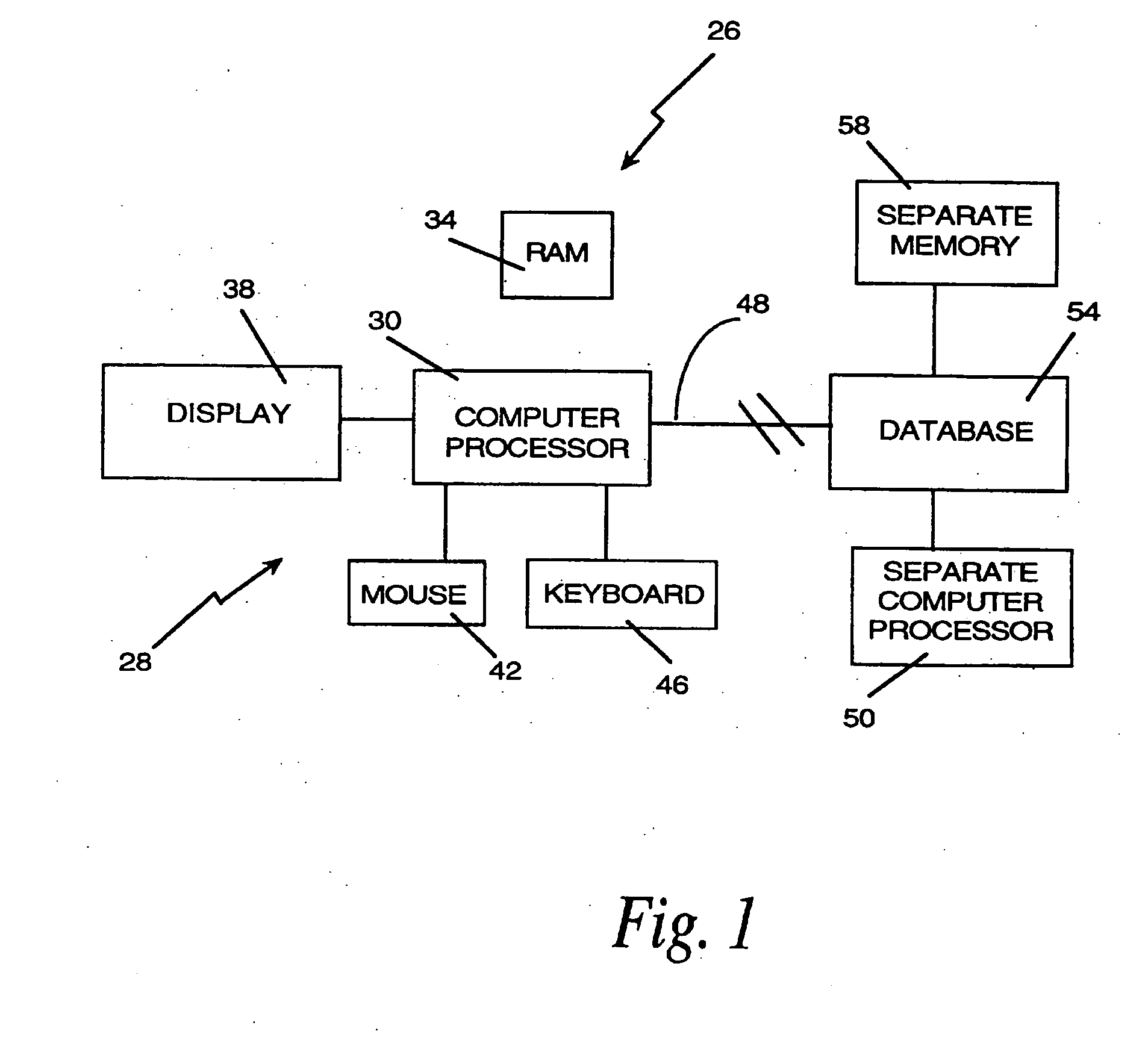
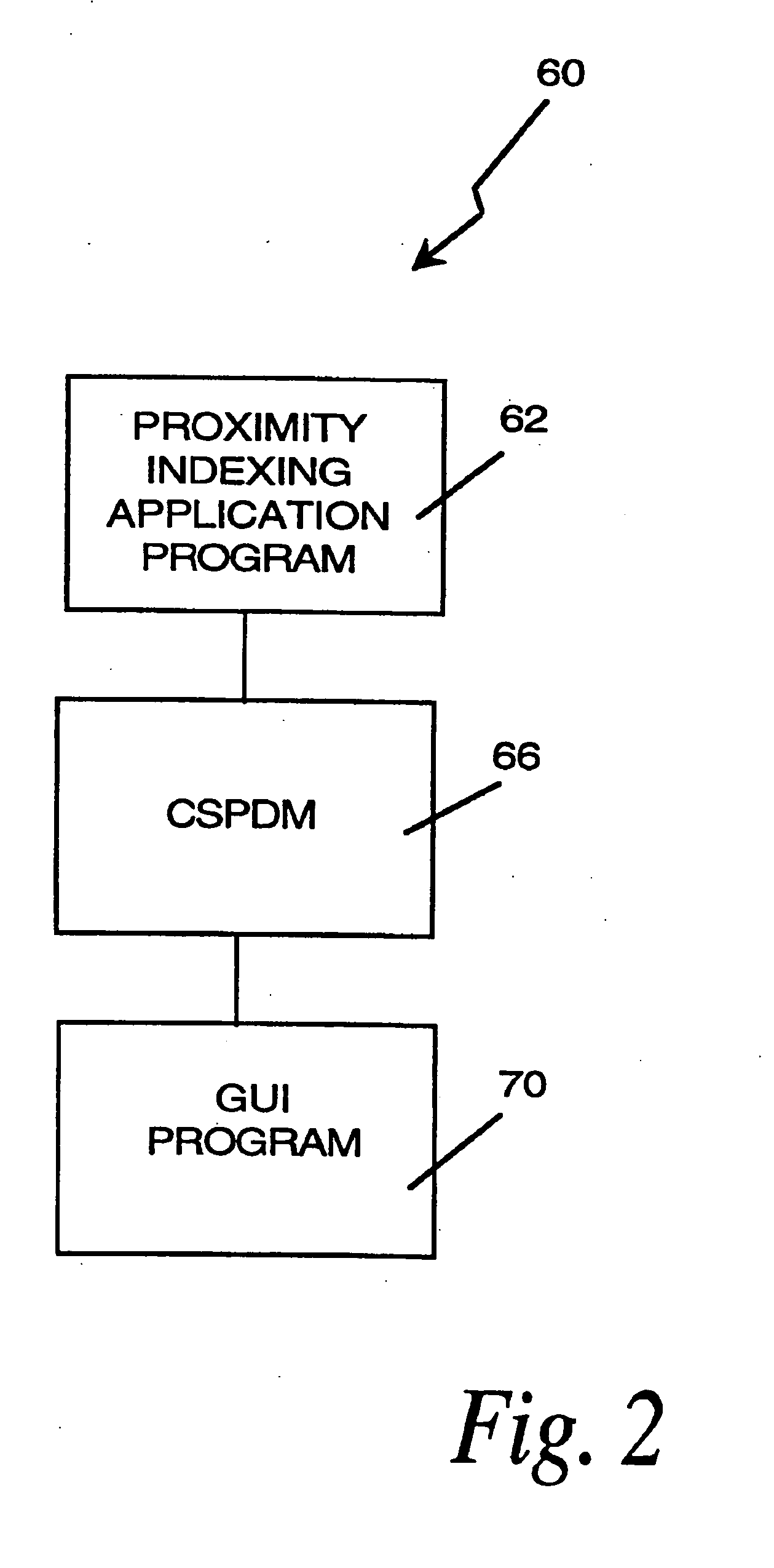
A computer research tool for indexing, searching and displaying data is disclosed. Specifically, a computer research tool for performing computerized research of data including textual objects in a database or a network and for providing a user interface that significantly enhances data presentation is described. Textual objects and other data in a database or network is indexed by creating a numerical representation of the data. The indexing technique called proximity indexing generates a quick-reference of the relations, patterns and similarity found among the data in the database. Proximity indexing indexes the data by using statistical techniques and empirically developed algorithms. Using this proximity index, an efficient search for pools of data having a particular relation, pattern or characteristic can be effectuated. The Computer Search program, called the Computer Search Program for Data represented in Matrices (CSPDM), provides efficient computer search methods. The CSPDM rank orders data in accordance with the data's relationship to time, a paradigm datum, or any similar reference. An alternative embodiment of the invention employs a cluster link generation algorithm which uses links and nodes to index and search a database or network. The algorithm searches for direct and indirect links to a search node and retrieves the nodes which are most closely related to the search node. The user interface program, called the Graphical User Interface (GUI), provides a user friendly method of interacting with the CSPDM program and prepares and presents a visual graphical display. The graphical display provides the user with a two or three dimensional spatial orientation of the data.
Owner:LIBERTECH
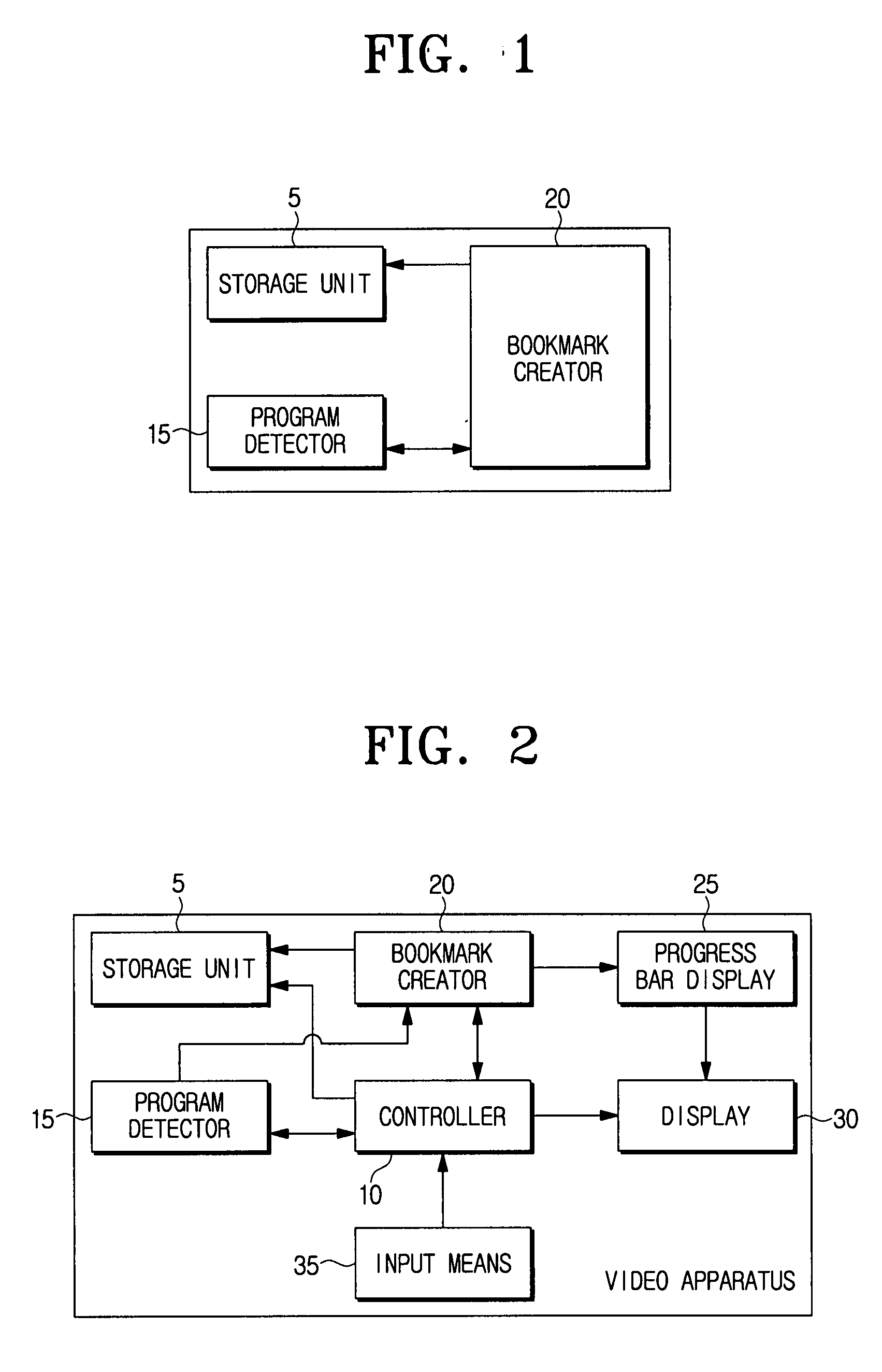
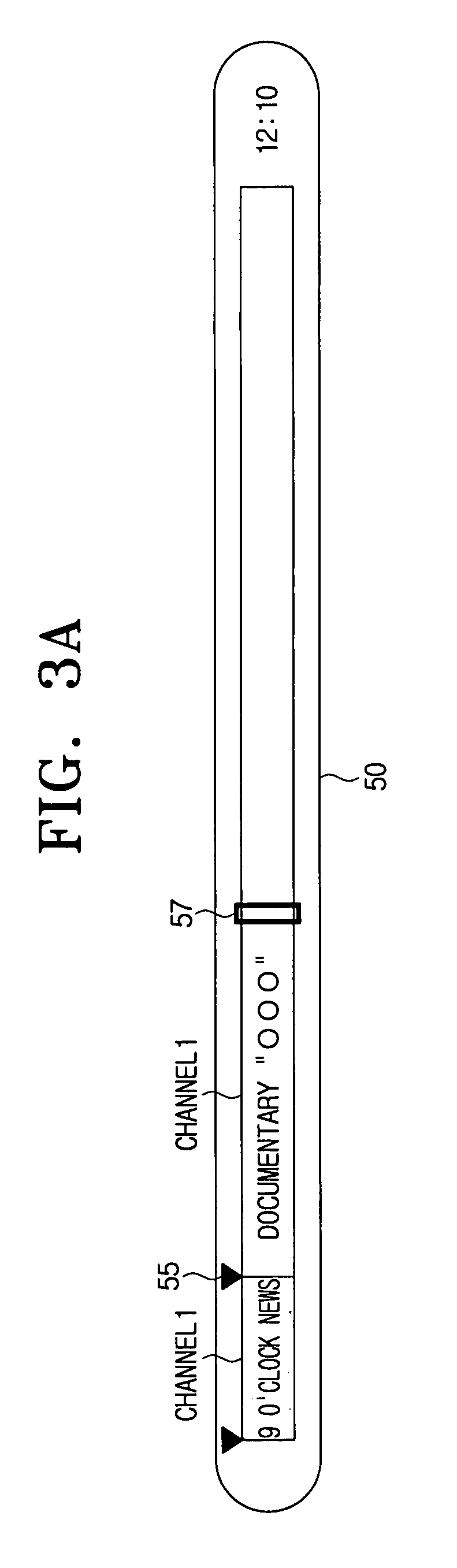
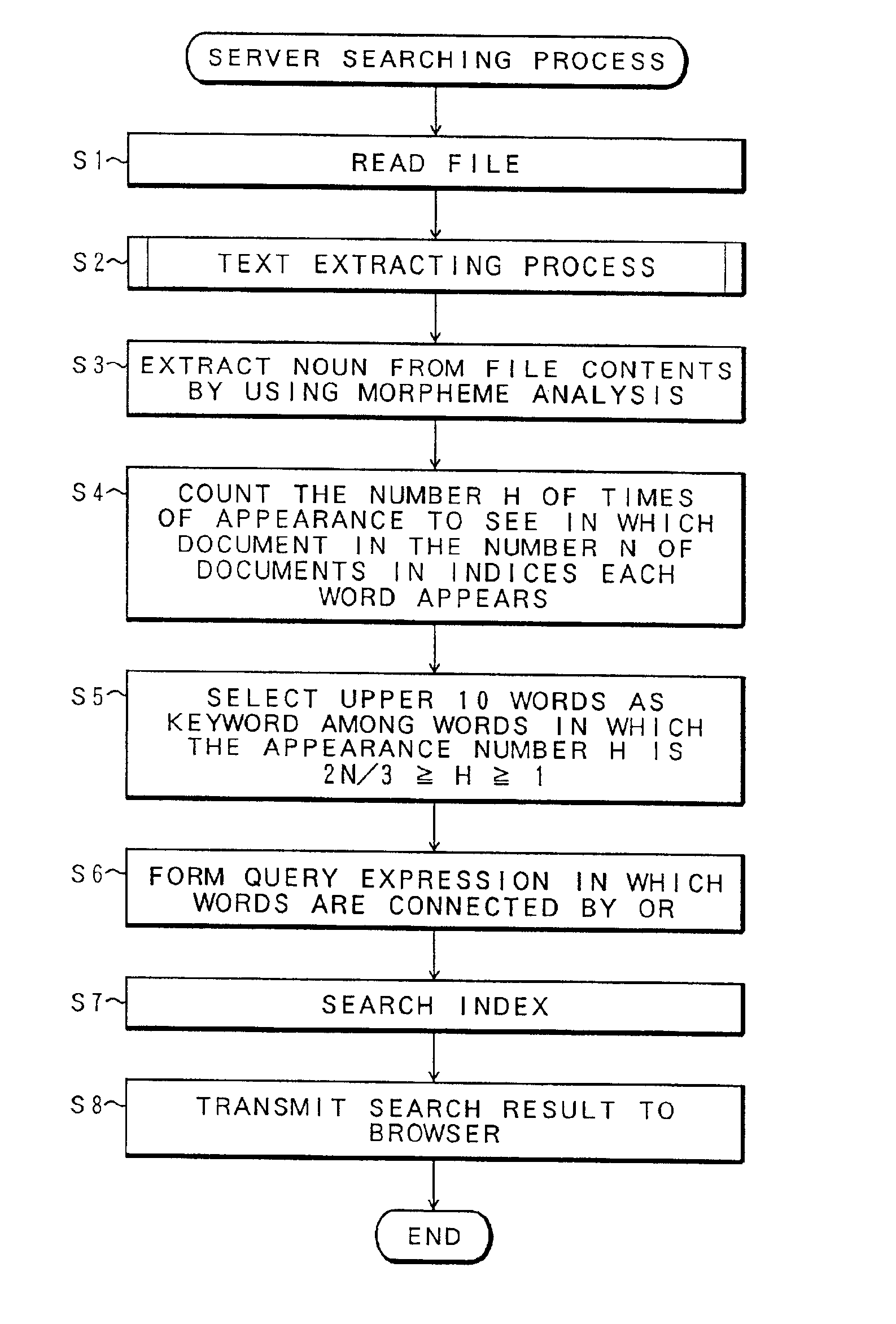
Video apparatus having bookmark function for searching programs and method for creating bookmarks
InactiveUS20080104534A1Easy searchTelevision system detailsDigital data information retrievalProgramming languageVideo equipment
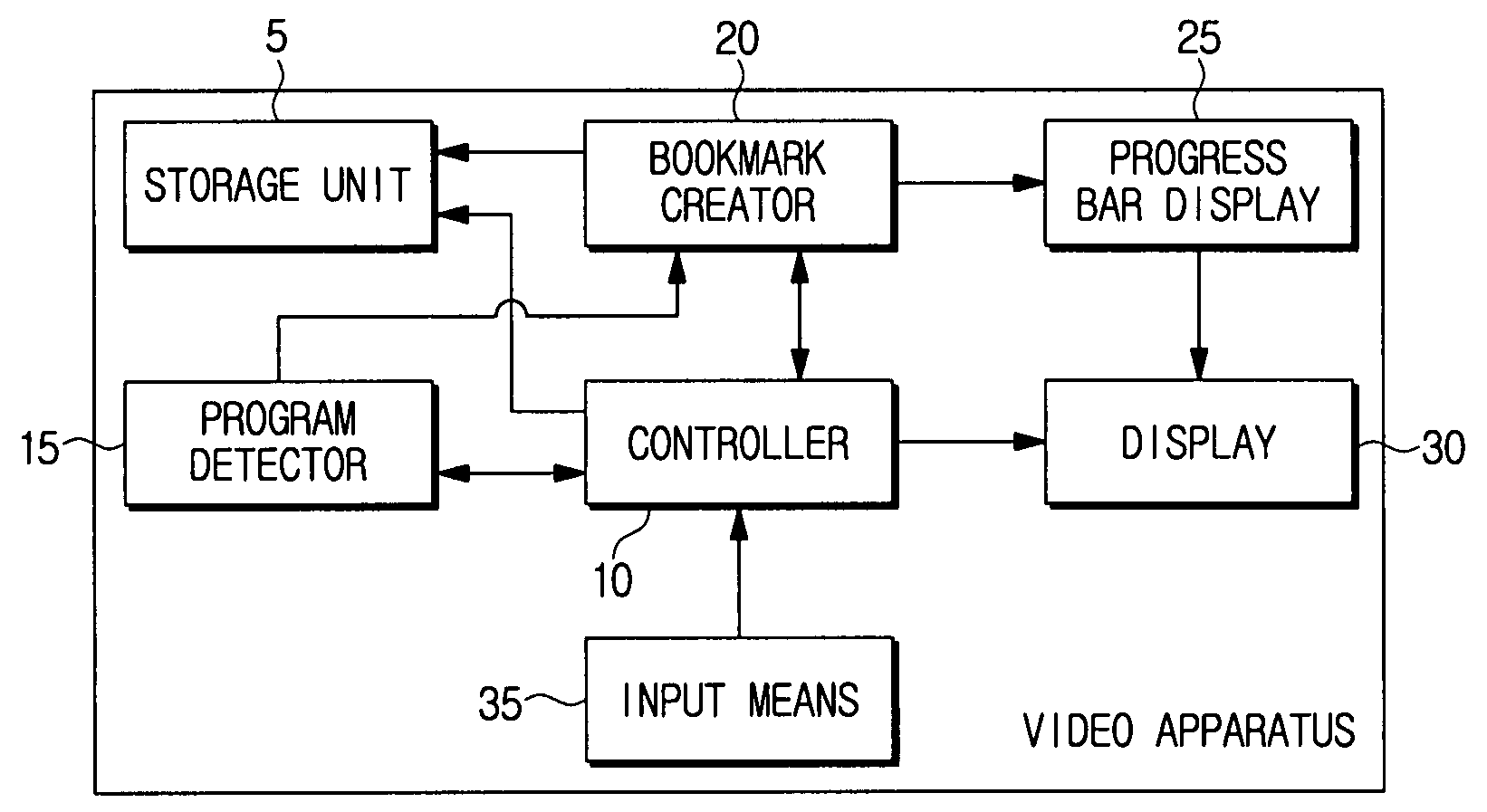
A video apparatus having a bookmark function for searching a program, and a method for creating a bookmark are provided. The video apparatus includes a storage unit which stores at least one program, a program detector which detects whether the program changes, and a bookmark creator which creates a bookmark at a point where the program changes, and stores the created bookmark in the storage unit if the program detector detects the program change. Accordingly, a bookmark is automatically created at the start position of the program, and thus, each of the stored programs can be easily played back using the bookmark and it is possible to play back the program from the beginning.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
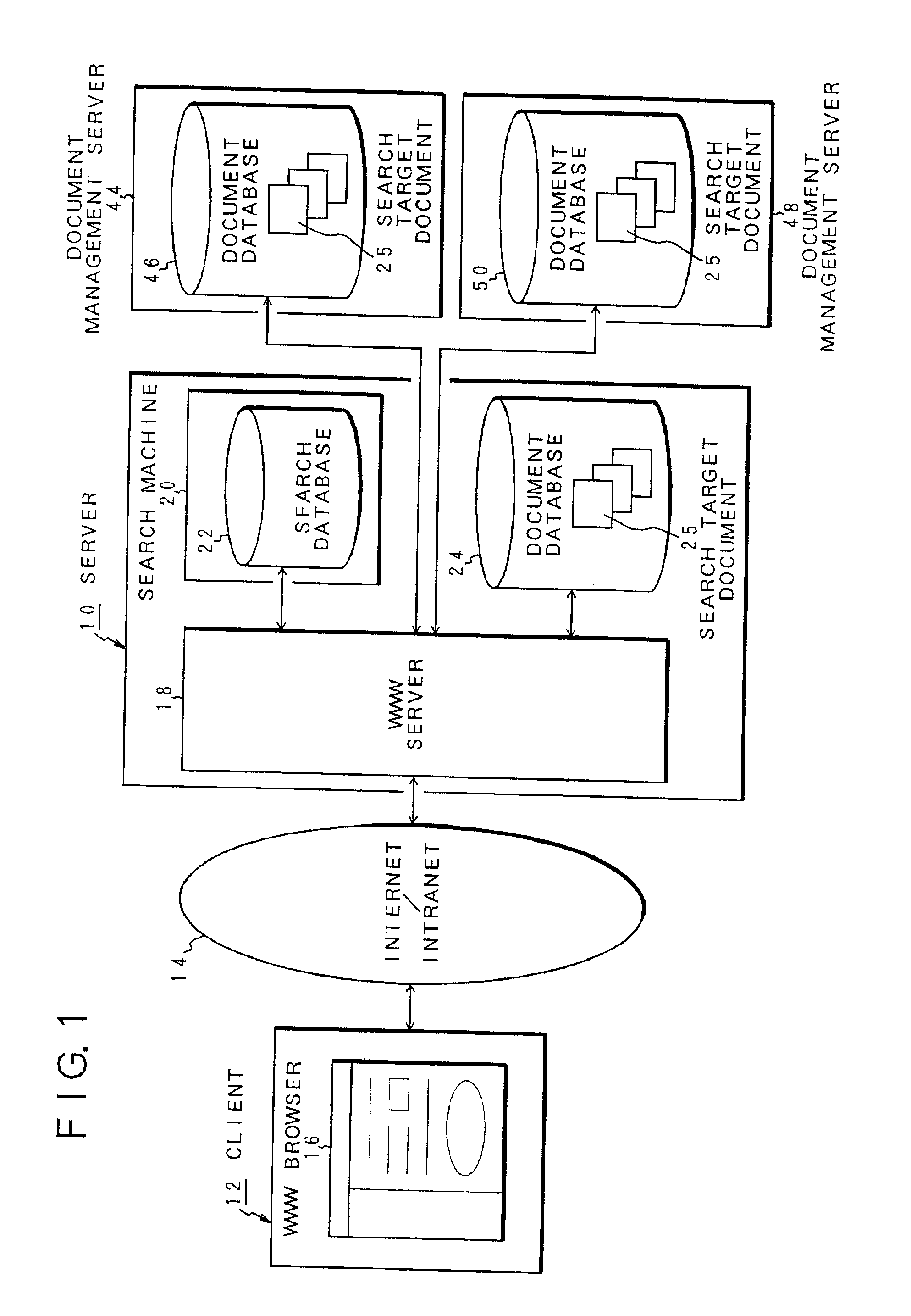
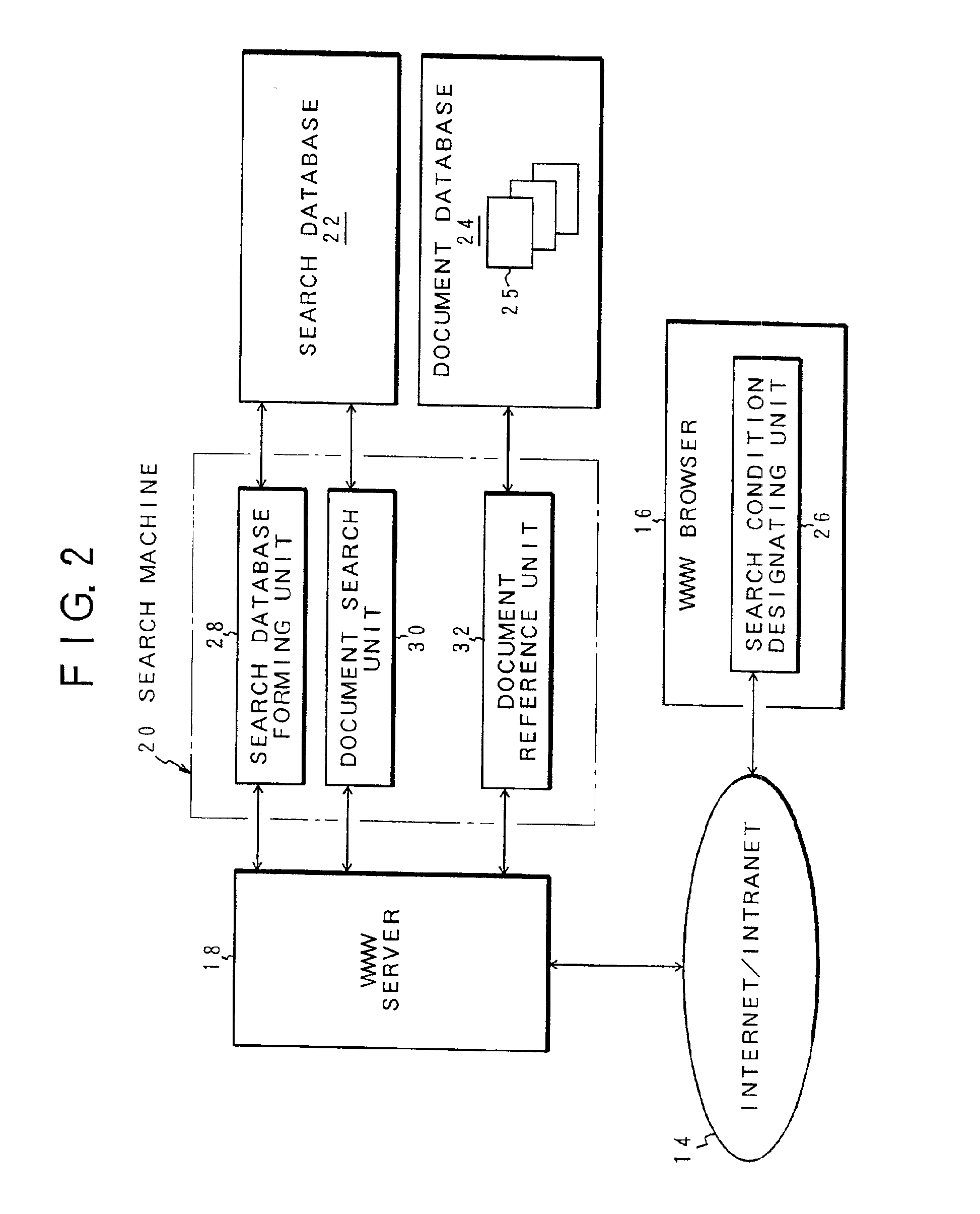
Document information search apparatus and method and recording medium storing document information search program therein
InactiveUS6883001B2Easily and promptly searchedMetadata text retrievalData processing applicationsInformation searchingClient-side
An apparatus for searching document information in response to a search request from a client is disclosed. When a document file is designated as a search condition by a search condition designating unit of the client, the unit causes contents of the designated file to be transmitted via a network. A document search unit of a search machine forms a keyword based on the file contents transmitted from the search condition designating unit, and searches similar documents from an index or selection of important words extracted from search target documents provided in a search database.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
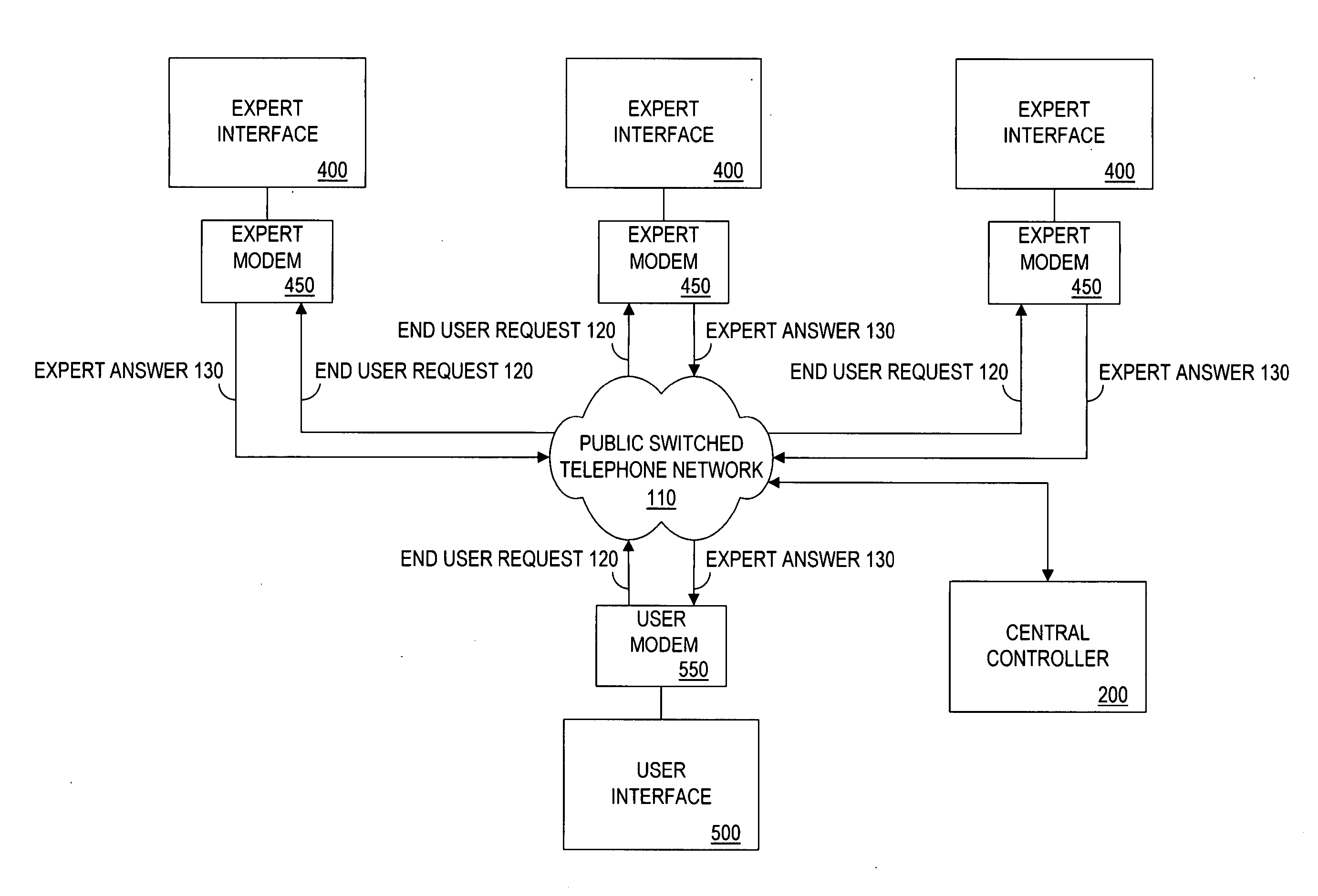
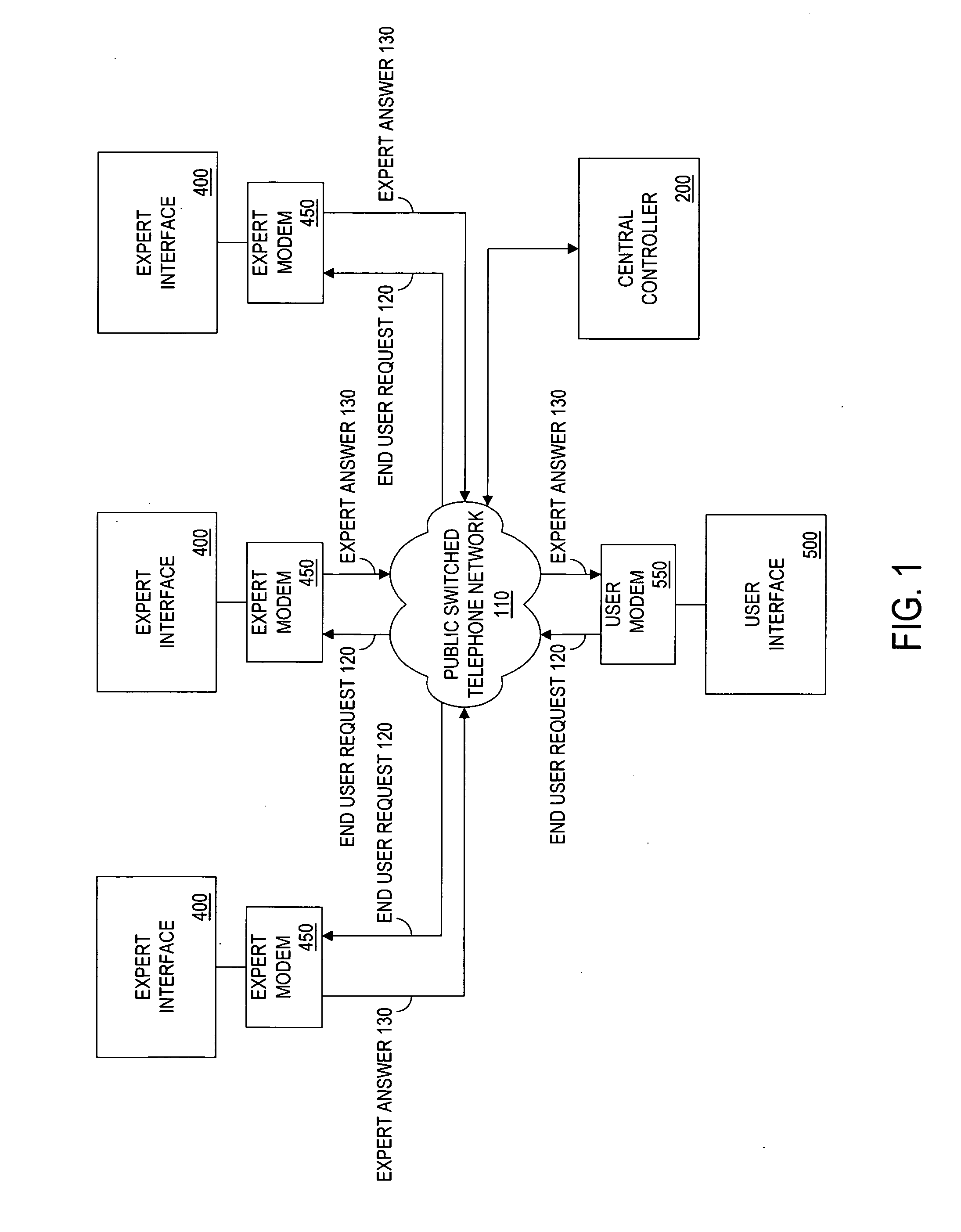
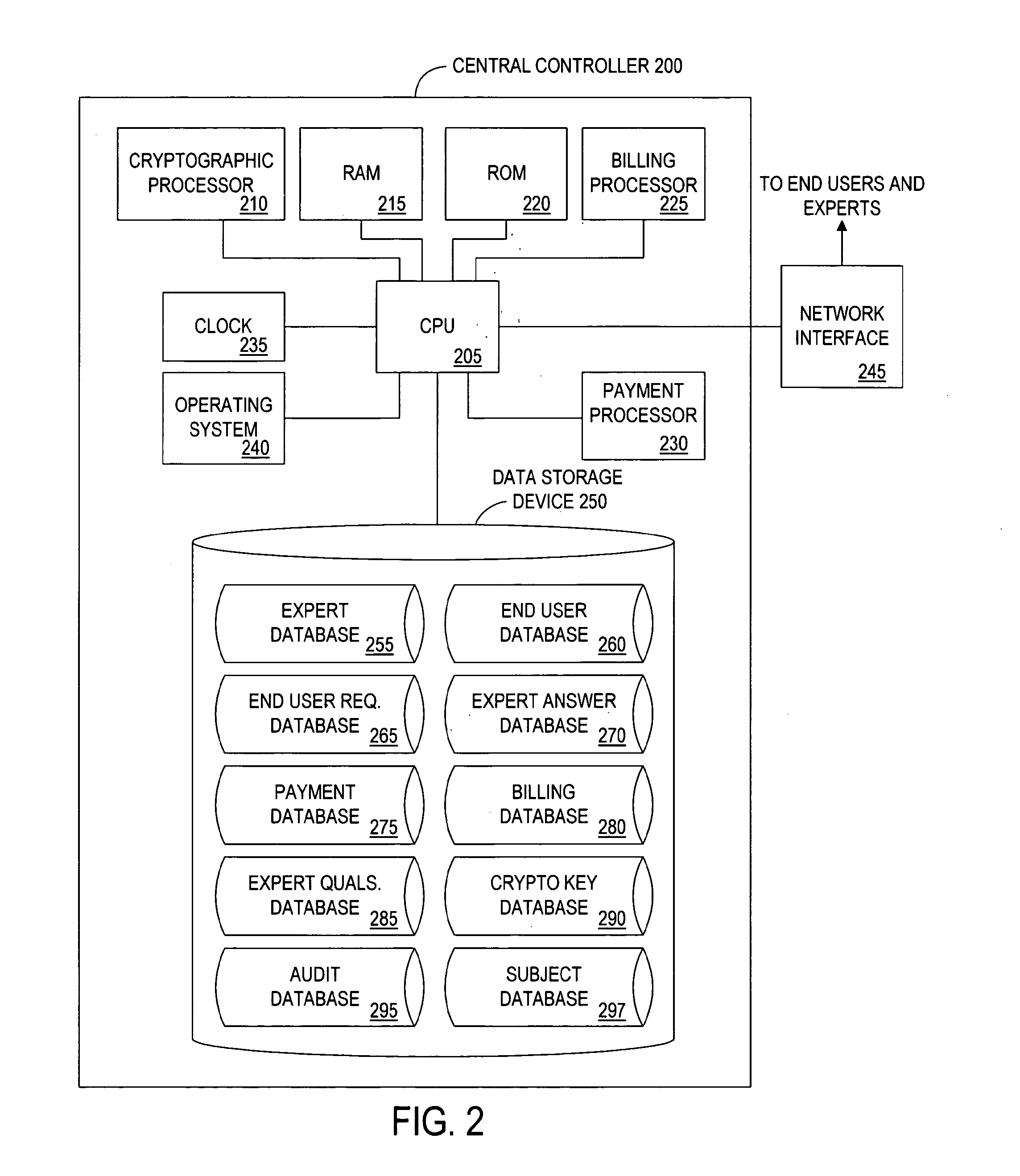
Method and apparatus for a cryptographically-assisted commerical network system designed to facilitate and support expert-based commerce
InactiveUS20130013362A1Ensure integrityFinanceBroadcast components for monitoring/identification/recognitionNetworked systemThe Internet
The present invention is an expert matching method and apparatus for managing communications between an expert having particular qualifications and an end user seeking a solution to an expert request. In a preferred embodiment, the apparatus of the present invention includes a controller having a database for storing expert qualifications. In one embodiment, the controller receives an expert request. A search program identifies experts qualified to respond to the expert request. The expert request is then transmitted to the expert, which results in an expert answer transmitted to and received by the central controller. After authentication of the expert answer, using a wide range of security levels from passwords to cryptography, the answer is forwarded to the end user. The method and apparatus of the present invention have applications on the Internet as well as conventional voice telephony systems.
Owner:COMMUNITY UNITED IP
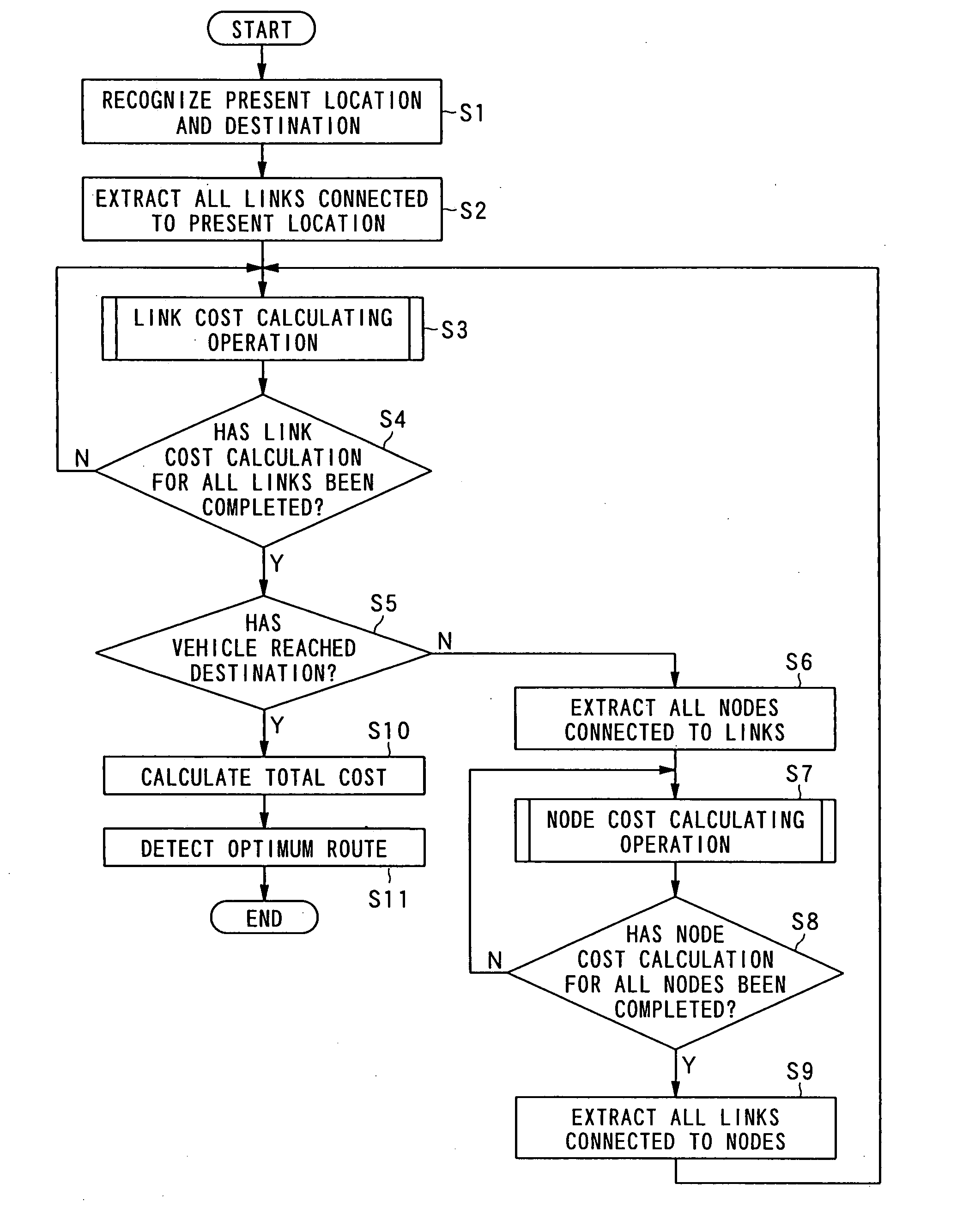
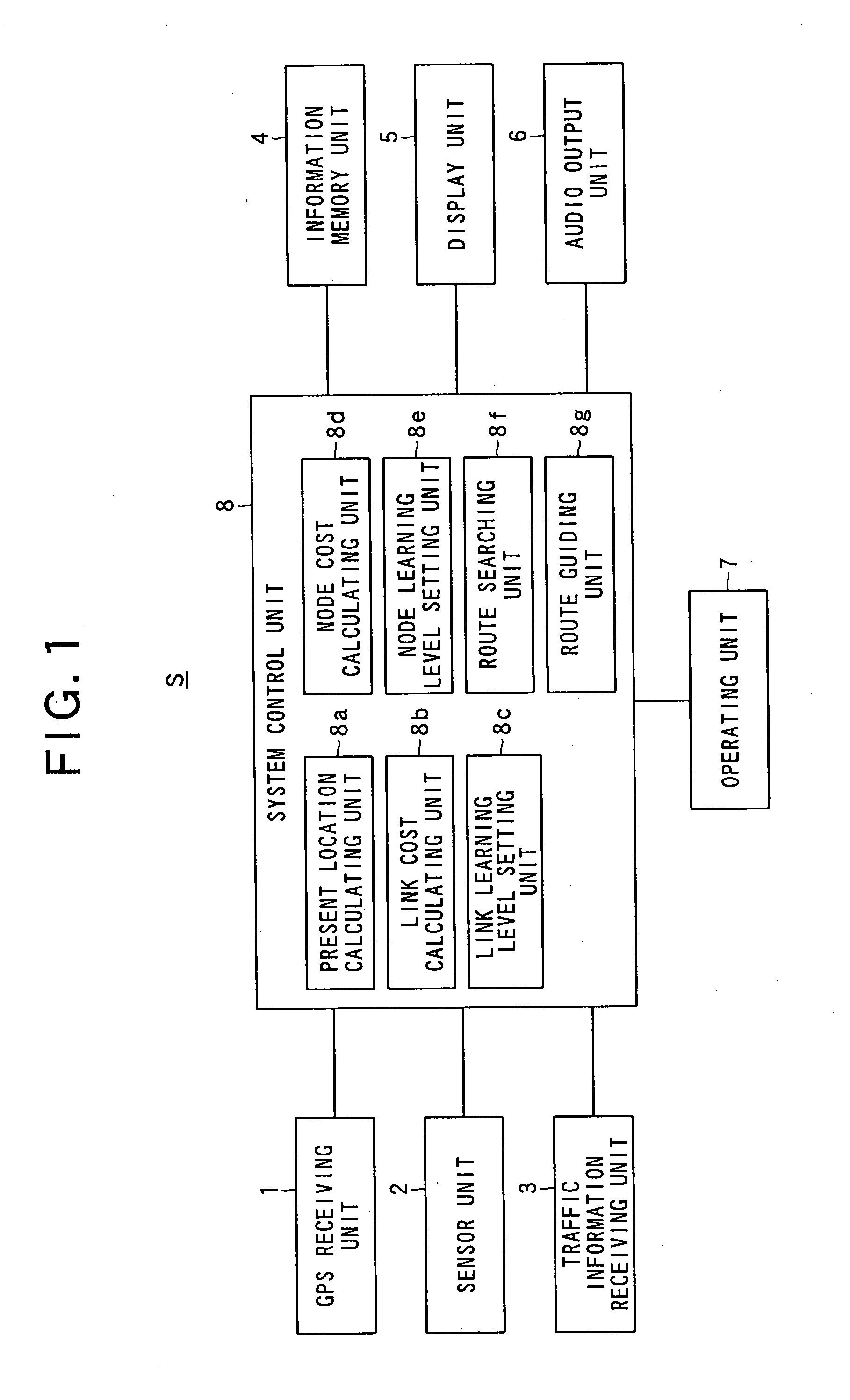
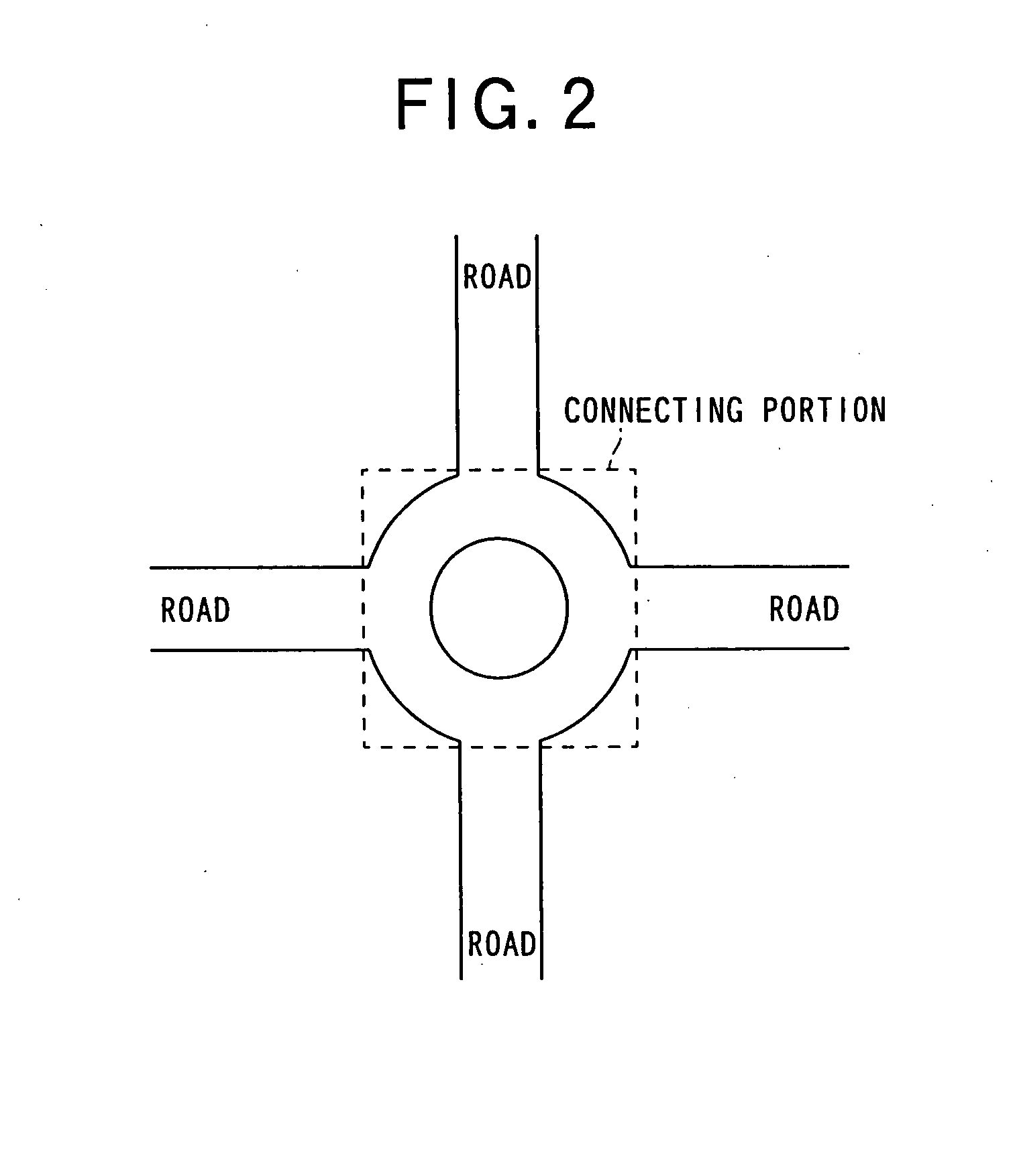
Route Searching Device, Route Searching Method, and Route Searching Processing Program
InactiveUS20080114542A1Improve accuracyEliminate disadvantagesInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlRoute searchOptimum route
The present invention provides a route searching device that can detect an optimum route with higher precision, a route searching method, and a route searching program.The route searching device detects an optimum route among possible routes from a first point to a second point, on the basis of link costs that are set for a plurality of links constituting the possible routes. The route searching device makes at least one of a determination on whether there is a restricting element for restricting the movement of a movable body at the time of moving from the road corresponding to one link to the road corresponding to another link via the connecting portion corresponding to a node to which at least two links are connected, a determination on the number of links connected to the node, a determination on the shape formed with the roads corresponding to the links connected to the connecting portion corresponding to the node, a determination on attributes of at least one of the roads corresponding to the links connected to the node, and a determination on the conditions of the roads. The route searching device then acquires a node cost that represents the difficulty of the movement from the road corresponding to the one link to the road corresponding to the another link, the node cost being in accordance with one or a combination of two or more of factors including the existence of a restricting element, the number of connected links, the shape formed with the roads corresponding to the links, the attributes of the roads, and the conditions of the roads, the factors being on the basis of the determination results of the determining means. On the basis of the link cost and the acquired node cost, the route searching device searches for the optimum route.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Efficient navigation of autonomous carriers
InactiveUS20040117079A1Reduce complexityReduce stepsSuction cleanersDistance measurementComputation complexityEngineering
According to the invention, autonomous carriers or vehicles are efficiently navigated over a field of operation. The carriers are equipped to execute a selected procedure at more than one desired location on the field, and the navigation system of the invention directs the carrier to the location that is preferentially accessible to it, based on a defined criterion. After the carrier has executed the selected procedure at the location which is preferentially accessible to it, the navigation system directs the carrier to the location which is preferentially accessible to the carrier from the carrier's new position. This procedure is repeated until all the locations at which the procedure is to be executed have been reached. The task of determining a navigation route to a location that can be preferentially accessed is based on an efficient, structured search procedure of low computational complexity.
Owner:AB ELECTROLUX
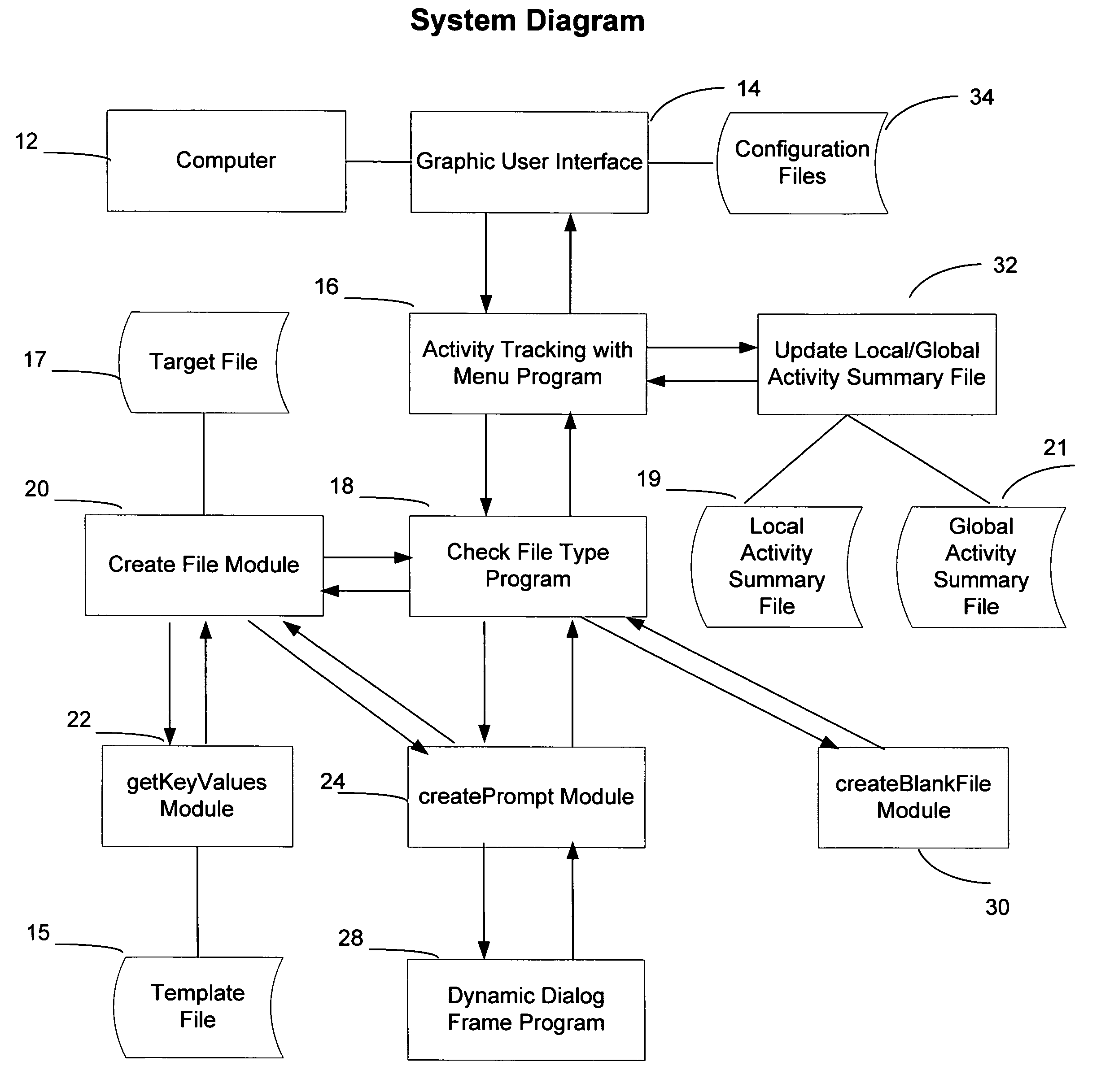
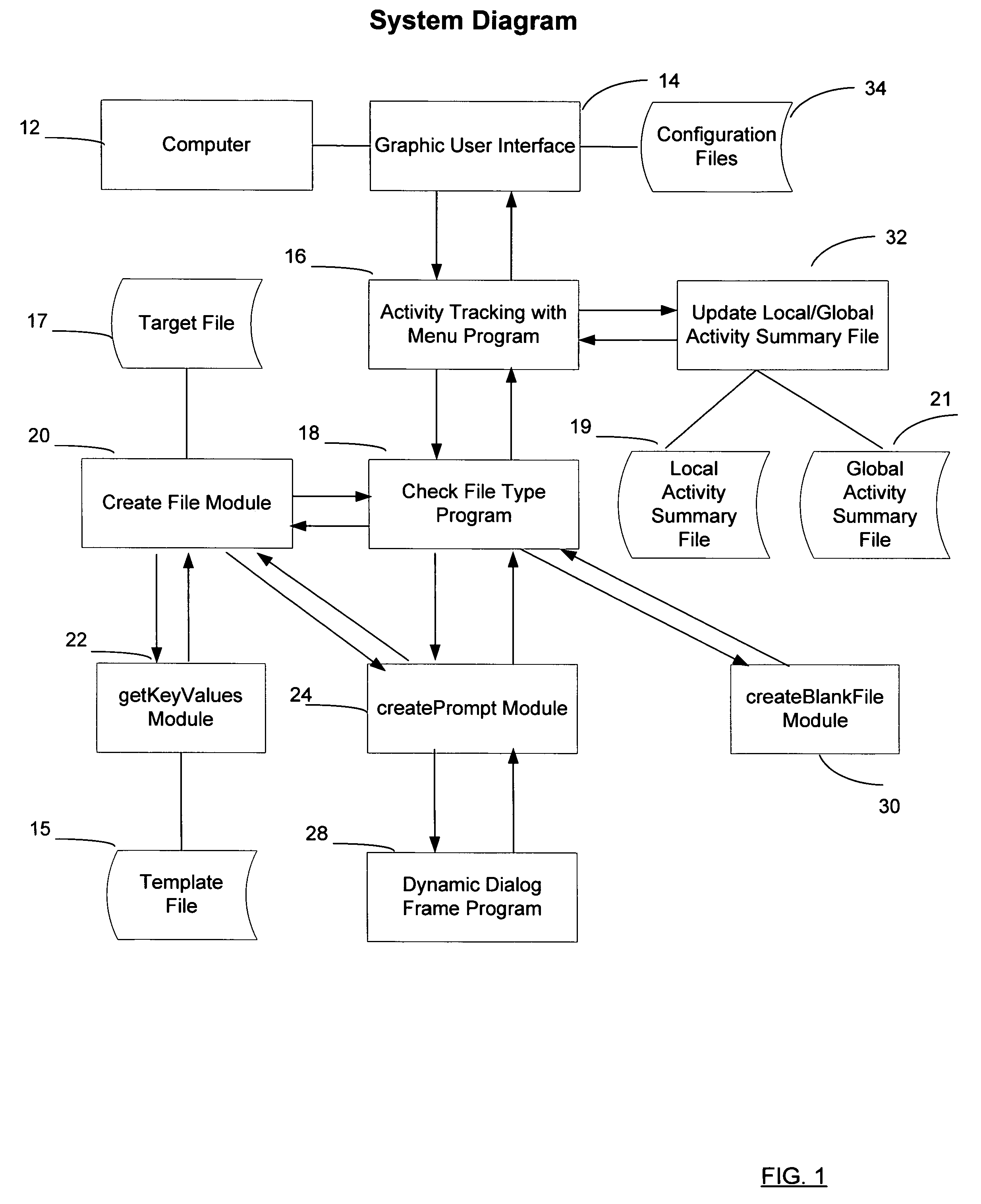
Dynamic generation of target files from template files and tracking of the processing of target files
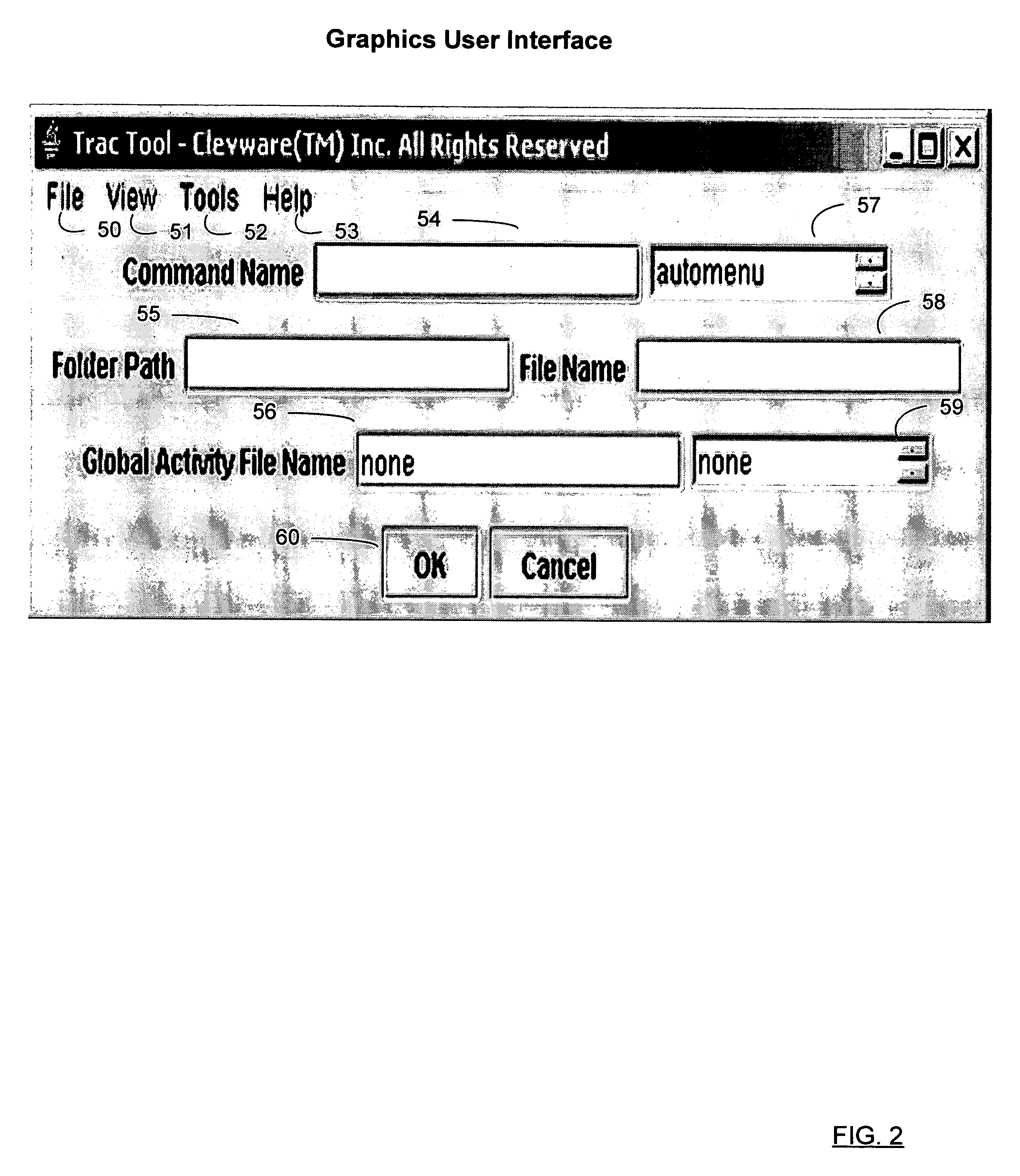
ActiveUS7320007B1Easily includedEasy to trackData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsGraphicsComputer users
A target file generation system and method for use by ordinary computer users to readily generate target files. The program includes various components. The first component promps for and receives user's selections of a folder or directory location where a new target file will reside, of an operating system command or application program that will process this new target file, of an optional global activity summary data repository that stores user'summaries of the processing of the target file. The second component dynamically generates an information exchange user interface that prompts for and receives input data provided by the user on information of menu configuration file and name of template file. The third component dynamically generates an information exchange user interface. The fourth component provides graphics user interfaces to start a menu program, a a merge programe, and a search program, respectively.
Owner:KNAPP INVESTMENT
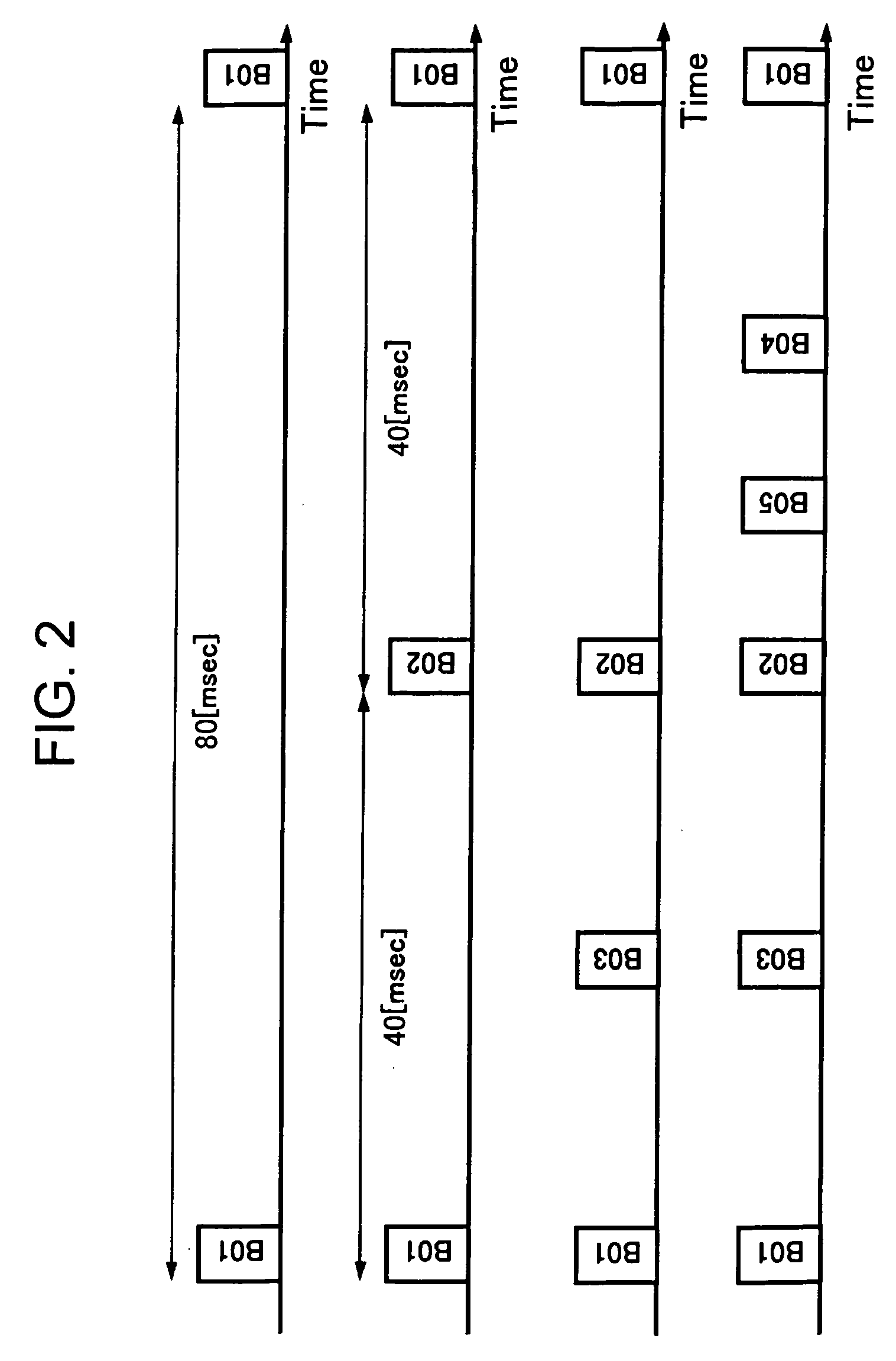
Wireless communication system, wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication method and computer program
ActiveUS20050243782A1Avoid mutual interferenceGuaranteed bandwidthNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionCommunications systemTime zone
The present invention eliminates a transmission-waiting operation which is unnecessary while accommodating a prioritized traffic. Although a communication station enters a transmission-disallowed state in response to detection of a signal addressed to another station in accordance with medium access control based on CSMA, if the communication station receives a frame transmitted with priority to a local station during the transmission waiting, it cancels the transmission-disallowed state, sends back a frame responding the frame transmitted with priority and effectively operates a transmission prioritized period. The communication station starts a search procedure to perform a processing of evading duplication of the transmission prioritized periods if it judges a possibility of a problem occurring in a time zone in which reception with priority is possible.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Node-search method, device, and medium on which a node-search program is recorded
InactiveUS7009941B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationBroadcast packetDomain name
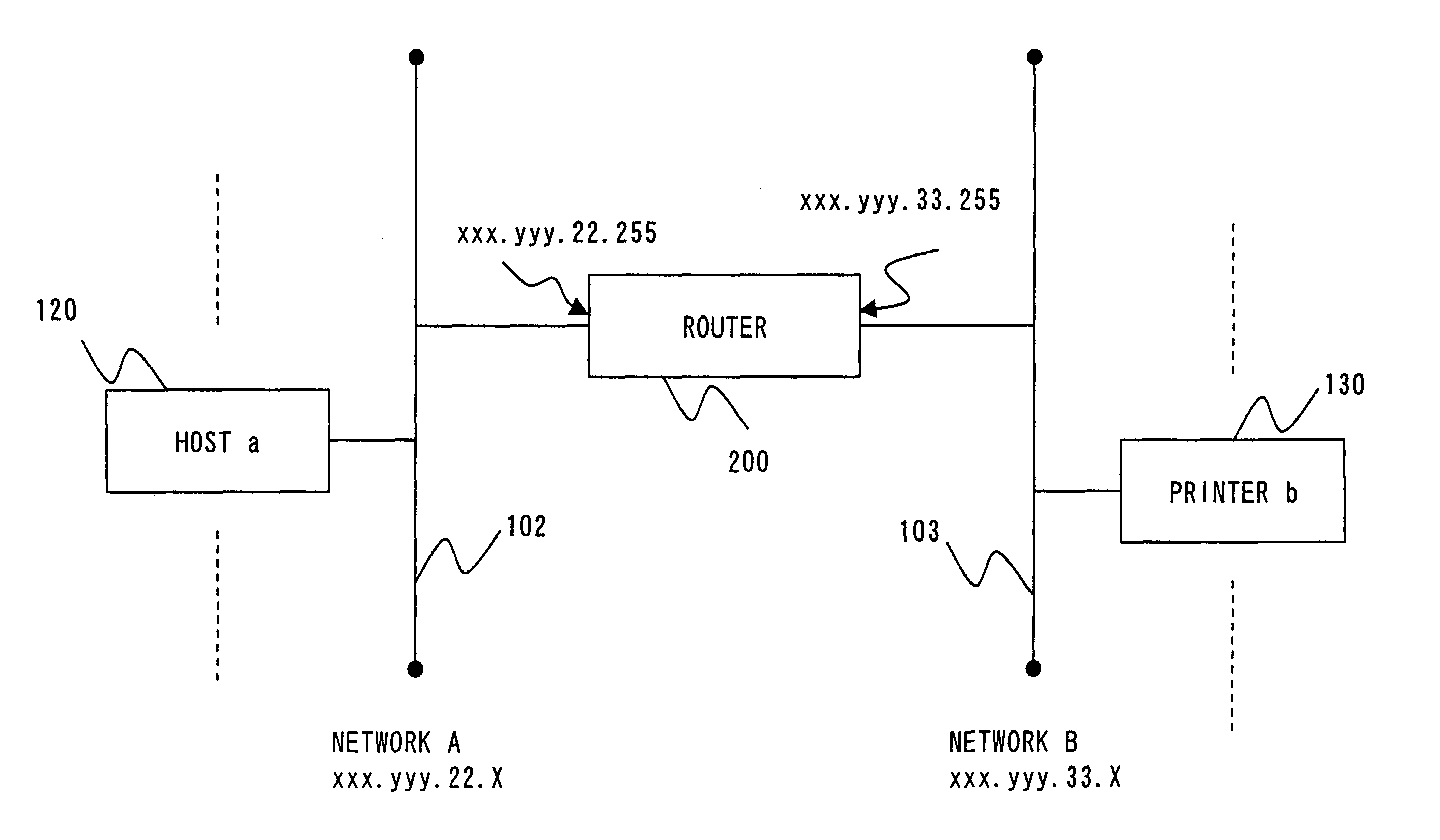
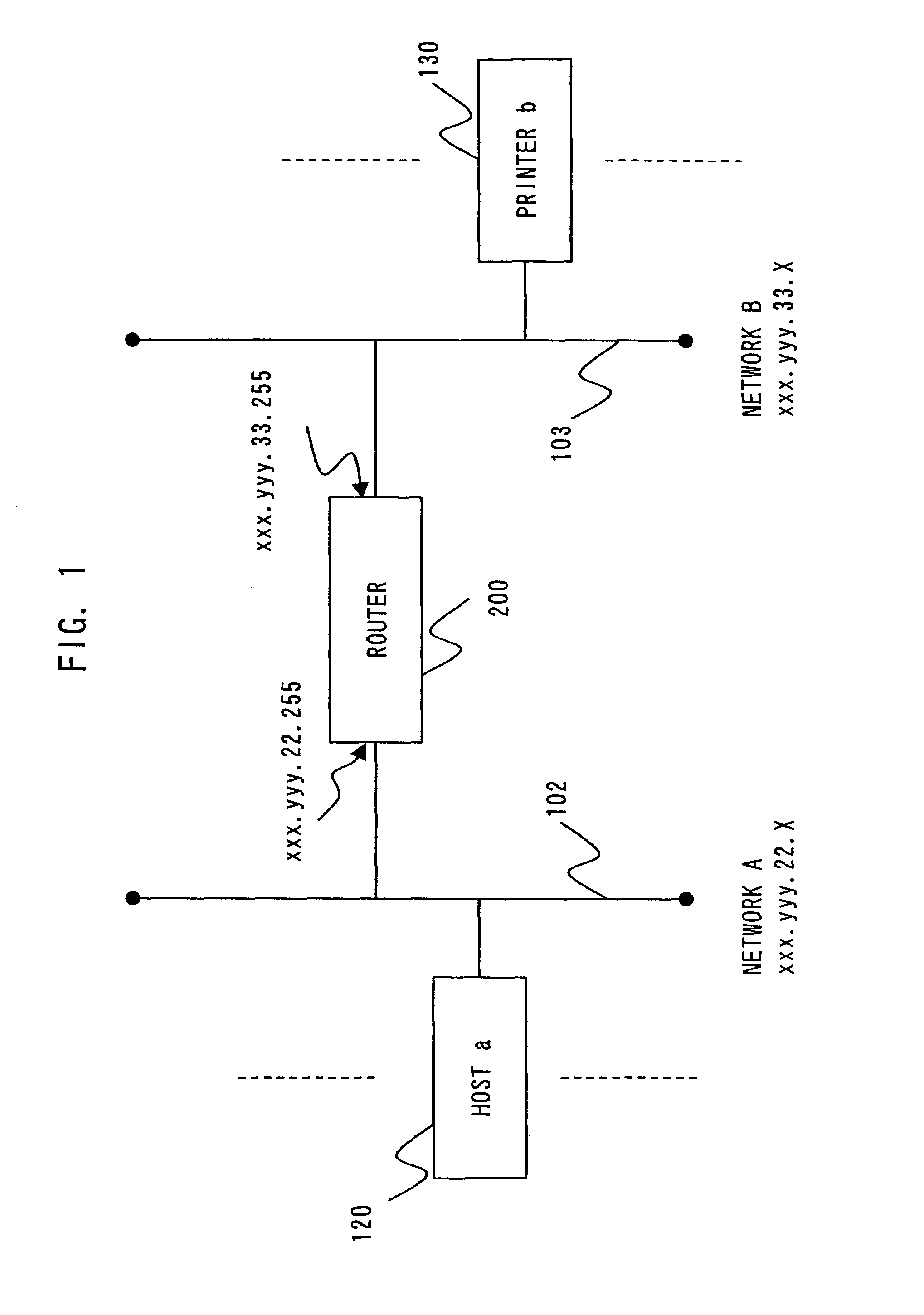
There are disclosed a method and device for searching equipment, such as a printer, connected to a network through a router by using a broadcast packet are disclosed. A host 110 acquires routing information from a router 200. The host 110 analyzes a domain name of a sub network B103 in the routing information so as to acquire a broadcast address in the domain, then, send a broadcast packet requesting a printer name addressed to the broadcast address through the router 200. The host 110 searches a printer 120 by receiving a response packet for the broadcast packet.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Wireless communication system, wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication method and computer program
ActiveUS7664130B2Eliminate operationEffective bandwidthNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionCommunications systemTime zone
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC
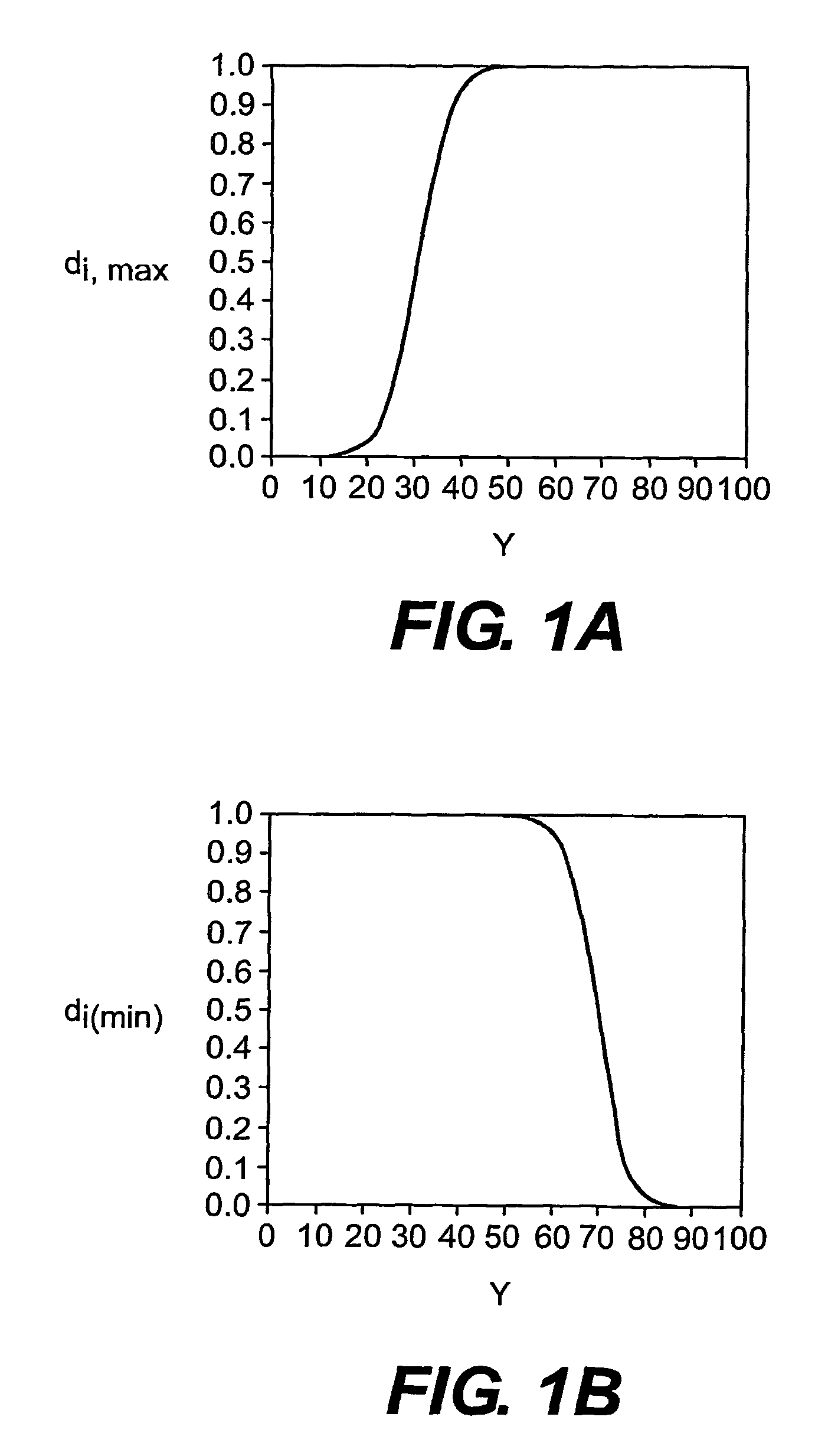
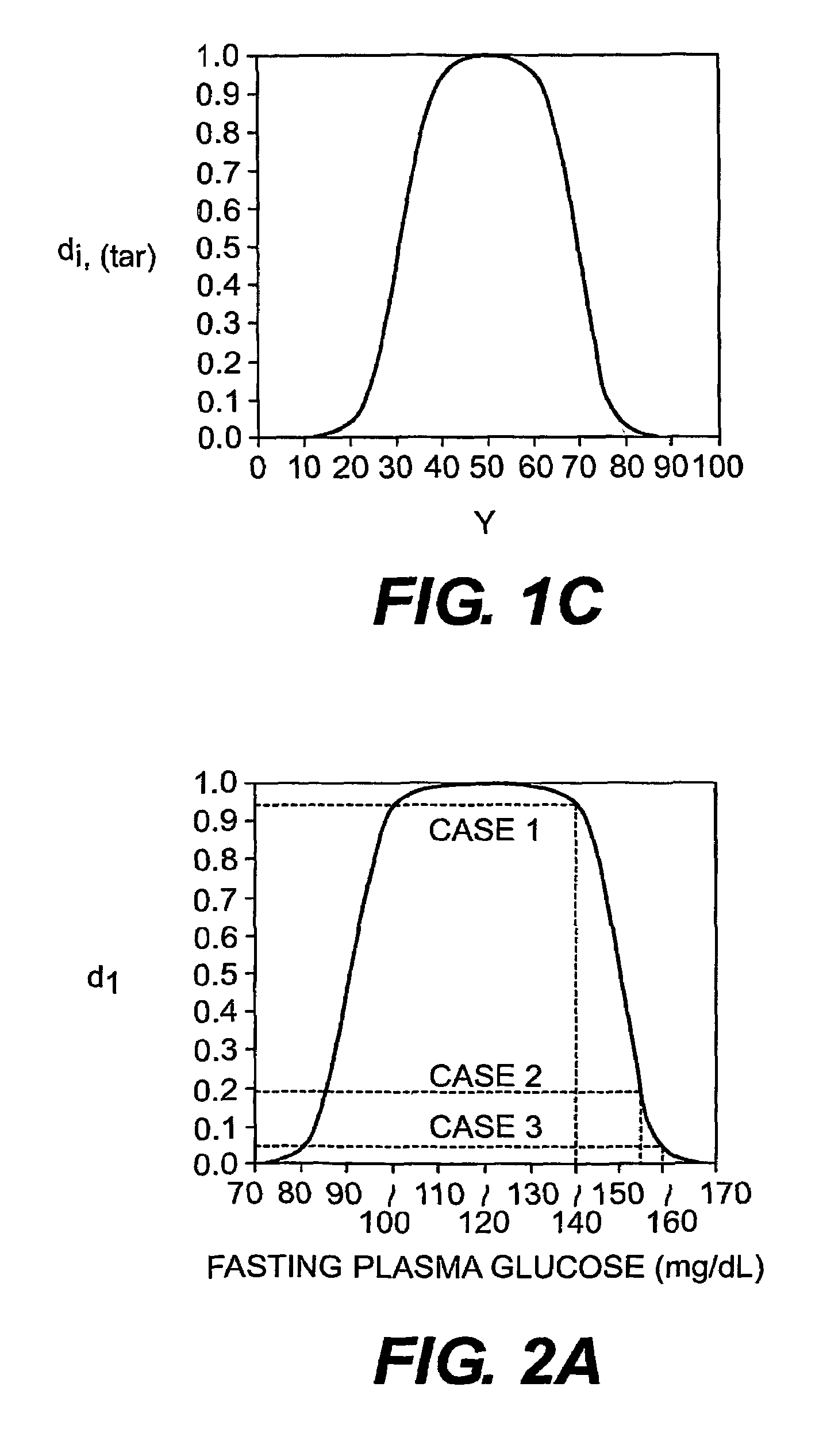
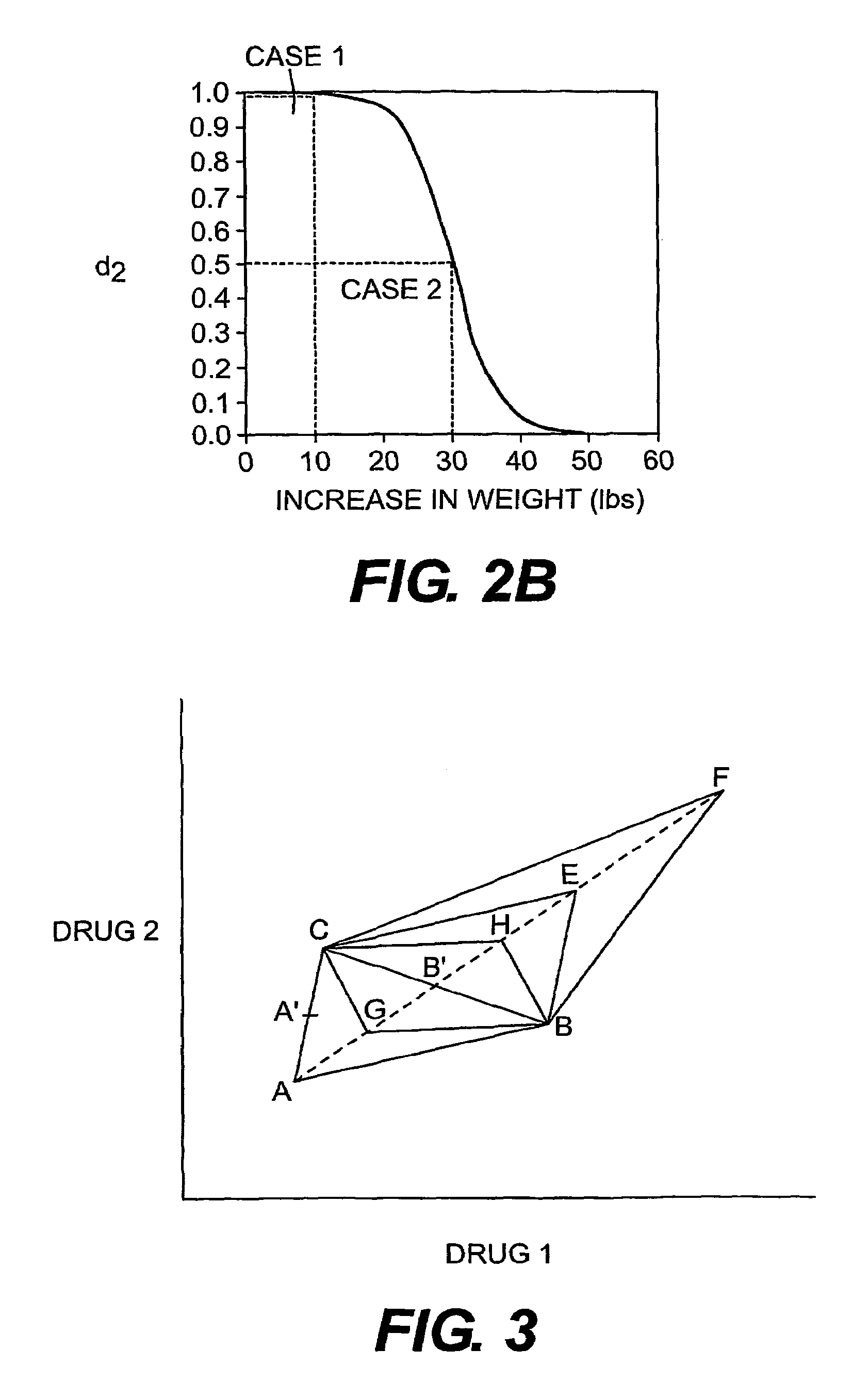
Multi-drug titration and evaluation
Titration of a combination of drugs or treatment modalities within individual subjects is carried out using an evolutionary operation (EVOP) direct-search procedure such as the Nelder-Mead simplex. Desirability functions are incorporated to define the main response of interest and additional responses or constraints. Statistical methodology for determining whether the titrated treatment combination has resulted in an improvement in patient response and for evaluating whether a therapeutic synergism exists is also incorporated. Inferences can be made about the efficacy of the combination or about the individual drugs or treatment modalities that comprise the combination. This approach allows every patient the potential to benefit from the combination under study and permits the consideration of multiple endpoints simultaneously.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
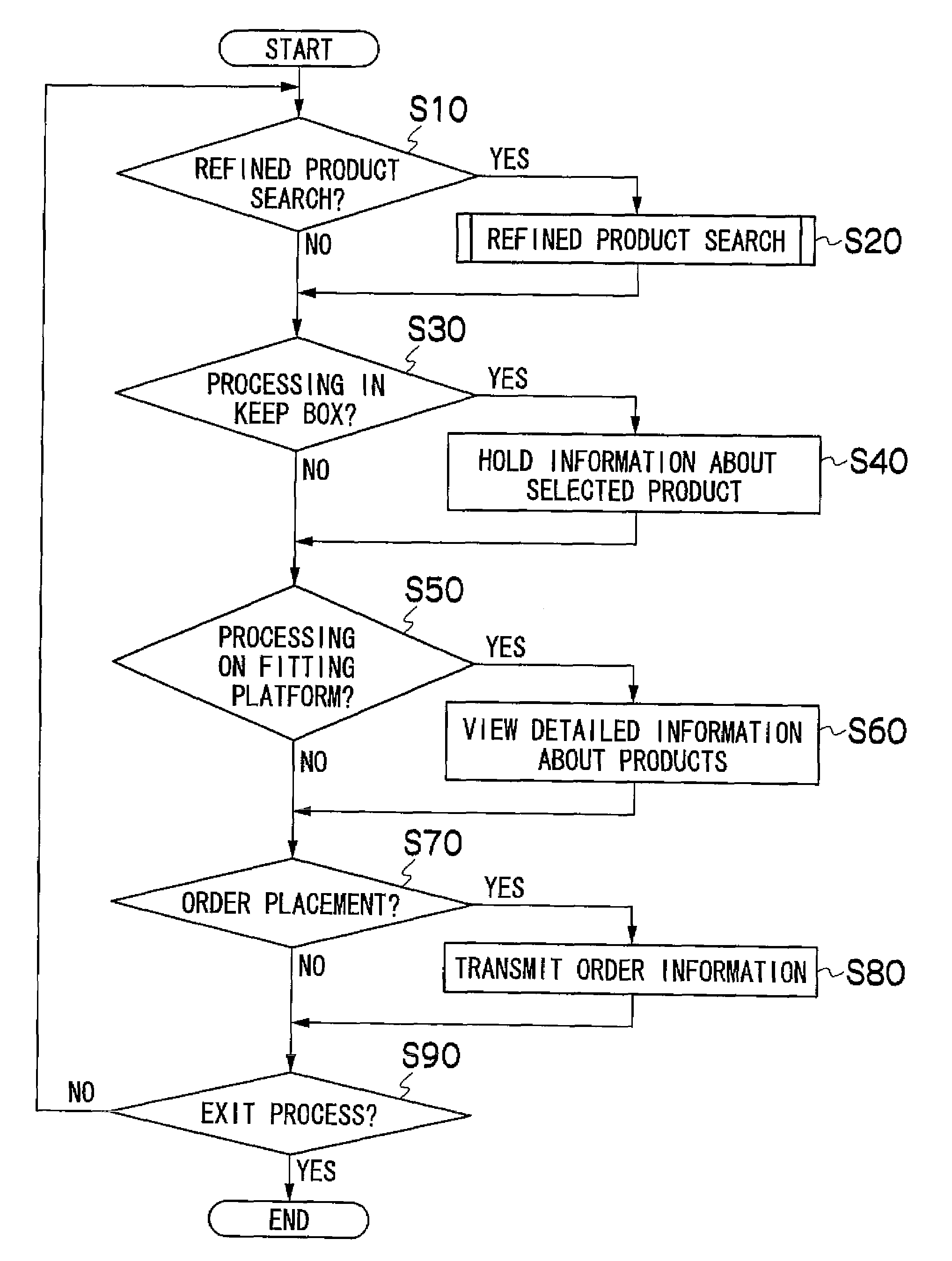
Product search system, product search method, and product search program
ActiveUS20090132388A1Narrow down products comfortably and efficientlyDigital data processing detailsVisual data miningDrag and dropComputer compatibility
The present invention makes it possible to narrow down desired products comfortably and efficiently while comparing products and checking a combination of products for compatibility on an EC site. An EC site screen containing a list screen of a product group, fitting platform, keep box, and the like is displayed on a client terminal accessing the EC site. When a user drags and drops thumbnail images of one or more products of interest from the list screen to the keep box, information about the products is held in the keep box. To view detailed information including the held images of the products, the user drags and drops the thumbnail images from the keep box to the fitting platform. Mannequin images and are provided on the fitting platform, and the user can compare products and check a combination of the products for compatibility by placing the images of the products (apparel products) on the mannequin images.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
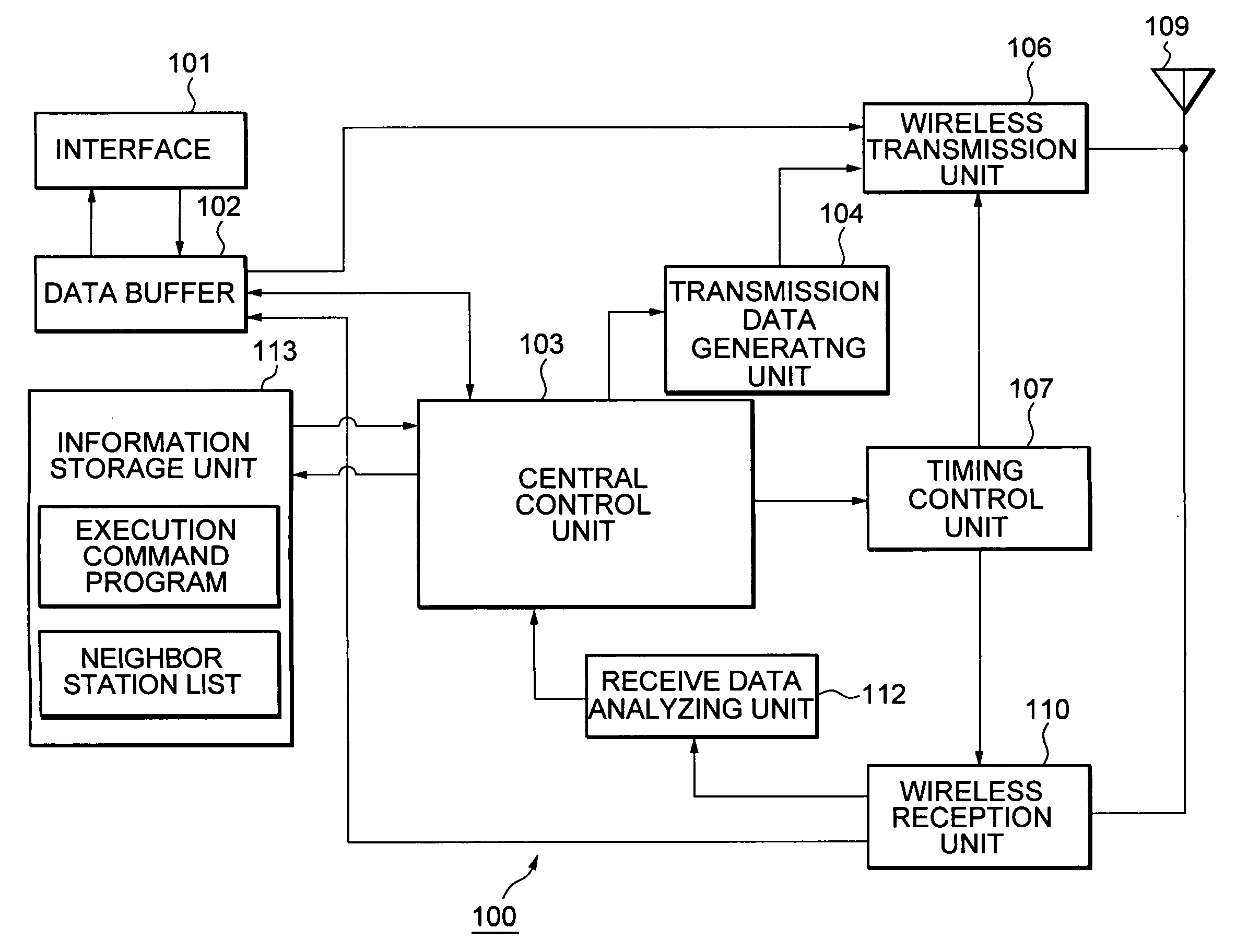
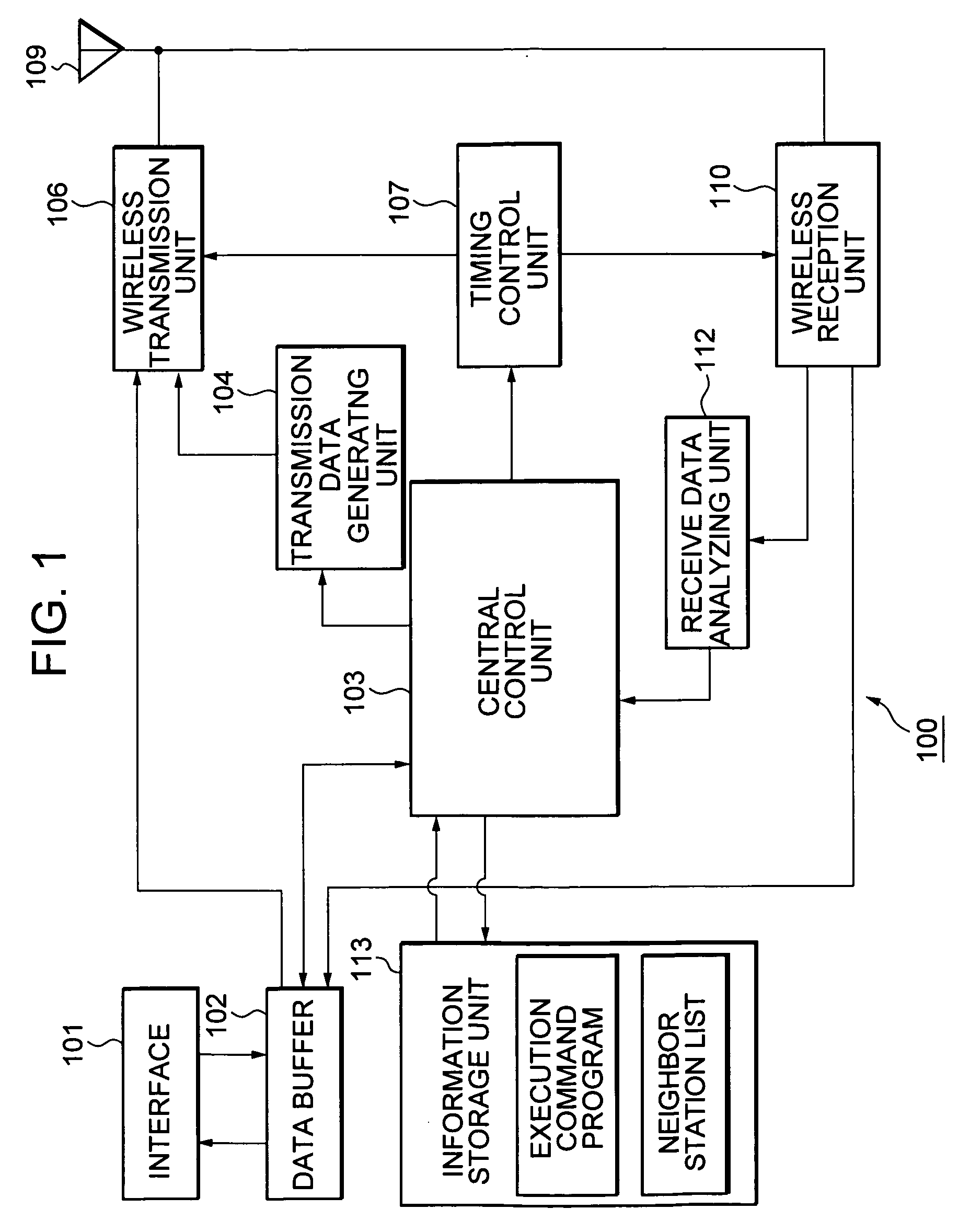
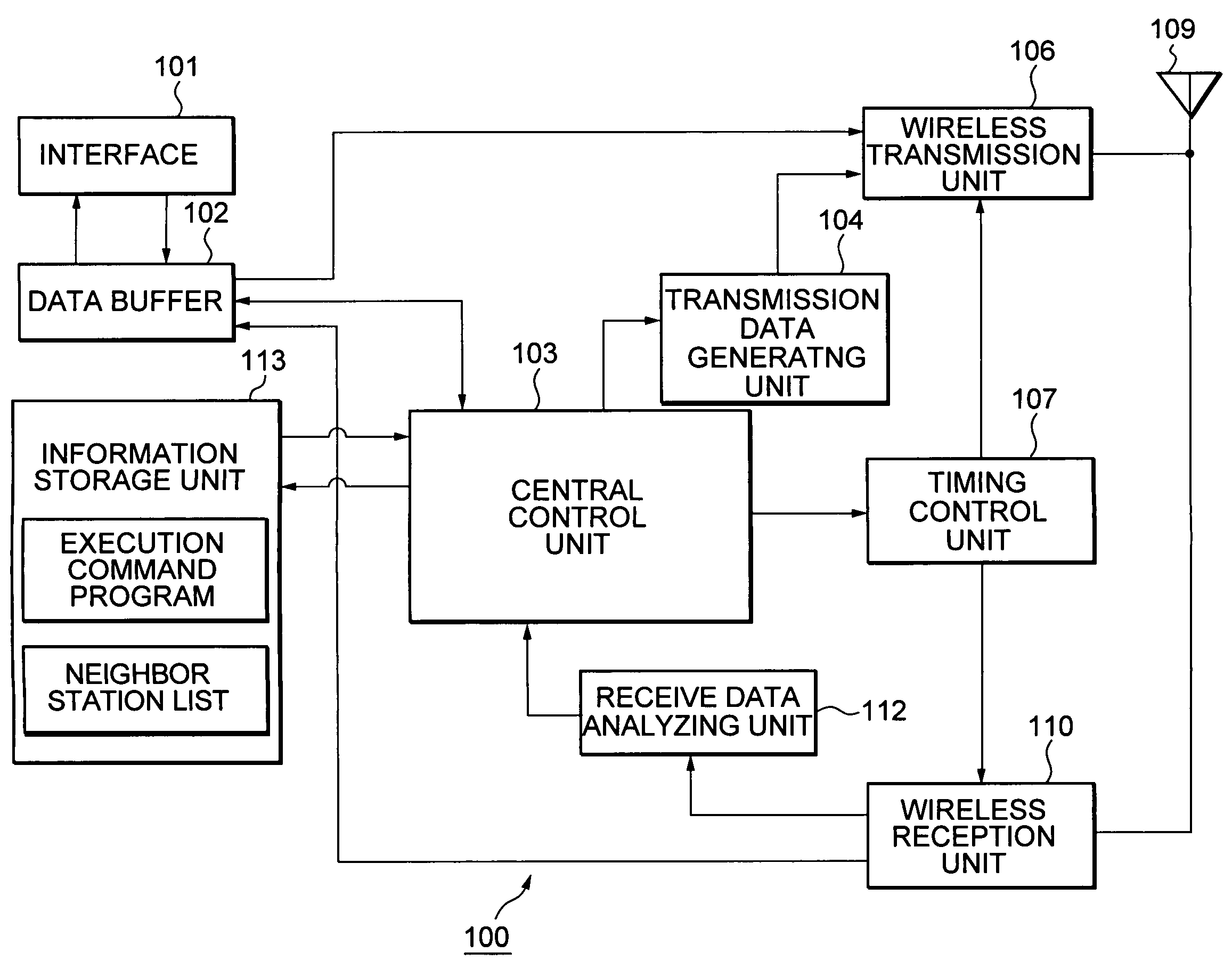
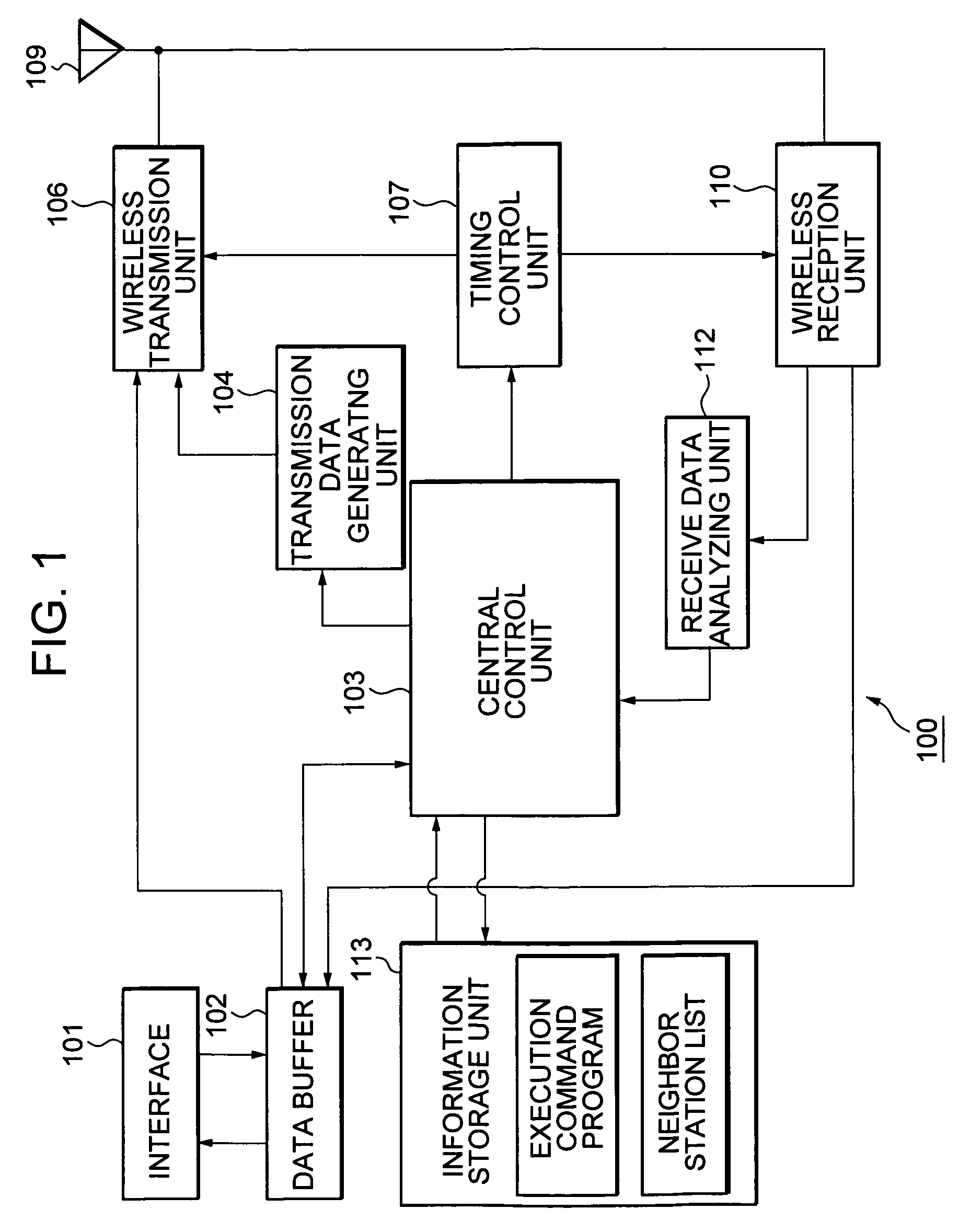
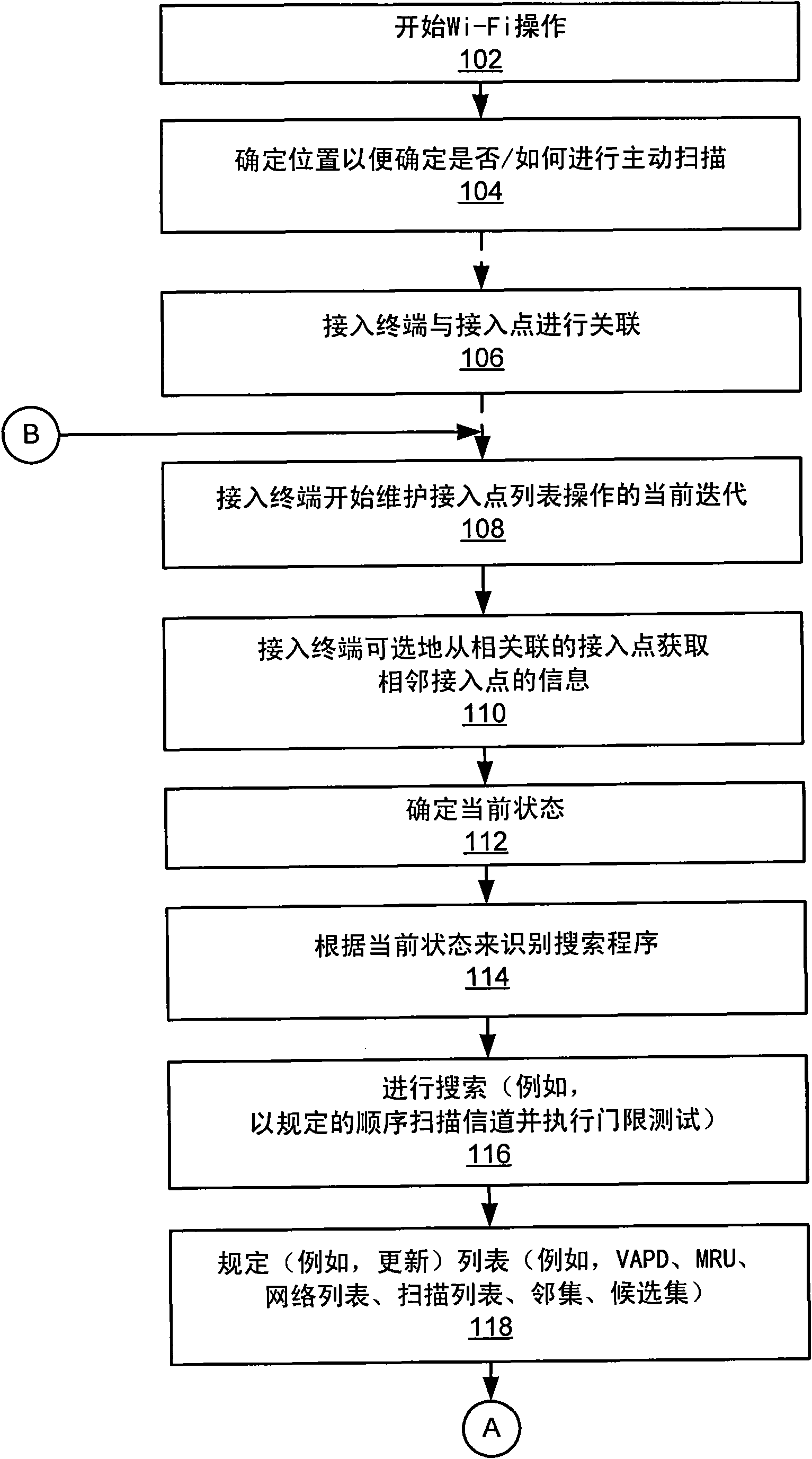
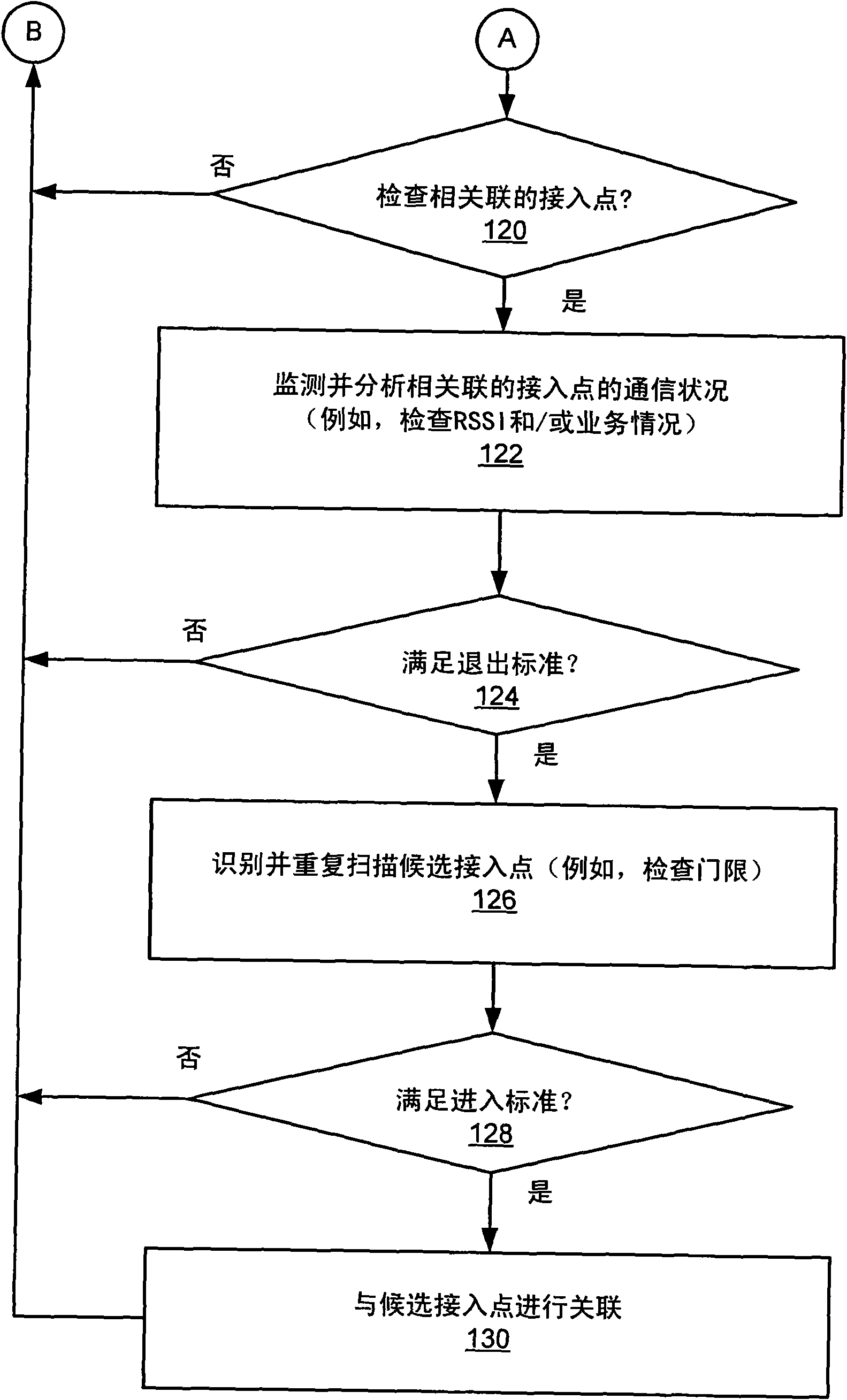
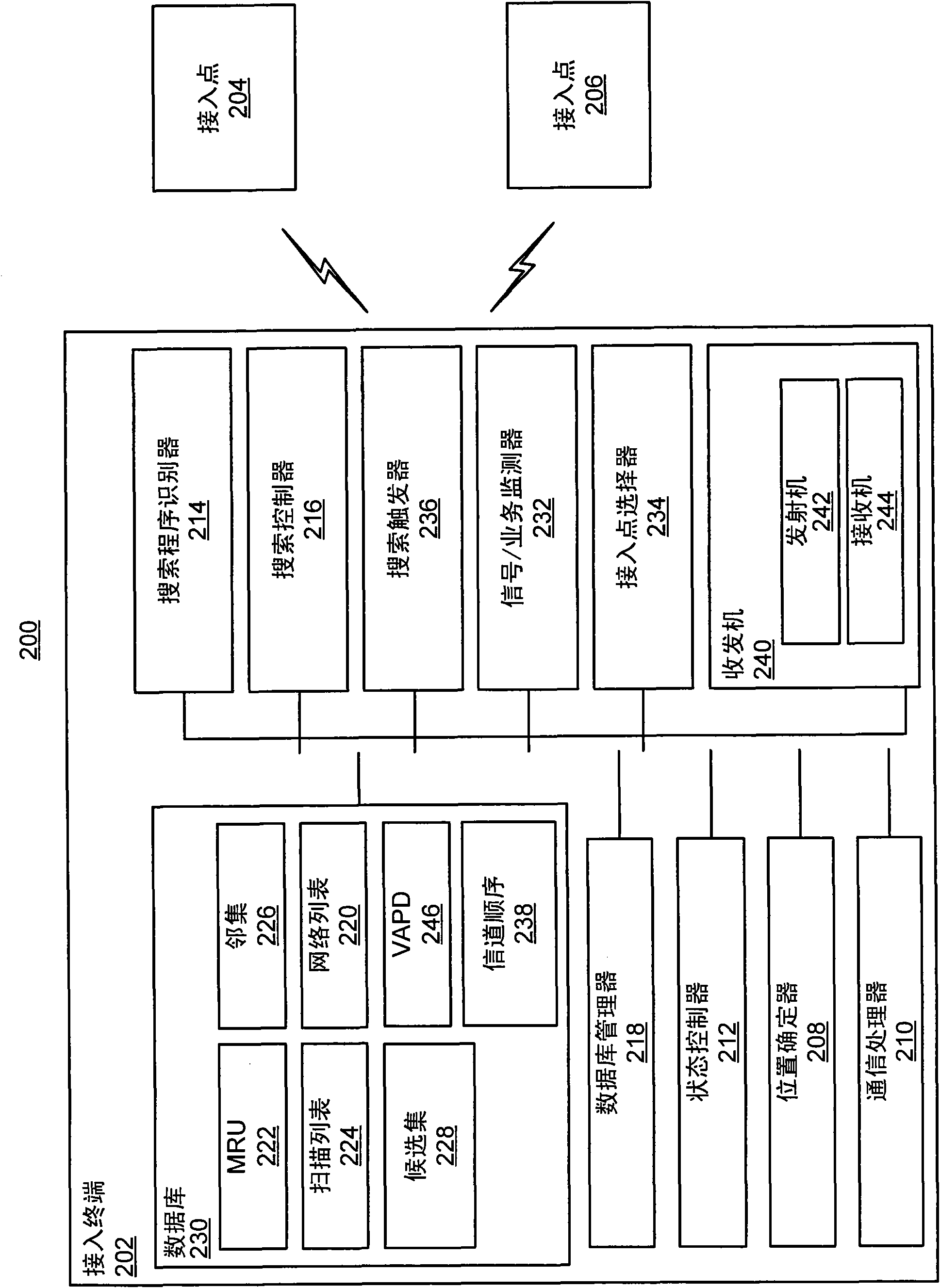
Wireless node search procedure
InactiveCN101622887AReduce power consumptionOptimize search programAssess restrictionLocation information based serviceRogue access pointComputer science
An access terminal scans for nearby access points and maintains a candidate list of access point with which the access terminal may associate in the event the access terminal's communication with its current access point deteriorates for some reason. This search procedure may be performed in a proactive manner whereby the access terminal repeatedly performs scans and updates its list of candidateaccess points when it is powered on. In some aspects, the search procedure used by the access terminal may be based on a state of the wireless device. In addition, different states of the access terminal may be associated with different optimization criteria.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
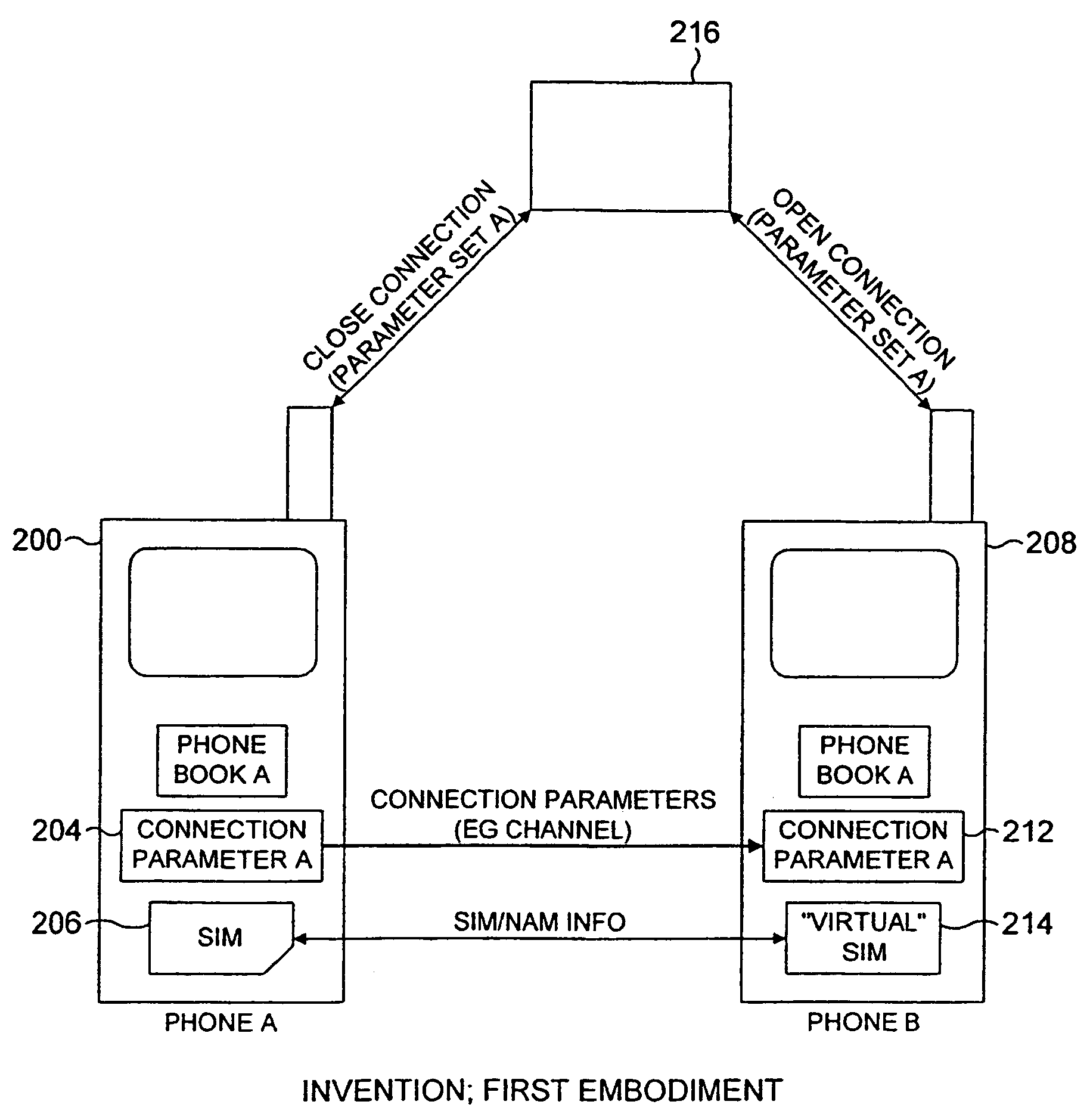
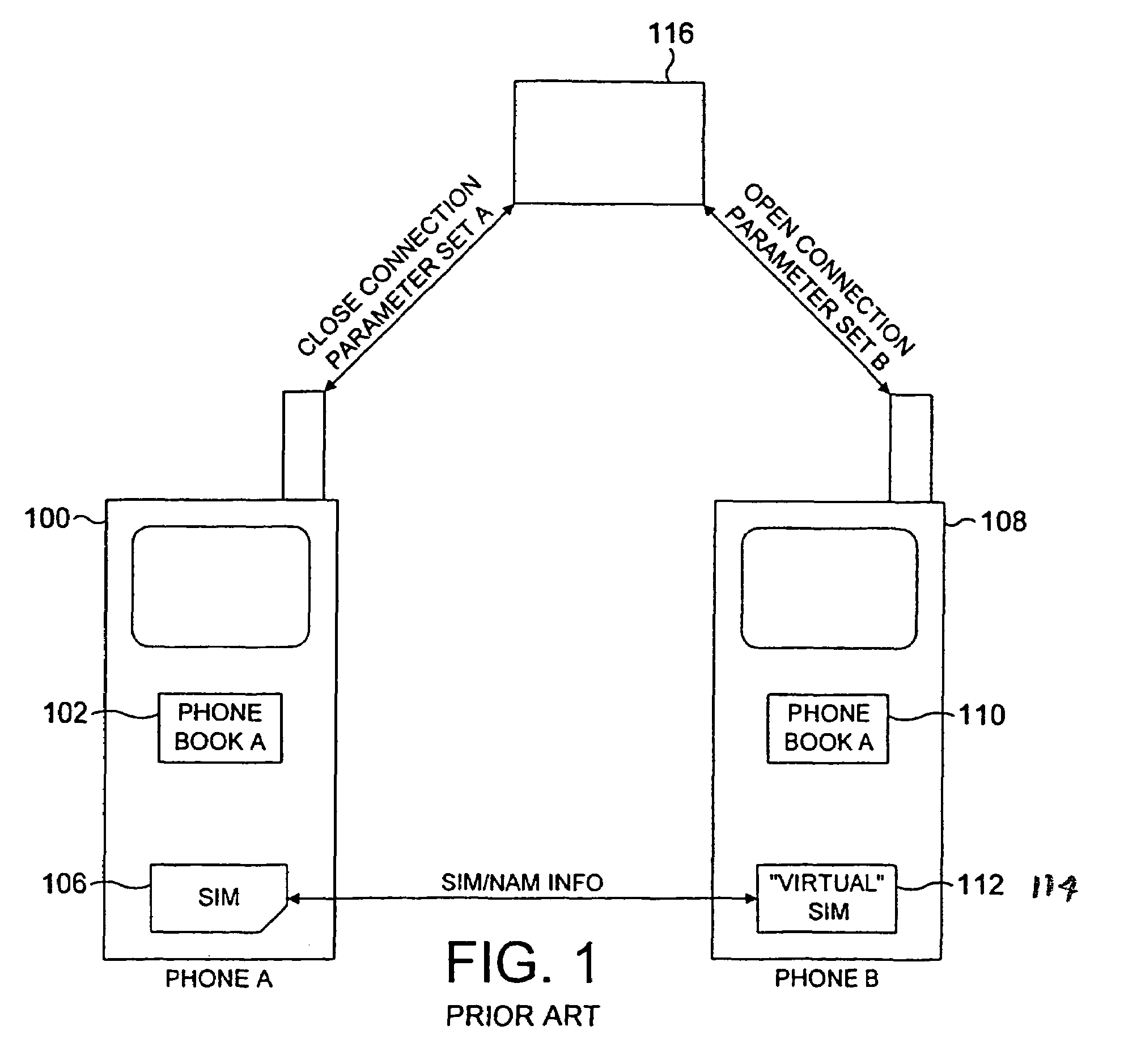
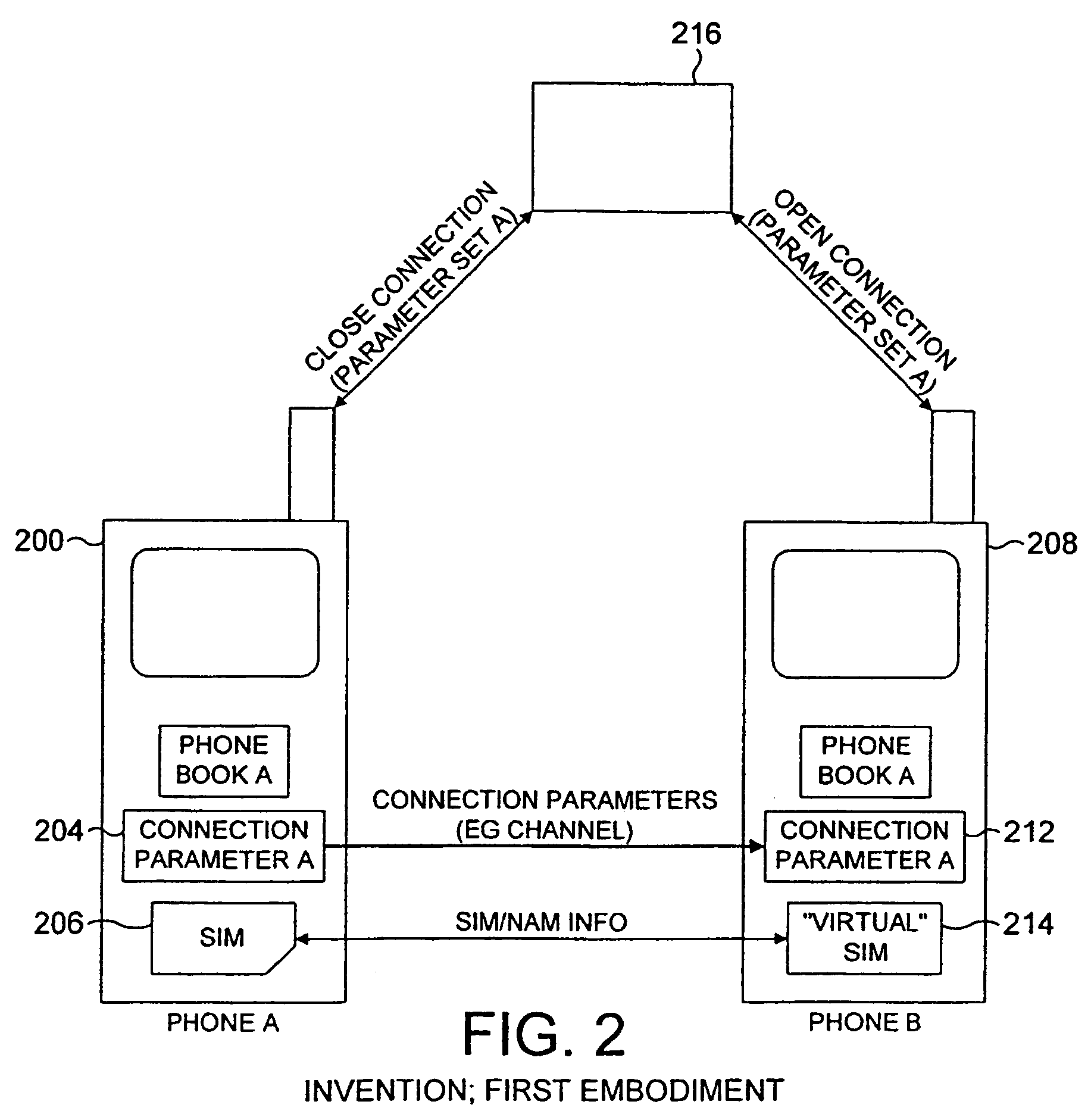
Radio telephone system allowing exchange of call setup parameters between associated or commonly owned mobile devices
InactiveUS7603107B2Improvement in amount of timeEasy to manageSpecial service for subscribersConnection managementCommunications systemTelecommunications network
A communication system includes first and second radiotelephones capable of communicating with a telecommunications network. The second radiotelephone is capable of remotely acquiring at least some of the identification information of the first radiotelephone and is further capable of acquiring connection parameters from the first radiotelephone. The communication parameters may include information relating to any of: the strongest radio channel; available frequency bands; and radio channels in use. The acquired parameters are applied to effect a connection to the network, without going through channel searching procedures. This overcomes the need to physically transfer subscriber identification modules (SIMs).
Owner:NOKIA CORP
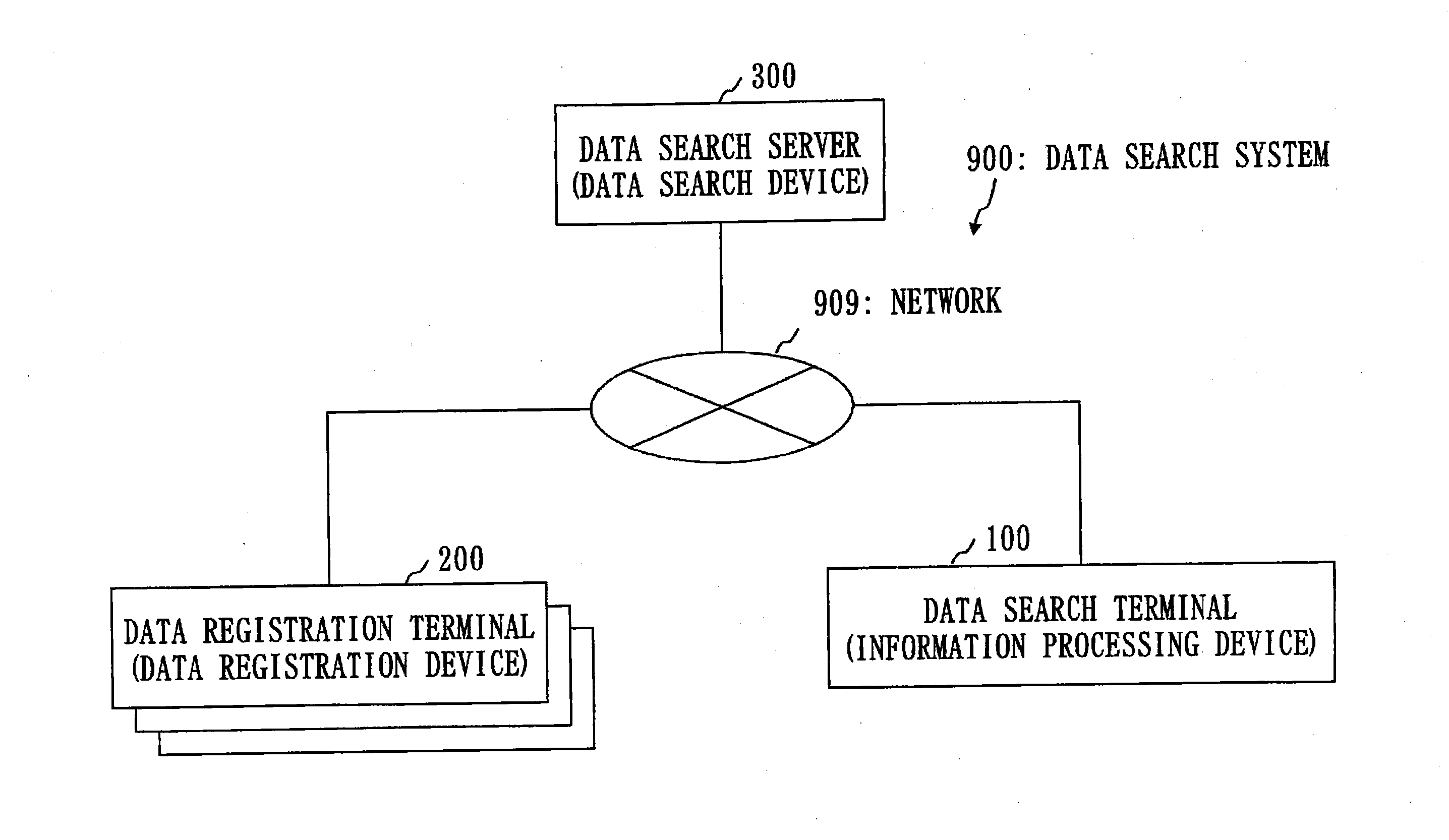
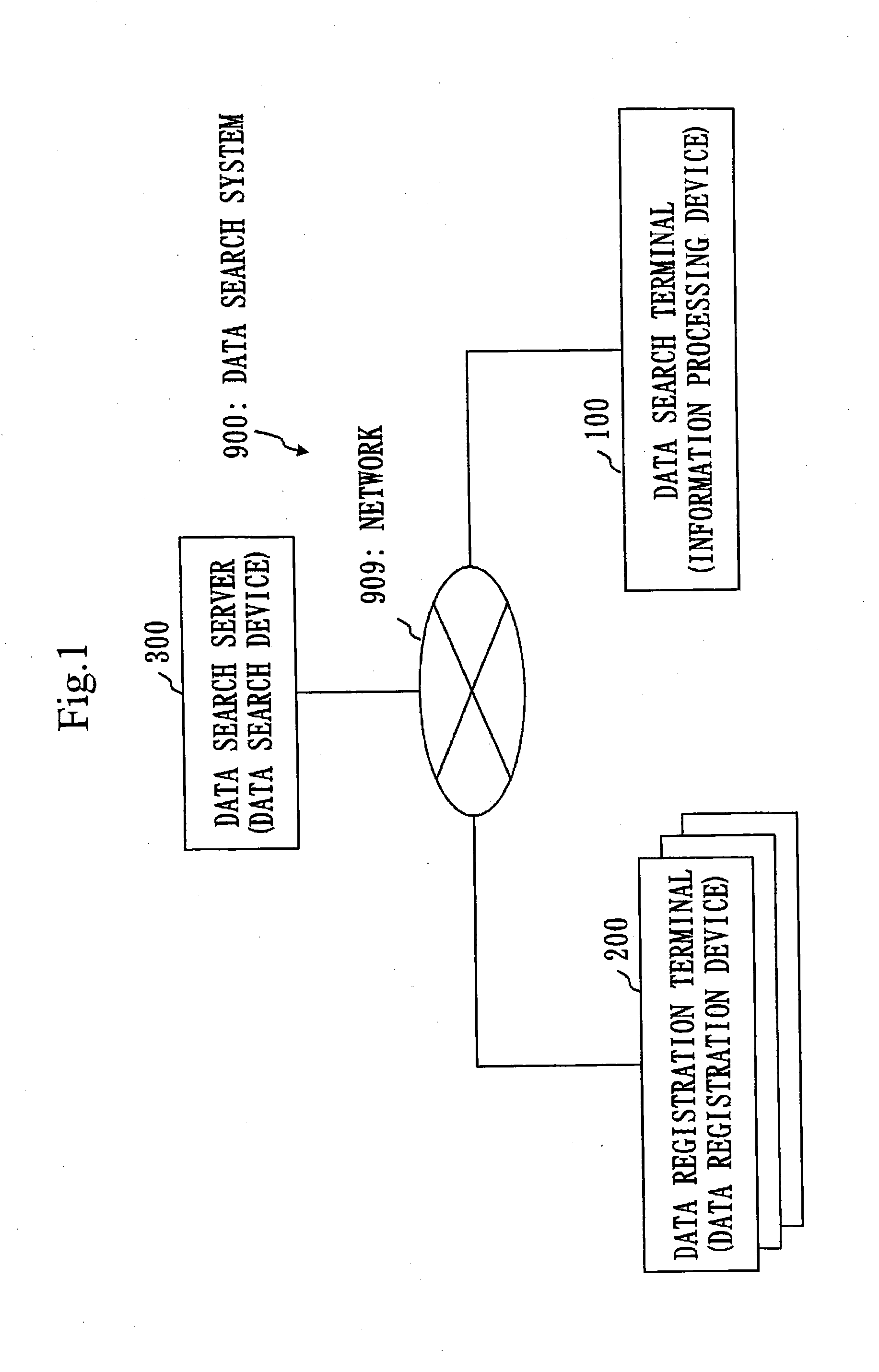
Data search device, data search method, data search program, data registration device, data registration method, data registration program, and information processing device
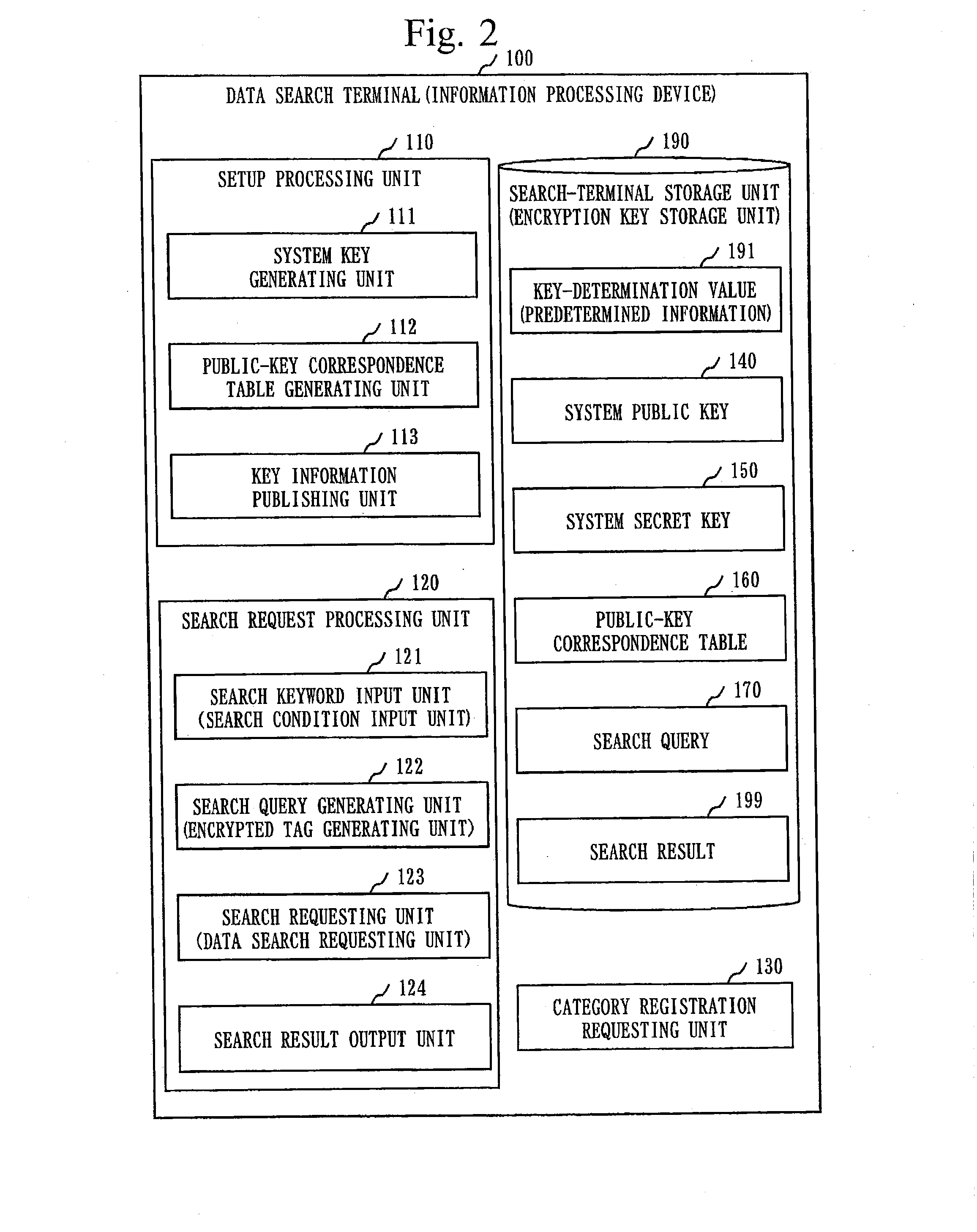
ActiveUS20140298009A1Faster search processFast processingDatabase queryingPublic key for secure communicationInformation processingCiphertext
A data search server stores a system ciphertext including a data ciphertext and a keyword ciphertext in each category-specific DB unit for each data category, and stores each category-determination secret key being associated with each category-specific DB unit. A search request receiving unit receives from a data search terminal a search request including a search trapdoor and an index tag. A data searching unit searches for a category-determination secret key with which the index tag is decrypted to the same value as a key-determination value. Using the search trapdoor, the data searching unit performs a search of a Public-key Encryption with Keyword Search scheme on system ciphertexts in a category-specific DB unit associated with this category-determination secret key. A search result transmitting unit transmits to the data search terminal a data ciphertext included in a system ciphertext which has been found as a hit in the search.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
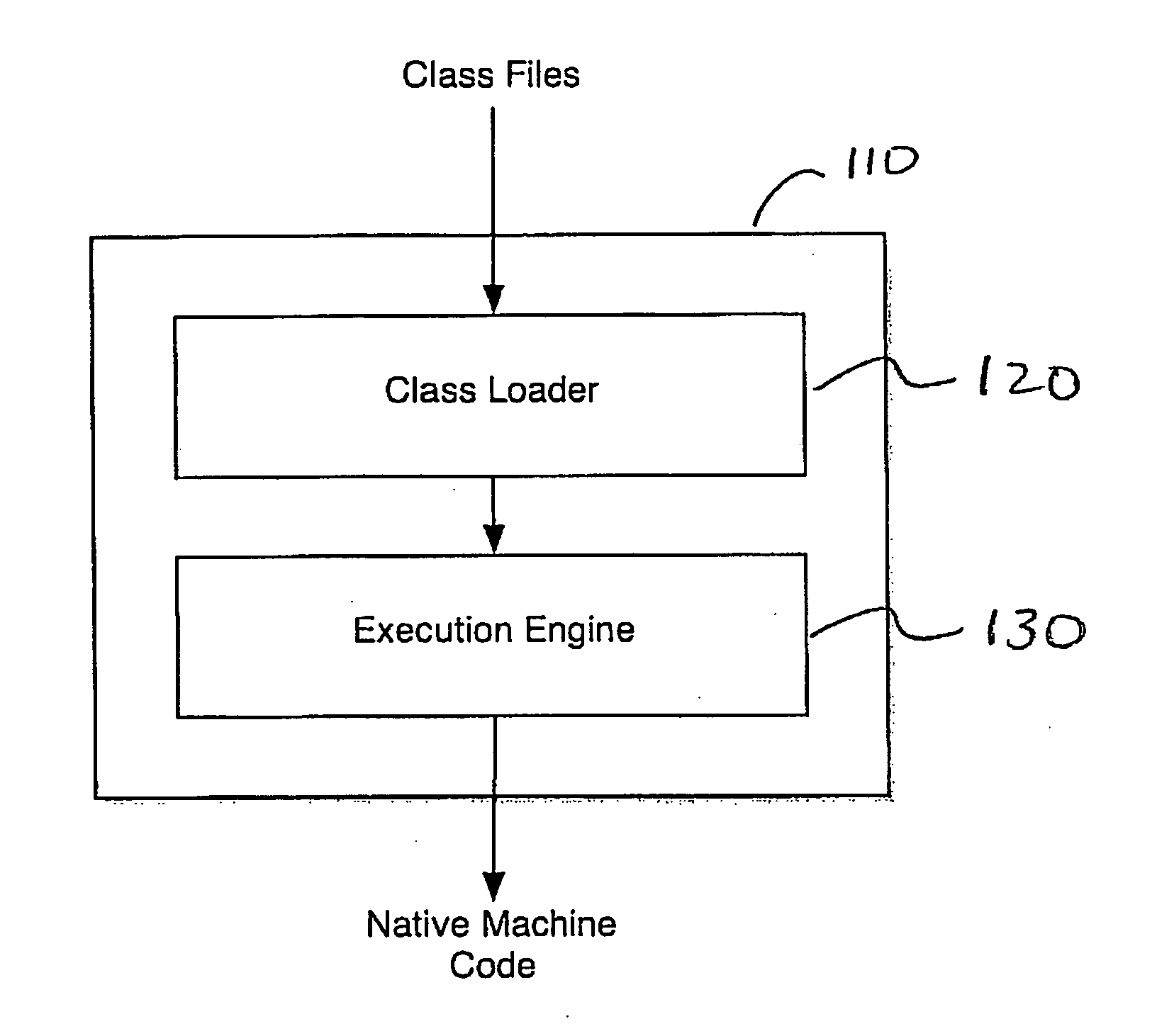
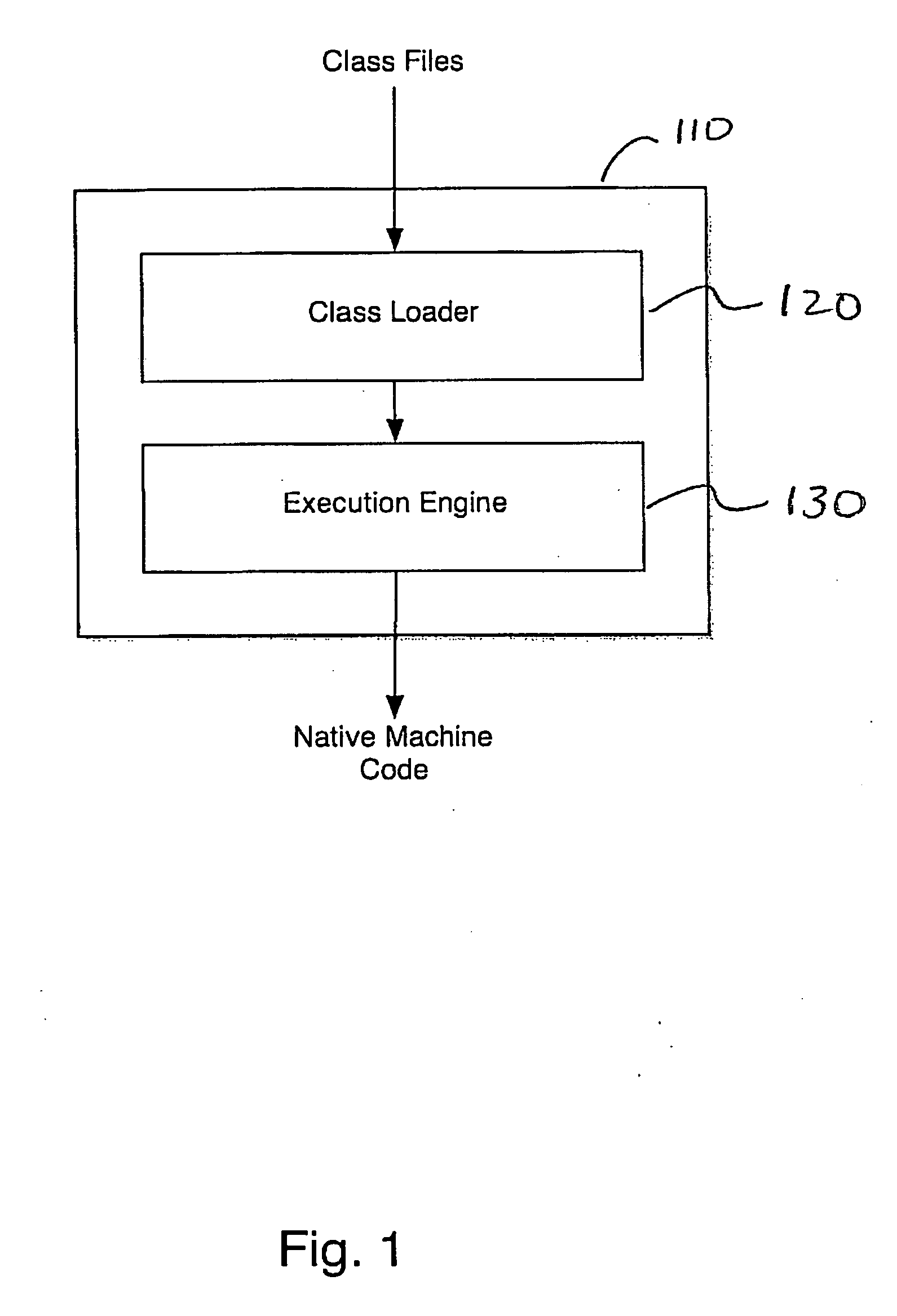
Method and system for automated root-cause analysis for class loading failures in Java
ActiveUS20070061792A1Specific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsProgramming languageObject definition
A method and system for automated root-cause analysis for failures in class loading in a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) environment. Specifically, a class loader comprises a class loader for loading classes which comprises an identifier, a search policy object, a configuration policy object, and metadata. The identifier is unique to the JVM environment. The search policy object defines search procedures for discovering and loading a class by the class loader. The configuration policy object manages configuration of the class loader. Metadata describes the interrelationships between the class loader to other class loaders in a class loader tree supporting the JVM environment.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
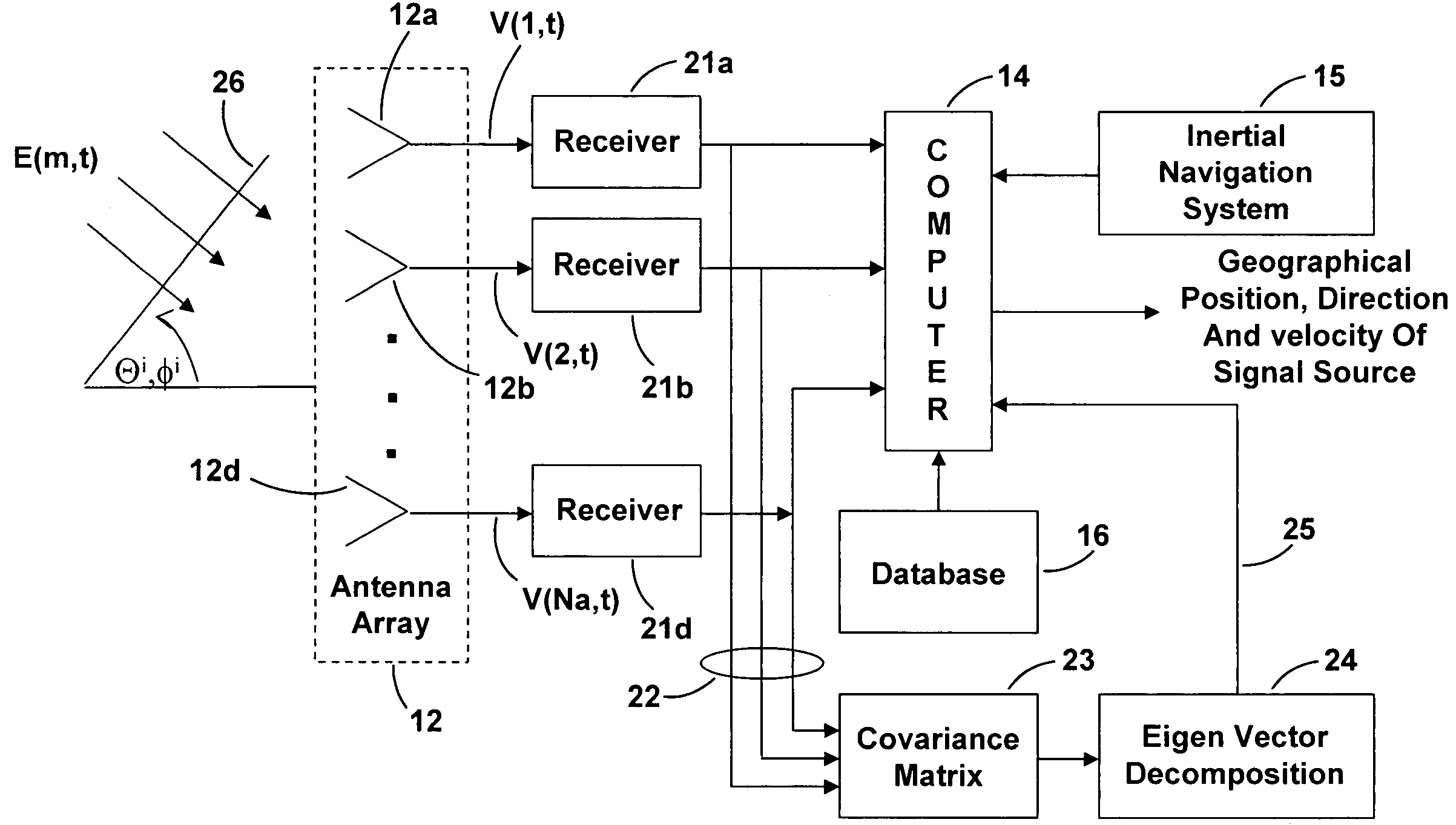
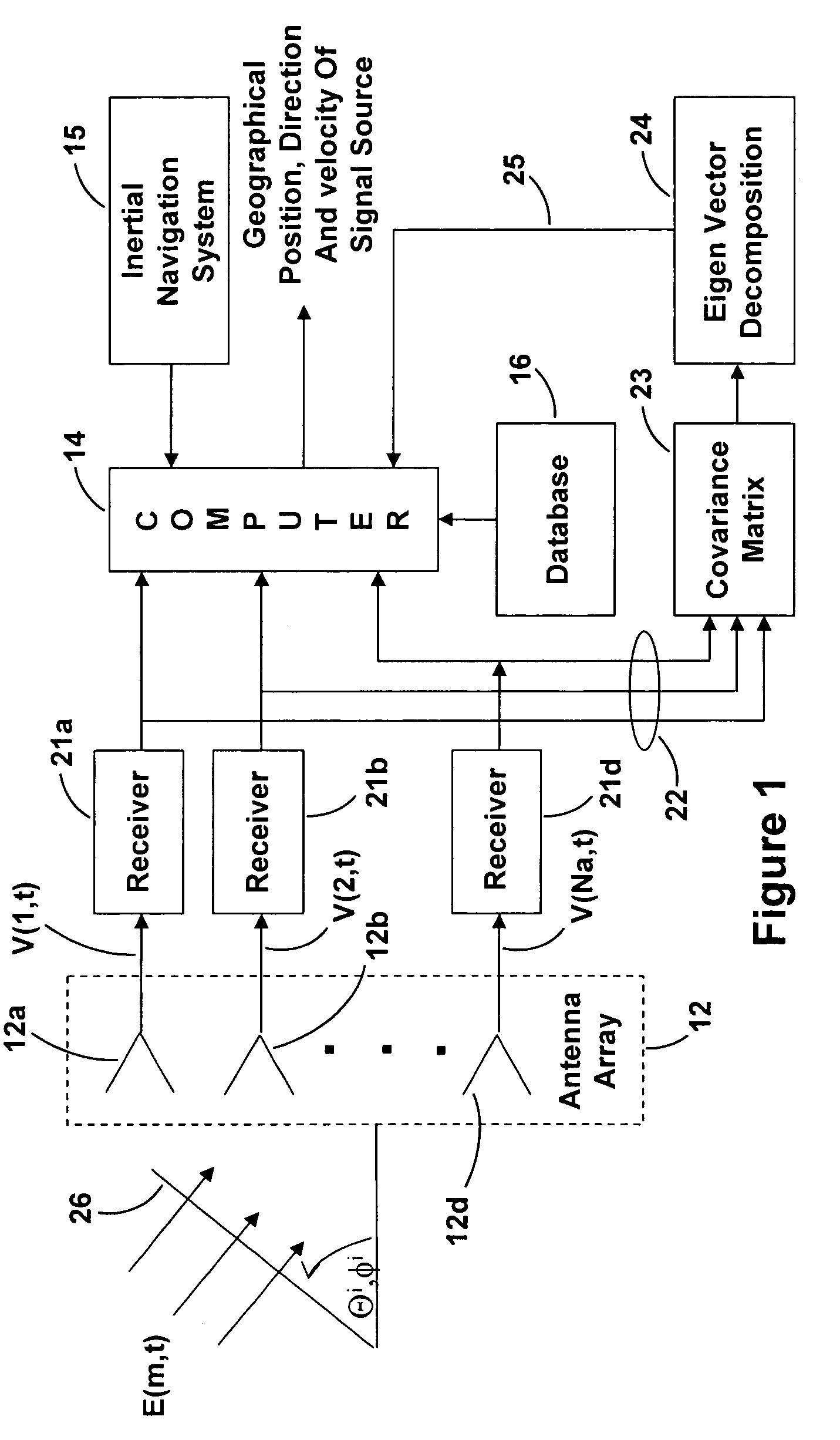
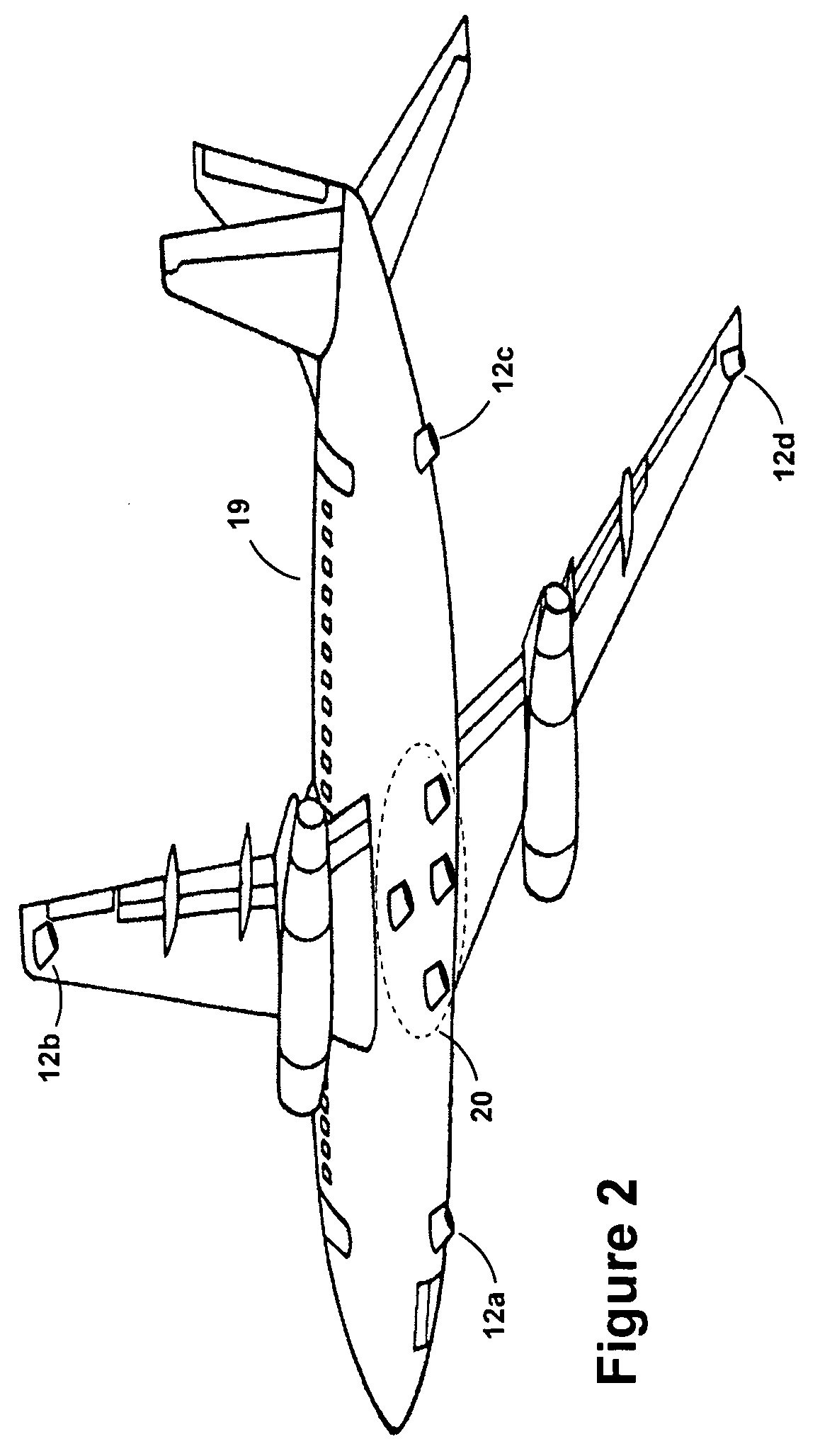
Moving transmitter correlation interferometer geolocation
ActiveUS7268728B1Reliable and accurate informationAccurate informationMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesPosition fixationGeolocationEngineering
A Moving Transmitter Correlation Interferometer Geo-Location (MT-CIGL) system is disclosed that permits locating both moving and stationary transmitters from moving DF equipment. A conjugate gradient based search routine is utilized which solves for the location of moving and stationary transmitters at the start of each measurement sequence and then solves for the velocity and direction of motion of the moving transmitter. This information is used to track the moving transmitter. Received signals are sampled, digitized and stored in covariance matrices. They are then summed and normalized using an equation that has velocity terms that are set to zero to minimize extraneous correlation peaks, and a maximum correlation peak is developed. A conjugate gradient search routine is used to find the correlation peak of the summed data. The value of the peak is then analyzed to see if it is above or below a predetermined value. If the peak value is above the predetermined value the transmitter is stationary and the located correlation peak is the location of the transmitter. If the peak value is below the predetermined value the transmitter is moving and the peak does not indicate the correct location of the transmitter. Another conjugate gradient search routine is performed using the previous erroneous peak as the starting point for the search to identify the actual location of the moving transmitter at the beginning of a search sequence. That location is then processed through the same equation, but without the velocity terms set to zero, to calculate the velocity and direction of motion of the transmitter. This information can then be used to plot a track for the moving transmitter.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
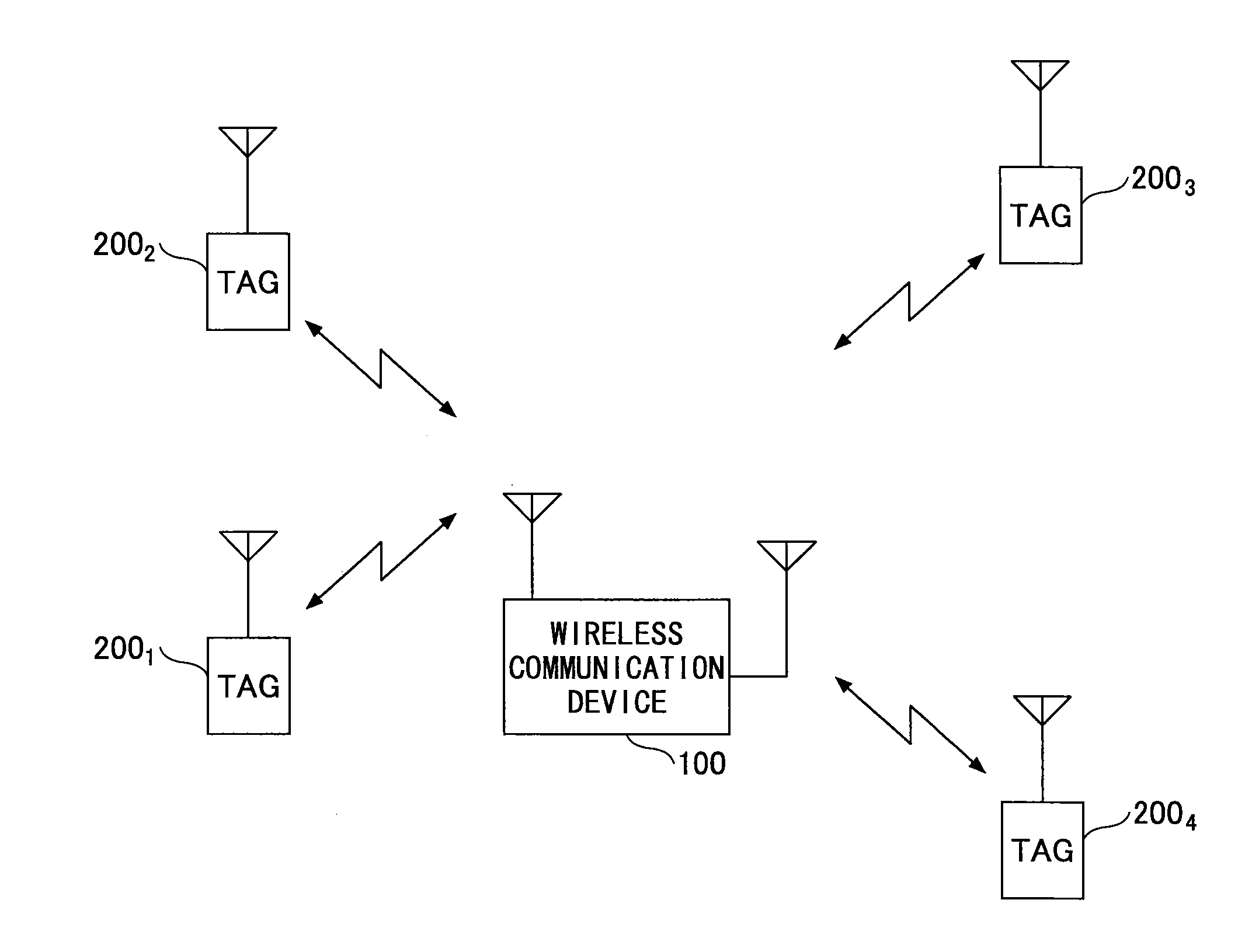
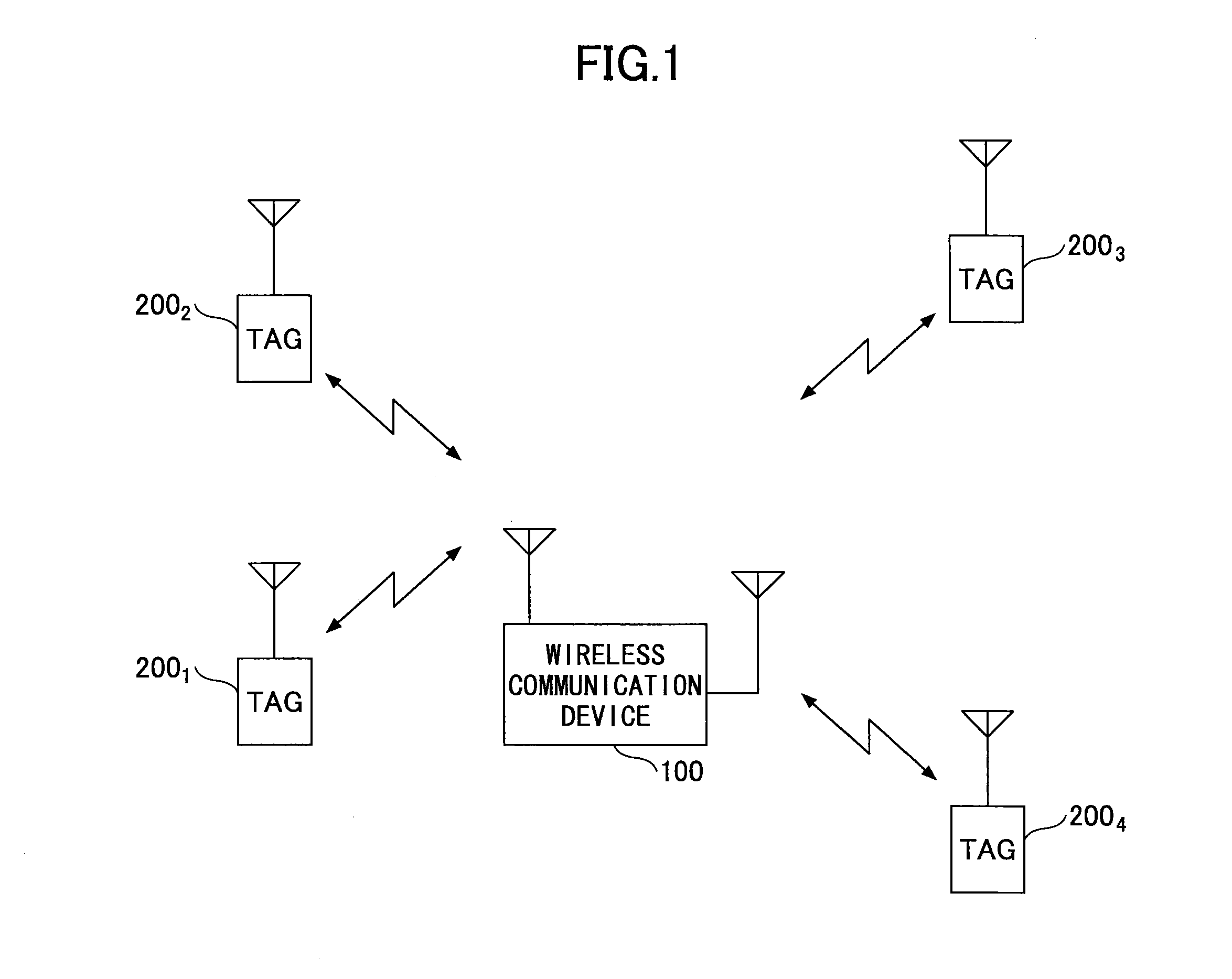
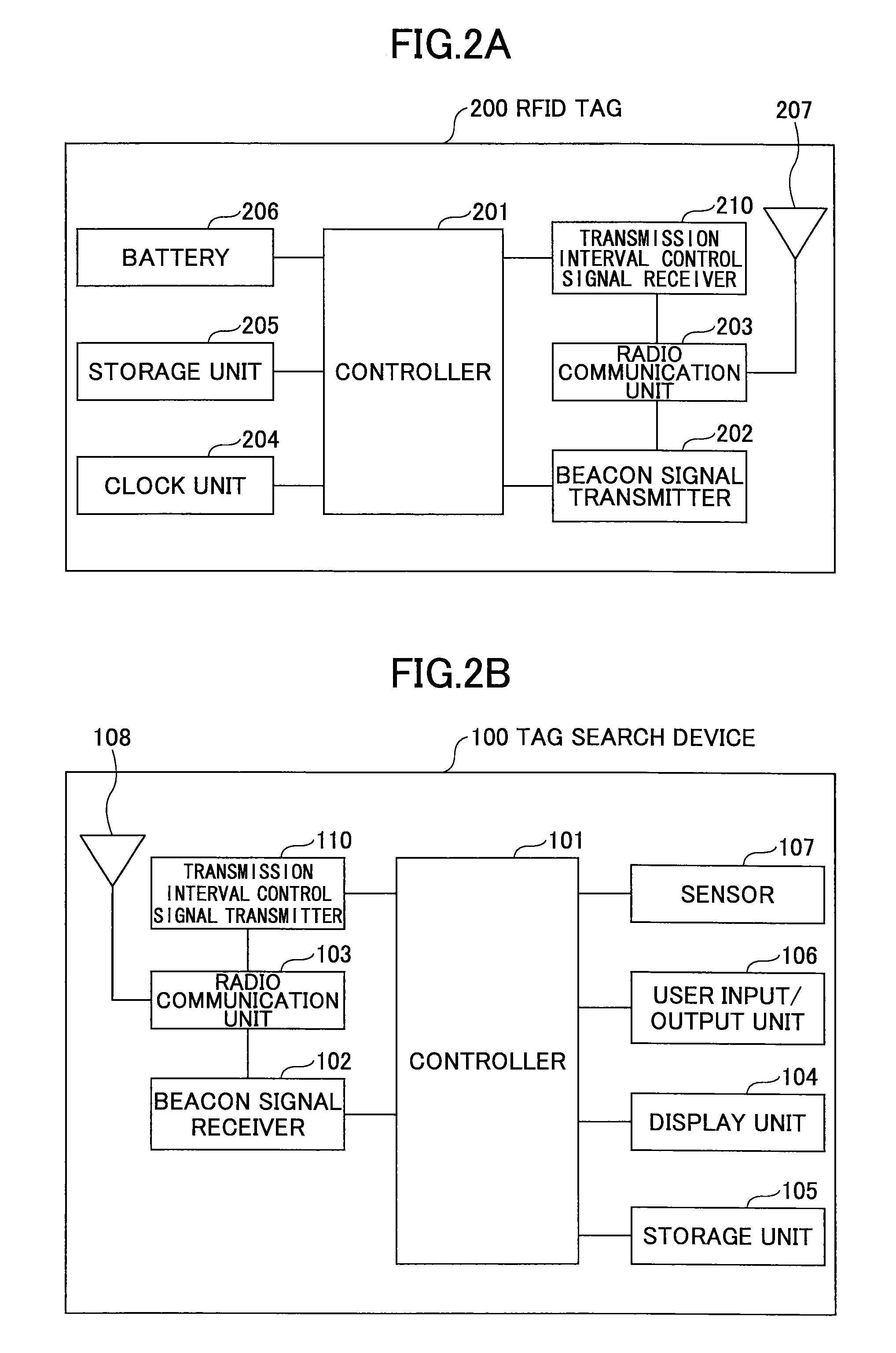
RFID tag search method, non-transitory storage medium storing RFID tag search program, and RFID tag search device
ActiveUS20150355308A1Beacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationComputer terminalSearch procedure
A method to be executed by a user terminal for searching for locations of one or more wireless devices that are located within an area in which the one or more wireless devices can wirelessly communicate with the user terminal, wherein each of the one or more wireless devices periodically transmits a beacon signal. The method includes detecting a number of the one or more wireless devices that are located within the area based on the beacon signals; determining a transmission period for transmitting the beacon signals depending on the number of the one or more wireless devices; and instructing the one or more wireless devices that are located within the area to transmit the beacon signals in accordance with the determined transmission period.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com