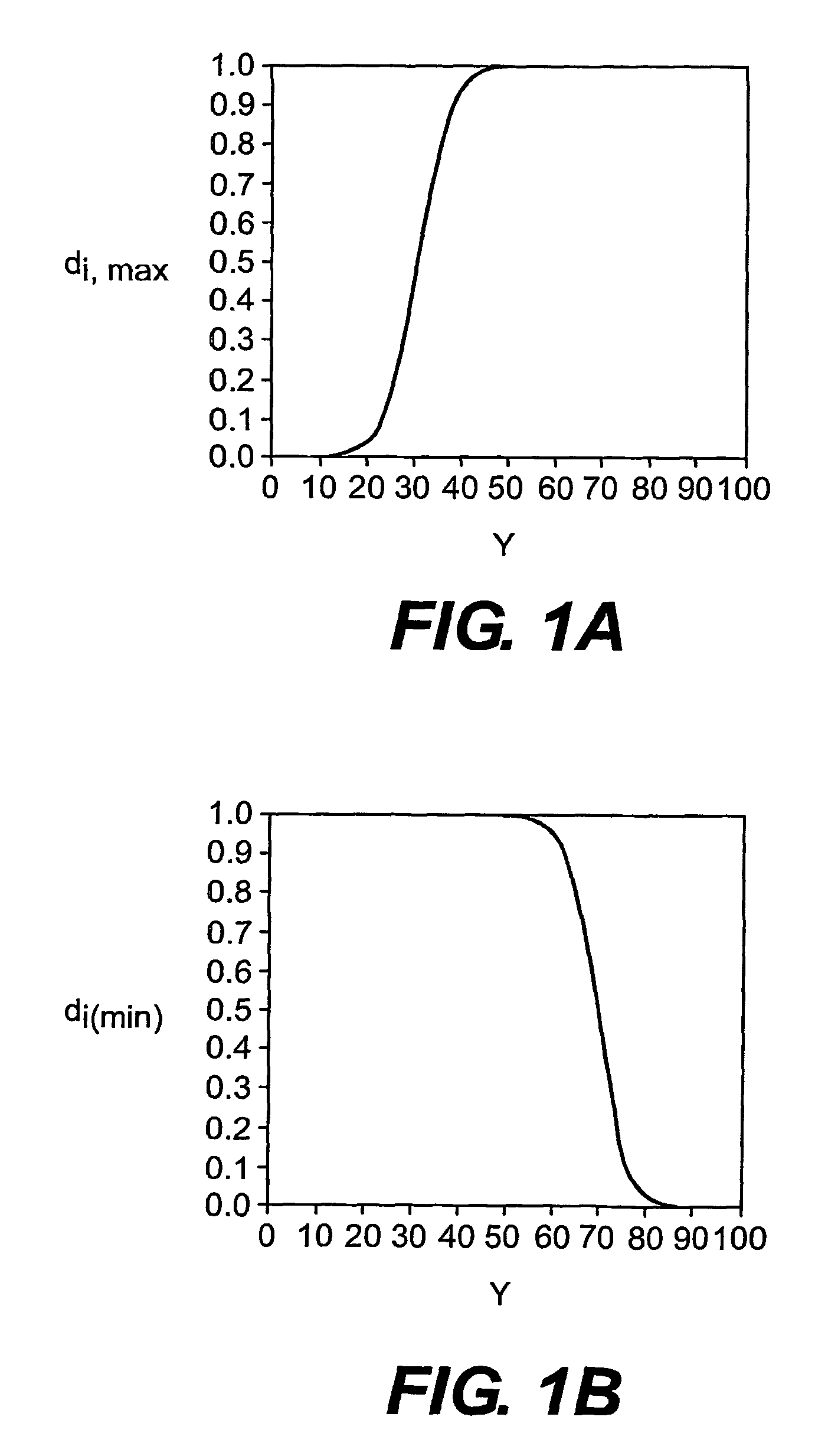
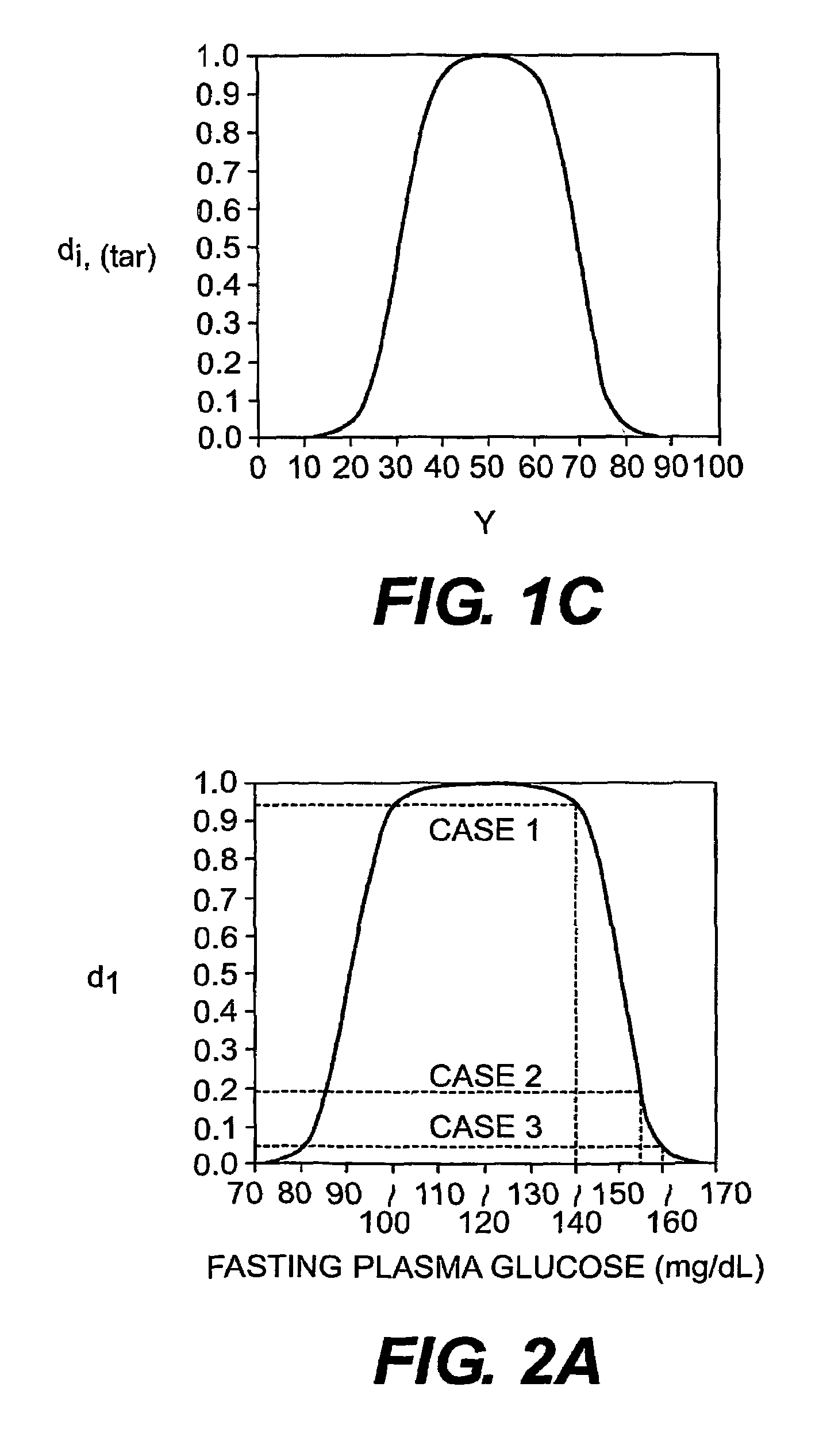
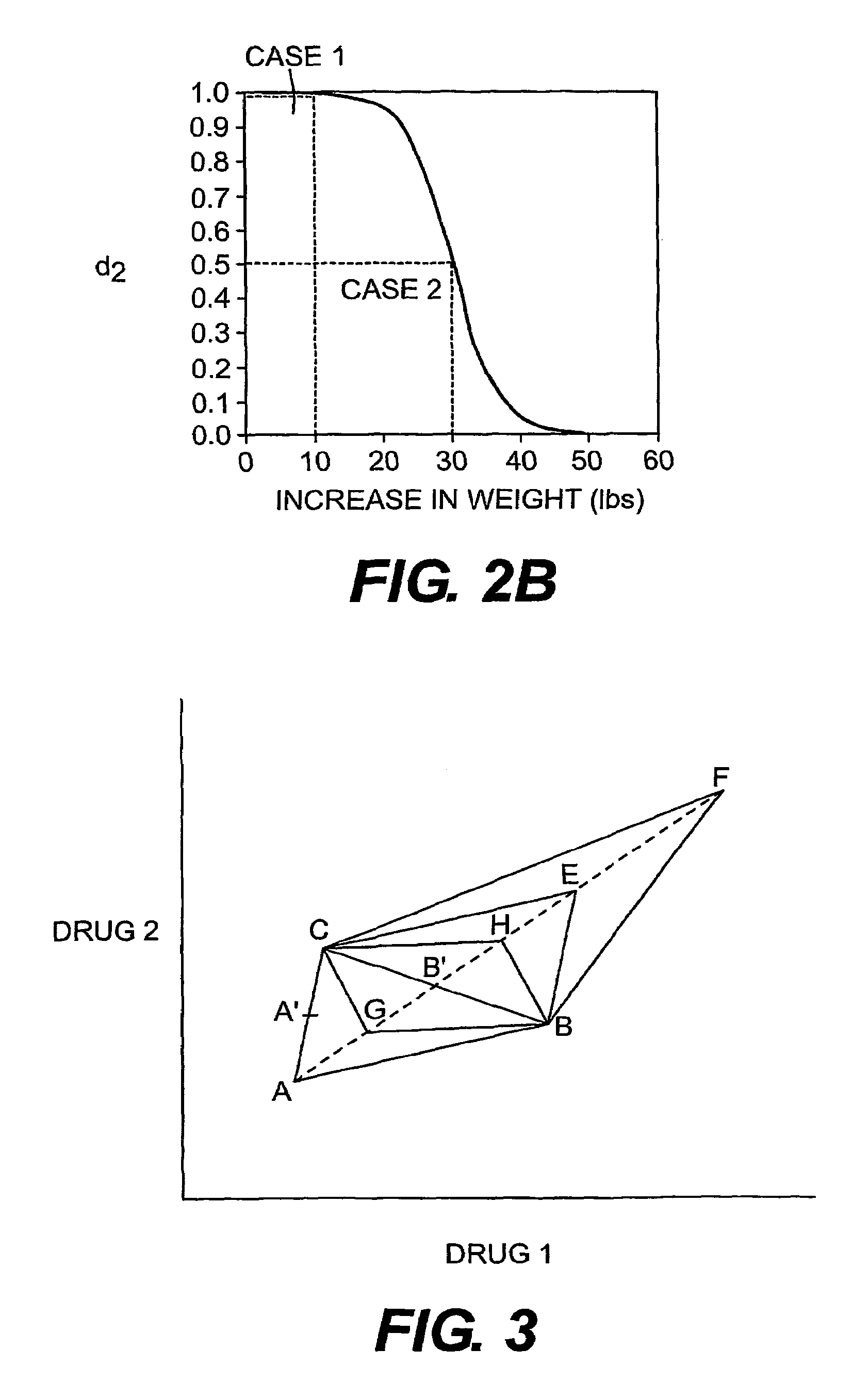
Multi-drug titration and evaluation
a multi-modality therapy and drug therapy technology, applied in the field of multi-modality therapy regimen titration and evaluation, can solve the problems of no systematic or efficient method for determining dosages of multi-modality therapy regimens, unable to translate this approach, and increasing the potential for drug interactions and adverse drug reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
A Comparison of Multi-drug Titration with Glyburide and Metformin to Treatment with Glucovance
[0083]It is estimated that approximately 16 million people in the U.S. have diabetes, only one third of which are diagnosed. Type 2 diabetes accounts for 90-95% of all patients diagnosed with diabetes. An additional 15 million people have impaired glucose tolerance, putting them at a high risk for developing type 2 diabetes. Diabetes is currently the 4th leading cause of death by disease in the U.S., the leading cause of blindness in adults 20-74 years old, and the leading cause of end-stage renal disease. Sixty to seventy percent of diabetics have some form of mild to severe neuropathy, and diabetes is associated with a 2 to 4 fold increase in risk for both heart disease and stroke. The considerable morbidity and mortality associated with this disease is estimated to cost $98 billion each year in direct medical costs and indirect costs to industry (Centers for Disease Control, 1998).
[0084]...
example 2
Simulation Studies Examining the Effectiveness of the EVOP Multi-drug Titration Algorithm in Dosing a Combination of Therapeutic Agents
[0112]Simulation studies were carried out using the estimated dose response surface from a published multicenter, factorial design clinical trial conducted by Burris, et.al. (1990), which studied the efficacy of the combination therapy of the diuretic hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) and a slow-release formulation of diltiazem hydrochloride (DLTZ), a calcium channel blocker, in the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension. The trial was conducted over a period of six weeks, following a 4- to 6-week placebo ‘run-in’ period. A 4 by 5 factorial grid of treatment doses was used, with 4 twice-a-day doses of hydrochlorothiazide ranging from 0 to 25 mg, and 5 twice-a-day doses of diltiazem hydrochloride ranging from 0 to 180 mg. Mild-to-moderate essential hypertension was defined as supine diastolic blood pressure in the range of 95 to 110 mm Hg. The goal of tr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diastolic blood pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com