Patents
Literature
282 results about "Object definition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
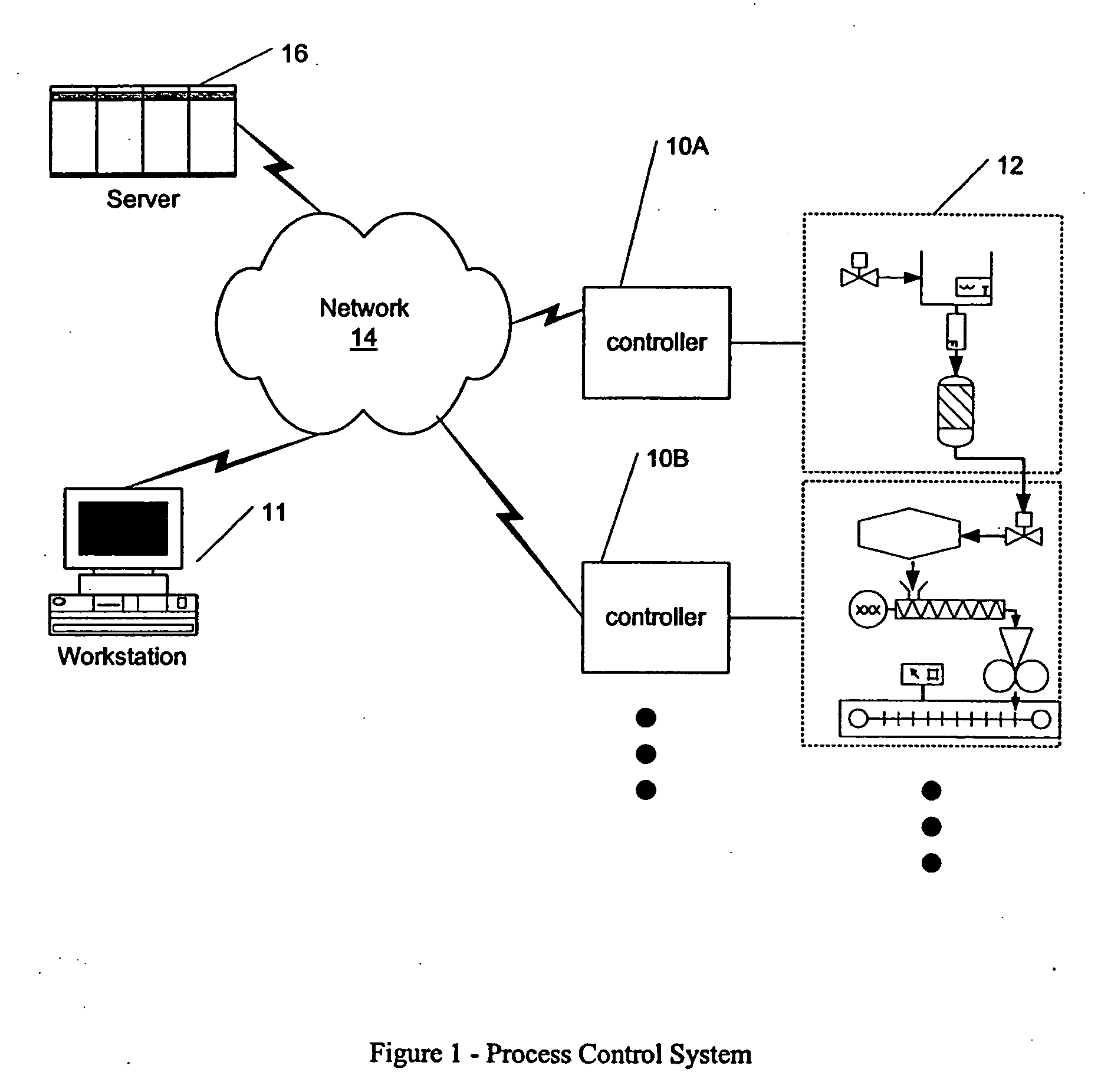
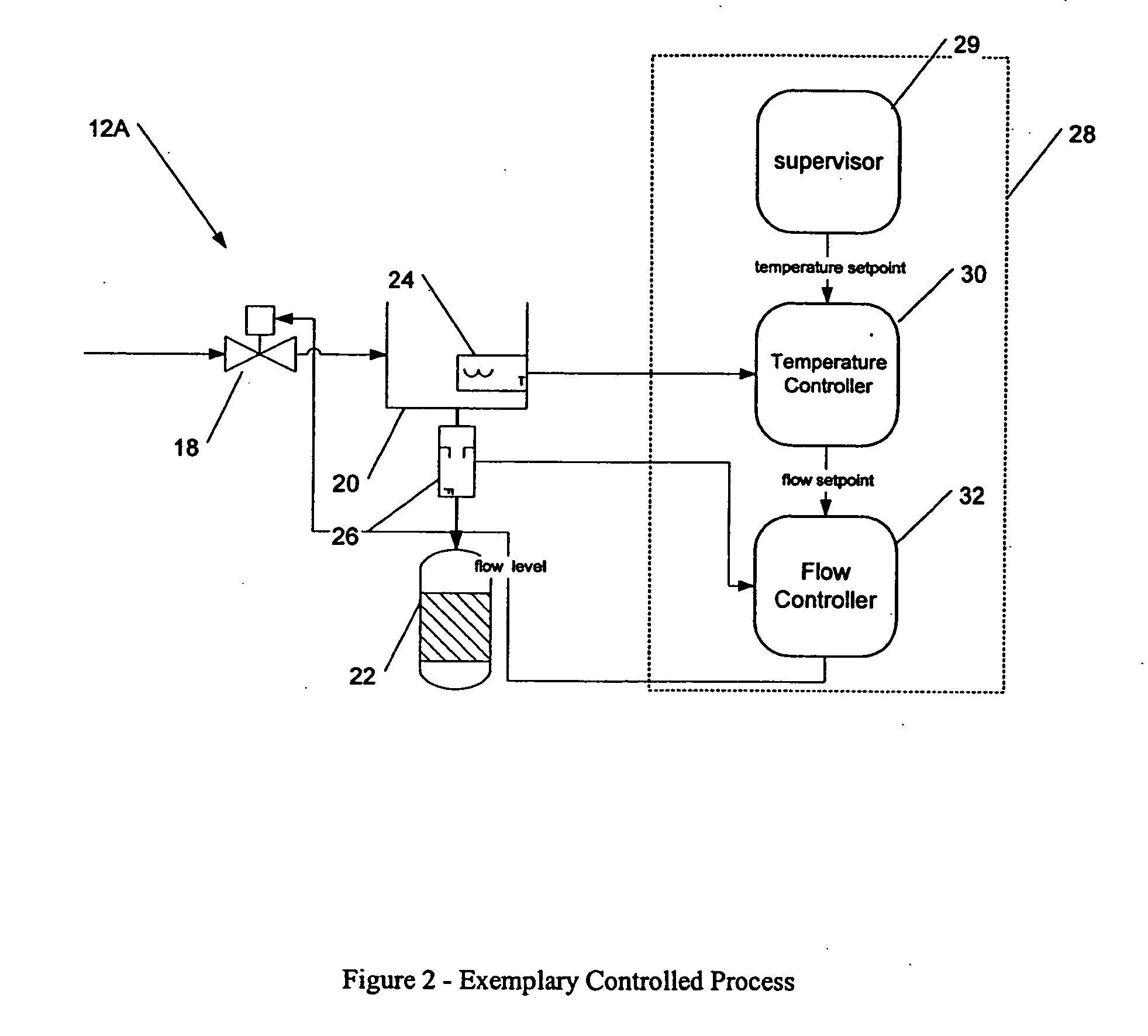
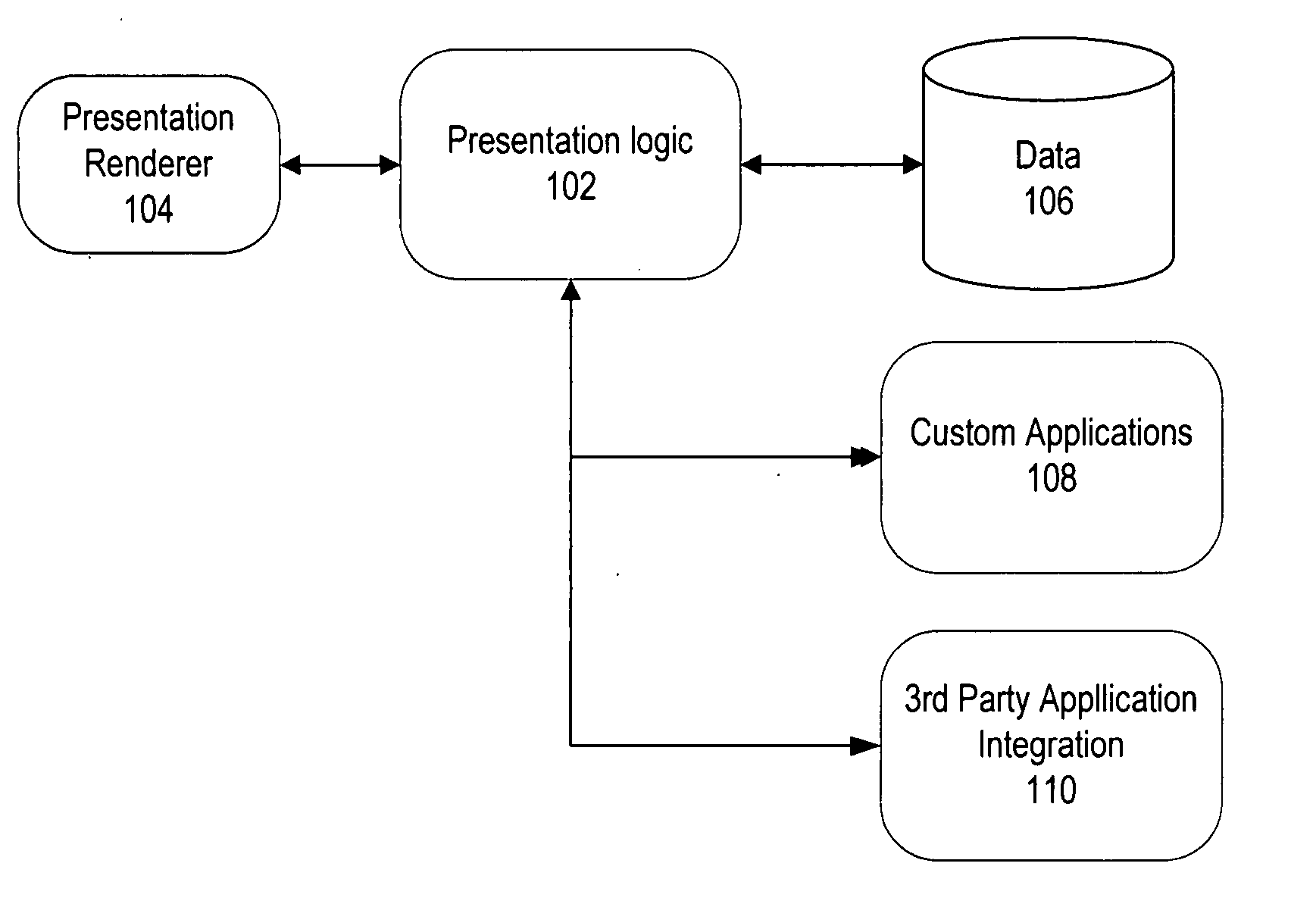
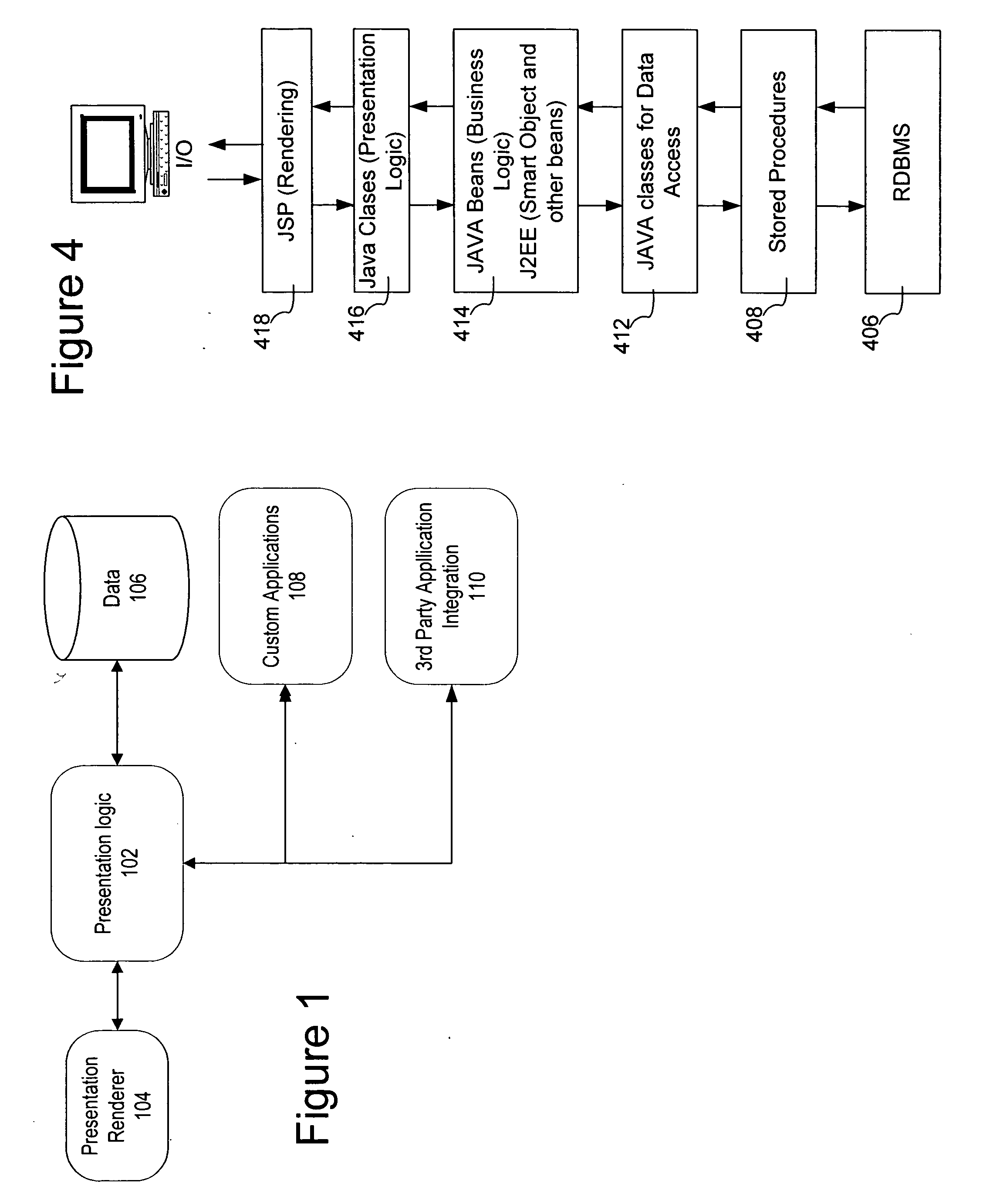
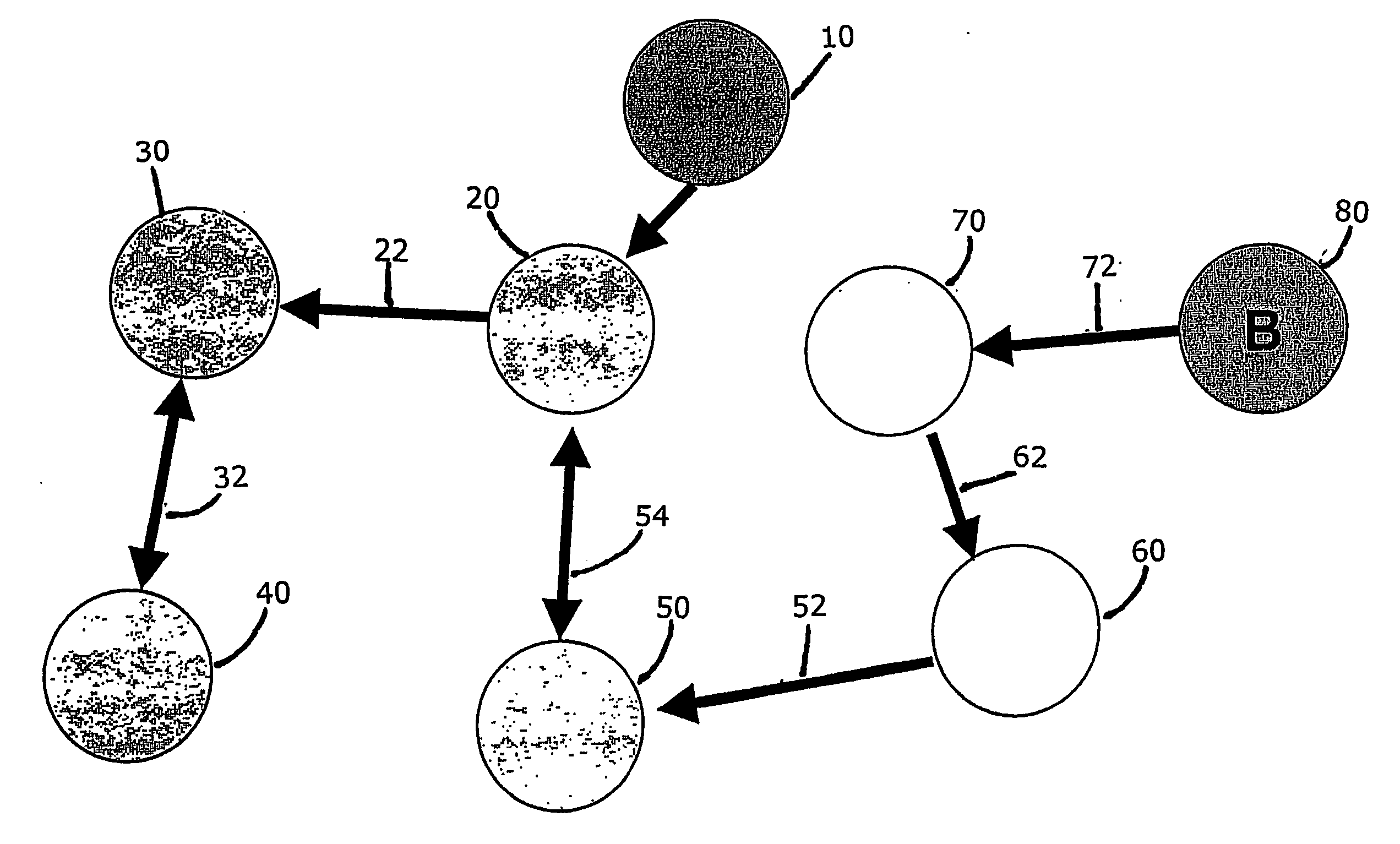
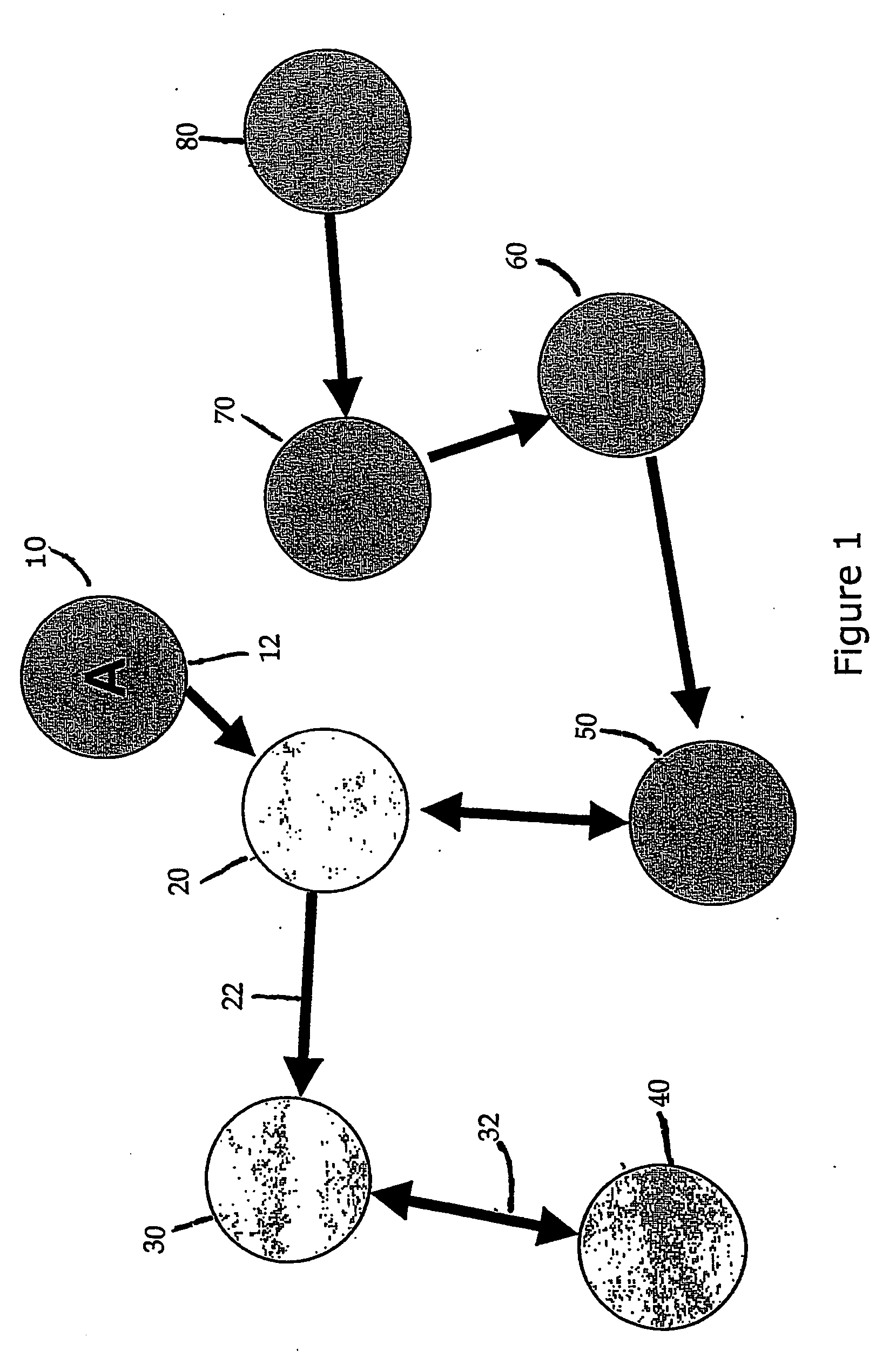
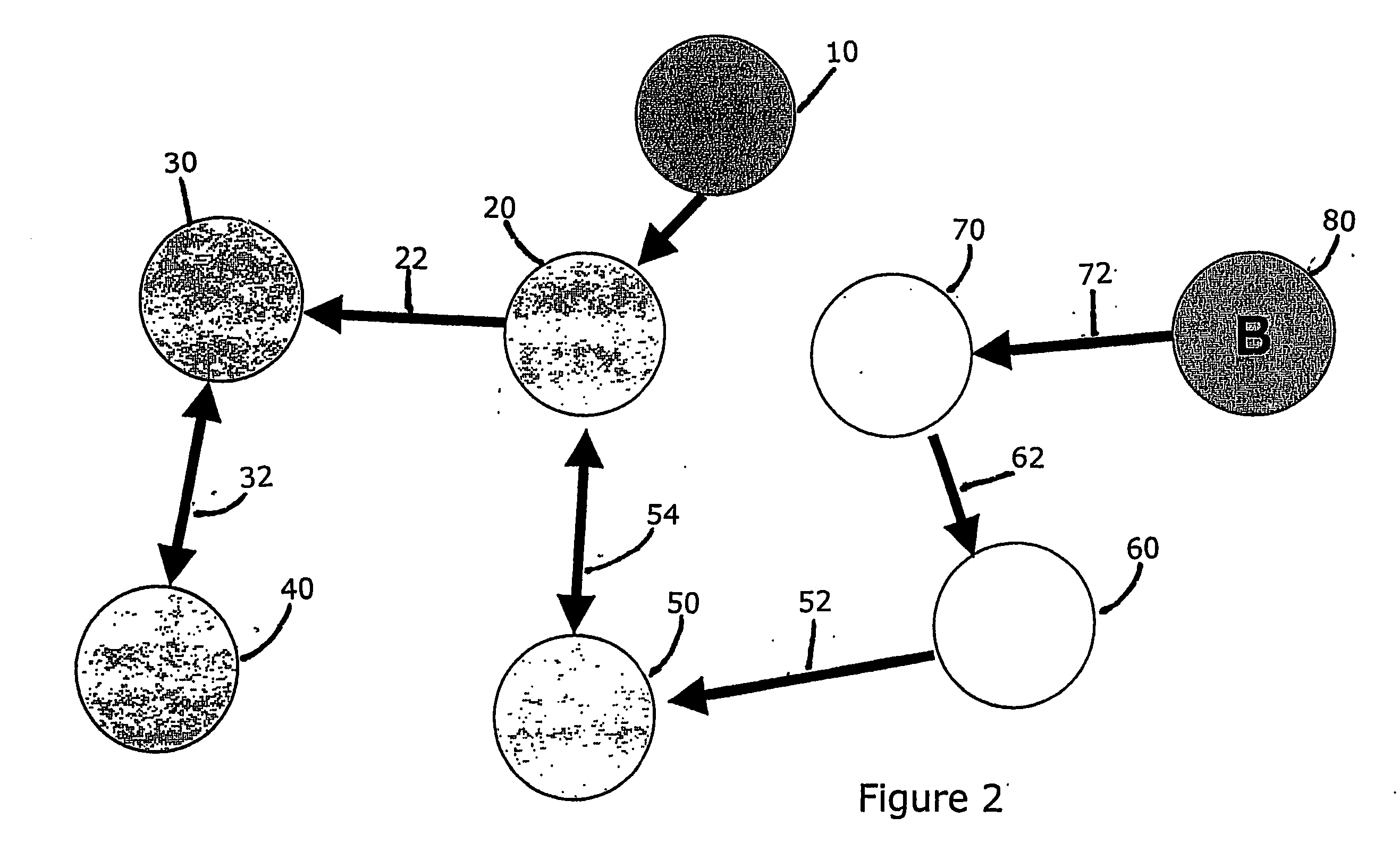
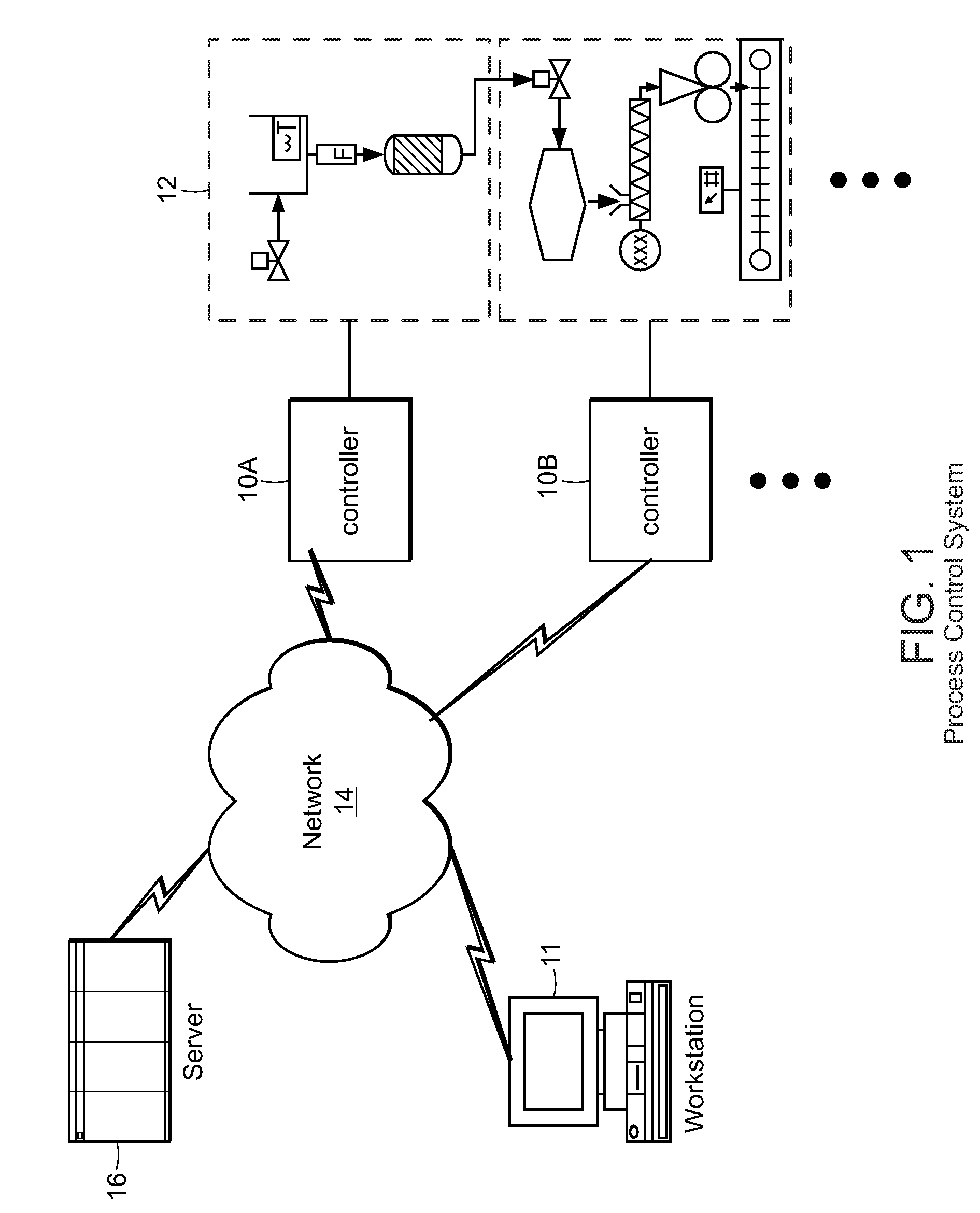
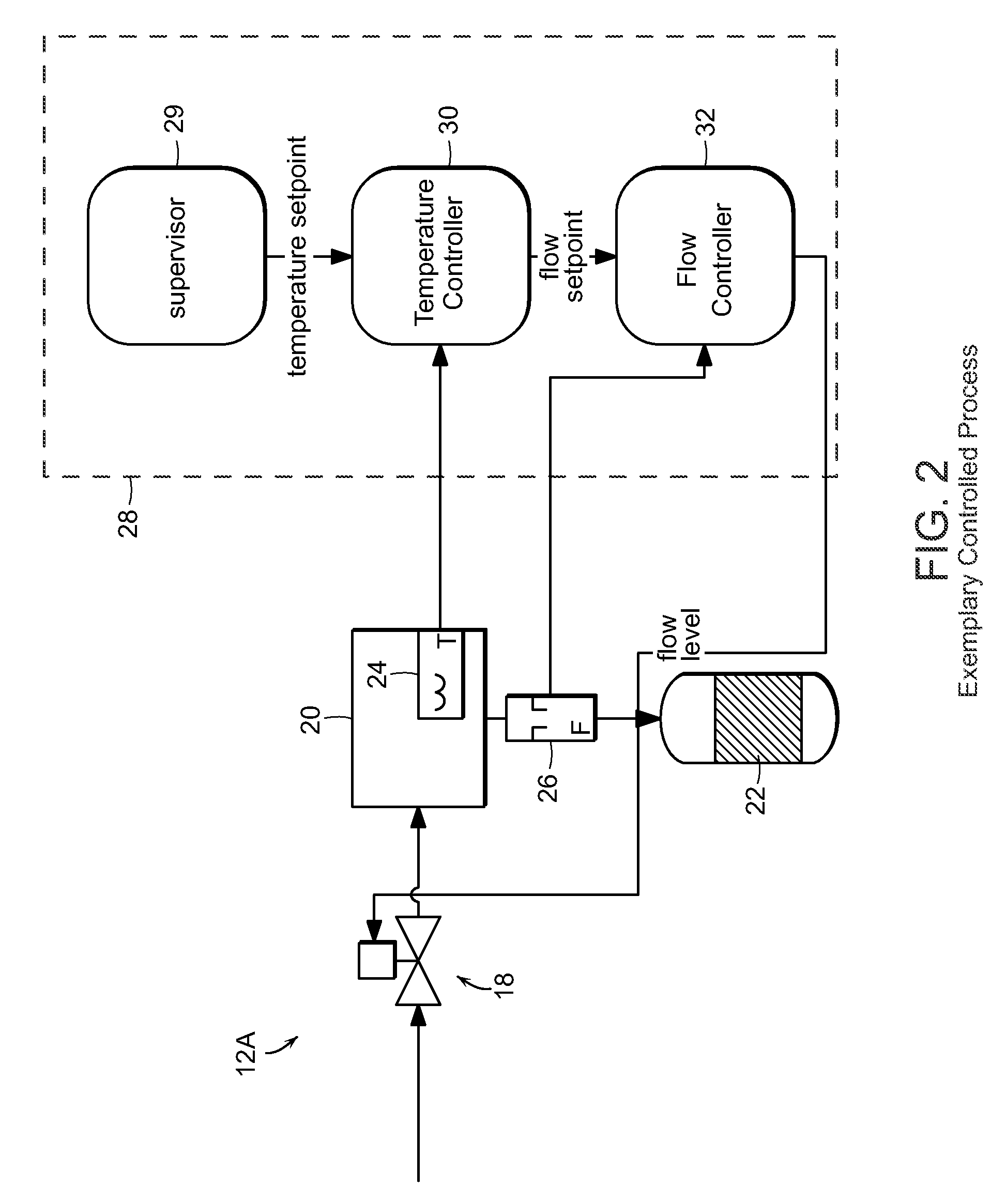
Methods and apparatus for control configuration with versioning, security, composite blocks, edit selection, object swapping, formulaic values and other aspects
InactiveUS7272815B1OptimizationOptimize system configurationData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsGraphical user interfaceComposite object
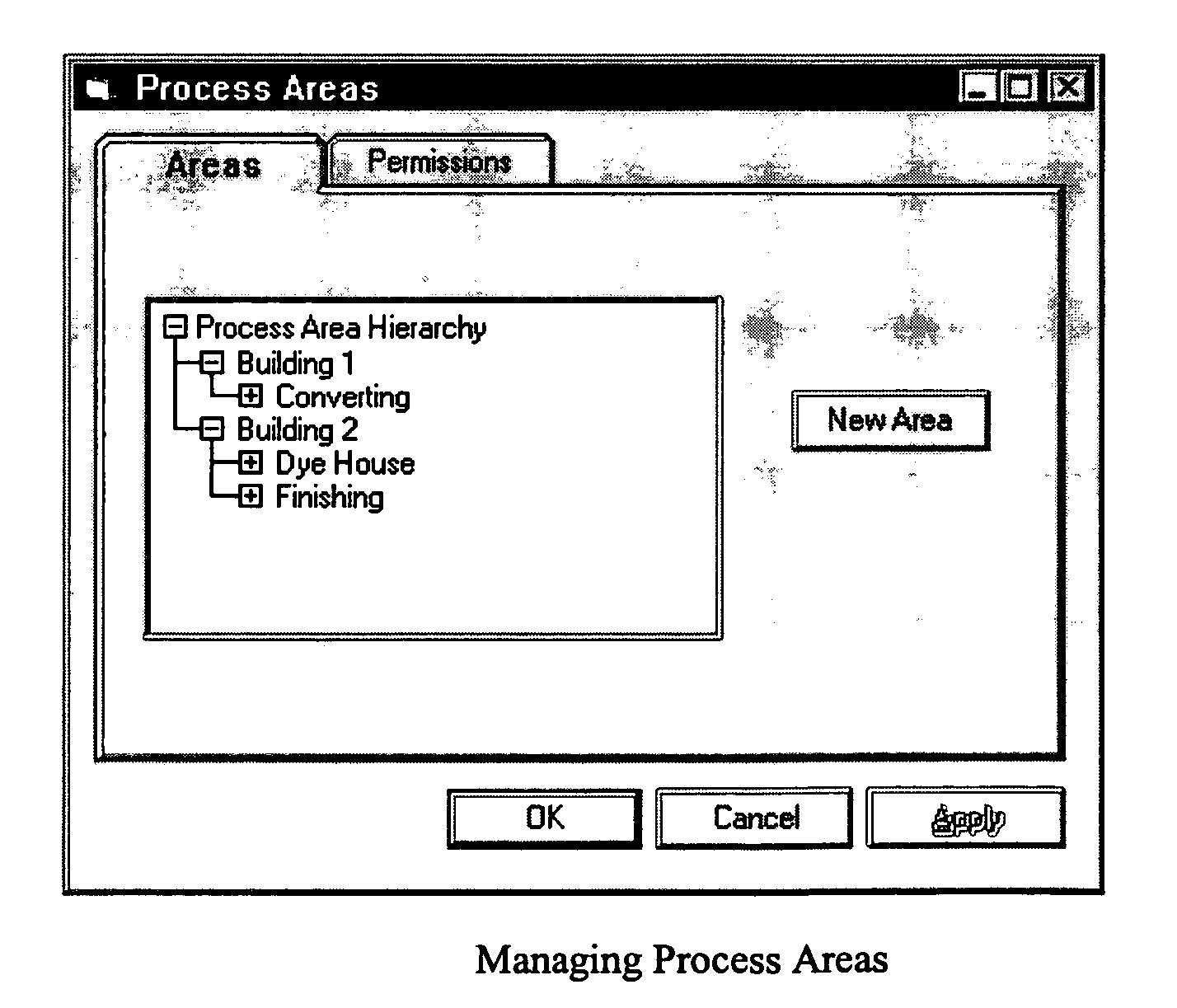
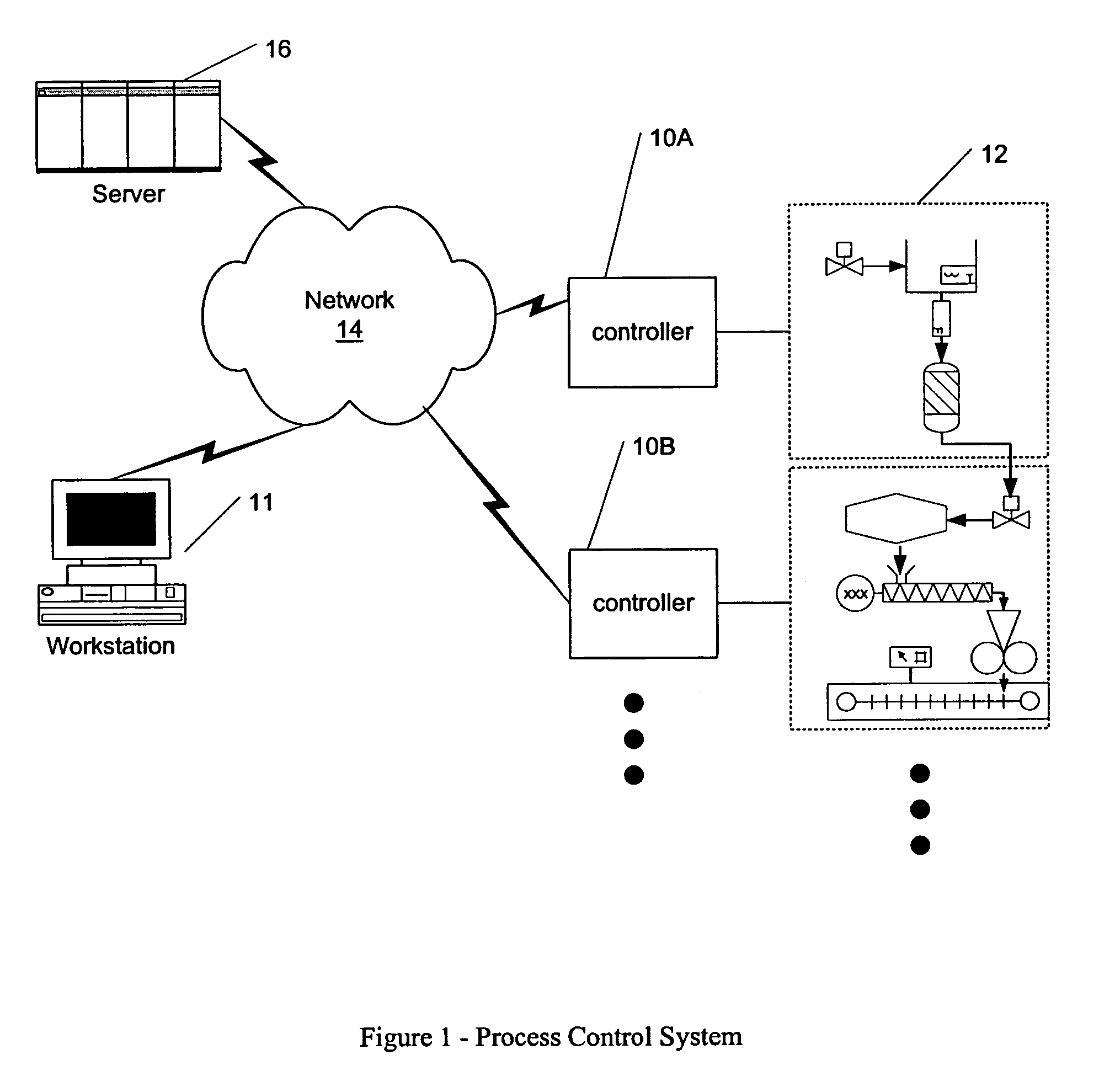
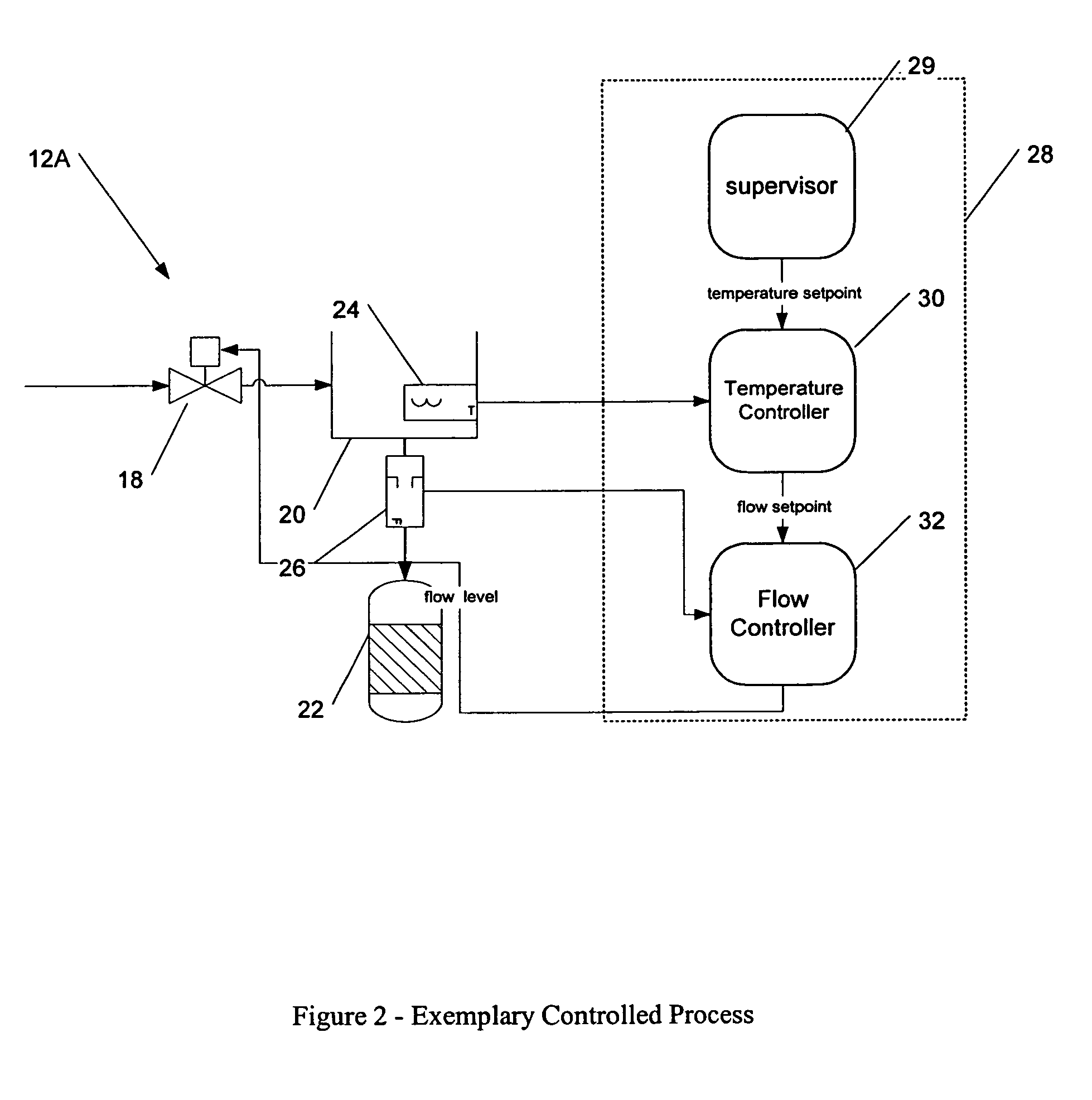
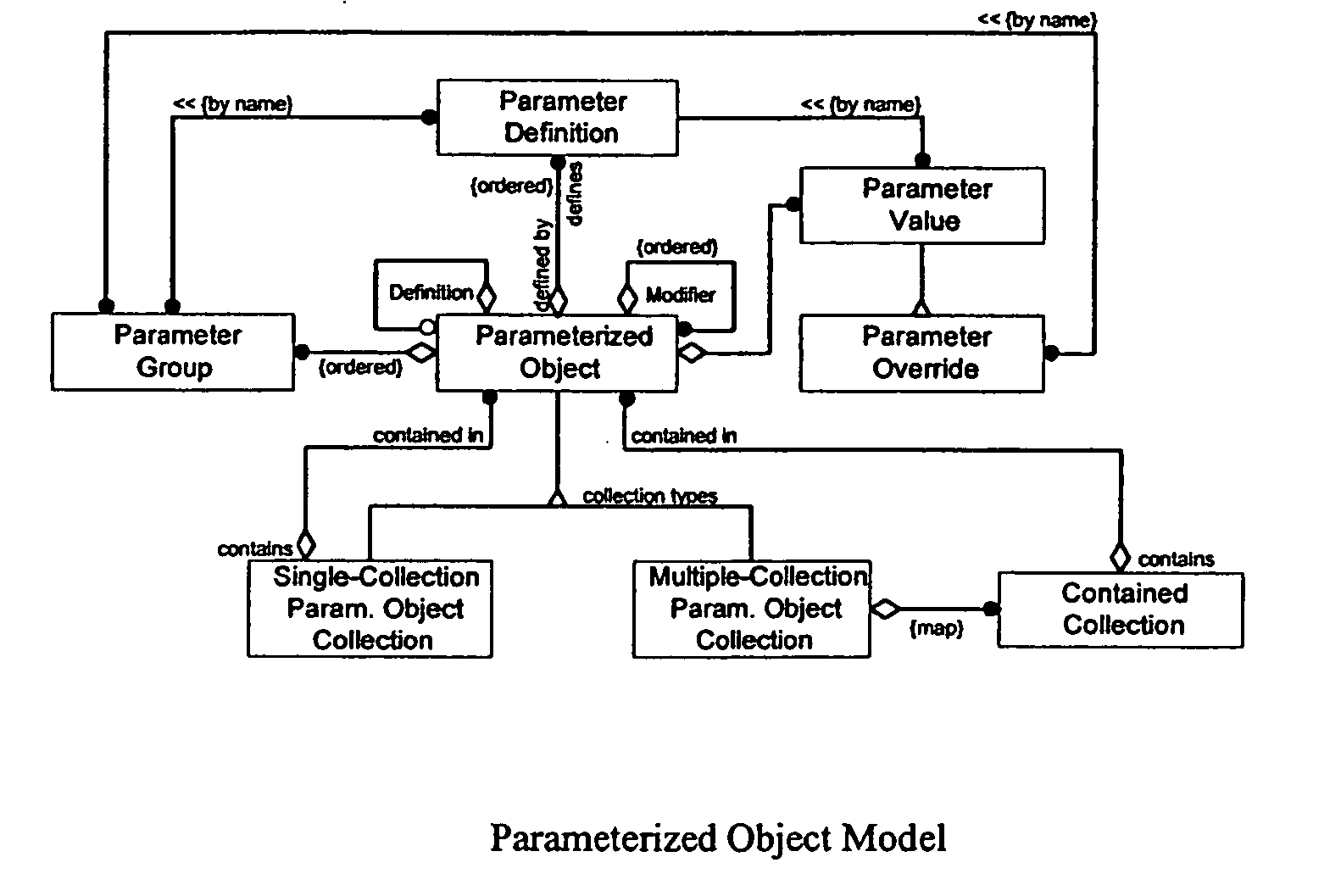
Methods and apparatus for configuring process, environmental, industrial and other control systems generate and / or utilize models representing configurations of control systems and / or the systems controlled by them. Records of changes to the models or the configurations represented by them are maintained, thereby, for example, providing bases for determining current states, prior states and histories of changes. Objects in the model have characteristics, such as an object type characteristic and an area characteristic. Users can have corresponding permissions. A security mechanism apparatus controls access by users to the objects. Composite objects are defined by definition objects and are displayed in encapsulated or expanded formats. Objects can include an edit control type identifier that determines how they are presented for editing. Functionality responds to user commands by transferring characteristics of a first object depicted by the graphical user interface to a second object. Configuration-time formulas contained objects are evaluated to constants prior to downloading to the control system.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SYST USA INC
Methods and apparatus for control configuration using live data
InactiveUS20060206866A1OptimizationOptimize system configurationData processing applicationsComputer controlGraphicsReal-time data
Methods and apparatus for configuring process, environmental, industrial and other control systems generate and / or utilize models representing configurations of control systems and / or the systems controlled by them. Records of changes to the models or the configurations represented by them are maintained, thereby, for example, providing bases for determining current states, prior states and histories of changes. Objects in the model have characteristics, such as an object type characteristic and an area characteristic. Users can have corresponding permissions. A security mechanism apparatus controls access by users to the objects. Composite objects are defined by definition objects and are displayed in encapsulated or expanded formats. Objects can include an edit control type identifier that determines how they are presented for editing. Functionality responds to user commands by transferring characteristics of a first object depicted by the graphical user interface to a second object. Configuration-time formulas contained objects are evaluated to constants prior to downloading to the control system.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
Method for Configuring an Optical Network
InactiveUS20090296719A1Huge complexityHuge timeData switching by path configurationOptical multiplexObject definitionNetwork model
A network model for the planning and / or the provisioning of traffic flows in a communication network includes nodes interconnected with each other by links according to a given network topology. The network model uses a graph defined by arc objects storing information related to both the links and adjacent nodes thereof.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
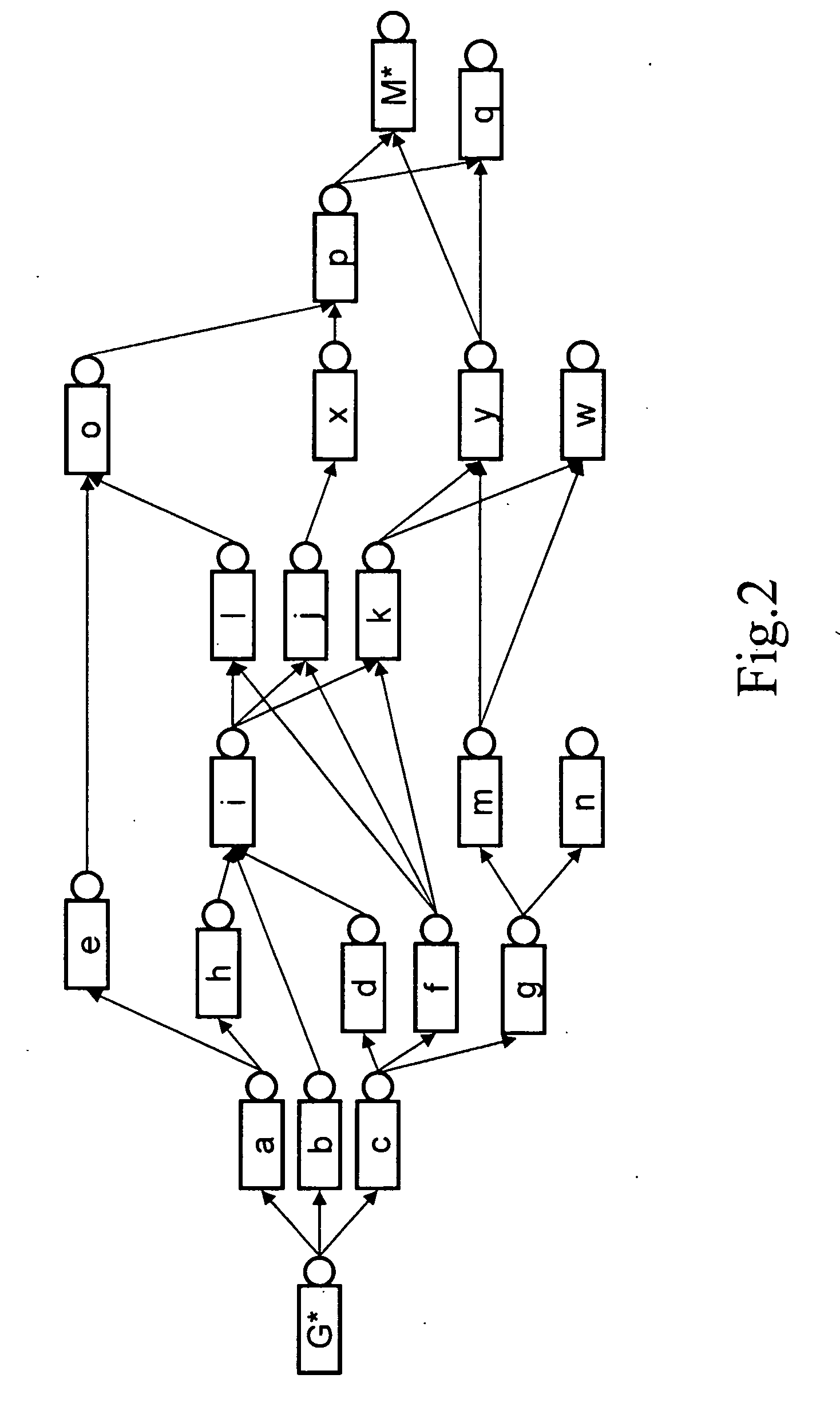
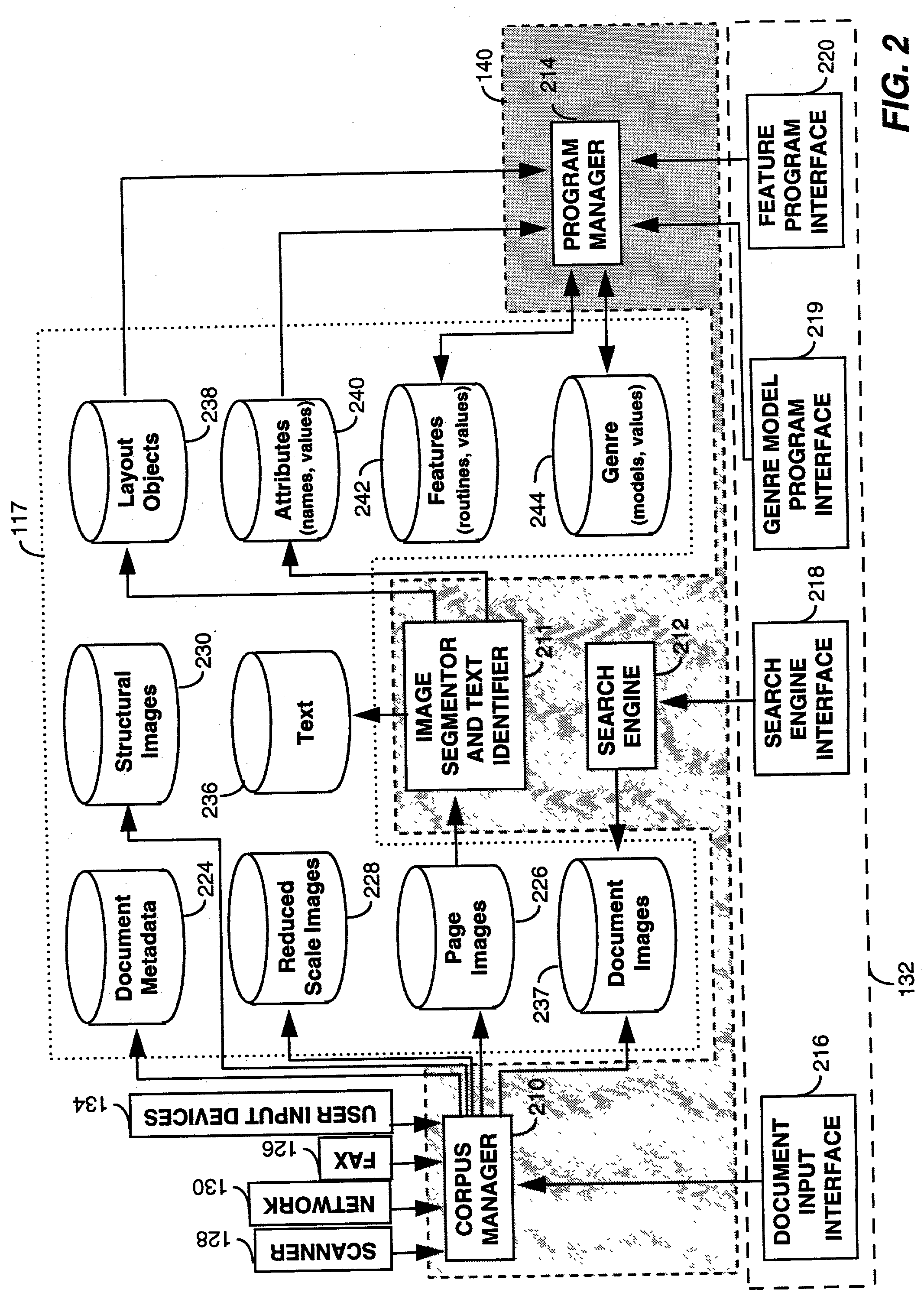
System for sorting document images by shape comparisons among corresponding layout components
A programming interface of document search system enables a user to dynamically specifying features of documents recorded in a corpus of documents. The programming interface provides category and format flexibility for defining different genre of documents. The document search system initially segments document images into one or more layout objects. Each layout object identifies a structural element in a document such as text blocks, graphics, or halftones. Subsequently, the document search system computes a set of attributes for each of the identified layout objects. The set of attributes are used to describe the layout structure of a page image of a document in terms of the spatial relations that layout objects have to frames of reference that are defined by other layout objects. Using the set of attributes a user defines features of a document with the programming interface. After receiving a feature or attribute and a set of document images selected by a user, the system forms a set of image segments by identifying those layout objects in the set of document images that make up the selected feature or attribute. The system then sorts the set of image segments into meaningful groupings of objects which have similarities and / or recurring patterns. In operation, the system sorts images in the image domain based on segments (or portions) of a document image which have been automatically extracted by the system. As a result, searching becomes more efficient because it is performed on limited portions of a document. Subsequently, document images in the set of document images are order and displayed to a user in accordance with the meaningful groupings.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Software application framework using meta-data defined object definitions
InactiveUS20060143220A1More independentSoftware designSpecial data processing applicationsObject definitionApplication software
An application framework for creating business process management software applications. The framework includes a data store including application data and information describing said data for a runtime environment. The information describing the application data includes presentation information and relational information. The framework further includes presentation logic outputting said data based on said information describing said data, and one or more automated business processes operable on said data.
Owner:TRIRIGA
Spreadsheet programming
InactiveUS20060224946A1Great computational capabilityGreat expressive powerText processingDigital computer detailsElectronic formObject definition
Spreadsheet programming model and language is extended to create objects, with their associated state and set of defined behaviors, as first-class spreadsheet cell residents. Desired object behaviors can be invoked by calling methods on the objects through an event-based imperative programming language that potentially modifies the state of an object. Expressions can also be defined by calling methods on objects that produce new objects in combination with operations on objects in other cells. Programming constructs are defined that allows users to perform a sequence of operations on one or more objects. Operations can also be performed automatically similar to spreadsheet triggering mechanism. Users can program to trigger operations either manually or automatically based on changes to objects, or based on conditions defined.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and Systems for Performing Transparent Object Migration Across Storage Tiers
ActiveUS20110258225A1For quick maintenanceMore reliableDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsObject definitionObject migration
In accordance with embodiments, there are provided mechanisms and methods for performing transparent object migration across storage tiers. In an embodiment and by way of example, a method for appending data to large data volumes is provided. The method embodiment includes a) setting a CustomEntityOption bit that determines (at object creation time) where the object is stored, either in the relational or the non-relational data store portion, b) loading the CustomEntityOption bit in a cached CustomEntityDefinition, c) showing the CustomEntityOption bit as EntityInfo, and d) allowing custom object definition and Metadata API functionality when the bit is shown.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
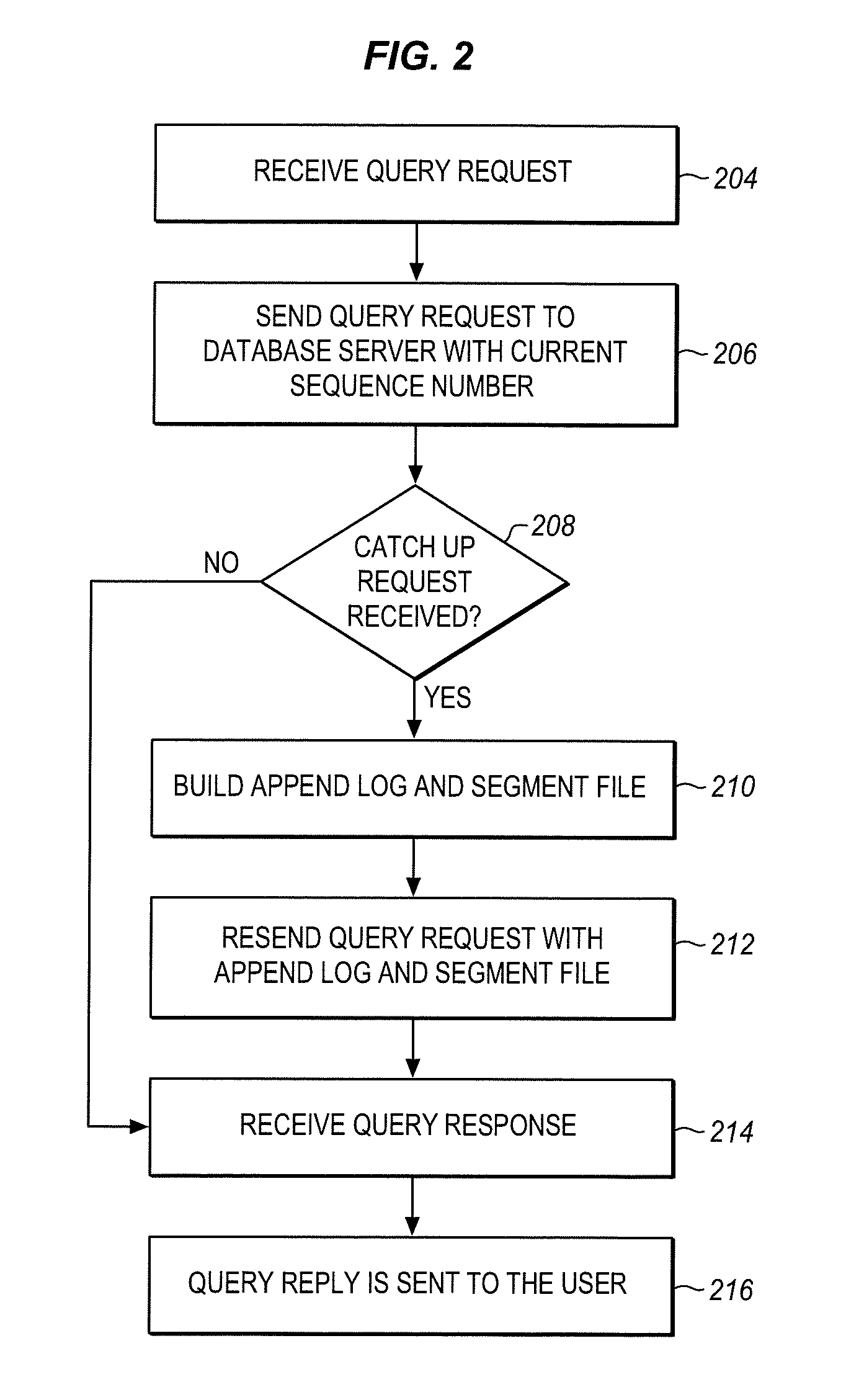
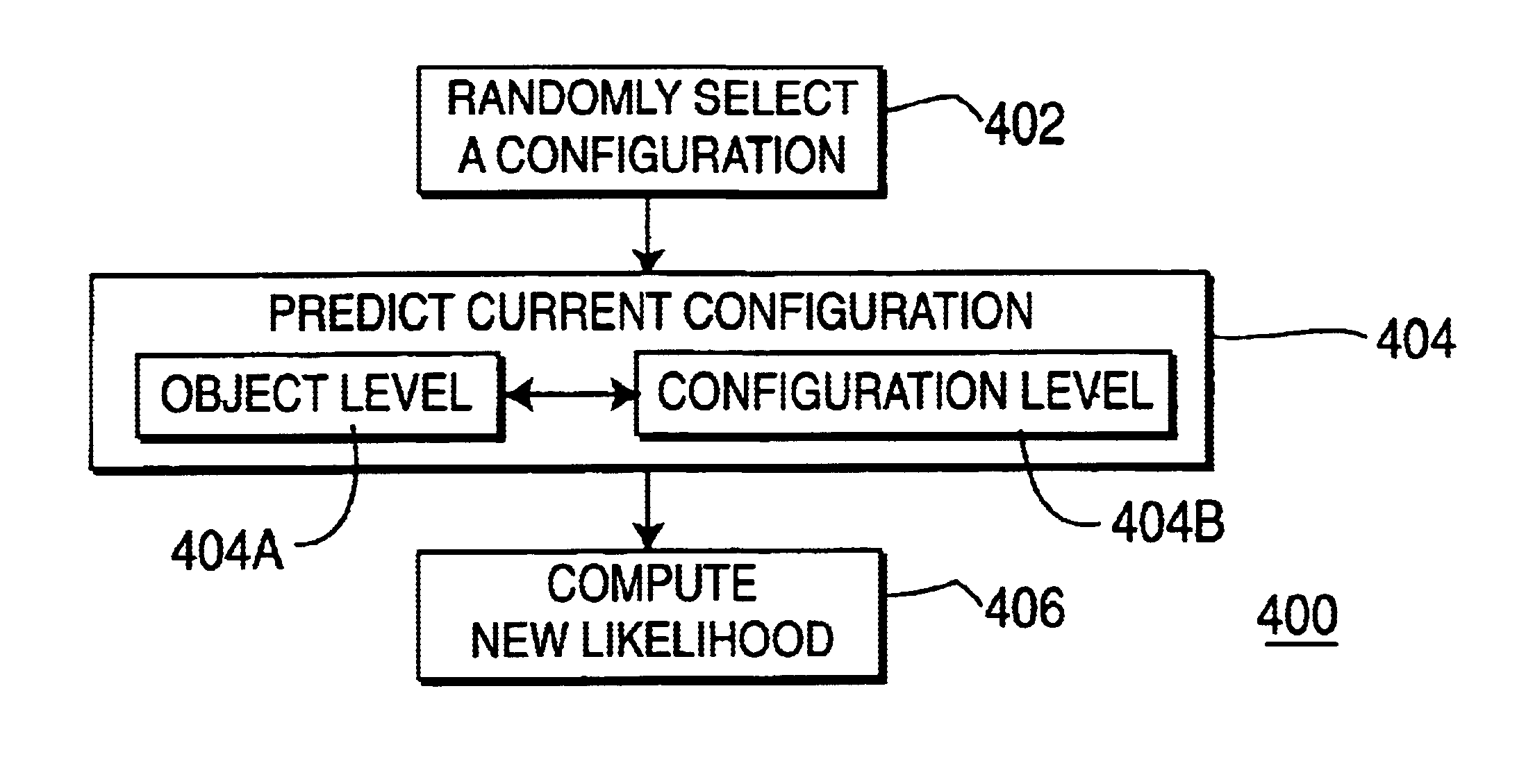
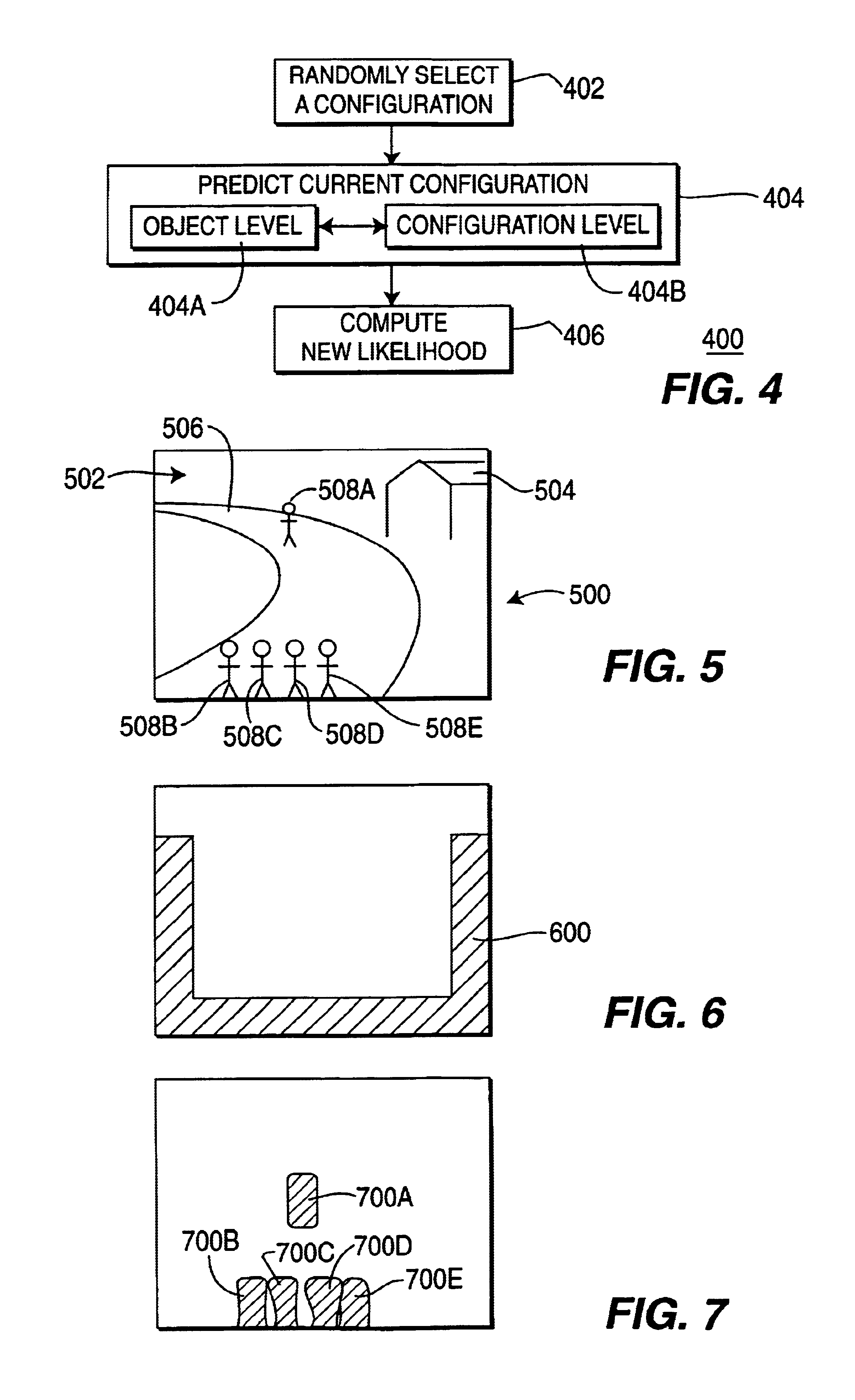
Method and apparatus for tracking multiple objects in a video sequence
InactiveUS6879705B1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A method and apparatus for tracking multiple objects in a video sequence. The method defines a group of objects as a configuration, selects a configuration for a current video frame, predicts a configuration using a two-level process and computes the likelihood of the configuration. Using this method in an iterative manner on a sequence of frames, tracks the object group through the sequence.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Rich drag drop user interface
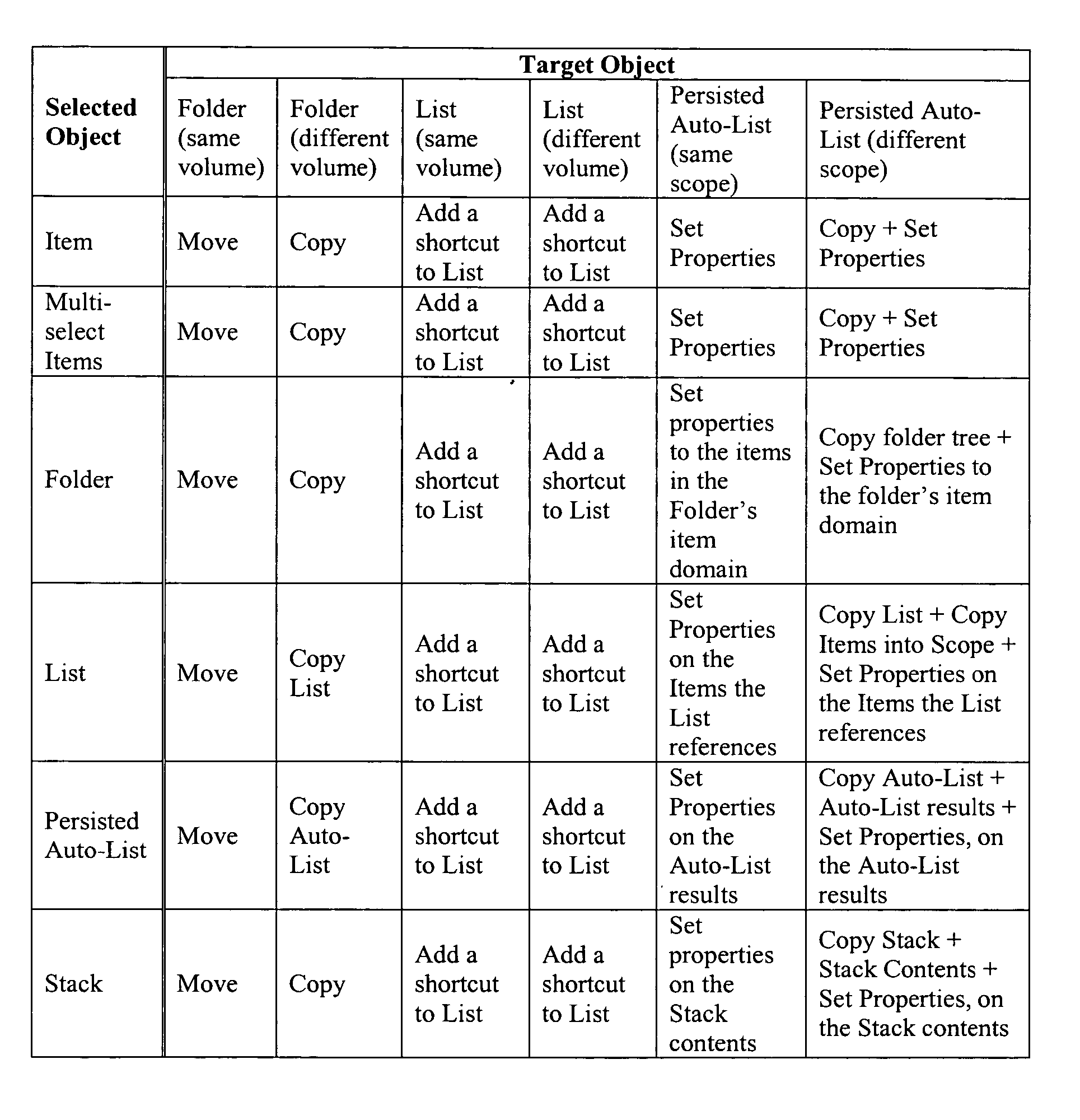
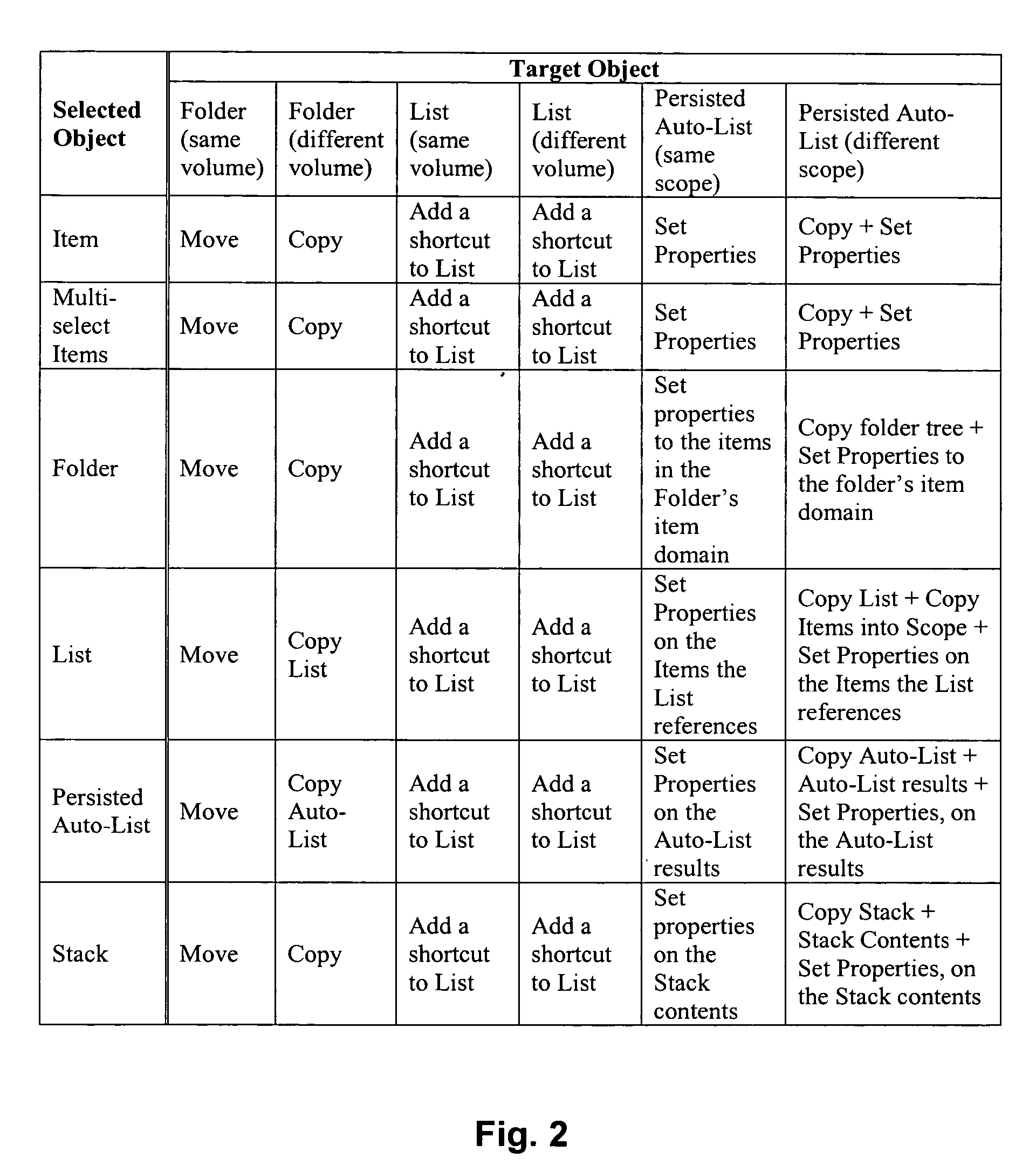
ActiveUS20070016872A1Rich relevant informationSpecial data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingFile systemObject definition
In an electronic file system, preview information is provided to the user during a drag operation of a selected object onto a target object. The information indicates what type(s) of action is to be taken should the selected object be dropped onto the target object. The action(s) to be taken may depend upon the type of the selected object and / or the type of the target object. For example, where the selected object is an item and the target object is a persisted auto-list, the action may include adding, removing, or modifying one or more properties of the selected object to conform to one or more criteria defined by the persisted auto-list. Also, numerical feedback may be provided to the user where multiple objects are selected. For example, where seven objects are selected, the textual number “7” may appear next to the cursor.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Automatic Creation And Management Of Dynamic Content
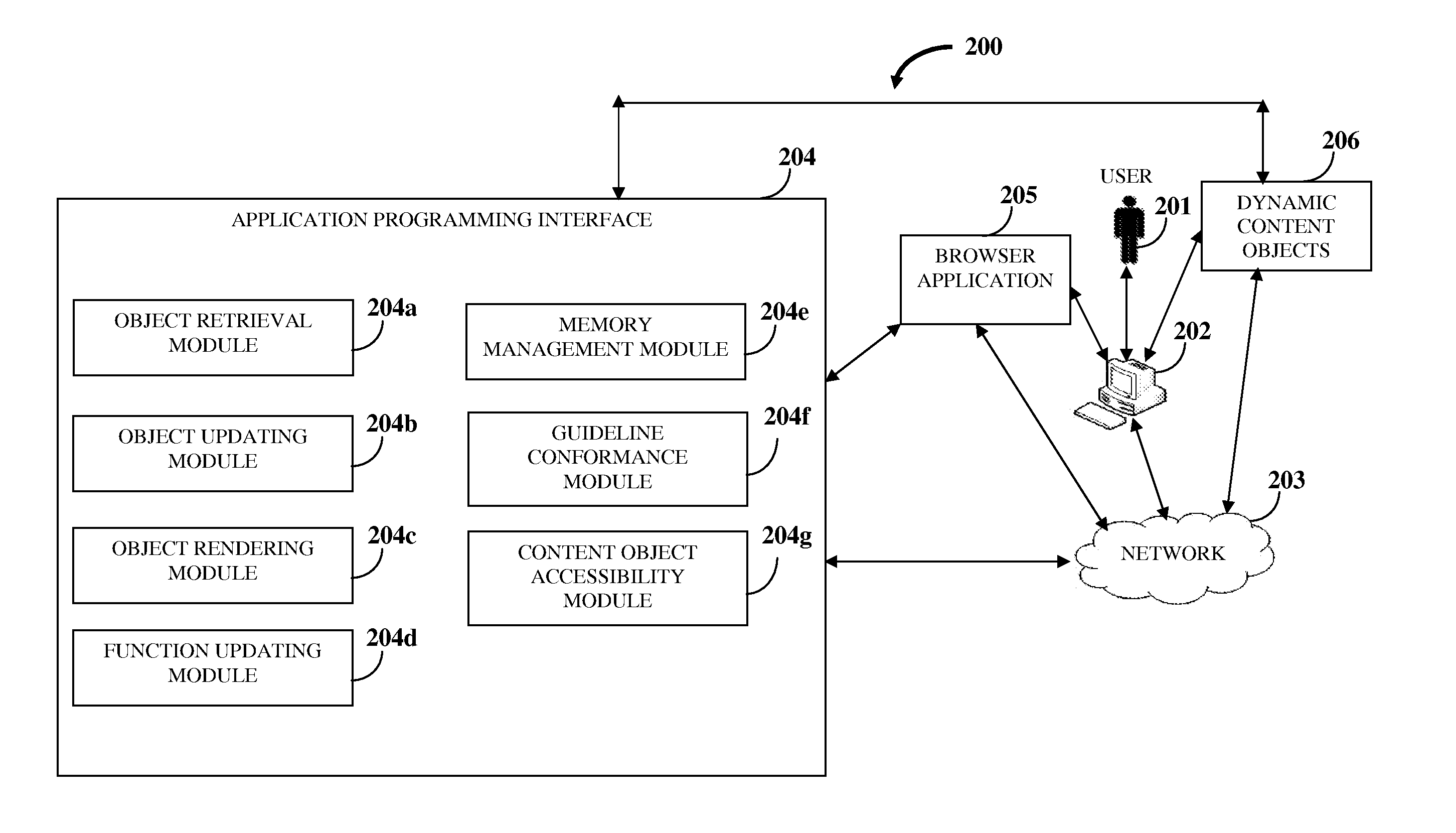
InactiveUS20110197124A1Website content managementSpecial data processing applicationsApplication programming interfaceUser input
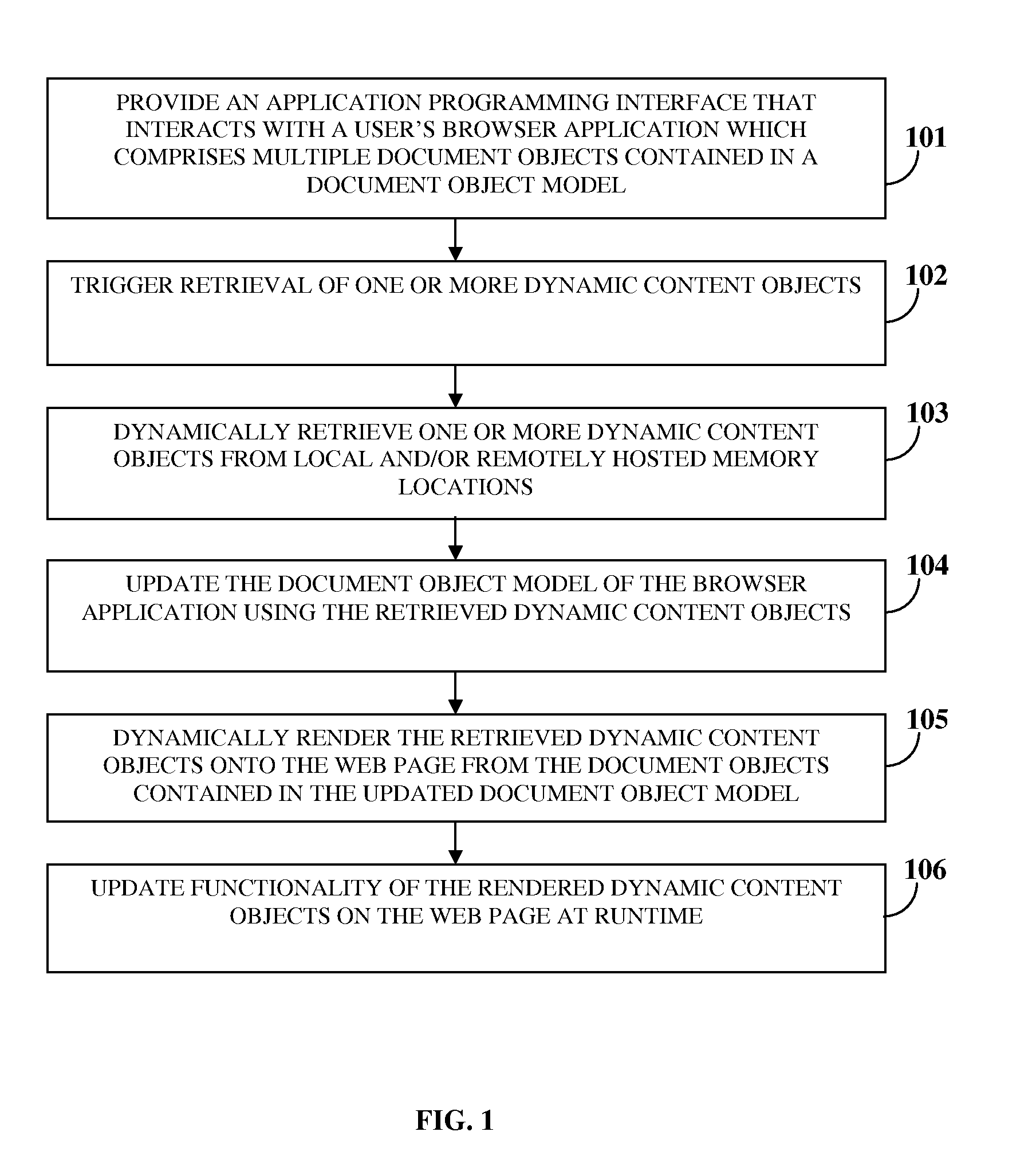
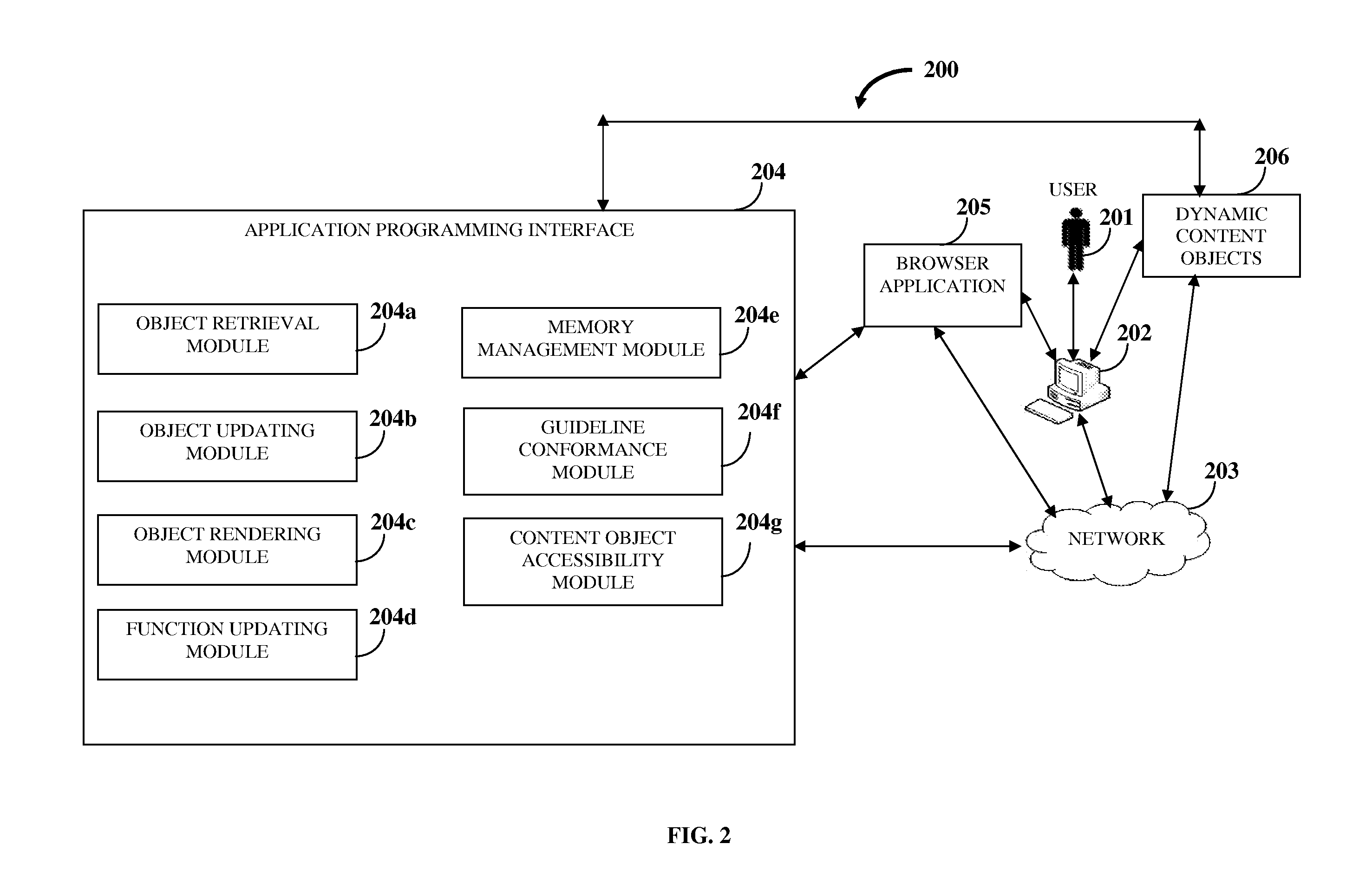
A computer implemented method and system for creating and managing dynamic content on a web page is provided. An application programming interface that interacts with a user's browser application is provided. The browser application comprises multiple document objects contained in a document object model. A user input triggers retrieval of one or more dynamic content objects on the web page. The application programming interface dynamically retrieves the dynamic content objects from local and / or remotely hosted memory locations. The application programming interface updates the document object model using the retrieved dynamic content objects. The retrieved dynamic content objects define the document objects in the document object model. The application programming interface dynamically renders the retrieved dynamic content objects onto the web page from the document objects contained in the updated document object model. The application programming interface updates functionality of the rendered dynamic content objects on the web page at runtime.
Owner:GARAVENTA BRYAN ELI
Object versioning
ActiveUS20050131964A1Eliminate needData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalRevision controlUnique identifier
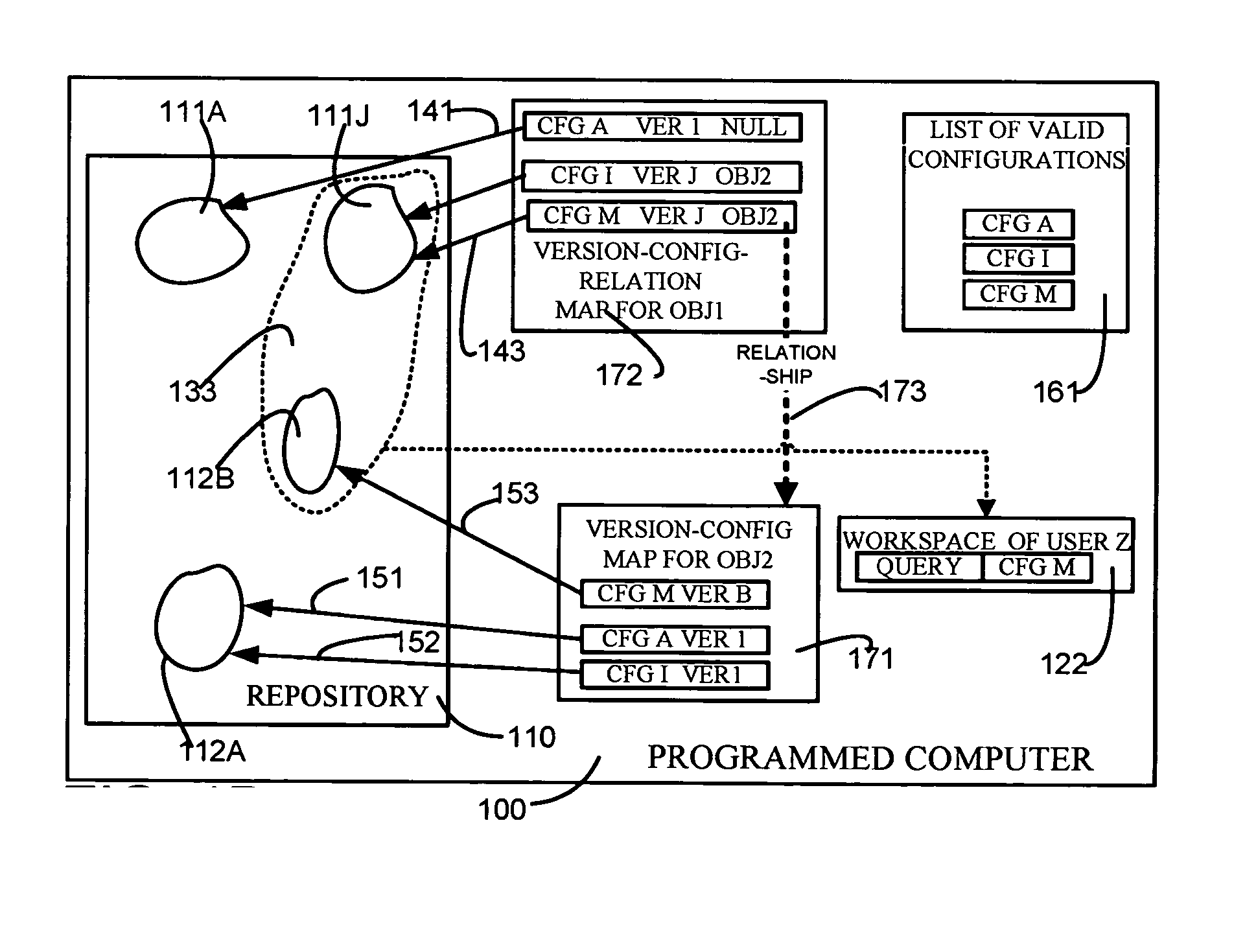
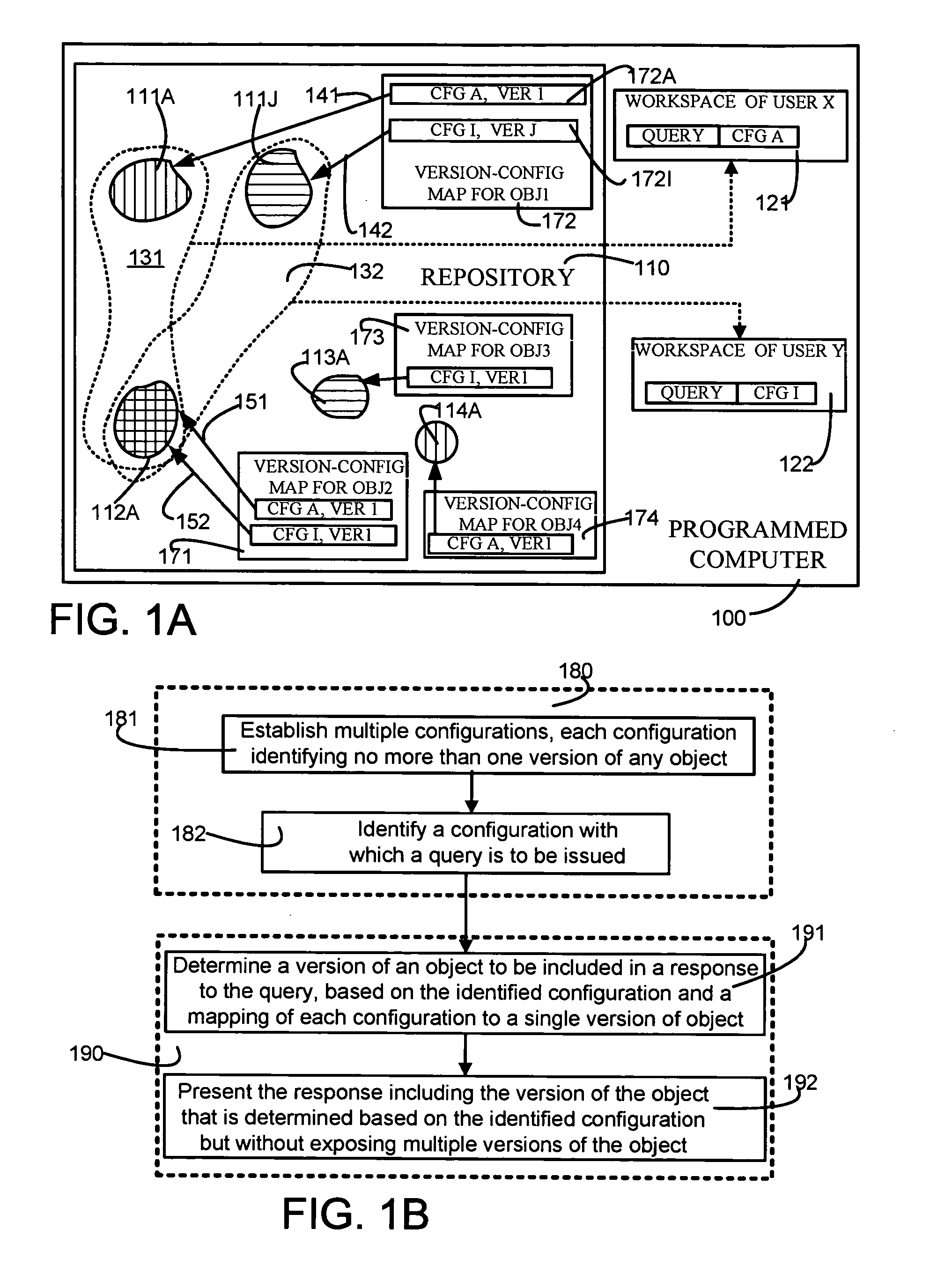
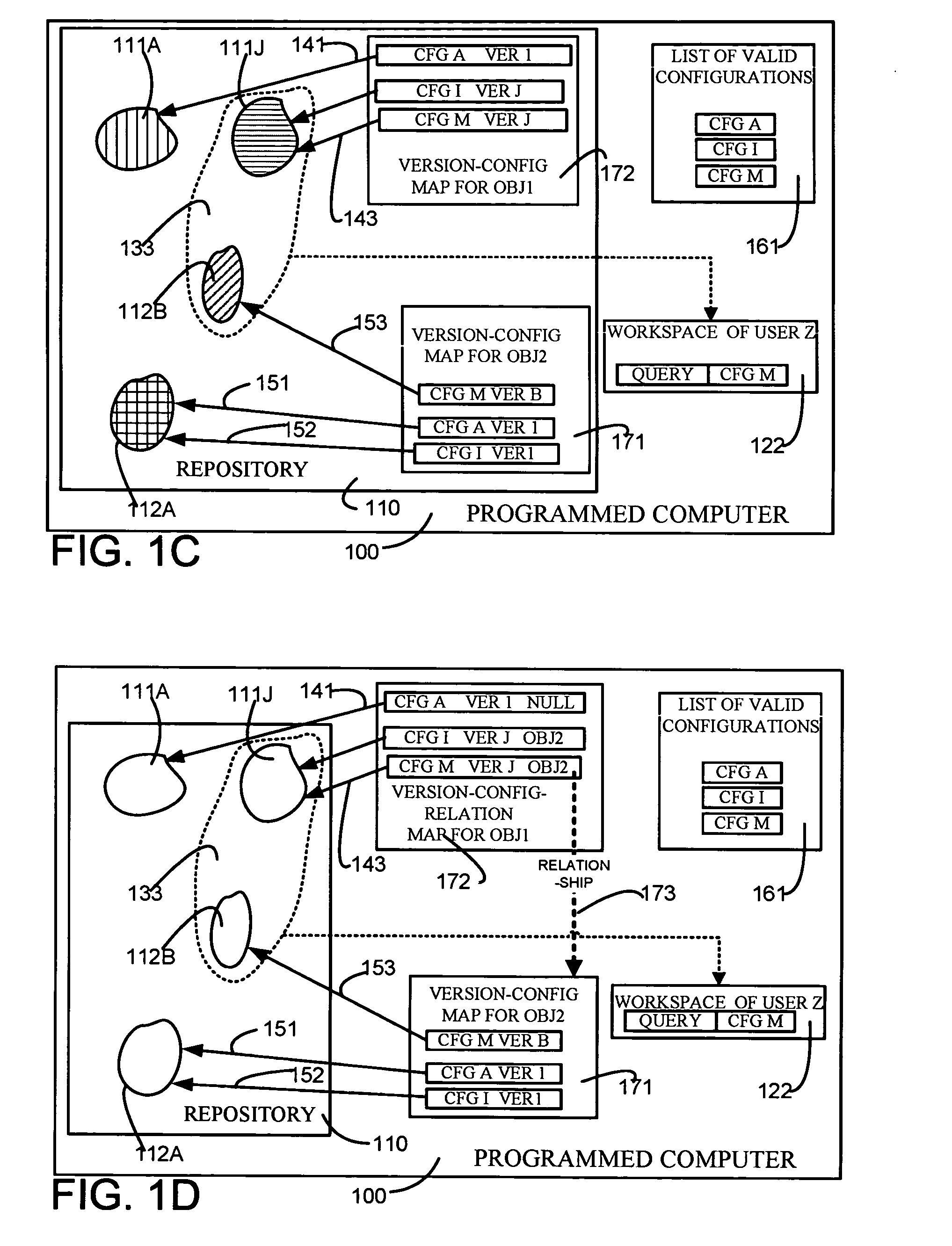
A repository contains multiple versions of an object, and any version of the object can be modified by a user, as and when necessary. A table for one object (“first object”) that is contained in another object (“second object”) has at least two columns, namely one column for a minimum version of the second object and another column for a maximum version of the second object. If a number of versions of the first object are responsive to a query, then one version of the first object is selected if a version of the second object that is responsive to the query happens to be in the range defined by the just-described minimum version number and the maximum version number. Depending on the embodiment, the second object can be an immediate parent of the first object, or can be an ancestor (also called “first class object”) of the first object that is not contained in any other object. In some embodiments, one or more attributes of the first object are stored in a first table along with a unique identifier and a version number. In addition, information on relations of the first object to other objects as well as an identity of a configuration (to which the current version of the first object belongs) are stored in a second table. Therefore, a pair of tables are used for each object, so as to decouple information that defines an object from information on relationships of the object. If a change happens in just the relationship of an object then no change is made to the table containing the definition of the object. Similarly, if a change happens in just the definition of the object, then no change is made to the table containing the relations of the object. Moreover, when a change happens to an object, if the object has a number of ancestors and decendants only an immediate parent of the object is updated, thereby to eliminate a versioning chain reaction (i.e. other objects are not affected).
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Factor analysis of information risk
InactiveUS20050066195A1Risk management decisions can become more effective and efficientGood return on investmentDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsSalient objectsObject definition
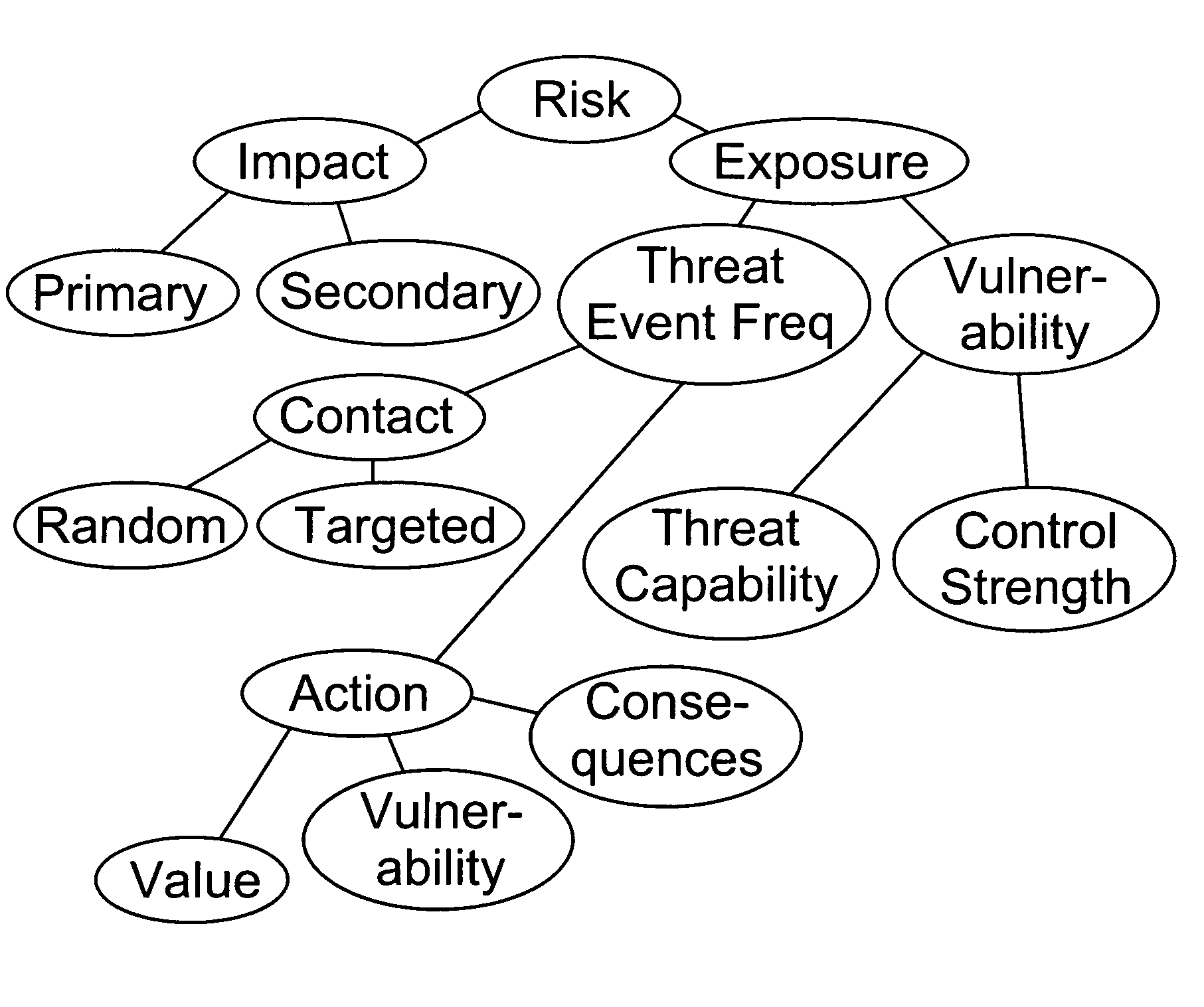
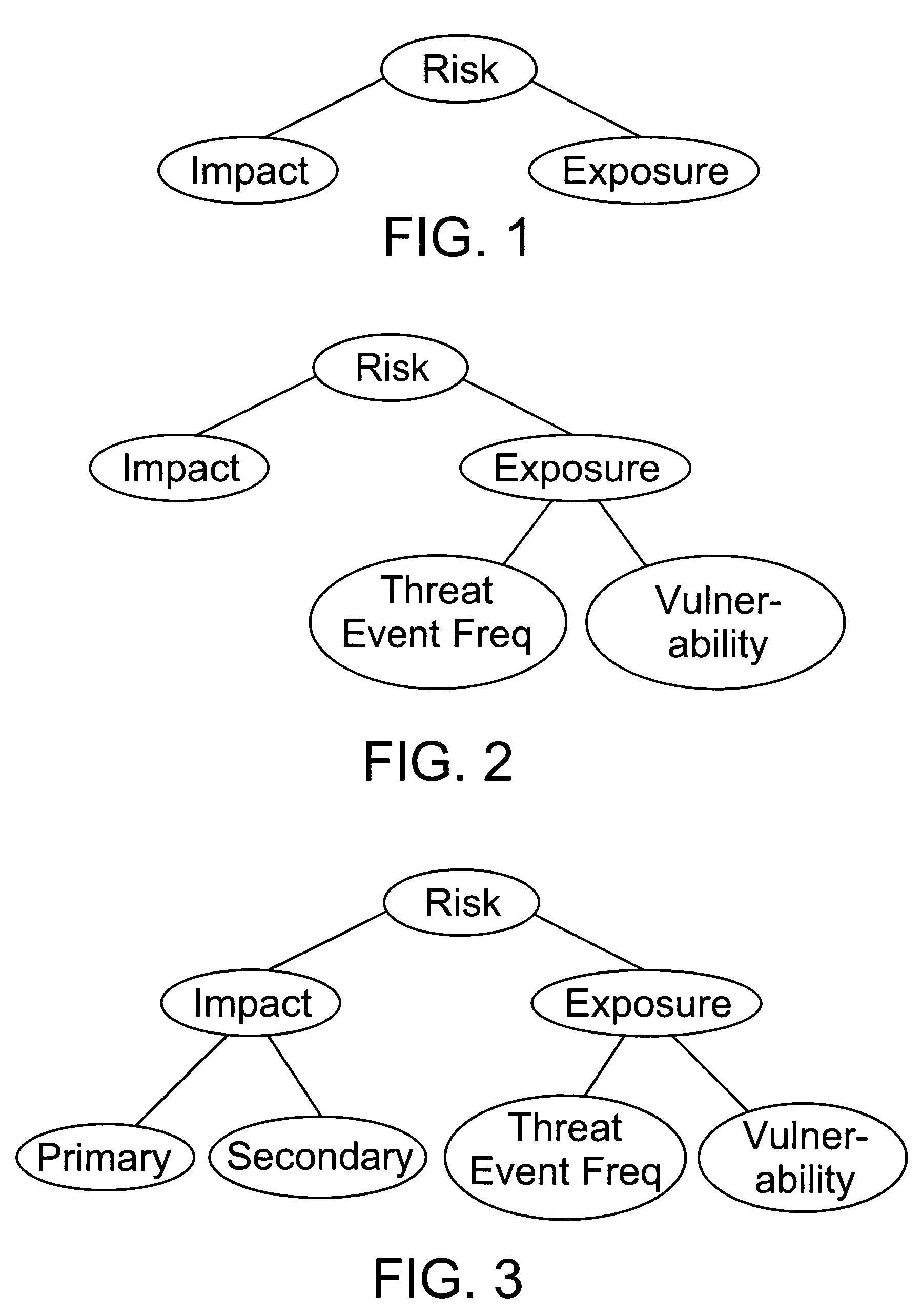
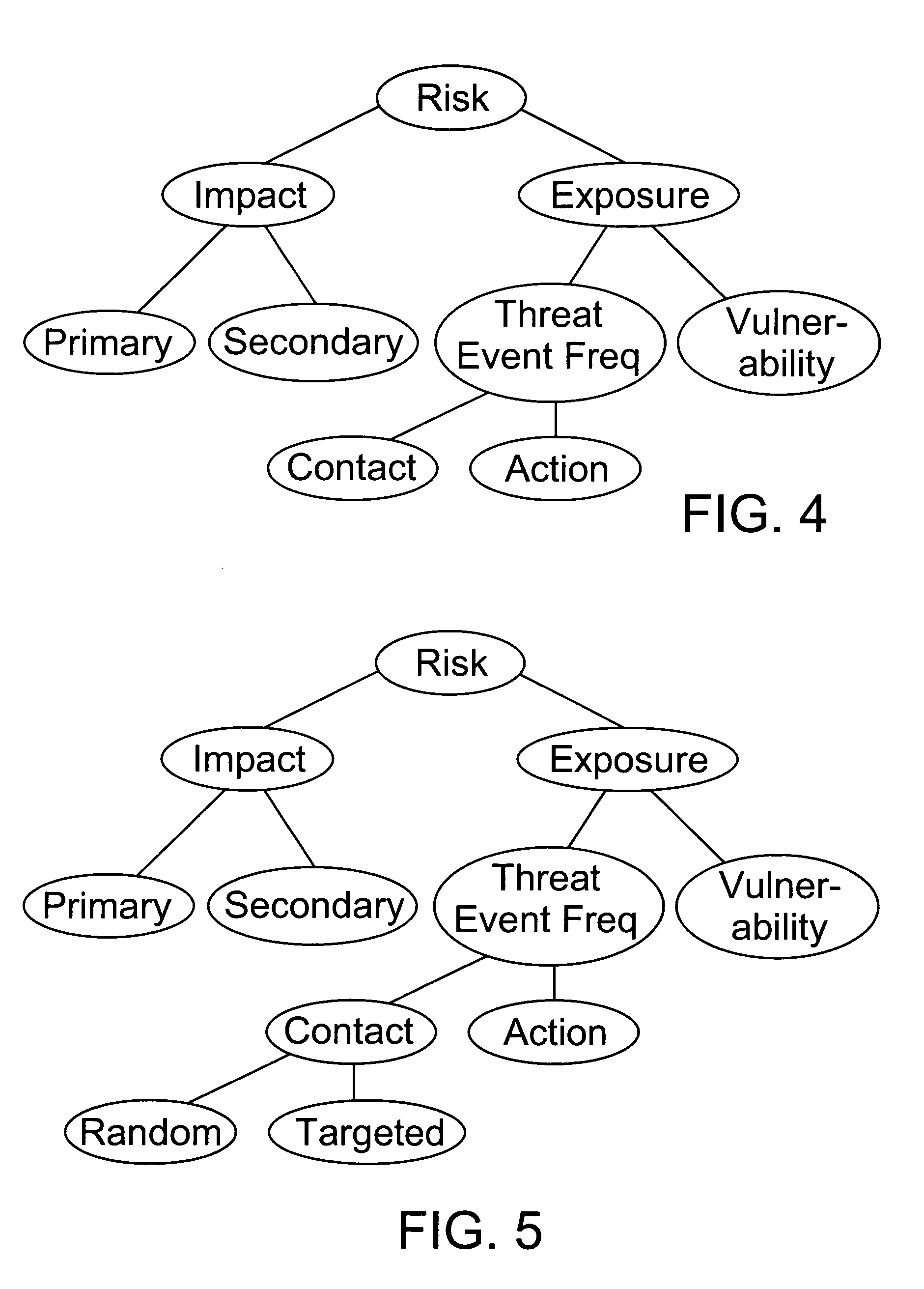
The invention is a method of measuring and representing security risk. The method comprises selecting at least one object within an environment and quantifying the strength of controls of at least one object within that environment. This is done by quantifying authentication controls, quantifying authorization controls, and then quantifying structural integrity. In the preferred method, the next step is setting global variables for the environment, for example, whether the environment is subject to regulatory laws, and then selecting at least one threat community, for example, professional hackers, and then calculating information risk. This calculation is accomplished by performing a statistical analysis using the strengths of controls of said at least one object, the characteristics of at least one threat community, and the global variables of the environment, to compute a value representing information risk. The method identifies the salient objects within a risk environment, defines their characteristics and how they interact with one another, utilizing a means of measuring the characteristics, and a statistically sound mathematical calculation to emulate these interactions and then derives probabilities. The method then represents the security risk, such as the risk to information security, such as by an integer, a distribution or some other means.
Owner:JONES JACK A
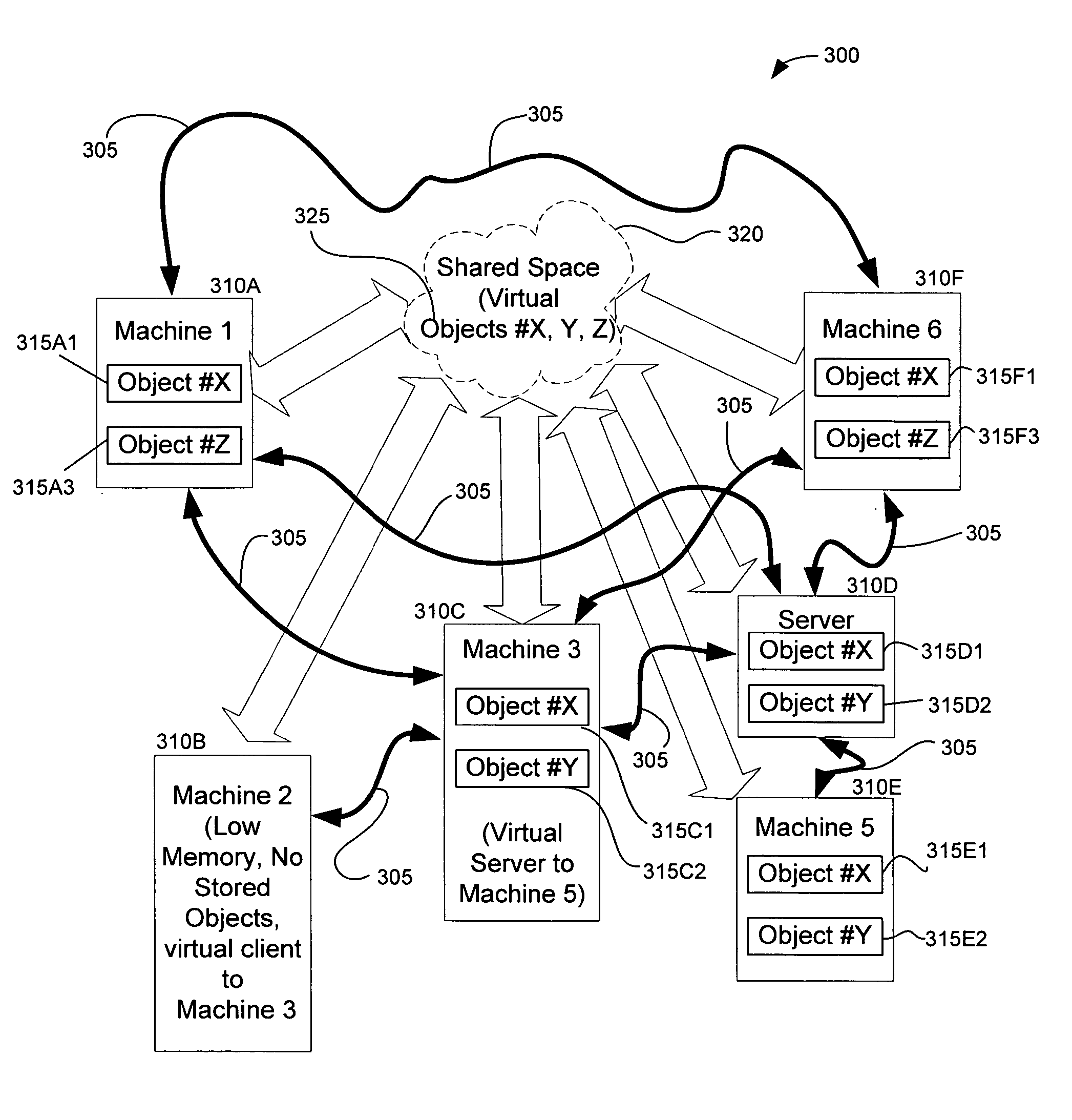
System and method for sharing objects between computers over a network
InactiveUS20050218739A1Easy to shareLimited memoryDigital data protectionMultiple digital computer combinationsApplication programming interfaceObject definition
A method and system to share objects that may reside on different machines. These objects can be accessed and shared using a computer network such as the Internet. The objects can comprise computer programming objects, that may include but are not limited to, application programming interfaces (APIs), programming object libraries, computer program object definitions, and other like information for computer network based applications. The method and system do not require a computer server since the invention may operate more like a peer-to-peer or multipoint computer network. The method and system can work with both peer-to-peer networks and client-server networks without requiring computers in a network to be identified as servers or as non-server (client) type computers.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
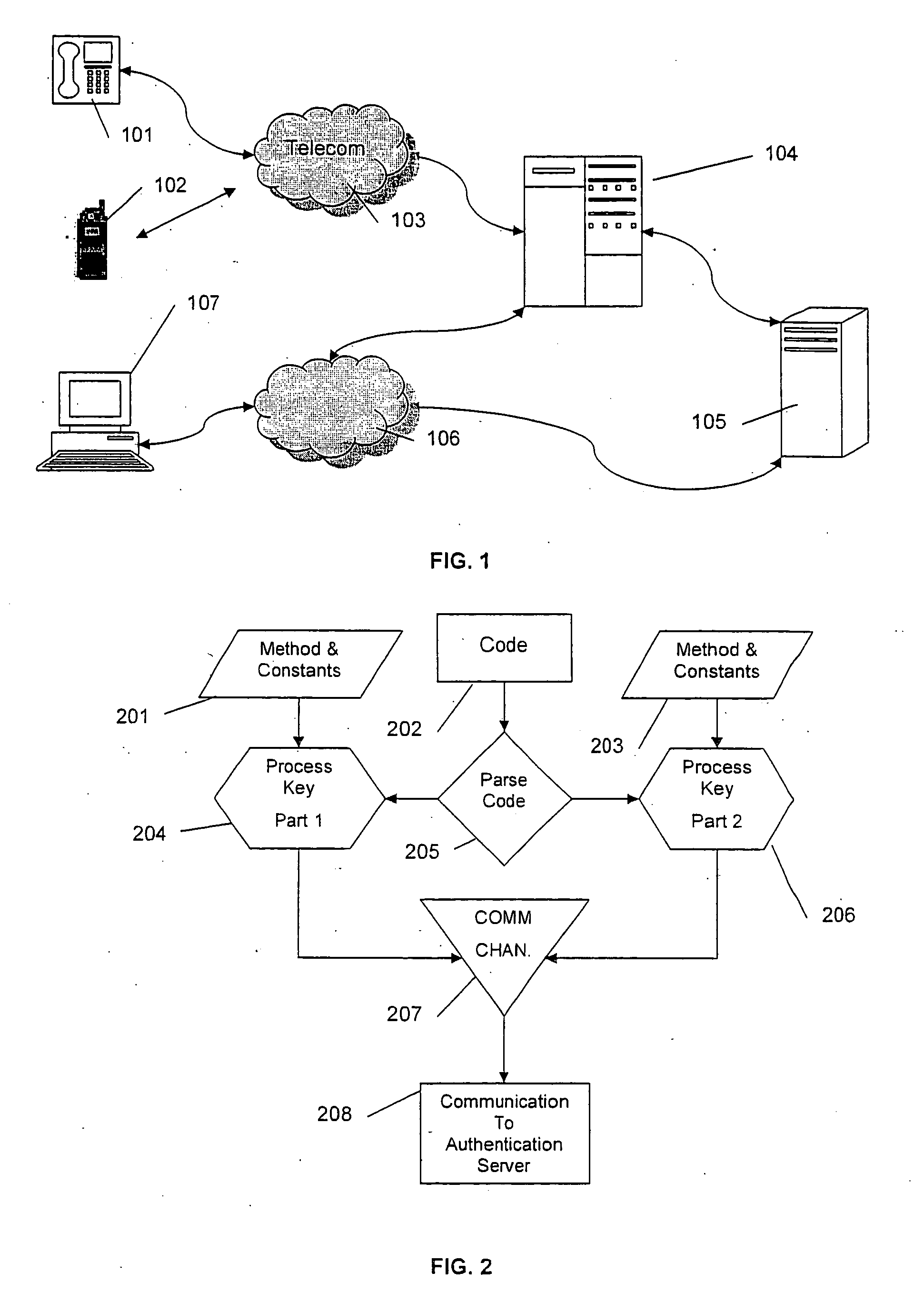
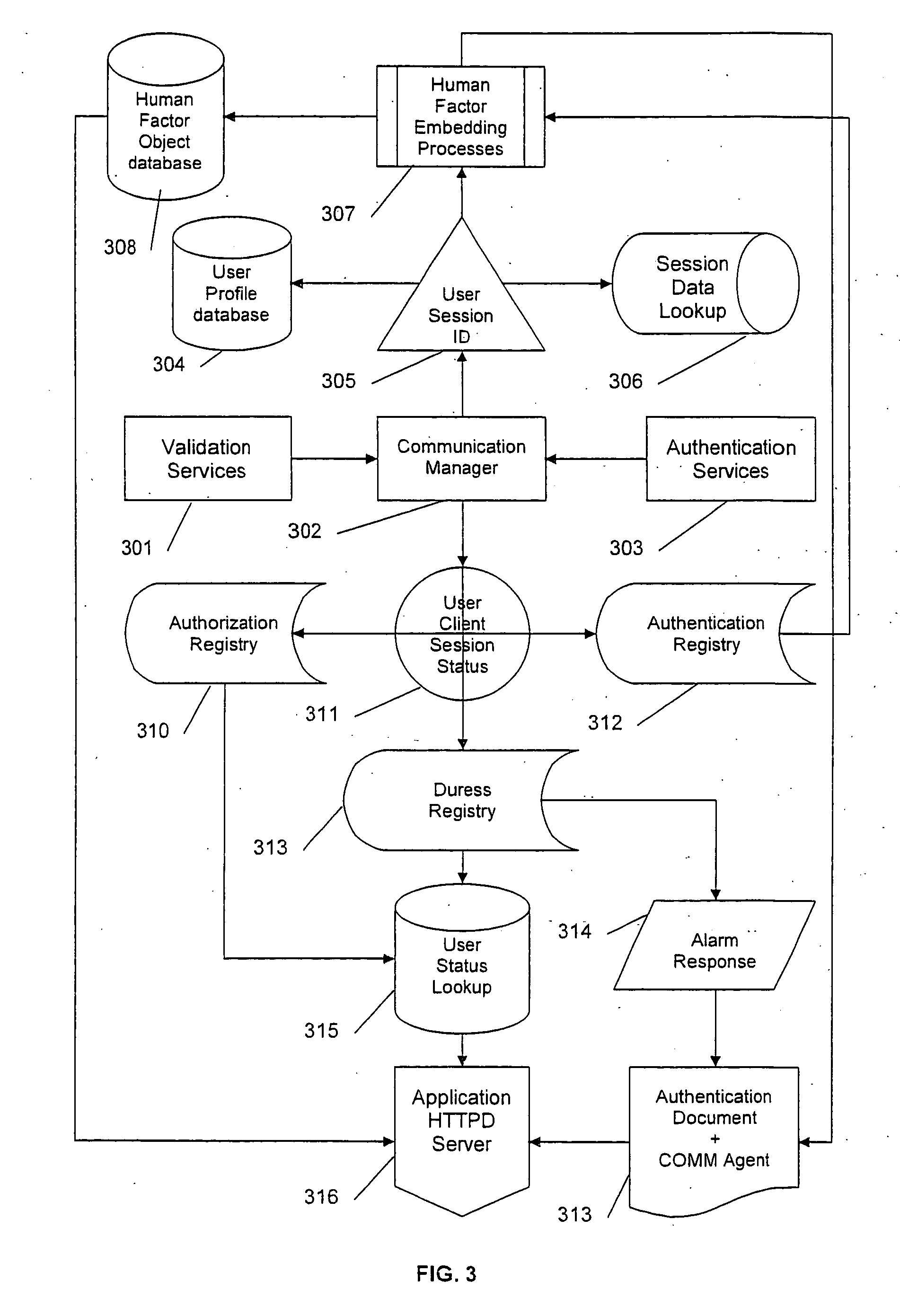
Human-factors authentication
InactiveUS20070130618A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationObject definitionHuman–computer interaction
A method of enhancing online security by requiring the user to choose from among multiple objects presented to the user an object which falls within an abstract object definition previously provided by the user. The presented objects are therefore unknown to the user but include at least one with a particular quality known to the user.
Owner:CHEN CHUAN PEI
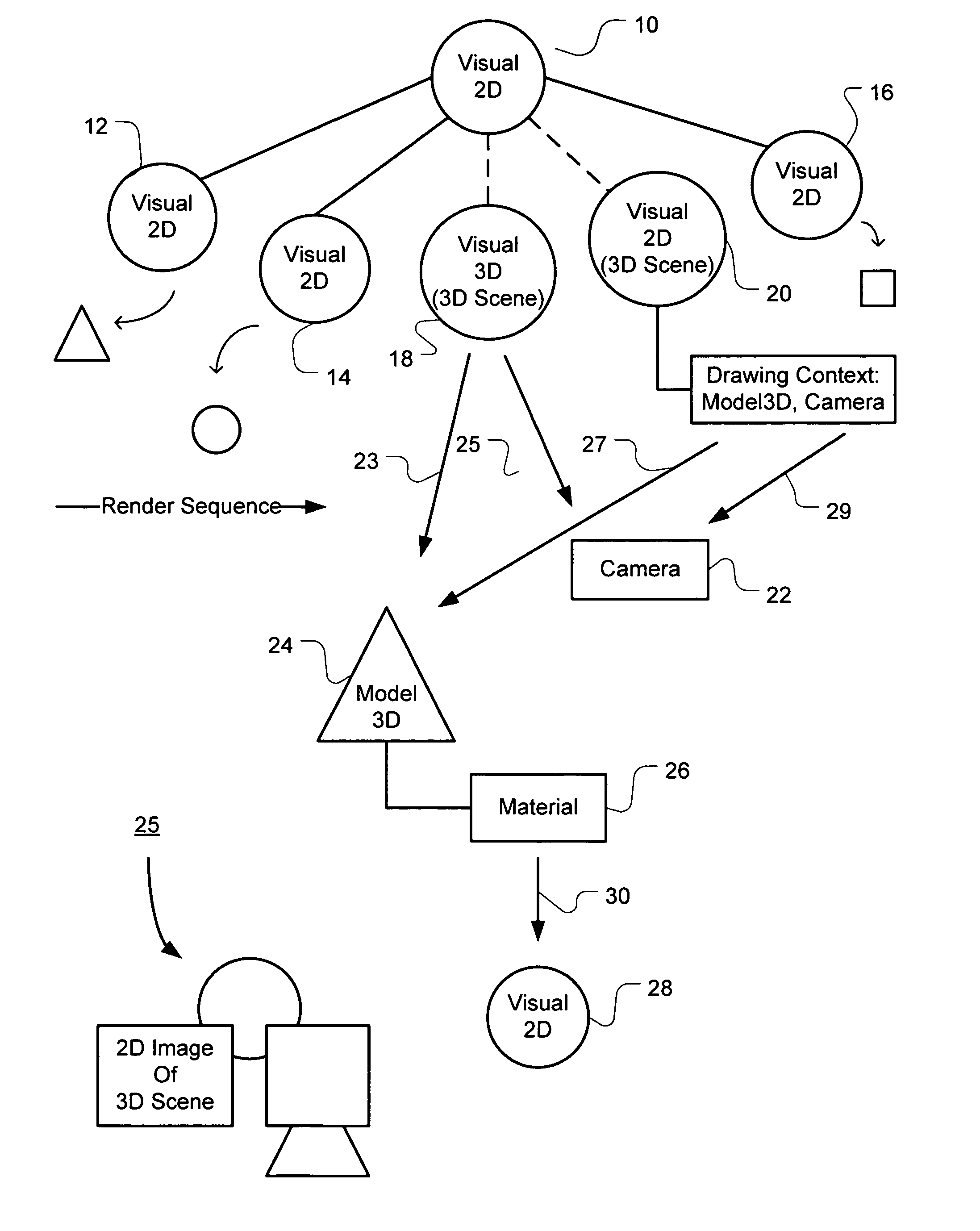
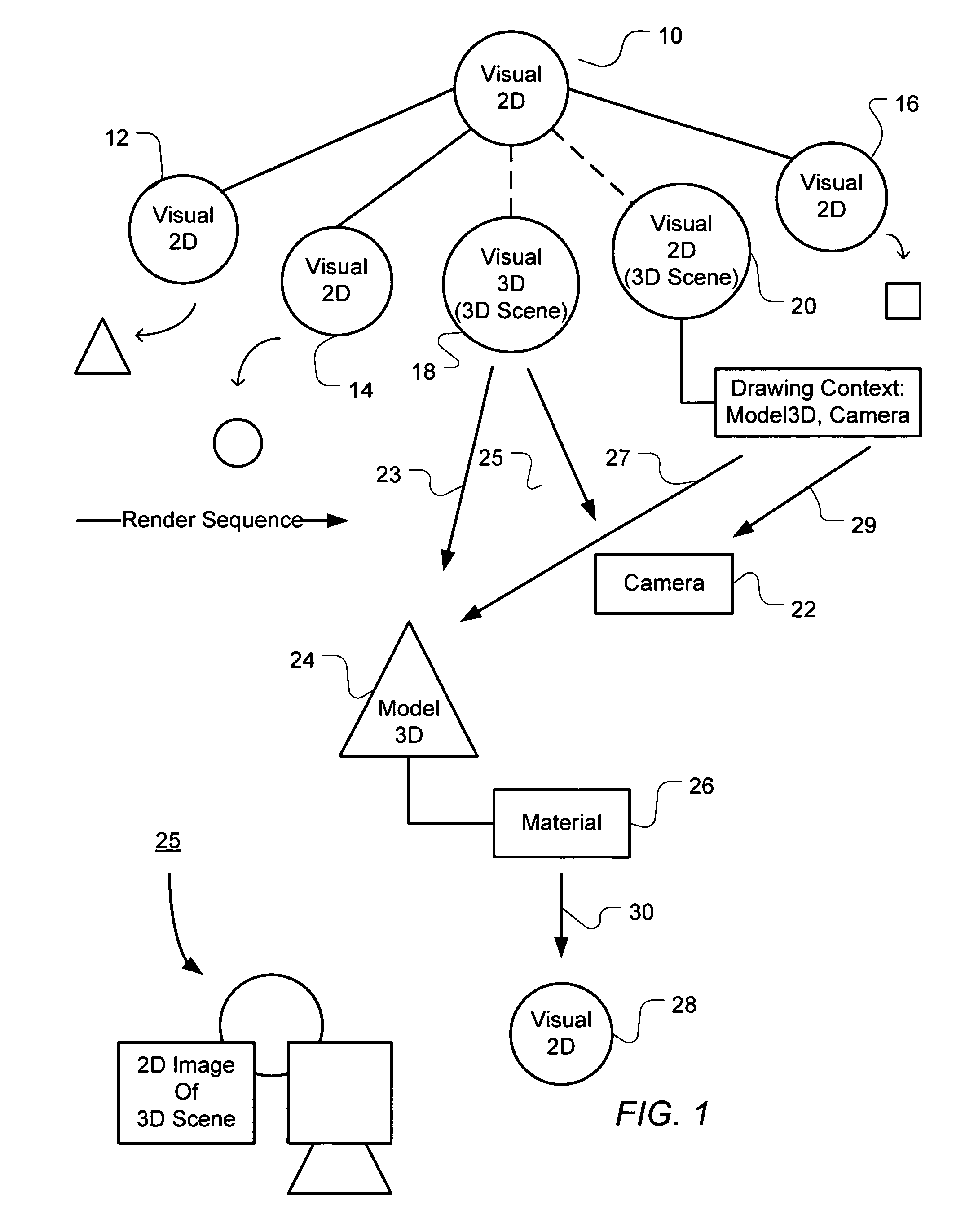
Integration of three dimensional scene hierarchy into two dimensional compositing system
A hierarchy of 2D visual objects and 3D scene objects are integrated for seamless processing to render 2D images including a 2D view of a 3D scene on a 2D computer display. The processing of the 3D model objects and 2D visual objects in the visual hierarchy is integrated so that the processing is readily handed off between 3D and 2D operations. Further the number of transitions between processing visual 2D objects and 3D model objects when creating a display image has no architectural limit. A data structure integrates computer program objects for creating 3D images and 2D images in a visual tree object hierarchy having visual 2D objects or 3D scene objects pointing to 3D model objects. The data structure comprises an object tree hierarchy, one or more visual 2D objects, and one or more 3D reference or scene objects pointing to 3D model objects. The visual 2D objects define operations drawing a 2D image. The 3D reference or scene objects define references pointing to objects with operations that together draw a two-dimensional view of a three-dimensional scene made up of one or more 3D models. The 3D reference or scene objects point to 3D model objects and a camera object. The camera object defines a two-dimensional view of the 3D scene. The 3D model objects draw the 3D models and define mesh information used in drawing contours of a model and material information used in drawing surface texture of a model. The material information for the surface texture of a model may be defined by a visual 2D object, a 3D reference or scene object or a tree hierarchy of visual 2D objects and / or 3D reference scene objects.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
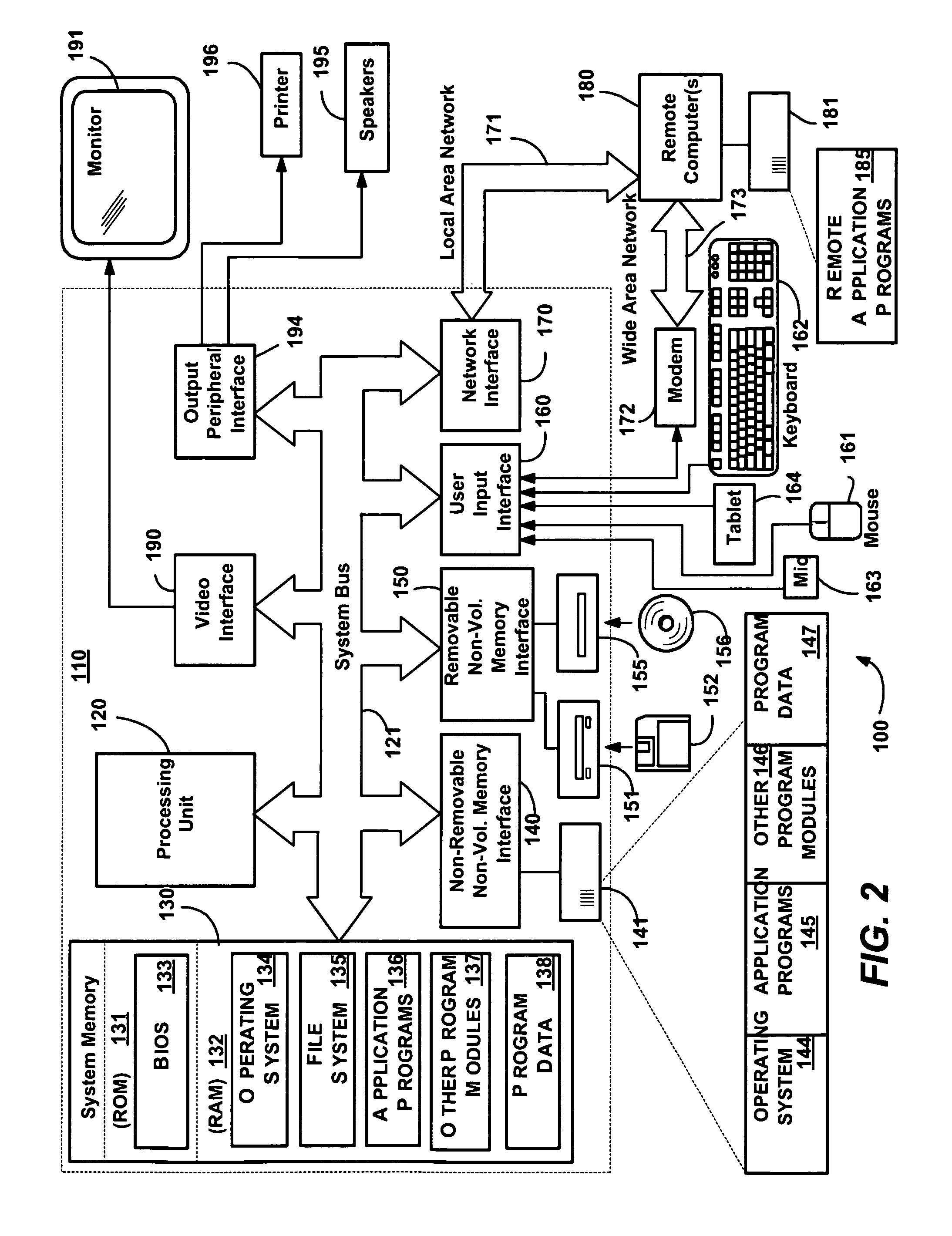
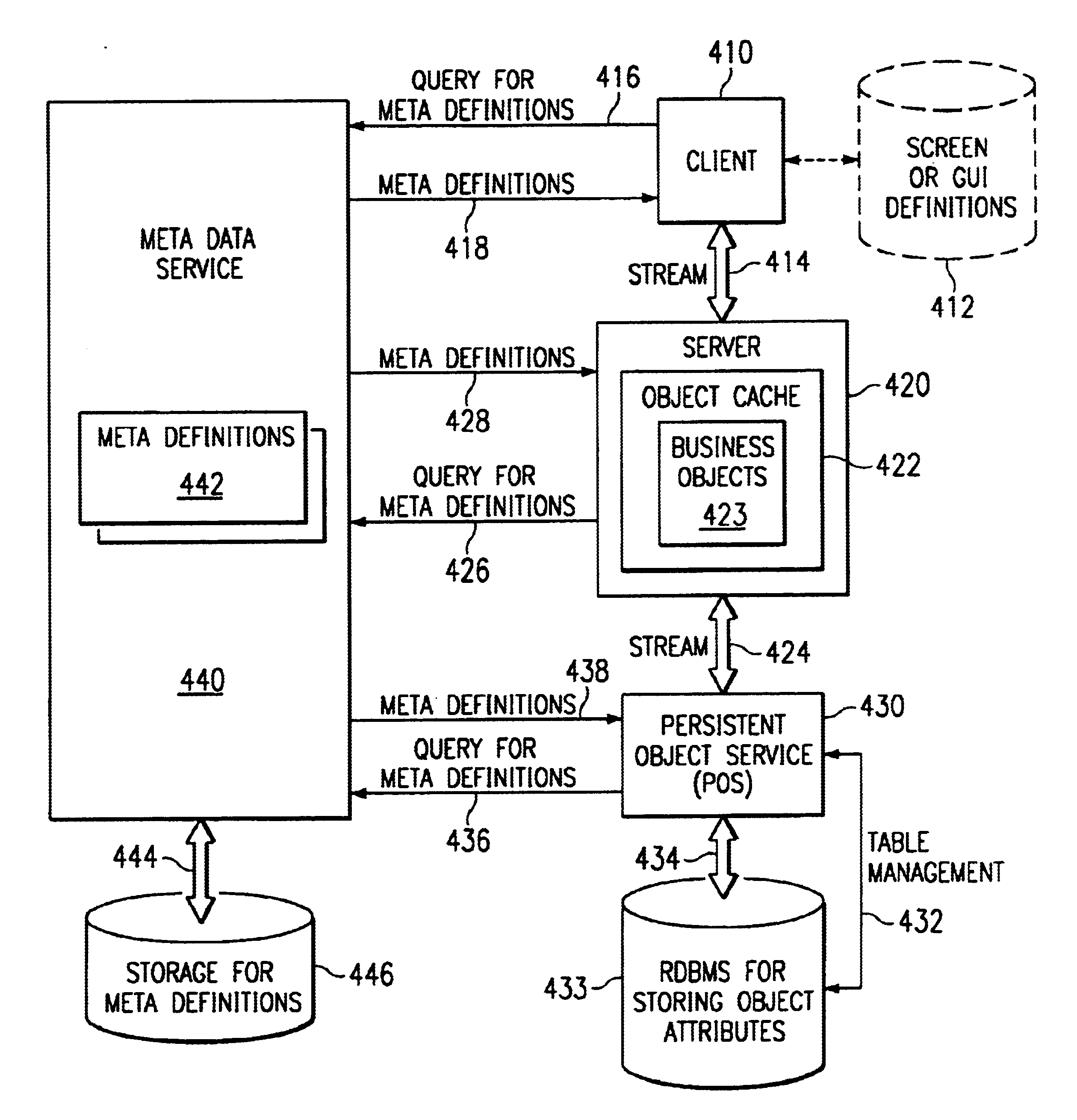
Method and apparatus for a Meta Data Service in a data processing system
InactiveUS6857123B1Precise processingData processing applicationsInterprogram communicationHard codingData processing system
As a solution to the problem of distributed knowledge of data object definitions, data object definitions are removed from the source code. A Meta Data Service is created and made available on a network which knows the definitions of all of the objects that are used by applications that are designed to use the Meta Data Service. When an object is created, the Meta Data Service creates and stores a meta definition for the object. Data objects are passed over a network in a “soft” format. Applications within a distributed data processing system are designed in such a manner such that, at any stage of object processing, an application does not assume to understand the definition or structure of an object, nor is an application hard-coded with the object definitions. At each stage, an application queries the Meta Data Service for the meta definition of the object before proceeding with the processing of an object. The application then receives a meta definition for the data object that allows the application to perform properly tailored processing for the data object.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method of augmented reality interaction
A method of augmented reality interaction for repositioning a virtual object on an image of a surface comprises capturing successive video images of the surface and first and second control objects and defining an interaction start area over the surface with respect to the virtual object. The method detects the control objects in successive video images, detects whether the control objects are brought together over the interaction start area, and if so, analyses a region of successive video images using optical flow analysis to determine the overall direction of motion of the control objects and augmenting the video image to show the virtual object being held by the control objects. Augmenting the video image itself comprises superposing a graphical effect on the video image prior to superposition of the virtual object, such that the graphical effect visually disconnects the virtual object from the video image in the resulting augmented image.
Owner:SONY COMP ENTERTAINMENT EURO
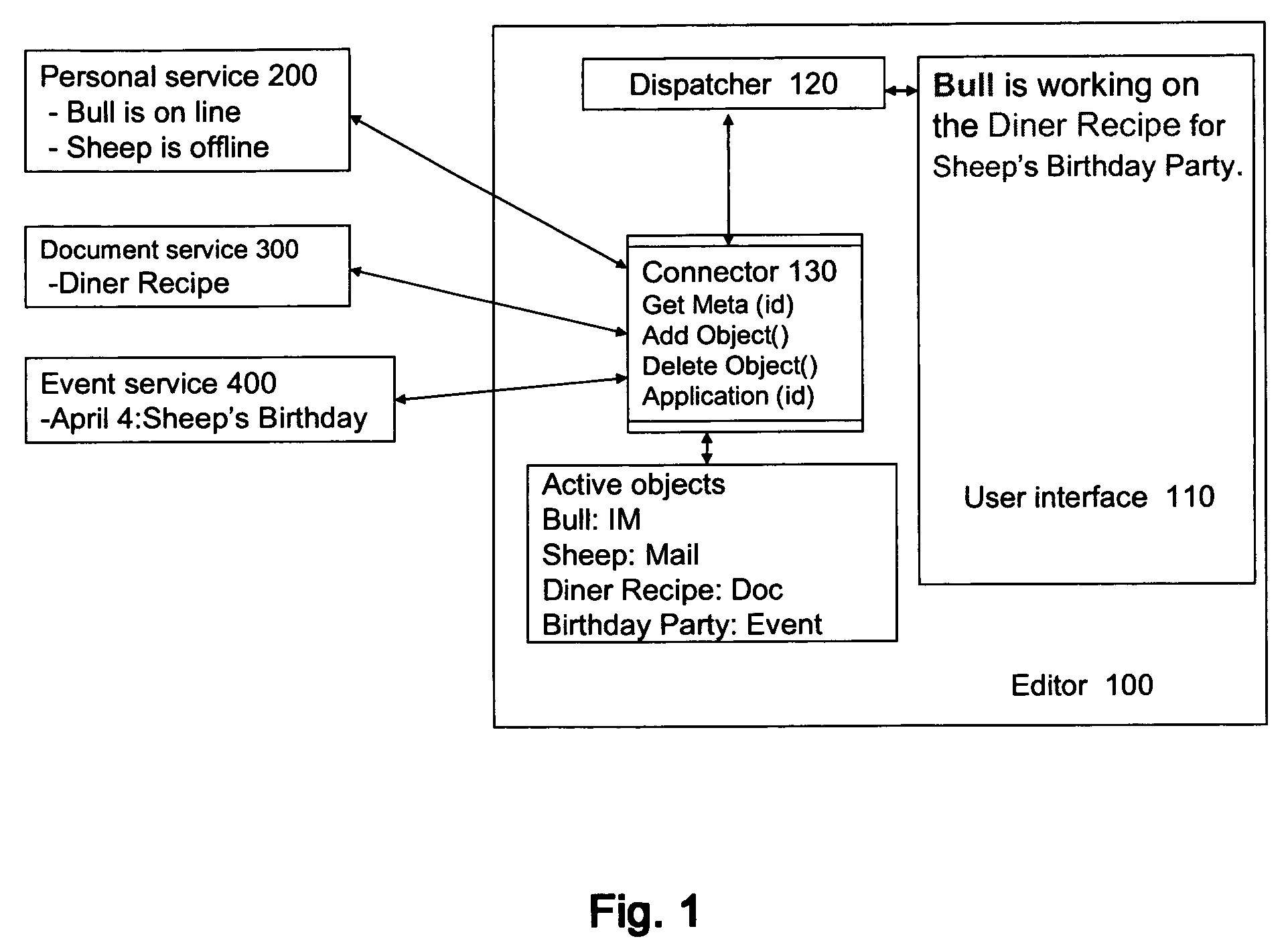
Document editor and method for editing document
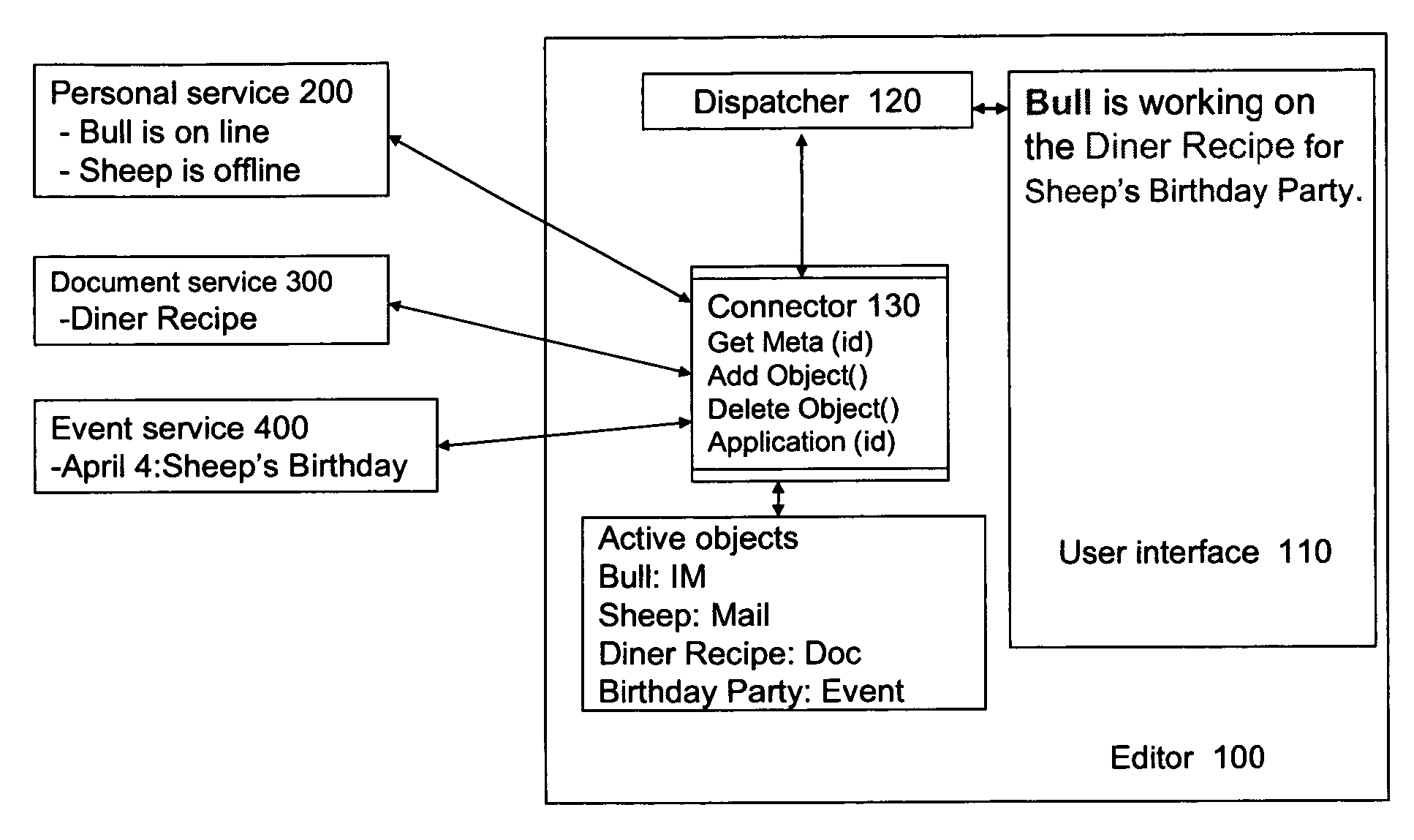
ActiveUS20060117249A1Promote collaborationReduce overheadText processingDigital computer detailsObject definitionPaper document
The present invention provides a document editor and a method for editing document to facilitate the collaboration between users. The document editor comprises a user interface for editing and displaying document information; a dispatcher for identifying objects in the user interface and their identifiers according to object definition, and providing the object information to the user interface; and at least one connector, for communicating with remote or local service using the identifier and address of at least one of the objects, to exchange the object information with the remote or local service and transfer the information to the dispatcher. According to the document editor and the method for editing document, a user could obtain more information of the object embedded in the document and effectively avoid operation failure on the object.
Owner:HCL TECH LTD
Identifying anomalous object types during classification
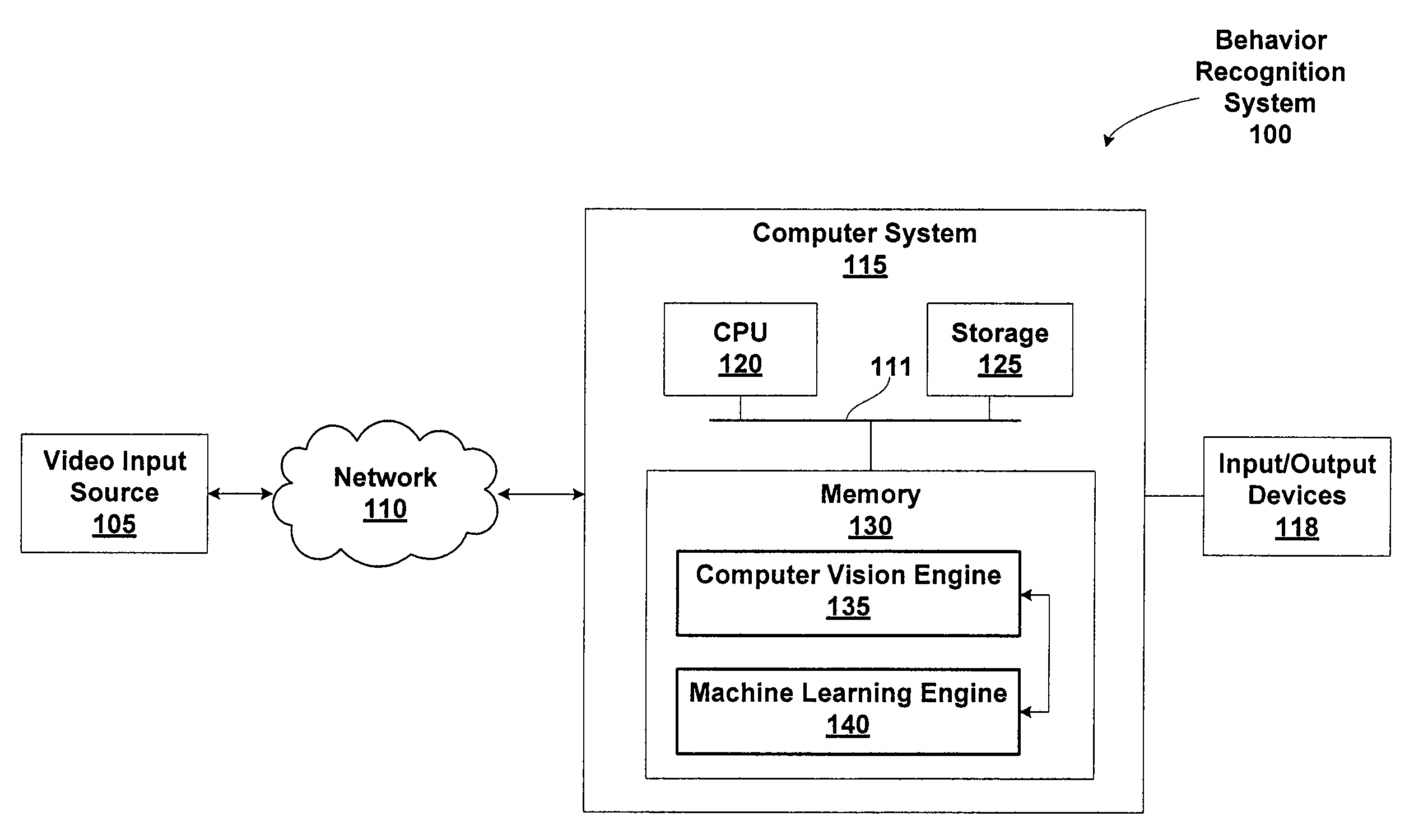
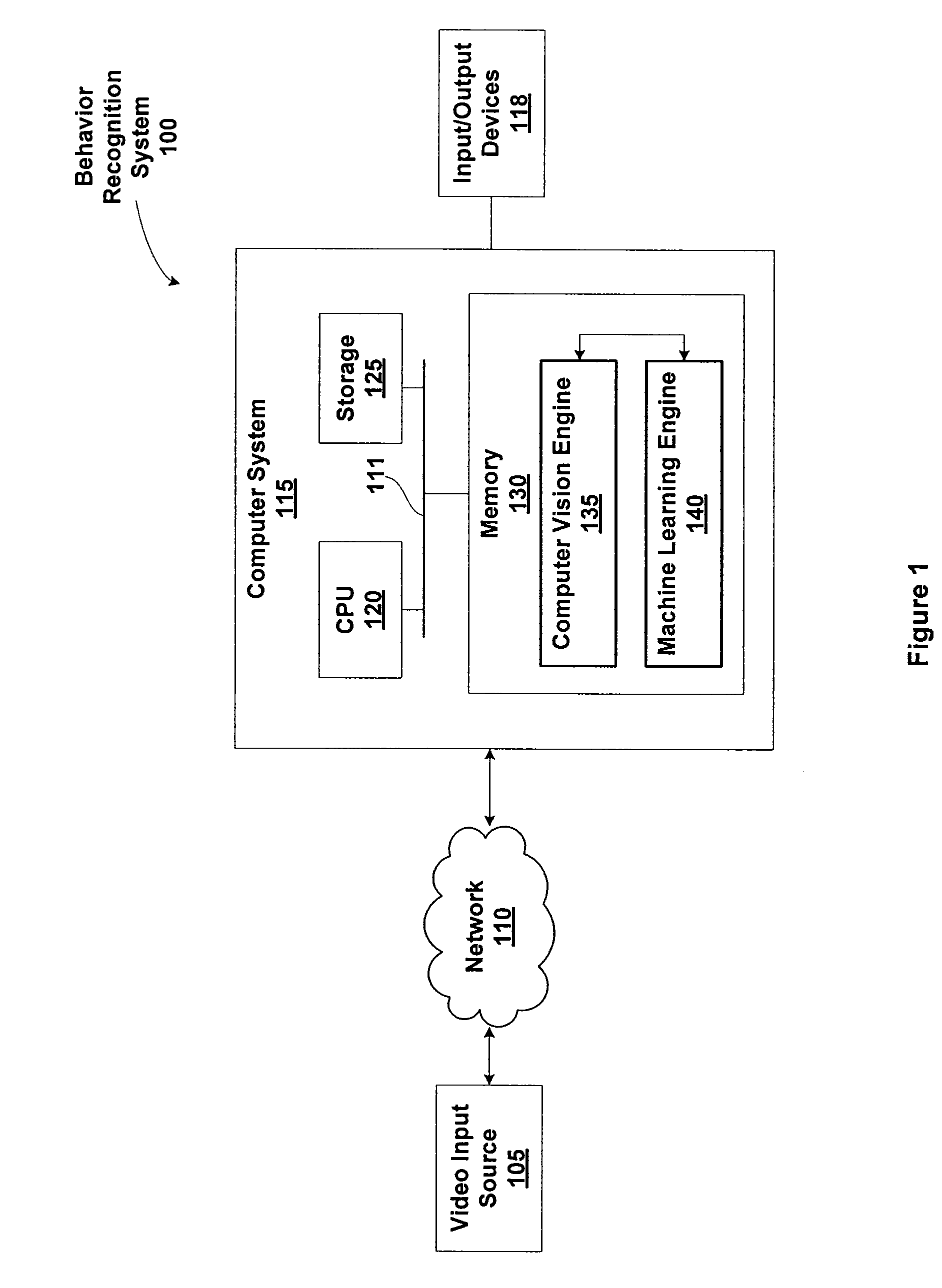
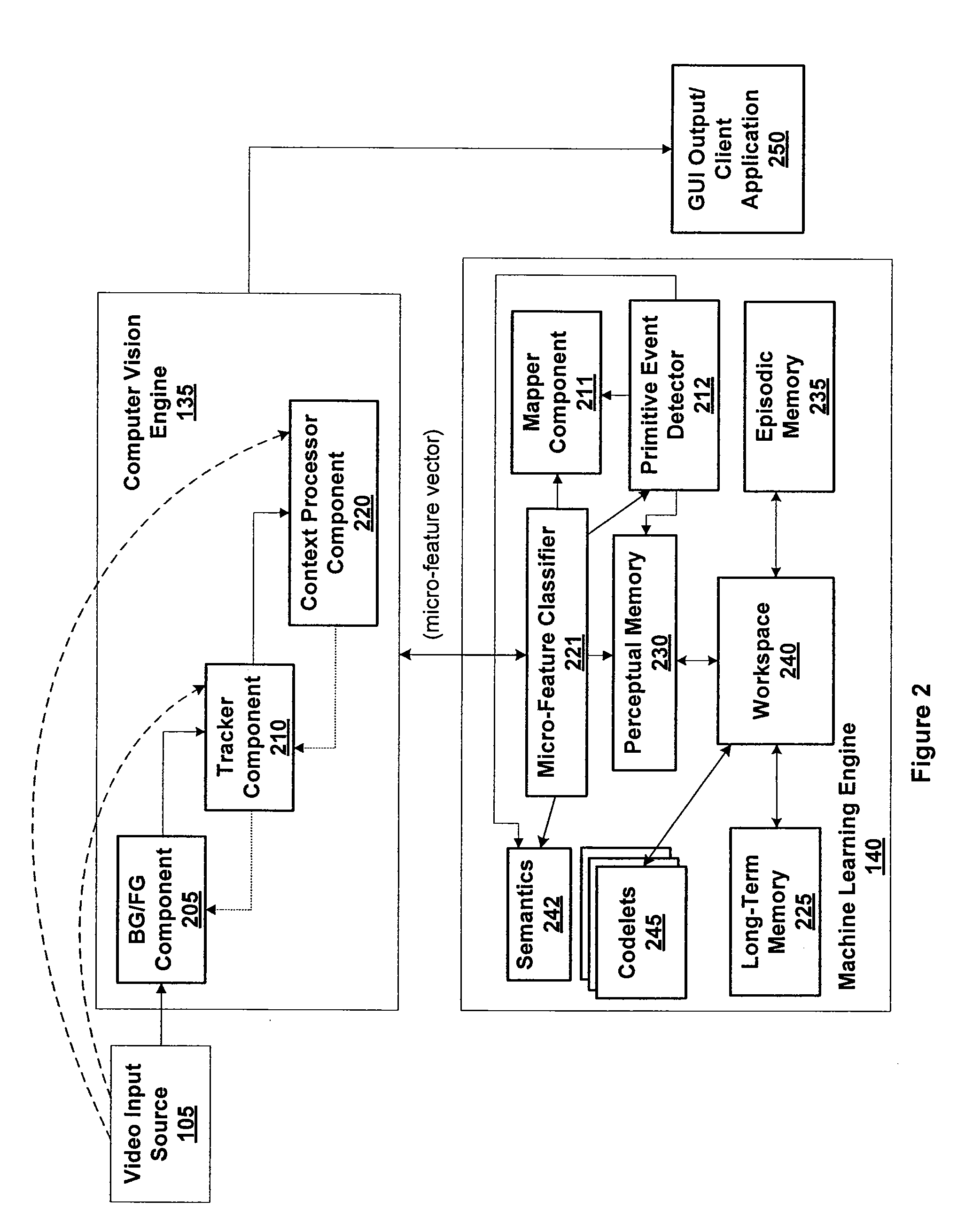
ActiveUS20110052068A1Character and pattern recognitionElectric/magnetic detectionTraining phaseObject definition
Techniques are disclosed for identifying anomaly object types during classification of foreground objects extracted from image data. A self-organizing map and adaptive resonance theory (SOM-ART) network is used to discover object type clusters and classify objects depicted in the image data based on pixel-level micro-features that are extracted from the image data. Importantly, the discovery of the object type clusters is unsupervised, i.e., performed independent of any training data that defines particular objects, allowing a behavior-recognition system to forgo a training phase and for object classification to proceed without being constrained by specific object definitions. The SOM-ART network is adaptive and able to learn while discovering the object type clusters and classifying objects and identifying anomaly object types.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Delivery of data and formatting information to allow client-side manipulation
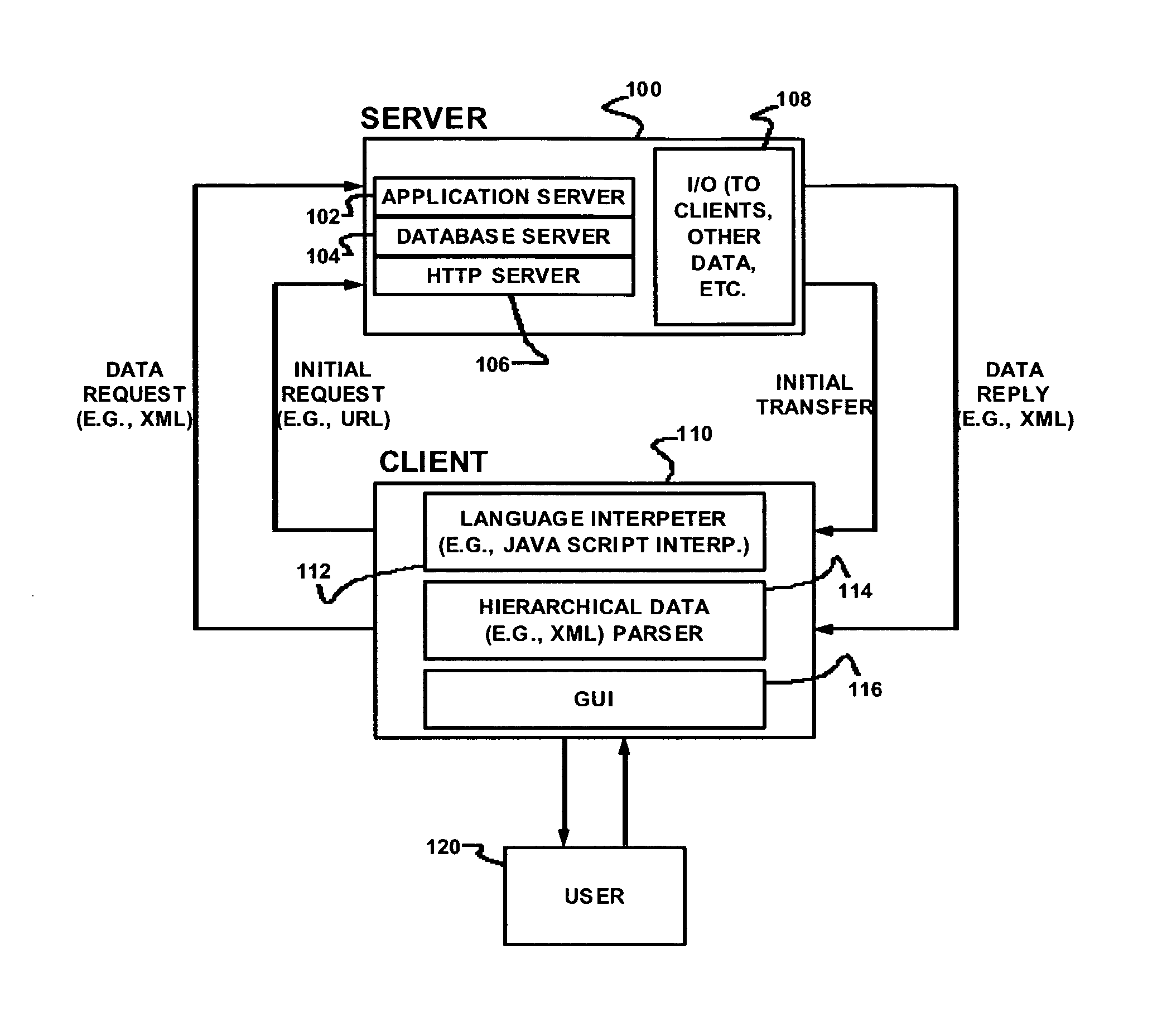
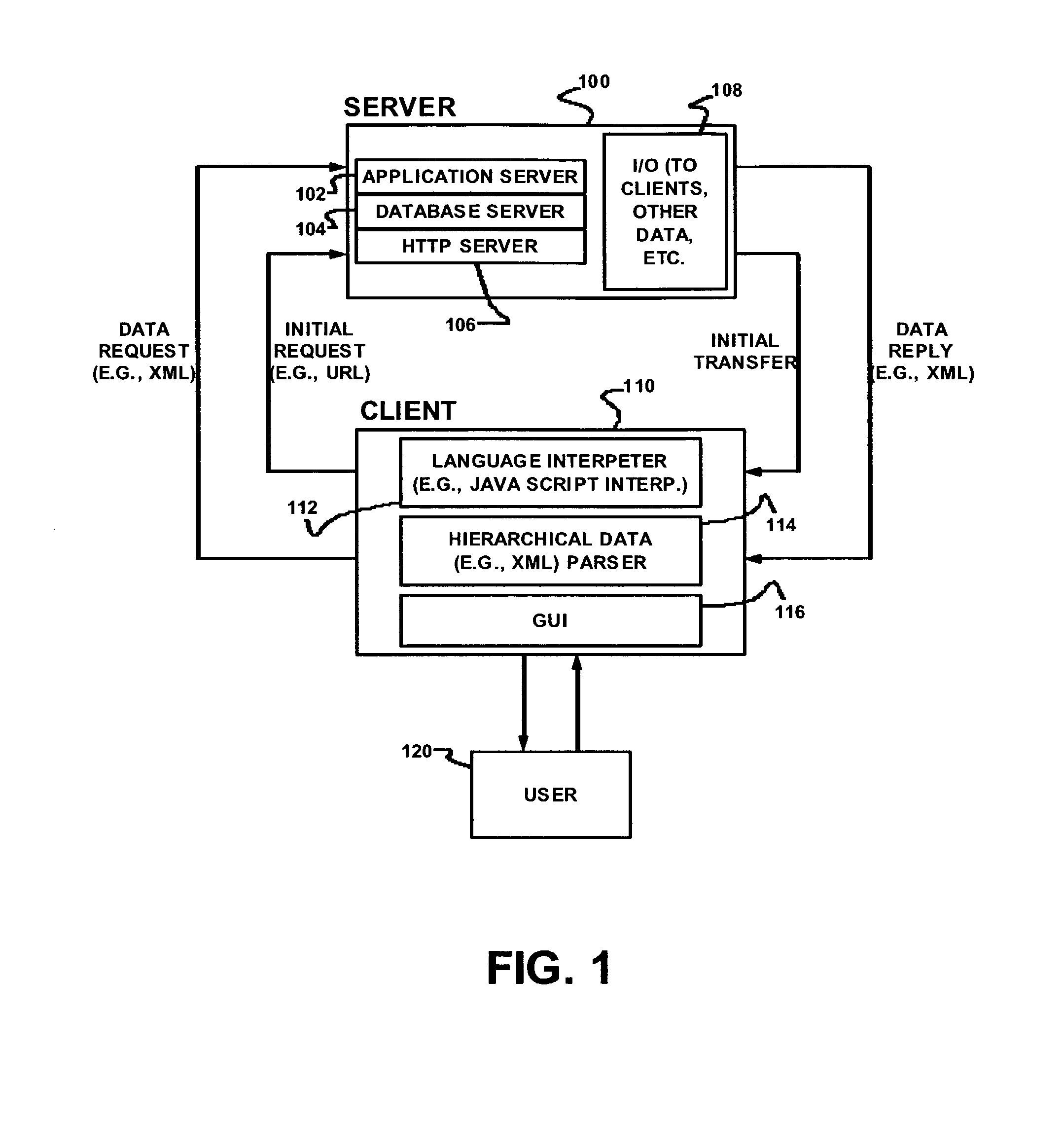
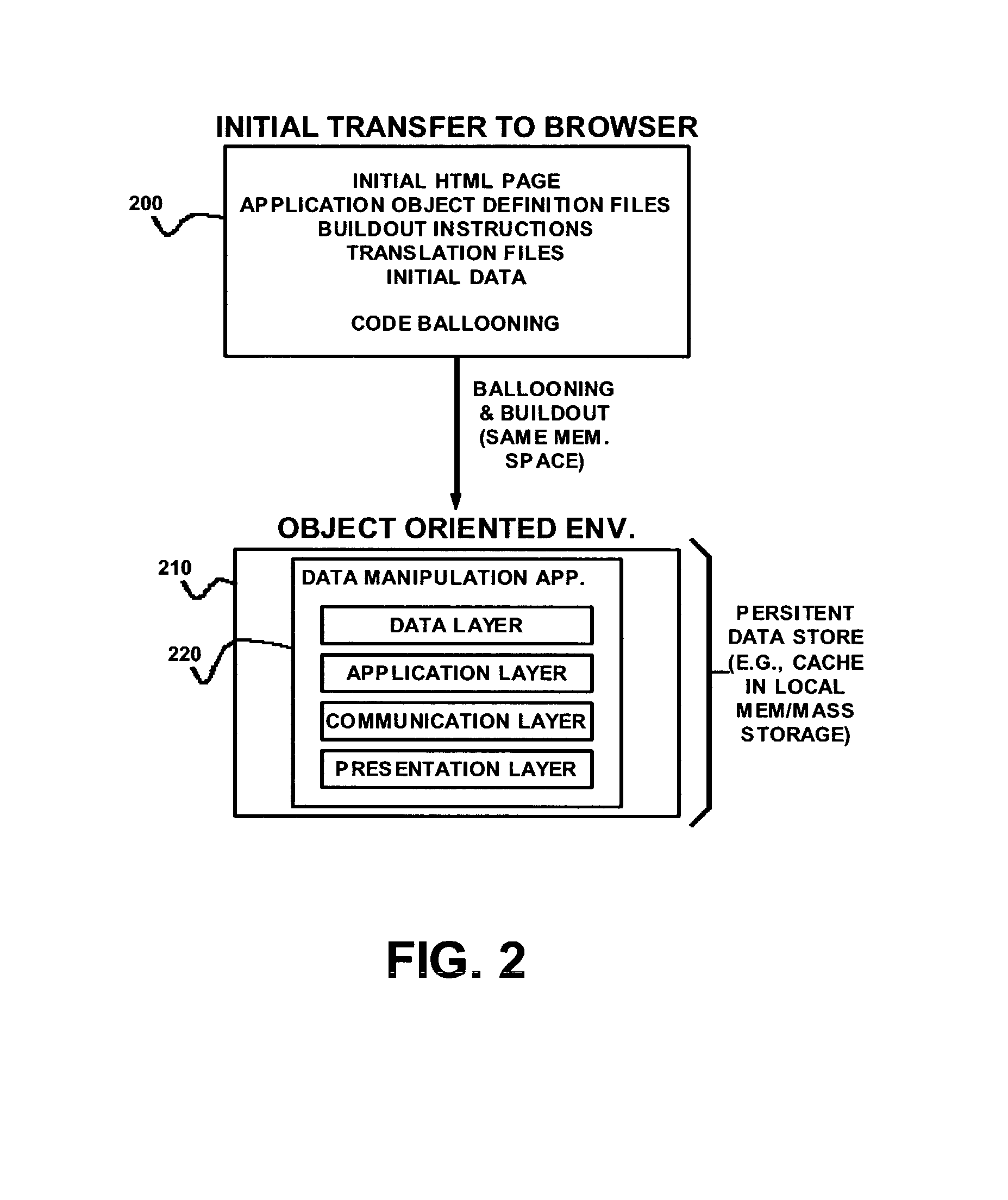
ActiveUS8136109B1A large amountSoftware designProgram loading/initiatingInterpreted languageWeb browser
Delivering data and formatting information includes delivering object definition files from a server to a client; generating definitions and object instantiations at a client using JavaScript or another simple browser-interpreted language, for objects relating to data modeling and presentation; and presenting data using those objects at the client, using a web browser without a separate runtime environment or application plug-in, but maintaining substantial state at the web browser regarding the data itself and the format for its presentation. Definition files are modified to provide object properties consistent with a full object-oriented language, including for example hierarchical inheritance of object properties. Code ballooning generates definitions and individual instantiations, with the effect that a very large amount of DHTML, or another markup or presentation definition language for use with the application, can be generated from relatively small aggregate size of definition files communicated from the server to the client.
Owner:CLOUD SOFTWARE GRP INC
System and method for business object discovery
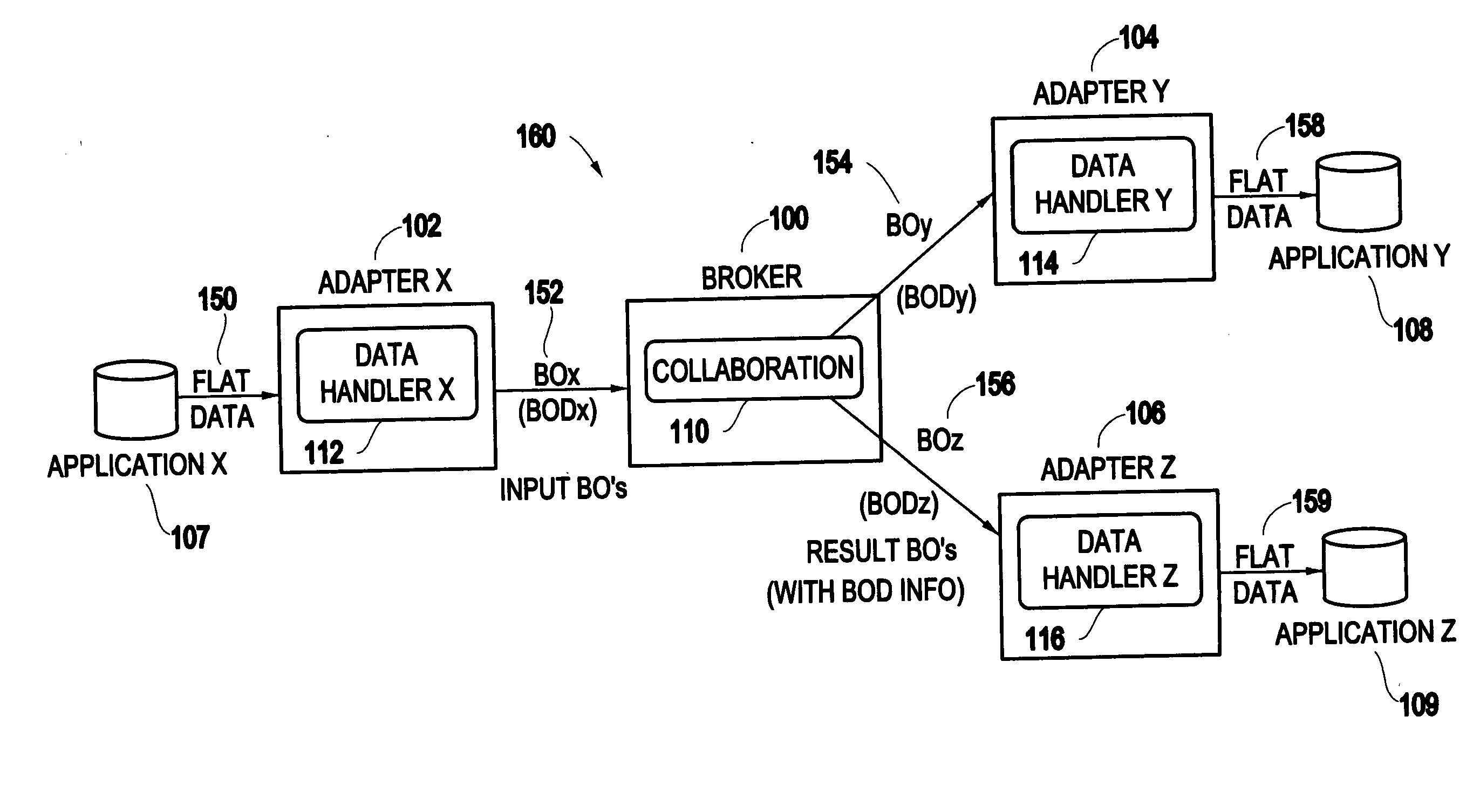
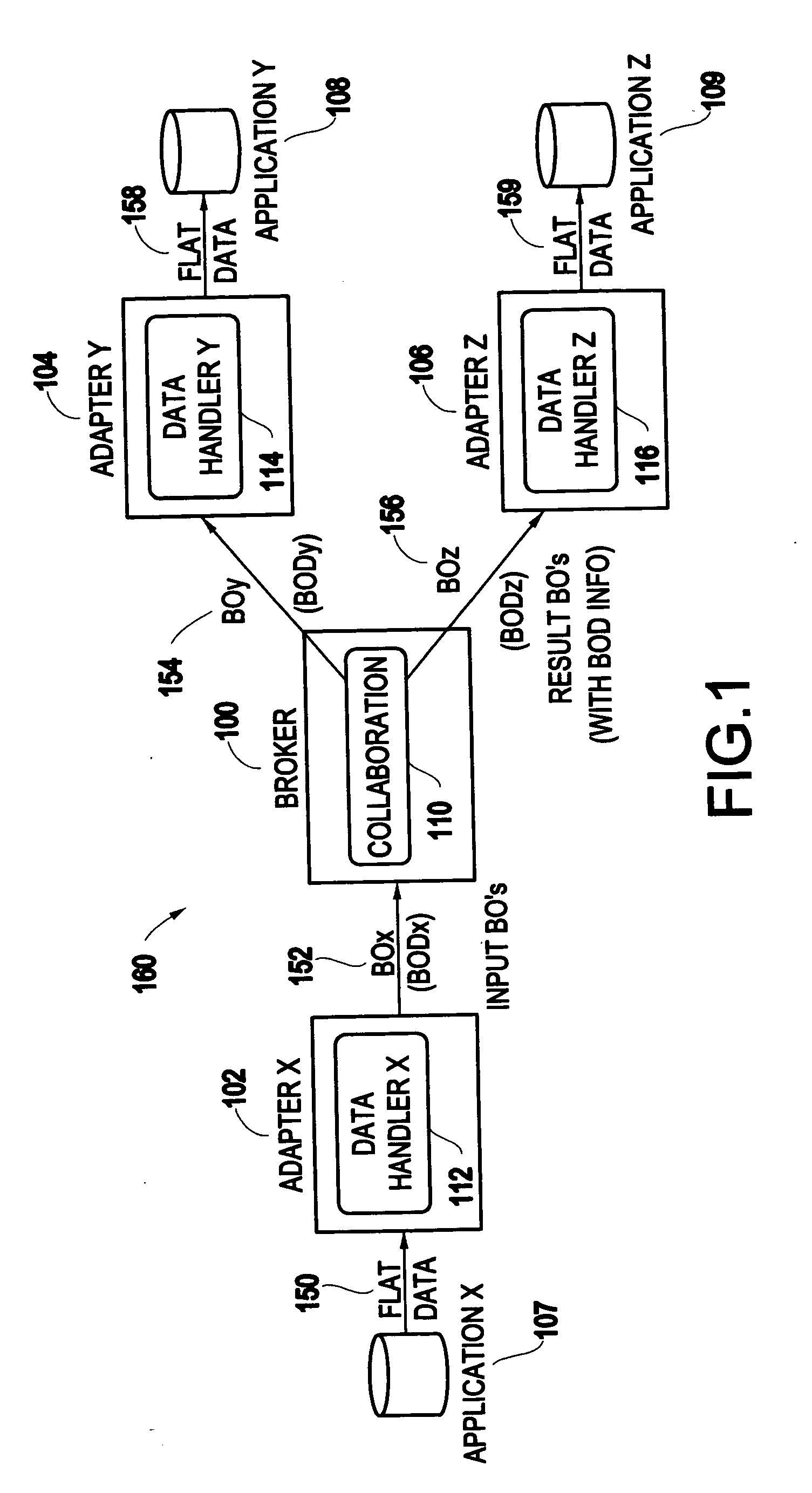
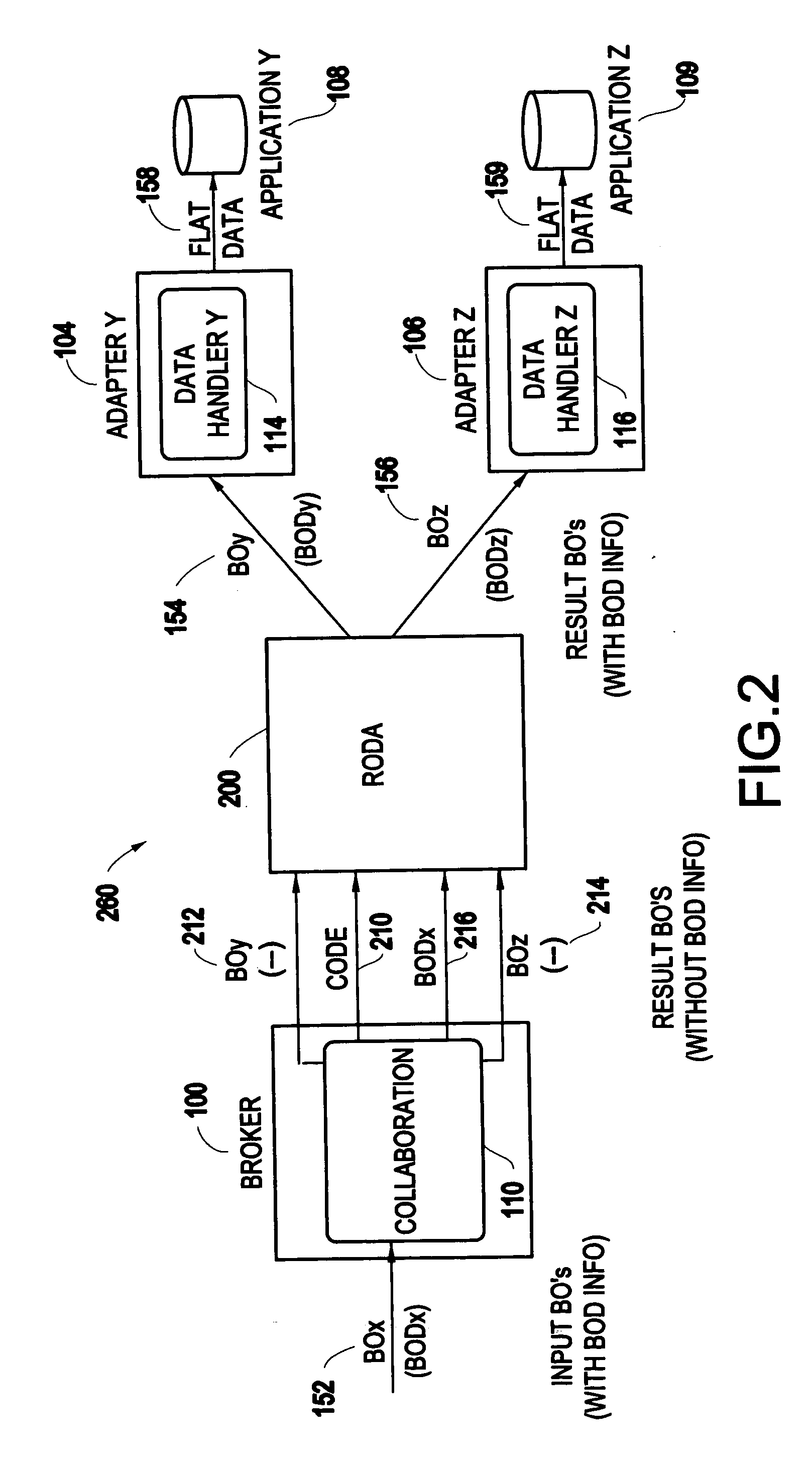
InactiveUS20050216282A1Simple compositionInterprogram communicationObject oriented databasesObject basedObject definition
A method and system discovers object definitions by receiving an object and a collaboration code, and determining an object definition for the object based upon the collaboration code.
Owner:IBM CORP
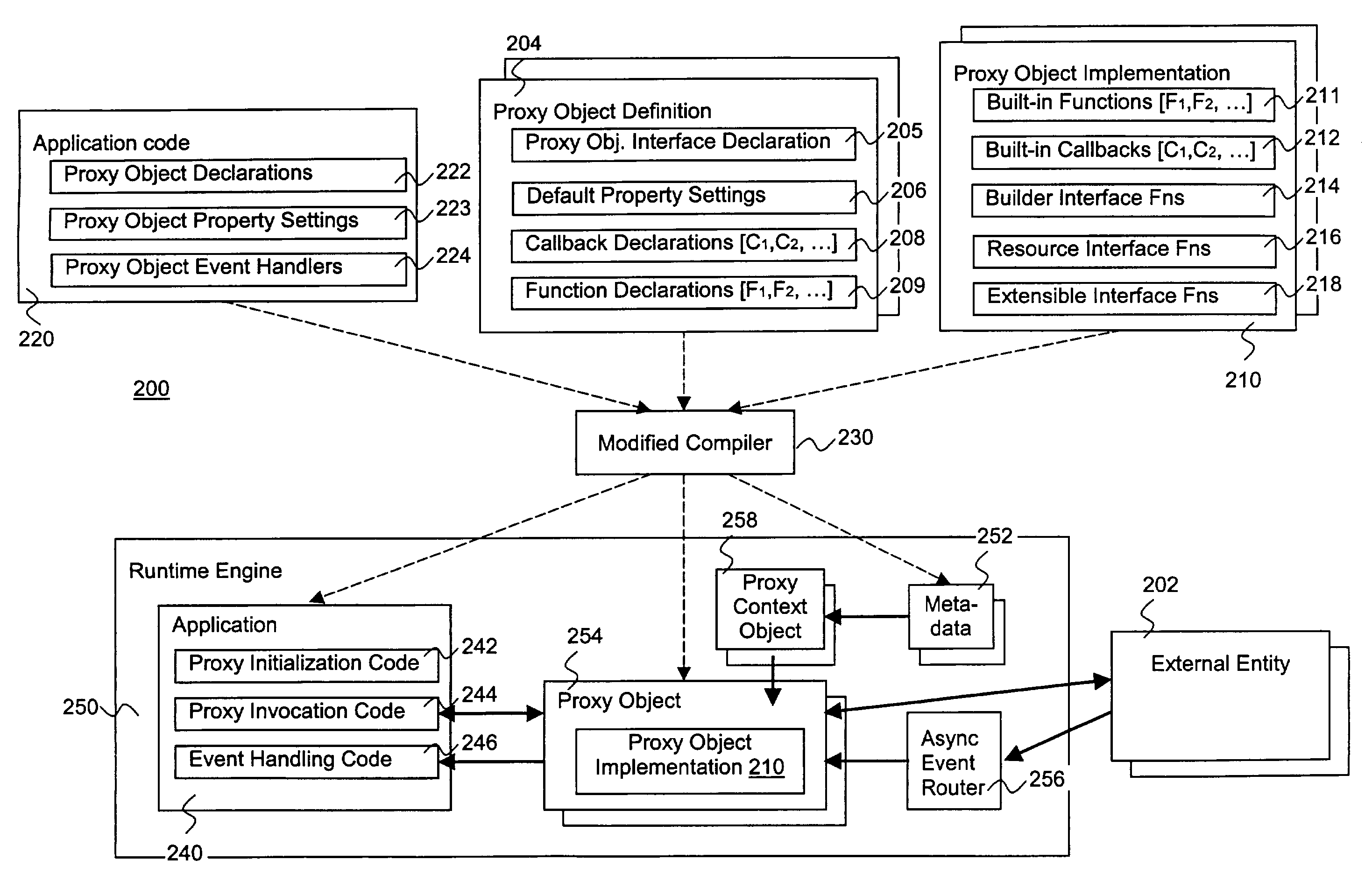
Methods and apparatus for building, customizing and using software abstractions of external entities
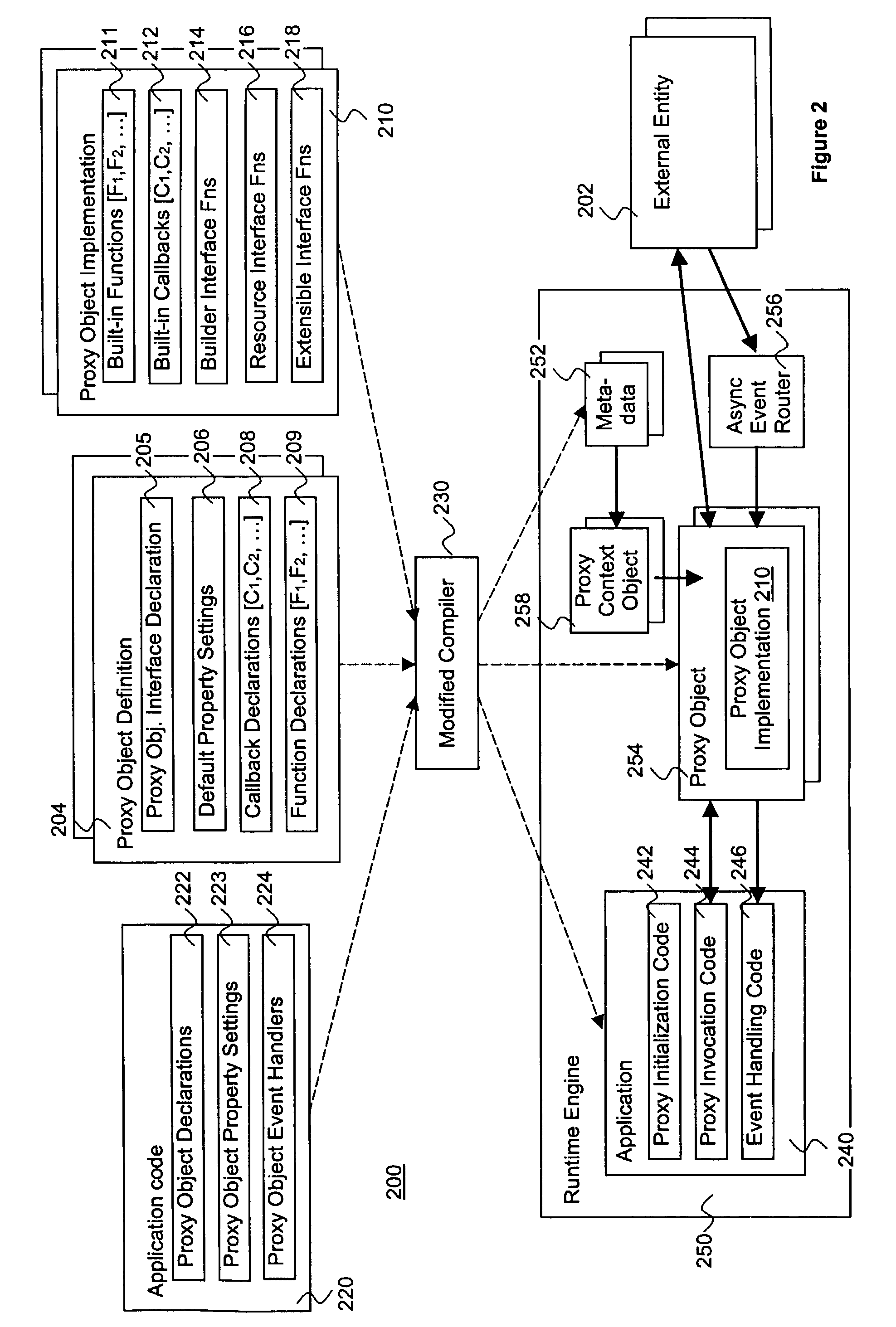
InactiveUS7516447B2Facilitate generation and routingSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsObject codeObject definition
An entity is abstracted through implementation of a proxy object of the present invention, including functions for a software application to programmatically interact with the entity at runtime, as well as optional compile and design time implementation classes to support the development and customization of declarative proxy object definitions. In one embodiment, builder and resource interfaces are provided to assist in the creation of the implementation classes. In one embodiment, an extension interface is also provided to facilitate extension of an implementation of the proxy object. Software applications including programmatic usage of proxy object functions are compiled into object codes with proxy objects and meta data files. The compiled object codes are executed using a runtime engine, which includes proxy context objects to facilitate interaction on an instance basis, and an asynchronous event router to route asynchronous events for the entity.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Control system configuration and methods with object characteristic swapping
InactiveUS20090118845A1OptimizationOptimize system configurationVersion controlElectric testing/monitoringGraphicsComposite object
Methods and apparatus for configuring process, environmental, industrial and other control systems generate and / or utilize models representing configurations of control systems and / or the systems controlled by them. Records of changes to the models or the configurations represented by them are maintained, thereby, for example, providing bases for determining current states, prior states and histories of changes. Objects in the model have characteristics, such as an object type characteristic and an area characteristic. Users can have corresponding permissions. A security mechanism apparatus controls access by users to the objects. Composite objects are defined by definition objects and are displayed in encapsulated or expanded formats. Objects can include an edit control type identifier that determines how they are presented for editing. Functionality responds to user commands by transferring characteristics of a first object depicted by the graphical user interface to a second object. Configuration-time formulas contained objects are evaluated to constants prior to downloading to the control system.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SYST USA INC
Software componentization for building a software product
ActiveUS7562346B2Easy to createLess laborLink editingProgram control using stored programsComponent Object ModelOperational system
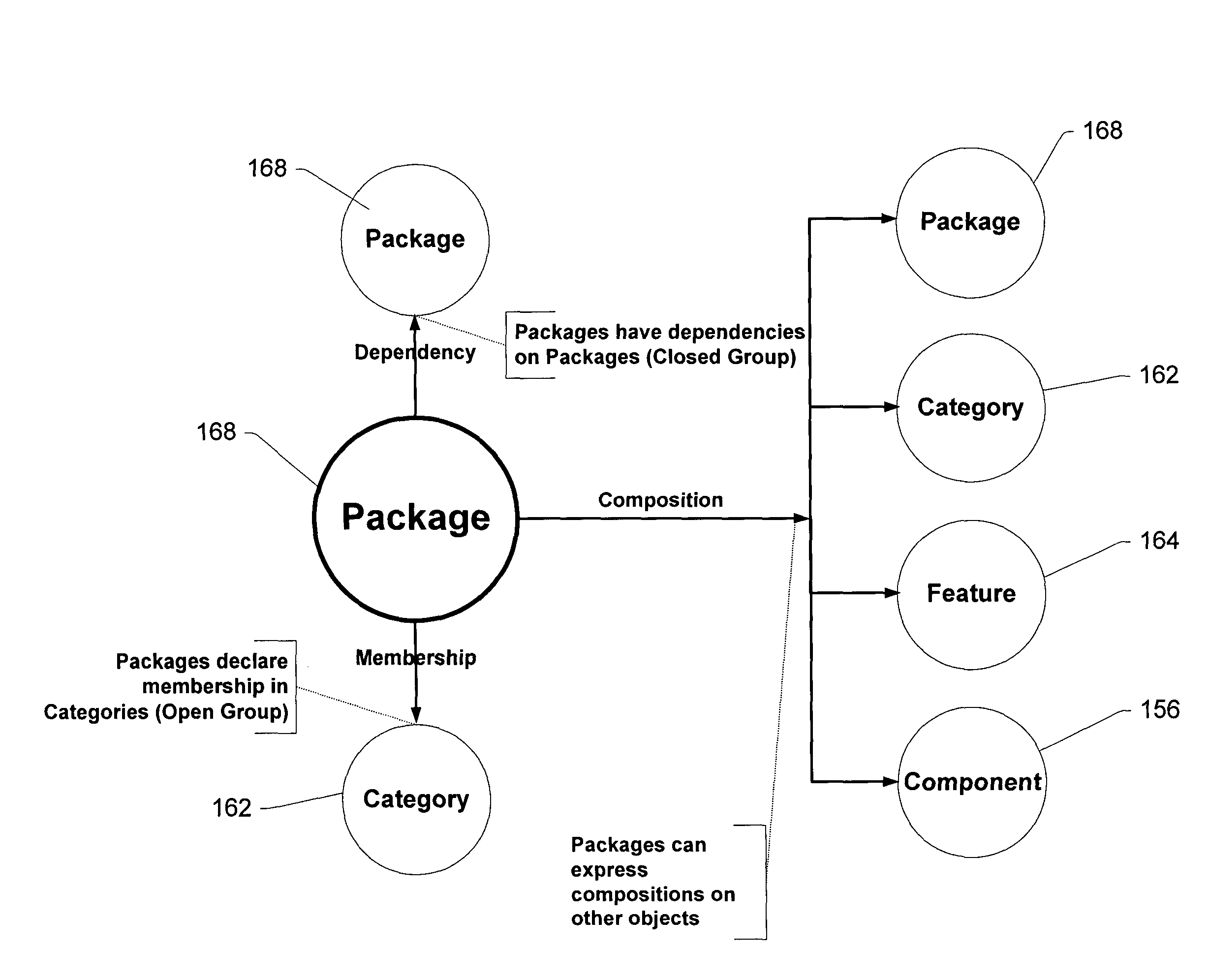
A componentization schema representing files from which an operating system or other software product is built. According to the schema, a component object represents one or more of the files. The component object has a manifest that identifies the component and specifies any dependencies between the component and other objects. Grouping objects according to the dependencies specified in manifests permits building the software product. A feature object defined by at least one component object represents a feature of the software product and a product object defined by at least one feature object represents the software product.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Search interface server and storage management
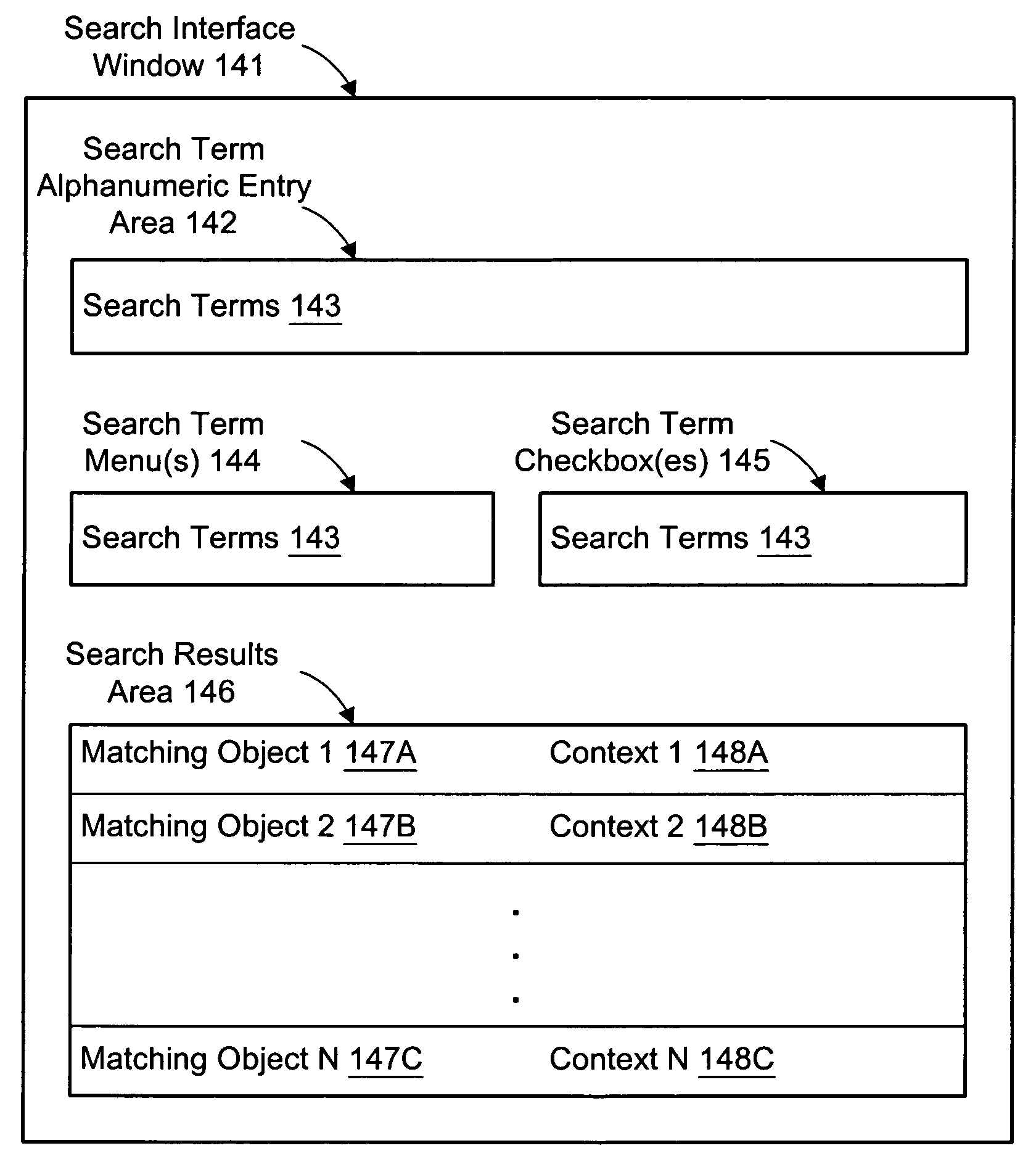
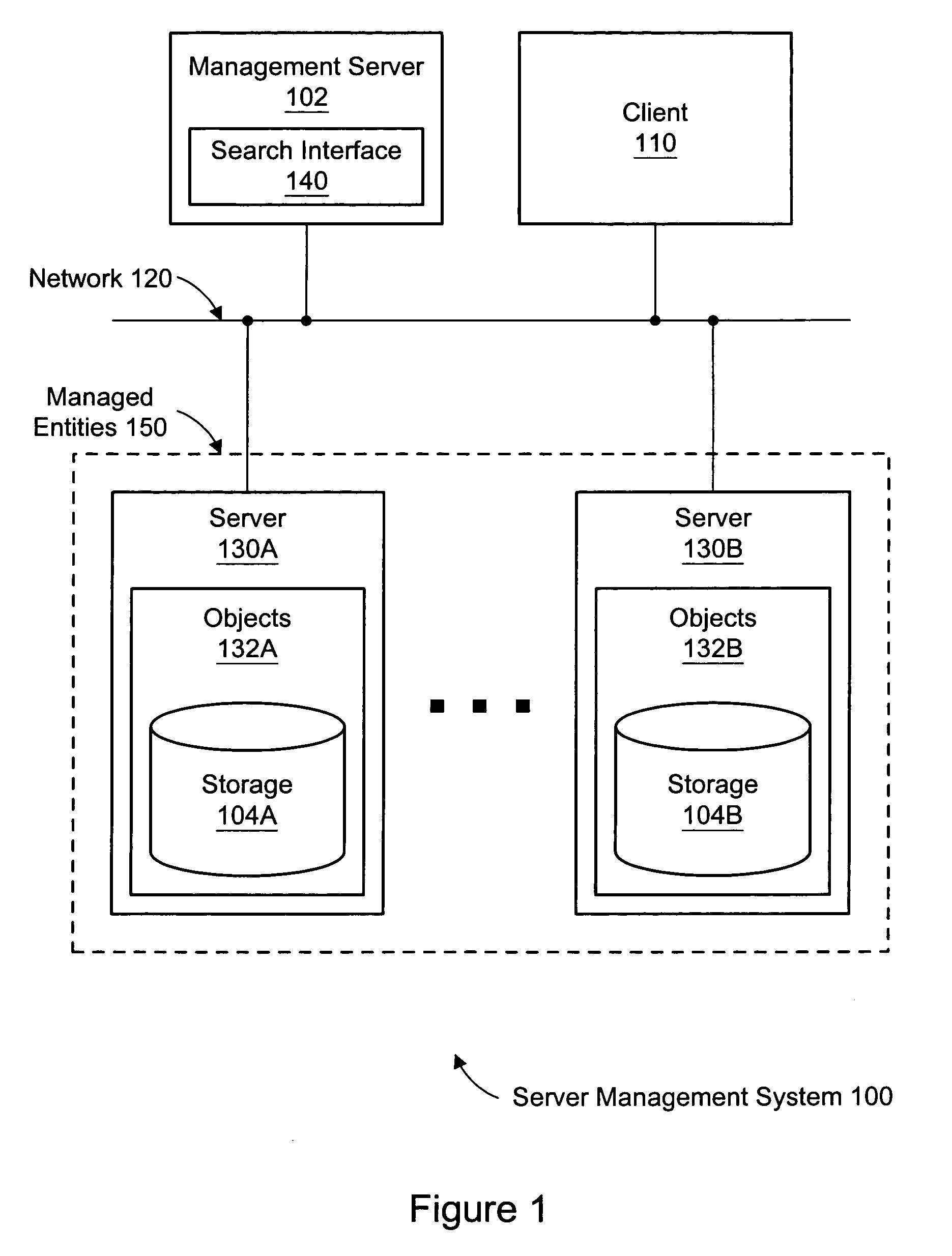
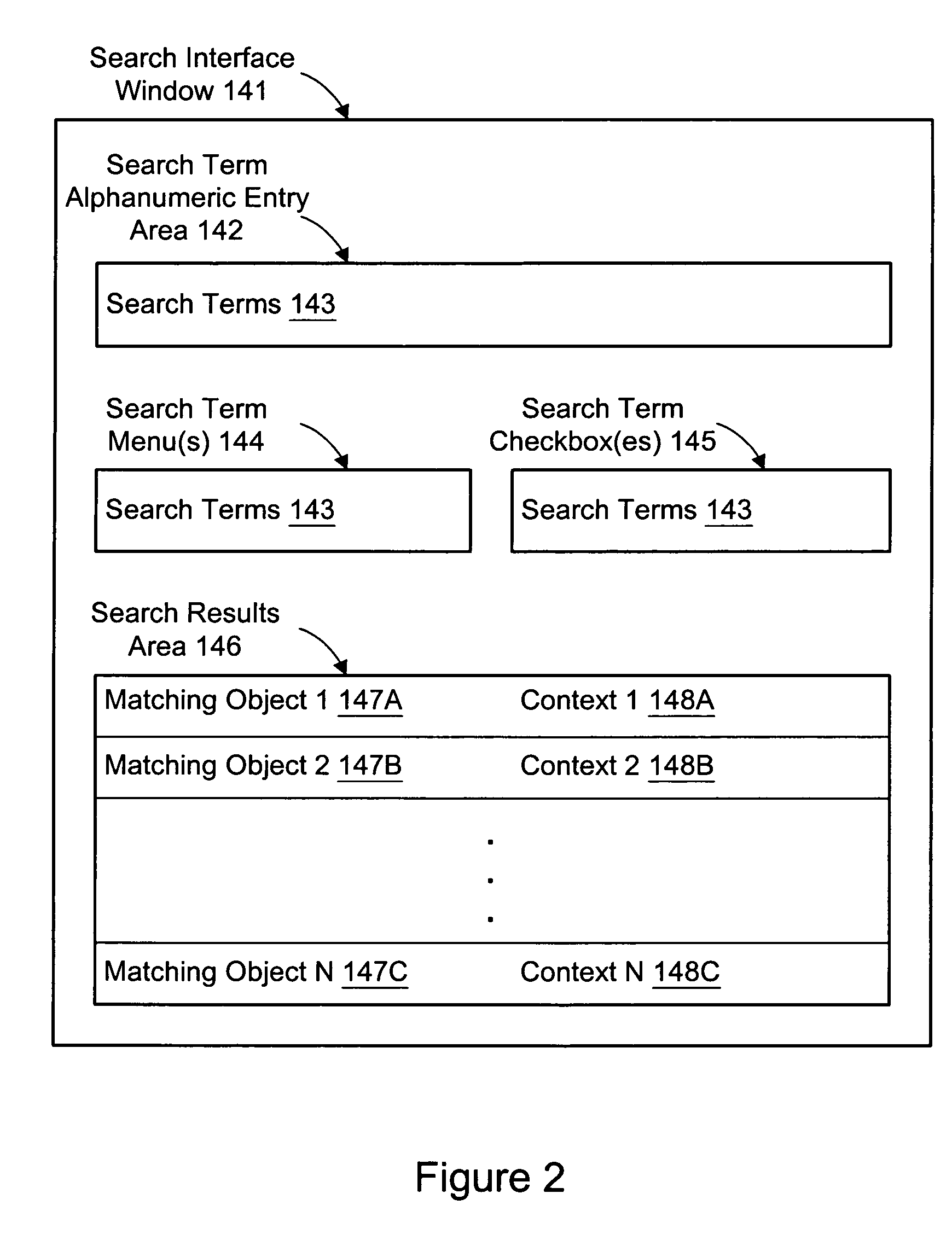
InactiveUS7529744B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalObject definitionStorage management
A system, method, and computer-accessible medium for searching in a server management system are disclosed. One or more search terms are determined. A search is performed for object definitions which match the search terms, thereby determining one or more matching objects corresponding to the object definitions which match the one or more search terms. The matching objects are reported.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
System and method for presentation of wireless application data using repetitive UI layouts
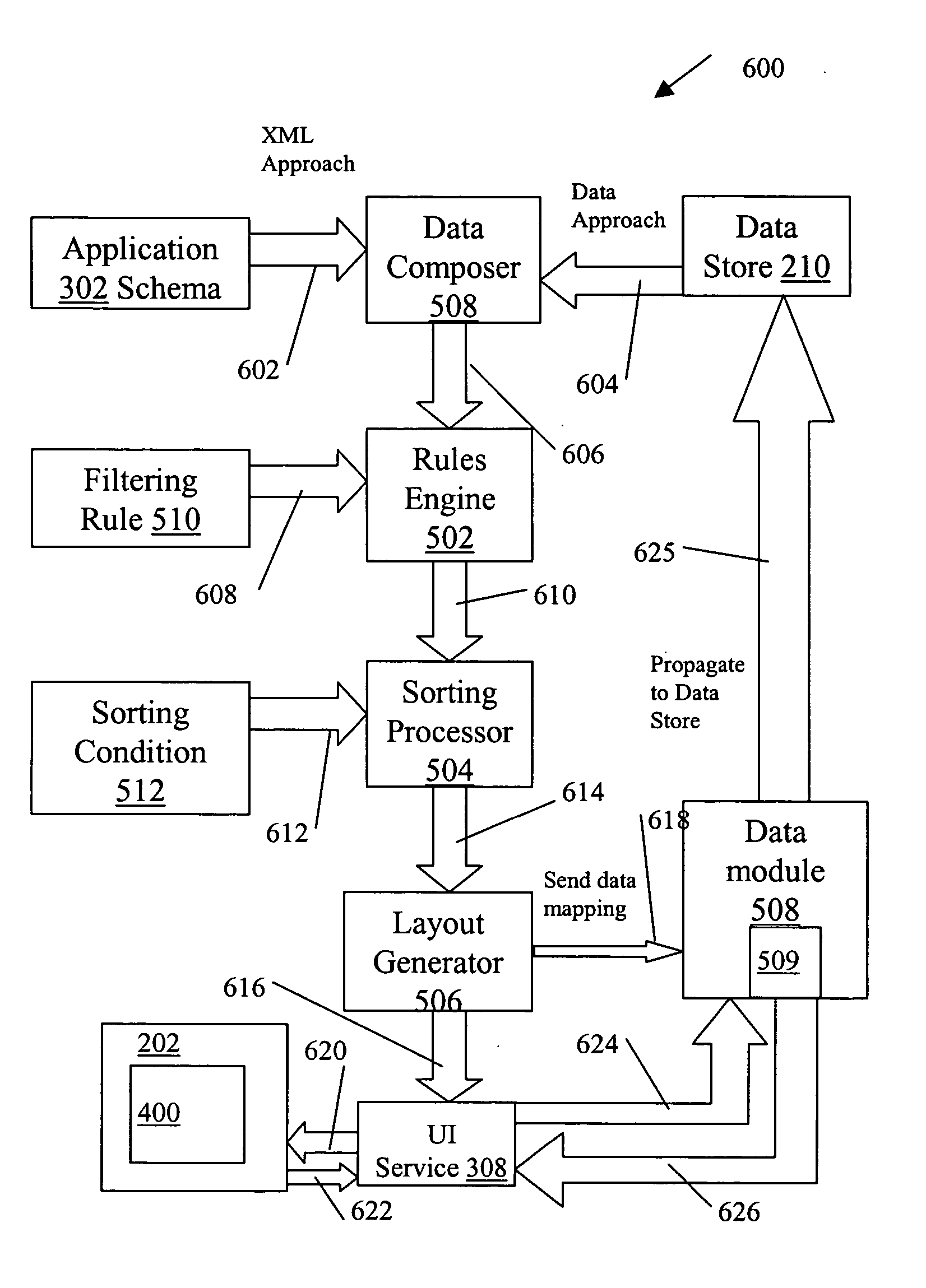
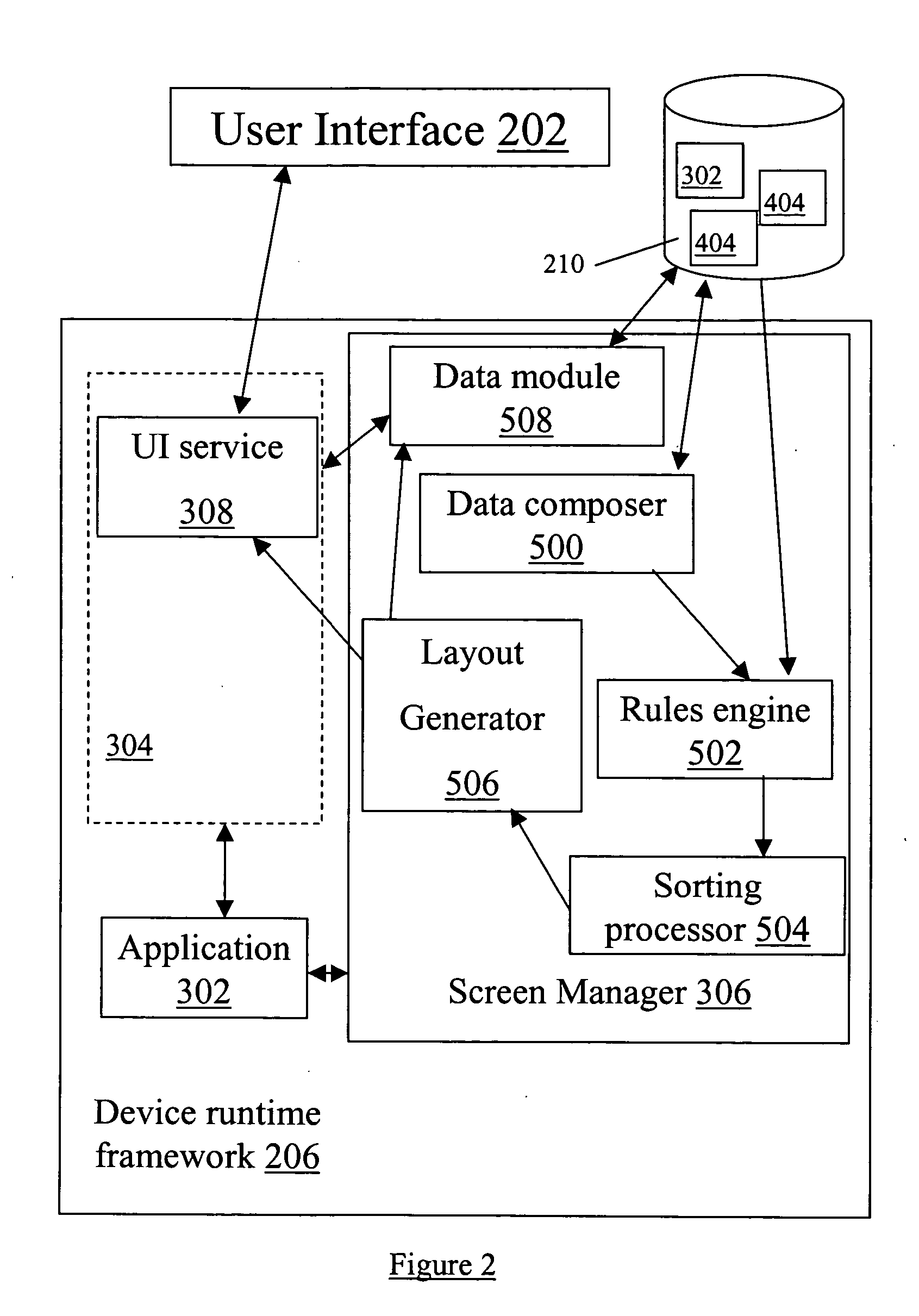
InactiveUS20050193361A1Reduced executable codeDegree of flexibility and efficiencyProgram loading/initiatingExecution for user interfacesObject definitionData field
A Repetitive Layout scheme is provided that operates on a collection of data objects, such that each data object accords to the same data object definition (data model) expressed in a structured definition language. The Repetitive Layout consists of one UI section repeated for every object in the collection. Each UI section is composed of a set of UI controls or sub-layouts. The UI controls in each section are associated with the data fields of the corresponding data object. A user of a wireless application interacting with the data objects can select UI sections and edit the controls within them via the user interface of the wireless device executing the application. Any modifications are propagated to the data objects mapped to the respective UI sections. Similarly, all modifications (driven by the application logic or incoming server messages) to the data objects are reflected in the UI section mapped to these objects. The generation and application of the repetitive layout scheme can include the steps: dynamic data entity generation (Data Composer stage); determining the collection of data objects that need to be presented by the user interface (Rules Engine stage); sorting the collection of data objects (Sorting Processor stage); generating the UI Layout (Layout Generator stage); propagating UI changes back to the Data Model having the definitions of the data objects (Data Dispatcher stage); propagating data changes to the Repetitive Layout; and propagating changes to nodes of the data model.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
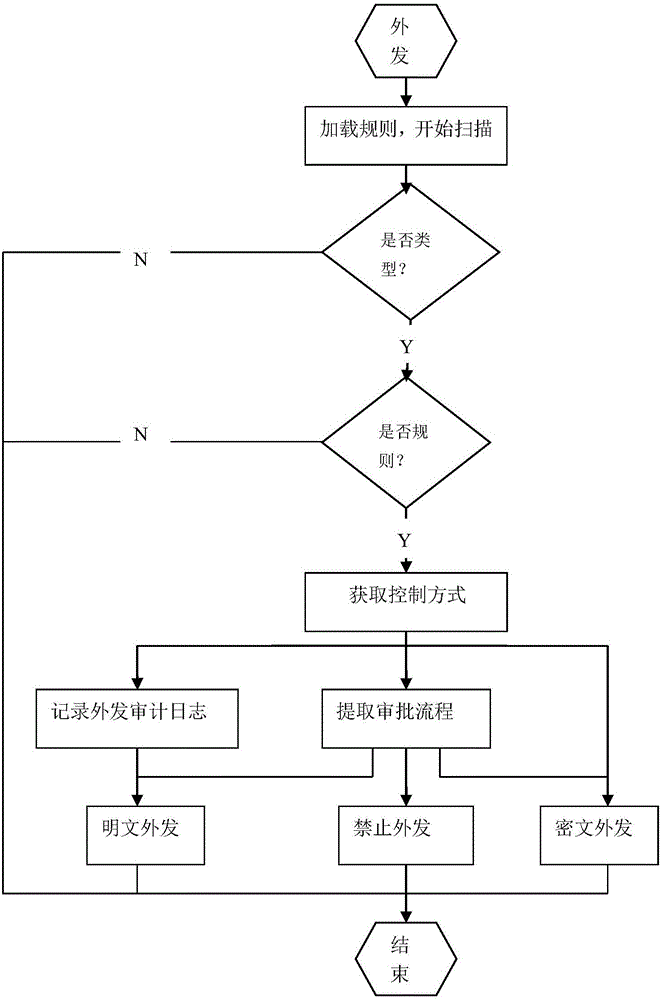
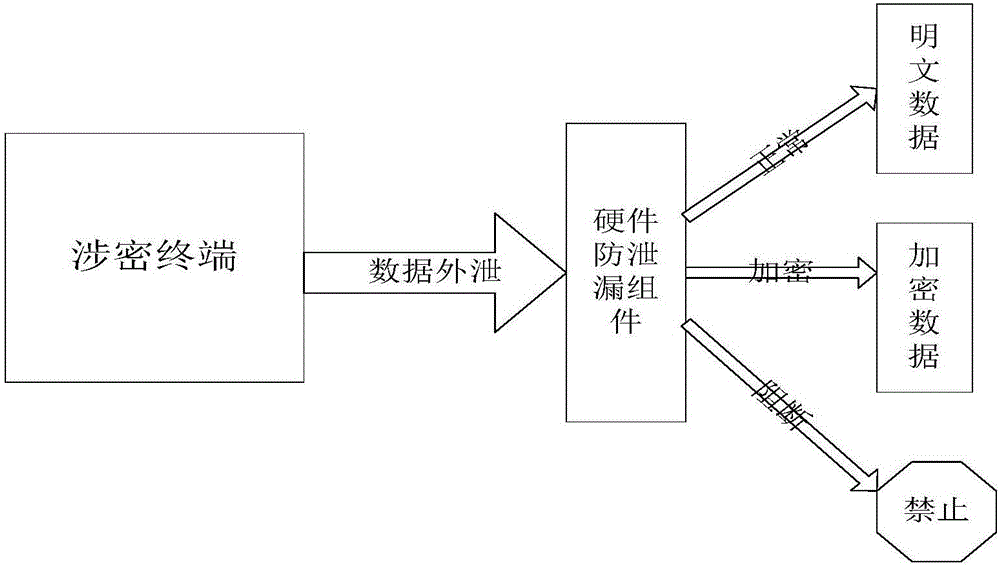
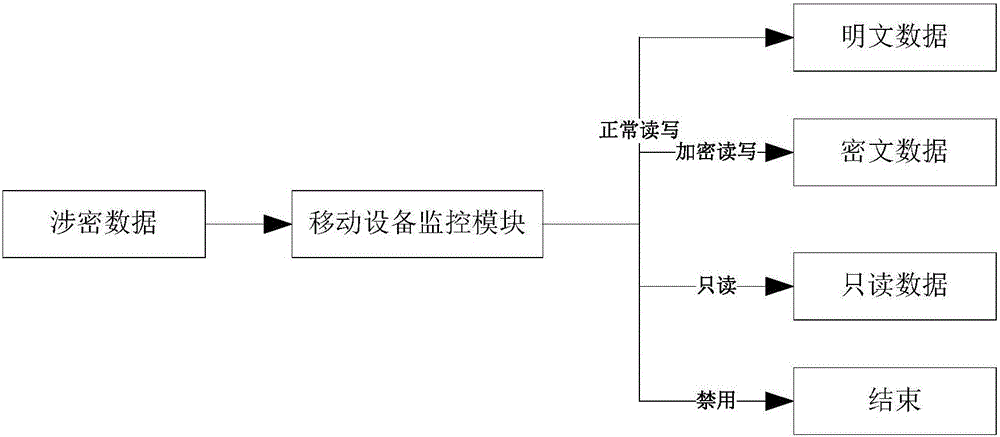
Dynamic data leakage prevention system and method
InactiveCN106446707AAvoid wastingAvoid affecting work efficiencyDigital data protectionObject definitionFiltering rules
The invention discloses a dynamic data leakage prevention system and method. The method comprises a data filtering rule file storage module, a data management control policy storage module and a file scanning engine, wherein the data filtering rule file storage module is used for storing a data filtering file, and the data filtering rule file comprises a plurality of different types of data filtering rules; the data management control policy storage module is used for storing a data management control policy, and the data management control policy comprises corresponding relationships between the different types of data filtering rules and different levels of data management control schemes; and the file scanning engine loads the data filtering rule file and the data management control policy, scans data sent to outside according to the data filtering rule file when the data needs to be sent to the outside, and performs corresponding outside sending control on the data sent to the outside. According to the system and the method, data leakage prevention can be dynamically performed, a leakage prevention management control object is defined in data, and a terminal or a user is no longer taken as a subject, so that the flexibility and security of data security control are improved.
Owner:北京明朝万达科技股份有限公司
Method for controlling access to informational objects
ActiveUS20060117389A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationInternet privacyInformation object
The described embodiments of invention comprises a method and an apparatus for regulating access to objects by authorized entities. Authorized entities are entities authorized for access by either an owner entity of the regulated object or an entity authorized to authorize access to the regulated object. Each user, which may be a physical person or another information system, is identified using standard user validation techniques. When an object is first created or introduced to the system, that information is associated with an owner, who is one user on the system. The present embodiment allows the owner to define relationships with other users, either generally or regarding a particular object. The owner may or may not have trusted relationships with other users. A second user that has a trusted relationship with the owner automatically has access to the object without additional intervention by the owner. In addition, the second user may have a trusted relationship with another user. In the above example, the records administrator may have an assistant. This third user will also have access to the records. This Web of Trust may link users infinitely, but such a case would create an undue risk of compromise of the information. Thus, the present embodiment includes a facility for the owner to designate a maximum number of trusted links from the owner and other users.
Owner:OPTIMIZATION ZORN CORP DBA OZ SYST INC
Control systems and methods with smart blocks
InactiveUS20090118846A1OptimizationOptimize system configurationData processing applicationsComputer controlGraphicsGraphical user interface
Methods and apparatus for configuring process, environmental, industrial and other control systems generate and / or utilize models representing configurations of control systems and / or the systems controlled by them. Records of changes to the models or the configurations represented by them are maintained, thereby, for example, providing bases for determining current states, prior states and histories of changes. Objects in the model have characteristics, such as an object type characteristic and an area characteristic. Users can have corresponding permissions. A security mechanism apparatus controls access by users to the objects. Composite objects are defined by definition objects and are displayed in encapsulated or expanded formats. Objects can include an edit control type identifier that determines how they are presented for editing. Functionality responds to user commands by transferring characteristics of a first object depicted by the graphical user interface to a second object. Configuration-time formulas contained objects are evaluated to constants prior to downloading to the control system.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SYST USA INC
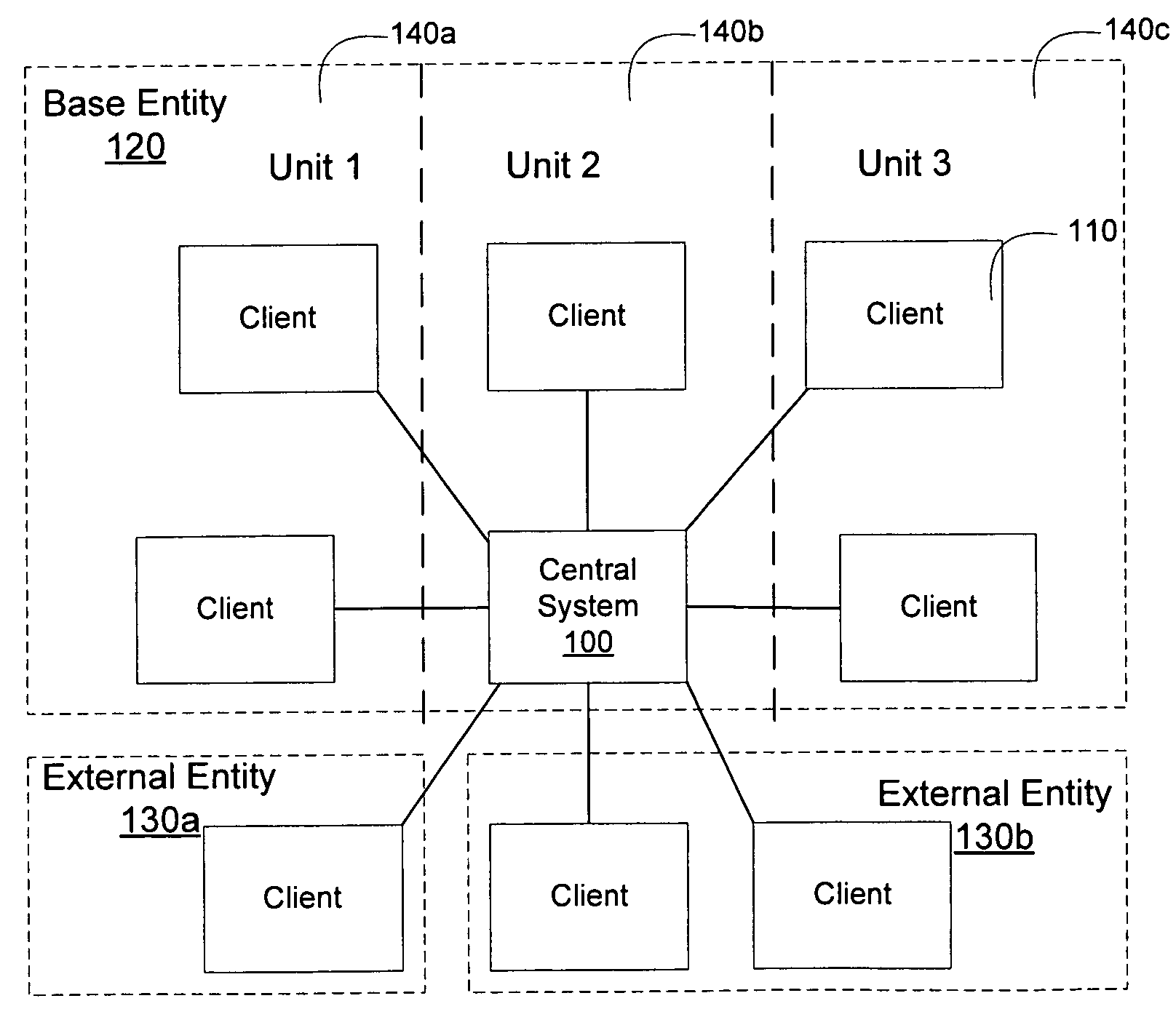
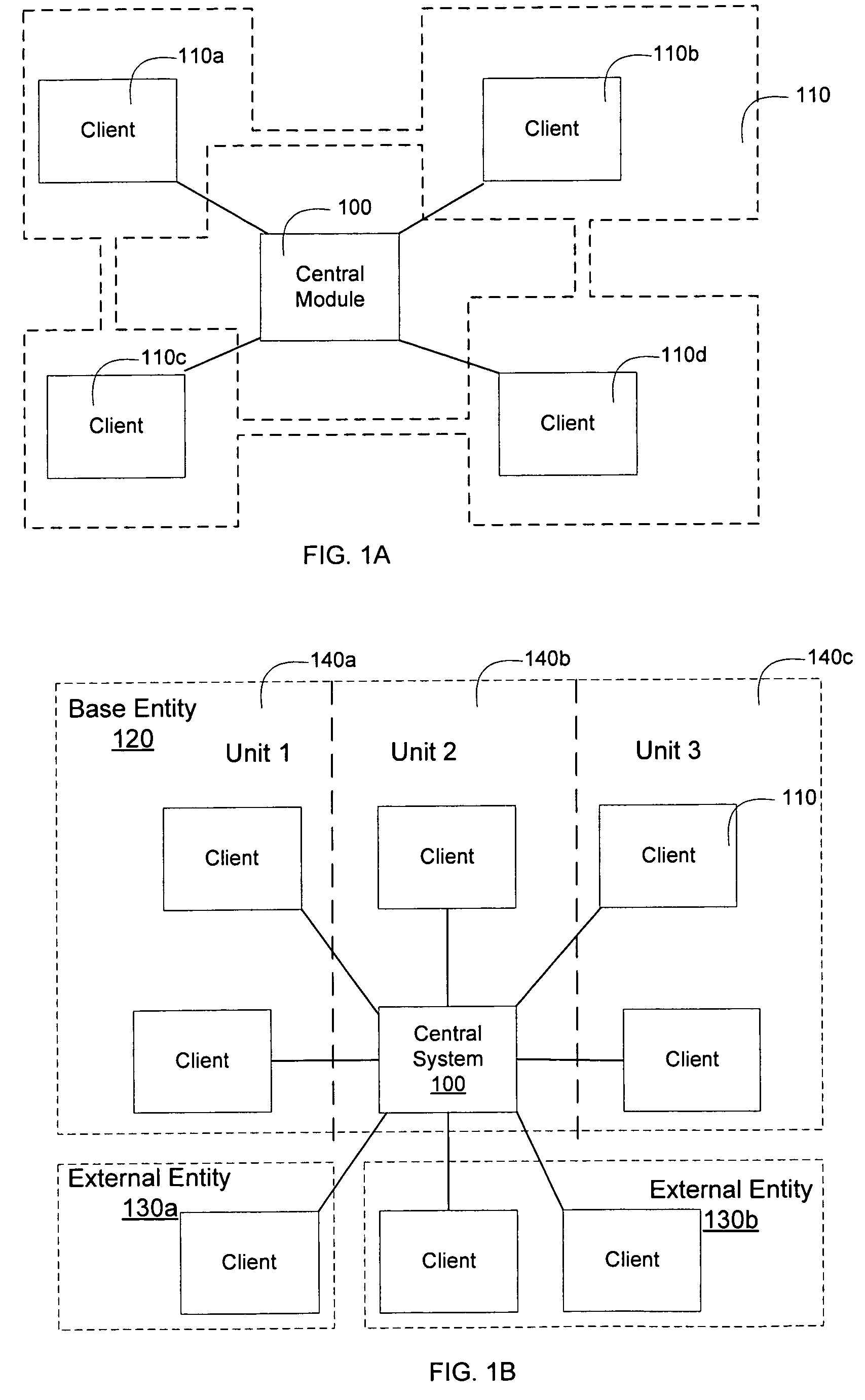
Central master data management
ActiveUS7509326B2Avoid data redundancyImproved cross-group reportingDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsObject definitionClient-side
Methods and apparatus, including computer program products, for sharing data. The technique includes creating at least one data object in a central system, the data object including a complete object definition, and dependencies to other objects, mapping at least one data object to other data objects in the central system, and distributing data objects from the central system to one or more client systems, where the one or more client systems.
Owner:SAP AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com