Patents
Literature
393 results about "Application logic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
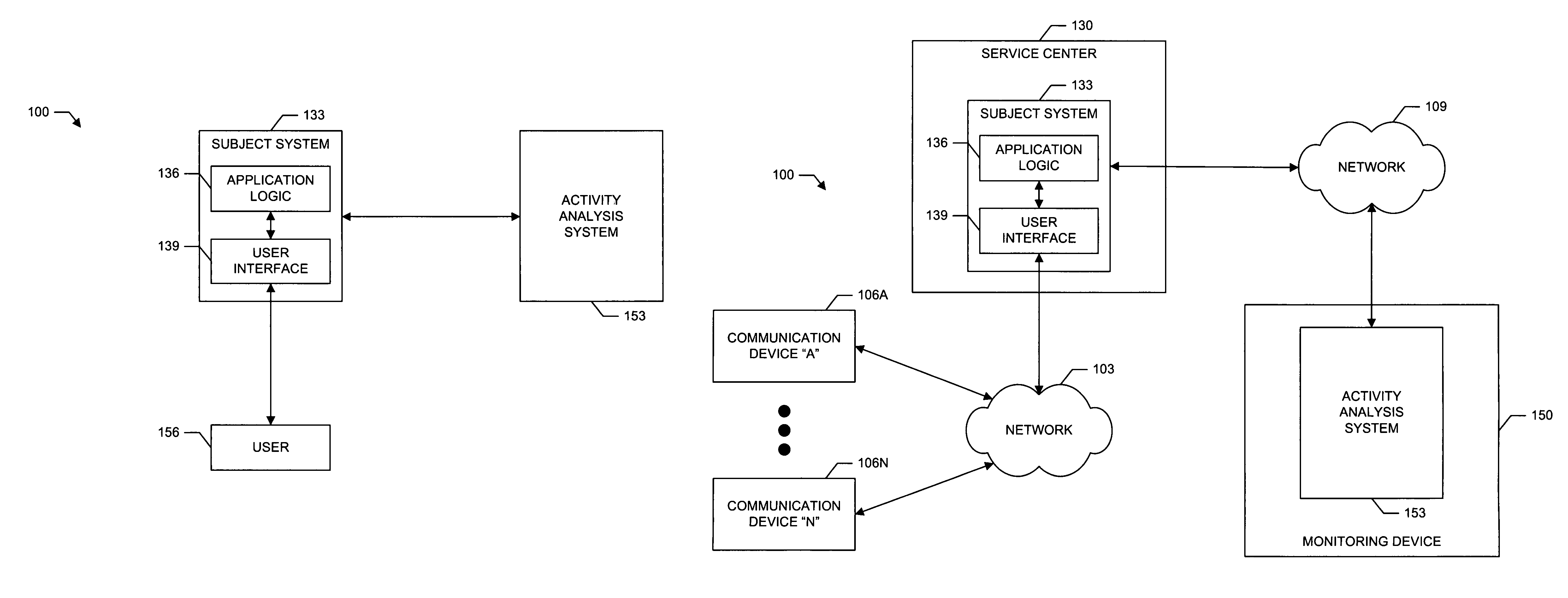
System and method for analyzing system user behavior
A system and method for monitoring and analyzing user activity of an interactive system, providing insight and recommendations to improve the interactive system based on the user activity. The present invention analyzes user behavior in the context of the structure of the interactive system as experienced by the user, the analysis of business-critical user tasks, the automated generation of recommendations for improving the interactive system, reports on the interactive system's application logic and data, unique visualizations of user behavior through the use of graphical displays, and secure report viewing and creation. The present invention can be applied to number of interactive systems or a combination thereof.
Owner:IGNITE ENTERPISE SOFTWARE SOLUTIONS INC
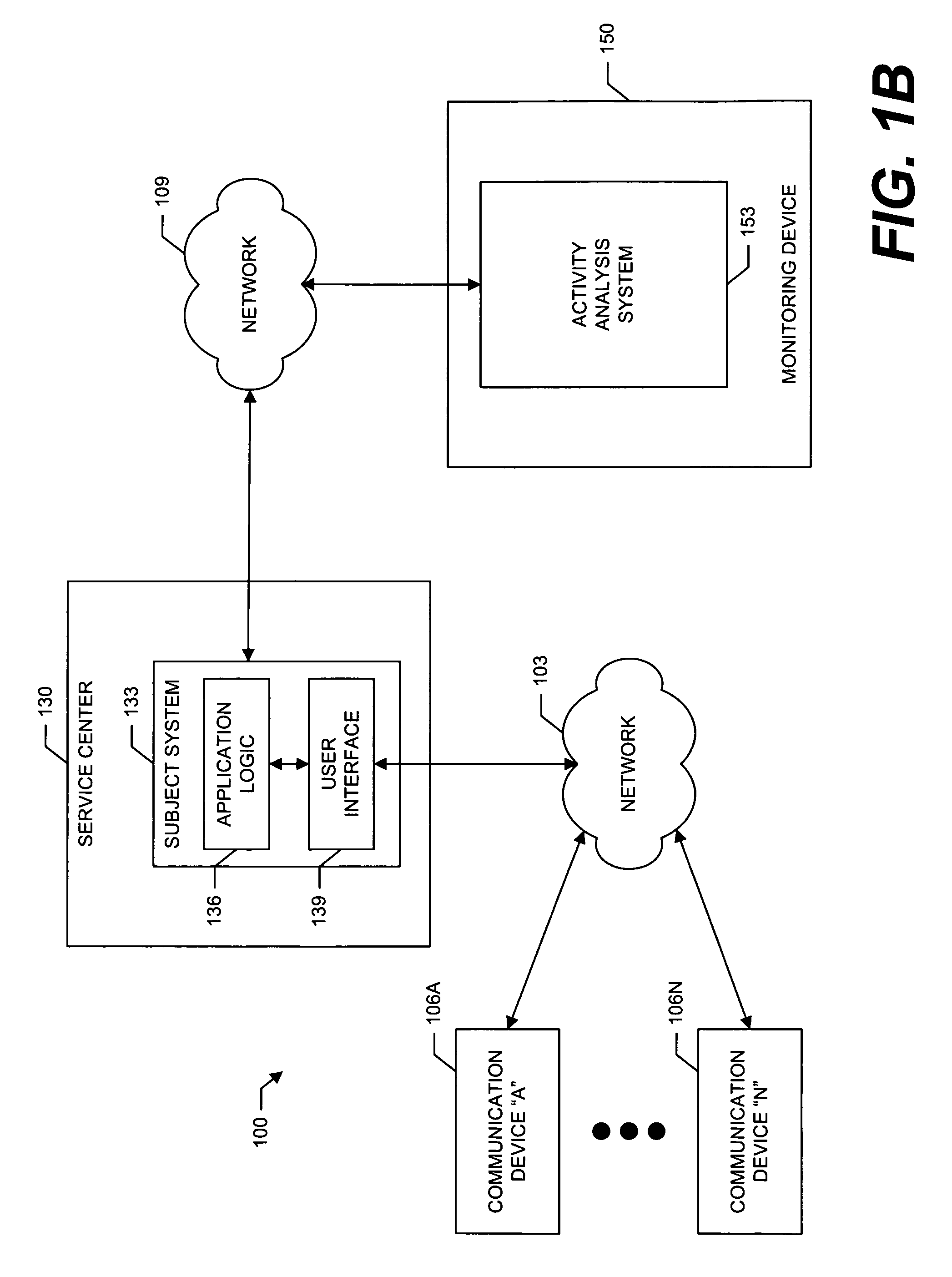
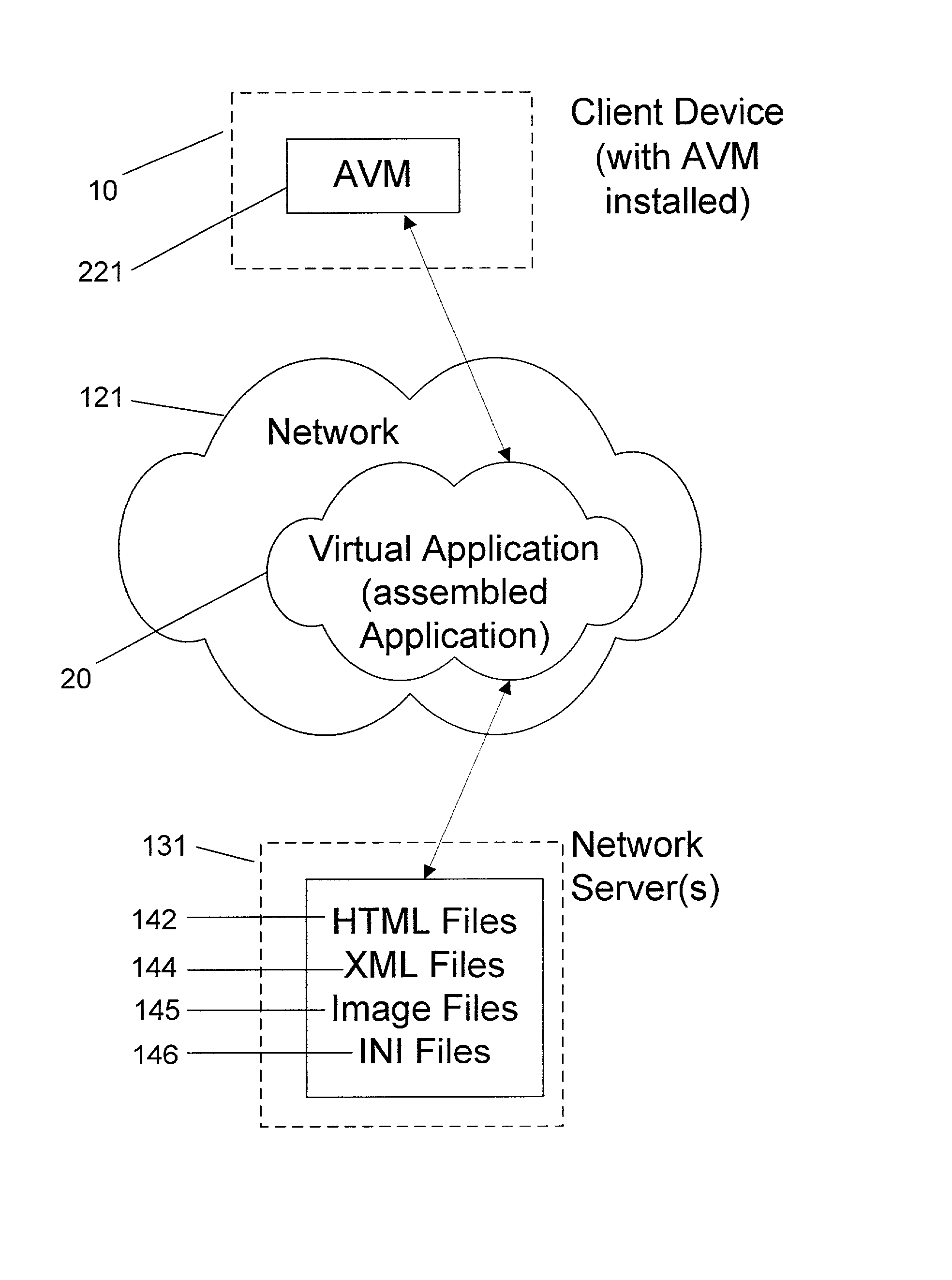
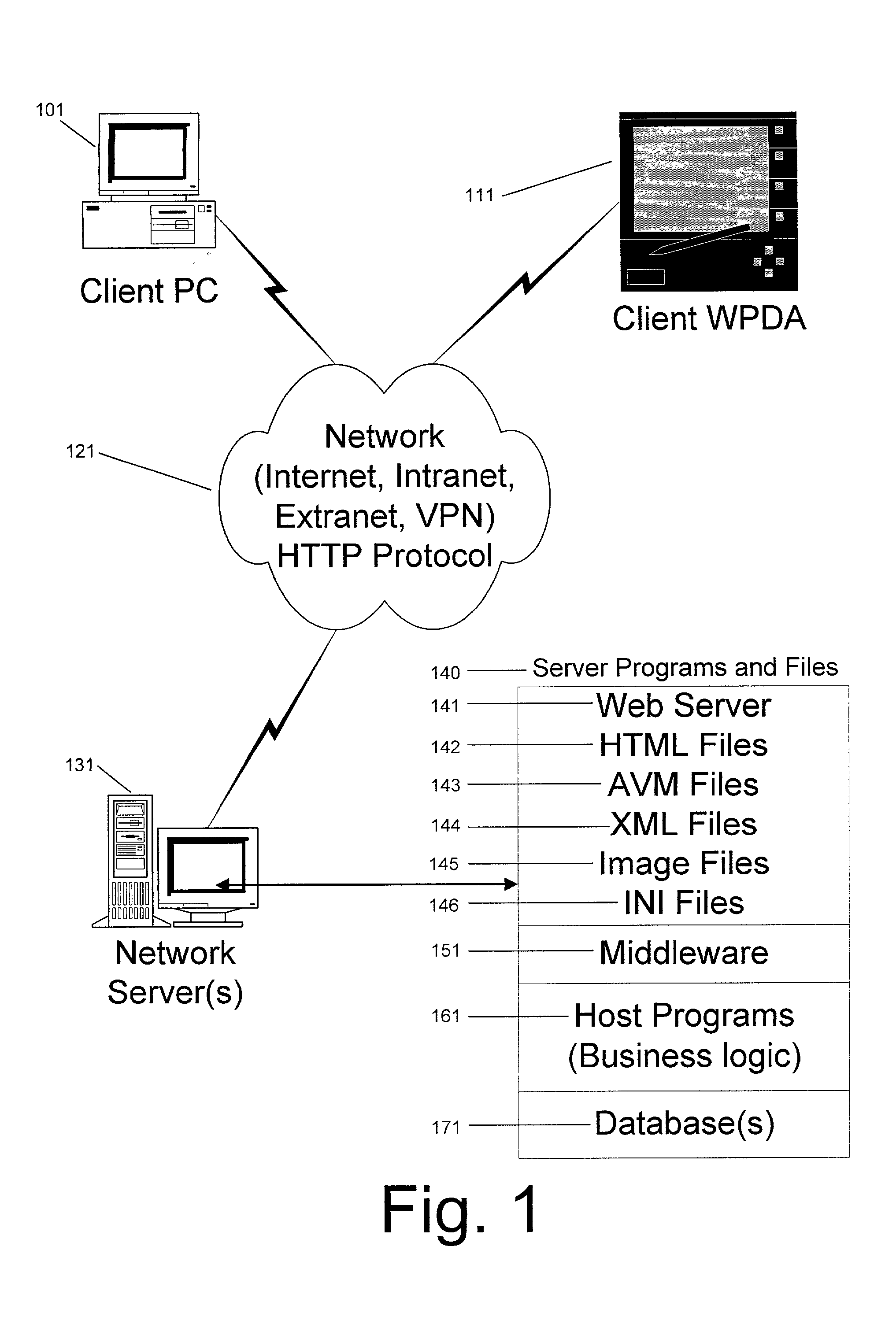
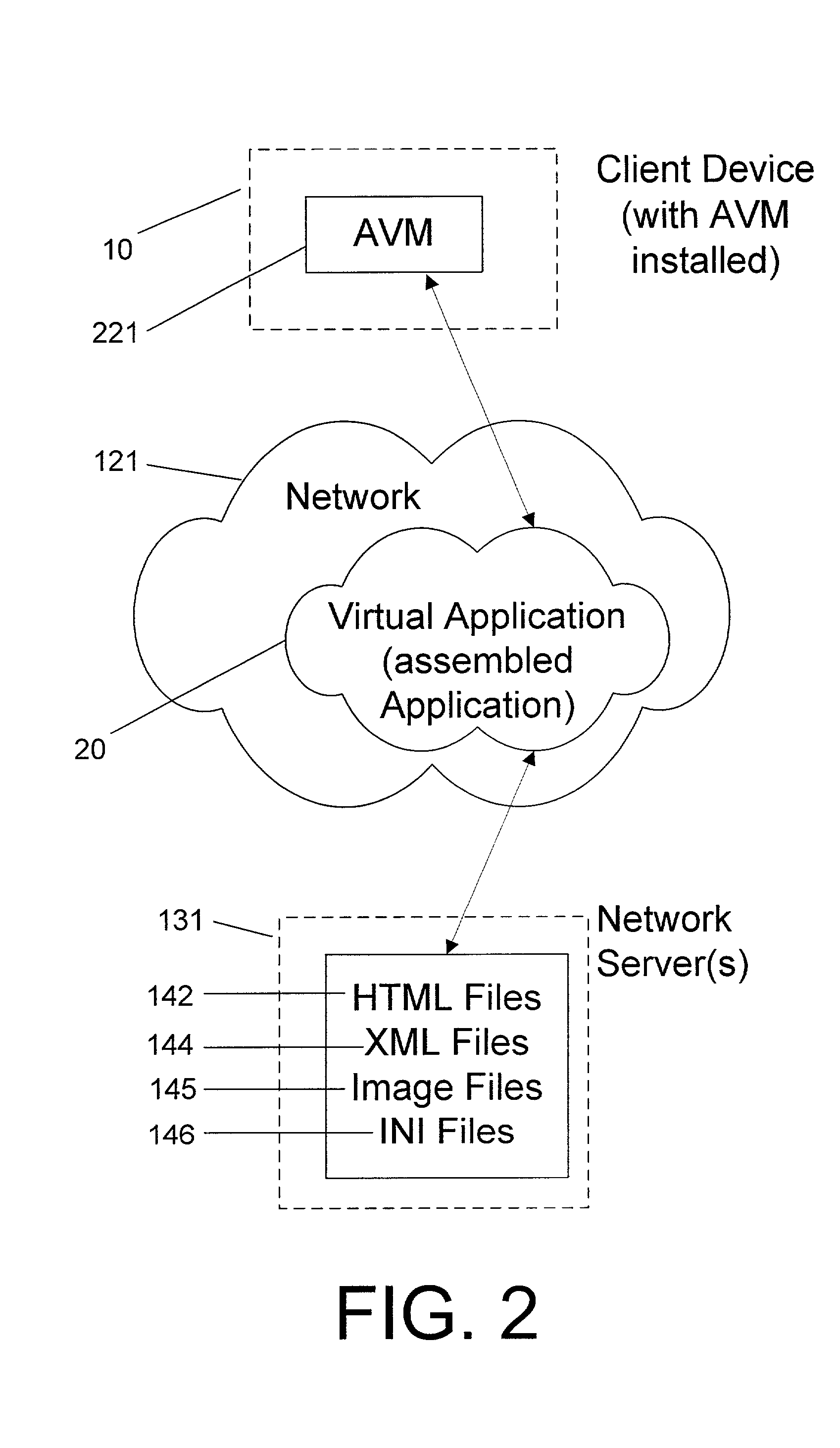
System and method for deploying and implementing software applications over a distributed network
ActiveUS20020129129A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram loading/initiatingApplication softwareProgram logic
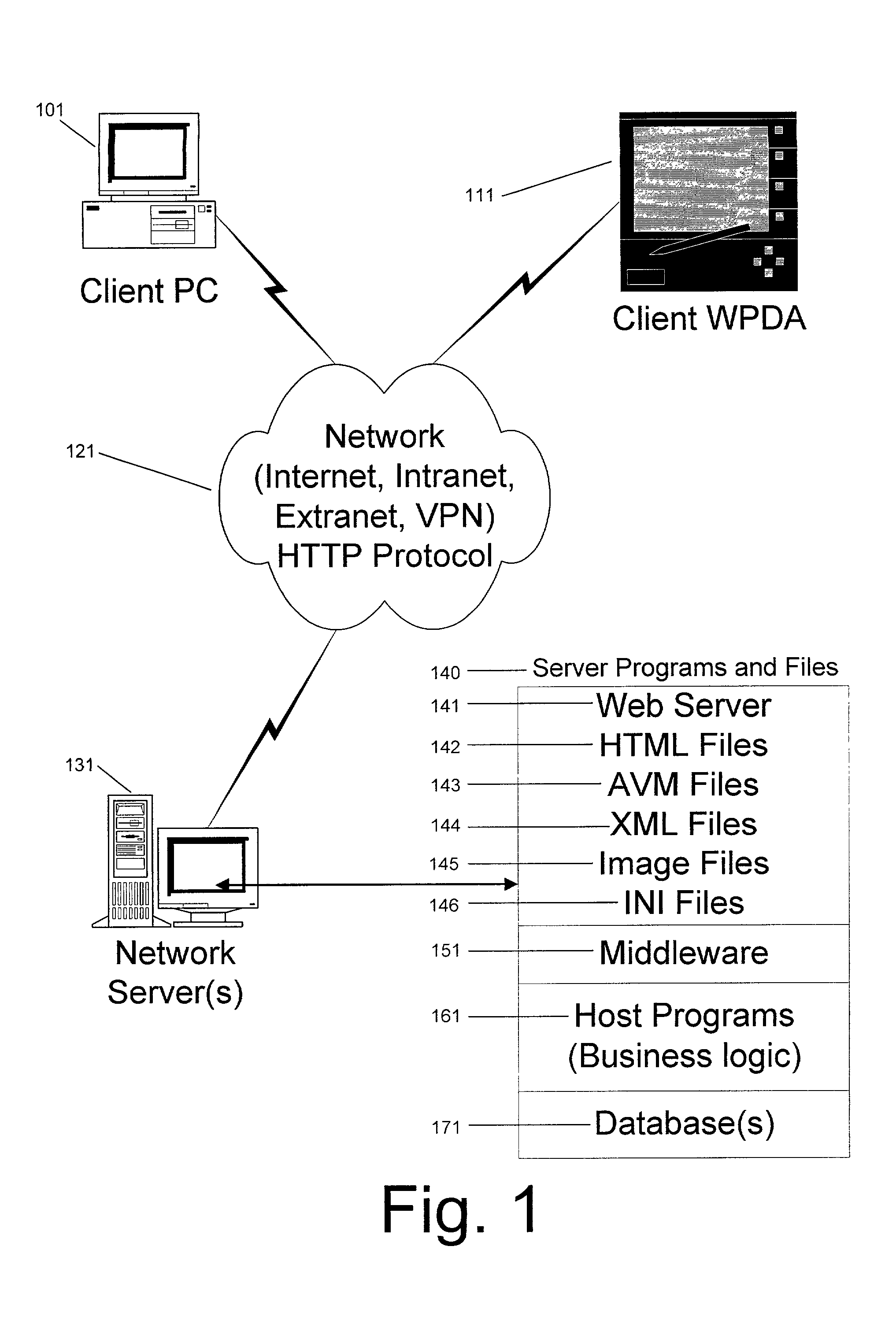
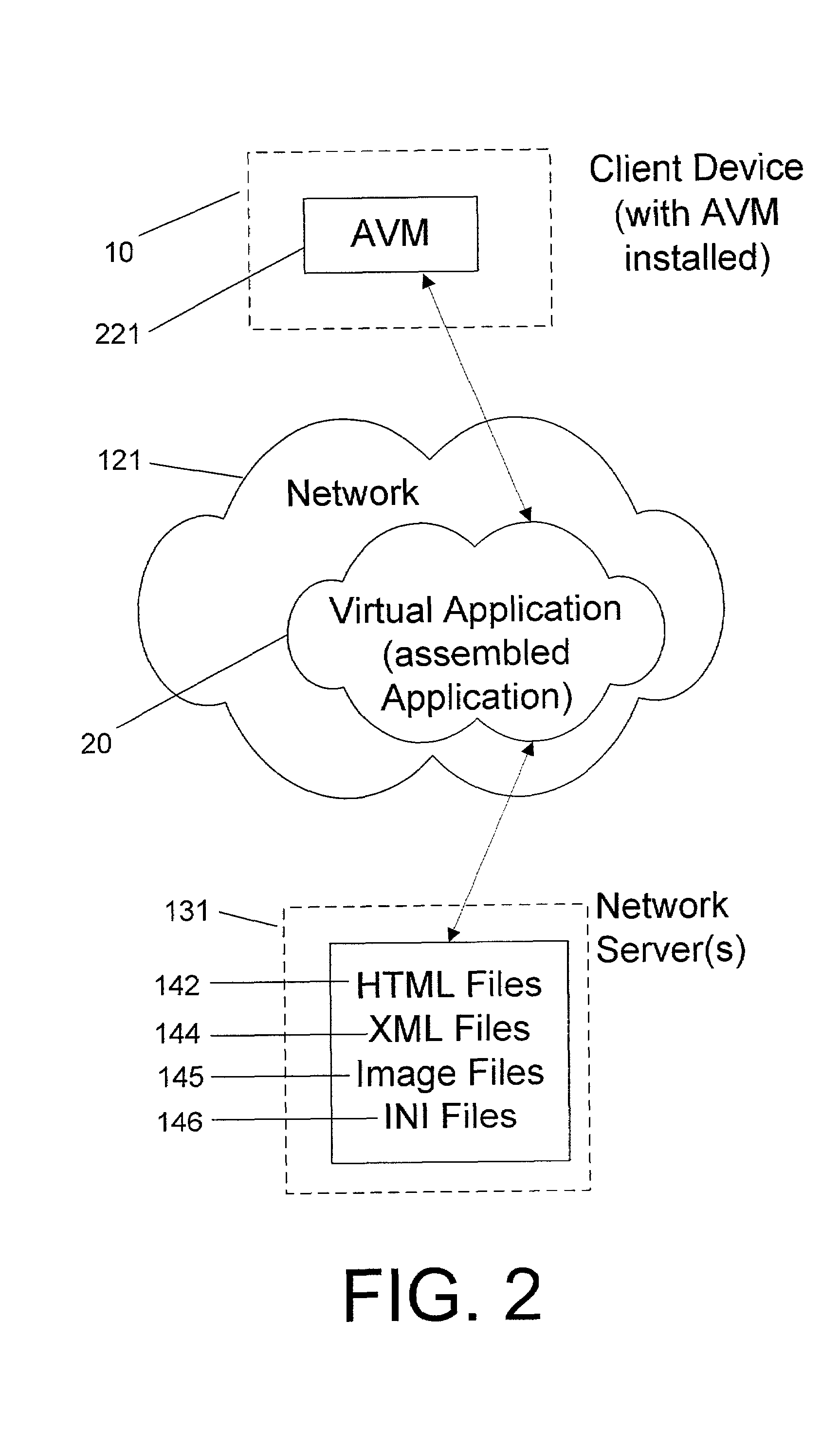
A system for deploying applications over a distributed network to web-enabled devices uses a server, with stored text files containing application logic, and an application assembler. The application assembler downloads and installs on each web-enabled device. Then, the application assembler downloads one or more text files from the server, retrieves program logic from each of the downloaded text files, and assembles the retrieved program logic into a functioning application. In some instances, a plugin that is downloaded and installed on each web-enabled device is activated by web pages on the server to launch the application assembler.
Owner:DATACLOUD TECH LLC
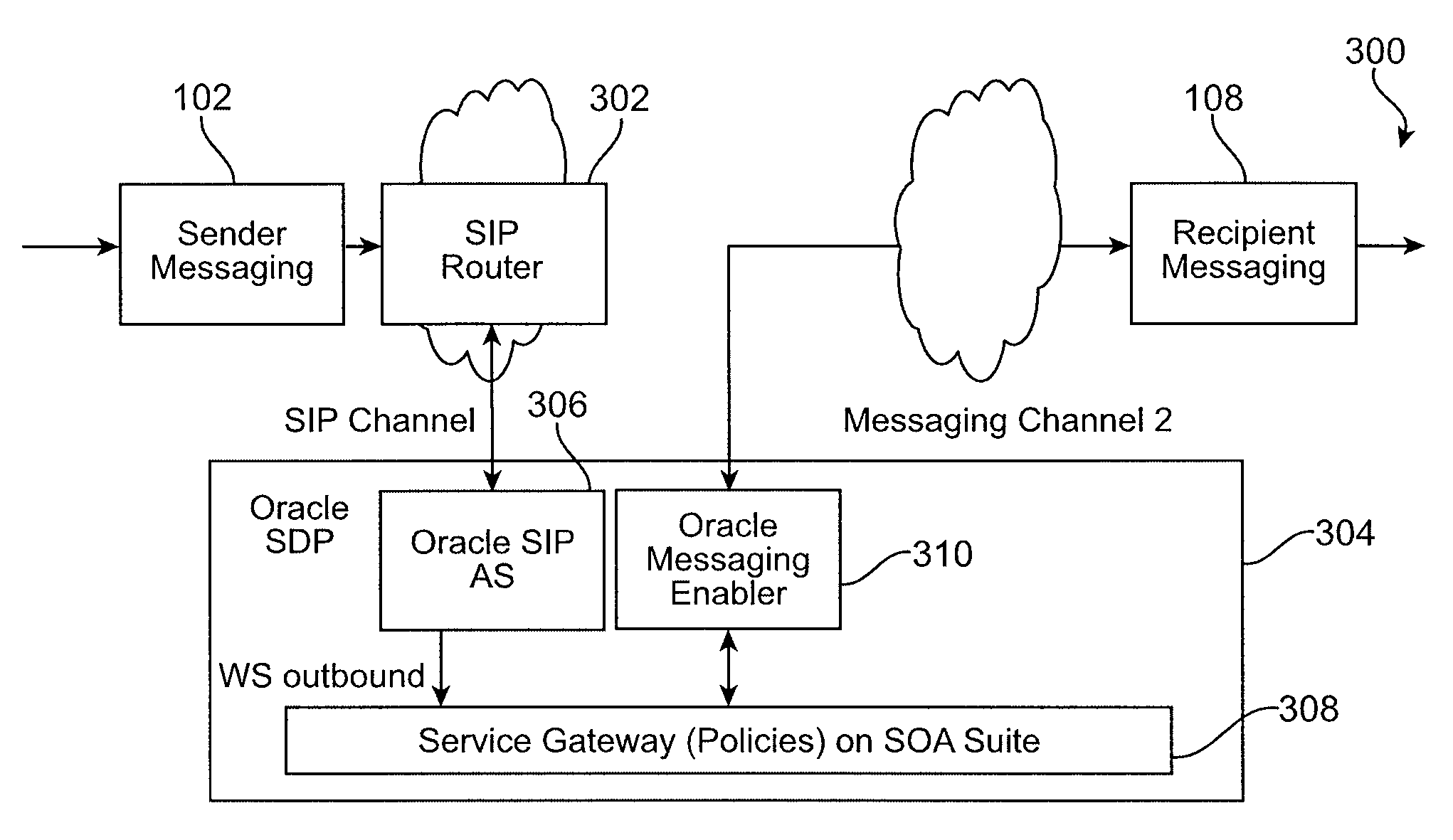
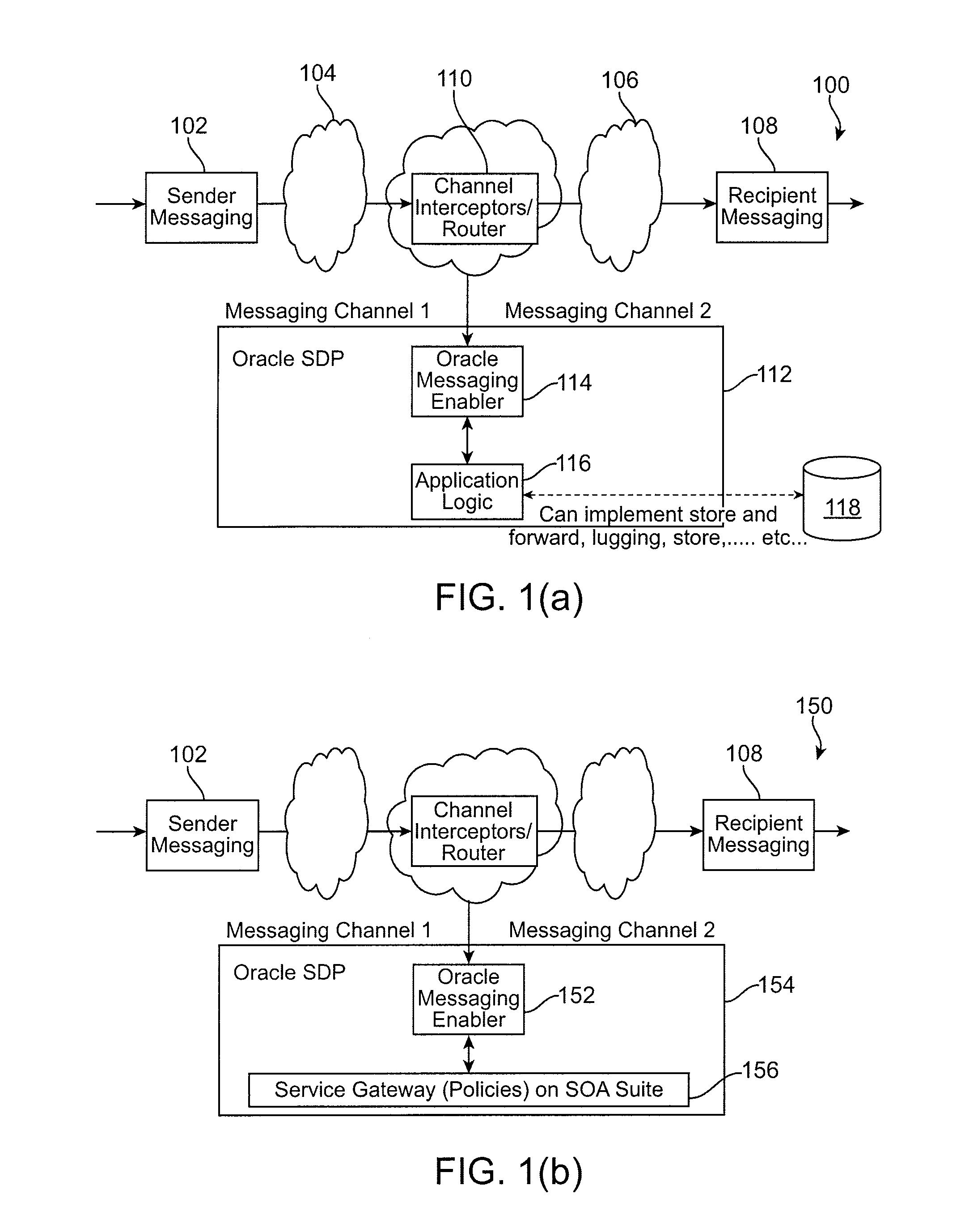
Intelligent message processing
ActiveUS20090125595A1Overcome deficienciesIntelligent processingTelephonic communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer hardwareWeb service
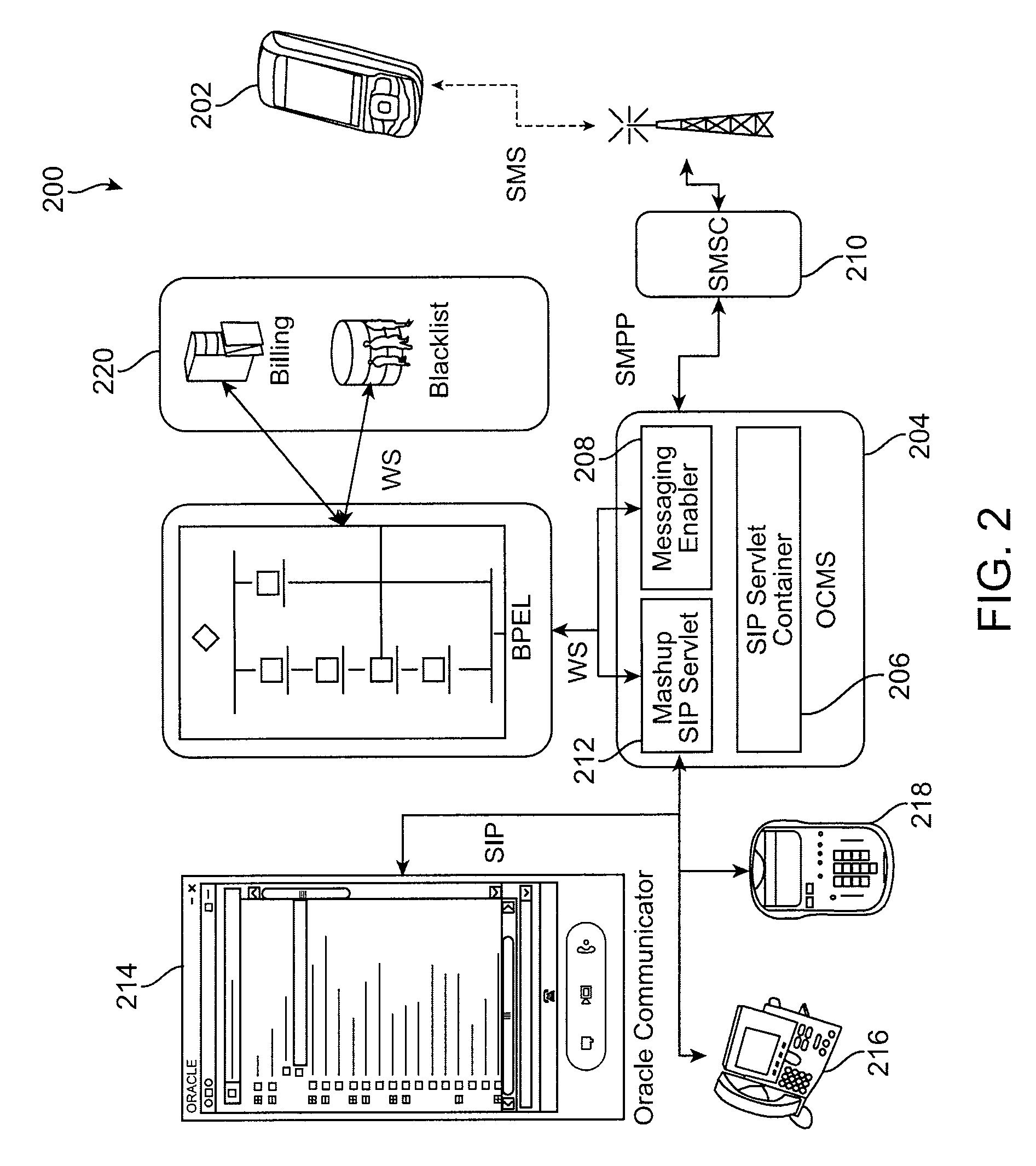
Intelligent message processing is provided for person to person (P2P) messaging by intercepting the message and processing the message before directing the message to the recipient. The messaging system then acts as a person to application (P2A) and application to person (A2P) system, wherein any P2P message can be intercepted and processed as necessary. Such functionality allows any desired processing of the message, such as to allow for transformation, charging, content filtering, screening, parsing, and any other such processing. Further, such an approach allows the message to be received from the sender and directed to the recipient on different channels. A messaging enabler allows the message to be processed using application logic and / or Web services, for example.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method for deploying and implementing software applications over a distributed network
ActiveUS7246351B2Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram loading/initiatingSystem usageProgram logic
Owner:DATACLOUD TECH LLC
Guest relationship management system
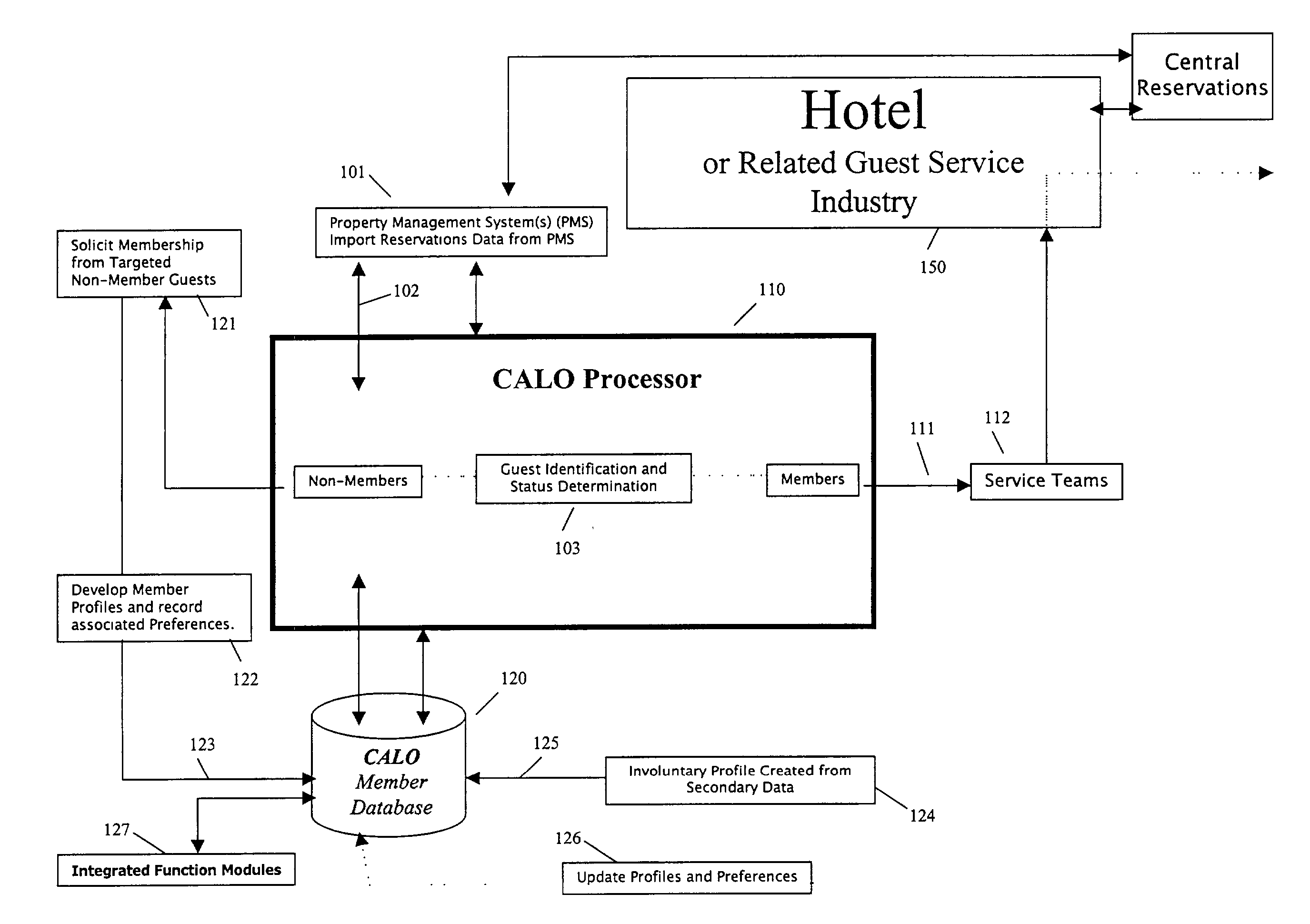
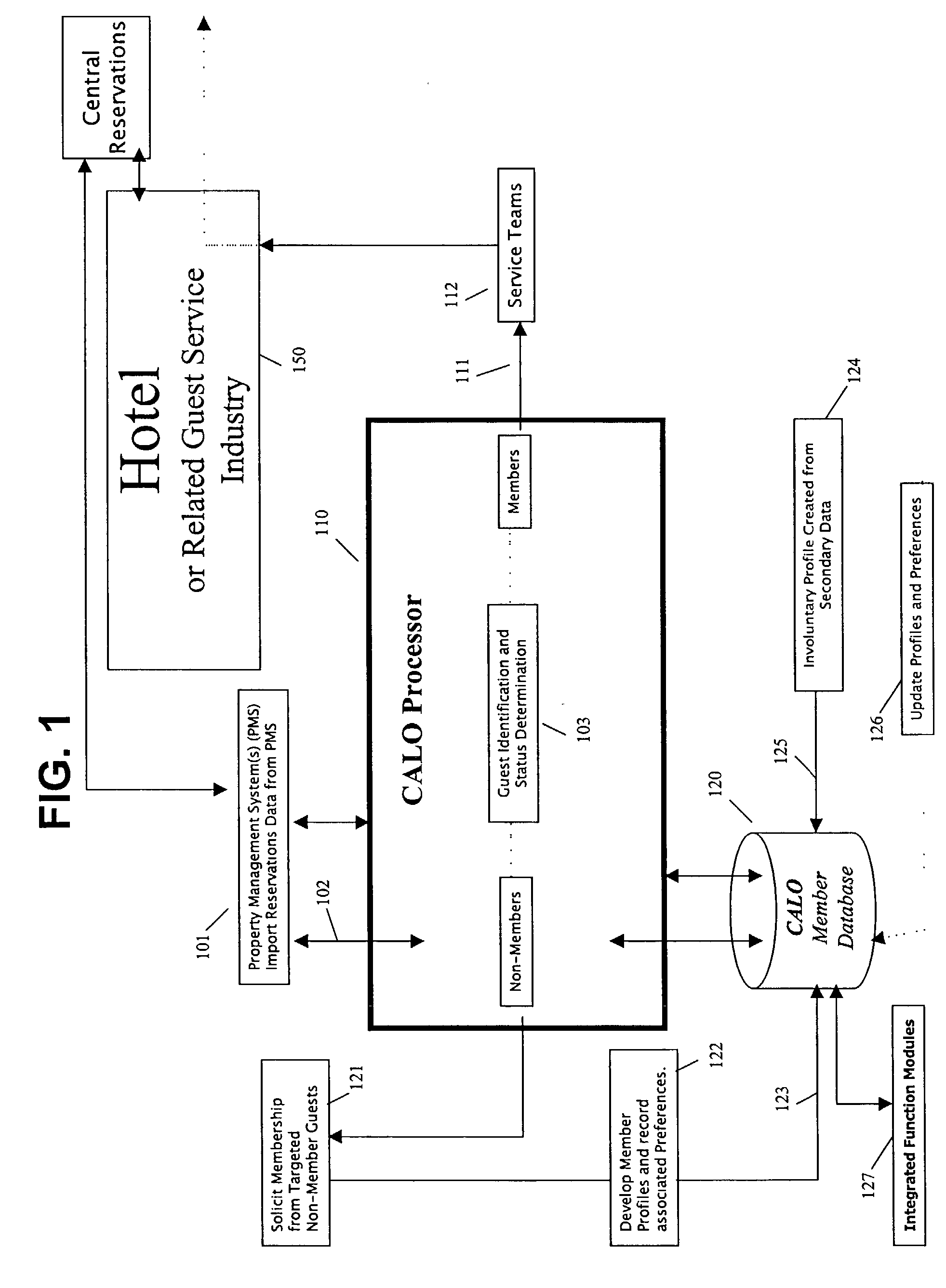
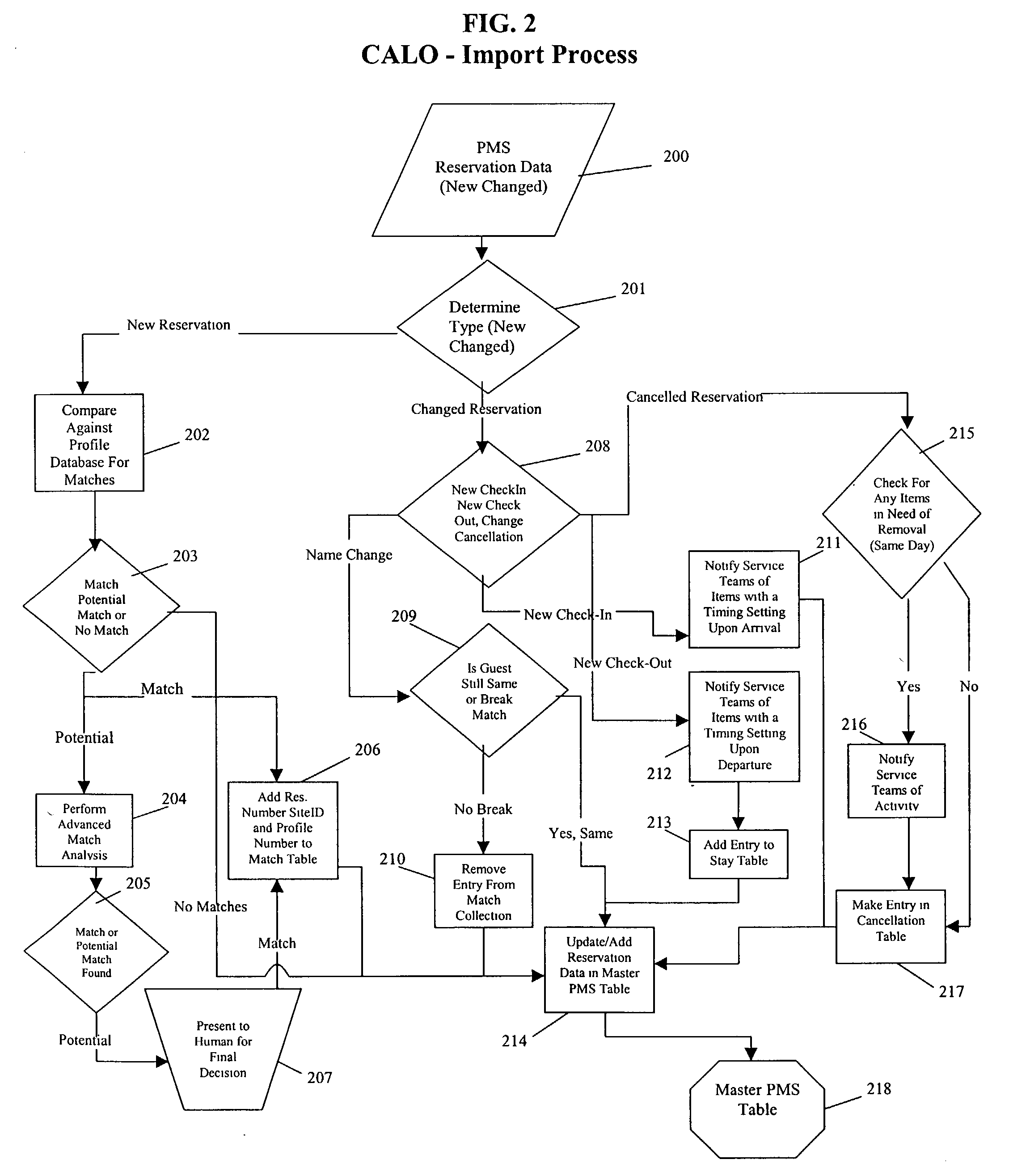
A method for implementing a guest profiling program that utilizes guest profiles, which. are developed and expanded by information gathered from various sources and managed in a central Guest Relationship Management System (GRMS). The GRMS is a web-architected internet application. The primary interface between the GRMS and hotel systems is a connection to each hotel's property management system (PMS). The GRMS extracts data from PMSs. PMS data is updated to the central GRMS for processing. The core application logic includes capabilities to identify reservations with attributes and to match guest reservations extracted from each hotel's PMS with profiled guests. Both automated and user-initiated data manipulation processes utilize the central GRMS profiles and PMS data to generate outputs designed to increase the quality and timeliness of services and to assist marketing efforts. The web-based architecture of GRMS enables consistent data sharing and processing capabilities with a plurality of hotels.
Owner:GENGARELLA JOHN S
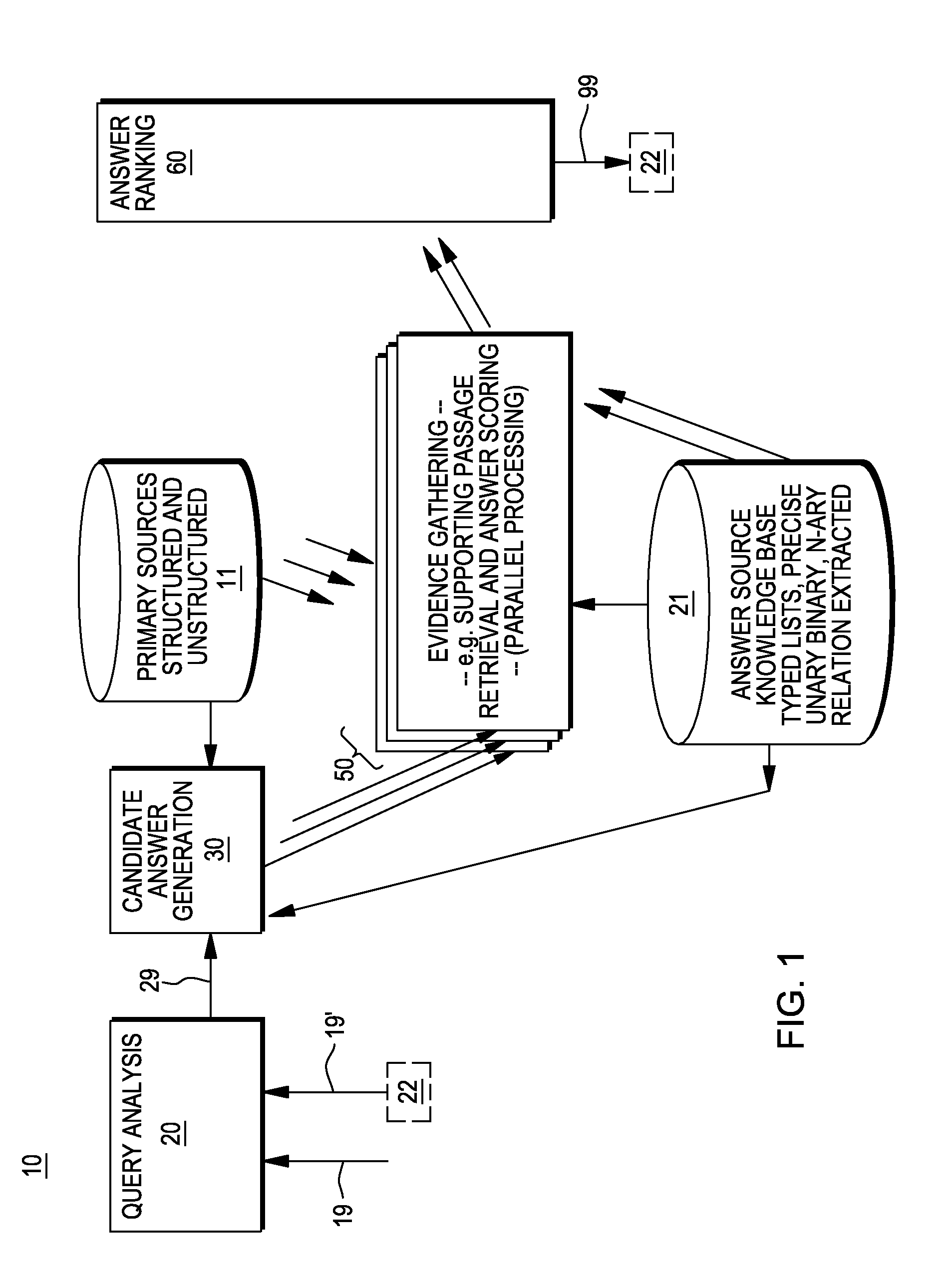
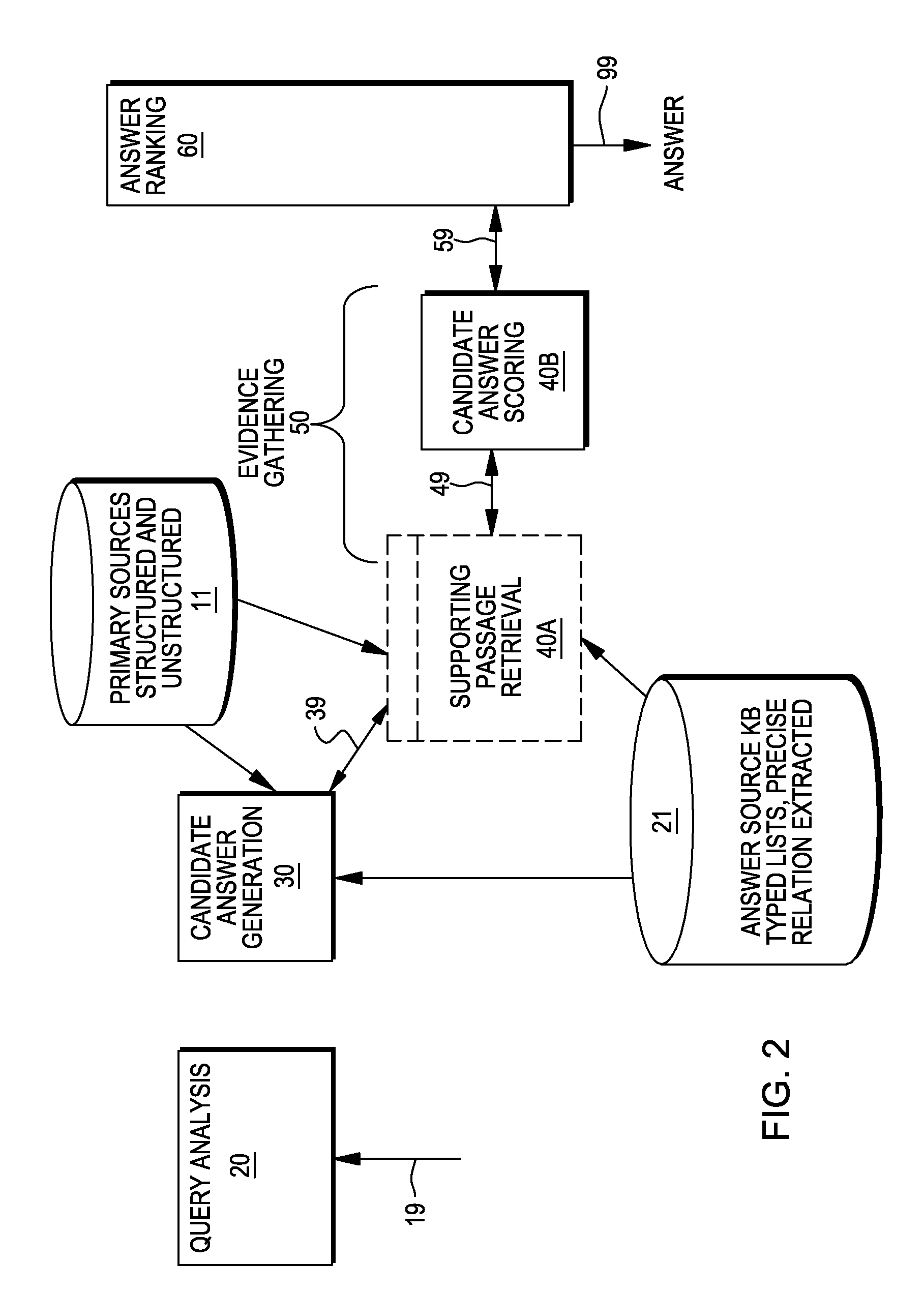
Providing answers to questions using logical synthesis of candidate answers
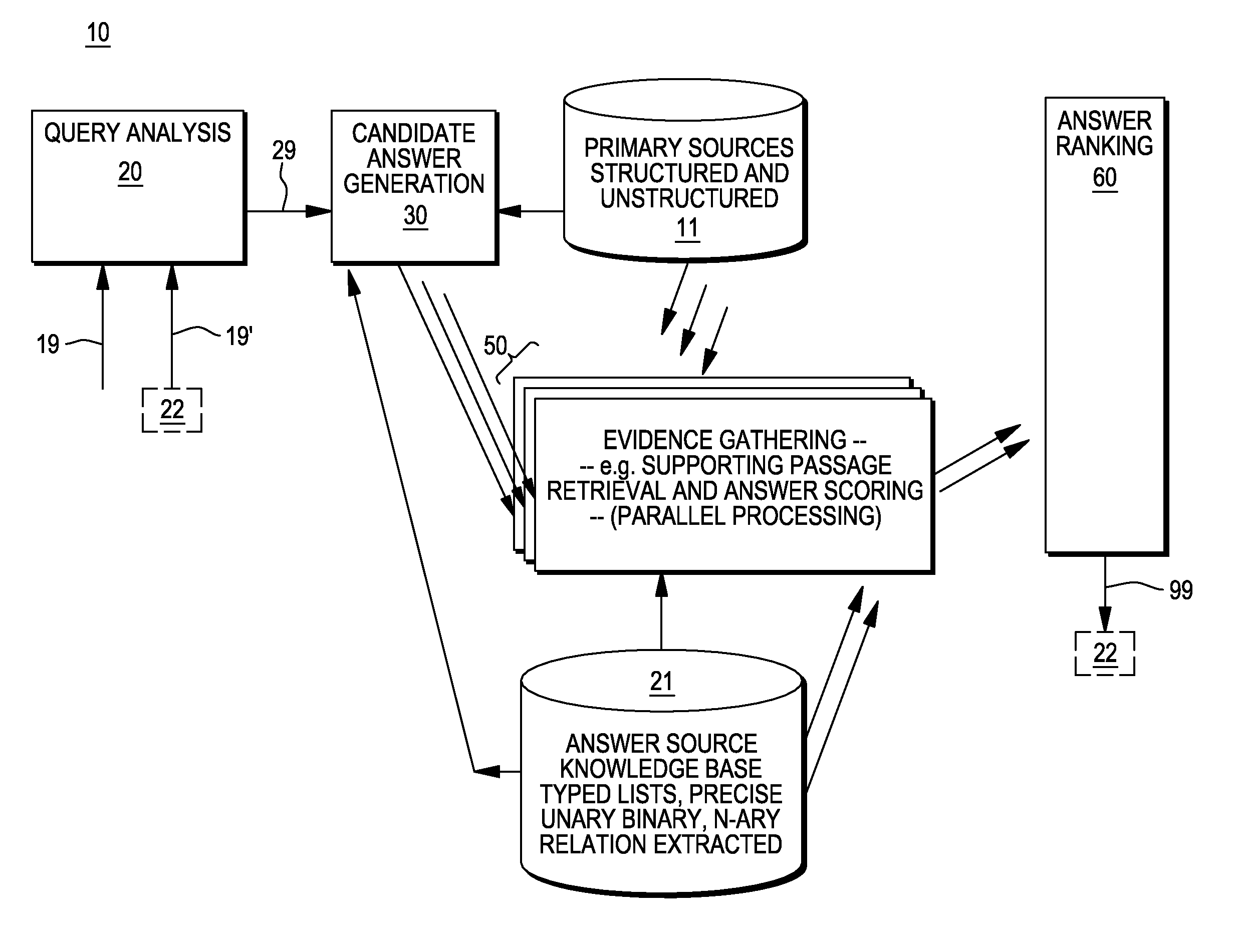
A method, system and computer program product for generating answers to questions. In one embodiment, the method comprises receiving an input query, decomposing the input query into a plurality of different subqueries, and conducting a search in one or more data sources to identify at least one candidate answer to each of the subqueries. A ranking function is applied to each of the candidate answers to determine a ranking for each of these candidate answers; and for each of the subqueries, one of the candidate answers to the subquery is selected based on this ranking. A logical synthesis component is applied to synthesize a candidate answer for the input query from the selected the candidate answers to the subqueries. In one embodiment, the procedure applied by the logical synthesis component to synthesize the candidate answer for the input query is determined from the input query.
Owner:IBM CORP
System, method and apparatus for providing functions to applications on a digital electronic device
InactiveUS20100257539A1Enabling and simplifying application developmentShorten development timeService provisioningInterprogram communicationDiscrete functionsApplication software
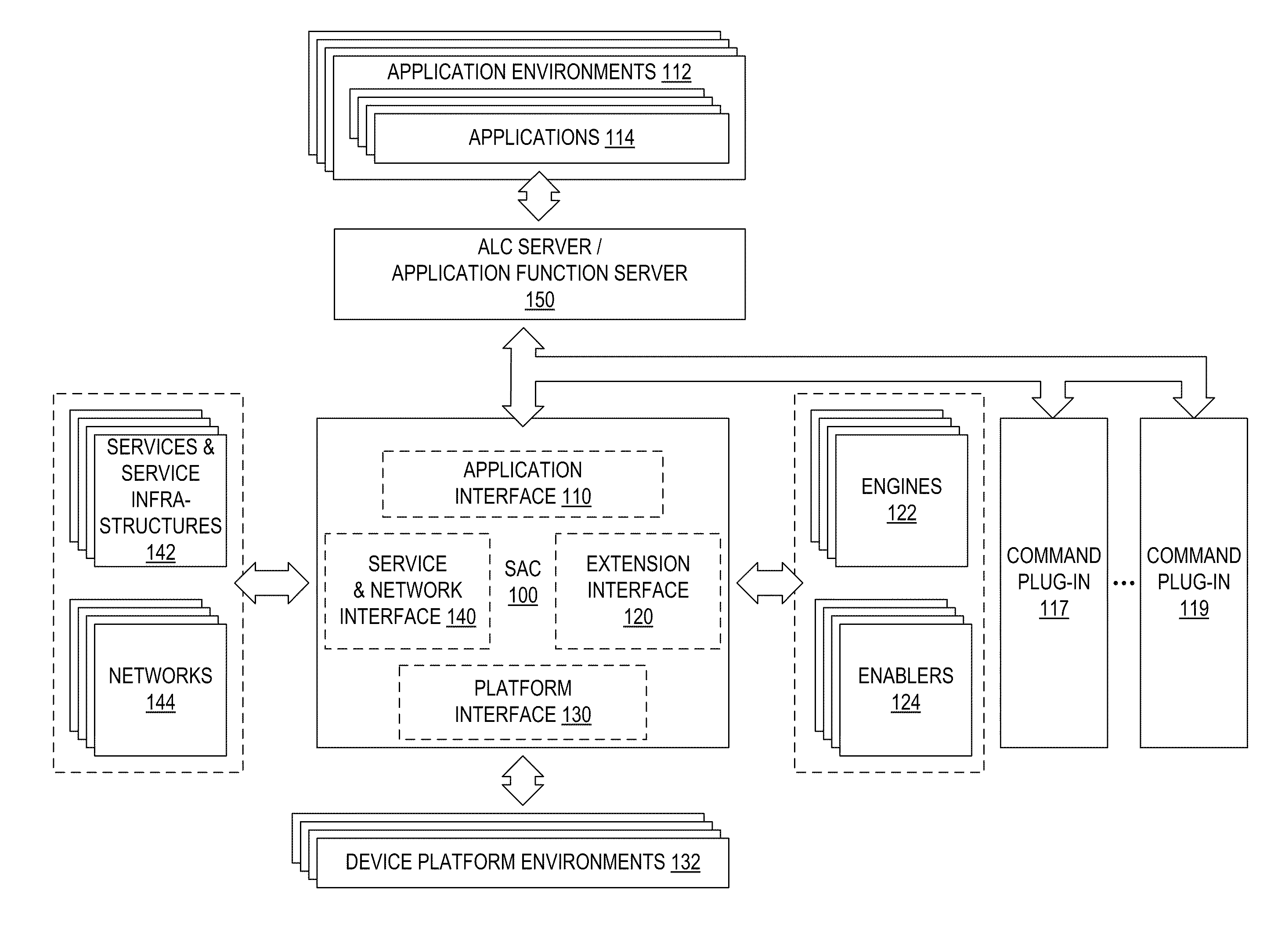
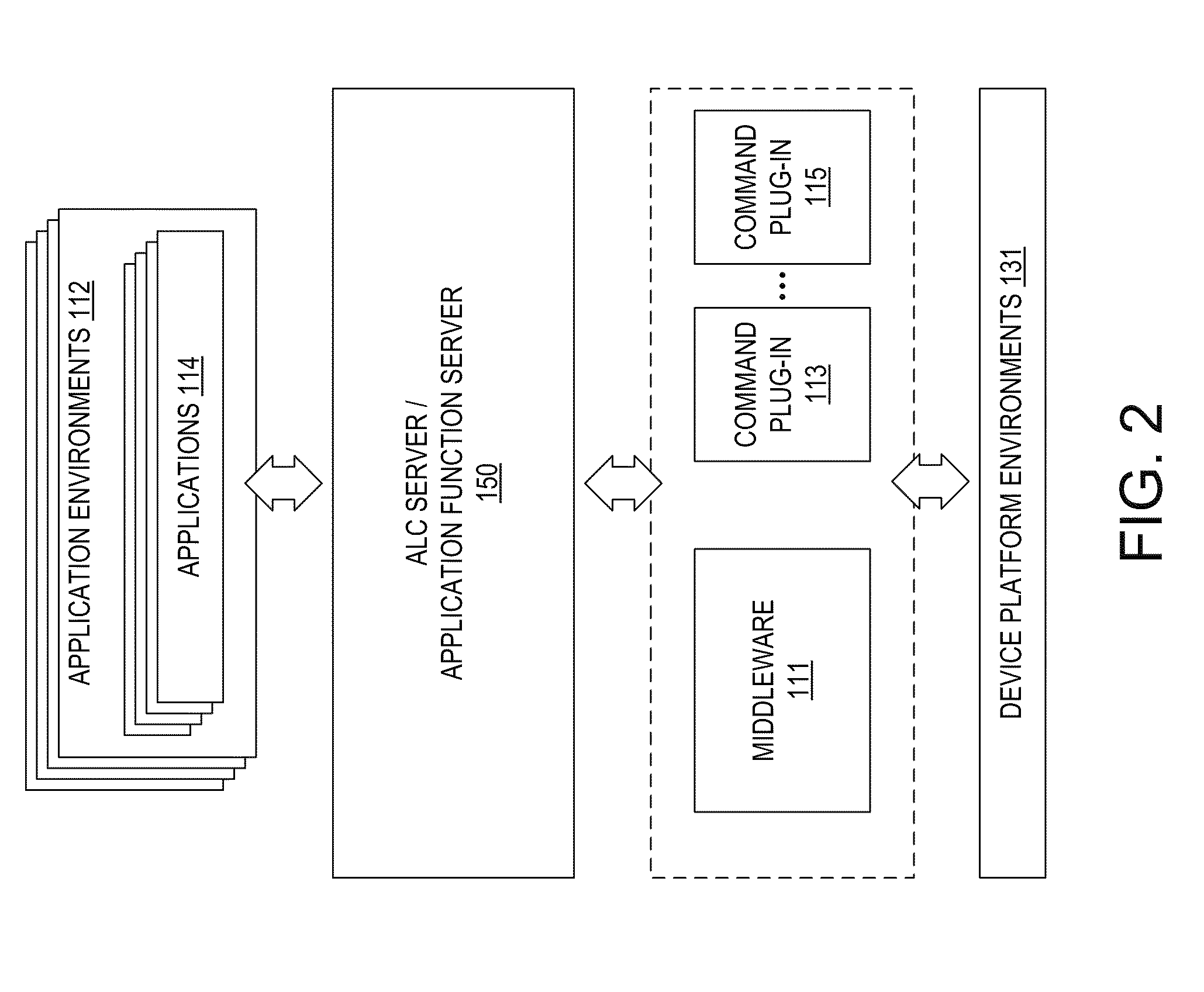
To greatly simplify the developer's task, an application function server or application logic controller (“ALC”) server runs on a digital electronic device with a common set of tools and methods to deliver high-value capabilities to applications developed in different application languages and running in various different application environments. The applications and the application function server have a local client-server relationship. The functions themselves are provided by various plug-ins. The interface of a plug-in illustratively is a discrete set of functions, common to the command plug-ins. The ALC Server accepts simplified commands directly from the applications, applies the appropriate policy, and interacts with the plug-ins to perform the requested functions on behalf of the applications. The result is that applications can use various capabilities without dealing with the complex methods, standards, and system interoperability required to make the technologies work, and technology additions and upgrades can be performed independently from the applications that use them.
Owner:ECRIO
Multidimensional digital platform for building integration and analysis
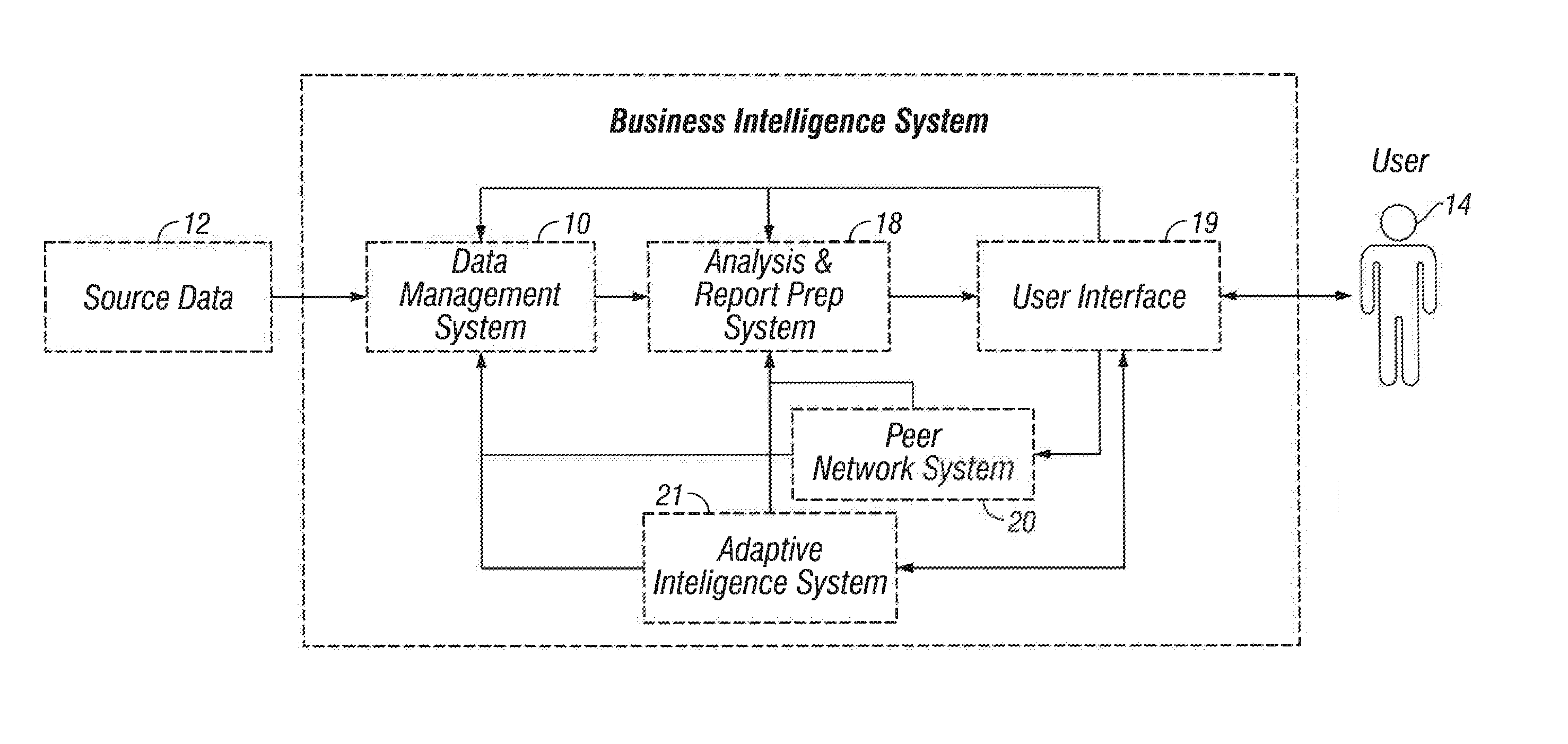
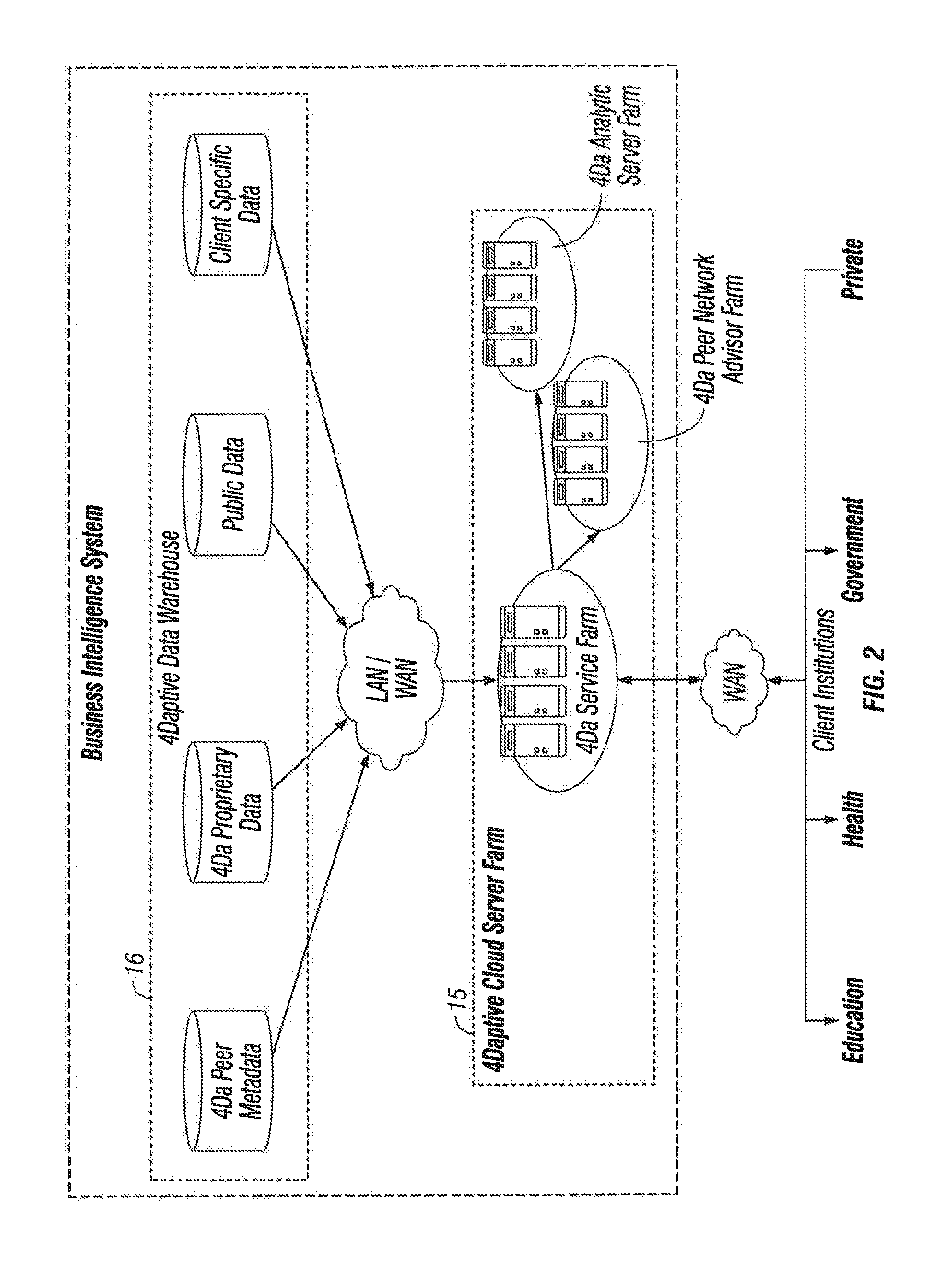
A method is provided for qualifying and analyzing business intelligence. At a first part of a data management system receives first, second and third streams of data. The first stream is client provided source data, the second is public source data and the third is data management system internal data previously collected and managed source data in the data management system. The three streams of data are organized into items and their attributes at the data management system. The source data is transformed at a data warehouse where it becomes normalized. Logic is applied to provide multi-dimensional analysis of transformed source data relative to a scale for at least one business intelligence. The data warehouse includes updated data from the multi-dimensional analysis. A user interface communicates with the data management system to create statistical information that illustrates impact over time and value.
Owner:ROUNDHOUSE ONE
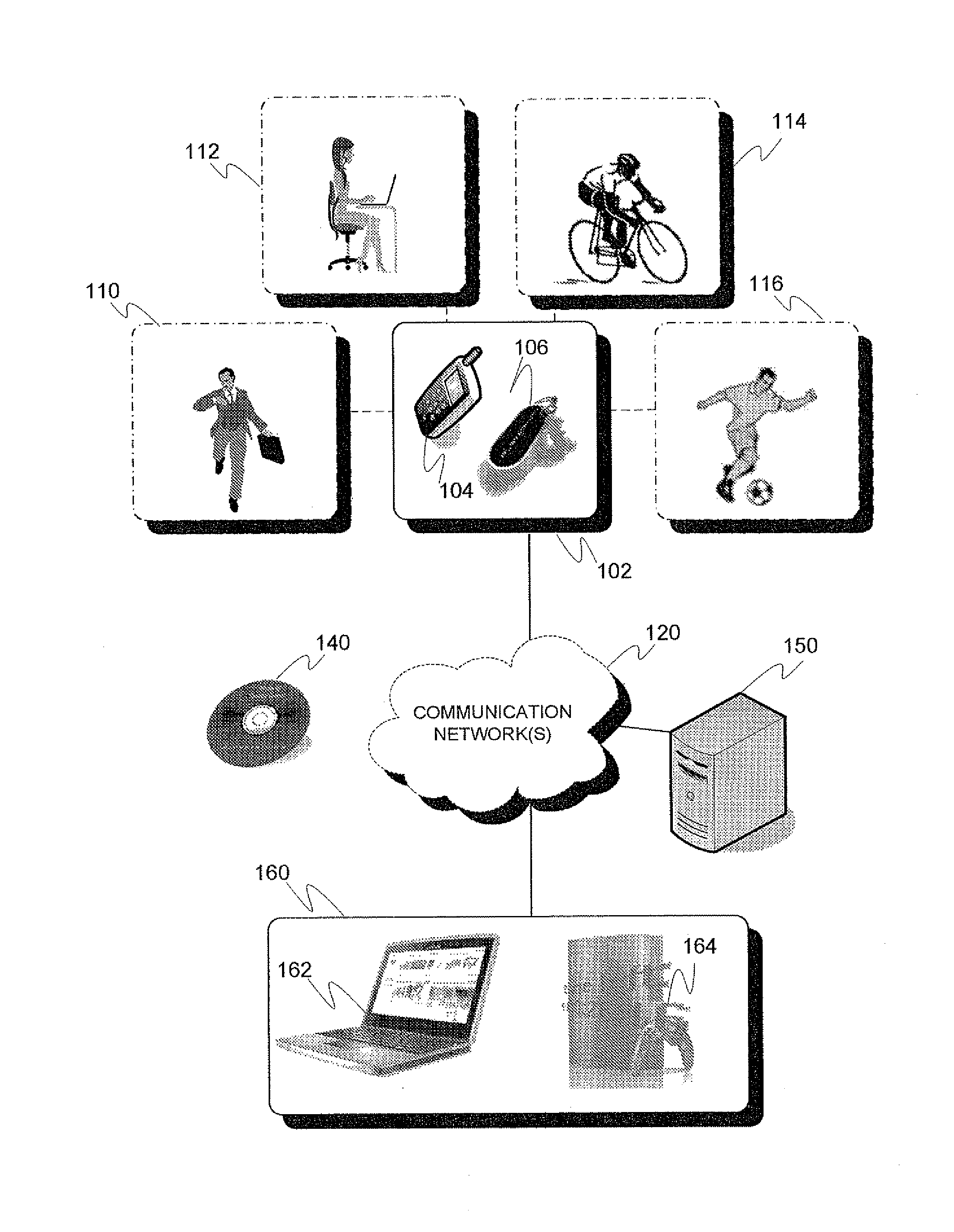
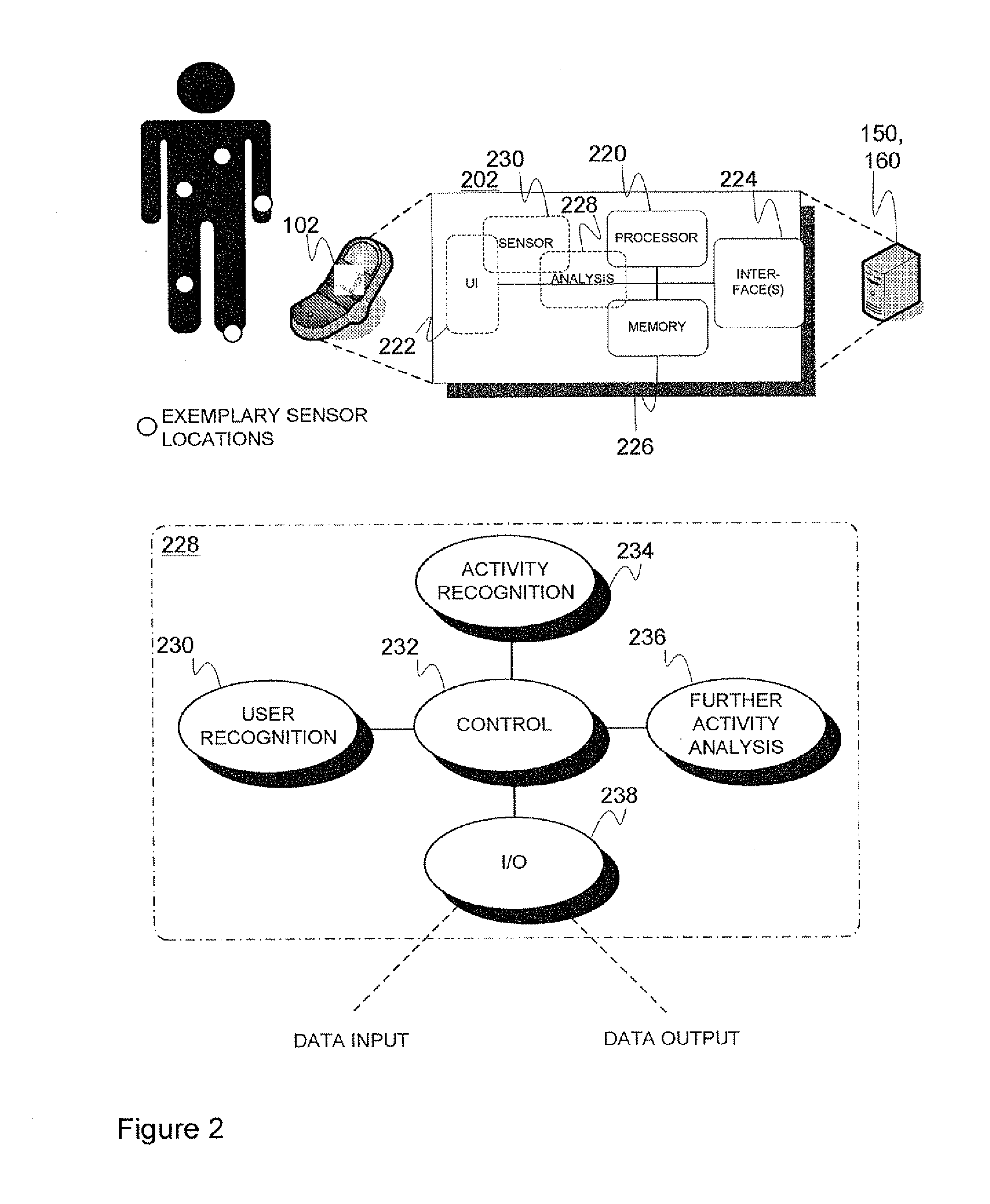
Physical activity-based device control
ActiveUS20120239173A1Reduce problemsHighly automated, flexible, and versatile physical activity-basedPhysical therapies and activitiesGymnastic exercisingMobile deviceElectronic equipment
A method for controlling the configuration, such as access and / or one or more other features, of an application in an electronic device from the standpoint of a particular user, comprising obtaining an indication of the identity of the user determined based on sensor data associated with physical activity by the user, obtaining an indication of the physical activity identified based on the sensor data, and modifying or at least providing information enabling to modify the identified user's configuration of an application logic based on the identified activity and optionally other activity information derived utilizing the sensor data. Related mobile device, electronic arrangement and system are presented.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
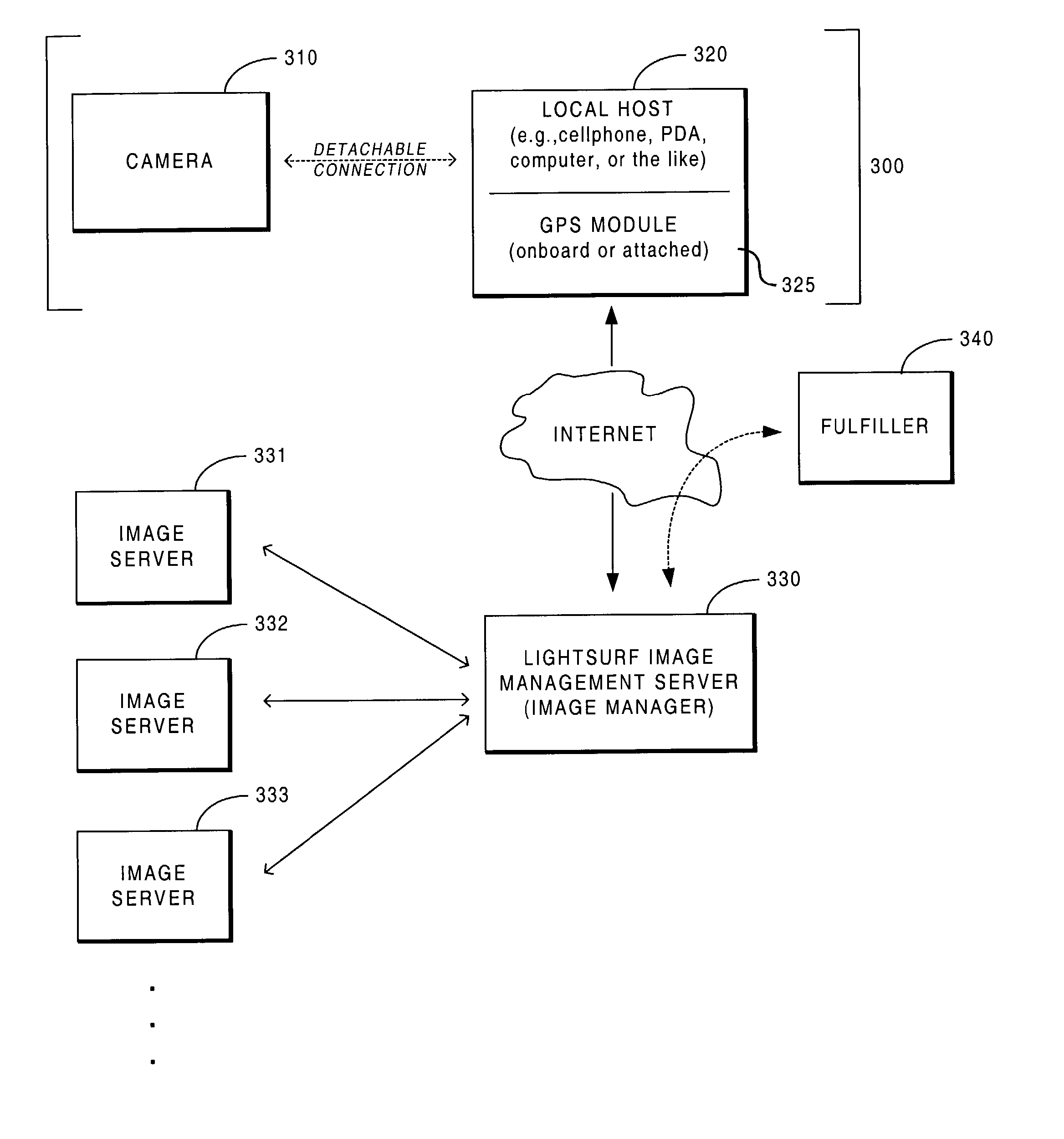
Imaging system providing automatic organization and processing of images based on location
InactiveUS20040004663A1Television system detailsColor television detailsImaging equipmentGlobal Positioning System
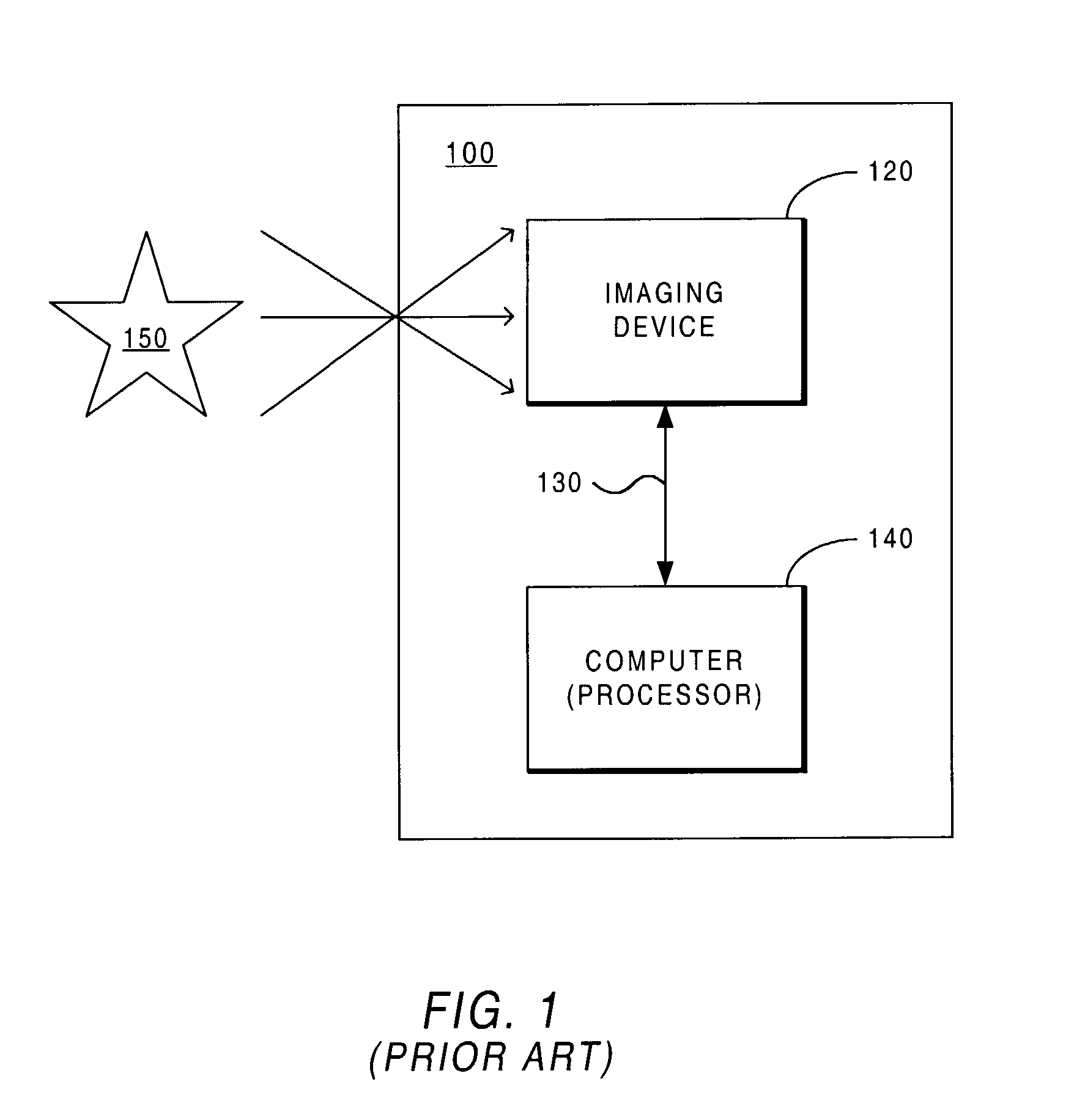
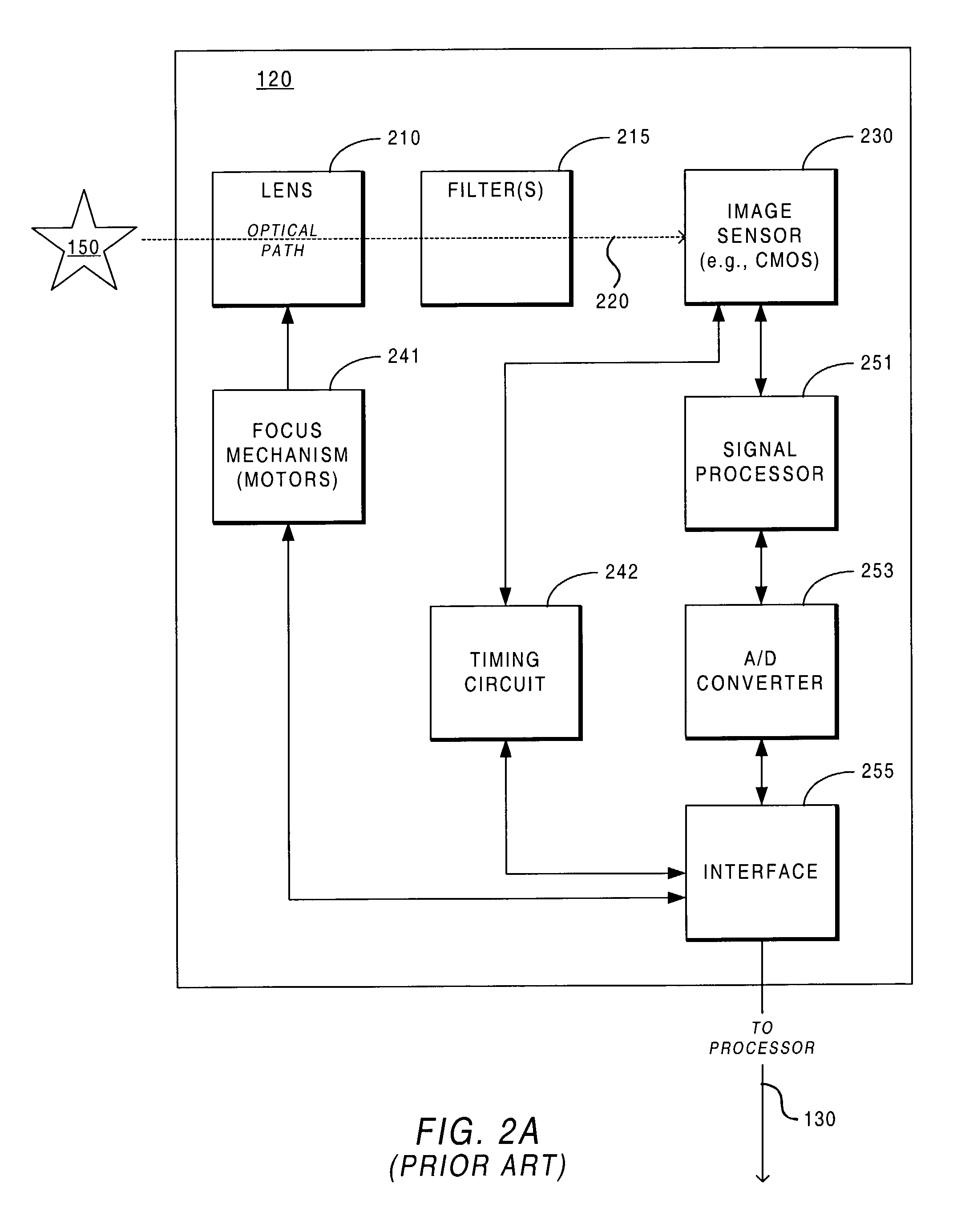
An imaging system is described that automatically identifies where images are captured. The system includes the following components: an imaging device for capturing images; a GPS (Global Positioning System) module providing location information; a host device (e.g., local host) that is at least occasionally connected to the imaging device, and application logic for querying the GPS module for determining location information and for associating each captured image with a location identifier indicating where each image was captured.
Owner:LIGHTSURF
Service-oriented architecture component processing model
InactiveUS20090193432A1Sufficient flexibility in granularityResourcesElectric digital data processingHandling systemBusiness object
A service-oriented architecture can include a service provider comprising a plurality of service objects, each service object comprising a self-describing, self-contained, platform independent, modular unit of application logic. The service oriented architecture further includes a service object among the plurality of service objects that is a service implementation having a pre-ordained message processing system. The service implementation can respond to client requests at different levels of granularity and can use a common transfer object message format that separates a business object into its constituent parts. The common set of operations can include at least the Read, Create, Update, Delete, and Execute functions.
Owner:IBM CORP
Extensible interactive voice response
InactiveUS7068643B1Easy to operateInterconnection arrangementsAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingApplication serverApplication software
In implementing an interactive voice response mechanism, a communication device establishes a communication connection with an application server. Application logic on the communication device, which may pre-exist on the device or be downloaded from the application server, defines at least one voice response application. The communication device includes a processor that operates to execute the application logic and locally administer the voice response application. Therefore, the voice response application is executed on the communication device instead of in a centralized interactive voice response unit (IVR).
Owner:INTERVOICE PARTNERSHIP
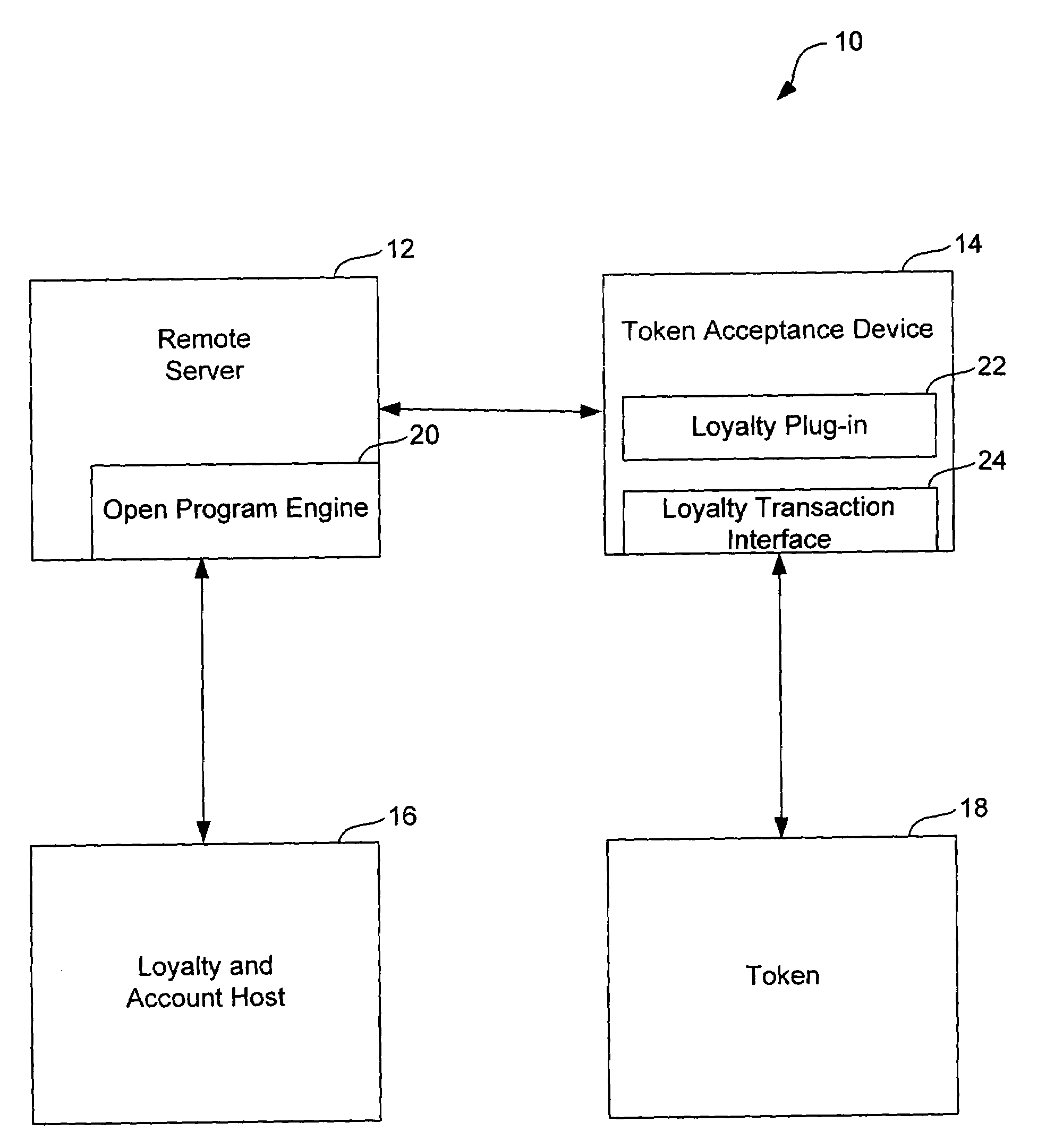
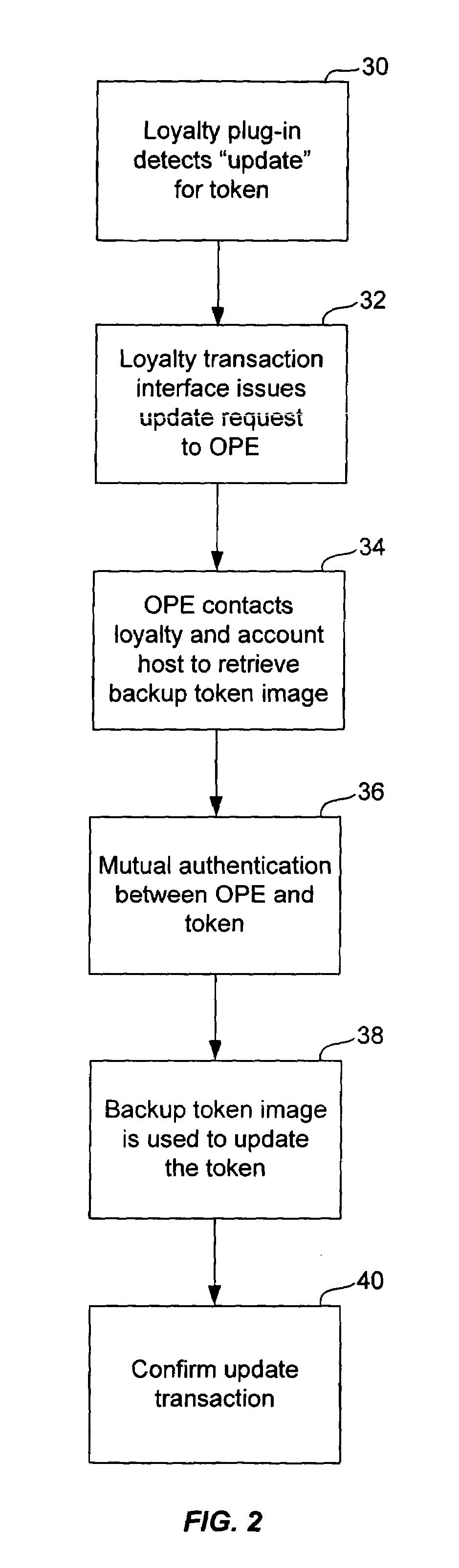
Method and system for managing token image replacement
Owner:VISA USA INC (US)
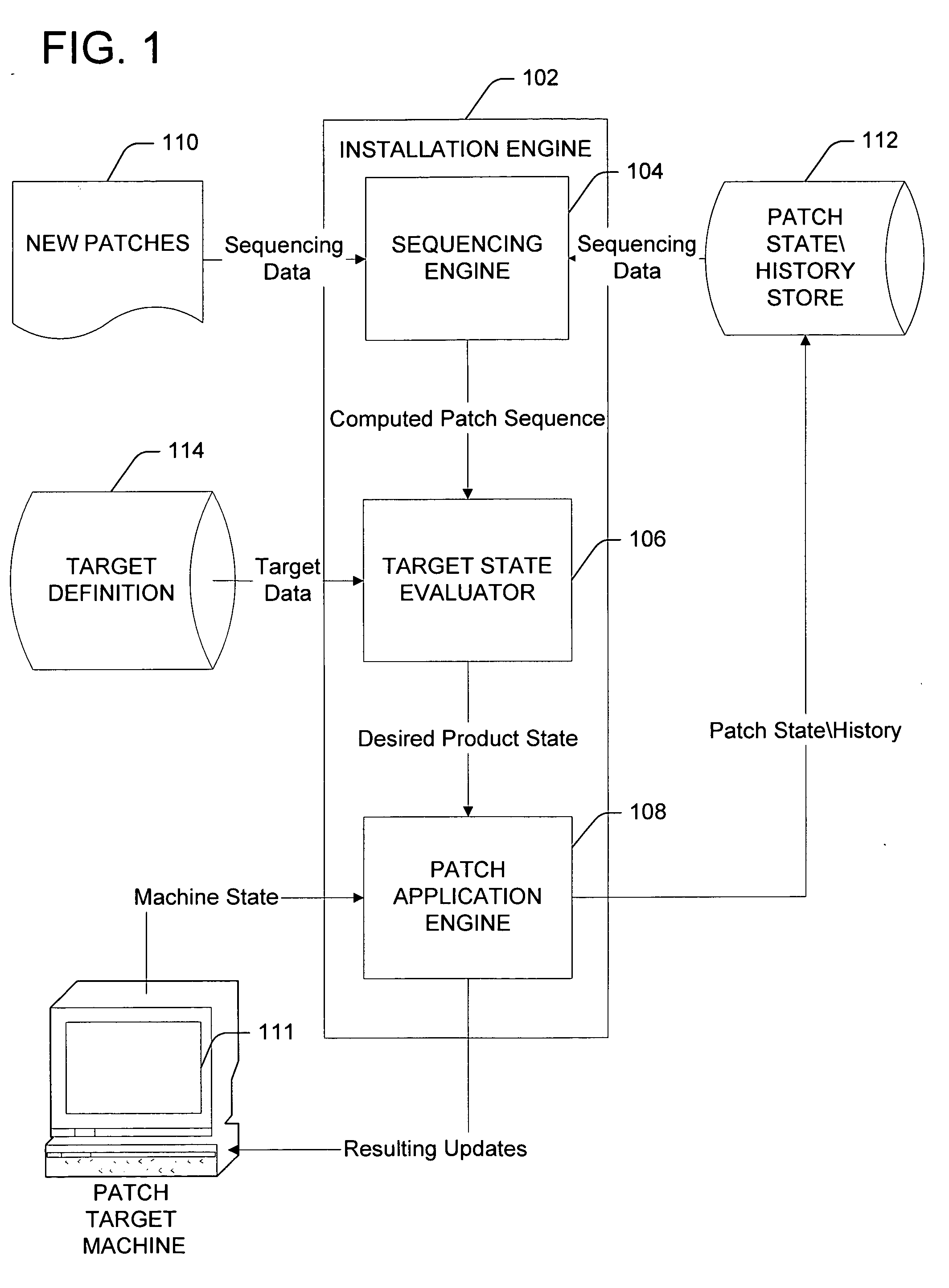
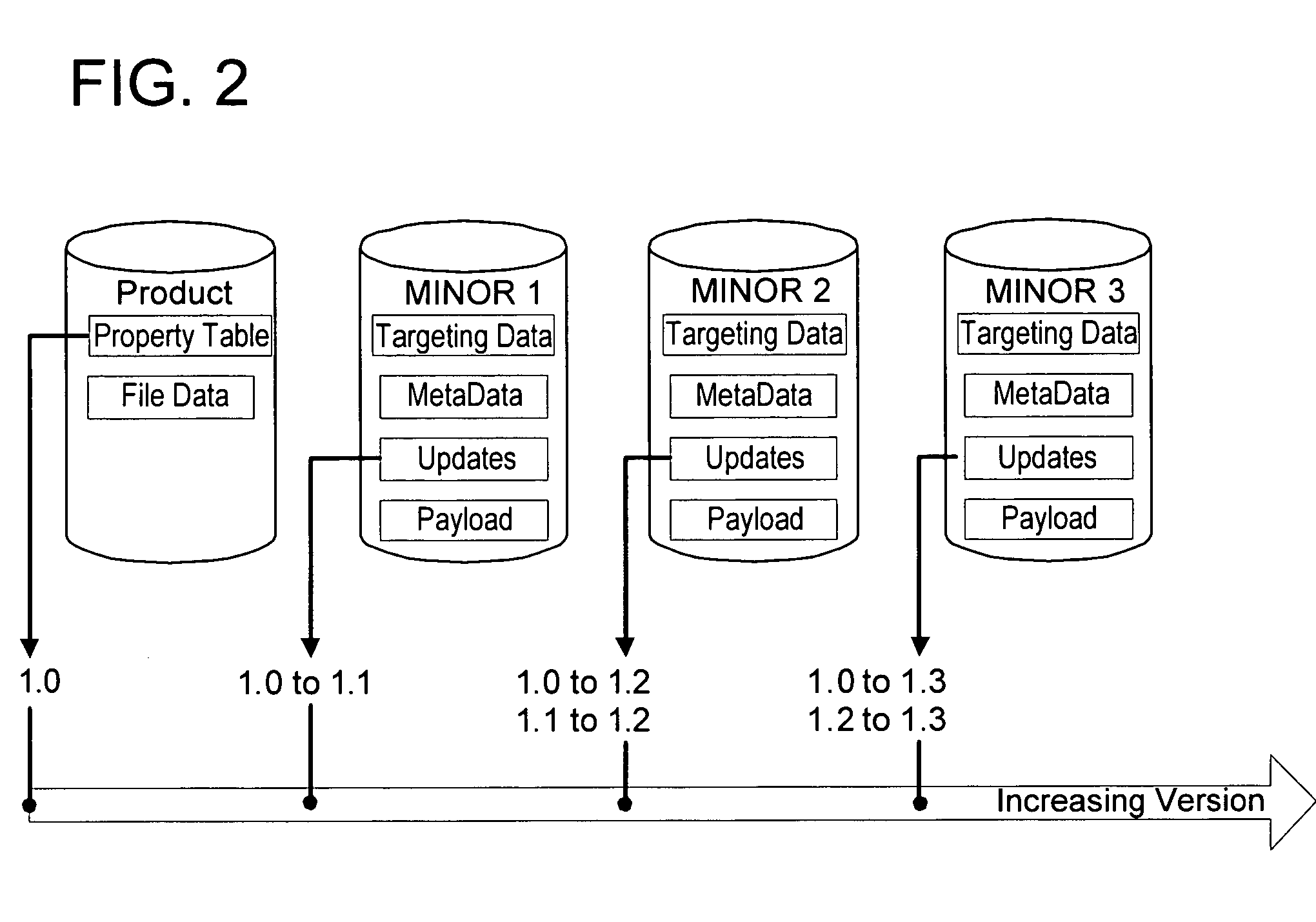
Patch sequencing
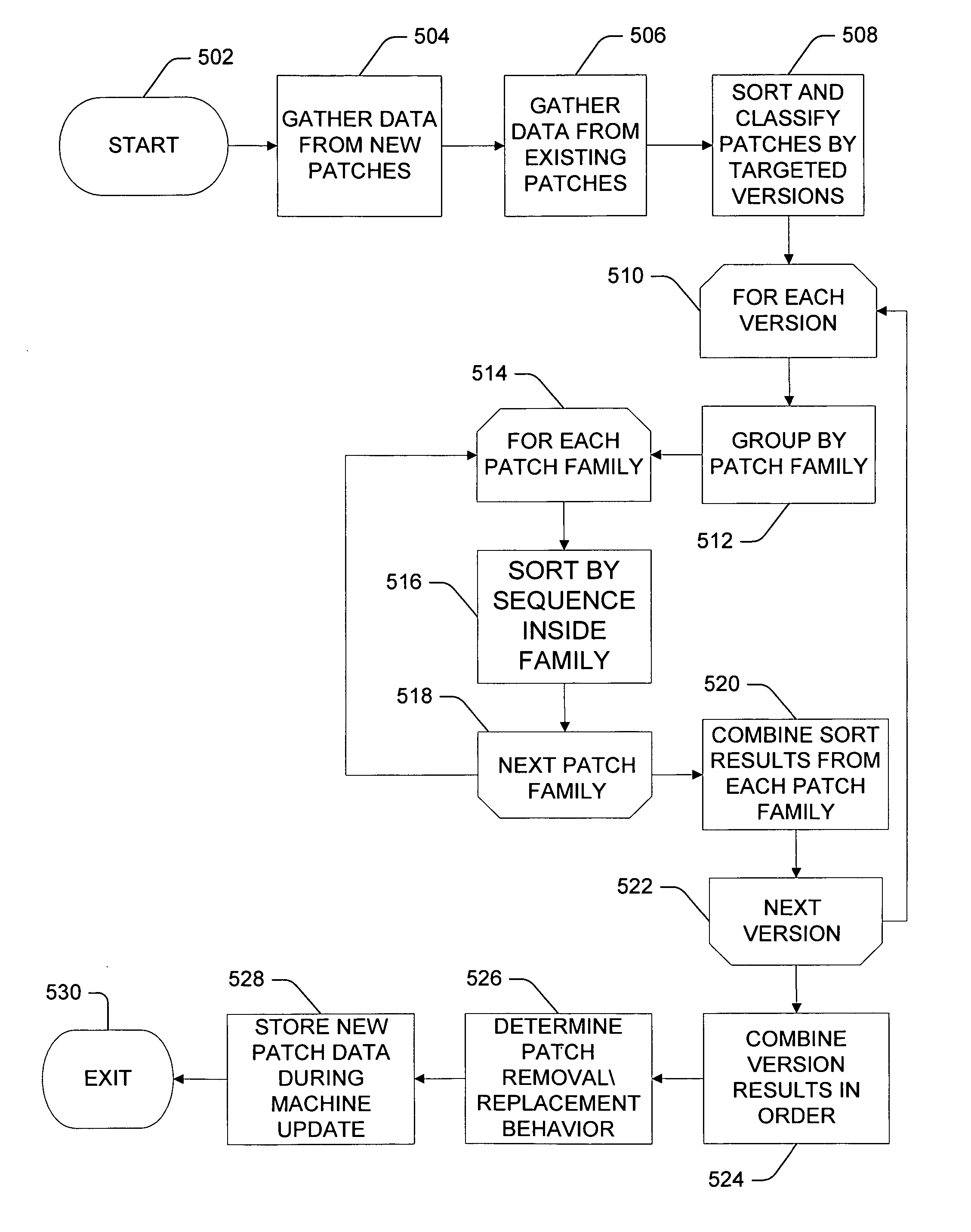
ActiveUS20060048130A1Simplifies patch creation processSimple processSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsSequencing dataSoftware
Updating a software product by a plurality of patches. Sequencing data of each patch of the plurality of patches is received from a user such as a patch author. Each patch of the plurality of patches has a defined membership in a portion of the software product and has a defined order in the portion relative to one or more other patches that are members of the portion. The sequencing data indicates a portion of the software product of which the patch is a member and a relative ordering between the patch and one or more other members of the portion. A logical order of application for the plurality of patches is determined based on the received sequencing data. The plurality of patches is applied to the software product according to the determined logical order of application.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Portable and dynamic distributed transaction management method
InactiveUS6115710AImprove productivityReduce needData processing applicationsProgram control using stored programsComputer resourcesGoal system
A system and method is shown for enabling a plurality of computers and associated computer resources, some or all of which may be of heterogeneous configuration, to cooperatively process various applications such that the execution is transparent to the user regardless of where the application is actually executing. This distributed applications architecture performs an information distribution service between multiple transaction processing systems by working with a transaction processor via communication channels to other hosts within the network and a dialog manager which uses a transaction processor interface to communicate with the transaction processor. The architecture employs a map service which provides an editor to create the maps for the application panels, a compiler to generate the maps into a linkable form, and a linkable interpreter which translates the linkable form into the screen presentation format for that platform. To distribute an application, the source code for the procedures, view and panels are moved as a block to the new system. This is possible because once the application source code is complete, all application logic, user interface control tables, view definitions, and other application-specific tables for one transaction definition are packaged by the present invention in a single load module on the system where the application will reside. The load module is then compiled using the target system's compiler, link editor, and bind process. Thus, all environment-dependent variations of import / export are automatically integrated with the application at load module bind time, requiring no source code changes.
Owner:COMP ASSOC THINK INC
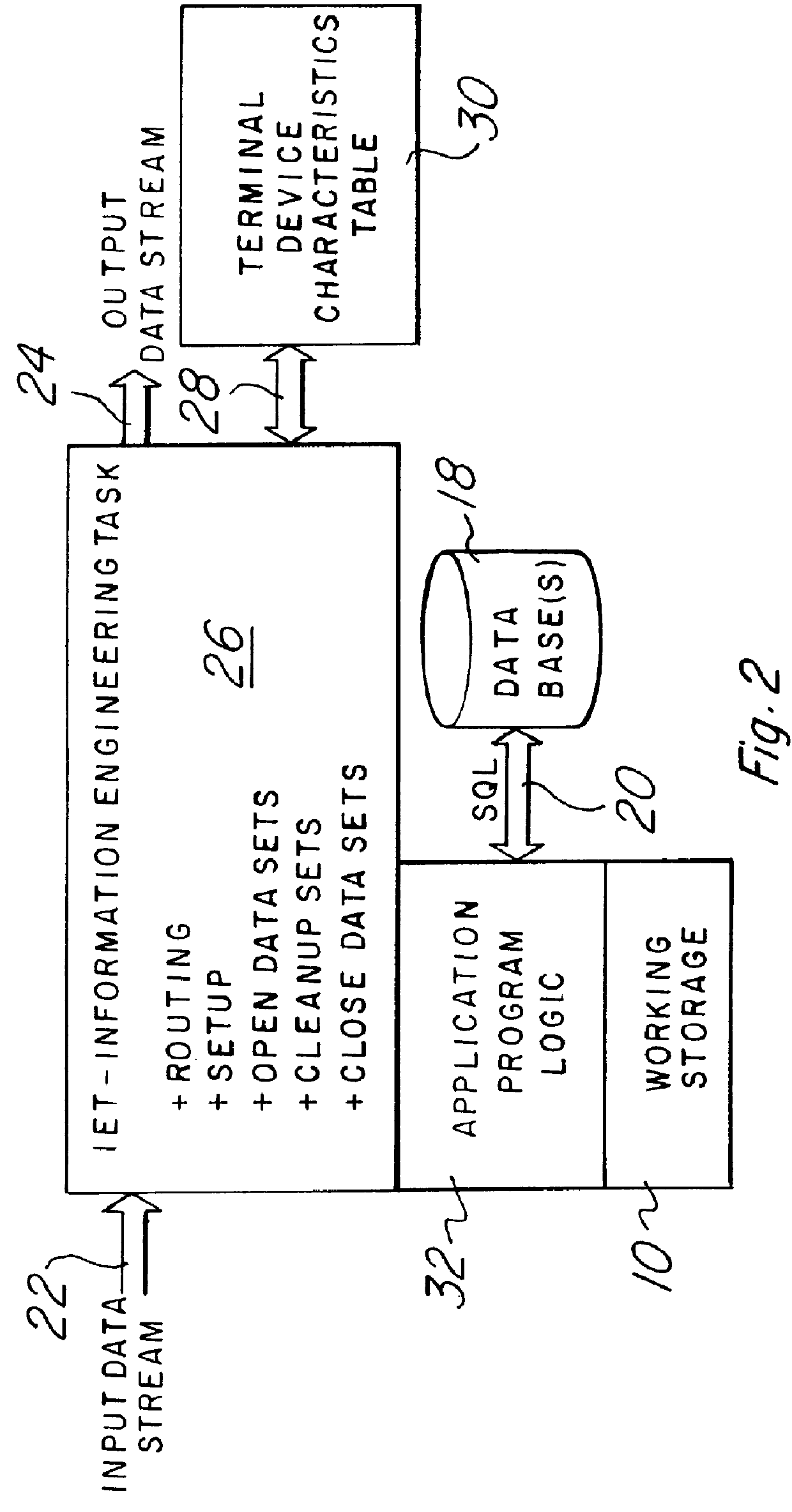
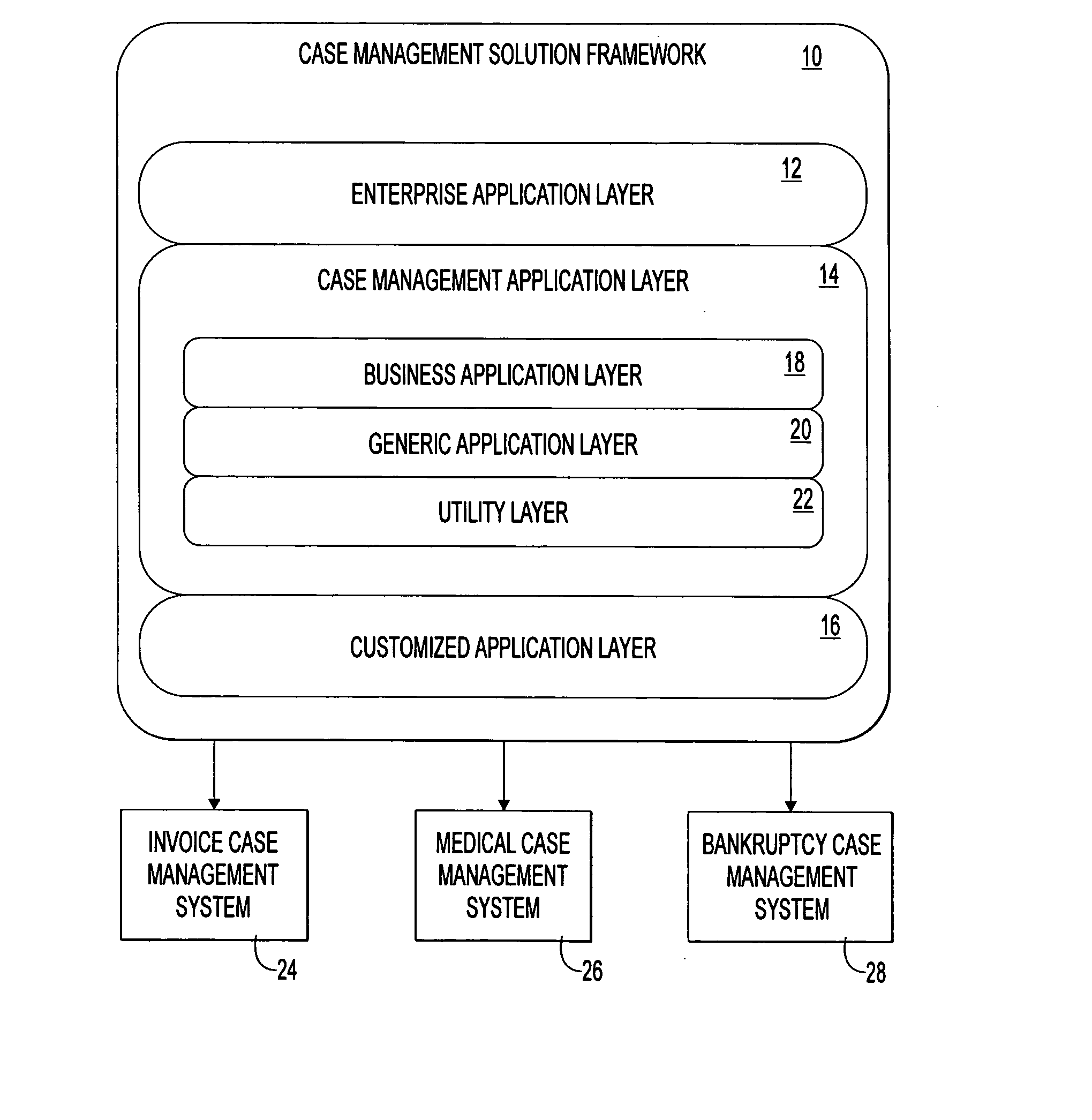
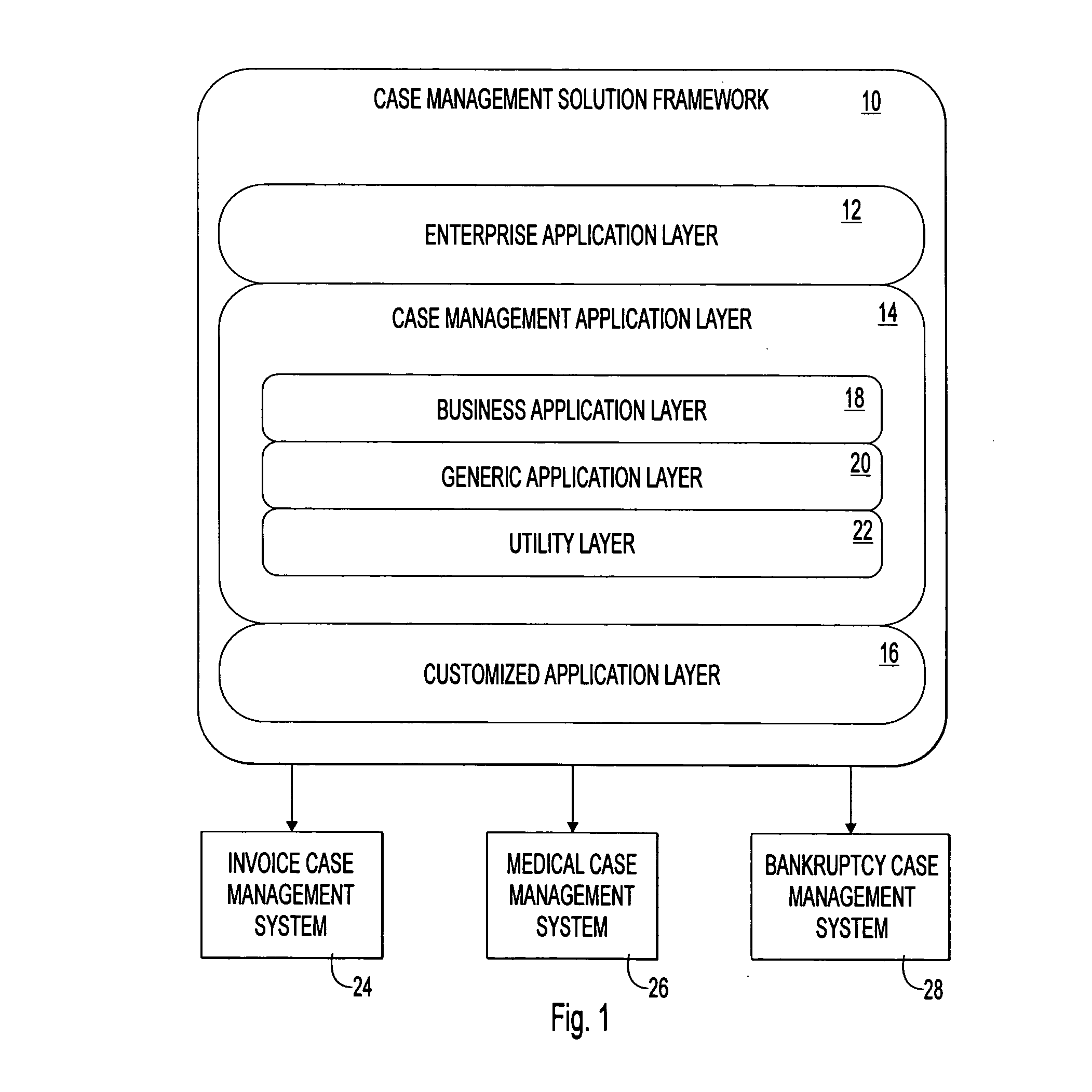
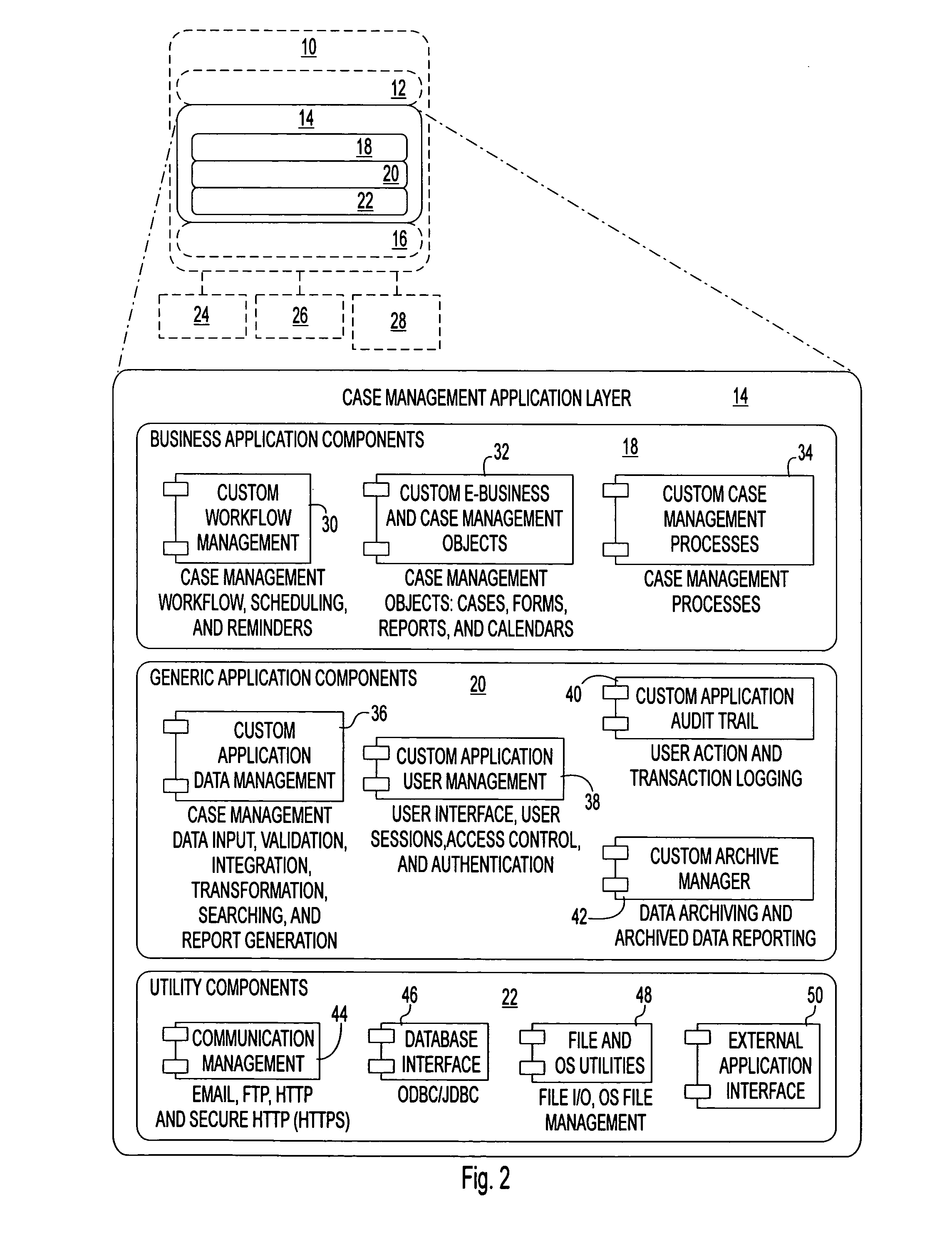
Programming toolkit for developing case management software applications
InactiveUS20070174810A1Reduce riskLow costSoftware designSpecific program execution arrangementsOff the shelfSoftware engineering
A robust toolkit that can be configured and assembled in an object-oriented manner to develop a custom case management software application. The toolkit provides a set of software components that serve as a framework for integration with off-the-shelf components. The software components are organized in a vertical layered architecture, with each layer depending upon the layers below it. The toolkit includes a top enterprise application layer, a middle case management application layer, and a bottom customized application layer. The toolkit allows developer to focus on meeting the specific case management needs of a target business / organization, instead of developing case management business logic and application logic from the ground up.
Owner:CONCURRENT TECH
System and method for executing wireless applications using common UI components from a UI repository
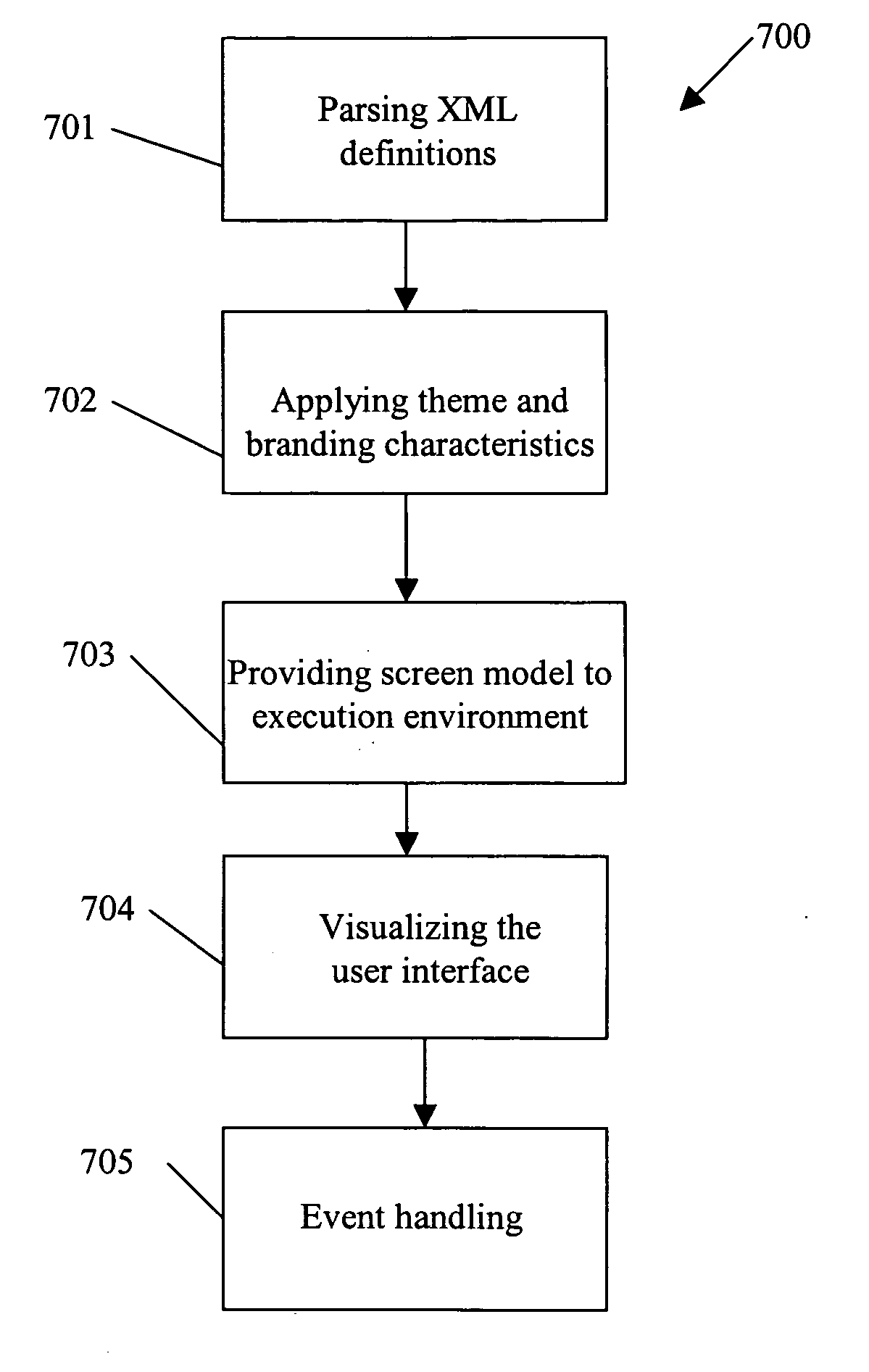
InactiveUS20050193380A1Maximum degreeMaximum efficiencyExecution for user interfacesMemory systemsModularityLook and feel
A system and method is provided having an execution environment of an intelligent runtime device framework for generating user interface elements on a user interface (UI), declared on the device. The proposed method allows user interface definitions through XML metadata UI definitions (or other structured definition language schema) instead of requiring an implementation of the screen elements in executable code for the application. The UI definitions are stored in a common UI repository as a common resource of the applications on the device and is processed at runtime. The UI definitions are independent from the target platform of the device. The “look and feel” of all the applications on the device can be customized and branded as required. Defining layout and ordering of UI elements separately from the applications logic offers modularization of the applications. Such modularization allows reuse of already defined UI screens and sharing them between different applications. The system has a themes and branding repository, a UI repository, a visualization engine, an execution environment, and a UI service. The method includes steps of parsing the XML definitions, applying theme and branding characteristics, providing a screen model to the execution environment, visualizing the user interface, and event handling.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
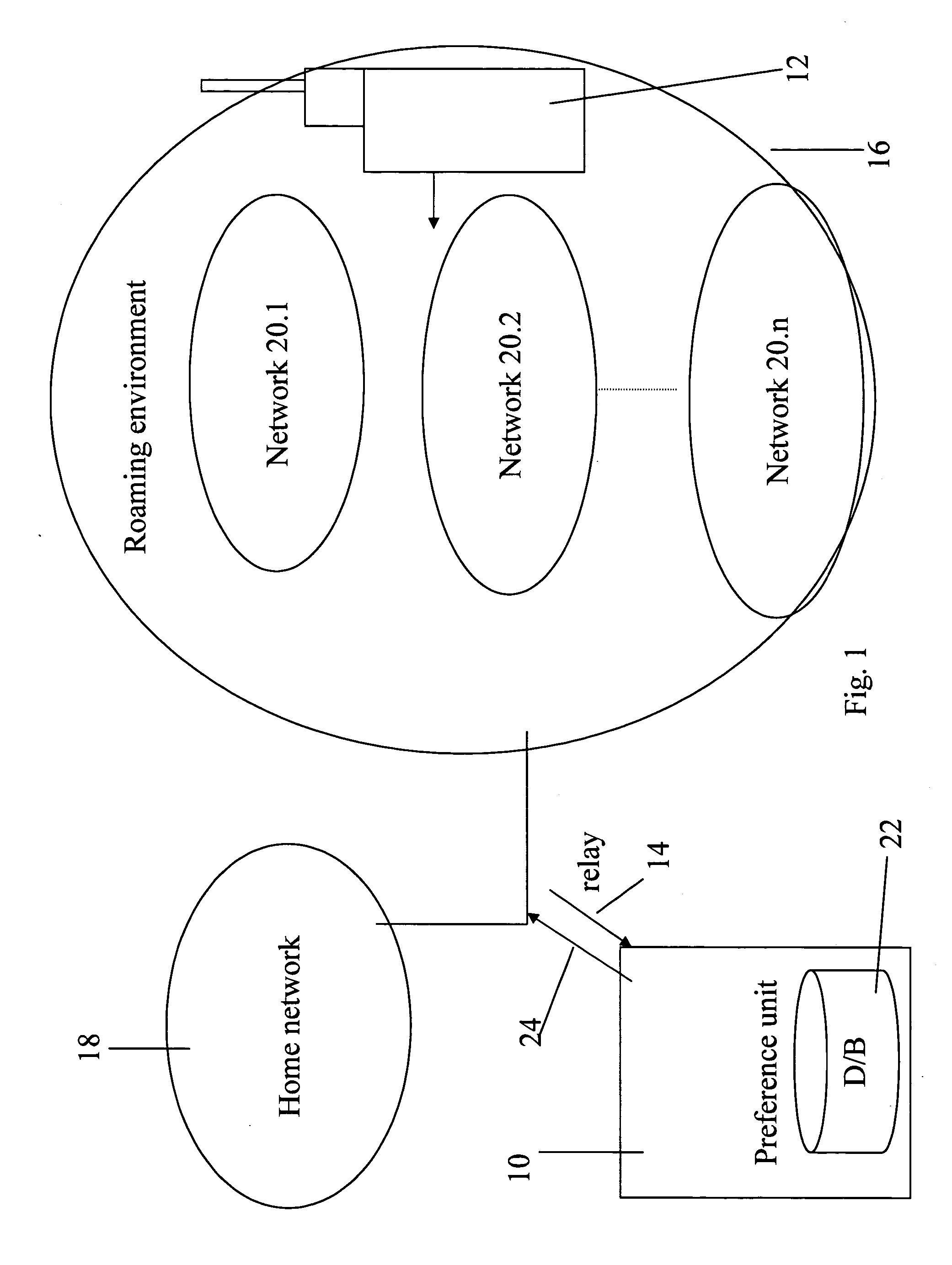
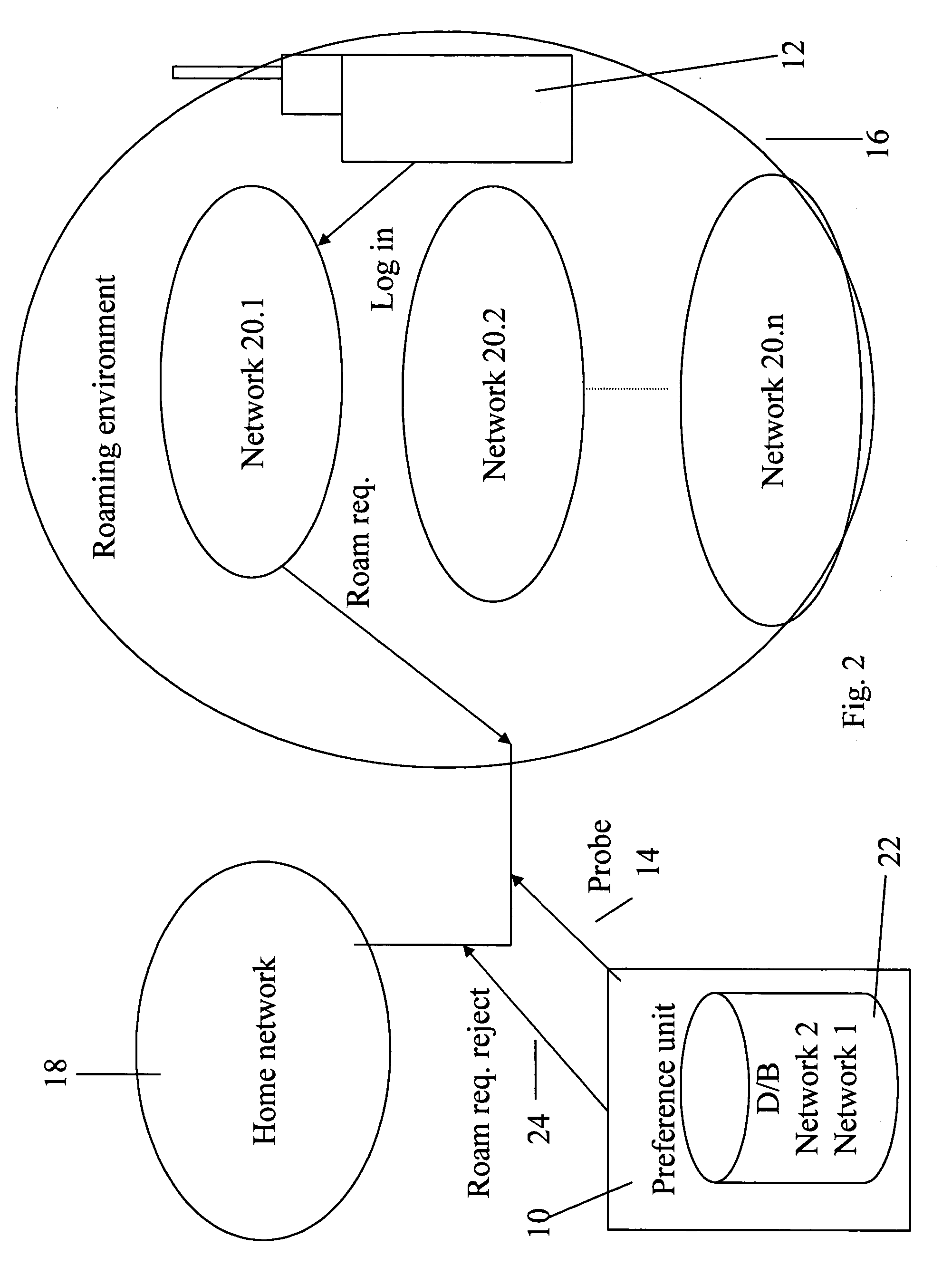
Dialing services via SIM toolkit
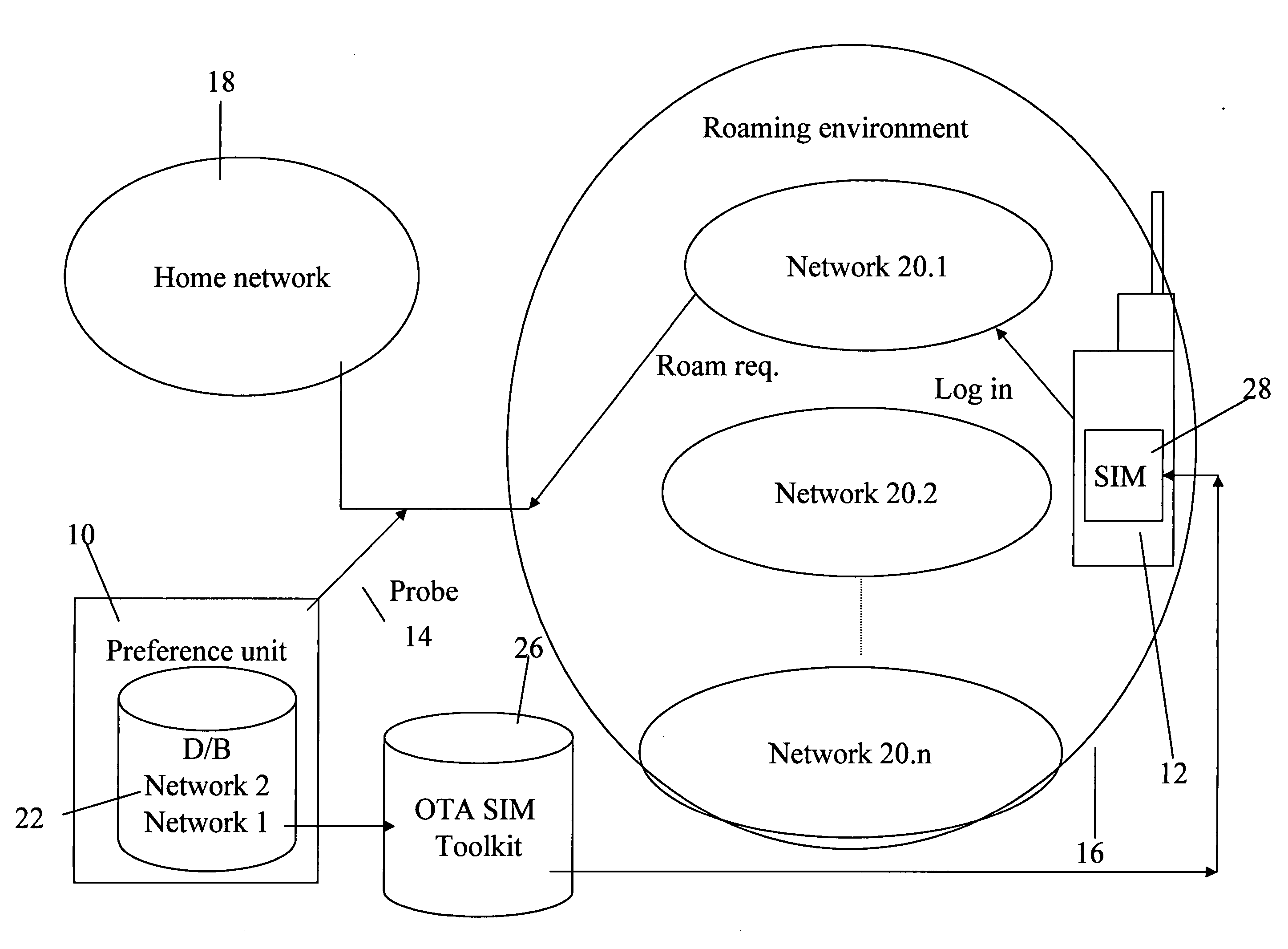
A remote preference unit for influencing visited network selection by roaming mobile units, comprises a detection signaling relay / probe on International signaling connections, for detection of roaming activity by mobile units, a database indicative of preferred networks in the given country that the network operator prefers his roamers to use, application logic with certain criteria, determining the output, and an output unit, associated with said detection probe and said database to output indications to influence network selection by said detected roaming mobile units. In one embodiment the output is simply a rejection of the location update signal that forms the roaming request. In an alternative embodiment the signal is a copy of the relevant section of the database which is uploaded to the SIM card of the roaming unit. The SIM card upgrade may or may not be accompanied by a stage of forcing the handset to re-initiate the network selection process.
Owner:STARHOME GMBH
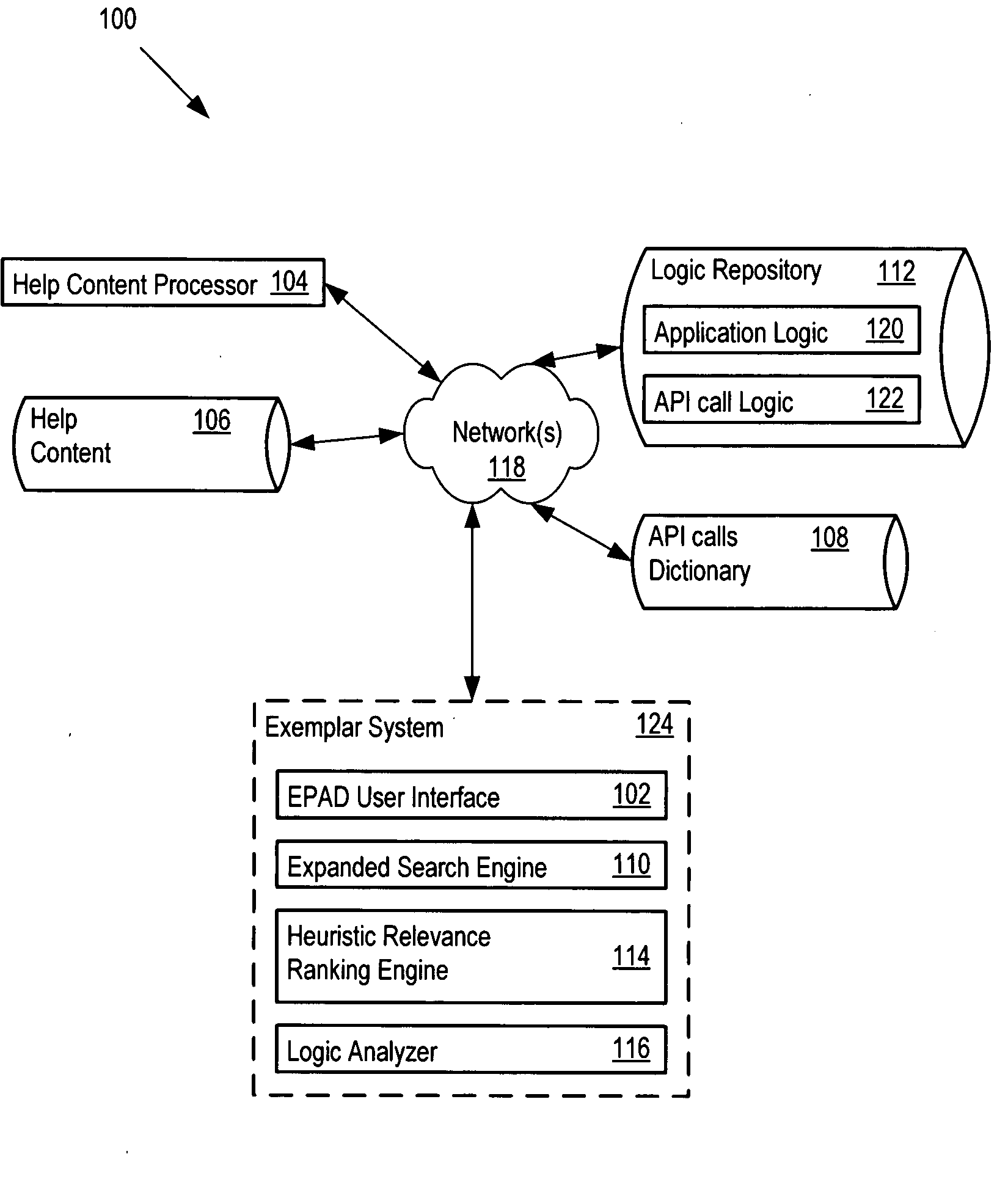
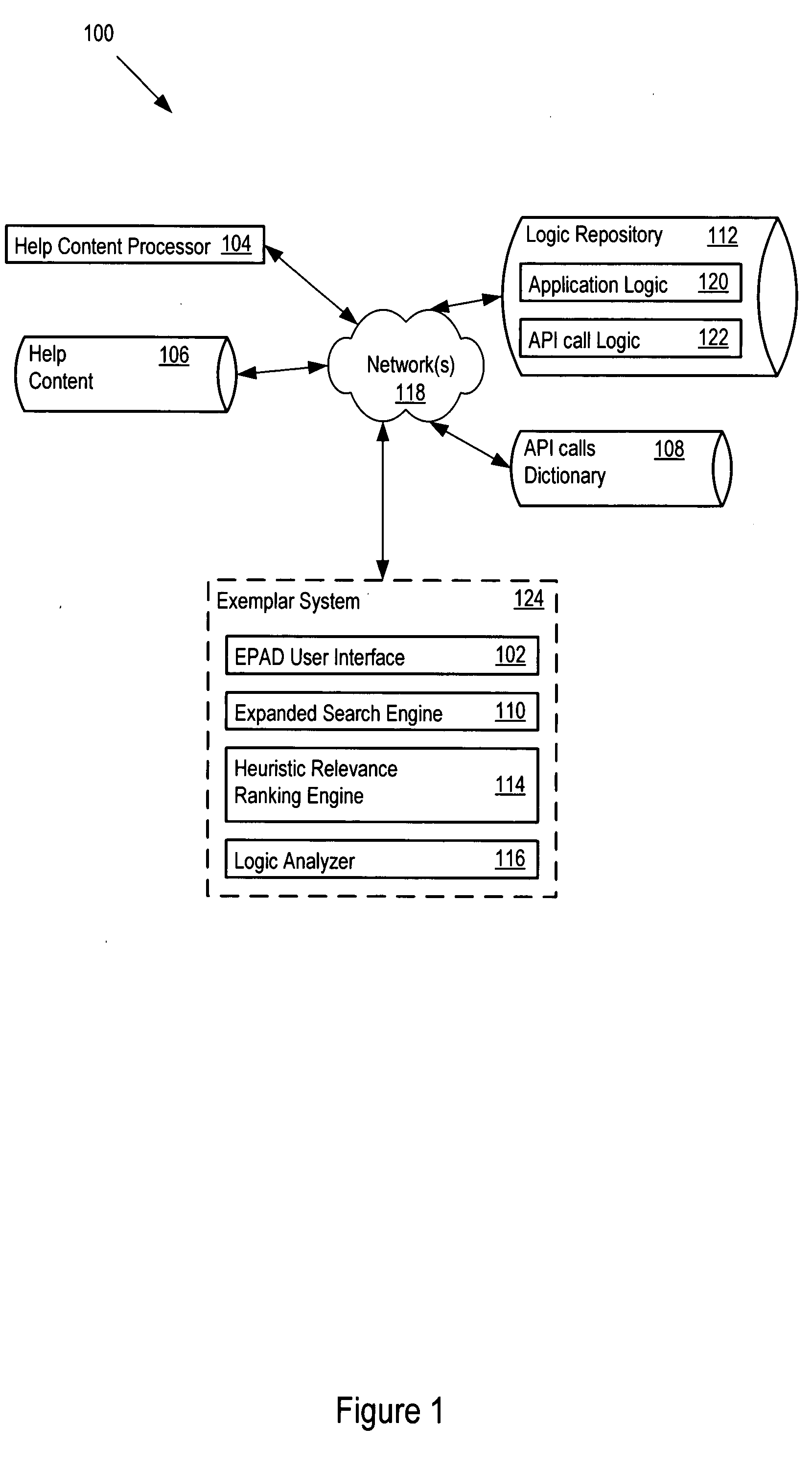
Application search tool for rapid prototyping and development of new applications
ActiveUS20080288965A1Rapidly and efficiently identifiesIncrease probabilityDigital data information retrievalSoftware reuseSoftware engineeringSoftware development
A code search tool greatly reduces time, cost, and other resource expenditures associated with implementing a new application. The tool is a search, navigation and visualization tool that accepts high-level processing concepts as inputs to identify, rank, and return the code of relevant existing applications. A software developer may use the relevant applications to rapidly build prototypes, identify requirements, and develop new applications. The tool provides an efficient way to improve the reuse of application logic to realize the high-level processing concepts, and more efficiently deliver proof of concept.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
Geospatial information system and method for updating same
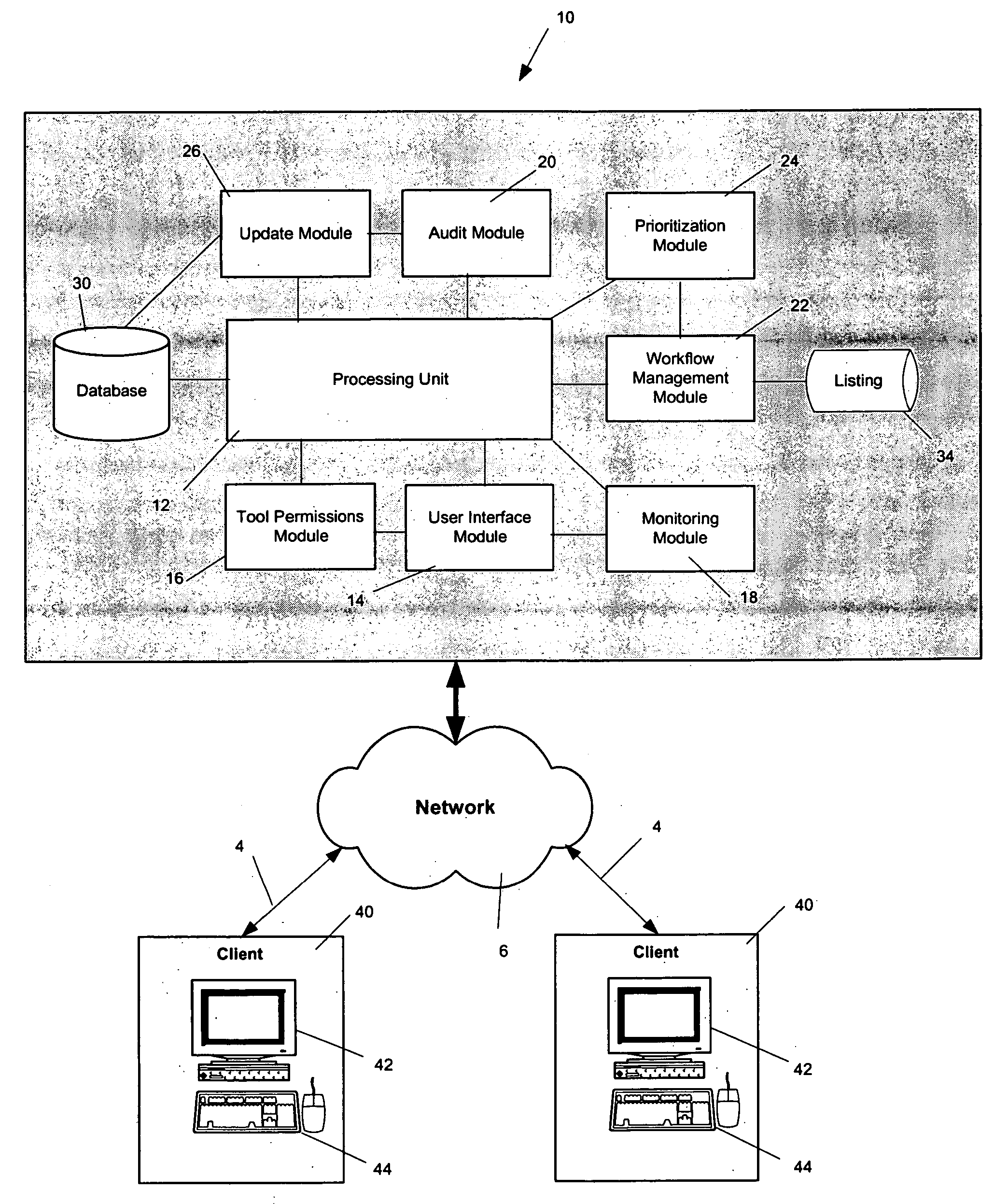
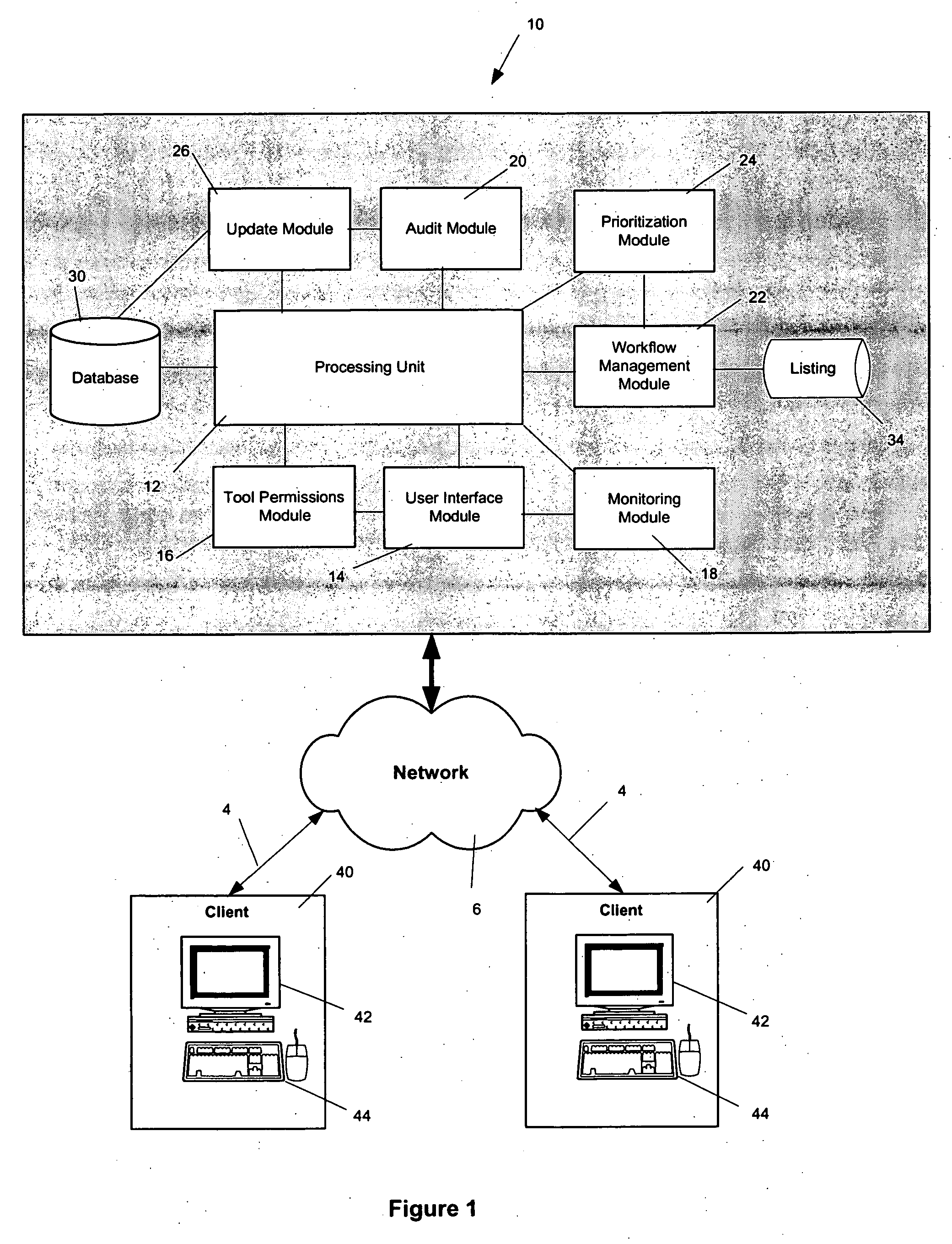
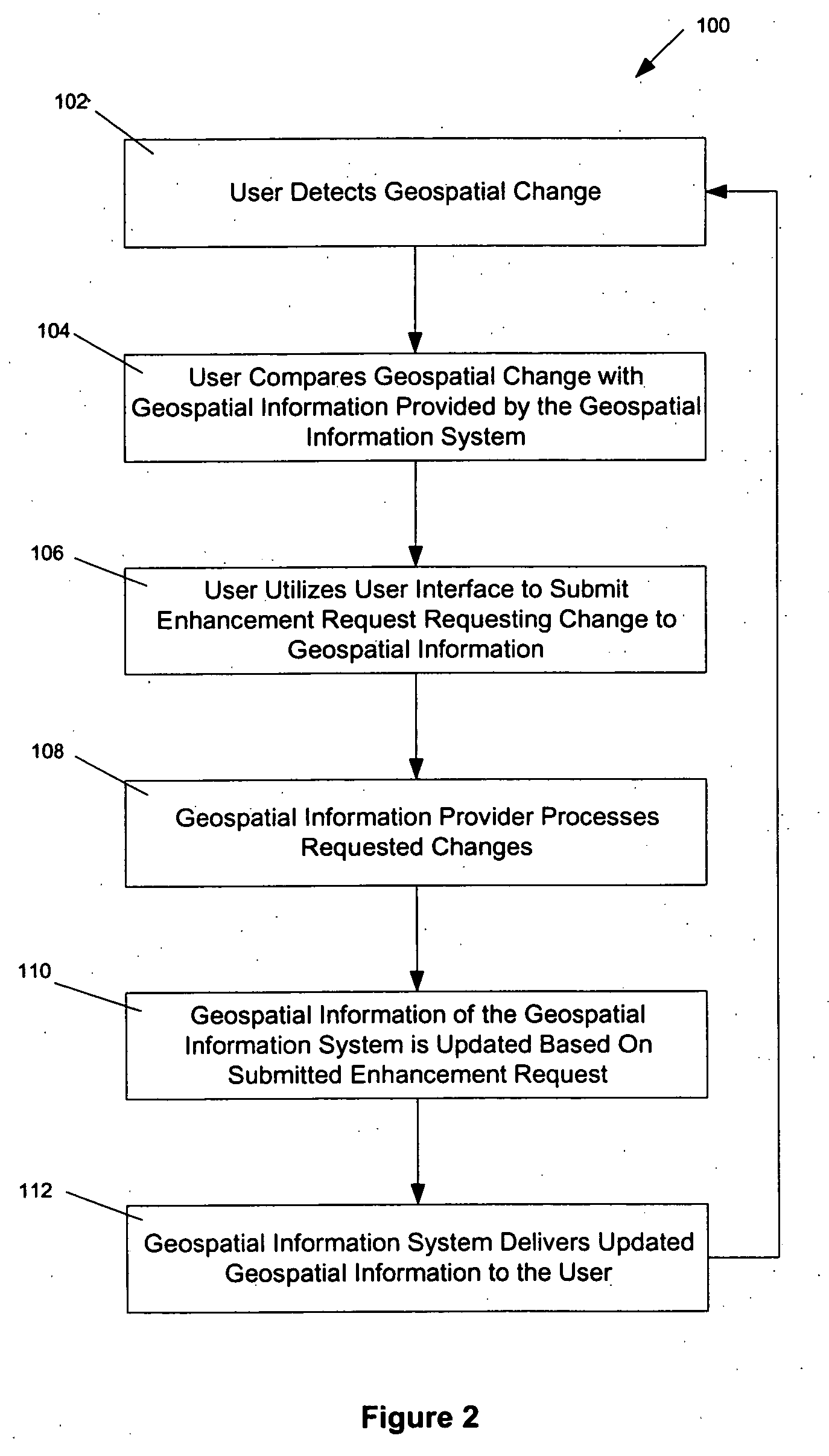
InactiveUS20050278386A1Easy to updateImprove information qualityInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsSpatial information systemsProcessing element
A geospatial information system is provided including a database, a processing unit adapted to access and retrieve the geospatial information from the database, a tool permissions module, a user interface module, a monitoring module, an audit module, a workflow management module, and an update module. Also, a method for updating geospatial information is provided including the steps of providing a database, accessing the database to retrieve geospatial information, associating a tool permission level to a user, generating a customized interface including a plurality of enhancement tools to request a change to the geospatial information, applying a logic check, selecting a map technician, prioritizing the order in which the changes are processed, monitoring the status of the requested change, and updating the geospatial information.
Owner:TELE ATLAS NORTH AMERICA
Method and apparatus for video services
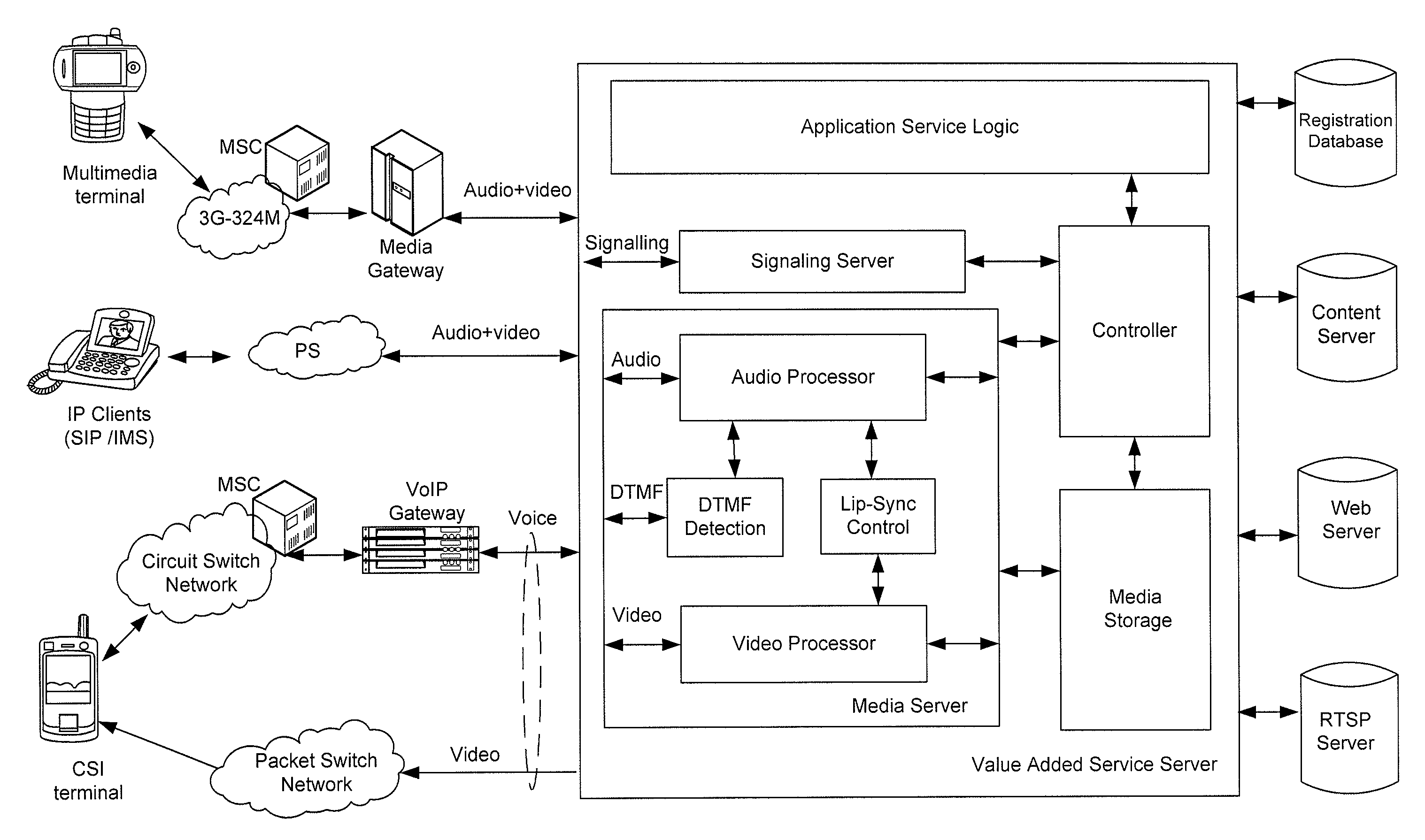
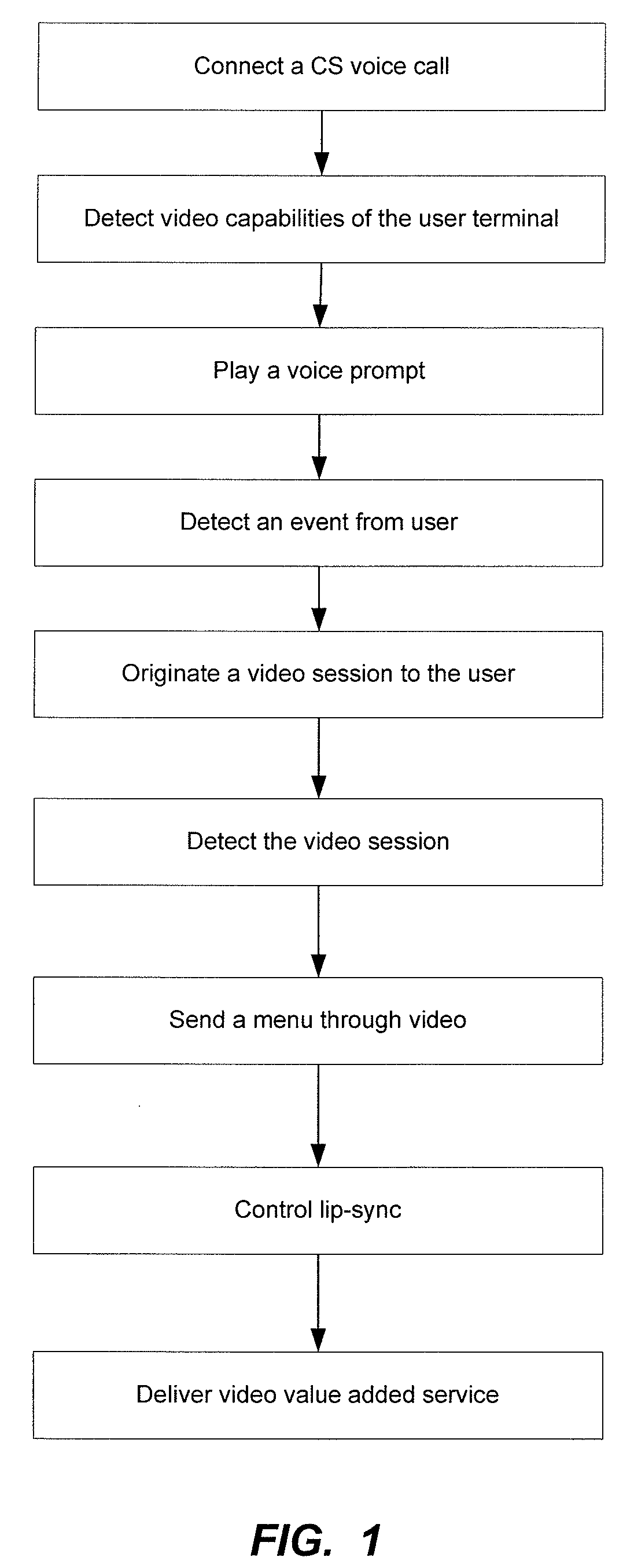
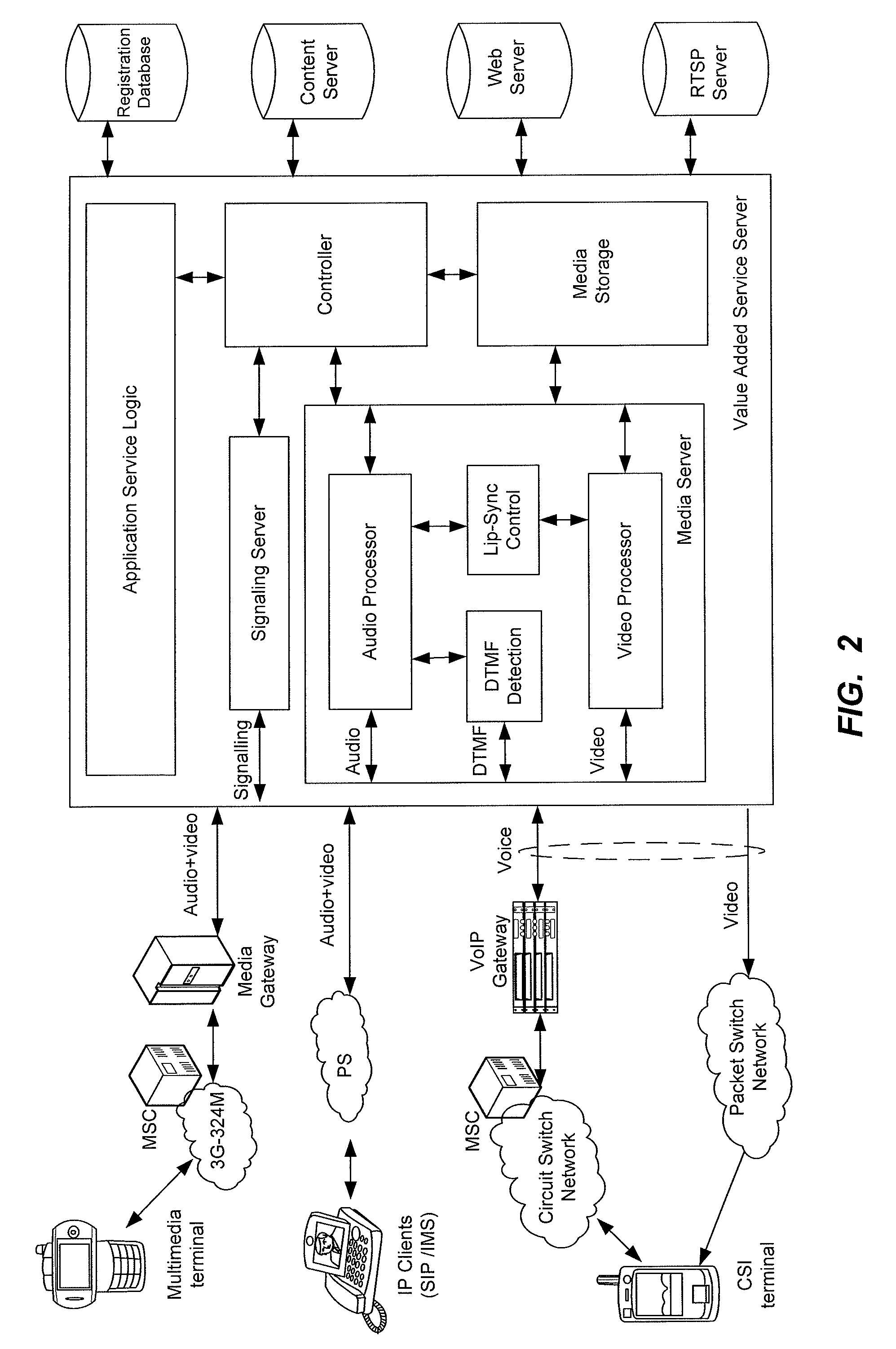
InactiveUS20090232129A1Promote absorptionImprove retentionSelective content distributionNetwork connectionsTransmission timeApplication logic
A method for providing a multimedia service to a multimedia terminal includes establishing an audio link between the multimedia terminal and a server over an audio channel, and detecting one or more media capabilities of the multimedia terminal. The method also includes providing an application logic for the multimedia service, establishing a visual link between the multimedia terminal and the server over a video channel, providing an audio stream for the multimedia service over the audio link, and providing a visual stream for the multimedia service over the video link. The method further includes combining the video link and the audio link, and adjusting a transmission time of one or more packets in the visual stream to synchronize the visual stream with the audio stream.
Owner:ONMOBILE GLOBAL LTD
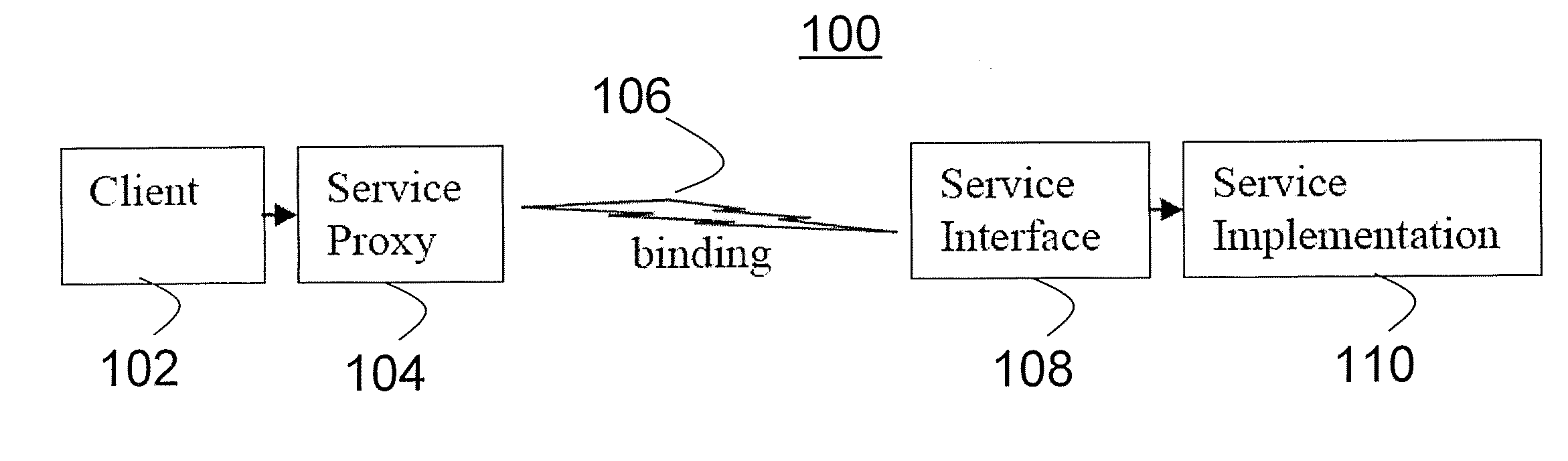
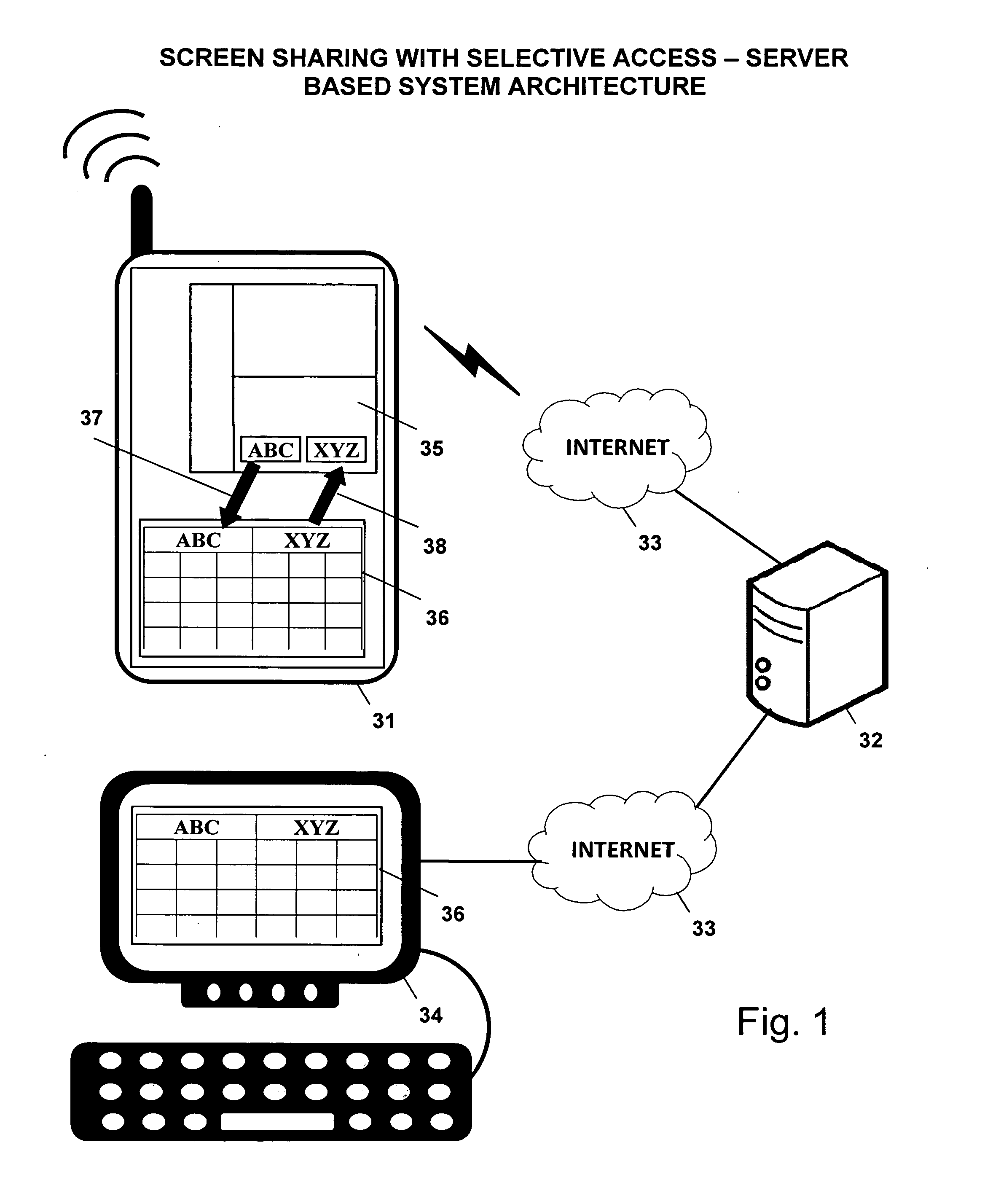
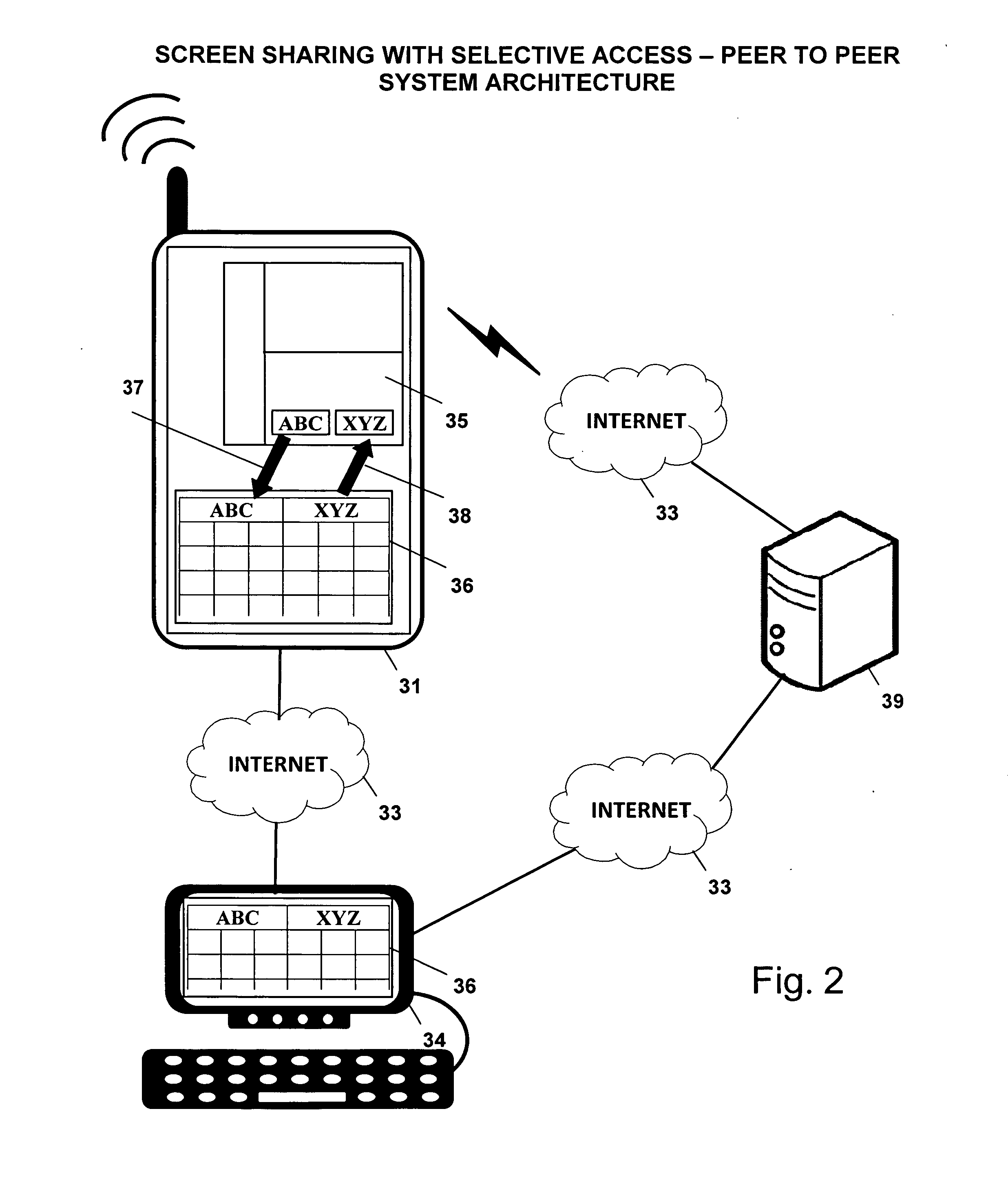
Screen sharing method with selective access to both data and logic of a shared application using a helper application
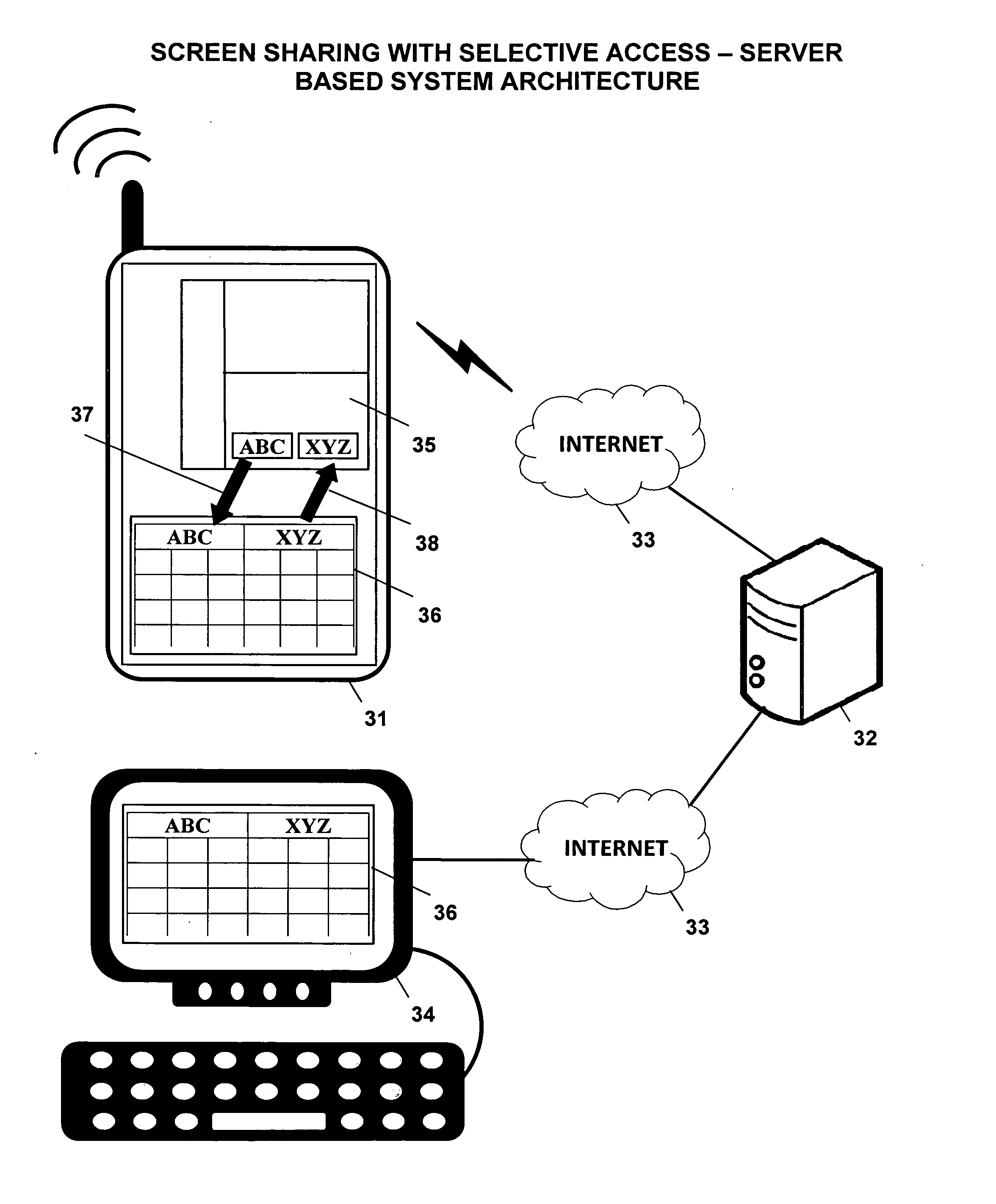
InactiveUS20110004888A1Guaranteed normal executionSelectively accessedInterprogram communicationExecution for user interfacesGraphicsGraphical user interface
A screen sharing system that enables selective access to application data and application logic is described. This screen sharing system is implemented by coupling a helper application (36) to an application that provides content referred to as content application (35).The helper application is an application that has the ability to programmatically access the content application (35) using window system graphical user interface application programming interface. Helper application (36) is used to get and set content application data and interact with the content application using window system input events that simulate user input.This method enables selective access to both application data and application logic that is necessary for use in a screen sharing system used by participants that may be trusted or may not be fully trusted.
Owner:SRINIVASAN SUDHARSHAN +2
Apparatus, systems and methods for managing incoming and outgoing communication
InactiveUS20070248220A1Telephone data network interconnectionsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionInbound communicationOutbound communication
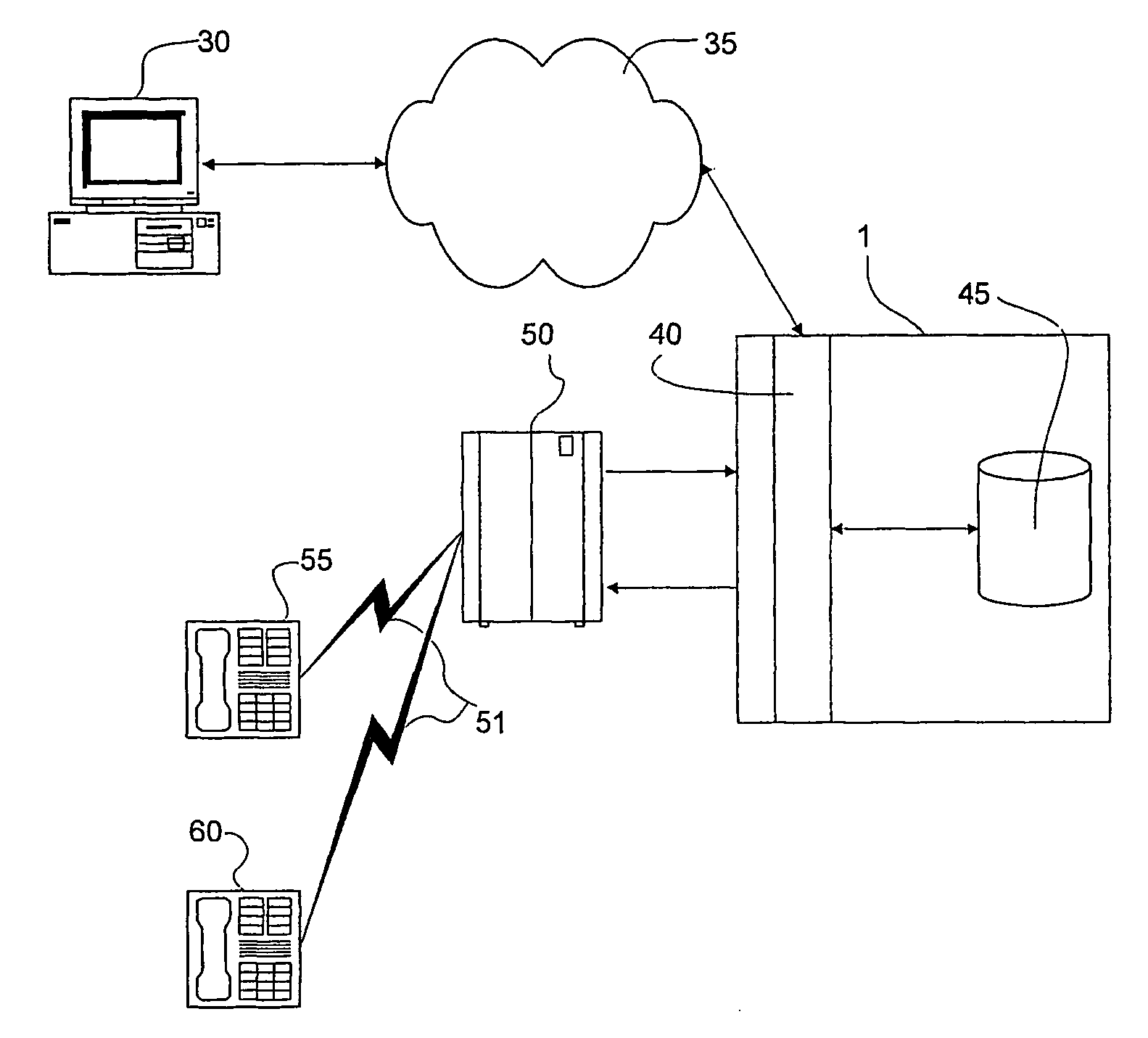
The present invention provides apparatus, systems and methods for managing incoming and outgoing communications for various communications methods. The invention provides control over inbound communications including definition of if, when, and who may communicate with a recipient. The invention also supports concealed identification communication in that no actual addresses, phone numbers, or other addressing IDs are required to be exchanged by the communication initiator and recipient. The invention also provides the capability to initiate immediate, delayed, scheduled, or recurring outbound communications. As depicted in FIG. 1, if the database (45) contains call management settings for a call recipient, the application logic (40) will evaluate the rules to determine if a particular caller is authorized to connect with the call recipient at the current time and date. If the caller is authorized by the recipient to connect to the recipient phone number, and is furthermore authorized to do so for the current time and date, the application logic (40) will connect the call utilizing the public telephone switch (50). The computer (1) passes the caller and call recipient phone numbers as stored in the database (45) to the telephone switch (50) using an application programming interface (“API”) appropriate to the service provider or telephone switch manufacturer. The exemplary embodiment of the invention utilizes an API provided by a telephone service provider as an interface to its switching infrastructure (50). The API captures both caller and recipient telephone numbers along with other variables useful for call setup and tracking. The telephone service provider then connects both parties' telephones (55), (60) to a phone call by dialing both numbers and connecting the call upon the parties' answer.
Owner:CRANDELL JEFFREY L +1
Methods of transforming application layer structure as objects
InactiveUS20060242197A1Code refactoringSpecial data processing applicationsSoftware engineeringProtocol Application
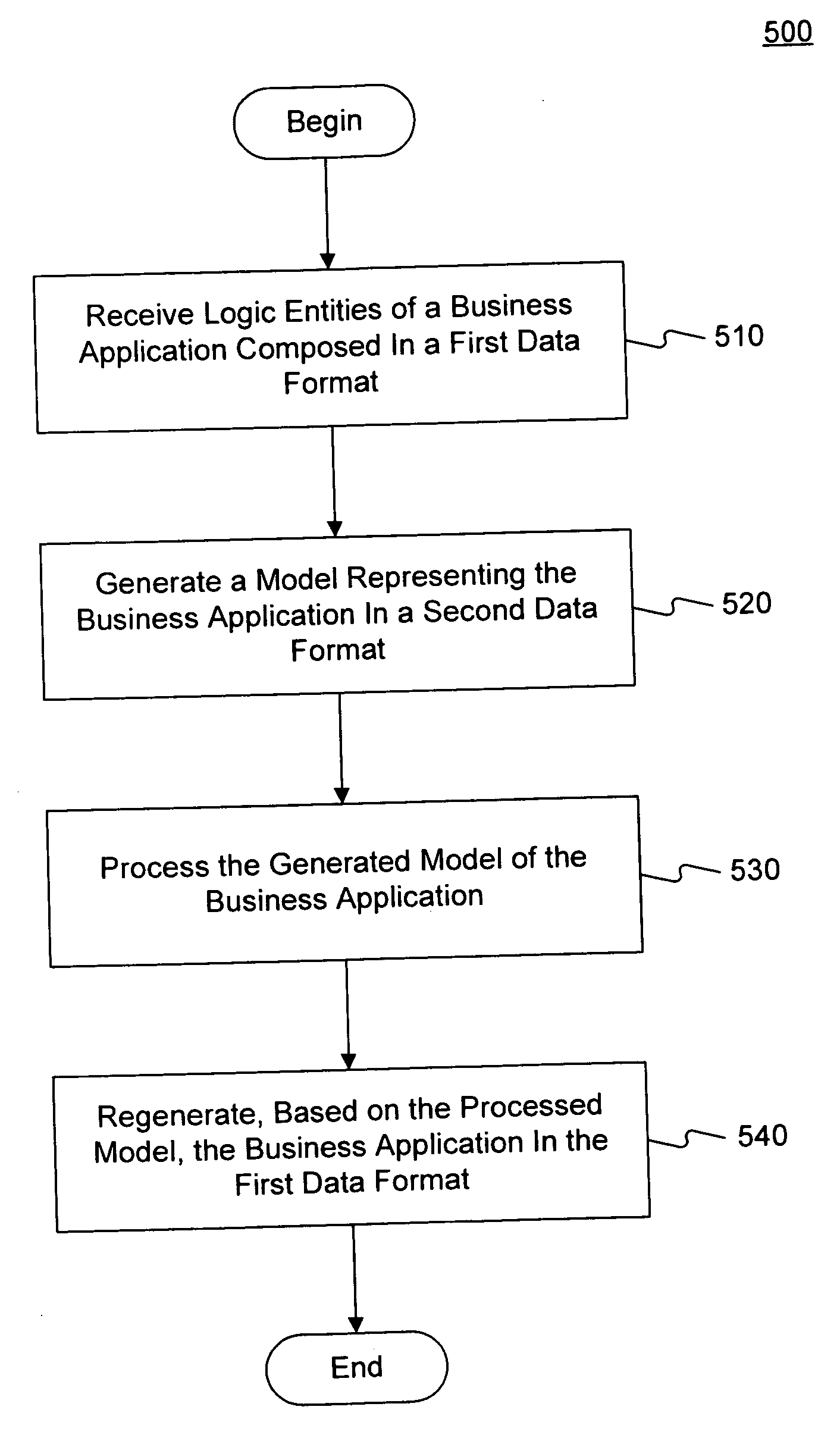
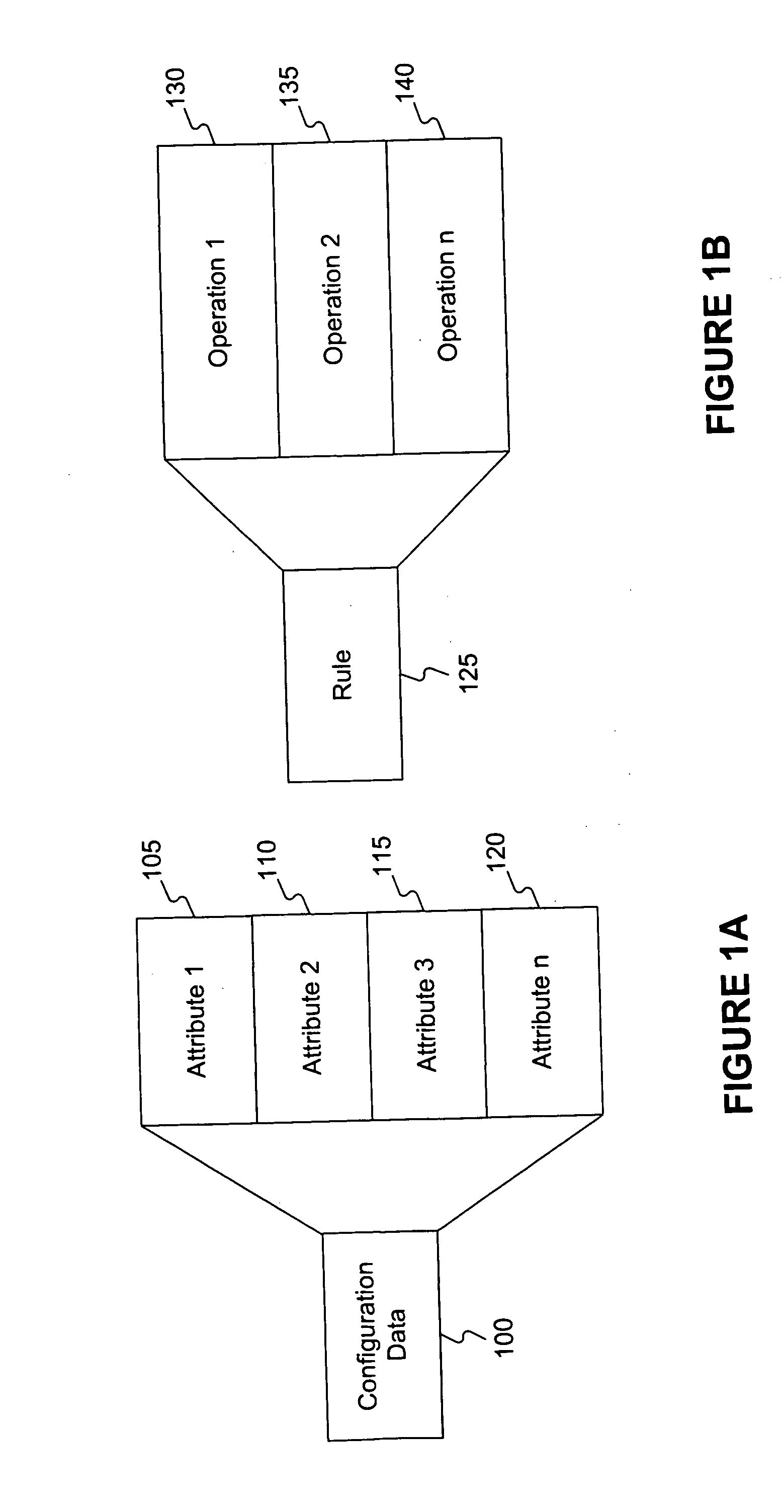
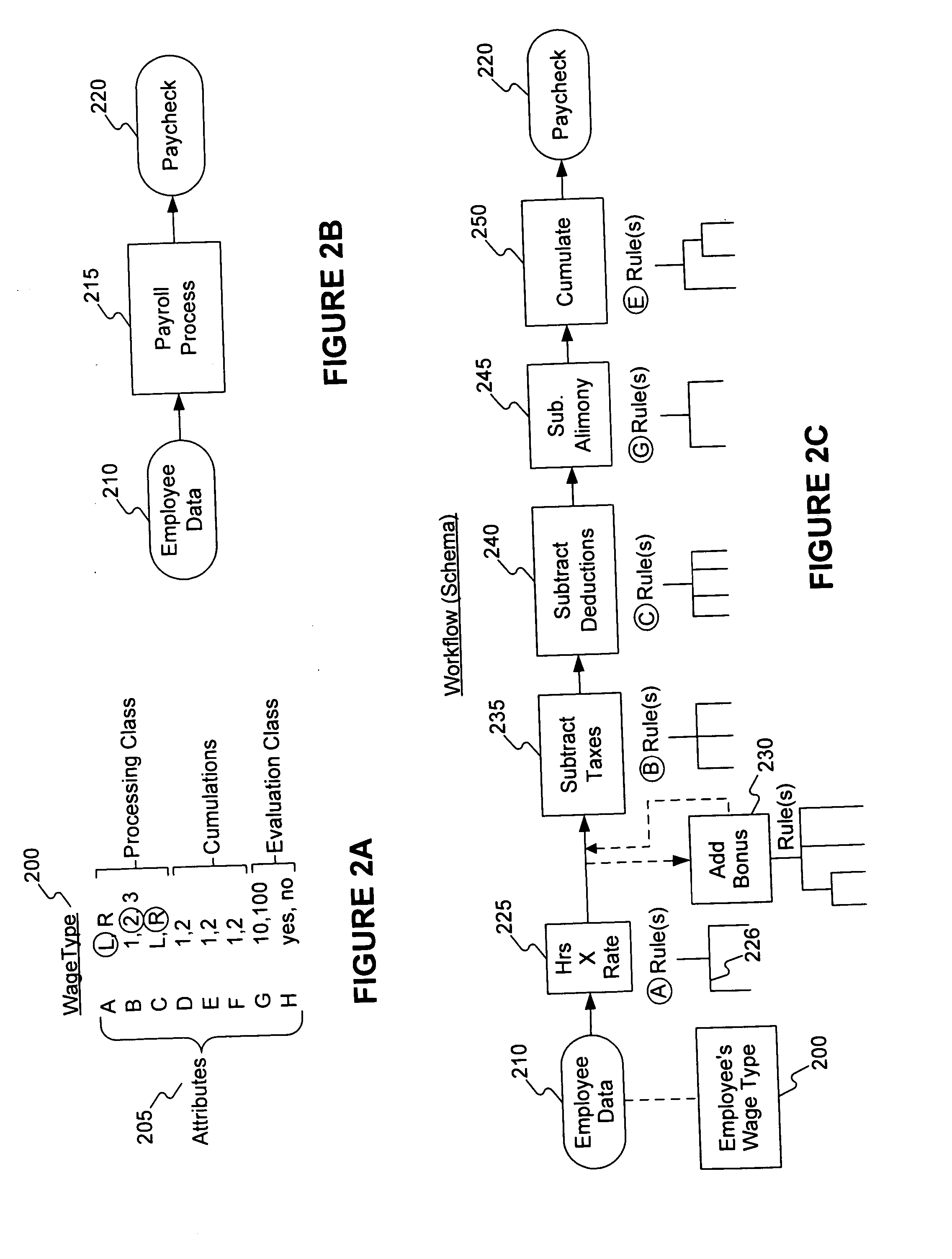
Embodiments consistent with the invention transform business application logic entities or structures into OOP structures that represent the data, relationships, and operations of the business application structures. The business application structures are transformed from the application level, including consideration of the business application logic and relationships. In one embodiment, transformation is done using a set of automated transformation rules. The resulting OOP structure model of the business application structure may be used with OOP tools to analyze, maintain, debug, modify, and revise the business application structure, and to create new structures for the business application.
Owner:SAP AG
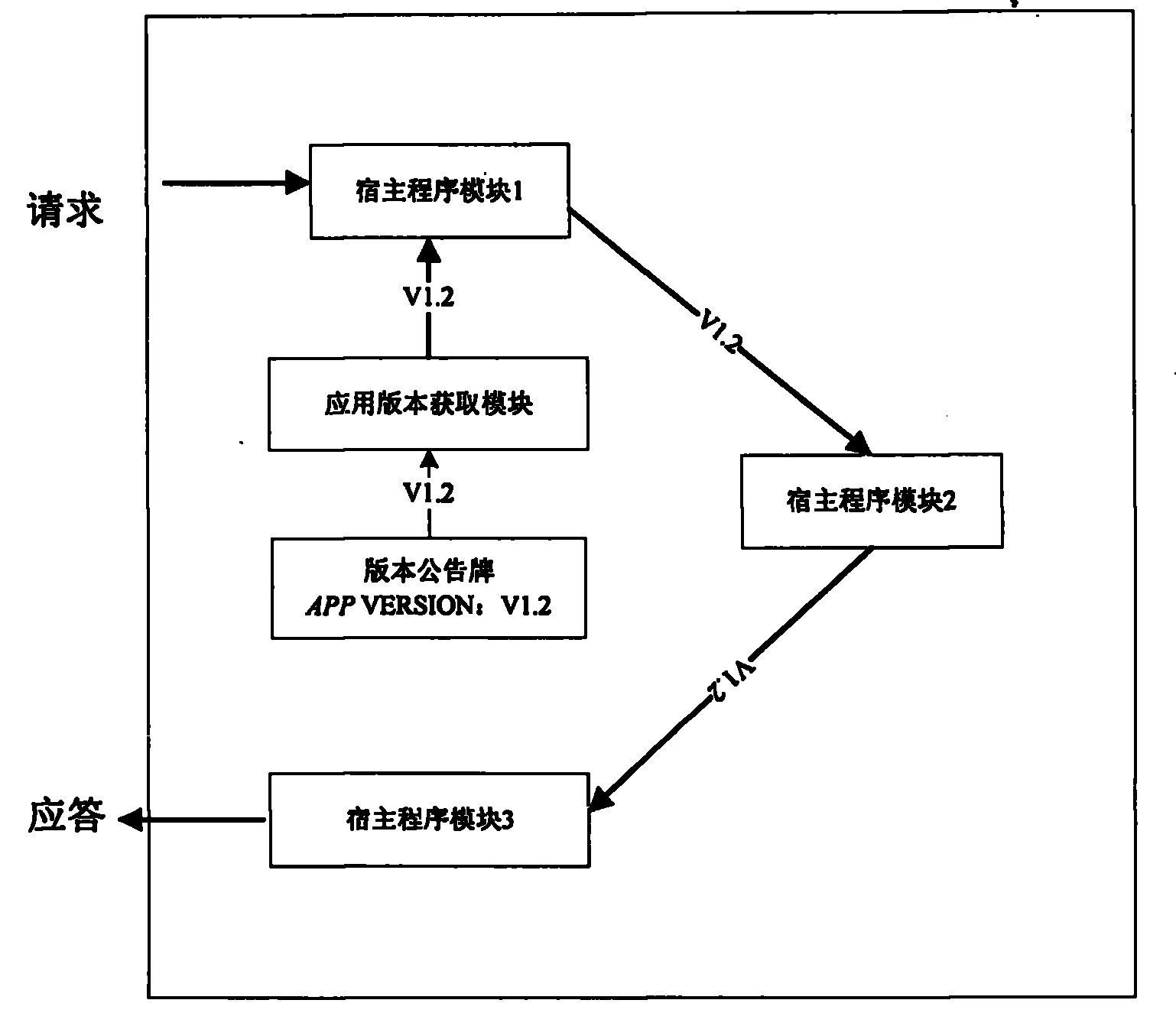
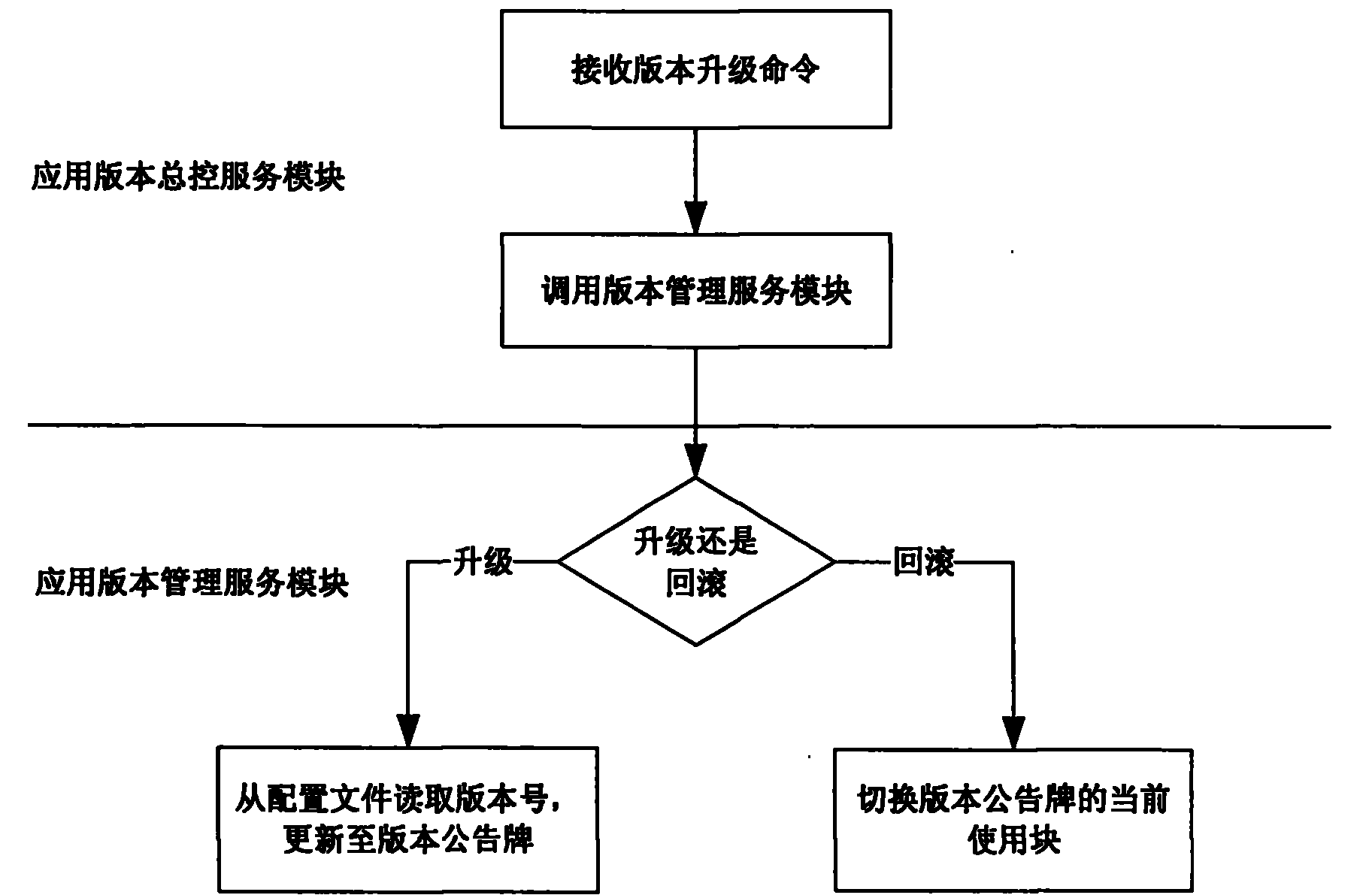
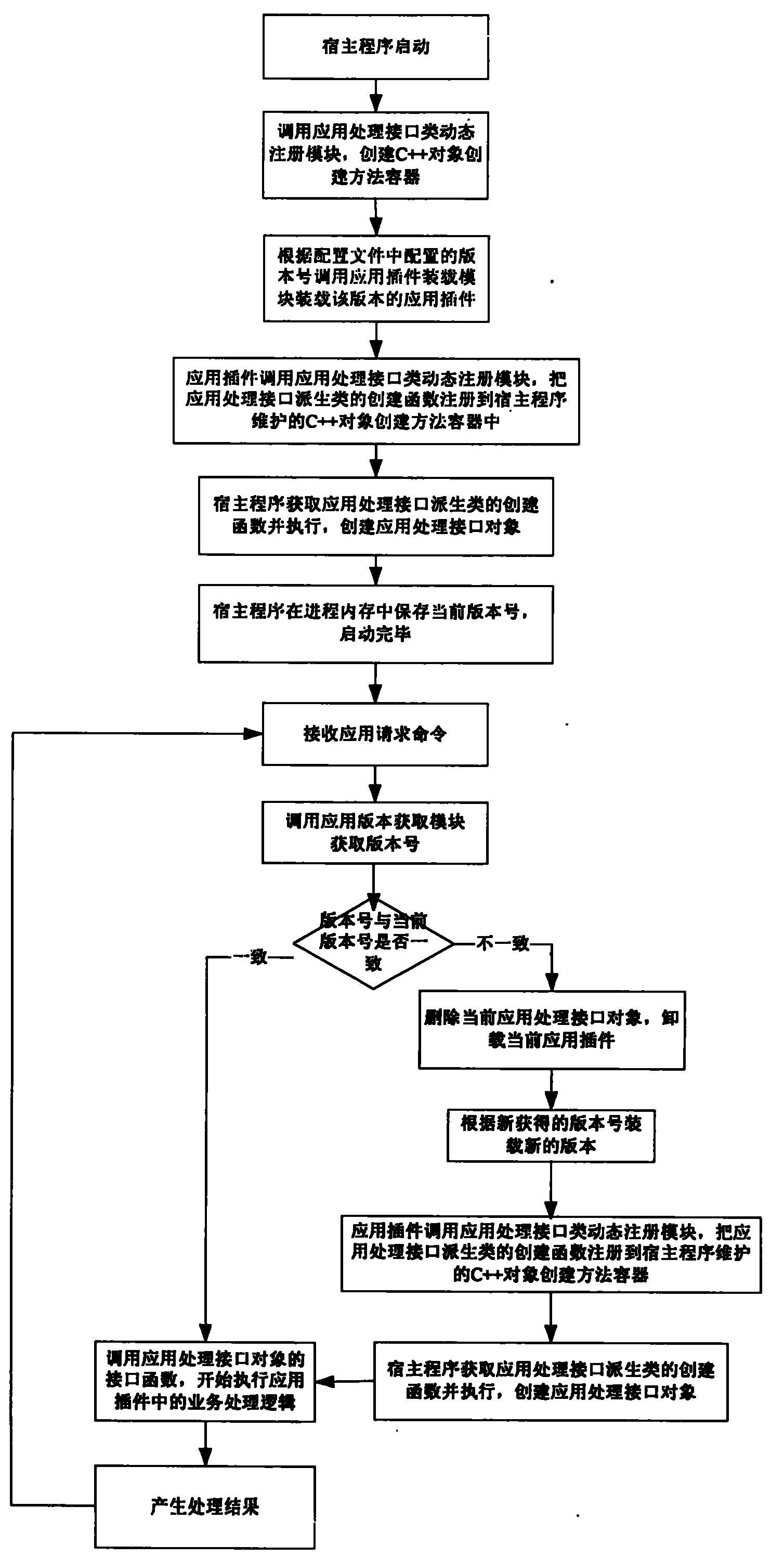
Dynamic management system and method for C++ application program version
InactiveCN102073520AReduce downtimeImprove service qualityProgram loading/initiatingSoftware engineeringDynamic management
The invention provides a dynamic management system and a dynamic management method for a C++ application program version. The system comprises an application plug-in module, a host program module, an application processing interface module, an application processing interface dynamic registration module, an application plug-in loading / unloading module, an application version distribution module and an application version acquisition module. Application logics are encapsulated into a dynamic shared library by reasonably using dynamic shared library technology, and meanwhile, the application logics are dynamically loaded by designing a system framework; and when the application program version is upgraded, only corresponding dynamic shared library files are upgraded and then loaded through the system framework to realize online update of an application program, and the whole process does not need to shut down and interrupt the service, namely hot plug.
Owner:TRAVELSKY
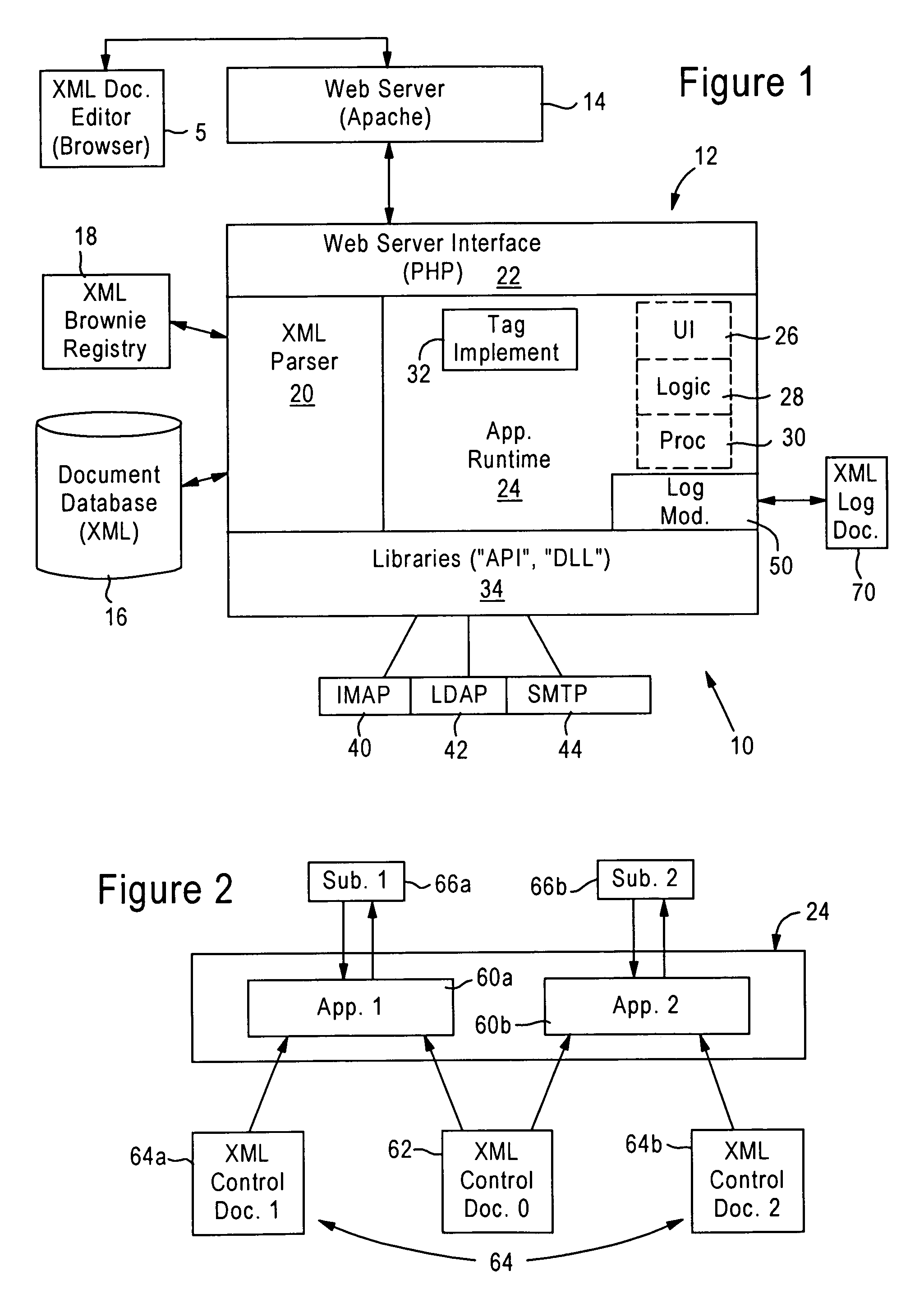
Arrangement for controlling and logging voice enabled web applications using extensible markup language documents
InactiveUS6952800B1Flexible controlReduce necessityDigital computer detailsWebsite content managementWeb serviceApplication software
A unified web-based voice messaging system provides voice application control between a web browser and an application server via an hypertext transport protocol (HTTP) connection on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The web browser receives an HTML page from the application server having an XML element that defines data for an audio operation to be performed by an executable audio resource. The application server executes the voice-enabled web application by runtime execution of extensible markup language (XML) documents that define the voice-enabled web application to be executed. The application server includes a runtime environment that establishes an efficient, high-speed connection to a web server. The application server, in response to receiving a user request from a user, accesses a selected XML page that defines at least a part of the voice application to be executed for the user. The XML page may describe any one of a user interface such as dynamic generation of a menu of options or a prompt for a password, an application logic operation, or a function capability such as generating a function call to an external resource. The application server then parses the XML page, and executes the operation described by the XML page, for example dynamically generating an HTML page having voice application control content, or fetching another XML page to continue application processing. In addition, the application server may access an XML page that stores application state information, enabling the application server to be state-aware relative to the user interaction. Hence, the XML page, which can be written using a conventional editor or word processor, defines the application to be executed by the application server within the runtime environment, enabling voice enabled web applications to be generated and executed without the necessity of programming language environments.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
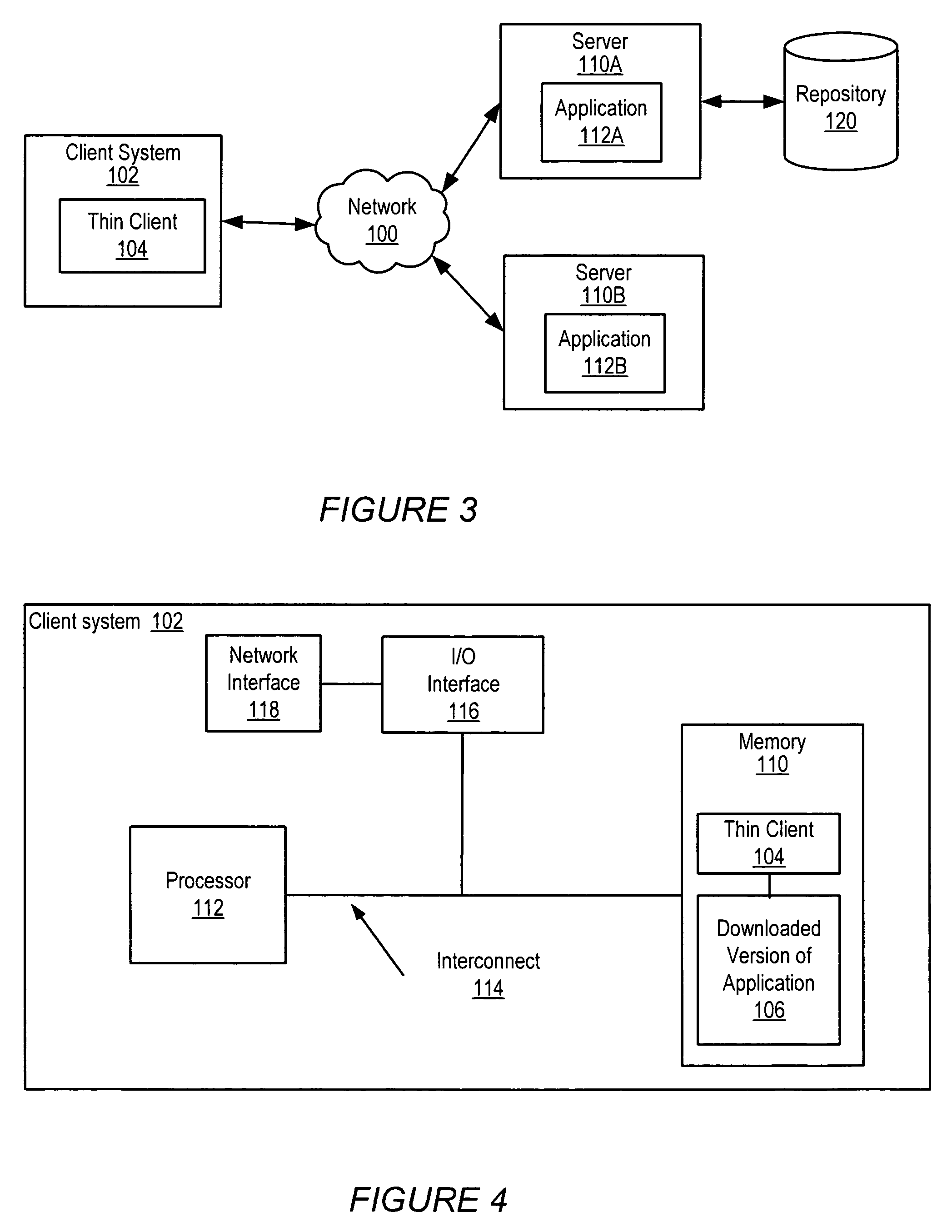
System and method for disconnected operation of thin-client applications
System and method for disconnected operation of thin-client applications. In embodiments, a thin client on a client system may be used to access an application on a server via a network. Prior to the thin client disconnecting from the application, a version of the application including at least a portion of the application logic of the application may be downloaded to the client system to be accessed using the thin client during disconnected operation of the client system. After reconnection of the thin client to the application, changes made, if any, to application data on the client system may be integrated into the application data on the server.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
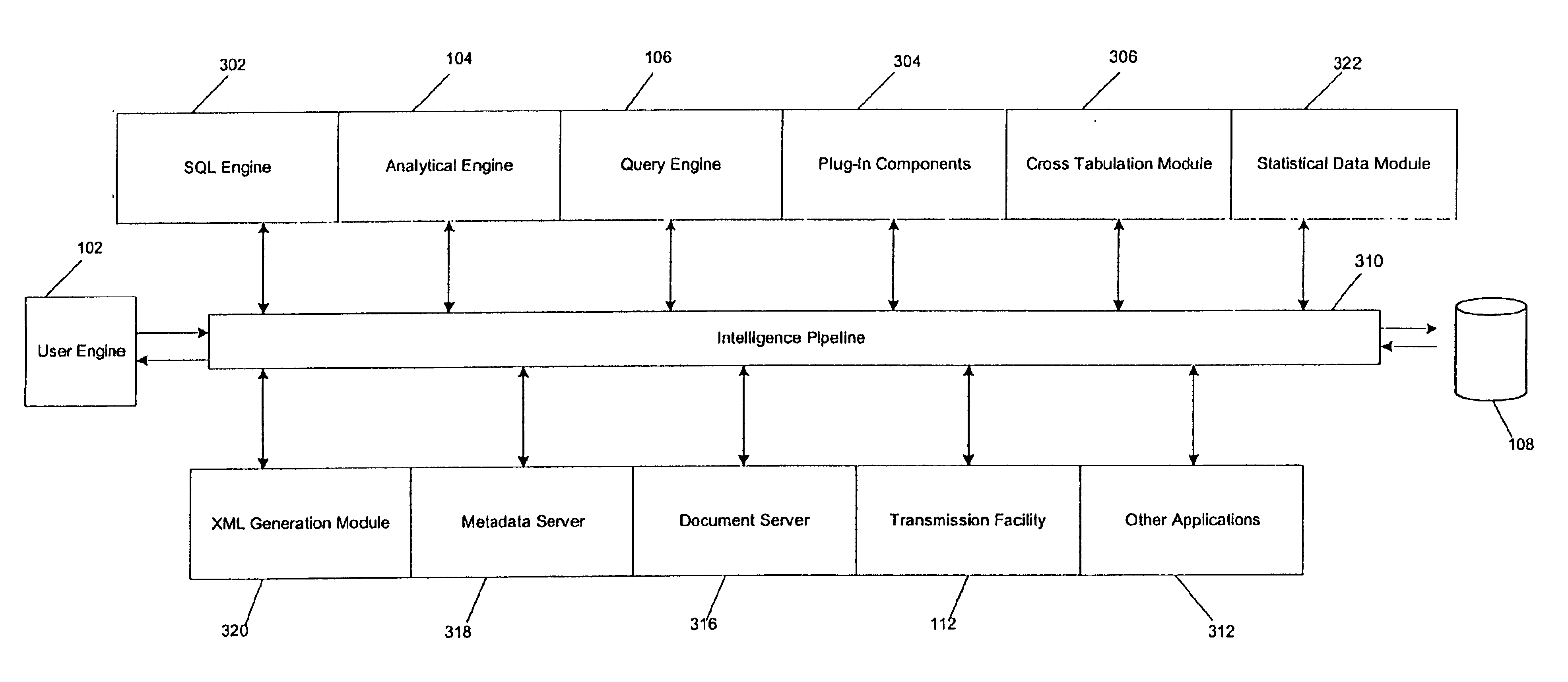
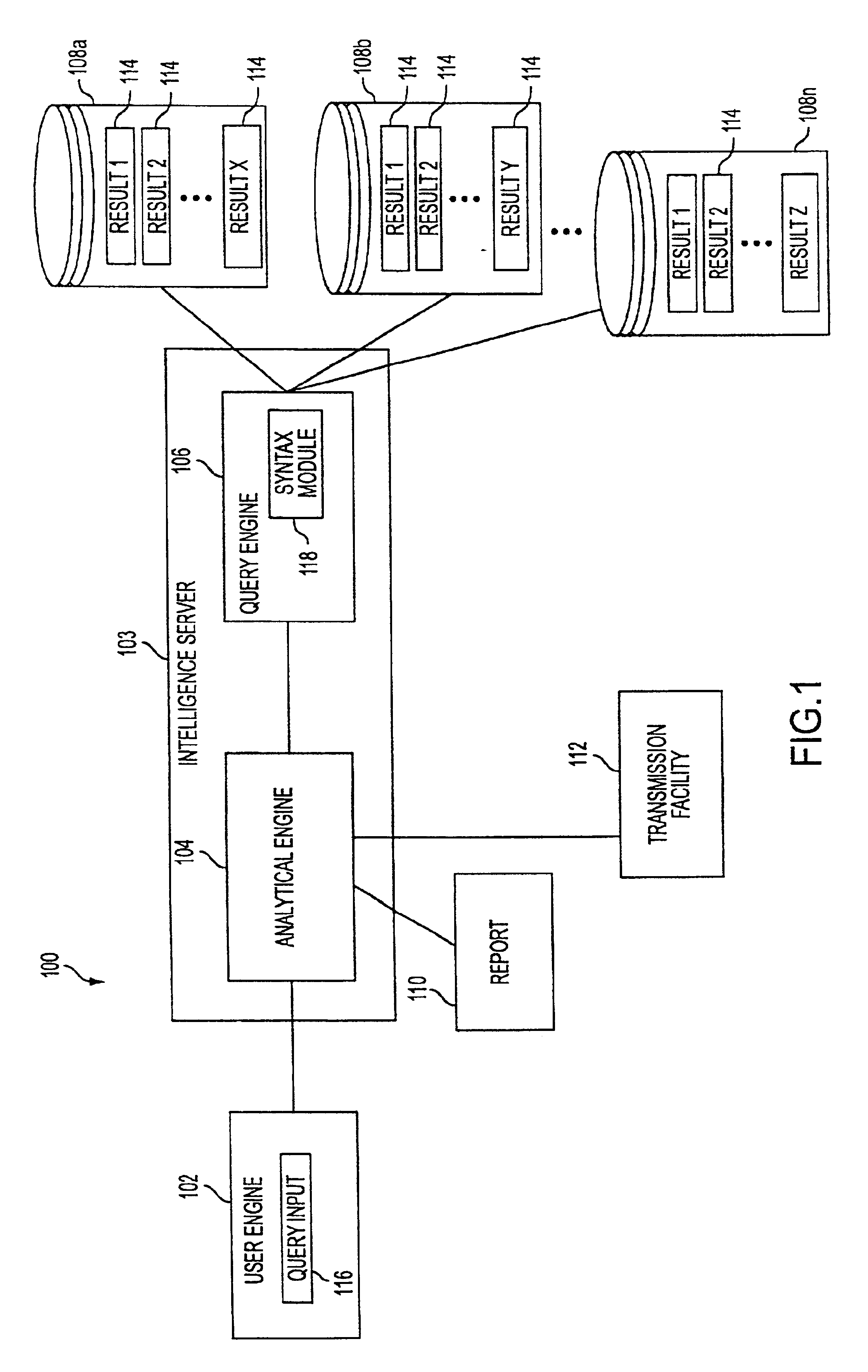
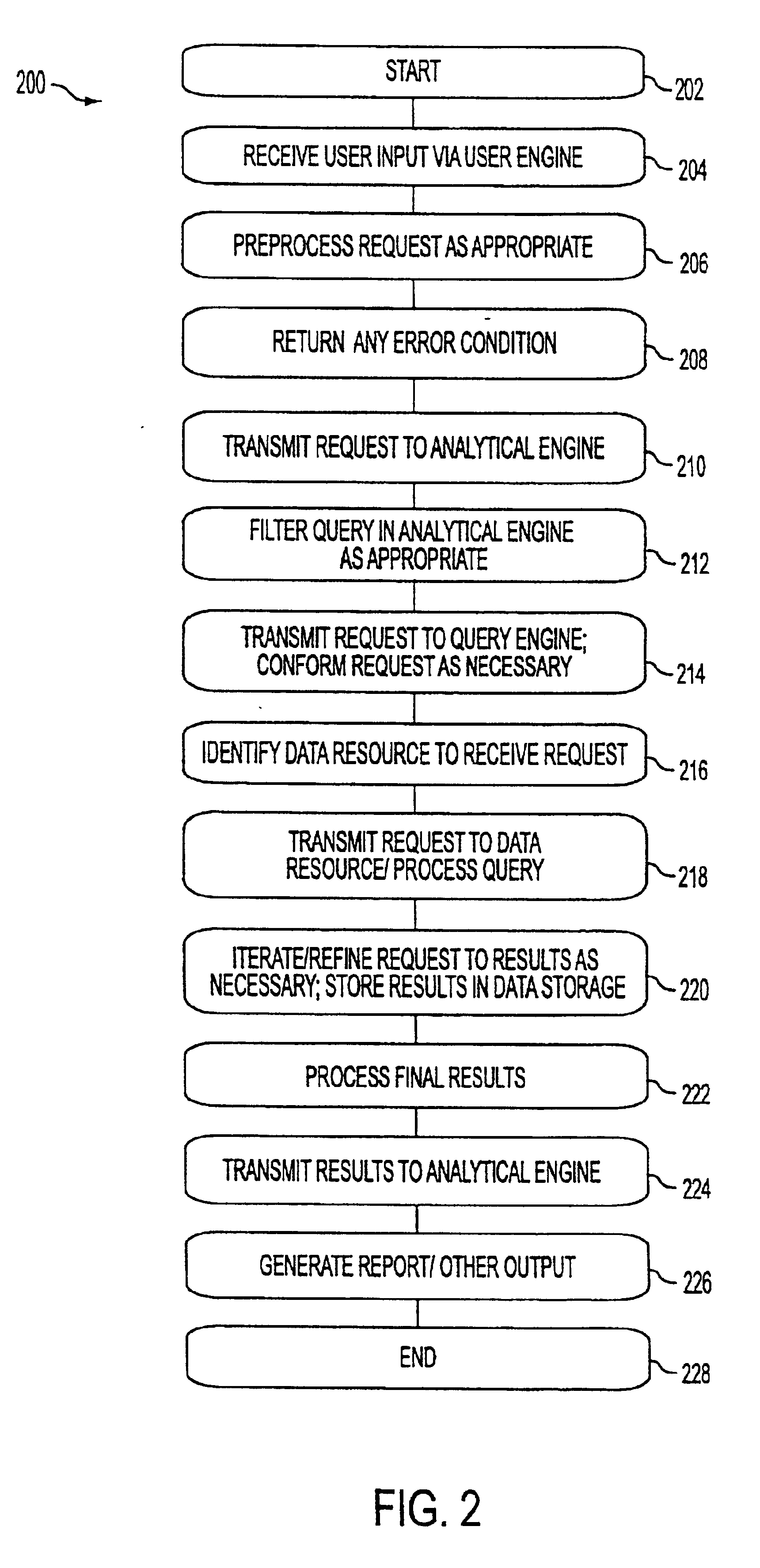
Intelligence server system
InactiveUS6859798B1Limited bandwidthDigital computer detailsResourcesApplication softwareBusiness intelligence
Owner:MICROSTRATEGY
System and method for secure content sharing and synchronization
ActiveUS20130097687A1Easy accessCustomer relationshipDigital data information retrievalContent distributionGate-keeper
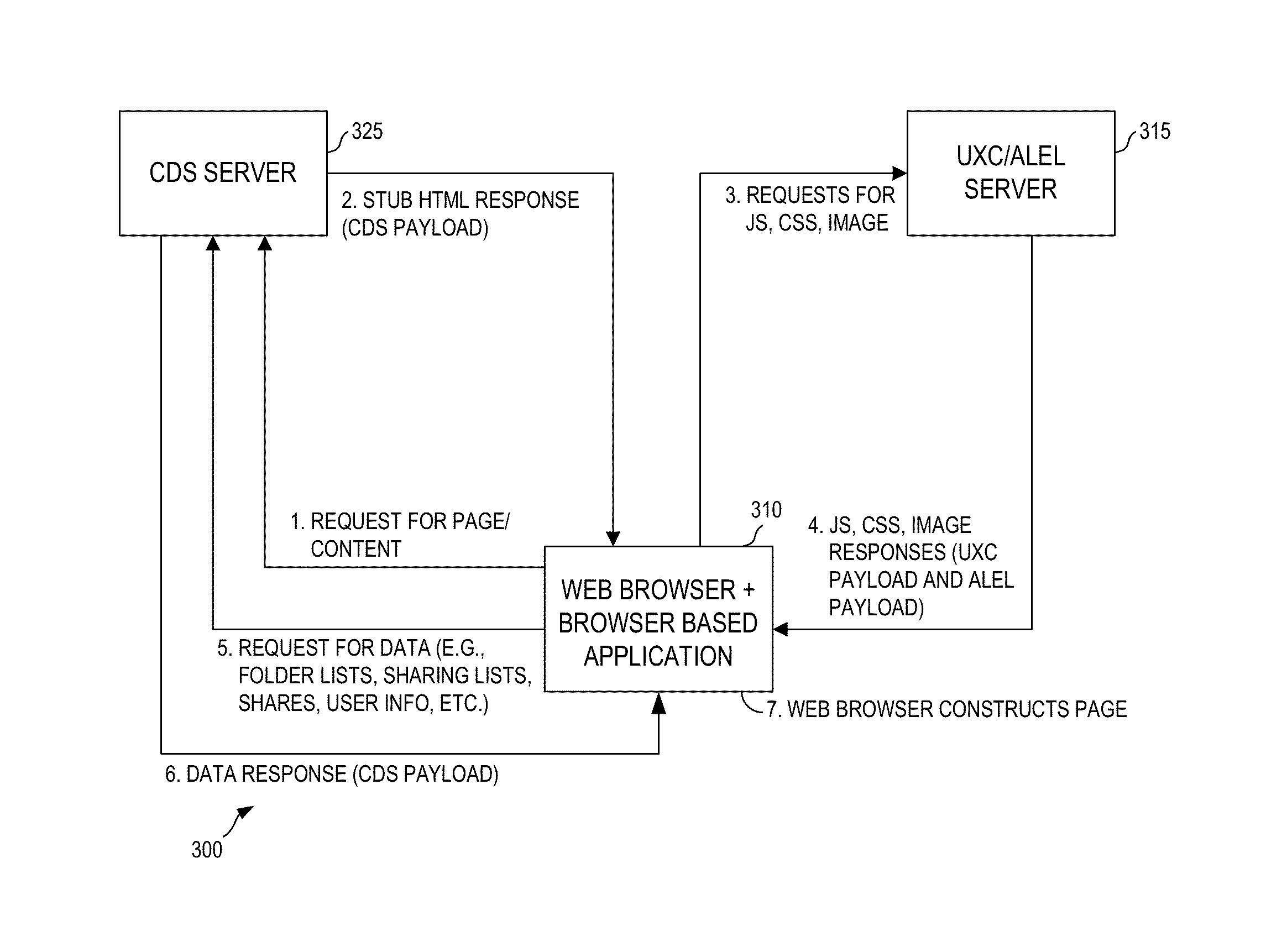
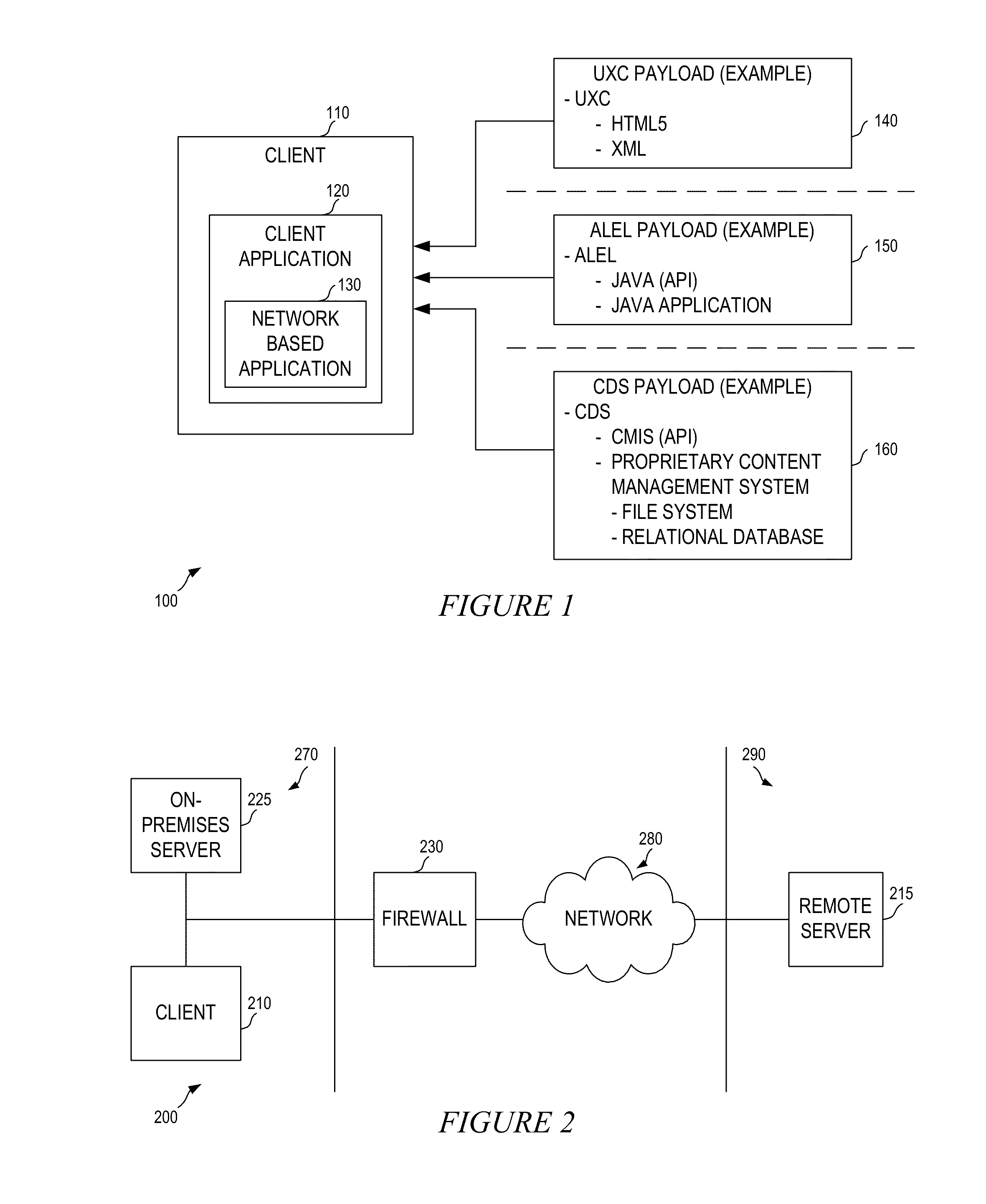
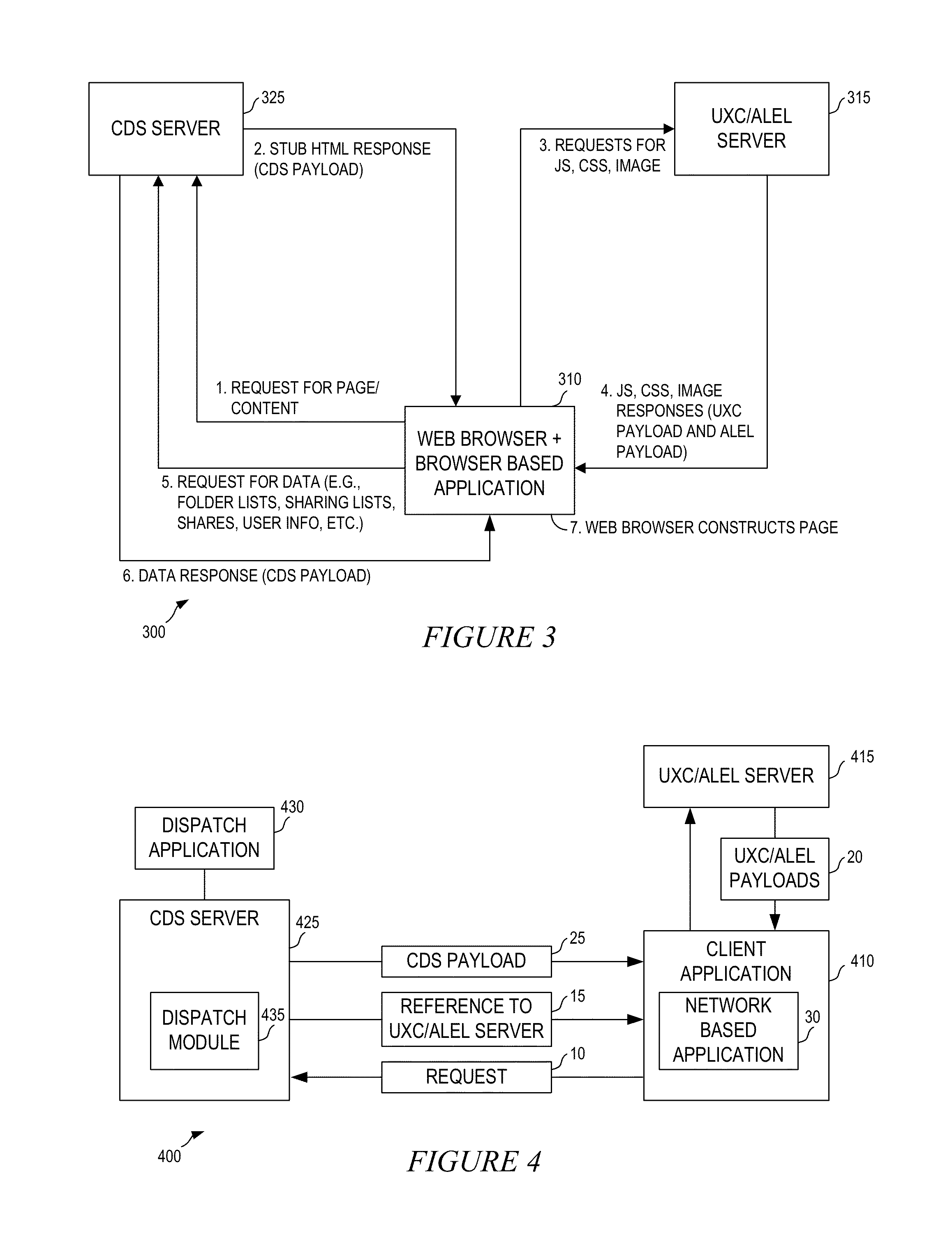
A flexible content sharing system may comprise a network based application built on a client device using information from dissociated user experience component (UXC), application logic and execution layer (ALEL), and content distribution system (CDS) payloads. An ALEL engine may communicate a request from the network based application to a CDS module. The CDS module may interface the ALEL engine and a CDS server. The ALEL engine can act as a gate keeper and securely communicates requests from client devices to the CDS server. The CDS server is configured to manage and alert the ALEL of any enterprise policies that may be applicable to the client devices connected to the ALEL engine which, in turn, notifies the client devices to comply with the enterprise policies. The CDS server may synchronize any change made to the content by any of the client devices running network based applications.
Owner:OPEN TEXT SA ULC
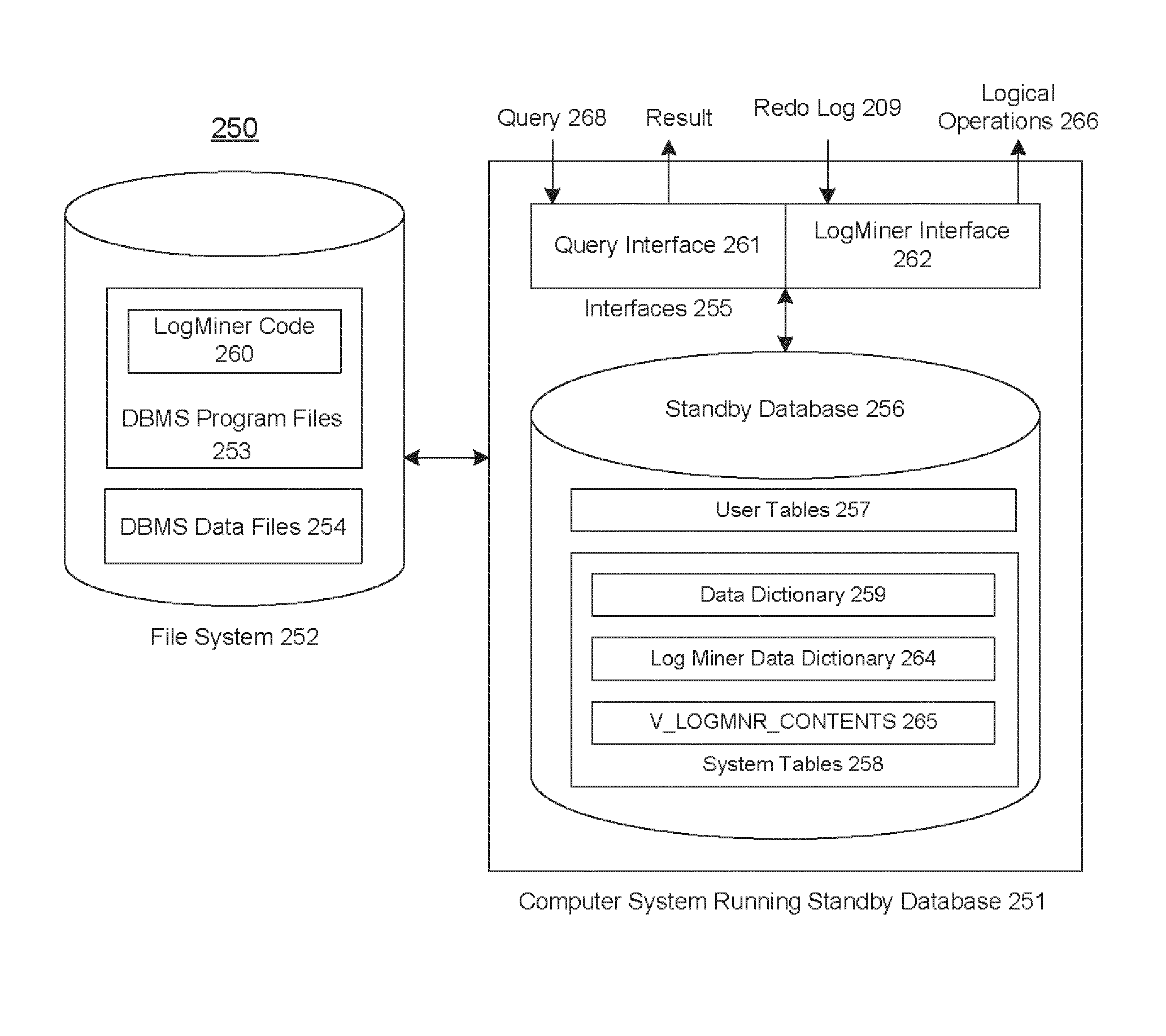
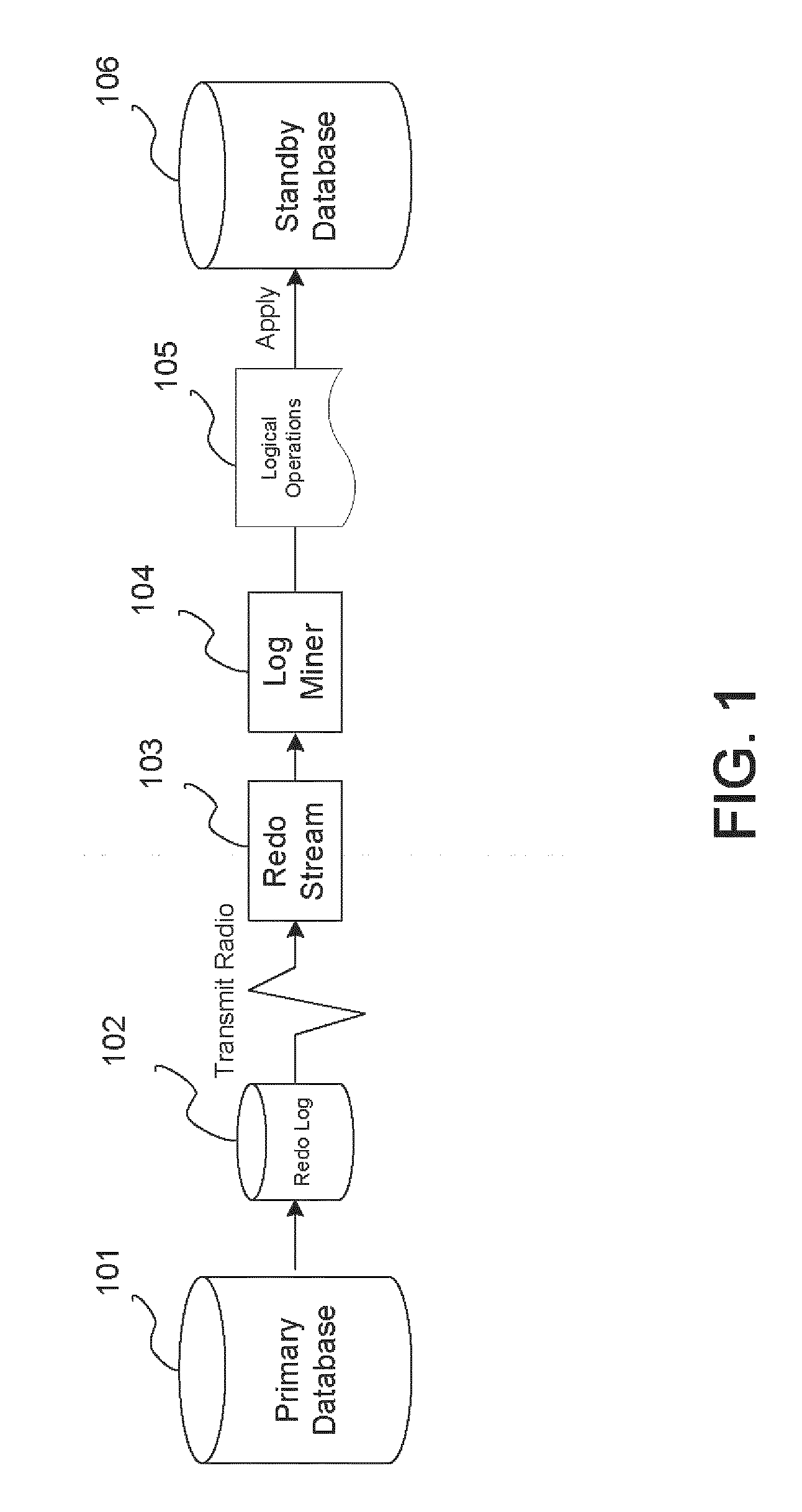
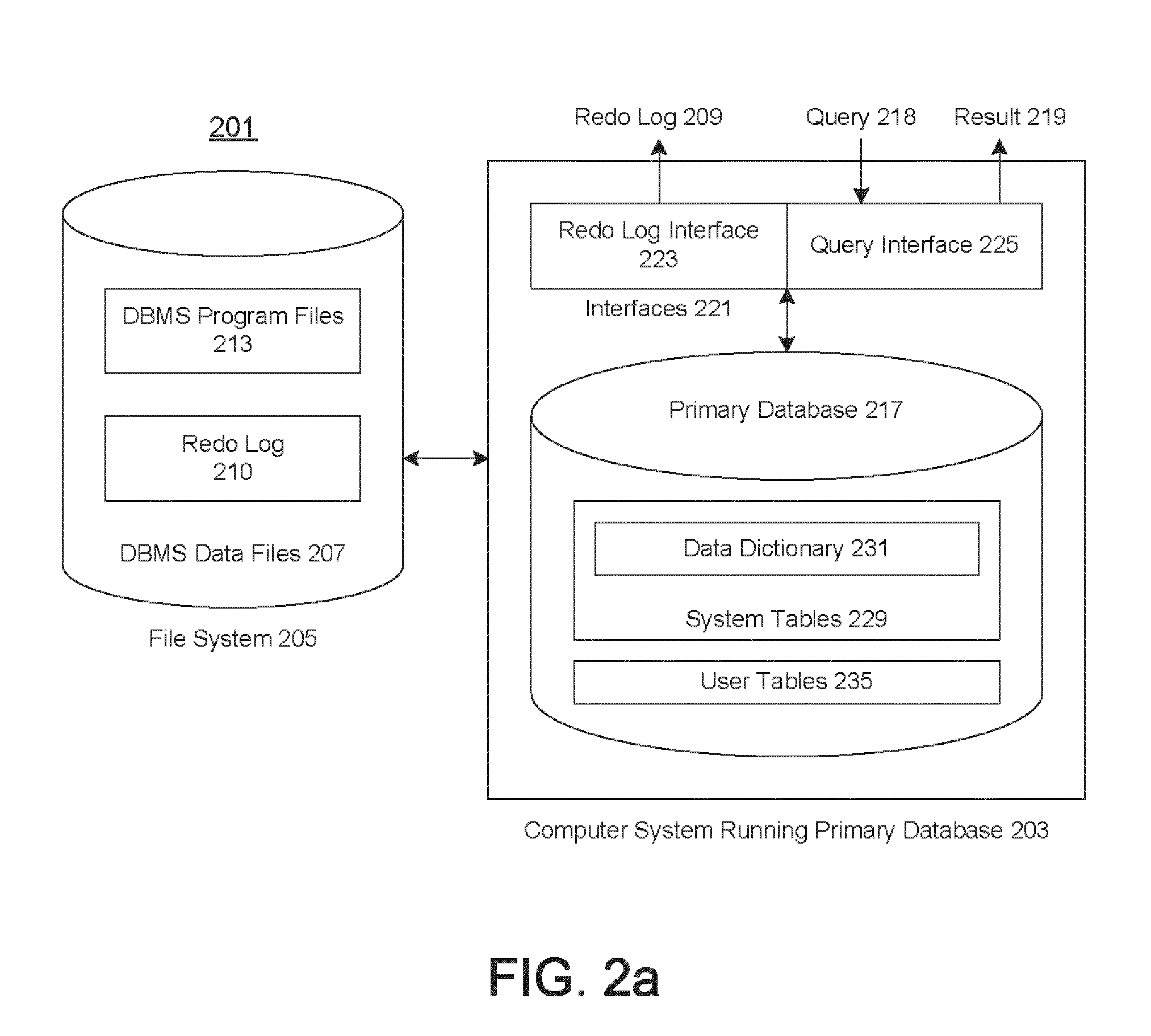
Techniques for the log-based replication of high-level procedures
A method and system that annotates a redo log to provide information concerning the execution of a procedure at a primary database. The annotations include entry and exit markers that indicate the beginning and the end of the execution along with any arguments passed to the procedure, and whether the execution of the procedure was successful. At the standby database, these markers are used to create a logical transaction associated with the procedure. The operations performed by the procedure are grouped into individual transactions, and these individual transactions are grouped as belonging to the logical transaction. If the execution of the procedure was successful at the primary database, then the individual transactions are discarded, and the logical transaction is applied by executing the procedure at the standby database. If the execution of the procedure failed at the primary database, then the individual transactions and the logical transaction are discarded.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com