Patents
Literature
2533 results about "Abdominal cavity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contains many organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle under the lungs, and its floor is the pelvic inlet, opening into the pelvis.
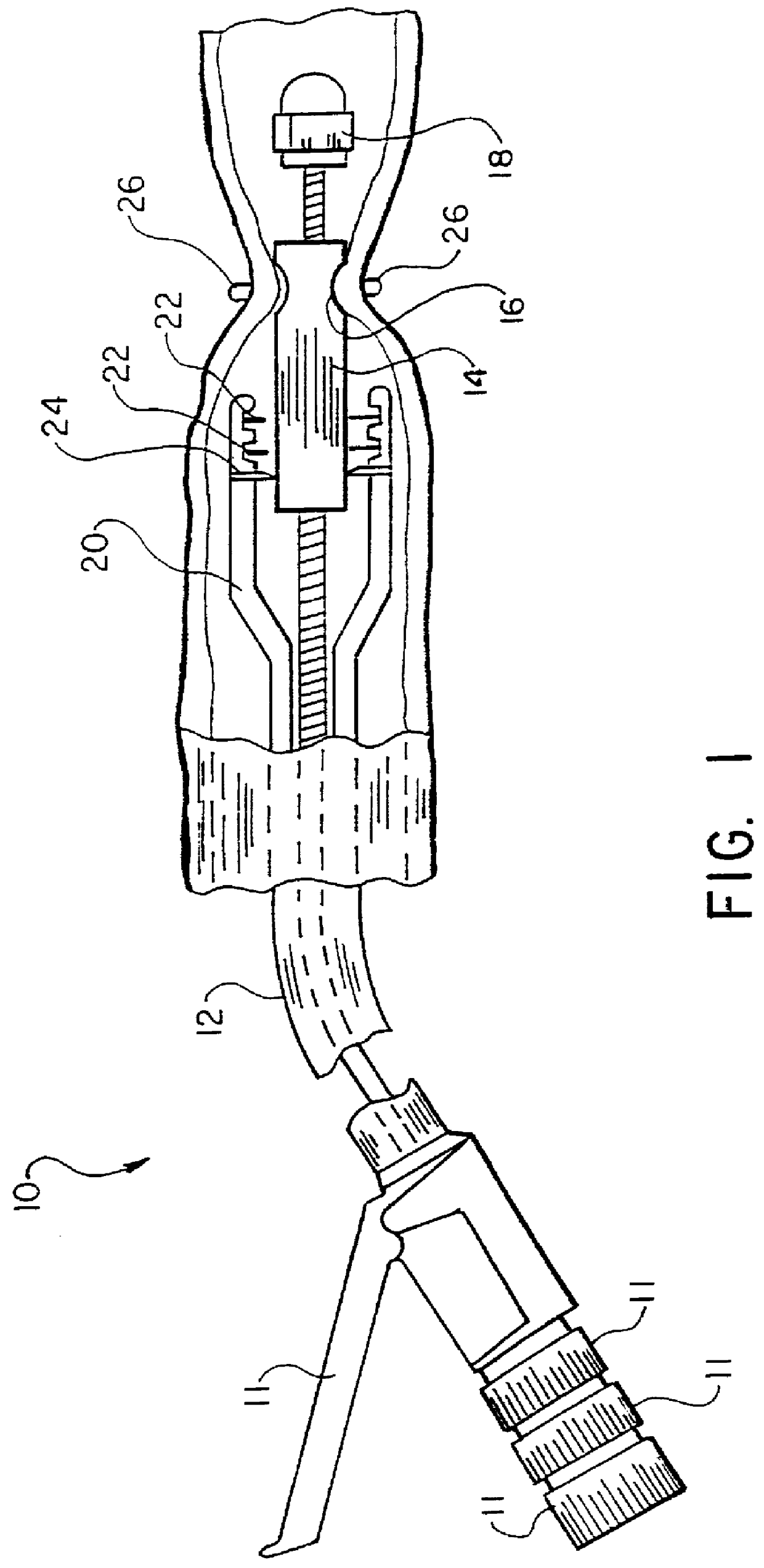
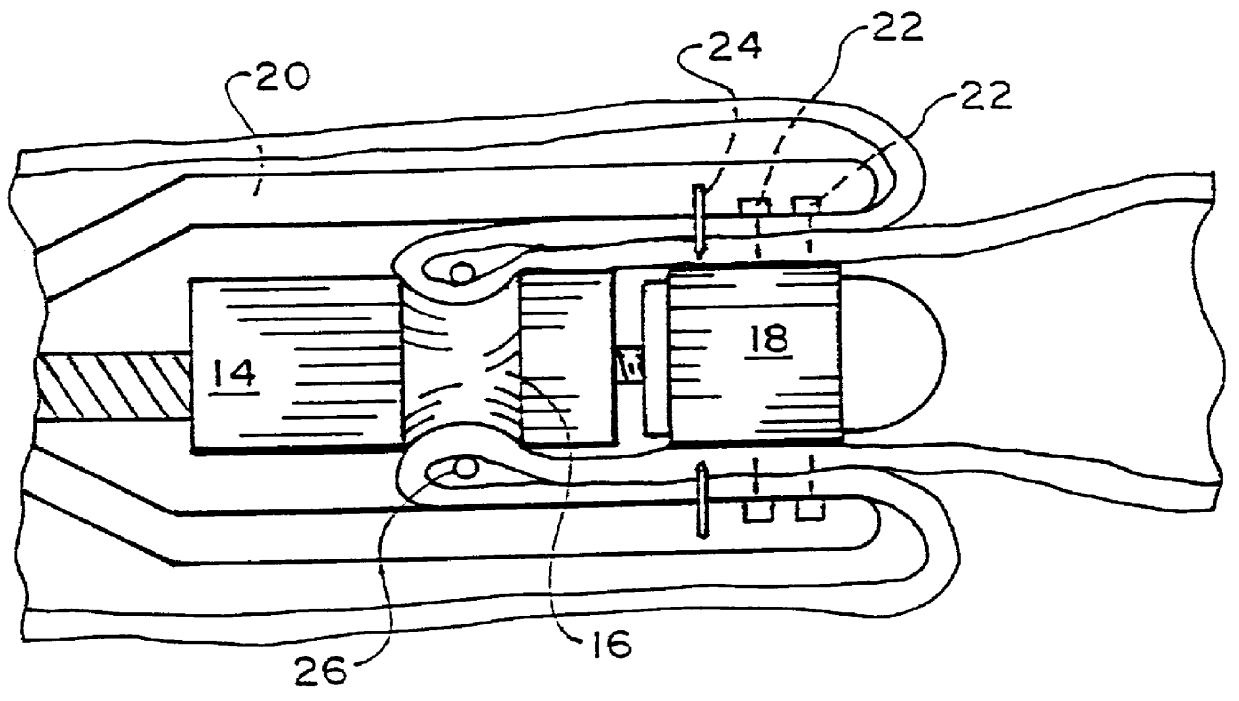
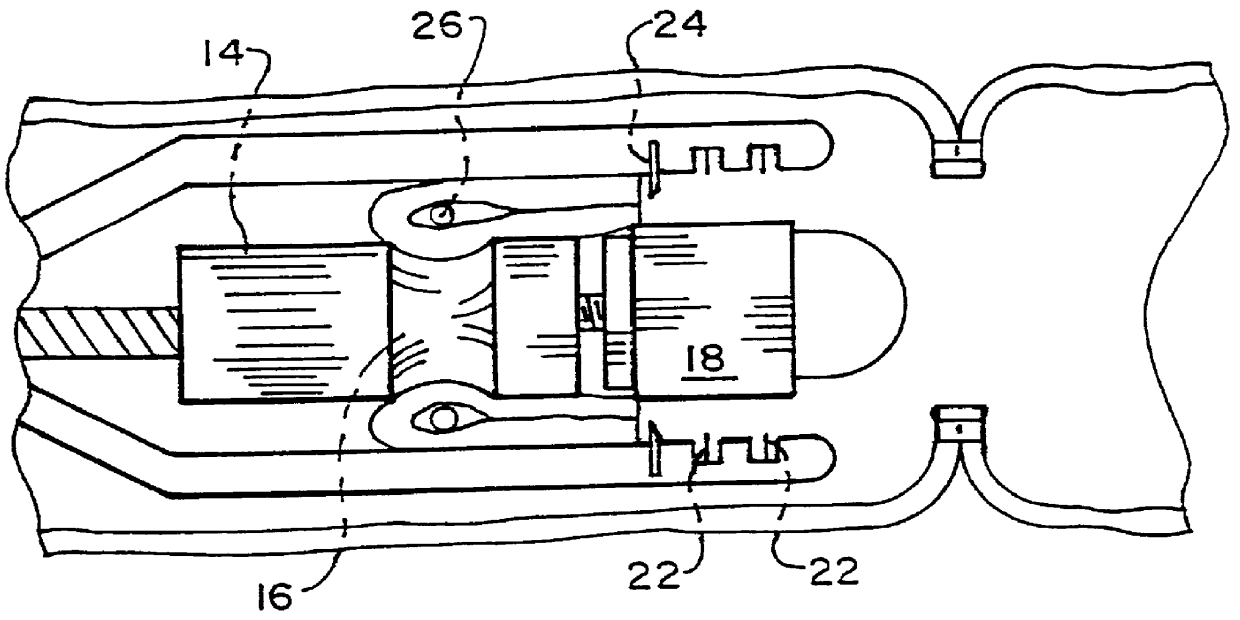
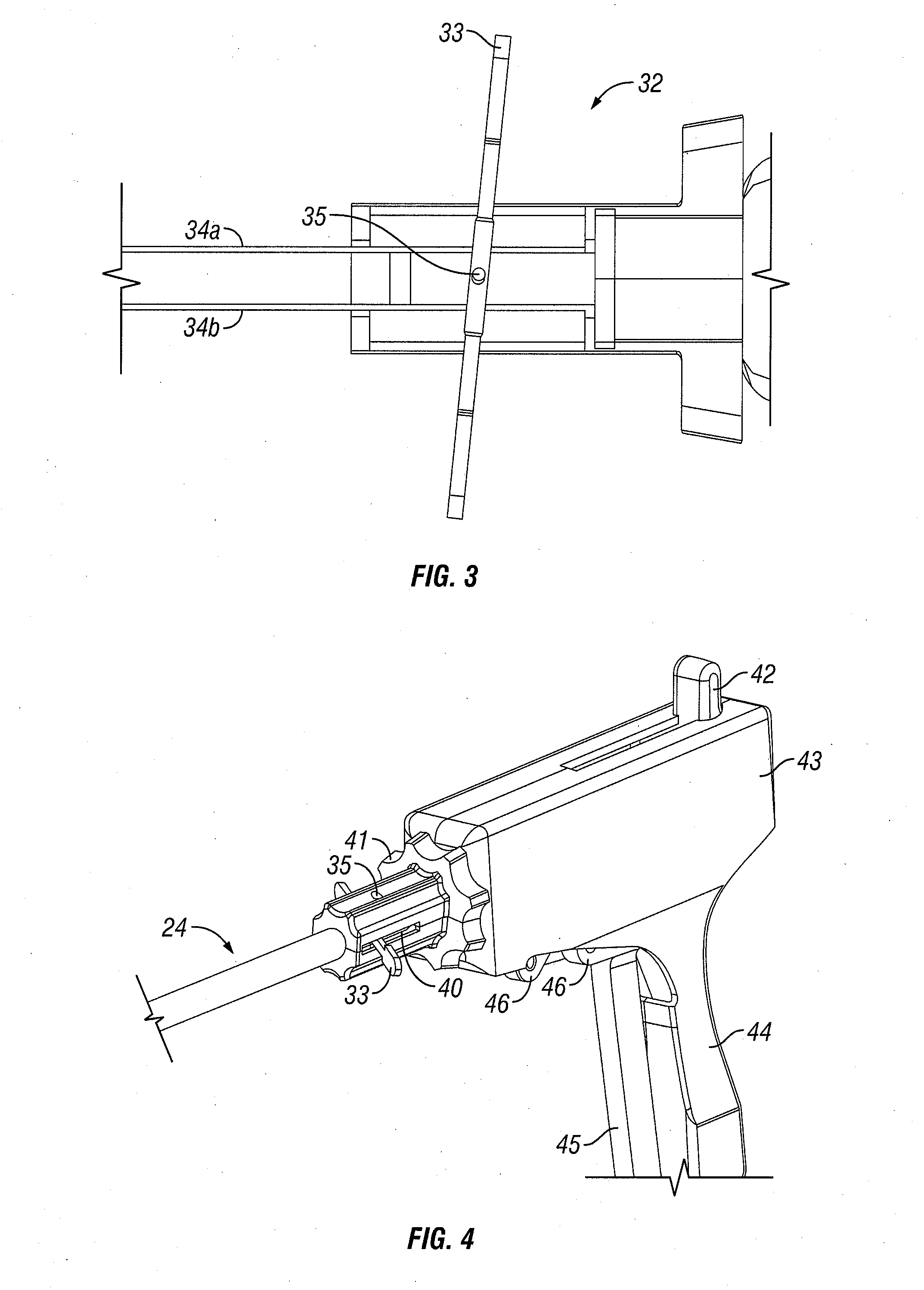
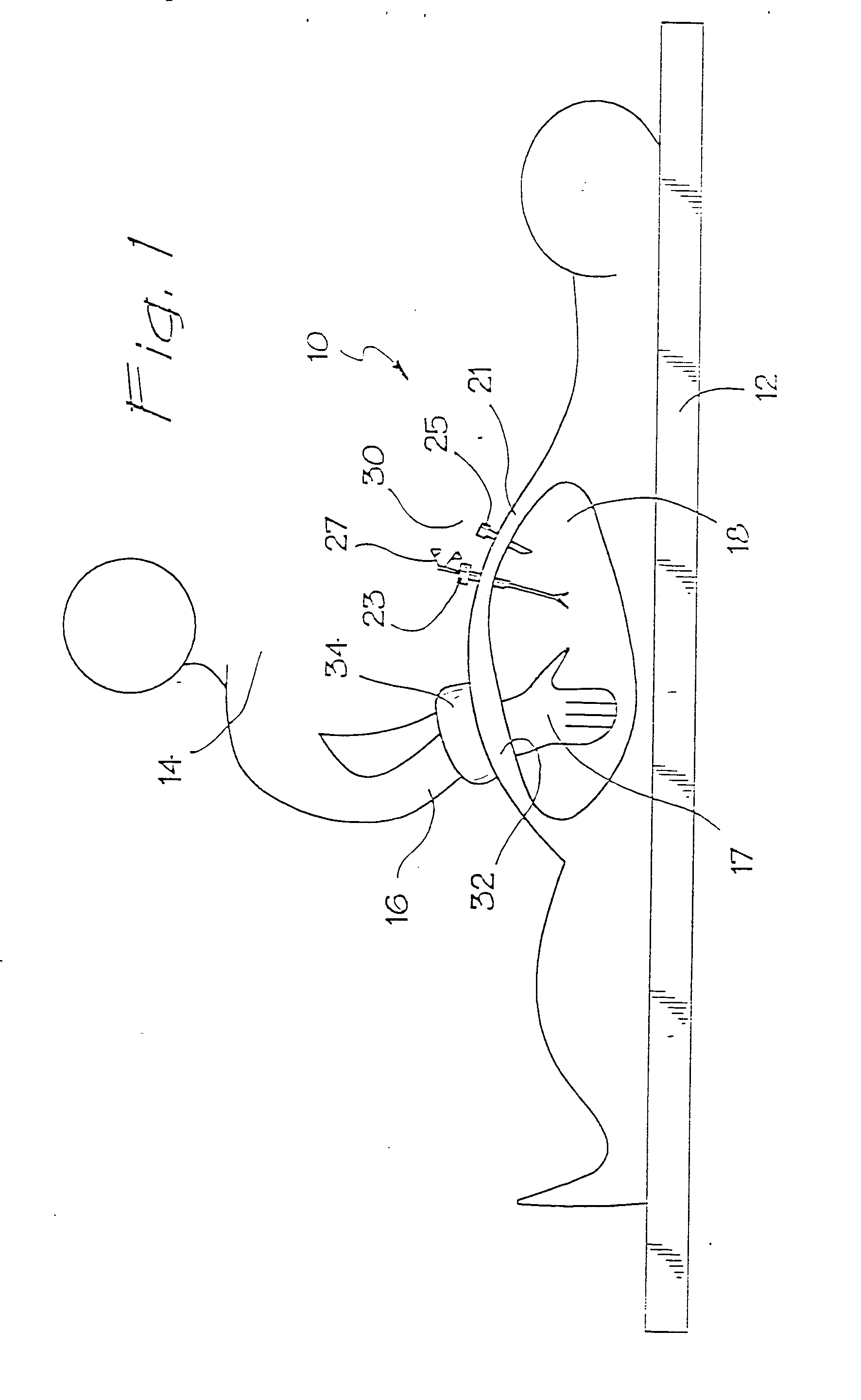
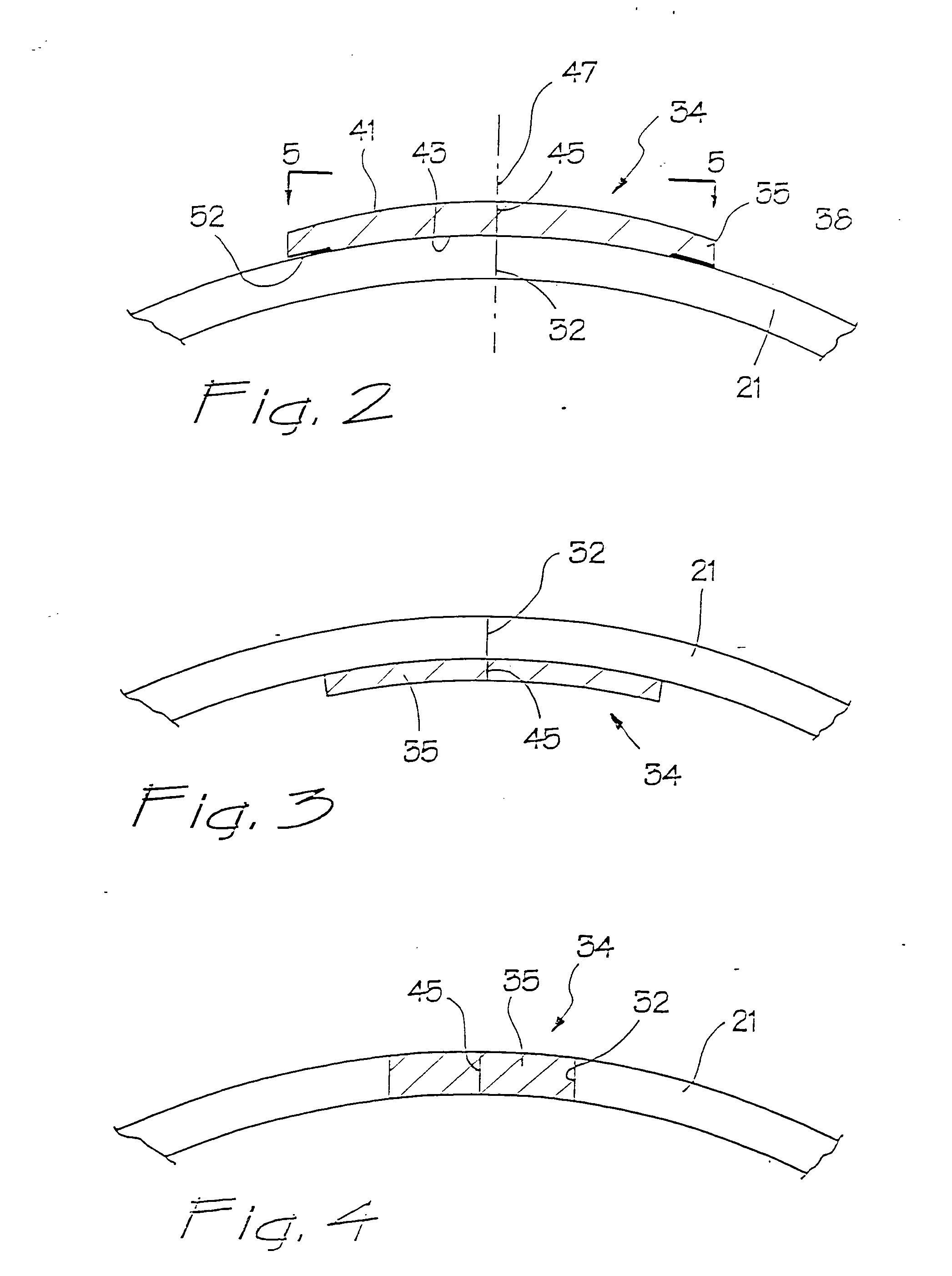
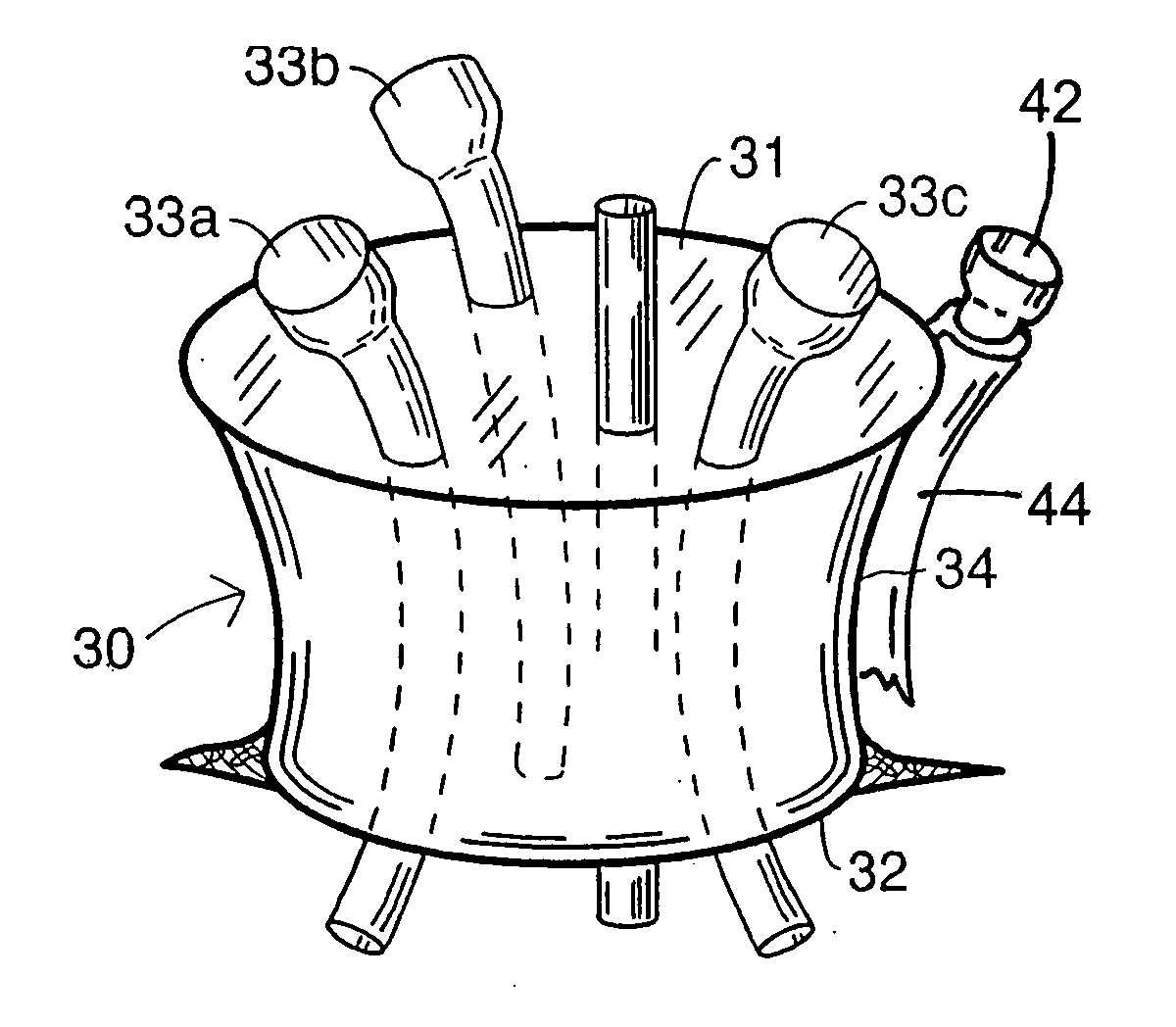
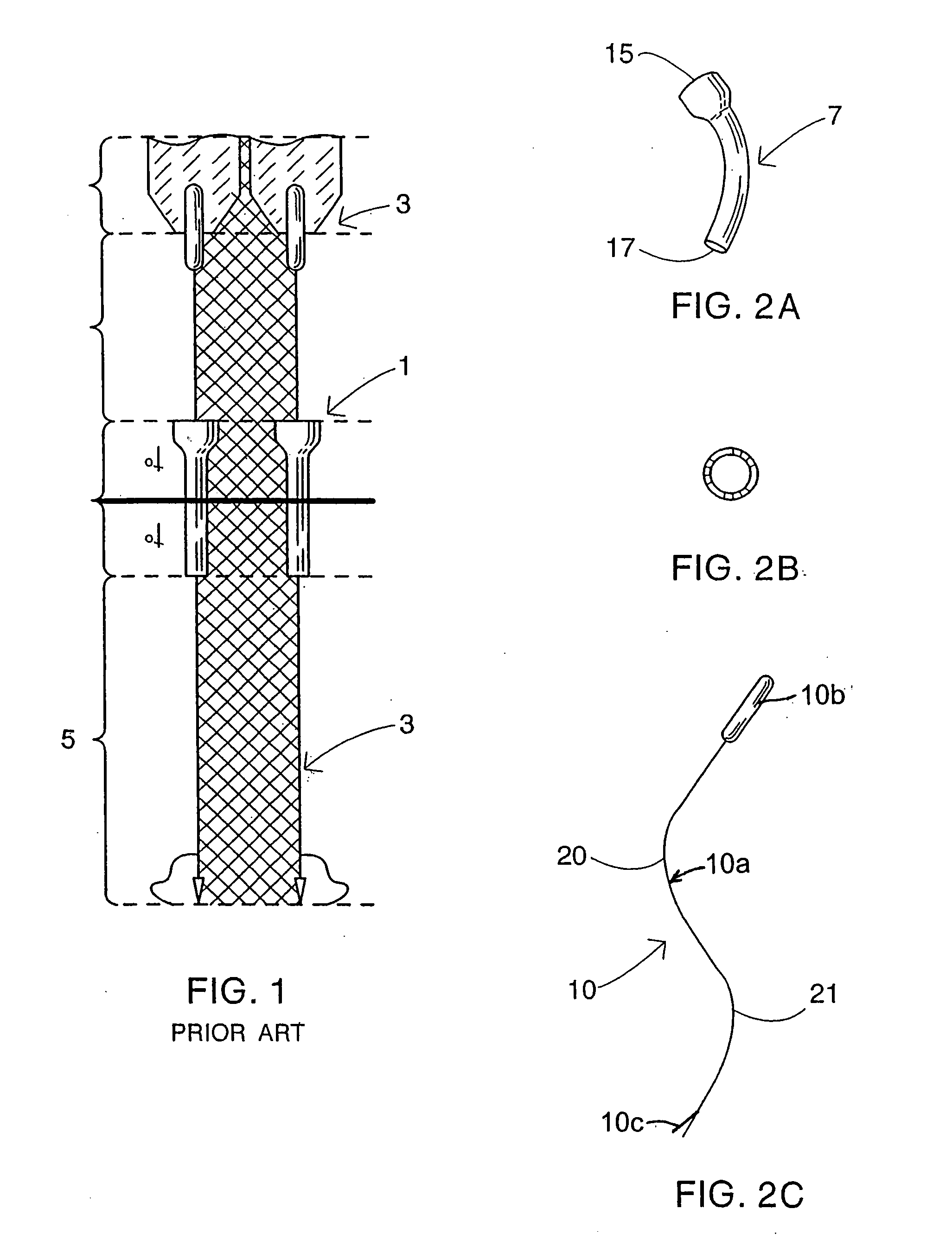
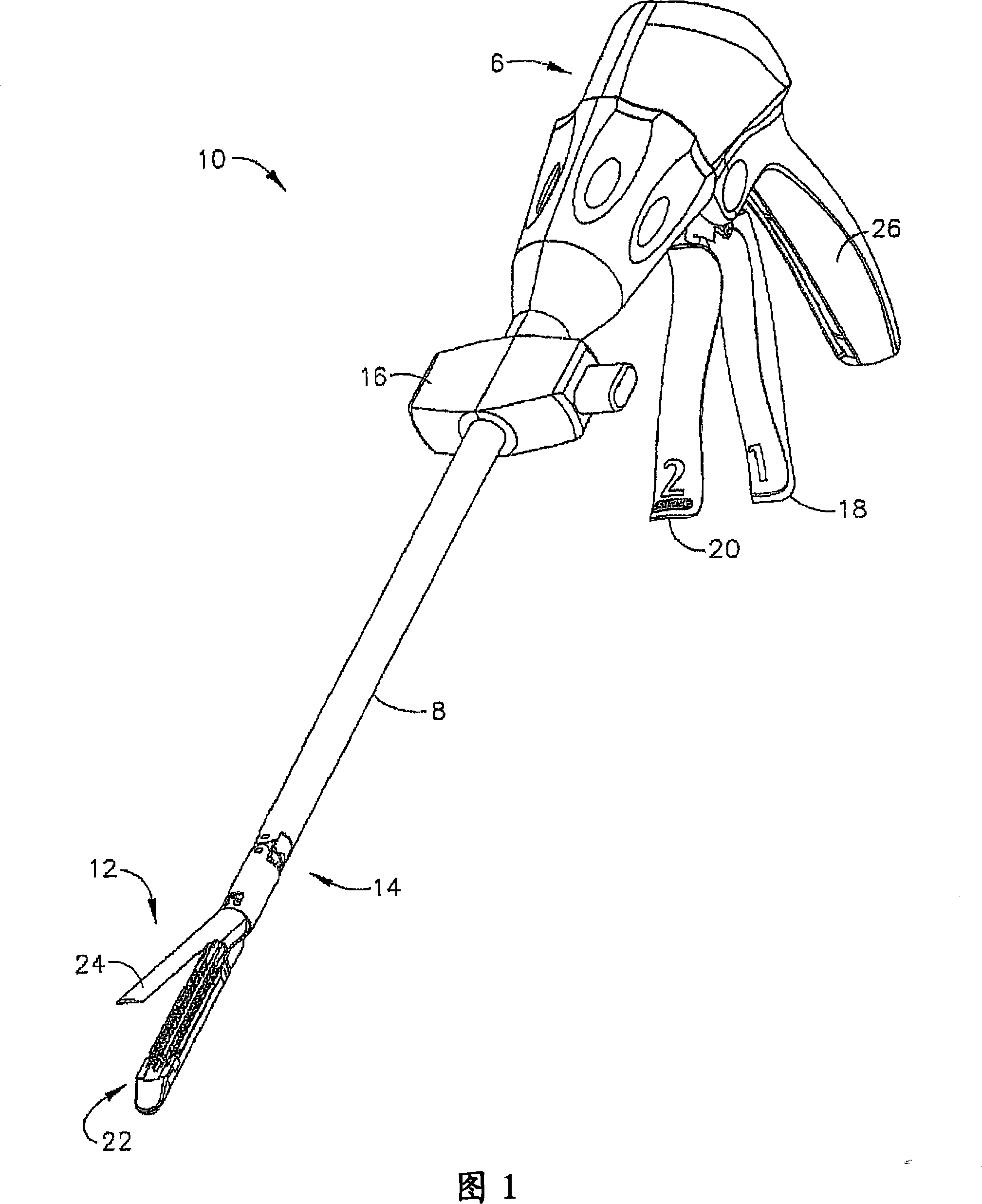
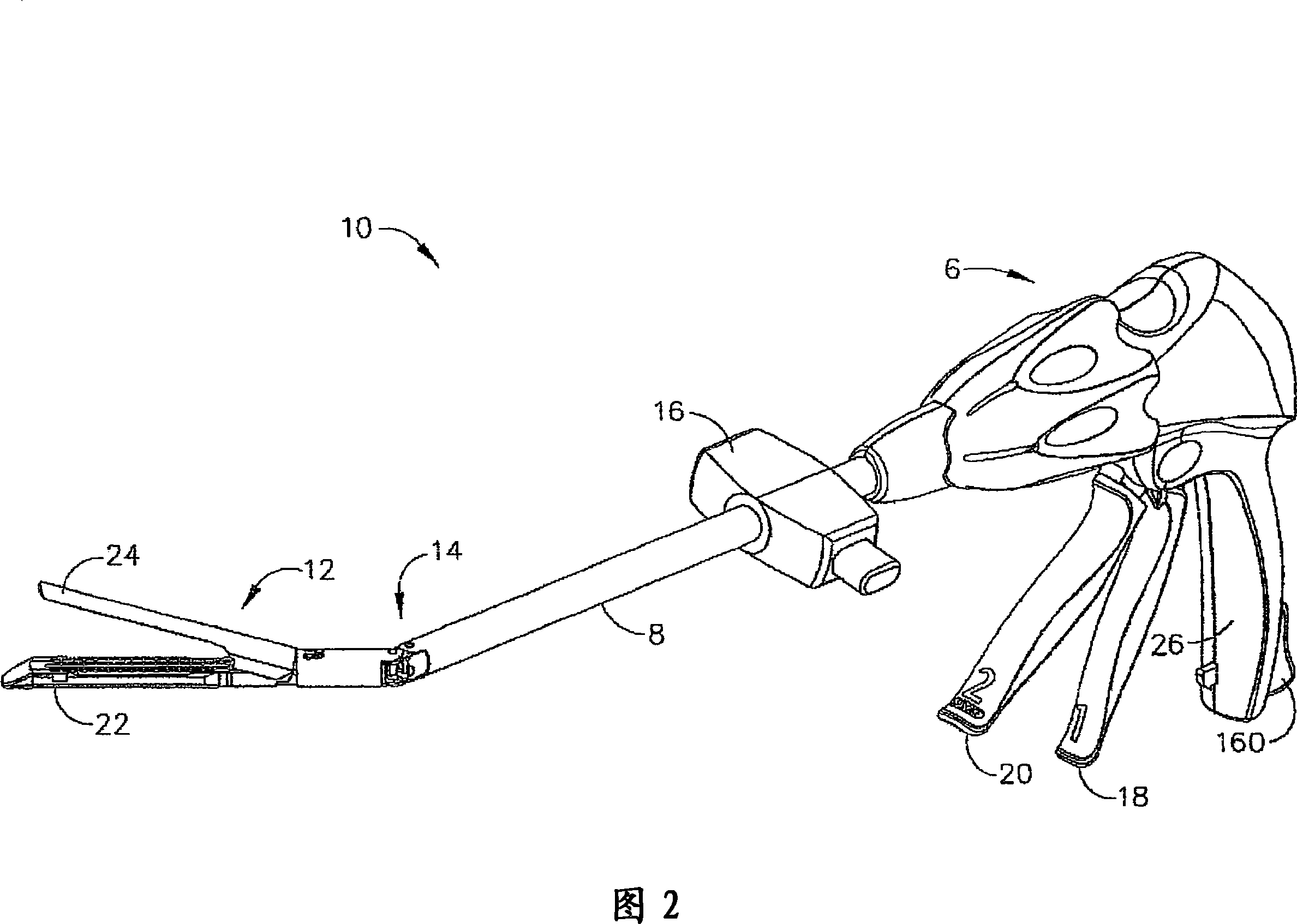
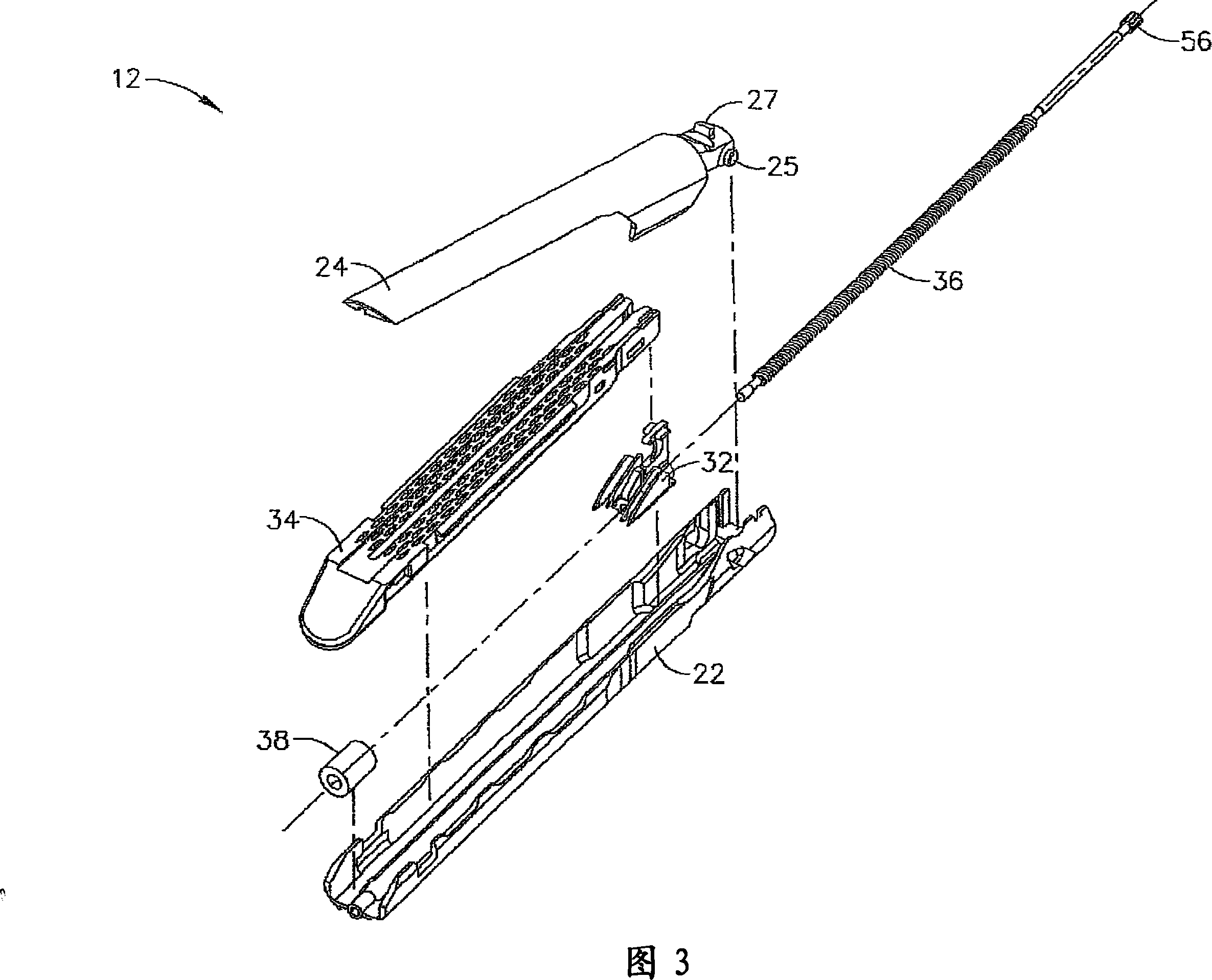
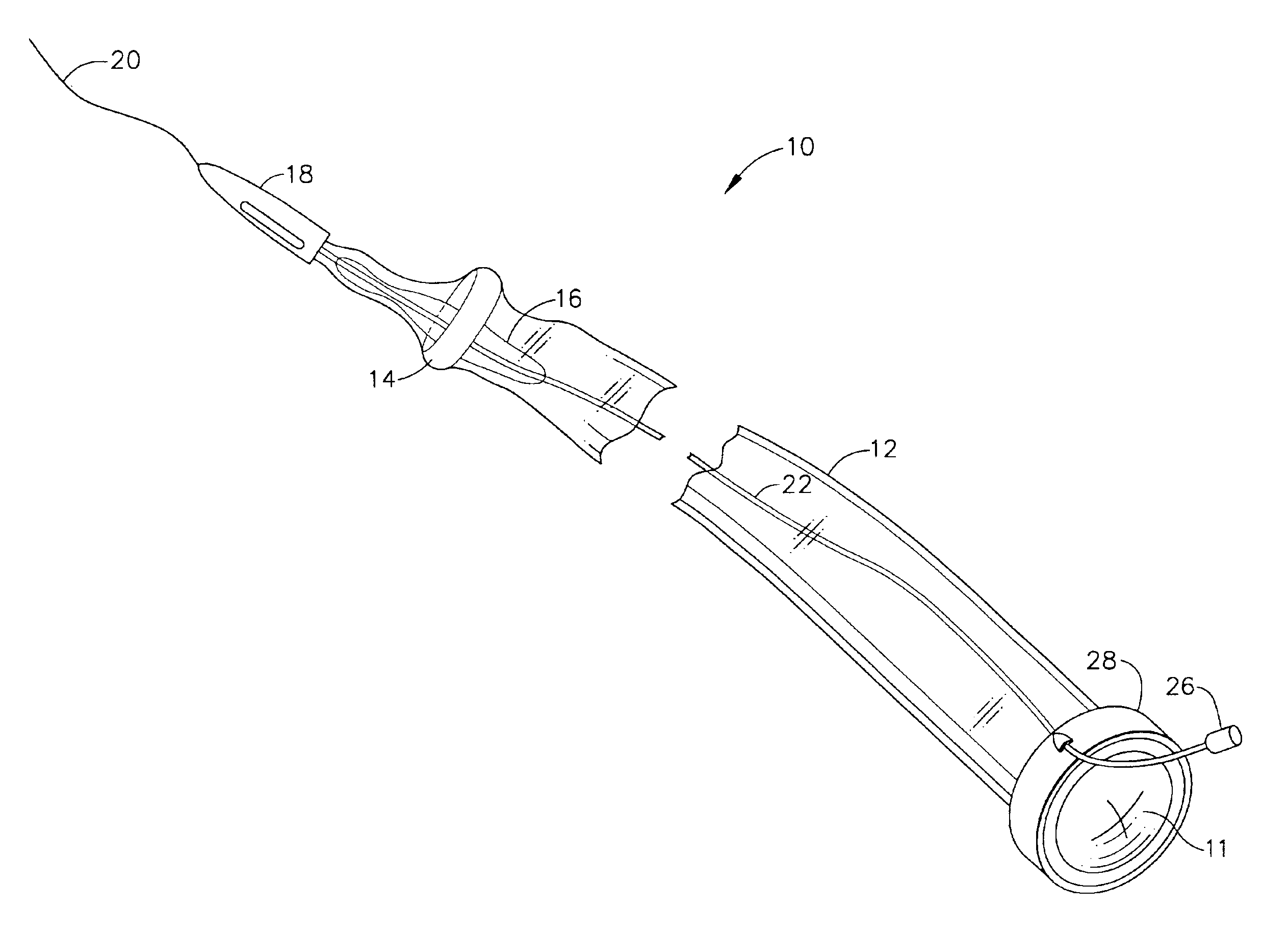
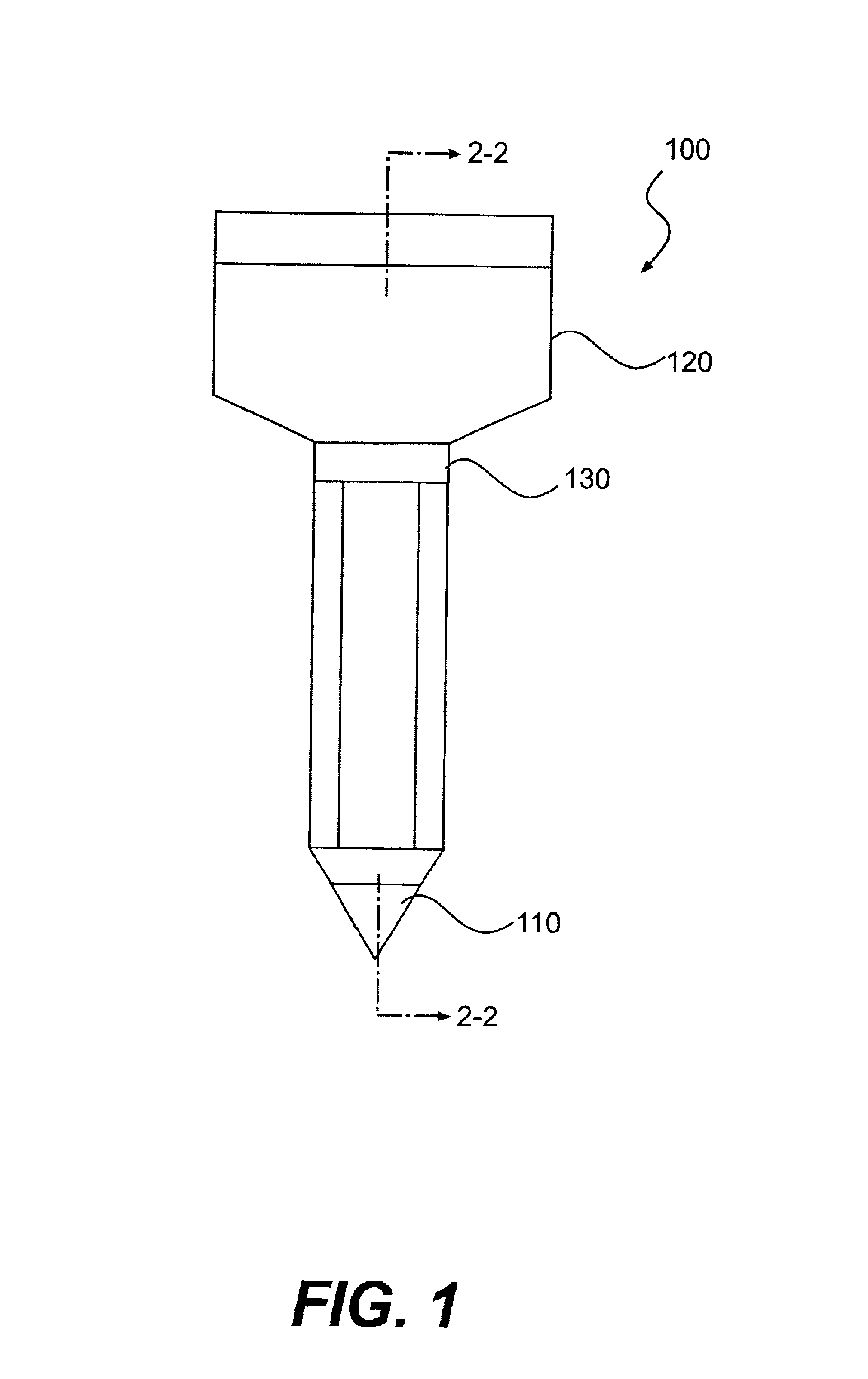
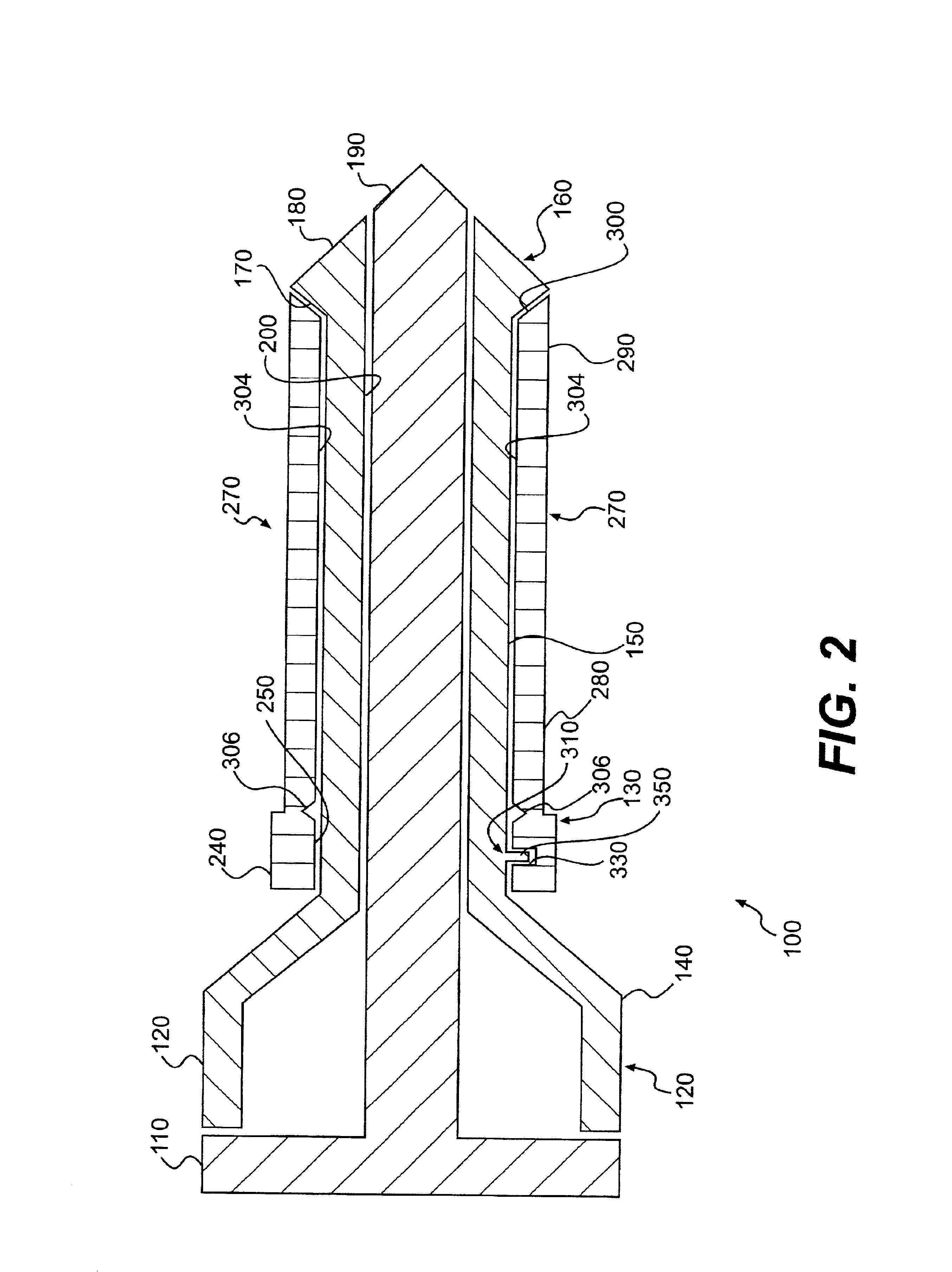
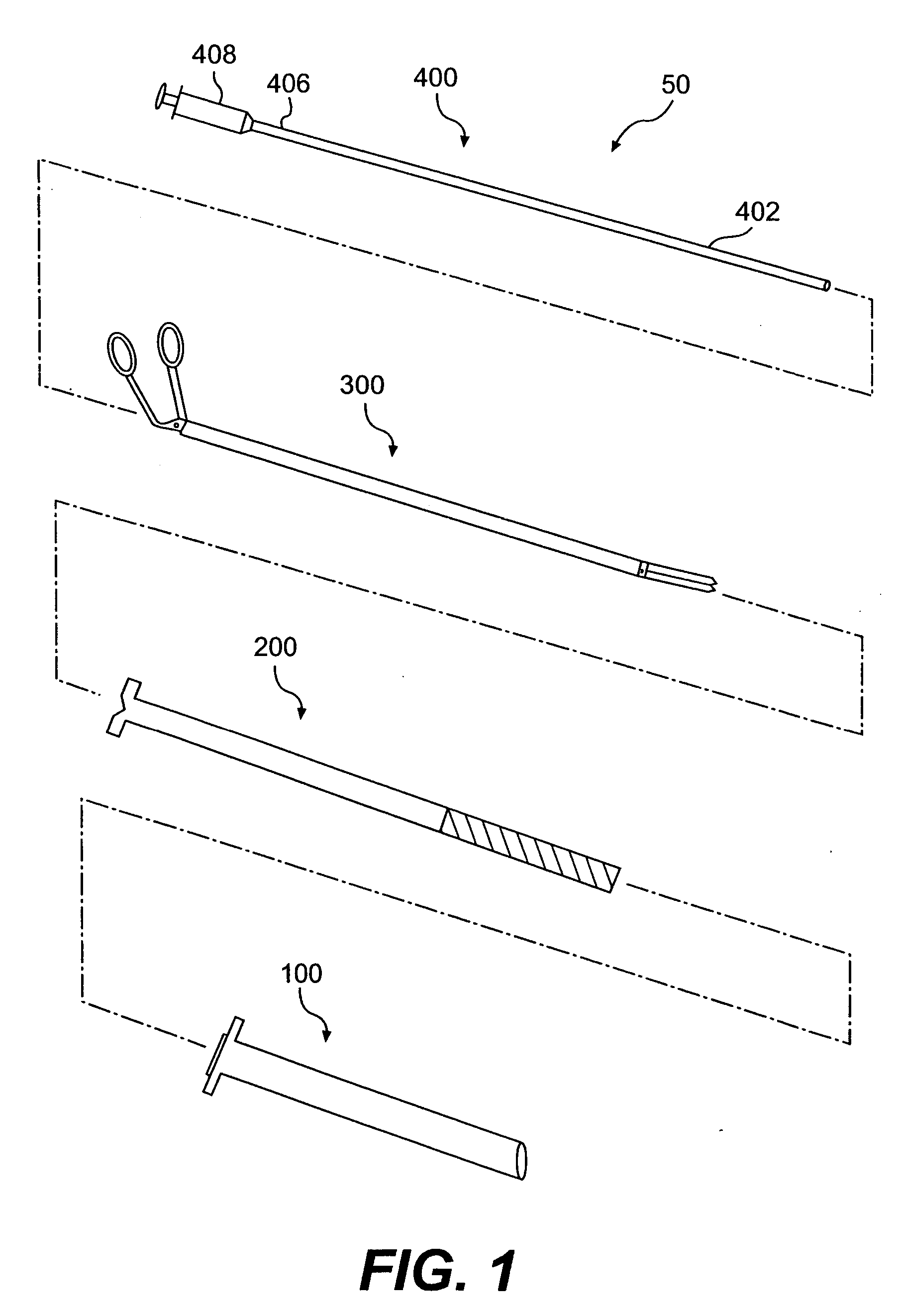
Intraluminal anastomotic device
InactiveUS6117148AEasy to disassembleSuture equipmentsStapling toolsThoracic structureAbdominal cavity
An intestinal intraluminal reconstruction and resection device includes a mechanism for intussusception of the bowel, a bowel anastomosis mechanism and a mechanism for severing the resected bowel. The surgical device allows the user to carry out intraluminally an anastomosis first, prior to resection of the intestine or any hollow viscus, therefore not exposing the dirty intraluminal content to the clean abdominal or thoracic cavities. The above is achieved by first intussuscepting the hollow viscus, then anastomosis and finally intraluminal resection.
Owner:RAVO BIAGIO +1
Insertable device and system for minimal access procedure
ActiveUS7066879B2Limited mobilityWide field of viewEndoscopesLaproscopesAbdominal cavityProcedure Indication
The present invention provides a system and single or multi-functional element device that can be inserted and temporarily placed or implanted into a structure having a lumen or hollow space, such as a subject's abdominal cavity to provide therewith access to the site of interest in connection with minimally invasive surgical procedures. The insertable device may be configured such that the functional elements have various degrees of freedom of movement with respect to orienting the functional elements or elements to provide access to the site from multiple and different orientations / perspectives as the procedure dictates, e.g., to provide multiple selectable views of the site, and may provide a stereoscopic view of the site of interest.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
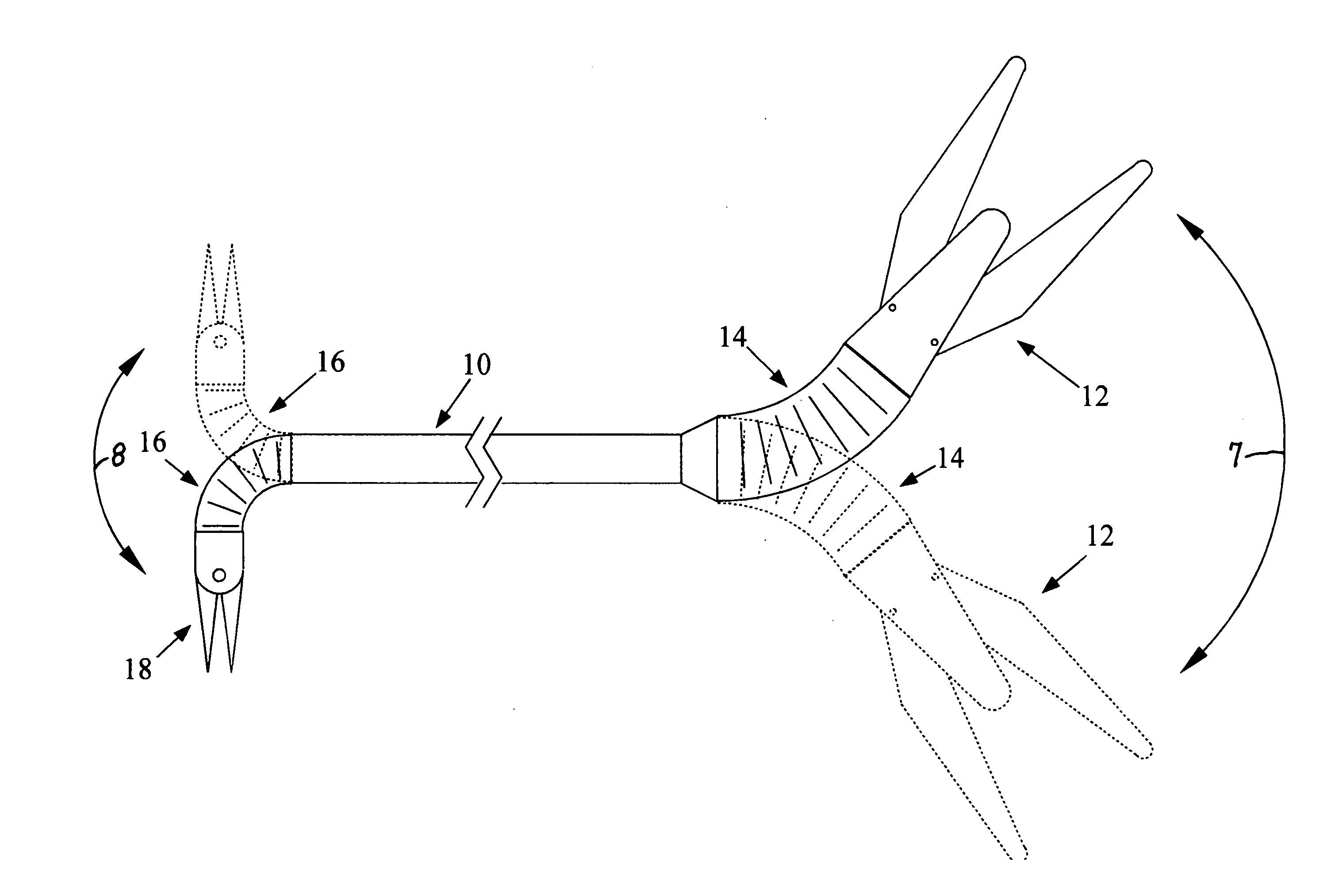
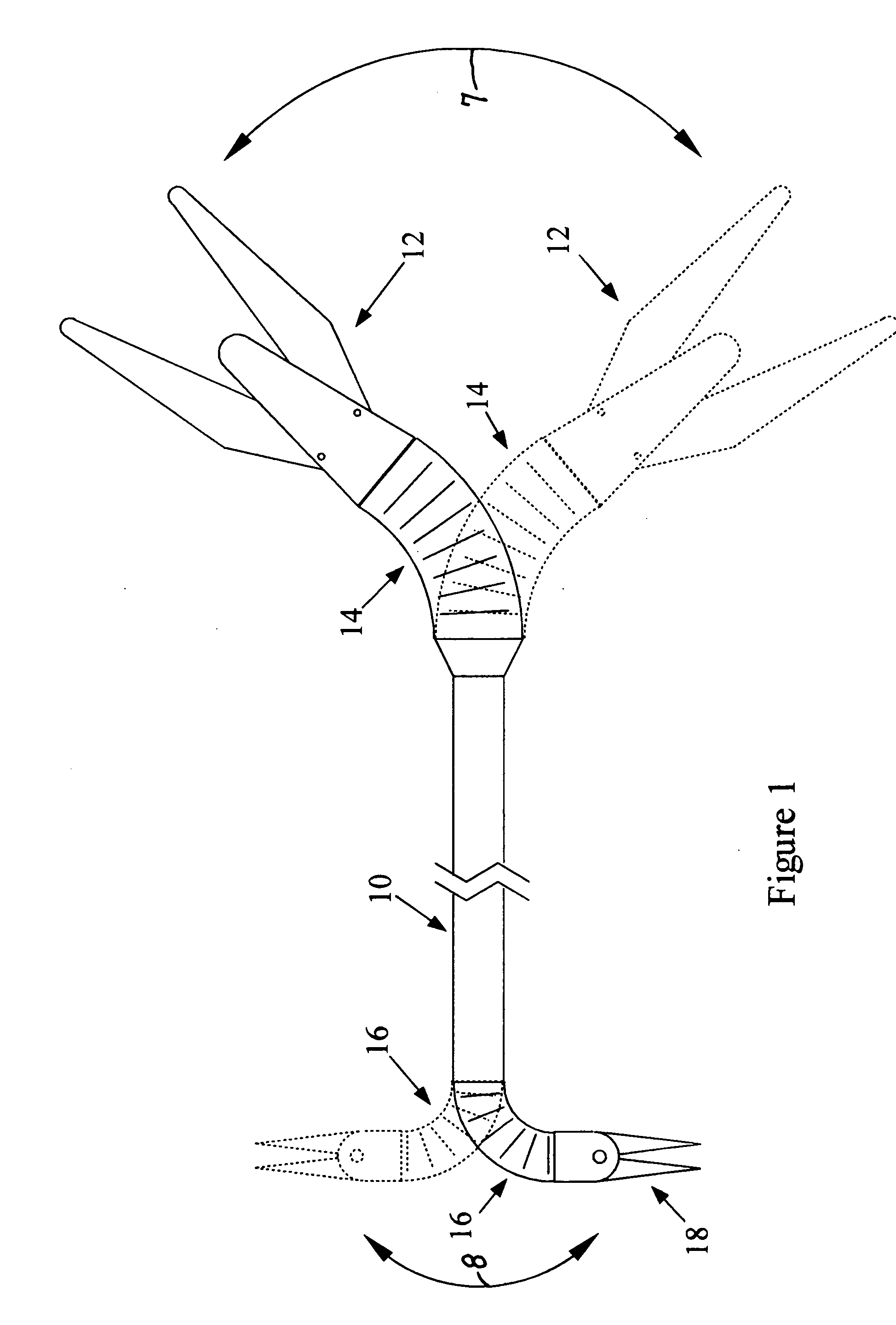
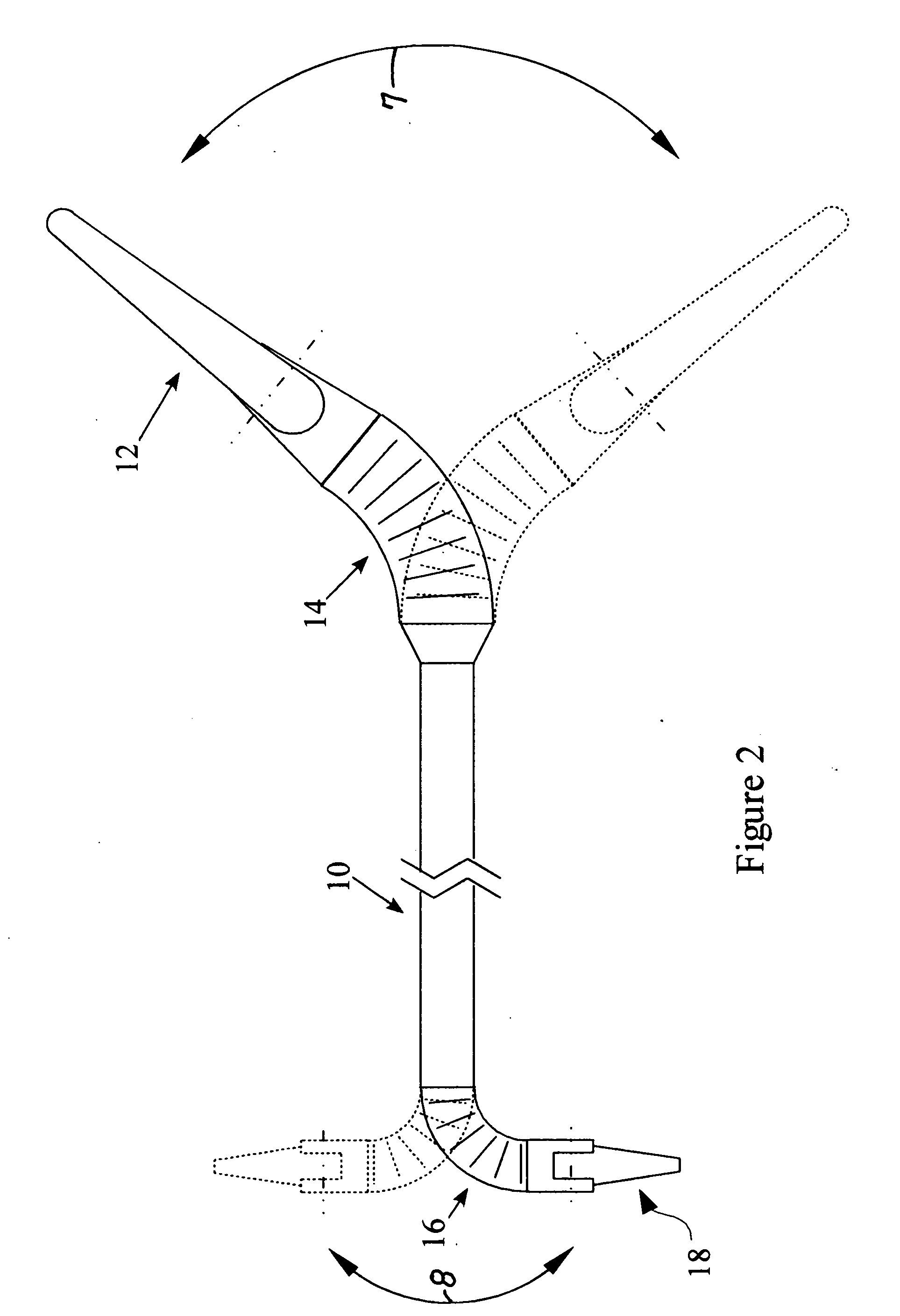
Method and apparatus for articulating the wrist of a laparoscopic grasping instrument
InactiveUS20090198272A1Avoid relative motionDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsAbdominal cavityLocking mechanism
A medical instrument has a set of opposing jaws that can be articulated, both left and right, from centerline. The instrument has a proper bend radius and support for the jaw actuation member and cutter driving member. The bendable support for the drive members comprises tightly wound coil springs. Another embodiment of the invention controls the degree of articulation at the handle of the laparoscopic instrument. A further embodiment of the invention incorporates a locking mechanism to prevent motion of the wrist while the user performs other operations on the device. The locking mechanism also includes an indexing feature with which the user can index and choose the necessary amount of angle between preset angles.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
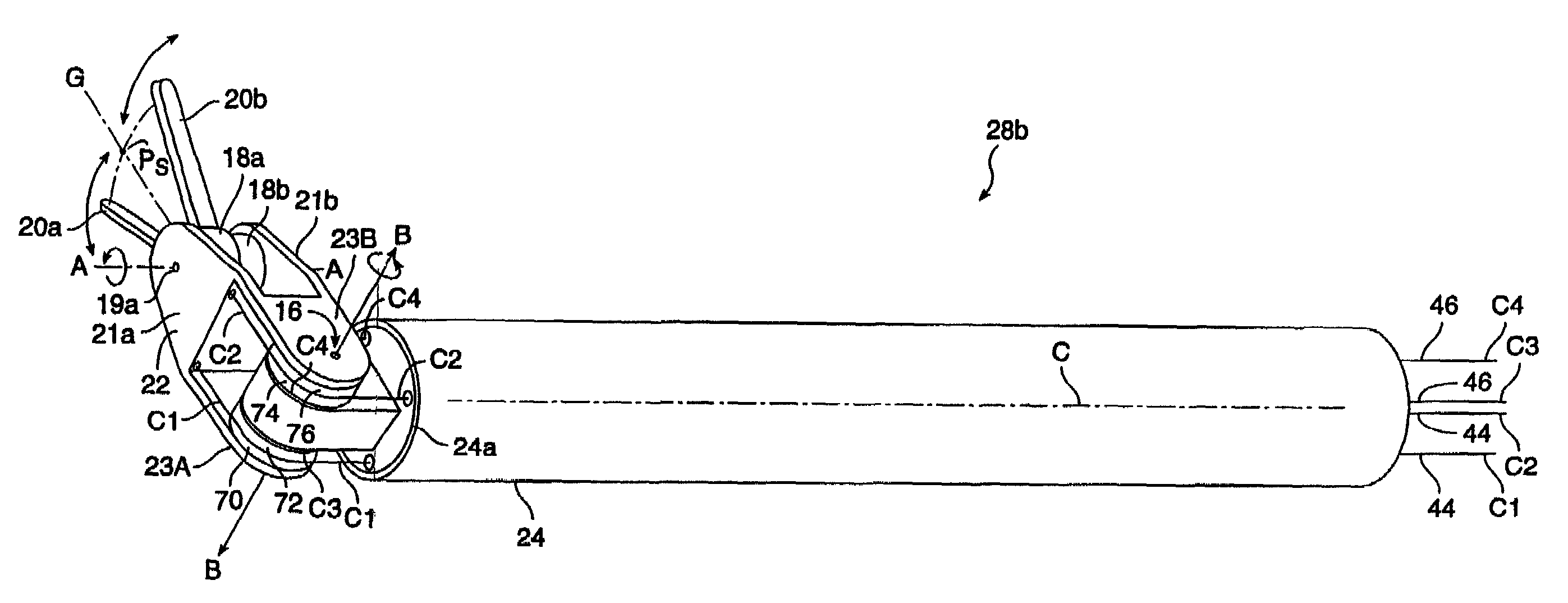
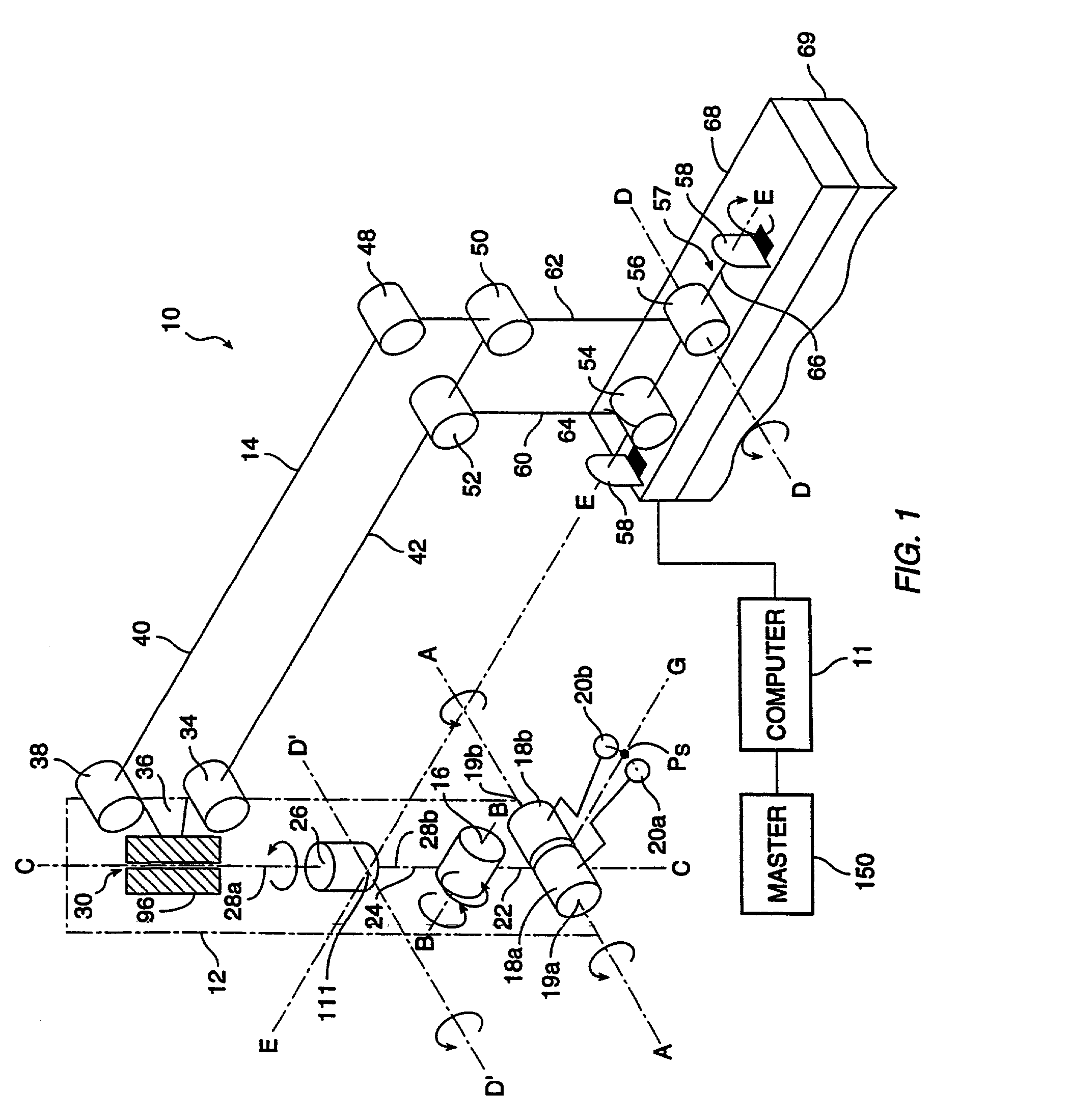
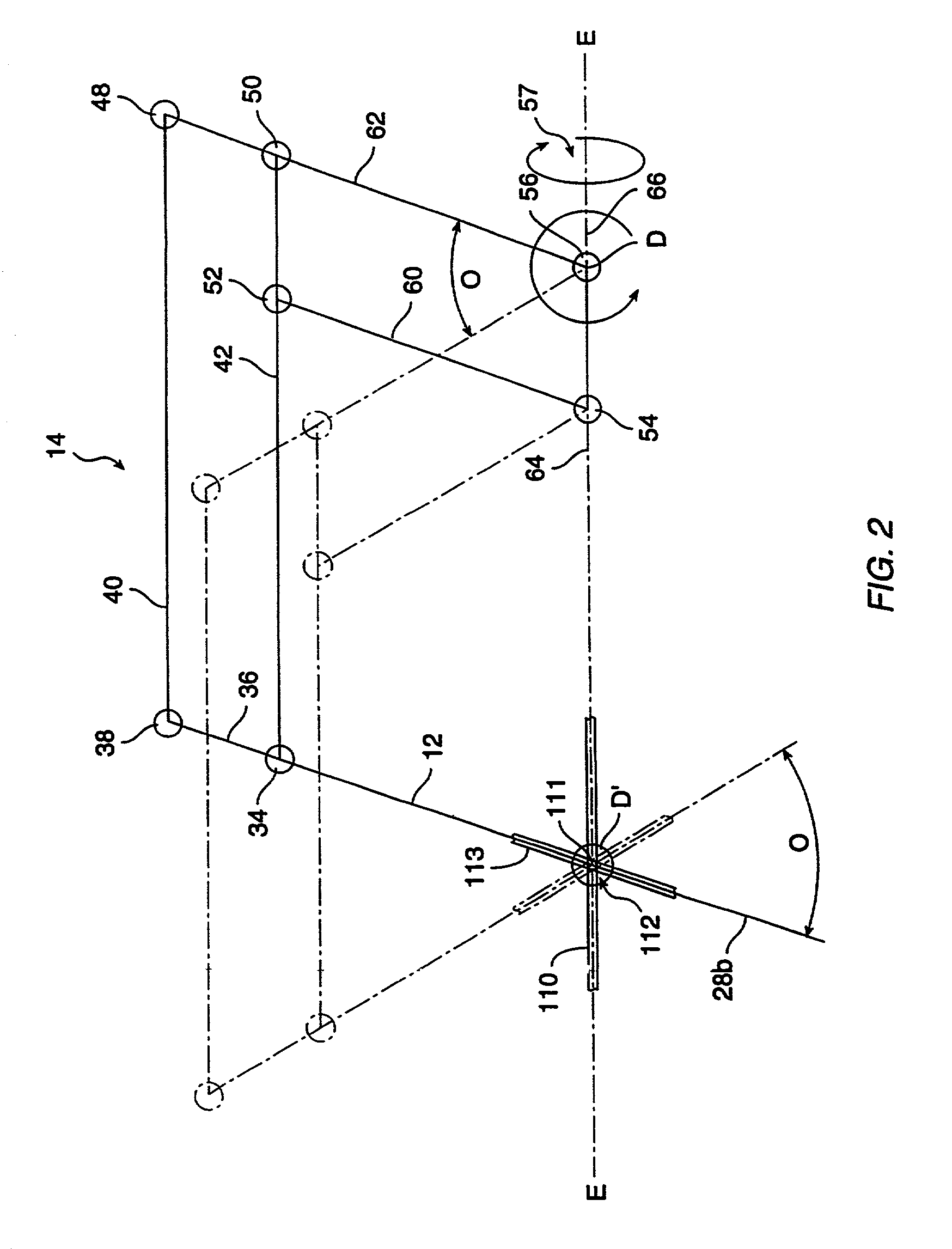
Articulated surgical instrument for performing minimally invasive surgery with enhanced dexterity and sensitivity
InactiveUS6991627B2Increase flexibilityInvasive surgical procedureProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusEngineeringActuator
An articulated surgical instrument for enhancing the performance of minimally invasive surgical procedures. The instrument has a high degree of dexterity, low friction, low inertia and good force reflection. A unique cable and pulley drive system operates to reduce friction and enhance force reflection. A unique wrist mechanism operates to enhance surgical dexterity compared to standard laparoscopic instruments. The system is optimized to reduce the number of actuators required and thus produce a fully functional articulated surgical instrument of minimum size.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Surgical instrument
An endoscopic or laparoscopic instrument includes a distal tool, a rigid or flexible elongated shaft that supports the distal tool, and a proximal handle or control member, where the tool and the handle are coupled to the respective distal and proximal ends of the elongated shaft via bendable motion members. The tool and the tool motion member are coupled to the handle and the handle motion member via cables and a push rod in such a way that the movement of the handle with respect to the elongated shaft in any direction is replicated by the tool at the distal end of the shaft. The magnitude of the tool motion with respect to the handle motion may be scaled depending on the size of the handle motion member with respect to that of the tool motion member.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENDOSCOPIC DEVICES
Surgical access apparatus and method
A surgical access device includes a single valve that forms a seal with the body wall and provides an access charnel into a body cavity. The valve has properties for creating a zero seal in the absence of an instrument as well as an instrument seal with instruments having a full range of instrument diameter. The valve can include a gel and preferably an ultragel comprised of an elastomer and an oil providing elongation greater than 1000 percent and durometer less than 5 Shore A. The shore valve can be used as a hand port where the instrument comprises the arm of a surgeon, thereby providing hand access into the cavity. A method for making the surgical access device includes the combining or a gelling agent with an oil, preferably in a molding process. A method for using the device includes steps for creating an opening with the instrument. In a particular process, an organ can be removed from the body cavity through the single valve to create an organ seal while the organ is addressed externally of the body cavity. The valve and method are particularly adapted for laparoscopic surgery wherein the abdominal cavity is insufflated with a gas thereby requiring the zero seal, the instrument seal, and the organ seal in various procedures.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Laparoscopic instruments and trocar systems and related surgical method
InactiveUS20080027476A1Increase workspaceEasy to take backSuture equipmentsCannulasAbdominal cavityPERITONEOSCOPE
Laparoscopic instruments and trocars are provided for performing laparoscopic procedures entirely through the umbilicus. A generally C-shaped trocar provides increased work space between the hands of the surgeon as well as S-shaped laparoscopic instruments placed through the trocar when laparoscopic instrument-trocar units are placed through the umbilicus. In order to facilitate retraction of intra-abdominal structures during a laparoscopic procedure, an angulated needle and thread with either one-or two sharp ends is provided. Alternatively, an inflatable unit having at least one generally C-shaped trocar incorporated within the unit's walls can be placed through the umbilicus following a single incision. Generally S-shaped laparoscopic instruments may be placed through the generally C-shaped trocars to facilitate access to intra-abdominal structures.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Medical treatment method and apparatus
A medical treatment method comprises orally inserting a first endoscope having a first treatment tool provided thereto into a body cavity, inserting a first insertion member insertion support tool from at least one of abdominal and transdermal cavities into the body cavity, inserting a second endoscope having a second treatment tool provided thereto into the body cavity through the first insertion member insertion support tool, grasping a lesioned part by the second treatment tool inserted into the body cavity by the second endoscope, cutting the lesioned part by the first treatment tool inserted into the body cavity by the first endoscope, and collecting the lesioned part.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Surgical instrument with wireless communication between control unit and remote sensor
Discloses a surgical instrument capable of wireless communication between the control unit and the remote sensor, such as an endoscopic or laparoscopic instrument. Surgical instruments may include an end actuator having at least one sensor. The surgical instrument further comprises a conductive shaft, the distal end of which is connected to the end actuator, the sensor is electrically insulated from the shaft. The surgical instrument may further comprise a handle, which is connected to the proximal end of the axis. The handle comprises a control unit, the control unit is electrically connected to the shaft, so that the axis can act as an antenna to transmit a signal from the control unit to the sensor and receive the transmitted signal from the sensor. Other components electrically connected to the shaft can also send signals.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Method for electrosurgical tissue treatment near a patient's heart
InactiveUS7217268B2Control depthControl damageEnemata/irrigatorsHeart valvesElectricityHigh frequency power
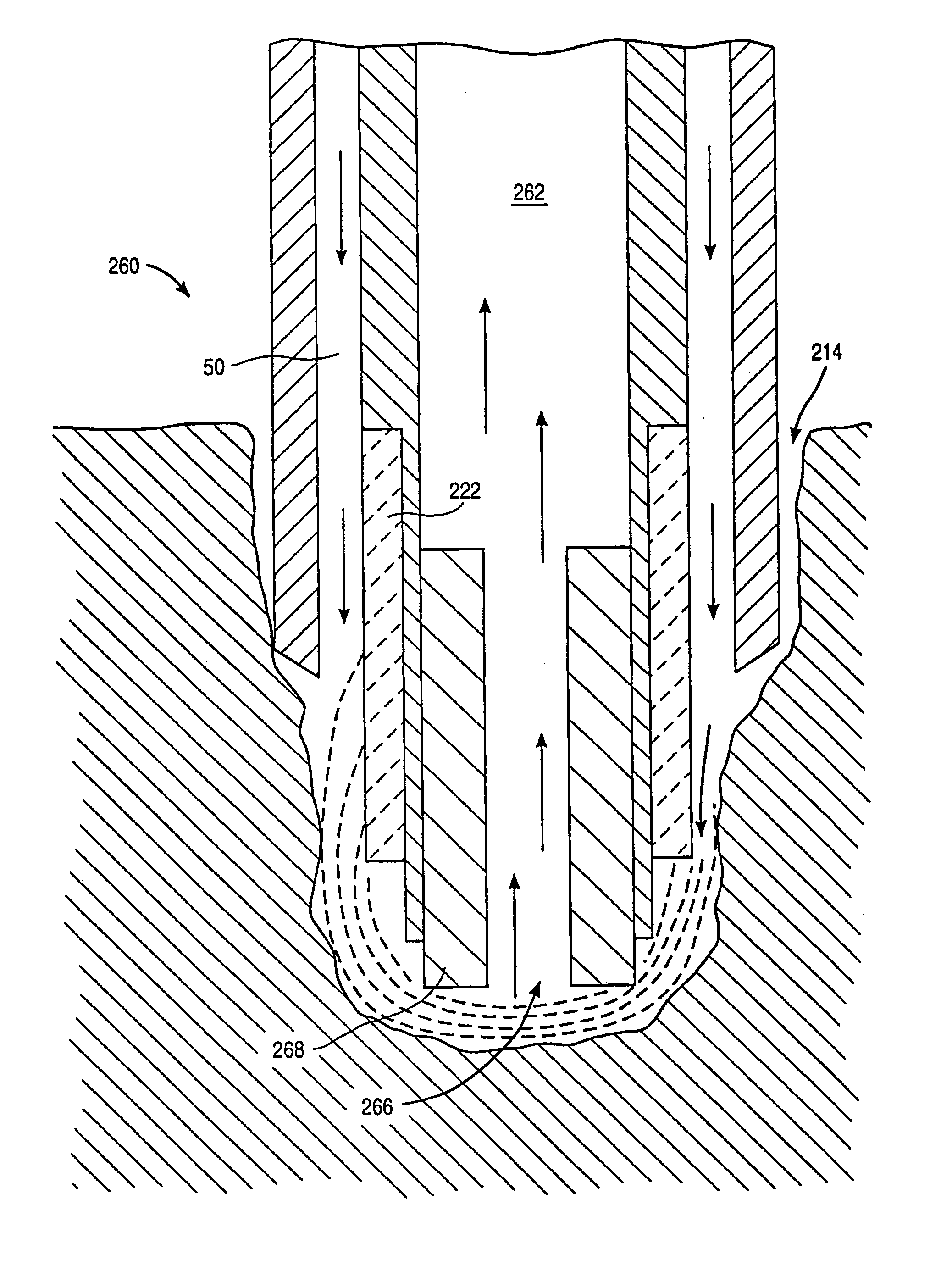
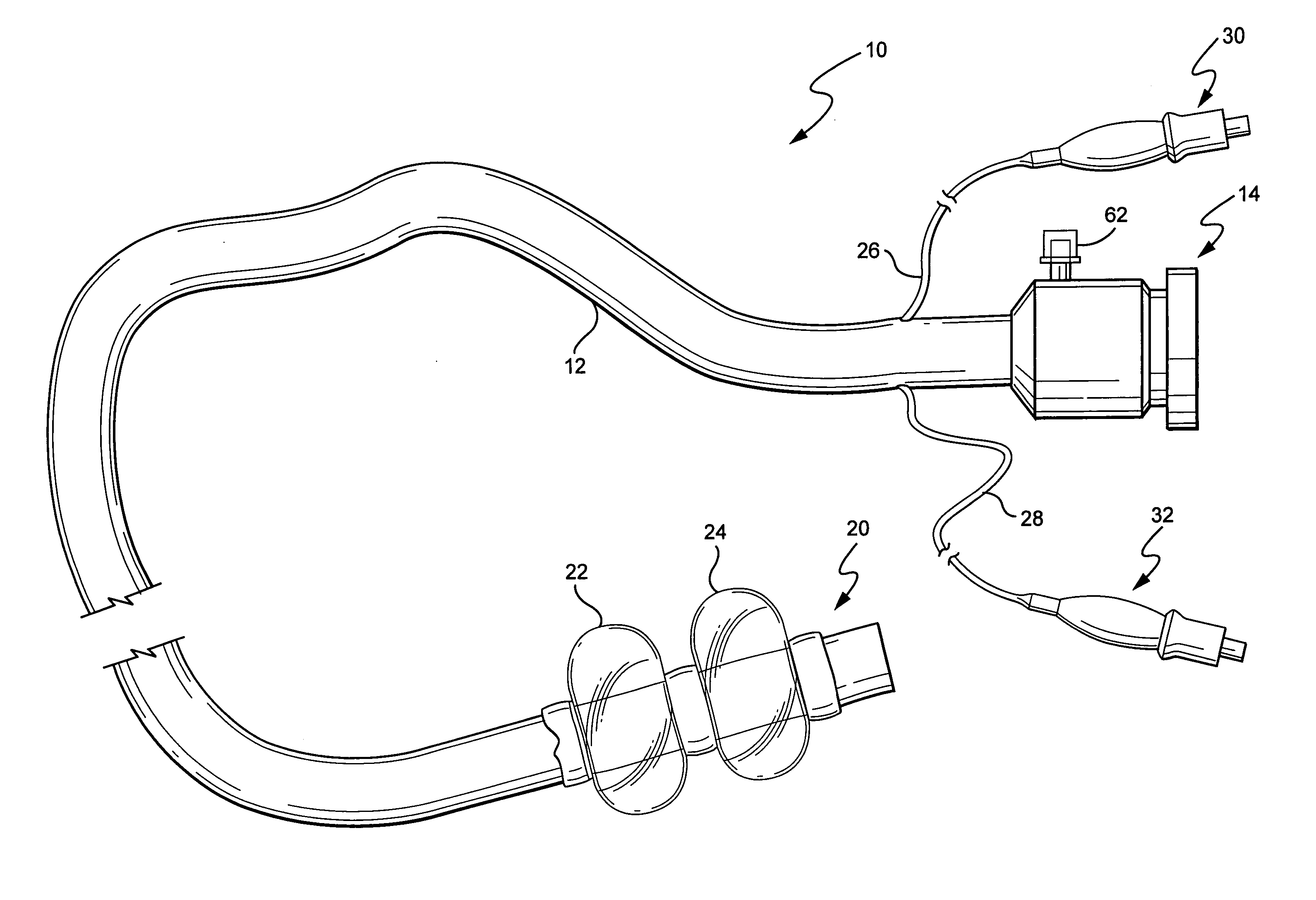
An electrosurgical probe (10) comprises a shaft (13) having an electrode array (58) at its distal end and a connector (19) at its proximal end for coupling the electrode array to a high frequency power supply (28). The shaft includes a return electrode (56) recessed from its distal end and enclosed within an insulating jacket (18). The return electrode defines an inner passage (83) electrically connected to both the return electrode and the electrode array for passage of an electrically conducting liquid (50). By applying high frequency voltage to the electrode array and the return electrode, the electrically conducting liquid generates a current flow path between the return electrode and the electrode array so that target tissue may be cut or ablated. The probe is particularly useful in dry environments, such as the mouth or abdominal cavity, because the electrically conducting liquid provides the necessary return current path between the active and return electrodes.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Filter cartridge with internal gaseous seal for multimodal surgical gas delivery system having a smoke evacuation mode
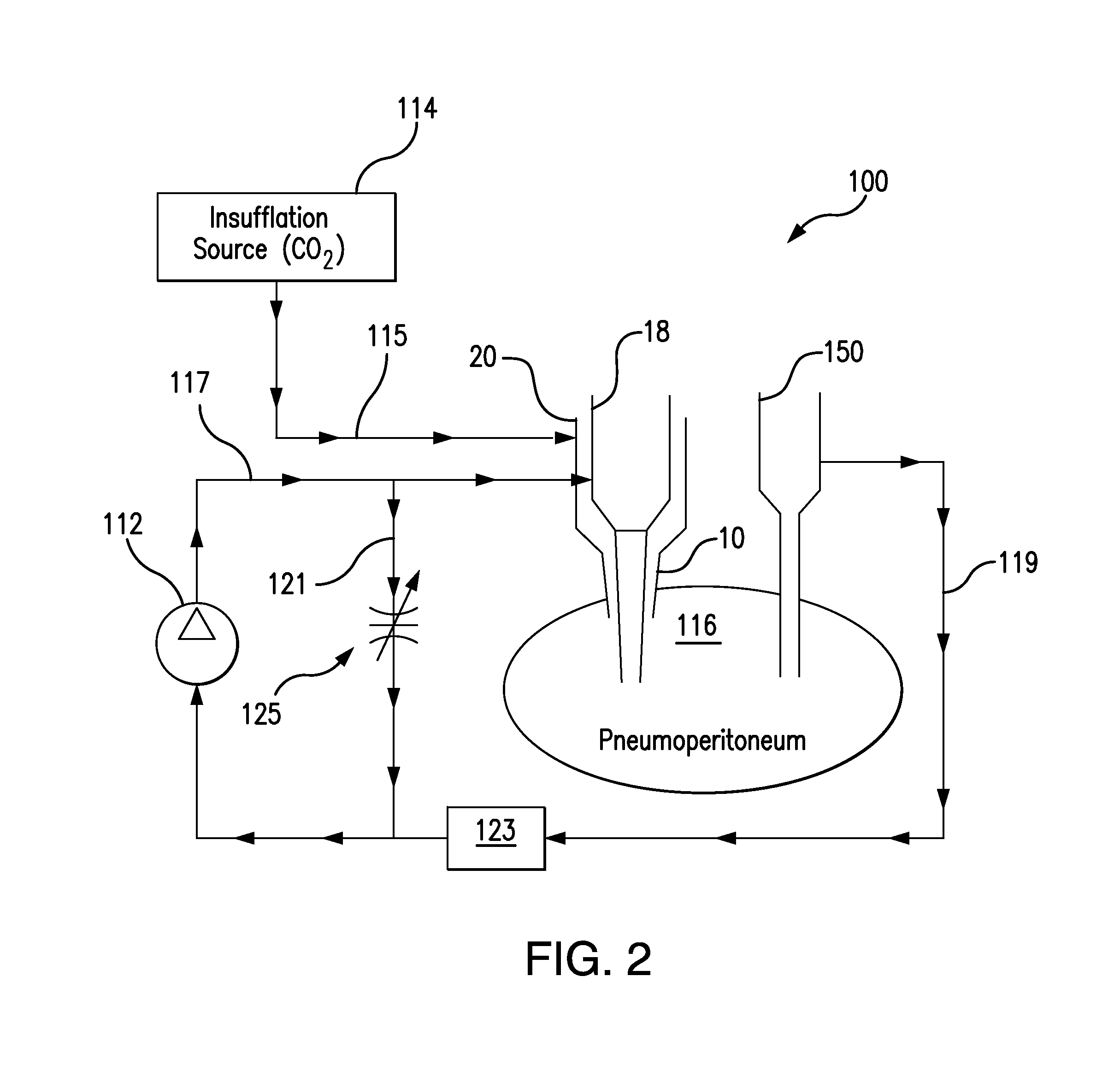
A system is disclosed for delivering gas during a laparoscopic surgical procedure performed within a patient's abdominal cavity requiring smoke evacuation which includes a gas delivery device having a housing with a port for receiving pressurized insufflating gas from a gas source, a pump assembly for circulating gas throughout the system, and a disposable gas conditioning unit or filter cartridge configured for operative association with the gas delivery device.
Owner:SURGIQUEST
Surgical access apparatus and method
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Guide tube
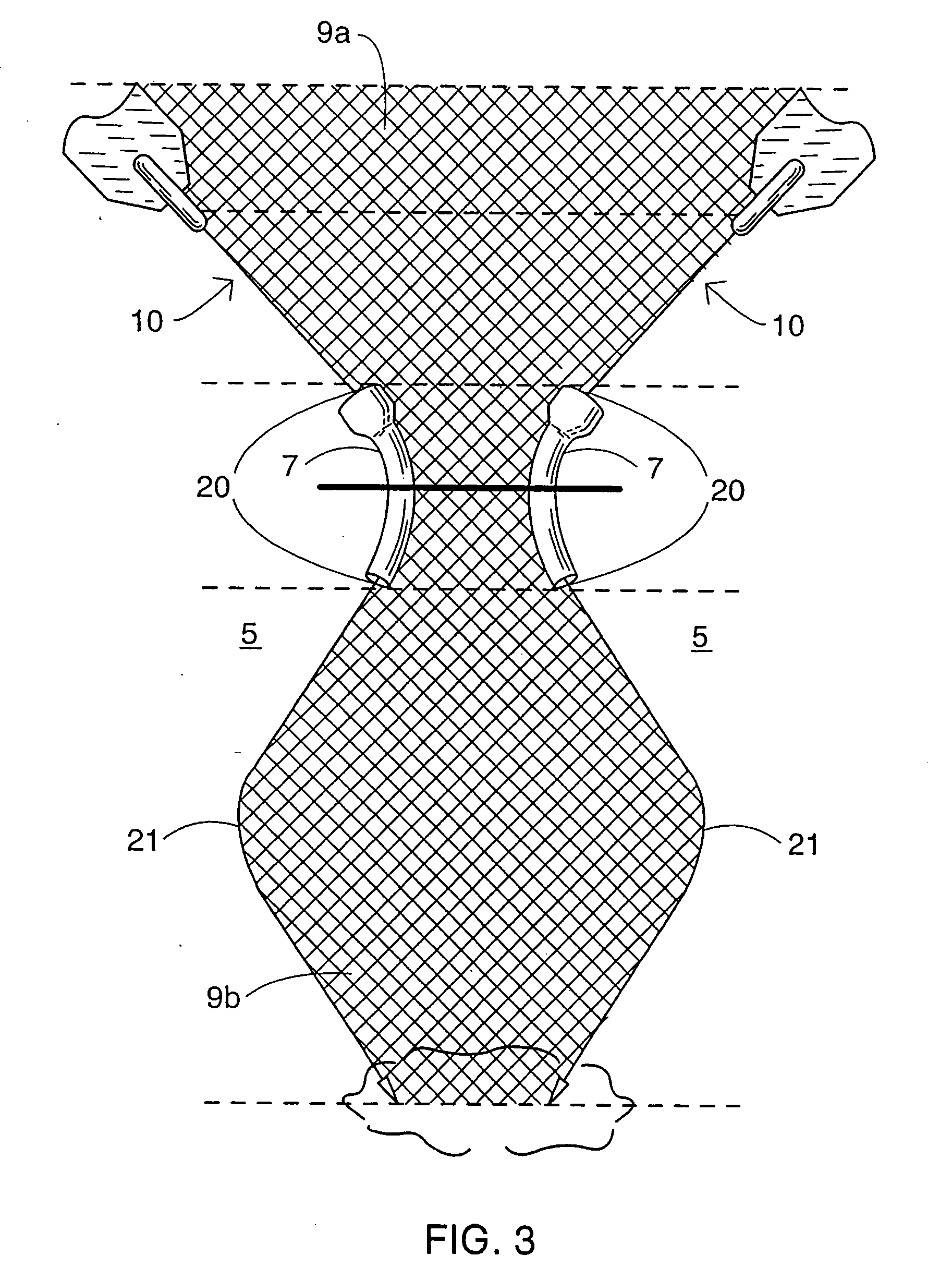
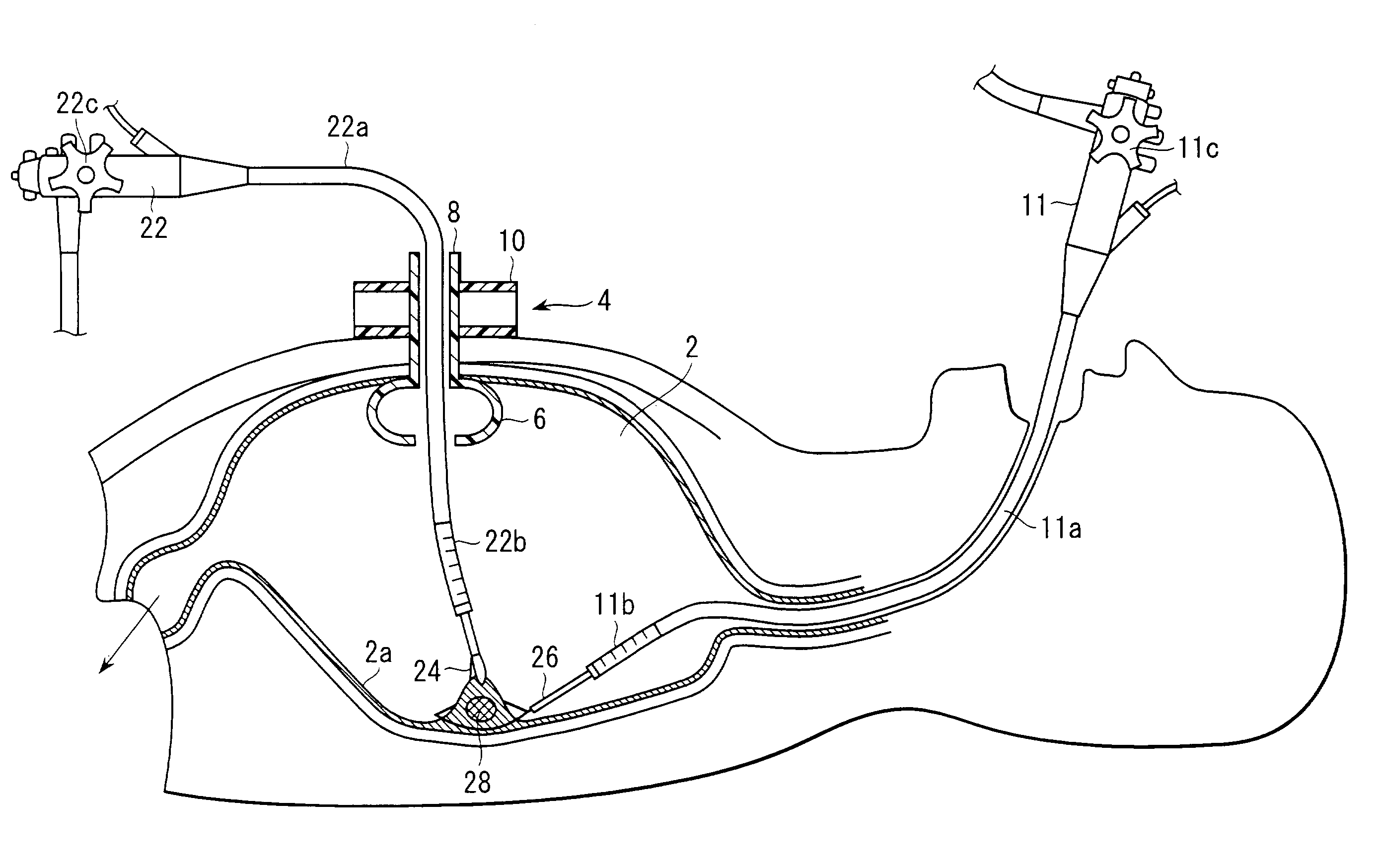
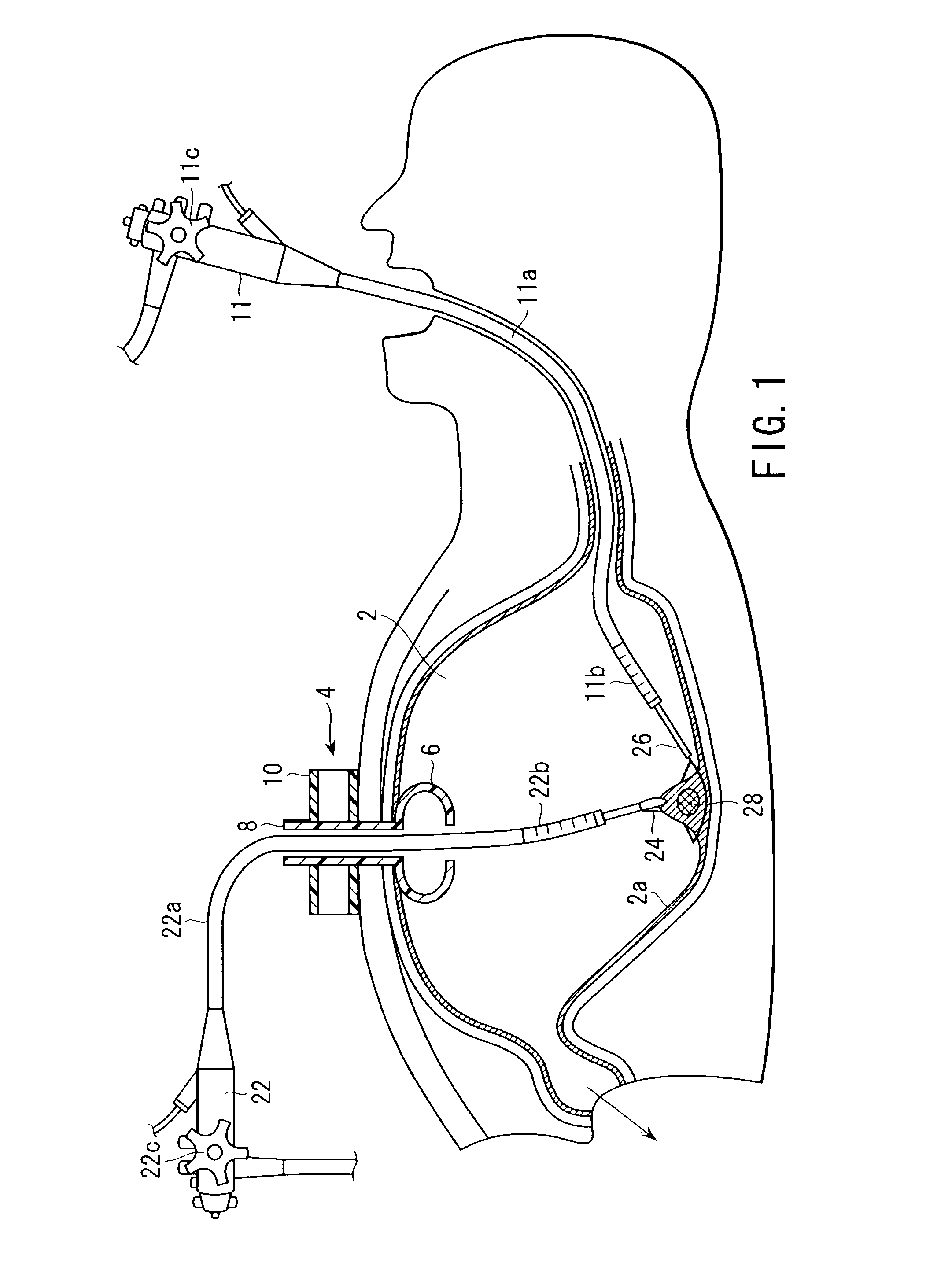
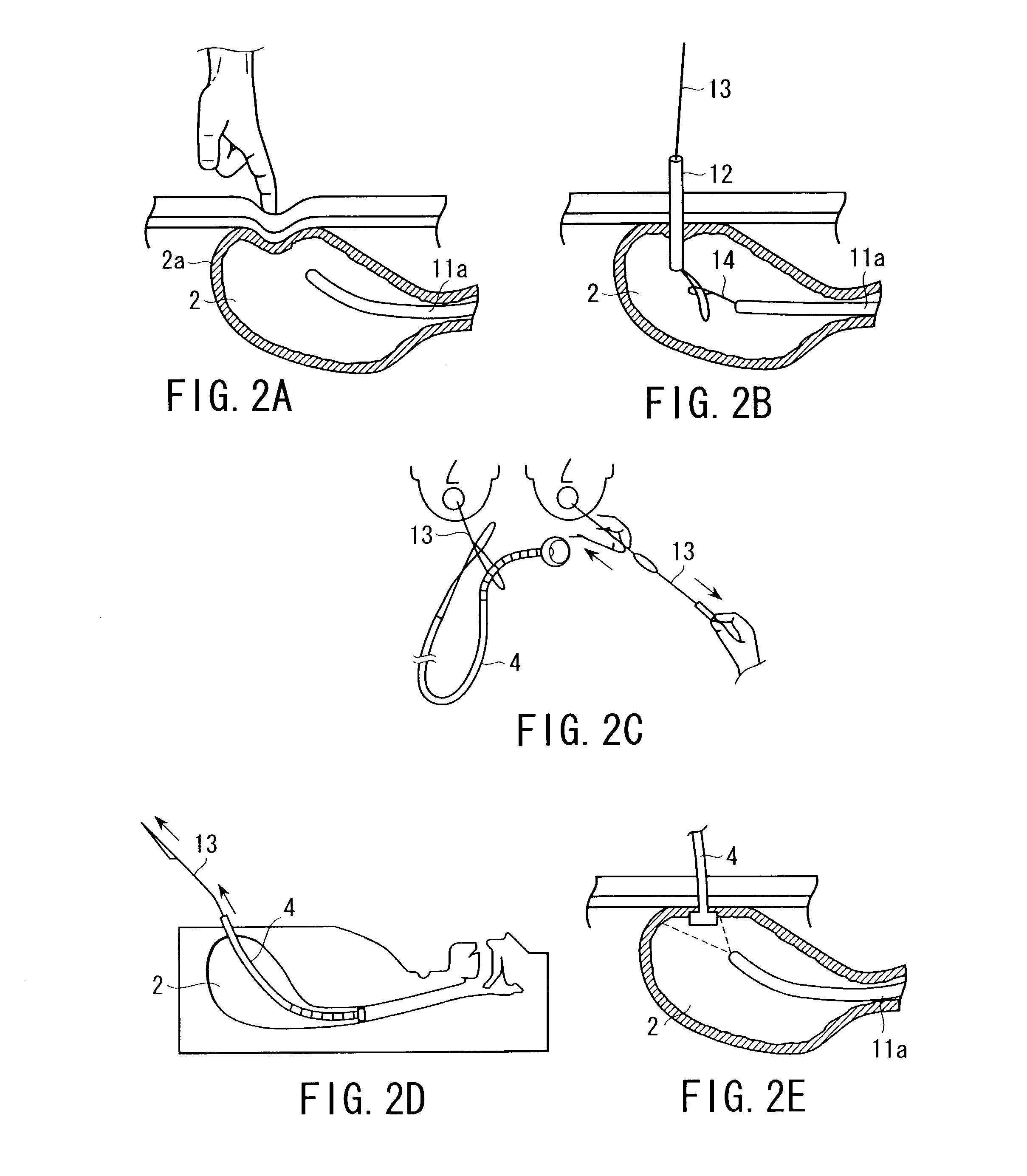
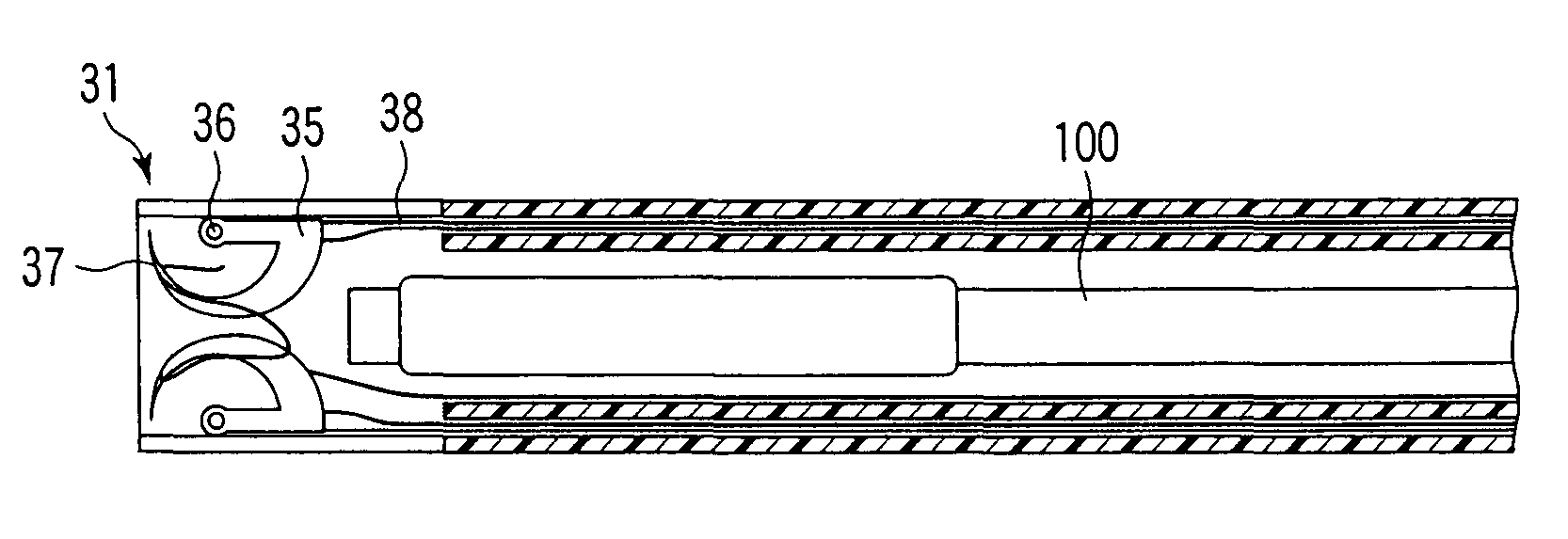
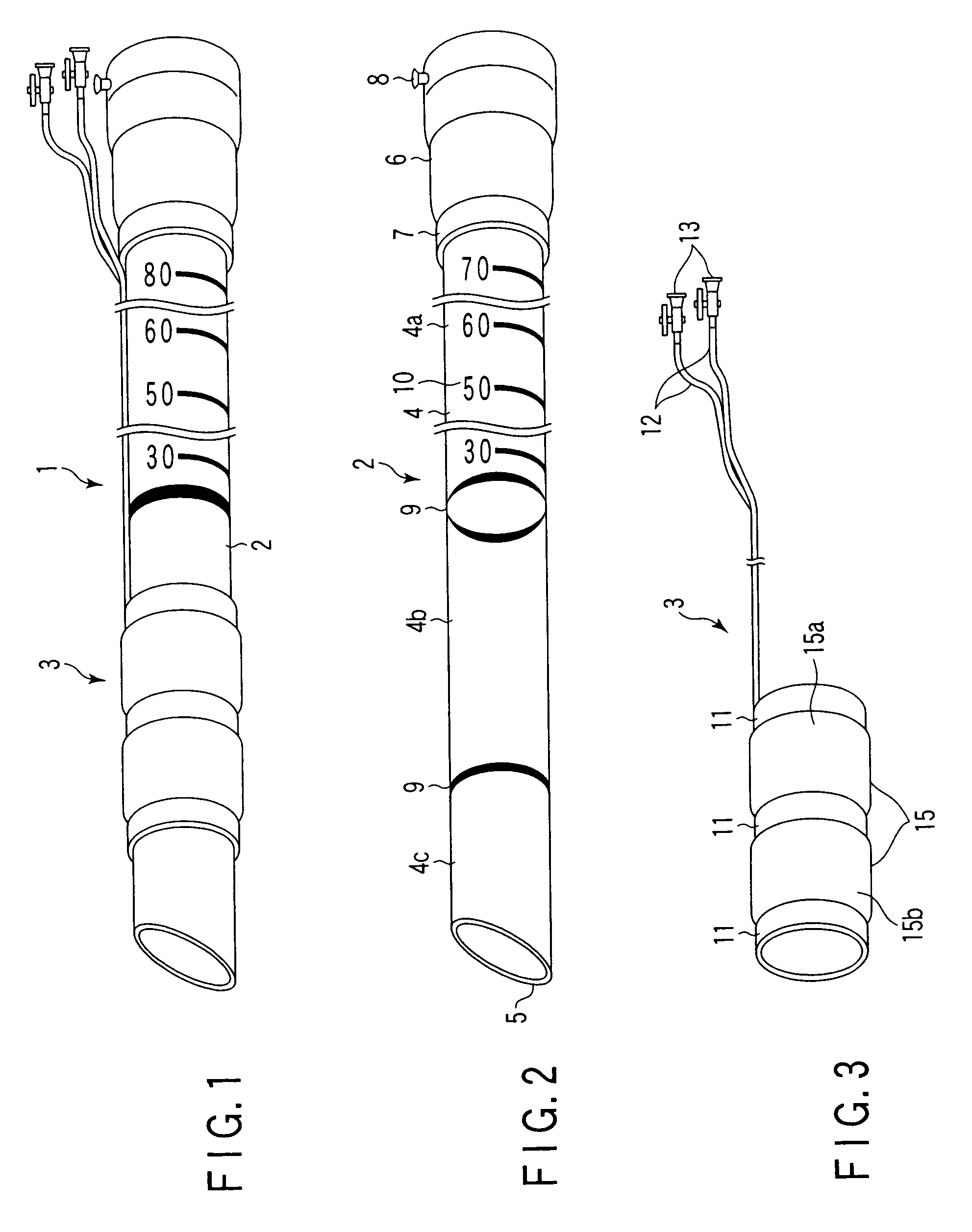
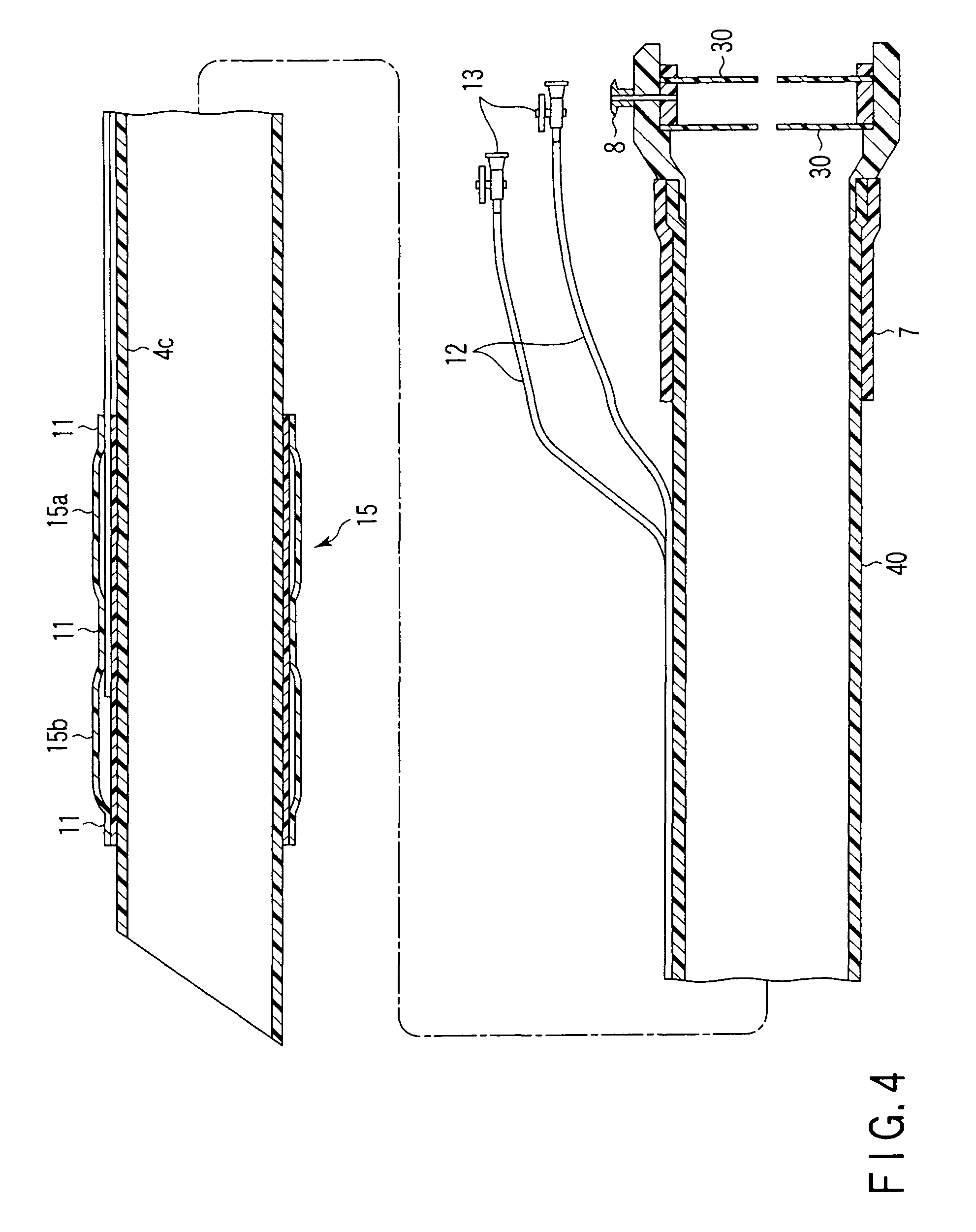
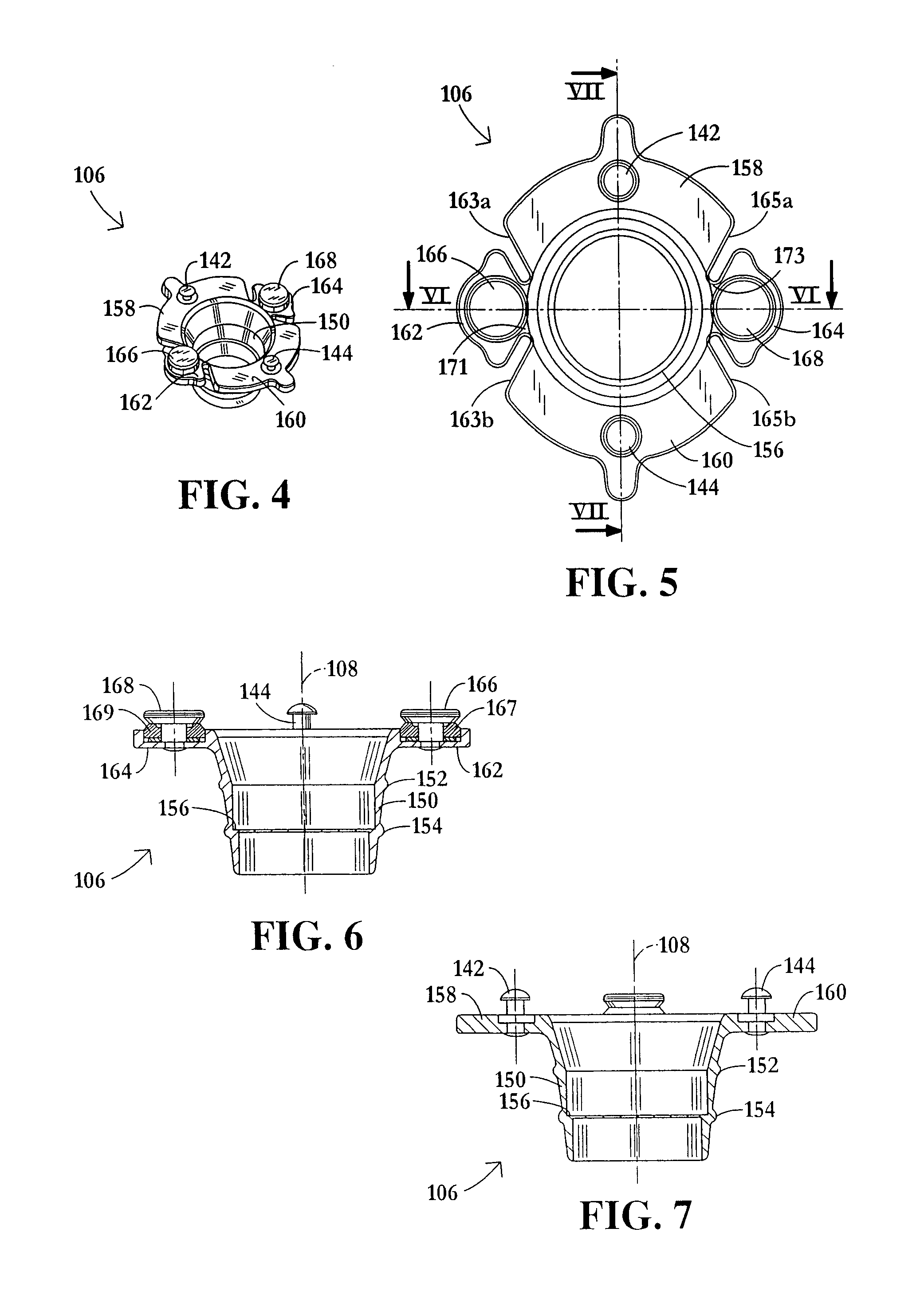
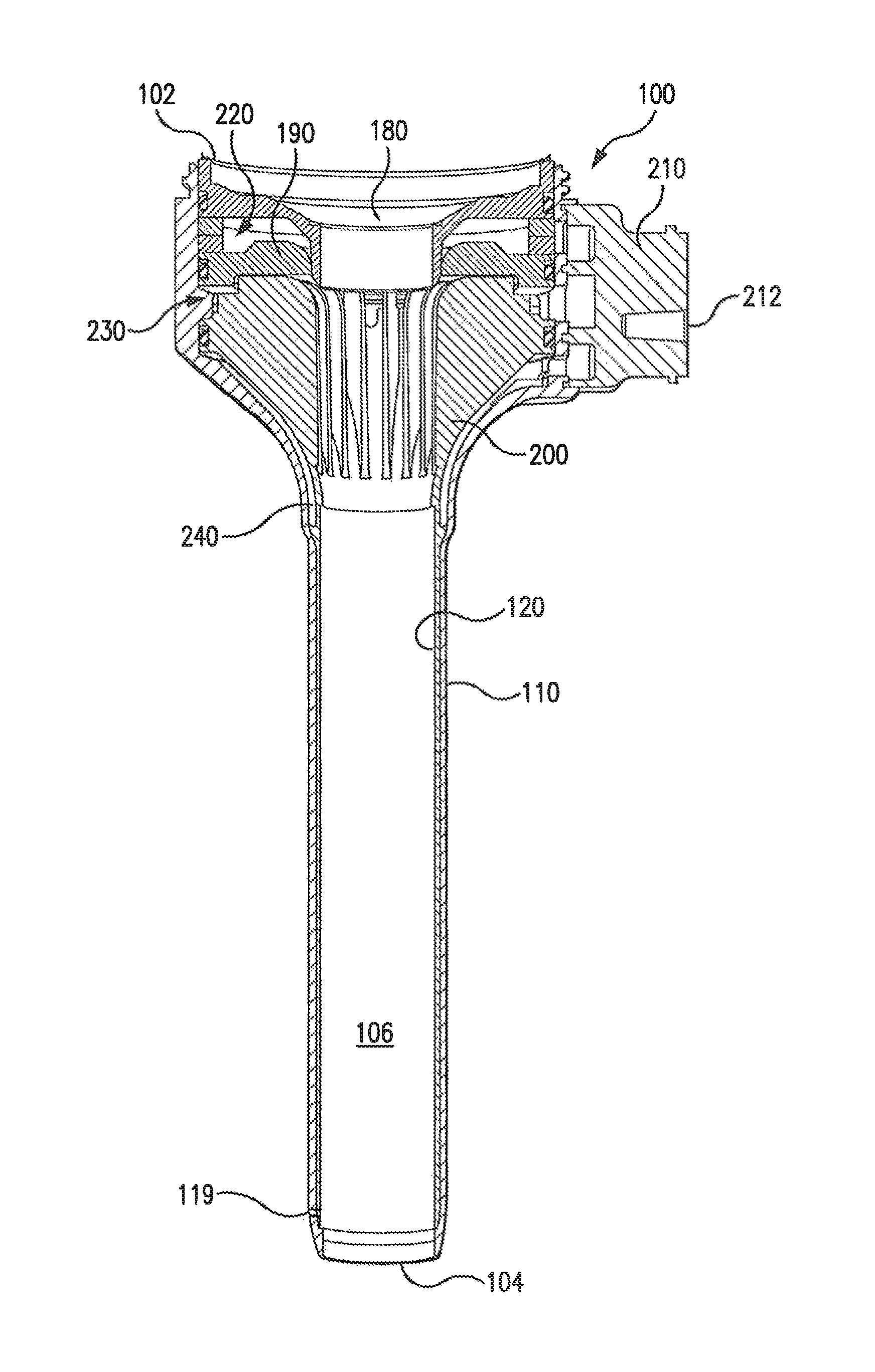
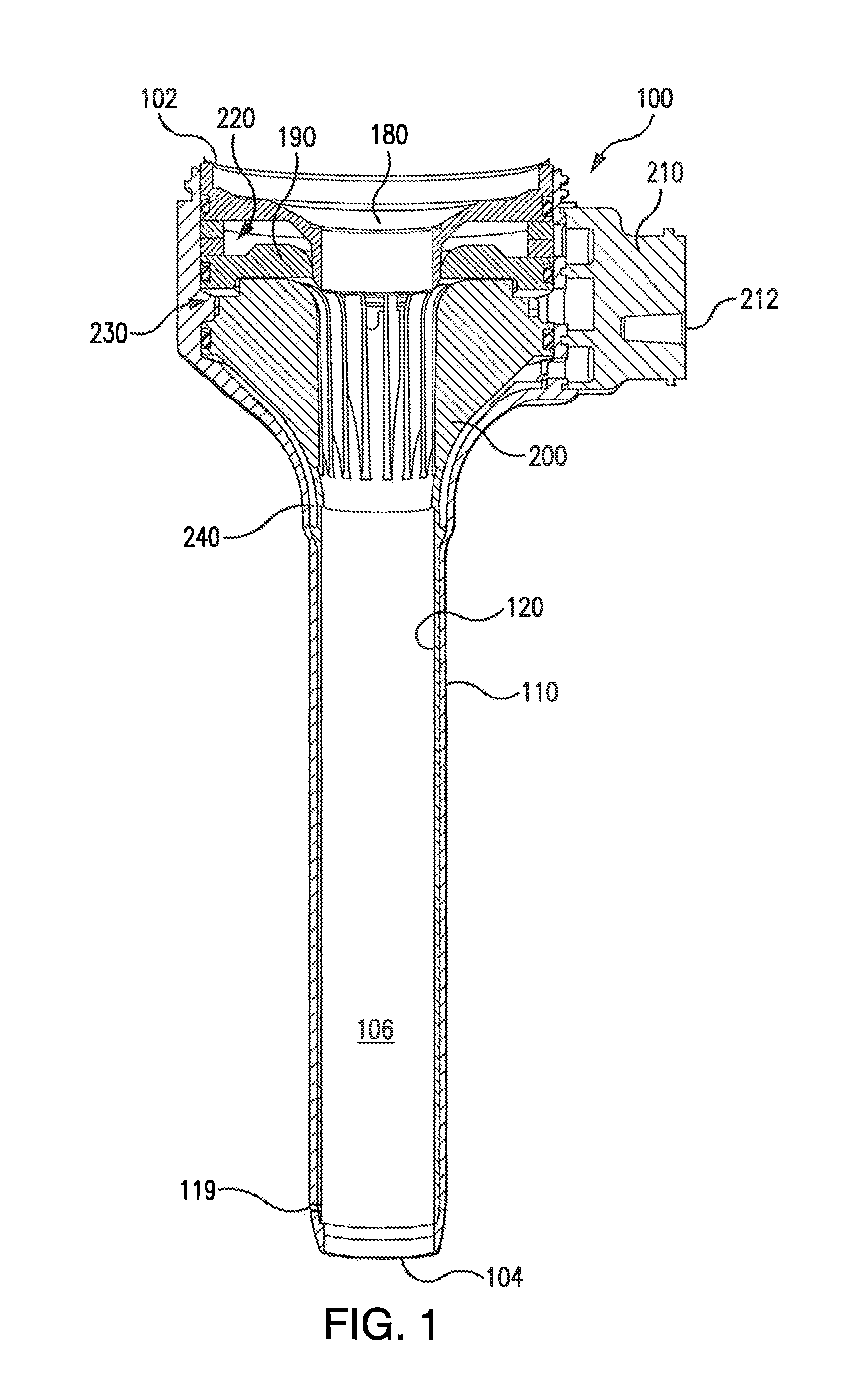
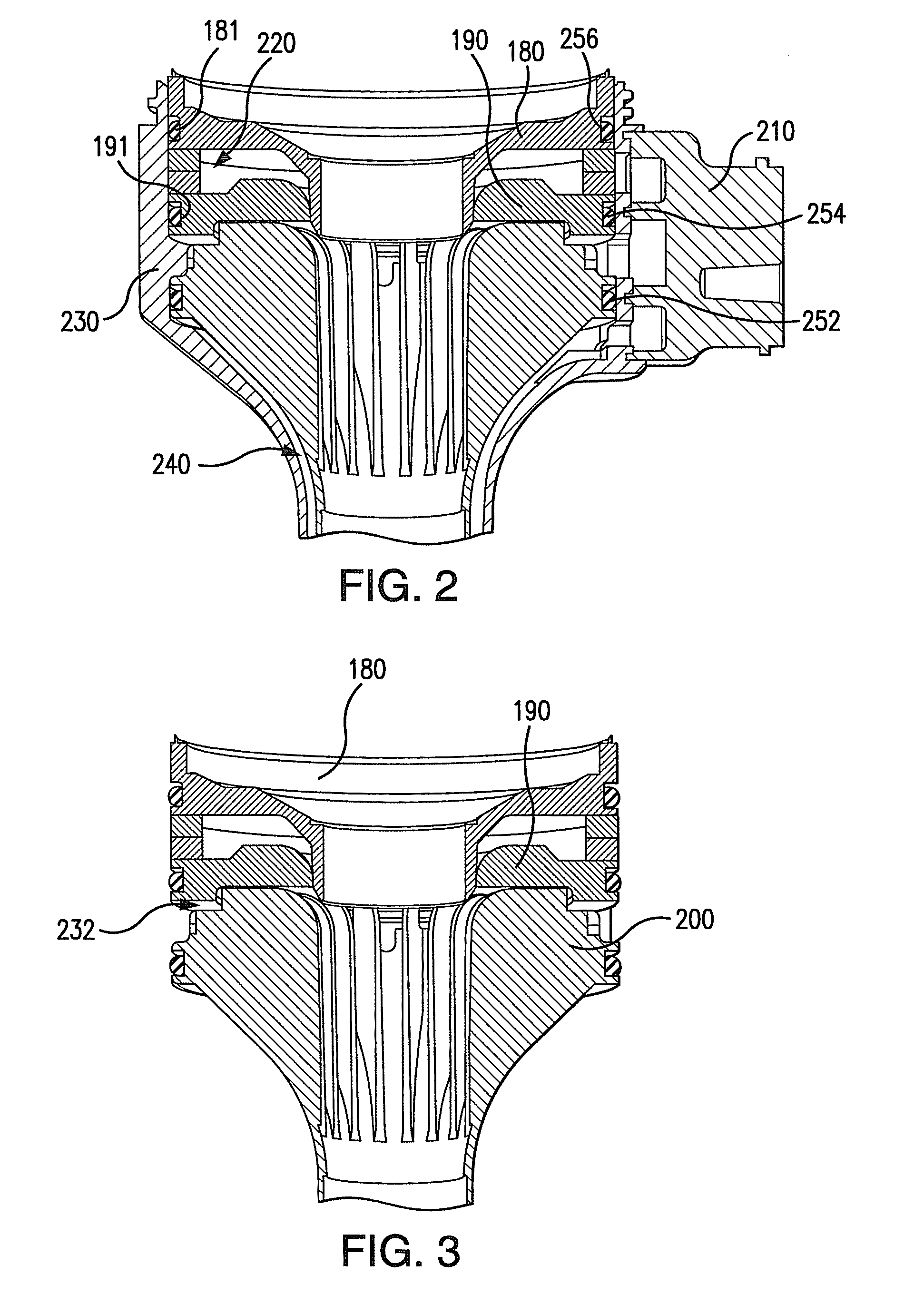
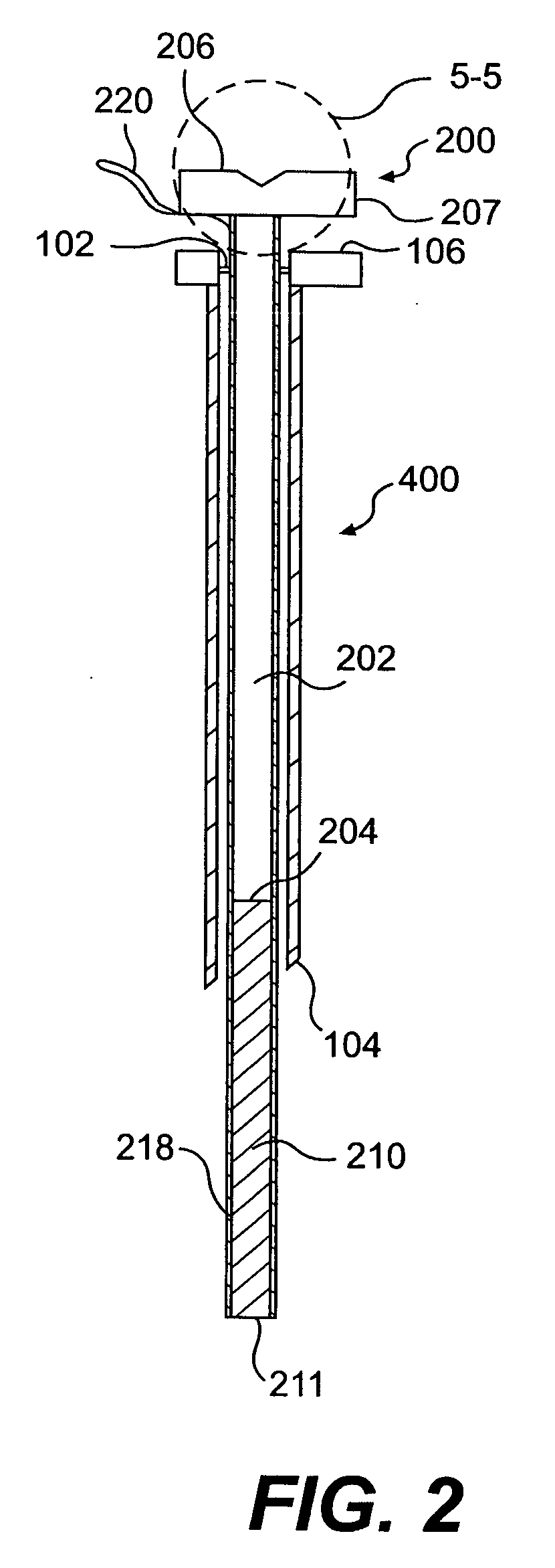
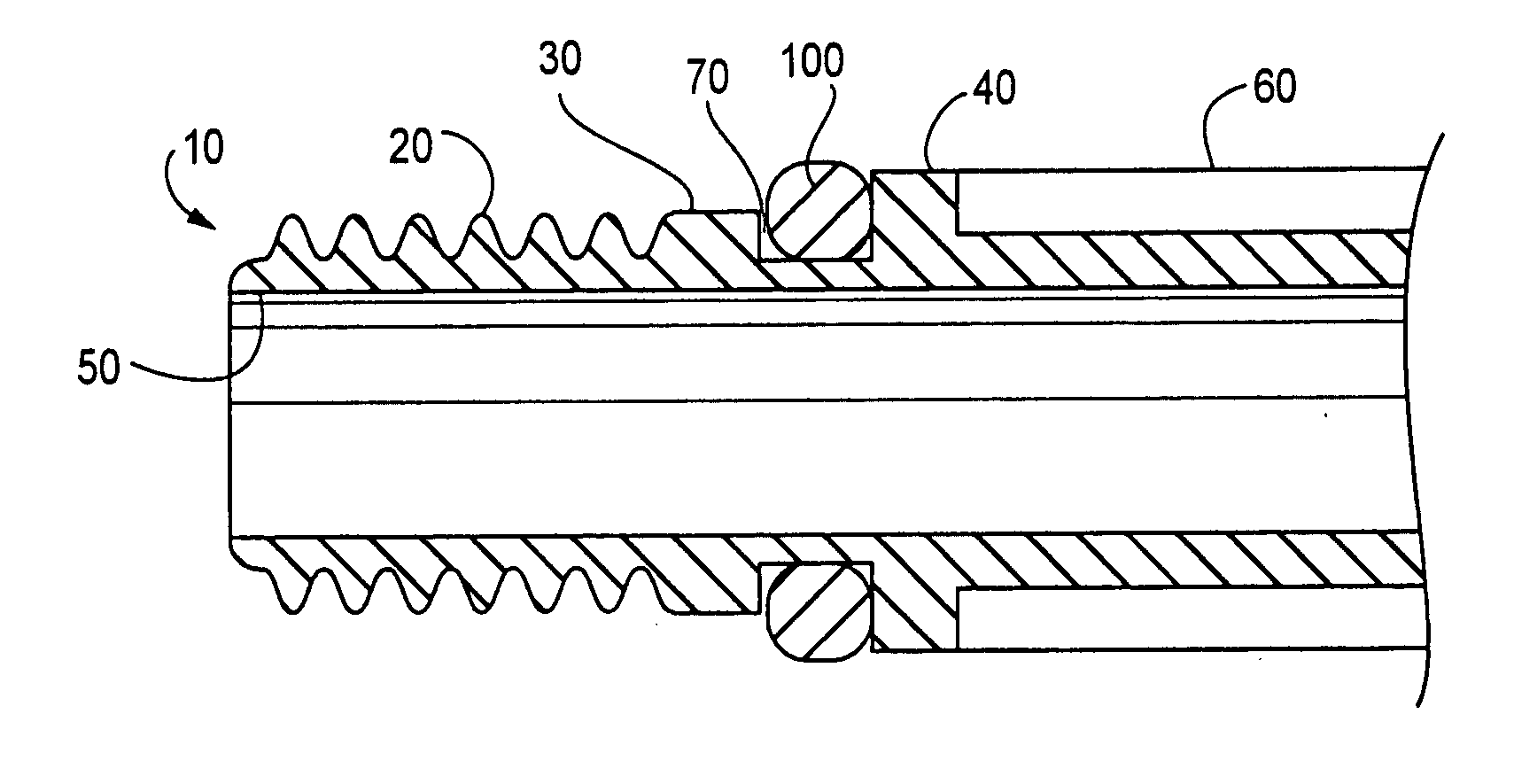
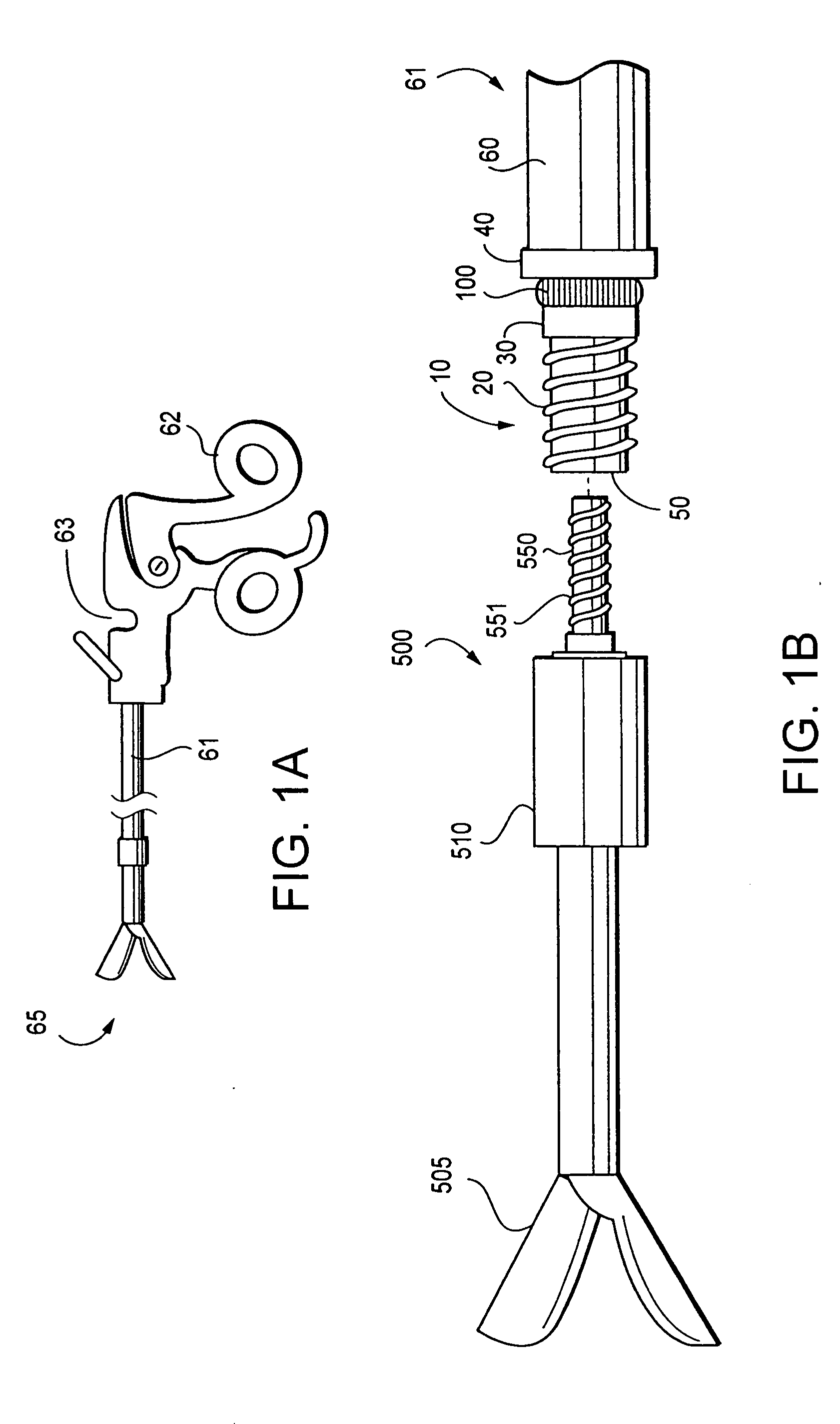
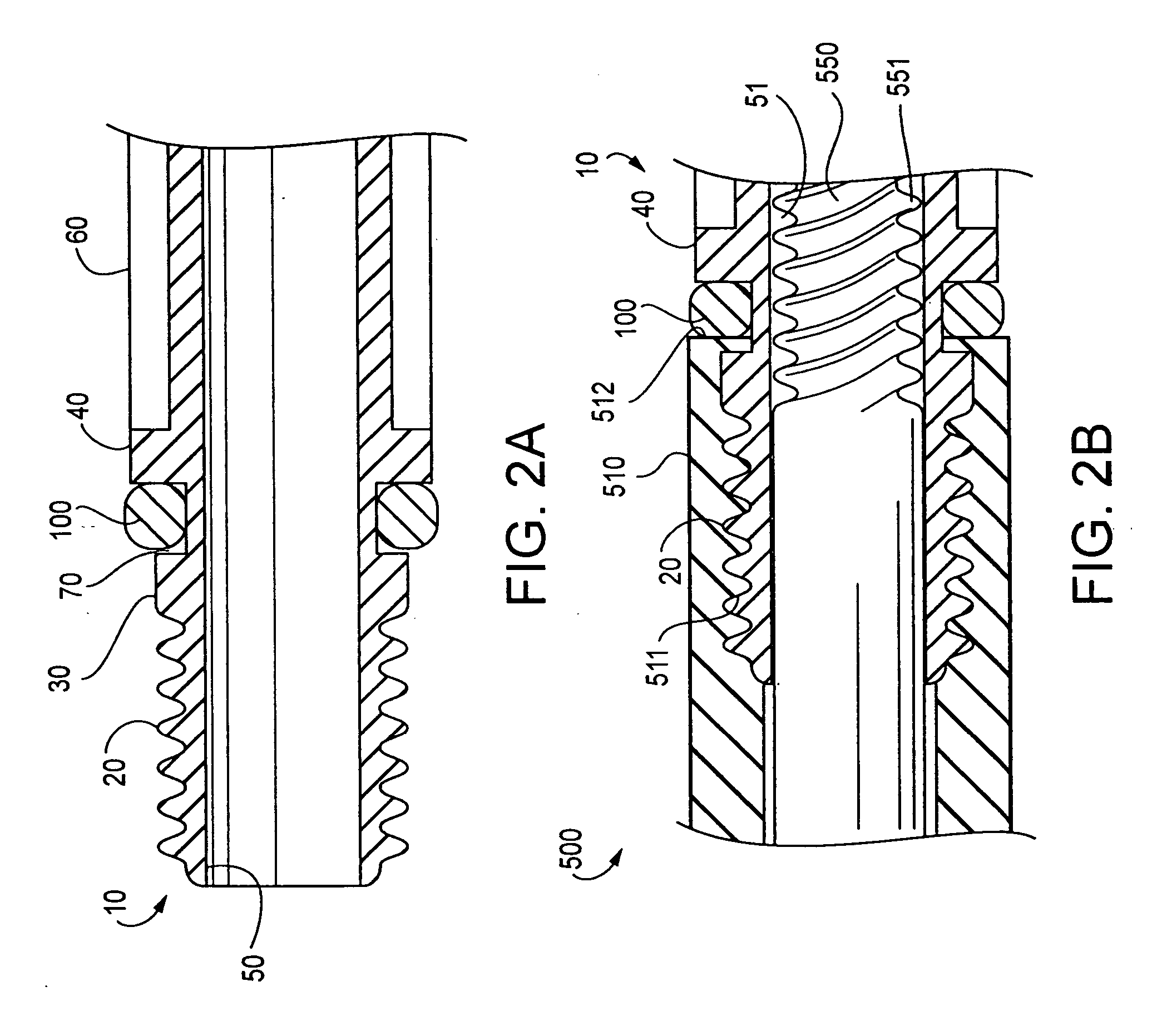
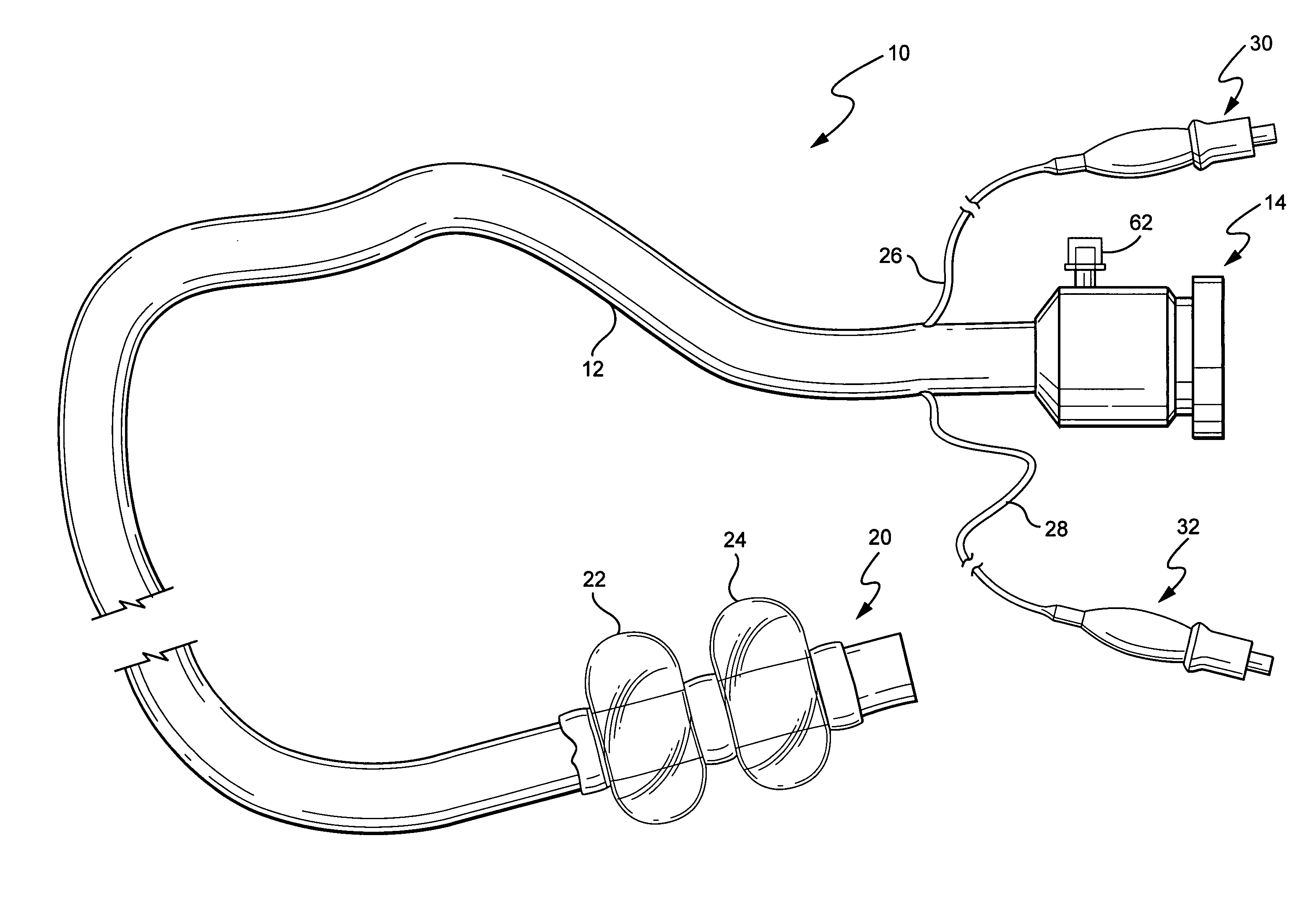
ActiveUS6988987B2Easily and stablyClose a perforation easily and surelySuture equipmentsSurgical needlesAbdominal cavityTherapeutic Devices
There is provided a flexible guide tube which guides an endoscope or a therapeutic device into an abdominal cavity through the mouth and stomach to conduct an observation or a therapeutic treatment in the abdominal cavity. The guide tube includes an insertion section which has a distal end, a peripheral section, and a central axis, and which is capable of being inserted into a body through the mouth, and two expandable and shrinkable balloons arranged in the vicinity of the distal end at a predetermined distance from each other in the axial direction on the periphery of the insertion section. The predetermined distance is preferably set to 3 to 8 mm, and the length of the insertion section is preferably set to about 600 to 1000 mm.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Methods and devices for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity
A novel approach to diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity is described. More specifically, a technique for accessing the peritoneal cavity via the wall of the digestive tract is provided so that examination of and / or a surgical procedure in the peritoneal cavity can be conducted via the wall of the digestive tract with the use of a flexible endoscope. As presently proposed, the technique is particularly adapted to transgastric peritoneoscopy. However, access in addition or in the alternative through the intestinal wall is contemplated and described as well. Transgastric and / or transintestinal peritoneoscopy will have an excellent cosmetic result as there are no incisions in the abdominal wall and no potential for visible post-surgical scars or hernias.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC
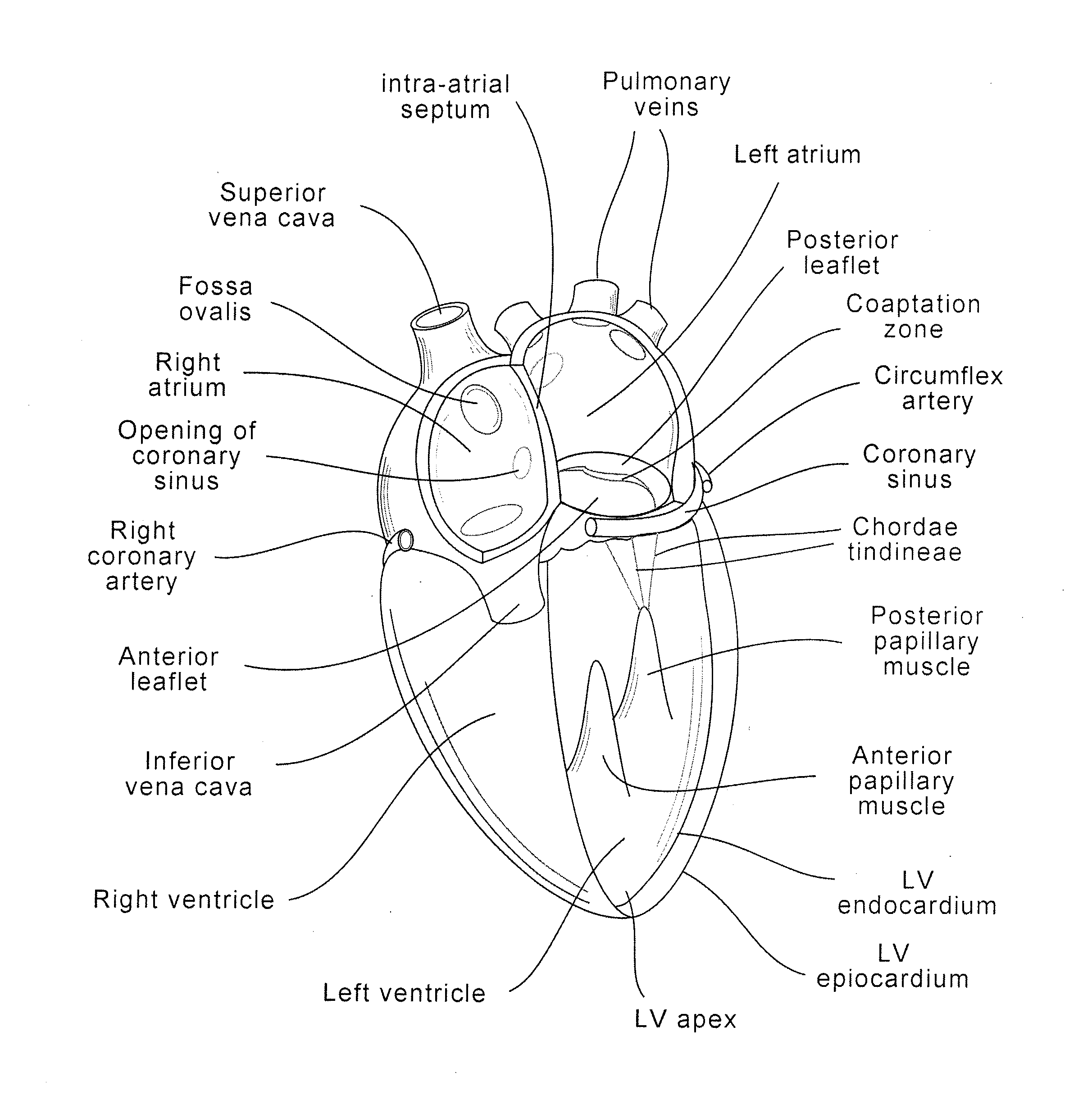
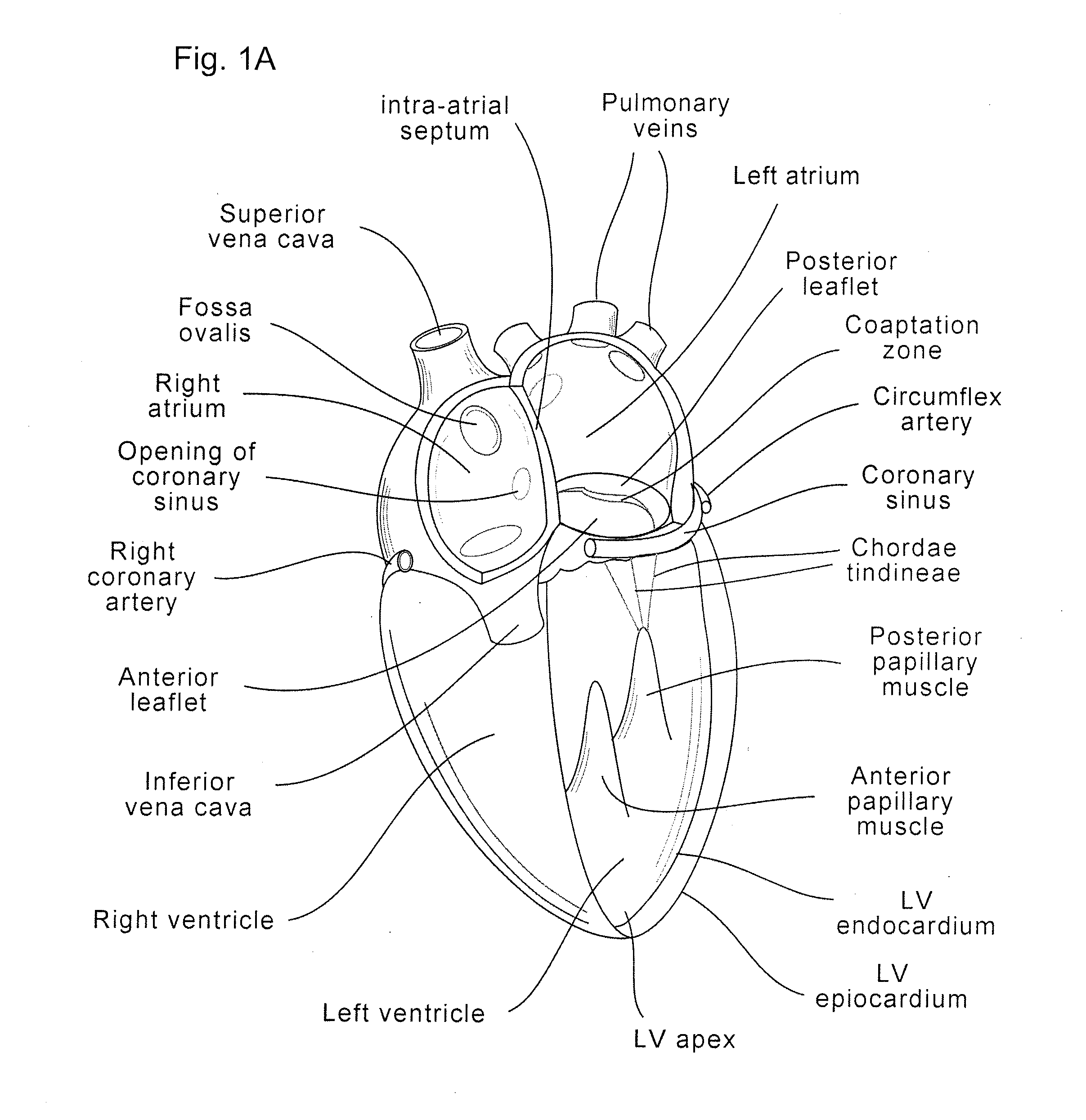
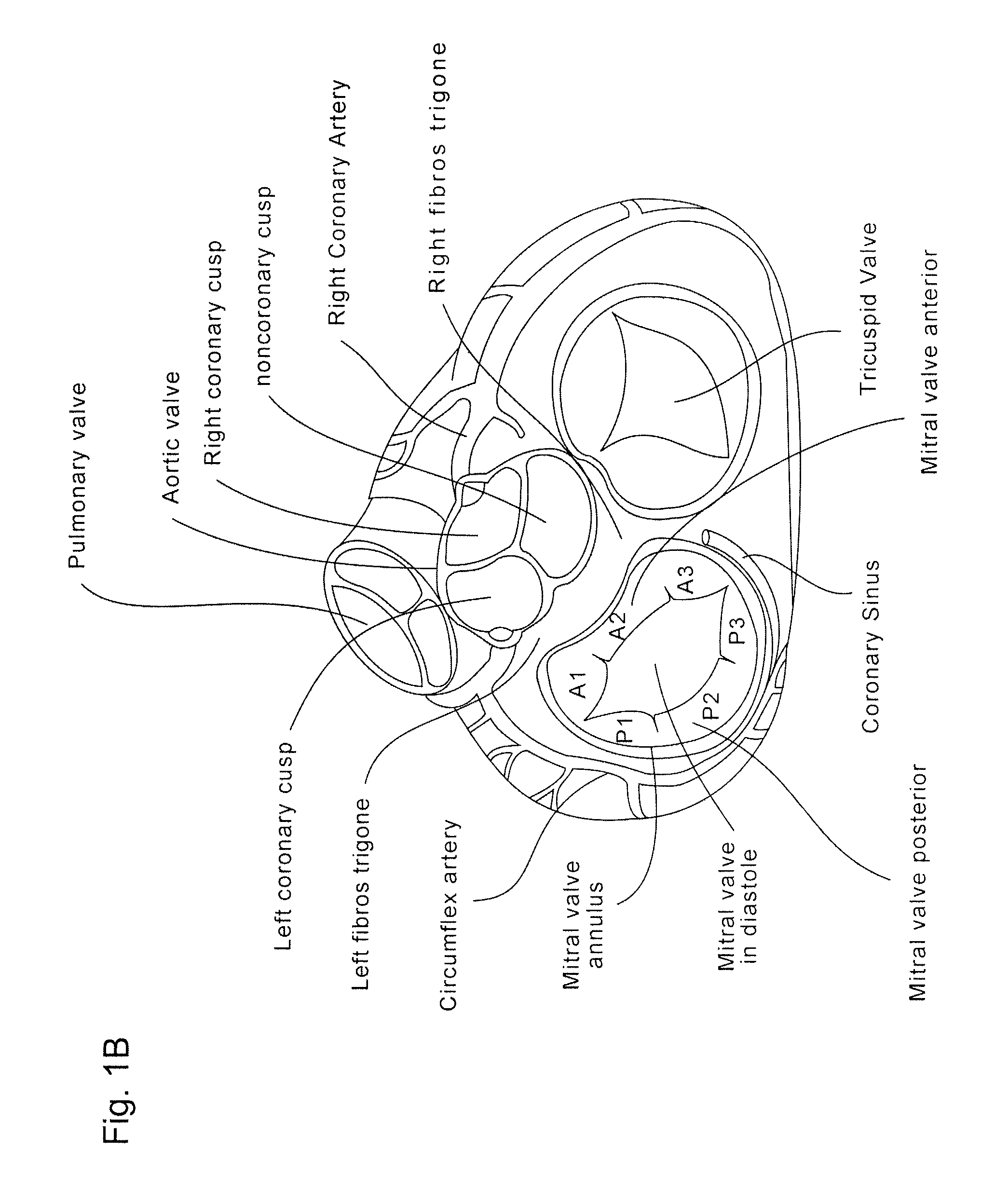
Coaptation enhancement implant, system, and method
ActiveUS20120197388A1Mal-coaptation is mitigatedImprove valve functionSuture equipmentsBone implantBody shapeAbdominal cavity
Implants, implant systems, and methods for treatment of mitral valve regurgitation and other valve diseases generally include a coaptation assist body which remains within the blood flow path as the leaflets of the valve move, the valve bodies often being relatively thin, elongate (along the blood flow path), and / or conformable structures which extend laterally from commissure to commissure, allowing the native leaflets to engage and seal against the large, opposed surfaces on either side of the valve body during the heart cycle phase when the ventricle contracts to empty that chamber of blood, and allows blood to pass around the valve body so that blood flows from the atrium to the ventricle during the filling phase of the heart cycle. Separate deployment of independent anchors near each of the commissures may facilitate positioning and support of an exemplary triangular valve body, with a third anchor being deployed in the ventricle. An outer surface of the valve body may accommodate tissue ingrowth or endothelialization, while a fluid-absorbing matrix can swell after introduction into the heart. The valve body shape may be selected after an anchor has been deployed, and catheter-based deployment systems may have a desirable low profile.
Owner:POLARES MEDICAL INC
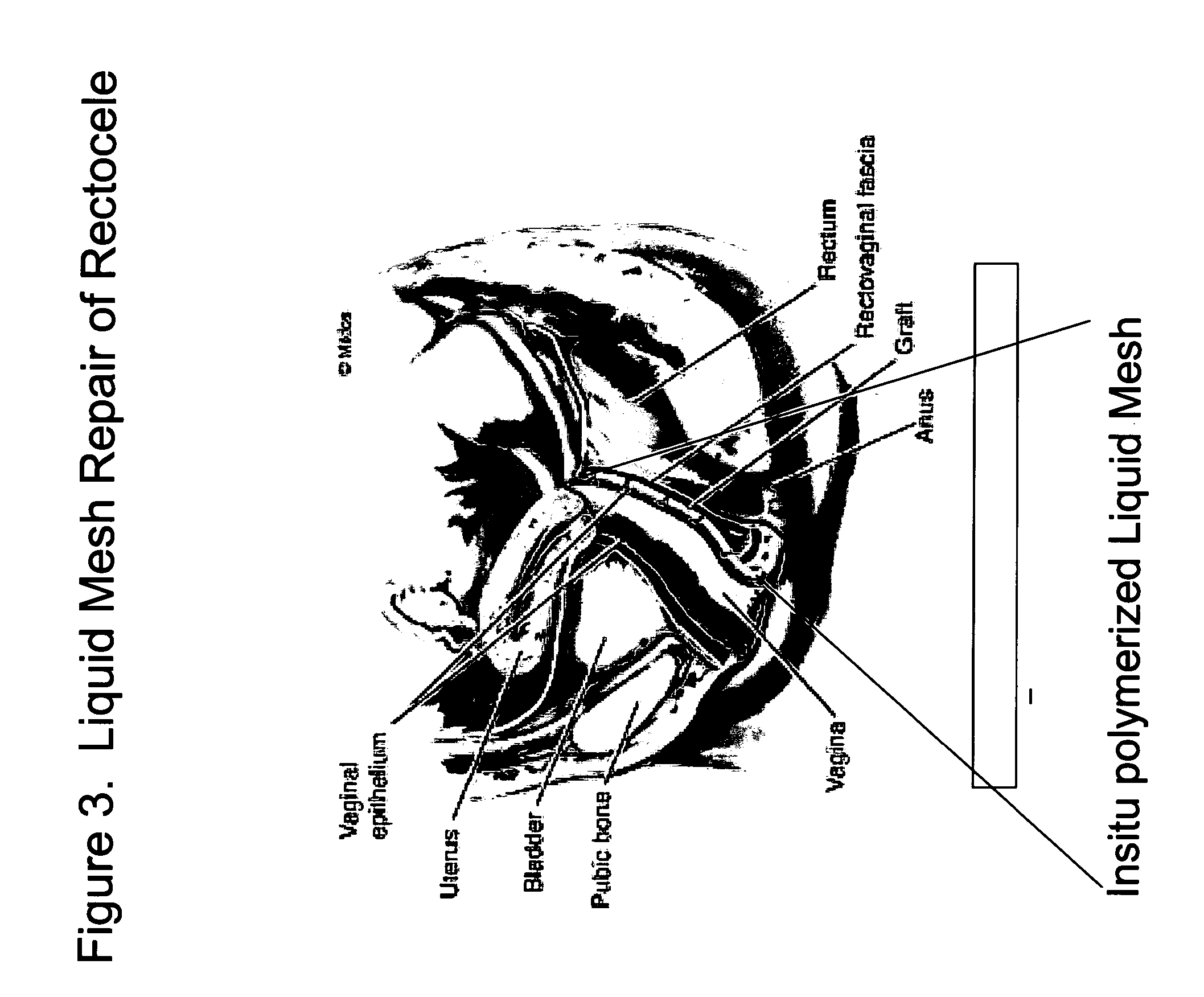
Surgical adhesive and uses therefore
InactiveUS20050129733A1Controlled strengthLess erosiveSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismIn situ polymerizationEnteroceles
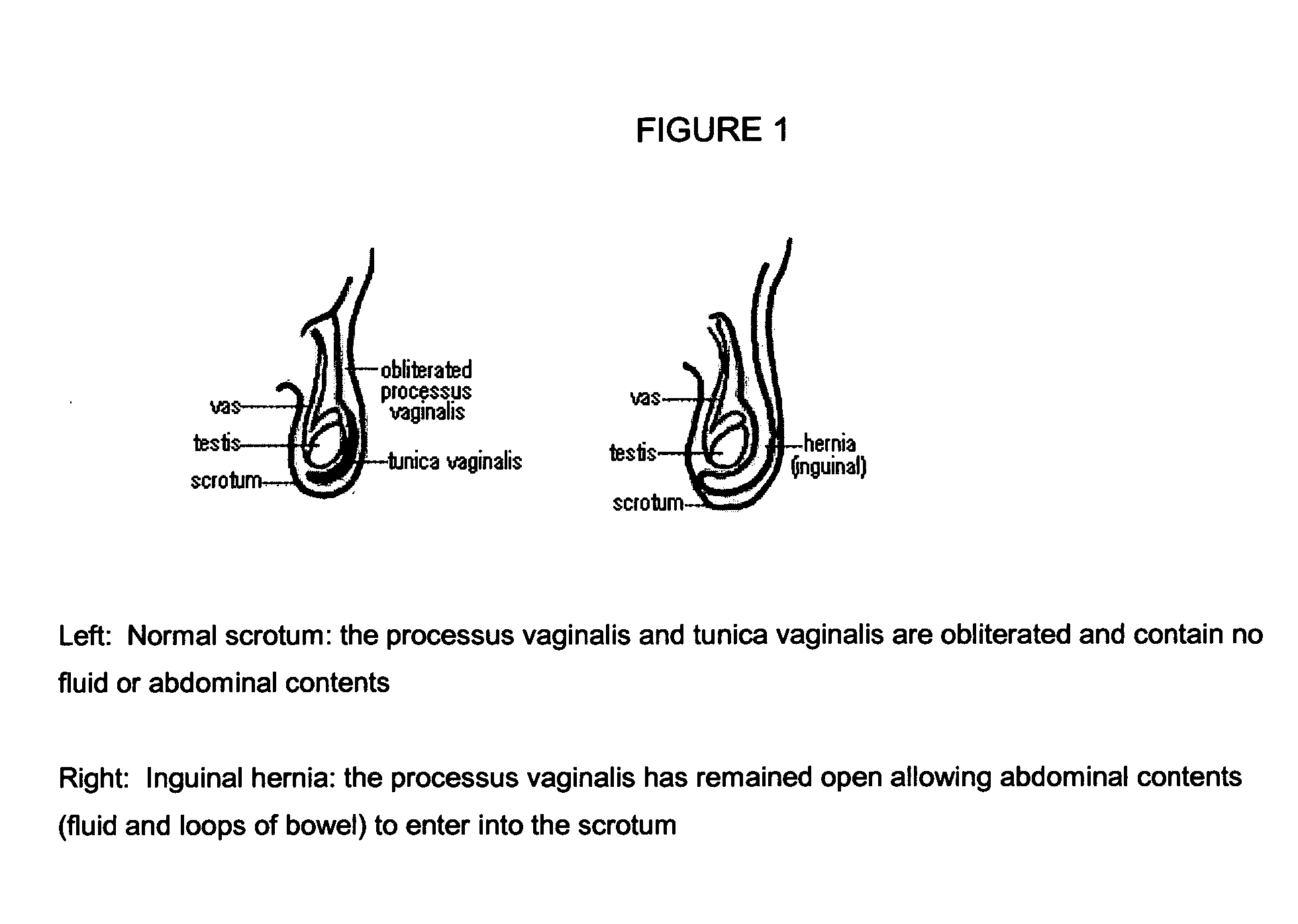
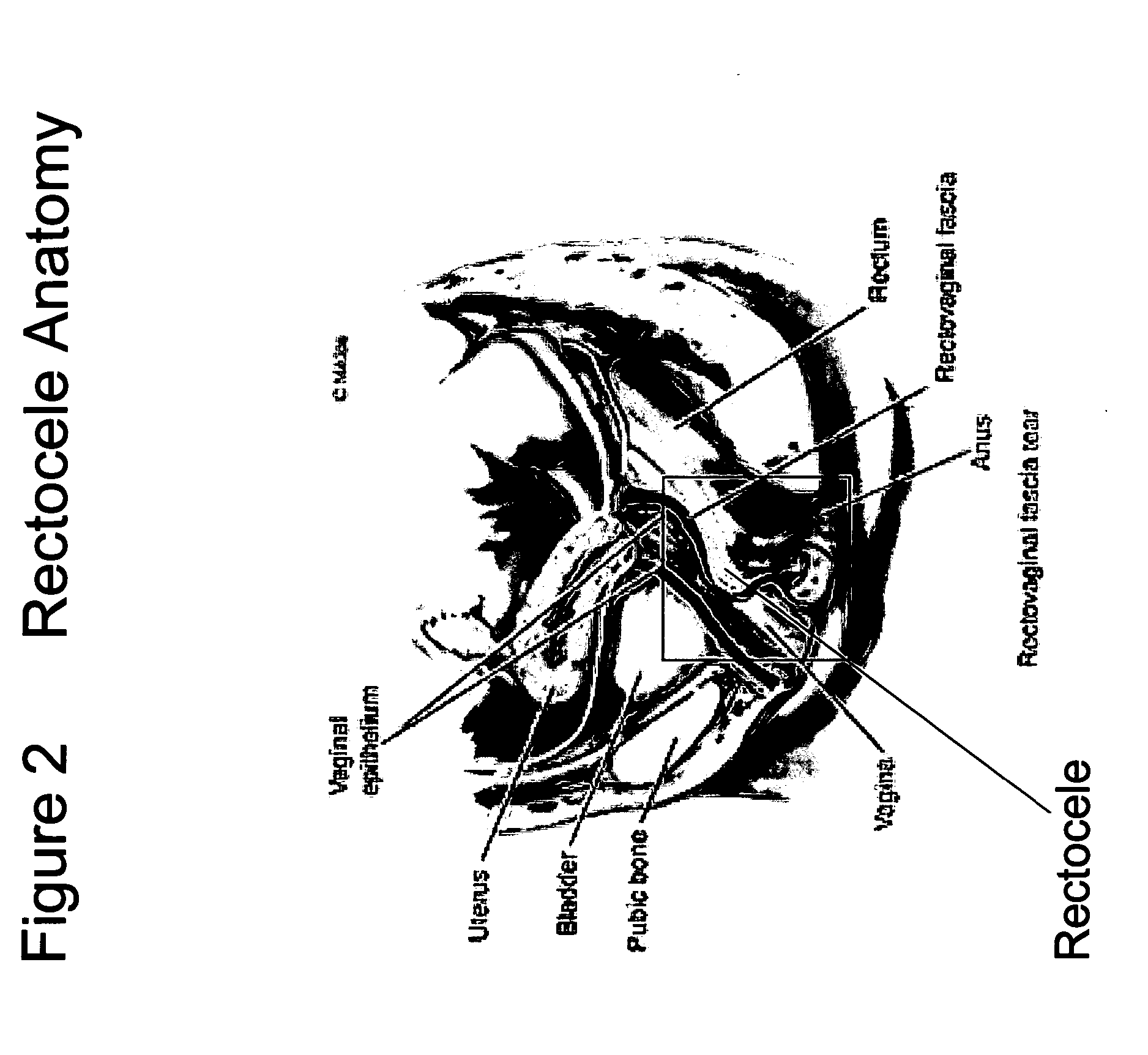
The present invention provides a liquid polymer composition which can be implanted into a living mammal and which forms a solid hydrogel by in situ polymerization upon contact with body fluid and tissue. The composition also can be used as a coating on a medical device, or for the formation of a medical device. Formation of a solid implant or coating involves crosslinking of the adhesive with itself and with surrounding tissue. The liquid implant, by itself or in conjunction with various prostheses, can be used for many purposed, including fixation of the urethra for providing treatment for incontinence, and repair of herniations in the abdominal cavity, including rectocele, cystocele, enterocele, and inguinal hernia. The adhesive may be used to establish adhesion prevention during such repairs, in part by coating or being the material of a repair mesh.
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
Laparoscopic instrument and cannula assembly and related surgical method
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
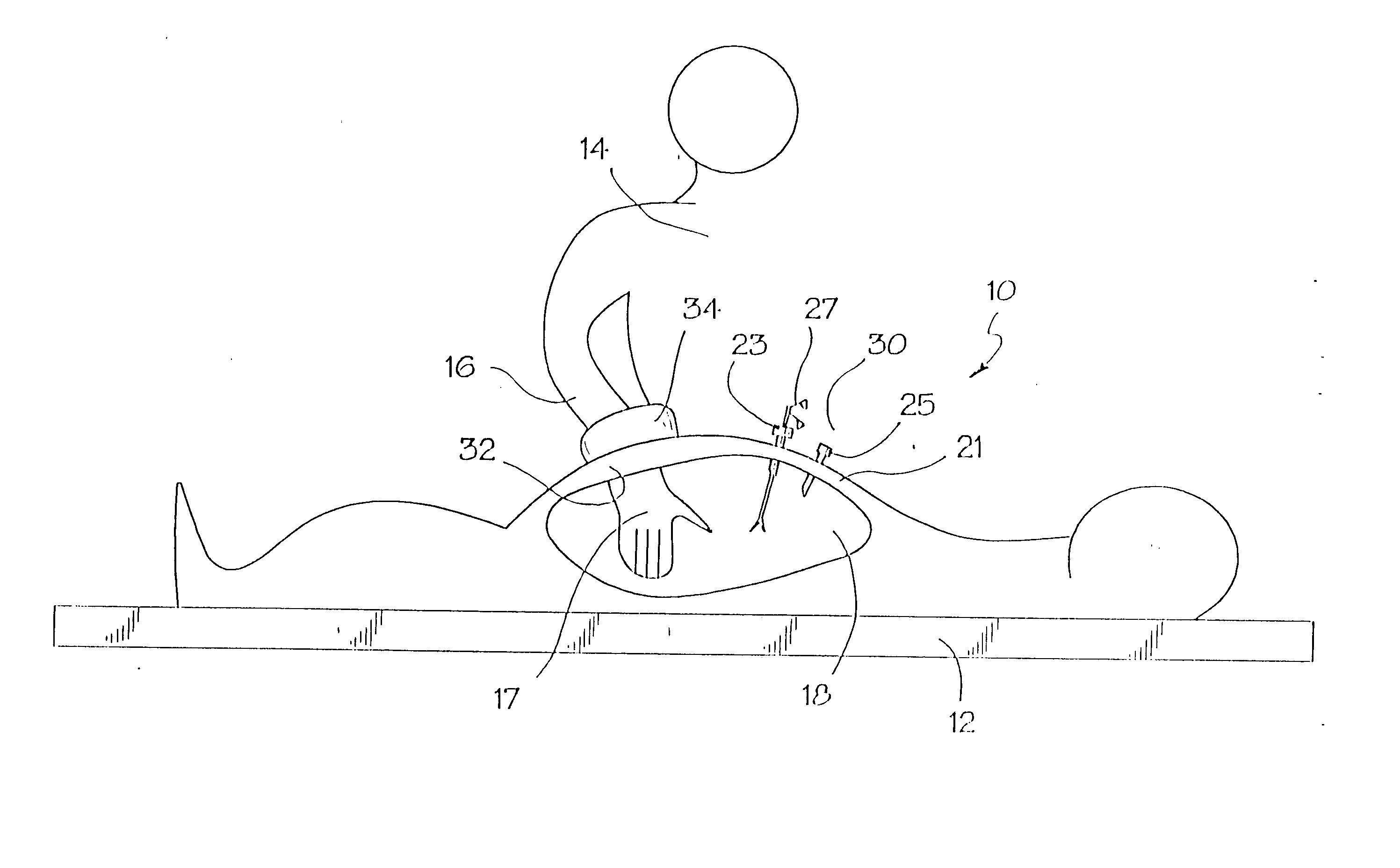
Method for accessing cavity
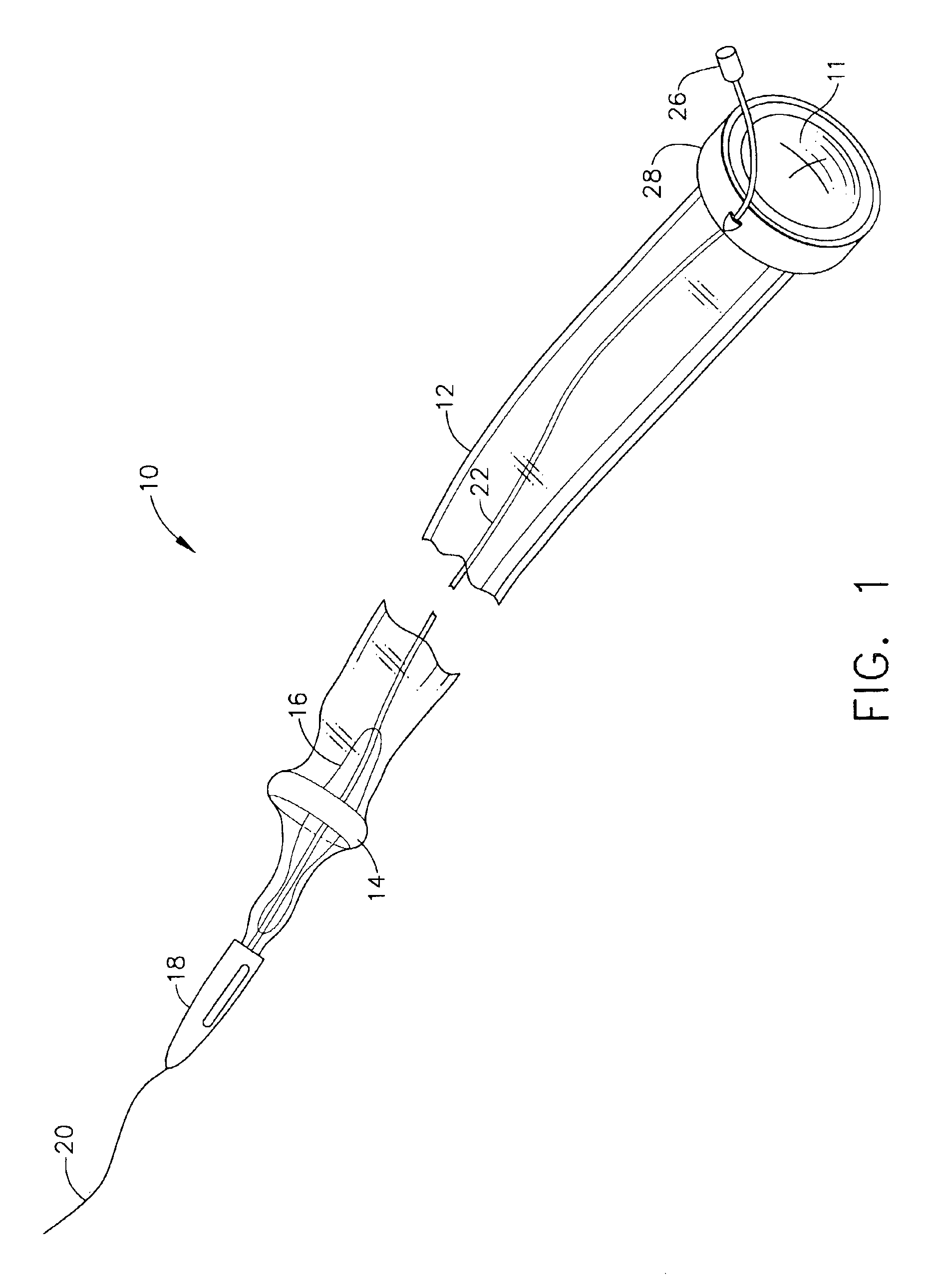
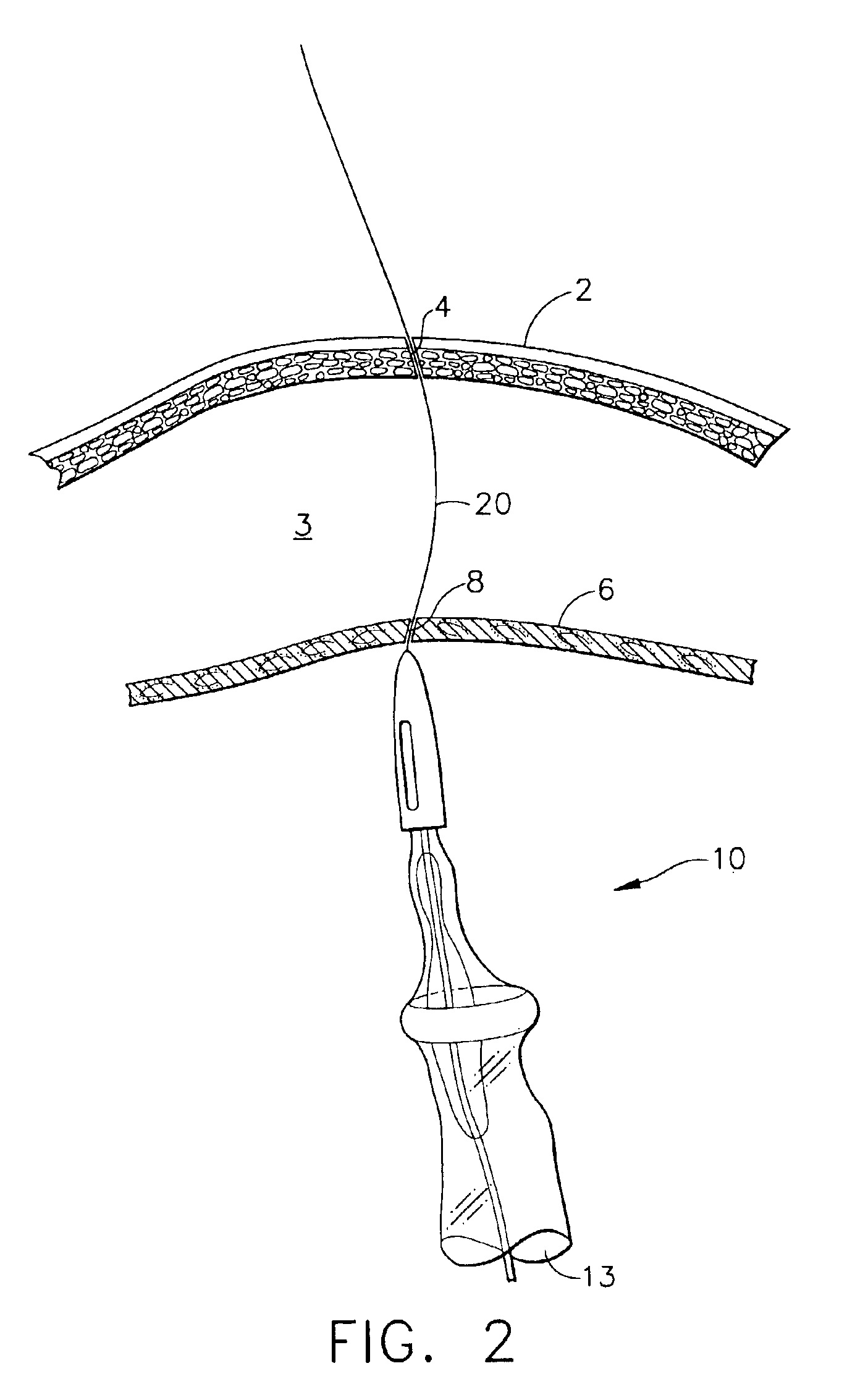
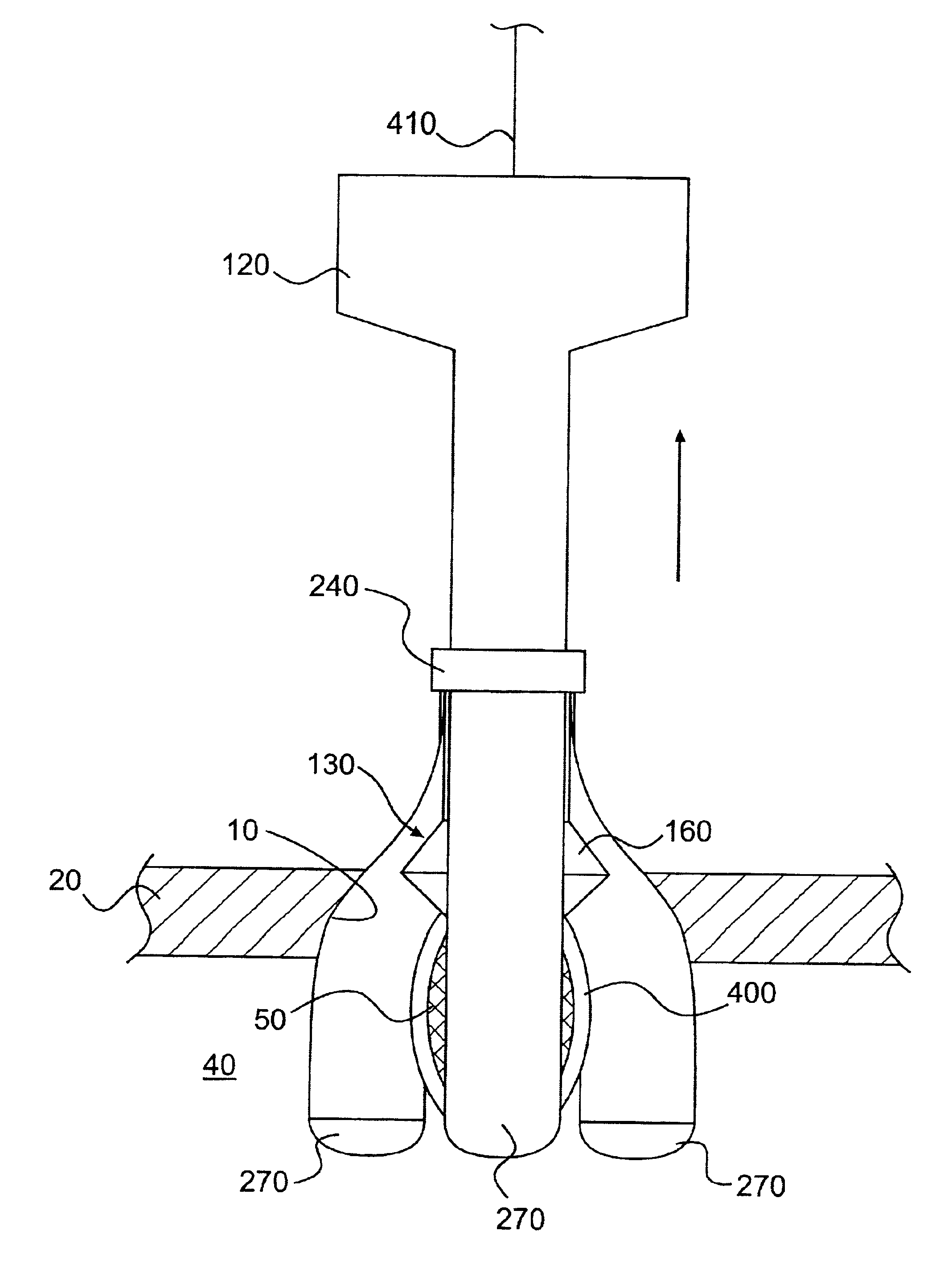
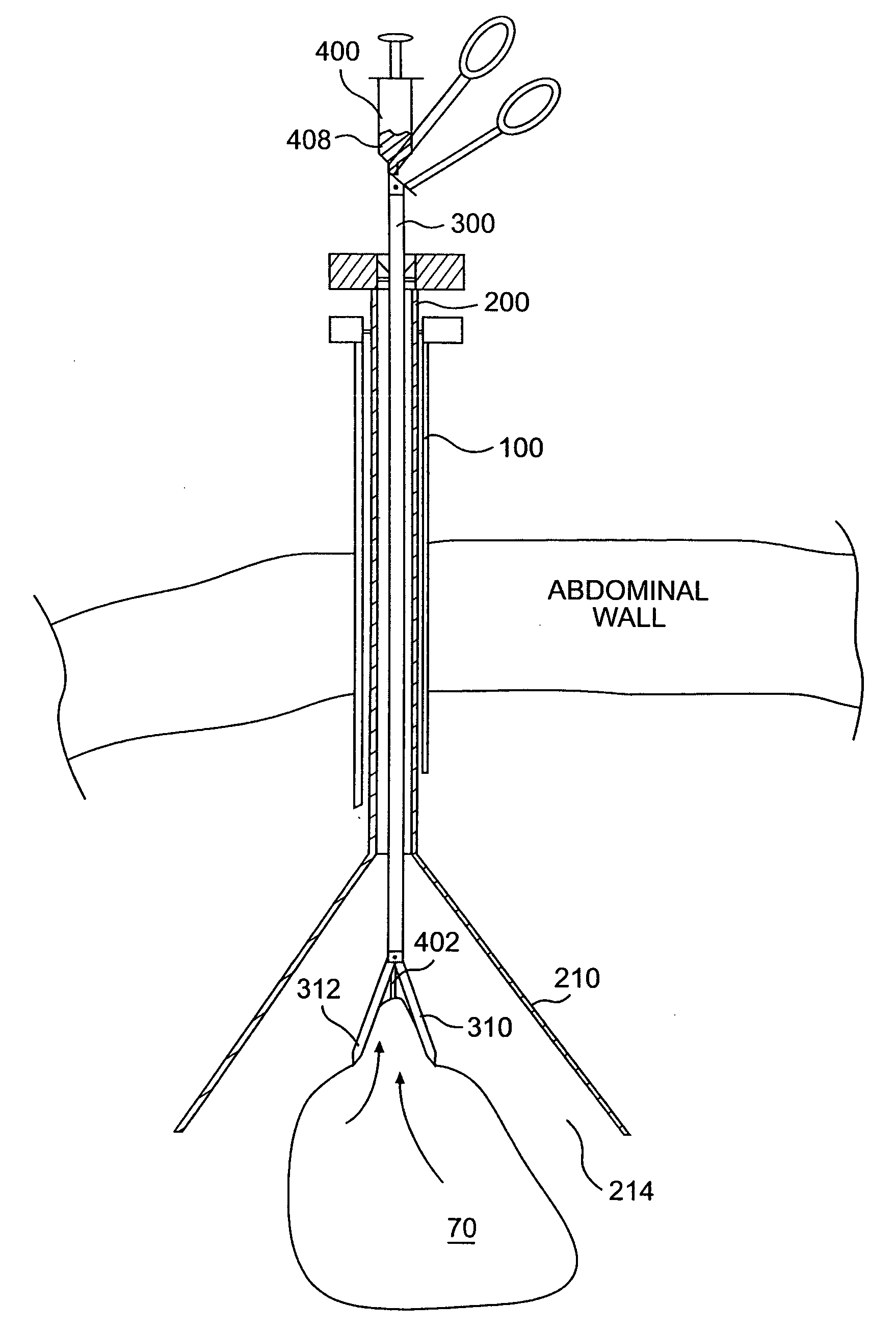
The present invention is a method for accessing the abdominal cavity of a patient in order to perform a medical procedure therein. The method can include the steps of introducing a medical device into the body cavity; providing a percutaneous incision to access the body cavity; and steering the medical device through the percutaneous incision. In one embodiment, a hollow steering element is advanced through the incision to guide a flexible endoscope postioned in the abdominal cavity.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Non-Immediate Effects of Therapy
InactiveUS20090131993A1Loss can be compensatedReduced glucose levelElectrotherapyAbdominal cavityMedicine
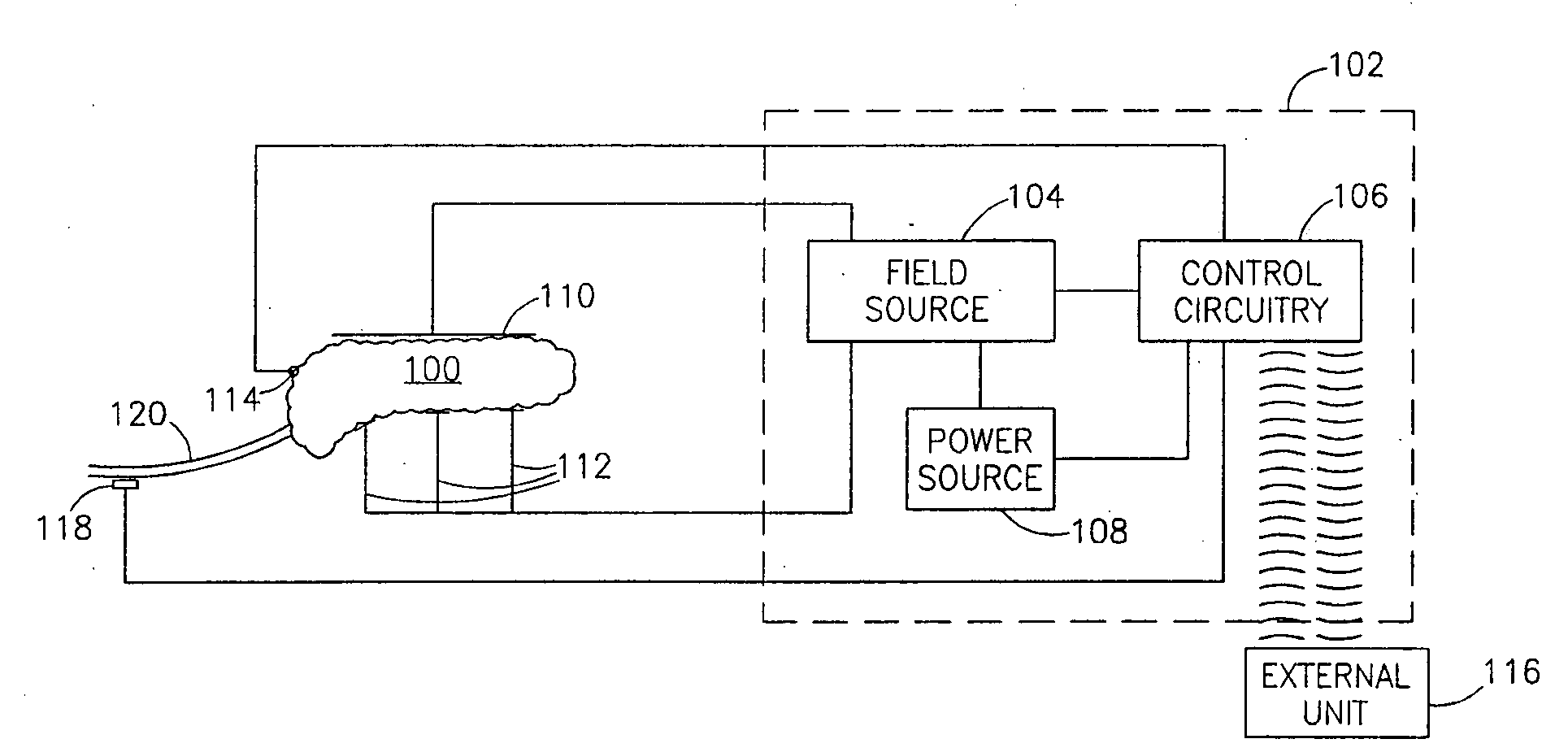
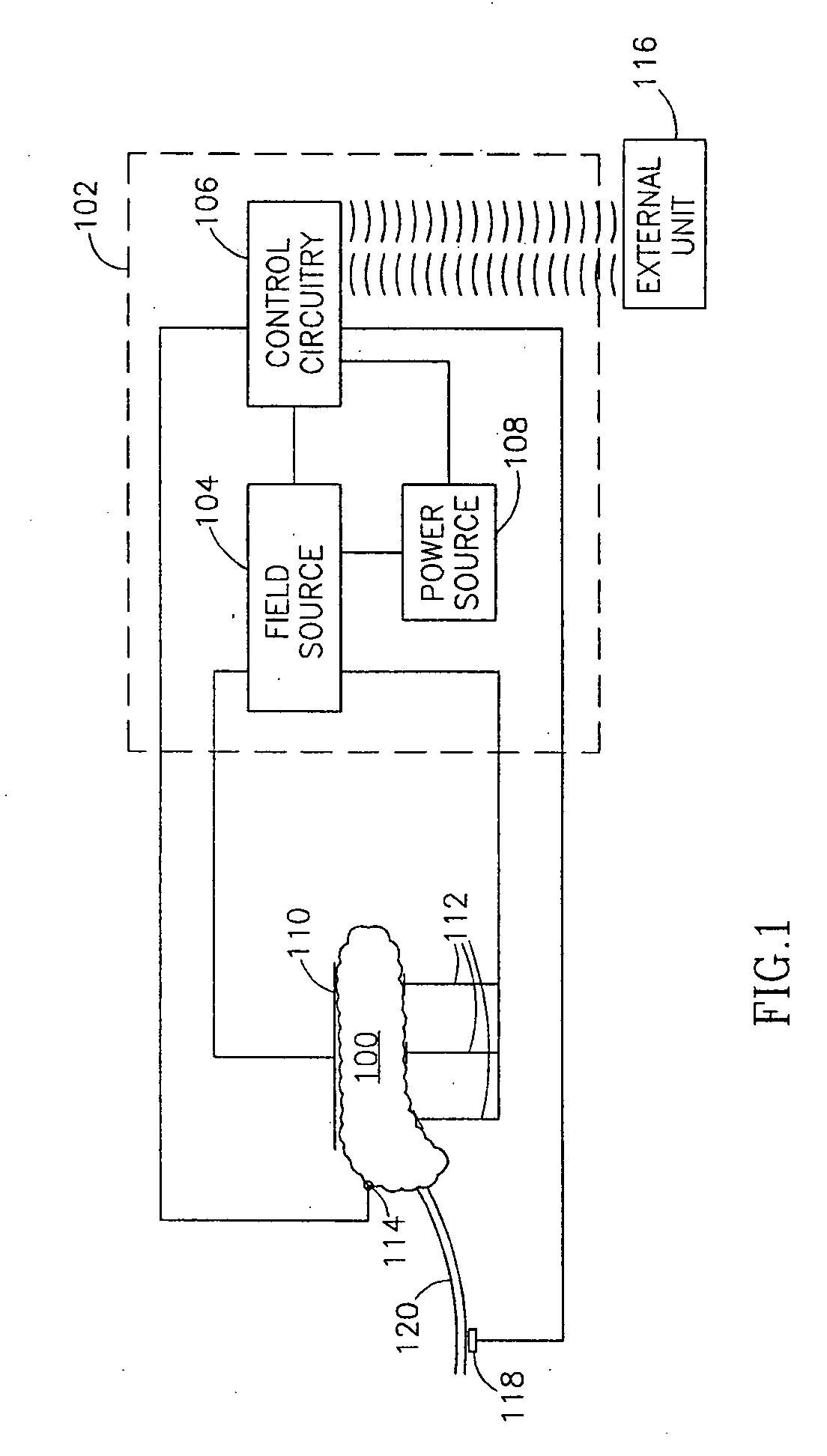
A method of treating a metabolic condition in a patient, comprising:determining a target non-immediate effect of a therapy relating to treatment of a metabolic condition; andapplying an electric field to an abdominal cavity of the patient in a manner designed to at least approach said target.
Owner:TYLERTON INT INC
Endoscopic system for treating inside of body cavity
InactiveUS20060025654A1Safe and reliableHelp positioningCannulasSurgical needlesThoracic structureHuman body
There is provided an endoscopic inserting system. The system includes an endoscope which is inserted into a lumen inside a body through a natural opening of a human body, an opening member which forms an opening for inserting the endoscope into a thoracic cavity or an abdominal cavity from the lumen inside the body at a wall portion of the lumen, and a retracting member which, when forming the opening, retracts the wall portion of the lumen.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC
Mechanical manipulator for surgical instruments
ActiveUS20130304084A1Solve the lack of stiffnessSolve the lack of precisionDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsConventional laparoscopyEngineering
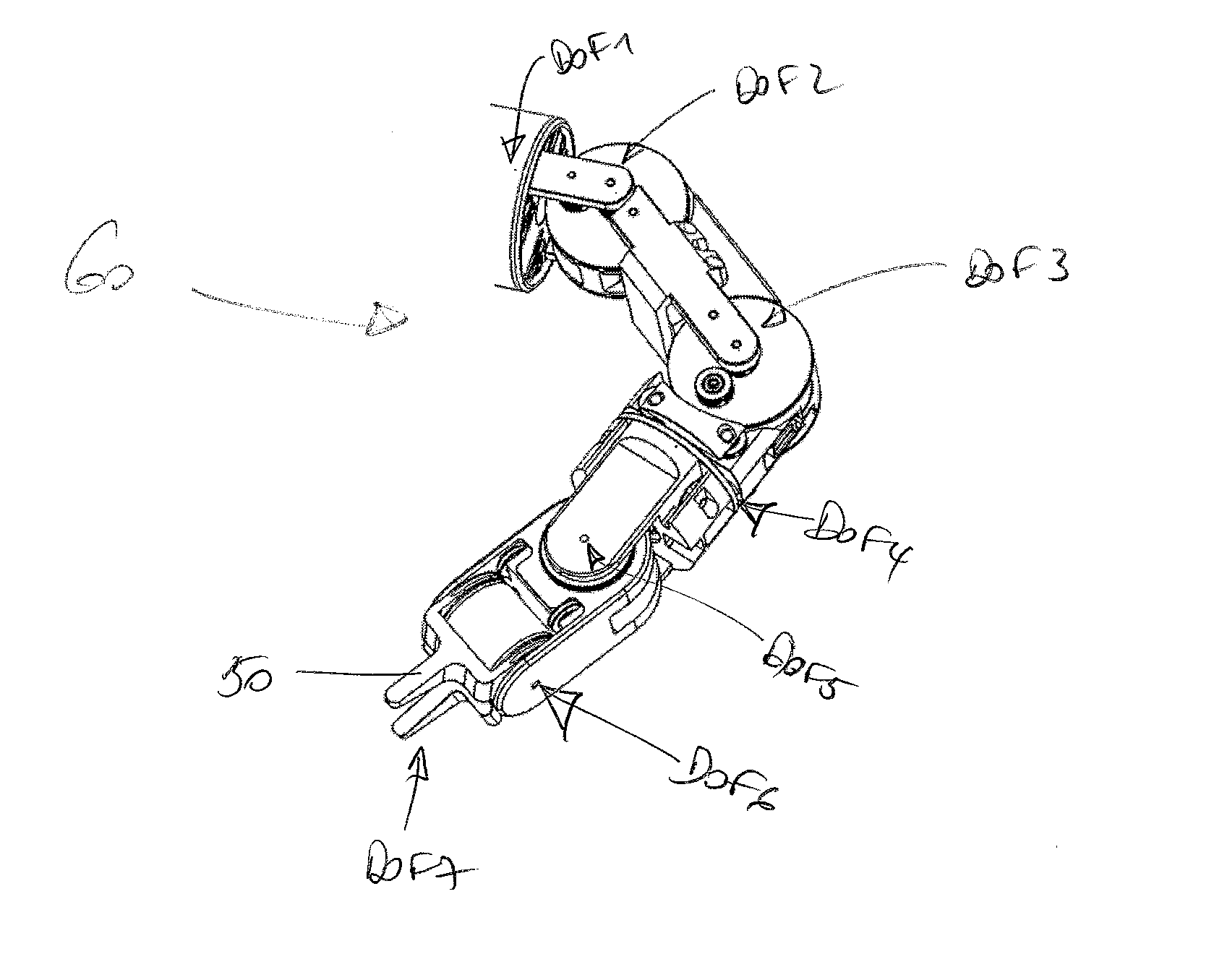
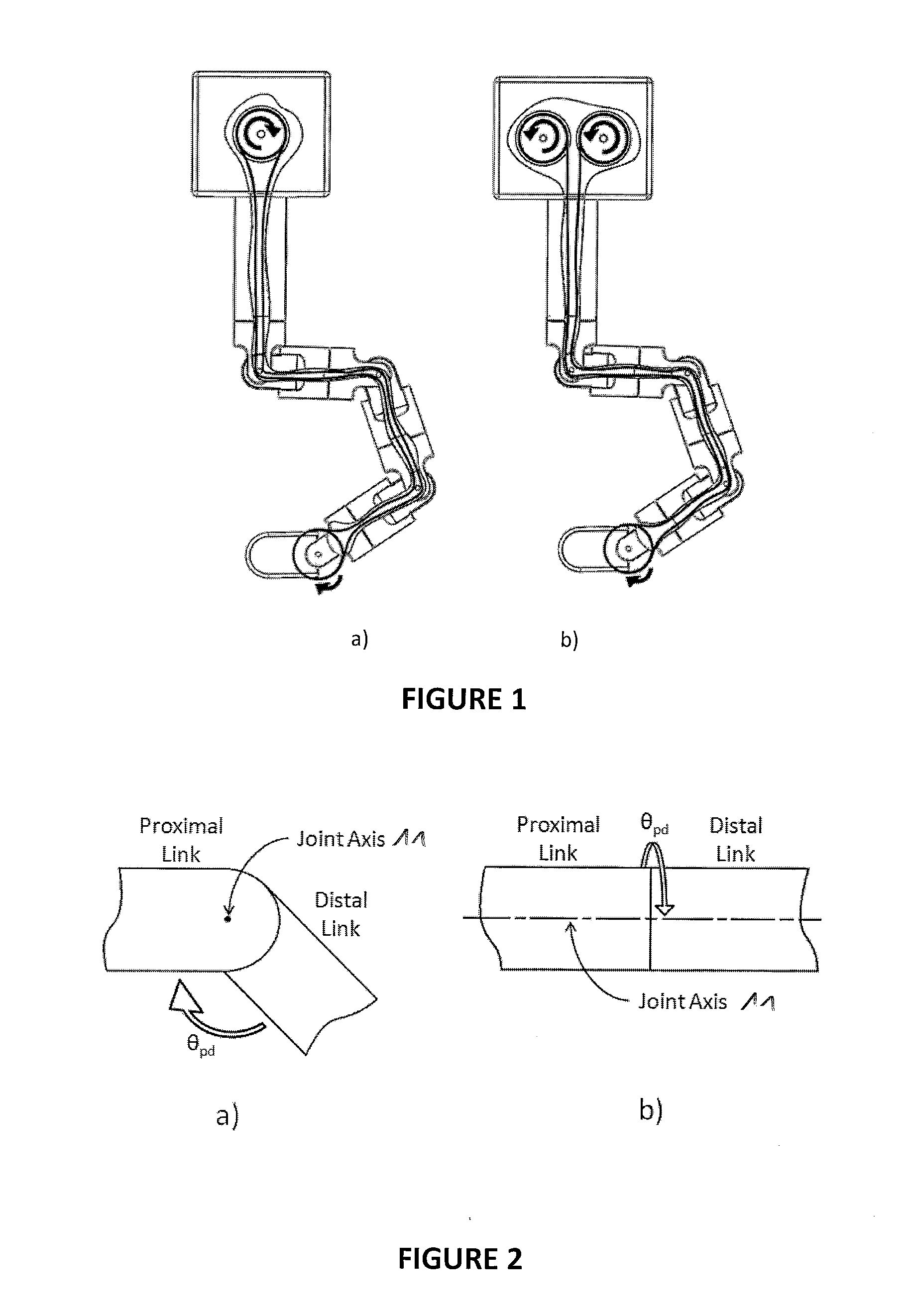
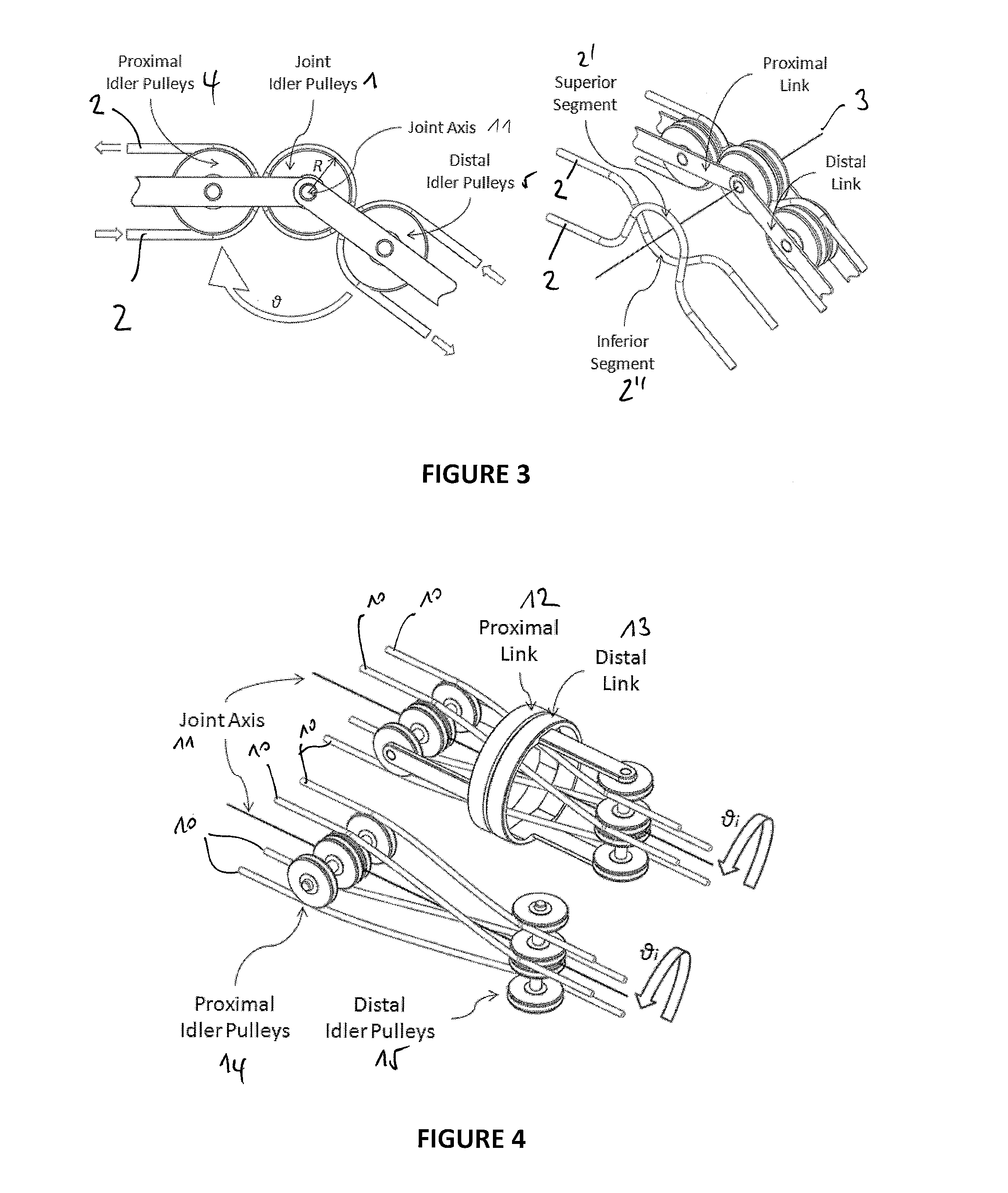
A novel mechanical system, based on a new cable driven mechanical transmission, able to provide sufficient dexterity, stiffness, speed, precision and payload capacity to actuate multi-DOF micro-manipulators. Besides the possibility of being used in several articulated surgical instruments and robotic systems for surgery or other applications involving remote manipulation, it enables the design of a novel fully mechanical surgical instrument, which offer the advantages of conventional laparoscopy (low cost, tactile feedback, high payload capacity) combined with the advantages of single port surgery (single incision, scarless surgery, navigation through several quadrants of the abdominal cavity) and robotic surgery (greater degrees of freedom, short learning curve, high stiffness, high precision, increased intuition). The unique design of the proposed system provides an intuitive user interface to achieve such enhanced manoeuvrability, allowing each joint of a teleoperated slave system to be driven by controlling the position of a mechanically connected master unit.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Laparoscopic specimen extraction port
A laparoscopic surgical extraction port (LSEP) includes a port having a radially-enlarged distal end. A sheath having a plurality of circumferentially-spaced prongs is slidingly mounted onto the port. With the prongs contracted radially-inwardly and the LSEP in its contracted position, a surgeon inserts the LSEP into a patient's abdominal cavity through an incision. The surgeon then expands the LSEP by pulling the port rearwardly such that the radially-enlarged distal end expands the prongs radially-outwardly. The surgeon then positions a specimen and endo-bag in the funnel formed by the expanded prongs. The specimen, endo-bag, and prongs are thereafter simultaneously extracted through the incision. A radially-inward force that is applied to the prongs by the incision substantially prevents the specimen from bunching or rupturing during the extraction process.
Owner:SHIMM PETER
Surgical instrument with wireless communication between control unit and remote sensor
Disclosed is a surgical instrument with wireless communication between control unit and remote sensor, such as an endoscopic or laparoscopic instrument. The surgical instrument may comprise an end effector comprising at least one sensor. The surgical instrument may also comprise an electrically conductive shaft having a distal end connected to the end effector wherein the sensor is electrically insulated from the shaft. The surgical instrument may also comprise a handle connected to a proximate end of the shaft. The handle may comprise a control unit electrically coupled to the shaft such that the shaft radiates signals as an antenna from the control unit to the sensor and receives radiated signals from the sensor. Other components electrically coupled to the shaft may also radiate the signals.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Surgical training simulator
A simulator (1) has a body form apparatus (2) with a skin-like panel (4) through which laproscopic instruments (5) are inserted. Cameras (10) capture video images of internal movement of the instruments (5) and a computer (6) processes them. 3D positional data is generated using stereo triangulation and is linked with the associated video images. A graphics engine (60) uses the 3D data to generate graphical representations of internal scenes. A blending function (70) blends real and recorded images, or real and simulated images to allow demonstration of effects such as internal bleeding or suturing.
Owner:CAE HEALTHCARE
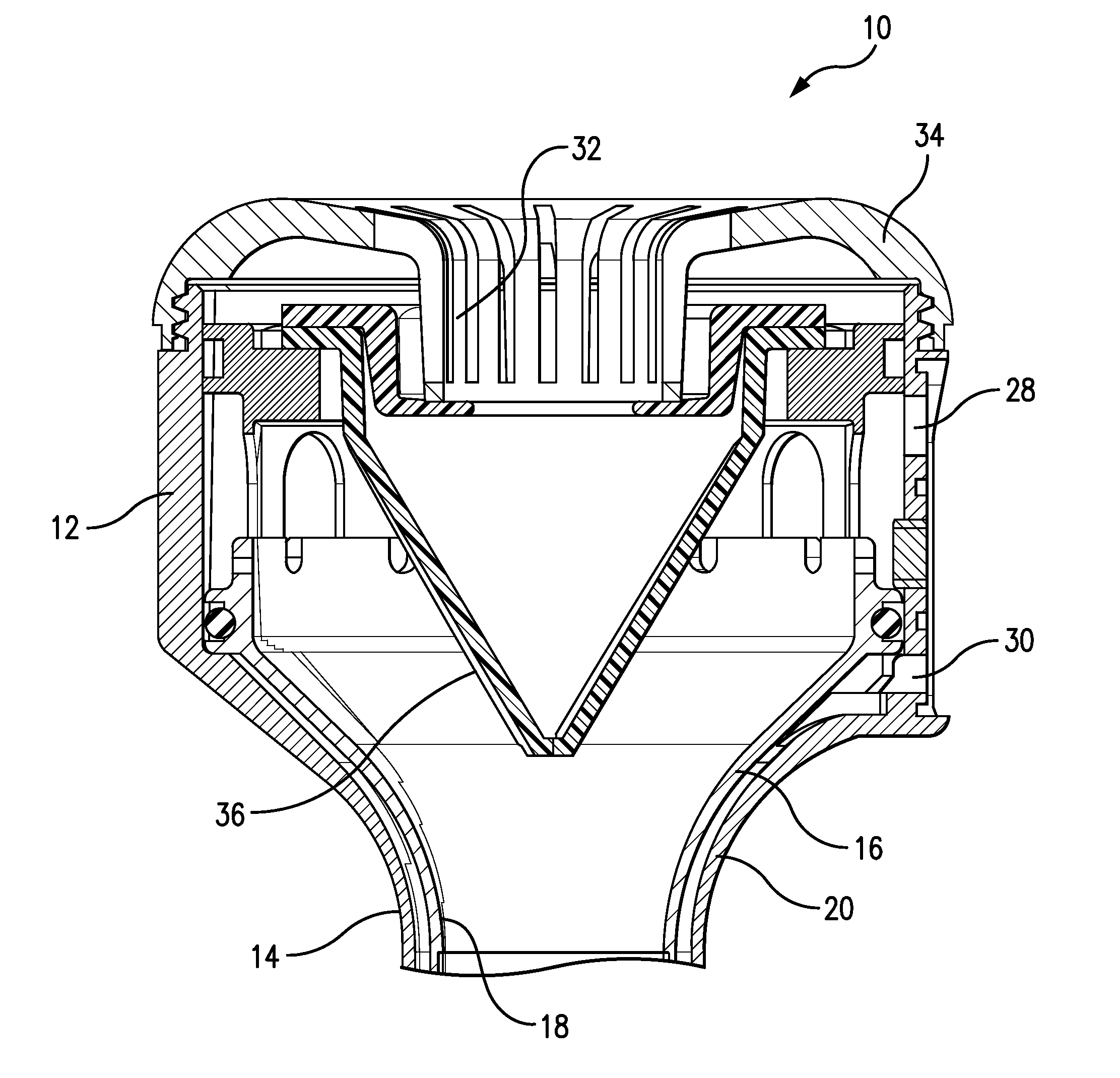
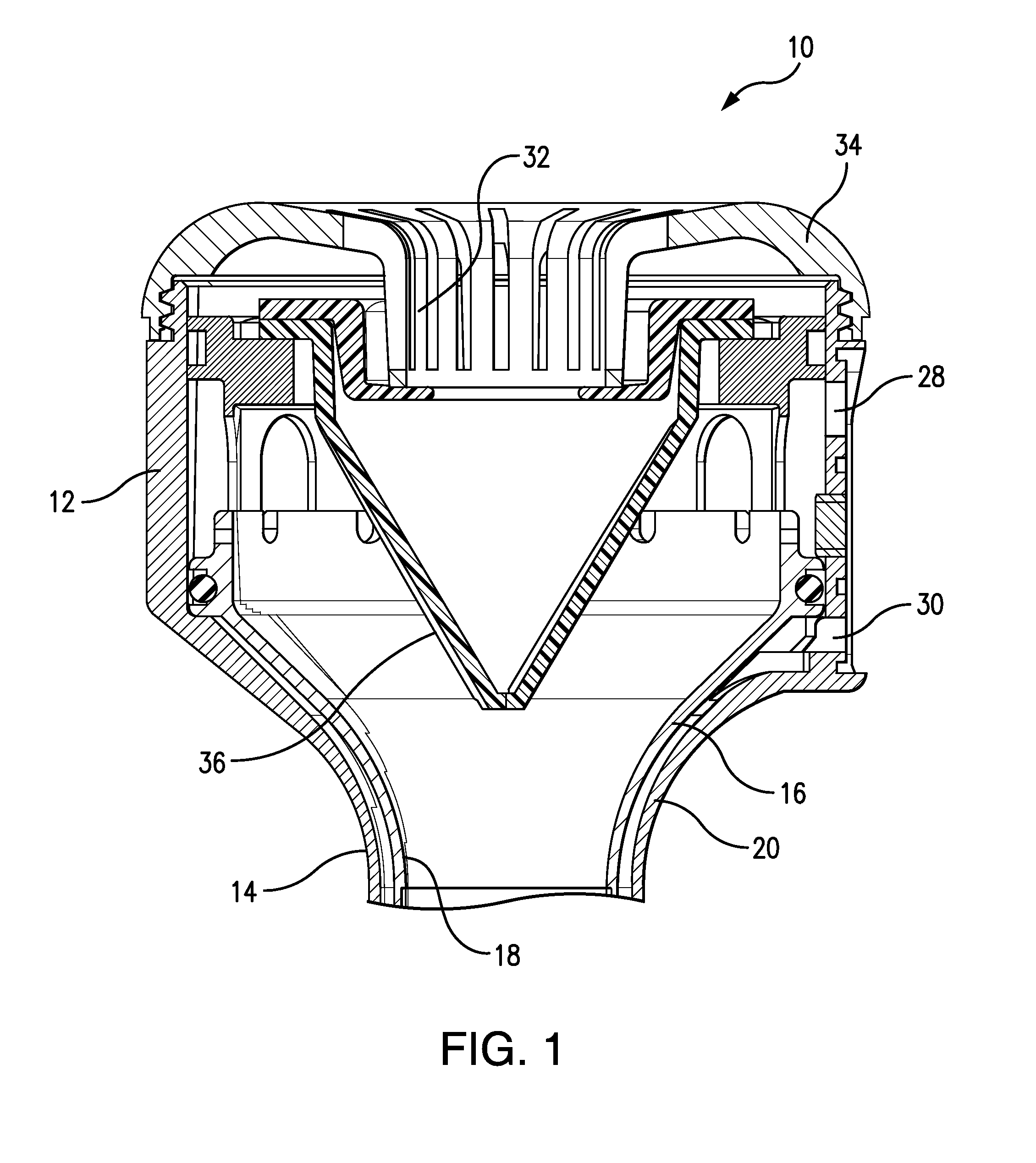
Trocar assembly with pneumatic sealing
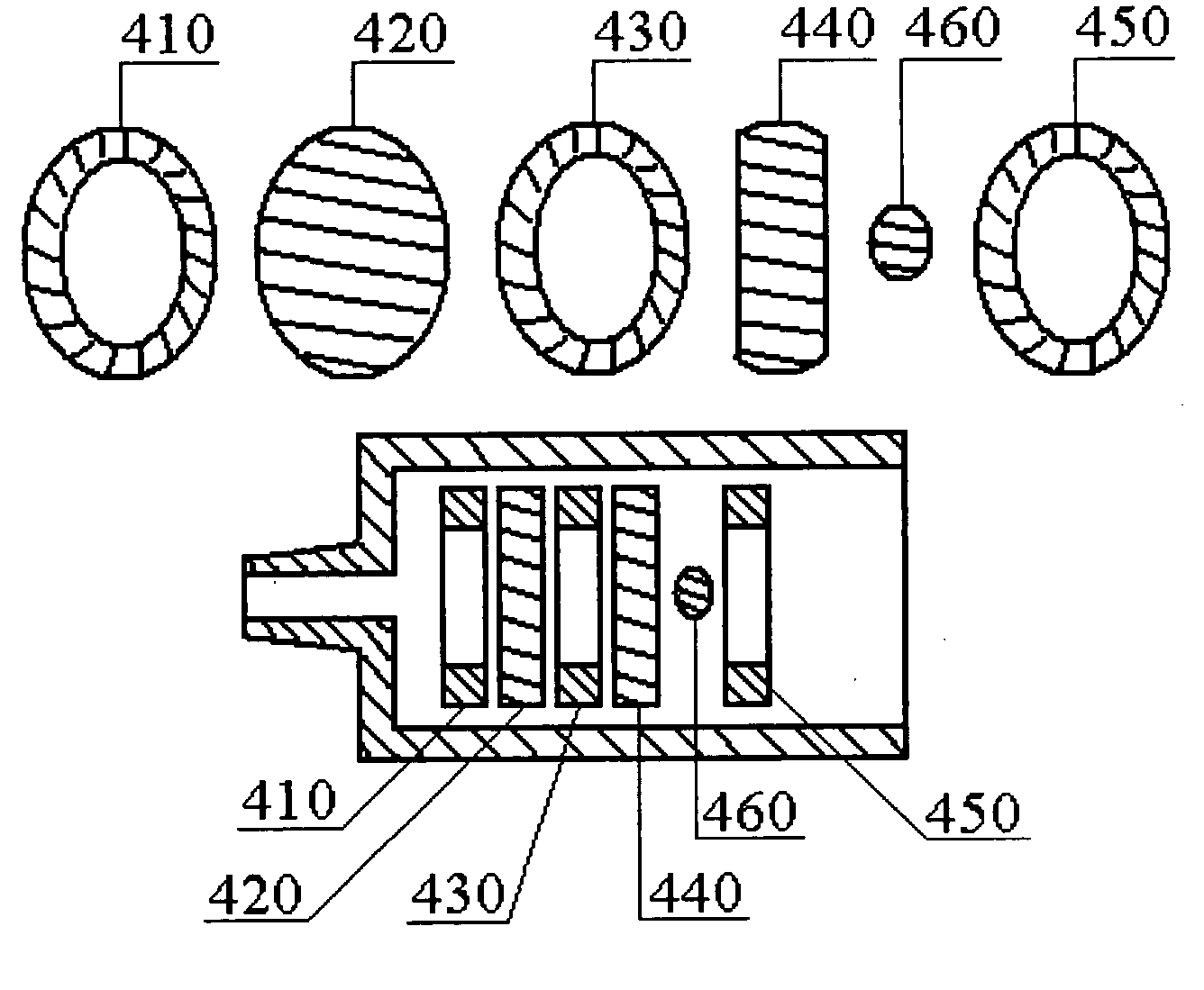
A trocar assembly for creating a pneumatic seal during a minimally-invasive surgical procedure. The trocar assembly including an elongated body having a lumen extending therethrough. The proximal end portion of the body defining a housing. A fluid supply plenum is defined in the housing configured to deliver pressurized insufflation fluid to a nozzle. The nozzle configured for directing pressurized fluid into the lumen and creating a pneumatic seal. A fluid return plenum is defined in the housing configured to collect spent insufflation fluid from as patient's abdominal cavity. The fluid return plenum including a plurality of axially and radially oriented elongate vanes configured to permit spent insufflation fluid to proceed between the vanes and direct spent insufflation fluid back to the fluid return plenum.
Owner:SURGIQUEST
Laparoscopic instruments and methods utilizing suction
InactiveUS20060025781A1Minimized cross sectionLittle strengthSurgical pincettesSurgical forcepsAbdominal cavityDilator
A surgical dilator extractor is introduced into the abdominal cavity through a trocar cannula and expanded, forming a tissue receiving space, at the distal end. The tissue that is to be extracted is then suctioned to the dilator. The tissue is then removed from the cavity by the surgeon applying a force onto the dilator extractor that insures the elongation of the tissue and temporarily dilates the entry wound to the extent necessary for the tissue to be removed. Alternative embodiments of the surgical dilator extractor and related instrument tool sets and methods for the use thereof also are disclosed.
Owner:LOGUIDICE MARK
Systems and methods for conducting smoke evacuation during laparoscopic surgical procedures
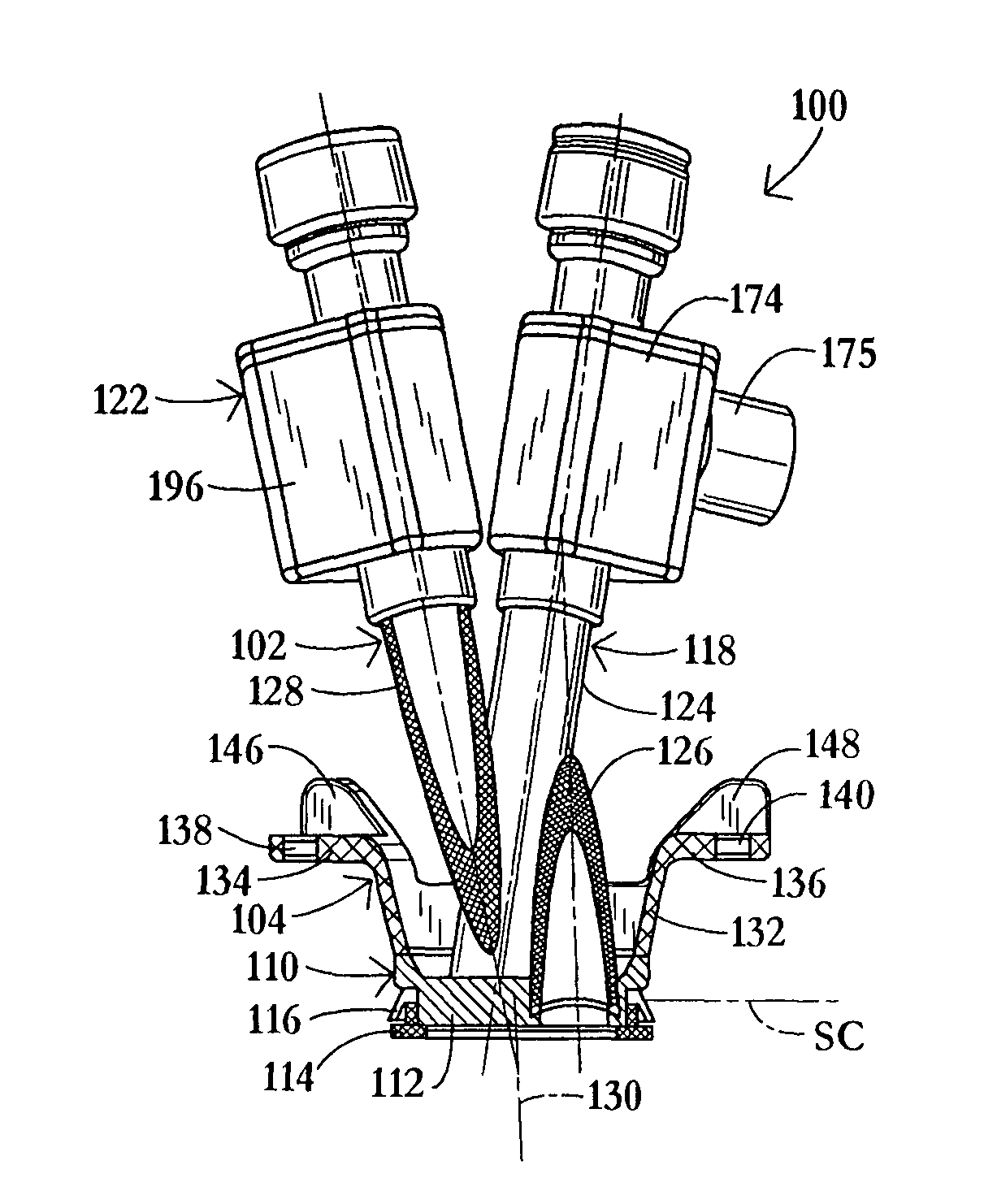
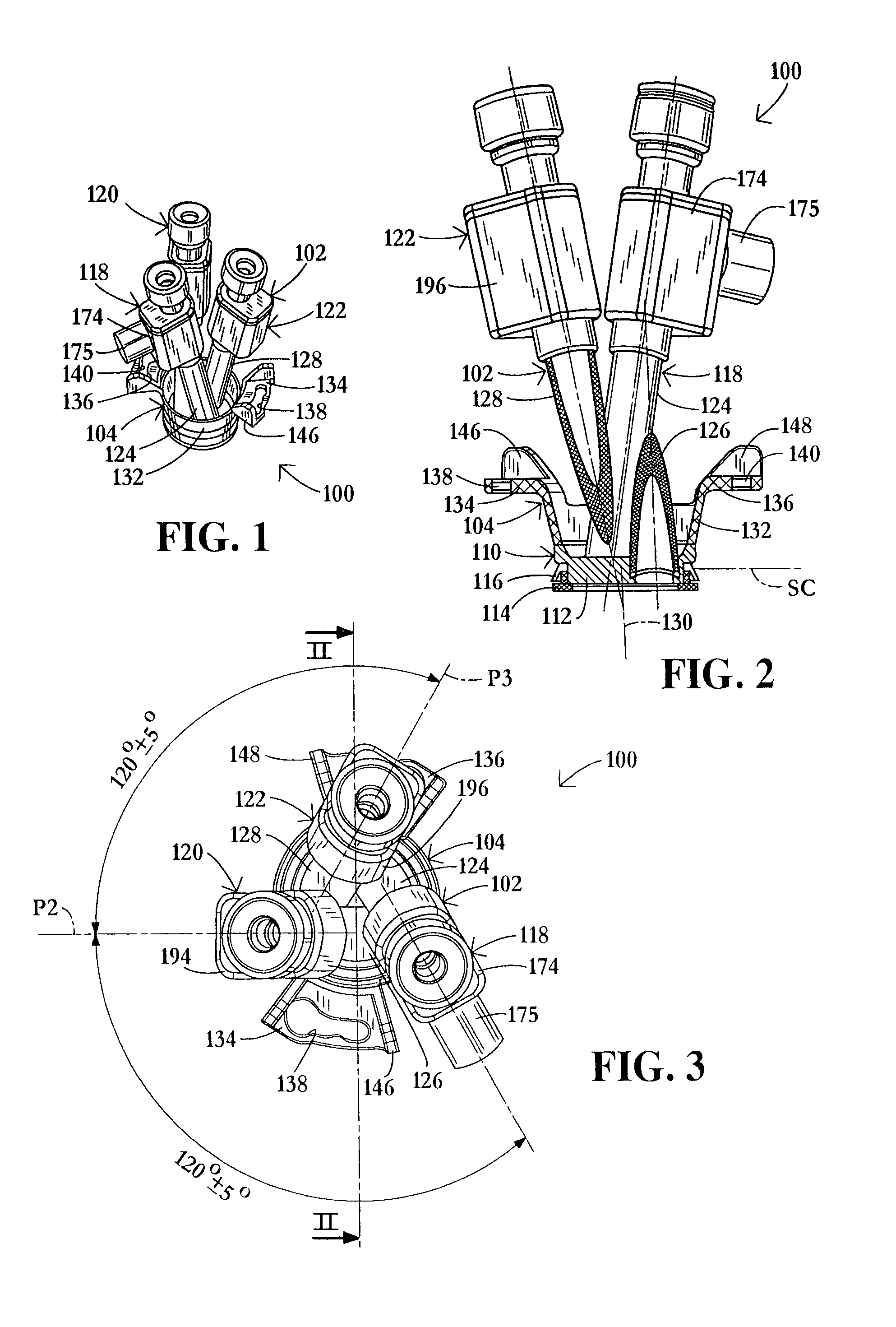
An insufflation and smoke evacuation system for use during laparoscopic surgical procedures in an abdominal cavity of a patient is disclosed that includes a pump for circulating pressurized gas within the system, and a dual lumen cannula configured to provide access to the abdominal cavity of a patient, which includes a first lumen communicating with a source of insufflation fluid and a second lumen communicating with the pump.
Owner:SURGIQUEST
Safety penetrating method and apparatus into body cavities, organs, or potential spaces
InactiveUS20060173480A1Reduce riskDanger can be reducedDiagnosticsSurgical needlesVeinElectrical resistance and conductance
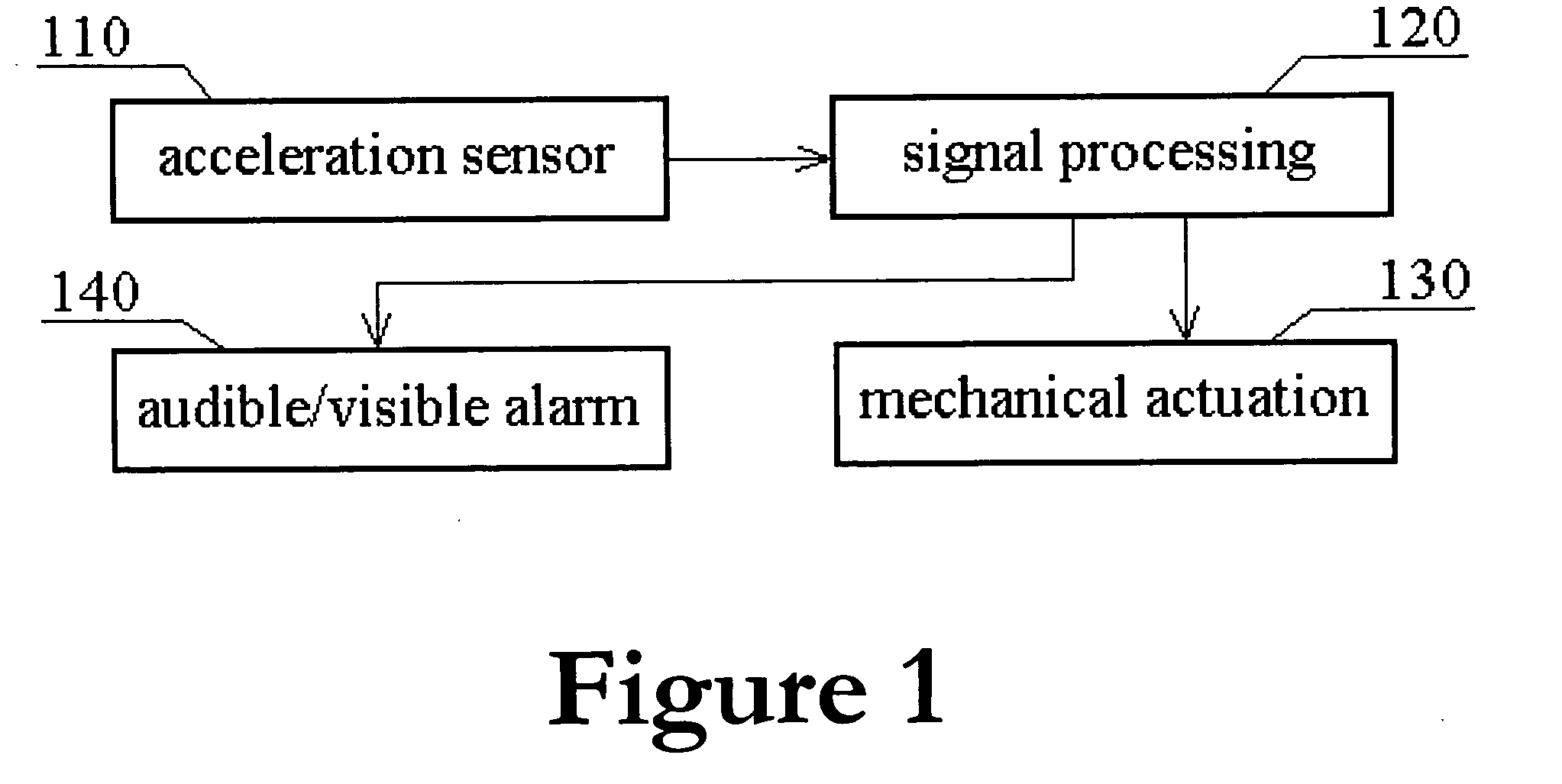
To more accurately control insertion of penetrating instruments (e.g., trocars, needles, or the like) into a body cavity, organ, or potential space, an accelerometer is coupled to the penetrating instrument. The accelerometer may by employed to measure or detect the sudden lack of resistance which occurs when the penetrating instrument penetrates to a predetermined depth (e.g., through the abdominal cavity, vein, or outer bone) in a more accurate and reliable way instead of practitioners' subjective feeling. An acceleration sensor (i.e., accelerometer) coupled to the penetrating instrument (e.g., trocar or the like) may transform the physical variable ‘resistance change’ into an electronic signal that is then processed in an electronic circuit, and finally triggers an audible / visible alarm and / or feeds an actuating mechanism to control movement of the penetrating instrument.
Owner:ZHANG YI
Seal for medical instrument
InactiveUS20070027447A1Reduce riskSurgical instrument detailsSurgical forcepsAbdominal cavityEngineering
A laparoscopic tube end for interfacing a tube with a tip may include an attachment portion to attach to the tip, and a tapered flare portion to frictionally abut the tip when the tip is attached to the tube end.
Owner:MICROLINE PENTAX
Methods and devices for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity
A novel approach to diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity is described. More specifically, a technique for accessing the peritoneal cavity via the wall of the digestive tract is provided so that examination of and / or a surgical procedure in the peritoneal cavity can be conducted via the wall of the digestive tract with the use of a flexible endoscope. As presently proposed, the technique is particularly adapted to transgastric peritoneoscopy. However, access in addition or in the alternative through the intestinal wall is contemplated and described as well. Transgastric and / or transintestinal peritoneoscopy will have an excellent cosmetic result as there are no incisions in the abdominal wall and no potential for visible post-surgical scars or hernias.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com