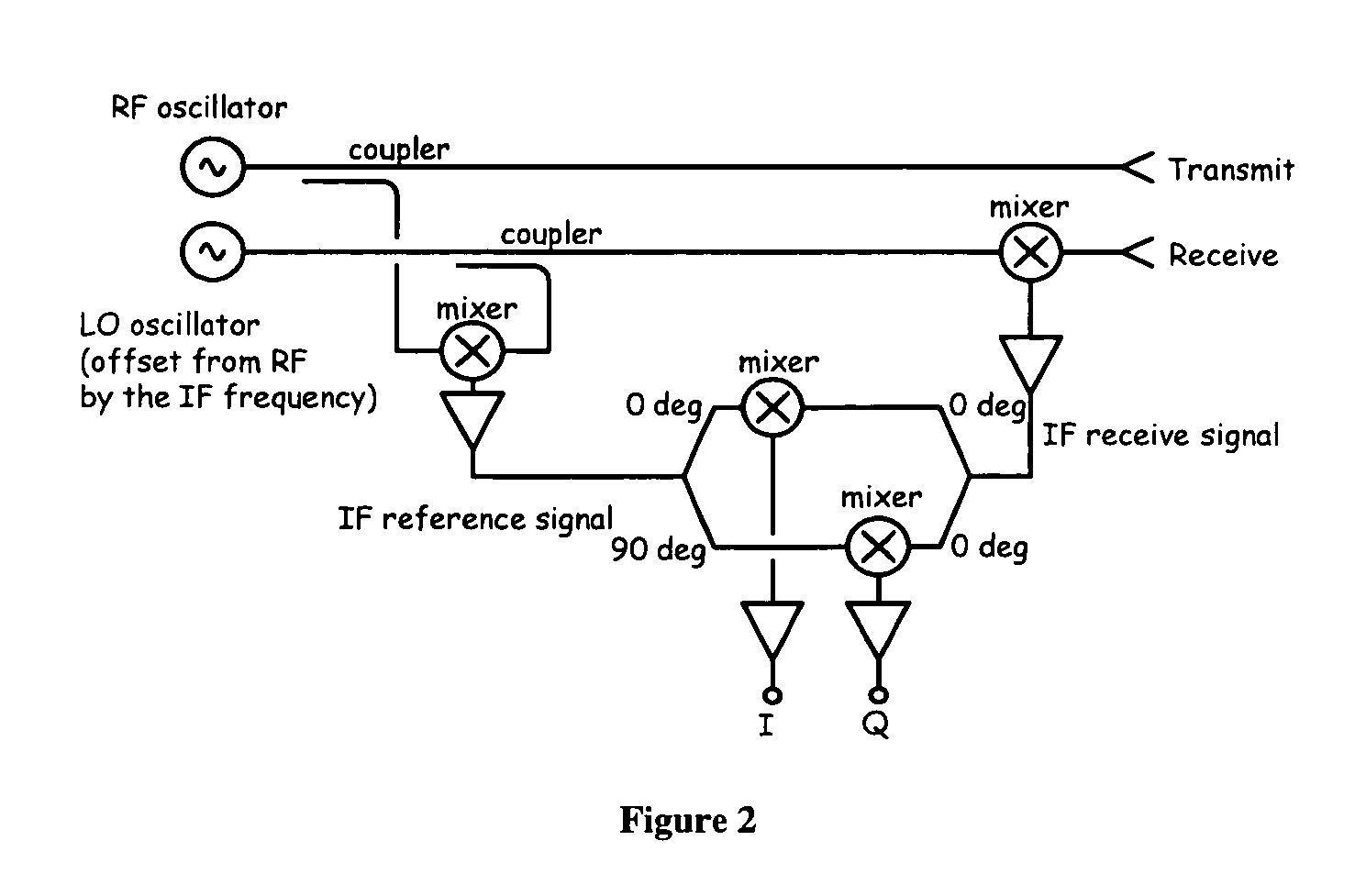
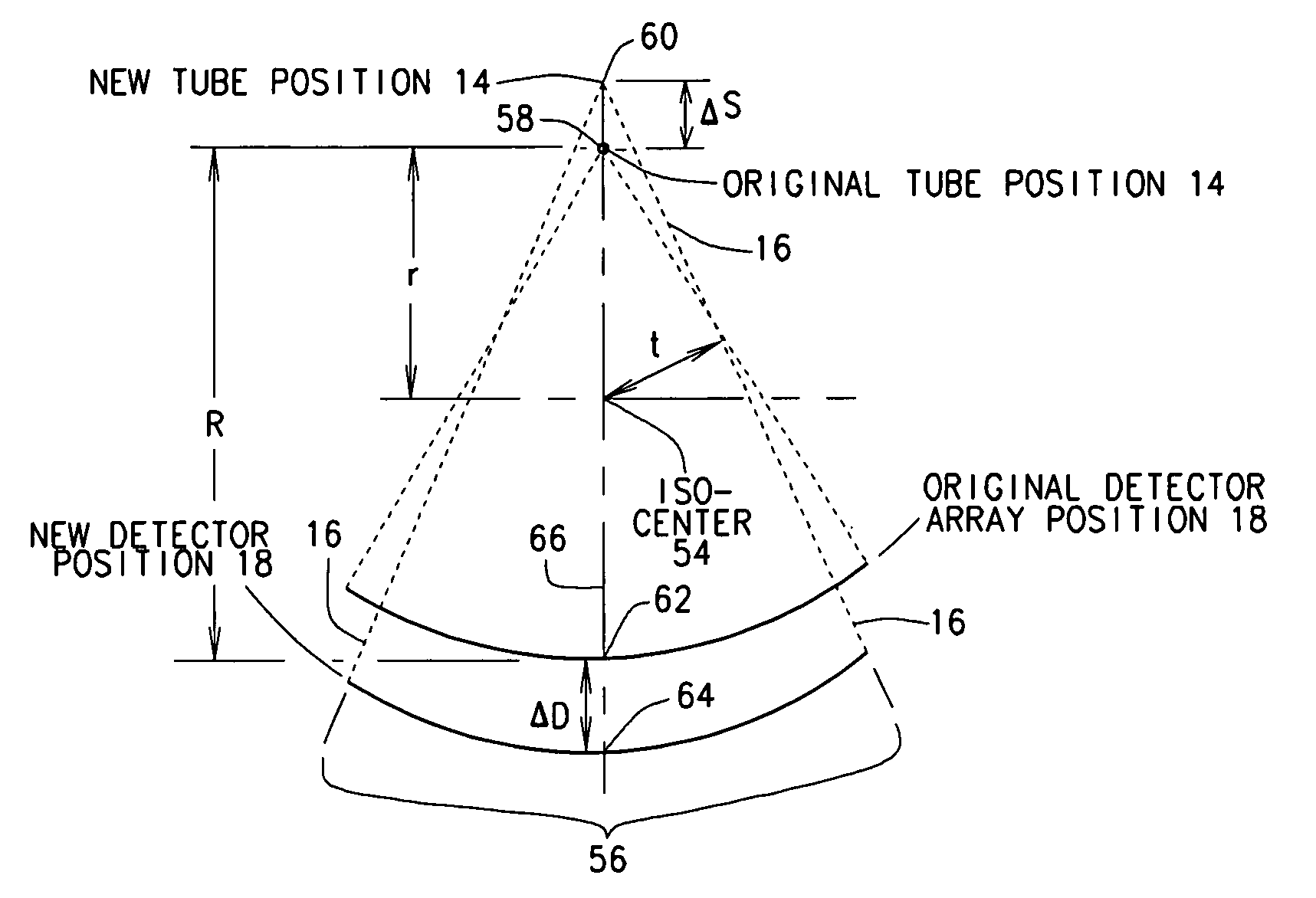
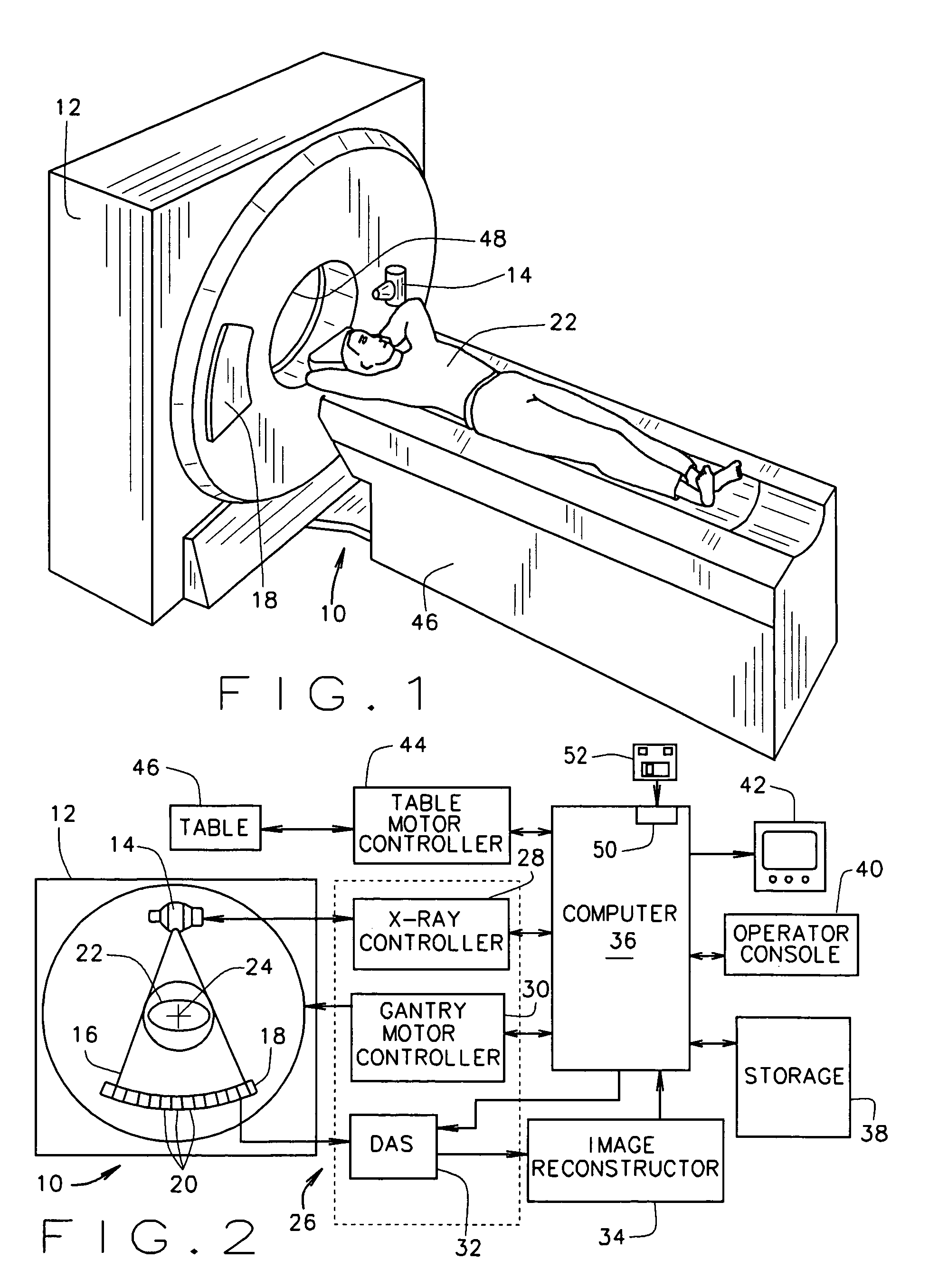
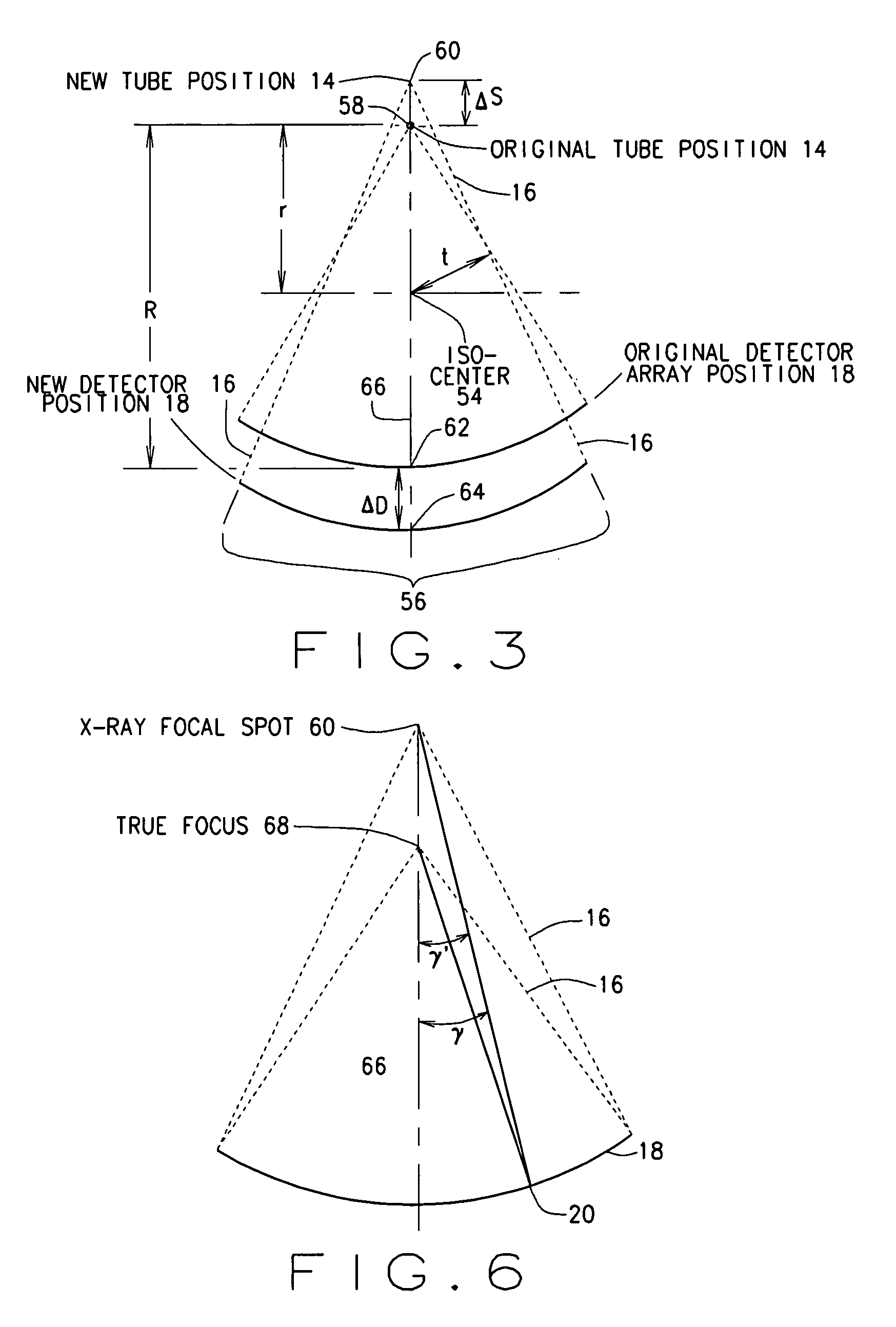
Patents
Literature
190 results about "Artifact reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
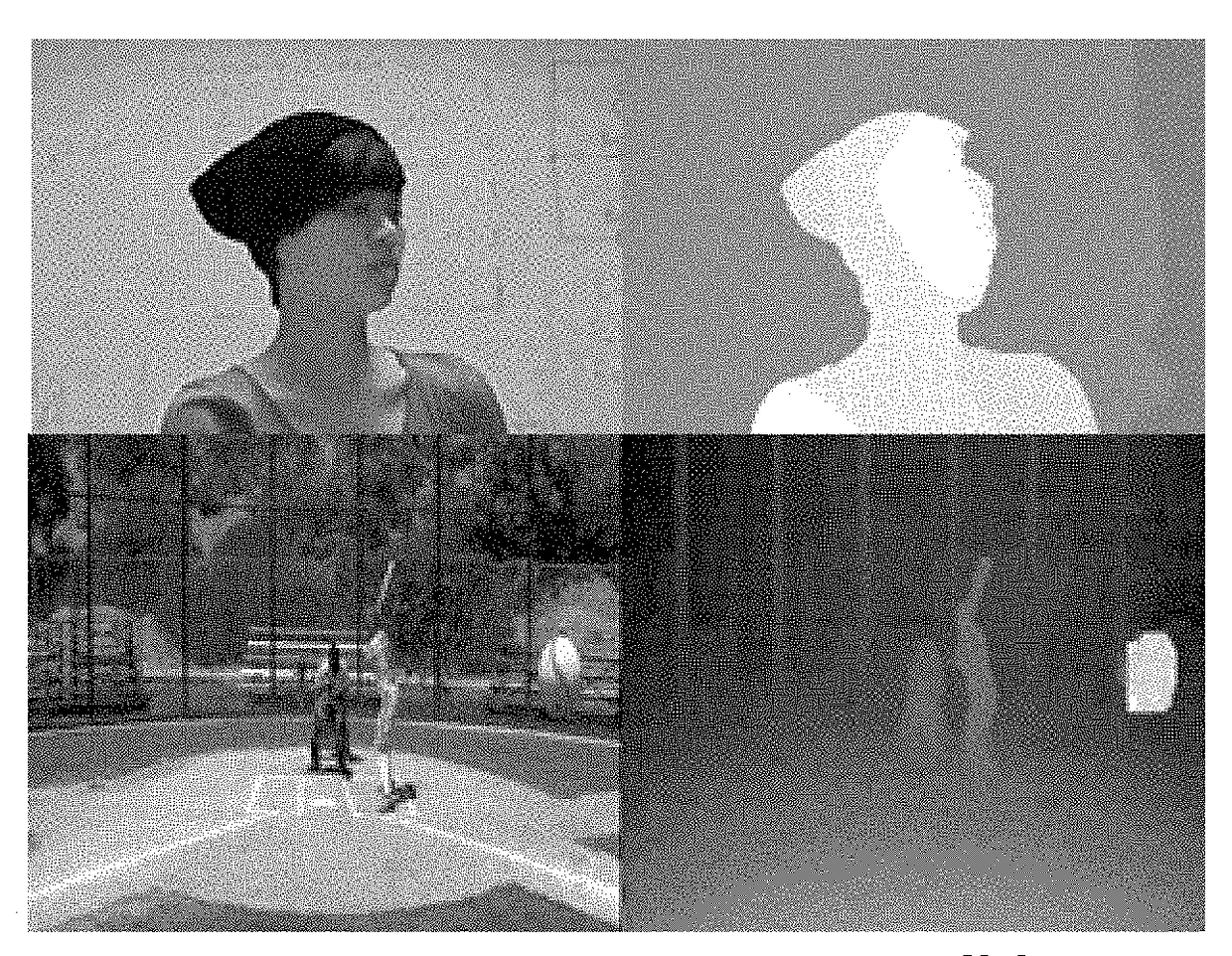
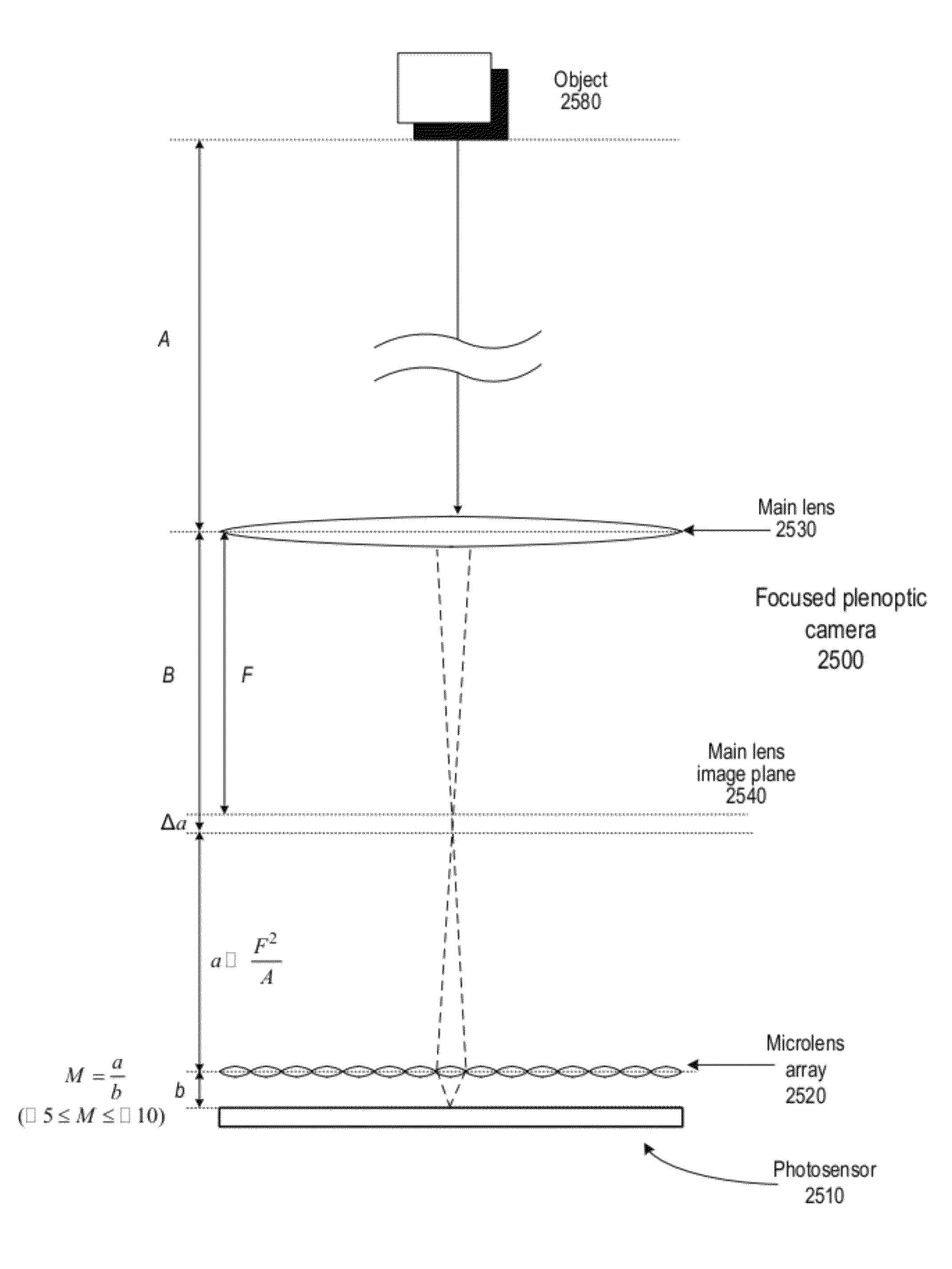
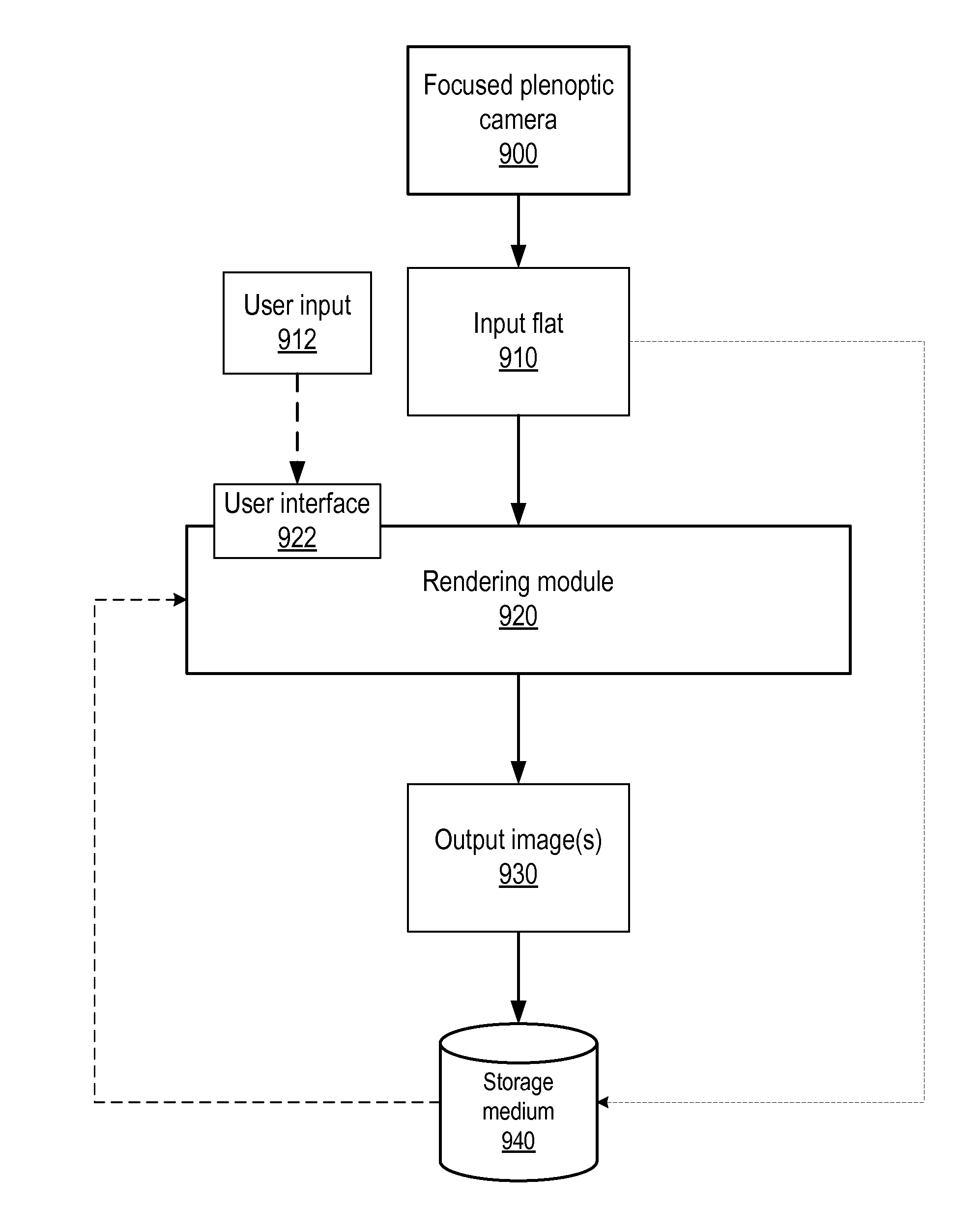
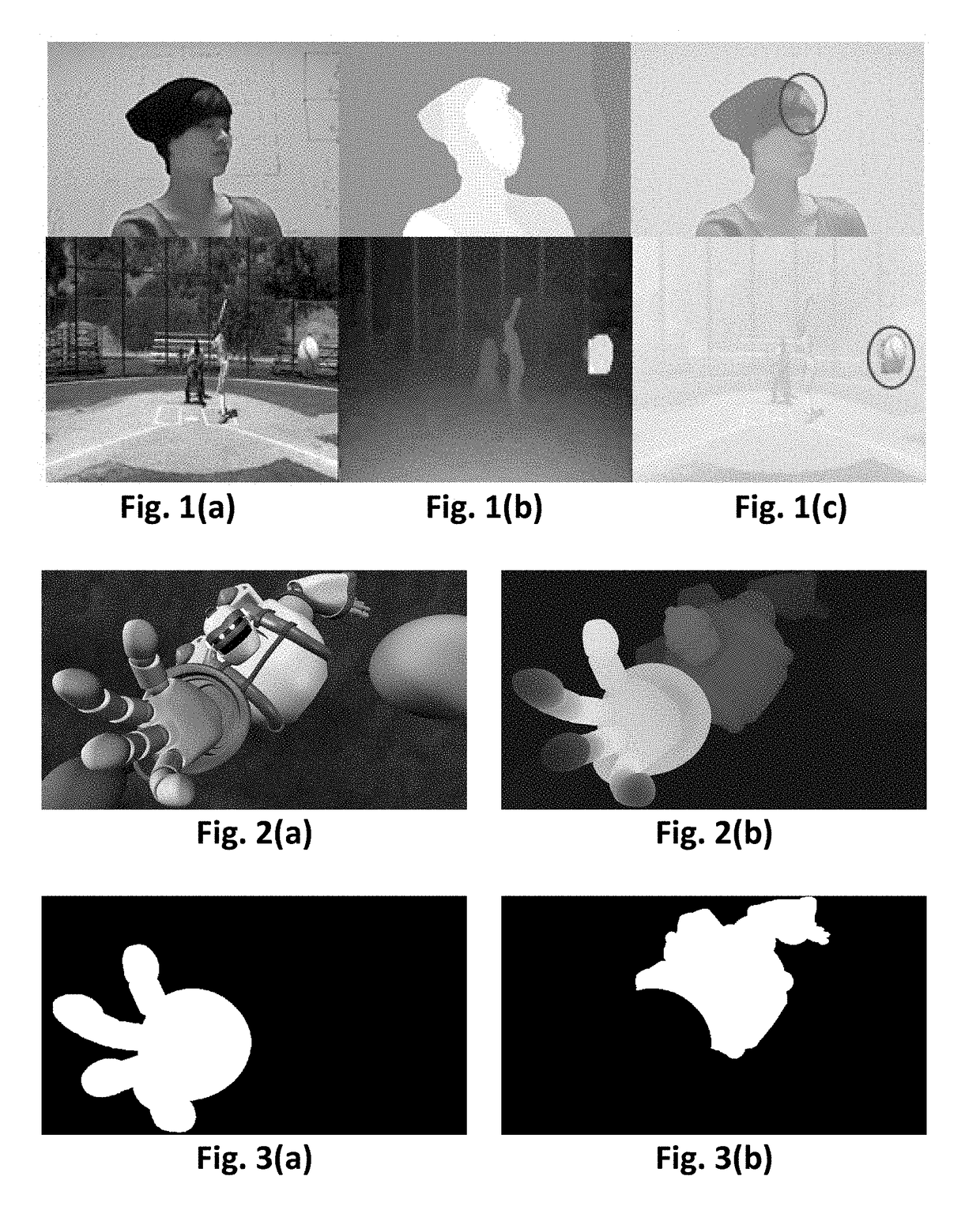
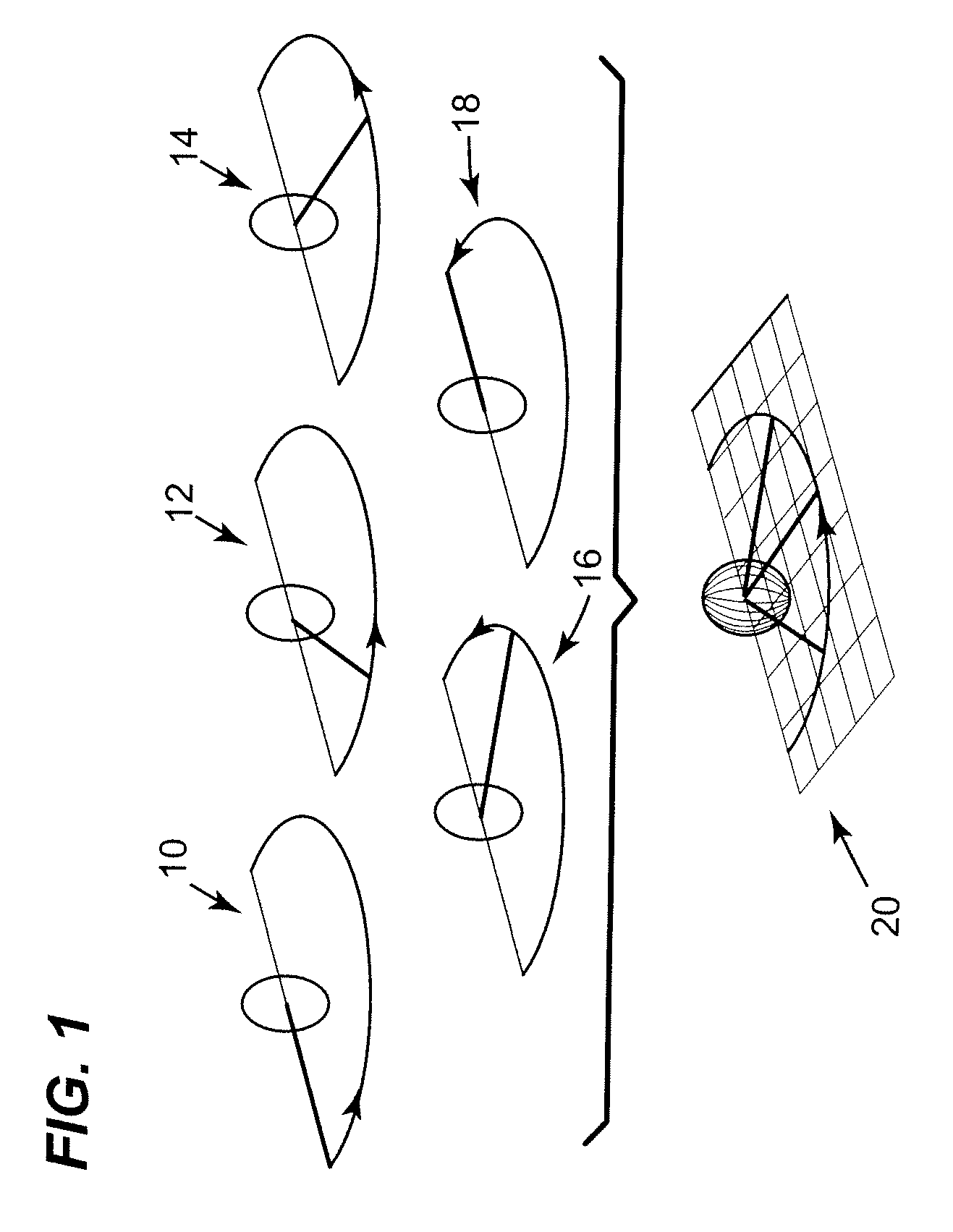
Methods and apparatus for reducing plenoptic camera artifacts
ActiveUS8189089B1Reduce artifactsQuality improvementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptic systemRendering algorithms
Methods and apparatus for reducing plenoptic camera artifacts. A first method is based on careful design of the optical system of the focused plenoptic camera to reduce artifacts that result in differences in depth in the microimages. A second method is computational; a focused plenoptic camera rendering algorithm is provided that corrects for artifacts resulting from differences in depth in the microimages. While both the artifact-reducing focused plenoptic camera design and the artifact-reducing rendering algorithm work by themselves to reduce artifacts, the two approaches may be combined.
Owner:ADOBE INC
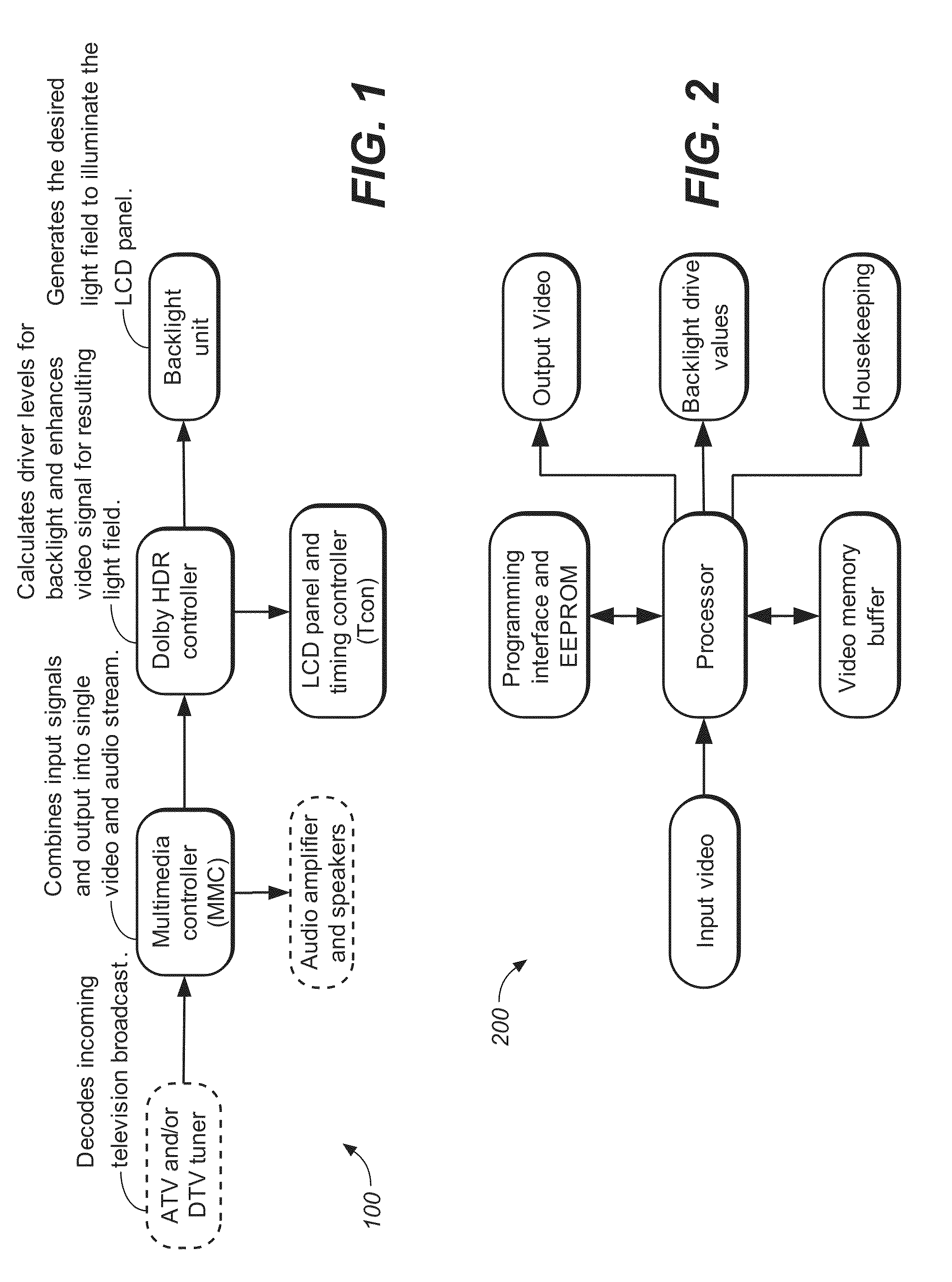
Method and apparatus in various embodiments for hdr implementation in display devices
InactiveUS20090322800A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLed arrayDisplay device
An HDR display is a combination of technologies including, for example, a dual modulation architecture incorporating algorithms for artifact reduction, selection of individual components, and a design process for the display and / or pipeline for preserving the visual dynamic range from capture to display of an image or images. In one embodiment, the dual modulation architecture includes a backlight with an array of RGB LEDs and a combination of a heat sink and thermally conductive vias for maintaining a desired operating temperature.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Methods and apparatus for facilitating a reduction in artifacts
InactiveUS7272429B2Reduce artifactsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputer scienceEnergy spectrum
A method for facilitating a reduction in artifacts includes receiving data regarding a first energy spectrum of a scan of an object, and receiving data regarding a second energy spectrum of a scan of the object, wherein the second energy spectrum is different than the first energy spectrum. The method further includes reconstructing at least one original first energy image using the first energy spectrum data, reconstructing at least one original second energy image using the second energy spectrum data, transforming at least one original second energy image into at least one transformed first energy image, and combining at least one original first energy image with at least one transformed first energy image to generate a combined first energy image.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Method and system for providing a continuous motion sequential lateral solidification for reducing or eliminating artifacts, and a mask for facilitating such artifact reduction/elimination
InactiveUS20070020942A1Reduce and eliminate artifactArtifact is reduced and eliminatedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusComputer scienceGrain growth
An arrangement, process and mask for implementing single-scan continuous motion sequential lateral solidification of a thin film provided on a sample such that artifacts formed at the edges of the beamlets irradiating the thin film are significantly reduced. According to this invention, the edge areas of the previously irradiated and resolidified areas which likely have artifacts provided therein are overlapped by the subsequent beamlets. In this manner, the edge areas of the previously resolidified irradiated areas and artifacts therein are completely melted throughout their thickness. At least the subsequent beamlets are shaped such that the grains of the previously irradiated and resolidified areas which border the edge areas melted by the subsequent beamlets grow into these resolidifying edges areas so as to substantially reduce or eliminate the artifacts.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
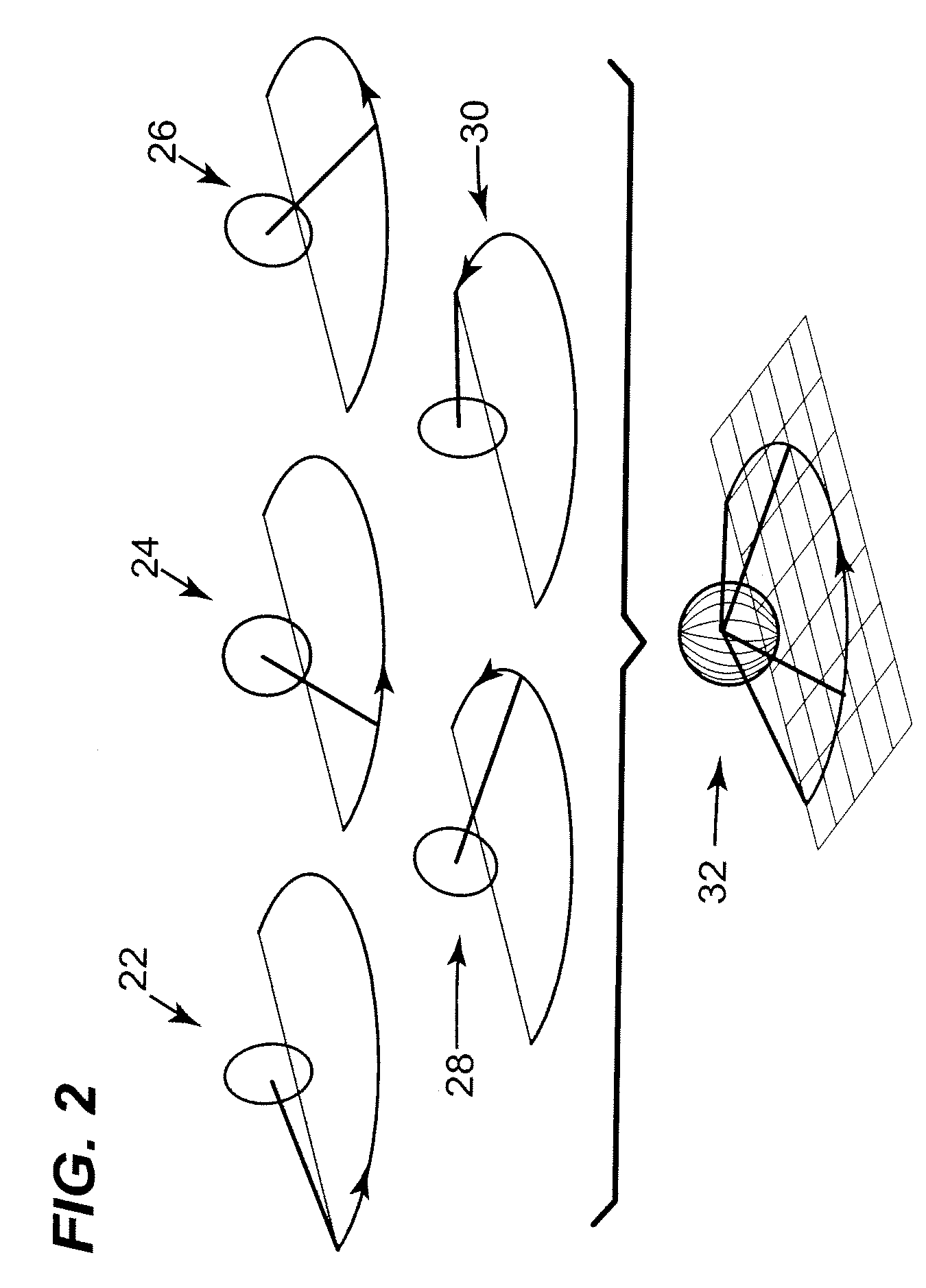
Methods and Apparatus for Reducing Plenoptic Camera Artifacts
ActiveUS20130128081A1High resolutionReduce artifactsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer scienceRendering algorithms
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
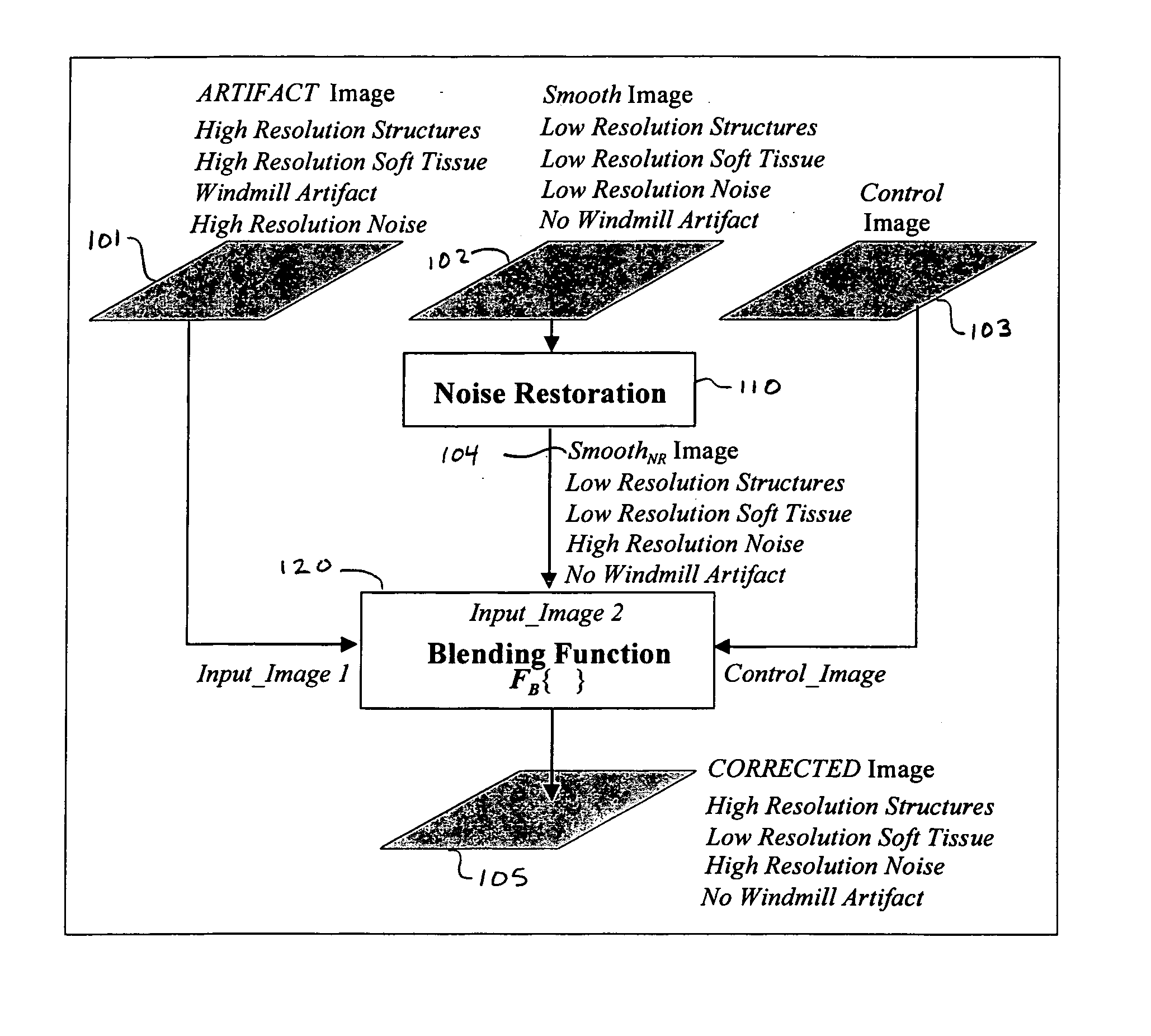
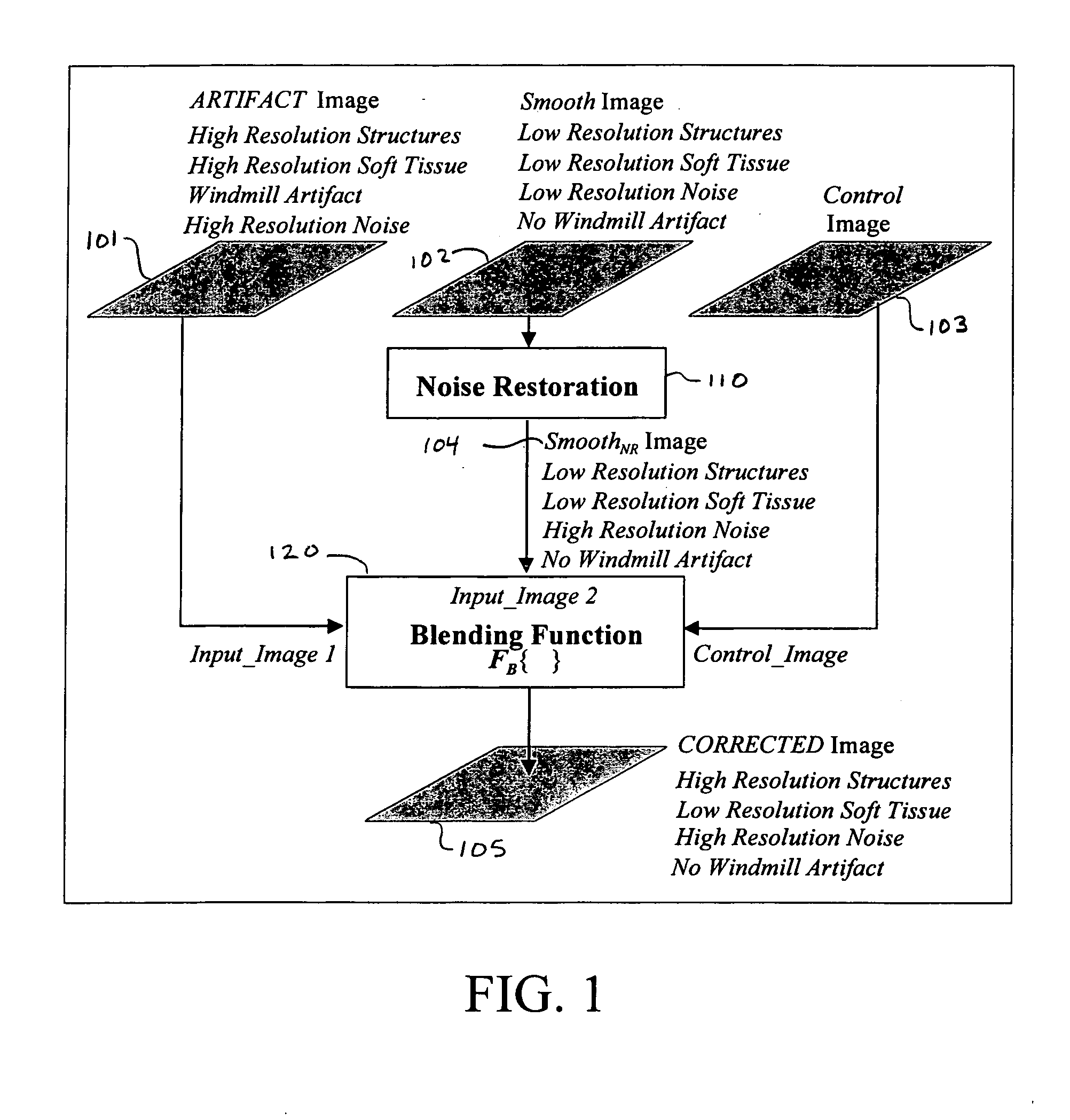
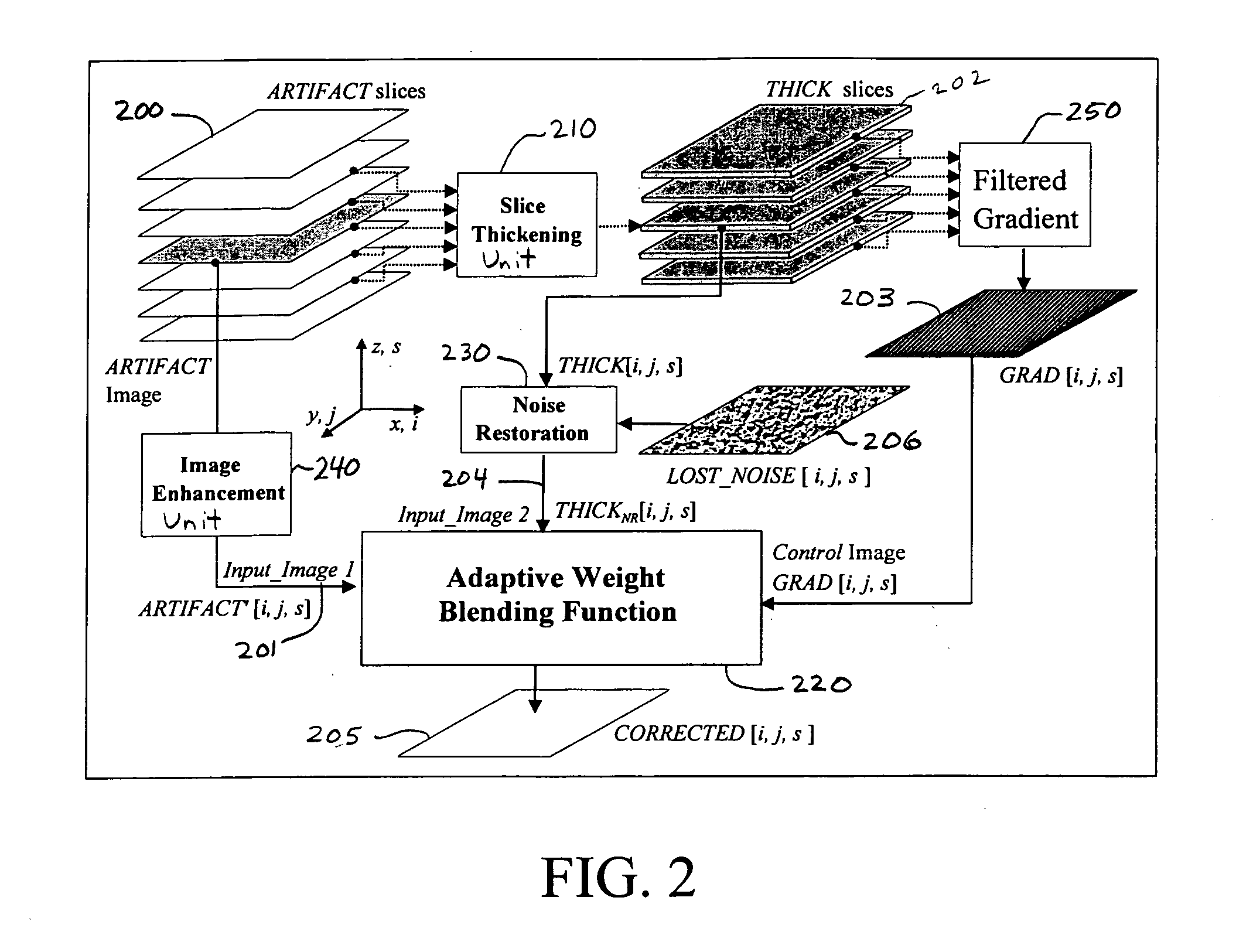
Method for helical windmill artifact reduction with noise restoration for helical multislice CT
A method of removing an imaging artifact in a medical image, including obtaining a first plurality of images, the first plurality of images collectively defining a first image volume; filtering the first plurality of images to create a second plurality of images, each image in the second plurality of images comprising an average of at least two images in the first plurality of images; selecting a first image from the first plurality of images; adding a lost noise image to a second image in the second plurality of images to create a noise restored image, the second image in the second plurality of images corresponding to the first image in the first plurality of images; determining a gradient image based on pixel values in the second plurality of images, the gradient image comprising a gradient value at each pixel location in the second image; and combining, based on the determined gradient image, the first image and the noise restored image to obtain a corrected image that does not contain the imaging artifact.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
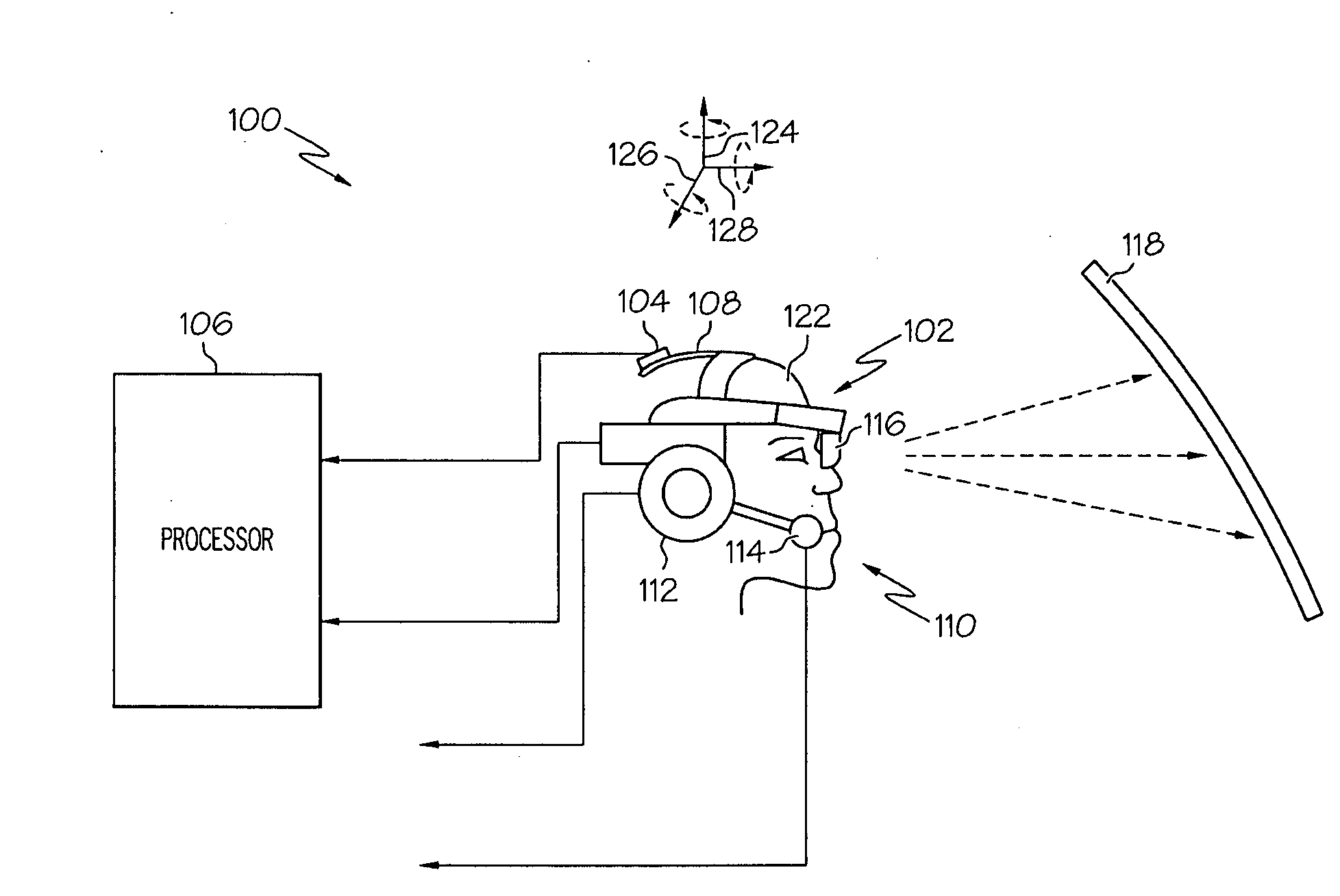
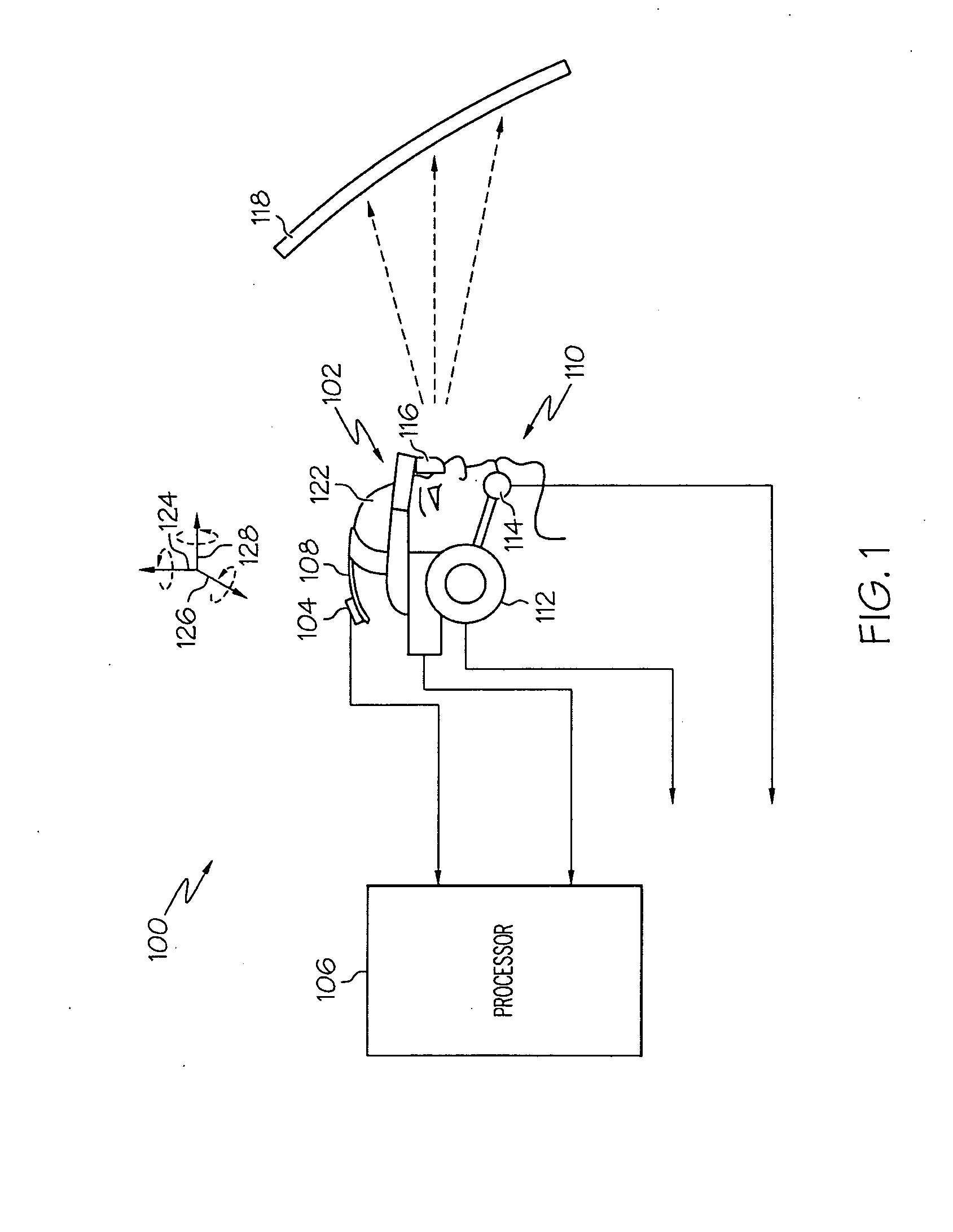
Near-to-eye display artifact reduction system and method
ActiveUS20100039353A1Reduce artifactsCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsComputer graphics (images)Display device
A near-to-eye (NTE) display system and method are provided for reducing artifact display in a NTE display that is worn, at least partially, on a viewer's head. The movement of the NTE display is sensed while displaying an image that comprises individual content frames on the NTE display. A characteristic of the individual content frames of the displayed image is varied based on the sensed movement.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
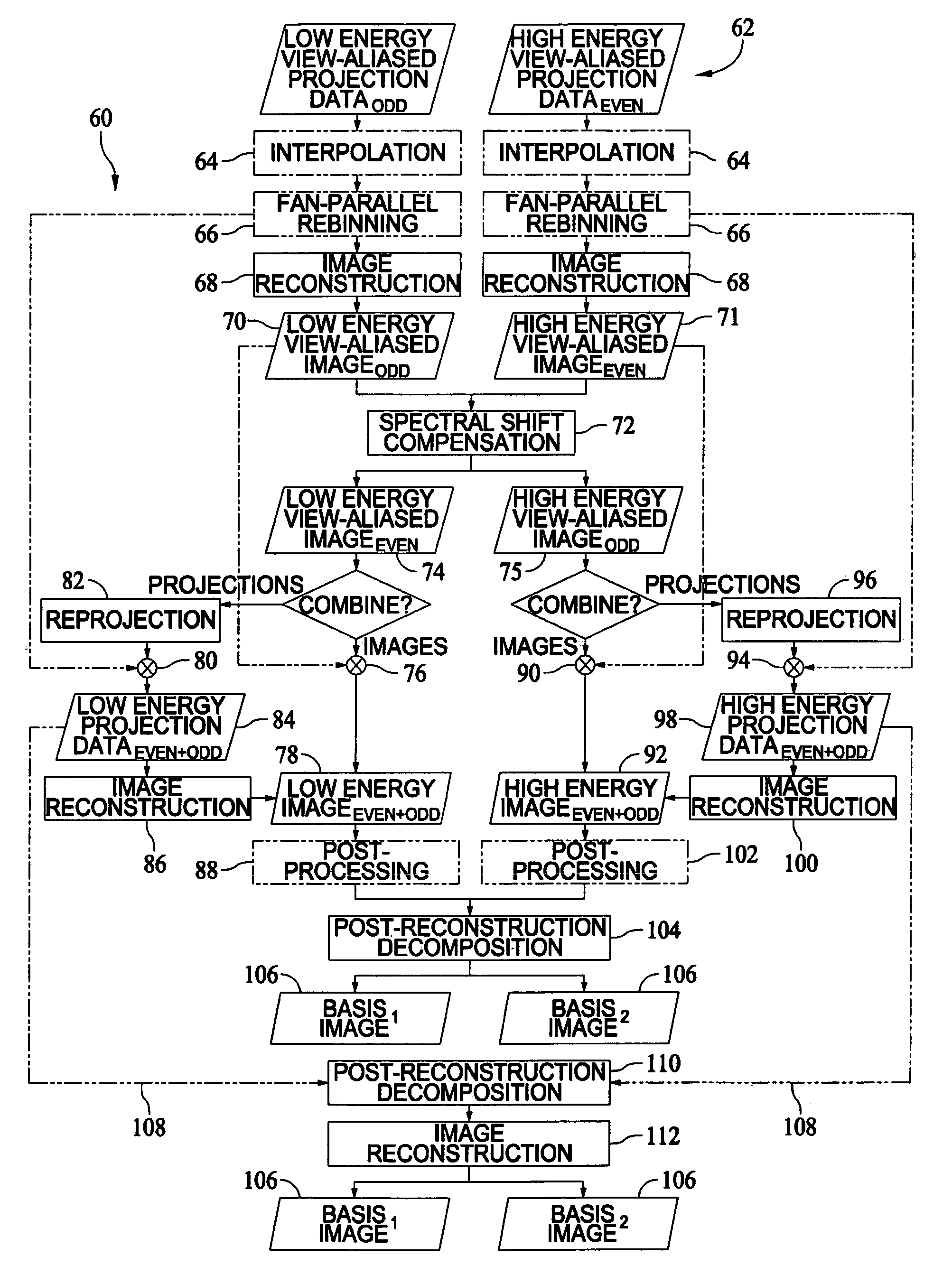
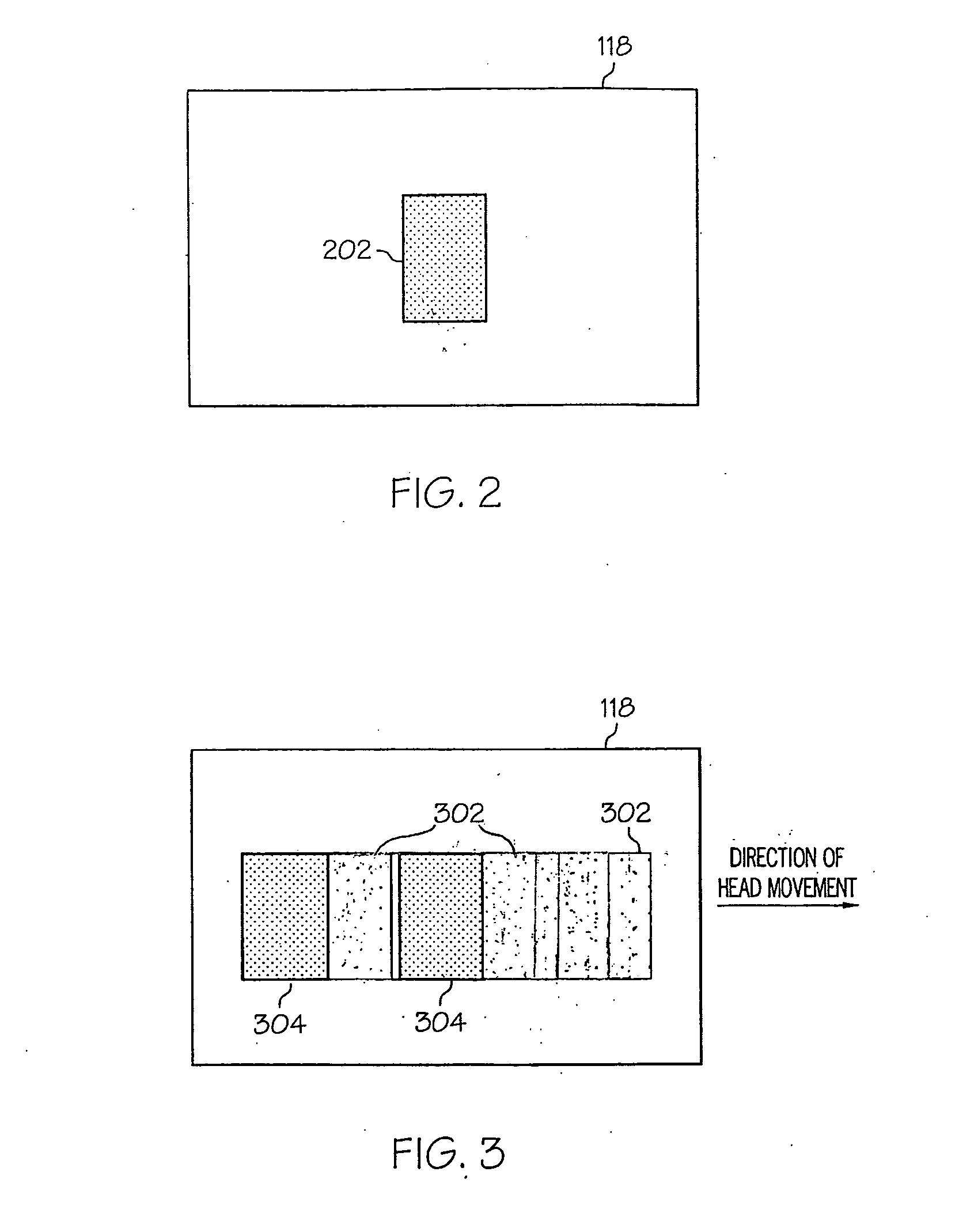
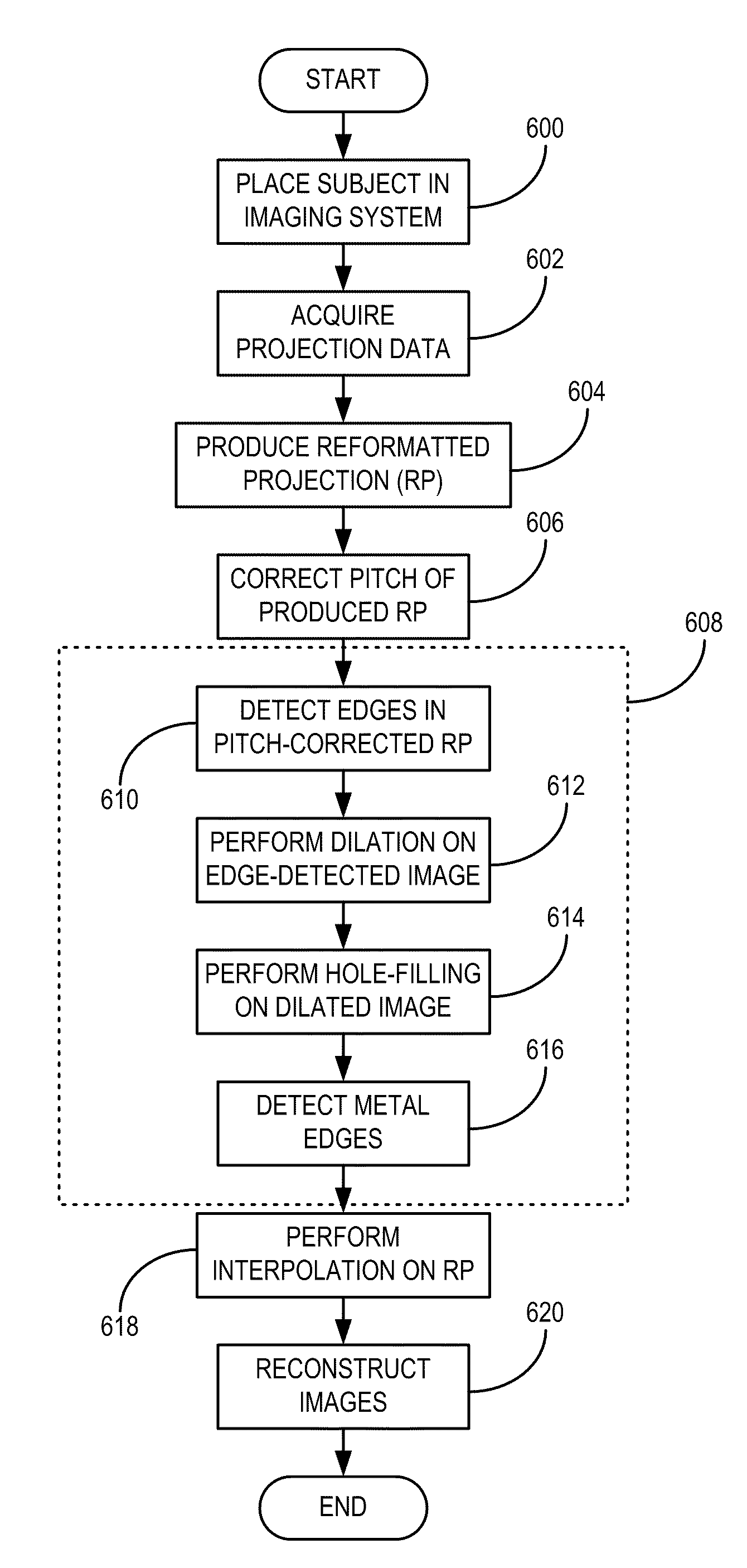
System and Method for Highly Attenuating Material Artifact Reduction in X-Ray Computed Tomography
The present invention is a method for reducing artifacts caused by highly attenuating materials in x-ray computed tomography (“CT”) images. The method includes combining projection views acquired at equivalent view angles to generate a projection plane data set, from which a reformatted projection is produced. The reformatted projection is then processed to detect and segment regions corresponding to objects composed of metals, metal alloys, or other highly attenuating materials. These segmented regions are then removed from the reformatted projection and the removed portions replaced by attenuation information interpolated from portions of the reformatted projection adjacent the removed portions. The interpolated reformatted projection is then mapped back to a projection plane data set, and an image of the subject is reconstructed from the projection views contained in that data set. The reconstructed image, therefore, is one in which artifacts caused by highly attenuating materials are substantially suppressed.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
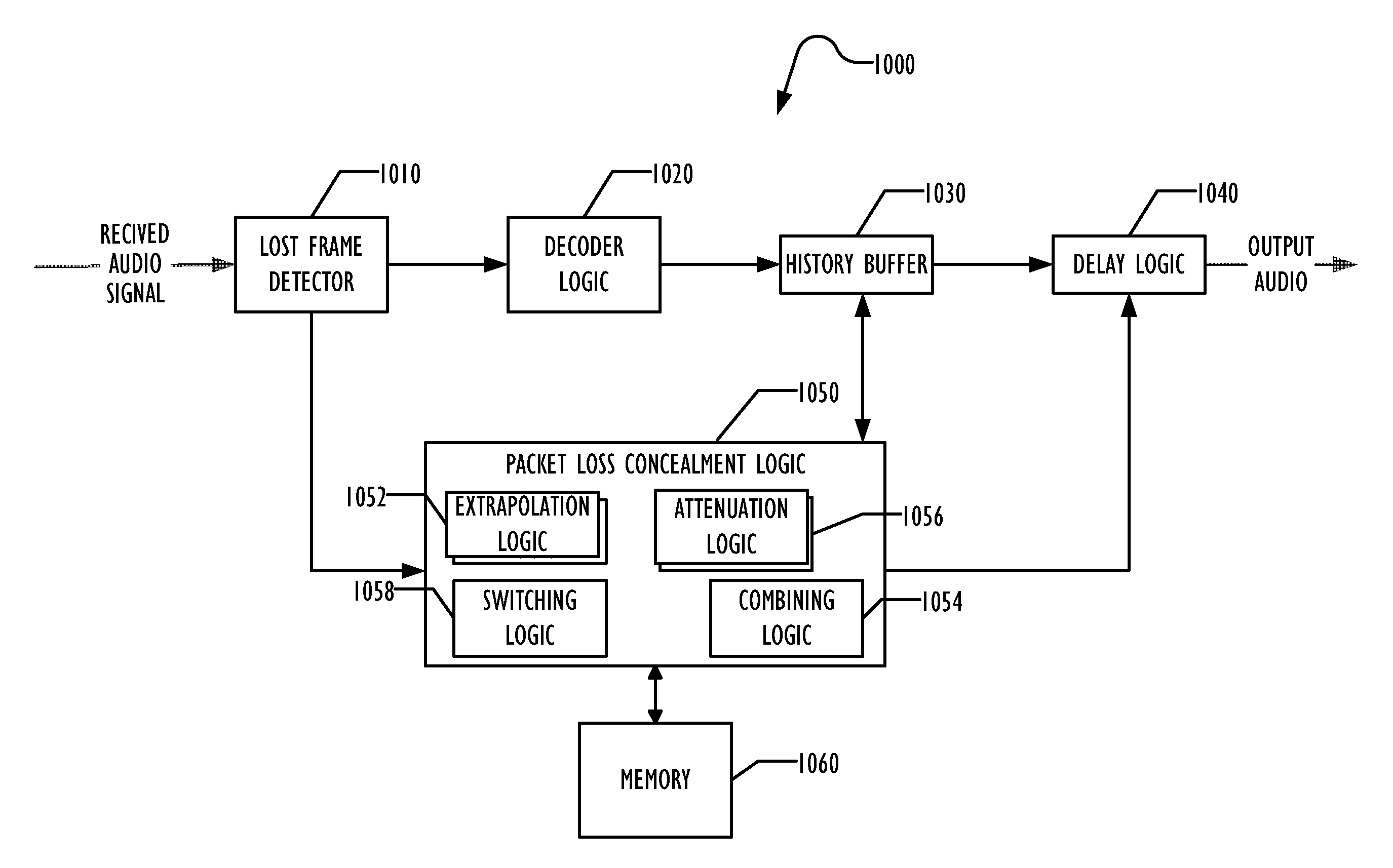
Artifact Reduction in Packet Loss Concealment
ActiveUS20120101814A1Improving packet loss concealmentReduce artifactsSpeech analysisUltrasound attenuationPacket loss concealment
Various techniques are disclosed for improving packet loss concealment to reduce artifacts by using audio character measures of the audio signal. These techniques include attenuation to a noise fill instead of attenuation to silence, varying how long to wait before attenuating the extrapolation, varying the rate of attenuation of the extrapolation, attenuating periodic extrapolation at a different rate than non-periodic extrapolation, and performing period extrapolation on successively longer fill data based on the audio character measures, adjusting weighting between periodic and non-periodic extrapolation based on the audio character measures, and adjusting weighting between periodic extrapolation and non-periodic extrapolation non-linearly.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
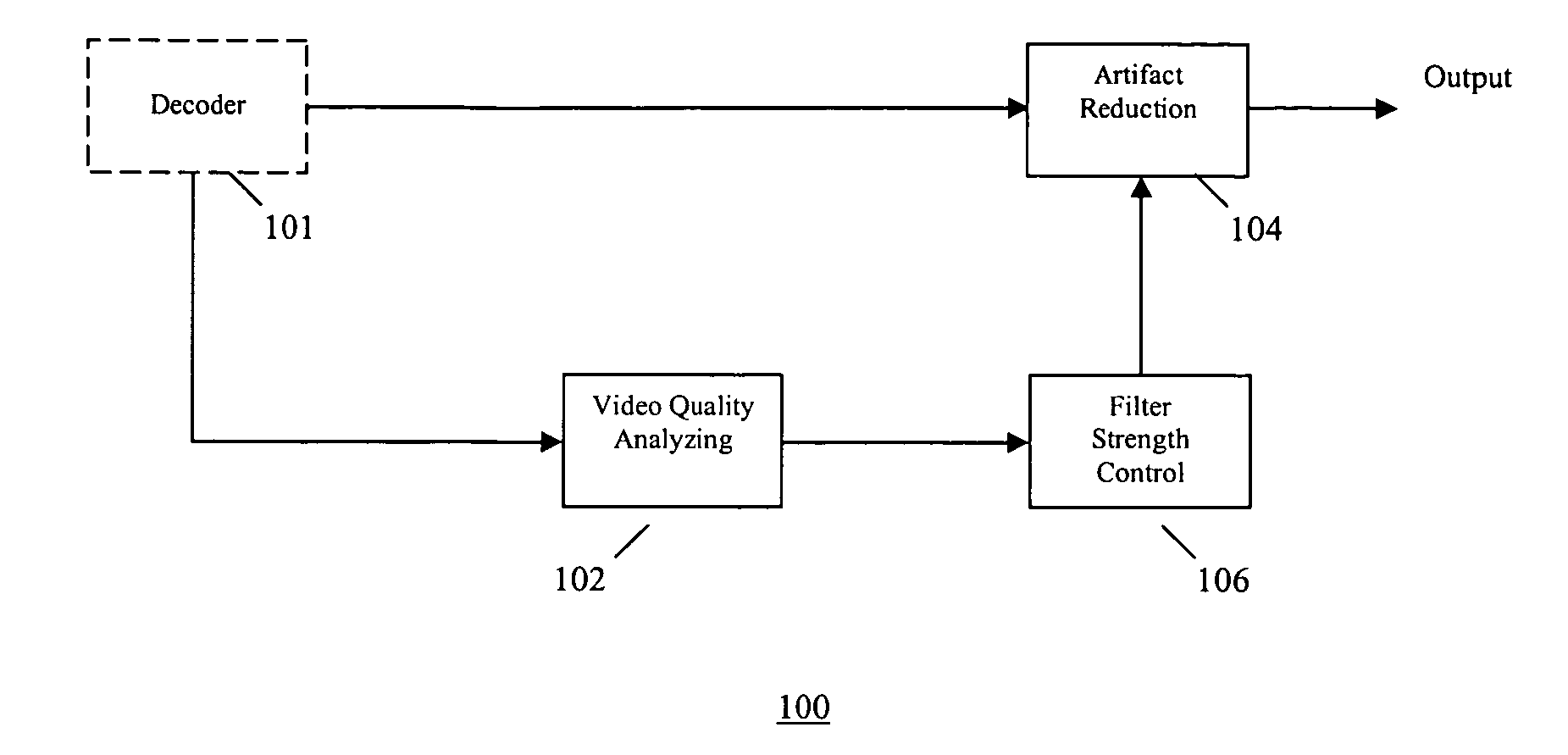
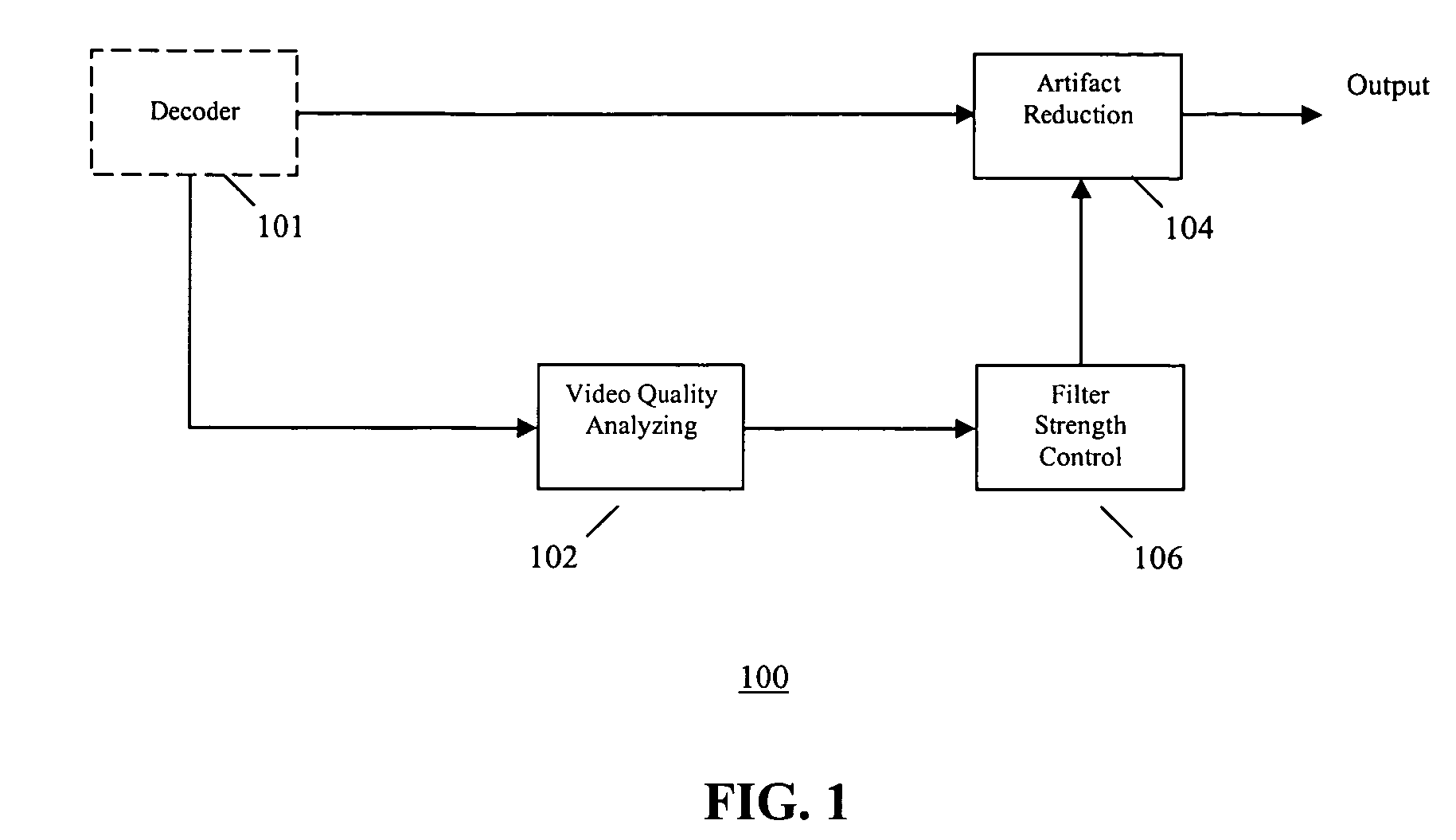
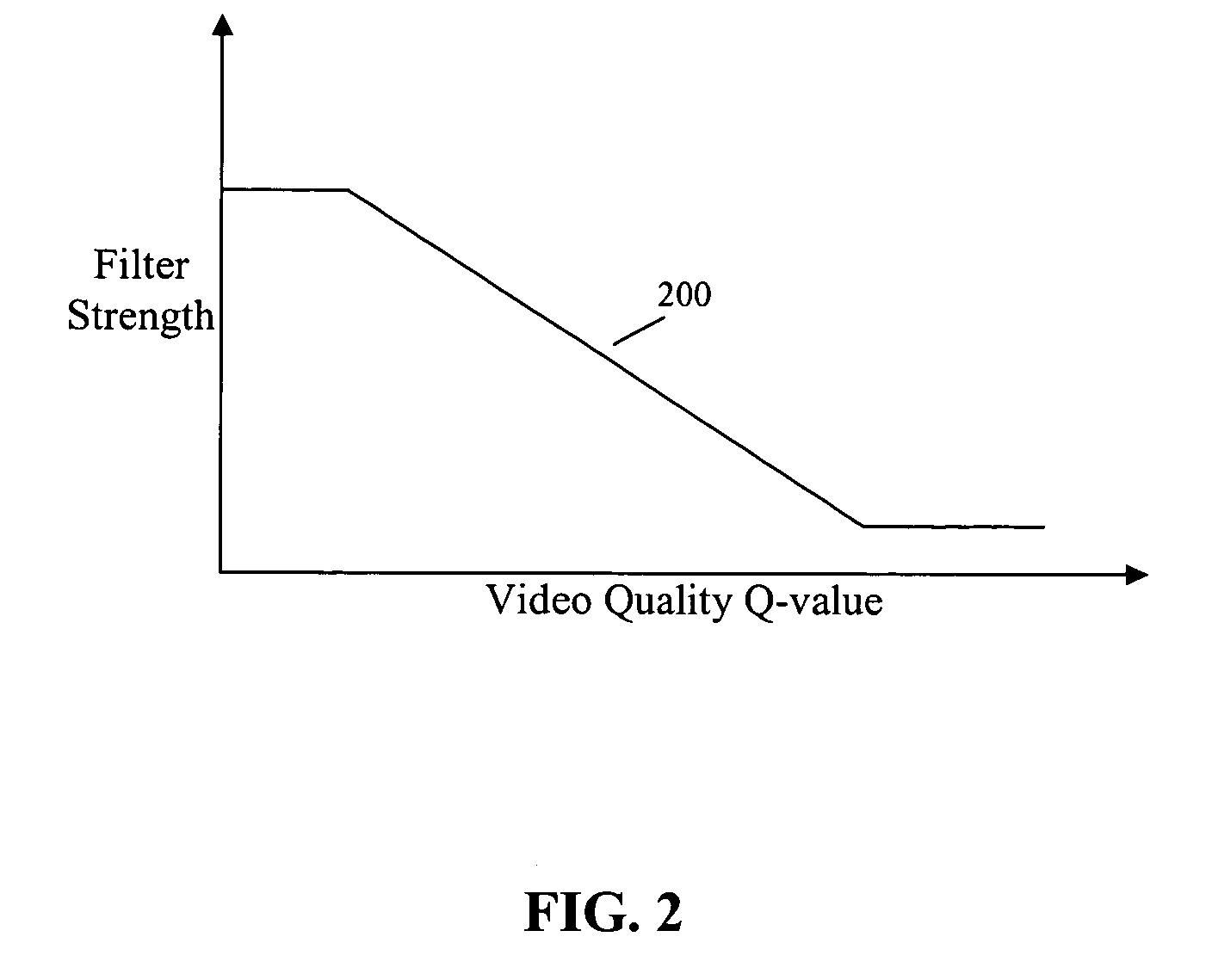
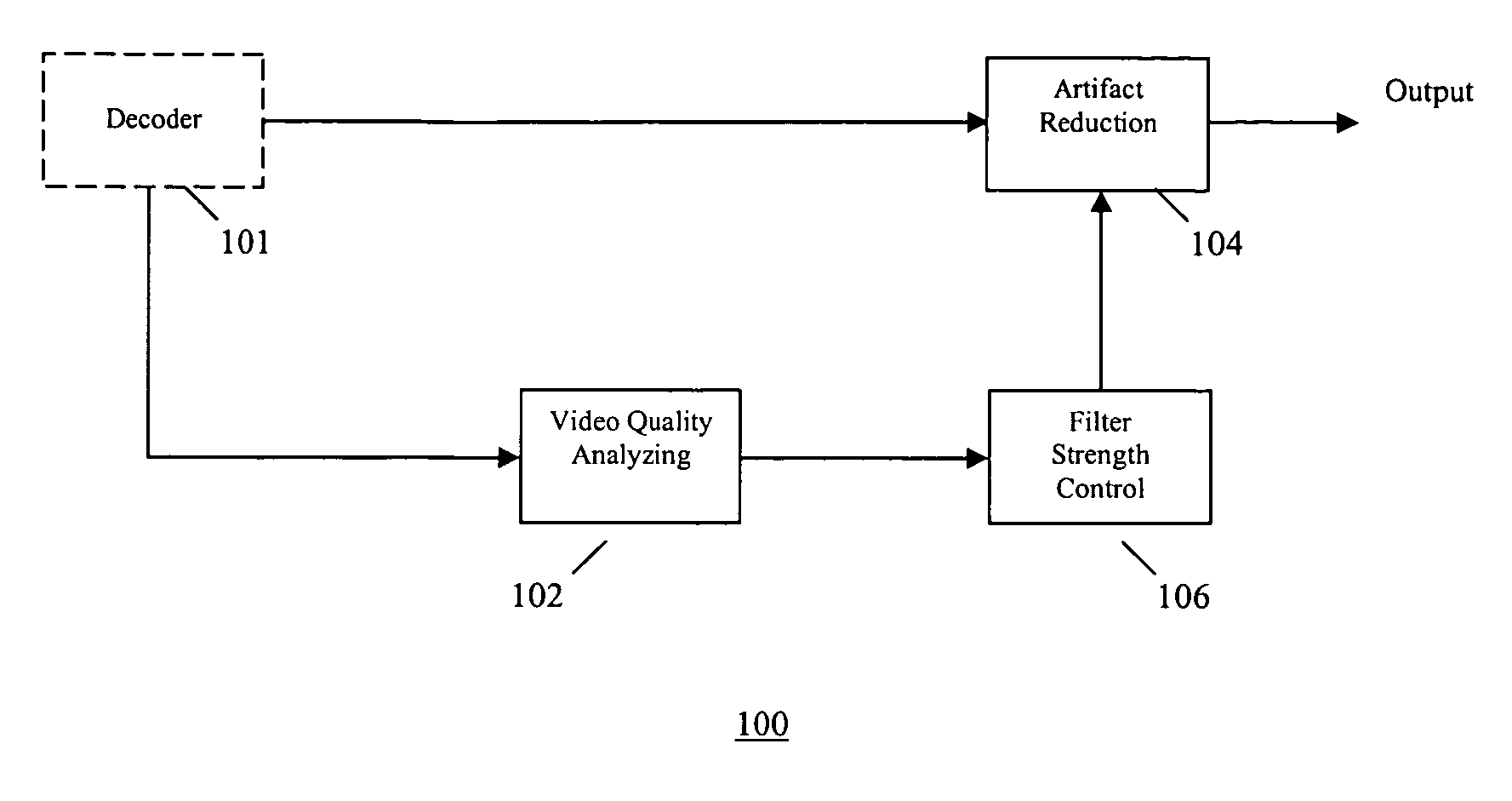
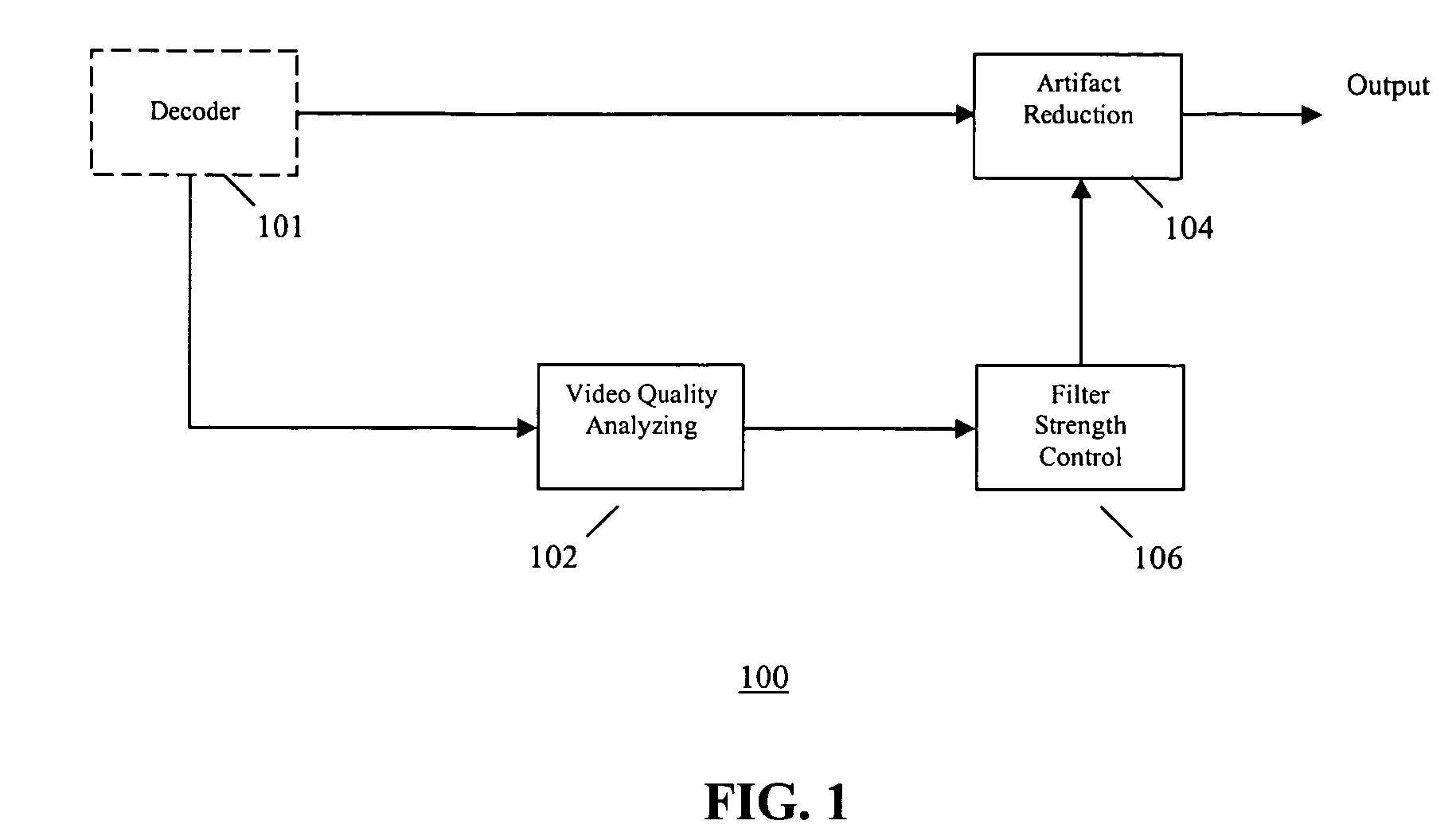
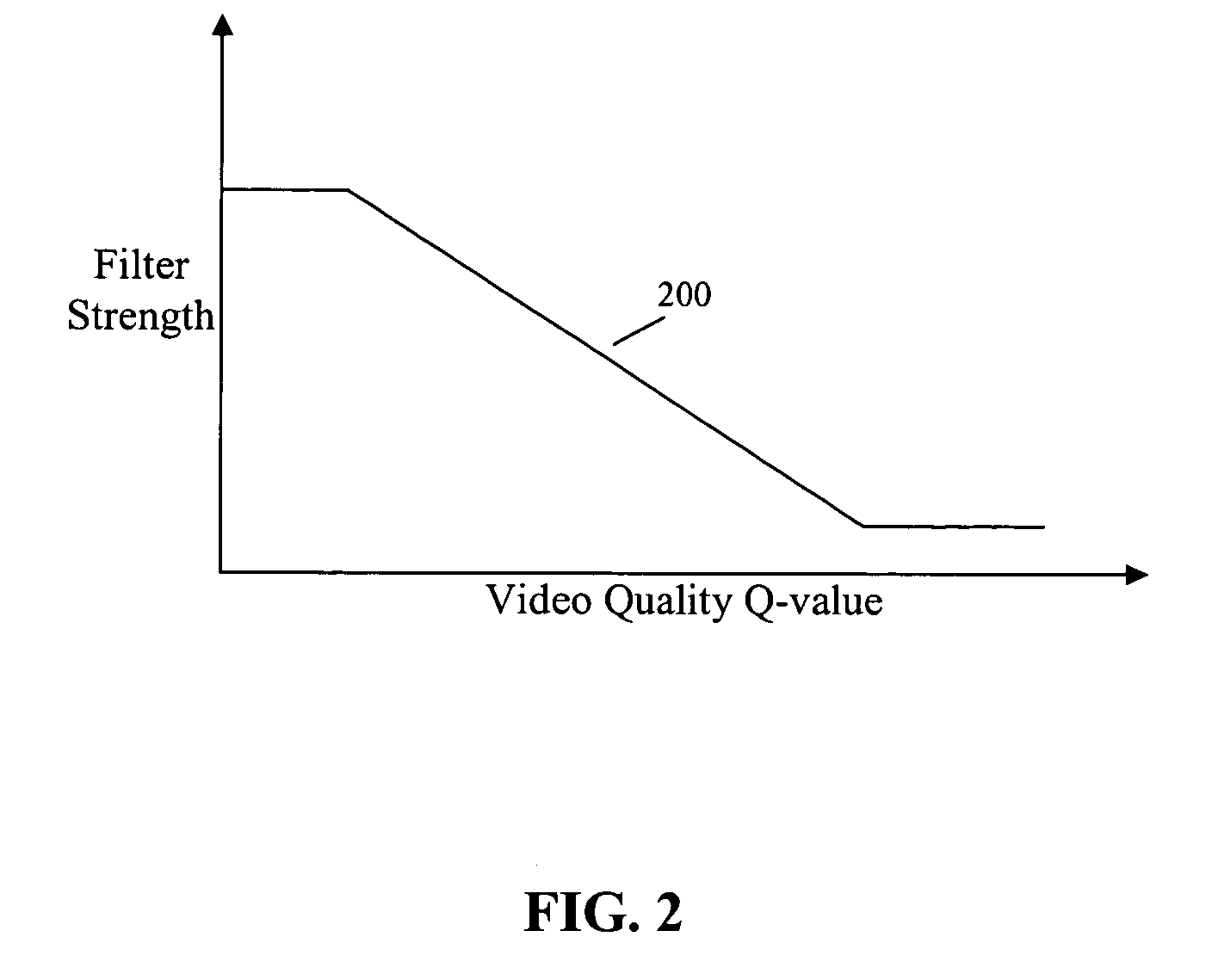
Video quality adaptive coding artifact reduction
InactiveUS20070081596A1Reduce artifactsReduce filter strengthPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesLight protection screensPattern recognitionAdaptive coding
A video quality adaptive coding artifact reduction system has a video quality analyzer, an artifact reducer, and a filter strength controller. The video quality analyzer employs input video quality analysis to control artifact reduction. The video quality analyzer accesses the video quality of the decoded video sequence to estimate the input video quality. The filter strength controller globally controls the filter strength of the artifact reducer based on the video quality estimate by the video quality analyzer. For low quality input video, the filter strength controller increases the artifact reduction filter strength to more efficiently reduce the artifact. For high quality input video, the filter strength controller decreases the artifact reduction filter strength to avoid blurring image detail.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
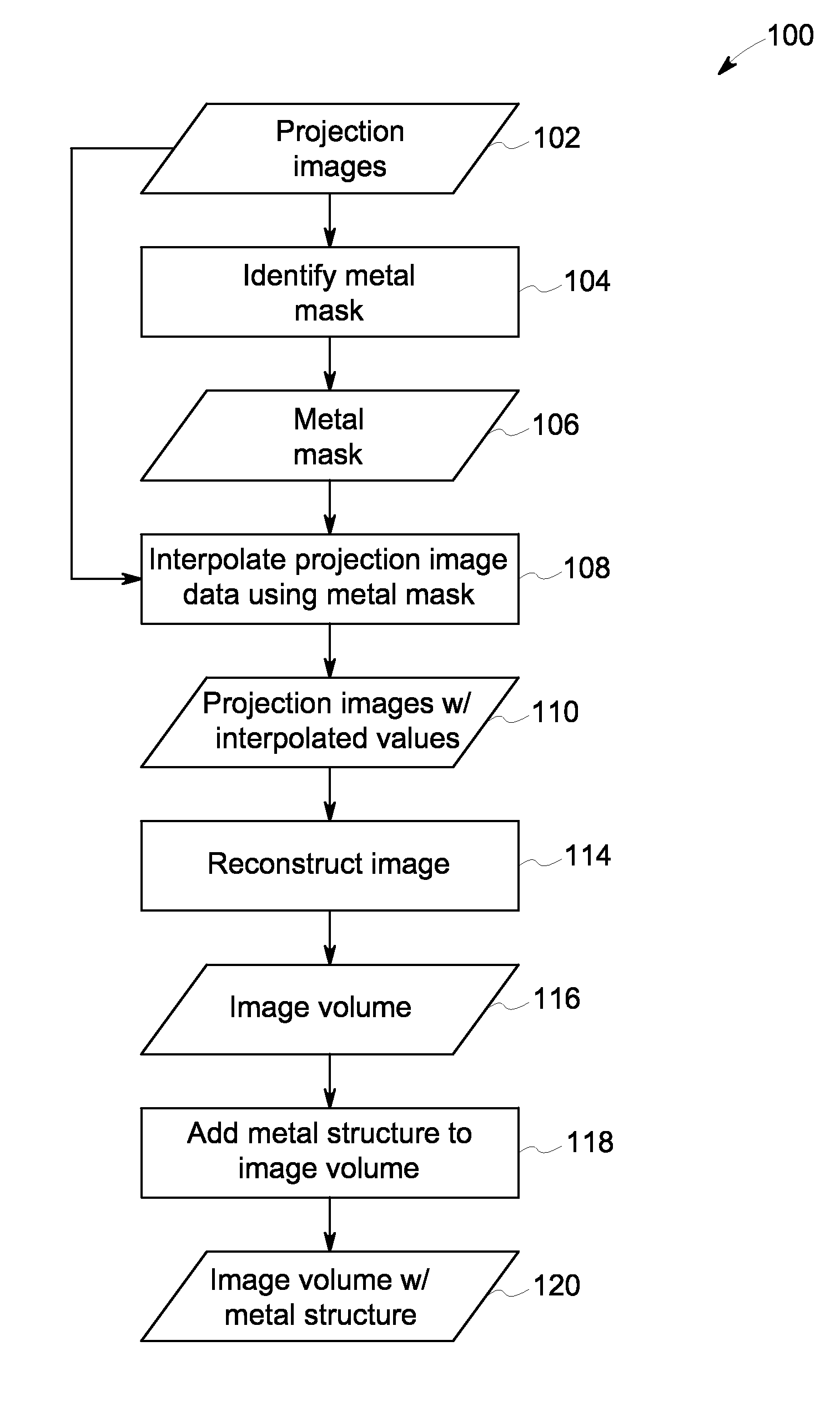
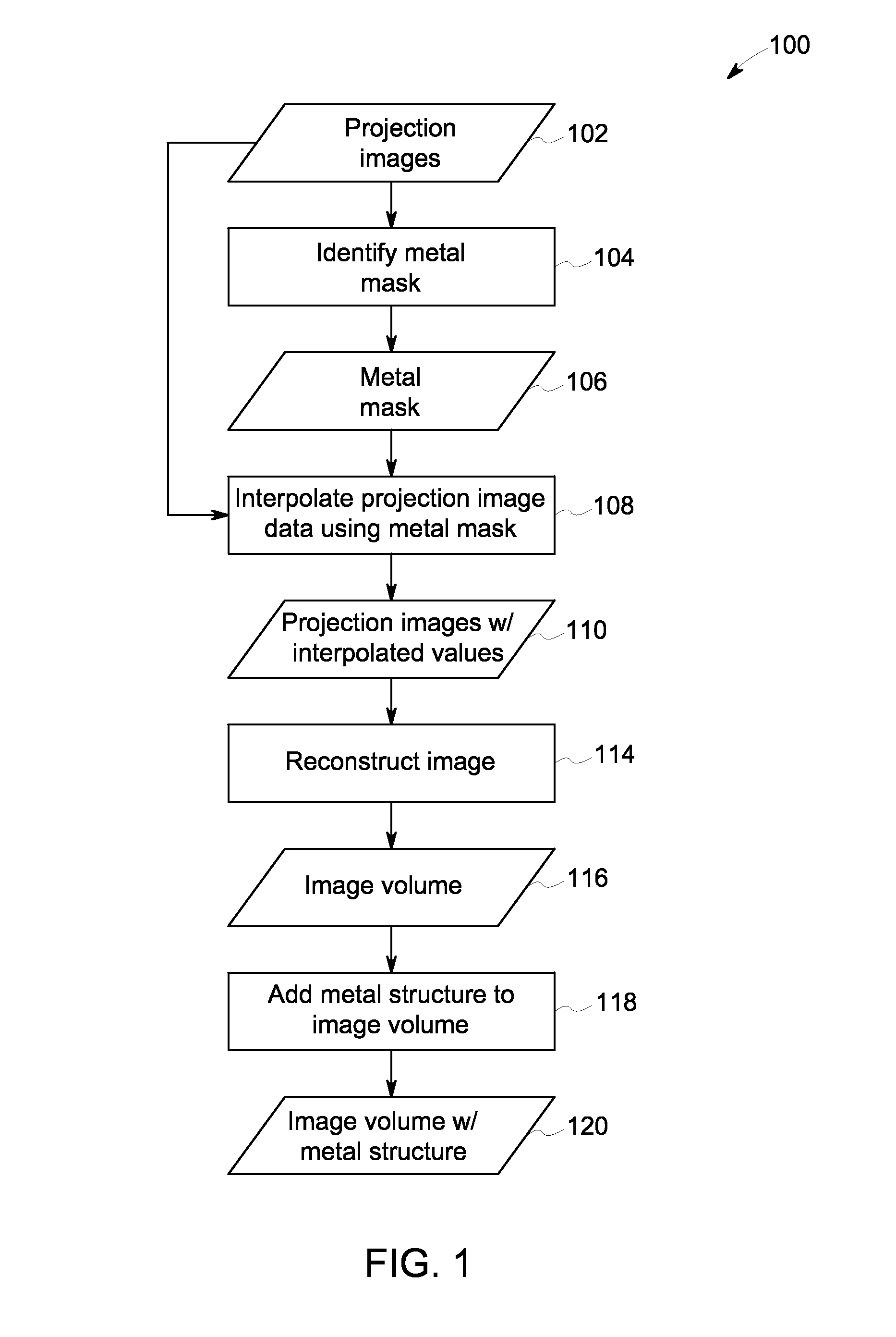
Robust artifact reduction in image reconstruction
ActiveUS20150029178A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionMetal ArtifactArtifact reduction
Approaches are disclosed for removing or reducing metal artifacts in reconstructed images. The approaches include creating a metal mask in the projection domain, interpolating data within the metal mask, and perform a reconstruction using the interpolated data. In certain embodiments the metal structure is separately reconstructed and combined with the reconstructed volume.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
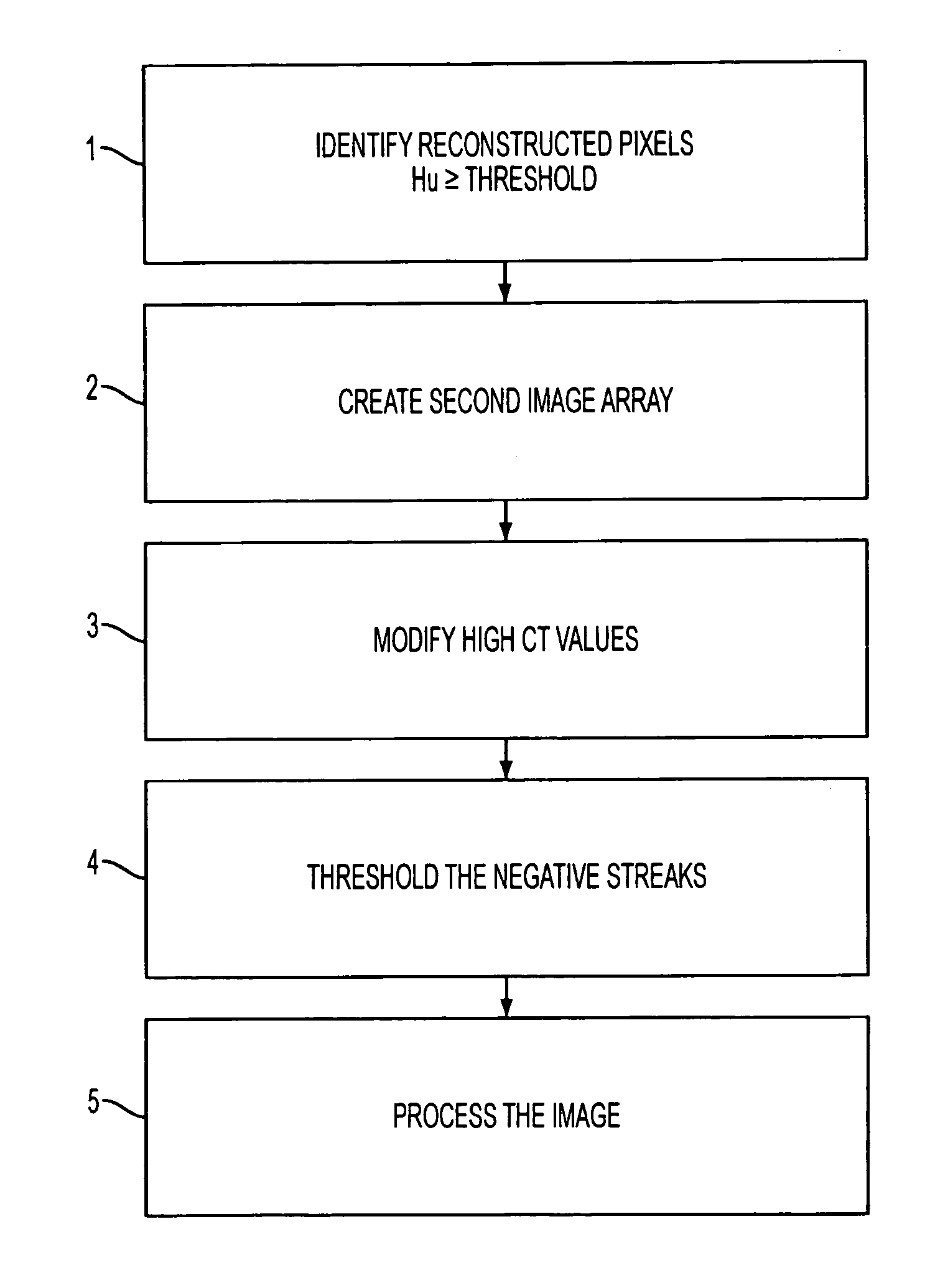
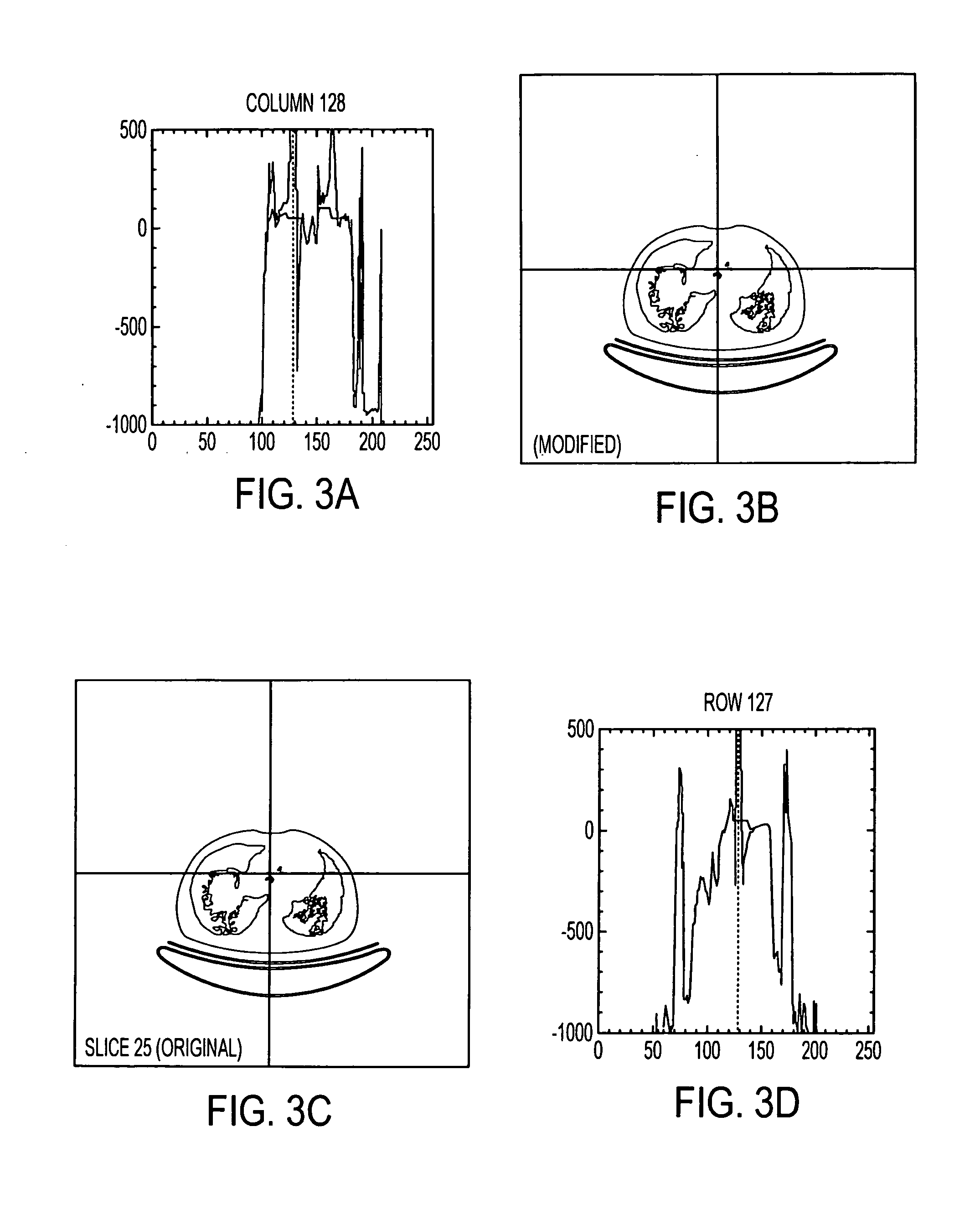
Image-based artifact reduction in PET/CT imaging
InactiveUS20060285737A1Reduce errorsSimple and robustImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionComputing tomographyCompanion animal
A method for reducing image-based artifacts in combined positron emission tomography and computed tomography (PET / CT) scans. The method includes identifying pixels in a CT image having a large HU value, identifying a region surrounding the pixels, and modifying a value of each pixel within the region.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
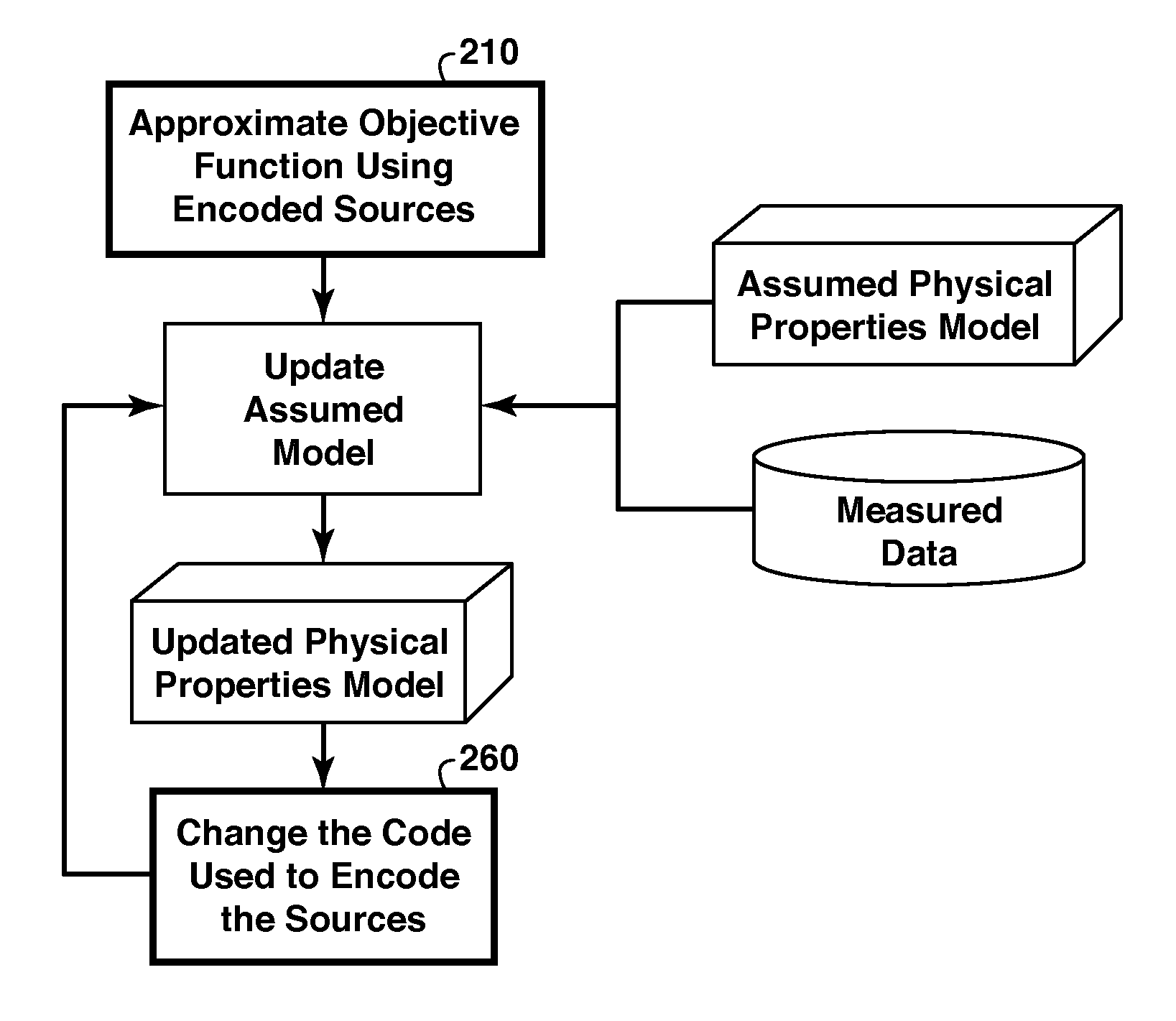
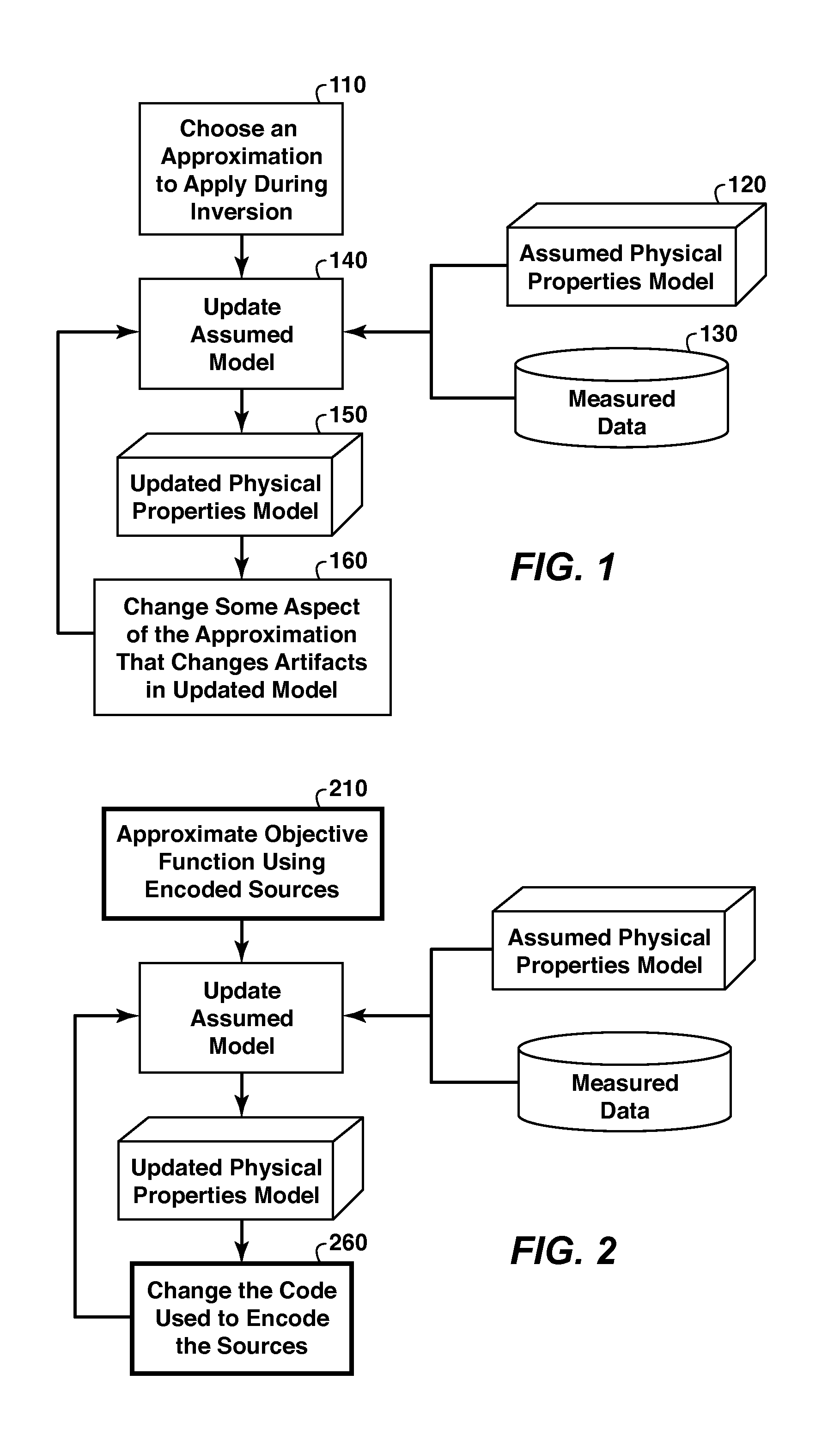
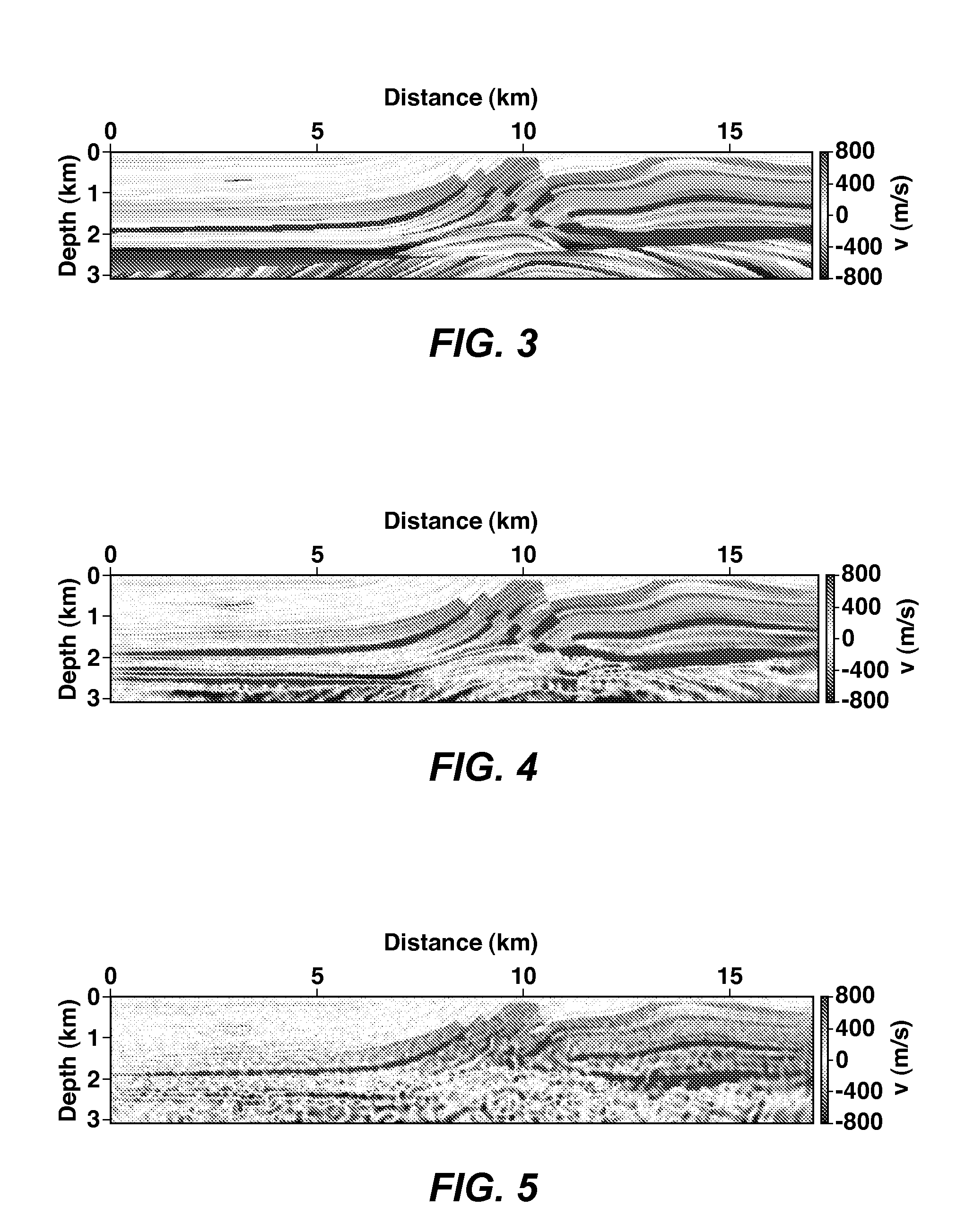
Artifact Reduction In Iterative Inversion Of Geophysical Data
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
System and method for image and video encoding artifacts reduction and quality improvement
InactiveUS20100027905A1Improve image qualityHigh quality imagingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionVideo encoding
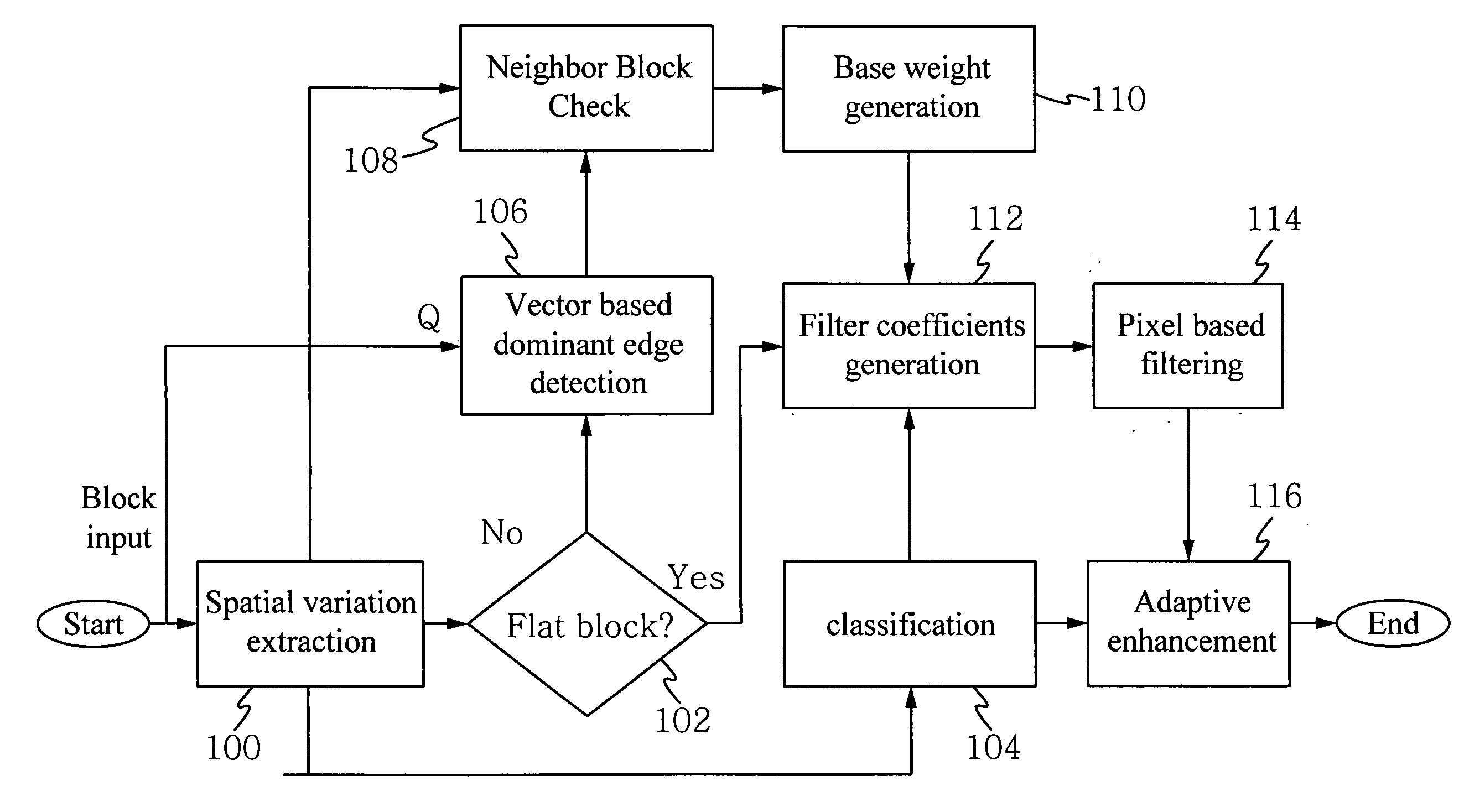
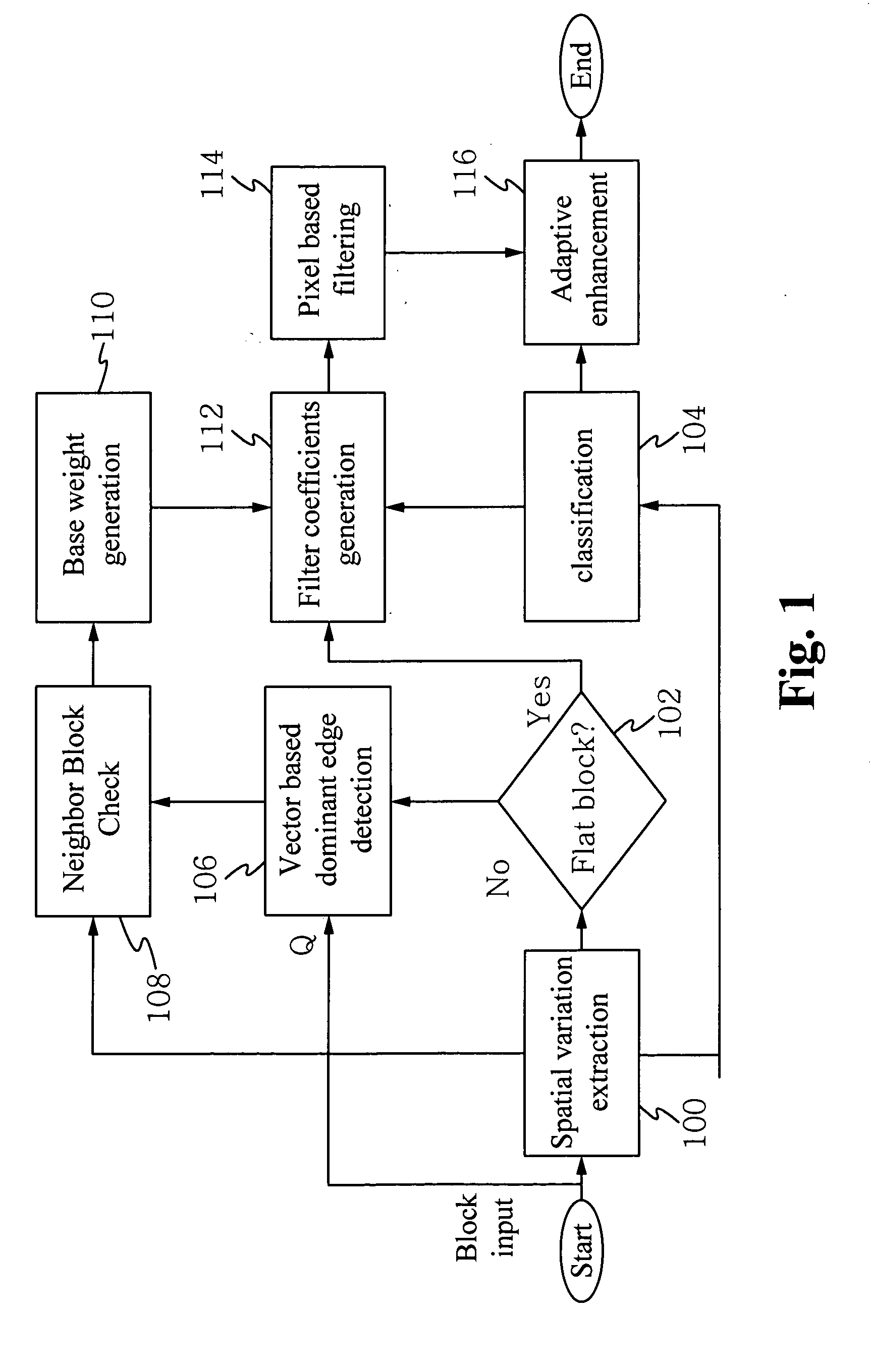
Reducing artifacts and improving quality for image and video encoding is performed in one pass to preserve natural edge smoothness and sharpness. To reduce artifacts and improve quality, several steps are implemented including spatial variation extraction, determining if a block is flat or texture / edge, classifying the pixels as texture or noise, detecting a dominant edge, checking the spatial variation of neighboring blocks, generating base weights, generating filter coefficients, filtering pixels and adaptive enhancement. A device which utilizes the method of reducing artifacts and improving quality achieves higher quality images and / or video with reduced artifacts.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Method and system for artifact reduction
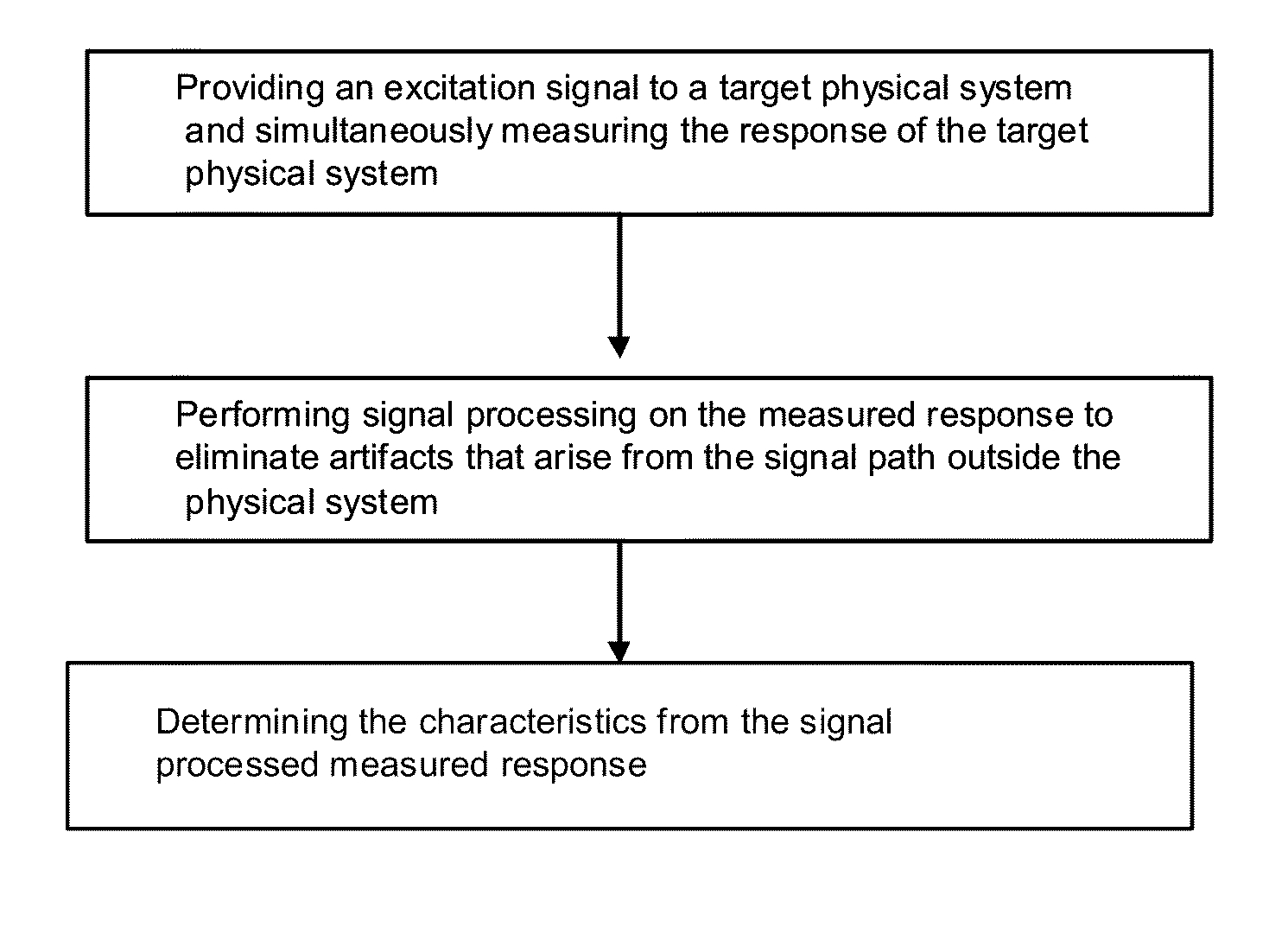
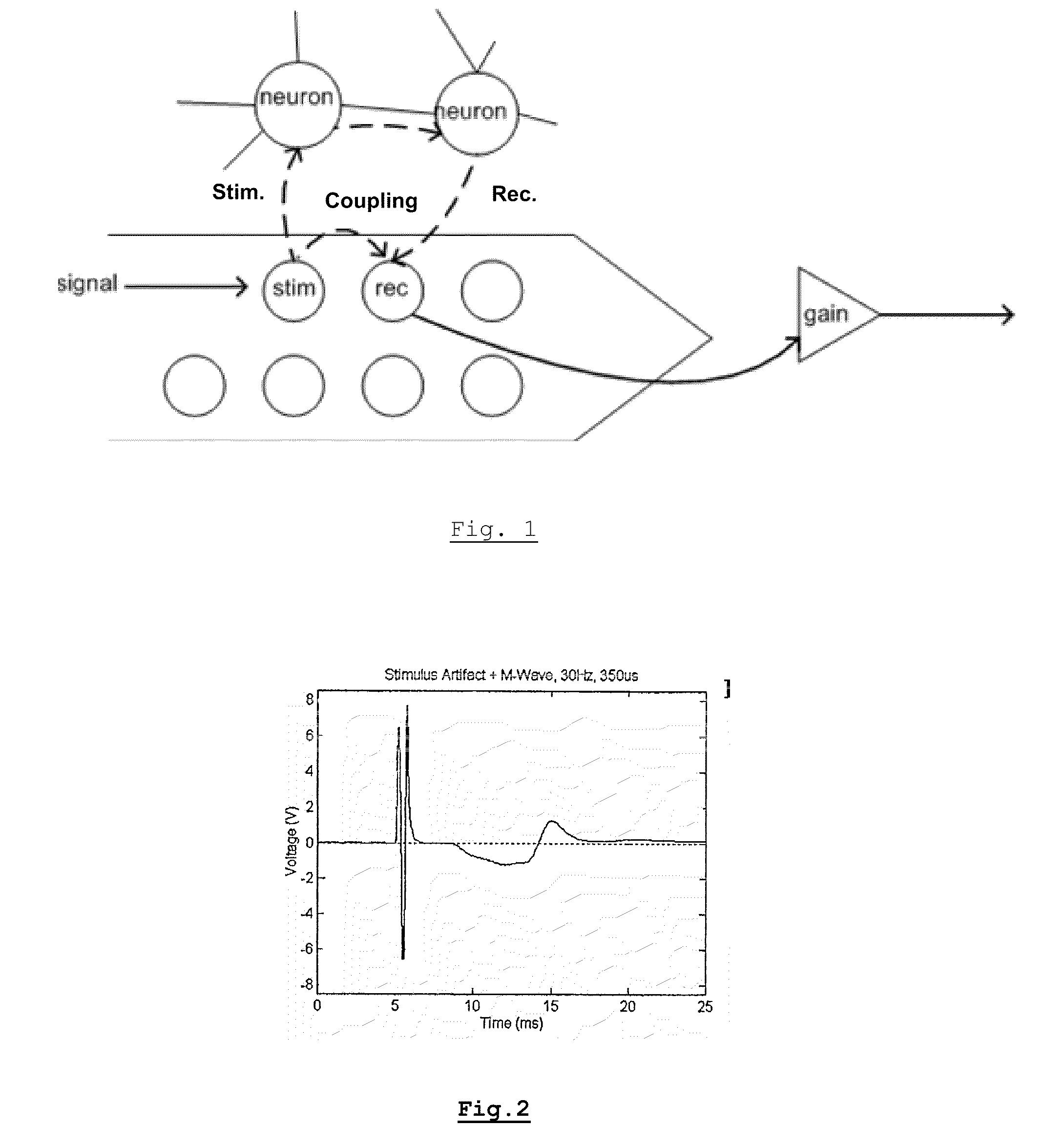
ActiveUS8335664B2Eliminate artifactsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhysical entityAnalog signal processing
A method is presented for obtaining characteristics of a target physical entity by providing an excitation signal to the target physical entity and simultaneously measuring the response of the target physical entity. Analog signal processing is performed on the measured response to eliminate artifacts arising from a signal path outside the target physical entity and determining the characteristics from the signal processed measured response. The excitation signal and the analog signal processing are selected such that after analog signal processing of the measured signal, the analog measured signal contains artifacts which are localized in time.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
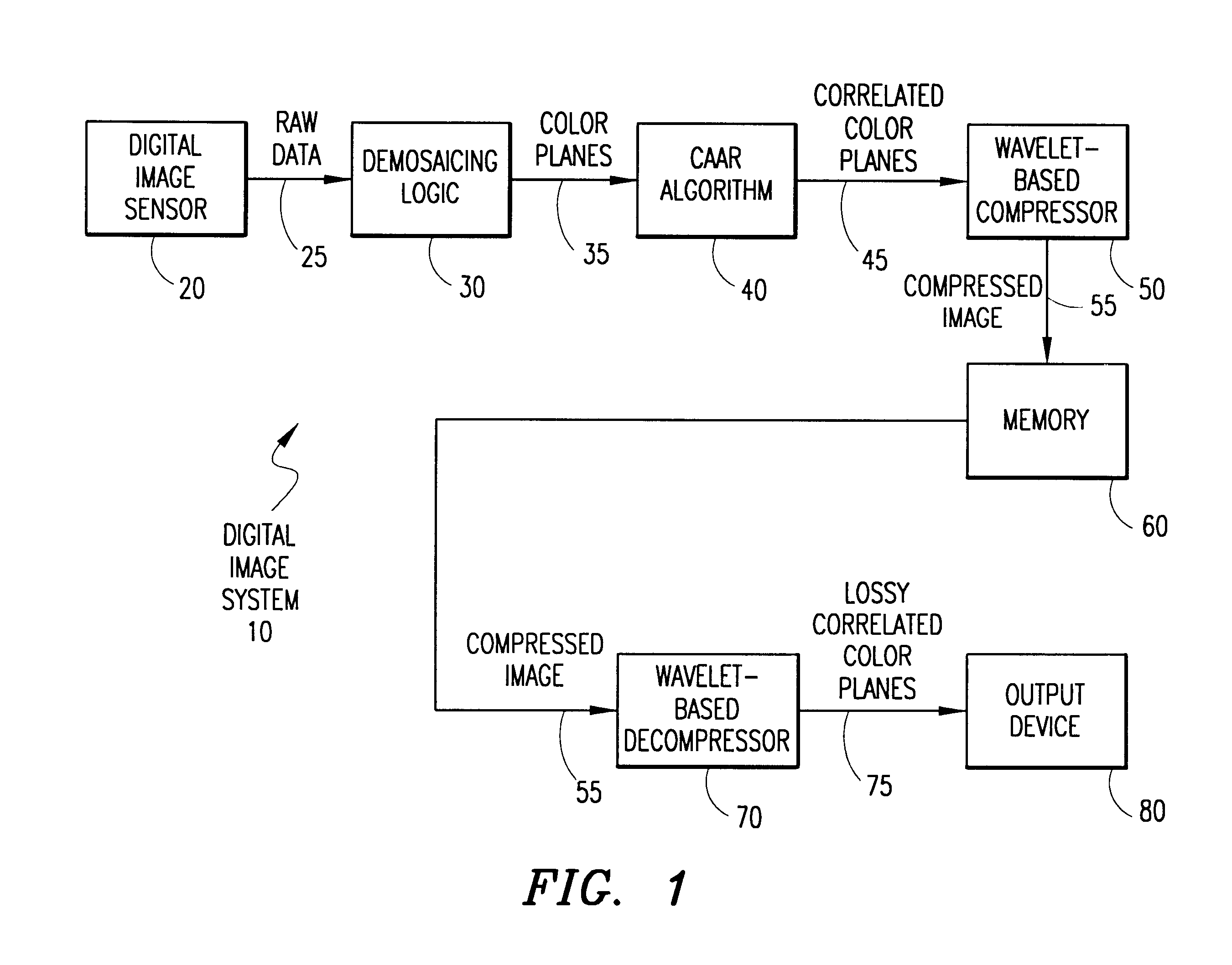
System and method for processing demosaiced images to reduce color aliasing artifacts
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Auxiliary data for artifacts - aware view synthesis
ActiveUS20170188002A1Reduce artifactsLarge discontinuityCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processingData packMissing data
Original or compressed Auxiliary Data, including possibly major depth discontinuities in the form of shape images, partial occlusion data, associated tuned and control parameters, and depth information of the original video(s), are used to facilitate the interactive display and generation of new views (view synthesis) of conventional 2D, stereo, and multi-view videos in conventional 2D, 3D (stereo) and multi-view or autostereoscopic displays with reduced artifacts. The partial or full occlusion data includes image, depth and opacity data of possibly partially occluded areas to facilitate the reduction of artifacts in the synthesized view. An efficient method is used for extracting objects at partially occluded regions as defined by the auxiliary data from the texture videos to facilitate view synthesis with reduced artifacts. Further, a method for updating the image background and the depth values uses the auxiliary data after extraction of each object to reduce the artifacts due to limited performance of online inpainting of missing data or holes during view synthesis.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
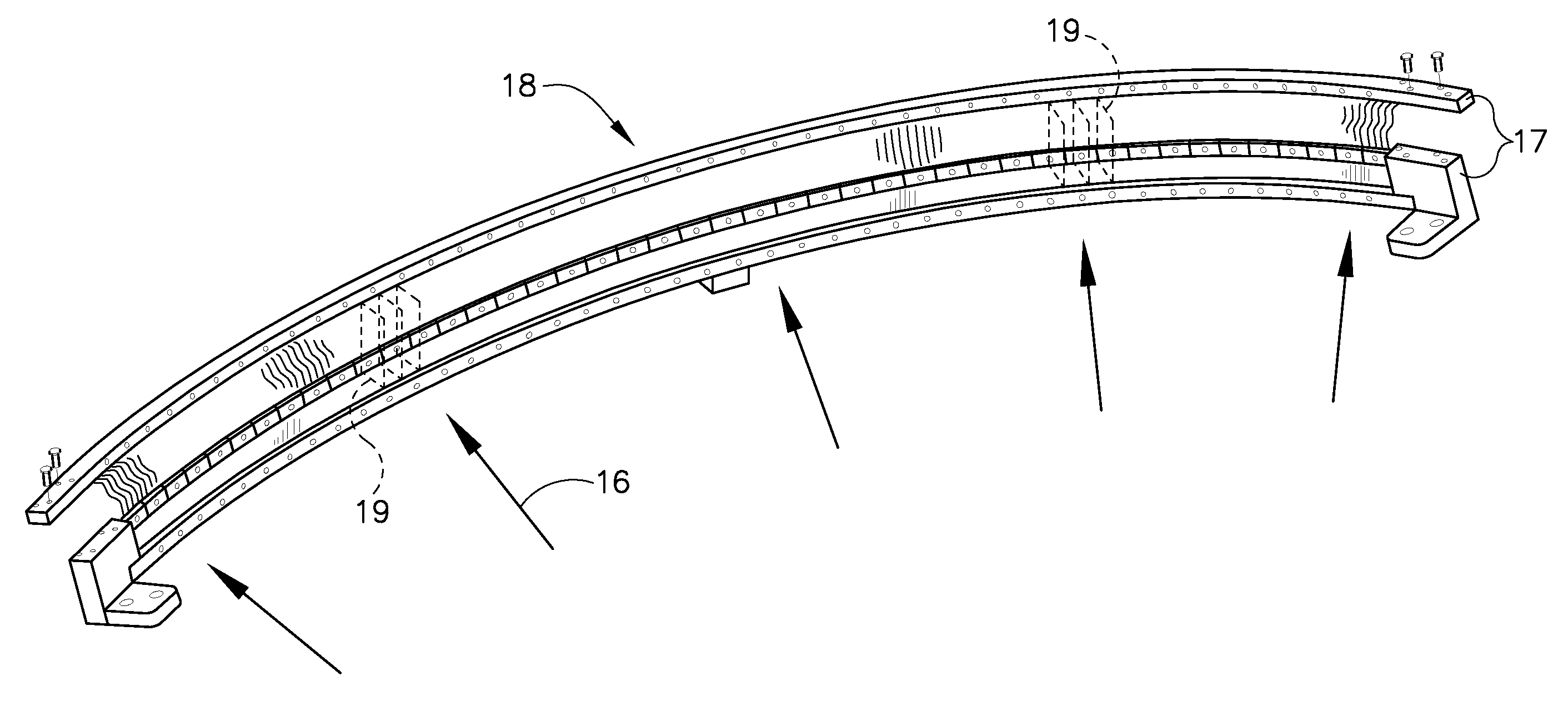
Holographic arrays for multi-path imaging artifact reduction
ActiveUS7295146B2Antenna supports/mountingsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionElectrical polarityElectromagnetic radiation
A method and apparatus to remove human features utilizing at least one transmitter transmitting a signal between 200 MHz and 1 THz, the signal having at least one characteristic of elliptical polarization, and at least one receiver receiving the reflection of the signal from the transmitter. A plurality of such receivers and transmitters are arranged together in an array which is in turn mounted to a scanner, allowing the array to be passed adjacent to the surface of the item being imaged while the transmitter is transmitting electromagnetic radiation. The array is passed adjacent to the surface of the item, such as a human being, that is being imaged. The portions of the received signals wherein the polarity of the characteristic has been reversed and those portions of the received signal wherein the polarity of the characteristic has not been reversed are identified. An image of the item from those portions of the received signal wherein the polarity of the characteristic was reversed is then created.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
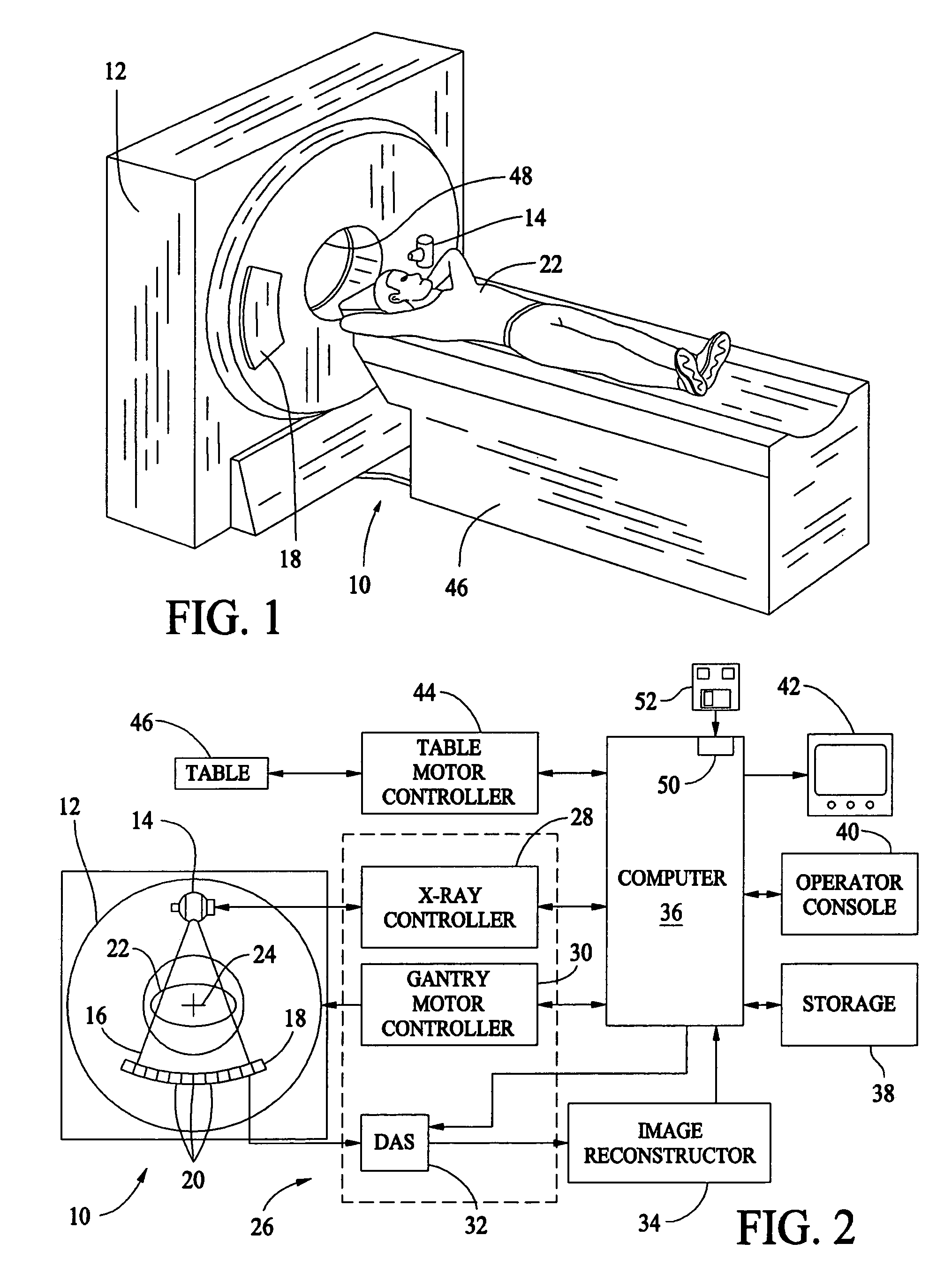
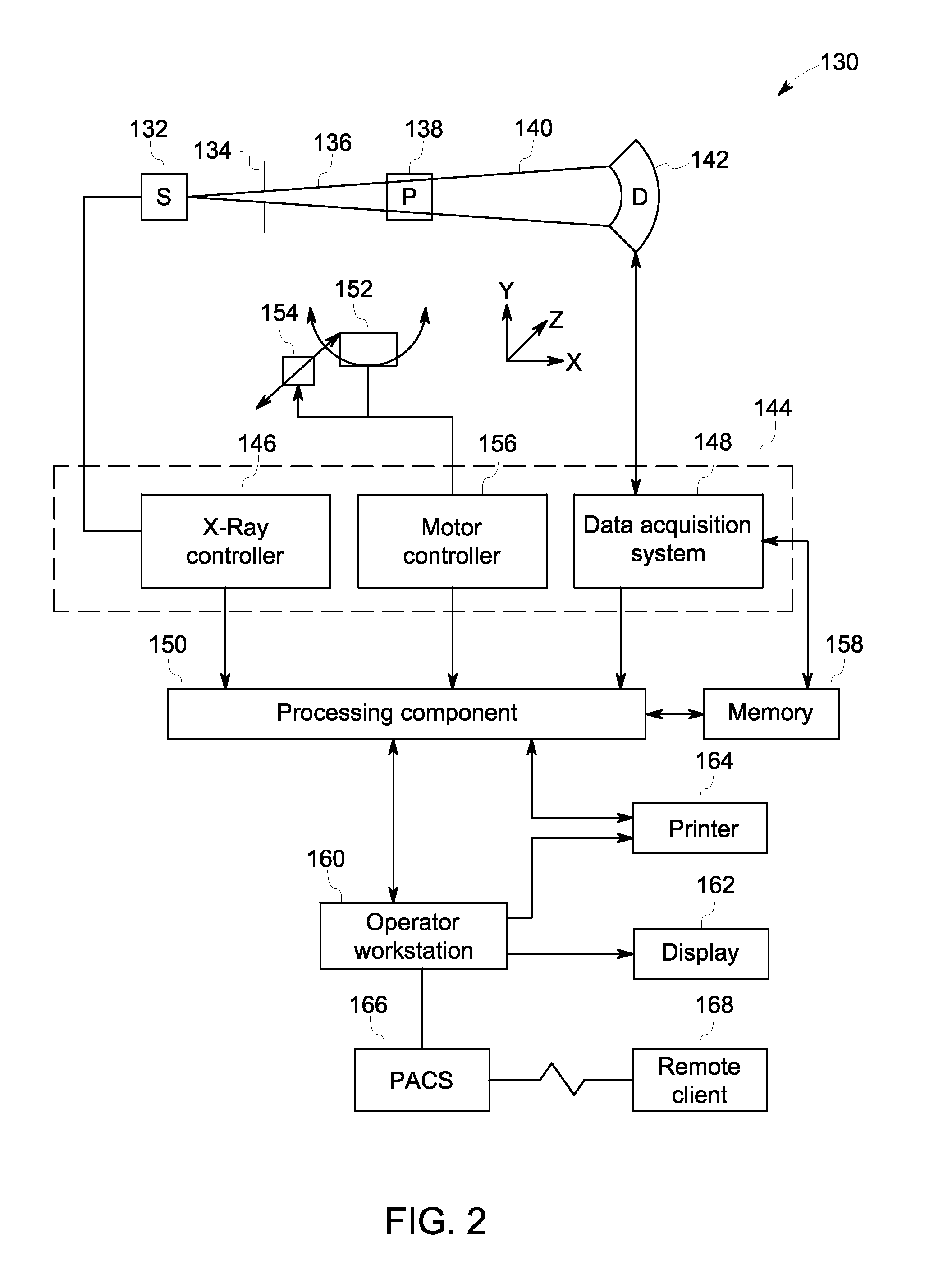
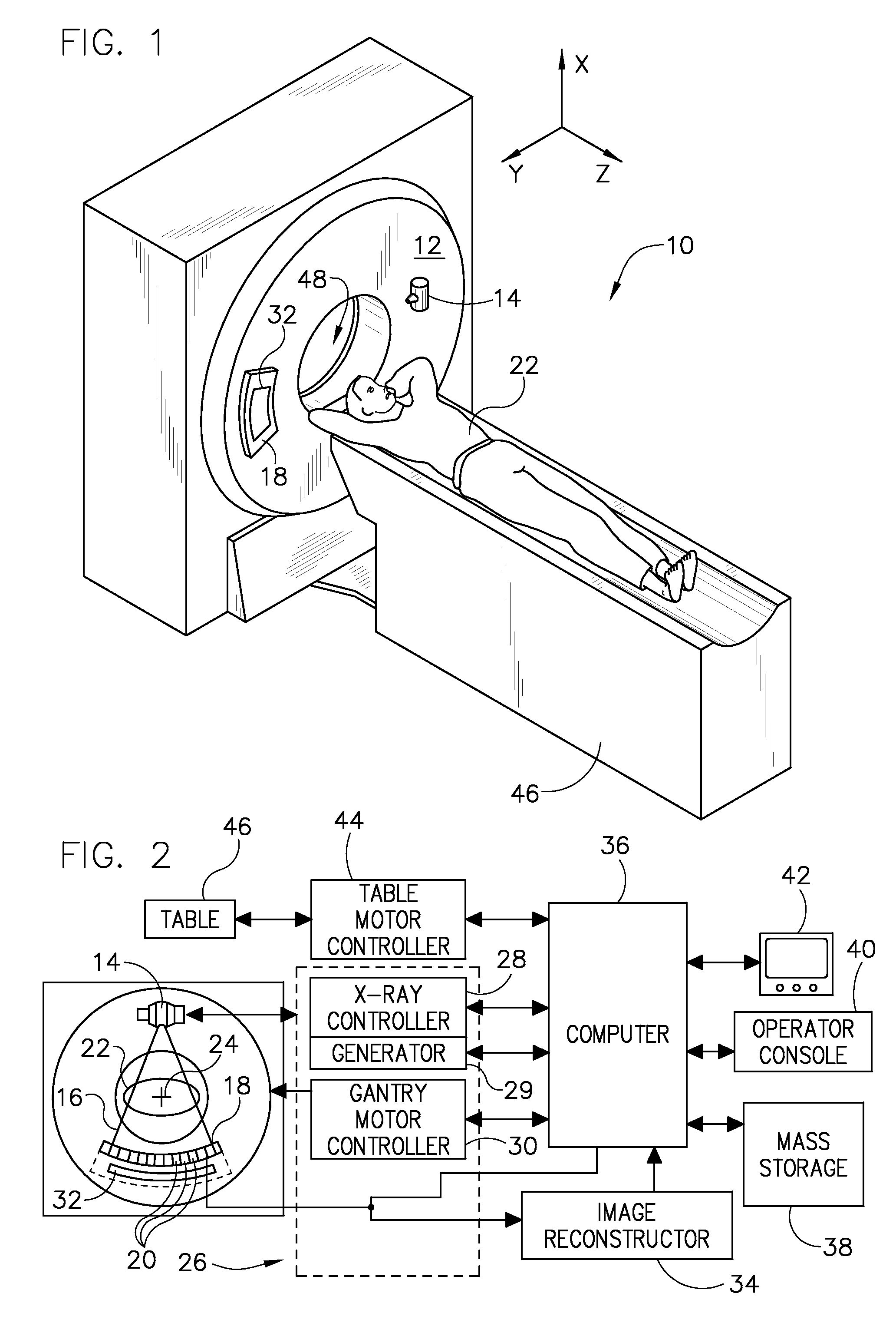
Methods and apparatus for artifact reduction in computed tomography imaging systems
ActiveUS6944260B2Reduce artifactsStay flexibleReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData setDetector array
Some configurations of the present invention provide a method for reconstructing an image of an object of a computed tomographic imaging system having a detector array and a radiation source, wherein an arc of the detector array is not concentric to a focal spot of the radiation source. The method includes scanning the object with the computed tomographic imaging system to obtain a fan beam dataset, rebinning the fan beam dataset into a set of parallel datasets; and reconstructing an image utilizing the set of parallel datasets.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Image blocking artifact reduction via transform pair
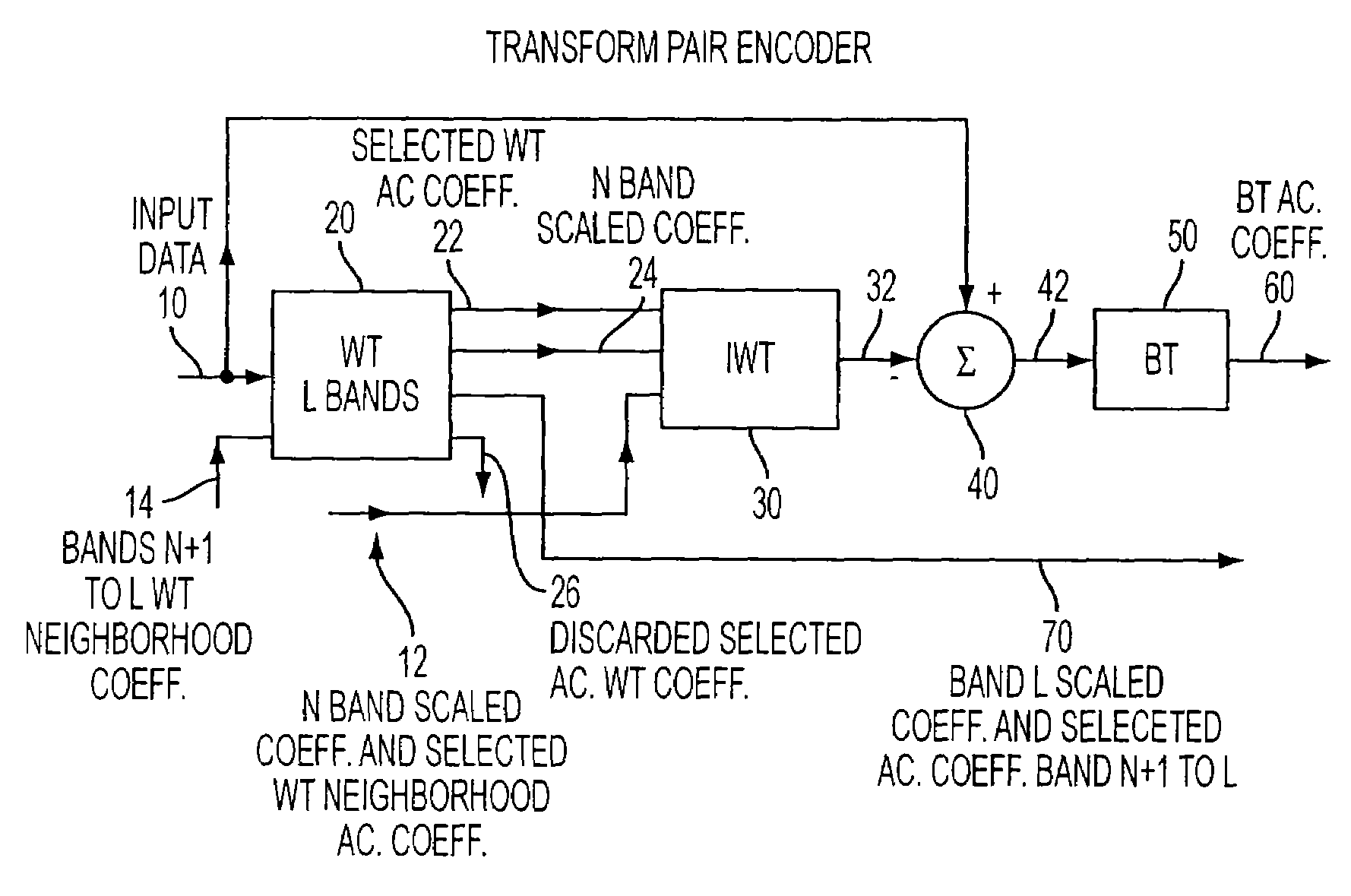
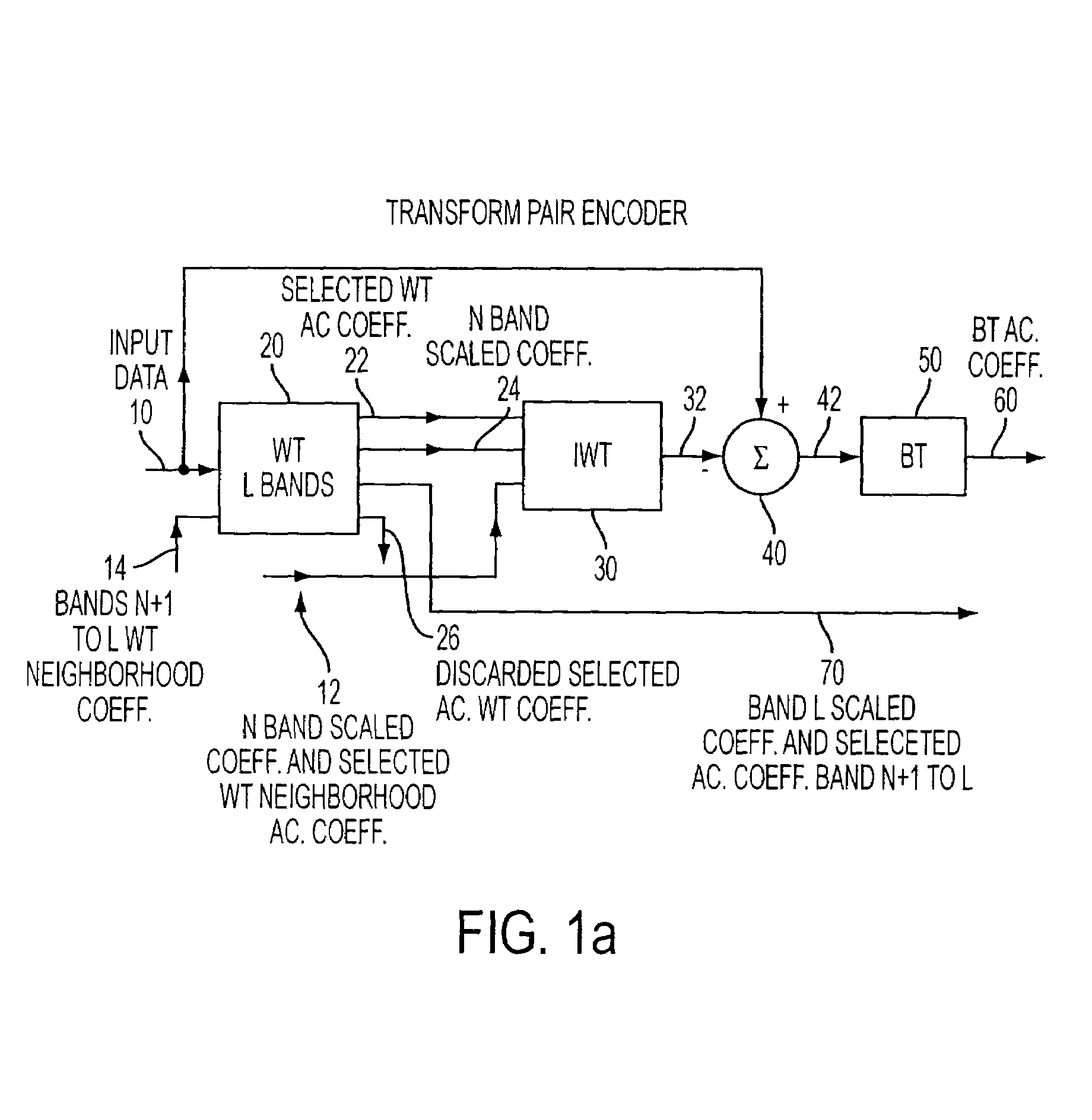
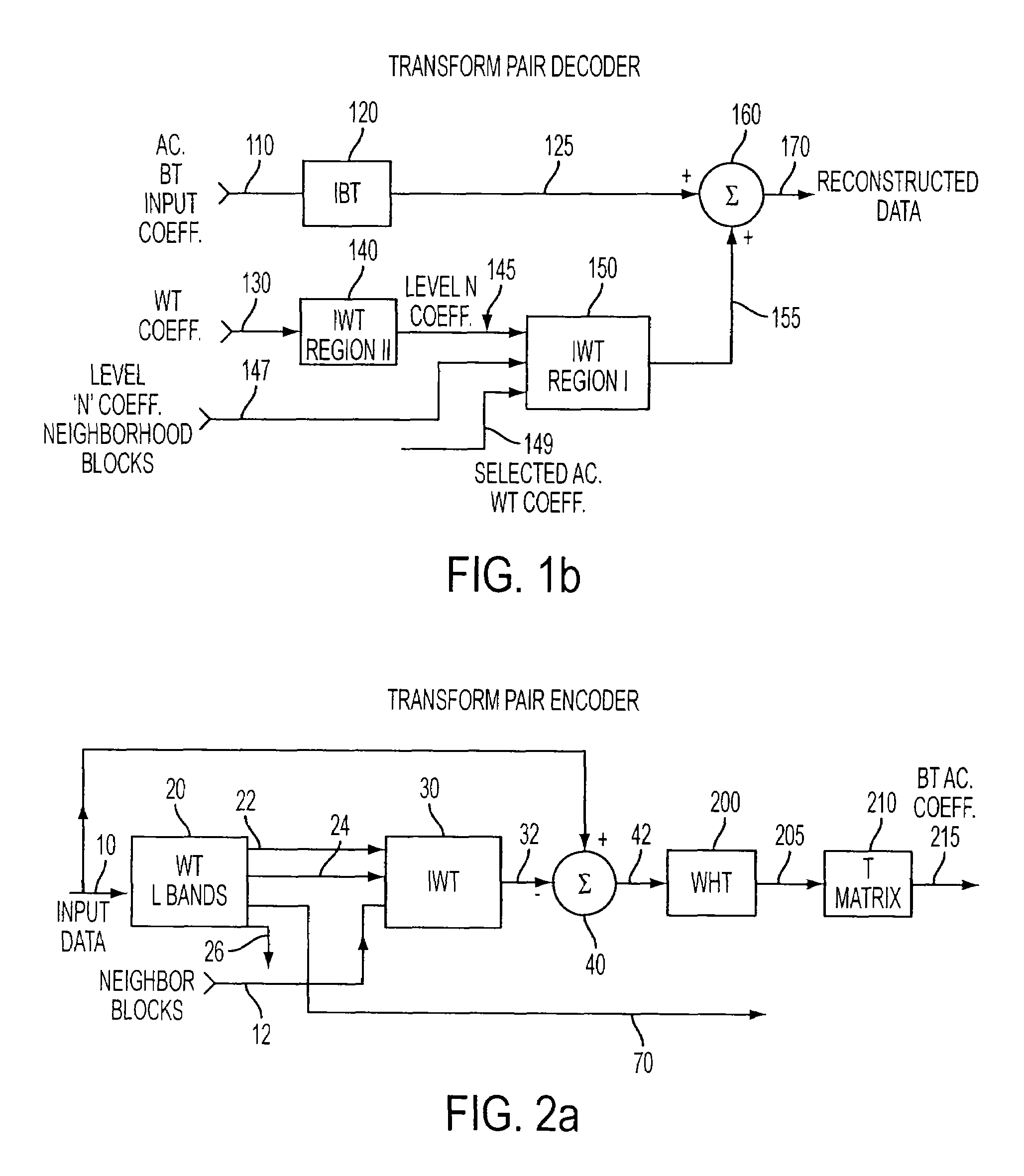
InactiveUS7545988B2Reduction in block edge artifact distortionImprove smoothnessCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationBlock transformImage compression
An apparatus using a compact blocked and Wavelet transform pair suppresses block artifacts in image compression systems by re-purposing one or more block transform coefficients with Wavelet coefficients. A general architecture and class of transforms is disclosed including integer types having Wavelet features but which can be processed one block at a time. An exemplary integer, non-separable two-dimensional Wavelet Transform is disclosed to partner with a Walsh-Hadamard blocked transform to serve as the core for the apparatus then tailored to function as a DCT, DST or other signal transform.
Owner:ELECTRIC PICTURE
Ghost Artifact Reduction for Rendering 2.5D Graphics
ActiveUS20080267527A1Easy to detect occlusionImprove completenessCharacter and pattern recognition3D-image renderingGraphicsImaging processing
An image processing system for performing a transformation of an input image associated with an input viewpoint to an output image associated with an output viewpoint. The input image is a pre-filtered 2D representation of 3D objects as seen from the input viewpoint, and comprises for each input pixel an associated input pixel value and an associated input pixel depth. Additional to the input image a hidden image is received, being another 2D representation of the 3D objects and comprising information, which information is occluded from the input viewpoint.The system comprises a video processor being operative to create the output image by transforming each input pixel to a transformed input pixel. The transformation is a function of the input pixel depth. The output image is created, based on the transformed input pixels, using hidden image pixels for filling de-occluded areas and for at least one pixel position adjacent to the de-occluded areas. As a consequence ghost line artifacts, caused by transformation of the pre-filtered input image, are prevented.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
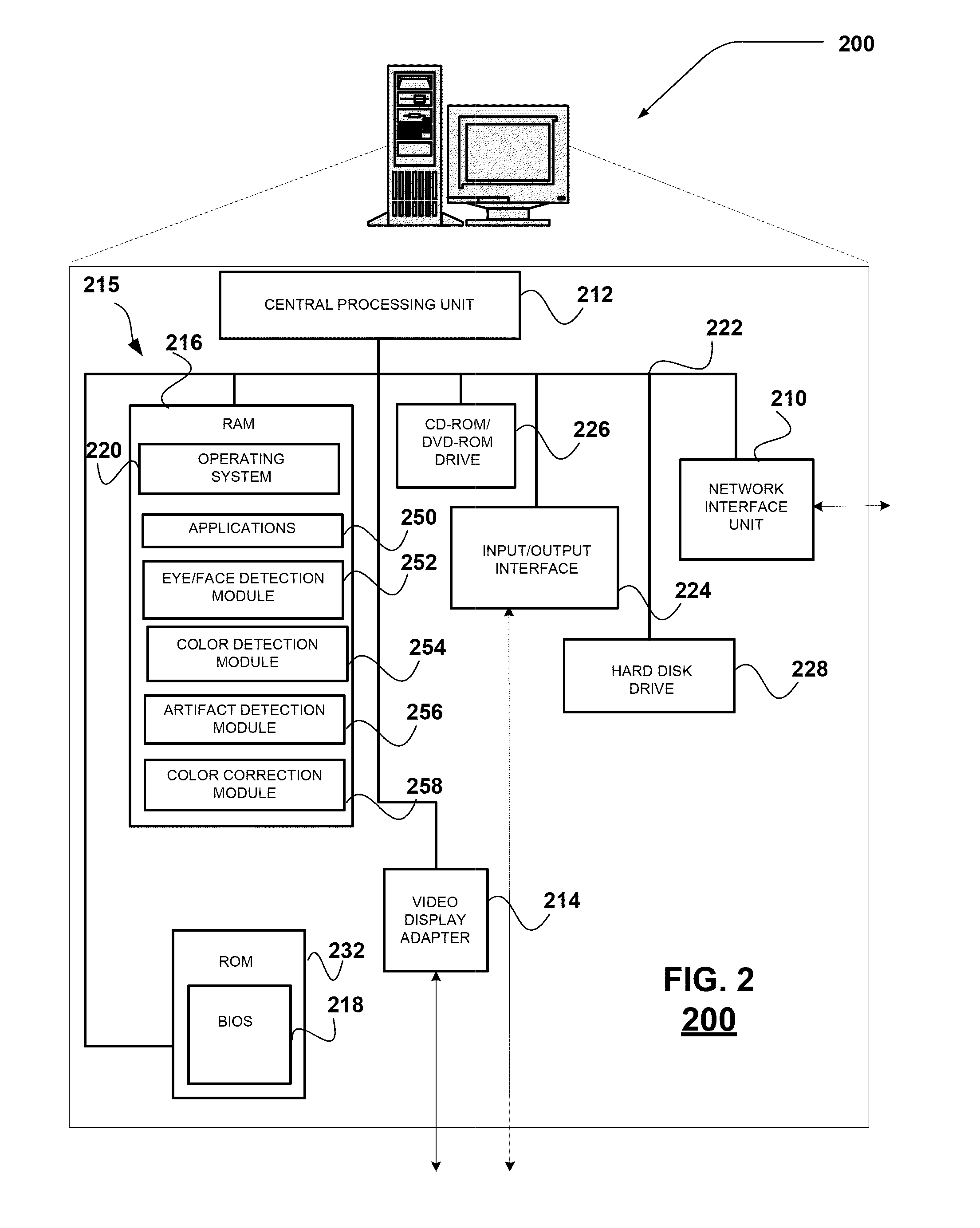
Automatic red eye artifact reduction for images
Systems and methods are provided for reducing eye coloration artifacts in an image. In the system and method, an eye is detected in the image and a pupil color for the eye in the image and a skin color of skin in the image associated with the eye are determined. At least one region of artifact coloration in the eye in the image is then identified based on the pupil color and the skin color, and a coloration of the region is modified to compensate for the artifact coloration.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Video quality adaptive coding artifact reduction
InactiveUS7865035B2Reduce artifactsReduce filter strengthPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesLight protection screensPattern recognitionAdaptive coding
A video quality adaptive coding artifact reduction system has a video quality analyzer, an artifact reducer, and a filter strength controller. The video quality analyzer employs input video quality analysis to control artifact reduction. The video quality analyzer accesses the video quality of the decoded video sequence to estimate the input video quality. The filter strength controller globally controls the filter strength of the artifact reducer based on the video quality estimate by the video quality analyzer. For low quality input video, the filter strength controller increases the artifact reduction filter strength to more efficiently reduce the artifact. For high quality input video, the filter strength controller decreases the artifact reduction filter strength to avoid blurring image detail.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
A method and system for reducing artifacts in a tomosynthesis imaging system
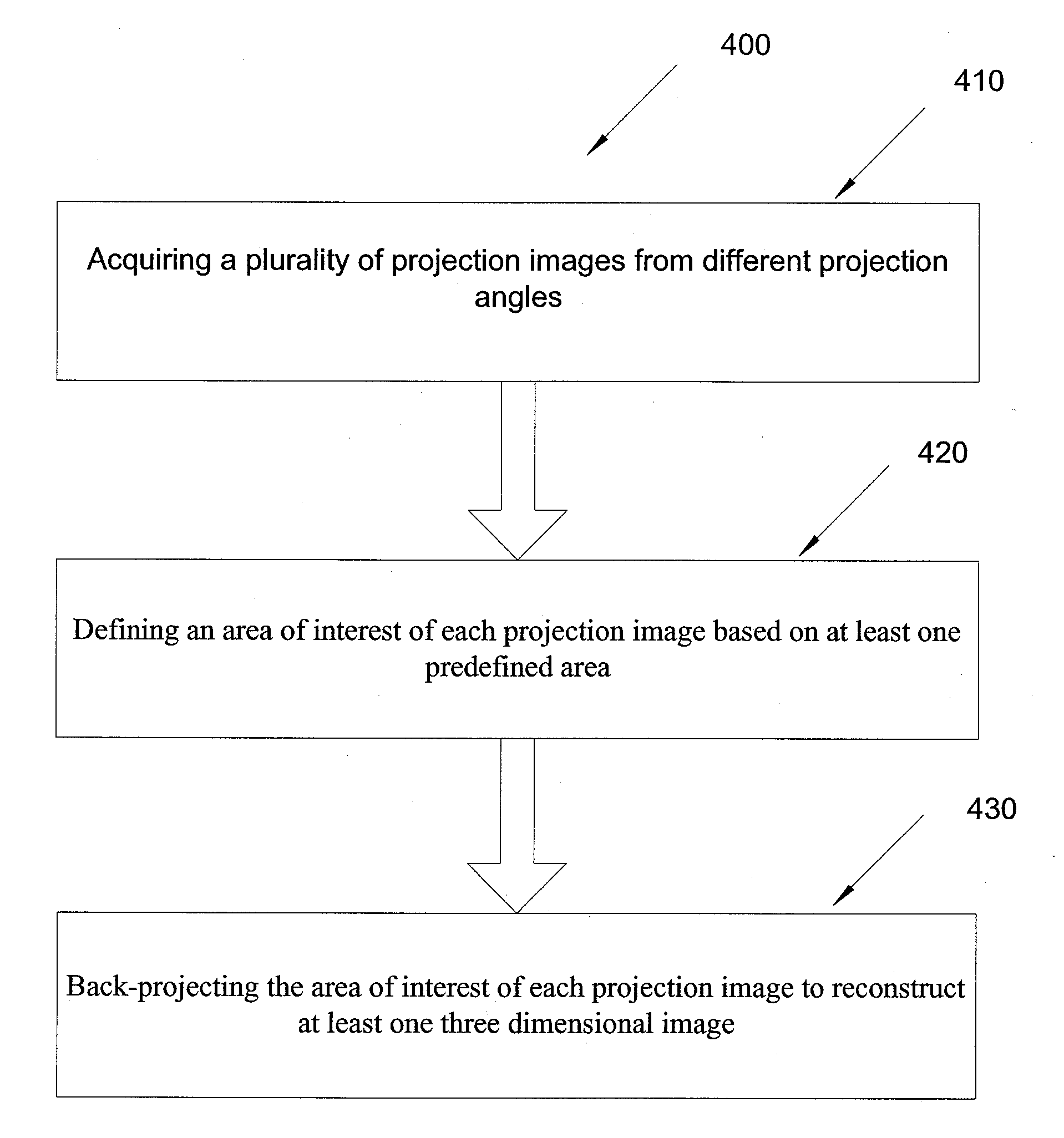
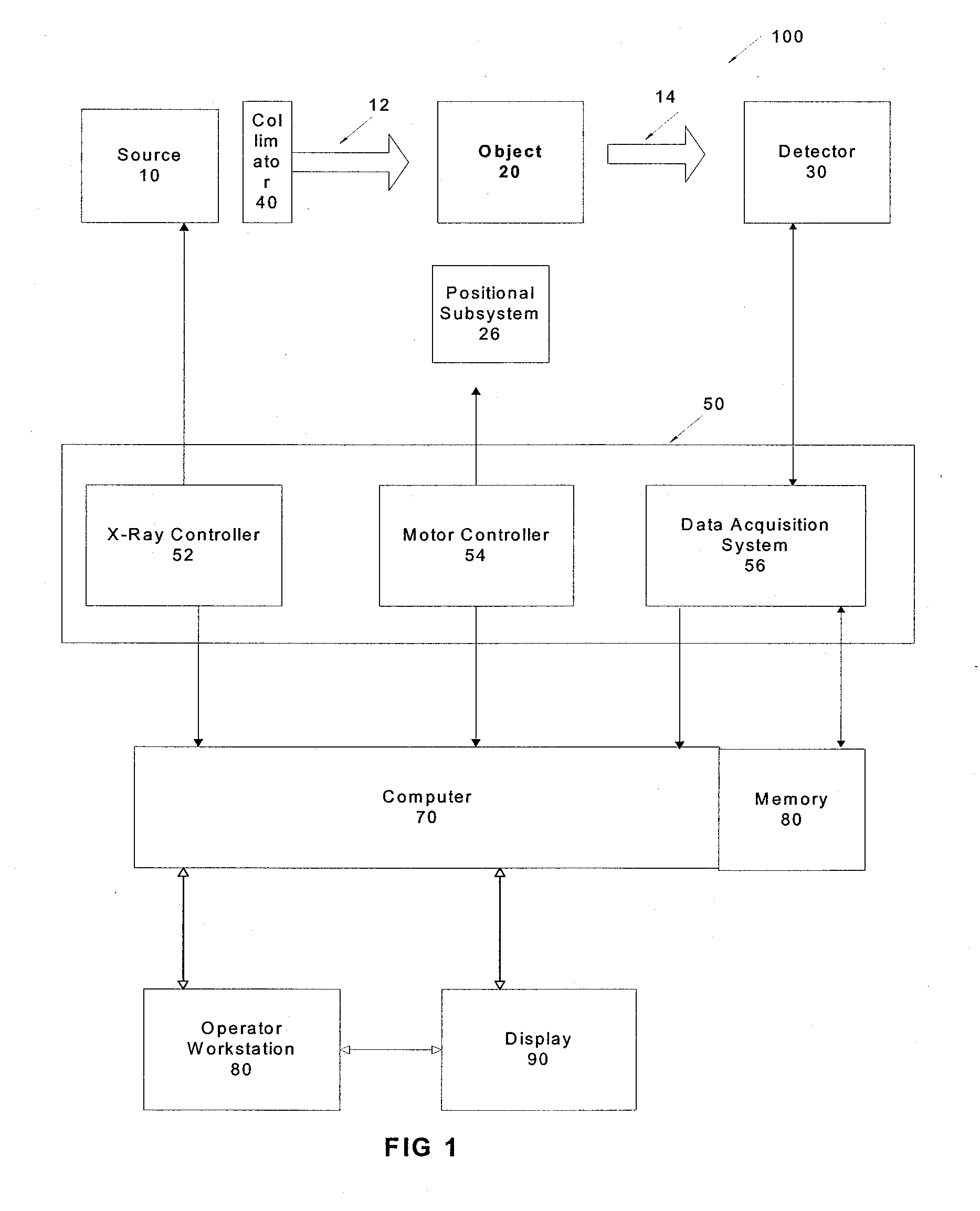
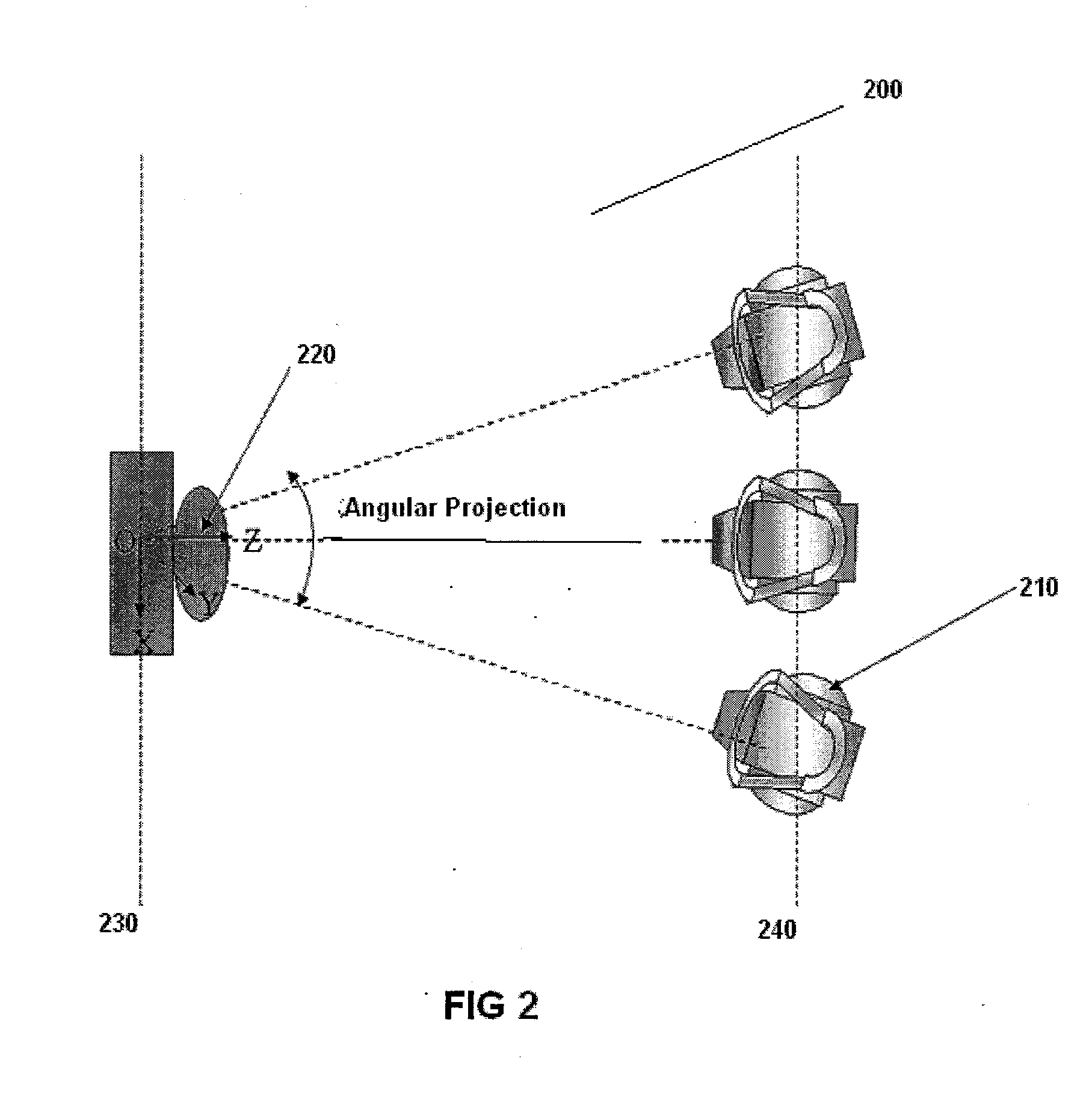
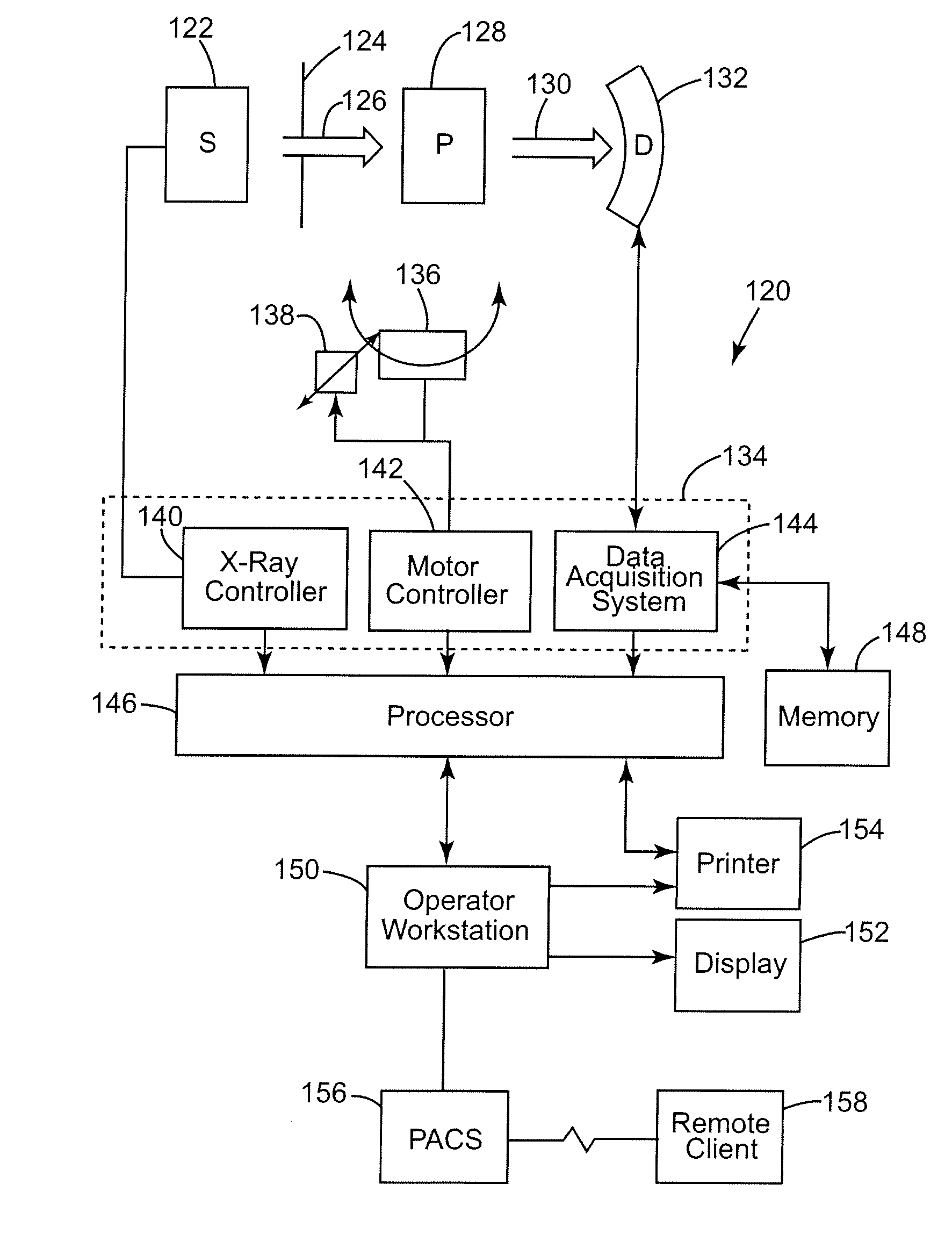
InactiveUS20080008372A1Improved artifact reductionAdditional artifactImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisProjection image
The present invention provides a method and system for reducing artifacts in tomosynthesis reconstructed images. The artifacts reduction method comprises back-projecting only a part of the projection image. The method includes acquiring plurality of projection images from different projection angles. It further includes identifying an area of interest of each projection image based on a predefined area and back project the area of interest of each projection image to reconstruct at least one three dimensional image. In an embodiment the area of interest of the projection image is identified based on field of view of the collimator. In another embodiment the invention provides a tomosynthesis system producing a 3-D image with reduced reducing artifacts.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system for reconstructing cone-beam projection data with reduced artifacts
ActiveUS20090207964A1Need be addressReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData setProjection View
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method of image artifact reduction in fast kvp switching ct
A CT system includes a generator configured to energize an x-ray source to a first kilovoltage (kVp) and to a second kVp, and a computer that is programmed to acquire a first view dataset with the x-ray source energized to the first kVp and a second view dataset with the x-ray source energized to the second kVp, generate a base correction image using the first view dataset and the second view dataset, and reconstruct a pair of base material images from the first view dataset and from the second view dataset. The computer is also programmed to estimate artifact correlation in the pair of base material images using the base correction image, generate a pair of final base material images and a final monochromatic image, and correct one of the pair of final base material images and the final monochromatic image at a keV value using the estimated artifact correlation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
X-ray therapy electronic portal imaging system and method for artifact reduction
InactiveUS7027558B2Reduce variationReduce removalTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayPulse rate
X-ray therapy EPI artifact reduction and control of imaging is provided. Scanning of images is synchronized with the pulse rate of the x-rays. The scanning period is longer than the pulse rate period, so artifacts are generated within the resulting images. Due to the synchronization, the pulse variation artifacts are aligned across multiple images. The synchronization and resulting alignment of linear artifacts allows for gain correction as a function of lines within the image. Such gain correction reduces or removes non-linearities associated with pulse rate variation.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
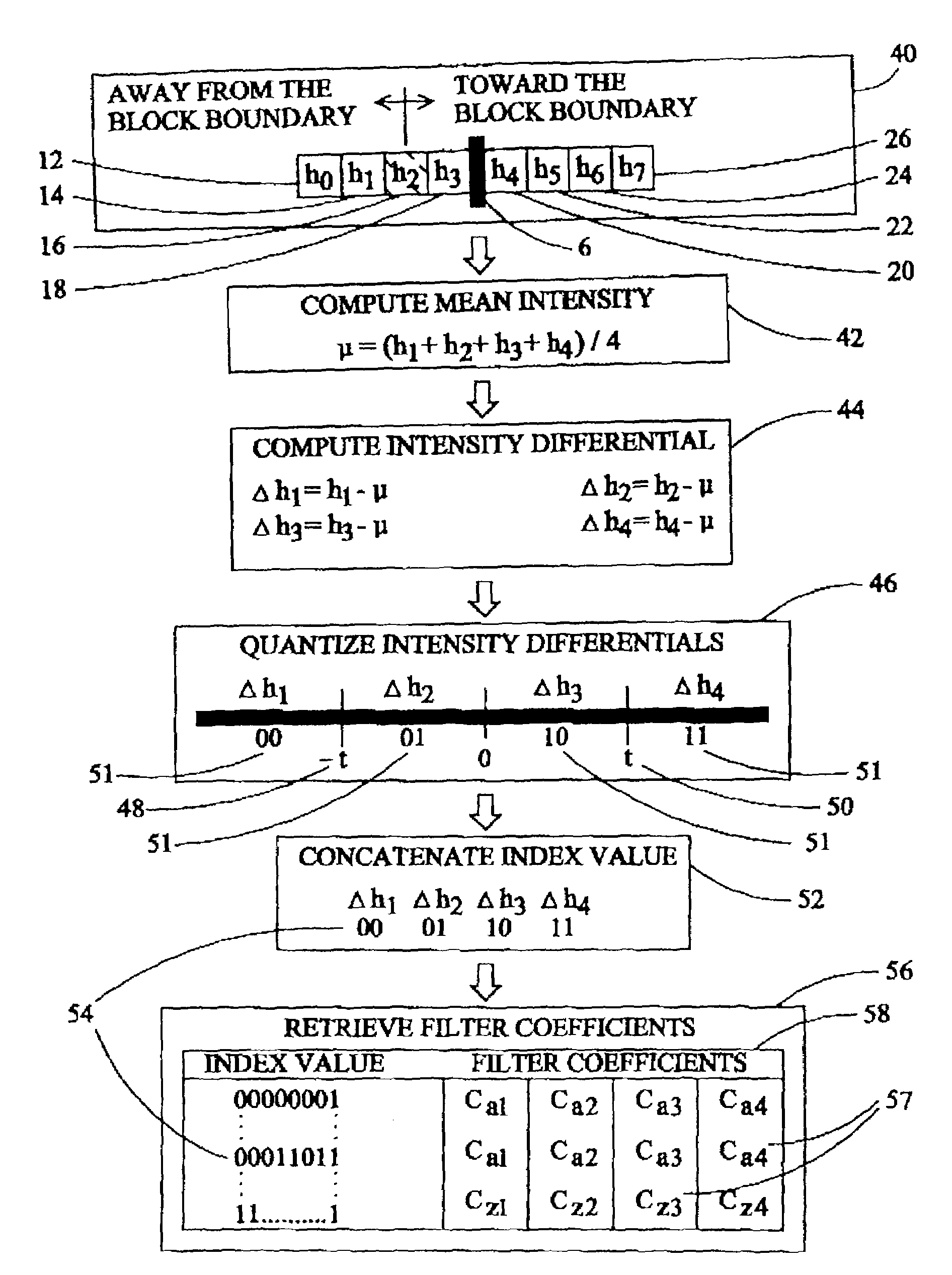
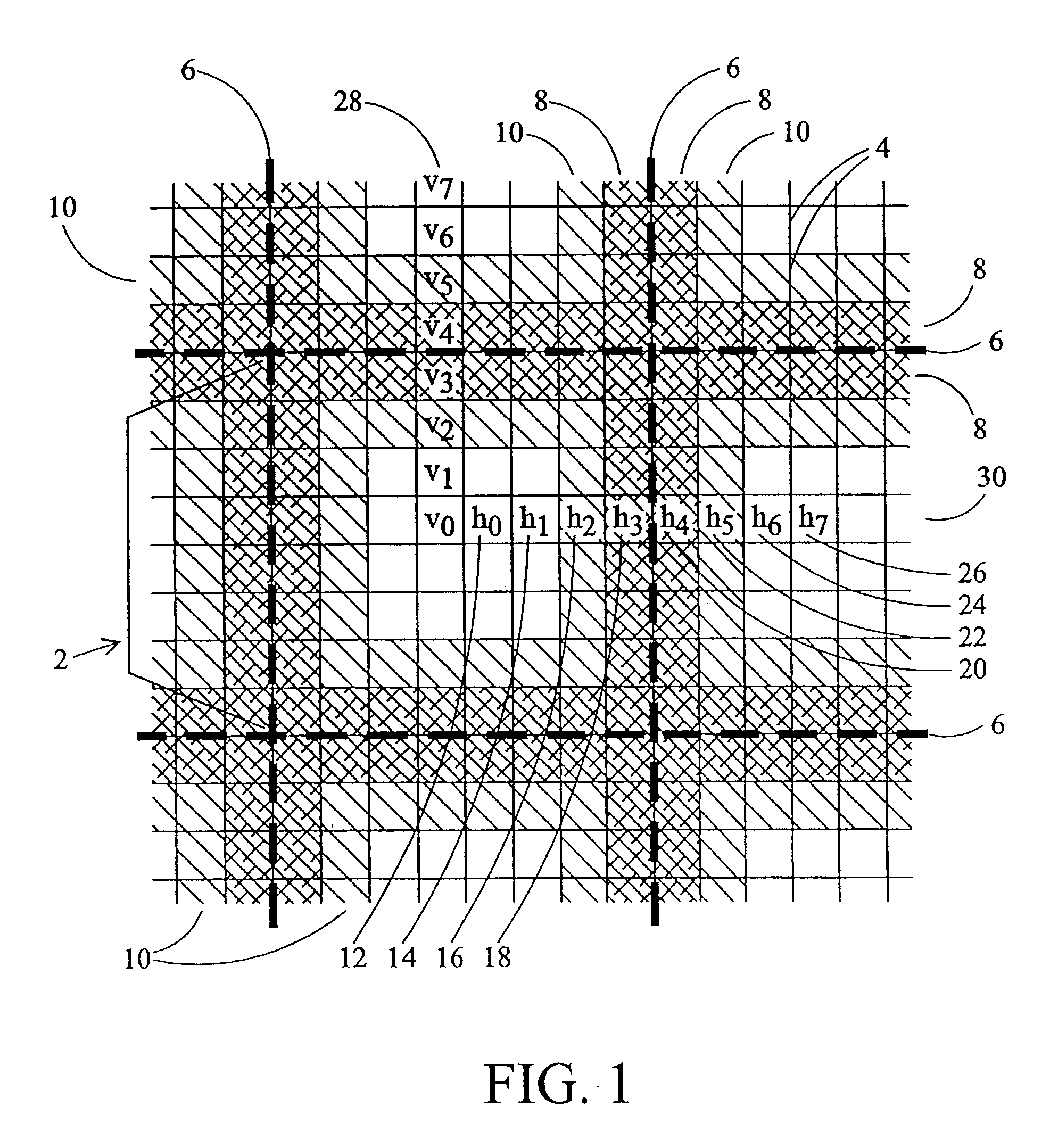
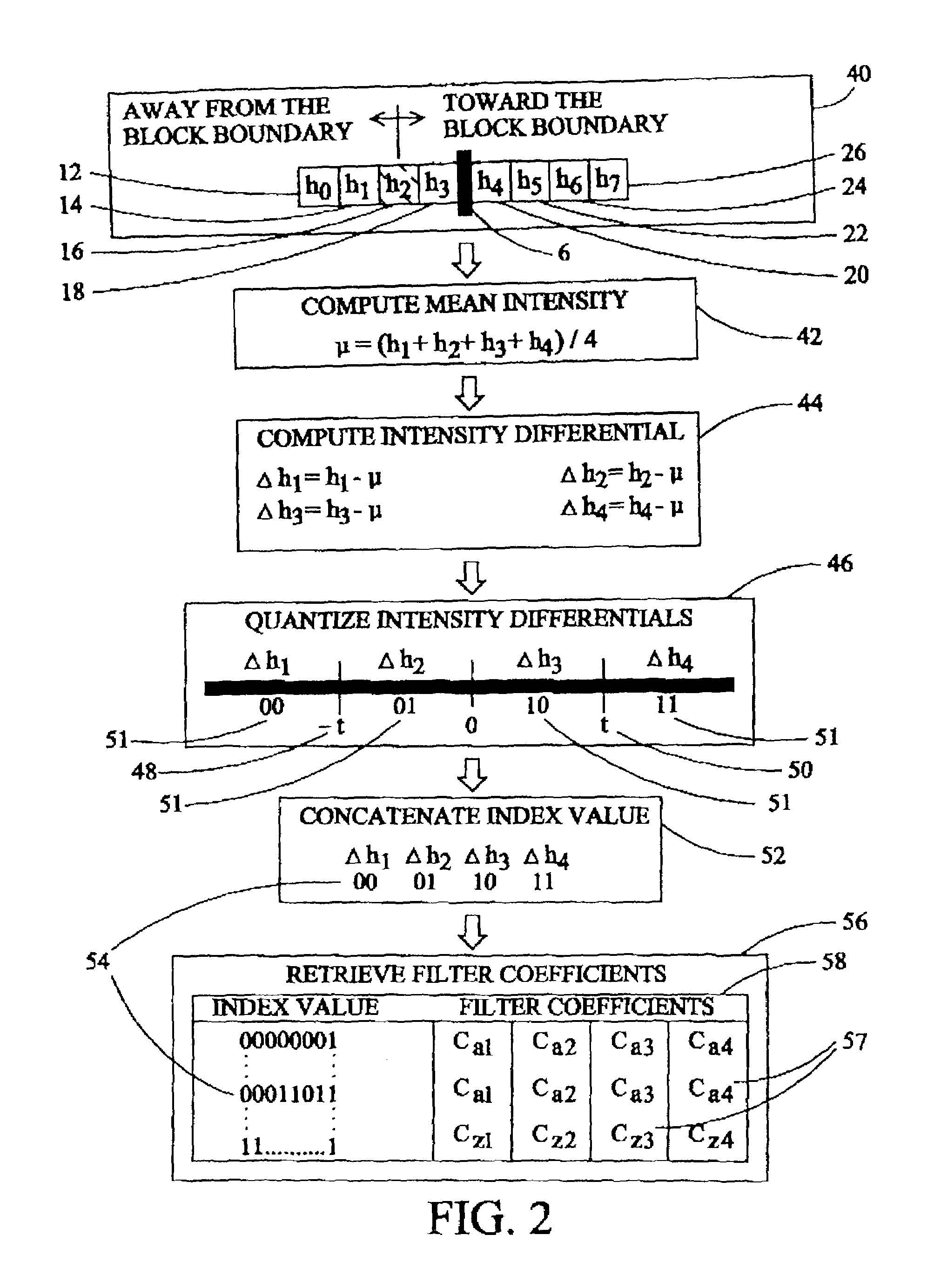
Block boundary artifact reduction for block-based image compression
InactiveUS7076114B2Reduce suddennessImproves block boundary artifact reductionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImage compressionDigital image
Block boundary artifact reduction in decompressed digital images is accomplished by filtering the intensity of pixels in the vicinity of the block boundary. The filter utilizes filter coefficients selected from tables on the basis of the distribution of a scalar quantity describing the pixels neighboring the pixel to which the intensity adjustment is to be applied. The intensities of pixels at the boundary and one pixel removed from the boundary are adjusted. If interpolation pixels in each of neighboring blocks are of relatively constant intensity, the intensities of additional pixels, more remote from the boundary, are adjusted. Filter coefficients can be selected from different arrays for pixels on the boundary or removed from the boundary or if the pixel intensity adjustment is based on the intensities of pixels in a horizontal row or vertical column of interpolation pixels.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
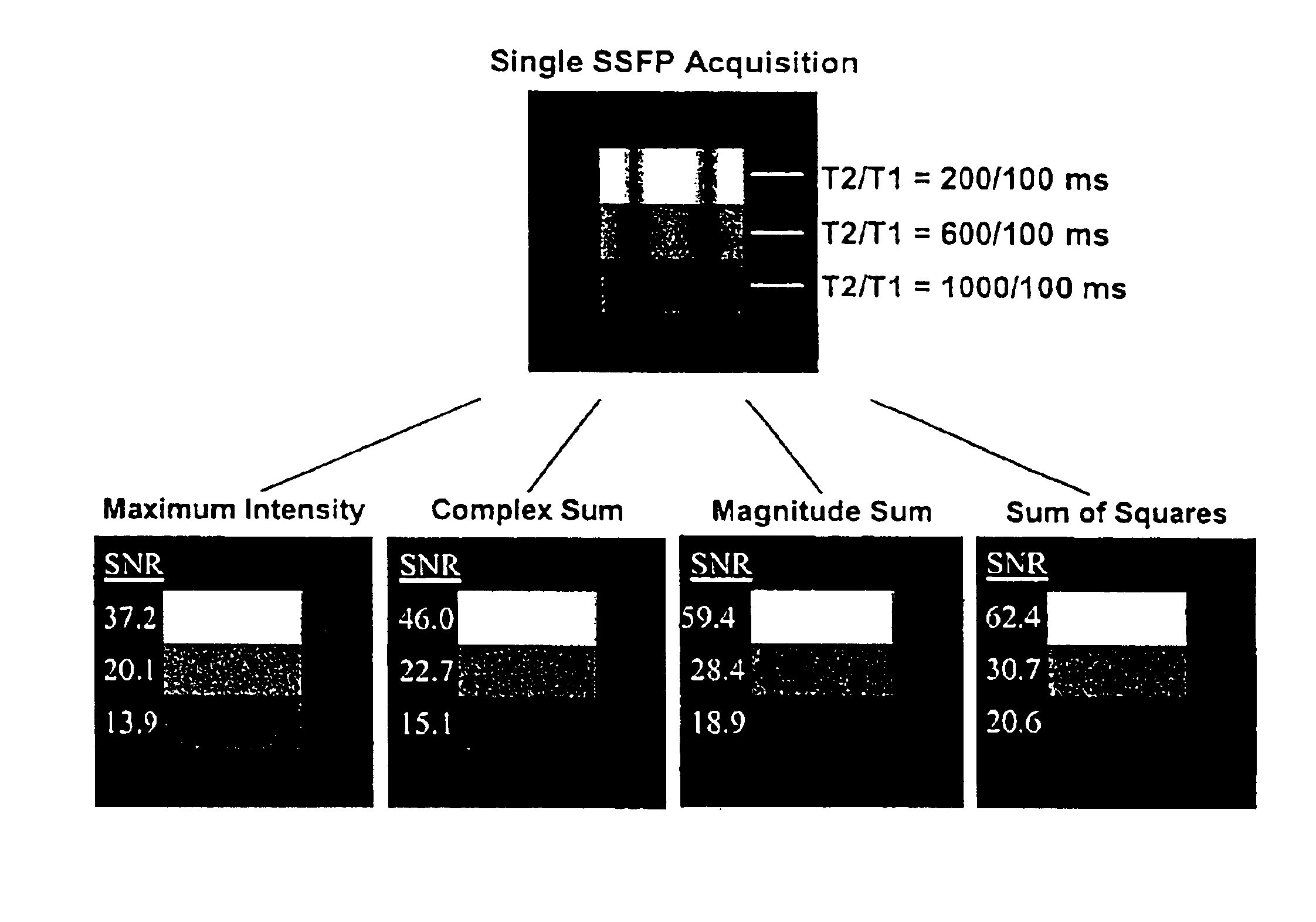
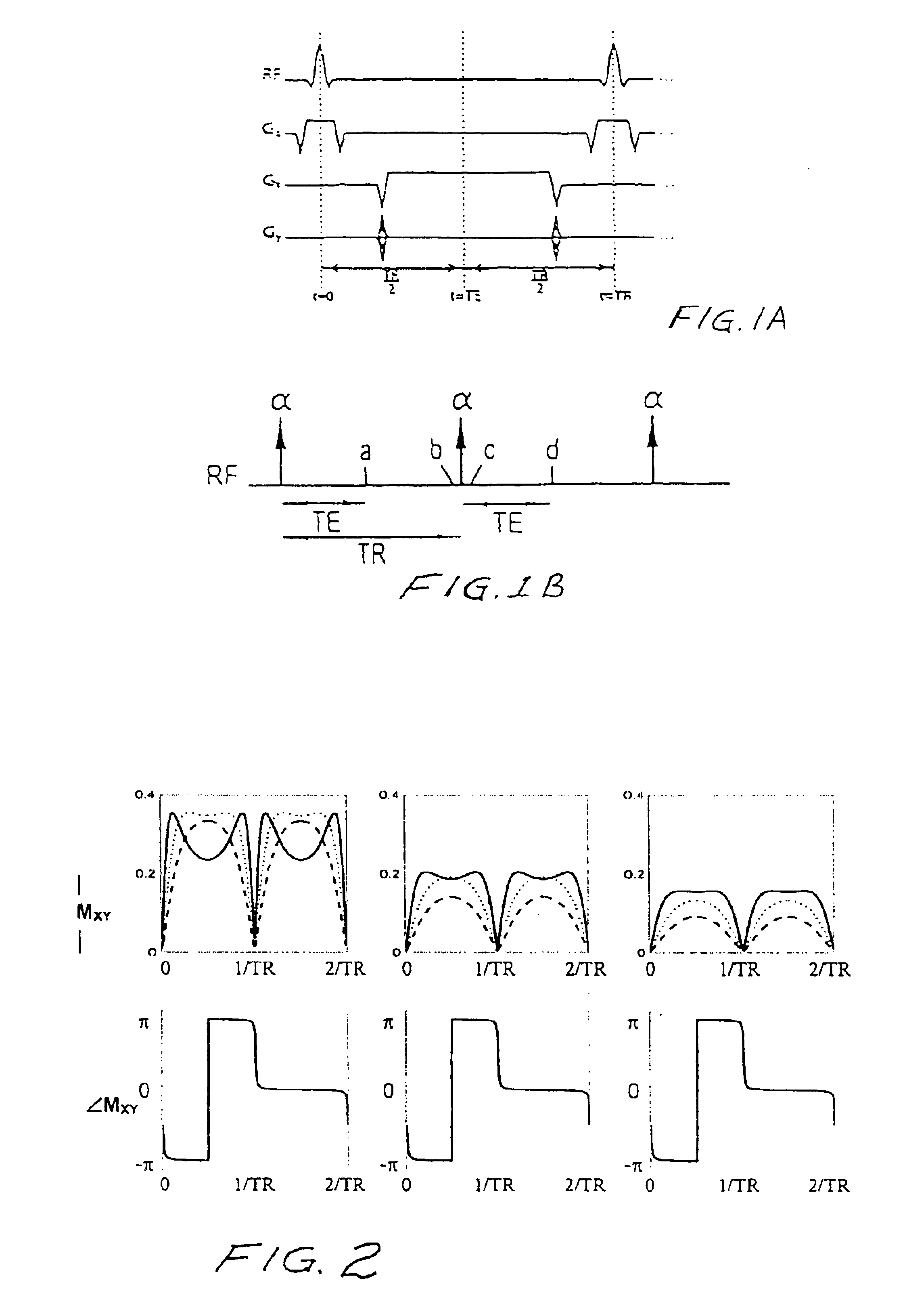
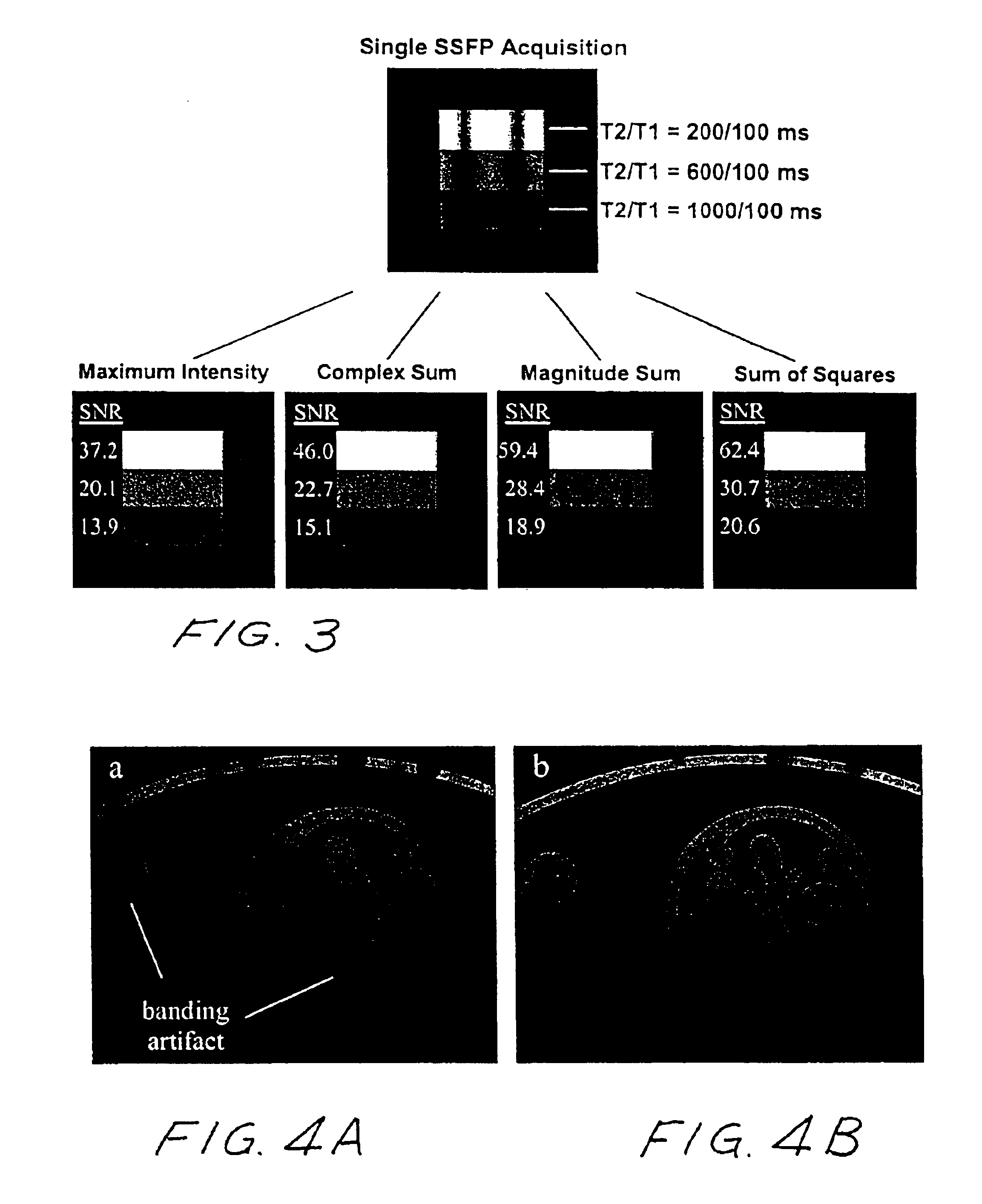
Artifact reduction in SSFP MRI using weighted sum of combined signals
InactiveUS6906516B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionPattern recognitionImage signal
Artifact reduction in steady state free precession magnetic resonance imaging uses weighting of acquired image data to emphasize higher signals and then establishing an image signal based on the combined weighted signals. In one embodiment, a SSFP imaging sequence uses phase cycling and acquired image data is squared with the squared data then combined. The final image signal is based on the square root of the squared data.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
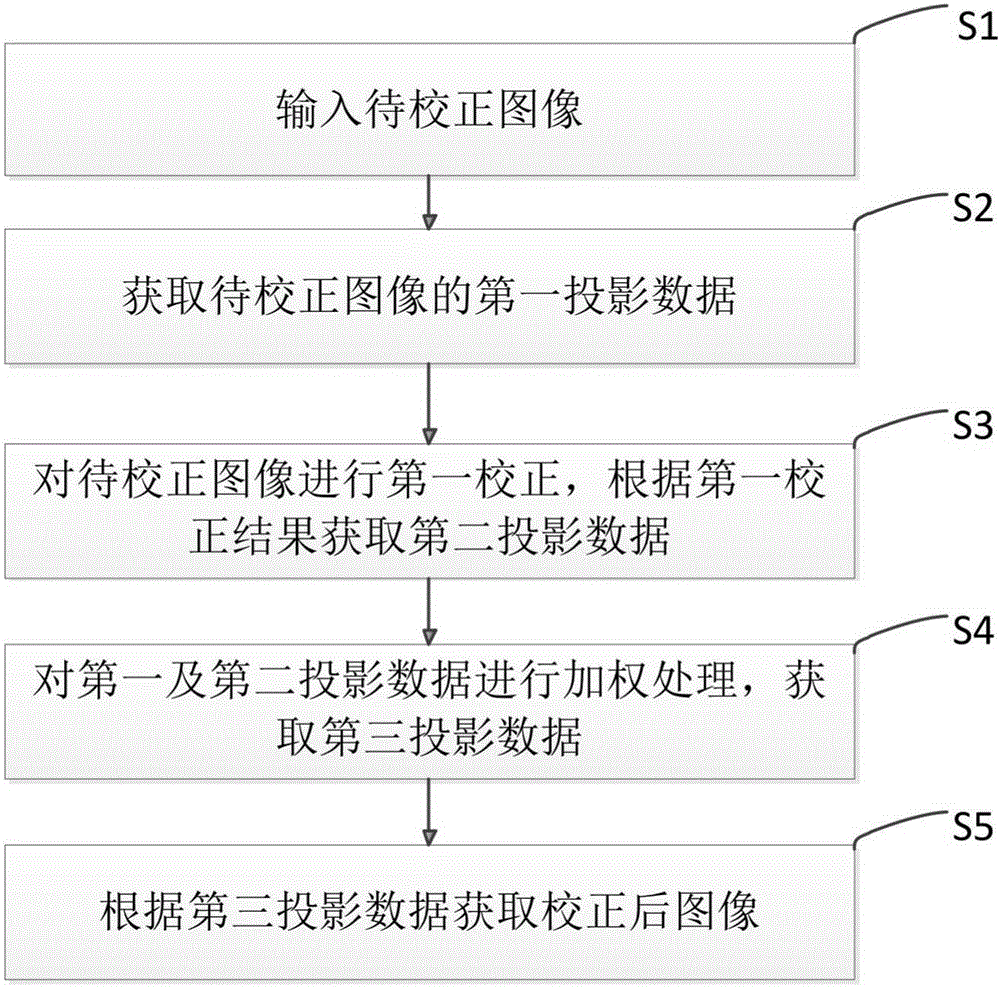
Computed tomography metal artifact correction method and apparatus
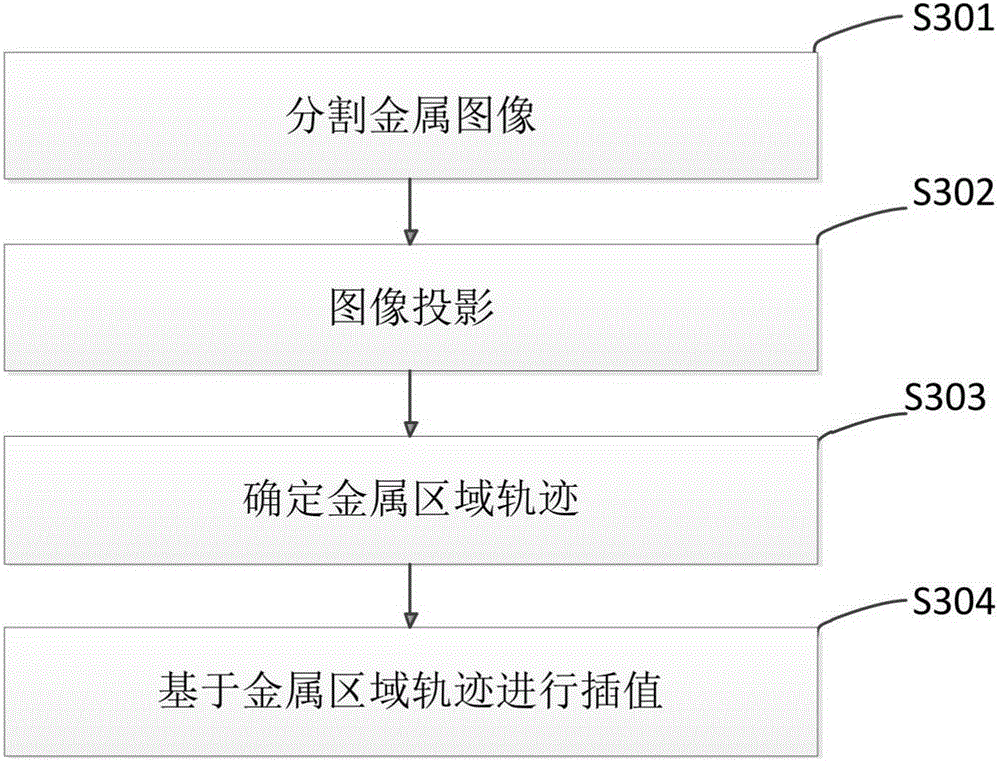
ActiveCN105225208ATrue restorationQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisMetal ArtifactCorrection method
The present invention discloses a computed tomography metal artifact correction method. The method comprises: inputting a to-be-corrected image; acquiring first projection data of the to-be-corrected image; performing first correction on the to-be-corrected image and acquiring second projection data according to a result of the first correction; performing a weighting process on the first and second projection data to acquire third projection data; and obtaining a corrected image according to the third projection data. The present invention further discloses a metal artifact correction apparatus. According to the method and the apparatus provided by the present invention, artifacts can be further reduced and the quality of images can be improved on the premise of reserving available information of original images.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com