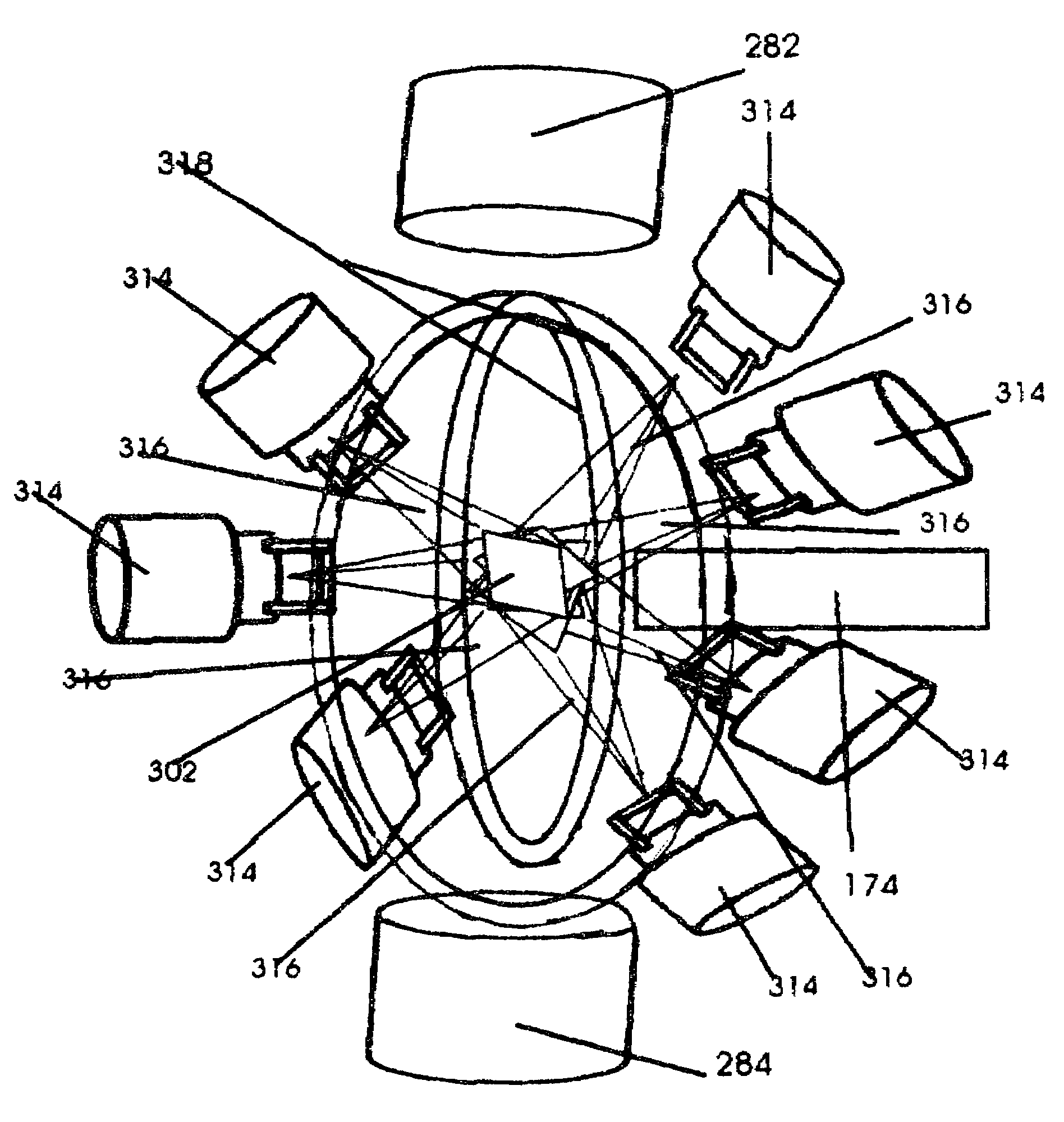
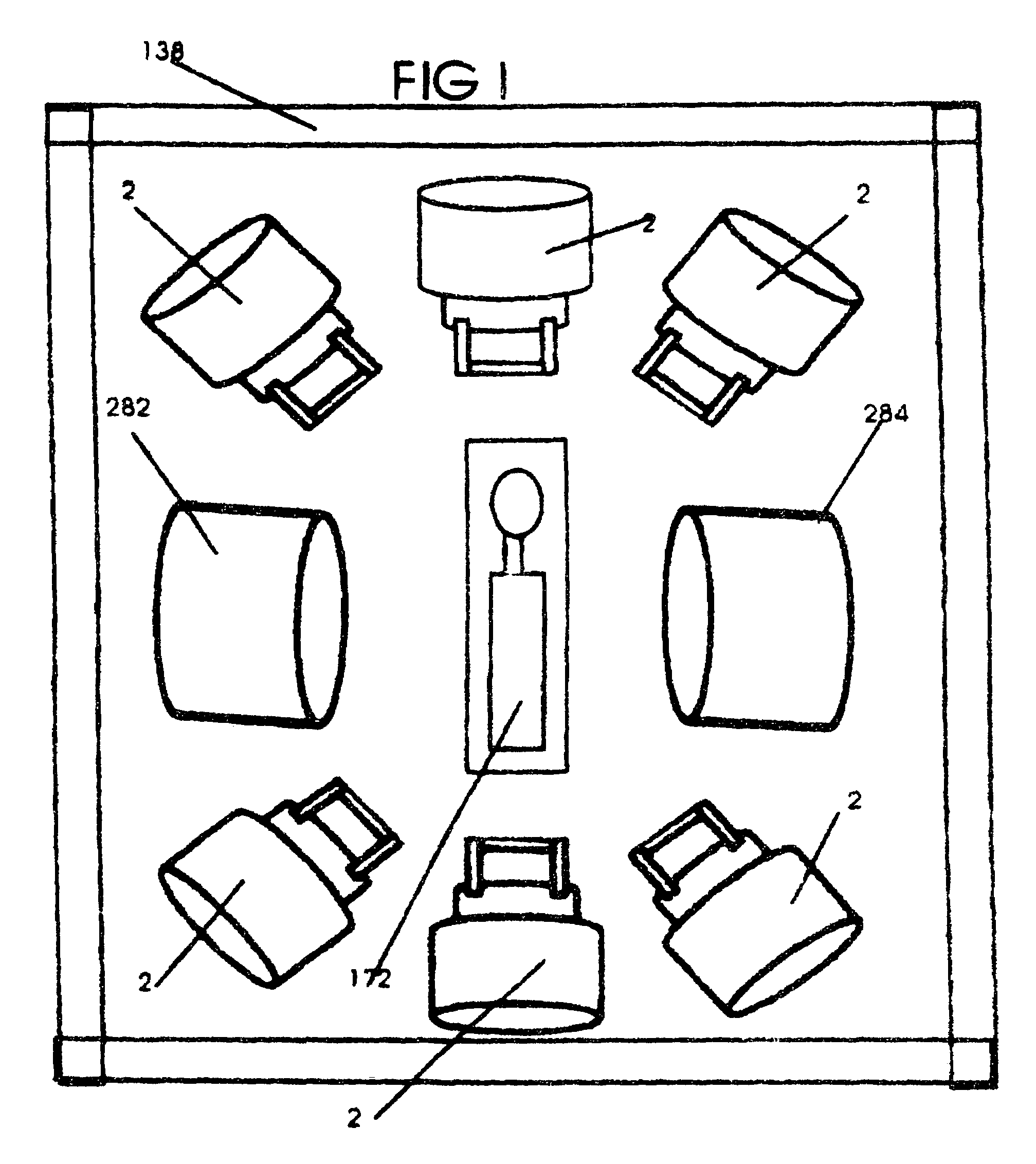
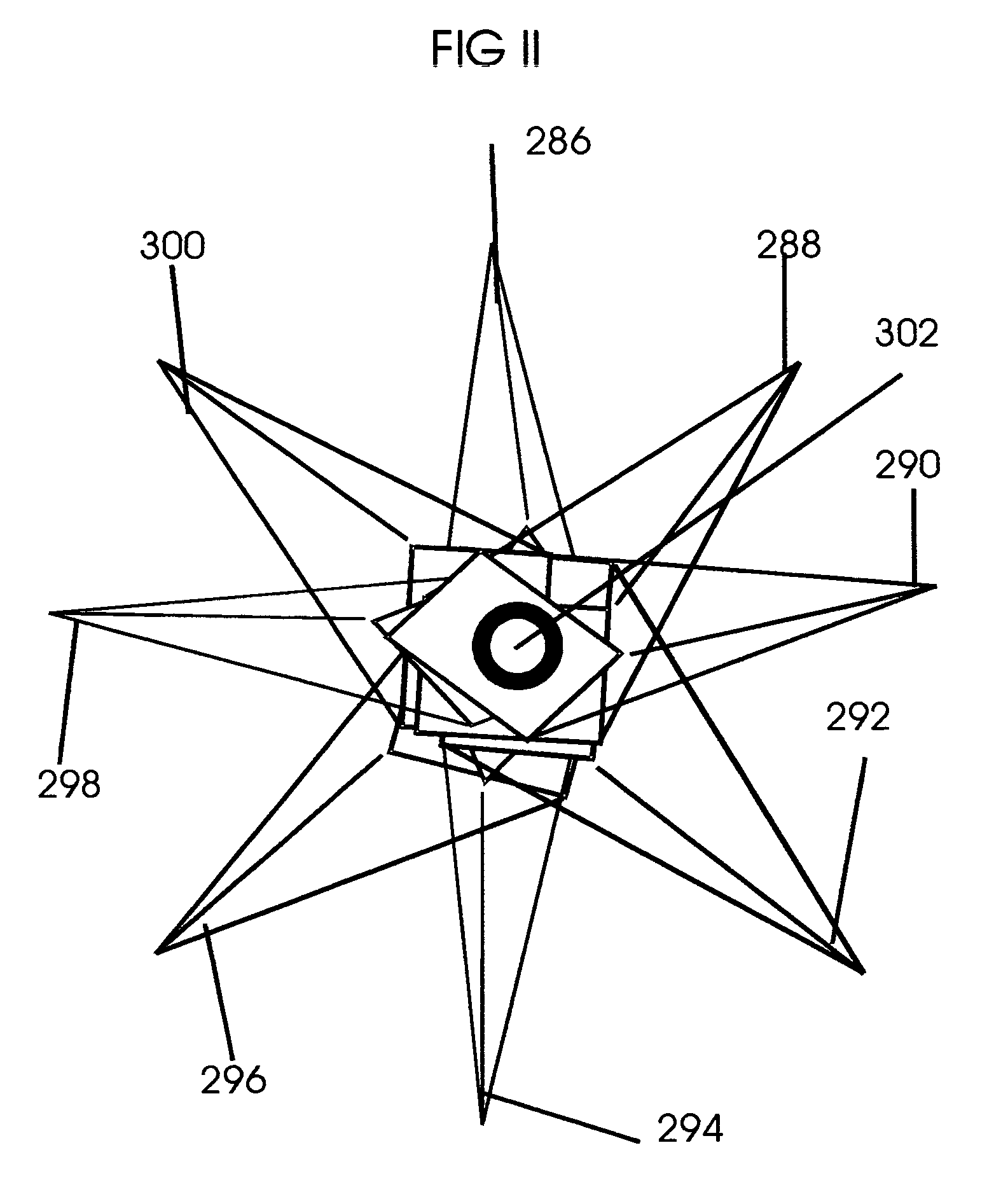
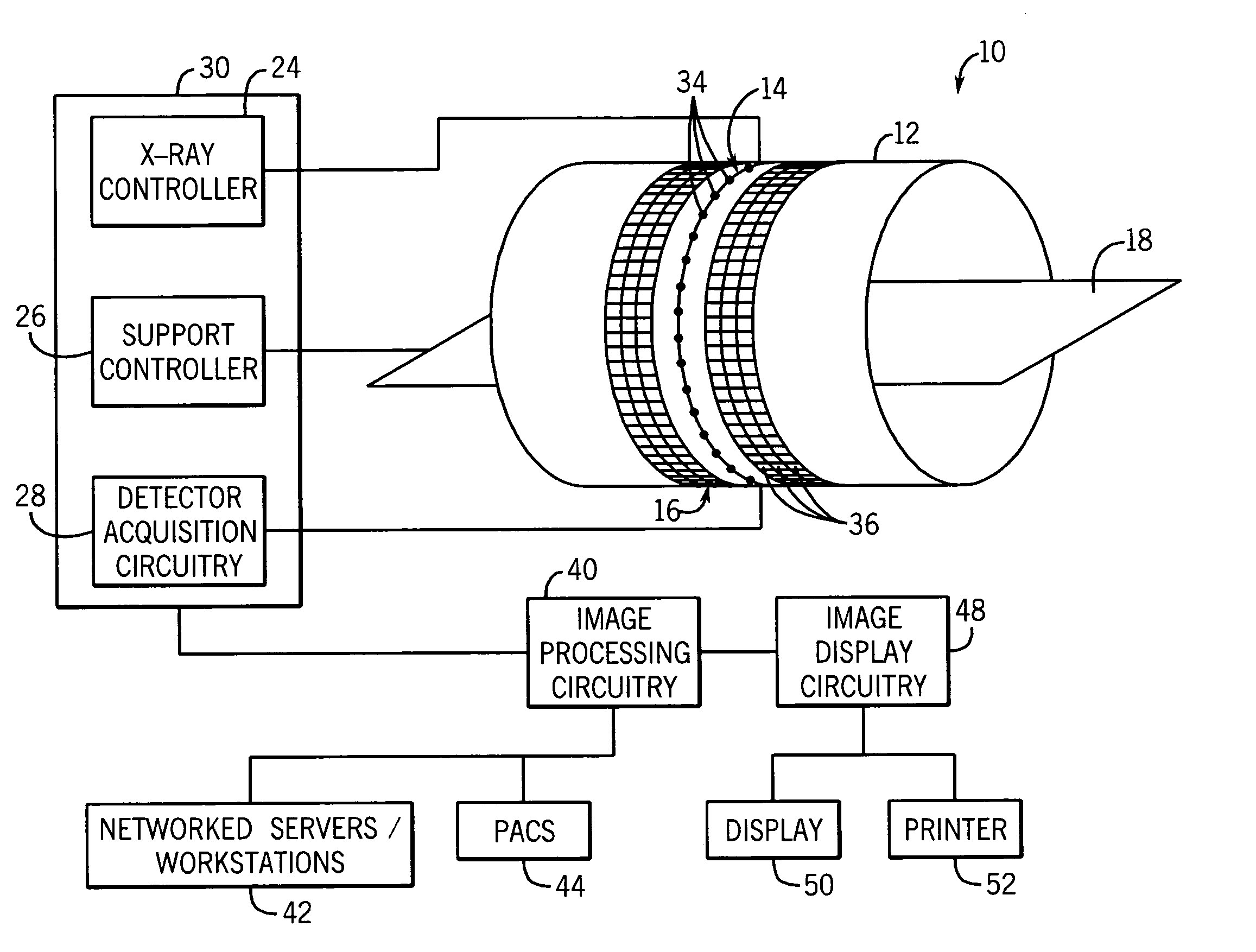
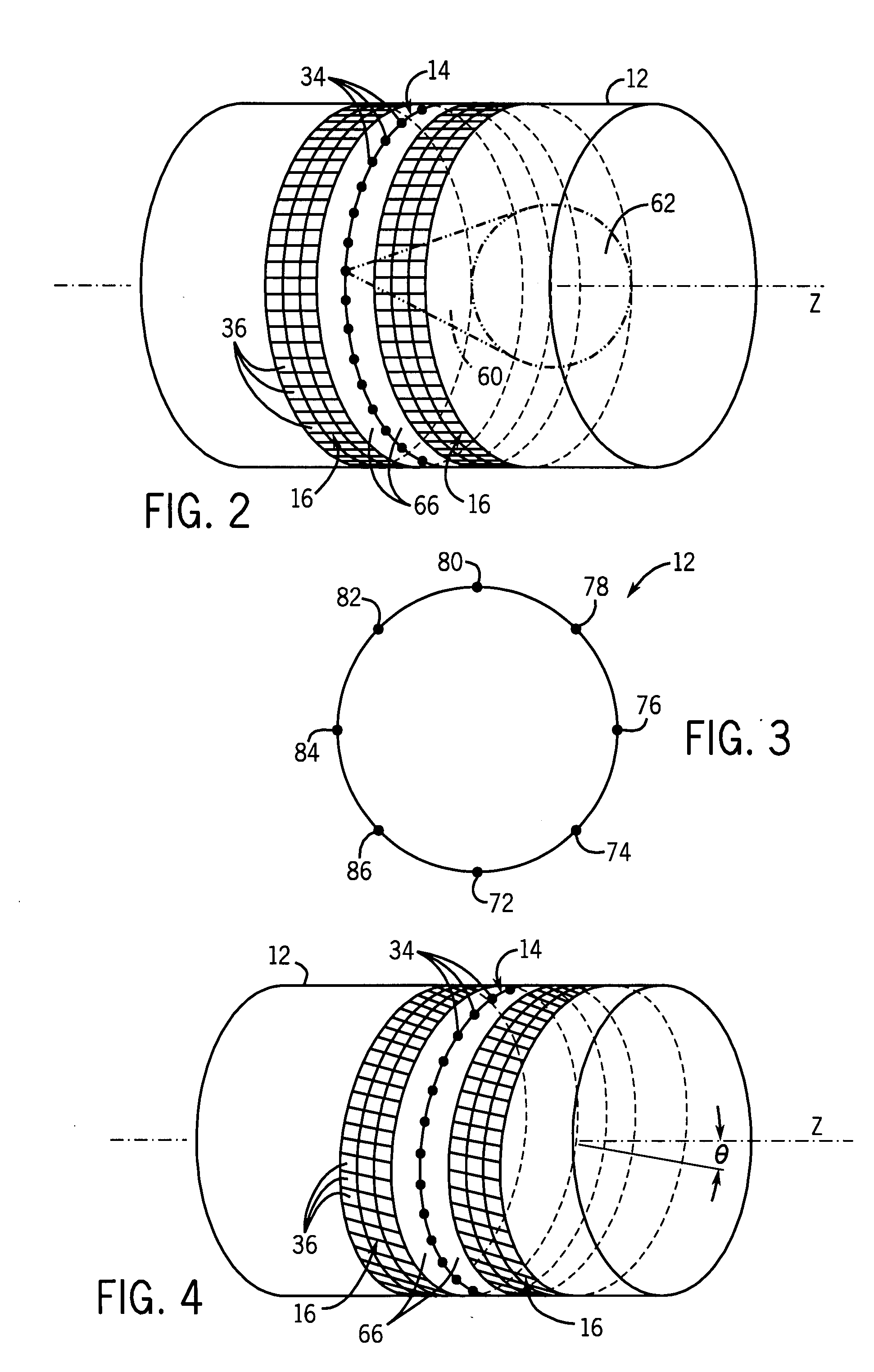
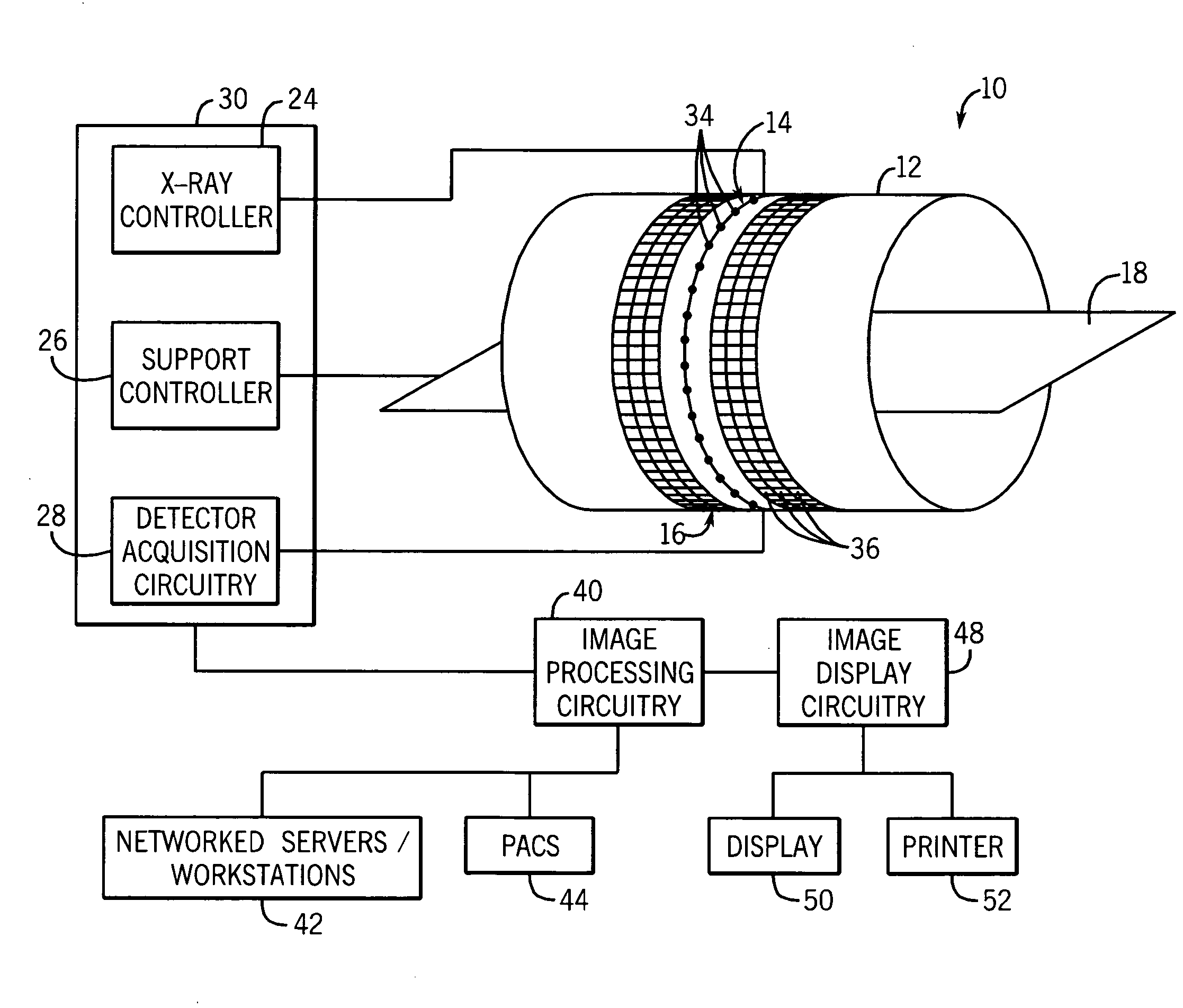
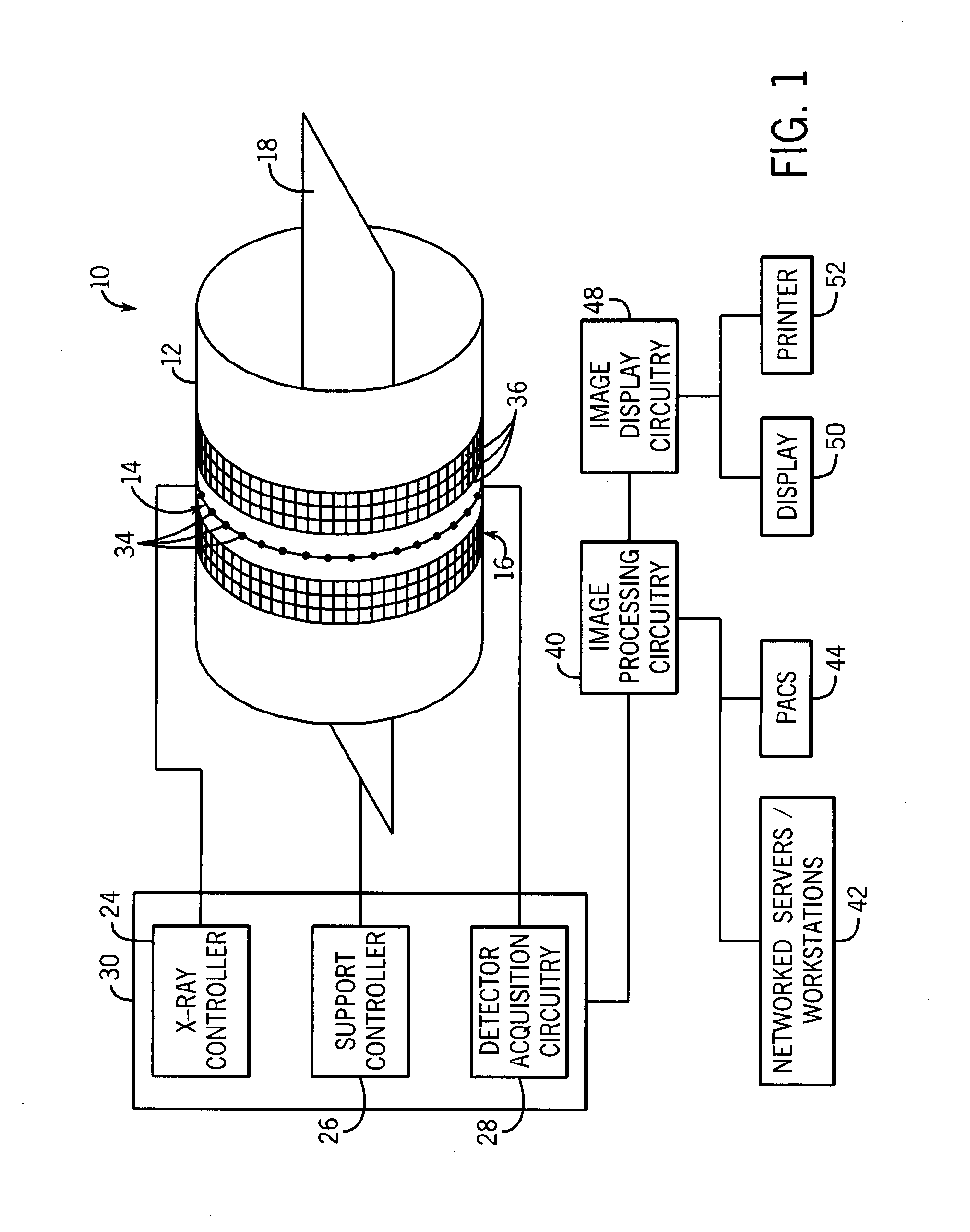
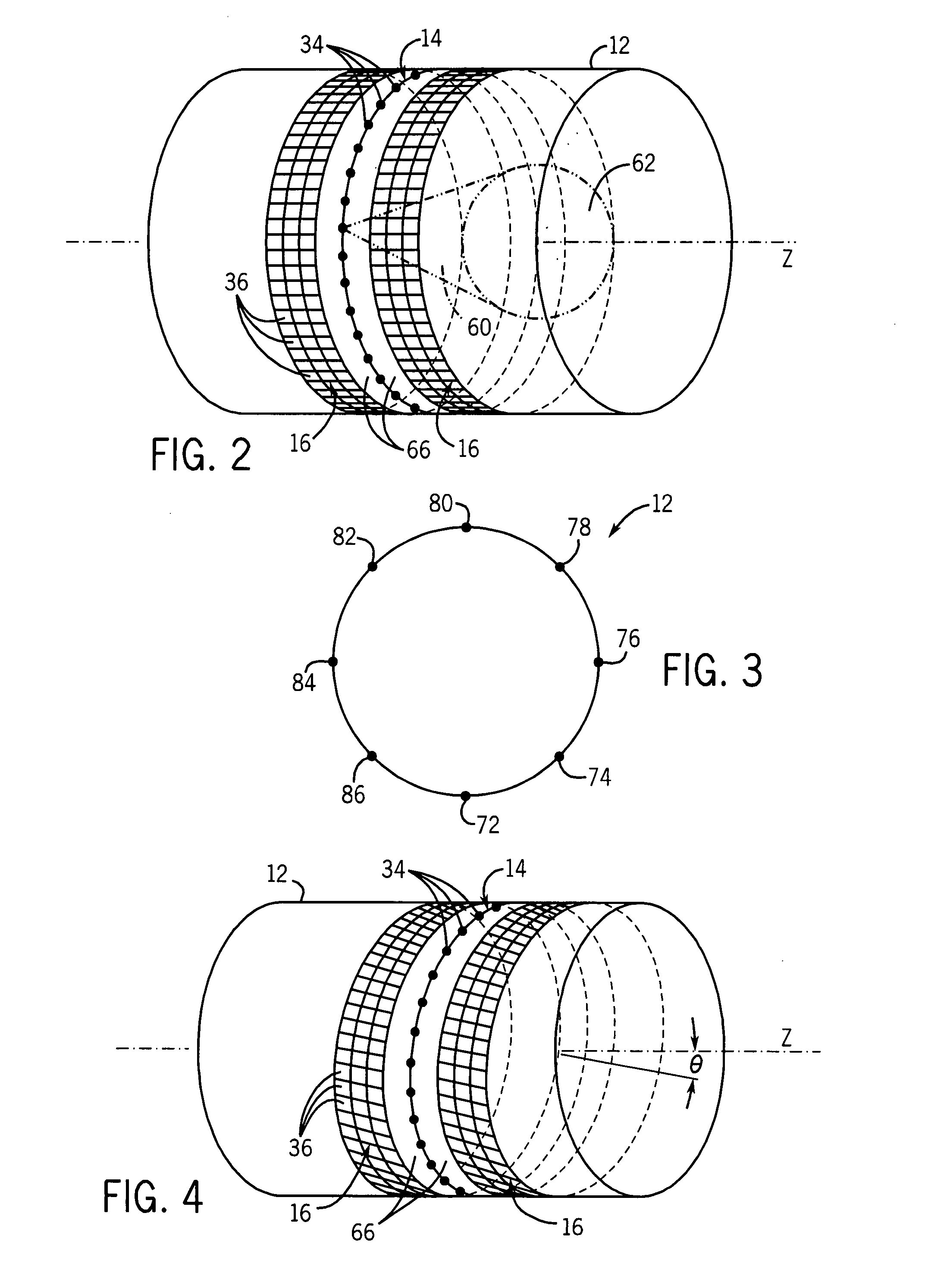
Patents
Literature
396 results about "Computed tomographic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
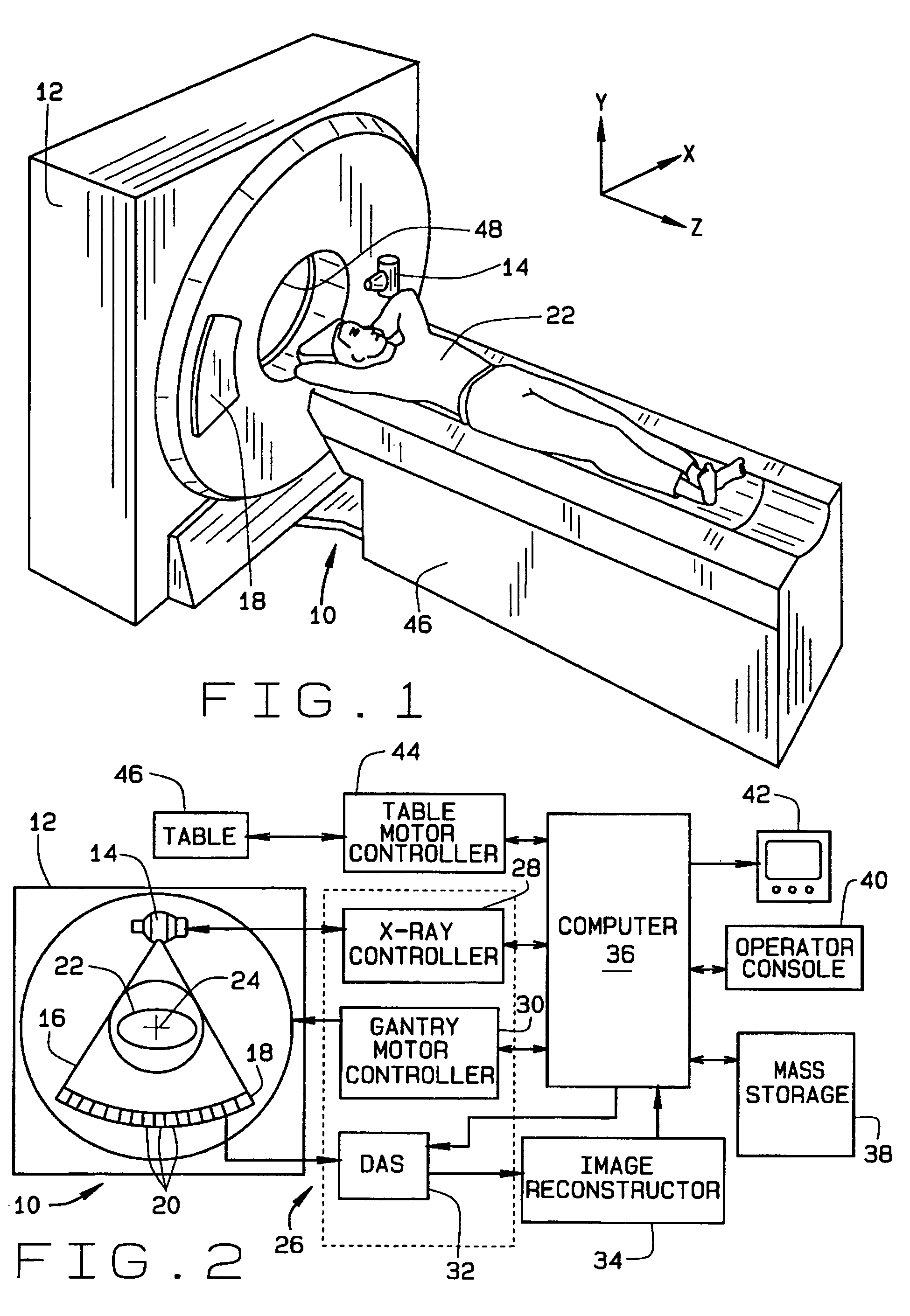
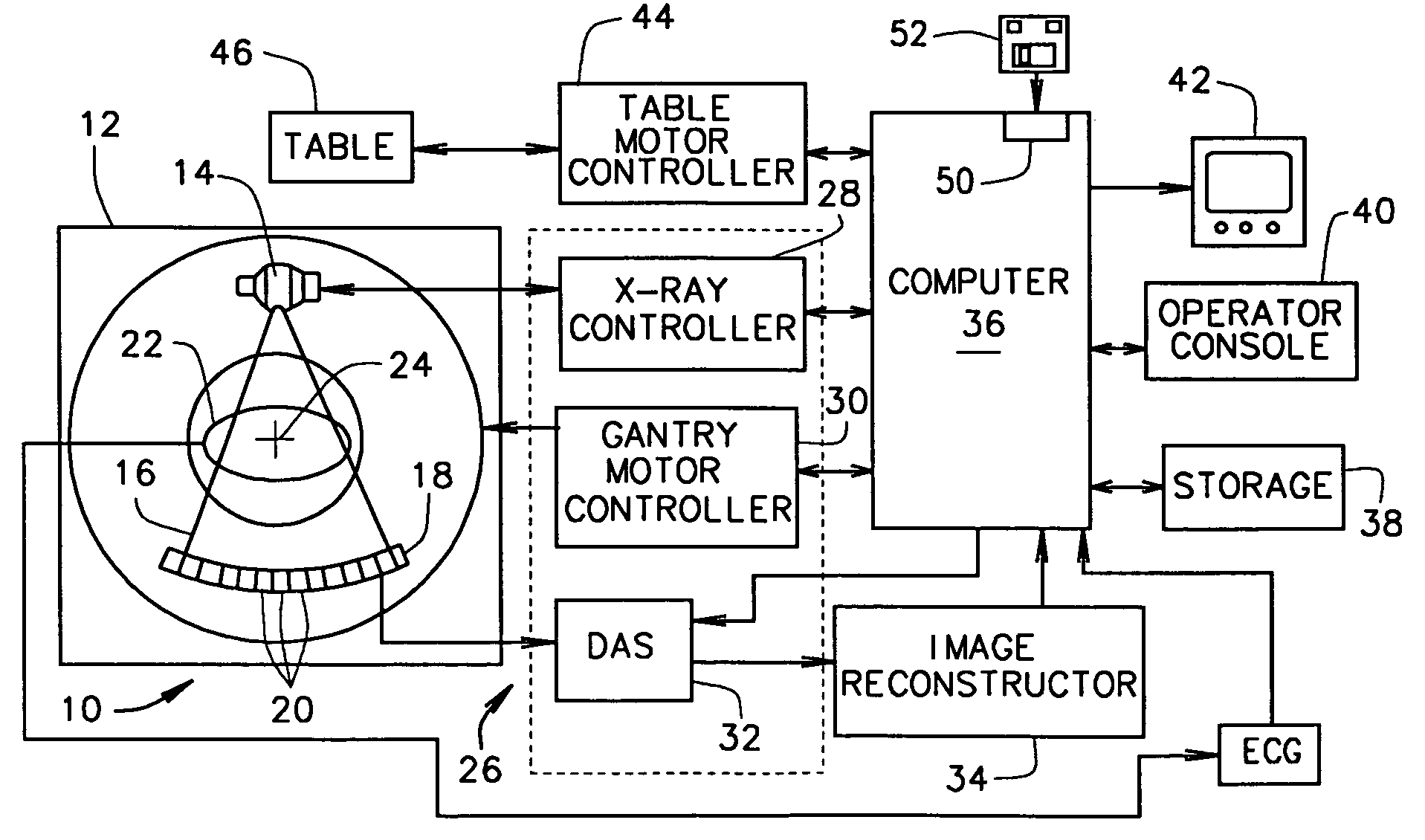
Computed tomography. X-ray computed tomography, also computed tomography, computed axial tomography or computer assisted tomography is a medical imaging procedure that uses computer-processed X-rays to produce tomographic images or 'slices' of specific areas of the body.
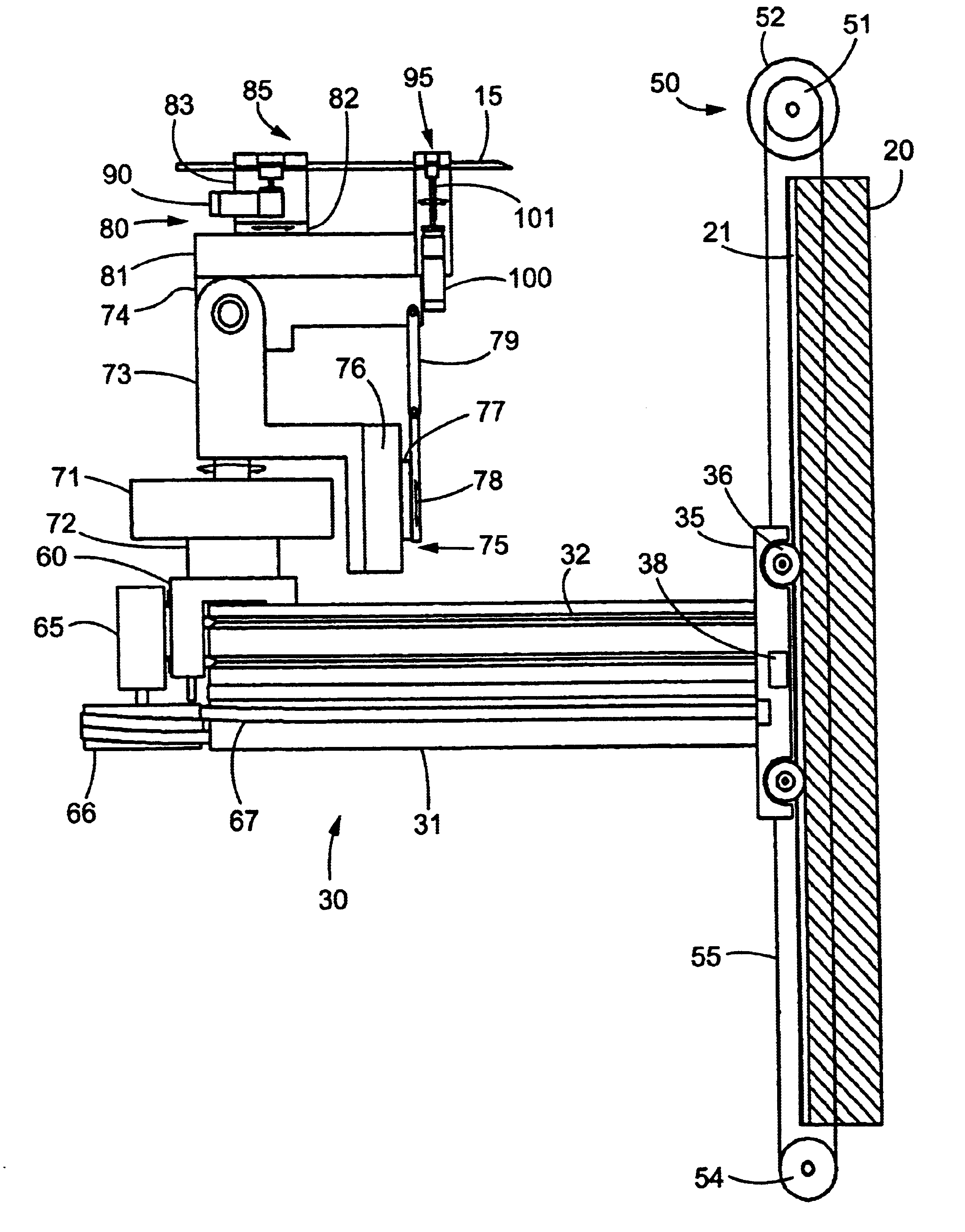
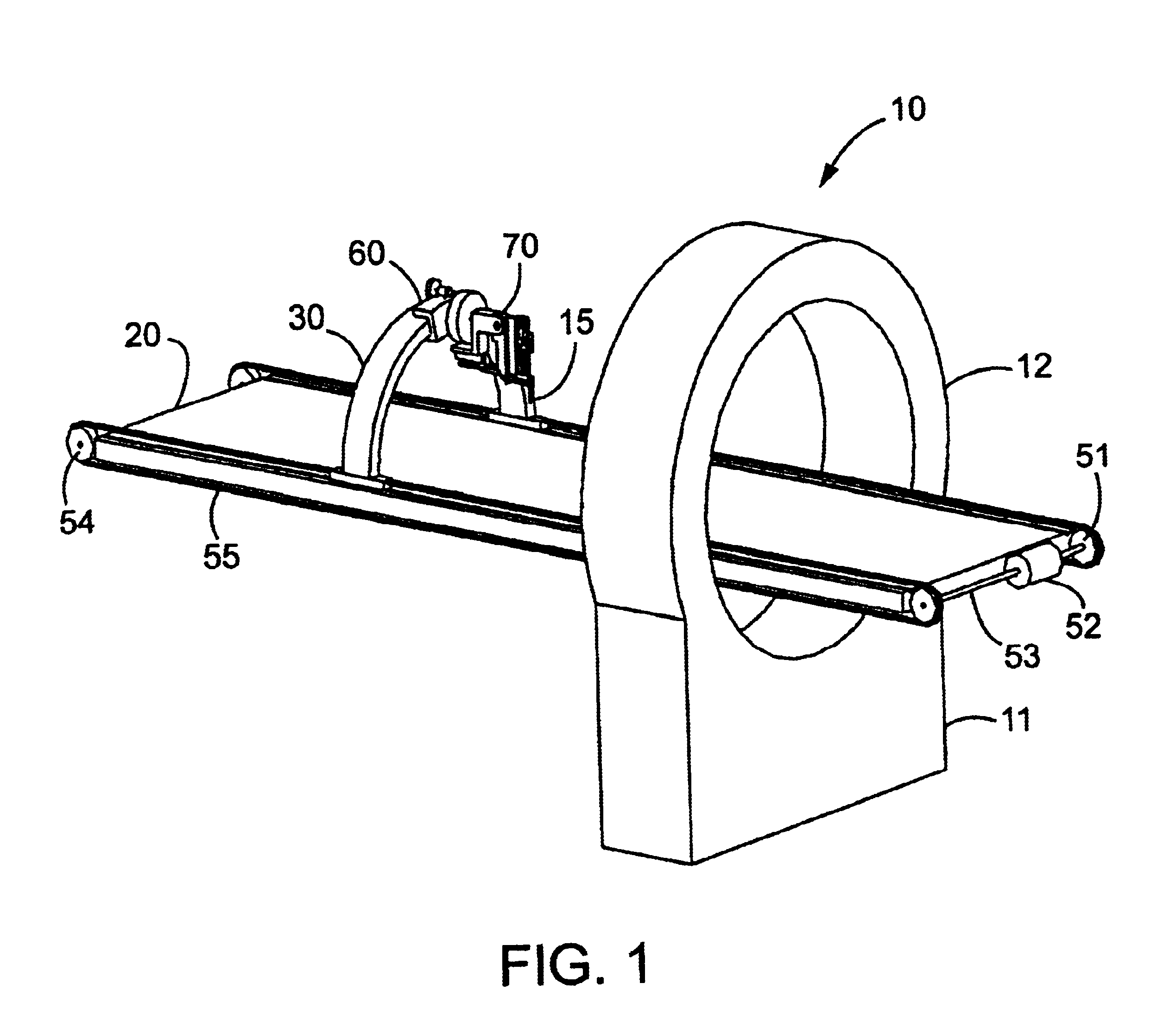
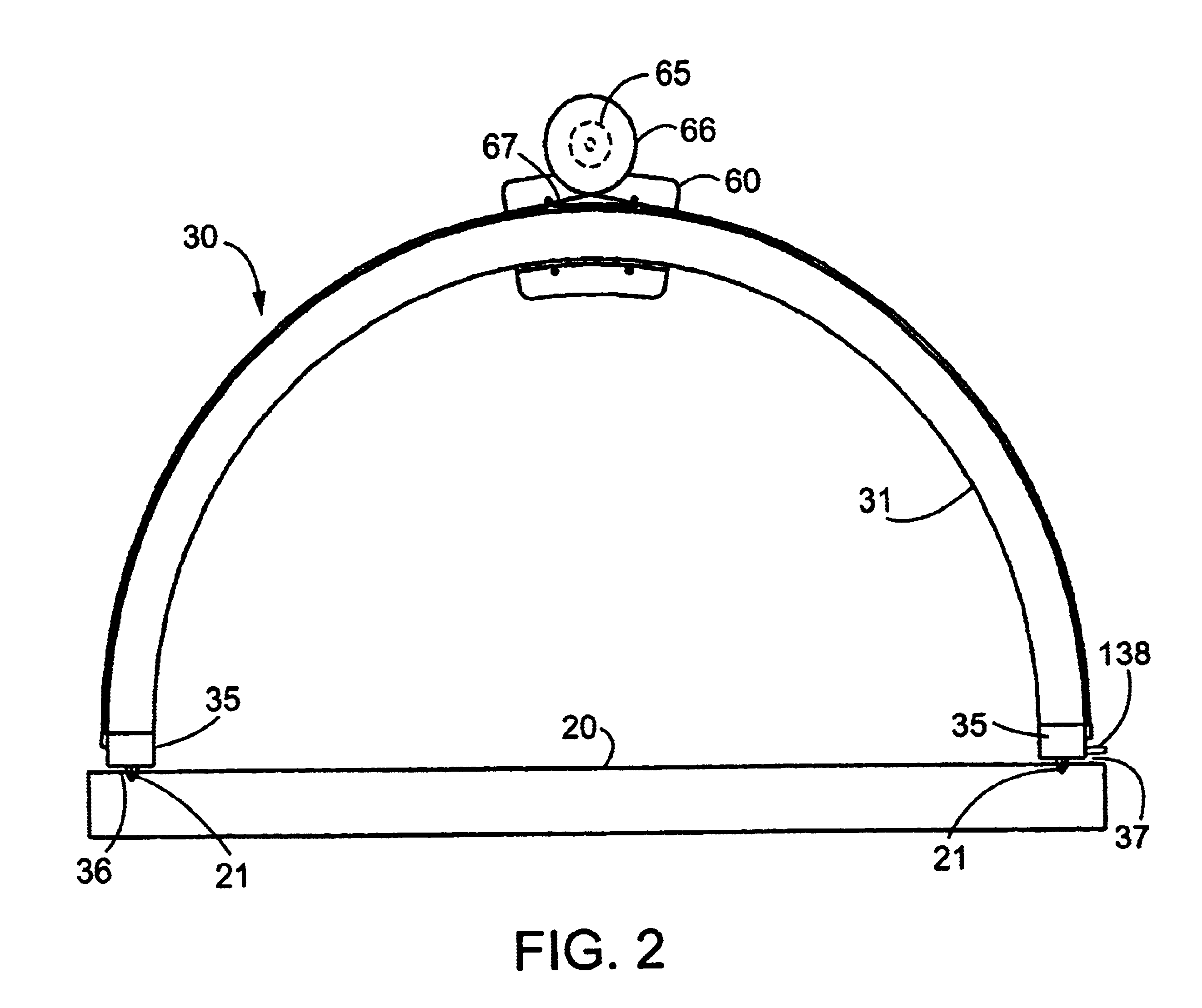
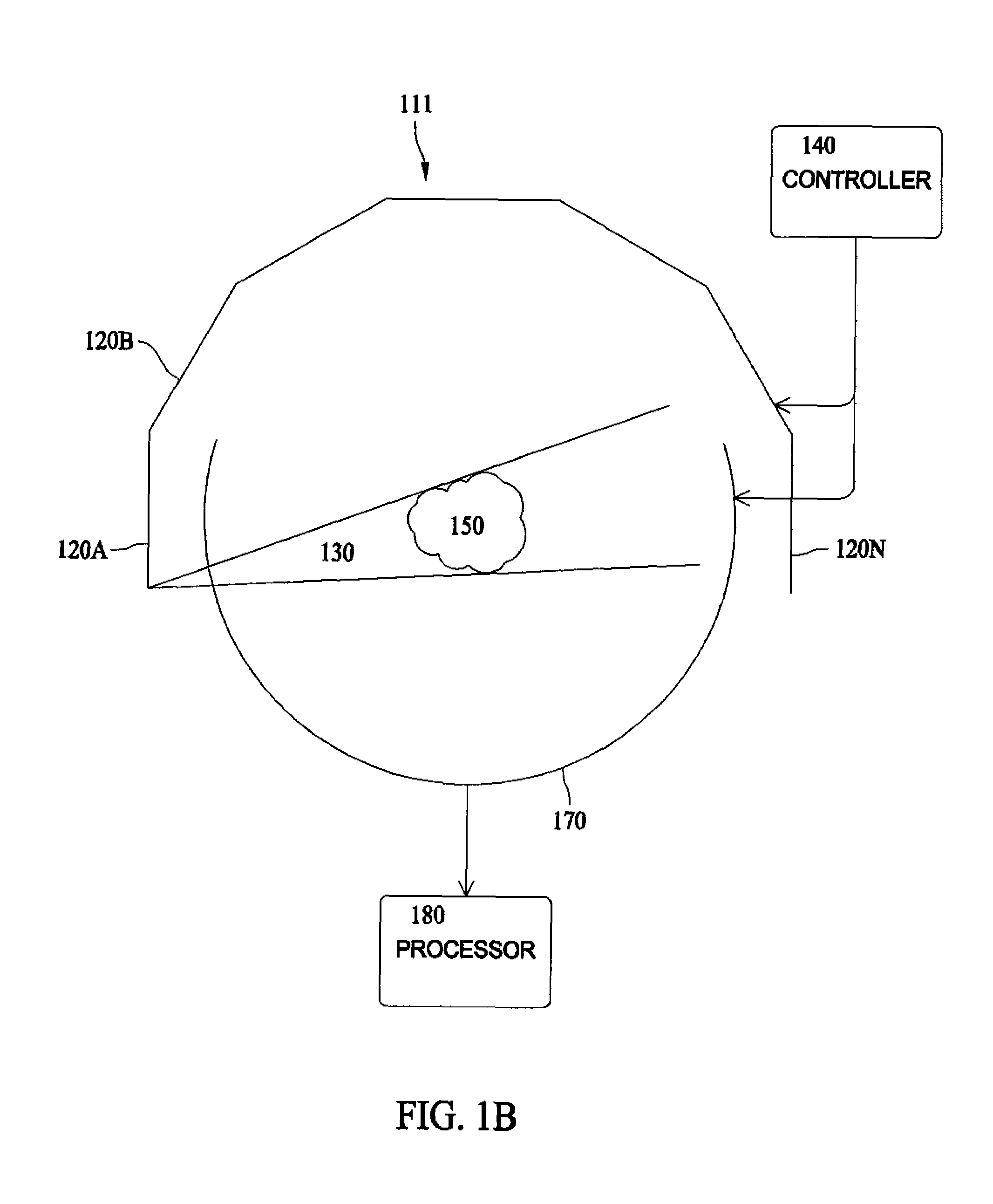
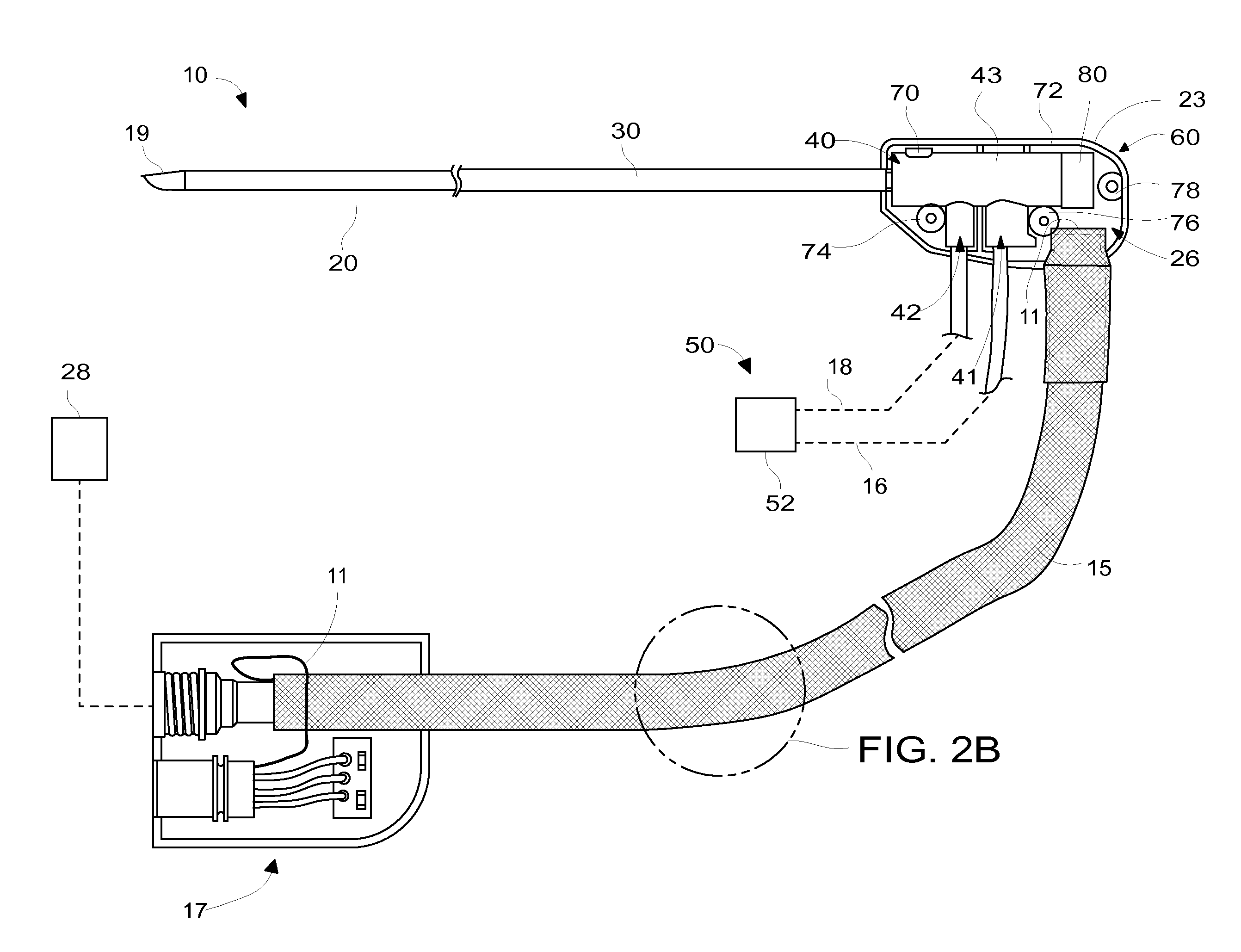
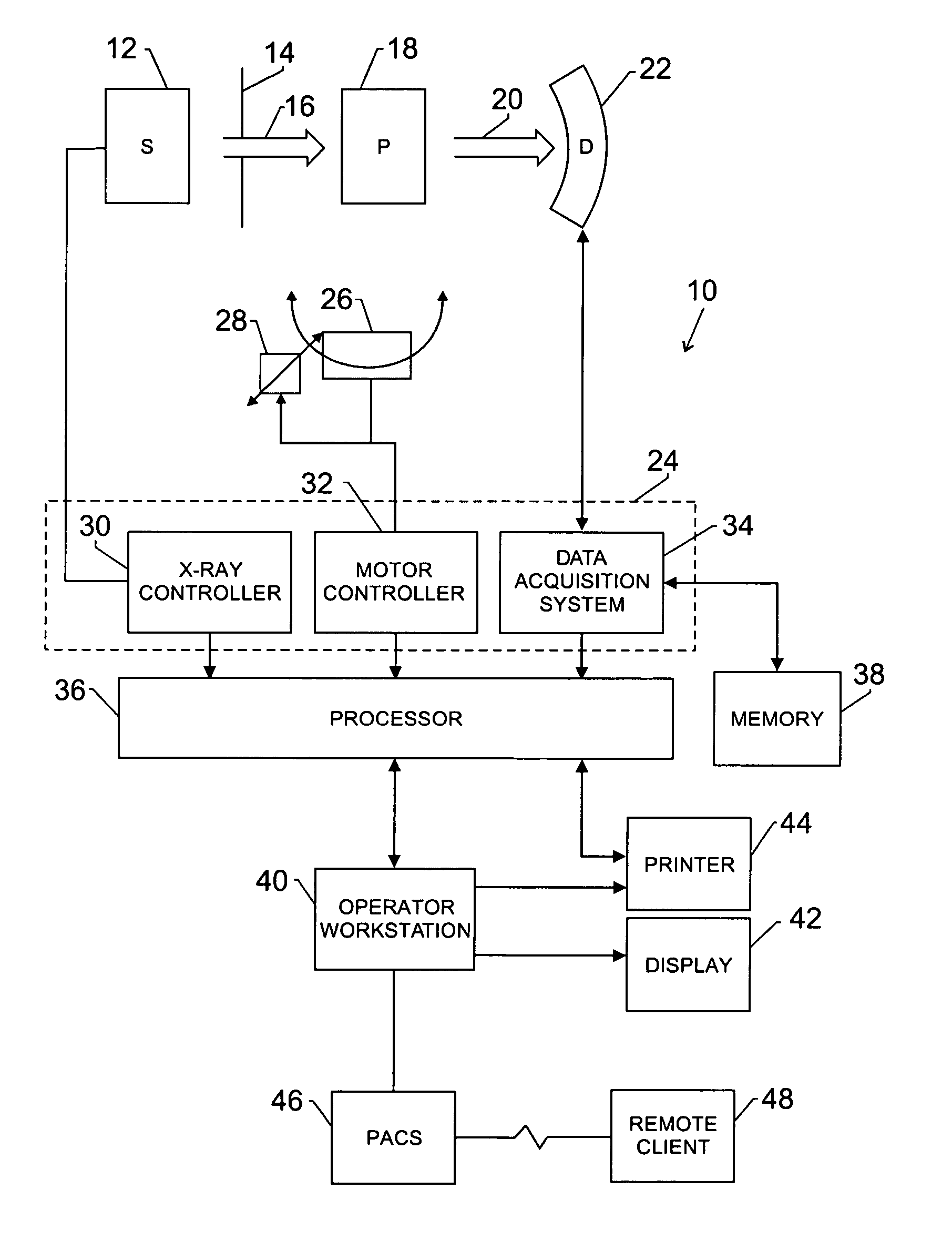
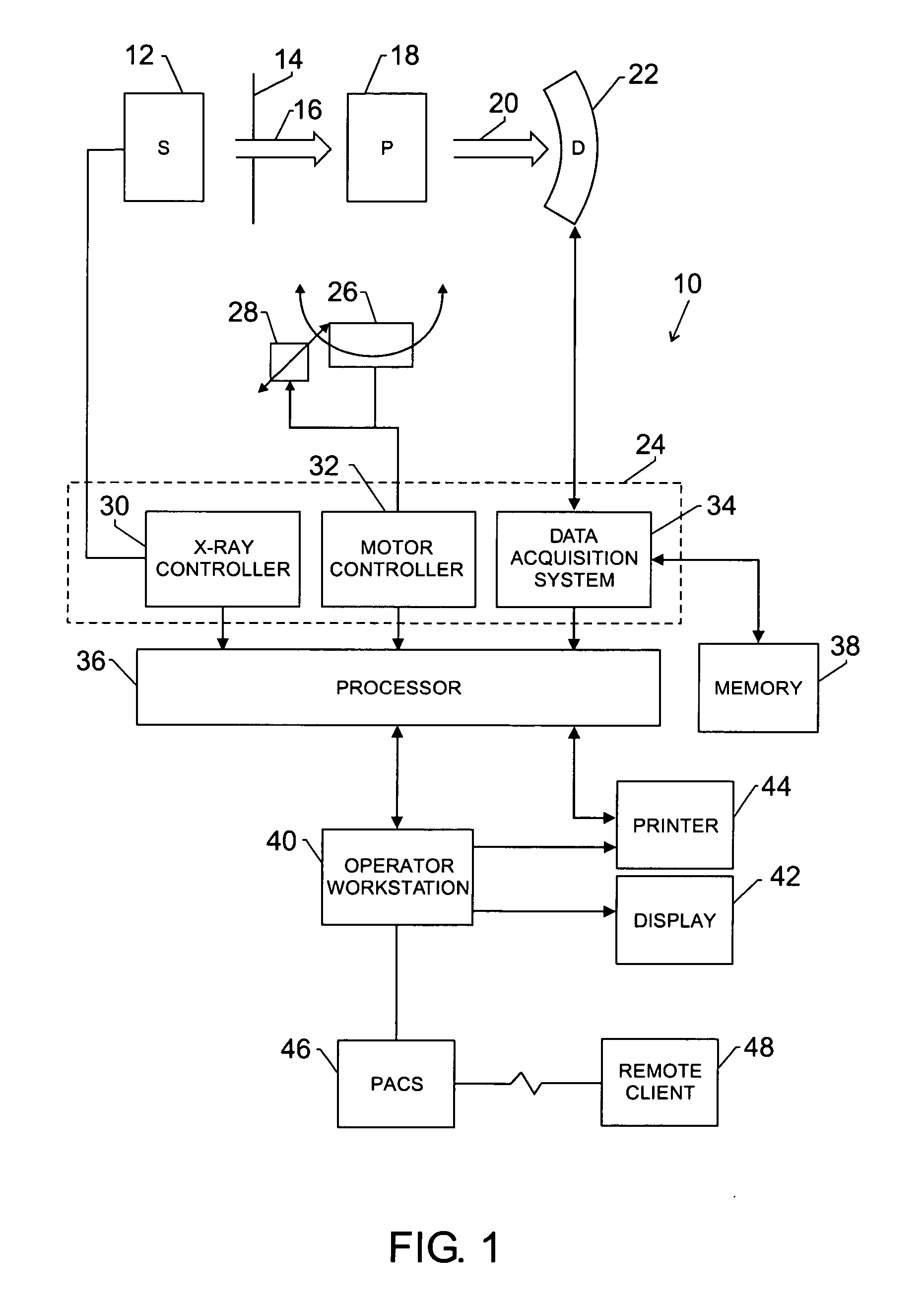
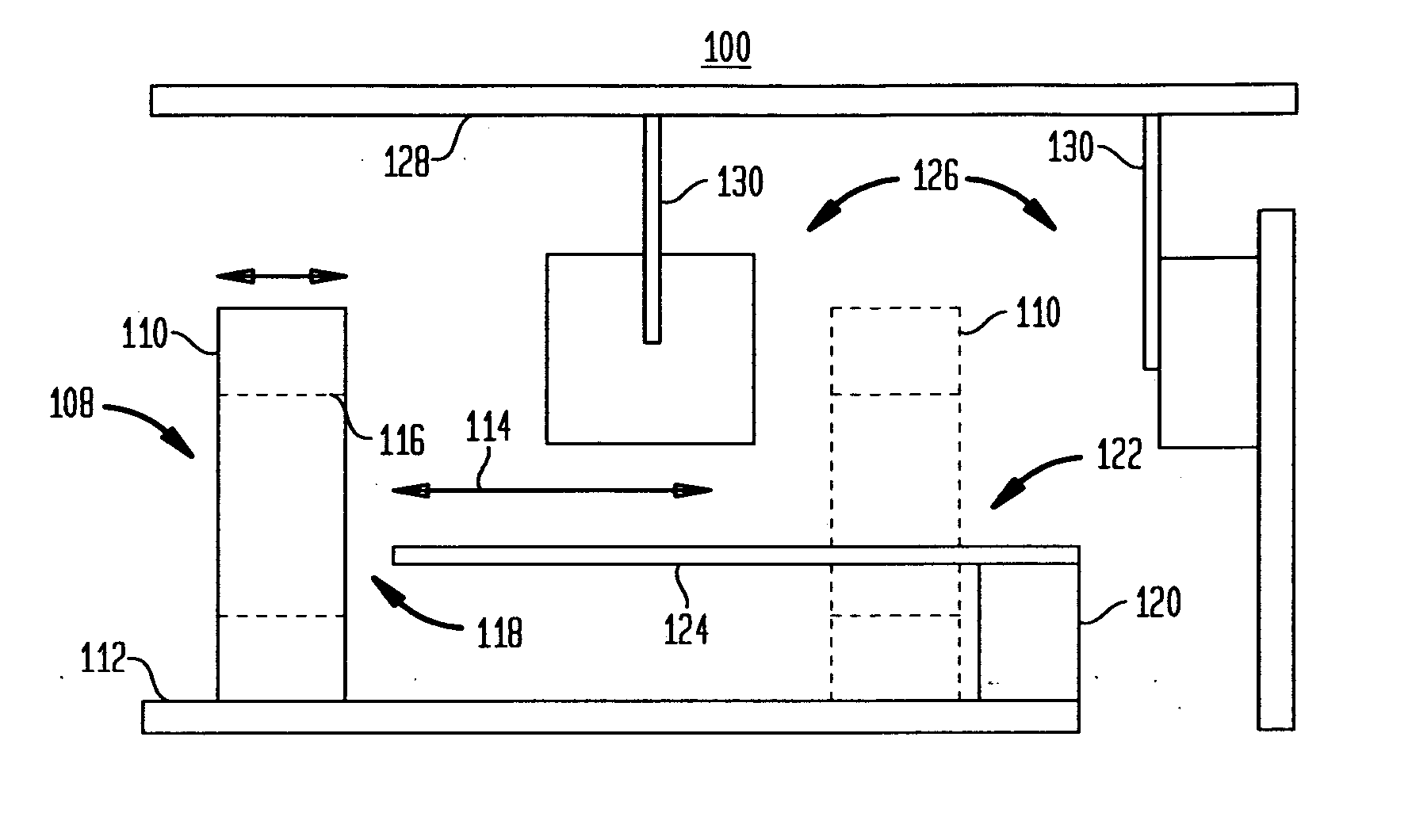
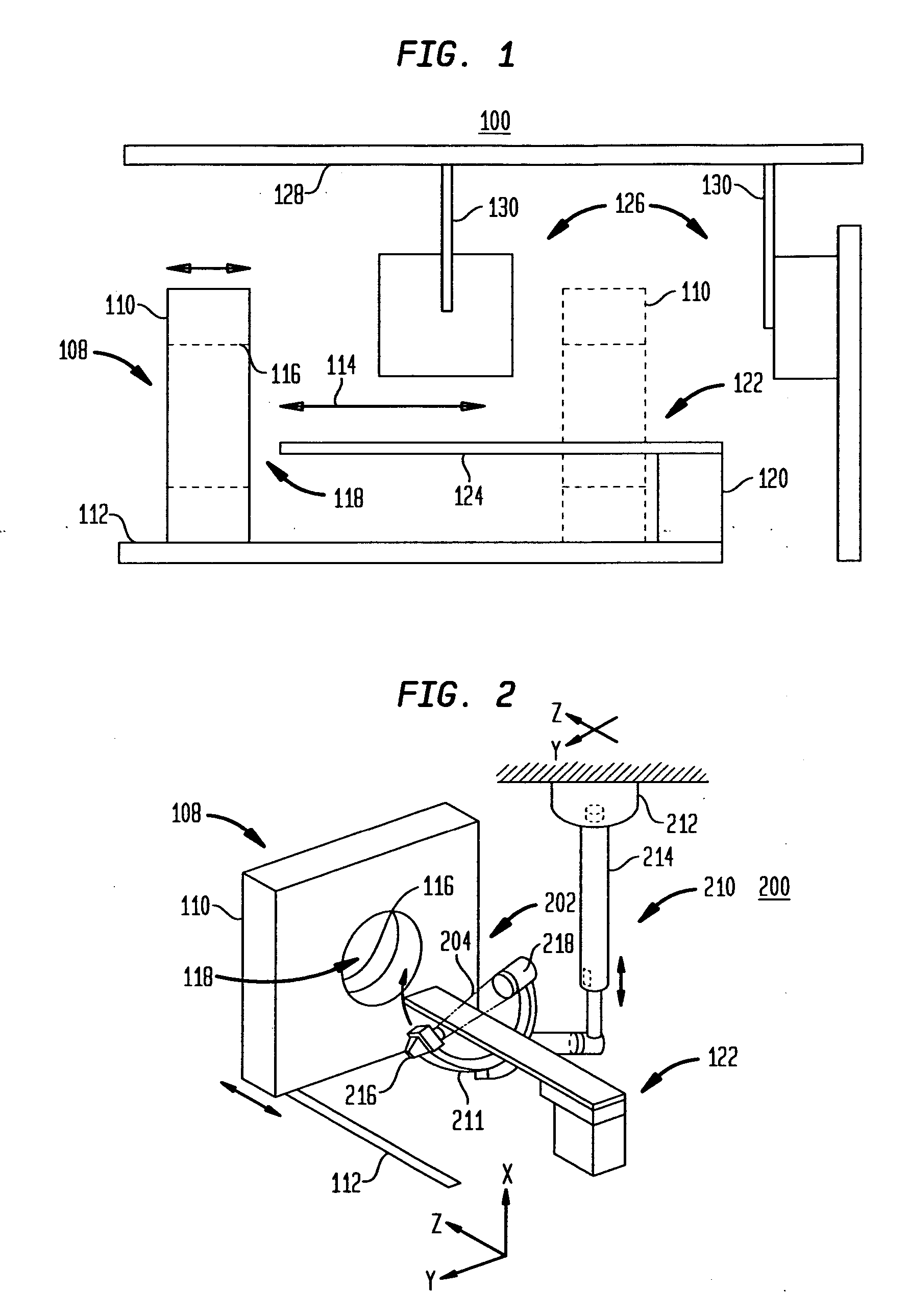
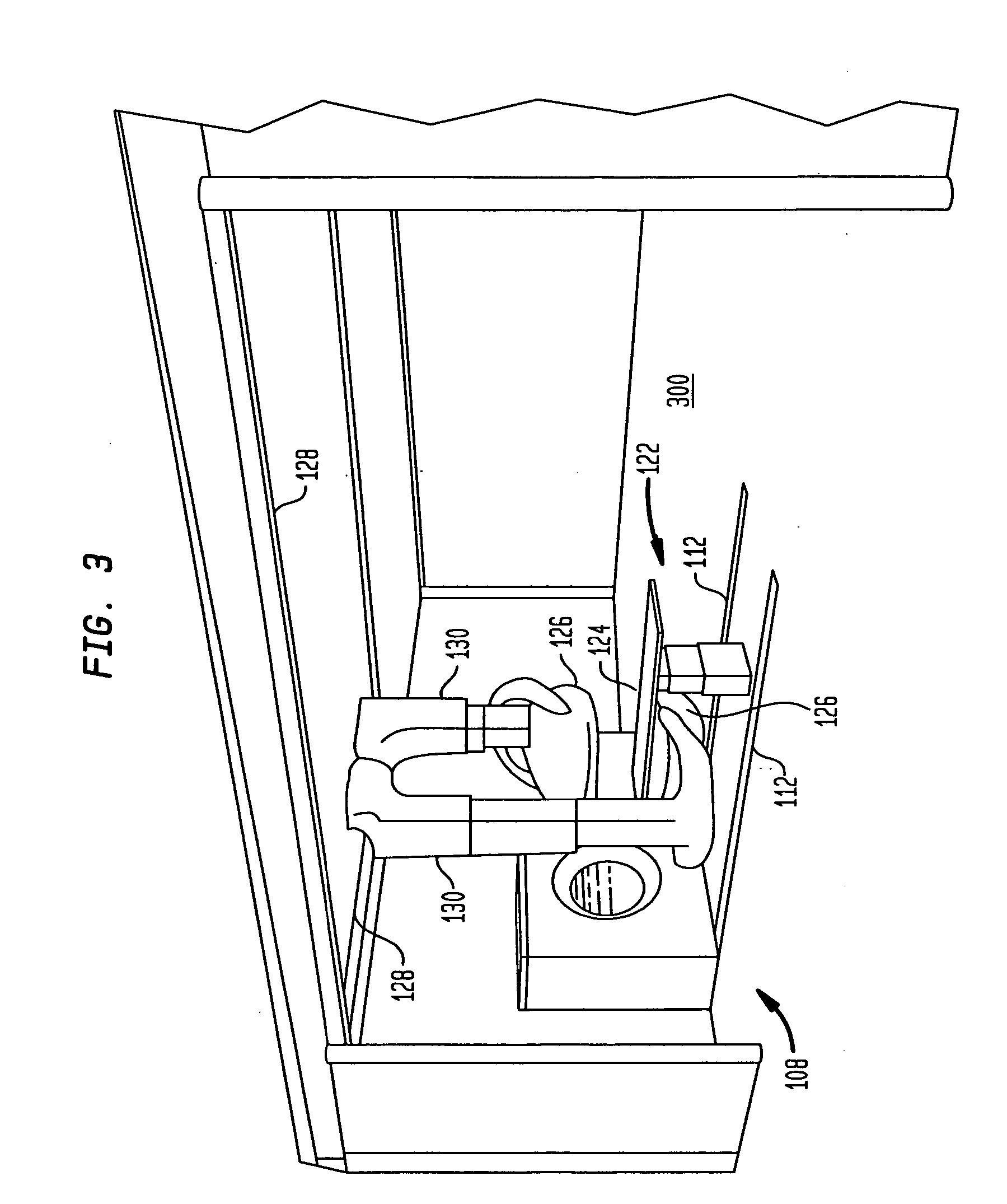
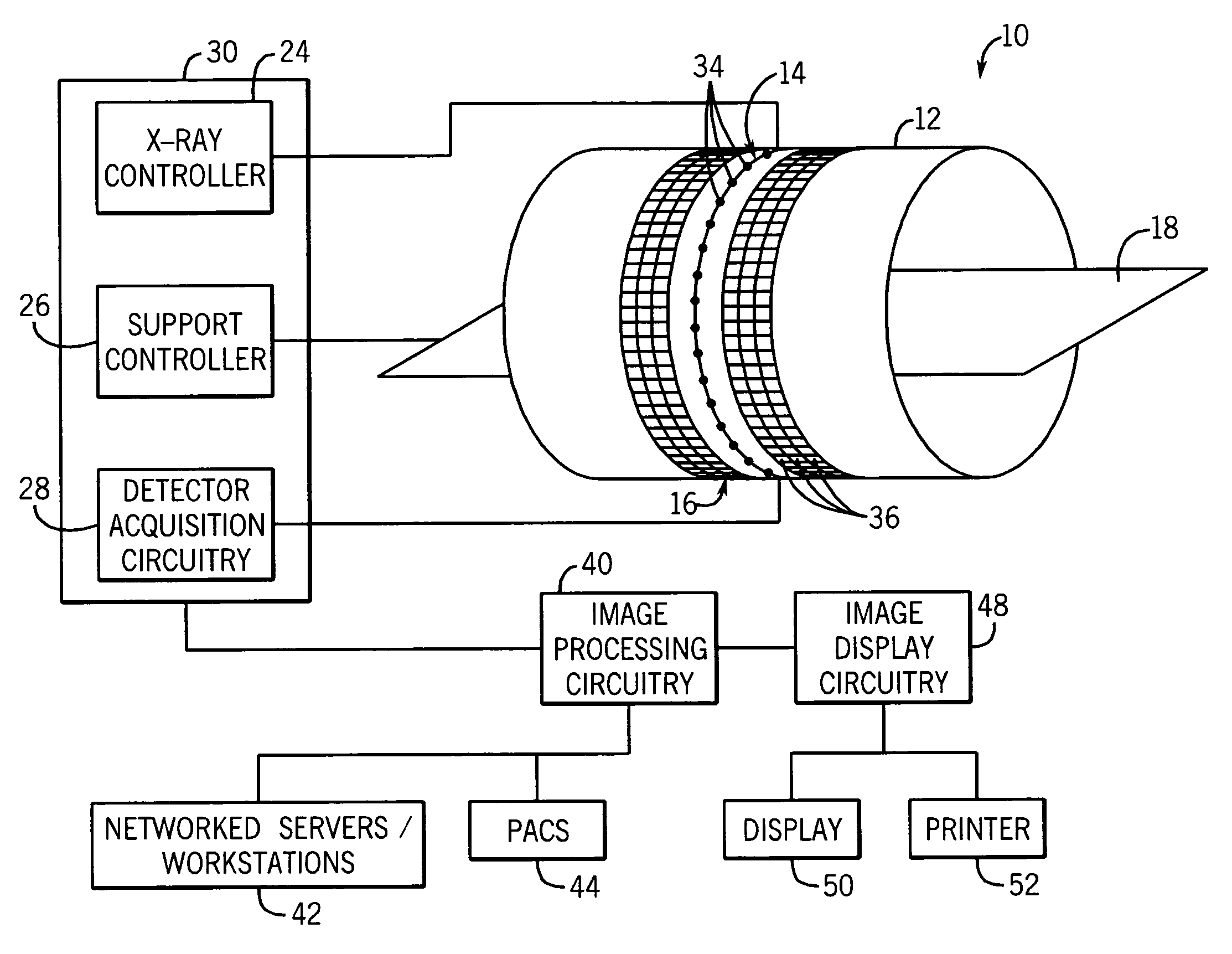
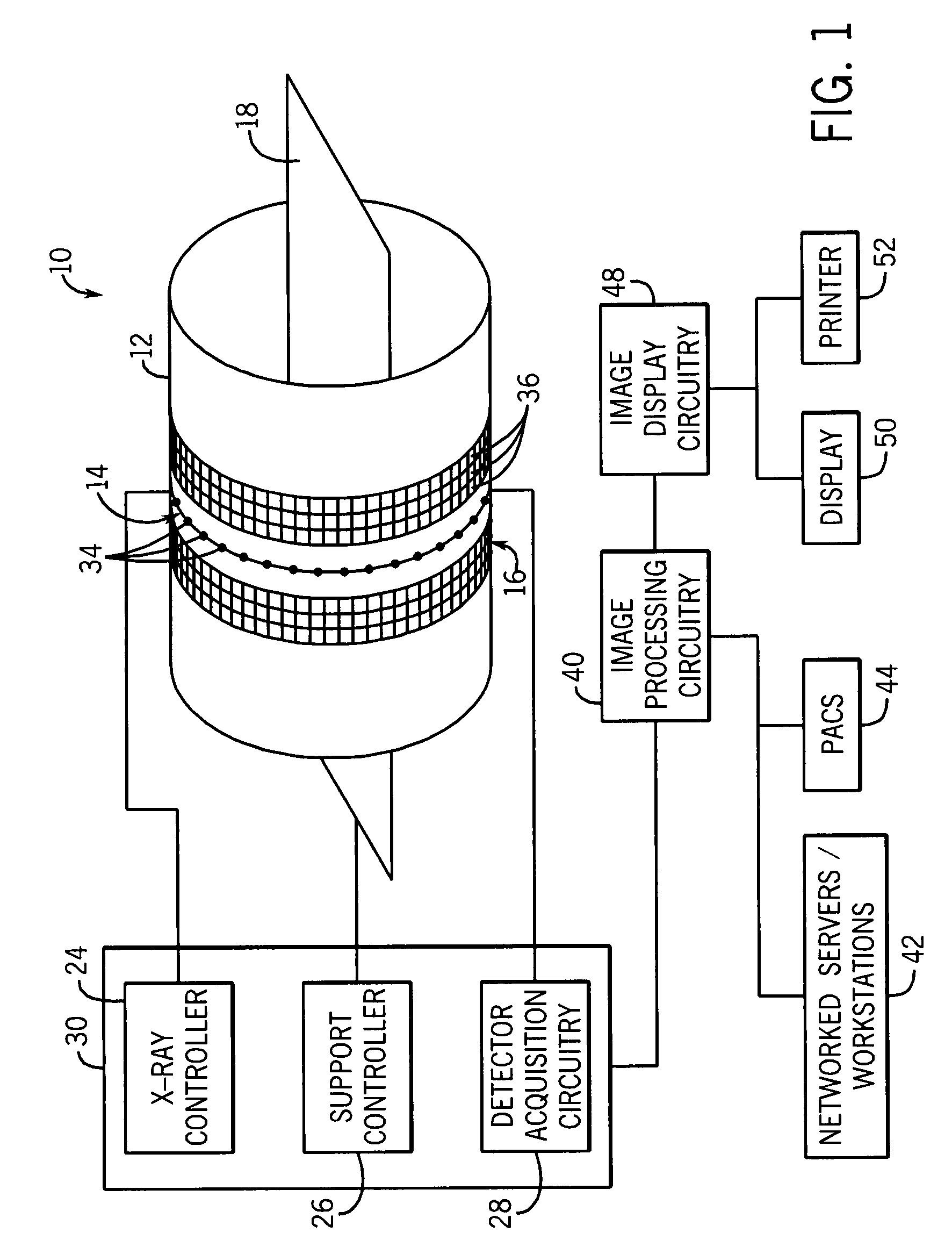
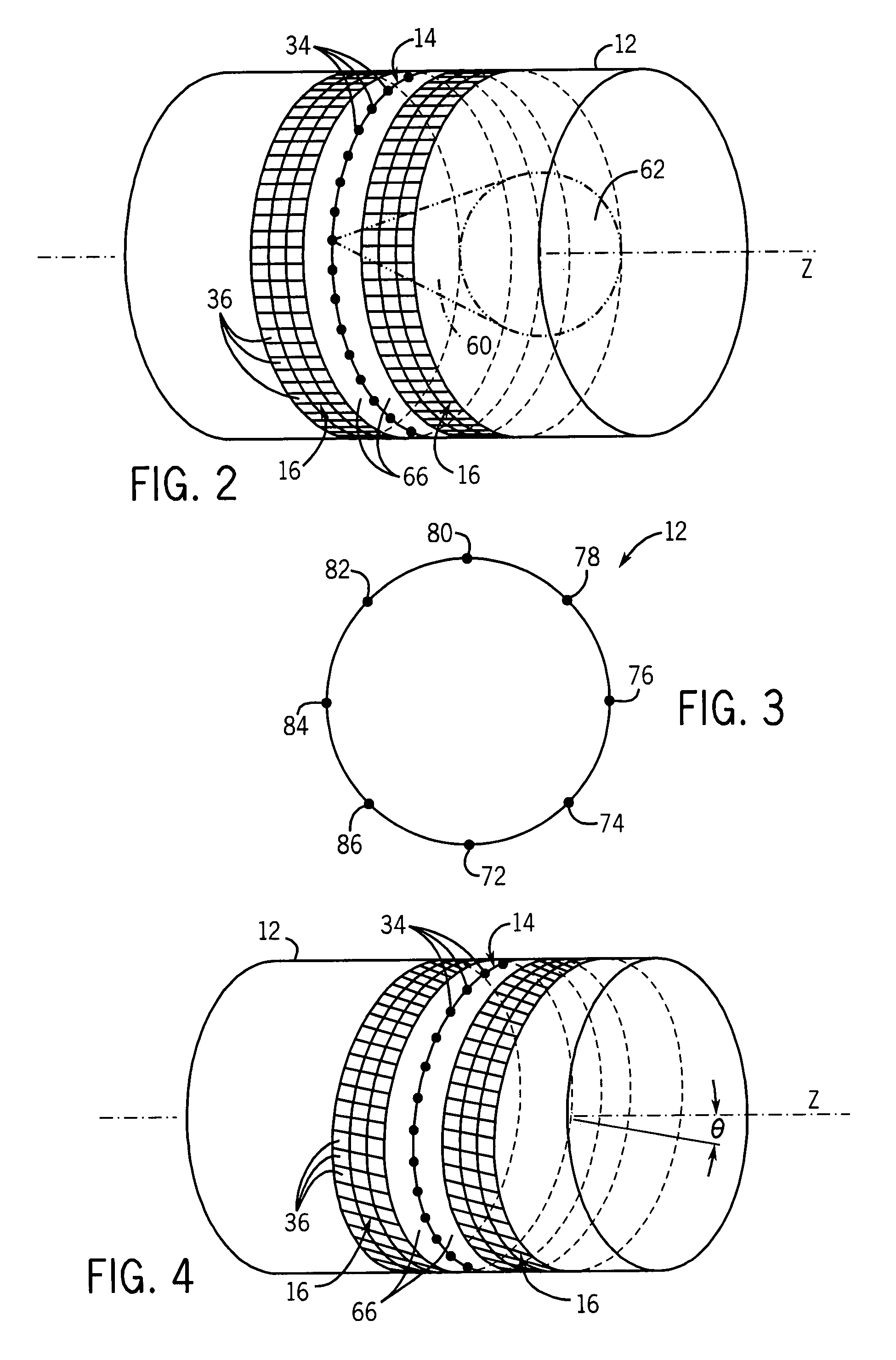
Medical manipulator for use with an imaging device
InactiveUS6665554B1Easy to insertLess stressSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDegrees of freedomEngineering
A manipulator for use in medical procedures can manipulate a medical tool with one or more degrees of freedom with respect to a patient. The manipulator is particularly useful for positioning a medical tool with respect to a patient disposed inside an imaging device such as a computer tomography machine.
Owner:MICRODEXTERITY SYST
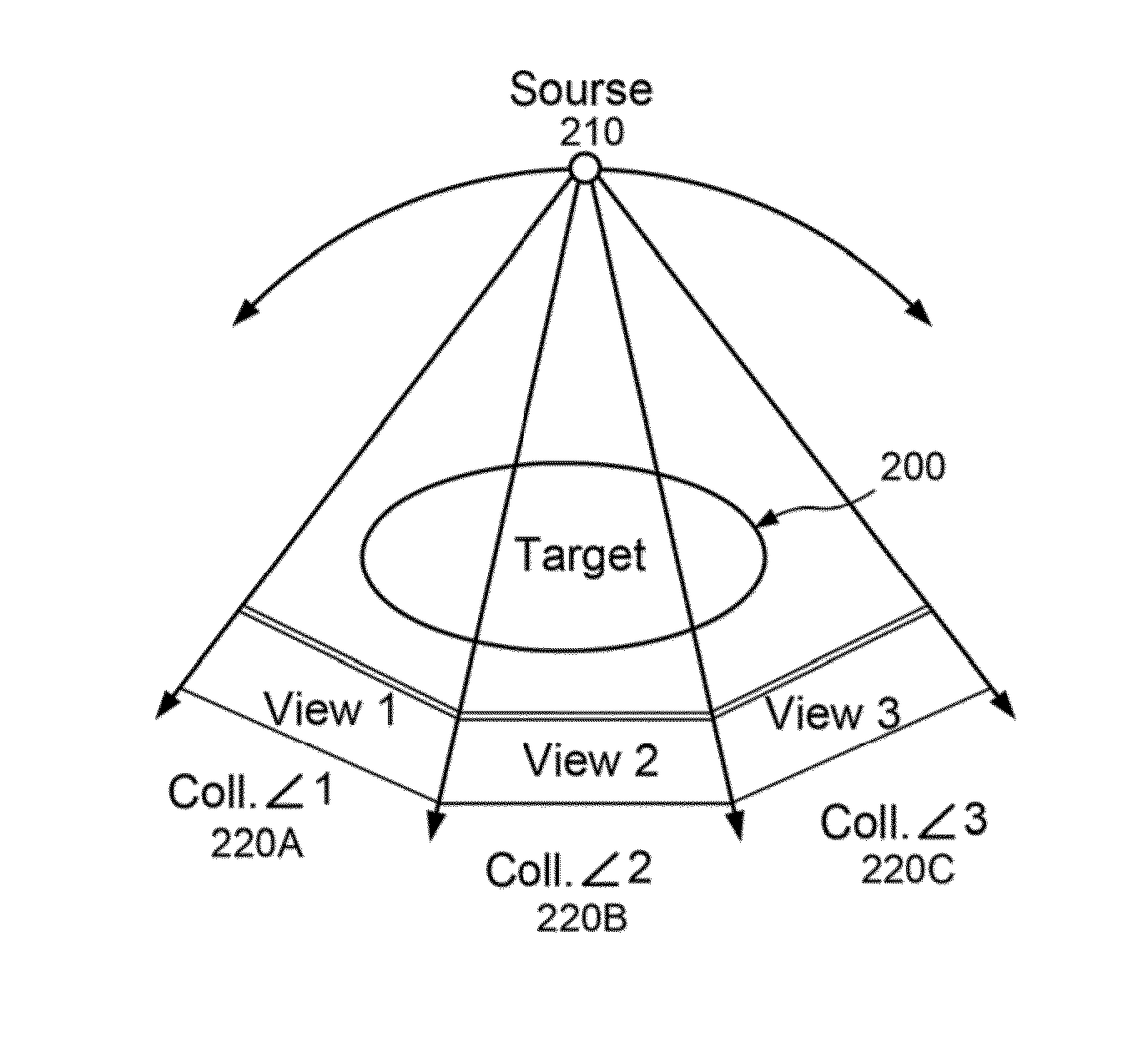
System, method and computer-accessible medium for providing a panoramic cone beam computed tomography (CBCT)
InactiveUS20150213633A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionProjection imageCone beam computed tomography
Exemplary devices, procedures and computer-readable mediums for providing a projection image associated with at least one target. The projection image can be formed from a plurality of locations of a source arrangement. At each source location, a plurality of panoramic projection images associated with a target can be acquired. At least two of the panoramic projection images can be obtained at view angles which are different from one another. These panoramic projection images can be stitched together or otherwise combined. A resulting image can then be generated using a computed tomography procedure based on the stitched or combined projection images that are generated at the plurality of location.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Computed tomographic scanner using rastered x-ray tubes
ActiveUS7233644B1Reduce coolingReduced Power RequirementsRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusComputing tomographyComputed tomography scanner
A high speed computed tomography x-ray scanner using a plurality of x-ray generators. Each x-ray generator is scanned along a source path that is a segment of the scanner's source path such that each point in the source path is scanned by at least one tube. X-ray generators and detectors can be arranged in different scan planes depending on the available hardware so that a complete and near planar scan of a moving object can be assembled and reconstructed into an image of the object.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Microwave energy-device and system
ActiveUS20140276033A1Controlling energy of instrumentSurgical navigation systemsComputed tomographyMicrowave
An ablation system including an image database storing a plurality of computed tomography (CT) images of a luminal network and a navigation system enabling, in combination with an endoscope and the CT images, navigation of a locatable guide and an extended working channel to a point of interest. The system further includes one or more fiducial markers, placed in proximity to the point of interest and a percutaneous microwave ablation device for applying energy to the point of interest.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
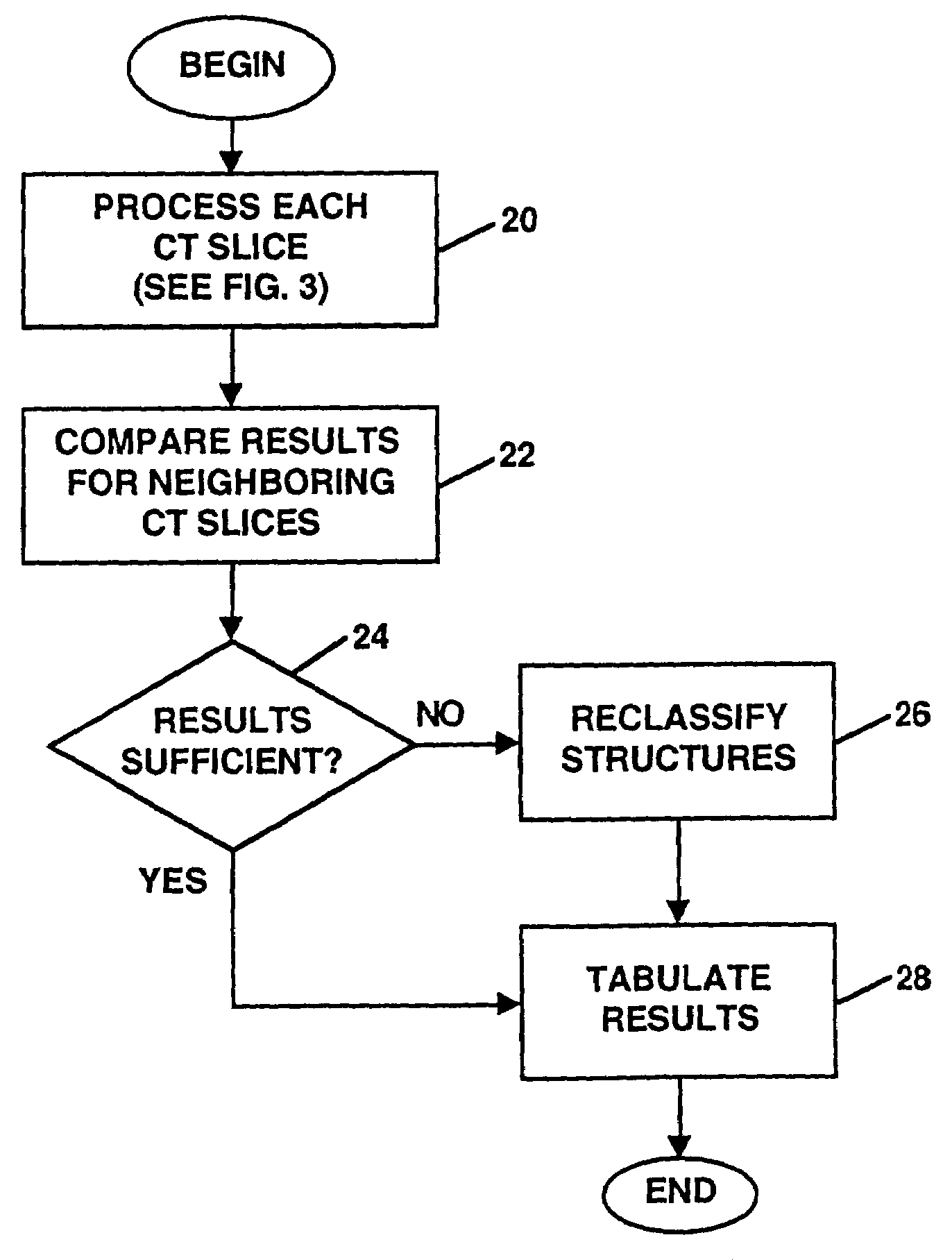
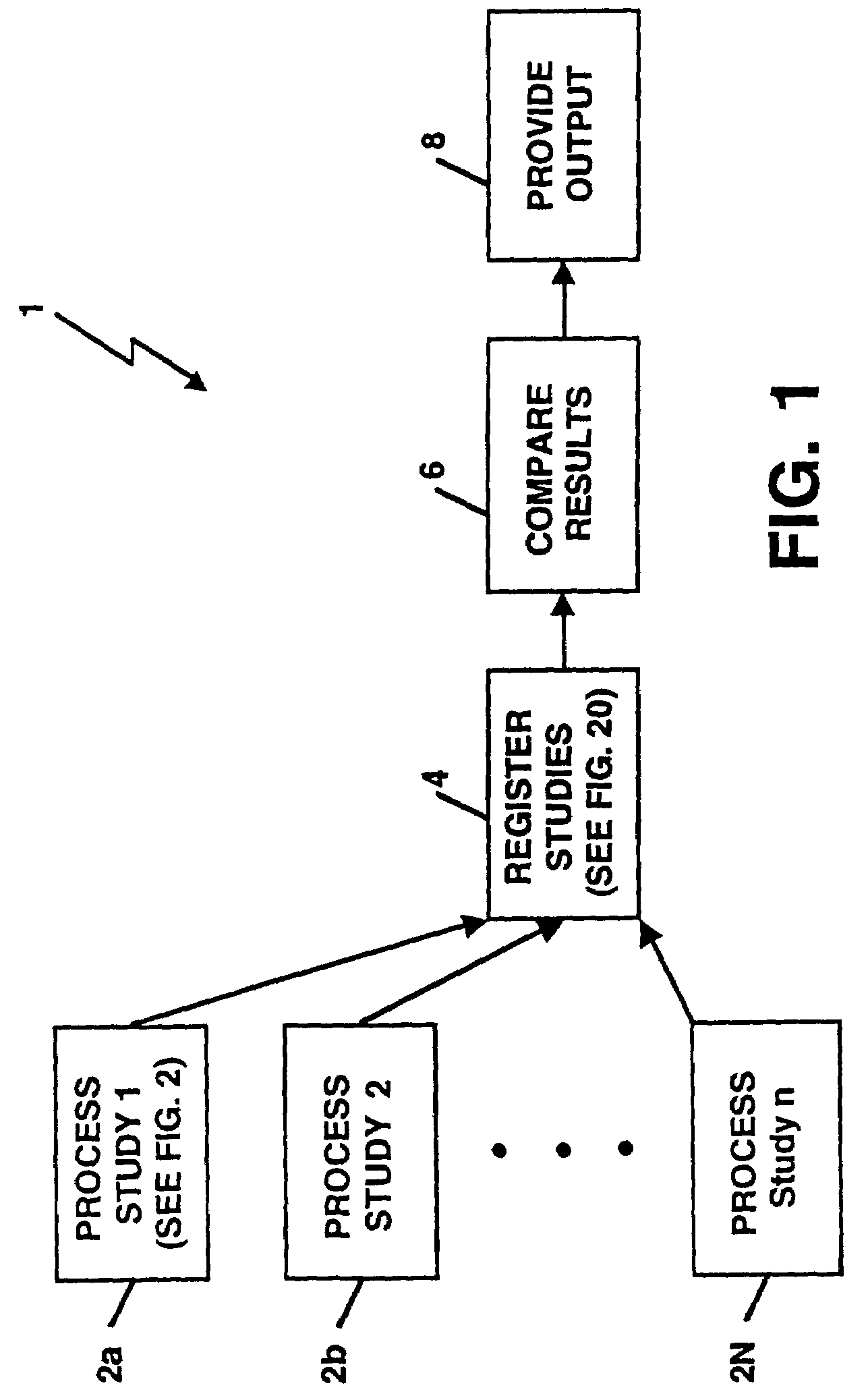
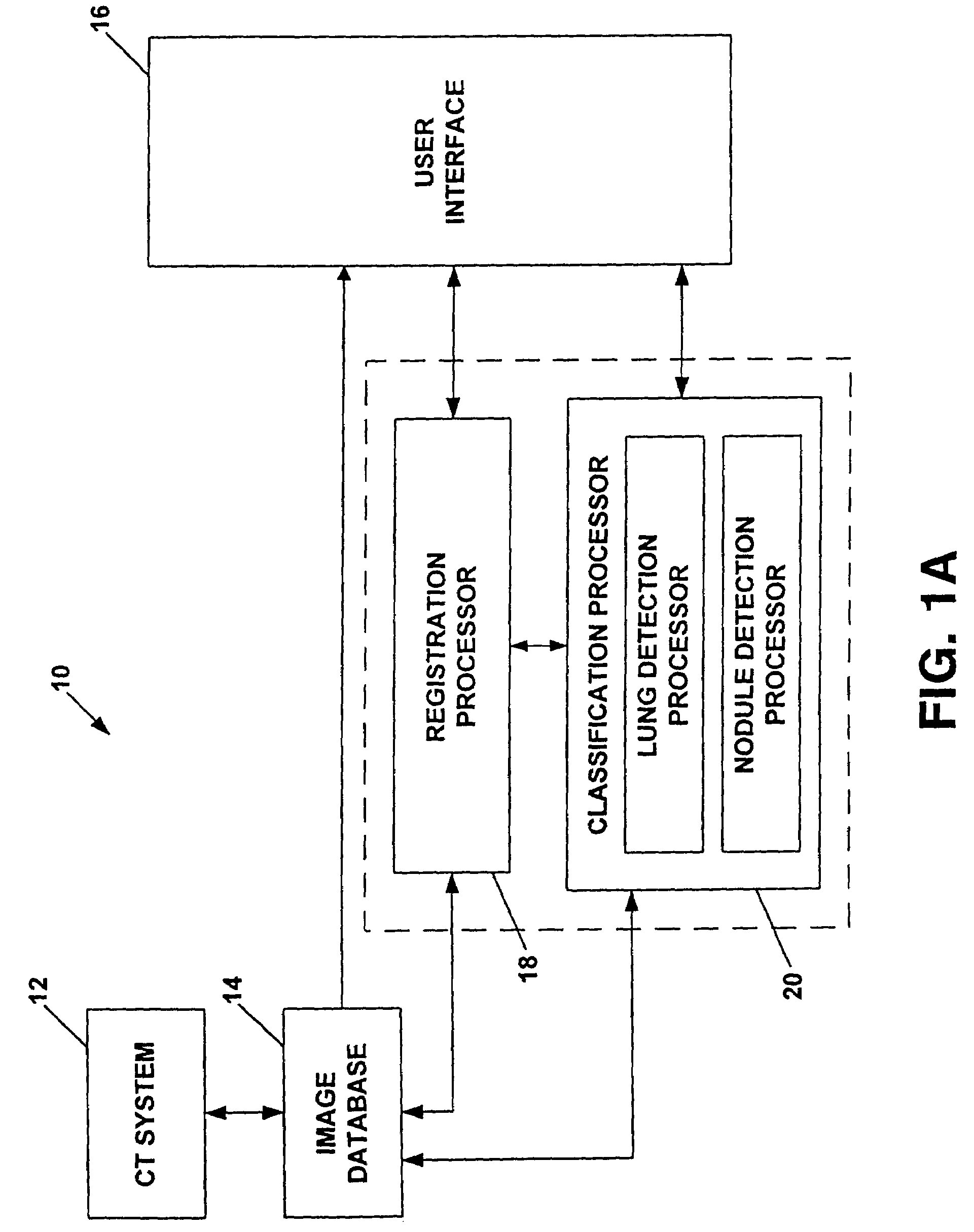
Method and system for the detection, comparison and volumetric quantification of pulmonary nodules on medical computed tomography scans
InactiveUS7206462B1Rapidly and accurately quantitate tumor loadLess time reviewing imageImage analysisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPulmonary noduleComputed tomographic
A method and system for the automated detection and analysis of pulmonary nodules in computed tomographic scans which uses data from computed tomography (CT) scans taken at different times is described. The method and system includes processing CT lung images to identify structures in the images for one patient in each of a plurality of different studies and then relating the plurality of CT lung images taken from the patient in one CT study with a plurality of CT lung images taken from the same patient in at least one other different study to detect changes in structures within the CT images.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method and apparatus for calibrating volumetric computed tomography systems
InactiveUS7016456B2Simplified determinationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingProjection imageX-ray
The present invention provides a method for determining a geometry of a scanning volumetric computed tomographic (CT) system having a rotation axis, a rotational plane, an x-ray source and a detector. The method includes scanning a phantom having a series of spatially separated discrete markers with the scanning volumetric computed tomographic system, wherein the markers are configured on a supporting structure of the phantom so as to permit separate identification of each marker in a collection of projection images. The method further includes locating images of the markers in each projection, using the located marker images to assign marker locations to tracks, and using the assigned tracks, determining a relative alignment between the detector, the source, and the rotation axis of the scanning volumetric computed tomographic system.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
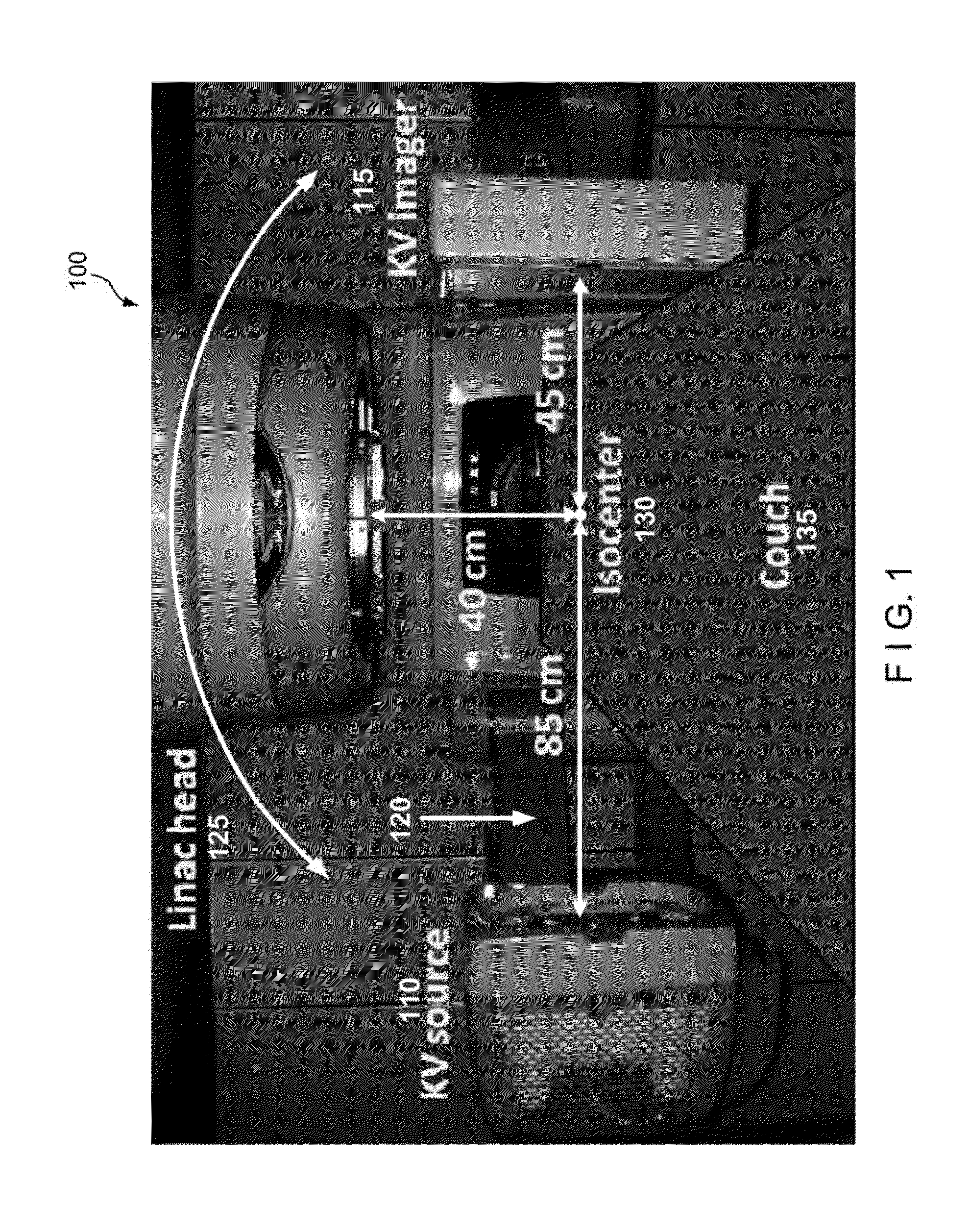
Contrast-enhanced cone beam X-ray imaging, evaluation, monitoring and treatment delivery
ActiveUS20070269000A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingVoxelData set
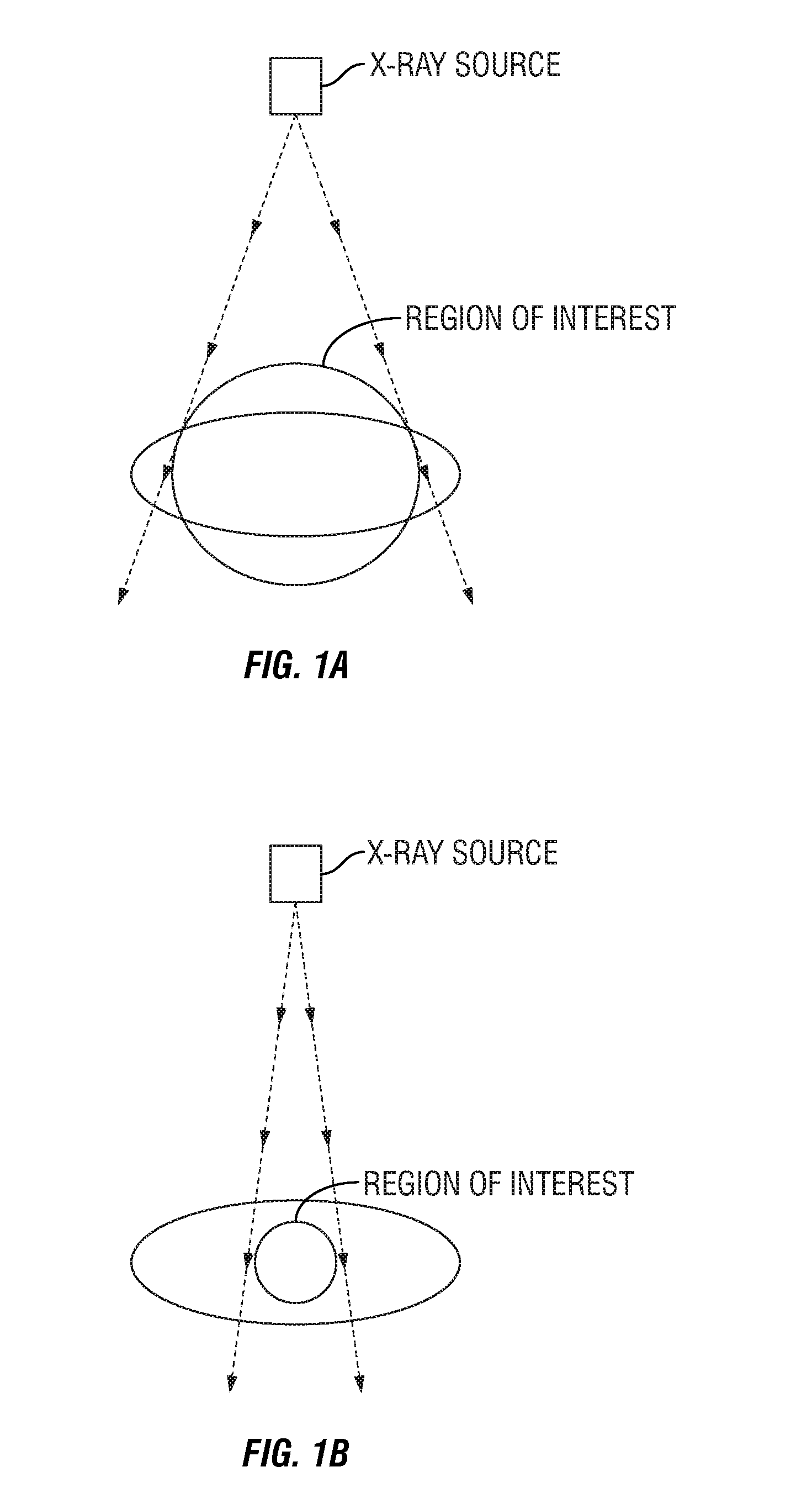
A method of imaging a patient's uncompressed region of interest using X-ray cone beam computed tomography or cone beam digital tomography comprises the step of introducing an effective amount of a contrast agent to the uncompressed region of interest. A system for imaging a patient's uncompressed region of interest using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) or cone beam digital tomography (CBDT) comprises an X-ray source transmitting an X-ray to the uncompressed region of interest, an image acquisition system acquiring a plurality of two-dimensional projection images data for a CBCT or CBDT data set with at least one of the projection images acquired in 35 milliseconds or less, and a processor generating a three-dimensional computed tomography image data set resolving voxels with dimensions of 0.4 mm or less in at least two orthogonal directions.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +2
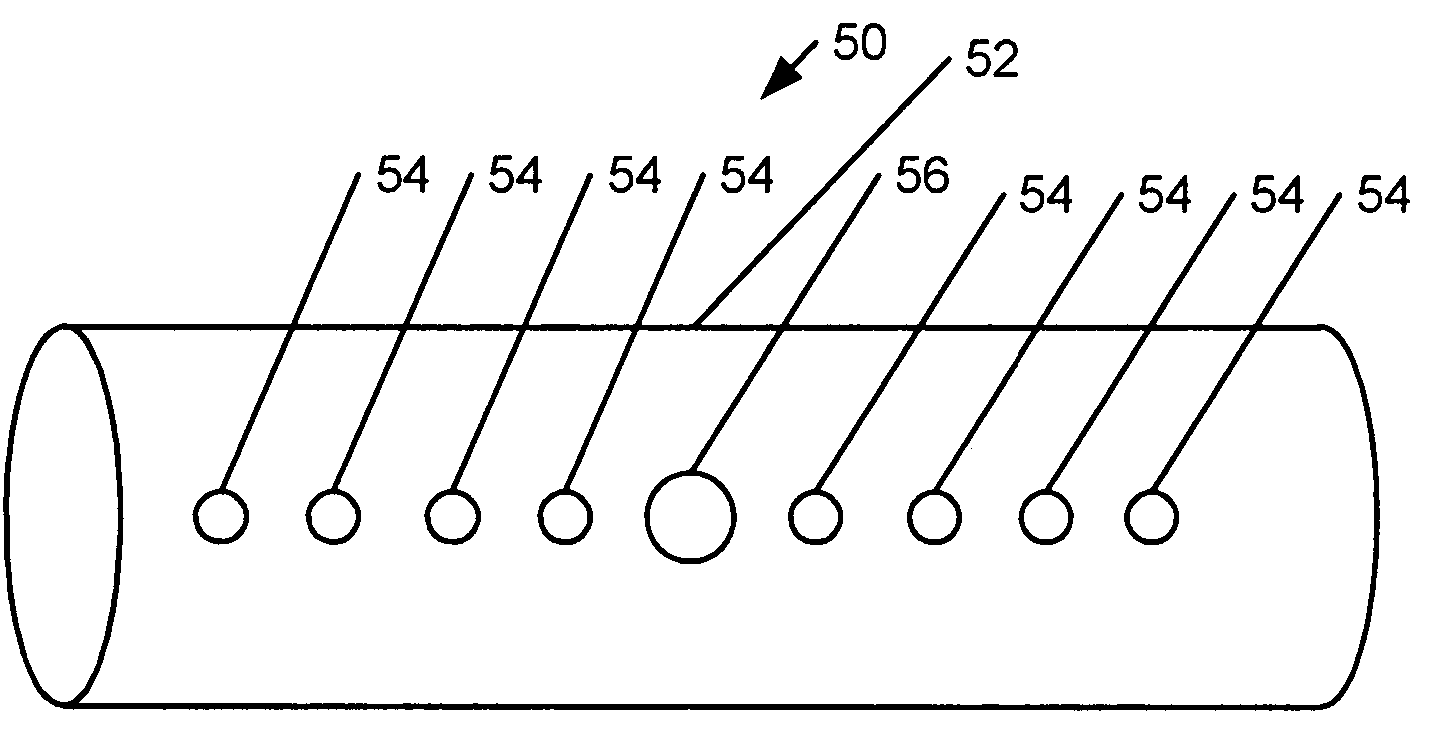
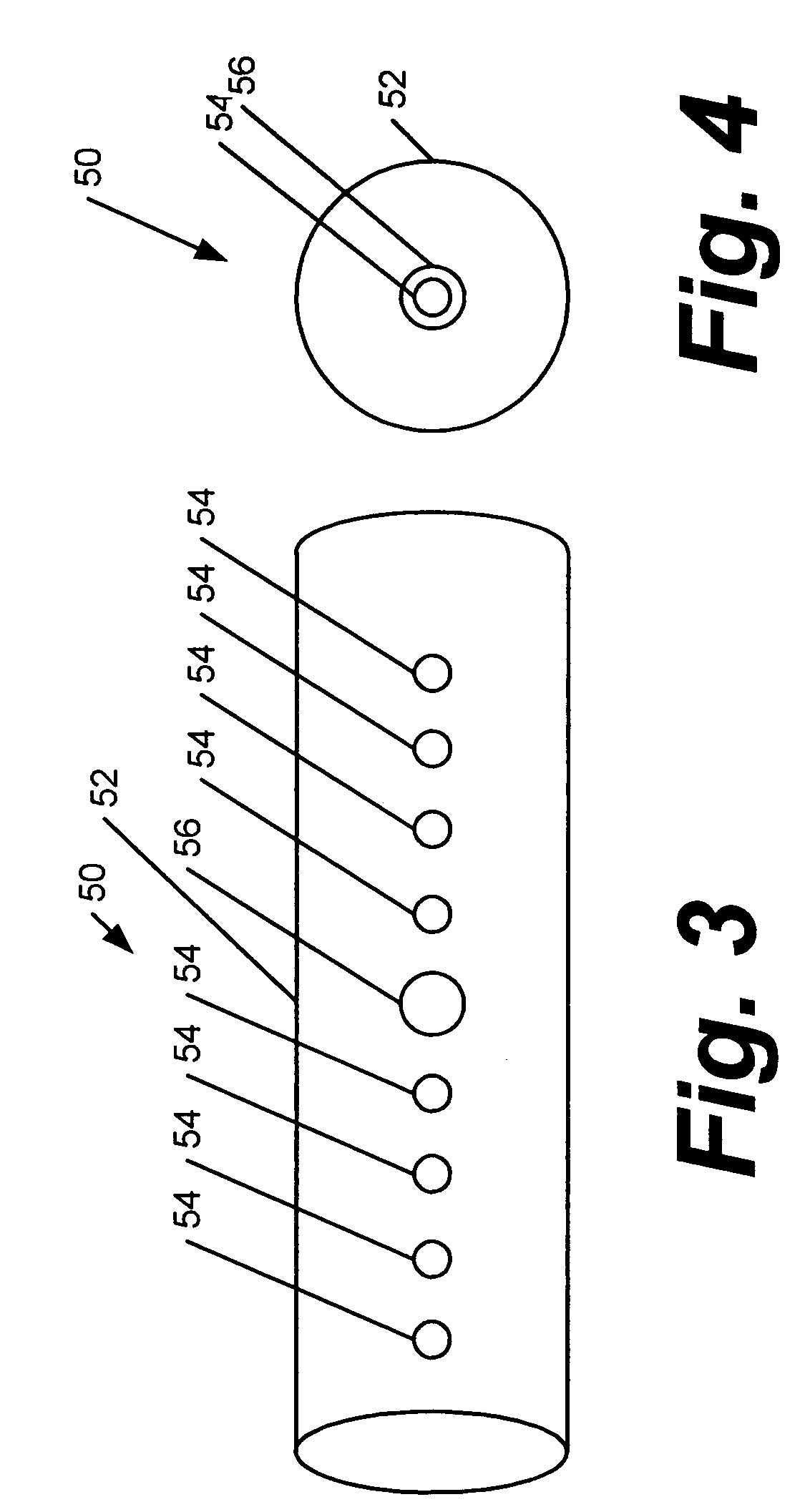
Multi-layer radiation detector assembly
InactiveUS20100102242A1Need can be overcomeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotodetectorData acquisition
A technique is provided for forming a multi-layer radiation detector. The technique includes a charge-integrating photodetector layer provided in conjunction with a photon-counting photodetector layer. In one embodiment, a plurality of photon-counting photosensor elements are disposed adjacent to a plurality of charge-integrating photosensor elements of the respective layers. Both sets of elements are connected to readout circuitry and a data acquisition system. The detector arrangement may be used for energy discriminating computed tomography imaging and similar computed tomography systems.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for calibrating volumetric computed tomography systems
InactiveUS20050094771A1Simplified determinationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingProjection imageX-ray
The present invention provides a method for determining a geometry of a scanning volumetric computed tomographic (CT) system having a rotation axis, a rotational plane, an x-ray source and a detector. The method includes scanning a phantom having a series of spatially separated discrete markers with the scanning volumetric computed tomographic system, wherein the markers are configured on a supporting structure of the phantom so as to permit separate identification of each marker in a collection of projection images. The method further includes locating images of the markers in each projection, using the located marker images to assign marker locations to tracks, and using the assigned tracks, determining a relative alignment between the detector, the source, and the rotation axis of the scanning volumetric computed tomographic system.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
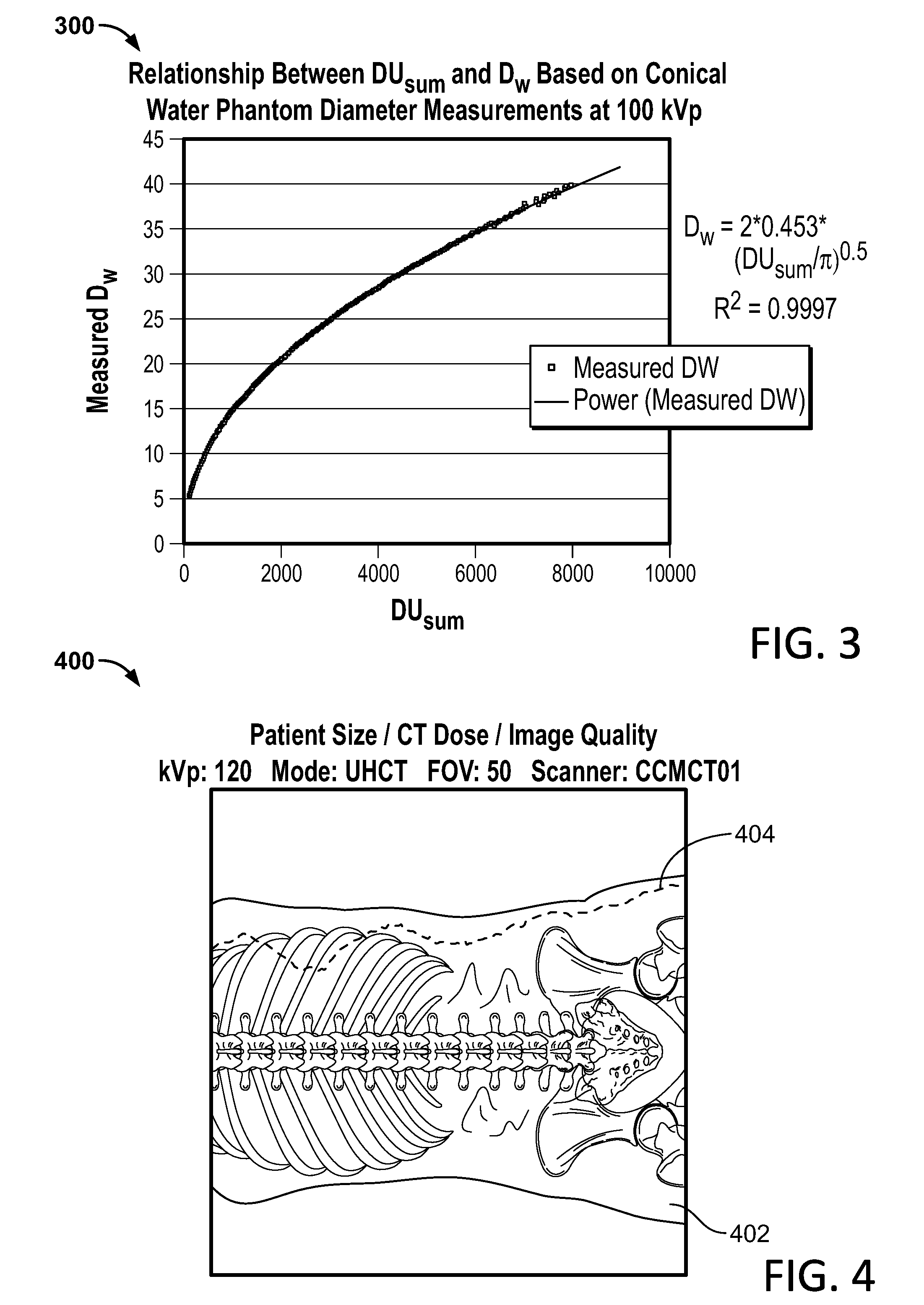
Method for Consistent and Verifiable Optimization of Computed Tomography (CT) Radiation Dose
InactiveUS20140270053A1Minimal disruptionGreat noise leverMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingClinical settingsMathematical model
A system and a method is disclosed for consistently and verifiably optimizing computed tomography (CT) radiation dose in the clinical setting. Mathematical models allow for estimation of patient size, image noise, size-specific radiation dose, and image quality targets based on digital image data and radiologists preferences. A prediction model estimates the scanner's tube current modulation and predicts image noise and size-specific radiation dose over a range of patient sizes. An optimization model calculates specific scanner settings needed to attain target image quality at the minimum radiation dose possible. An automated system processes the image and dose data according to the mathematical models and stores and displays the information, enabling verification and ongoing monitoring of consistent dose optimization.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
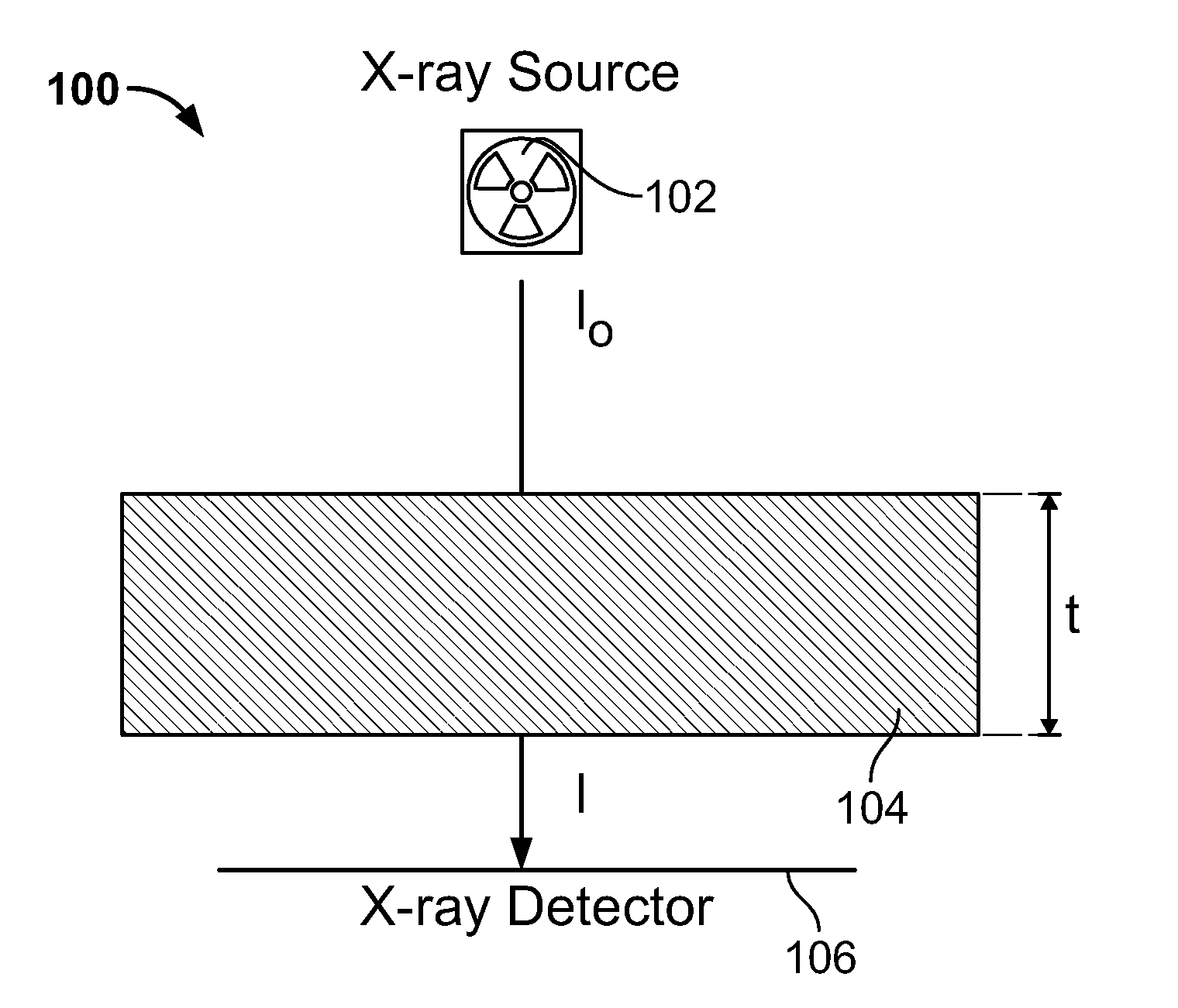
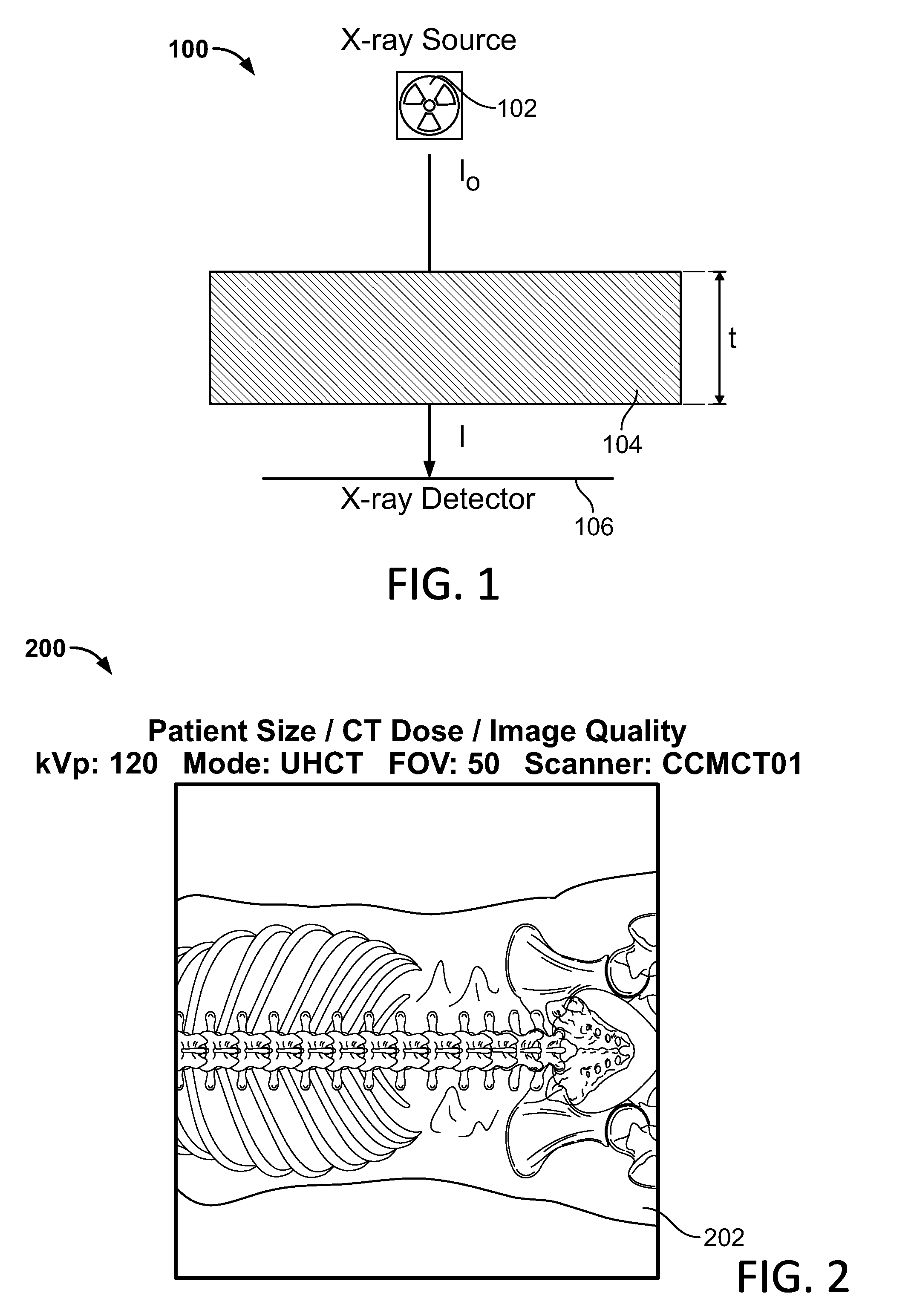
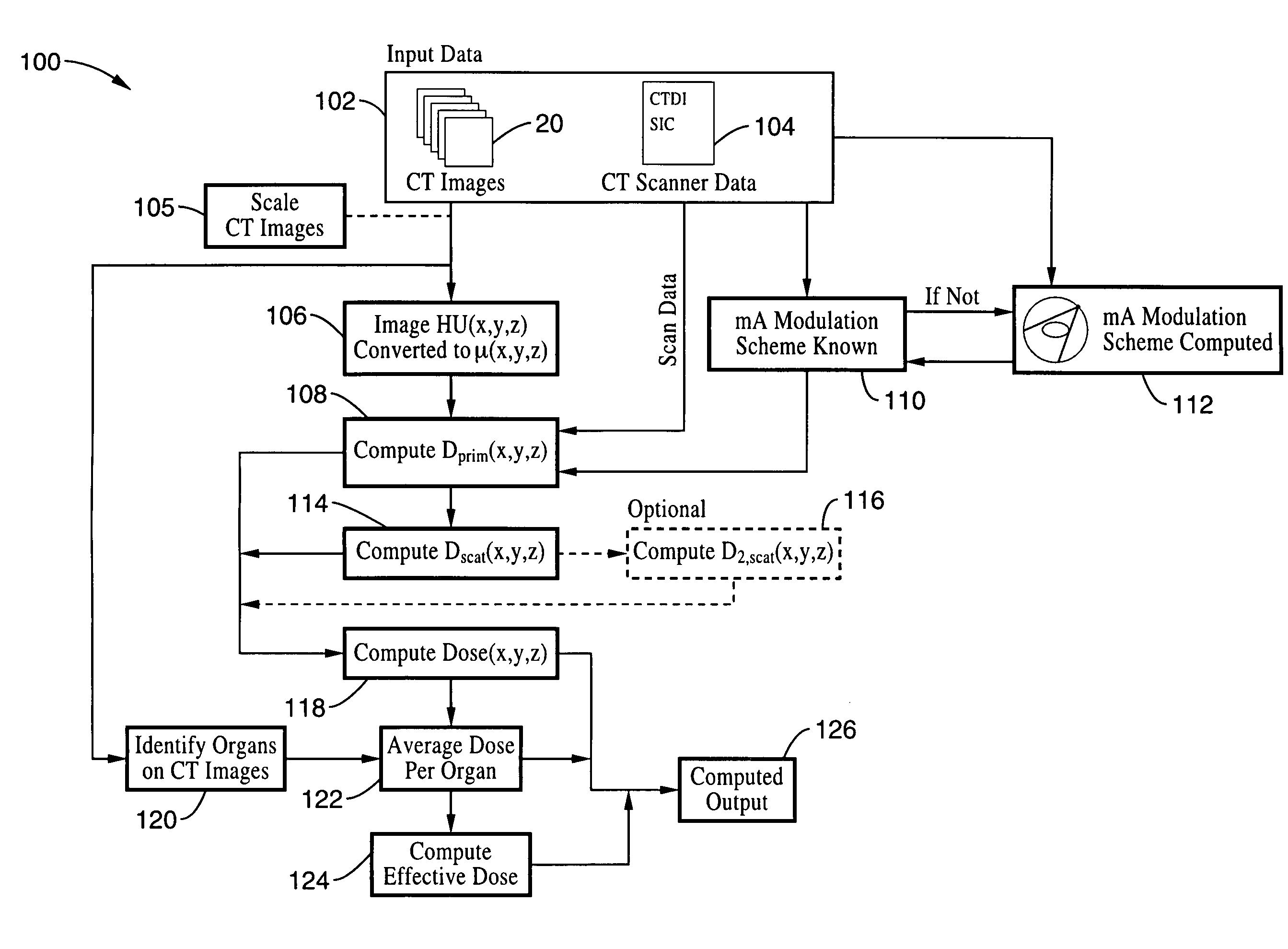
Method for computing patient radiation dose in computed tomography
ActiveUS20080292055A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputed tomographyX-ray
A system and method are disclosed for computing a radiation dose delivered to a patient during a computed tomography (CT) scan of the patient. The CT image dataset generated during the scan of the patient, and one or more parameters relating to a x-ray source are used to calculate the radiation dose delivered to the patient as a function of the CT image data set and the one or more parameters of the x-ray source. The radiation dose is generally found by calculating a primary x-ray dose distribution and scattered x-ray dose distribution from the CT image dataset and taking the sum of the primary x-ray dose distribution and scattered x-ray dose distribution.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method, apparatus, and computer-readable medium for pre-reconstruction decomposition and calibration in dual energy computed tomography
ActiveUS20090262997A1Easy to handleReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDecompositionDual energy
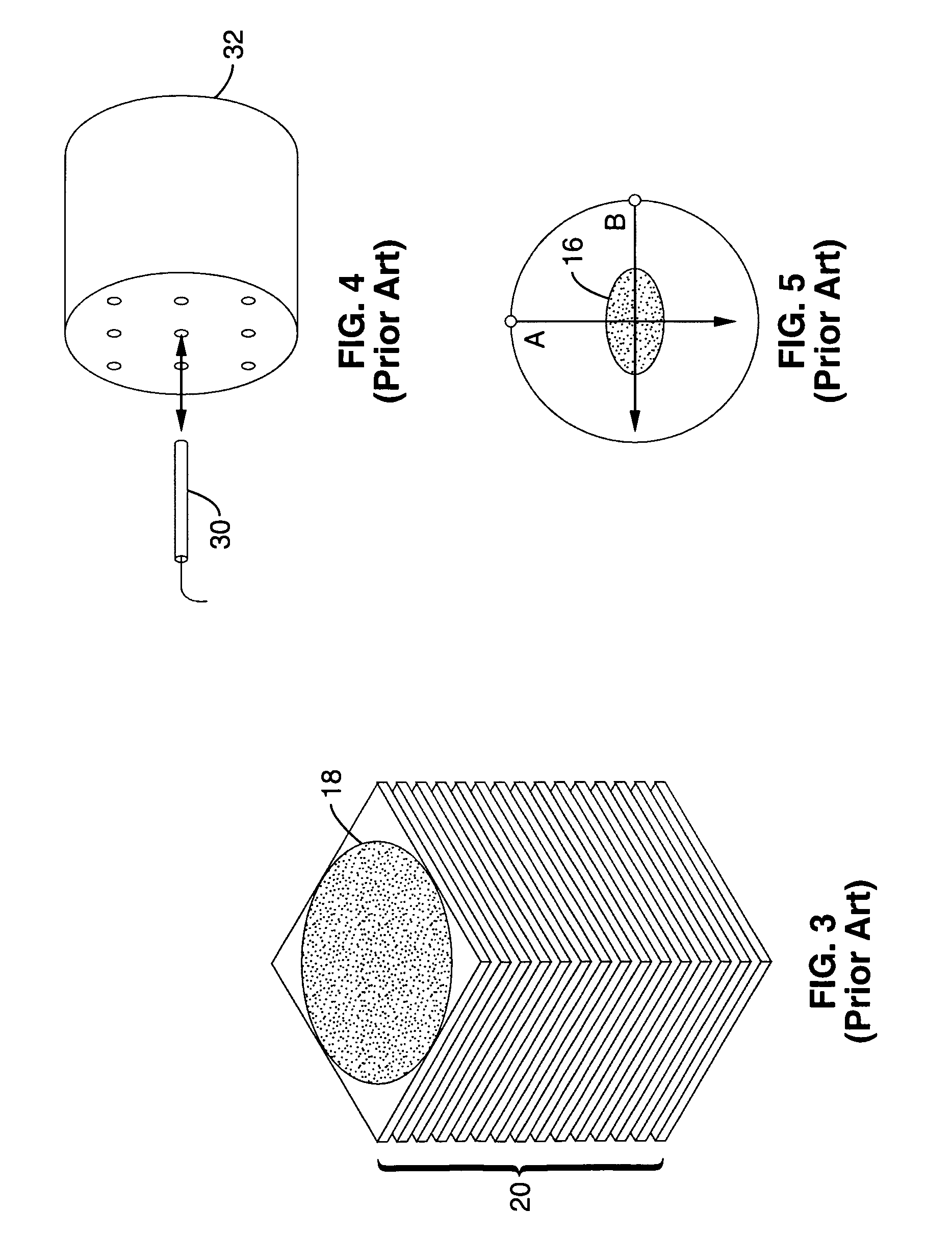
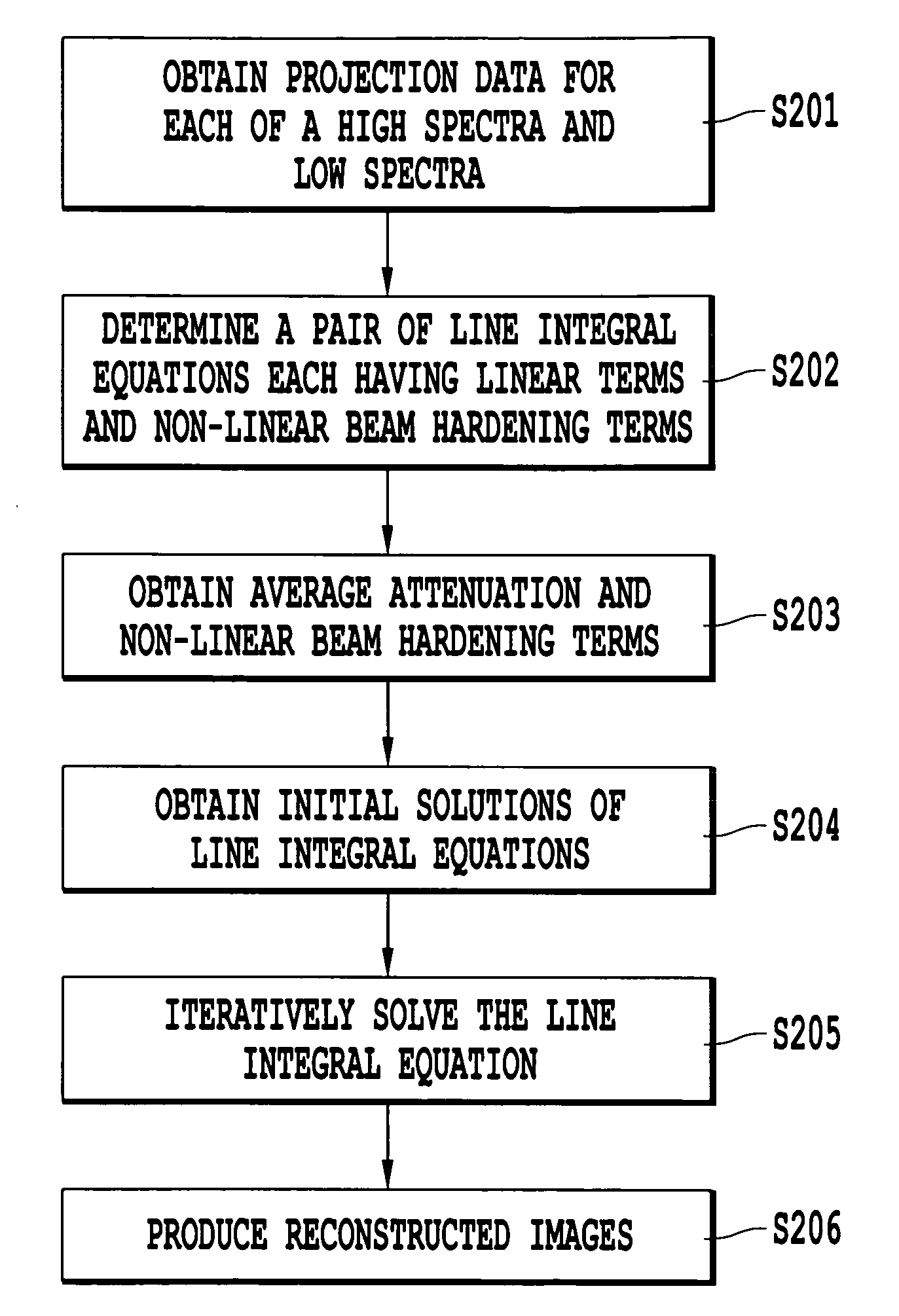
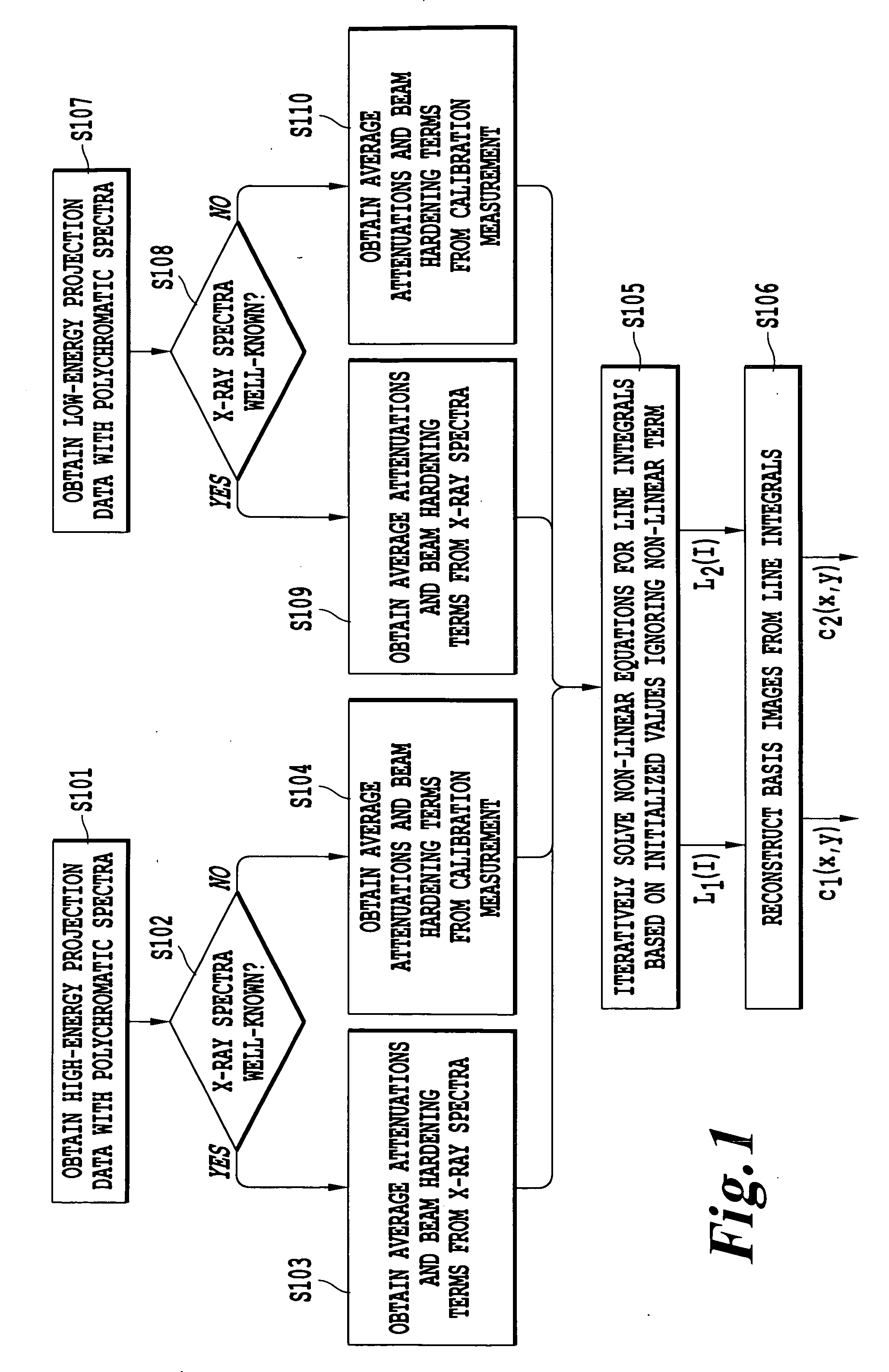
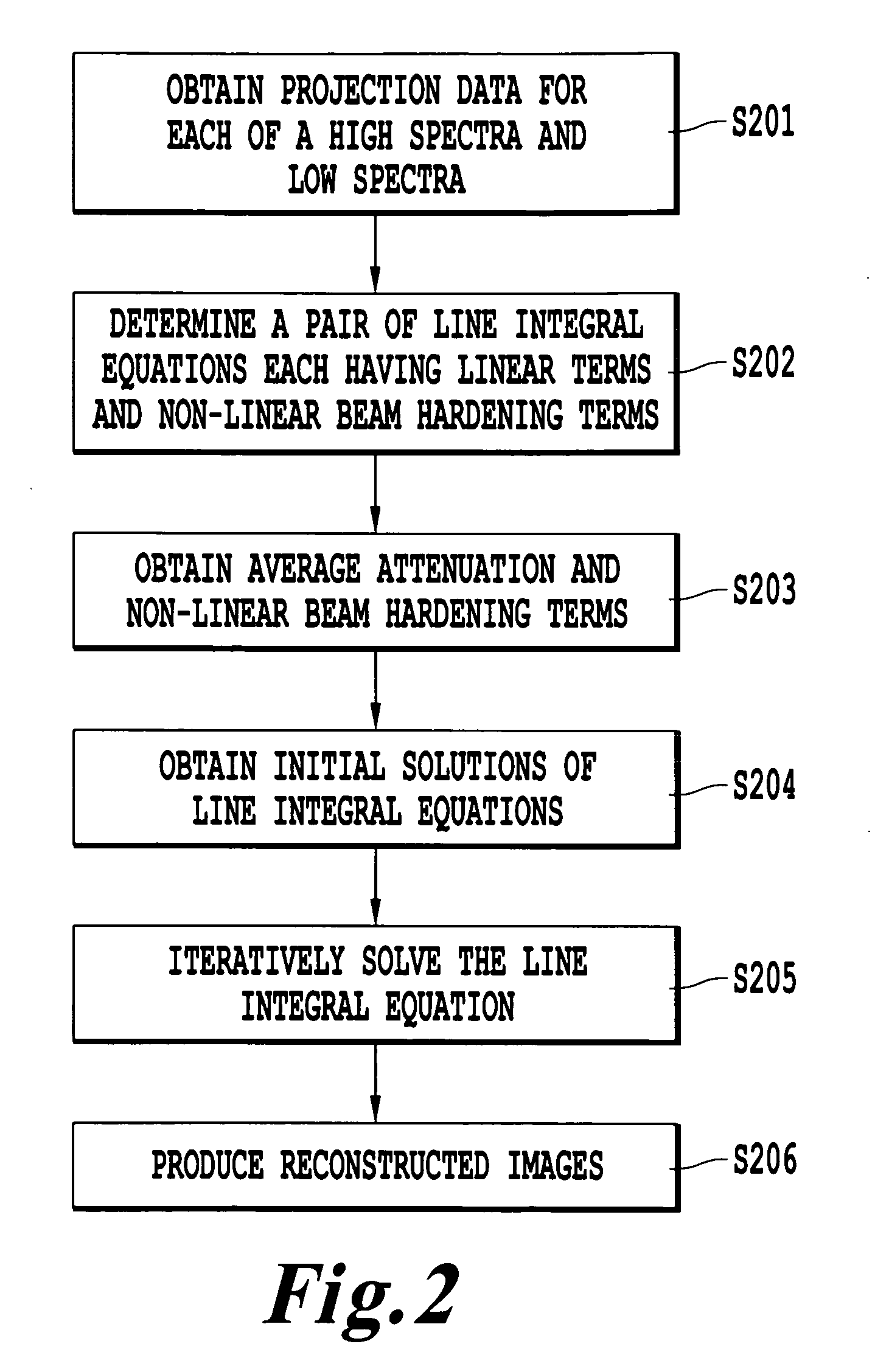
A method of obtaining a computed tomography image of an object includes determining linear terms and non-linear beam hardening terms in a pair of line integral equations for dual-energy projection data from inserting average and difference from average attenuation terms, obtaining an initial solution of the line integral equation by setting the non-linear beam hardening terms to zero, and iteratively solving the line integral equations to obtain one line integral equations for each basis material. Attenuation by the first basis material corresponds to a photoelectric attenuation process, and attenuation by the second basis material corresponds to a Compton attenuation process. The line integral equations can be inverted by an inverse Radon procedure such as filtered backprojection to give images of each basis material. The images of each basis material can then be optionally combined to give monochromatic images, density and effective atomic number images, or photoelectric and Compton processes images.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Single session interactive ultra-short duration super-high biological dose rate radiation therapy and radiosurgery
A medical accelerator system consisting of coplanar and non-coplanar beams, on line magnetic resonance anatomic and functional imaging and cone beam computed tomographic imaging for single session image guided all field simultaneous radiation therapy and radiosurgery is provided. This system enables single session simulation, field-shaping block making, treatment planning, dose calculations and treatment of tumors. The radiation exposure time to the tumor and the normal tissue is reduced to a few seconds to less than a minute. In filed intensity modulated radiation is rendered by combined divergent and pencil beam, multiple smaller fields within a larger field, selectively varying beam's energy, dose rate and beam weight. Since all the treatment fields are treated simultaneously the dose rate at the tumor site is the sum of each of the converging beam's dose rate at depth. This super-high biological dose rate impairs the lethal and sublethal damage repair.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
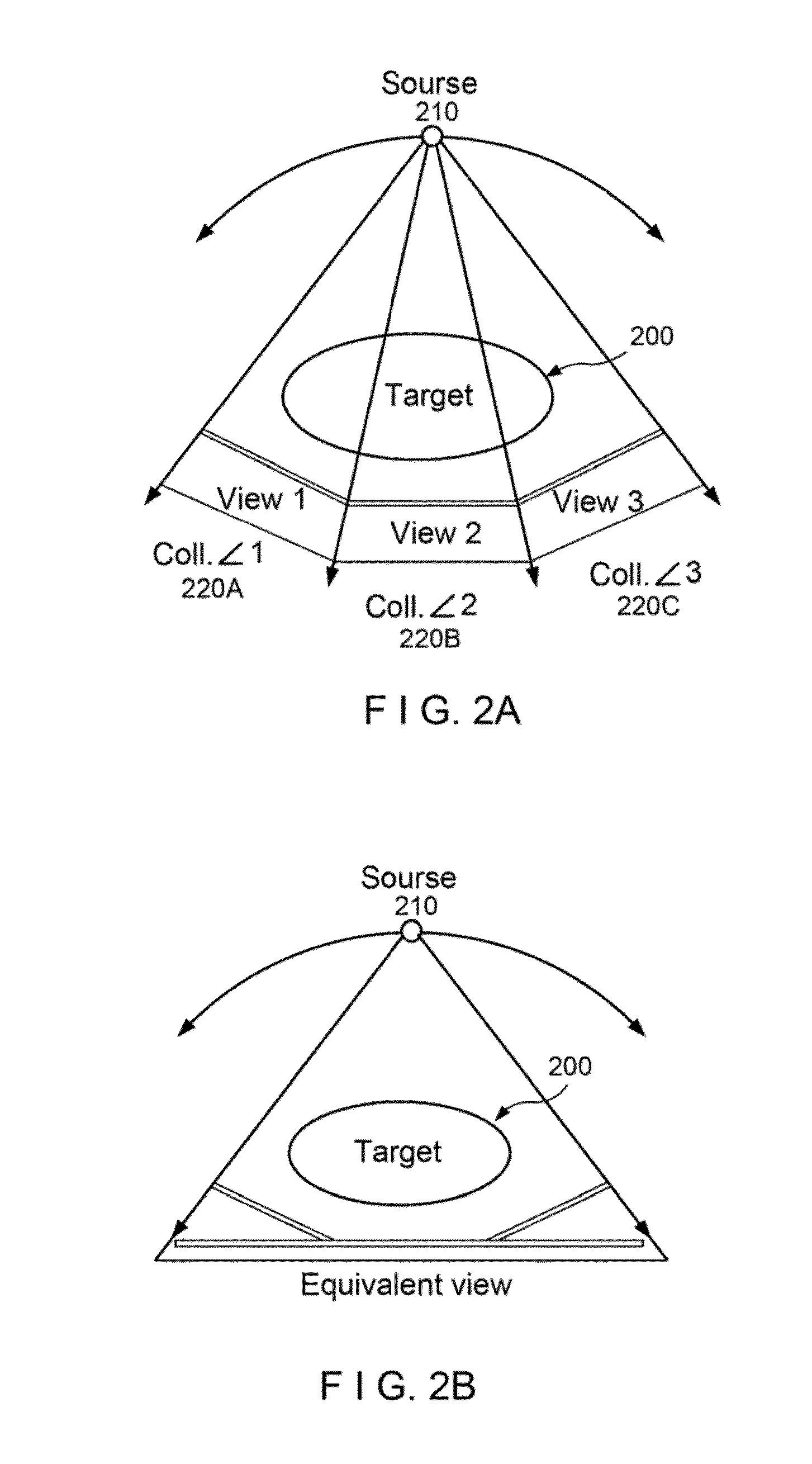
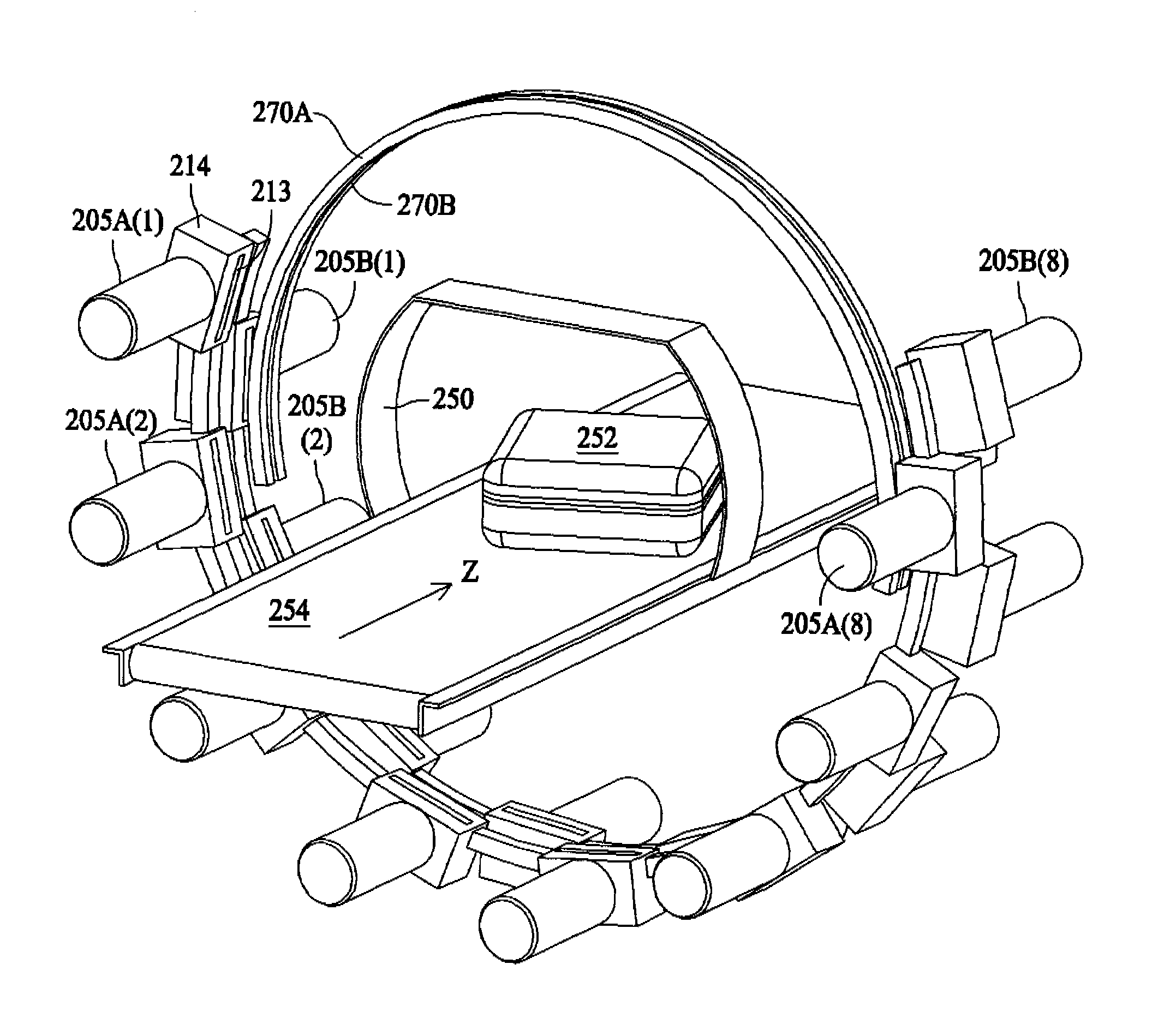
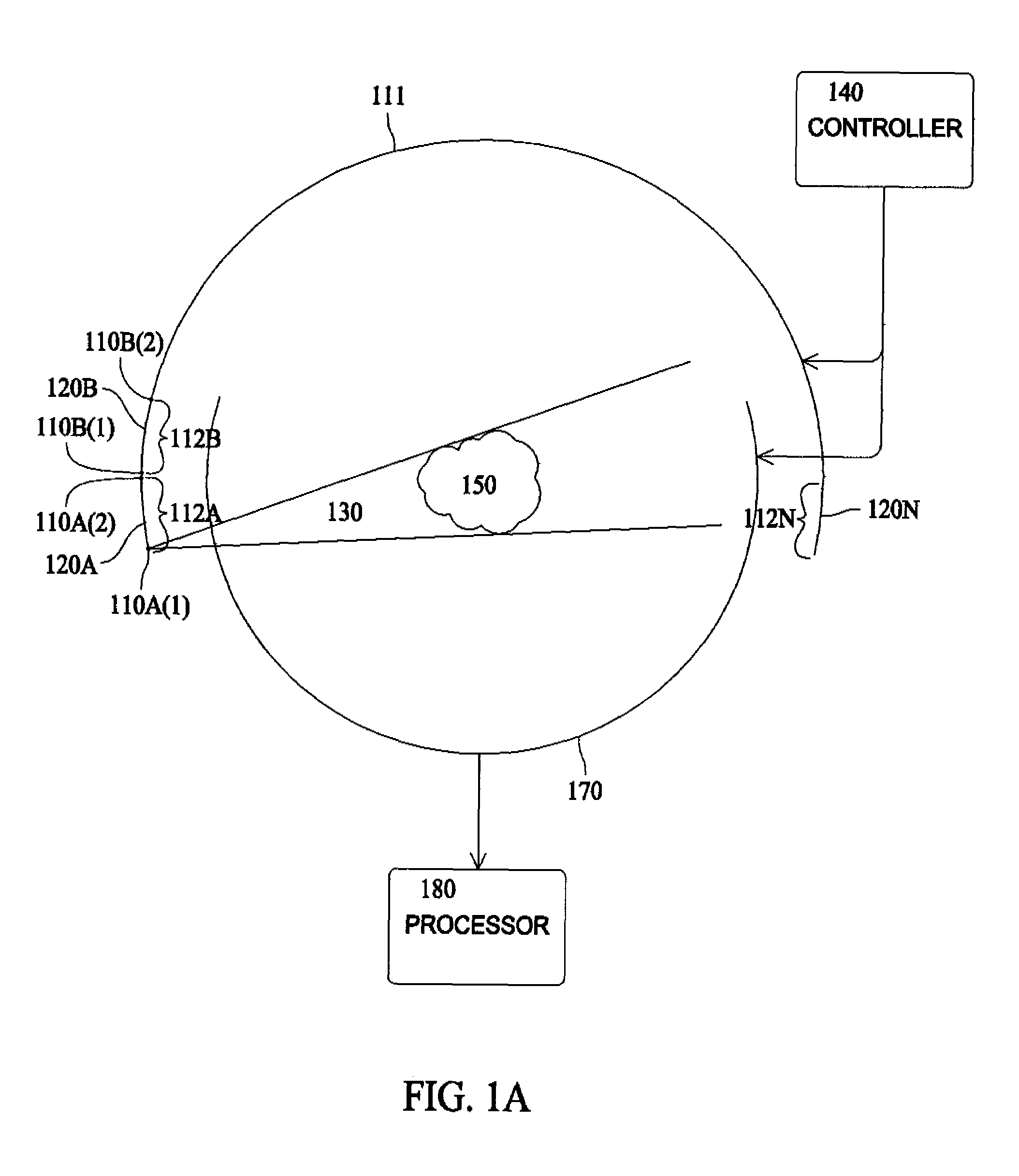
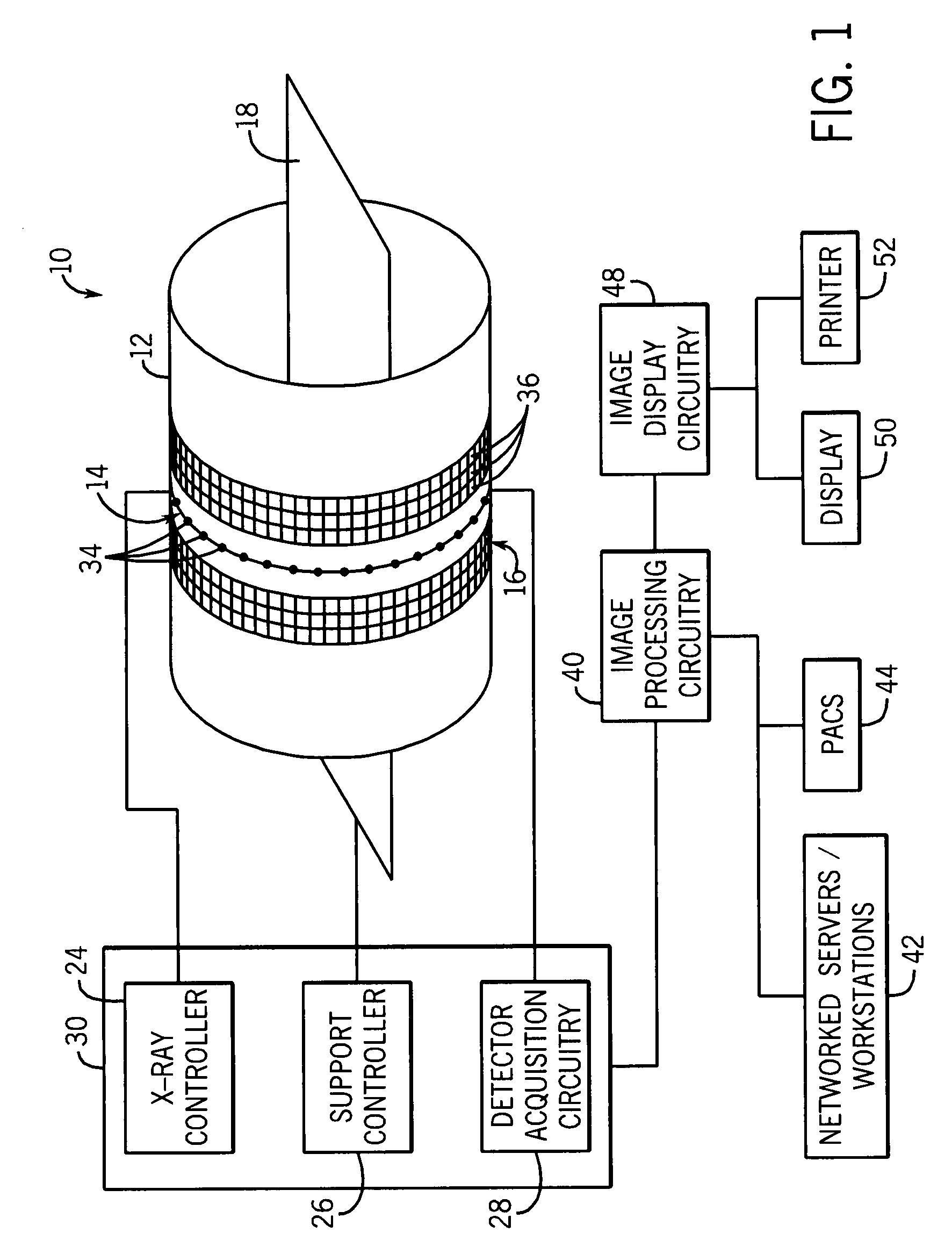
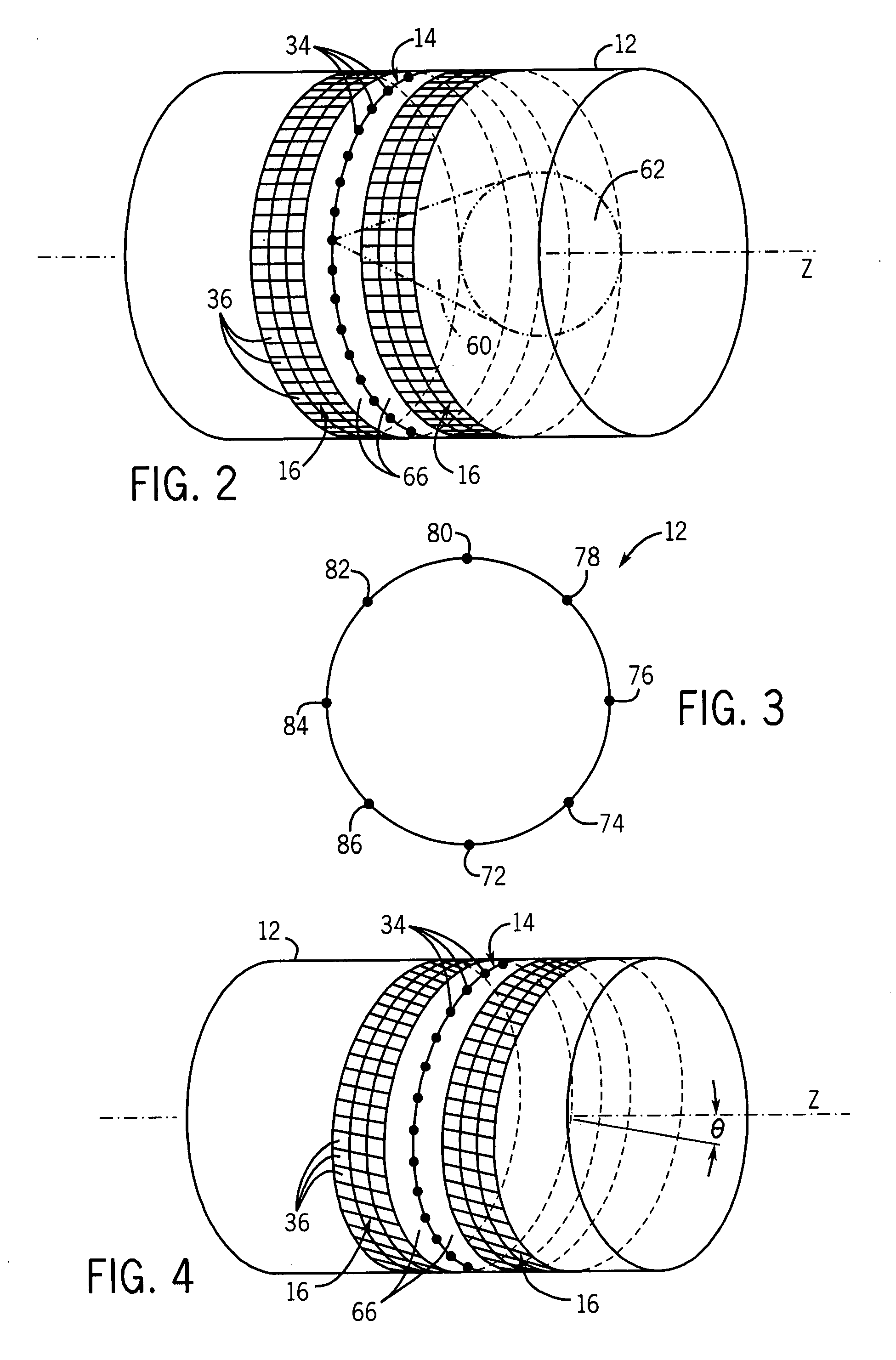
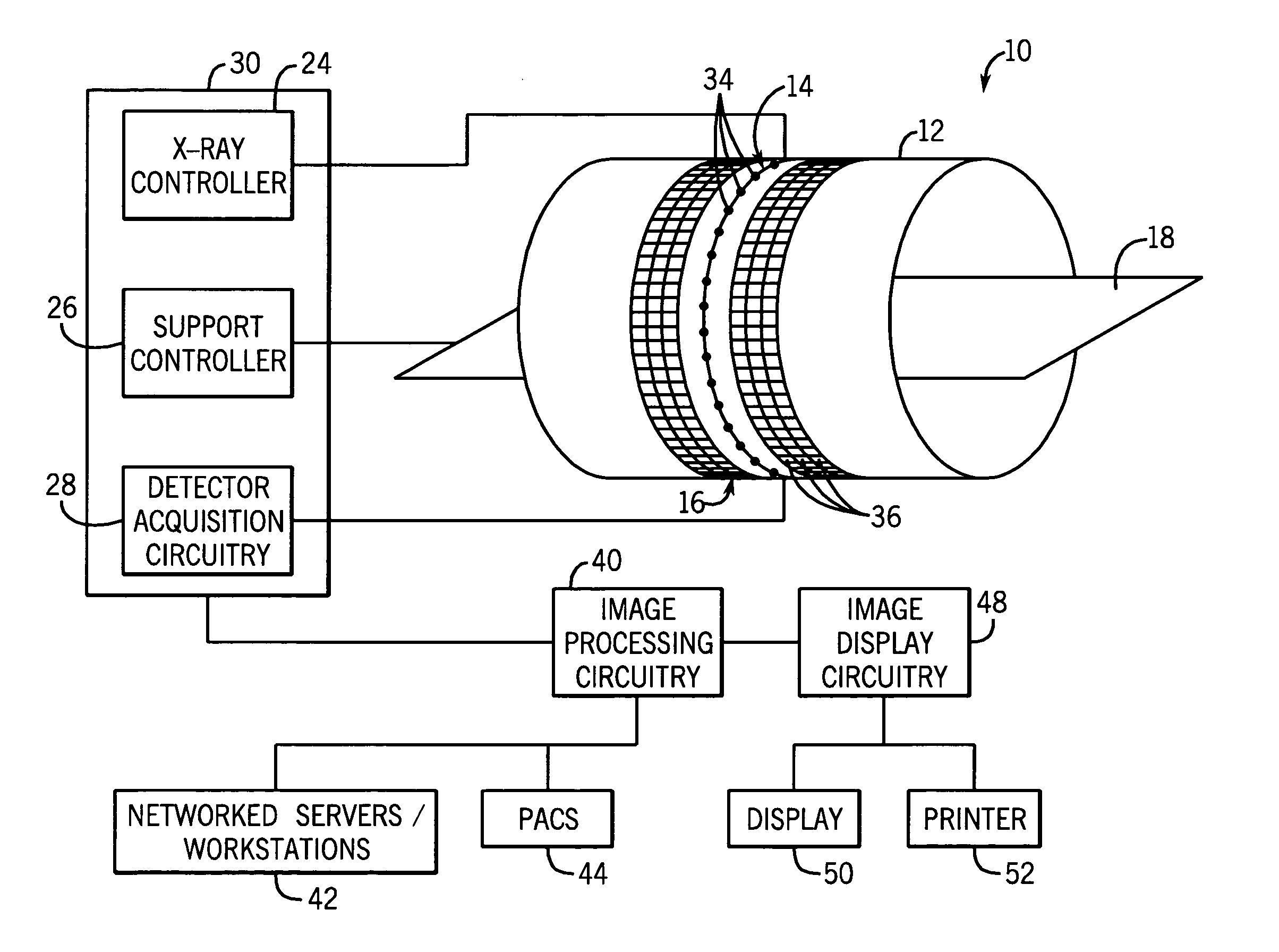
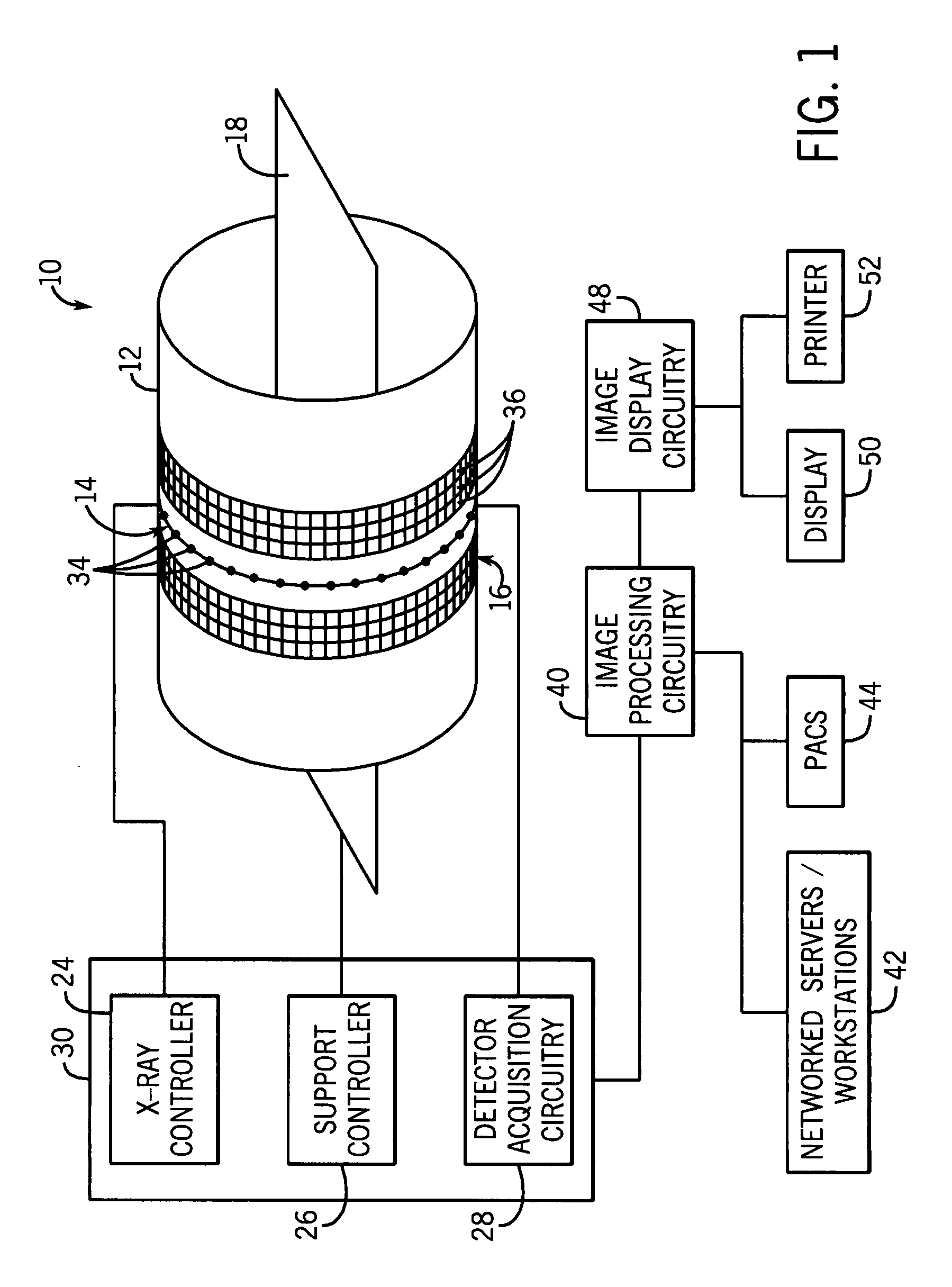
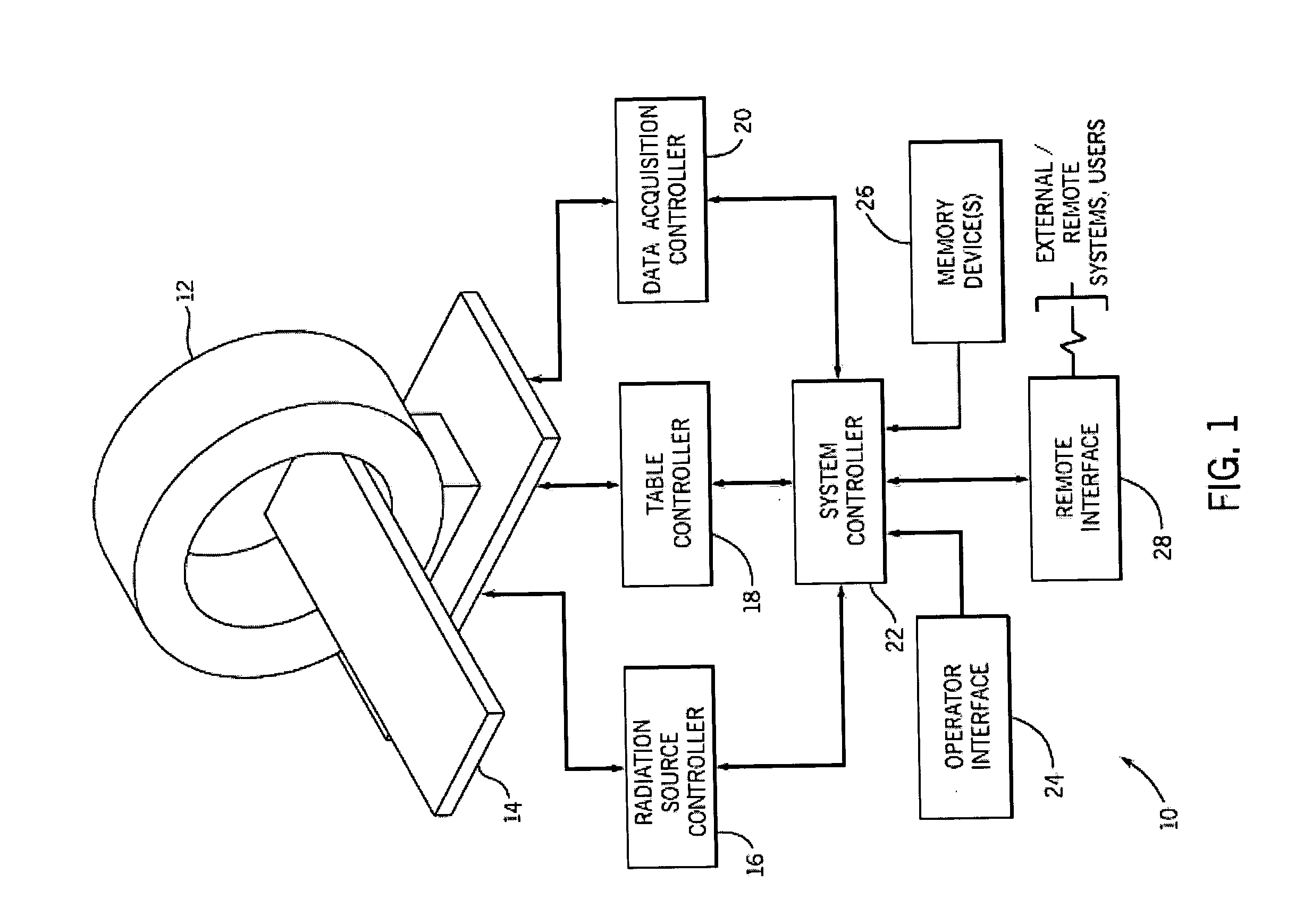
Acquisition and reconstruction of projection data using a stationary CT geometry
ActiveUS20080056436A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingDistributed sourceX-ray
Systems and methods are provided for acquiring and reconstructing projection data that is mathematically complete or sufficient using a computed tomography (CT) system having stationary distributed X-ray sources and detector arrays. In one embodiment, a non-sequential activation is employed to acquire mathematically complete or sufficient projection data. In another embodiment, a distributed source is provided as a generally semicircular segment. In such an embodiment, an alternating activation scheme may be employed to allow one or more helices of image data to be acquired.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Reconstruction of CT projection data
InactiveUS20080056432A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData setComputing tomography
Systems and methods are provided for reconstructing projection data that is mathematically complete or sufficient acquired using a computed tomography (CT) system. In one embodiment, a set of projection data representative of a sampled portion of a cylindrical surface is provided. The set of projection data is reconstructed using a suitable cone-beam reconstruction algorithm. In another embodiment, two or more sets of spatially interleaved helical projection data are processed using helical interpolation. The helically interpolated set of projection data is reconstructed using a two-dimensional axial reconstruction algorithm or a three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Acquisition and reconstruction of projection data using a stationary CT geometry
ActiveUS20080056435A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingDistributed sourceX-ray
Systems and methods are provided for acquiring and reconstructing projection data that is mathematically complete or sufficient using a computed tomography (CT) system having stationary distributed X-ray sources and detector arrays. In one embodiment, a distributed source is provided as arcuate segments offset in the X-Y plane and along the Z-axis.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
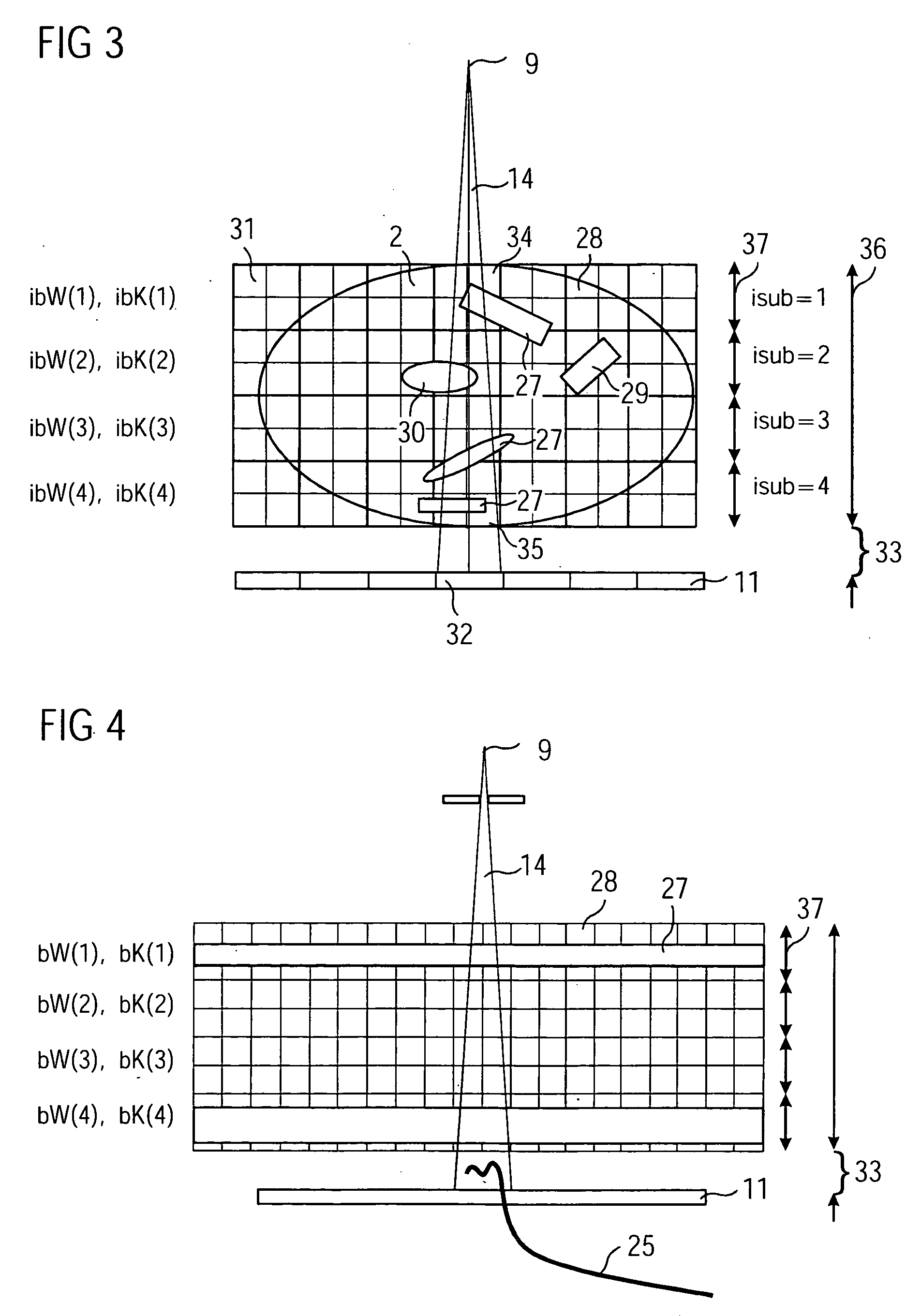
Method and apparatus for reduction of artifacts in computed tomography images
ActiveUS20050123089A1Reduce artifactsReconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingPattern recognitionComputed tomography
A method and computer-readable medium for reducing artifacts in image data generated by a computed tomography system is provided. The artifacts are due to the presence of a high density object in a subject of interest. The method comprises receiving measured sinogram data from the computed tomography system. The sinogram data is representative of sinogram elements. The measured sinogram data is reconstructed to generate initial reconstructed image data. Then corrected sinogram data is generated using the measured sinogram data. The corrected sinogram data is iteratively reconstructed to generate an improved reconstructed image data based on a weight measure derived from the measured sinogram data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Device and method for x-ray scatter correction in computer tomography
InactiveUS20060008046A1Simple parameter settingSimple calculationReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayTomography
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
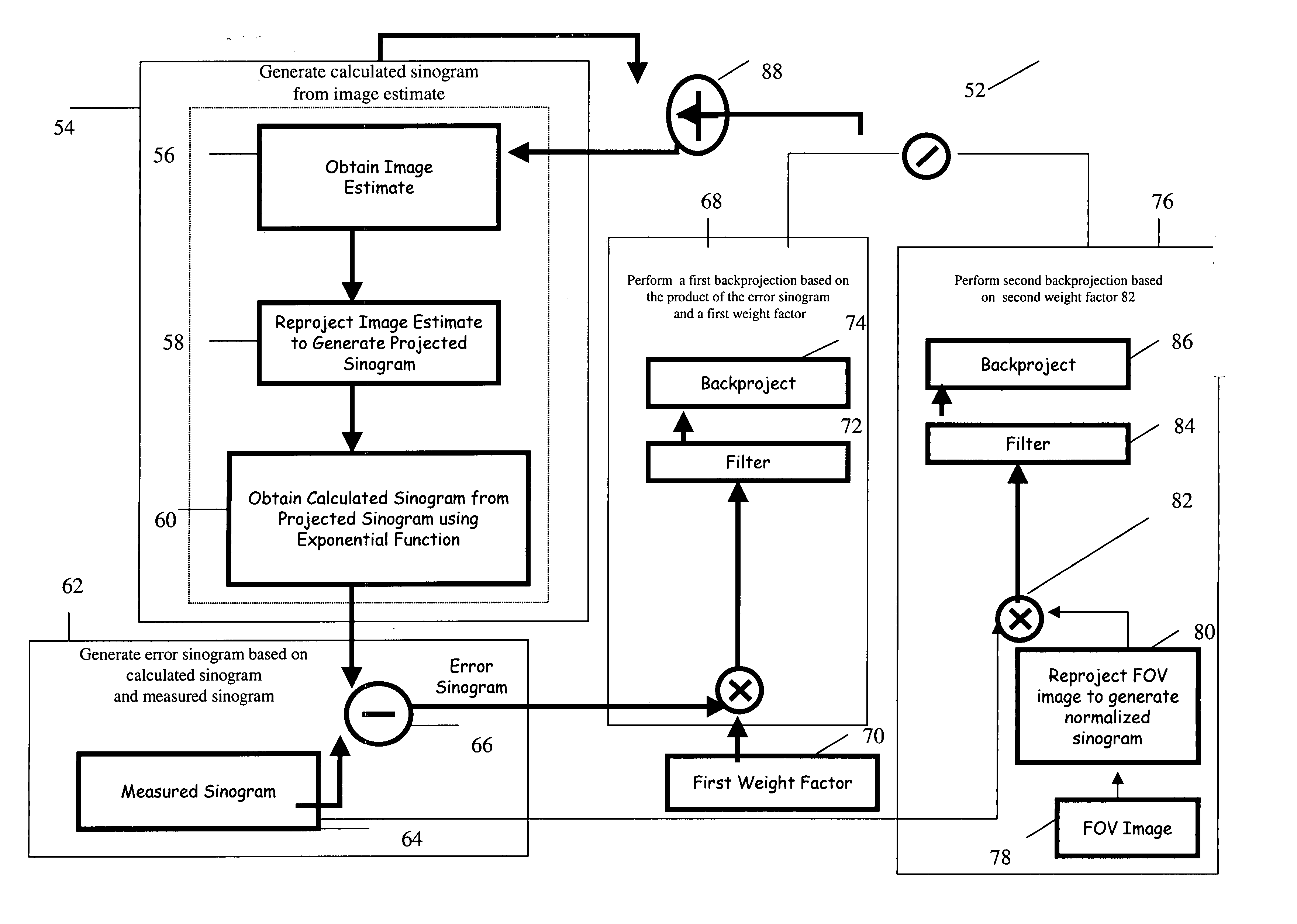
Method and system for iterative image reconstruction
InactiveUS20060072801A1Need be addressReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputed tomographyImage estimation
A method for iteratively reconstructing image data acquired by a computed tomography system is provided. The method comprises generating a calculated sinogram from an image estimate and generating an error sinogram based on the calculated sinogram and a measured sinogram. Then, one or more backprojections are performed, each based upon a reconstruction parameter. The reconstruction parameter impacts at least one of convergence speed and computational cost of each iterative step and corresponding reconstruction. A filtering step is performed prior to performing the one or more backprojections. Finally, the initial image is updated by adding corresponding results of the one or more backprojections to the image estimate to obtain the reconstructed image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method For Image Reconstruction Using Low-Dimensional-Structure Self-Learning and Thresholding
InactiveUS20120099774A1Improve reconstructionPromote reconstructionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImage resolutionPrincipal component pursuit
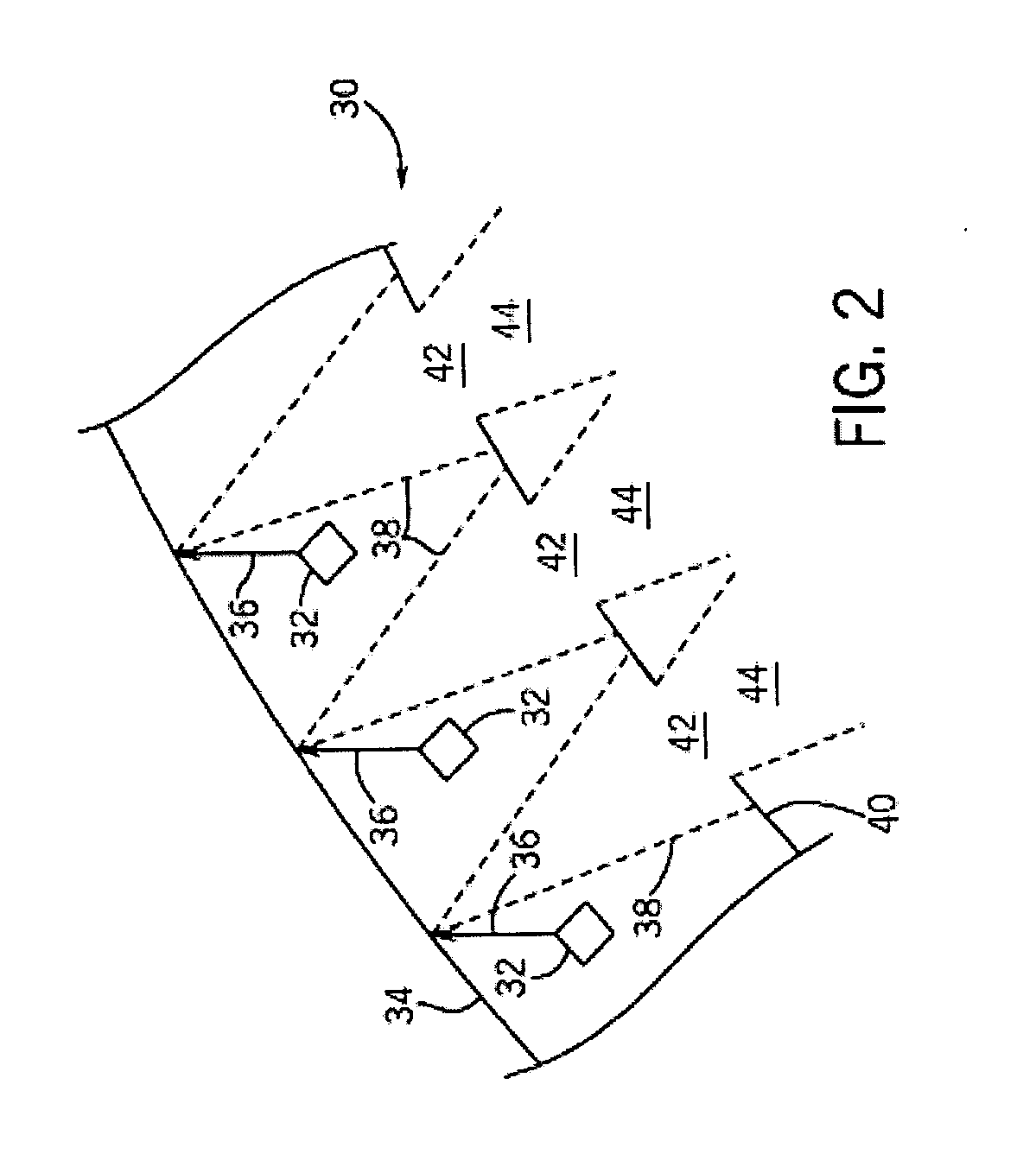
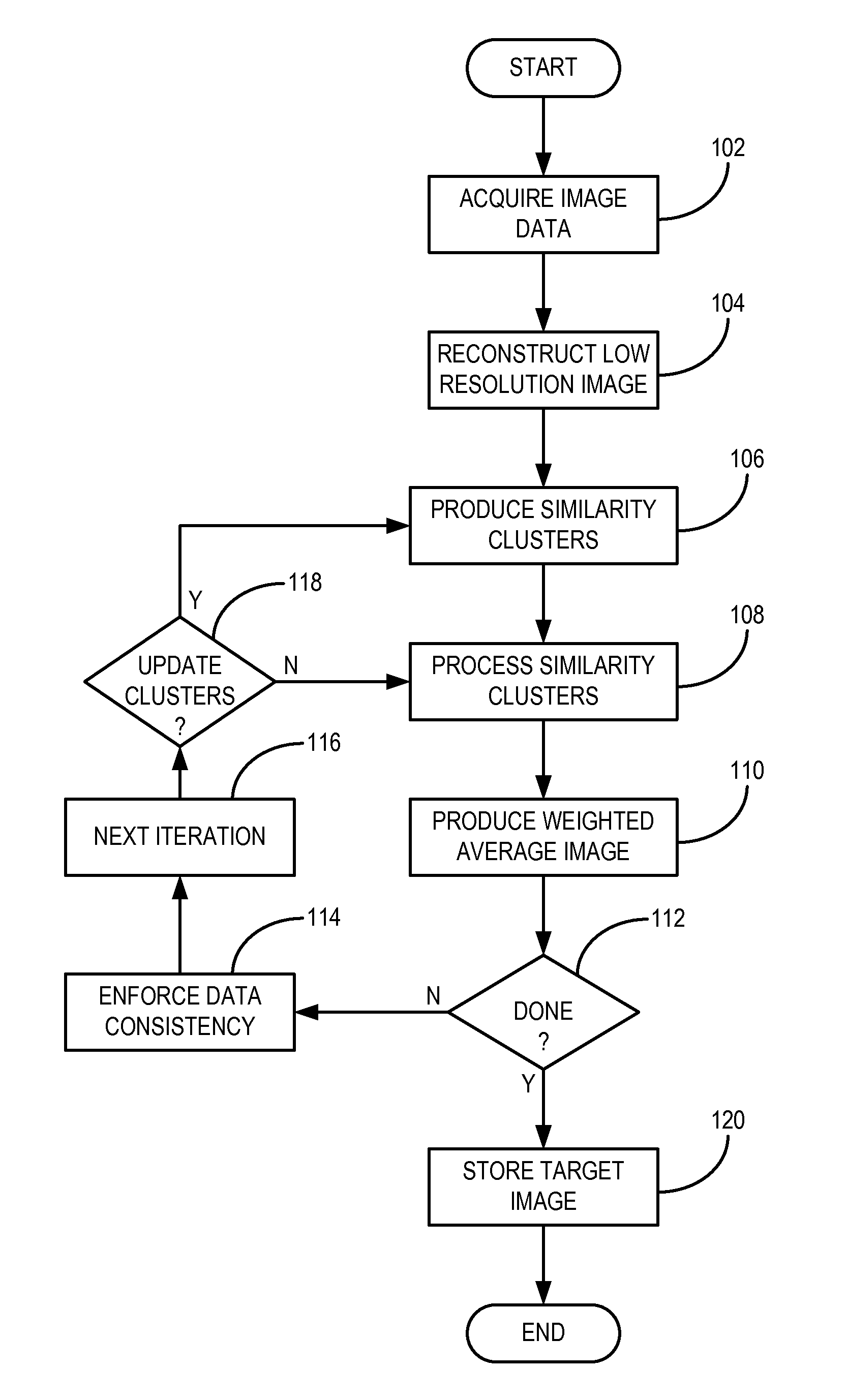
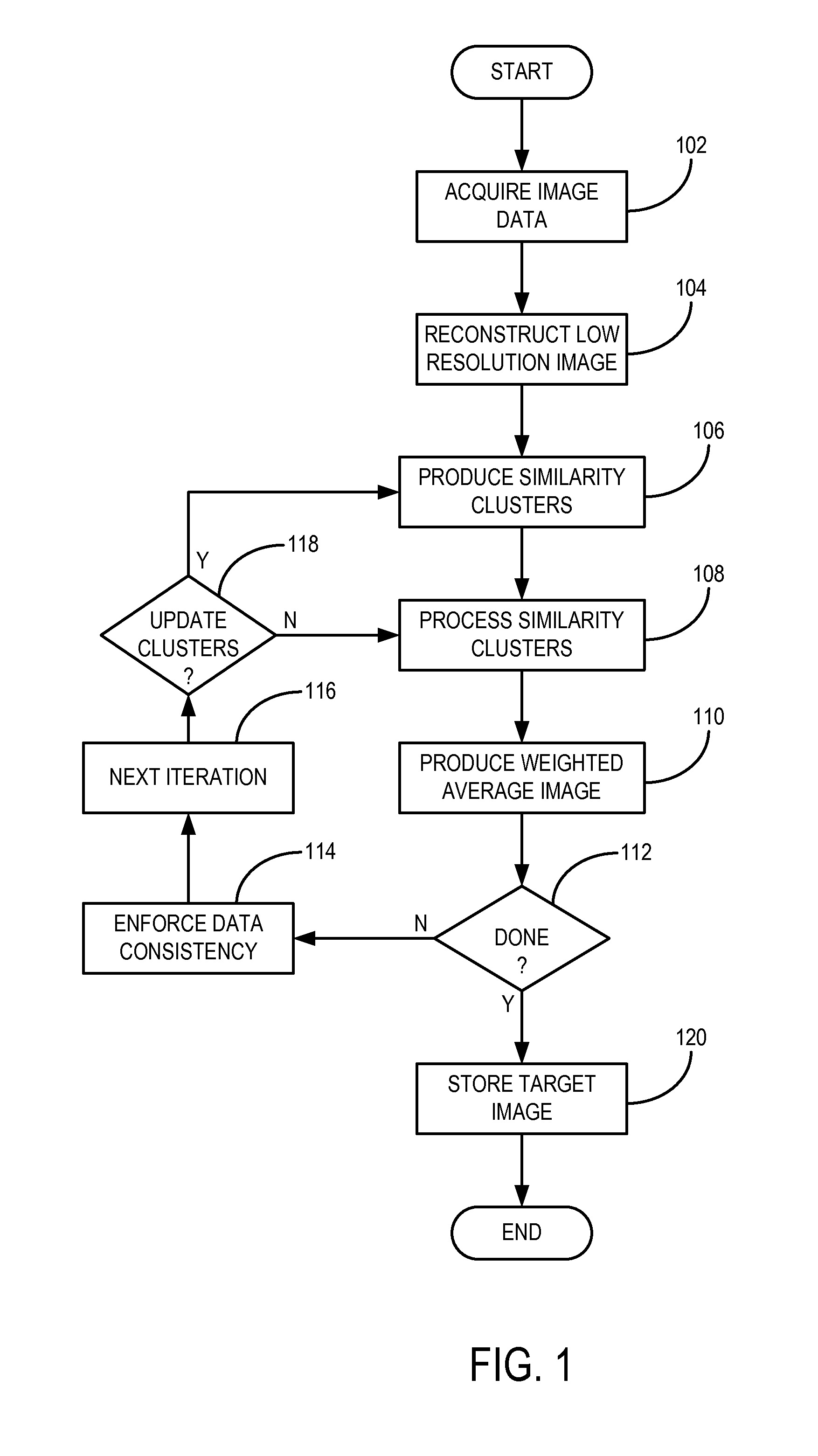
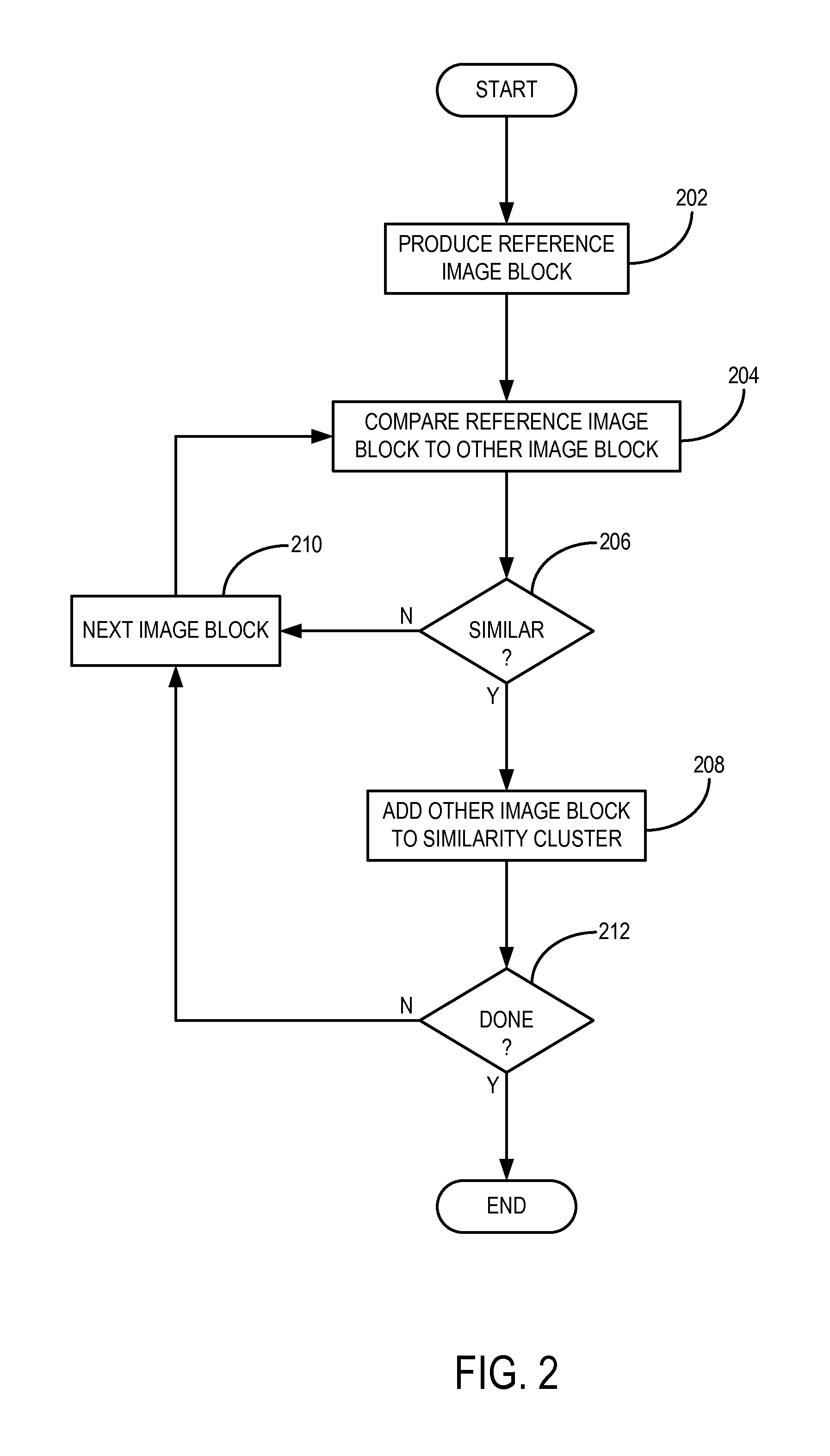
A method for reconstructing an image of a subject from undersampled image data that is acquired with an imaging system, such as a magnetic resonance imaging system or computed tomography system, is provided. From the acquired undersampled image data, an image of the subject is reconstructed and used to guide further image reconstruction. For example, a low resolution image is reconstructed from a portion of the undersampled image data, such as from a portion corresponding to the center of k-space when MRI is used. From this image, a number of similarity clusters are produced and processed. The processing may be by hard thresholding, Wiener filtering, principal component pursuit, or other similar techniques. These processed similarity clusters are then used to reconstruct a final, target image of the subject using, for example, a weighted average combination of the similarity clusters.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
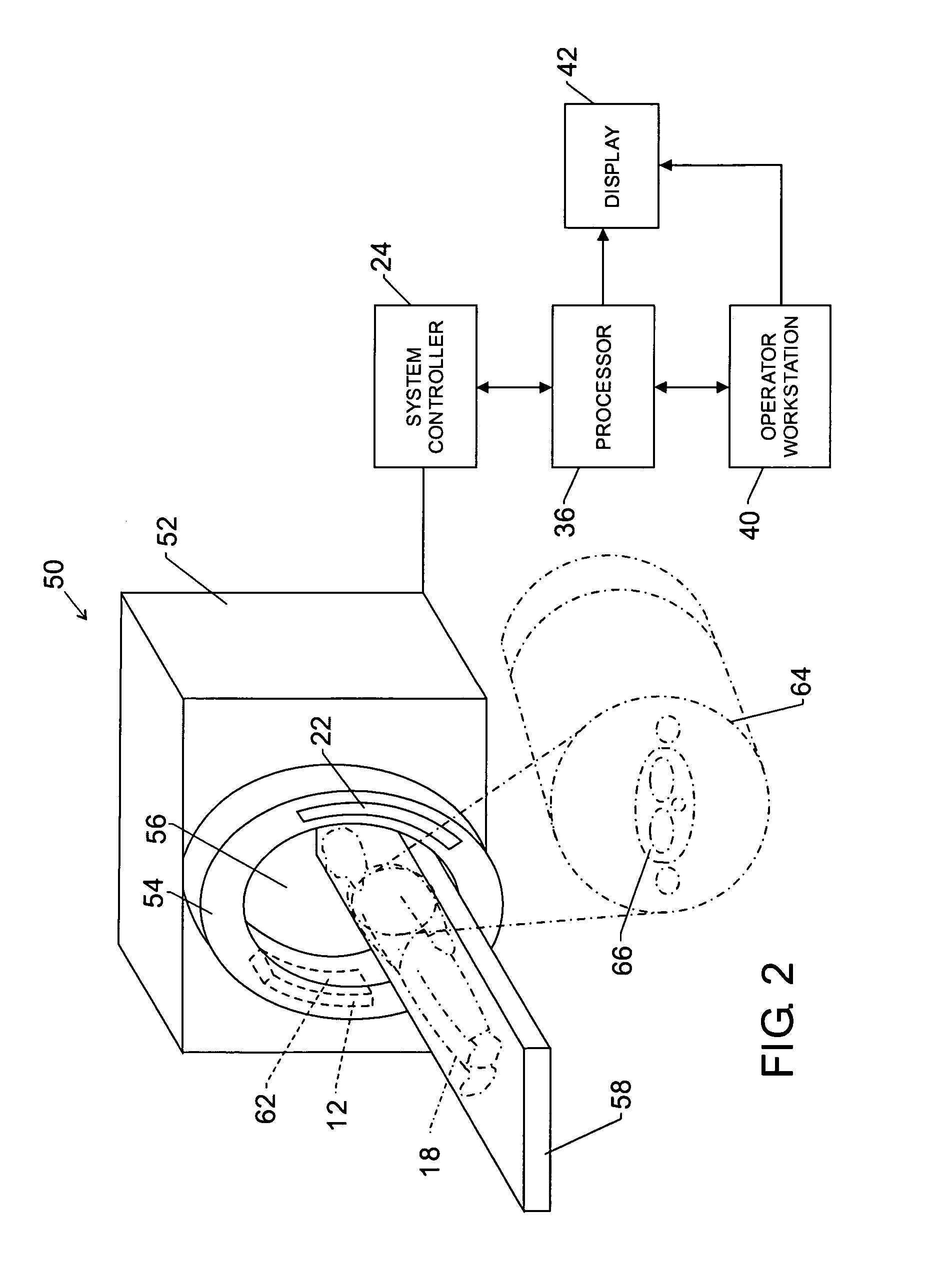
Separate and combined multi-modality diagnostic imaging system
InactiveUS20070238950A1Improve productivityApparent advantageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPatient positioning for diagnosticsNuclear medicineOrbit
A multi-modality diagnostic imaging system includes a first imaging subsystem, such as a computed tomographic (CT) system, for performing a first imaging procedure on a subject. The first imaging system has a gantry that slides along rails. A second imaging subsystem, such as a nuclear medicine system (NUC), performs a second imaging procedure on a subject. The second imaging subsystem is separate from the first imaging system, but in the same room. The second imaging subsystem has a gantry or is gantryless. A patient couch supports a subject. The patient couch is supported on a couch support having vertical adjustment and horizontally fixed. In this manner, the patient is maintained in the same position for multiple types of scans using the same couch support without horizontal translation of the patient couch and patient.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
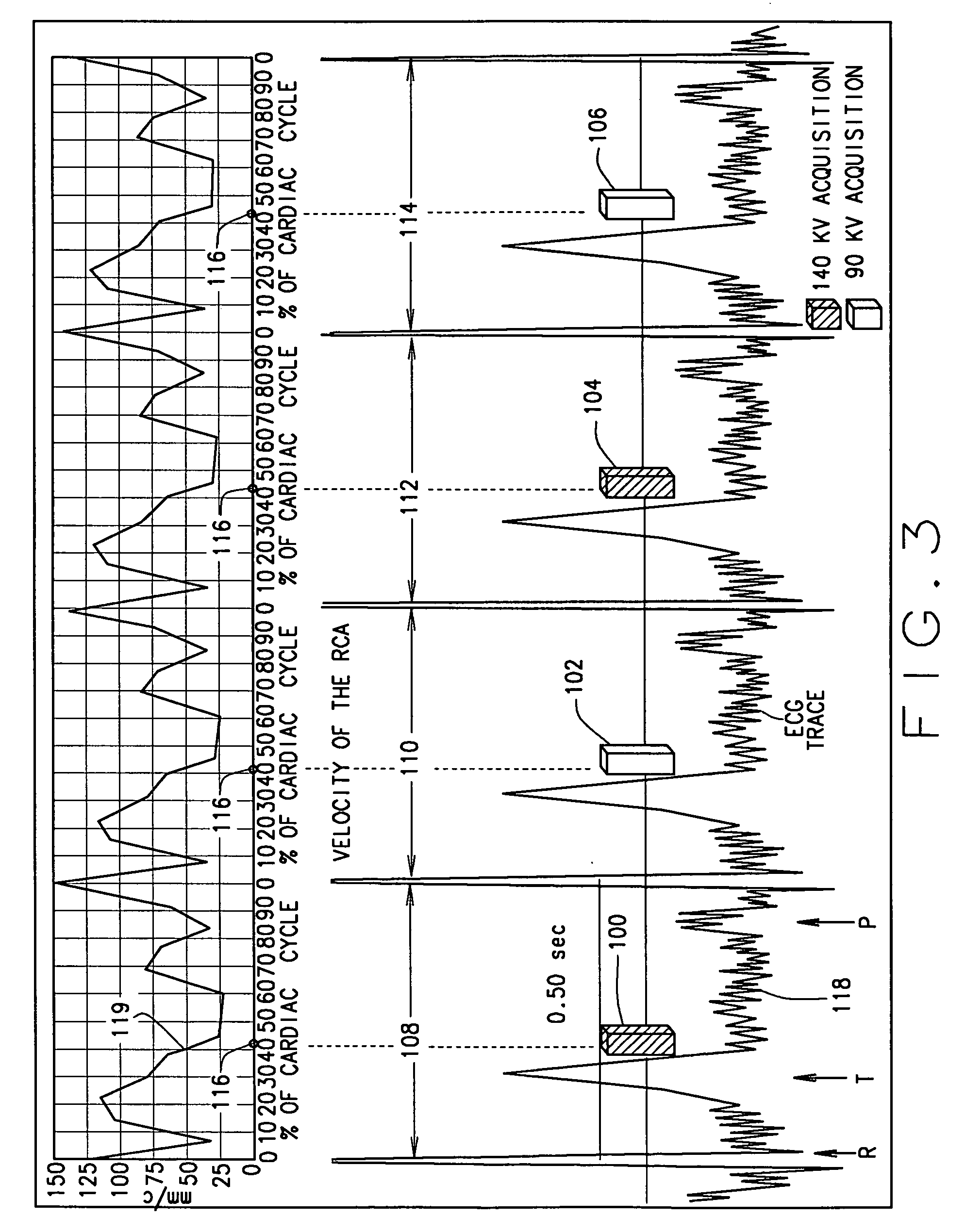
Dual energy scanning protocols for motion mitigation and material differentiation
ActiveUS20070041490A1Reducing mis-registrationMinimal mis-registrationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomographyDual energy
A method for reducing mis-registration during multiple energy scanning on computed tomographic (CT) imaging systems or multiple energy electron beam tomographic (EBT) systems includes scanning a portion of a patient including a cyclically moving body part using a multiple energy computed tomographic (CT) imaging system or multiple energy electron beam tomographic (EBT) system having at least two different energies, monitoring the cyclically moving body part, and gating the multiple energy CT imaging system or multiple energy EBT system in accordance with the monitored cyclically moving body part so that acquisitions are acquired at at least two different kVps. The data acquired at the different kVps are then utilized to generate material decomposition images of the cyclically moving body part.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Tissue marker for multimodality radiographic imaging
ActiveUS7702378B2Increase intensityImprove featuresUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsUltrasound imagingDiagnostic Radiology Modality
An implantable tissue marker incorporates a contrast agent sealed within a chamber in a container formed from a solid material. The contrast agent is selected to produce a change, such as an increase, in signal intensity under magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). An additional contrast agent may also be sealed within the chamber to provide visibility under another imaging modality, such as computed tomographic (CT) imaging or ultrasound imaging.
Owner:BREAST MED
Intensity-modulated, cone-beam computed tomographic imaging system, methods, and apparatus
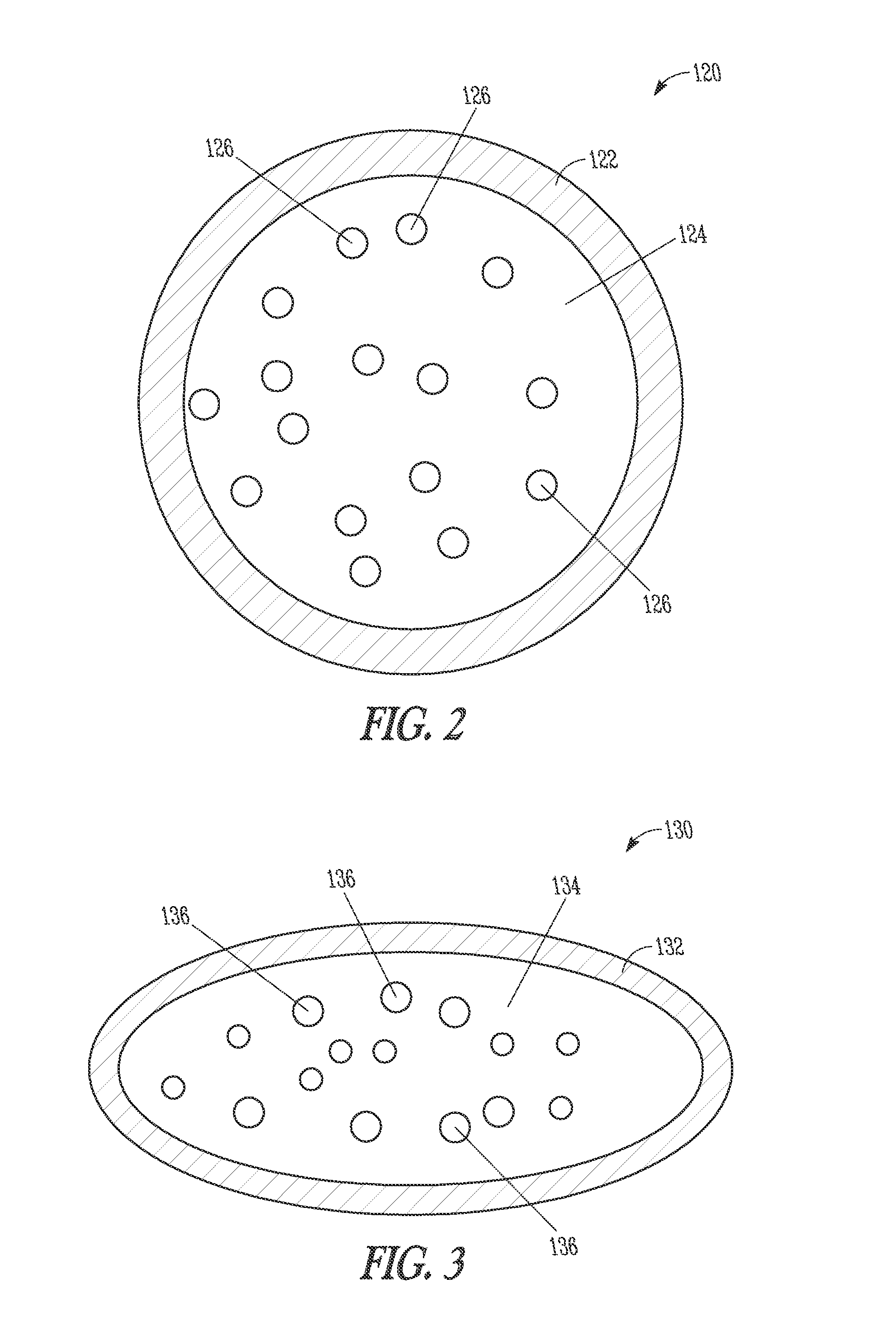
InactiveUS20100119033A1Reduce radiation exposureNarrowed windowMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersImaging processing3d image
Owner:THE METHODIST HOSPITAL RES INST
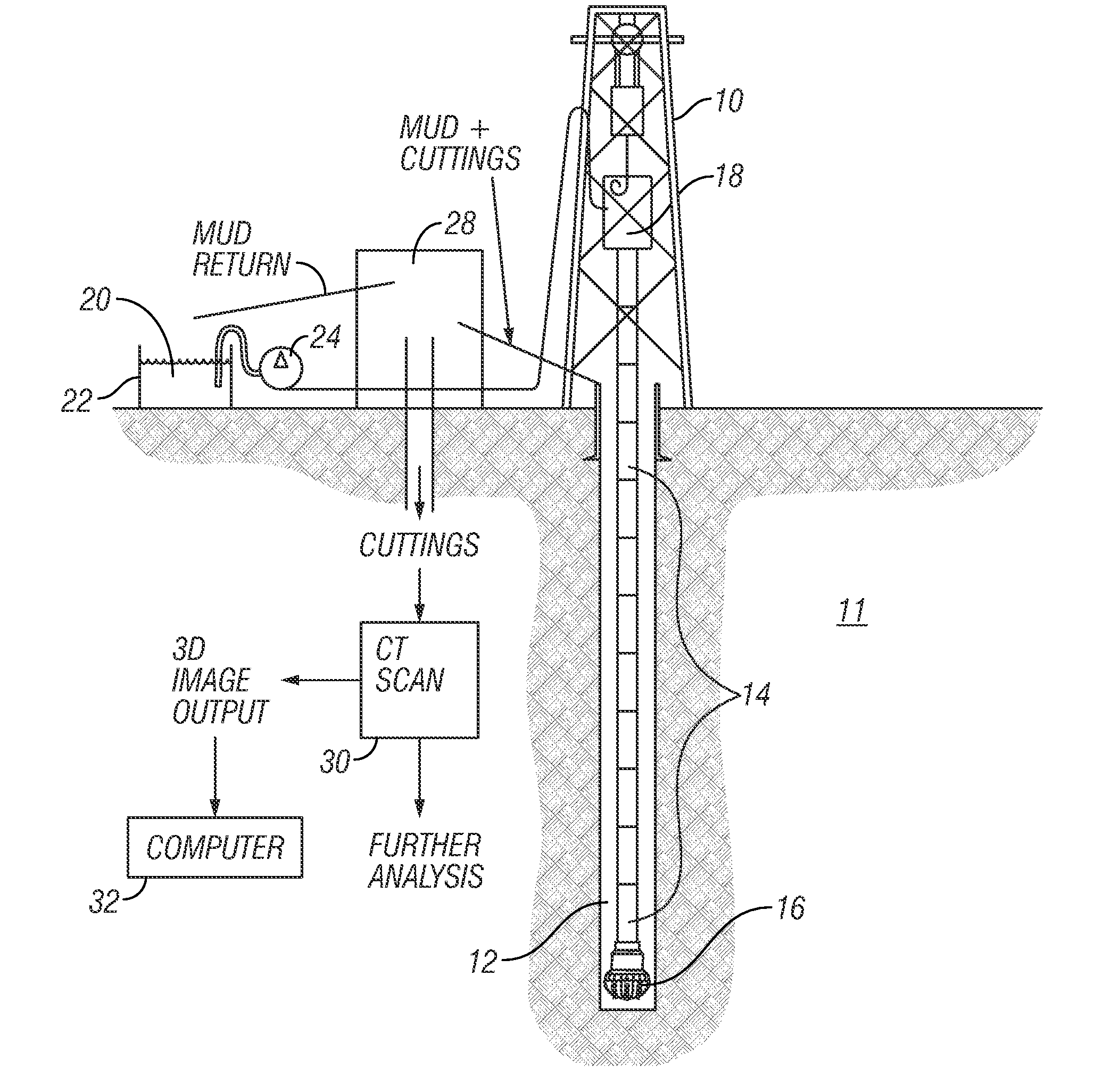
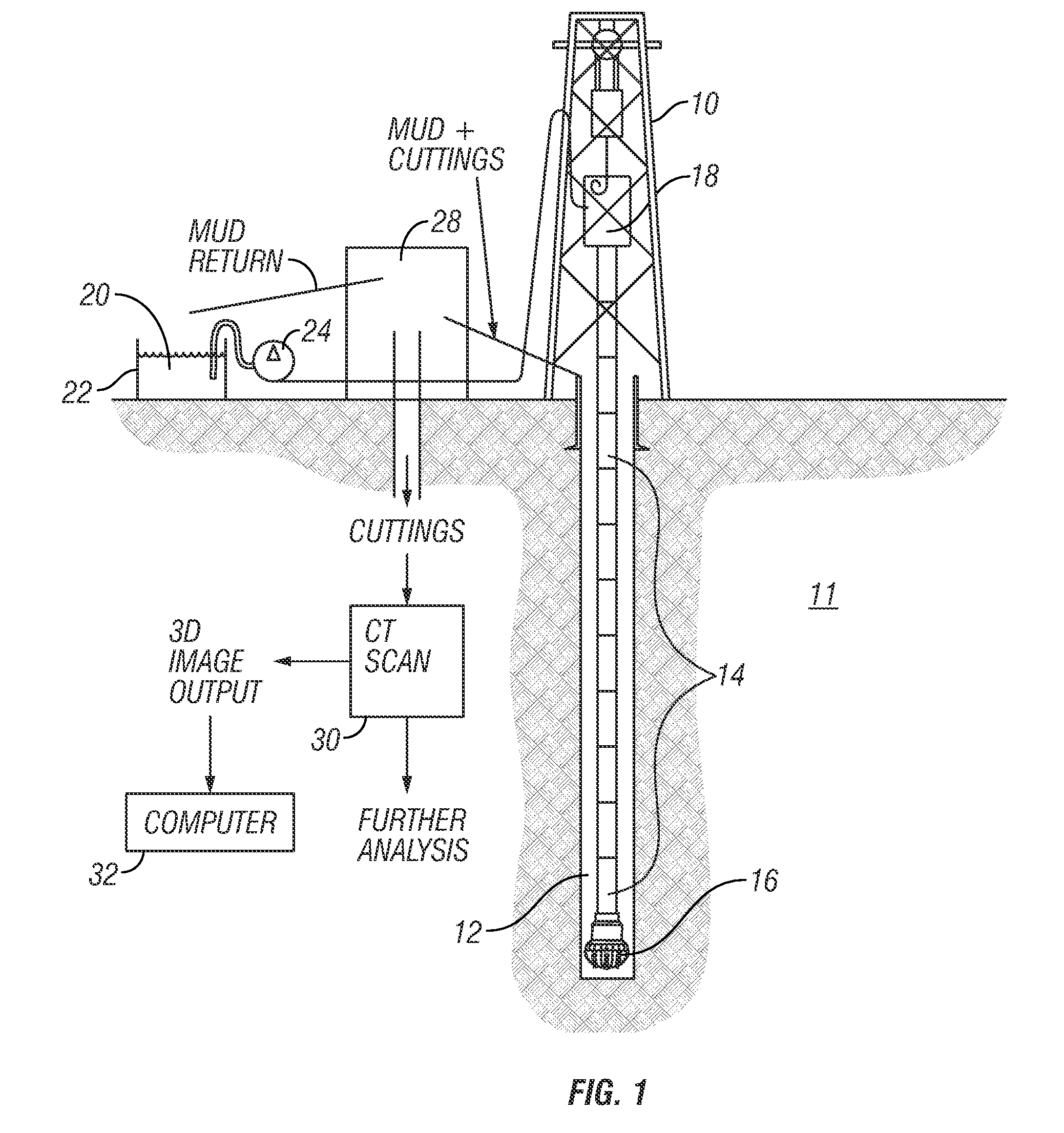
Method for determining properties of fractured rock formations using computer tomograpic images thereof
A method for estimating a petrophysical parameter from a rock sample includes making a three dimensional tomographic image of the sample of the material. The image is segmented into pixels each representing pore space or rock grain. Porosity of the sample is determined from the segmented image. An image of at least one fracture is introduced into the segmented image to generate a fractured image. The porosity of the fractured image is determined. At least one petrophysical parameter related to the pore-space geometry is estimated from the fractured image.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
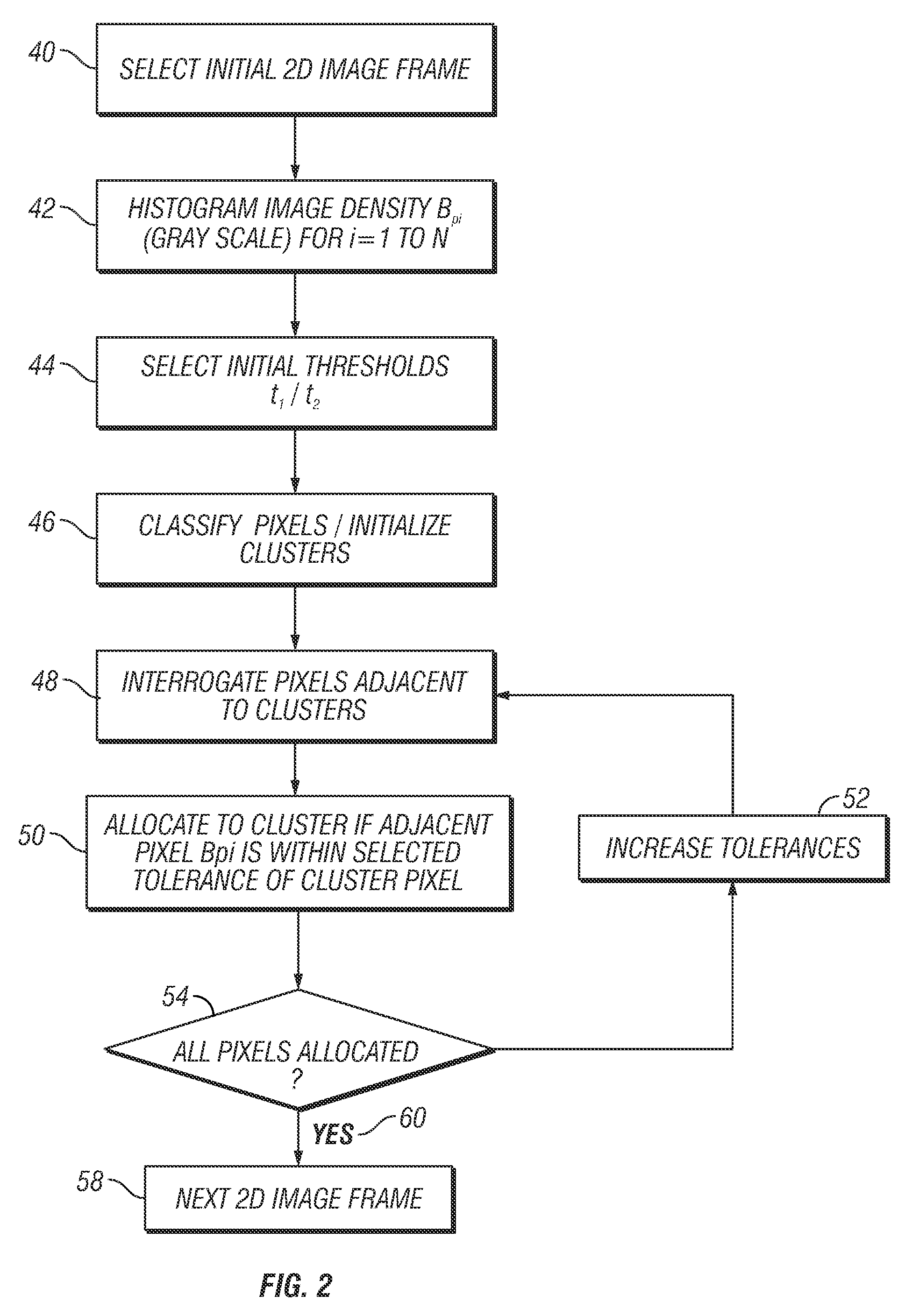
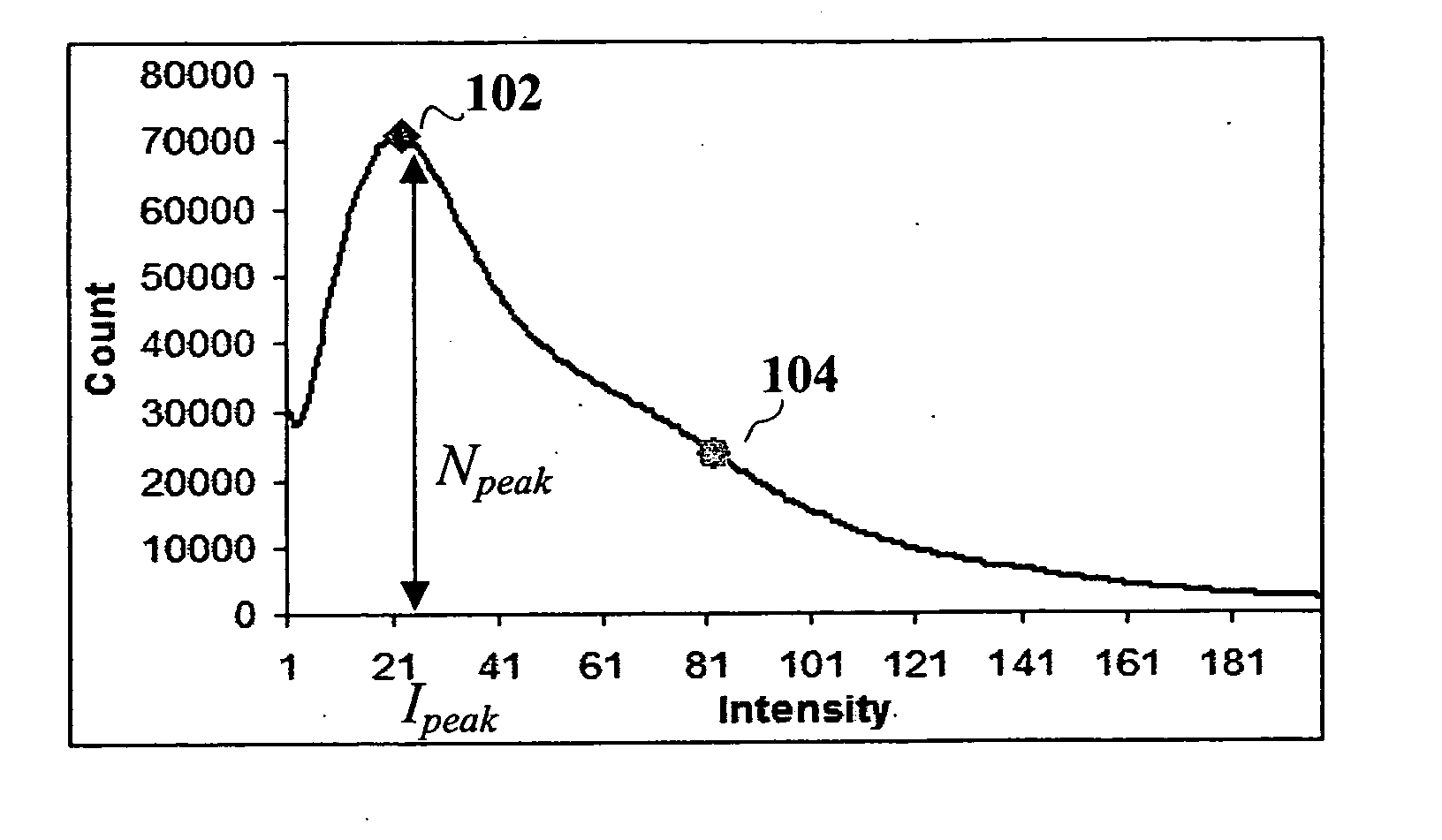
Automated methods for pre-selection of voxels and implementation of pharmacokinetic and parametric analysis for dynamic contrast enhanced MRI and CT
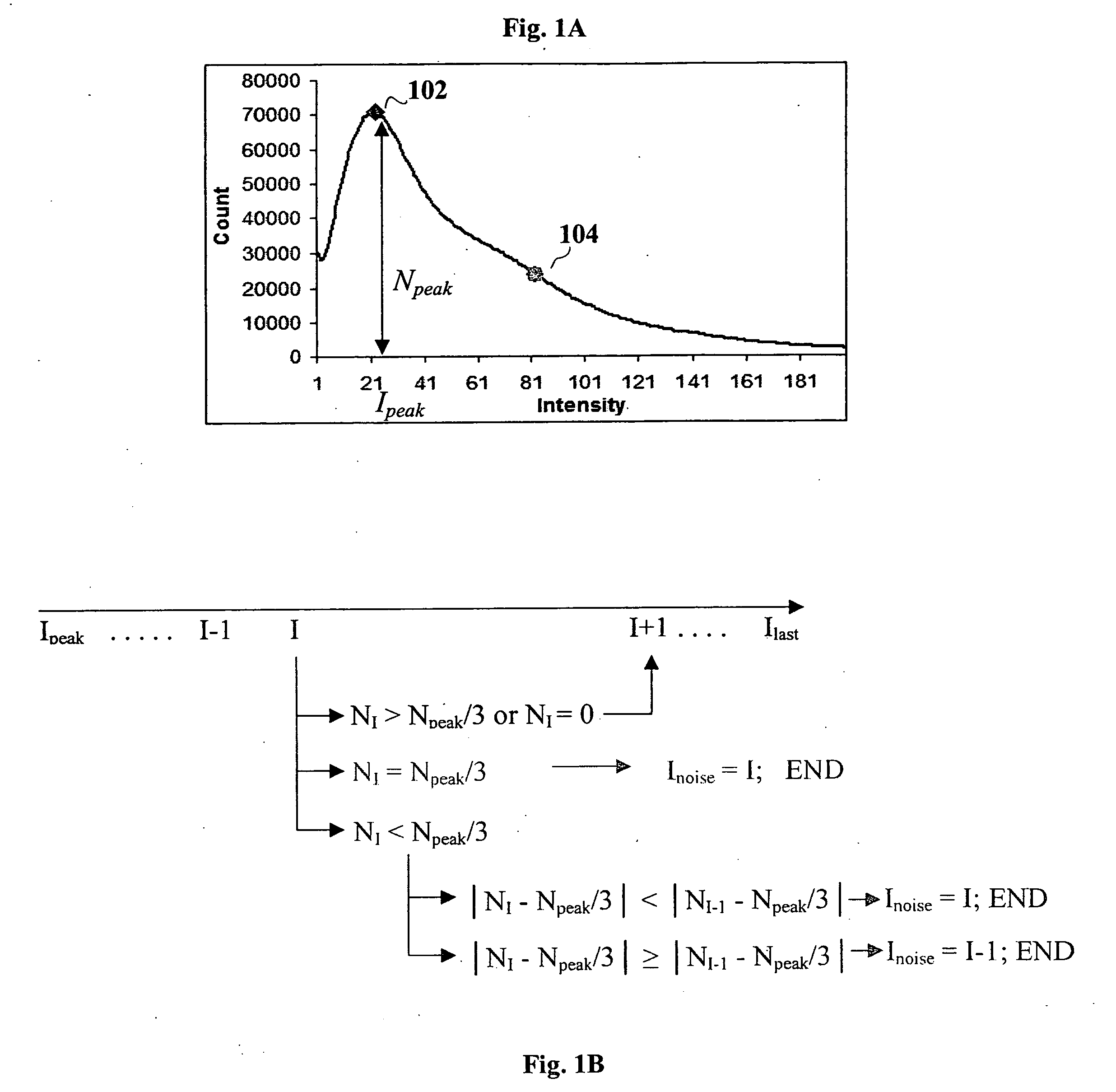
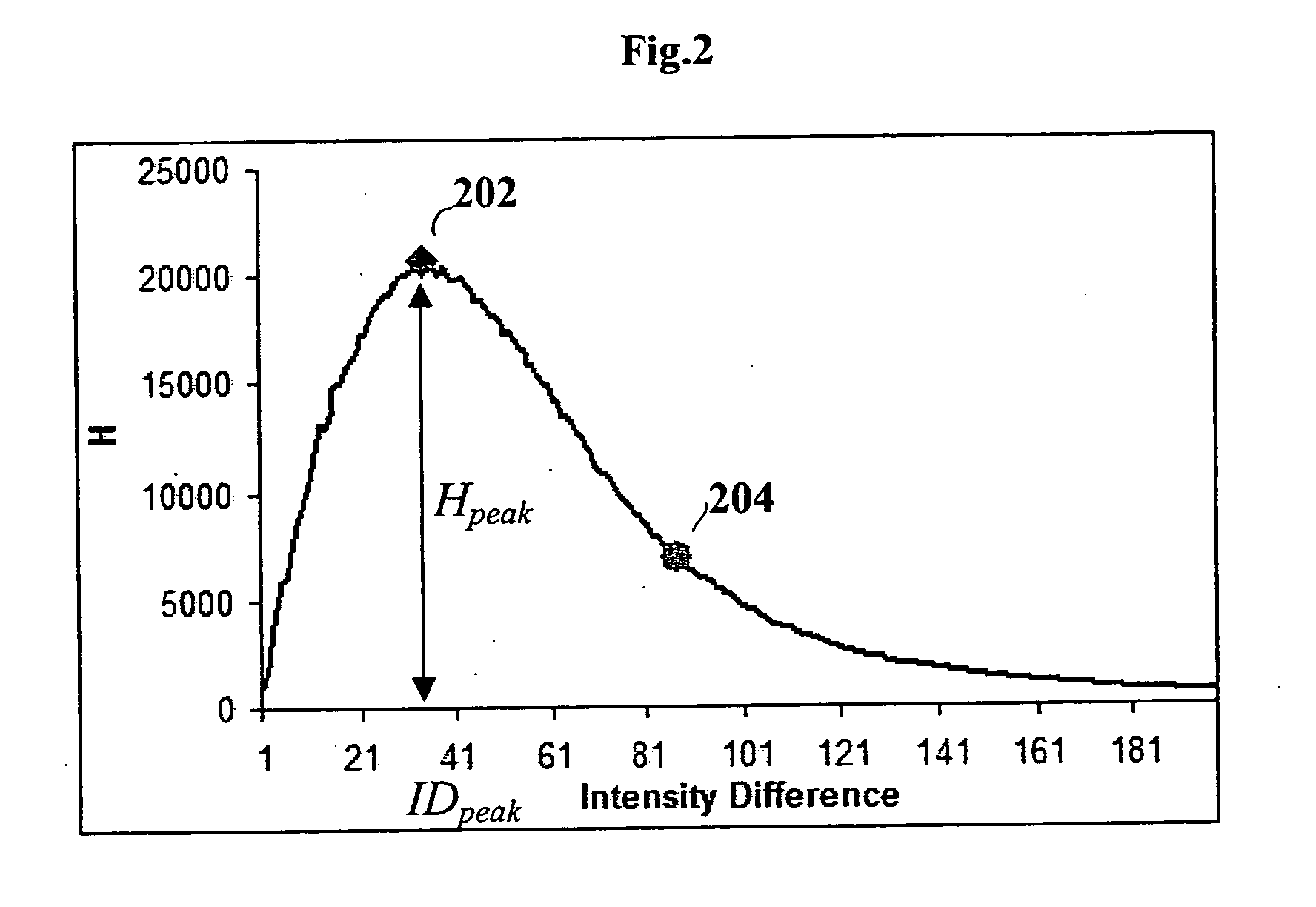
A method, system and computer-readable medium of filtering noise pixels and other extraneous data, including saturated fat tissue and air data in image data is provided. Examples of image data may include but are not limited to magnetic resonance imaging data and computed tomography data. The method includes receiving pixel count for each signal intensity value of the image data; determining a signal intensity value, Ipeak, corresponding to a pixel count of a greatest number of pixels, Npeak; setting a noise threshold at a signal intensity value, Inoise, corresponding to a pixel count, NI, such that NI, is determined based on Npeak; and filtering from the image data one or more pixels with signal intensity values below the noise threshold. NI, may be determined such that NI=Npeak / 3 or close to Npeak / 3.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
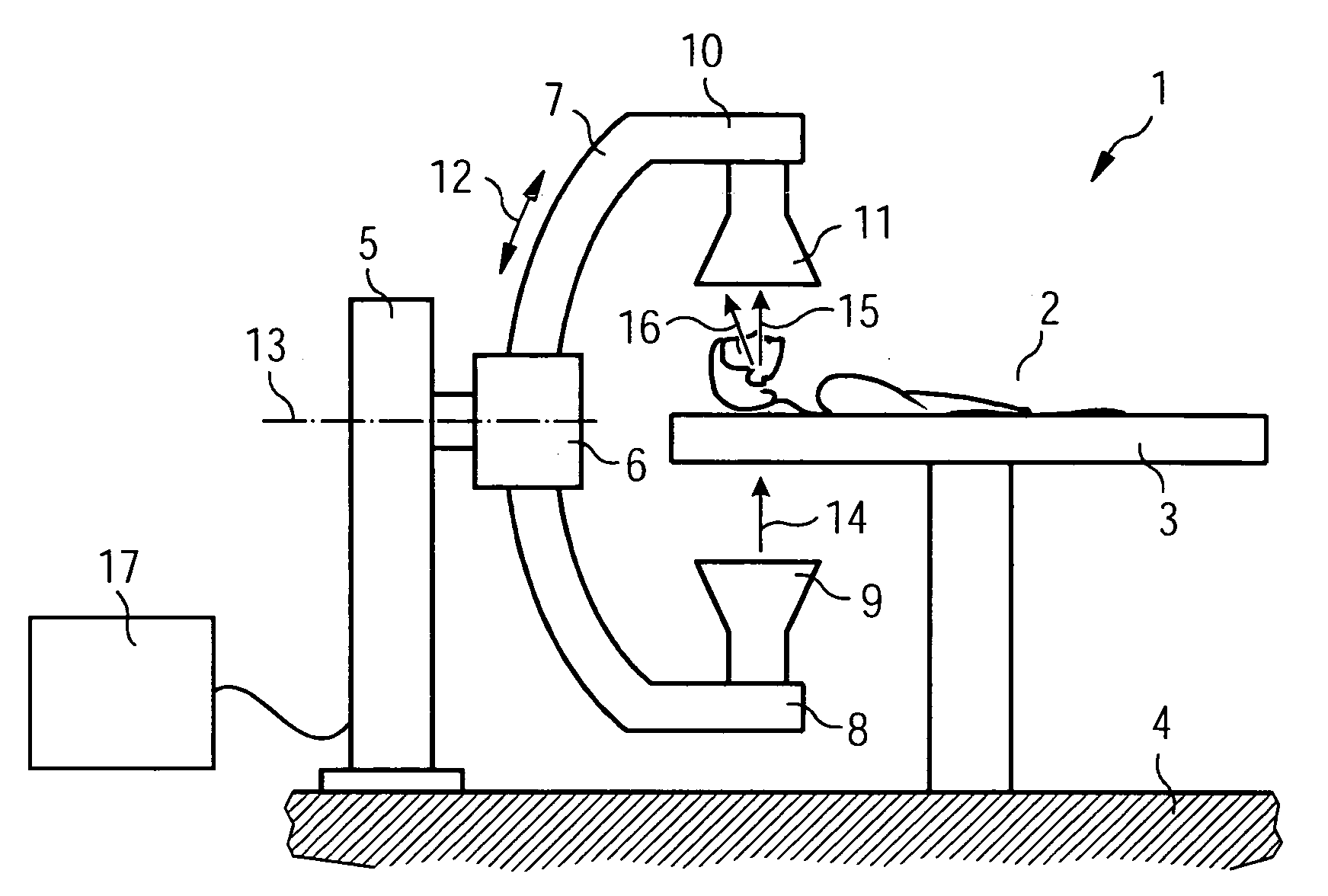
Radiotherapeutic device
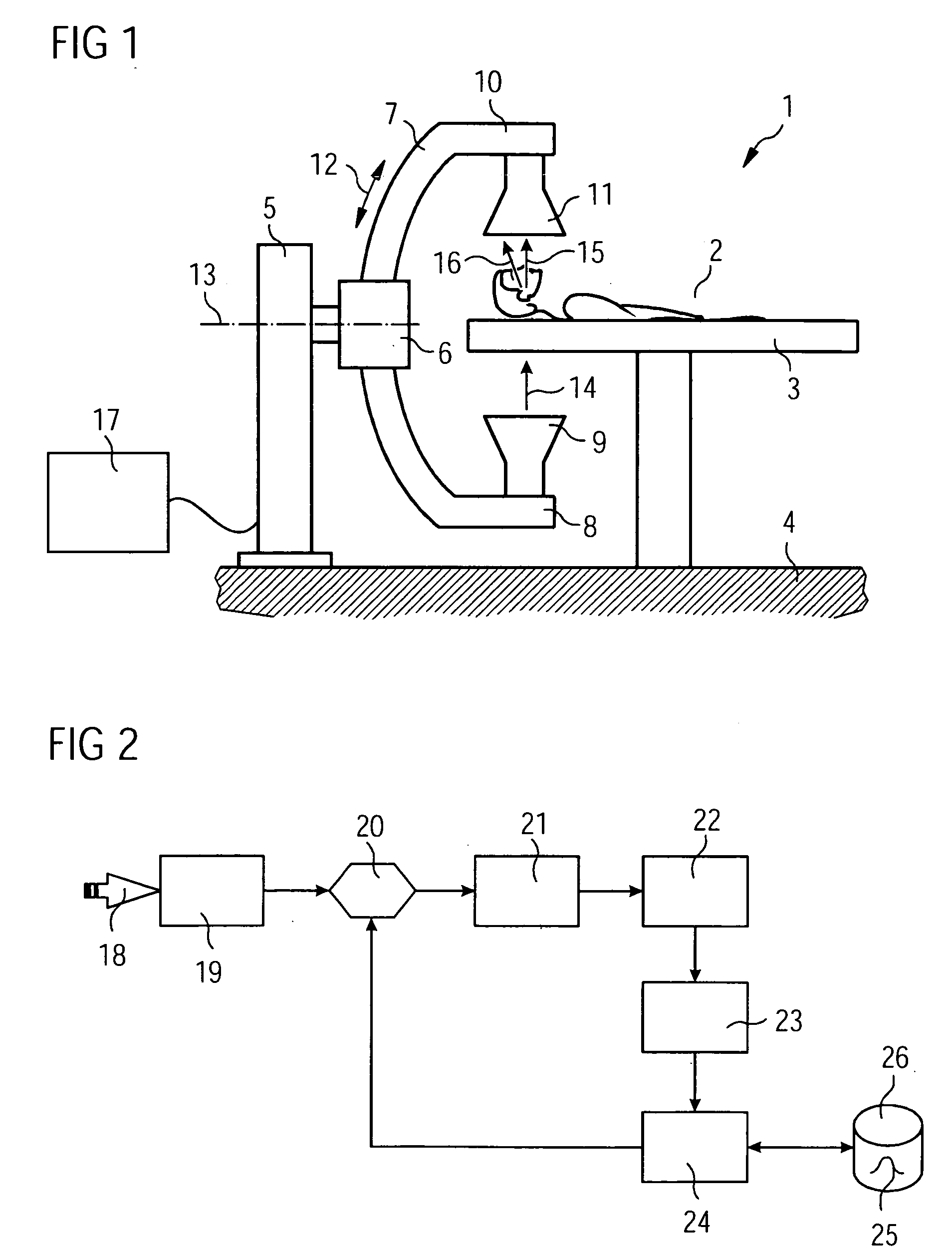
InactiveUS20070153969A1Improve securityEnsure proper implementationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTherapeutic DevicesRadiotherapy unit
A radiotherapeutic device has a radiotherapeutic irradiation unit with a radiation source for generation of radiotherapeutic radiation and a beam guidance and / or beam shaping device in order to direct the radiotherapeutic radiation in a defined manner onto a specific irradiation region. The radiotherapeutic device additionally has an imaging unit that includes a radionuclide emission tomography acquisition unit and a computed tomography scanner. The radiotherapeutic device also has a support device with a positioning device in order to position the support device in an image acquisition position in which a body region to be irradiated of a patient borne on or in the support device is located in an acquisition region of the image acquisition unit, or in order to position the support device in an irradiation position in which the body region to be irradiated of the patient is at least partially located in congruence with the irradiation region of the irradiation unit. The radiotherapeutic device additionally has a coordinate registration device that registers changes of all position coordinates of the support device given a movement of the support device between the image acquisition position and the irradiation position.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Radiation scanning units with reduced detector requirements
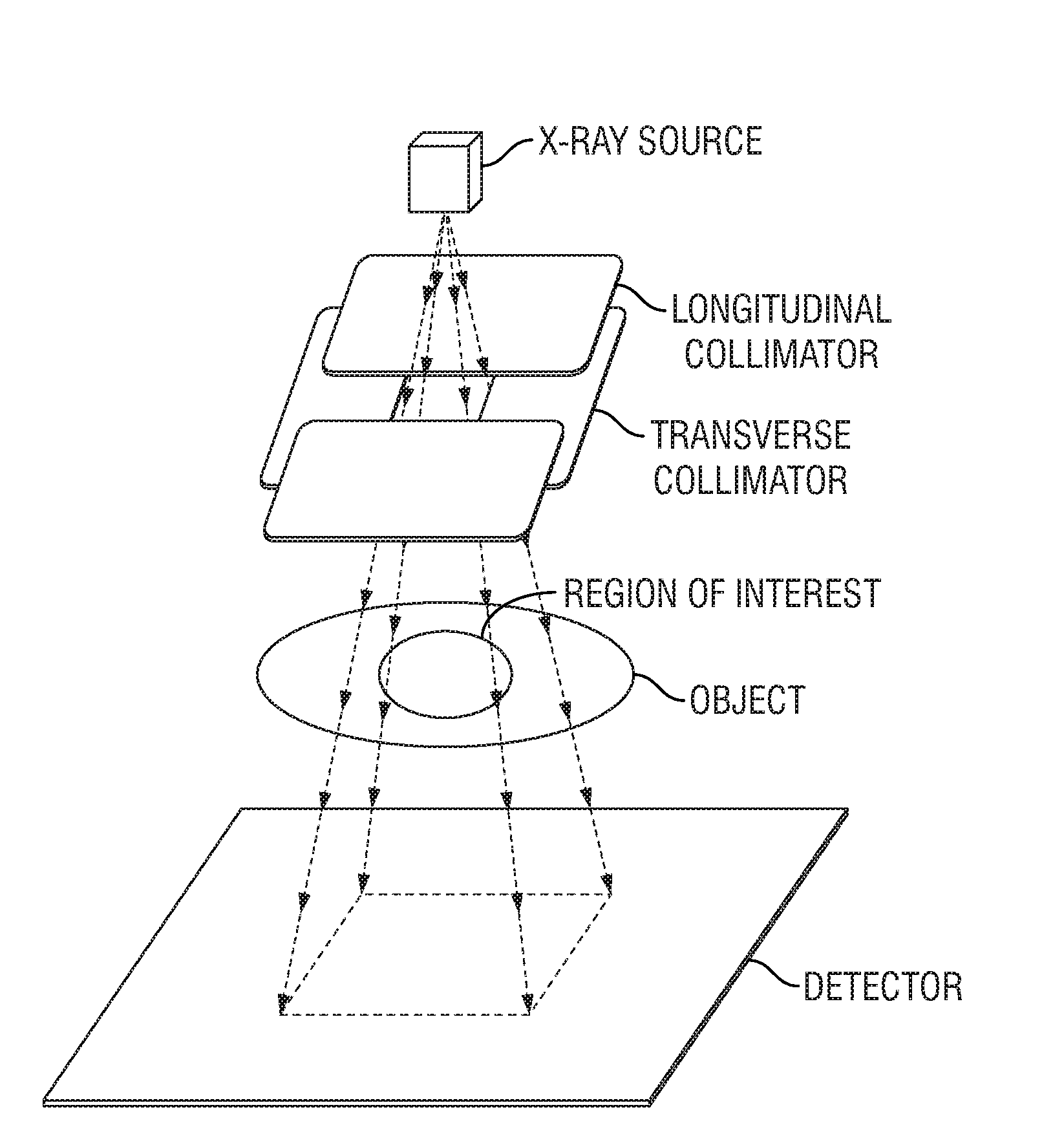
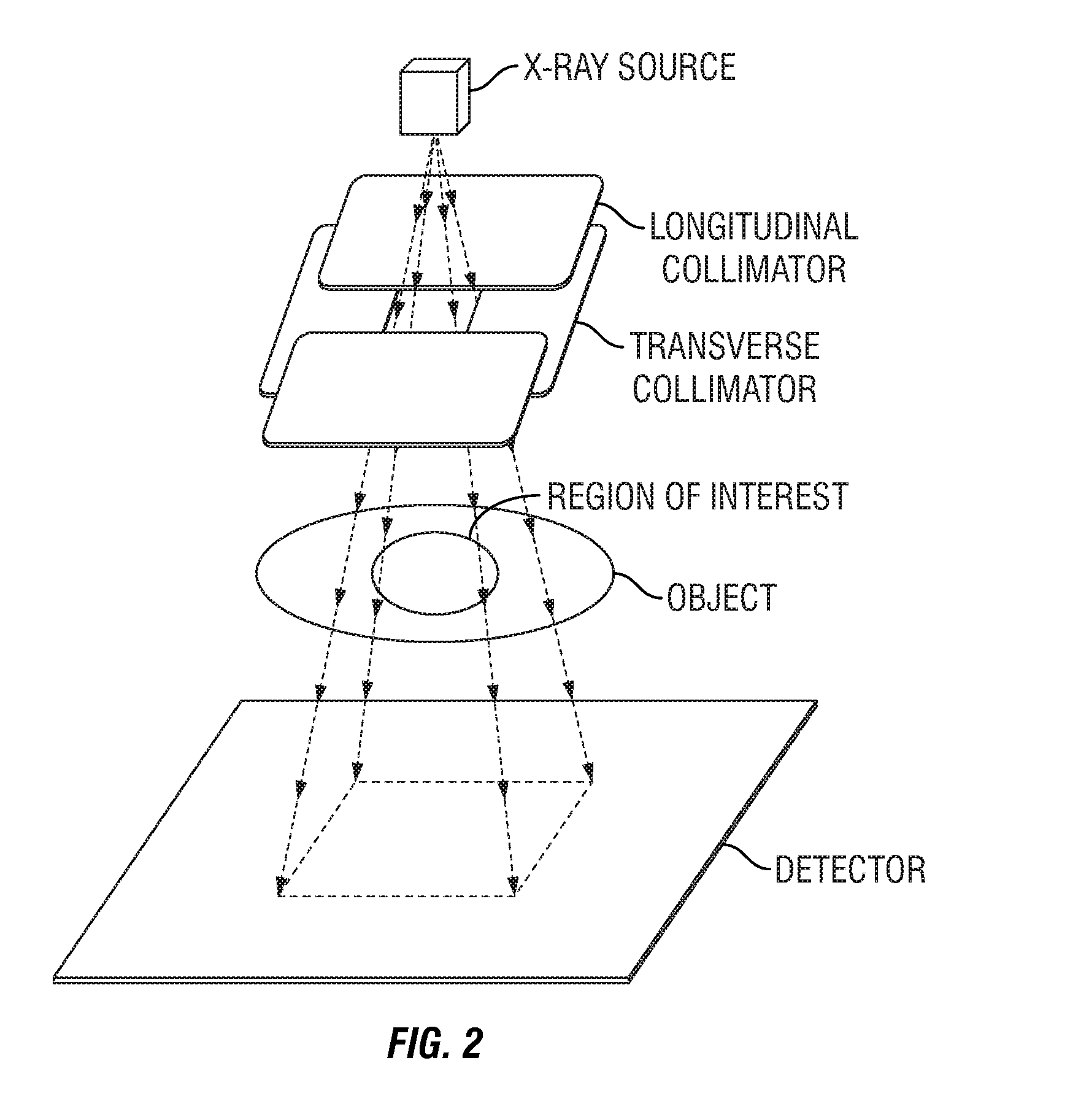
In one embodiment, a scanning unit for inspecting cargo conveyances uses a partial radiation beam and a detector of reduced length. In another embodiment, a scanning unit for inspecting objects comprises a detector with gaps along its expanse. In both cases, the cost of the scanning system may be reduced. The object, the source, and or the detector may be moved to enable generation of computed tomographic images. Methods are disclosed, as well.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
Acquisition and reconstruction of projection data using a stationary CT geometry
ActiveUS7616731B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingDistributed sourceX-ray
Systems and methods are provided for acquiring and reconstructing projection data that is mathematically complete or sufficient using a computed tomography (CT) system having stationary distributed X-ray sources and detector arrays. In one embodiment, a non-sequential activation is employed to acquire mathematically complete or sufficient projection data. In another embodiment, a distributed source is provided as a generally semicircular segment. In such an embodiment, an alternating activation scheme may be employed to allow one or more helices of image data to be acquired.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
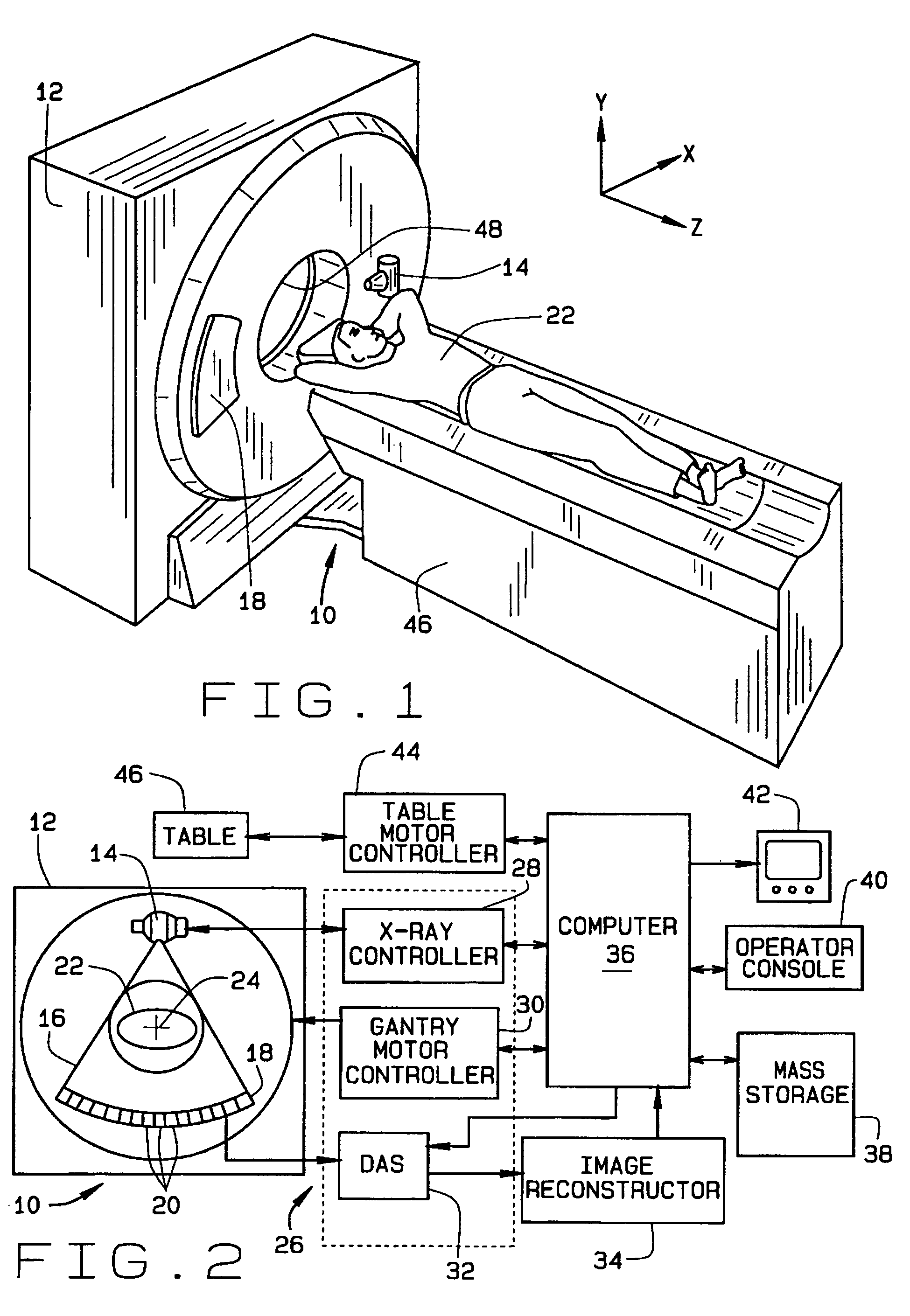
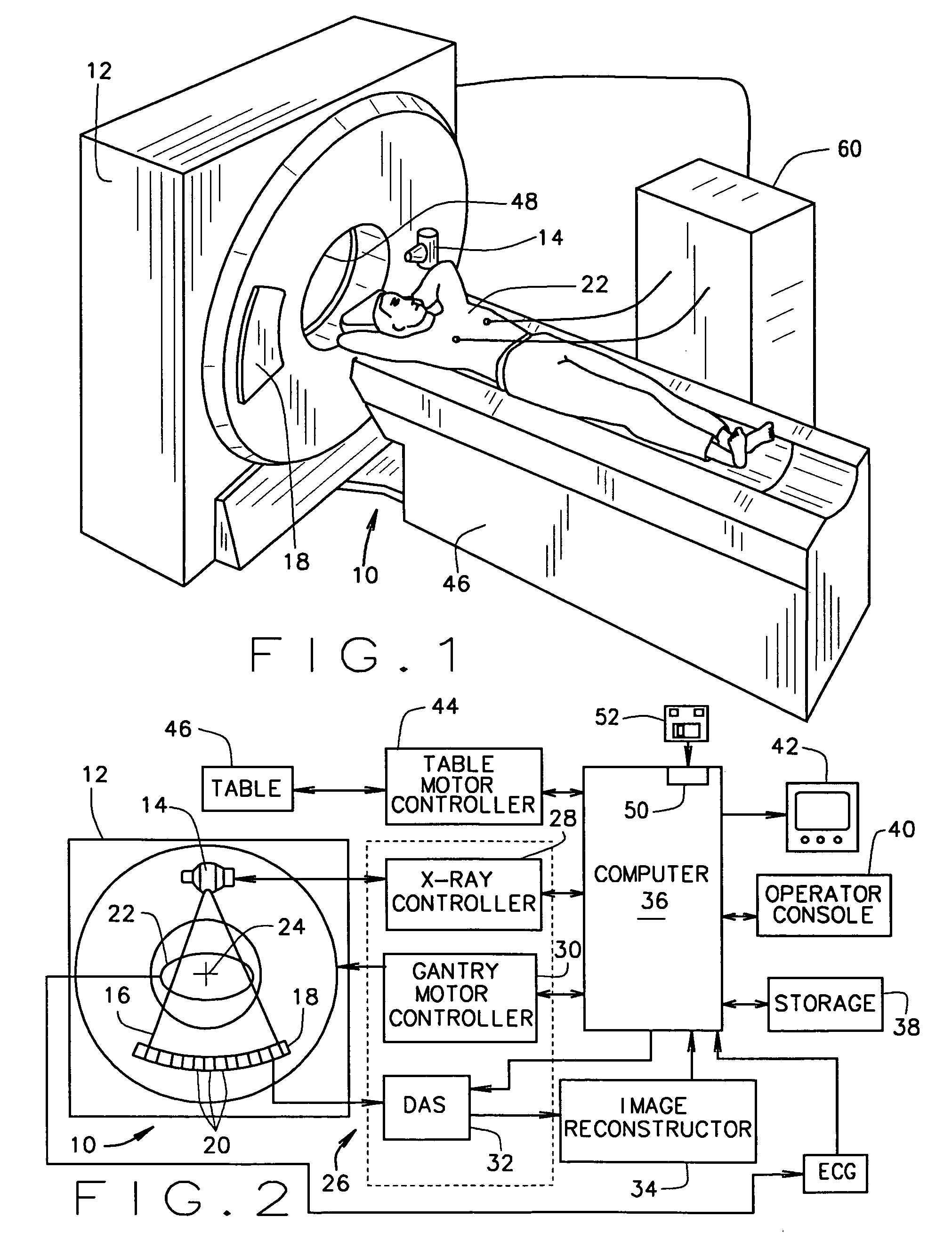
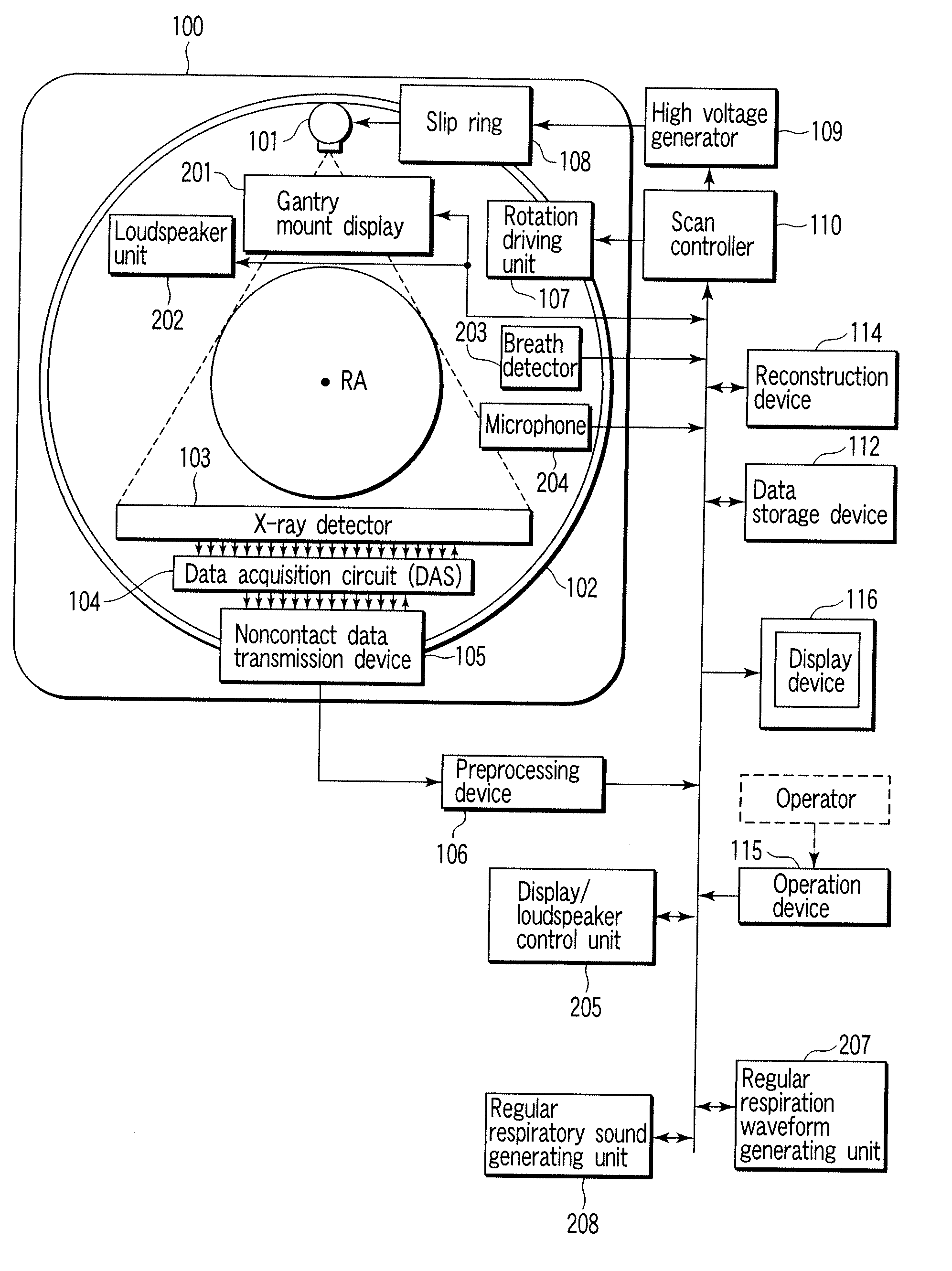
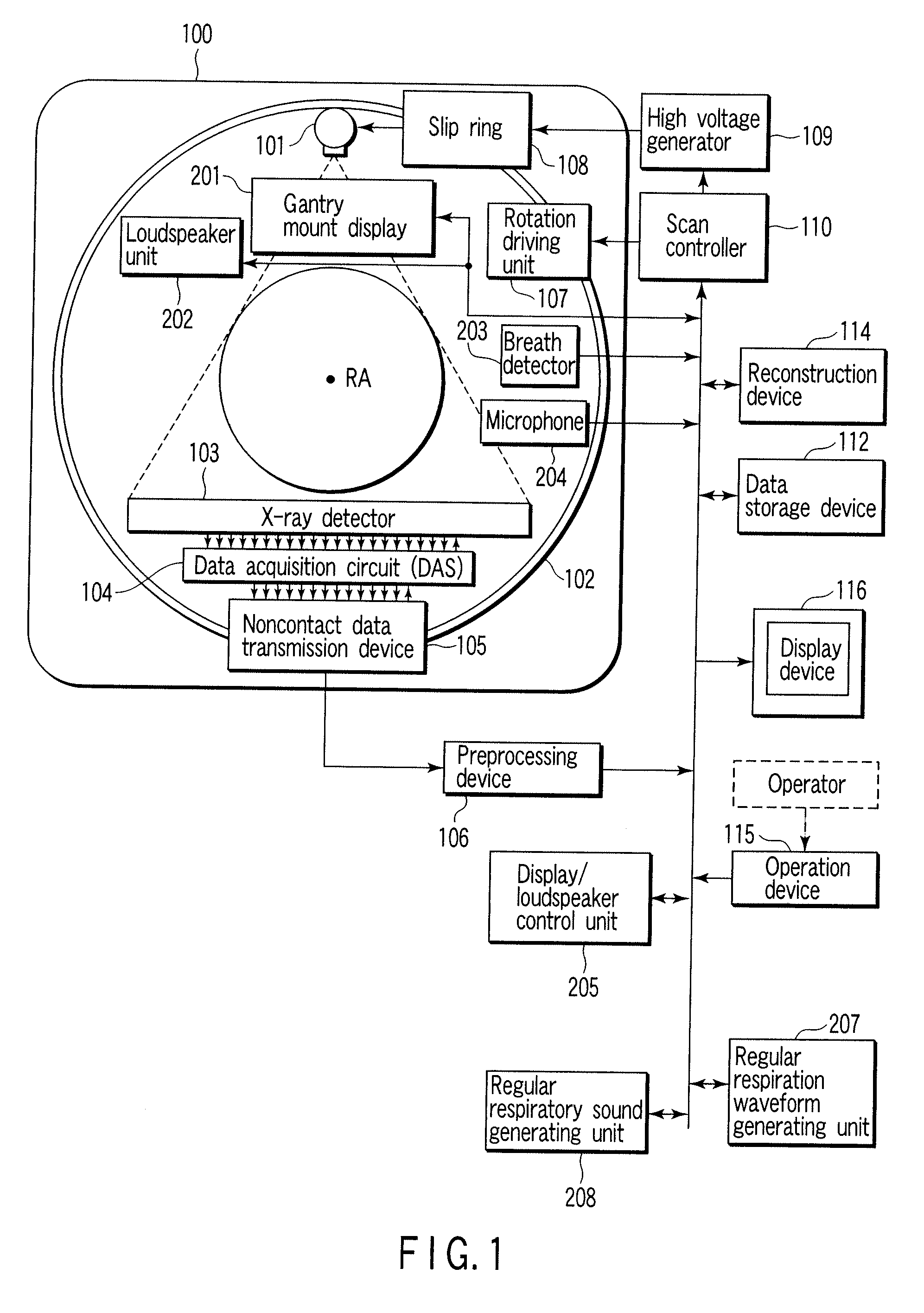
X-ray computerized tomography apparatus, breathing indication apparatus and medical imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20080089463A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic measurementsTemporal changeX-ray
An X-ray computed tomographic apparatus includes a gantry 100 including an X-ray tube 101 which generates X-rays and an X-ray detector 103 which detects X-rays transmitted through a subject to be examined, a reconstruction device 114 which generates tomogram data on the basis of an output from the X-ray detector, a breath detector 203 which detects a respiration waveform representing a temporal change in respiration index value associated with the subject, a regular respiration waveform generating unit 207 which generates a respiration waveform with a regular respiration cycle which originates from the detected respiration waveform, and a gantry mount display 201 which displays the generated regular respiration waveform.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com