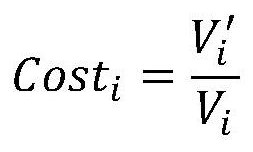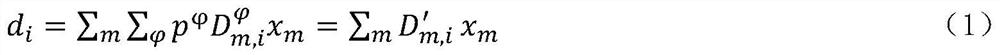Patents
Literature
42 results about "Dose optimization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dose optimization usually means in creasing the amount of a medication so that you only have to take it once a day, ins tead of taking a lower dose two times each day. The goal of dose optimization in these cases is to help make sure you take a single dosage at the higher strength as soon as your doctor thinks it’s appropriate.
Method for Consistent and Verifiable Optimization of Computed Tomography (CT) Radiation Dose
InactiveUS20140270053A1Minimal disruptionGreat noise leverMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingClinical settingsMathematical model
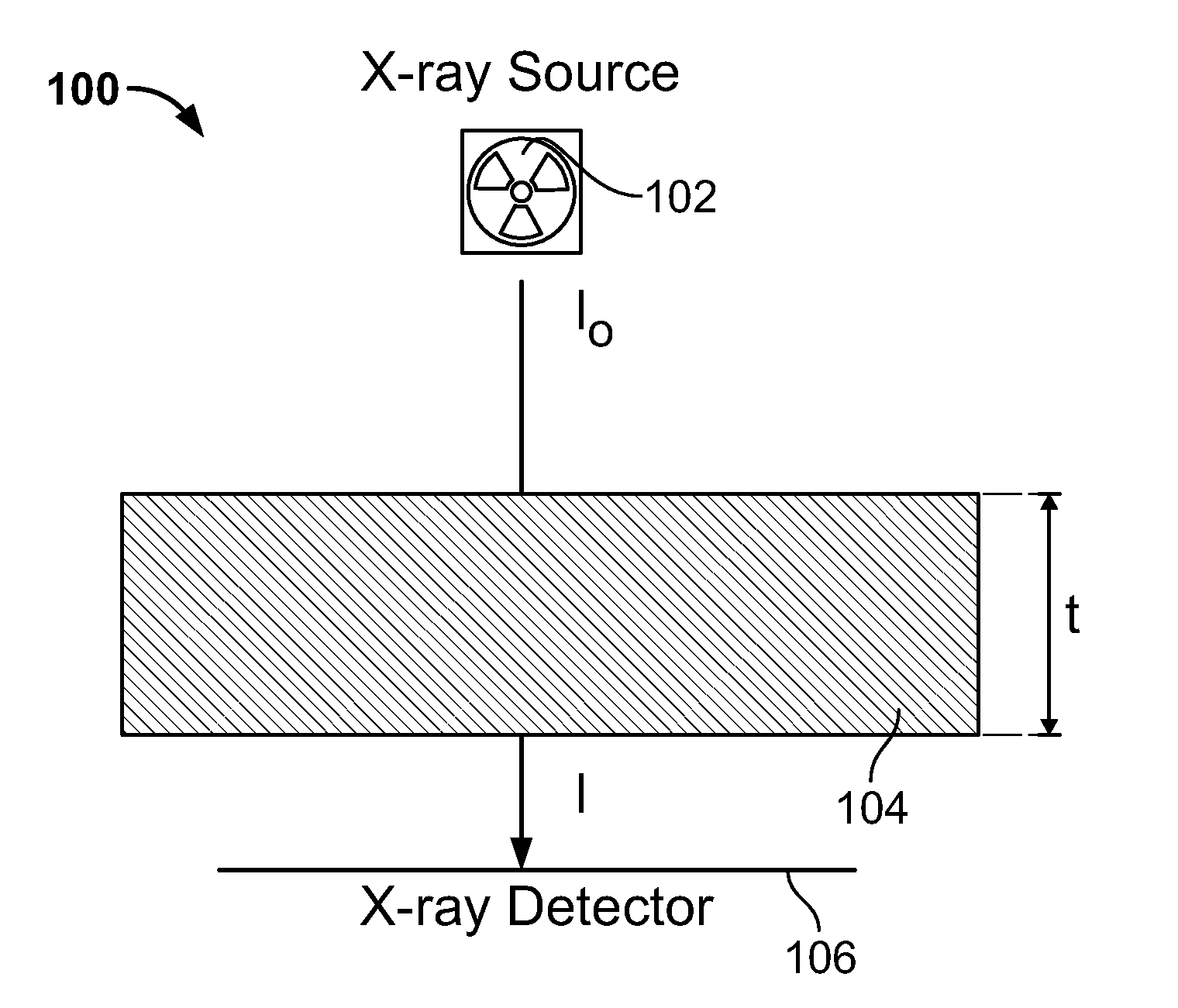
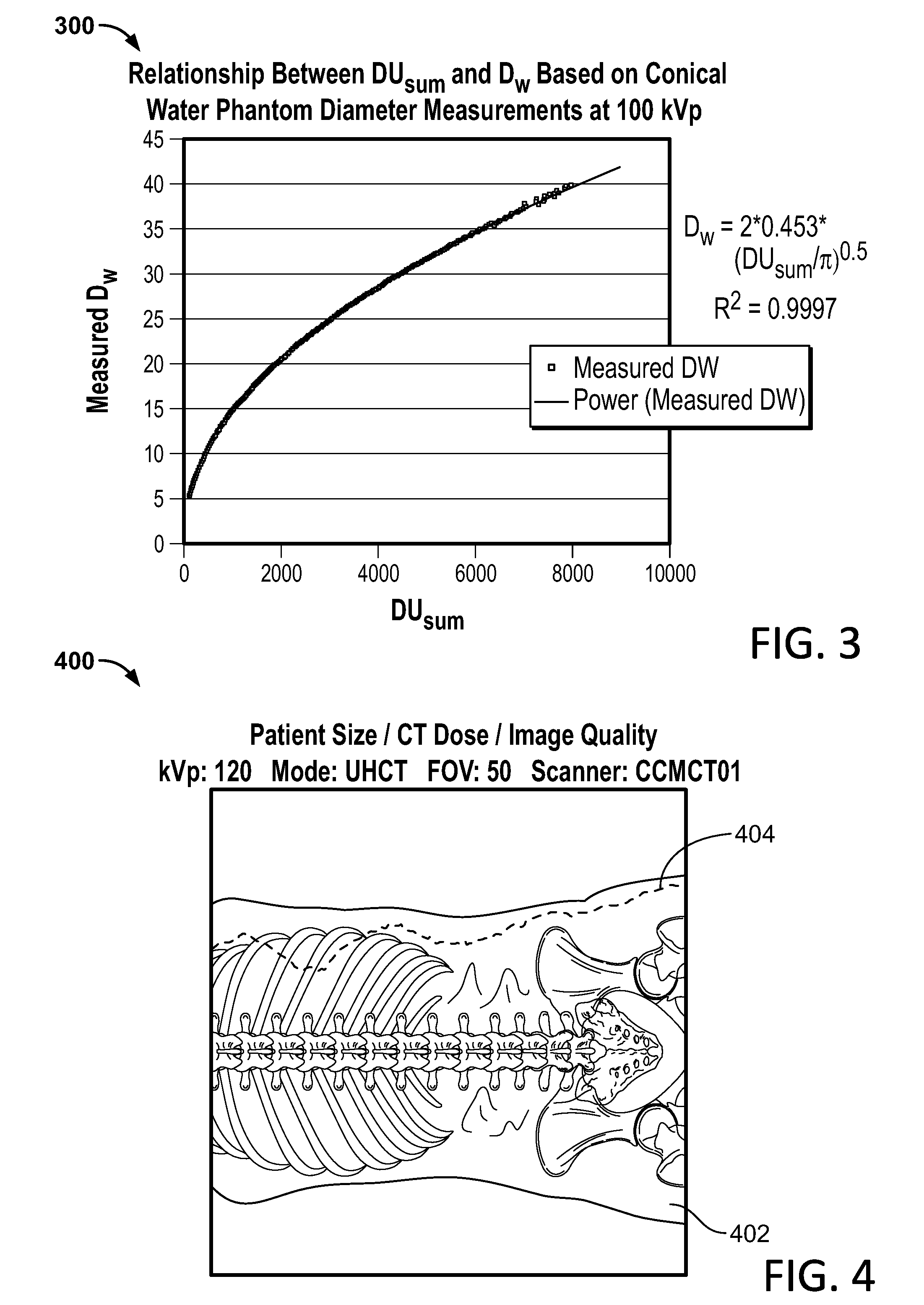
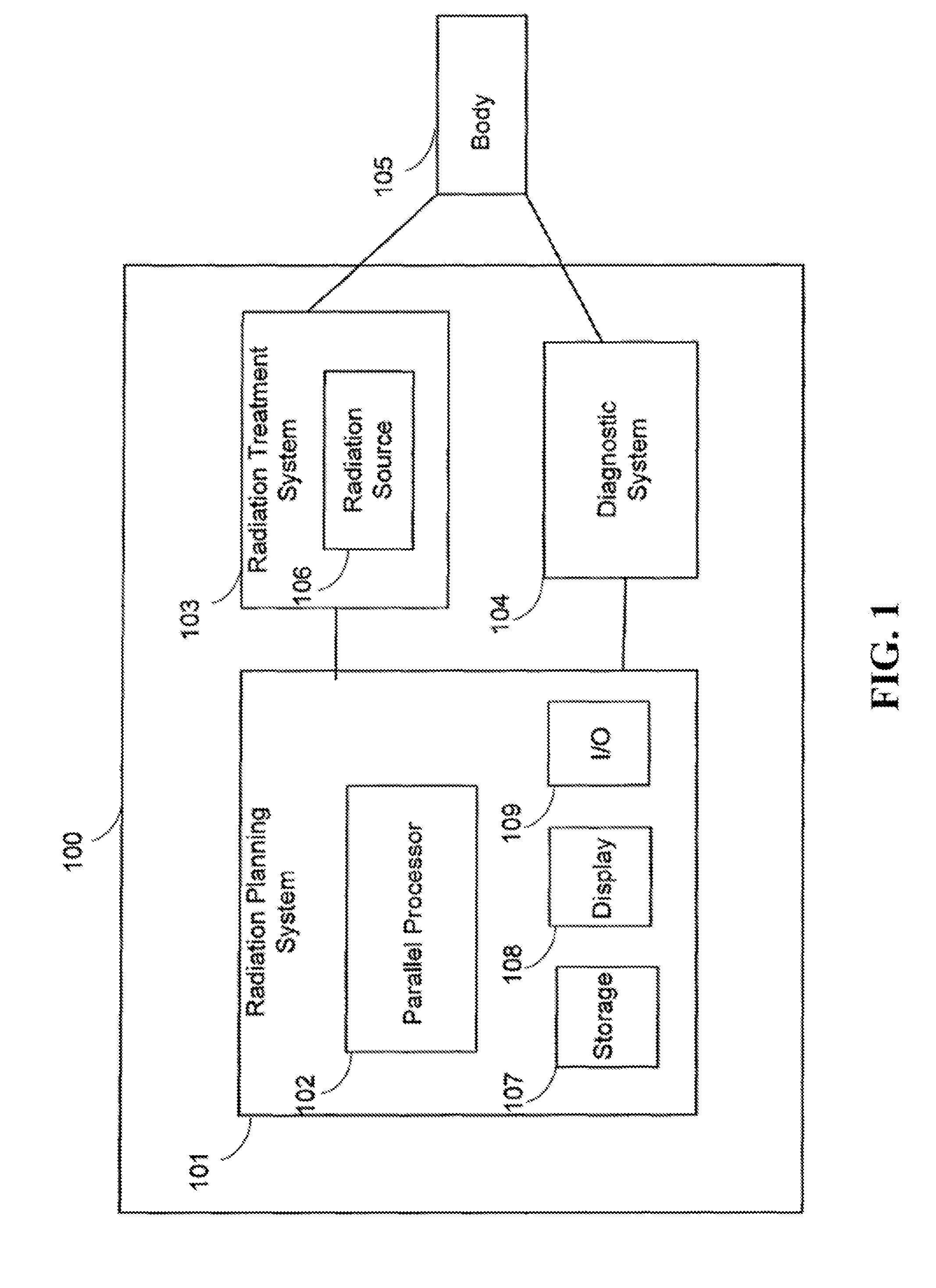
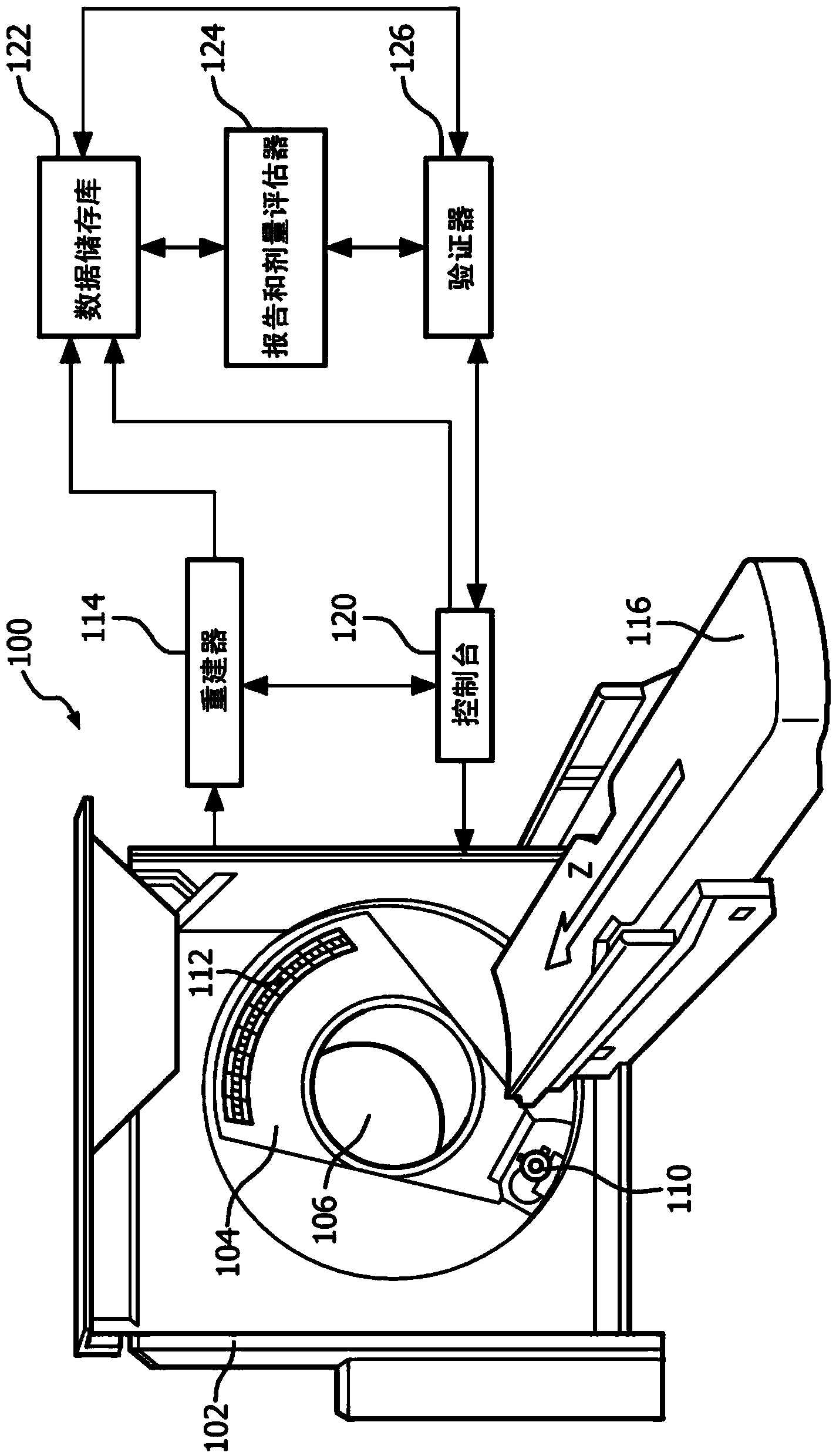
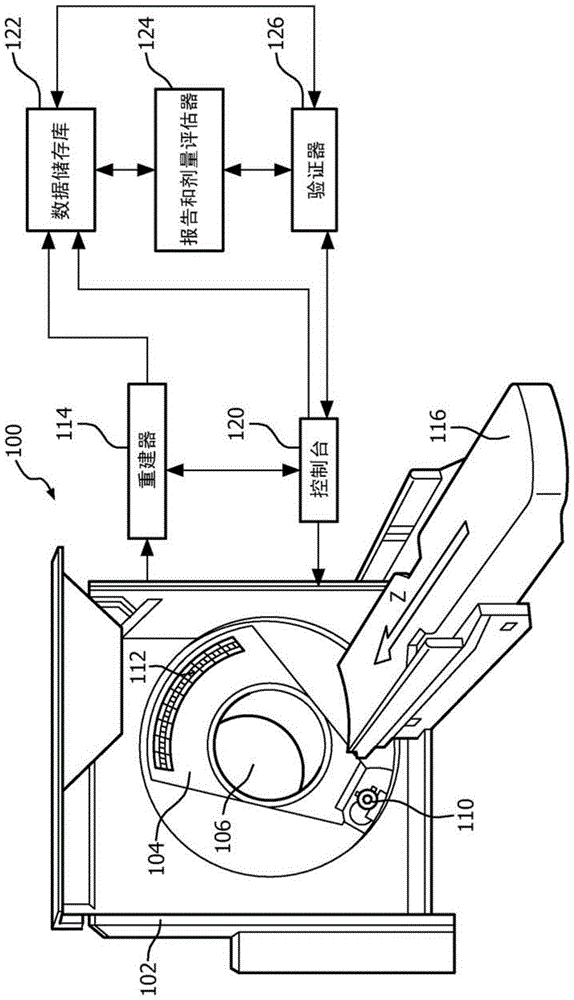
A system and a method is disclosed for consistently and verifiably optimizing computed tomography (CT) radiation dose in the clinical setting. Mathematical models allow for estimation of patient size, image noise, size-specific radiation dose, and image quality targets based on digital image data and radiologists preferences. A prediction model estimates the scanner's tube current modulation and predicts image noise and size-specific radiation dose over a range of patient sizes. An optimization model calculates specific scanner settings needed to attain target image quality at the minimum radiation dose possible. An automated system processes the image and dose data according to the mathematical models and stores and displays the information, enabling verification and ongoing monitoring of consistent dose optimization.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
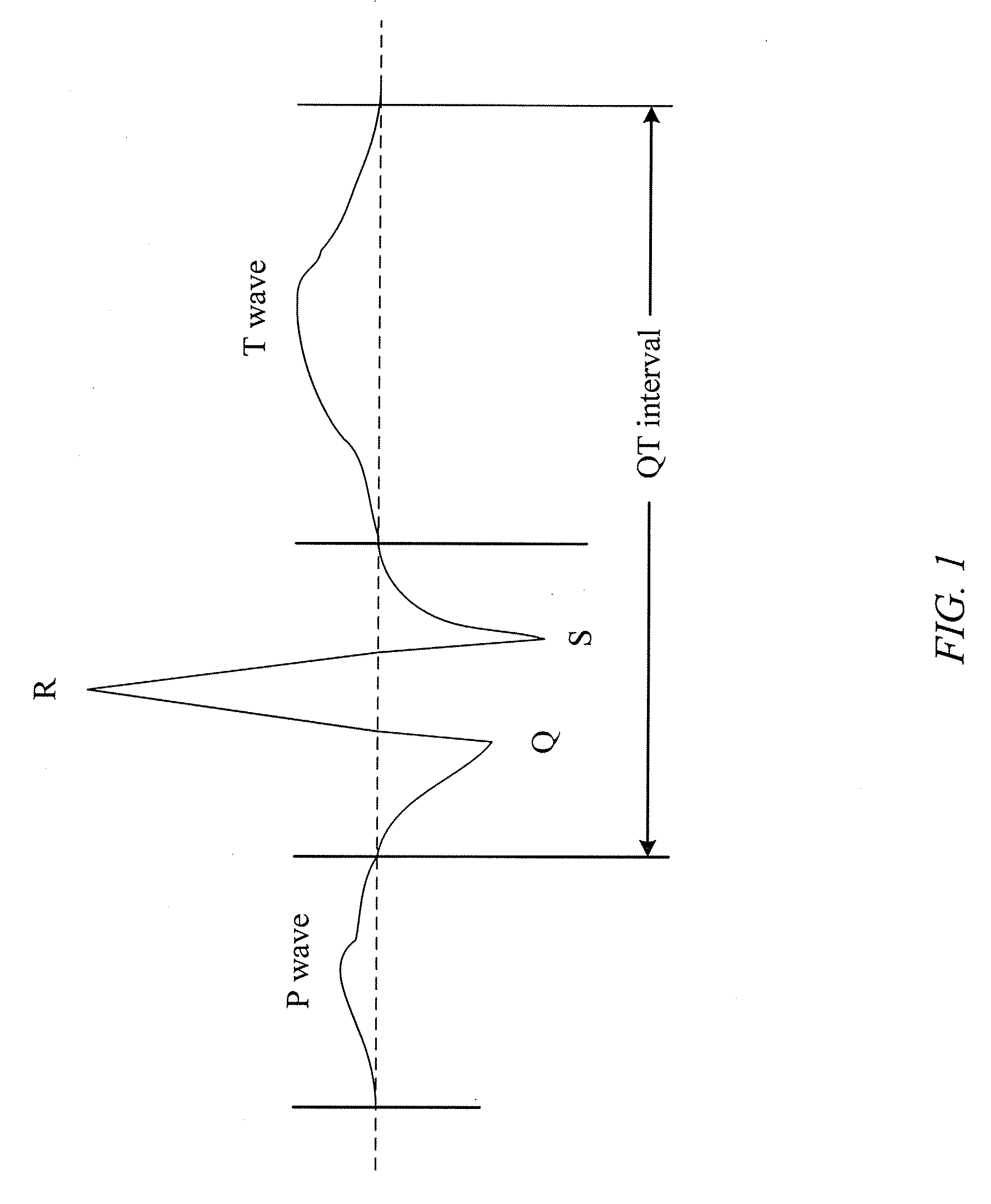
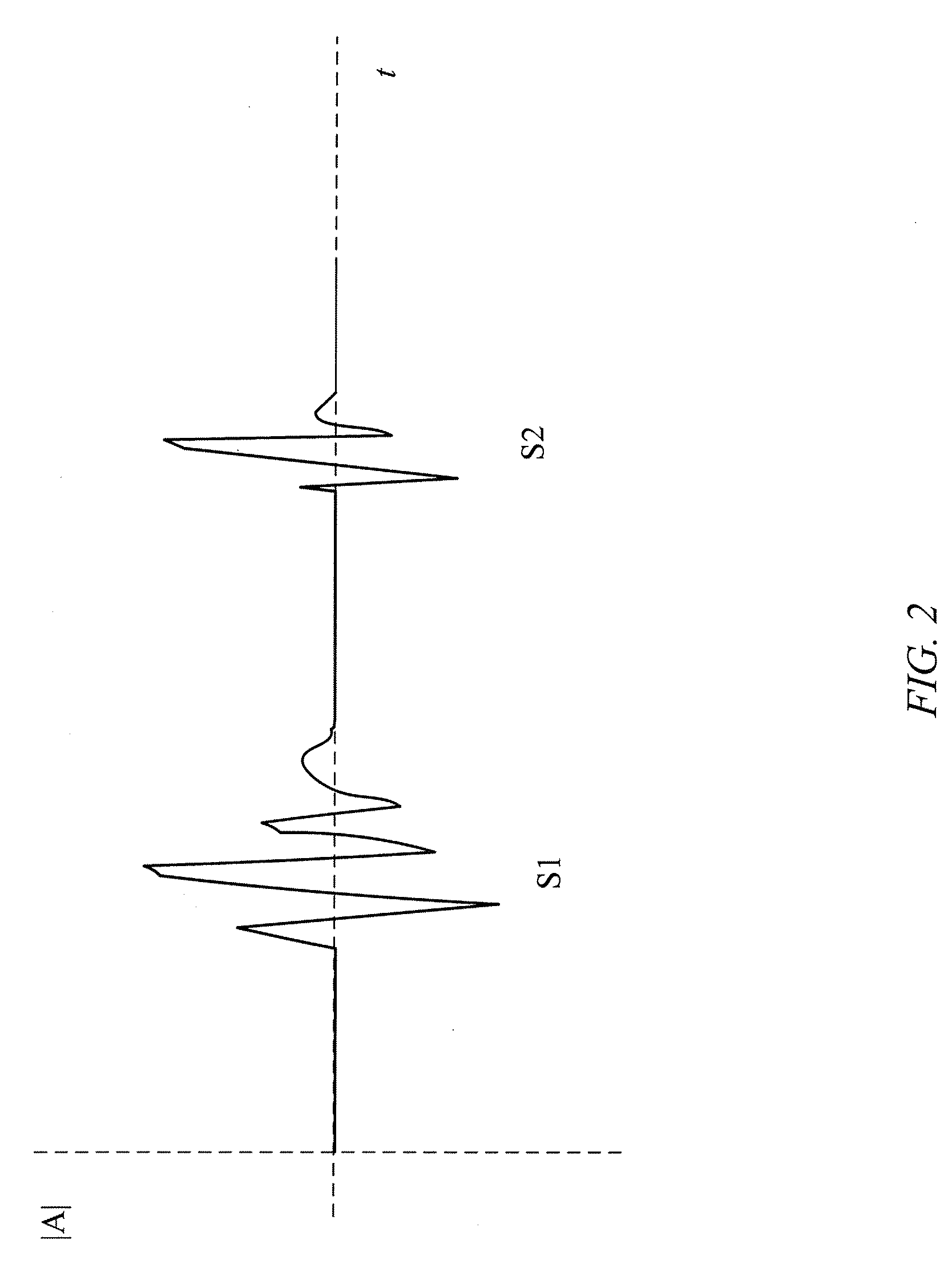
System and method for diagnosing and treating long qt syndrome
InactiveUS20080255464A1Easy to identifySimple methodElectrocardiographyAuscultation instrumentsSystoleCardiac cycle
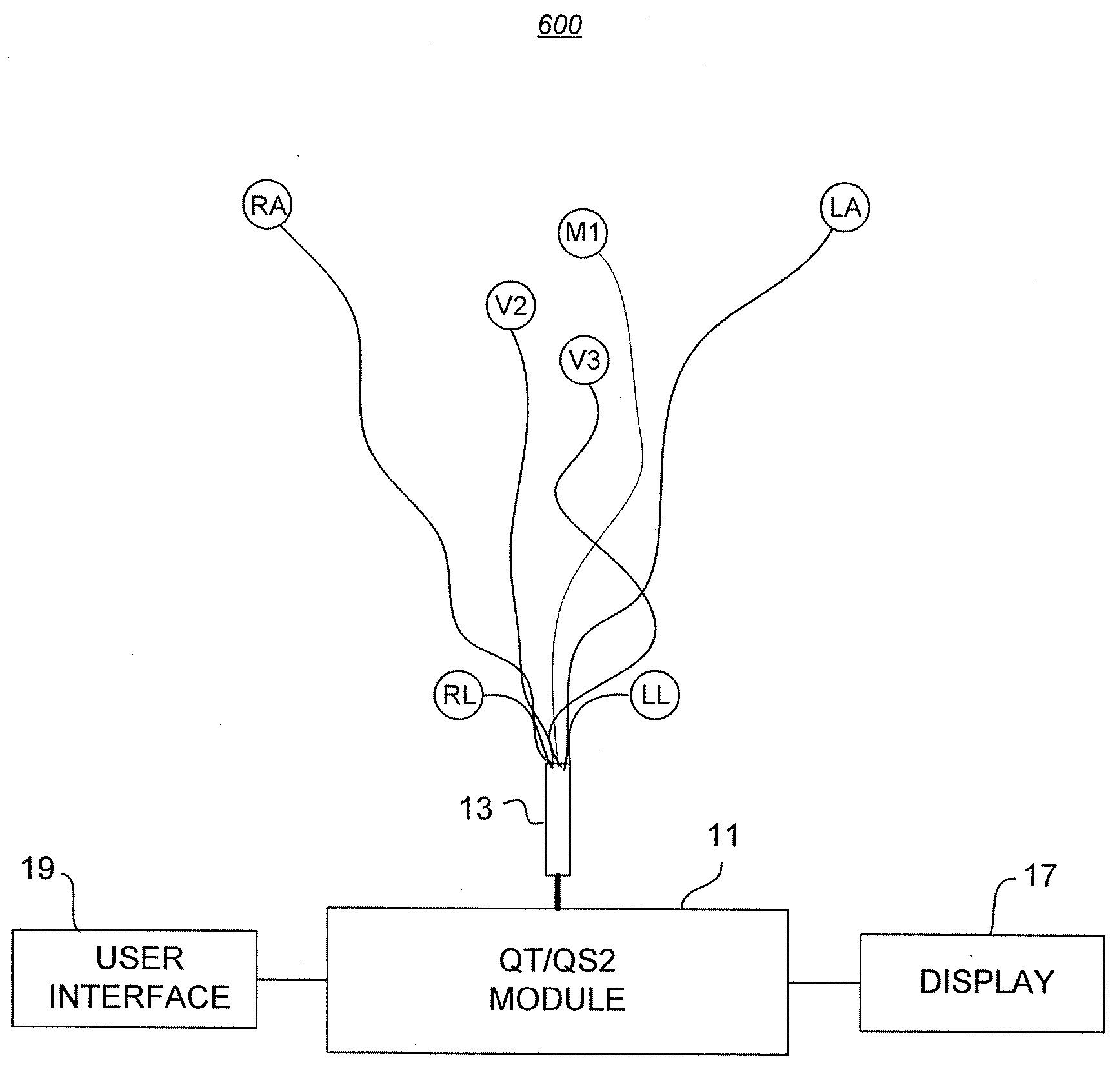
A system for diagnosing Long QT Syndrome (LQTS) derives a QT / QS2 ratio from an electrical systole (QT) and a mechanical systole (QS2) to detect a prolonged QT interval in a patient's cardiac cycle. A processor acquires the systoles from a microphone and chest electrodes, calculates the QT / QS2 ratio, and outputs the result to a display. The processor may compare the QT / QS2 ratio to a threshold value stored in memory for diagnosing LQTS in the patient. A user interface provides for programming, set-up, and customizing the display. A mode selector allows the system to operate alternatively as a phonocardiograph, a 12 lead electrocardiograph, or a machine for diagnosing LQTS. A related method for diagnosing cardiac disorders such as LQTS includes measuring QT and QS2 during a same cardiac cycle, calculating a QT / QS2 ratio, and comparing the result to a threshold value derived from empirical data. The method may include measuring systoles both at rest and during exercise, and may be used for drug efficacy, dosage optimization, and acquired LQTS causality tests.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL ASSET MANAGEMENT
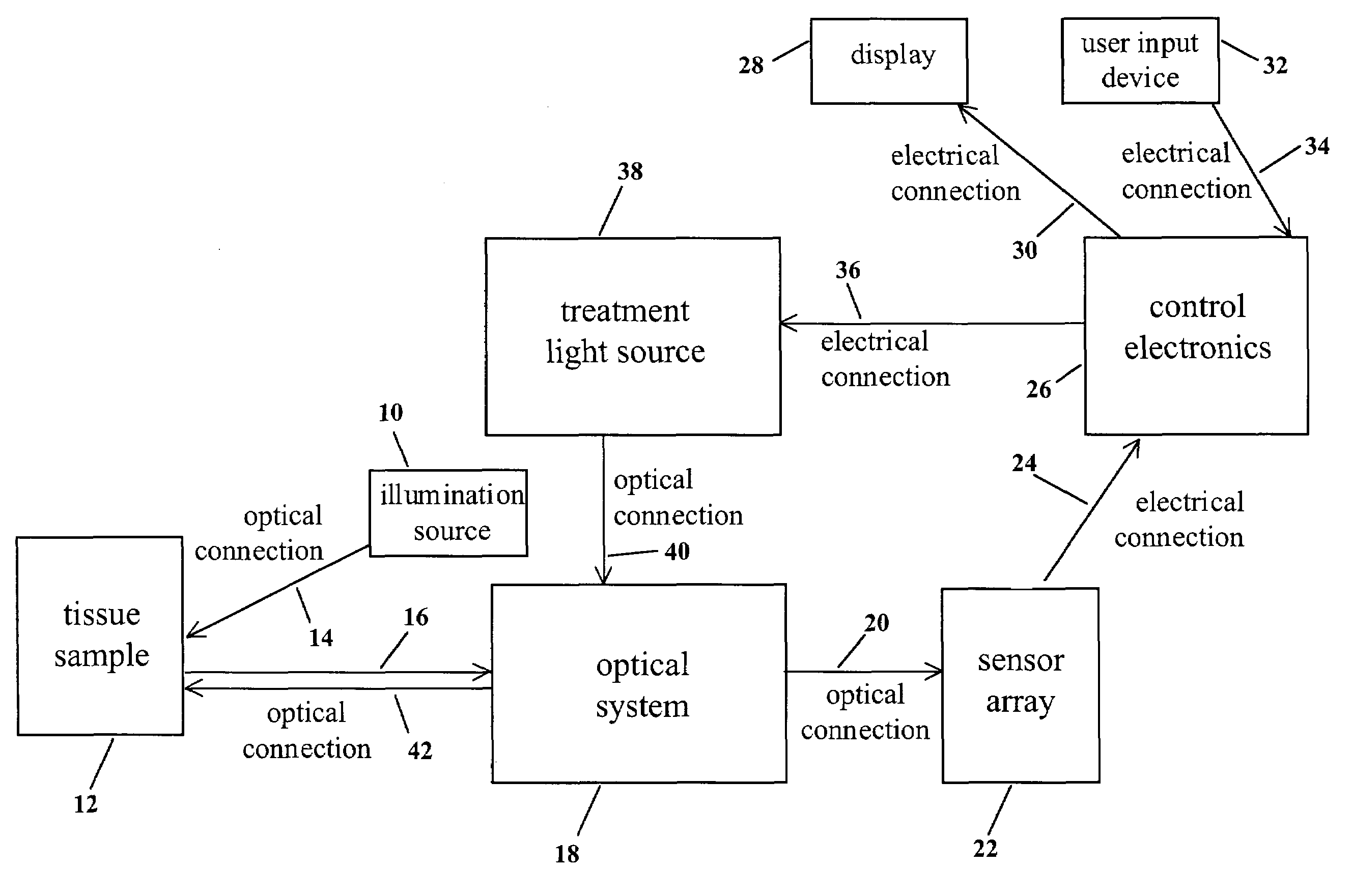
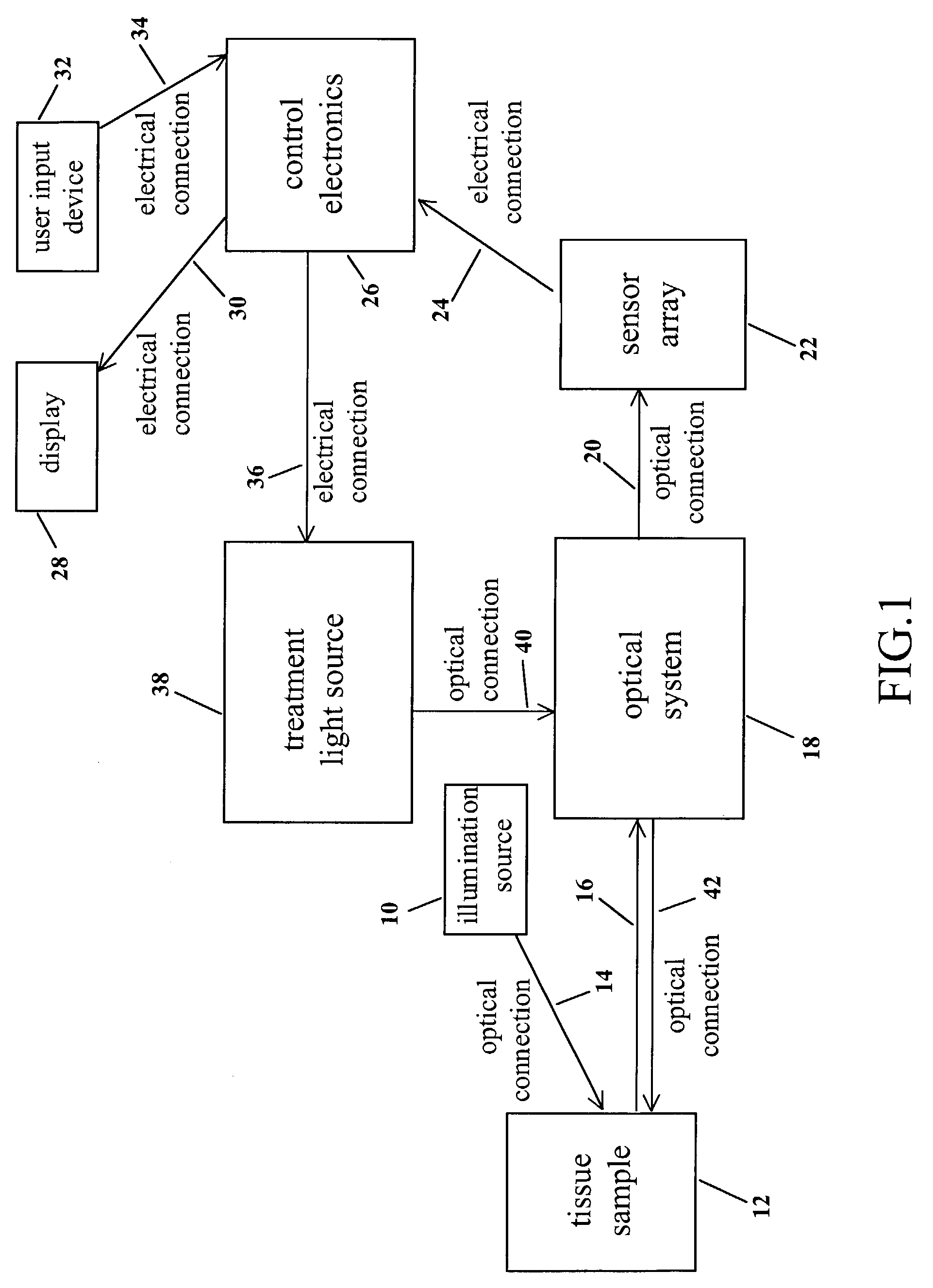
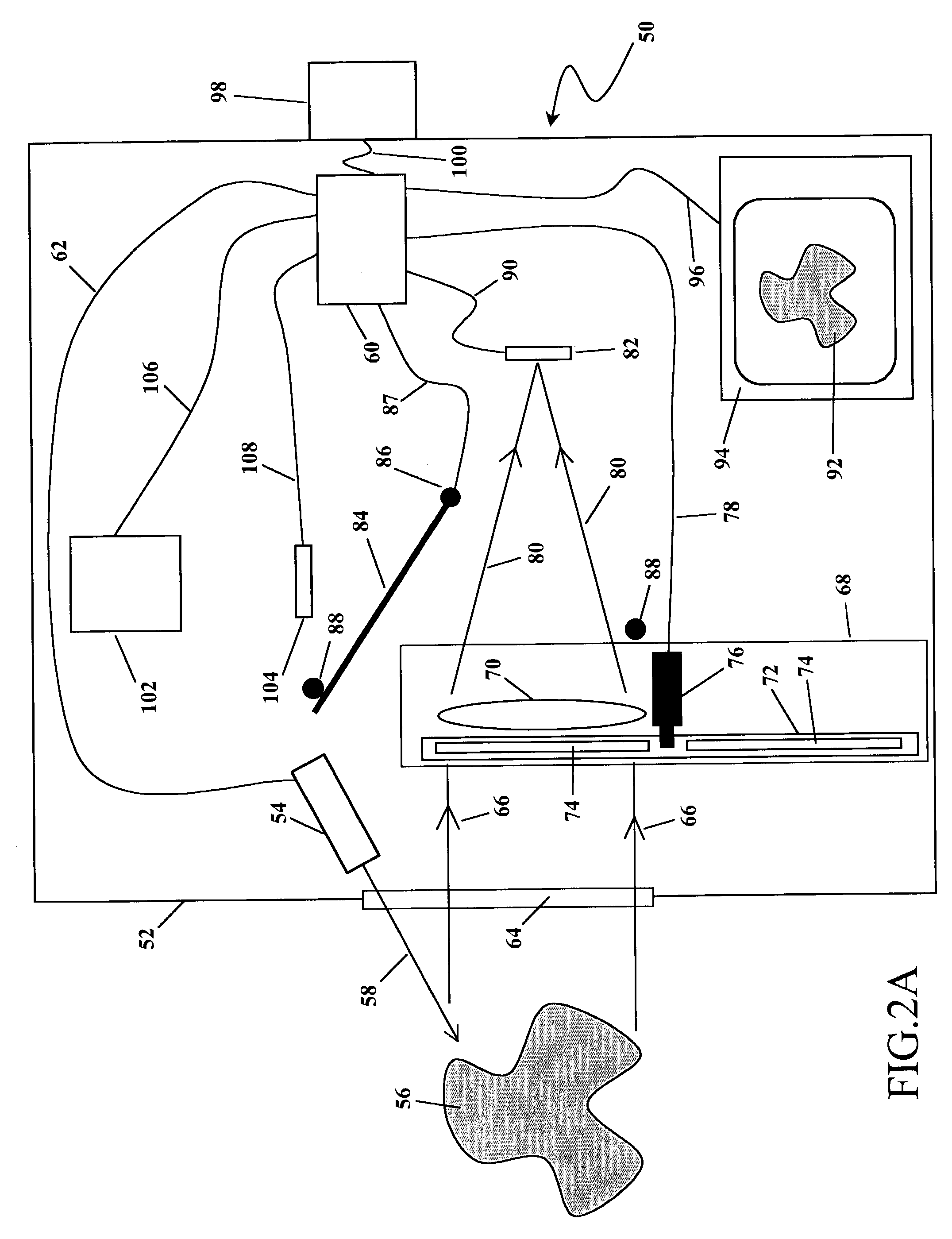
Cancer detection and adaptive dose optimization treatment system
The present invention utilizes a series of optical and electronic elements to detect and image cancerous and / or pre-cancerous cells in living tissue. The invention further uses the images thus obtained to adaptively and dynamically shape a treatment light beam so as to maximize the beam's intensity in proportion to the areas with the most cancer or pre-cancer and to minimize the irradiation of normal tissue by the beam.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
Dosage optimization method and system
ActiveCN105031819AQuickly transform into each otherFast mutual conversionRadiation therapyDose optimizationAnesthesia
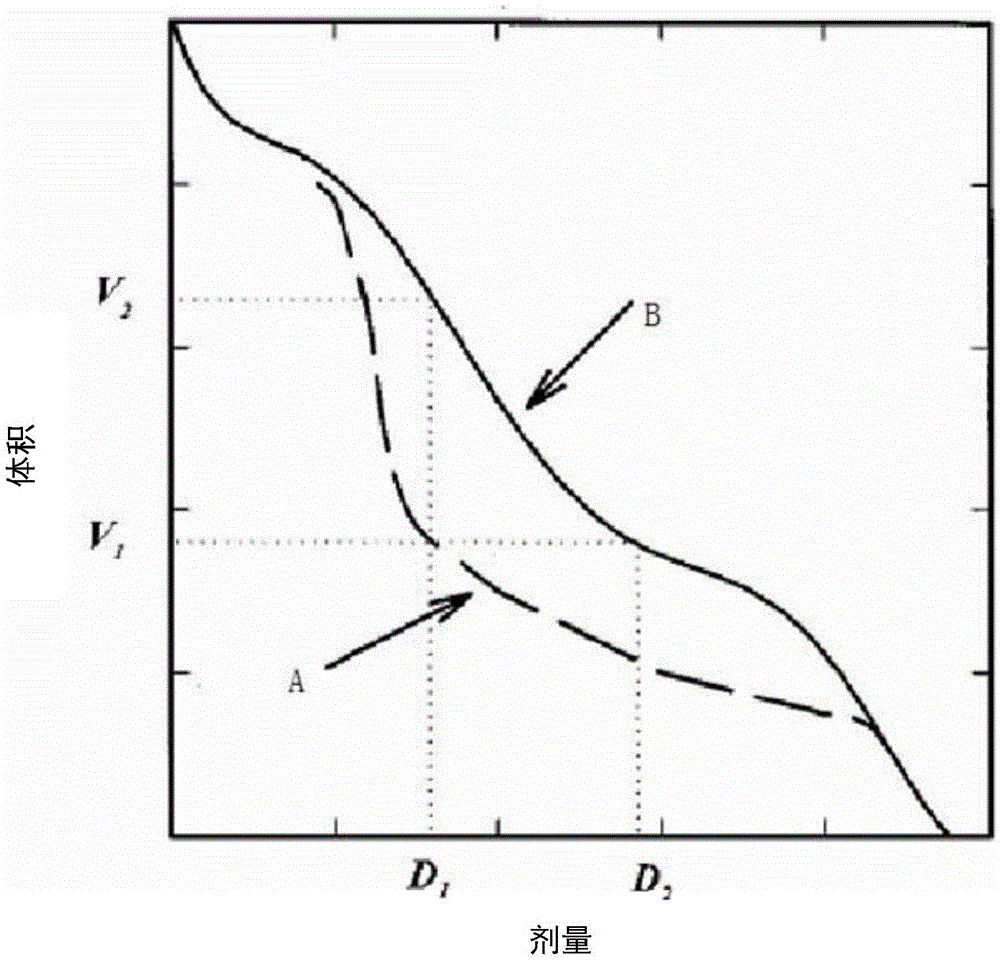
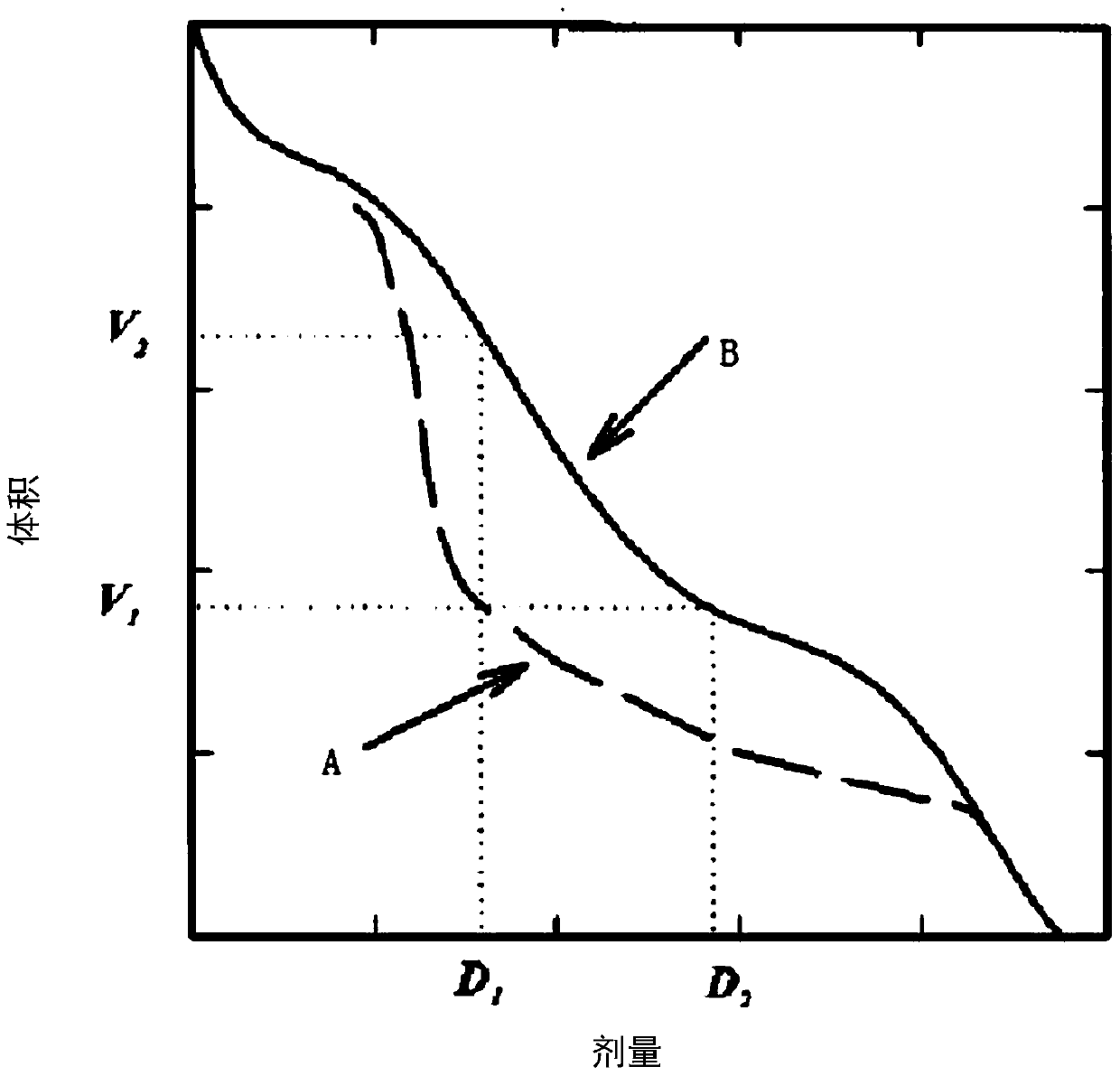
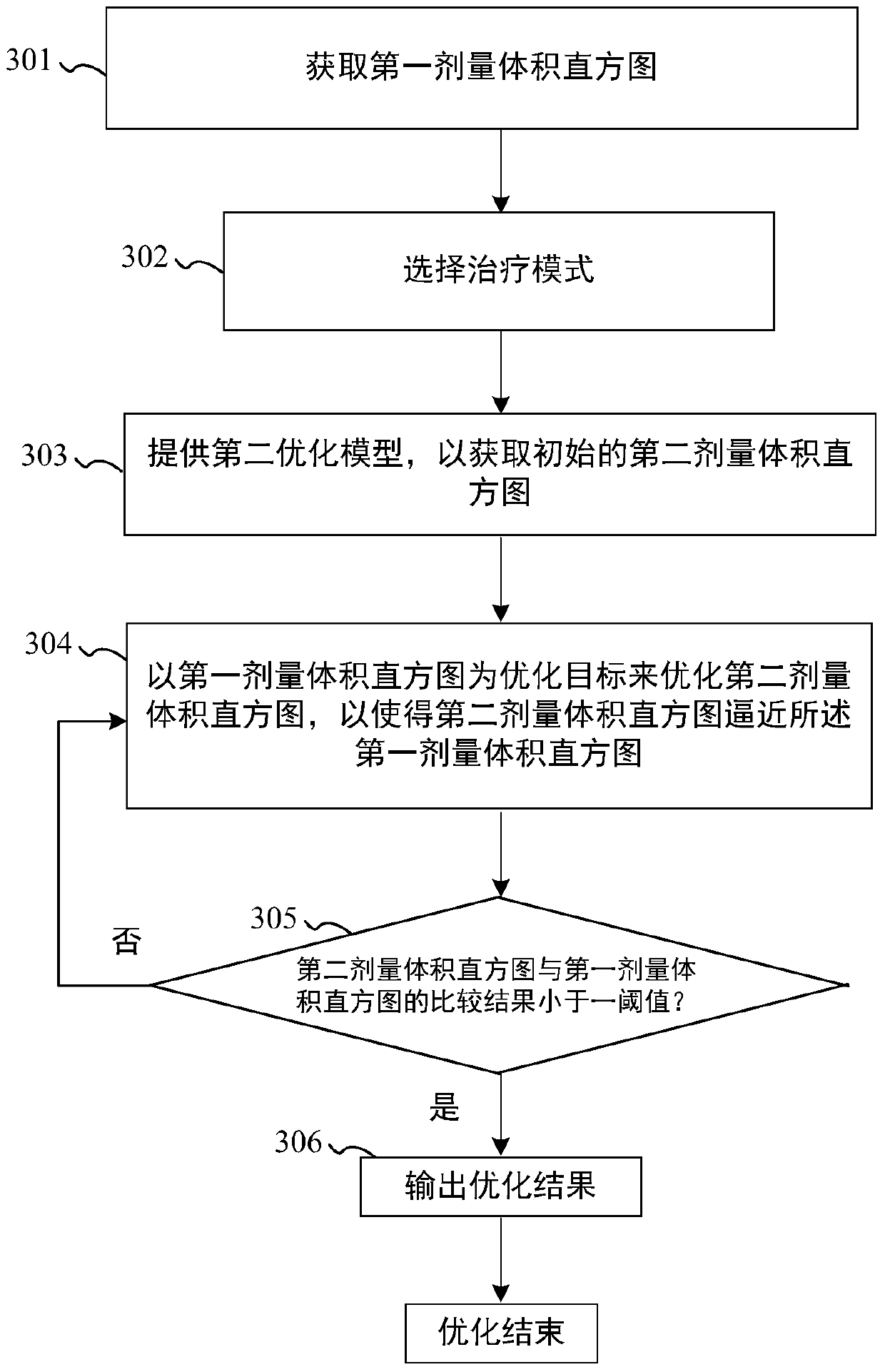
The invention provides a dosage optimization method and a system. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring a first dosage volume histogram, wherein a first dosage volume histogram is a result of fluxgraph optimization; providing a second optimization model, and taking the first dosage volume histogram as an optimization target so as to optimize a parameter of a second optimization model and acquiring a second dosage volume histogram, wherein if a comparison result of the second dosage volume histogram and the first dosage volume histogram is less than a threshold, optimization is finished; otherwise, the optimization is continued.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
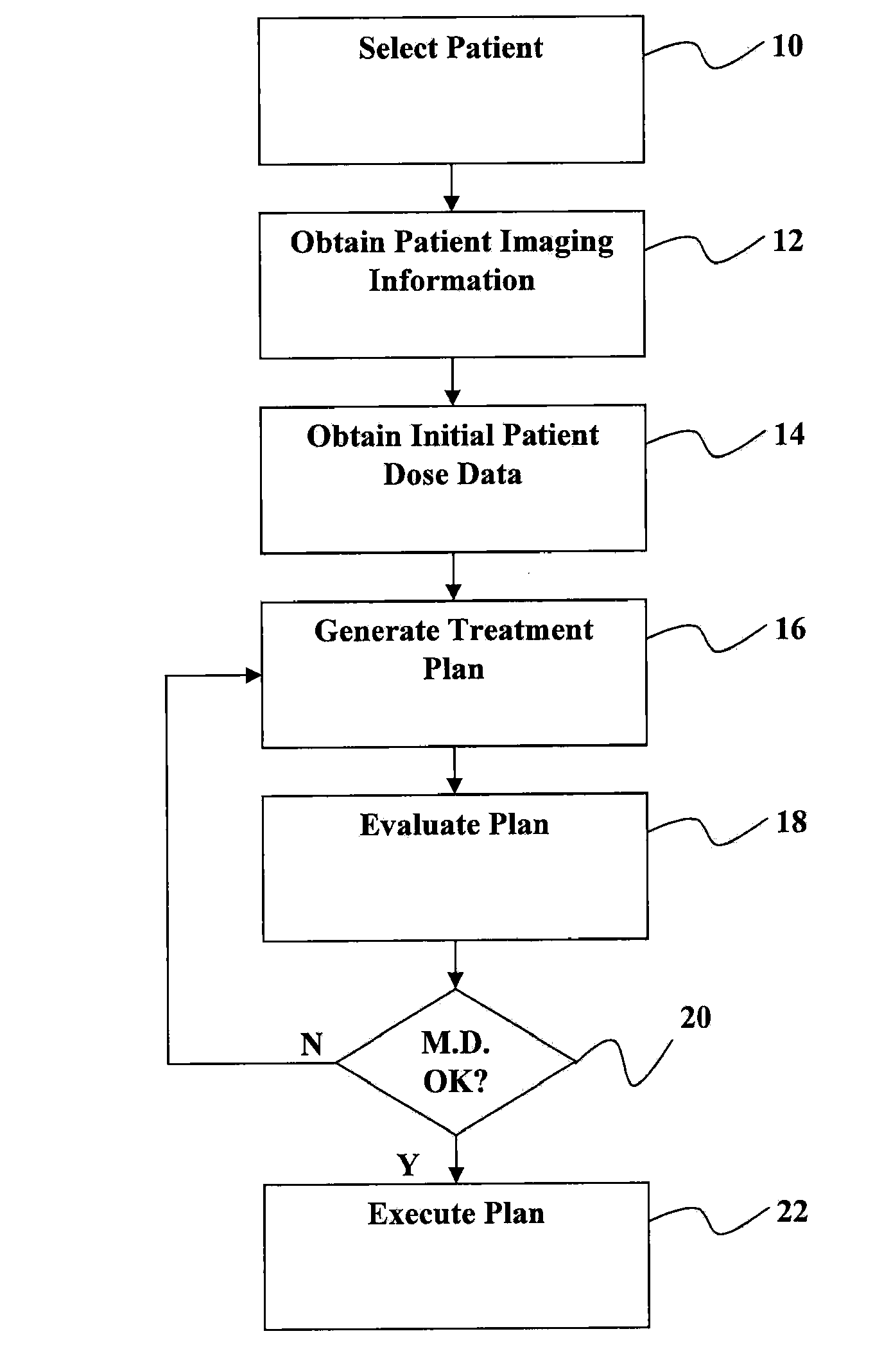
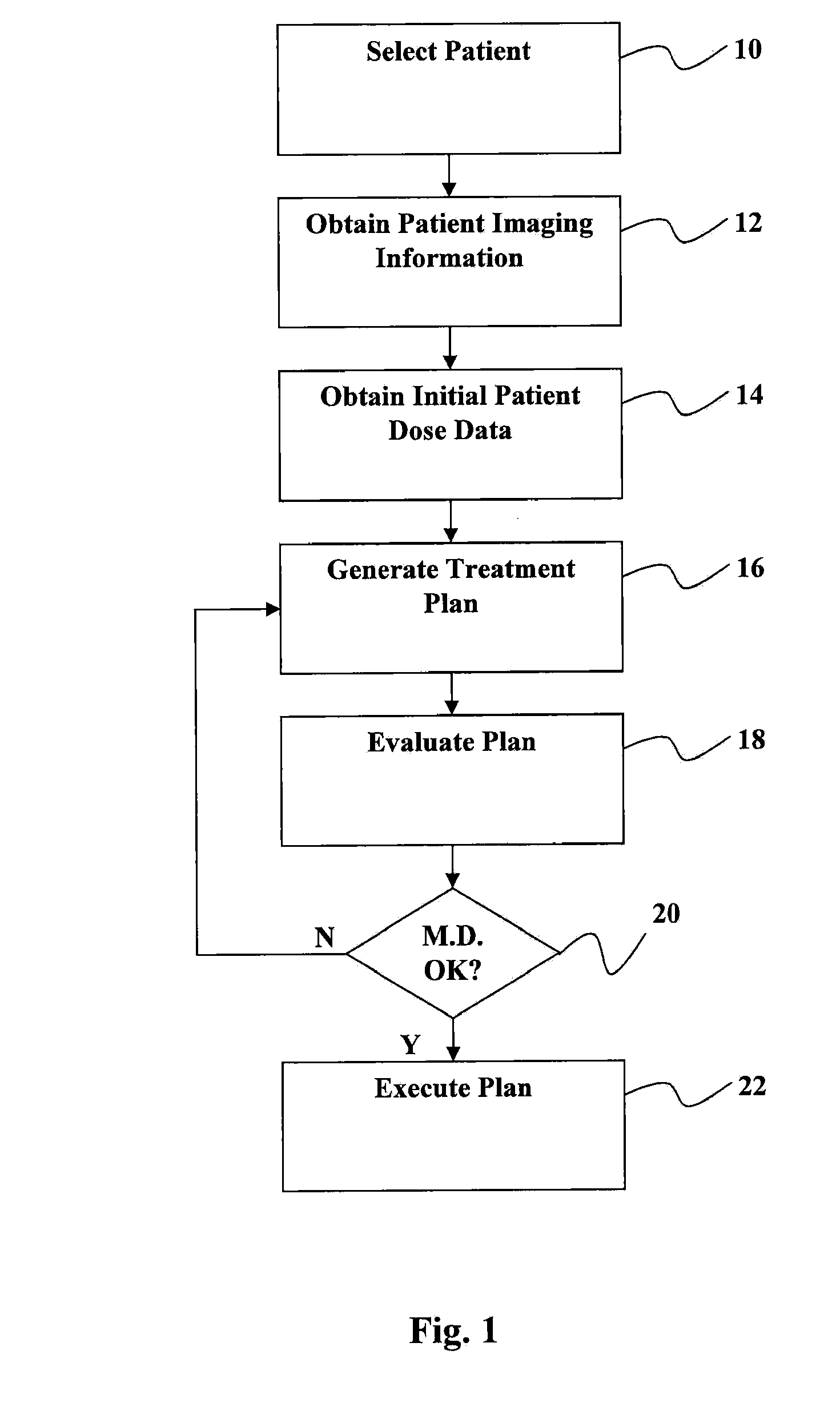
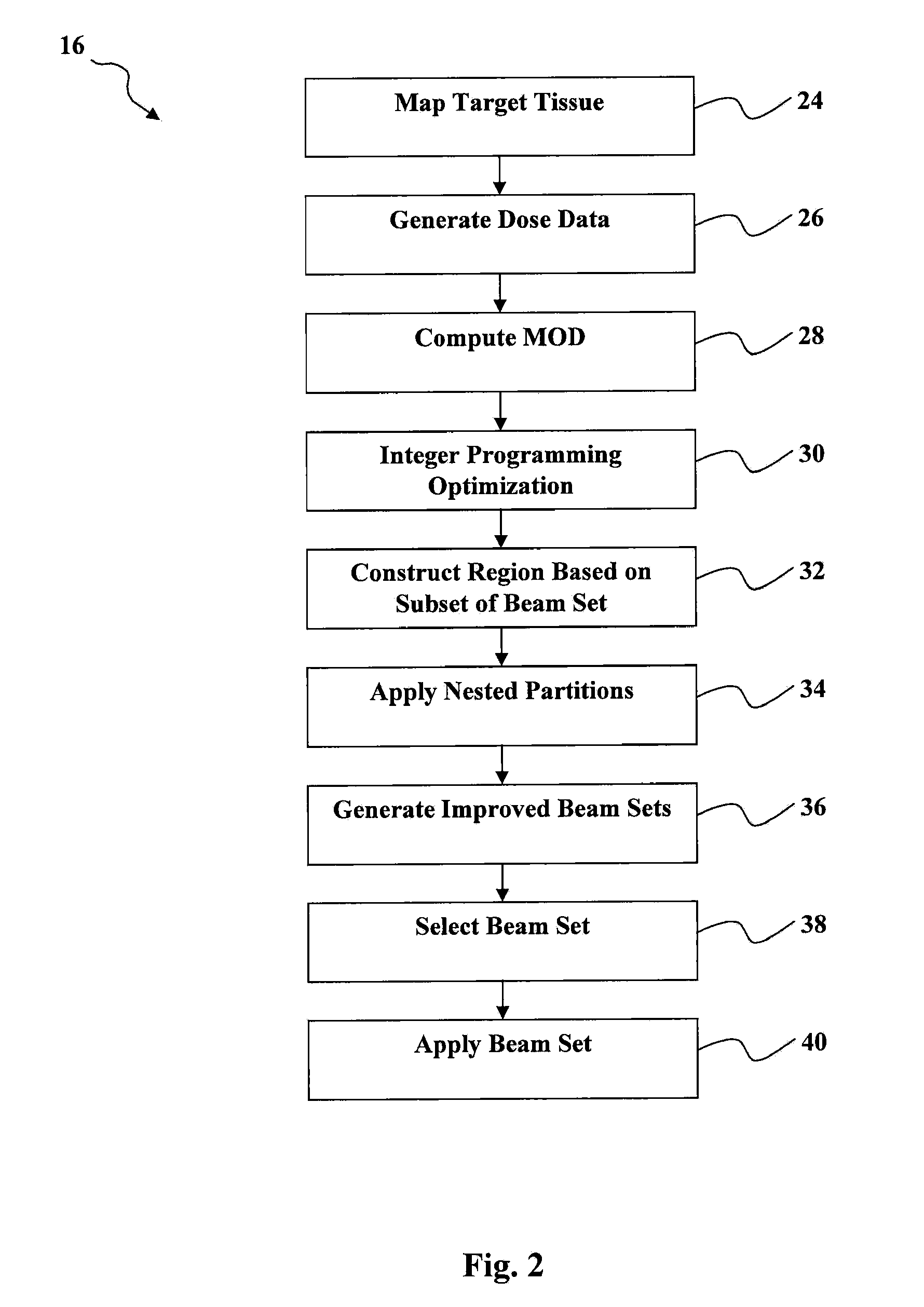
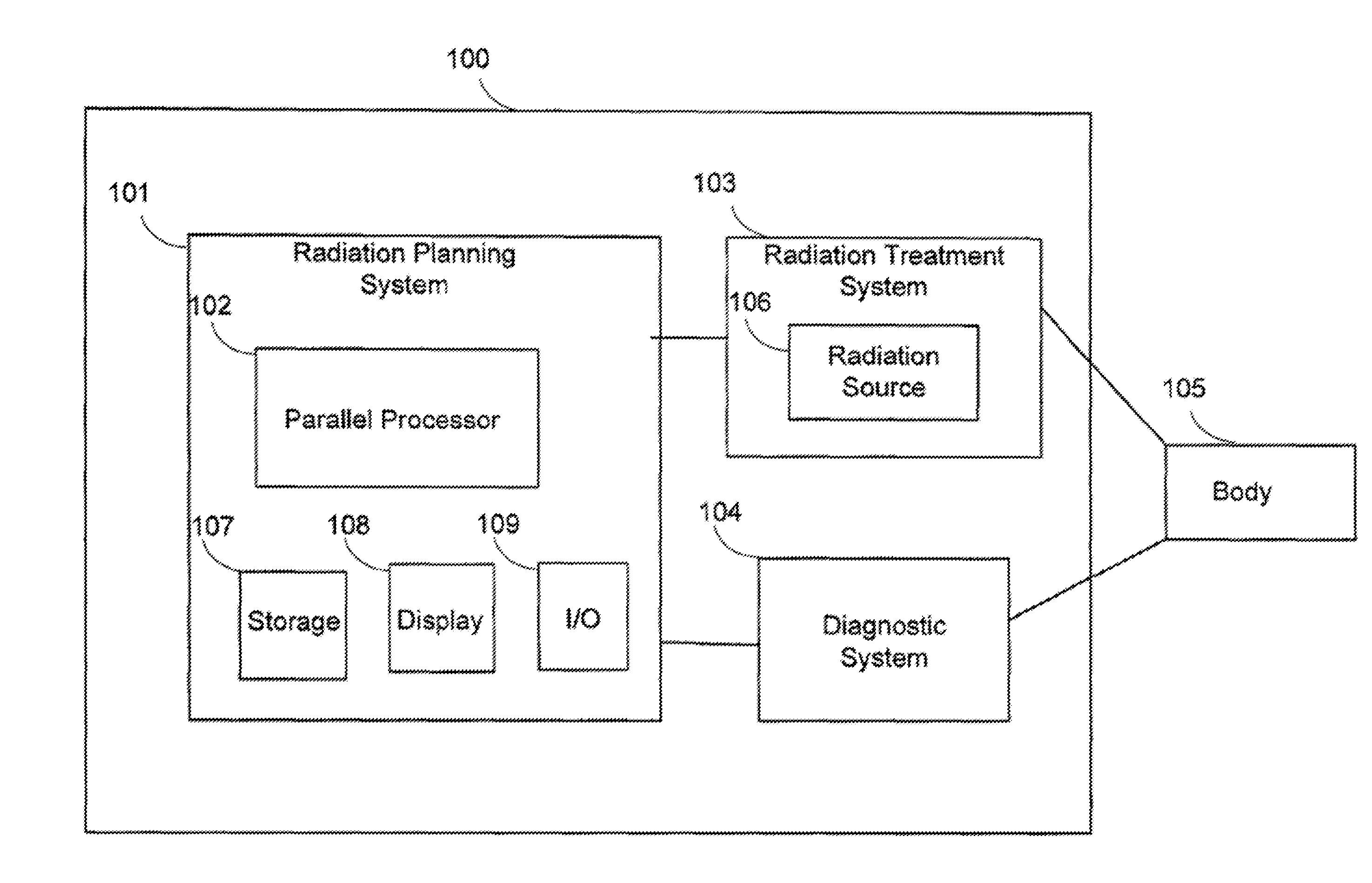
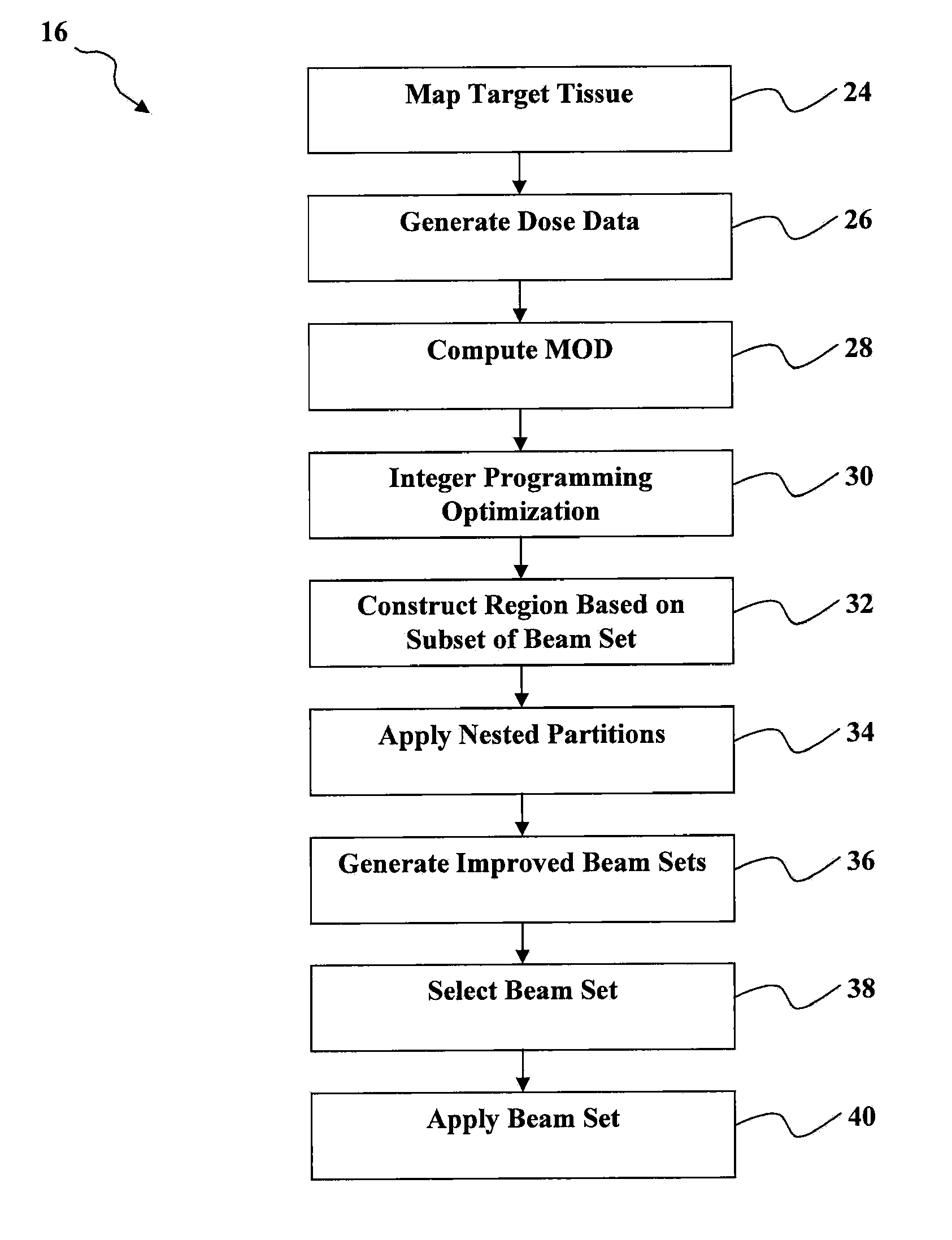
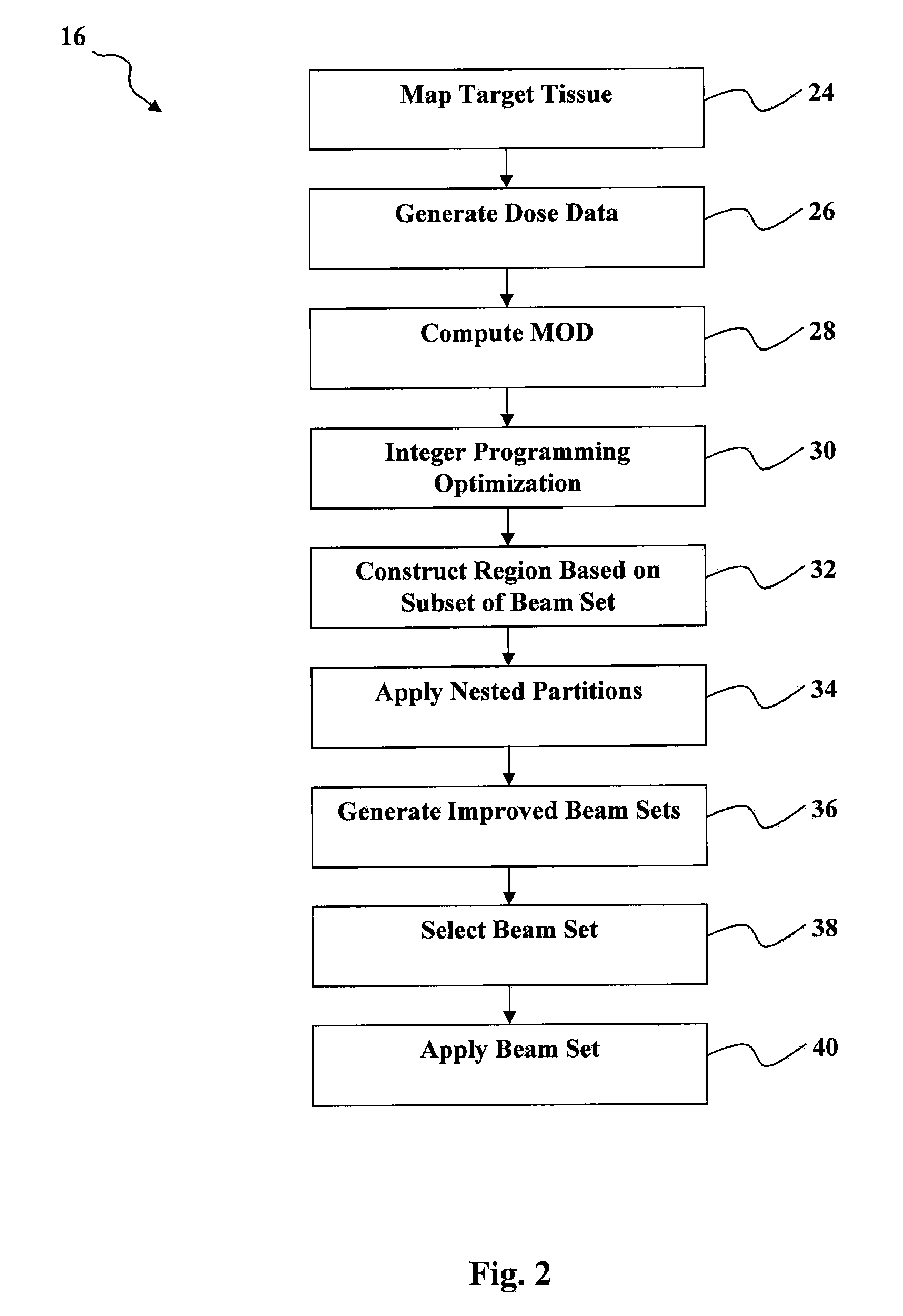
Automated software system for beam angle selection in teletherapy
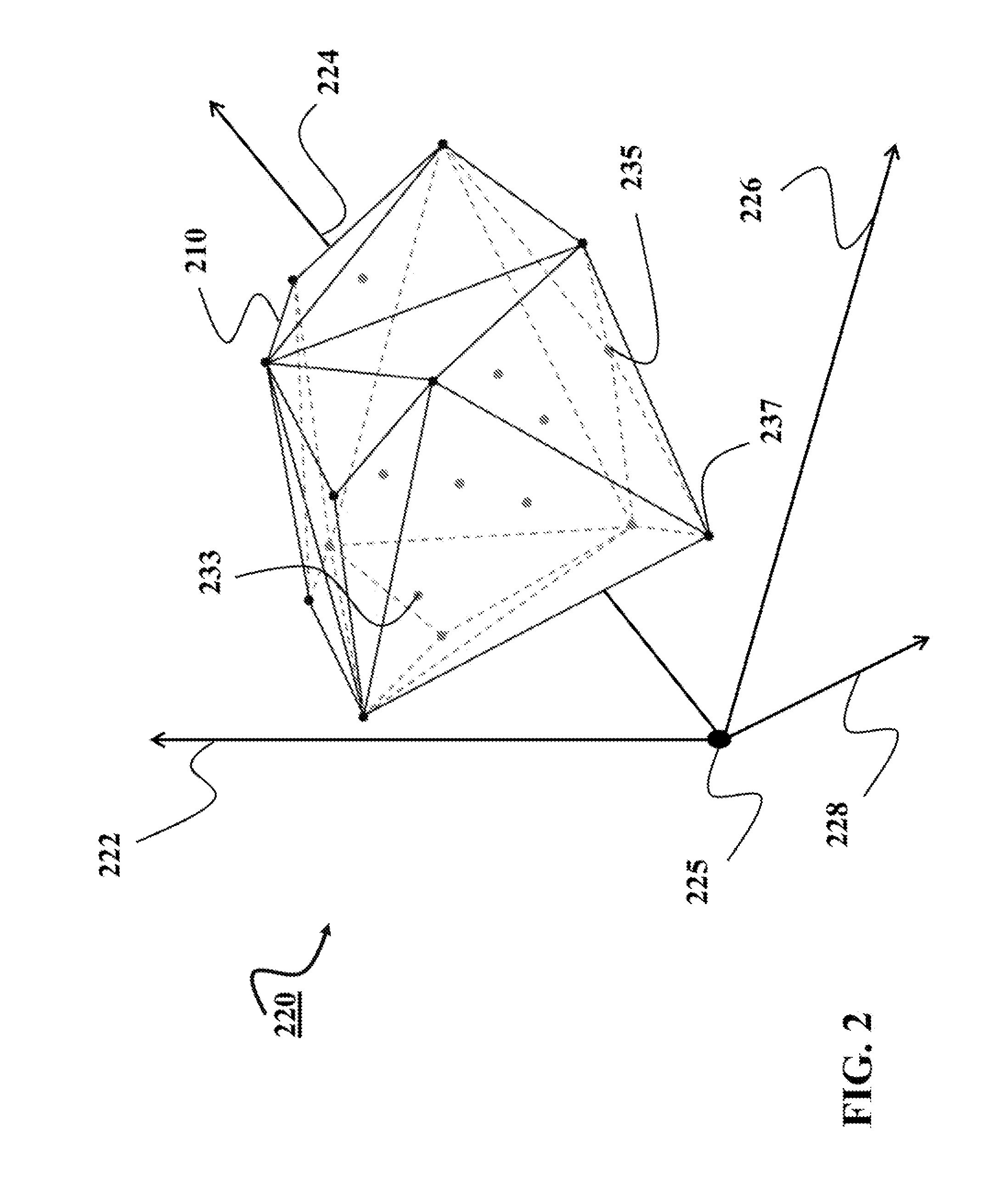
A novel approach to generating radiation treatment plans through a nested partitions framework provides an optimization of radiation delivery. The nested partitions approach couples beam angle selection and dose optimization to solve treatment planning problems. An optimal beam angle selection is provided to best treat tumors, while minimizing exposure to the surrounding healthy tissues.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Multi-Criteria Optimization in Particle Beam Dose Optimization
InactiveUS20150202464A1Minimizes a weighted norm of the total irradiationSatisfy constraintsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMedical automated diagnosisClosest pointParticle beam
A method optimizes a dose of radiation for a radio-therapy treatment subject to constraints on diagnostic parameters of the radio-therapy treatment. The method determines a point of a polytope arranged in a coordinate system of the diagnostic parameters, such that a position of the point in the coordinate system is determined at least in part by values of each diagnostic parameter. The polytope is convex with boundaries formed by intersecting half-spaces of feasible values of each diagnostic parameter specified by the constraints. The point is the closest point of the polytope to an origin of the coordinate system with regard to a weighted Euclidean distance norm. The method determines a distribution of the dose of radiation for the radio-therapy treatment using the values of the diagnostic parameters corresponding to the position of the point.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
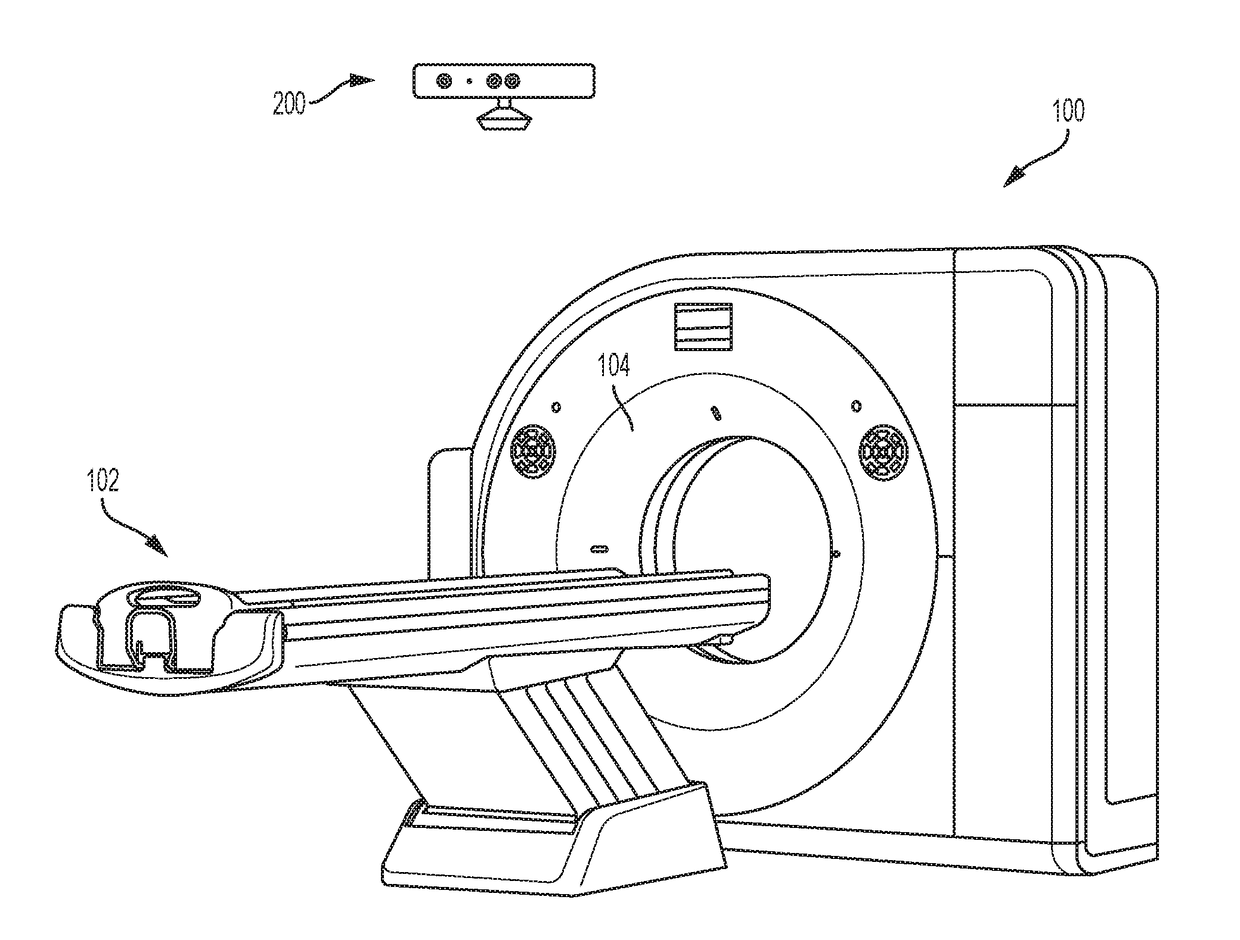
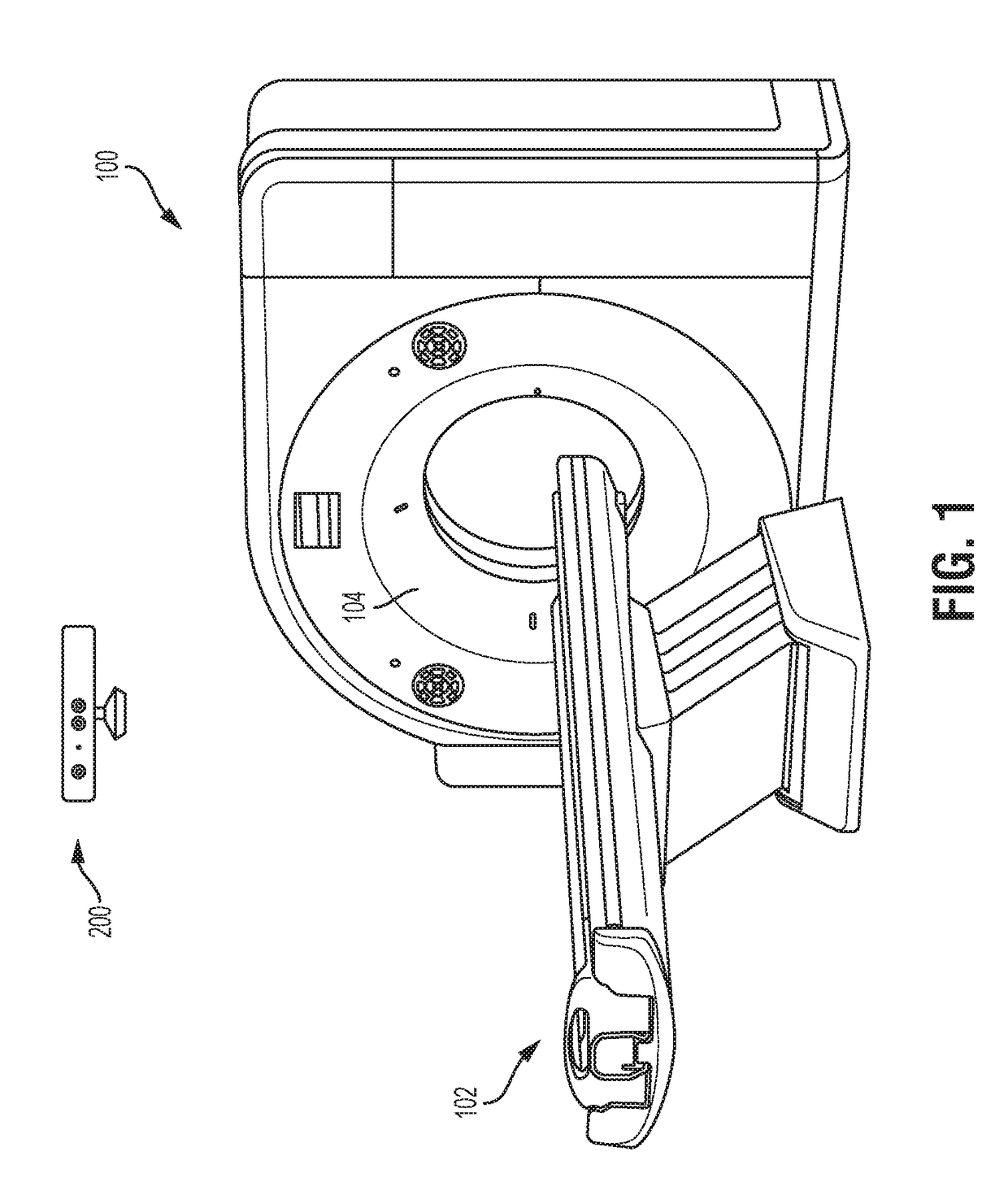
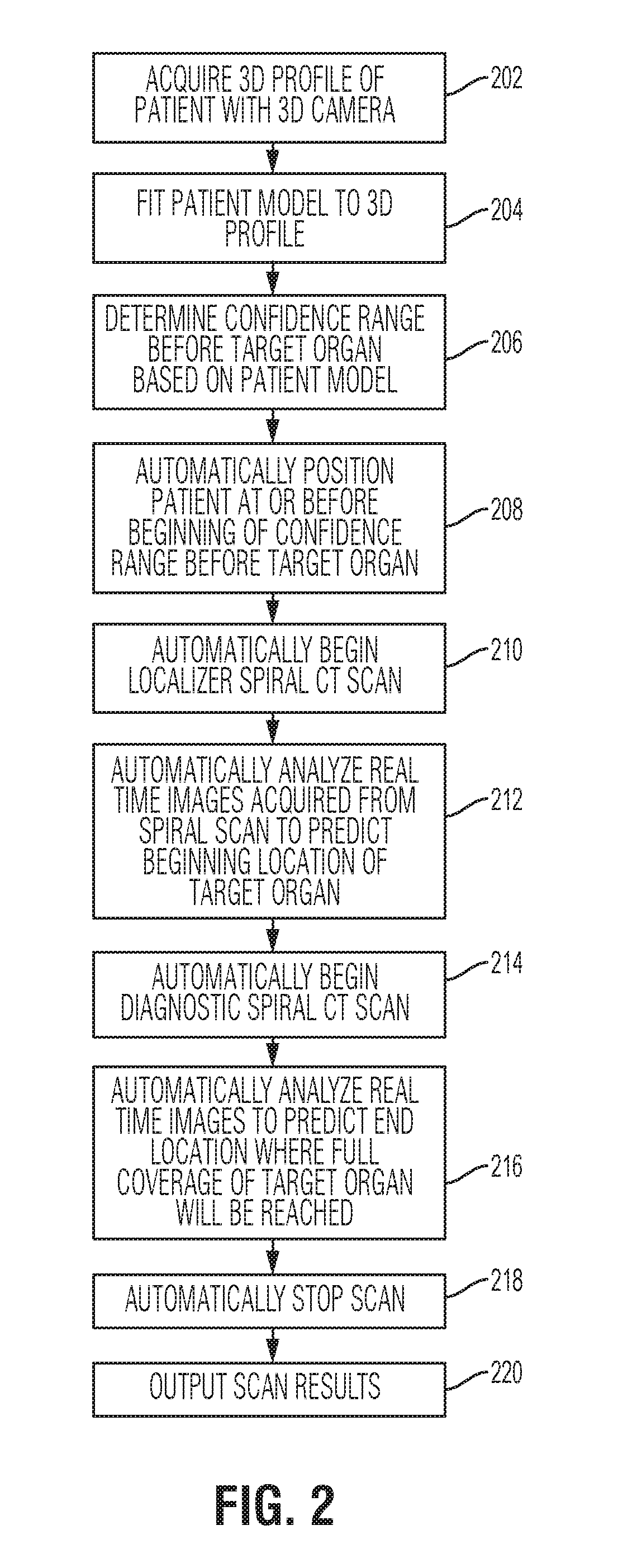
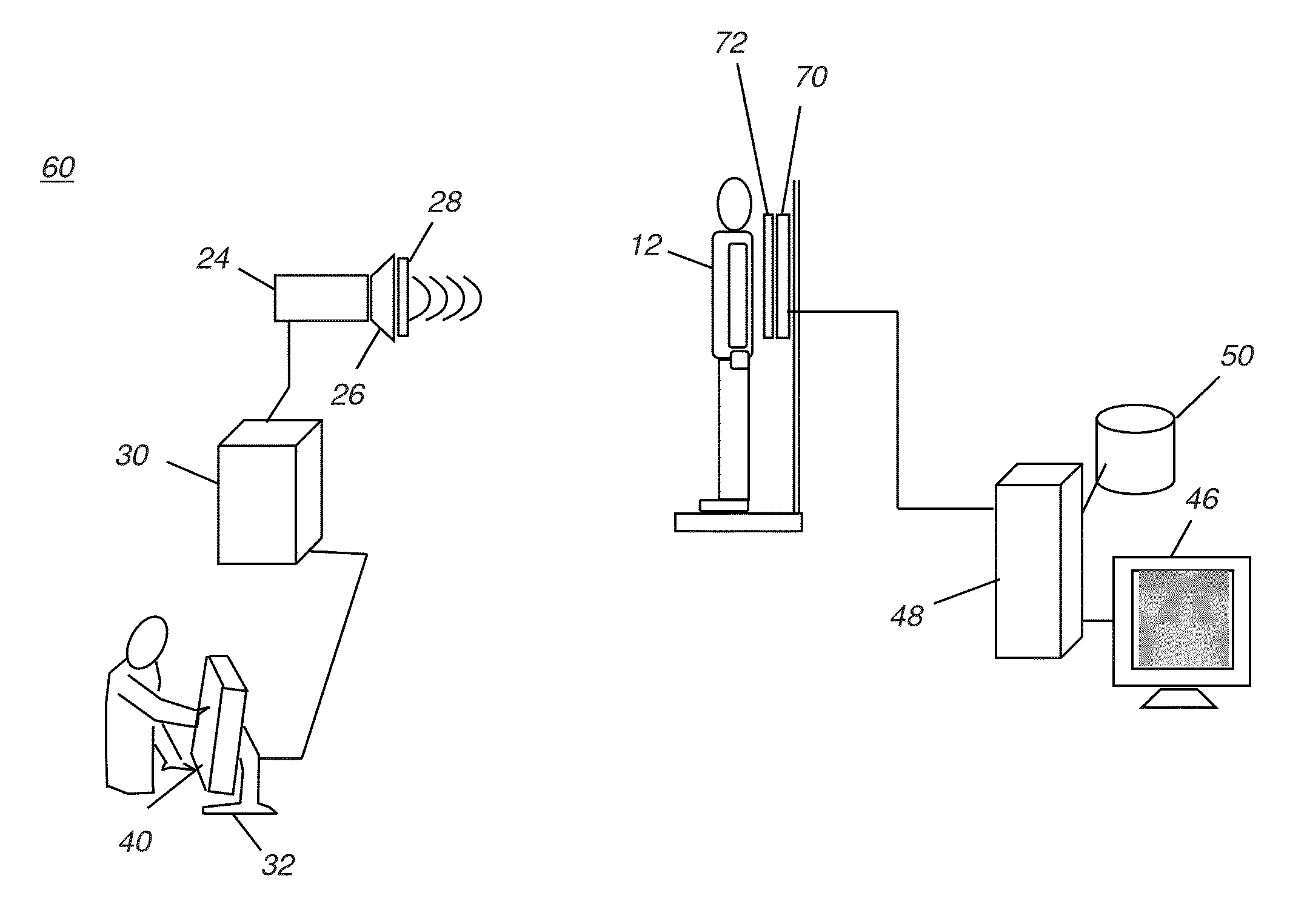
Method and System for Dose-Optimized Computed Tomography Scanning of a Target Organ
ActiveUS20180228450A1Health-index calculationRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsComputed tomographyConfidence interval
A method and system for dose-optimized acquisition of a computed tomography (CT) scan of a target organ is disclosed. A localizer spiral CT scan is started at a beginning of a confidence range before a target organ. Real-time localizer scan images are automatically analyzed to predict a beginning location of the target organ based on the real-time localizer scan images. A diagnostic spiral CT scan is automatically started at the predicted beginning location of the target organ. Real-time diagnostic scan images are automatically analyzed to predict an end location of the target organ where full coverage of the target organ will be reached. The diagnostic spiral CT scan is automatically stopped in response to reaching the predicted end location of the target organ. A 3D profile can be acquired using a 3D camera and used to determine the confidence range before the target organ.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Microwave ablation treatment planning method based on CT image
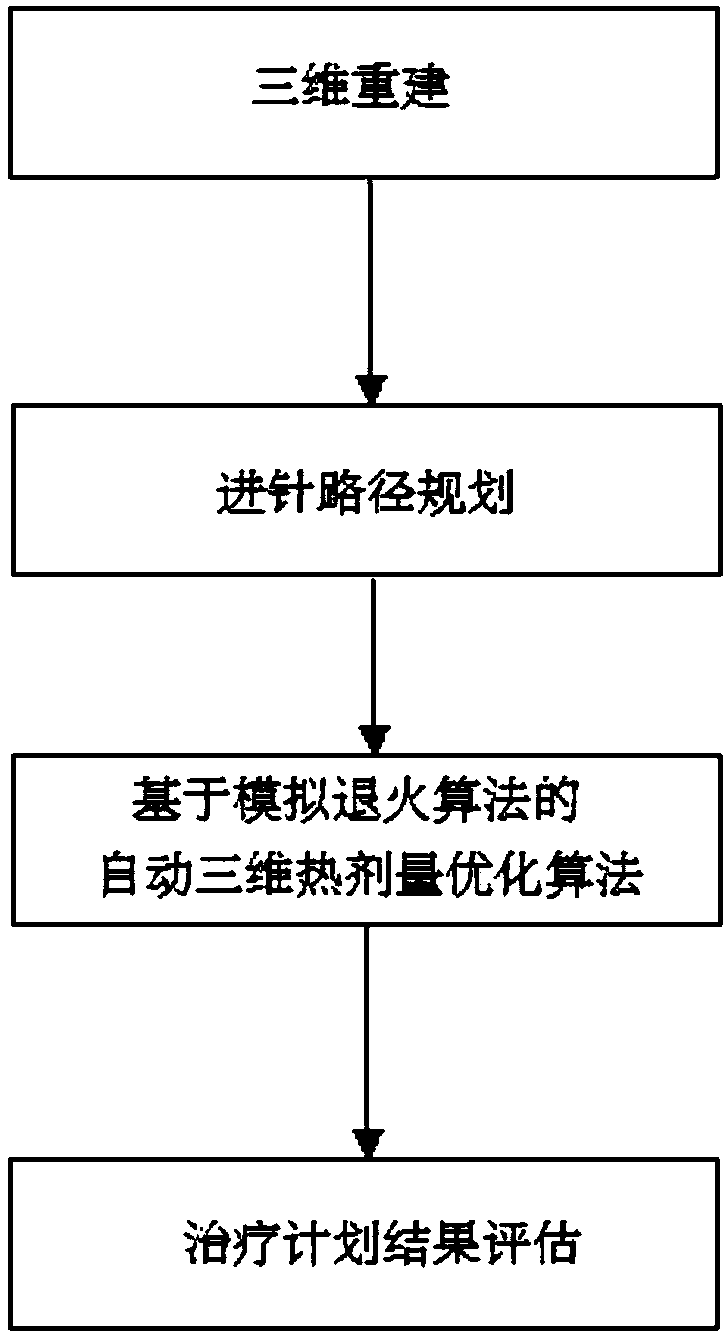
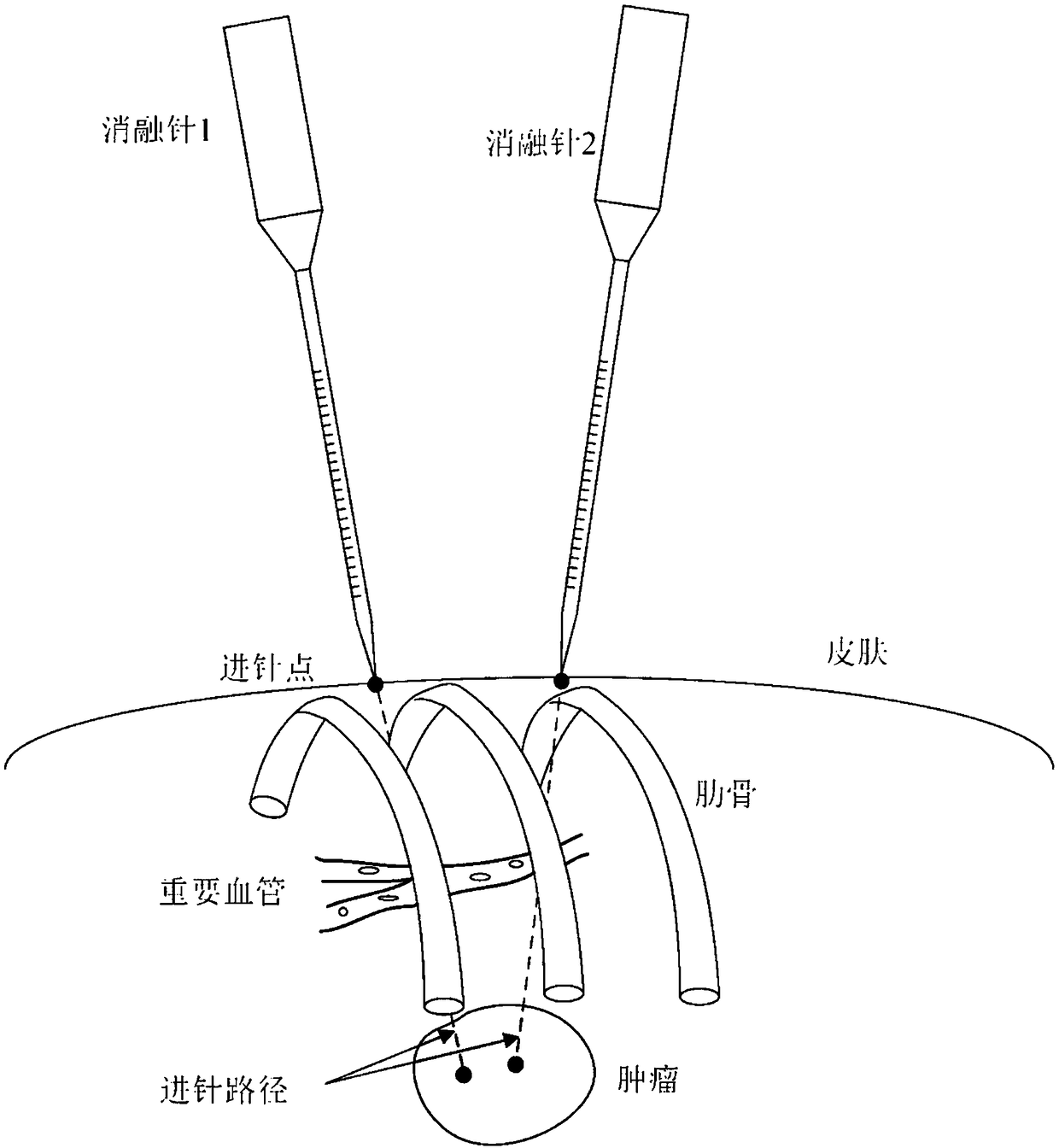
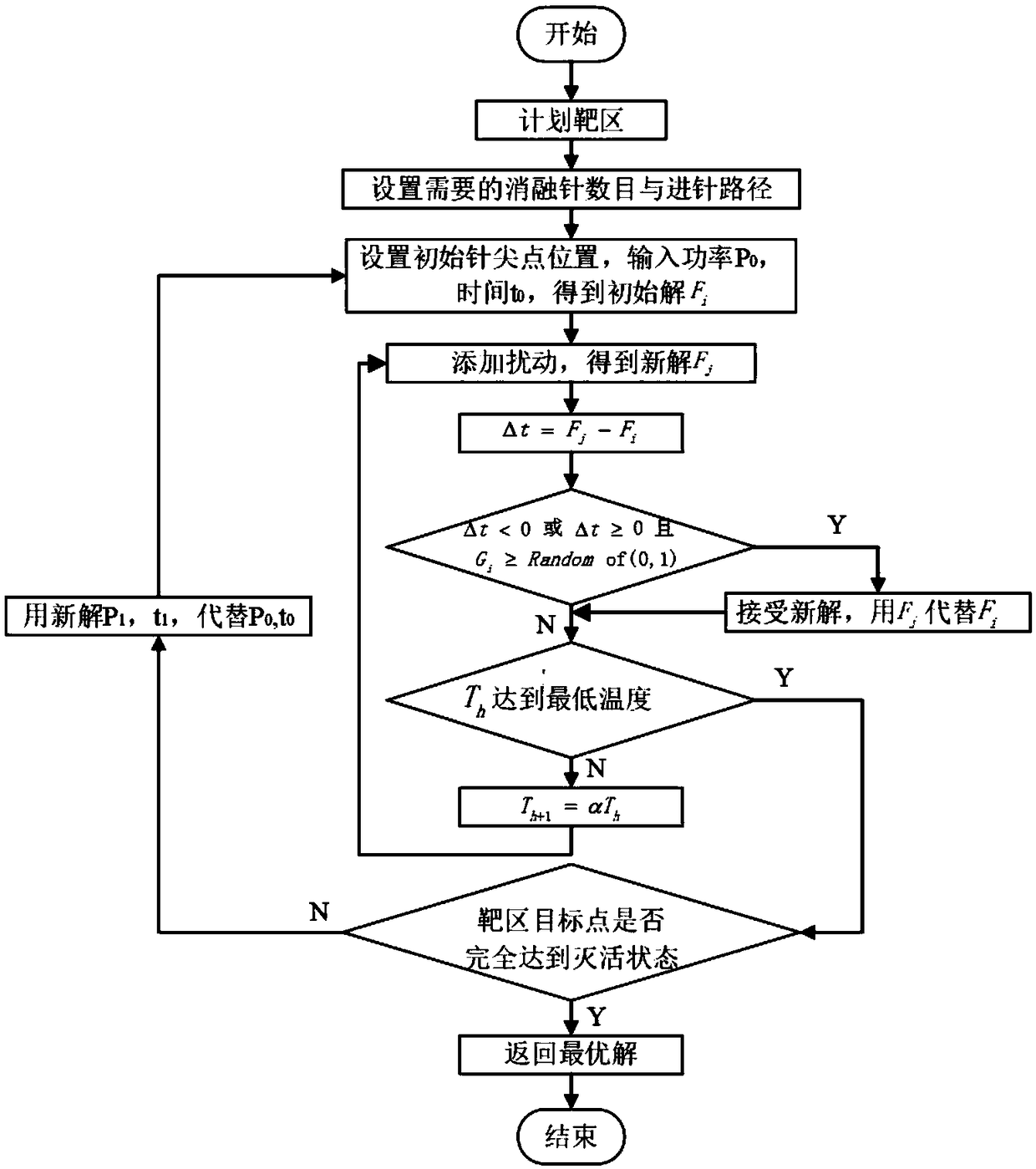
InactiveCN109077804AReduce blindnessAvoid damageComputer-aided planning/modellingSurgical instruments using microwavesPlanning methodTherapy planning
The invention discloses a microwave ablation treatment planning method based on a CT image. The method comprises the steps that a medical image sequence of a patient is read and displayed to perform three-dimensional reconstruction; the best needle inserting number and needle inserting route are selected according to a three-dimensional visualized result, wherein the route can avoid important tissues and organs, safety distance is reserved, and the route is the shortest route between a cutaneous needle inserting point and a target region; the optimal input parameters are inversely resolved according to the geometry of a tumor and a preset needle inserting route using an automatic three-dimensional thermal-dose optimization algorithm; the range of a three-dimensional tissue damage field anda temperature field is displayed to evaluate a treatment planning result. By means of the method, a doctor can be assisted in making a reasonable preoperative plan of microwave ablation operation, the clinical executing effect of an operation scheme designed by the doctor using a computer simulation method before the operation is conducted to provide a reliable operation guidance for the doctor,the executing difficulty of the operation is reduced, the operation is safer, and excess damage on the patient is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
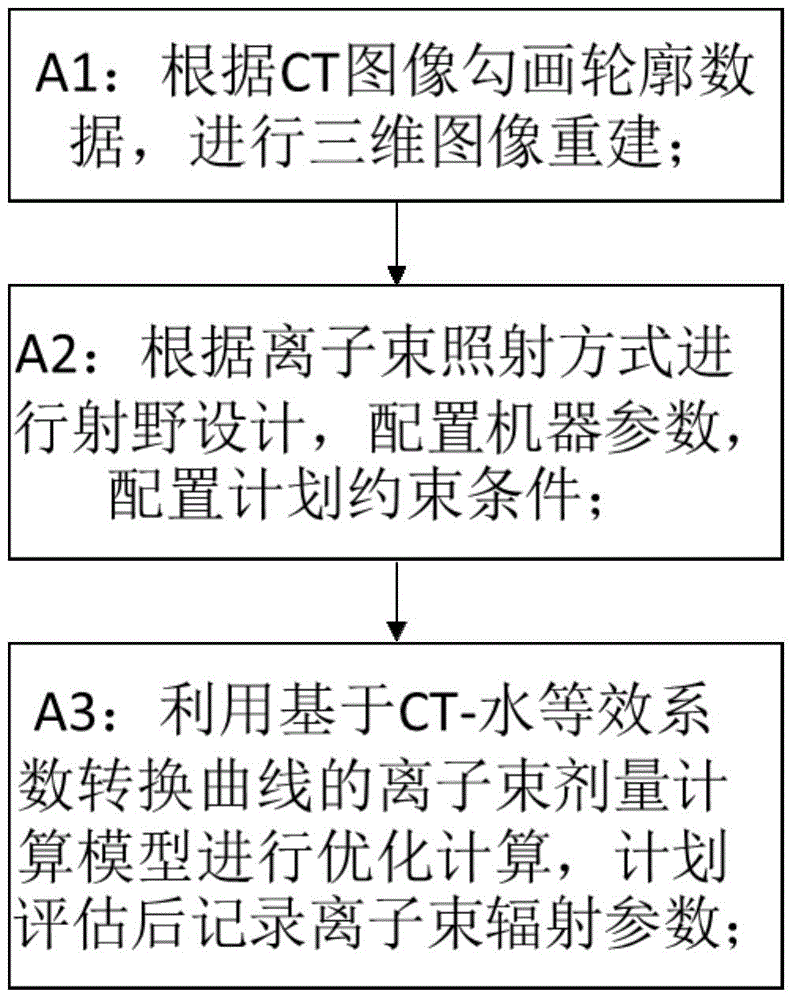
Ion beam radiotherapy dosage verification method based on water equivalent coefficients
ActiveCN104888364AEasy to movePrecise positioningX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose profileTherapy planning
The invention relates to an ion beam radiotherapy dosage verification method based on water equivalent coefficients. The ion beam radiotherapy dosage verification method based on the water equivalent coefficients includes the following steps that A, CT image data of a cancer patient are obtained, a treatment planning system (TPS) is utilized for plan design according to a CT-water equivalent coefficient transformation curve, and ion beam radiation parameters are recorded after the plan is determined; B, a virtual three-dimensional water phantom CT image is generated based on the water equivalent coefficients, the ion beam radiation parameters are transplanted to the water phantom through the TPS, dosage optimal computation is carried out again, and three-dimensional rasterization dose distribution in the water phantom is obtained; C, an ionization chamber is placed at an interest point in the three-dimensional water phantom, interpolating calculation is carried out in the three-dimensional rasterization dose distribution according to the three-dimensional coordinates of the sensitive volume of the ionization chamber in the water phantom, and planned dosage of the interest point is obtained; D, the ion beam radiation parameters designed as planned control a medical heavy-ion accelerator to perform simulated irradiation on the water phantom, and the measured absolute dosage value of the interest point for the ionization chamber in the water phantom is compared with the planned dosage.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for consistent and verifiable optimization of computed tomography (CT) radiation dose
InactiveUS9592022B2More transparentLess dauntingComputerised tomographsMachines/enginesClinical settingsPower flow
A system and a method is disclosed for consistently and verifiably optimizing computed tomography (CT) radiation dose in the clinical setting. Mathematical models allow for estimation of patient size, image noise, size-specific radiation dose, and image quality targets based on digital image data and radiologists preferences. A prediction model estimates the scanner's tube current modulation and predicts image noise and size-specific radiation dose over a range of patient sizes. An optimization model calculates specific scanner settings needed to attain target image quality at the minimum radiation dose possible. An automated system processes the image and dose data according to the mathematical models and stores and displays the information, enabling verification and ongoing monitoring of consistent dose optimization.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Automated software system for beam angle selection in teletherapy
A novel approach to generating radiation treatment plans through a nested partitions framework provides an optimization of radiation delivery. The nested partitions approach couples beam angle selection and dose optimization to solve treatment planning problems. An optimal beam angle selection is provided to best treat tumors, while minimizing exposure to the surrounding healthy tissues.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
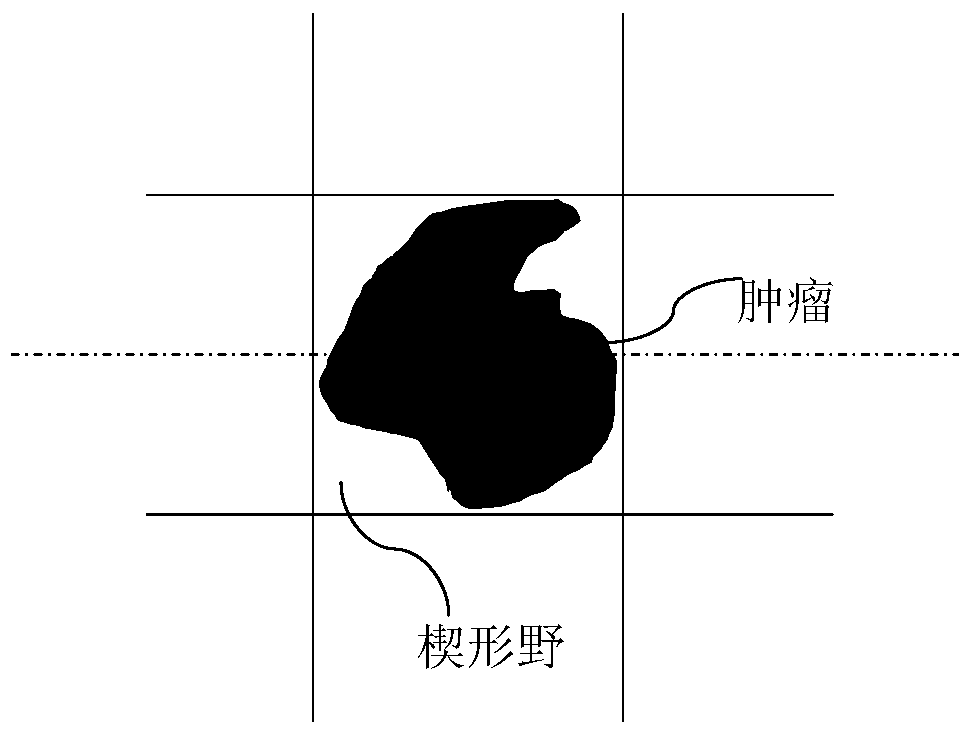
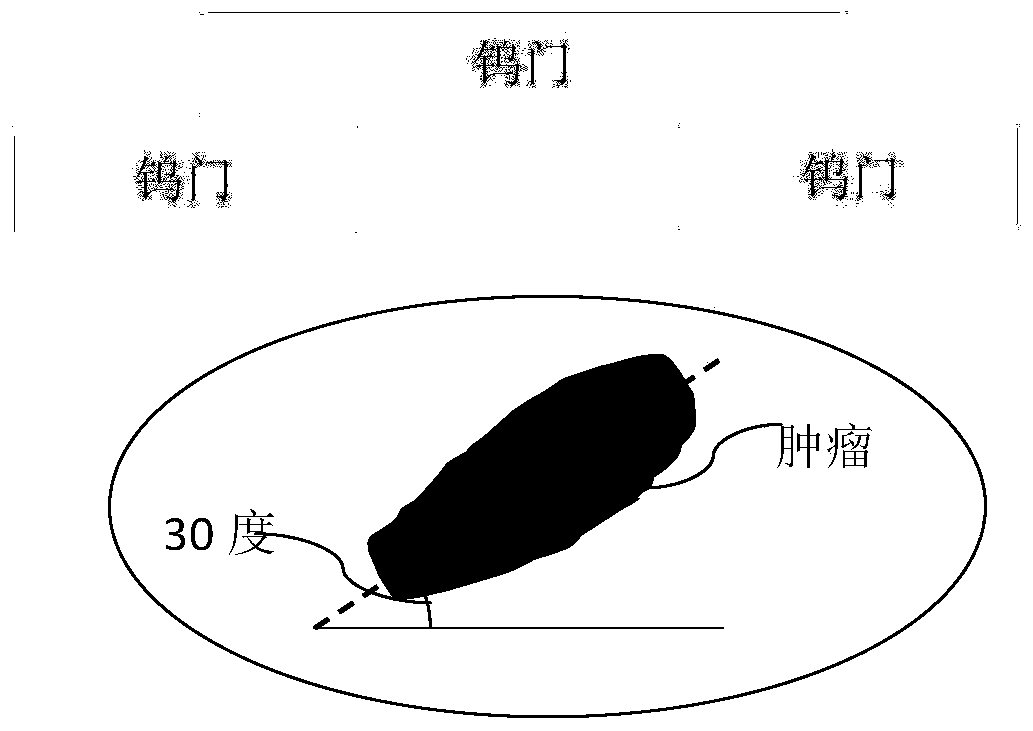
Radiotherapy target section dose regulating personalized silicone compensator and preparation method thereof
PendingCN108187242AImprove protectionSame distanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing processesSide effectCurative effect
The invention relates to a radiotherapy target section dose regulating personalized silicone compensator and a preparation method thereof. The radiotherapy target section dose regulating personalizedsilicone compensator comprises an skin expanding part, a normal tissue expanding part and positioning mark lines. According to conditions of patient's skin in the target section and normal organic contour needed to be protected, silicone comensators in different thickness are customized by the 3D printing technology, so that the compensators fit the skin better; as the compensators have differentthickness, the distances from the surfaces of the compensators in a treatment region to the deep normal tissue are the same, the radiotherapy dose of the target section near the skin can be increasedand the expose dose of the target section can also be unformized by means of dose optimization, and further, the deep normal organs can be protected better to some degrees; thus, the core of the modern precise radiotherapy is achieved, treatment effect is improved and side effect in radiotherapy to patients can also be reduced to the utmost extent. Besides, as medical silicone molding through medical silicone molds is utilized, manufacturing cost is lowered, manufacturing speed is high, and the technique is superior to the method of direct printing of silicone in terms of economical efficiencyand application and promotion.
Owner:于江平
Dose optimization based on outcome quality
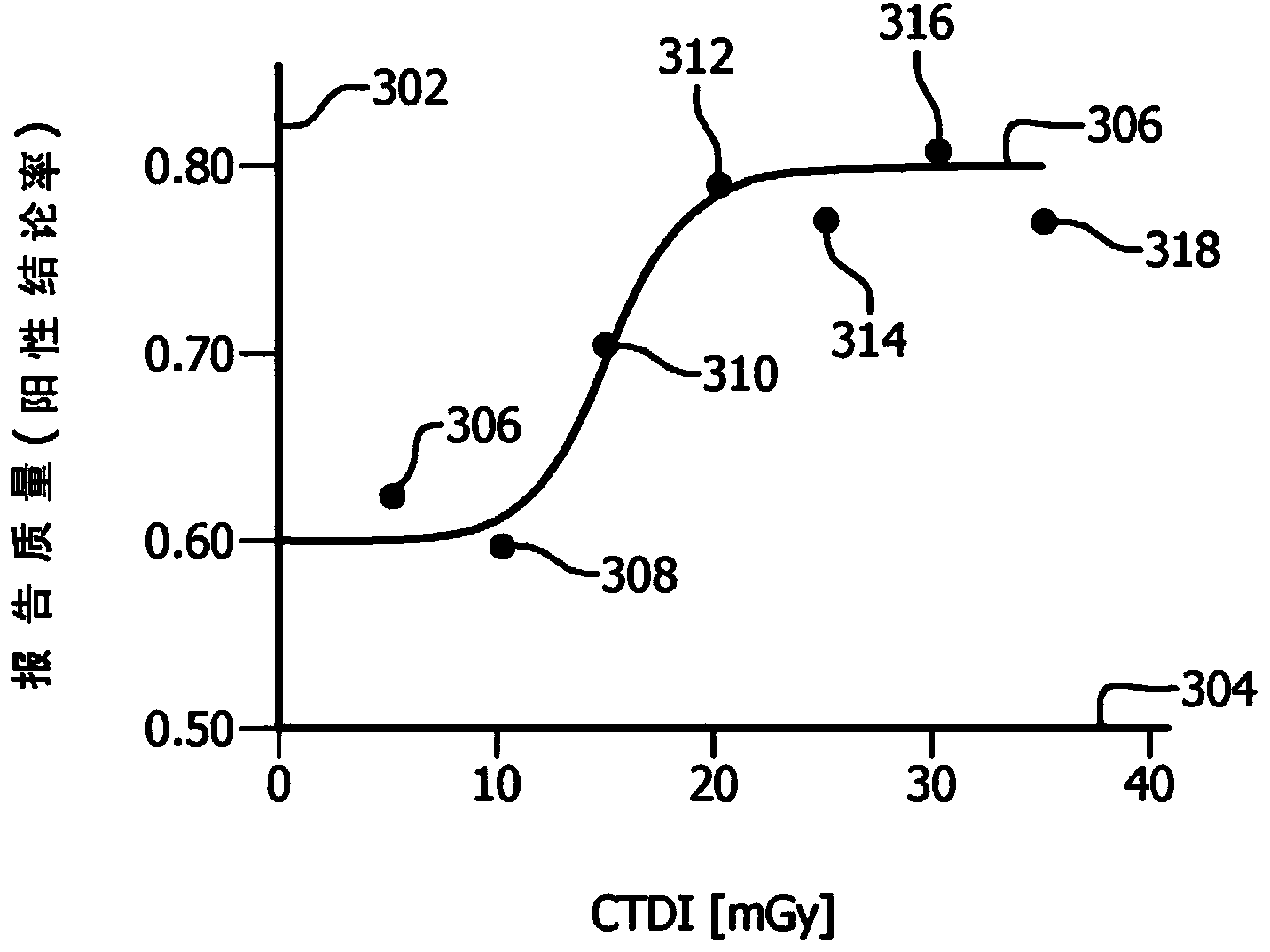
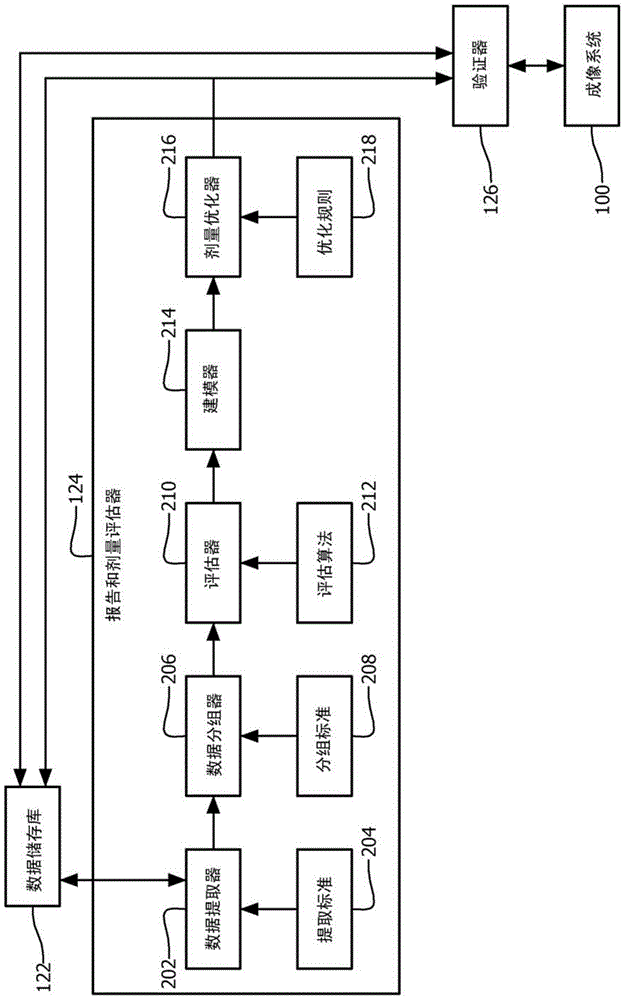
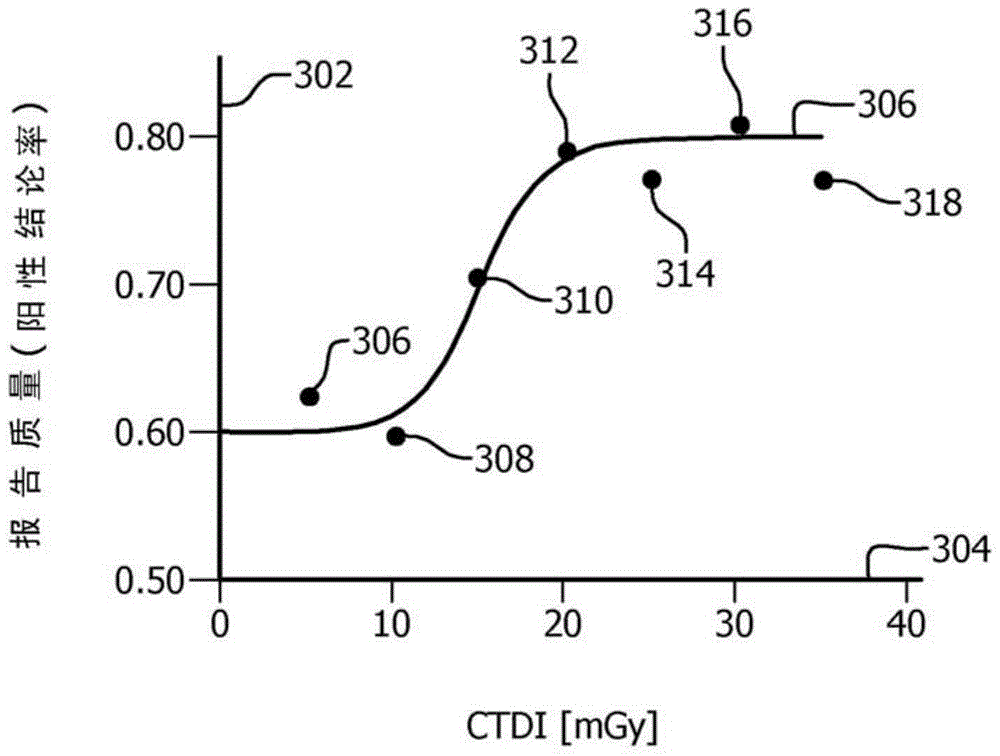
ActiveCN103987321ASolve the real problemLocal control/monitoringComputerised tomographsDose optimizationGenerative model
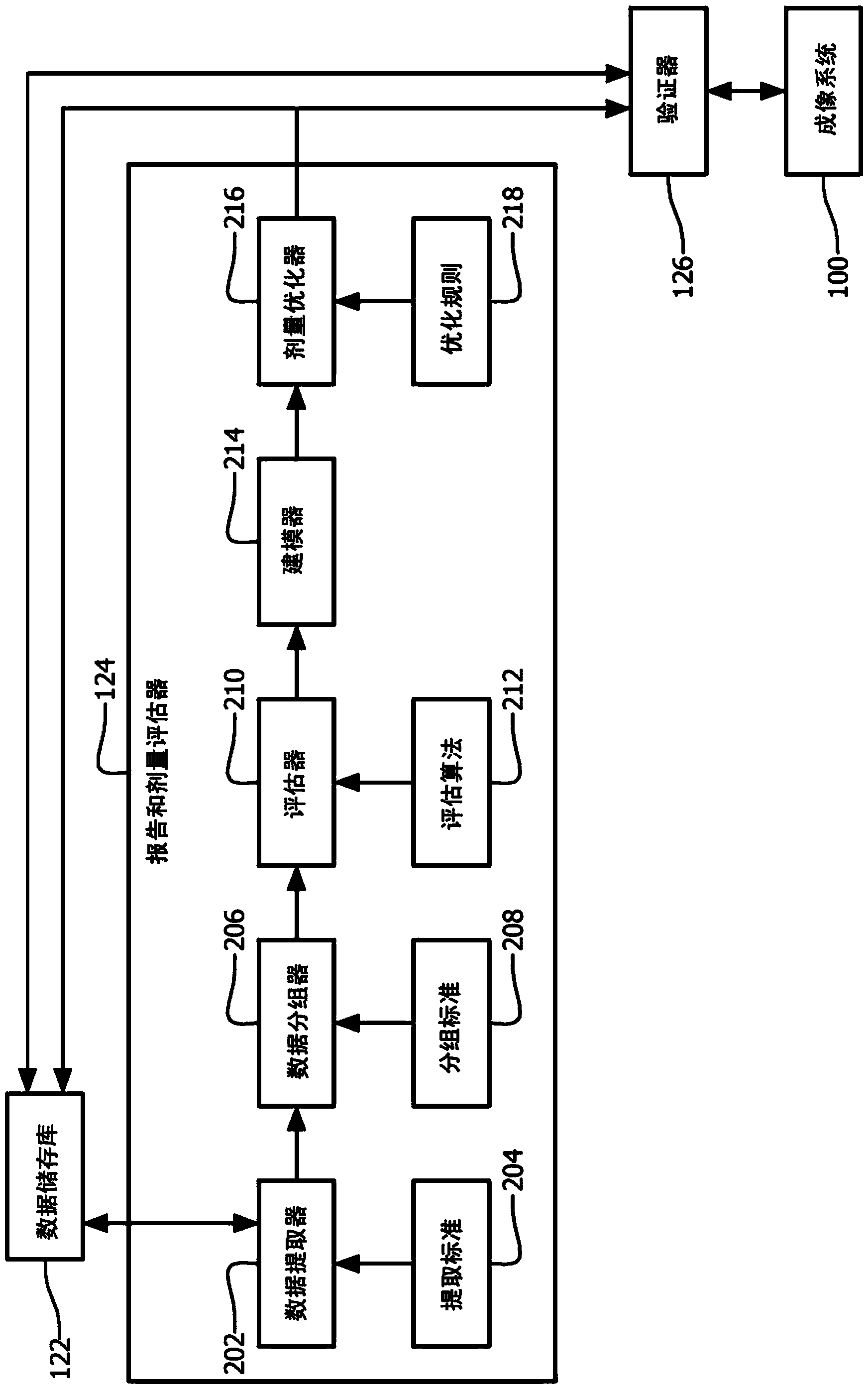
A system includes a modeler (214) that generates a model which models a quality of findings in radiologist reports as function of deposited dose of scans from which the radiologist reports are created and a dose optimizer (216) that determines an optimal dose value for a planned scan based on the model and one or more optimization rules (218). A method includes generating a model which models a quality of fmdings in radiologist reports as a function of deposited dose of scans from which the radiologist reports are created and determining an optimal dose value for a planned scan based on the model and one or more optimization rules.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
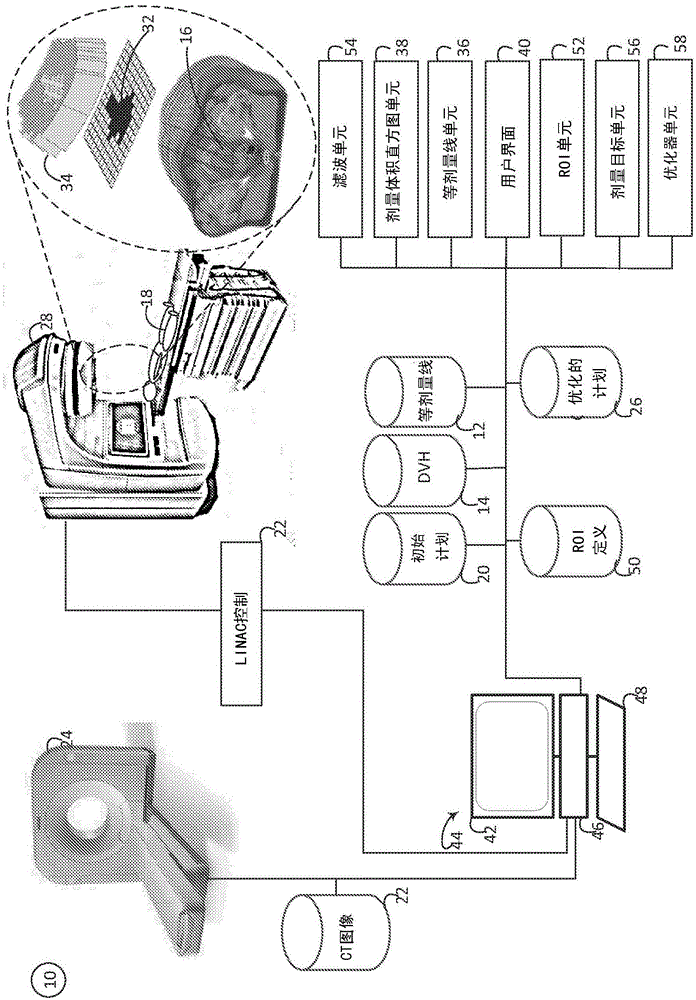
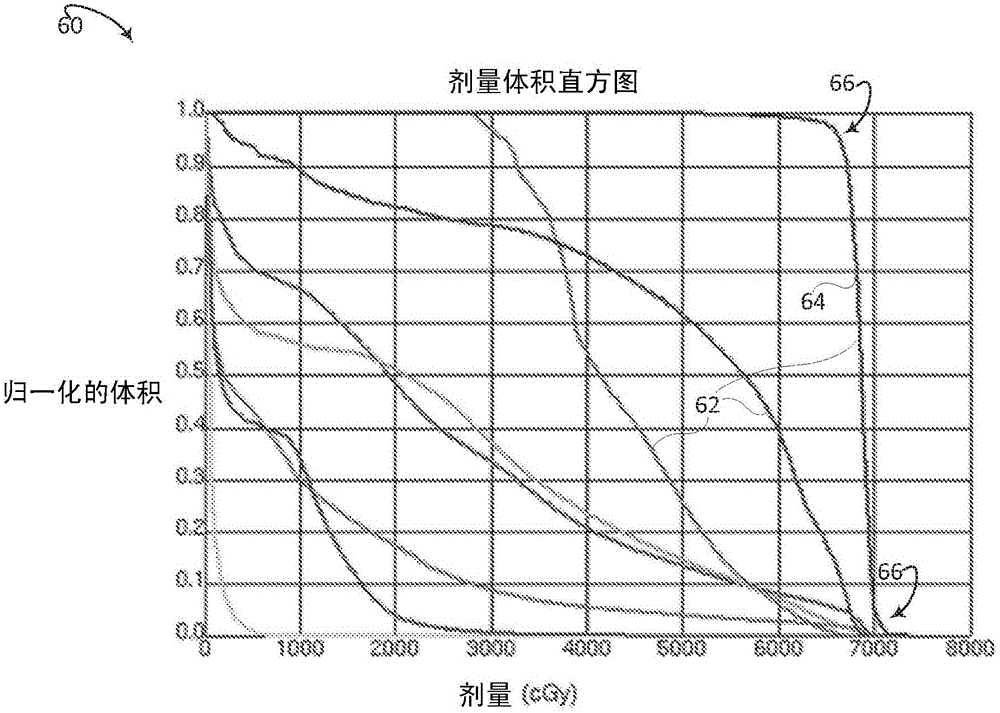
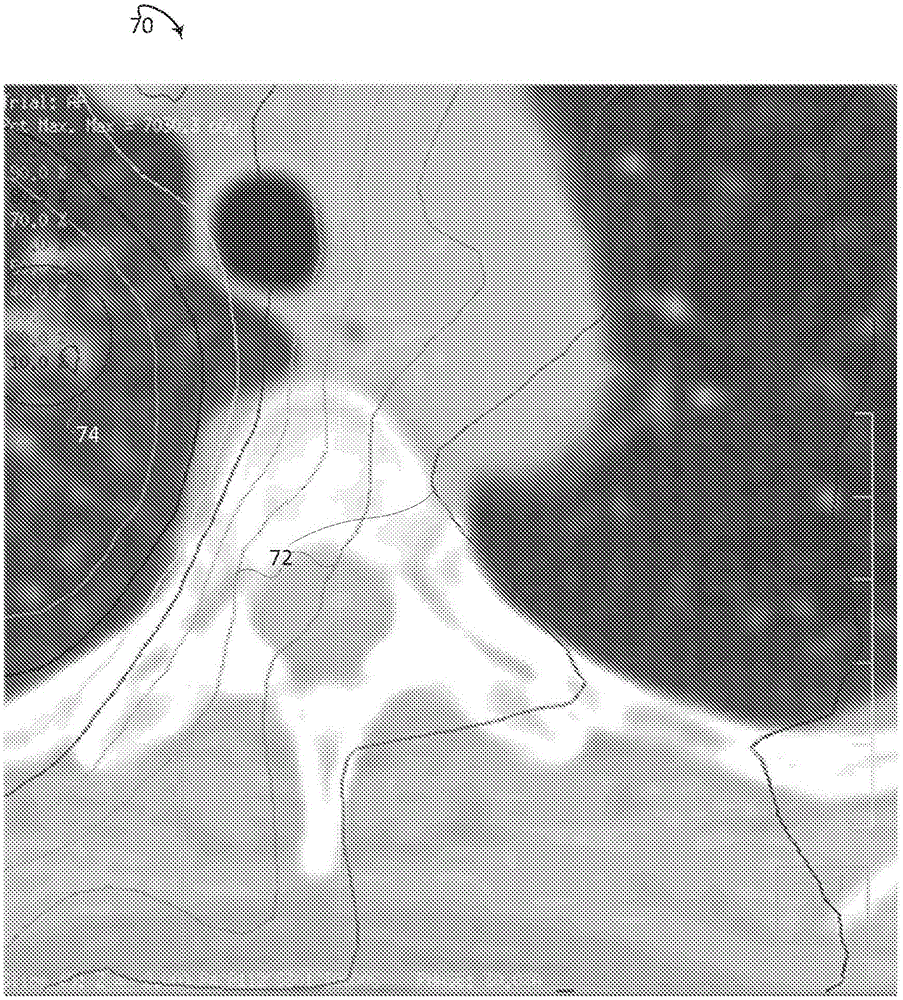
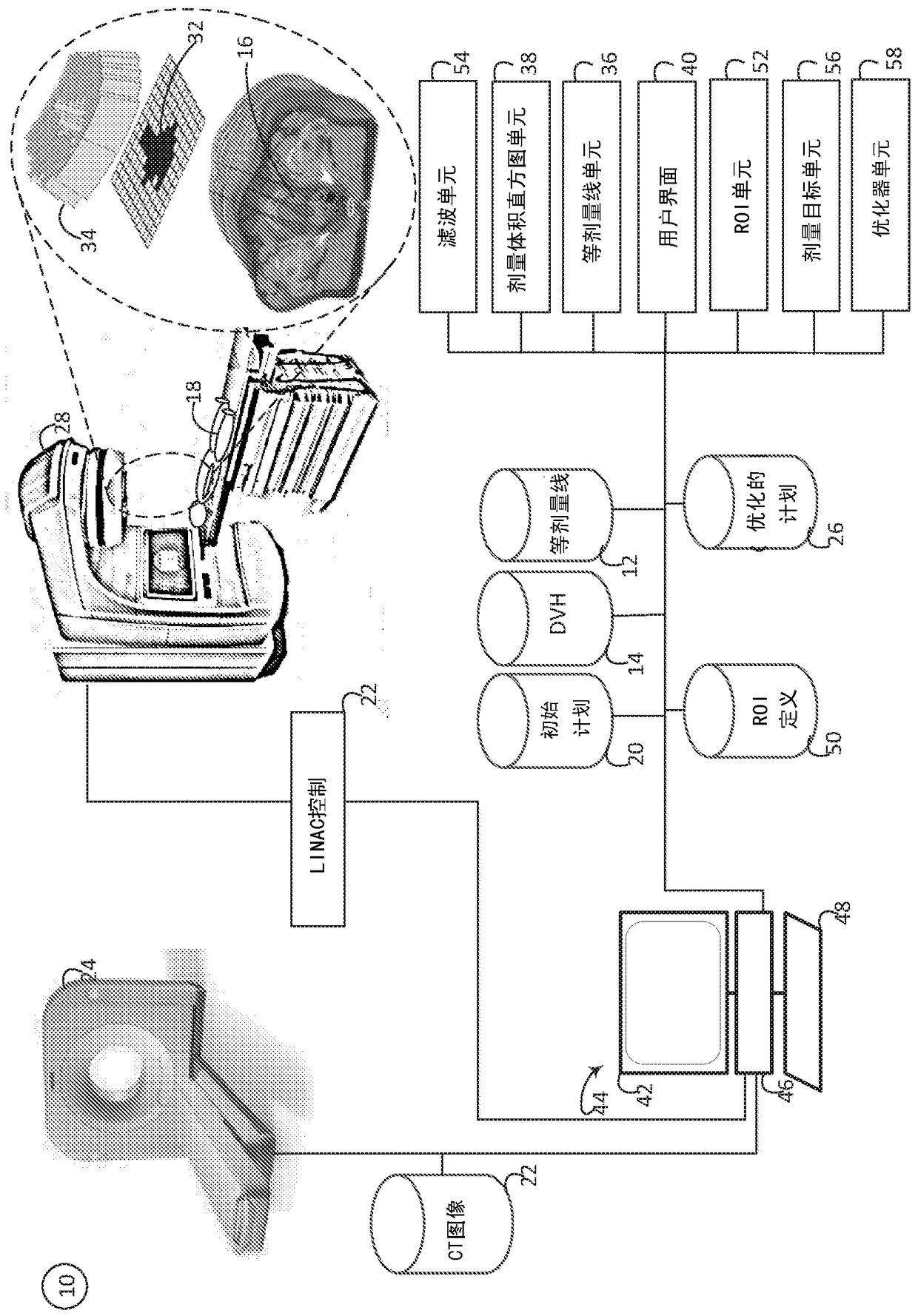
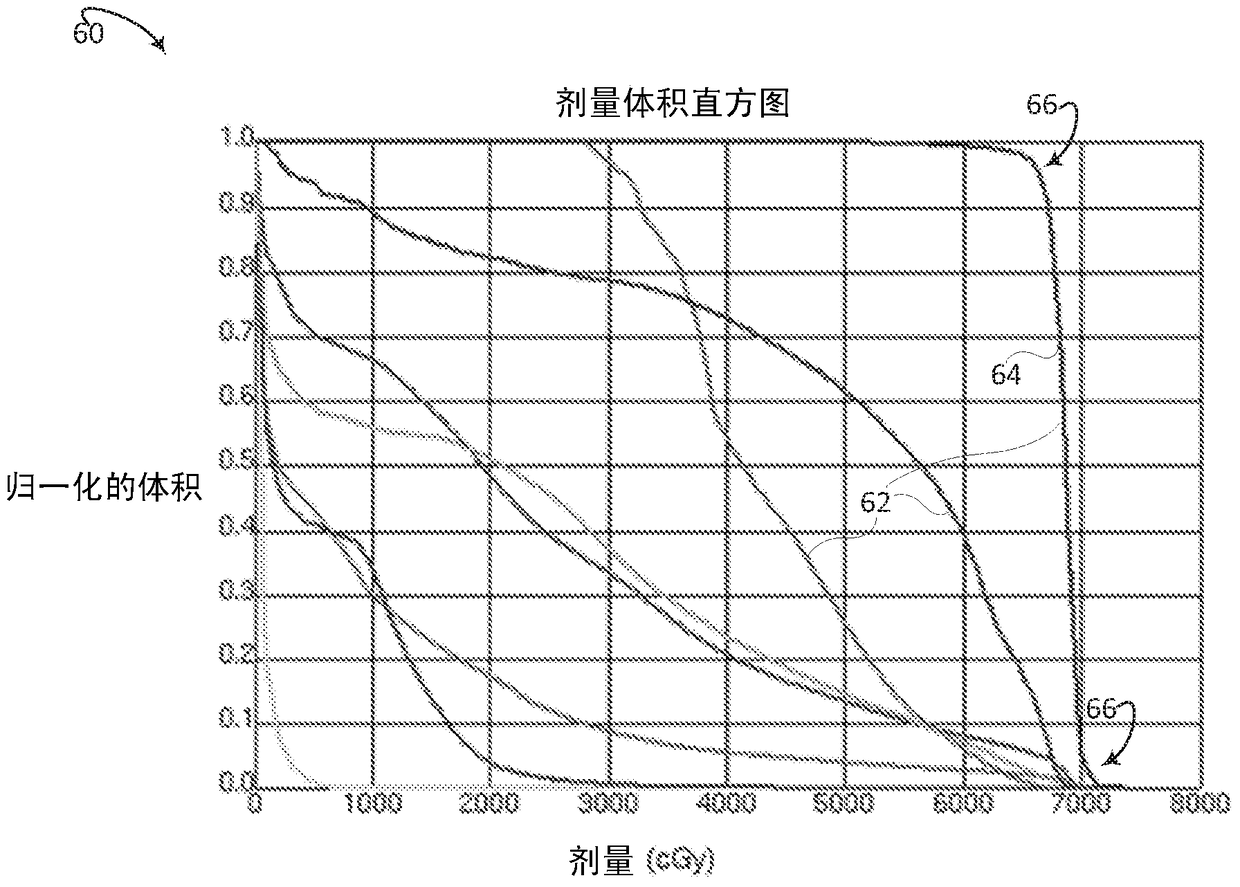
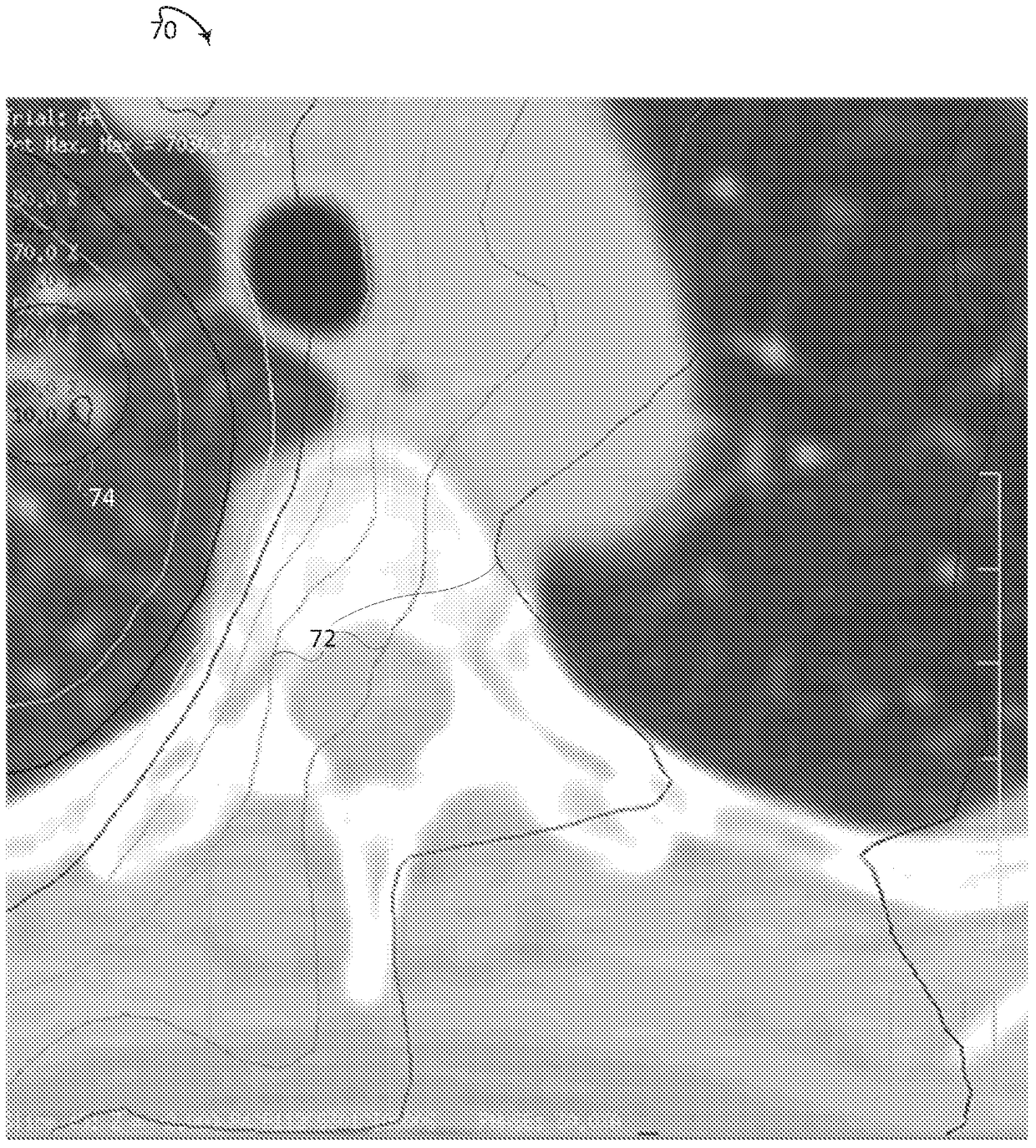
Isodose optimization
A radiation therapy planning system (10) includes an isodose line unit (36), a region of interest unit (52), and an optimization unit (58). The isodose line unit (36) receives isodose lines planned for a volume of a subject. The region of interest unit (52) defines at least one isodose region of interest based on the received isodose lines. The optimization unit (58) generates an optimized radiation therapy plan based on the at least one defined isodose region of interest and at least one dose objective for the defined region of interest.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Dose optimization method and device based on Monte Carlo and storage medium
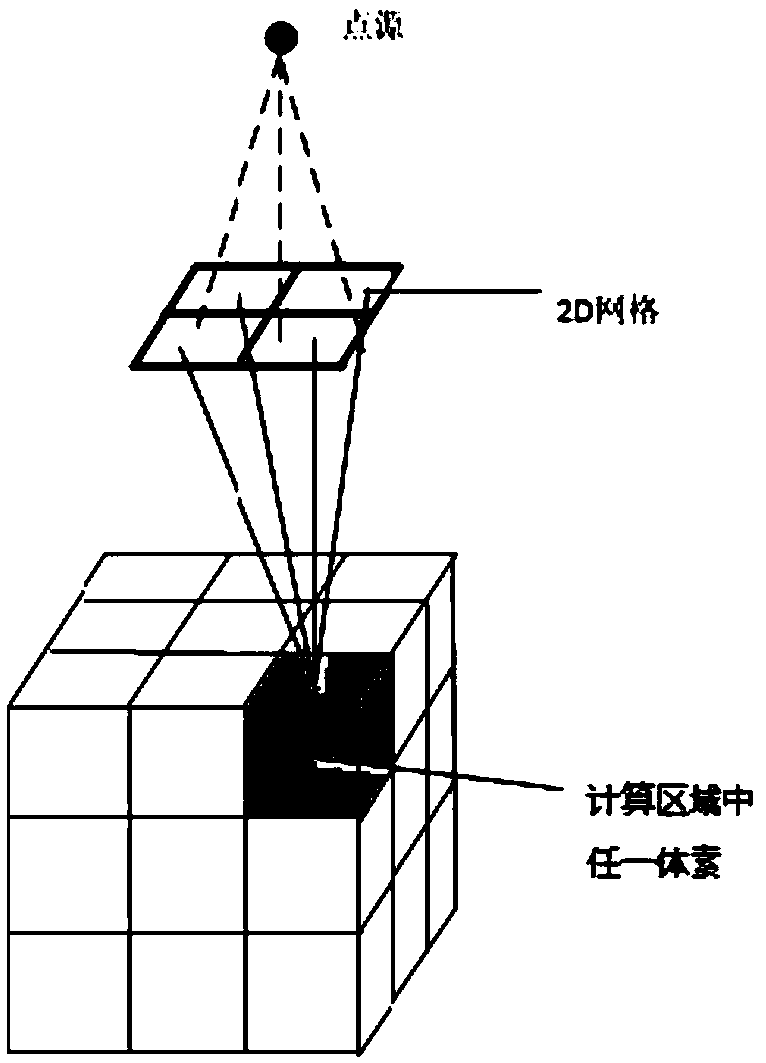
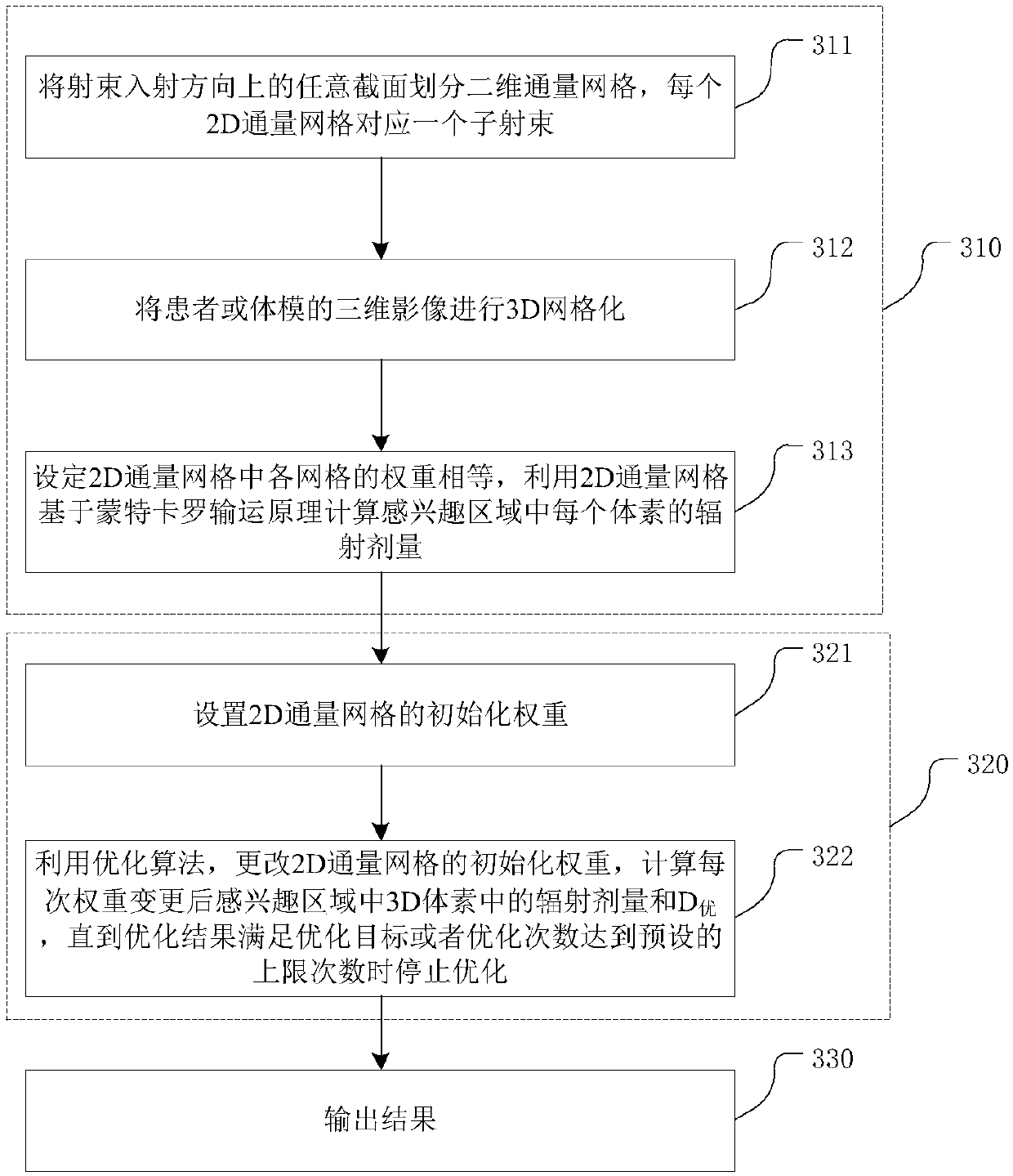
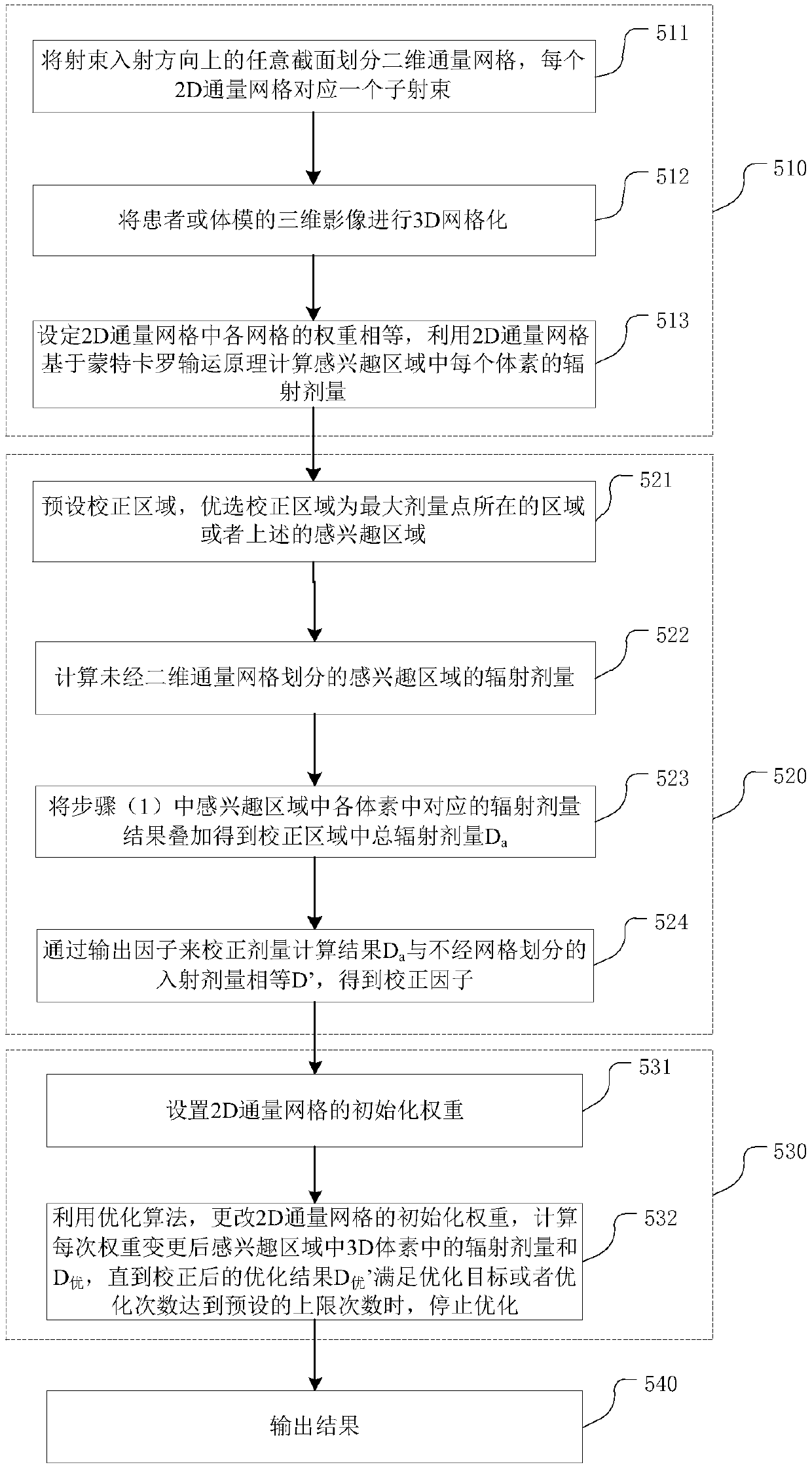
ActiveCN110556176ASolve the defect of slow calculation speedThe calculation result is accurateMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesArtificial lifeVoxelGrid based
The invention belongs to the field of radiotherapy dose calculation, and relates to a dose optimization method and device based on Monte Carlo, and a storage medium. The method comprises the followingsteps: dividing any cross section in the incident direction of a beam into two-dimensional flux grids, wherein each two-dimensional flux grid is corresponding to one sub-beam; carrying out 3D gridding on the three-dimensional image of a patient or a phantom, wherein each grid is a voxel; setting the weight of each grid in the 2D flux grid to be equal, and calculating the radiation dose of each voxel in the region of interest by utilizing the 2D flux grid based on the Monte Carlo transport principle; optimizing the 2D flux grid weight by using an optimization algorithm to realize an optimization target; and outputting results. The method provided by the invention overcomes the defect of low calculation speed caused by participation of MC in each optimization in the optimization process inthe prior art; and an output factor correction step is added, so that the corrected calculation result of the radiation dose of the 3D grid is accurate, and the error is greatly reduced.
Owner:BEIJING LINKING MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
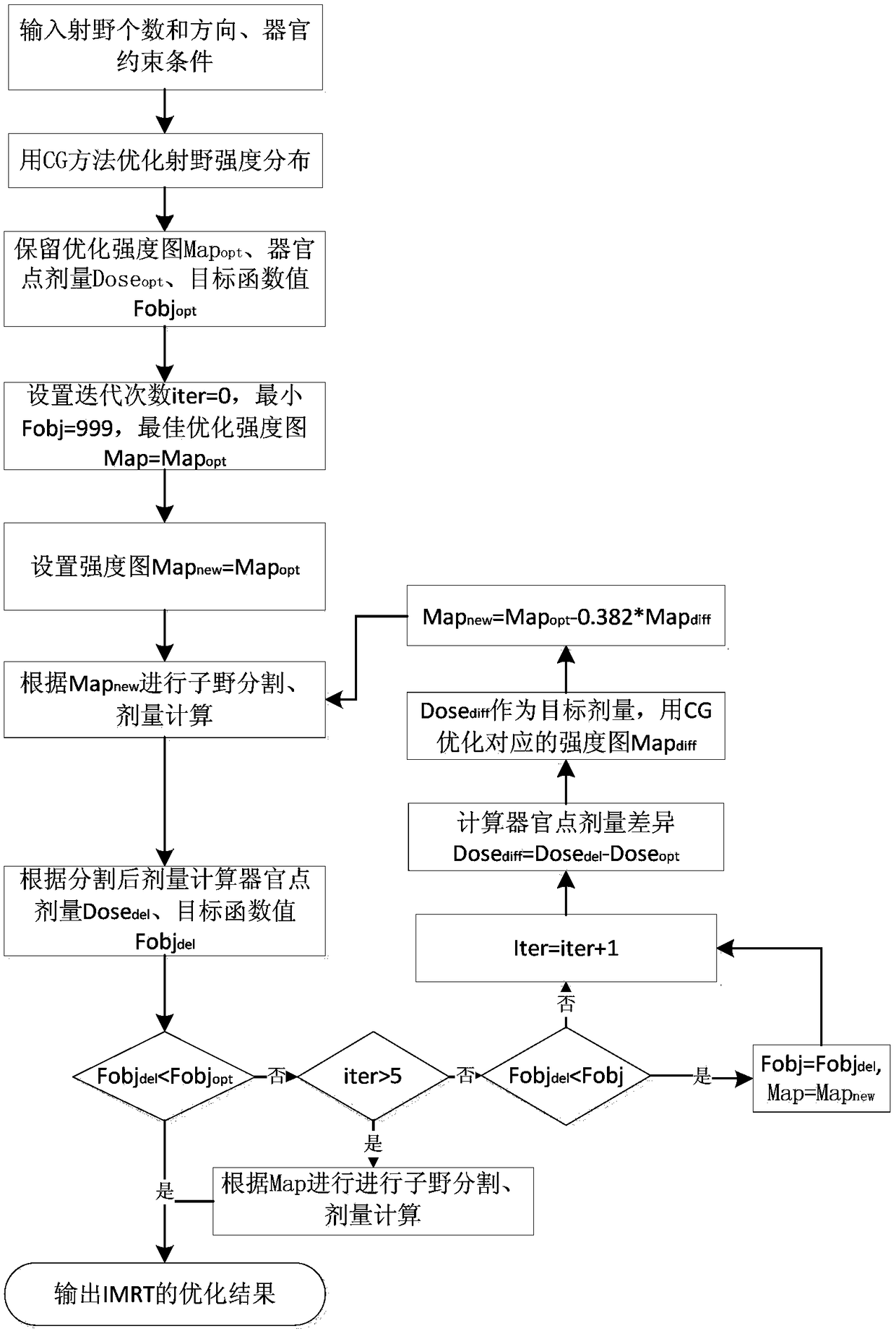
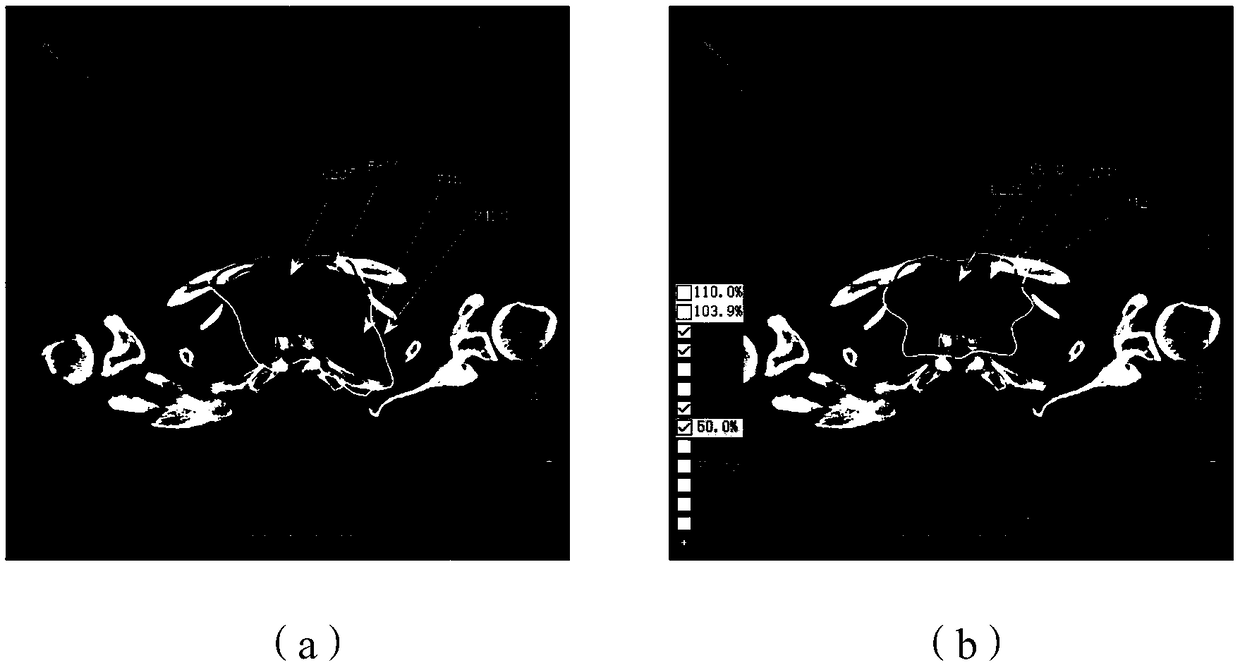
Dose optimization guided TPS (transaction per second) automatic iterative optimization algorithm
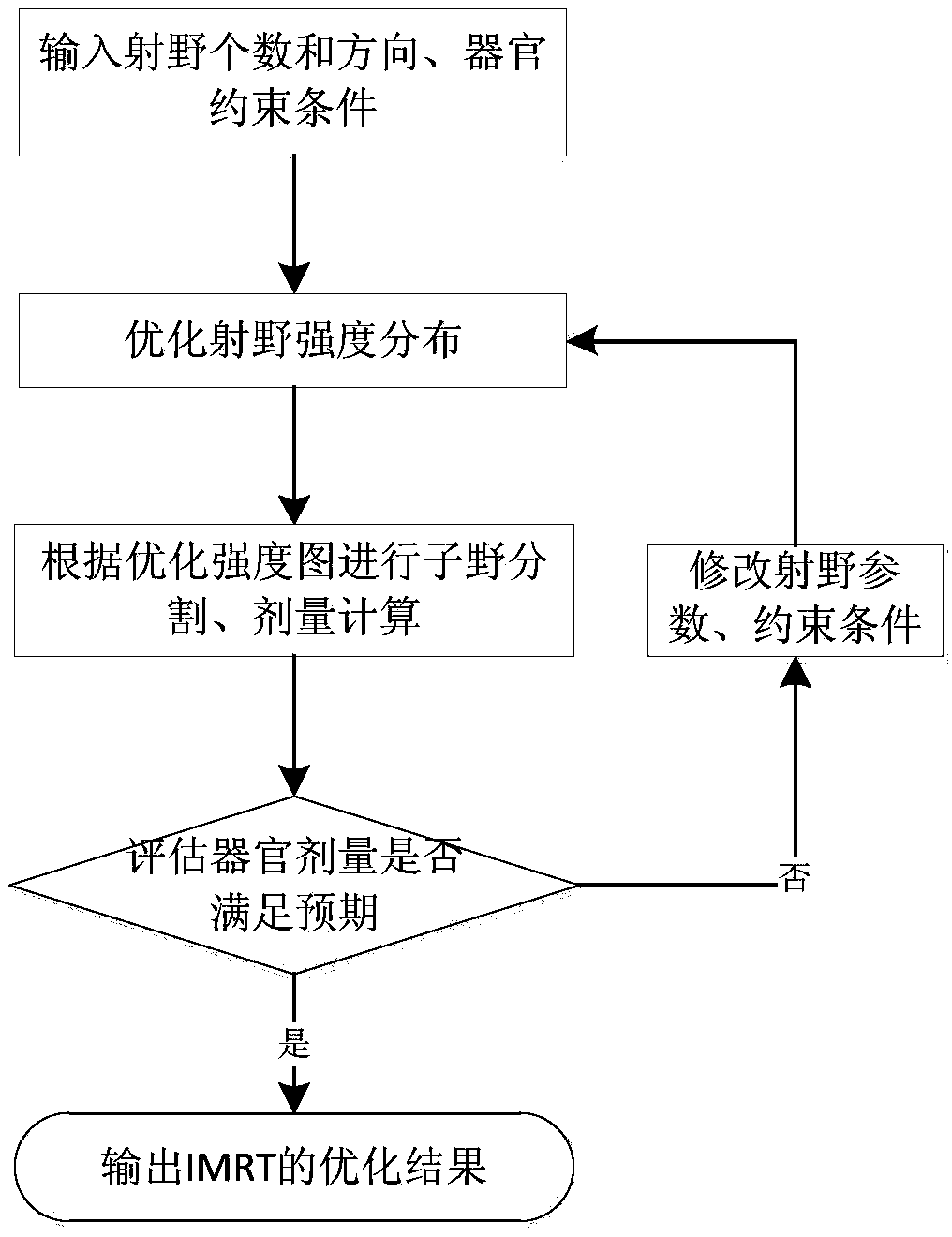
ActiveCN109499012AShorten the timeSolving for Optimal Dose DistributionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAlgorithmDose optimization
The invention discloses a dose optimization guided TPS (transaction per second) automatic iterative optimization algorithm which includes the steps: first, calculating the difference of the dose and the optimization result of each point in each organ according to fractionated dose as optimization engine input to obtain strength map contribution of the difference; second, subtracting the strength map of the difference from an original optimized strength map to serve as strength map input of sub-domain segmentation to obtain iterated sub-domains, and calculating the dose; finally, repeating thewhole process, enabling final dose distribution to be approximate to the optimized dose to obtain expected dose distribution. The step of sub-domain segmentation is taken into the whole optimization process, dose deviation caused by sub-domain segmentation is continuously corrected, planning quality can be remarkably improved, and plan making efficiency is accelerated.
Owner:SUZHOU LINATECH MEDICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
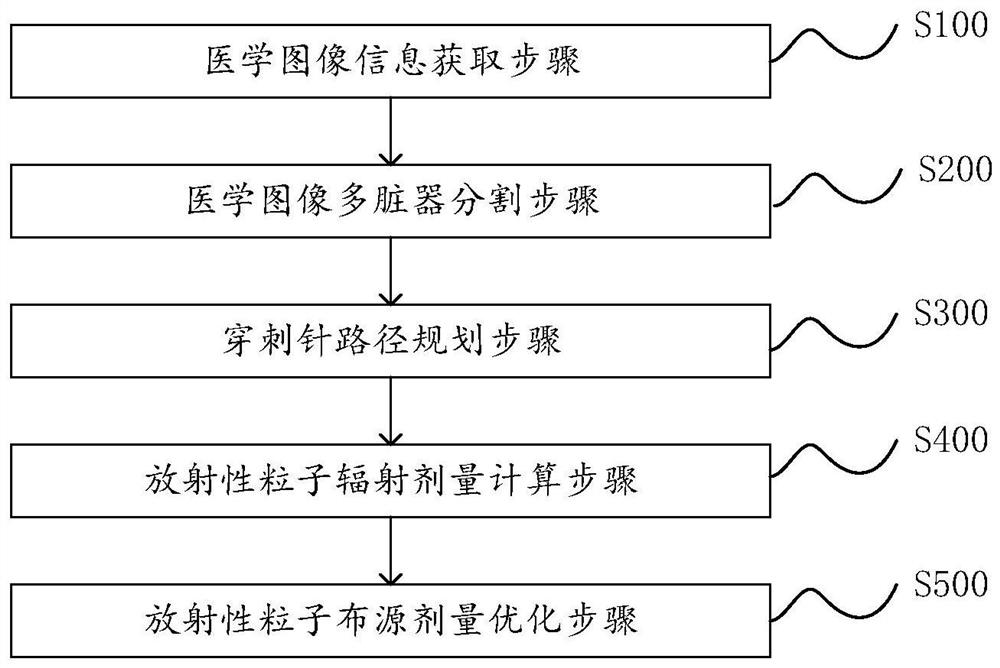
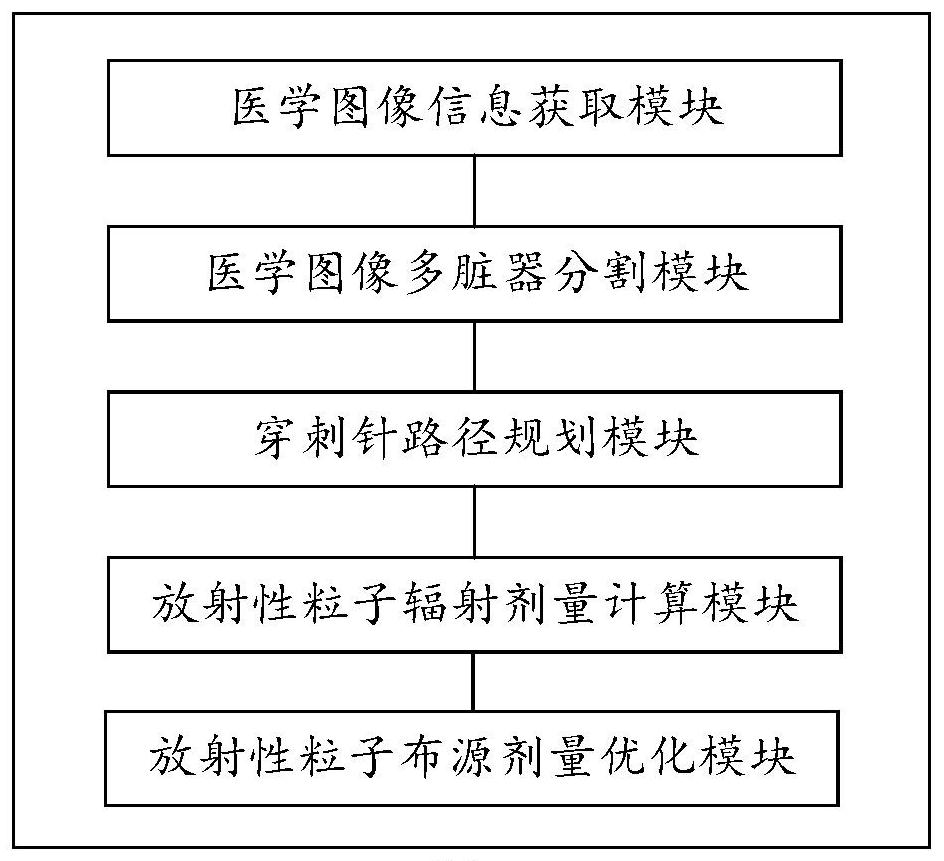
Radiotherapy dose planning method and system for implanting particles into tumor, and medium
ActiveCN113181563AStable and accurate outputStable outputImage enhancementImage analysisDose optimizationSeed Implantation
The invention discloses a radiotherapy dose planning method and system for implanting particles into a tumor, and a medium, and is used for a radiotherapy interventional surgical robot in radioactive particles. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining medical image information; a medical image multi-organ segmentation step of performing multi-organ segmentation on the medical image, including labeling one or more organs on the medical image; a puncture needle path planning step: limiting a feasible path of a puncture needle based on the marked organ and the virtual needle insertion panel; a radioactive particle radiation dose calculation step: calculating the radiation dose of the radioactive particles in the in-vivo environment; and a radioactive particle source arrangement dose optimization step: optimizing the number and spatial positions of the implanted particles according to the radiation dose of the particles and the form and volume of the tumor focus to obtain a particle source arrangement result with the accumulated radiation dose meeting the set dose. According to the invention, radiation particle dose distribution meets clinical requirements.
Owner:珠海横乐医学科技有限公司
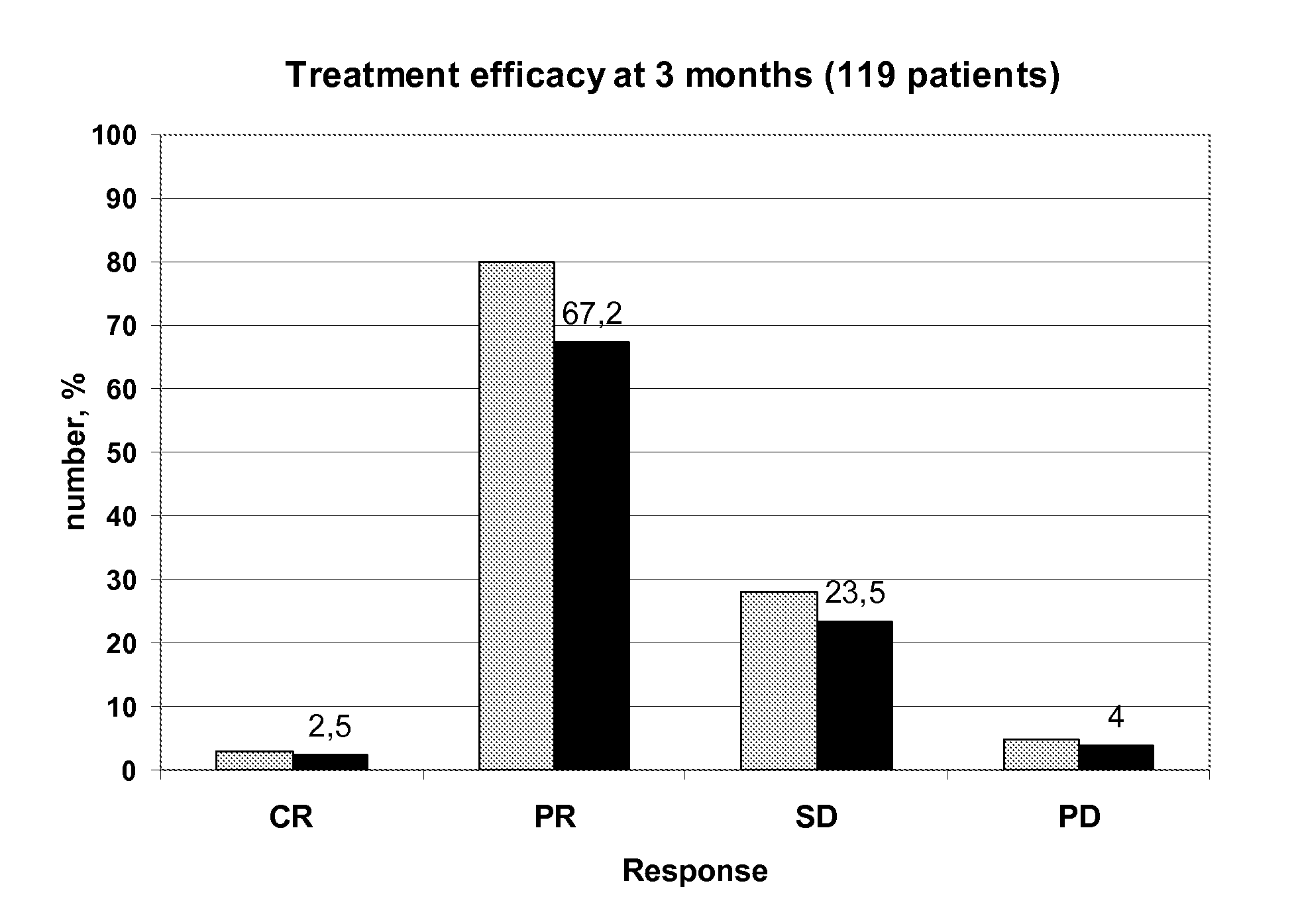
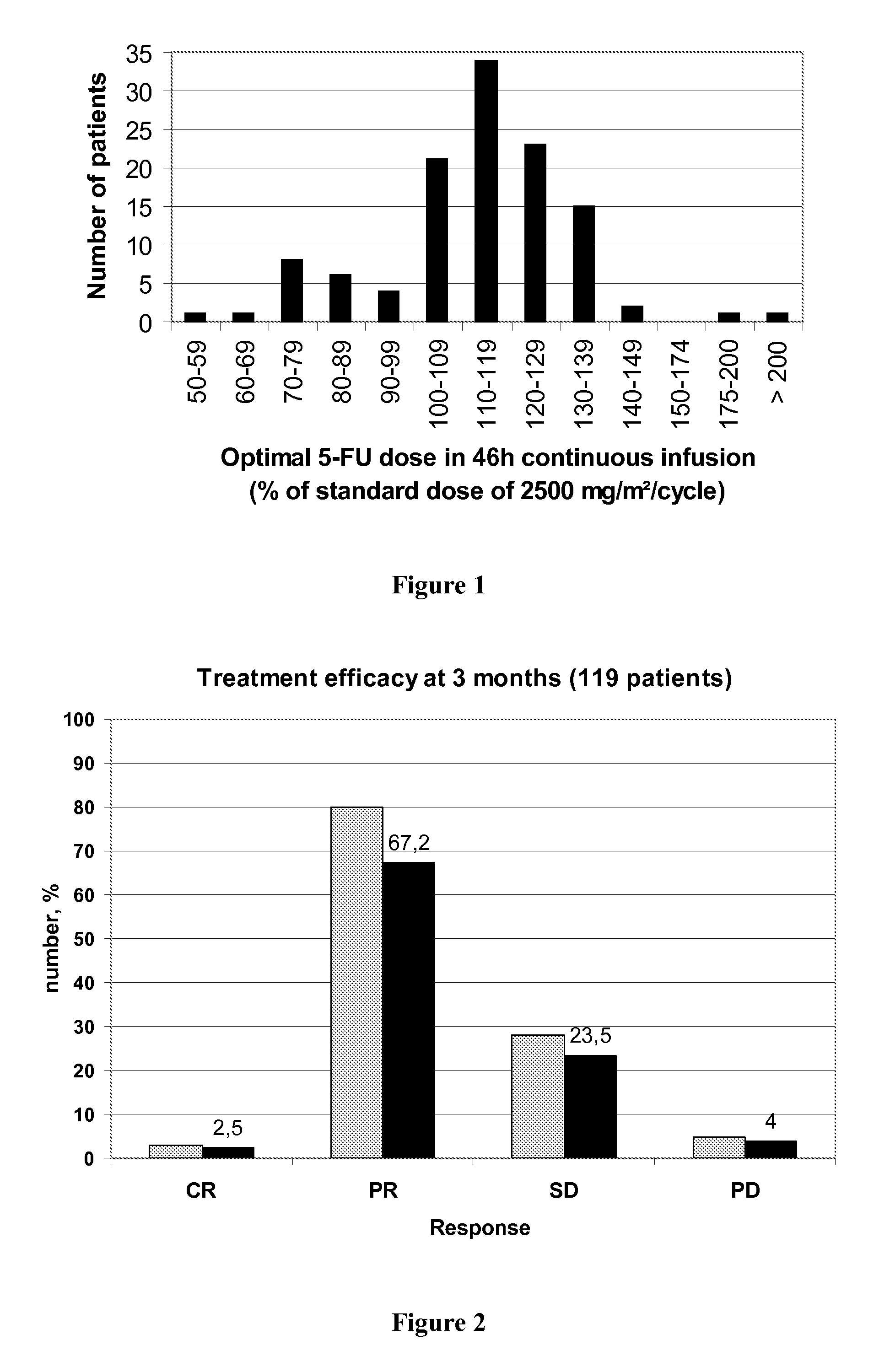
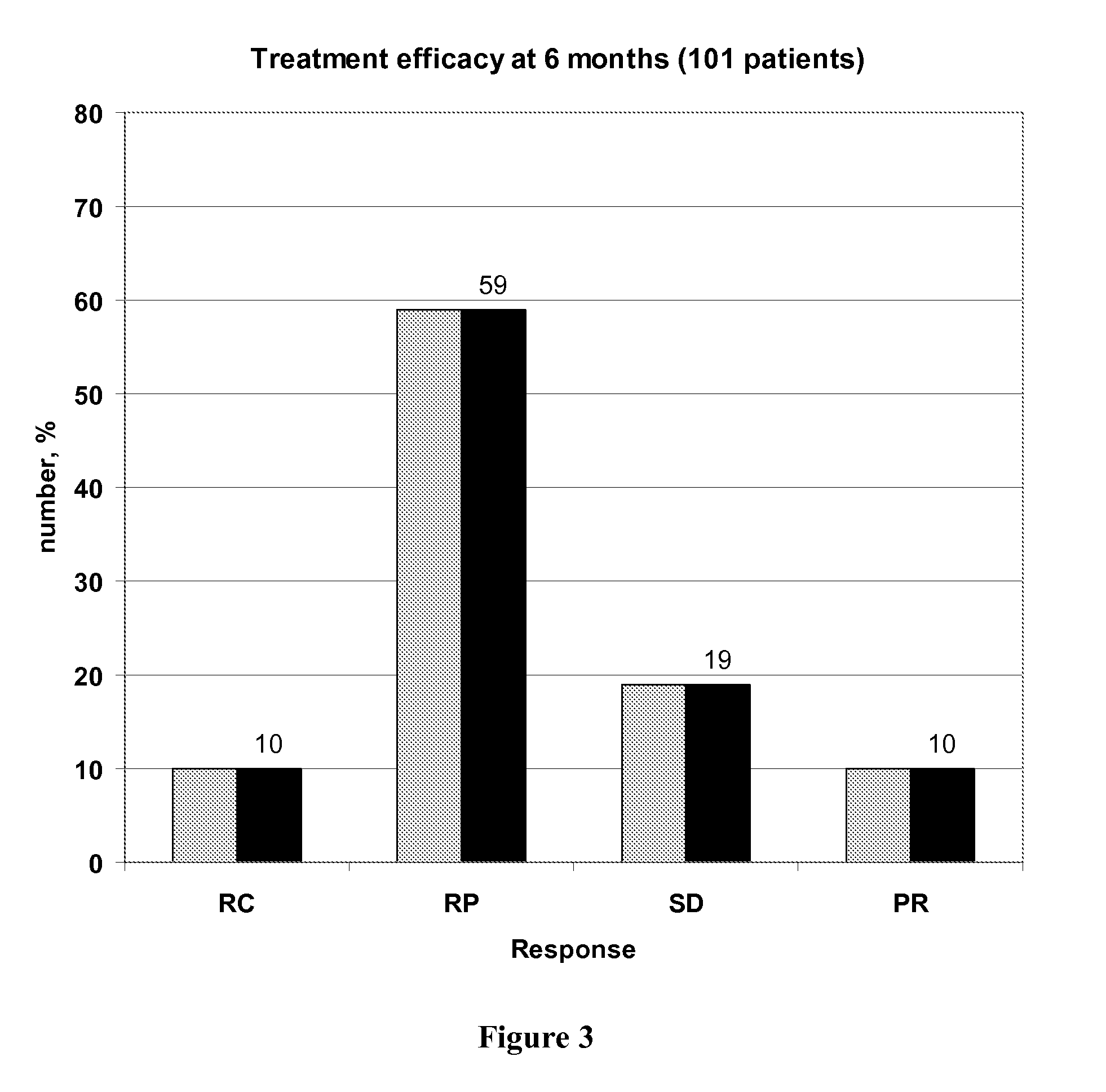
Individual 5-fluorouracile dose optimization in folfox treatment
InactiveUS20110246079A1Short half-lifeImprove the quality of lifeDisease diagnosisBiological testingFOLFOX RegimenPersonalization
The present invention belongs to the field of improved personalized medicine. More precisely, the present invention relates to a method for progressively optimizing the 5-FU dose administered by continuous infusion in patients treated by a FOLFOX regimen or a similar regimen, based on the 5-FU plasmatic concentration measured during the previous 5-FU continuous infusion and on a herein described decision algorithm. The present invention also relates to a method for treating a cancer patient in which the 5-FU dose administered in continuous infusion in each FOLFOX or similar treatment cycle is optimized using the decision algorithm according to the invention.
Owner:UNIV DANGERS +1
Dose optimization method of radiotherapy interventional surgical robot in radioactive particles and medium
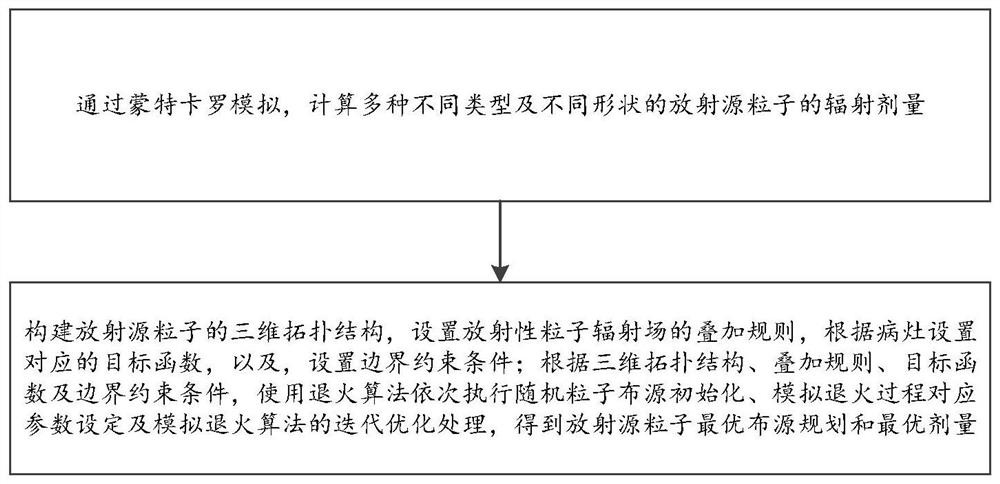
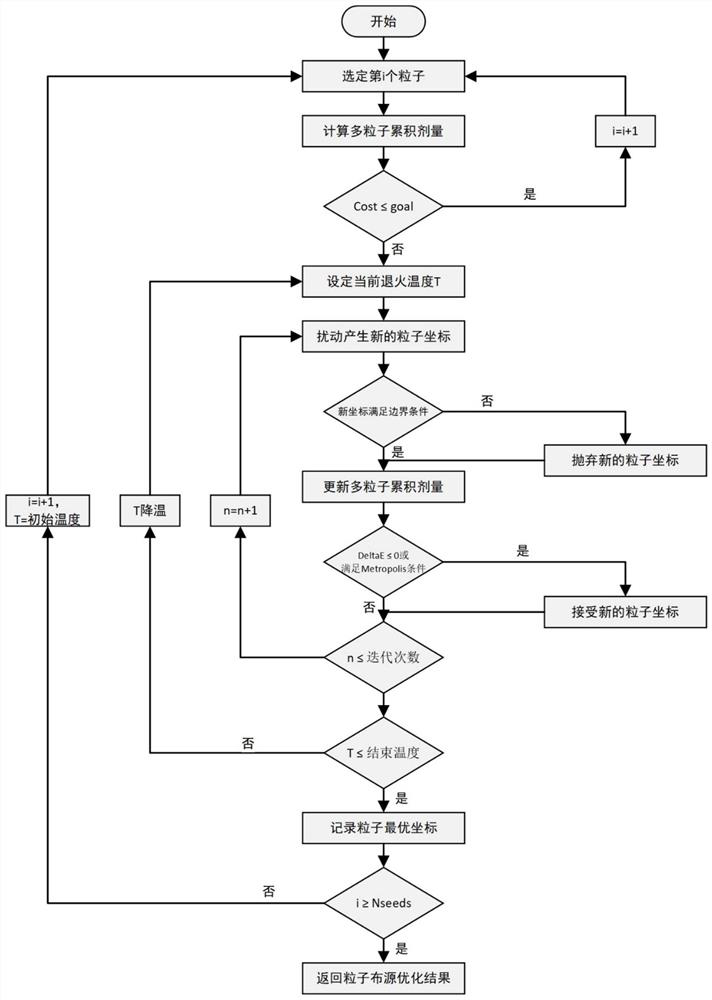
PendingCN113192554AOptimal Particle Distribution PlanningExcellent dosageArtificial lifeMolecular structuresNuclear engineeringRadiation field
The invention relates to a dose optimization method of a radiotherapy interventional surgical robot in radioactive particles and a medium. The dose optimization method comprises the steps of particle dose calculation and particle dose optimization. The particle dose calculation comprises the following steps: calculating radiation doses of various radioactive source particles with different types and different shapes through Monte Carlo simulation; wherein the particle dose optimization comprises the steps of constructing a three-dimensional topological structure of radioactive source particles, setting a superposition rule of a radioactive particle radiation field, setting a corresponding objective function according to a focus, and setting a boundary constraint condition; according to the three-dimensional topological structure, the superposition rule, the objective function and the boundary constraint condition, carrying out an annealing algorithm sequentially executing random particle source arrangement initialization, corresponding parameter setting of the simulated annealing process and iterative optimization processing of the simulated annealing algorithm, thus acquiring the optimal source arrangement plan and the optimal dosage of radioactive source particles. The method has the beneficial effects that the optimal particle source arrangement planning and dosage of the radiotherapy interventional surgical robot in the radioactive particles are realized.
Owner:珠海横乐医学科技有限公司
Individual 5-fluorouracile dose optimization in folfiri treatment
ActiveUS9463193B2Short half-lifeImprove the quality of lifeOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementRegimenDose optimization
Owner:UNIV DANGERS +1
Intelligent optimization setting adjustment for radiotherapy treatment planning using patient geometry information and artificial intelligence
PendingUS20220126116A1Save calculationShorten the timeMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMedical automated diagnosisDose prescriptionEngineering
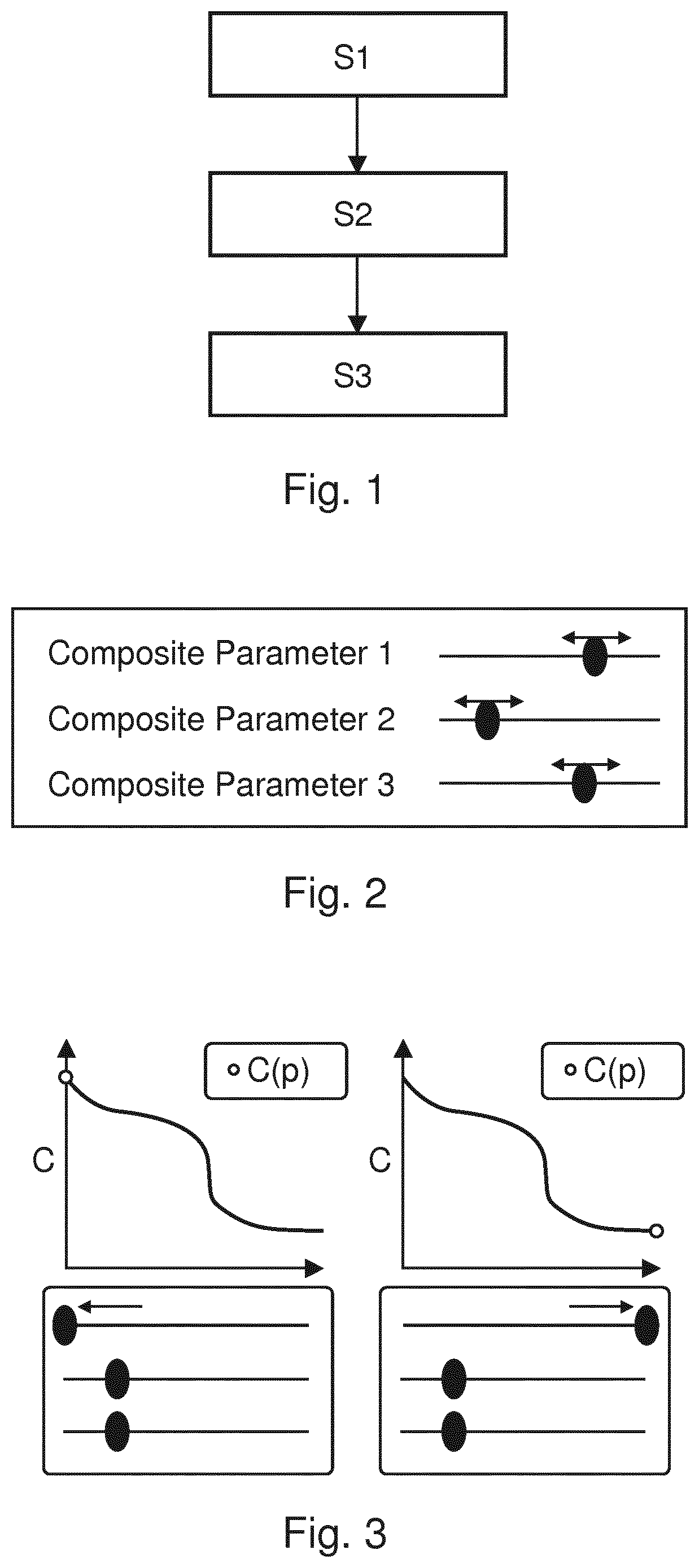
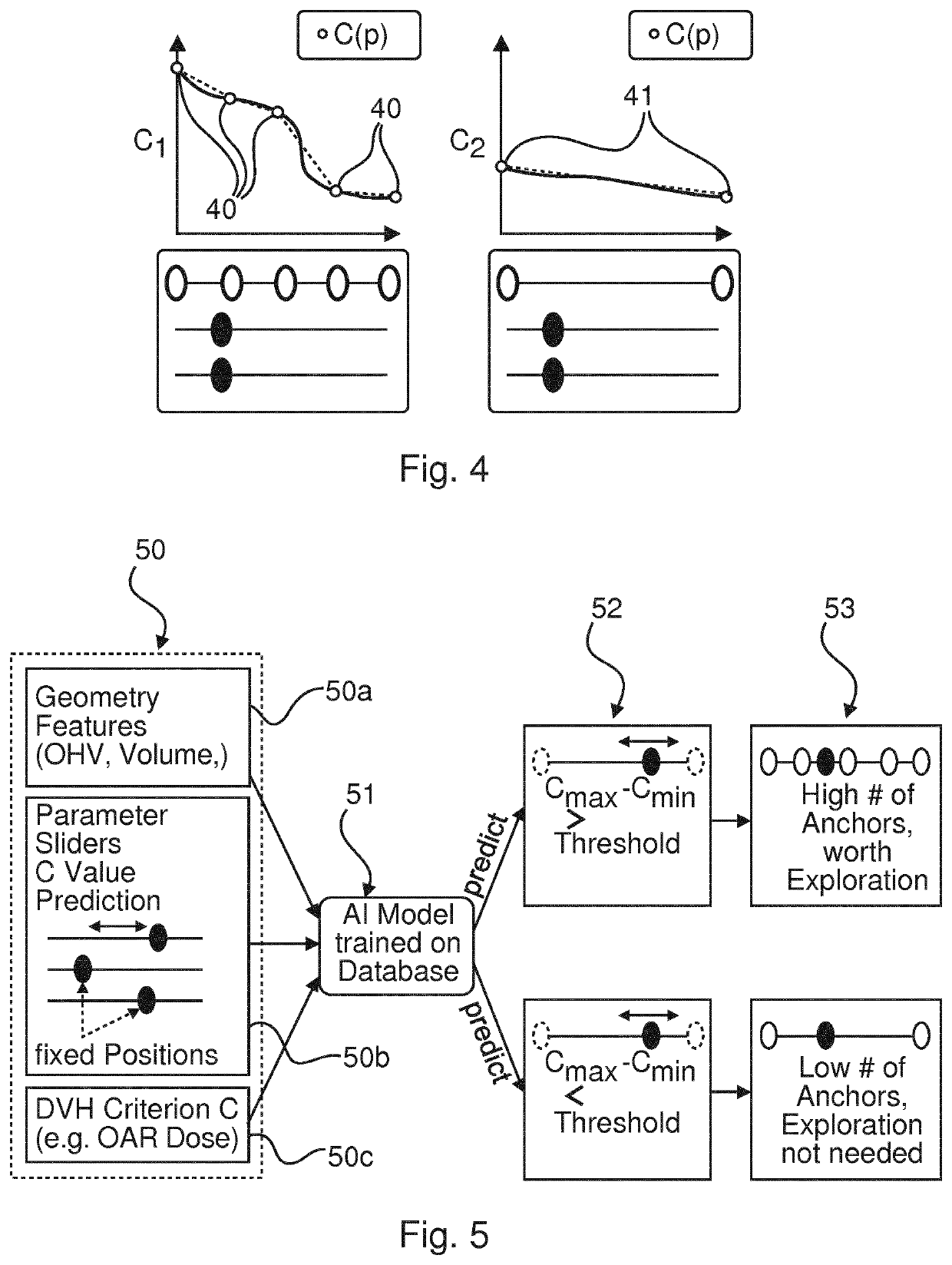
By using the Al module, the method of the present invention calculates, i.e. predicts, the dependency Ci (pi) of a radiotherapy (RT) quality criterion C, from an adjustment of such a radiotherapy planning parameter pi. In this way, the decision making process in RT treatment plan optimization is streamlined by prediction of promising settings of one or more radiotherapy planning parameters p, before the actual time intensive iterative optimization process is carried out. This is achieved by applying an Al module, which has been trained to predict the specific behaviour of the dose optimization algorithm, i.e. the optimizer, with respect to geometric patient data, dose prescription and treatment indication data. Thus, a computer-implemented medical method of predicting a dependency Ci (pi) of a radiotherapy (RT) quality criterion Ci from an adjustment of a radiotherapy planning parameter p, is presented. The method comprises the following steps of providing geometric patient data geometrically describing an area of a patient, which is to be irradiated according to a radiotherapy treatment plan (step S1), providing dose prescription data and treatment indication data for said patient (step S2), and predicting with a trained Artificial Intelligence (Al) module the dependency Ci (pi) of the radiotherapy quality criterion Ci from the radiotherapy planning parameter p, when adjusting said radiotherapy planning parameter pi, thereby using the geometric patient data, the dose prescription data and the treatment indication data as input for the Al module (step S3).
Owner:BRAINLAB
Method for detecting influence of electronic cigarette aerosol water extract on activity of superoxide dismutase of cells
InactiveCN107807233AAssessing the effects of oxidative damageColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingMode of actionCell selection
The invention discloses a method for detecting the influence of an electronic cigarette aerosol water extract on the activity of superoxide dismutase of cells. The method comprises: sample pre-treatment, single cell suspension preparation, cell concentration calculation, cell inoculation, subject exposure, cell collection, cell lysis, sample determination, superoxide dismutase enzyme activity calculation, and other steps. According to the present invention, the expose way and the action mode of the electronic cigarette product are comprehensively inspected, the completely-new electronic cigarette product smoke pre-treatment method is established, human lung fibroblasts HPF are selected as detection cells, and the sample detection dose is determined; and through the effective sample treatment, the detection dose optimization and the correct target cell selection, the method can accurately determine the influence of the electronic cigarette aerosol water extract on the activity of the superoxide dismutase of the cells, such that the influence of the electronic cigarette product on the oxidative damage of cells can be effectively evaluated.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
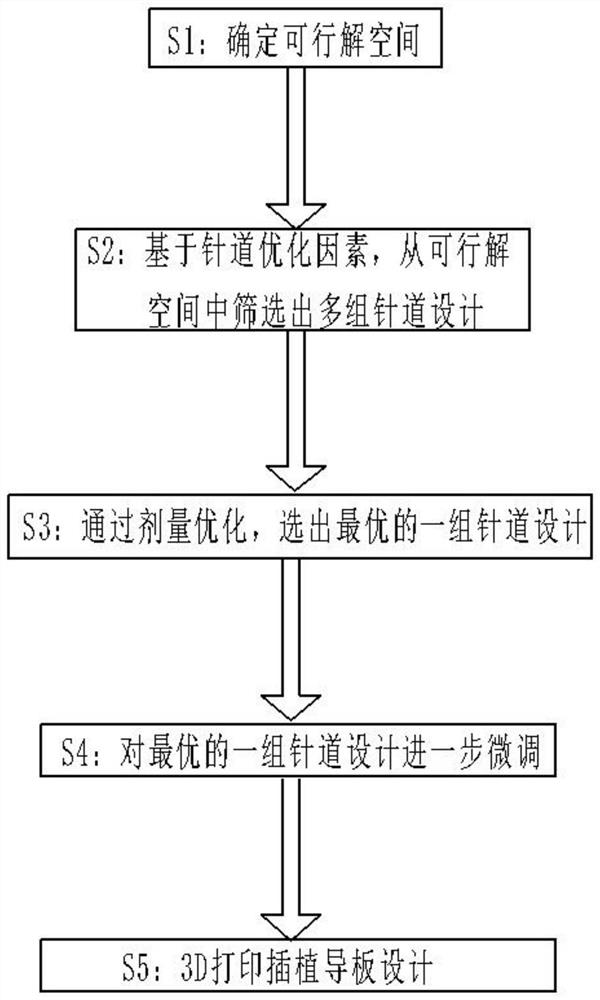
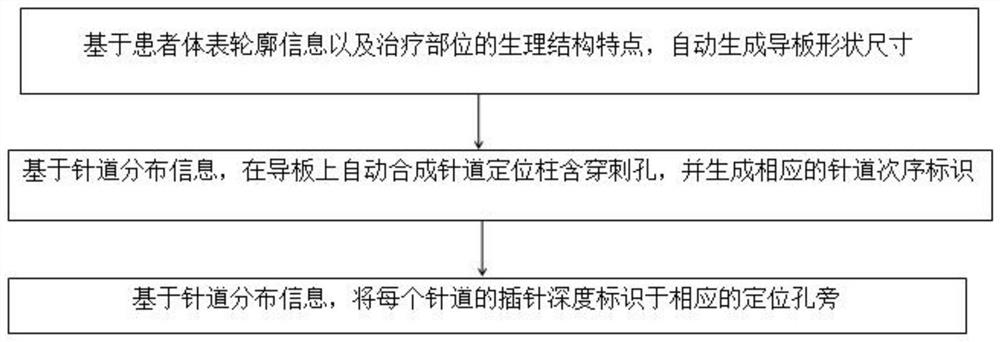
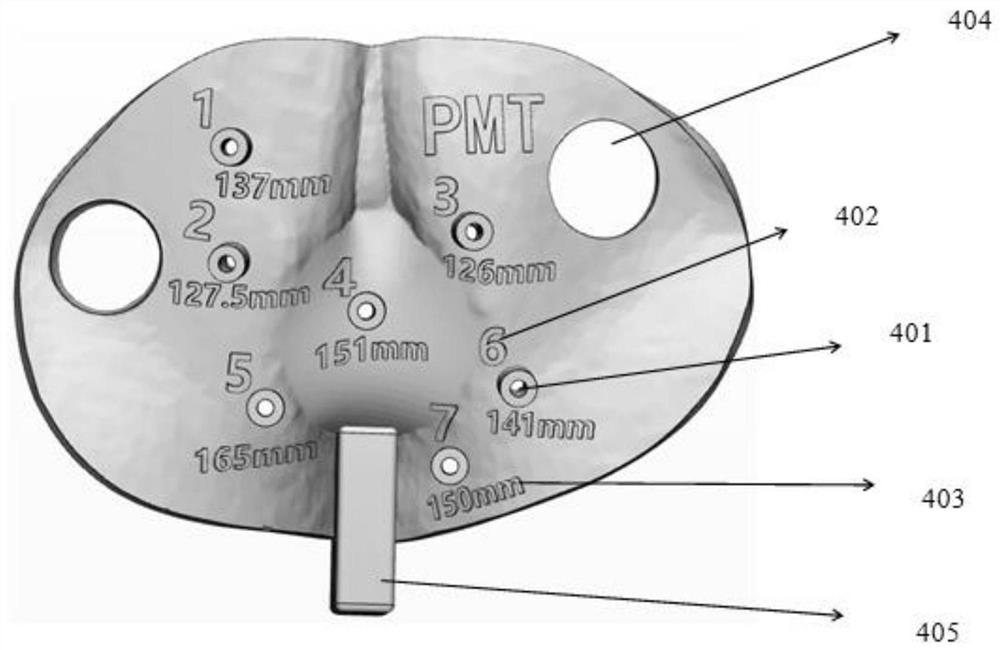
Implantation guide plate design method and implantation guide plate
The invention provides an implantation guide plate design method and an implantation guide plate, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, determining a feasible solution space based on the image information of a patient; S2, based on needle passage optimization factors, screening out multiple groups of needle passage designs from the feasible solution space determined in the step S1; and S3, performing dose optimization on the multiple groups of needle passage designs screened out in the step S2 to select a group of needle passage designs with the optimal dose volume. According to the implantation guide plate design method, the needle passage design of the implantation guide plate is optimized by adopting objective evaluation indexes to replace manual experience, so that the personalized implantation guide plate is obtained, and when the personalized implantation guide plate is applied to an internal irradiation plan, the irradiation dose endangering organs can be reduced to the greatest extent while the irradiation dose of a target region is improved.
Owner:苏州普能医疗科技有限公司
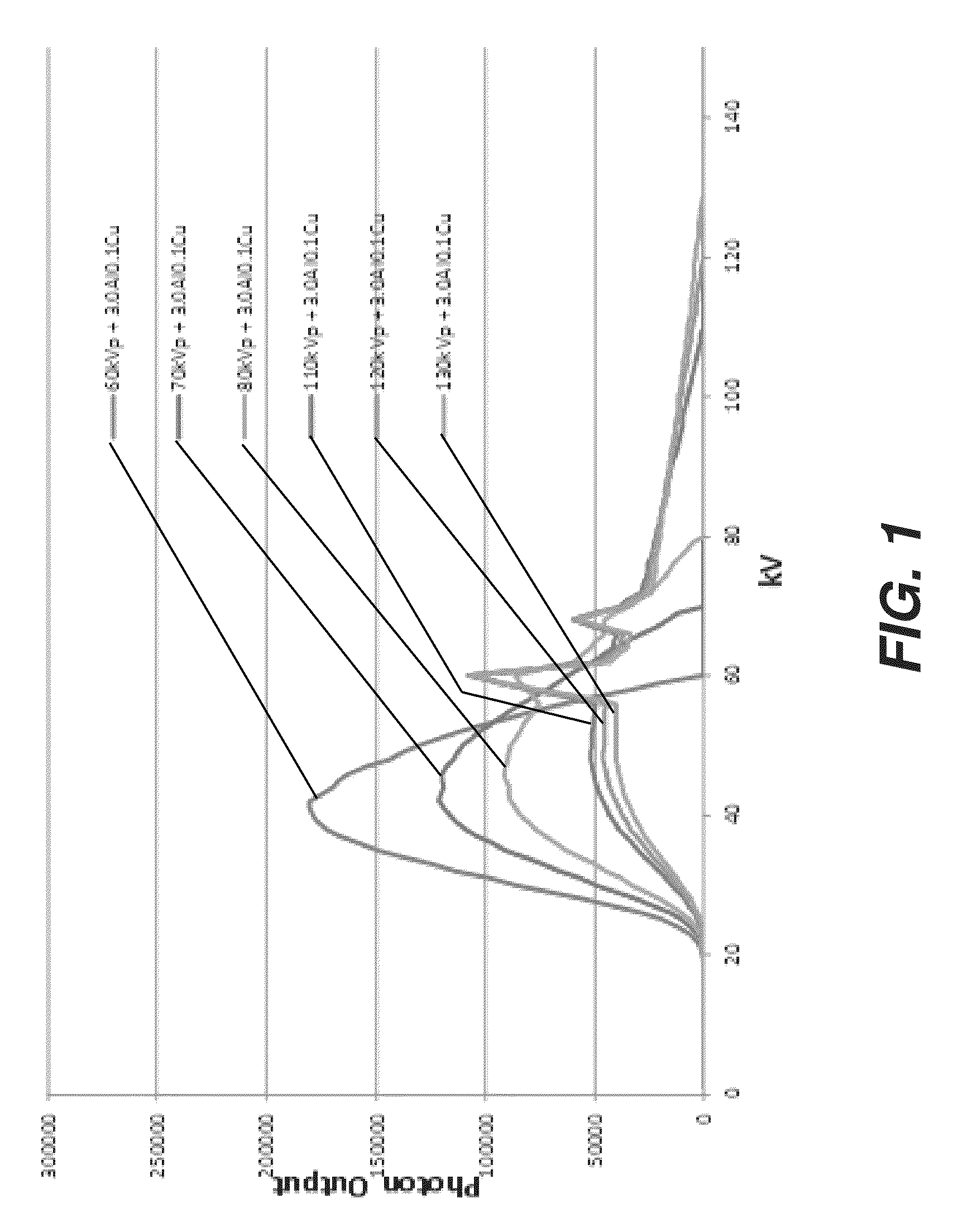
Chest radiography image contrast and exposure dose optimization
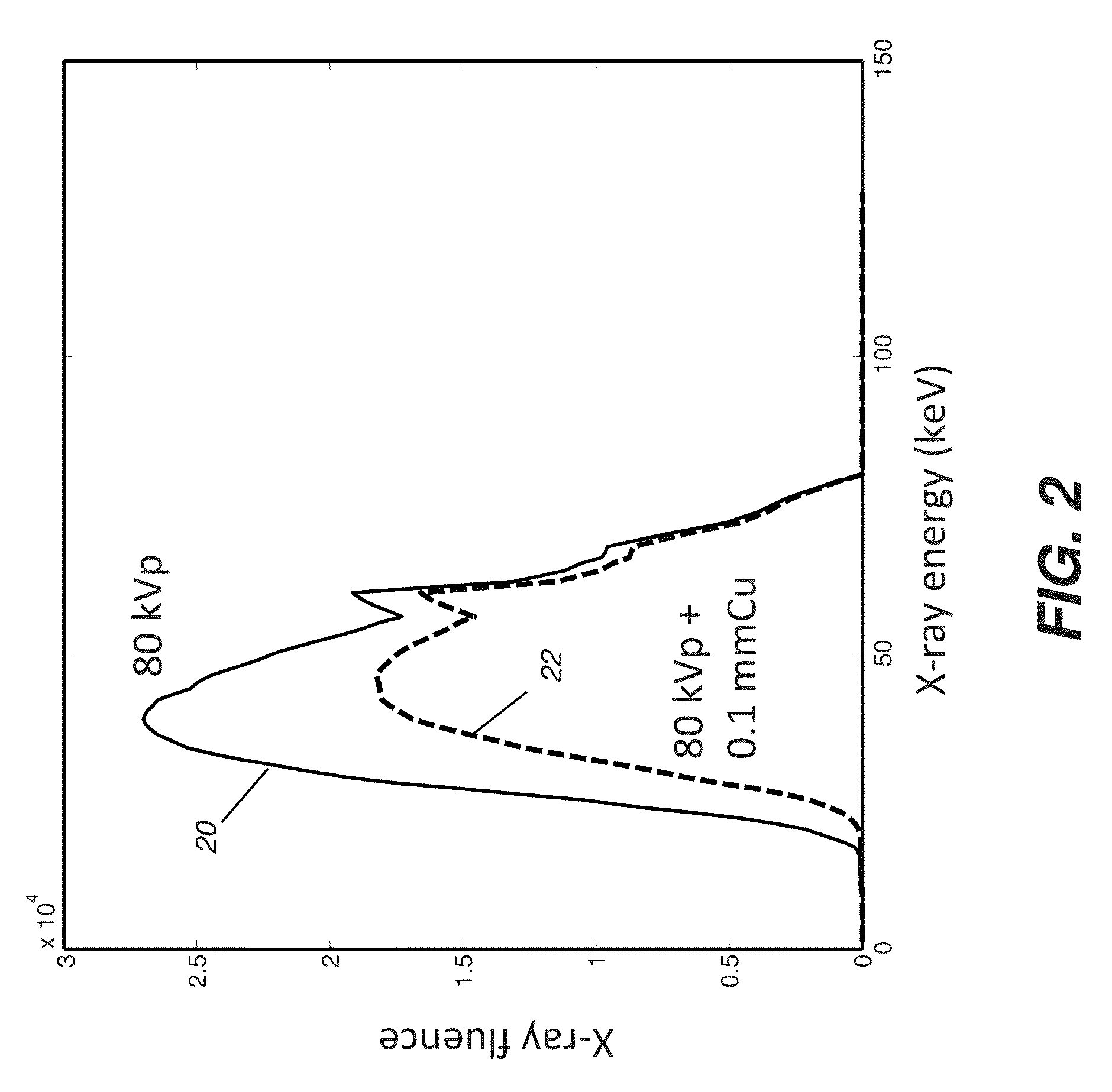
ActiveUS9101325B2Improved imaging parameter and processingIncrease contrastRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionSoft x rayImage contrast
A method for obtaining a digital chest x-ray image of a patient. The method includes providing a default set of technique settings for the chest x-ray, wherein the default set is selectable by an operator command and includes using a peak kilovoltage exposure setting that is below 90 kVp with beam filtration of the x-ray, and applying a rib contrast suppression algorithm to the digital chest x-ray image data acquired from the exposure.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Dynamic optimization system based on respiratory movement
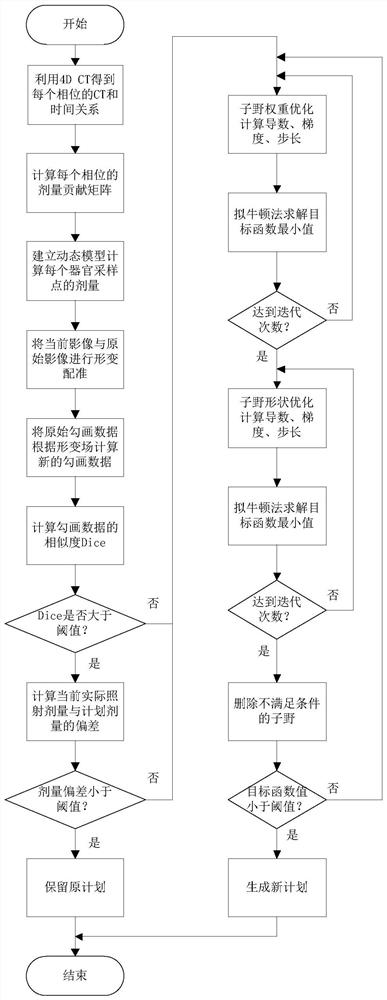
ActiveCN112999531AOptimizing the Optimal Plan ParametersImage enhancementImage analysisRespiratory phaseDynamical optimization
The invention discloses a dynamic optimization system based on respiratory movement, and belongs to a radiotherapy plan optimization system. The dynamic optimization system specifically comprises a time phase data processing module which obtains a CT image and acquisition time of each breathing phase by using 4D CT, a dose calculation module used for calculating a dose contribution matrix of each respiratory phase, and calculating the dose of an organ sampling point with the time probability according to a dynamic model formula, an optimization judgment module used for verifying the organ position and the irradiation dose, conducting plan optimization if deformation of the organ position or an error of the irradiation dose exists, and otherwise, adopting original plan parameters, and a sub-field optimization module used for adopting a sub-field optimization method for plan optimization, obtaining the dose of each organ point according to a dynamic model, calculating the shape and weight of a sub-field meeting the expected dose when the minimum value of the target function is calculated, and outputing a result. According to the method, plan optimization is carried out by considering a dynamic model, and the optimal plan parameters are automatically optimized.
Owner:中科超精(南京)科技有限公司
A dose optimization system
ActiveCN105031819BFast mutual conversionFast convergenceRadiation therapyAnesthesiaDose optimization
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Method and device for generating dynamic wedge plate control points
ActiveCN105105780BMeet needsAccurate estimateComputerised tomographsTomographyIsodose curvesDose optimization
The invention provides a method for generating control points of a dynamic wedge plate, comprising: determining a target isodose curve and a target dose; generating a one-dimensional fluence distribution according to the target isodose curve and the target dose; The dose is optimized for the one-dimensional fluence distribution, and the control points of the dynamic wedge are generated according to the optimized one-dimensional fluence distribution.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Systems and methods for dose optimization based on quality of results
ActiveCN103987321BSolve the real problemComputerised tomographsTomographyDose optimizationQuality of results
A system includes a modeler (214) that generates a model that models quality of conclusions in a radiologist's report as a function of deposited dose for a scan, and a dose optimizer (216) , creating a radiologist's report from the scan, the dose optimizer (216) determines an optimal dose value for the planned scan based on the model and one or more optimization rules (218). A method comprising: generating a model that models the quality of conclusions in a radiologist's report as a function of deposited dose of a scan, creating the radiologist's report from the scan; and, based on the model and one or Multiple optimization rules to determine optimal dose values for planned scans.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
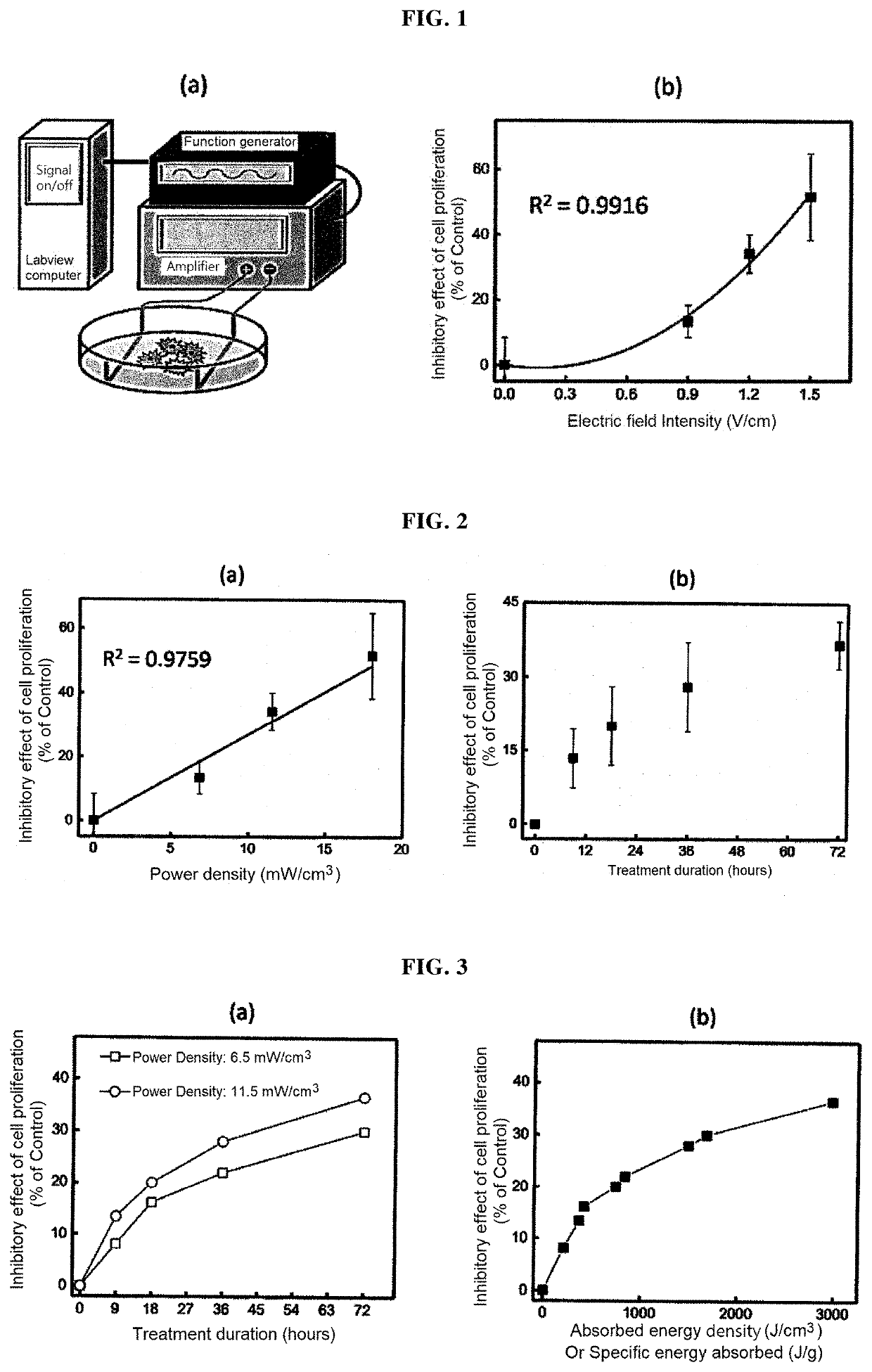
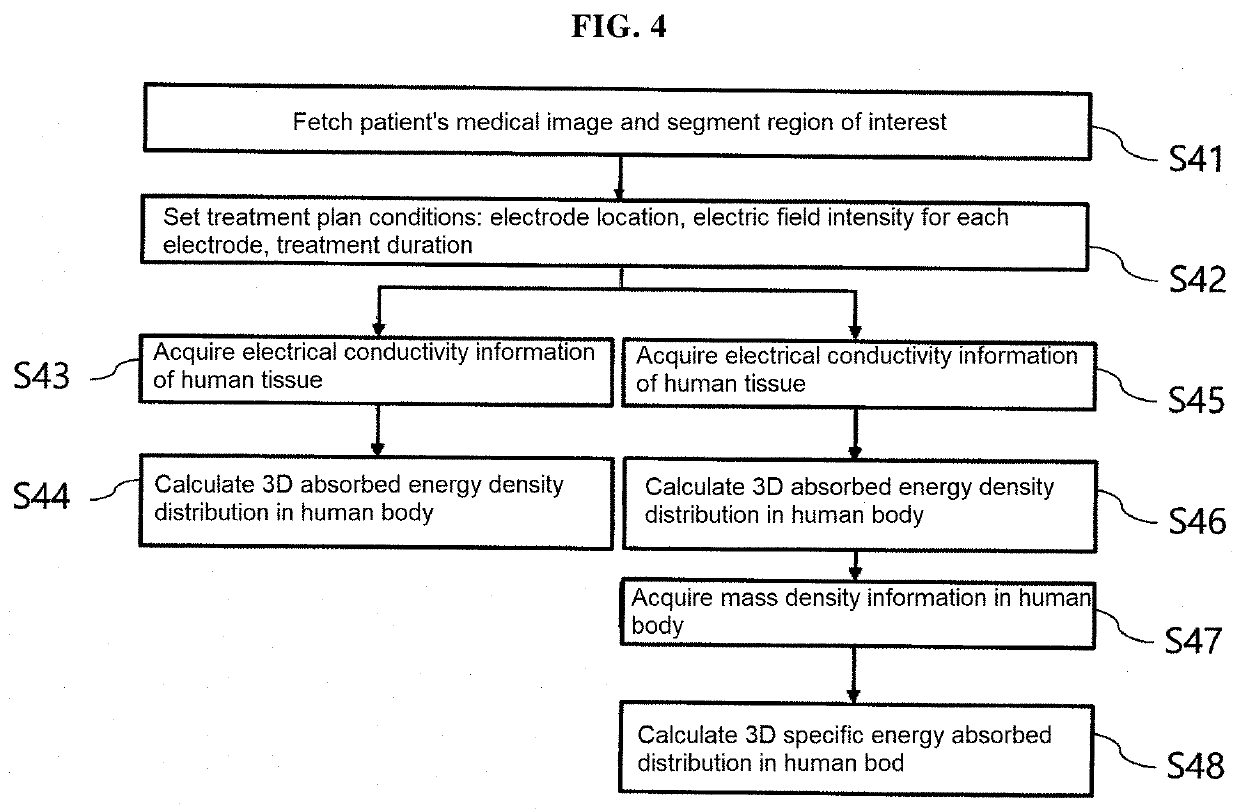
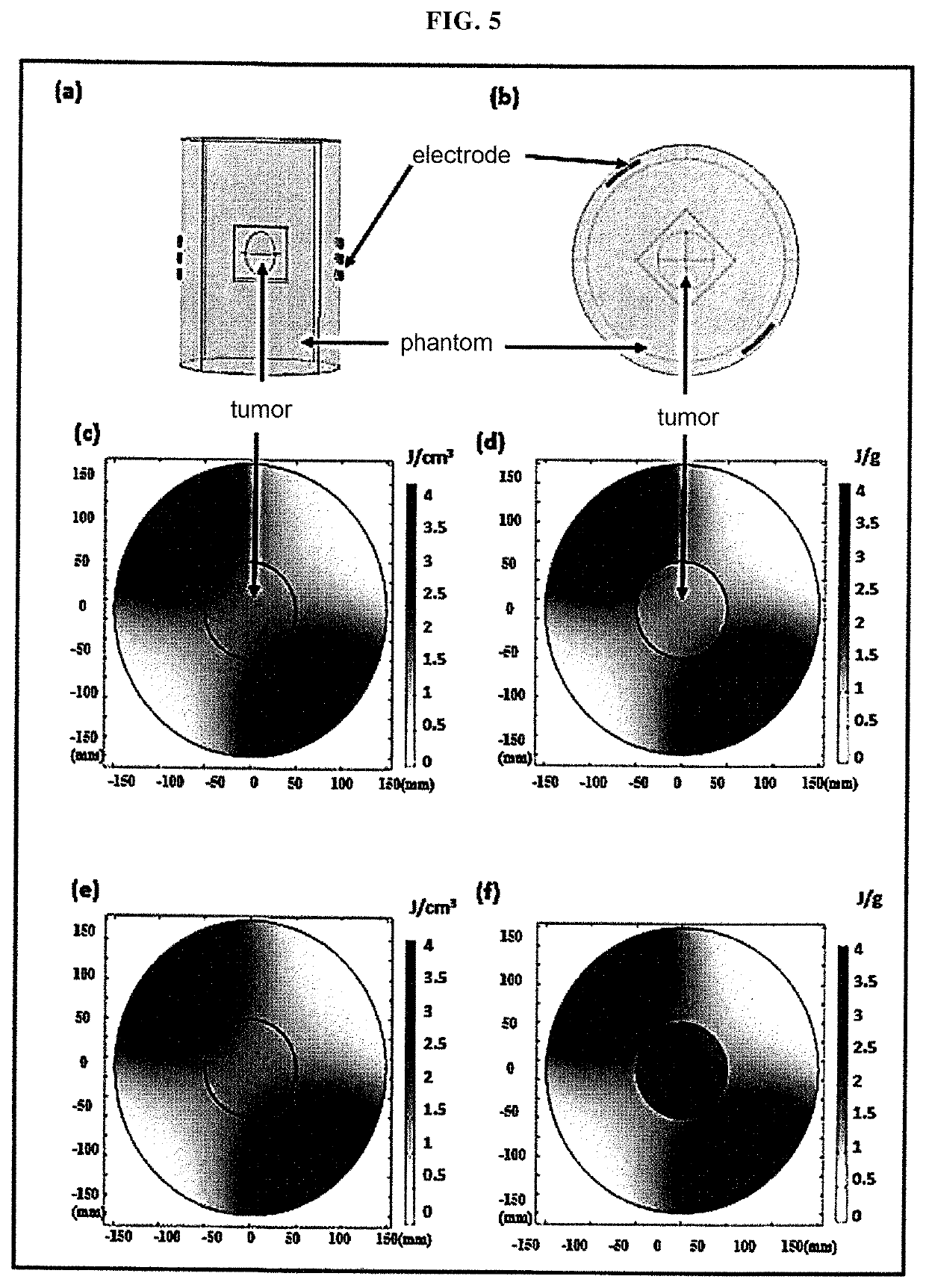
System and method for planning electric field cancer treatment based on absorbed energy
PendingUS20220184391A1Maximize the effectImage enhancementElectrotherapyDose optimizationCancer treatment
Owner:FIELDCURE CO LTD +1
isodose optimization
ActiveCN105142725BEasy doseRadiation diagnosticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyEngineeringDose optimization
A radiation therapy planning system (10) includes an isodose line unit (36), a region of interest unit (52), and an optimization unit (58). The isodose line unit (36) receives isodose lines planned for a volume of a subject. The region of interest unit (52) defines at least one isodose region of interest based on the received isodose lines. The optimization unit (58) generates an optimized radiation therapy plan based on the at least one defined isodose region of interest and at least one dose objective for the defined region of interest.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com