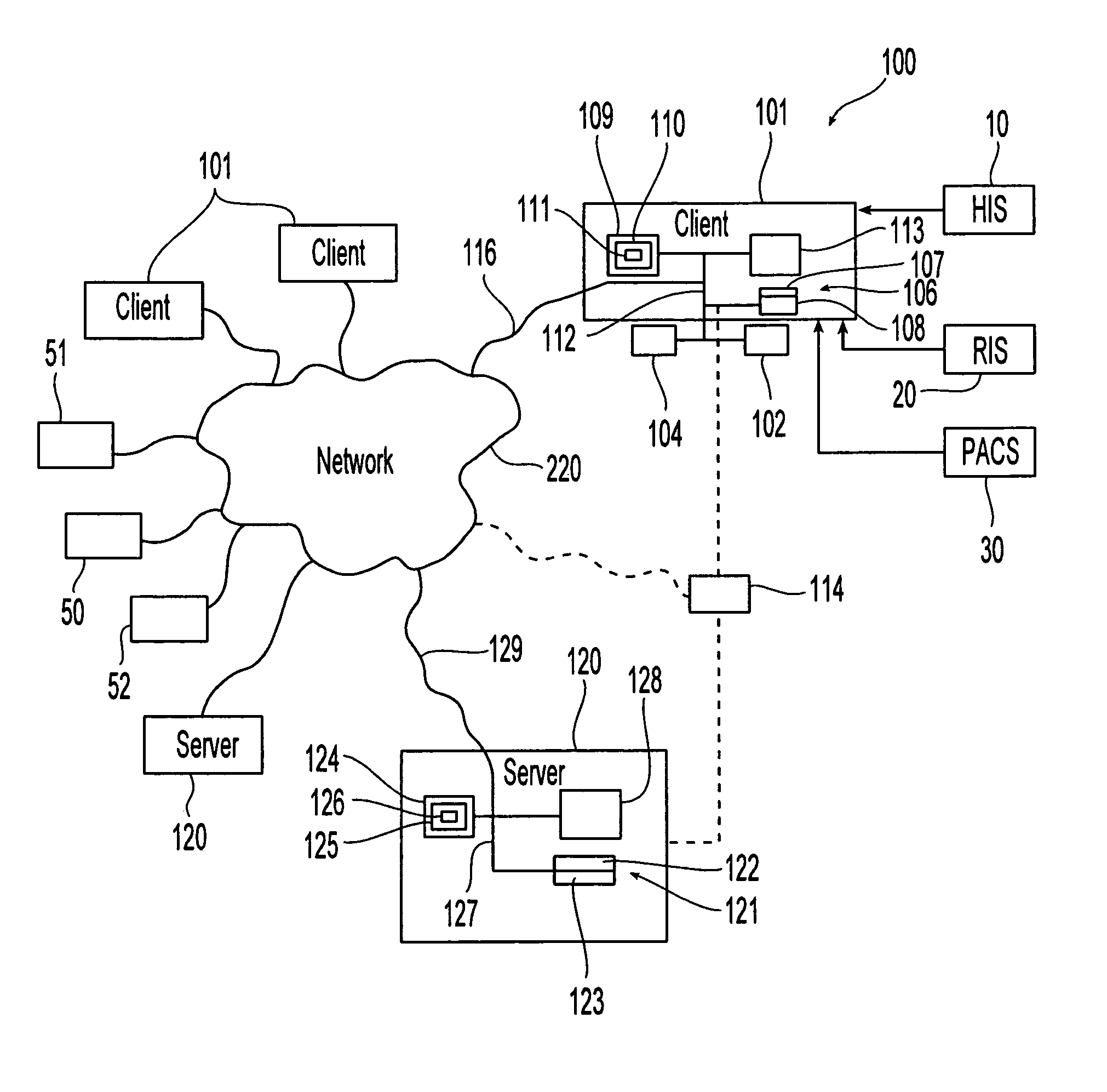
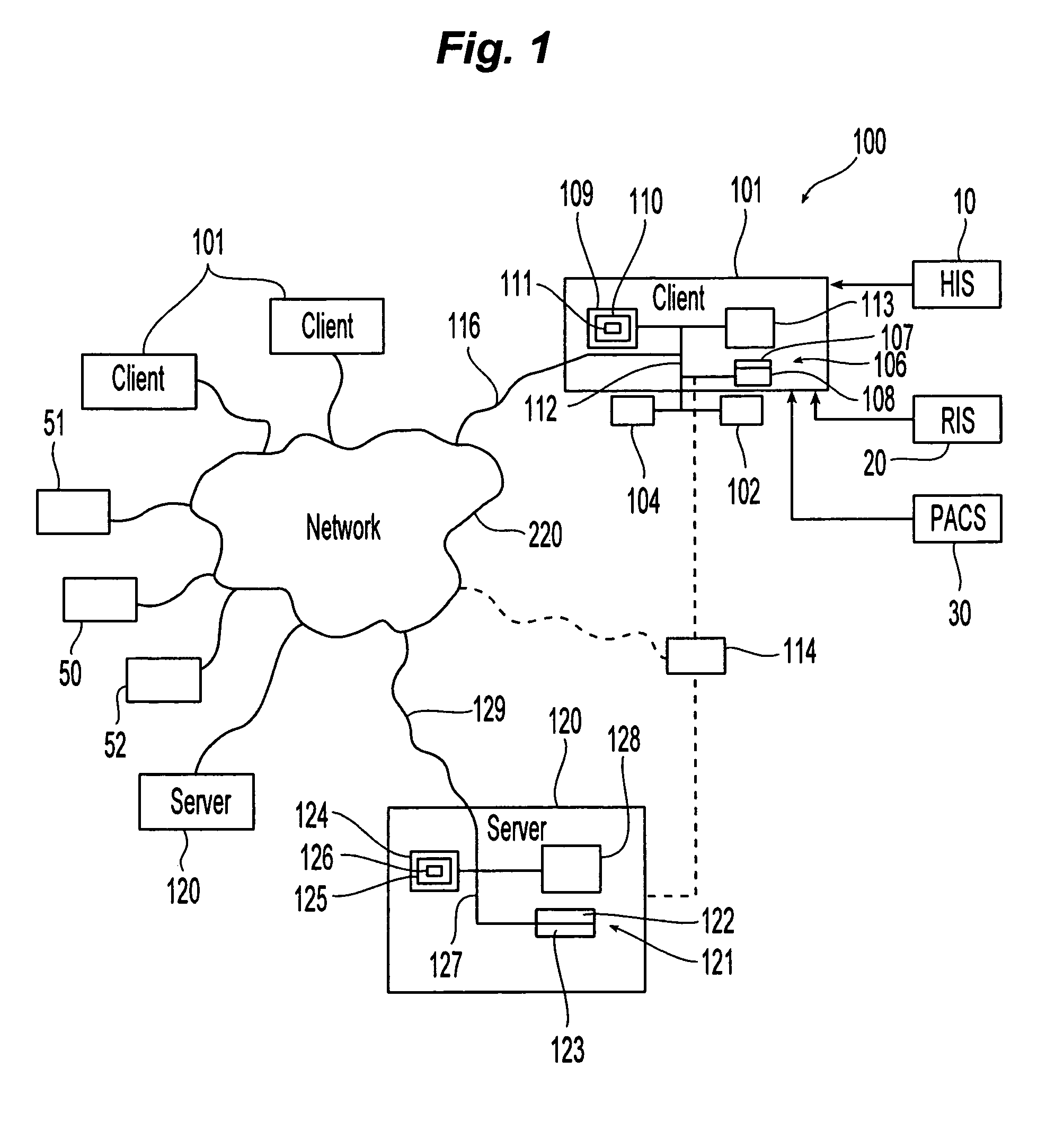
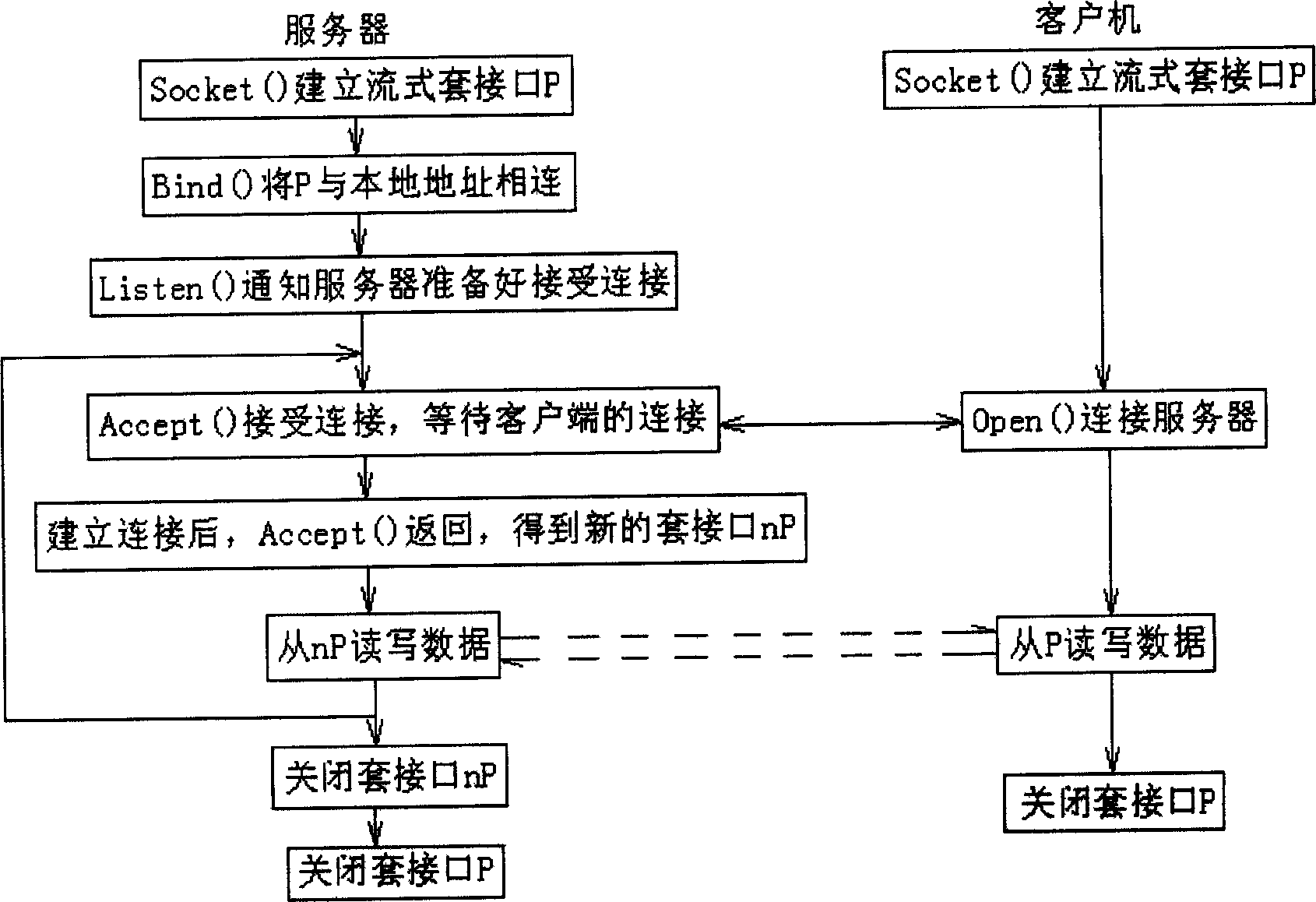
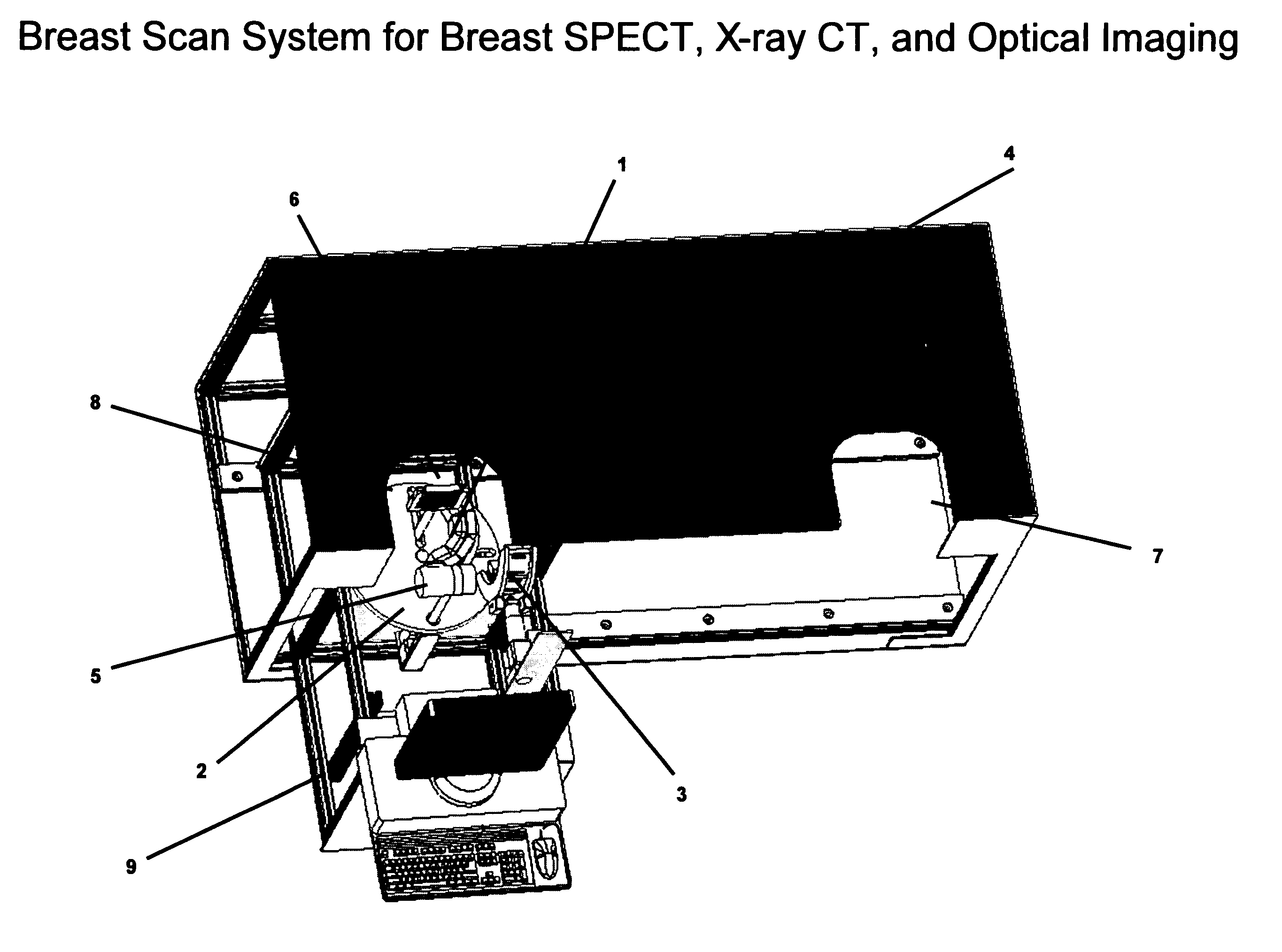
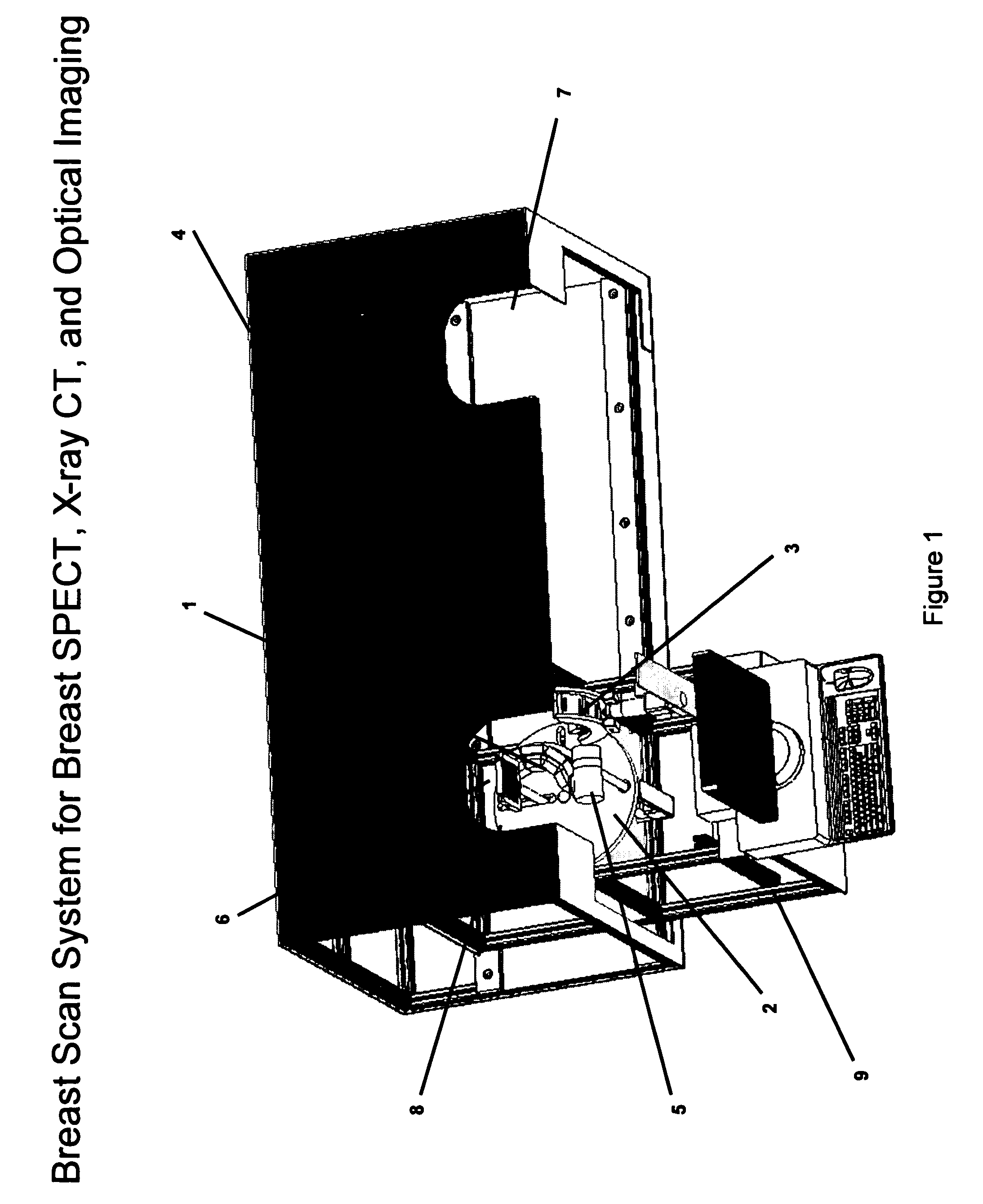
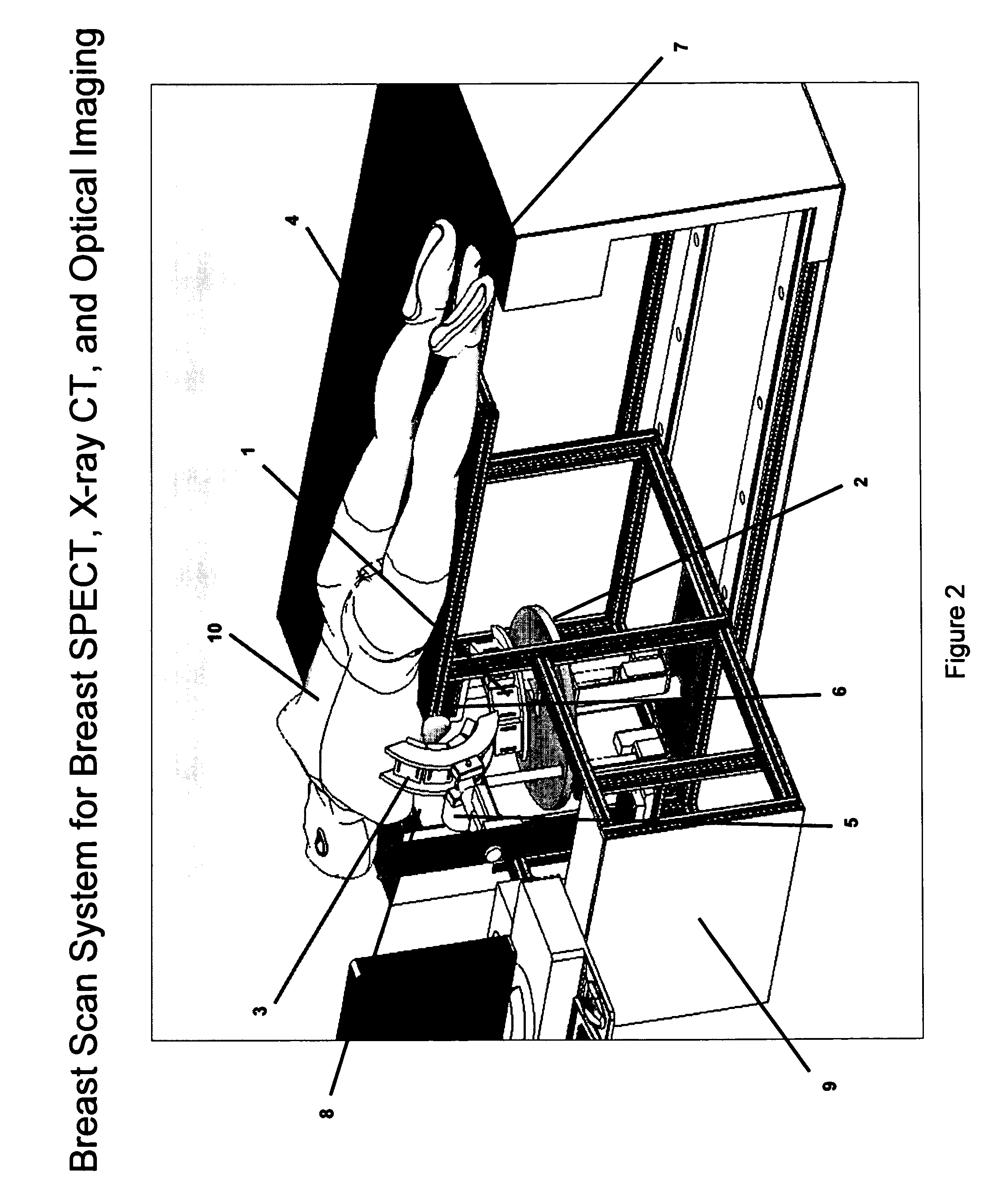
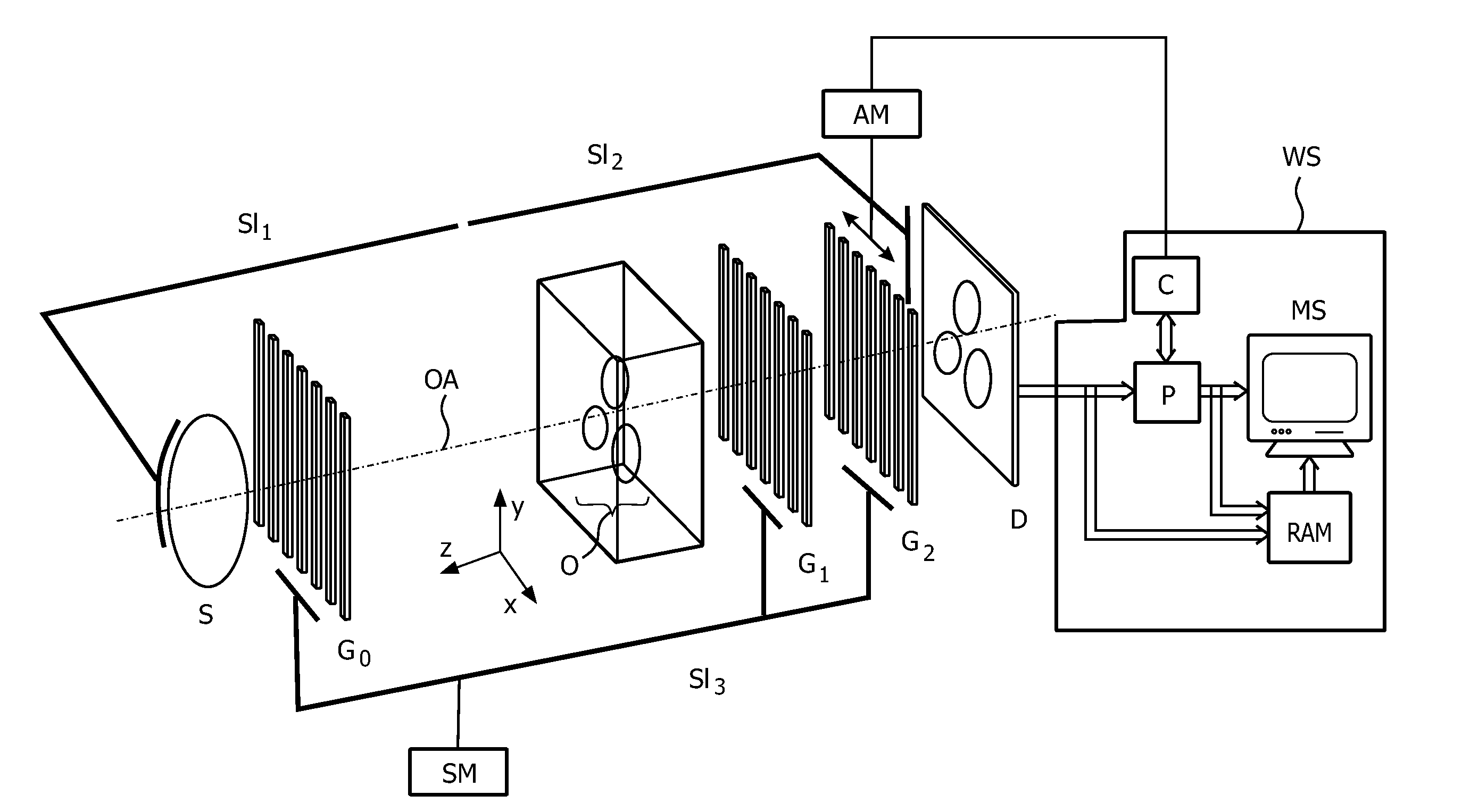
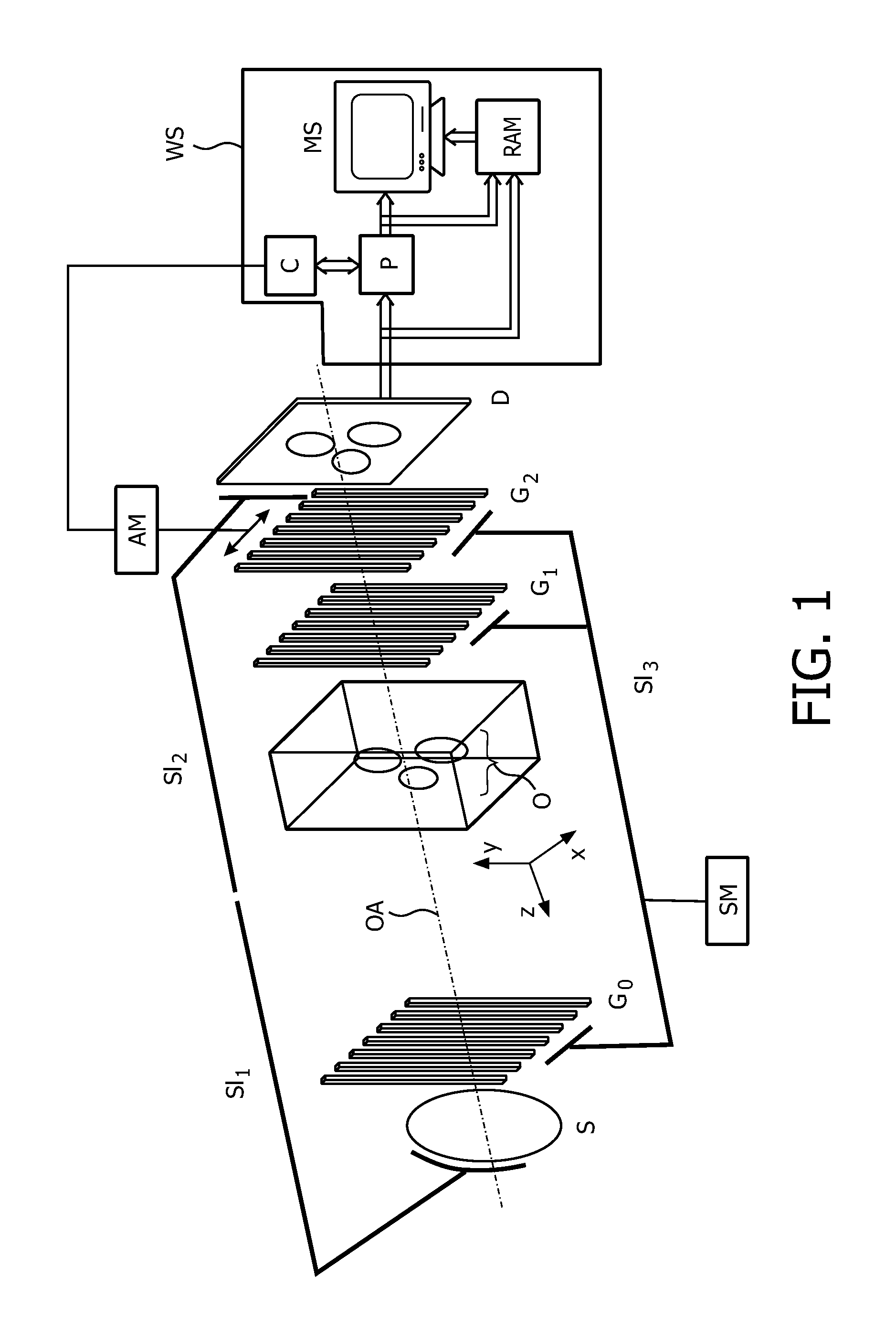
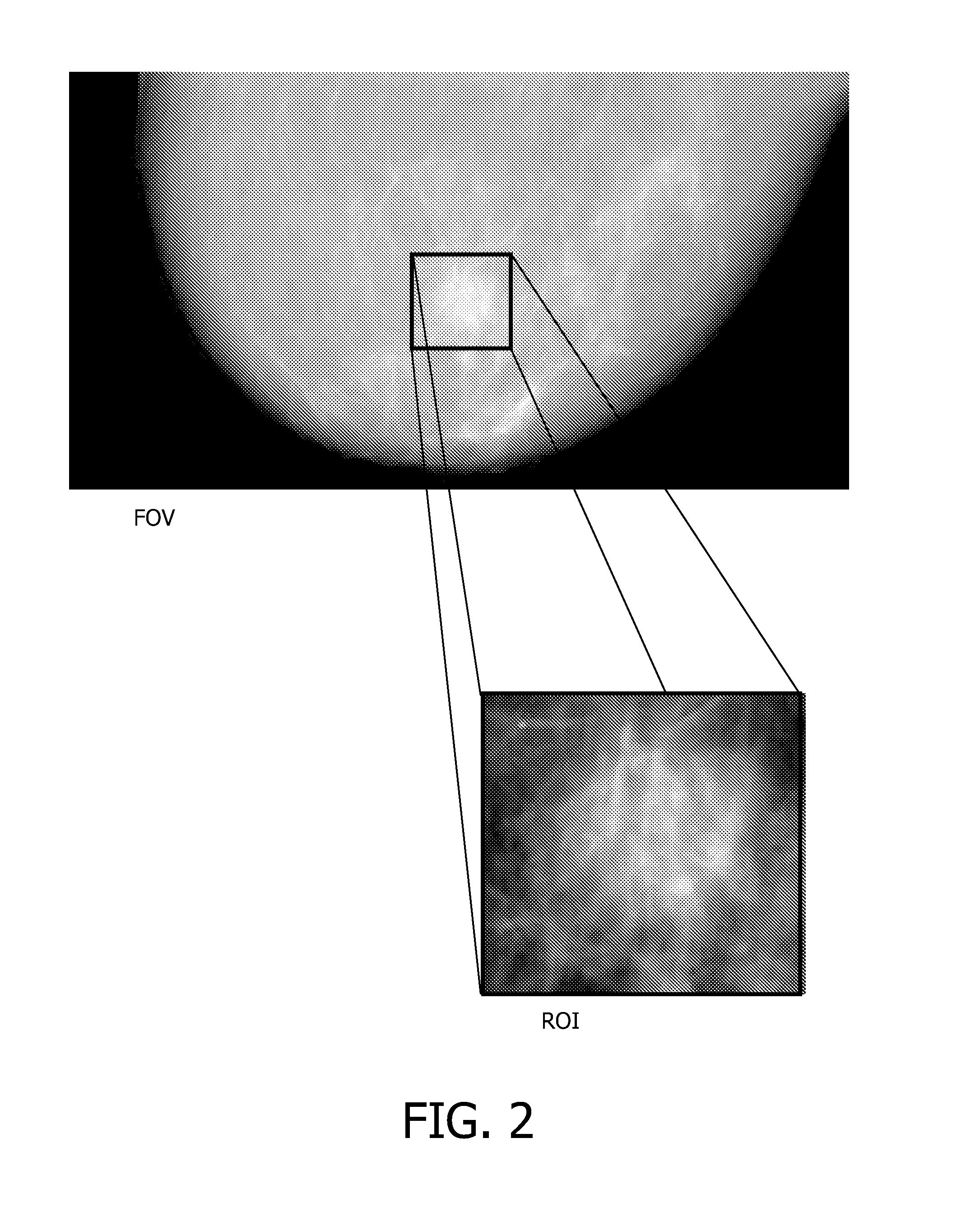
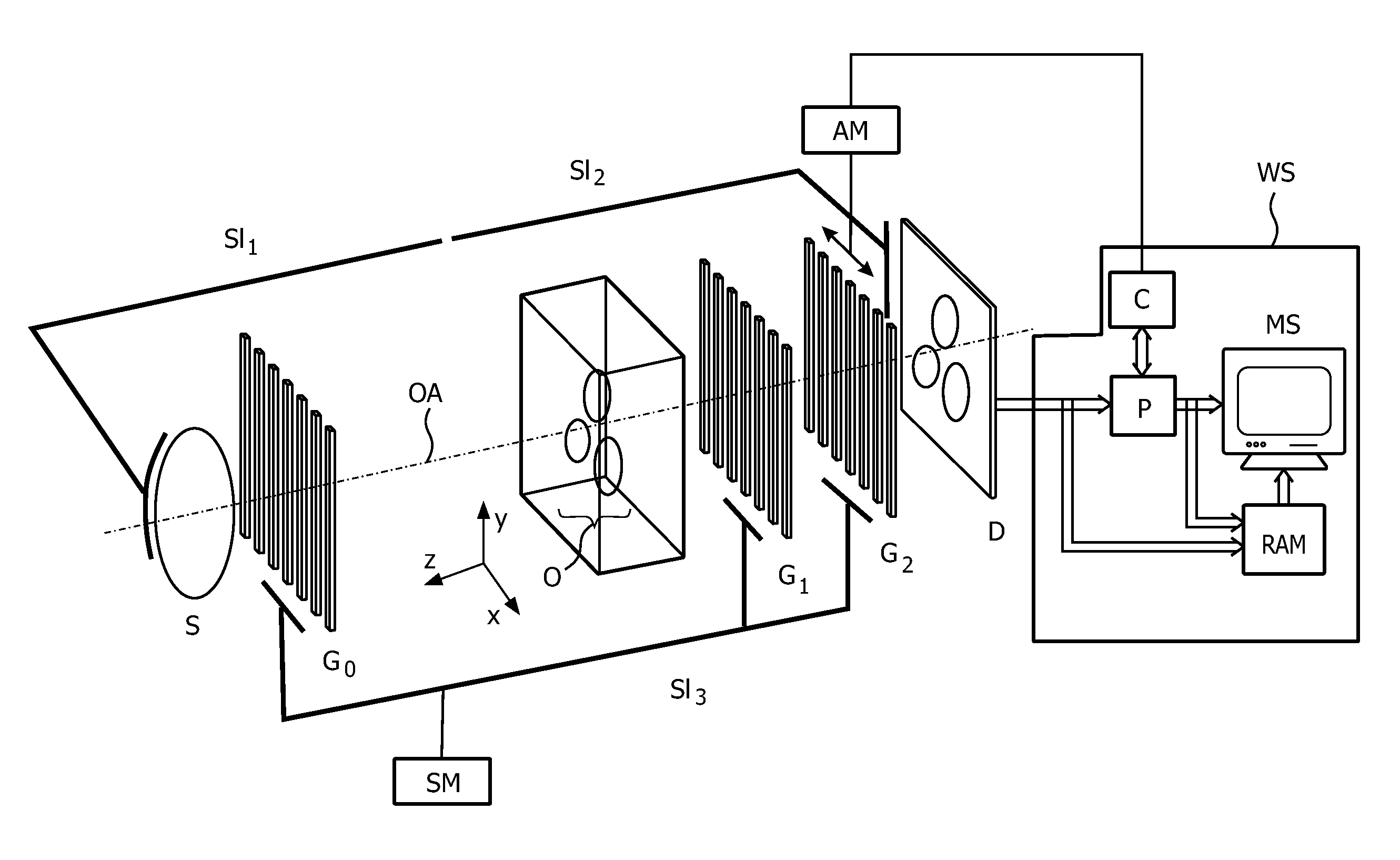
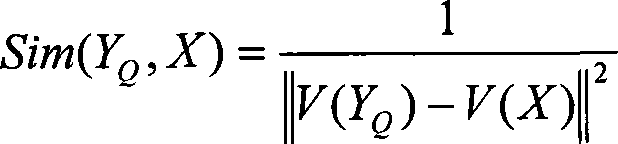Patents
Literature
467 results about "Radiology Unit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radiology Unit. The primary aim of our radiology department is to provide an imaging service combined of a high standard of technical excellence and an equally high quality of patient care. The branch of medicine that deals with the diagnostic and therapeutic applications of radiation.
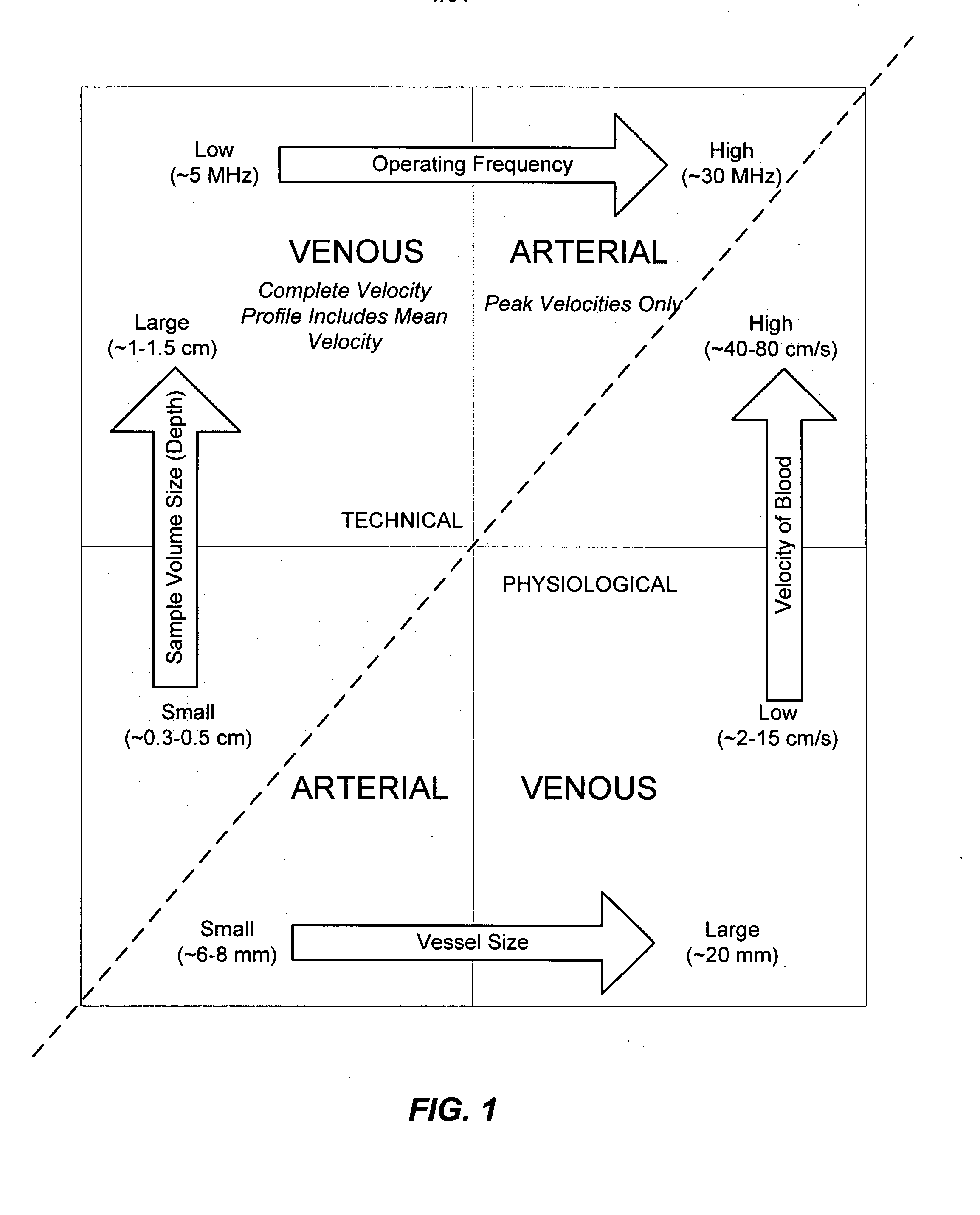
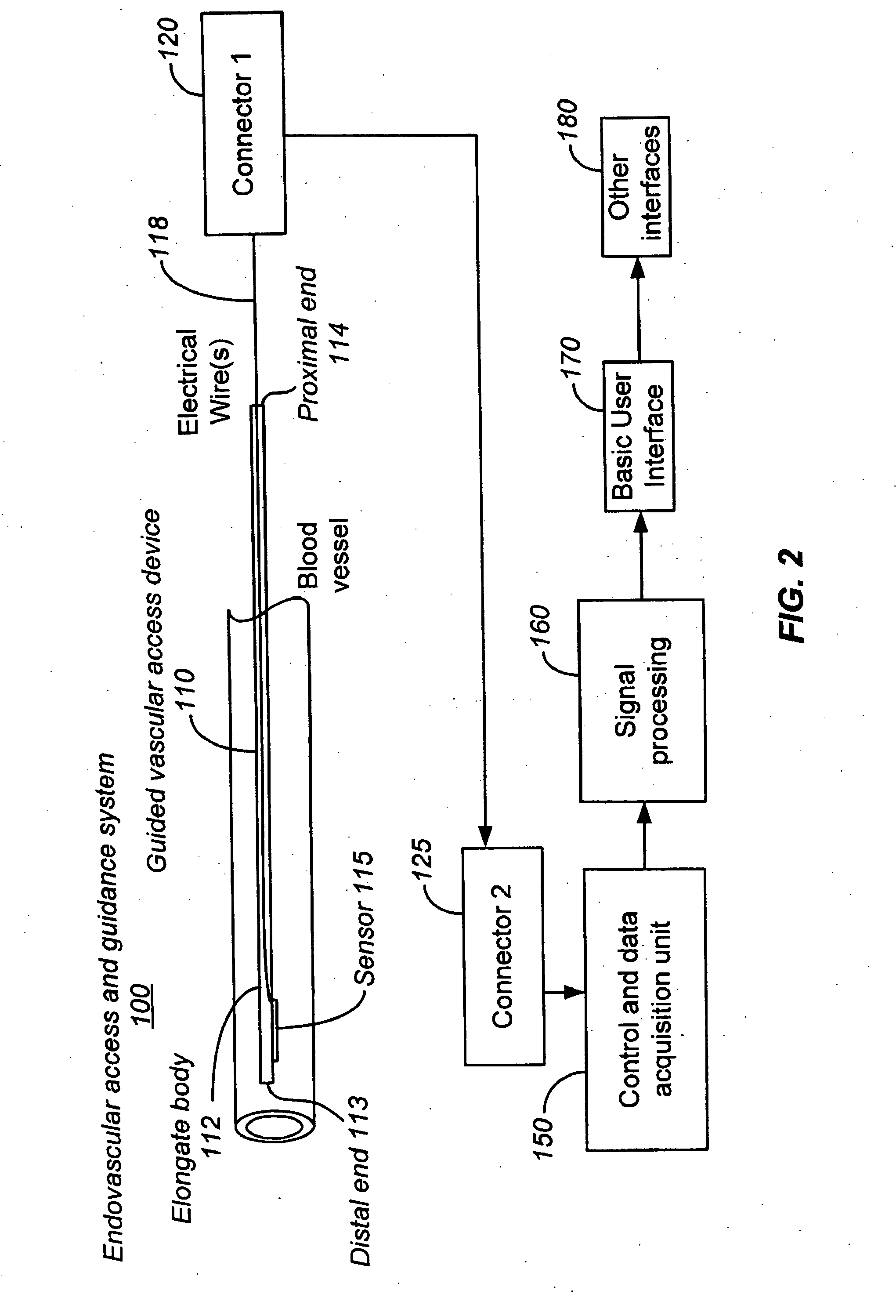
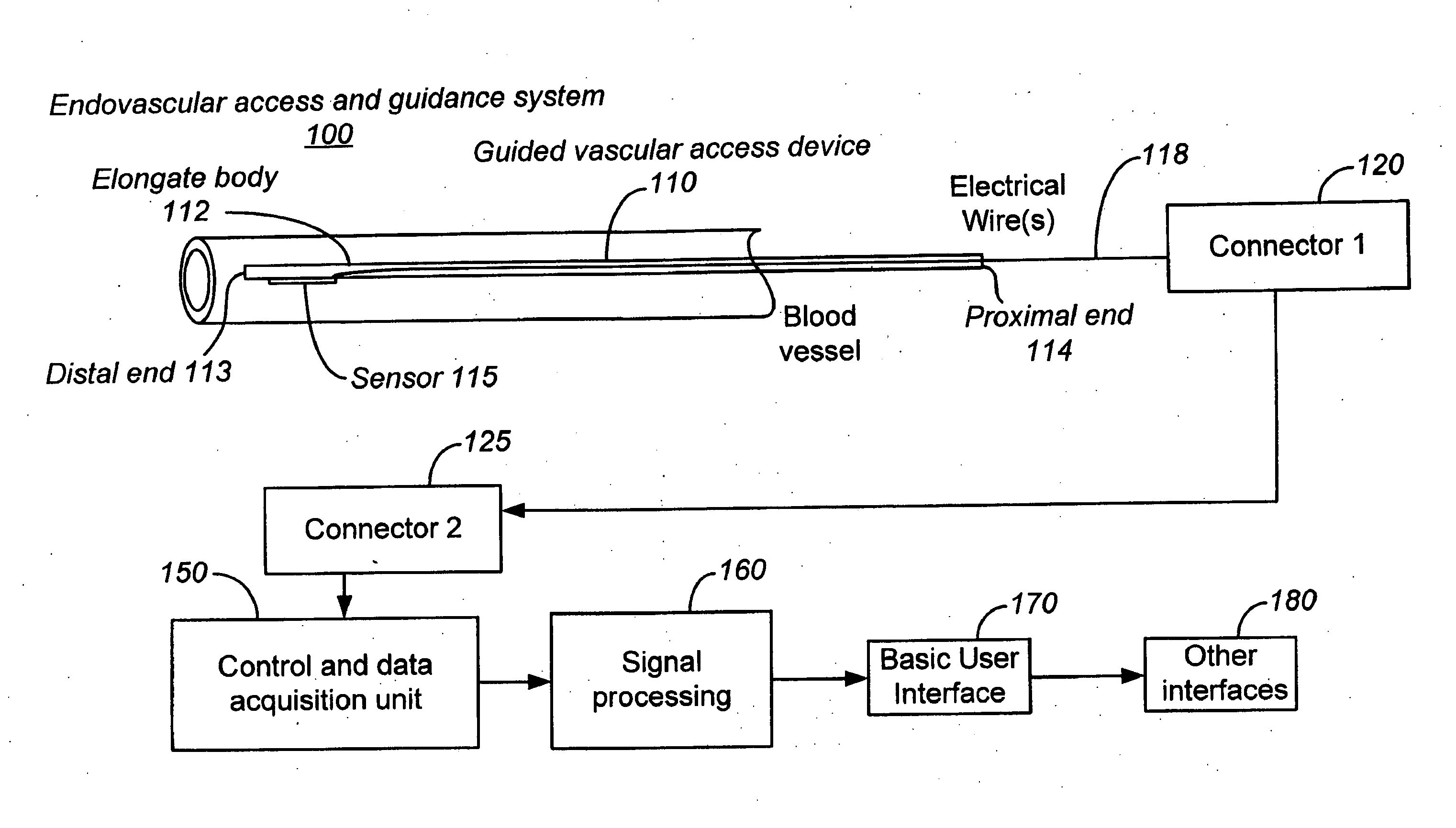
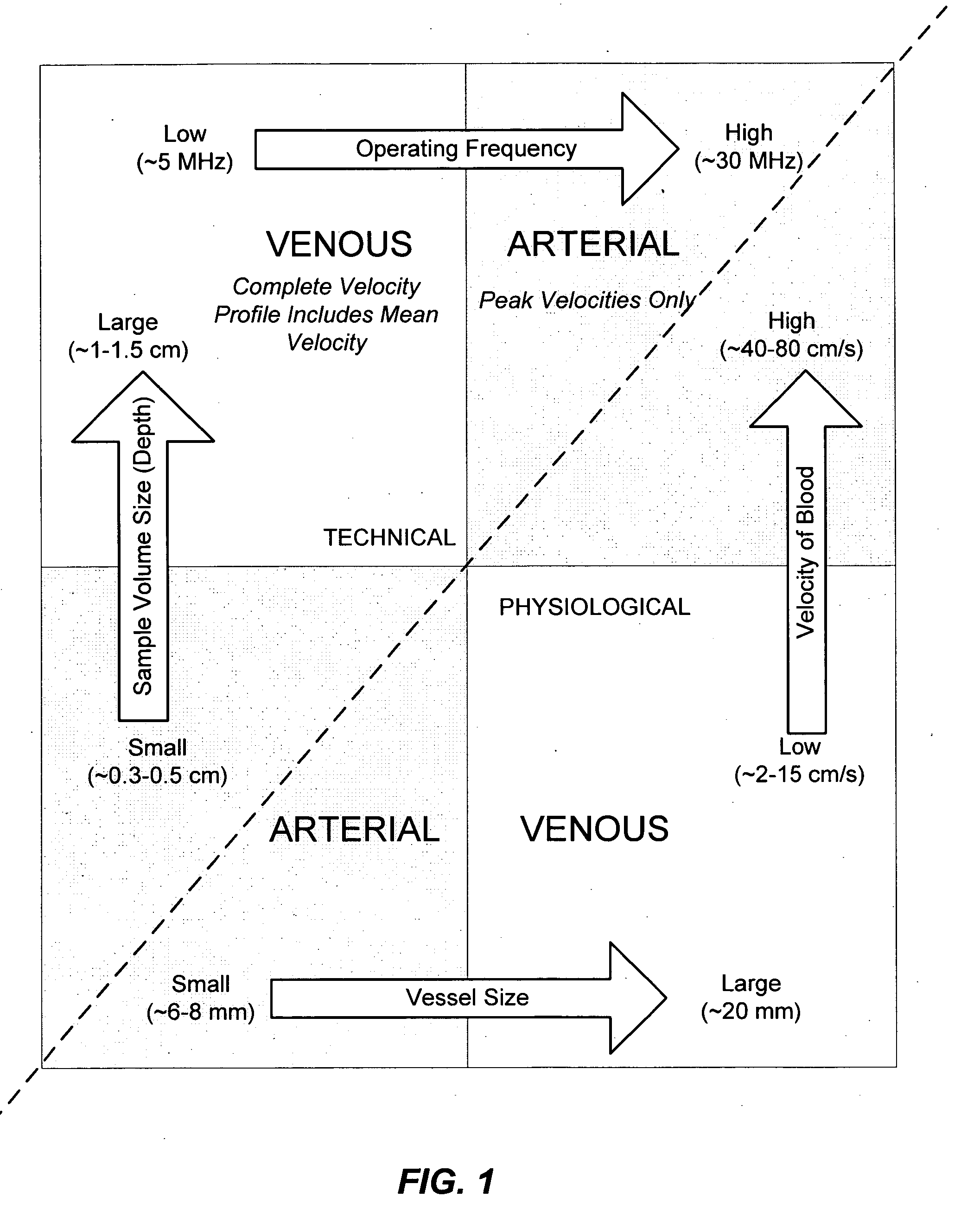
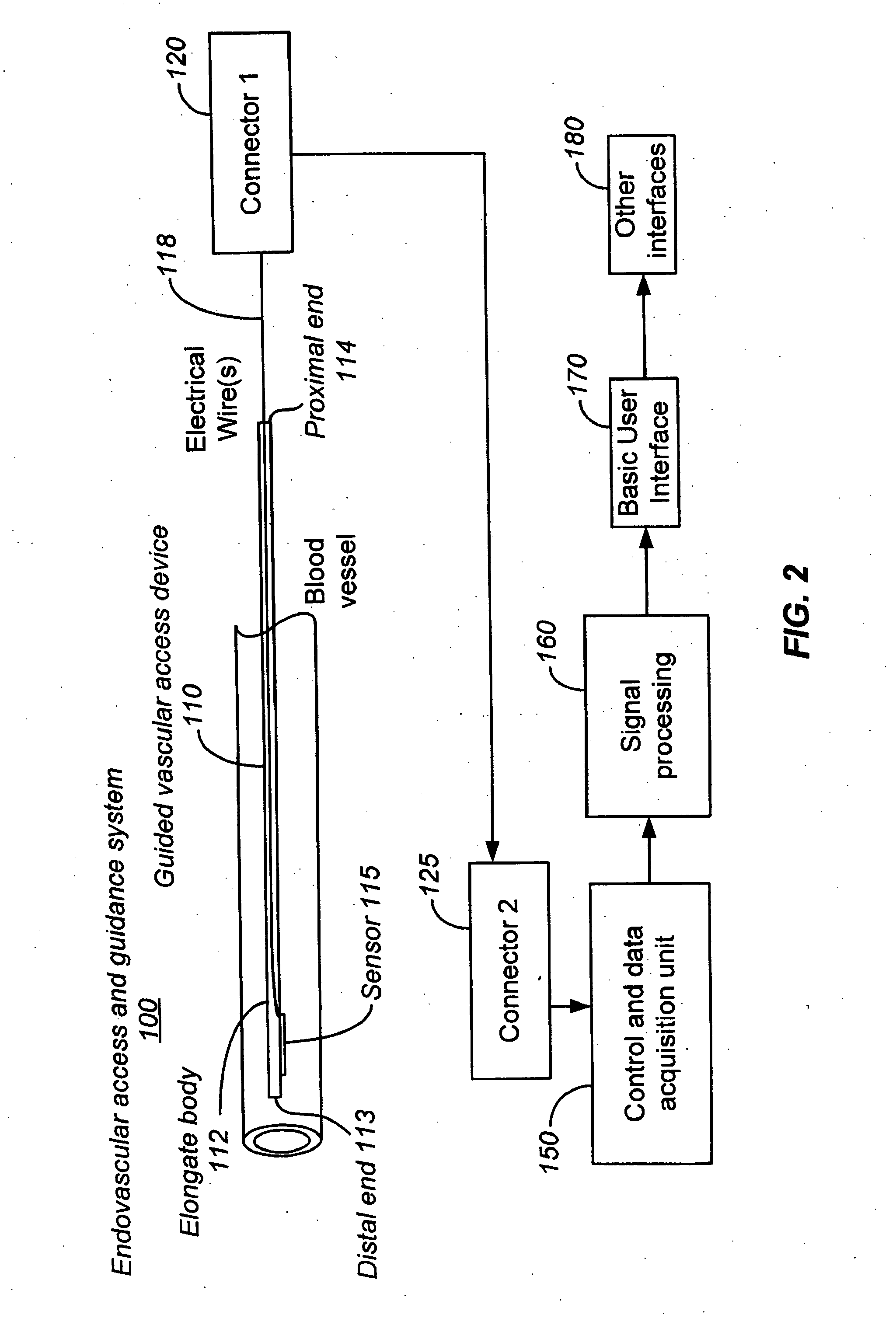
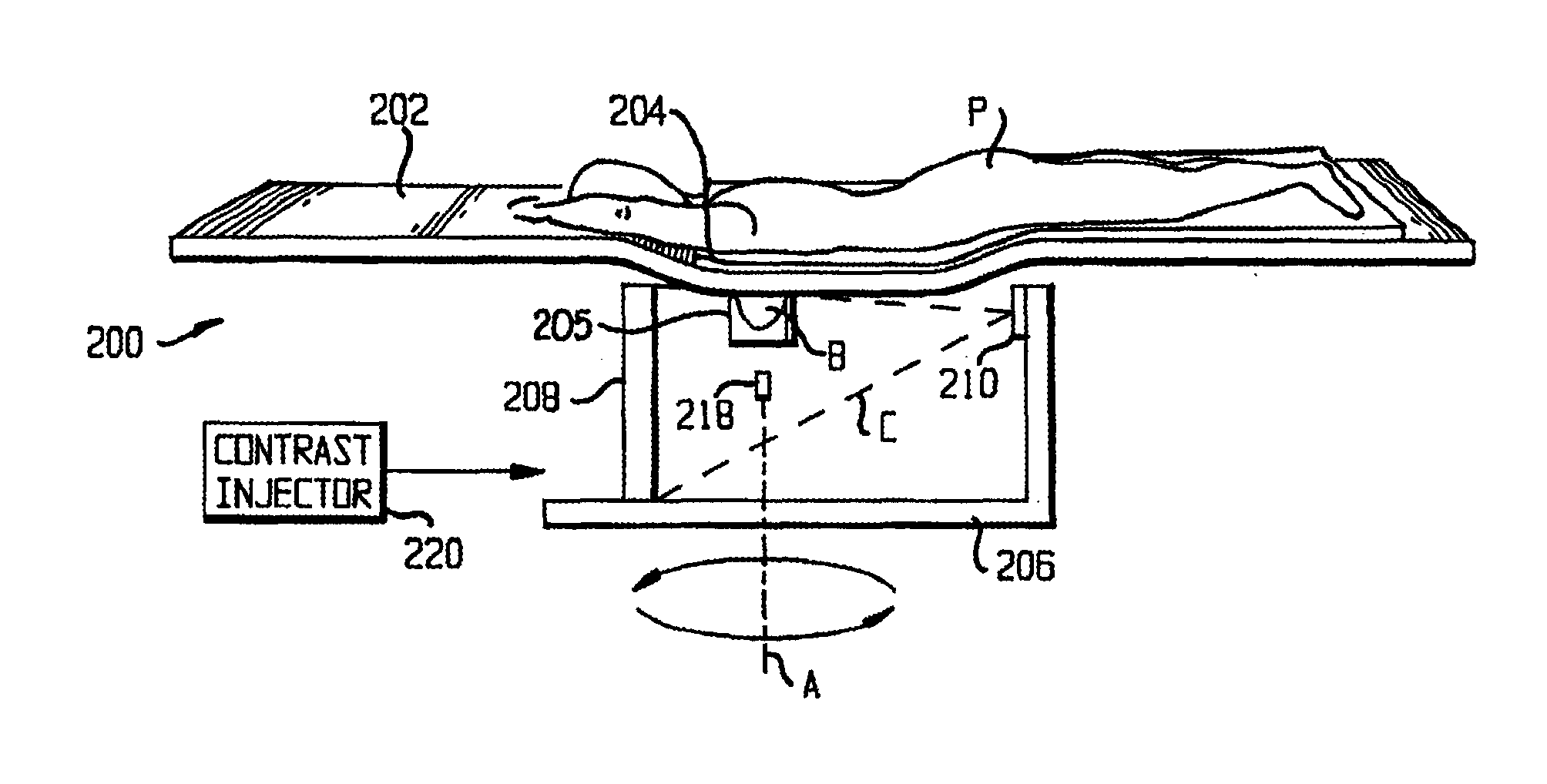
Ultrasound methods of positioning guided vascular access devices in the venous system
ActiveUS20070016068A1Diagnostic probe attachmentBlood flow measurement devicesGuidance systemVascular Access Devices
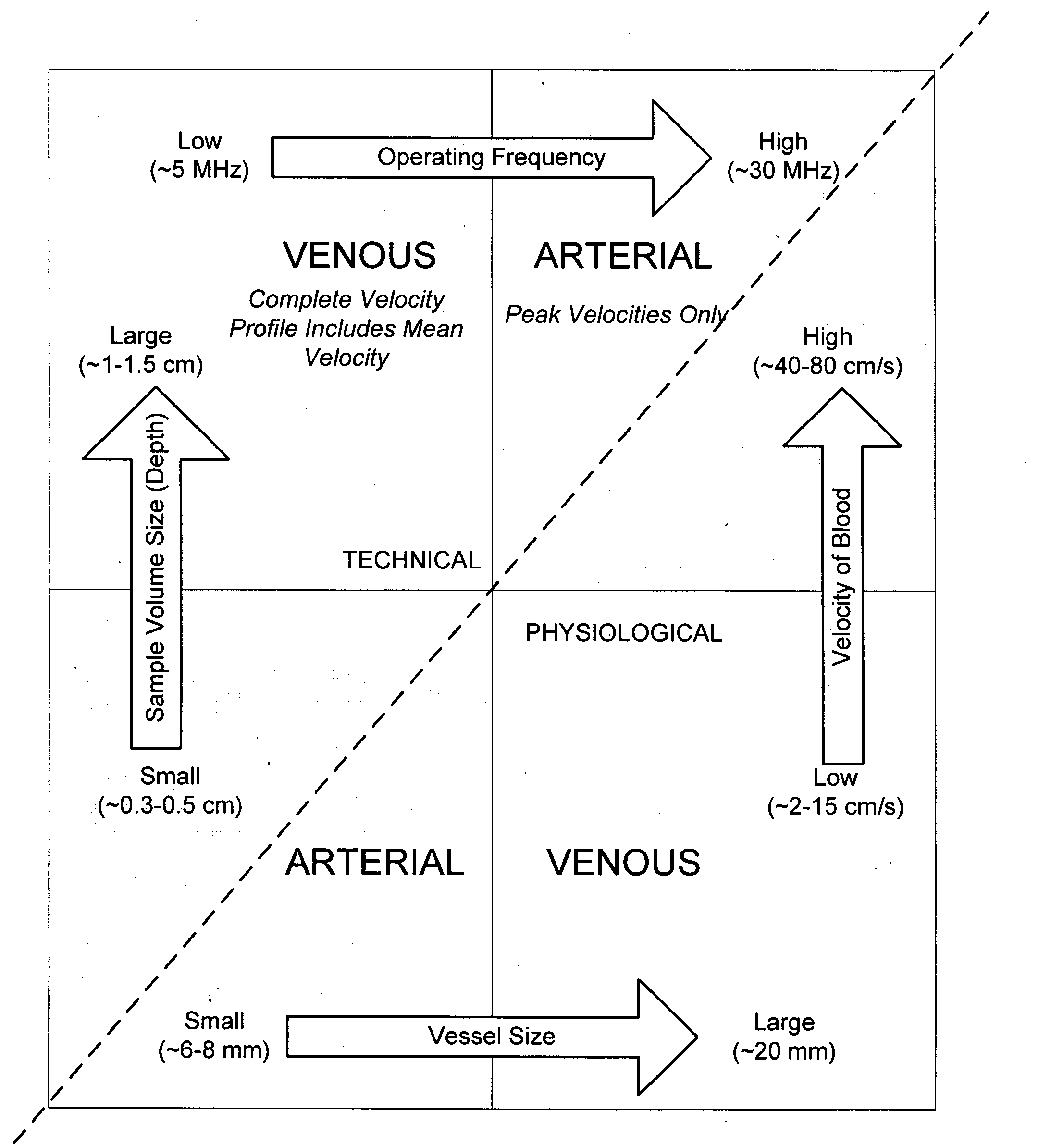
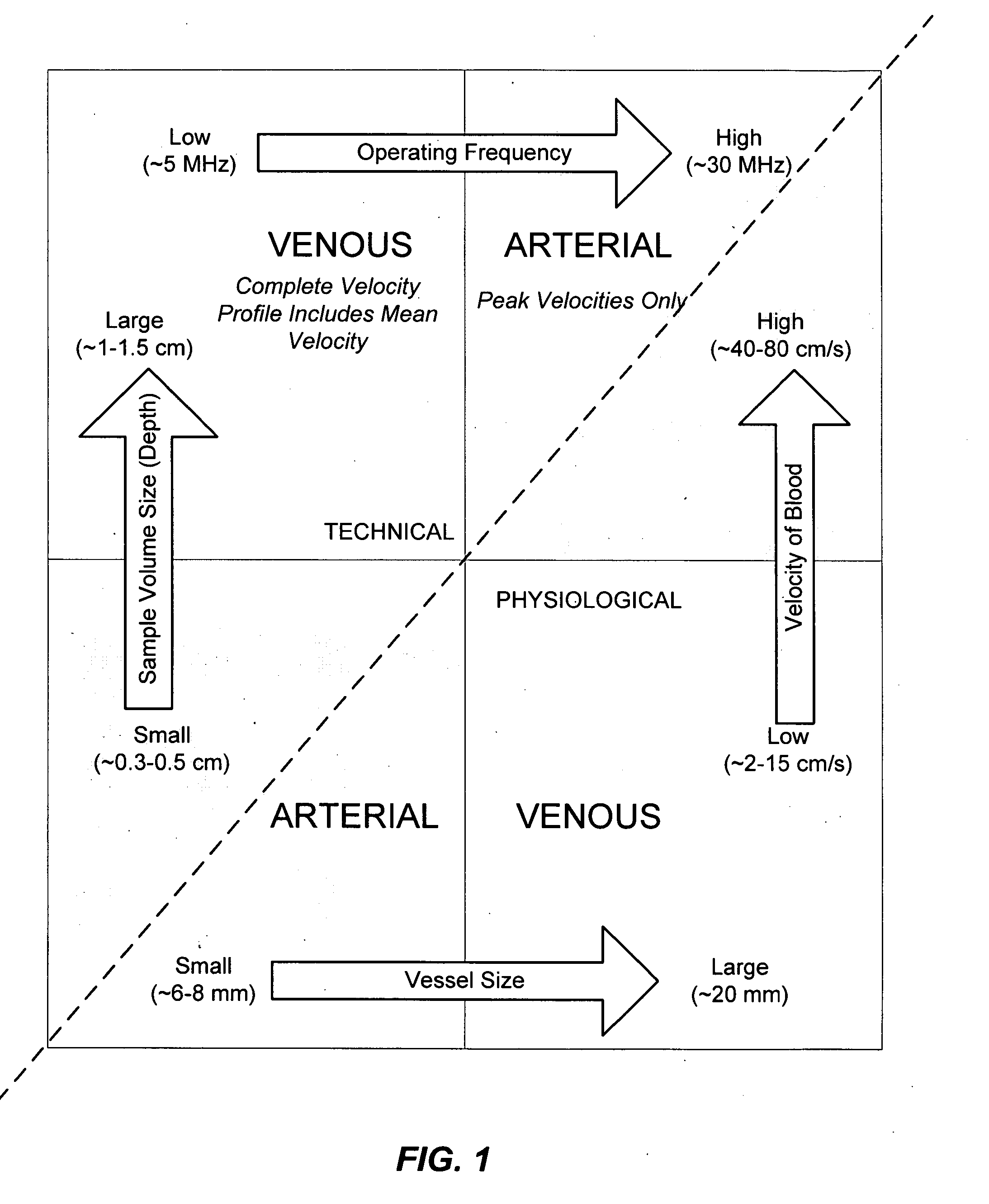
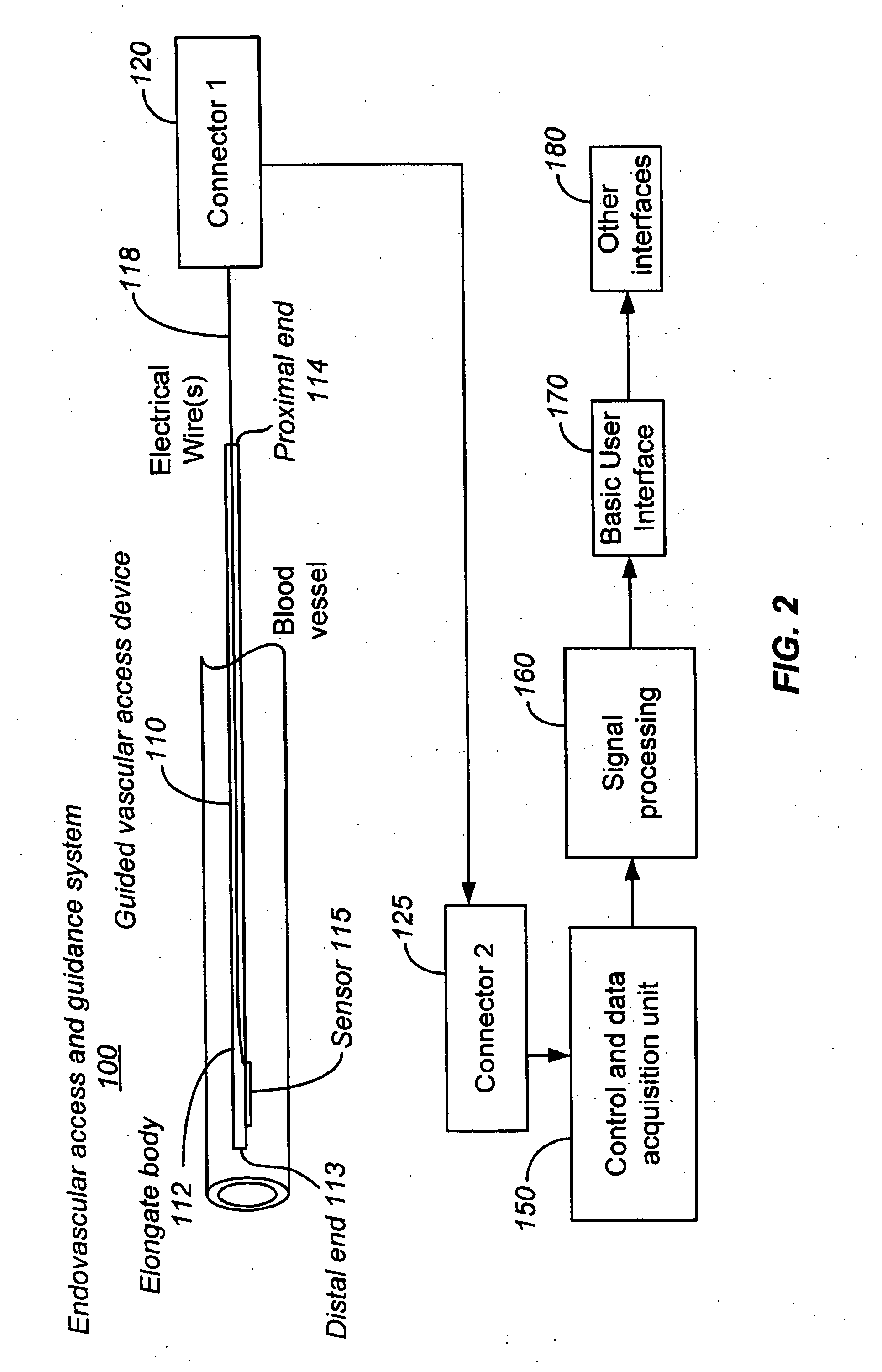
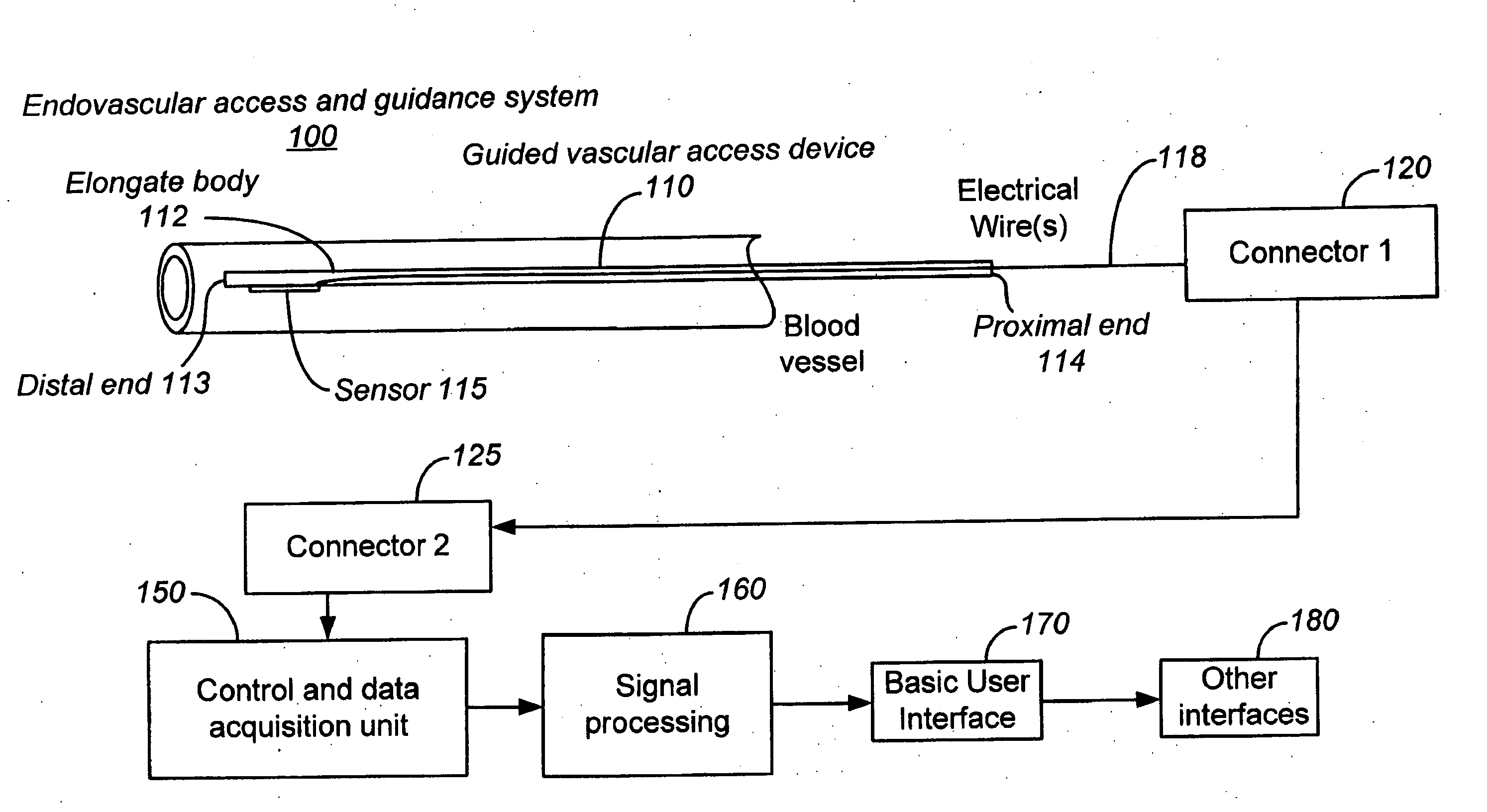
The invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices, such as catheters, stylets, guidewires and other flexible elongate bodies that are typically inserted percutaneously into the venous or arterial vasculature. Currently these goals are achieved using x-ray imaging and in some cases ultrasound imaging. This invention provides a method to substantially reduce the need for imaging related to placing an intravascular catheter or other device. Reduced imaging needs also reduce the amount of radiation that patients are subjected to, reduce the time required for the procedure, and decrease the cost of the procedure by reducing the time needed in the radiology department. An aspect of the invention includes, for example, an endovenous access and guidance system. The system comprises: an elongate flexible member adapted and configured to access the venous vasculature of a patient; a sensor disposed at a distal end of the elongate flexible member and configured to provide in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient; a processor configured to receive and process in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient provided by the sensor and to provide position information regarding the position of the distal end of the elongate flexible member within the venous vasculature of the patient; and an output device adapted to output the position information from the processor.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Endovenous access and guidance system utilizing non-image based ultrasound
The invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices, such as catheters, stylets, guidewires and other flexible elongate bodies that are typically inserted percutaneously into the venous or arterial vasculature. Currently these goals are achieved using x-ray imaging and in some cases ultrasound imaging. This invention provides a method to substantially reduce the need for imaging related to placing an intravascular catheter or other device. Reduced imaging needs also reduce the amount of radiation that patients are subjected to, reduce the time required for the procedure, and decrease the cost of the procedure by reducing the time needed in the radiology department. An aspect of the invention includes, for example, an endovenous access and guidance system. The system comprises: an elongate flexible member adapted and configured to access the venous vasculature of a patient; a sensor disposed at a distal end of the elongate flexible member and configured to provide in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient; a processor configured to receive and process in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient provided by the sensor and to provide position information regarding the position of the distal end of the elongate flexible member within the venous vasculature of the patient; and an output device adapted to output the position information from the processor.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
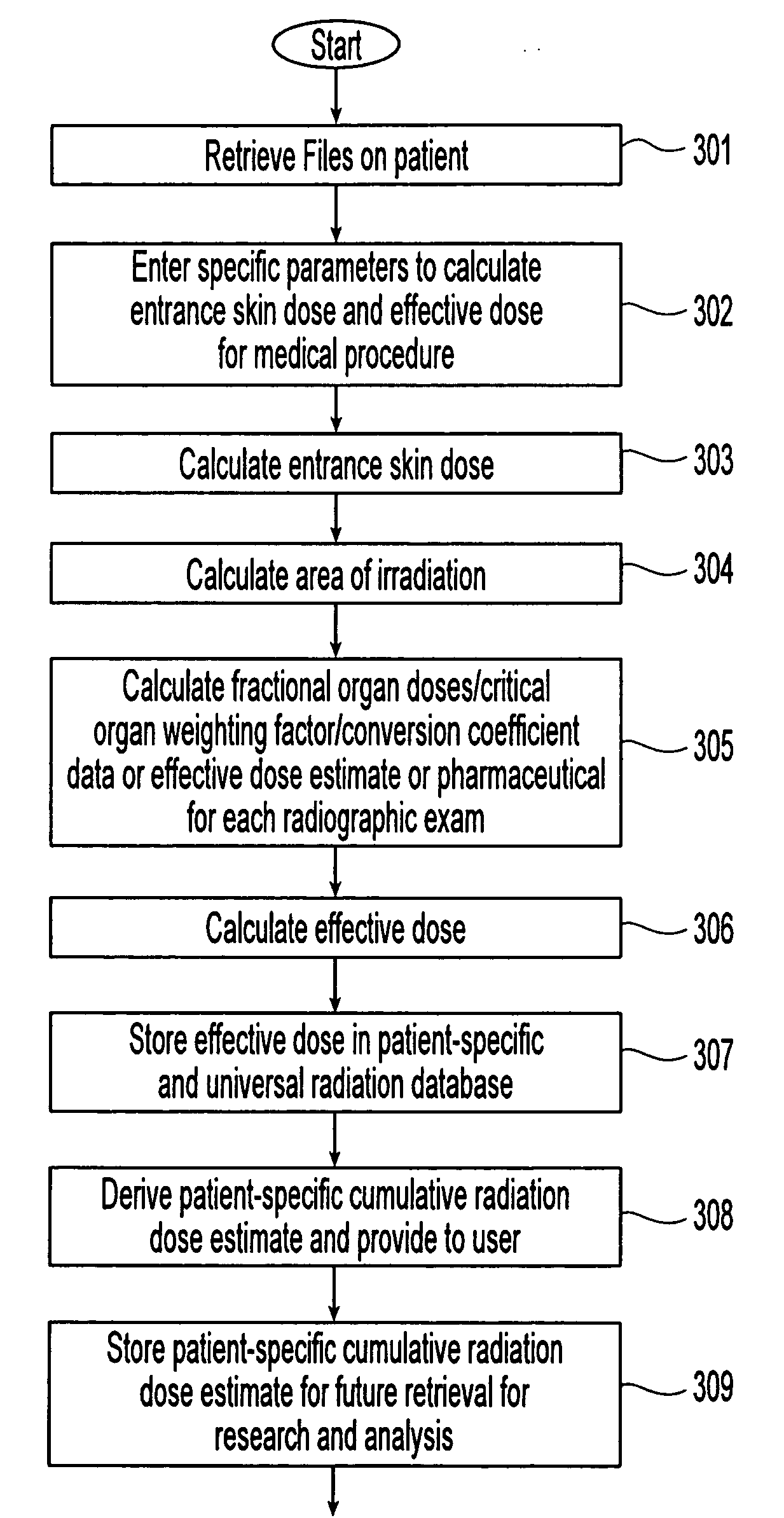
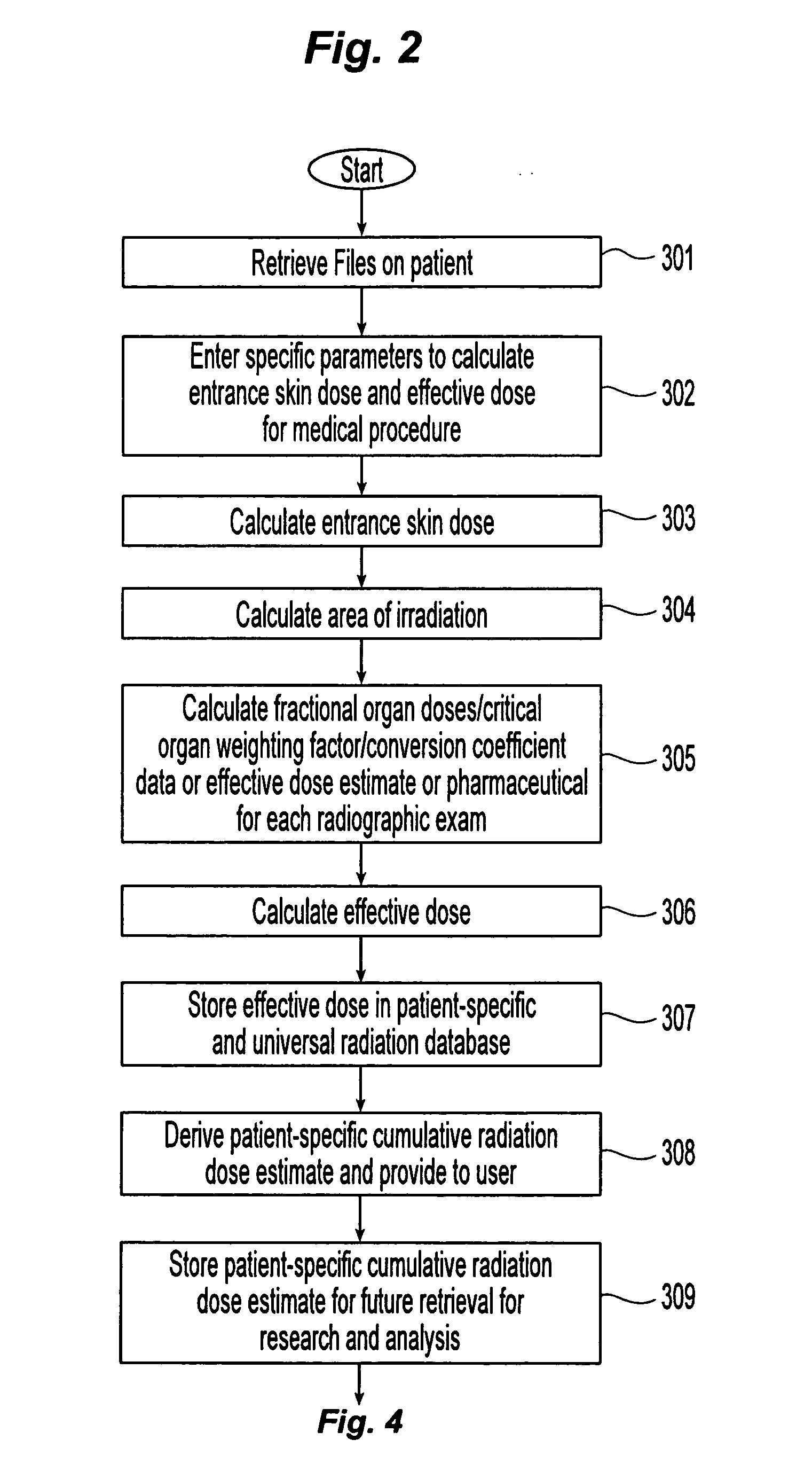
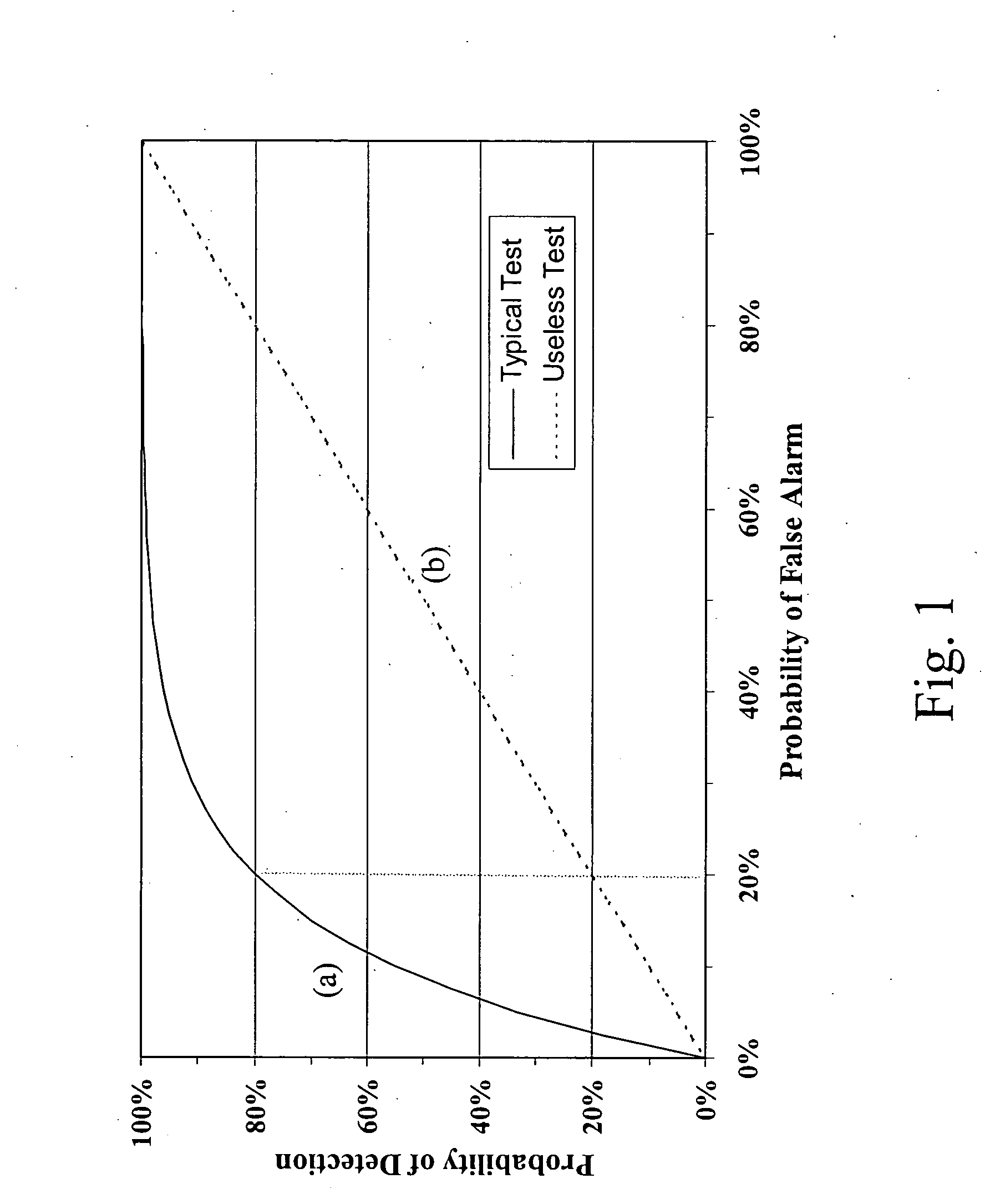
Method and apparatus of providing a radiation scorecard
ActiveUS20080103834A1Improve patient safetyReduce the environmentMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesColor television detailsRadiation exposureRetrospective analysis
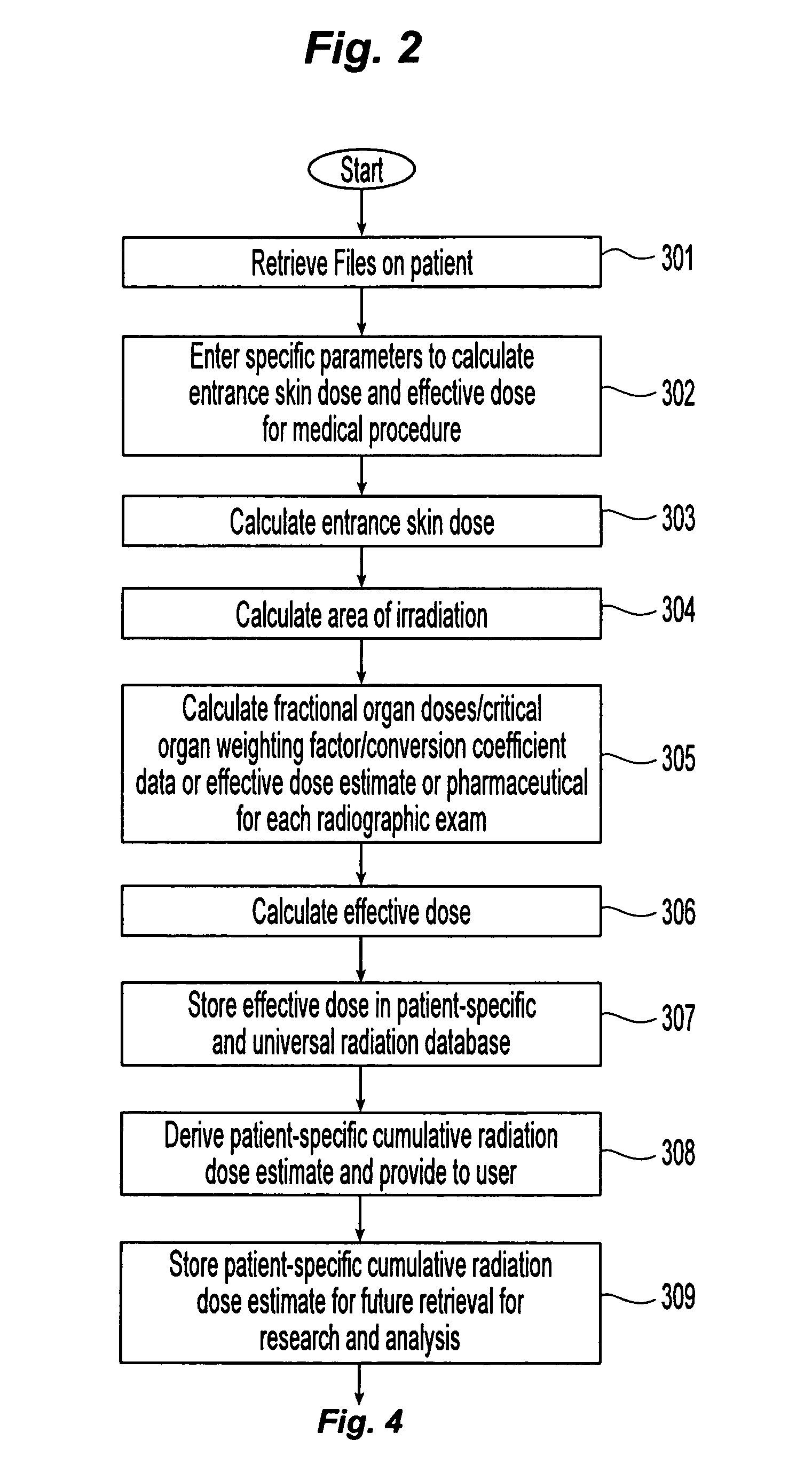
The present invention relates to a method to measure, record, analyze, and report cumulative radiation exposure to the patient population and provide automated feedback and recommendations to ordering clinicians and consultant radiologists. The data provided from this “radiation scorecard” would in turn be automatically recorded into a centralized data repository (radiation database), which would be independent to the acquisition site, technology employed, and individual end-user. Retrospective analysis can also be performed using a set of pre-defined scorecard data points tied to the individual patient's historical medical imaging database, thereby allowing for comprehensive (both retrospective and prospective) medical radiation exposure quantitative analysis. Patient safety can be improved by a combination of radiation dose reduction, exposure optimization, rigorous equipment quality control (QC), education and training of medical imaging professionals, and integration with computerized physician order entry (CPOE).
Owner:REINER BRUCE
Endovascular access and guidance system utilizing divergent beam ultrasound
The invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices, such as catheters, stylets, guidewires and other flexible elongate bodies that are typically inserted percutaneously into the venous or arterial vasculature. Currently these goals are achieved using x-ray imaging and in some cases ultrasound imaging. This invention provides a method to substantially reduce the need for imaging related to placing an intravascular catheter or other device. Reduced imaging needs also reduce the amount of radiation that patients are subjected to, reduce the time required for the procedure, and decrease the cost of the procedure by reducing the time needed in the radiology department. An aspect of the invention includes, for example, an endovenous access and guidance system. The system comprises: an elongate flexible member adapted and configured to access the venous vasculature of a patient; a sensor disposed at a distal end of the elongate flexible member and configured to provide in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient; a processor configured to receive and process in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient provided by the sensor and to provide position information regarding the position of the distal end of the elongate flexible member within the venous vasculature of the patient; and an output device adapted to output the position information from the processor.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Device and method for margin marking tissue to be radiographed
InactiveUS7127040B2Eliminate confusionEasy to holdSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsPathology diagnosisRadiography
Owner:BEEKLEY A CT
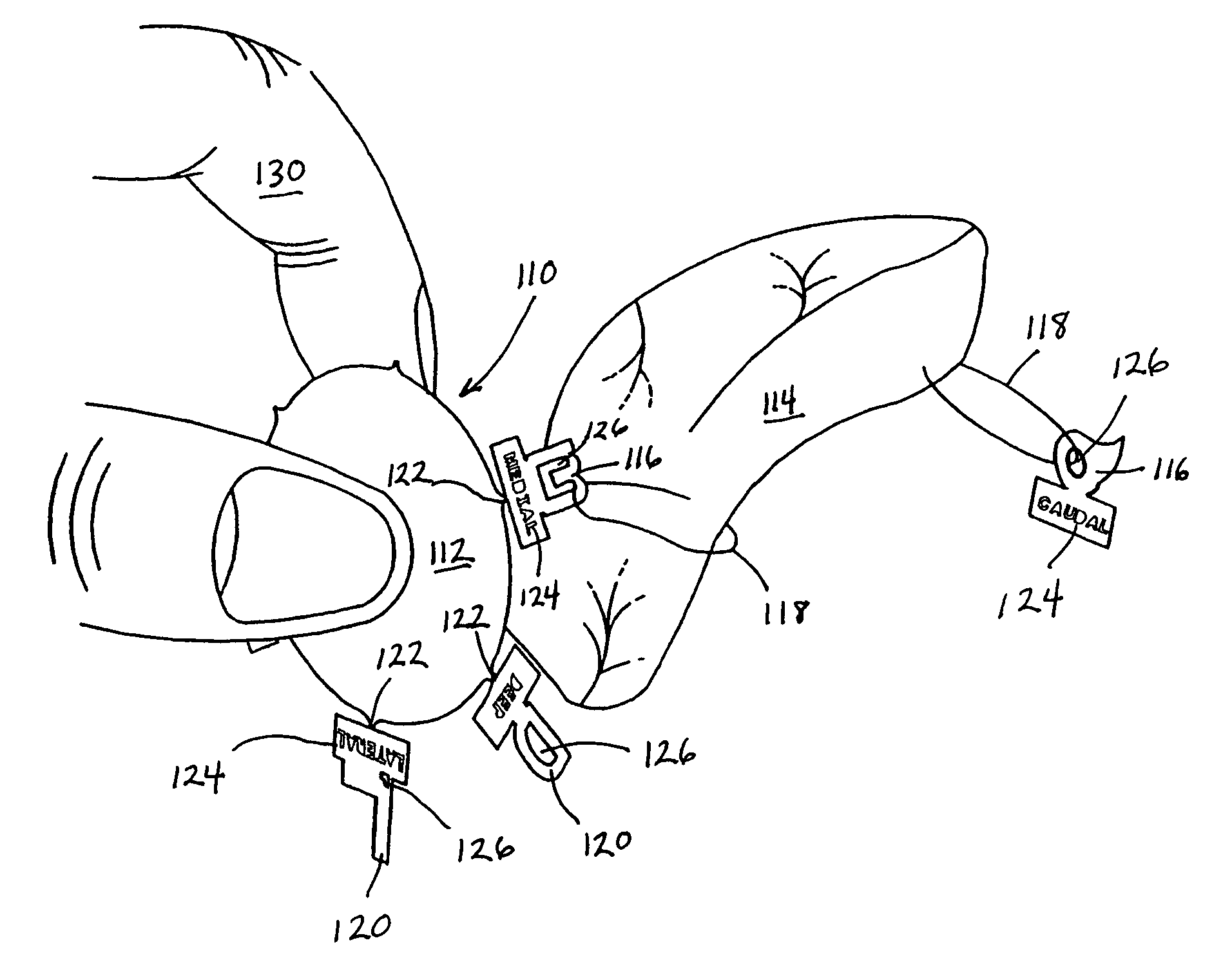
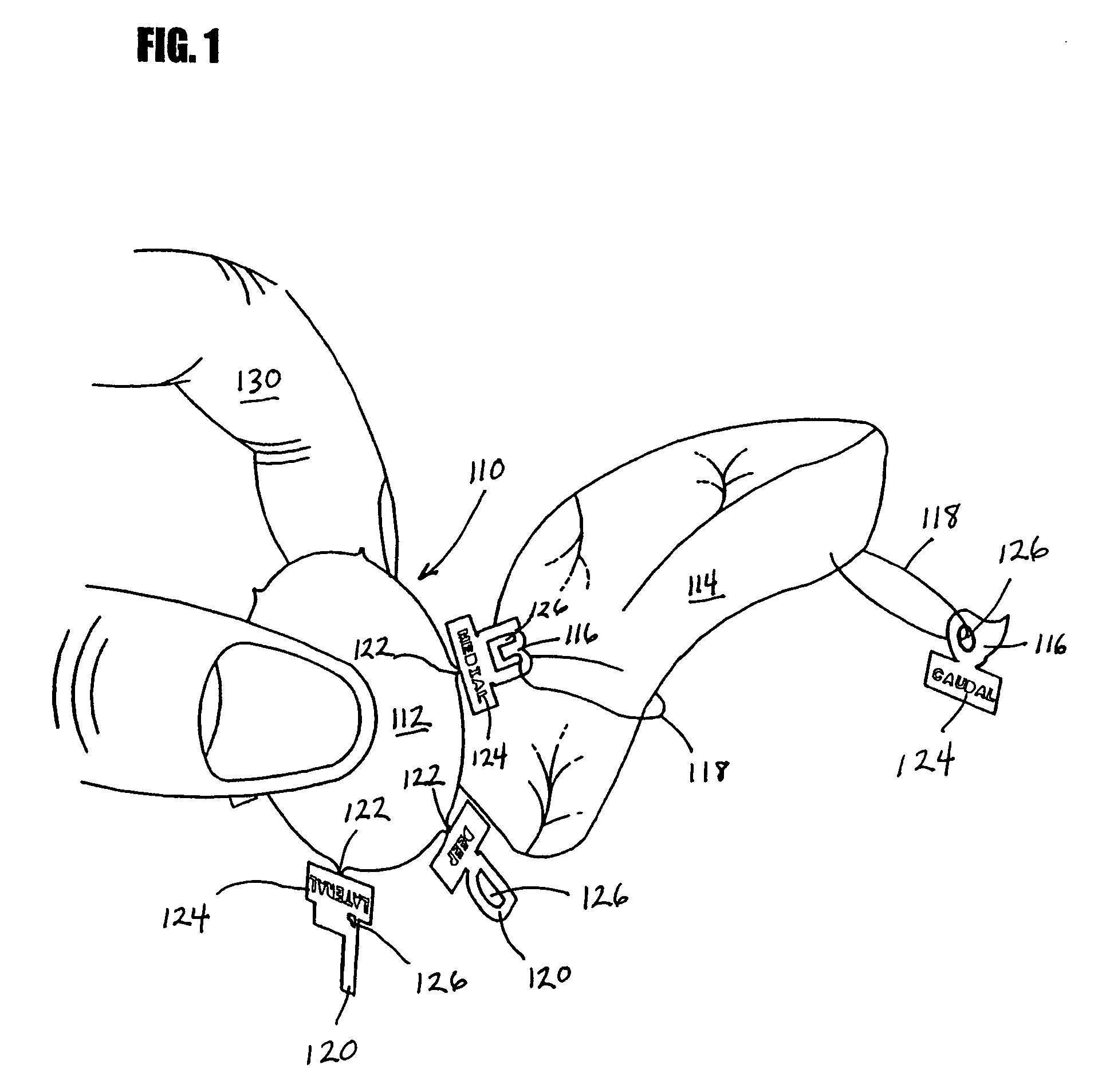
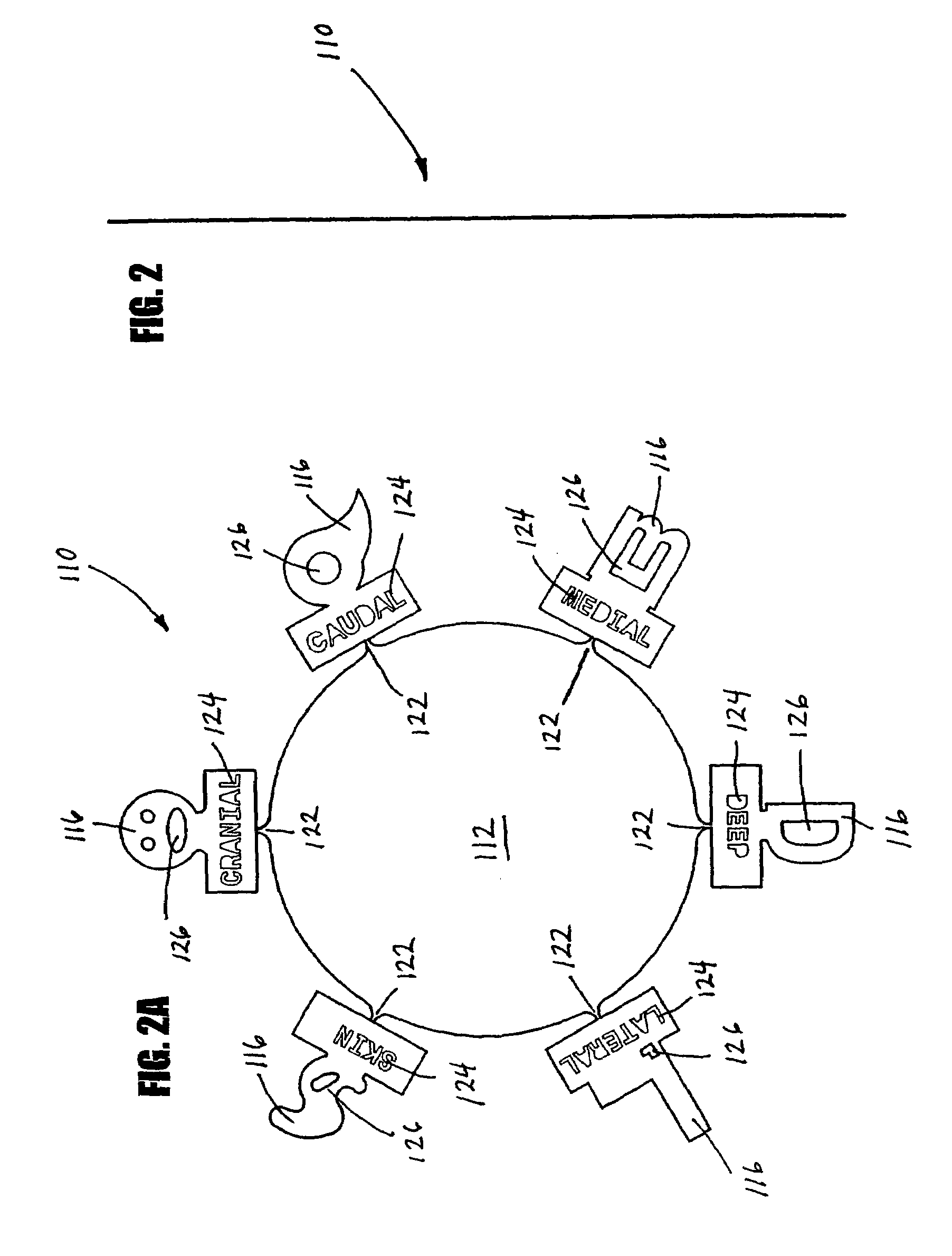
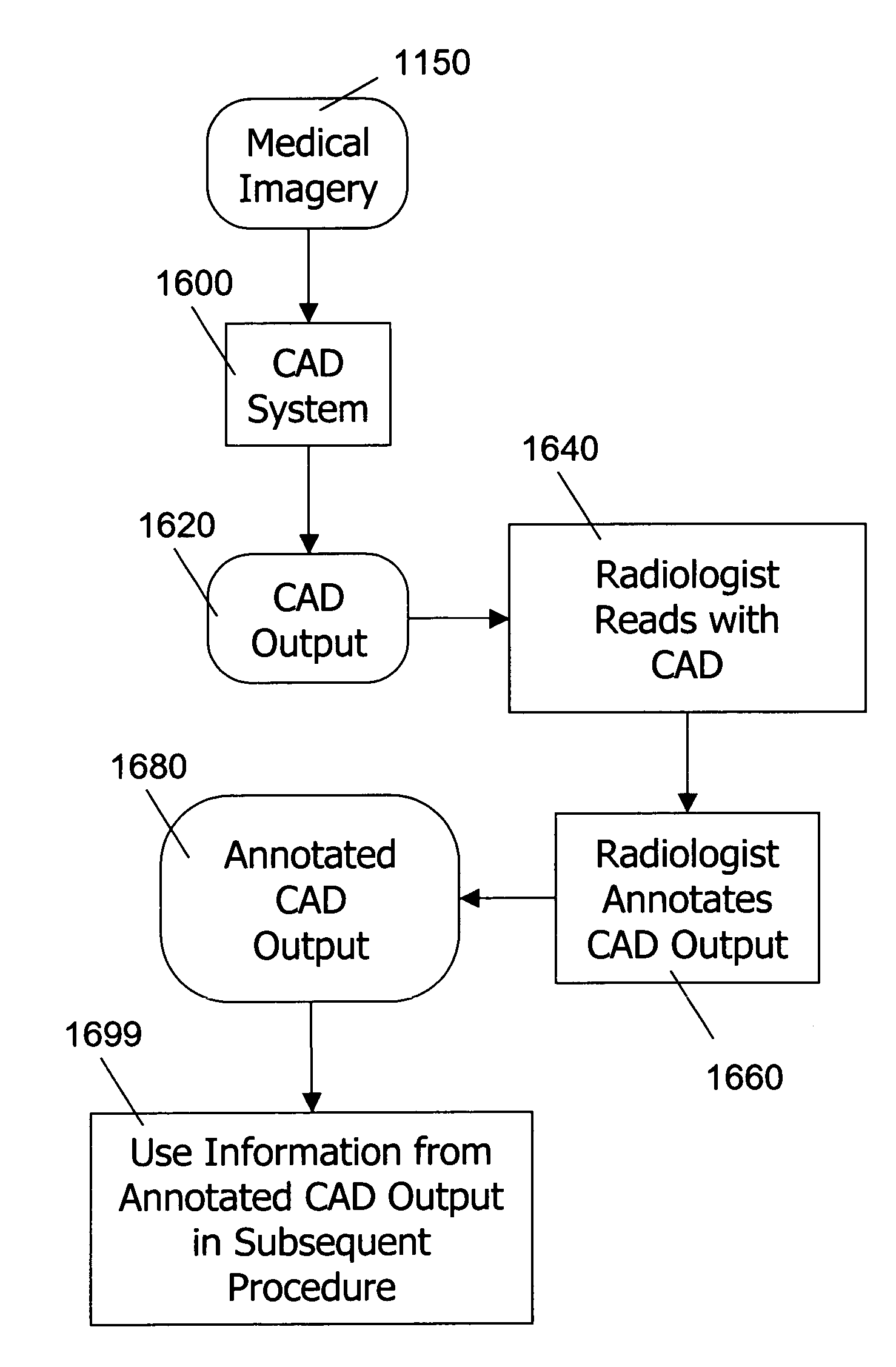
Use of computer-aided detection system outputs in clinical practice
InactiveUS6970587B1Accurate representationEfficient and precise positioningImage enhancementImage analysisDisplay deviceMinutiae
The present invention provides for the use of computer-aided detection (CAD) system output displays for providing accurate representations of areas for subsequent exams. Since the CAD output, unlike the original medical imagery, is not used during the initial reading, the radiologist does not mark it until a final determination is reached regarding subsequent procedures. Additionally, since the CAD output contains versions of the original imagery, the regions indicated by the radiologist are shown in the context of the particular anatomical detail for the given patient. This detail assists the technologist in more efficiently and accurately locating the exact area for subsequent exams.
Owner:ICAD INC
Device and method for margin marking of radiography specimens
InactiveUS20050152841A1Eliminate confusionEasy to holdSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsEngineeringVisual perception
A marking device for defining the margins and orientation of radiography specimens includes a plurality of visually distinctive markers joined by a base that holds the markers until the markers are secured to a specimen. The base serves as a holder for the individual markers as the markers are secured to a specimen with sutures or staples, at which time the markers are disconnected from the base. One or more markers may be secured to a specimen as needed to define the orientation of the specimen. By securing markers to specific locations on a specimen, a surgeon can indicate to radiologists and pathologists the specimen's orientation in the body before removal, thus aiding in future study of the specimen. Since the markers are made either wholly or partially from radiopaque material, the markers are visible when radiographed.
Owner:BEEKLEY A CT
Method for Consistent and Verifiable Optimization of Computed Tomography (CT) Radiation Dose
InactiveUS20140270053A1Minimal disruptionGreat noise leverMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingClinical settingsMathematical model
A system and a method is disclosed for consistently and verifiably optimizing computed tomography (CT) radiation dose in the clinical setting. Mathematical models allow for estimation of patient size, image noise, size-specific radiation dose, and image quality targets based on digital image data and radiologists preferences. A prediction model estimates the scanner's tube current modulation and predicts image noise and size-specific radiation dose over a range of patient sizes. An optimization model calculates specific scanner settings needed to attain target image quality at the minimum radiation dose possible. An automated system processes the image and dose data according to the mathematical models and stores and displays the information, enabling verification and ongoing monitoring of consistent dose optimization.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
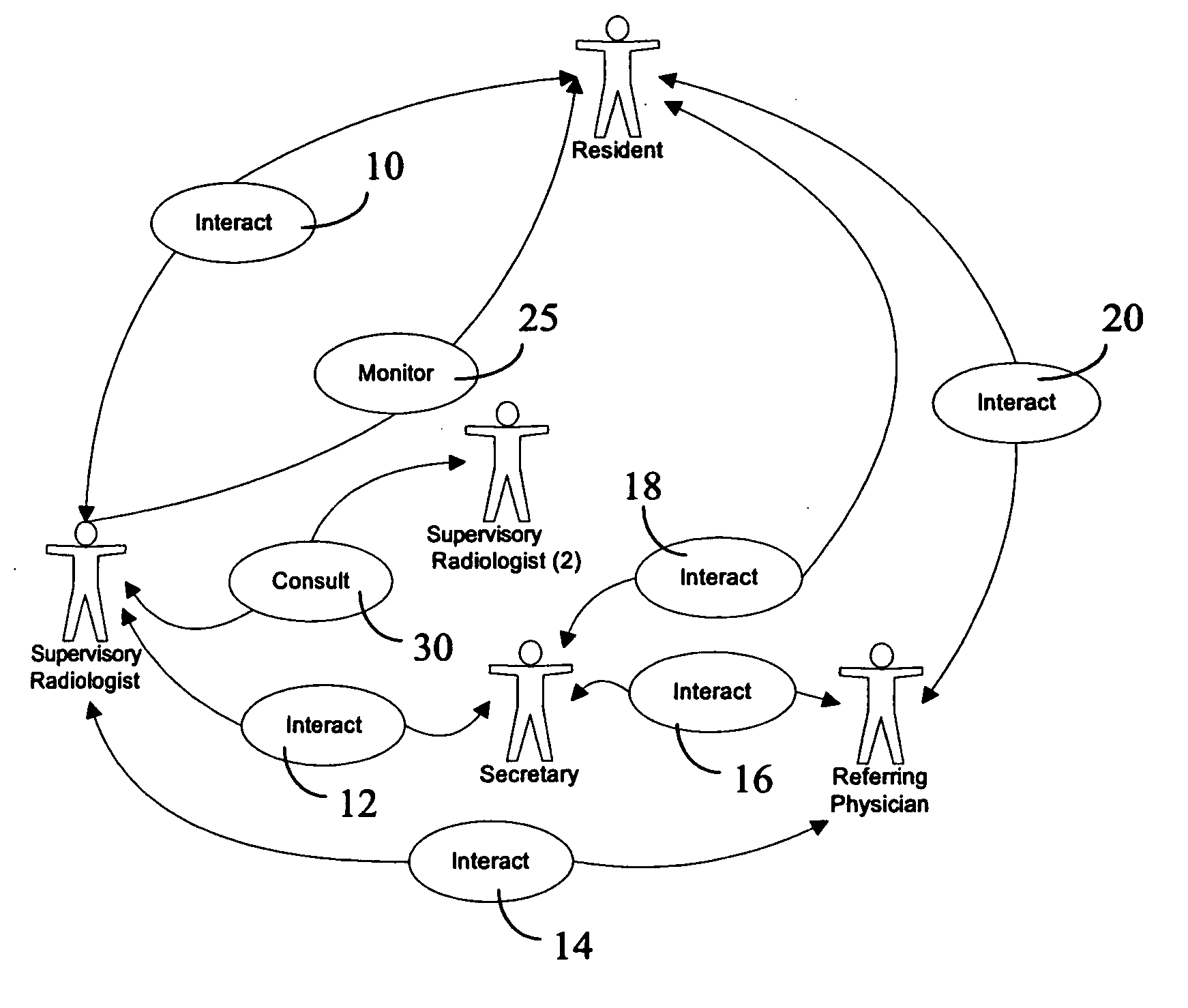
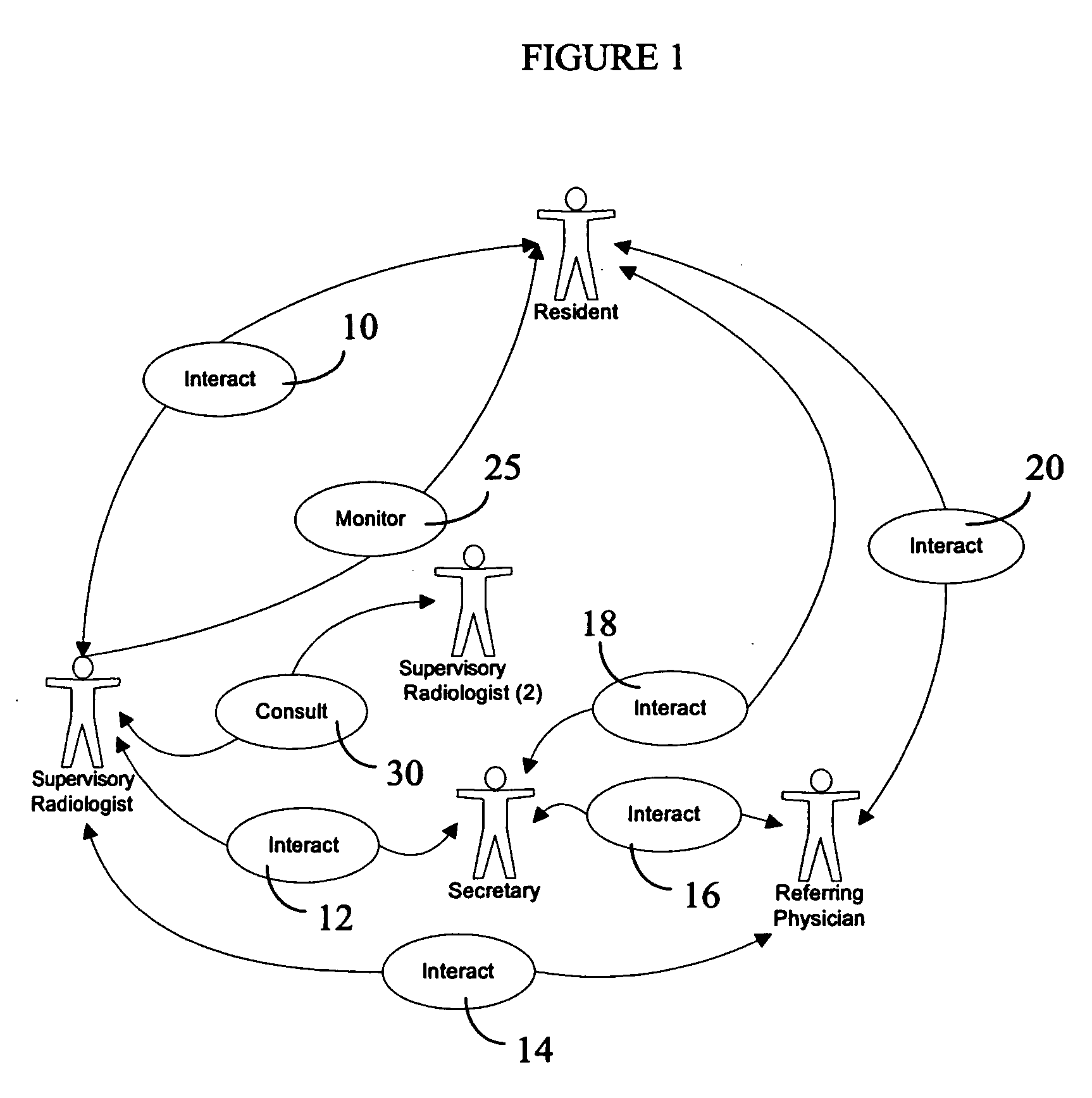
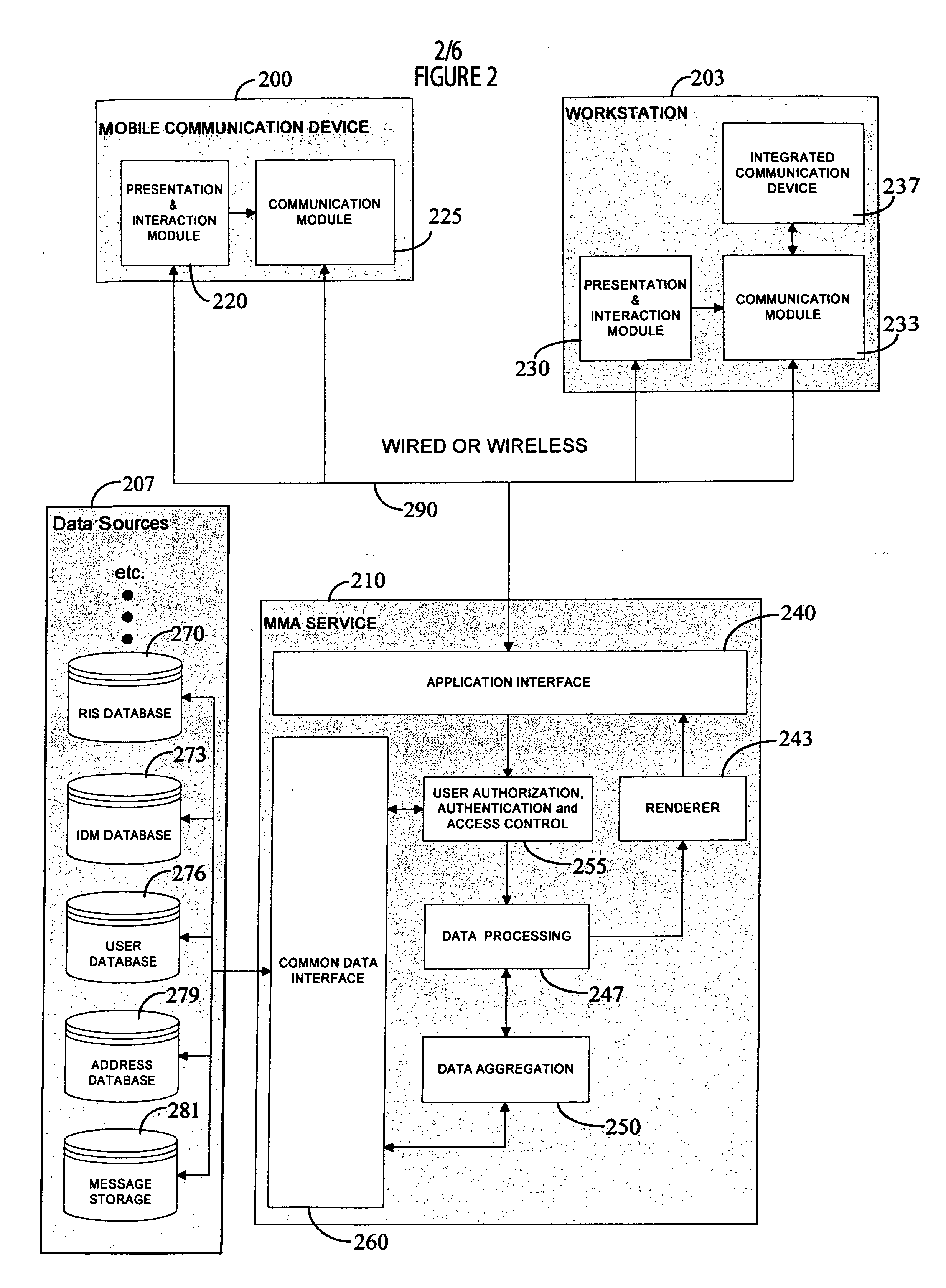
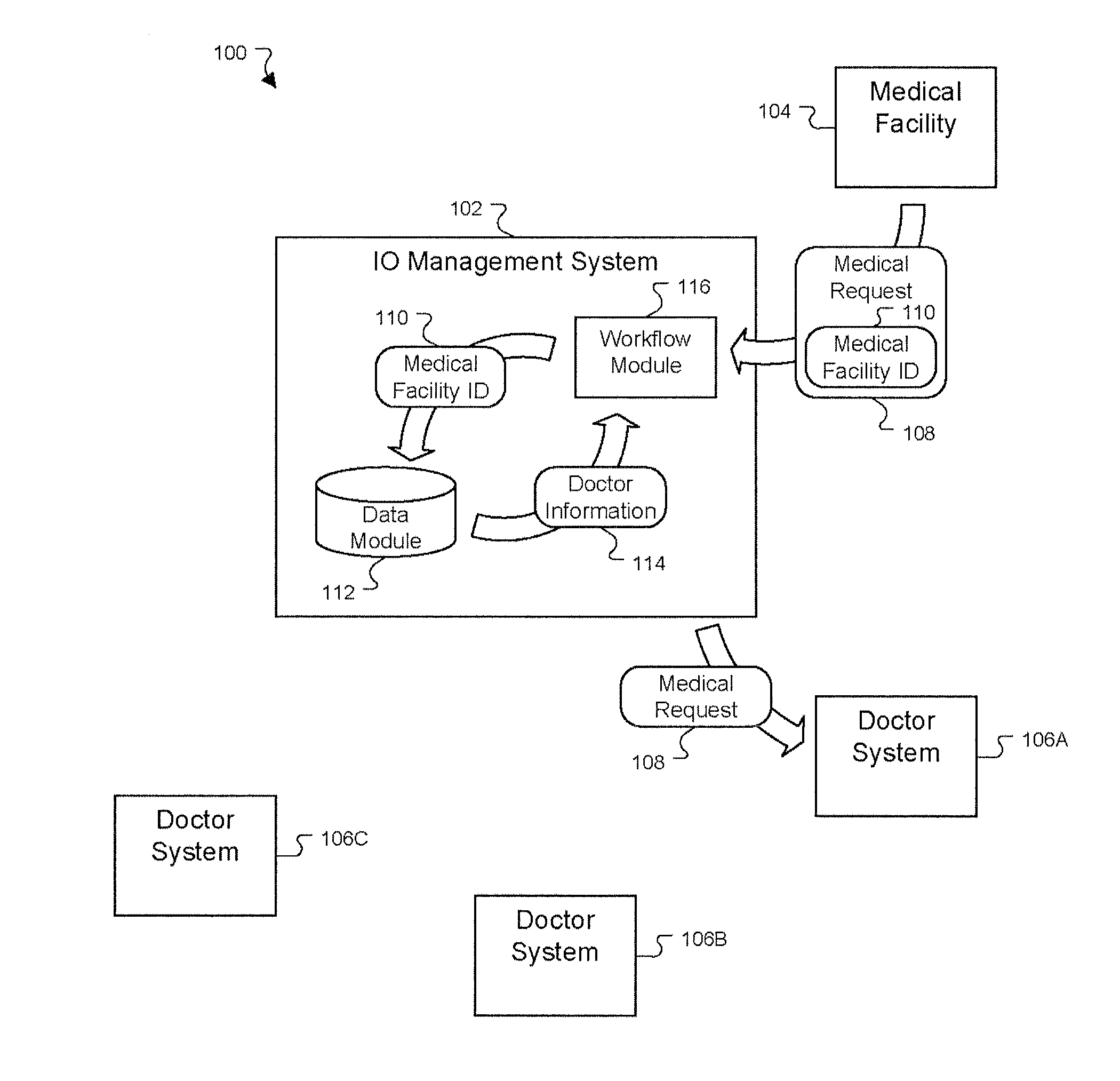
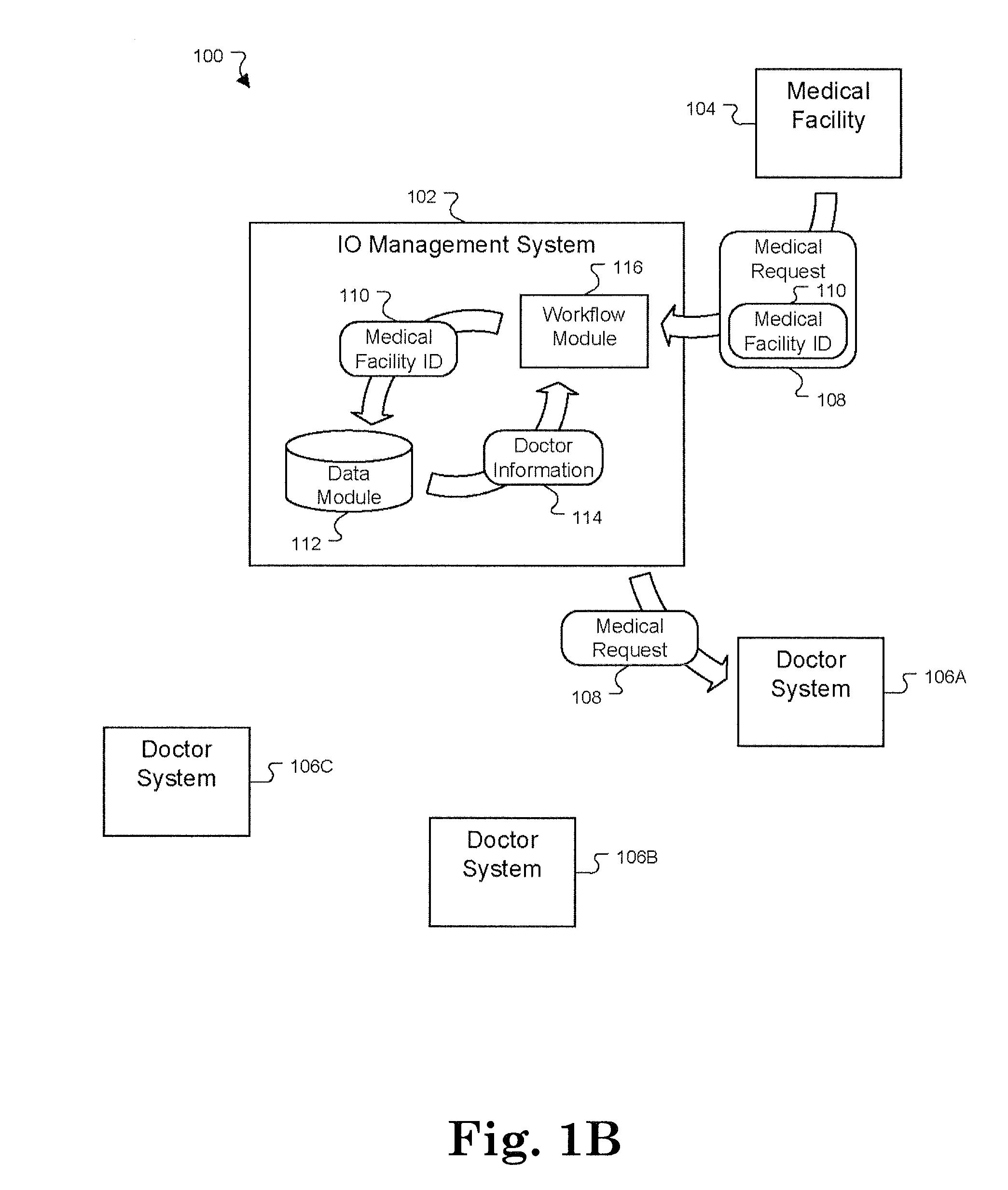
Portable task management system for healthcare and other uses
InactiveUS20060106641A1Medical communicationData processing applicationsMedical recordTask management
A mobile monitoring and communication system integrates communication services (text, voice, video, and data) with medical information (e.g., patient medical record, patient demographics, reason for procedure, workflow information, etc.) within a radiology department, for example. A medical information system for use with portable processing devices involves a portable processing device including a communication processor for receiving messages from one or more different healthcare workers. An individual message identifies, a task for performance by a particular healthcare worker for a patient, patient and task associated context information and a priority level of the task. A user interface provides data representing at least one display image for display to a user and comprising an overview of tasks of the different healthcare workers including the task for performance by the particular healthcare worker.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
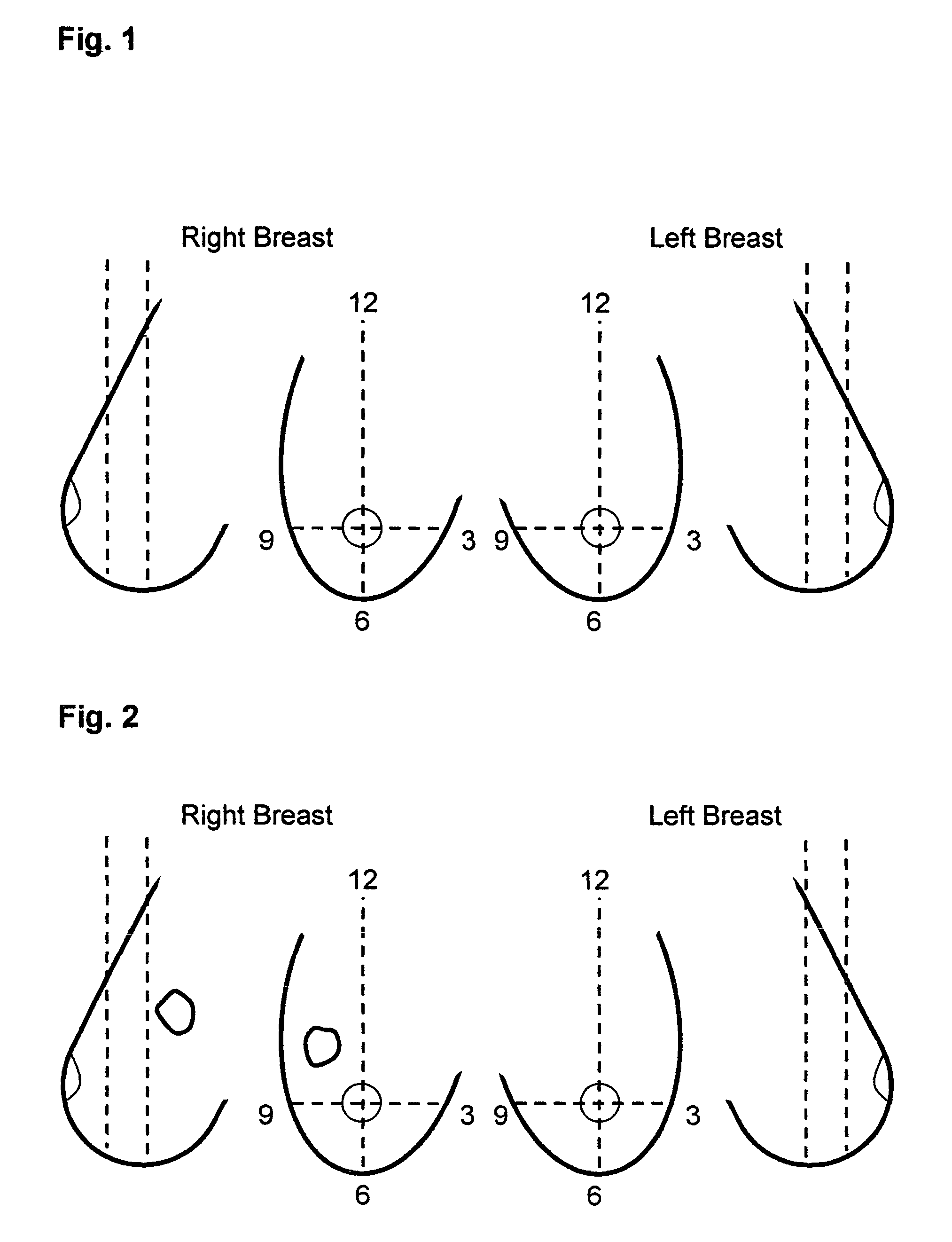
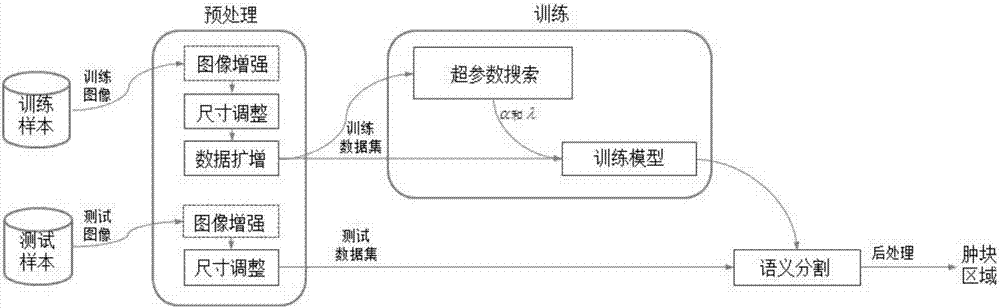
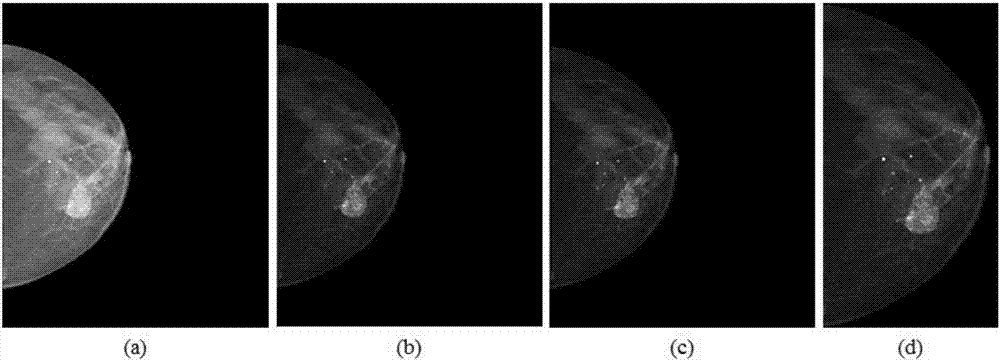
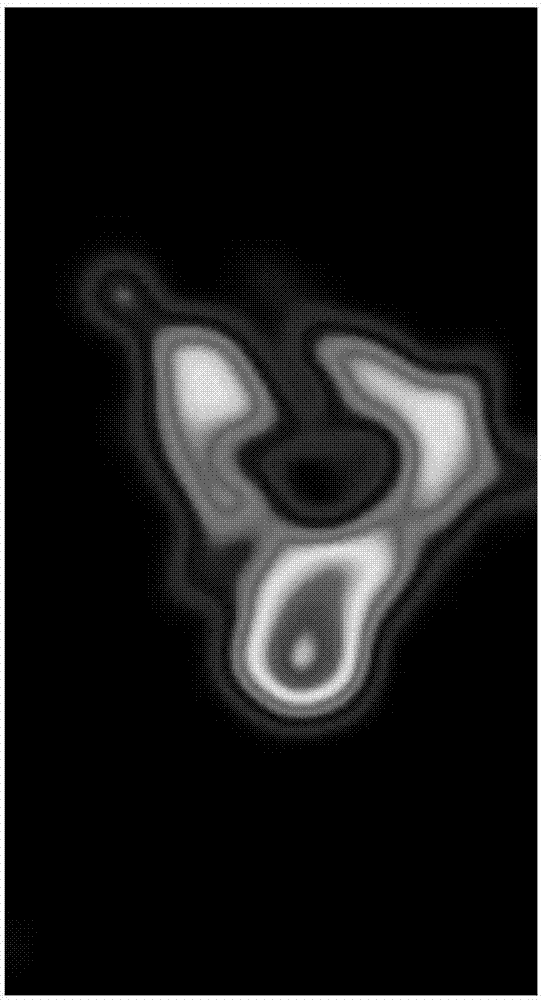
Deep residual network-based semantic mammary gland molybdenum target image lump segmentation method
ActiveCN107886514ALess parameters to learnImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionData set
The invention discloses a deep residual network-based semantic mammary gland molybdenum target image lump segmentation method. The method comprises the following steps of: labelling pixel categories of lumps and normal tissues corresponding to a collected mammary gland molybdenum target image so as to generate label images, and dividing the mammary gland molybdenum target image and the corresponding label images into training samples and test samples; preprocessing the training samples to form a training data set; constructing a deep residual network, and training the network by utilizing thetraining data set, so as to obtain a deep residual network training model; after a to-be-segmented mammary gland molybdenum target image lump is preprocessed, carrying out binary classification and post-processing on a pixel of the to-be-segmented mammary gland molybdenum target image by utilizing the deep residual network training model, and outputting lump segmentation image to realize semanticsegmentation of the mammary gland molybdenum target image lump. The method is capable of effectively improving the automatic and intelligent levels of mammary gland molybdenum target image lump segmentation, and can be applied to the technical field of assisting radiologists to carry out medical diagnosis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Enhanced multiple resource planning and forecasting
ActiveUS20110066449A1Avoid service interruptionAccurate volumeHospital data managementHealthcare resources and facilitiesSystem configurationResource efficiency
A system configuration and techniques for optimizing schedules and associated use predictions of a multiple resource planning workflow are disclosed herein, applicable to environments such as radiologist scheduling in a teleradiology workflow. In one embodiment, a series of computing engines and components are provided to allow detailed forecasting and the generation of customized recommendations for scheduling and other resource usage scenarios. This forecasting can factor resource efficiencies, changes in resource demand volume, resource specialties, resource usage preferences, expected future events such as the removal or addition of resources at future times, and other resource availability or usage changes. The forecasts may be further enhanced through the use of historical data models and estimated future data models. Additionally, a calendar and other tools may be presented through a user interface to allow forecast and scenario customization based on selection of a series of future dates.
Owner:VIRTUAL RADIOLOGIC
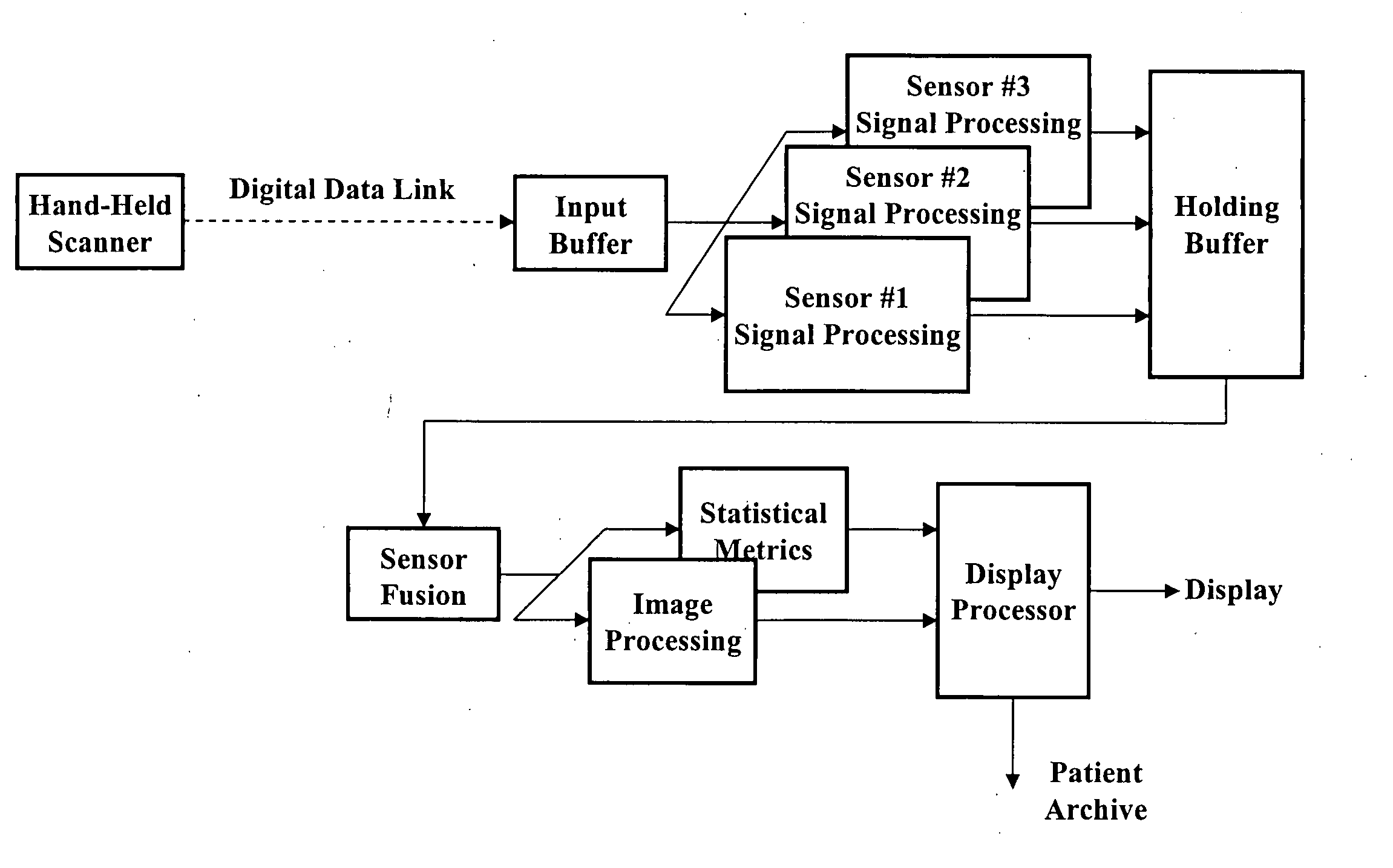
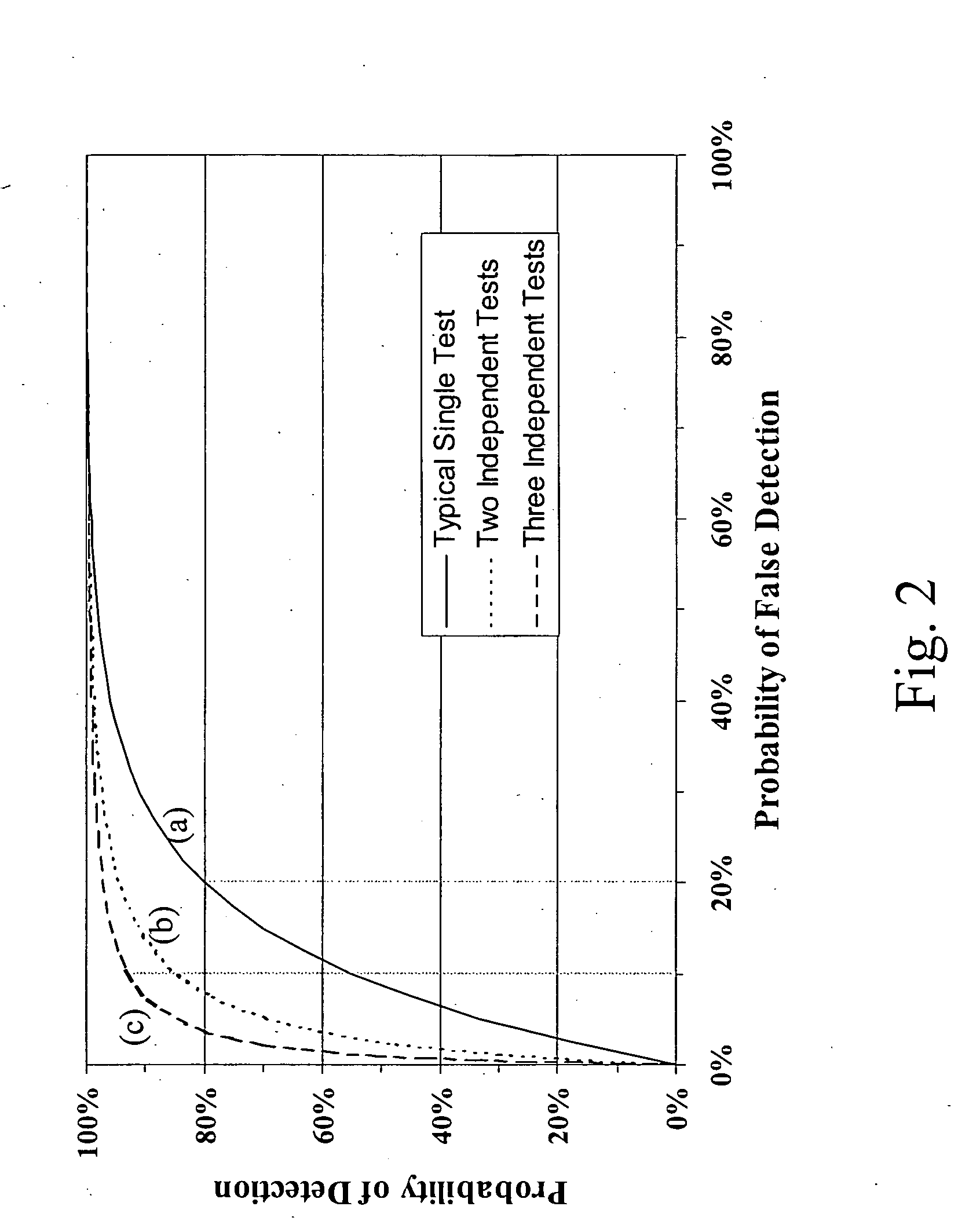
Multi-sensor breast tumor detection
InactiveUS20040220465A1Strong specificityIncrease cost/complexityOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringGeneral practionerBreast cancer screening
X-ray mammography has been the standard for breast cancer screening for three decades, but offers poor statistical reliability; it also requires a radiologist for interpretation, employs ionizing radiation, and is expensive. The combination of multiple independent tests, performed effectively at the same time and co-registered, can produce substantially more reliable detection performance than that of the individual tests. The multi-sensor approach offers greatly improved reliability for detection of early breast tumors, with few false positives, and also can be designed to support machine decision, thus enabling screening by general practitioners and clinicians; it avoids ionizing radiation, and can ultimately be relatively inexpensive.
Owner:CAFARELLA JOHN H
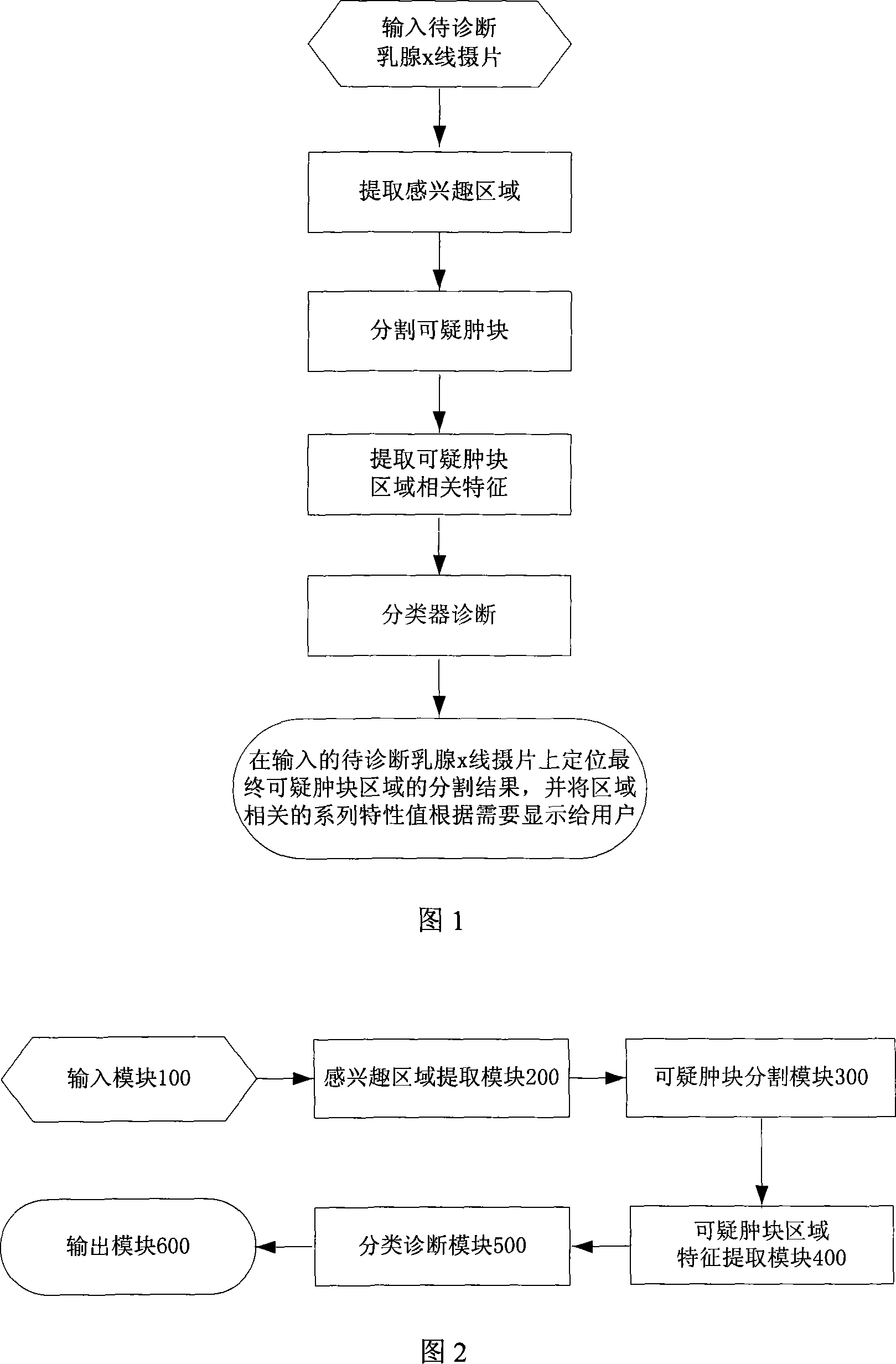
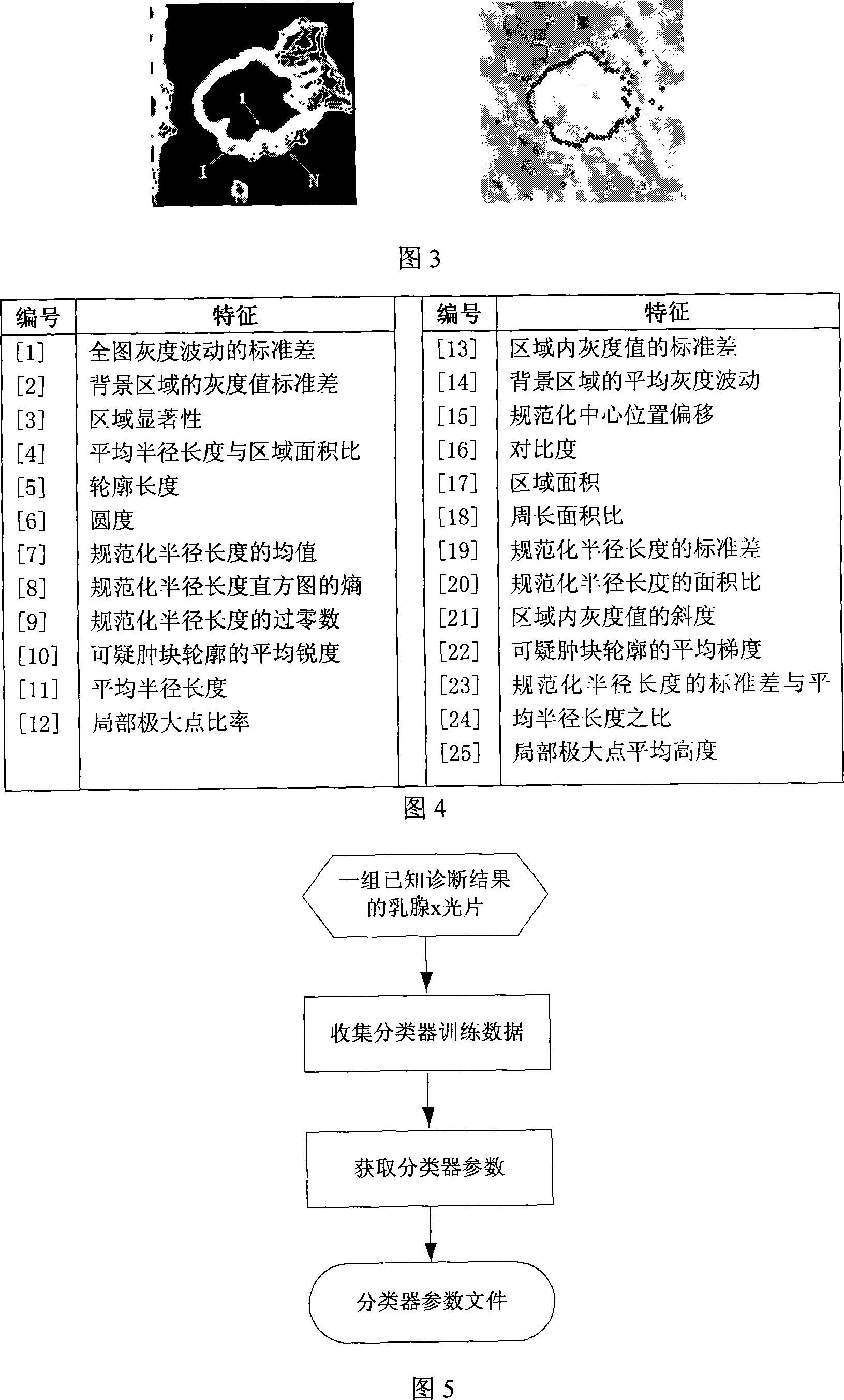
Galactophore cancer computer auxiliary diagnosis method based on galactophore X-ray radiography and system thereof
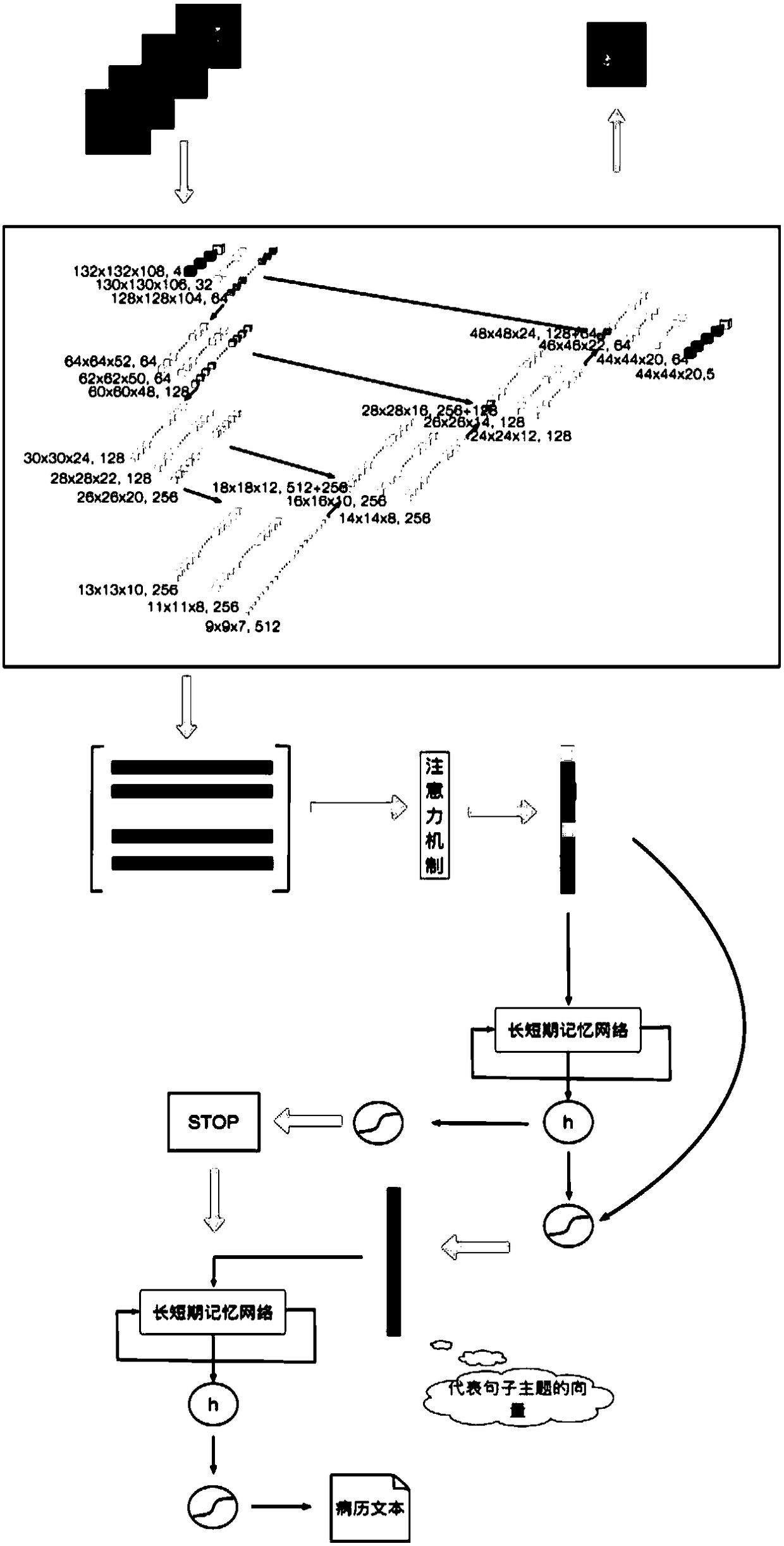
InactiveCN101103924AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsRadiation diagnosticsFeature extractionDiagnosis methods
The invention discloses a breast cancer computer auxiliary diagnosis method and system based on galactophore X-ray radiograph. A galactophore X-ray radiograph for diagnosis is input into the system of the invention firstly, and is treated through an extracting module in a region of interest, a partitioning module and a feature extracting module in a region of doubtful lump, hereby a series of relative feature values about the doubtful lump region; then the feature values are input into a trained classifier which classifies and identifies the doubtful lump region and lastly the computer automatic examined final result of portioning the doubtful lump region is located on the input galactophore X-ray radiograph for diagnosis and the calculated relative feature values of the region are displayed to a roentgenologist according to requirements to indicate the roentgenologist about the region needing special attention and relative important parameters of the region. The invention can improve the accurateness and efficiency of the breast cancer diagnosis by the roentgenologist to some extent and help the roentgenologist to bring forward a diagnostic opinion and a therapeutic schedule more objectively and effectively.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-modal nuclear magnetic resonance image case report automatic generation method
ActiveCN108376558ANo human intervention requiredEase workMedical automated diagnosisMedical imagesMedical recordNerve network
The invention belongs to the medical data analysis and intelligent processing technical field, and specifically relates to a multi-modal nuclear magnetic resonance image case report automatic generation method employing a deep learning model; the method comprises the following steps: importing an attention matrix on the basis of using a convolution nerve network to extract image characteristics; giving different weights on characteristics of different positions via point multiplication operation, thus obtaining image characteristics under different attentions; using a long-short period memorycycle nerve network to form a subject vector of each sentence in a case report according to the image characteristics under different attentions; using another long-short period memory cycle nerve network to form each word according to the subject vector of the sentence; connecting the words so as to obtain the final case report. The method can automatically form a description text of a magnetic resonance image case without using a case template, thus providing deep meanings for mitigating works of radiology department doctors and building an intelligent computer auxiliary diagnosis system.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method and apparatus of providing a radiation scorecard
ActiveUS8538776B2Improve securityReduce exposureMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesColor television detailsRetrospective analysisRadiation exposure
The present invention relates to a method to measure, record, analyze, and report cumulative radiation exposure to the patient population and provide automated feedback and recommendations to ordering clinicians and consultant radiologists. The data provided from this “radiation scorecard” would in turn be automatically recorded into a centralized data repository (radiation database), which would be independent to the acquisition site, technology employed, and individual end-user. Retrospective analysis can also be performed using a set of pre-defined scorecard data points tied to the individual patient's historical medical imaging database, thereby allowing for comprehensive (both retrospective and prospective) medical radiation exposure quantitative analysis. Patient safety can be improved by a combination of radiation dose reduction, exposure optimization, rigorous equipment quality control (QC), education and training of medical imaging professionals, and integration with computerized physician order entry (CPOE).
Owner:REINER BRUCE
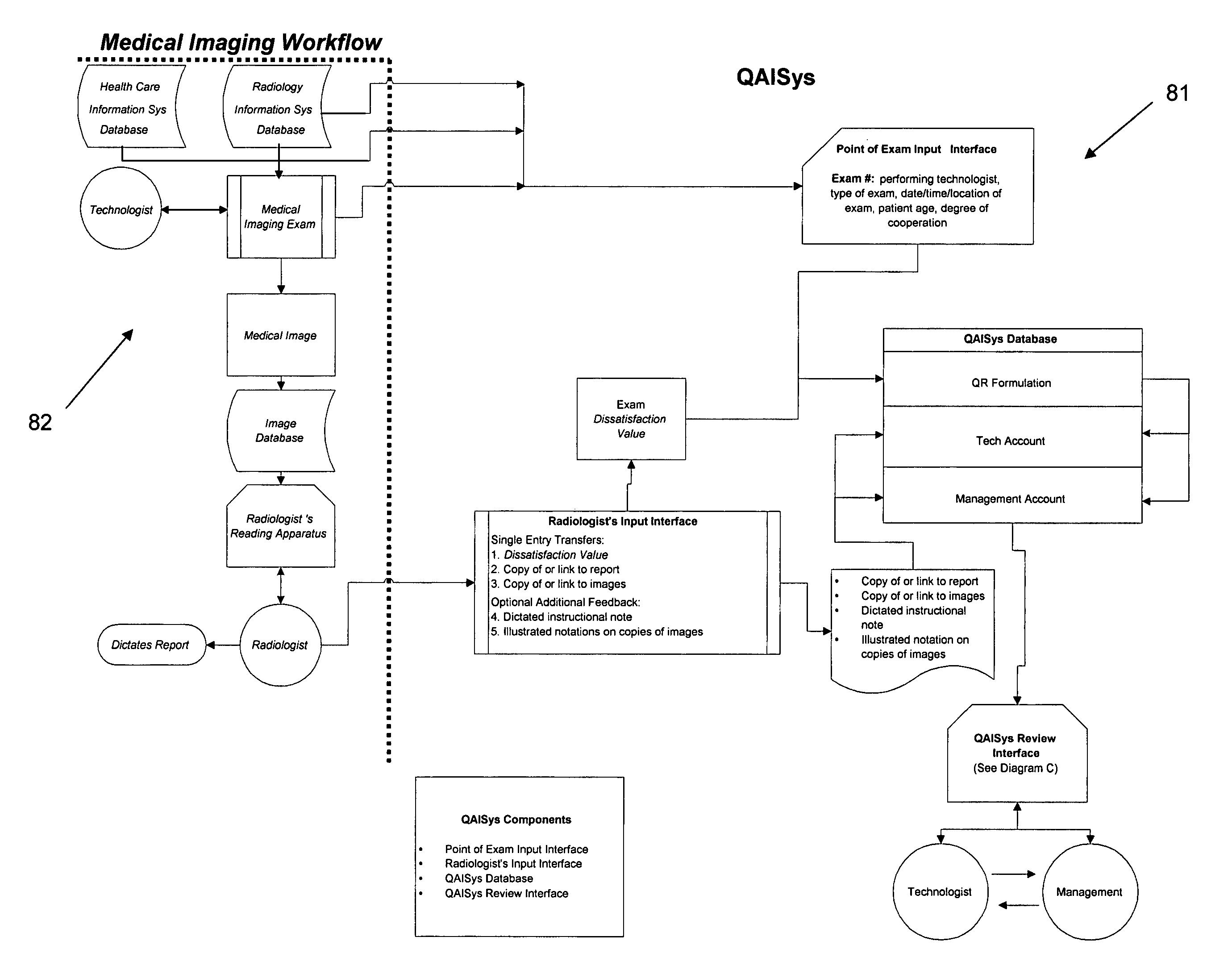
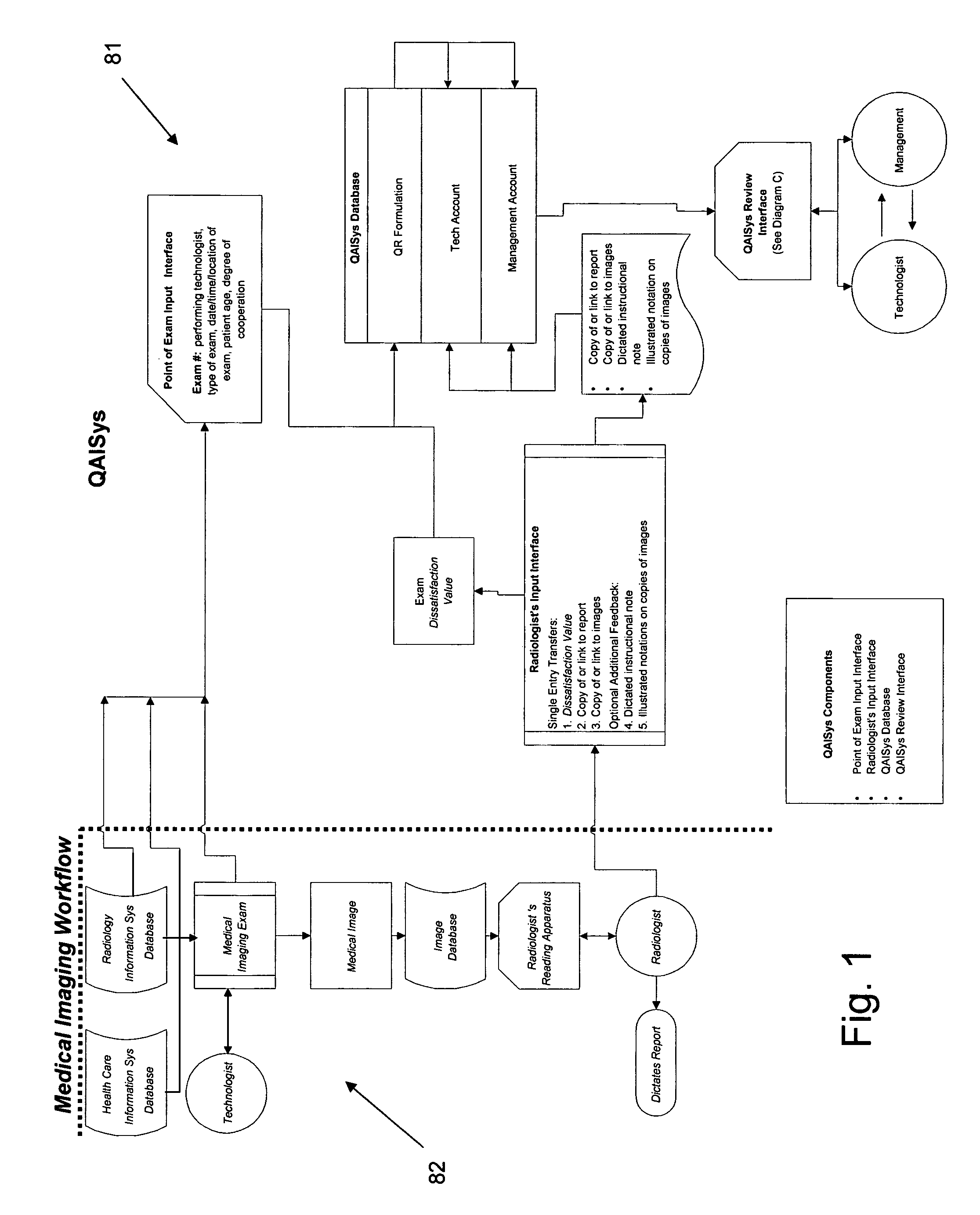
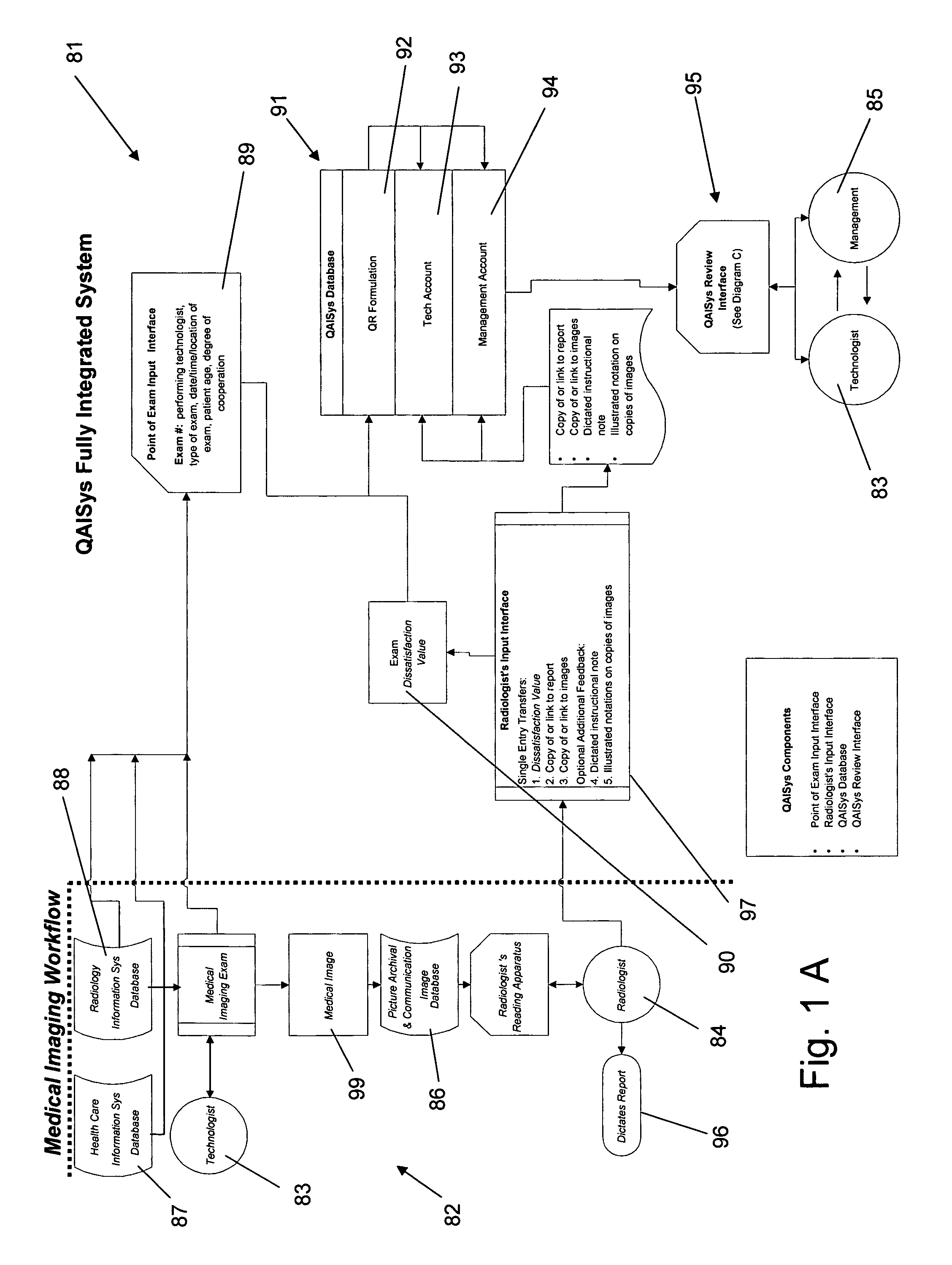
Medical imaging-quality assessment and improvement system (QAISys)
The business method known as QAISys (Quality Assessment and Improvement System) is a process that rates comprehensively and continually the quality of medical images as determined by the interpreting radiologist. The output of this system conveys feedback from the radiologist to the performing technologist and his / her supervisor. This feedback enables medical radiologists, technologists, and managers to bridge any communication gaps between themselves in respect to the quality and effectiveness of medical images. It permits management to assess and track image quality for an entire medical imaging department by modality, location, and / or shift, and for each individual technologist. The QAISys method reveals the nature of recurrent quality failures and highlights which exam types need to be improved. QAISys then indicates practical, cost-effective means of assessing and improving the overall medical images for future patients.
Owner:DALE RICHARD B
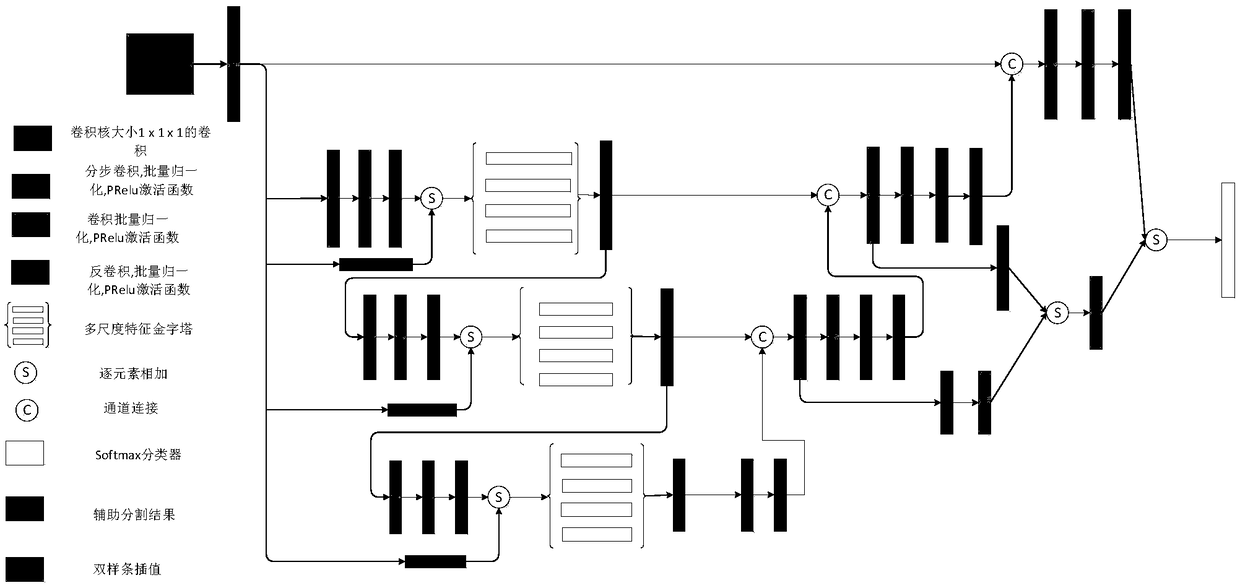
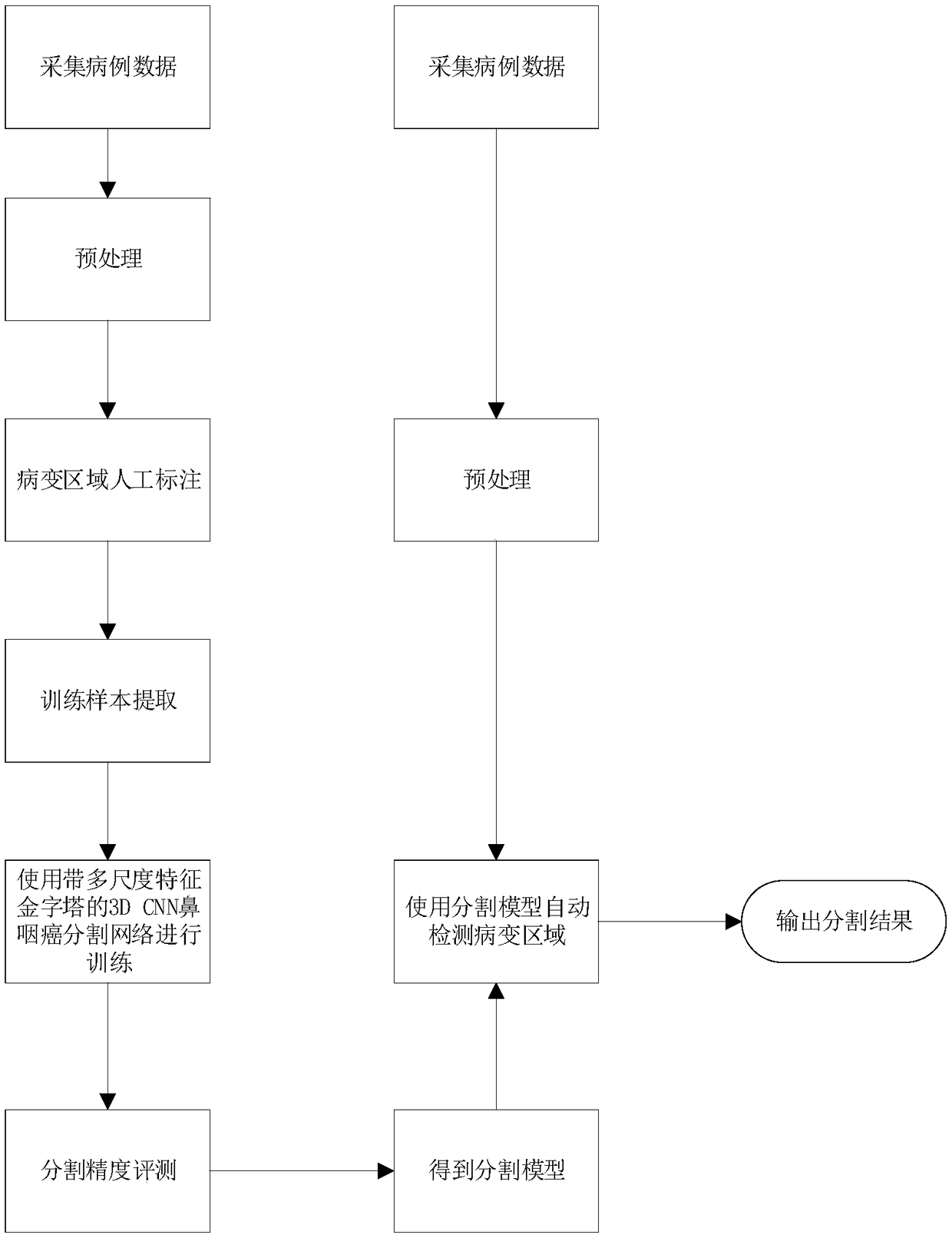
Segmentation of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Using 3D CNN Based on Multi-scale Feature Pyramid
ActiveCN109063710ARealize automatic segmentationHigh precisionNeural architecturesRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsData setTraining phase
The invention relates to a nasopharyngeal tumor image segmentation technology in the image segmentation field, in particular to a 3D CNN nasopharyngeal carcinoma segmentation method based on a multi-scale feature pyramid. For the training samples, the experienced radiologist should label several cases of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, use the whole three-dimensional MRI image to establish the data set,and preprocess the data set, then train the training data set with network to obtain high-precision segmentation model. For new cases, the segmentation model can be used to segment MRI images. Compared with the traditional methods, except for manual labeling in the training phase, the other parts can be processed automatically, which greatly reduces the demand for experienced physicians and achieves higher accuracy compared with the five mainstream networks.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
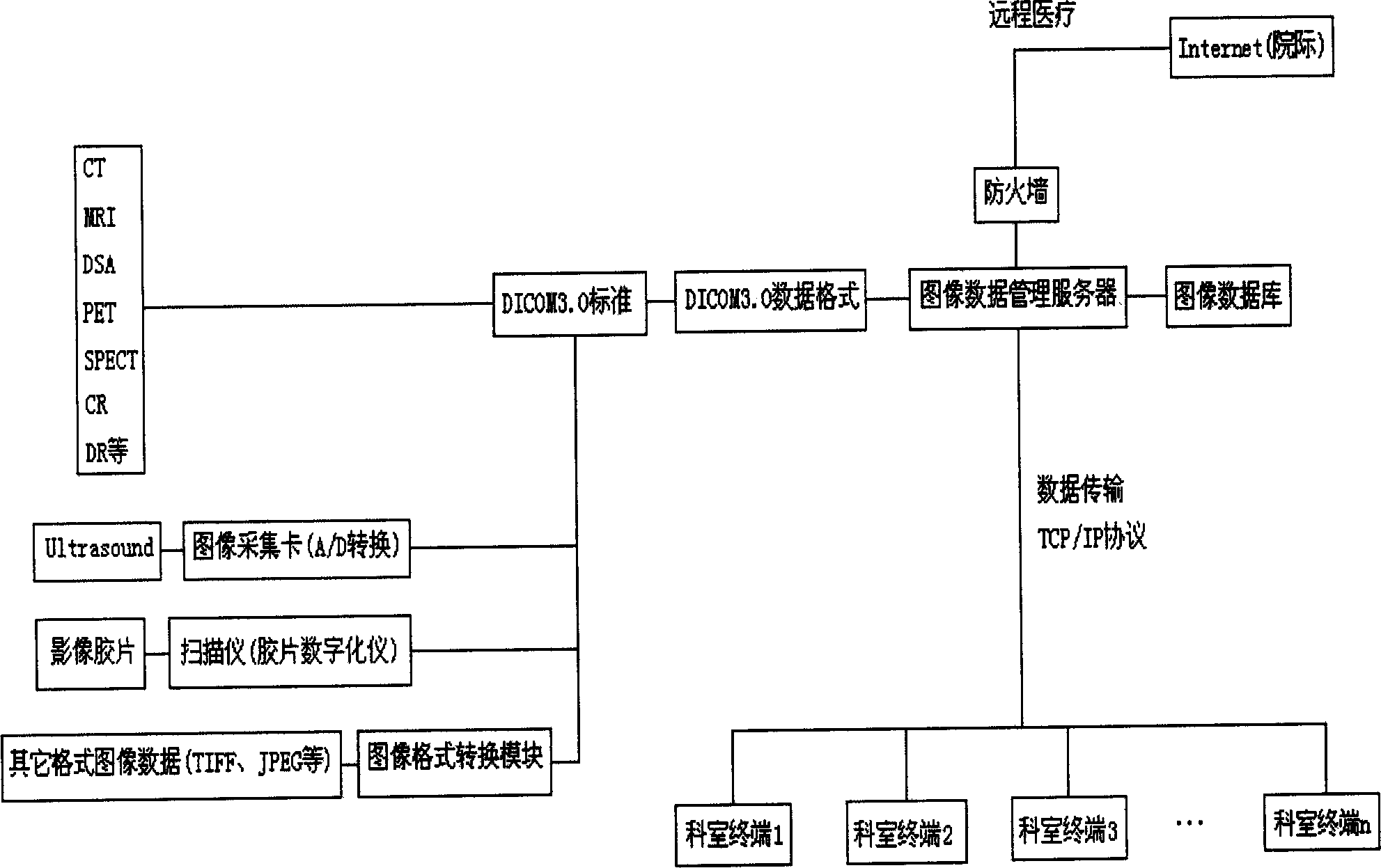
Medical image data transmission and three-dimension visible sysem and its implementing method
InactiveCN1794246AImprove efficiencyEasy to useTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsProcess functionMedical imaging data
This invention discloses a medical image transmission and 3-D visual system and a realizing method, which develops an iconography diagnosis system operated by stand-alones and single persons to expand the image data process function of a radiation section or an image working station to computer terminals of hospitals, so that, doctors in hospitals can get the image data of patients directly from the terminals in their offices to carry out 3-D display interaction operations.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Breast diagnostic apparatus for fused SPECT, PET, x-ray CT, and optical surface imaging of breast cancer
InactiveUS20060239398A1Improve spatial resolutionImprove system capabilitiesDiagnostics using lightPatient positioning for diagnosticsOptical reflectionImage-Guided Therapy
A new method of breast imaging to improve the detection of cancer during early stages of development is disclosed. The system combines molecular images of radioisotope uptake in cancerous cells with three dimensional high resolution single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), positron emission tomography (PET), x-ray computed tomography (CT) and optical reflectance and emission (ORE) images of the breast. The system acquires data from nuclear isotopes within the breast and processes the data into three dimensional molecular tomographic images of cancerous cellular activity, morphological three dimensional x-ray density tomographic images and three dimensional optical surface images. These three sets of images or data are then combined to provide information as to the sensitivity and specificity as to the type of cancer present, three dimensional information as to the physical location of the cancer and reference information for radiologists, surgeons, oncologists and patients in order to plan stereo-tactic biopsy, minimally invasive surgery and image guided therapy, if necessary.
Owner:FUSED MULTIMODALITY IMAGING
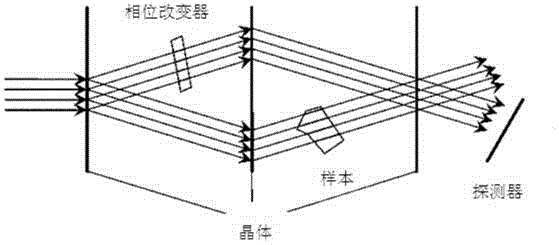
Phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS20120243658A1High contrast-to-noise ratioReduce exposureRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusLarge fovGrating
X-ray devices for Phase Contrast Imaging (PCI) are often built up with the help of gratings. For large field-of-views (FOV), production cost and complexity of these gratings could increase significantly as they need to have a focused geometry. Instead of a pure PCI with a large FOV, this invention suggests to combine a traditional absorption X-ray-imaging system with large-FOV with an insertable low-cost PCI system with small-FOV, The invention supports the user to direct the PCI system with reduced FOV to a region that he regards as most interesting for performing a PCI scan thus eliminating X-ray dose exposure for scanning regions not interesting for a radiologist. The PCI scan may be generated on the basis of local tomography.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS9084528B2Reducing X-ray dose exposureReduce intensityRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusLarge fovGrating
X-ray devices for Phase Contrast Imaging (PCI) are often built up with the help of gratings. For large field-of-views (FOV), production cost and complexity of these gratings could increase significantly as they need to have a focused geometry. Instead of a pure PCI with a large FOV, this invention suggests to combine a traditional absorption X-ray-imaging system with large-FOV with an insertable low-cost PCI system with small-FOV, The invention supports the user to direct the PCI system with reduced FOV to a region that he regards as most interesting for performing a PCI scan thus eliminating X-ray dose exposure for scanning regions not interesting for a radiologist. The PCI scan may be generated on the basis of local tomography.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
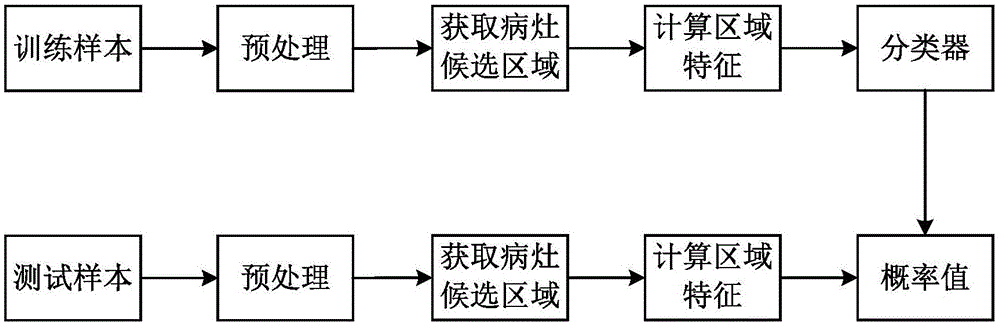
Prostatic cancer computer-assisted detection method and system based on multi-parameter MRI
ActiveCN106778005AAuxiliary diagnosisImprove performanceImage enhancementImage analysisMalignancyTest phase
The invention discloses a prostatic cancer computer-assisted detection method and system based on multi-parameter MRI and relates to the field of medical image processing. The method includes the following steps that at a training stage, firstly, a clinical case sample is preprocessed, then a prostate region and a focus candidate region are automatically extracted, and then features of the focus candidate region are calculated and used for training a classifier; at a testing stage, the trained classier is used for classifying the features of the focus candidate region automatically extracted from the tested clinical case sample, and a corresponding diagnosis result is obtained and serves as reference comments to be provided for doctors. A series of quantitative indexes and corresponding malignancy probability values are provided for radiologists, and the doctors can be effectively assisted in diagnosing the prostatic cancer through an MRI image.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
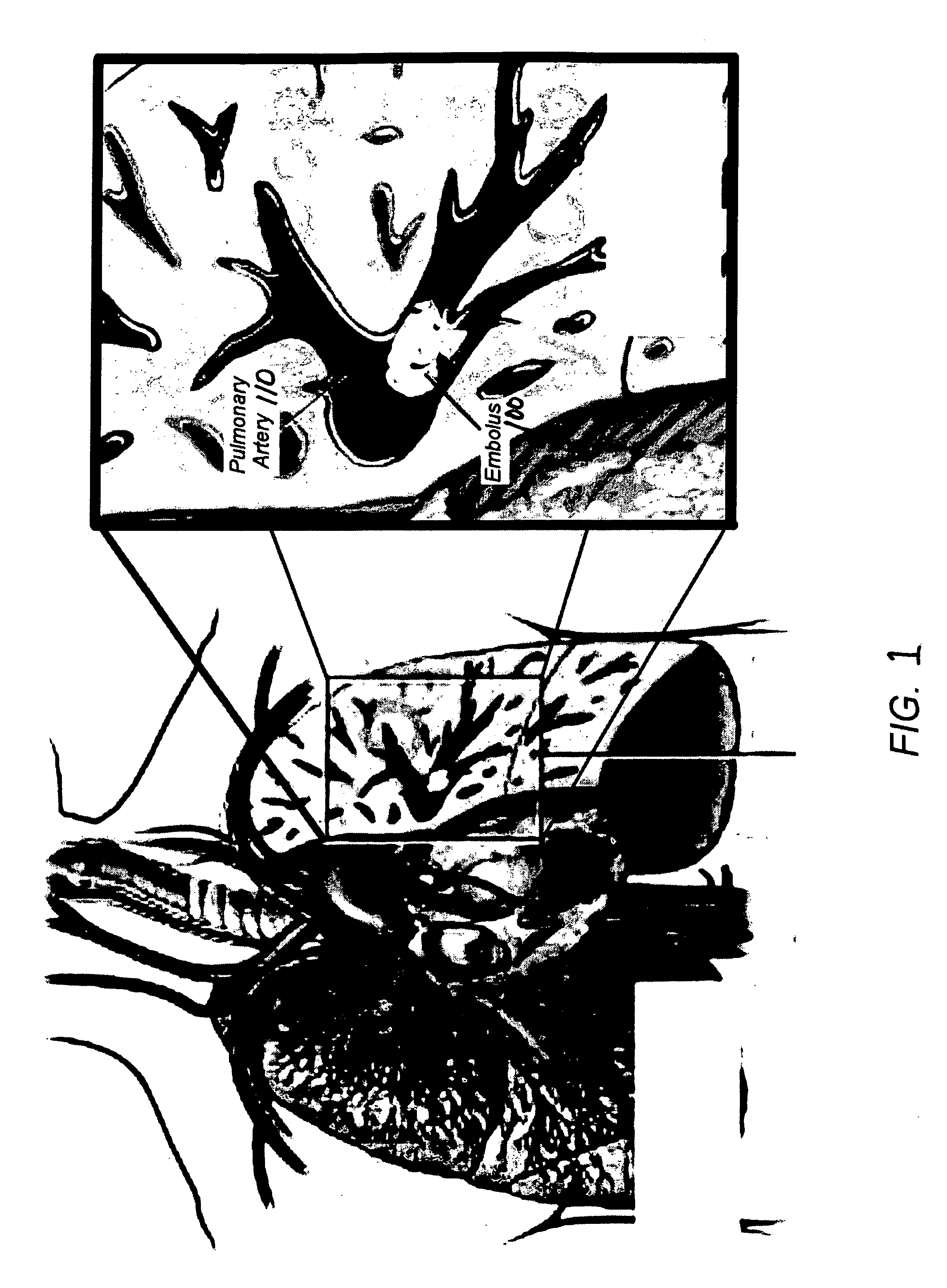
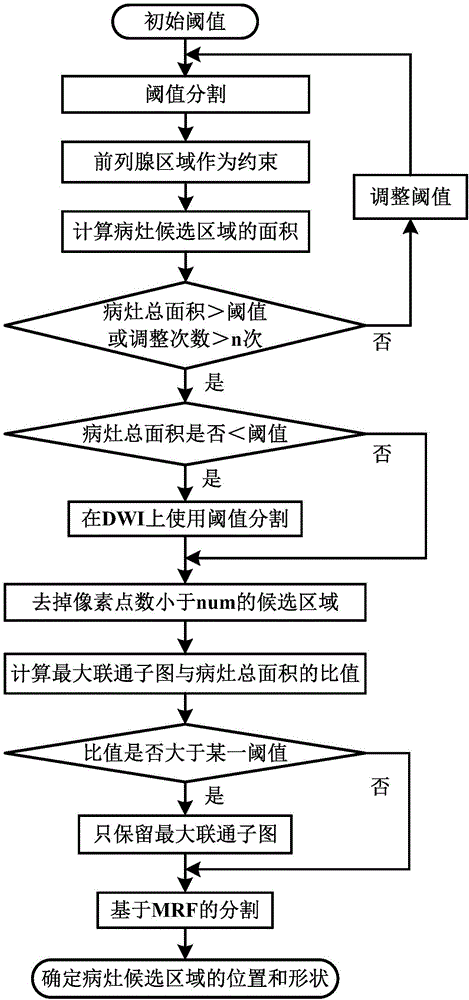
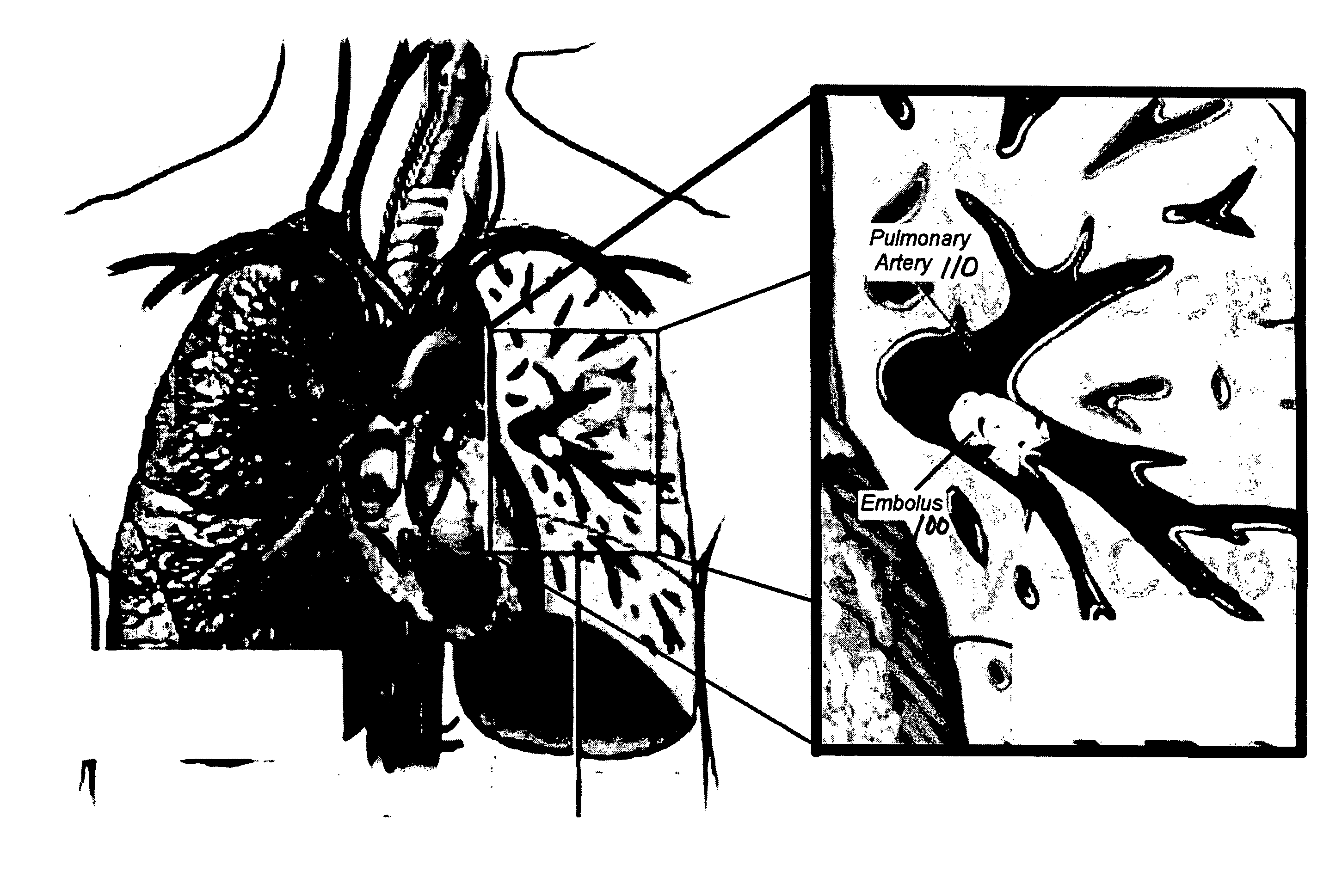
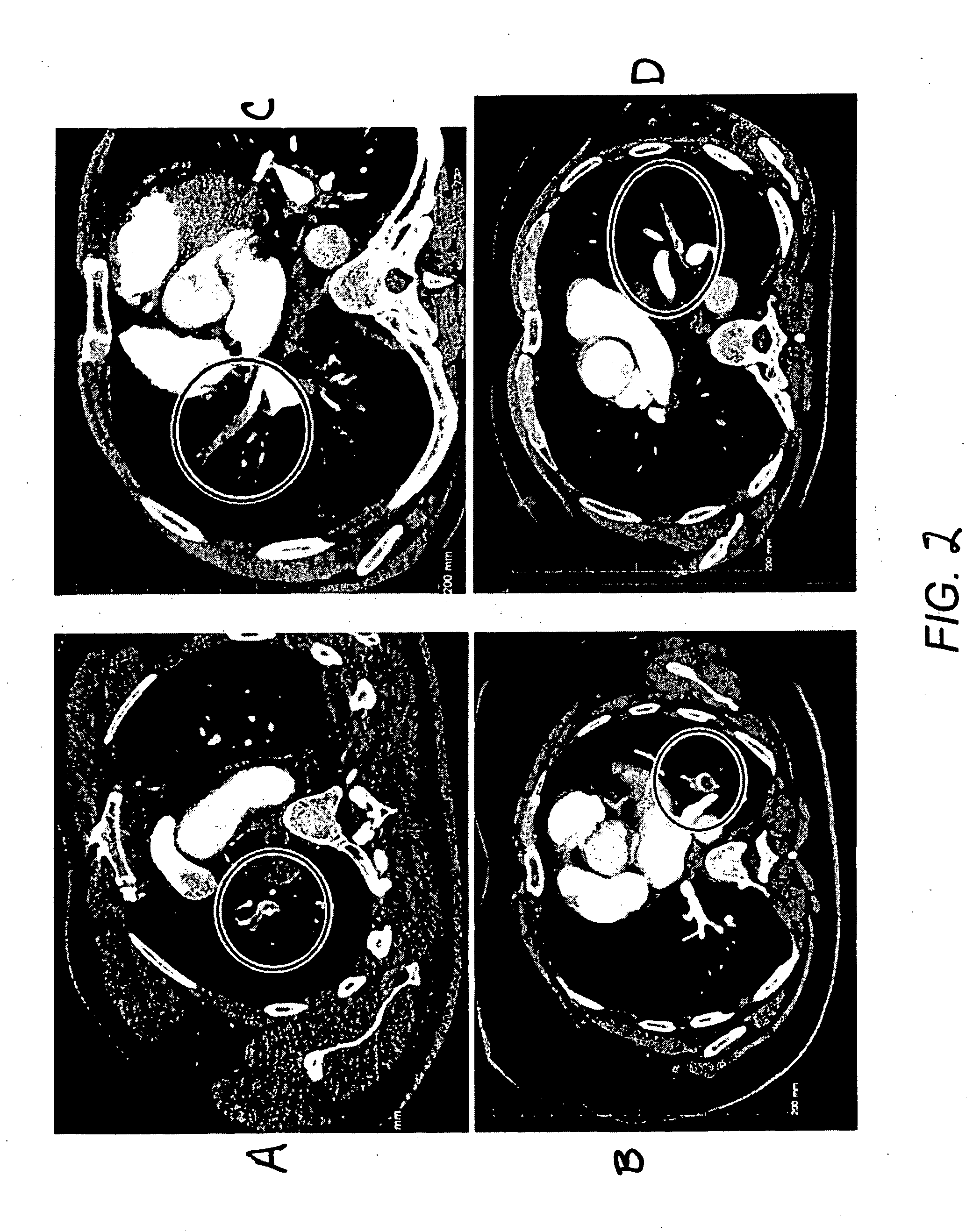
Method for segmenting arteries and veins
In a preferred embodiment a radiologist traces the pulmonary artery and pulmonary veins visible in a set of CT images and identifies the arteries and veins. The radiologist's identification of the pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins is then received by an image analyzer and combined with the analyzer's identification of the pulmonary arteries to form a combined identification; and the analyzer then reviews this combined identification of the pulmonary arteries to detect any pulmonary embolisms. The radiologist's identification of any pulmonary embolisms is compared with the analyzer's identification of any pulmonary embolisms to determine if there are any embolisms identified by the analyzer that were not identified by the radiologist.
Owner:MEVIS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS
Mammography Systems and Methods, Including Methods for Improving the Sensitivity and Specificity of the Computer-Assisted Detection (CAD) Process
InactiveUS20070223652A1Breast motionFlow of bloodStethoscopePatient positioning for diagnosticsSound detectionBlood flow
Provided are systems using compression devices for a mammography unit, and methods of using the same, for example, in conjunction with imaging of a patient's breast. The instant mammography units can comprise at least one x-ray transparent inflatable chamber for containing a fluid. When fluid is introduced into the chamber, at least one surface of the chamber expands, breast motion is limited, and the breast and its vasculature are compressed. Fluid may also be released from the chamber, and as the chamber deflates, blood flow to the breast is restored, producing Korotkoff sounds that may be detected by a sound detection device. The detected sounds may be used to assist a radiologist in identifying regions of interest on a mammogram, and additionally or alternatively may be used to a enhance a computer-assisted detection (CAD) process by contributing an additional data parameter.
Owner:GALKIN BENJAMIN M
Method of data mining in medical applications
InactiveUS20110218815A1Increase productivityQuality improvementMedical data miningFinanceData dredgingPersonalization
The present invention relates to a method of creating databases for data mining in medical applications. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to providing a data-driven objective reimbursement model incorporating performance and quality measures, tied to patient, exam, context, and provider-specific variables. In another embodiment, the present invention creates standardized databases where context, patient, provider, and technology specific variables are used to create an objective quantitative measure of exam complexity, which can be correlated with performance times and outcomes measures for iterative refinement. In another embodiment, through the combined analysis of examination complexity, interpretation accuracy, and interpretation times, specific to each individual radiologist, external pacers are created which can be customized to a radiologist's individual needs and preferences. The derived data is used to identify best practice patterns and end-user performance, which can be used by radiologists for individualized education and training.
Owner:REINER BRUCE
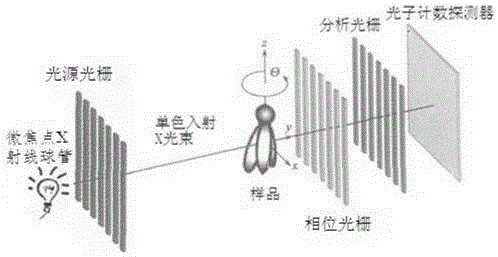
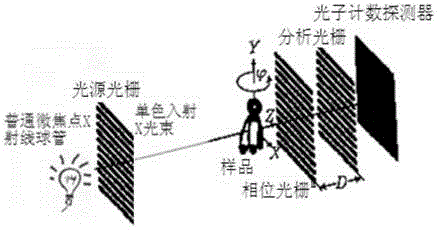
X-ray imaging system and method based on grating phase contrast and photon counting
The invention discloses an X-ray imaging system and method based on grating phase contrast and photon counting. X-rays become coherent X-rays after being shaped through a light source grating; the coherent X-rays containing phase changes after penetrating through samples form beam-split X-rays through a phase grating; the phase changes of the X-rays are converted into light intensity changes after the X-rays pass an analyzing grating; a photon counting detector is used for recording phase contrast information of the X-rays with different intensities; sectional images based on phase contrast are obtained through a three-dimensional reconstruction system; finally, components and interior fine structure information of the soft tissue samples are obtained. The system and method can be used for detecting soft tissue samples in the pathology department, the radiology department and the scientific research department of a hospital, early lesion information such as small lesions in the tissue samples can be found easily, and the detection rate is greatly increased.
Owner:NANOVISION TECHNOLOGY (BEIJING) CO LTD
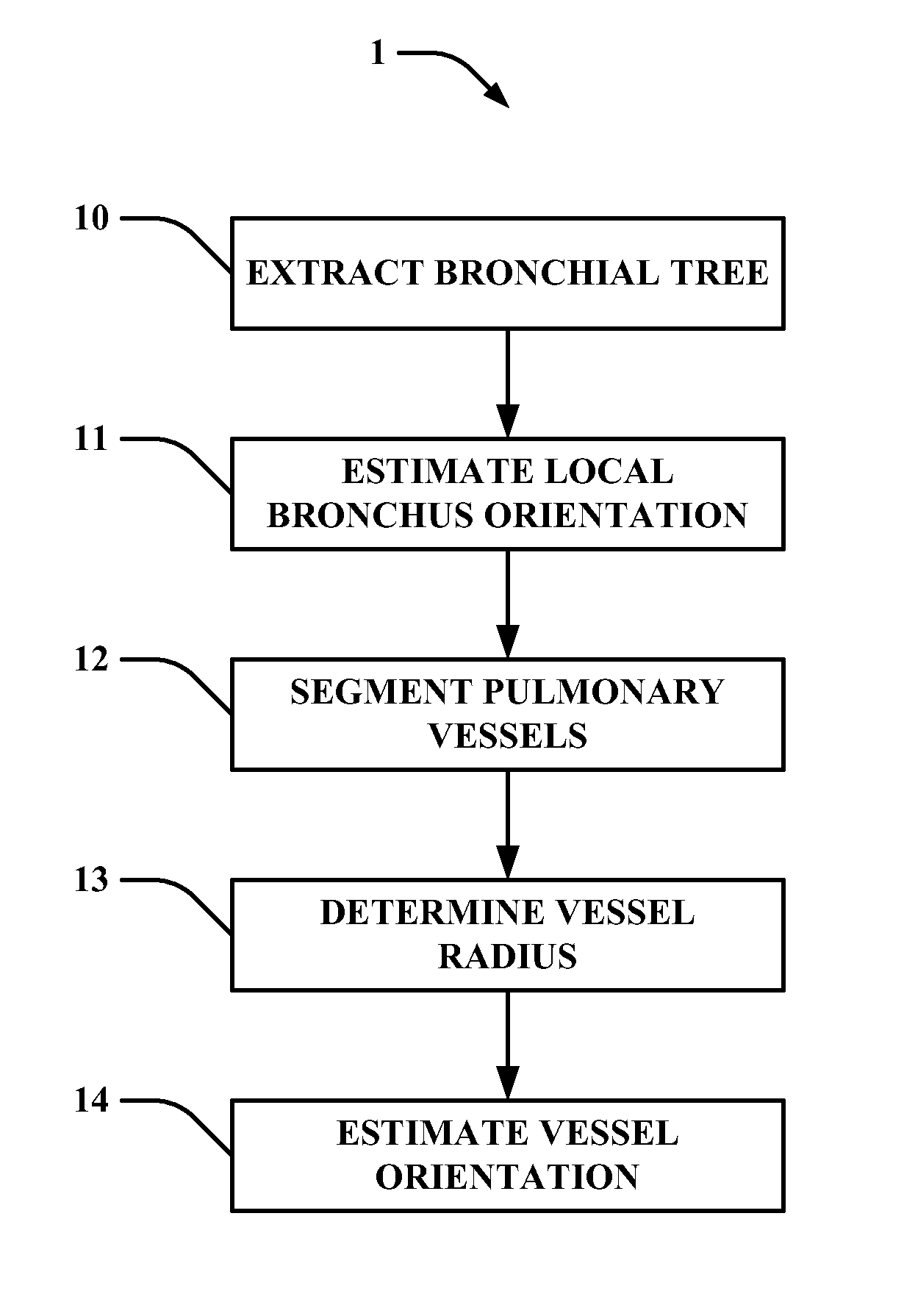
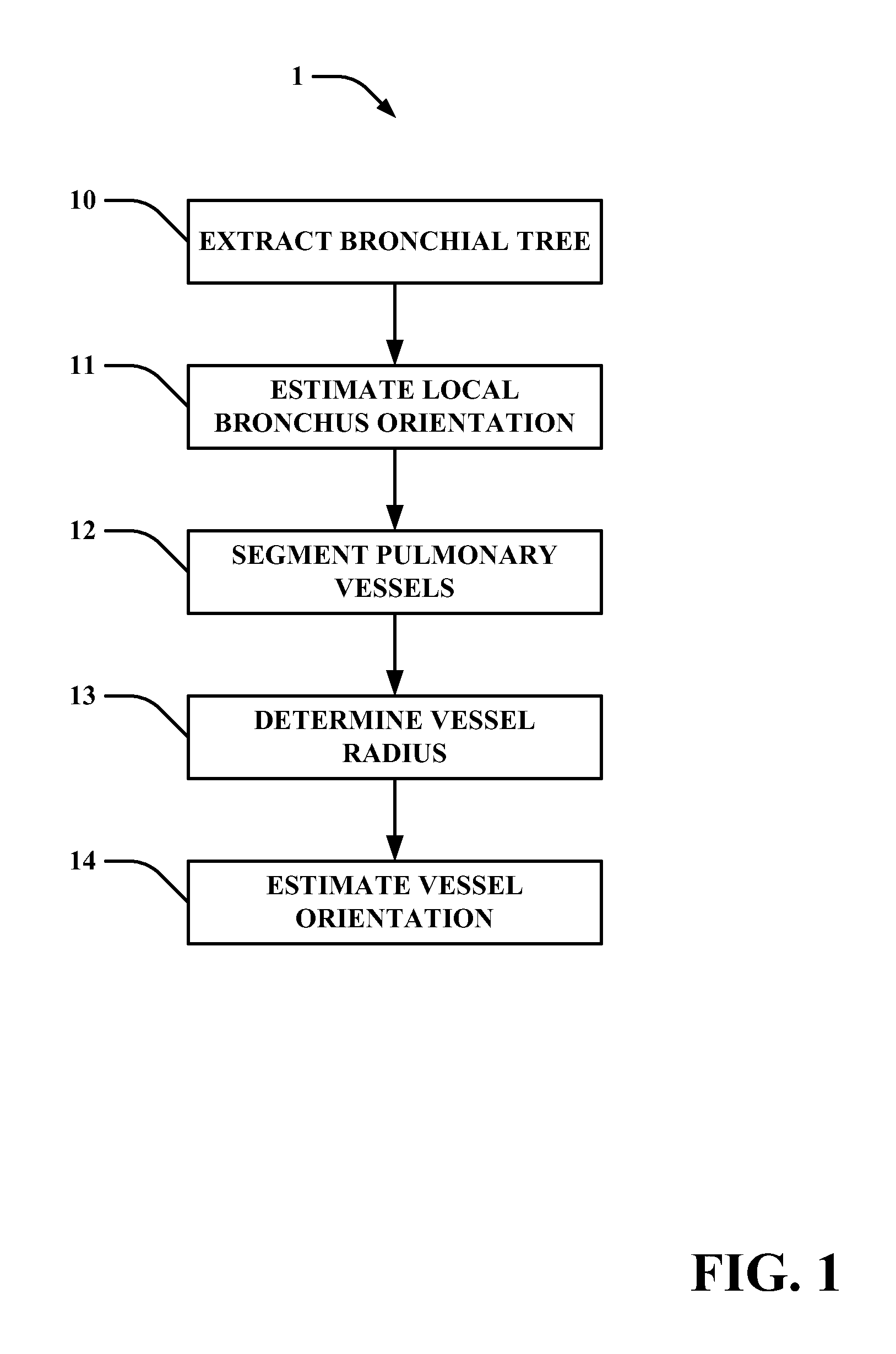
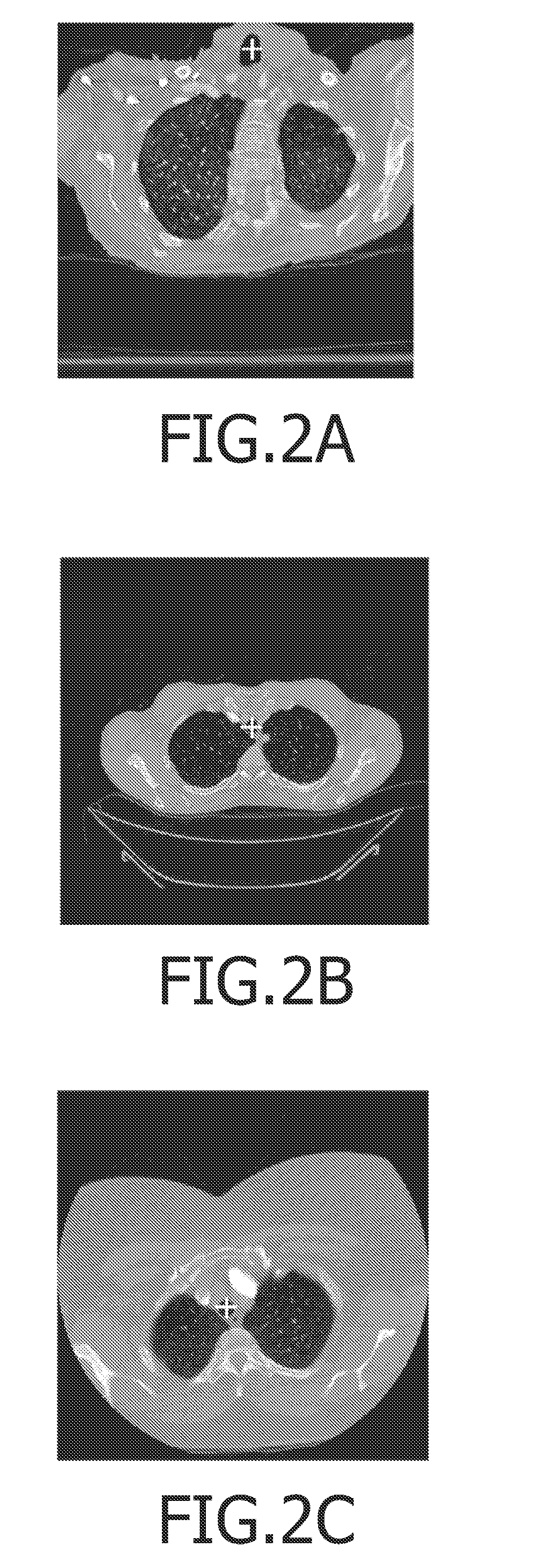
Method of automatic extraction of the pulmonary artery tree from 3D medical images
An automated method (1) for the automatic extraction of a pulmonary vessel tree from a 3D medical image, such as multi-slice CT data, is disclosed. A segmented pulmonary vessel is identified as either an artery or a vein by determining a measure for arterialness for the vessel. The measure is based on a relation of the orientation of a local bronchus to the orientation of the segmented pulmonary vessel of the local bronchus. When a vessel is identified as a pulmonary artery, it is added to the pulmonary artery tree. Radii of the pulmonary artery and bronchus are measured automatically and positions where a ratio of these radii exhibits unusual values are presented in a display, preferably for suggesting further assessment by a radiologist, which for instance is useful for pulmonary embolism detection.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
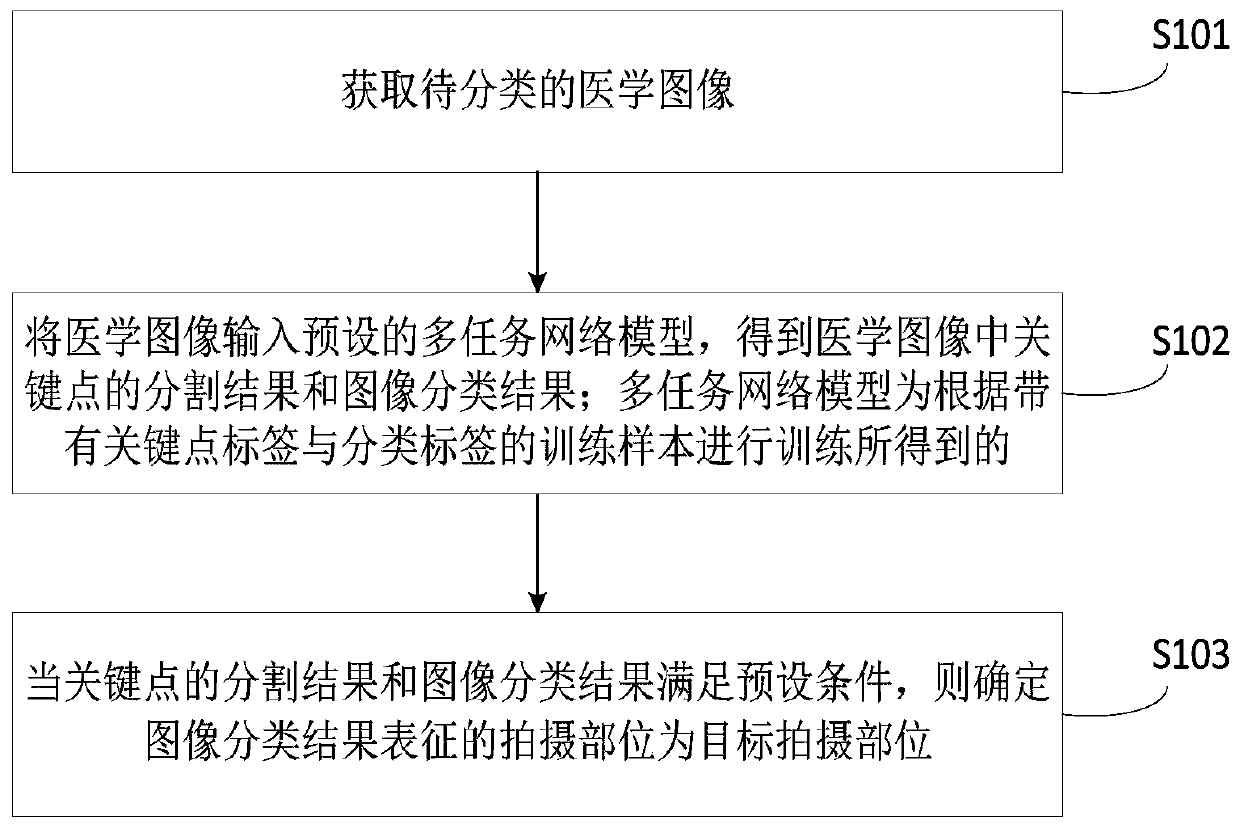
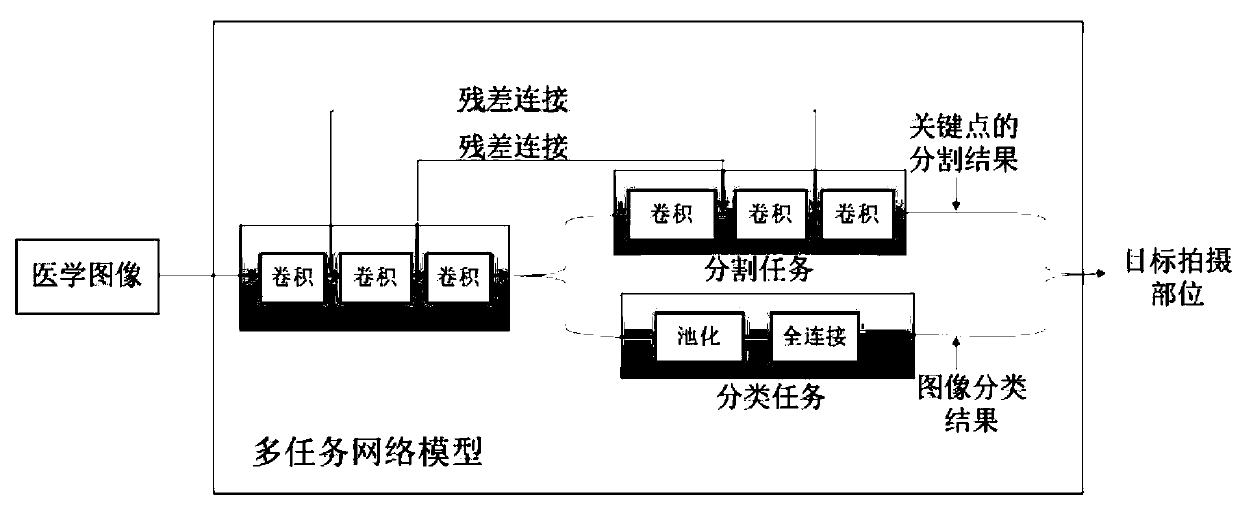
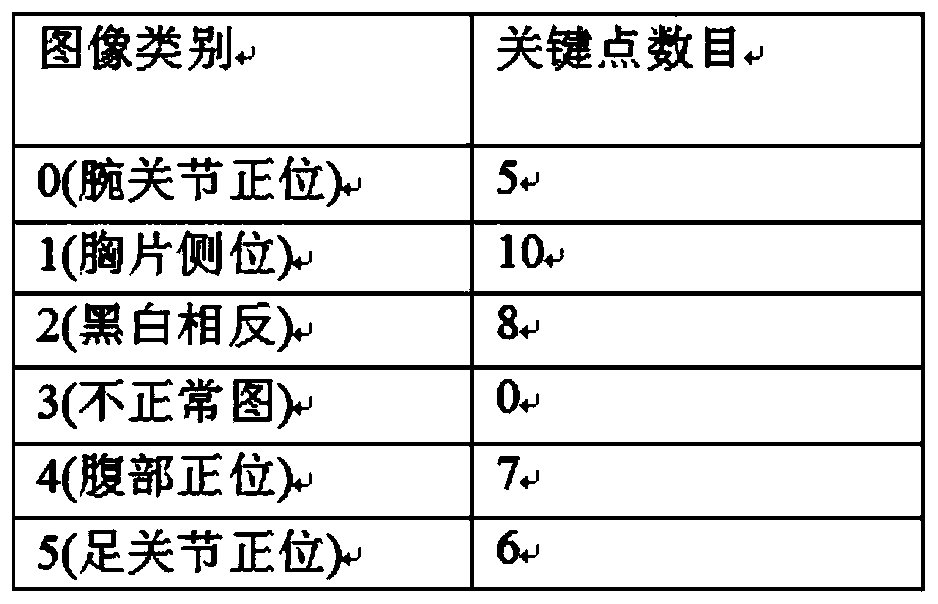
Image classification method and device, computer equipment and readable storage medium
PendingCN111160367AImprove accuracyImprove recognition efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionTask networkClassification methods
The invention relates to an image classification method and device, computer equipment and a readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a to-be-classified medical image; inputting the medical image into a preset multi-task network model to obtain a segmentation result and an image classification result of key points in the medical image; the multi-task network model beingobtained by training according to a training sample with a key point label and a classification label; and when the segmentation result of the key points and the image classification result meet a preset condition, determining the shooting part represented by the image classification result as a target shooting part. According to the method, the computer equipment determines the shooting part inthe medical image by adopting the multi-task network model, so that the accuracy of a target shooting part result can be improved, and the accuracy of a subsequent focus identification process is further improved; a radiologist does not need to make a confirmation process, and meanwhile, the efficiency of a focus recognition process is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING INTELLIGENT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for cone beam breast ct image-based computer-aided detection and diagnosis
ActiveUS20140037044A1High contrast resolutionNo tissue overlapImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityCalcification
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER +1
Medical robot device, system and method
PendingCN111916195AImprove work efficiencyEffective Joint OperationMedical communicationStethoscopePatient roomMedical equipment
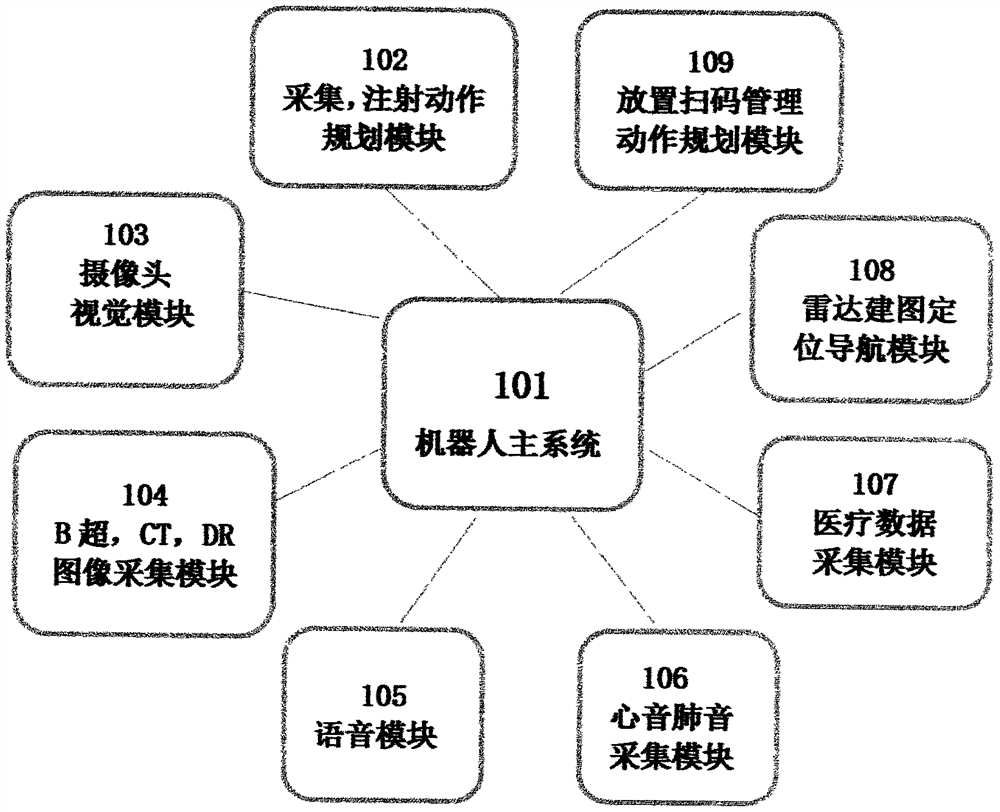
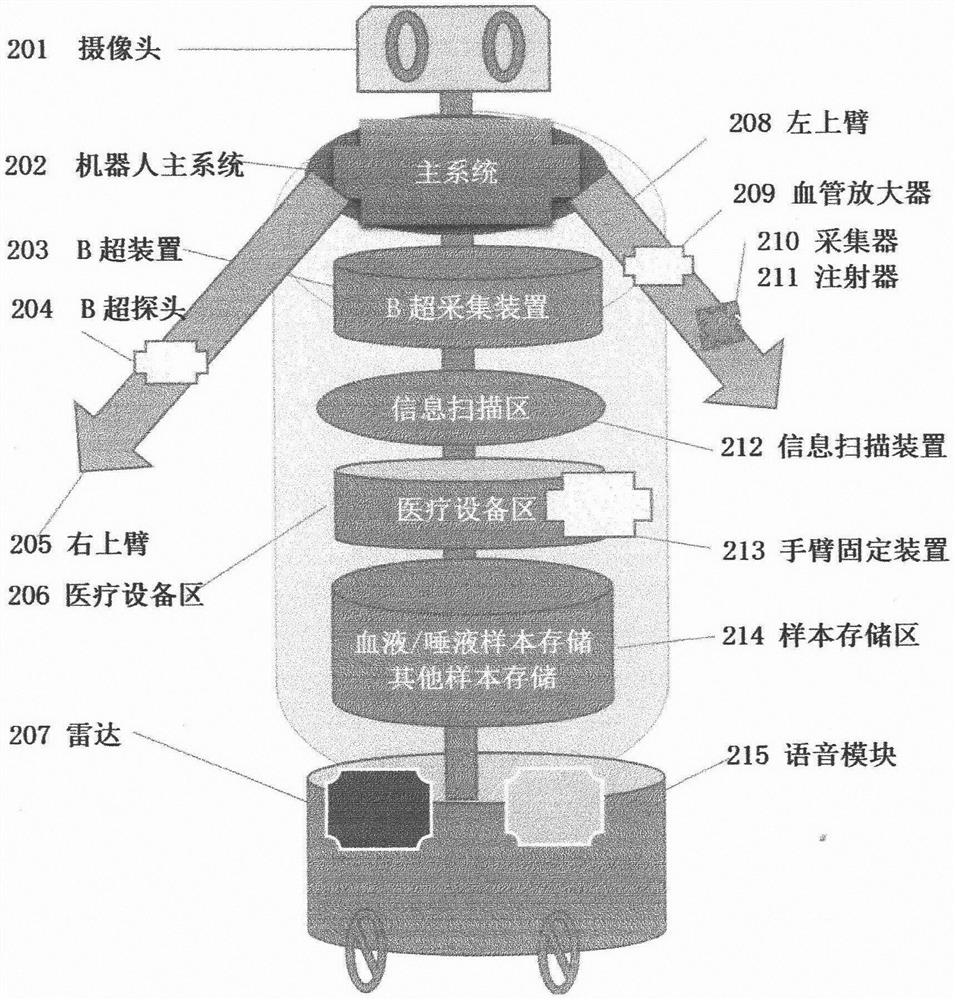
The invention relates to a medical robot device, system and method, provides a medical far-end joint diagnosis adjuvant therapy robot device, far-end consultation, multi-department joint consultationand far-end medical advice by utilizing an artificial intelligence robot technology, and solves the problems of unsmooth communication of patient doctors, unclear understanding of illness conditions,unmatched treatment methods and the like. A B-ultrasonic image acquisition device, an intraoral acquisition device, a blood acquisition device, a CT image and a DR radiology department image which arecarried by a robot are used for remotely controlling acquisition and sharing to realize image sharing, so that the problems of human diagnosis and treatment errors, diagnosis limitation of a single diagnosis and treatment department, singleness of a diagnosis scheme and the like are solved; through a blood vessel amplifier, an intravenous injector and other injection devices carried by the robot,robot far-end control, autonomous injection, autonomous medicine configuration and cyclic taking and placing of medical equipment are achieved, and the problems that the operation pressure of medicalstaff is large, and many night shifts exist are solved. The flexibility of far-end inquiry, ward round and multi-department joint consultation of experts and doctors is improved, and clinical cases are efficiently solved by multiple treatment schemes and multiple experts. The system is applied to outpatient service, wards and overseas medical institutions.
Owner:谈斯聪 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com