Patents
Literature
403 results about "Image estimation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
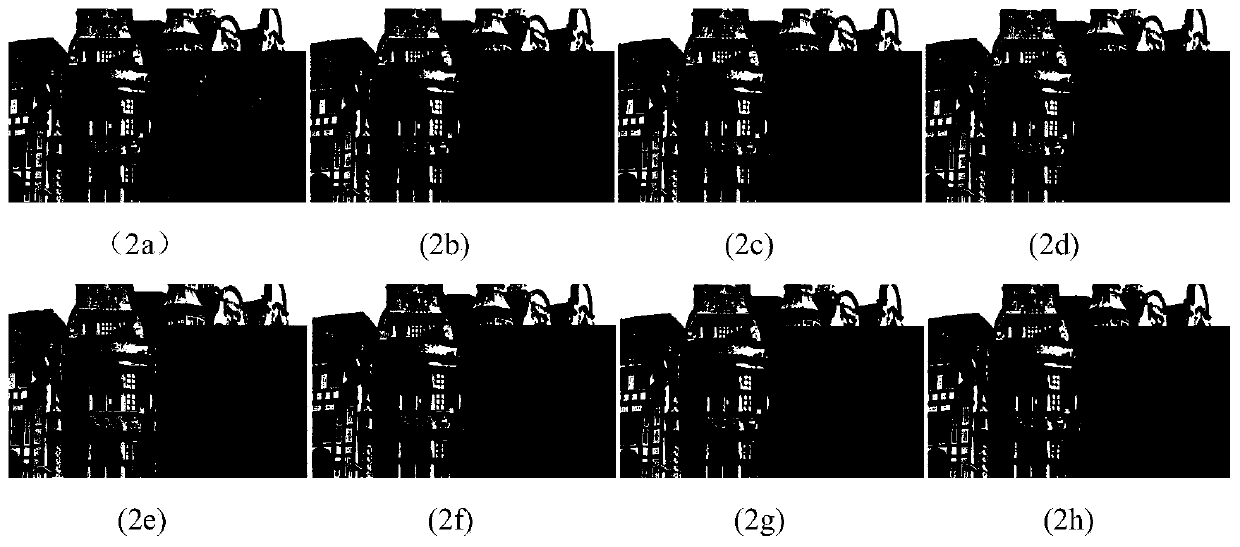
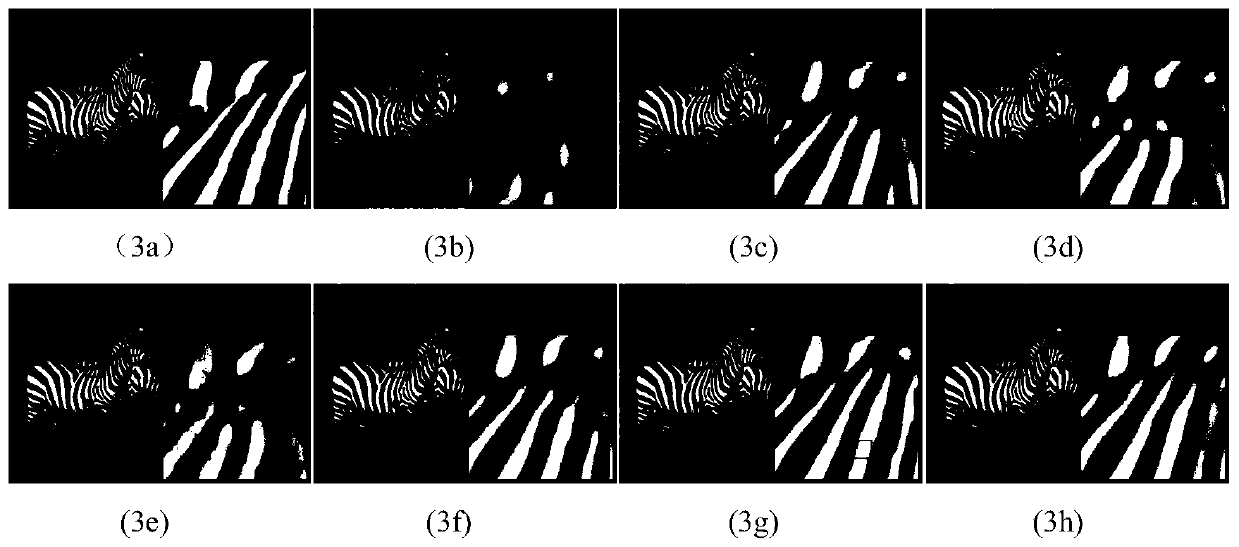
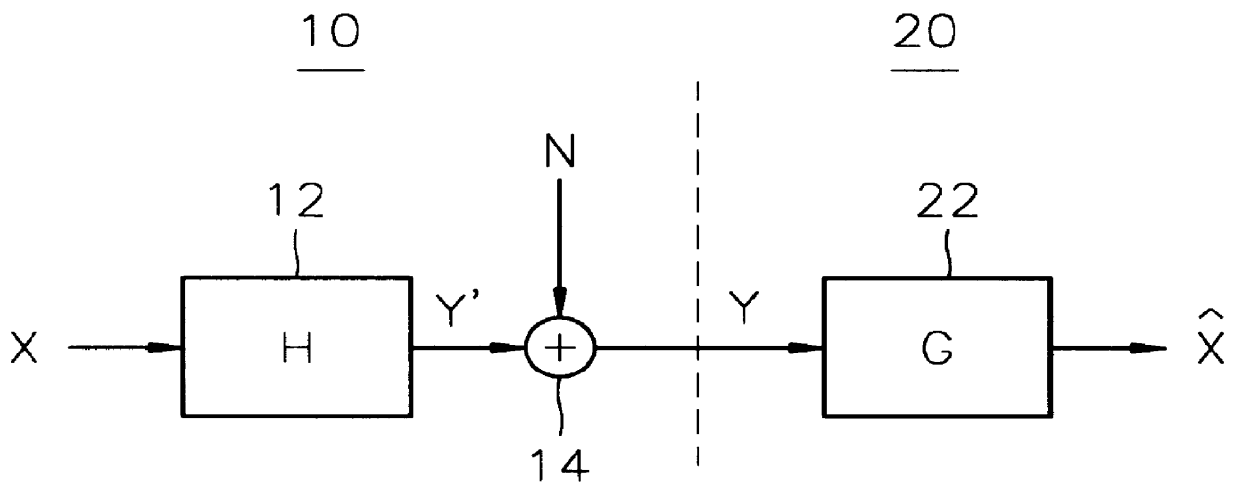
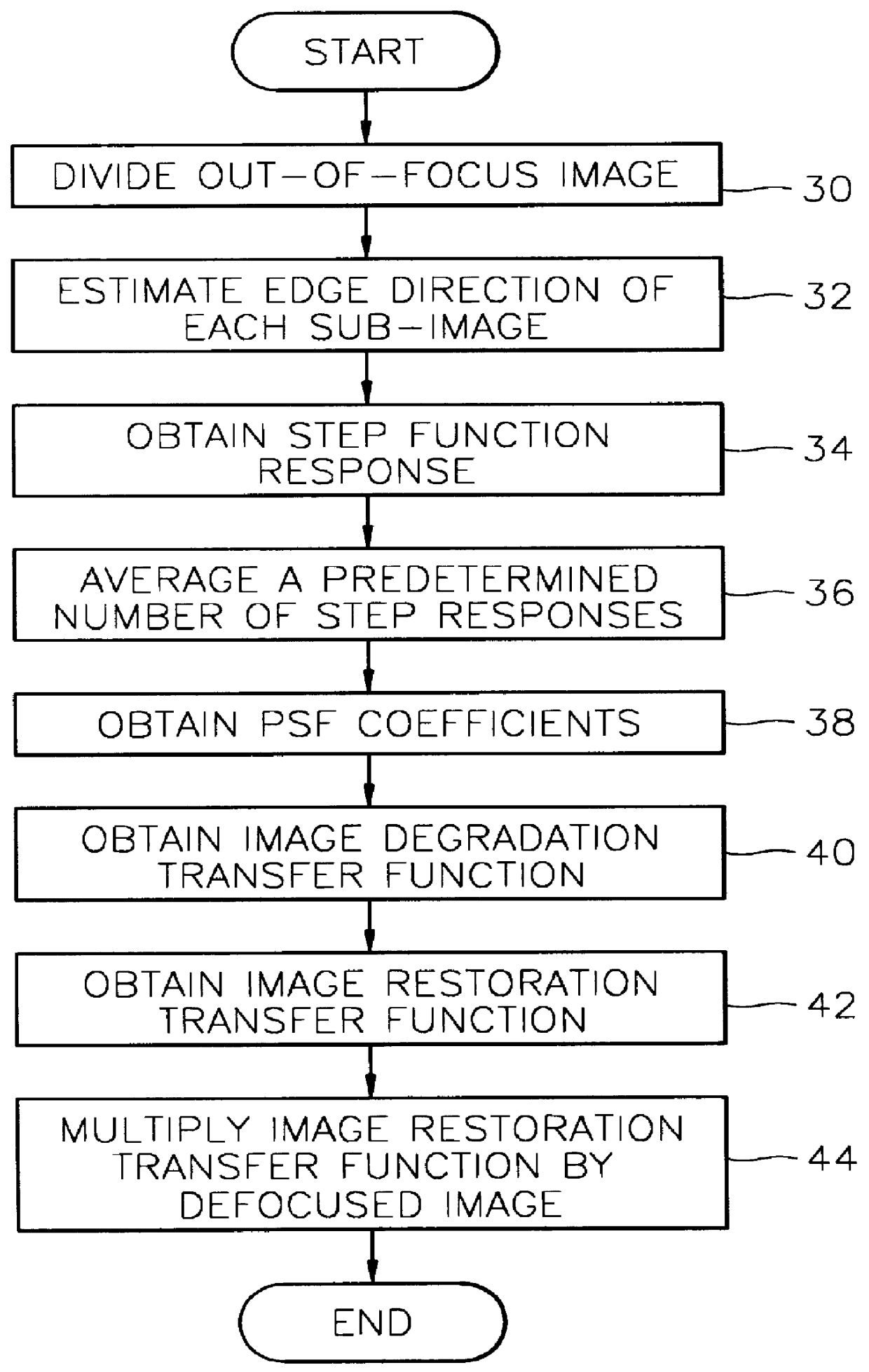
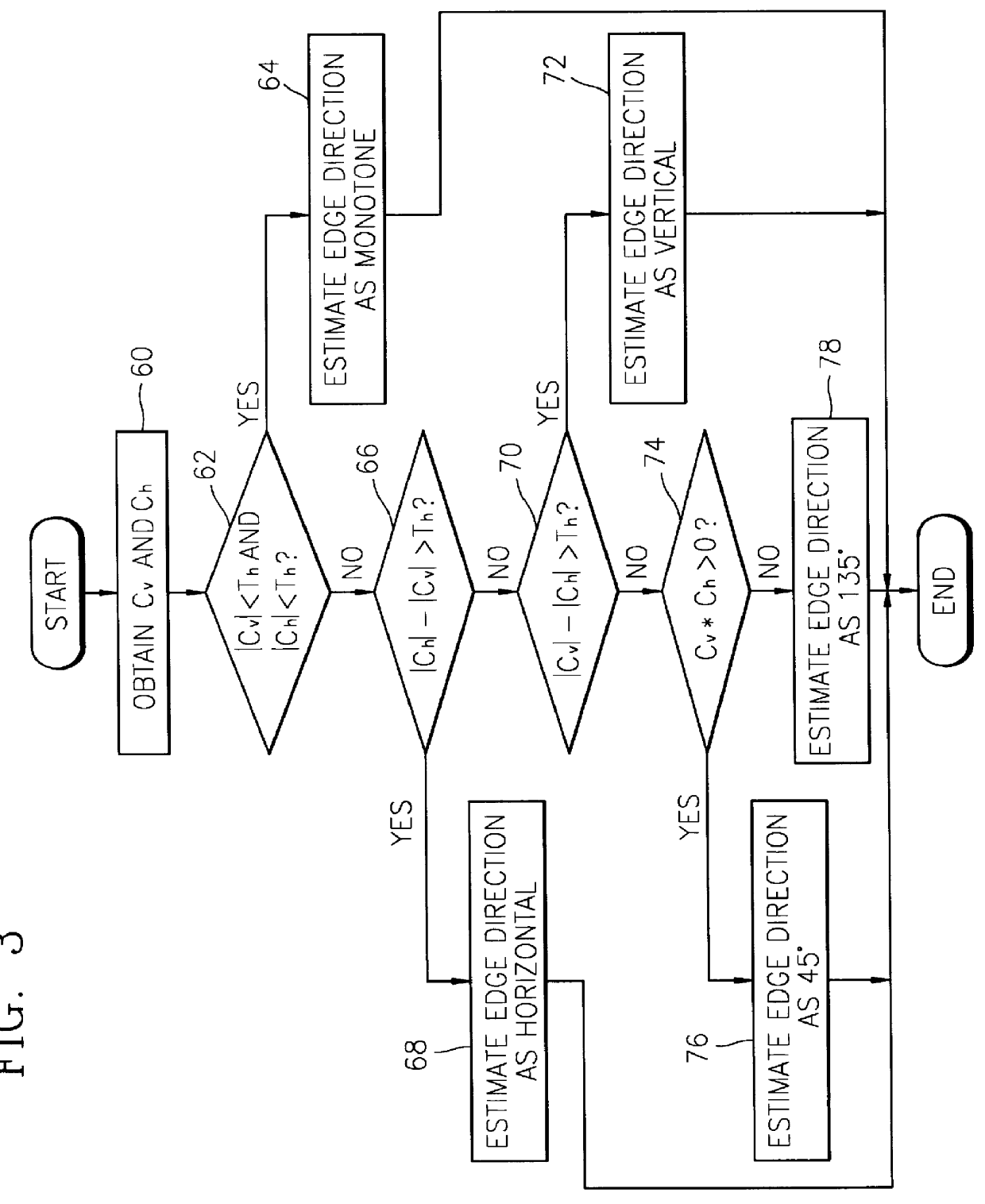
Digital focusing method and apparatus in image processing system
Digital focusing method and apparatus in an image processing system, for digitally focusing an out-of-focus image, are provided. A defocused image is divided into sub-images of a predetermined size. An edge direction of each of the divided sub-images is estimated. Step responses with respect to the respective edge directions are calculated. A mean step response is obtained by averaging a predetermined number of the step responses. Point Spread Function (PSF) coefficients are obtained using the mean step response. An image blur transfer function is obtained using the PSF coefficients. An image restoration transfer function is obtained using the image blur transfer function. An original in-focused image is obtained by multiplying the image restoration transfer function by the defocused image in a frequency domain. Thus, an image can be restored in real time, and the size and weight of the image processing system can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
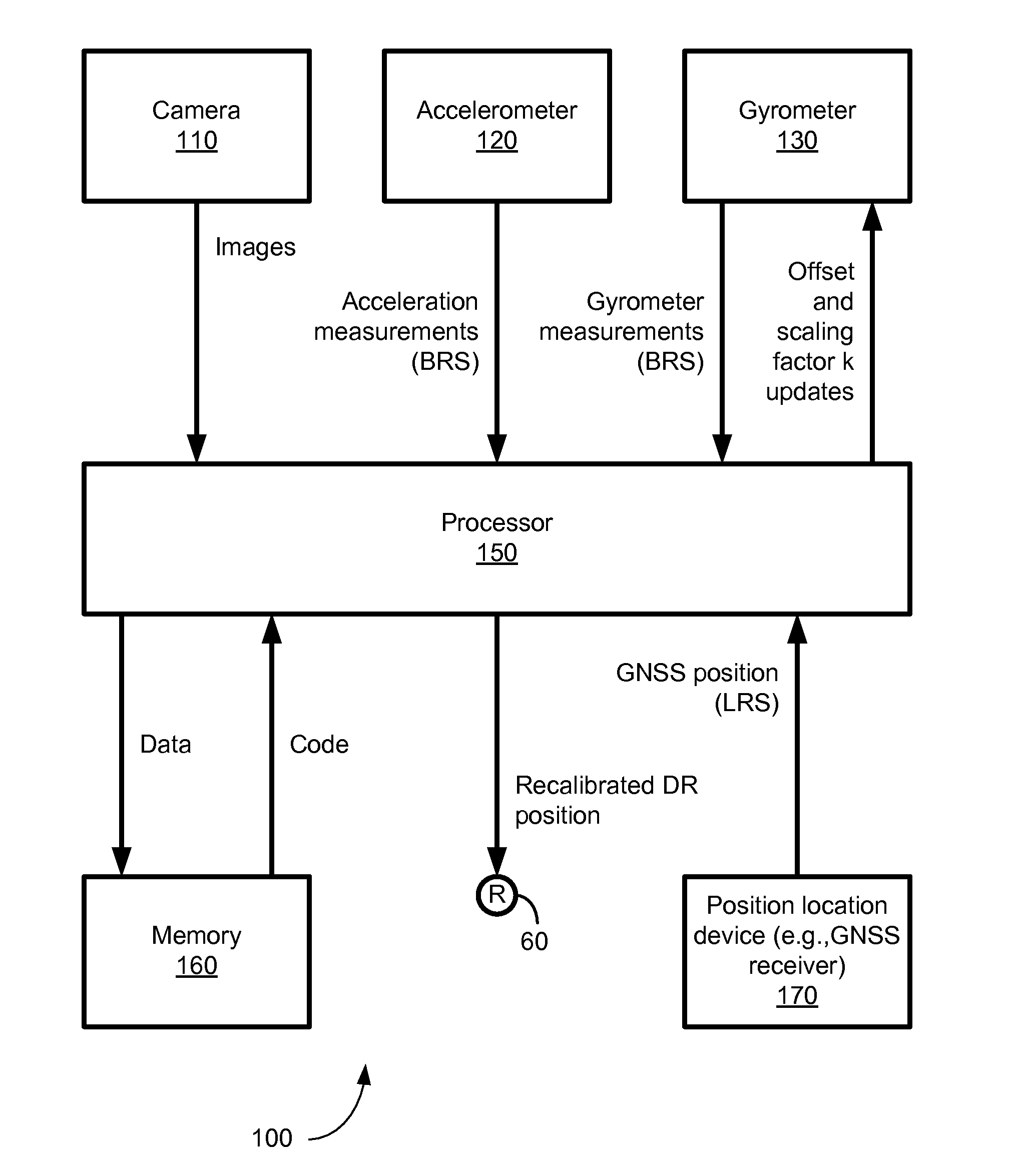
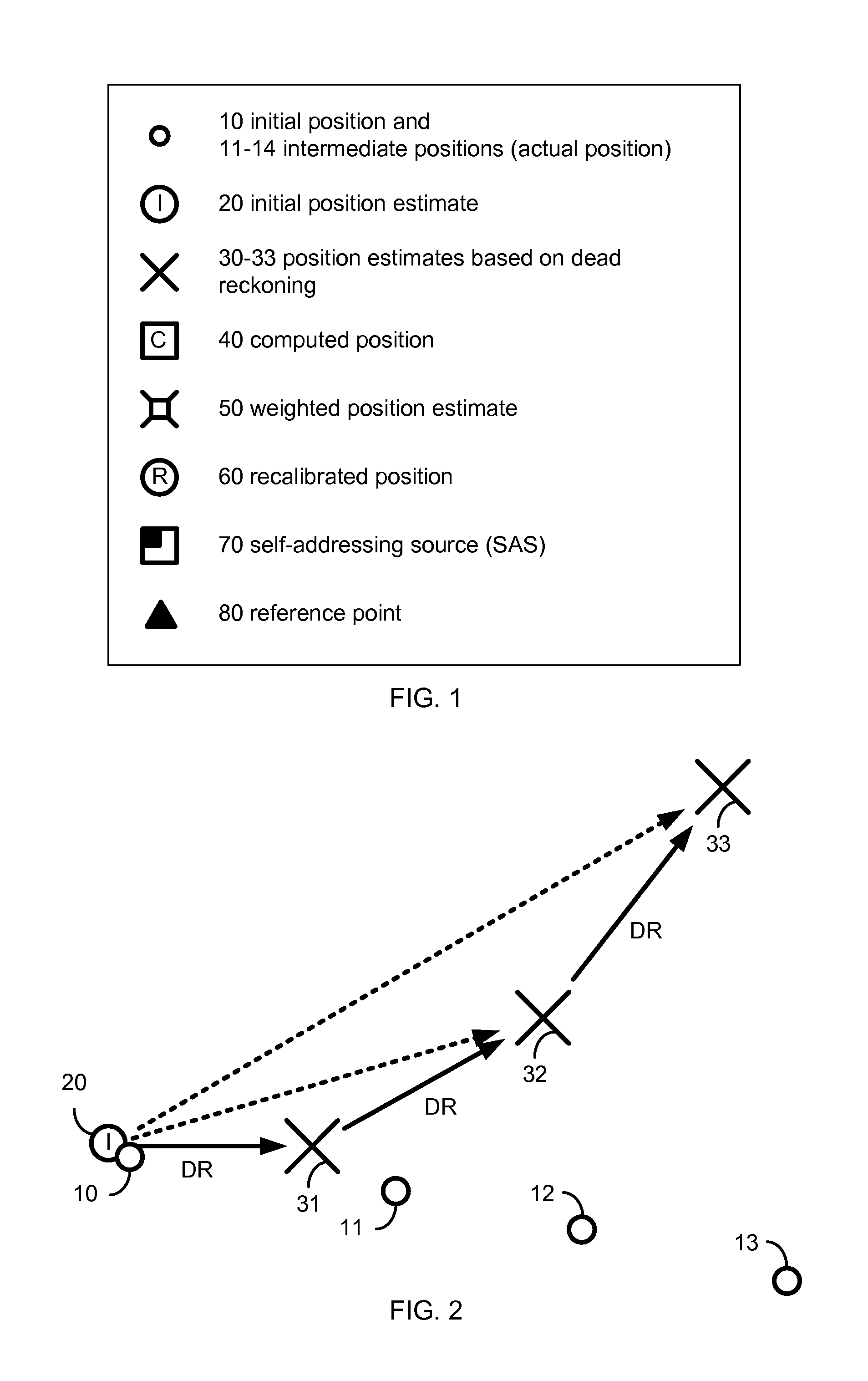
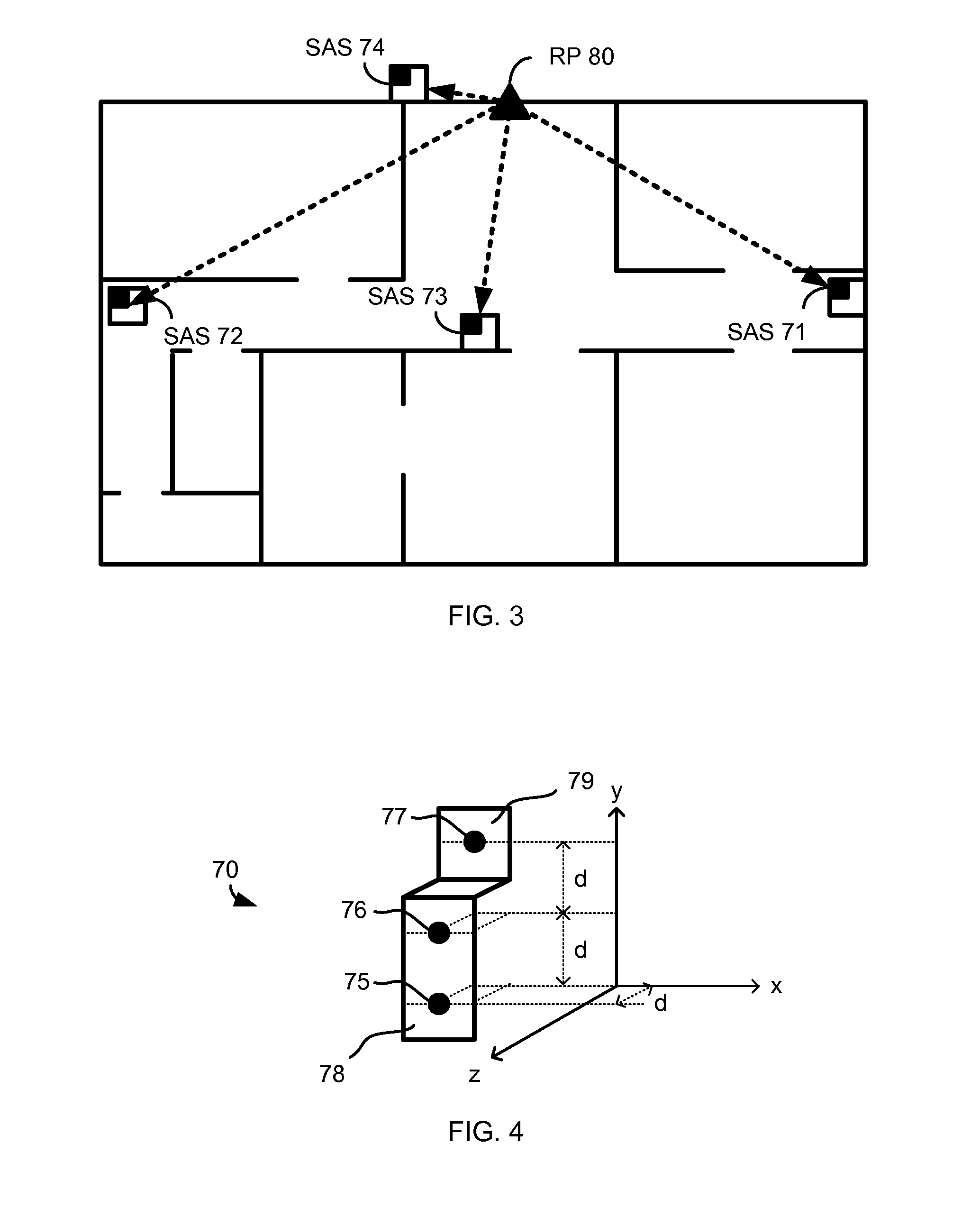
Camera-based position location and navigation based on image processing
ActiveUS20120176491A1Instruments for road network navigationColor television detailsPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
An apparatus and method for estimating a position of a mobile device based on one or more images is disclosed. Positioning information is derived from an image containing an SAS (self-addressing source such as a QR code), thereby setting a first vector V1 and an SAS pose. The image is also used to determine a displacement between the mobile device and the self-addressing source, thereby setting a second vector V2. Using the first vector V1, the SAS pose and the second vector V2, the mobile device may estimate its position with high accuracy and may also recalibrate dead-reckoning navigation and a gyrometer.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
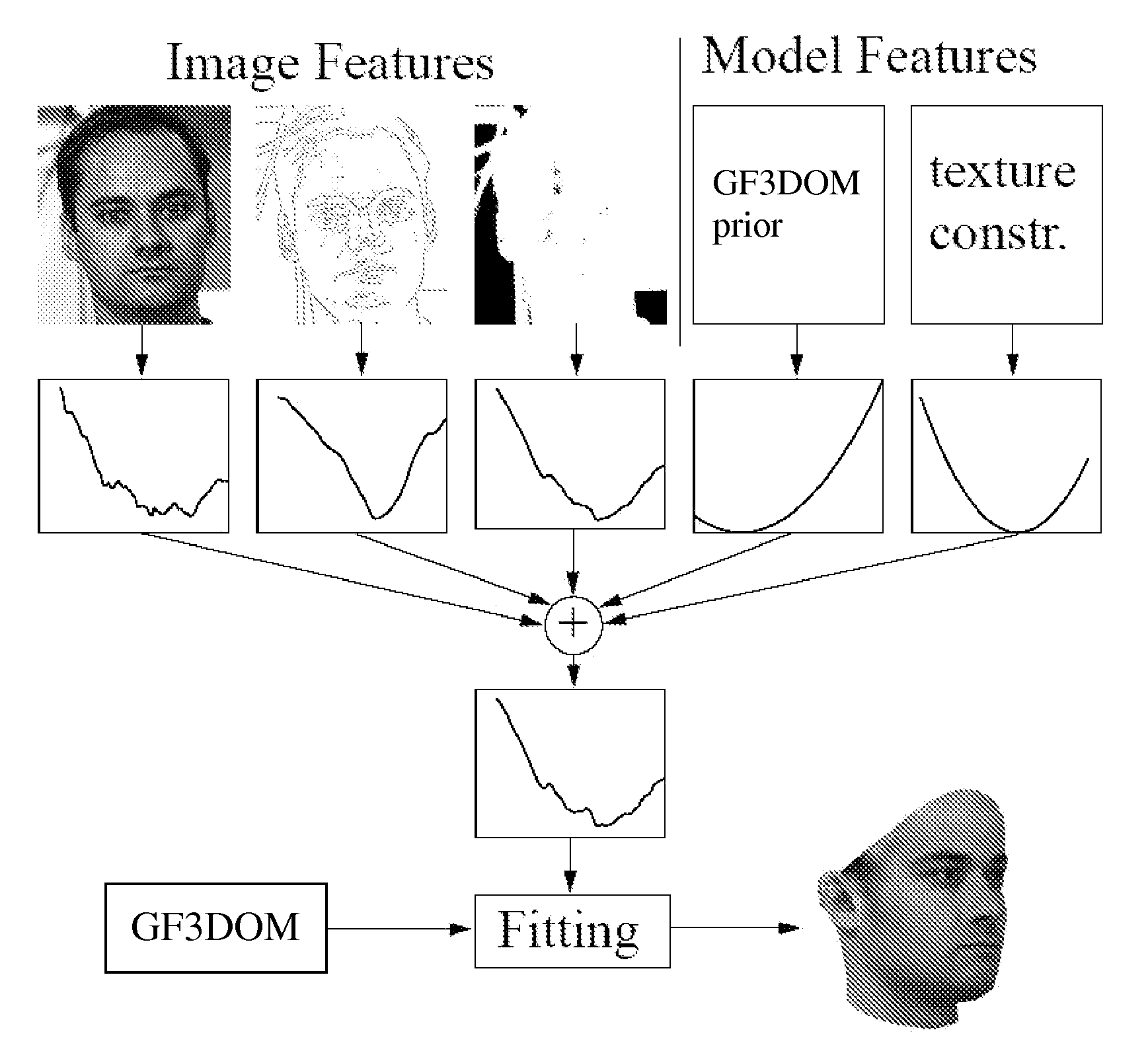
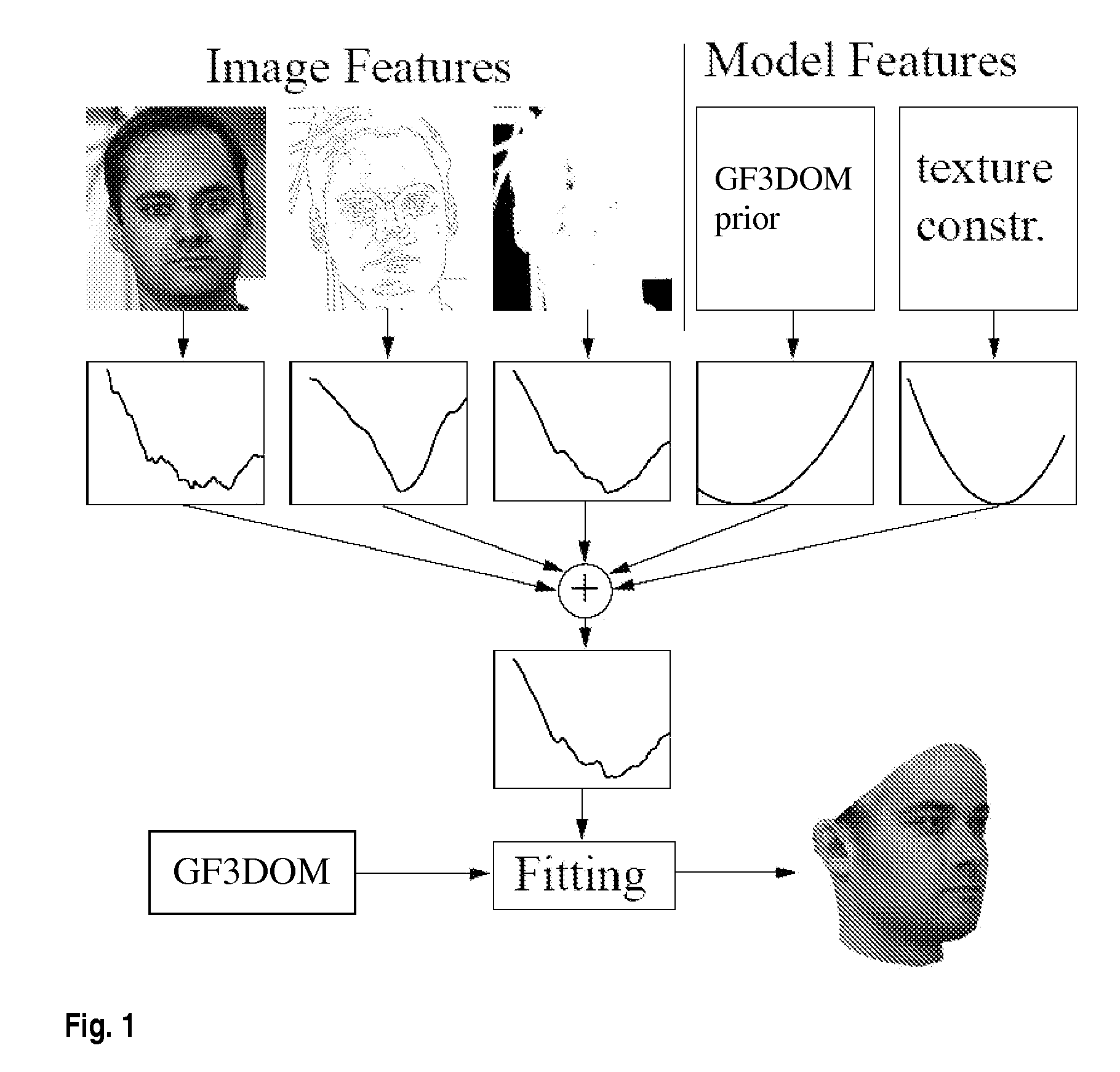
Estimating 3D shape and texture of a 3D object based on a 2d image of the 3D object
InactiveUS20070031028A1Maximizing posterior probabilityPerformance maximizationAdditive manufacturing apparatusDrawing from basic elements3d shapesObject based
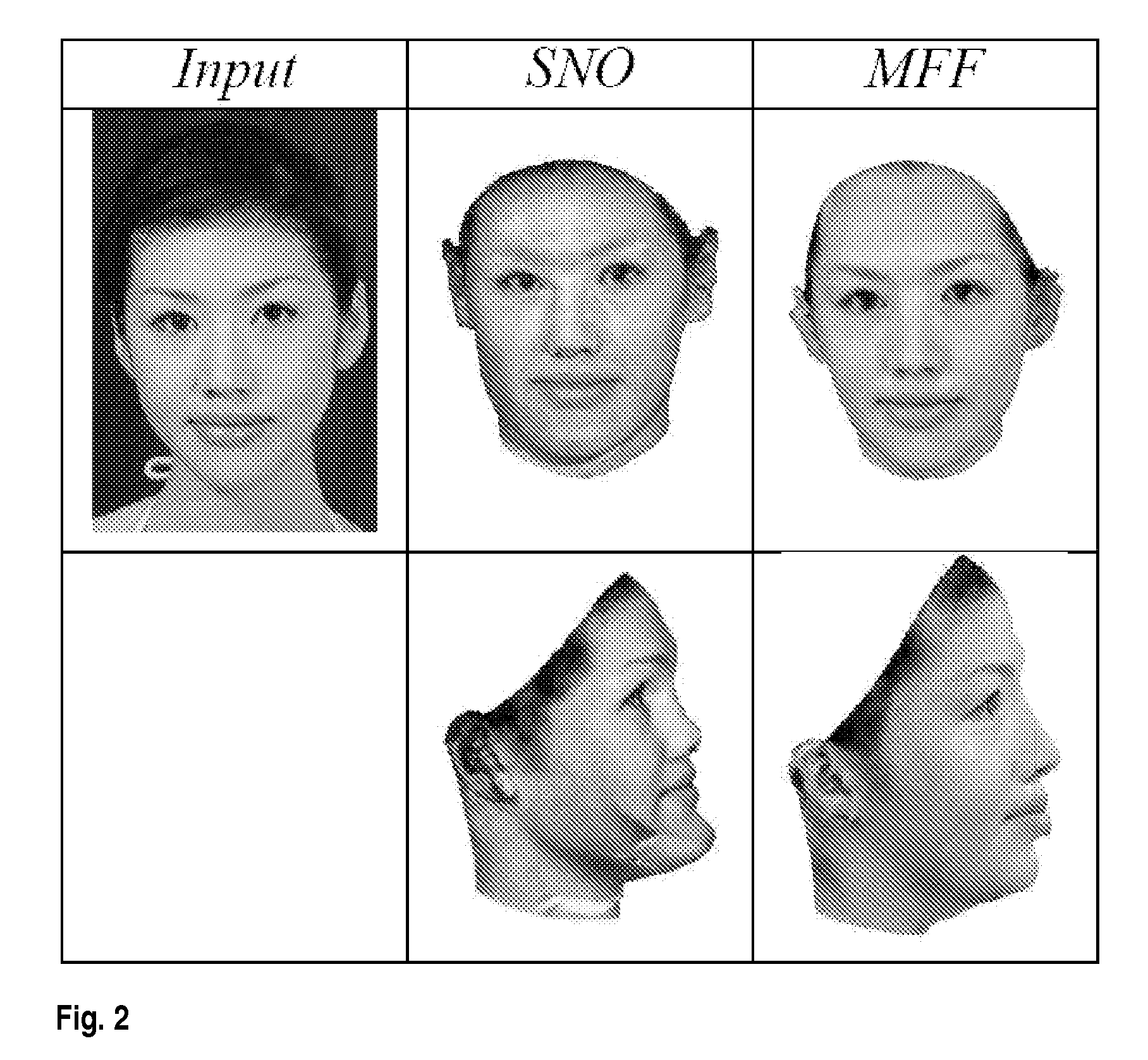
Disclosed is an improved algorithm for estimating the 3D shape of a 3-dimensional object, such as a human face, based on information retrieved from a single photograph by recovering parameters of a 3-dimensional model and methods and systems using the same. Beside the pixel intensity, the invention uses various image features in a multi-features fitting algorithm (MFF) that has a wider radius of convergence and a higher level of precision and provides thereby better results.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BASEL
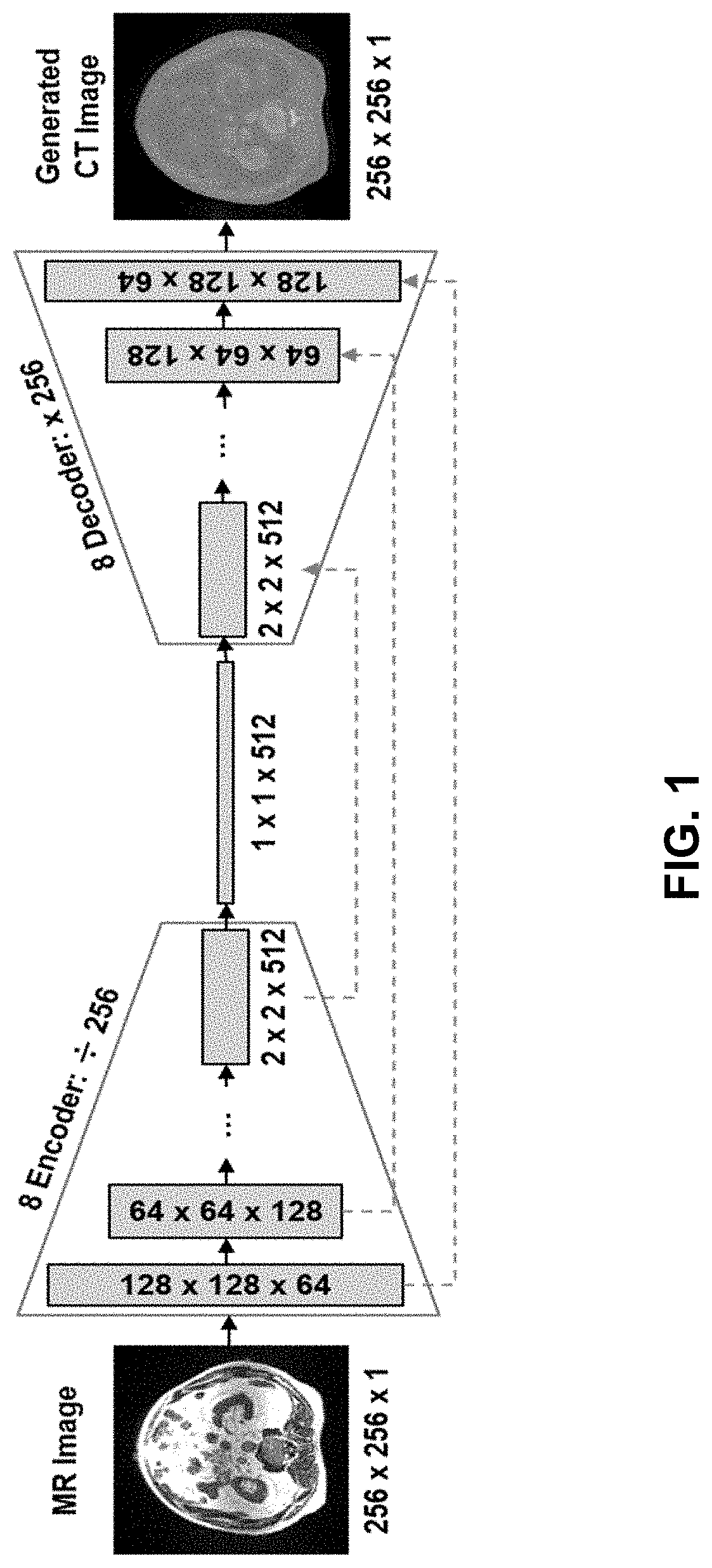
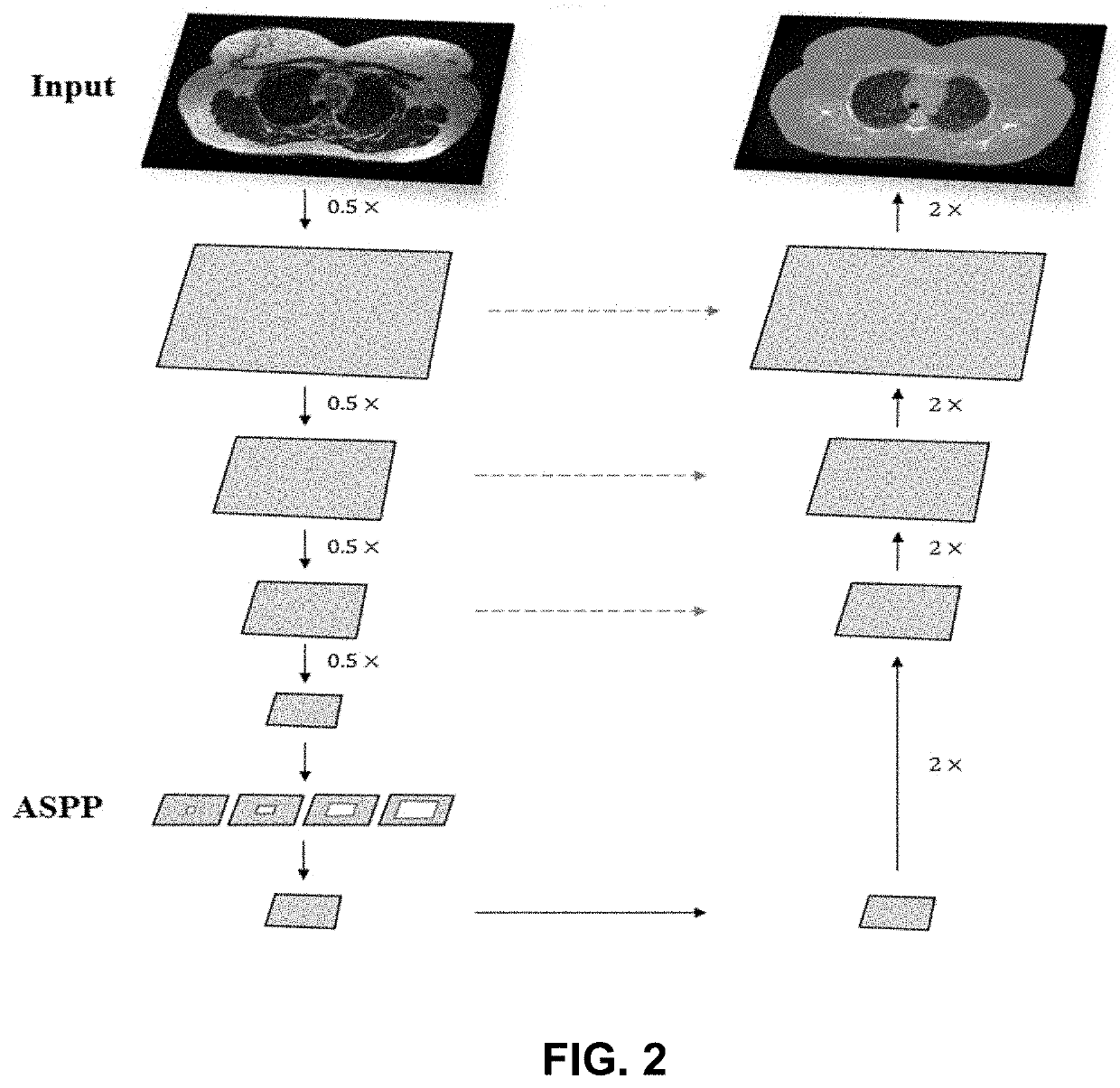
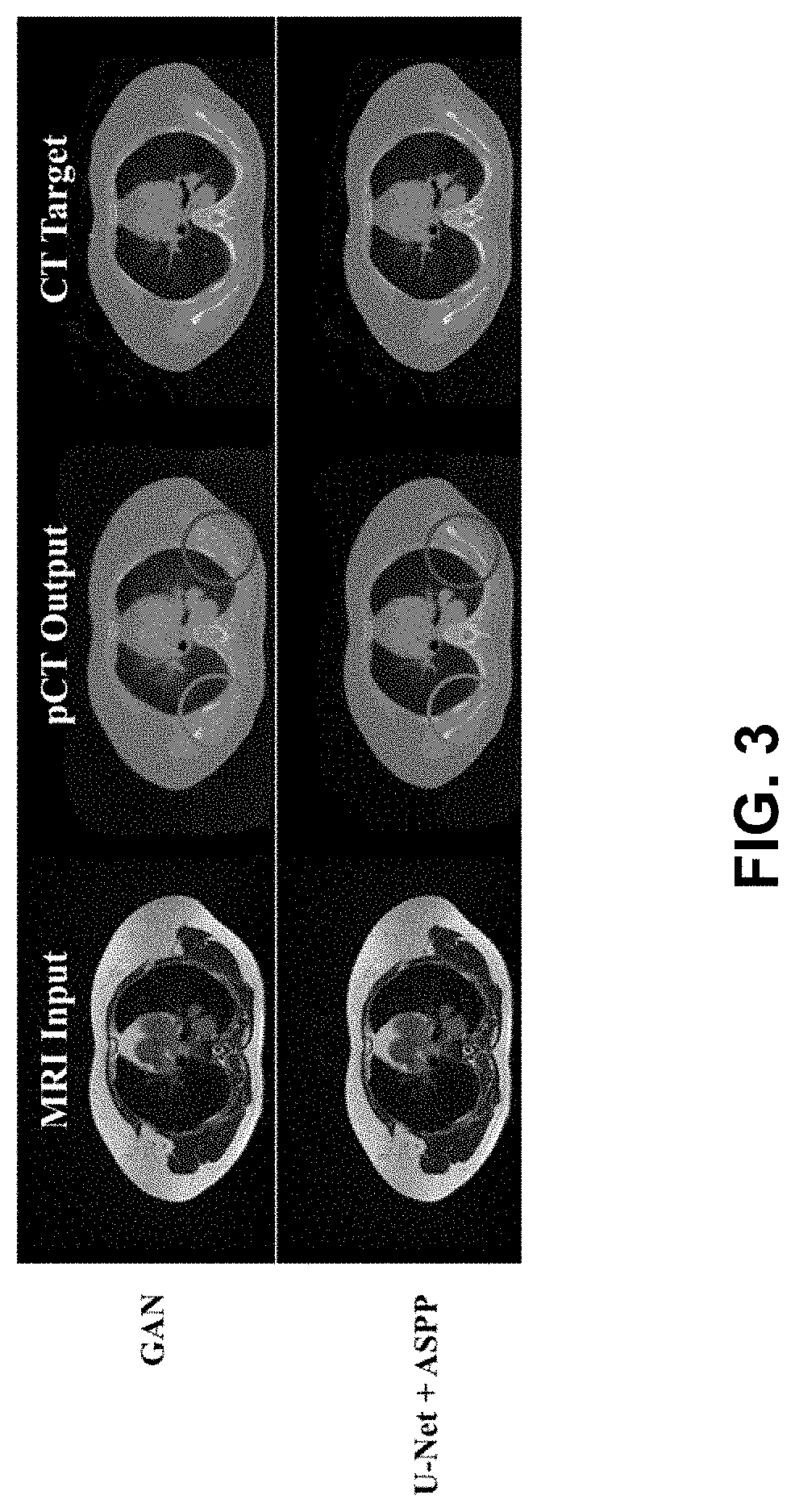
Ml-based methods for pseudo-ct and hr mr image estimation
The present disclosure describes a computer-implemented method of transforming a low-resolution MR image to a high-resolution MR image using a deep CNN-based MRI SR network and a computer-implemented method of transforming an MR image to a pseudo-CT (sCT) image using a deep CNN-based sCT network. The present disclosure further describes a MR image-guided radiation treatment system that includes a computing device to implement the MRI SR and CT networks and to produce a radiation plan based in the resulting high resolution MR images and sCT images.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
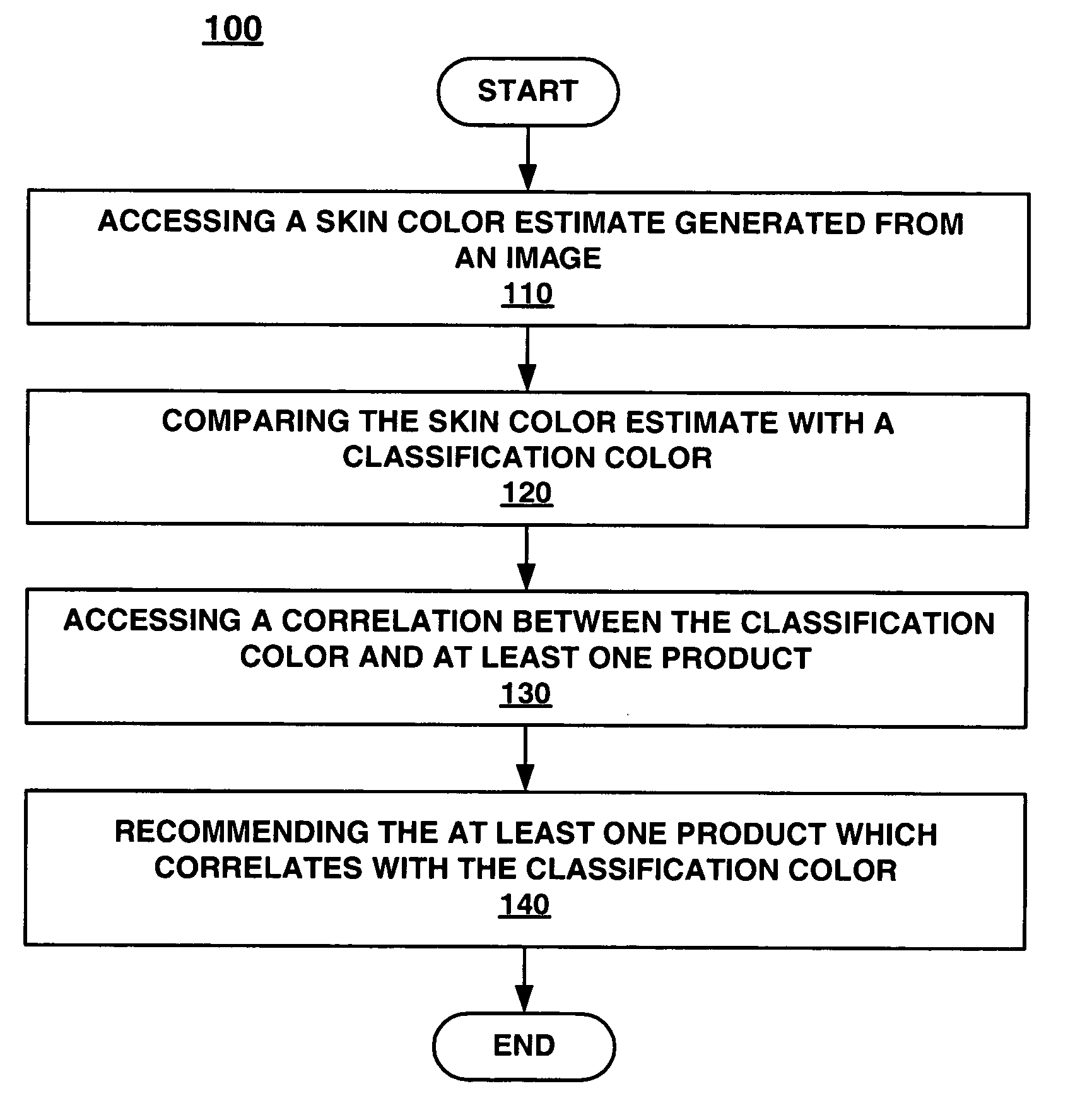
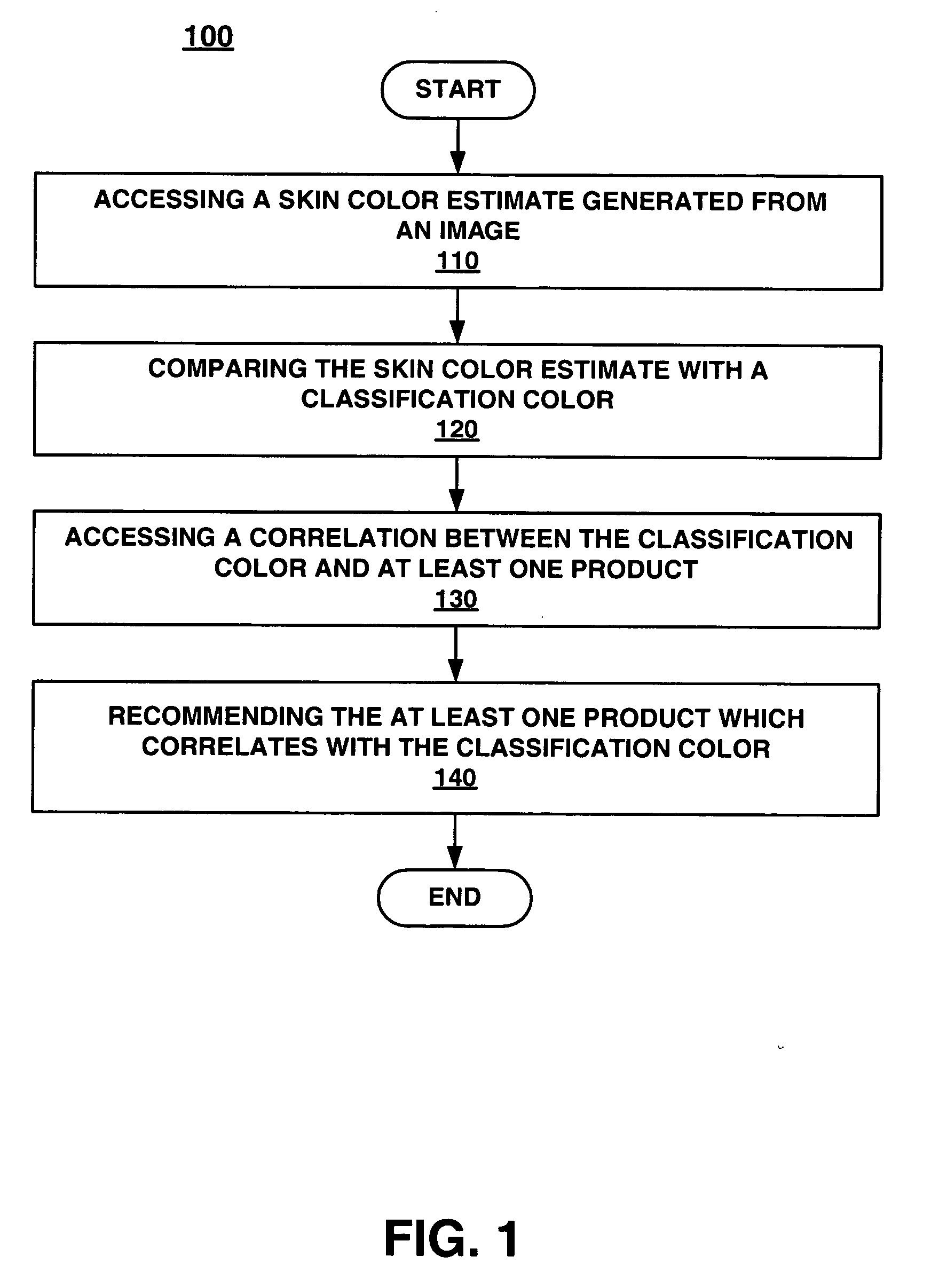
Method and system for recommending a product based upon skin color estimated from an image
Embodiments of the present invention recite a computer implemented method for recommending a product based upon skin color estimated from a single captured image. In one embodiment of the present invention, a skin color estimate which is generated from a single captured image is accessed. The skin color estimate is then compared with a classification color. A correlation between the classification color and at least one product is accessed. Then, at least one of the products which corresponds with the classification color is recommended.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
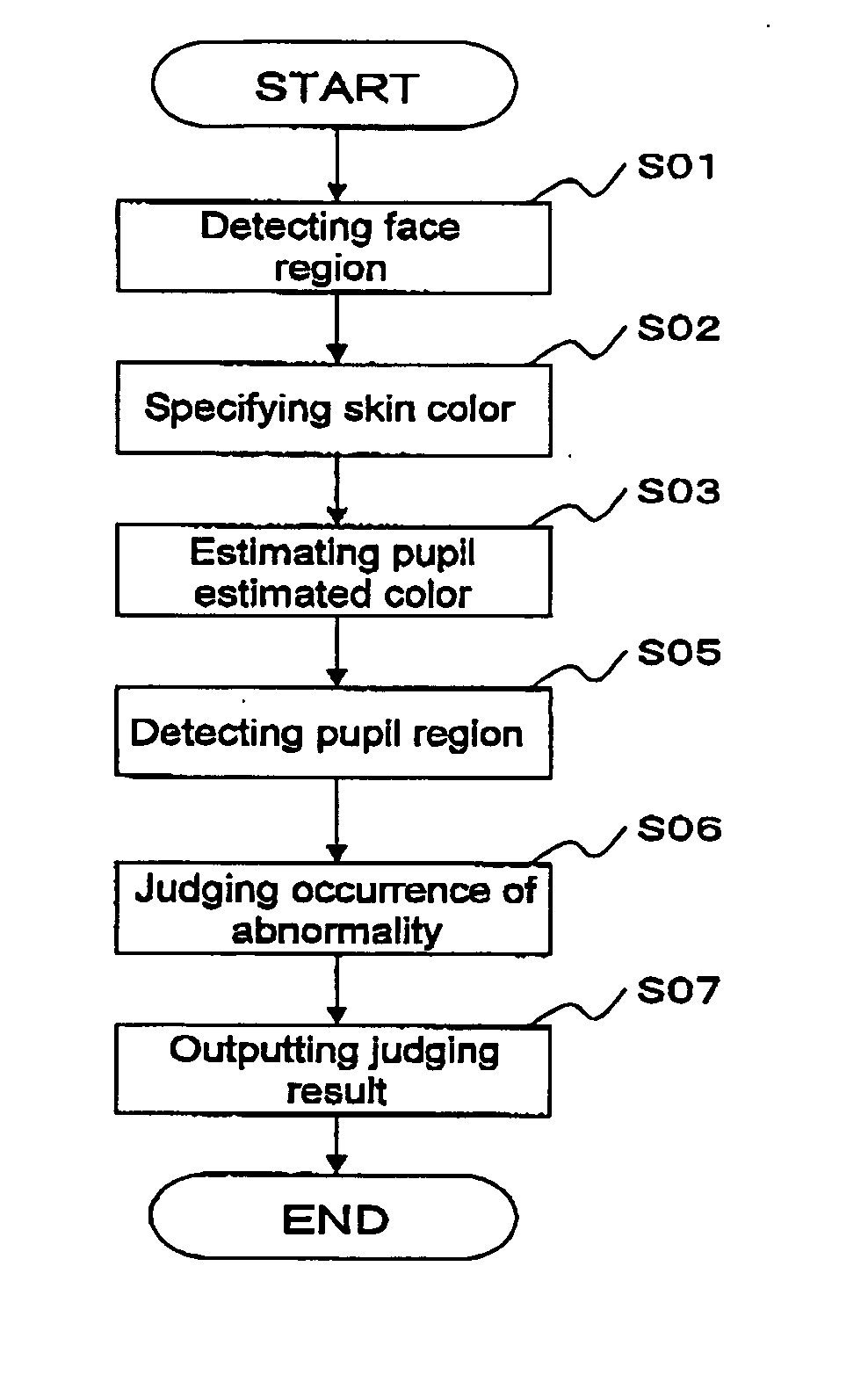
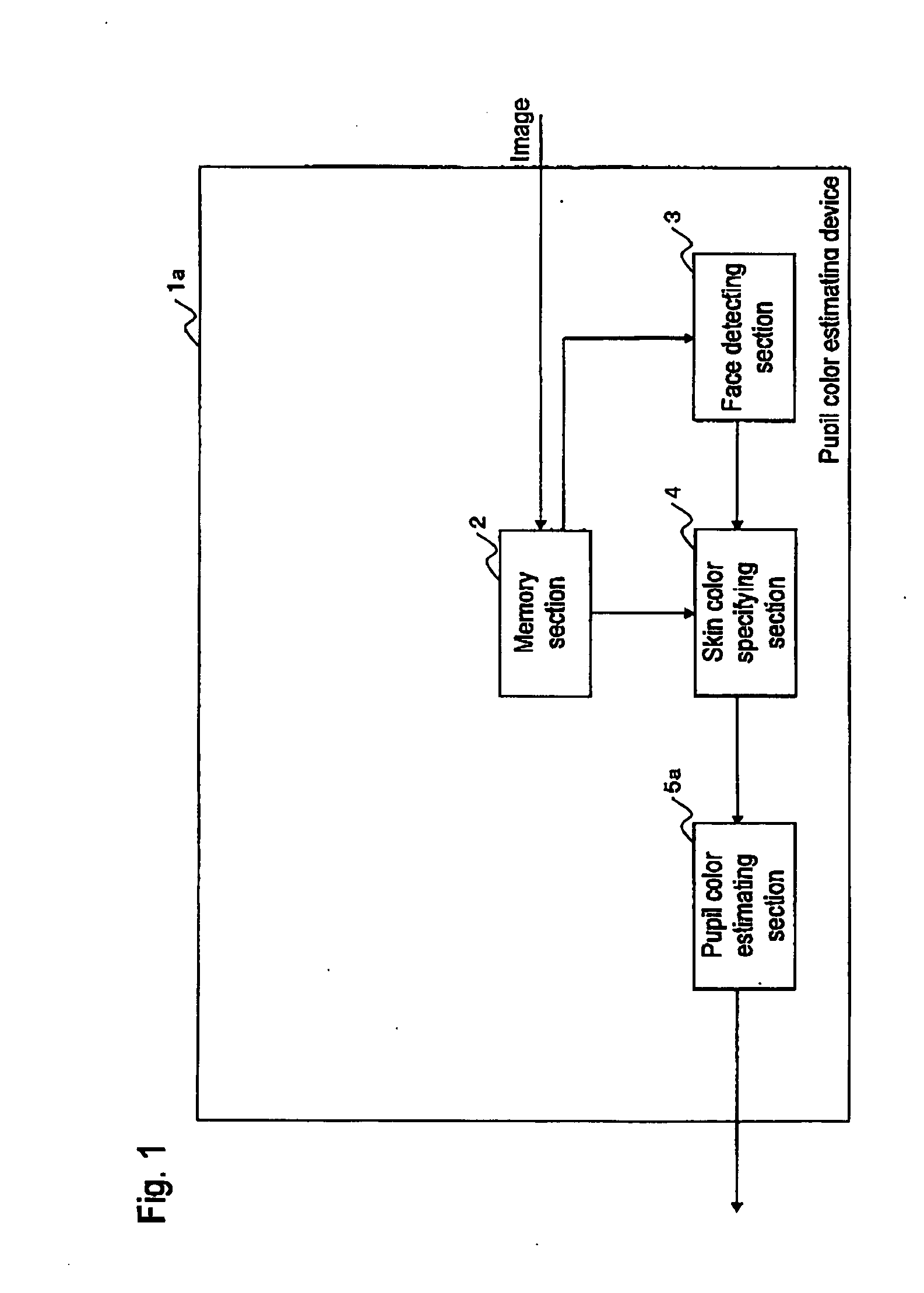
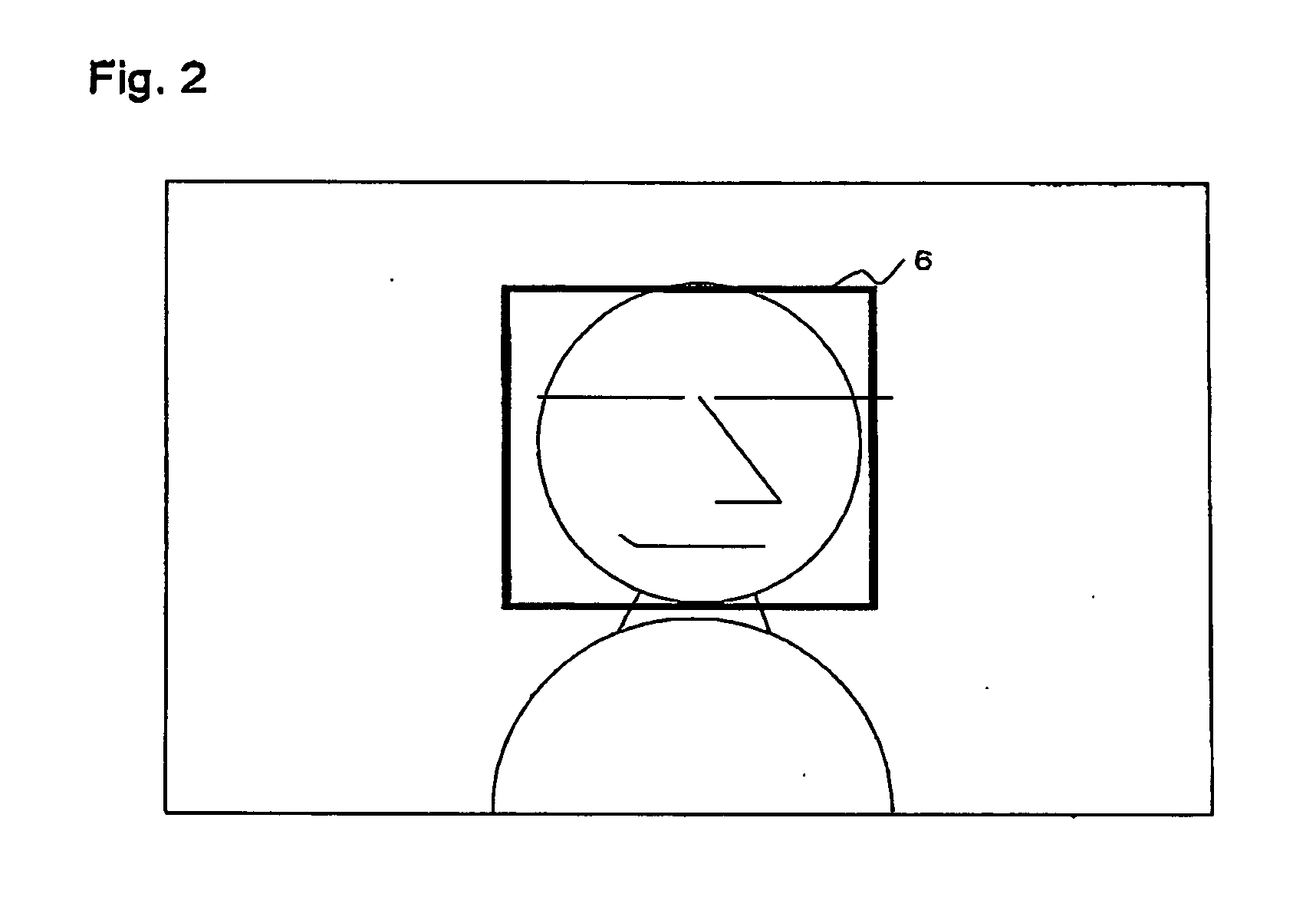
Pupil color estimating device
An original pupil color of a subject person in an image in which an abnormality such as a red-eye or gold-eye occurs is estimated. Further, whether an image correction is required or not and to produce an image having a natural pupil color in the image correction by estimating the original pupil color from the image is judged. A pupil color estimating device has a skin color of a subject person specified from an inputted image, regardless of whether an abnormality such as a red-eye or gold-eye occurs. This skin color is substituted in an approximate equation based upon a statistical result carried out in advance, and thereby a normal color component of a pupil is estimated from the skin color of the subject person.
Owner:ORMON CORP
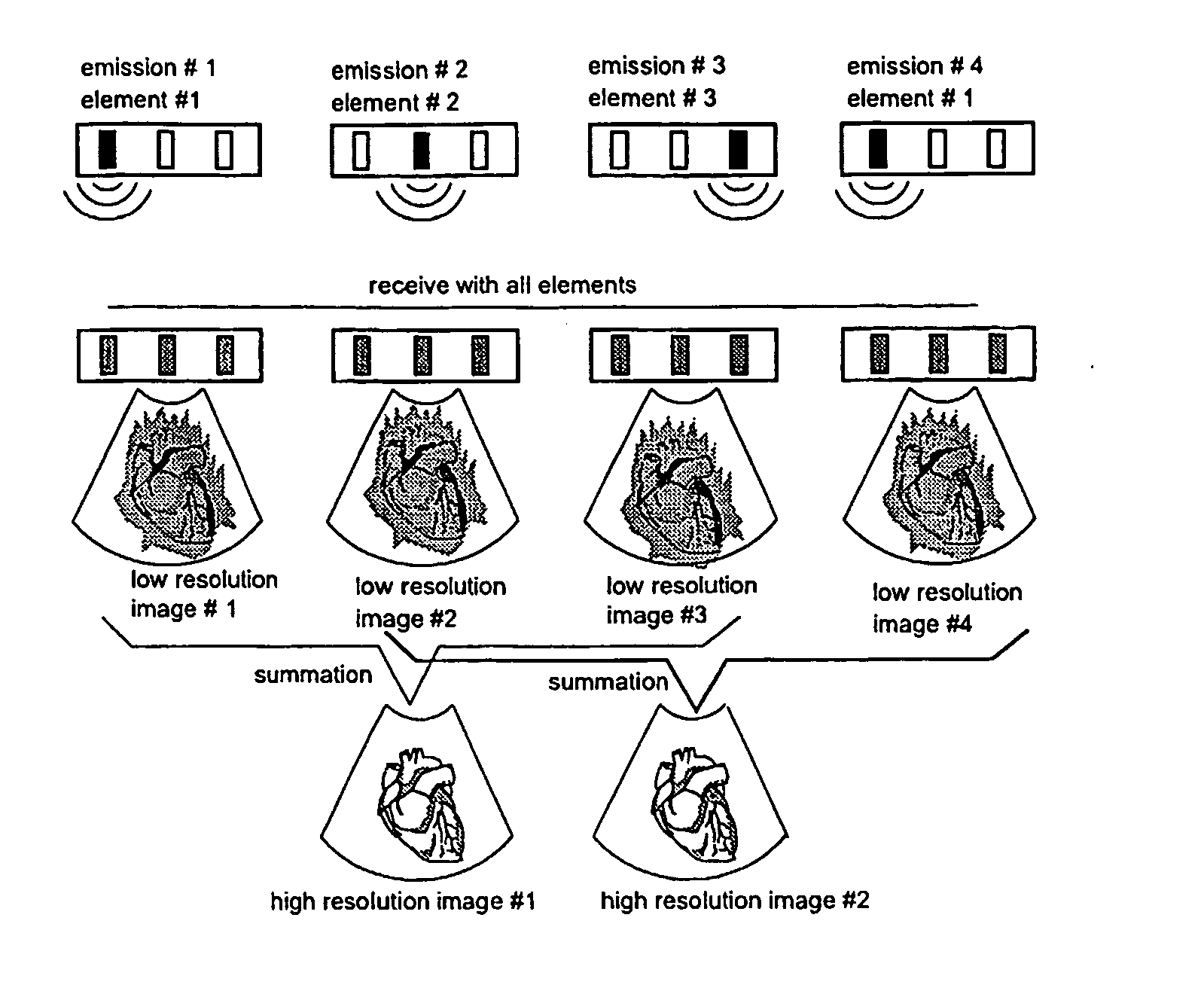
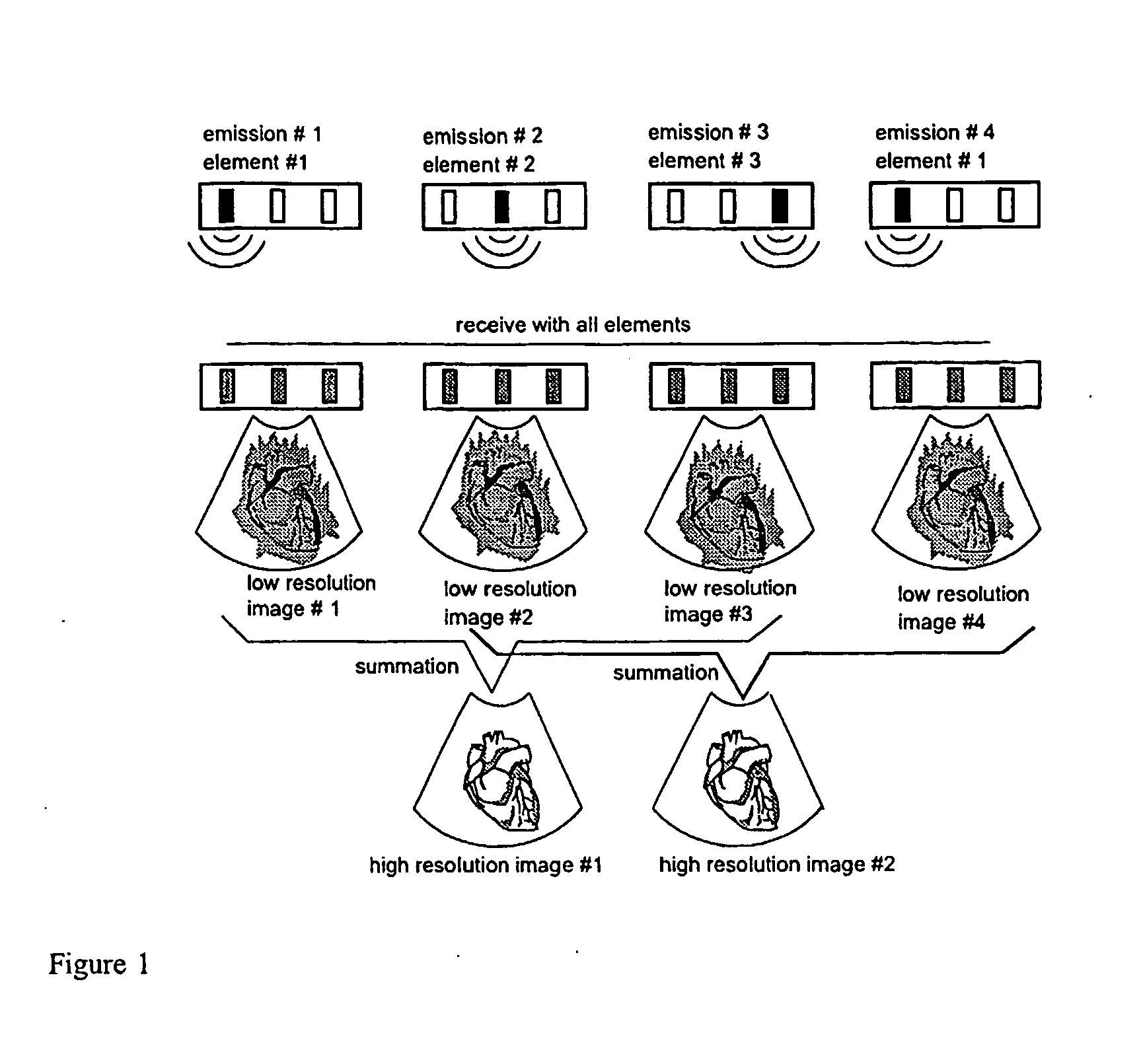
Apparatus and method for velocity estimation in synthetic aperture imaging
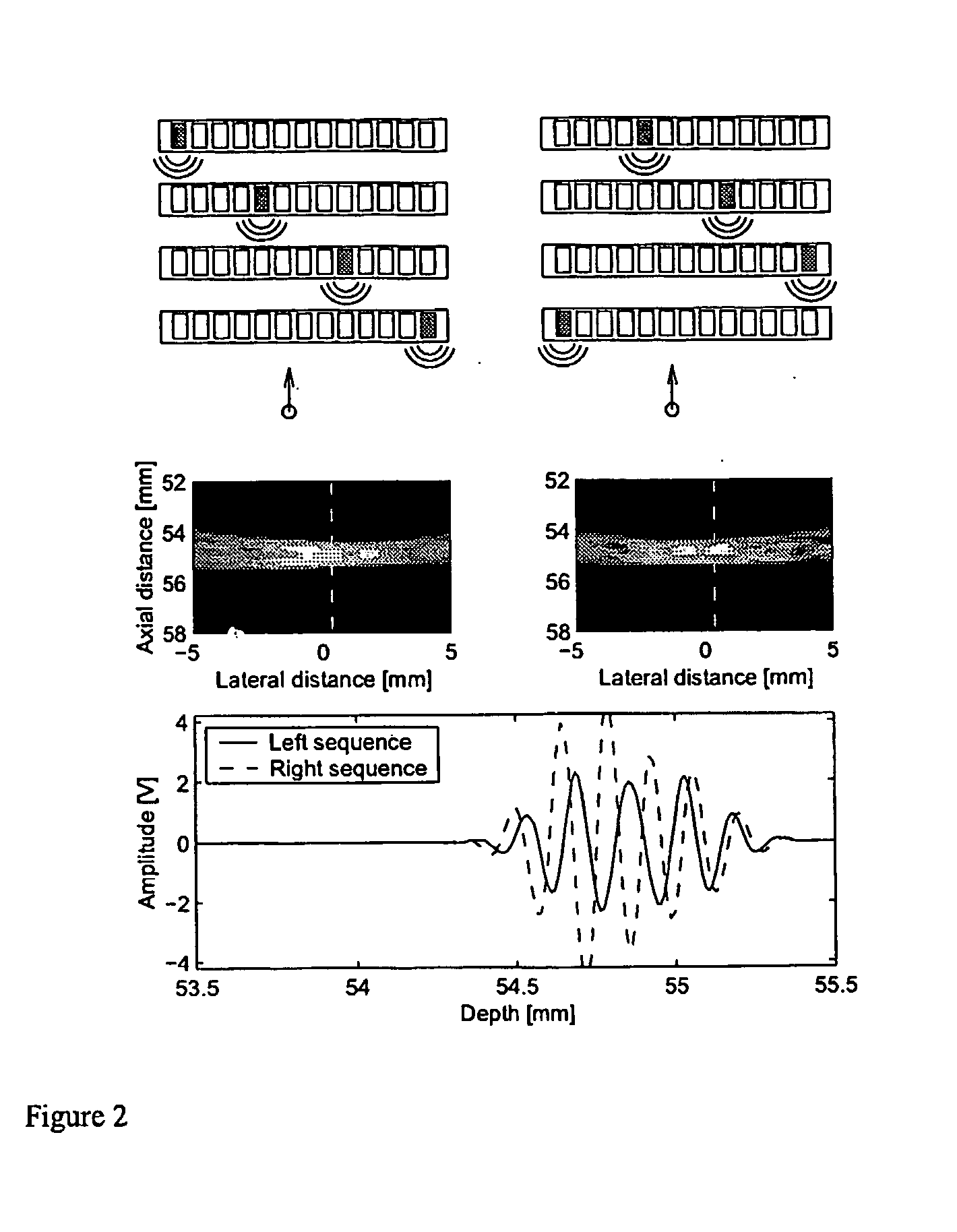
The invention relates to an apparatus for flow estimation using synthetic aperture imaging. The method uses a Synthetic Transmit Aperture, but unlike previous approaches a new frame is created after every pulse emission. In receive mode parallel beam forming is implemented. The beam formed RF data is added to the previously created RF lines obtained by the same transmit sequence. The apparatus comprises a pulser (1) to generate a pulsed voltage signal, that is fed to the emit beam former (2). The emit beam former (2) is connected to the emitting transducer array (3). The ultrasound is reflected by the object (4) and received by the elements of the transducer array (5). All of these signals are then combined in the beam processor (6) to focus all of the beams in the image in both transmit and receive mode and the simultaneously focused signals are used for updating the image in the processor (7). The estimation processor (8) to correlate the individual measurements to obtain the displacement between high-resolution images and thereby determine the velocity.
Owner:B K MEDICAL
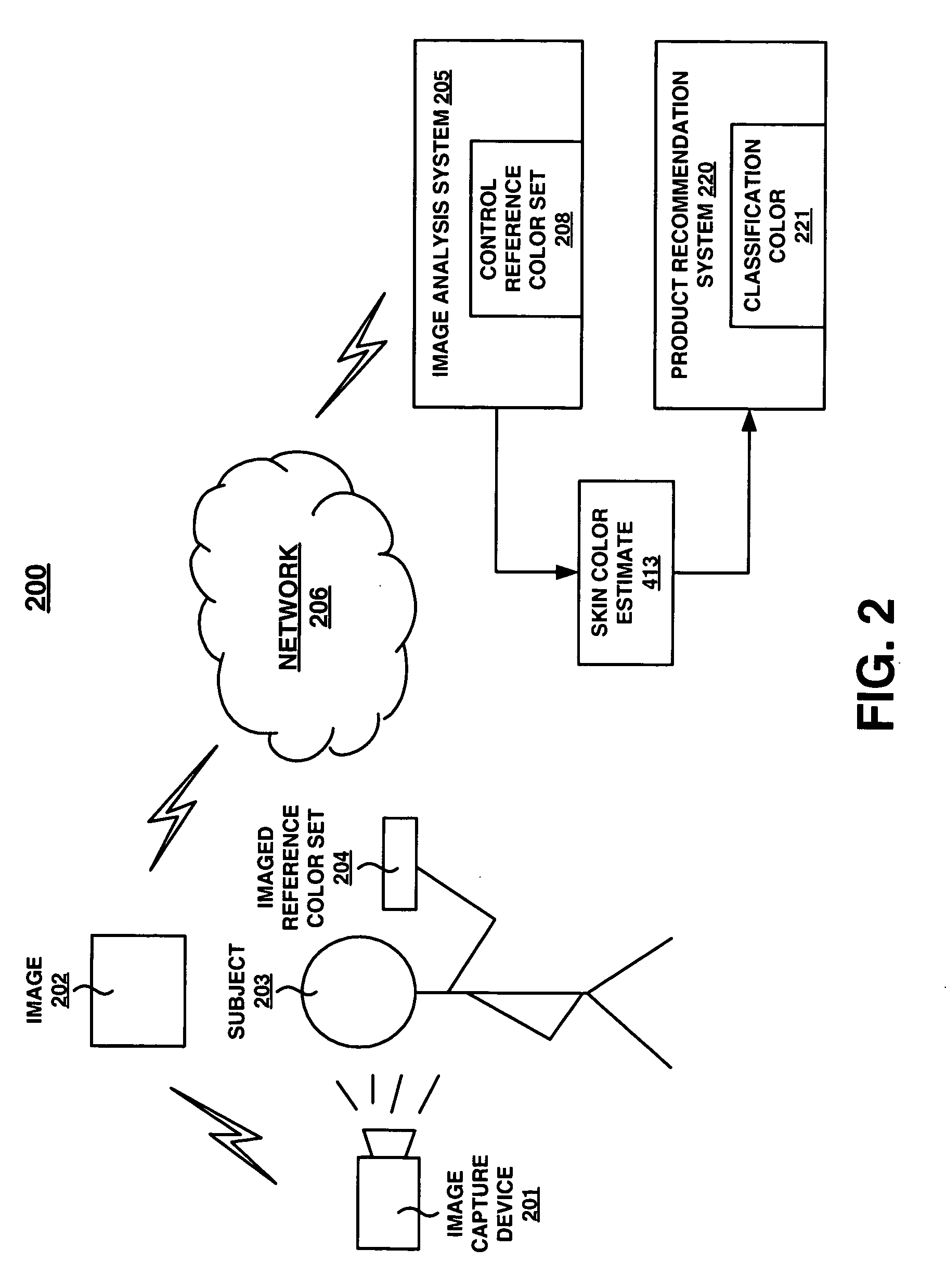
Method and system for skin color estimation from an image
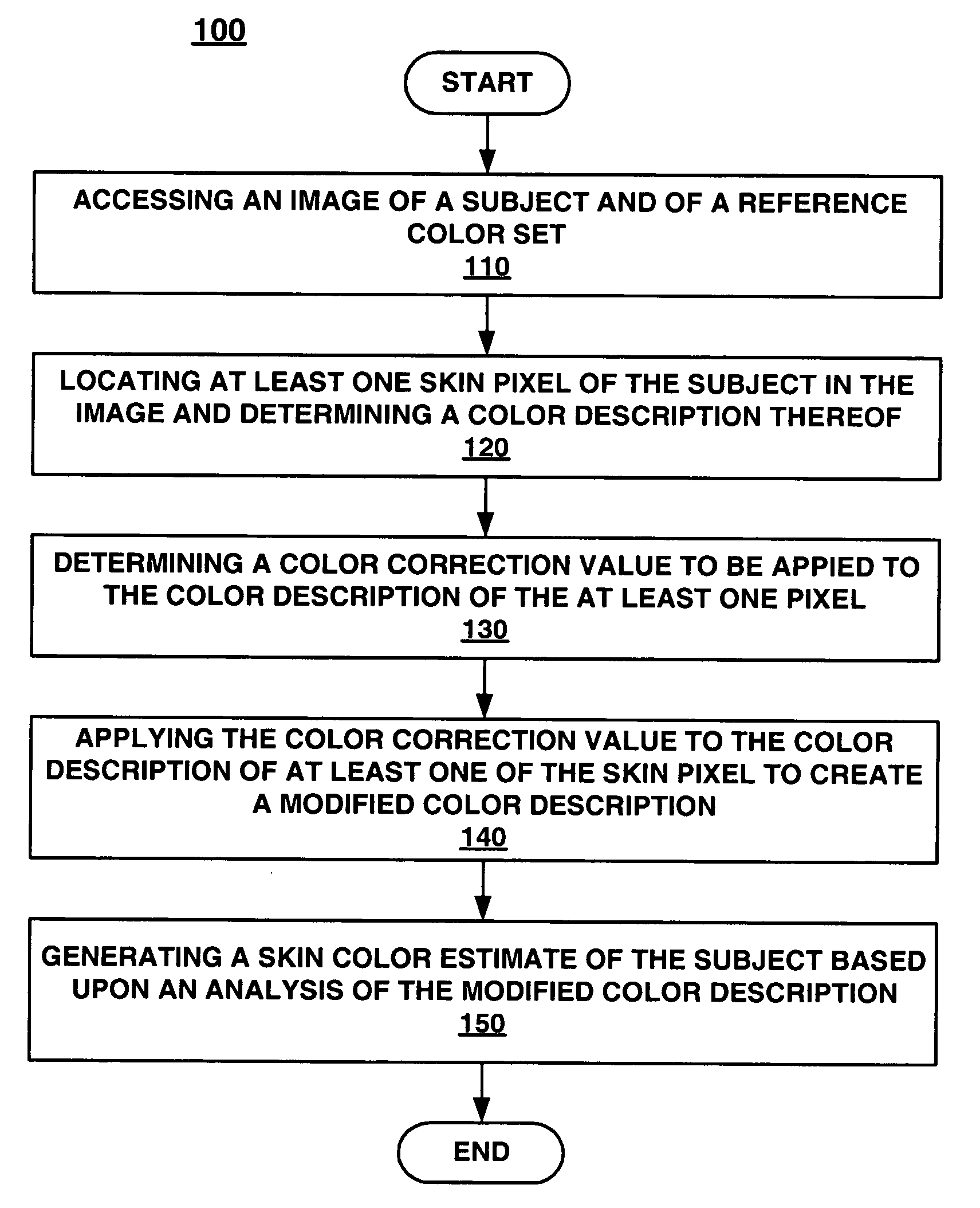
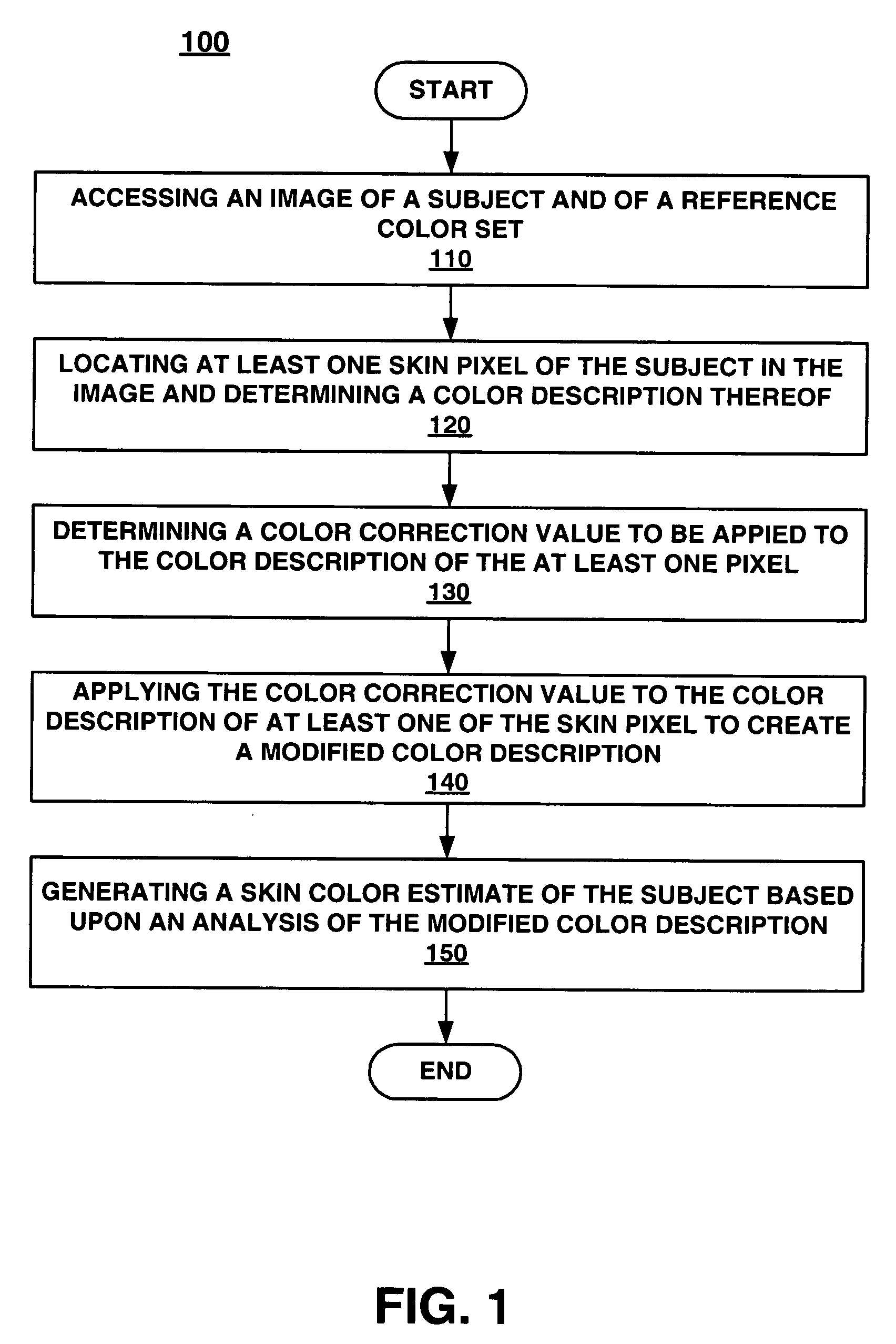
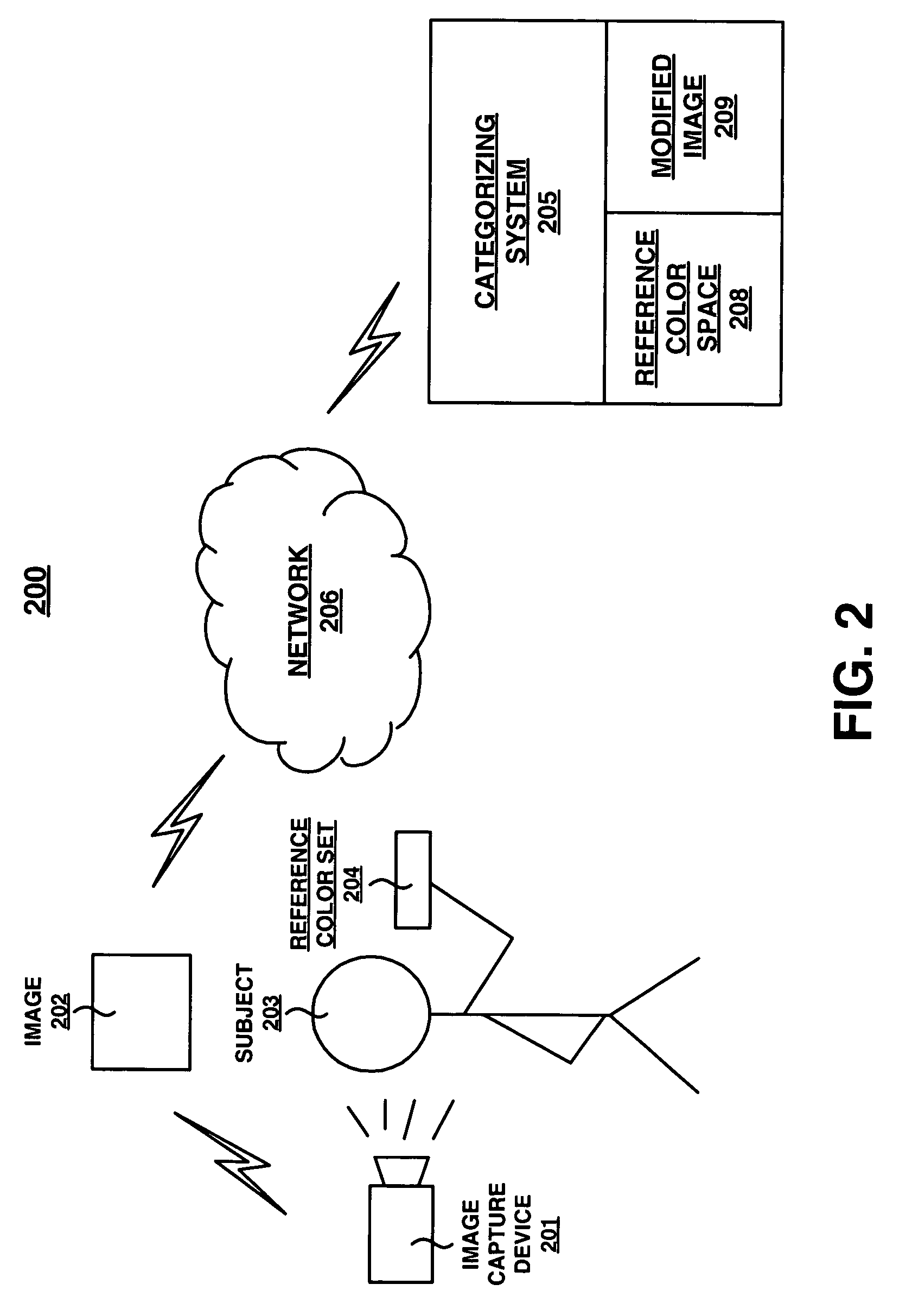
Embodiments of the present invention recite a computer implemented method and system for estimating skin color from an image. In embodiments of the present invention, an image of a subject and of an imaged reference color set is accessed. In embodiments of the present invention, a controlled infrastructure is not required when capturing the image. At least one skin pixel of the subject is located in the image and a color description of the at least one skin pixel is determined. Then, a color correction function to be applied to the color description of the at least one skin pixel is determined. The color correction function is applied to the color description of the at least one skin pixel to create a modified color description. Finally, the skin color of the subject is estimated based upon an analysis of the modified color description.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
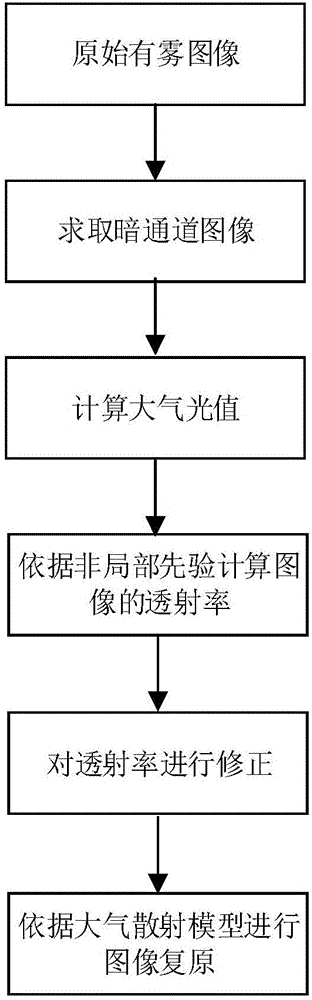
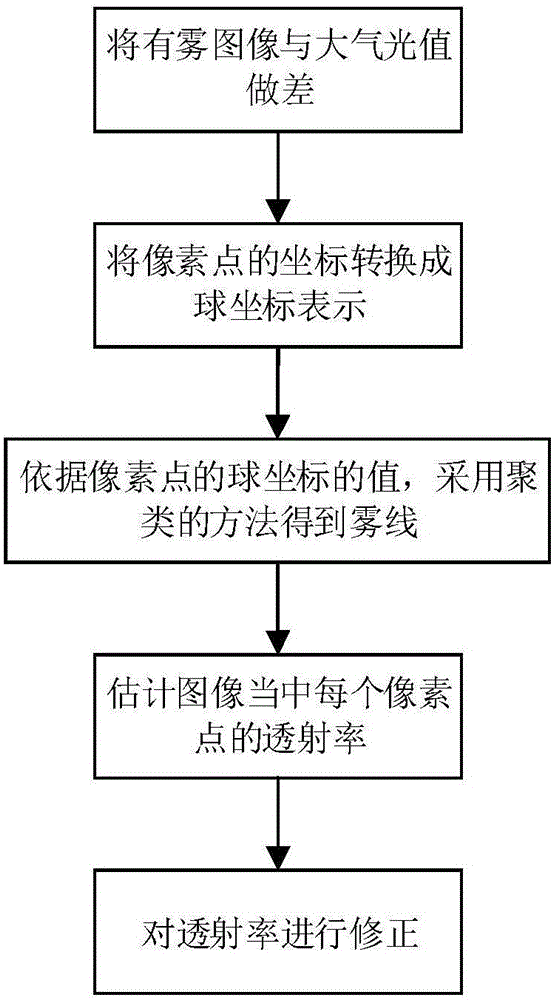
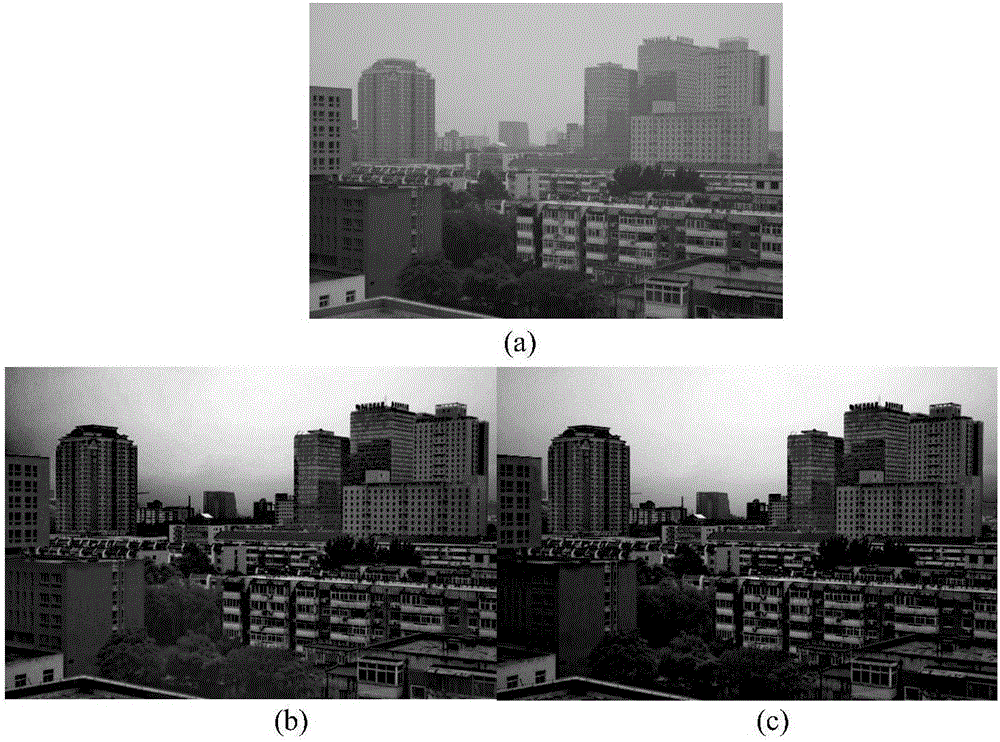
Image dehazing method and system based on dark channel and non-local prior
ActiveCN106530246AImprove transmittanceImprove color distortionImage enhancementImage analysisInformation processingTransmittance
The invention discloses an image dehazing method and system based on a dark channel and a non-local prior, which belongs to the technical field of image information processing. The image dehazing method can reasonably recover a degraded image collected in the haze weather. The method comprises the following steps of (1) calculating a dark channel image of a hazed image; (2) estimating the atmospheric light intensity of the hazed image according to the dark channel image; (3) estimating the transmissivity of the image based on the non-local prior; (4) correcting a transmittance image; and (5) using an atmospheric scattering model to restore a dehazed image. The invention also discloses an image dehazing system based on the dark channel and the non-local prior. The invention can restore scene information in the image realistically and naturally, and the algorithm has the advantages of low complexity, fast running speed and wide application prospect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
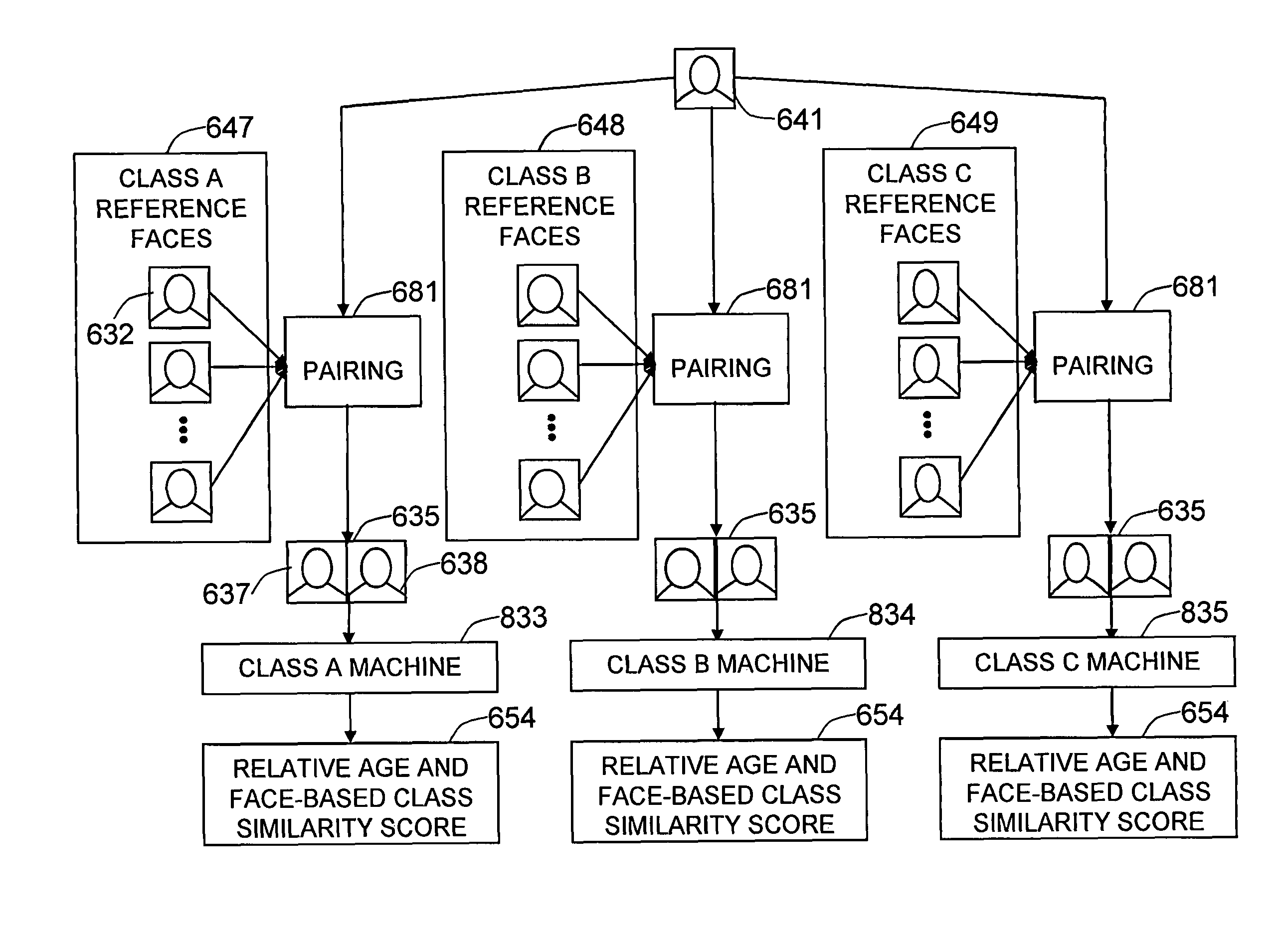
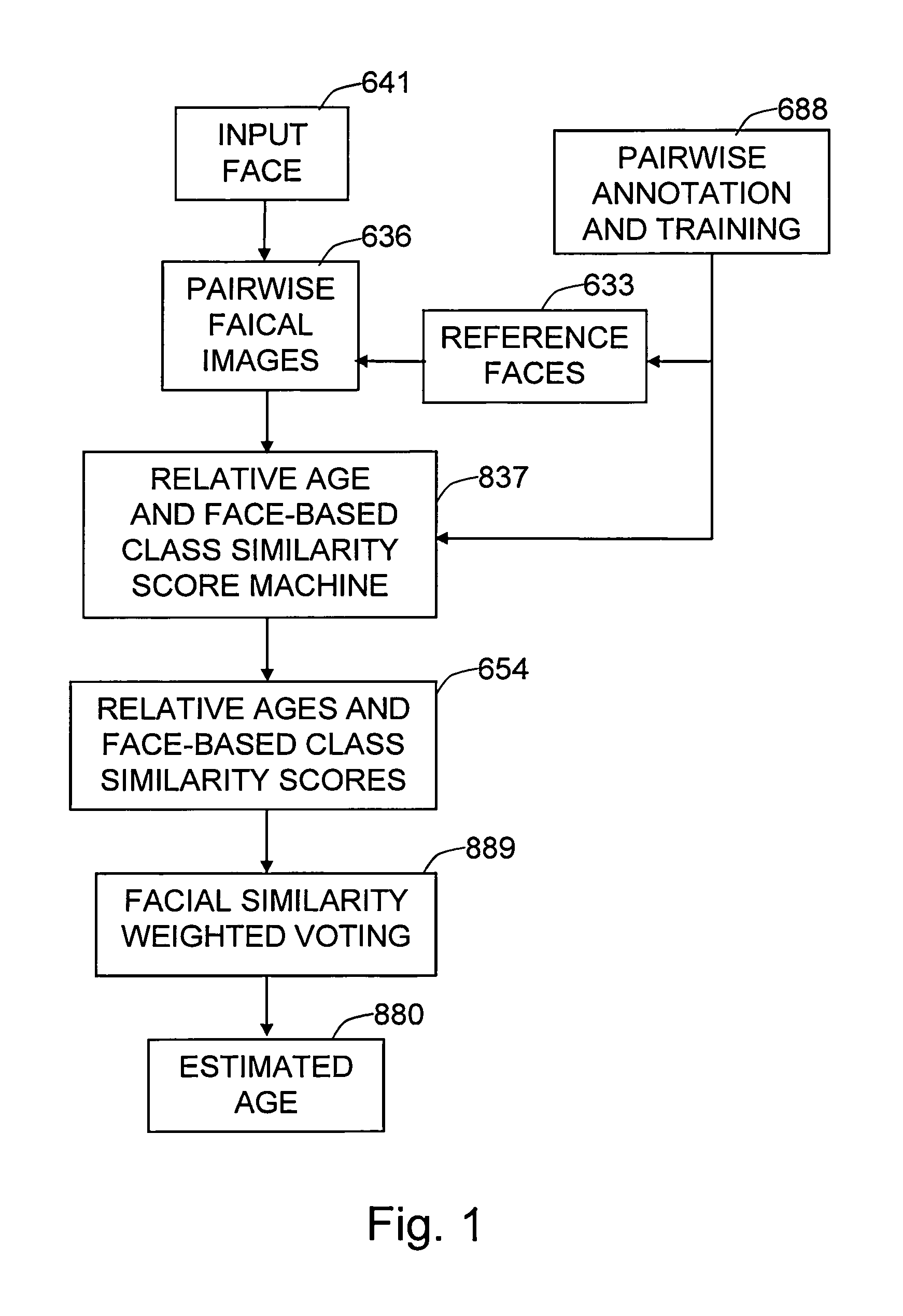
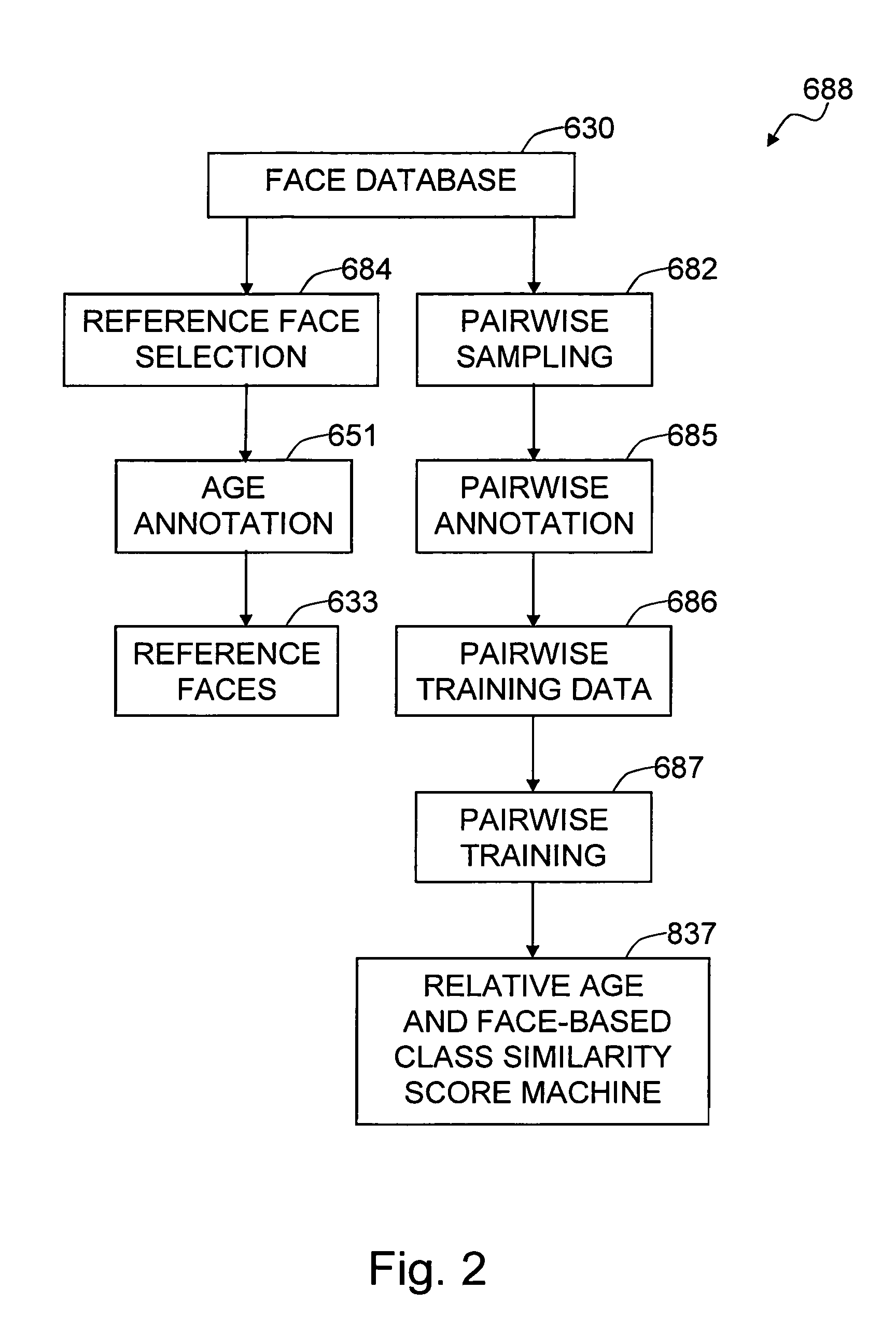
Method and system for age estimation based on relative ages of pairwise facial images of people
The present invention is a system and method for estimating the age of people based on their facial images. It addresses the difficulty of annotating the age of a person from facial image by utilizing relative age (such as older than, or younger than) and face-based class similarity (gender, ethnicity or appearance-based cluster) of sampled pair-wise facial images. It involves a unique method for the pair-wise face training and a learning machine (or multiple learning machines) which output the relative age along with the face-based class similarity, of the pairwise facial images. At the testing stage, the given input face image is paired with some number of reference images to be fed to the trained machines. The age of the input face is determined by comparing the estimated relative ages of the pairwise facial images to the ages of reference face images. Because age comparison is more meaningful when the pair belongs to the same demographics category (such as gender and ethnicity) or when the pair has similar appearance, the estimated relative ages are weighted according to the face-based class similarity score between the reference face and the input face.
Owner:VIDEOMINING CORP
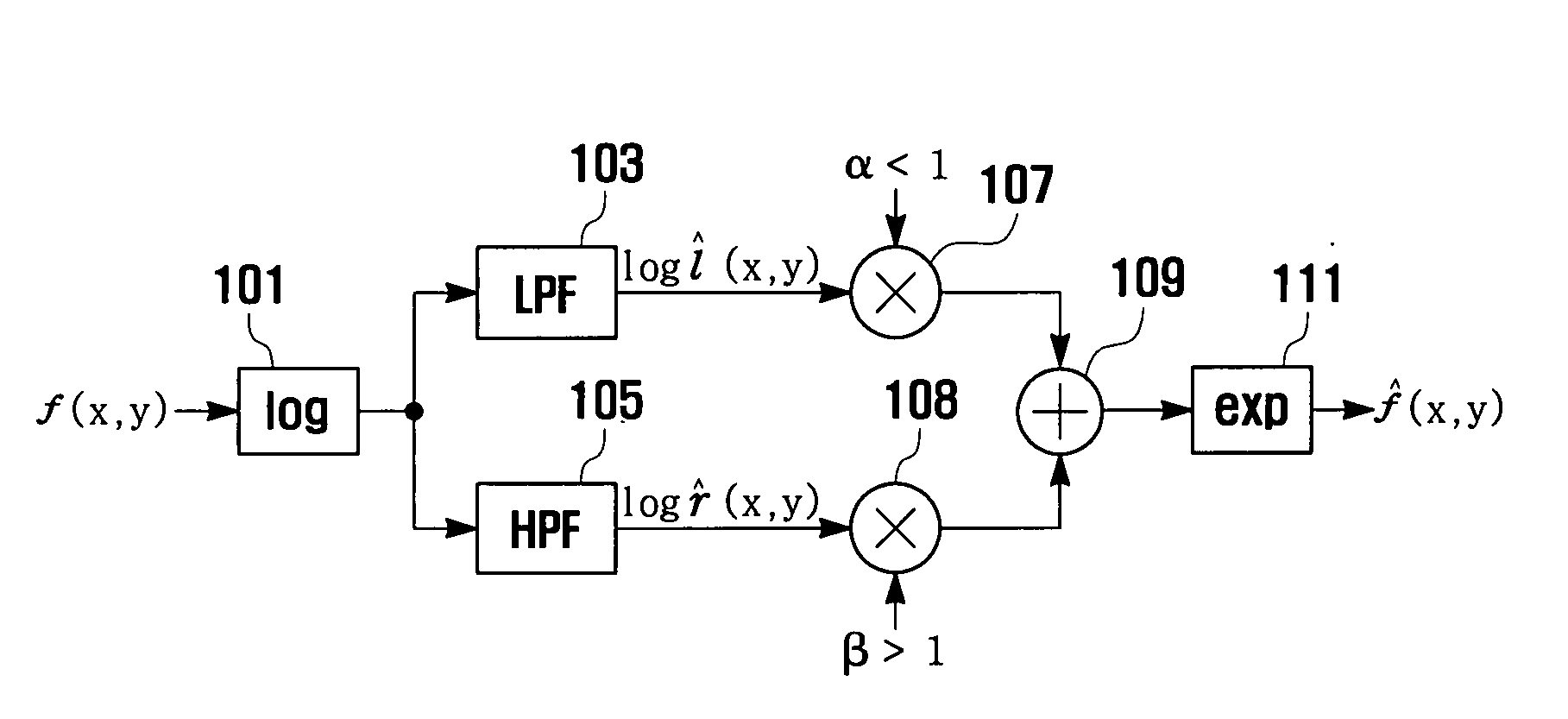
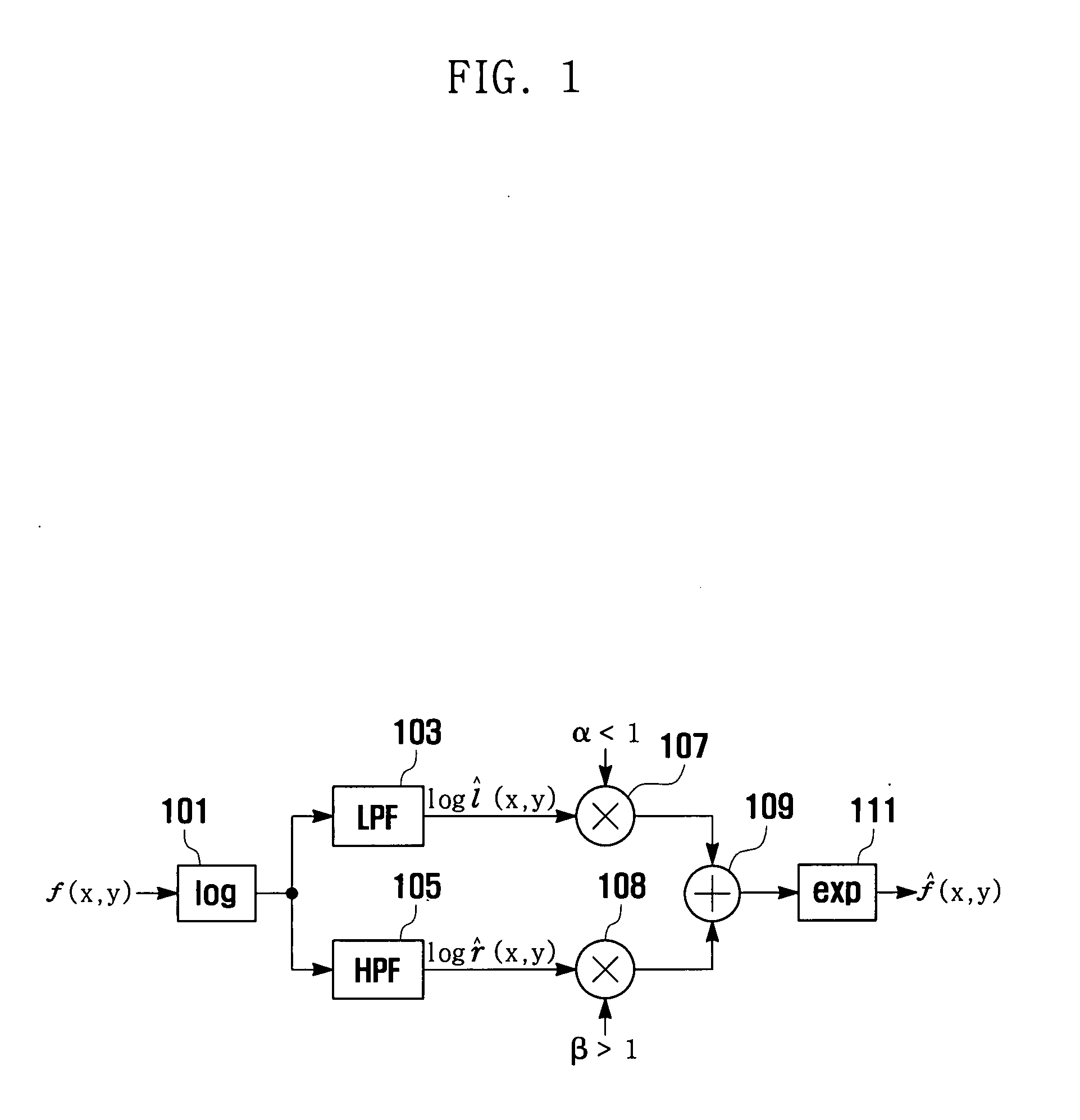
Image enhancement method and system
InactiveUS20080101719A1Reduced dynamic rangeIncrease contrastTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageImaging quality
An image enhancement method and system are provided. The image enhancement method and system are capable of improving image quality by performing gamma corrections on global and local illuminations and reflectance estimated from an input image, in consideration of dynamic range and contrast of the image, respectively. Particularly, in a case of a color image, the red, green, and blue (RGB) component images are converted into hue, saturation, and value (HSV) component images, and the global and local illuminations and reflectance estimated from the V component image. By converting the hue (H), saturation (S), and enhanced value (V) into RGB, an enhanced color image can be obtained.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
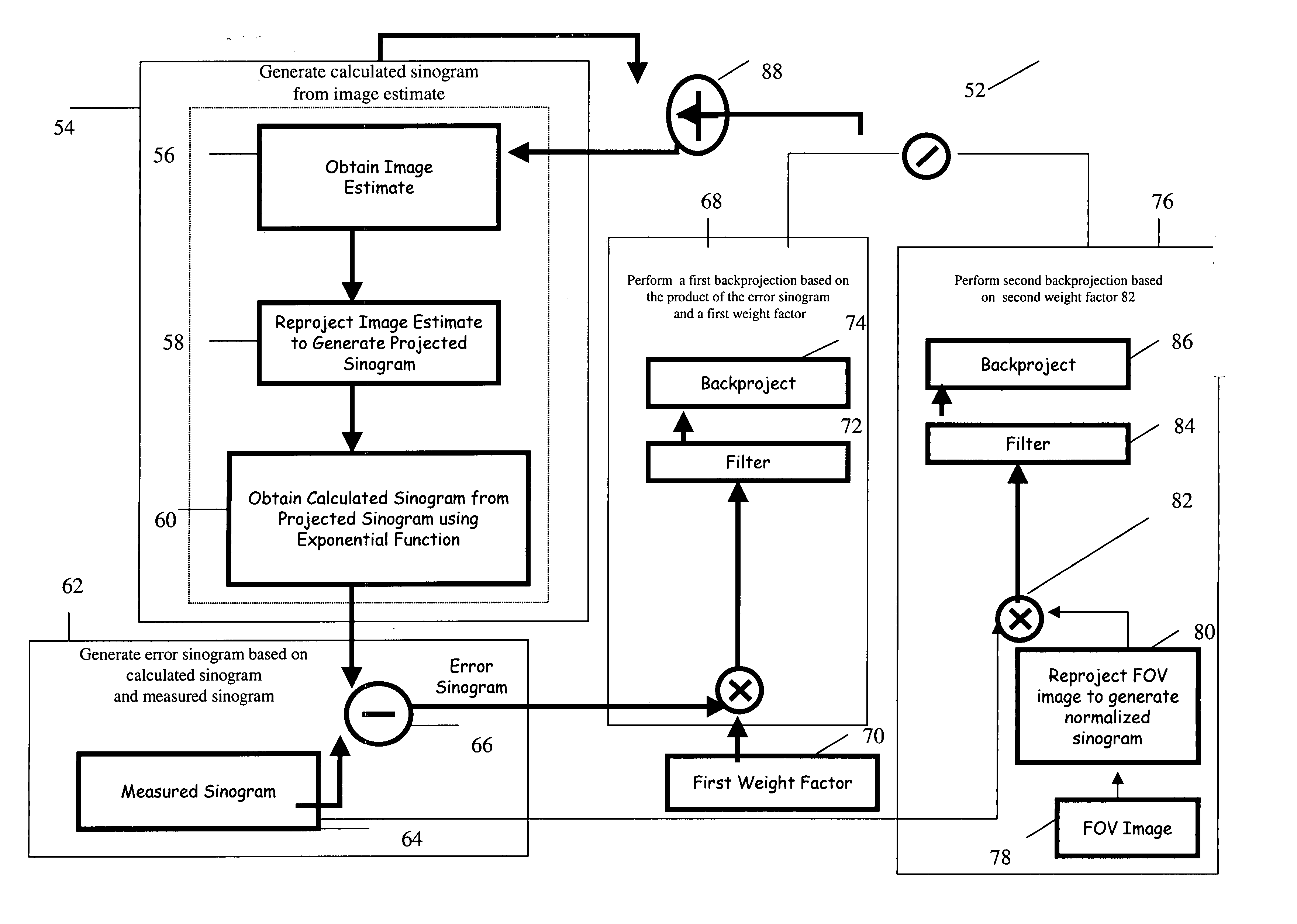
Method and system for iterative image reconstruction
InactiveUS20060072801A1Need be addressReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputed tomographyImage estimation
A method for iteratively reconstructing image data acquired by a computed tomography system is provided. The method comprises generating a calculated sinogram from an image estimate and generating an error sinogram based on the calculated sinogram and a measured sinogram. Then, one or more backprojections are performed, each based upon a reconstruction parameter. The reconstruction parameter impacts at least one of convergence speed and computational cost of each iterative step and corresponding reconstruction. A filtering step is performed prior to performing the one or more backprojections. Finally, the initial image is updated by adding corresponding results of the one or more backprojections to the image estimate to obtain the reconstructed image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
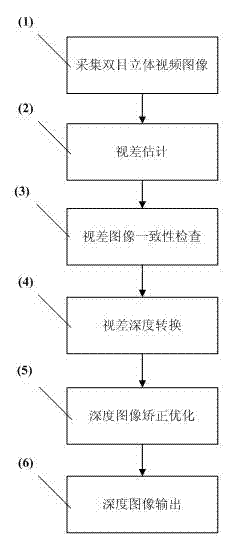
Depth image estimating method of binocular stereo video
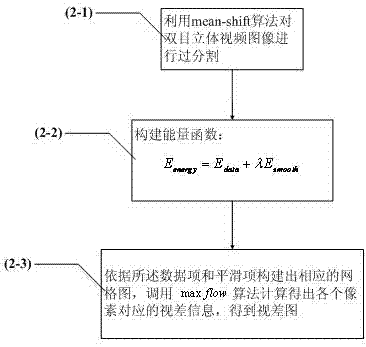
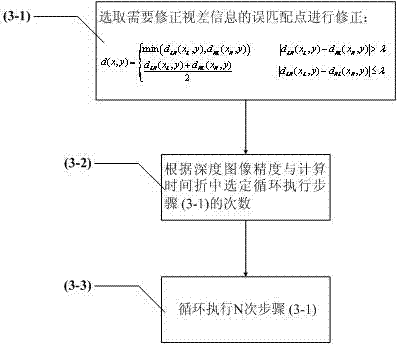
InactiveCN102523464AEliminate errorsReduce complexityImage analysisSteroscopic systemsStereoscopic videoImaging quality
The invention discloses a depth image estimating method of a binocular stereo video, which comprises the following steps of: (1) collecting a binocular stereo video image from a binocular stereo camera; (2) performing parallax estimation based on graph cut stereo matching on the binocular stereo video image; (3) performing uniformity check on a parallax image obtained by the graph cut stereo matching, and deleting the unreliable matching by self-adapting matching to reduce the wrong matching of the depth image; (4) converting the parallax image into a depth image according to the relation of the parallax and the depth; (5) performing correction optimization on the obtained depth image by a multilateral filter; and (6) outputting the depth image to finish the depth image estimation of the binocular stereo video. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of effectively eliminating the errors in the depth image estimation, and finally obtaining an accurate and dense depth image so as to satisfy the demand of rebuilding image quality based on a real scene.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Two-dimensional polynomial model for depth estimation based on two-picture matching
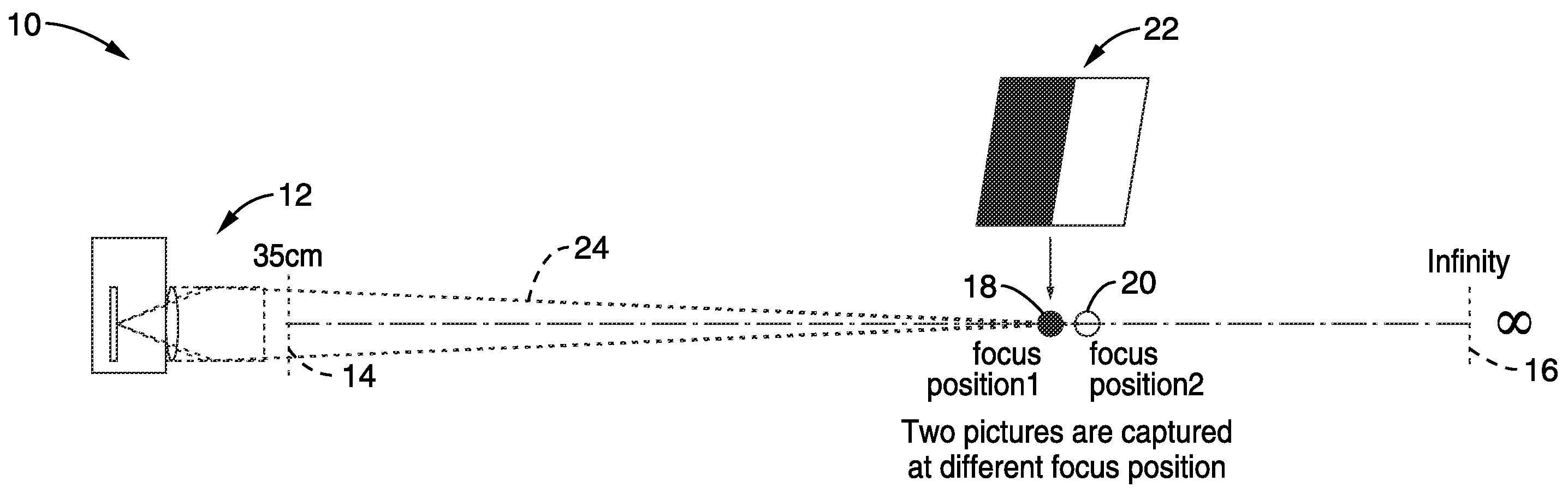
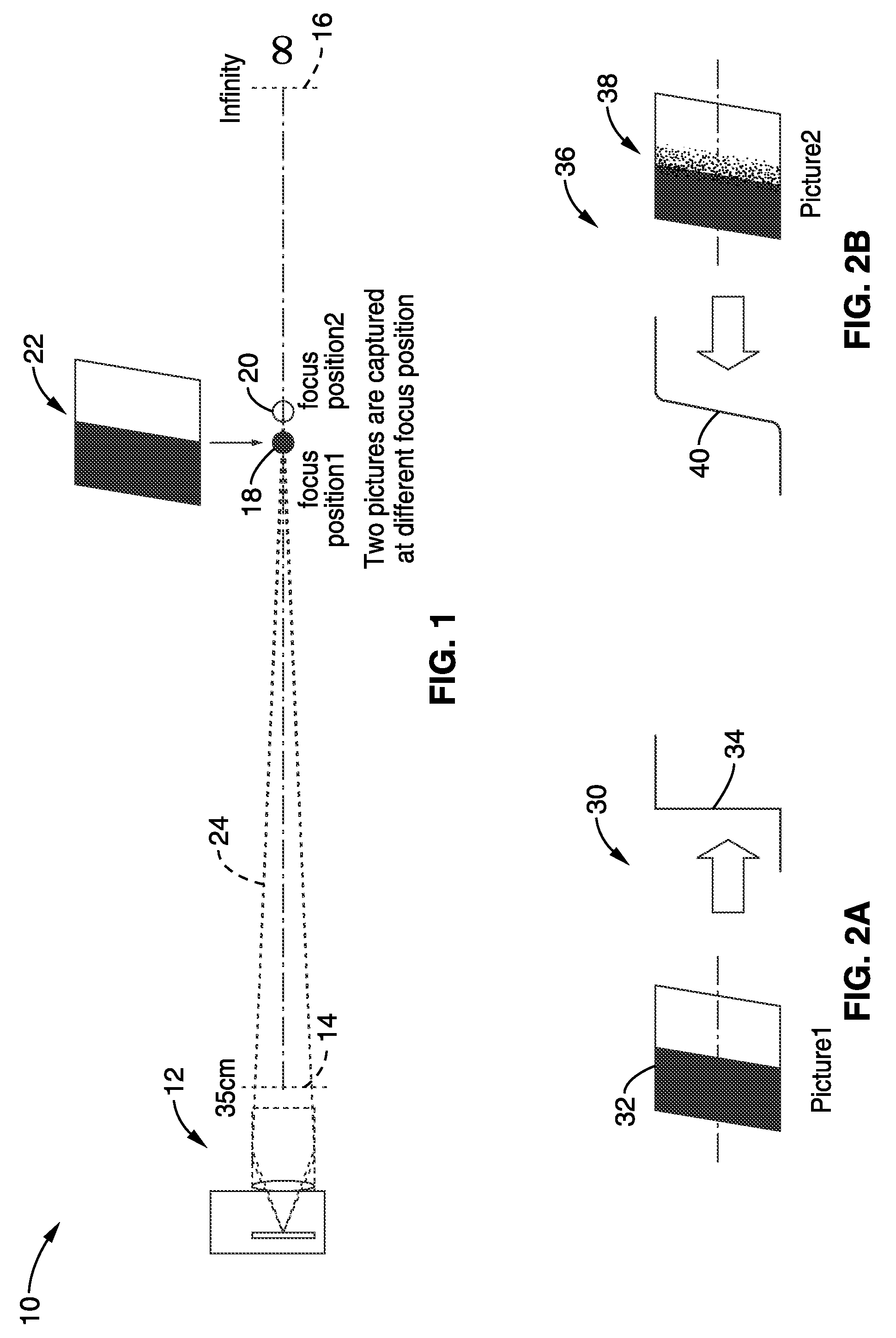
InactiveUS20100194971A1Accurate distanceReducing noiseTelevision system detailsImage analysisImage estimationFocal position
Apparatus and method for electronically estimating focusing distance between a camera (still and / or video camera) and a subject. Images at different focal positions of a calibration target are collected with distances between subject positions. In one aspect, histogram matching is performed to reduce noise error. A focus matching model is then generated in response to detected blur differences between successive images of the calibration target. The focus matching model is preferably converted to a polynomial equation of a desired order to smooth out image collection noise. The focus matching model is stored for access during operation. In use, the distance to subject is estimated in response to capturing images, detecting blur differences between the images and entering the blur difference information into the matching model.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
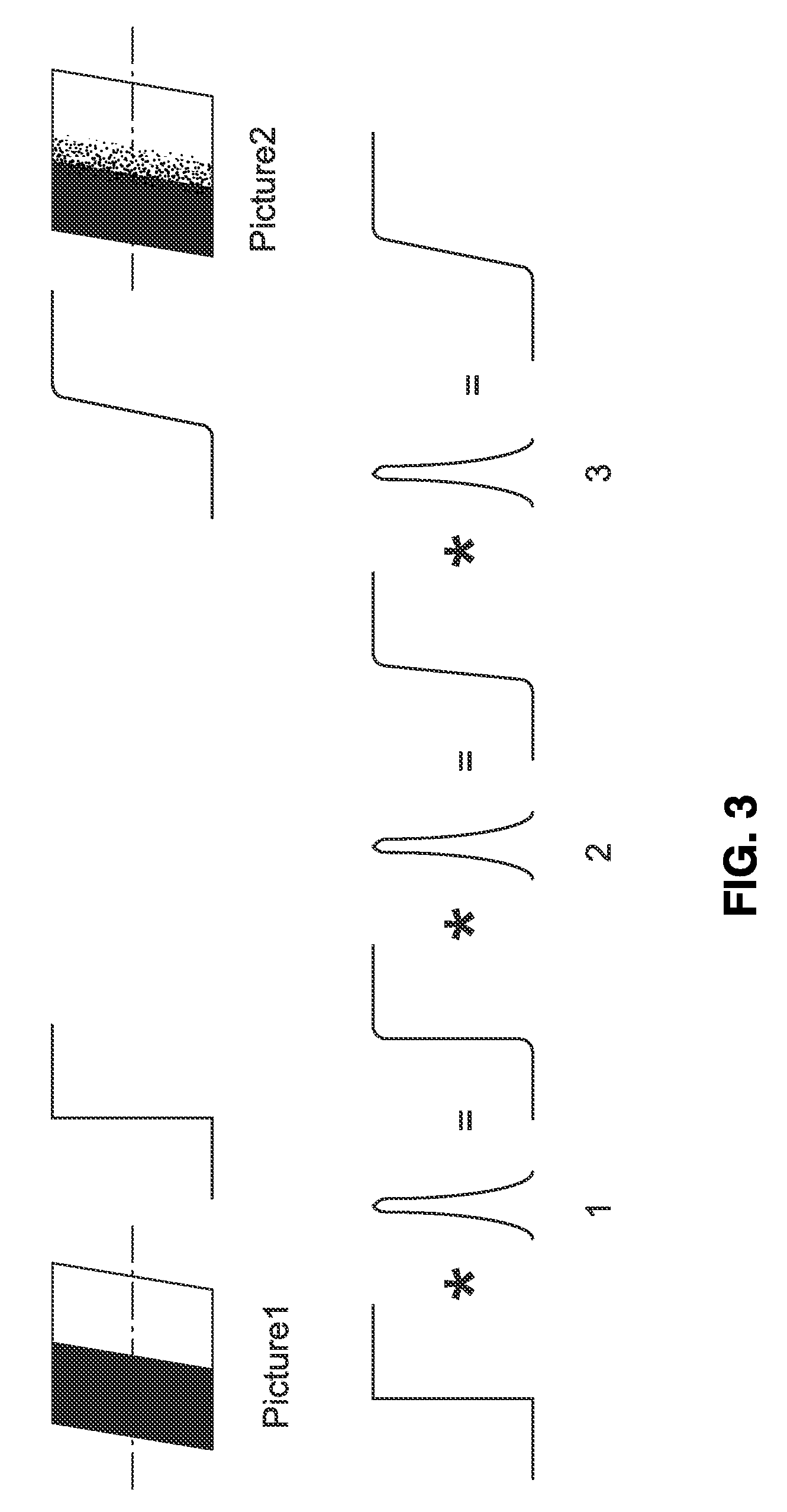
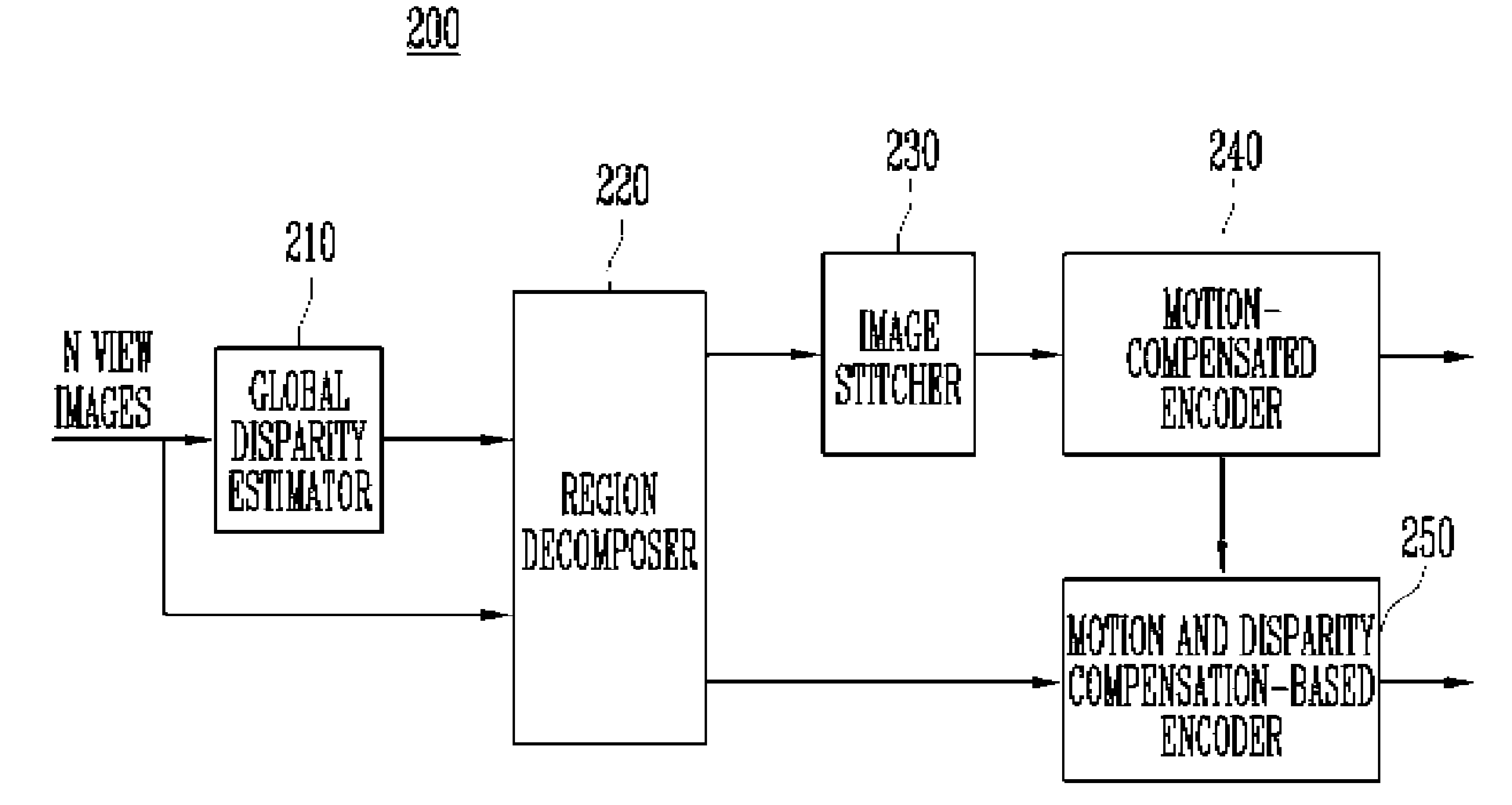
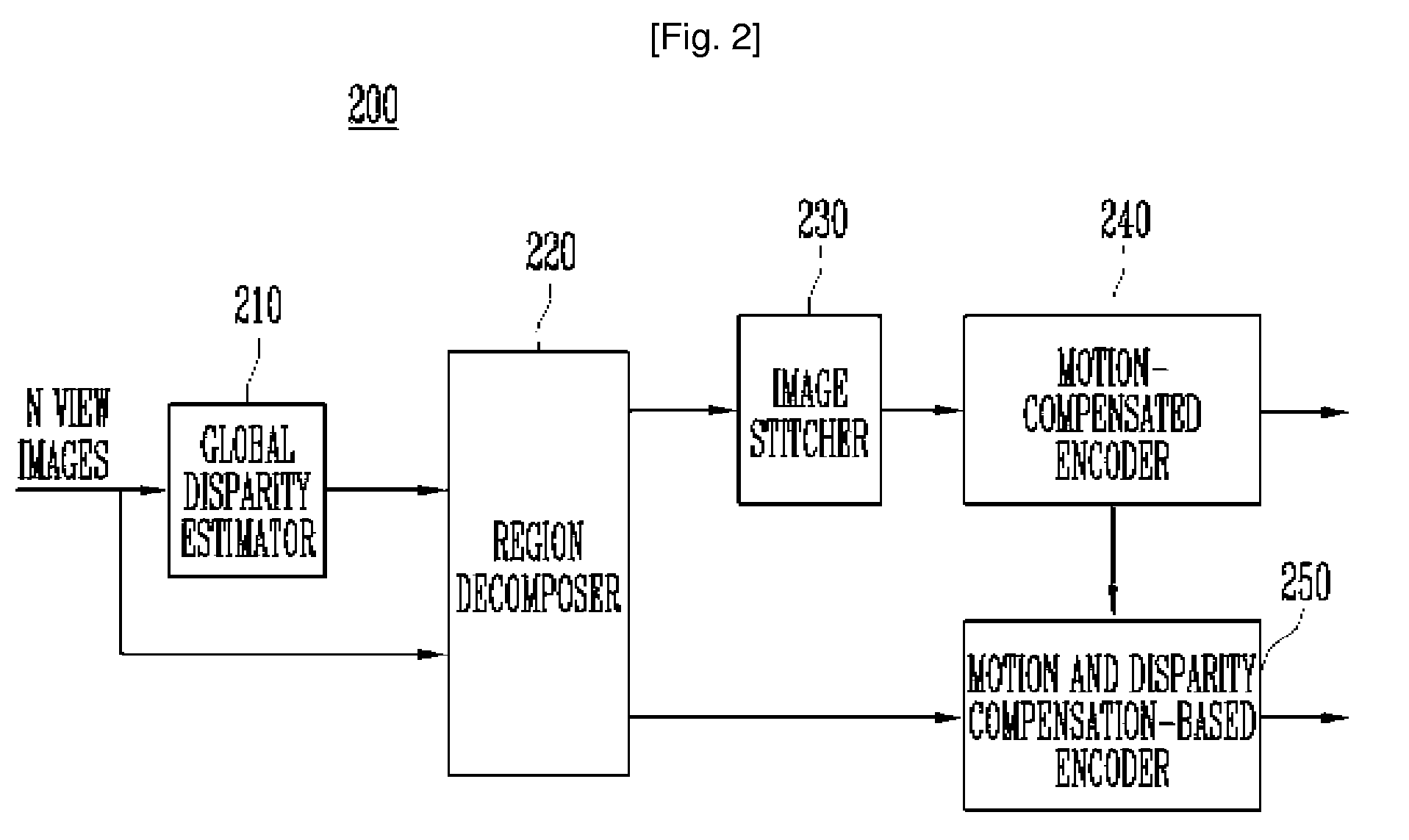
Method and Apparatus for Encoding and Decoding Multi-View Video Using Image Stitching
InactiveUS20080089405A1Increase the compression ratioImprove decoding efficiencyTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesParallaxImage estimation
Provided is a method and apparatus for encoding and decoding multi-view video data. The encoding method includes: decomposing each view image of the multi-view video into an overlapped region and a non-overlapped region, the overlapped region being overlapped with other view image and the non-overlapped region not being overlapped with other view image; generating a stitched image by combining the non-overlapped region of each view image and a middle view image; encoding the stitched image using a first encoding algorithm; and encoding the overlapped region of each view image, using a second encoding algorithm. Further, the decomposing step includes the steps of estimating disparity information for each view image, based on a predetermined view image; and decomposing each view image into said overlapped region and said non-overlapped region using the estimated disparity information.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Equipment and method for detecting head posture
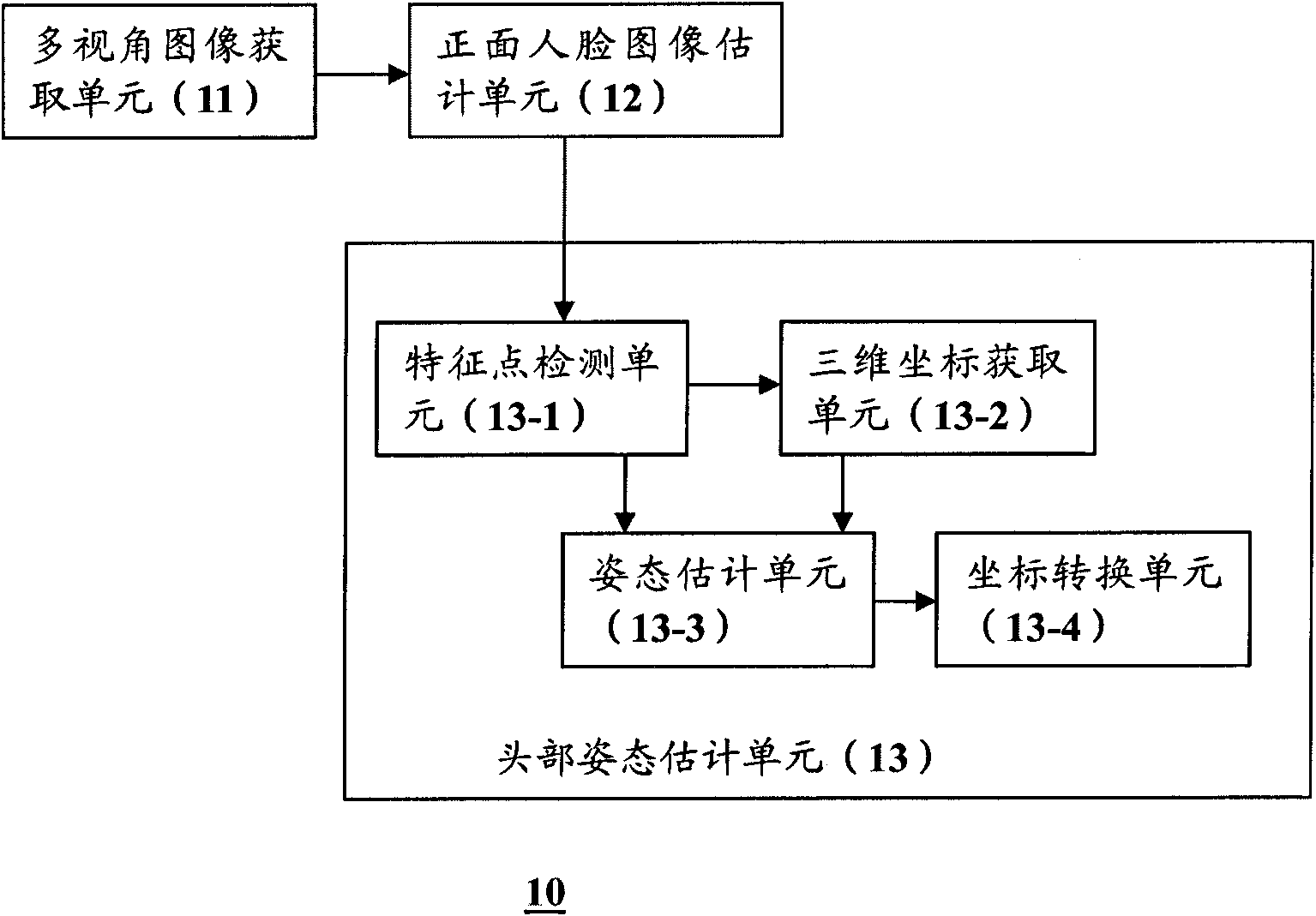
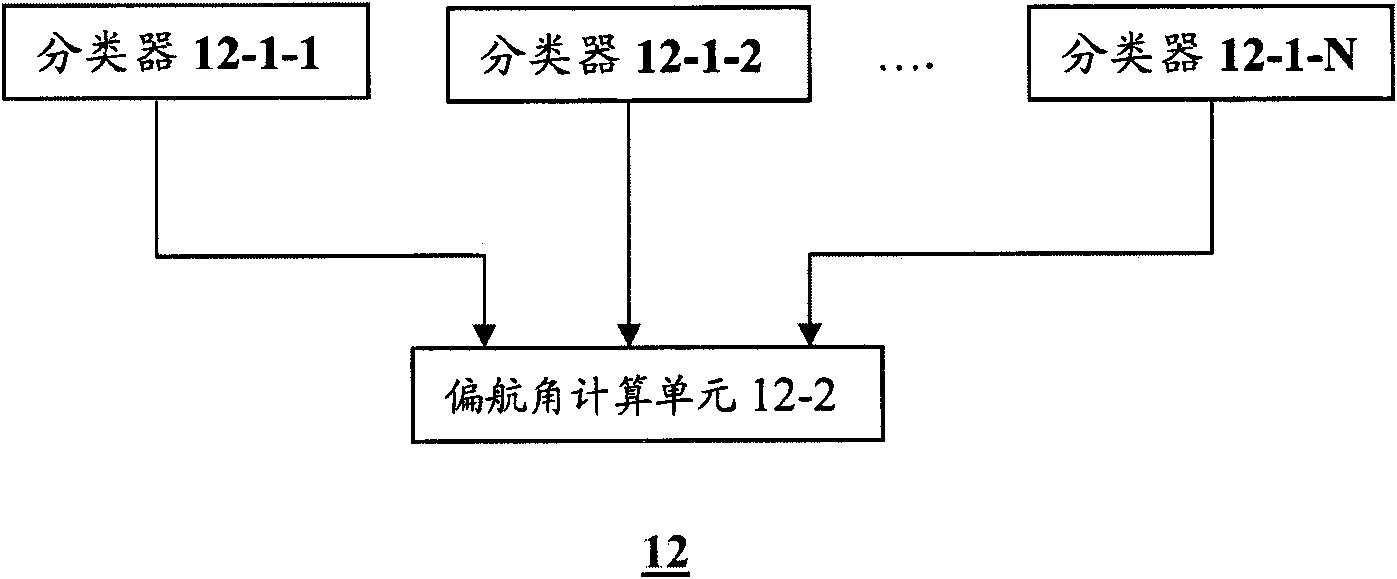
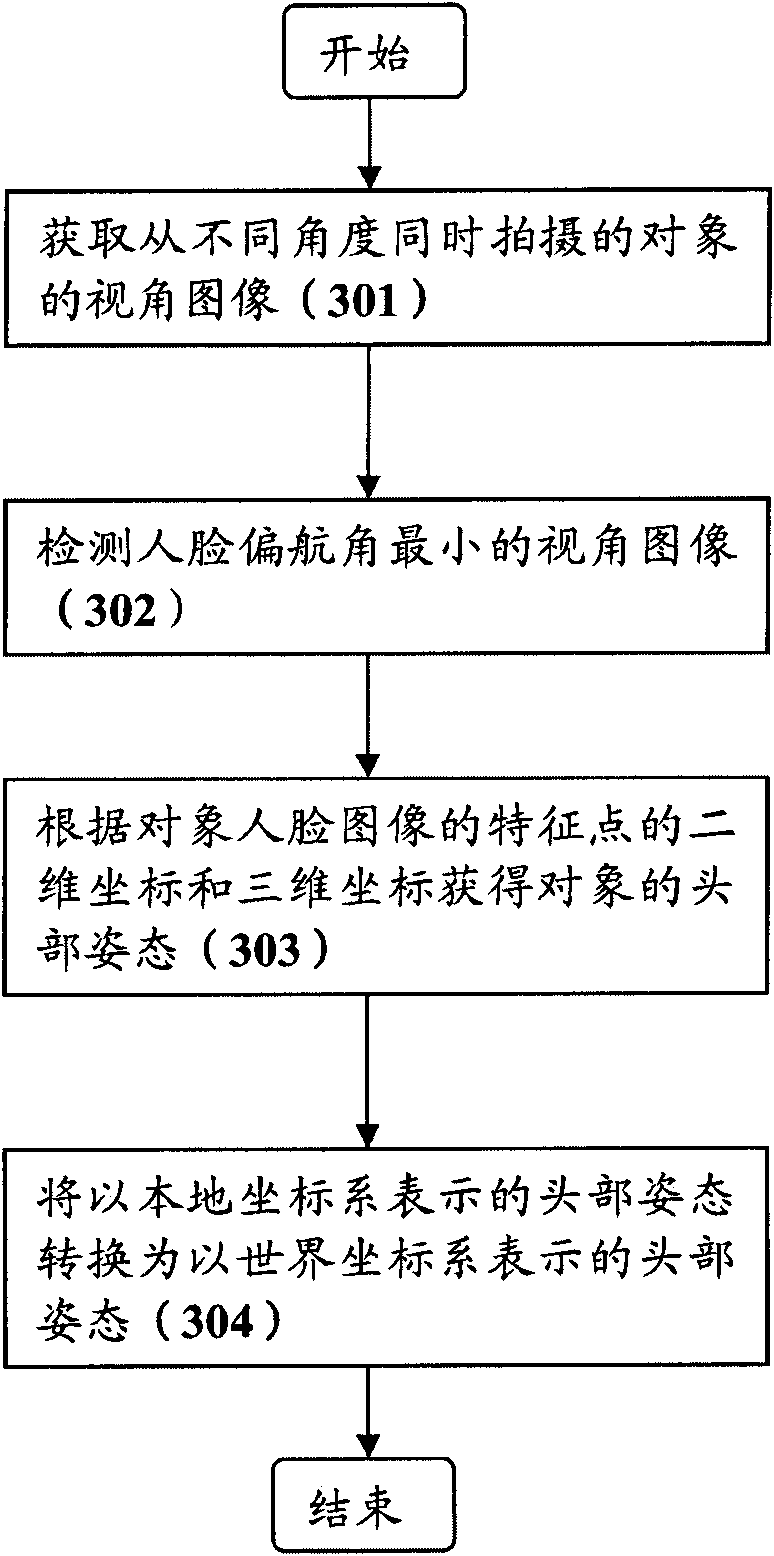
InactiveCN102156537AAccurate detectionEasy to useInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingImage estimationAngular degrees
The invention provides equipment and a method for detecting a head posture. The equipment for detecting the head posture comprises a multi-visual-angle image acquiring unit, a front human face image estimation unit, a head posture estimation unit and a coordinate conversion unit, wherein the multi-visual-angle image acquiring unit is used for acquiring visual angle images, which is shot from different angles, of an object; the front human face image estimation unit detects a visual angle image of a human face having a minimum yaw angle from the acquired visual angle images; the head posture estimation unit acquires a three-dimensional coordinate of a predetermined human face characteristic point from a human face three-dimensional model, detects the predetermined human face characteristic point and a two-dimensional coordinate of the predetermined human face characteristic point from the detected visual angle image, and calculates a first head posture relative to image capturing equipment for shooting the visual angle image of the human face having the minimum yaw angle according to the two-dimensional coordinate and the three-dimensional coordinate of the predetermined human face characteristic point; and the coordinate conversion unit converts the first head posture into a second head posture represented by a world coordinate system according to the world coordinate system coordinates of the image capturing equipment.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
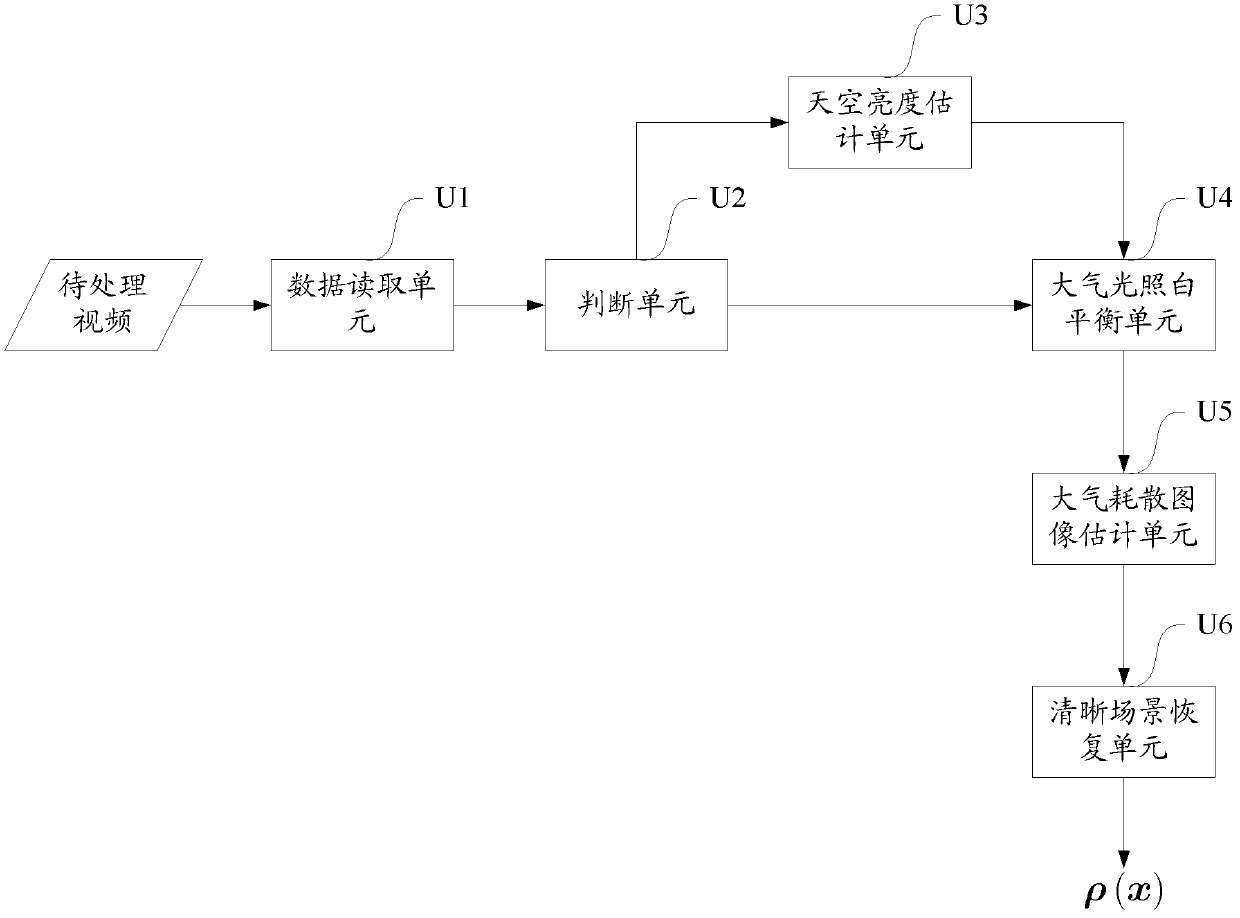
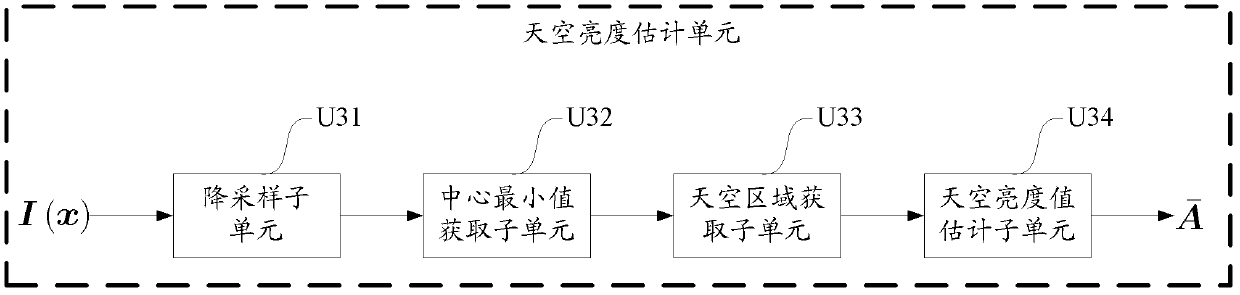
Real-time video defogging system
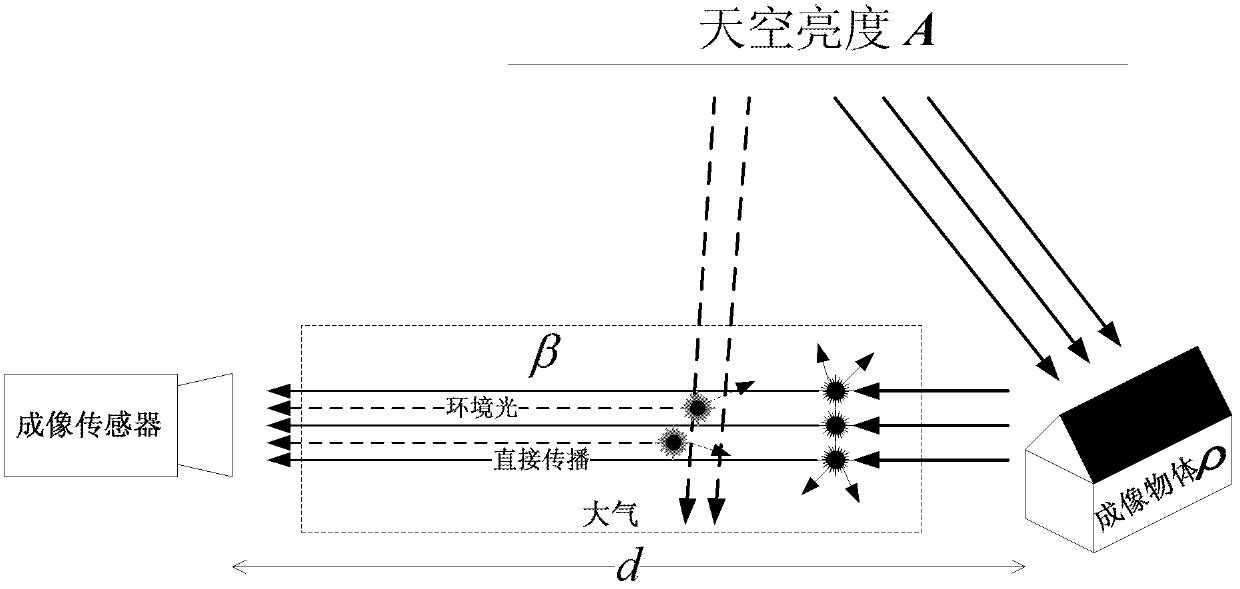
InactiveCN102170574AAcceleration of defogging processingImprove defogging effectImage enhancementColor signal processing circuitsSky brightnessImage estimation
The invention provides a real-time video defogging system which belongs to the field of image processing and is characterized by being realized in a digital integrated circuit and comprising a data reading unit, a judgment unit, a sky brightness estimation unit, an atmosphere illumination white balance unit, an atmosphere dissipation image estimation unit and a clear scene recovery unit. As for the former K frames in the current lens of a video to be processed, the sky region thereof is estimated so that the sky brightness value is calculated; then the atmosphere illumination color of an image to be processed is corrected according to the sky brightness value by utilizing a white balance algorithm and a white balance image is normalized, the minimum values, minimum values of various colorcomponent are solved out so as to serve as rough estimated image; and based on the minimum values, an refined atmosphere dissipation image is calculated by utilizing an edge maintained flatting method, and the atmosphere scene albedo is calculated based on the atmosphere dissipation image, so that defogging recovery processing is carried out. As for a common-intermediate-format (CIF) video with the resolution of 288*352, the processing speed can be up to 60 fps (frames per second); and as for a D1-format video with the resolution of 578*720, the processing speed can be up to 15 fps, thus the system provided by the invention can be applied to monitoring systems and meet the requirement on real-time performance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
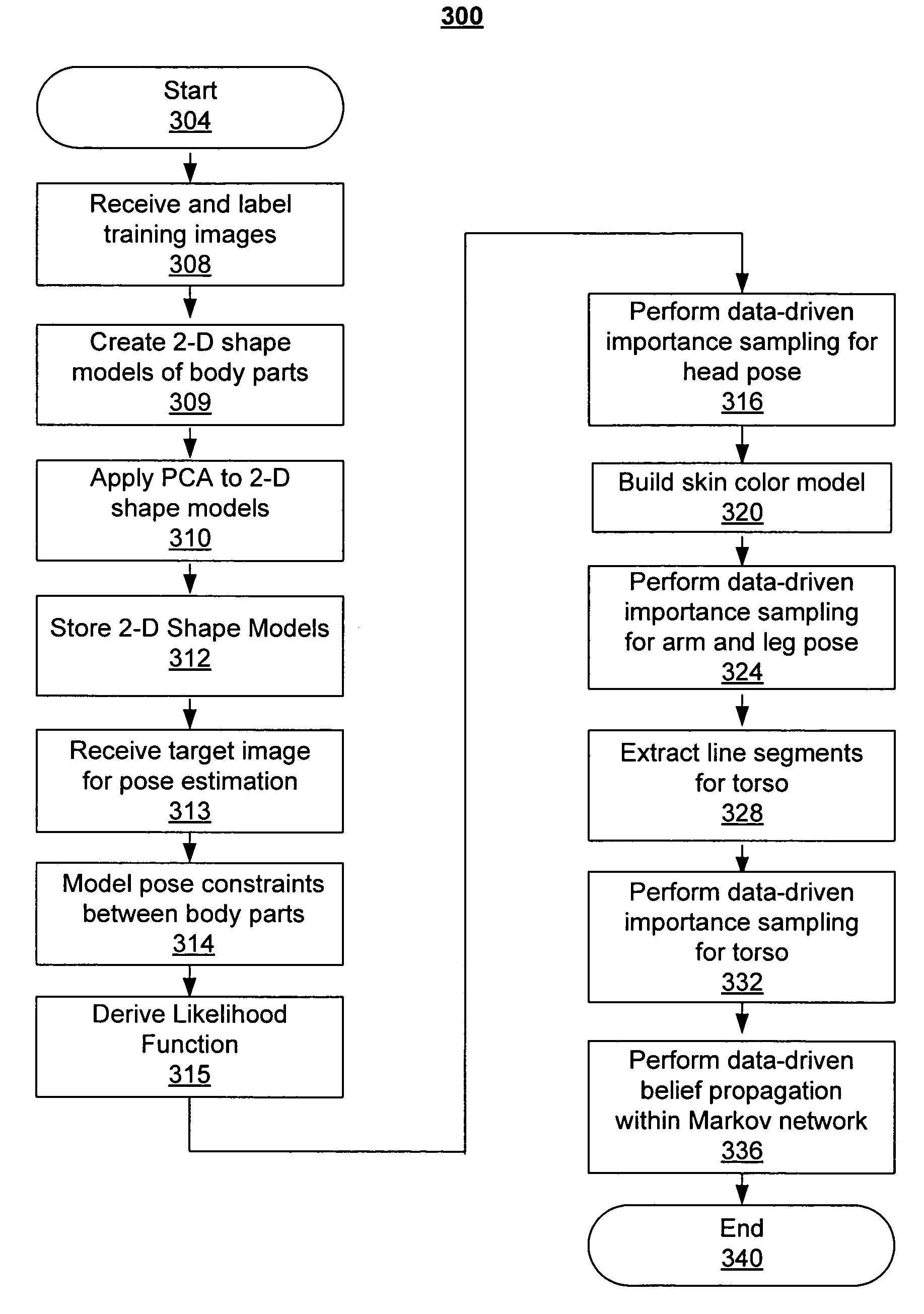
Human pose estimation with data driven belief propagation
A statistical formulation estimates two-dimensional human pose from single images. This is based on a Markov network and on inferring pose parameters from cues such as appearance, shape, edge, and color. A data-driven belief propagation Monte Carlo algorithm performs efficient Bayesian inferencing within a rigorous statistical framework. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the method in estimating human pose from single images.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
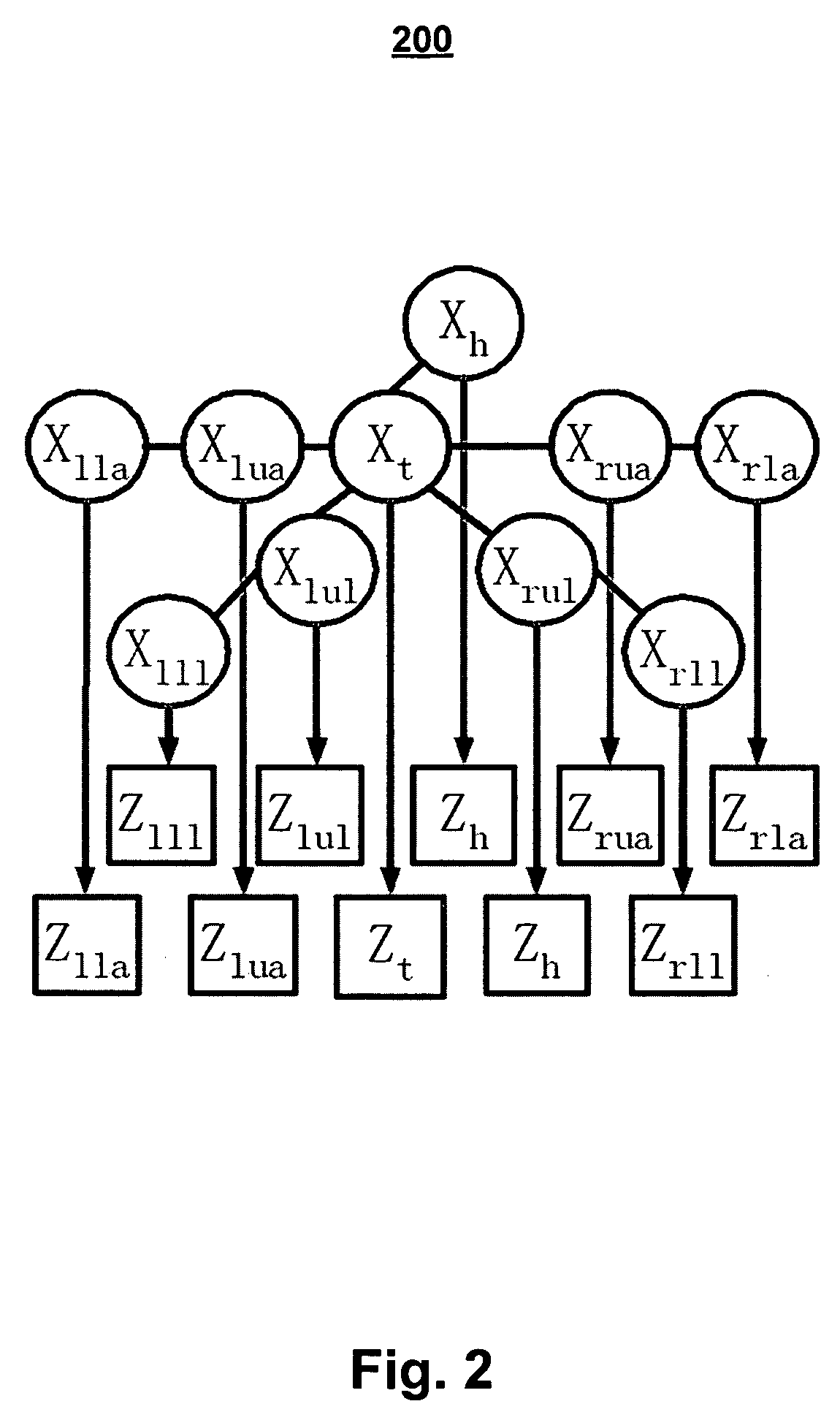
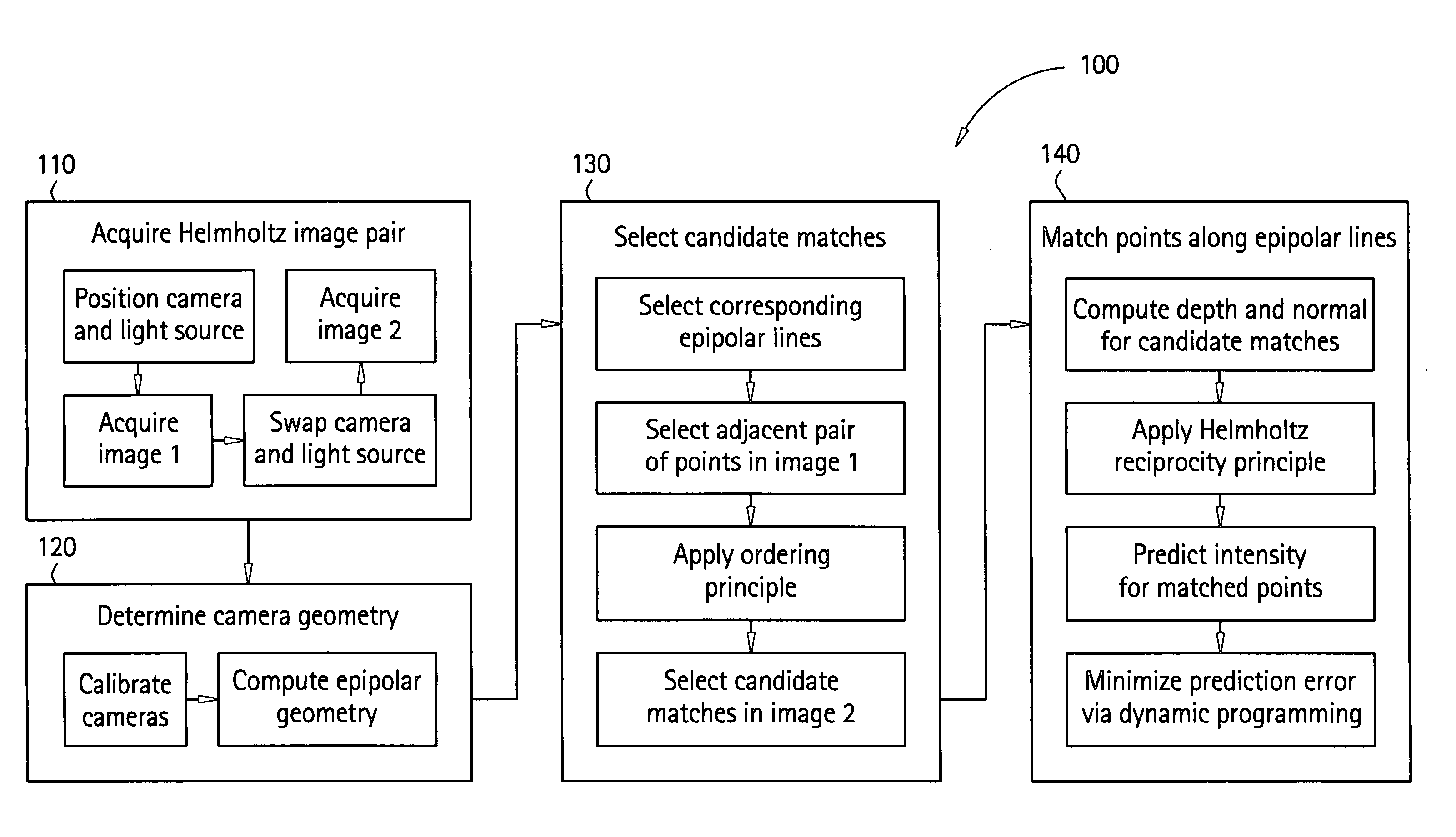
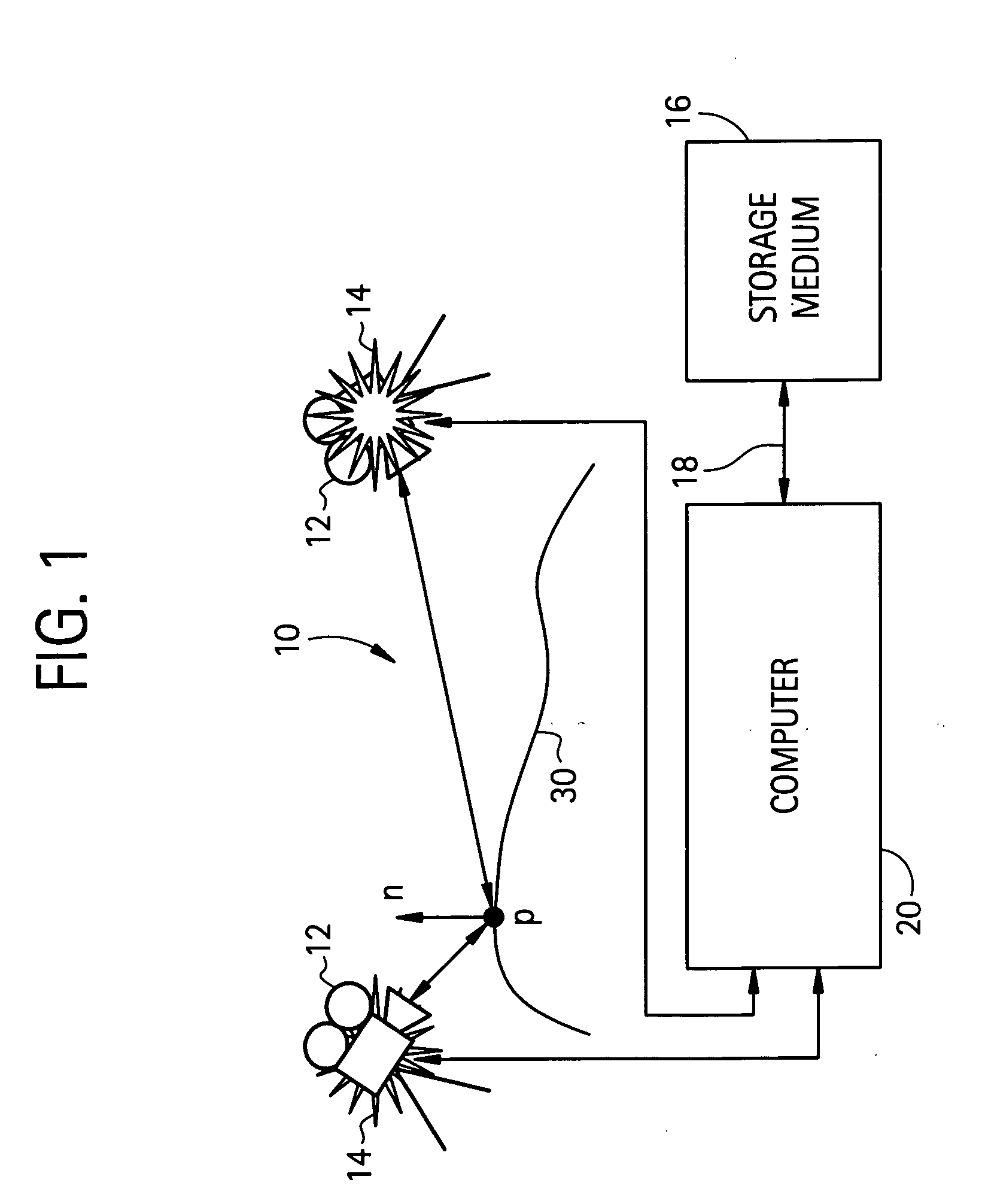
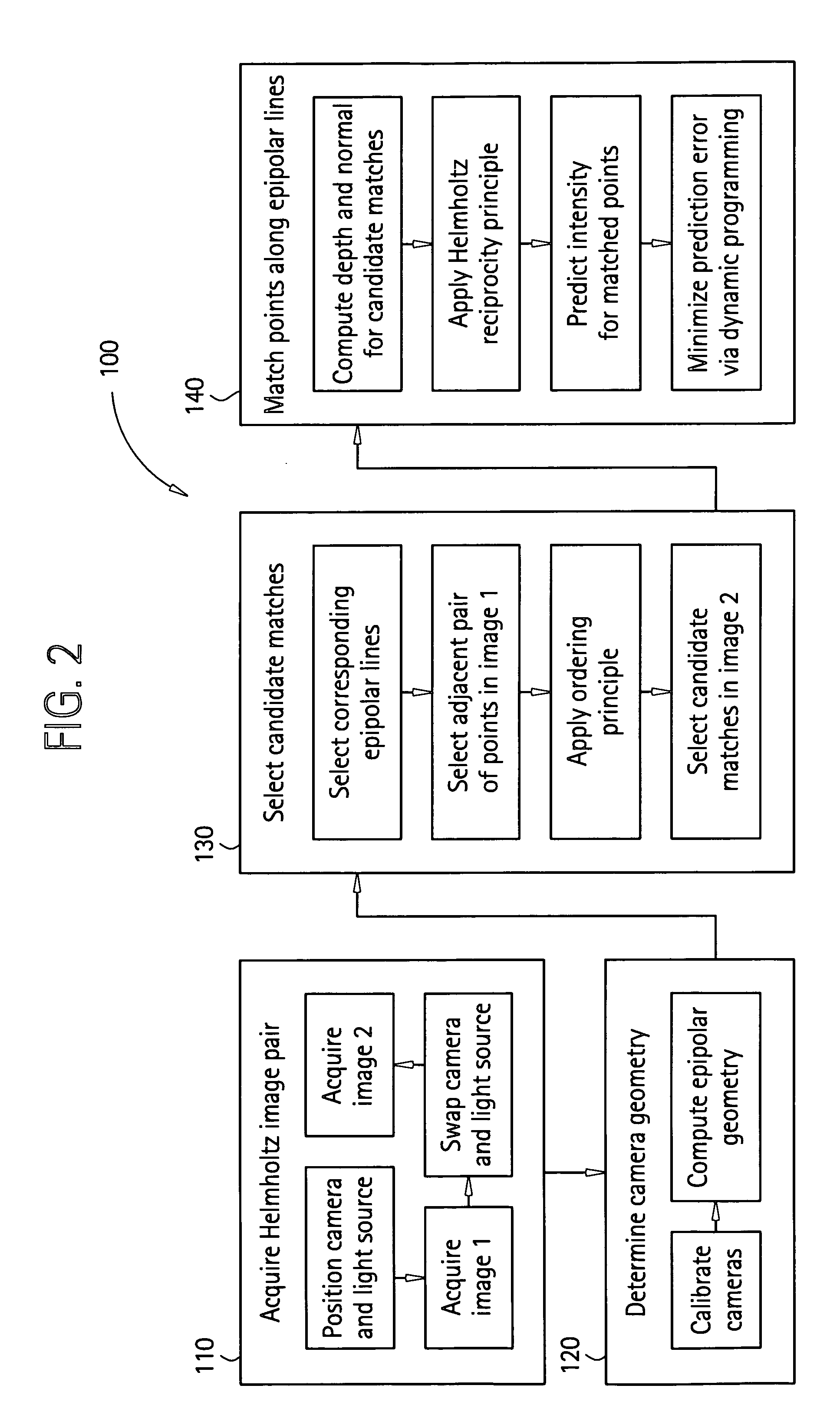
Surface reconstruction and registration with a Helmholtz reciprocal image pair
InactiveUS20050074162A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImage estimationMethod of images
A method of image reconstruction comprising: obtaining a Helmholtz reciprocal pair of images of an object, the images comprising a first image and a corresponding reciprocal image; determining an imaging geometry associated with the obtaining; selecting a plurality of points in the first image and identifying corresponding candidate points in the corresponding reciprocal image; matching a selected point of the plurality of points and a candidate point of the corresponding candidate points. A method of image registration with an object comprising: obtaining a Helmholtz reciprocal pair of images of an object, the Helmholtz reciprocal pair of images comprising a first image and a corresponding reciprocal image; estimating a pose for the object; predicting an estimated image corresponding to the pose and one image of the reciprocal pair of images; comparing the estimated image with a corresponding actual image from the pair of images; and refining the estimating a pose based on the comparing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
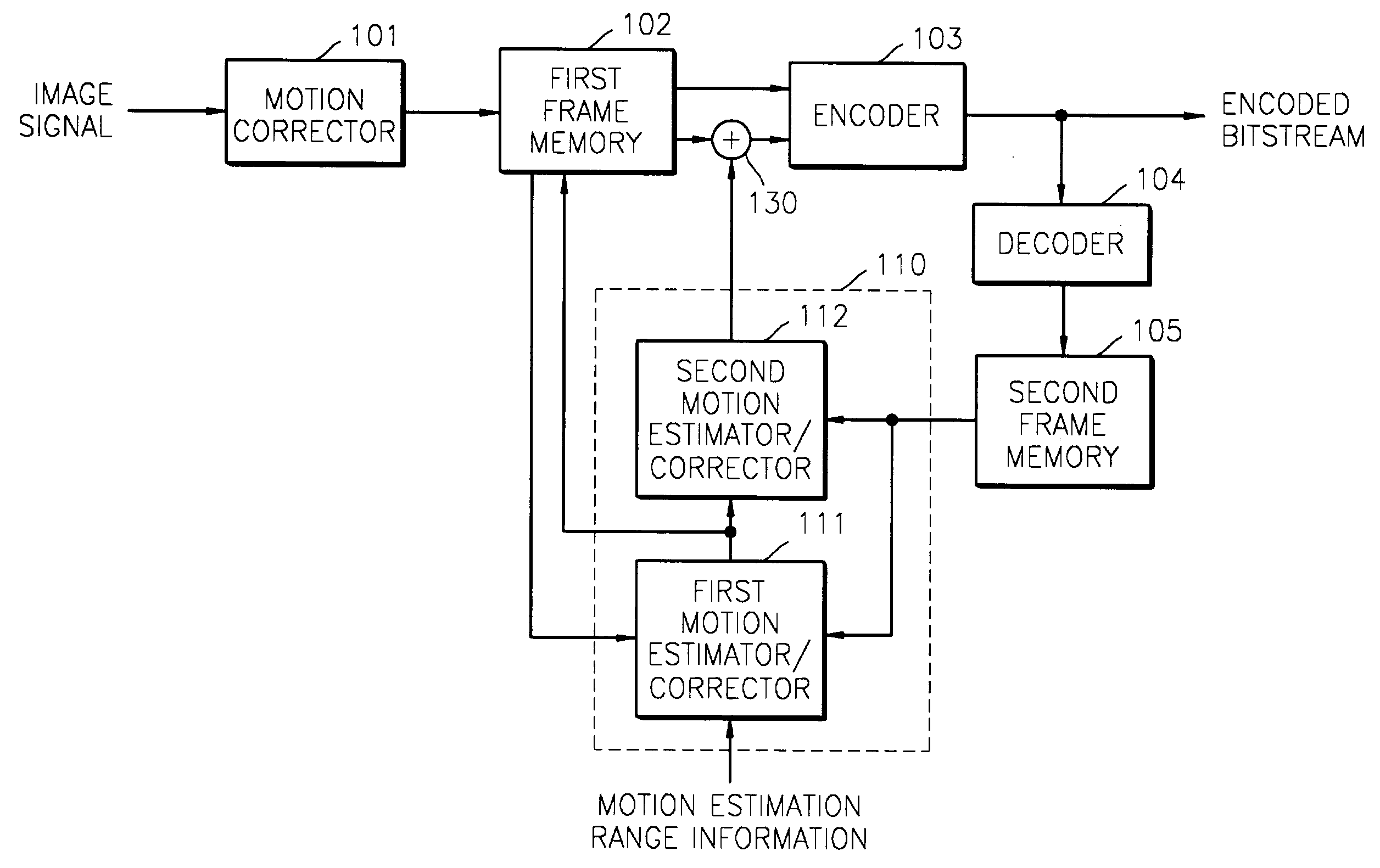
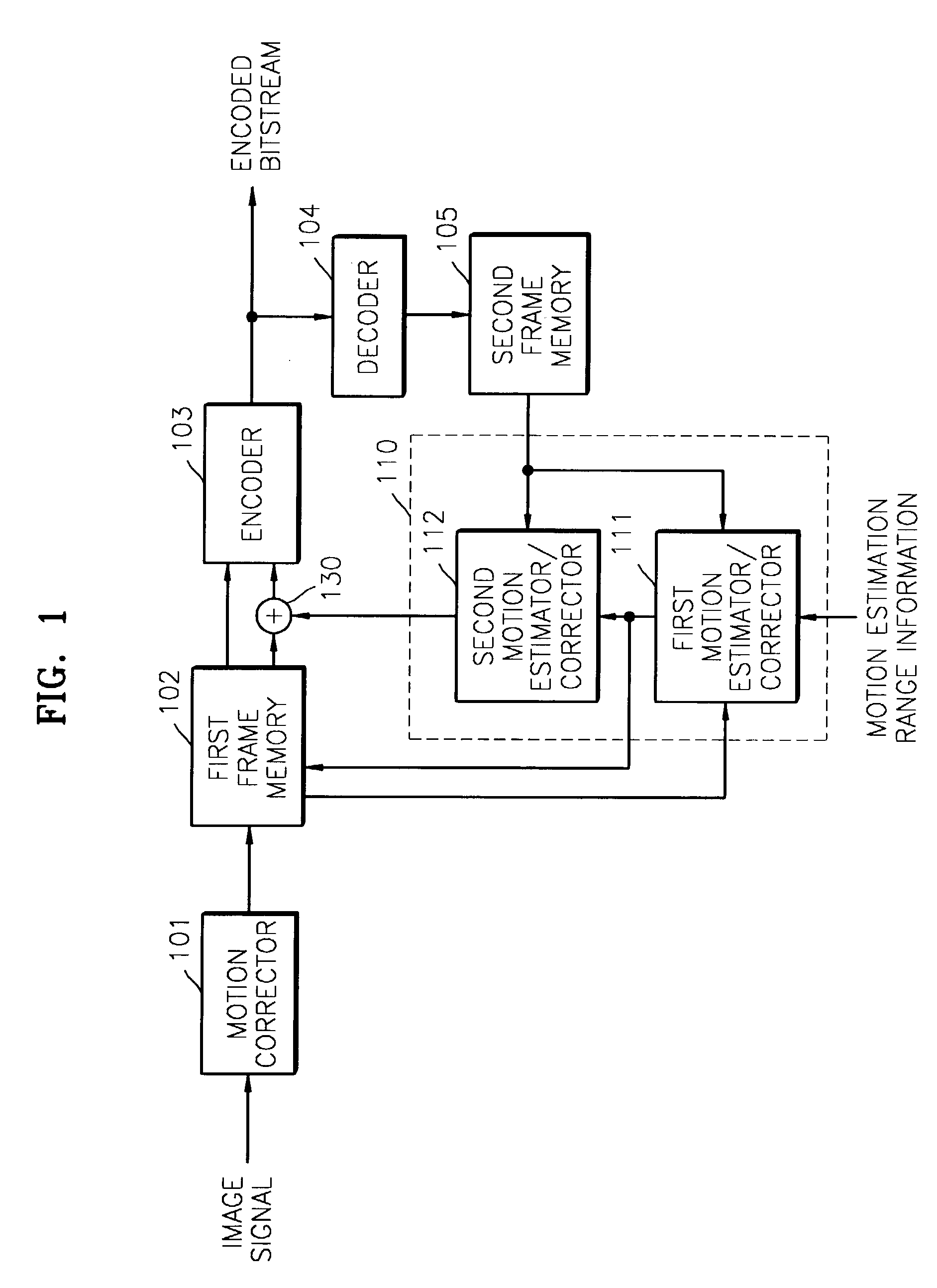
Apparatus and method for correcting motion of image
InactiveUS7171052B2Improve efficiencyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingImage estimation
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
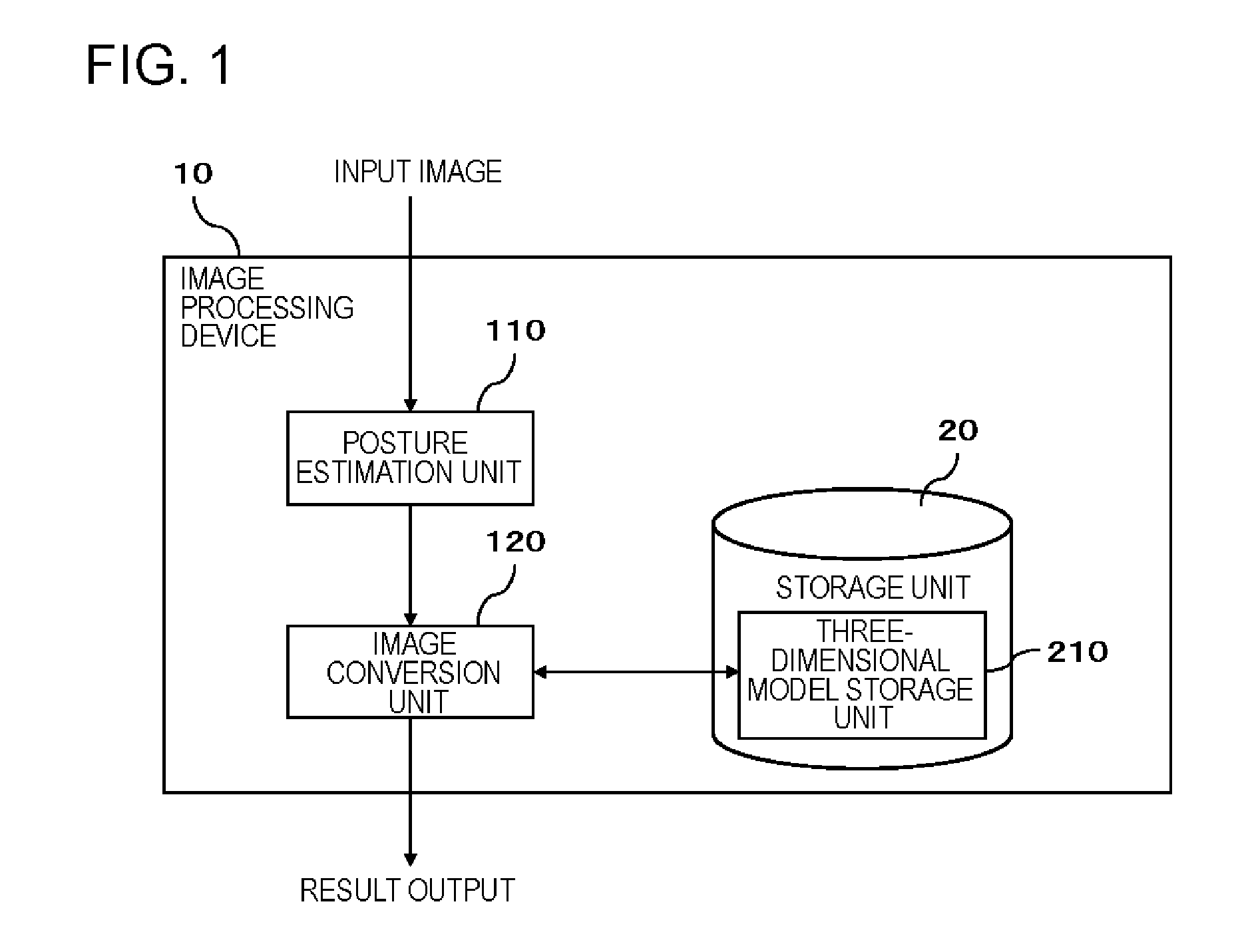
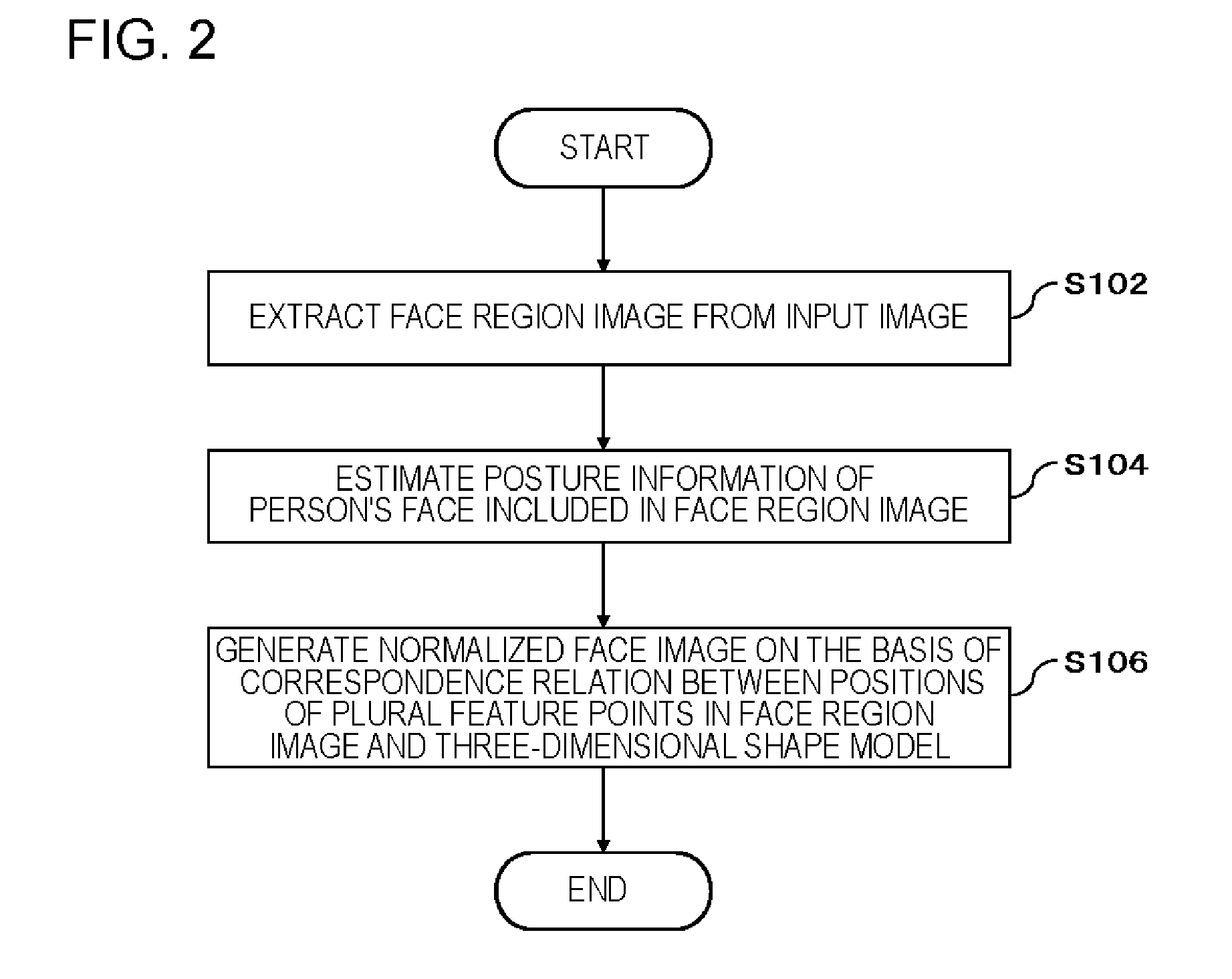
Image processing device, image processing method, and program
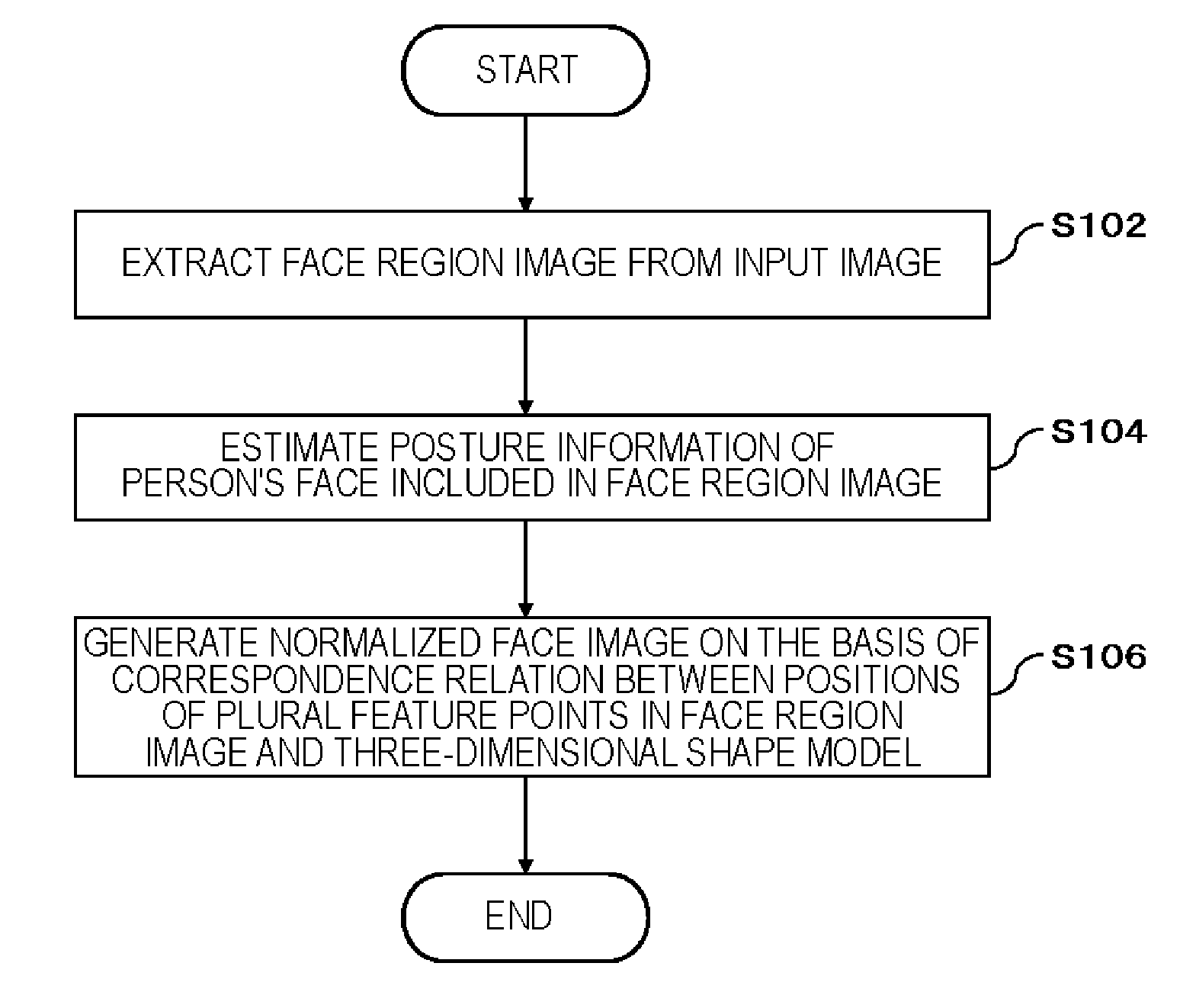
ActiveUS20160217318A1Generate accuratelyGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingImage estimation
An image processing device (10) includes a posture estimation unit (110) that estimates posture information including a yaw angle and a pitch angle of a person's face from an input image including the person's face, and an image conversion unit (120) that generates a normalized face image in which an orientation of a face is corrected, on the basis of positions of a plurality of feature points in a face region image which is a region including the person's face in the input image, positions of the plurality of feature points in a three-dimensional shape model of a person's face, and the posture information.
Owner:NEC CORP
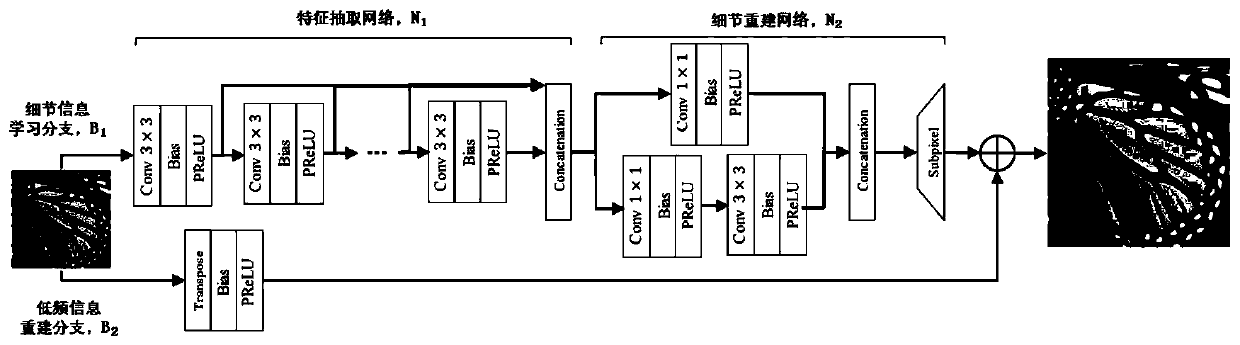
A fast image super-resolution reconstruction method based on deep learning
InactiveCN109767386ALessen the training loadGood edge informationGeometric image transformationImage estimationReconstruction method
The invention relates to a fast image super-resolution reconstruction method based on deep learning, and belongs to the field of image processing. The method comprises the following steps of selectingan image training set and a test set, and performing feature extraction, nested network feature refinement and sub-pixel up-sampling operation on a low-resolution image by using a deep neural networkto obtain high-resolution detail residual information of the image; carrying out transposition convolution processing on the low-resolution image to obtain high-resolution space low-frequency featureinformation of the image; combining the high-resolution detail residual information of the image with the high-resolution space low-frequency characteristic information to obtain a high-resolution reconstruction result of image estimation; performing loss value measurement on the high-resolution reconstruction result of the image estimation and the high-resolution image block; updating the network weight by using an Adam operator to obtain a trained network model; and inputting a low-resolution image into the trained network model to obtain a high-resolution reconstructed image. According tothe method, the super-resolution reconstruction of the image is accelerated, and a good reconstruction effect is kept.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
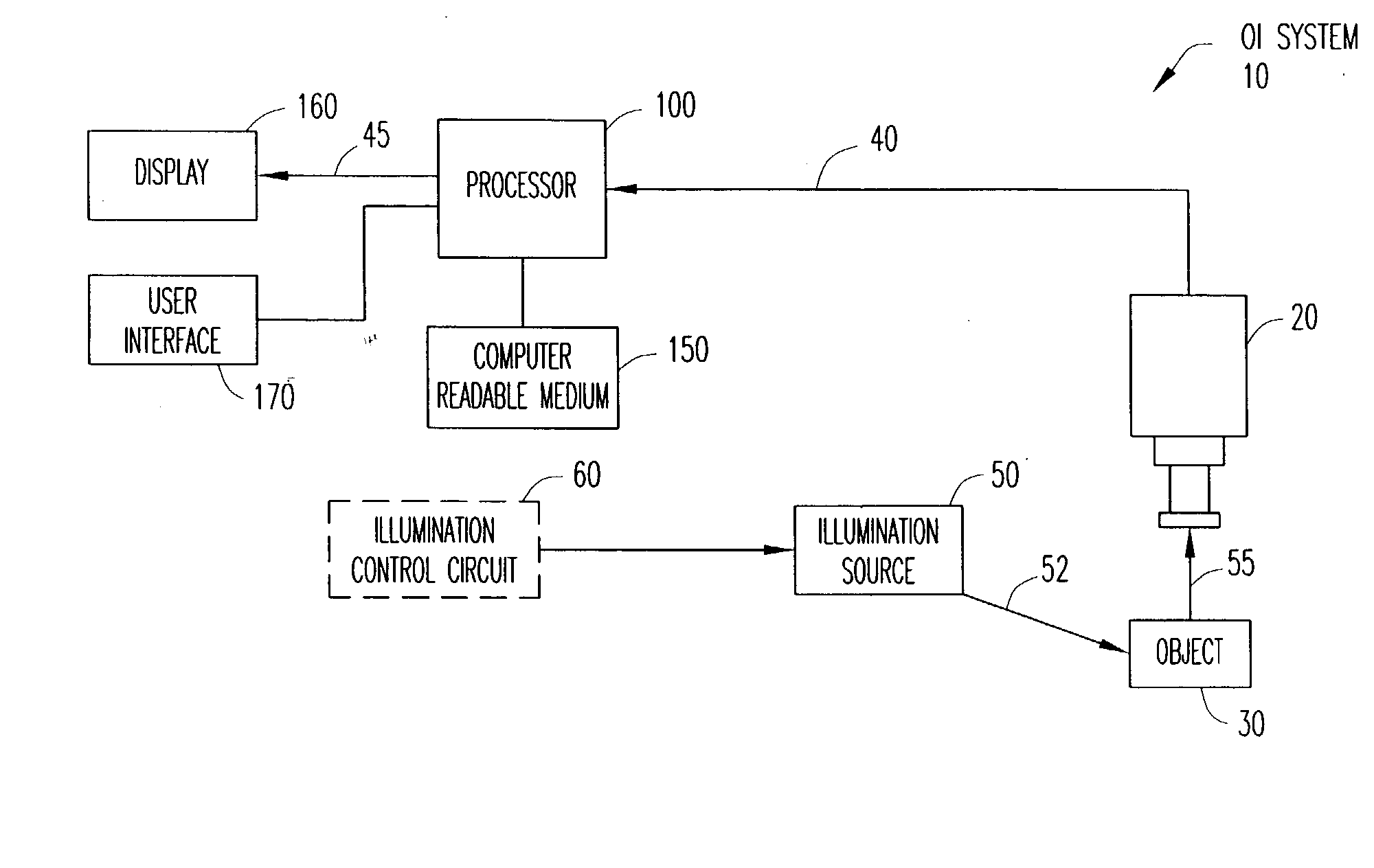
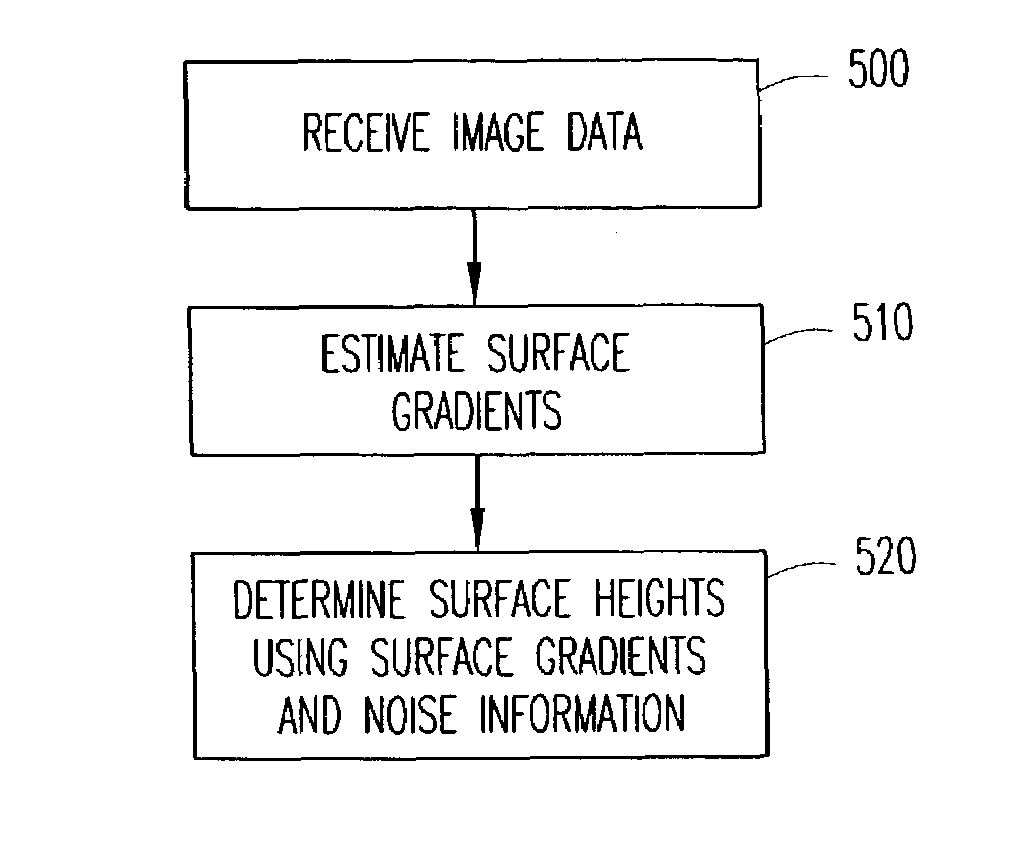
System and method for shape reconstruction from optical images
Reconstructing the shape of the surface of an object in greater than two dimensions is performed using a noise-tolerant reconstruction process and / or a multi-resolution reconstruction process. The noise-tolerant reconstruction process can be a Bayesian reconstruction process that adds noise information representing the noise distribution in optical image(s) of the object to surface gradient information estimated from the images to determine surface height information that defines the shape of the surface of the object in greater than two dimensions. In the multi-resolution reconstruction process, for each resolution of the image, the surface gradient information is estimated and the surface height information is calculated using the estimated surface gradient information. To obtain the final surface height map, the surface height information from each resolution is combined to reconstruct the shape of the surface of the object in greater than two dimensions. The multi-resolution reconstruction process can be used with the Bayesian reconstruction process or with another decomposition process, such as a wavelet decomposition process.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
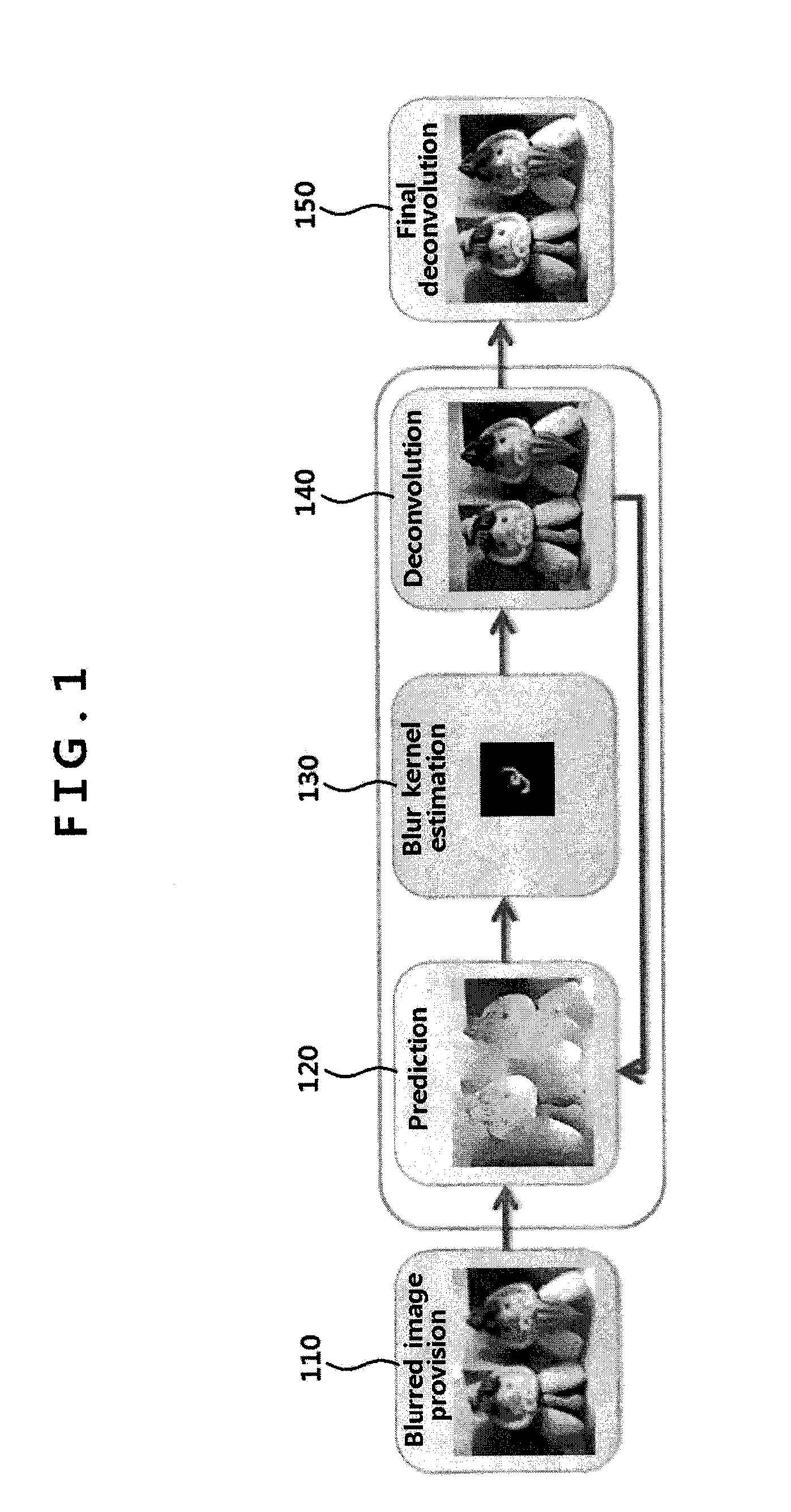
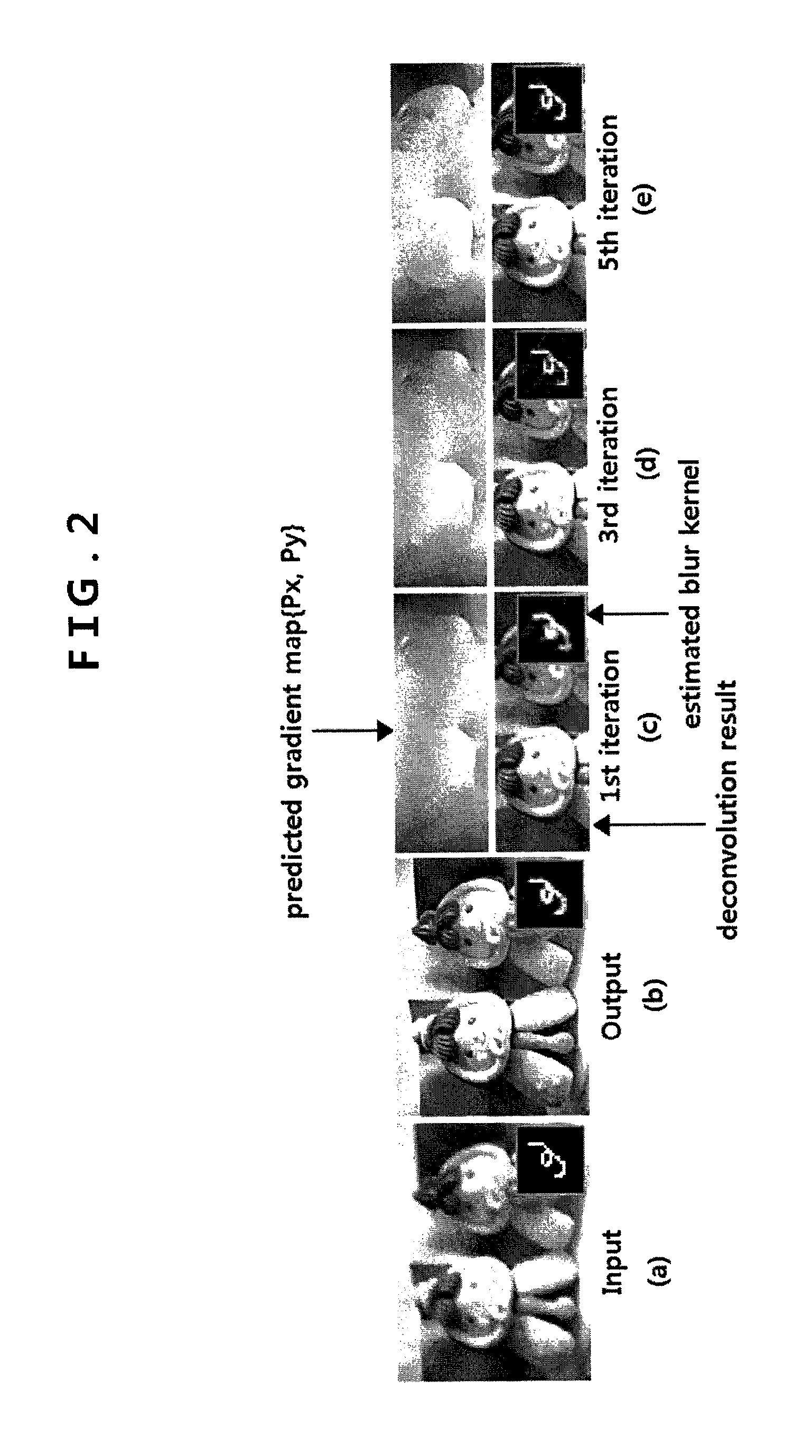
Methods of deblurring image and recording mediums having the same recorded thereon
ActiveUS20100166332A1Easily and rapidly deblurredImprove image qualityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage estimationRecording media
A method of deblurring an image by which blur can be easily and rapidly eliminated from one image and the quality of the image can be improved is provided. The method includes receiving a blurred image, an image estimation step of estimating a non-blurred image from the blurred image, a blur information estimation step of estimating blur information from the blurred image and the estimated non-blurred image, and a deblurring step of deblurring the blurred image based on the blurred image and the estimated blur information, wherein the image estimation step and the blur information estimation step are iteratively performed. Thus, blur can be rapidly and effectively eliminated from one image, thereby improving the quality of an image.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
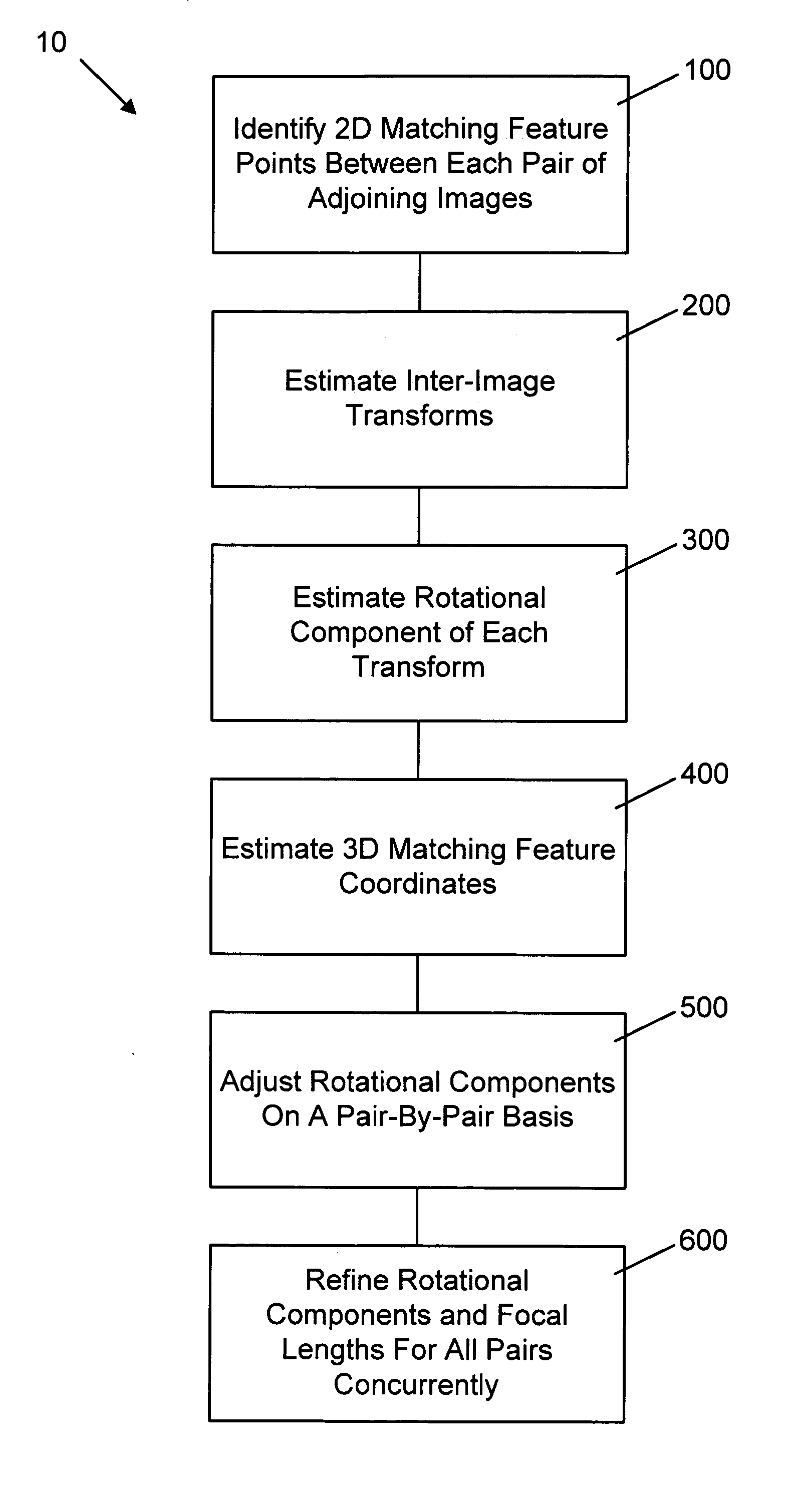
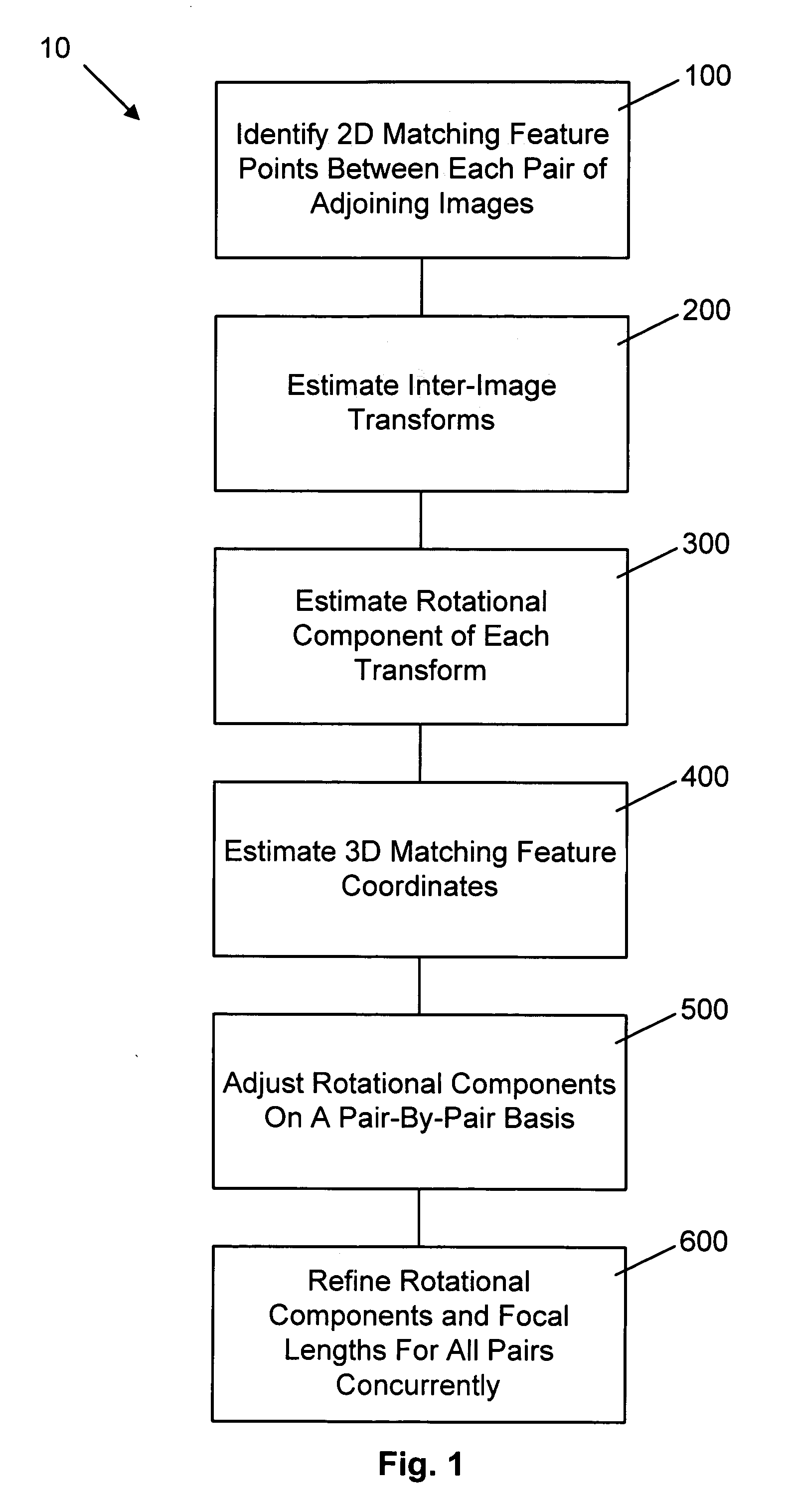
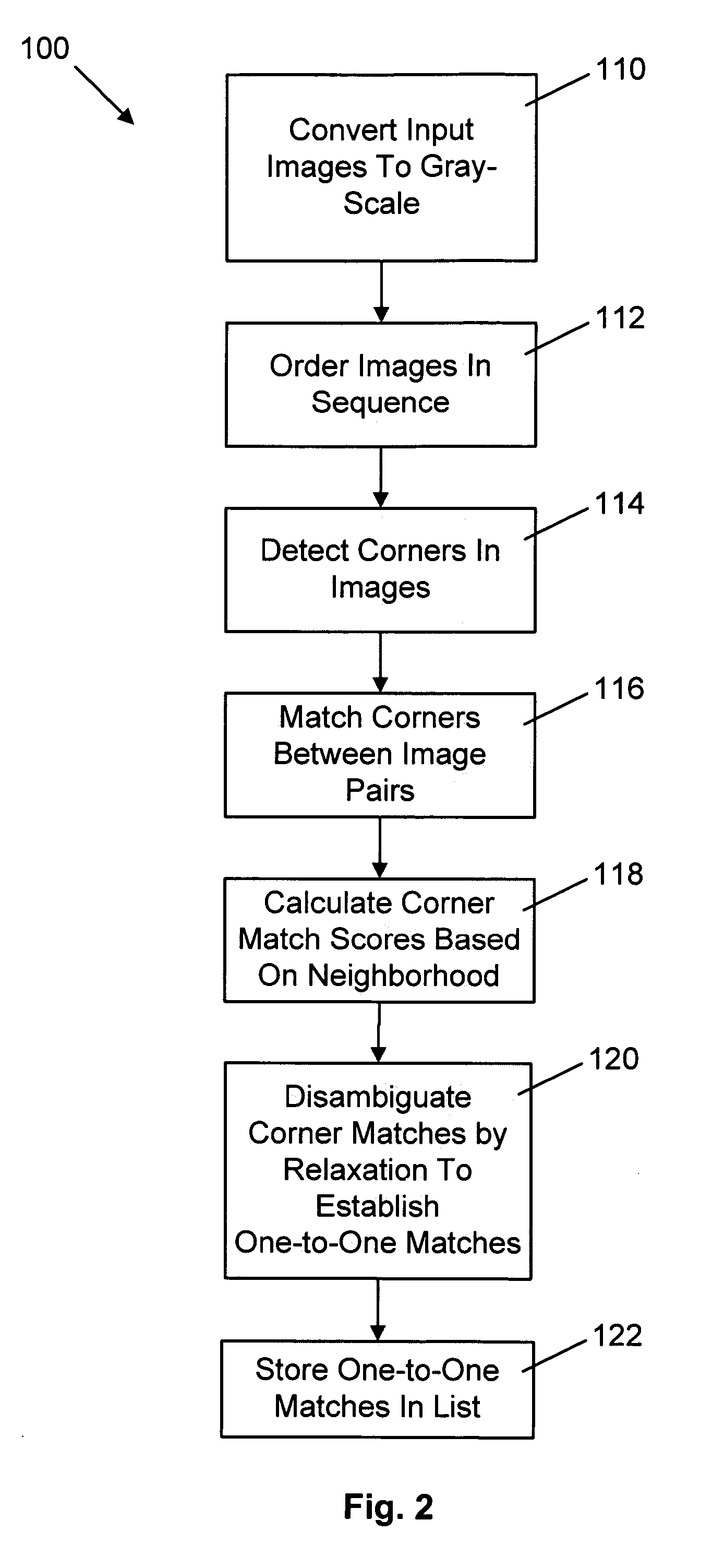
Method for determining camera position from two-dimensional images that form a panorama
InactiveUS7565029B2Reduce errorsReduce the differenceImage enhancementImage analysisImage estimationThree-dimensional space
A method of estimating three-dimensional camera position information from a series of two-dimensional images that form a panorama employs common features in adjoining image pairs in the series to estimate a transform between the images in the pairs. The common features are subsequently employed to adjust an estimated rotational component of each transform by reducing error between coordinates corresponding to the common features in three-dimensional space in image pairs, on a pair-by-pair basis. A global optimization of the position estimation, used for long sequences of images such as 360 degree panoramas, refines the estimates of the rotational and focal length components of the transforms by concurrently reducing error between all 3D common feature coordinates for all adjoining pairs.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
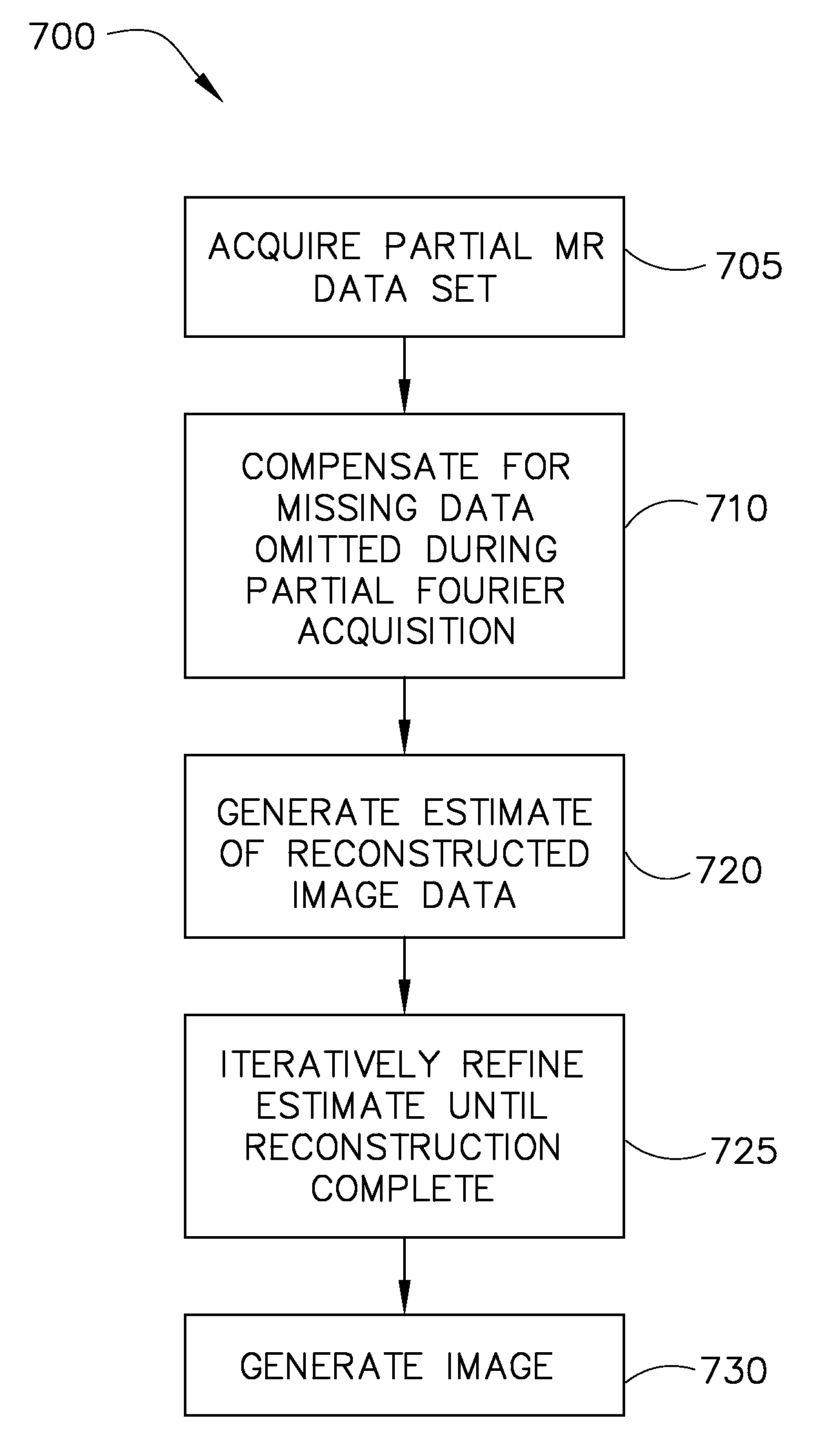
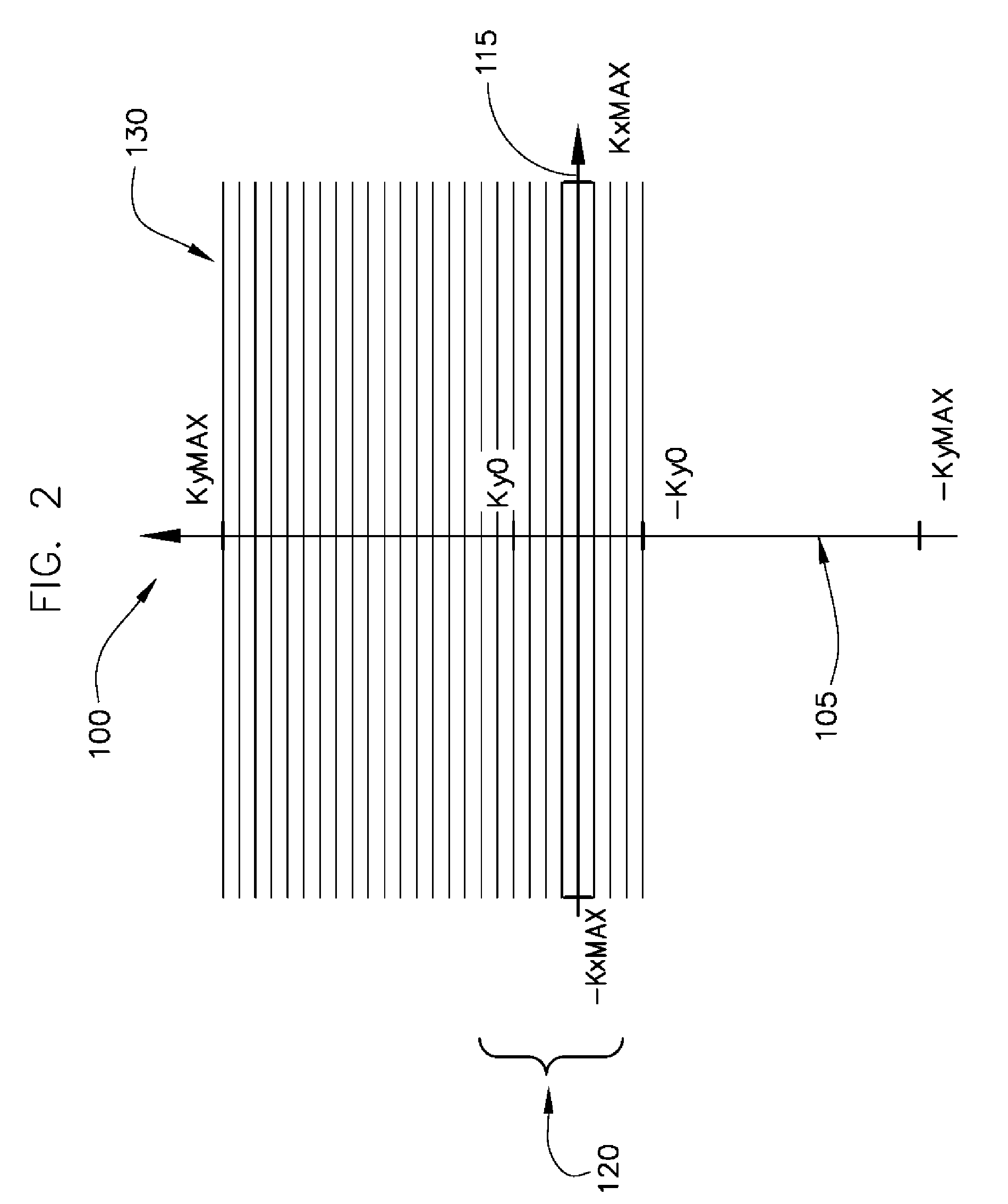
System and method for reducing MR scan time using partial fourier acquisition and compressed sensing
A system and method for reducing the scan time of an MR imaging system using a data acquisition technique that combines partial Fourier acquisition and compressed sensing includes a computer programmed to acquire a partial MR data set in k-space along a phase encoding direction, the data set having missing data in the phase encoding direction due to the omission of phase encoding steps. The computer is further programmed to generate an estimate of a reconstructed image, compensate the partial MR data set for the missing data, and reconstruct an MR image by iteratively minimizing the total squared difference between the k-space data of the estimate of the reconstructed image and the measured k-space data of the compensated partial MR data set.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for shape reconstruction from optical images
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
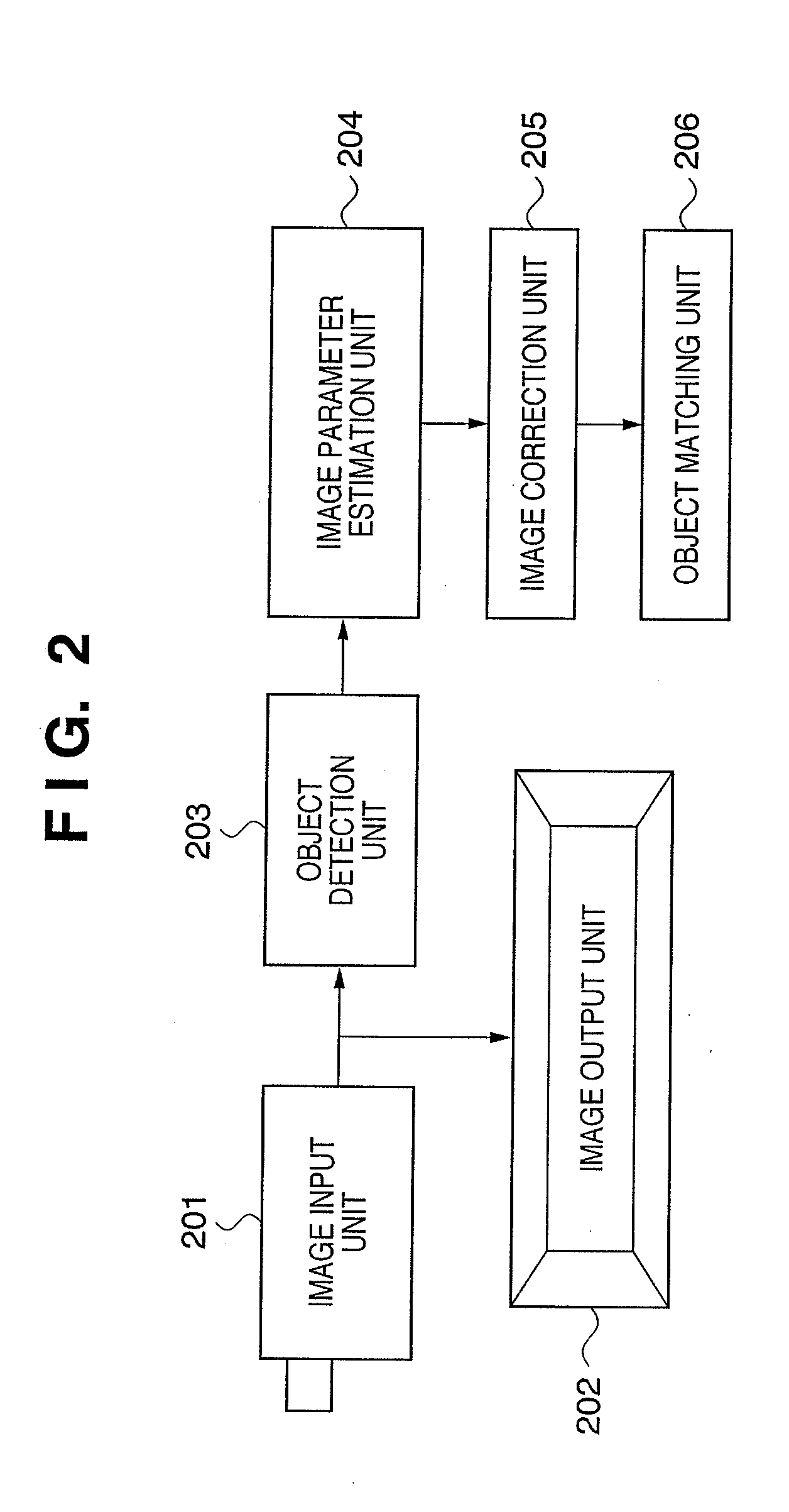
Image matching apparatus, image matching method, computer program and computer-readable storage medium
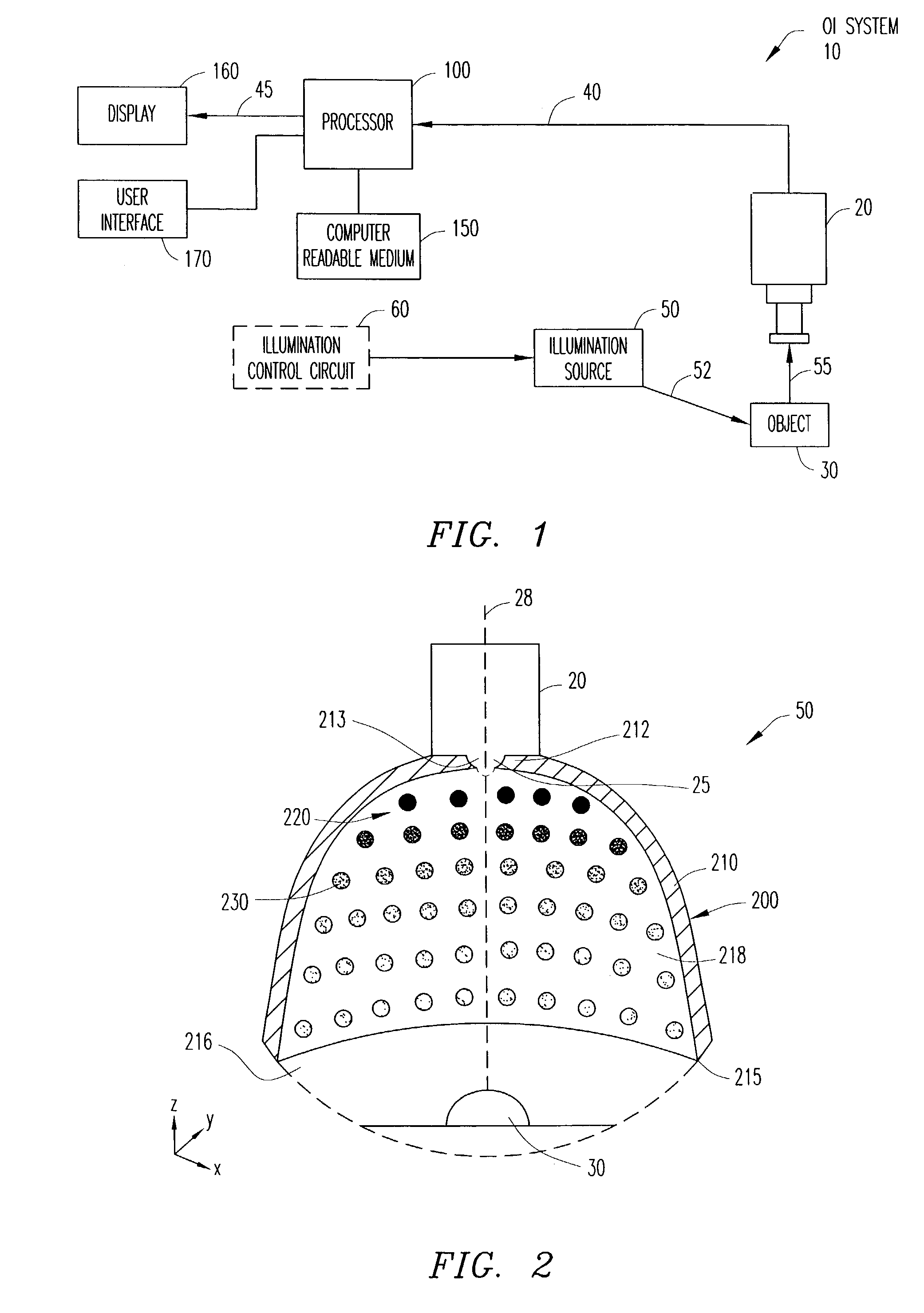
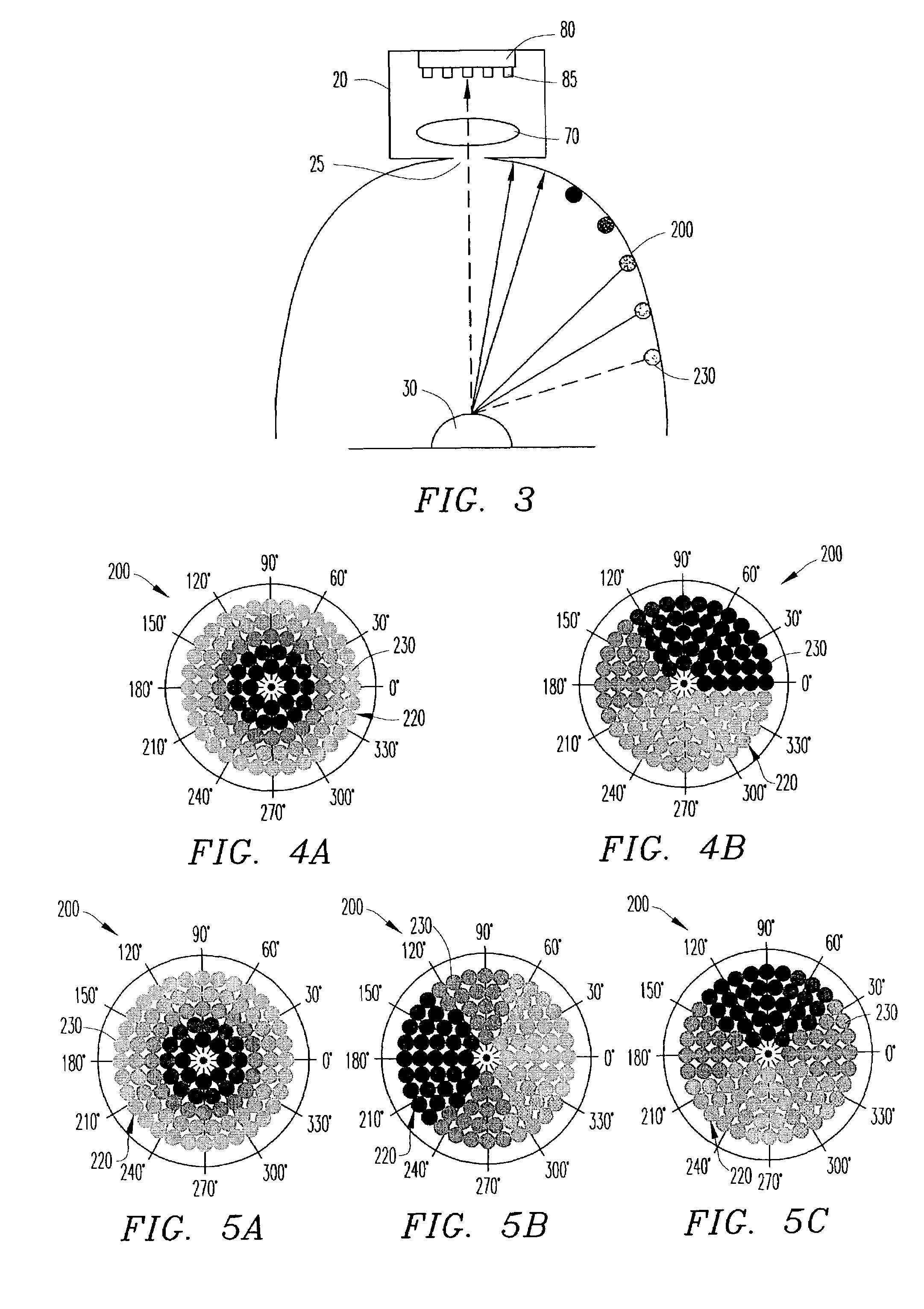
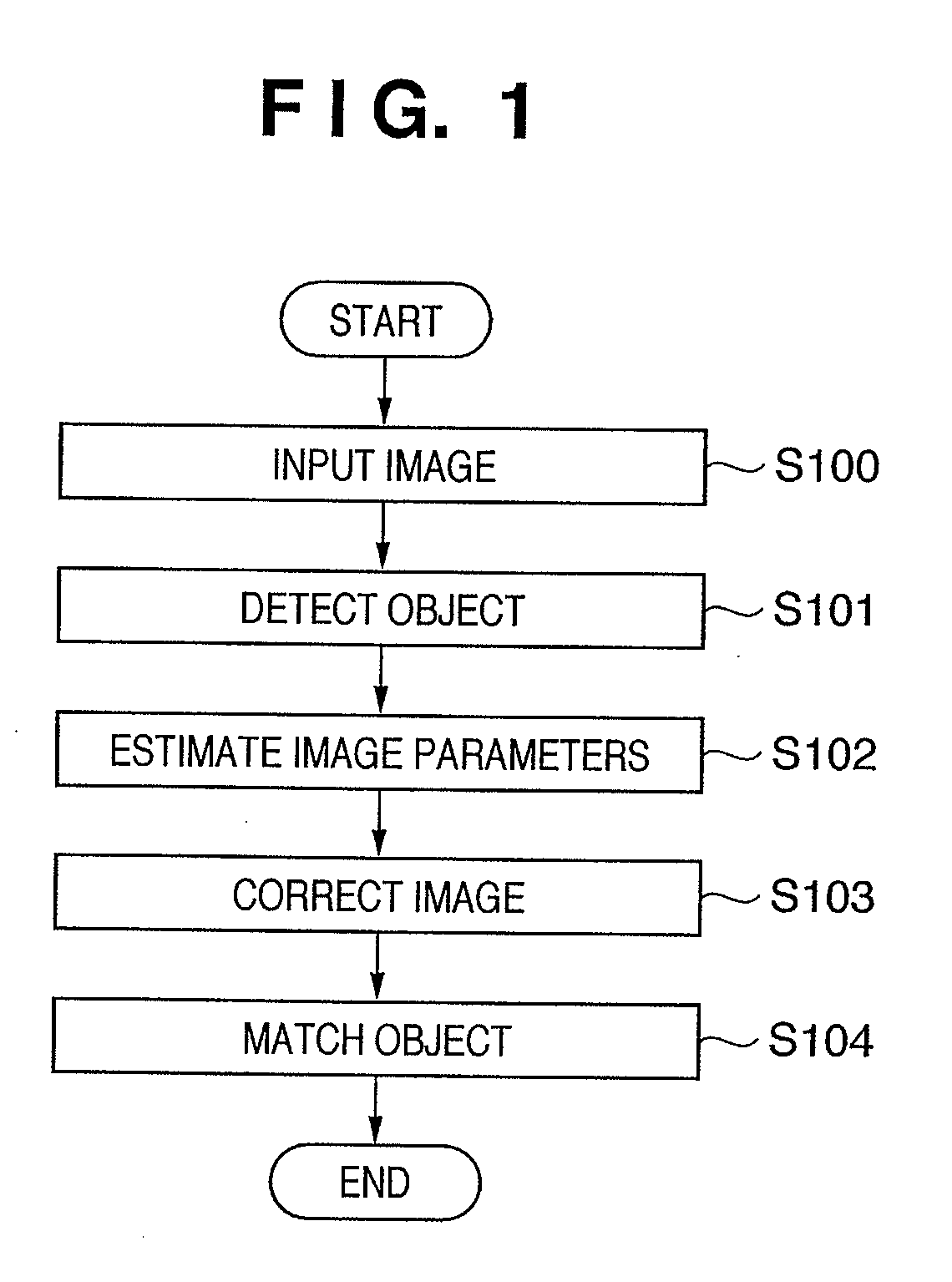
An image matching apparatus comprising, a detector adapted to detects, from an input image containing an object to be matched, a region where the object exists, an estimation unit adapted to estimates a parameter regarding a displaying characteristic based on an image of the region, a correction unit adapted to corrects the displaying characteristic of the input image based on the parameter, and a matching unit adapted to matches the corrected input image containing the object to be matched with an image containing a matching object.
Owner:CANON KK
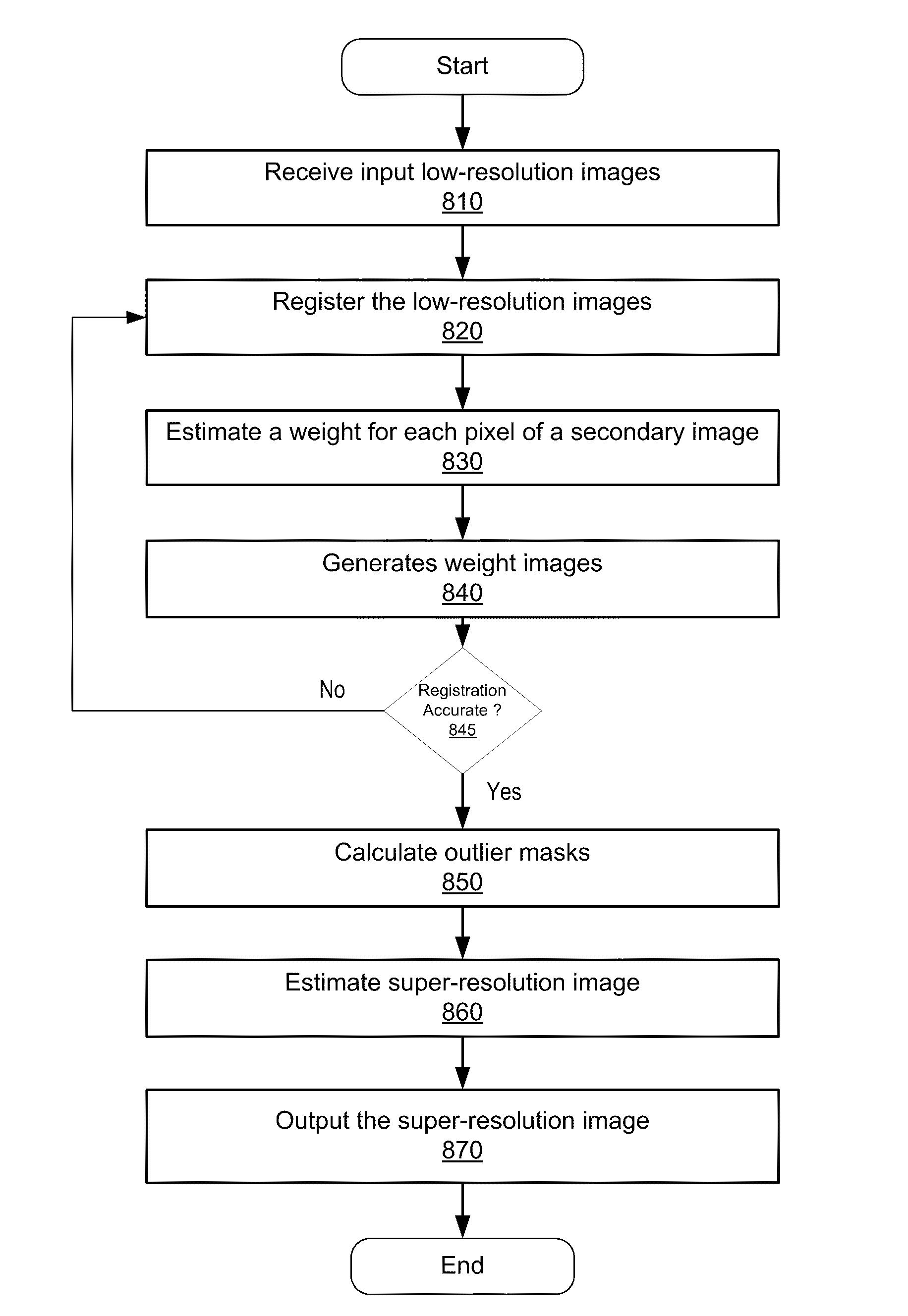
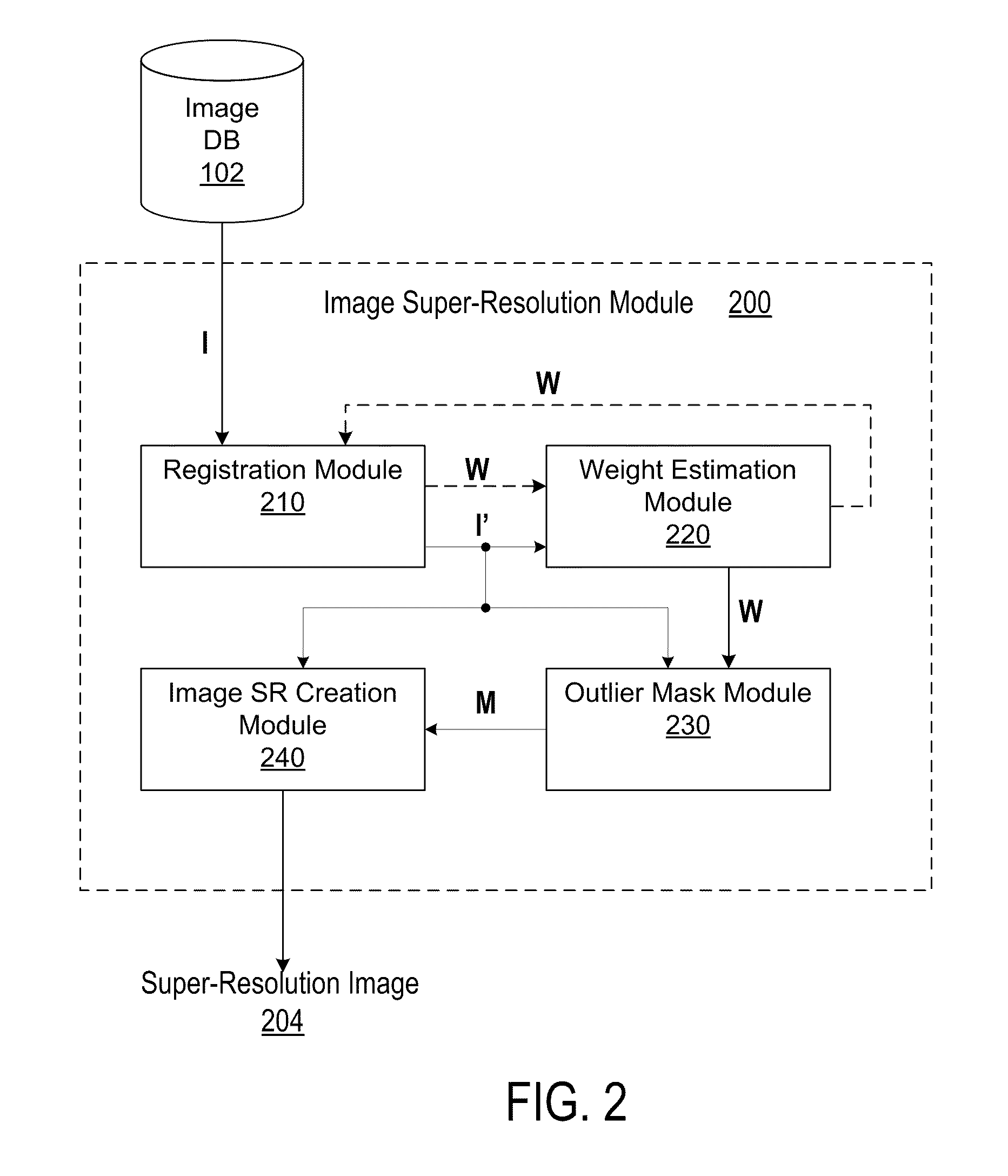
Enhanced image and video super-resolution processing
ActiveUS20110037894A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImage resolutionImage estimation
A system and method generates super-resolution images and videos using motion-compensated low-resolution images and videos. An image is selected as a primary image from a plurality of low-resolution images and the rest of the low-resolution images are registered as secondary images with respect to the primary image. Each registered secondary image is transformed to a motion compensated image. A mask value for a pixel in each motion compensated image is estimated. The super-resolution image of the primary image is generated by combining the mask values and the motion compensated secondary images. Similarly, a low-resolution video is segmented into a plurality of video objects, each of which is represented by an alpha layer. A super-resolution frame of the segmented video object is generated. The super-resolution frames of each segmented video object are combined using the alpha layers to create a super-resolution frame of the resulting video.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
System and method for controlling a camera based on processing an image captured by other camera
InactiveCN106030614AAcquiring/recognising eyesDigital video signal modificationFace detectionImage estimation
A device comprises a first digital camera having a first center line of sight and a second digital camera having a second center line of sight that is parallel and opposing the first camera. A method for controlling the first camera based on estimating the angular deviation between a person gaze direction and the line of sight of the first digital camera. A human face is detected in an image captured as an image file by the second digital camera, using a face detection algorithm. An angular deviation a is estimated, defined between the second center line of sight and an imaginary line from the second camera to the detected human face based on the captured image, and an angular deviation beta is estimated, defined between the imaginary line from the second camera to the detected face and the human face gaze direction based on the captured image.
Owner:史奈普辅助专利有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com