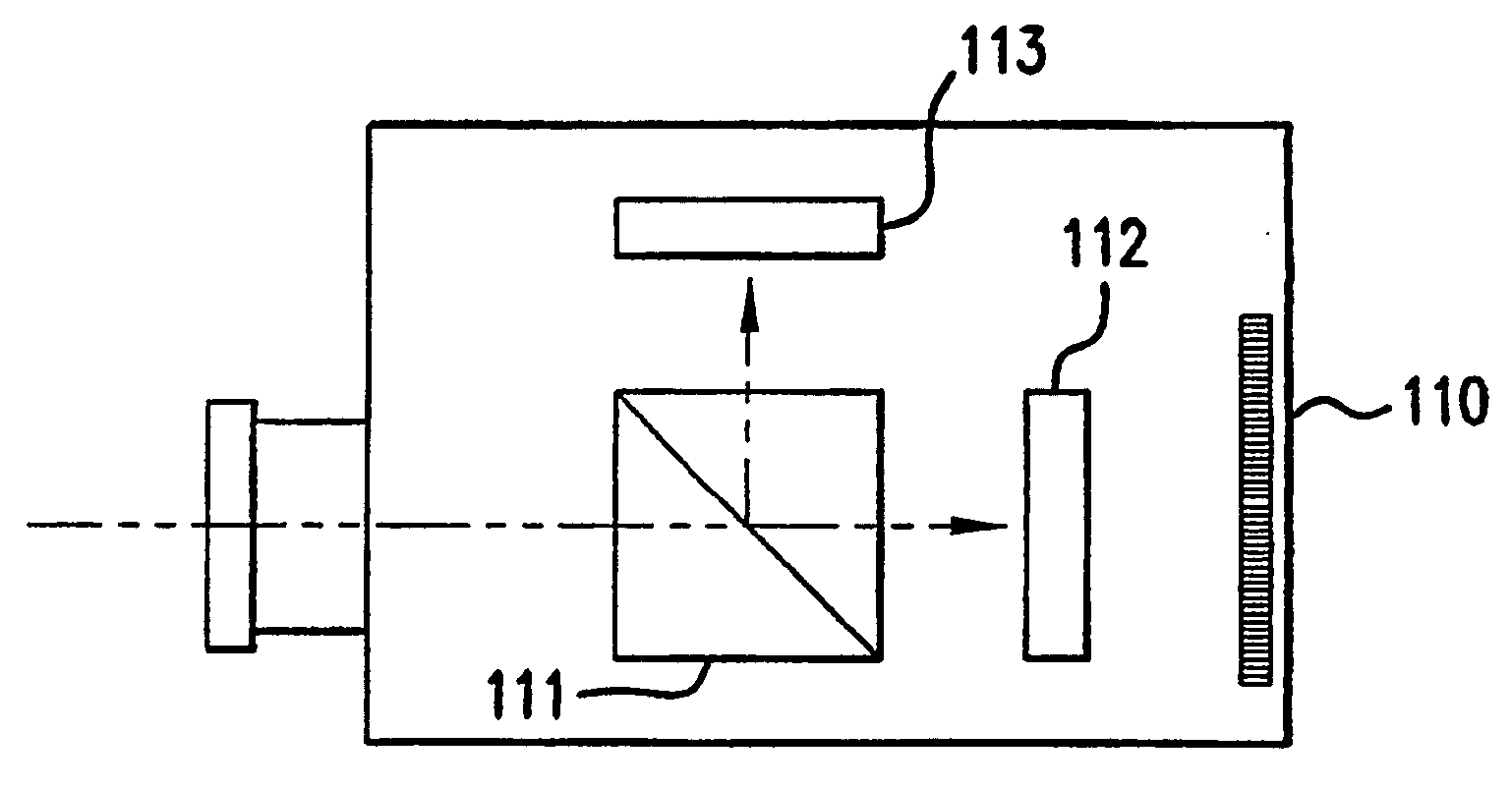
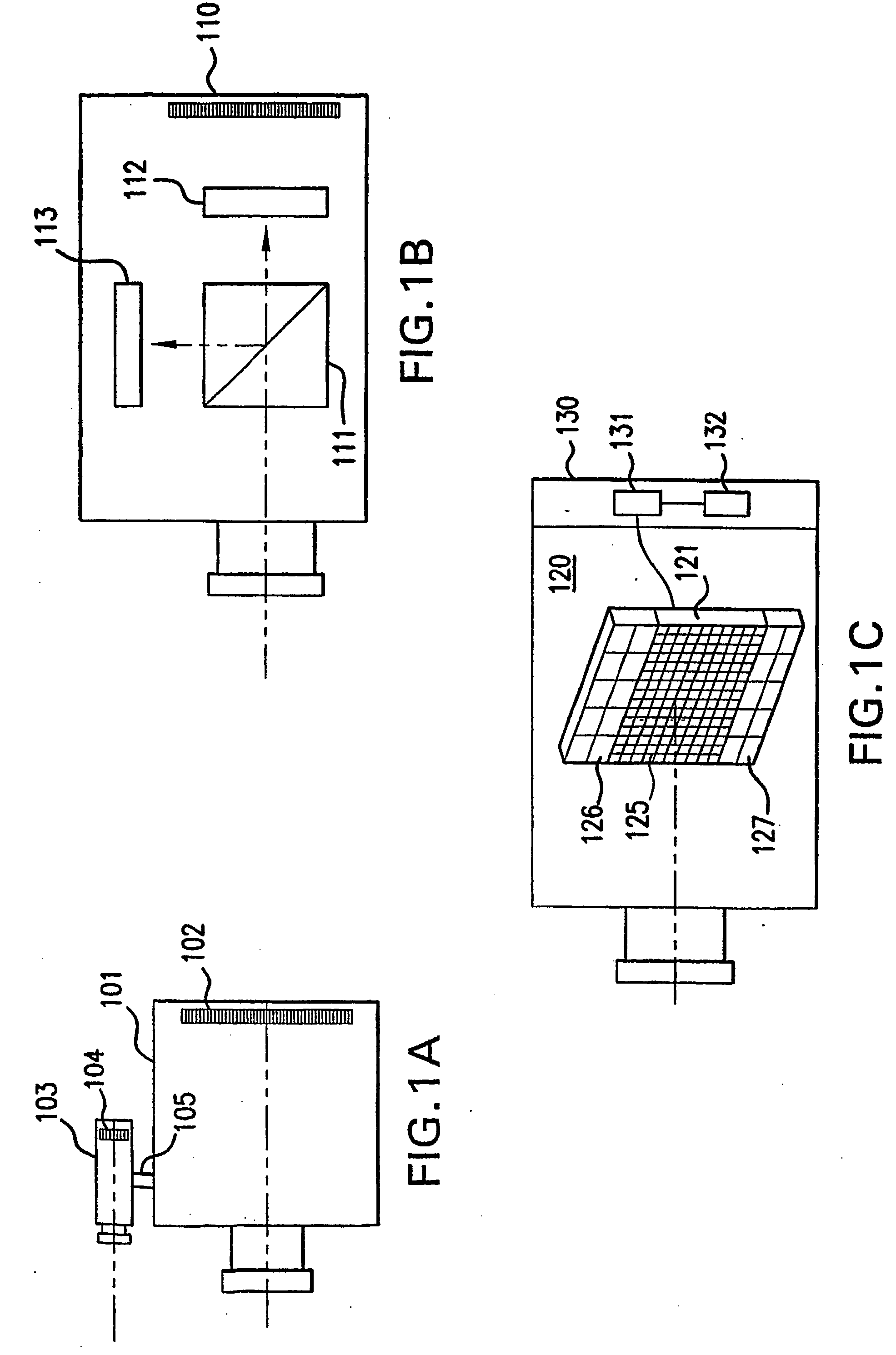
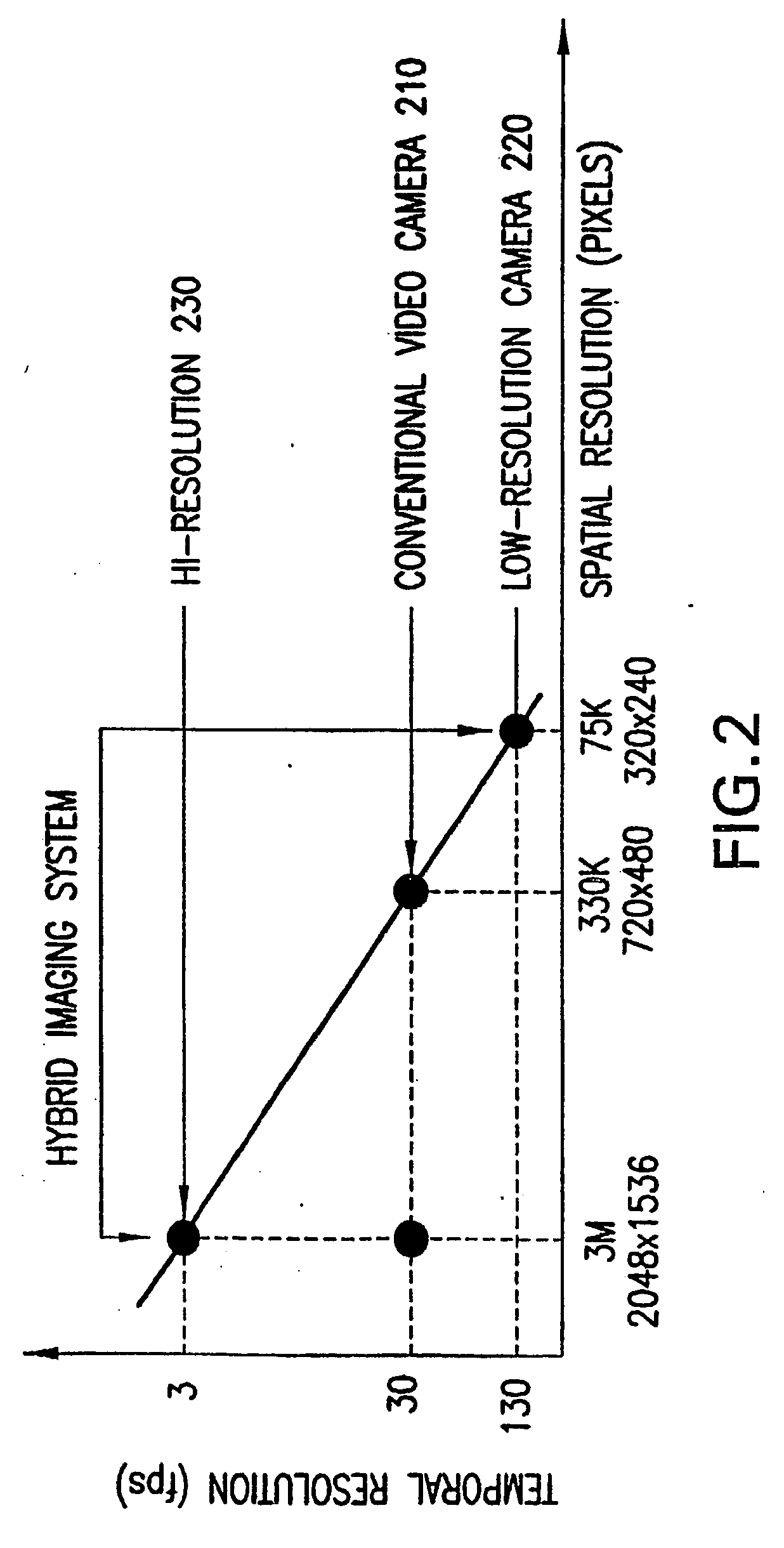
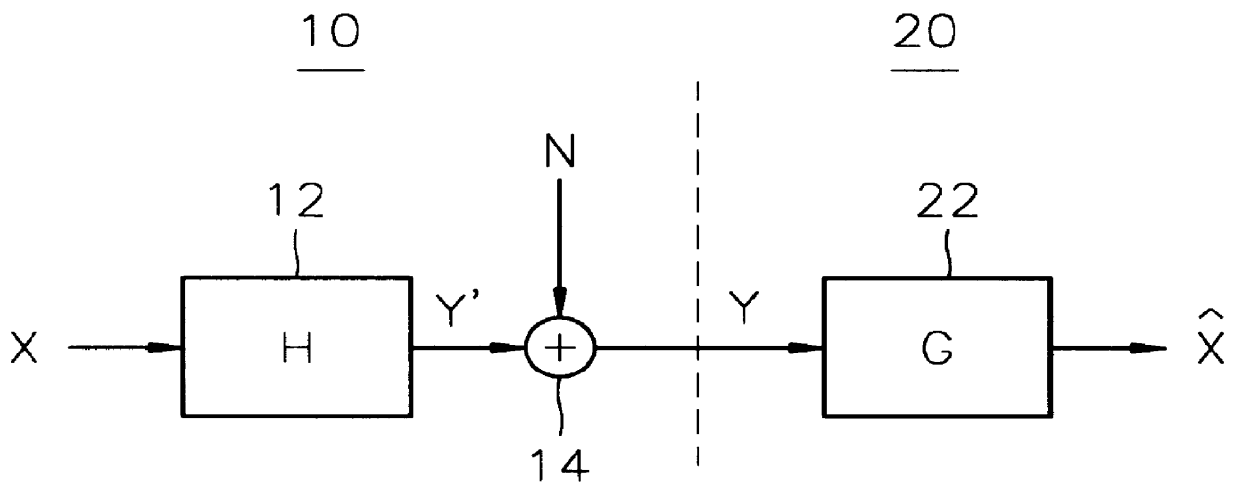
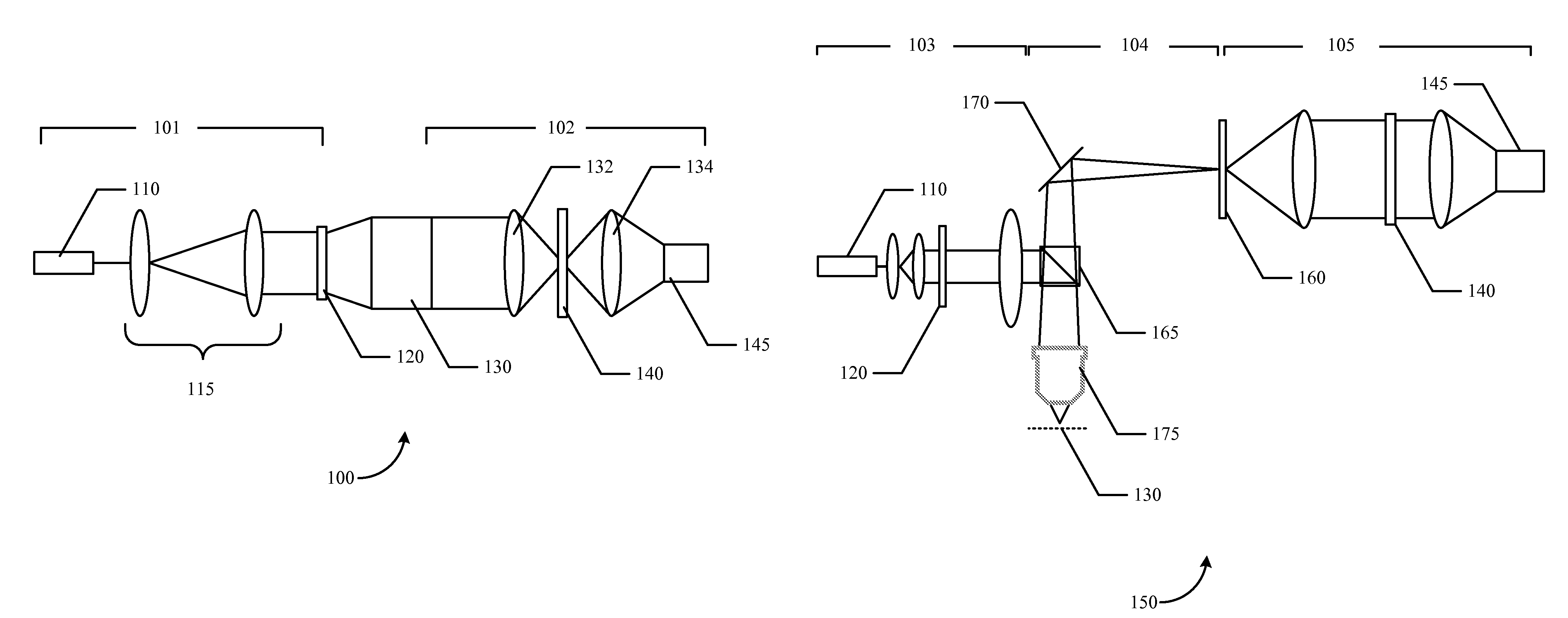
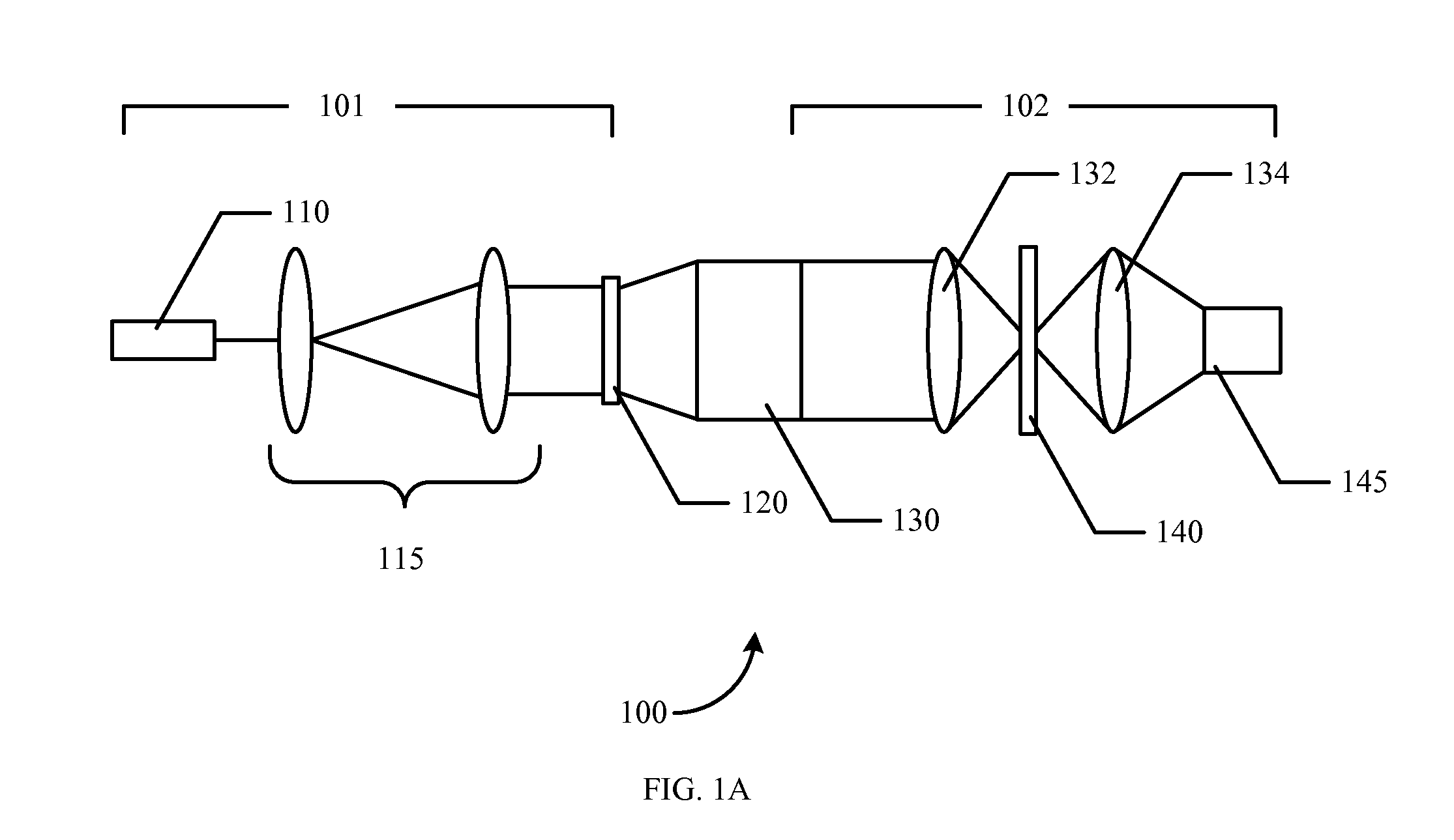
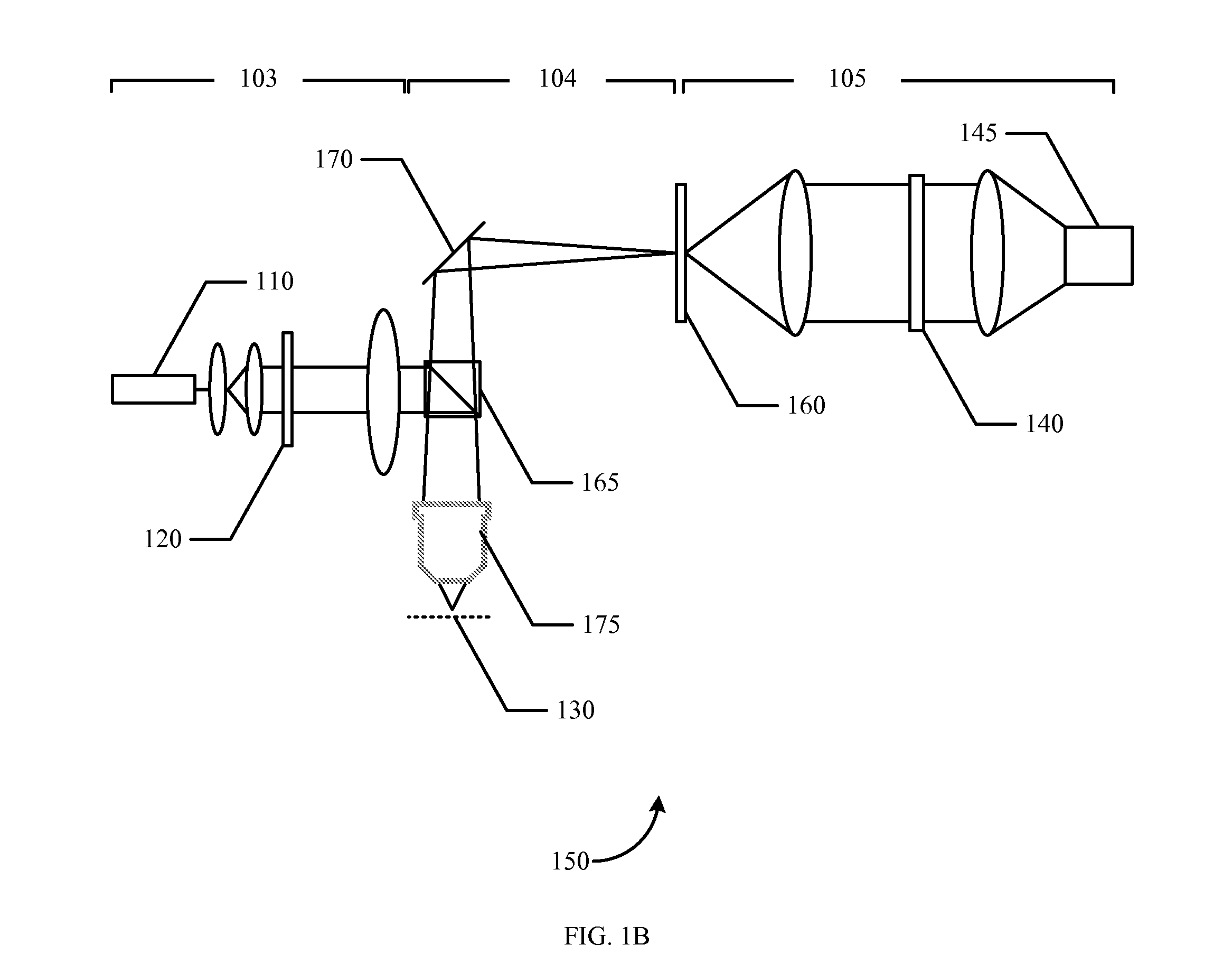
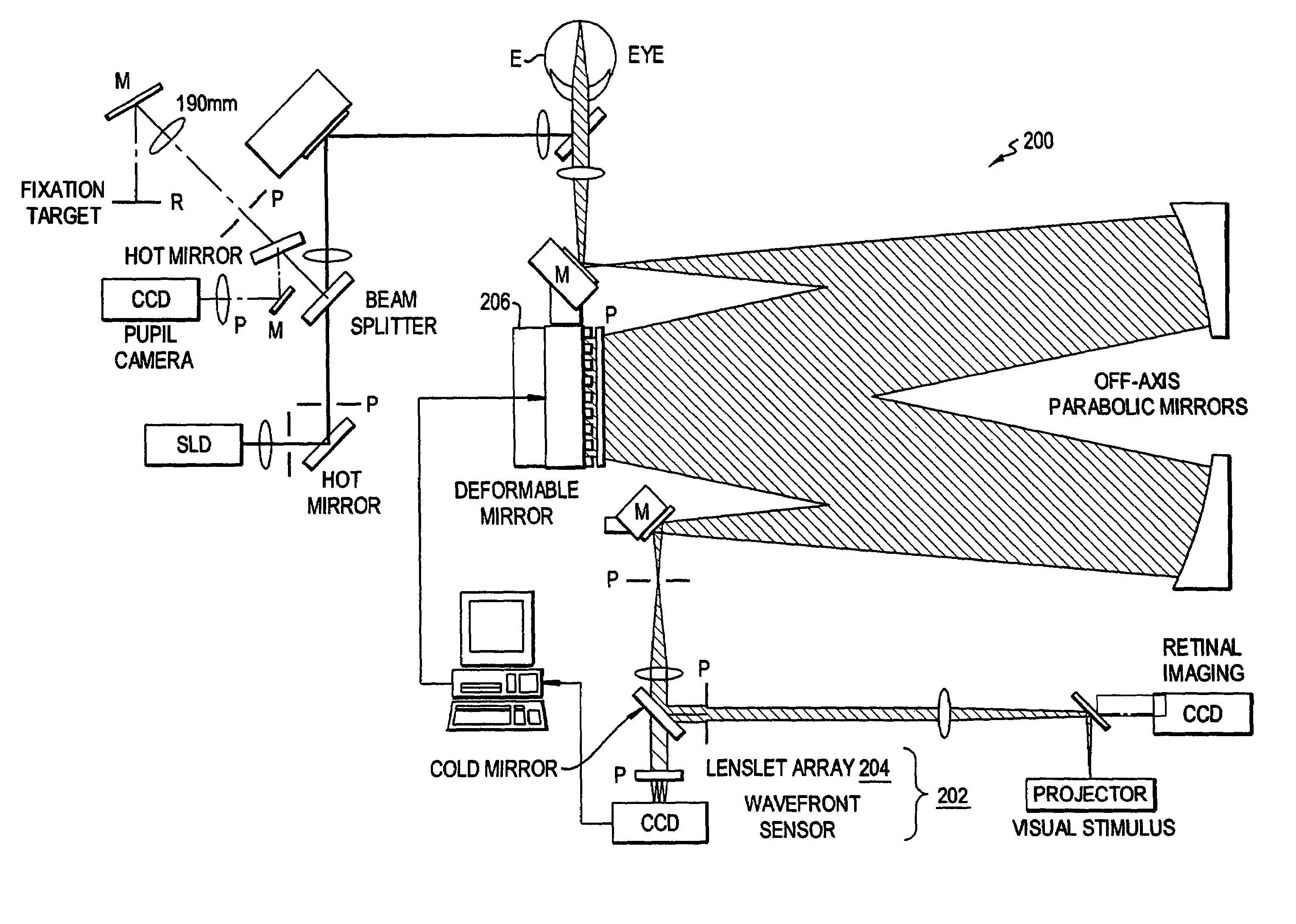
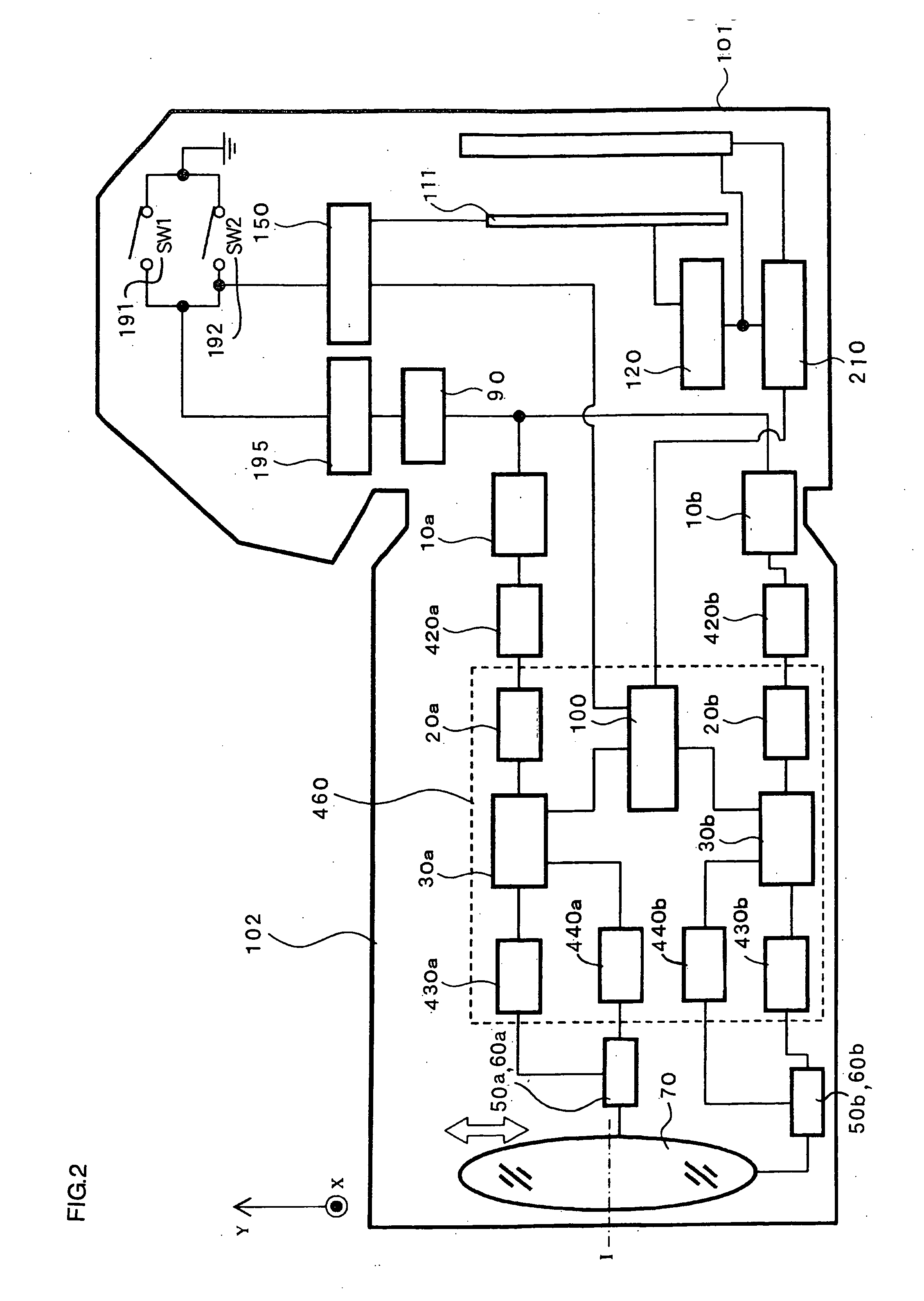
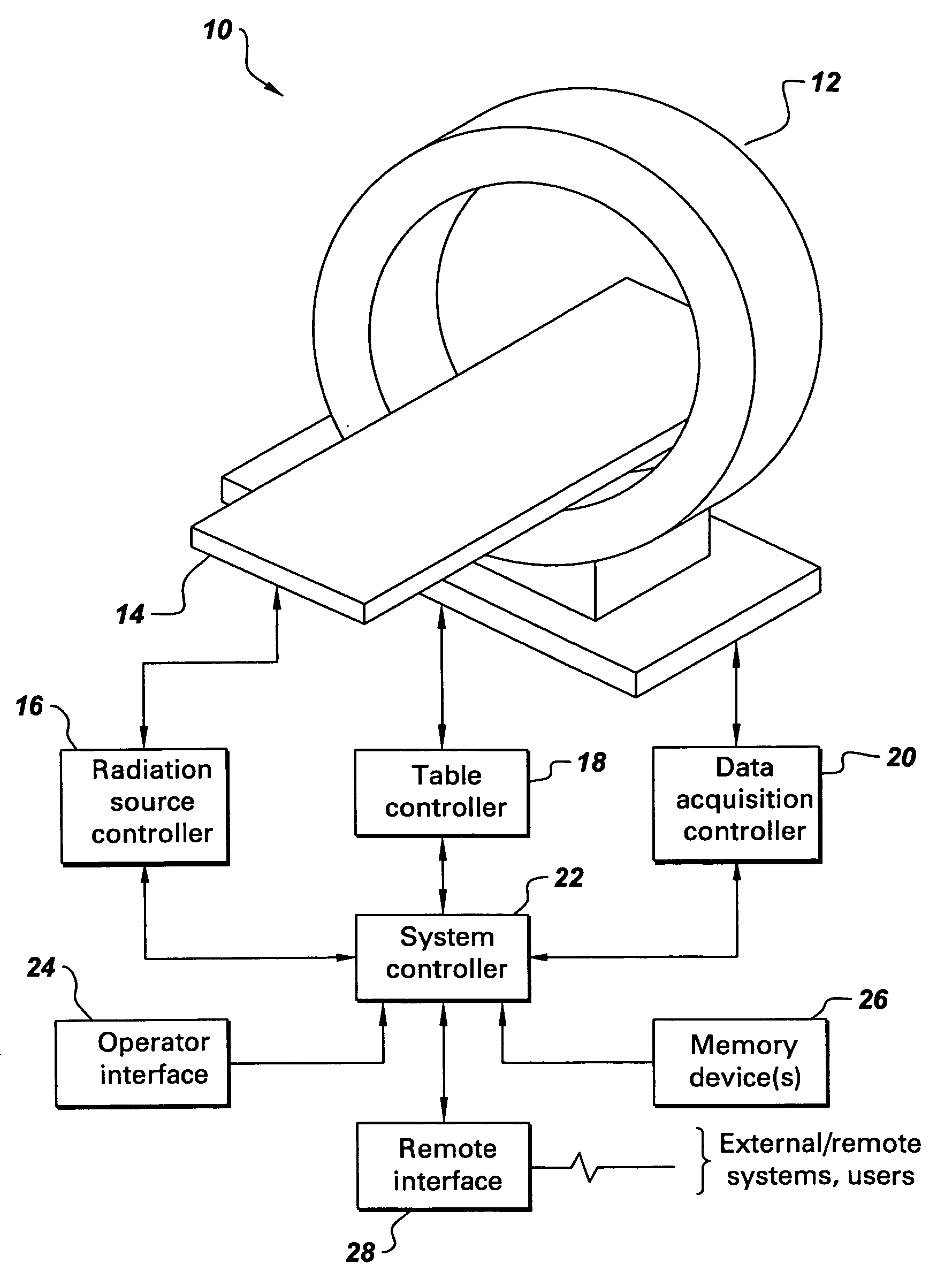
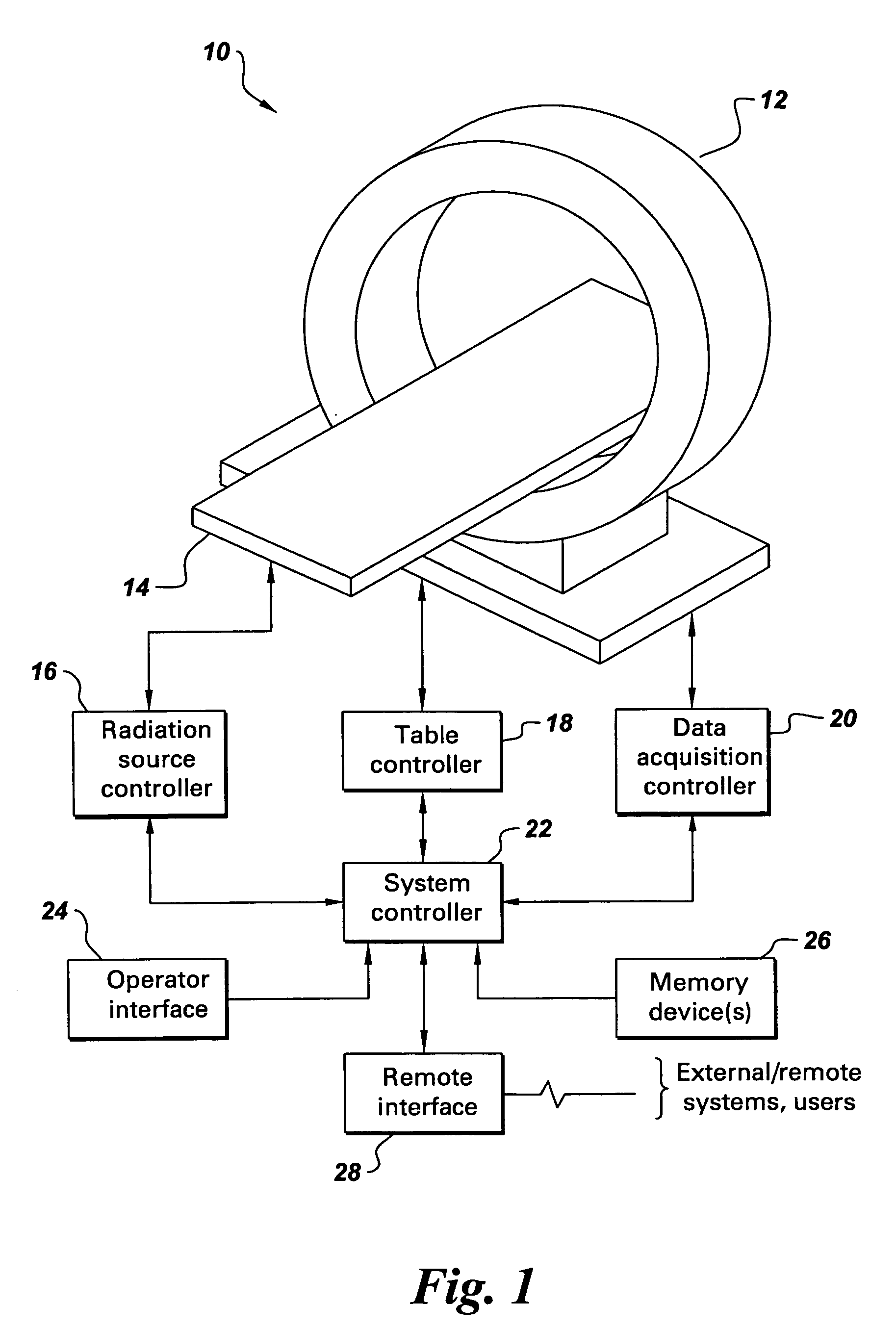
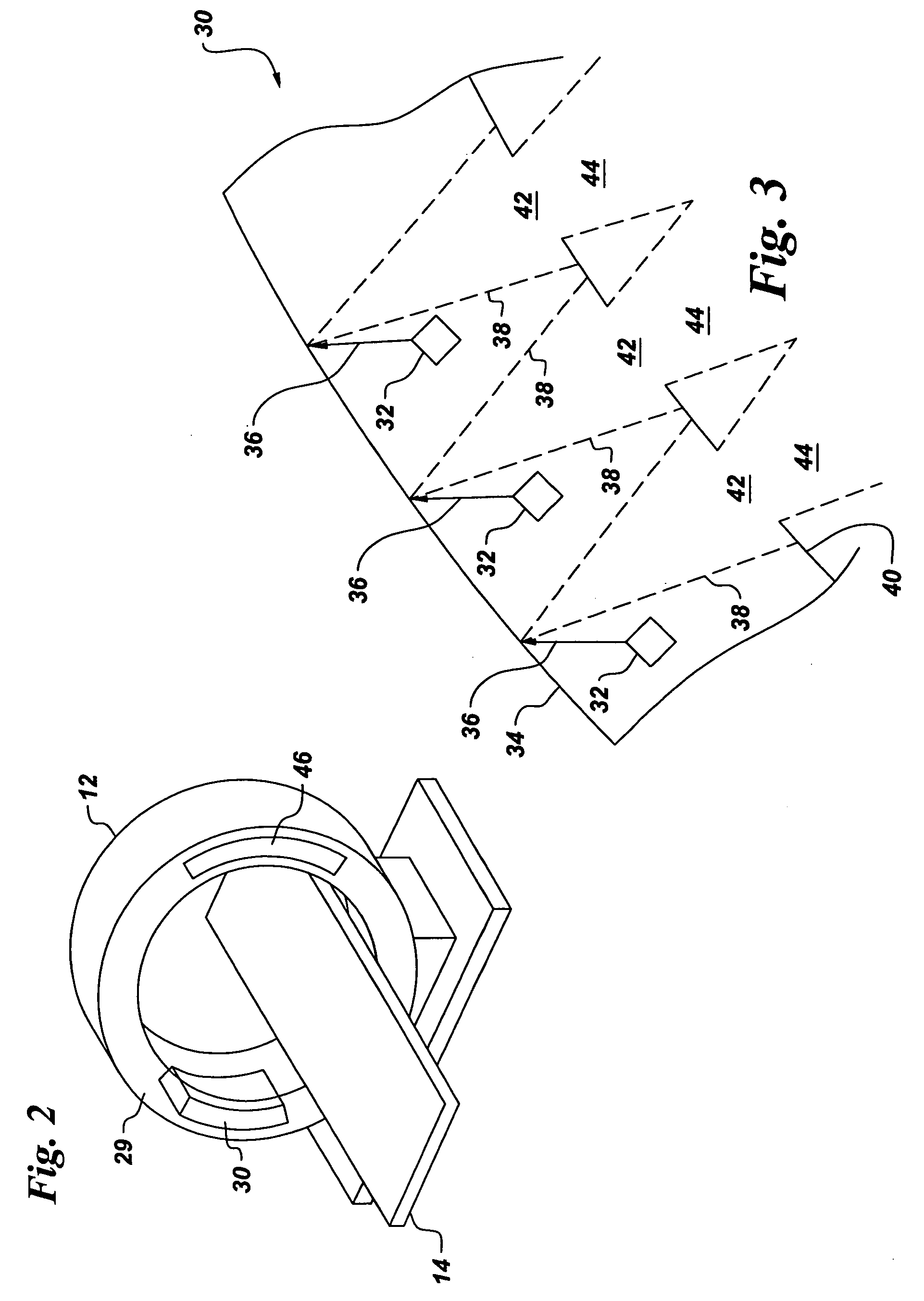
Patents
Literature
1043 results about "Point spread function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
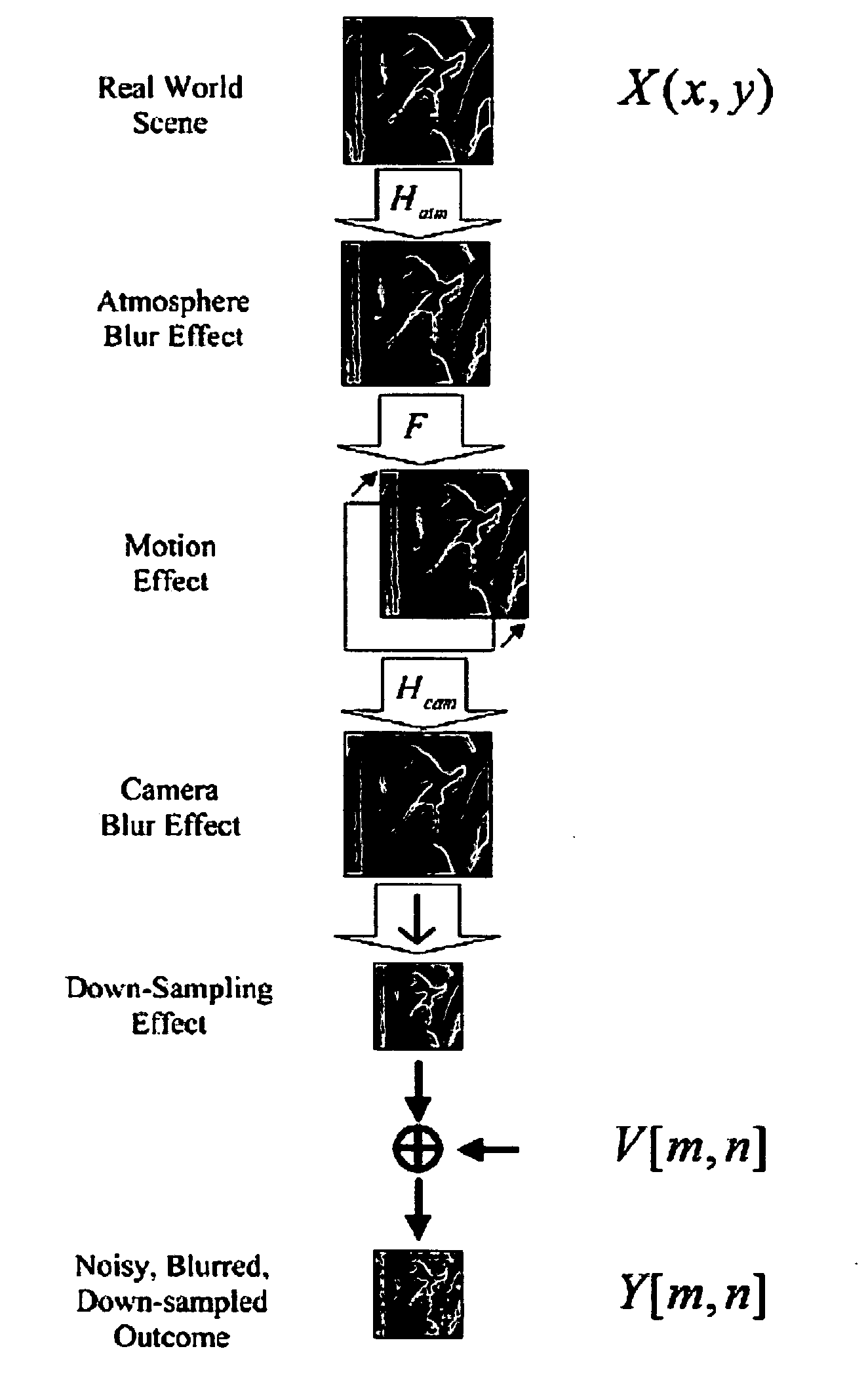
The point spread function (PSF) describes the response of an imaging system to a point source or point object. A more general term for the PSF is a system's impulse response, the PSF being the impulse response of a focused optical system. The PSF in many contexts can be thought of as the extended blob in an image that represents a single point object. In functional terms it is the spatial domain version of the optical transfer function of the imaging system. It is a useful concept in Fourier optics, astronomical imaging, medical imaging, electron microscopy and other imaging techniques such as 3D microscopy (like in confocal laser scanning microscopy) and fluorescence microscopy. The degree of spreading (blurring) of the point object is a measure for the quality of an imaging system. In non-coherent imaging systems such as fluorescent microscopes, telescopes or optical microscopes, the image formation process is linear in the image intensity and described by linear system theory. This means that when two objects A and B are imaged simultaneously, the resulting image is equal to the sum of the independently imaged objects. In other words: the imaging of A is unaffected by the imaging of B and vice versa, owing to the non-interacting property of photons. In space-invariant system, i.e. the PSF is the same everywhere in the imaging space, the image of a complex object is then the convolution of the true object and the PSF. However, when the detected light is coherent, image formation is linear in the complex field. The recorded intensity image then can show cancellations or other non-linear effects.
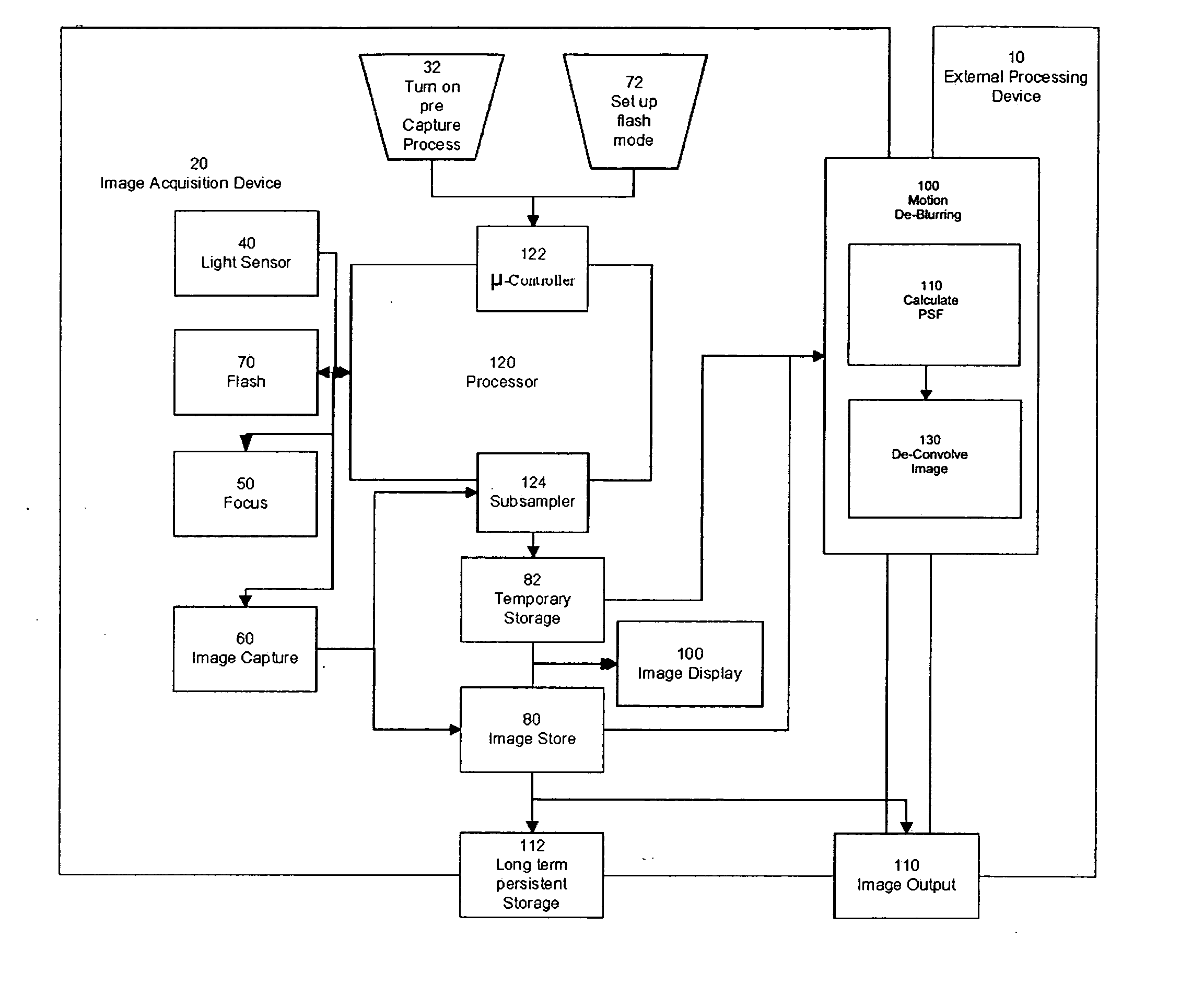
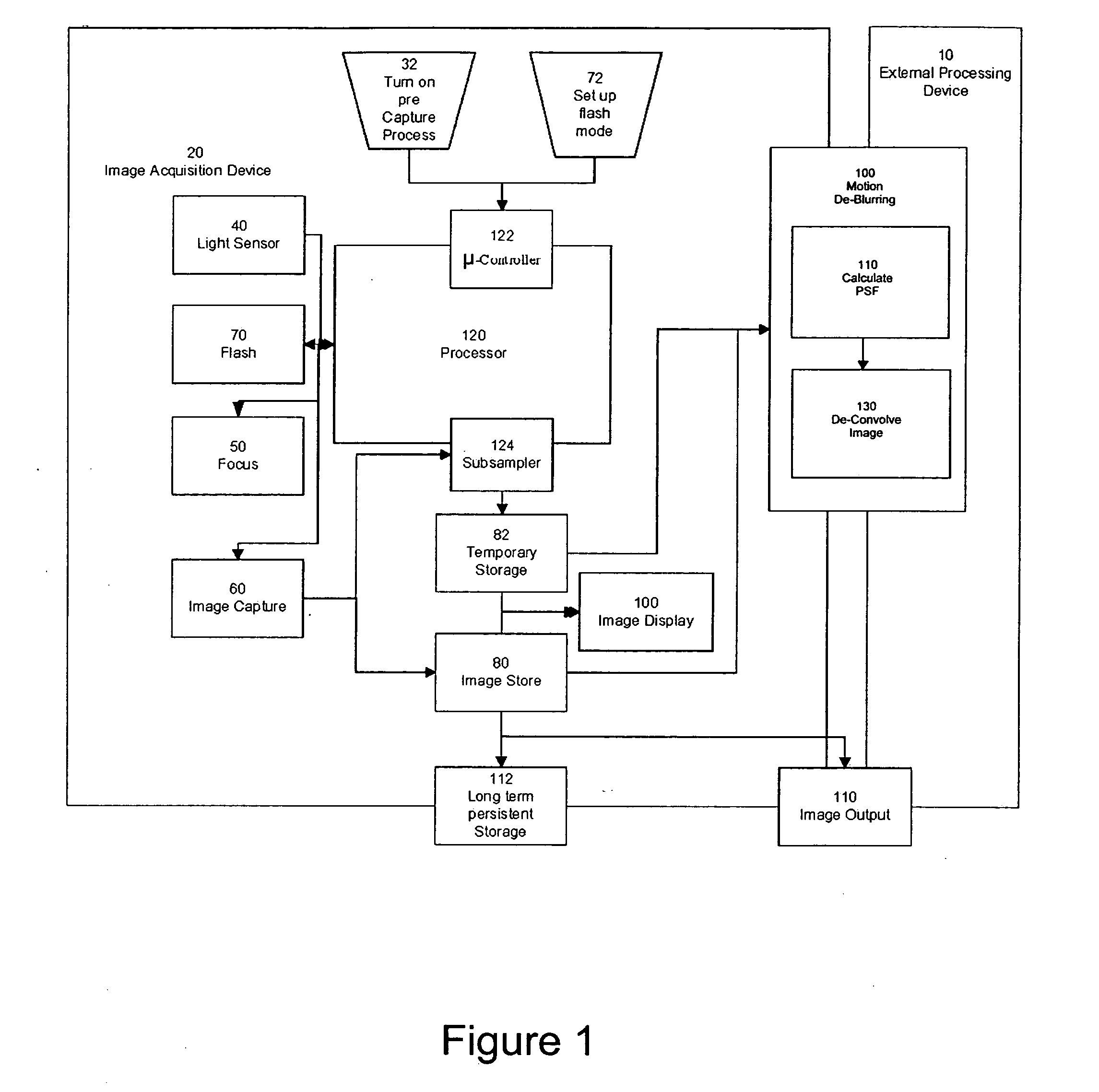
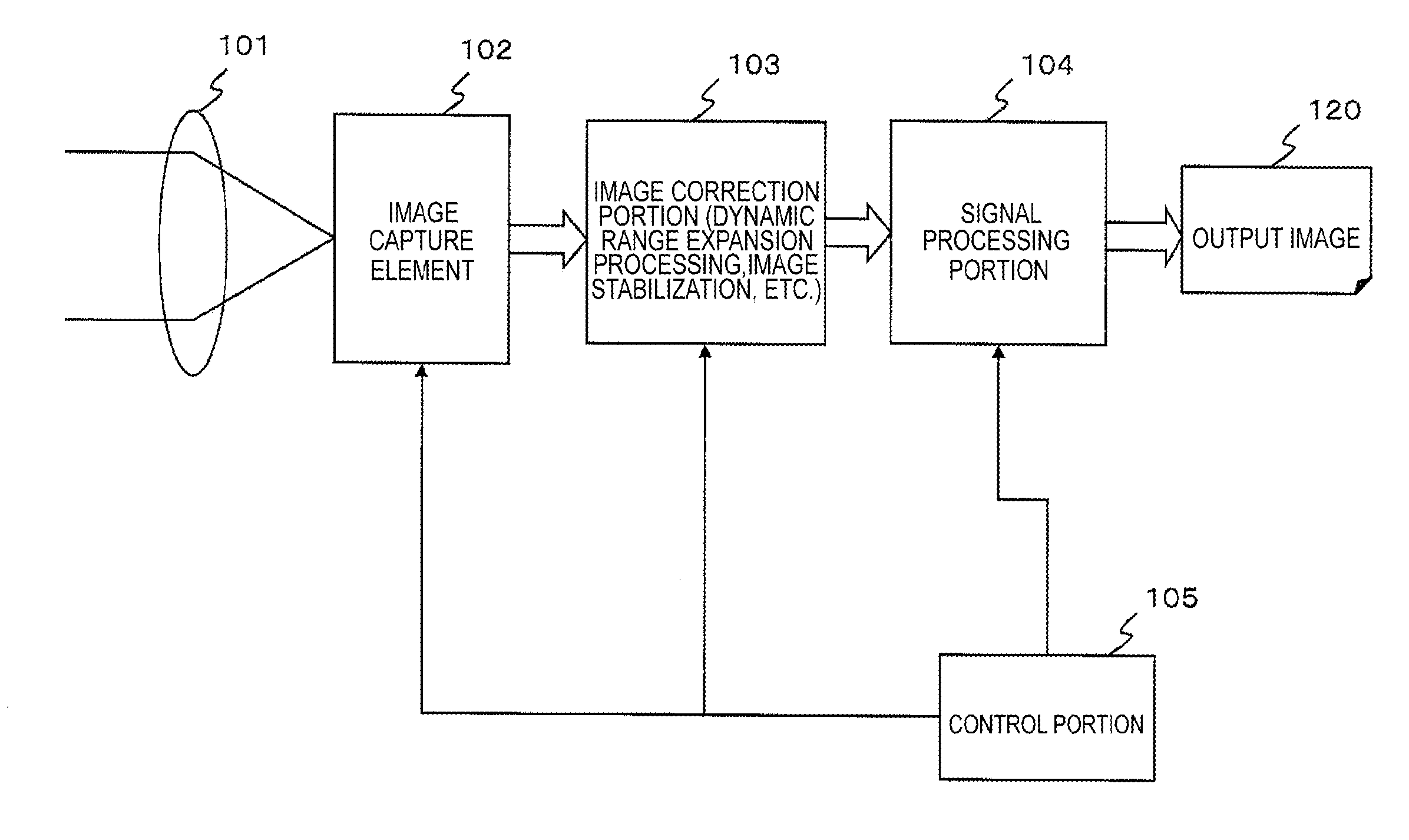
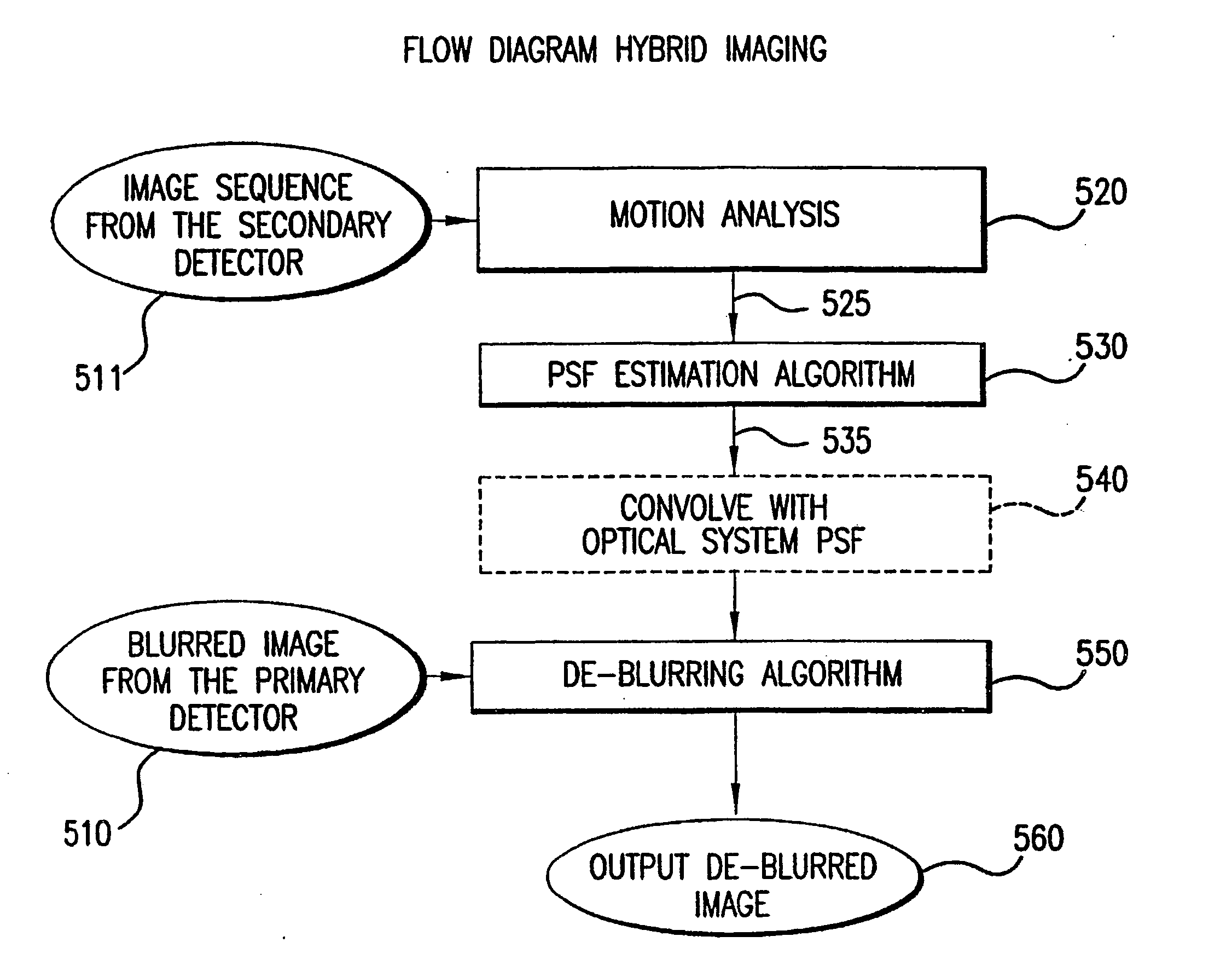
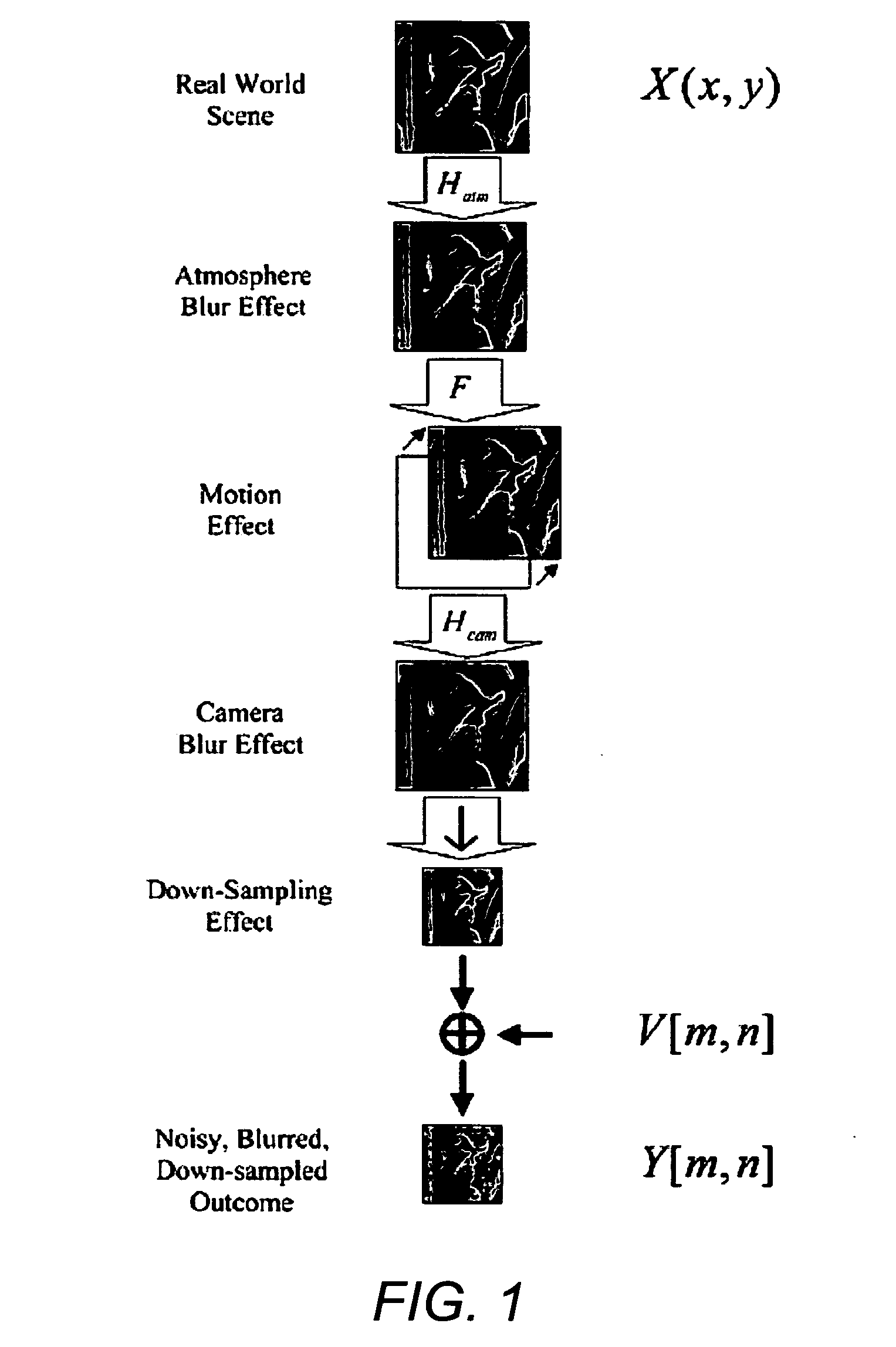
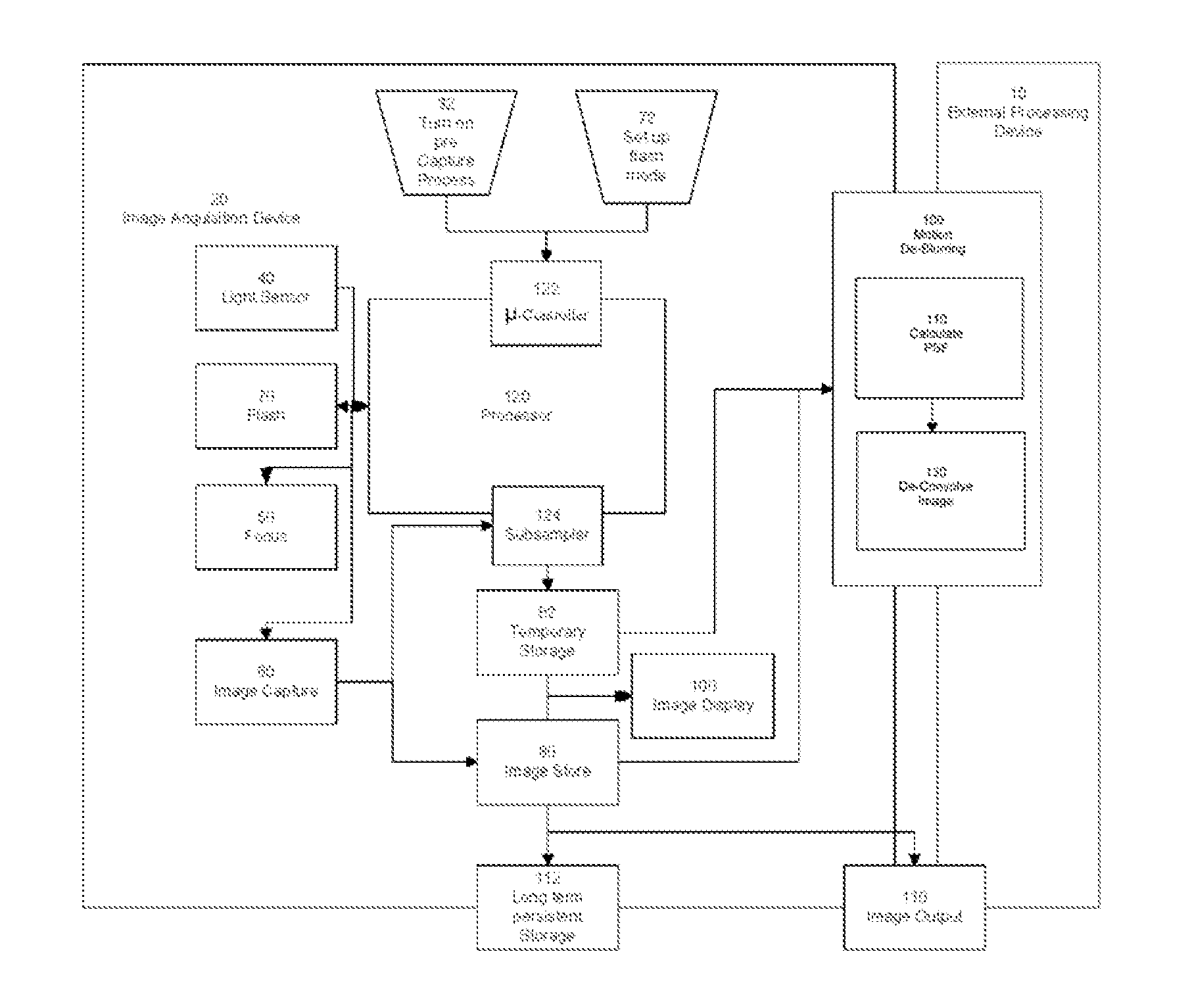
Systems and methods for de-blurring motion blurred images
ActiveUS20060119710A1Correcting blurringTelevision system detailsImage enhancementComputer graphics (images)Deblurring
Systems and methods for providing a substantially de-blurred image of a scene from a motion blurred image of the scene are disclosed. An exemplary system includes a primary detector for sensing the motion blurred image and generating primary image information representing the blurred image, a secondary detector for sensing two or more secondary images of the scene and for generating secondary image information representing the two or more secondary images, and a processor for determining motion information from the secondary image information, estimating a point spread function for the motion blurred image from the motion information, and applying the estimated point spread function to the primary image information to generate information representing the substantially de-blurred image.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
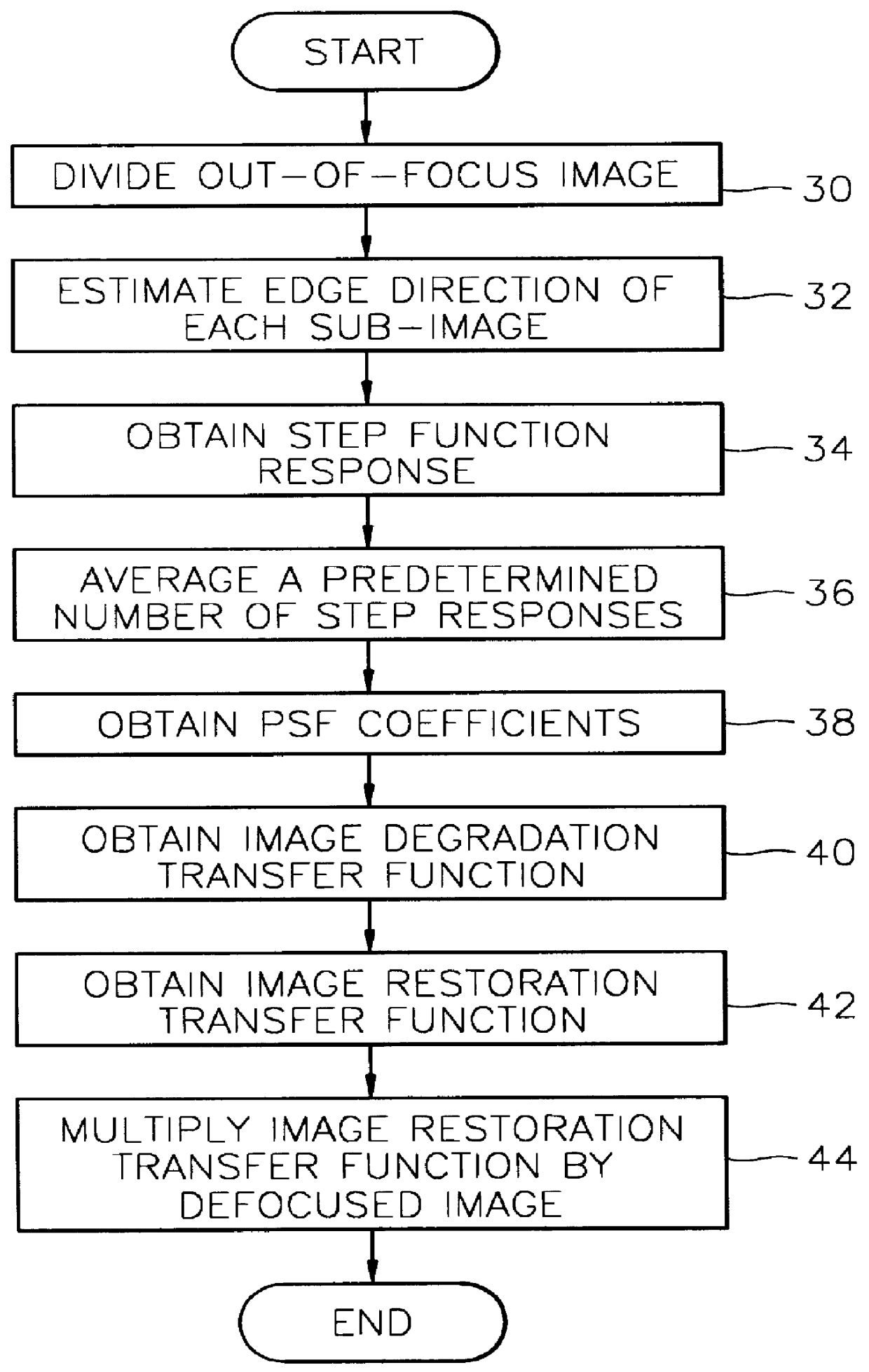
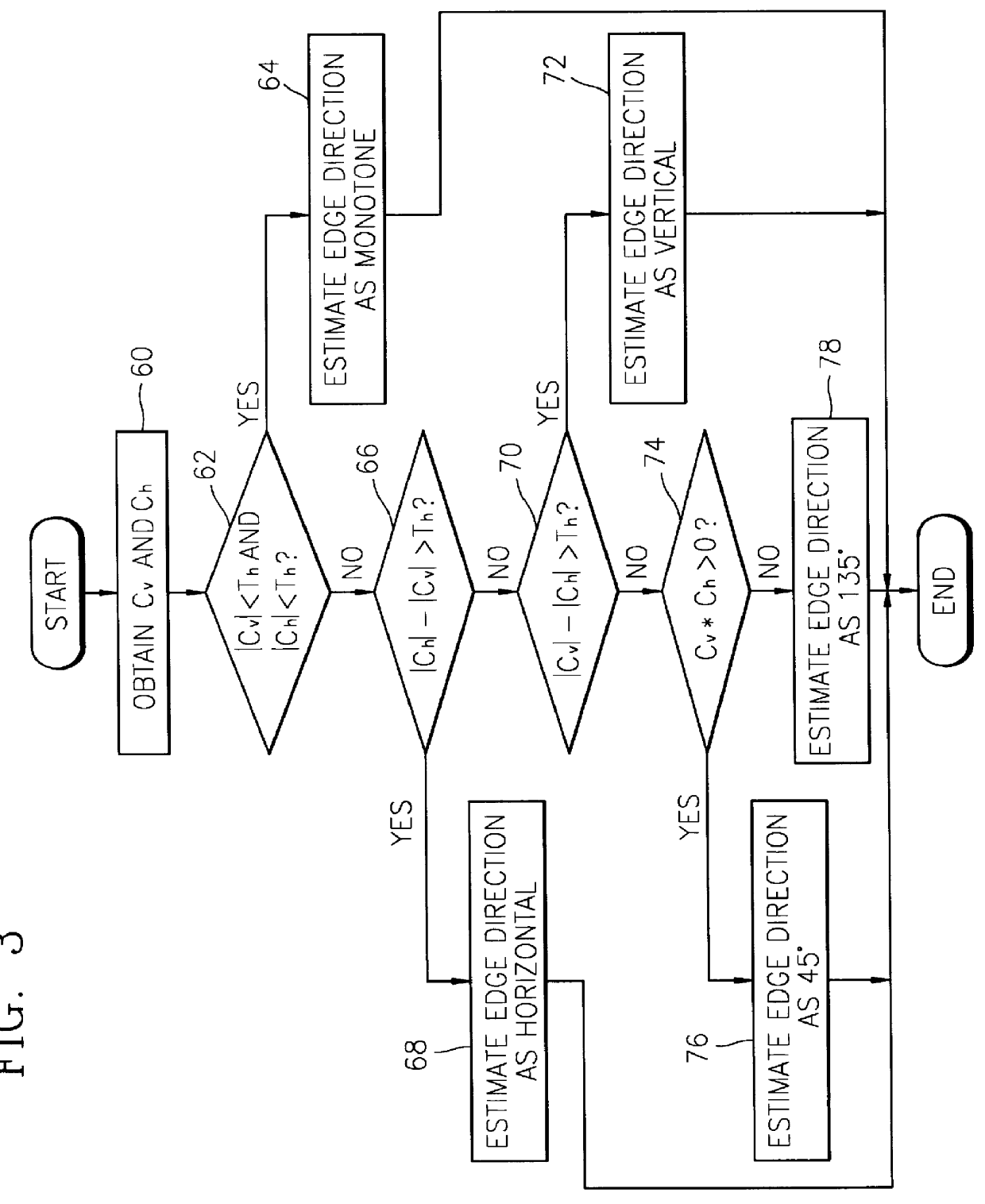
Digital focusing method and apparatus in image processing system
Digital focusing method and apparatus in an image processing system, for digitally focusing an out-of-focus image, are provided. A defocused image is divided into sub-images of a predetermined size. An edge direction of each of the divided sub-images is estimated. Step responses with respect to the respective edge directions are calculated. A mean step response is obtained by averaging a predetermined number of the step responses. Point Spread Function (PSF) coefficients are obtained using the mean step response. An image blur transfer function is obtained using the PSF coefficients. An image restoration transfer function is obtained using the image blur transfer function. An original in-focused image is obtained by multiplying the image restoration transfer function by the defocused image in a frequency domain. Thus, an image can be restored in real time, and the size and weight of the image processing system can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of determining PSF using multiple instances of a nominally similar scene
InactiveUS20060098890A1Image enhancementTelevision system detailsPoint spread functionExposure period
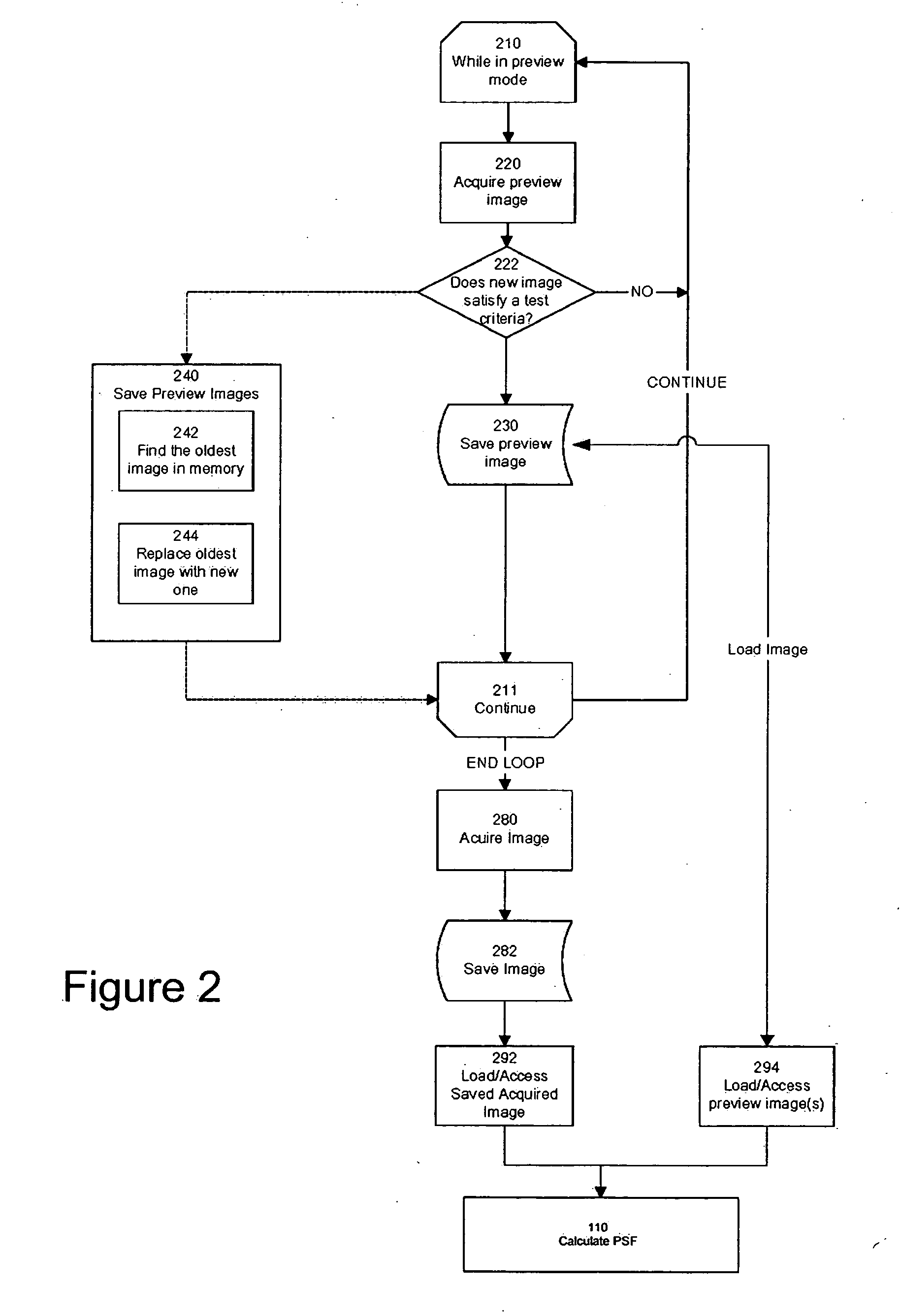
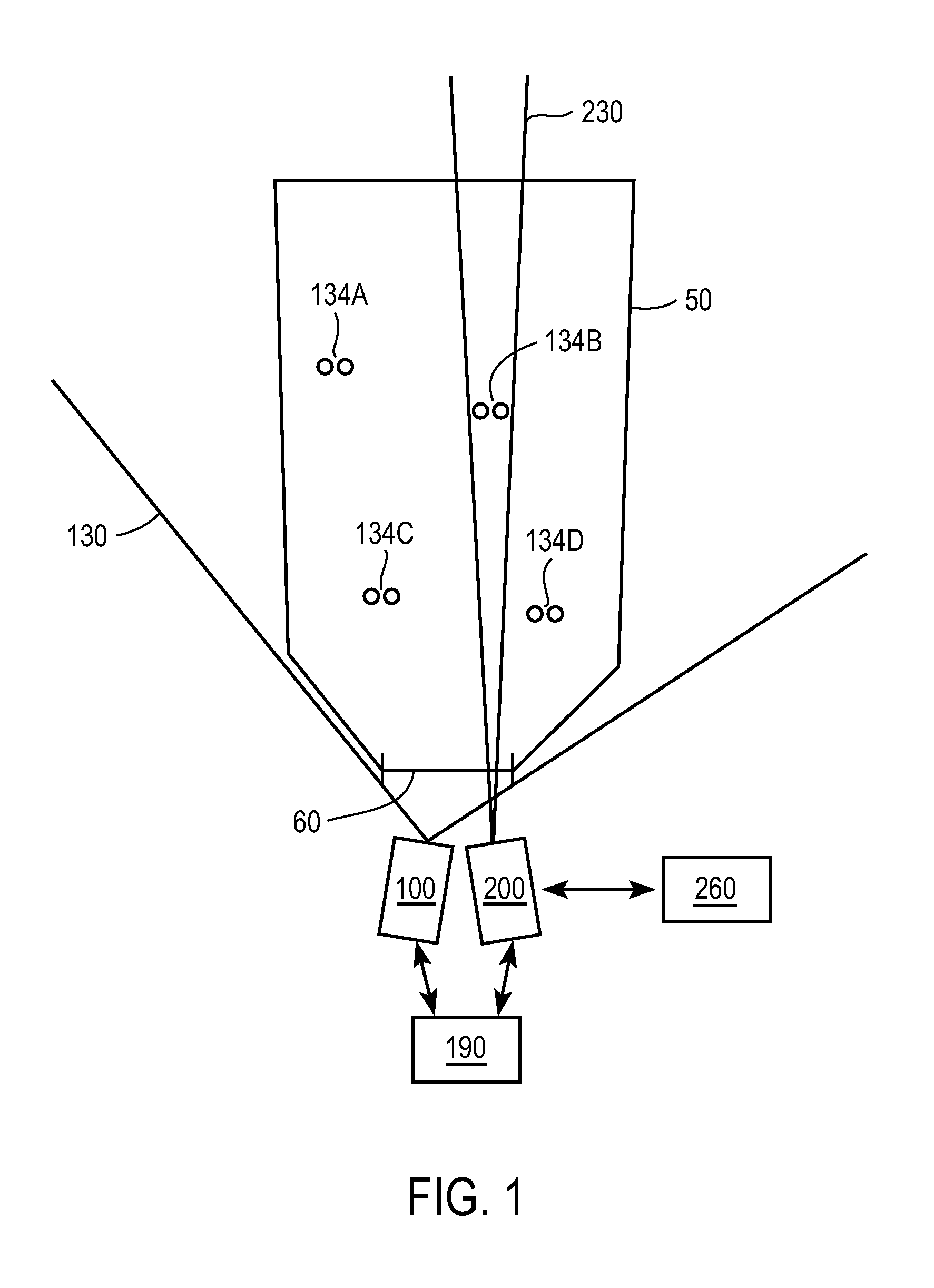
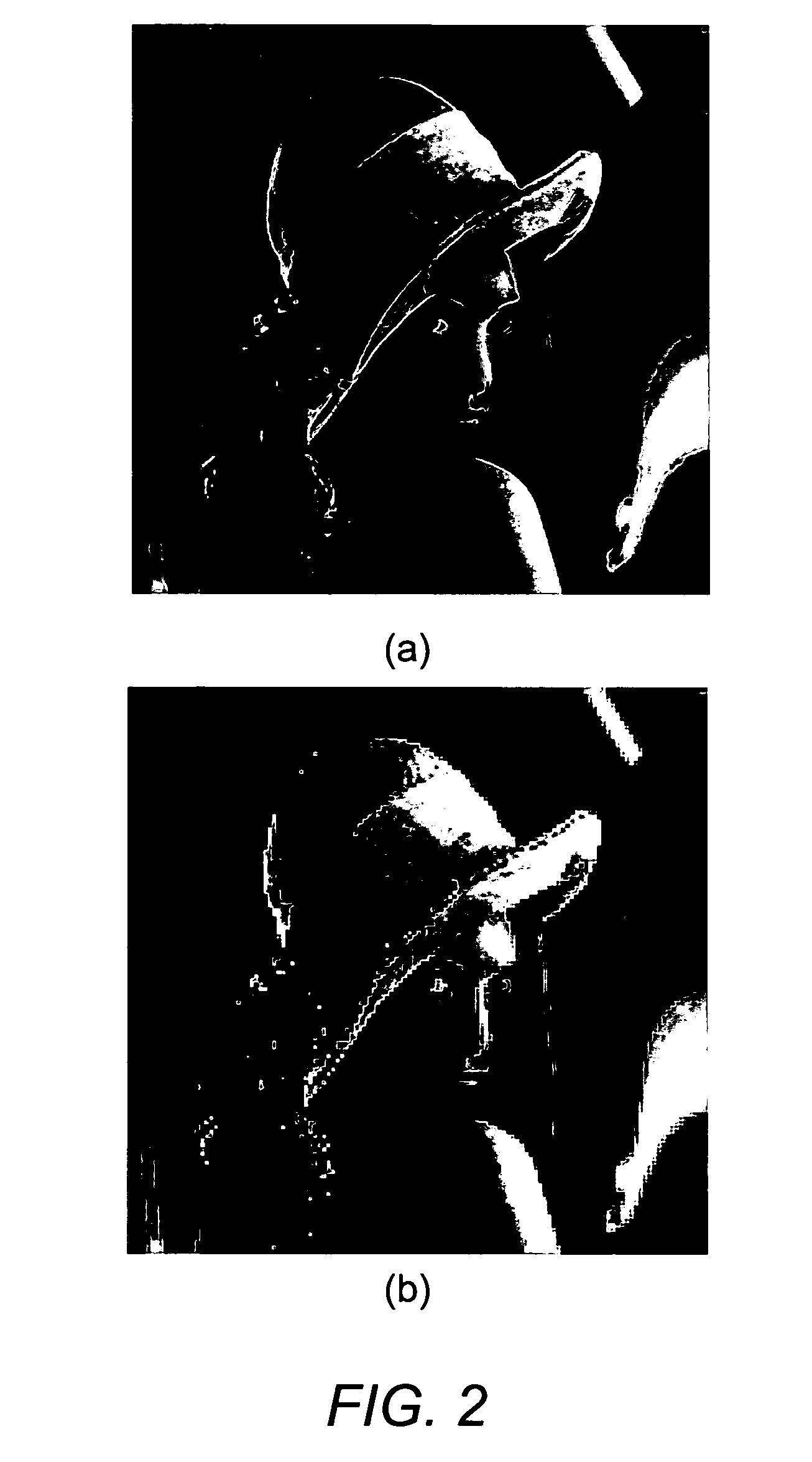
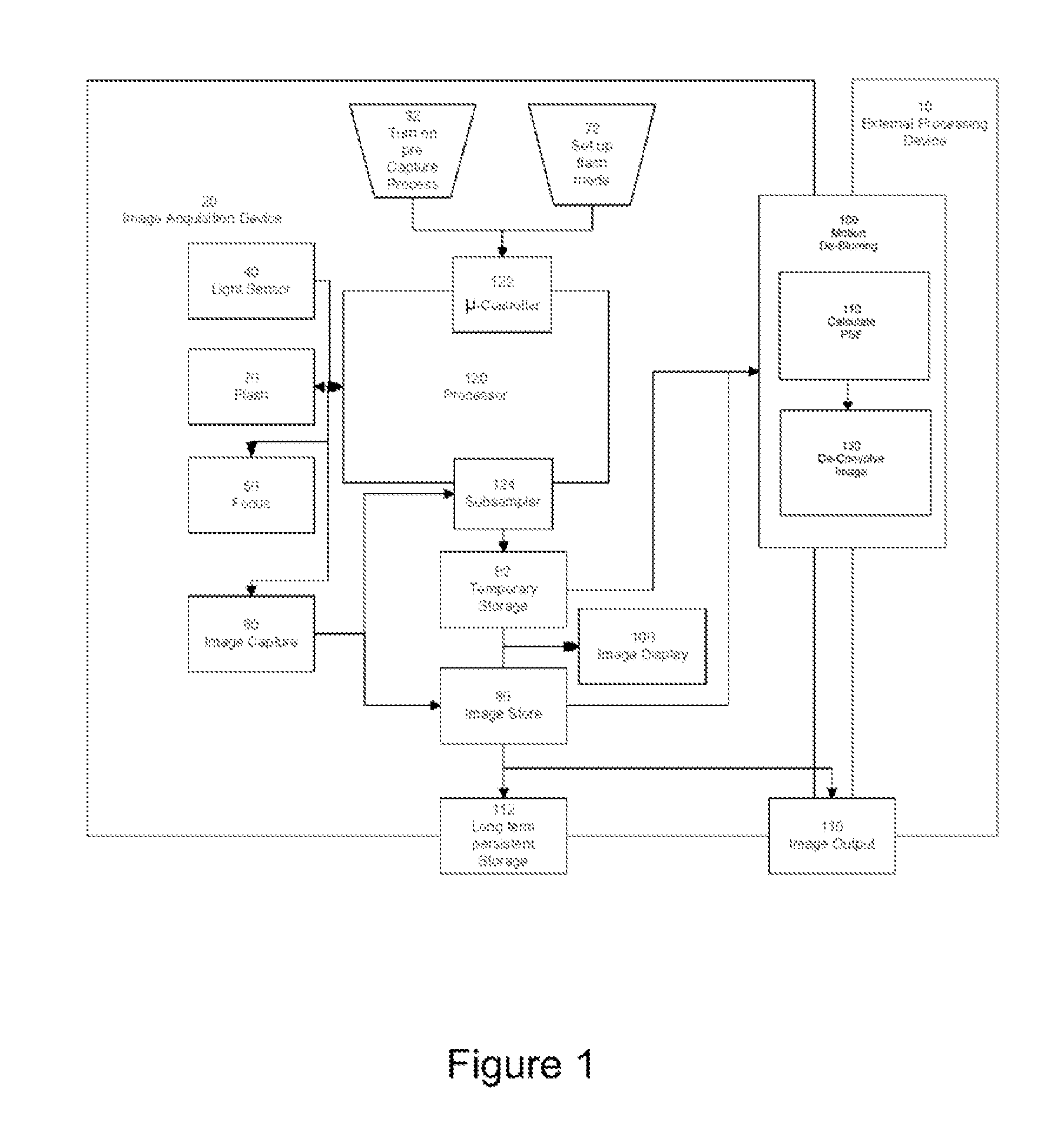
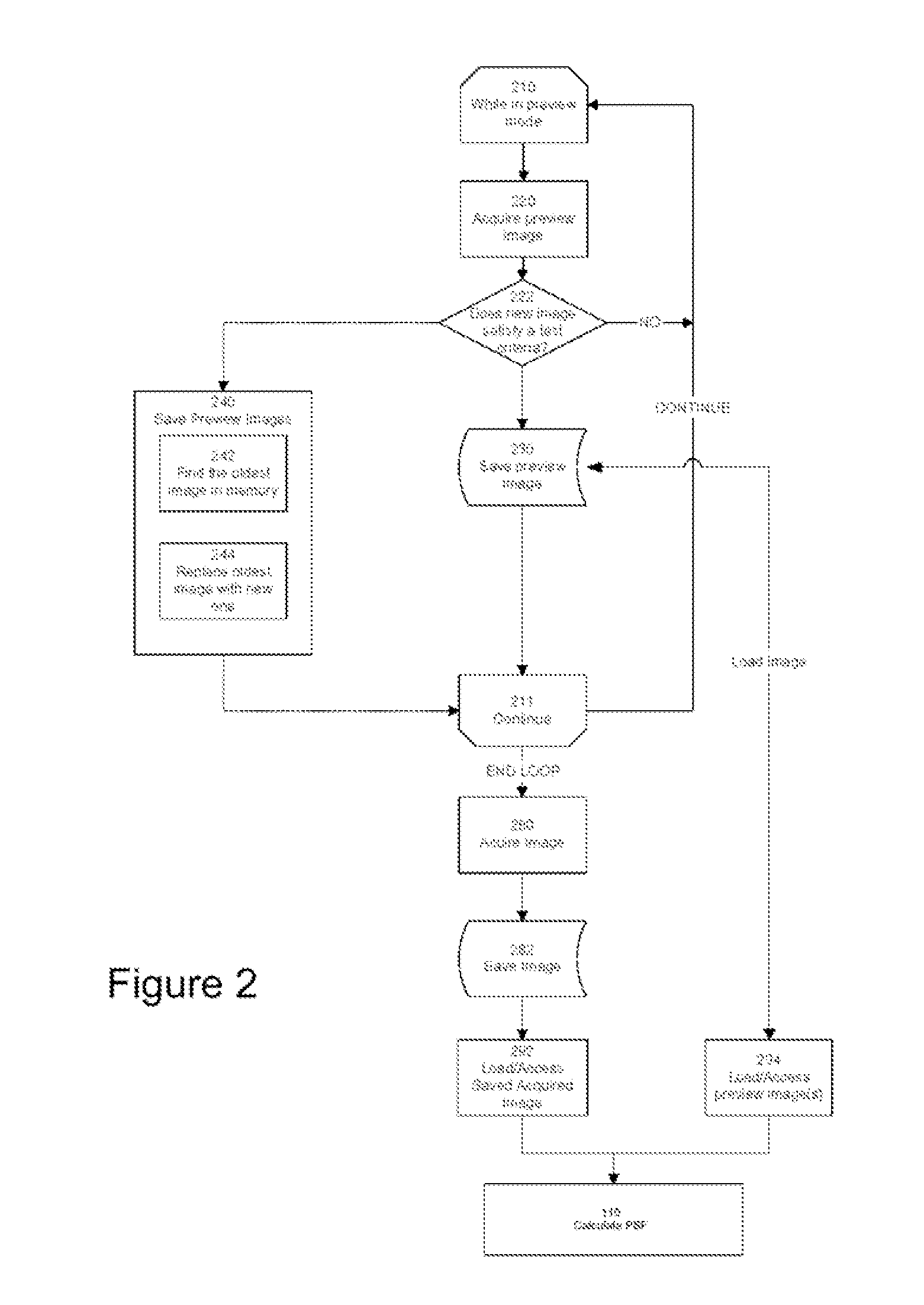
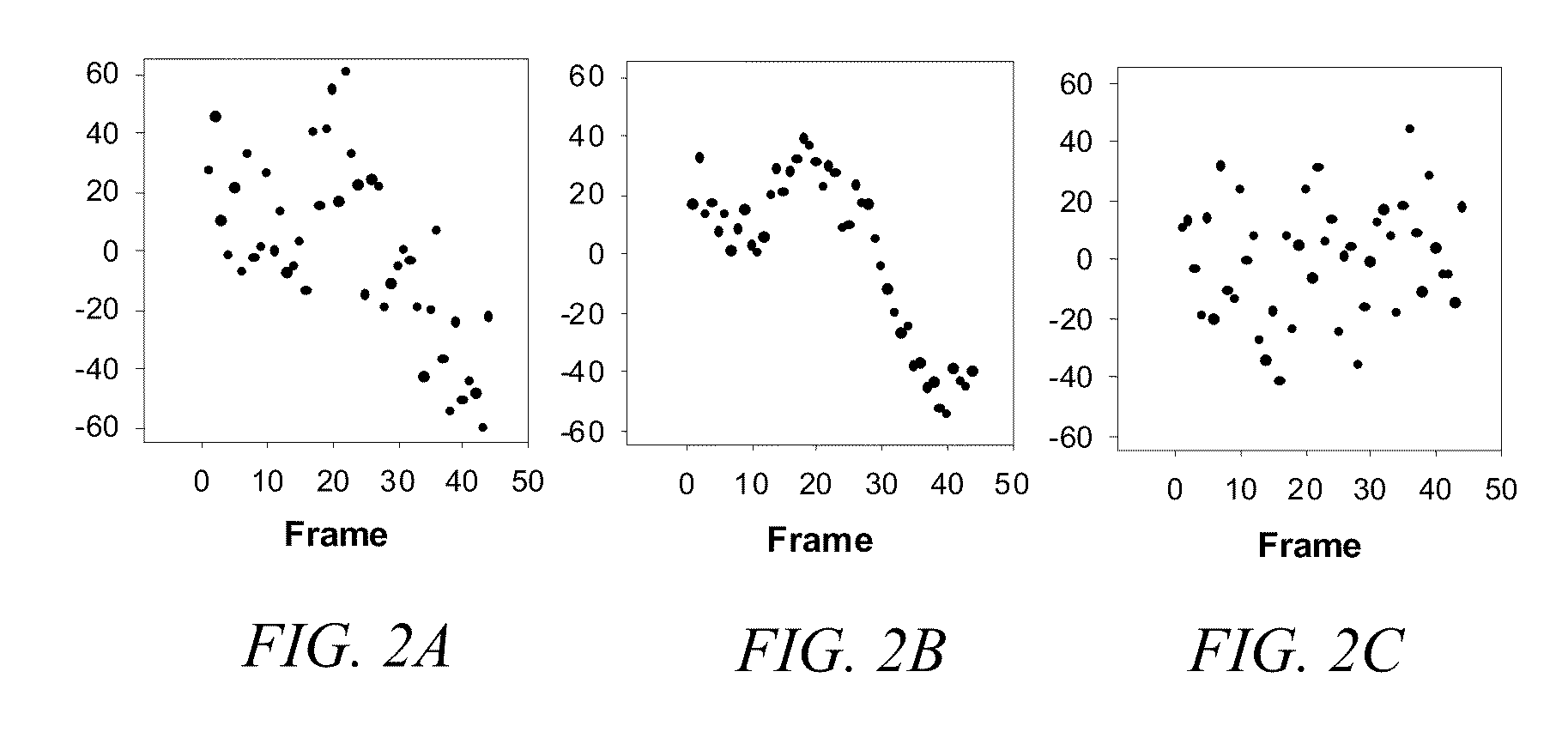
A digital image acquisition system includes a portable apparatus for capturing digital images and a digital processing component for detecting, analyzing and informing the photographer regarding motion blur, and for reducing camera motion blur in an image captured by the apparatus. The digital processing component operates by comparing the image with at least one other image, for example a preview image, of nominally the same scene taken outside the exposure period of the main image. In one embodiment the digital processing component identifies at least one feature in a single preview image which is relatively less blurred than the corresponding feature in the main image, calculates a point spread function (PSF) in respect of such feature, and de-convolves the main image using the PSF. In another embodiment, the digital processing component calculates a trajectory of at least one feature in a plurality of preview images, extrapolates such feature on to the main image, calculates a PSF in respect of the feature, and de-convolves the main image using the PSF. In another embodiment the digital processing unit after determining the degree of blur notifies the photographer of the existing blur or automatically invokes consecutive captures.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Method and system for producing a virtual output image from data obtained by an array of image capturing devices
ActiveUS20130088489A1Raise the possibilityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPoint spread functionImaging data
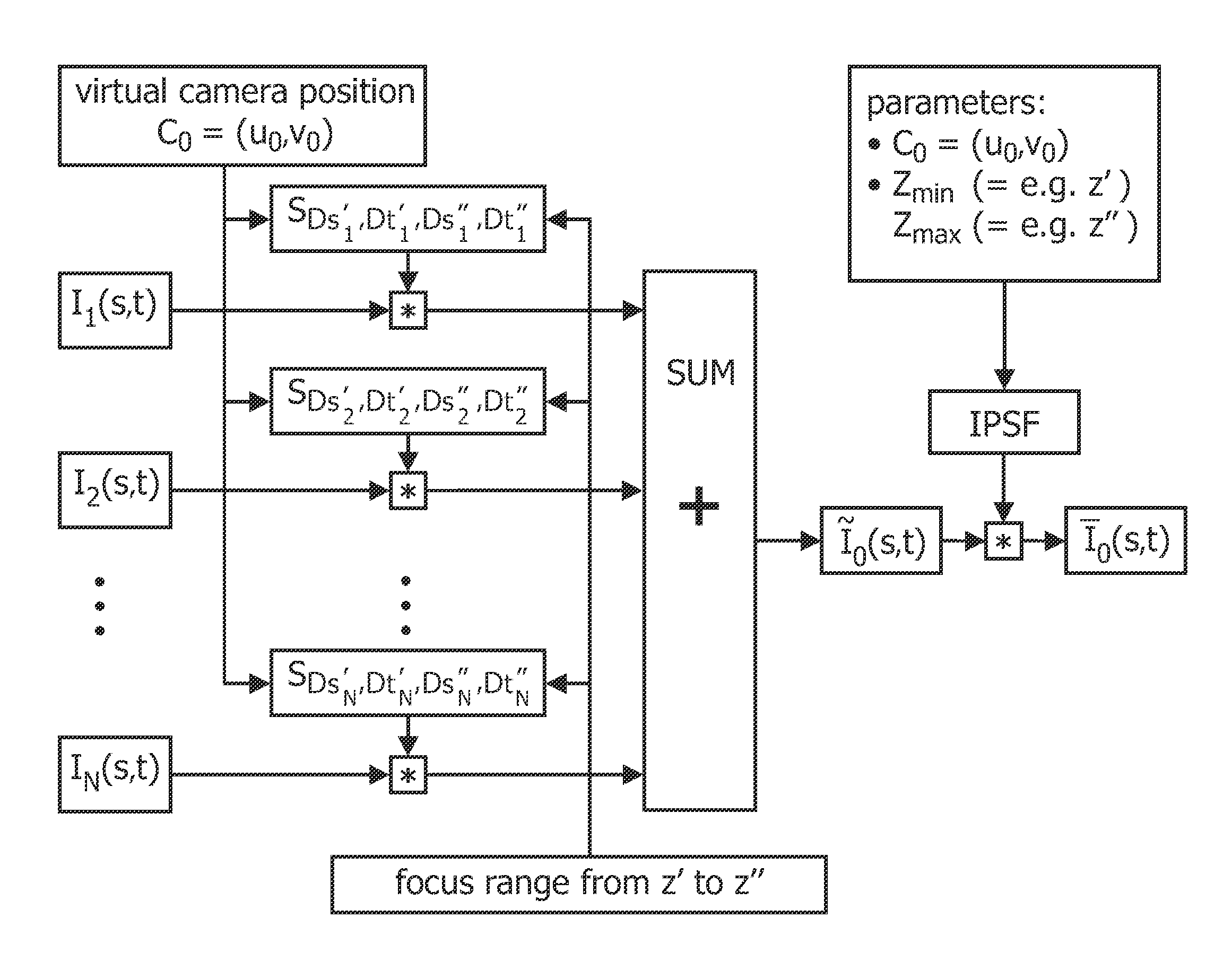
In a method and system for providing virtual output images from an array of image capturing devices image data (Ii(s,t), I2(s,t)) is taken from the devices (Ci, C2). This image data is processed by convolving the image data with a function, e.g. the path (S) and thereafter deconvolving them, either after or before summation (SUM), with an inverse point spread function (IPSF) or a filter (HP) equivalent thereto to produce all-focus image data (I0(s,t)).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method to control point spread function of an image
ActiveUS20060103951A1Guaranteed preservation qualityMore interferenceTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityPoint spread function
A method of controlling the point spread function of an image projected with said image being diffused by a filter; said point spread function is a result of the application of spatial filter(s) on said image; with said control of the point spread function effected by varying the distance between such image and said spatial filter(s) and varying the bidirectional scattering transmission function of the spatial filter(s). Said spatial filter may be a holographic diffuser, which by method of manufacture has a ell defined bi-directional scattering transmission spread function. Control of said spread function is particularly useful to maintain image quality while abating moiré interference in situations where two periodic patterns are layered causing moiré interference.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
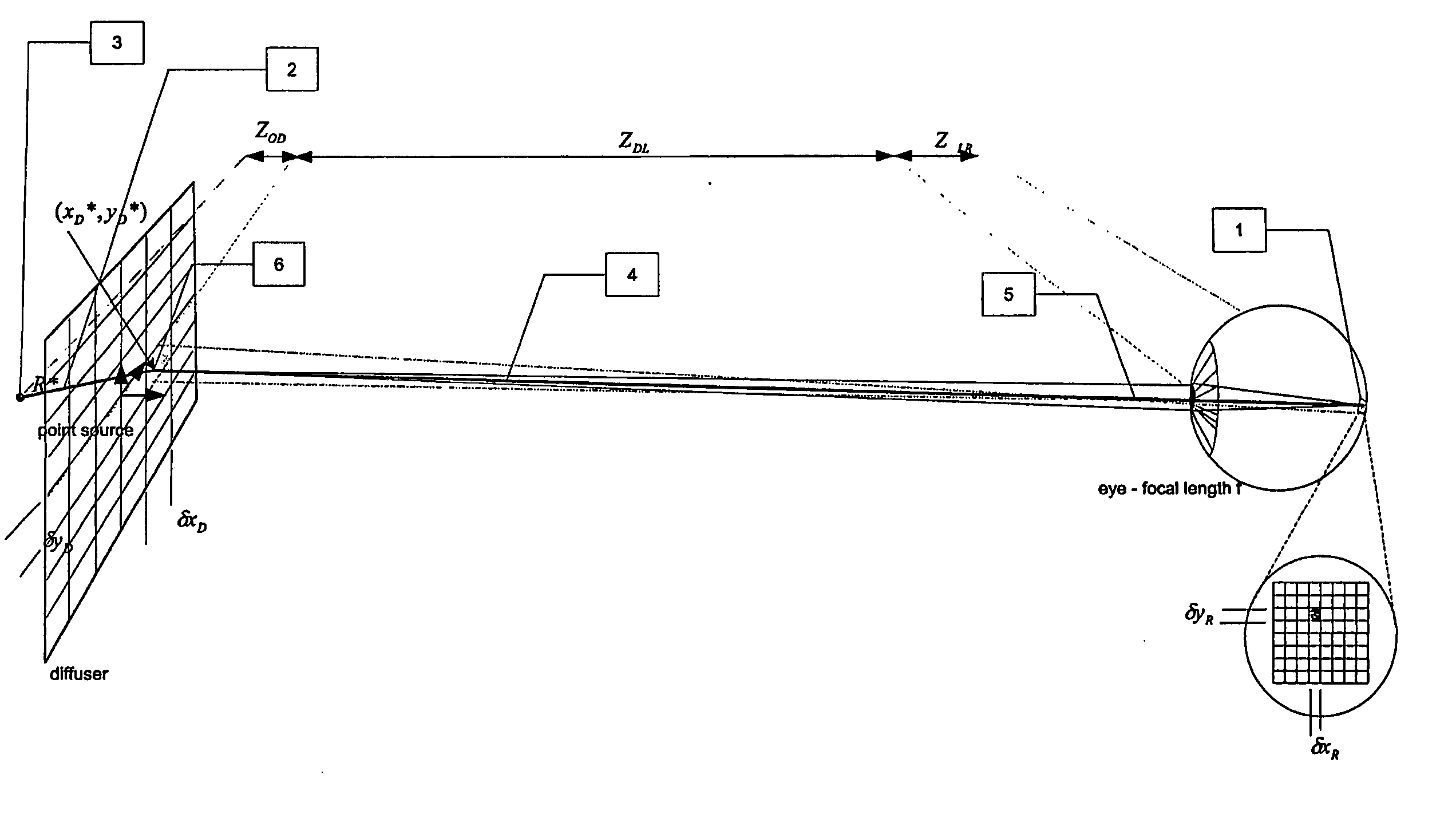
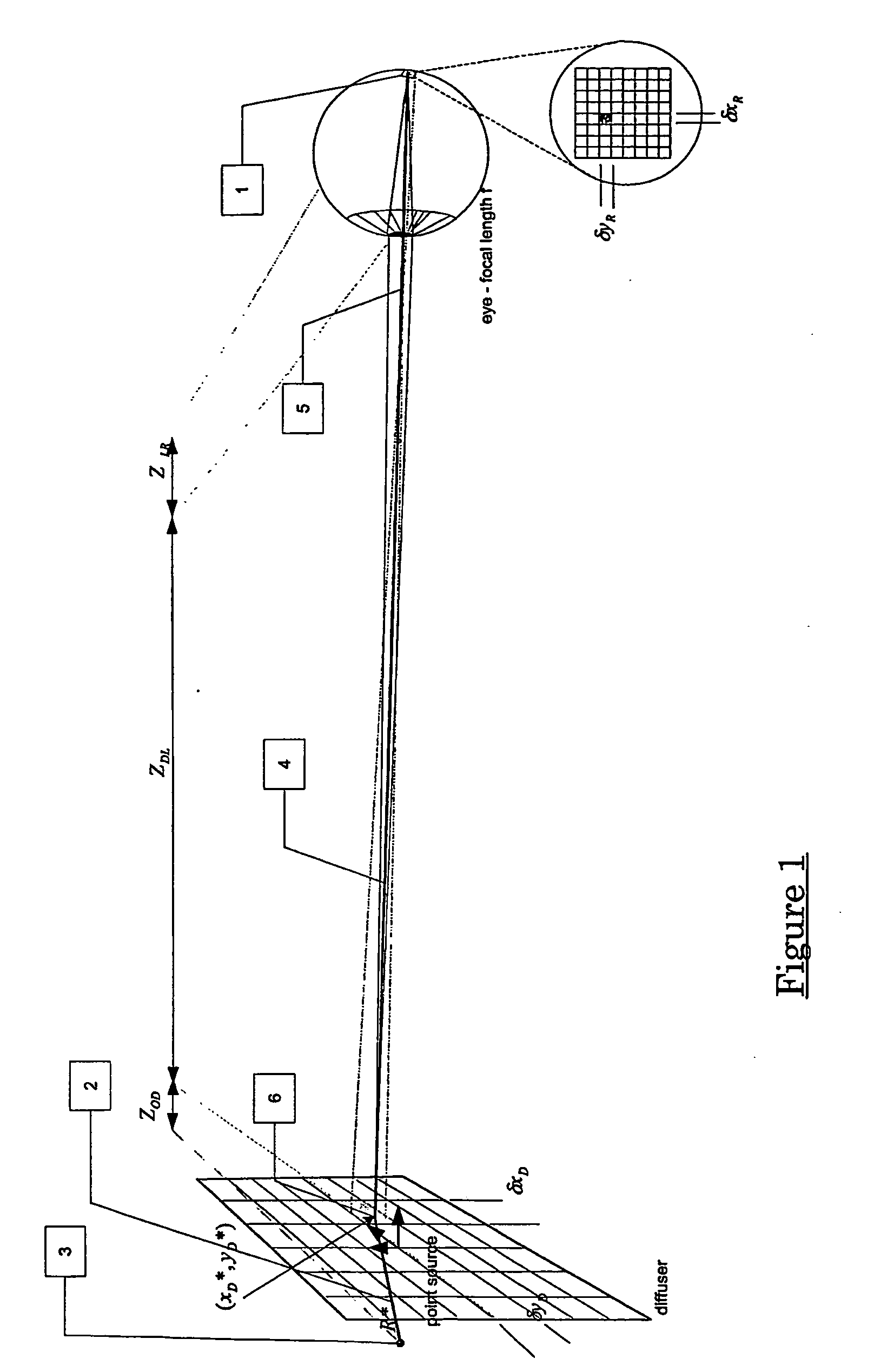
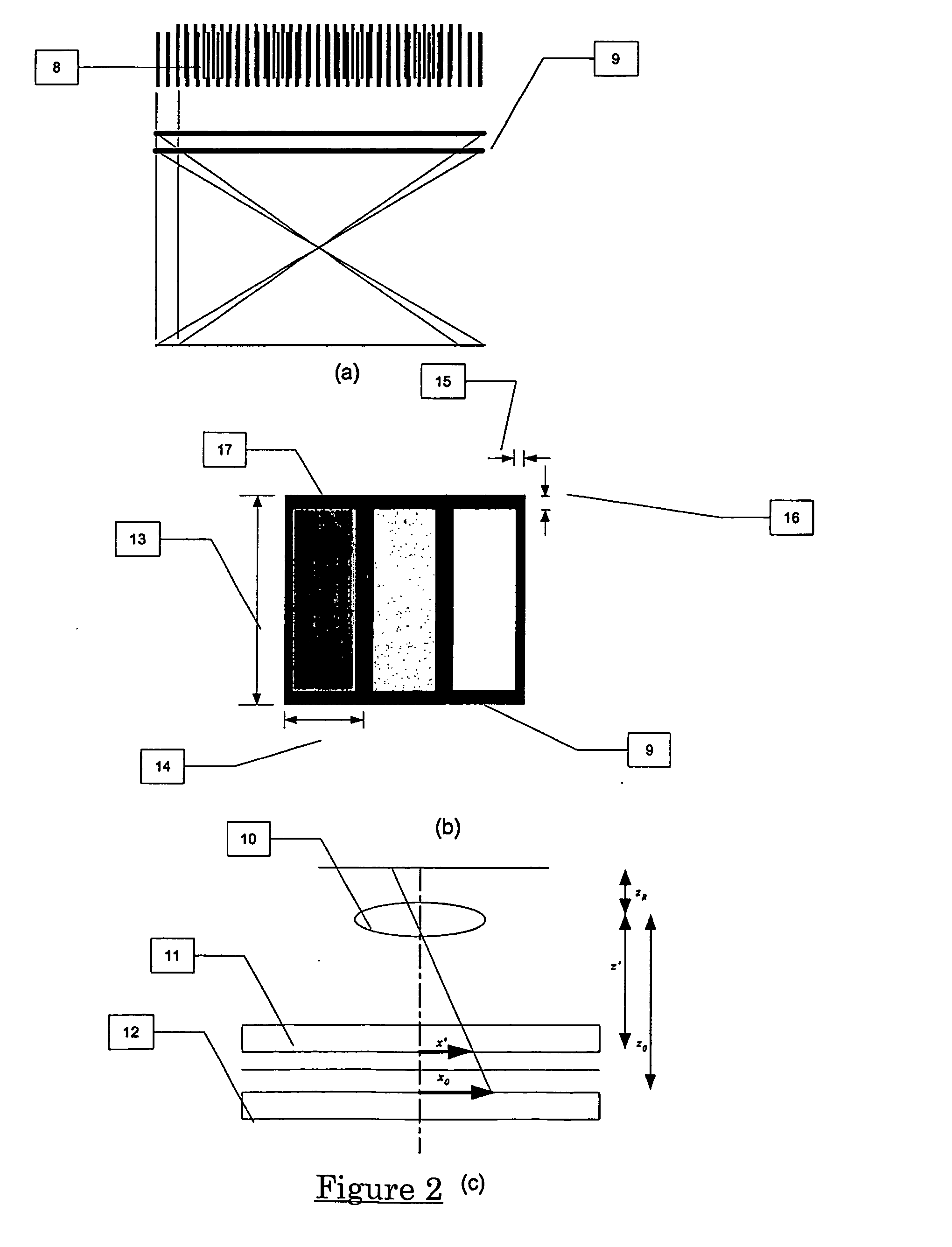
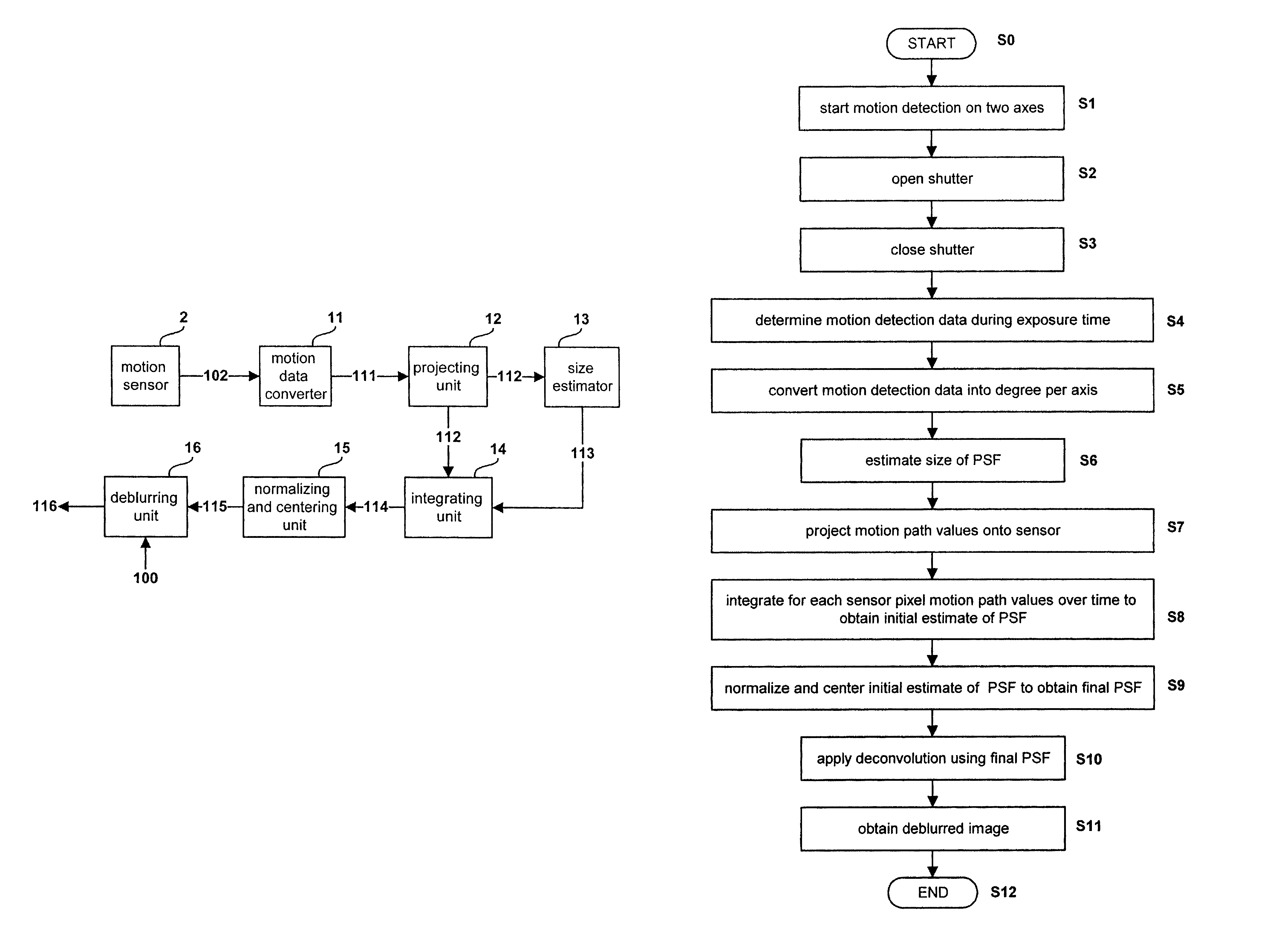
Method and system for obtaining a point spread function using motion information
InactiveUS8648918B2Function increaseLess complexImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDiffusion functionPoint spread function
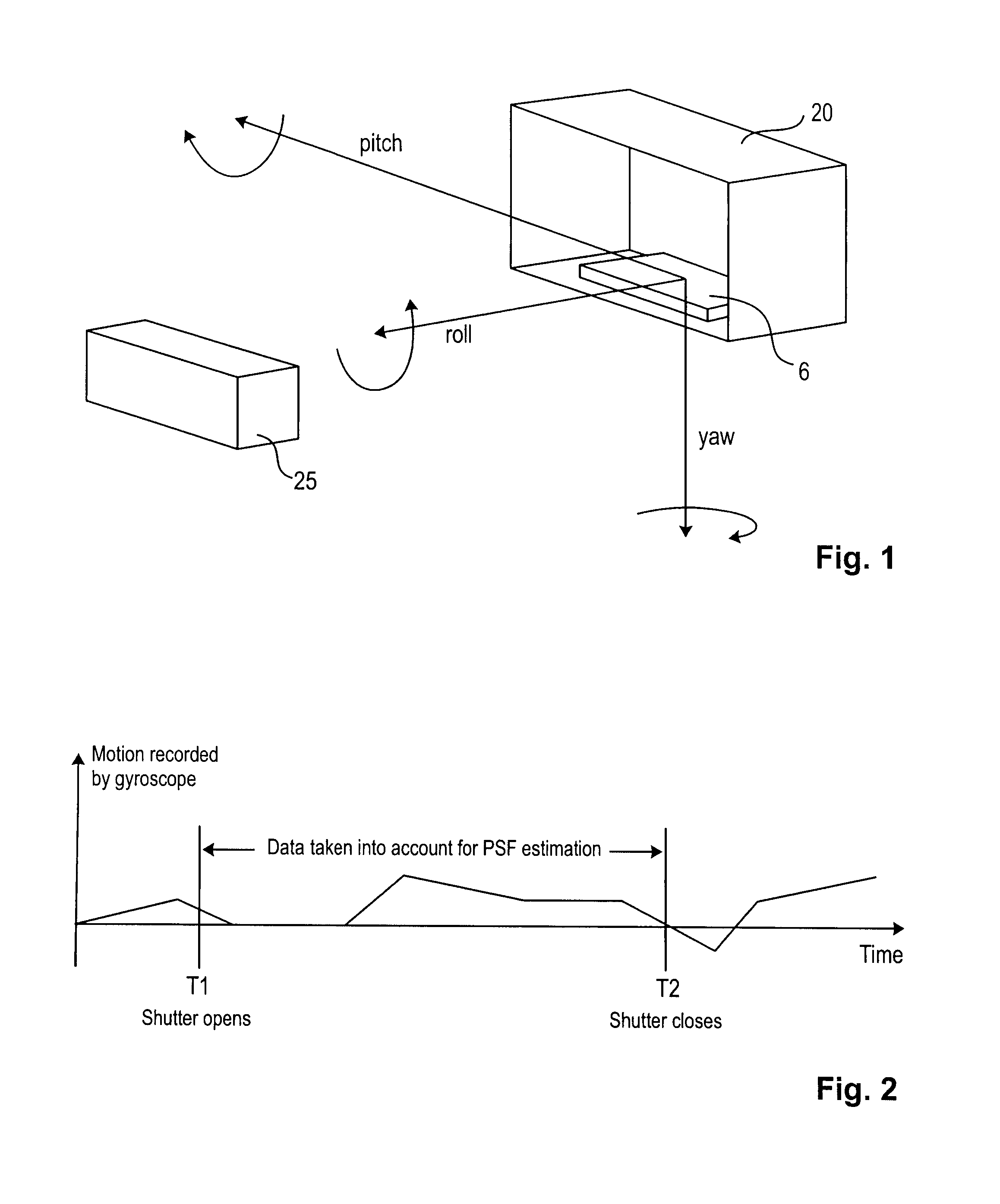
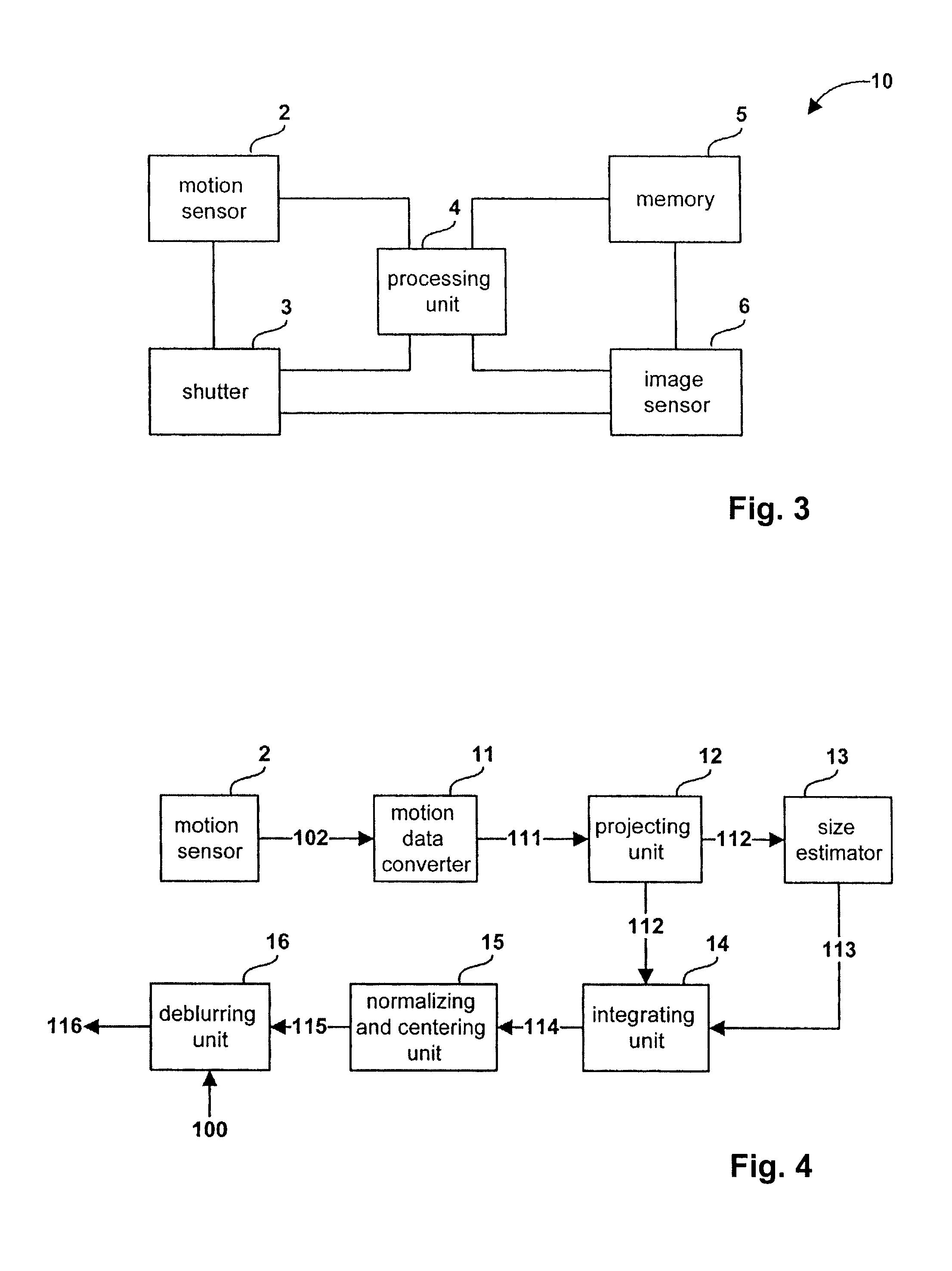
The present invention relates to a method and system for obtaining a point spread function for deblurring image data captured by an imaging device comprising a motion sensor. First, motion path values indicating the motion of the imaging device during the exposure time are acquired. The motion path values of the imaging device are then projected onto the sensor plane and for each sensor pixel the projected motion path values are integrated over time. Said integrated value represents for each sensor pixel an initial estimate of the point spread function. Optionally, the size of the point spread function can also be estimated based on the distance of the focused object and taken into account during the projecting step.
Owner:SONY CORP
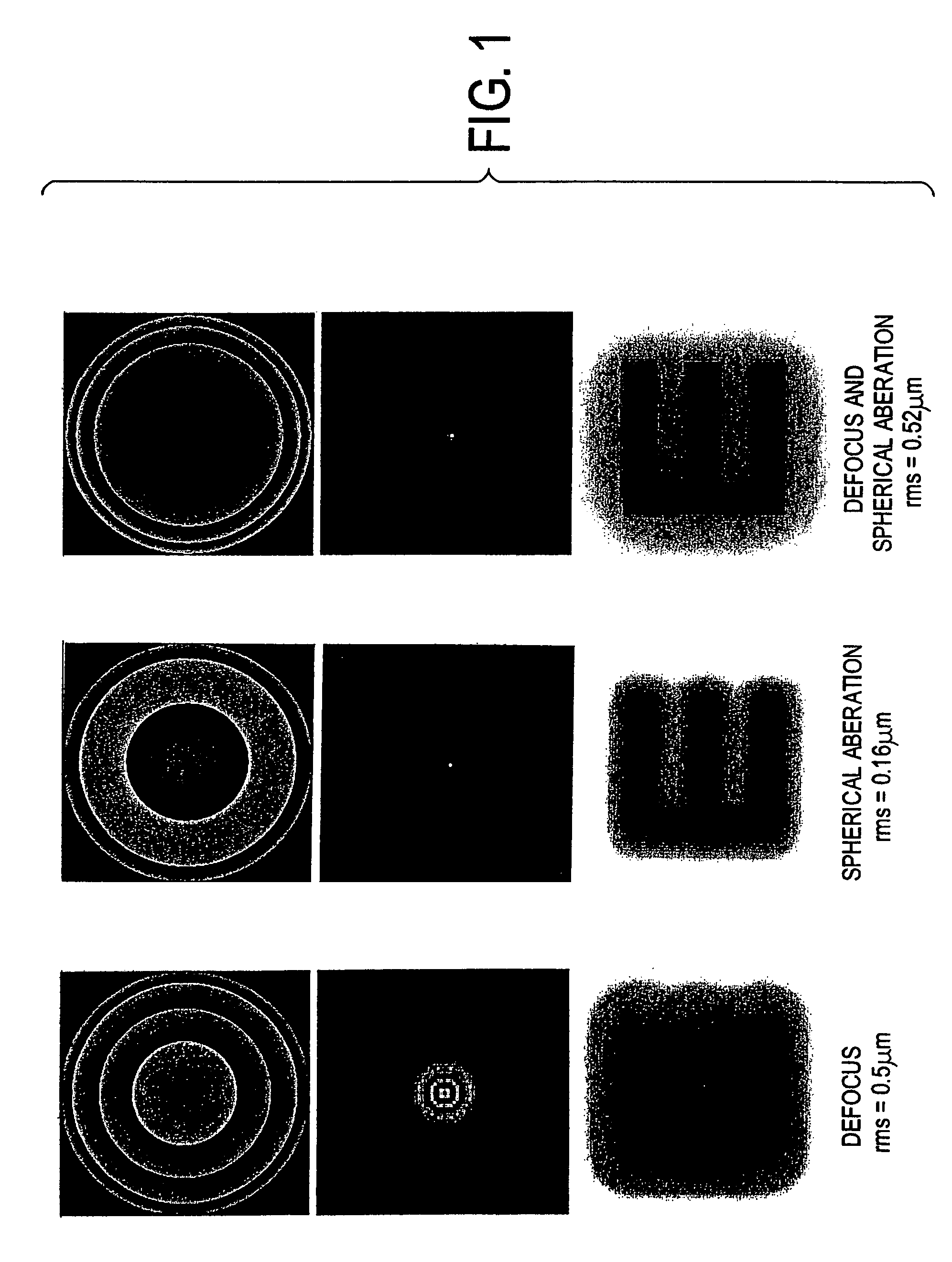
Extended depth of field using a multi-focal length lens with a controlled range of spherical aberration and a centrally obscured aperture
ActiveUS7336430B2Easy to manufactureUniform responseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsIntermediate imageImaging quality
An extended depth of field is achieved by a computational imaging system that combines a multifocal imaging subsystem for producing a purposefully blurred intermediate image with a digital processing subsystem for producing a recovered image having an extended depth of field. The multifocal imaging system preferably exhibits spherical aberration as the dominant feature of the purposeful blur. A central obscuration of the multifocal imaging subsystem renders point-spread functions of object points more uniform over a range of object distances. An iterative digital deconvolution algorithm for converting the intermediate image into the recovered image contains a metric parameter that speeds convergence, avoids stagnations, and enhances image quality.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Camera with image enhancement functions
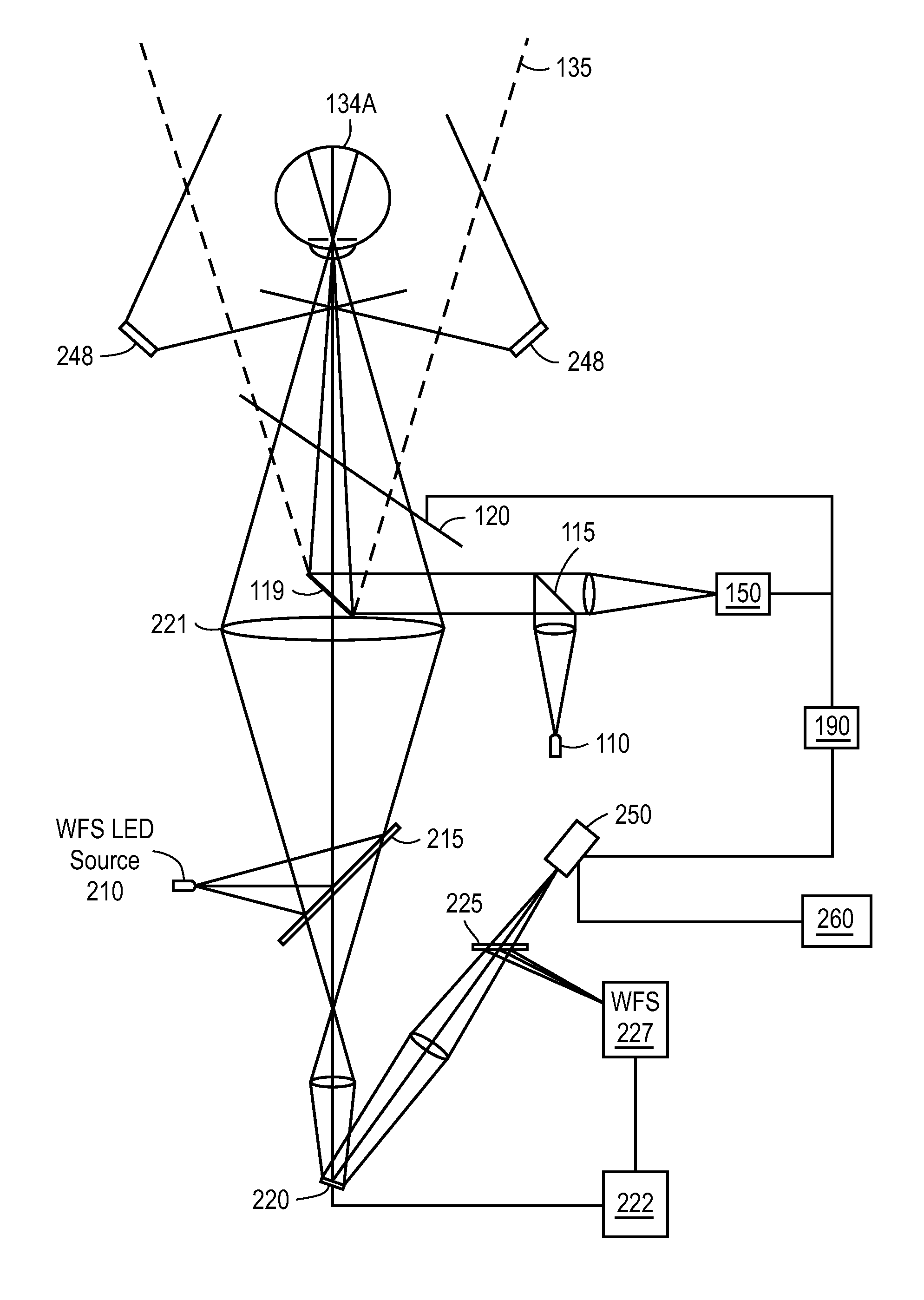
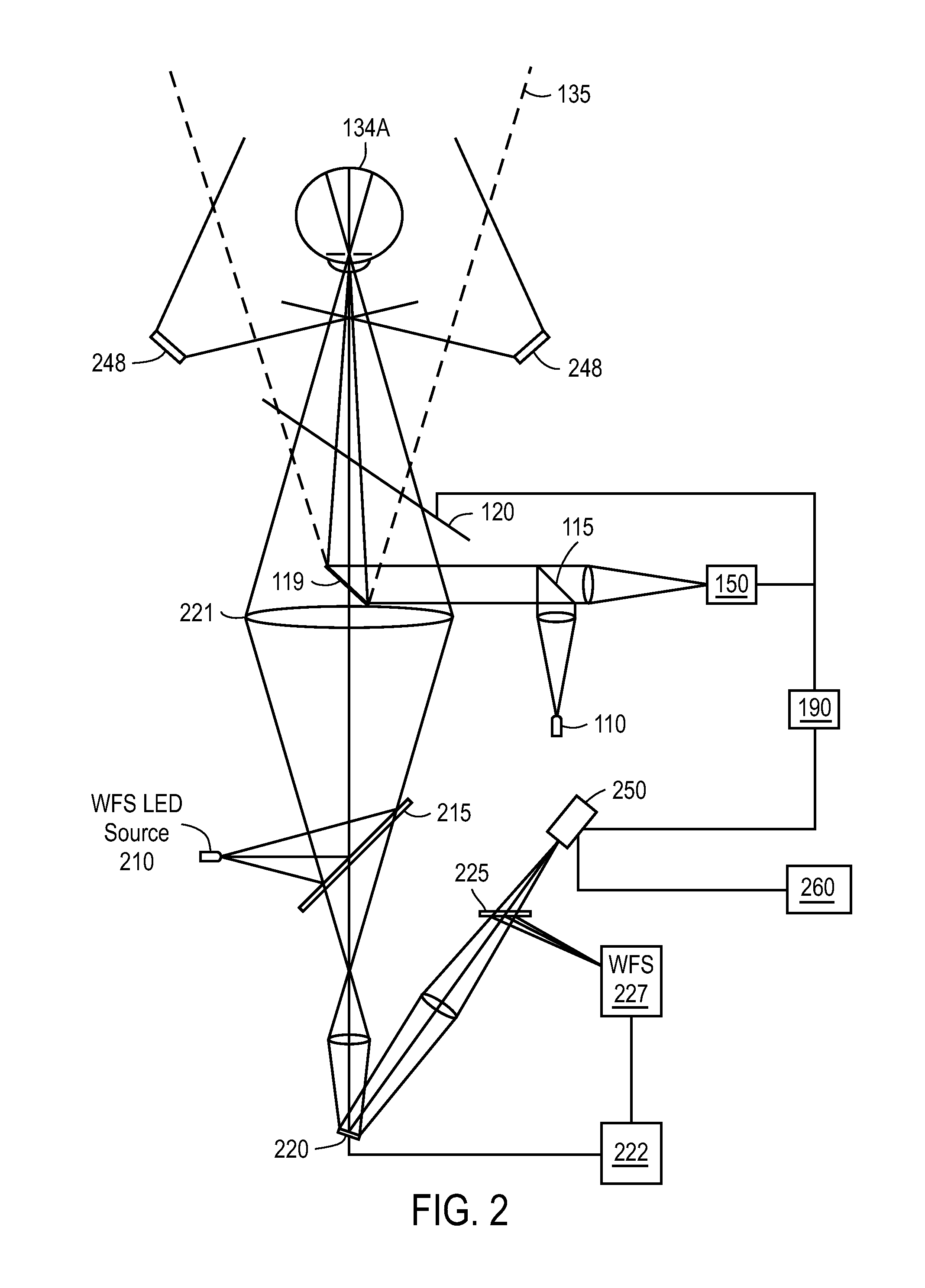
ActiveUS20060256226A1Improve image qualityHigh quality imagingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsOptical radiationOptical axis
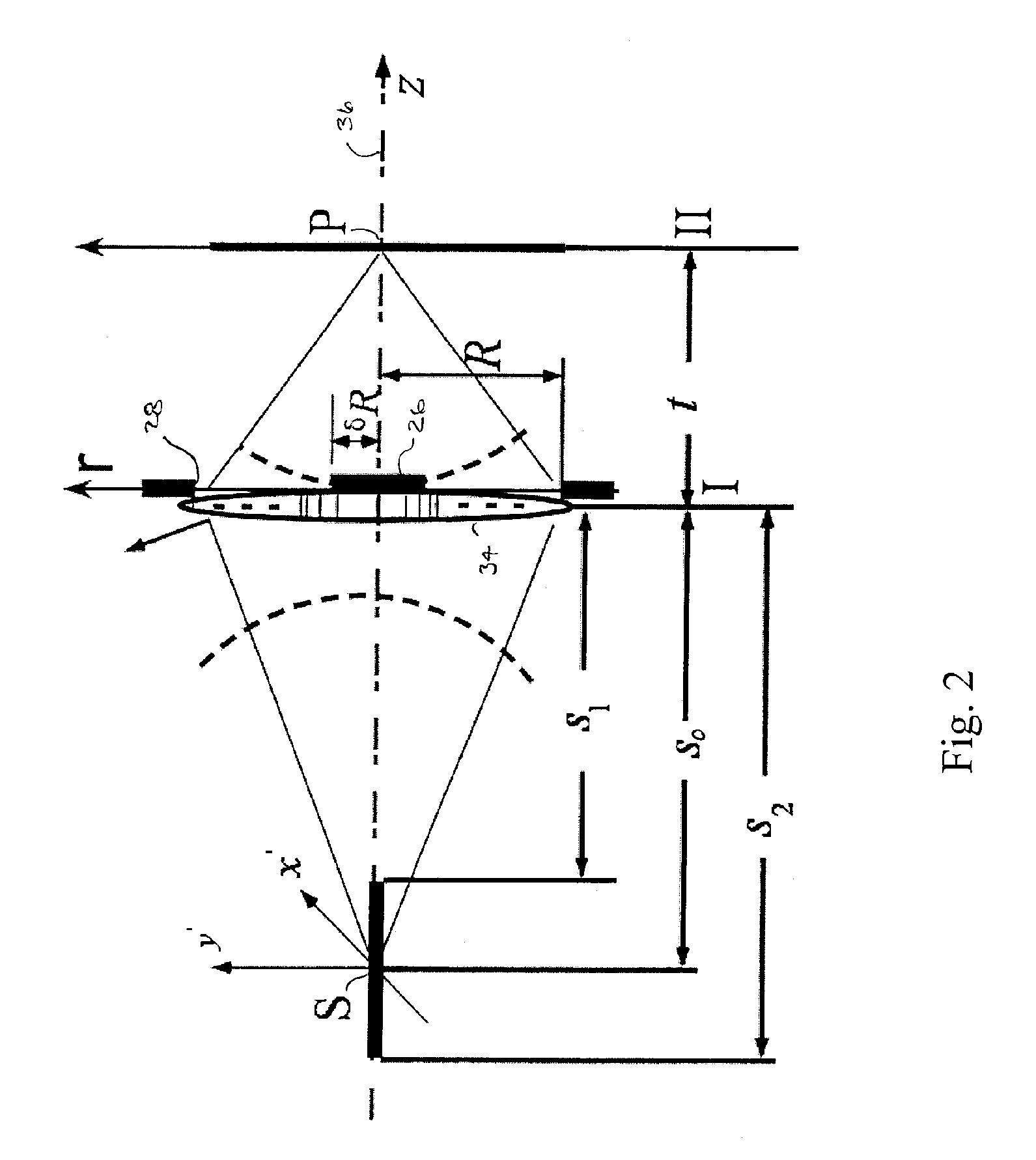
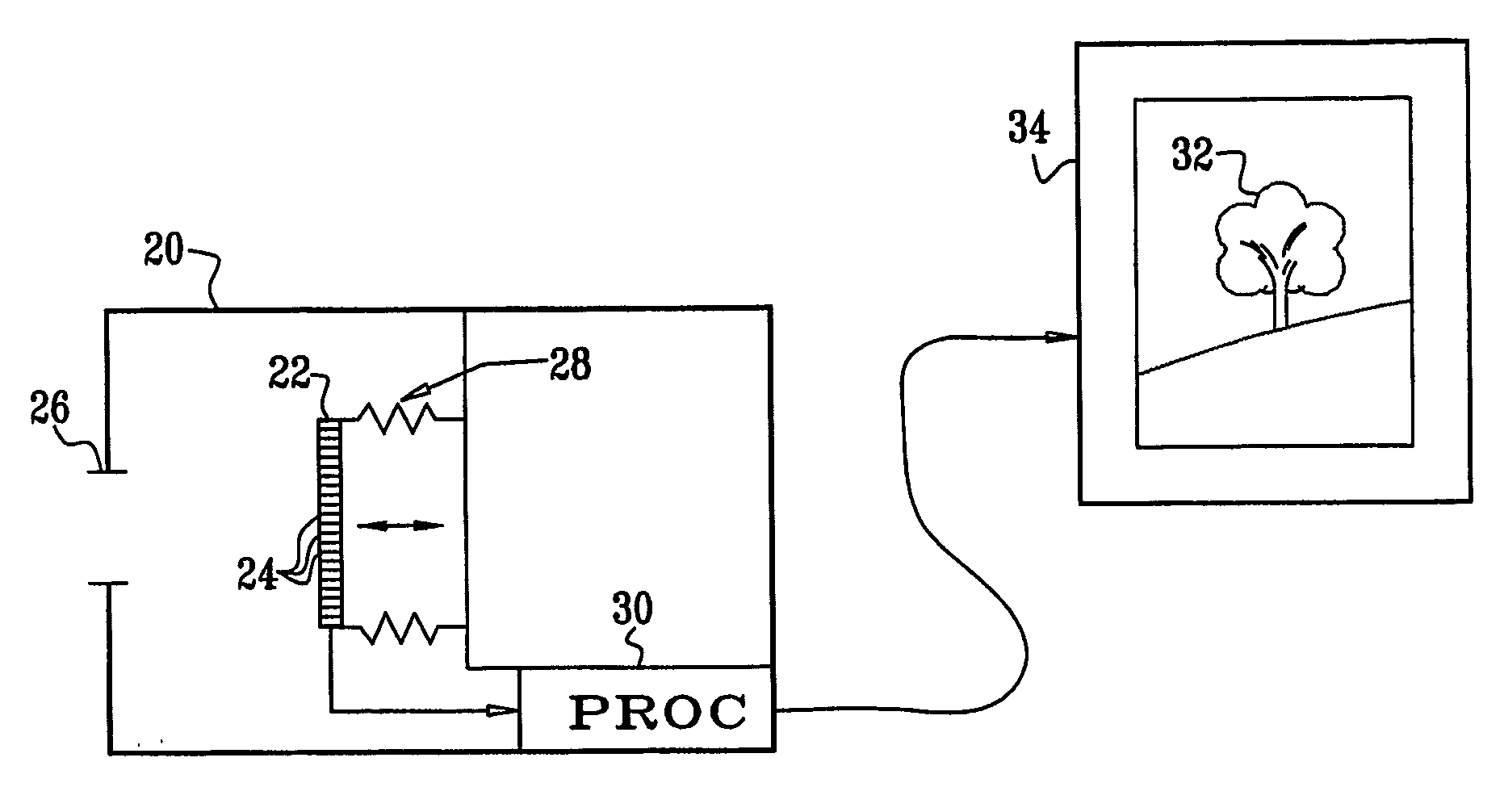
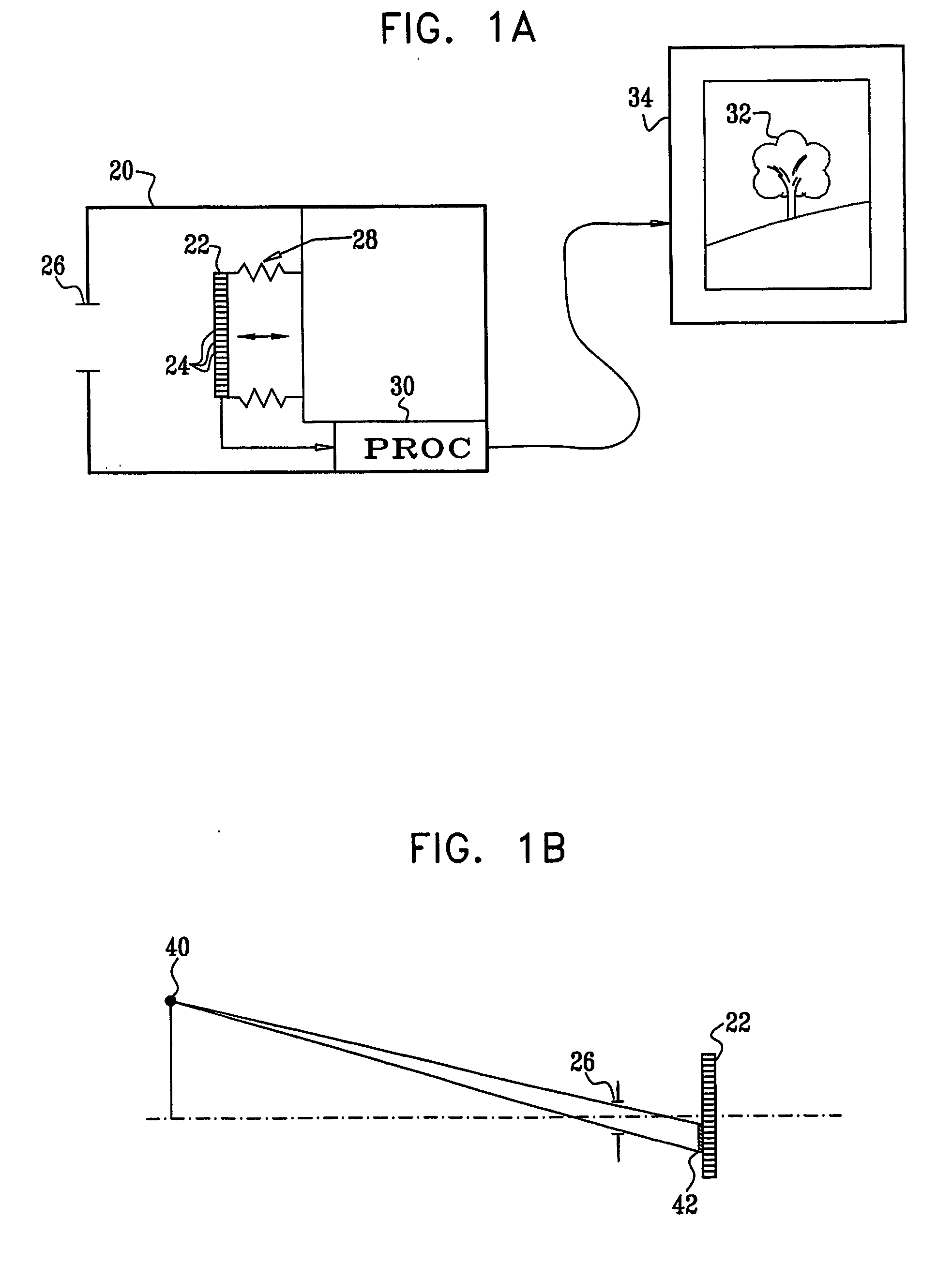
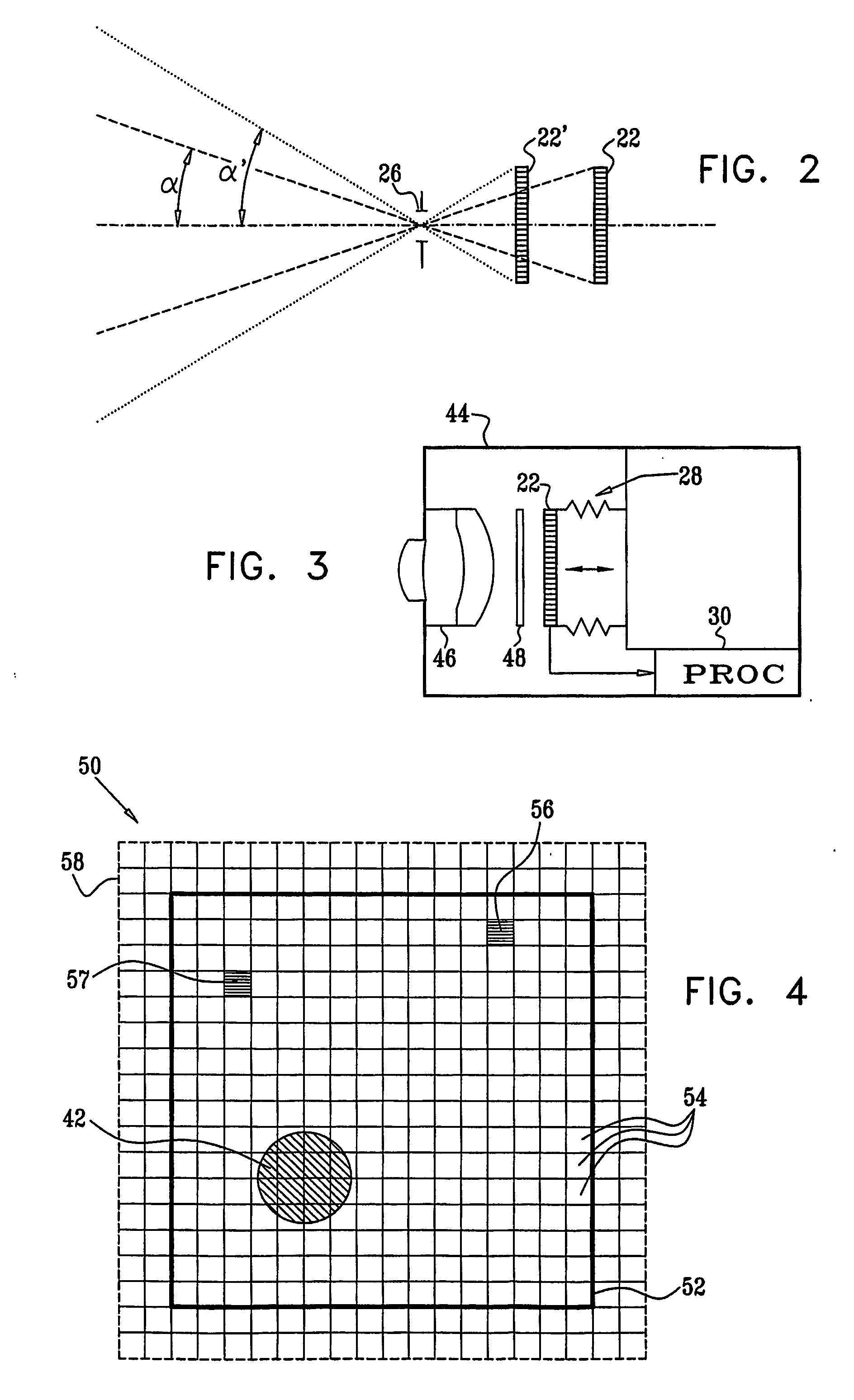
Imaging apparatus (20, 44) includes an array (22) of optical sensing elements (24), characterized by a pitch, which is adapted to generate a signal in response to optical radiation that is incident on the elements. Objective optics (26, 46), which have an optical axis (134) and are characterized by a cylindrical symmetry about the axis, are arranged to focus the optical radiation from an object onto the array with a point spread function (PSF) having an extent greater than twice the pitch of the array at an optimal focus of the objective optics.
Owner:DIGITALOPTICS CORPORATION
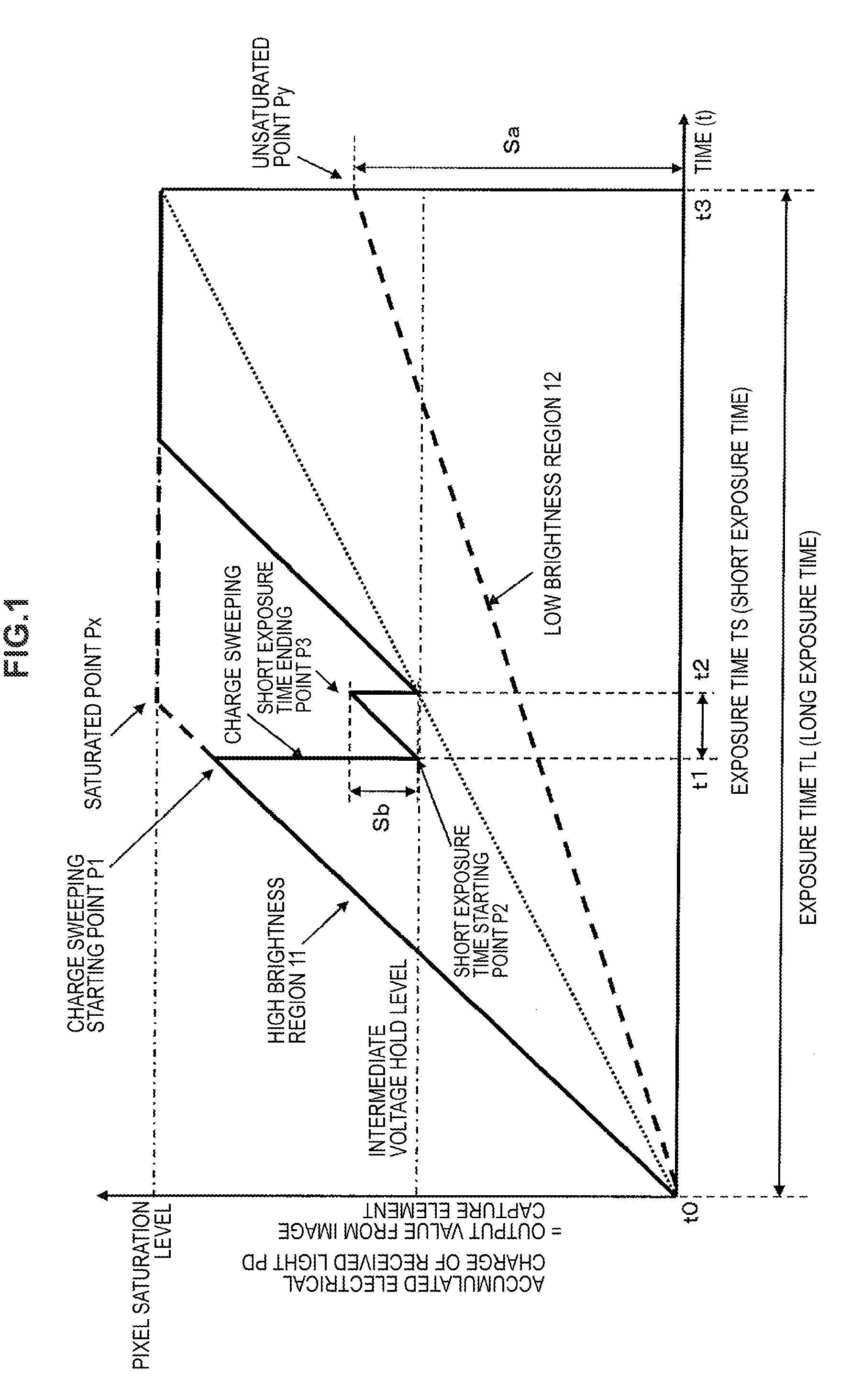
Image processing device, image processing method, and program
InactiveUS20120281111A1Reduce blurWide dynamic rangeImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingPoint spread function
Long and short exposure time pixel information are input to pixel information. A long exposure time image set with the pixel values assuming all of the pixels have been exposed for a long time and a short exposure time image set with the pixel values assuming all of the pixels have been exposed for a short time are generated. A point spread function corresponding to the long exposure time image is computed as a long exposure time image PSF. A corrected image is generated using the short exposure time image, the long exposure time image, and the long exposure time image PSF. The corrected image is generated as a wide dynamic range image utilizing the pixel information for the long and short exposure time image. Utilizing the pixel information for the short exposure time image with little blurring, makes the corrected image a high quality corrected image with little blurring.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Systems and methods for de-blurring motion blurred images
Systems and methods for providing a substantially de-blurred image of a scene from a motion blurred image of the scene are disclosed. An exemplary system includes a primary detector for sensing the motion blurred image and generating primary image information representing the blurred image, a secondary detector for sensing two or more secondary images of the scene and for generating secondary image information representing the two or more secondary images, and a processor for determining motion information from the secondary image information, estimating a point spread function for the motion blurred image from the motion information, and applying the estimated point spread function to the primary image information to generate information representing the substantially de-blurred image.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Methods of calibrating an imaging system using calibration beads
InactiveUS6906792B2Improve liquidityEasy procedureImage analysisIndividual particle analysisPoint spreadSmall sample
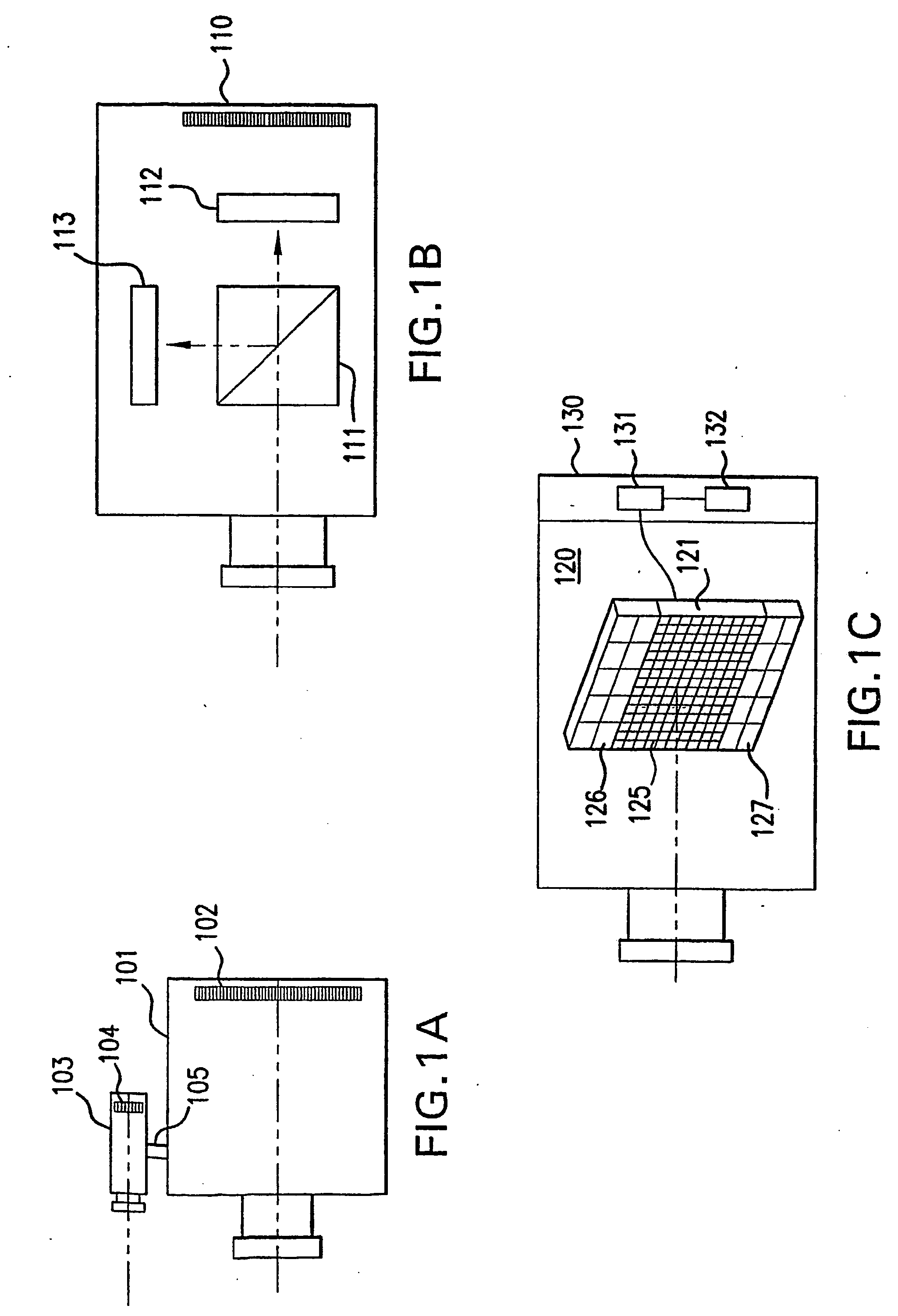
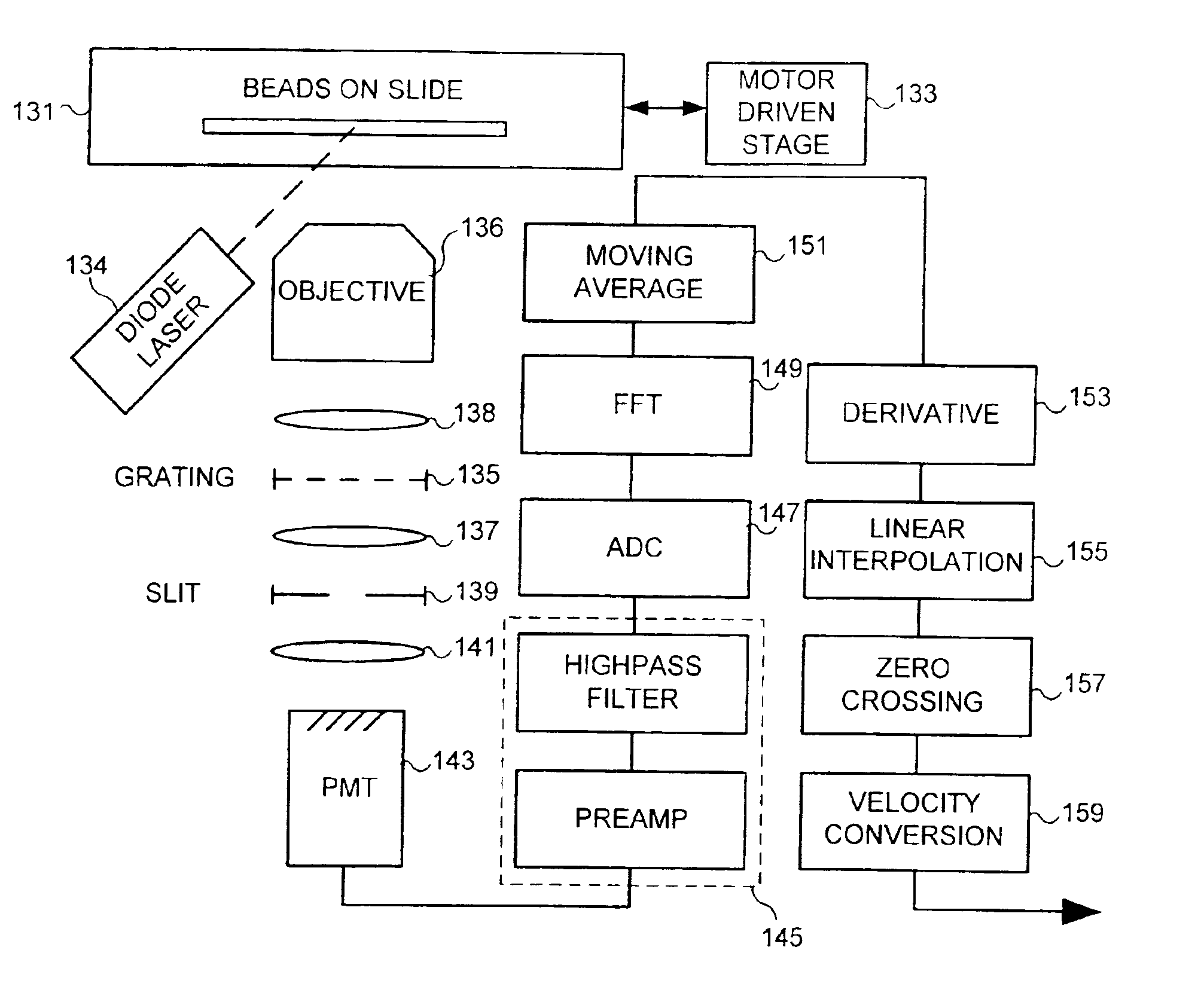
When utilized in a flow imaging instrument, calibration beads provide a known data source that can be employed in various self-diagnostic, calibration and quality metric applications for the both the optical system of the flow imaging instrument, as well as the flow cell of the flow imaging instrument. Such data can be used to determine point spread functions associated with an imaging system, to determine a sensitivity of an imaging system, and to determine a focal point of the imaging system. Imagery collected from calibration beads can be used to determine core size and stability and TDI / flow speed synchronization. Calibration beads can be beneficially employed to enable stable system operation, even when very low sample concentration, or very small sample sizes are to be analyzed.
Owner:AMNIS CORP
Method and apparatus for initiating subsequent exposures based on determination of motion blurring artifacts
InactiveUS20060098237A1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionReal time analysisPoint spread function
A digital image acquisition system includes a portable apparatus for capturing digital images and a digital processing component for detecting, analyzing, invoking subsequent image captures and informing the photographer regarding motion blur, and for reducing camera motion blur in an image captured by the apparatus. The digital processing component operates by comparing the image with at least one other image, for example a preview image, of nominally the same scene taken outside the exposure period of the main image. In one embodiment the digital processing component identifies at least one feature in a single preview image which is relatively less blurred than the corresponding feature in the main image, calculates a point spread function (PSF) in respect of such feature, and initiates a subsequent capture if determined that the motion blur exceeds a certain threshold. In another embodiment the digital processing determines the degree of blur by analyzing the motion blur in the captured image itself, and initiates a subsequent capture if determined that the motion blur exceeds a certain threshold. Such real time analysis may use the auto focusing mechanism to qualitatively determine the PSF.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Post processing of iris images to increase image quality
ActiveUS7869627B2Quality improvementLow resolution imageTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersDiffusion functionImage resolution
A rapid iris acquisition, tracking, and imaging system can be used at longer standoff distances and over larger capture volumes, without the active cooperation of subjects. Light illuminates the subjects' eyes and a high resolution camera captures images of the irises. The images of the irises are processed by a post processing module to improve their quality. In one approach, the point spread function of the image capture subsystem is estimated using glint reflections from the eye, and the estimated point spread function is used in deconvolution to increase the resolution of the iris images. The post processed iris images have sufficient resolution to be used for biometric identification.
Owner:TASCENT INC
Robust reconstruction of high resolution grayscale images from a sequence of low resolution frames
ActiveUS20070217713A1Fast and robust super-resolutionImprove performanceImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersPoint spread functionImage resolution
A computer method of creating a super-resolved grayscale image from lower-resolution images using an L1 norm data fidelity penalty term to enforce similarities between low and a high-resolution image estimates is provided. A spatial penalty term encourages sharp edges in the high-resolution image, the data fidelity penalty term is applied to space invariant point spread function, translational, affine, projective and dense motion models including fusing the lower-resolution images, to estimate a blurred higher-resolution image and then a deblurred image. The data fidelity penalty term uses the L1 norm in a likelihood fidelity term for motion estimation errors. The spatial penalty term uses bilateral-TV regularization with an image having horizontal and vertical pixel-shift terms, and a scalar weight between 0 and 1. The penalty terms create an overall cost function having steepest descent optimization applied for minimization. Direct image operator effects replace matrices for speed and efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
Use of wavefront coding to create a depth image
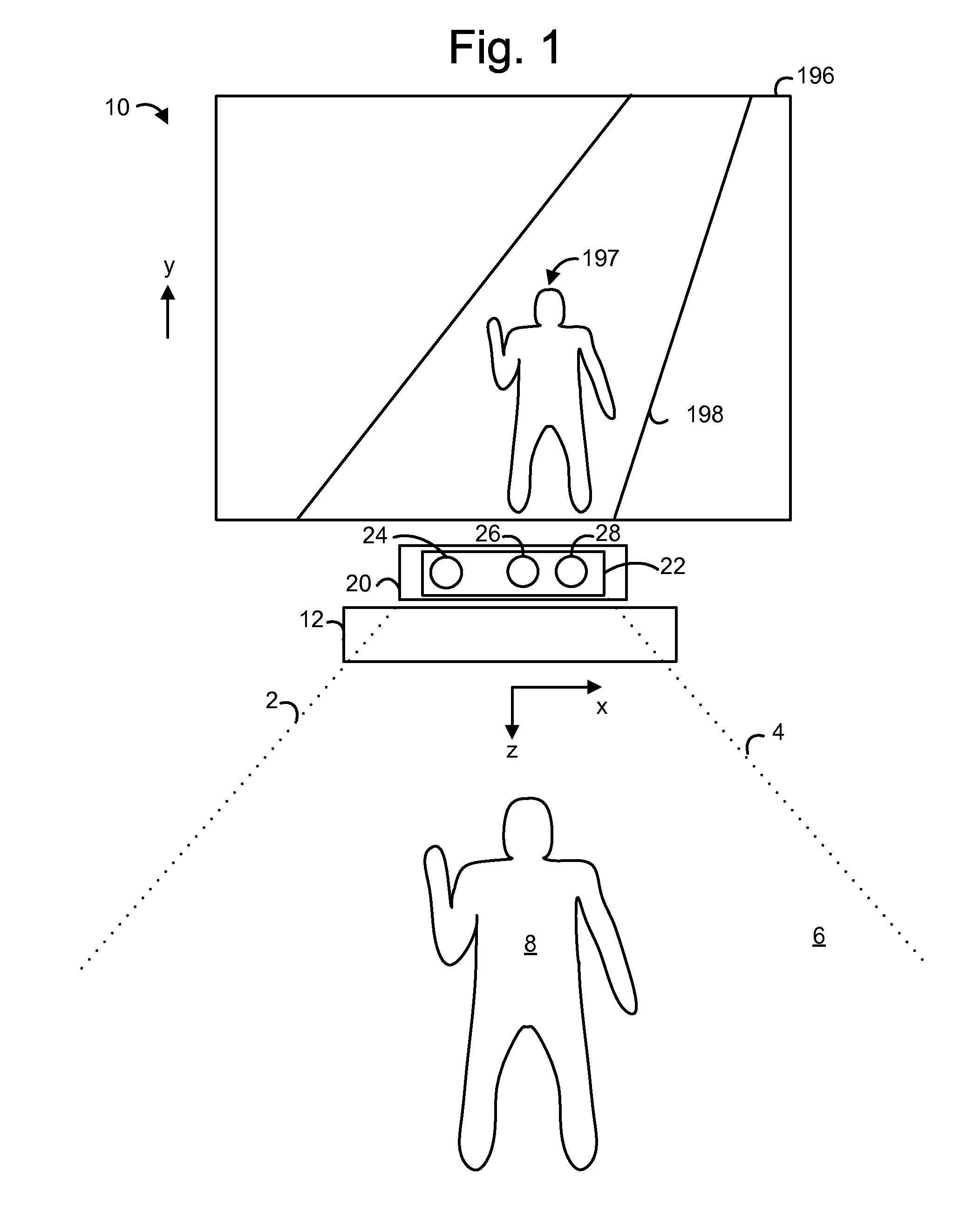
ActiveUS20110310226A1Well formedCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansDiffusion functionMotion capture
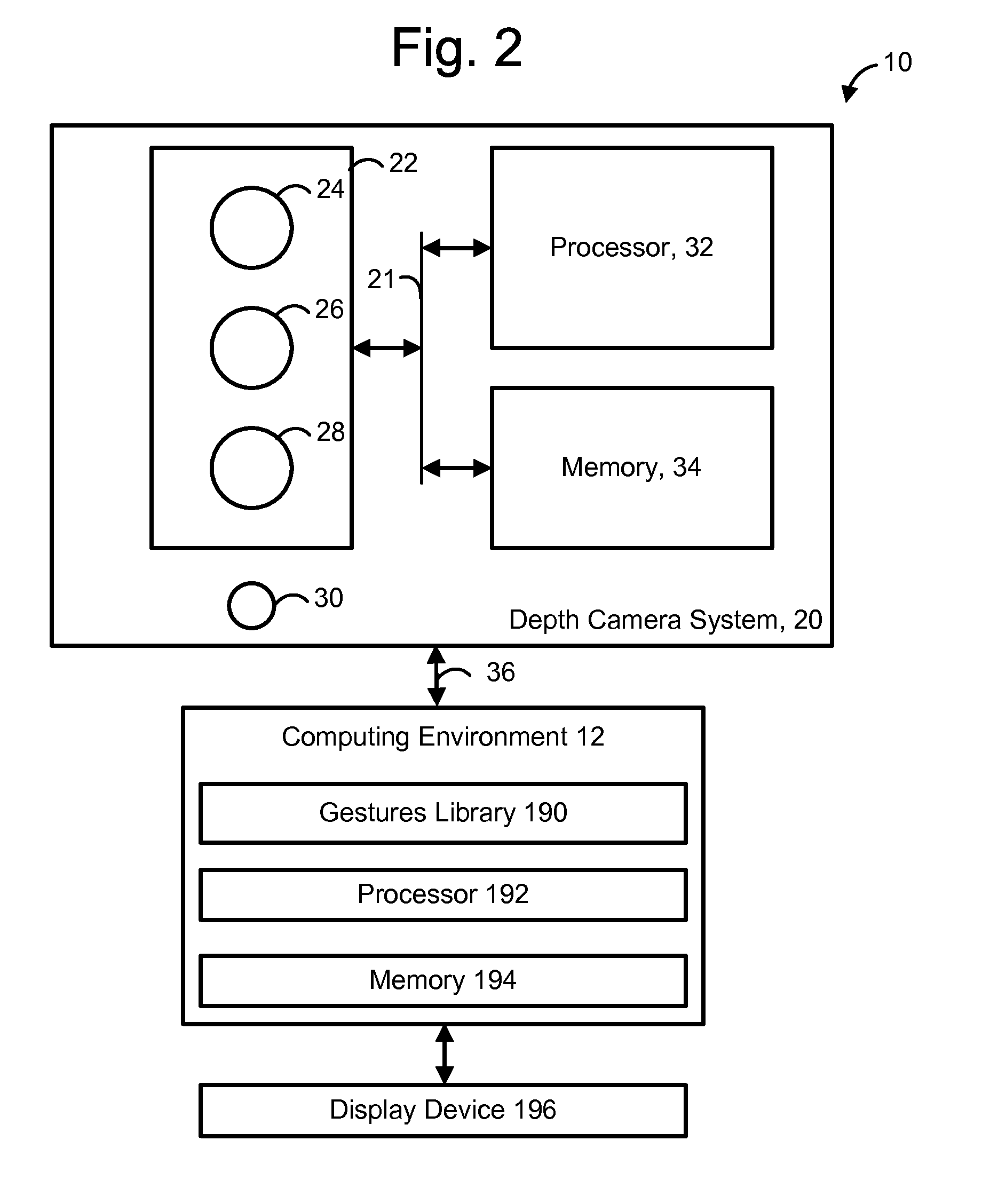
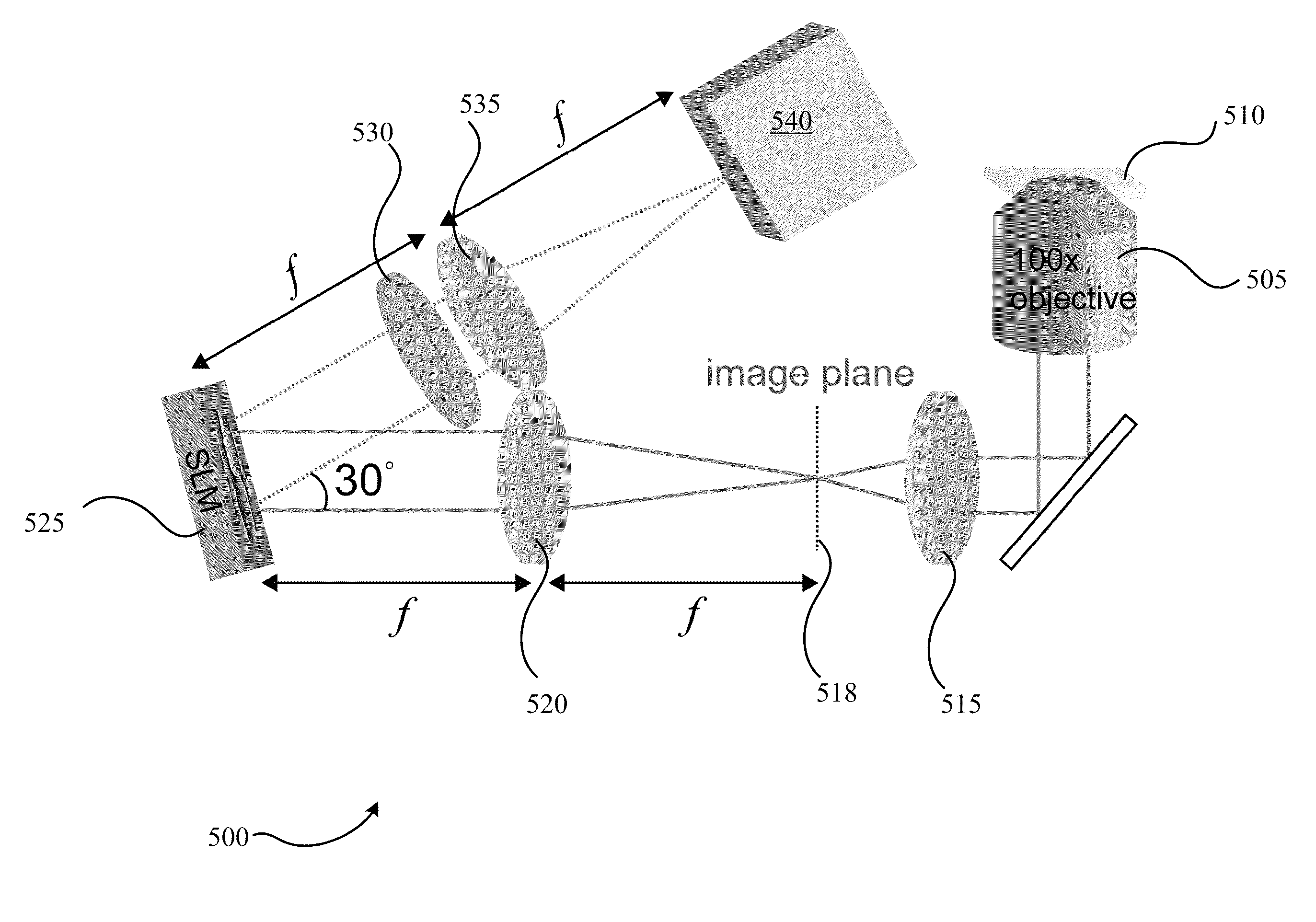
A 3-D depth camera system, such as in a motion capture system, tracks an object such as a human in a field of view using an illuminator, where the field of view is illuminated using multiple diffracted beams. An image sensing component obtains an image of the object using a phase mask according to a double-helix point spread function, and determines a depth of each portion of the image based on a relative rotation of dots of light of the double-helix point spread function. In another aspect, dual image sensors are used to obtain a reference image and a phase-encoded image. A relative rotation of features in the images can be correlated with a depth. Depth information can be obtained using an optical transfer function of a point spread function of the reference image.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method And System For Optical Imaging And Ranging
ActiveUS20080137059A1Maximises informationOptimize depth estimationOptical rangefindersSensor arrayCMOS
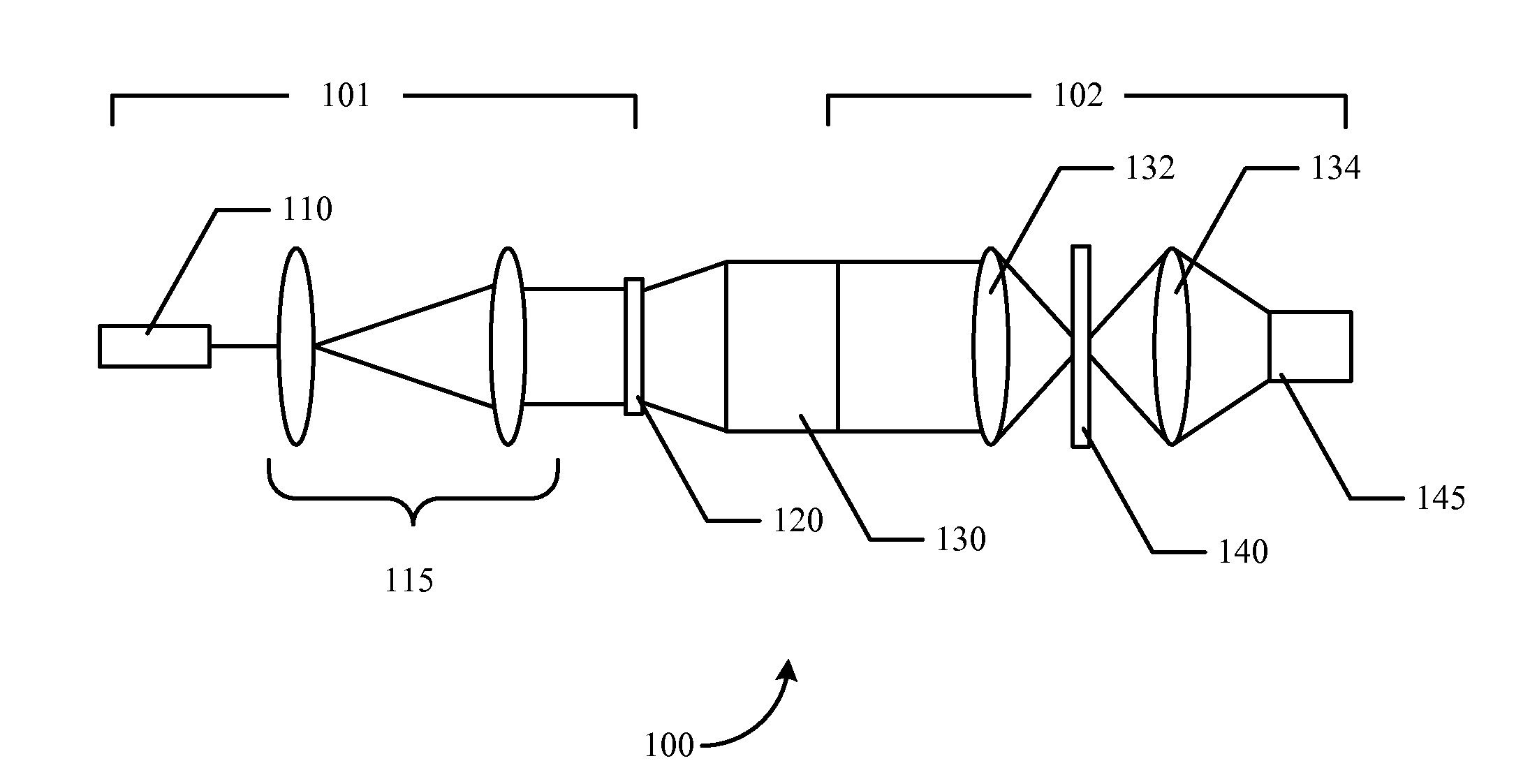
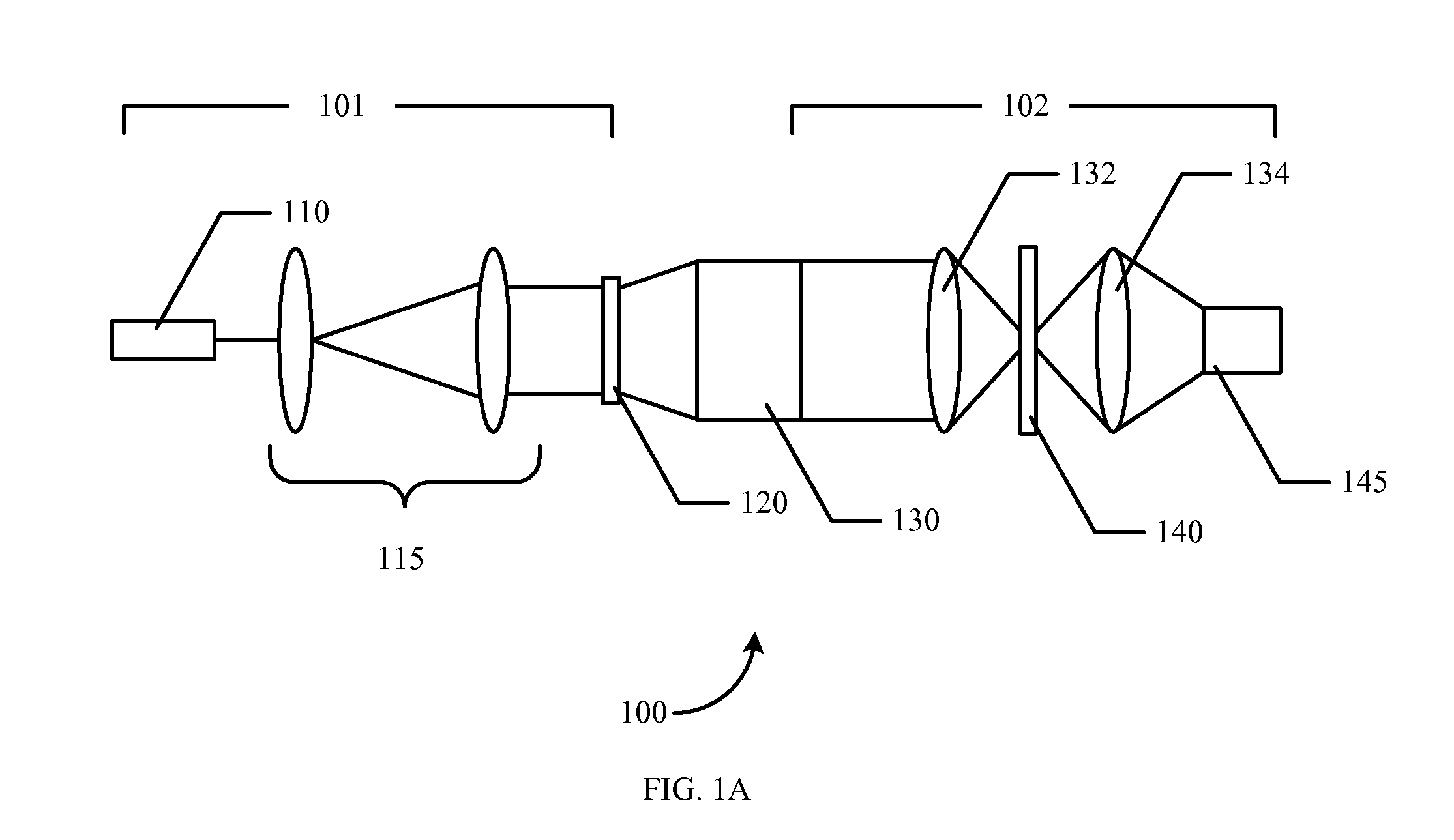
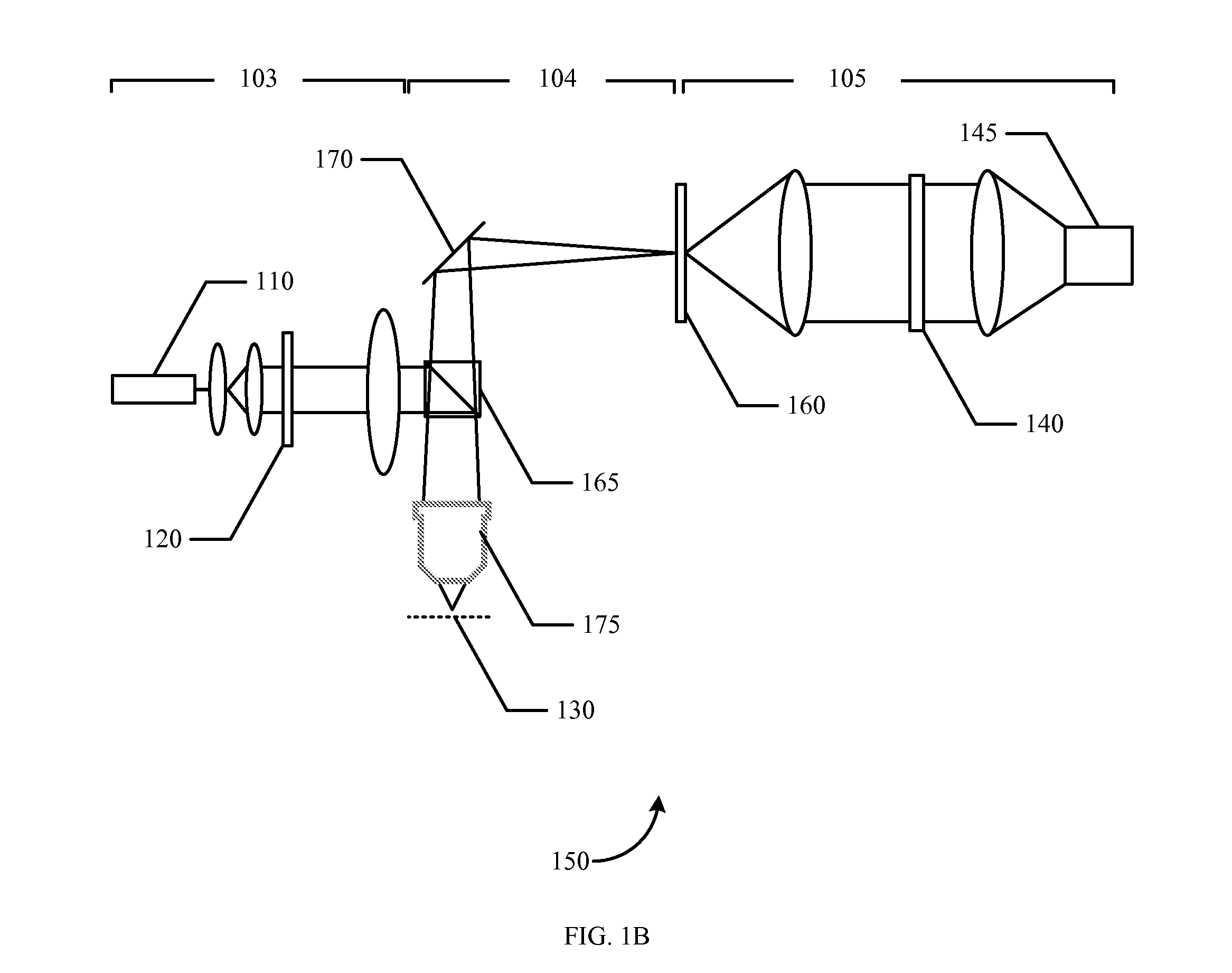
The distance of objects to an optical system is estimated. An optical mask such as a diffractive optical element, continuous phase mask, hologram, amplitude mask, or combination thereof is placed within the optics in front of a sensor array such as a CCD, CID or CMOS device. The optical mask encodes the three-dimensional response of the system. The mask is designed to optimize depth estimation, for example, by maximizing Fisher information. A particular implementation creates a point spread function (“PSF”) that rotates as a function of the object position. The image or images obtained with different PSFs may be digitally processed to recover both a depth map of the scene and other parameters such as image brightness. The digital processing used to recover the depth map of the object may include deconvolution of a PSF from detected images.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD +1
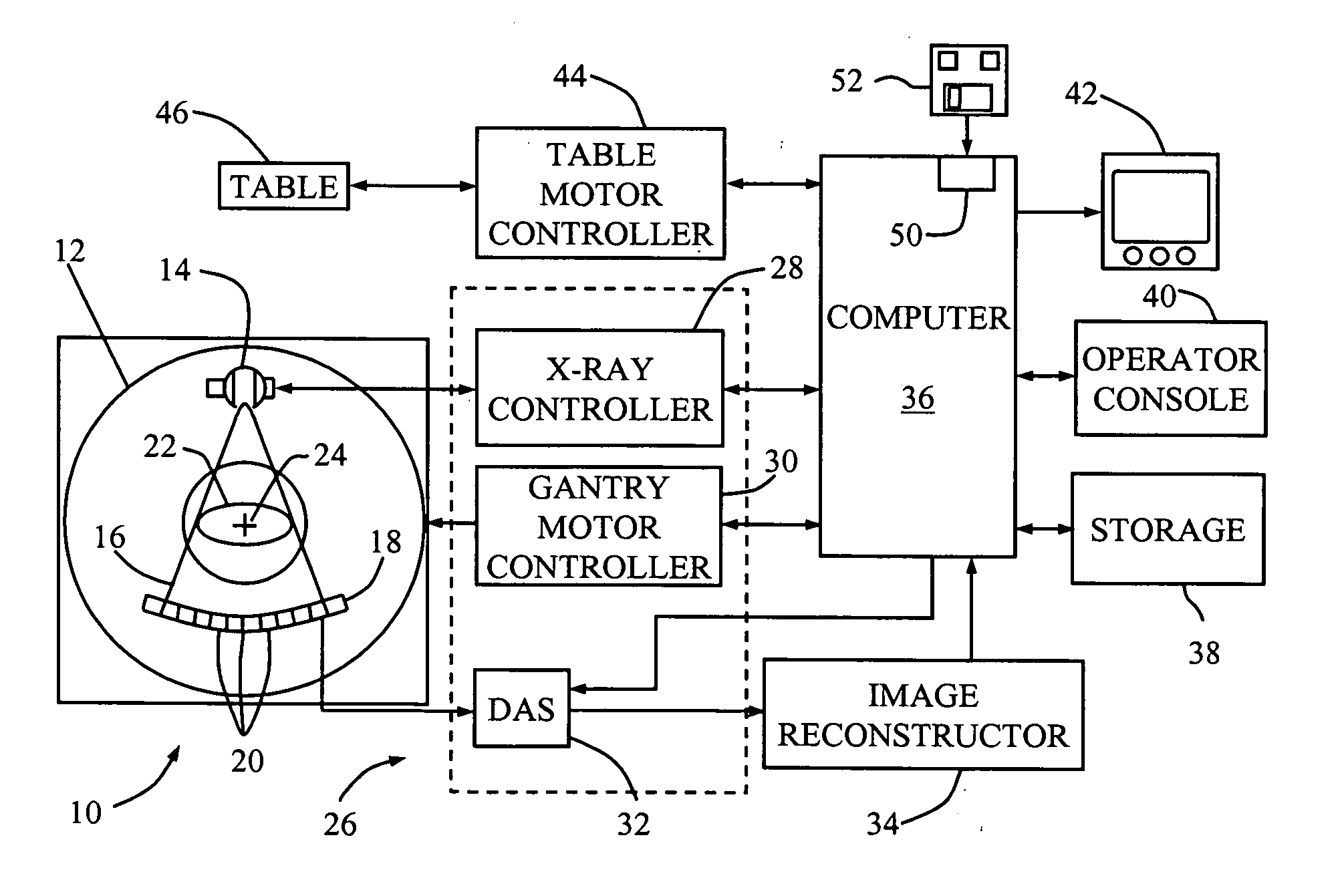
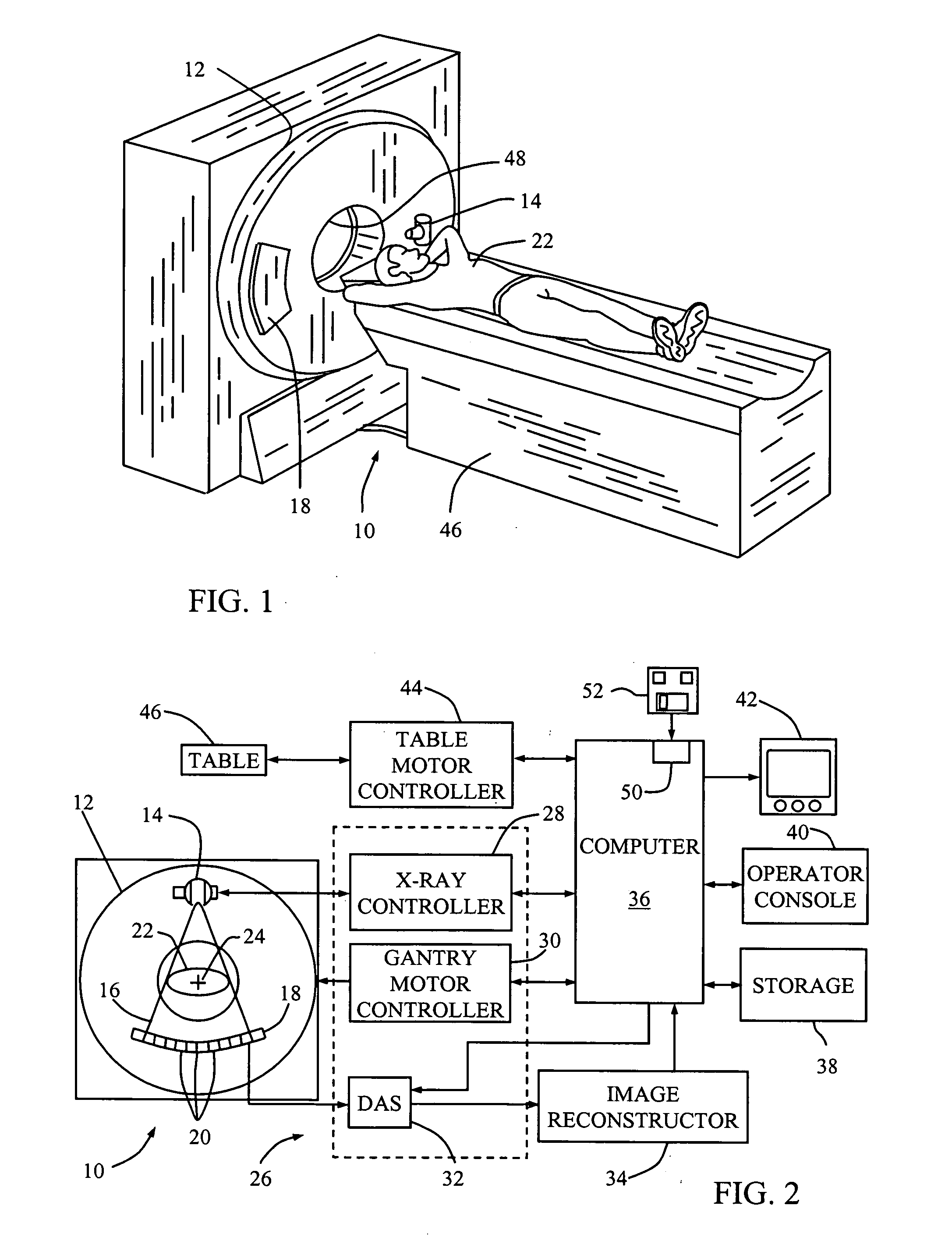
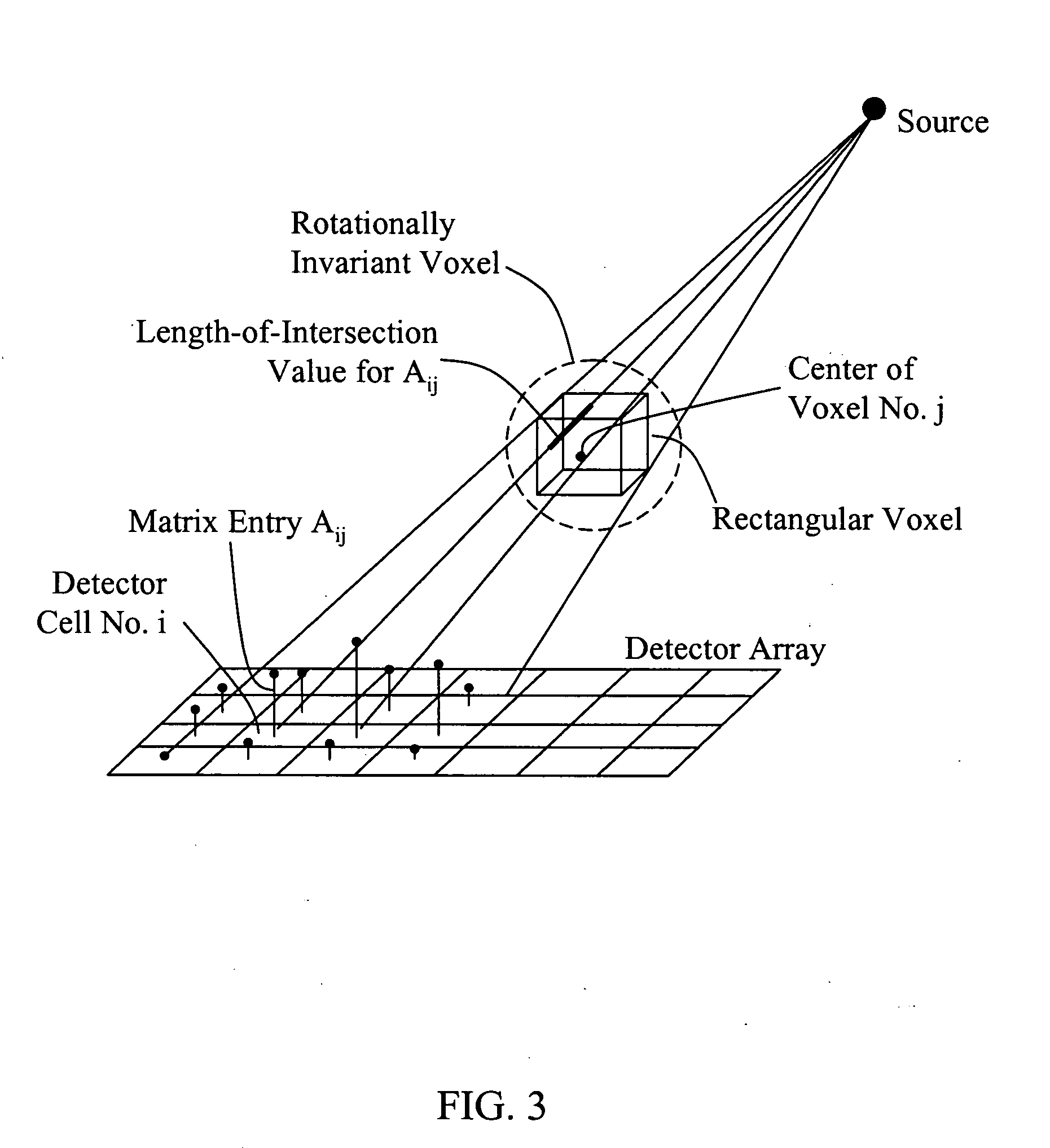
Methods, apparatus, and software to facilitate iterative reconstruction of images
ActiveUS20060104410A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPoint spread functionX ray image
A method of reconstructing an image includes performing an iterative CT X-ray image reconstruction using a model including a point spread function (PSF) to reconstruct an image.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +2
Method of Determining PSF Using Multiple Instances of a Nominally Scene
A digital image acquisition system includes a portable apparatus for capturing digital images and a digital processing component for detecting, analyzing and informing the photographer regarding motion blur, and for reducing camera motion blur in an image captured by the apparatus. The digital processing component operates by comparing the image with at least one other image, for example a preview image, of nominally the same scene taken outside the exposure period of the main image. In one embodiment the digital processing component identifies at least one feature in a single preview image which is relatively less blurred than the corresponding feature in the main image, calculates a point spread function (PSF) in respect of such feature, and de-convolves the main image using the PSF. In another embodiment, the digital processing component calculates a trajectory of at least one feature in a plurality of preview images, extrapolates such feature on to the main image, calculates a PSF in respect of the feature, and de-convolves the main image using the PSF. In another embodiment the digital processing unit after determining the degree of blur notifies the photographer of the existing blur or automatically invokes consecutive captures.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
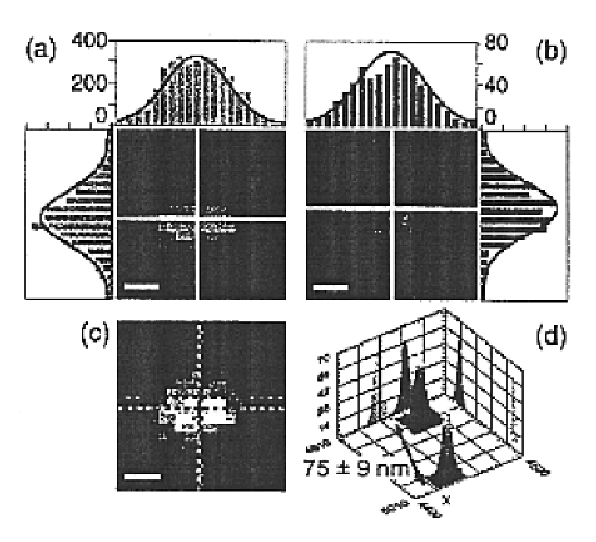
Three-dimensional single-molecule fluorescence imaging beyond the diffraction limit using a double-helix point spread function
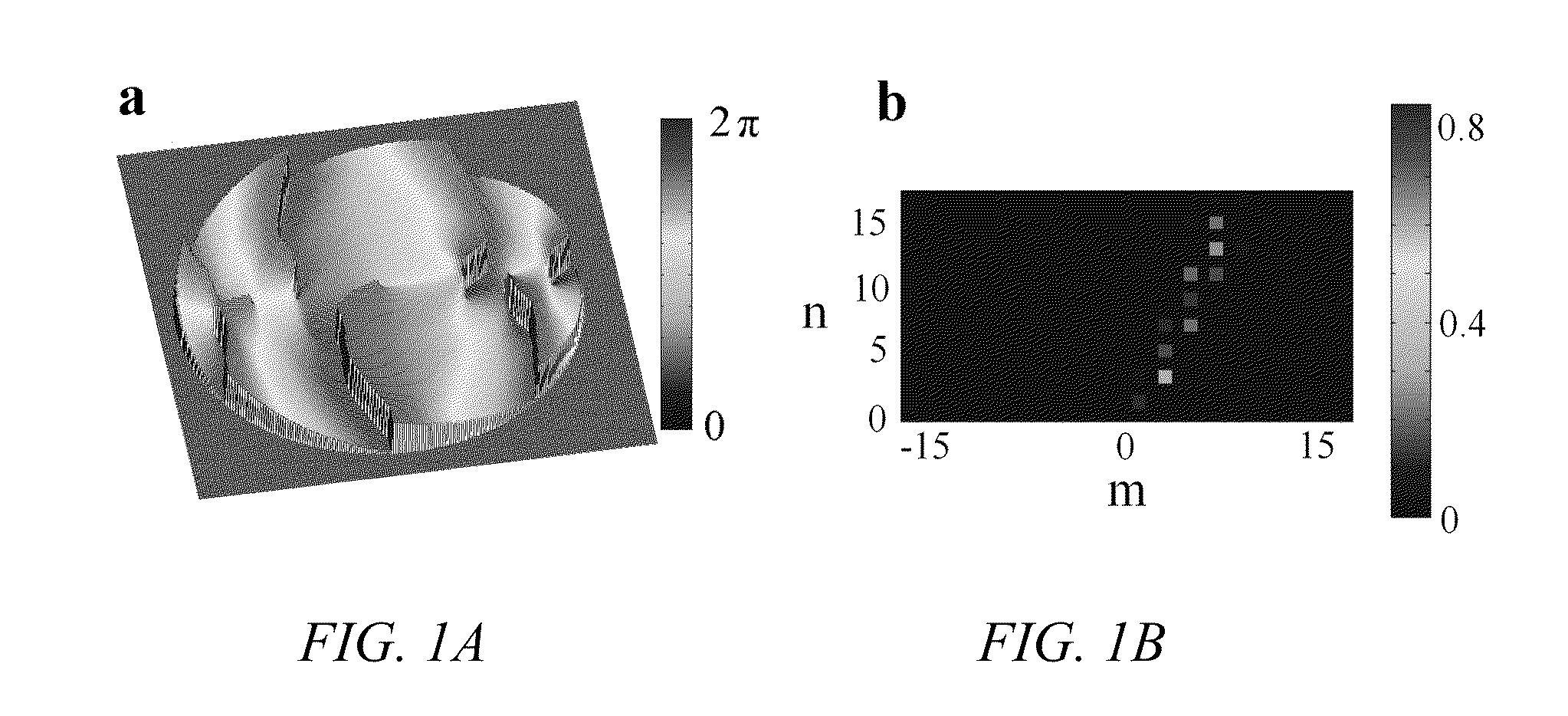
Embodiments of the present invention can resolve molecules beyond the optical diffraction limit in three dimensions. A double-helix point spread function can be used to in conjunction with a microscope to provide dual-lobed images of a molecule. Based on the rotation of the dual-lobed image, the axial position of the molecule can be estimated or determined. In some embodiments, the angular rotation of the dual-lobed imaged can be determined using a centroid fit calculation or by finding the midpoints of the centers of the two lobes. Regardless of the technique, the correspondence between the rotation and axial position can be utilized. A double-helix point spread function can also be used to determine the lateral positions of molecules and hence their three-dimensional location.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
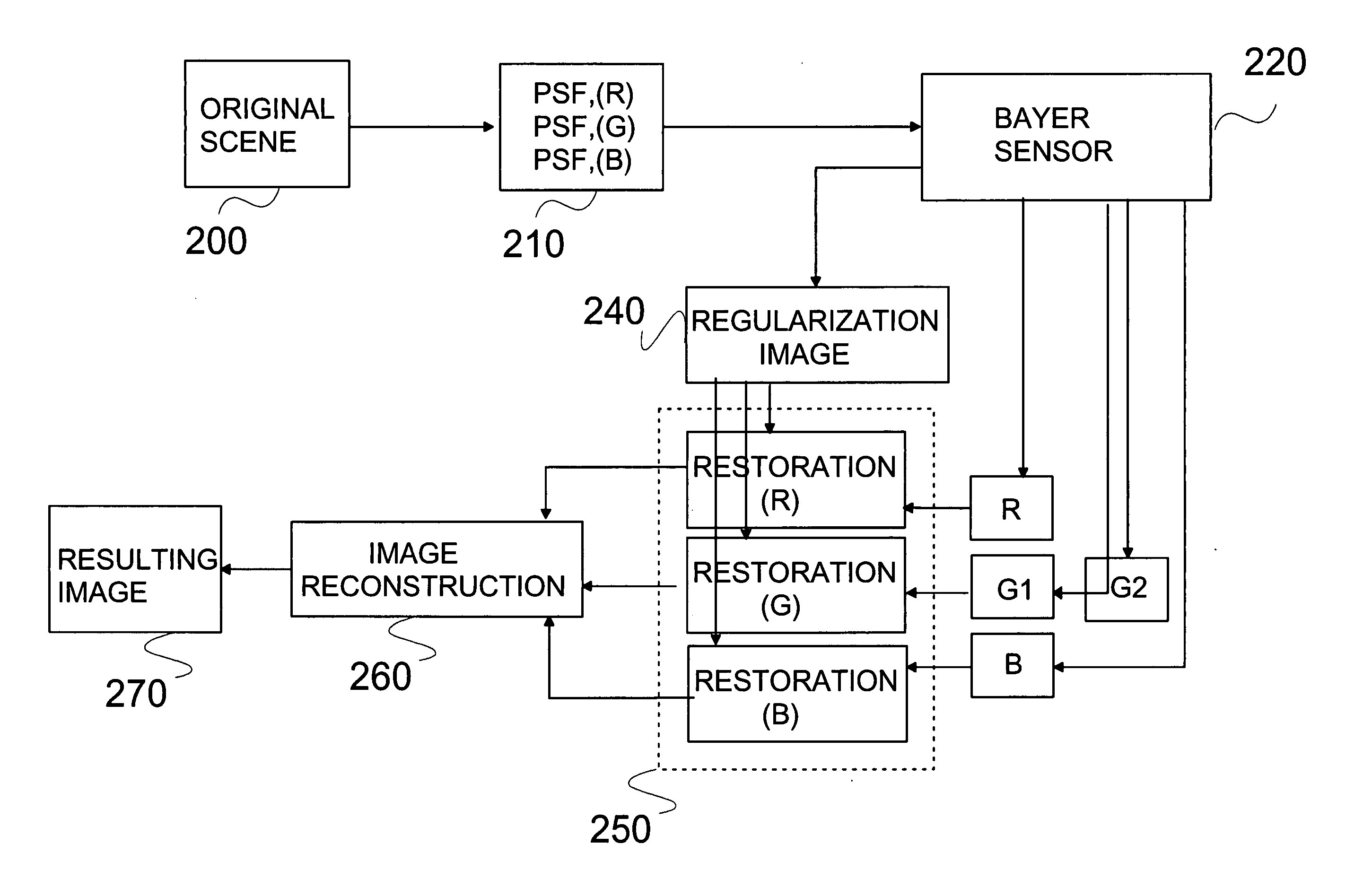
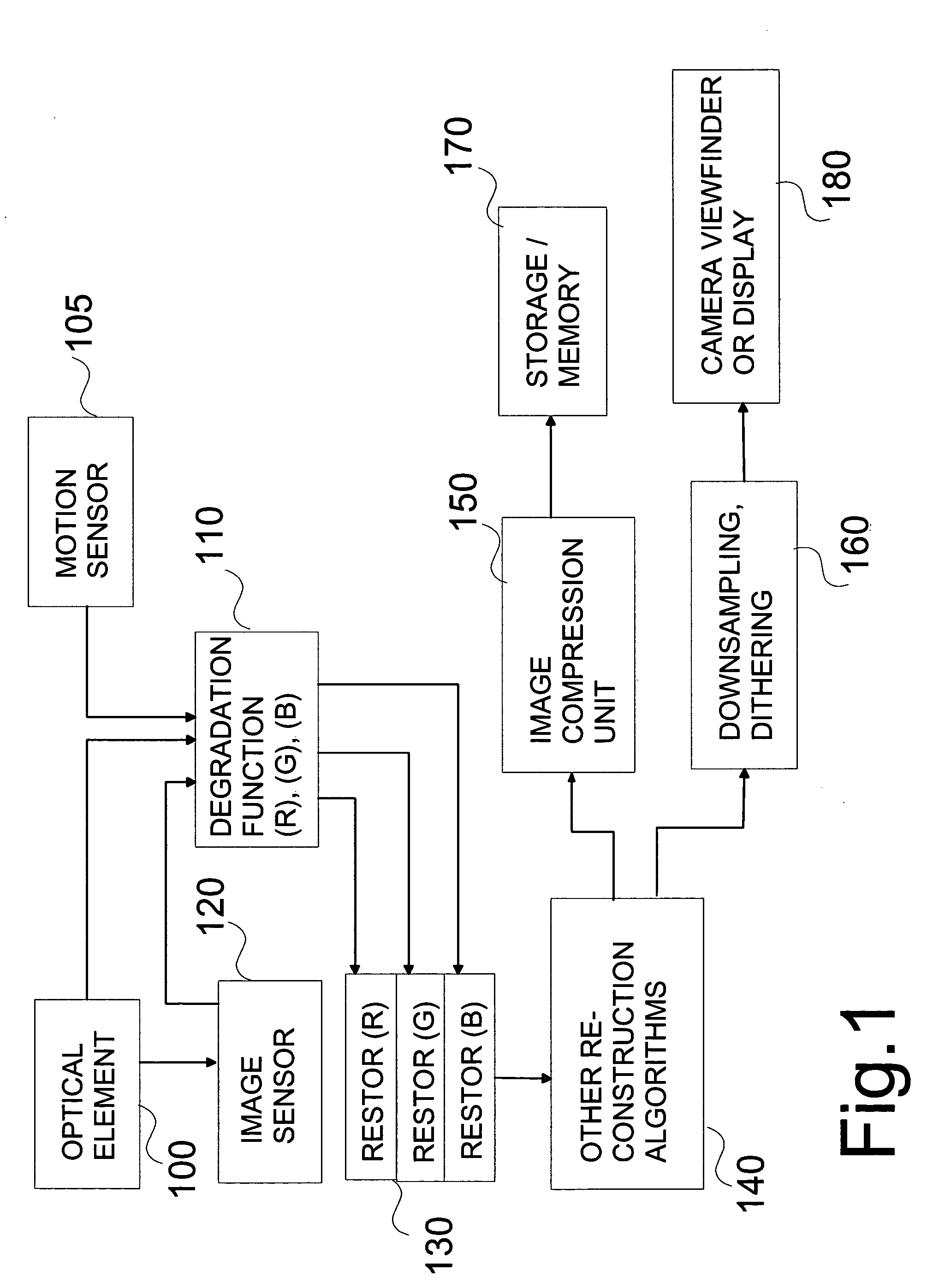
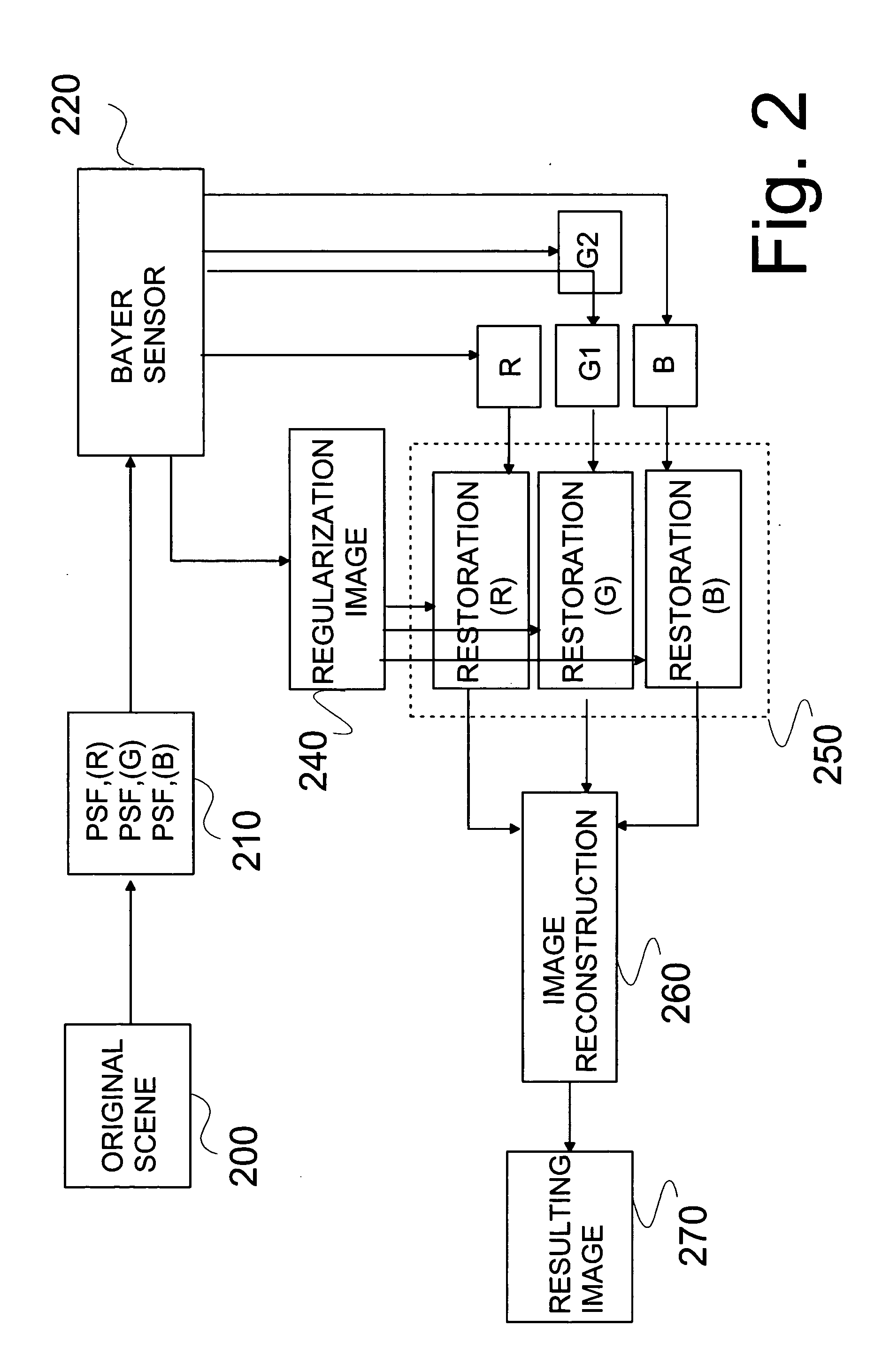
Restoration of color components in an image model
InactiveUS20060013479A1Improve resolutionIncrease contrastImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityPoint spread function
This invention relates to a method for improving image quality of a digital image captured with an imaging module comprising at least imaging optics and an image sensor, where the image is formed through the imaging optics, the image consisting of at least one colour component. In the method degradation information of each colour component of the image is found and is used for obtaining a degradation function. Each colour component is restored by said degradation function. The image is unprocessed image data, and the degradation information of each colour component can be found by a point-spread function. The invention also relates to a device, to a module, to a system and to a computer program product and to a program module.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method and system for optical imaging and ranging
ActiveUS7705970B2Maximises informationOptimize depth estimationOptical rangefindersSensor arrayPoint spread function
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD +1
Sharpness metric for vision quality
InactiveUS7077522B2Remove wave aberrationSubjective blurRefractometersSkiascopesQuality of visionPoint spread function
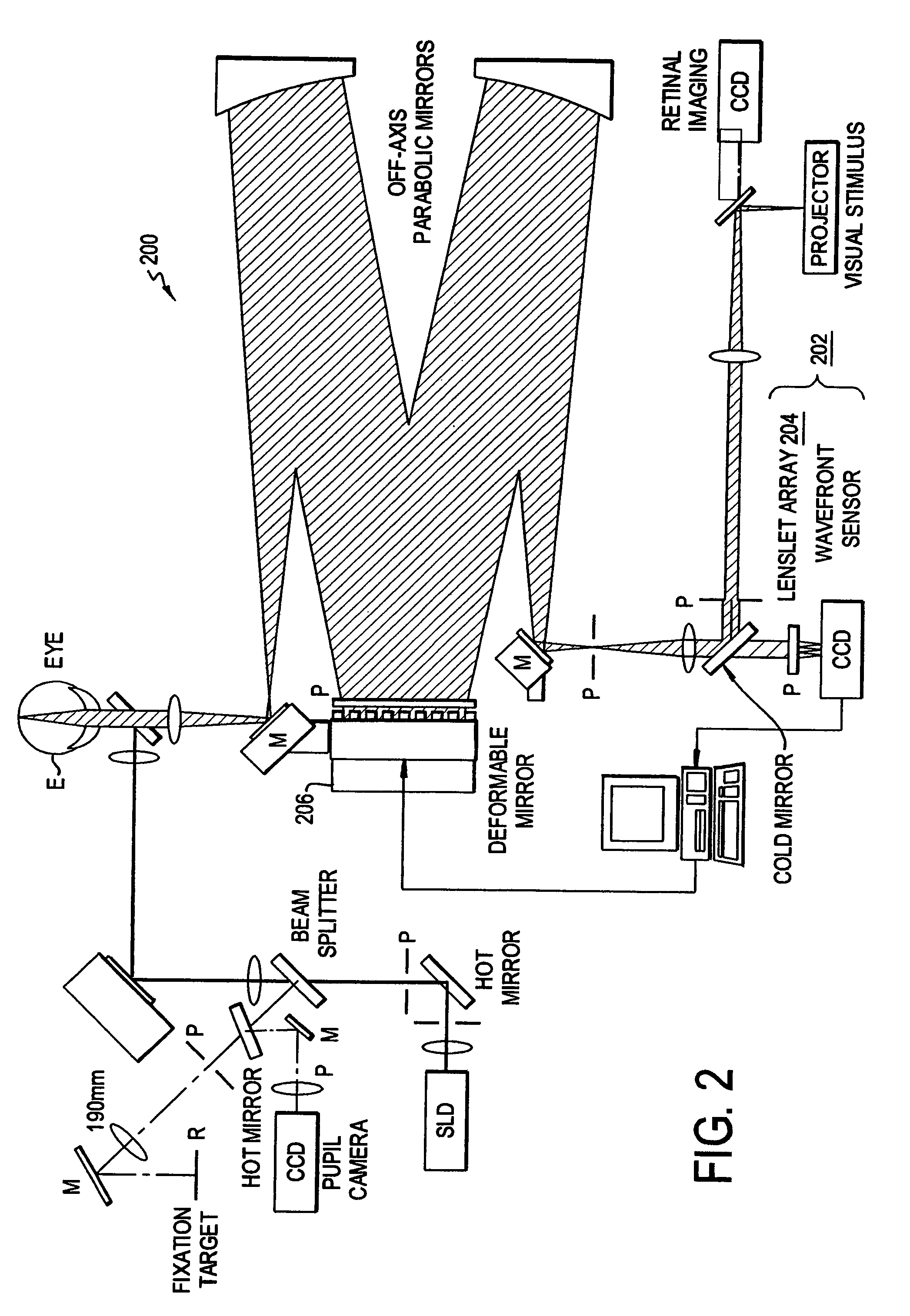
A vision metric, called the sharpness metric, indicates the subjective sharpness of a patient's vision by taking into account both the wavefront aberration and the retinal response to the image. A retinal image quality function such as the point spread function is convolved by a neural quality function, and the maximum of the convolution over the retinal plane provides the sharpness metric. The sharpness metric can be used to control eye surgery or the fabrication of a lens.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Constrained image deblurring for imaging devices with motion sensing
InactiveUS20070009169A1Image enhancementTelevision system detailsPoint spread functionMotion sensing
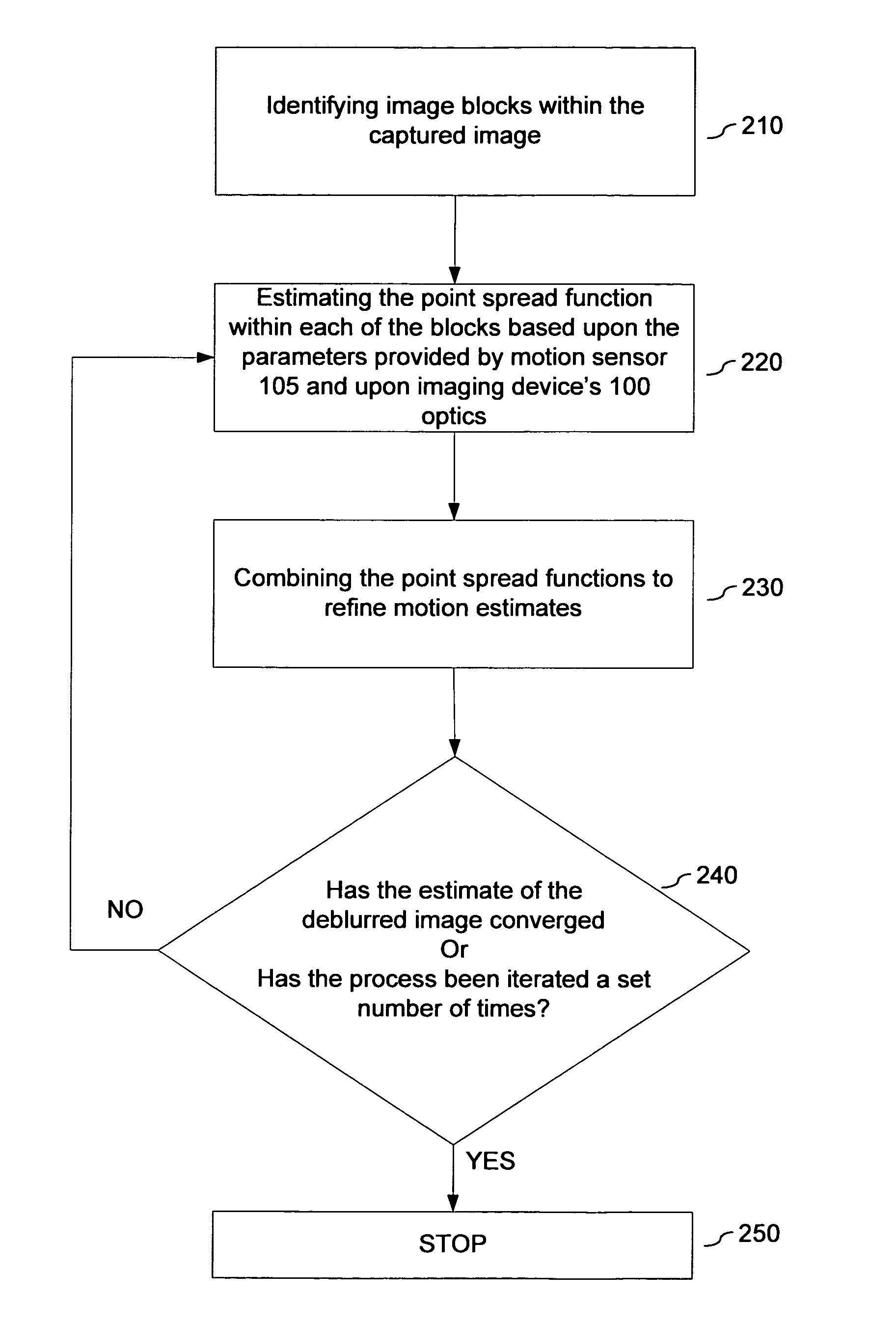
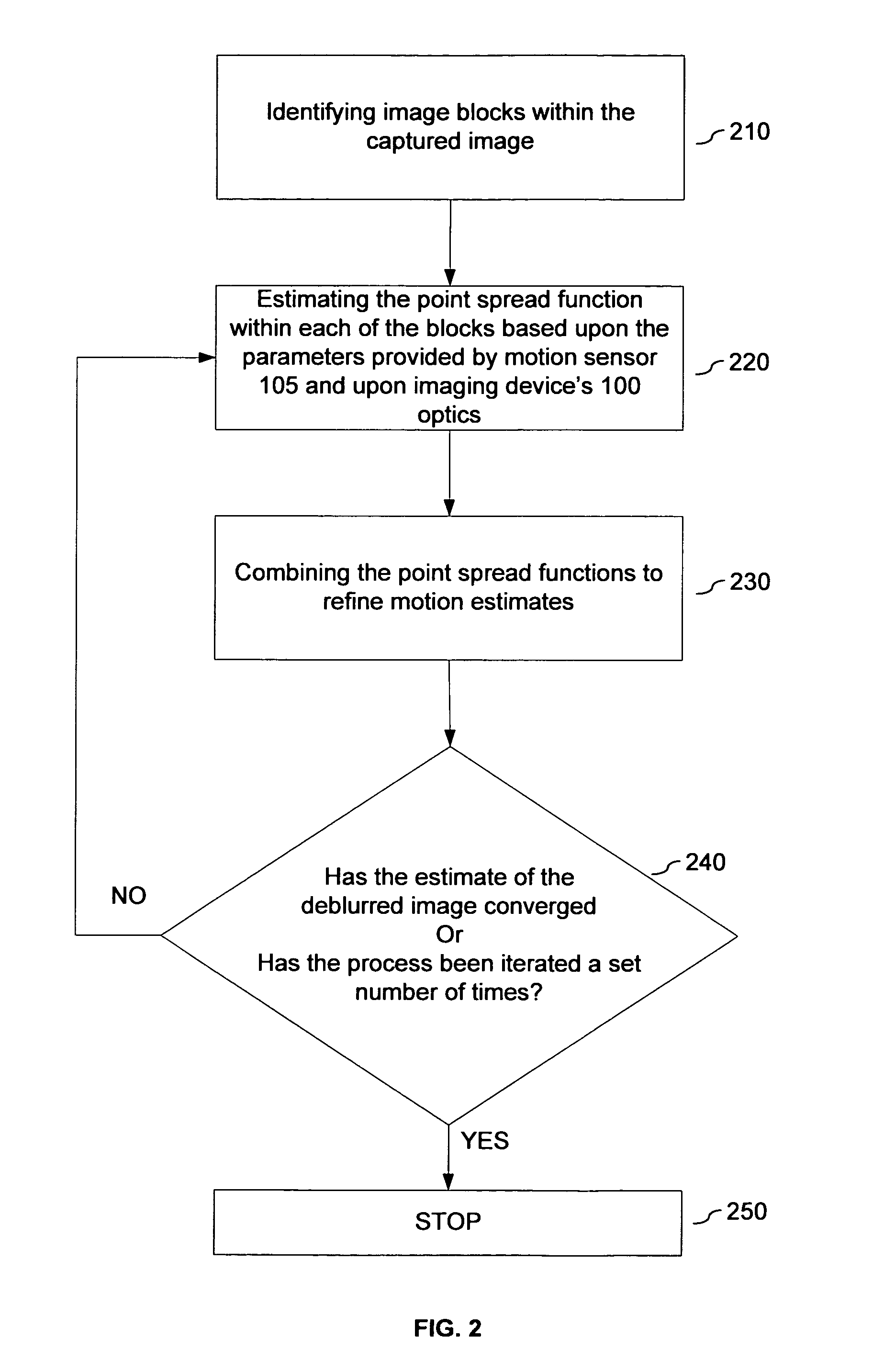
Systems and methods are disclosed for deblurring a captured image using parametric deconvolution, instead of a blind, non-parametric deconvolution, by incorporating physical constraints derived from sensor inputs, such as a motion sensor, into the deconvolution process to constrain modifications to the point spread function. In an embodiment, a captured image is deblurred using a point spread function obtained from the cross-validation of information across a plurality of image blocks taken from the capture image, which image blocks are deconvolved using parametric deconvolution to constrain modifications to the point spread function.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Ultrahigh resolution multicolor colocalization of single fluorescent probes
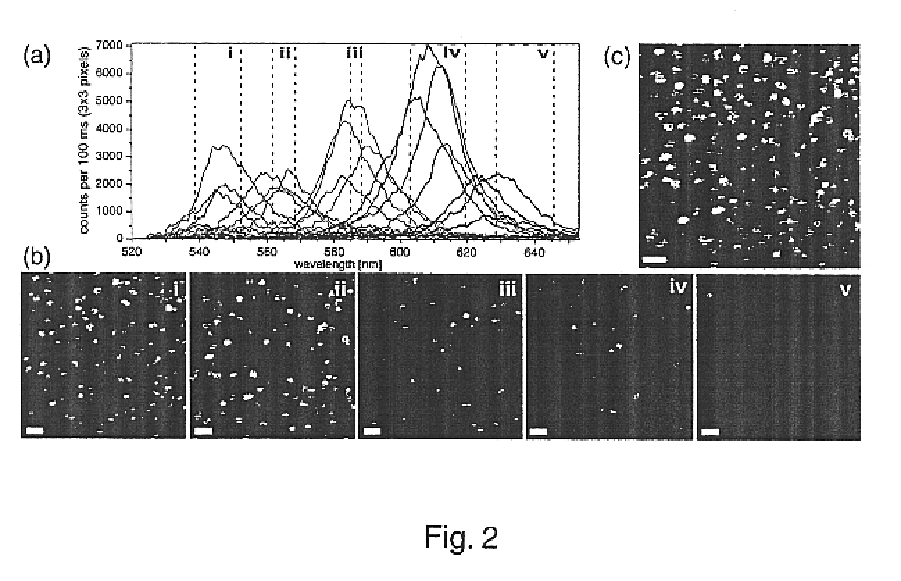
InactiveUS6844150B2Improve spatial resolutionLimited ability to compensate for aberrationSamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementDiffusion functionLasing wavelength
A novel optical ruler based on ultrahigh-resolution colocalization of single fluorescent probes is described. Two unique families of fluorophores are used, namely energy-transfer fluorescent beads and semiconductor nanocrystal (NC) quantum dots, that can be excited by a single laser wavelength but emit at different wavelengths. A novel multicolor sample-scanning confocal microscope was constructed which allows one to image each fluorescent light emitter, free of chromatic aberrations, by scanning the sample with nanometer scale steps using a piezo-scanner. The resulting spots are accurately localized by fitting them to the known shape of the excitation point-spread-function of the microscope.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
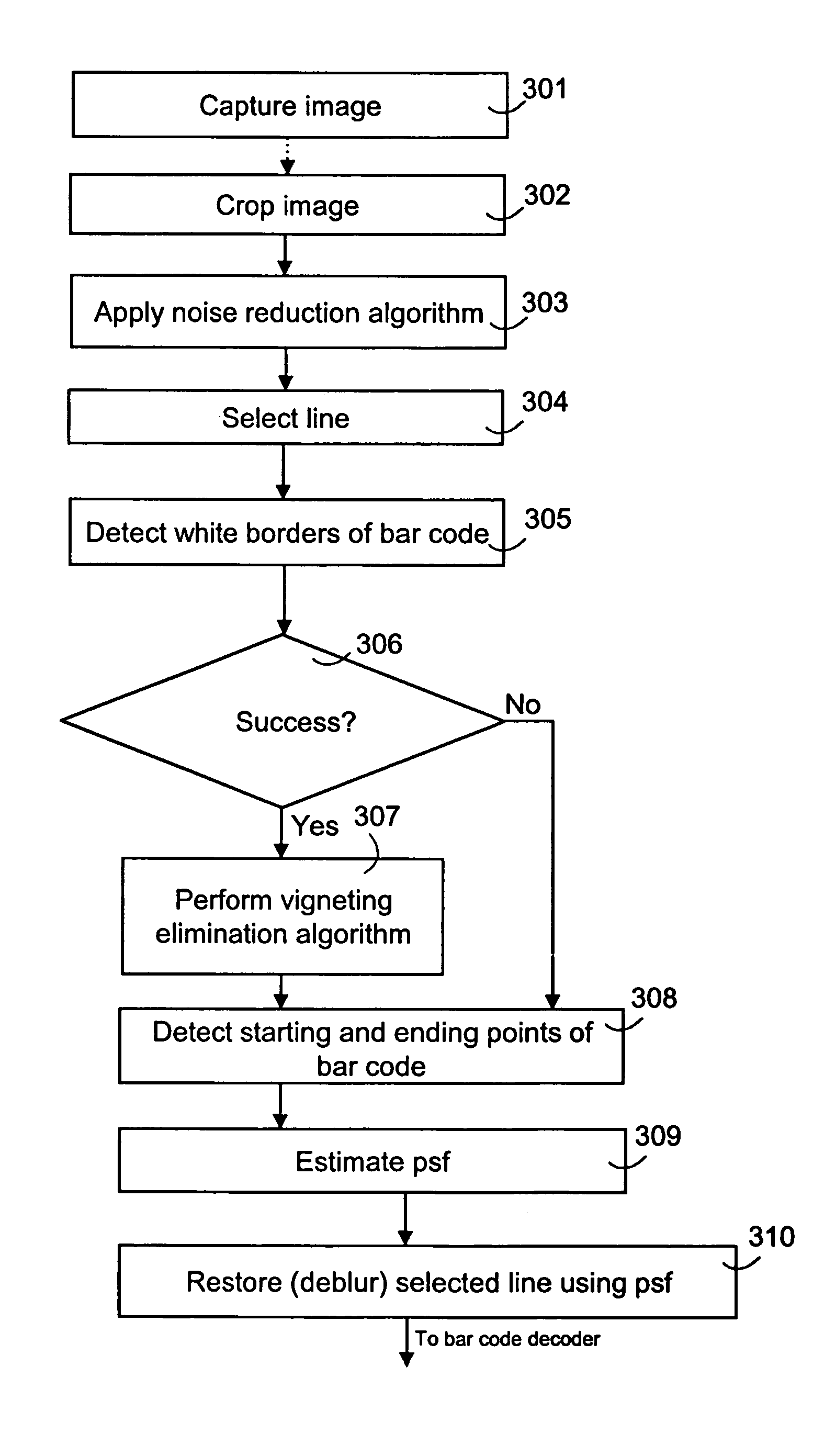
Image processing for pattern detection
InactiveUS7237721B2Improve captured image qualityReliable detectionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
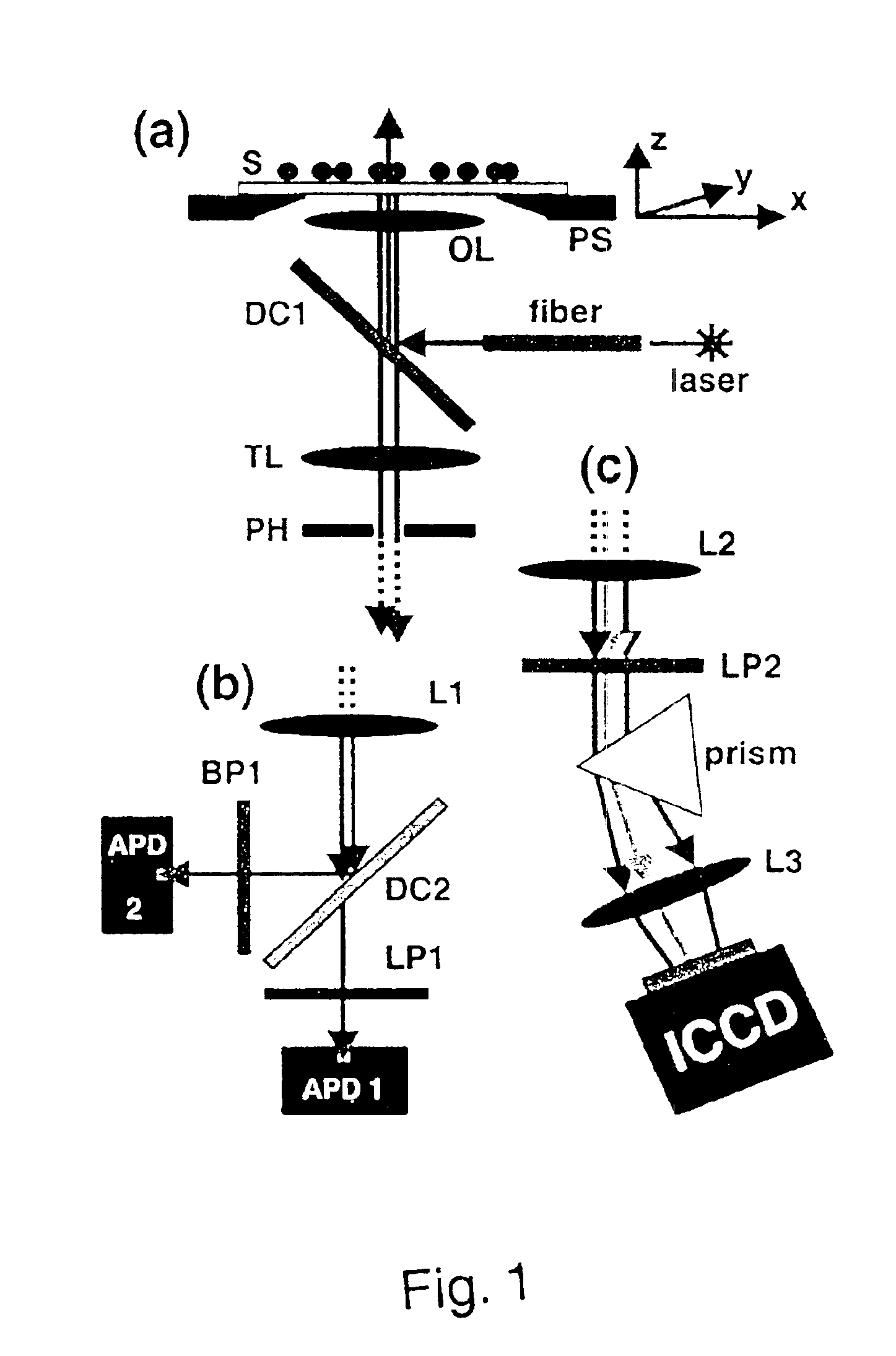
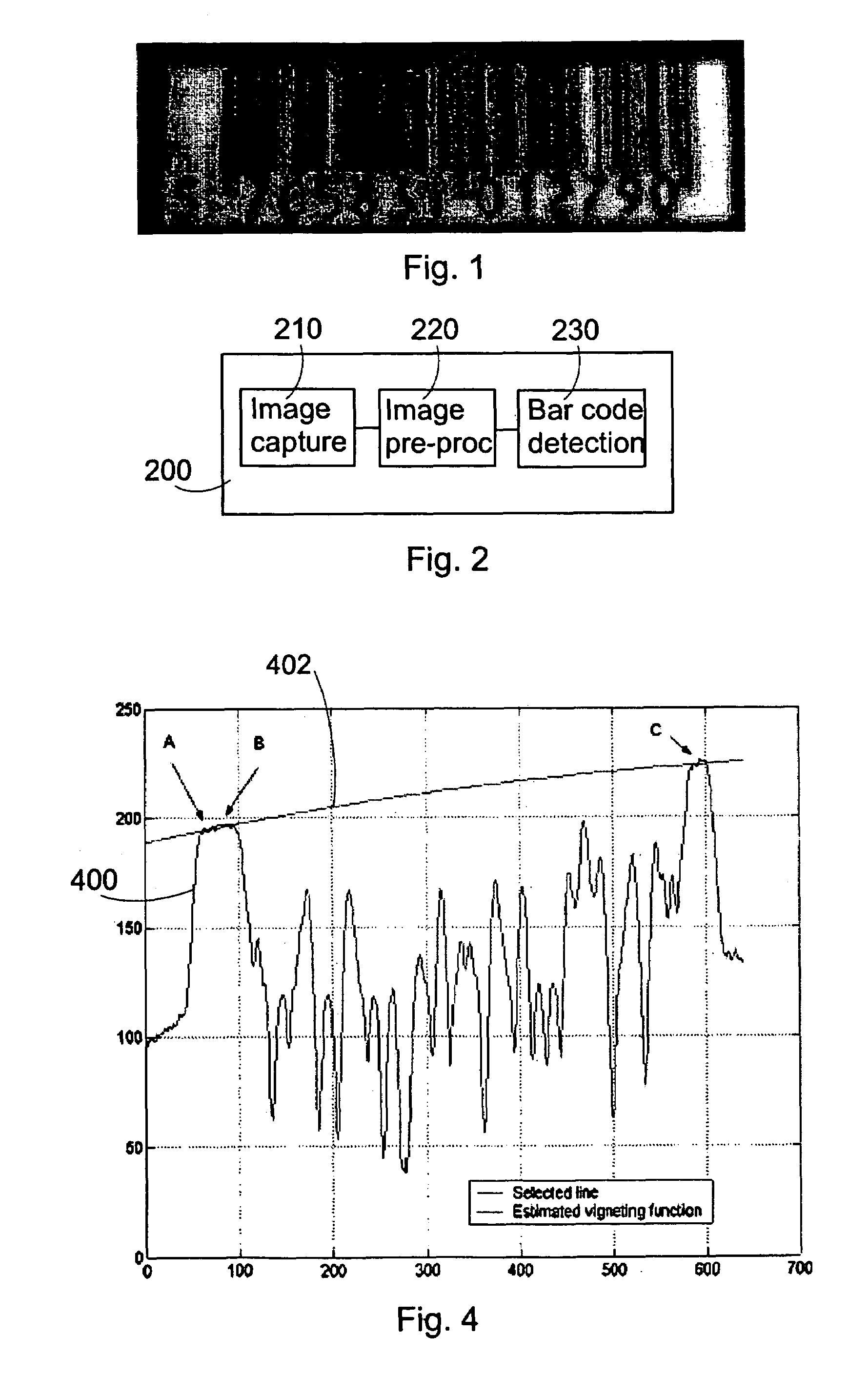
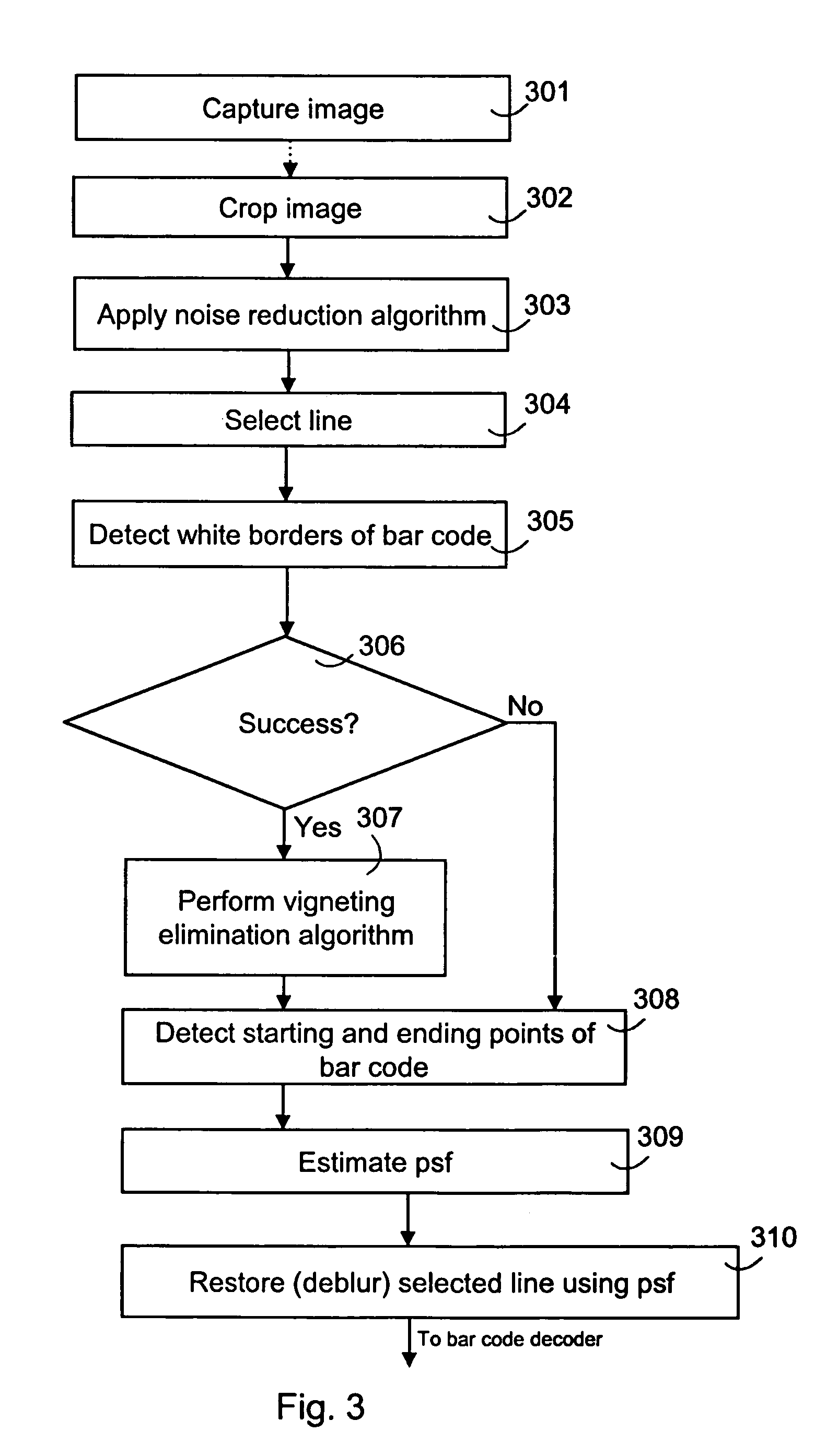
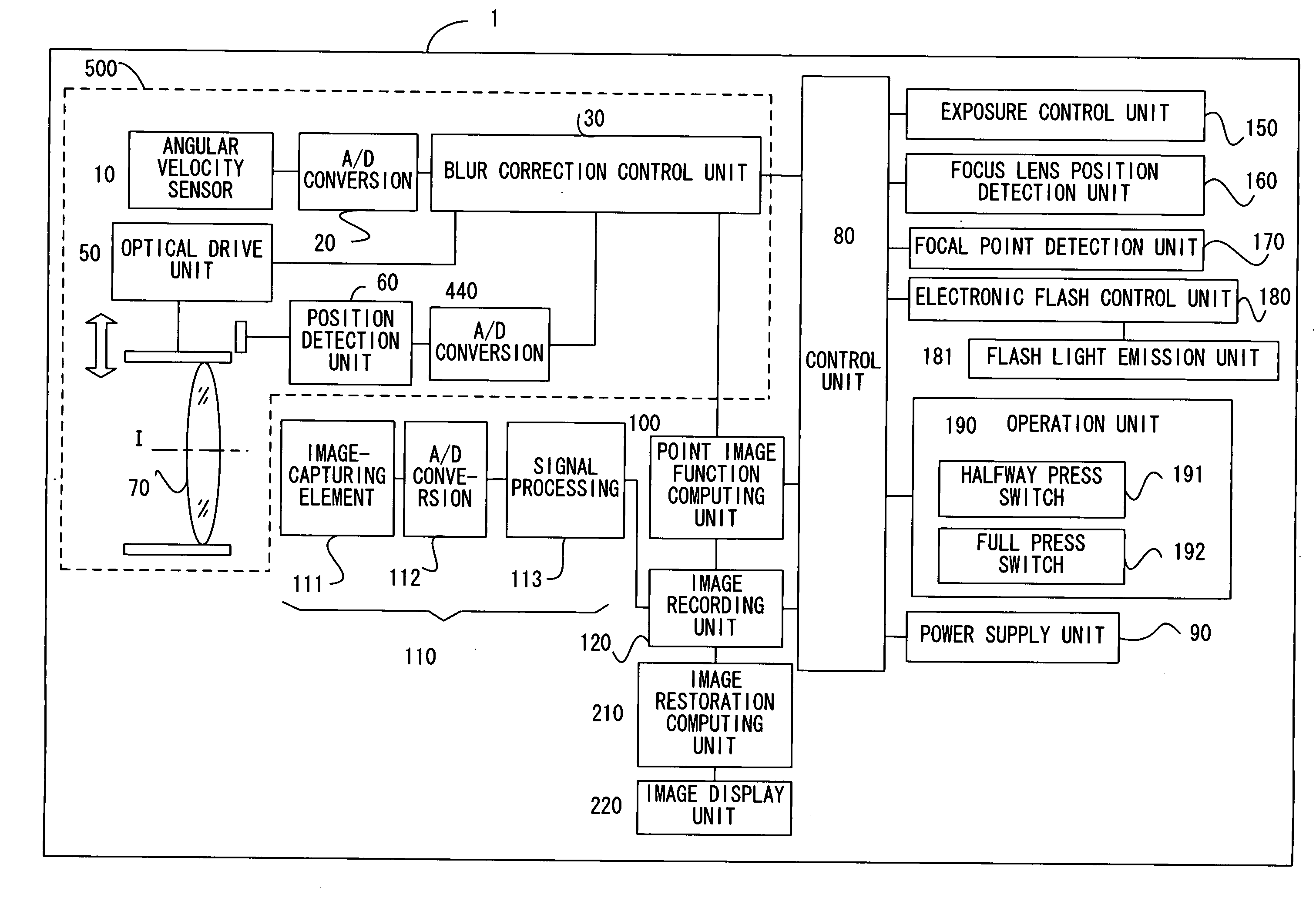
The present invention relates to an image pre-processing method for a pattern detection system, such as a bar code detection system. The method comprises the steps of: detecting a start point and an end point of a pattern on the basis of image data of at least a portion of a captured image, estimating a point spread function from the image data or a modified image data on the basis of the detected start point and the end point, and restoring the image data or the modified image data using the estimated point spread function.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Blur correction camera system
InactiveUS20060110147A1Lower the volumeIncrease in sizeTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementImaging processingPoint spread function
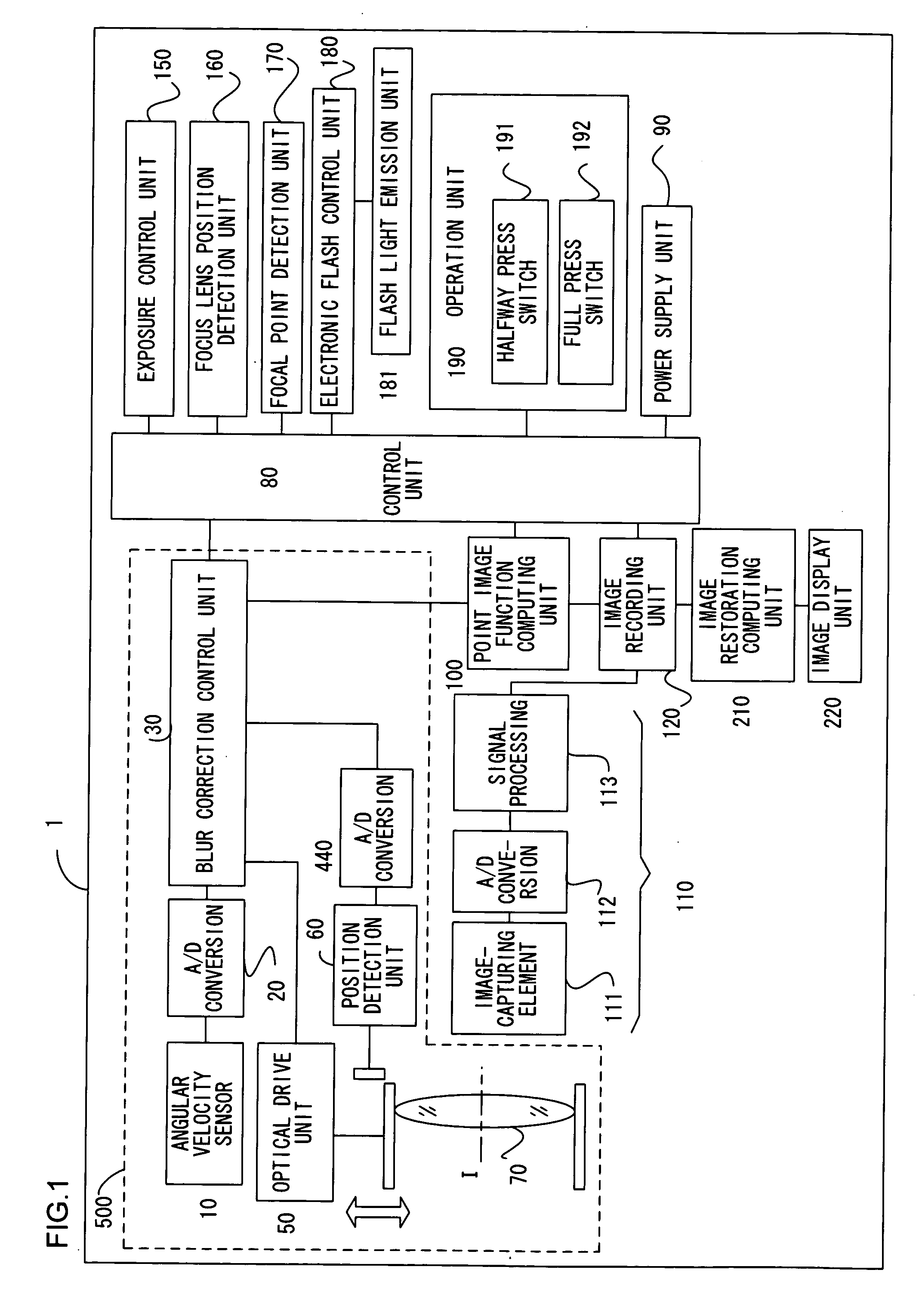
A blur correction camera system includes a blur correction lens driven based upon the vibration detection signal detected by an angular velocity sensor, that corrects an image blur, a point-image function computing unit that computes a point spread function, and an image restoration computing unit that corrects an image blur by executing image restoration through image processing on a captured image by using the point spread function. The image blur that cannot be completely corrected by the blur correction lens is further corrected through image restoration so as to obtain a high quality image.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Method and system for CT reconstruction with pre-correction
InactiveUS20060067461A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionPoint spread functionBeam hardening
A method for reconstructing image data from measured sinogram data acquired from a CT system is provided. The CT system is configured for industrial imaging. The method includes pre-processing the measured sinogram data. The pre-processing includes performing a beam hardening correction on the measured sinogram data and performing a detector point spread function (PSF) correction and a detector lag correction on the measured sinogram data. The pre-processed sinogram data is reconstructed to generate the image data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
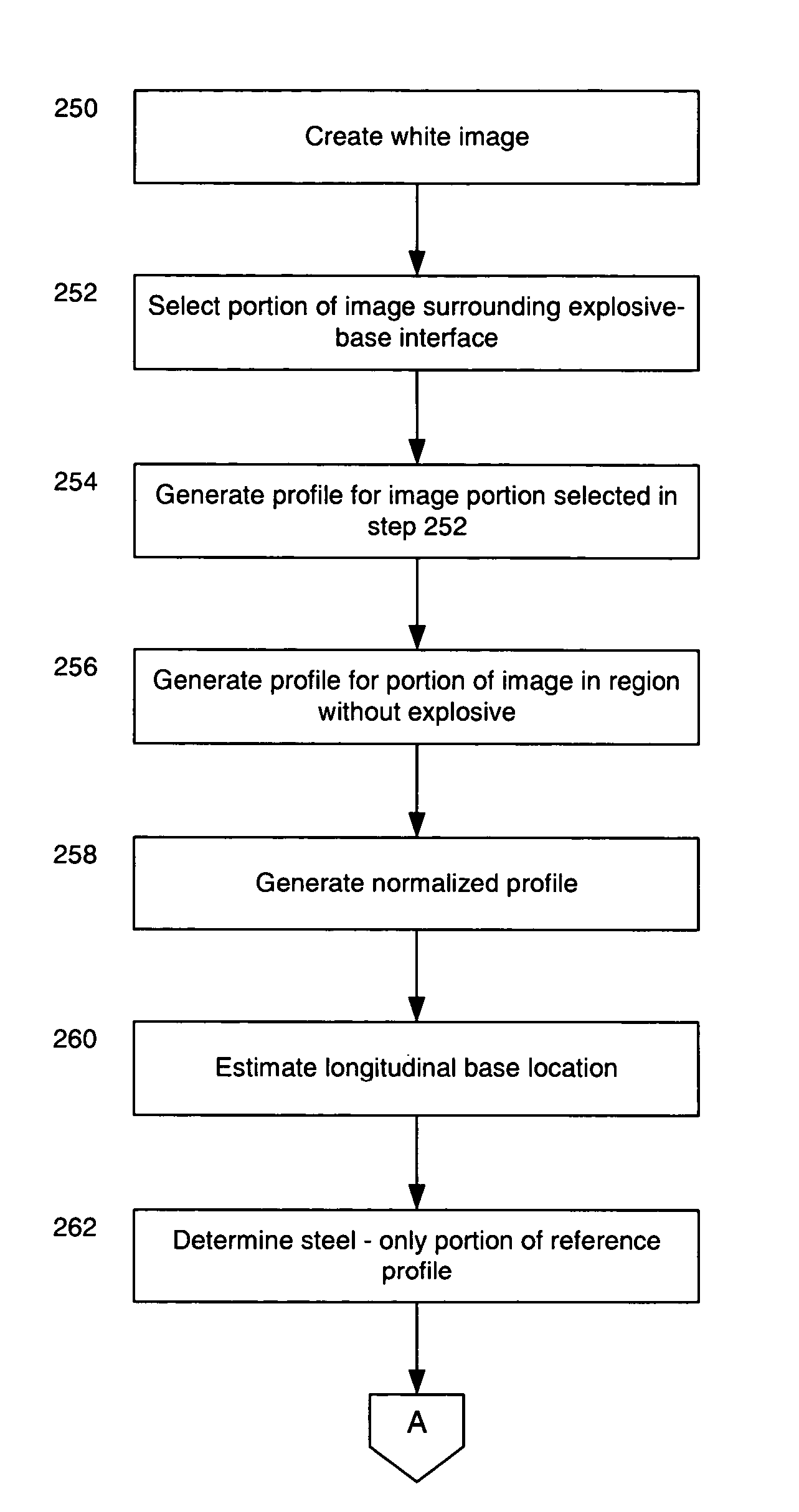
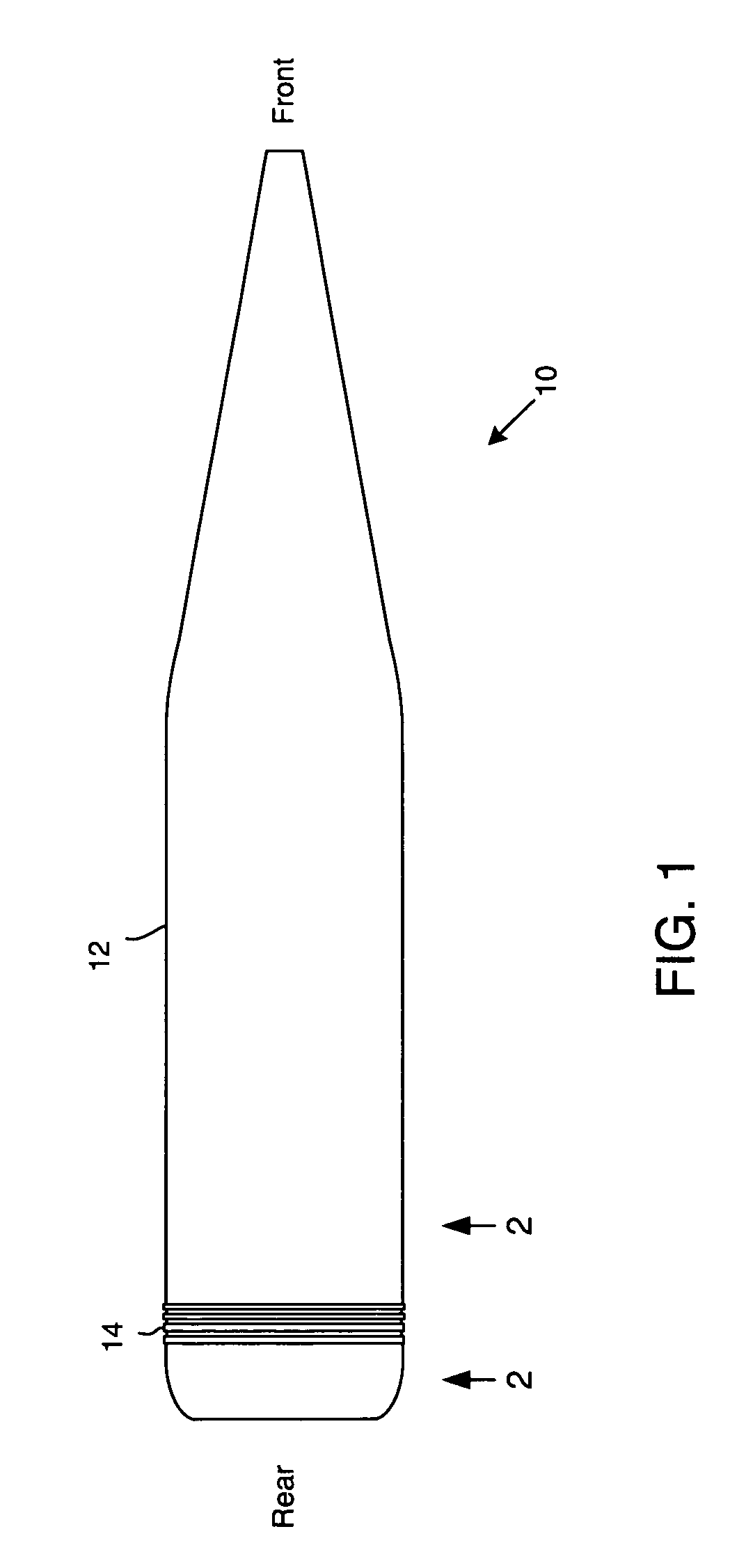
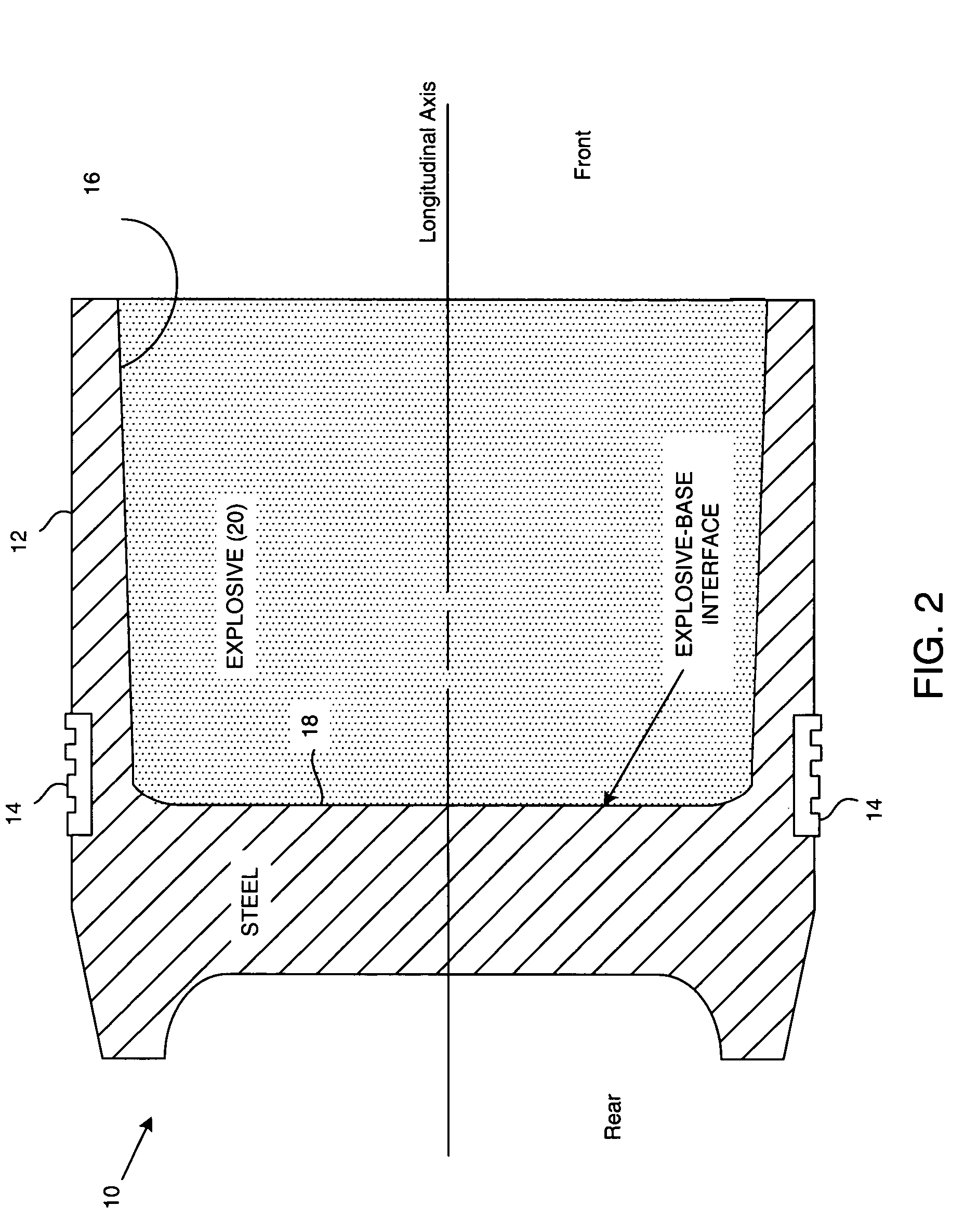
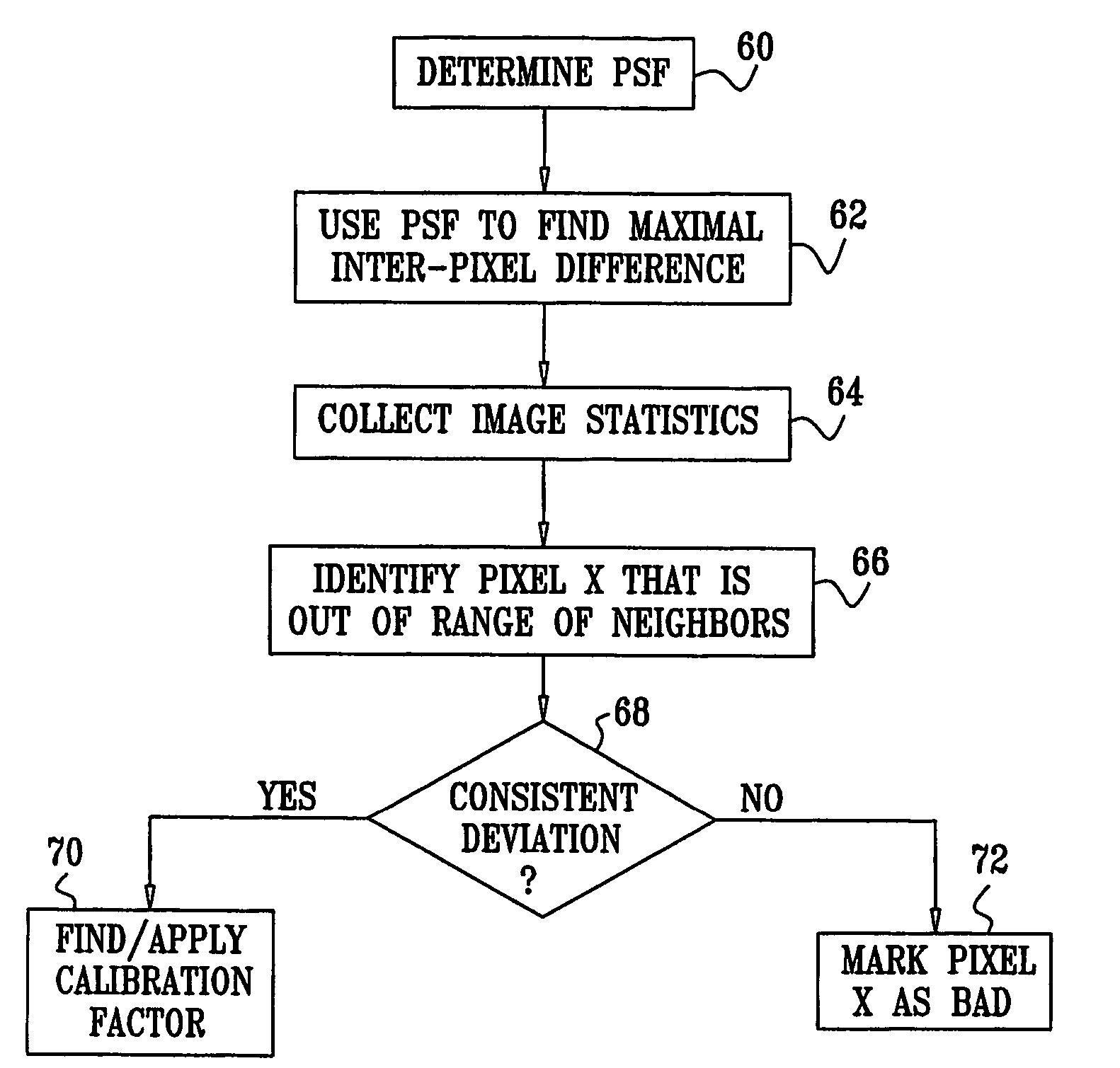
Measuring linear separations in digital radiographs
ActiveUS20050135668A1Character and pattern recognitionNuclear radiation detectionPoint spread functionLookup table
Digital pixel data is obtained from radiographic imaging of one or more objects, and corresponds to an imaged area containing a feature to be measured. A data profile for a region around the measured feature is created from the digital pixel data. A reference profile is then created from the data profile. The reference profile represents an expected data profile for a reference condition of the objects, and accounts for the point spread function of the imager. The difference between the data profile and the reference profile is calculated. Based on that difference, the degree by which the actual condition of the objects varies from the reference condition is determined. The calculated difference can be compared to a lookup table mapping previously calculated differences to degrees of variation from the reference condition. The calculated difference can also be used as an input to an experimentally derived formula.
Owner:LEIDOS
Camera with image enhancement functions
ActiveUS7627193B2Improve image qualityHigh quality imagingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsOptical radiationOptical axis
Imaging apparatus (20, 44) includes an array (22) of optical sensing elements (24), characterized by a pitch, which is adapted to generate a signal in response to optical radiation that is incident on the elements. Objective optics (26, 46), which have an optical axis (134) and are characterized by a cylindrical symmetry about the axis, are arranged to focus the optical radiation from an object onto the array with a point spread function (PSF) having an extent greater than twice the pitch of the array at an optimal focus of the objective optics.
Owner:DIGITALOPTICS CORPORATION
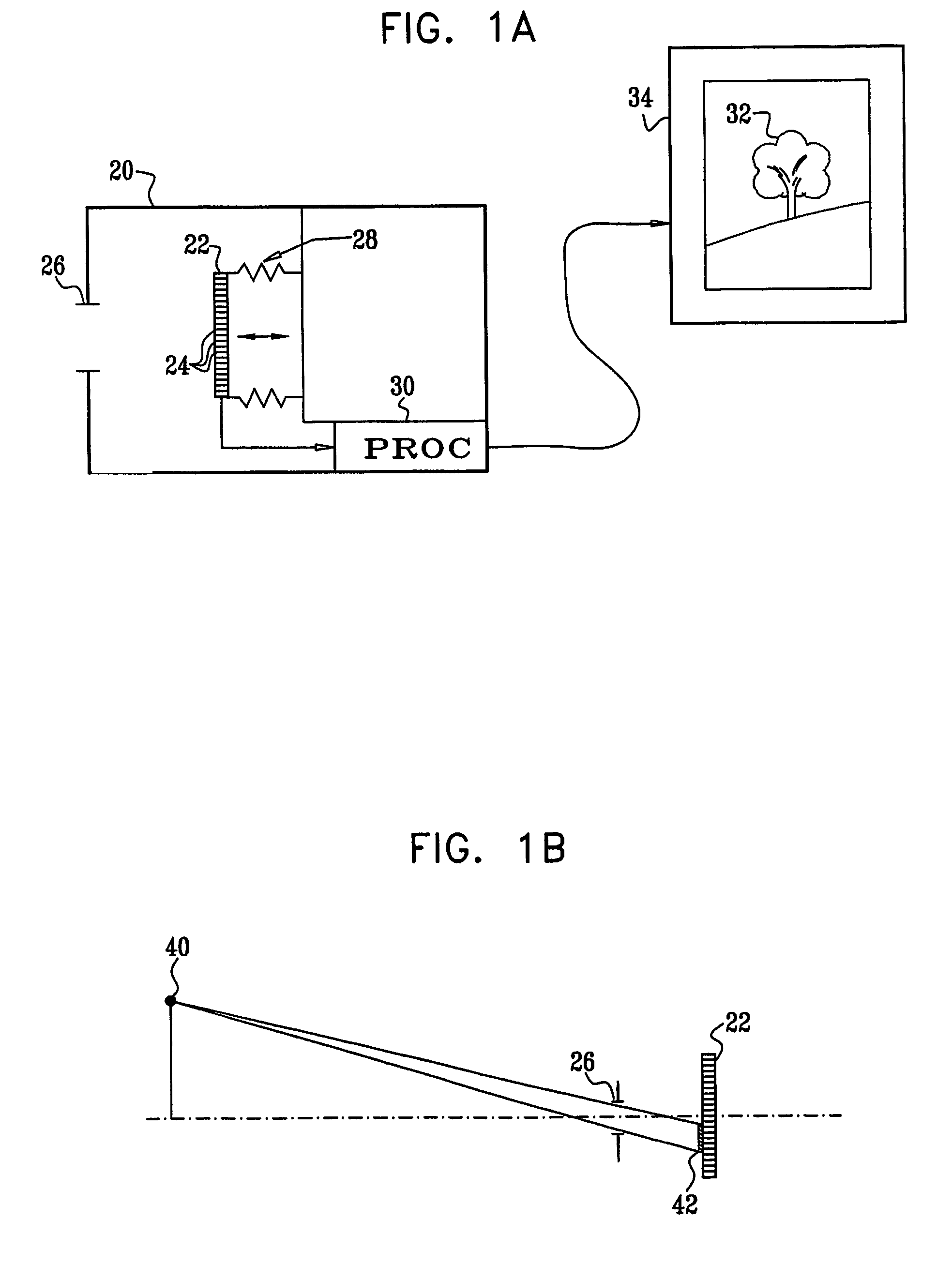
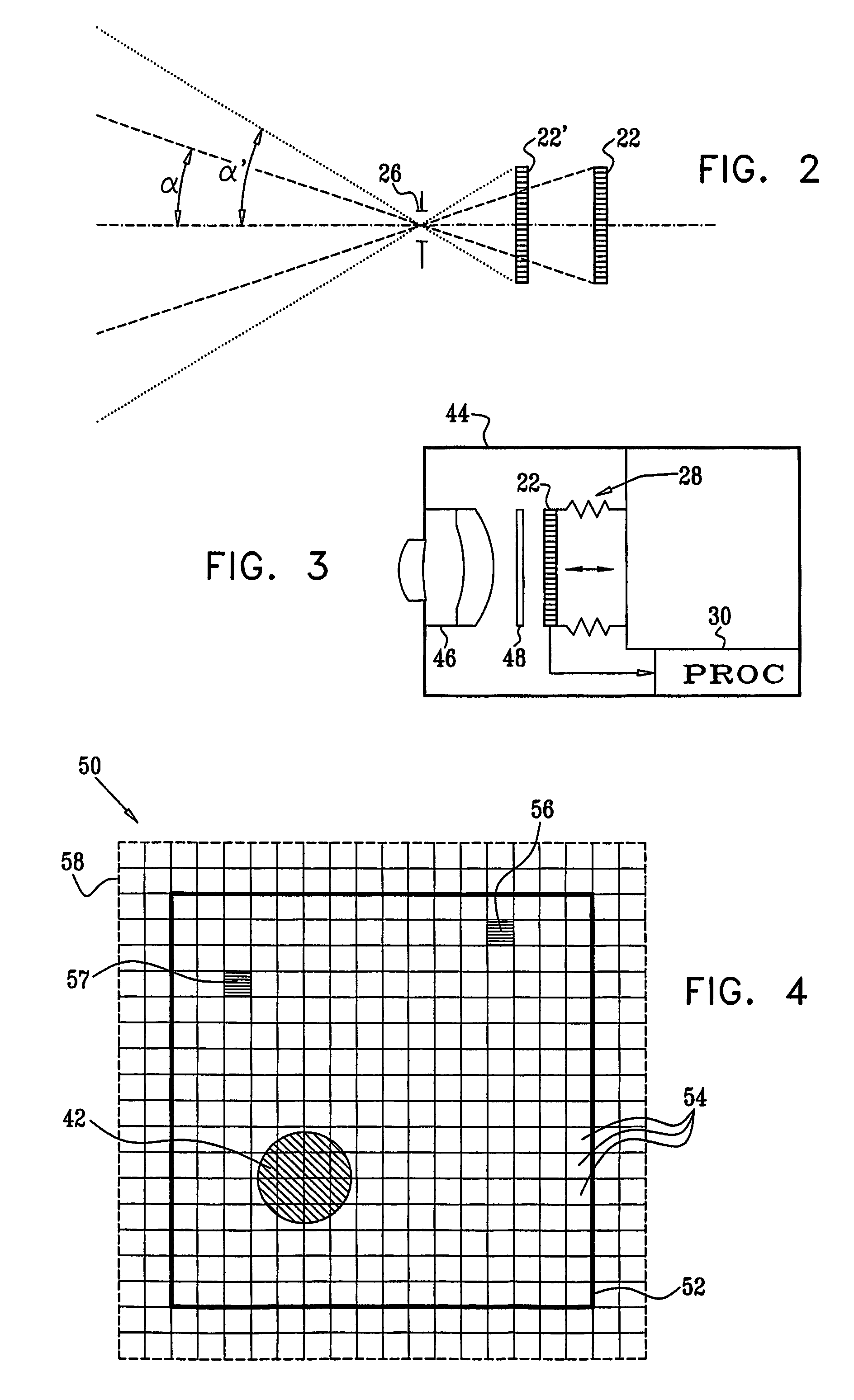
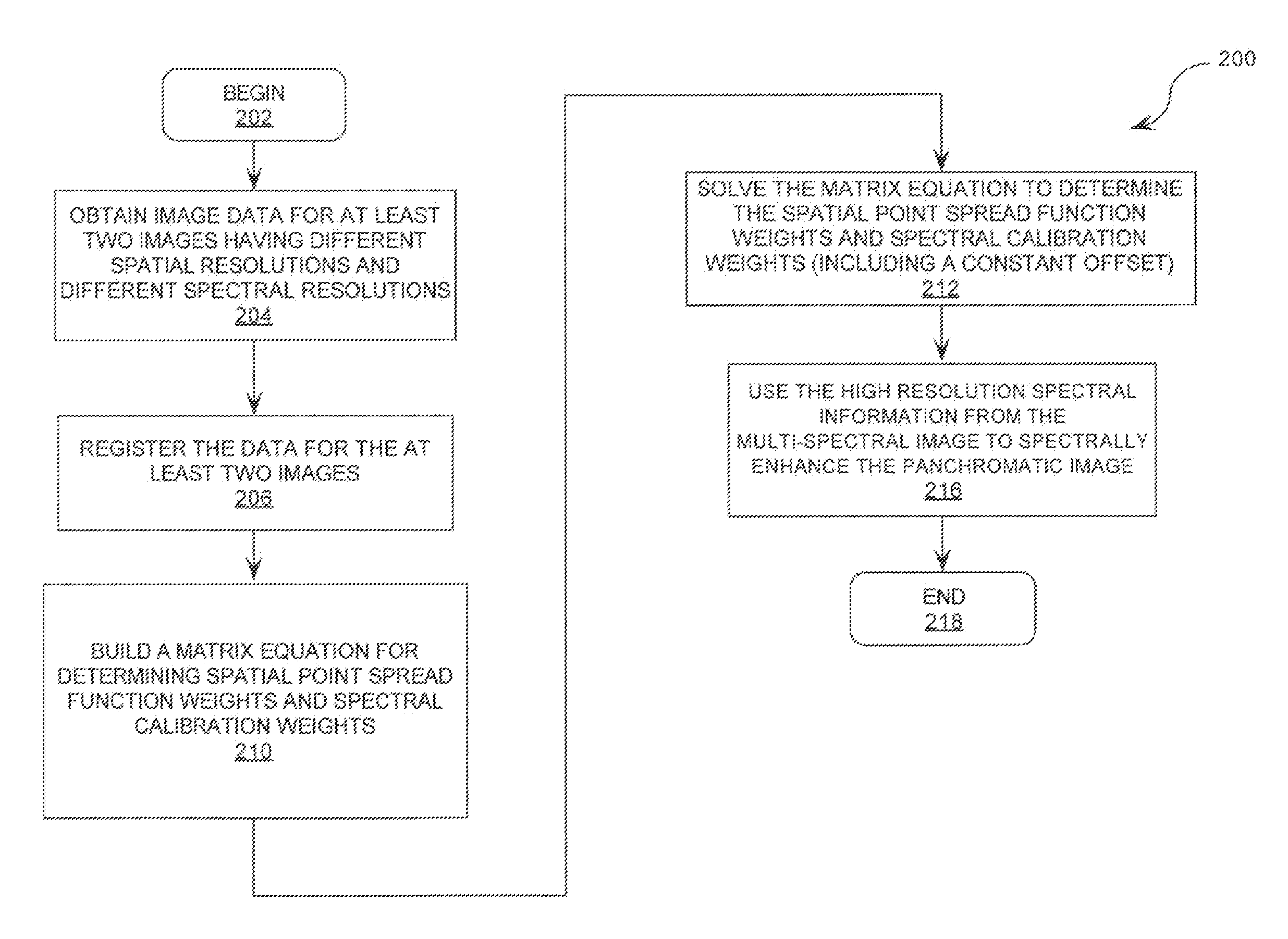
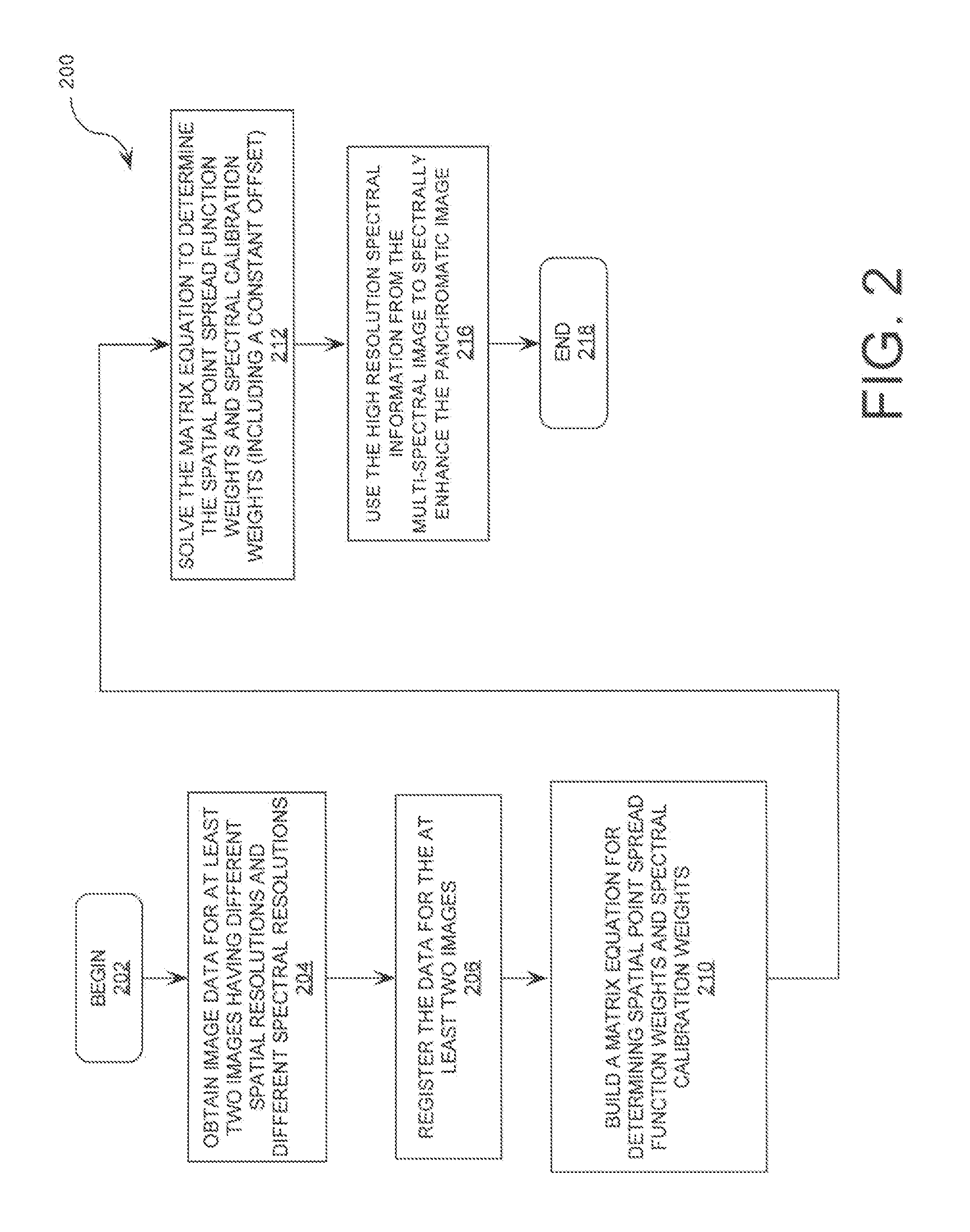
Spatial and Spectral Calibration of a Panchromatic, Multispectral Image Pair
InactiveUS20080129752A1Image enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionPoint spread function
Method and system for creating a fused image from an image pair comprising a high resolution panchromatic image and lower resolution multi-spectral image. The method includes obtaining image data (204) defining a first image of a panchromatic image type and a second image of a multi-spectral image type. The first image has a first spatial resolution and a first spectral resolution. The second image has a second spatial resolution which is lower than the first spatial resolution and a second spectral resolution higher than the first spectral resolution. The method also includes a step (212) of concurrently calculating a point-spread function for down-sampling the first image to the second spatial resolution, and a set of weights for down-sampling the second image to the first spectral resolution.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com