Patents
Literature
39 results about "Colocalization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In fluorescence microscopy, colocalization refers to observation of the spatial overlap between two (or more) different fluorescent labels, each having a separate emission wavelength, to see if the different "targets" are located in the same area of the cell or very near to one another. The definition can be split into two different phenomena, co-occurrence, which refers to the presence of two (possibly unrelated) fluorophores in the same pixel, and correlation, a much more significant statistical relationship between the fluorophores indicative of a biological interaction. This technique is important to many cell biological and physiological studies during the demonstration of a relationship between pairs of bio-molecules.
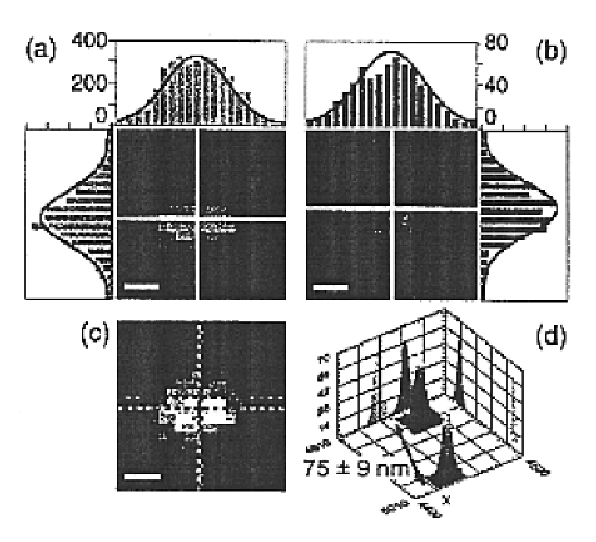
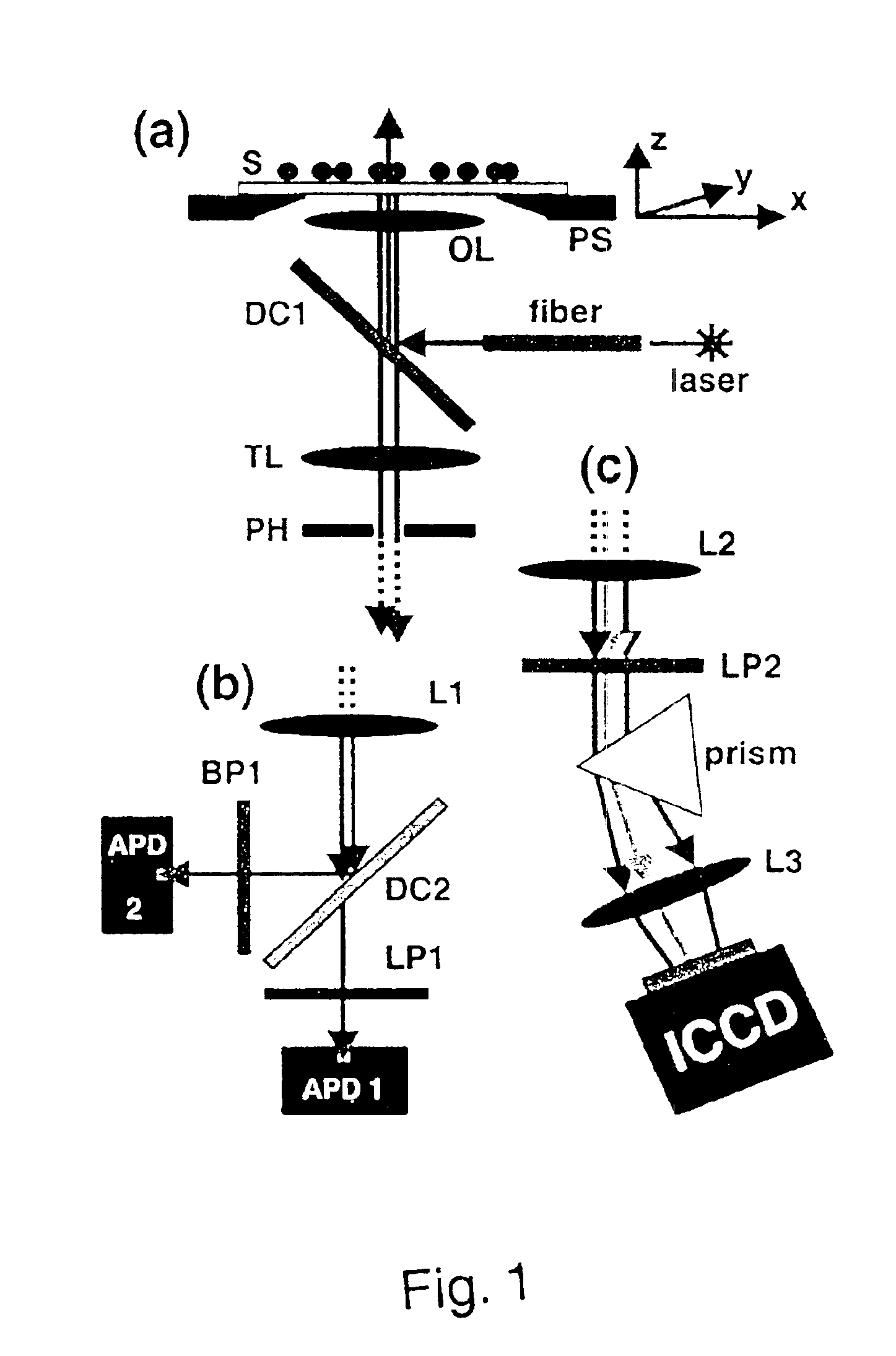
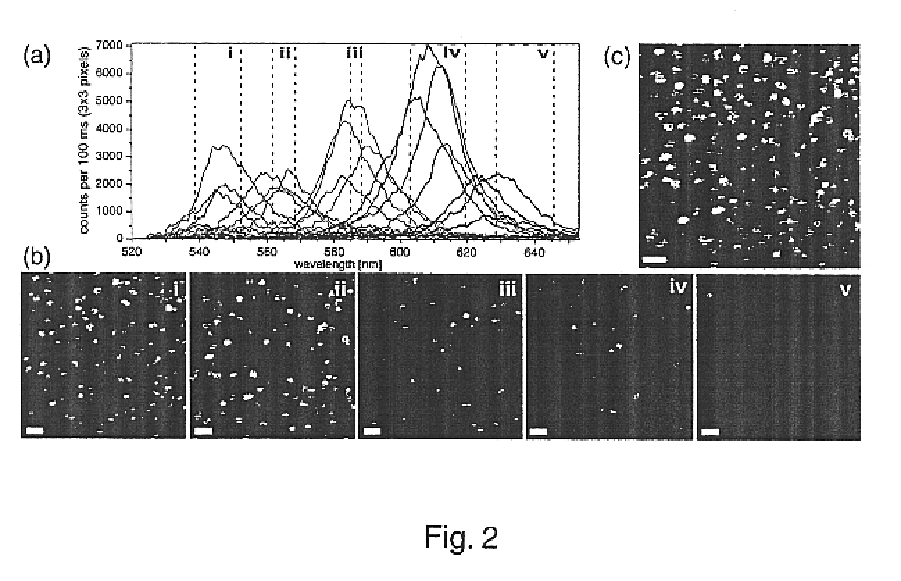
Ultrahigh resolution multicolor colocalization of single fluorescent probes
InactiveUS6844150B2Improve spatial resolutionLimited ability to compensate for aberrationSamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementDiffusion functionLasing wavelength
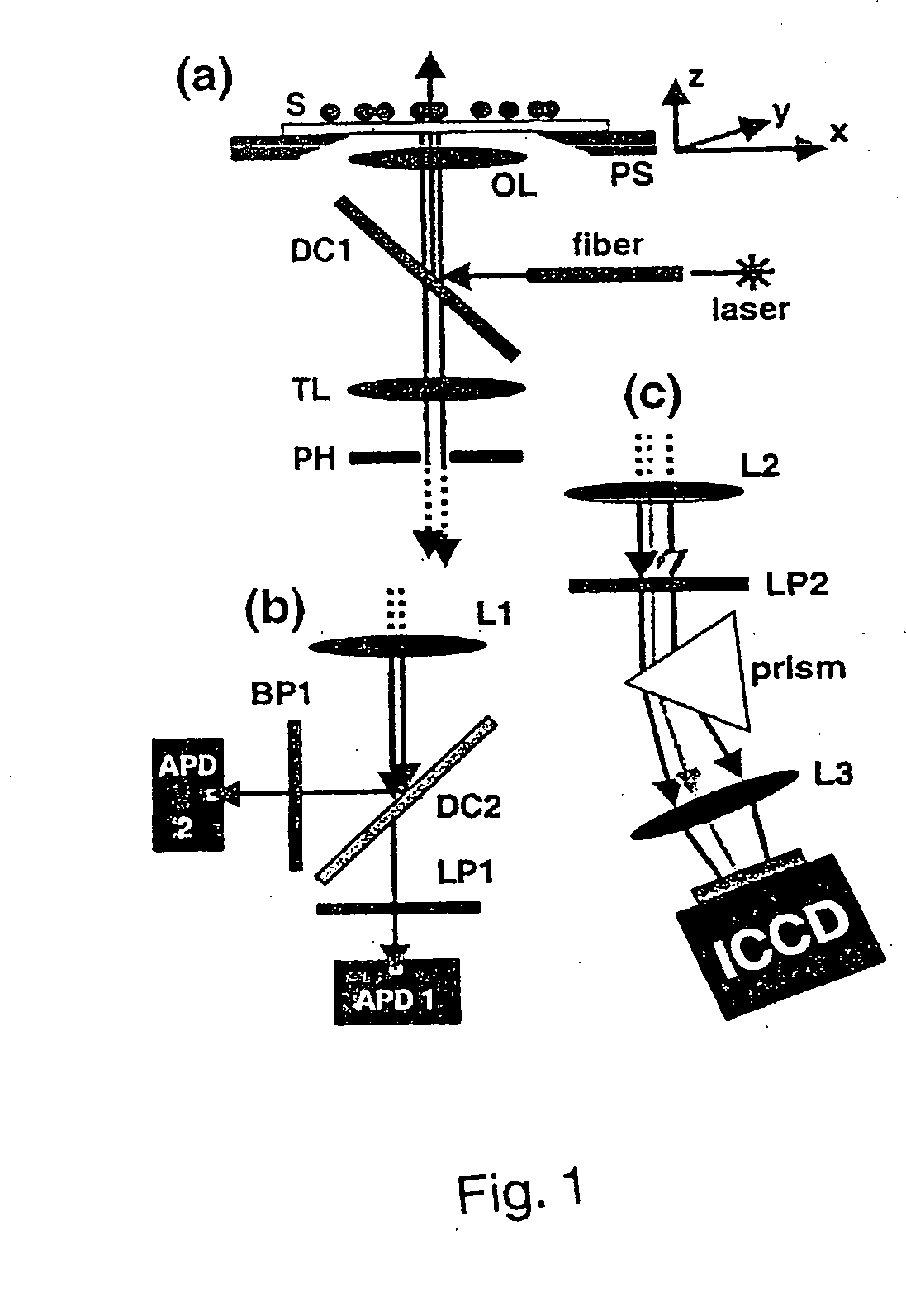
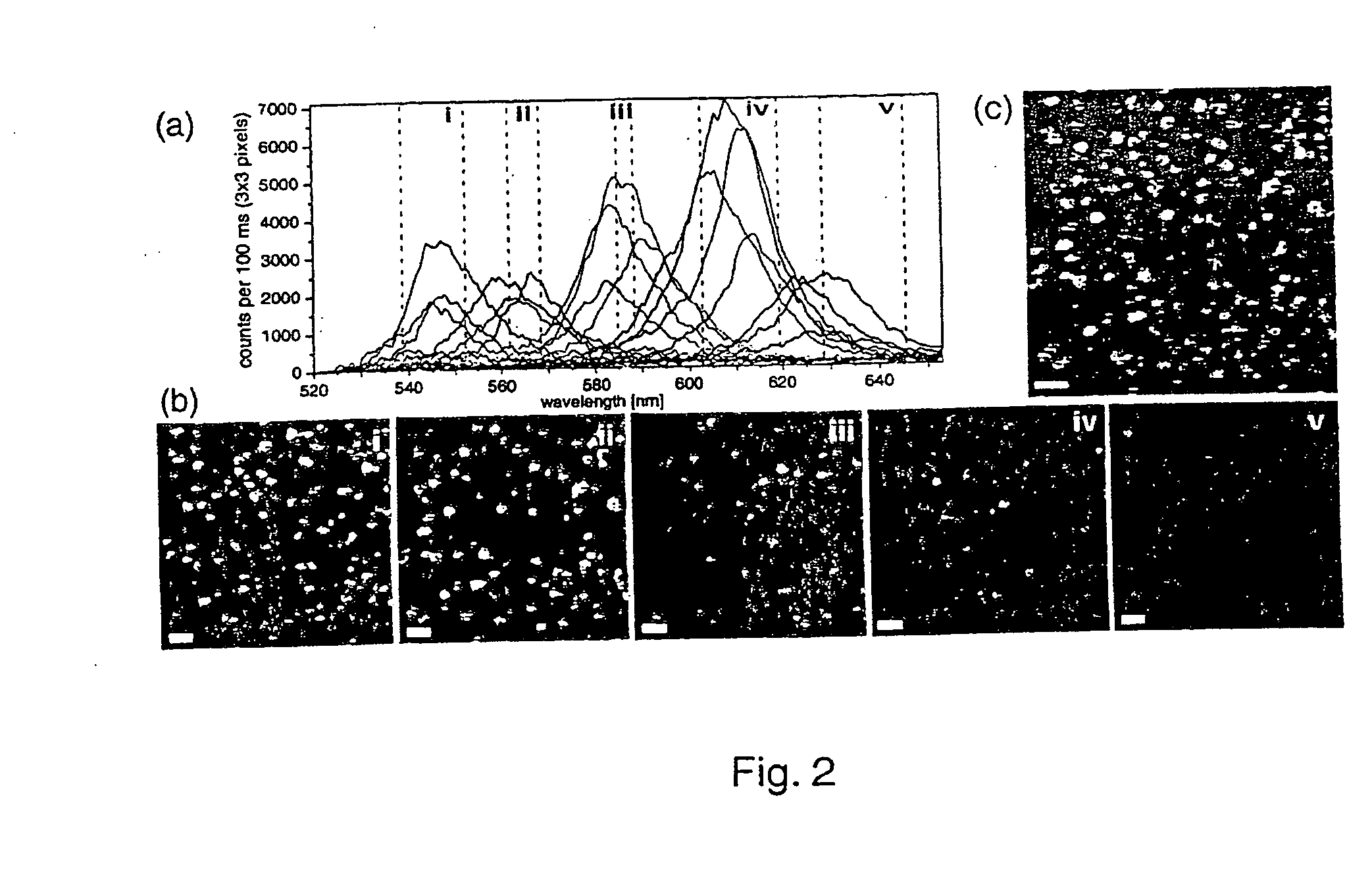
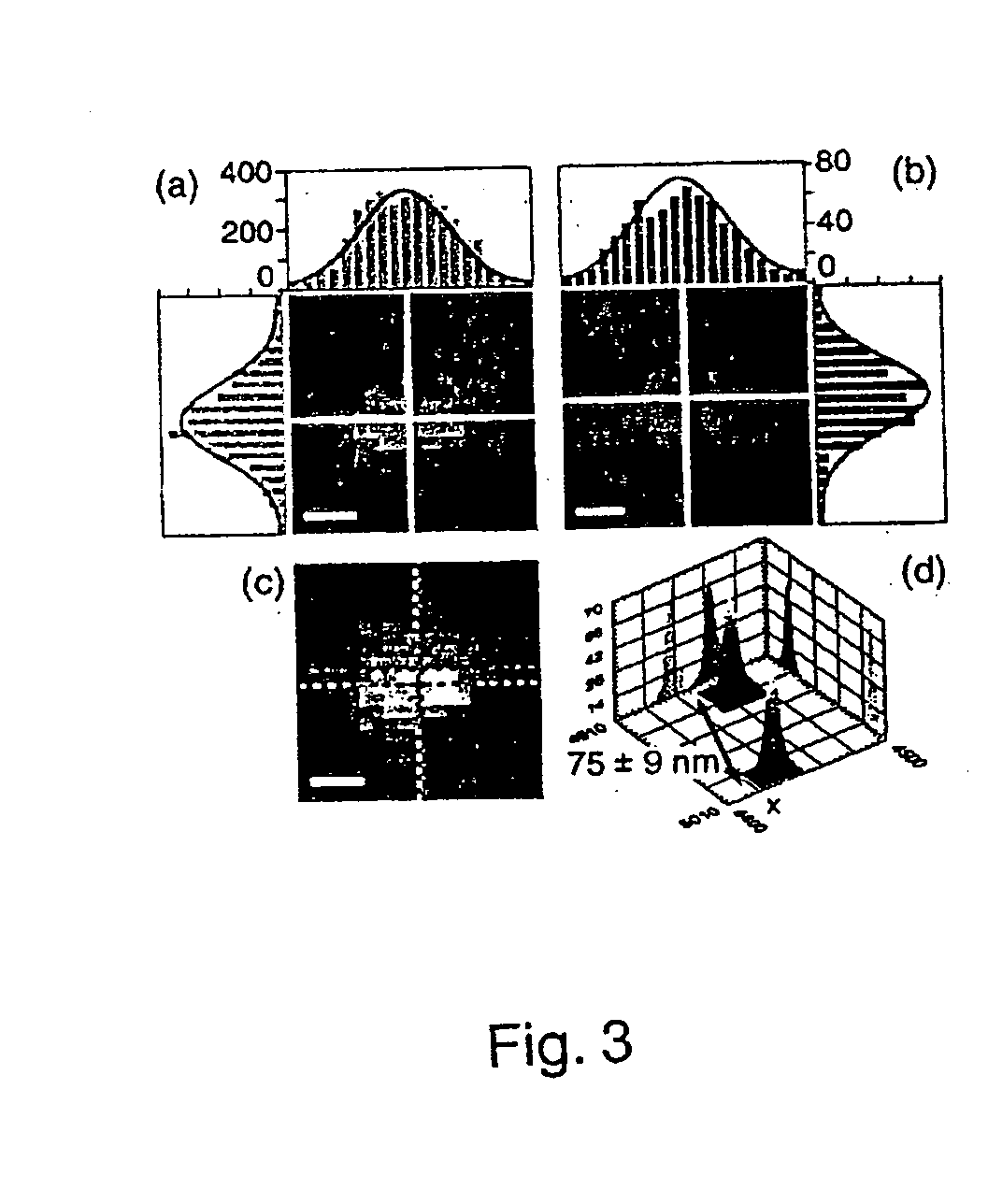
A novel optical ruler based on ultrahigh-resolution colocalization of single fluorescent probes is described. Two unique families of fluorophores are used, namely energy-transfer fluorescent beads and semiconductor nanocrystal (NC) quantum dots, that can be excited by a single laser wavelength but emit at different wavelengths. A novel multicolor sample-scanning confocal microscope was constructed which allows one to image each fluorescent light emitter, free of chromatic aberrations, by scanning the sample with nanometer scale steps using a piezo-scanner. The resulting spots are accurately localized by fitting them to the known shape of the excitation point-spread-function of the microscope.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
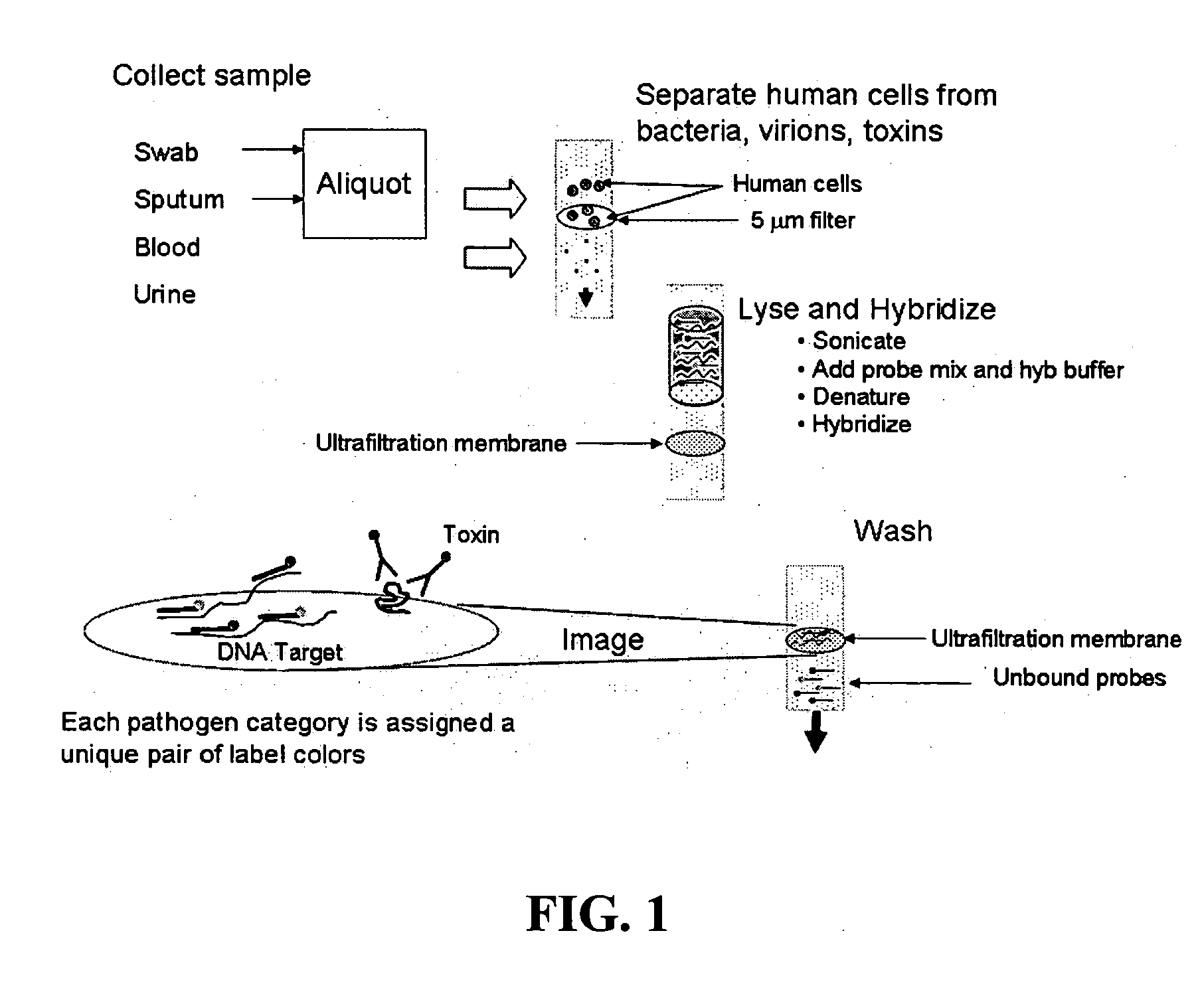
Methods and compositions for identifying chemical or biological agents using multiplexed labeling and colocalization detection
InactiveUS20070026391A1High degreeMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsColocalizationBiology
The present invention provides methods for detecting a target pathogenic agent, e.g., a virus, a bacterium, and / or a toxic substance, using colocalization detection. The invention also provides methods for parallel detection of different target pathogenic agents in a sample using multiplexed labeling and colocalization detection. The invention also provides kits comprising sets of probes for detecting pathogenic agents. The invention further provides computer systems and computer program products for carrying out the method of determining degrees of colocalization.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
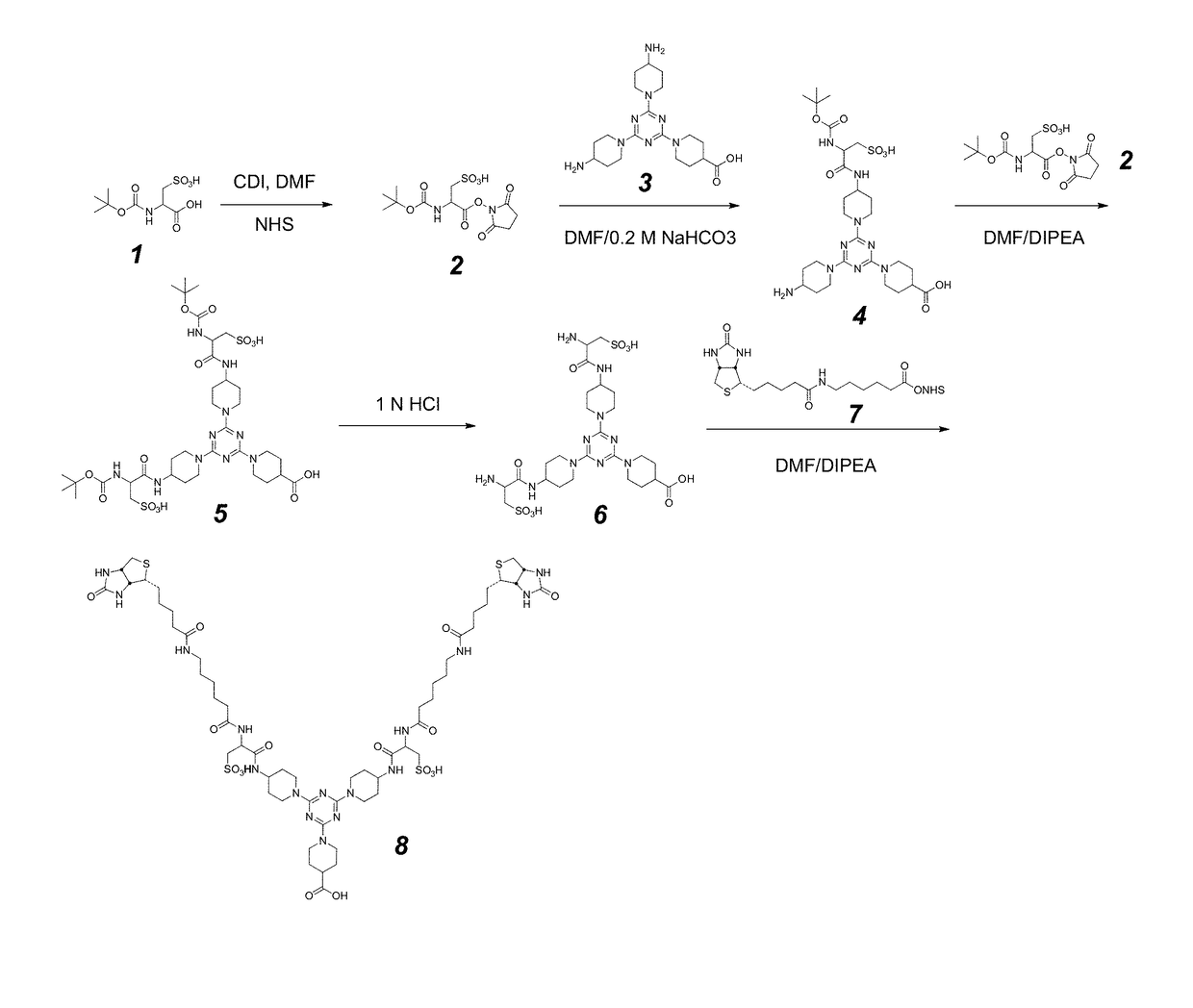
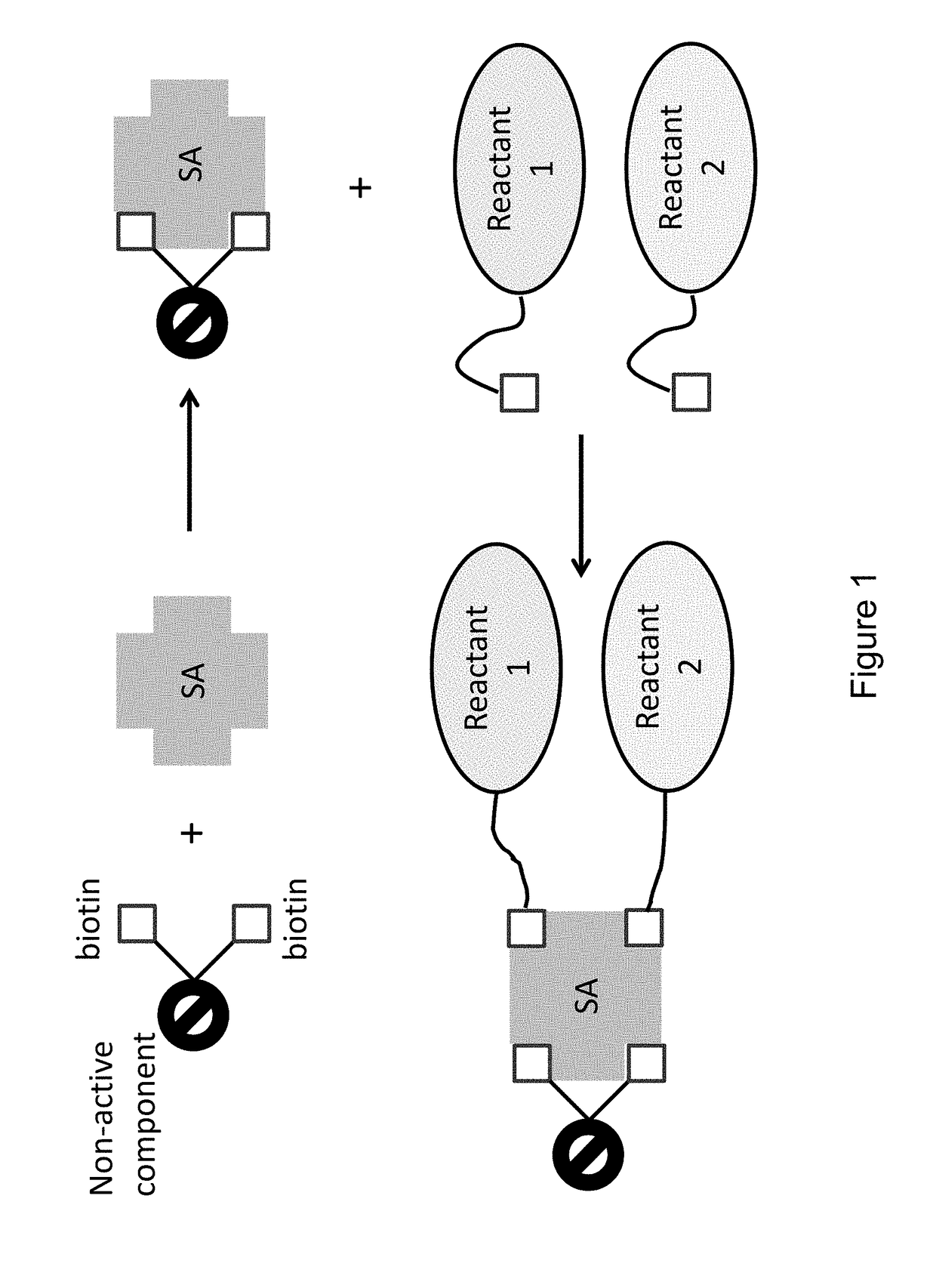
Bis-biotinylation tags
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods of cytodiagnostic staging of neoplasia and squamous cell carcinoma
InactiveUS7258987B2Microbiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsEpitheliumSquamous Carcinomas
Methods of diagnosing whether an epithelial tissue is an abnormal tissue by determining an expression pattern for PML in the epithelial tissue; determining an expression pattern for nuclear bodies in the epithelial tissue; determining SUMO-1 colocalization and comparing the expression pattern for PML and the expression pattern for nuclear bodies with a control are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for diagnosing whether a subject has mild dysplasia, moderate dysplasia, Type A severe dysplasia, Type B severe dysplasia, cervical squamous cell carcinoma, or poorly-differentiated cervical squamous cell carcinoma, by determining an expression pattern for PML, an expression pattern for nuclear bodies, and SUMO-1 colocalization and determining whether the sample is consistent with expression patterns expected for mild dysplasia, moderate dysplasia, Type A severe dysplasia, Type B severe dysplasia, cervical squamous cell carcinoma, or poorly-differentiated cervical squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Rhodamine B targeted lysosome pH fluorescent probe with cysteine ethyl ester structure and application of rhodamine B targeted lysosome pH fluorescent probe
InactiveCN103320120AQuick responseHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryBiological testingLysosomePh regulation
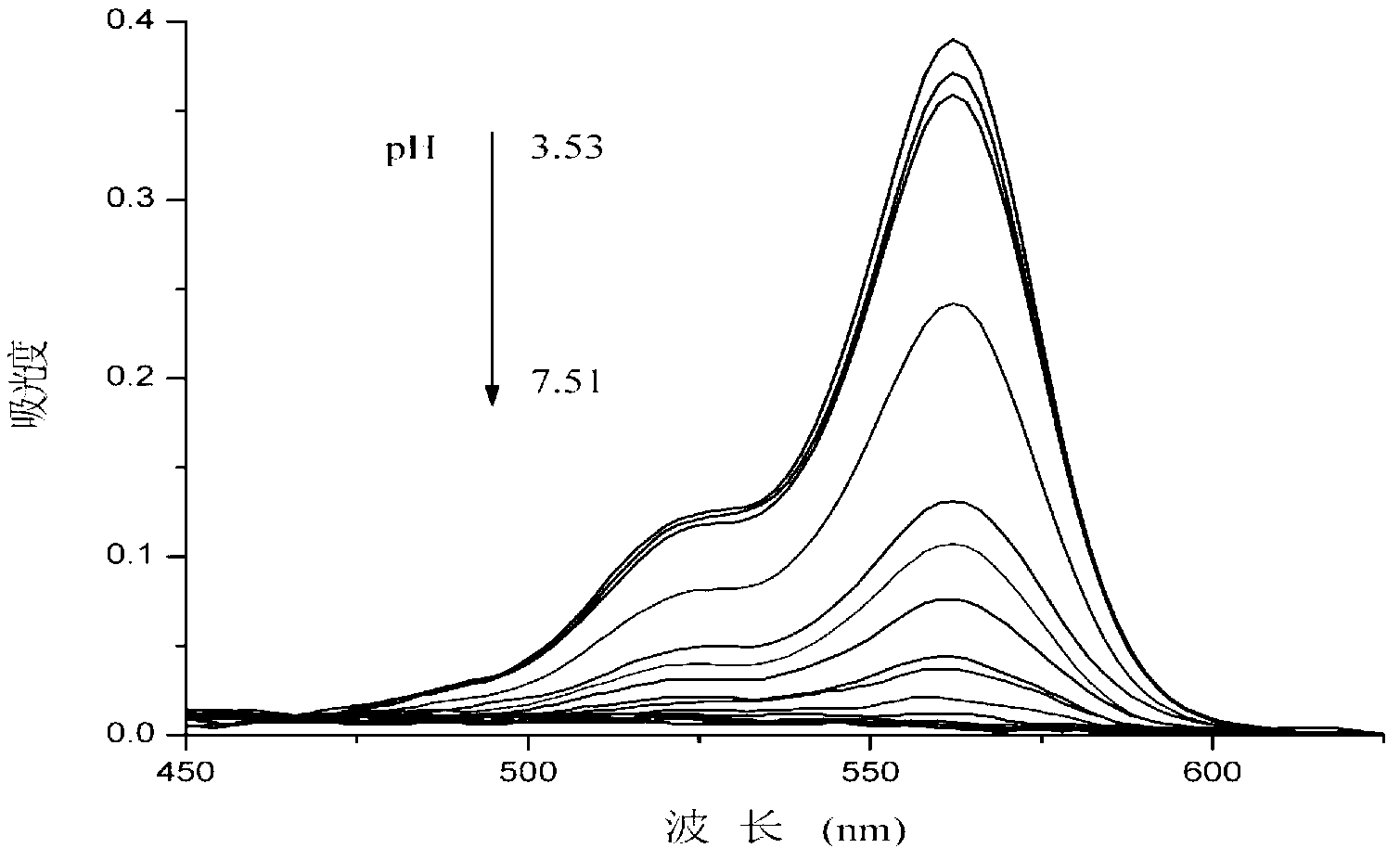
The invention discloses a rhodamine B targeted lysosome pH fluorescent probe with a cysteine ethyl ester structure, wherein the rhodamine B targeted lysosome pH fluorescent probe has the structure as shown in a formula (I). Meanwhile, the invention discloses an application of the probe as a living cell lysosome pH fluorescent probe. Experiments show that the probe provided by the invention does not generate fluorescence under the neutral and alkaline conditions, the fluorescence intensity is rapidly enhanced along with the reduction of the pH value of the solution, is up to the maximum value when the pH value is about 4.0 and is enhanced by about 150 times when the pH value ranges from 7.51 to 3.53, and the probe has favorable antijamming capability and reversibility in the presence of various metal ions. An intracellular colocalization experiment and an interlysosome pH regulation experiment prove that the probe can specially mark a lysosome and sensitively monitor the small change of the interlysosome pH value. A cell survival rate experiment shows that the probe is nontoxic to cells, which indicates that the probe disclosed by the invention has an important application value in the aspects of imaging the cells and monitoring the change of the interlysosome pH value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
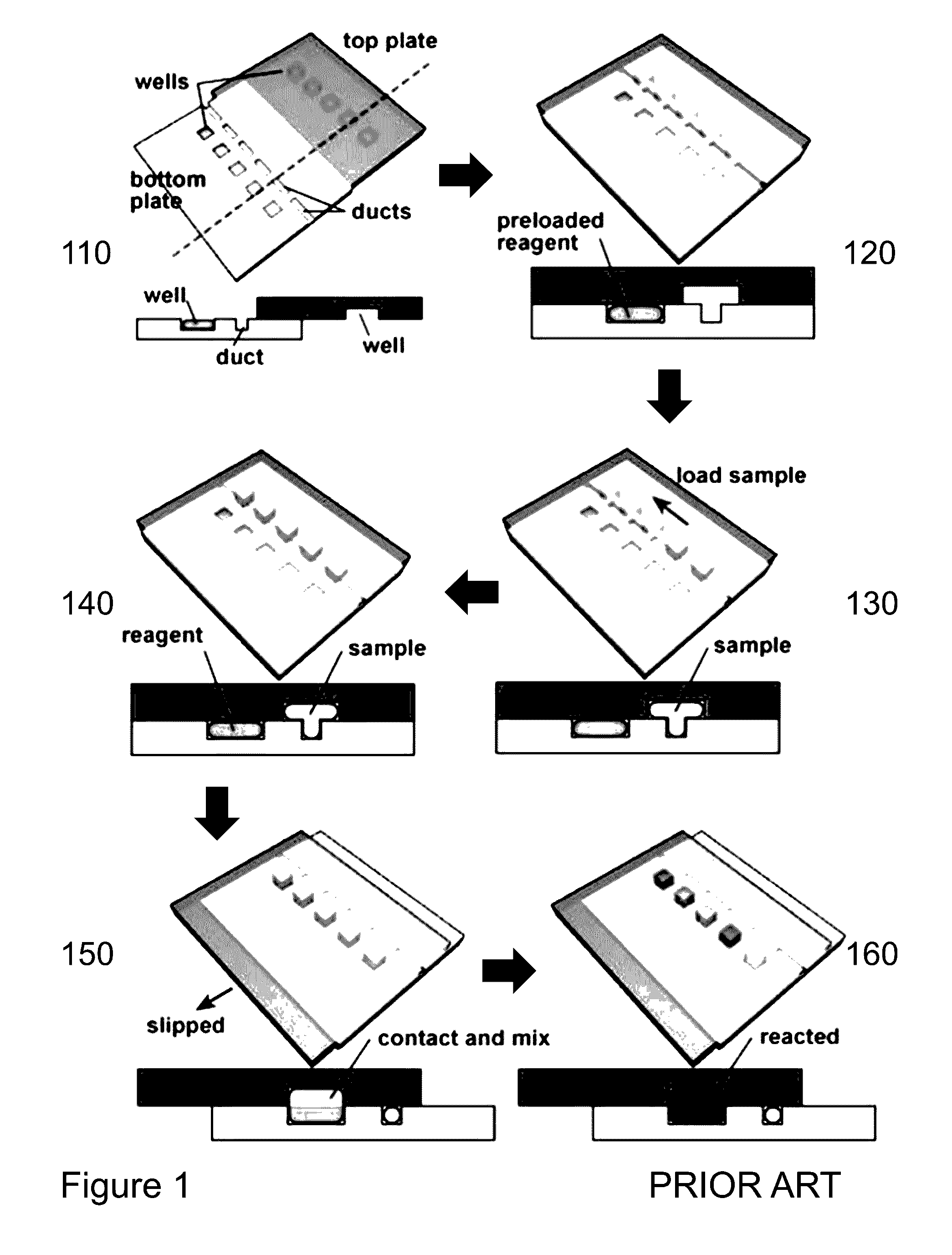
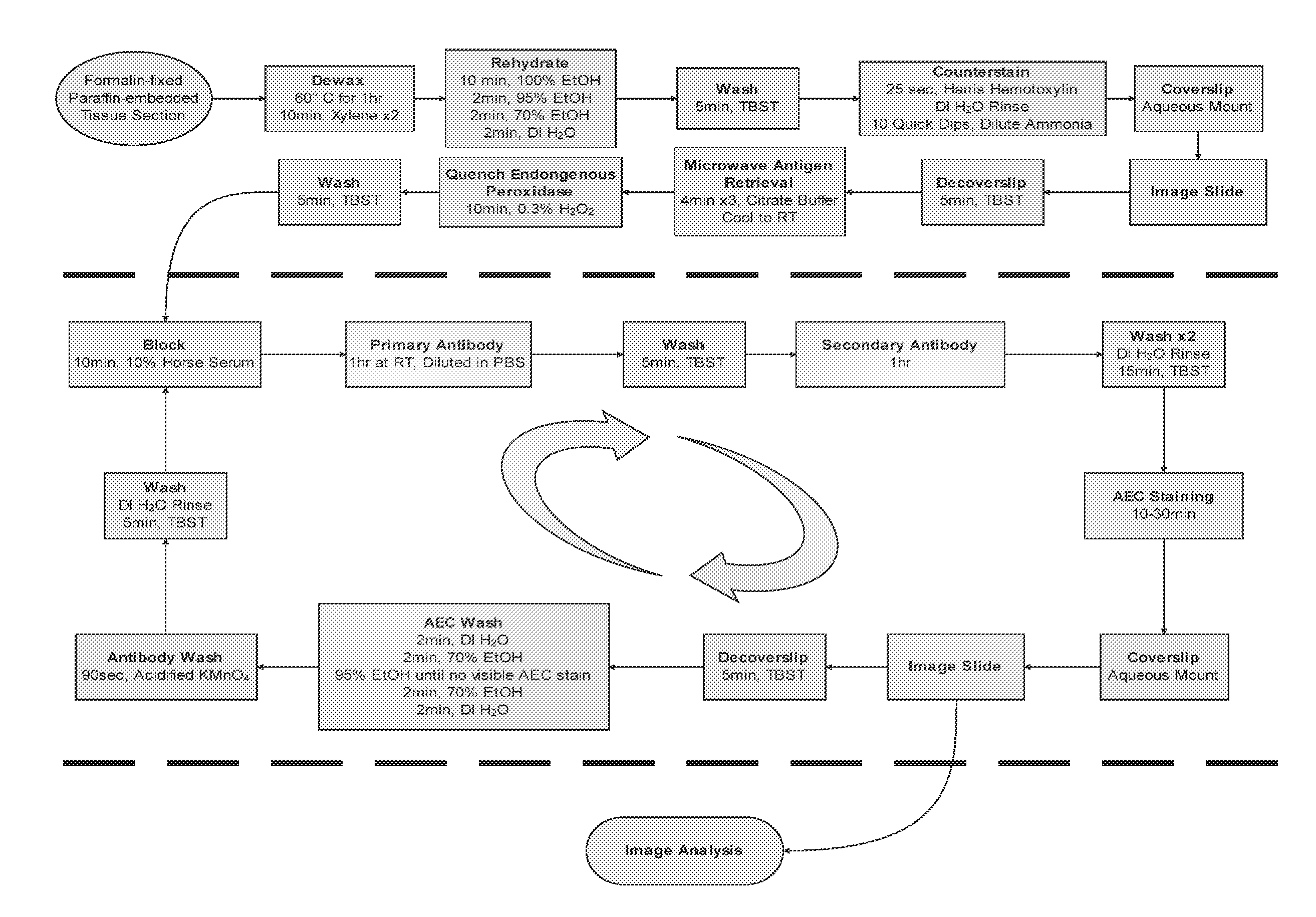
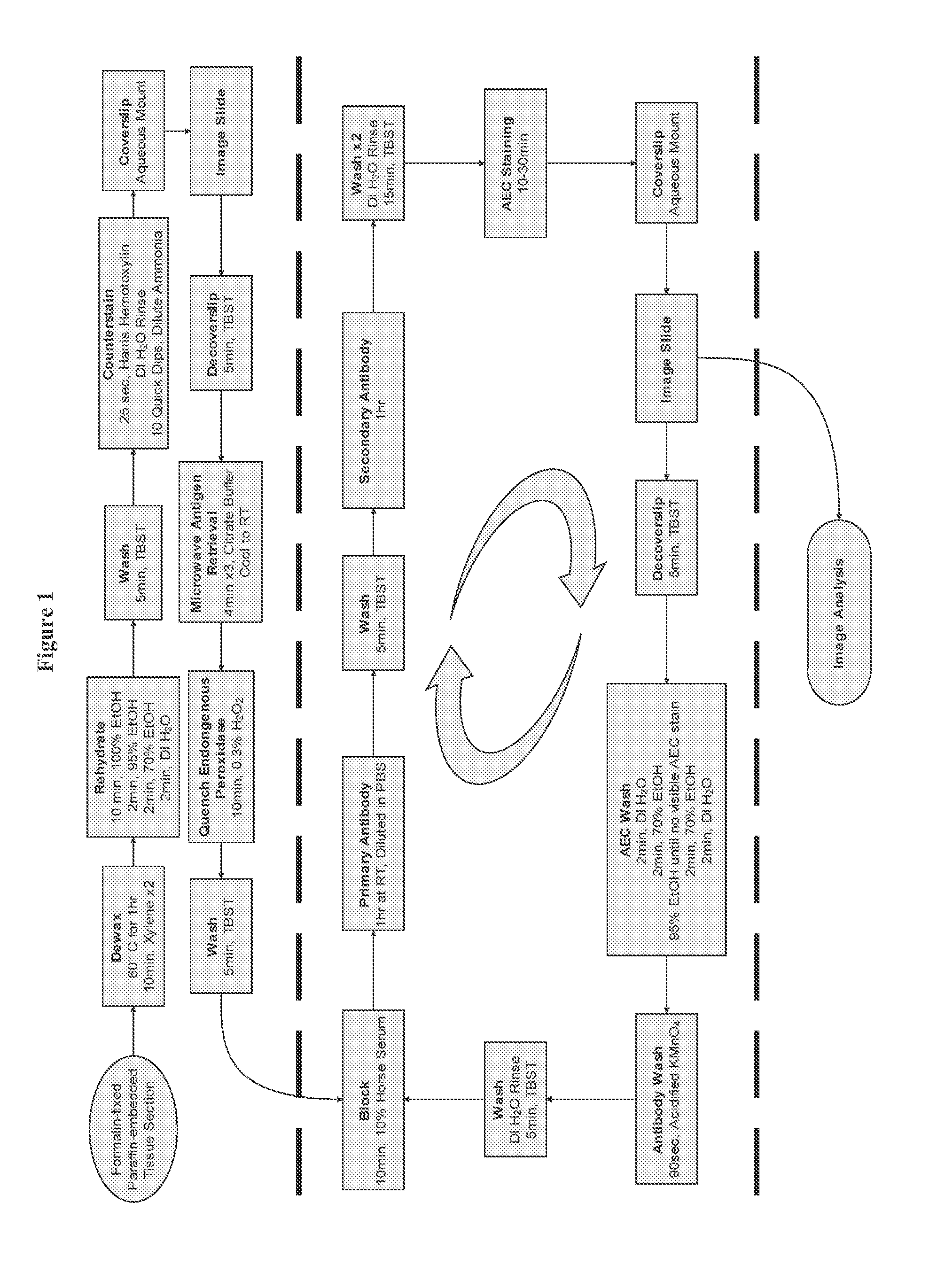
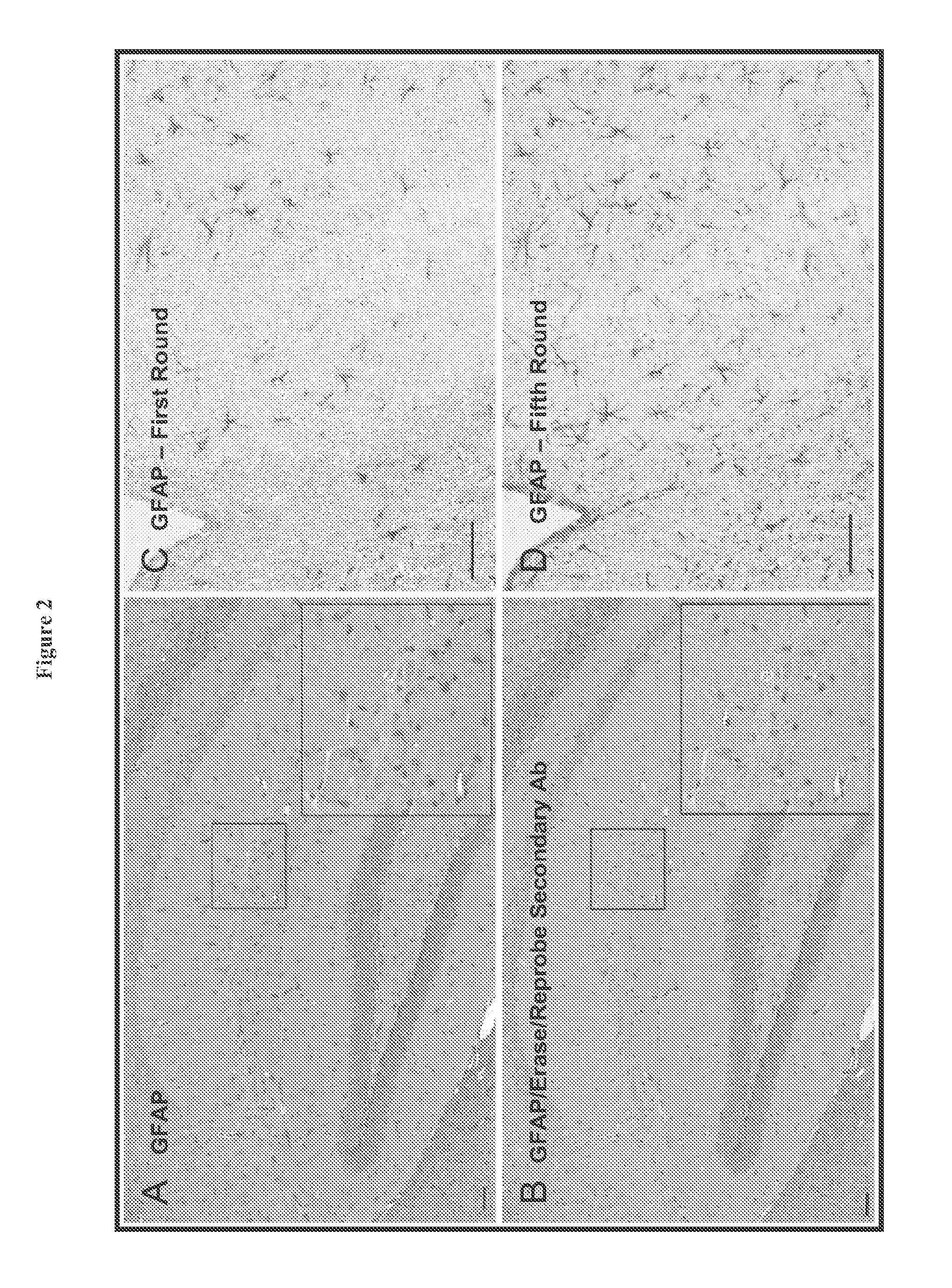
Serial multiple antigen colocalization in paraffin-embedded tissue
ActiveUS8753824B2Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPeroxidase3-amino-9-ethylcarbazole
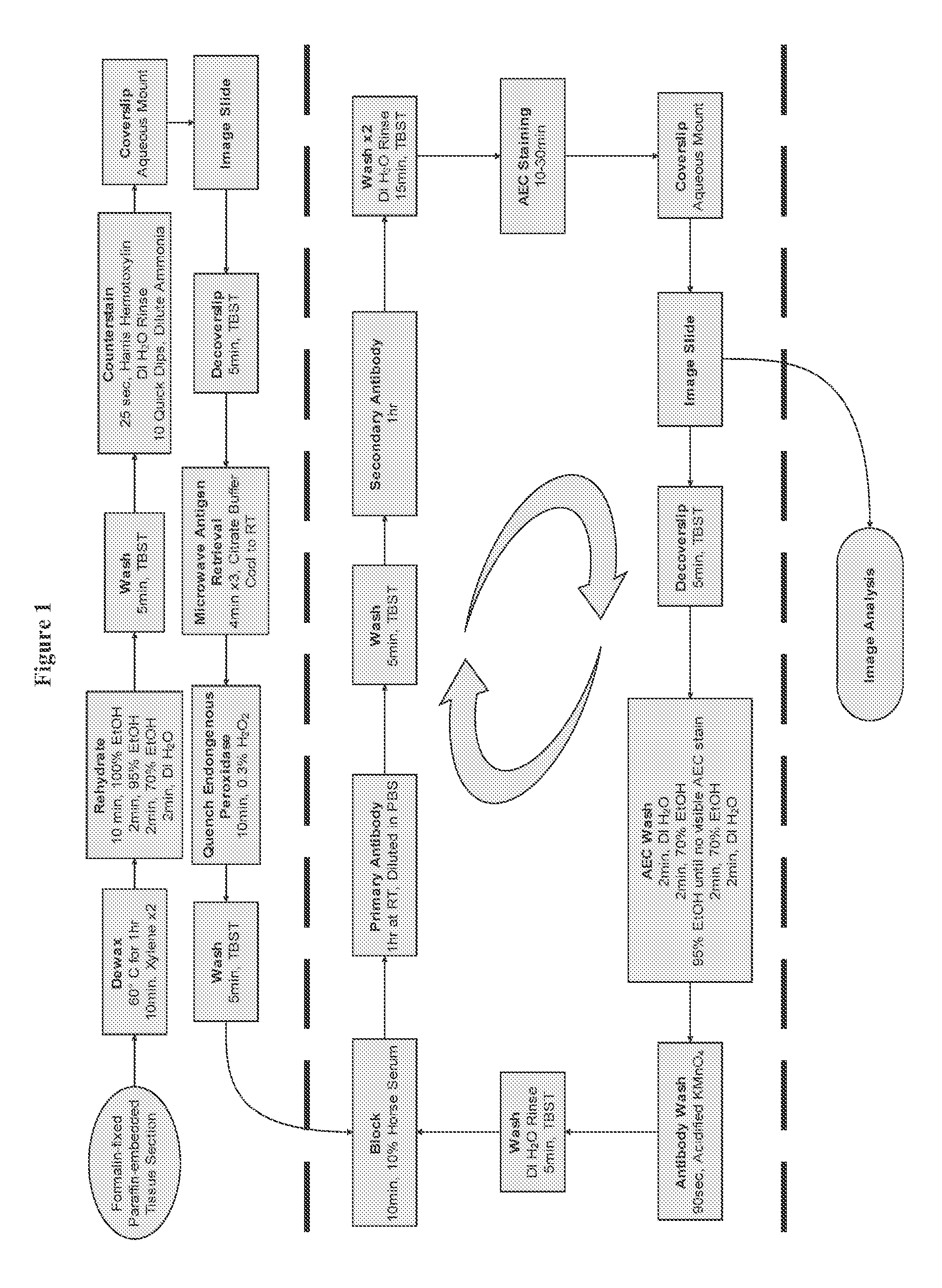
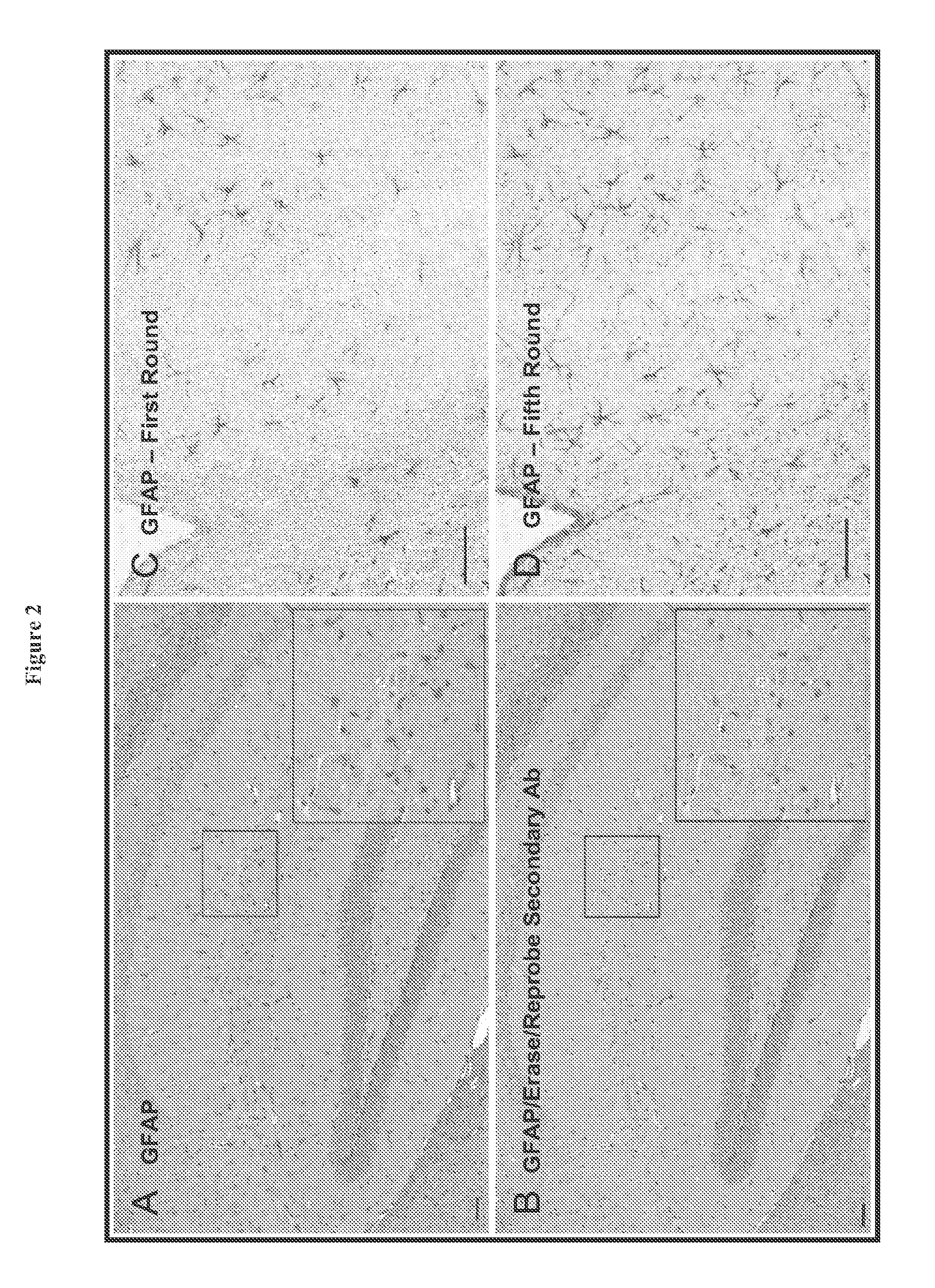
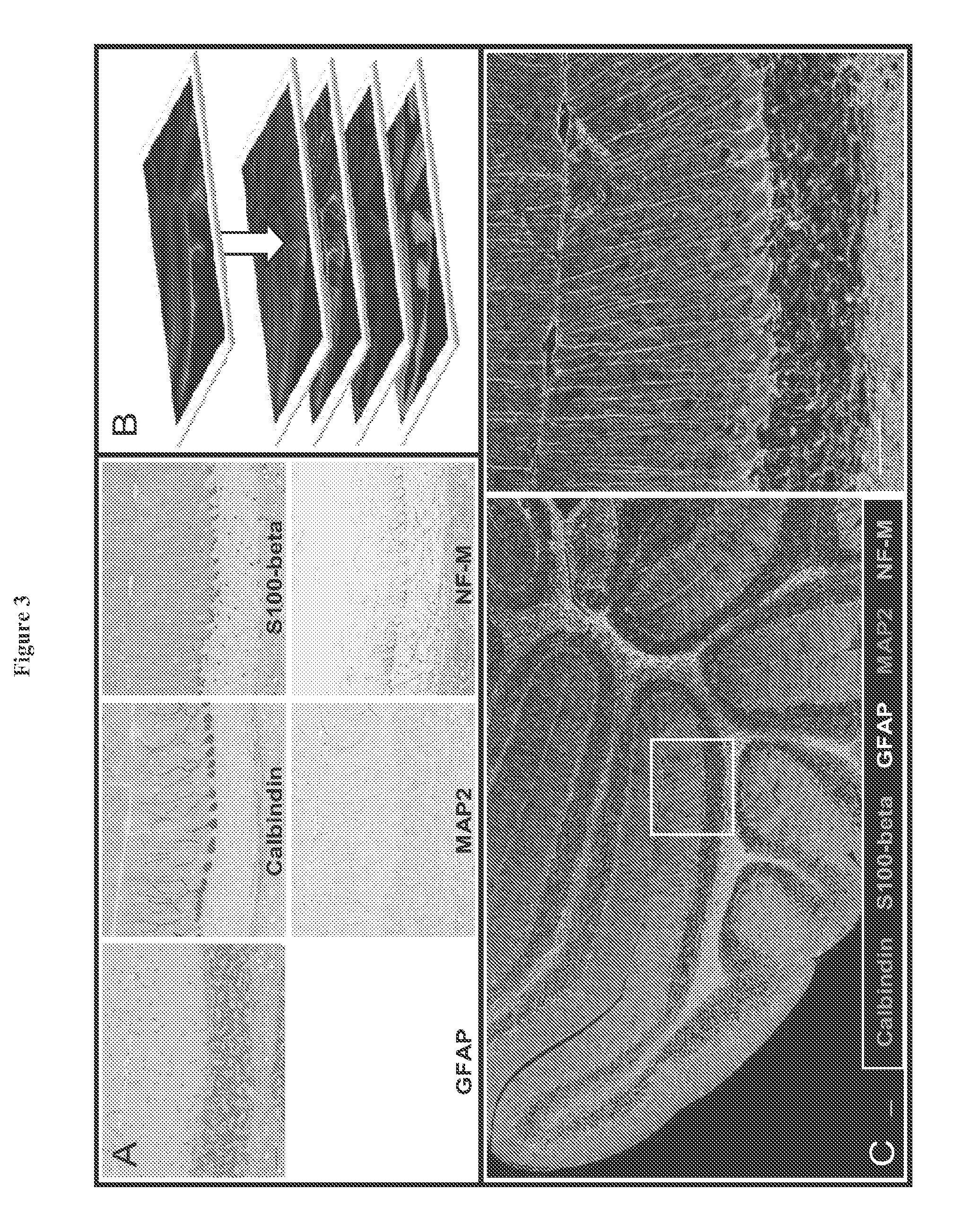
The present invention provides a novel method called Sequential IMmunoPeroxidase Labeling and Erasing (SIMPLE) that enables the simultaneous visualization of at least five markers within a single tissue section. Utilizing the alcohol-soluble peroxidase substrate 3-amino-9-ethylcarbazole (AEC), combined with a rapid non-destructive method for antibody-antigen dissociation, the present application discloses the ability to erase the results of a single immunohistochemical stain while preserving tissue antigenicity for repeated rounds of labeling. The present invention also provides methods for visualizing multiple antigens simultaneously.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Ultrahigh resolution multi-color colocalization of single fluorescent probes
A novel optical ruler based on ultrahigh-resolution colocalization of single fluorescent probes is described. Two unique families of fluorophores are used, namely energy-transfer fluorescent beads and semiconductor nanocrystal (NC) quantum dots, that can be excited by a single laser wavelength but emit at different wavelengths. A novel multicolor sample-scanning confocal microscope was constructed which allows one to image each fluorescent light emitter, free of chromatic aberrations, by scanning the sample with nanometer scale steps using a piezo-scanner. The resulting spots are accurately localized by fitting them to the known shape of the excitation point-spread-function of the microscope.
Owner:WEISS SHIMON +2
Bis-biotinylation tags
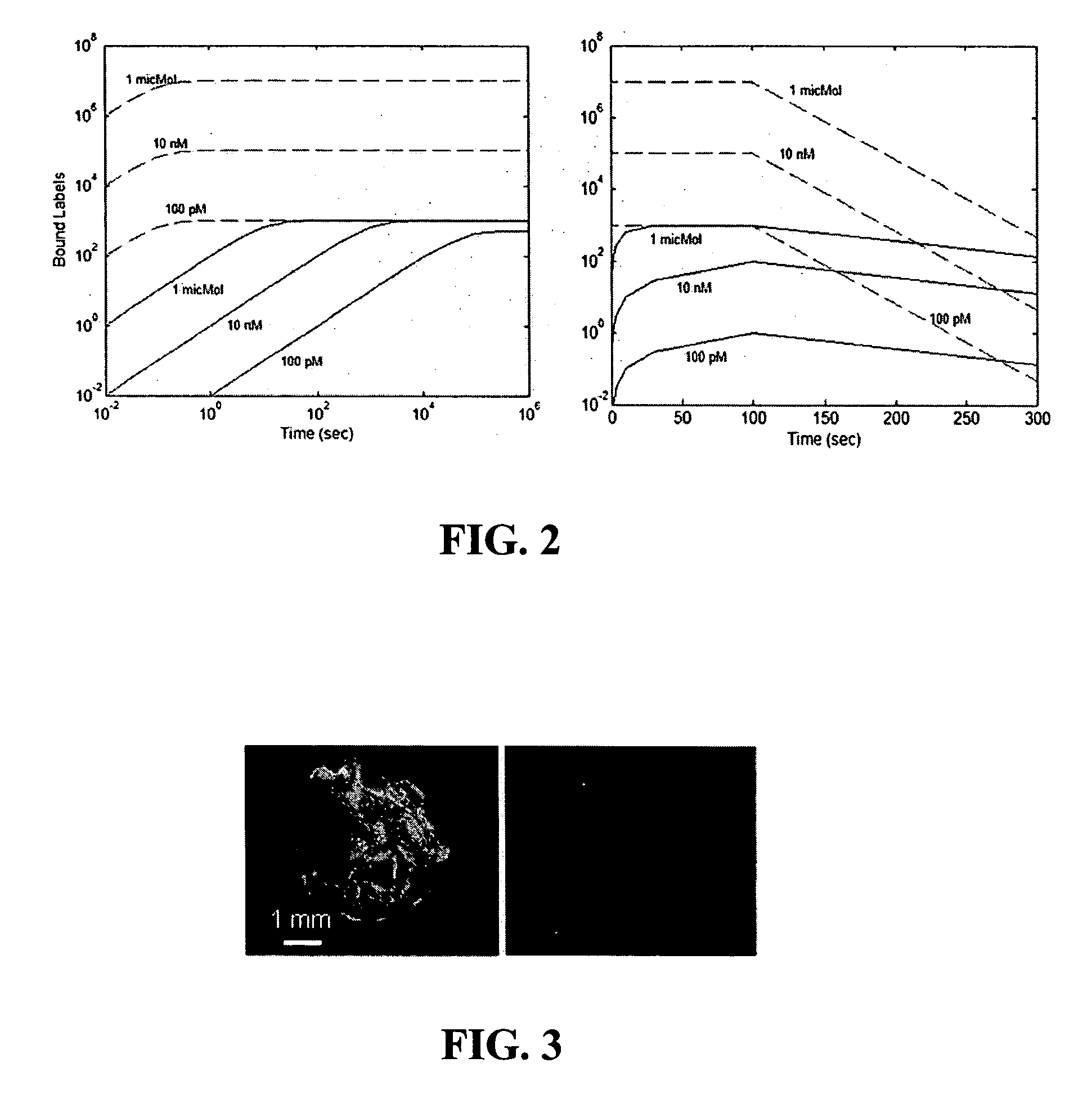
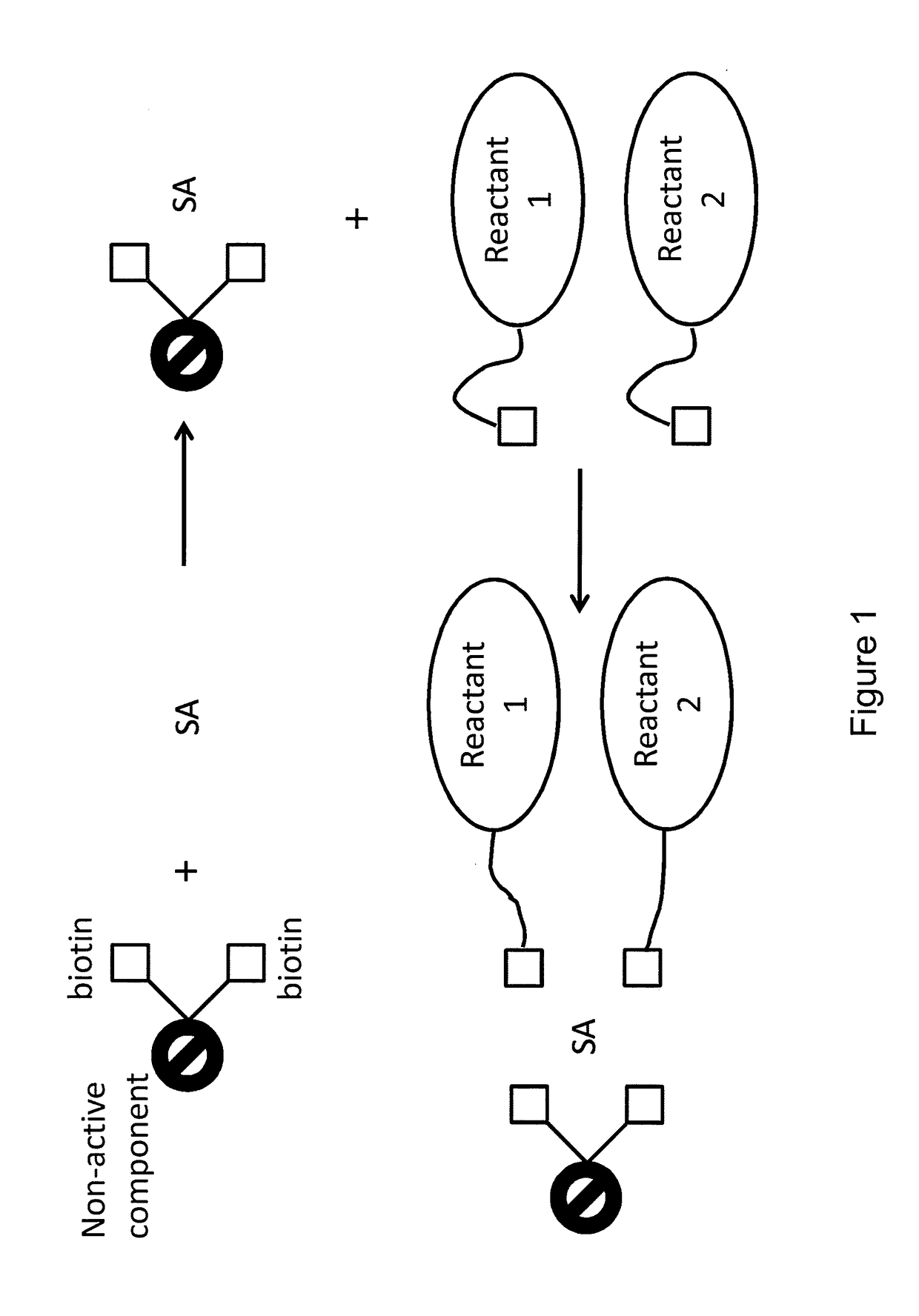
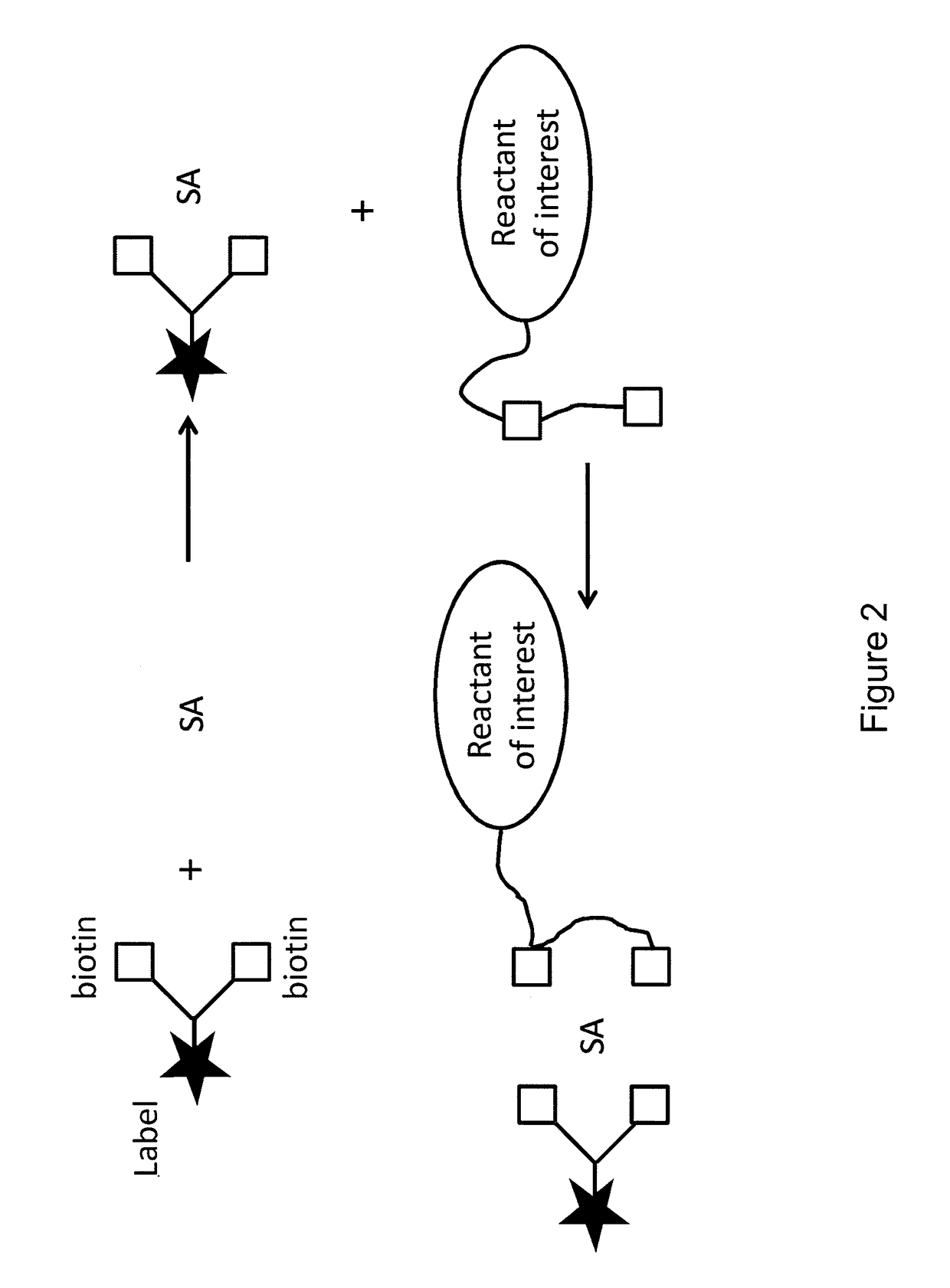
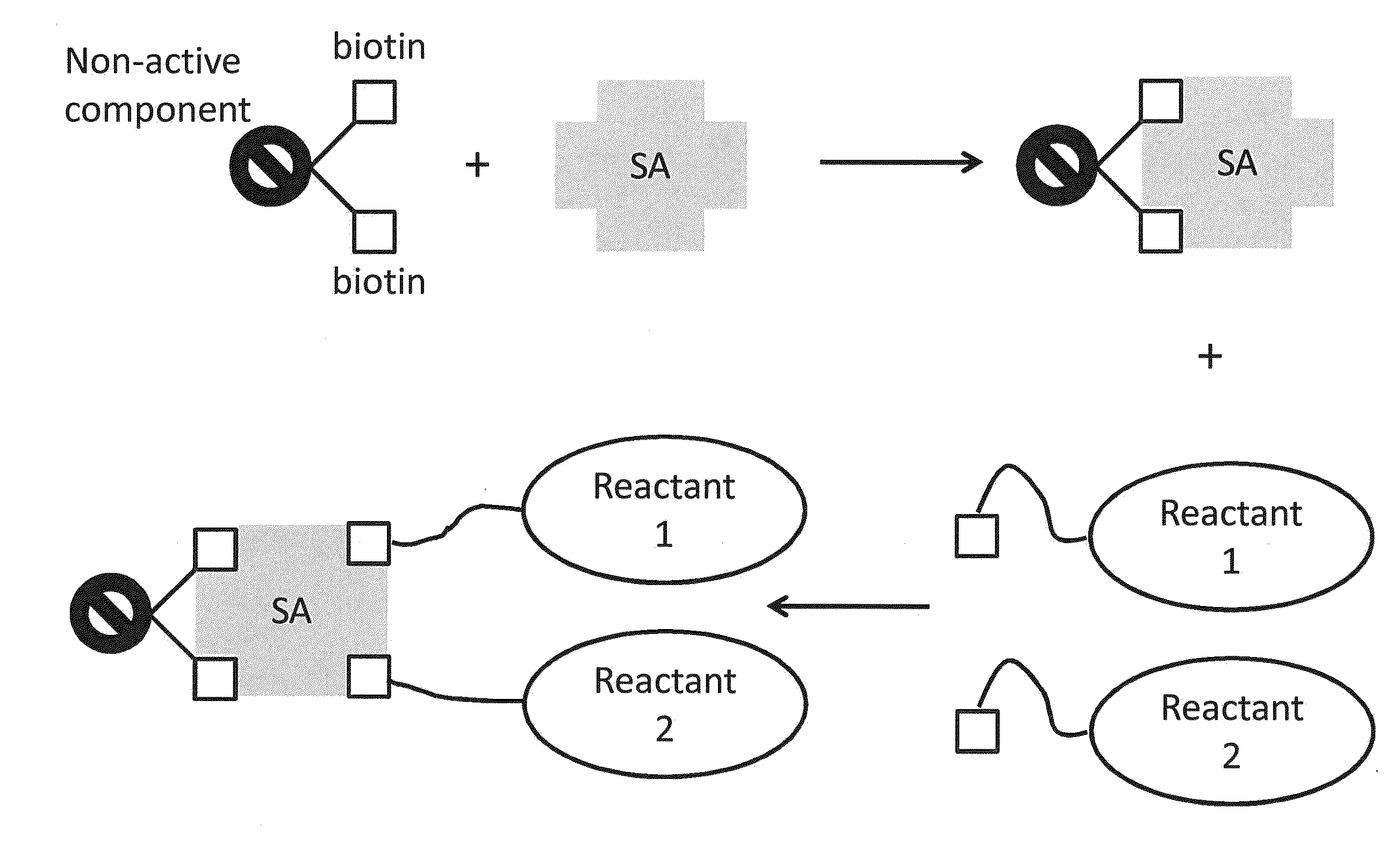
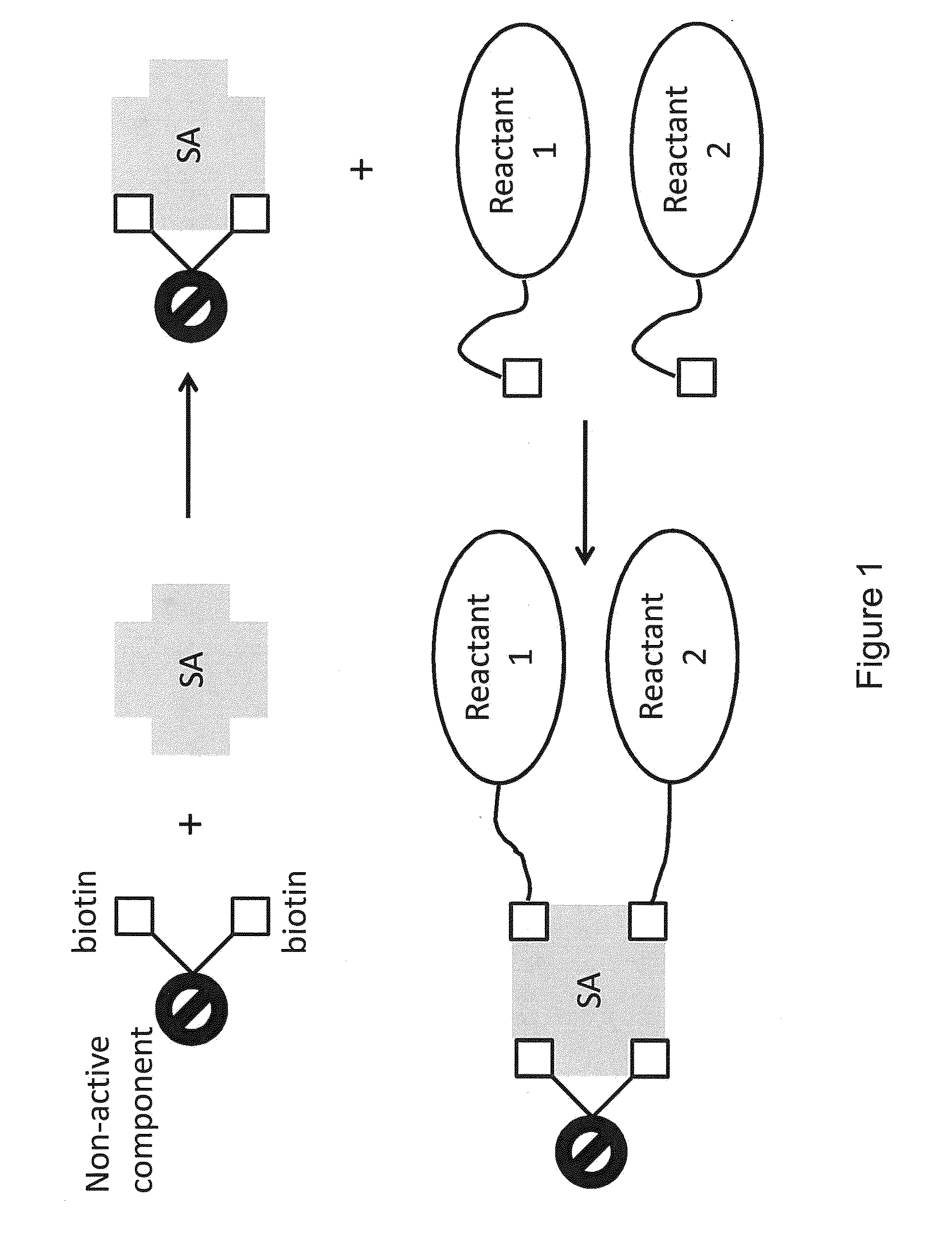
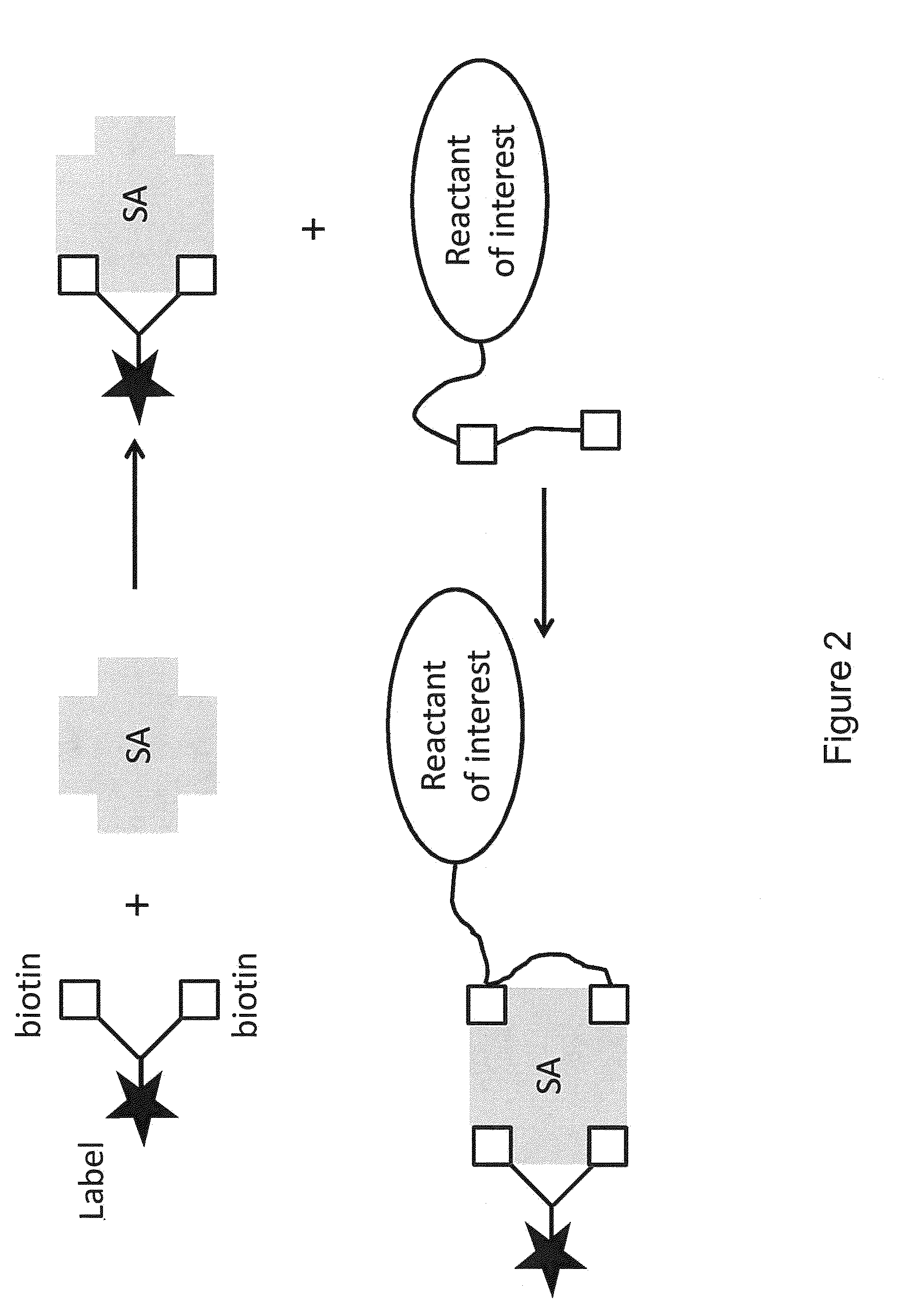
ActiveUS20150011433A1Enhanced interactionWide commercial utilityPeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotin-streptavidin complexColocalization
Multi-biotinylated reactants are provided which can be used in divalent complexes for various applications such as colocalization, labeling, immobilization, and purification. Methods for constructing, purifying, and using the bis-biotinylated reactants are also provided. In certain embodiments, two bis-biotinylated reactants are bound to a single streptavidin tetramer to provide a complex having a 1:1 stoichiometry with respect to the bis-biotinylated reactants.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Data transmission control method, network side device and terminal
ActiveCN108288985ARealize data transmissionRadio transmissionSignalling characterisationComputer hardwareColocalization
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
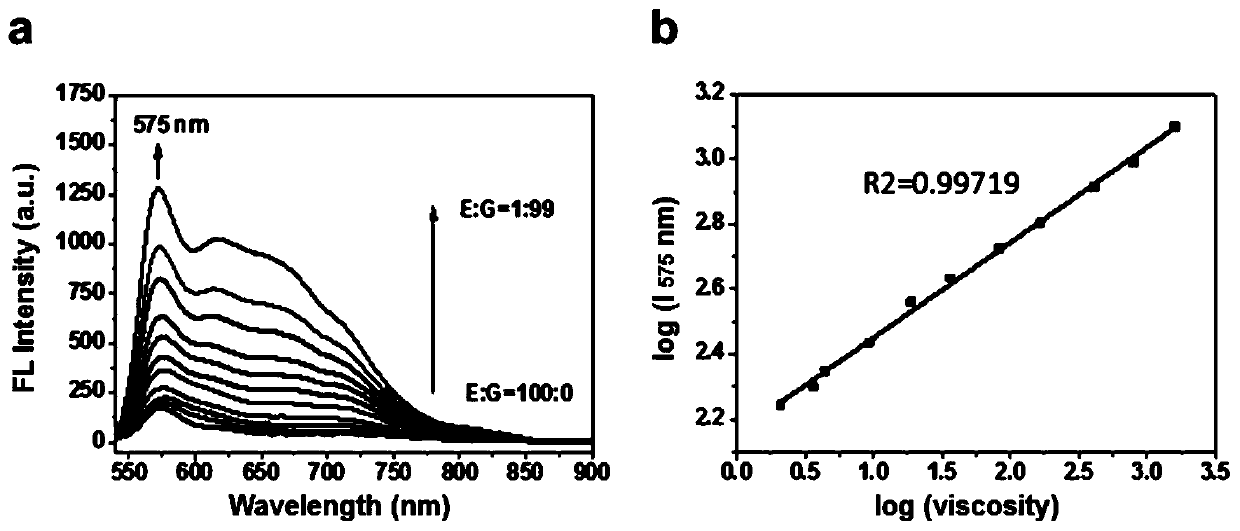
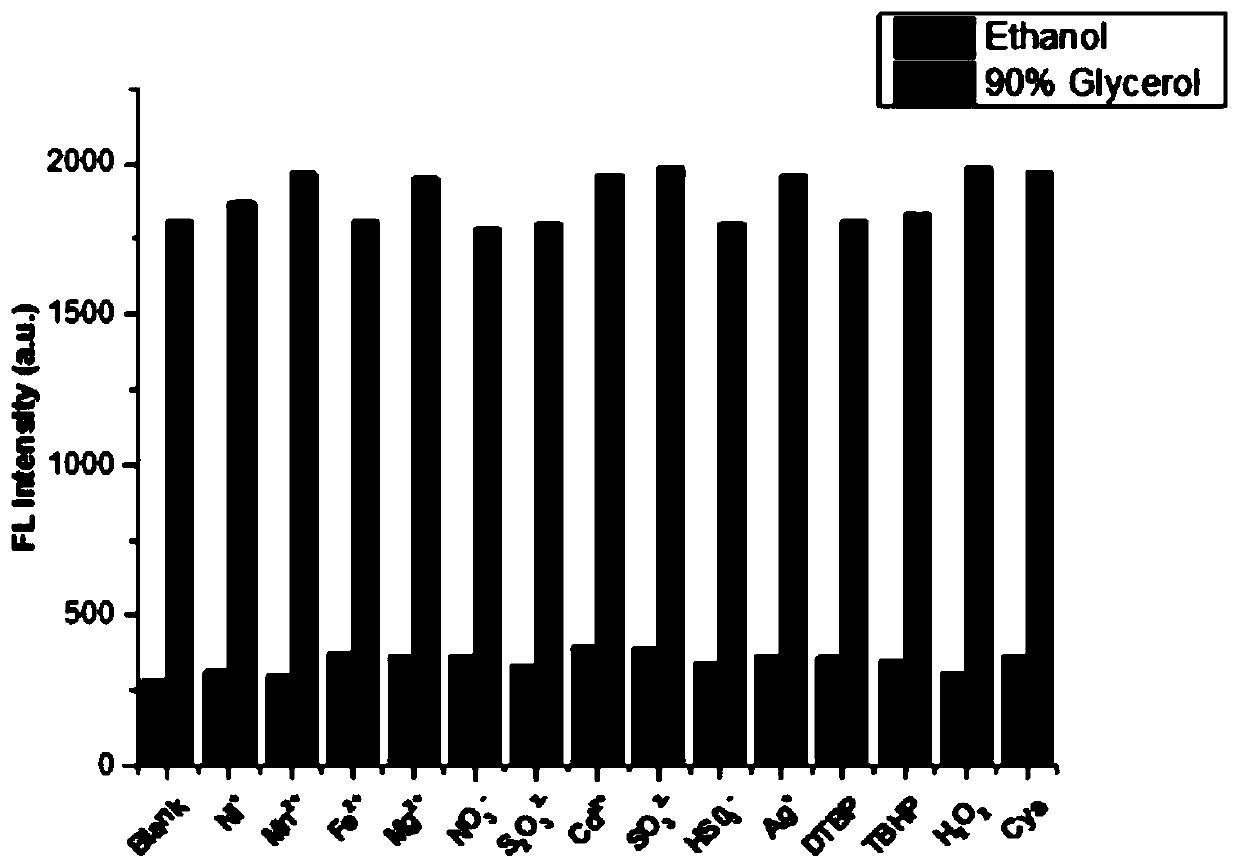
Fluorescent probe for detecting viscosity, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110129037AStrong specificityWith color sensing functionOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceColocalizationFluorescence
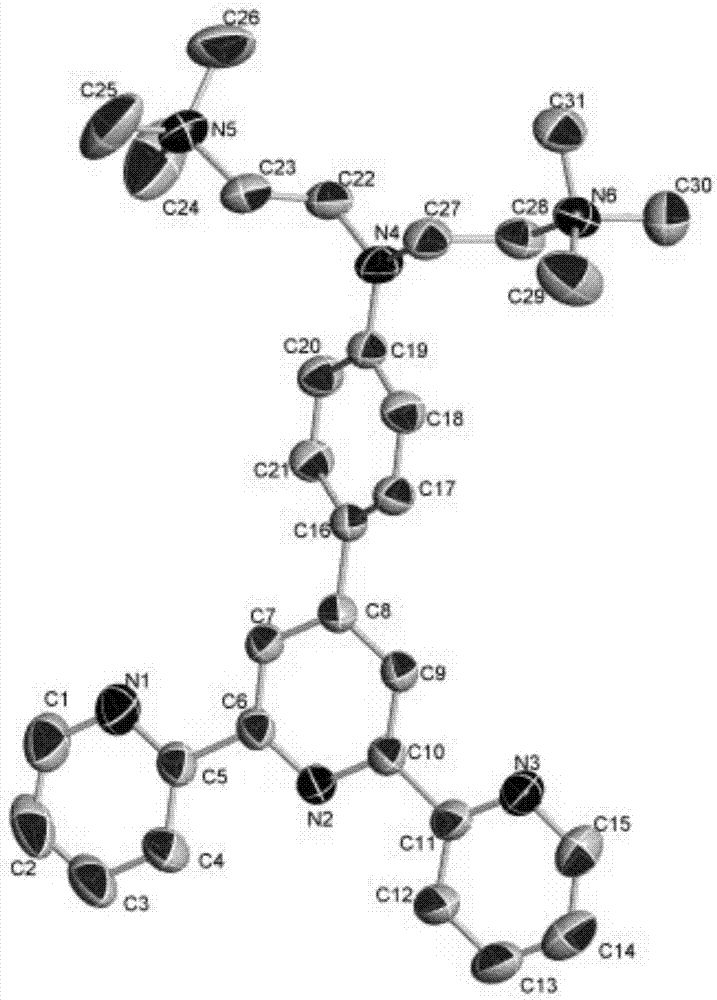
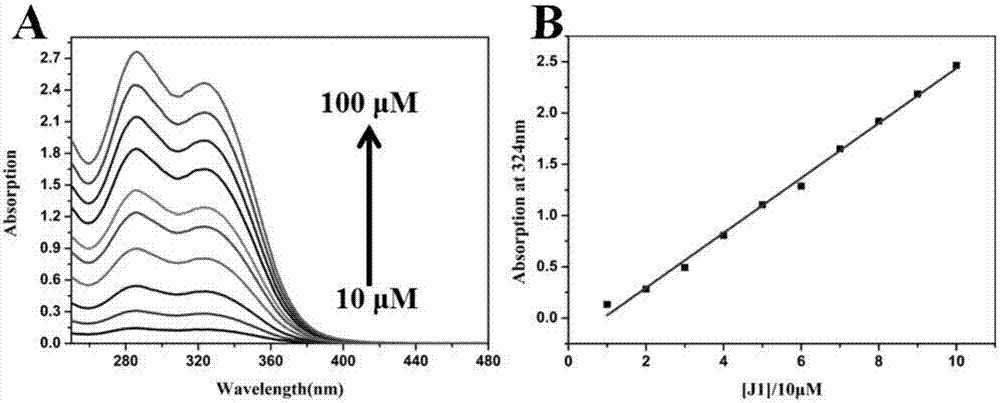
The invention provides a fluorescent probe for detecting the viscosity. The chemical structural formula of the fluorescent probe is shown in the description. The fluorescent probe can be used for detecting the viscosity of a solution or a cell. The donor of the probe is an imidazolyl group, the acceptor of the probe is a hemicyanine group, and the donor and the acceptor are combined through a phenyl ring. The probe has the advantages of short synthesis steps, and simplicity in post-treatment; the probe can realize precise location of mitochondria, and has a high colocalization coefficient; andthe enhancement of the fluorescence color can be observed under an ultraviolet lamp, so the fluorescent probe has a chromophoric sensing function. The probe of the invention is a simple and sensitiveaccurate-location viscosity specific detection reagent, and has a broad application prospect in the field of biomolecule detection.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
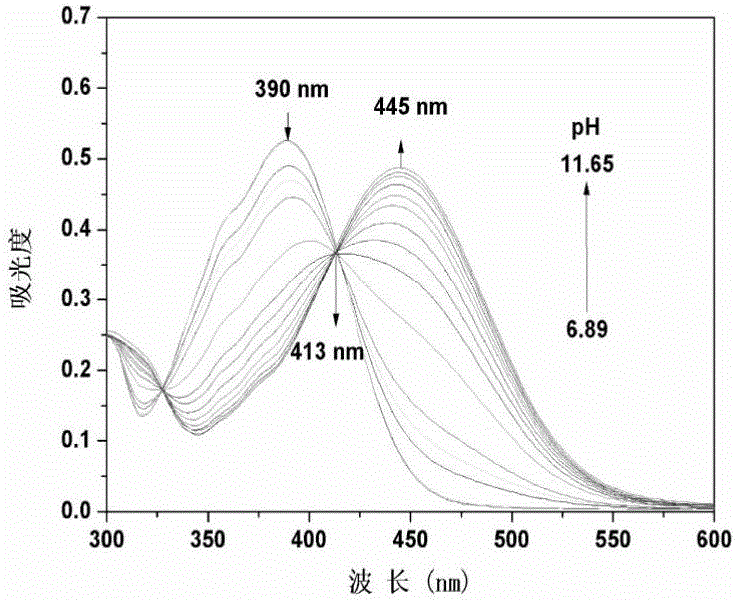
Application of naphthyl derivatives used as targeted pH fluorescent probes for mitochondria
InactiveCN106565596AGood cell membrane permeabilityIncrease polarityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilityPhosphate
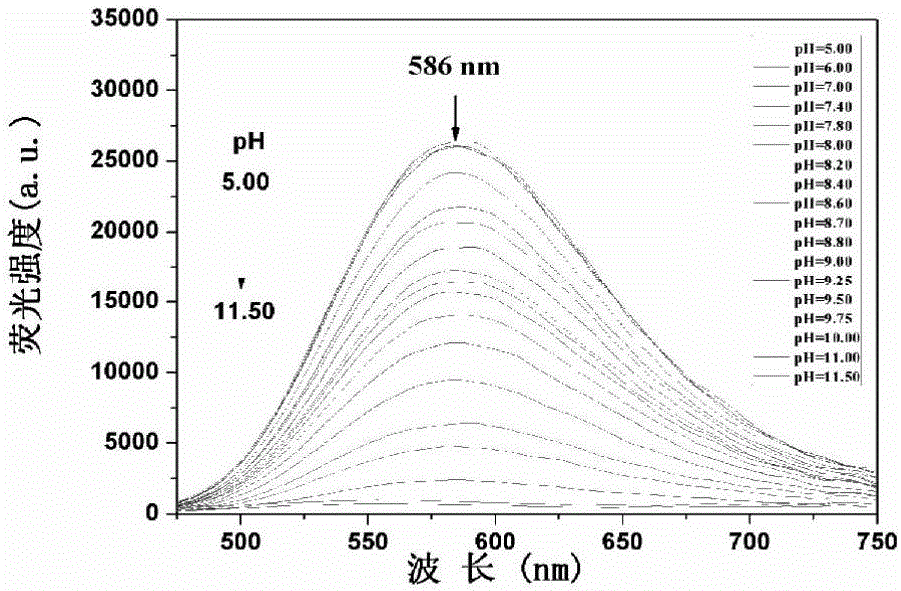
The invention discloses an application of naphthyl derivatives used as targeted pH fluorescent probes for mitochondria, and specifically discloses targeted marking of 1- methyl-4-[2-(6-hydroxyl-2-naphthalene)- vinyl]-pyridium (HNEP<+>) in the mitochondria of living cells, and an application thereof in pH detection. The derivatives are excited at a wavelength of 390nm, and achieve maximum fluorescence emission at a wavelength of 586nm. The fluorescence intensity at a wavelength of 586nm is gradually weakened with the rising of the pH value from 5.00 to 11.50 in a phosphate buffer system. The pKa value is 8.8, and the linear range of the pH value is 7.8-10.0 and suitable for detection for the mitochondria in an alkaline environment (with a pH value of 8.0). In addition, the probes have an ultra-large Stokes displacement (196nm), and are high in selectivity and water solubility, low in toxicity and beneficial to fluorescence imaging study in the cells. A colocalization experiment in the cells and a pH adjustment experiment for the mitochondria prove that the probes are capable of realizing specific targeted marking for the mitochondria, and capable of detecting the change of the pH value in the mitochondria with high sensitivity.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Technology for preparing double-loaded or multi-loaded liposome through liposome fusion induction
InactiveCN105832670AHigh fluorescence intensityNo fluorescence quenchingOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsColocalizationDrug administration
The invention belongs to the field of medicines and relates to a technology for preparing double-loaded or multi-loaded liposome through liposome fusion induction. The technology utilizes liposome fusion induction to prepare a double-loaded or multi-loaded liposome. The technology provides a feasible solution scheme for double-loaded or multi-loaded liposome preparation. The liposome realizes synergism of two or more drugs in vitro and vivo through colocalization of two or more drug structures and cell levels and provides a novel choice for clinical, safe and effective combined drug administration.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Bis-biotinylation tags
ActiveUS20170184580A1Group 4/14 element organic compoundsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotin-streptavidin complexColocalization
Multi-biotinylated reactants are provided which can be used in divalent complexes for various applications such as colocalization, labeling, immobilization, and purification. Methods for constructing, purifying, and using the bis-biotinylated reactants are also provided. In certain embodiments, two bis-biotinylated reactants are bound to a single streptavidin tetramer to provide a complex having a 1:1 stoichiometry with respect to the bis-biotinylated reactants.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods and devices for multiplexed microarray microfluidic analysis of biomolecules
Rapid and specific detection of biological cells and biomolecules is important to biological assays across diverse fields including genomics, proteomics, diagnoses, and pathological studies. Microarrays and microfluidics increasingly dominate such detection techniques due to the ability to perform significant numbers of tests with limited sample volumes. A snap chip assembly is provided for the transfer of a microarray of reagents within semi-spherical liquid droplets on a transfer chip to a target assay microarray on an assay chip following assembly of the two chips and physical contact of the droplets with the target array. Reagents in nanoliter quantities are spotted on both chips and selectively transferred as liquid droplets between transfer chip and assay chip within the contact areas. Using the snap chip structure the inventors performed immunoassays with colocalization of capture and detection antibodies with 10 targets and bead-in-gel droplet microarrays with 9 targets in the low pg / ml regime.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Serial multiple antigen colocalization in paraffin-embedded tissue
ActiveUS20120021439A1Less tissue damageMore roundedMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPeroxidase3-amino-9-ethylcarbazole
The present invention provides a novel method called Sequential IMmunoPeroxidase Labeling and Erasing (SIMPLE) that enables the simultaneous visualization of at least five markers within a single tissue section. Utilizing the alcohol-soluble peroxidase substrate 3-amino-9-ethylcarbazole (AEC), combined with a rapid non-destructive method for antibody-antigen dissociation, the present application discloses the ability to erase the results of a single immunohistochemical stain while preserving tissue antigenicity for repeated rounds of labeling. The present invention also provides methods for visualizing multiple antigens simultaneously.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Methods for modeling infectious disease and chemosensitivity in cultured cells and tissues
InactiveUS20040175707A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisHost–pathogen interactionIn vivo
The present invention provides methods for utilizing a form of optimized suspension culture to examine the infectivity of pathogenic organisms and agents in human cells and tissues. Also provided are methods using a rotating wall vessel to predict chemosensitivity of cells and tissues to toxins and chemotherapeutic agents. These culture conditions potentiate spatial colocalization and three-dimensional assembly of individual cells into large aggregates which more closely resemble the in vivo tissue equivalent. In this environment, dissociated cells can assemble and differentiate into macroscopic tissue aggregates several millimeters in size. These culture conditions allow for better cellular differentiation and formation of three-dimensional cellular aggregates, more efficient cell-to-cell interactions, the in in vivo-like exchange of growth factors and greater molecular scaffolding facilitating mechanical stability for cells. The suspension culture system offers a new approach for studying microbial infectivity from the perspective of the host-pathogen interaction and also for analyzing chemosensitivity to toxins and chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
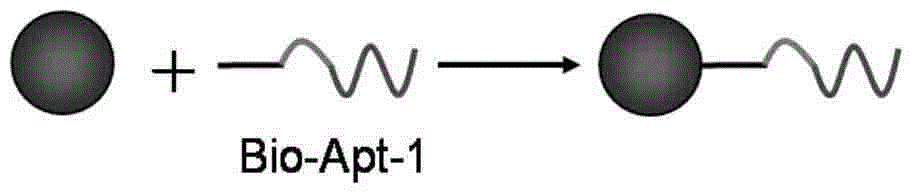
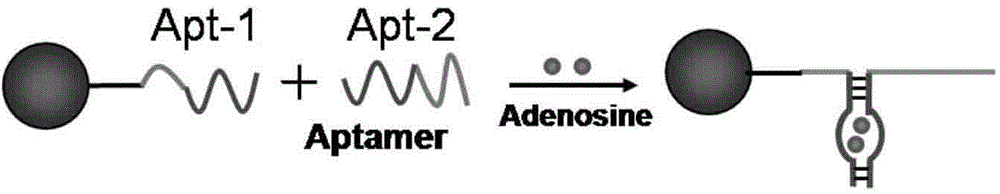
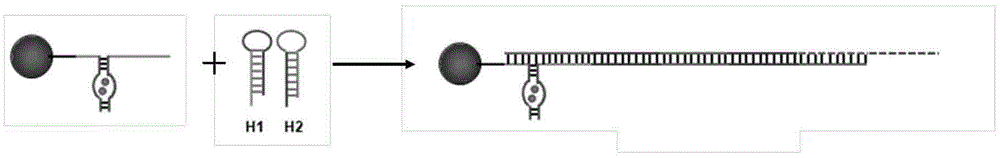
Colocalization trigger chain type hybridization reaction based aptamer sensor for detecting adenosine
ActiveCN104152552ATroubleshooting Nonspecific ResponsesLimit sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotin-streptavidin complexFluorescence
The invention discloses a colocalization trigger chain type hybridization reaction based aptamer sensor for detecting adenosine. The colocalization trigger chain type hybridization reaction based aptamer sensor consists of an aptamer chain 1, an aptamer chain 2 and a hairpin probe which are biotinylated and a magnetic nano-sphere modified by streptavidin. The aptamer sensor is used for detecting adenosine, and a detection method comprises the following steps: (1) activation of a streptavidin modified magnetic sphere; (2) fixation of the biotinylated aptamer chain 1; (3) colocalization of adenosine-induced double aptamers; (4) colocalization trigger chain type hybridization reaction; (5) addition of a dye SYBR Green I and fluorescence detection; (6) calculation: calculating the concentration of adenosine in a to-be-detected object containing adenosine according to a measured fluorescence value. The aptamer sensor disclosed by the invention can be used for reducing the non-specific reaction of conventional chain type hybridization reaction by virtue of the colocalization-induced hybridization reaction, has the advantages of high detection sensitivity and less sample usage without enzyme amplification, and can achieve the analysis and detection of low-concentration adenosine.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Methods for modeling infectious disease and chemosensitivity in cultured cells and tissues
InactiveUS7244578B2Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisHost–pathogen interactionCultured cell
The present invention provides methods for utilizing a form of optimized suspension culture to examine the infectivity of pathogenic organisms and agents in human cells and tissues. Also provided are methods using a rotating wall vessel to predict chemosensitivity of cells and tissues to toxins and chemotherapeutic agents. These culture conditions potentiate spatial colocalization and three-dimensional assembly of individual cells into large aggregates which more closely resemble the in vivo tissue equivalent. In this environment, dissociated cells can assemble and differentiate into macroscopic tissue aggregates several millimeters in size. These culture conditions allow for better cellular differentiation and formation of three-dimensional cellular aggregates, more efficient cell-to-cell interactions, the in in vivo-like exchange of growth factors and greater molecular scaffolding facilitating mechanical stability for cells. The suspension culture system offers a new approach for studying microbial infectivity from the perspective of the host-pathogen interaction and also for analyzing chemosensitivity to toxins and chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
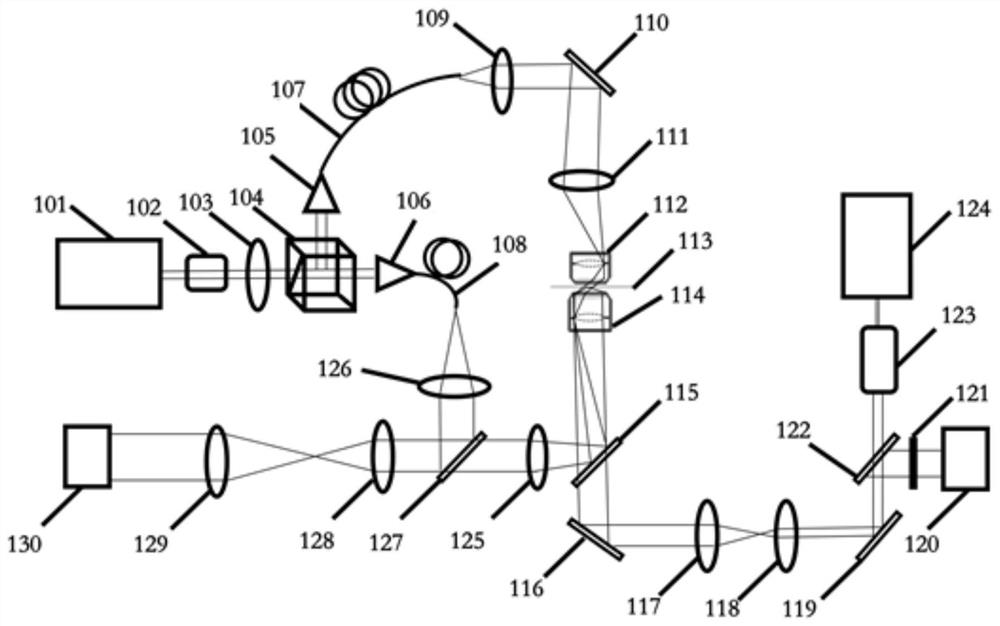
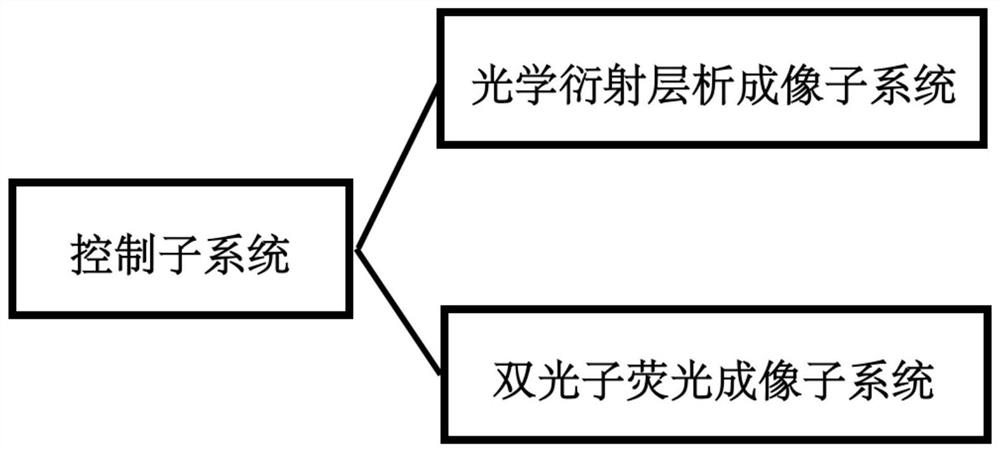
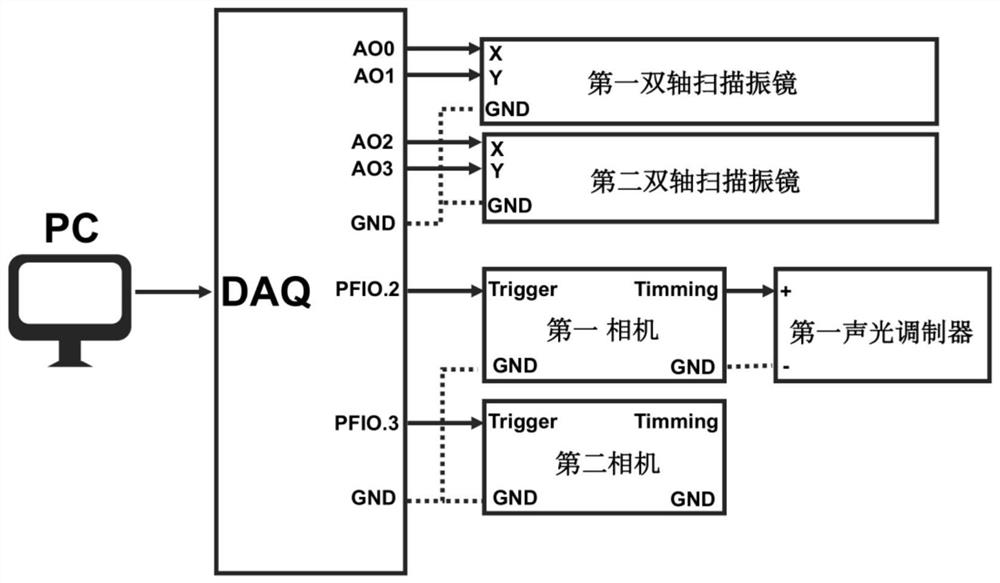
Bimodal microscopic imaging system and imaging method thereof
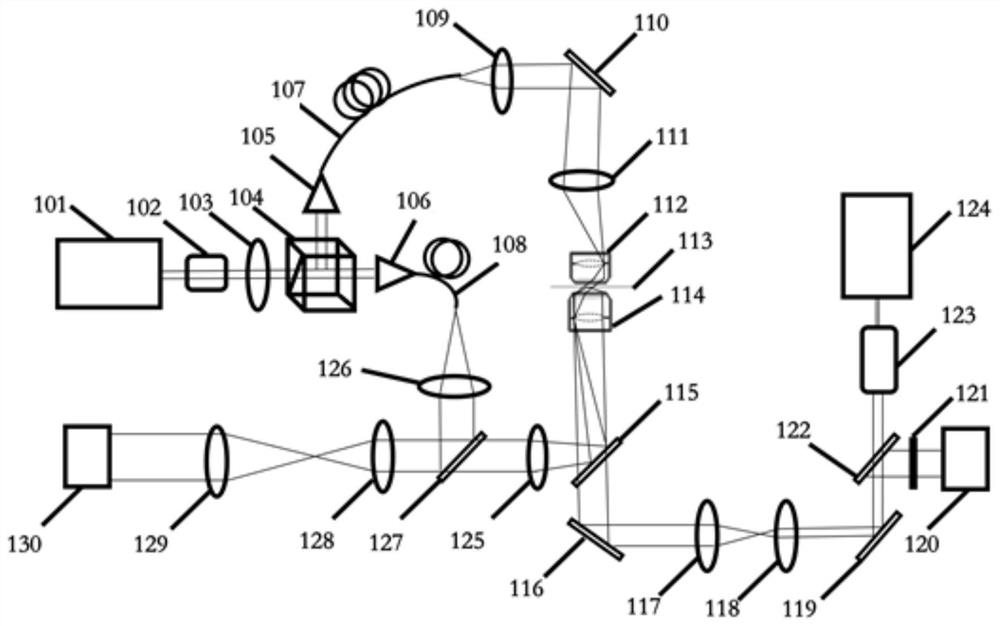
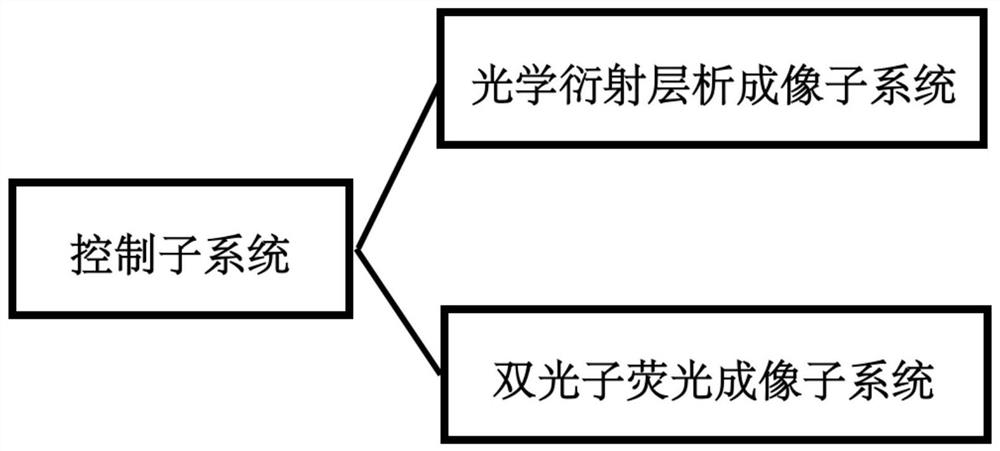
ActiveCN113702288AEnabling Dual-Modal MicroscopyPhase-affecting property measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingFluorescence
The invention discloses a bimodal microscopic imaging system and an imaging method thereof. According to the bimodal microscopic imaging system combining two-photon fluorescence and optical diffraction tomography, synchronous control is achieved through the control subsystem, and the problems encountered by two-photon fluorescence imaging are solved by means of the characteristics of no mark, no invasion and small phototoxicity of optical diffraction tomography; meanwhile, a result in diffraction chromatography is calibrated by utilizing two-photon fluorescence, so that a biological sample is imaged from morphological and chemical specificity, and the two-photon fluorescence imaging device is simple and can realize relatively high resolution without a complicated imaging light path; the two modalities are fused based on the control subsystem, and parallel imaging characterization of local specificity and global morphology of the sample is achieved; and according to the invention, the three-dimensional high-resolution refractive index distribution of the to-be-detected sample can be recovered through optical diffraction tomography, and co-positioning is carried out on the two-photon fluorescence imaging of the to-be-detected sample at the same time, so that bimodal microscopic imaging is realized.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Mitochondria targeted membrane-permeable cyclopeptide as well as preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN110627875ATarget stabilizationPrecise positioningPeptide preparation methodsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMembrane permeabilityColocalization
The invention discloses a mitochondria targeted membrane-permeable cyclopeptide as well as a preparation method and a use thereof, wherein the structure of a mitochondria targeted peptide is as follows: the mitochondria targeted membrane-permeable cyclopeptide can be specific to targeting cell mitochondria, and a confocal inverted fluorescence microscopic imaging experiment shows that the structure has good membrane permeability to Hela cells, and the colocalization coefficient Pr of the structure and a commercial mitochondrial dye is equal to 0.74, and the structure can be efficiently targeted and localized to mitochondria.
Owner:合肥修合生物科技有限公司
Ribosome rRNA (ribosomal Ribonucleic Acid) two-photon fluorescent probe-quaternary ammonium salt terpyridine derivative as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107311916AGood water solubilityGood light stabilityOrganic chemistry methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyColocalization
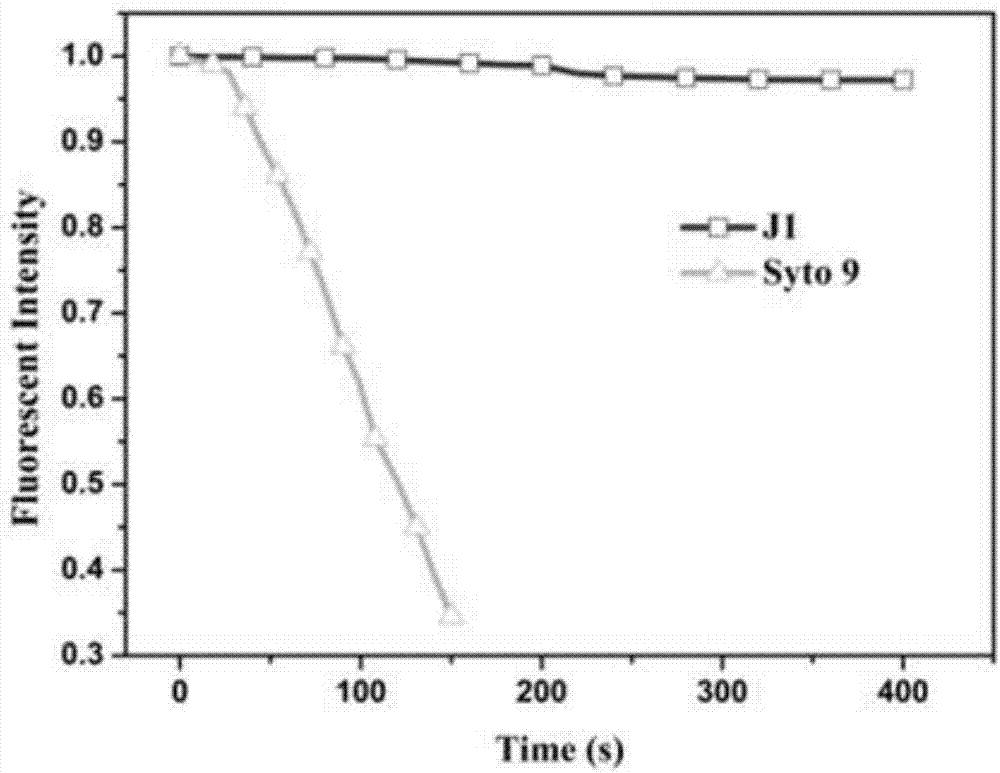
The invention discloses a ribosome rRNA two-photon fluorescent probe-quaternary ammonium salt terpyridine derivative as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the ribosome rRNA two-photon fluorescent probe-quaternary ammonium salt terpyridine derivative is as shown in the description. A target product disclosed by the invention can identify RNA by two-photon fluorescent enhancement and realizes a two-photon fluorescent enhancement identification effect; and low-energy long wave (710 nm) excitation has little damage to a living body. The rRNA in cell nucleolus is specifically identified. The colocalization effect of the target product disclosed by the invention and nucleolus Syto9 at the cell nucleolus is good, and a Pearson coefficient can reach 90 percent.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Bis-biotinylation tags
Multi-biotinylated reactants are provided which can be used in divalent complexes for various applications such as colocalization, labeling, immobilization, and purification. Methods for constructing, purifying, and using the bis-biotinylated reactants are also provided. In certain embodiments, two bis-biotinylated reactants are bound to a single streptavidin tetramer to provide a complex having a 1:1 stoichiometry with respect to the bis-biotinylated reactants.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Method and system for visualising colocalised fluorescence signals
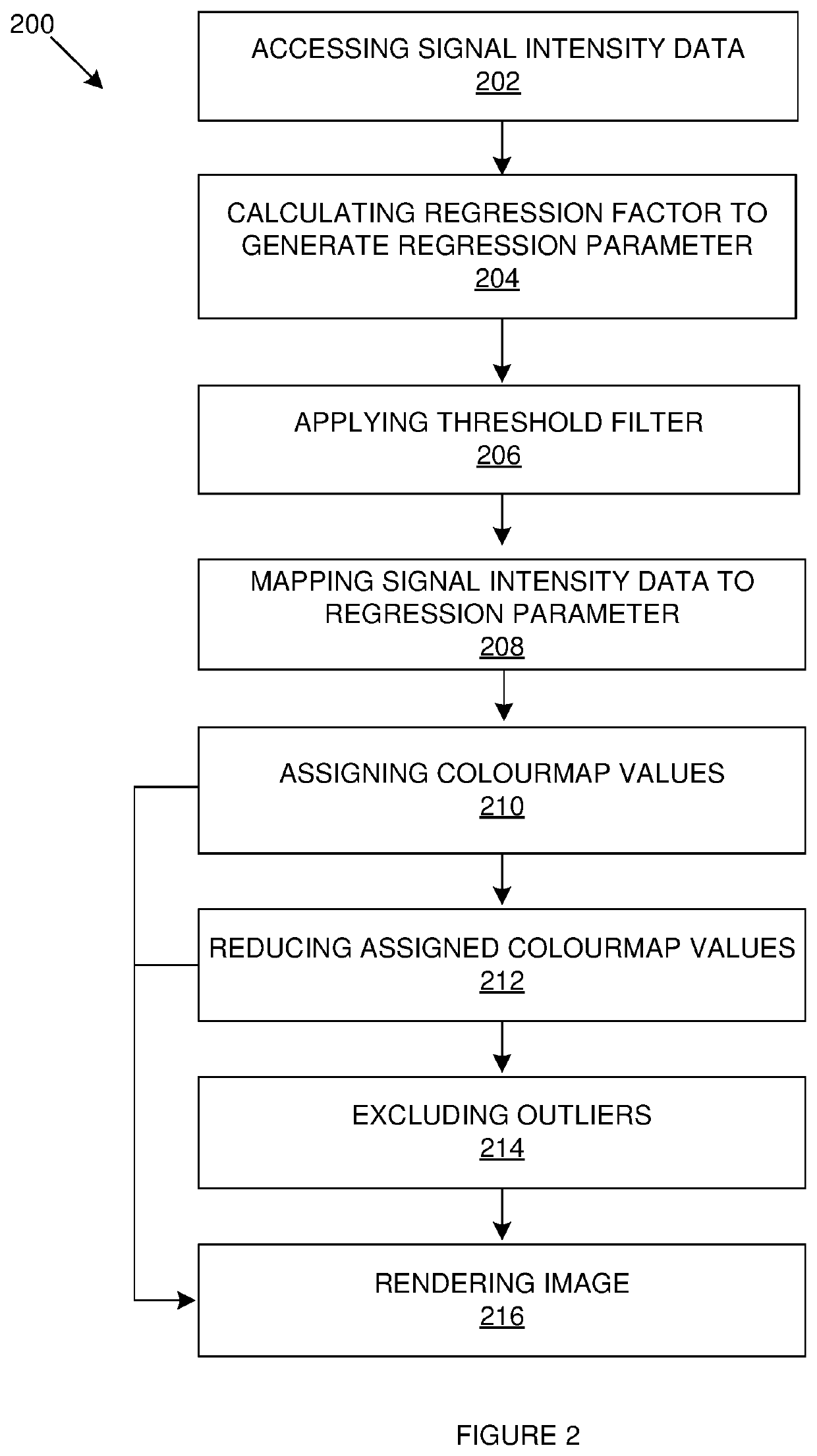
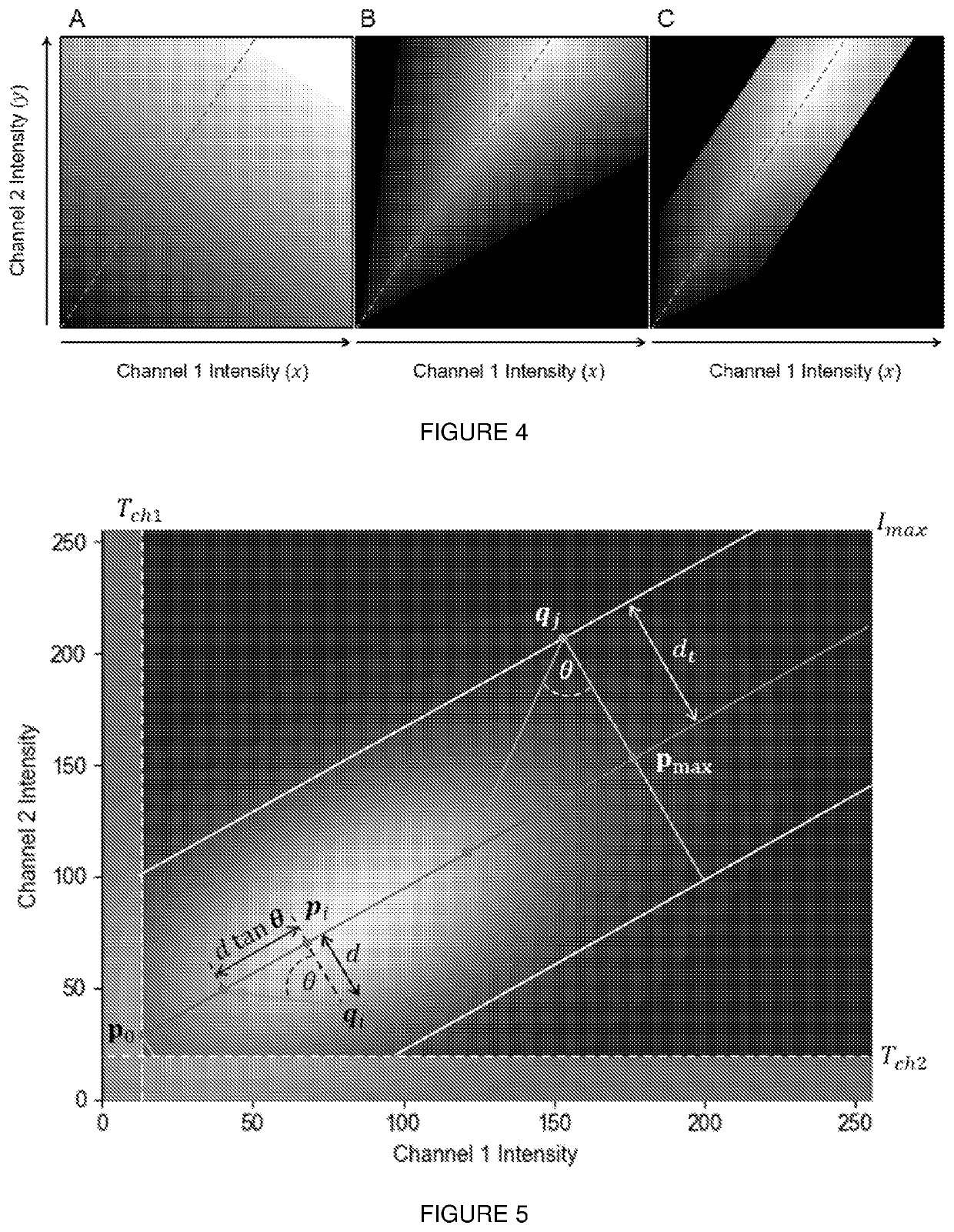
A computer-implemented method and a system are provided for visualising colocalised fluorescence signals. The method accesses signal intensity data obtained from a first fluorescence channel and a second fluorescence channel in which the signal intensity data is associated with voxels in an image. A regression factor on the signal intensity data is calculated to generate a regression parameter corresponding to a degree of correlation between the signal intensity data obtained from the first and second fluorescence channels The signal intensity data is mapped to the regression parameter and colourmap values are assigned to each voxel based on the mapped signal intensity data in which colourmap values of voxels embodying poorly correlated signal intensity data are reduced. The method renders the voxels in the image in colours according to their colourmap values to visualise colocalisation in the image.
Owner:STELLENBOSCH UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of super-resolution imaging probe based on silicon dioxide
InactiveCN111044496ASimple manufacturing methodSmall and uniform particle sizeFluorescence/phosphorescenceAptamerSingle molecule localization
The invention discloses a super-resolution imaging probe based on silicon dioxide and a preparation method and application of the probe.The super-resolution imaging probe includes silicon dioxide nanoparticles connected with an Alexa Fluor 647 dye, and the surface of the super-resolution imaging probe is coupled with an HER2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor-2) nucleic acid aptamer; the probe can be used for targeted recognition of HER2 overexpression cell exosomes, that is, the HER2 overexpression cell exosomes are subjected to fluorescence labeling; super-resolution optical imaging canbe carried out on the cell exosome which specifically recognizes the probe by utilizing an ultra-high resolution microscope; the probe is uniform in particle size, small in size, high in positioningprecision, excellent in scintillation performance and suitable for ultrahigh-resolution optical imaging based on a single-molecule positioning method; and the exosome is marked by the super-resolutionimaging probe, and the exosome of the cell can be accurately marked by using a single-molecule positioning microscope in a double-channel co-positioning mode.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A dual-modality microscope imaging system and imaging method thereof
ActiveCN113702288BEnabling Dual-Modal MicroscopyPhase-affecting property measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingFluorescence
The invention discloses a dual-mode microscopic imaging system and an imaging method thereof. The invention combines the dual-mode microscopic imaging system of two-photon fluorescence and optical diffraction tomography, through the synchronous control of the control subsystem, and utilizes the features of the optical diffraction tomography to be label-free, non-invasive and low in phototoxicity to solve the problem of two-photon fluorescence imaging. At the same time, two-photon fluorescence is used to calibrate the results in diffraction tomography, so as to image biological samples from morphological and chemical specificity, and the two-photon fluorescence imaging device is simple and does not require complex imaging optical paths. High resolution; the fusion of two modes based on the control subsystem realizes the parallel imaging characterization of the local specificity and the global morphology of the sample; the invention can restore the three-dimensional high-resolution refractive index distribution of the test sample through optical diffraction tomography , and at the same time co-localize the two-photon fluorescence imaging of the sample to be tested to achieve dual-modal microscopic imaging.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for double staining colocalized nuclear-markers in histological lymphoid or bone marrow tissue sample
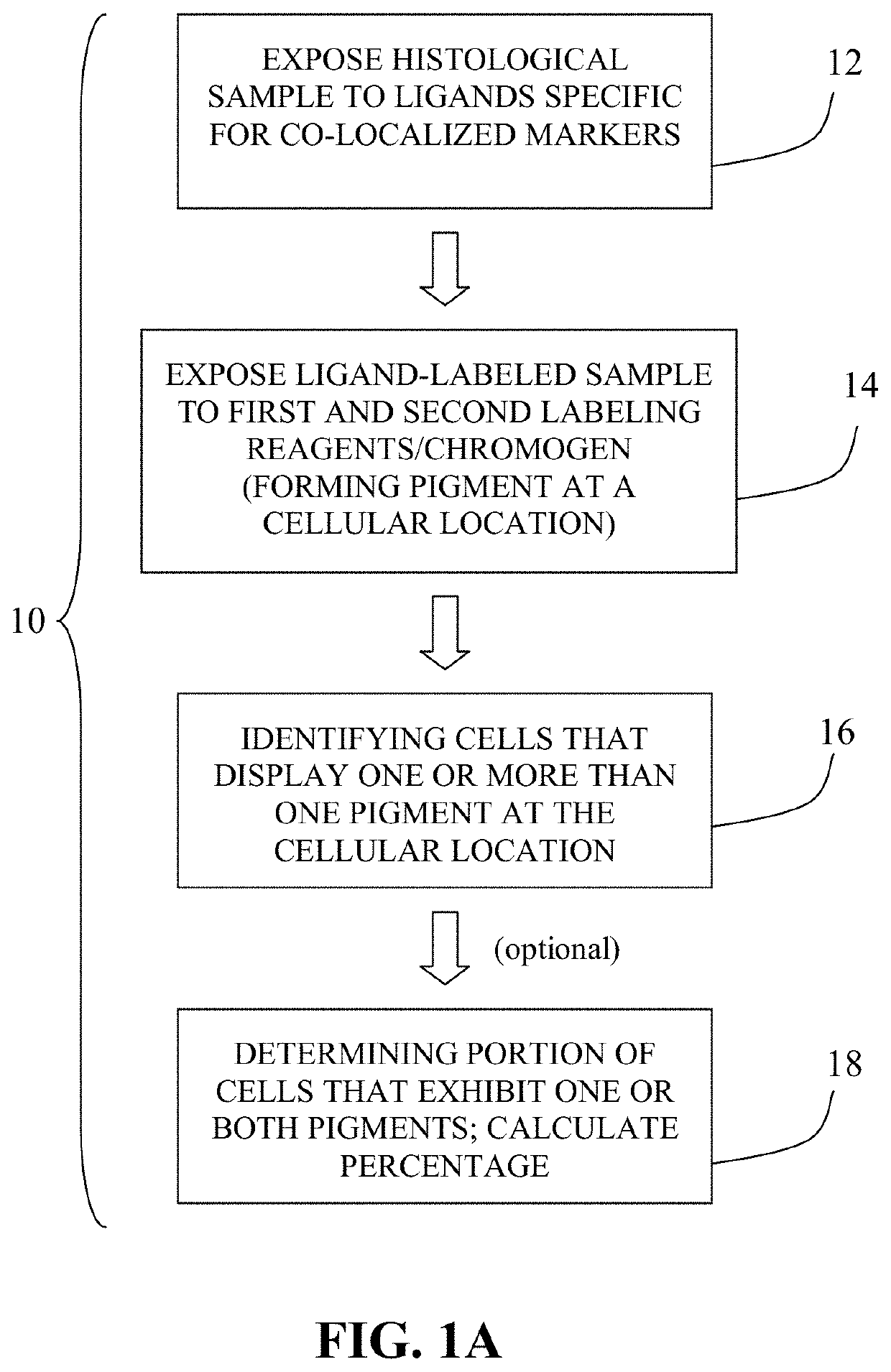
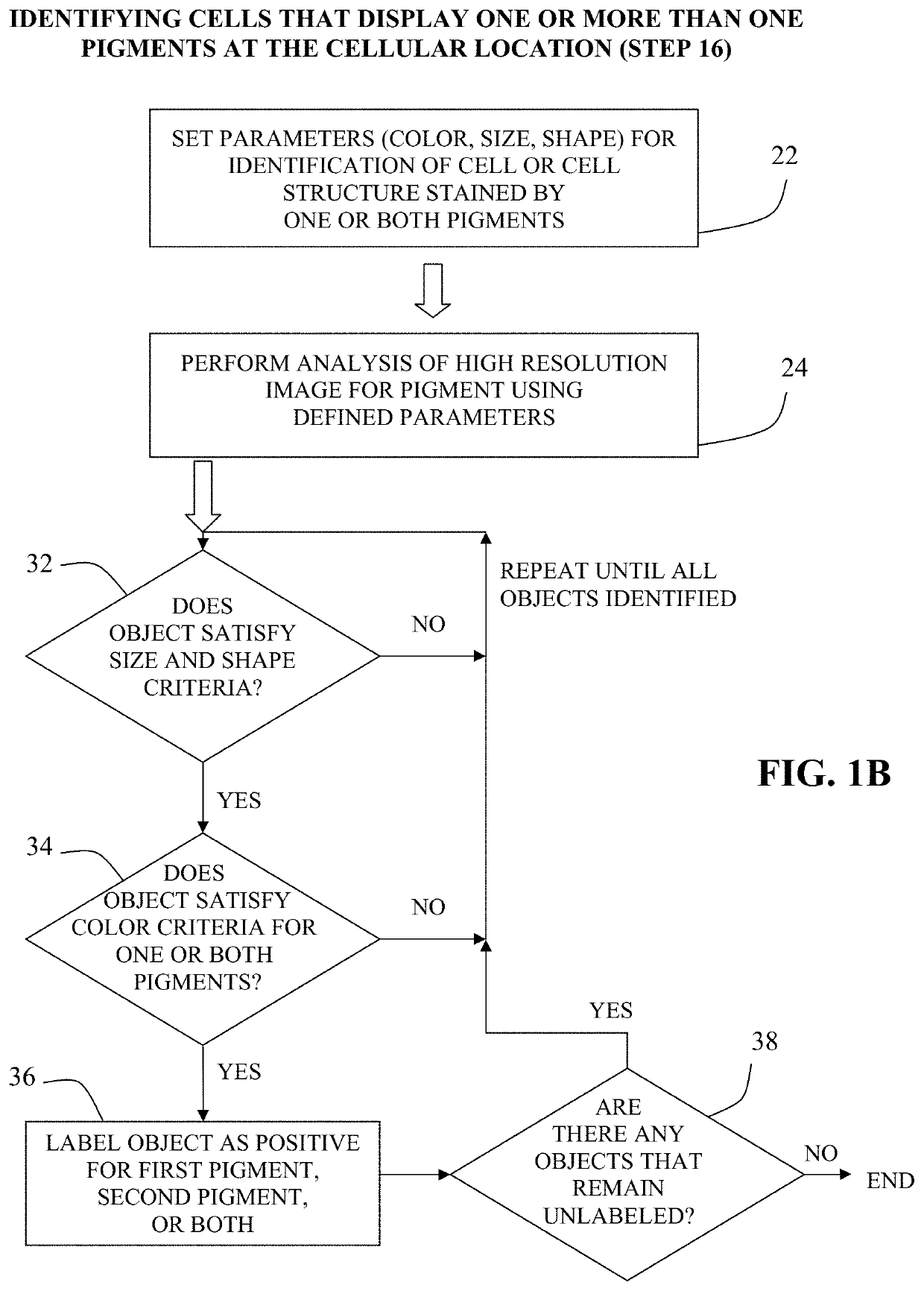
The present invention relates to kits and methods for performing dual-staining immunohistochemistry (IHC) for the detection of specific cell populations in tissue samples containing heterogeneous populations of cells, which can be observed by a light microscope for co-localization of distinct pigments. The method includes providing a tissue sample comprising fixed cells; exposing the sample to first and second ligands that recognize different marker proteins found at the same cellular location, thereby forming a ligand-labeled sample; exposing the ligand-labeled sample to first and second labeling reagents, the first labeling reagent binding to the first ligand and the second labeling reagent binding to the second ligand, the first and second labeling reagents each forming distinct pigments; and identifying the number of cells that display only one particular pigment, or more than one pigment, by the different coloration of the cellular location labeled by the distinct pigment.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
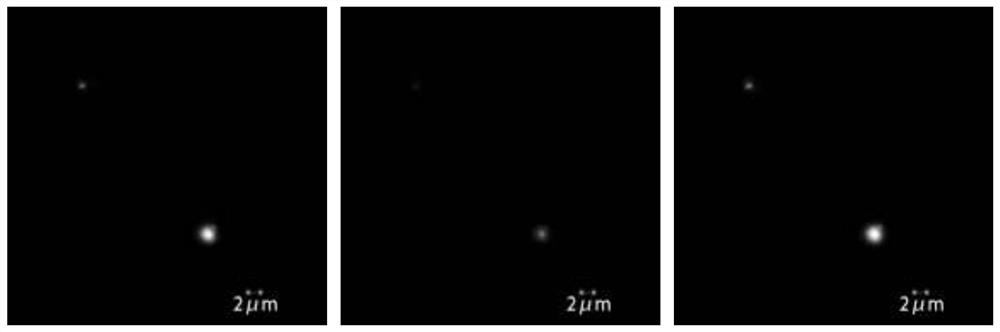
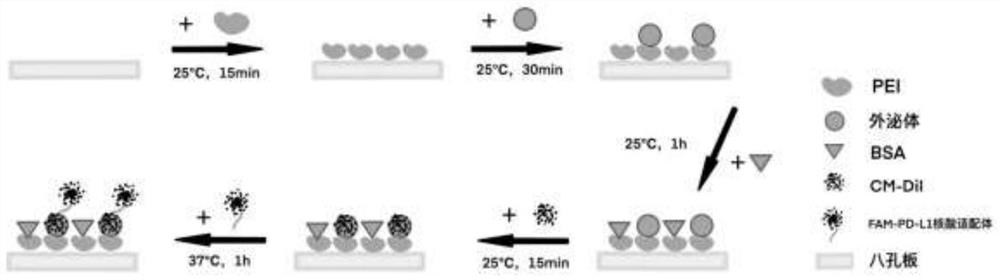
MDA-MB-231 cell exosome detection method based on two-color co-localization and application
PendingCN114705663AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceExtracellularFluorescence immunoassay
The invention discloses an MDA-MB-231 exosome detection method based on two-color co-localization and application. The detection method comprises the following steps: marking an MDA-MB-231 cell exosome through a cell membrane probe CM-DiI; meanwhile, a PD-L1 nucleic acid aptamer probe with another fluorophore FAM is used, and the probe can specifically capture exosomes secreted by MDA-MB-231 cells highly expressed by PD-L1; the captured exosome can be subjected to fluorescence imaging through a total internal reflection (TIRF) imaging technology; and by combining a two-color fluorescence co-localization technology, a false positive event can be judged on a single particle level, and the accuracy of an exosome fluorescence immunoassay technology is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A kind of ribosomal rRNA two-photon fluorescent probe-quaternary ammonium salt terpyridine derivative and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN107311916BGood water solubilityGood light stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganic chemistry methodsStructural formulaBiology
The invention discloses a ribosome rRNA two-photon fluorescent probe-quaternary ammonium salt terpyridine derivative as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the ribosome rRNA two-photon fluorescent probe-quaternary ammonium salt terpyridine derivative is as shown in the description. A target product disclosed by the invention can identify RNA by two-photon fluorescent enhancement and realizes a two-photon fluorescent enhancement identification effect; and low-energy long wave (710 nm) excitation has little damage to a living body. The rRNA in cell nucleolus is specifically identified. The colocalization effect of the target product disclosed by the invention and nucleolus Syto9 at the cell nucleolus is good, and a Pearson coefficient can reach 90 percent.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Imaging-based pooled crispr screening
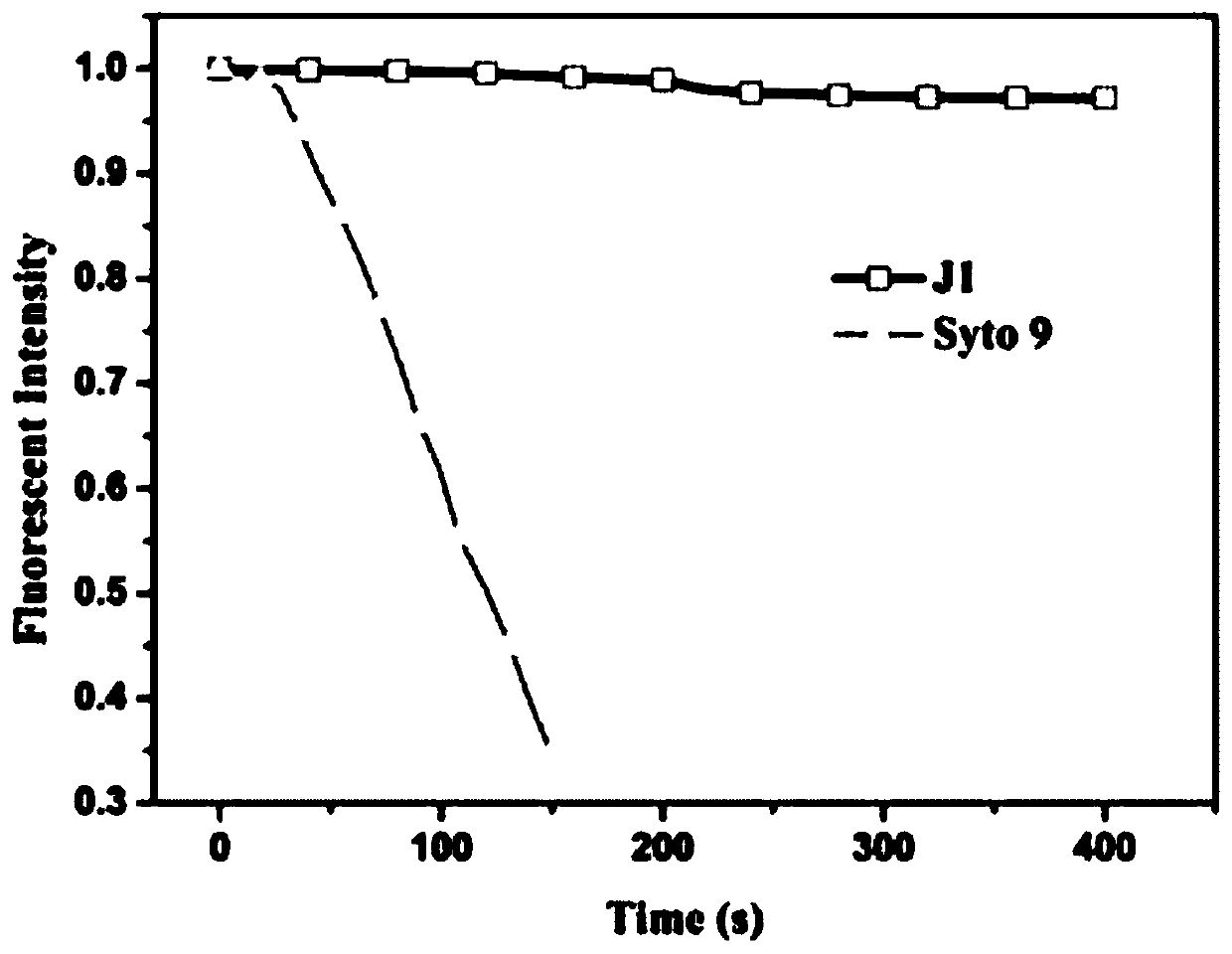
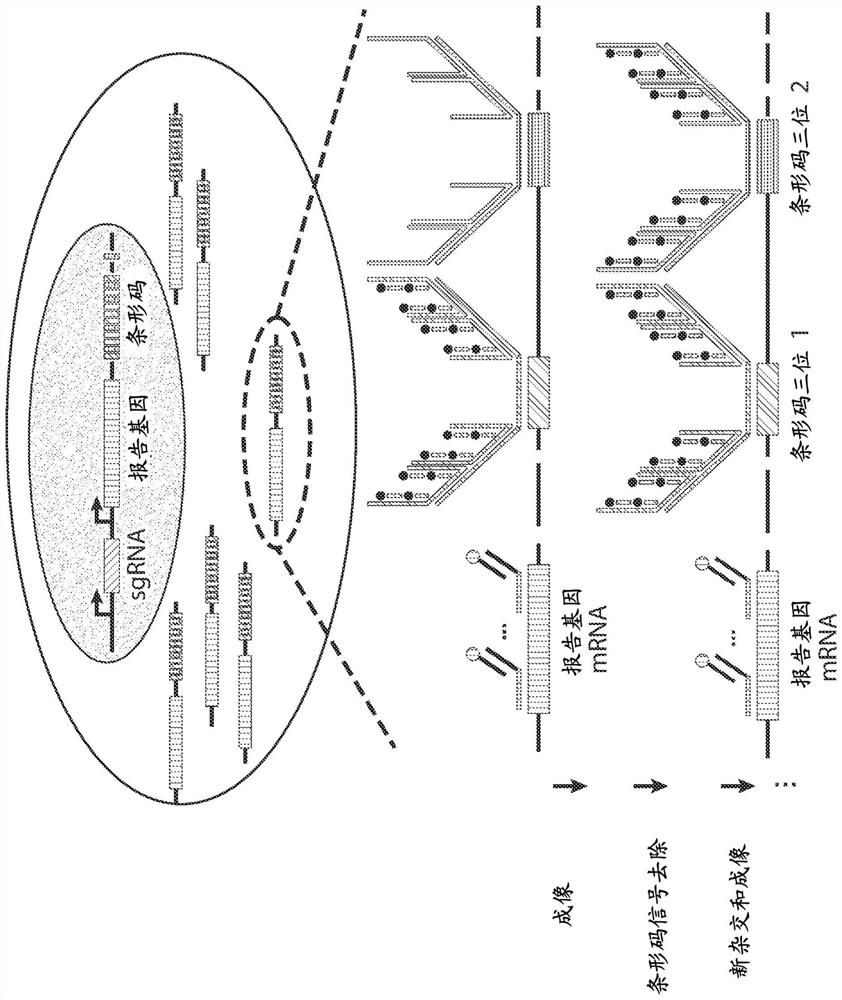
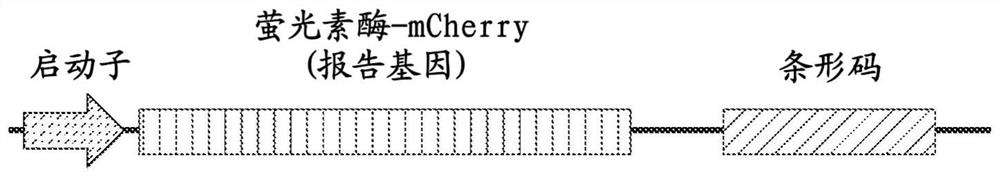
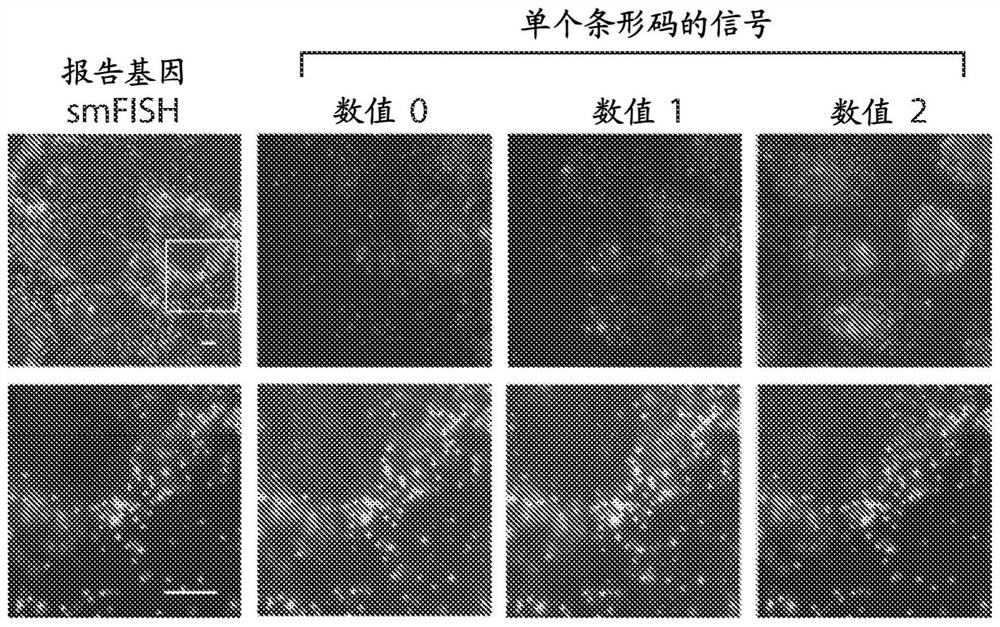
The present invention generally relates to imaging cells, for example, to determine phenotypes and / or genotypes in populations of cells, e.g., to build genotype-phenotype corresponse for high-throughput screening. In some cases, the cells may be manipulated, e.g., using CRISPR or other techniques. In certain embodiments, nucleic acids may be introduced to the cell, e.g., using a lentivirus. The nucleic acids may contain a guide portion comprising a DNA or RNA recognition sequence, a reporter portion, and an identification portion comprising one or more read sequences. The guide portion may be used to alter the phenotype of the cells, e.g., using a sequence, e.g., an sgRNA sequence, that can be targeted using CRISPR or other techniques, and in some cases, the phenotype of the cells may be determined using various imaging approaches. The identification portion may be determined using MERFISH or other suitable techniques. In addition, in some cases, association or colocalization between determination of the reporter and the read sequences may substantially improve decoding accuracy, e.g., due to lowered misidentification of background signals. Other aspects are generally directed to compositions or devices for use in such methods, kits for use in such methods, or the like.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
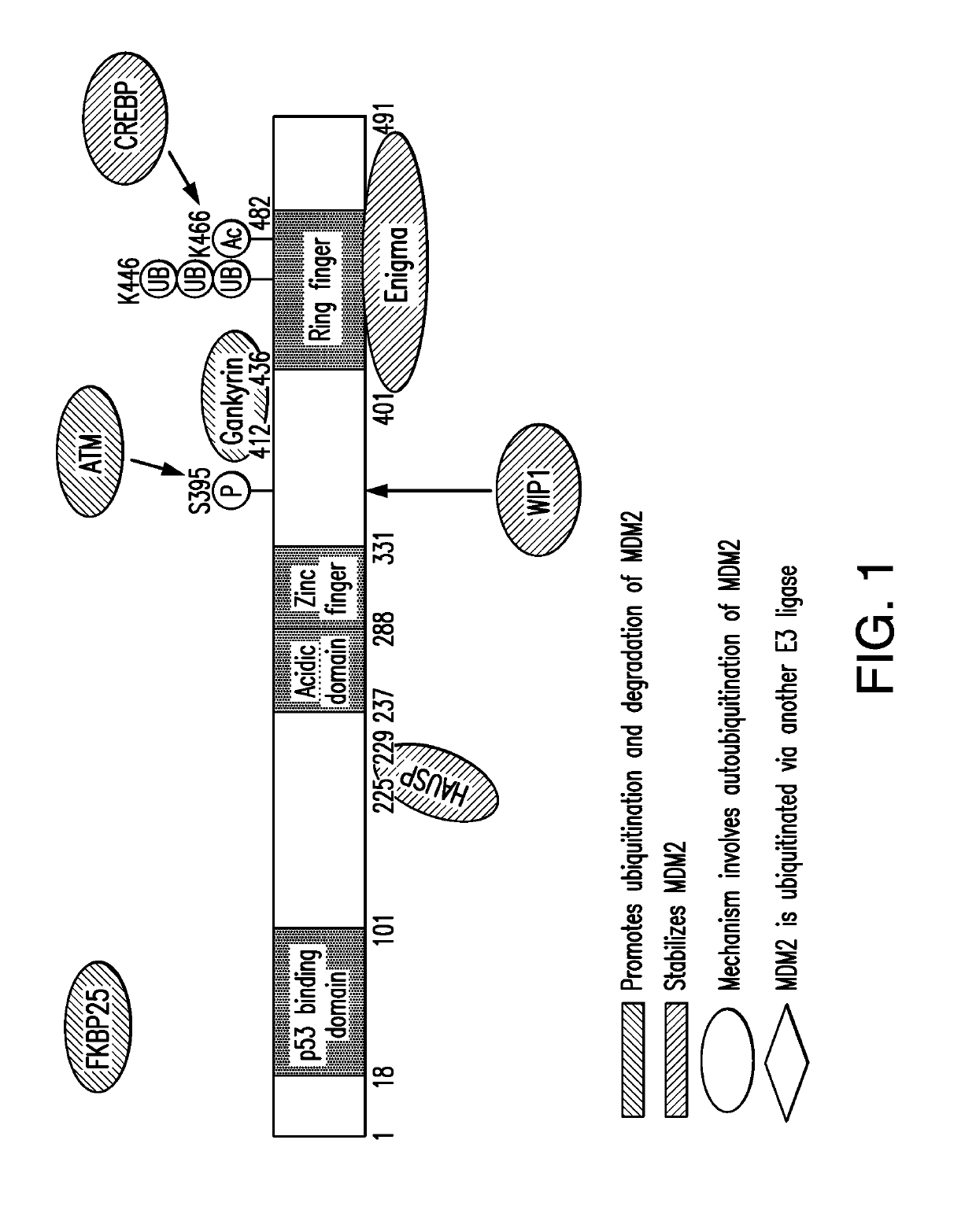
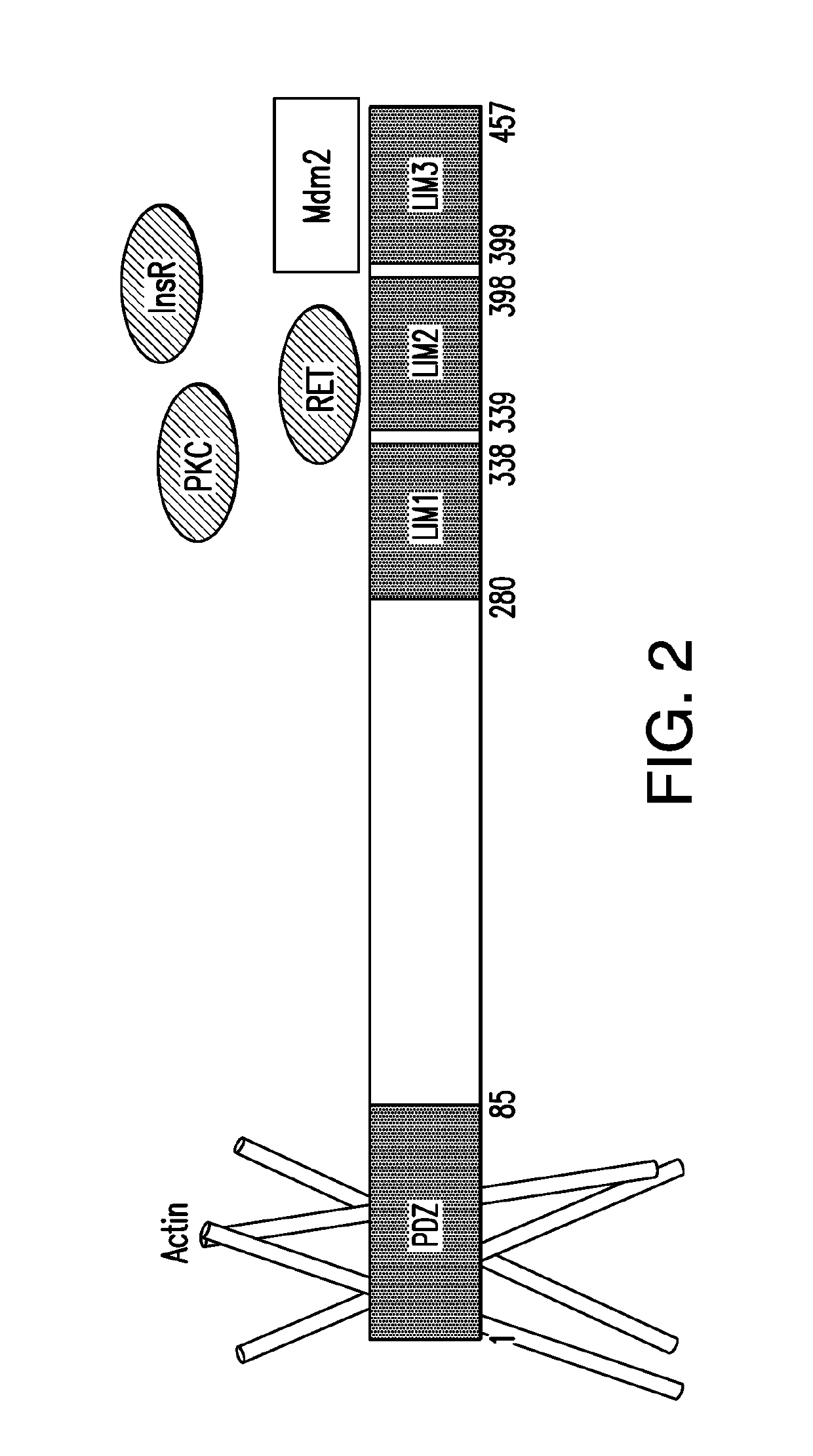
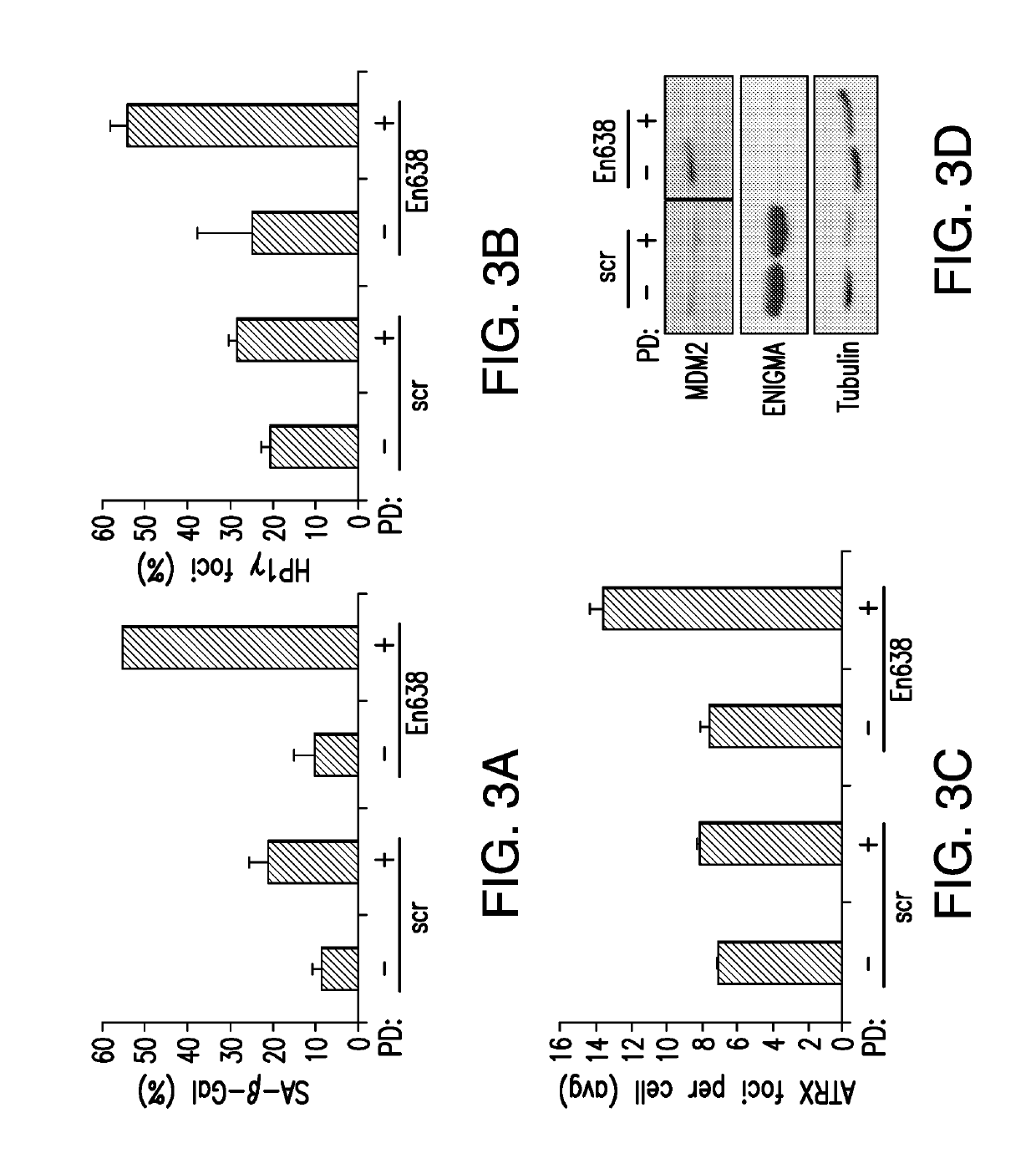
Enigma and cdh18 as companion diagnostics for cdk4 inhibitors
PendingUS20190310259A1High expressionEffective treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisColocalizationCancer research
The present invention relates to the use of one or more biomarkers to evaluate the likelihood that a CDK4 inhibitor would produce an anti-cancer effect in a subject. Accordingly, in certain non-limiting embodiments, the present invention provides for methods, compositions and kits for a companion diagnostic for CDK4 inhibitors, and in particular, for the use of the colocalization of Enigma and CDH18 biomarkers to foci within the cancer for determining whether the cancer can be successfully treated by CDK4 inhibition.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com