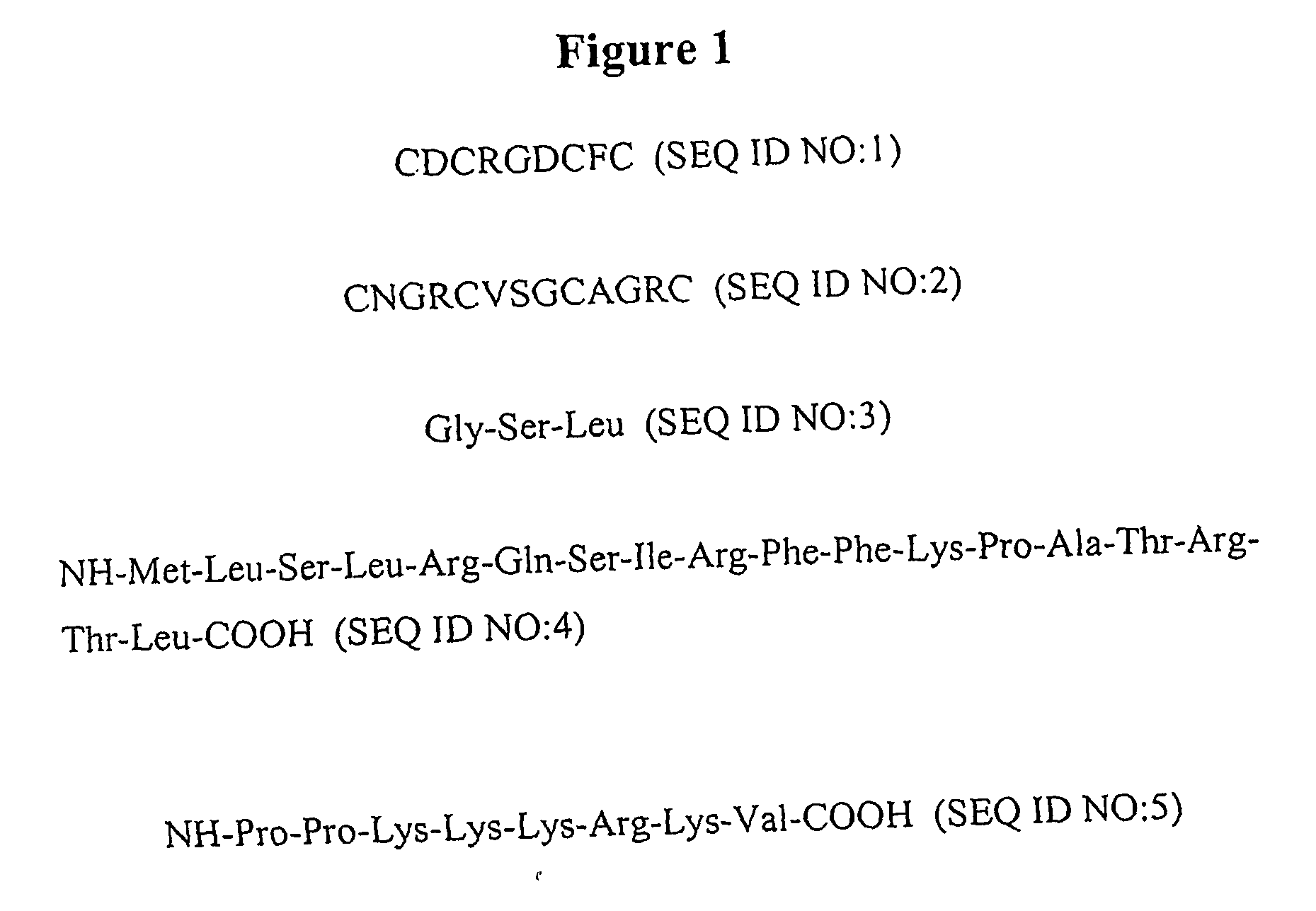
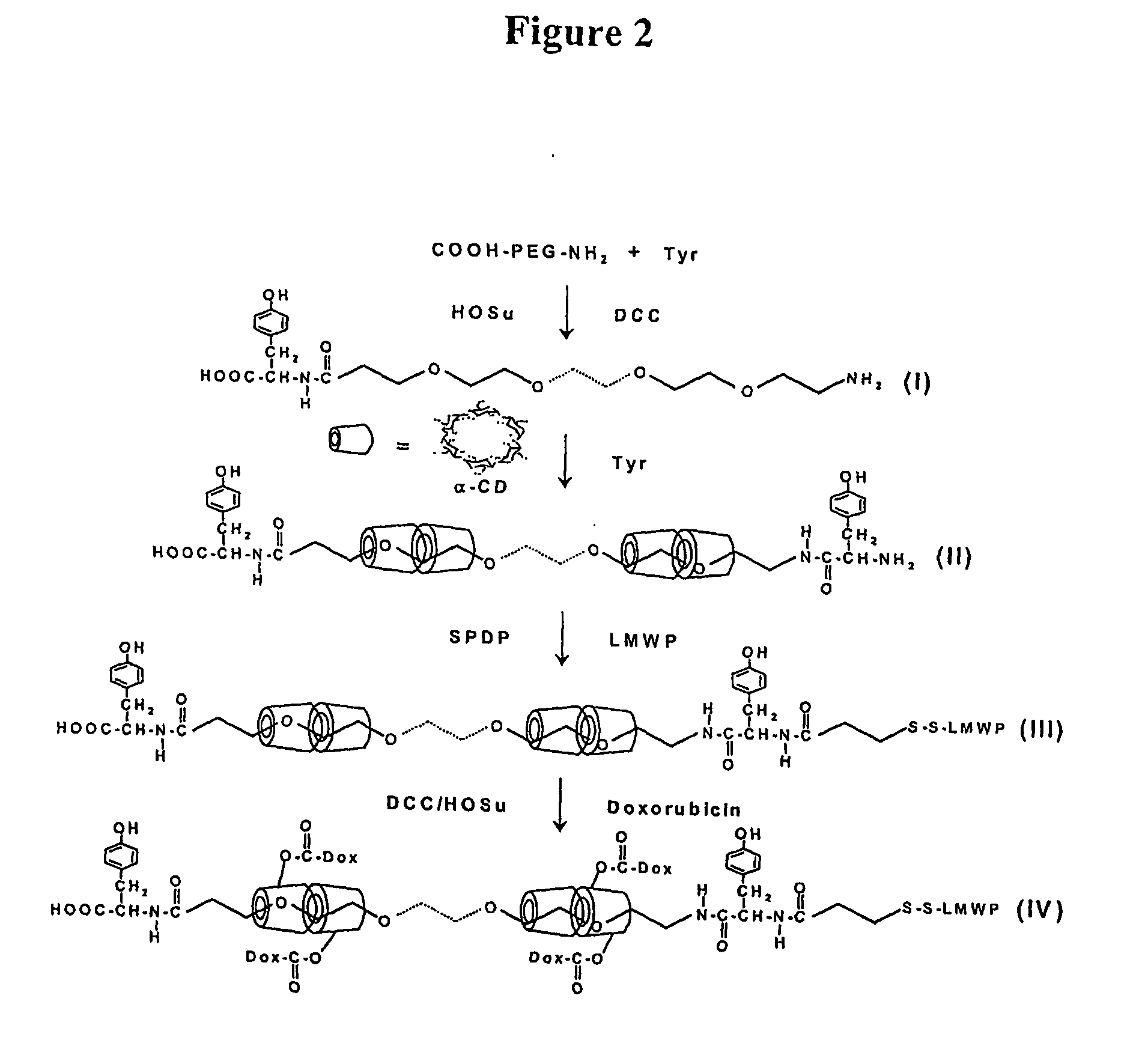
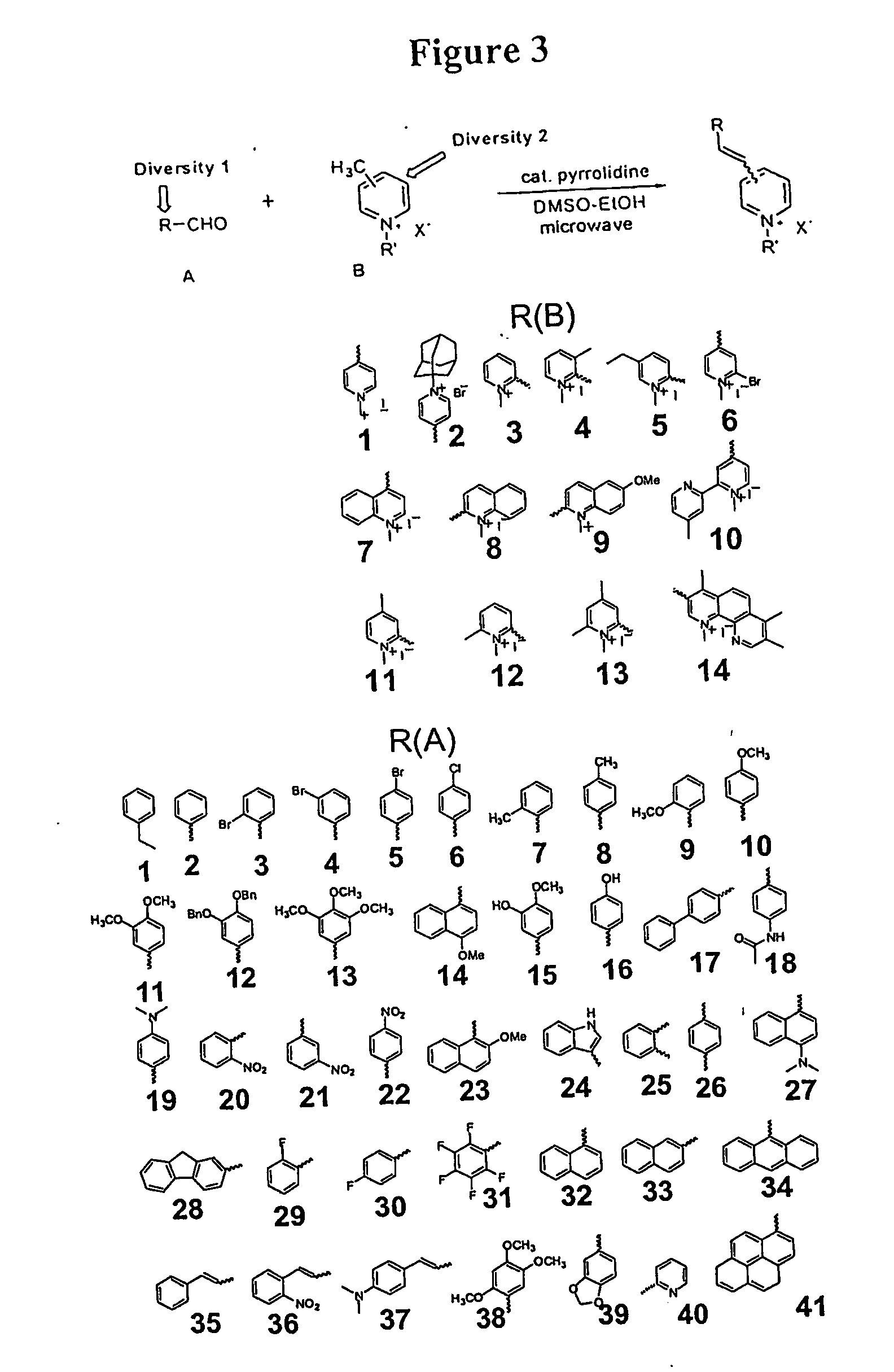
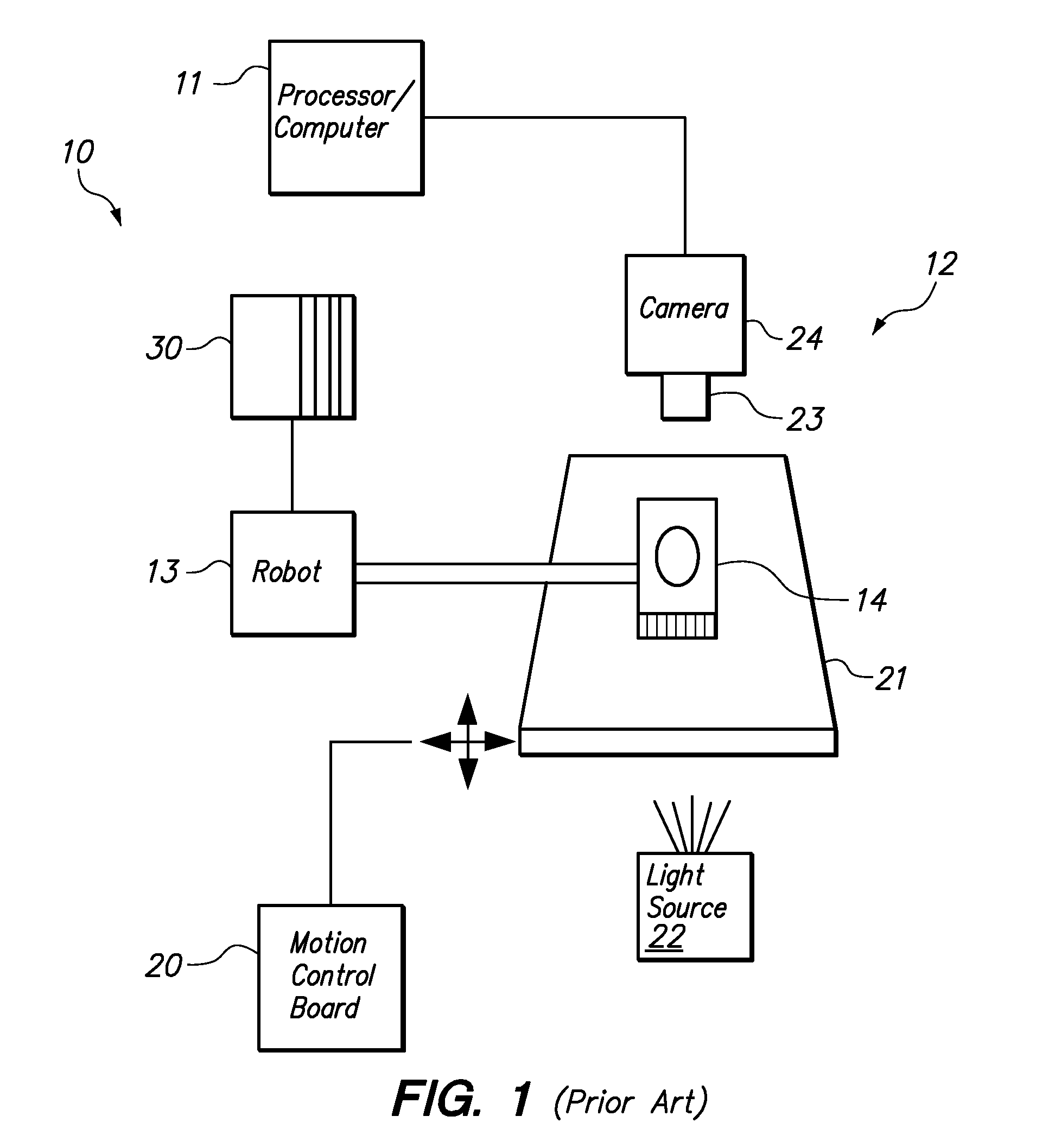
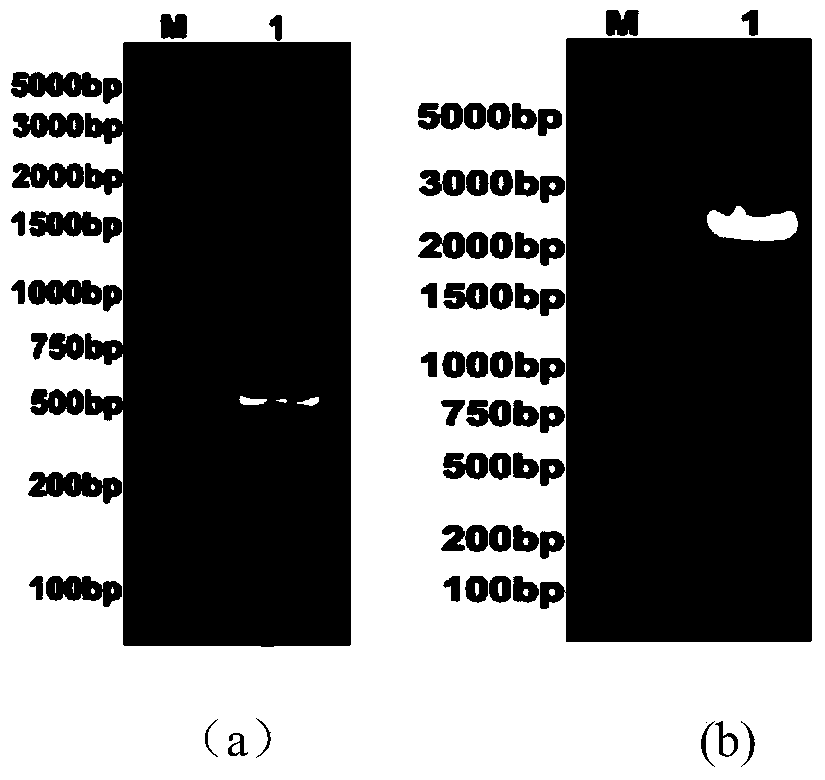
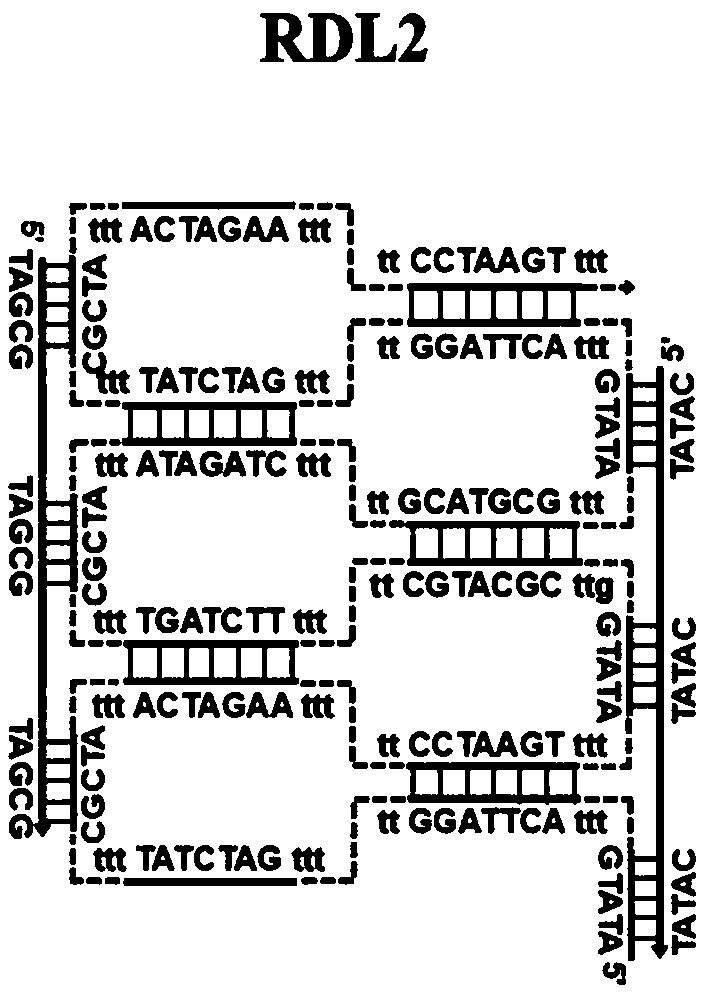
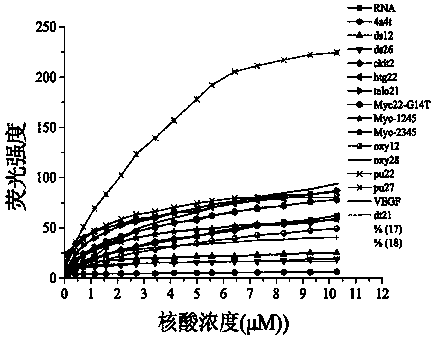
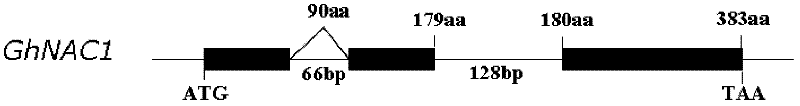Patents
Literature
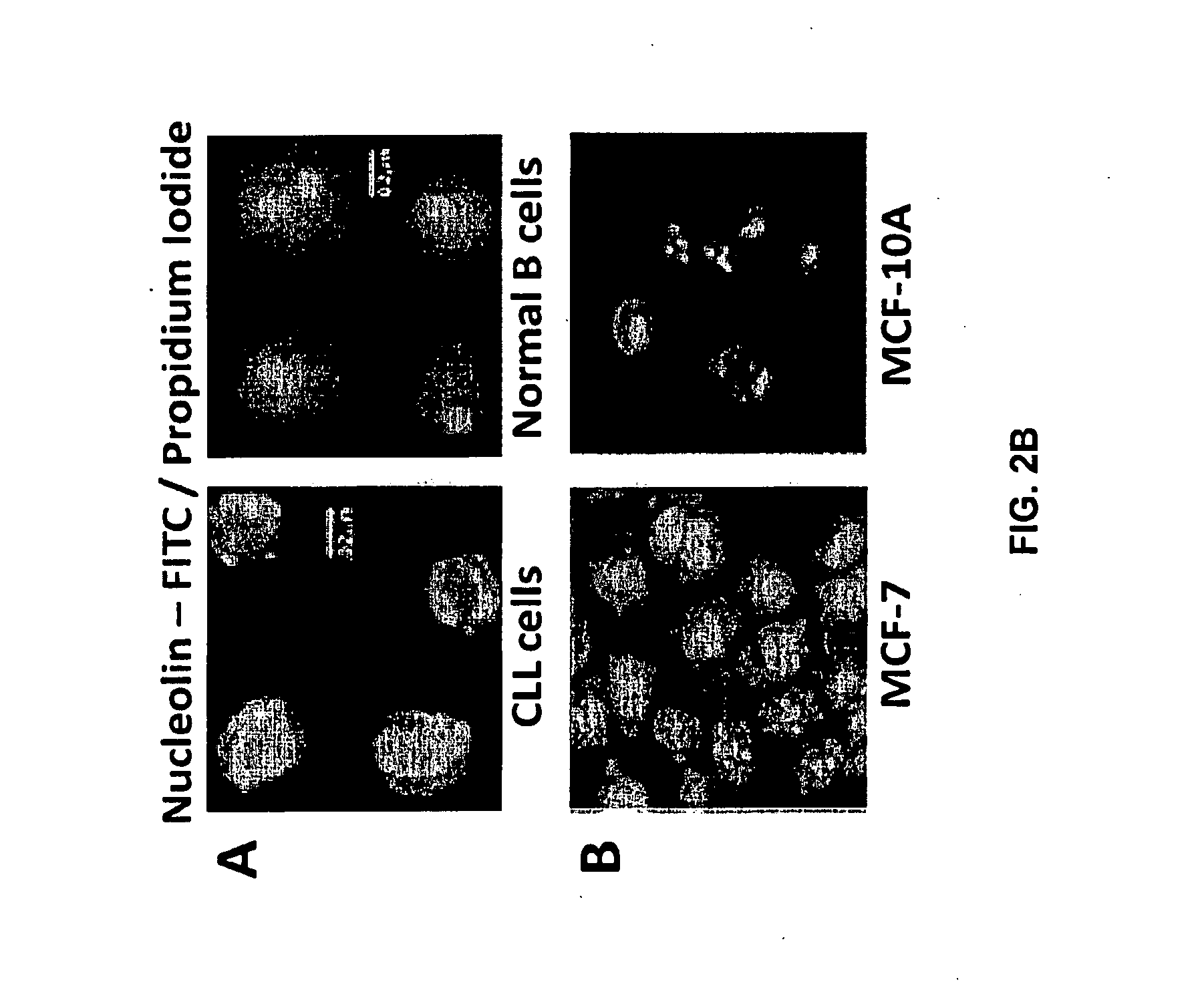
139 results about "Nucleolus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The nucleolus (/njuːˈkliːələs, -kliˈoʊləs/, plural: nucleoli /-laɪ/) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis. Nucleoli also participate in the formation of signal recognition particles and play a role in the cell's response to stress. Nucleoli are made of proteins, DNA and RNA and form around specific chromosomal regions called nucleolar organizing regions. Malfunction of nucleoli can be the cause of several human conditions called "nucleolopathies" and the nucleolus is being investigated as a target for cancer chemotherapy.
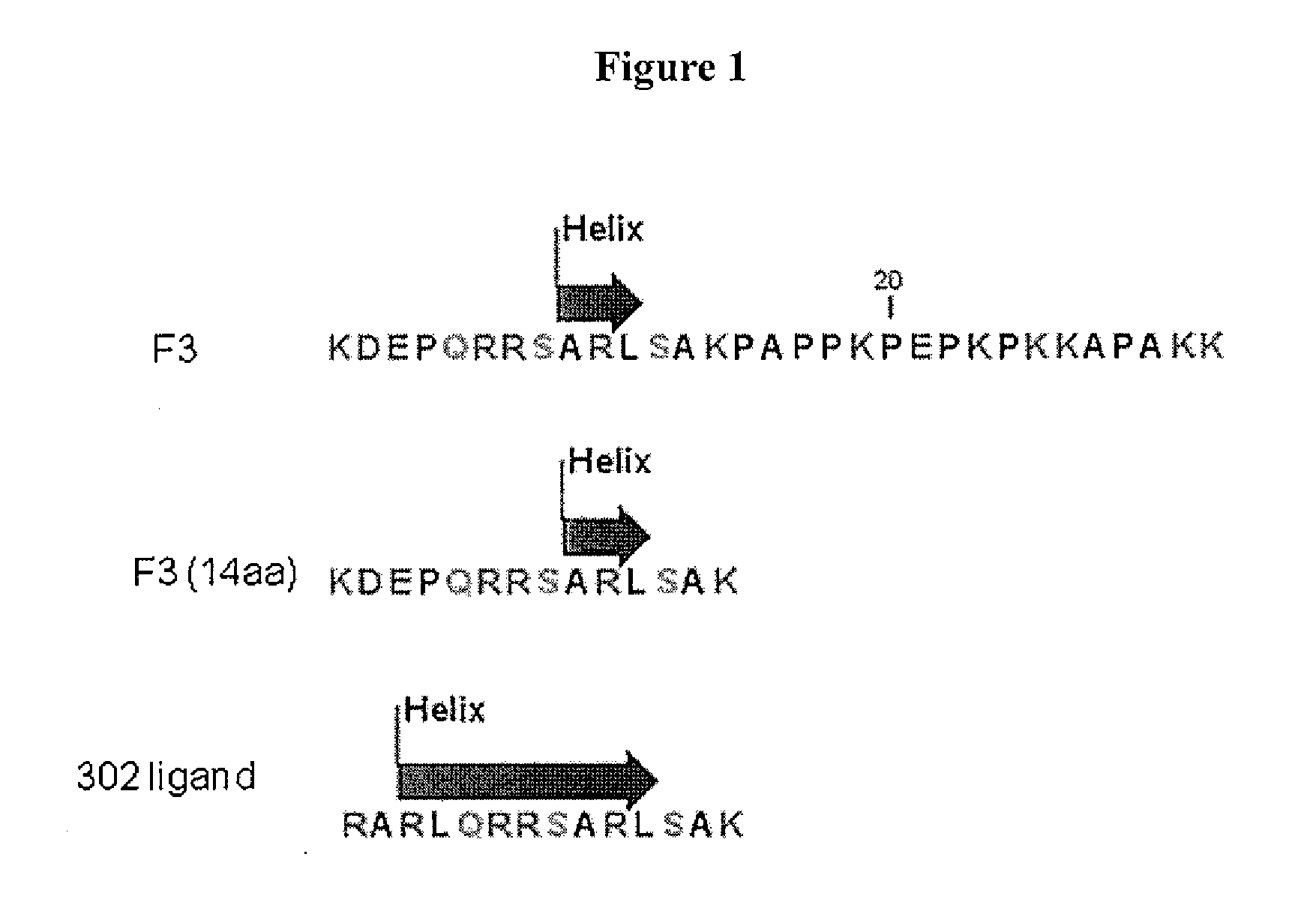
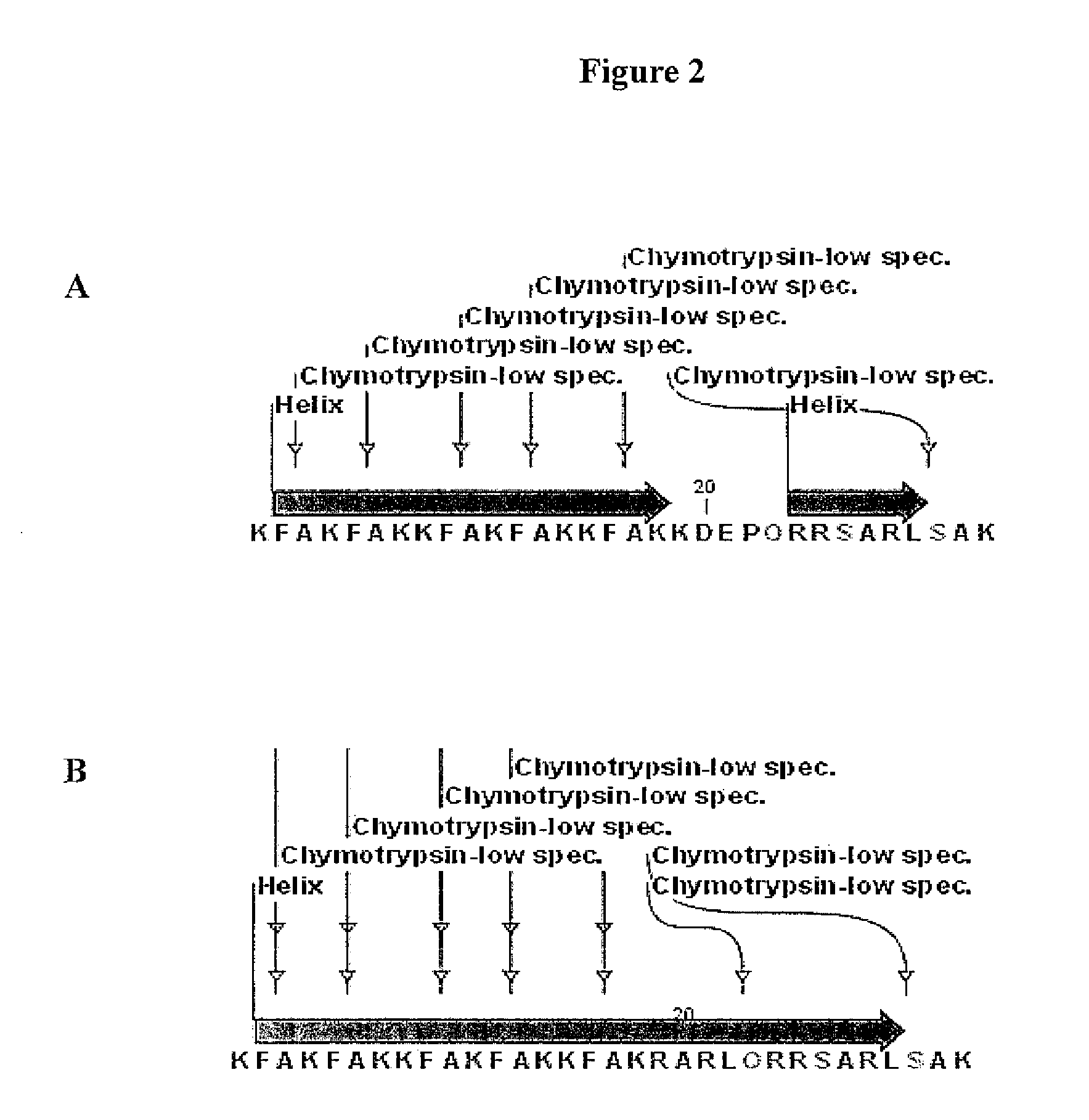
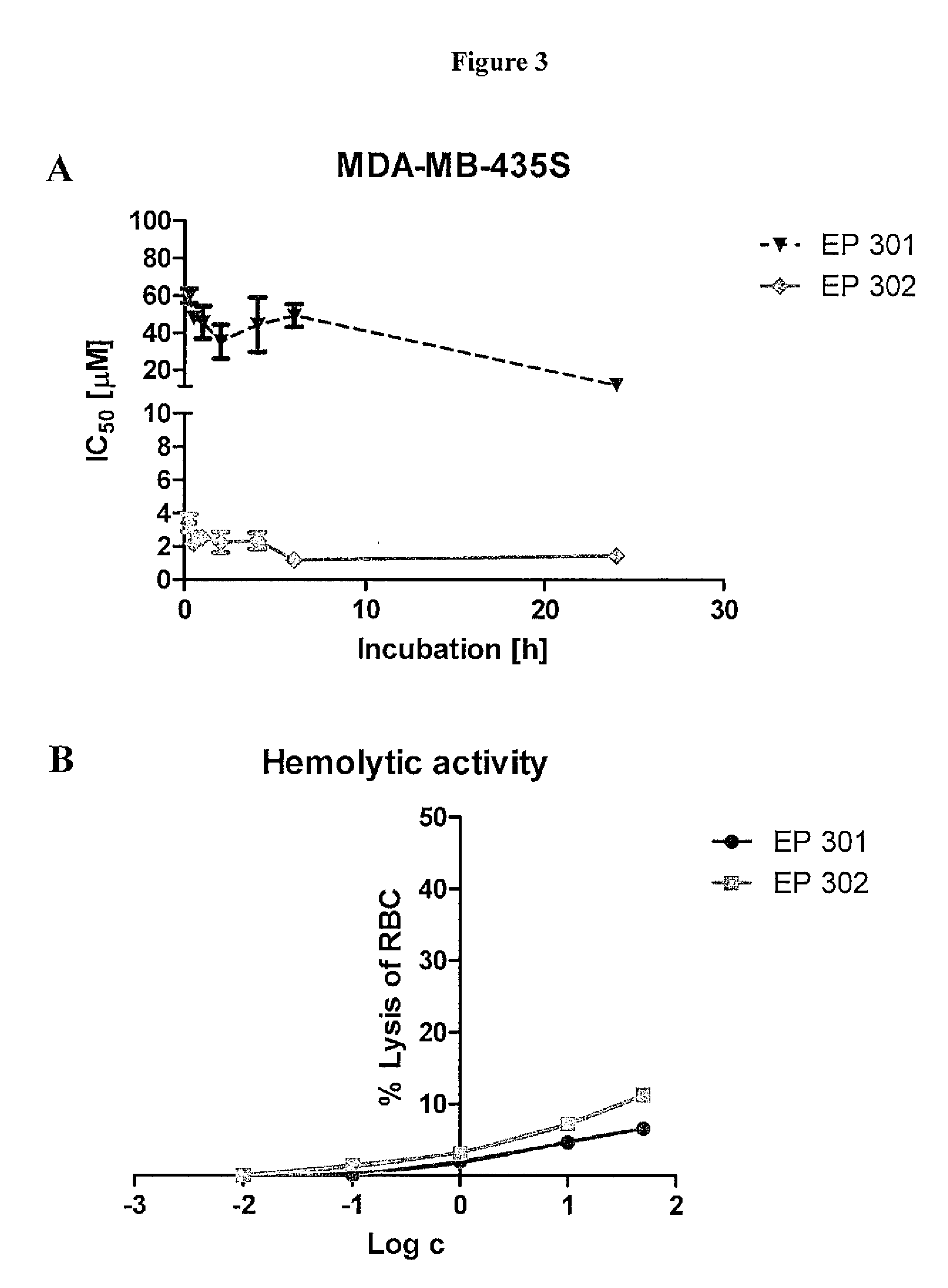
Chemical address tags
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to the fields of chemoinformatics, chemogenomics, drug discovery and development, and drug targeting. In particular, the present invention provides subcellular localization signals (e.g., chemical address tags) that influence (e.g., direct) subcellular and organelle level localization of associated compounds (e.g., drugs and small molecule therapeutics, radioactive species, dyes and imagining agents, proapoptotic agents, antibiotics, etc) in target cells and tissues. The compositions of the present invention modulate the pharmacological profiles of associated compounds by influencing the compound's accumulation, or exclusion, from subcellular loci such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, vesicles, granules, nuclei and nucleoli and other subcellular organelles and compartments. The present invention also provides methods for identifying chemical address tags, predicting their targeting characteristics, and for rational designing chemical libraries comprising chemical address tags.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Nucleolar targeting of therapeutics against HIV
InactiveUS6995258B1Improve the immunityImprove the level ofSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHiv 1 rnaT cell
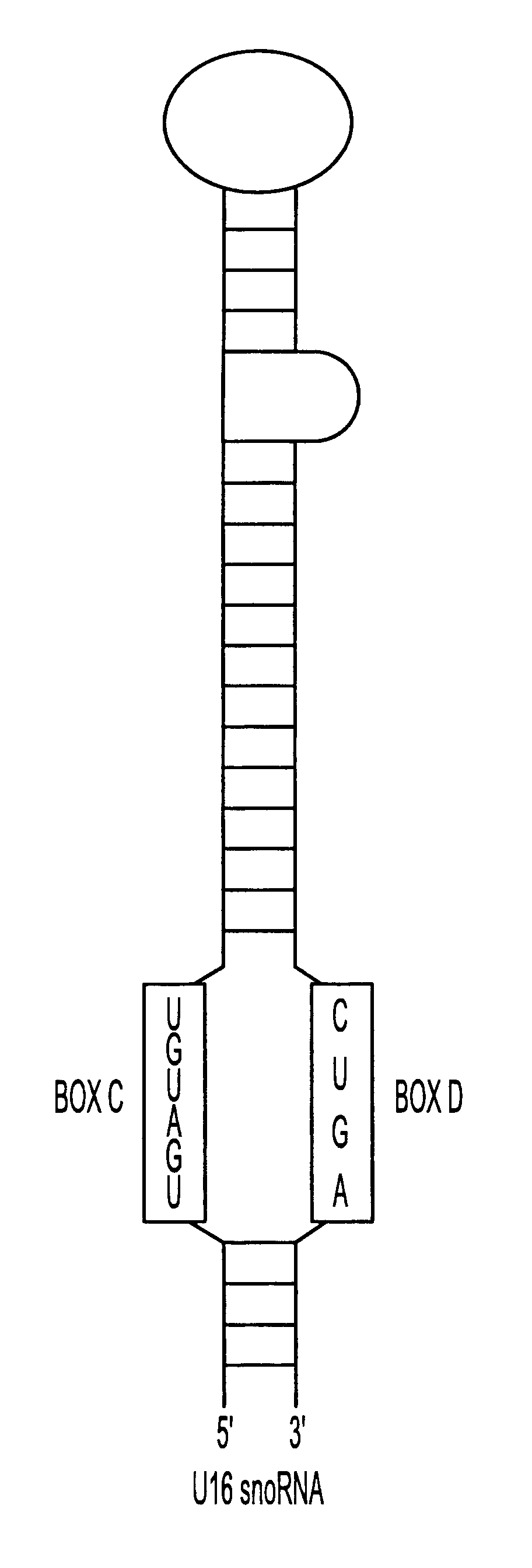
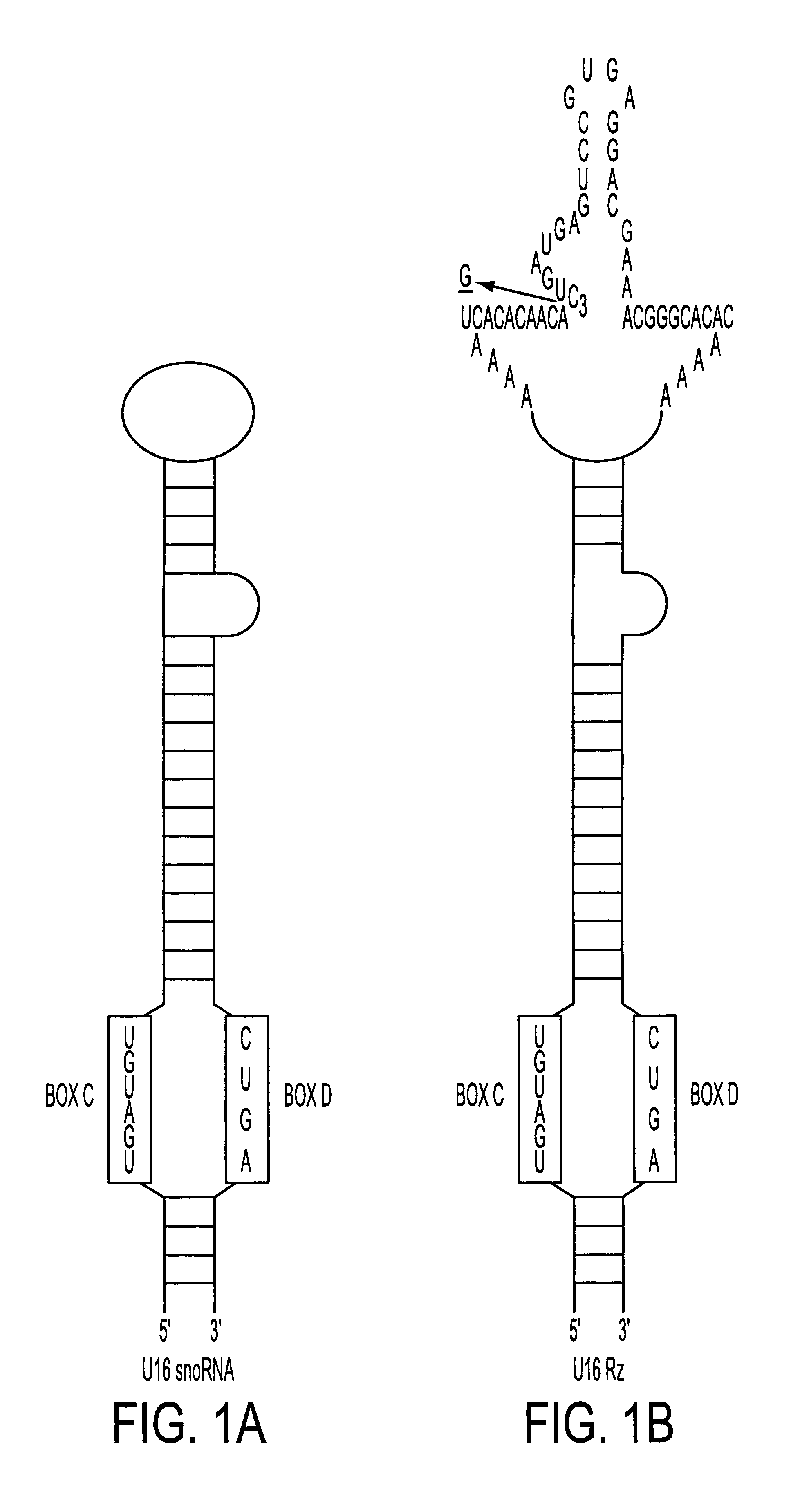
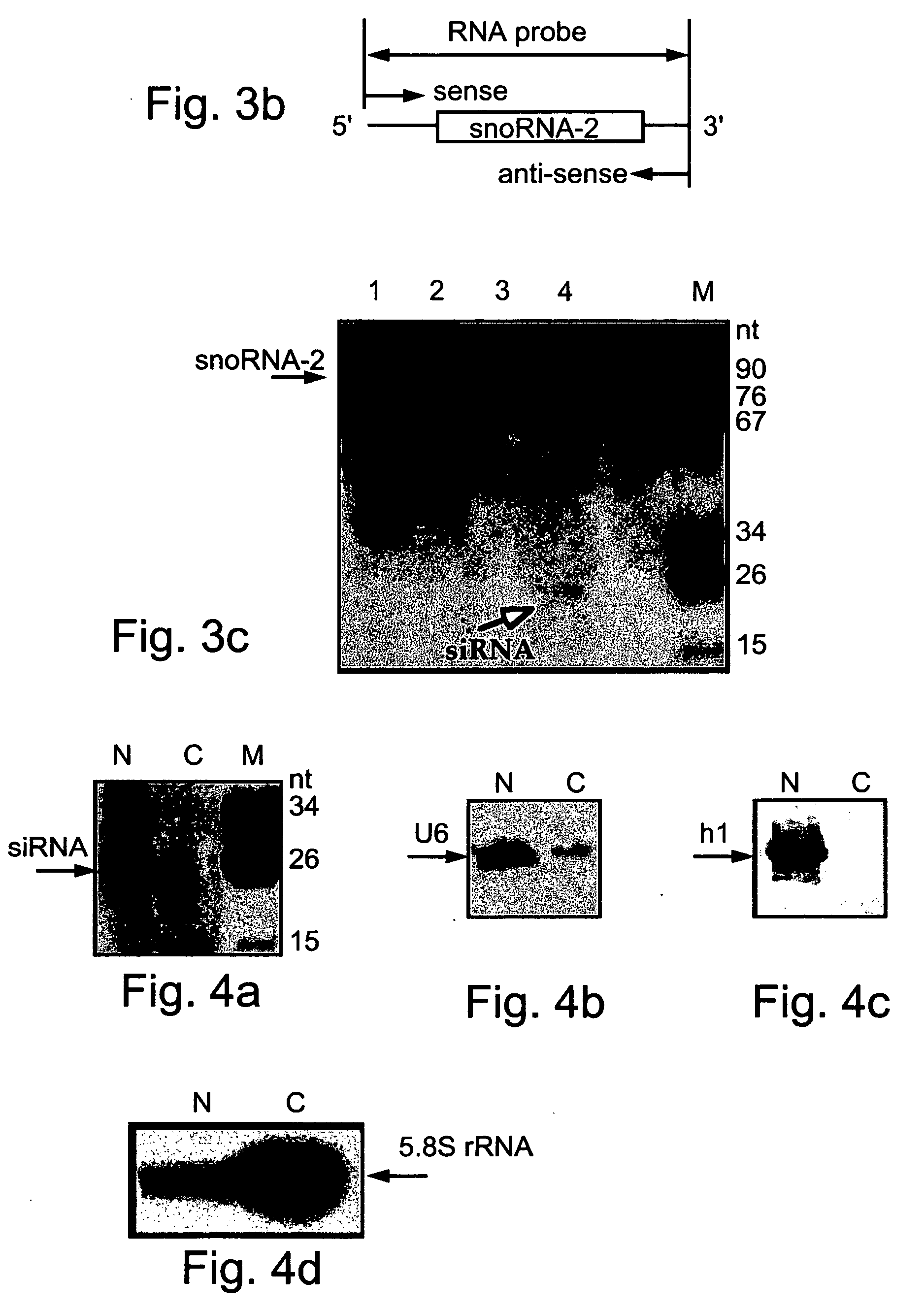
The HIV regulatory proteins Tat and Rev accumulate in nucleoli of human cells. No functional role has been attributed to this localization. Recently it was demonstrated that expression of Rev induces nucleolar re-localization of some nuclear factors involved in Rev export. Thus, it is likely that the nucleolus plays a critical role in Rev-mediated export of singly spliced and unspliced HIV-1 RNAs. As a test for trafficking of HIV-1 RNAs into the nucleolus, a hammerhead ribozyme which specifically cleaves HIV-1 RNA was joined to the U16 snoRNA resulting in accumulation of the ribozyme within nucleoli of human cells. Stably transduced human T-cells expressing this nucleolar localized ribozyme dramatically suppressed HIV-1 replication, confirming a possible trafficking of the HIV RNA through the nucleoli of human cells. In addition, a TAR element which binds Tat was joined to the U16 snoRNA, also resulting in localization in the nucleoli and inhibiting HIV replication.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Artificial peptide and use thereof
InactiveUS20100297758A1Improve efficiencyChemical synthesis is easyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsCell membraneCulture mediums
The present invention provides a method of transporting a peptide motif of interest into a nucleus of a eukaryotic cell from outside the cell, including: synthesizing a peptide chain having an amino acid sequence constituting the peptide motif of interest at an N-terminal end or a C-terminal end of a cell membrane-permeable nucleolar localization signal sequence defined by the amino acid sequence KKRTLRKNDRKKR (SEQ ID NO: 1); adding the synthesized peptide to a culture medium which includes the eukaryotic cell or a tissue containing the eukaryotic cell; and culturing the eukaryotic cell to which the synthesized peptide is added, or the tissue containing the cell.
Owner:TOAGOSEI CO LTD
Human Monoclonal Antibodies to Human Nucleolin
ActiveUS20130115674A1Reduces BCL- levelInduce cytotoxicityAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseNon malignant
The present invention provides for methods of producing human monoclonal antibodies to human nucleolin, cells producing such antibodies, and the antibodies themselves. Also provided are methods of using the antibodies in diagnosing and treating malignant and non-malignant diseases wherein cells that express nucleolin on the cell surface contribute to the pathophysi-ology of the disease.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Indolpyridine type fluorescent probe for imaging RNA and nucleolus in living cell
ActiveCN103265947AGood membrane permeabilityGood colorOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceDead stateMembrane permeability
The invention discloses an indolpyridine type fluorescent probe for imaging RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) and nucleolus in a living cell. The structural general formula of the fluorescent probe is shown in the specification, wherein R1 and R2 represent alkyl, hydroxyalkyl or ether group, respectively. The invention also discloses application of the fluorescent probe in marking or displaying of the distribution of the RNA and the nucleolus in the living cell and distinguishing of the dead state and the live state of the cell. The probe provided by the invention has the characteristics of wide application range, good membrane permeability, low cytotoxicity and ability of exclusively realizing fluorescent imaging of RNA in the living cell.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
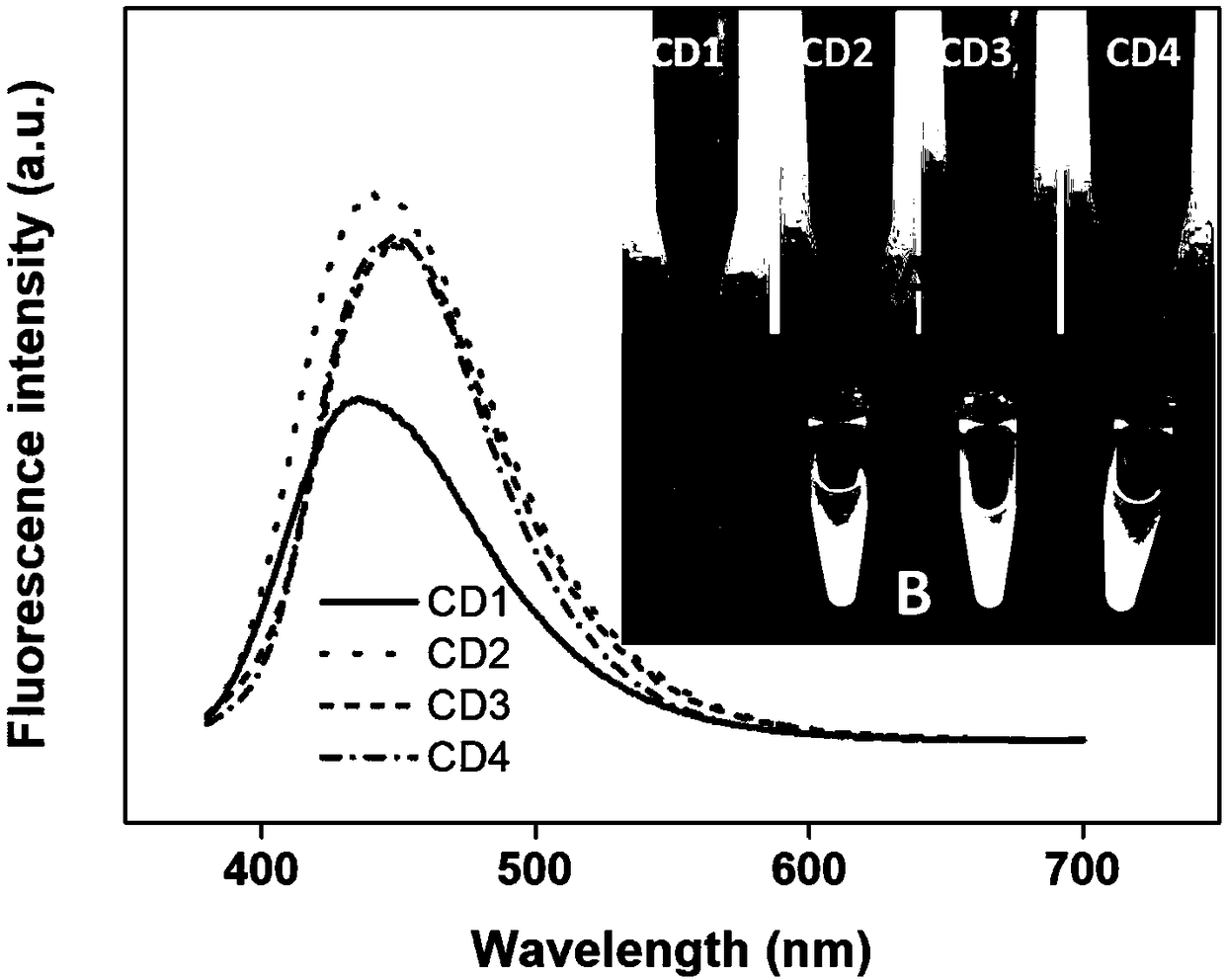
Application of fluorescent carbon dots in living cell nucleolus imaging or RNA labeling or display
InactiveCN106610376AHigh selectivityImprove imaging resolutionFluorescence/phosphorescenceStainingRNA marker
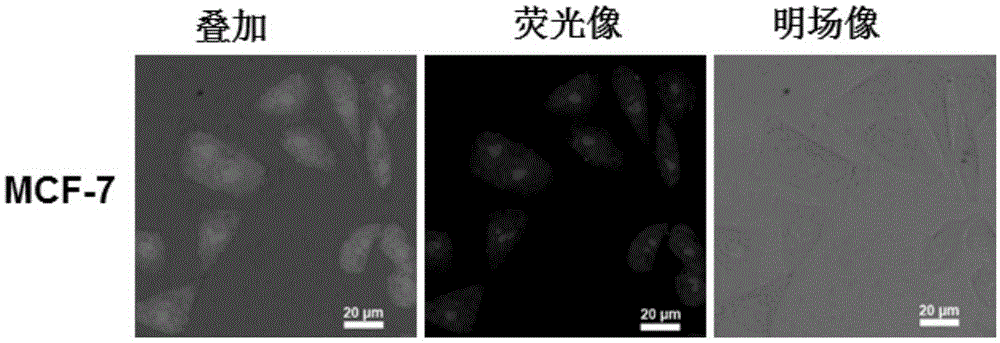
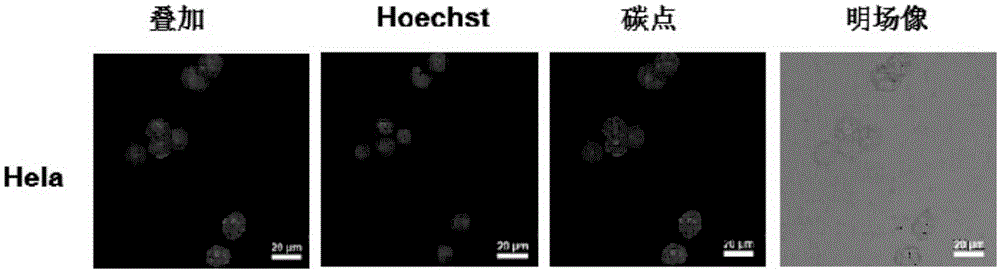
The invention discloses an application of fluorescent carbon dots in living cell nucleolus imaging or RNA labeling or display. The fluorescent carbon dots adopt red light emitting fluorescent carbon dots with an up-and-down conversion function, and particularly adopt fluorescent carbon dots disclosed in the CN104263366A. In some embodiments, the living cell nucleolus imaging can be accomplished by the use of the fluorescent carbon dots through cell culture, dye solution preparation, staining and imaging. With the help of the fluorescent carbon dots, the living cell nucleolus imaging or labeling or display of RNA in living cells can be realized, and the fluorescent carbon dots have the advantages of high selectivity on nucleolus imaging, high imaging resolution, simpliness, rapidness, low cost, low biological toxicity, and quite high practical value.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Snornai-small nucleolar rna degradation by rna interference in trypanosomatids
ActiveUS20060079471A1Downregulating levelSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseSmall nucleolar RNA
Polynucleotides and a method suitable for downregulation of small nuclear RNA which can be used to treat diseases associated with activity of small nuclear RNA are provided. Specifically, the present invention can be used to downregulate snoRNA molecules or box H / ACA-containing RNA molecules which are involved in diseases such as cancer.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV
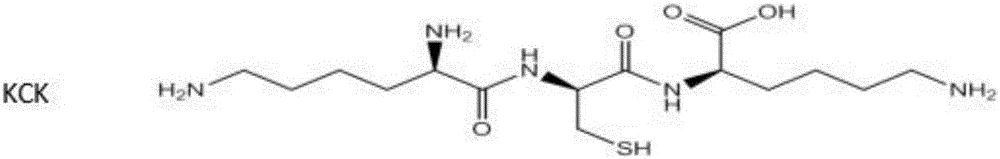
KCK polypeptide modified gold nanocluster and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106010513AEasy to prepareEasy to operateTransportation and packagingMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantum yieldPhotochemistry
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Pyrrole pyridine salt fluorescent probe used for RNA (ribonucleic acid) and nucleolus imaging in living cell
ActiveCN103275699AGood membrane permeabilityGood colorOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceEtherCytotoxicity
The invention discloses a pyrrole pyridine salt fluorescent probe used for RNA (ribonucleic acid) and nucleolus imaging in a living cell. The structural general formula of the fluorescent probe is shown in a formula (I), wherein R<1> and R<2> represent an alkyl group, a hydroxyalkyl or an ether group. The invention also discloses application of marking or displaying distribution of RNA and nucleolus in the living cell and identifying life or death state of the cell of the fluorescent probe. The probe has the characteristics of wide application scope, good membrane permeability and low cytotoxicity and can be used for specific fluorescence imaging of RNA in the living cell.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for observing embryo sac of paddy rice by using stone peculiar fluorescent dye, and transparent technique of whole ovary
InactiveCN1916609ADifficult to penetrateNot easy to dyePreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceEmbryo
A method of utilizing nuclear specific fluorescent staining and ovary being made to be completely transparent technique to observe blastocyst of rice includes using certain concentration of sodium hydroxide solution to carry out softening treatment on blastocyst of rice before staining then utilizing specific combination of nucleus fluorescent staining DAPI with nucleus to observe structure of cell and nucleus in blastocyst, enabling to use laser scan confocal microscope to observe internal structure of cell clearly.
Owner:代西梅
Method for homologous recombining by using spirulina and expressing human gene
InactiveCN1528902AImprove conversion rateEasy to detectOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationHuman bodyRecombinant expression
The invention refers to a method for reconstructing the cloned and constructed human body tumor death factor TRAIL gene expression carrier into spirulina gene group to be expressed stably with gene gun. The special components of the reconstructed TRAIL expression carrier include resistant mark gene expression box CAT, chlorophyll body photosynthetic gene promotor and ender, spirulina homologous segment, TRAIL gene segment without coding film combining part, the expression system also includes characters of primary nucleus and eukarya. The invention sets suitable striking parameter, uses gene gun to guide the reconstructed expression carrier into spirulina silk body, and through several times of sifting of chloramphenicol with incremental density and molecular biology testing, the invention gets spirulina converter of TRAIL gene. The invention applies to spirulina reconstruction and human body gene expression, it also applies to reconstruct and express other primary nucleolus and eukarya.
Owner:广东梅雁蓝藻有限公司
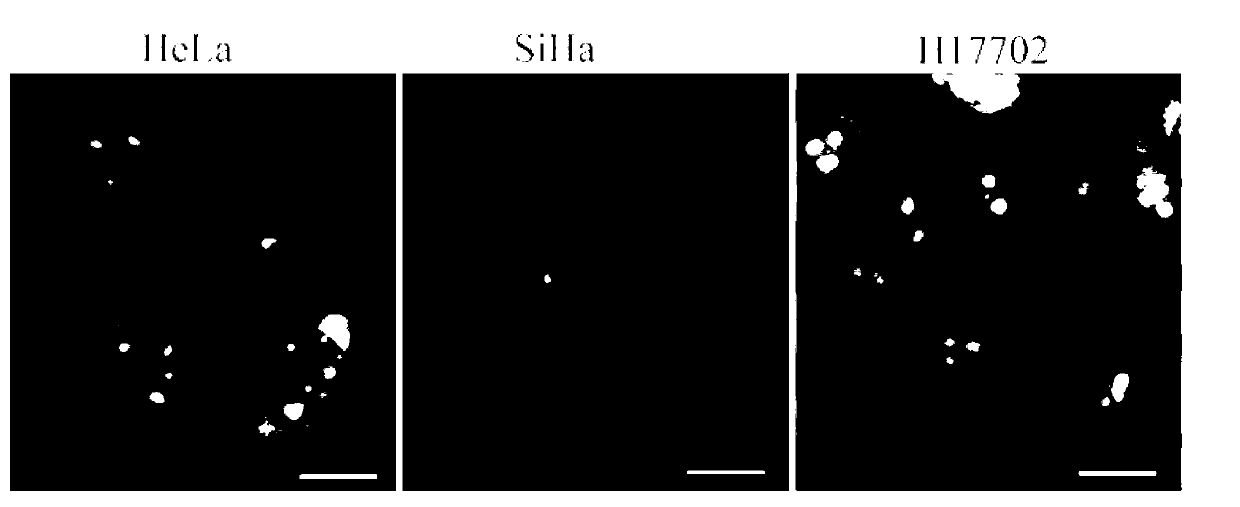
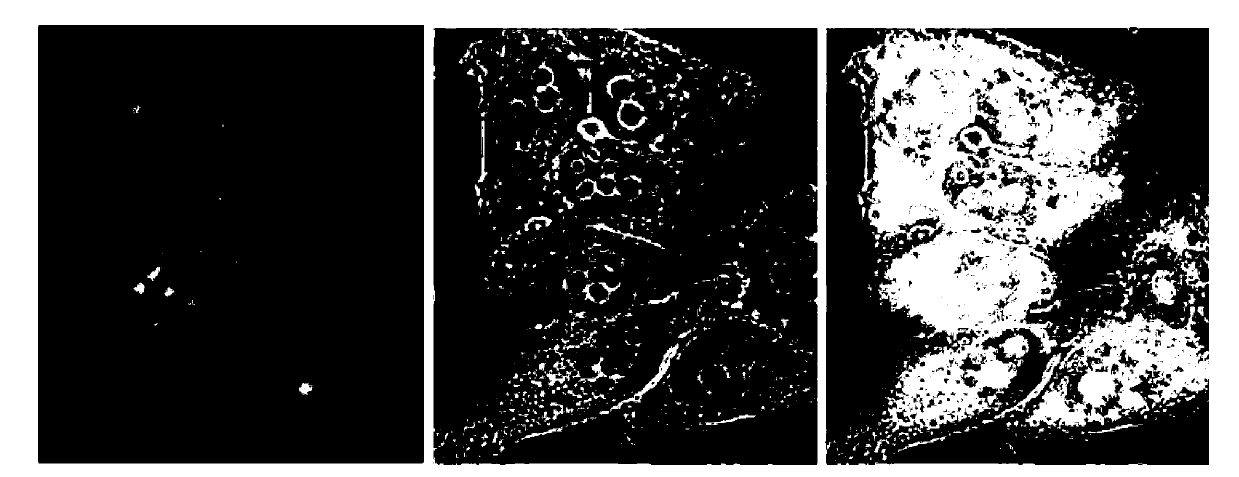
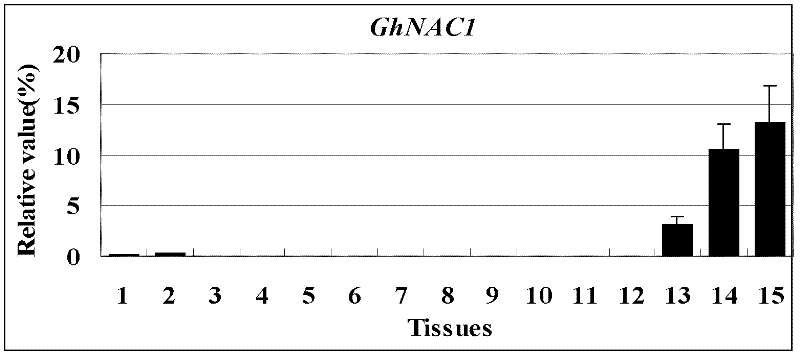
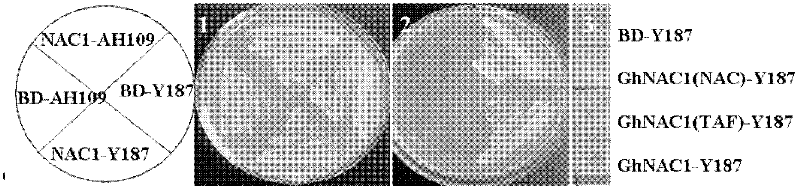
Cloning and identification of cotton fiber cell secondary wall development-associated GhNAC1 gene
InactiveCN102399792ATranscriptional self-activatingRegulates secondary wall developmentPlant peptidesFermentationExonCell wall
The invention discloses a novel cotton fiber secondary development specific expression gene GhNAC1 full-length sequence, and relates to an important cotton fiber development-associated regulator gene element. The GhNAC1 gene contains three exons and two introns, and is coded with an NAC (N Acetyl L Cysteine) transcription factor. A large quantity of mRNAs (messenger Ribonucleic Acids) of the gene are accumulated specifically at the secondary development stage of the cotton fiber cells, which indicates that the gene is a fiber secondary wall development specific gene. GhNAC1 protein is positioned in a cell nucleolus and has the capability of activating transcription independently, which indicates that the protein serving as a transcription activating factor plays a role in cotton fiber development. GhNAC1 is expressed excessively in arabidopsis, so that leaves crimp upwards, cell walls are thickened, ectopic sedimentation of lignin and the like is detected in foliar epidermic cells, so that the hemicellulose content of foliar cells is greatly increased. As proved by the results, the GhNAC1 can be used for regulating the biosynthesis of cell secondary walls, and plays a key role in the developing process of cotton fiber.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Litsea cubeba nucleolus deep-processing and comprehensive utilization process
ActiveCN101328446AHigh reaction conversion rateShort reaction timeBio-organic fraction processingOrganic chemistryBiodieselDistillation
The invention provides a technique for deeply processing and comprehensively utilizing of a litsea cubeba kernel. In the invention, the litsea cubeba kernel is crushed and subject to heated reflux extraction in a Soxhlet extractor for 0.5 to 4 hours by taking a low boiling point nonlinear solvent as an extraction solvent, and the litsea cubeba kernel oil is obtained; the obtained litsea cubeba kernel oil, methanol, concentrated sulfuric acid and anhydrous sodium sulfate are mixed according to the ratio of 100:(between15 and 50):(between 1and 2):(between 3 and 5) and then put in a reaction kettle for degreaseing reaction, after the reaction, the mixed liquid are added with the anhydrous sodium sulfate to neutralize the sulphuric acid so as to obtain solid salt, by the reduced pressure distillation, the methanol is recovered and the moisture is dried, and the solid salt is removed by centrifugation; the obtained filtrate, the methanol, a phase transfer catalyst and sodium hydroxide are mixed according to the ratio of 100:(between15 and 50):(between 0.1 and 1):(between 0.5 and 2) and then put in the reactor reaction kettle for ester exchange reaction, after the reaction, the concentrated sulfuric acid are added to neutralize the sodium hydroxide, the obtained mixed liquid are kept stand and layered, the upper layer of coarse biodiesel is subject to the reduced pressure distillation to obtain the finished biodiesel, and the lower layer of the methanol and the glycerin are vaporized to recover the methanol for repeated use.
Owner:YONGZHOU SAMSHIANG FLAVOURS & FRAGRANCES CORP
Nucleolin-binding peptides, nucleolin- binding lytic peptides, fusion constructs and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20110124564A1Reducing and decreasing and durationReducing and decreasing and and frequencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody conjugateBinding peptide
The invention relates to nucleolin binding peptides, nucleolin binding peptides and anti-nucleolin antibody conjugates with cytotoxic activity, fusion constructs, methods of using nucleolin binding peptides and antibodies and fusion constructs thereof, and methods of treating various disorders, undesirable conditions and diseases treatable with nucleolin binding peptides and fusion constructs, such as undesirable or aberrant cell proliferation (hyperproliferation) or hyperproliferative disorders, including tumors, cancers, neoplasia and malignancies, angiogenesis related or dependent diseases, and inflammatory diseases and inflammation.
Owner:A28 THERAPEUTICS INC
Novel near-infrared high-quantum-yield dye as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN107141840AReduce the incubation concentrationPrecise positioningOrganic chemistryBenzoxanthene dyesQuantum yieldHalogen
The invention discloses a novel near-infrared high-quantum-yield dye which has the following structural formula I shown as the original specification, wherein R1, R2, R6 and R7 are hydrogen, a low-level alkyl, an ether group and a substituted alkyl or acyl that are independent respectively; R3, R4, R5, R8, R9 and R10 are hydrogen, a low-level alkyl or halogen that are independent respectively; R11 is hydrogen, methyl, a cyano group or trifluoromethyl; X<theta> is a negative ion. The invention discloses a preparation method of the dye. The dye has good biocompatibility, low toxicity, longer fluorescence-emission and high fluorescence quantum yield, the autofluorescence of a background is avoided, a fluorescence image with high signal-to-noise ratio can be obtained, and the dye is used for fluorescence labeling for nucleolar RNA in a biological system and plays an important pole in a study process of physiology related to the nucleolar RNA.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
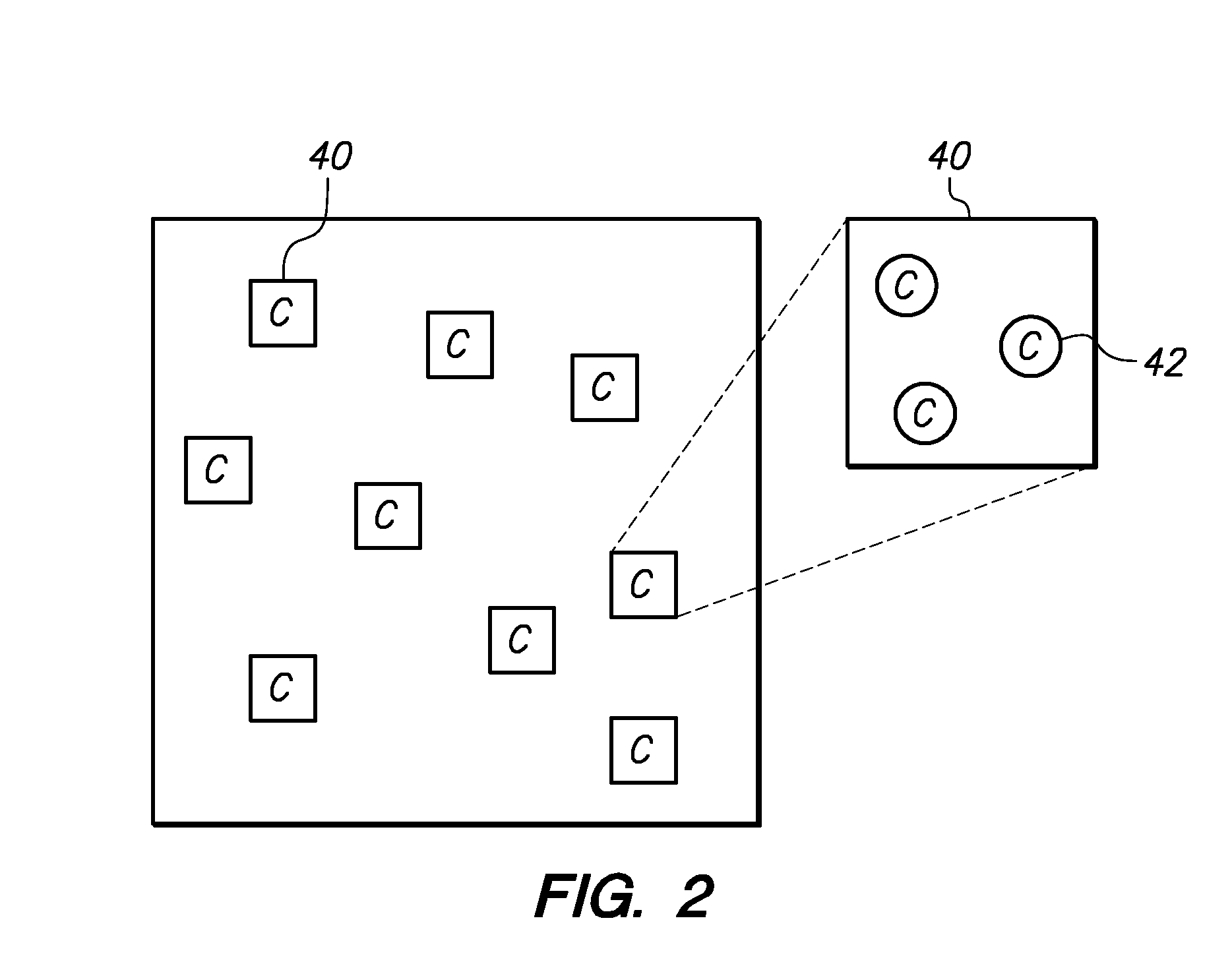
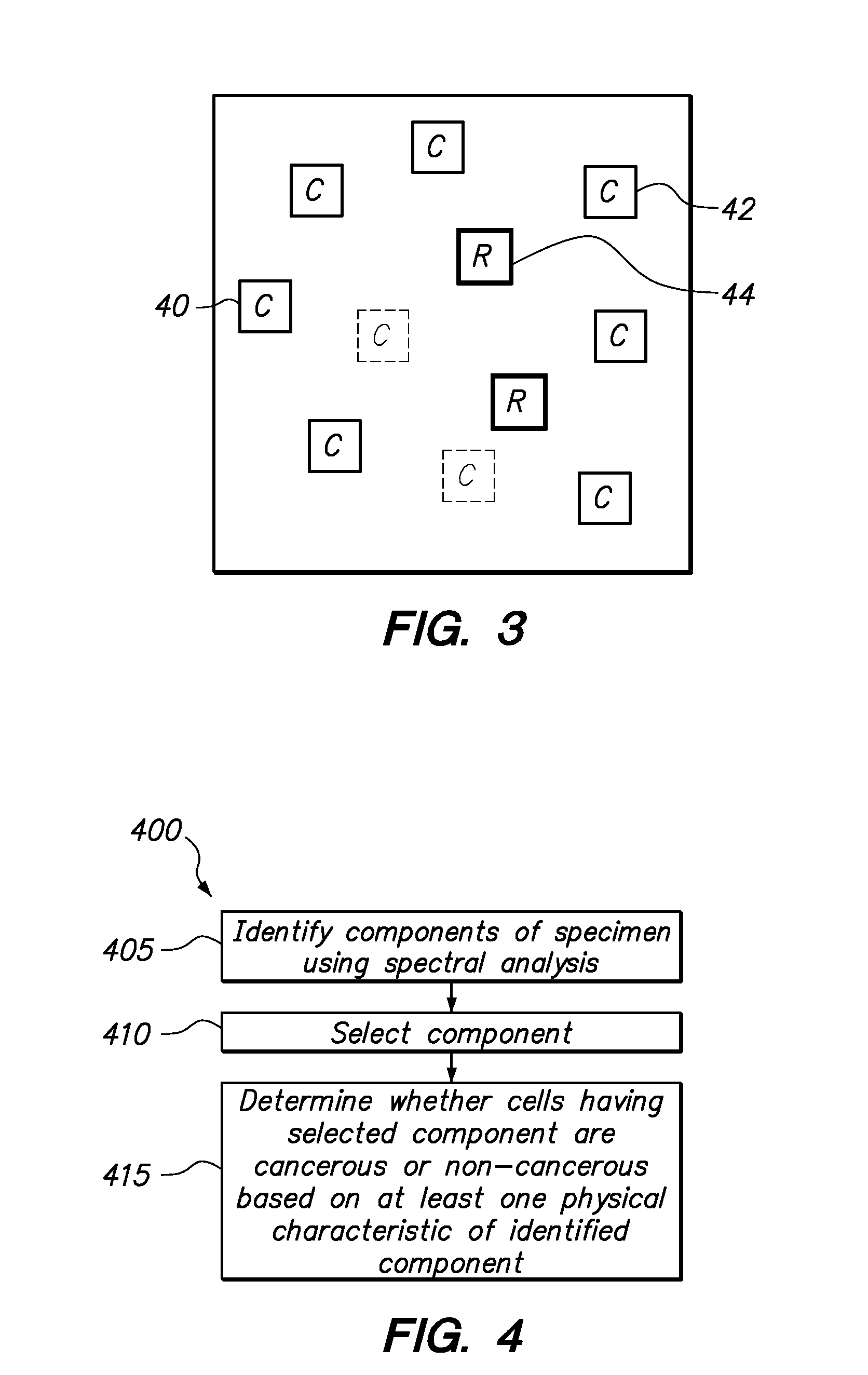
Method and system for processing an image of a biological specimen
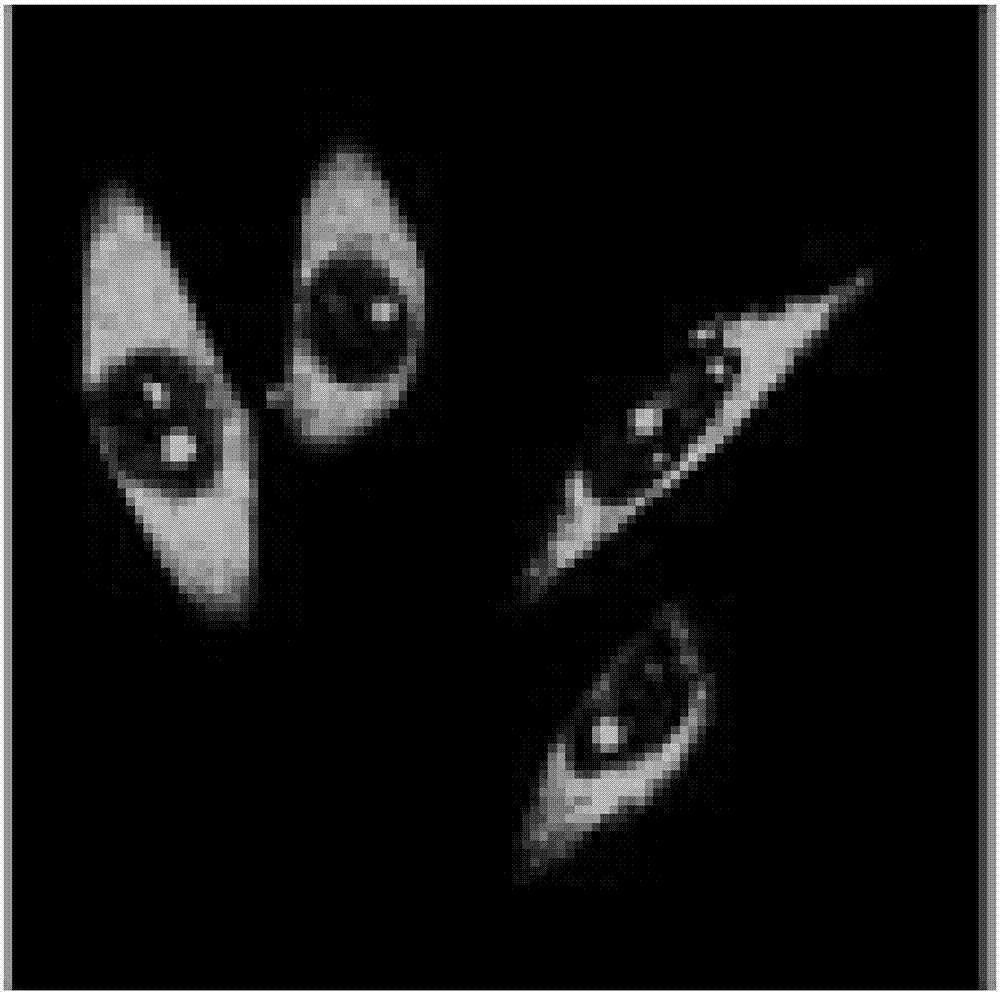
Components, e.g., background, cytoplasm, nucleus and nucleolus, of a biological specimen are identified using multi-wavelength analysis. Specimen components, such as nucleoli, are selected, and a determination is made whether cells having nucleoli are cancer cells or regular repair cells based on one or more physical characteristics of the identified component. The physical characteristics can be one or more of a shape, size, texture and gray value.
Owner:CYTYC CORP
Immunofluorescence method for rapidly detecting nucleolus protein positioning under the stress of heavy metal
InactiveCN101650310APrecise positioningStrong specificityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescencePlant cellThermostat
The invention discloses an immunofluorescence method for detecting plant cell nucleolus B23 protein positioning under the stress of heavy metal, which comprises the following steps: cutting a plant root meristematic tissue cell processed by heavy metal and fixing for 1 hour in 4% paraformaldehyde; carrying out enzyme solution enzymolysis, using a burette to sucke out 0.1ml of sample liquid and uniformly spreading the sample liquid on a glass slide to be dispersed into a single cell; marking and then naturally drying by air; soaking in1 % TritonX-100 for 15 minutes; then dropwise adding 15 microliters of prepared first antibodies, covering a cover glass slide and hatching for 1 hour in a thermostat at 37 DEG C; dropwise dropping 15 microliters of prepared second antibodies; processing and then dropwise dropping 15 microliters of DAPI; finally dropwise adding 5 microliters of quenching preventing agent on a glass slide material, covering the cover glass slide and sealing the periphery ofthe cover glass slide with nail polish; and observing under a fluorescence microscope after 1 hour. The method has the characteristics of high specificity, accurate experimental result, and the likeand greatly improves the quantity of observation cells. The method provides a precise detecting method for discussing a heavy metal toxic cell mechanism and has wide application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method of improving directional imaging ability of carbon dots to cell nucleolus
InactiveCN108152261AImprove imaging effectExcellent directional imaging effectFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsEthylene diamineNeutral Charge
The invention discloses a method of improving directional imaging ability of carbon dots to cell nucleolus. The method includes: using citric acid and ethylene diamine as carbon sources to prepare carbon dots; adjusting the surfaces of the carbon dots from negative charge to close to neutral so as to improve directional imaging ability of the carbon dots to the cell nucleolus. Common organic saltis used as a carbon source and simply treated to prepare the carbon dots. Effect of the carbon dots on nucleolus imaging is improved by changing charge on the surfaces of the obtained carbon dots, andthe carbon dots with the surfaces in neutral charge have better directional imaging effect on the nucleolus.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Application of gold-silver mixed-metal cluster compound in preparing fluorescence staining reagent for cell nucleolus
InactiveCN102798561ARich structure-activity relationshipRapid specific stainingPreparing sample for investigationFluorescenceNucleolus
Application of gold-silver mixed-metal cluster compound in preparing fluorescence staining reagents for cell nucleoli relates to a fluorescence staining reagent. The invention provides an application of the gold-silver mixed-metal cluster compound which has excellent specific staining effect to cell nucleolus area quickly and stably, in preparing fluorescence staining reagents. The gold-silver mixed-metal cluster compound [Au6Ag2(C)(dppy)6](BF4)4 is synthesized using the method in the document: Jian-Hua Jia, Quan-Ming Wang; J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16634-16635. The dppy is diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine. The gold-silver mixed-metal cluster compound has fluorescence staining effect to cell nucleolus area, wherein the cell nucleolus fluorescence staining performance of the gold-silver mixed-metal cluster compound reaches or exceeds that of existing like products, so the compound can be used for preparing fluorescence staining reagents for cell nucleoli.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Application of carbon quantum dots in targeted cell nucleolus wash-free imaging
ActiveCN112461807AAvoid damageConvenient sourceMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsFreeze-dryingCell injury
The invention belongs to the technical field of fluorescence imaging, and provides application of carbon quantum dots in targeted cell nucleolus wash-free imaging. A preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking m-phenylenediamine and p-aminobenzoic acid as a carbon source and a nitrogen source, preparing brown-yellow carbon quantum dots (N-CDs) by a one-step hydrothermal method, andremoving an ethanol solvent by rotary evaporation to obtain a brown viscous material; dissolving the obtained brown viscous material in secondary water, centrifuging to remove insoluble substances, dialyzing to remove unreacted reaction precursor small molecules, and freeze-drying to obtain brown N-CDs solid powder, namely the carbon quantum dots for targeted cell nuclei wash-free imaging. High-resolution cell imaging images of HeLa and PC12 are obtained by laser confocal imaging, which shows that N-CDs can successfully target cell nucleolus for no-clean imaging, and the reagent is an excellent cell nucleolus imaging reagent. The preparation method is simple, can target cell nuclei without modification, has low requirements on instruments and equipment, is simple and convenient to operate, does not need to wash nuclei for imaging, saves time and can avoid cell damage.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Copper phthalocyanine molecule-based diagnosis and treatment integrated nanoprobe as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN111068051AGood singlet oxygen generating capacitySimplify complexityPowder deliveryEnergy modified materialsNucleotideHexagonal boron nitride
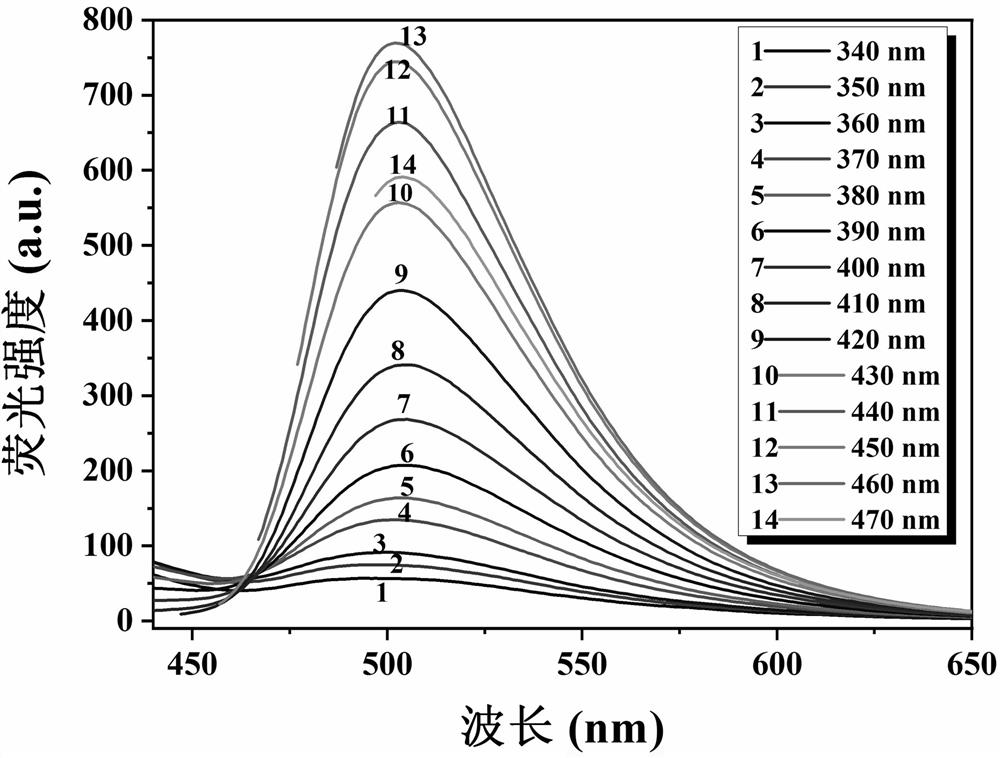
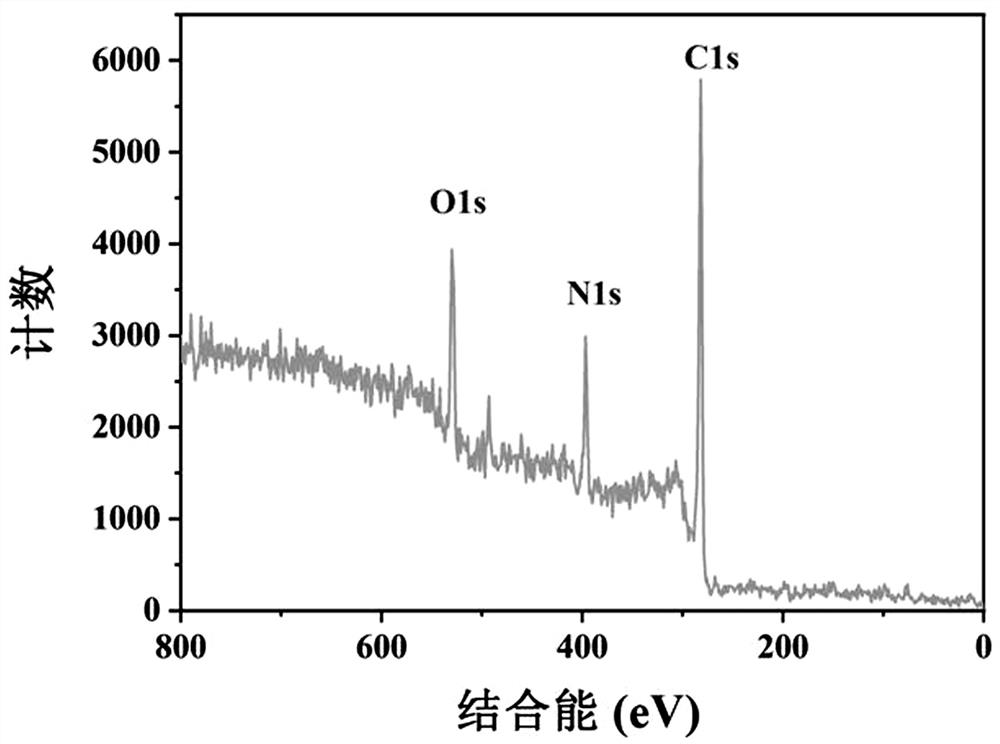
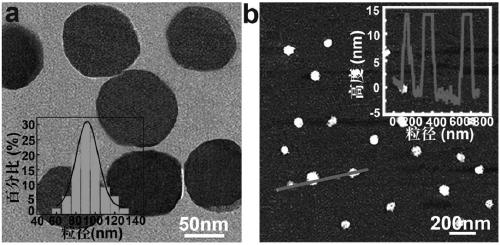
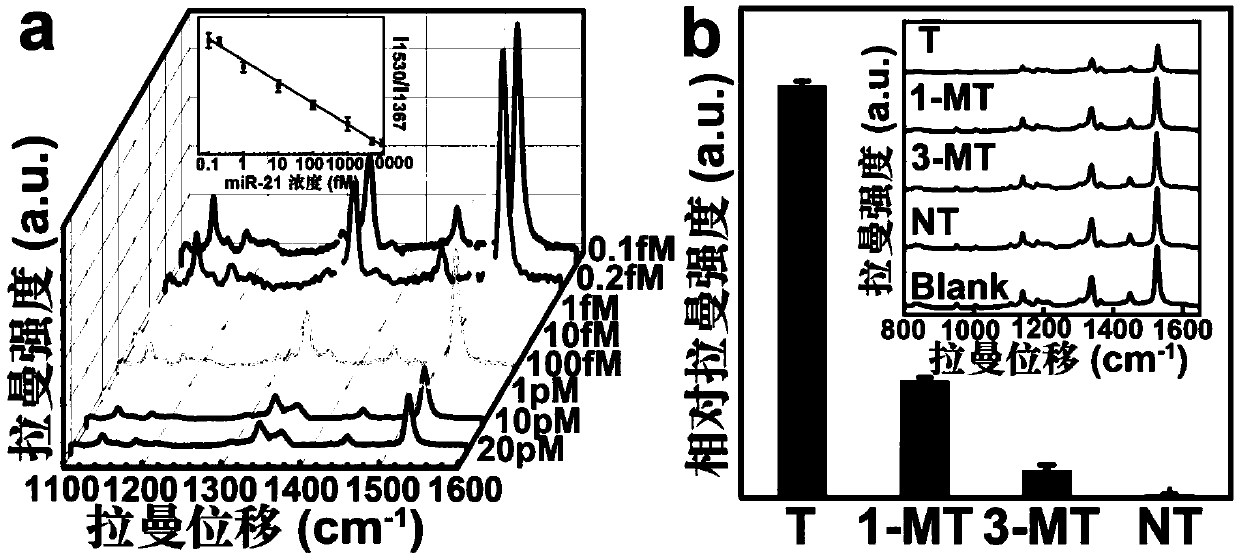
The invention relates to a copper phthalocyanine molecule-based detection, imaging and treatment integrated nanoprobe. The copper phthalocyanine molecule-based detection, imaging and treatment integrated nanoprobe comprises hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets, copper phthalocyanine molecules and two groups of oligonucleotide binding sequences. One end of each of the two groups of oligonucleotide sequences designed by the invention is a base pair for detecting and circularly amplifying microRNA-21, and the other end is an AS1411 sequence. The AS1411 sequence not only can recognize nucleolin highly expressed on the surfaces of tumor cells to play a role in targeted localization, but also can carry copper phthalocyanine molecules with poor water solubility based on a G quadruplex formed underspecific conditions, then, the nucleotide sequence loaded with copper phthalocyanine is adsorbed on the surfaces of the hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets through pi-pi accumulation to enter tumor cells. The invention further discloses application of the copper phthalocyanine molecule-based detection, imaging and treatment integrated nanoprobe in diagnosis and treatment of tumor cells and living bodies. The diagnosis and treatment integrated nanoprobe can perform in-situ Raman diagnosis on tumor cells, is high in sensitivity and specificity, can realize photodynamic therapy at the same time, and has a certain application value in biological medicine and clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Fluorescent probes for simultaneously displaying cell nucleus structure and cell integral morphology in live cells
ActiveCN107024462AGood membrane permeabilityGood colorFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsFluoProbesCell membrane
The invention discloses a group of fluorescent probes for simultaneously displaying cell nucleus structure and cell integral morphology in live cells. The group of fluorescent probes comprises a generalized RNA (ribonucleic acid) fluorescent probe with a chemical structure shown in a formula (I), a cell nucleus fluorescent probe with a chemical structure shown in a formula (II), and a cell membrane fluorescent probe with a chemical structure shown in a formula (III). The invention also discloses application of the group of fluorescent probes for labeling or displaying cell integral morphology, especially labeling or displaying the cell nucleus structure including nucleolus distribution. Proofed by experiment, the group of fluorescent probes has the characteristics that the application range is broad, the membrane permeability is good, the cell toxicity is low, and the cell nucleus, cell nucleolus, cell plasma and cell plasma member can be simultaneously imaged; the application prospect is broad.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
Method for preparing rose apple nucleolus polysaccharide
The invention relates to a method for preparing rose apple nucleolus polysaccharide, which comprises the following steps: (1) after drying and crushing rose apple nucleoli, adding the dried and crushed rose apple nucleoli into petroleum ether solution, performing water-bath heating reflux, then adding ethanol to carry out reflux after extraction filtration, and drying after extraction filtration; (2) adding dried powder into water and processing solution by using ultrasonic waves; (3) after finishing ultrasonic processing, regulating the pH value, adding cellulase and then performing enzymolysis and enzyme killing; and (4) removing precipitates in the solution which is subjected to enzyme killing and is cooled, taking out supernatant to carry out concentration, then adding chloroform and n-butyl alcohol mixed solution, centrifuging, taking out supernatant to be added with absolute ethyl alcohol precipitate polysaccharide, performing extraction filtration after standing, taking out solid matter to be washed sequentially by acetone, diethyl ether and absolute ethyl alcohol, and after drying, obtaining rose apple nucleolus polysaccharide powder. According to the invention, an ultrasonic-assisted enzymic method is adopted to extract the rose apple nucleolus polysaccharide; and not only is the method good in extracting effect, but also extraction time can be effectively shortened and production efficiency is improved.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Fast-fermenting bread yeast strain and construction method thereof
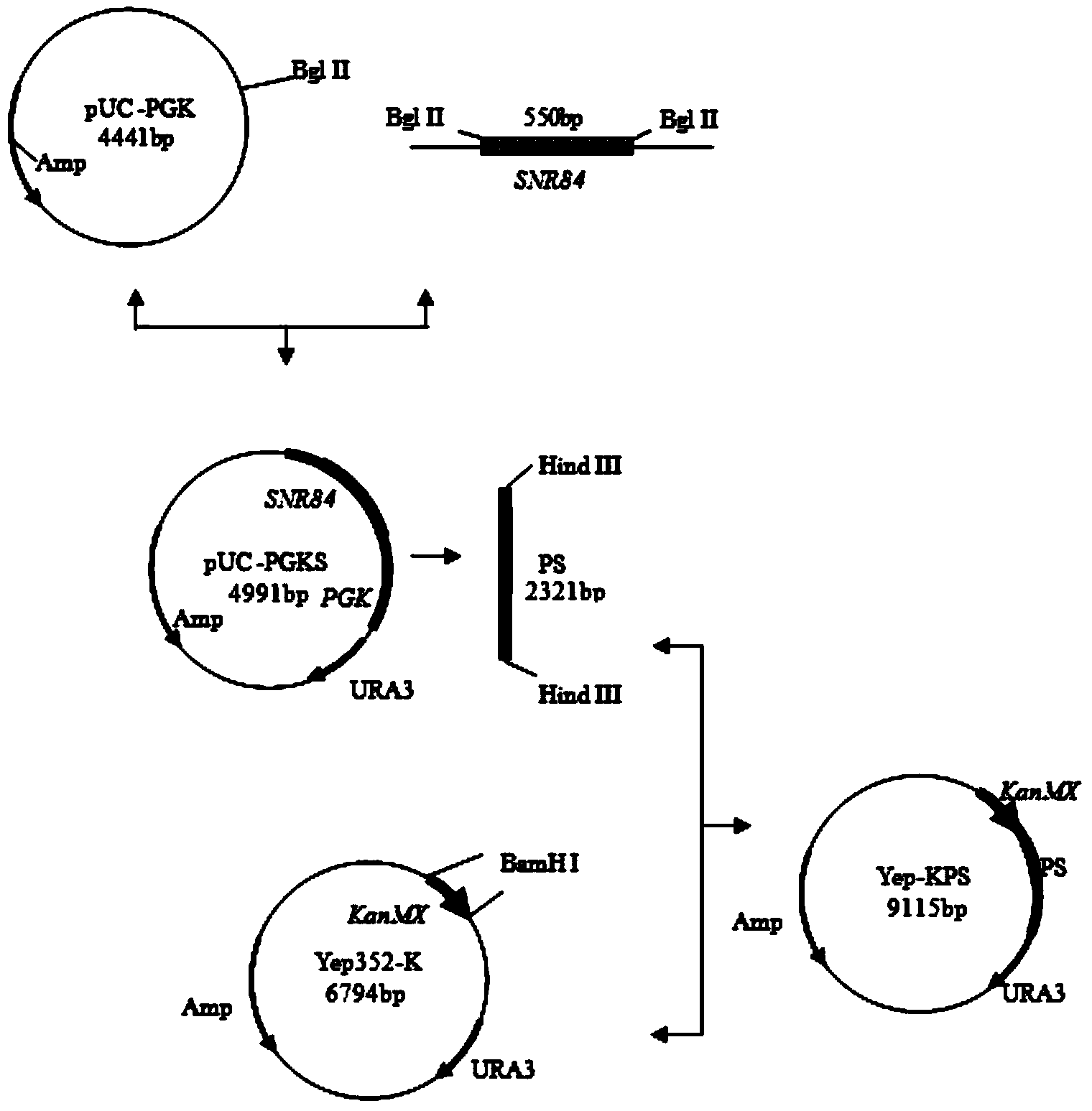
ActiveCN104073449AMeeting the needs of "fast" yeastHigh starting capacityFungiPre-baking dough treatmentBiotechnologyComplete sequence
The invention discloses a fast-fermenting bread yeast strain and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of a bioengineering technology. The construction method comprises the following steps: knocking out phosphoglucomutase genes PGM2 completely in the parent bread yeast strain; meanwhile, choosing a strong promoter PGK1 to over-express the complete sequence of H / ACA small nucleolus RNA (SNR84) to acquire the fast-fermenting yeast strain. The CO2 gas production of the fast-fermenting bread yeast strain in a non-sugaring paste for 1 hour reaches to 818mL; compared with the parent strain, the CO2 gas production is improved by 21.2% (the CO2 gas production of the parent strain fermenting in the non-sugaring paste for 1 hour reaches to 675mL); meanwhile, the fermenting time is shortened by 18.0%. The bread yeast strain has a good fermentability during fermenting in the non-sugaring paste, so that the requirement for the 'fast' yeast in a cooked wheaten food processing market is met. Therefore, the bread yeast strain has an extensive application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
DNA nano-material, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a DNA nano-material, and a preparation method and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of nano-materials. A DNA nano-stripe band is designed on the basis of a DNA origami theory, the nano-stripe is characterized in that a rolling circle amplification reaction product obtained through rolling circle reaction amplification of a ring template with a special structure is self-assembled to form a DNA nano-crystal lattice, and the DNA nano-crystal lattice is modified with an AS1411 aptamer of targeted nucleolin to form a DNA nano-material DNA nanostripe crystal lattice band-AS1411 compound; and the DNA nano-strip crystal lattice band-AS1411 compound is combined with nano-gold balls to form the DNA nano-material nano-gold-DNA nano-crystal lattice bandcompound. The prepared DNA nano-material has wide application values in tumor diagnosis and treatment as a targeting drug carrier.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Compound and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108558853AHigh selectivityLow biological toxicityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceChemical compound
The invention provides a compound and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound serves as a fluorescent probe and can selectively recognize G-quadruplex DNA, and compared with fluorescent probes with similar functions, the probe has the advantages of being high in selectivity, low in biotoxicity, good in membrane permeability, high in color development, good in re-dyeing compatibility and relatively high in light stability. It is indicated that the probe has a wide application range as the G-quadruplex DNA and nucleolus fluorescent probe and is expected to be developed into asimple and visual biological detection reagent related to G-quadruplex DNA and nucleoli and used for physiological and pathology research. The experiment result shows that the compound serves as the fluorescent probe, a fluorescence image marked by the probe has obvious red light distribution when displayed in a cytoplasm and nucleuse area, and it shows that the probe can be used for recognizing specific imaging cytoplasm in living cells and G-quadruplex DNA in the nucleoli.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Telomerase encoding DNA vaccine
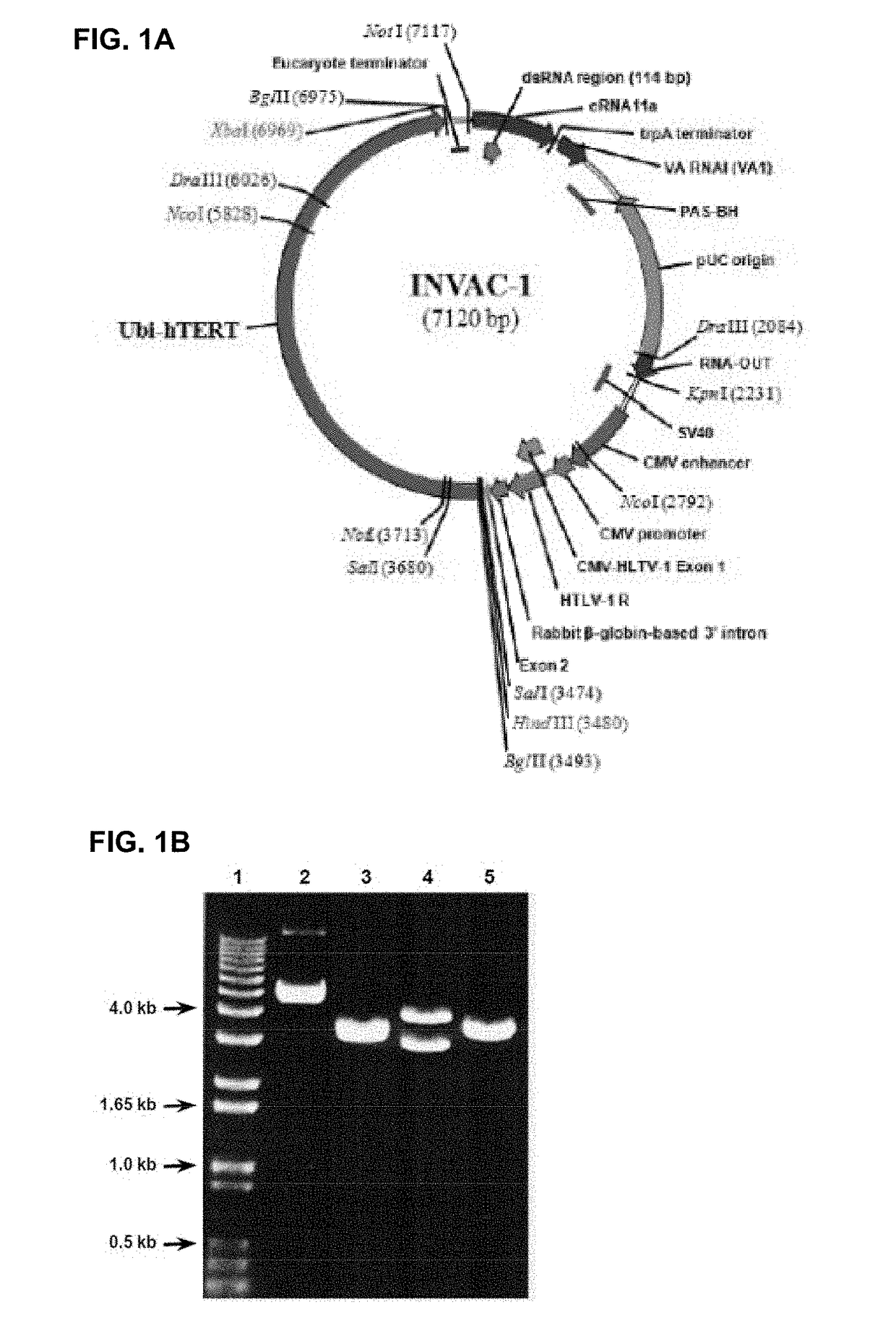
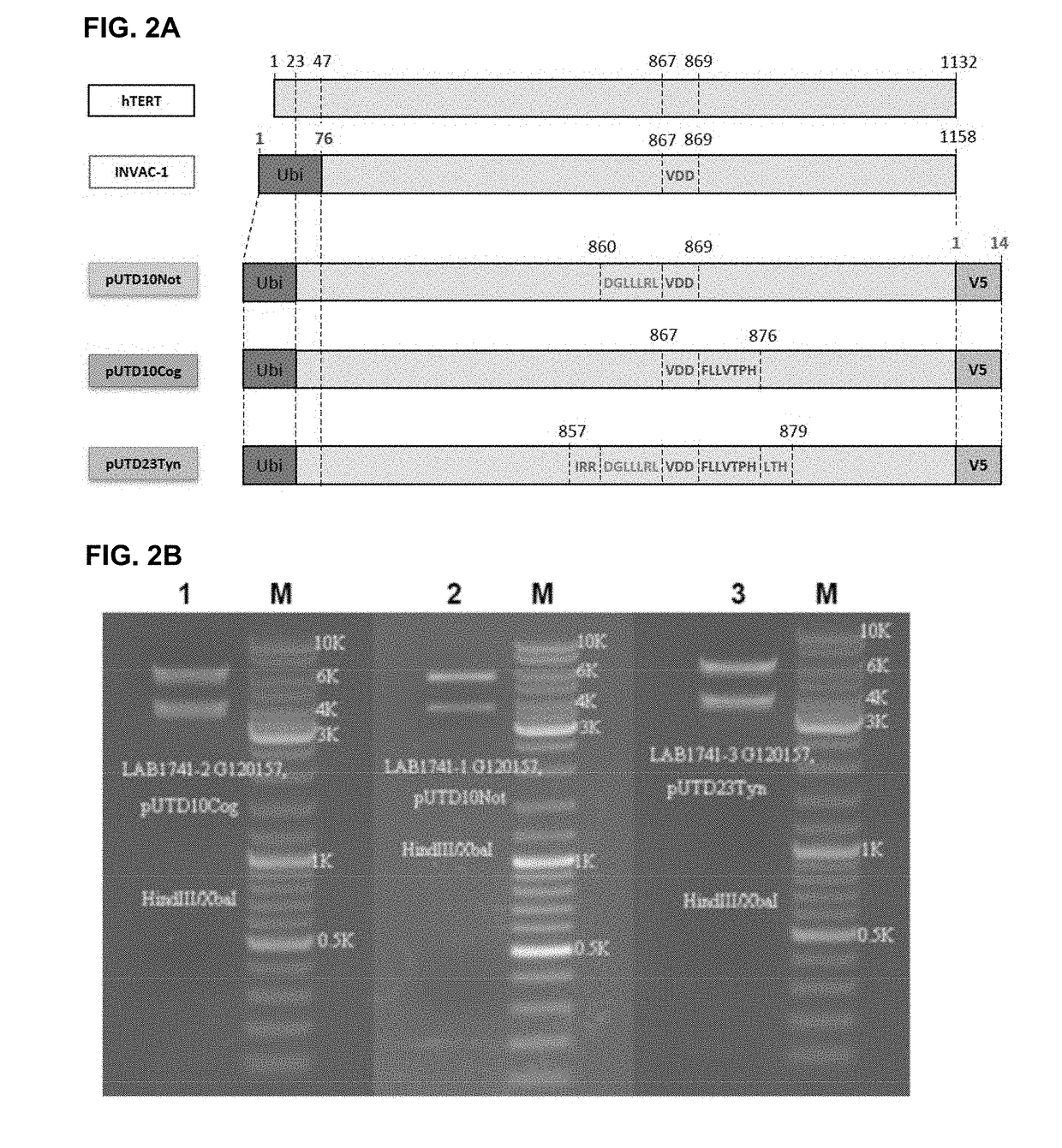
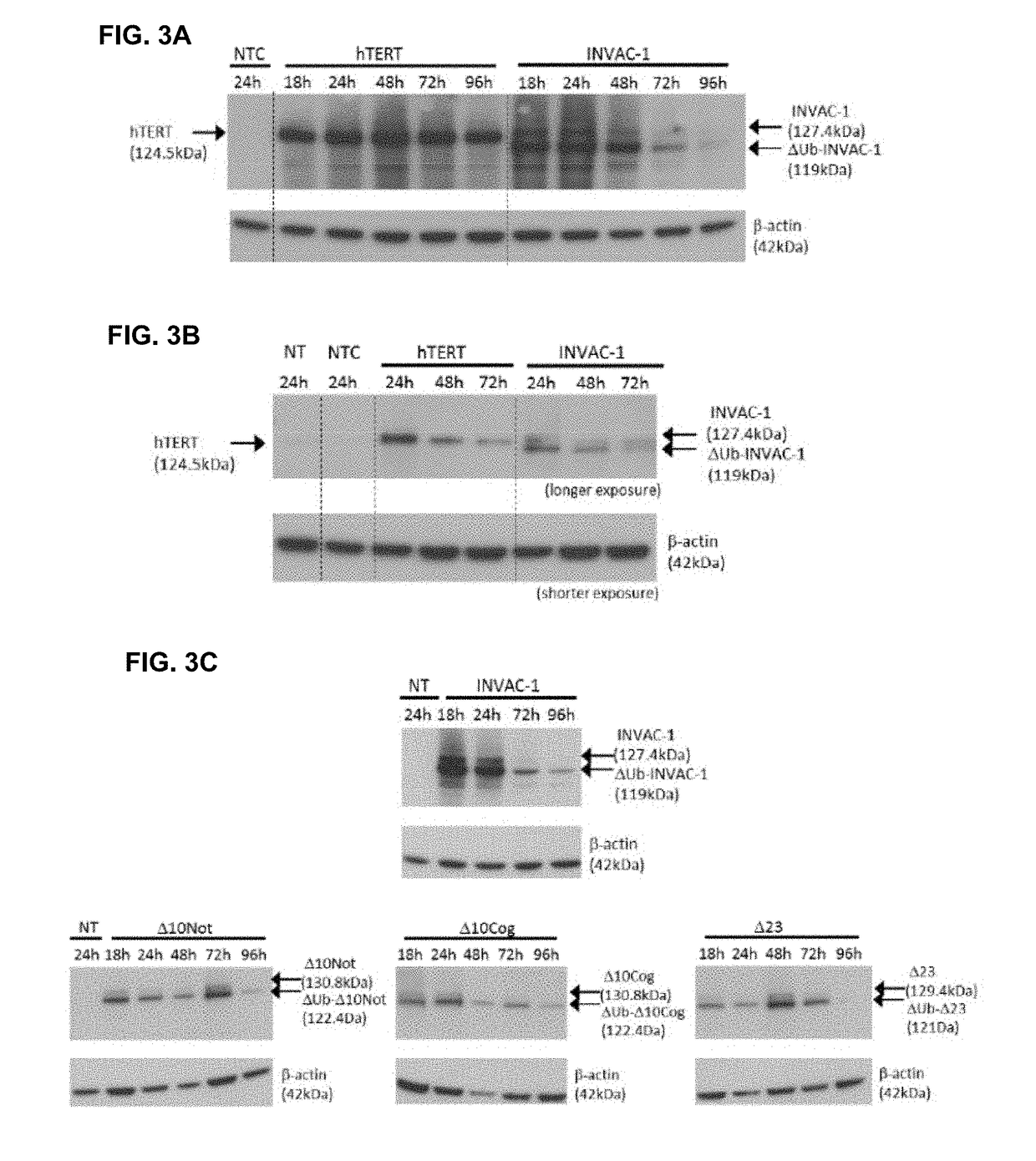
PendingUS20190000946A1Avoids expensive and complicated procedure for protein productionStimulate immune responsePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifTransferasesTelomeraseTelomerase Reverse Transcriptase Protein
Owner:INVECTYS
Segmentation method of cell nucleolus and cell membrane based on mixed contour model
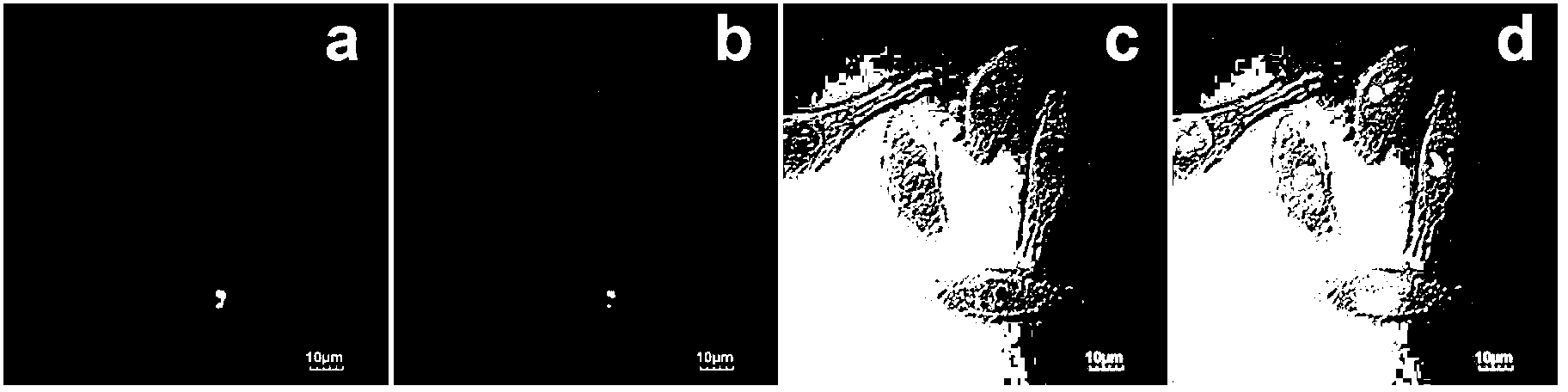
ActiveCN101661614AHigh precisionGood segmentation effectImage enhancementCell membranePartial differential equation
The invention relates to a segmentation method of cell nucleolus and cell membrane based on a mixed contour model. The method comprises the following steps: 1) according to the mixed contour model, establishing an energy function of a cell image to be segmented, the form of which is: such as E<E>(Phi, c1, c2, f1, f2)=E<M>(Phi, c1, c2, f1, f2)+P(Phi)+L(Phi); and 2) constructing and using a steepestdescent method to minimize the formula, calculating the border of the cell nucleolus and cell membrane of the cells by utilizing the level set function Phi being equal to zero through an iterative approach of discretization of partial differential equations. The invention provides a segmentation method of cell nucleolus and cell membrane based on the mixed contour model, which has high precisionand excellent segmentation effect.
Owner:山东盛世共青茶业有限公司
Kit for detecting colorectal cancer indicator bacteria
InactiveCN110643721AHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesClostridium symbiosumFusobacteria
The invention discloses a kit for detecting colorectal cancer indicator bacteria. The kit is characterized by comprising the following components: a specific primer combination for identifying the indicator bacteria, wherein the primer combination is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1-14, and the indicator bacteria are the combination of fusobacterium nucleatum (F.nucleolus), anaerobic digestion streptococcus(P.anaerobicus), clostridium symbiosum (C.symbiolum), Porphyromonas saccharolytica (P.asaccharolytica), Prevotella intermedia (P.intermedia), Bacteroides fragilis (B.fragilis) and Streptococcus salivarius (S.salivarius). The kit for detecting colorectal cancer indicator bacteria disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the colorectal cancer can be identified only by collecting astool sample. The principle is that the aim of identifying the colorectal cancer by detecting the colorectal cancer pathogenic bacteria in excrement, the sensitivity can reach 92.9%, and the specificity is 92.6%.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Nucleic acid dye compound and preparation method and application of nucleic acid dye compound
ActiveCN108165045AHigh selectivityLow biological toxicityStyryl dyesMethine/polymethine dyesMembrane permeabilityFluorescence
The invention provides a nucleic acid dye compound and a preparation method and application of the nucleic acid dye compound. The provided compound, as a fluorescence probe, can selectively recognizeG-quadruplex DNA and RNA; compared with the fluorescence probe having similar functions, the probe has the characteristics of strong selectivity, low bio-toxicity, good membrane permeability, strong developing, good counterstaining compatibility, and stronger light stability, and the characteristics indicate that the compound has extensive applications as the G-quadruplex DNA and the nucleolus fluorescence probe, and is expected to be developed into a simple convenient intuitive biological detection agent for the related physiological and pathological studies of the G-quadruplex DNA and nucleolus.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com