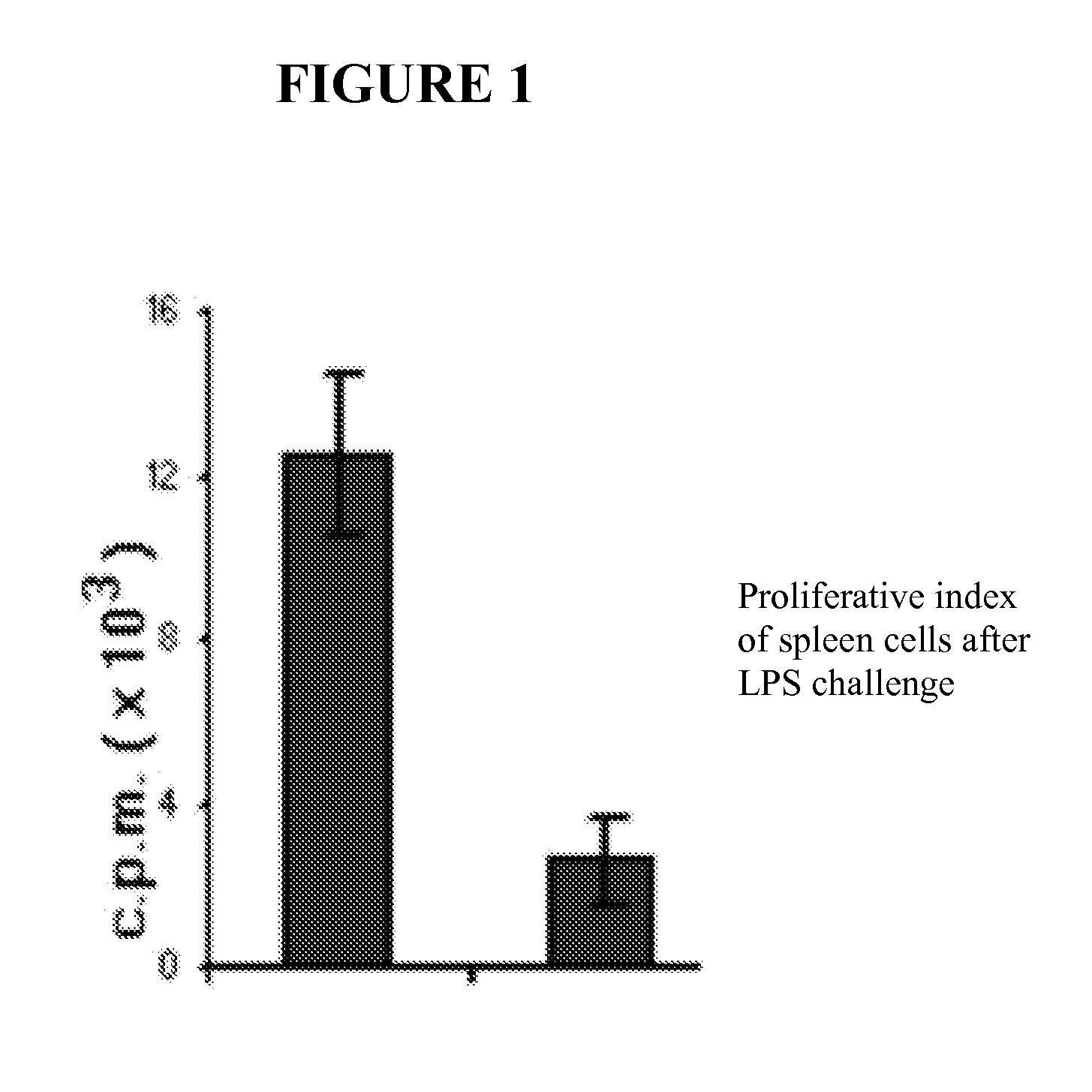
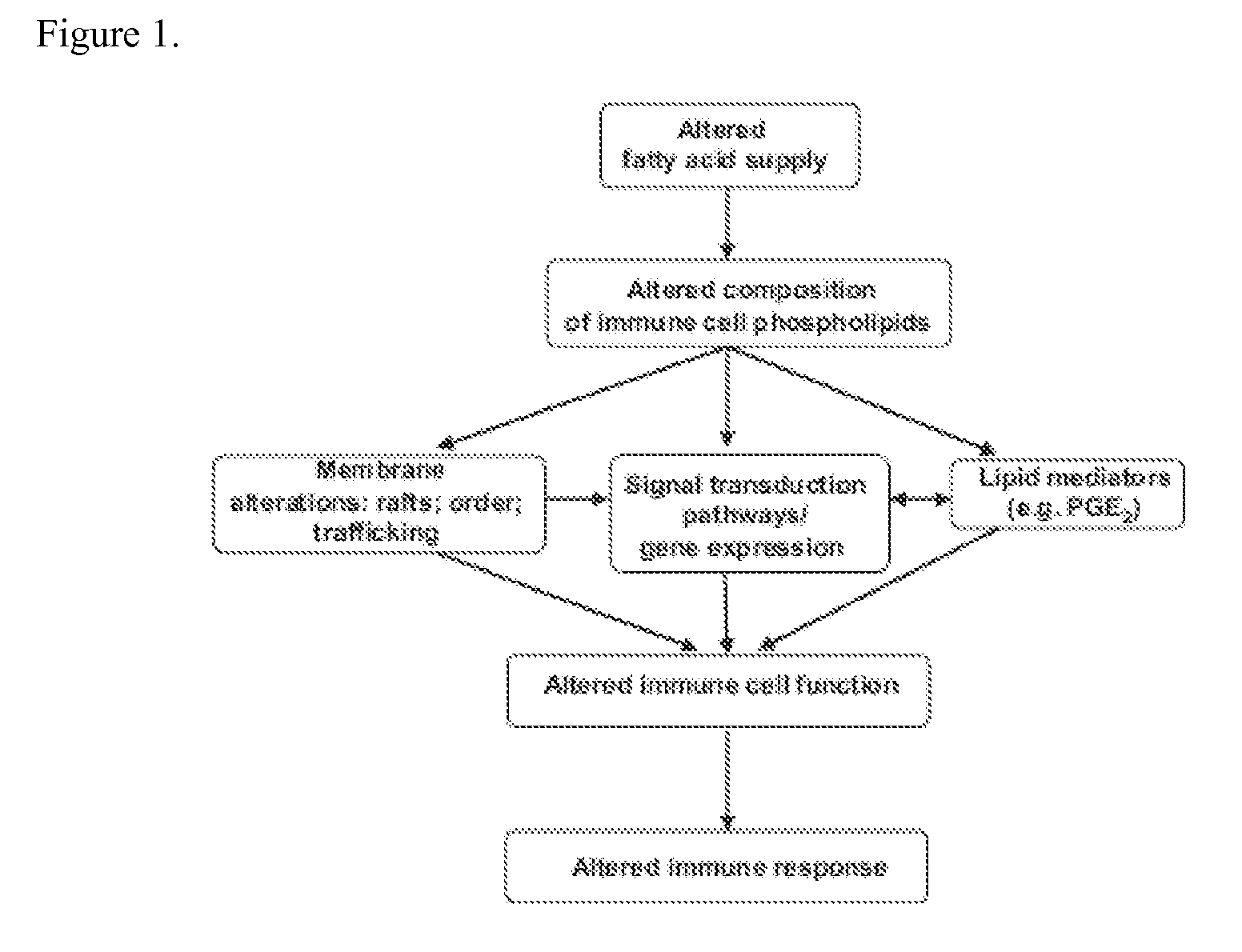
Patents
Literature
612 results about "Cell injury" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
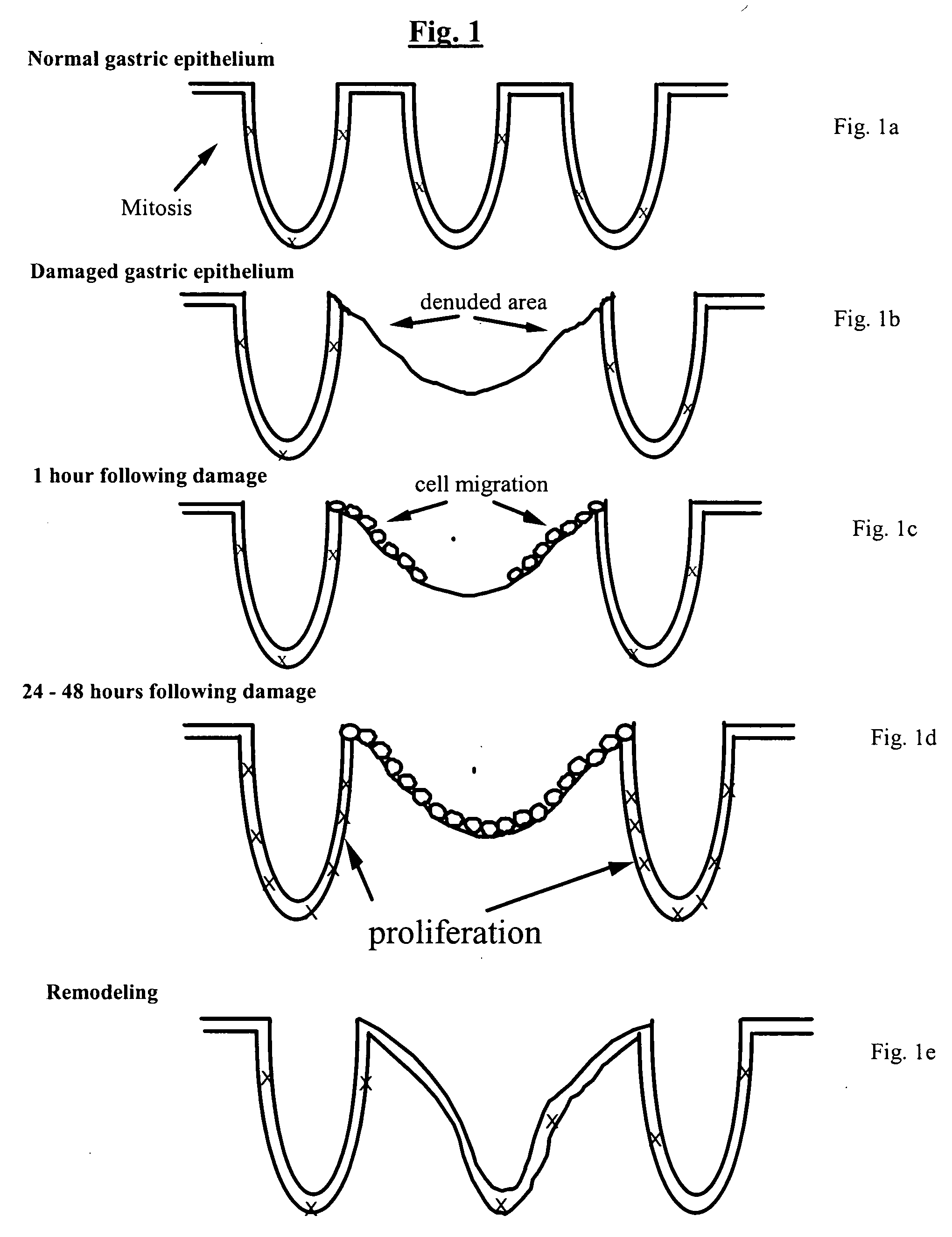
Cell damage (also known as cell injury) is a variety of changes of stress that a cell suffers due to external as well internal environmental changes. Among other causes, this can be due to physical, chemical, infectious, biological, nutritional or immunological factors.
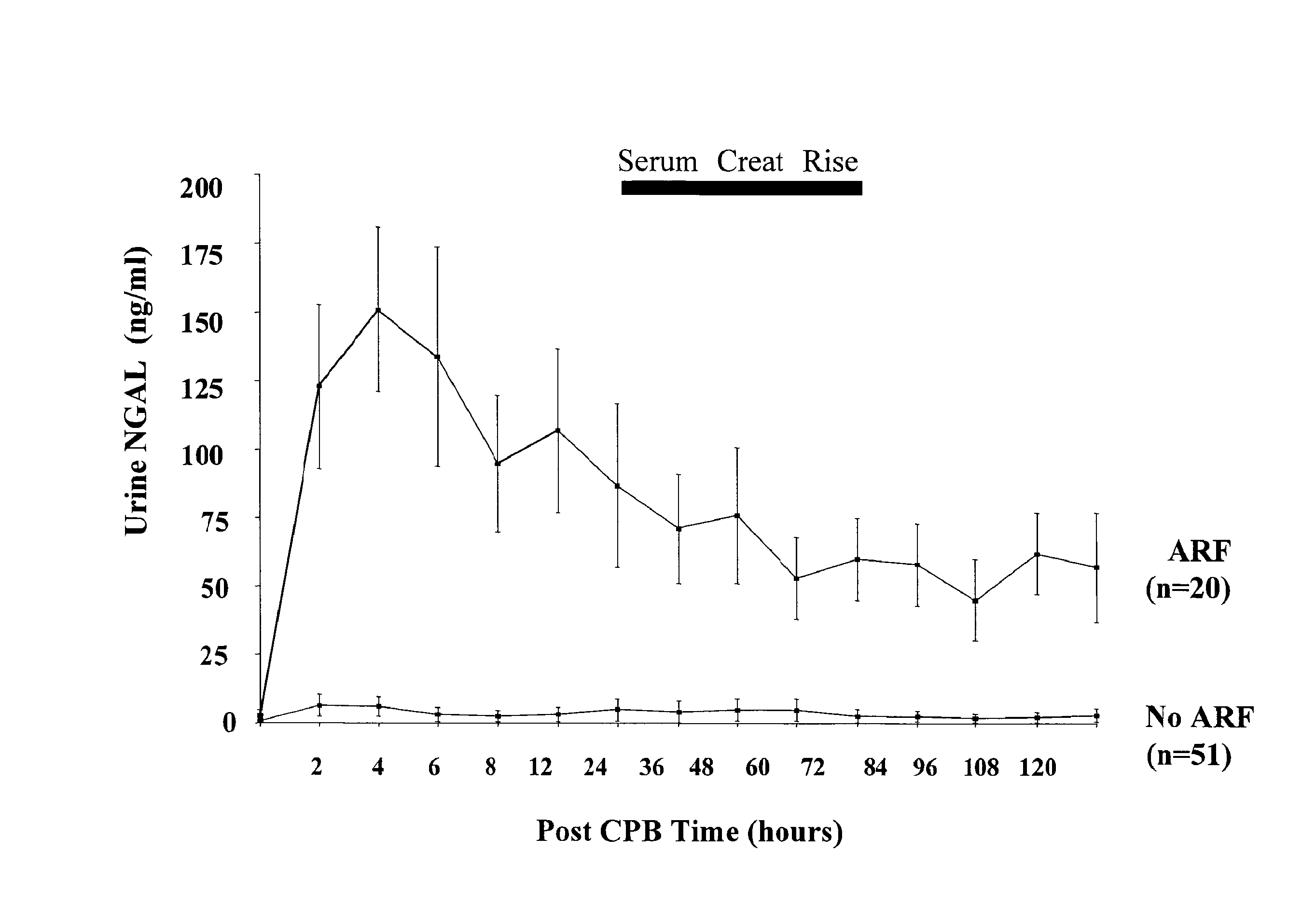
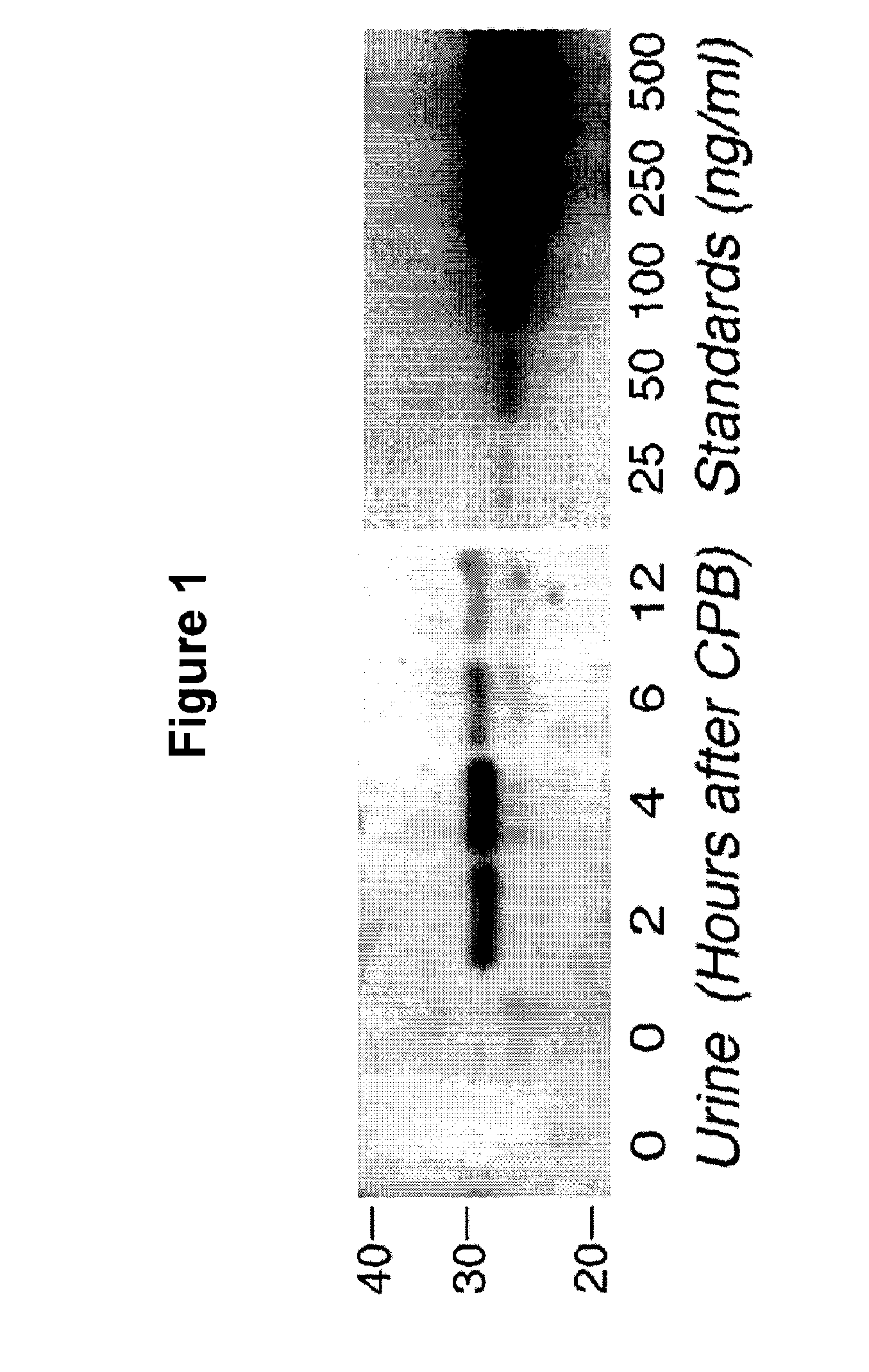
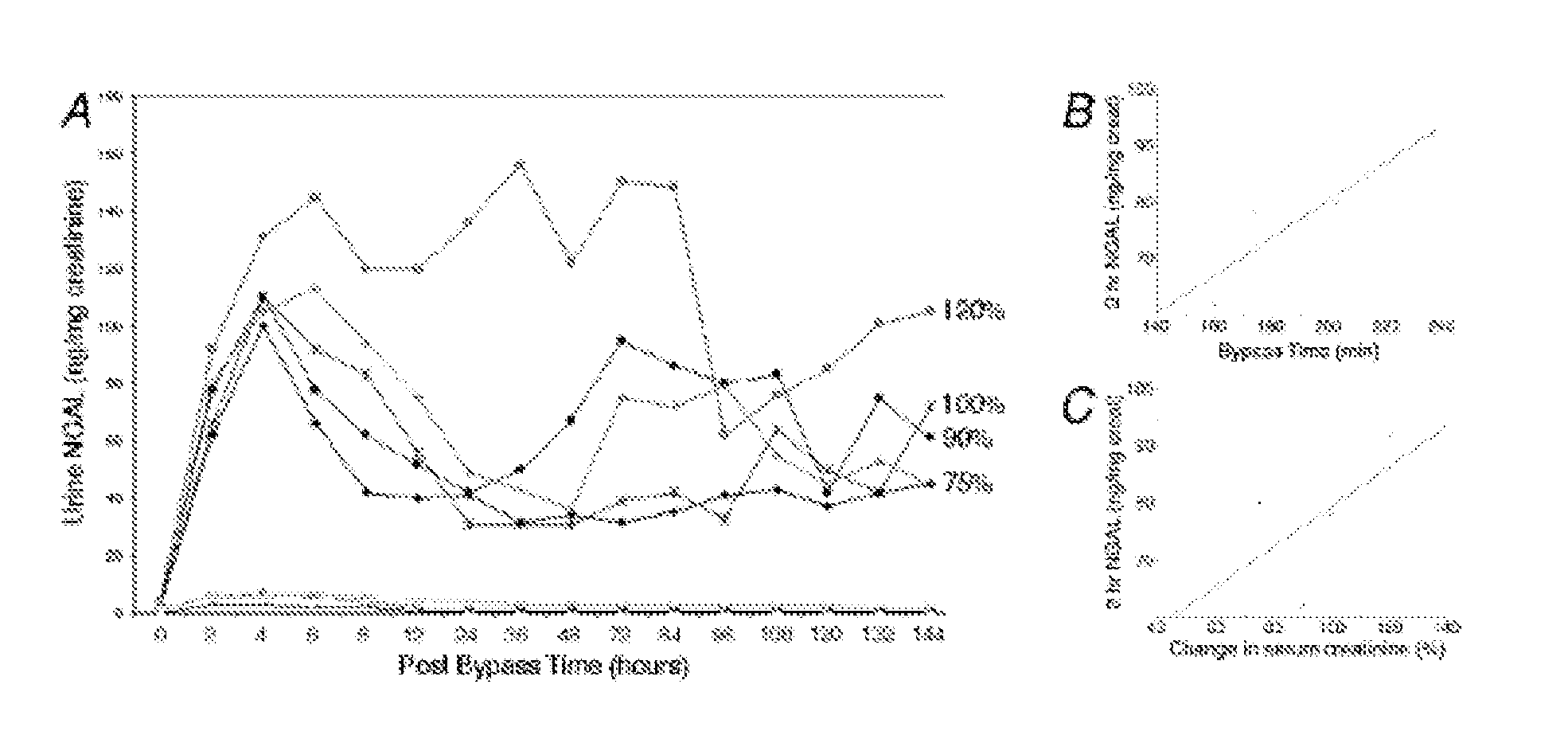
Method for the early detection of renal injury
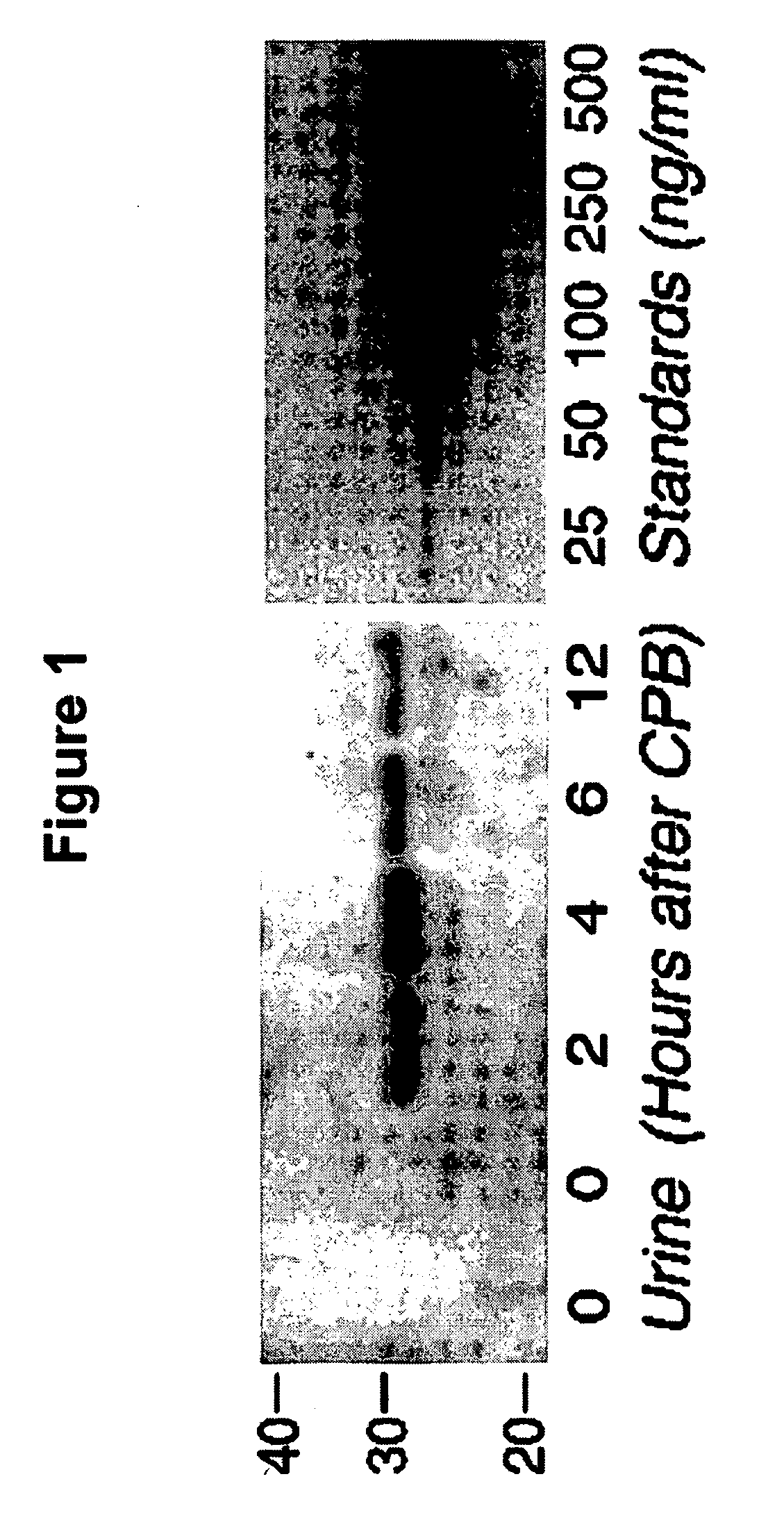
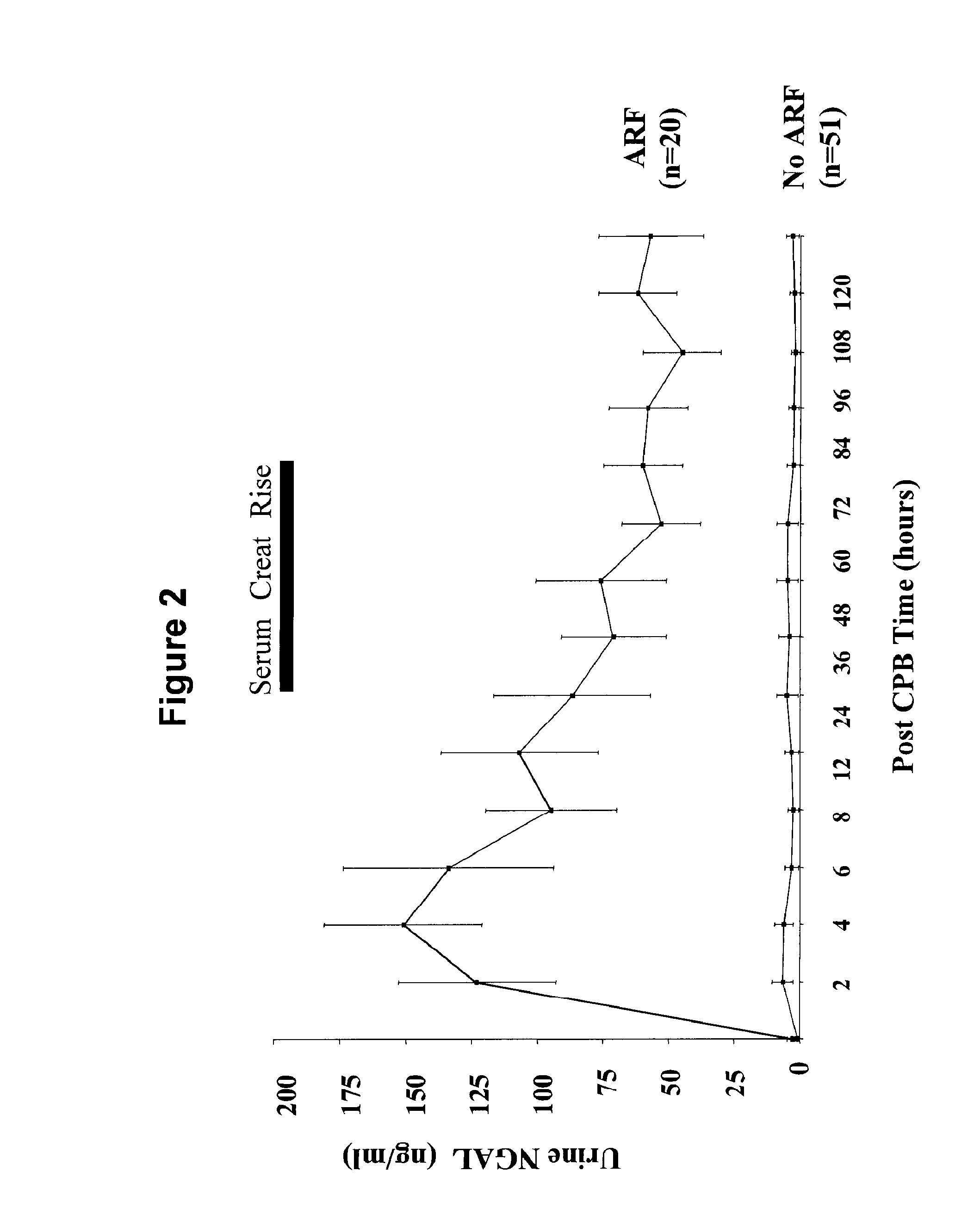
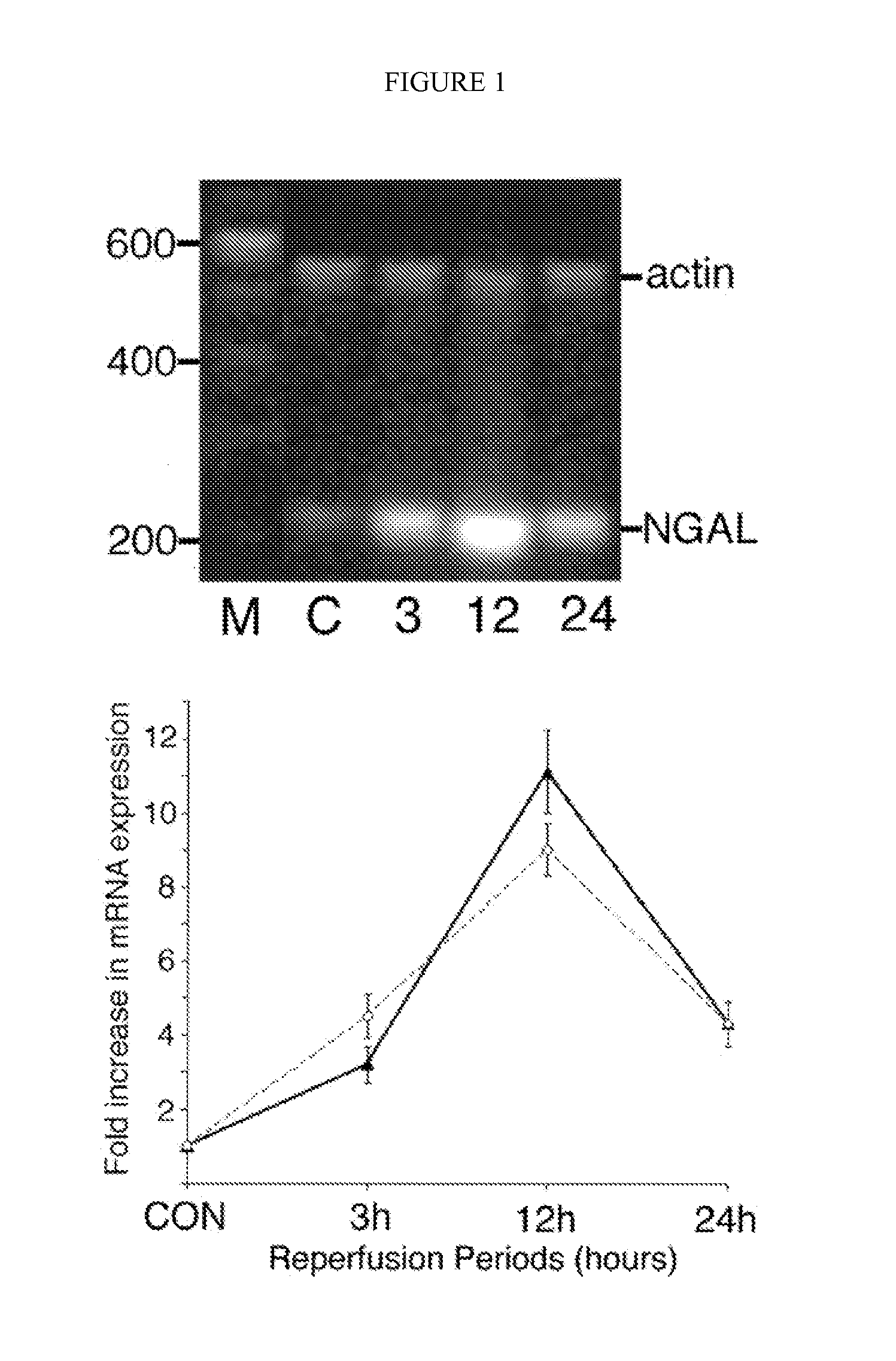
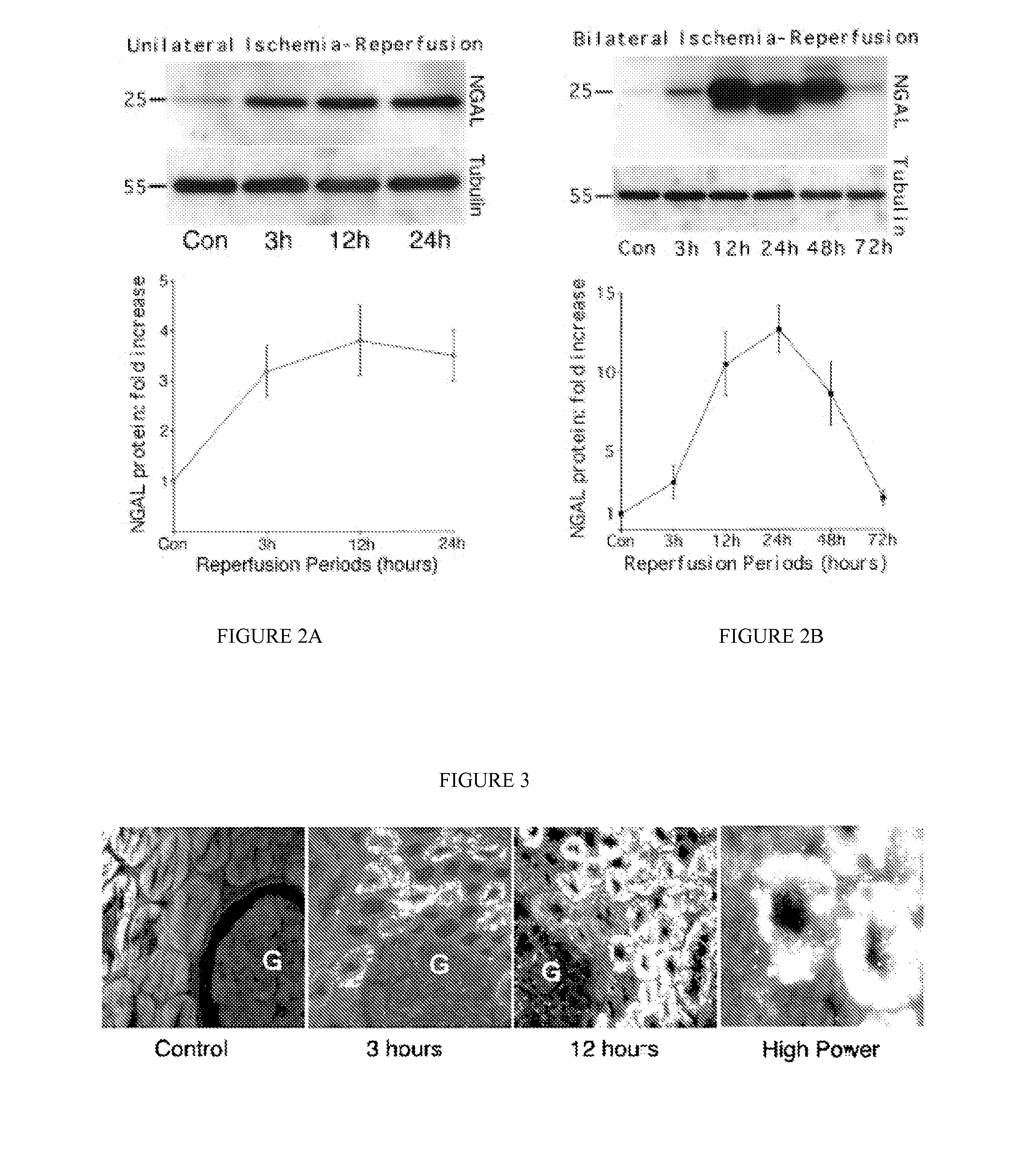
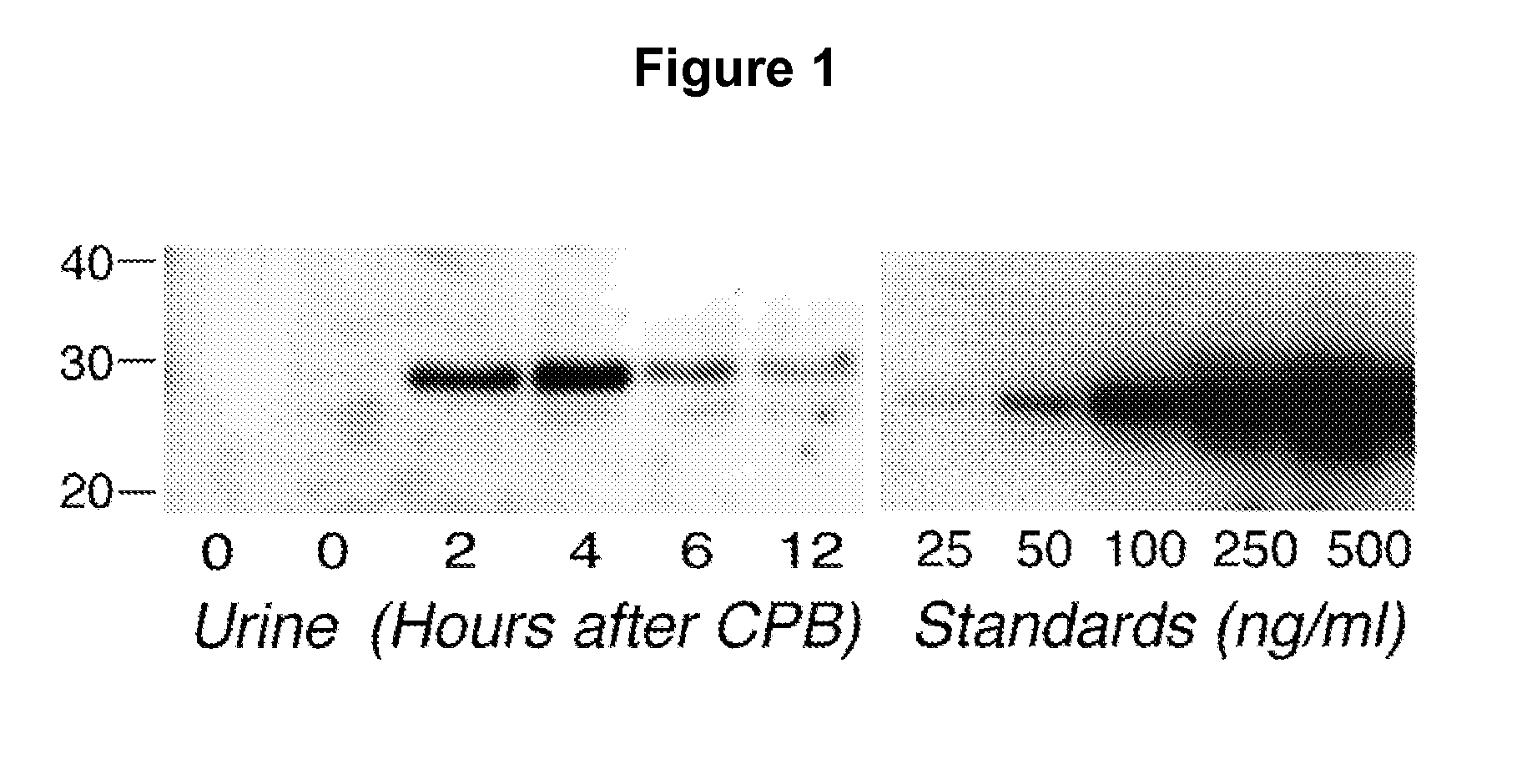
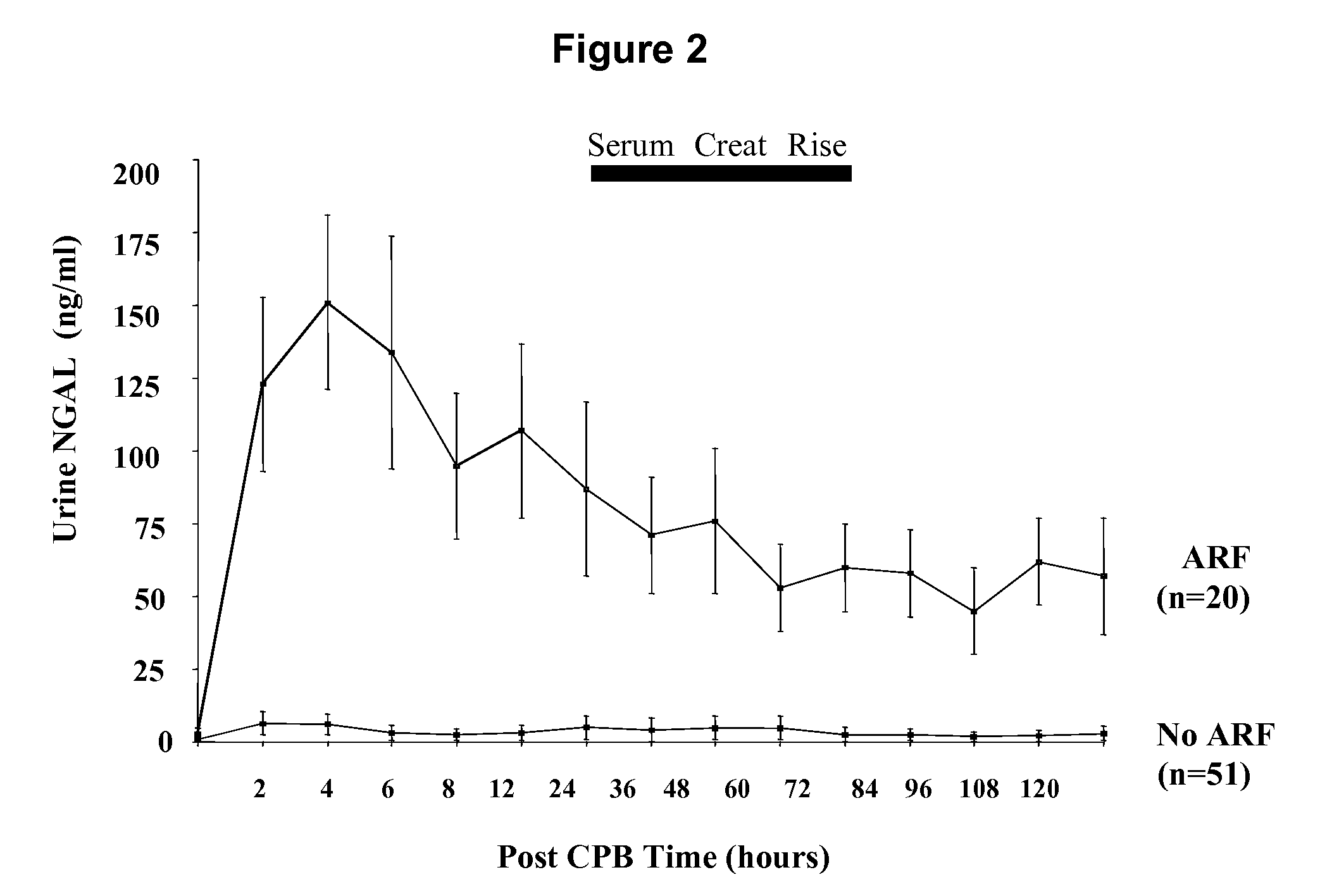
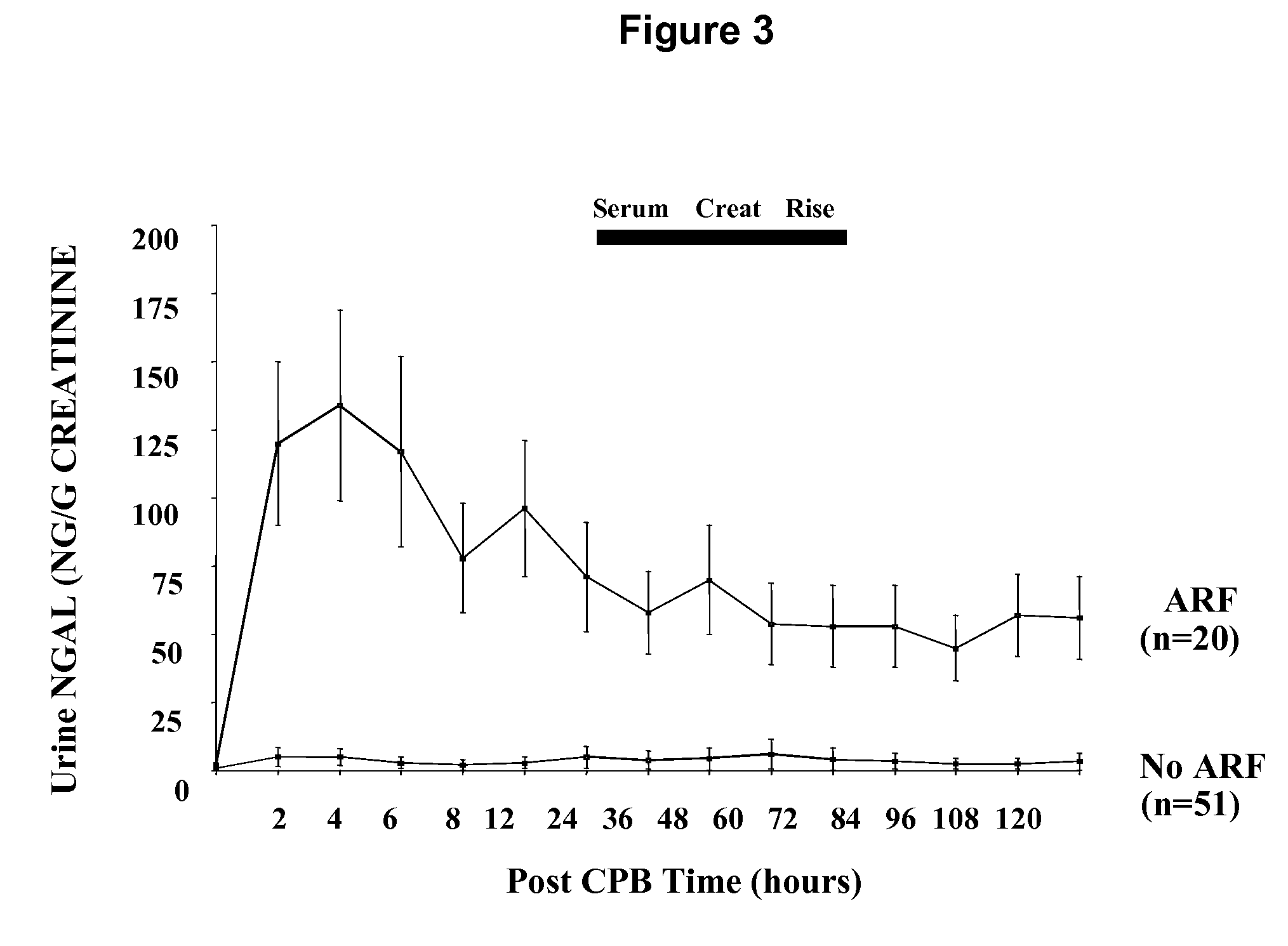
A method and kit for detecting the immediate or early onset of renal disease and injury, including renal tubular cell injury, utilizing NGAL as an immediate or early on-set biomarker in a sample of blood serum. NGAL is a small secreted polypeptide that is protease resistant and consequently readily detected in the blood serum following renal tubule cell injury. NGAL protein expression is detected predominantly in proximal tubule cells, in a punctuate cytoplasmic distribution reminiscent of a secreted protein. The appearance NGAL in the serum is related to the dose and duration of renal ischemia and nephrotoxemia, and is diagnostic of renal tubule cell injury and renal failure. NGAL detection is also a useful marker for monitoring the nephrotoxic side effects of drugs or other therapeutic agents.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI +1
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
This invention relates to methods of reducing the damaging effect of an injury to mammalian cells by treatment with compounds which reduce cell death or dysfunction, including cellular damage following episodes of tissue ischemia, trauma, epilepsy, and acute or chronic degeneration. The invention discloses methods of treating these disorders by administering inhibitors that disrupt protein-protein interactions involved in these disorders, screening methods to identify such inhibitors and specific compositions useful for treating these disorders.
Owner:NONO INC
Method for the early detection of renal injury
A method and kit for detecting the immediate or early onset of renal disease and injury, including renal tubular cell injury, utilizing NGAL as an immediate or early on-set biomarker in a sample of blood serum. NGAL is a small secreted polypeptide that is protease resistant and consequently readily detected in the blood serum following renal tubule cell injury. NGAL protein expression is detected predominantly in proximal tubule cells, in a punctuate cytoplasmic distribution reminiscent of a secreted protein. The appearance NGAL in the serum is related to the dose and duration of renal ischemia and nephrotoxemia, and is diagnostic of renal tubule cell injury and renal failure. NGAL detection is also a useful marker for monitoring the nephrotoxic side effects of drugs or other therapeutic agents.
Owner:DEVARAJAN PRASAD +1
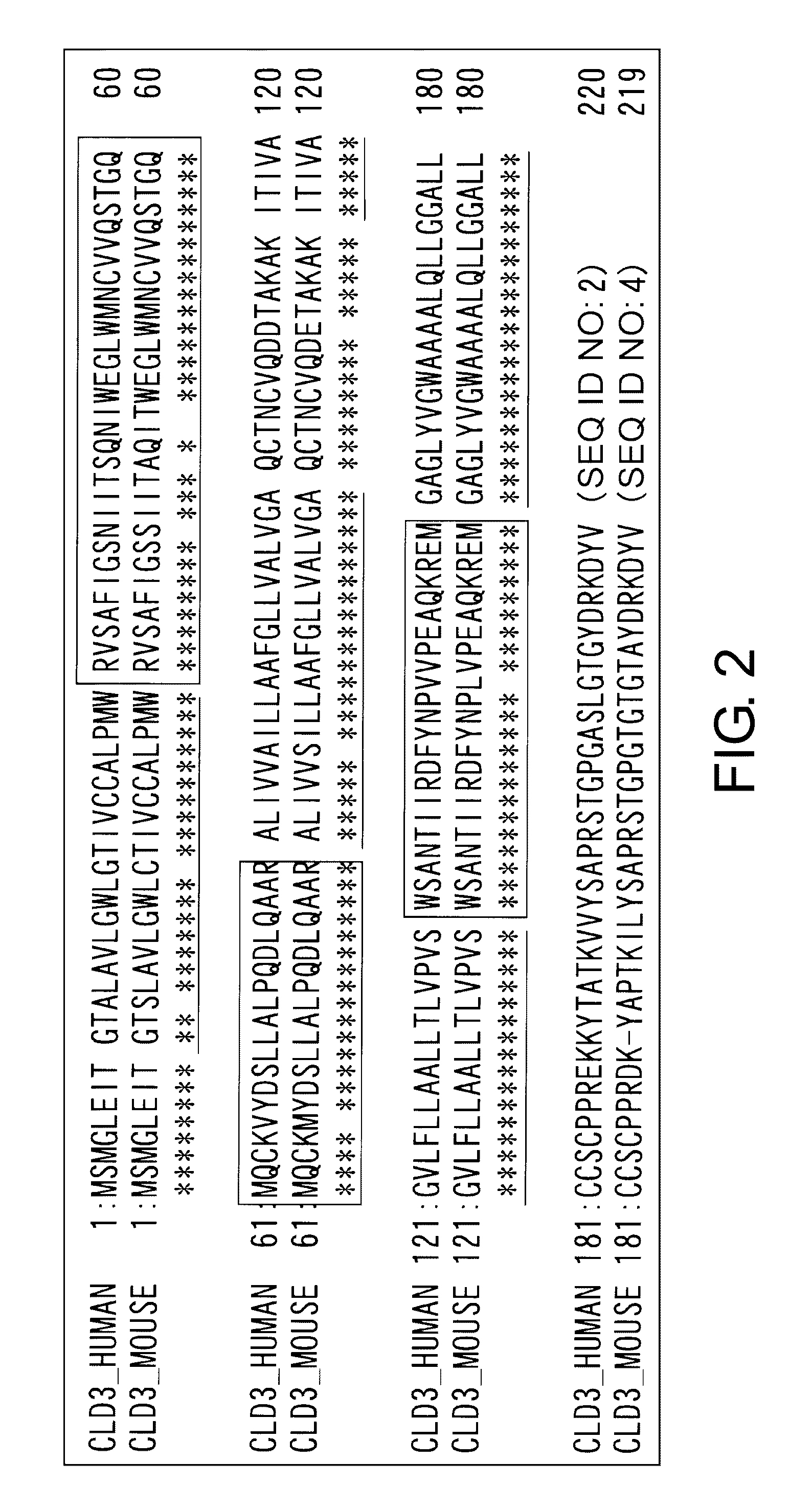
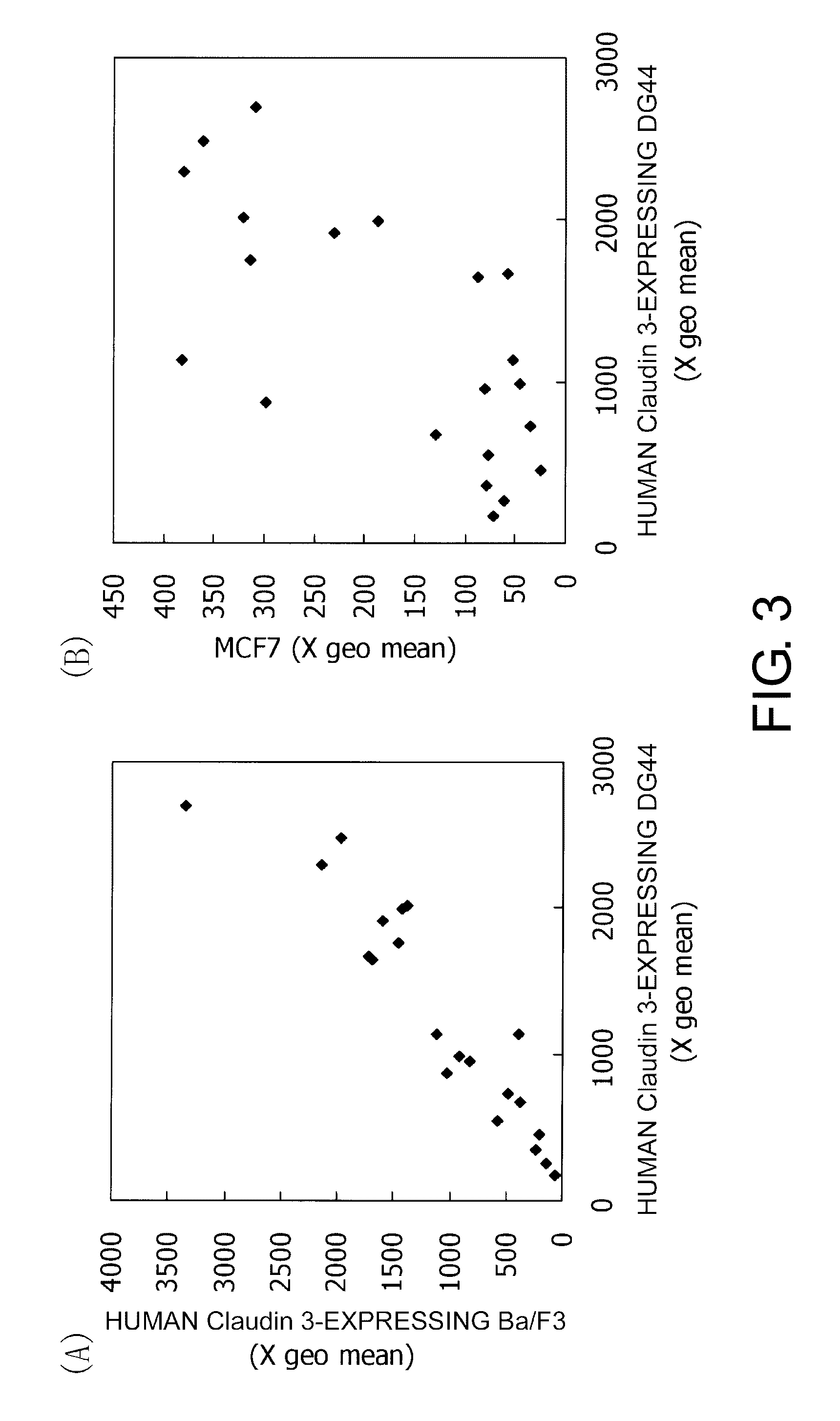
Anti-Claudin 3 Monoclonal Antibody and Treatment and Diagnosis of Cancer Using the Same
InactiveUS20100111852A1Inhibit cell proliferationIn-vivo radioactive preparationsBiological material analysisProstate cancerCytotoxicity
Monoclonal antibodies that bind specifically to Claudin 3 expressed on cell surface are provided. The antibodies of the present invention are useful for diagnosis of cancers that have enhanced expression of Claudin 3, such as ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, breast cancer, uterine cancer, liver cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, stomach cancer, bladder cancer, and colon cancer. The present invention provides monoclonal antibodies showing cytotoxic effects against cells of these cancers. Methods for inducing cell injury in Claudin 3-expressing cells and methods for suppressing proliferation of Claudin 3-expressing cells by contacting Claudin 3-expressing cells with a Claudin 3-binding antibody are disclosed. The present application also discloses methods for diagnosis or treatment of cancers.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
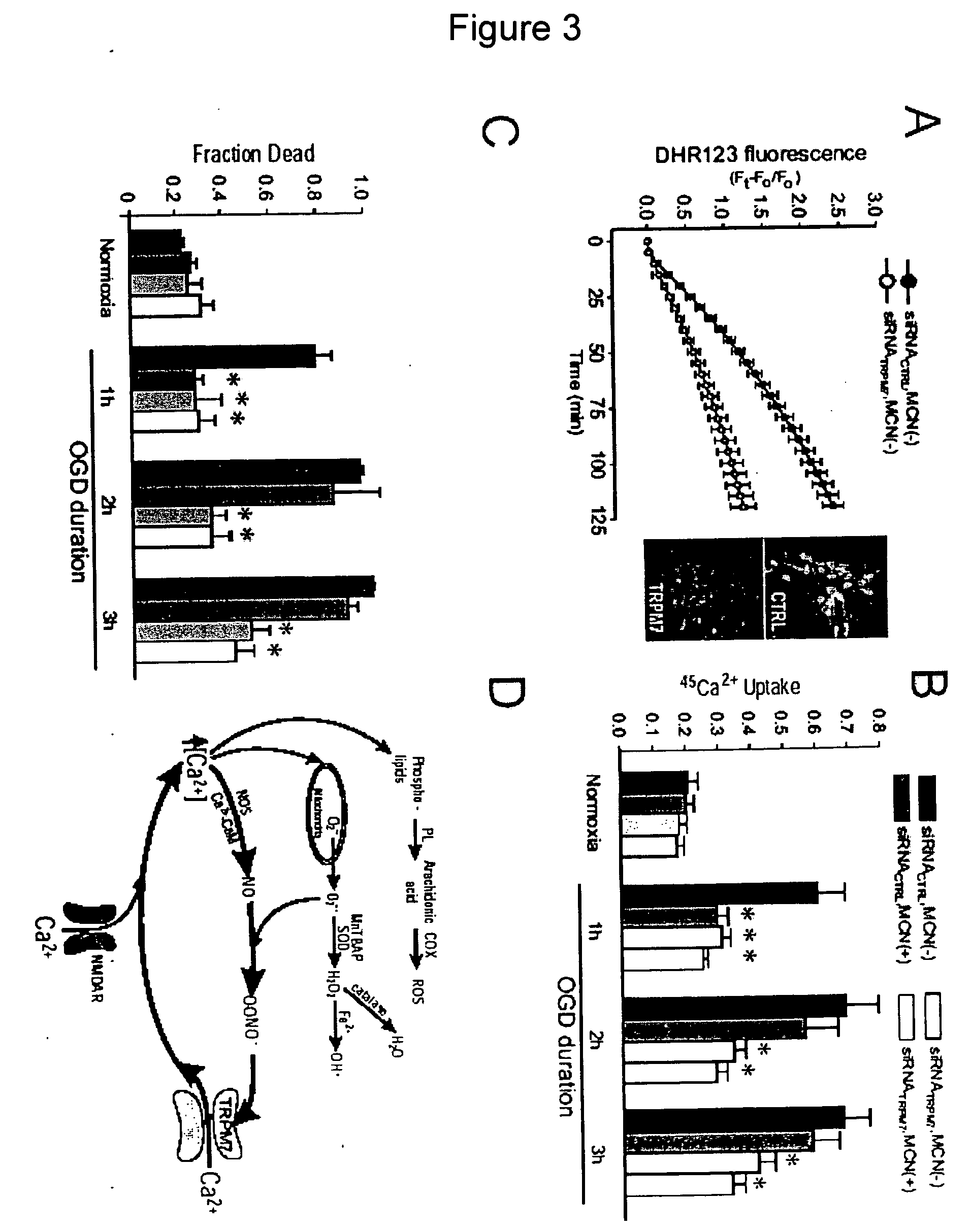
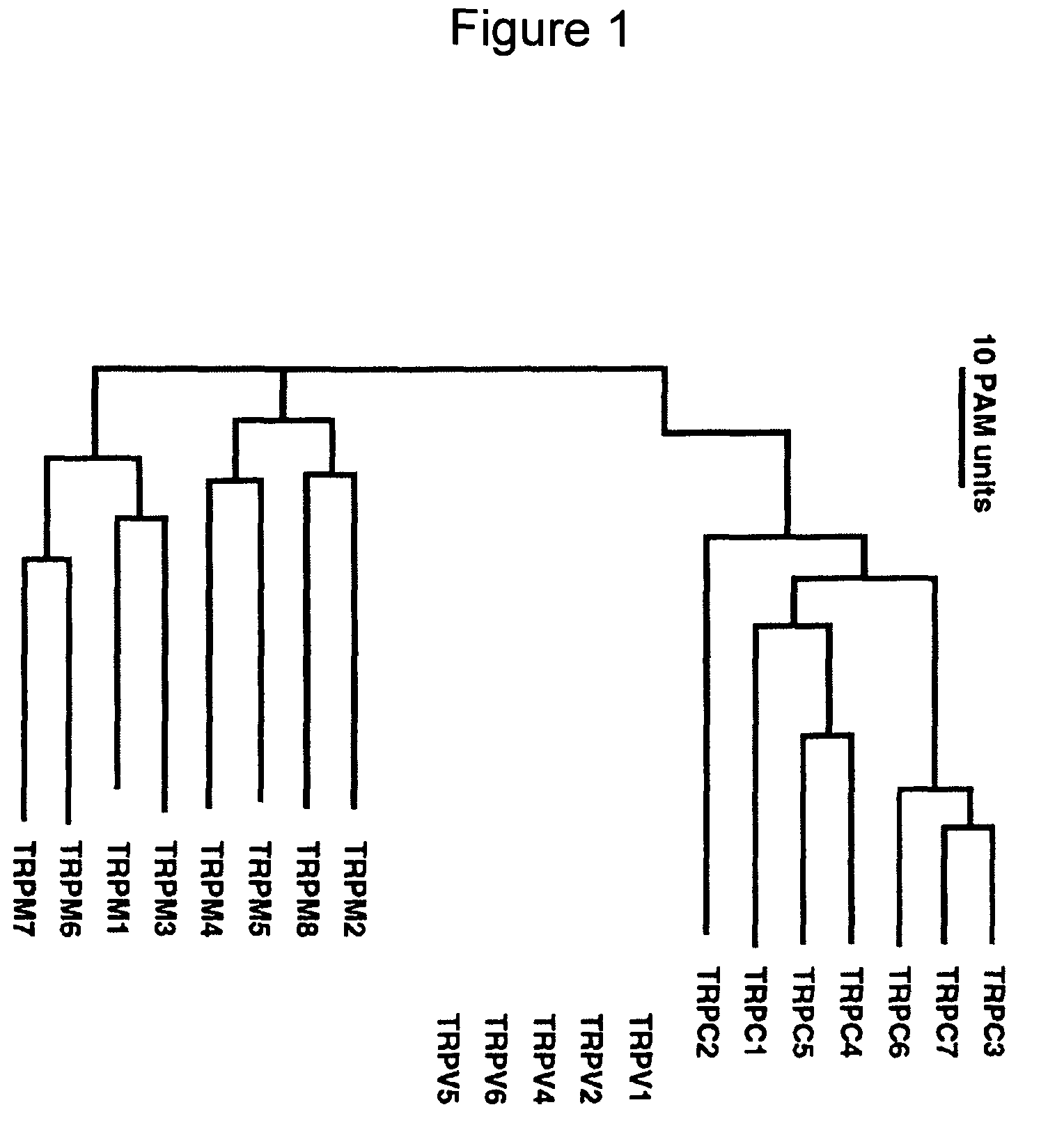
Method of determining inhibition of binding to TRPM7 protein
This invention relates to methods of reducing the damaging effect of an injury to mammalian cells by treatment with compounds which reduce cell death or dysfunction, including cellular damage following episodes of tissue ischemia, trauma, epilepsy, and acute or chronic degeneration. The invention discloses methods of treating these disorders by administering inhibitors that disrupt protein-protein interactions involved in these disorders, screening methods to identify such inhibitors and specific compositions useful for treating these disorders.
Owner:NONO INC
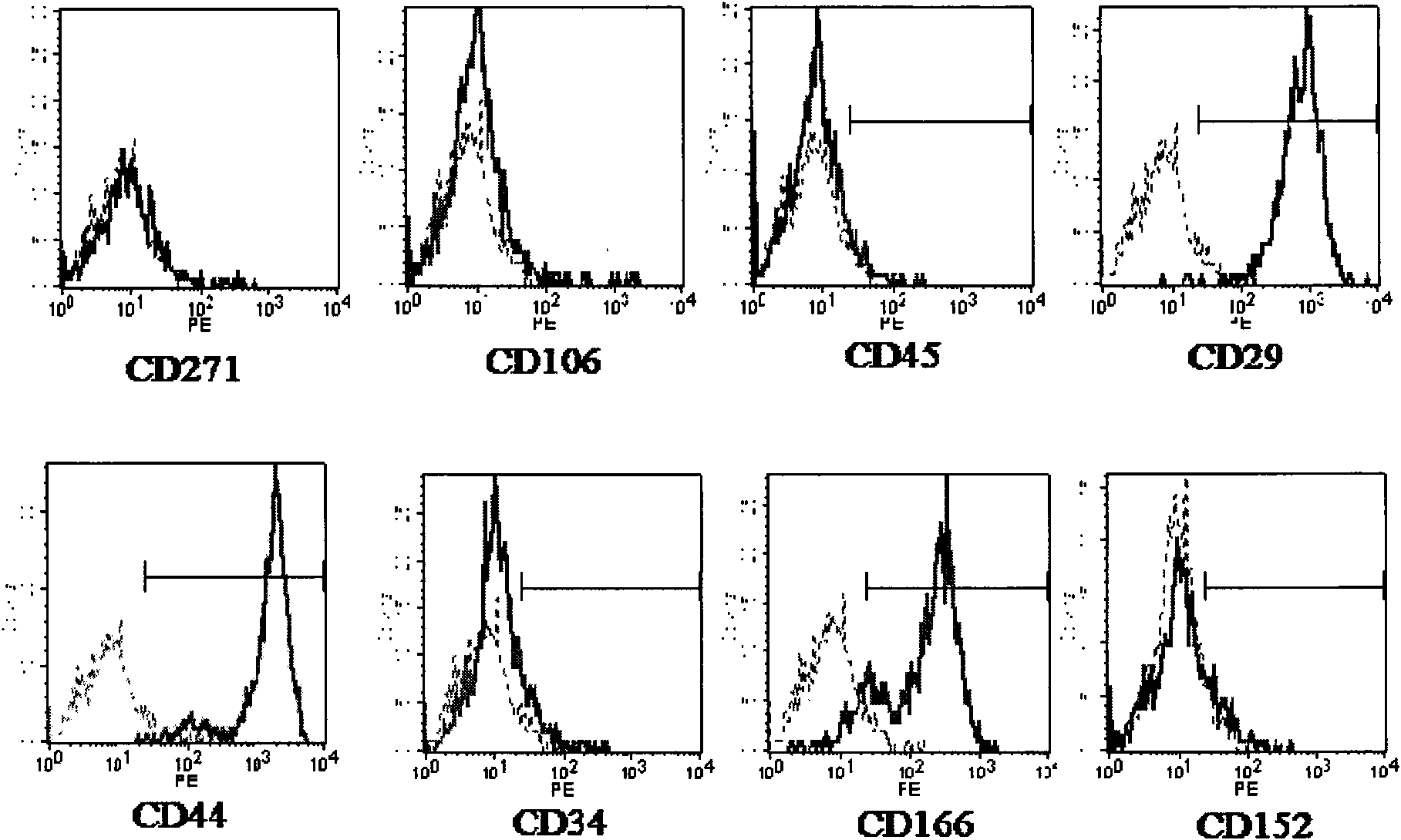
Method for preparing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
The invention relates to a method for preparing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, which comprises the steps of collection, transportation, handover, separation, freezing, recovering, primary culture and subculture of umbilical cords. The method has simple process, ensures low production cost, good freezing effect, little cell damage, low toxic side effect and no harm to human body and reduces the residual of the freezing protection liquid in the recovered cells of tissue blocks; and the prepared mesenchymal stem cells can be applied to the clinical treatment of various diseases.
Owner:江苏省北科生物科技有限公司 +1
Detection of NGAL in chronic renal disease
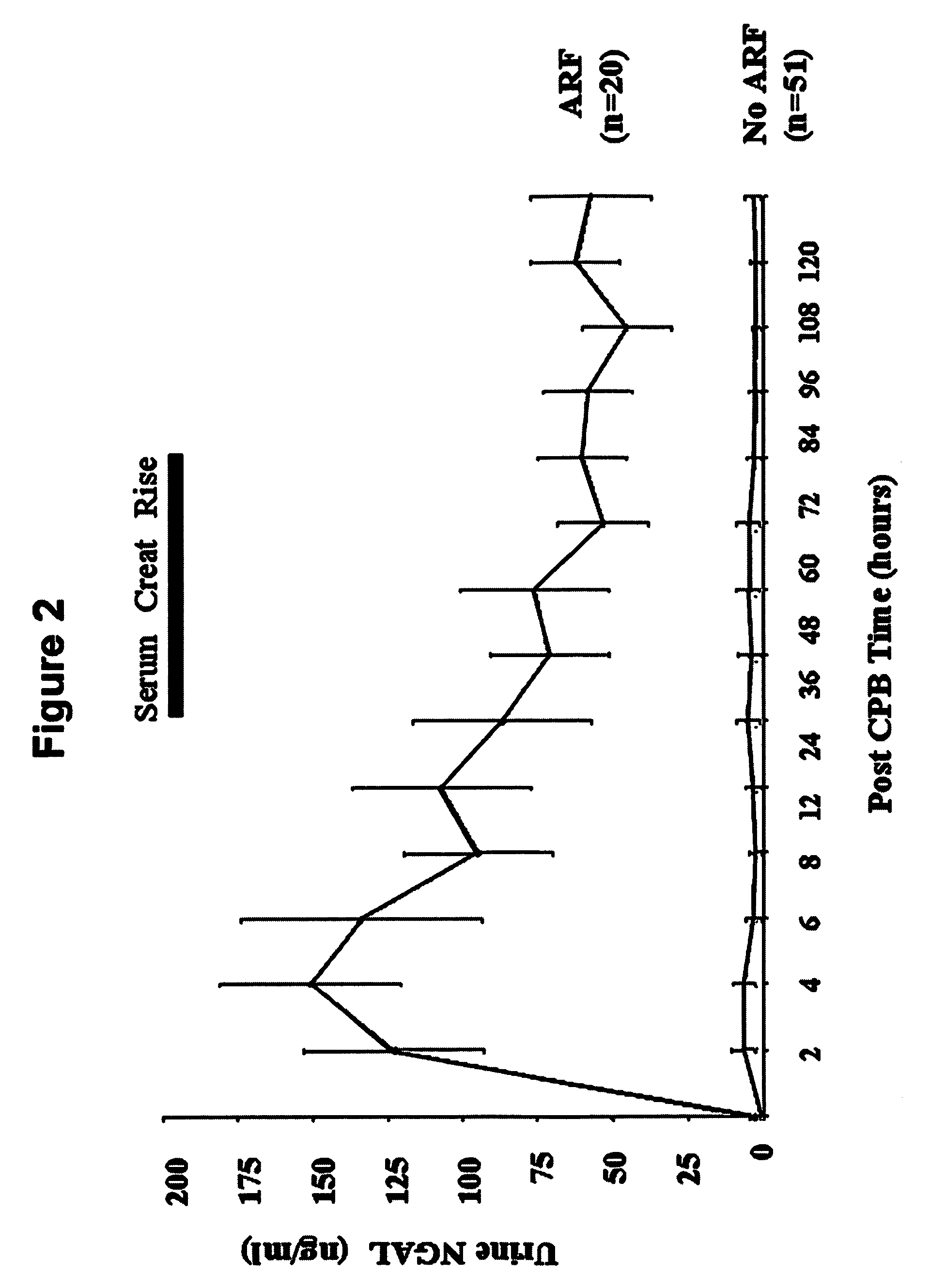
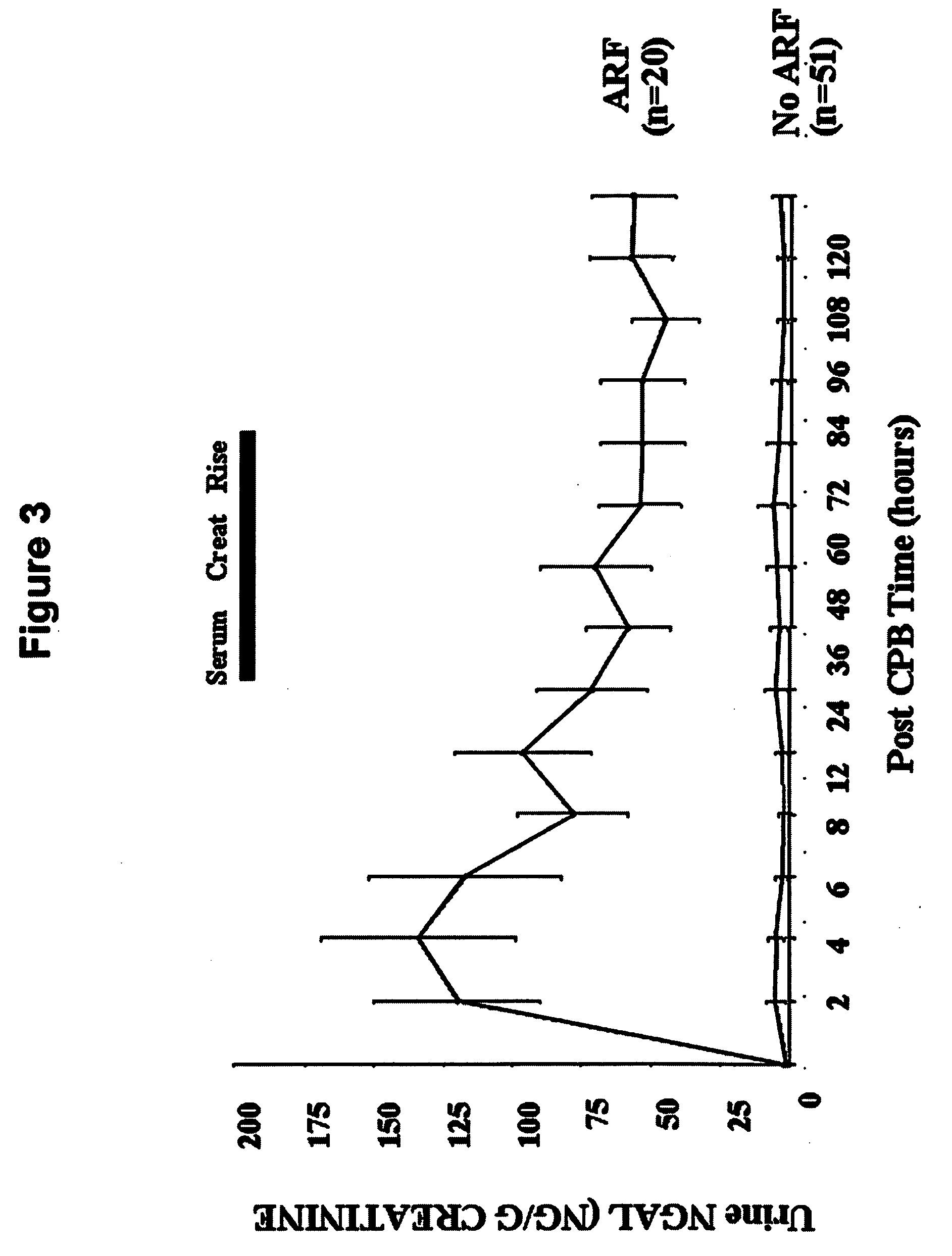
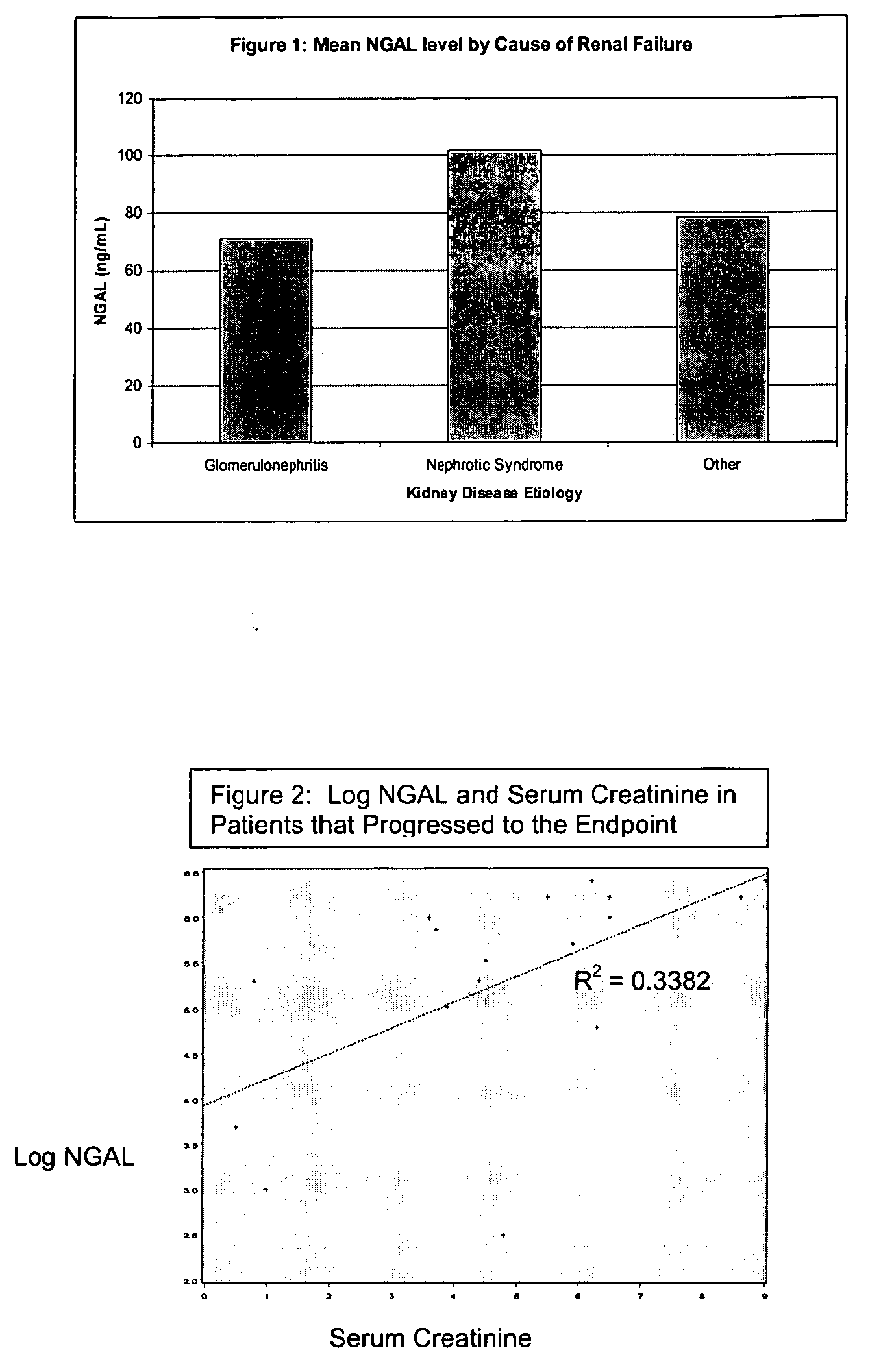
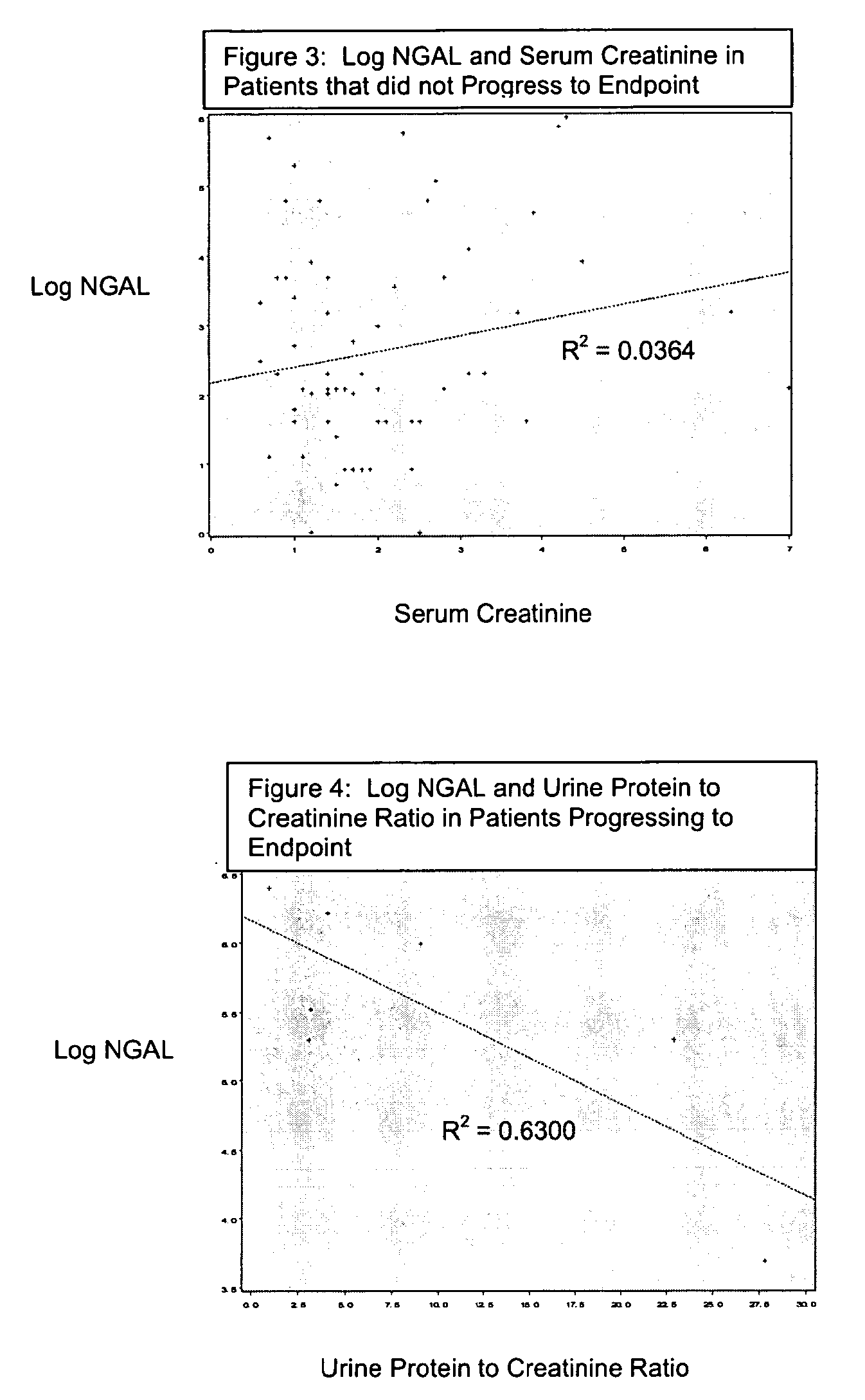
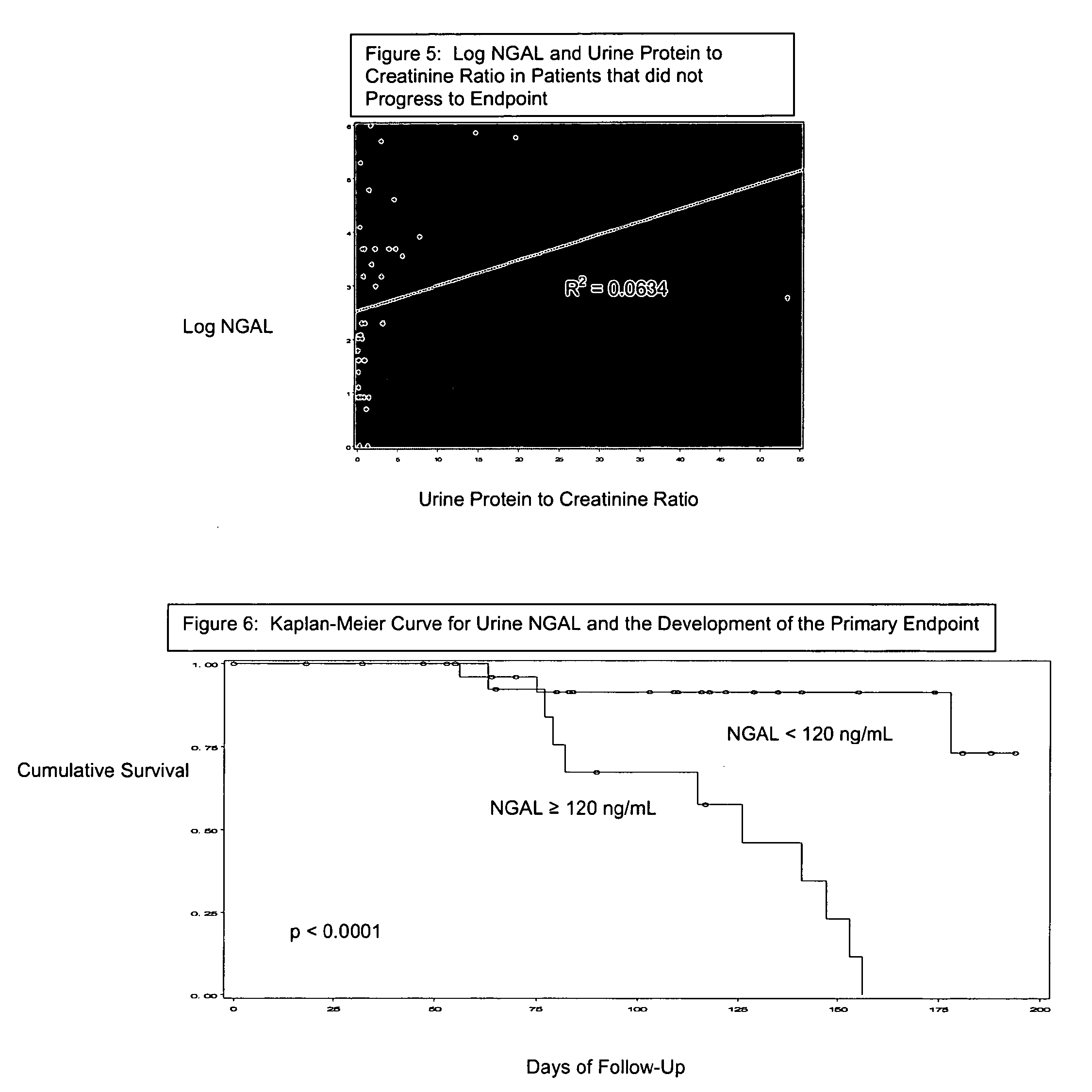
Methods of assessing the ongoing kidney status in a subject afflicted with chronic renal failure (CRF) by detecting the quantity of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) in fluid samples over time is disclosed. NGAL is a small secreted polypeptide that is protease resistant and consequently readily detected in the urine and serum as a result of chronic renal tubule cell injury. Incremental increases in NGAL levels in CRF patients over a prolonged period of time are diagnostic of worsening kidney disease. This increase in NGAL precedes and correlates with other indicators of worsening CRF, such as increased serum creatinine, increased urine protein secretion, and lower glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Proper detection of worsening (or improving, if treatment has been instituted) renal status over time, confirmed by pre- and post-treatment NGAL levels in the patient, can aid the clinical practitioner in designing and / or maintaining a proper treatment regimen to slow or stop the progression of CRF.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
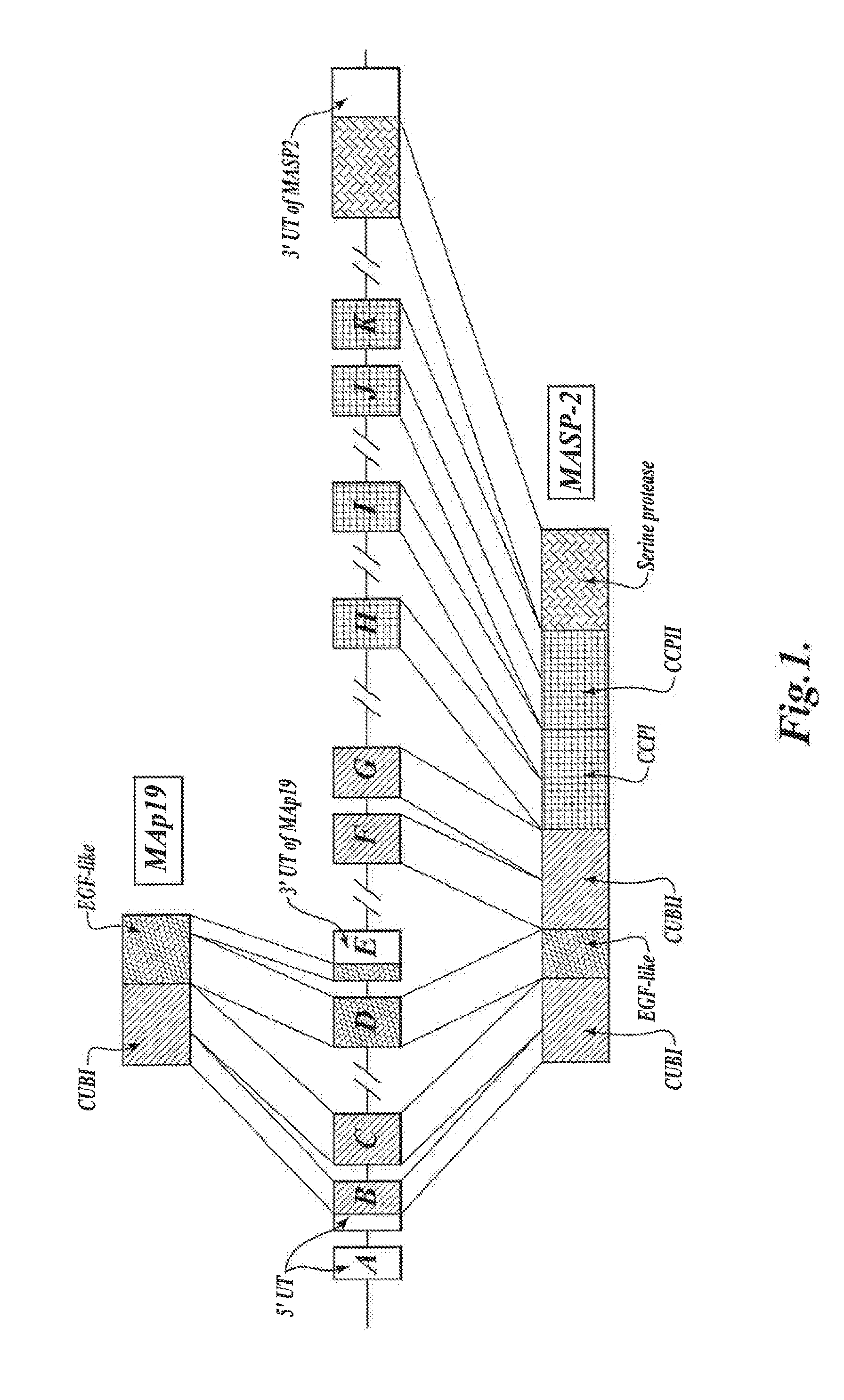
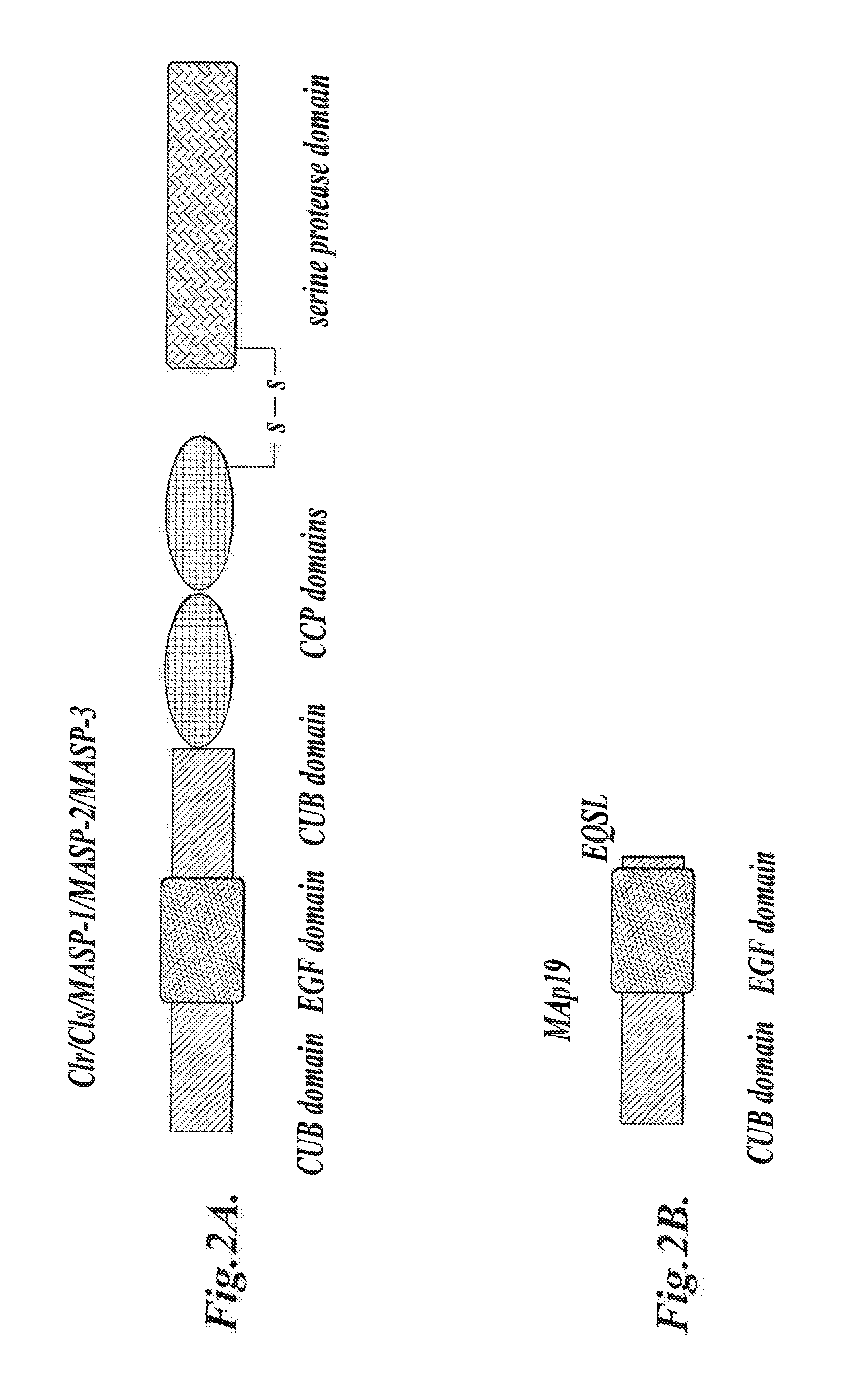
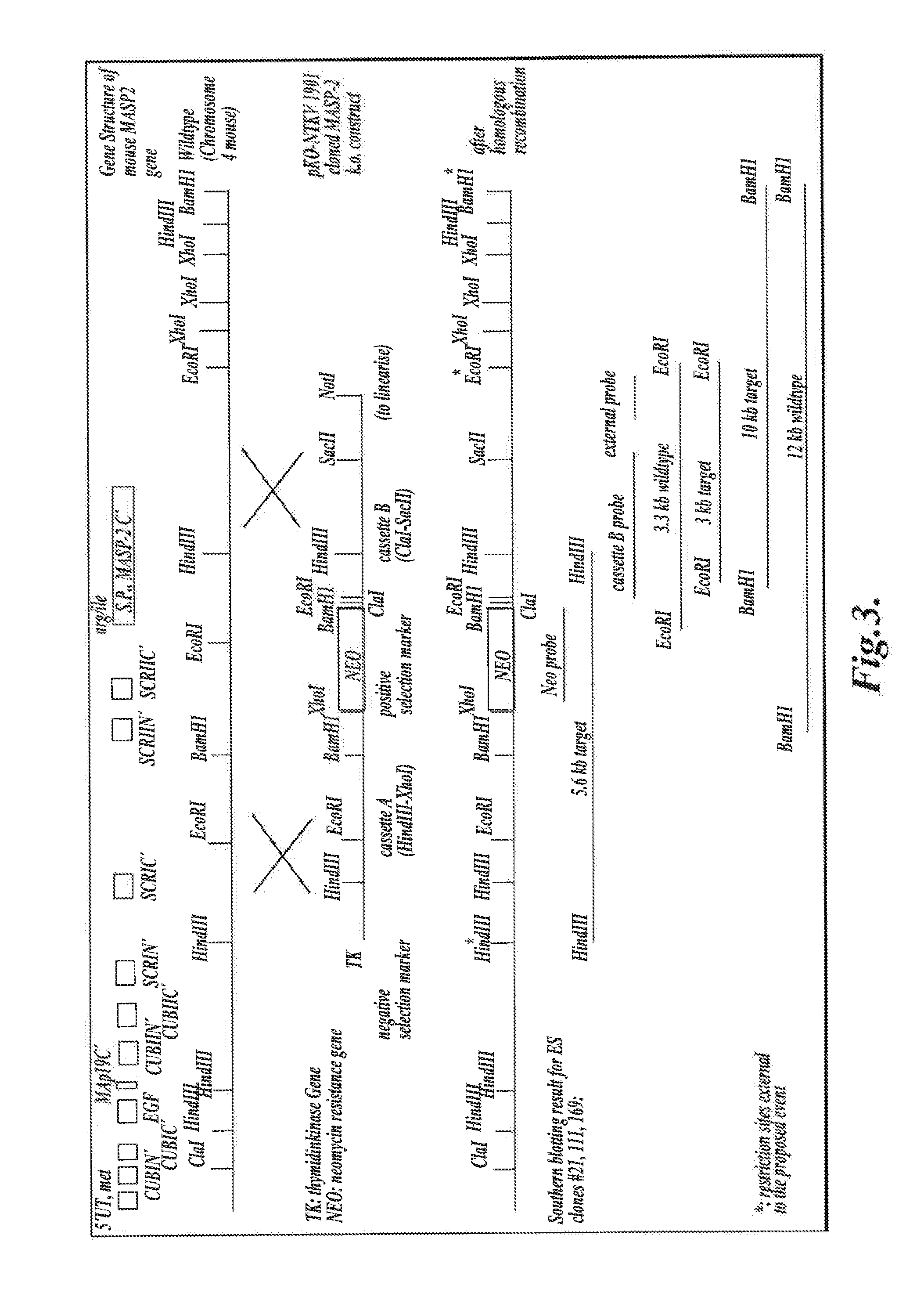
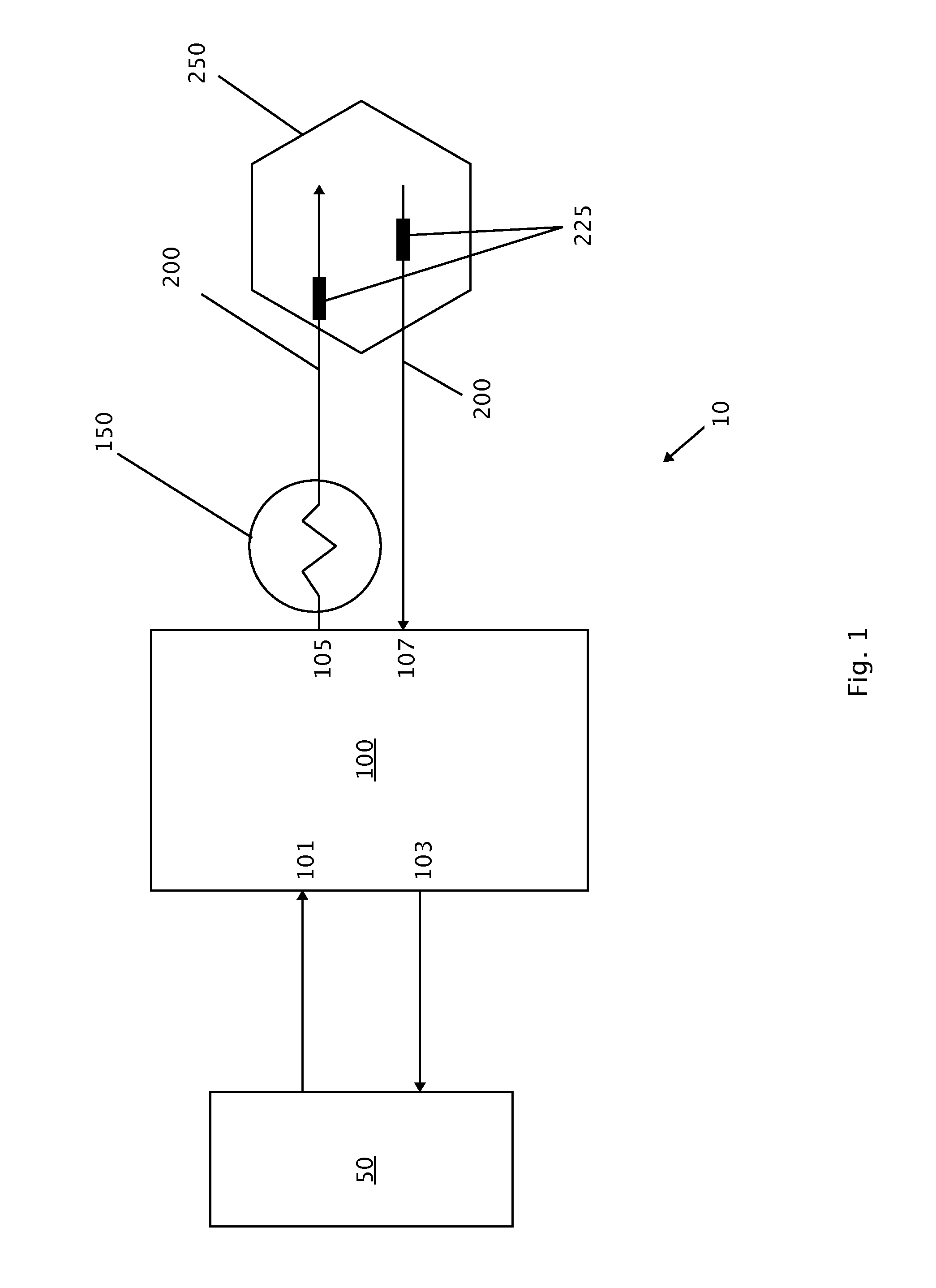
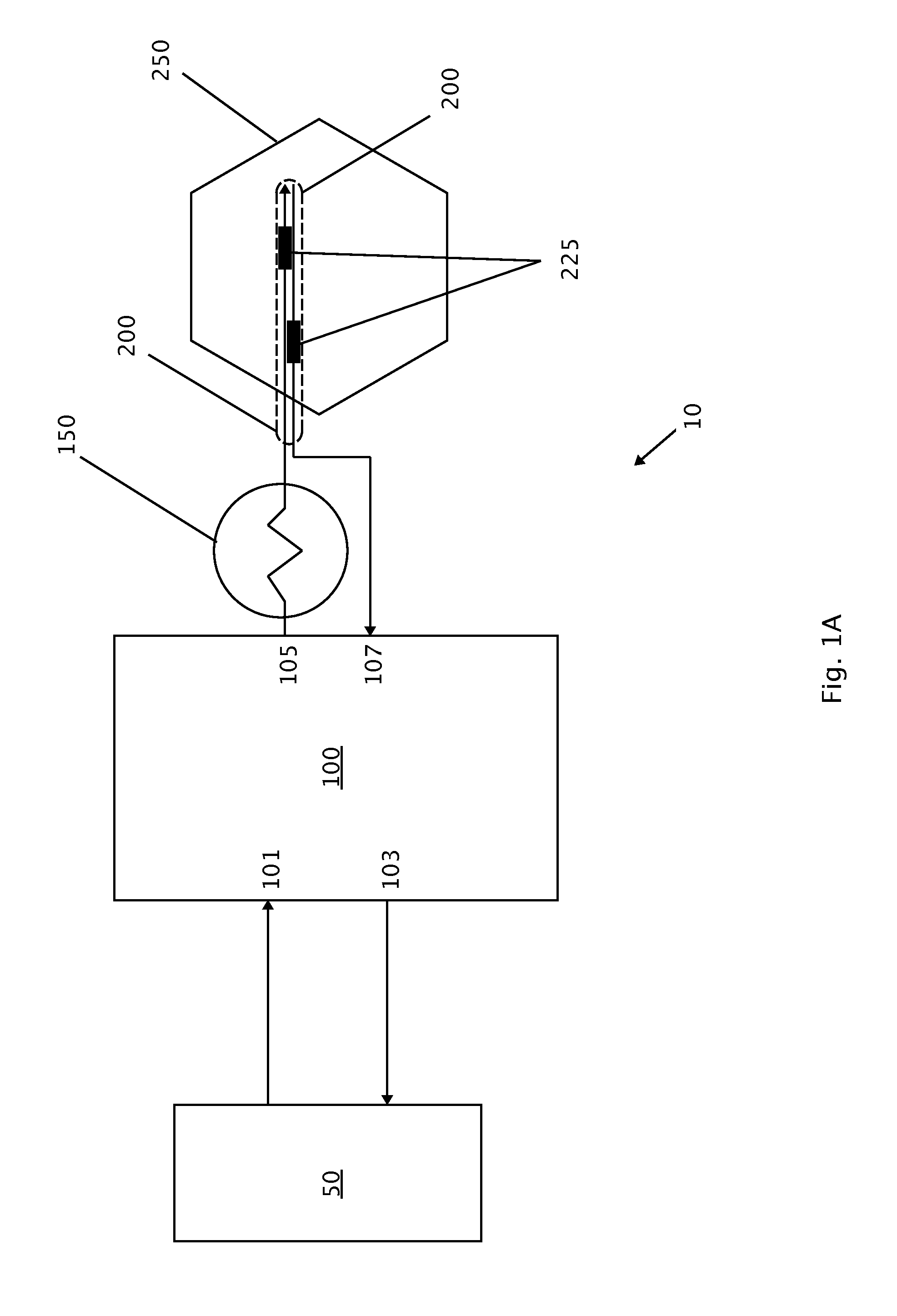
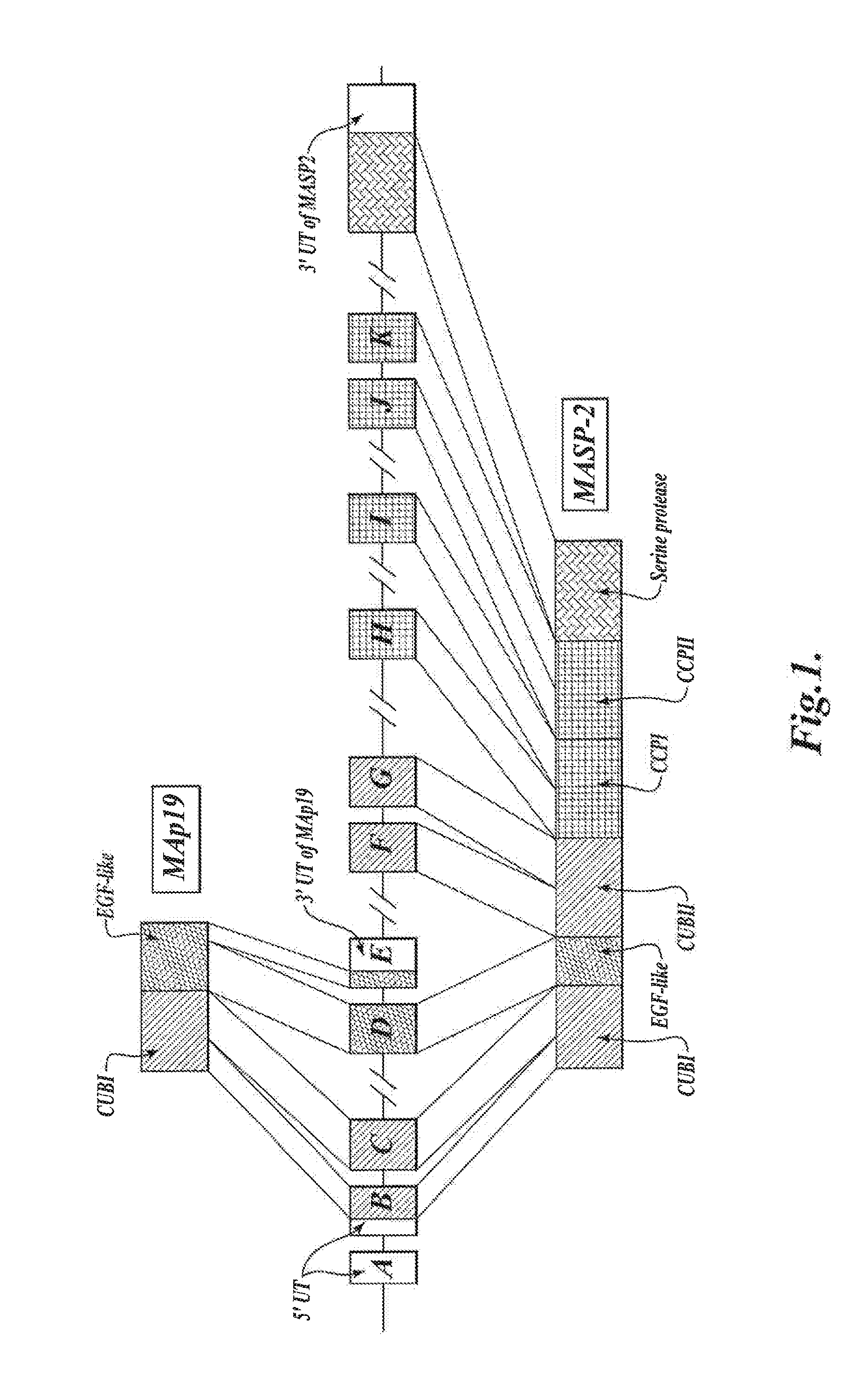
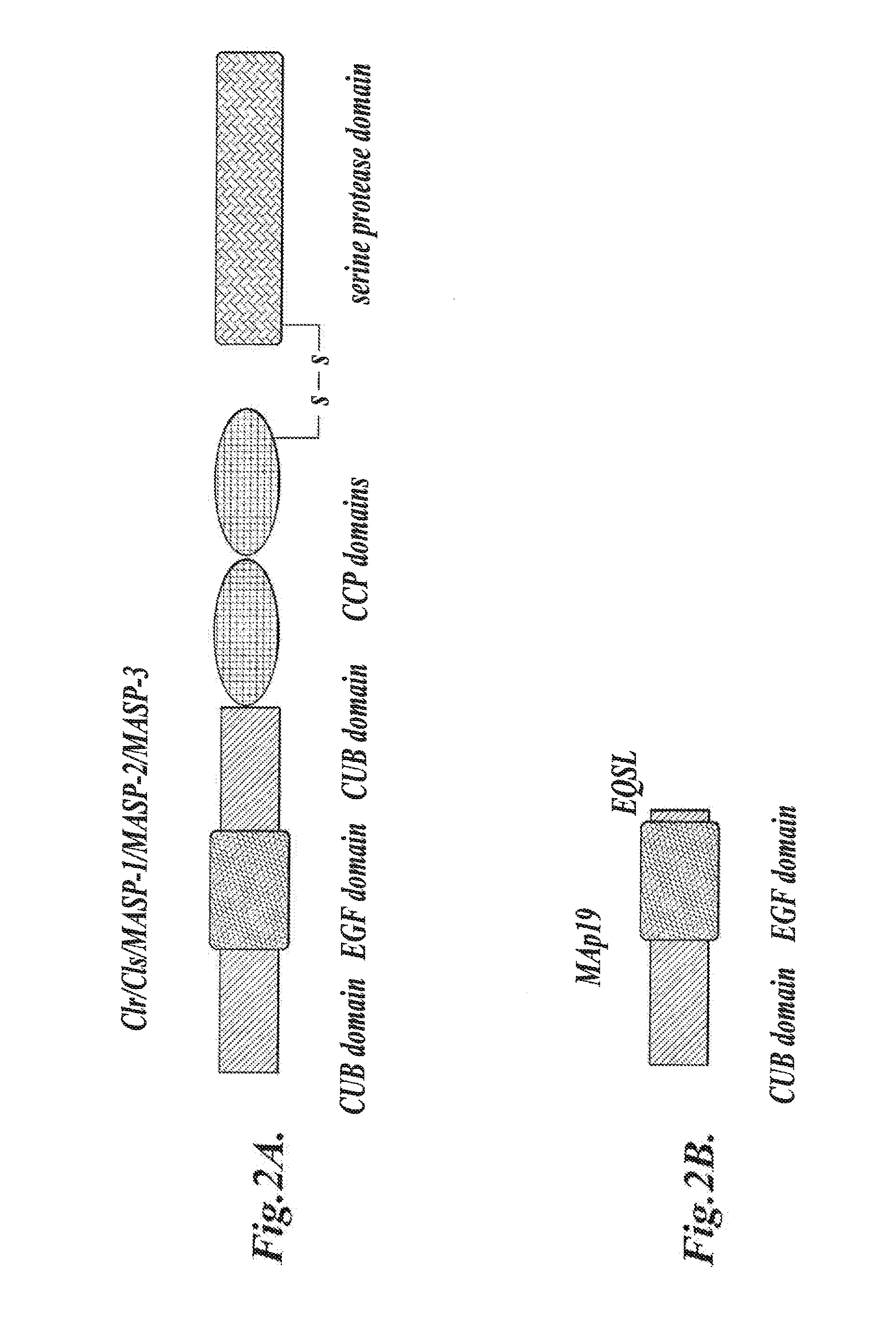
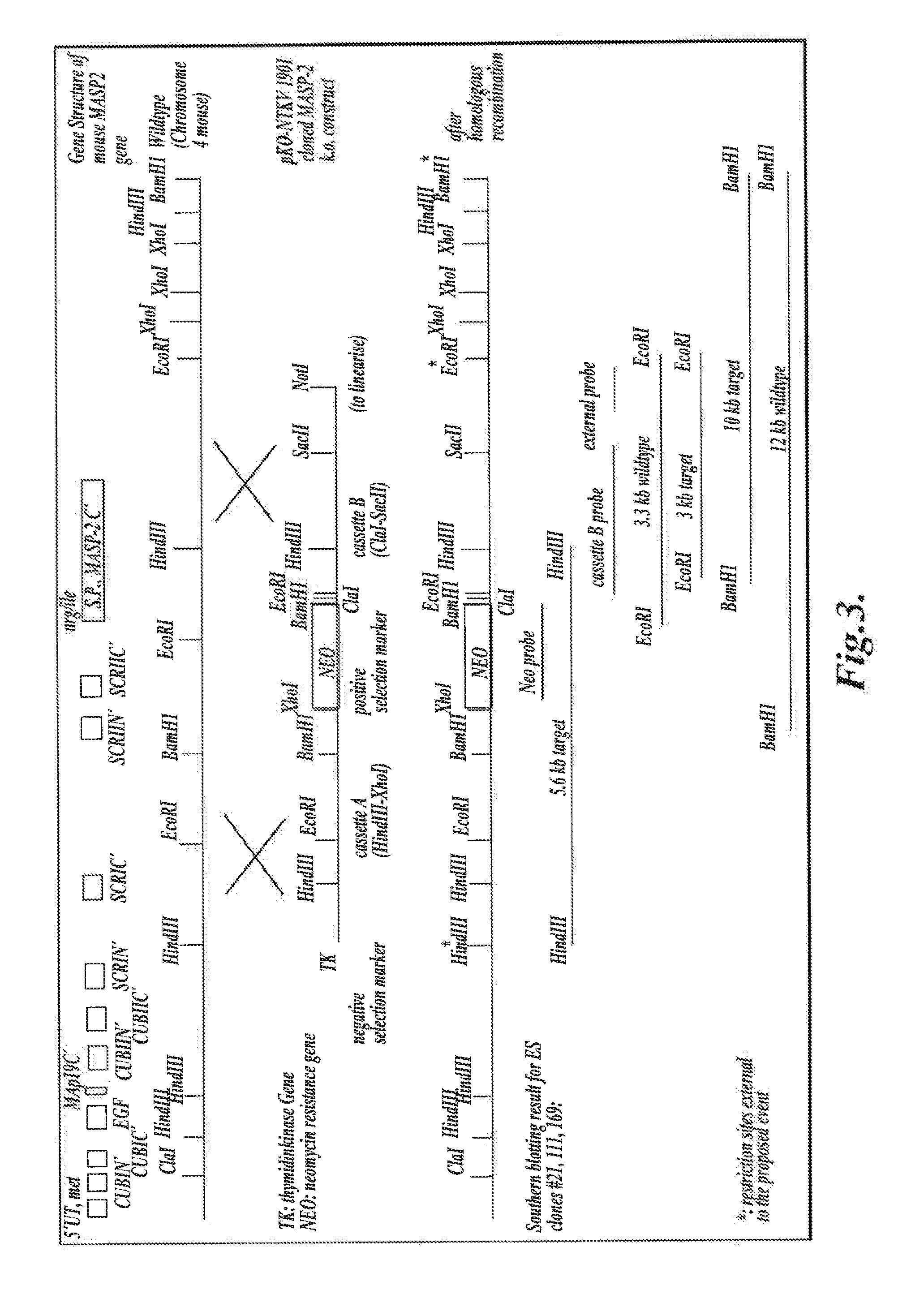
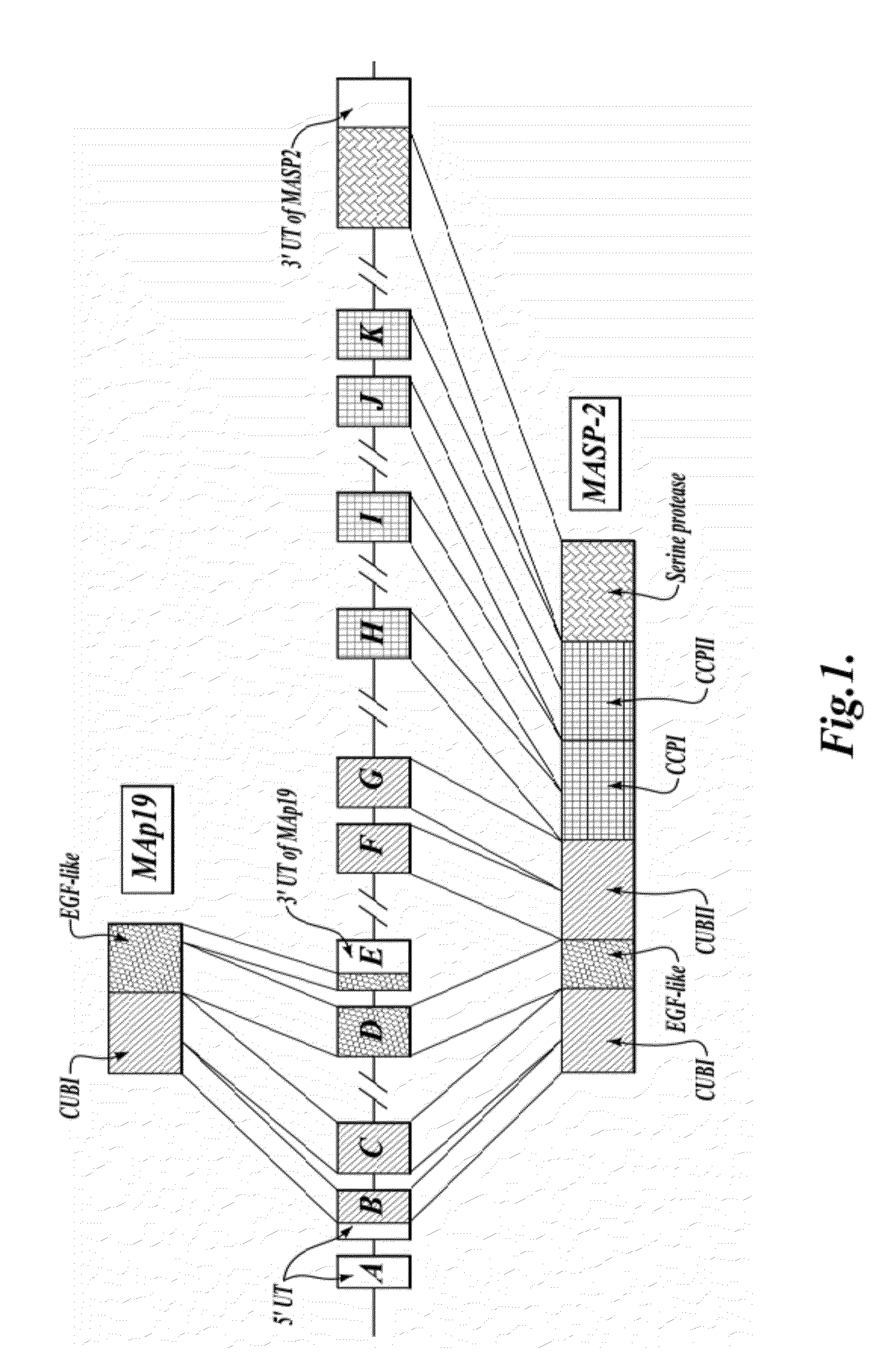
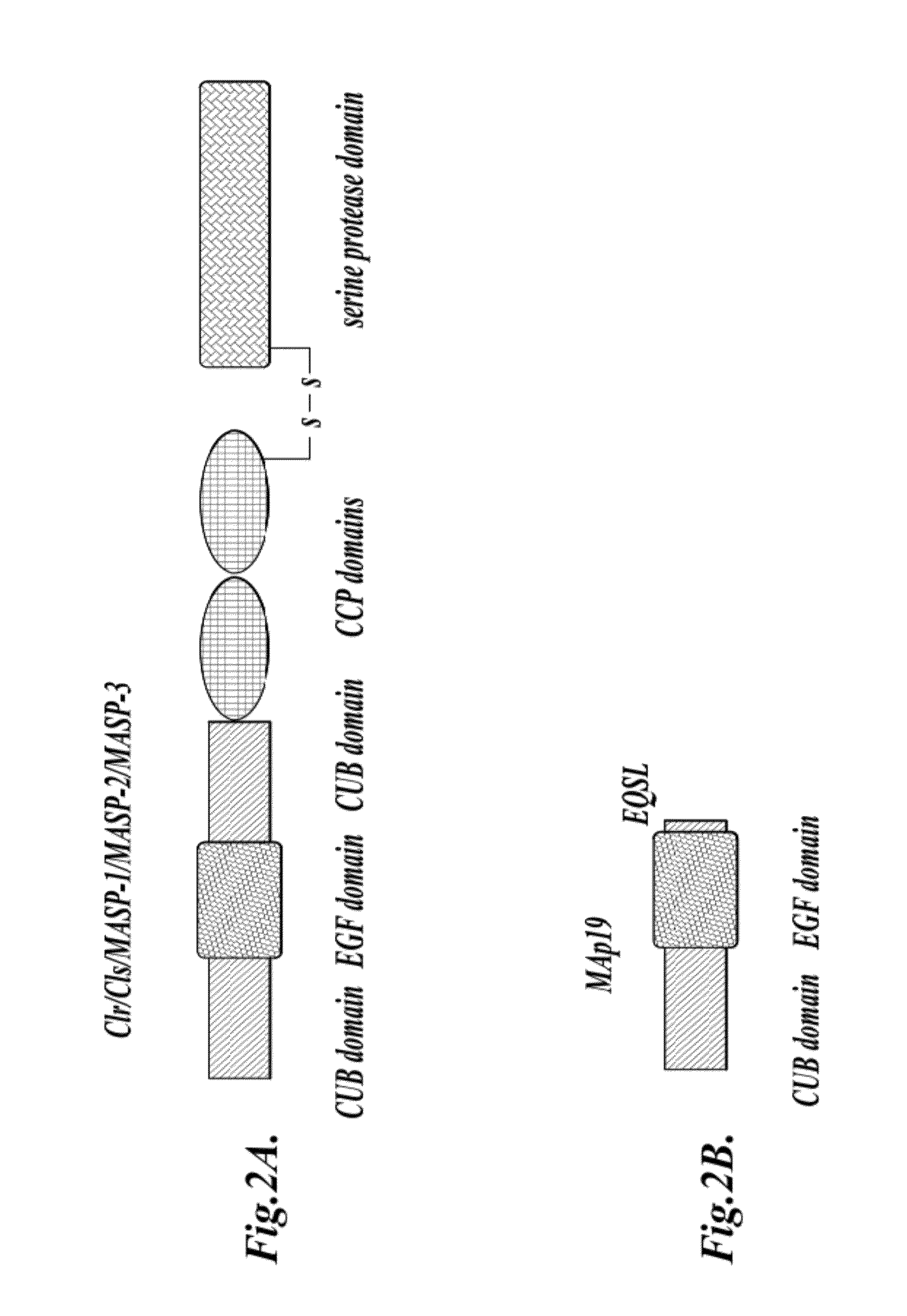
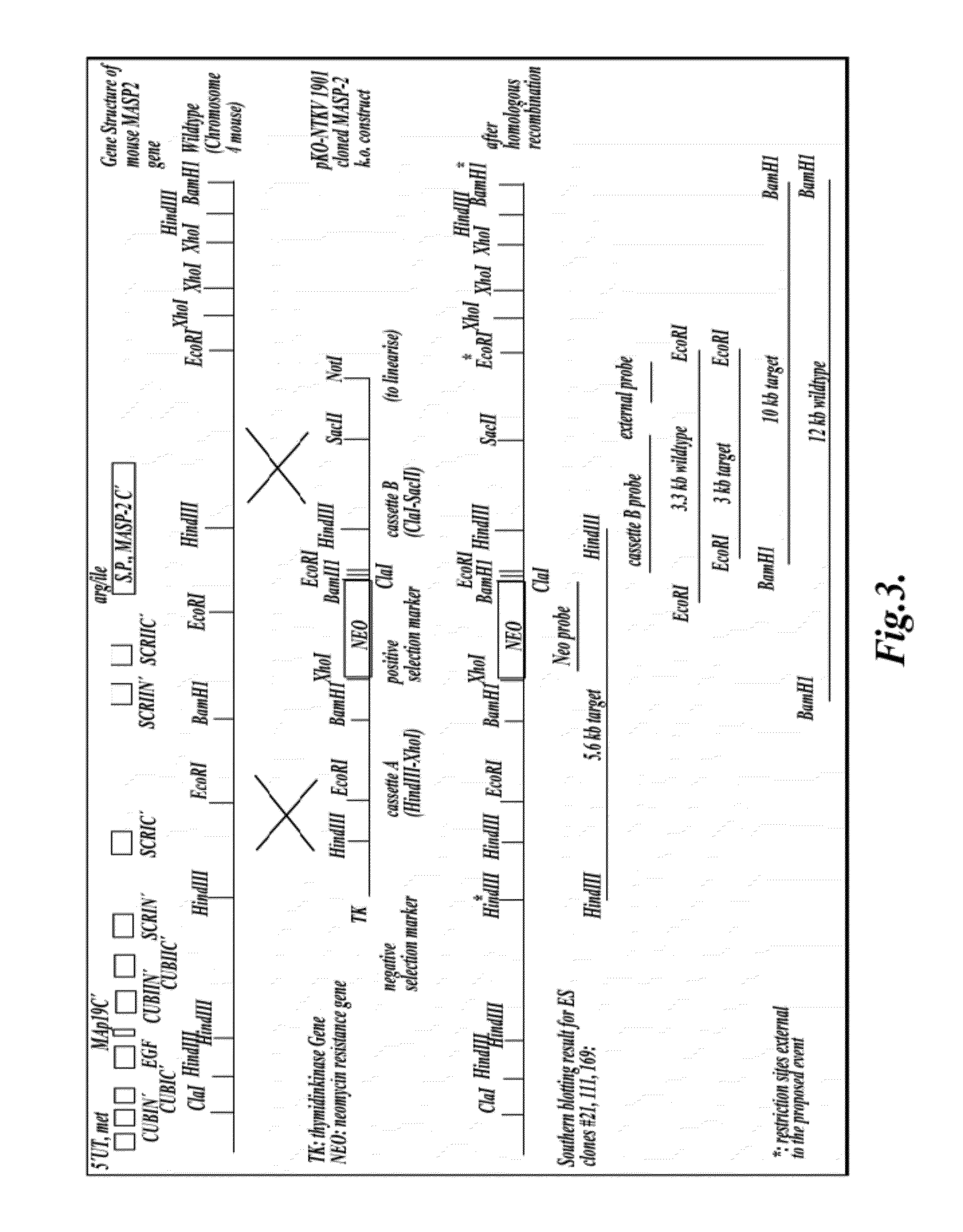
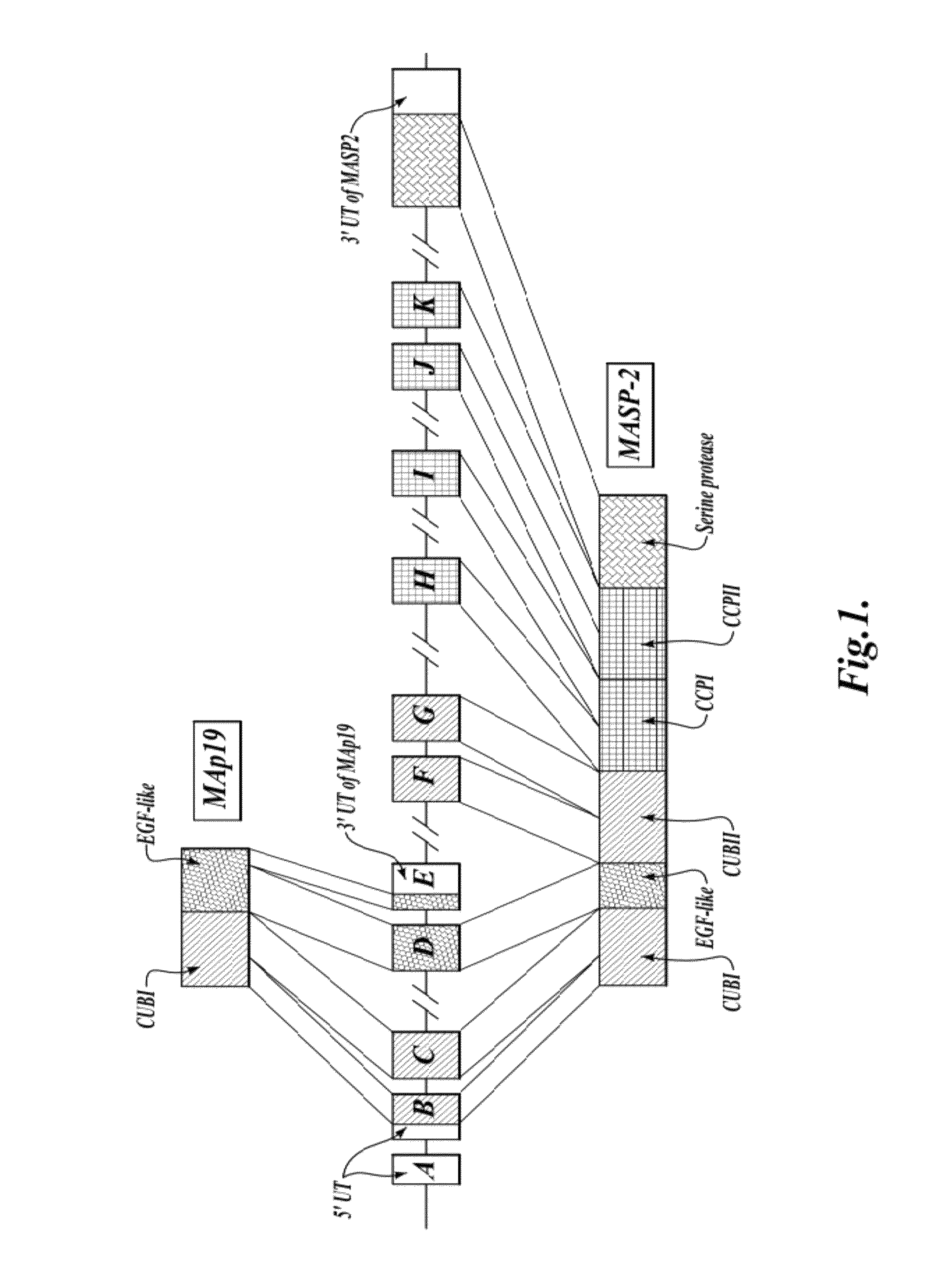
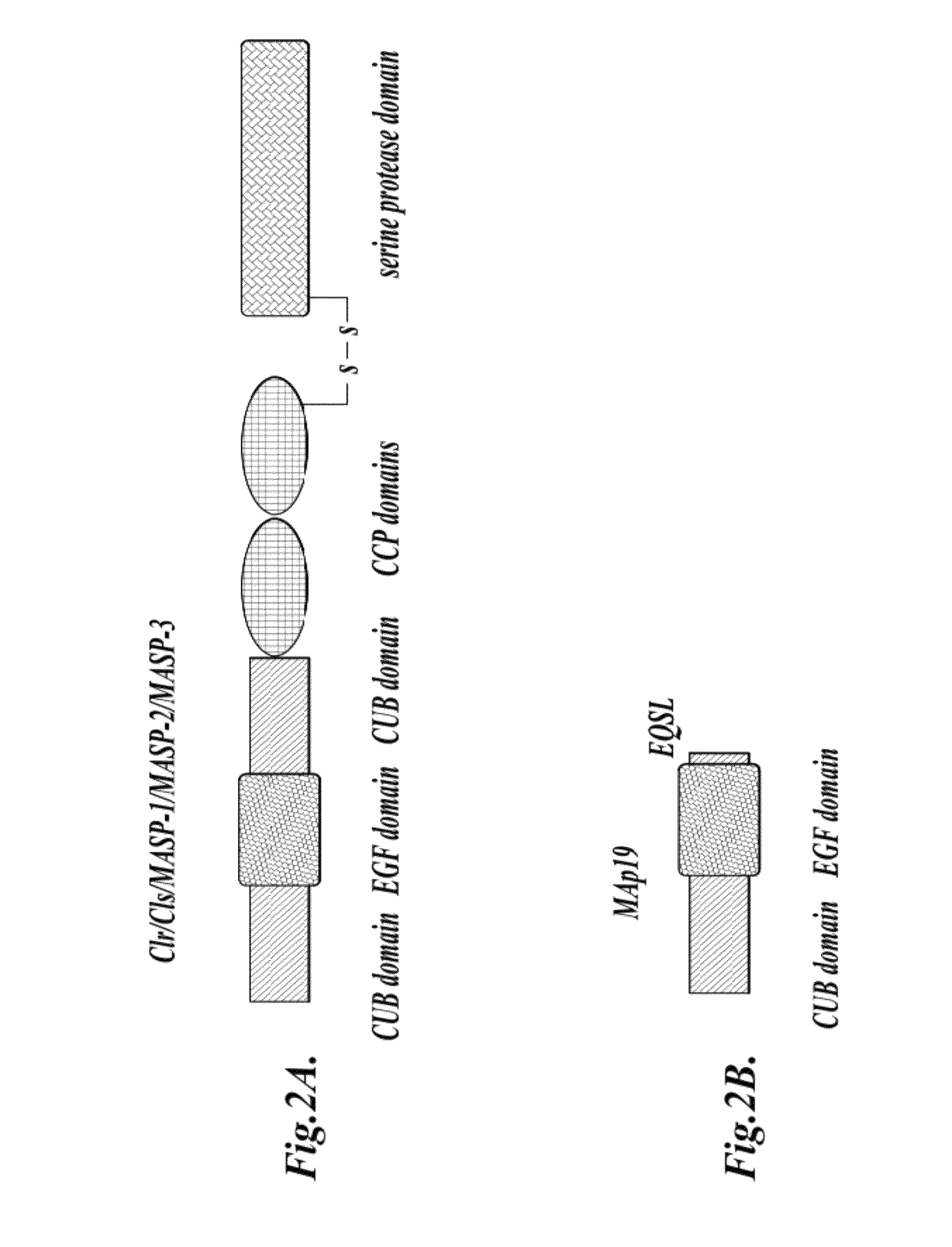
Methods for Treating Conditions Associated with MASP-2 Dependent Complement Activation
ActiveUS20130266560A1Improve survivalReduced survival rateAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulins against enzymesDiseasePharmaceutical medicine
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER +1
High frequency alternating current medical device with self-limiting conductive material and method
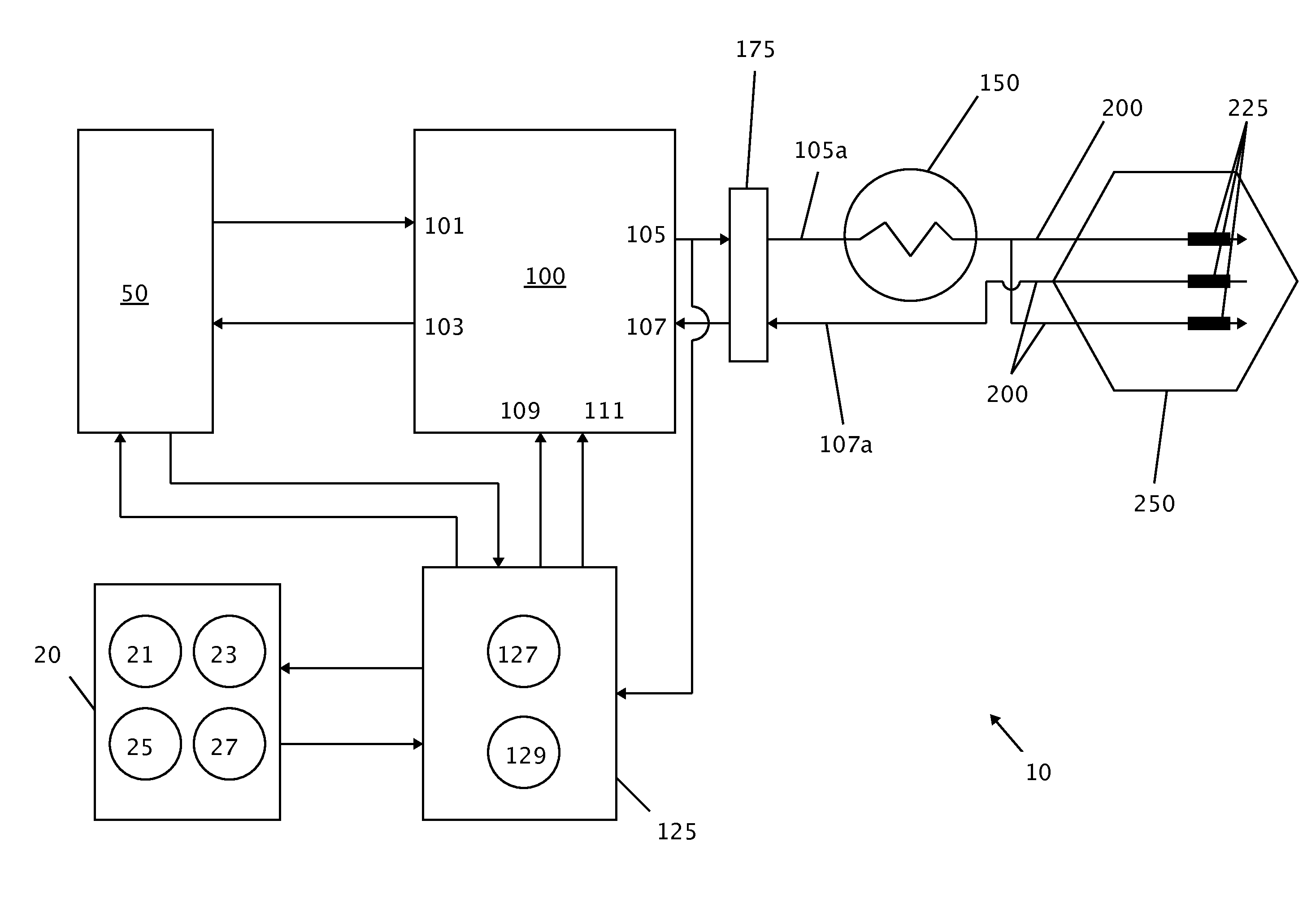
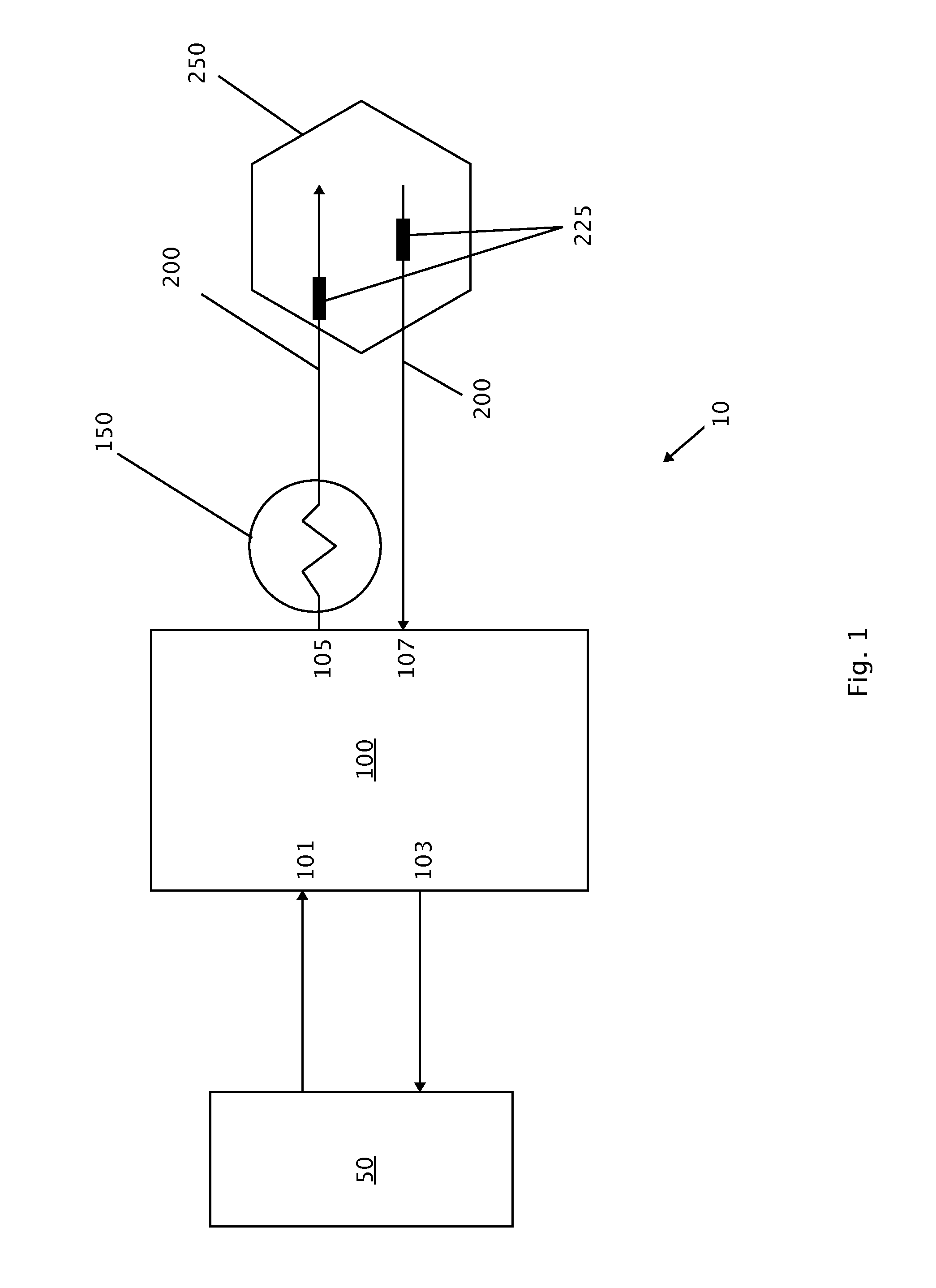
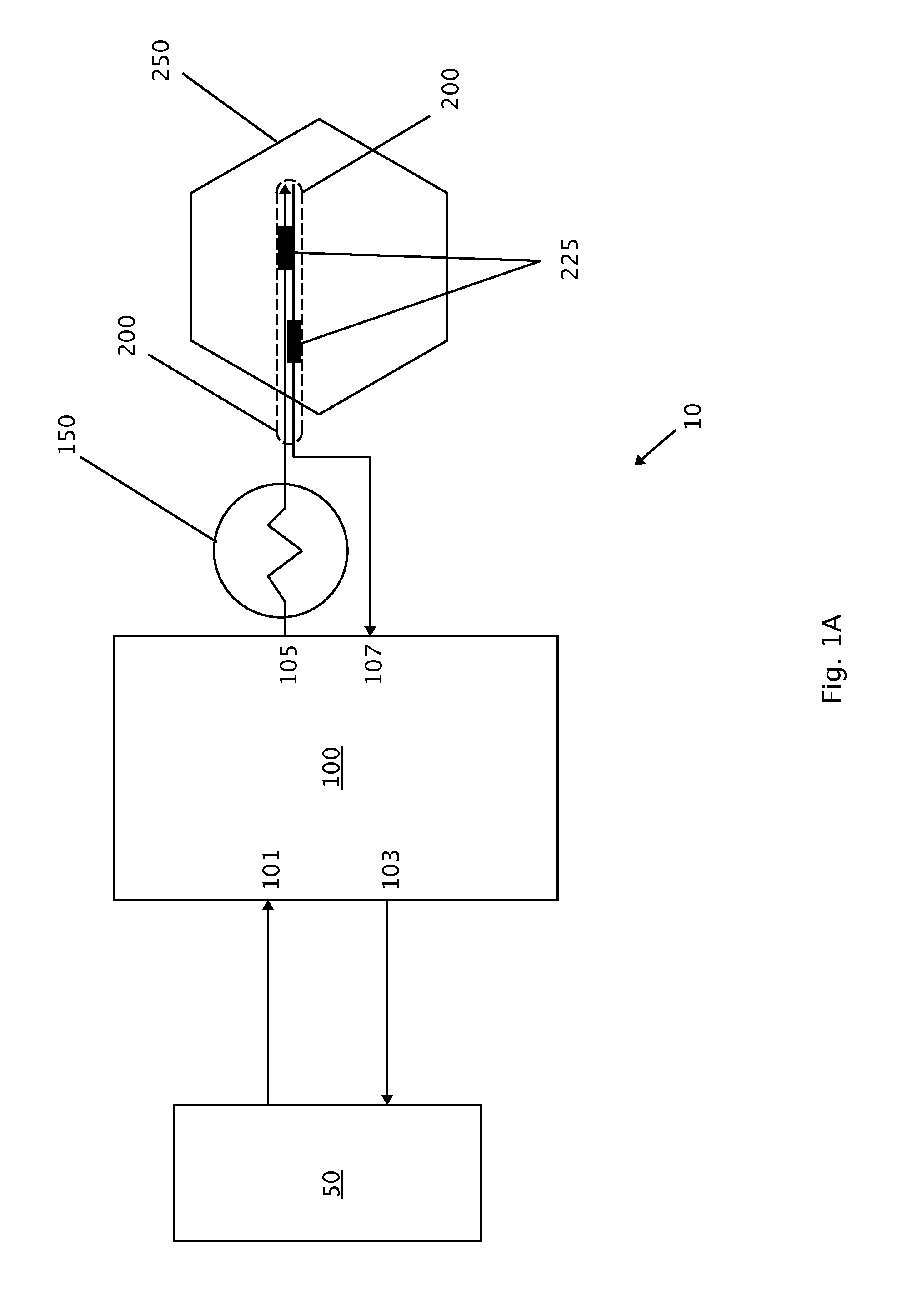
A high frequency alternating current medical device and method of using such is disclosed. High frequency alternating current medical device comprises a power source, an electric field generator, a self-limiting conductive material electrical component, at least one probe or needle-type projection, and at least two conductive segments located on probe or needle-type projection. At least two conductive segments are electrically connected to electric field generator so that an electric field is created between conductive segments, which induces an electrical current, which generates heat, and causes a certain desired precise cell injury. Self-limiting conductive material electrical component allows such precise cell injury because it limits electrical current through target tissue. Invention may be used in medical, dental, or veterinary applications. Exemplary embodiments include cosmetic applications, treatment of wrinkles, remodeling of subcutaneous tissue, treatment of muscle spasms, and others. Medical device can be small, hand-held, and easily manipulated to perform surgery.
Owner:CURO MEDICAL
Methods for Treating Conditions Associated with MASP-2 Dependent Complement Activation
InactiveUS20150166675A1Inhibiting complement activationReduce the possibilityAntibody ingredientsDermatological disorderCvd riskBiological activation
In one aspect, the invention provides methods of inhibiting the effects of MASP-2-dependent complement activation in a living subject suffering from, or at risk for developing a thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA). The methods comprise the step of administering, to a subject in need thereof, an amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent effective to inhibit MASP-2-dependent complement activation. In some embodiments, the MASP-2 inhibitory agent inhibits cellular injury associated with MASP-2-mediated alternative complement pathway activation, while leaving the classical (C1q-dependent) pathway component of the immune system intact.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER
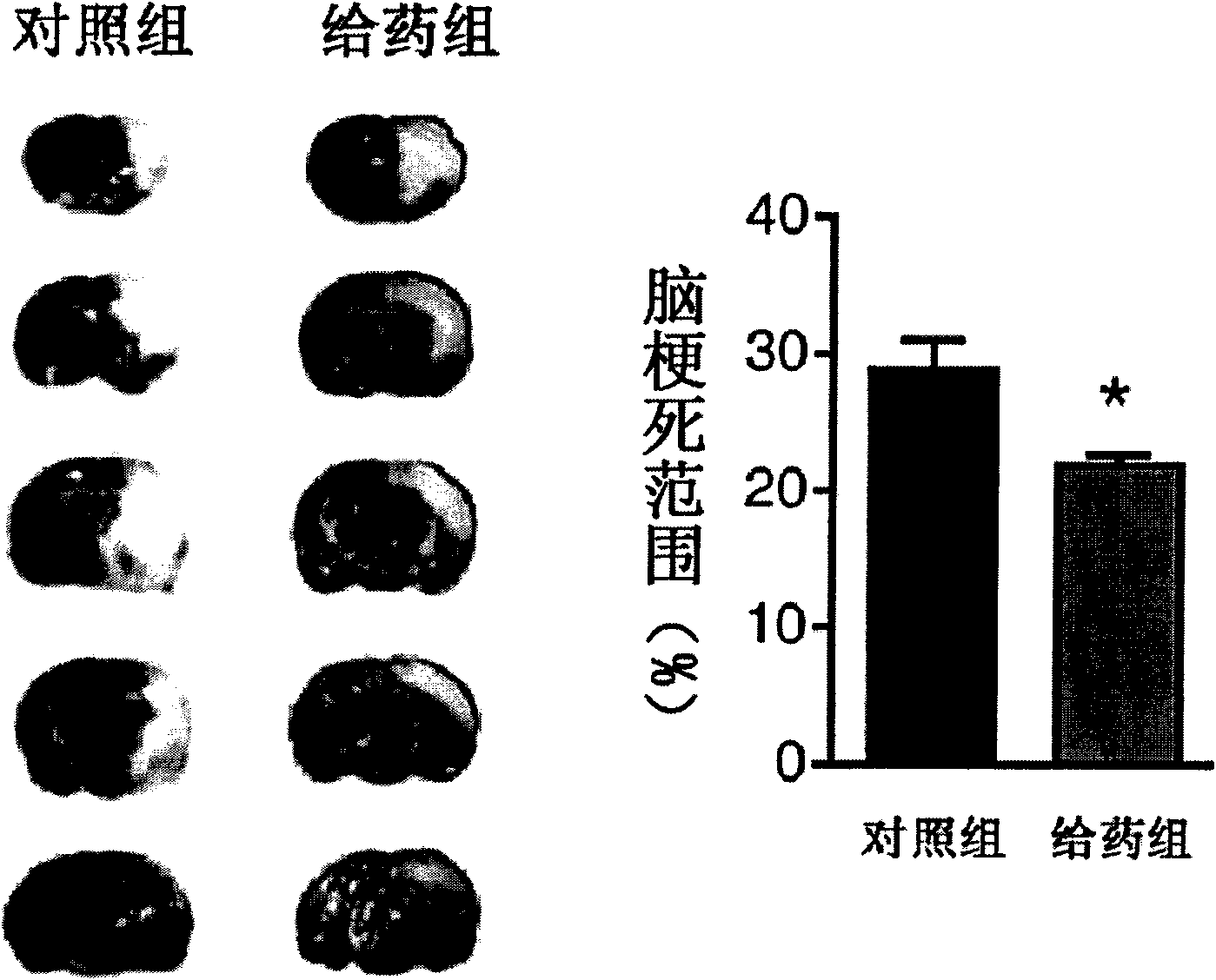
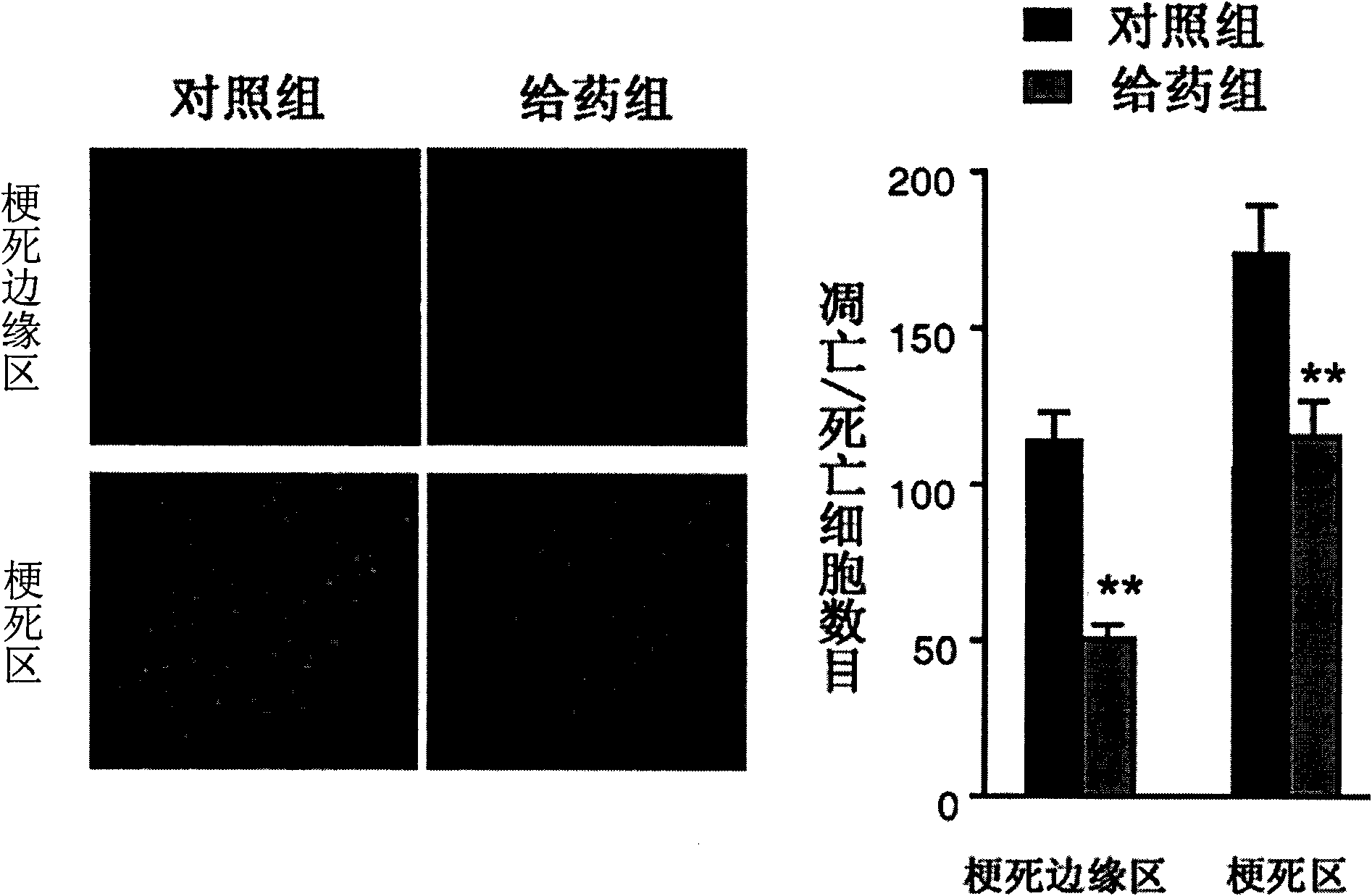
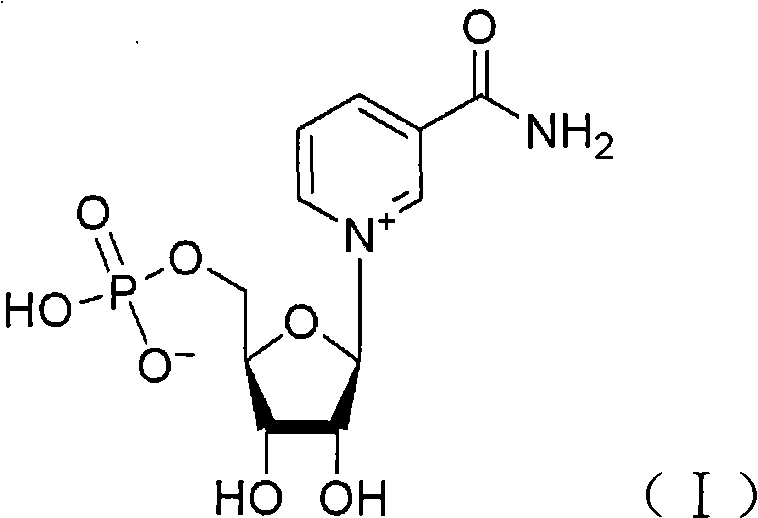
Application of nicotinamide mononucleotide
ActiveCN101601679AImprove securityEffective controlOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSide effectActive component
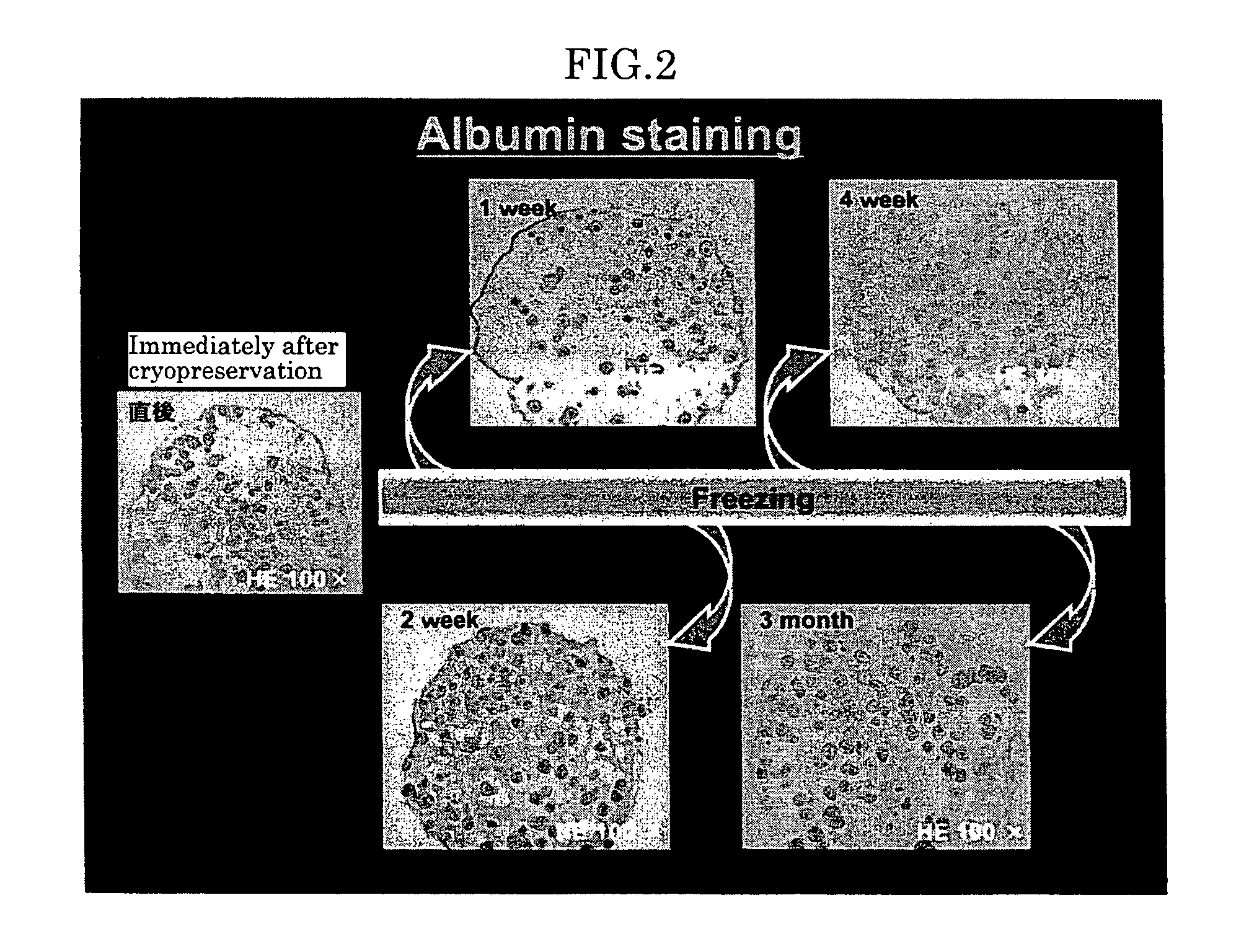
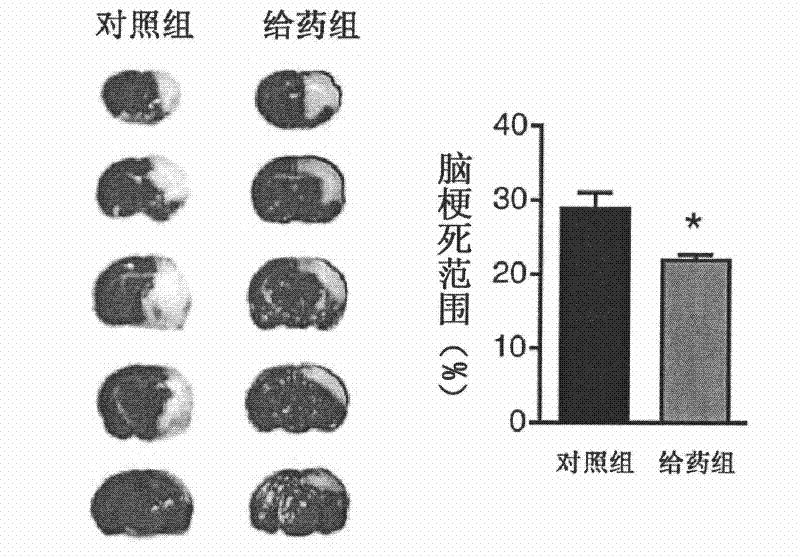
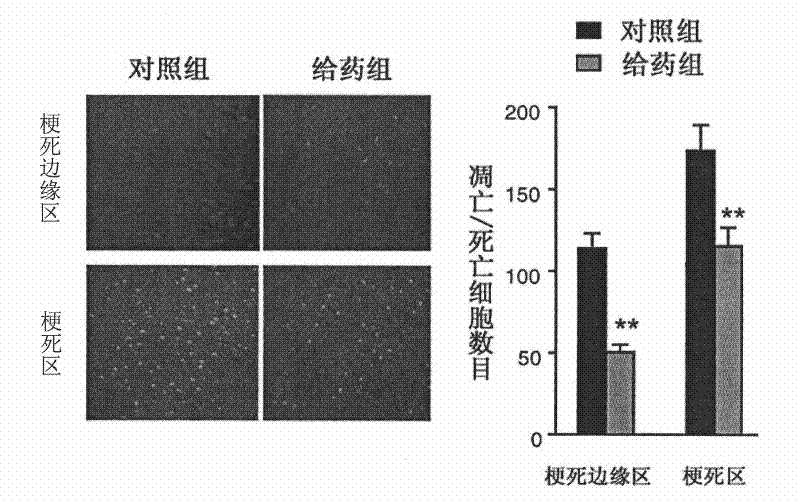
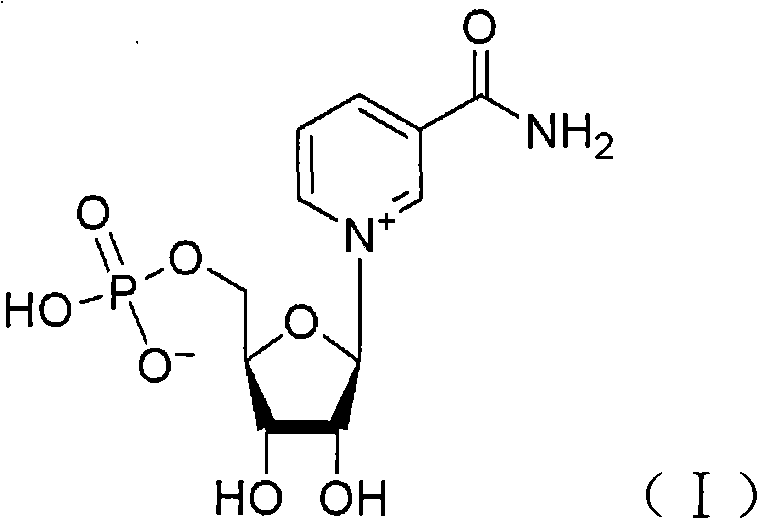
The invention discloses the application of nicotinamide mononucleotide on preparing medicines or health-care food for resisting neuronal cell injury cerebral apoplexy or oxygen-glucose deprivation. The invention also provides a novel medical composite which can effectively resist the neuronal cell injury caused by cerebral apoplexy and oxygen-glucose deprivation, thereby showing great significance to the treatment of cerebral apoplexy; and the active component in the medical composite is the nicotinamide mononucleotide which is an endogenic protective substance for an organic body and can not generate side effects according to current information, and therefore the nicotinamide mononucleotide used as a medicine has higher security and wide time window for treatment.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Methods for Treating Conditions Associated with MASP-2 Dependent Complement Activation
ActiveUS20120258095A1Improve survivalReduced survival rateAntibacterial agentsAntibody ingredientsPharmaceutical medicinePharmacology
In one aspect, the invention provides methods of inhibiting the effects of MASP-2-dependent complement activation in a living subject. The methods comprise the step of administering, to a subject in need thereof, an amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent effective to inhibit MASP-2-dependent complement activation. In some embodiments, the MASP-2 inhibitory agent inhibits cellular injury associated with MASP-2-mediated alternative complement pathway activation, while leaving the classical (C1q-dependent) pathway component of the immune system intact. In another aspect, the invention provides compositions for inhibiting the effects of lectin-dependent complement activation, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER
Method and kit for detecting the early onset of renal tubular cell injury
InactiveUS20070254370A1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementSide effectNGAL Protein
A method and kit for detecting the early onset of renal tubular cell injury, utilizing NGAL as an early urinary biomarker. NGAL is a small secreted polypeptide that is protease resistant and consequently readily detected in the urine following renal tubule cell injury. NGAL protein expression is detected predominantly in proximal tubule cells, in a punctate cytoplasmic distribution reminiscent of a secreted protein. The appearance NGAL in the urine is related to the dose and duration of renal ischemia and nephrotoxemia, and is diagnostic of renal tubule cell injury and renal failure. NGAL detection is also a useful marker for monitoring the nephrotoxic side effects of drugs or other therapeutic agents.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Construction method of human umbilical cord mesenchyma stem cell
ActiveCN101608174AAvoid damageActivity without lossDead animal preservationTissue cultureUmbilical cord tissueCell damage
The invention discloses a construction method of an umbilical cord mesenchyma stem cell bank utilizing newborn umbilical cords as resources, aiming at causing the steps to be less and the operation to be simpler and easier when constructing the umbilical cord mesenchyma stem cell bank. The invention comprises the following steps: (1), taking a human umbilical cord for detection, using a buffer solution to wash and remove residual blood, shearing to pieces, thus obtaining human umbilical cord tissue; (2), adding collagenase for digestion; (3), adding the buffer solution for diluting the digested tissue followed by organizing, mixing evenly and centrifuging; (4), abandoning the supernatant, adding the buffer solution for heavy suspension precipitation, screening, collecting filtrate and centrifuging, and repeating twice to obtain the human umbilical cord mesenchyma stem cell; (5), saving the obtained human umbilical cord mesenchyma stem cell in liquid nitrogen according to ABO / Rh parting and HLA parting thereof, establishing a cell information archive for retrieval, thus constructing the human umbilical cord mesenchyma stem cell bank. Compared with the existing method, the invention is more fast and convenient, and has less damage to the cell.
Owner:章毅 +7
High frequency alternating current medical device with self-limiting conductive material and method
A high frequency alternating current medical device and method of using such is disclosed. High frequency alternating current medical device comprises a power source, an electric field generator, a self-limiting conductive material electrical component, at least one probe or needle-type projection, and at least two conductive segments located on probe or needle-type projection. At least two conductive segments are electrically connected to electric field generator so that an electric field is created between conductive segments, which induces an electrical current, which generates heat, and causes a certain desired precise cell injury. Self-limiting conductive material electrical component allows such precise cell injury because it limits electrical current through target tissue. Invention may be used in medical, dental, or veterinary applications. Exemplary embodiments include cosmetic applications, treatment of wrinkles, remodeling of subcutaneous tissue, treatment of muscle spasms, and others. Medical device can be small, hand-held, and easily manipulated to perform surgery.
Owner:CURO MEDICAL
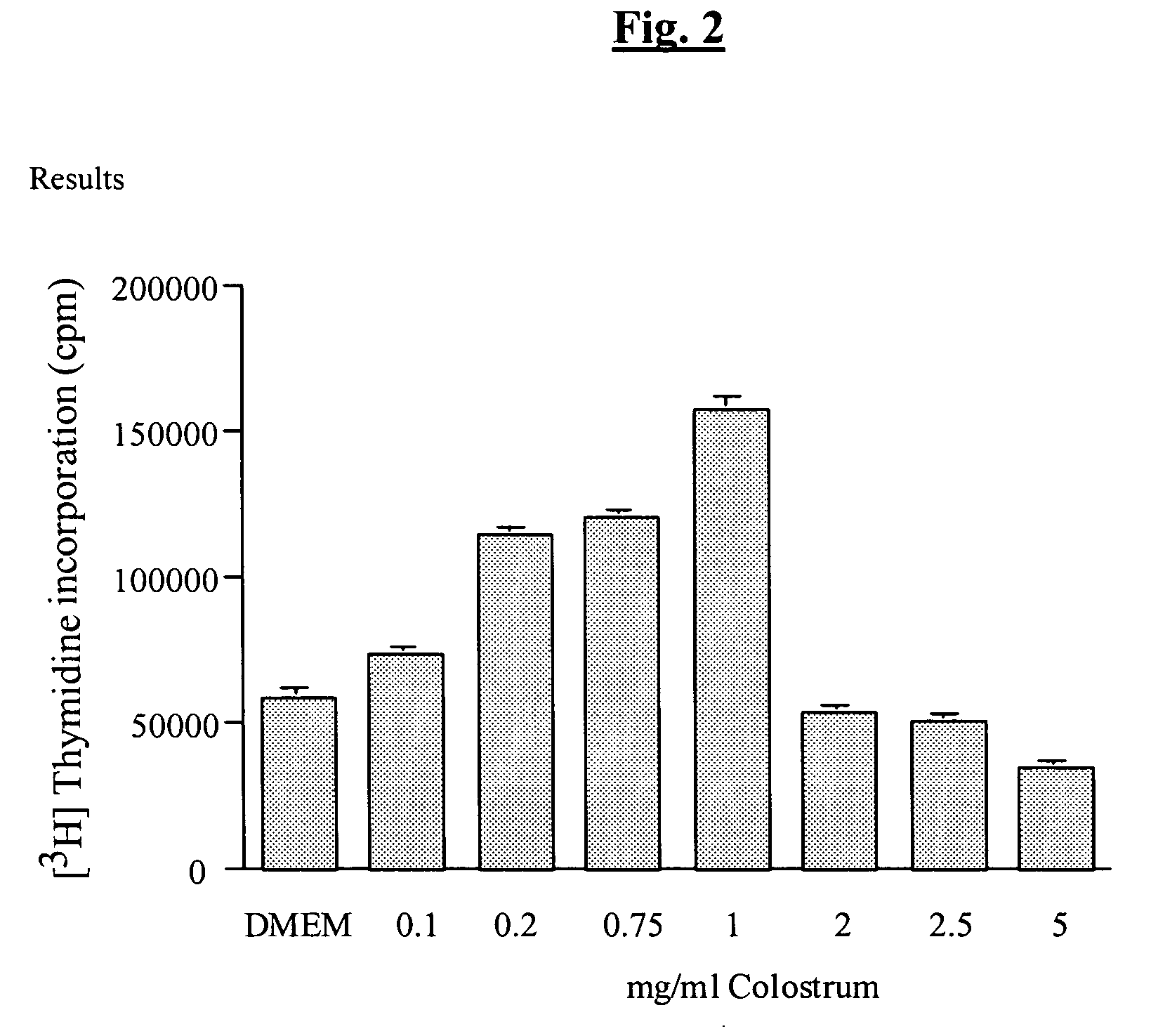
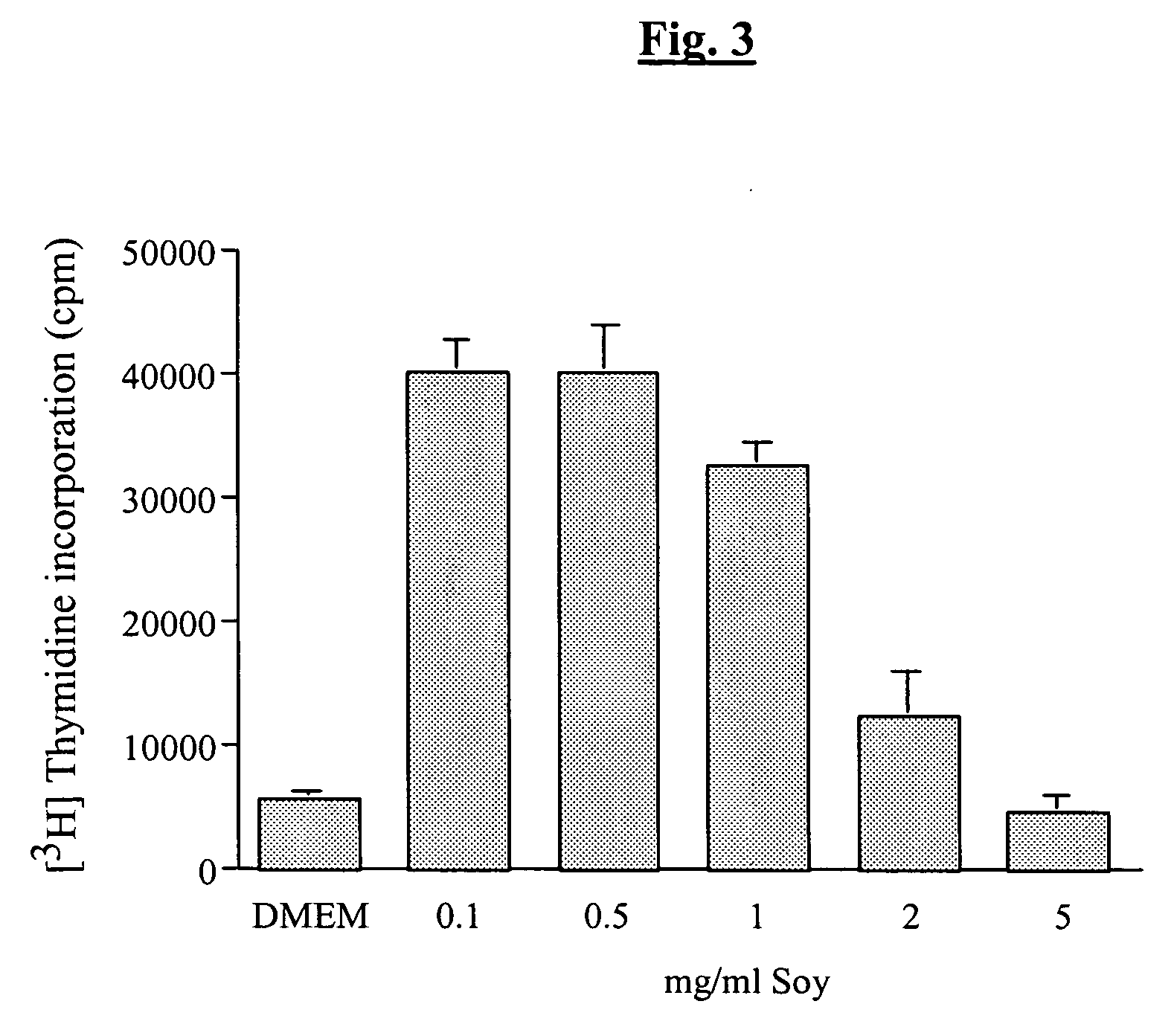
Bioactive agent compositions for repair of cell injuries
InactiveUS20060068022A1Enhanced bioactive agent compositionAvoid problemsBiocideInorganic active ingredientsSodium bicarbonateDisease
A method for prophylactically treating a gastrointestinal disorder or skin ailment in a mammal through the administration of an enhanced bioactive agent composition comprising a bioactive agent and at least one of a soy product, licorice product, or sodium bicarbonate (depending upon the indication to be treated) is provided according to the invention. The bioactive agent preferably is bovine colostrum. The effective amount of enhanced bioactive agent composition to be used will depend upon such factors as the age and weight of the mammal, the bioactivity level of the bioactive agent, the gastrointestinal disorder or skin ailment at issue, and whether treatment of existing symptoms of the gastrointestinal disorder or skin ailment, or prevention of the onset of such symptoms is desired. A medicament comprising an enhanced bioactive agent composition for prophylactically treating a gastrointestinal disorder or skin ailment in a mammal is also provided according to the invention.
Owner:NUTRITIONAL BIOSCI
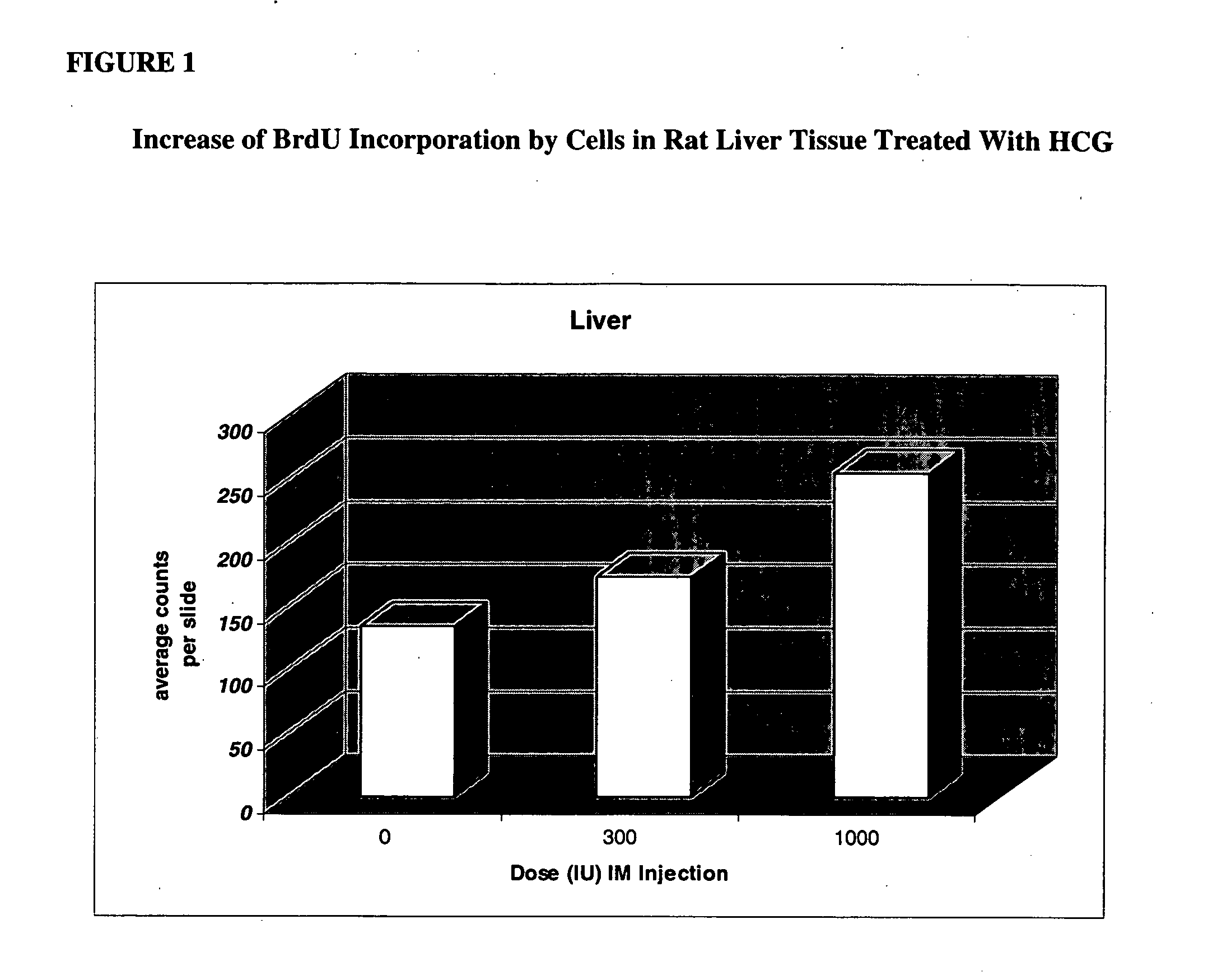
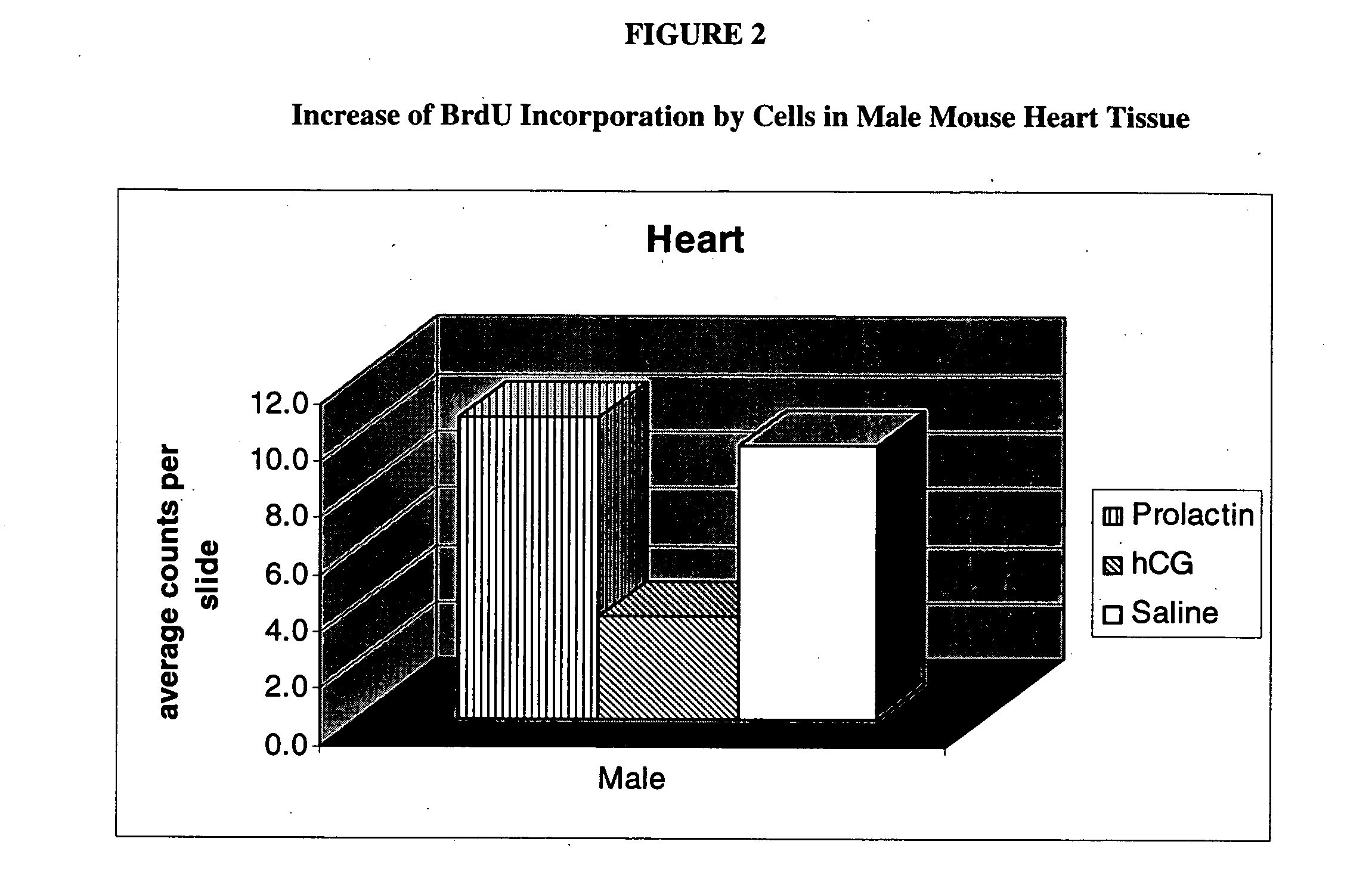
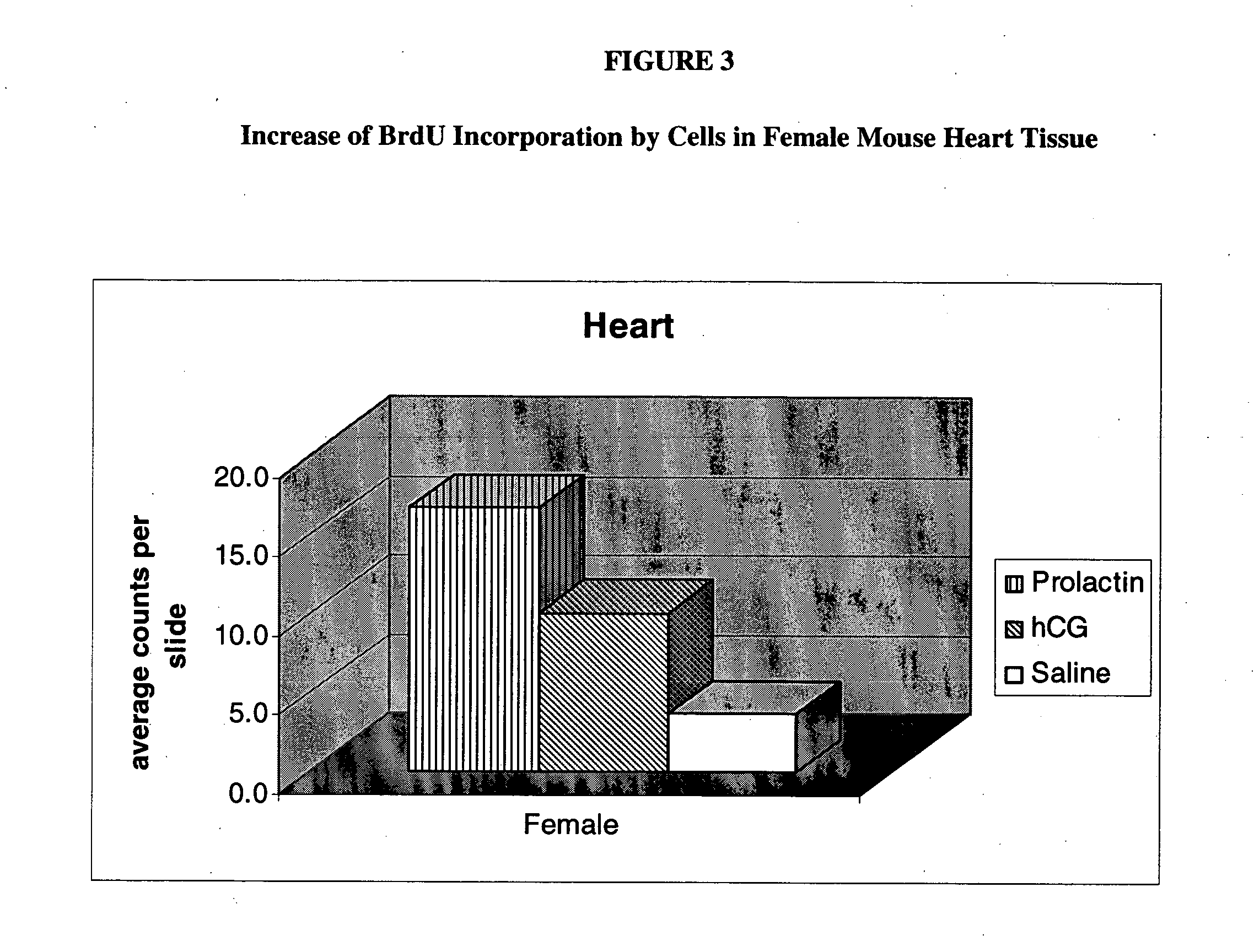
Stimulation of proliferation of pluripotential stem cells through administration of pregnancy associated compounds
The present invention provides for a method for stimulating the proliferation of pluripotential stem cells in a mammal comprising administration of pregnancy related compounds more particularly human chorionic gonadotropin, leutenizing hormone or prolactin. The present invention further provides for a method of treatment of tissues or organs experiencing cellular damage, injury or disease.
Owner:STEM CELL THERAPEUTICS
Use of compounds having ccr antagonism
InactiveUS20050245537A1Effective preventionEffective treatmentBiocideSenses disorderAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
It is intended to provide preventives / remedies for graft-versus-host disease and / or rejection in organ or bone marrow transplantation, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune diseases, allergic diseases, ischemic cerebral cell injury, myocardial infarction, chronic nephritis and arteriosclerosis. The above object can be achieved by preventives / remedies for graft-versus-host disease and / or rejection in organ or bone marrow transplantation, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune diseases, allergic diseases, ischemic cerebral cell injury, myocardial infarction, chronic nephritis and arteriosclerosis characterized by containing a specific compound having a CCR (CC chemokine receptor) antagonism.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD +1
Methods for treating conditions associated with MASP-2 dependent complement activation
ActiveUS8951522B2Reduce adverse effectsInhibition of activationAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderBiological activationLectin
In one aspect, the invention provides methods of inhibiting the effects of MASP-2-dependent complement activation in a living subject. The methods comprise the step of administering, to a subject in need thereof, an amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent effective to inhibit MASP-2-dependent complement activation. In some embodiments, the MASP-2 inhibitory agent inhibits cellular injury associated with MASP-2-mediated alternative complement pathway activation, while leaving the classical (C1q-dependent) pathway component of the immune system intact. In another aspect, the invention provides compositions for inhibiting the effects of lectin-dependent complement activation, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a MASP-2 inhibitory agent and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER
Nutritional support to prevent or moderate bone marrow paralysis or neutropenia during Anti-cancer treatment
InactiveUS20110229447A1Preserve activation capacityPreserve cell viabilityBiocideVitamin food ingredientsTolerabilityImmunocompetence
The present invention relates to methods and immunonutritional compositions for preventing the impairment of the immune function during anti-cancer therapy, thereby attaining a better efficacy of the treatment. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods and immunonutritional compositions that can transiently preventing or moderating, bone marrow paralysis or neutropenia of a subject undergoing anti-cancer therapy-induced apoptosis or necrosis or other cell damage such that the innate and adaptive immune functions and normal physiology of the bone marrow are preserved, at least in part, which, in turn, lead to (i) a better tolerance and increased efficacy to anti-cancer therapy; (ii) transient augmentation or enhancement of immunocompetence of the immune cell; and (iii) optimization of the effects of and increase of immunocompetence of the immune cell weakened by anti-cancer therapy.
Owner:NESTEC SA
A hemopoietic stem cell cryopreserving solution, and a hemopoietic stem cell cryopreserving method
InactiveCN107094753AImprove protectionDrop in recovery rateDead animal preservationHydroxyethyl starchCell culture media
The invention relates to the technical field of cytobiology, and particularly relates to a hemopoietic stem cell cryopreserving solution, and a hemopoietic stem cell cryopreserving method. The cryopreserving solution includes following raw materials by weight: 10-20 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, 6-10 g of hydroxyethyl starch, 4-8 mL of a cell culture medium, 6-10 mL of human serum albumin, and 60-100 mL of human autologous plasma. The formula of the cryopreserving solution is simple, and the raw materials are cheap. The cryopreserving solution can effectively protect hemopoietic stem cells from freezing injuries, is high in safety and low in cell injuries, can increase the resuscitation survival rate of hemopoietic stem cells. The survival rate after resuscitation can be 96% or above, and after resuscitation, the cell viability is high, the quantity of cell proliferation is high, the cells are not liable to age, physiological functions and biological characteristics of the hemopoietic stem cells after resuscitation can be ensured, and microbe detection indexes meet requirements. The survival time of the hemopoietic stem cells is prolonged.
Owner:DONGGUAN BOALAI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
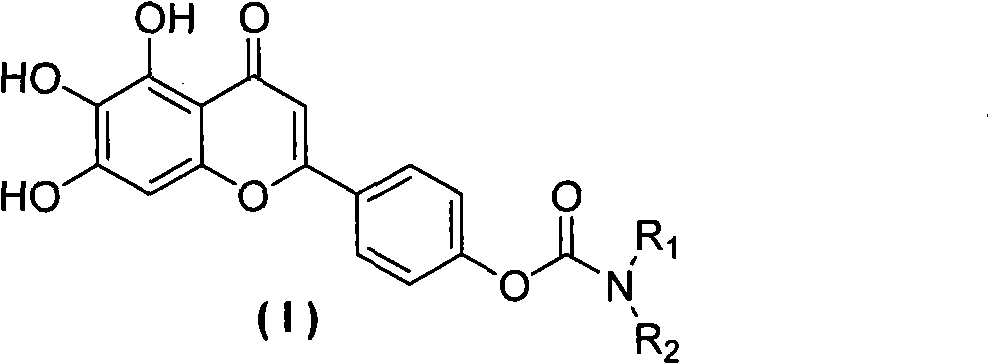
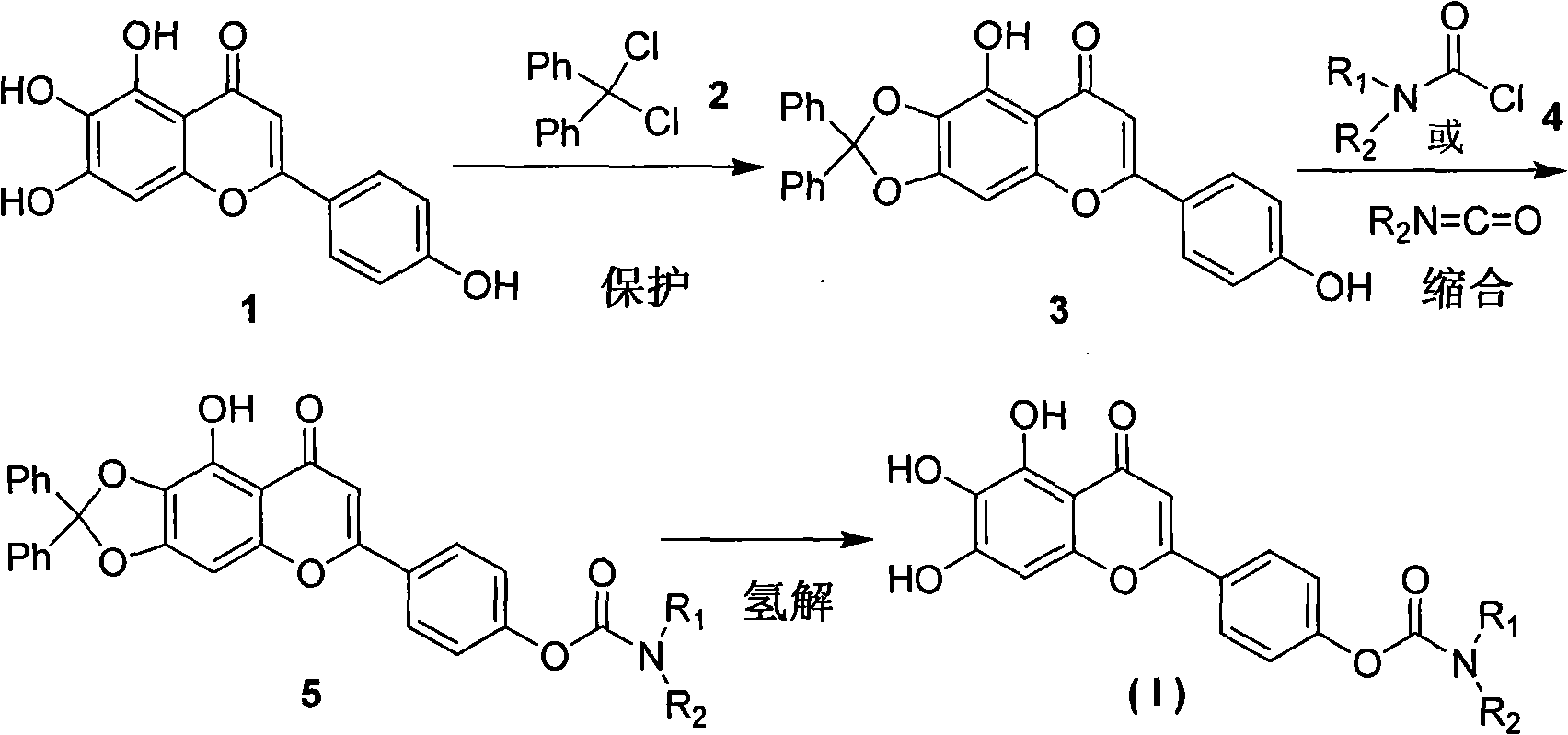
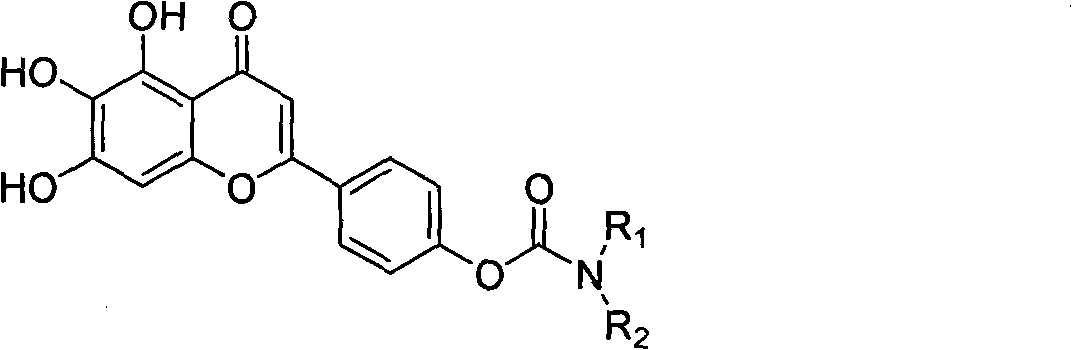
Scutellarein carbamate derivates, preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a novel scutellarin aglycon 4 (1)-position carbamate derivant (1), a preparation method and the application thereof. A pharmacological experiment proves that the compounds have obvious inhibitory activity of acetylcholinesterase and have protective effect with different degrees on PC12 cell trauma induced by H2O2, so the compounds can be used for preparing the drugs for treating neurodegenerative diseases such as vascular dementia, AD (presenile dementia), etc.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for the early detection of renal injury
InactiveUS20090142774A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiseaseSide effect
A method and kit for detecting the immediate or early onset of renal disease and injury, including renal tubular cell injury, utilizing NGAL as an immediate or early on-set biomarker in a sample of blood serum. NGAL is a small secreted polypeptide that is protease resistant and consequently readily detected in the blood serum following renal tubule cell injury. NGAL protein expression is detected predominantly in proximal tubule cells, in a punctuate cytoplasmic distribution reminiscent of a secreted protein. The appearance NGAL in the serum is related to the dose and duration of renal ischemia and nephrotoxemia, and is diagnostic of renal tubule cell injury and renal failure. NGAL detection is also a useful marker for monitoring the nephrotoxic side effects of drugs or other therapeutic agents.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Prevention of nuclear, solar, and other radiation-induced tissue damage
InactiveUS20070293458A1Reduced cell attachmentHigh strengthBiocideAntinoxious agentsPhosphorylationPyrophosphate
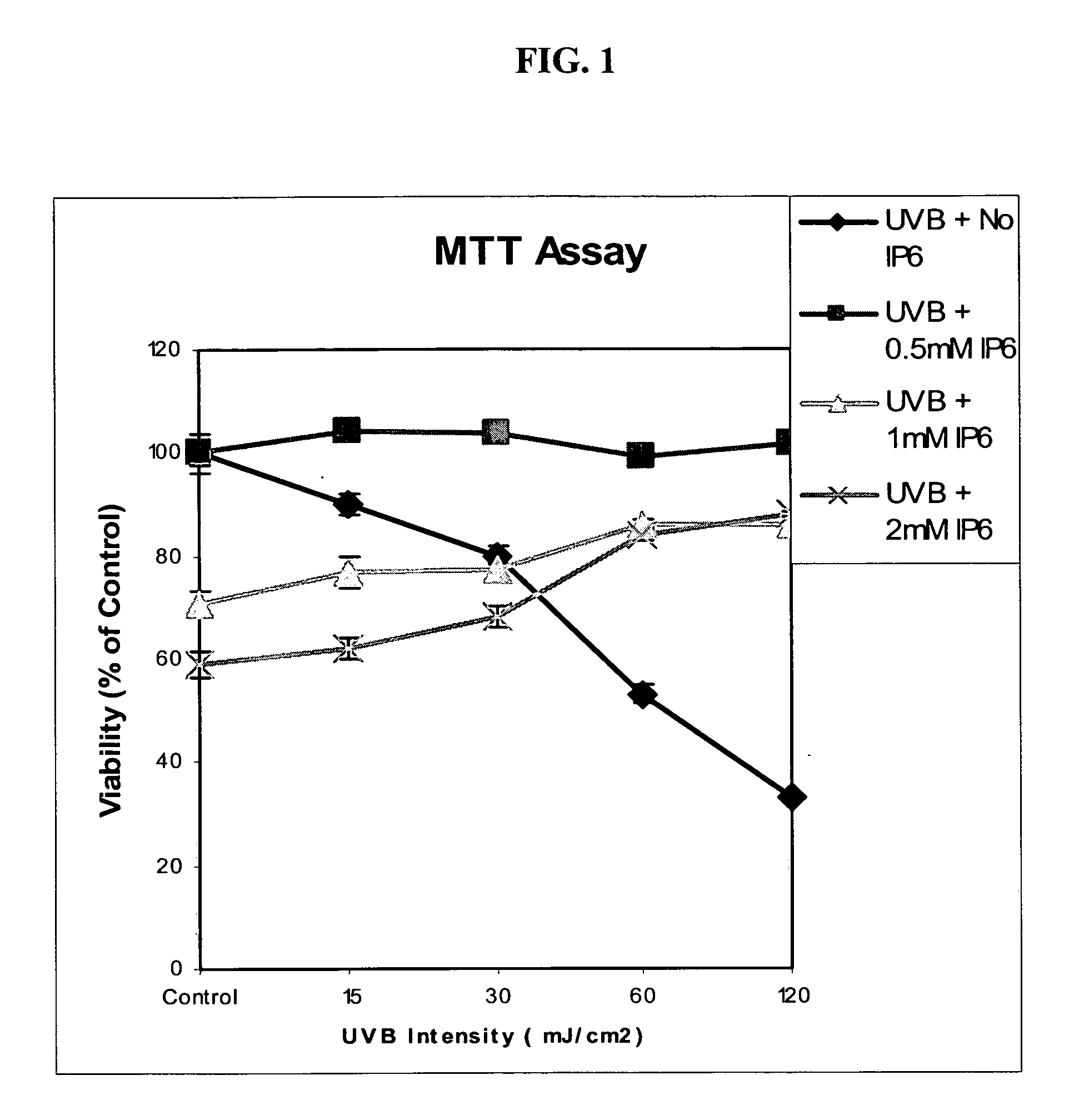
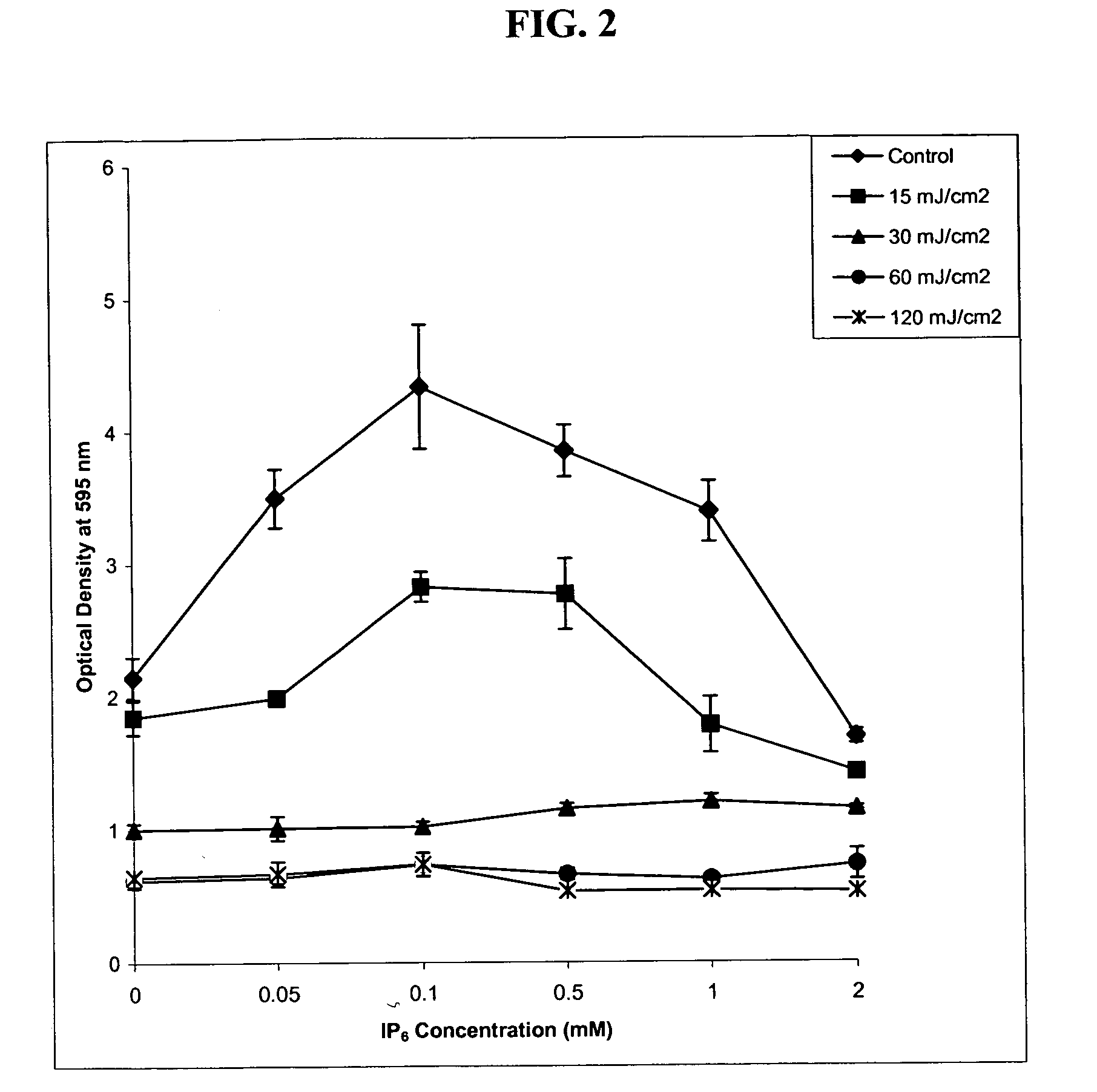
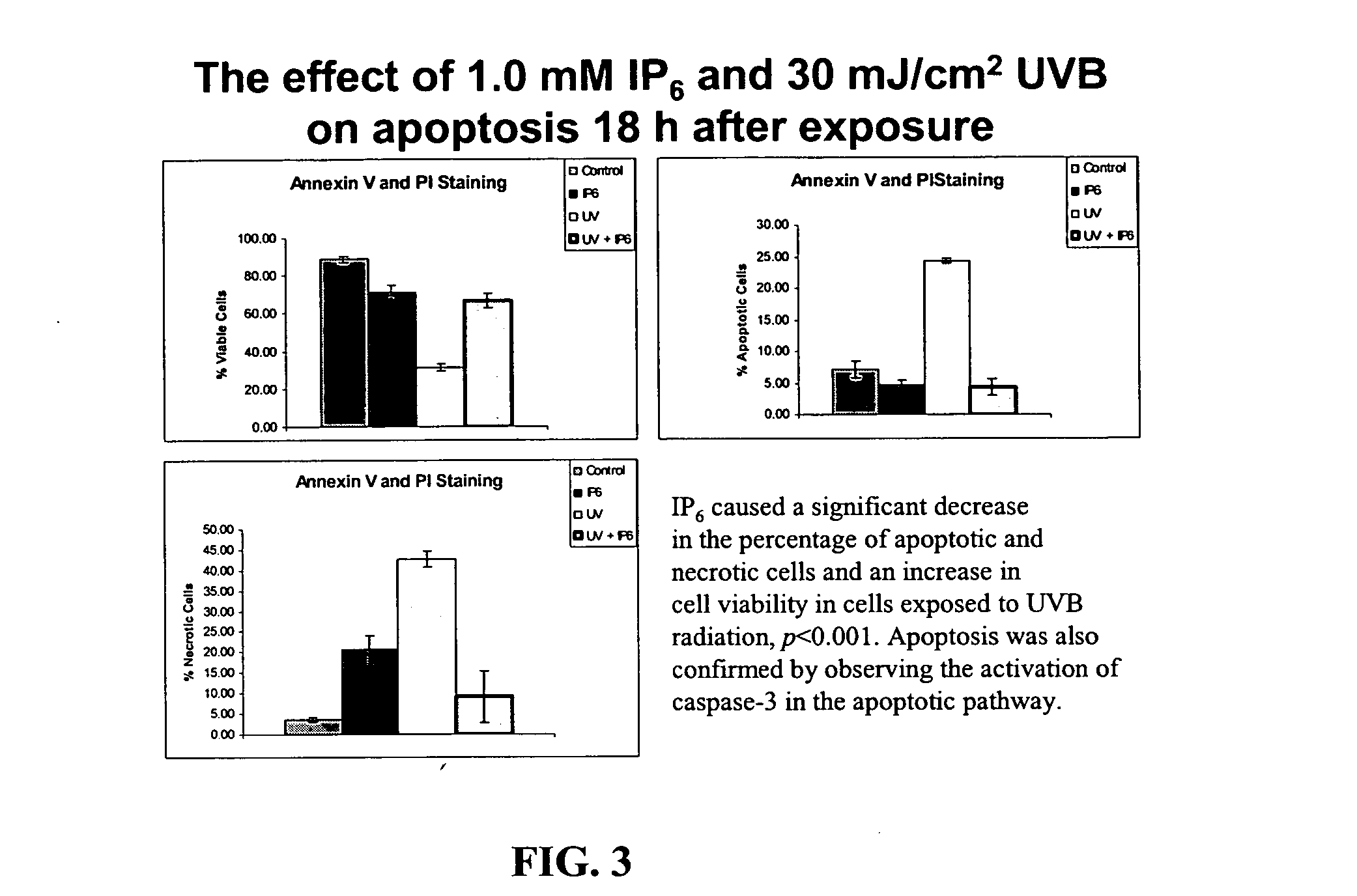
Inositol hexaphosphate (IP-6) is a polyphosphorylated carbohydrate with potent antioxidant activity to prevent active oxygen species-mediated mutagenesis, cell injury and carcinogenesis. IP-6 also activates DNA repair mechanisms. Sublethal radiation causes DNA damage through the formation of free radicals, reactive oxygen species, and pyrimidine crosslinks leading to cellular proliferation, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. In the skin it results in the induction of skin cancer, premature skin aging, immuno-suppression, inflammation, and cell death. Likewise sublethal exposure to ionizing radiation as in nuclear blasts (war-time, accidental, terrorist-induced etc), cosmic radiation, etc. also causes the same spectrum of damage to the cells and the organisms with acute symptoms and eventual high risk of many cancers. IP-6 and / or inositol and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and derivatives, including pyrophosphates and citrate derivatives, significantly counteract the harmful effects of radiation, affecting cell cycle progression in a protective manner (more cells in the protective GI phase) as well as decreasing apoptosis and caspase-3 activation. Various salts of IP-6 are used with comparable efficacy and the combination of IP-6+inositol affords the best protection against radiation-induced cell injury. Thus IP-6 and inositol are effective agents for protection against nuclear, solar and other radiation injuries.
Owner:IP 6 RES
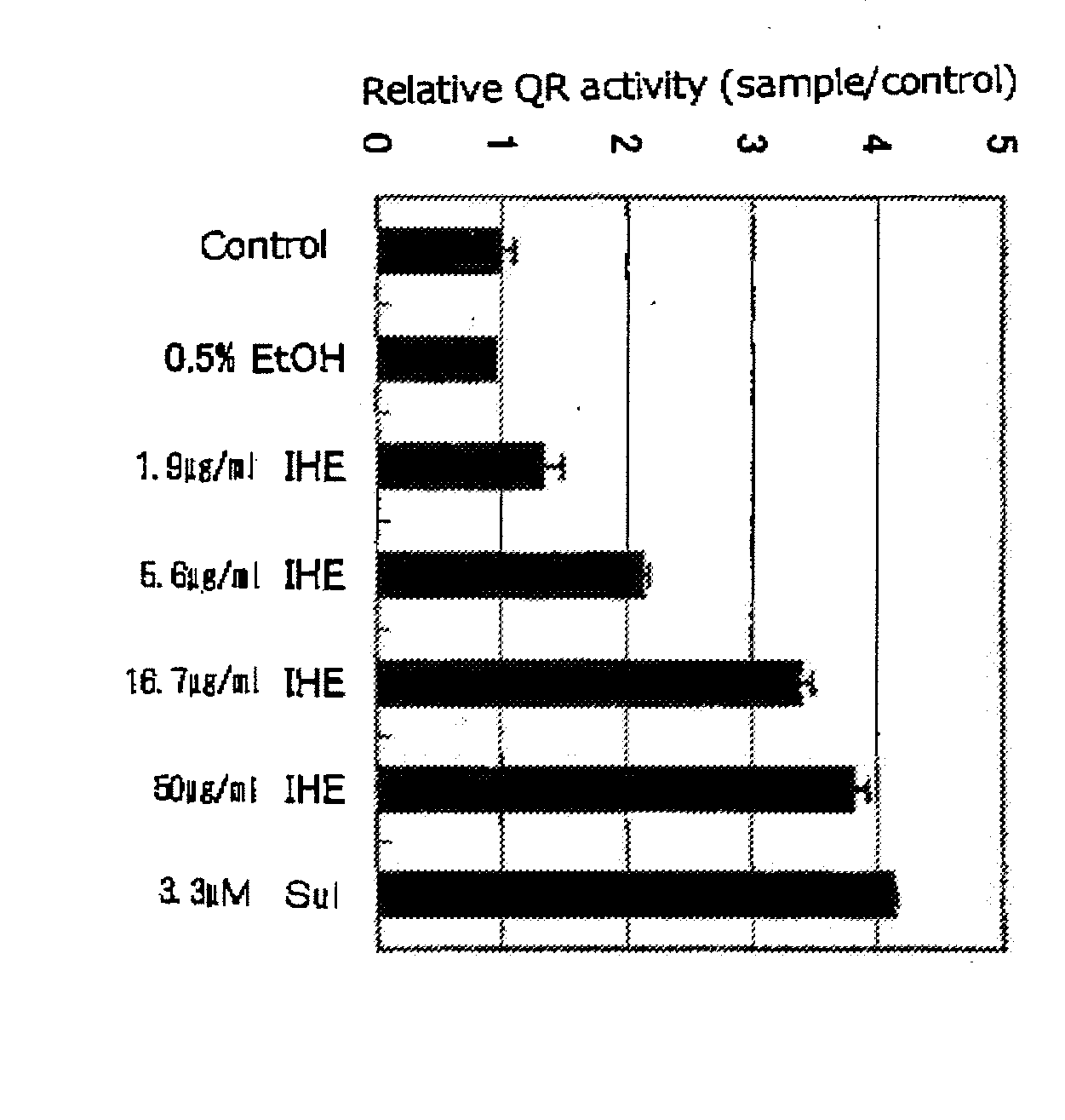
Agents for Activating the Transcription Factor Nrf2 and Foods Having Such Function
InactiveUS20070248705A1High activityReduce the amount of solutionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsFactor iiBiological activation
A composition, an Nrf2 activating agent, and a food according to the present invention comprise isohumulones or isomerized hop extract as an active ingredient. They are useful in treating, preventing, or ameliorating a disease of condition which is treatable, preventable, or ameliorable by the activation of transcription factor Nrf2. More specifically, the composition, the Nrf2 activating agent and the food according to the present invention are useful in treating, preventing, ameliorating, or alleviating chronic diseases which are believed to be caused or exacerbated by cellular damages due to oxidative stress in the body or environmental substances (for example, arteriosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes, cerebral nerve degenerative diseases, skin diseases, eye diseases, asthma, and cancer) or delaying progress of these diseases, or in detoxificating xenobiotic substances.
Owner:KIRIN BREWERY CO LTD
Compositions and methods for protecting organs, tissue and cells from immune system-mediated damage
InactiveUS20080241194A1Organic active ingredientsFungiVascular endotheliumNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
This invention concerns novel compositions and methods for for the protection of organs and cells from damage caused by activated lymphocytes, NK-cells and NK-like cells, more particularly compositions and methods for the protection of vascular endothelial cells from immune system-mediated damage.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
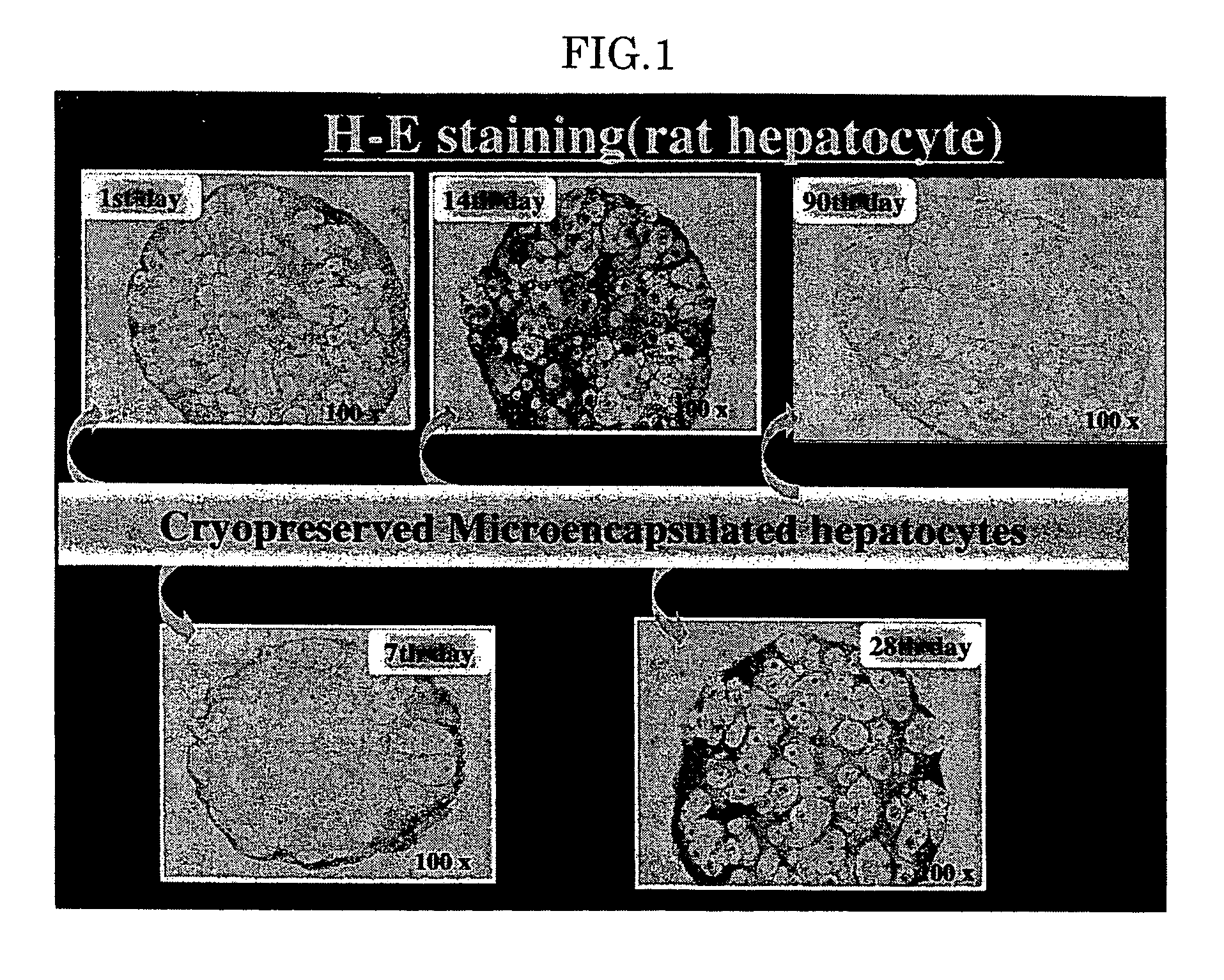
Method for cryopreserving microencapsulated living animal cells enclosed in immunoisolation membranes, such microencapsulated living animal cells in immunoisolation membranes, and biohybrid artificial organ modules using such microencapsulated living animal cells in immunoisolation membranes
ActiveUS20050265979A1Convenient for clinical operationSuppressing clinically harmful influenceBiocideDead animal preservationCell damageCryopreservation
A method is disclosed for cryopreserving living animal cells in immunoisolation membranes, including: (1) cutting out a living organ from an animal, (2) digesting the cutout organ into the discrete living animal cells and separating the discrete cells, (3) suspending the separated cells in a solution of sodium chloride containing sodium alginate and collagen, (4) forming microcapsules of the living animal cells by using the resulting suspension, (5) forming immunoisolation membranes around outer surfaces of the microcapsules of the living animal cells by covering the outer surfaces with alginate-(poly-L-lysine) and thereby obtaining the living animal cells enclosed in the immunoisolation membranes, (6) suspending the resulting living animal cells enclosed in the immunocapsules in a cell damage-preventing solution, and (7) immediately with liquid nitrogen.
Owner:SHOWA UNIVERSITY
Application of nicotinamide mononucleotide
ActiveCN101601679BImprove securityEffective controlOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSide effectActive component
The invention discloses the application of nicotinamide mononucleotide on preparing medicines or health-care food for resisting neuronal cell injury cerebral apoplexy or oxygen-glucose deprivation. The invention also provides a novel medical composite which can effectively resist the neuronal cell injury caused by cerebral apoplexy and oxygen-glucose deprivation, thereby showing great significance to the treatment of cerebral apoplexy; and the active component in the medical composite is the nicotinamide mononucleotide which is an endogenic protective substance for an organic body and can notgenerate side effects according to current information, and therefore the nicotinamide mononucleotide used as a medicine has higher security and wide time window for treatment.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Novel menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell separation method
ActiveCN103966162AEasily damagedReduce yieldSkeletal/connective tissue cellsStem Cell IsolationCentrifugation
The invention provides a novel menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell separation method, belonging to the field of methods for separating stem cells from menstrual blood. In order to solve the problems of long centrifugal time, relatively serious cell injury, low cell yield and the like existing in a lymph separating medium method in the traditional method, the invention provides the novel menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell separation method comprising the steps of with source-wide menstrual blood as a material, storing by using a special preserving fluid in a collecting process; then, carrying out primary separation by using a density gradient centrifugation method of a lymphocyte separation tube, and optimizing the centrifugal time and centrifugal rotating speed in separation; and next, carrying out secondary separation according to the wall attachment growth characteristic of the stem cells, simultaneously separating and amplifying the stem cells, and maintaining the activity of the stem cells to the maximum extent in the separation process. The obtained menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell is high in purity, quantity and application value. The novel menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell separation method is simple in operation and low in cost.
Owner:CHENGDU QINGKE BIOTECH
Clinic compliant method for banking human placental mesenchymal cells
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com