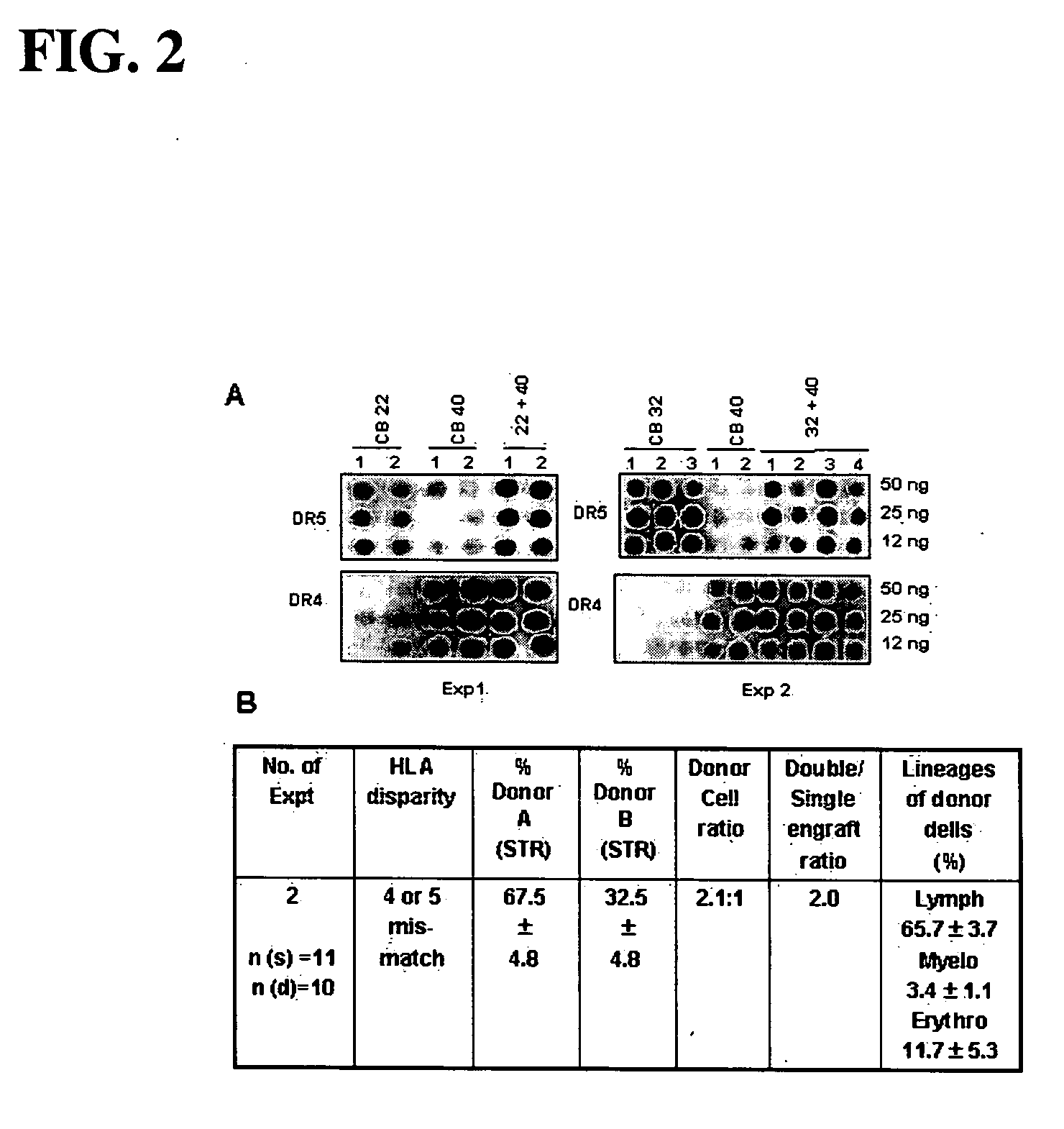
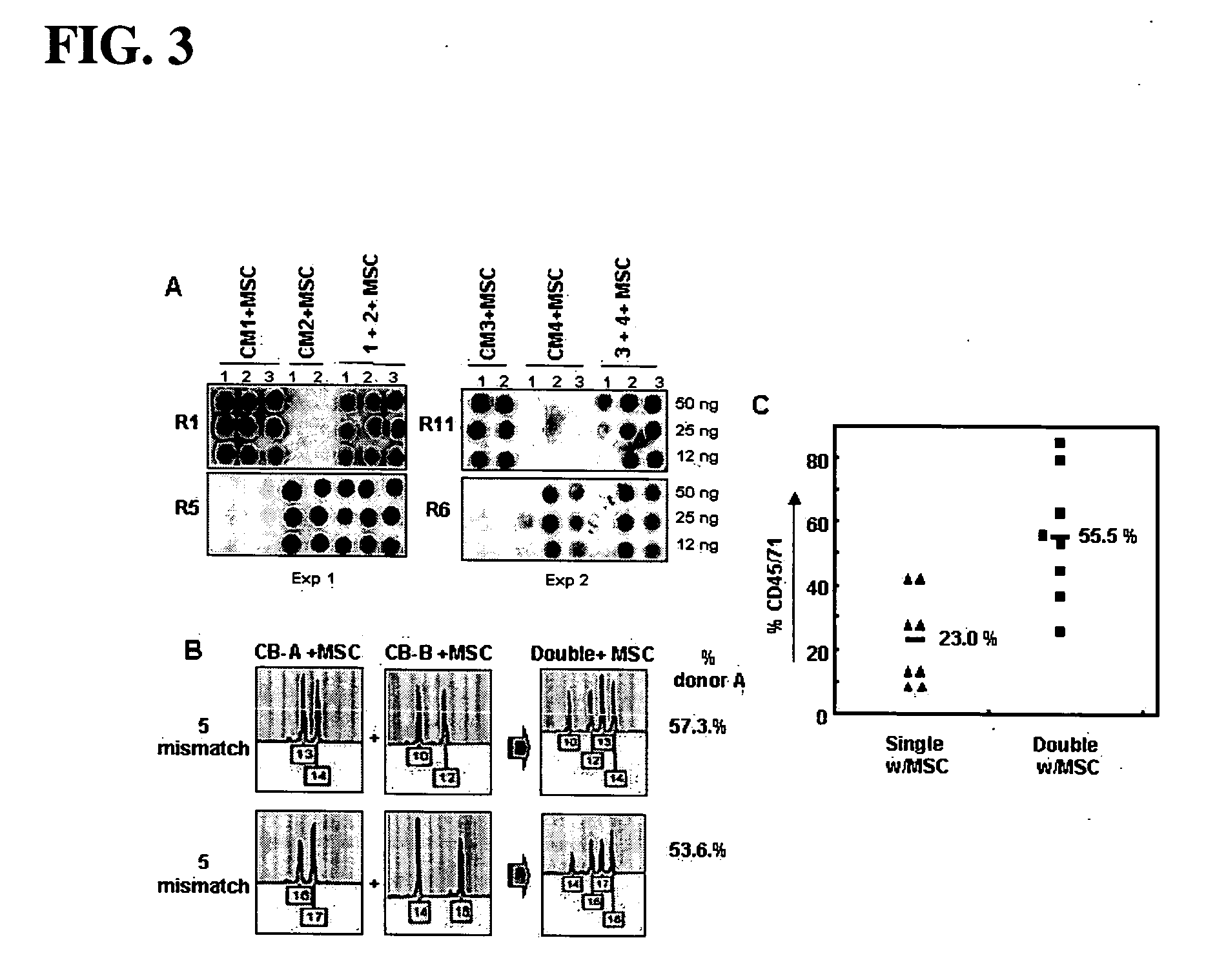
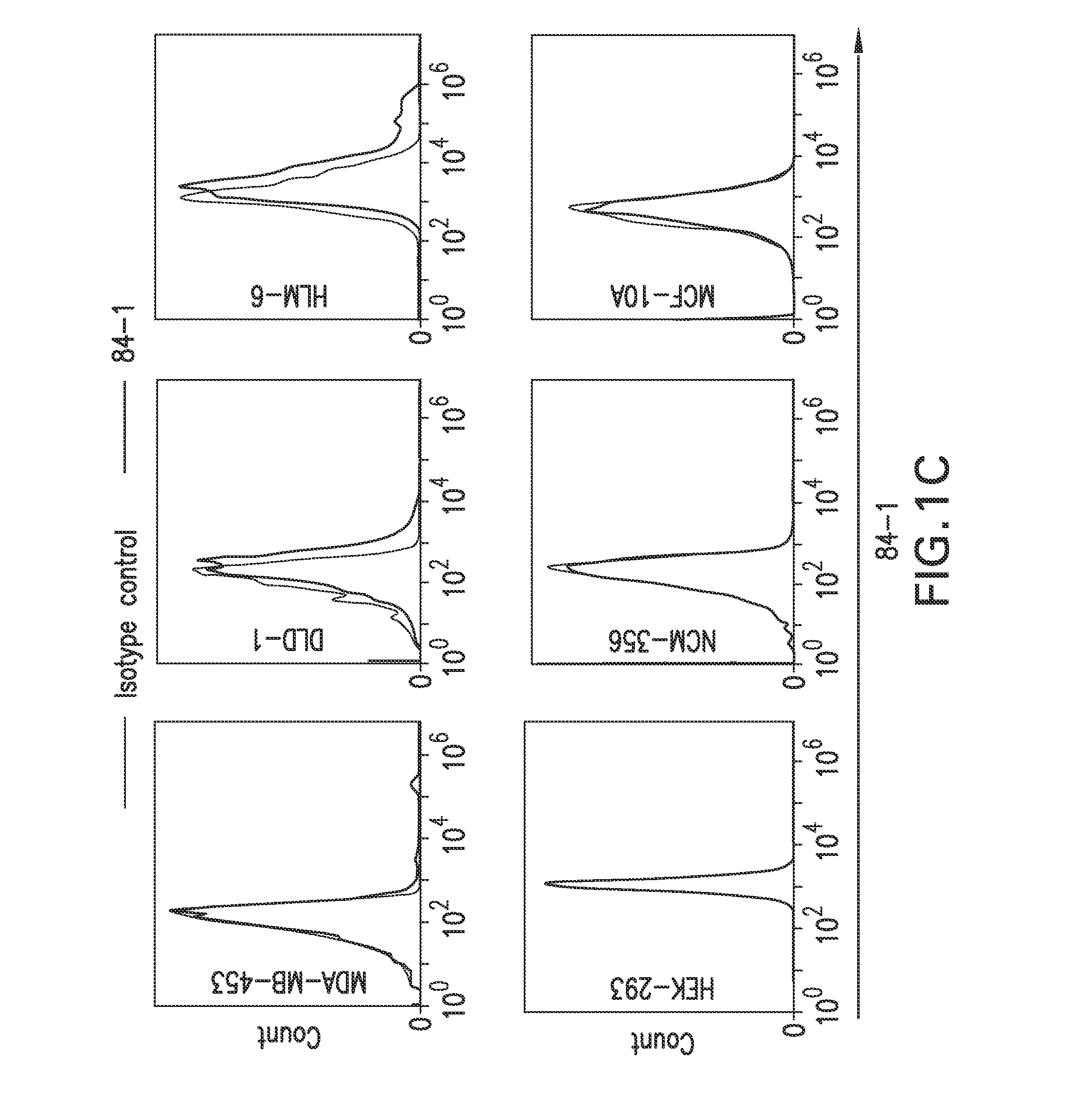
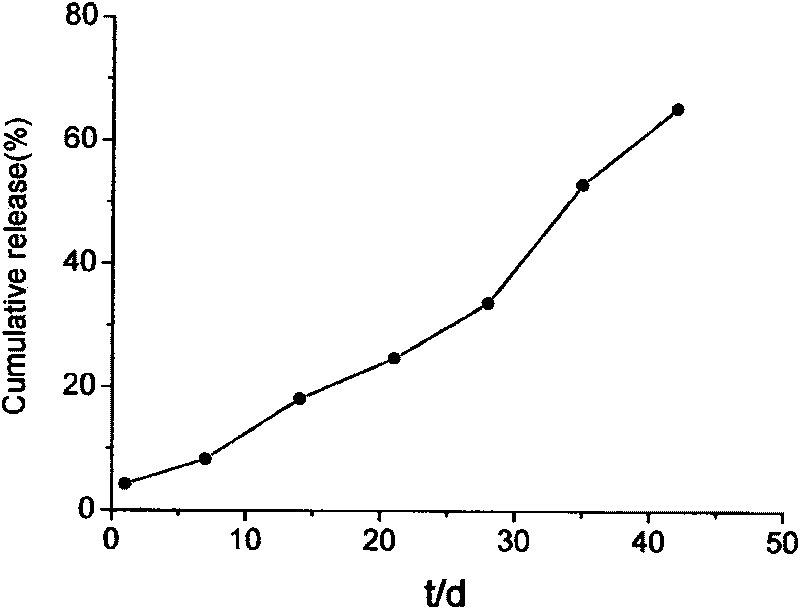
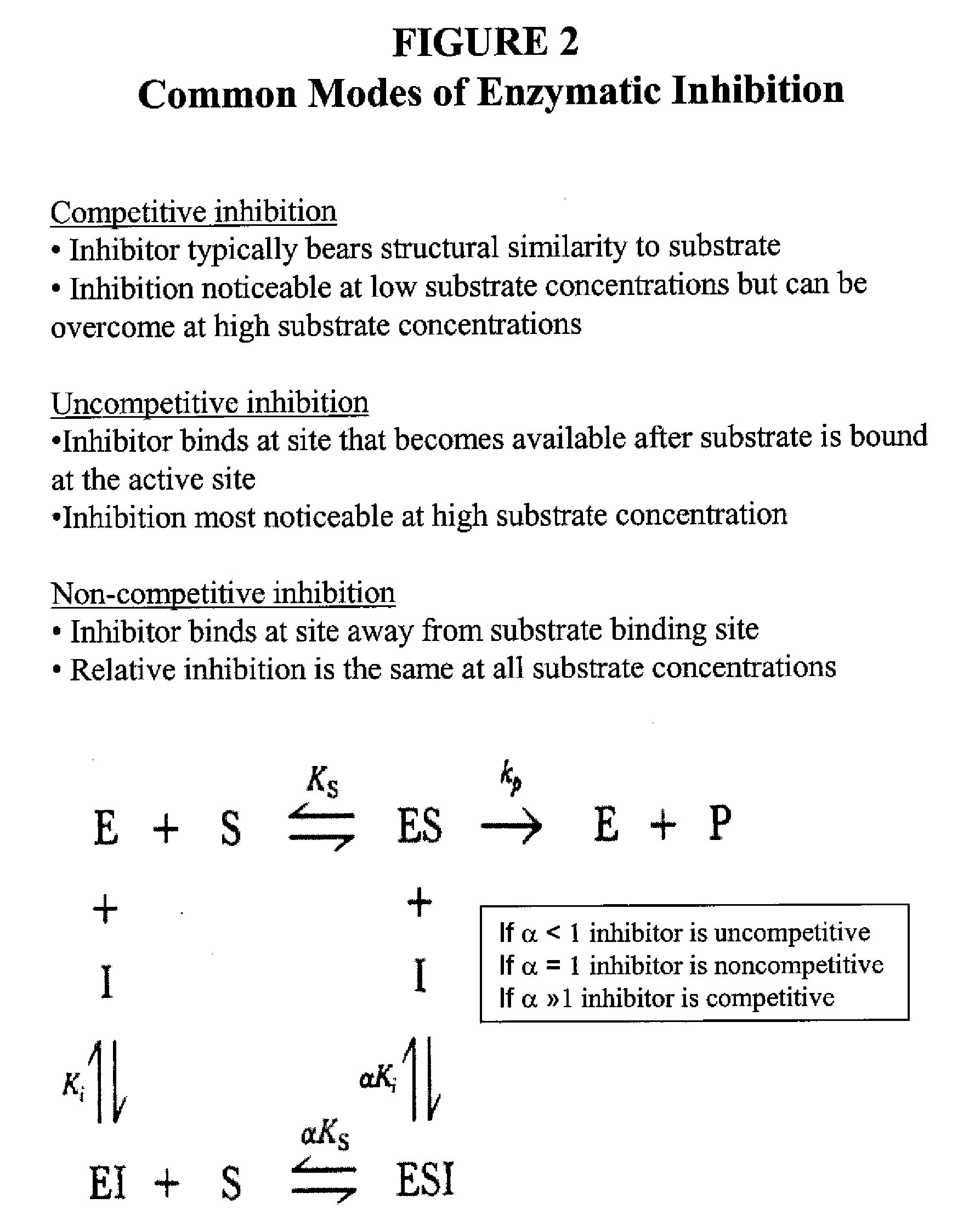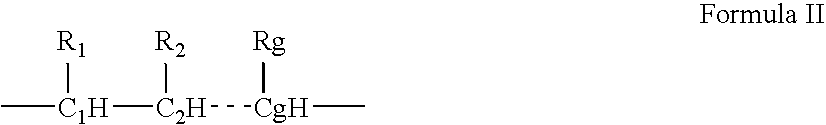Patents
Literature
209 results about "Mesenchyma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mesodermal tissue or tissue with mesodermal origin.
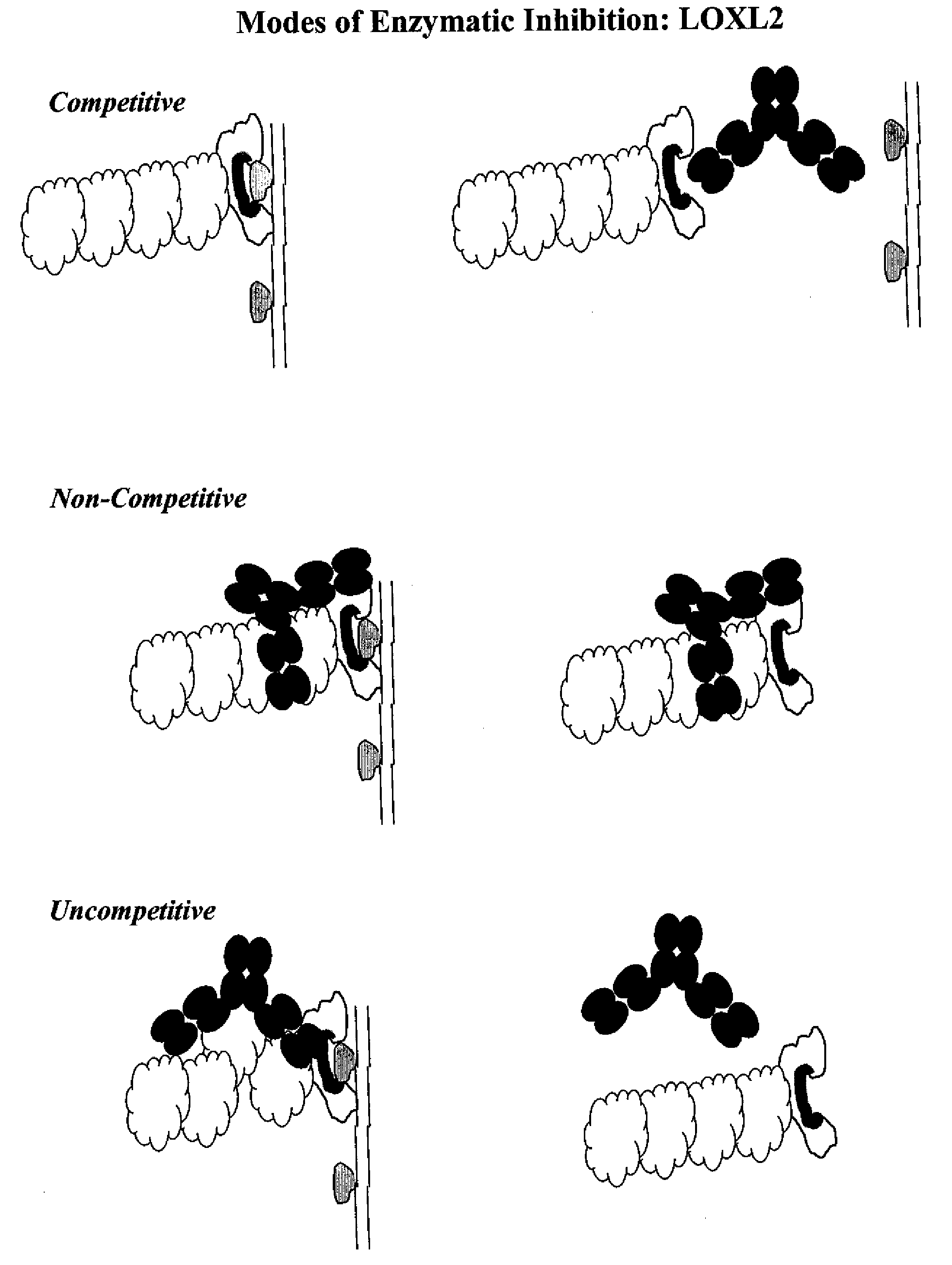
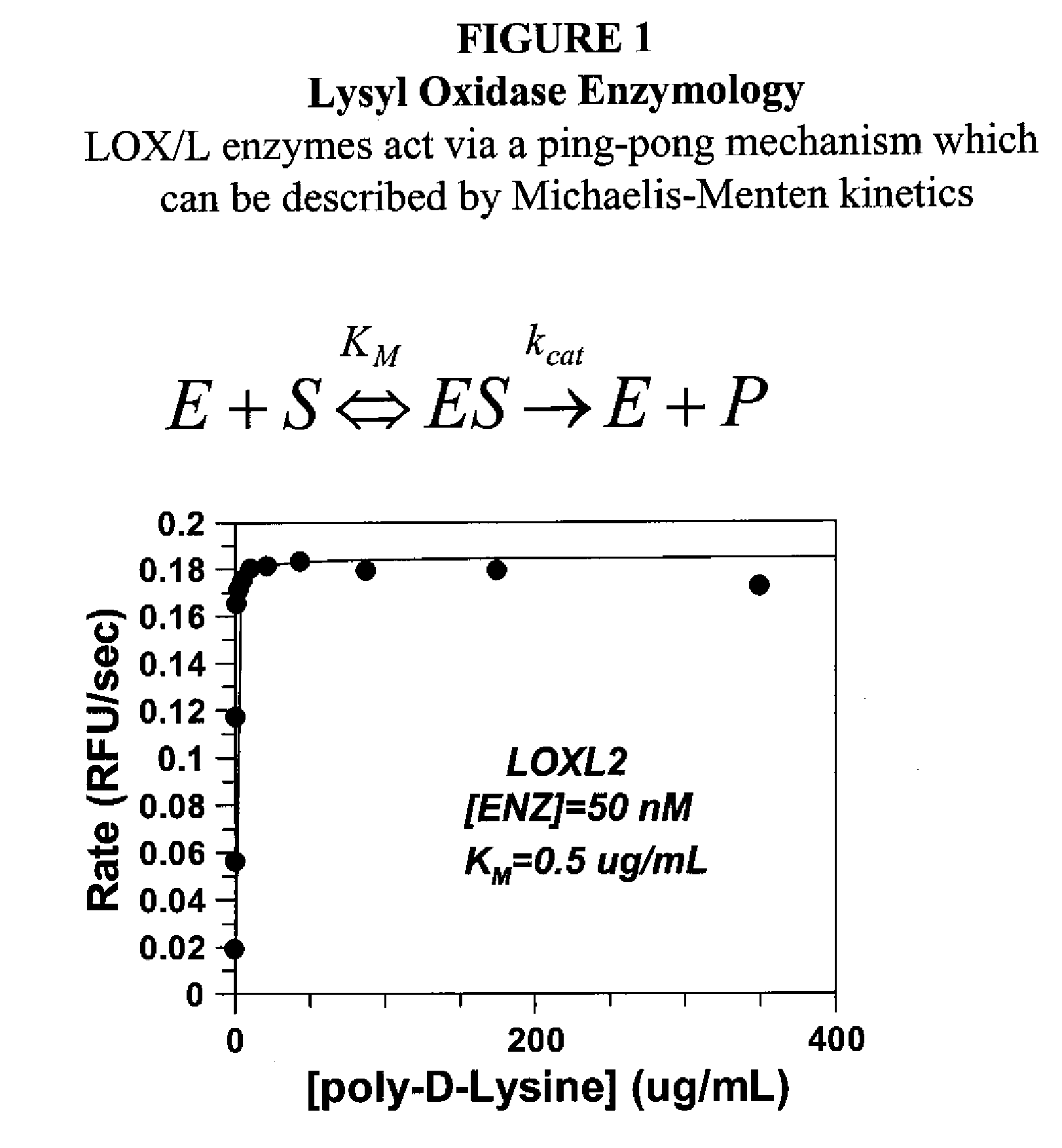
Lox and loxl2 inhibitors and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090053224A1Block enzymatic activitySlow tumor growthNervous disorderMuscular disorderAngiogenesis growth factorFibrosis
The present application relates to anti-LOX and anti-LOXL2 antibodies and their use in purification, diagnostic and therapeutic methods. Antibodies include monoclonal antibodies, humanized antibodies and functional fragments thereof. Anti-LOX and anti-LOXL2 antibodies can be used to identify and treat conditions such as a fibrotic condition, angiogenesis, or to prevent a transition from an epithelial cell state to a mesenchymal cell state.
Owner:GILEAD BIOLOGICS
Methods of ex vivo progenitor and stem cell expansion by co-culture with mesenchymal cells
Methods of ex-vivo expansion and at the same time inhibiting differentiation of stem cells by co-culture with mesenchymal cells, transplantable populations of renewable progenitor and stem cells expanded thereby, and their uses in therapeutic applications.
Owner:GAMIDA CELL
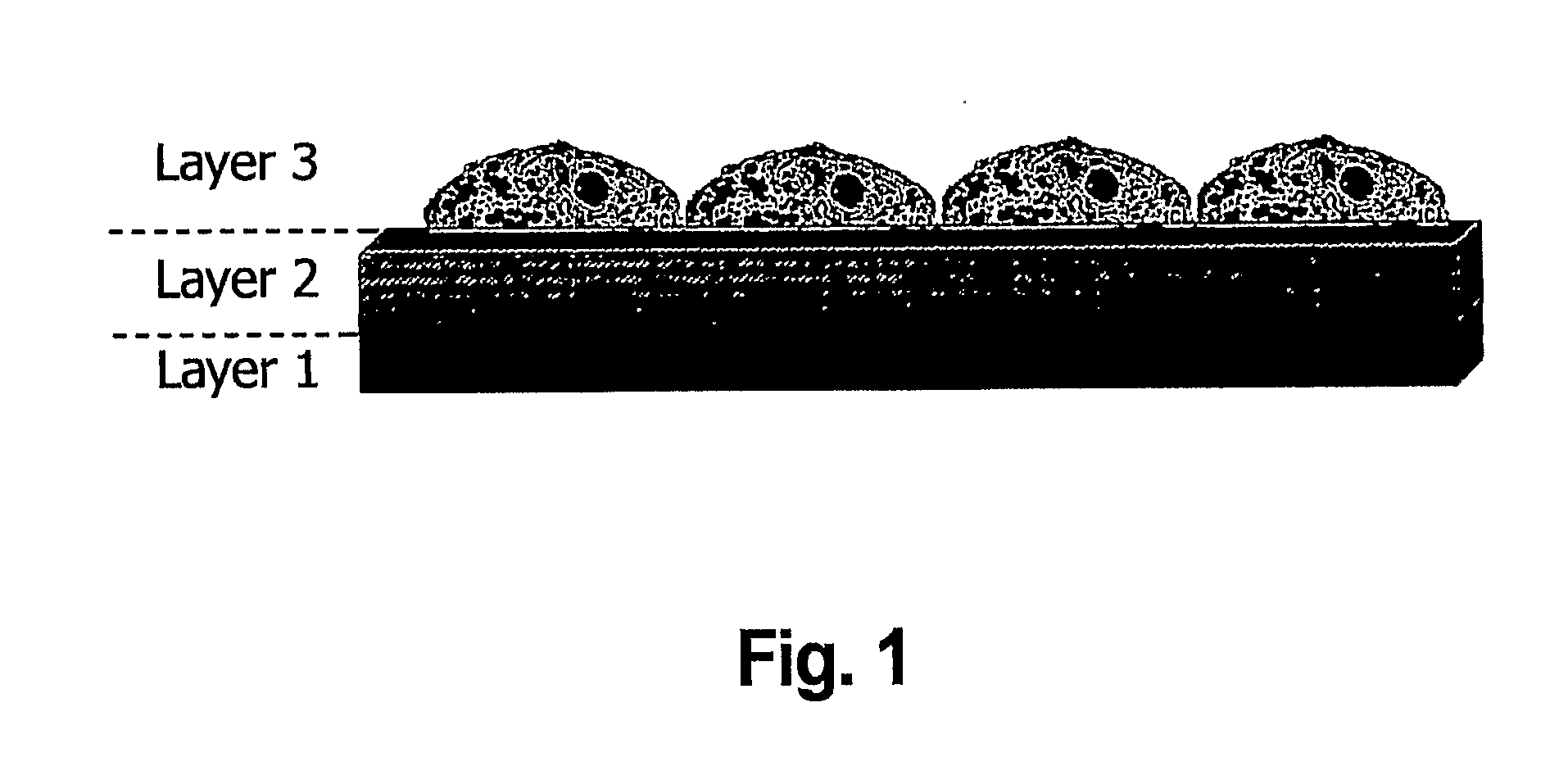
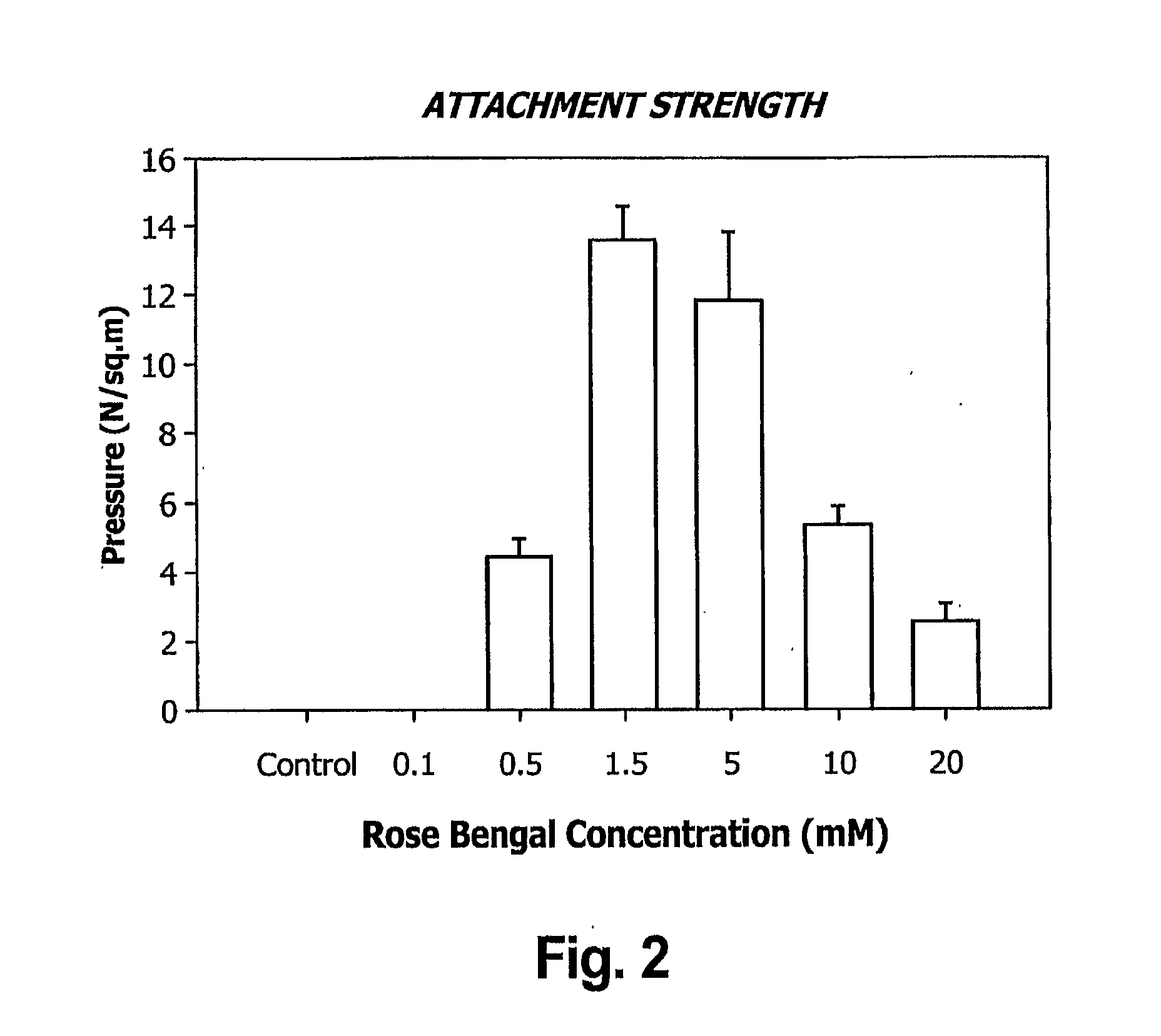
Layered bio-adhesive compositions and uses thereof
The invention generally provides compositions and methods for promoting and enhancing wound closure and healing. Specifically, the invention provides a biologic composition which comprises a support layer which serves as transport scaffold, for example made of gelatin, which is coated or impregnated with a bio-adhesive molecule such as rose bengal or glyceraldehyde. The composition can also comprise an artificial or biological matrix, optionally processed (i.e. cleaned and coated with extracellular matrix proteins) to enhance cell attachment and survival. The composition can further comprise a monolayer of epithelial, endothelial cells or mesenchymal cells. The invention provides methods for using the compositions for treating wounds due to disease, trauma or surgery. Specific methods for treating ocular wounds are provided.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Biological markers predictive of anti-cancer response to insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor kinase inhibitors
InactiveUS20070065858A1Restore sensitivityHigh sensitivityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionInsulin-like growth factorPancreatic hormone
The present invention provides diagnostic and prognostic methods for predicting the effectiveness of treatment of a cancer patient with an IGF-1R kinase inhibitor. Methods are provided for predicting the sensitivity of tumor cell growth to inhibition by an IGF-1R kinase inhibitor, comprising assessing whether the tumor cell has undergone an epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), by determining the expression level of epithelial and / or mesenchymal biomarkers, wherein tumor cells that have undergone an EMT are substantially less sensitive to inhibition by IGF-1R kinase inhibitors. Improved methods for treating cancer patients with IGF-1R kinase inhibitors that incorporate the above methodology are also provided. Additionally, methods are provided for the identification of new biomarkers that are predictive of responsiveness of tumors to IGF-1R kinase inhibitors. Furthermore, methods for the identification of agents that restore the sensitivity of tumor cells that have undergone EMT to inhibition by IGF-1R kinase inhibitors are also provided.
Owner:OSI PHARMA INC
Bioartificial filtration device for filtering blood to mimic kidney function
InactiveUS6942879B2Long life-timeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBioartificial liver deviceUltrafiltration
A novel cell seeded hollow fiber bioreactor is described as a potential bioartificial kidney. Endothelial cells along with pericyte, vascular smooth muscle, and / or mesangial cells or any mesenchymally derived support cells are seeded along a hollow fiber in a perfused bioreactor to reproduce the ultrafiltration function and transport function of the kidney. Maintenance of tissue specific function and ultrastructure suggest that this bioreactor provides an economical device for treating renal failure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
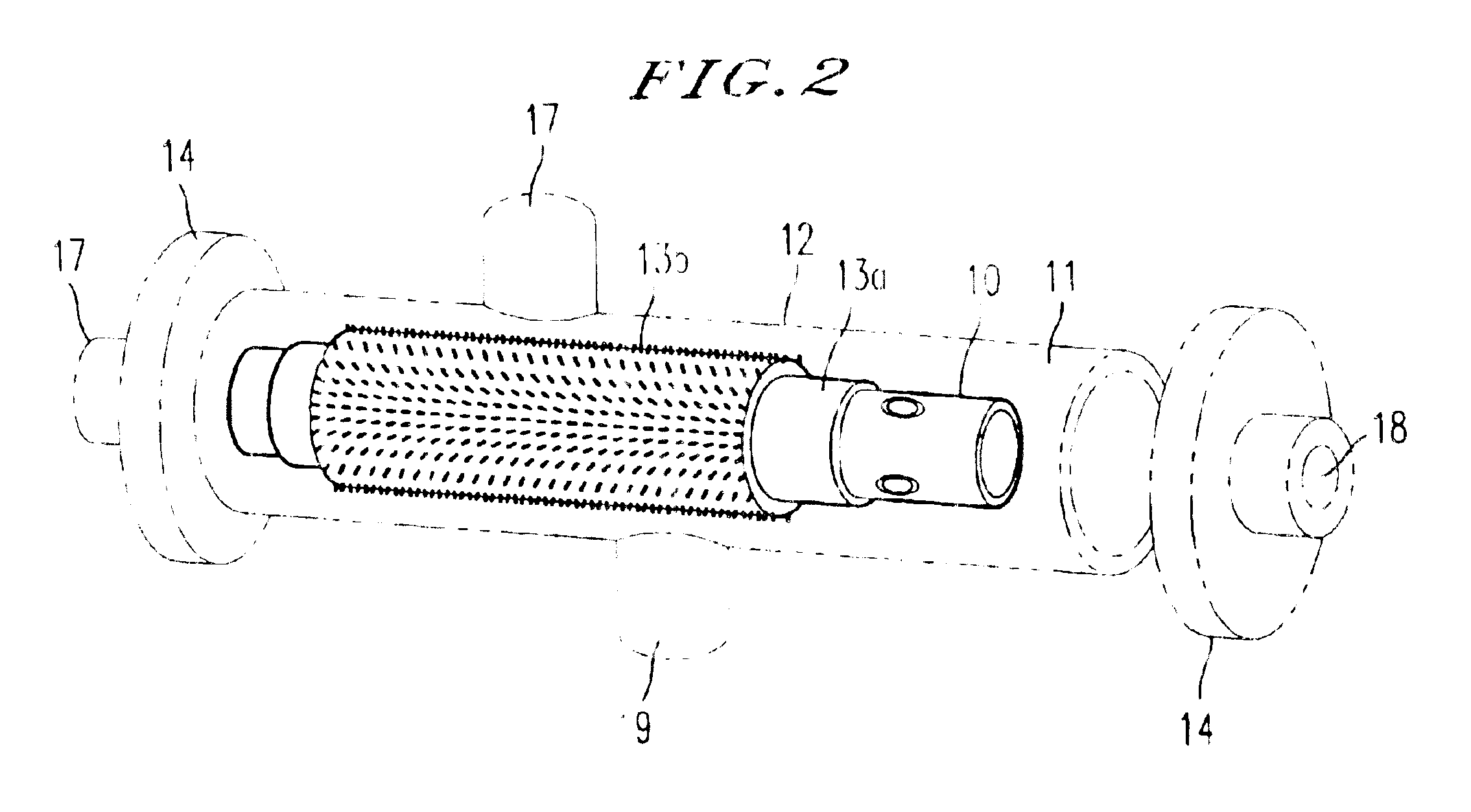
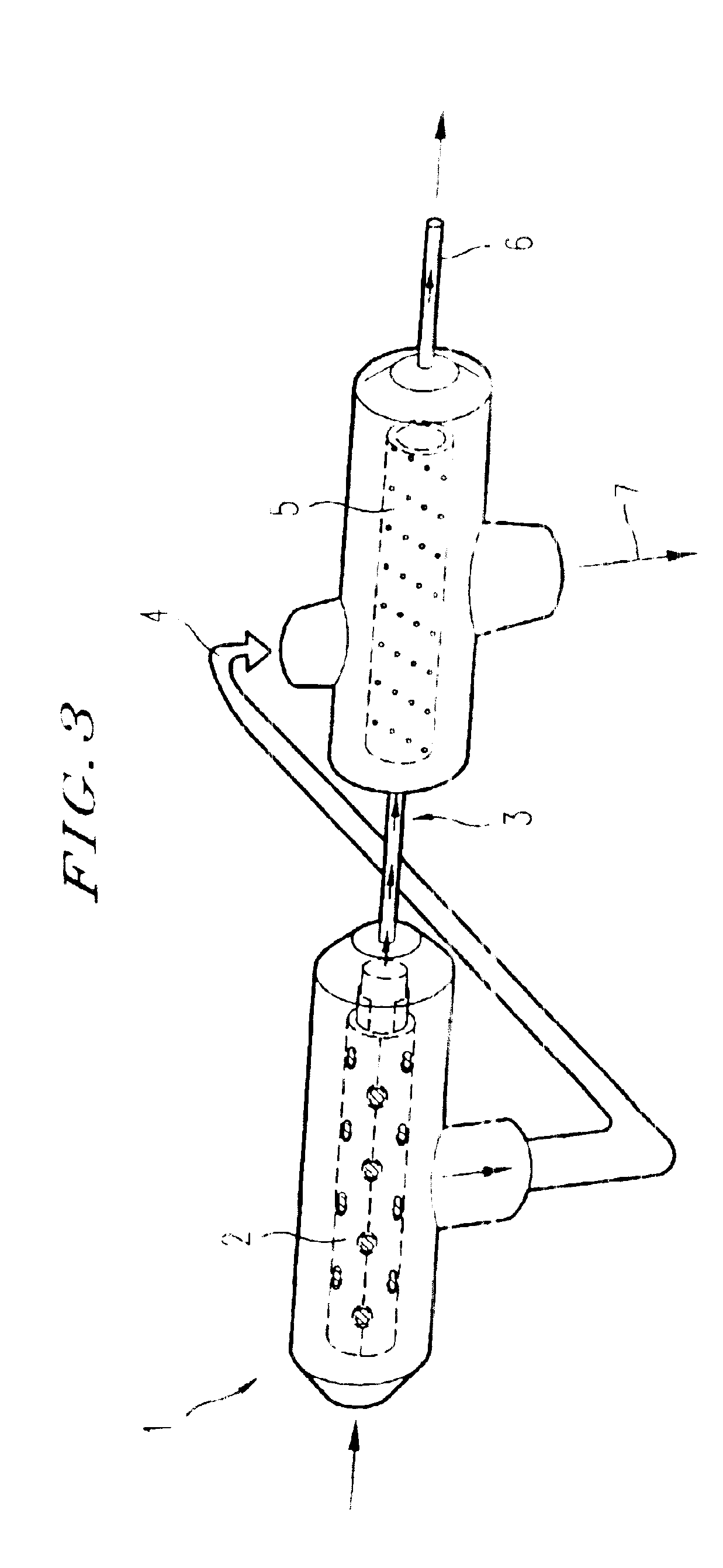
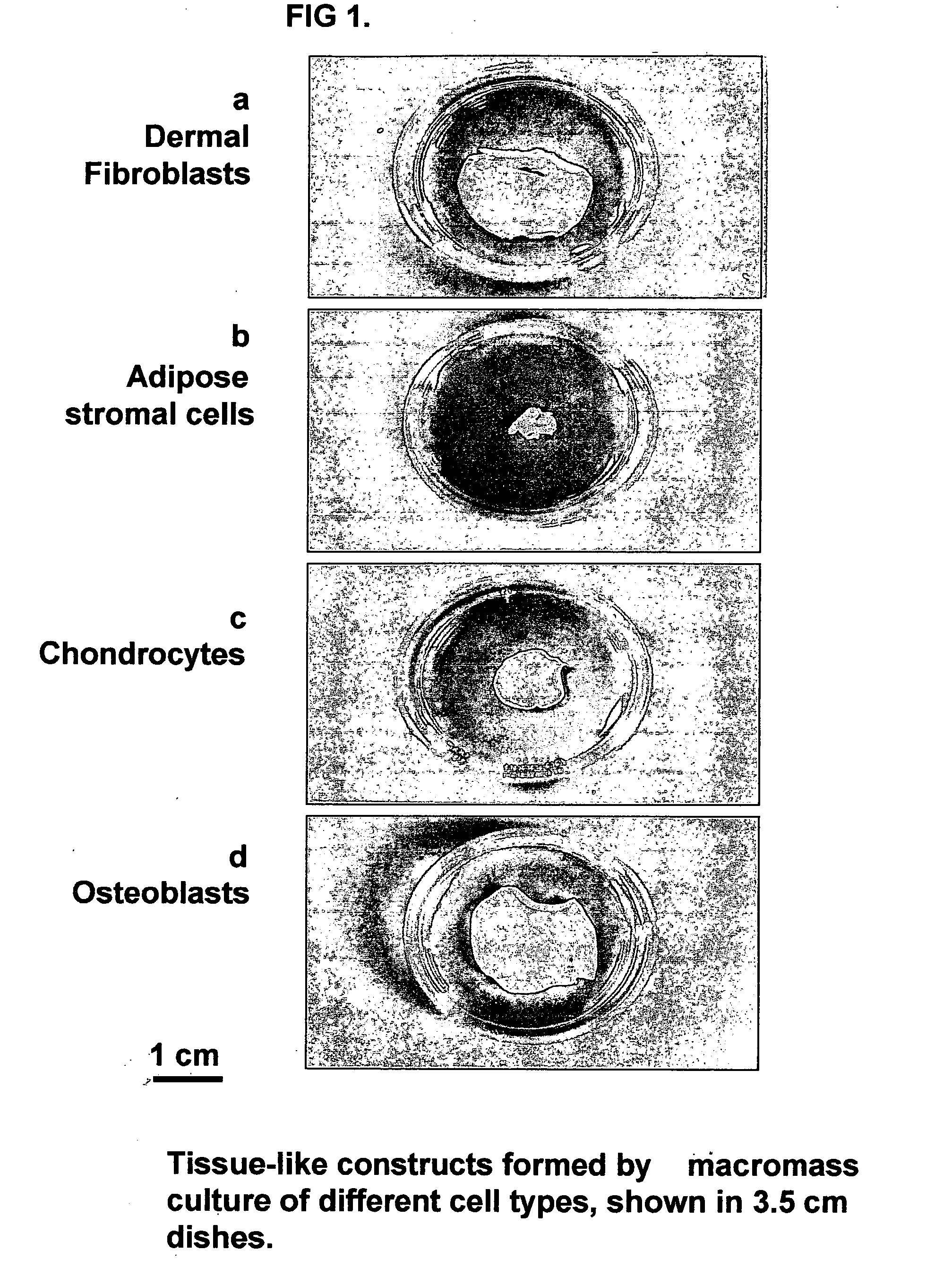
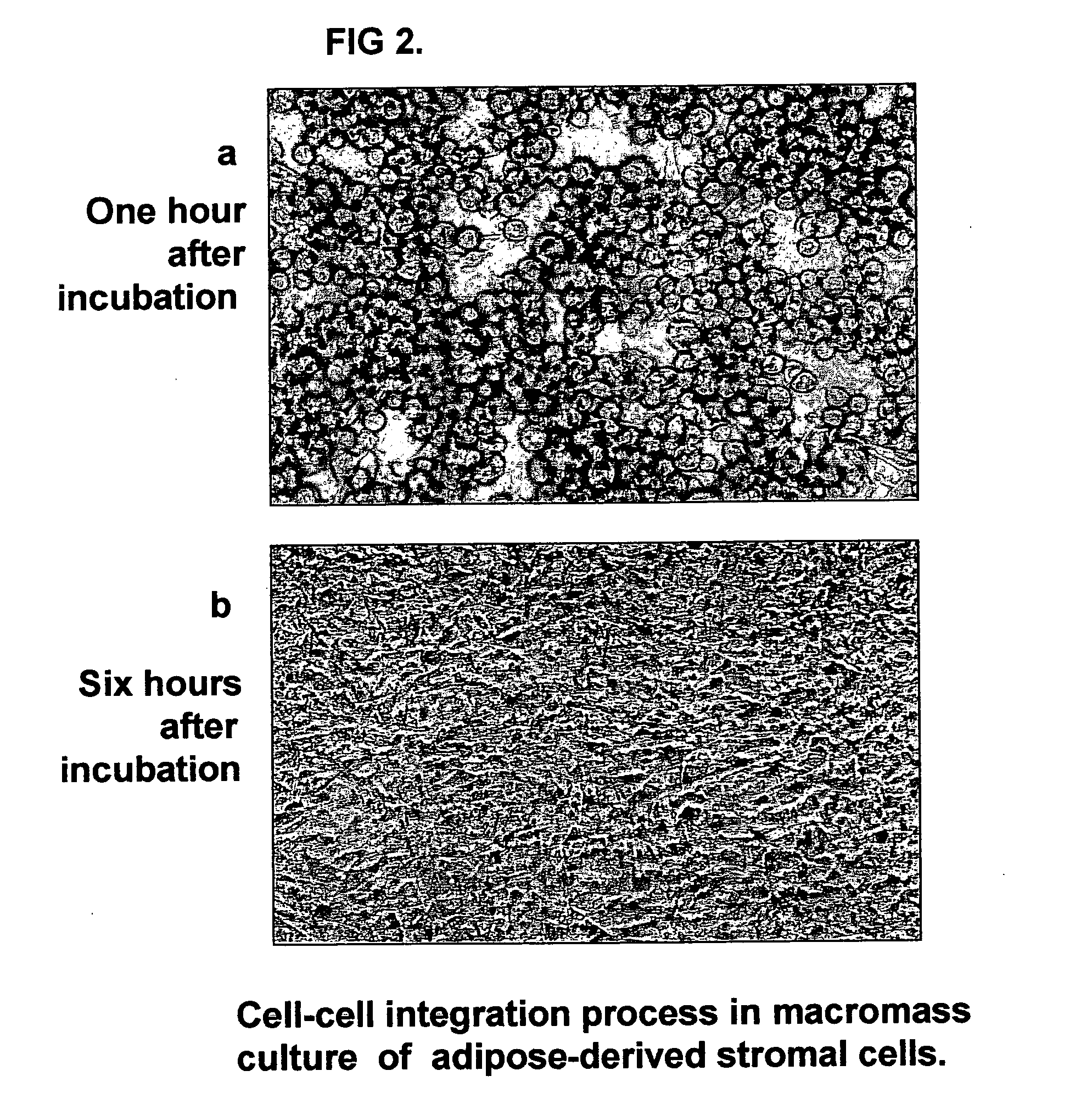
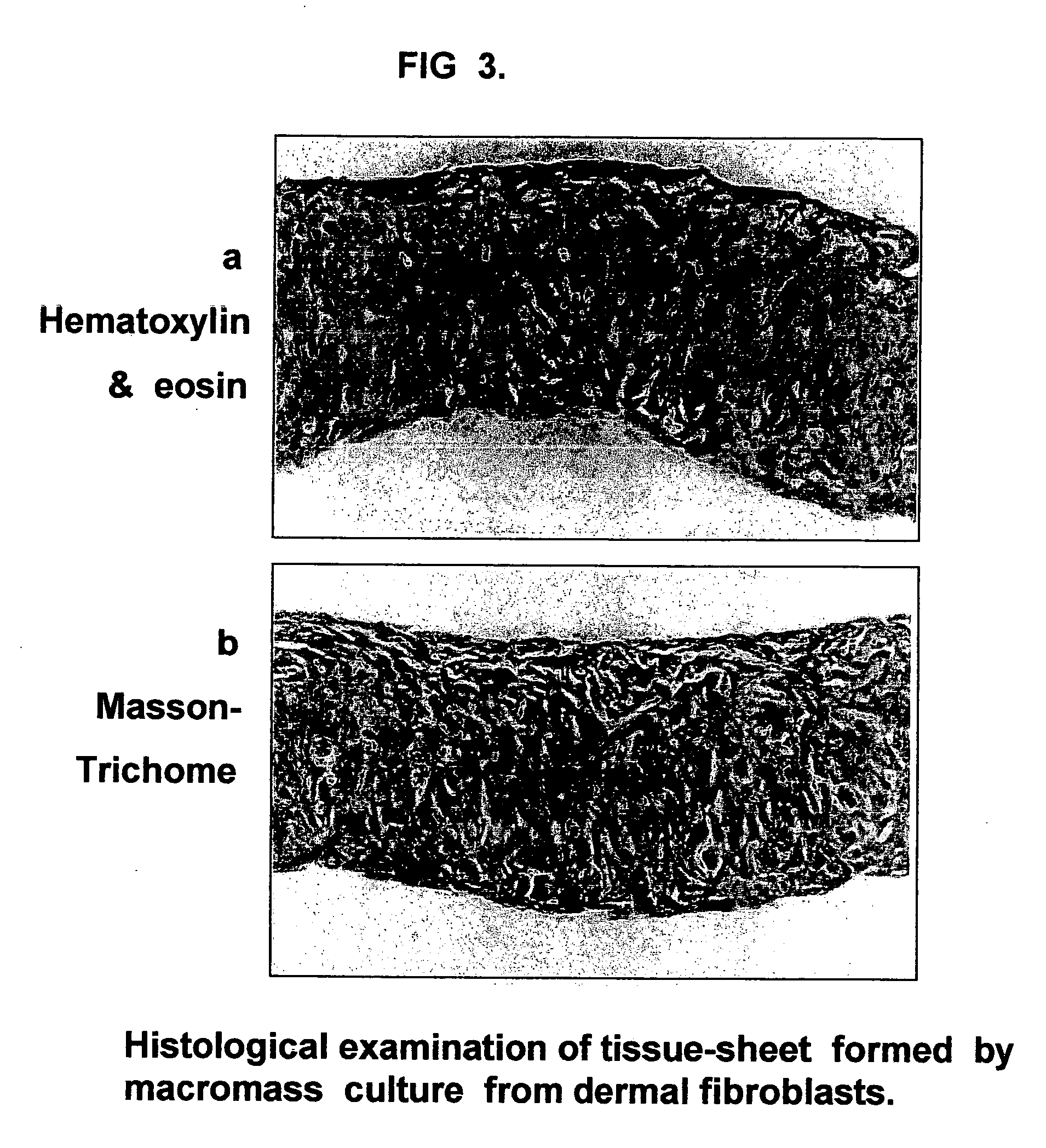
Tissue-like organization of cells and macroscopic tissue-like constructs, generated by macromass culture of cells, and the method of macromass culture
InactiveUS20040082063A1Sectioned easilySmall sizeEpidermal cells/skin cellsMammal material medical ingredientsHigh cellFiber
Three-dimensional tissue-like organization of cells by high cell-seeding-density culture termed as macromass culture is described. By macromass culture, cells can be made to organize themselves into a tissue-like form without the aid of a scaffold and three-dimensional macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be made wholly from cells. Tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be generated from fibroblastic cells of mesenchymal origin (at least), which can be either differentiated cells or multipotent adult stem cells. In this work, tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs have been generated from dermal fibroblasts, adipose stromal cells-derived osteogenic cells, chondrocytes, and from osteoblasts. The factor causing macroscopic tissue formation is large scale culture at high cell seeding density per unit area or three-dimensional space, that is, macromass culture done on a large scale. No scaffold or extraneous matrix is used for tissue generation, the tissues are of completely cellular origin. No other agents (except high cell-seeding-density) that aid in tissue formation such as tissue-inducing chemicals, tissue-inducing growth factors, substratum with special properties, rotational culture, etc, are employed for tissue formation. These tissue-like masses have the potential for use as tissue replacements in the human body. Tissue-like organization by high cell-seeding-density macromass culture can also be generated at the microscopic level.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Method of image guided intraoperative simultaneous several ports microbeam radiation therapy with microfocus X-ray tubes
This invention pertains to a method of low-cost intraoperative all field simultaneous parallel microbeam single fraction few seconds duration 100 to 1,000 Gy and higher dose radiosurgery with micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS)-carbon nanotube based microaccelerators. It ablates cancer cells including the mesenchymal epithelial transformation associated cancer stem cells. Microbeam brachy-therapeutic radiosurgery is performed. Microaccelerators are configured for simultaneous parallel microbeam emission from varying angels to an isocentric tumor. Their additive dose rate at the isocentric tumor is in the range of 10,000 to 20,000 Gy / s. It eliminates most tumor recurrence and metastasis which enhances cancer cure rates. It also exposes cancer antigens which induces cancer immunity. Stereotactic breast core biopsy is combined with, positron emission tomography and computerized tomography and phase-contrast imaging. Parallel microbeam brachytherapy preserves normal breast appearance. Migration of normal stem cells from unirradiated valley regions heals the radiation damage to the normal tissue.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
Substrate recognition by differentiable human mesenchymal stem cells
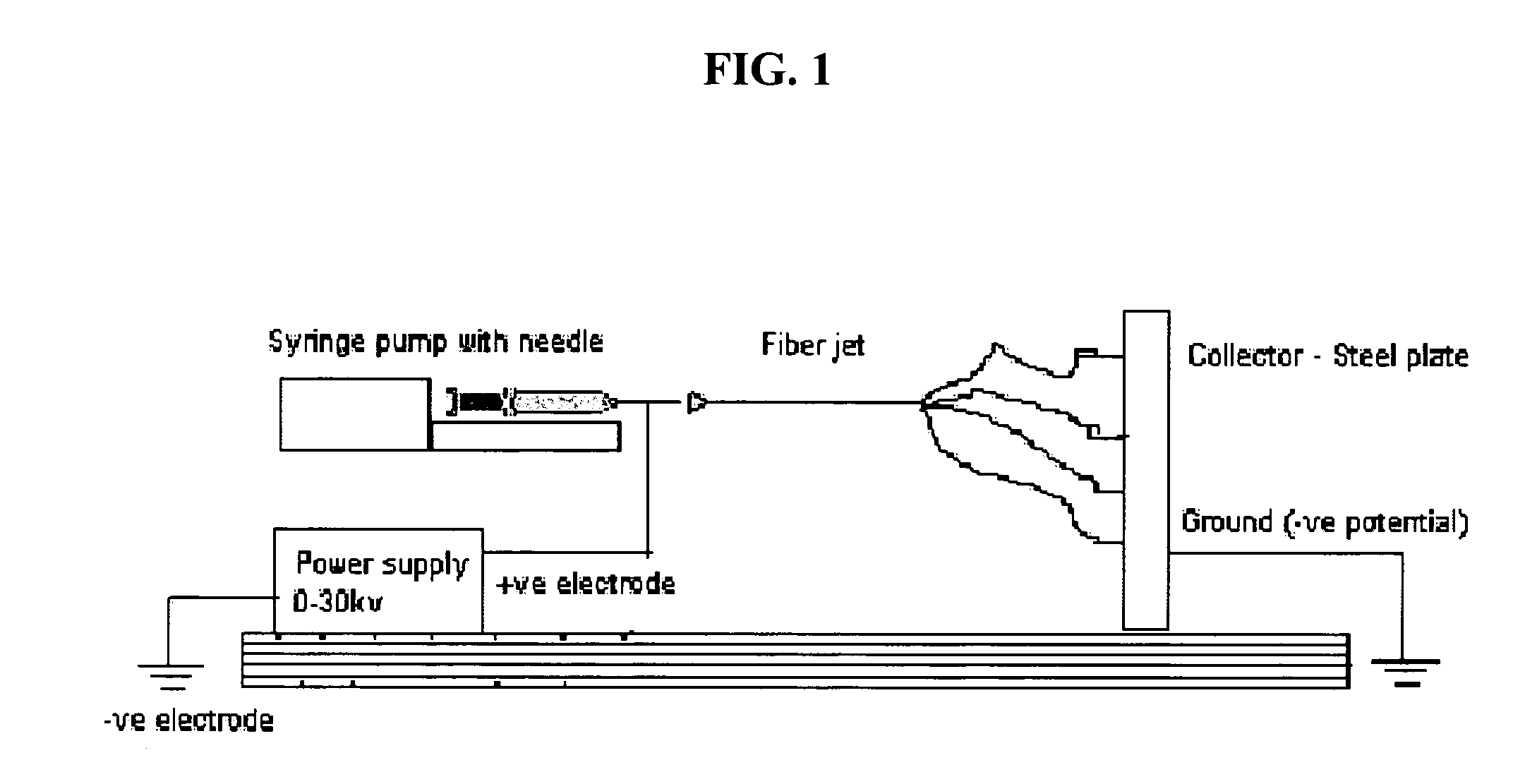
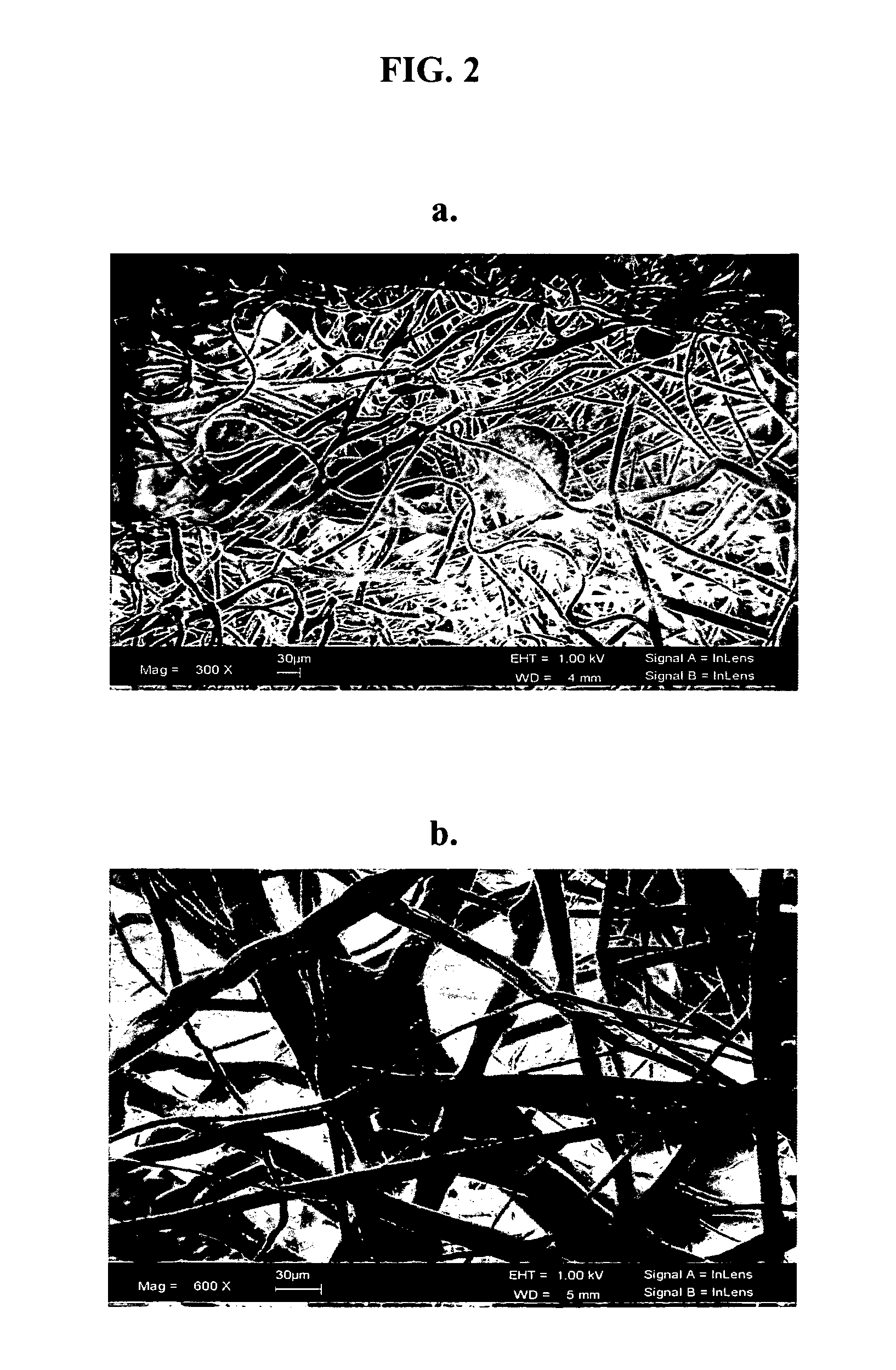
InactiveUS20060128012A1Effective therapyPulse automatic controlFilament/thread formingFiberNanofiber
The invention described herein provides a structure for growing isolated differentiable human mesenchymal cells, which includes a three-dimensional matrix of fibers. The matrix serves as an implantable scaffolding for delivery of differentiable human mesenchymal cells in tissue engineering. The invention further provides compositions that contain the three-dimensional matrix of fibers seeded with isolated differentiable human mesenchymal cells, wherein the matrix forms a supporting scaffold for growing the isolated differentiable human mesenchymal cells, and wherein the differentiable human mesenchymal cells differentiate into a mature cell phenotype. The invention further provides methods of preparing the implantable nanofiber matrix scaffolding seeded with differentiable human mesenchymal cells for use in tissue engineering.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Mesenchymal precursor cell
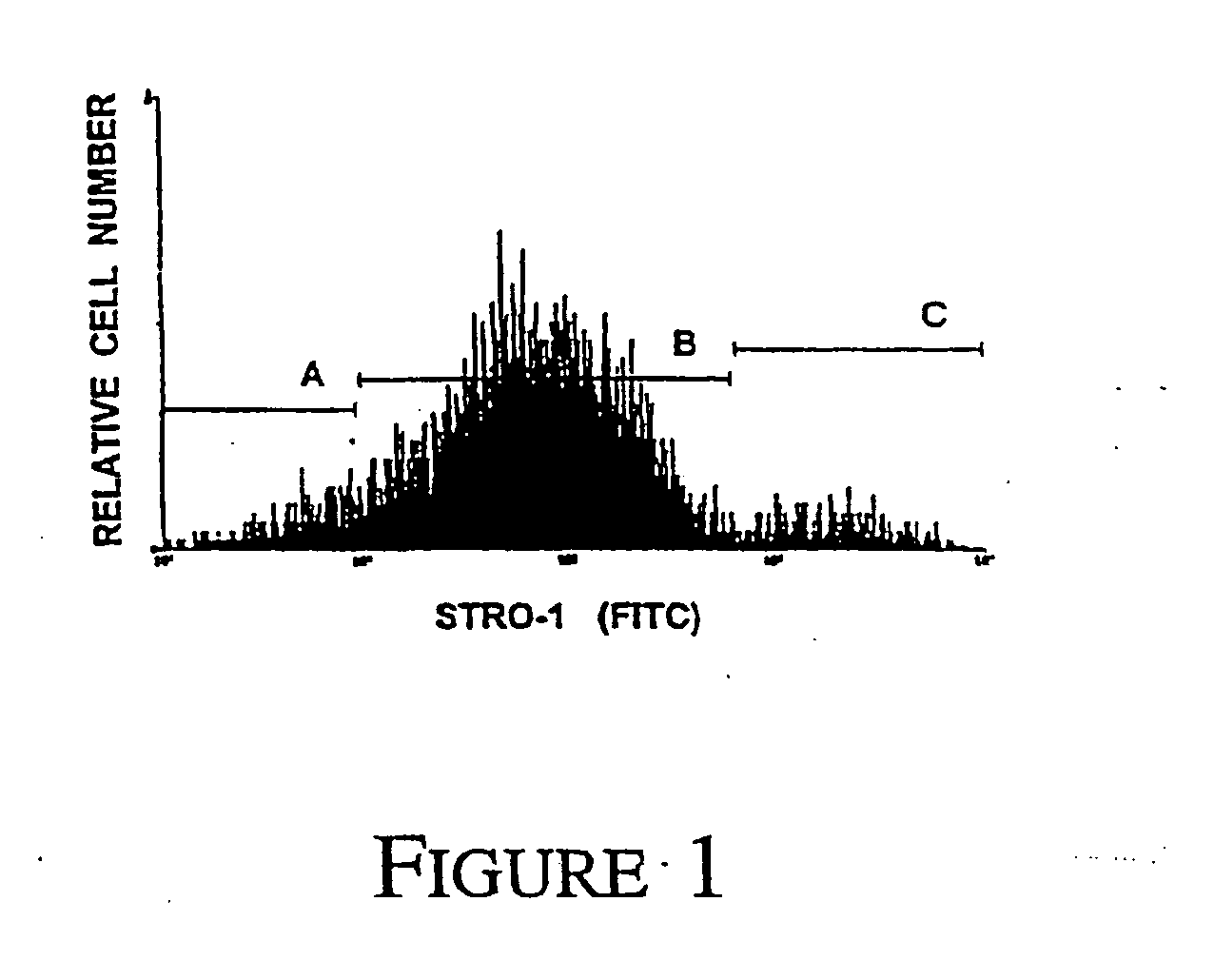
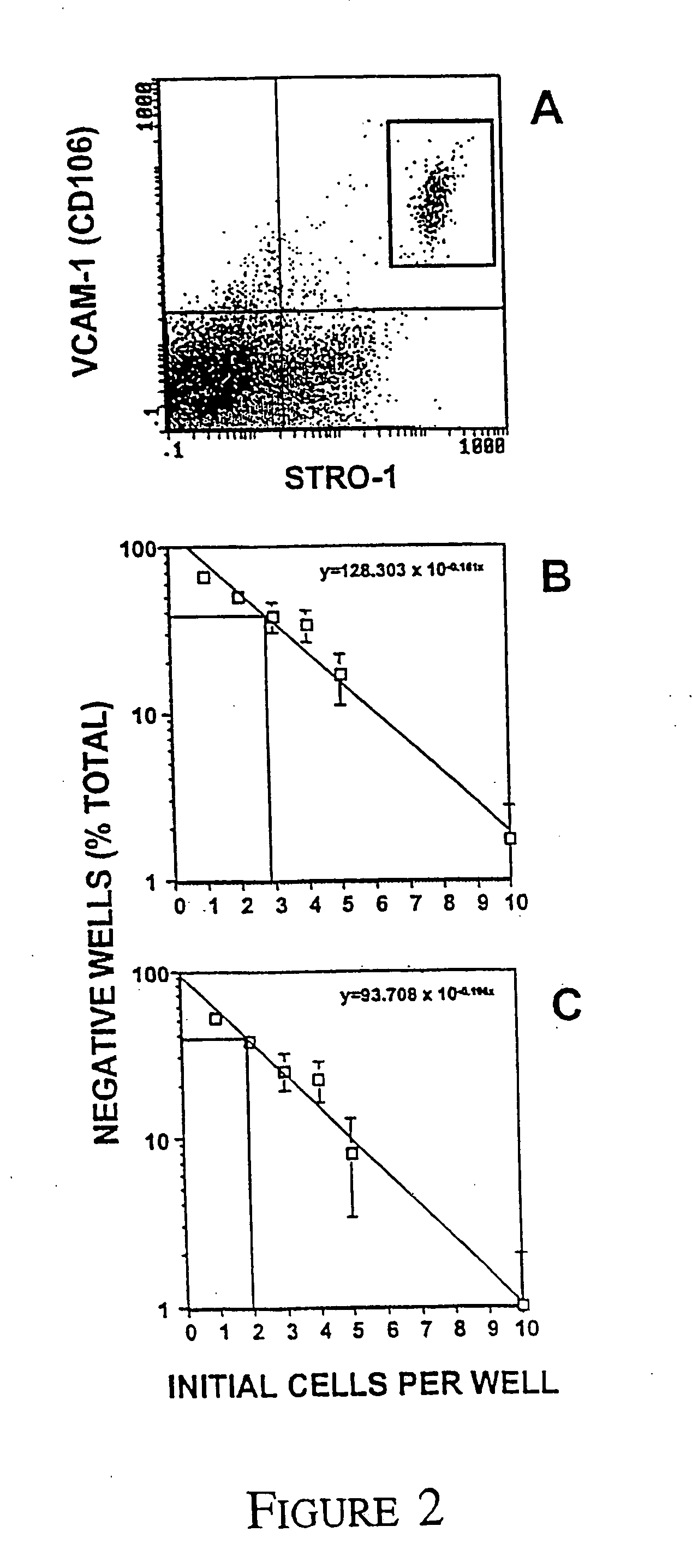
InactiveUS20060008452A1Improved implantIncrease ratingsBiocideGenetic material ingredientsVCAM-1Antigen
Owner:MESOBLAST
Genetic Alterations Useful For The Response Prediction of Malignant Neoplasia to Taxane-Based Medical Treatments
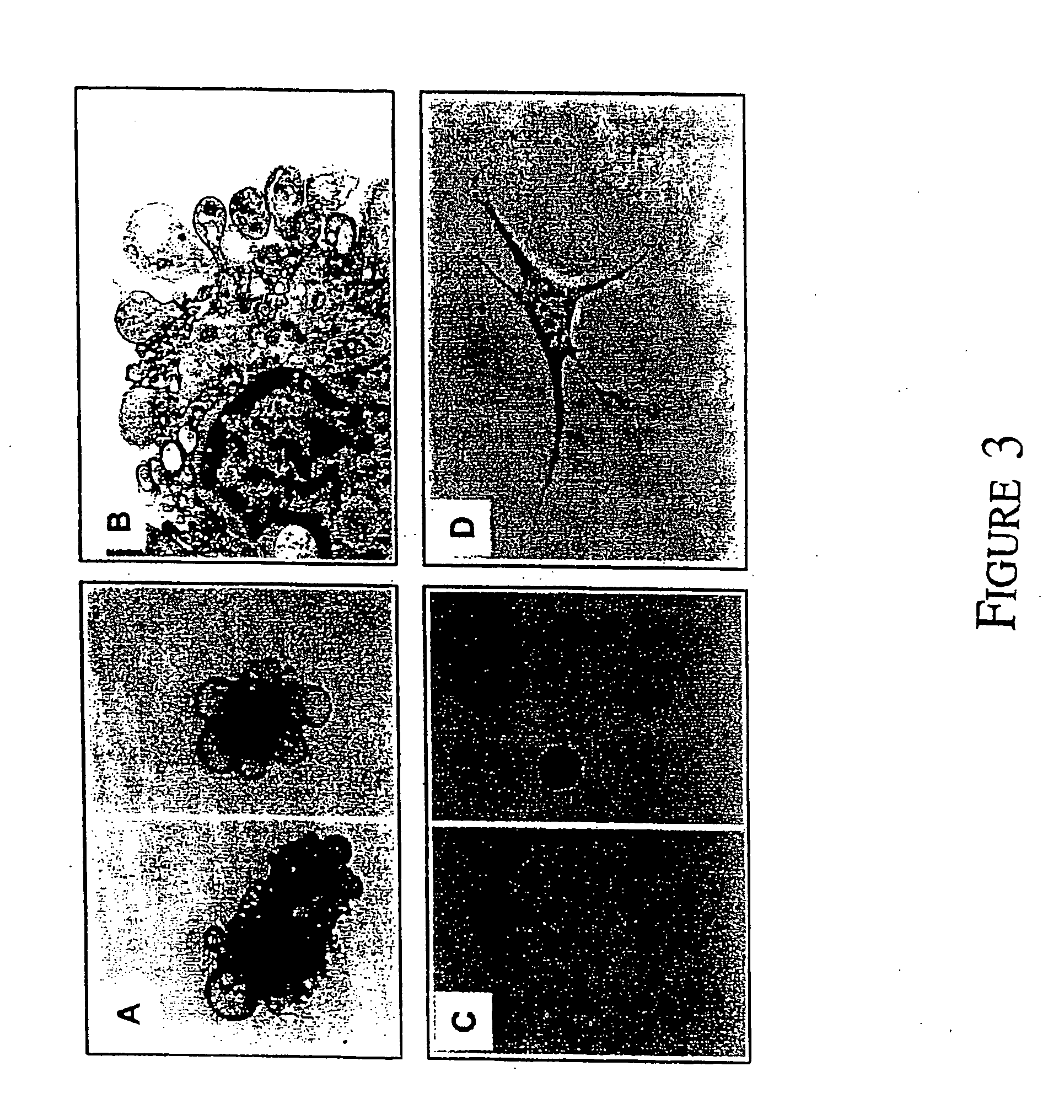
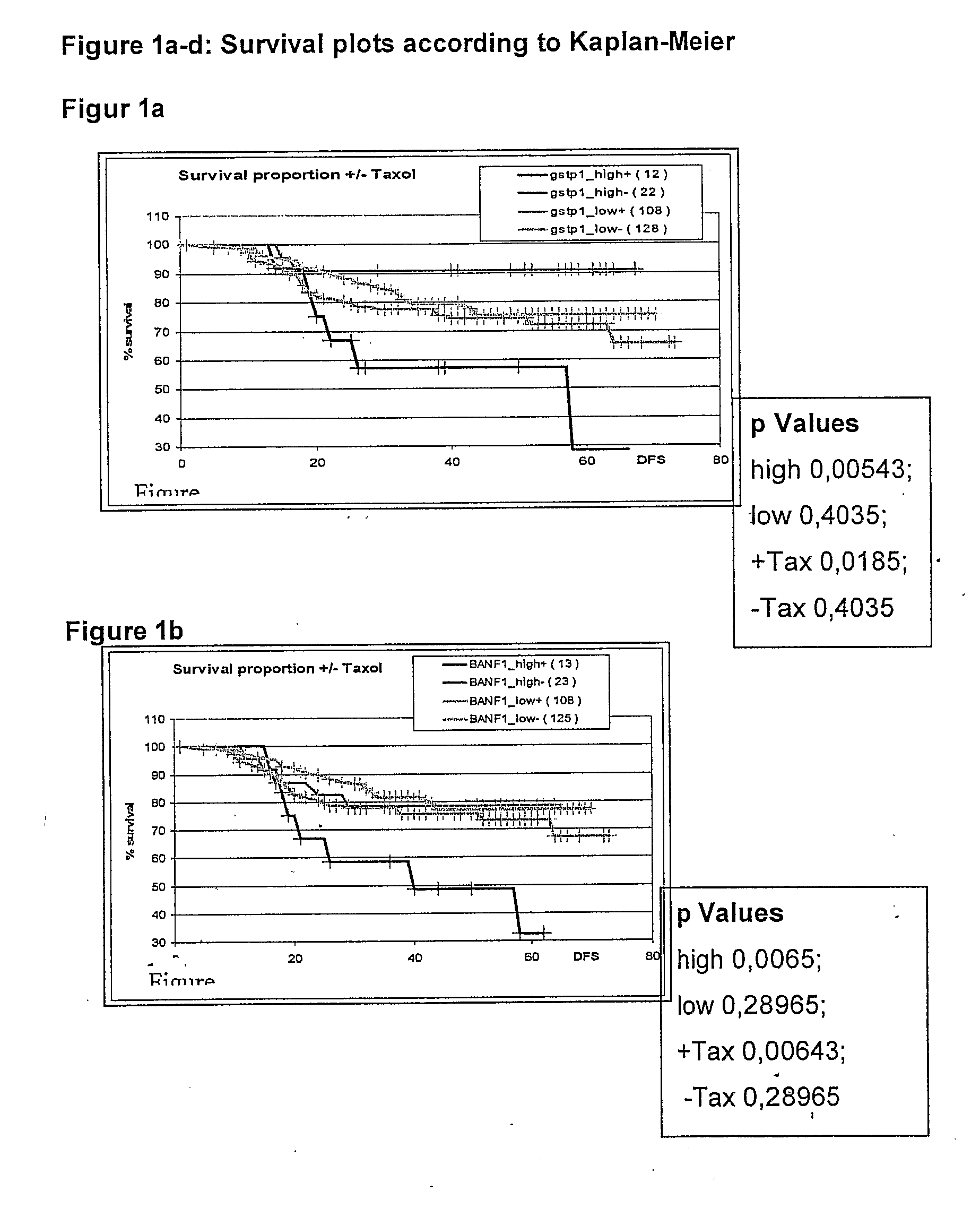
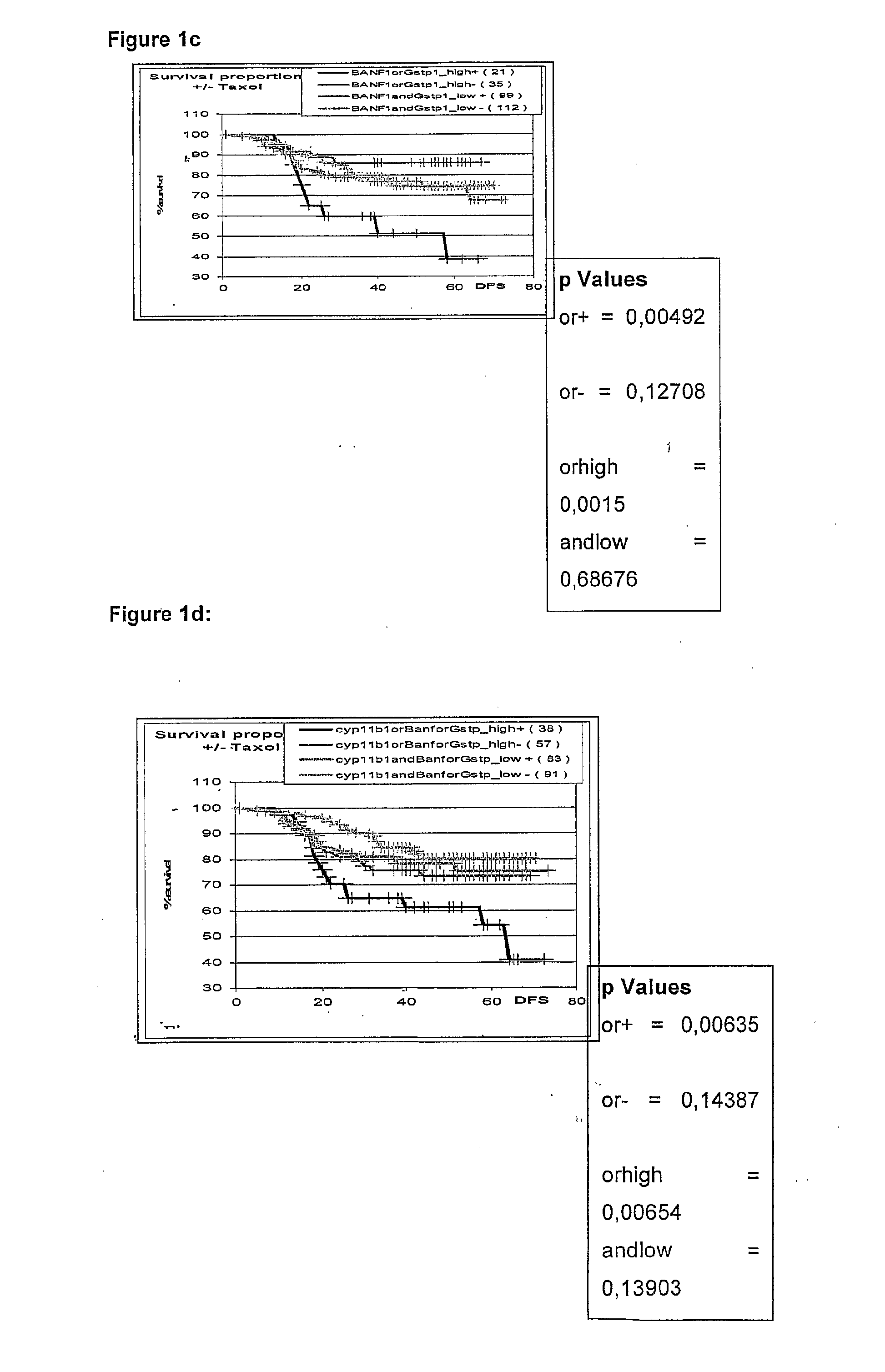
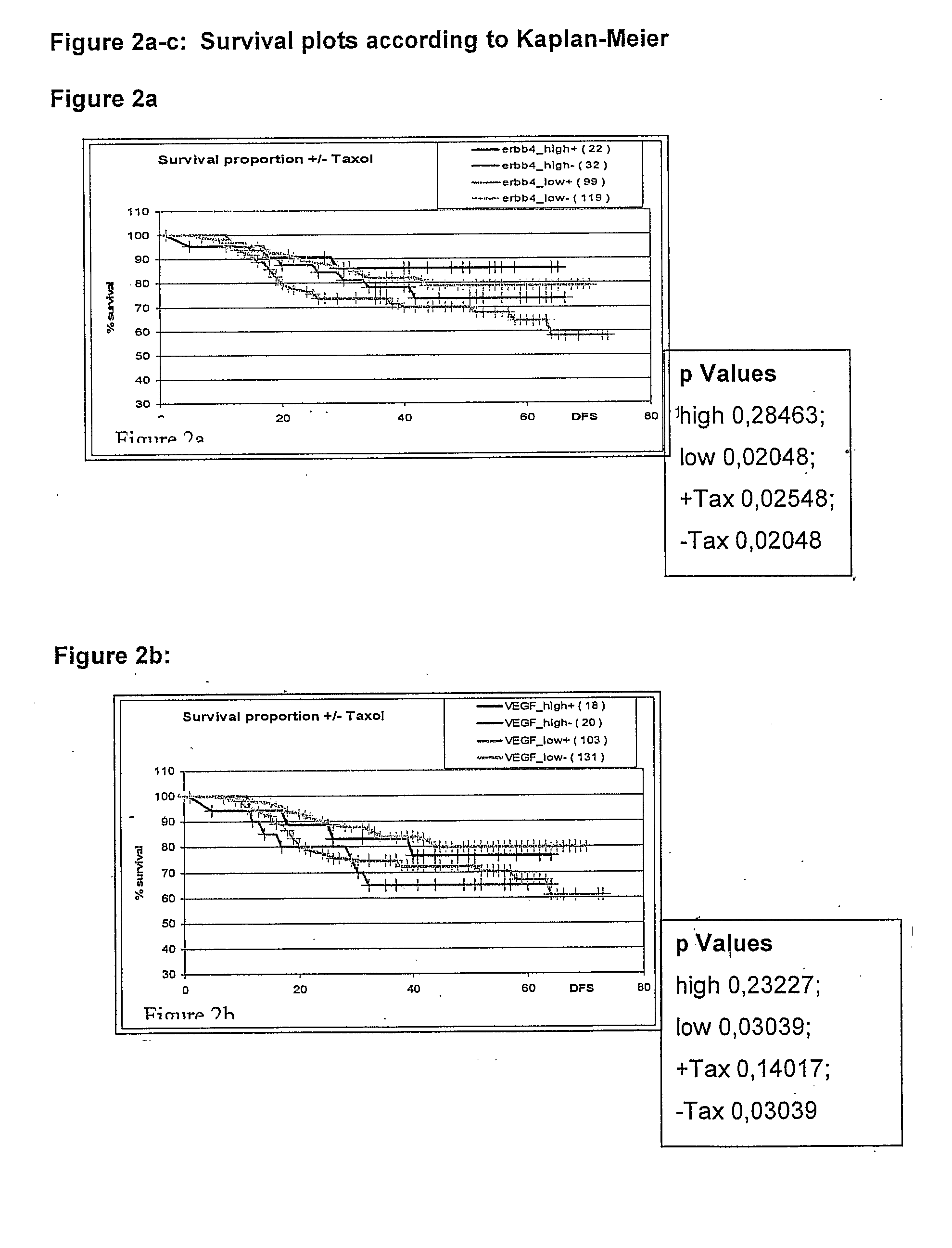
The invention provides novel compositions, methods and uses, for the diagnosis, prognosis, prediction, prevention and aid in treatment of malignant neoplasia such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, gastric cancer, colon cancer, esophageal cancer, mesenchymal cancer, bladder cancer or non-small cell lung cancer. Genes that are chromosomally amplified in breast tissue of breast cancer patients are disclosed. Further disclosed are chromosomally amplified genes and non-amplified genes that correlate to Taxane resistance, Taxane benefit or adverse Taxane reaction, which can be used as an aid to make therapy dicisions.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Serum-free medium for umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN105420182AOvercoming pollutionOvercoming Cell Expansion NumbersSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPancreatic hormoneStem cell culture
The invention provides a serum-free medium for umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and belongs to the technical field of cell culture. The serum-free medium for umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells comprises a basal culture medium body and added ingredients, wherein the basal culture medium body is a DMEM culture medium; the added ingredients include a basic fibroblast growth factor hFGF, a epidermal growth factor hEGF, insulin hI, a leukaemia inhibitory factor hLIF and astragalus polysaccharide. The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are subjected to subculture and amplification in the medium, and the surfaces of the cultured cells are marked and analyzed. The serum-free medium for umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells overcomes the defect of exogenous pollution of serum and solves the problem of contradiction between the cell expansion number and cost reduction. The medium is free of serum, thereby preventing influence of animal-derived serum ingredients on cell culture. The medium can be used for studying the differentiation and proliferation adjusting mechanism of the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.
Owner:SHANDONG JINGYUAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Construction method of human umbilical cord mesenchyma stem cell
ActiveCN101608174AAvoid damageActivity without lossDead animal preservationTissue cultureUmbilical cord tissueCell damage
The invention discloses a construction method of an umbilical cord mesenchyma stem cell bank utilizing newborn umbilical cords as resources, aiming at causing the steps to be less and the operation to be simpler and easier when constructing the umbilical cord mesenchyma stem cell bank. The invention comprises the following steps: (1), taking a human umbilical cord for detection, using a buffer solution to wash and remove residual blood, shearing to pieces, thus obtaining human umbilical cord tissue; (2), adding collagenase for digestion; (3), adding the buffer solution for diluting the digested tissue followed by organizing, mixing evenly and centrifuging; (4), abandoning the supernatant, adding the buffer solution for heavy suspension precipitation, screening, collecting filtrate and centrifuging, and repeating twice to obtain the human umbilical cord mesenchyma stem cell; (5), saving the obtained human umbilical cord mesenchyma stem cell in liquid nitrogen according to ABO / Rh parting and HLA parting thereof, establishing a cell information archive for retrieval, thus constructing the human umbilical cord mesenchyma stem cell bank. Compared with the existing method, the invention is more fast and convenient, and has less damage to the cell.
Owner:章毅 +7
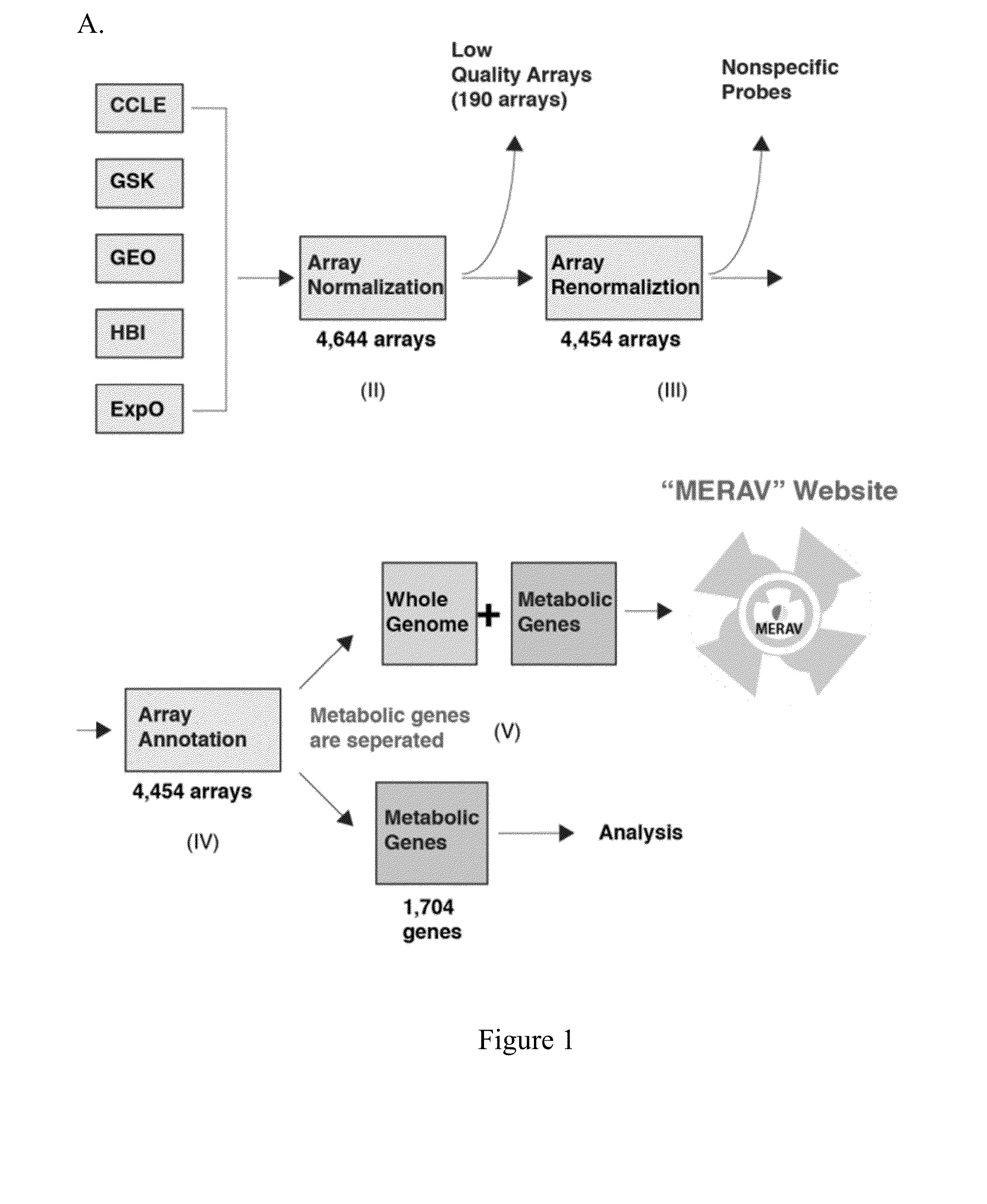
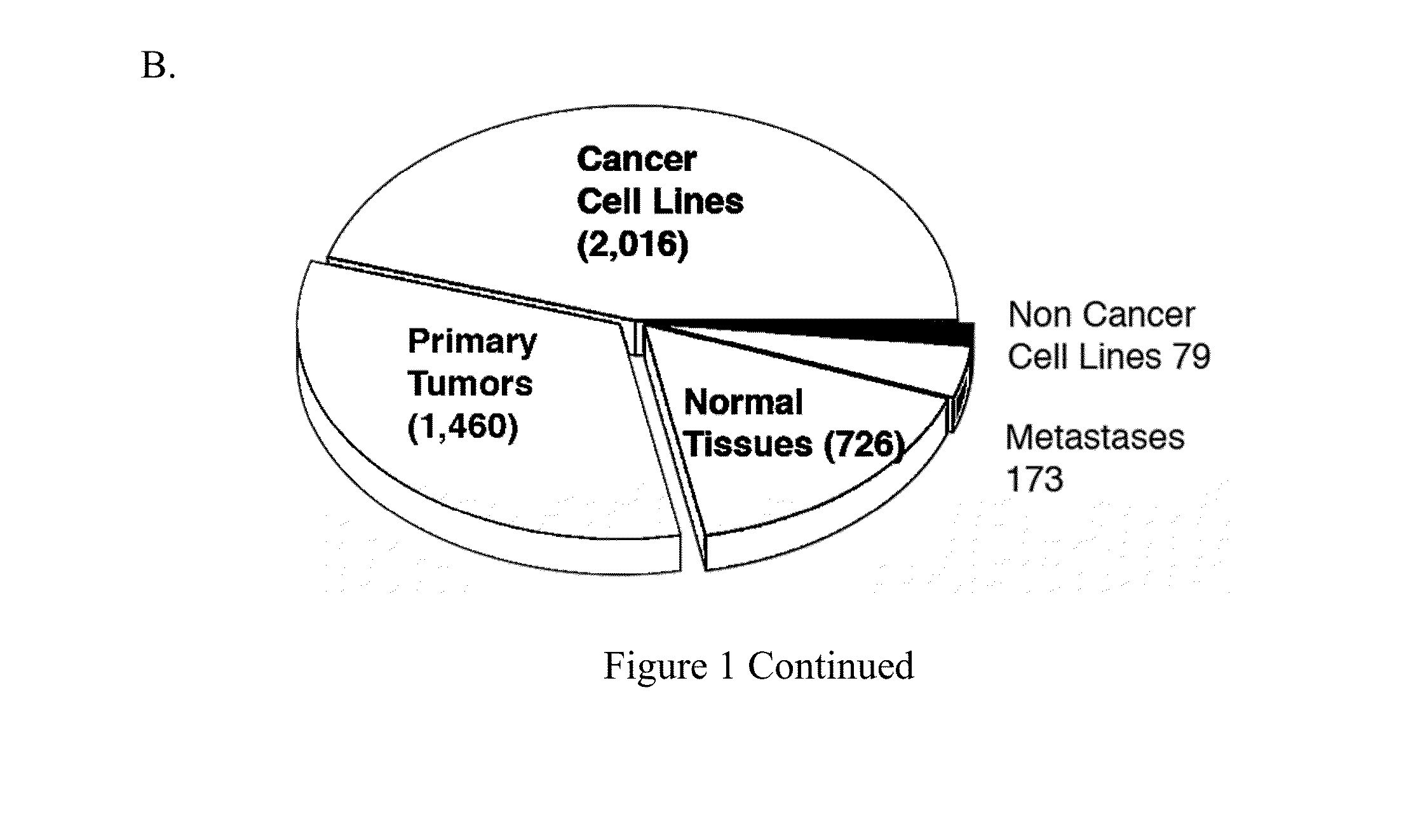
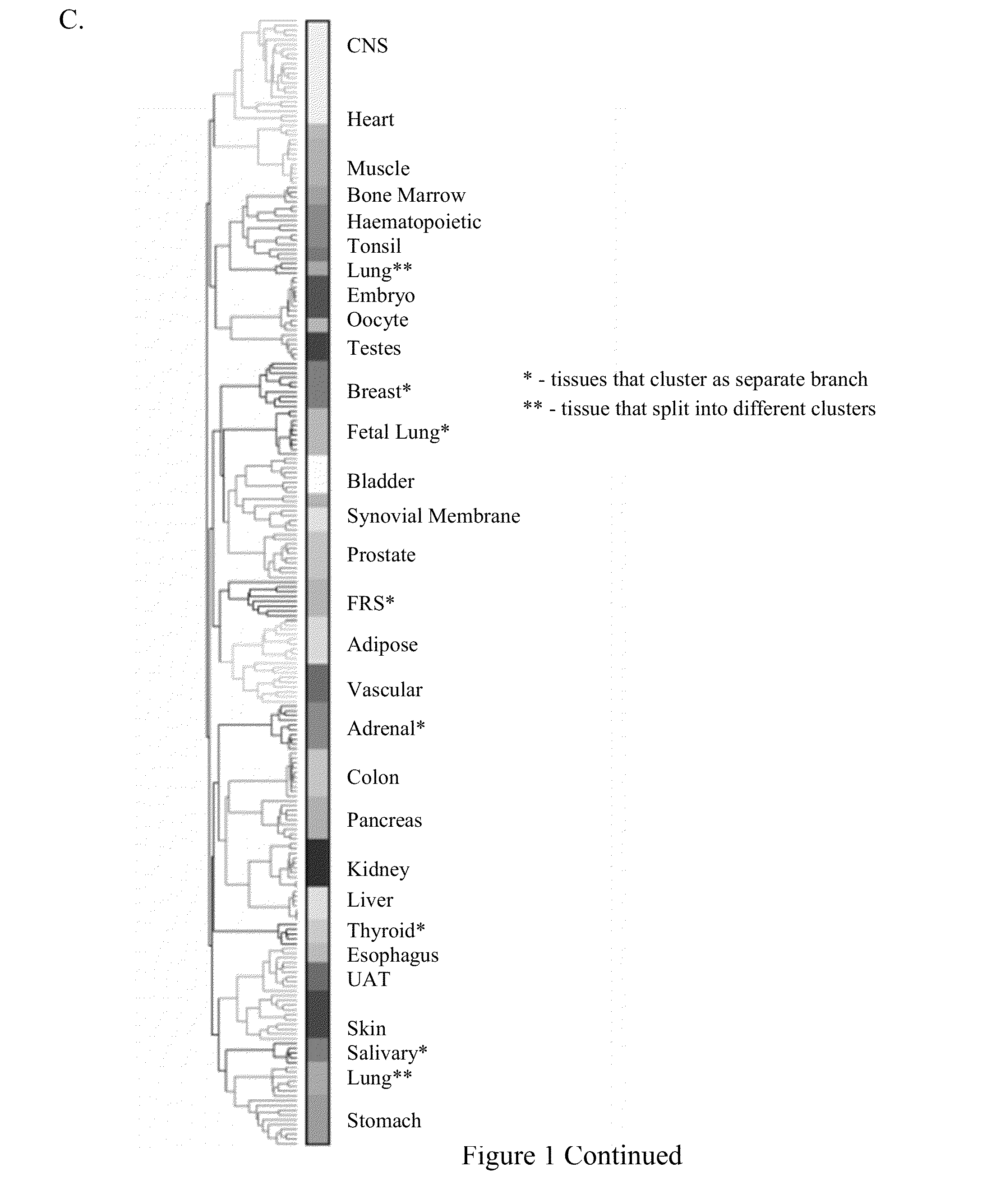
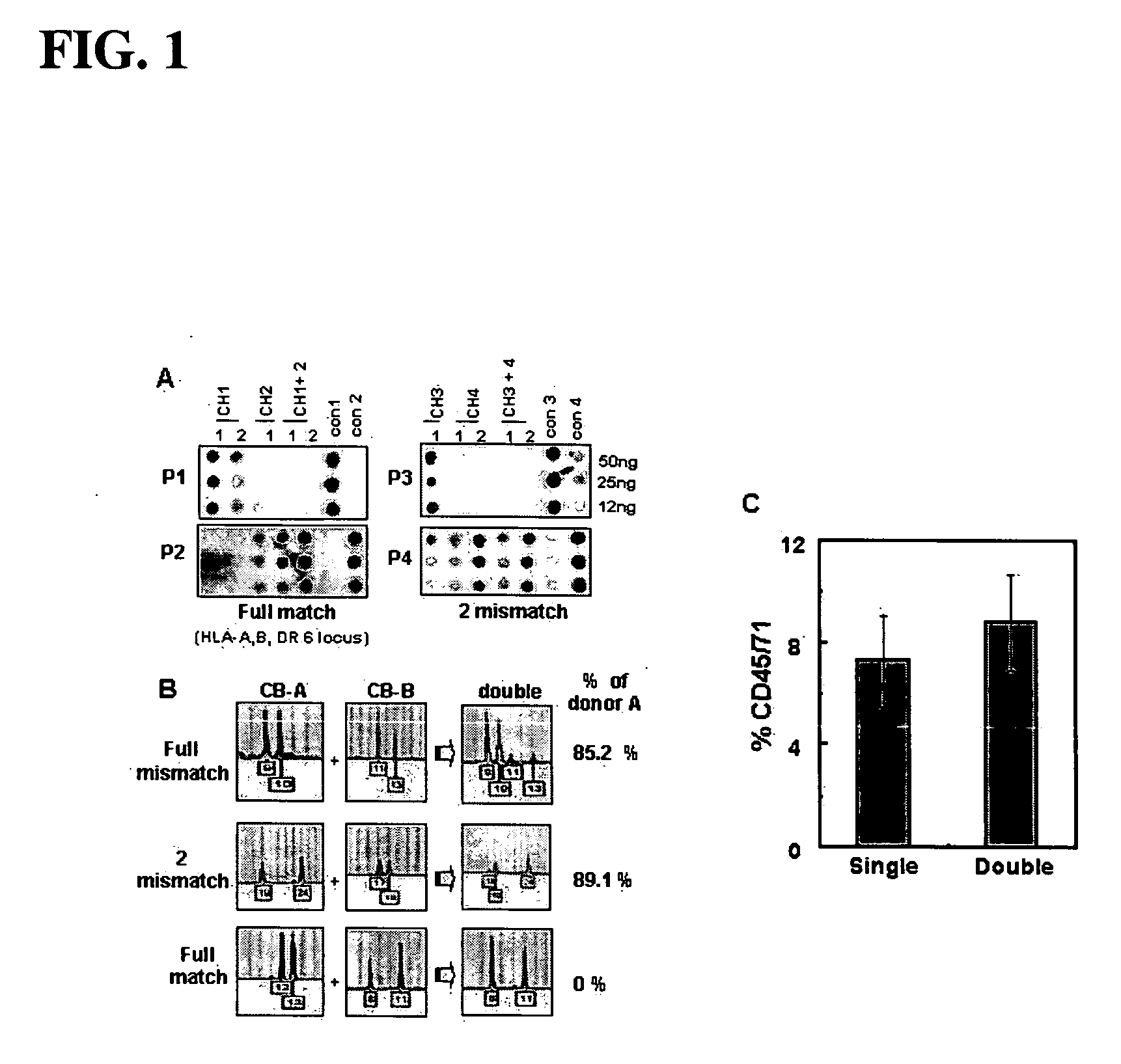
Metabolic gene mesenchymal signatures and uses thereof
InactiveUS20140357693A1Inhibits cell invasionInduce cell deathMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMedicineCell biology
Aspects of the invention relate to methods and compositions for characterizing or modulating the expression of metabolic mesenchymal genes. In some embodiments, methods for assessing the expression of metabolic mesenchymal genes and related gene signatures are provided that are useful for cancer classification, prognosis, diagnosis, or treatment selection.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Method for reshaping and beautifying by using tissue engineering fat regeneration technology
The invention provides a method for reshaping and beautifying by using tissue engineering fat regeneration technology, which is applicable to plastic surgery and reshaping and beautifying and belongs to the field of tissue engineering. The method comprises the following technical routes: directly extracting mesenchyme matrix cells with multiple differentiation capabilities from fatty tissues of a patient, culturing and propagating the mesenchyme matrix cells in vitro, wrapping a specific amount of cells and other necessary components in a hydrogel stent material, and implanting the hydrogel stent material into the corresponding part in the body of the patient. The cells are grown into fatty tissues along with degradation and absorption of the stent material so as to perform regenerative repair on the soft tissue defect of the patient. The method has the advantages that the cells of the patient do not bring immunological rejection to the patient, and the regenerative repair effect is safe, natural and durable because the used hydrogel stent material is finally degraded and absorbed in the body of the patient.
Owner:王影
Method of using mesenchymal stromal cells to increase engraftment
InactiveUS20050118147A1Improve the level ofReduce one-donor predominanceBiocideArtificial cell constructsStromal cellStem cell
Owner:THE CATHOLIC UNIV OF KOREA IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
Internally administered therapeutic agents for diseases in central and peripheral nervous system comprising mesenchymal cells as an active ingredient
InactiveUS20070178591A1Effective treatmentReduce riskVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsNervous systemCord blood stem cell
Intravenous administration of bone marrow cells collected from rat bone marrow to a rat cerebral infarction model was found to be effective in treating cerebral infarction. Human and murine bone marrow stem cells showed similar effects. Mesenchymal cells such as bone marrow cells, cord blood cells, or peripheral blood cells can be used as agents for in vivo administration against cranial nerve diseases.
Owner:NC MEDICAL RES +2
Method for isolated culture of human fat mesenchyma stem cell and special culture medium thereof
ActiveCN101314766AThe method of isolation and culture is simpleImprove efficiencySkeletal/connective tissue cellsAntigenMuscle injury
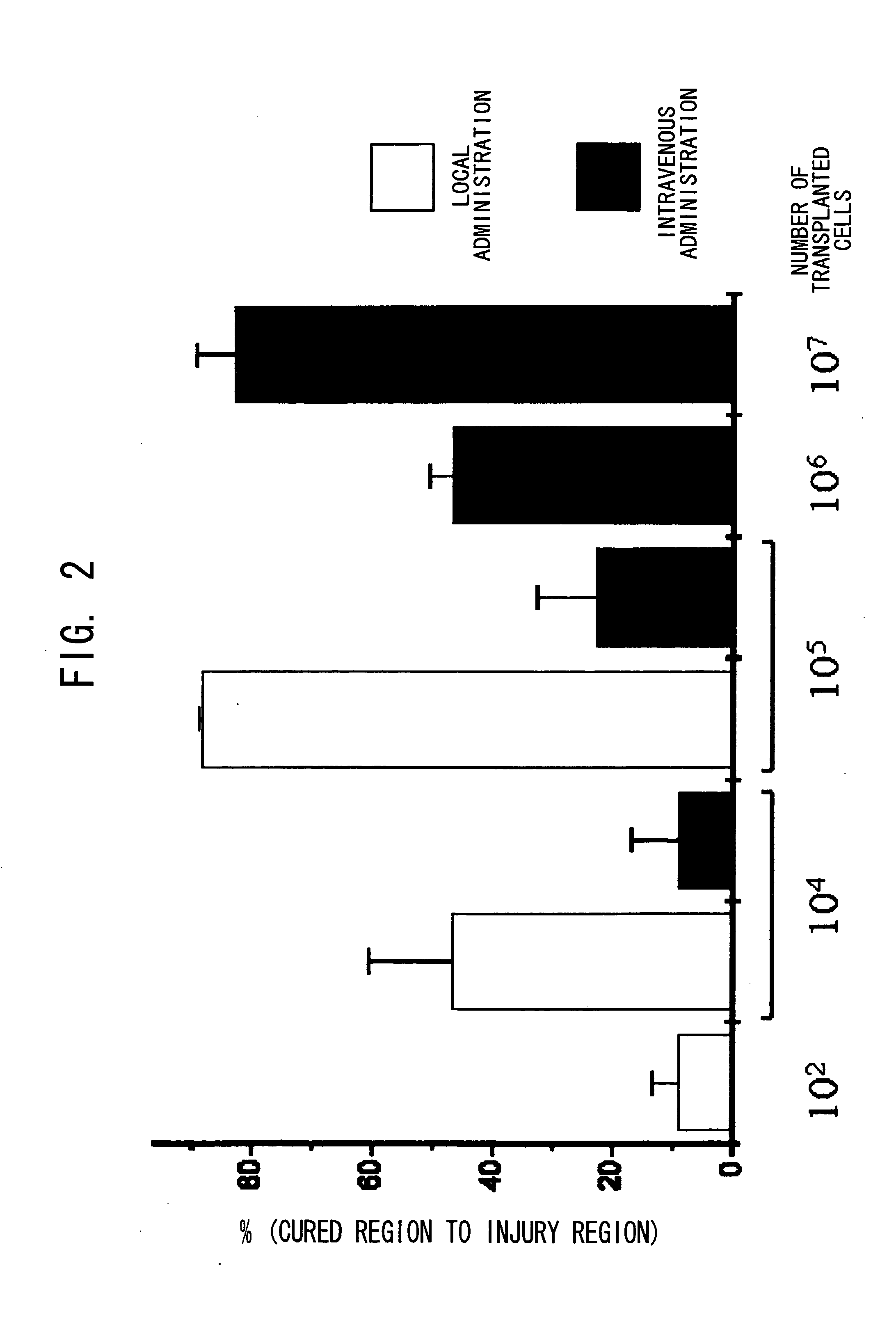
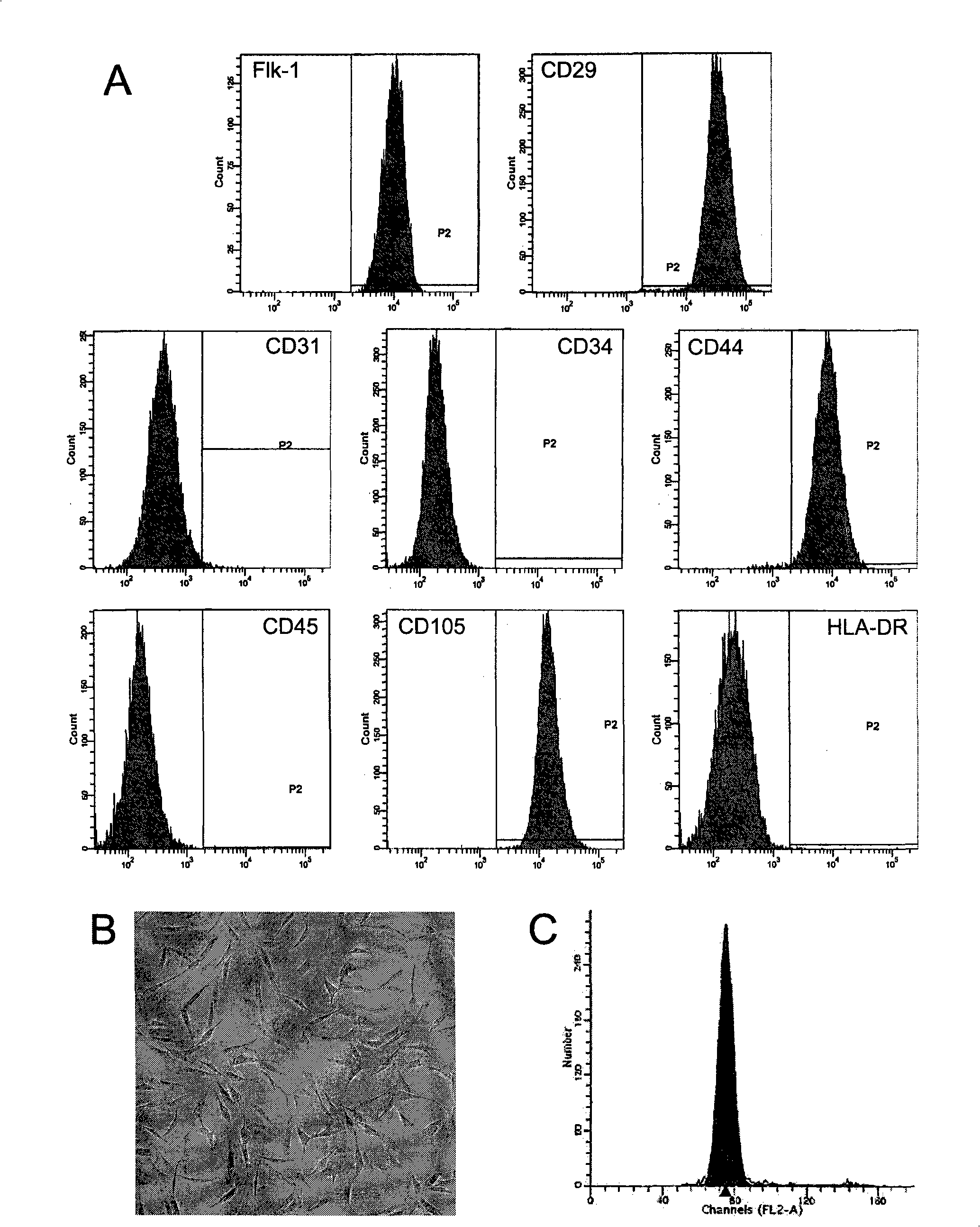
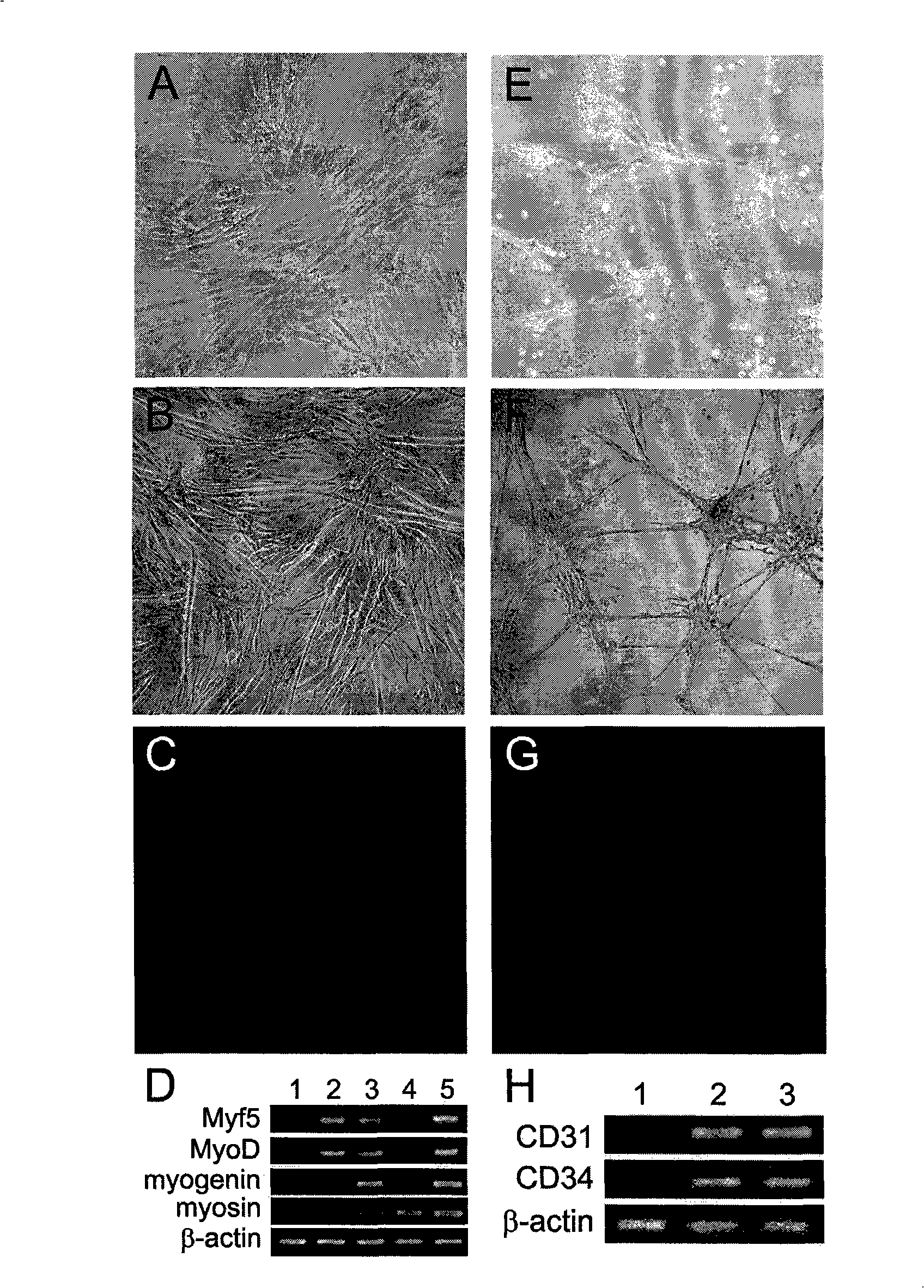
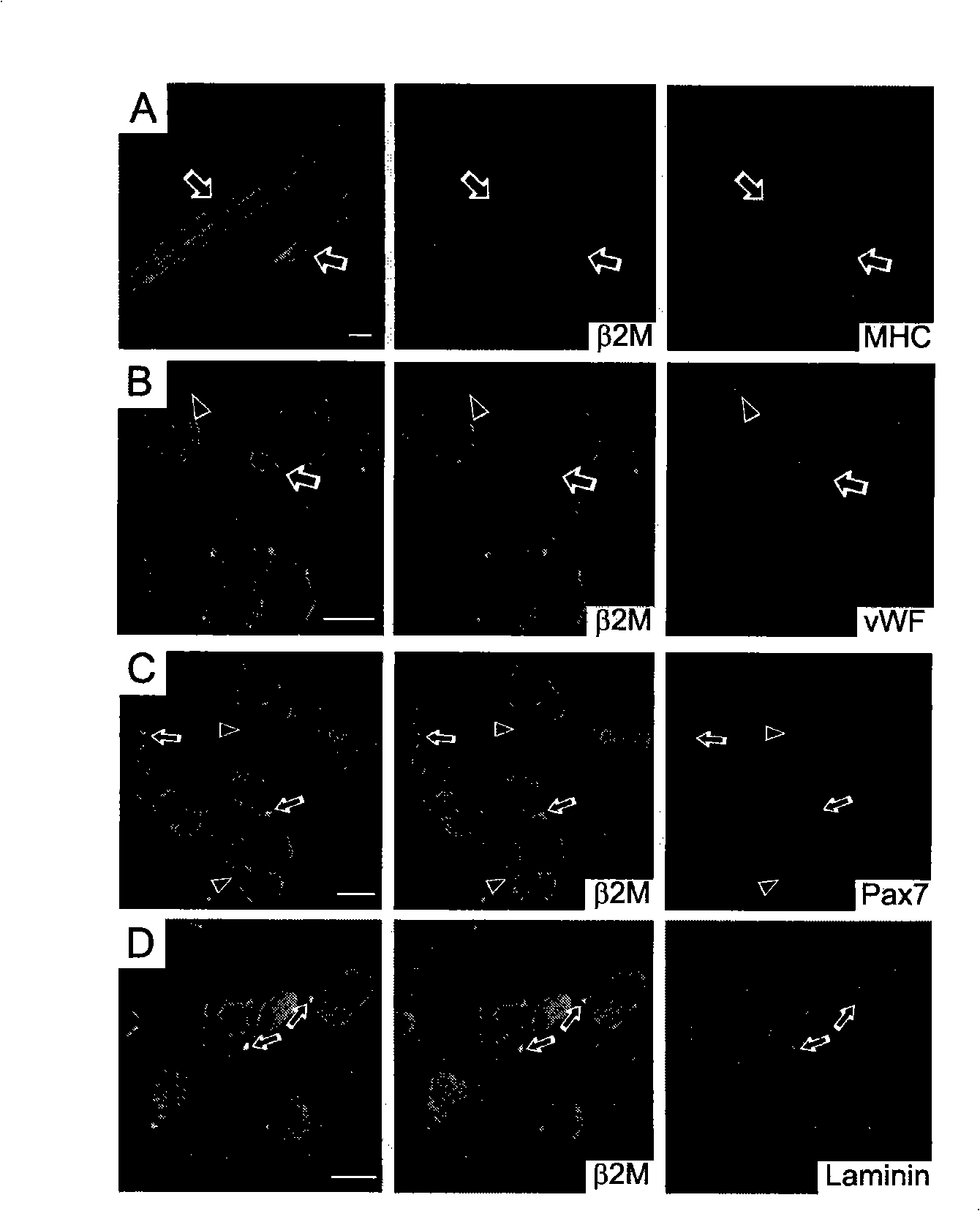
The invention discloses a method for separately culturing a human adipose mesenchymal stem cell and a dedicated culture medium thereof. The culture medium used for separately culturing the human adipose mesenchymal stem cell comprises an animal cell basic culture medium, fetal calf serum, an epidermal growth factor and a platelet-derived growth factor. The final concentration of the fetal calf serum is 1-200 mL / L, the final concentration of the epidermal growth factor is 1-100 ng / ml, and the final concentration of the platelet-derived growth factor is 1-100 ng / ml. The adipose mesenchymal stem cell of the invention has CD31-, CD34-, CD45- and HLA-DR-, as well as the phenotype of CD29+, CD44+, CD105+ and Flk-1+. The specificity cell surface marker and the relevant antihelion molecule of a skeletal muscle cell and a vascular endothelia cell can be expressed after inducement is performed in vitro. Muscle fiber, vascular endothelin and functional muscle satellite cells can be differentiated in a muscle injury model mouse body caused by medicine and the expression of dystrophin protein on the ducheme muscular dystrophy (DMD) model mouse (mdx) myolemma can be partially recovered, so as to release the pathological symptom of the model mouse.
Owner:微能生命科技集团有限公司
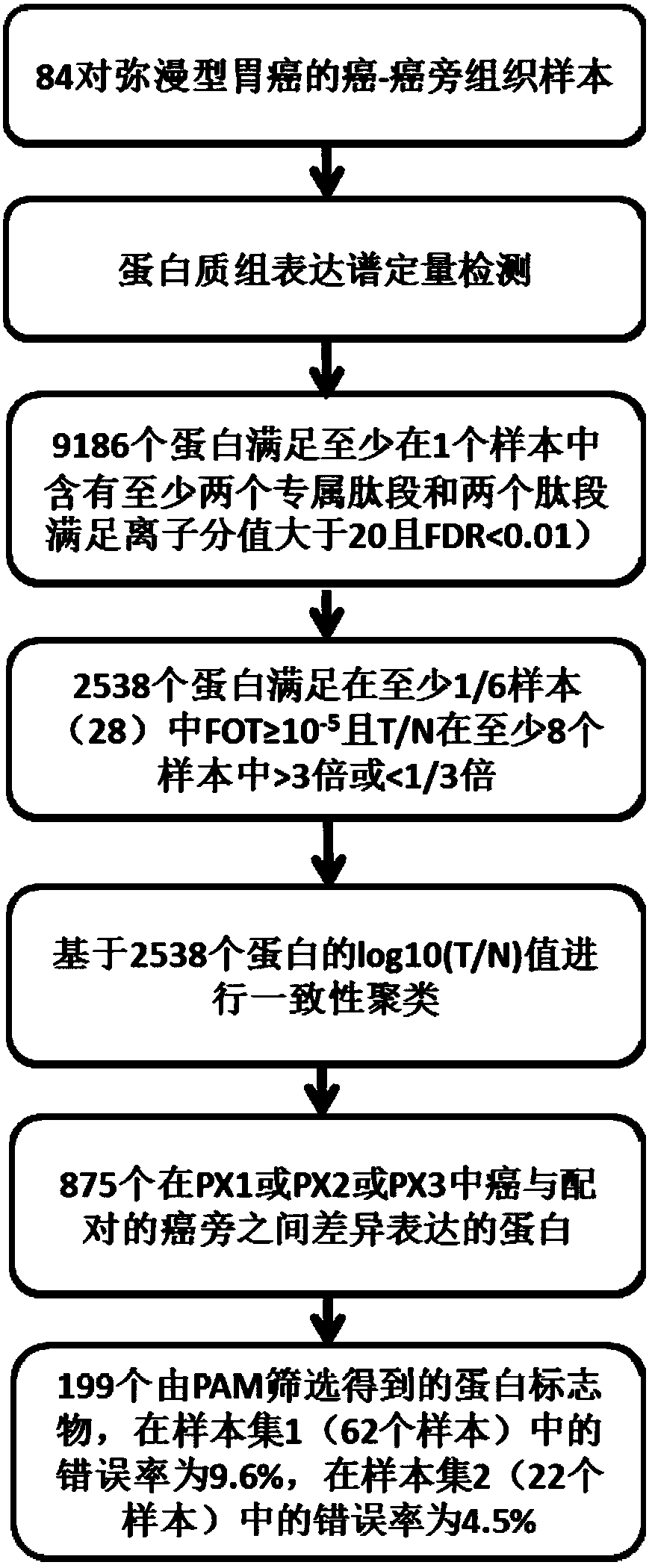
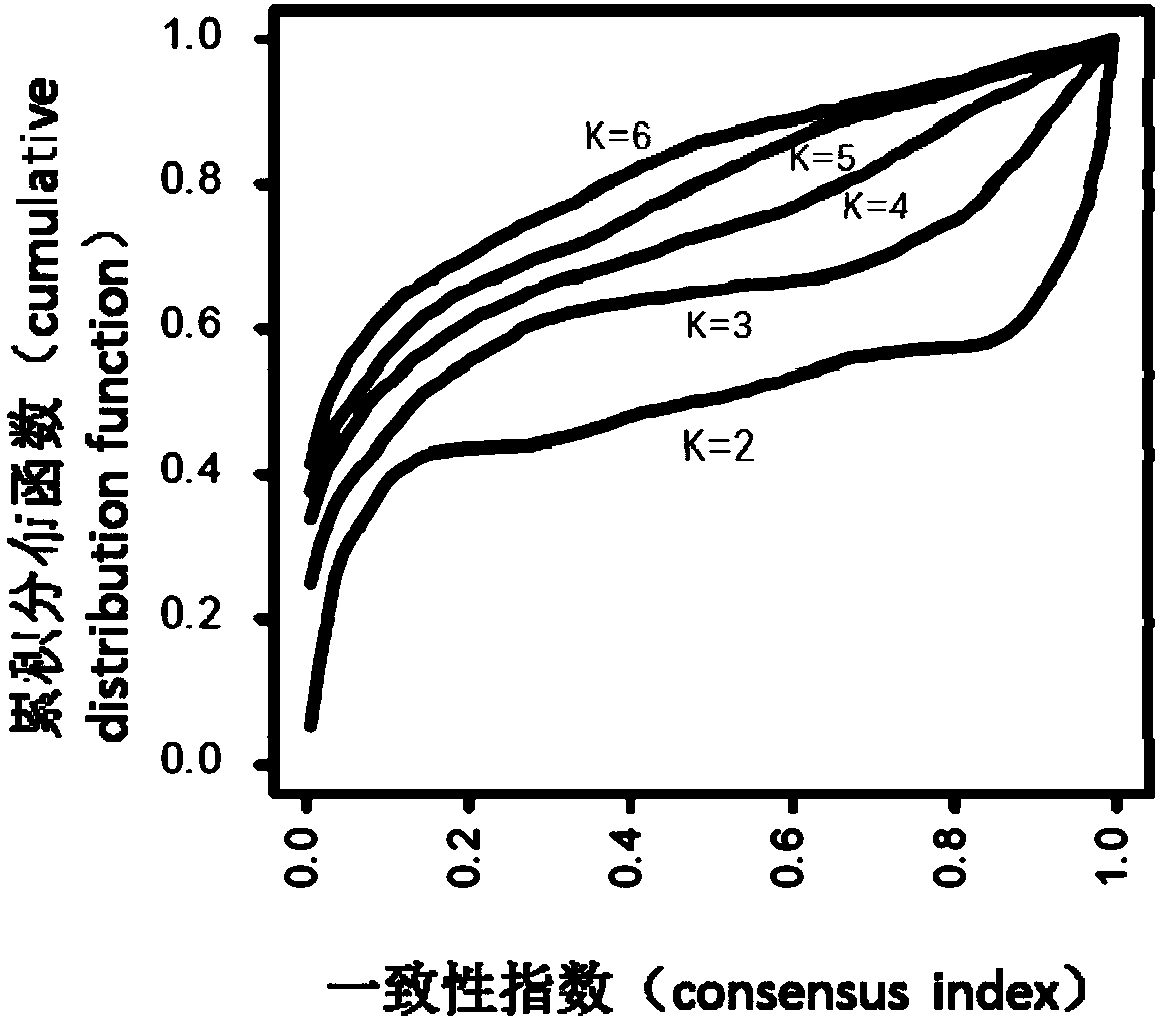
Molecular typing of diffuse gastric cancer and protein markers for typing and screening method and application thereof
The invention provides molecular typing of diffuse gastric cancer and protein markers for typing and a screening method and application thereof, and discloses protein expression profile data of tissues of 84 cases of diffuse gastric sample cancer and tissues adjacent to the cancer, a method for typing of the gastric cancer based on the protein expression profile data and 199 protein markers for gastric cancer typing. The method can be used for typing of the diffuse gastric cancer in Lauren typing into three subtypes comprising cell cycle diffuse gastric cancer PX1, epithelial-mesenchymal transition diffuse gastric cancer PX2 and immunoenriched diffuse gastric cancer PX3. The invention provides a method for classification, diagnosis and prognosis of the gastric cancer, and lays a foundationfor prognosis of the diffuse gastric cancer and designing of targeted drugs.
Owner:北京谷海天目生物医学科技有限公司
Mesenchymal stromal cell populations and methods of using same
InactiveUS20110123498A1Reduce the possibilityMinimize damageBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsStromal cellKidney
Owner:ALLOCURE
Compositions and Methods for Myogenesis of Fat-Derived Stem Cells Expressing Telomerase and Myocardin
An in vitro method of producing stem cells with potential to develop into cardiovascular myocytes is disclosed which comprises culturing myogenic stem cells obtained from the stromal or mesenchymal compartment of adult adipose tissue in a medium that favors myogenic development of the cells. These myogenic stem cells highly express telomerase and myocardin. A composition comprising fat-derived myogenic stem cells and / or differentiated cardiovascular myocytes and a method for treating a mammalian subject suffering from a cardiovascular disorder are also disclosed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
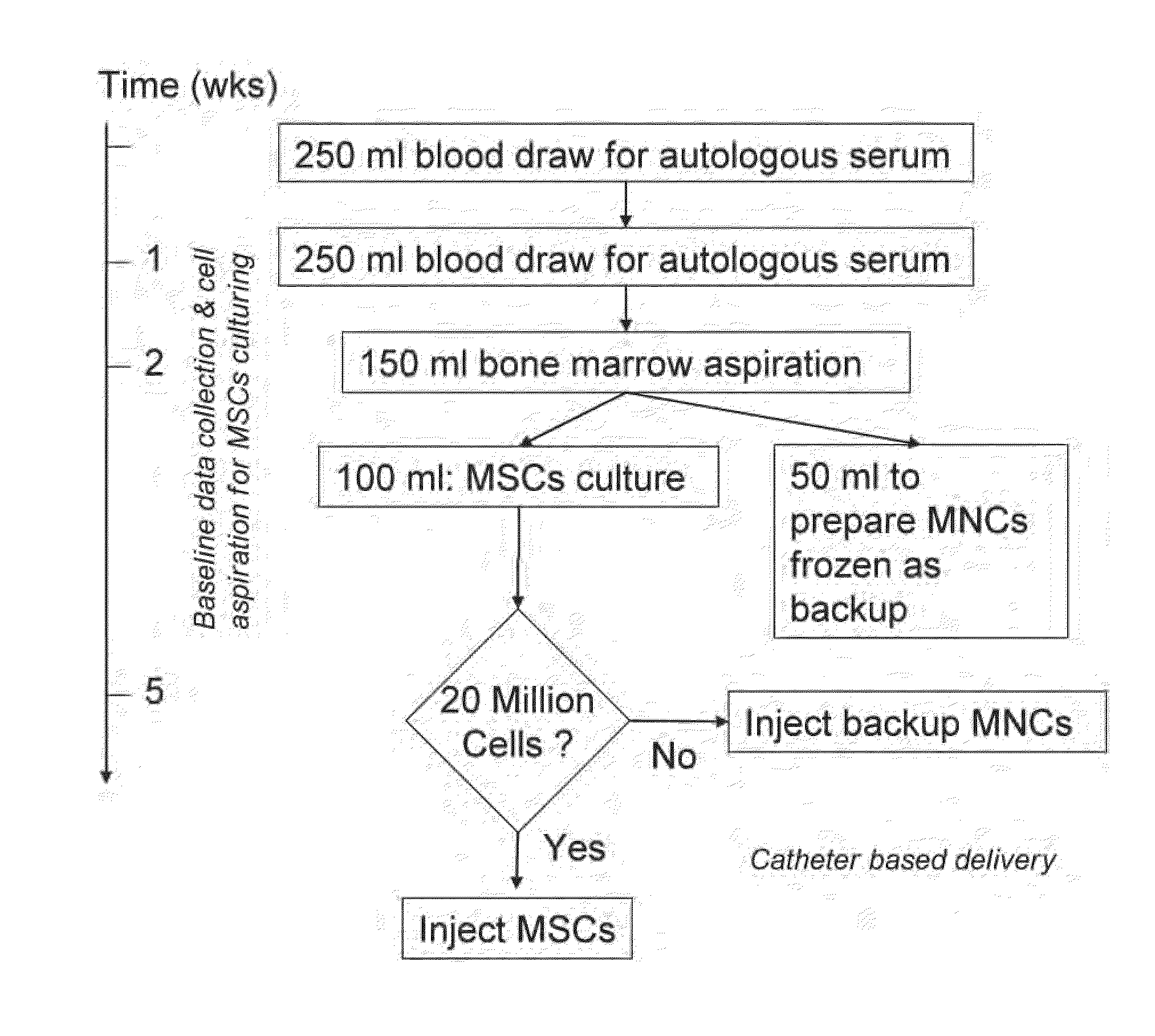
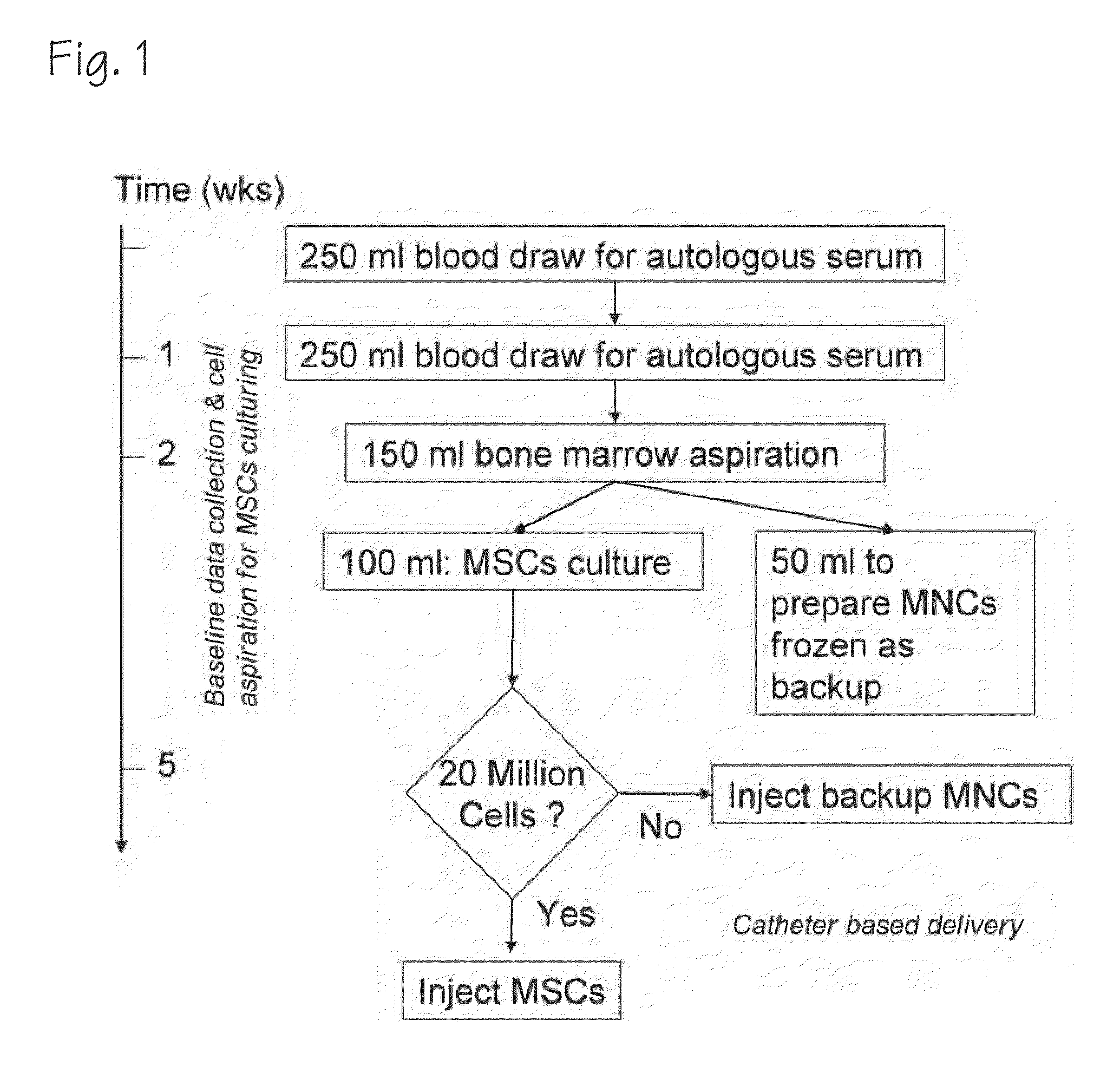
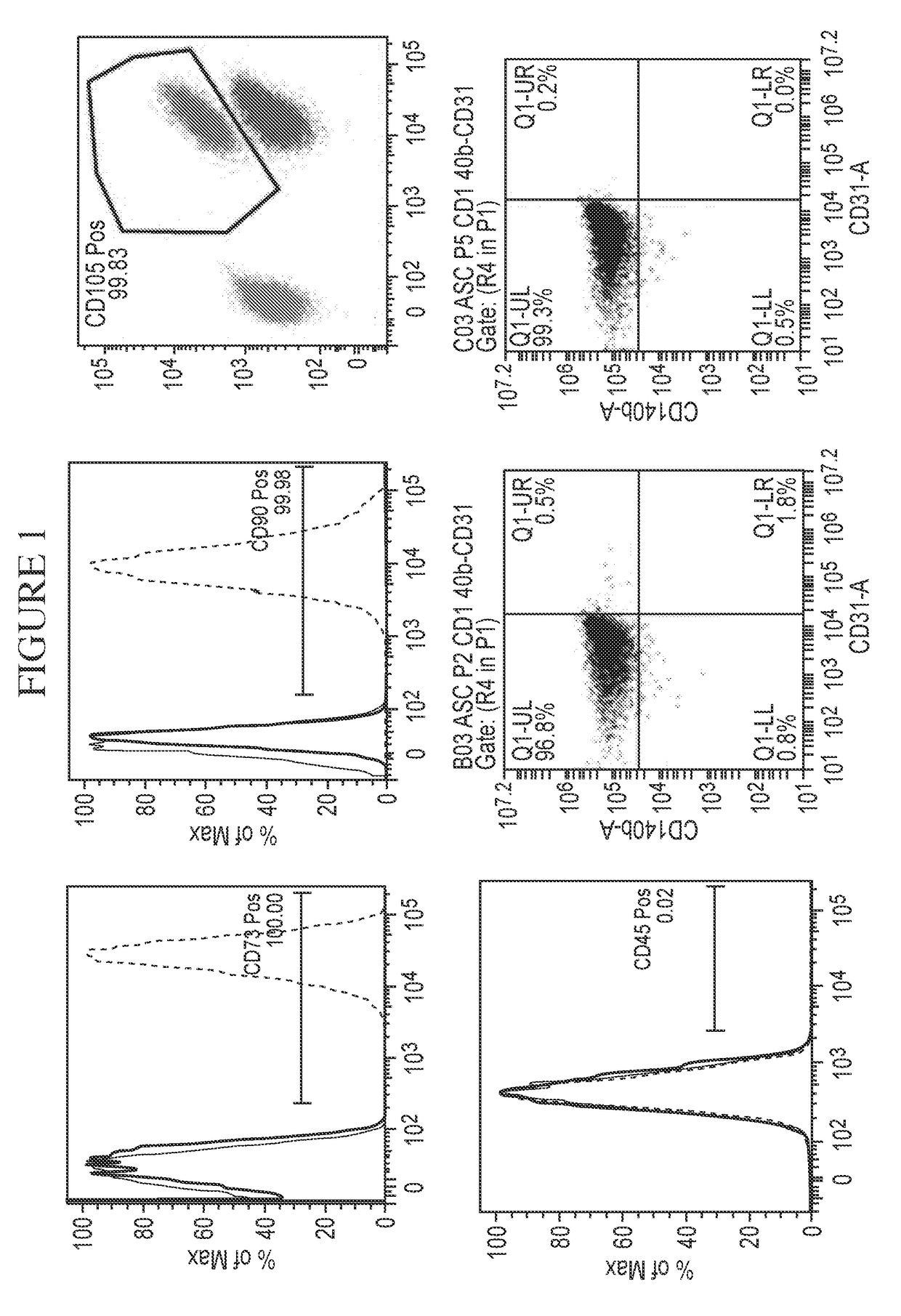
Method of Preparing Autologous Cells and Method of Use for Therapy
A method for expanding mesenchymal cells derived from autologous bone marrow in autologous culture medium which can be used in a clinical setting, and a business method for performing such expansions in the future as a service for patients. A method for expanding mesenchymal cells derived from autologous bone marrow in autologous culture medium including a diagnostic kit for the autologous cell therapy to determine whether a patient will respond to the autologous cell therapy for treatment of a disease, in which said kit comprising a system for detecting gene and protein expression comprising at least two isolated DNA molecules wherein each isolated DNA molecule detects expression of a gene that is differentially expressed in the tissue of the patient that is intended to be the source of the autologous cell therapy.
Owner:BIOCARDIA
Adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stromal cell conditioned media and methods of making and using the same
PendingUS20190046576A1Easy to refactorHigh potencyPowder deliverySenses disorderSustained release drugStromal cell
Provided herein are lyophilized compositions containing the secretome of cultured adipose cells, pharmaceutical compositions and that additionally contain a sustained release drug delivery matrix, as well as methods of making and using such compositions.
Owner:CELL CARE THERAPEUTICS INC
Mesenchymal stem cells populations, their products, and use thereof
PendingUS20190269739A1Improve survivalImpact can be more specific and efficientNervous disorderMetabolism disorderDiseaseExtracellular vesicle
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising a mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) population, extracellular vesicles secreted from said MSC population, and a combination thereof, and methods of use thereof in treatment of a disease or disorder.
Owner:EXOSTEM BIOTEC LTD
Use of chemokines, and pharmaceutical preparations containing the same
InactiveUS20070020230A1Organic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical formulationStem cell
The present invention relates to the use of chemokines and / or nucleic acids encoding a chemokine for recruiting mesenchymal precursor and / or stem cells in vivo and in vitro. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical preparations which comprise these substances and which are preferably intended for recruiting mesenchymal precursor and / or stem cells for tissue synthesis.
Owner:TRANSTISSUE TECH GMBH
Mesenchymal stromal cells and uses related thereto
ActiveUS8962321B2Improve the level ofSimple methodAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderMedicineStromal cell
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Mesenchymal stromal cells and uses related thereto
ActiveUS20130183272A1Retain potencyImproved therapeutic propertyAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderStromal cellMesenchymal stem cell
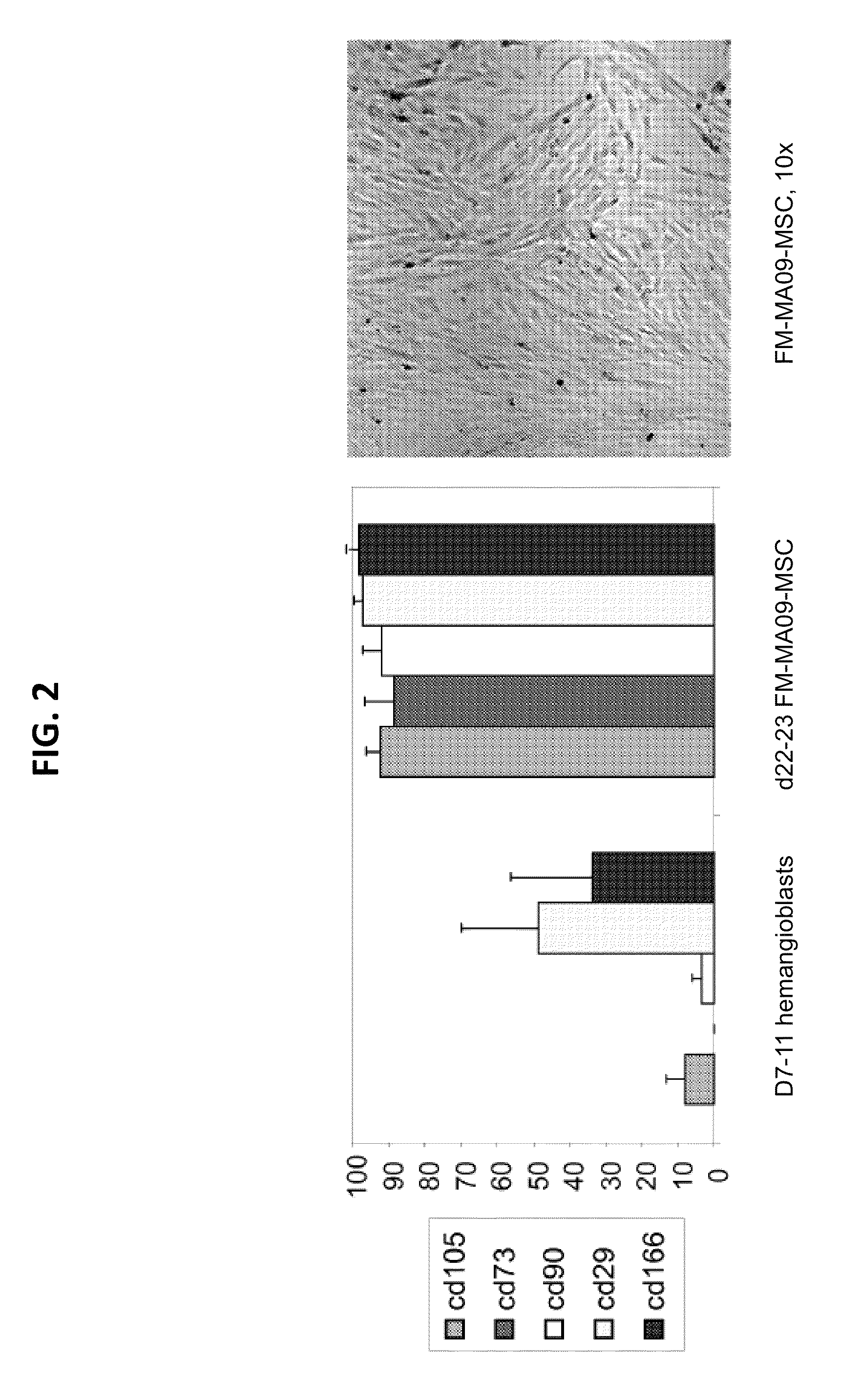
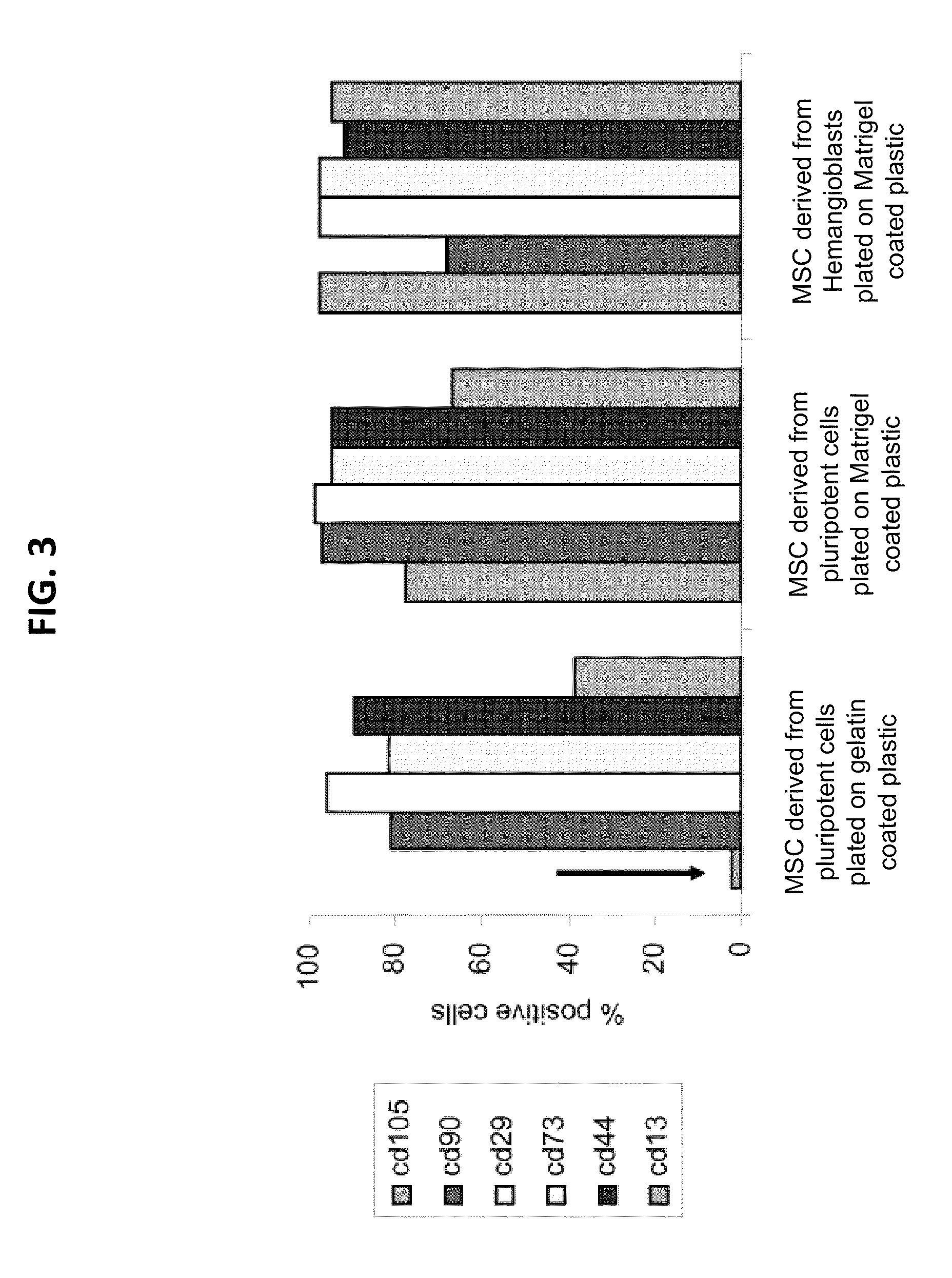
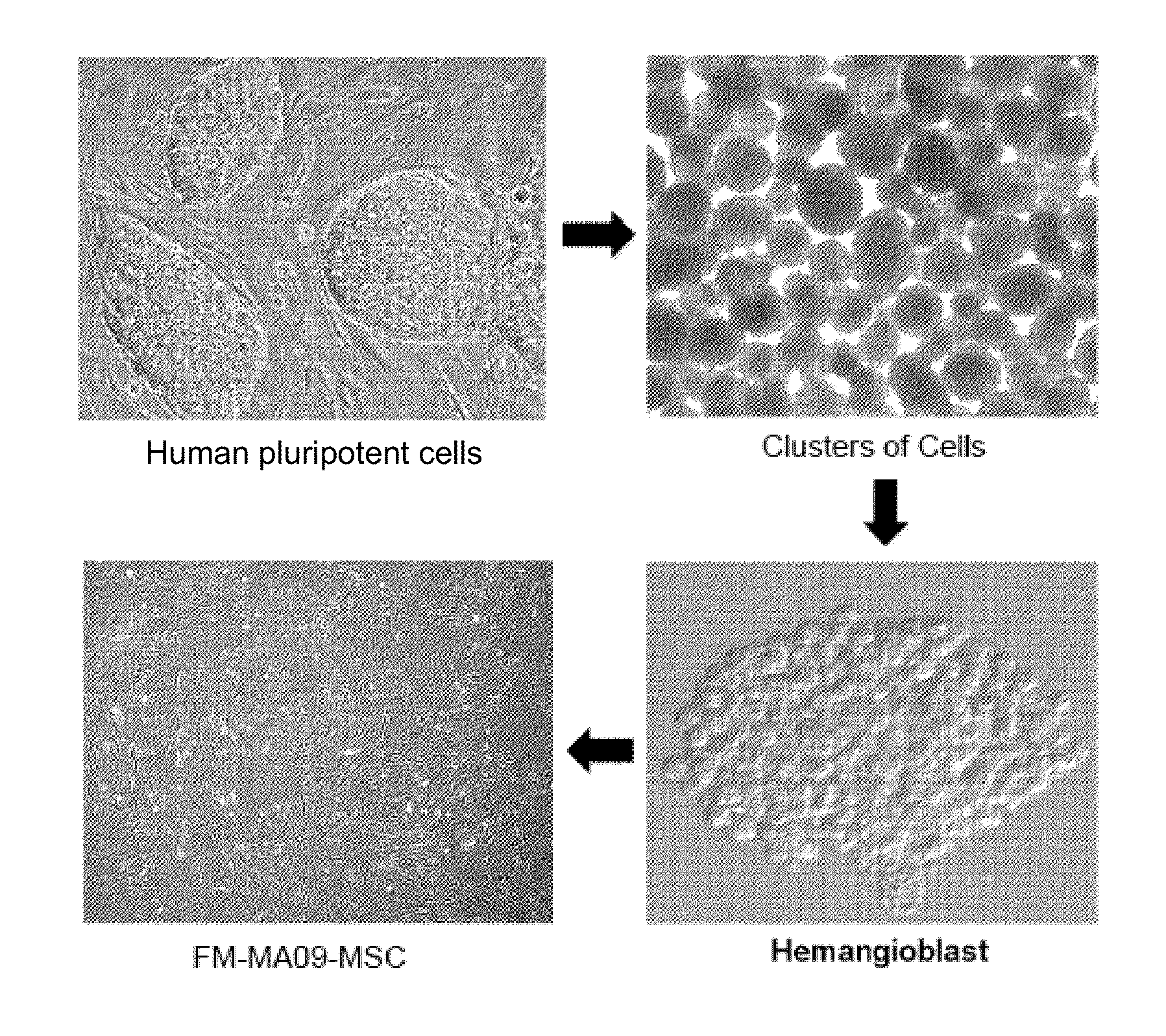
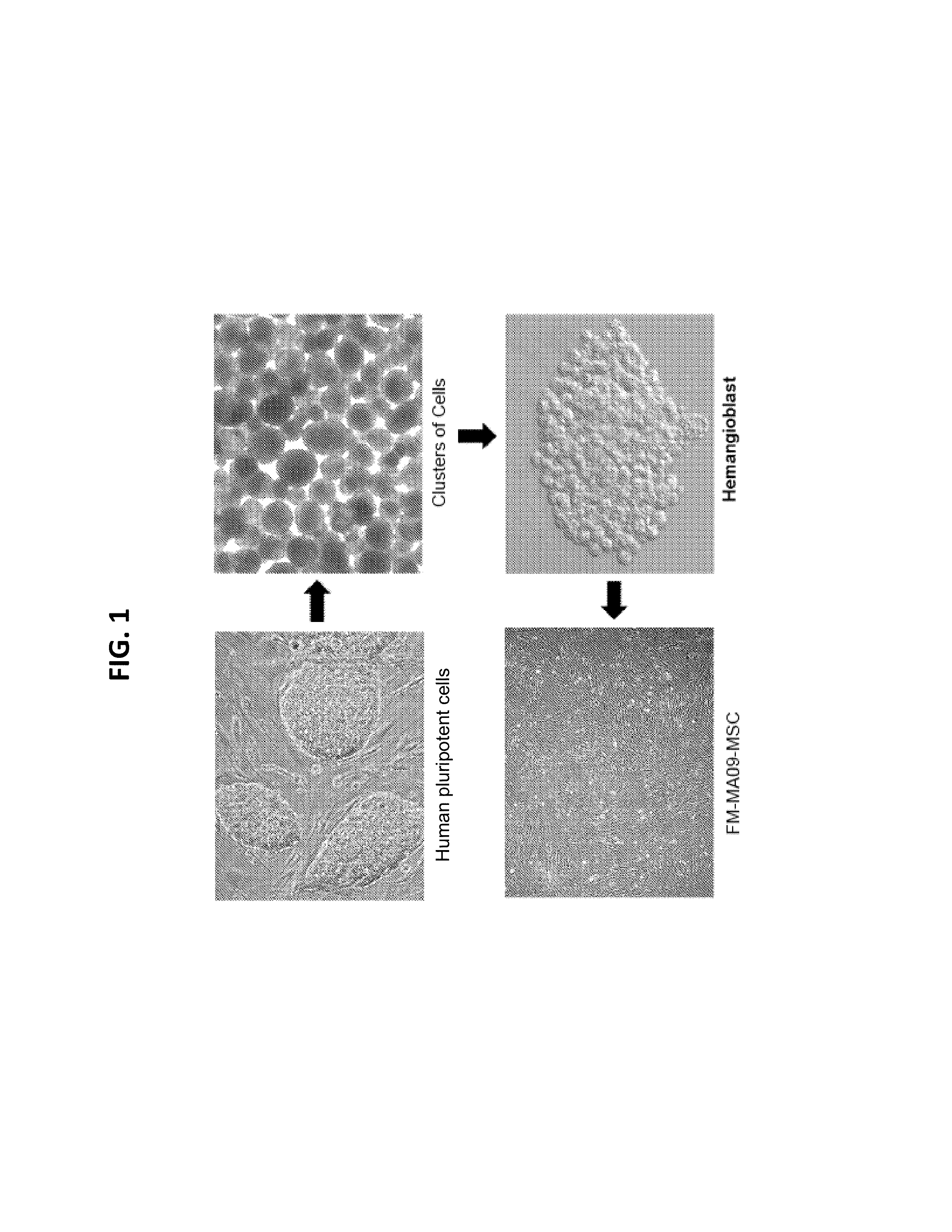
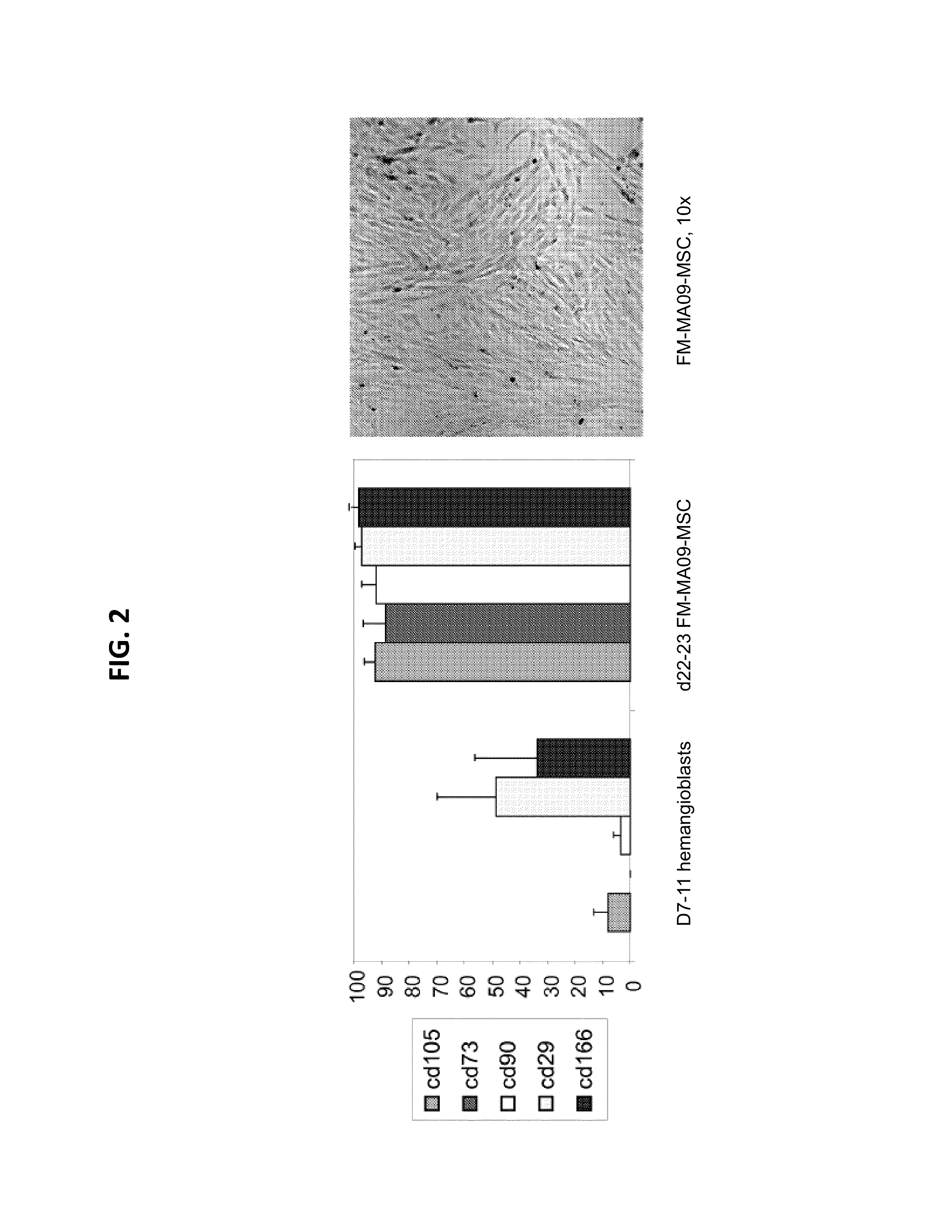
The present invention generally relates to novel preparations of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) derived from hemangioblasts, methods for obtaining such MSCs, and method sof treating a pathology using such MSCs. The methods of the present invention produce substantial numbers of MSCs having a potency-retaining youthful phenotype, which are useful in the treatment of pathologies.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
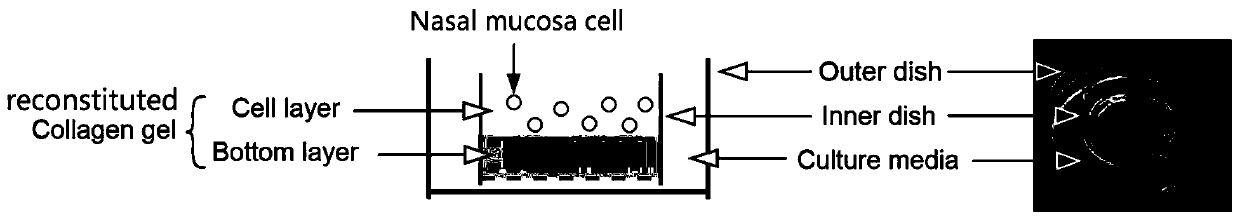
Nasal mucosa organoid culture medium and culture method
ActiveCN111117946AProliferateCapable of multi-lineage differentiationCulture processEpidermal cells/skin cellsEpitheliumGoblet cell
The invention discloses a culture medium and culture method of a nasal mucosa tissue. According to the culture medium and culture method of the nasal mucosa tissue, epithelial-mesenchymal / matrix components are integrated in an organoid culture system based on a gas-liquid interface method for the first time, and by inducing proliferation and differentiation of adult stem cells in a fresh nasal mucosa epithelial tissue, an organoid which is composed of multiple kinds of cells, including ciliated cells, goblet cells, club cells and basal cells, and is close to an internal mucosa in structure andfunction can be obtained, and becomes an in-vitro nasal mucosa model with proliferation and multi-lineage differentiation capability.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Specific detection tool for mesenchymal and epithelial-mesenchymal transformed circulating tumor cells
ActiveUS20160009812A1Animal cellsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSpecific detectionCirculating cancer cell
The present invention includes the discovery of cell-surface vimentin as a novel biomarker to detect and isolate mesenchymal and epithelial-mesenchymal transformed circulating tumor cells from blood of cancer patients. In addition, an antibody specific for the detection of cell-surface vimentin on circulating tumor cells and the use the antibody to detect, enumerate, and isolate CTC are provided.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for preparing PLGA slow-release microsphere carrying docetaxel and application thereof in chemotherapy of mesenchyma stroma of tumors under ultrasonic mediation
InactiveCN101697963AImprove protectionComplete structureOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectDocetaxel
The invention discloses a method for preparing a PLGA slow-release microsphere carrying docetaxel and an application thereof in the chemotherapy of the mesenchyma stroma of tumors under ultrasonic mediation. The PLGA slow-release microsphere carrying the docetaxel is a medicine-carrying microsphere prepared from PLGA and the docetaxel by a single emulsification method, the molecular weight of the PLGA in the medicine-carrying microsphere is 5000-50000dal, the mole ratio of lactic acid to glycollic acid is 75:25-50:50, the feeding ratio of the PLGA to the docetaxel is 100 / 1-100 / 10, and the PLGA slow-release microsphere carrying the docetaxel is prepared by emulsification in an organic solvent. The slow-release microsphere preparation carrying the docetaxel is injected into the tumor tissues of nude mice with human liver cancer, beast cancer and ovarian cancer, and the necrosis situation of the tumors is checked by pathological histology; the result shows that the slow-release microsphere carrying the docetaxel can thoroughly ablate and inactivate the tumors, reduces the whole-body toxic or side effect of the medicine obviously and is a novel method for the chemotherapy of the mesenchyma stroma of the tumors under ultrasonic intervention with very good clinical application prospect.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV UNION HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com