Patents
Literature
89 results about "Tissue formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
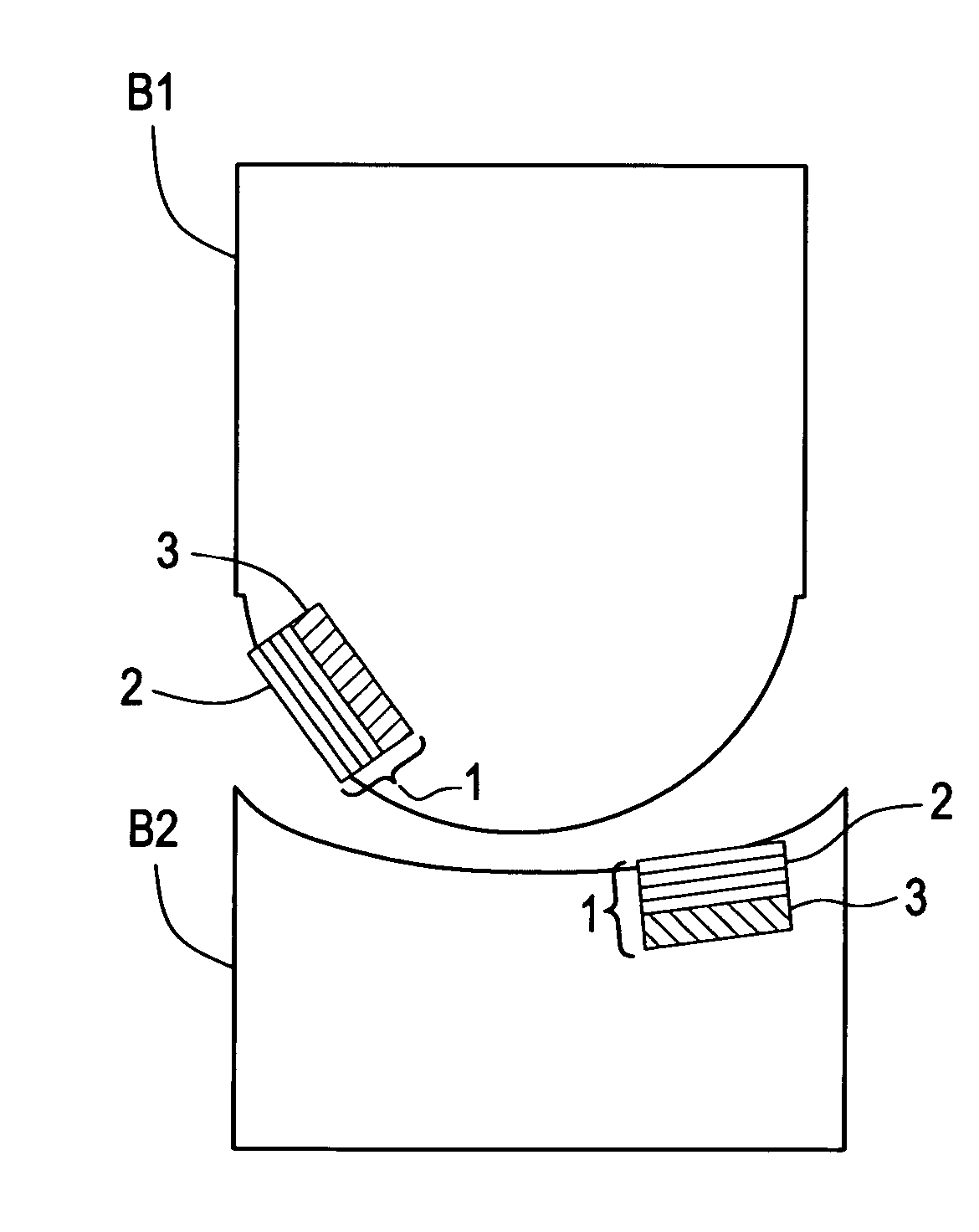
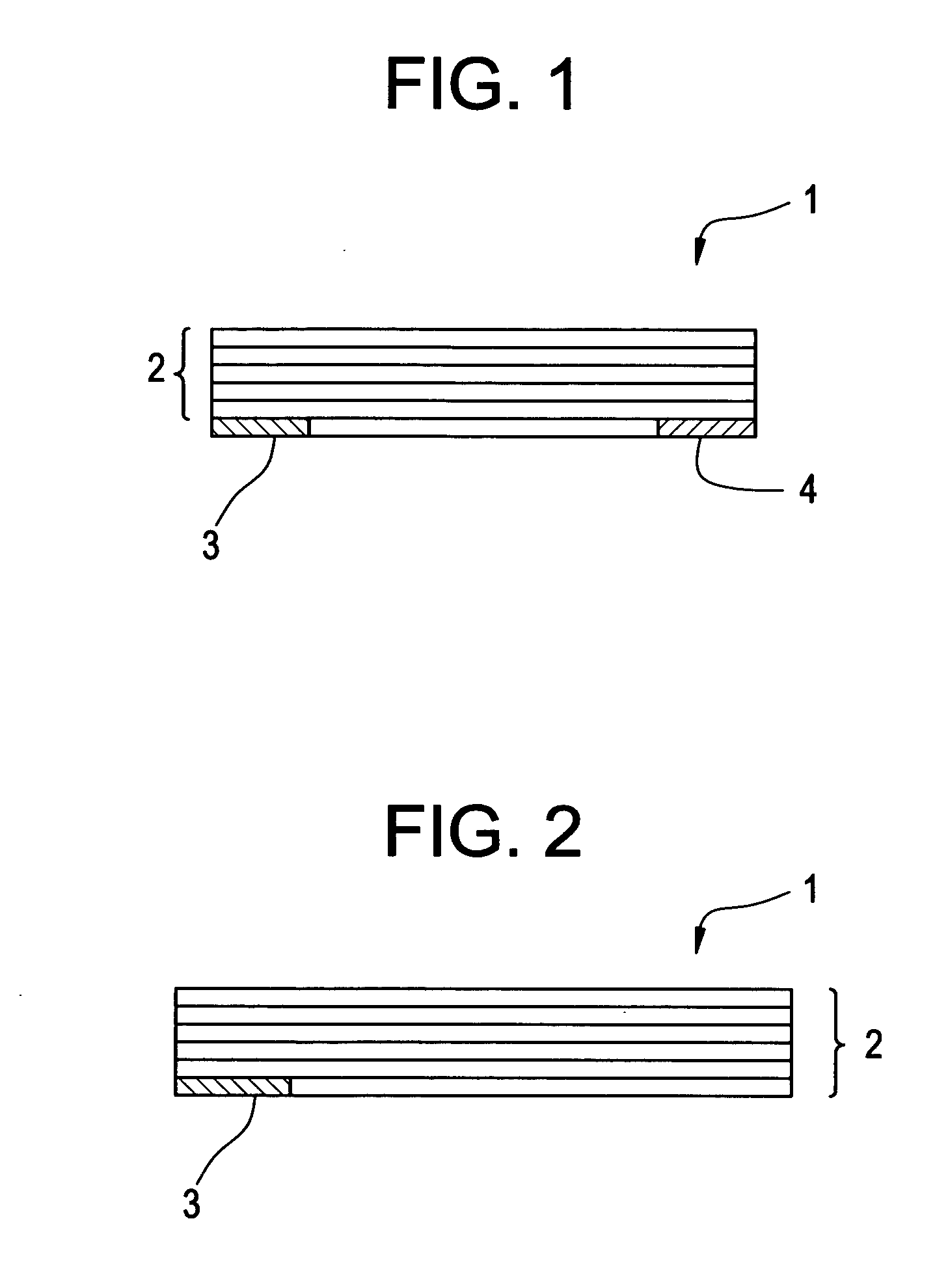
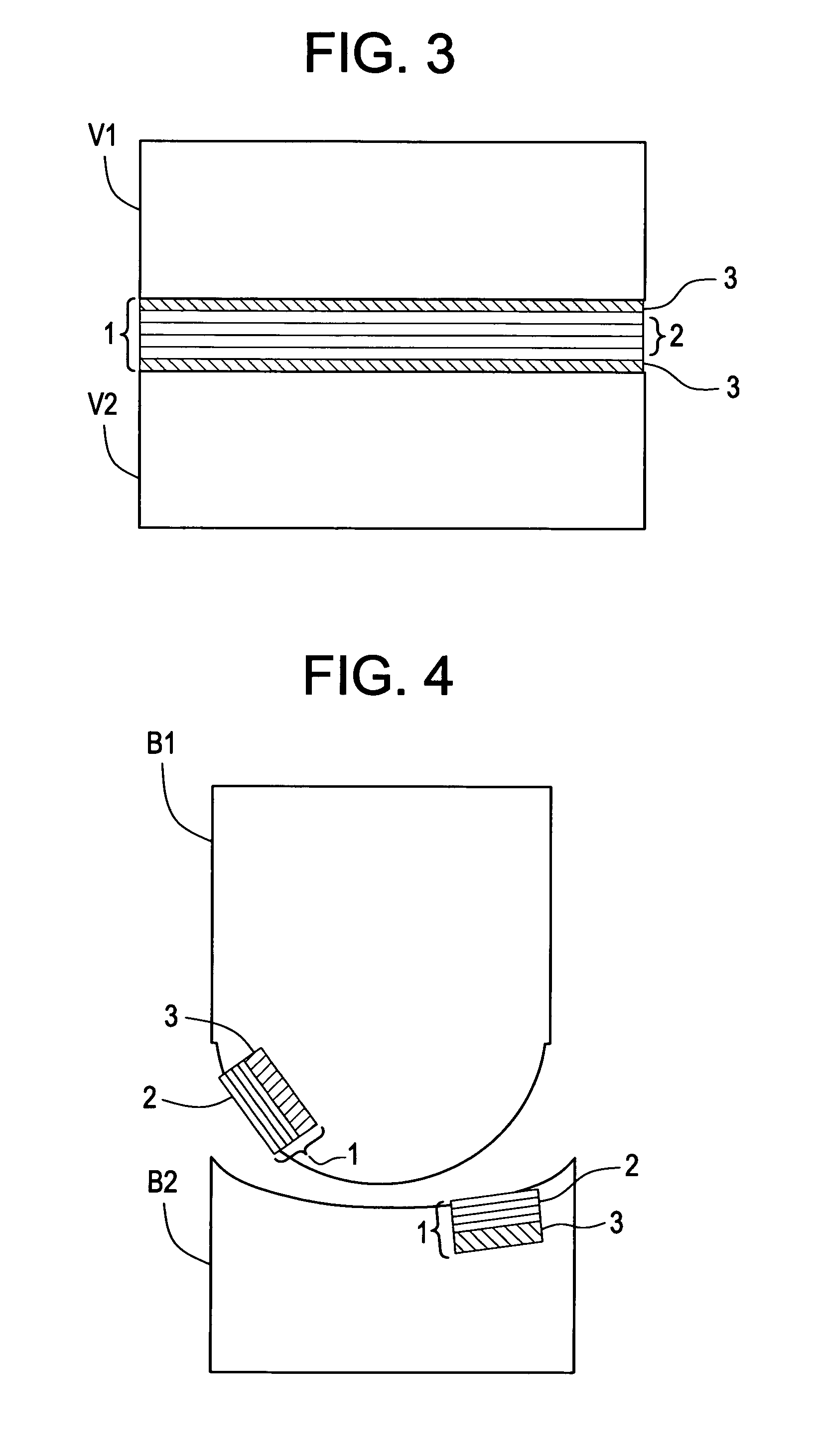
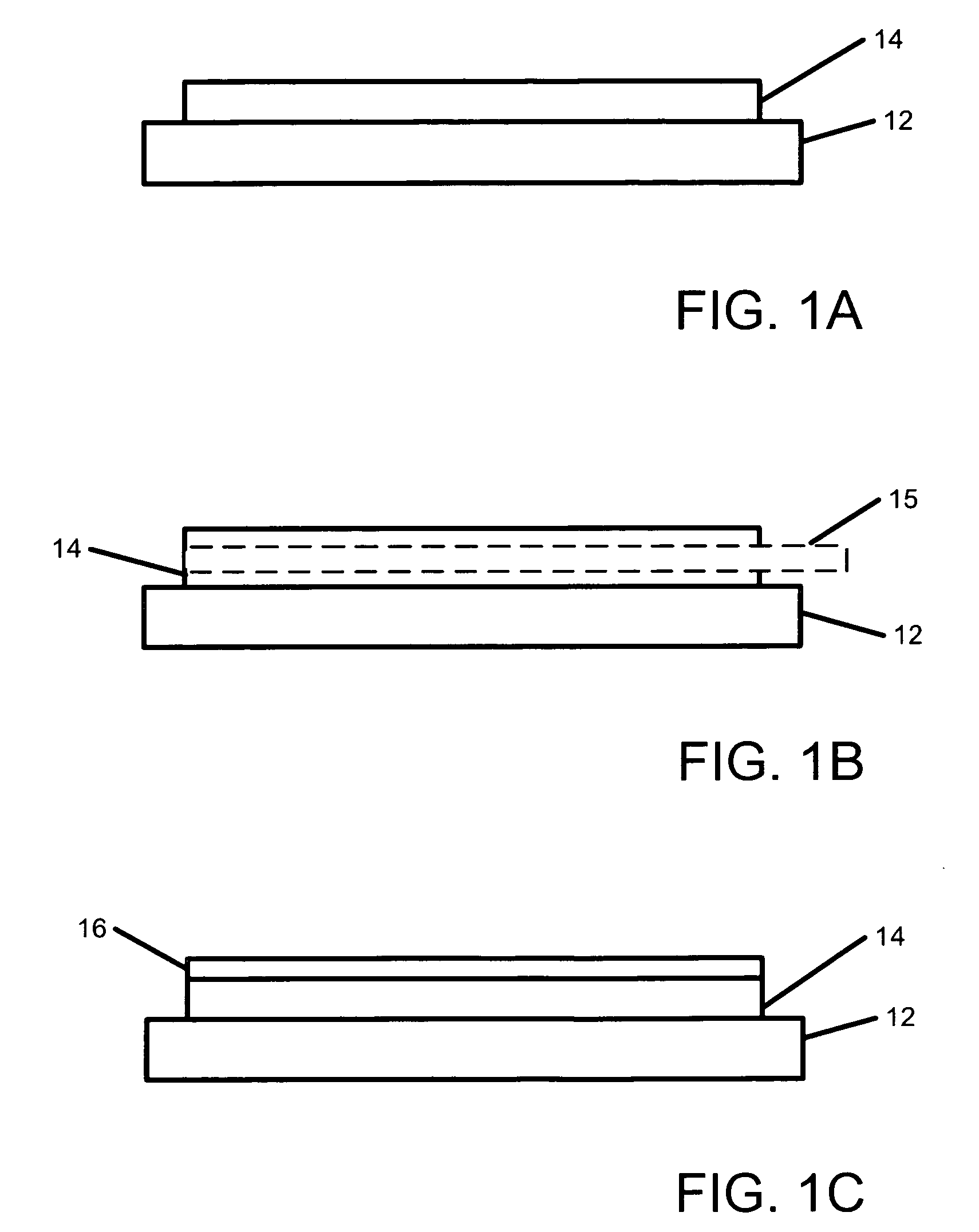
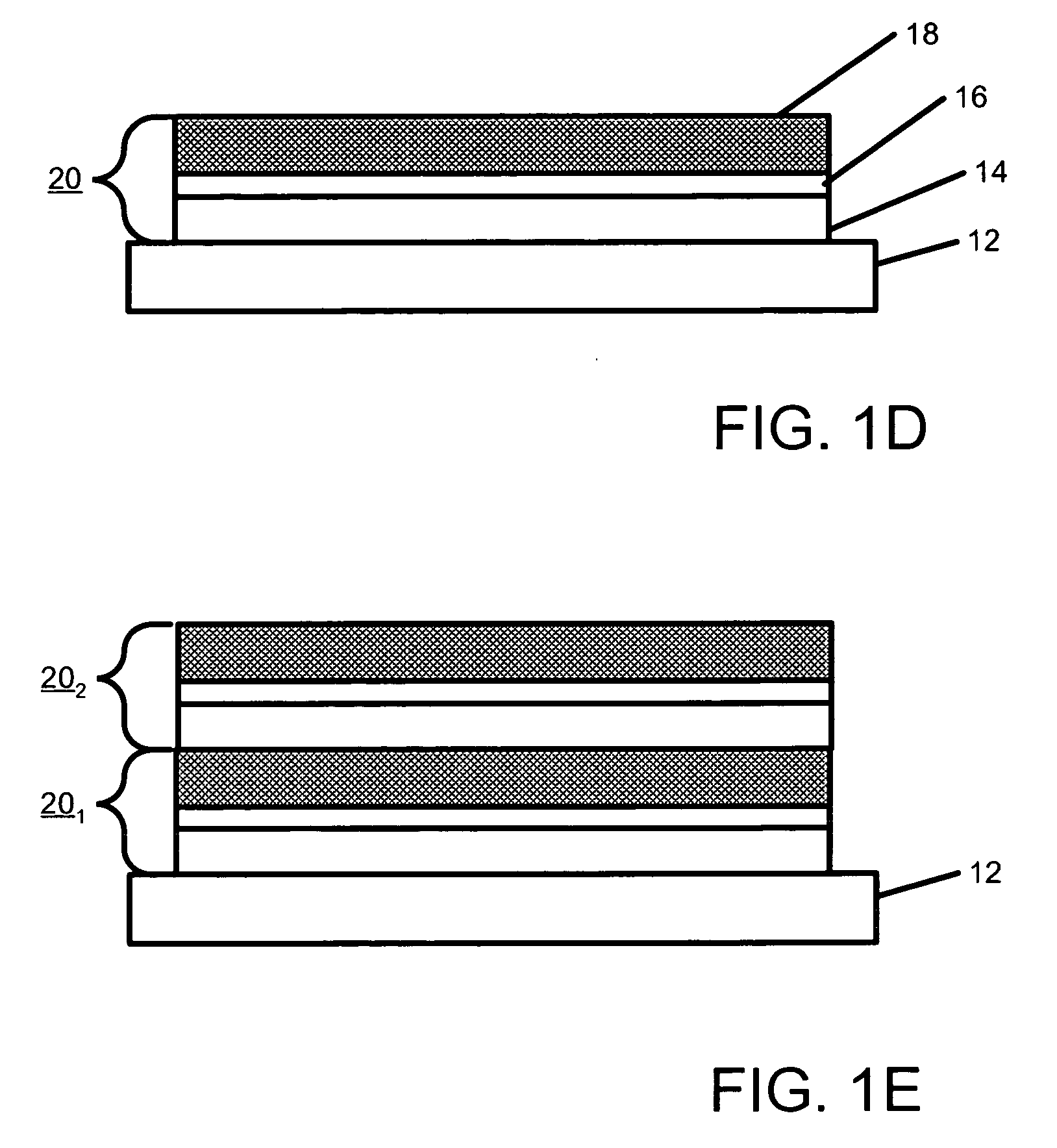
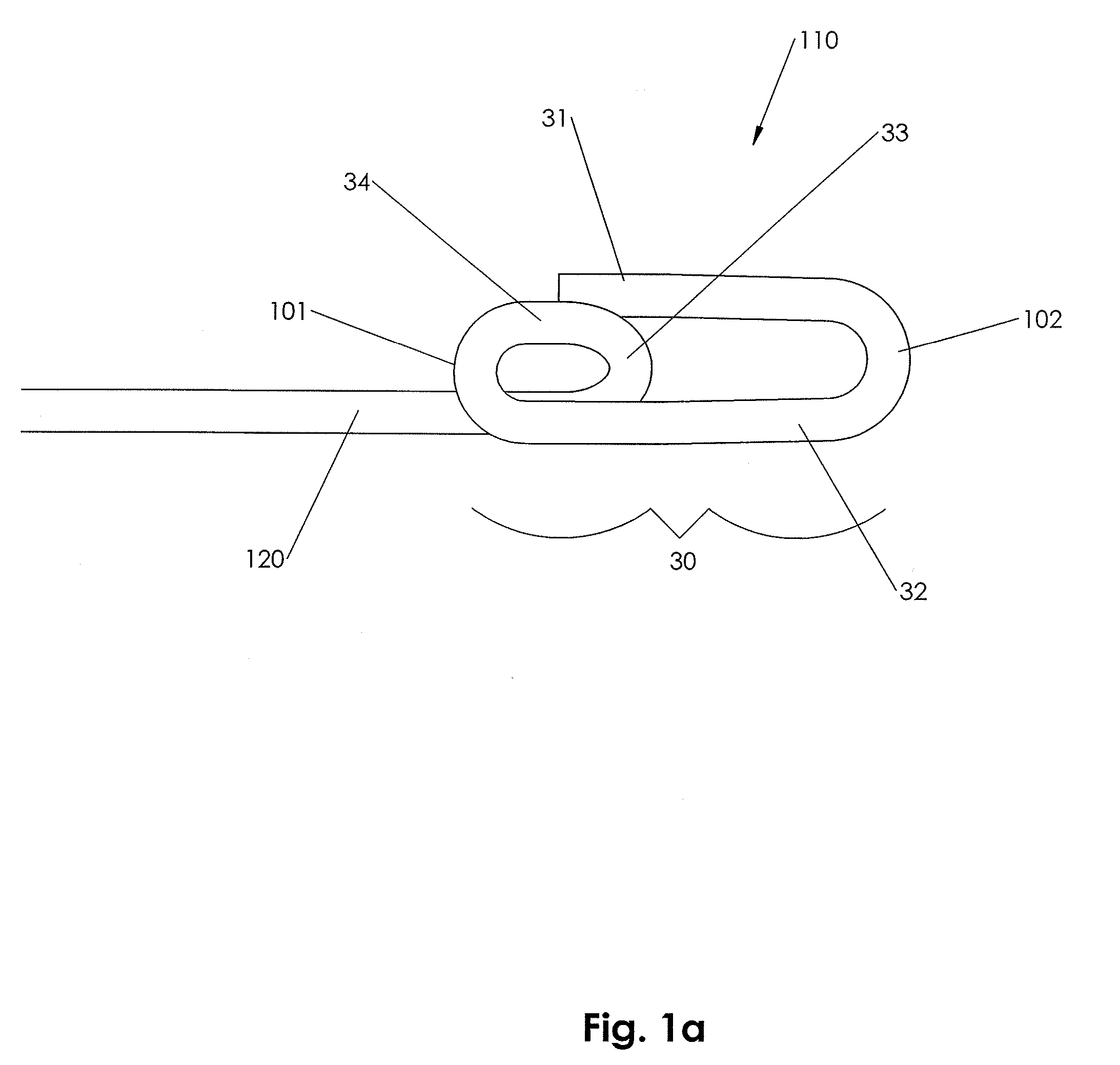
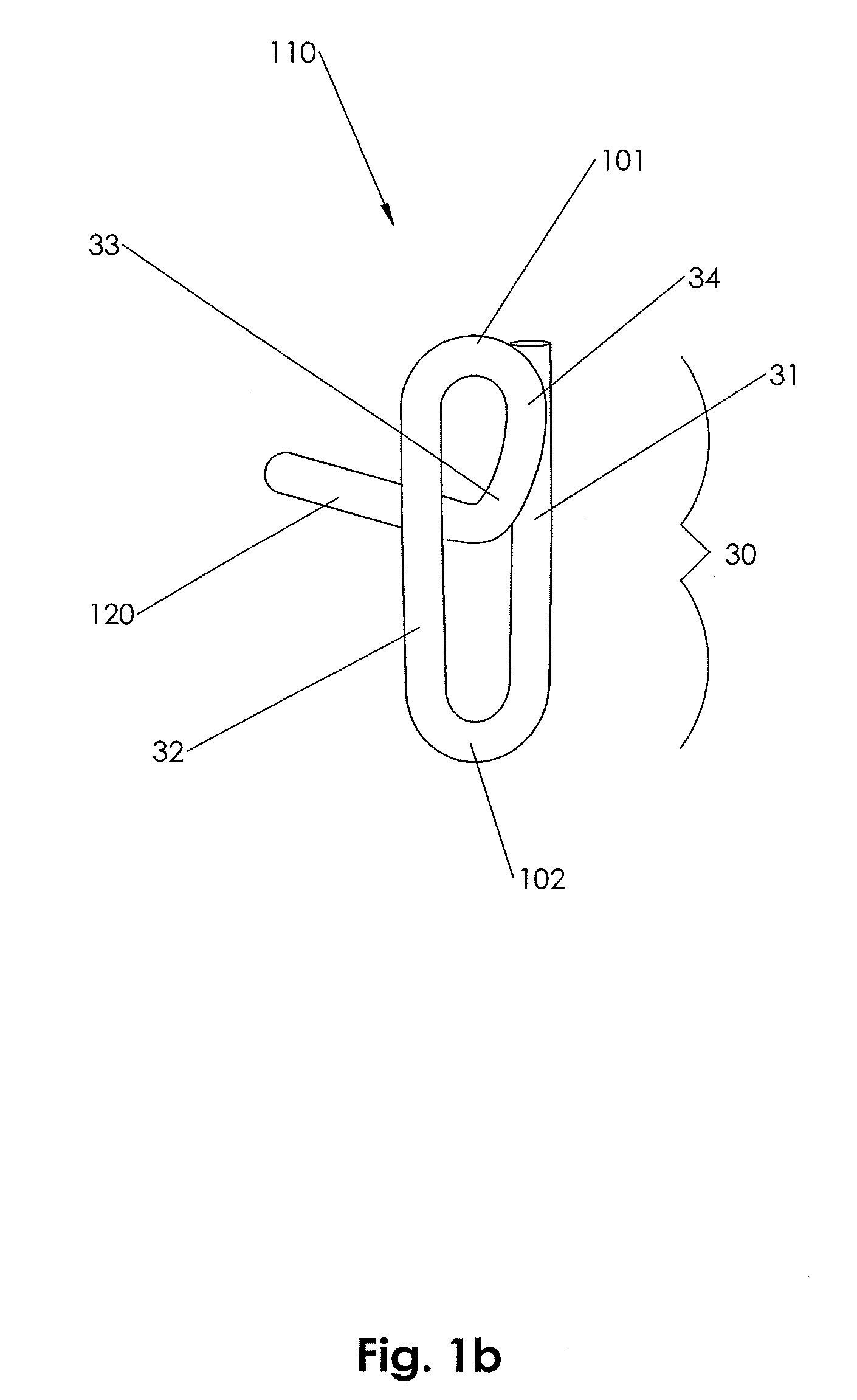
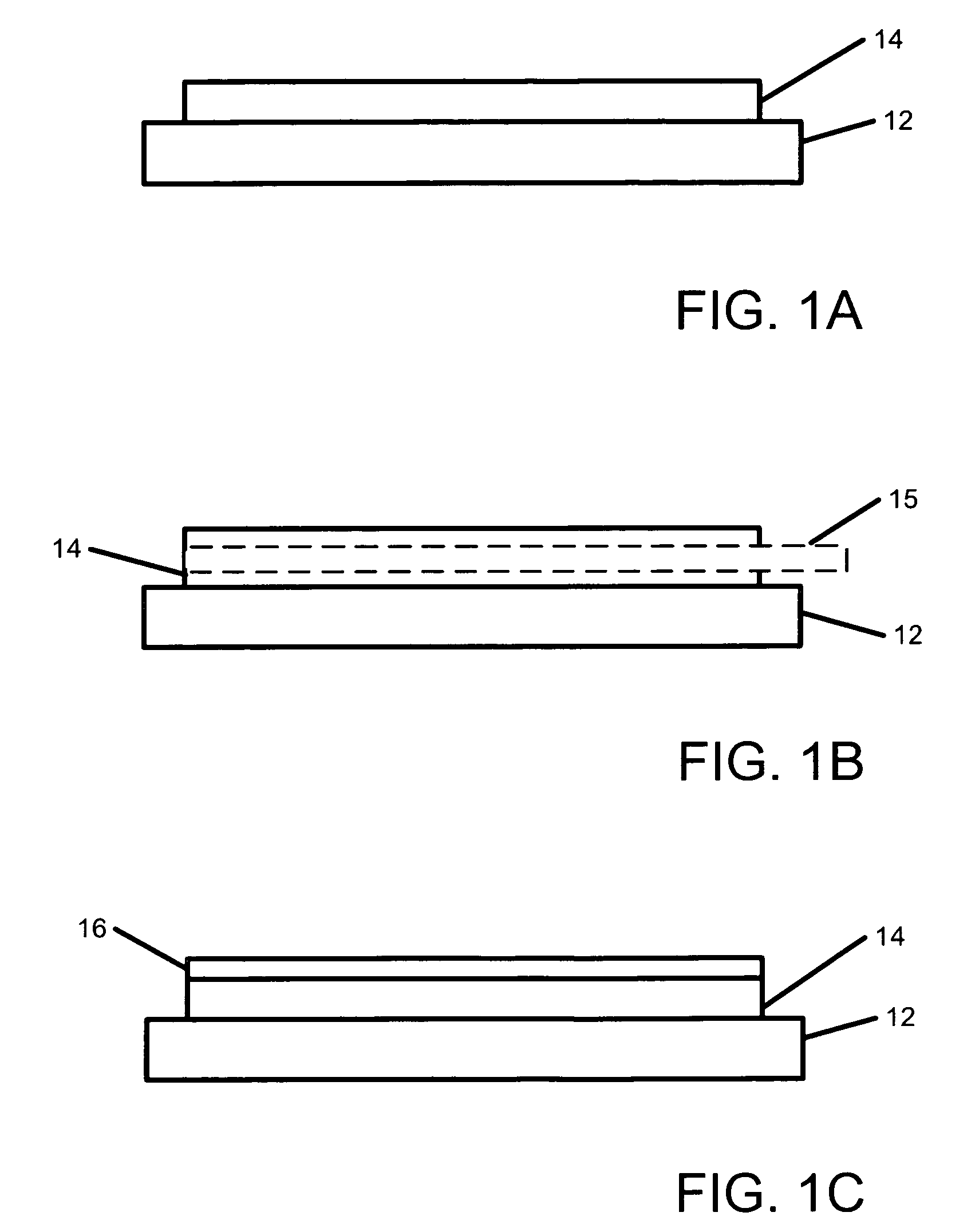
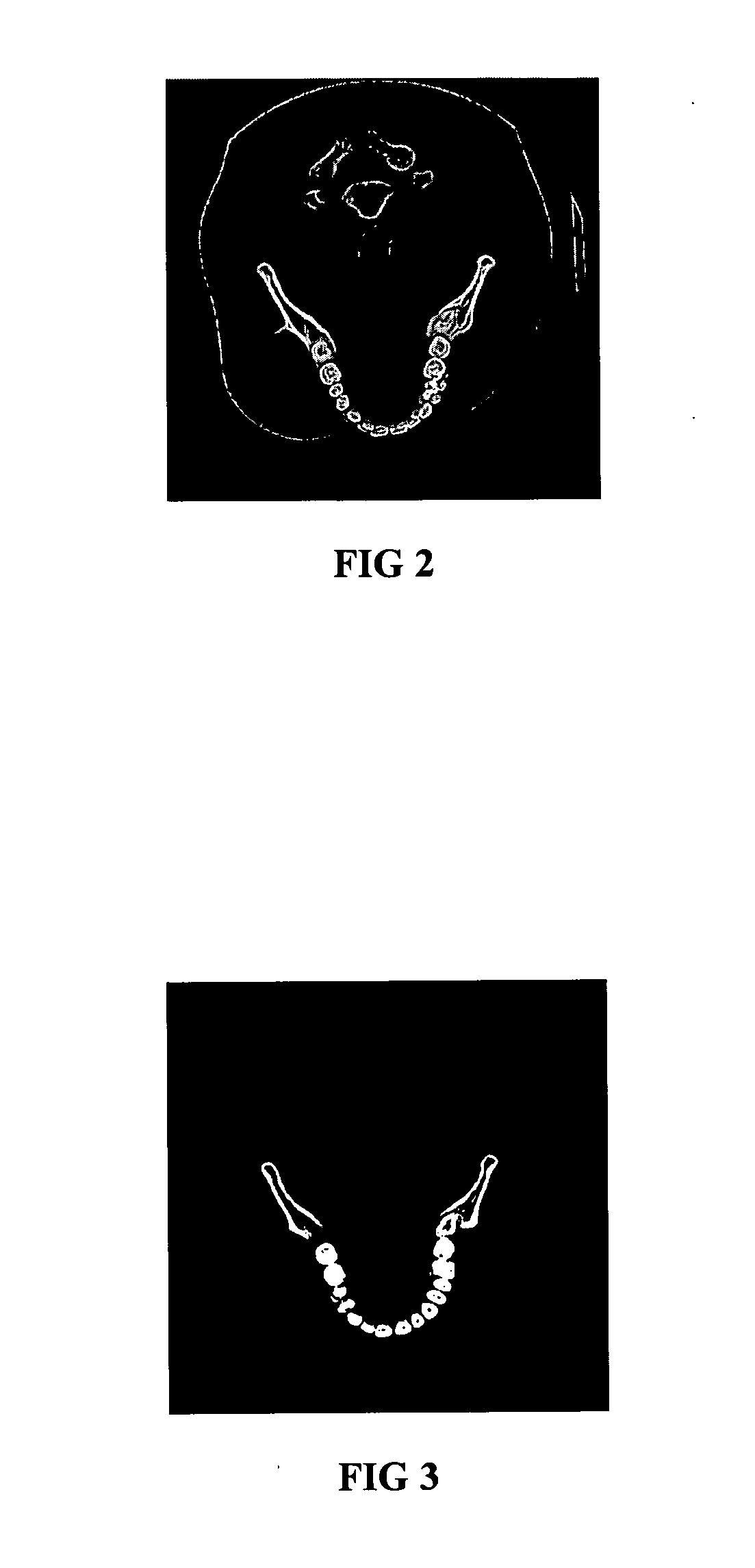
Soft tissue implants with improved interfaces
InactiveUS20060293760A1Facilitates dual functionInduce new tissue formationAnkle jointsBone implantHost tissueDual function
Specialization of the end(s) or host tissue contact points of biocompatible scaffolds brings a functionality to the scaffold that facilitates the dual function of inducing new tissue formation and facilitating attachment and site-specific tissue formation at the scaffolds' functionalized points of fixation.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US) +1
System and method for tissue generation and bone regeneration
ActiveUS20070061015A1Promotes bone formationIncrease surface areaImpression capsBone implantDamages tissueActive agent
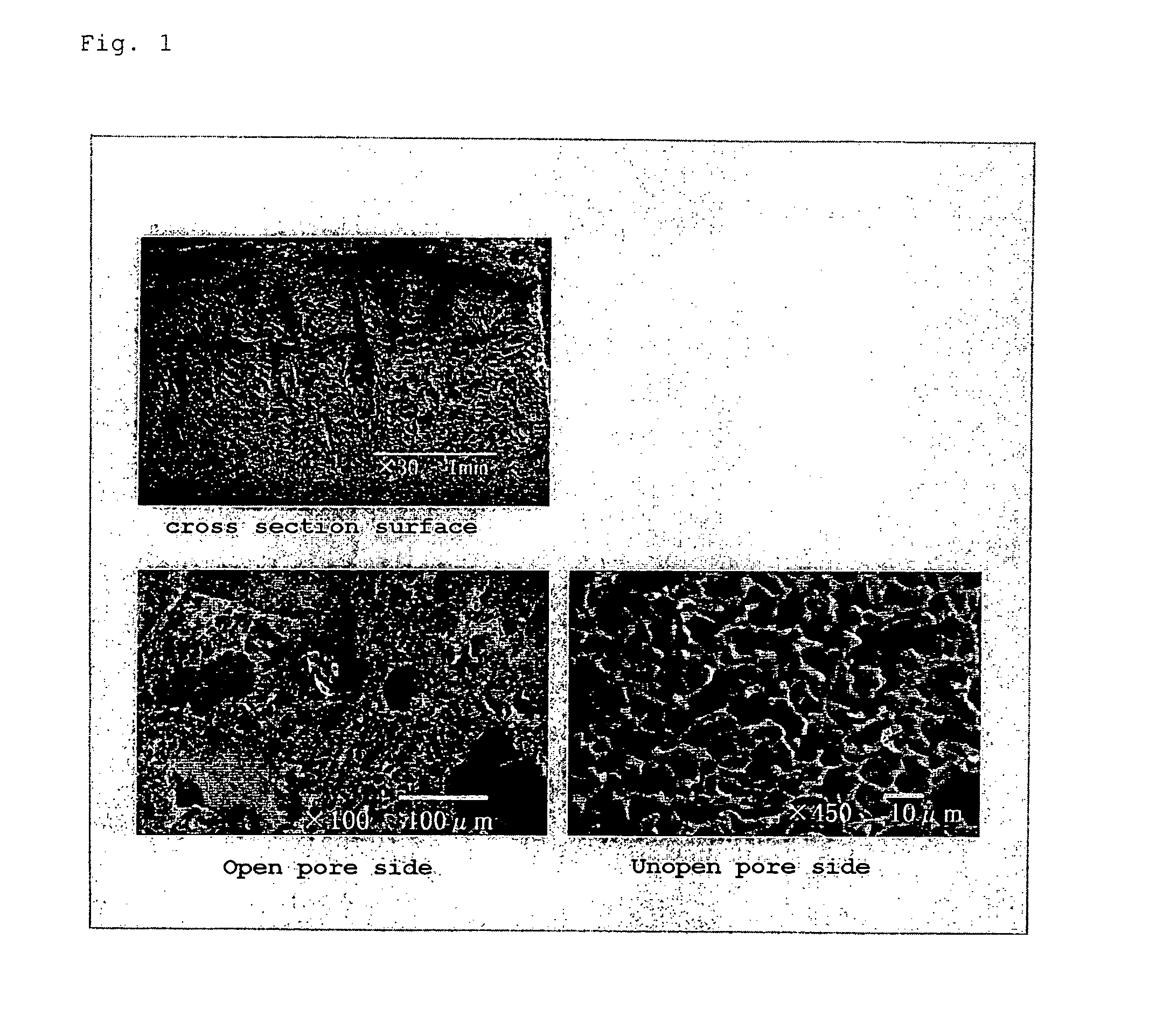
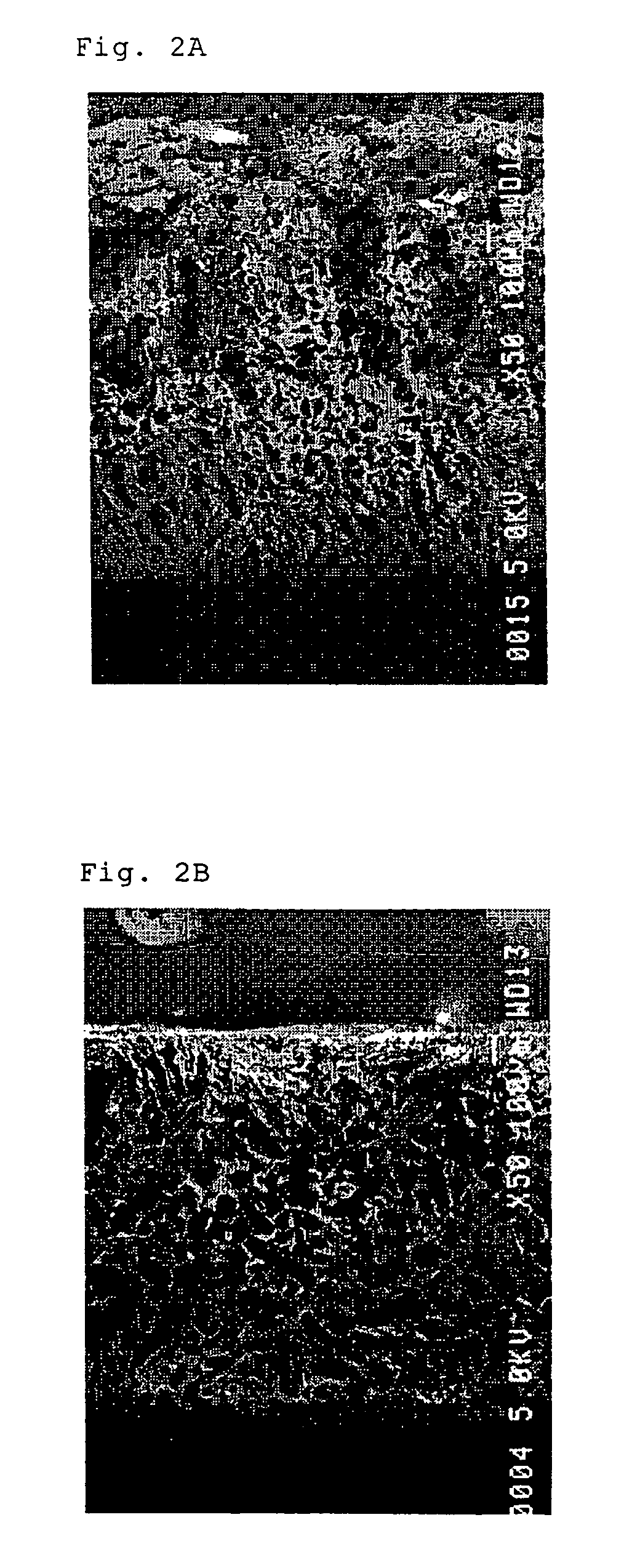
A system and method for the repair of damaged tissue and bones, congenitally missing tissue / cosmetic reconstruction of tissue is described. The system has a layered porous structure with a sufficiently large area of exposed pores to promote neo-vascularization as well as bone and tissue formation. The disclosed porous implant system can contain bioactive agents necessary for rapid tissue formation and keep ingrowth of unwanted tissue out of the implant surgical site. The implant can be reinforced with an additional, stronger polymer layer and / or may include an endoskeleton or exoskeleton for dimensional stability.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
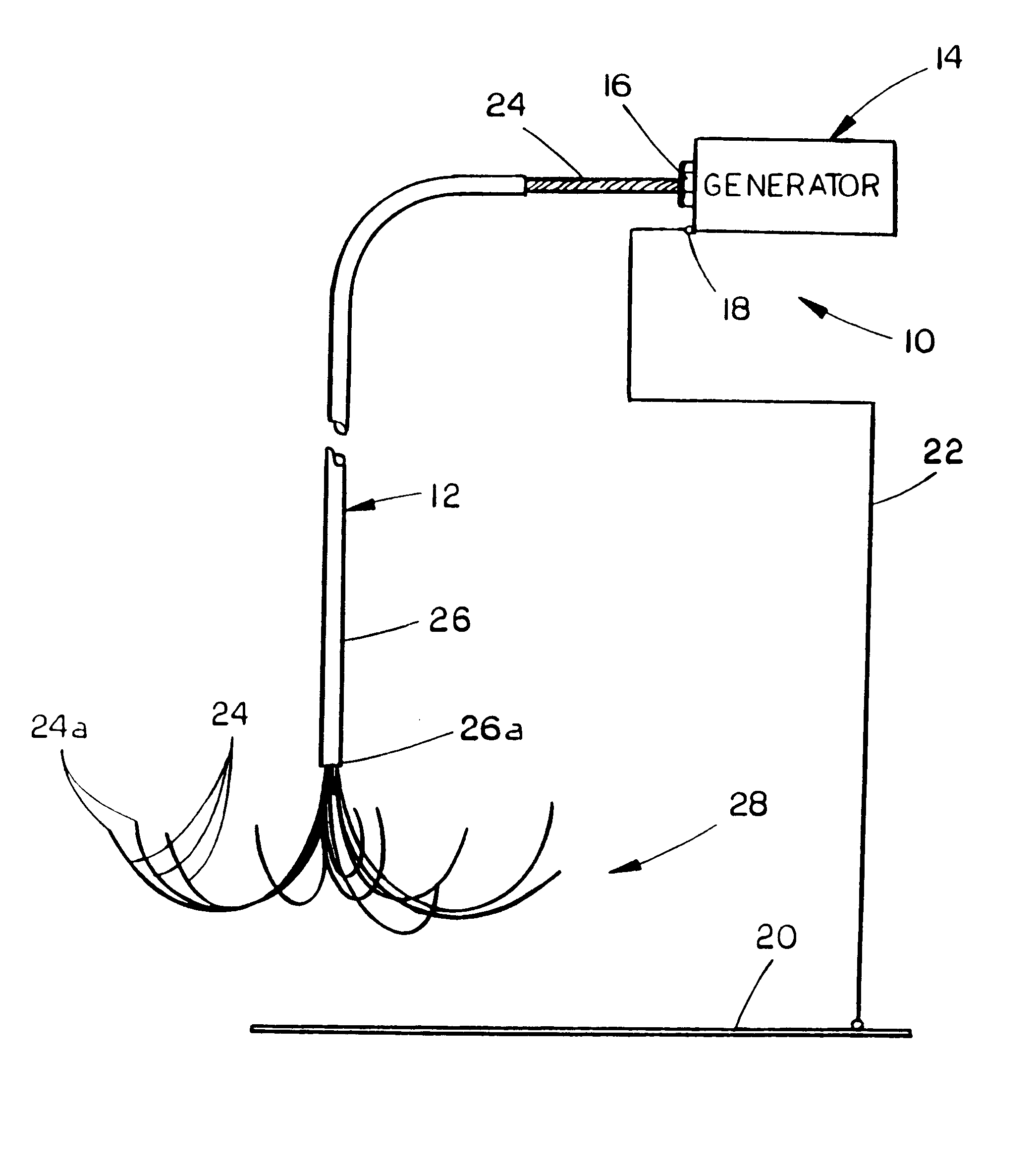
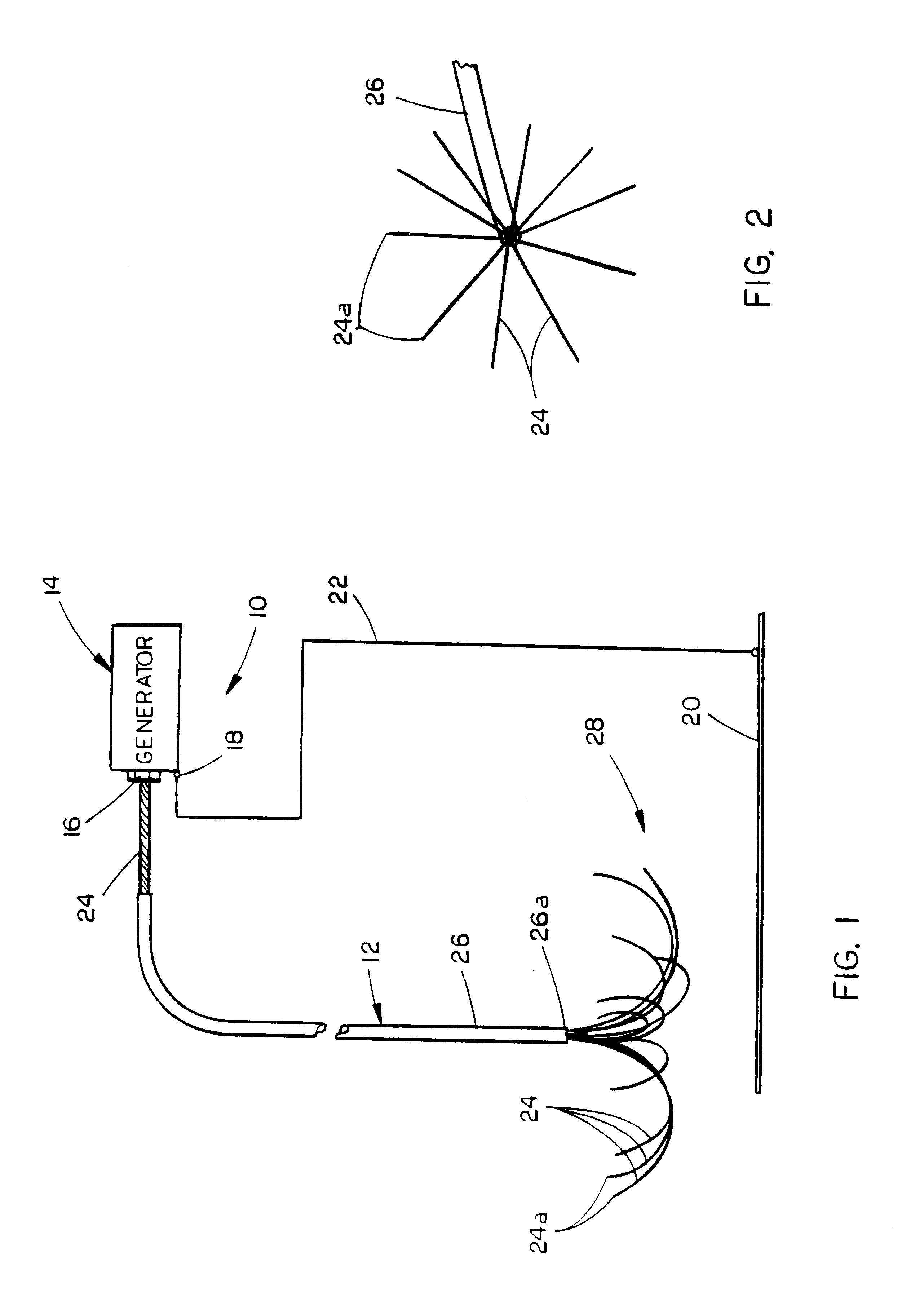
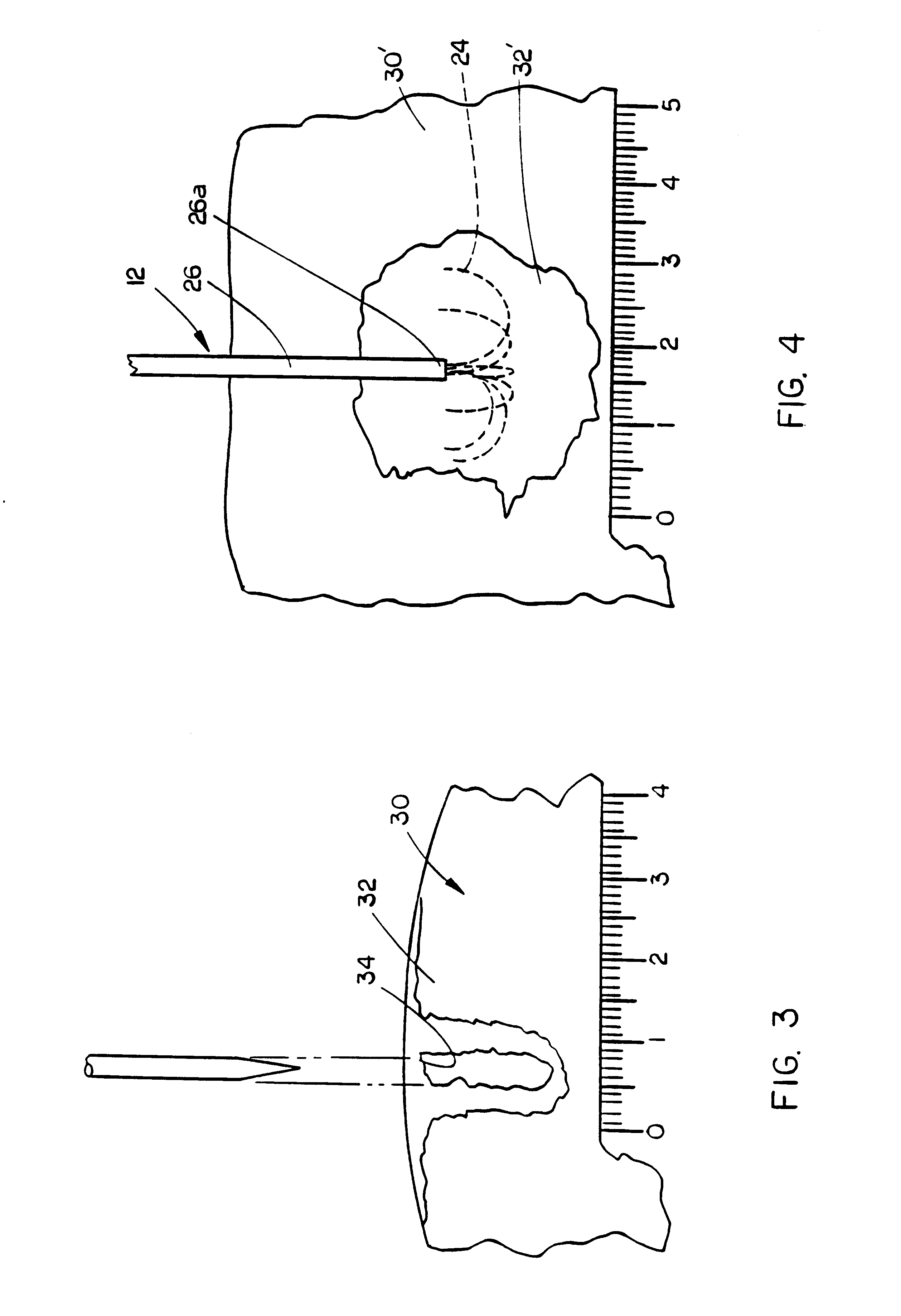
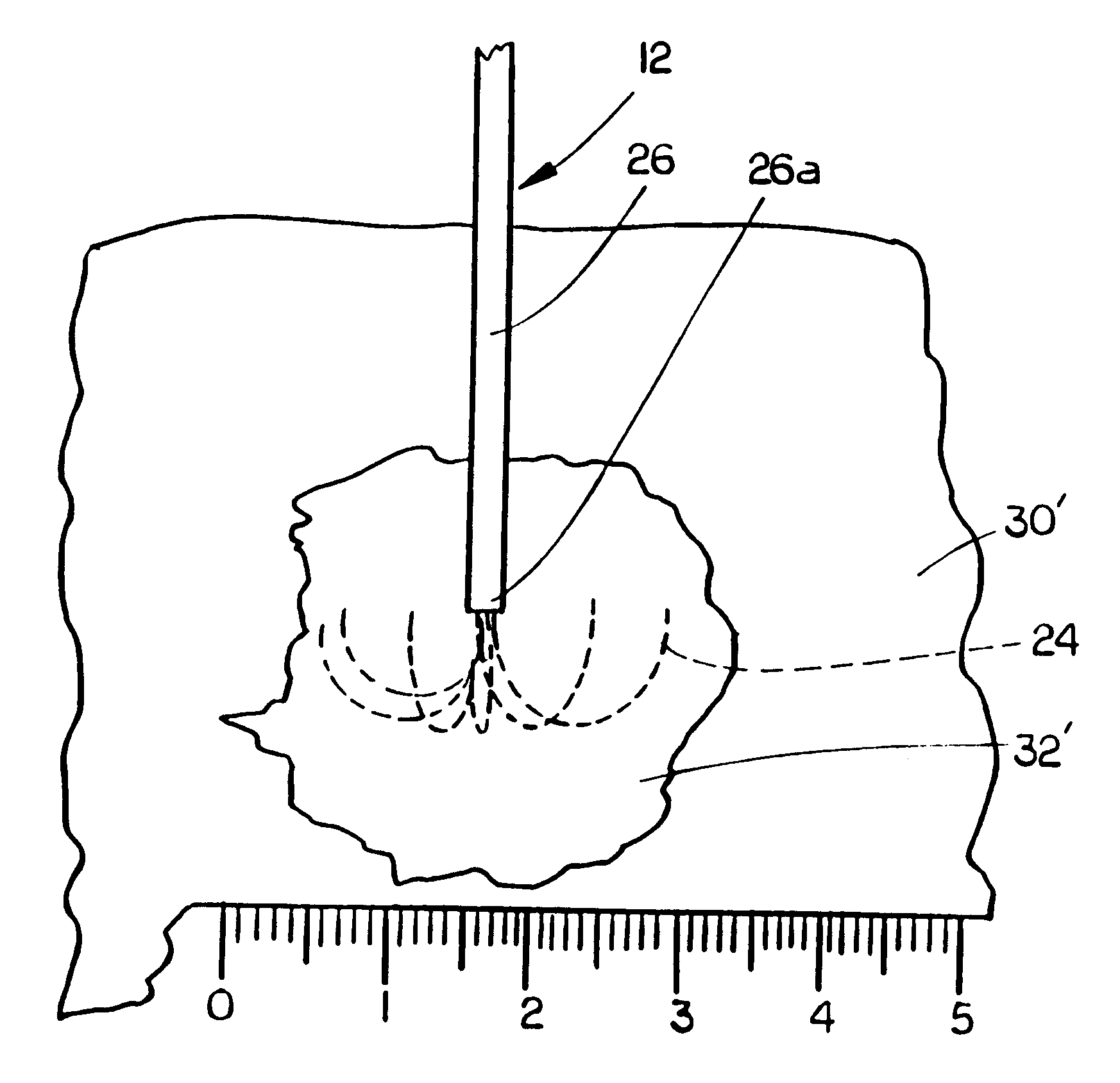
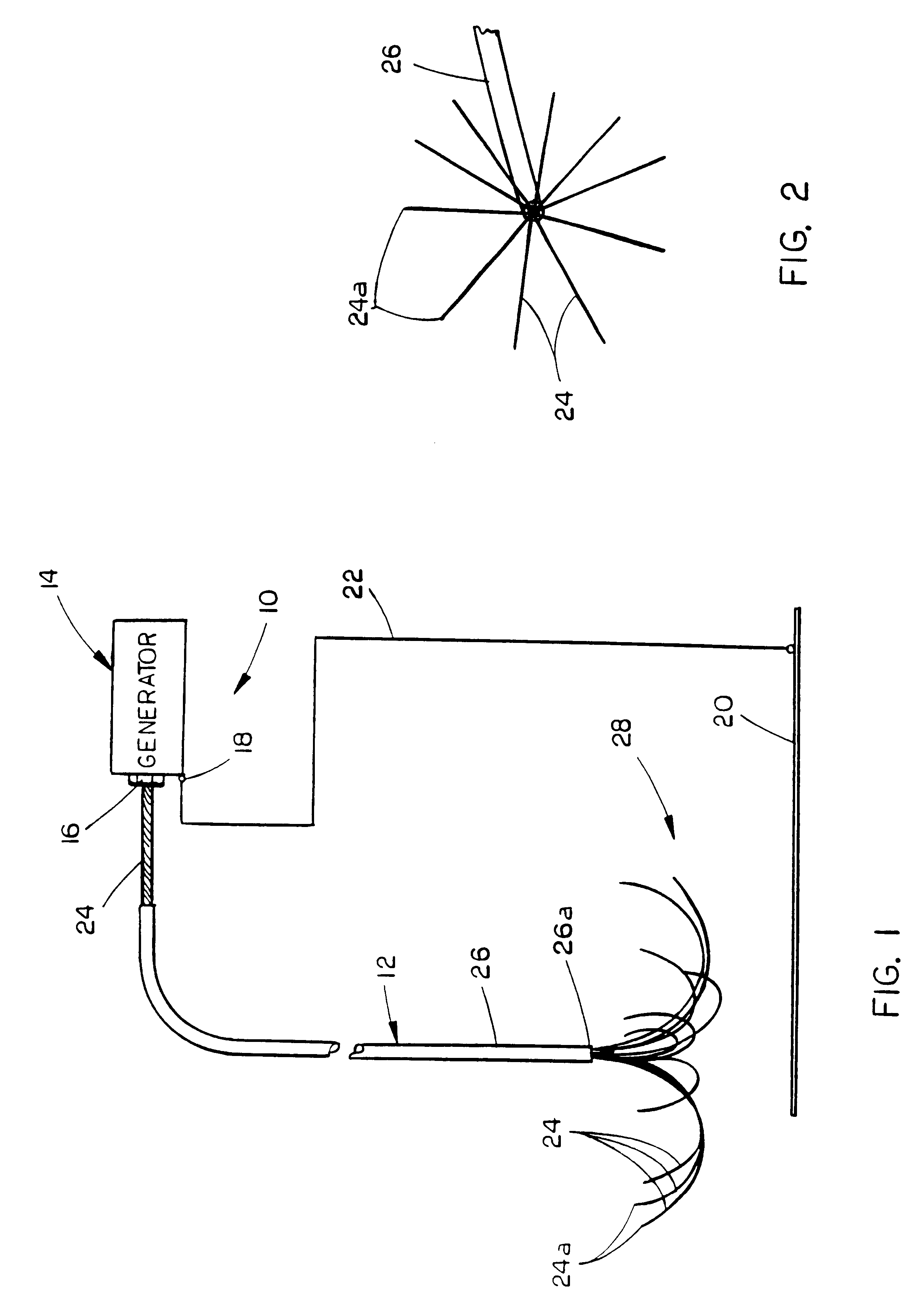
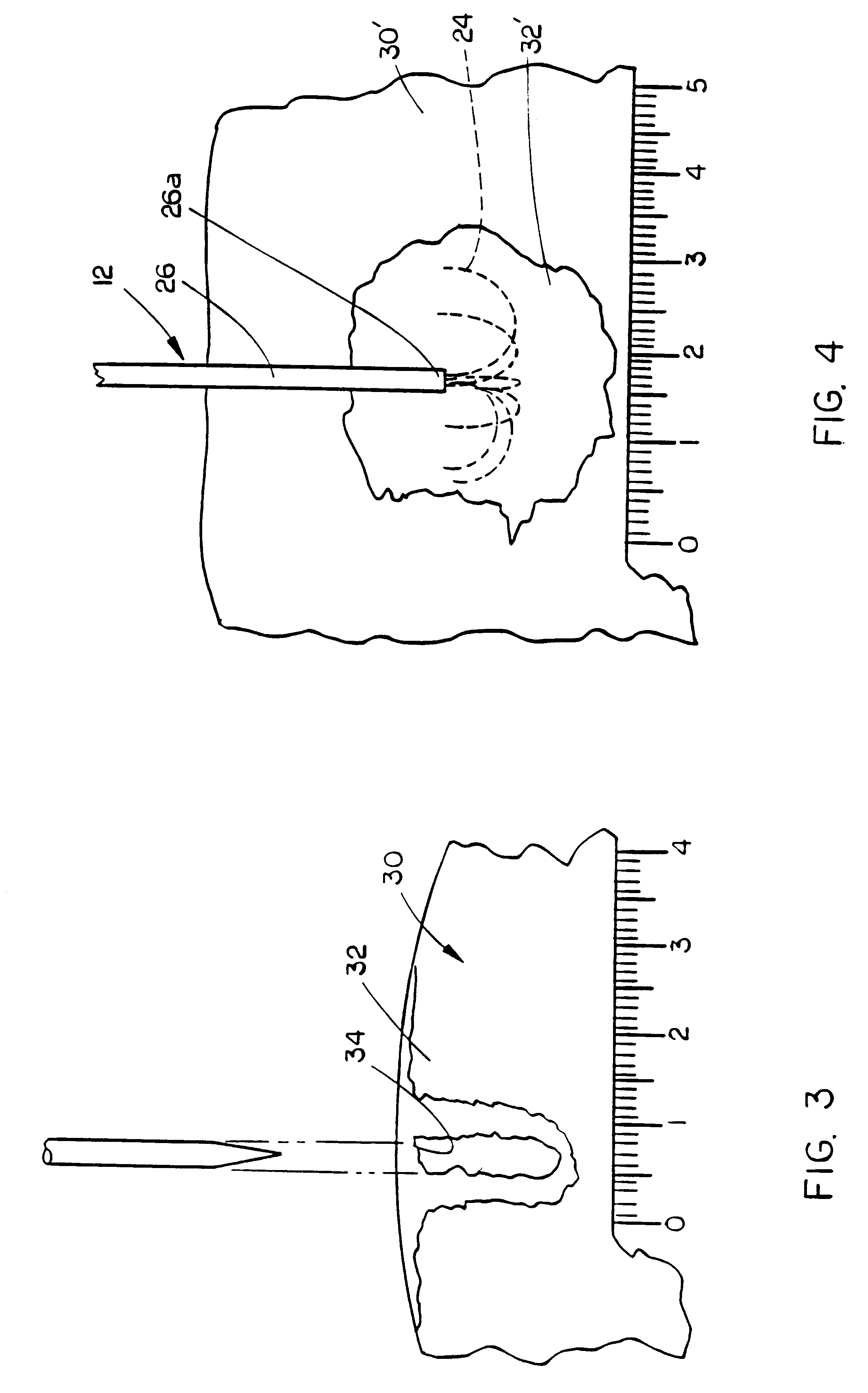
Methods for volumetric tissue ablation
A volumetric tissue ablation apparatus includes a probe having a plurality of wires journaled through a catheter with a proximal end connected to the active terminal of a generator and a distal end projecting from a distal end of the catheter. The probe wire distal ends are arranged in an array with the distal ends located generally radially and uniformly spaced-apart from the catheter distal end. A conductor connected to the return terminal of the generator is located relative to the probe wire array to form a closed electrical circuit through tissue to be ablated. Preferably, the probe wire array includes 10 wires, each formed in an arch from the catheter distal end. The conductor can be either a conventional ground plate upon which the tissue is supported, or a conductor wire extending through the probe and electrically insulated from the probe wires.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Innovative bottom-up cell assembly approach to three-dimensional tissue formation using nano-or micro-fibers
The present invention provides a synthetic tissue scaffold, the scaffold comprising alternating layers of electrospun polymers and mammalian cells sandwiched within. A novel method is also provided for generating a three-dimensional tissue by electrospinning polymers and seeding cells in alternating layers on an aqueous solution in a desired shape. This invention is suitable for generating animal tissue as well as for delivery of drugs or other substances to a recipient.
Owner:WANG HONGJUN
Use of bioactive glass compositions to stimulate osteoblast production
InactiveUS20040009598A1Expand the populationRapid apoptosisSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture supports/coatingOsteoblastMammal
Compositions comprising bioactive glass compositions or extracts thereof which include ions in an appropriate concentration and ratio that they enhance osteoblast production, and methods of preparation and use thereof, are disclosed. The compositions can be included in implantable devices that are capable of inducing tissue formation in autogeneic, allogeneic and xenogeneic implants, for example as coatings and / or matrix materials. Examples of such devices include prosthetic implants, sutures, stents, screws, plates, tubes, and the like. Aqueous extracts of the bioactive glass compositions, which extracts are capable of stimulating osteoblast production, are also disclosed. The compositions can be used, for example, to induce local tissue formation from a progenitor cell in a mammal, for accelerating allograft repair in a mammal, for promoting in vivo integration of an implantable prosthetic device to enhance the bond strength between the prosthesis and the existing target tissue at the joining site, and for treating tissue degenerative conditions.
Owner:NOVATHERA
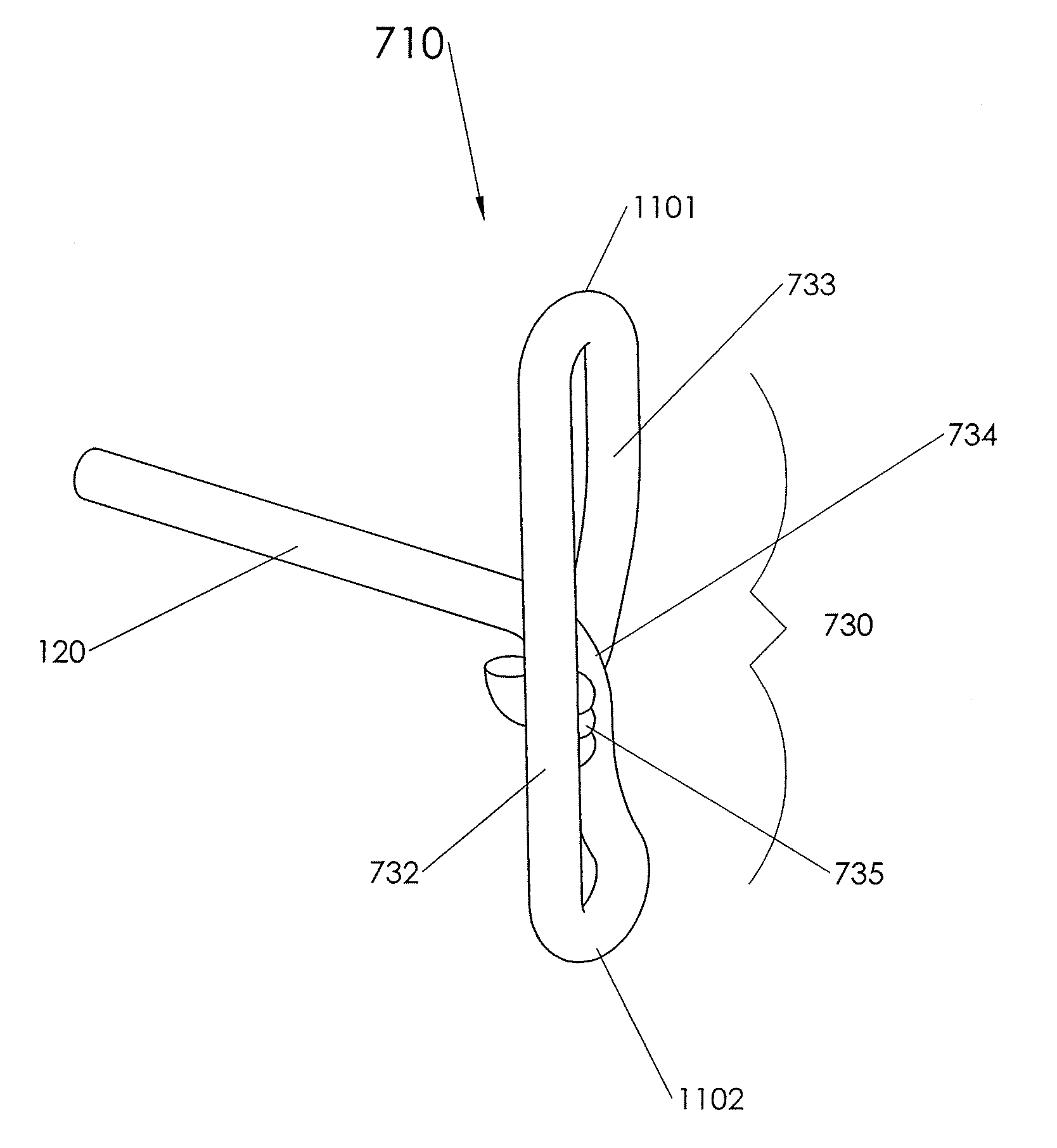
Closure Device, Deployment Apparatus, and Method of Deploying a Closure Device
ActiveUS20090069844A1Improve sealingSecure early ambulationSurgical veterinaryWound clampsMedical deviceBiological fluids
The present invention relates generally to medical devices and methods for sealing and closing passages formed through tissue. More specifically, the present invention relates to devices for sealing or closing an opening formed through biological tissue comprising a distal or outside margin or surface, and a proximal or inside margin or surface (i.e., a wall thickness), and to apparatuses and methods for delivering such devices, to control (or prevent or stop) bleeding (or the flow of other biological fluid or tissue). The openings comprise percutaneously formed punctures, incisions, or other openings formed through biological tissue, such as in blood vessels, organs, and the like.
Owner:TRANSLUMINAL TECH INC
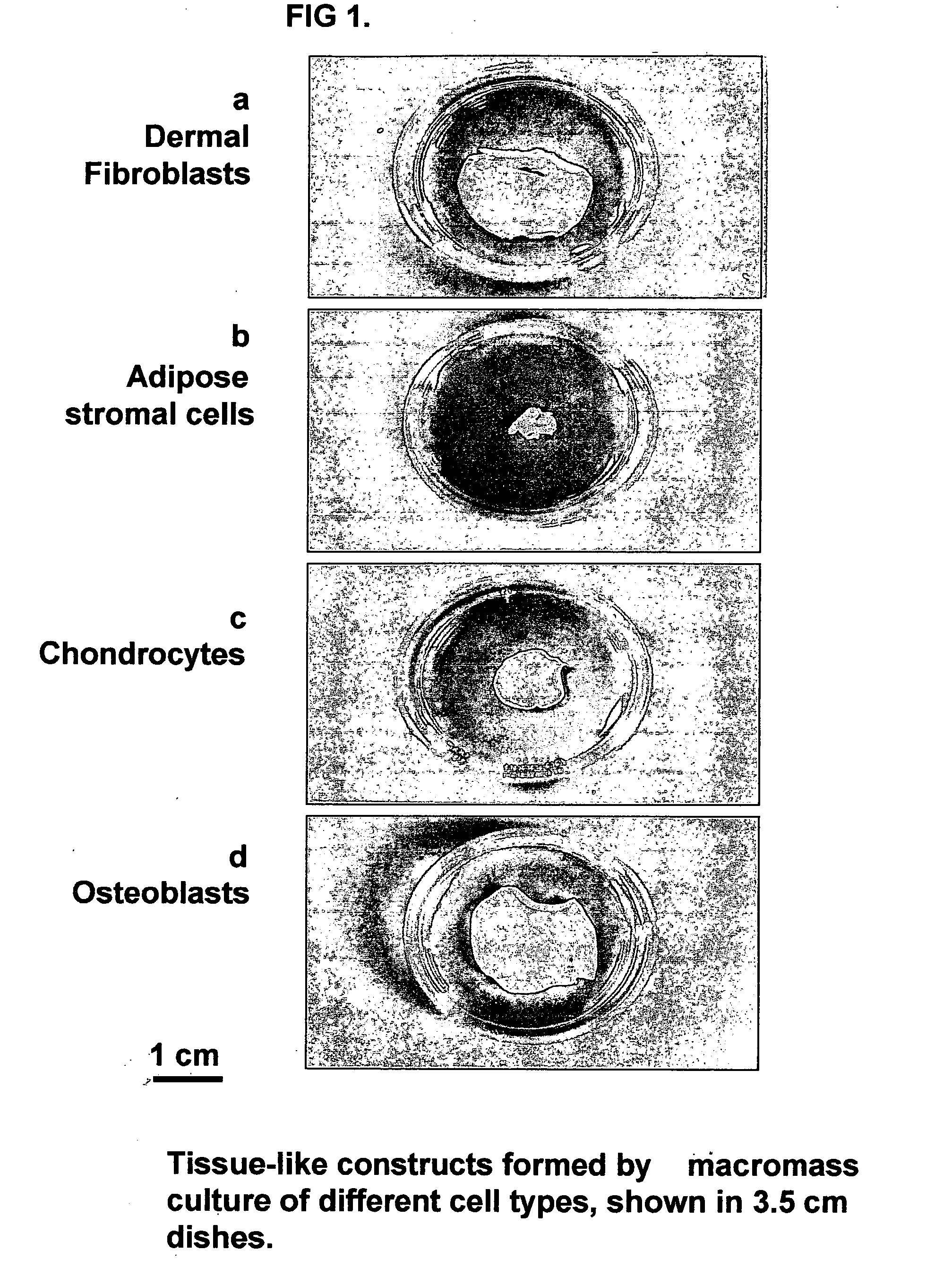
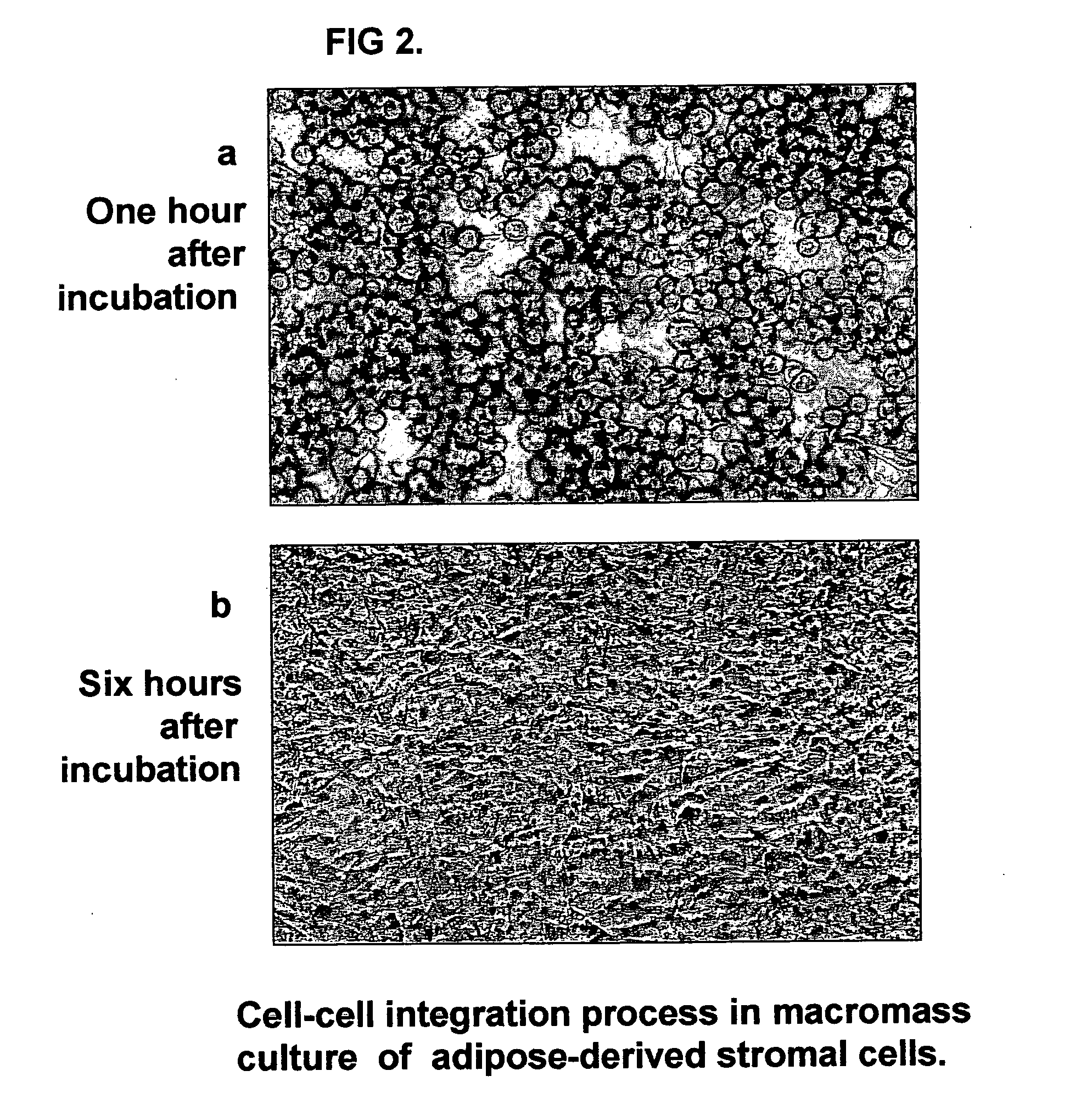
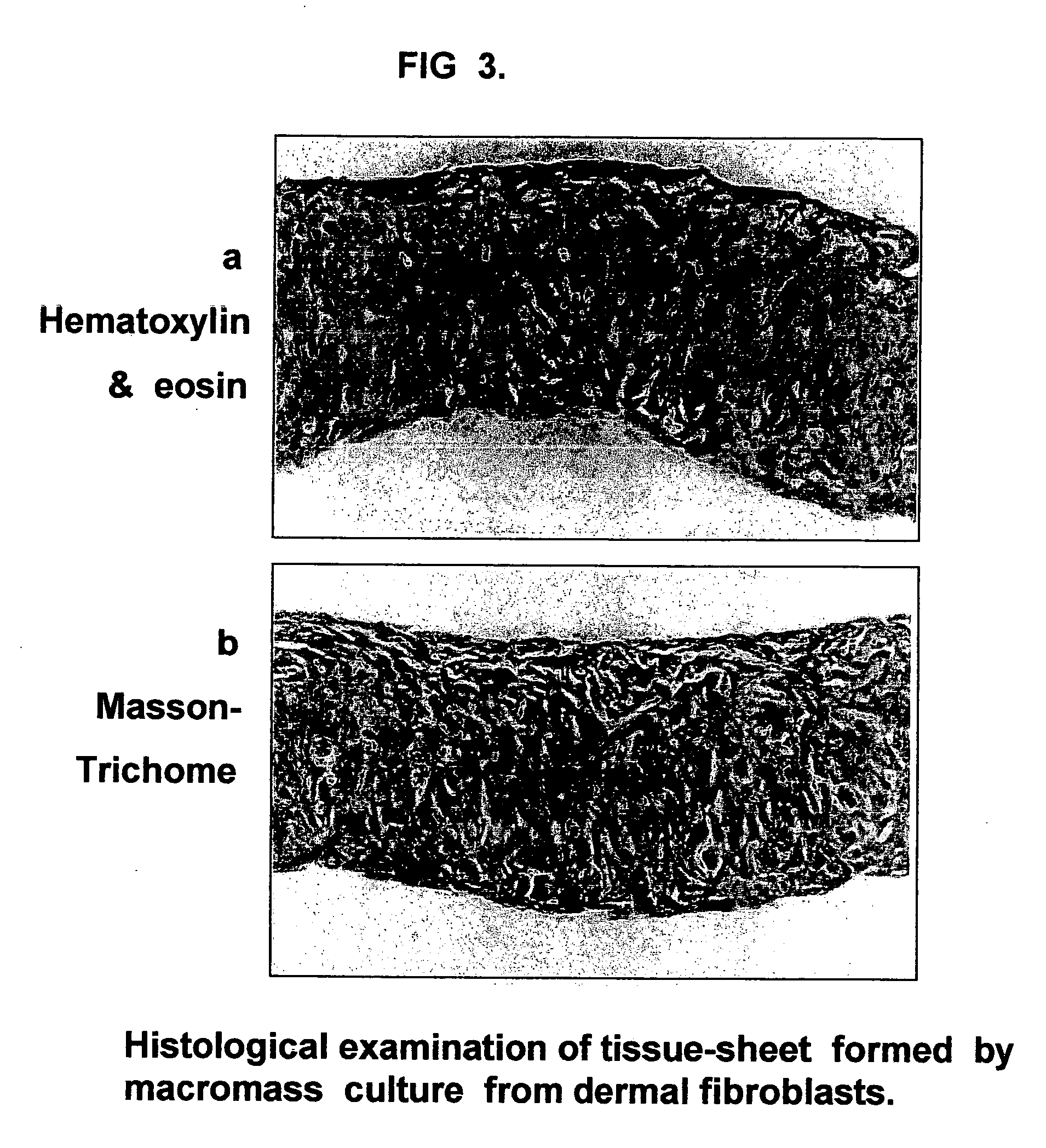
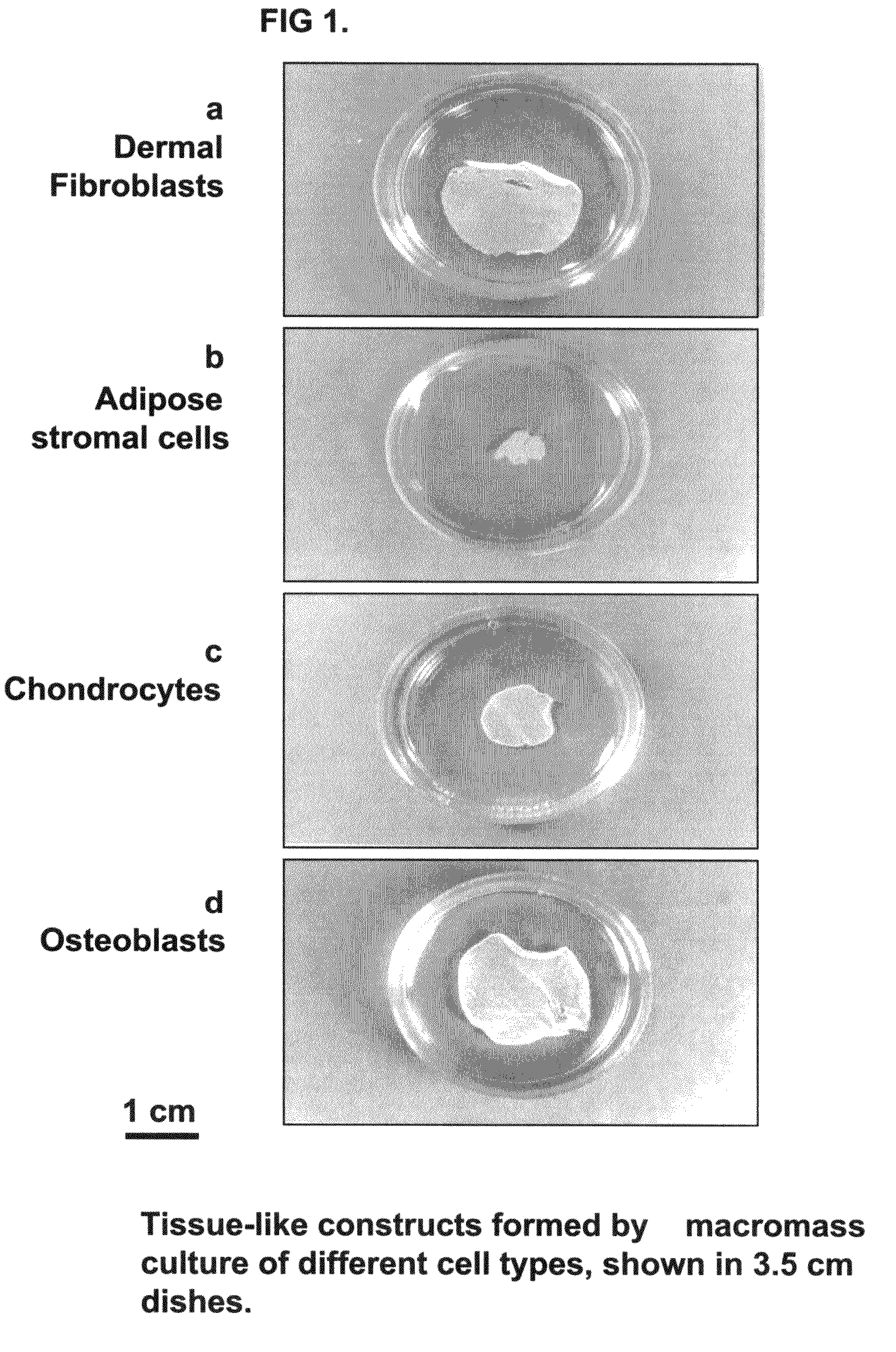
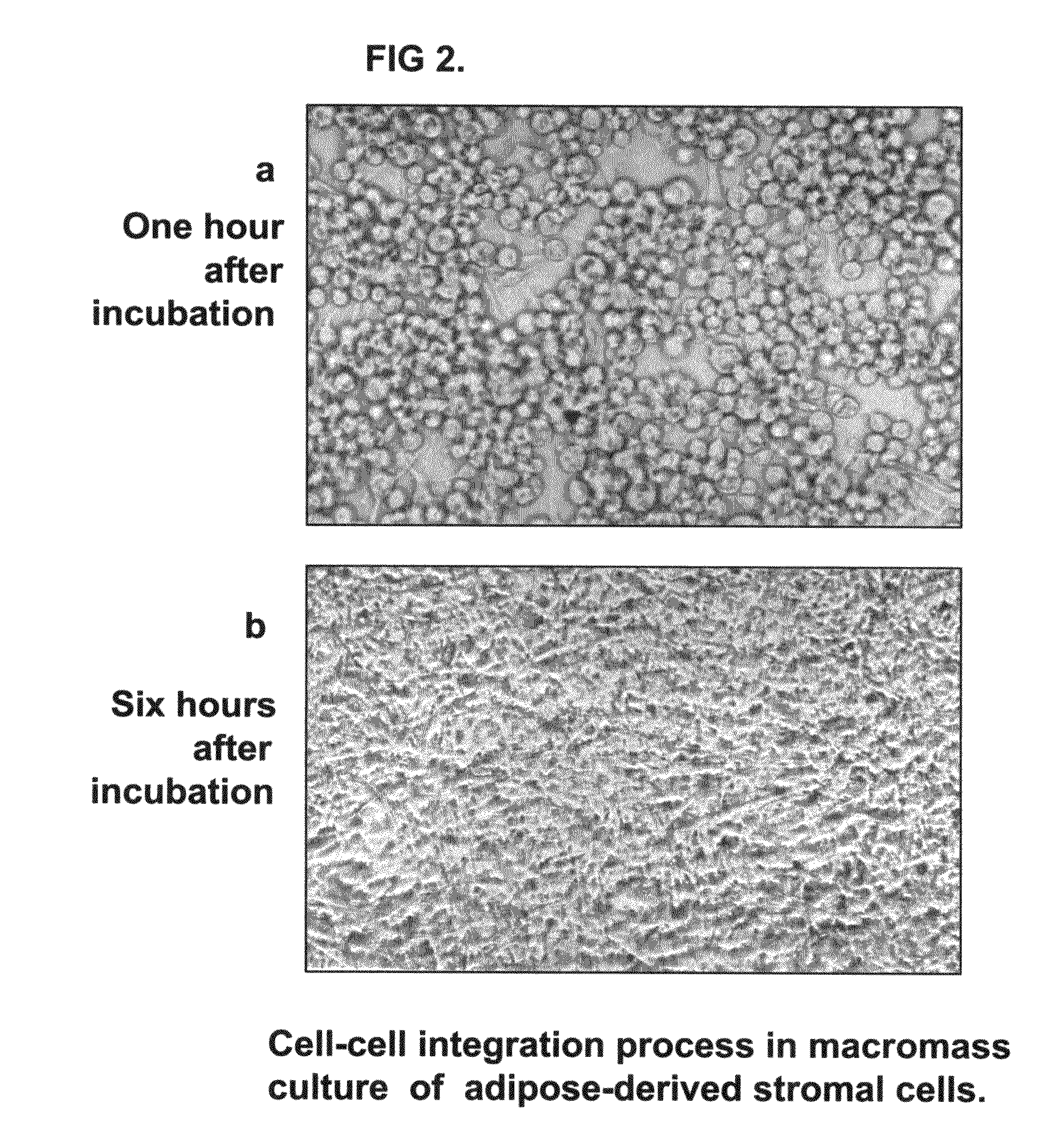
Tissue-like organization of cells and macroscopic tissue-like constructs, generated by macromass culture of cells, and the method of macromass culture
InactiveUS20040082063A1Sectioned easilySmall sizeEpidermal cells/skin cellsMammal material medical ingredientsHigh cellFiber
Three-dimensional tissue-like organization of cells by high cell-seeding-density culture termed as macromass culture is described. By macromass culture, cells can be made to organize themselves into a tissue-like form without the aid of a scaffold and three-dimensional macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be made wholly from cells. Tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be generated from fibroblastic cells of mesenchymal origin (at least), which can be either differentiated cells or multipotent adult stem cells. In this work, tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs have been generated from dermal fibroblasts, adipose stromal cells-derived osteogenic cells, chondrocytes, and from osteoblasts. The factor causing macroscopic tissue formation is large scale culture at high cell seeding density per unit area or three-dimensional space, that is, macromass culture done on a large scale. No scaffold or extraneous matrix is used for tissue generation, the tissues are of completely cellular origin. No other agents (except high cell-seeding-density) that aid in tissue formation such as tissue-inducing chemicals, tissue-inducing growth factors, substratum with special properties, rotational culture, etc, are employed for tissue formation. These tissue-like masses have the potential for use as tissue replacements in the human body. Tissue-like organization by high cell-seeding-density macromass culture can also be generated at the microscopic level.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Methods for volumetric tissue ablation
A volumetric tissue ablation apparatus includes a probe having a plurality of wires journaled through a catheter with a proximal end connected to the active terminal of a generator and a distal end projecting from a distal end of the catheter. The probe wire distal ends are arranged in an array with the distal ends located generally radially and uniformly spaced-apart from the catheter distal end. A conductor connected to the return terminal of the generator is located relative to the probe wire array to form a closed electrical circuit through tissue to be ablated. Preferably, the probe wire array includes 10 wires, each formed in an arch from the catheter distal end. The conductor can be either a conventional ground plate upon which the tissue is supported, or a conductor wire extending through the probe and electrically insulated from the probe wires.
Owner:NEBRASKA THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF
Bioabsorbable tissue tack with oval-shaped head and method of tissue fixation using the same
InactiveUS20070288027A1Low profileAvoid contactSuture equipmentsJoint implantsCancellous boneSacroiliac joint
A bioabsorbable, cannulated tissue tack having an oblong head is used in sutureless soft tissue fixation to bone, particularly in arthroscopic shoulder surgery. A plurality of ribs are formed along the shaft of the tack. Repair of the glenohumeral joint is performed by installing the tack through a hole formed through the soft tissue of the labrum and into the cancellous bone of the glenoid rim. Aligning the oblong head of the tack lengthwise along the glenoid rim provides a low profile that avoids articular impingement on the tack head.
Owner:GRAFTON R DONALD +1
Support for tissue regeneration and process for producing the same
ActiveUS7445793B2Excellent in retention and grafting abilityPrevent intrusionBiocidePowder deliveryFreeze-dryingBiology
Owner:GC CORP +2
Methods for transforming immature maize embryos
InactiveUS7057089B2Promote embryogenic-tissue formationSmall sizeStable introduction of DNAFermentationEmbryogenesisGenetically modified maize
Methods are provided for transforming freshly isolated, immature maize embryos and for producing transgenic maize plants. The methods comprise obtaining immature embryos from a maize plant, contacting the embryos with an auxin-depleted or phytohormone-depleted transformation support medium and introducing a nucleotide construct into cells from the embryos prior to subjecting the embryos to conditions which promote embryogenic-tissue formation. The methods additionally comprise identifying or selecting transformed cells and regenerating such cells into transformed maize plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
System and method for tissue generation and bone regeneration
ActiveUS8518123B2Promotes bone formationIncrease surface areaImpression capsBone implantDamages tissueSurgical site
A system and method for the repair of damaged tissue and bones, congenitally missing tissue / cosmetic reconstruction of tissue is described. The system has a layered porous structure with a sufficiently large area of exposed pores to promote neo-vascularization as well as bone and tissue formation. The disclosed porous implant system can contain bioactive agents necessary for rapid tissue formation and keep ingrowth of unwanted tissue out of the implant surgical site. The implant can be reinforced with an additional, stronger polymer layer and / or may include an endoskeleton or exoskeleton for dimensional stability.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Convective flow tissue assembly
InactiveUS7439057B2Accurate tissue morphologyAvoid delaminationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIn vivoBiology
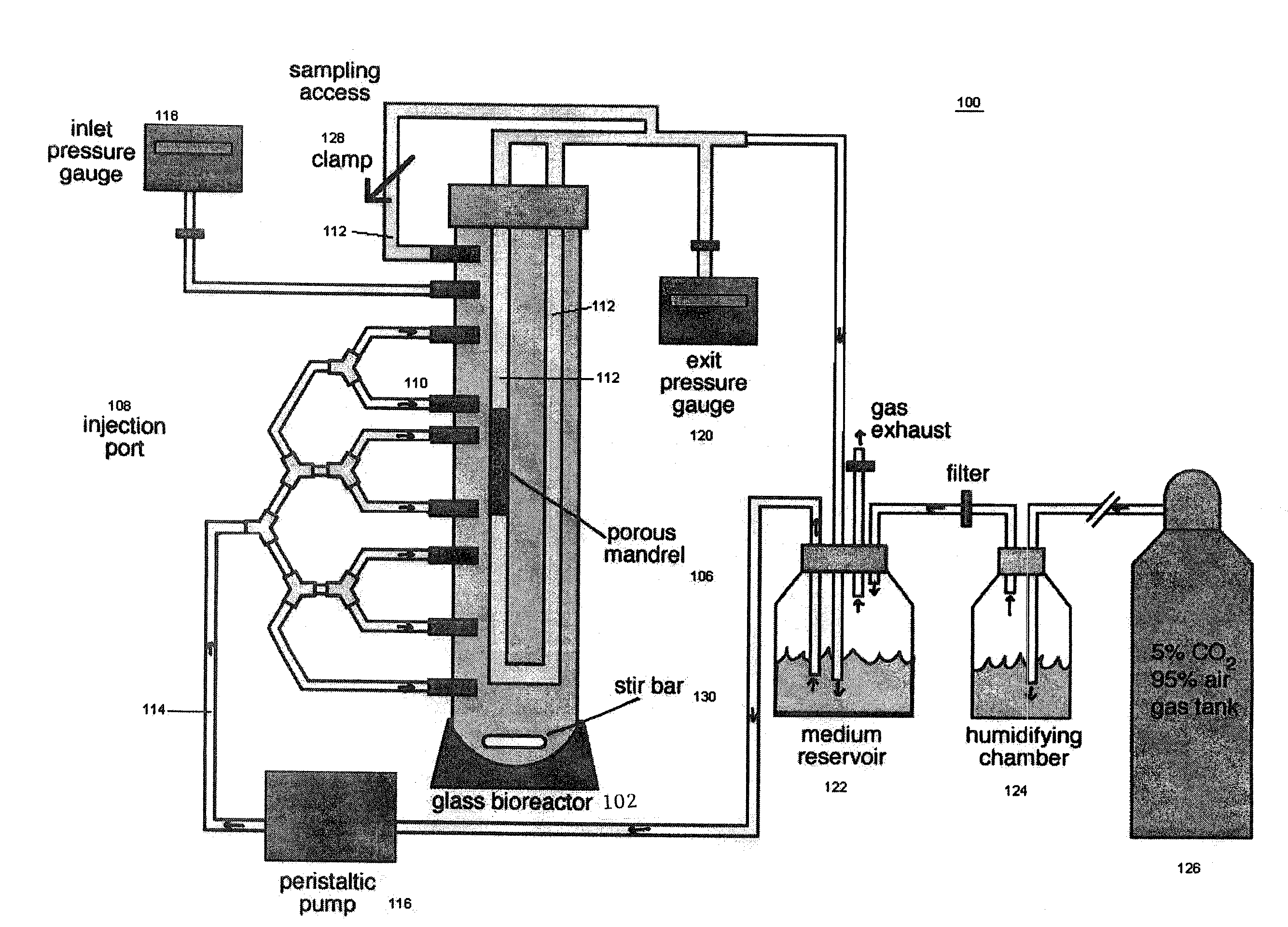
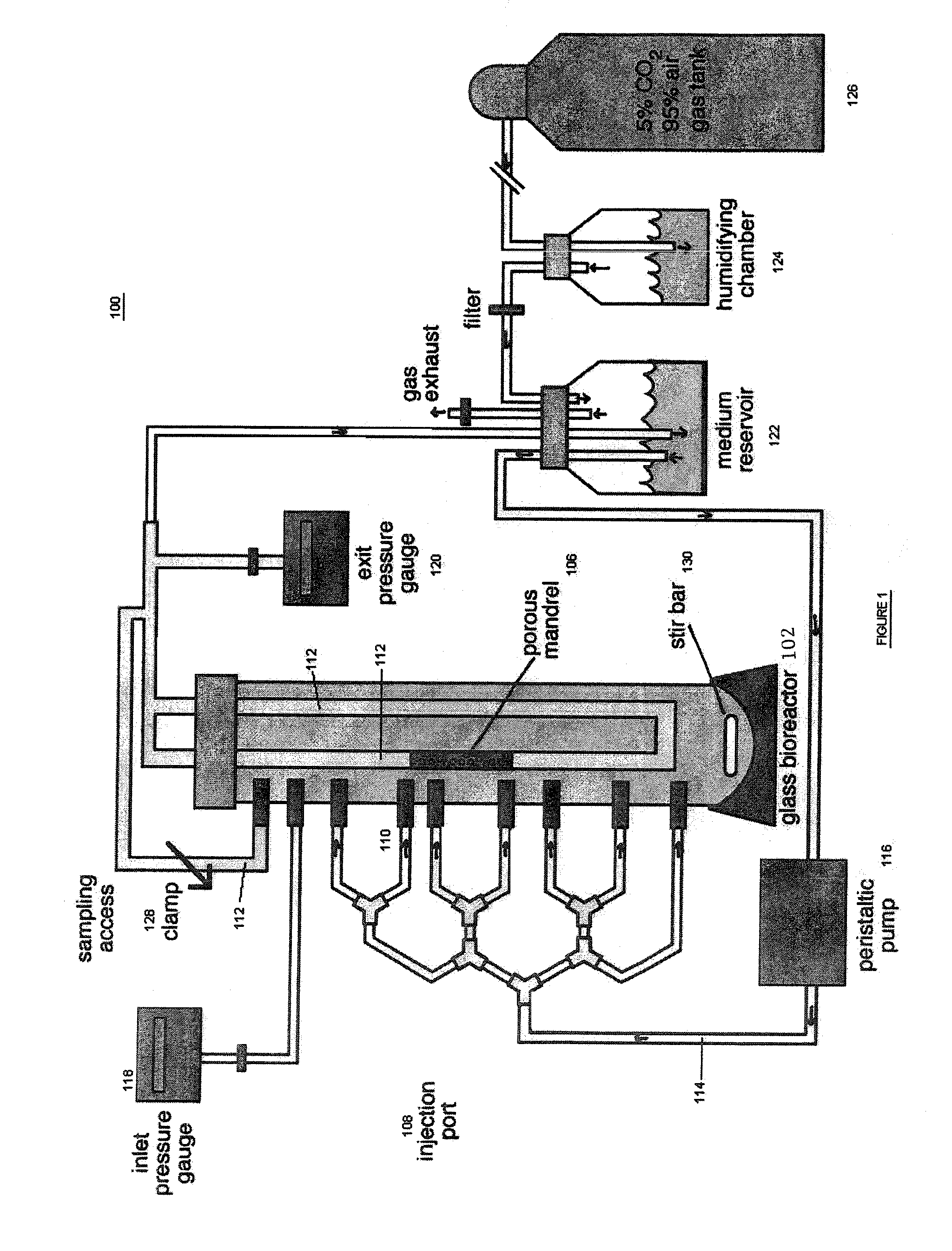
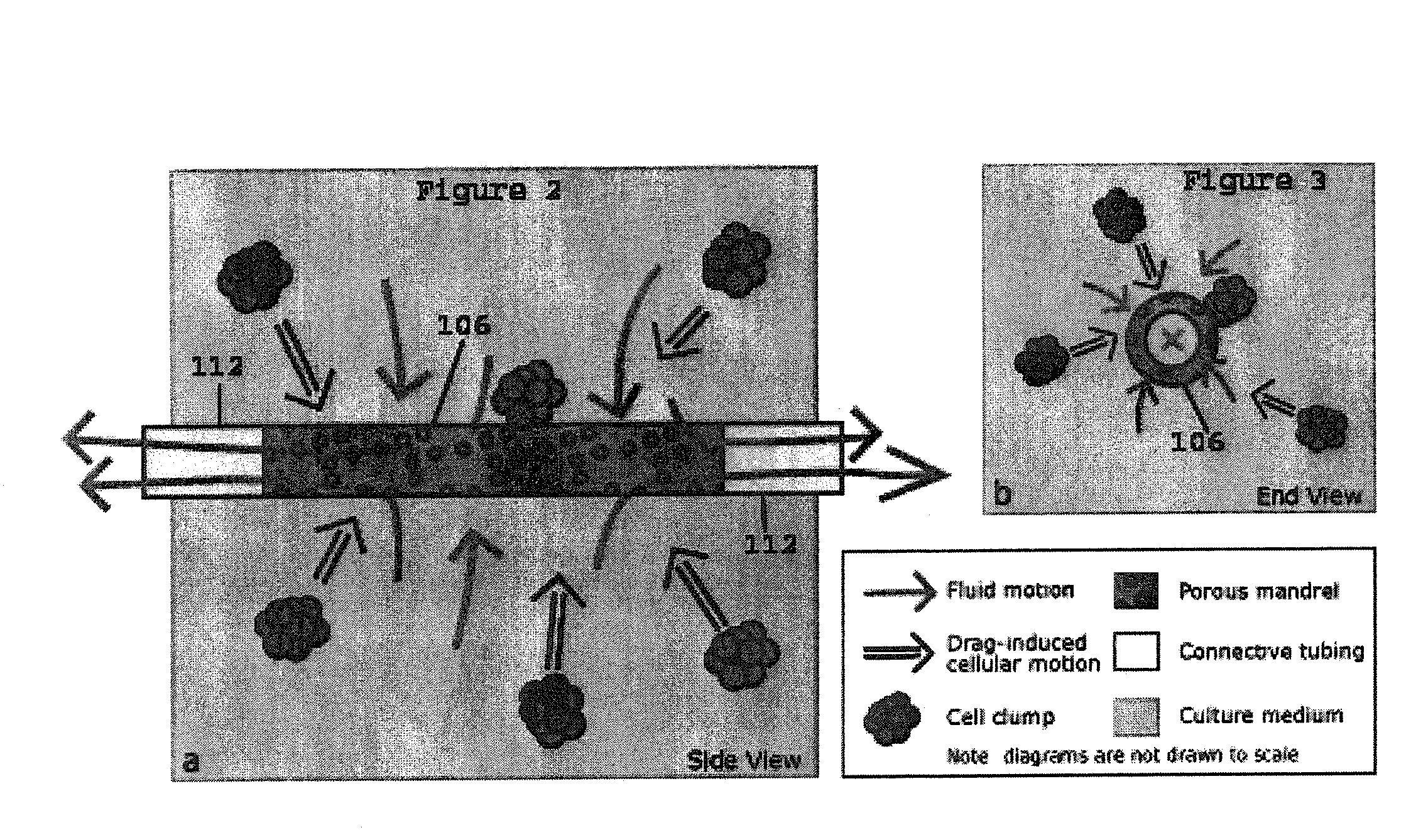
The present invention provides for an improved in vitro tissue assembly system and related methods that includes and uses a bioreactor, a porous mandrel disposed in the bioreactor, and components that provide for the circulation of culture media and cell suspensions within the bioreactor and through the porous mandrel. The circulation of the culture media and cell suspensions within the bioreactor produces a radial, convective flow and drag forces that result in the deposition of cells on the mandrel to form a tissue construct. Upon completion of the culture and tissue formation process, the tissue construct may be removed from the mandrel for subsequent in vivo use.
Owner:LA JOLLA BIOENG INST
Semi-interpenetrating or interpenetrating polymer networks for drug delivery and tissue engineering
Compositions for tissue engineering and drug delivery have been developed based on solutions of two or more polymers which form semi-interpenetrating or interpenetrating polymer networks upon exposure to active species following injection at a site in a patient in need thereof. The polymers crosslink to themselves but not to each other; semi-interpenetrating networks are formed when only one of the polymers crosslink. The resulting viscous solutions retain the biologically active molecules or cells at the site of injection until release or tissue formation, respectfully, occurs.As a result of studies conducted with polymer-cell suspensions forming interpenetrating polymer networks, it has been determined that polymer solutions can be formulated wherein the active species is provided by exposure of the polymer solution to an exogenous source of active species, typically electromagnetic radiation, preferably light. Studies demonstrate that light will penetrate through skin, body fluids (such as synovial fluid) and membranes and polymerize the polymer solutions. The polymer solutions can be crosslinked ionically or covalently, to form a hydrogel, semi-interpenetrating polymer network or an interpenetrating polymer network.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Selective destruction of cancerous cellular tissue
InactiveUS20070015949A1Optimize dynamic vacuum circulationImprove the immunityPneumatic massageAdhesive dressingsCancer cellControl manner
A method and apparatus for applying decompressive energy to tissue for the selective destruction of cancerous cells is disclose and claimed. The tissue to be treated is enclosed within a vessel subjected to decompressive energy supplied by said decompressive energy source to said vessel. The decompressive energy is applied in a controlled manner to said tissue in at a pre-selected level of decompressive energy. Loading forces generated by applied decompressive energy and the forces generated between the interior of said vessel and said tissue which said vessel encompasses are to be diffused. As disclosed and claimed, a mass of elastic material comprising an inner radius and outer radius with the inner radius forming a seal with said tissue while allowing said tissue to move in relation to said inner radius and a fluid pocket circumferentially positioned within said elastic mass in combination with a collar positioned at the perimeter of the vessel opening is claimed.
Owner:KAISER DANIEL E
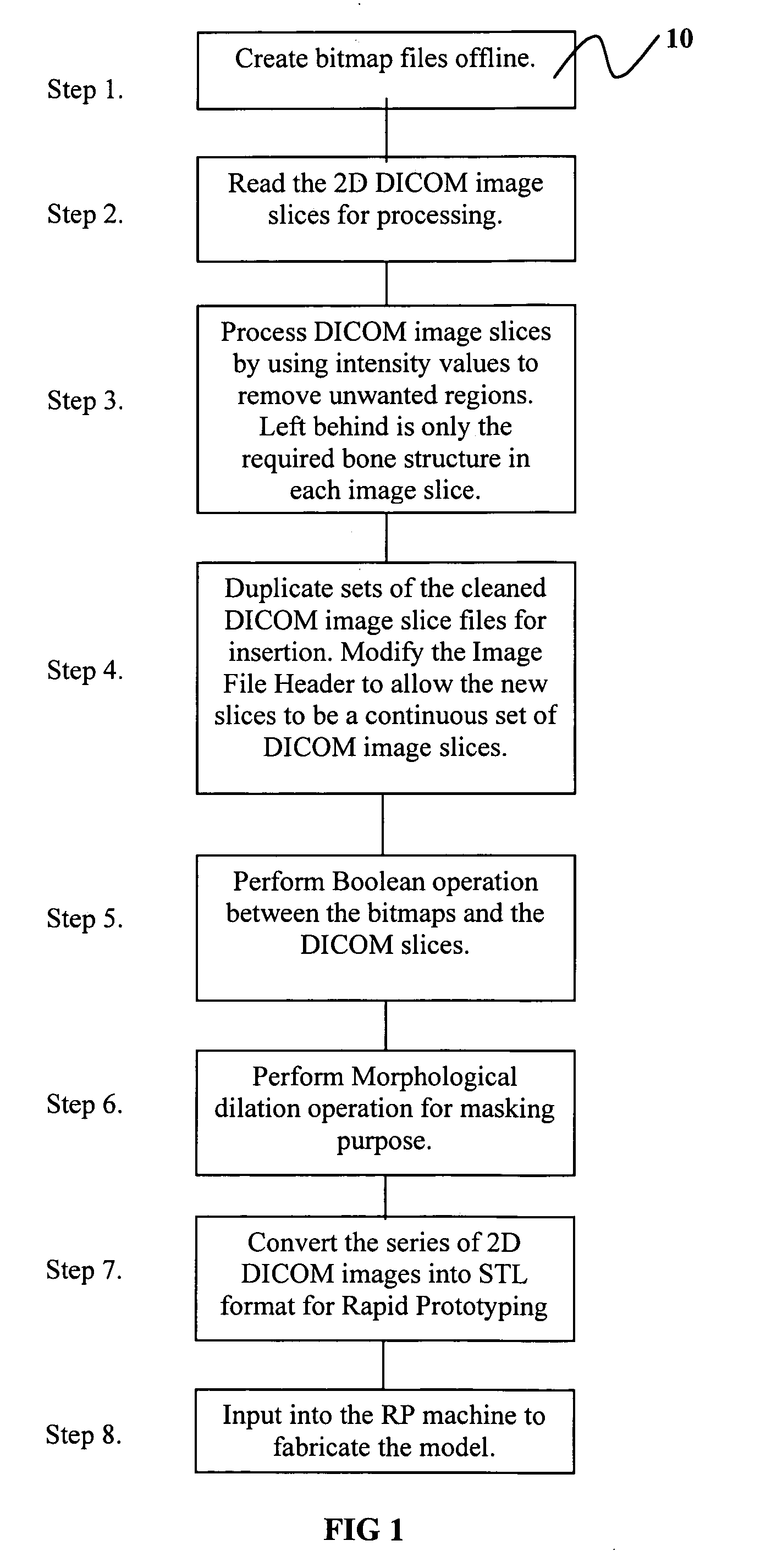
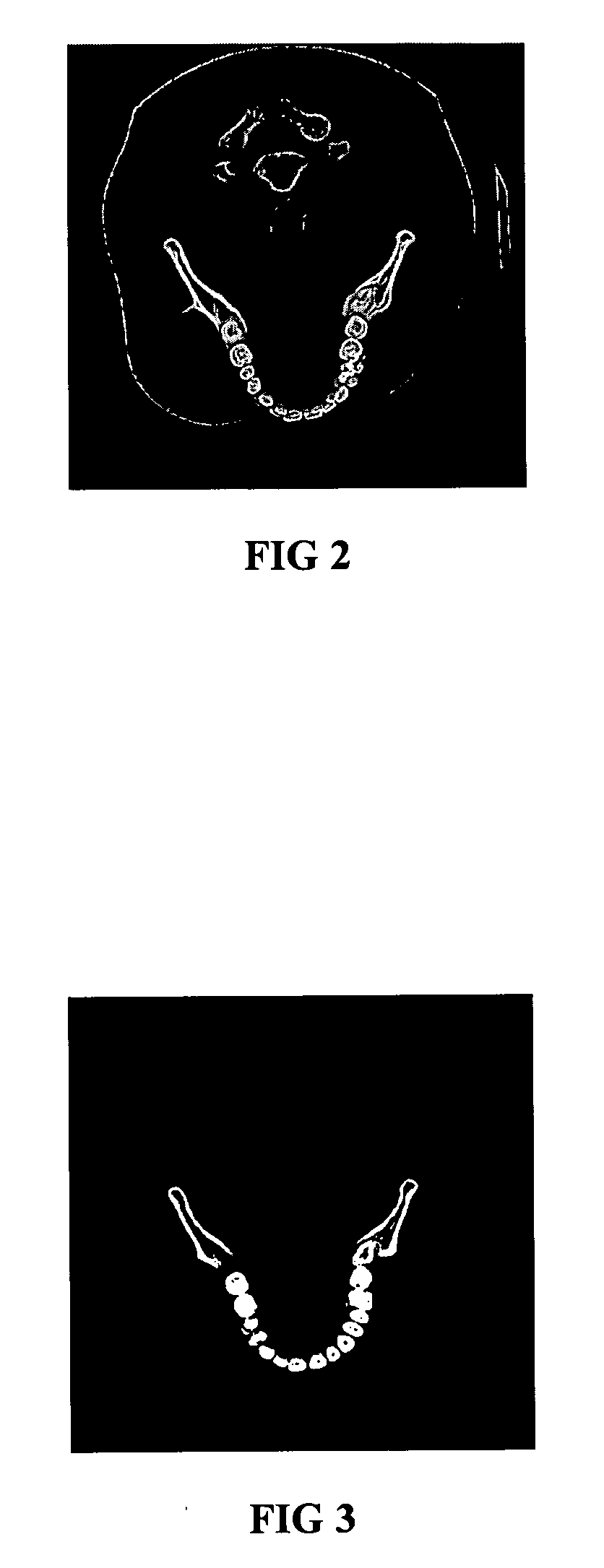
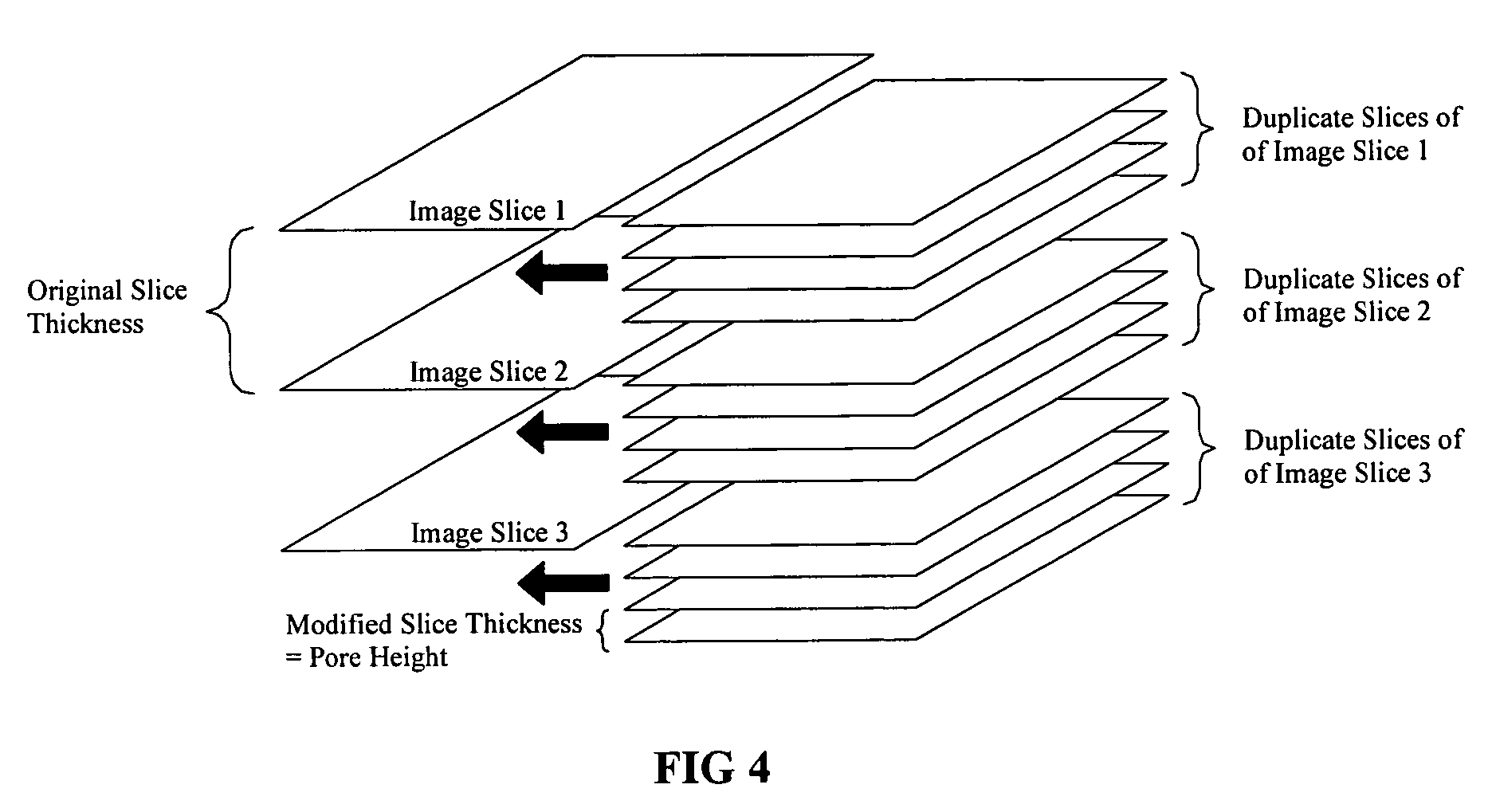
Method for designing 3-dimensional porous tissue engineering scaffold
InactiveUS20060129328A1Easy to manufactureRapid fabrication techniqueAnalogue computers for chemical processesTomographyDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPatient data
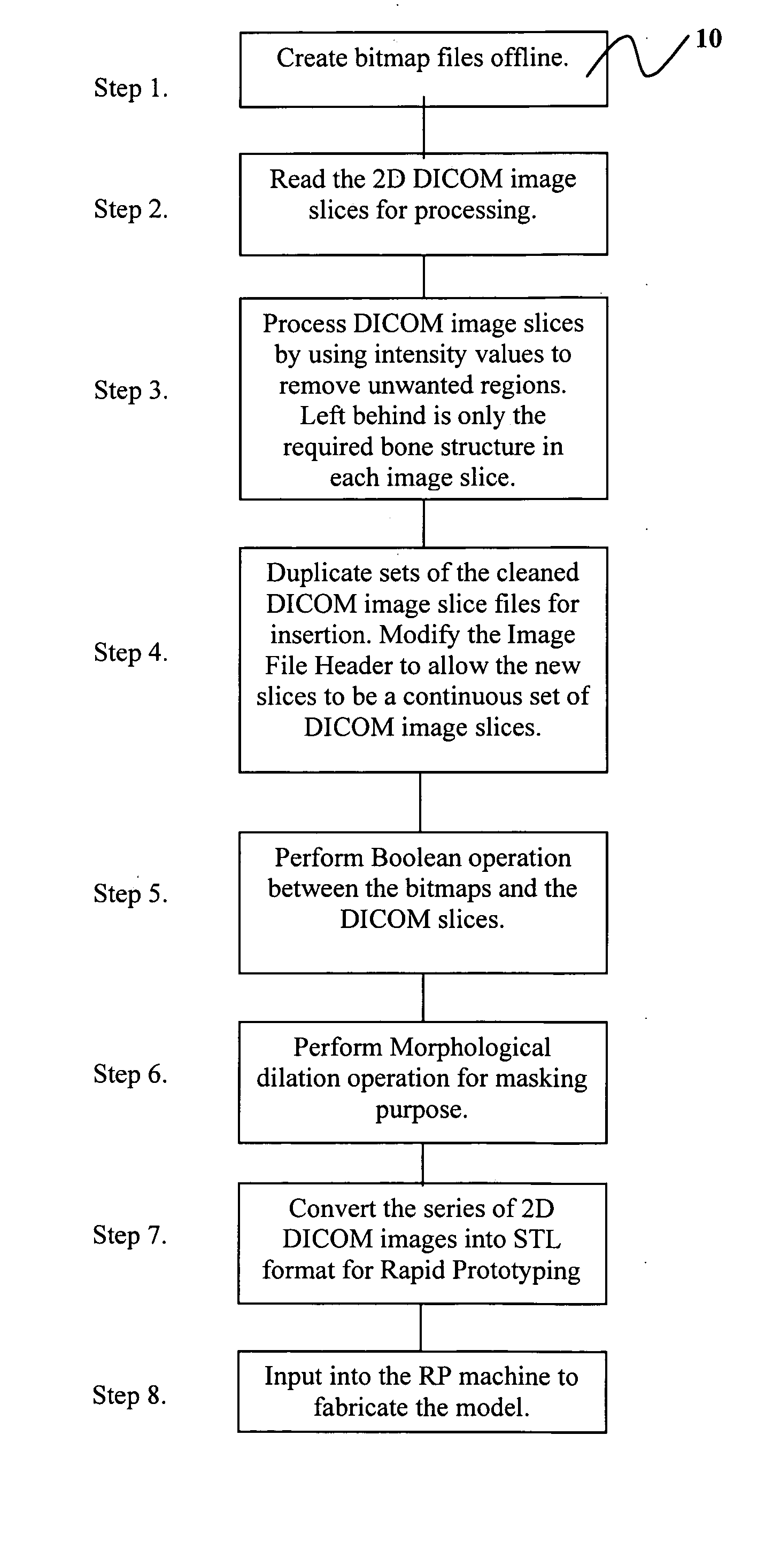
The present invention provides a method for designing three-dimensional scaffold structures that are anatomically accurate and possess the necessary internal porous micro-architecture design, wherein the porous micro-architecture is necessary for the proliferation and colonization of cultured cells that lead to tissue formation. The design method of the present invention utilizes the patient data derived from medical imaging modalities (e.g., CT or MRI) in combination with computer data manipulation techniques. The present invention further provides that the resultant scaffold design can be easily manufactured by Rapid Prototyping fabrication techniques.
Owner:NANYANG POLYTECHNIC
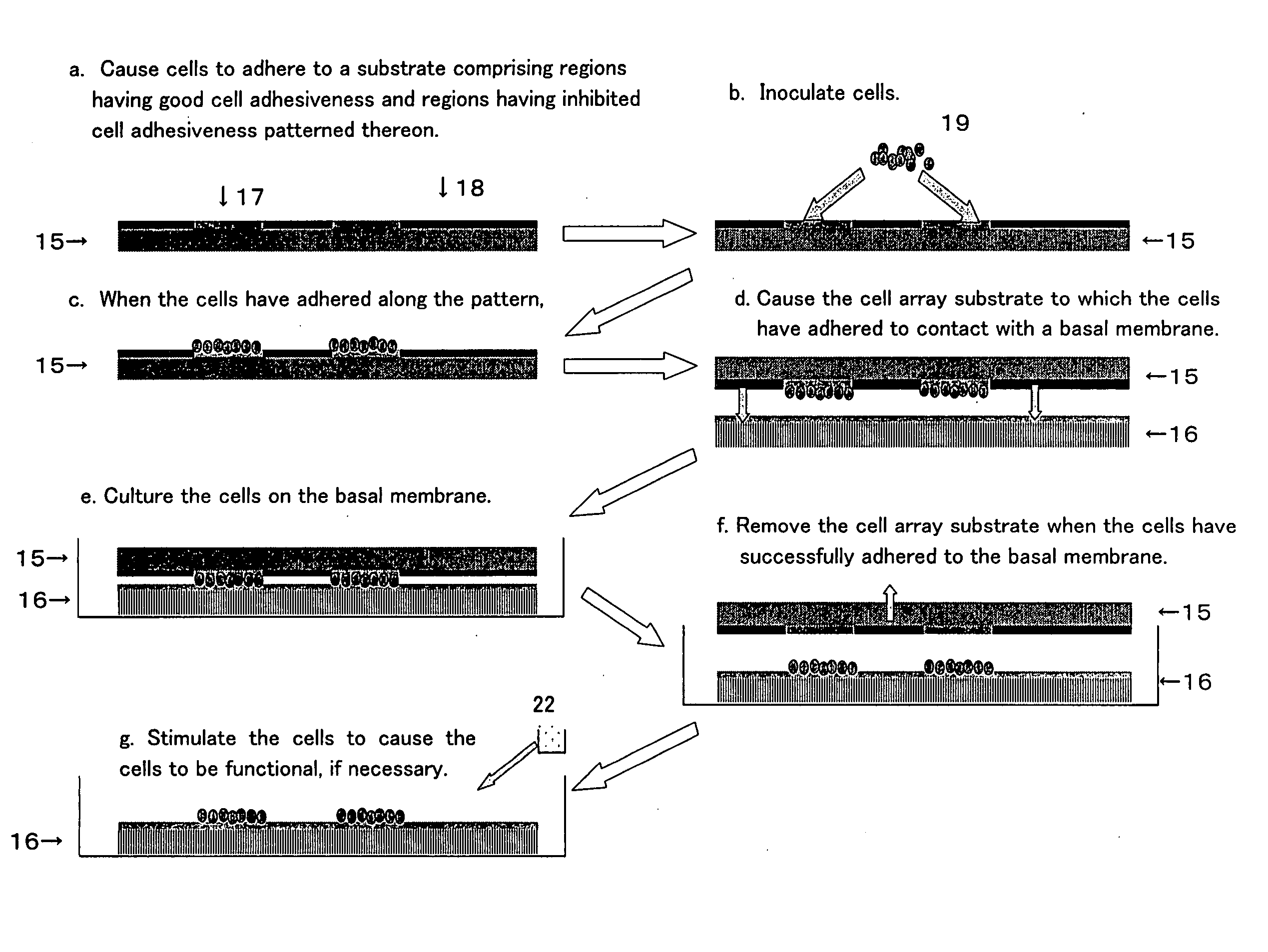
Artificial Tissue Construct and Method for Producing the Same
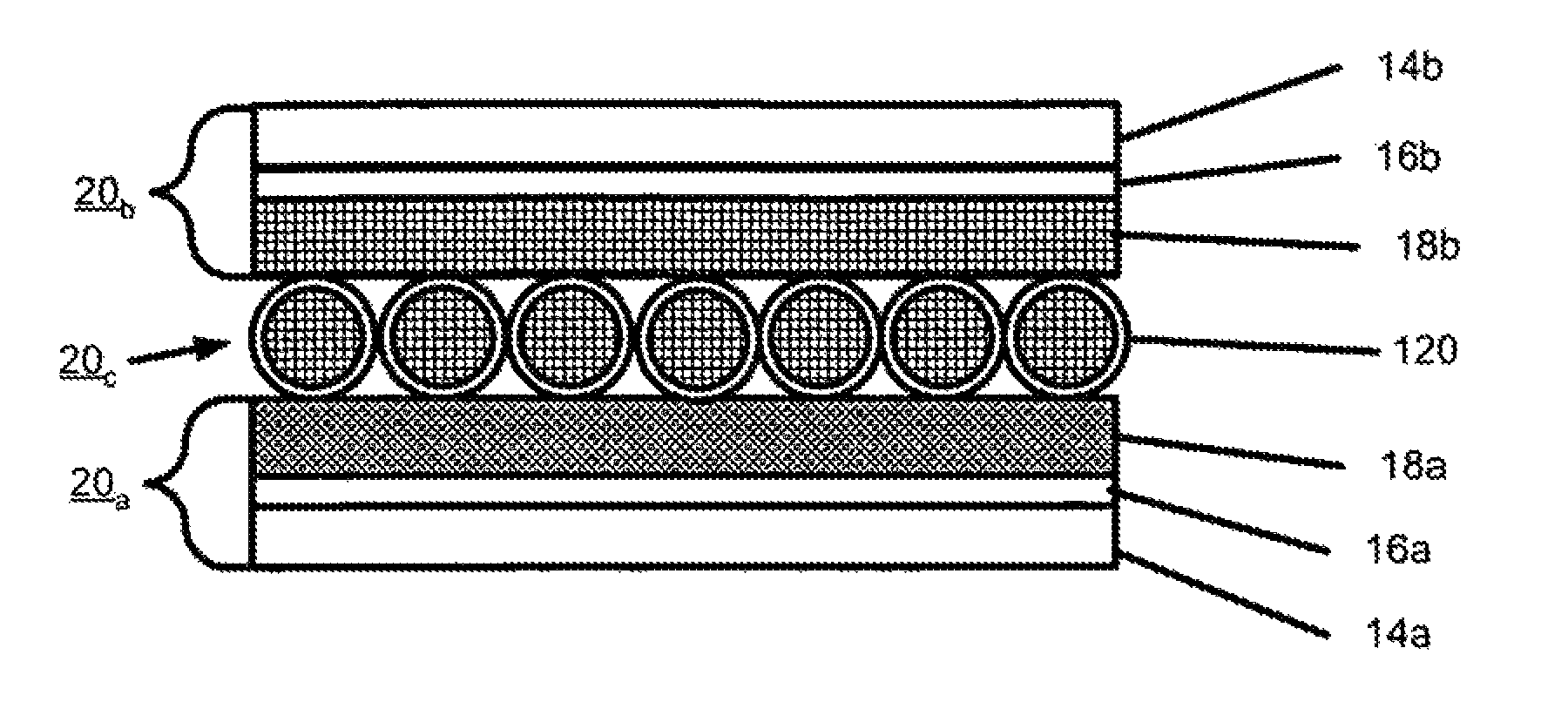
An object of the present invention is to provide an artificial tissue construct that has means for transporting nutrients, oxygen, waste products, or the like and is viable in vivo. The present invention relates to a tissue construct formed in vitro, which comprises a vascular layer, a basal membrane layer, and a tissue-forming cell layer.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Three-dimensional transversely-wrinkled fuzzing towel and weaving process thereof
ActiveCN102660824AGuaranteed uptimeStrong three-dimensional senseHeating/cooling textile fabricsWoven fabricsEngineeringPolymer science
Owner:SUNVIM GROUP
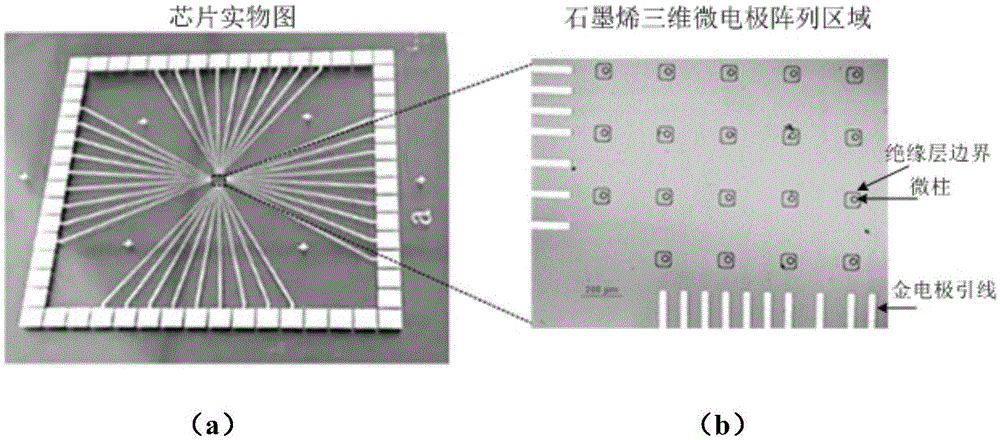
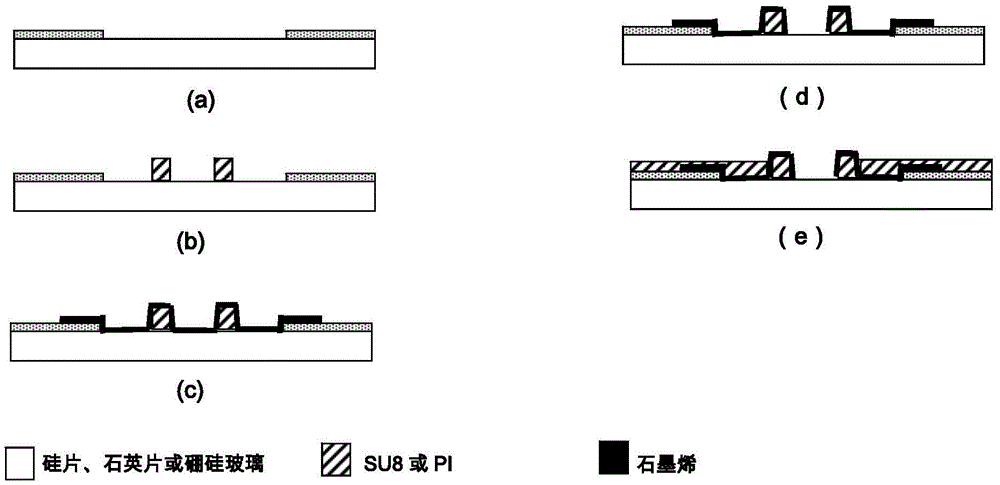
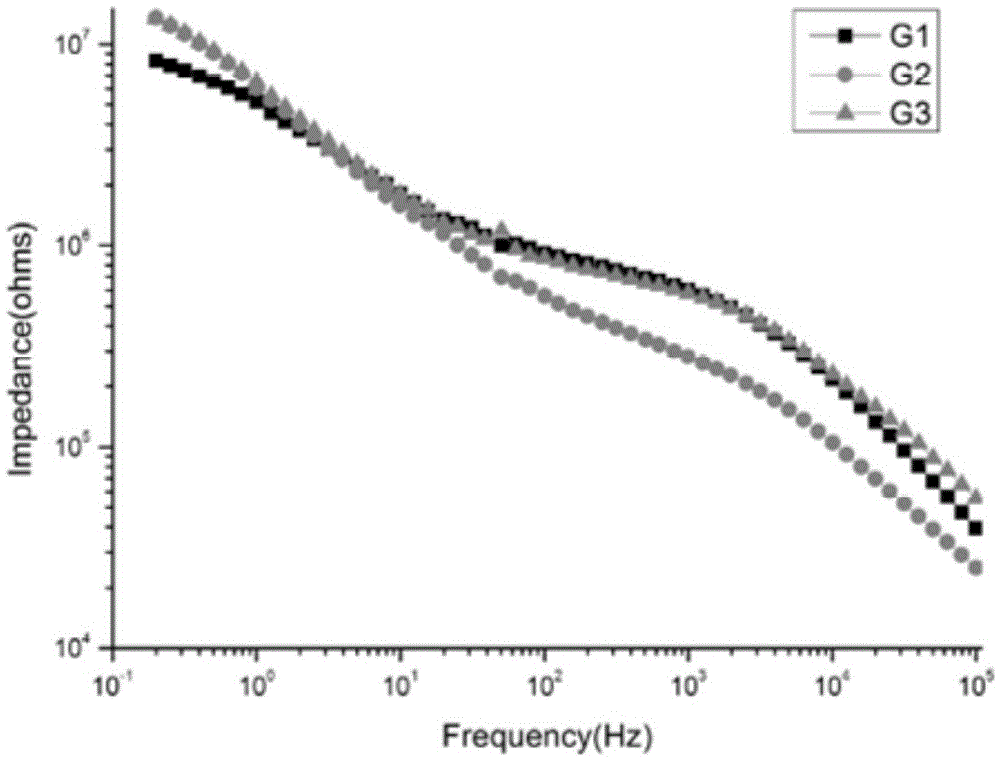
Graphene three-dimensional microelectrode array chip, and method and application thereof
ActiveCN105460882AImproved ability to detect weak electrical signalsGood light transmissionSemi-permeable membranesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsMicro columnMicroelectrode
The invention relates to a graphene three-dimensional microelectrode array chip, and a method and application thereof. The graphene three-dimensional microelectrode array chip is characterized in that a micro-column array is produced by utilizing negative photoresist, and a microelectrode array is produced by covering a single-layer graphene film on the microelectrode array; and the microelectrode array chip comprises two parts, namely a transparent graphene three-dimensional microelectrode array area and a peripheral gold electrode lead pin. A microelectrode site is a three-dimensional bulge. The three-dimensional microelectrode dome shaped (or hill shaped) microelectrode structure is beneficial for the rigid microelectrode site and the soft cell or tissue to form tight electric coupling, and the graphene has excellent electrical property, so that the electrophysiological detection sensitivity of the microelectrode array can be improved. In addition, the graphene three-dimensional microelectrode array on a transparent substrate is convenient for observation through an inverted microscope and application of various cell microscopic imaging methods, and can be combined with a micro-fluidic chip.
Owner:上海前瞻创新研究院有限公司
Tissue-like organization of cells and macroscopic tissue-like constructs, generated by macromass culture of cells and the method of macromass culture
InactiveUS20080026461A1Sectioned easilySimple processEpidermal cells/skin cellsMammal material medical ingredientsHigh cellHuman body
Three-dimensional tissue-like organization of cells by high cell-seeding-density culture termed as macromass culture is described. By macromass culture, cells can be made to organize themselves into a tissue-like form without the aid of a scaffold and three-dimensional macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be made wholly from cells. Tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be generated from fibroblastic cells of mesenchymal origin (at least), which can be either differentiated cells or multipotent adult stem cells. In this work, tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs have been generated from dermal fibroblasts, adipose stromal cells-derived osteogenic cells, chondrocytes, and from osteoblasts. The factor causing macroscopic tissue formation is large scale culture at high cell seeding density per unit area or three-dimensional space, that is, macromass culture done on a large scale. No scaffold or extraneous matrix is used for tissue generation, the tissues are of completely cellular origin. No other agents (except high cell-seeding-density) that aid in tissue formation such as tissue-inducing chemicals, tissue-inducing growth factors, substratum with special properties, rotational culture, etc, are employed for tissue formation. These tissue-like masses have the potential for use as tissue replacements in the human body. Tissue-like organization by high cell-seeding-density macromass culture can also be generated at the microscopic level.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
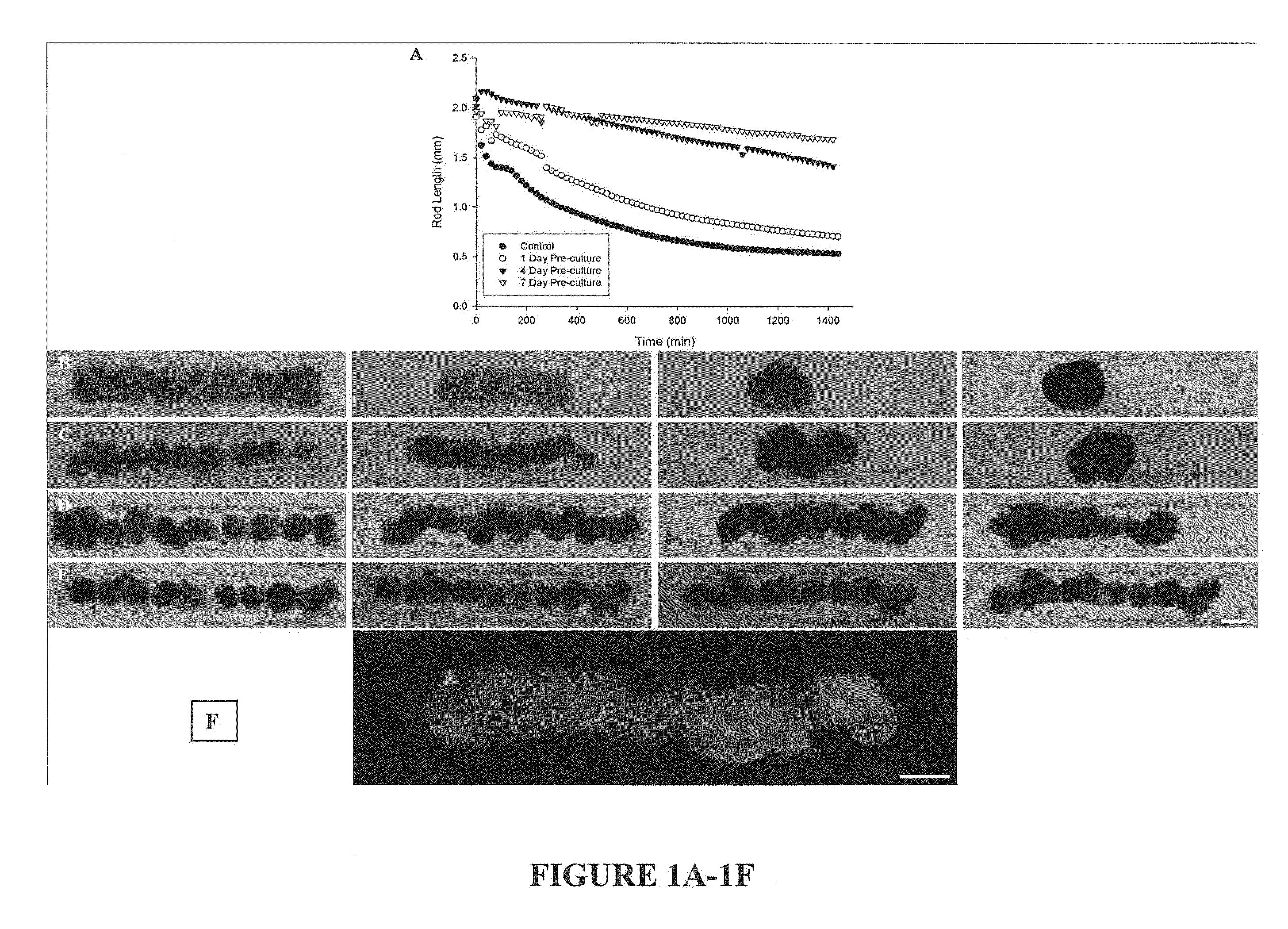
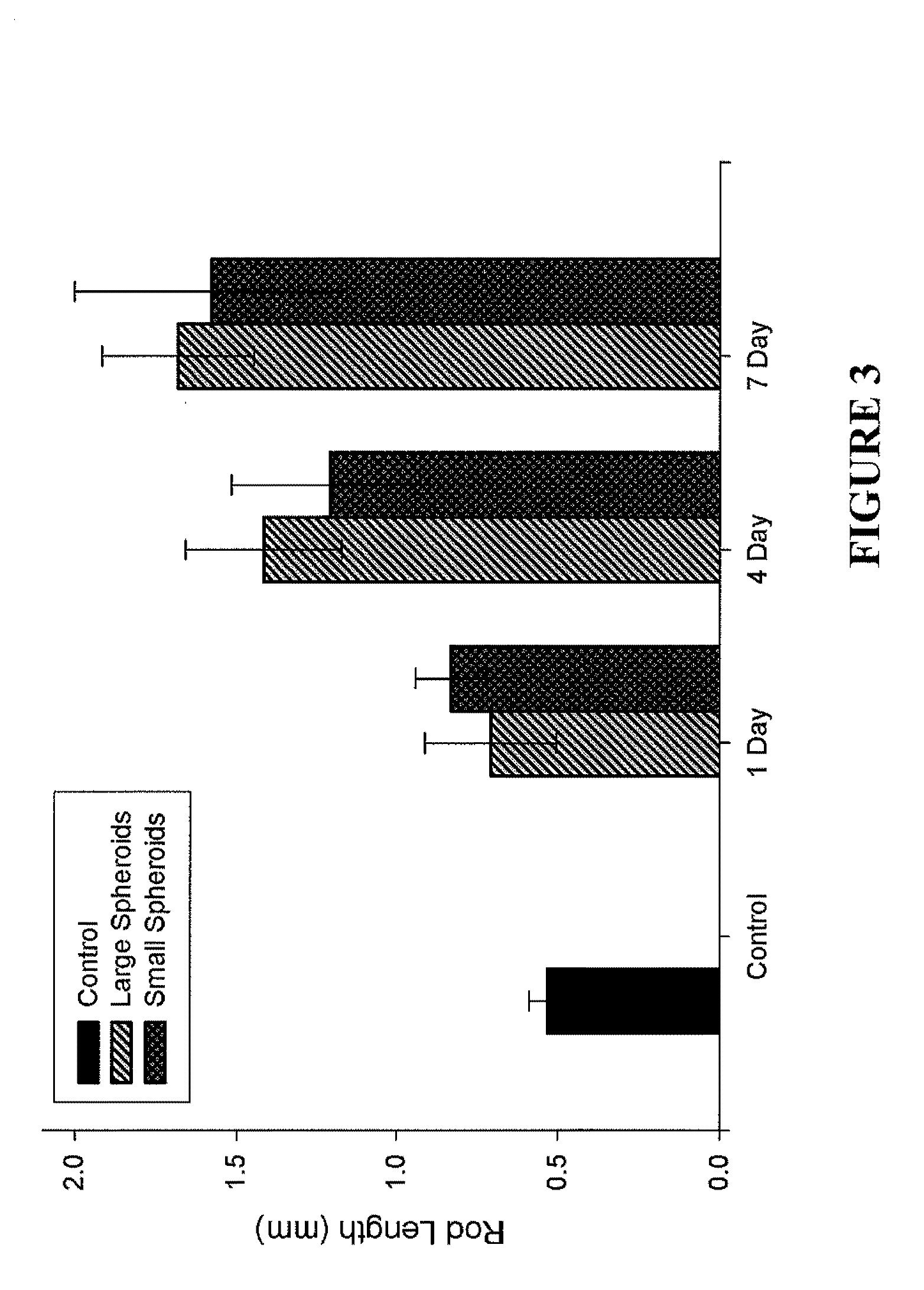
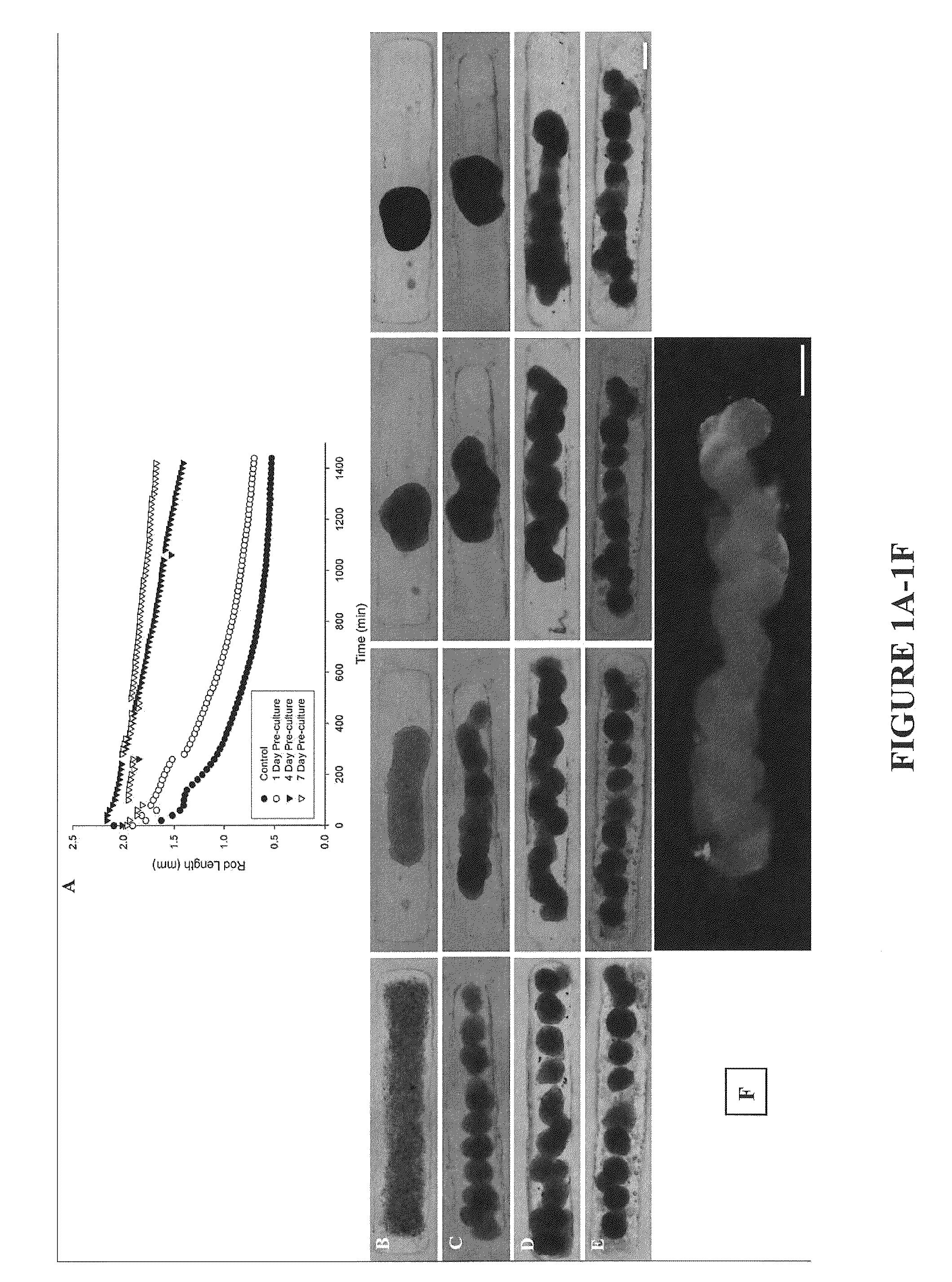
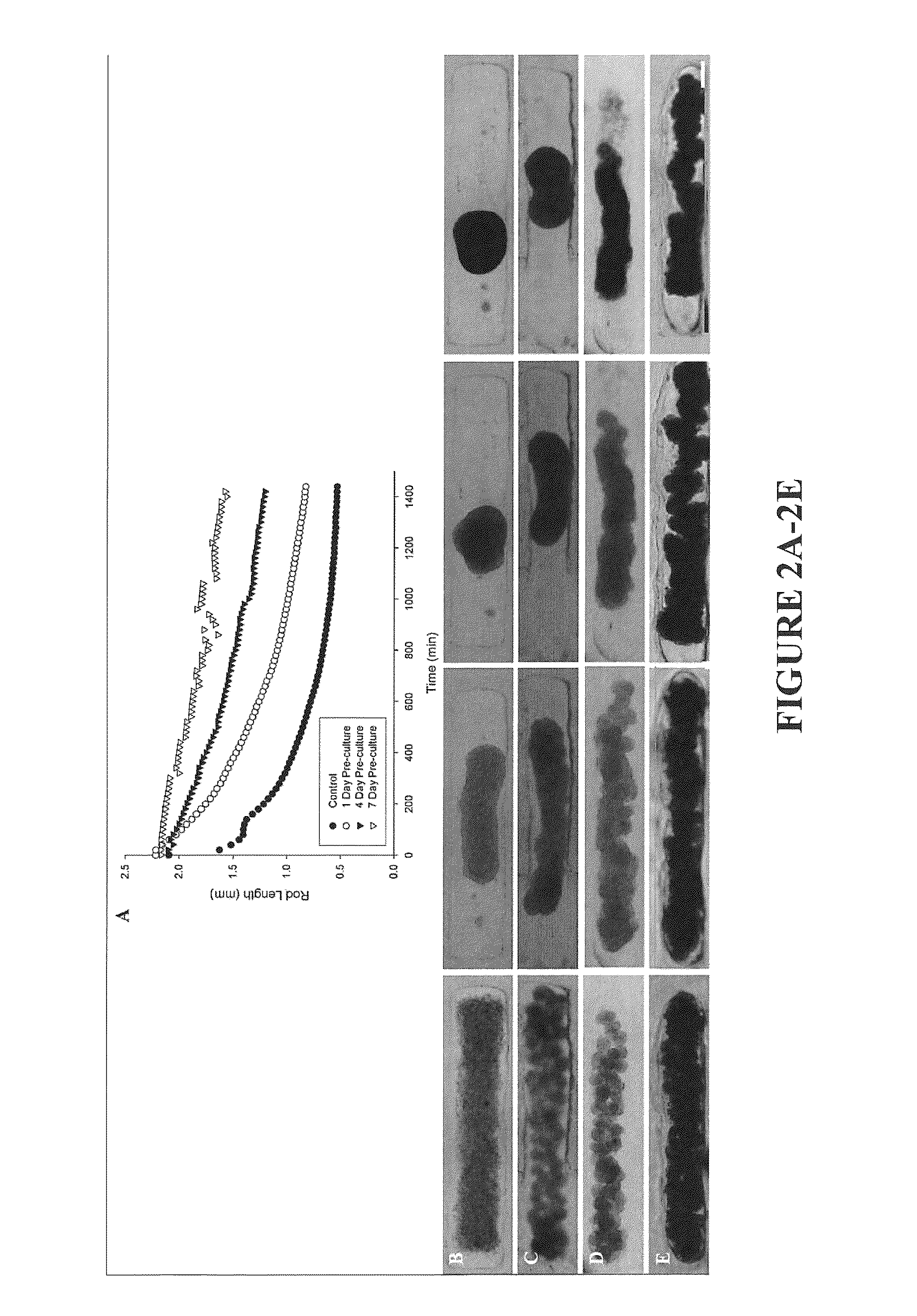
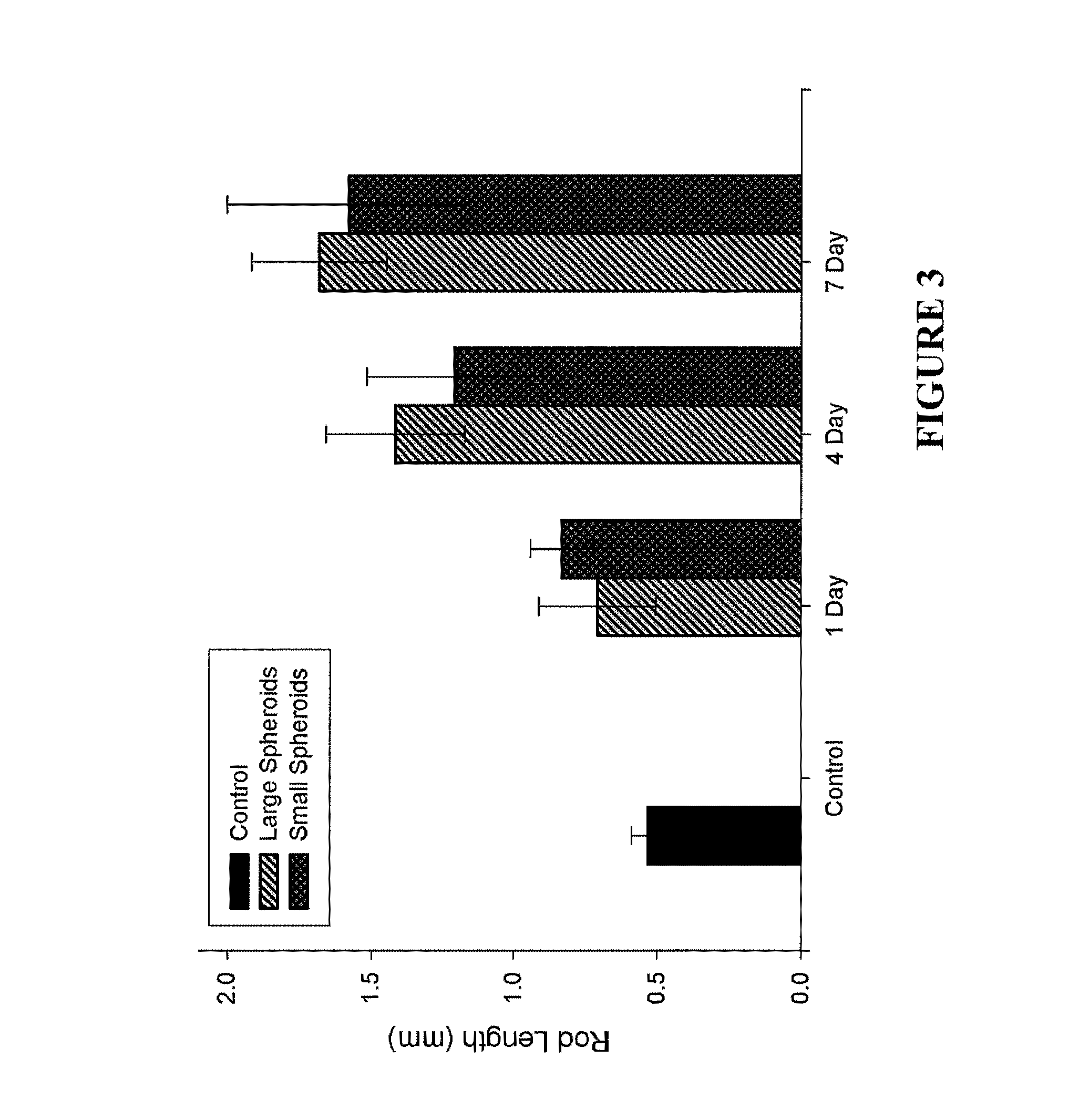
Assays and methods for fusing cell aggregates to form proto-tissues
ActiveUS20110212481A1Reduce rateLess cell sorting cellAdditive manufacturing apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementCell aggregationAggresome
Provided are assays and methods for creating proto-tissues from aggregates of cells. The invention concerns assays and methods useful in tissue engineering and reconstruction techniques, specifically in the formation of macrotissues from microtissues using microtissue pre-culture time as a controlling parameter.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
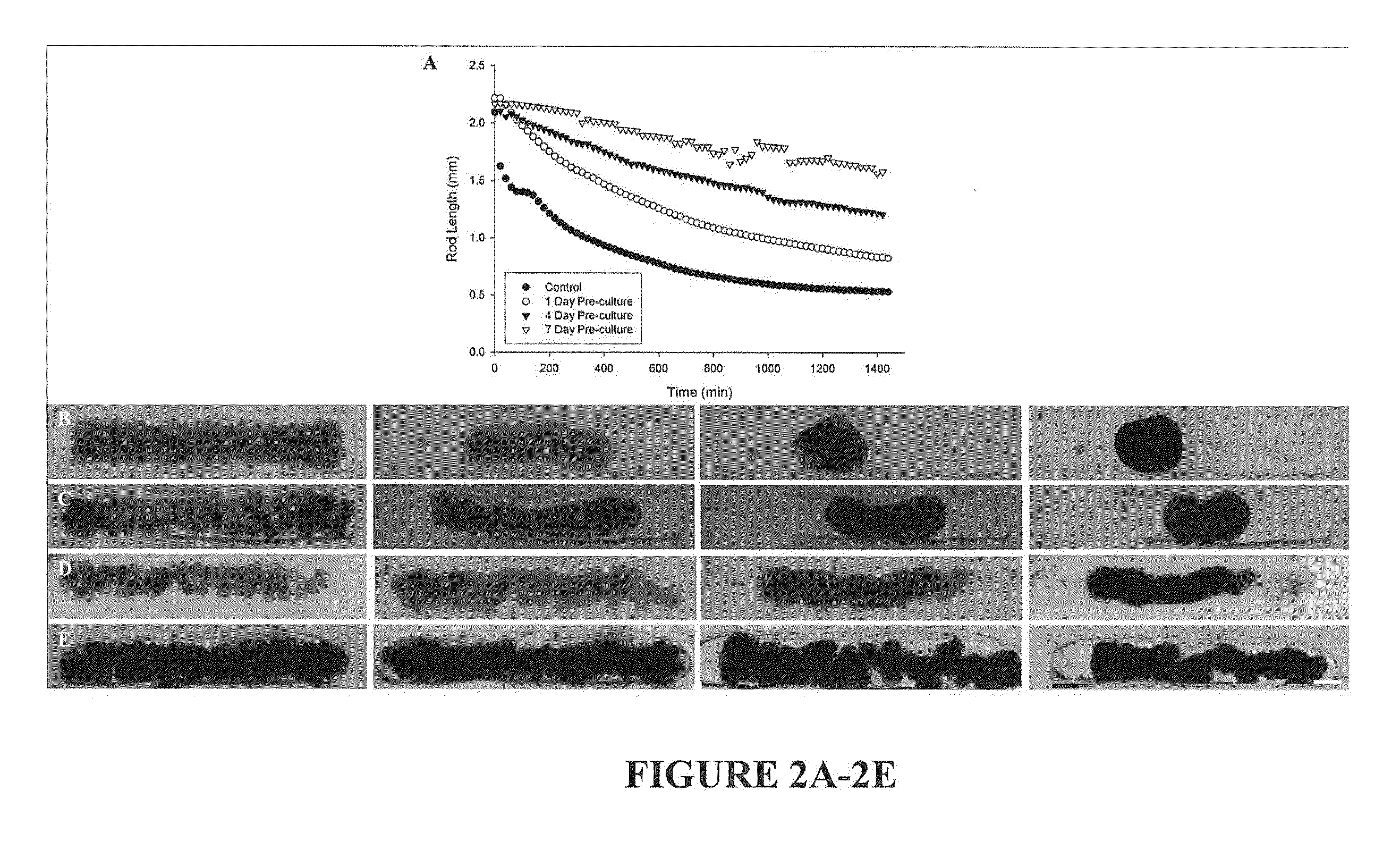
Assays and methods for fusing cell aggregates to form proto-tissues
Provided are assays and methods for creating proto-tissues from aggregates of cells. The invention concerns assays and methods useful in tissue engineering and reconstruction techniques, specifically in the formation of macrotissues from microtissues using microtissue pre-culture time as a controlling parameter.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
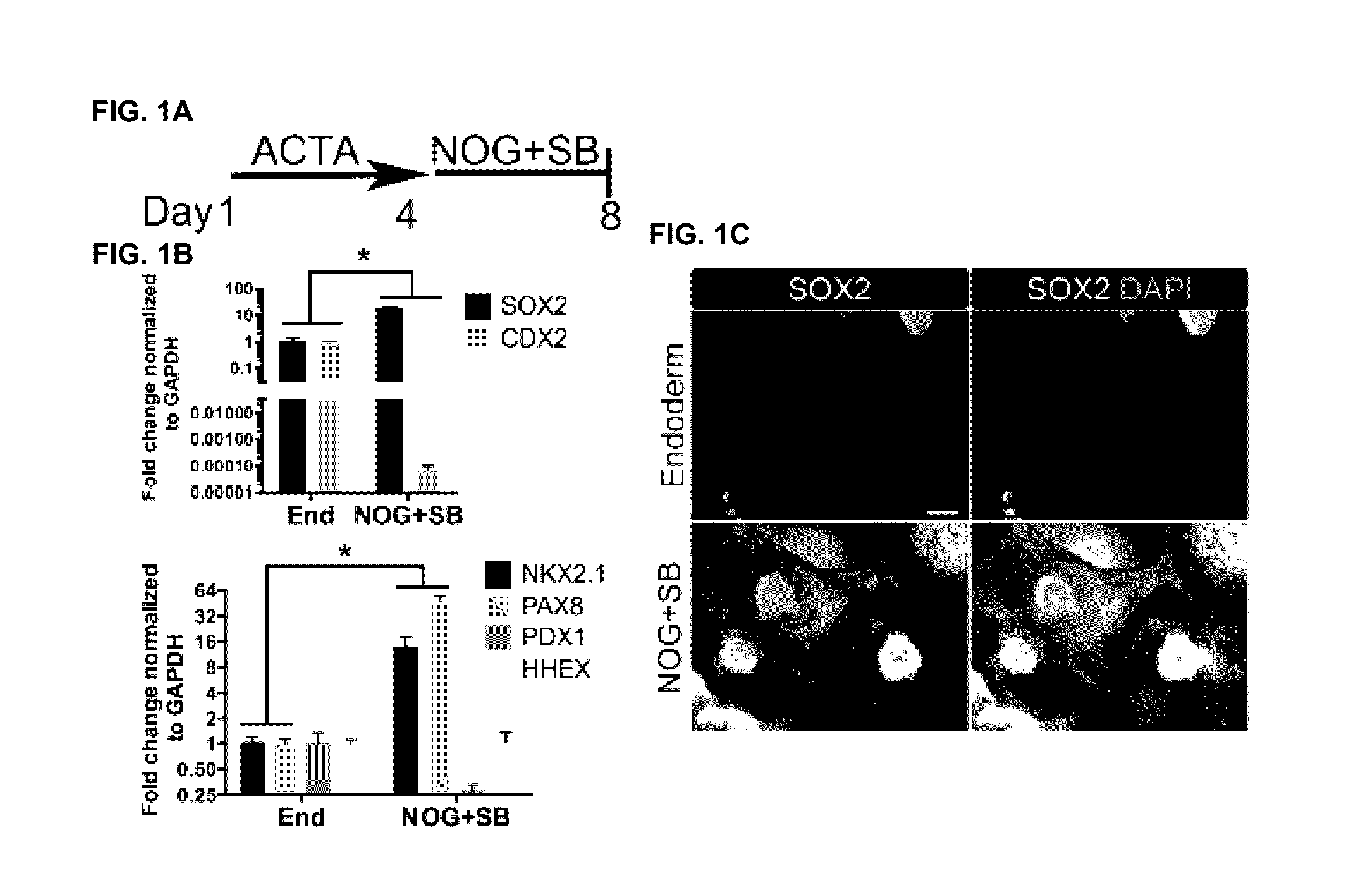
Compositions and methods for obtaining stem cell derived lung tissue, and related uses therof
ActiveUS20160312191A1Easy to shapeArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsGerm layerDirected differentiation
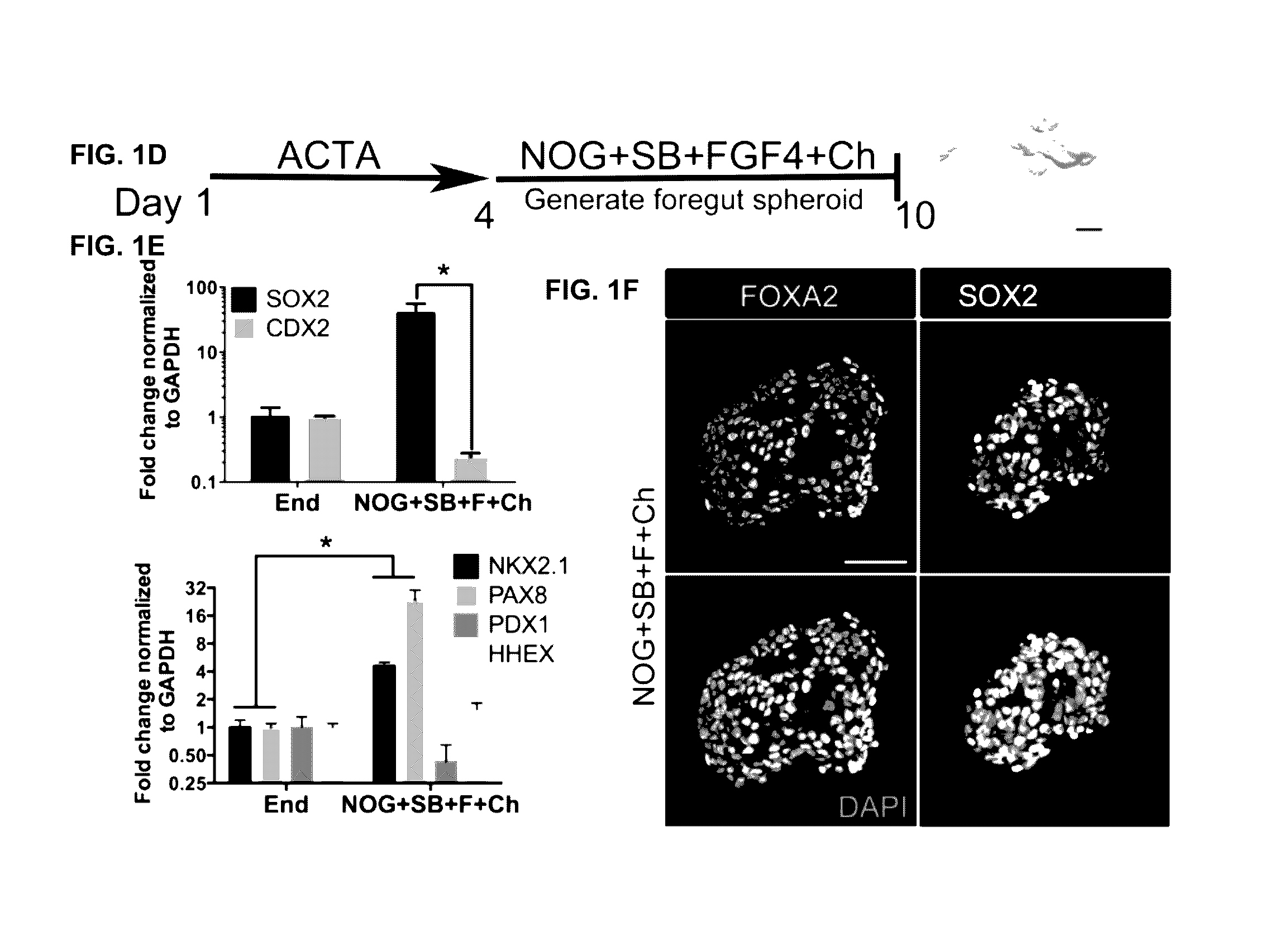
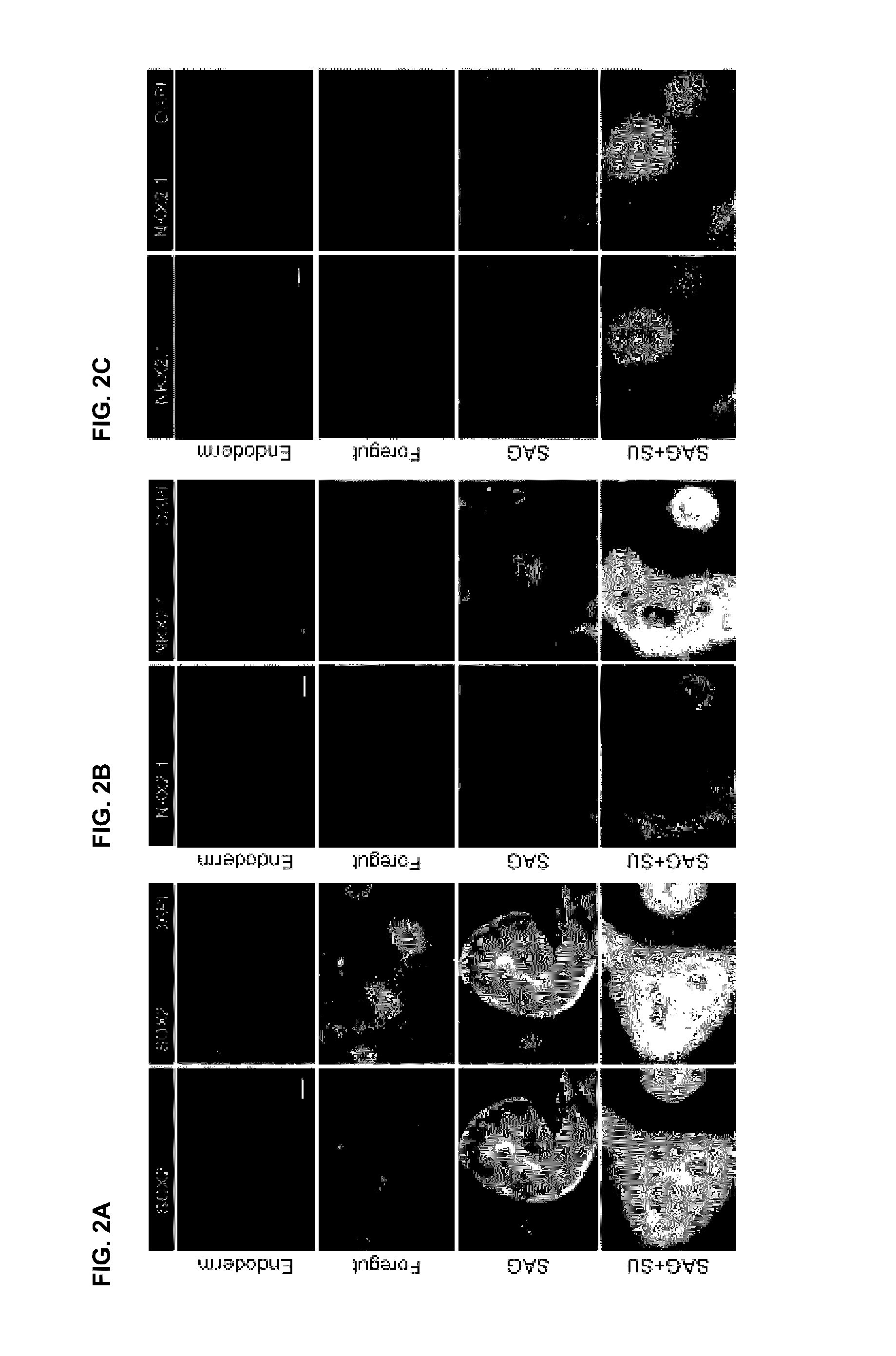
The invention disclosed herein generally relates to methods and systems for converting stem cells into specific tissue(s) or organ(s) through directed differentiation. In particular, the invention disclosed herein relates to methods and systems for promoting definitive endoderm formation from pluripotent stem cells. The invention disclosed herein further relates to methods and systems for promoting ventral-anterior foregut spheroid tissue formation, 3-dimensional lung tissue formation, and lung organoid tissue formation produced in vitro from the described methods
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Support for tissue regeneration and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20060127368A1Improve retentionExcellent in grafting abilityBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsFreeze-dryingMedical treatment
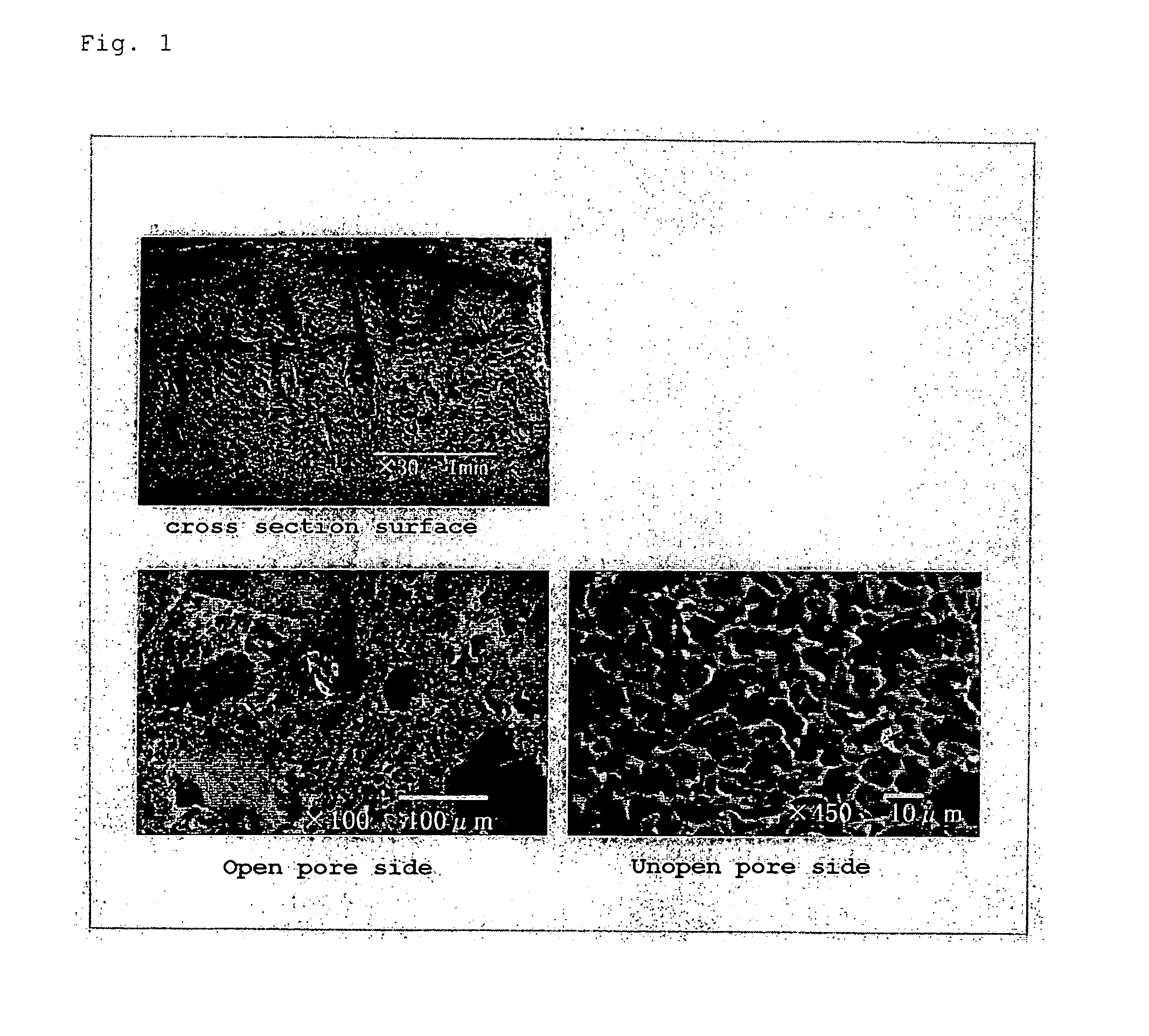
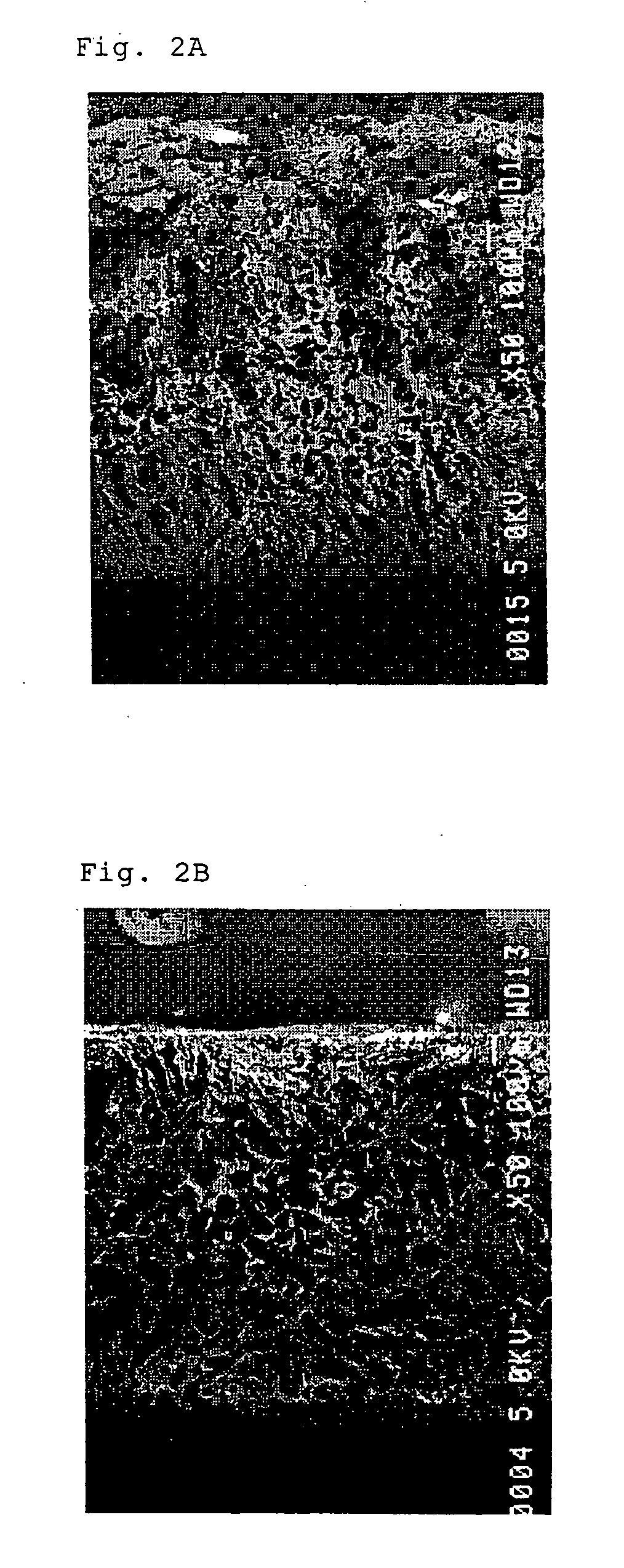
The present invention provides a scaffold in which cells can be stably retained and grafted in a uniform distribution state in the culture, preferable proliferation ability and viability can be secured, and particularly in the case of cartilage, fixation treatment such as suture can be carried out in the transplantation into affected parts after the culture, and the mechanical strength is provided sustainable for (weighted) compression at the initial stage of transplantation. The present invention relates to a 3-dimensional porous scaffold for tissue regeneration which comprises a structure composed of vertically long-shaped pores having a pore diameter of not less than 10 μm to not more than 500 μm and pore length of not less than 20 μm to not more than 1 cm being juxtaposedly arranged obtained by a production process comprising rapid freeze-drying as a key technology. Further, the invention relates to the above 3-dimensional porous scaffold in which seeding properties of cells are improved by a pore enlargement treatment of one side face by a separation operation, a salt elution operation of a surface part, or a combination of these operations. It becomes possible to produce a 3-dimensional cell combination having excellent degree of tissue formation and medical treatment effect by seeding a cell or precursor cell derived from a tissue in this scaffold, and culturing them in an artificial environment and / or the living body.
Owner:GC CORP +2
Method for designing 3-dimensional porous tissue engineering scaffold
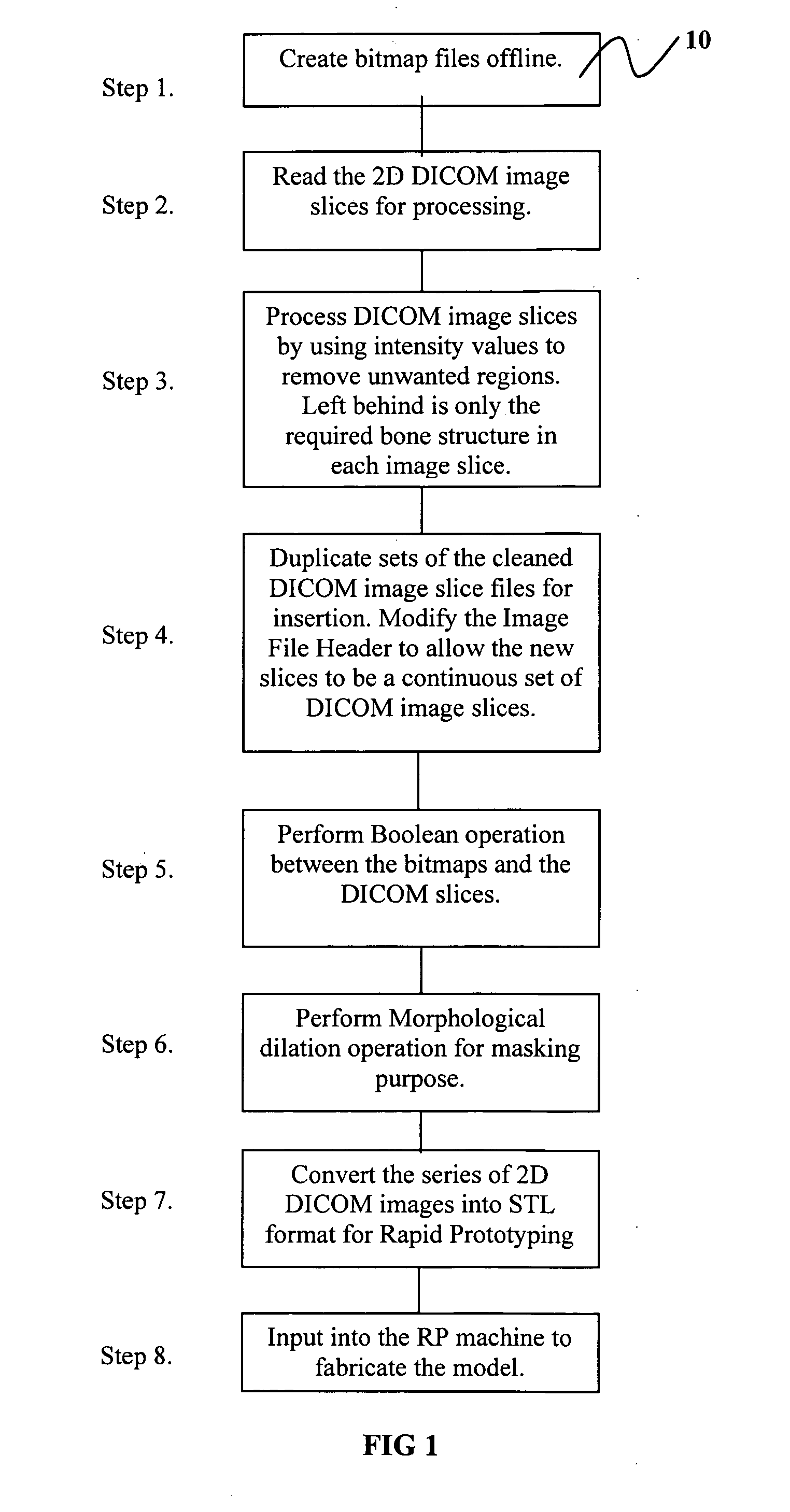
InactiveUS8090540B2Easy to manufactureRapid fabrication techniqueSamplingAnalogue computers for chemical processesDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPatient data
Owner:NANYANG POLYTECHNIC
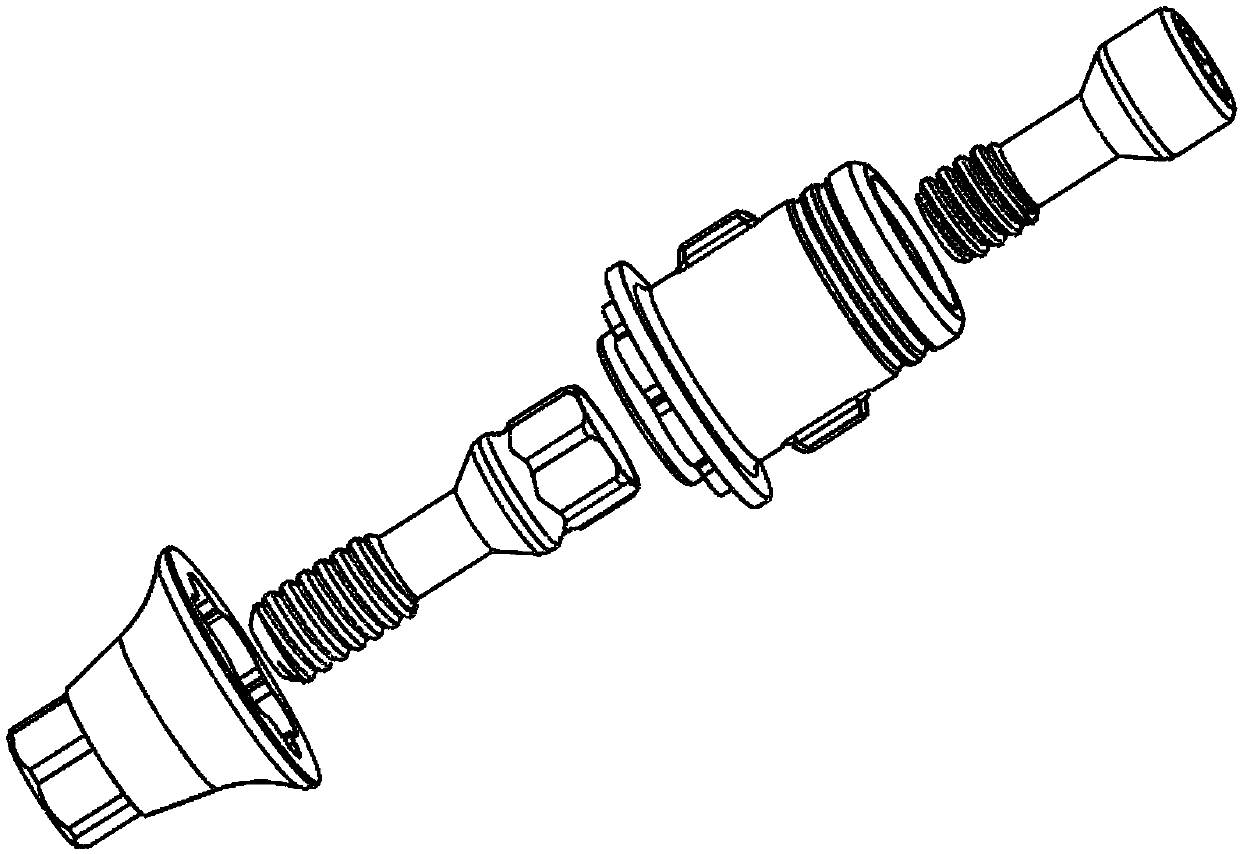
Composite base table assembly
PendingCN109567964AMeet the needs of personalized customizationAvoid secondary damageDental implantsEngineeringScrew thread
The invention discloses a composite base table assembly, which comprises a substrate, a substrate screw, a base table and a base table screw, wherein the substrate is fixed to a planting body throughthe substrate screw; the base table is arranged on the substrate through the base table screw; the lower part of the base table screw is connected with the upper end of the substrate screw through screw threads. The base table assembly is formed through the substrate, the substrate screw, the base table and the base table screw; the problem of non-adjustable base table position due to different implanting depth of planting bodies can be solved. The substrate is made into a reverse cone frustum structure, and helps the tissue formation in the postoperative healing period; a gum cuff matched with a gum curve of the patient is formed. Through the arrangement of a healing cap, an operation passage is reserved for the subsequent substrate replacement on the premise of isolating the bacteria andpreventing infection; the secondary harm to the gum caused by the substrate replacement is avoided; meanwhile, the entering of the bacteria into the alveoli fossa is effectively avoided.
Owner:苏州从冠医疗科技有限公司
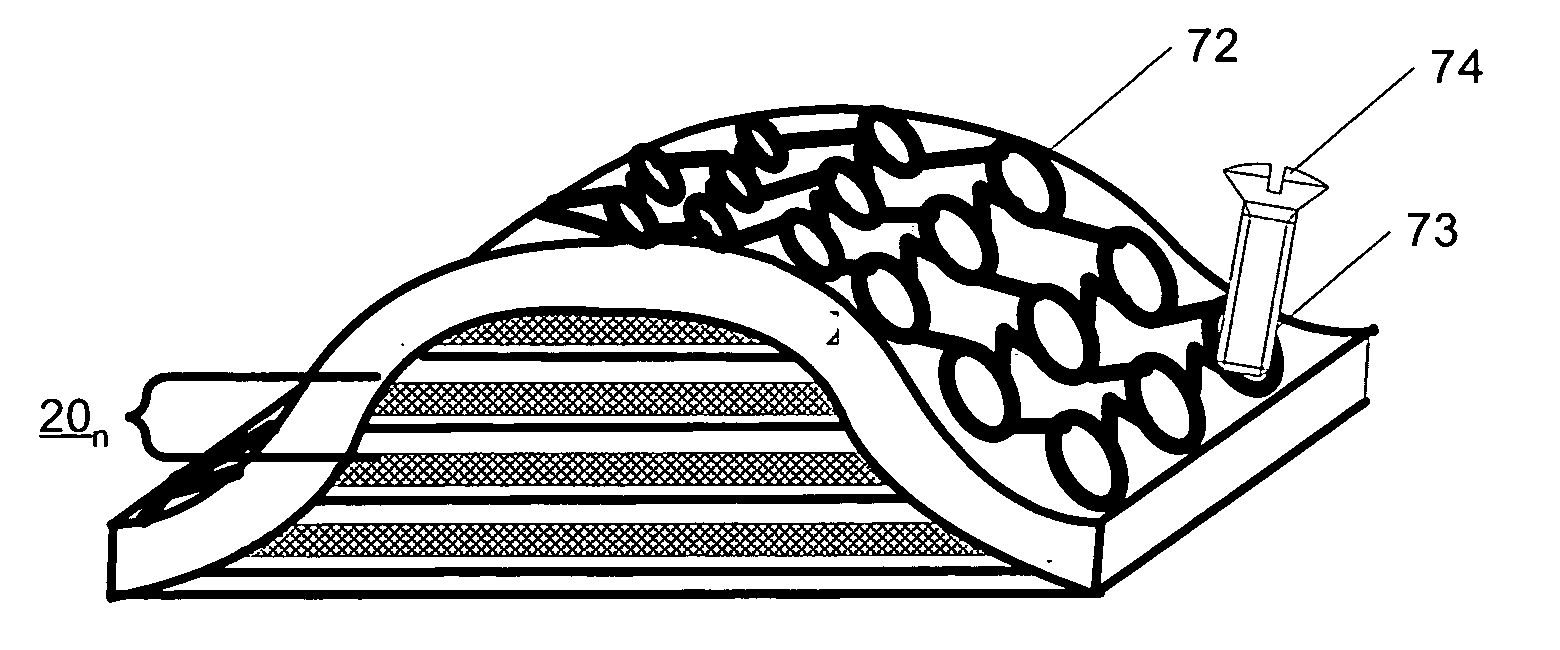
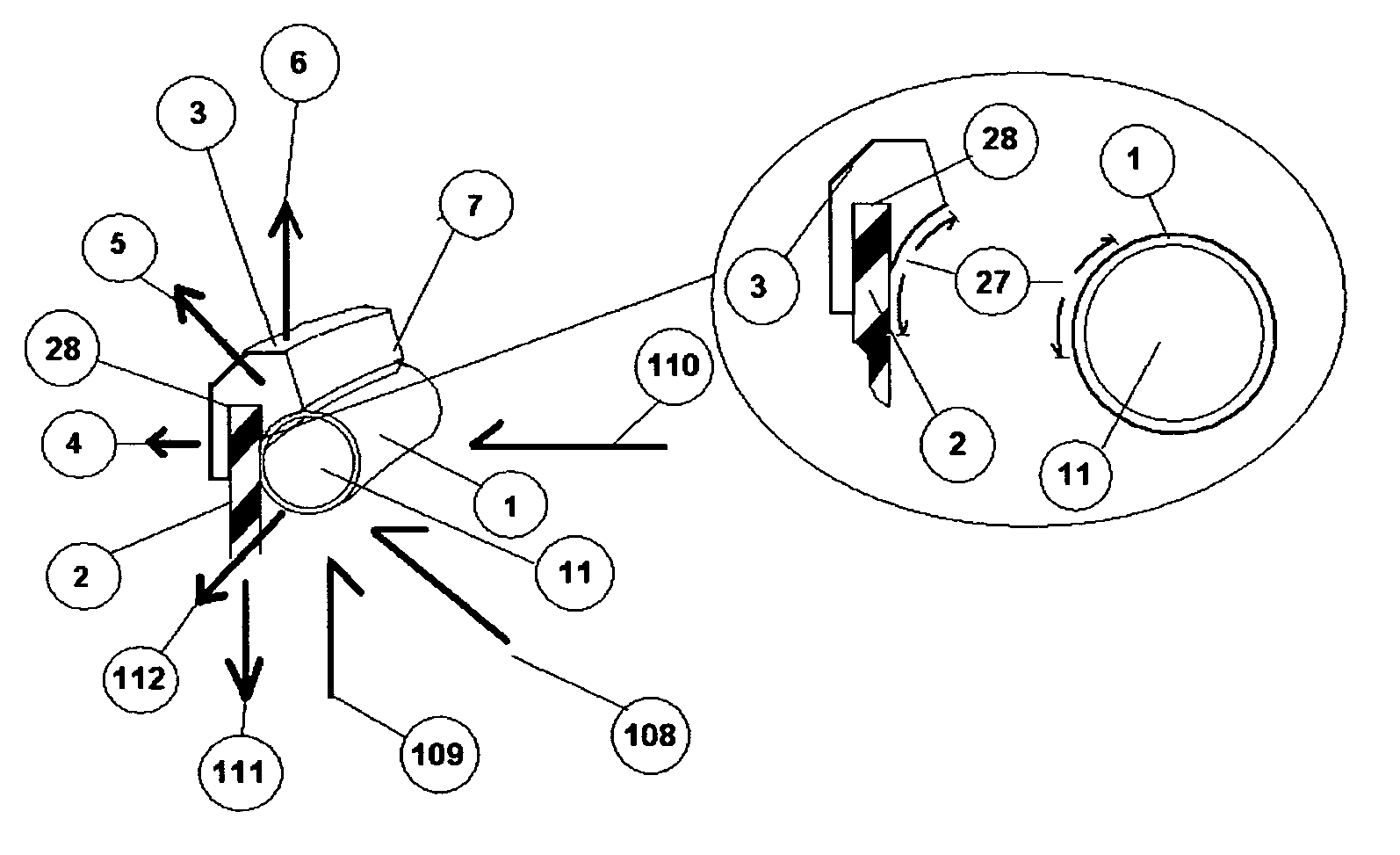
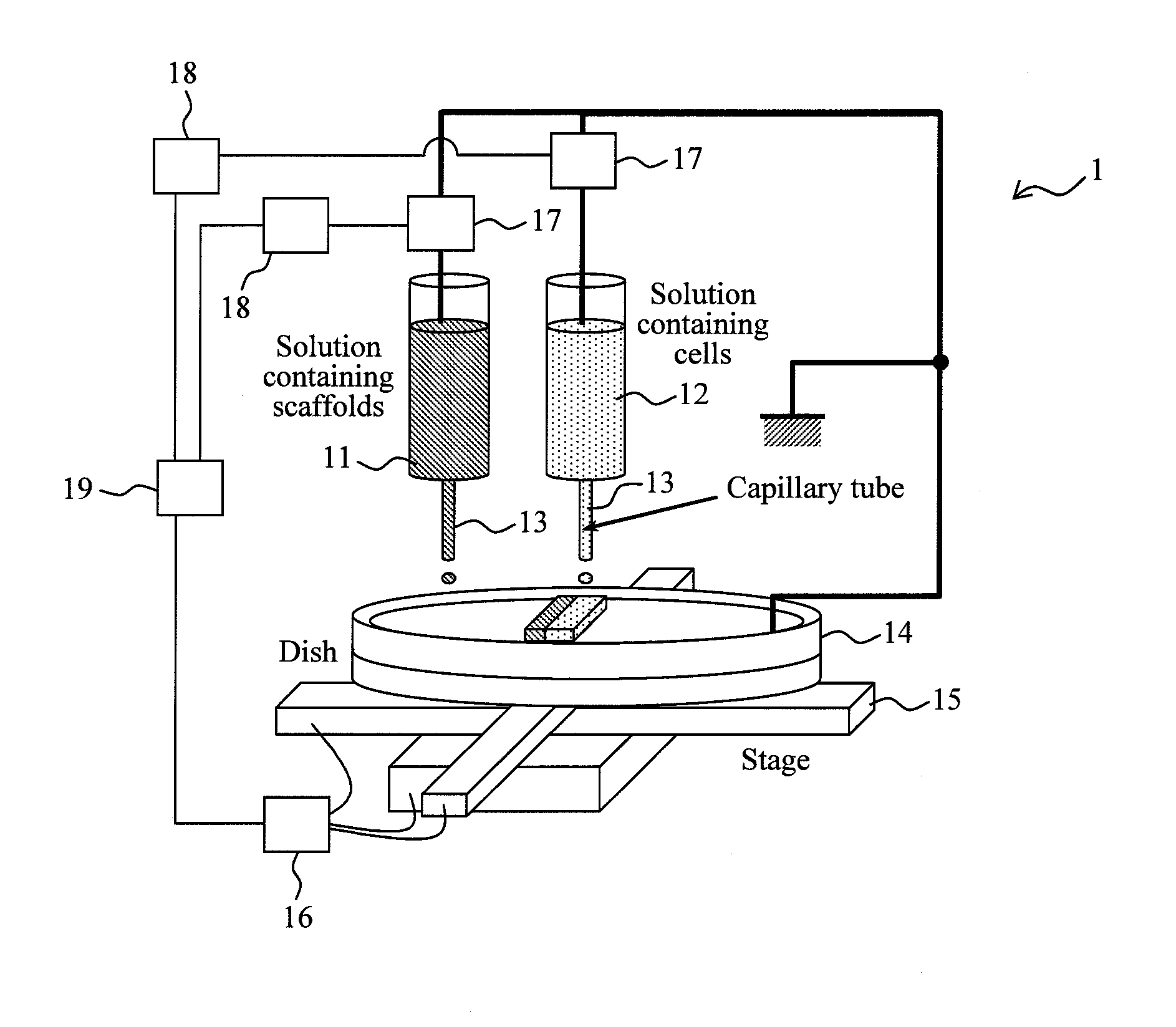
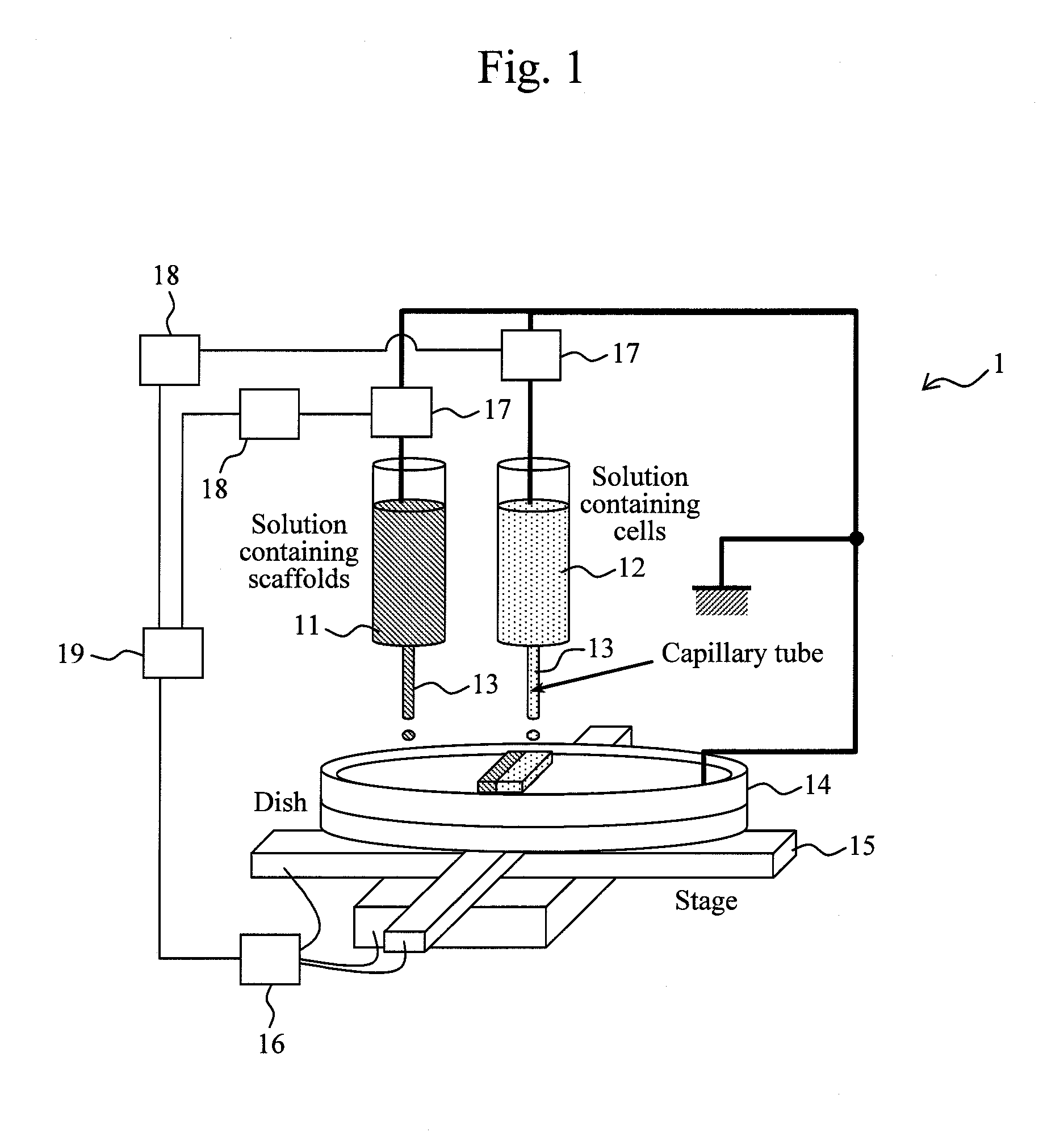
Production of cell tissue having three-dimensional structure using electrostatic ink jet phenomenon
InactiveUS20110129892A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBlood vesselBiomedical engineering
According to the present invention, a method and an apparatus for producing a cell tissue of blood vessels or the like with the use of an electrostatic ink jet phenomenon are provided.The following is provided: a pattern generator for cell tissue patterning on a substrate, which comprisesat least one vessel for holding a solution containing materials used for cell tissue formation,a substrate that is an object of patterning, anda voltage applying unit for applying a voltage to the vessel, wherein a voltage is applied to the vessel by the voltage applying unit in order to generate an electric field between the vessel and the substrate, causing the solution to be ejected from the vessel as a result of an electrostatic ink jet phenomenon and allowing the ejected solution to adhere to the substrate.
Owner:RIKEN
System and method for sinus surgery
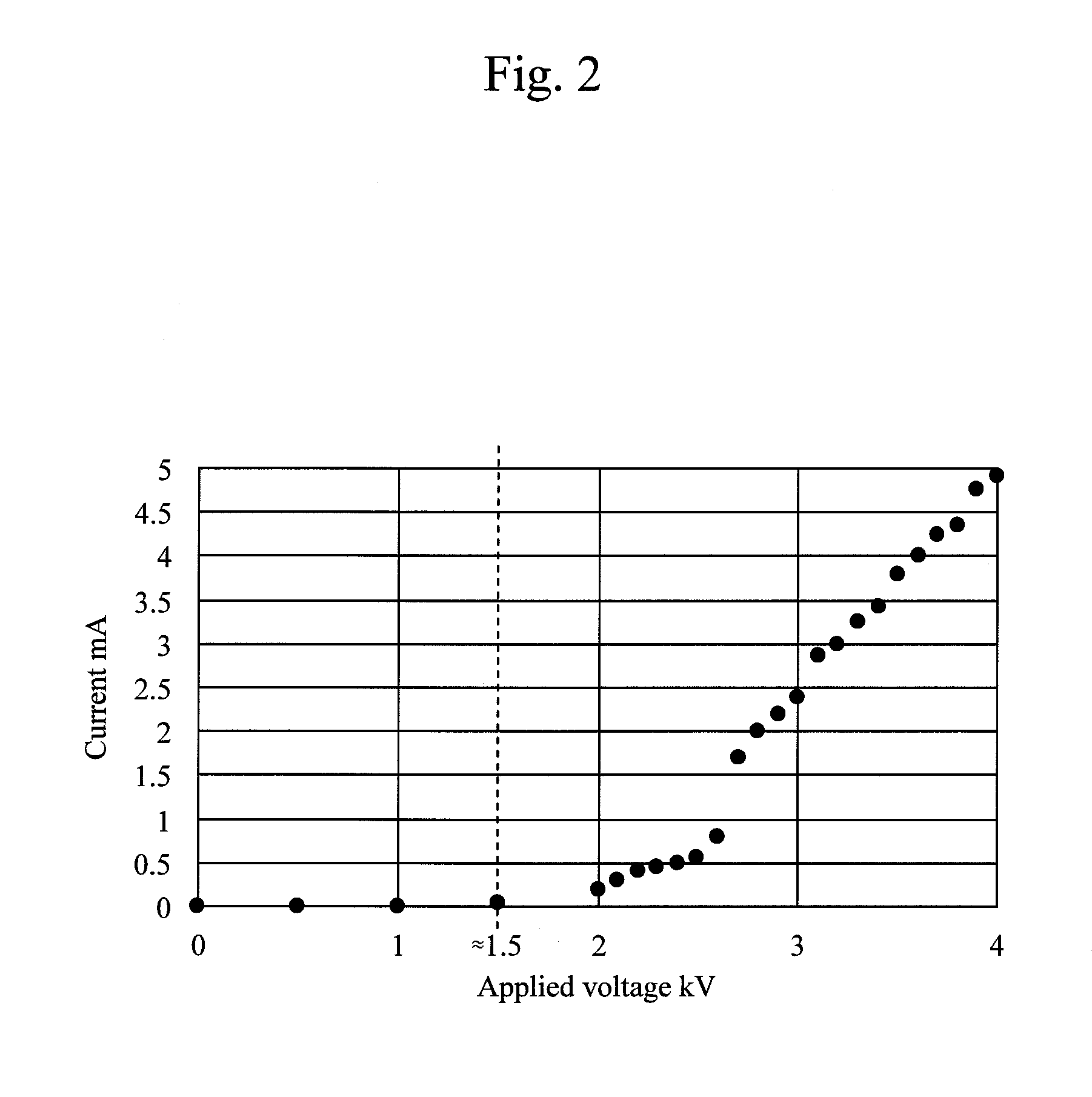
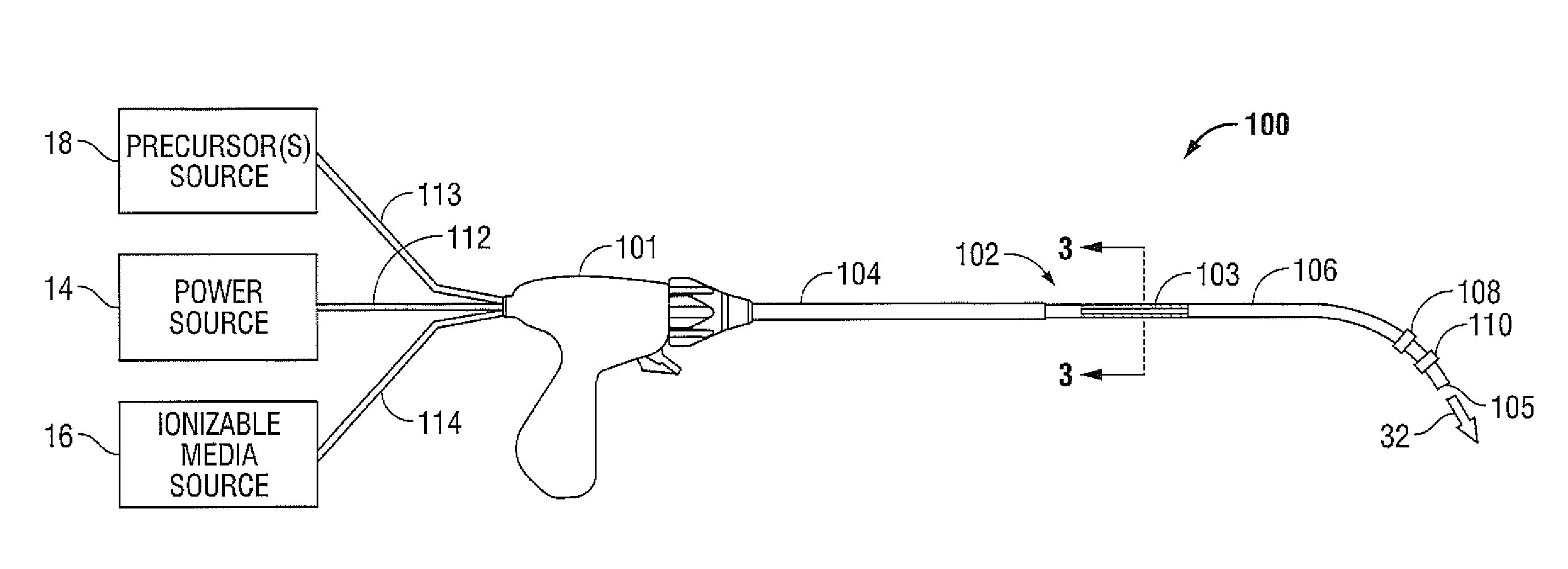
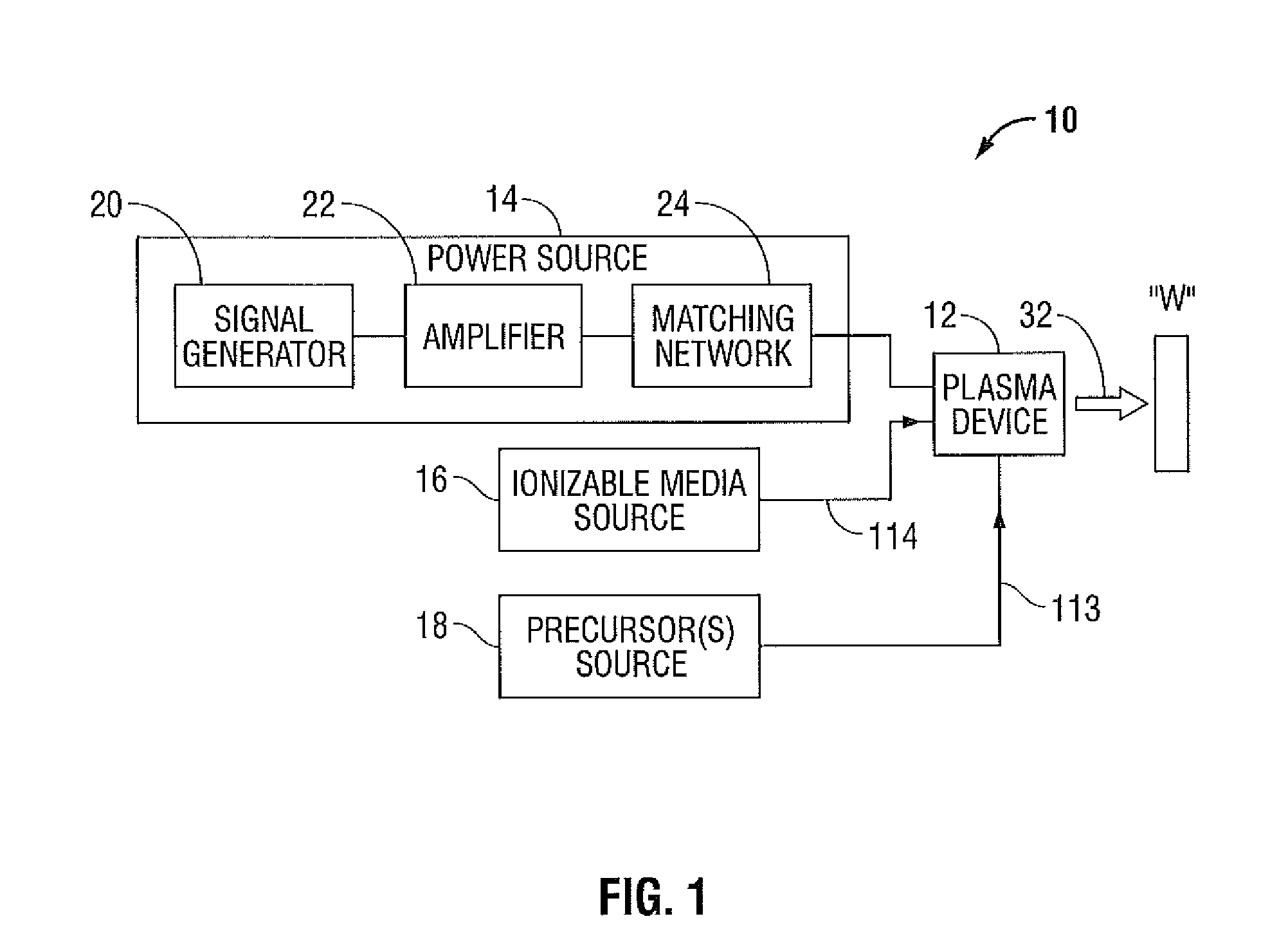
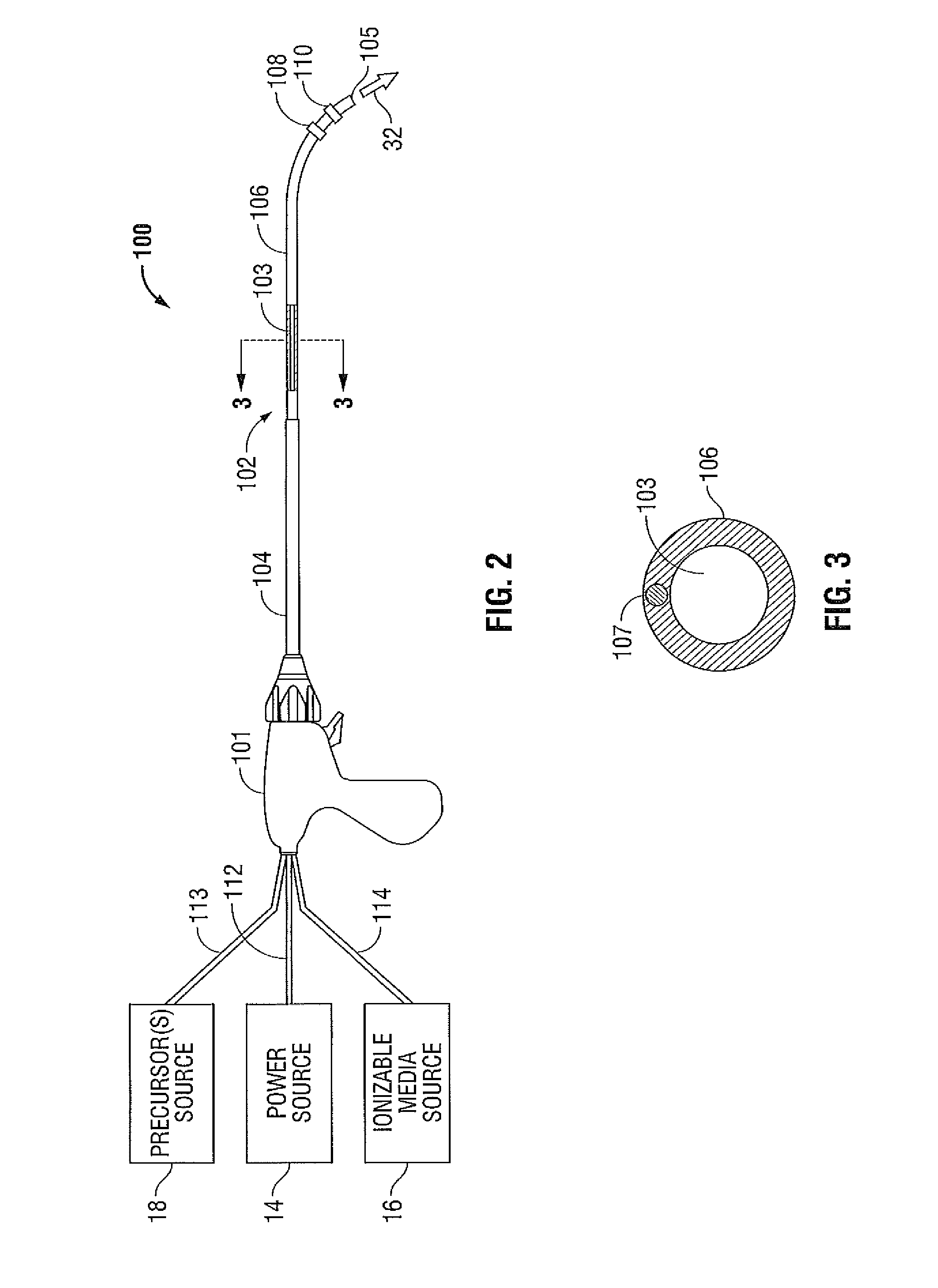
ActiveUS20140257276A1High spatialHigh material selectivitySurgical instruments for heatingSinus surgeryReactive plasma
A method for treating a sinus cavity is provided. The method includes the steps of inserting a plasma applicator into a sinus cavity defined in a bone mass, positioning the plasma applicator adjacent a tissue formation, generating a selectively reactive plasma effluent at the plasma applicator and directing the selectively reactive plasma effluent at the tissue formation. The selective nature of the reactive plasma enables treatment of specific targets inside the sinus while minimizing the effect on other tissues. Such treatment includes, but not limited to, sterilization of bacterial colonies, vaporization of unwanted tissues or foreign masses, stimulation of tissues by enriching the content of reactive oxygen and nitrous oxide pathways, and combinations thereof.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Bioartificial implant and its use and method of reducing the risk for formation of connective tissue after implantation
InactiveUS20060263405A1Eliminate the problemGrowth inhibitionBiocideAlgae medical ingredientsHuman bodyConnective tissue fiber
A bioartificial implant comprises a semipermeable barrier designed from one side to allow diffusion or prevent diffusion of predetermined substances / materials / molecules / cells / cell lines produced in the human body to the other opposite side of the barrier, and from said other opposite side to allow diffusion or prevent diffusion of predetermined substances which are the same as or different from the first mentioned substances / materials / molecules / cells / cell lines. The semipermeable barrier has a surface coating at least on said one side a bioactive metal, such as titanium, which surface coating is permeable to allow said diffusions. In a method for reducing the risk of formation / growth of connective tissue in connection with an implant which comprises a semipermeable barrier, the barrier is provided at least on one side with a permeable coating of bioactive metal. An example of the use of the implant is bioartificial pancreas.
Owner:TIKOMED
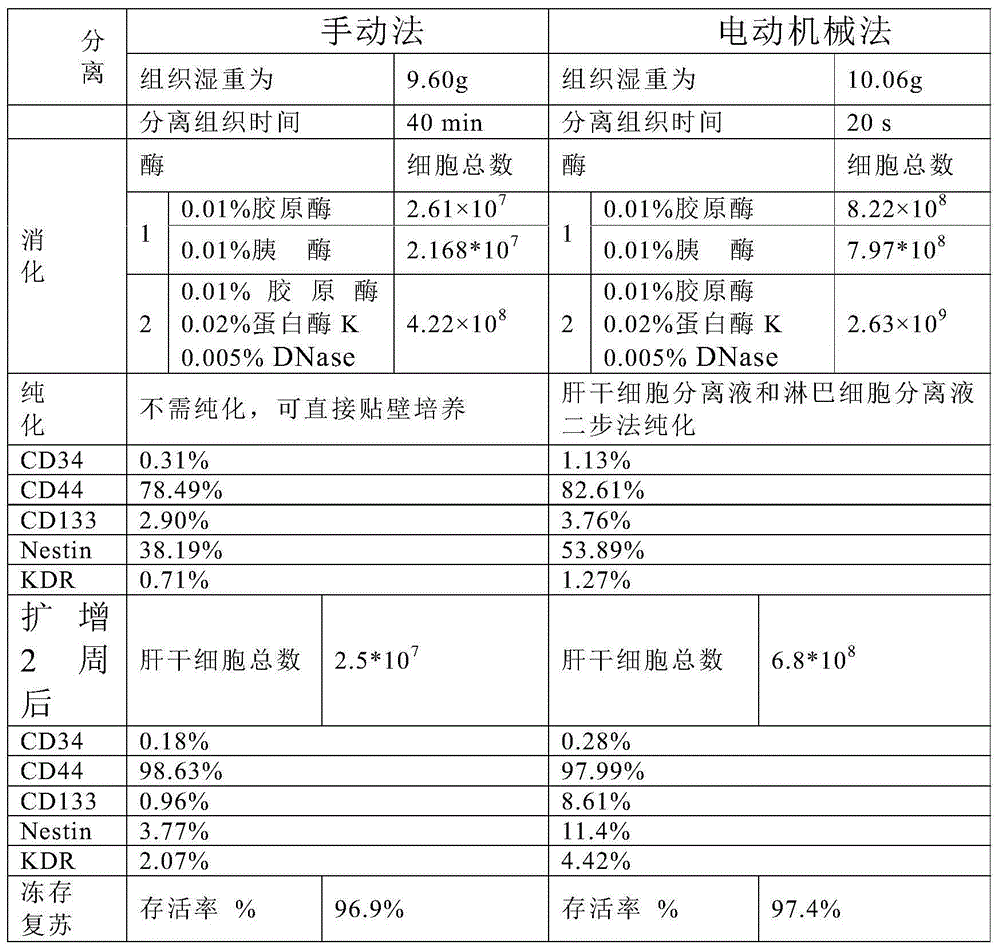
Method for large scale preparation of liver stem cells, and uses of liver stem cells
ActiveCN104630135AStable quantityQuality improvementDigestive systemUnknown materialsDirected differentiationStem cell culture
The invention relates to a method for large scale preparation of liver stem cells, and uses of the liver stem cells in the fields of cell transplantation, stem cell culture, amplification, directional differentiation and tissue formation. The preparation method of the liver stem cells includes the following steps: extracting the liver stem cells from animal or human liver tissues through using a mechanical method, enzymatic method and mechanical-enzymatic method and density gradient centrifuge method combined technology; and carrying out in-vitro large scale culture, amplifying, carrying out liver stem cell identification, and freezing the liver stem cells for later use. The liver stem cell preparation efficiency of the method disclosed in the invention is about 100-10000 times higher than that of conventional methods, and the method can be used in tissue engineering and the production of liver stem cell preparations or stem cell drugs in order to provide a new method for the treatment of human diseases.
Owner:GZ CEDICINE BIOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com