Patents
Literature
85 results about "Embryogenesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Embryonic development also embryogenesis is the process by which the embryo forms and develops. In mammals, the term refers chiefly to early stages of prenatal development, whereas the terms fetus and fetal development describe later stages.
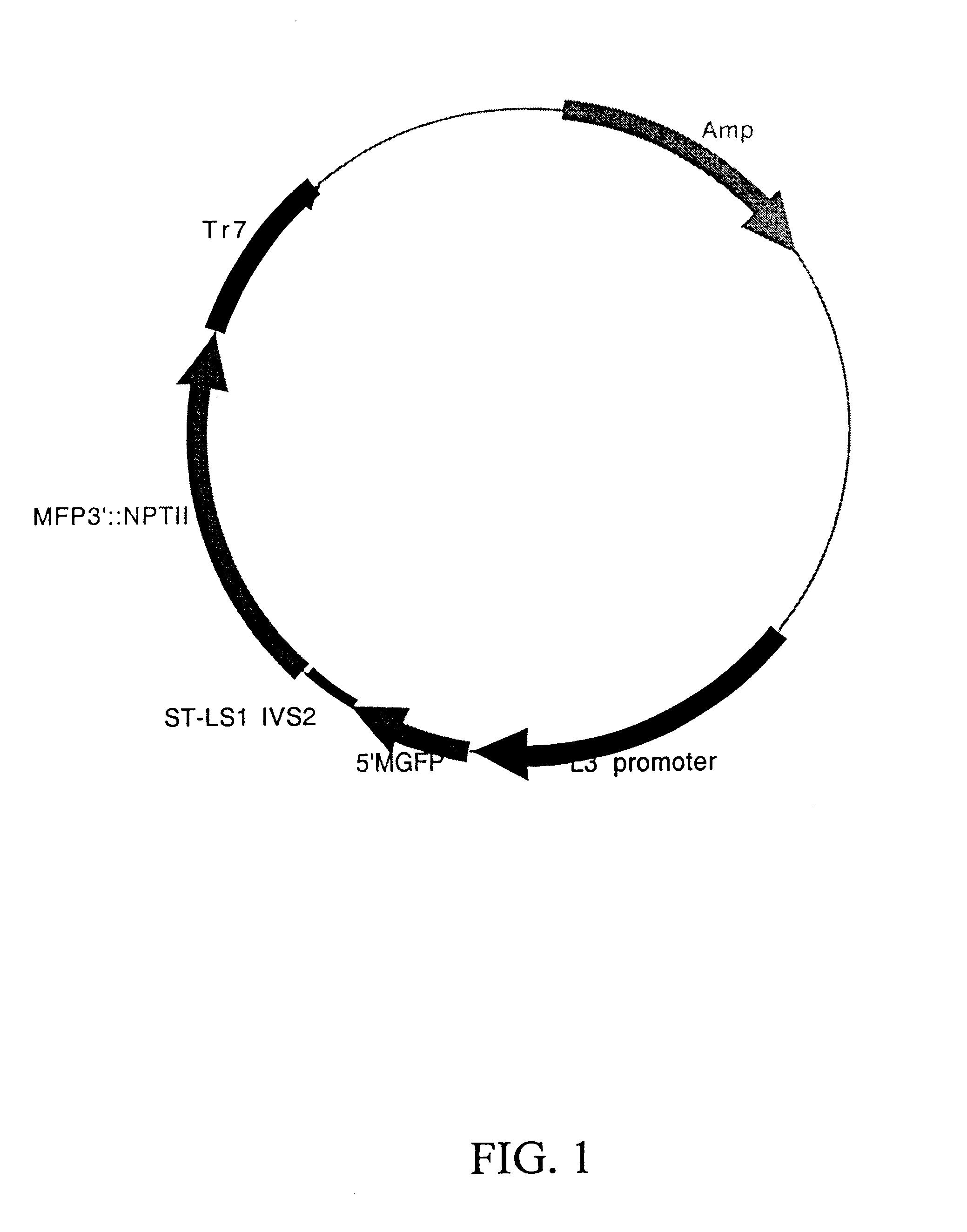
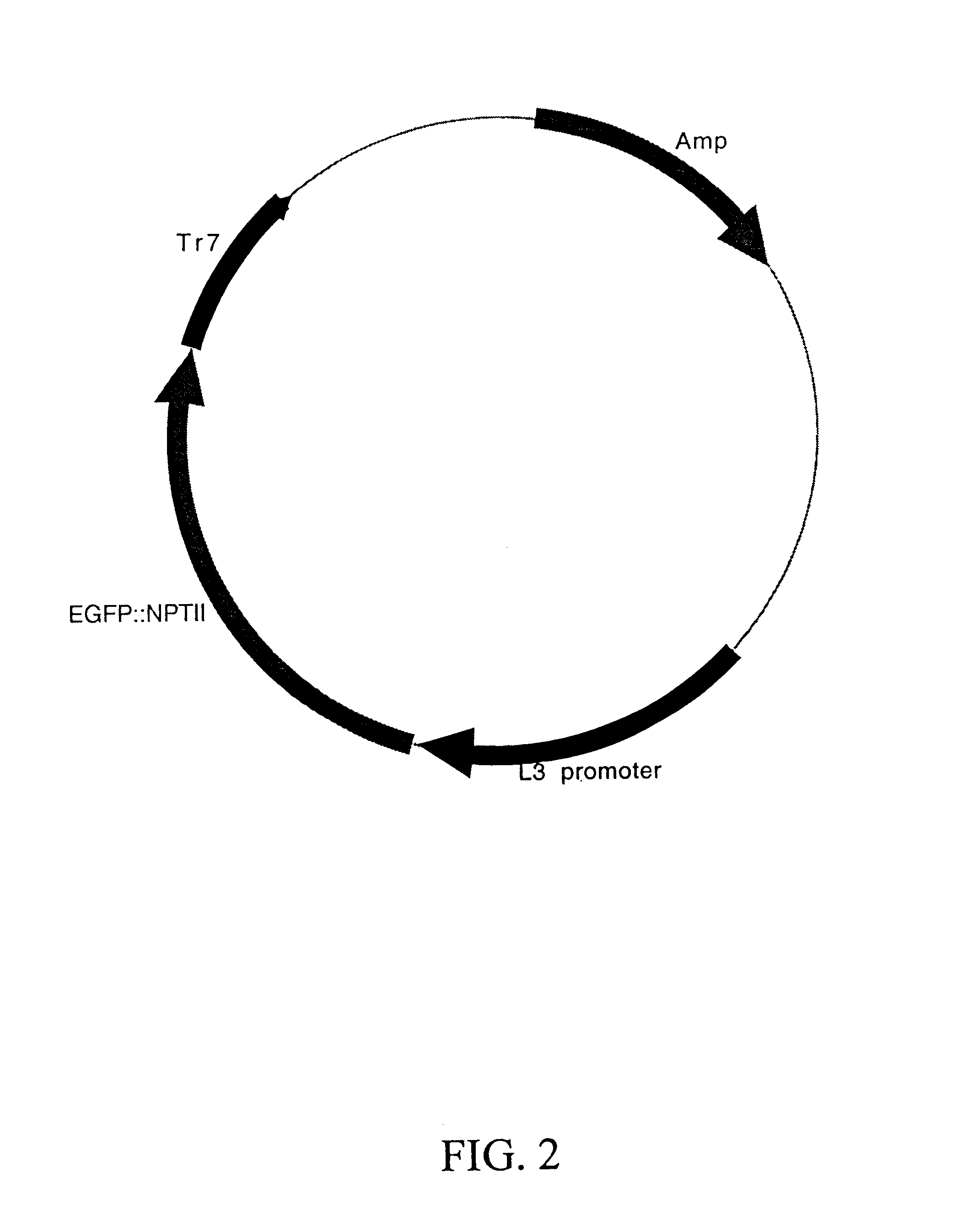
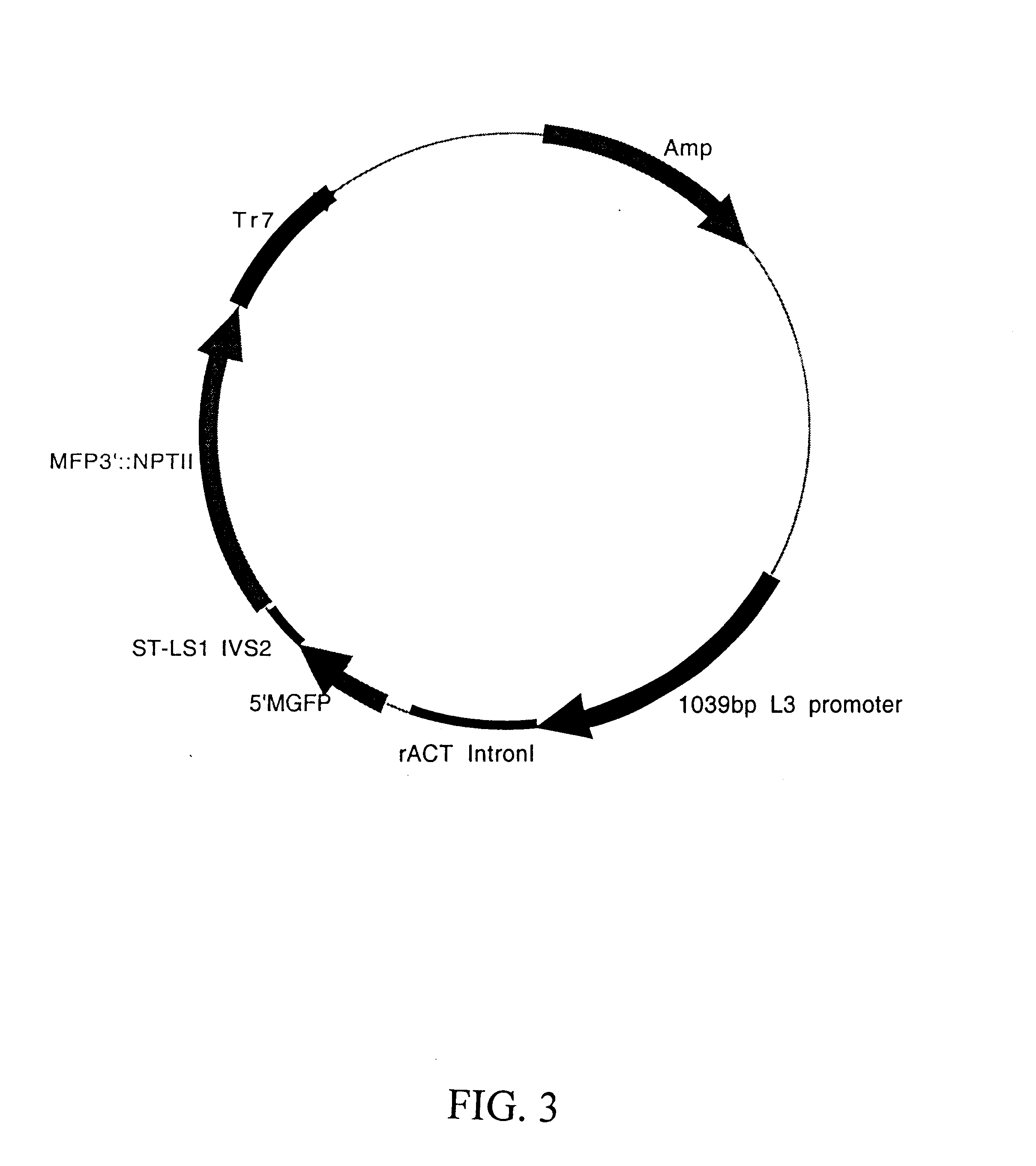
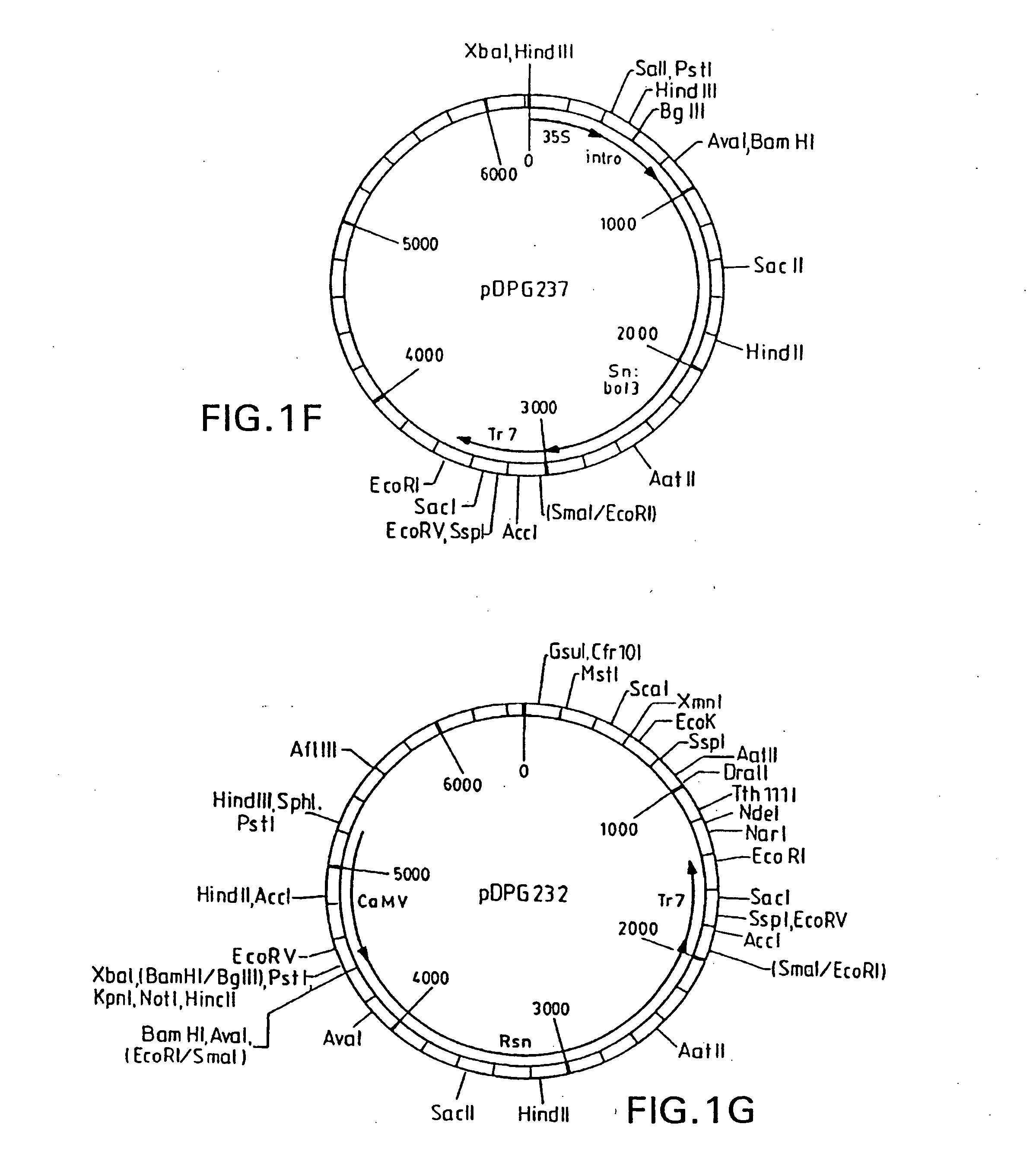
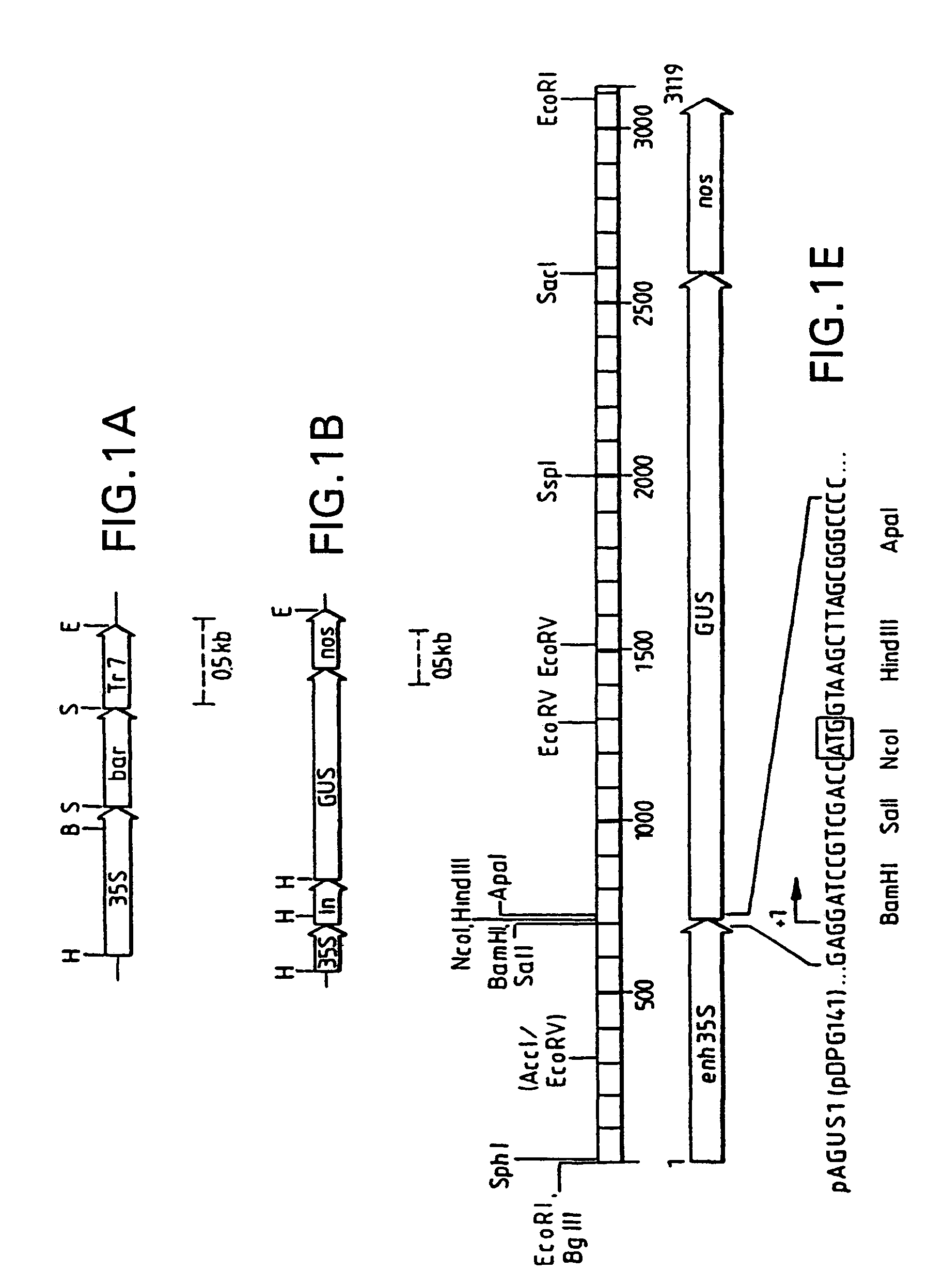
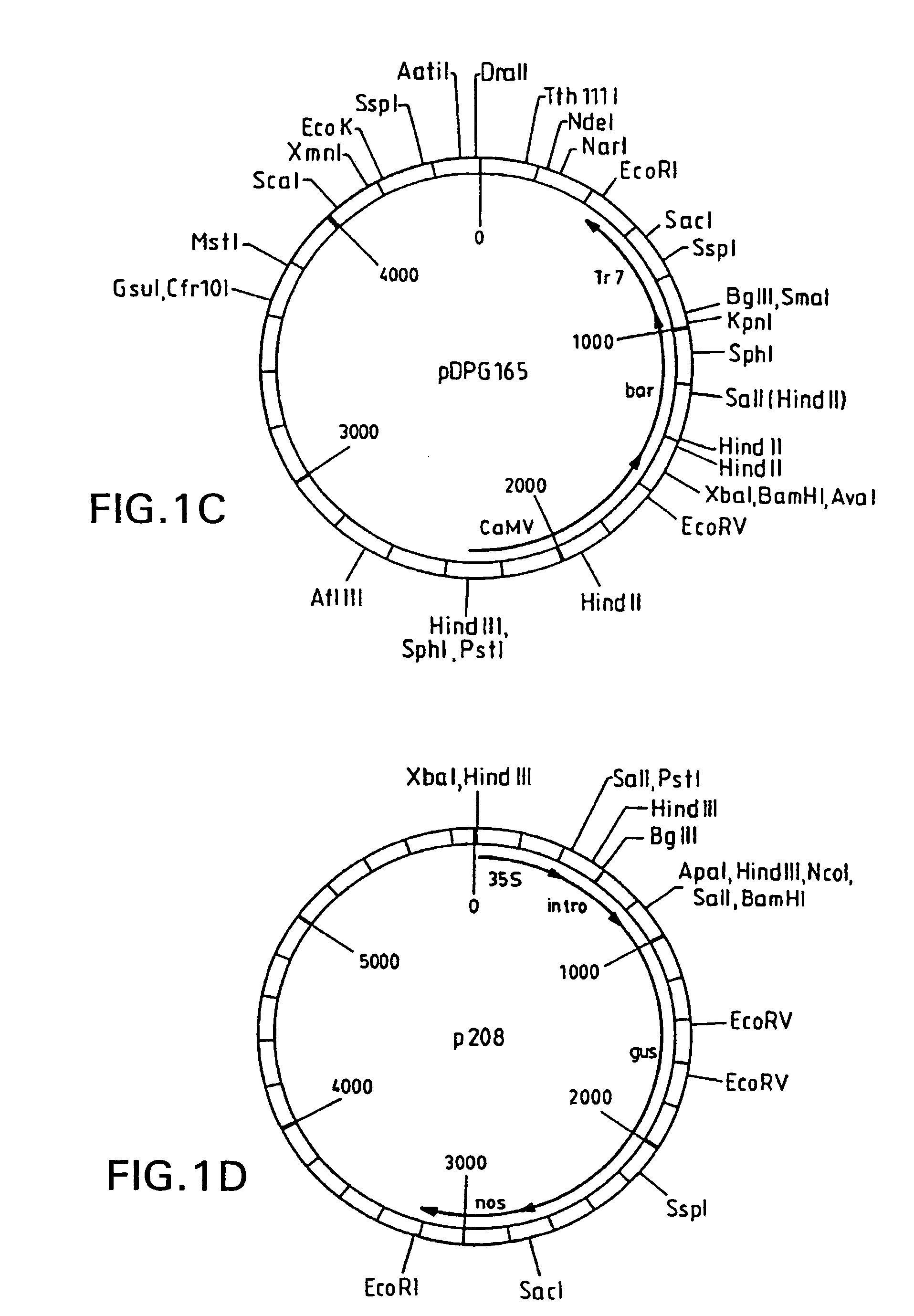
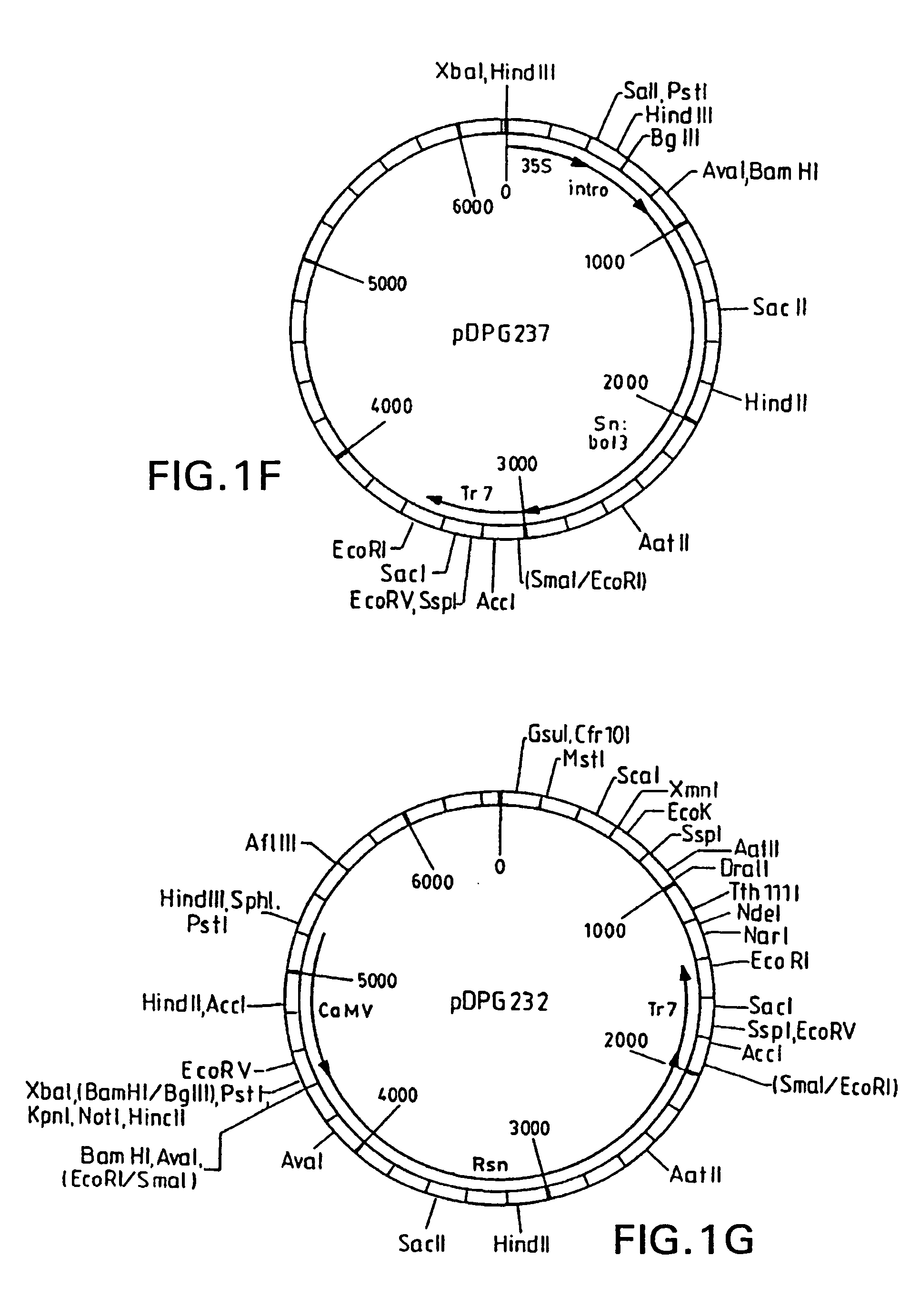
Maize L3 oleosin promoter
InactiveUS6433252B1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesAleuroneEmbryogenesis
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the identification of transgenic seeds. This is accomplished by use of screenable markers linked to aleurone-specific promoters. The screenable markers can be provided as gene fusions with selectable markers, allowing both selection and screening of transformants. The use of aleurone-specific promoters, which also direct expression in embryogenic tissues, allows efficient selection of transgenic cells and the screening of viable transgenic seeds, while avoiding the deleterious effects associated with constitutive expression of screenable marker genes. Screening of transgenic seeds avoids the need for growing and assaying of seeds for transgenes and allows implementation of automated seed screening techniques for the identification of transgenic seeds.
Owner:DEKALB GENETICS CORPORATION +1
Transformed embryogenic microspores for the generation of fertile homozygous plants
InactiveUS6316694B1Increase the number ofImprove conversion efficiencyBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesEmbryogenesisRegulatory control
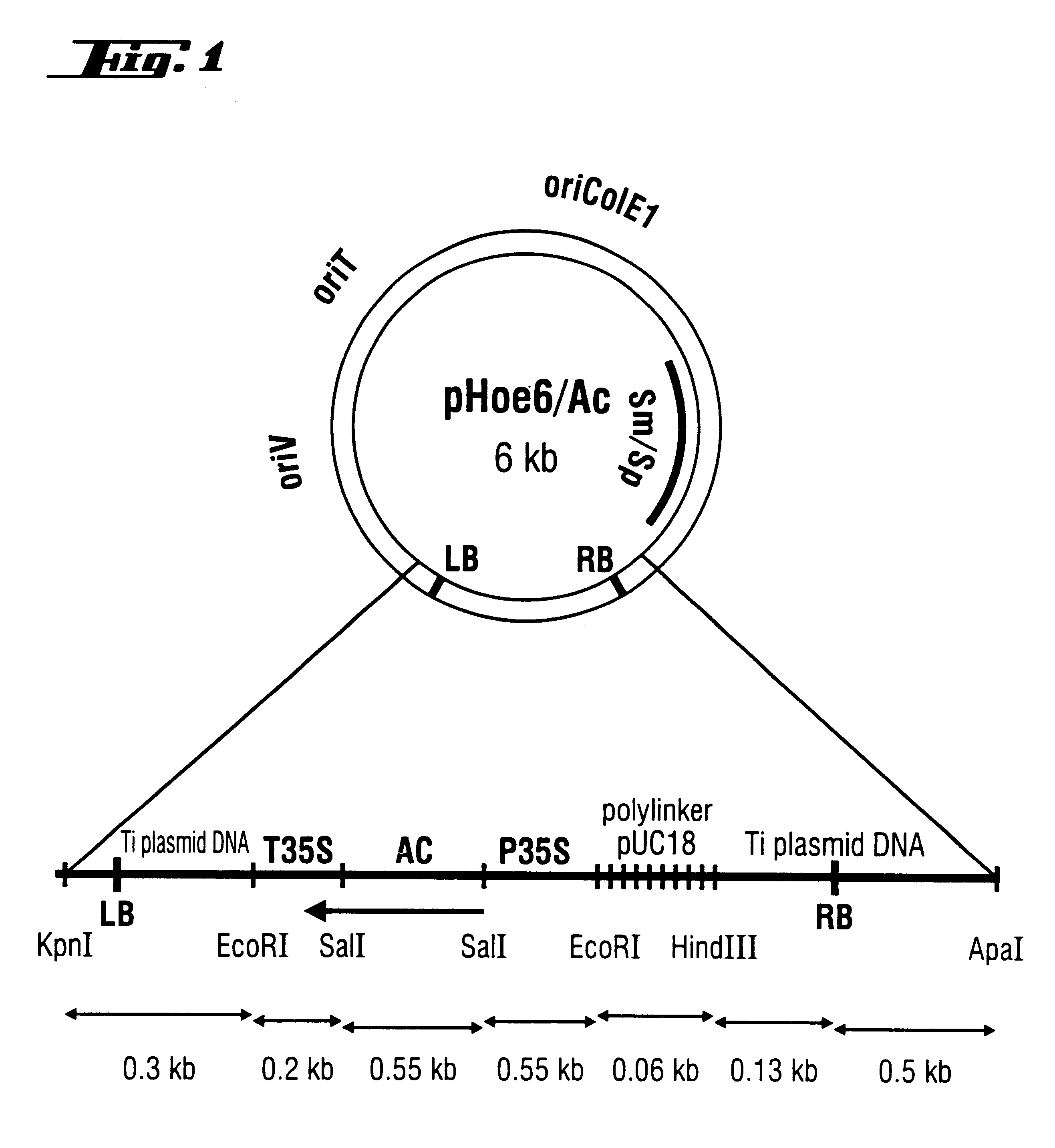
The invention relates to transformed, embryogenic microspores and progeny thereof characterized by being transformed by Agrobacterium tumefaciens, capable of leading to non-chimeric transformed haploid or doubled haploid embryos that develop into fertile homozygous plants within one generation and containing stably integrated into their genome a foreign DNA, said DNA being characterized in that it comprises at least one gene of interest and at least base pairs within the right border sequence of Agrobacterium T-DNA. The invention furthermore relates to a method for the incorporation of foreign DNA into chromosomes of microspores comprising the following steps: a) infecting of embryogenic microspores with Agrobacteria, which contain plasmid carrying a gene of interest under regulatory control of initiation and termination regions bordered by at least one T-DNA border, b) Washing out and killing the Agrobacteria after co-cultivation.
Owner:AGREVO CANADA
Methods for transforming immature maize embryos
InactiveUS7057089B2Promote embryogenic-tissue formationSmall sizeStable introduction of DNAFermentationEmbryogenesisGenetically modified maize
Methods are provided for transforming freshly isolated, immature maize embryos and for producing transgenic maize plants. The methods comprise obtaining immature embryos from a maize plant, contacting the embryos with an auxin-depleted or phytohormone-depleted transformation support medium and introducing a nucleotide construct into cells from the embryos prior to subjecting the embryos to conditions which promote embryogenic-tissue formation. The methods additionally comprise identifying or selecting transformed cells and regenerating such cells into transformed maize plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Zea mays (L.) with capability of long term, highly efficient plant regeneration including fertile transgenic maize plants having a heterologous gene, and their preparation
InactiveUS6284945B1Careful shakingPromote shakingTransferasesPlant tissue cultureHeterologousCallithamnion granulatum
Protoplasts which regenerate reproducibly in a short time to normal, fertile plants can be regenerated from an auxin-autotrophic genotype of Zea mays (L.). Starting from immature embryos on hormone-free media, an auxin-autotrophic, embryogenic callus is formed on the shoot basis of the seedlings, which callus retains its embryogenic potential over a substantial period of time when subcultured on hormone-free medium. In addition to fully-developed embryos, adventitious embryos are also formed under suitable culture conditions (6-9% of sucrose in the medium). When the sucrose content is reduced to 2-3% and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is added, soft, granular calli are formed which consist of embryogenic cell aggregates (type II callus). After subculturing the type II callus in the form of a cell suspension culture, totipotent protoplasts can be isolated. From these protoplasts, the maize plants according to the invention are regenerated.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG
Method of somatic embryogenesis of cassava and rapid propagation of regenerated plant
The invention relates to a tissue culture propagating method of Manihot esculenta Crantz. As one of the global three-top tuber crops and the number one alimentarn crop in Africa, the Manihot esculenta Crantz is currently ranked as a vital biological energy crop in our country. Stem section vegetative cottage is commonly adopted for propagation, and the low propagation rate thereof is a restrictive factor for popularizing the new variety and shortening the breeding period. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: the Manihot esculenta Crantz stem section with stem apexes or lateral buds is taken as an explant, and the Manihot esculenta Crantz tissue culture plantlets are quickly obtained in virtue of the micro-propagation method; young leaves, stem apexes and axillary buds of the sterile plantlets obtained from micro-propagation are taken as explants, somatic embryo generation and plant regeneration are induced, thus the Manihot esculenta Crantz somatic cell regeneration system is established. By adopting the method, the Manihot esculenta Crantz has the advantages of high propagation rate, no genotype dependence, and the like; the method has high value on the quick propagation and large-scale production of the Manihot esculenta Crantz improved variety in a short term, and establishes a technical basis for the Manihot esculenta Crantz transgene and other breeding.
Owner:朱文丽 +4
Methods for the production of stably-transformed, fertile wheat employing agrobacterium-mediated transformation and compositions derived therefrom
InactiveUS20030024014A1Efficient conversionOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureSomaclonal variationEmbryogenesis
Disclosed are processes for producing stably transformed fertile wheat a system of transforming wheat via Agrobacterium. This invention provides methods transforming a variety of explants, such as freshly isolated or pre-cultured immature embryos, embryogenic callus and suspension cells. Also disclosed are methods for recovering transgenic plants after transformation within a short period of time, if the explants are regenerable at the time of transformation. Thus the frequency of somaclonal variation associated with prolonged in vitro culture period is significantly reduced. The transformation frequency using this system is comparable to or better than published methods using other systems, such as microprojectile bombardment.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
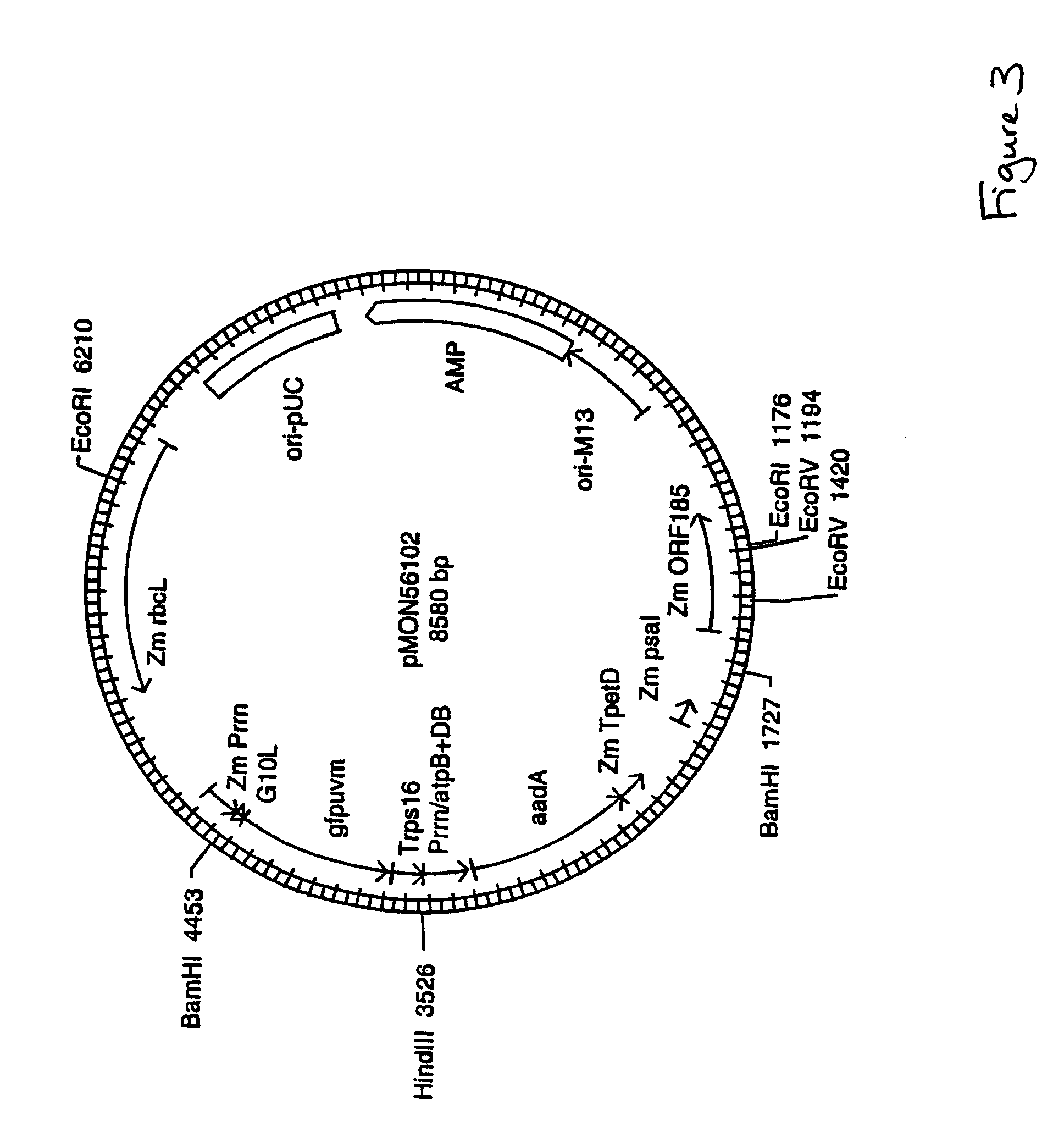
Plastid Transformation of Maize
ActiveUS20080289063A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationMicroorganismPlant tissue
A method is provided for transforming maize plants to express DNA sequences of interest from plant cell plastids. The method allows the transformation of maize plant tissue with heterologous DNA constructs by microprojectile bombardment of green light grown cultures and dark grown embryogenic cultures. The invention also provides for maize cells in which the plastids contain heterologous DNA constructs.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods of assaying for telomerase activity and compositions related to same
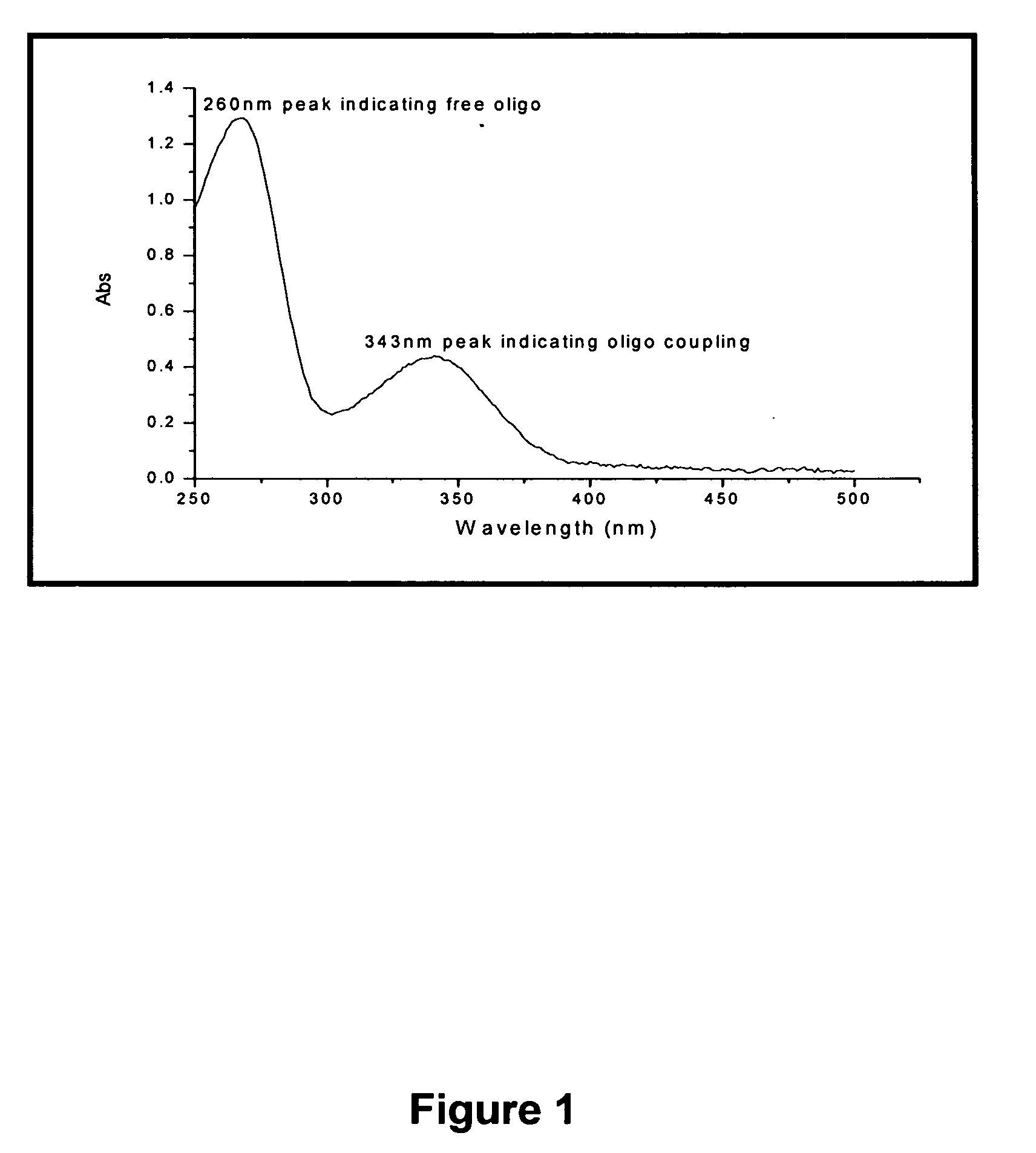
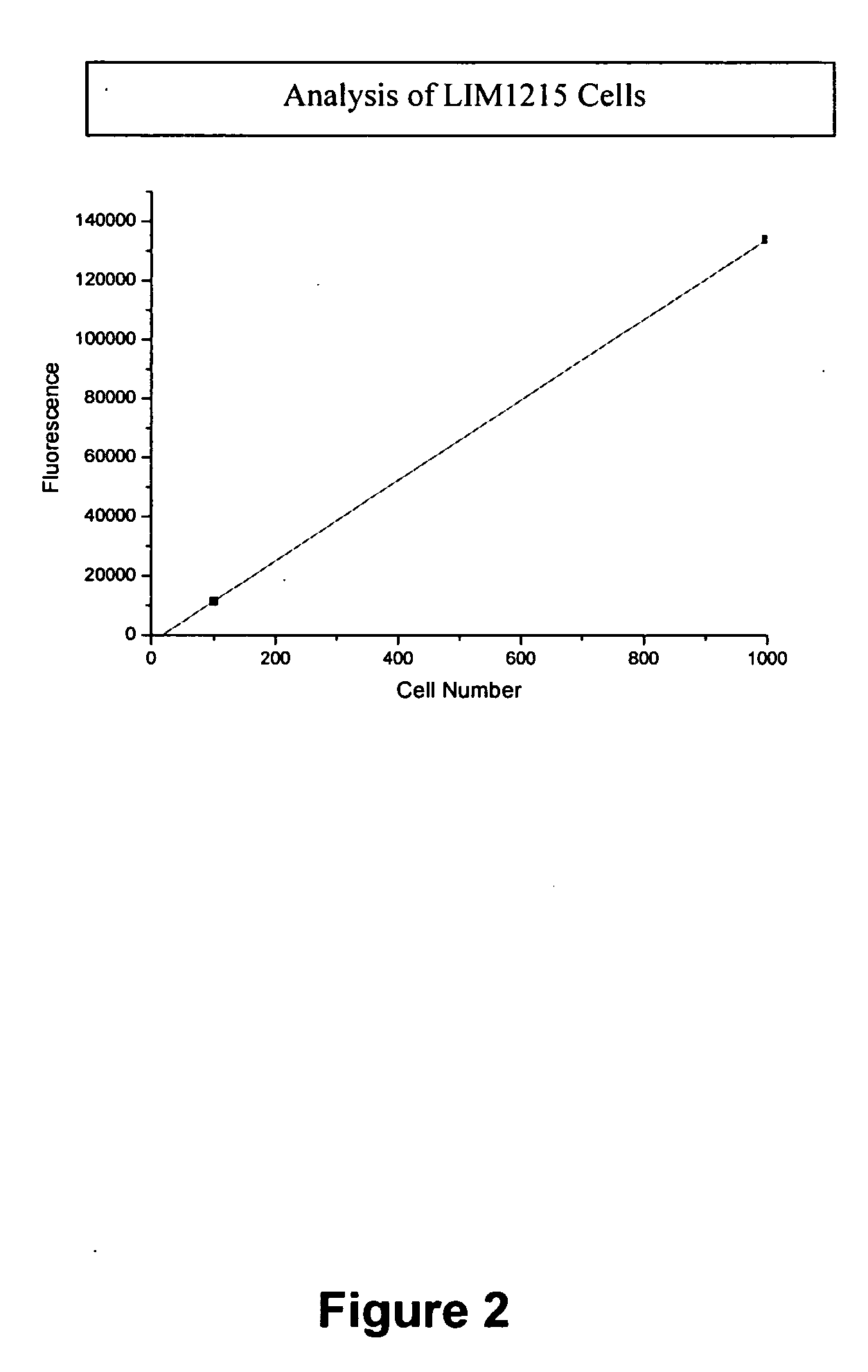
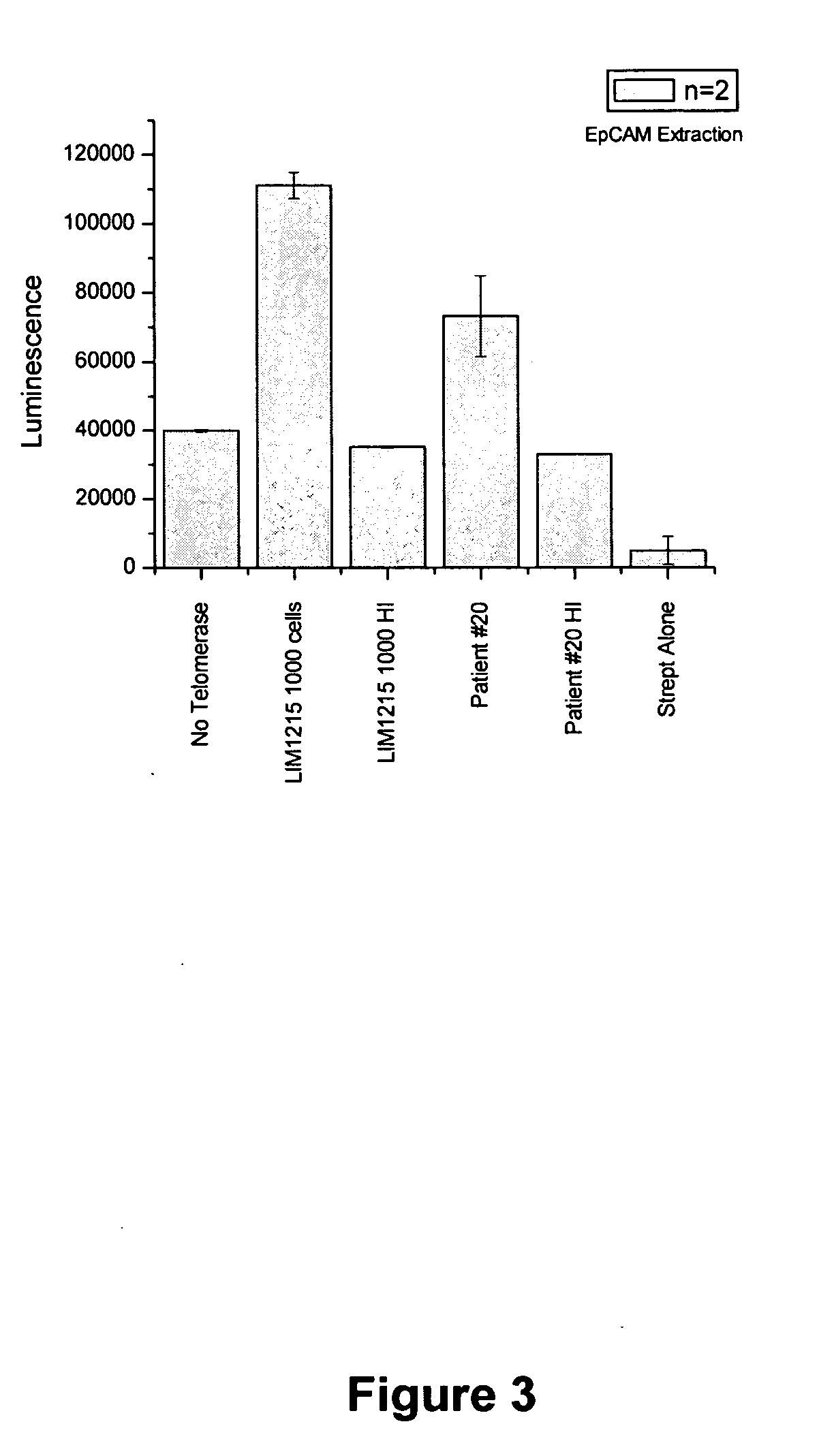
InactiveUS20100261162A1Conveniently automatedReduce the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementTelomeraseHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The present invention relates generally to the field of diagnostic and prognostic assays such as diagnostic assays for conditions associated with telomerase activity. More particularly, the present invention provides an assay for measuring telomerase activity as an indicator of cancer, an inflammatory disorder and / or a condition involving embryogenesis and / or requiring stem cell proliferation and agents and kits useful for same. Automated and partially automated assays permitting high throughput screening also form part of the present invention. The subject invention further contemplates methods of treatment using agents identified by the subject assay or where treatment protocols are monitored by the assay.
Owner:SIENNA CANCER DIAGNOSTICS
Eucalyptus urophylla*grandis embryoid induction seedling raising method
InactiveCN103155872AThe result is stableGood repeatabilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureEmbryogenesisPlantlet
The invention relates to a eucalyptus urophylla*grandis embryoid induction seedling raising method and belongs to the technical field of eucalyptus tissue culture and regeneration. The eucalyptus urophylla*grandis embryoid induction seedling raising method specifically comprises the steps of: taking a eucalyptus urophylla*grandis aseptic seedling stem segment as an explant, and obtaining a complete regenerated plant through embryonic callus induction, embryoid induction and embryoid germination. The eucalyptus urophylla*grandis embryoid induction seedling raising method can be adopted for obtaining the regenerated plant by an embryogenesis way with stable results and good repeatability, can be applied in the production and large-scale commercialization of seedlings, and also lays a foundation for eucalyptus urophylla*grandis breeding.
Owner:ZHANJIANG NORMAL UNIV
Eucalyptus urophylla*grandis embryoid induction seedling raising method
InactiveCN103155872BThe result is stableGood repeatabilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureEmbryogenesisPlantlet
The invention relates to a eucalyptus urophylla*grandis embryoid induction seedling raising method and belongs to the technical field of eucalyptus tissue culture and regeneration. The eucalyptus urophylla*grandis embryoid induction seedling raising method specifically comprises the steps of: taking a eucalyptus urophylla*grandis aseptic seedling stem segment as an explant, and obtaining a complete regenerated plant through embryonic callus induction, embryoid induction and embryoid germination. The eucalyptus urophylla*grandis embryoid induction seedling raising method can be adopted for obtaining the regenerated plant by an embryogenesis way with stable results and good repeatability, can be applied in the production and large-scale commercialization of seedlings, and also lays a foundation for eucalyptus urophylla*grandis breeding.
Owner:ZHANJIANG NORMAL UNIV
Regeneration system for grape and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050050592A1Promote formationIncrease frequencyBryophytesPlant tissue cultureEmbryogenesisHorticulture
The invention features methods of producing a plant or a mature somatic embryo from an embryogenic cell or embryogenic culture. The method includes the steps of: (a) providing a liquid culture that includes an embryogenic cell; (b) recovering embryogenic cell from the culture; (c) transferring the embryogenic cell to a second culture; and (d) growing a mature somatic grape embryo from the embryogenic cell.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method for breeding somatic embryo of immature soybean cotyledon, preserving succeed generation and revegetating plant
InactiveCN1415191ASolve the problem of induced plant regenerationSolve the regeneration problemHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySomatic embryogenesis
A tissue culture technique for soybean includes using the immature soybean cotyledon as explant to induce the reproduction of somatic embryo in solid culture medium, successive transfer storage in the solid culture medium, and normally germinating to regenerate plant.
Owner:MILITARY SUPPLIES UNIV THE CHINESE PLA
Induction of peony embryoid
InactiveCN1778169AFor long-term storageIncrease varietyPlant phenotype modificationPlant tissue cultureMicrobiologyEmbryogenesis
A method for inducing the embryoid of peony includes such steps as cleaning and disinfecting the explant, culturing in starting culture medium for 30-40 days, culturing in differentiating culture medium for 15-70 days to generate embryoid, separating the embryoid, culturing in culture medium of embryoid for 30-40 days, culturing in secondary culture medium for rooting, cold storage of rooted embryoid at 4 deg.C for 60-90 days, normal culturing in culture room, and transplanting.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for maturation of conifer somatic embryos
InactiveUS6897065B1Promote maturityBulk materialHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGrowth plantCell mass
According to the invention an embryogenic cell mass is cultured with a culture medium comprising an anti-auxin resulting in an unexpected shift in physiology from proliferation to maturation. Proliferation is reduced so that the formation of new immature embryos ceases. Reduction of proliferation facilitates the transition from proliferation to maturation and maturation frequency is increased to a much larger extend than expected. Surprisingly, it has been discovered that the quality of the somatic embryos is not reduced, although the activity of the important endogenous plant growth regulator, auxin, is reduced. As a mater of fact, the overall quality of the mature embryos harvested at the end of maturation is actually increased over the prior art.
Owner:WOODY PLANT BIOTECH
Transcription factor for enhancing embryogenesis of plant cell and synthesis of fatty acid as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a transcription factor for enhancing the embryogenesis of a plant cell and the synthesis of fatty acid as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. The transcription factor is the following proteins: (a) a protein formed by an amino acid sequence disclosed by the sequence 3 in a sequence table; (b) relevant proteins derived from (a), enhancing the embryogenesis of the plant cell and obtained through replacing and / or losing and / or adding one or a plurality of amino acids in the amino acid sequence disclosed by the sequence 3 in the sequence table. The invention also discloses the encoding gene of the transcription factor and a recombined expression vector containing the gene, a transgene clone or a recombined germ. The transcription factor for enhancing the embryogenesis of a plant cell and the synthesis of fatty acid and the encoding gene thereof have great application values, such as enhancing the embryogenesis of the plant cell, culturing transgene plants with improved fatty acid content, being used as screening marks of the transgene plates, enabling plants to have asexual reproduction capacity and producing synthetic seed.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for increasing conifer somatic embryo initiation, capture, and multiplication
InactiveUS20060051868A1Improve efficiencyInitiation efficiency is highCell culture mediaPlant tissue cultureSomatic embryogenesisBiotin
The present invention provides methods for initiating, capturing, maintaining and multiplying embryogenic cultures of coniferous plants. Methods include the use of novel media compositions containing folic acid, biotin, pH buffers, gibberellin inhibitors and gas-tight environment treatments to improve the frequency of embryogenic tissue initiation, capture, maintenance and multiplication. The methods are well suited for initiating embryogenic cultures in recalcitrant conifer varieties. The method is also well suited for producing somatic embryos that can be further cultured to produce large numbers of plants. Further, the invention provides novel methods that may be used to enhance somatic embryogenesis in a broad range of species.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Methods and compositions for the production of stably transformed, fertile monocot plants and cells thereof
InactiveUS20070044181A1Raise the ratioIncrease contentClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffStreptomycesPollen
This invention relates to a reproducible system for the production of stable, genetically transformed maize cells, and to methods of selecting cells that have been transformed. One method of selection disclosed employs the Streptomyces bar gene introduced by microprojectile bombardment into embryogenic maize cells which were grown in suspension cultures, followed by exposure to the herbicide bialaphos. The methods of achieving stable transformation disclosed herein include tissue culture methods and media, methods for the bombardment of recipient cells with the desired transforming DNA, and methods of growing fertile plants from the transformed cells. This invention also relates to the transformed cells and seeds and to the fertile plants grown from the transformed cells and to their pollen.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Wild tomato Solanum sitiens somatic embryo induction method and somatic embryo genetic transformation method
ActiveCN103314849AInduced fastStabilized receptor systemHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSomatic embryogenesisEmbryogenesis
The invention relates to the field of genetic transformation, specifically to a wild tomato Solanum sitiens somatic embryo induction method and a somatic embryo genetic transformation method. The induction method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) culturing Solanum sitiens aseptic seedlings;(2) carrying out dark culture and inducing roots, stems (without axillalry buds) and leaves of Solanum sitiens on a embryogenic callus induction medium ECIM to generate embryogenic callus;(3) transferring the generated embryogenic callus onto a somatic embryogenesis induction medium SEIM in the light to induce somatic embryogenesis; and (4) inducing budding and seedling.
Owner:ZHOUKOU NORMAL UNIV
Method for improving embryogenesis efficiency and plant regeneration efficiency of stem nodule mustard microspore embryo
ActiveCN103329804AImprove regeneration efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySporeling
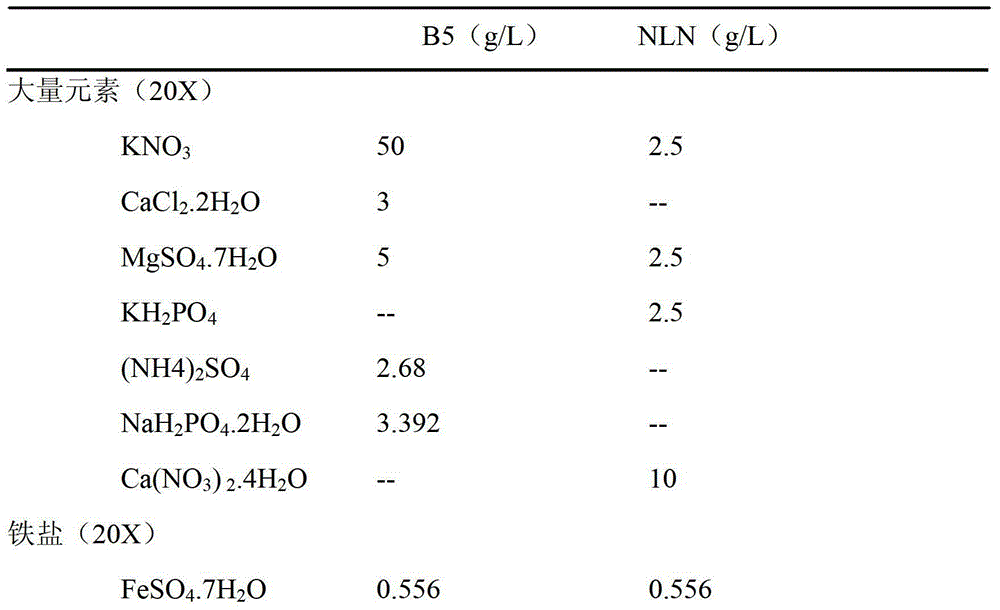
The invention discloses a method for improving the embryogenesis efficiency and the plant regeneration efficiency of a stem nodule mustard microspore embryo. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting materials, namely observing flower buds by a microscope, and selecting the flower buds with the diameters of 2-3 mm; (2) performing sterilization, namely performing sterilization by adopting 0.1 percent of mercury bichloride for 12 min, and washing the flower buds by germfree water for three times; (3) extracting pollens, namely adding a B5-13 liquid culture medium for grinding and filtration, and performing centrifugation; (4) performing heat-activation treatment, namely transferring sedimented pollens into an NLN-16 liquid culture medium containing a colchicine solution, culturing the pollens in the dark at the temperature of 32 DEG C for 48-52 hours; (5) performing induction to obtain the embryo, namely performing centrifugation, adding the NLN-13 liquid culture medium, packaging the pollens into a culture dish according to a unit of 1.5 flower buds per culture dish, and culturing the flower buds in the dark at the temperature of 25 DEG C; and (6) performing induction to obtain seedlings, namely after the embryo is formed, transferring the embryo into a B5-3 solid culture medium for culture. The invention creates a novel method of a stem nodule mustard free microspore culture technology and has a wide application prospect in breeding of stem nodule mustards.
Owner:NINGBO ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods and compositions for the production of stably transformed, fertile monocot plants and cells thereof
InactiveUS7211713B2Raise the ratioIncrease contentClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesStreptomycesPollen
This invention relates to a reproducible system for the production of stable, genetically transformed maize cells, and to methods of selecting cells that have been transformed. One method of selection disclosed employs the Streptomyces bar gene introduced by microprojectile bombardment into embryogenic maize cells which were grown in suspension cultures, followed by exposure to the herbicide bialaphos. The methods of achieving stable transformation disclosed herein include tissue culture methods and media, methods for the bombardment of recipient cells with the desired transforming DNA, and methods of growing fertile plants from the transformed cells. This invention also relates to the transformed cells and seeds and to the fertile plants grown from the transformed cells and to their pollen.
Owner:DEKALB GENETICS CORPORATION
Peanut breeding method of fast neutron irradiation combining with tissue culture
InactiveCN103125401AGenetic stabilityEffective mutagenPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsEmbryogenesisSomatic cell
The invention provides a peanut breeding method of fast neutron irradiation combining with tissue culture. The main steps are that a peanut seed is disposed through the neutron irradiation and the peanut seed is sterilized on the surface. Embryo lobules are separated and the embryo lobules are inoculated to the somatic embryo induction culture medium to be cultivated. An explant forming the somatic embryo is transferred to the somatic embryo germination culture medium and cultivated. The somatic embryo is transferred to the seedling culture medium to be cultivated after the somatic embryo germinates, thus the seedling is promoted to develop. Obtained regrowth- seedling is transplanted to the field after the regrowth- seedling is grafted. The field management is conventional. Clear variation and separation occur to obtained regrowth-plant progeny (M2). The seed disposed by the fast neutron irradiation is tissue cultured, thus a great quantity of regrowth-plants are obtained. A dozen of the regrowth-plants or even dozens of the regrowth-plants can be obtained through one grain seed. Selection probability is greatly increased. The problems that the seed of the peanut is large and a selection group of mutagenesis breeding is not achieved are solved. The somatic cell origins from a single cell through the embryo occurring way of the regeneration of the mutant, thus mosaic of the mutant can be avoided.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Method for promoting Chinese cabbage microspore embryogeny and direct seedling development
InactiveCN105028203APromote productionHigh seedling rate directlyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeMicrometer
The invention provides a method for promoting Chinese cabbage microspore embryogeny and direct seedling development so as to solve the problems that in an existing dissociative microspore culture technology, the microspore embryogeny rate is low, the direct seedling development rate is low, and the culture period is long. Histone histone deacetylase inhibitor-suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) is added to an induction medium NLN to increase the Chinese cabbage microspore embryogeny rate and the direct seedling development rate. In the NLN induction medium with SAHA of 0.025 micrometer to 0.10 micrometer added, the Chinese cabbage microspore embryogeny rate is increased by 1.42-4.35 times, and the direct seedling development rate is increased by 1.11-1.50 times.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Continuous culture of conifer embryogenic tissue
ActiveUS7625754B2Easy to produceIncrease probabilityCell culture mediaOther foreign material introduction processesEmbryogenesisBiology
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
Crossbred Chinese tulip tree clone trophozoite suspension cell line inducement method for the generating and regenerating of somatic embryo
The invention relates to a method for reducing somatic embryo generating and plant regenerating by clone vegetative suspension cell line of cross-bred liriodendron. The method adopts bud, stem tip, leaf, flower organ and new branch from different parts of a mother tree as induction materials for the generating of somatic embryo and young plant is obtained after the stage of callus induction, establishing and multiplication of suspension cell line, induction of suspension cell embryo development, maturity of embryo, somatic embryo germinating and plant regenerating. The method solves the problem of the somatic embryo generating and plant regenerating can not be reduced by adult cross-bred liriodendron vegetative directly, and provides the new way with short cycle, high propagation rate and low cost.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for increasing embryogenesis rate of microspores of Wucai
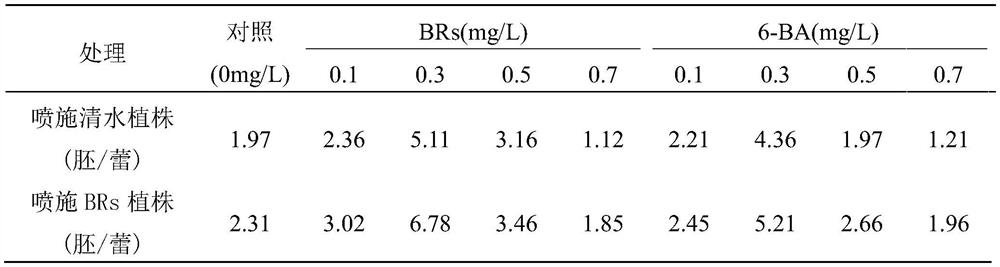
ActiveCN112385541AEasy to operateEasy to implementLeaf crop cultivationPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses a method for increasing the embryogenesis rate of microspores of Wucai, and belongs to the field of vegetable chemical control. The method further comprises the step of spraying brassinolide to seedlings with 6-7 main leaves before obtaining the microspores of the Wucai, the concentration of the brassinolide added to a culture medium is 0.3 mg / L, the concentration of the brassinolide sprayed to the seedlings of the Wucai is 50 mg / L, and the spraying parts of the seedlings of the Wucai are the back surfaces of the leaves until the surfaces of the leaves drip water. The method provided by the invention can effectively improve the occurrence rate of microspore embryos of the Wucai.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Separator device, deposition device and system for handling of somatic plant embryos
Methods and devices for separating fluid-suspended plant somatic embryos and embryogenic tissue based on differences in their fluid drag properties are disclosed. Deposition method and device for depositing plant somatic embryos into embryo receiver comprising growth substrate by means of a fluid jet is disclosed. An automated system for processing plant somatic embryos from the bioreactor to the growth substrate is also disclosed.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Methods for developing conifer somatic embryos
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
Armeniaca sibirica somatic embryogenesis method
InactiveCN106718893AGood apricot shapeProduction and Breeding GuaranteePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSomatic embryogenesisEmbryogenesis
The invention provides an armeniaca sibirica somatic embryogenesis method, and belongs to a seedling technology in the field of plant cultivation and is a method for inducing somatic embryogenesis with mature armeniaca sibirica embryos. In the method, fully matured armeniaca sibirica seeds are adopted, mature embryos are taken as an explant material, are inoculated on callus induction media for cultivation and are induced to generate an embryonic callus, and the callus are proliferated, so as to achieve the purpose of expanding propagation; further induction is performed by the embryonic callus, so that the embryonic callus is differentiated to form proembryos in the prior period; synchronized cultivation is performed by early proembryos under a certain condition, so that the development of the mature embryos are promoted to realize synchronization; and the early proembryos synchronously cultivated are further matured, so as to form somatic embryos with normal germination conditions. The method has the advantages that a large number of armeniaca sibirica somatic embryos are obtained by adopting the method, so that excellent armeniaca sibirica varieties are proliferated rapidly, and therefore, the propagation coefficient is greatly improved, and the propagation period is shortened.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for rapidly propagating akebia trifoliata varaustralis seedlings through somatic embryogenesis pathway
InactiveCN112586349AHigh cell totipotencyLow rate of bacterial infection in tissue culturePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyPlant hormone
The invention discloses a method for rapidly propagating akebia trifoliata varaustralis seedlings through a somatic embryogenesis pathway. According to the method for rapidly propagating the akebia trifoliata varaustralis seedlings through the somatic embryogenesis pathway, immature akebia trifoliata varaustralis seeds are used as explants for inducing somatic embryos. The method mainly has the advantages that 1) zygotic embryos of immature seeds have higher cell totipotency, the somatic embryogenesis process is easily induced, the immature seeds are in a relatively sterile environment in pulp, and the tissue culture contamination rate is low; 2) no exogenous plant hormones need to be added in the process of inducing somatic embryogenesis initiation and subculture multiplication, and initiation induction and subculture multiplication can be carried out in an MS culture medium; and 3) through the somatic embryogenesis pathway, the somatic embryo proliferation efficiency is high, and a large number of akebia trifoliata varaustralis aseptic seedlings can be obtained in a short time; and 4) the induced somatic embryos can be developed into complete plants, are originated from single cells, and have the advantages of low chimerism rate, low mutation rate and the like.
Owner:江西省·中国科学院庐山植物园
Plastid transformation of maize
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com