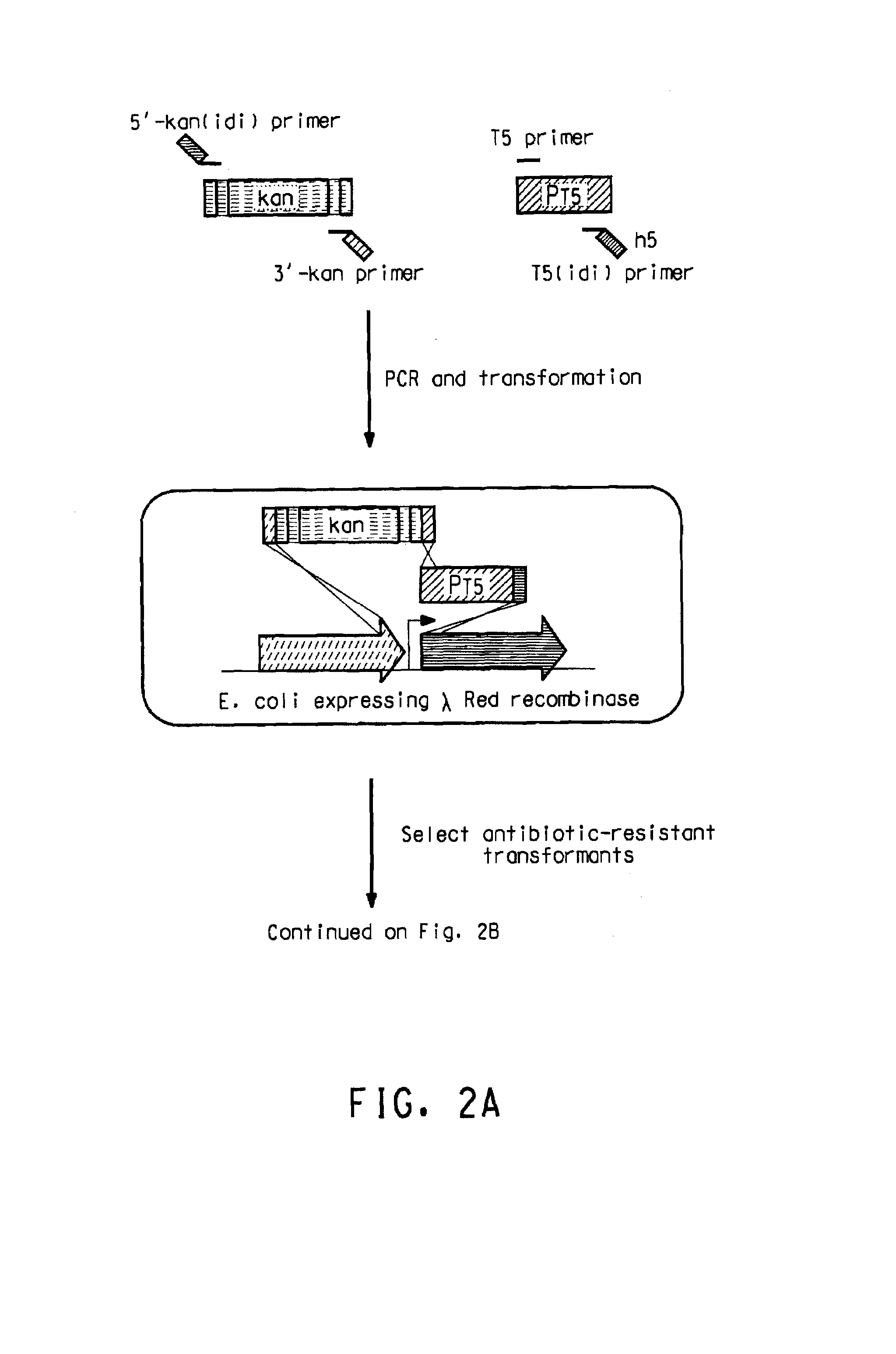
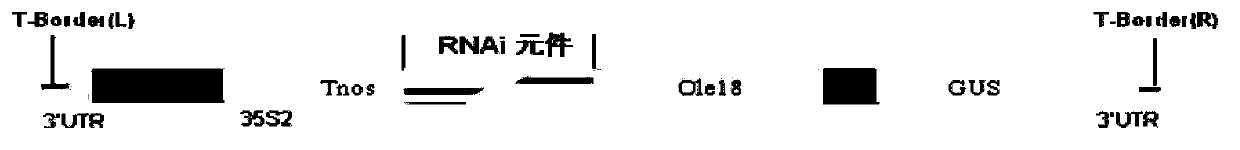Patents
Literature
55 results about "Oleosin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
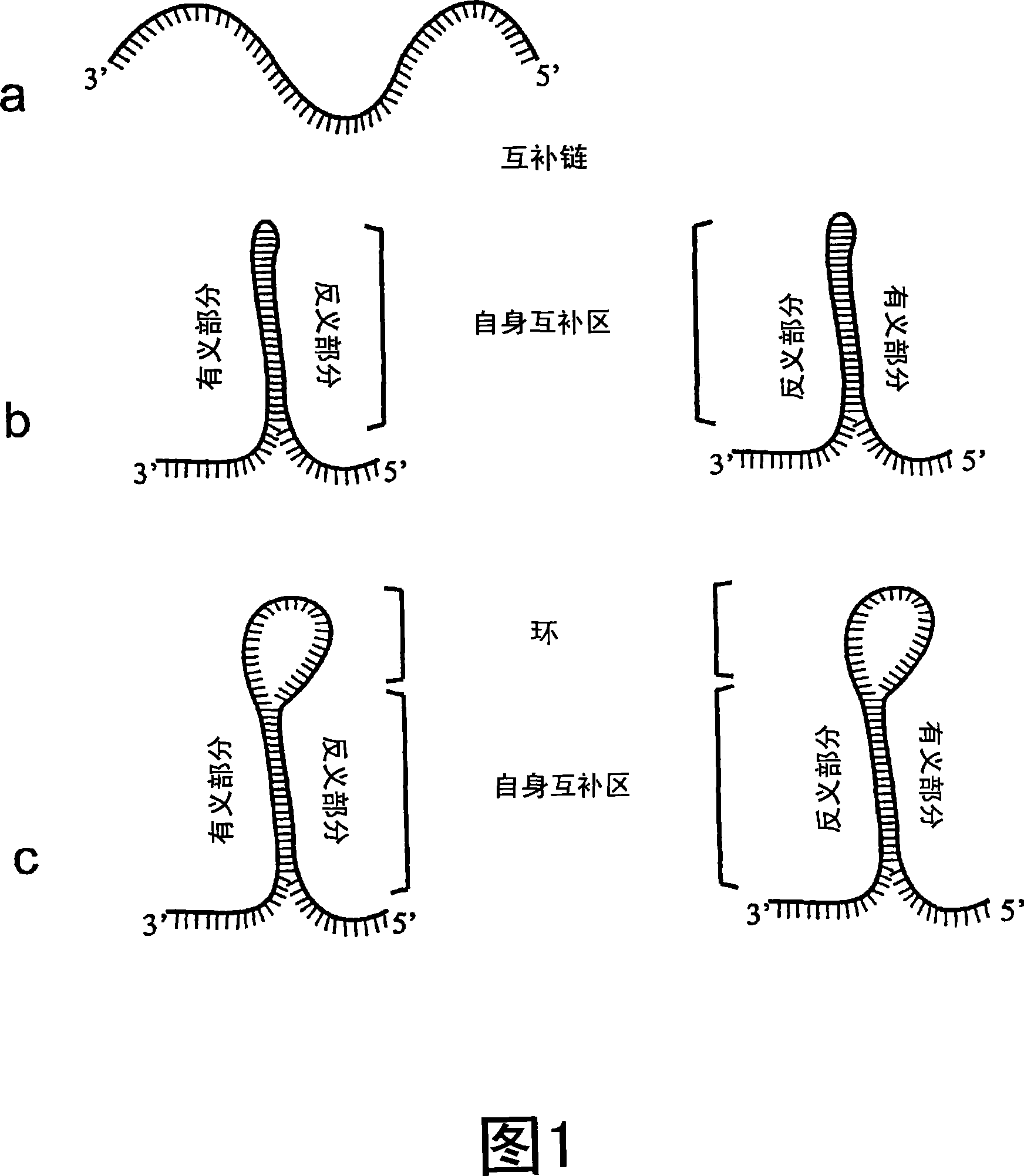
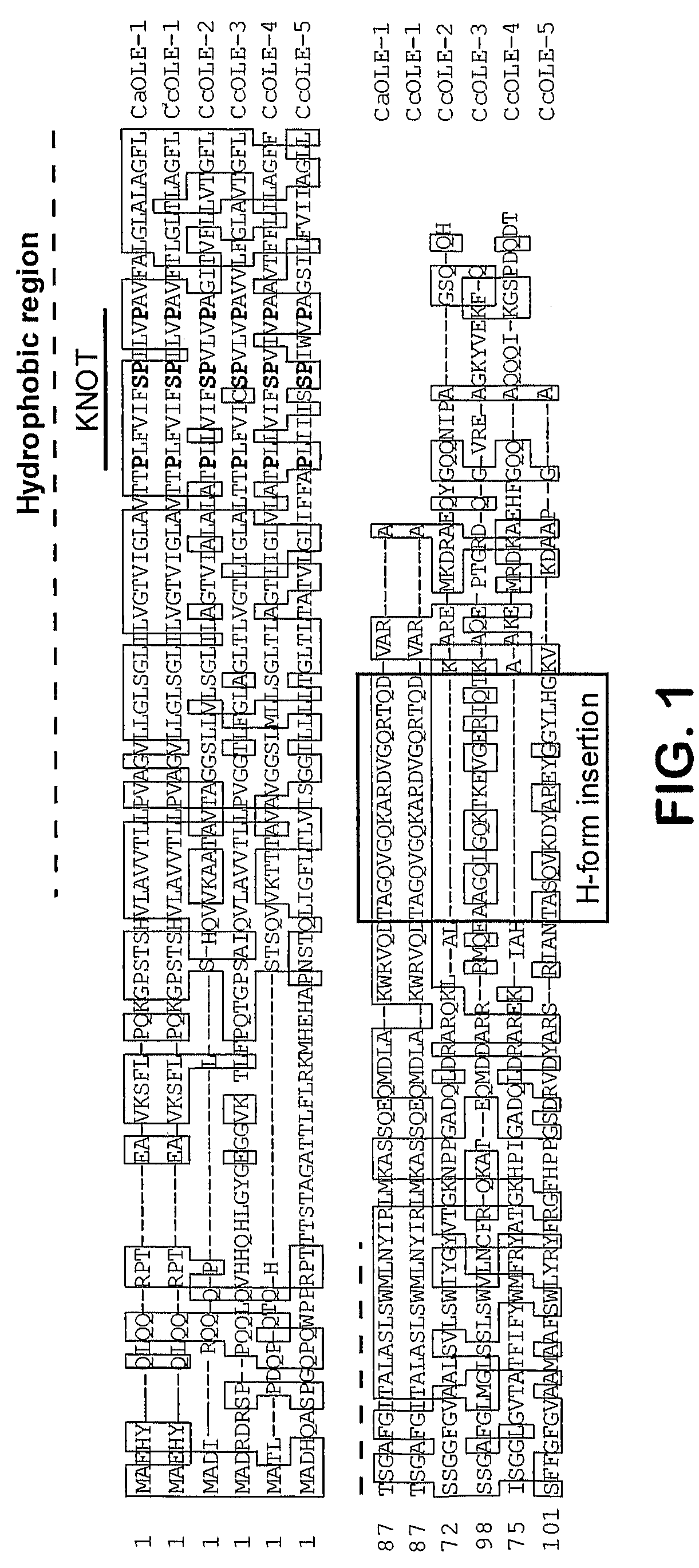
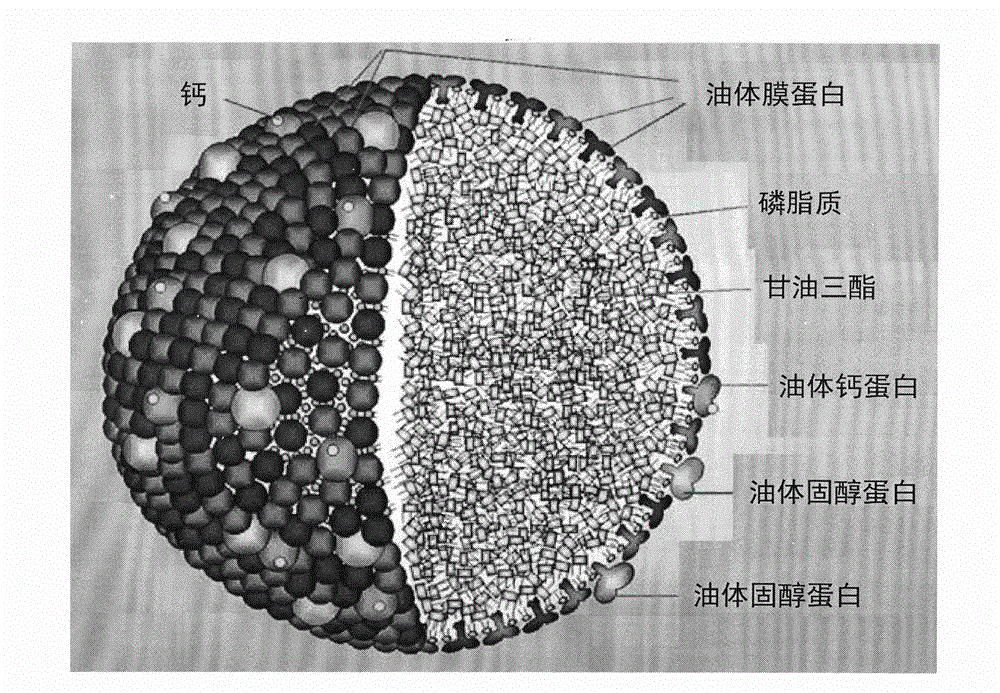
Oleosins are structural proteins found in vascular plant oil bodies and in plant cells. Oil bodies are not considered organelles because they have a single layer membrane and lack the pre-requisite double layer membrane in order to be considered an organelle. They are found in plant parts with high oil content that undergo extreme desiccation as part of their maturation process, and help stabilize the bodies.
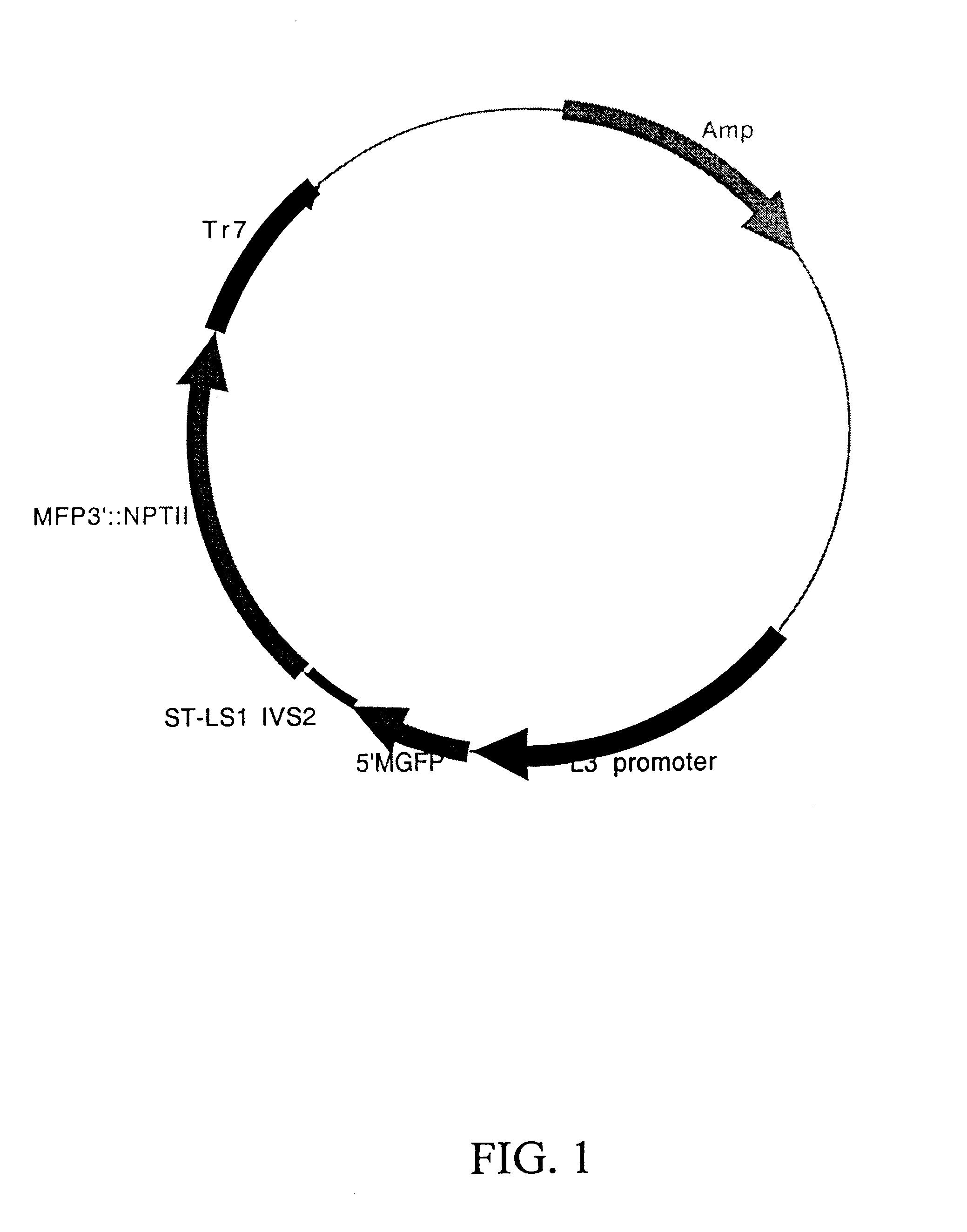
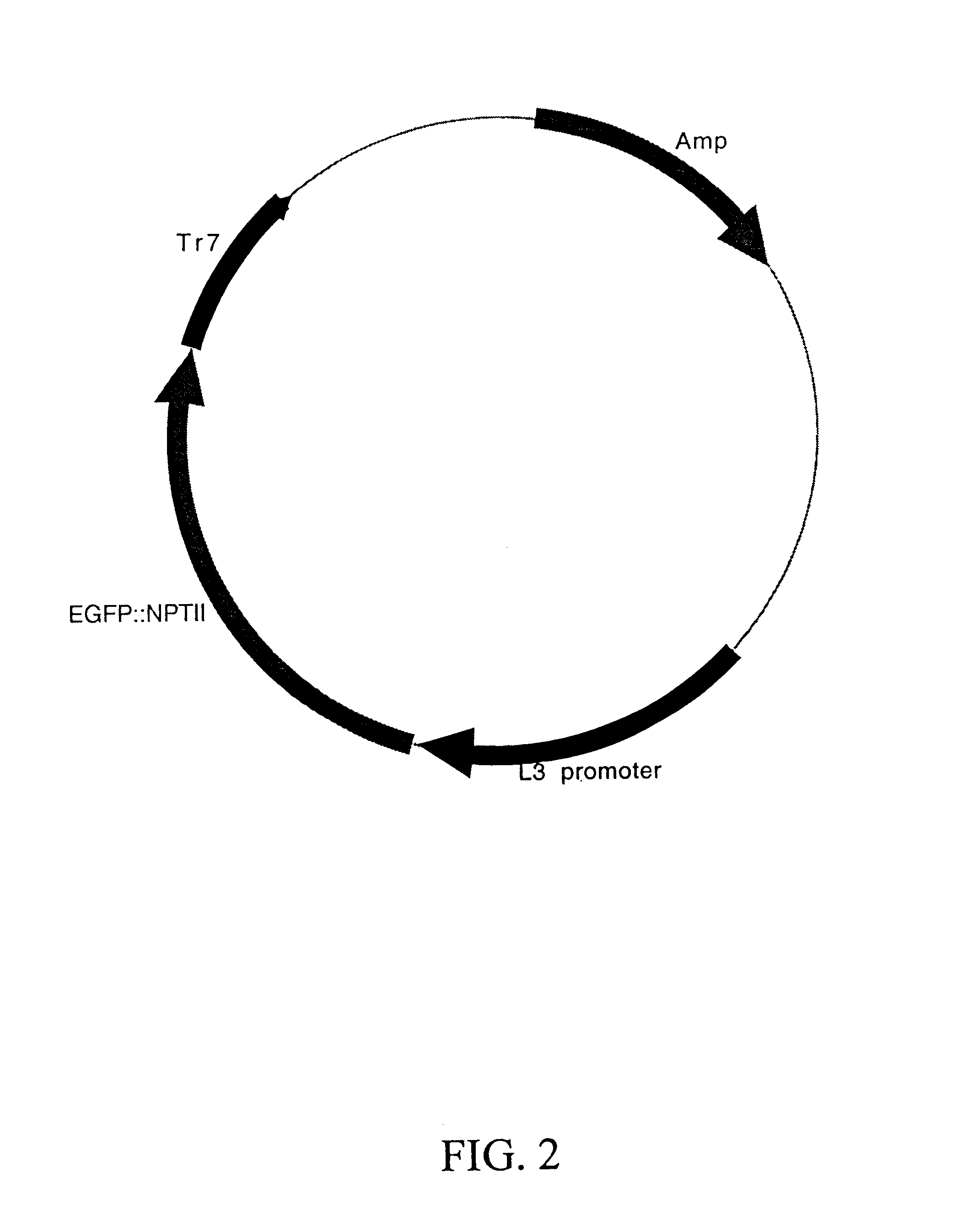
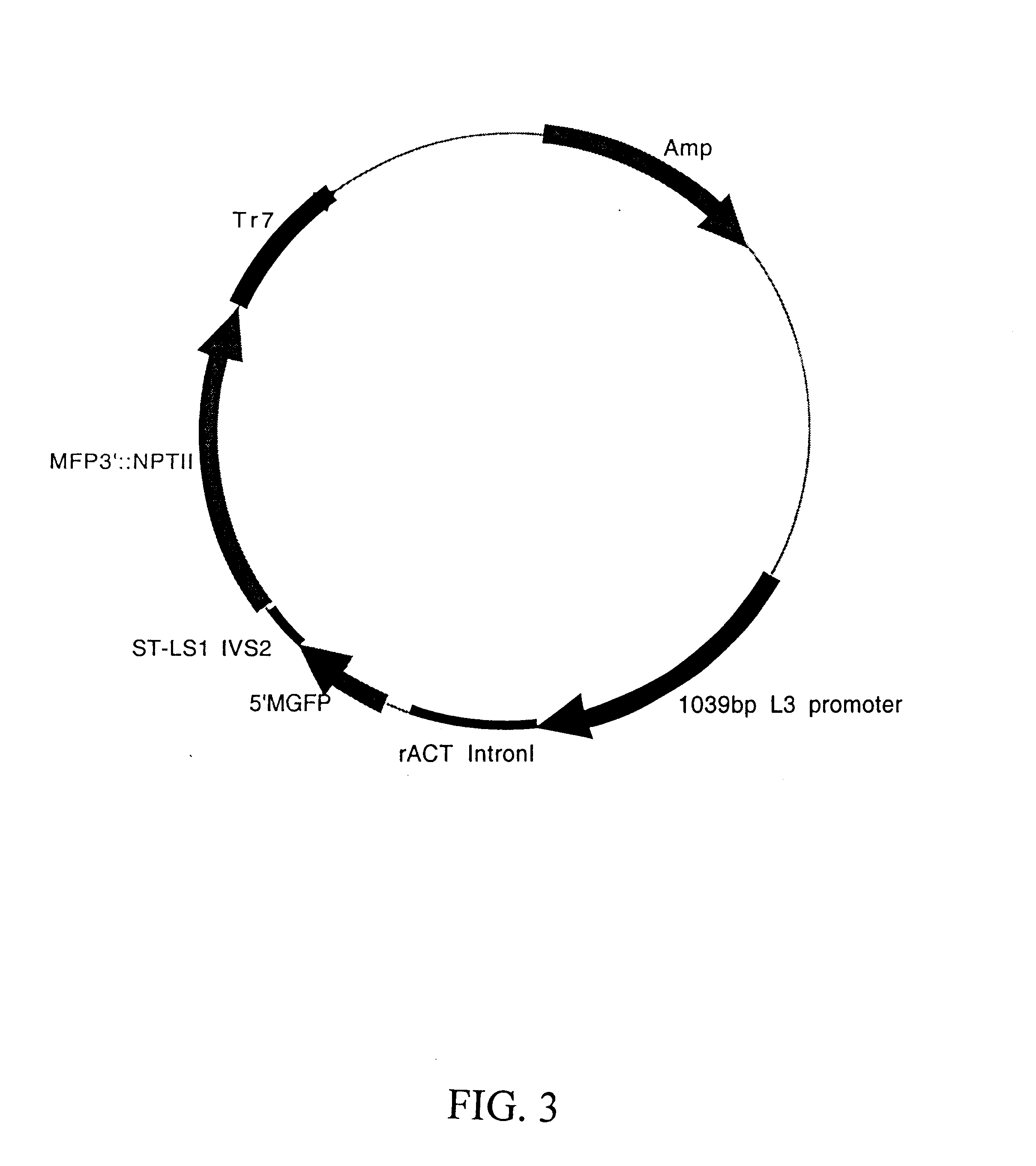
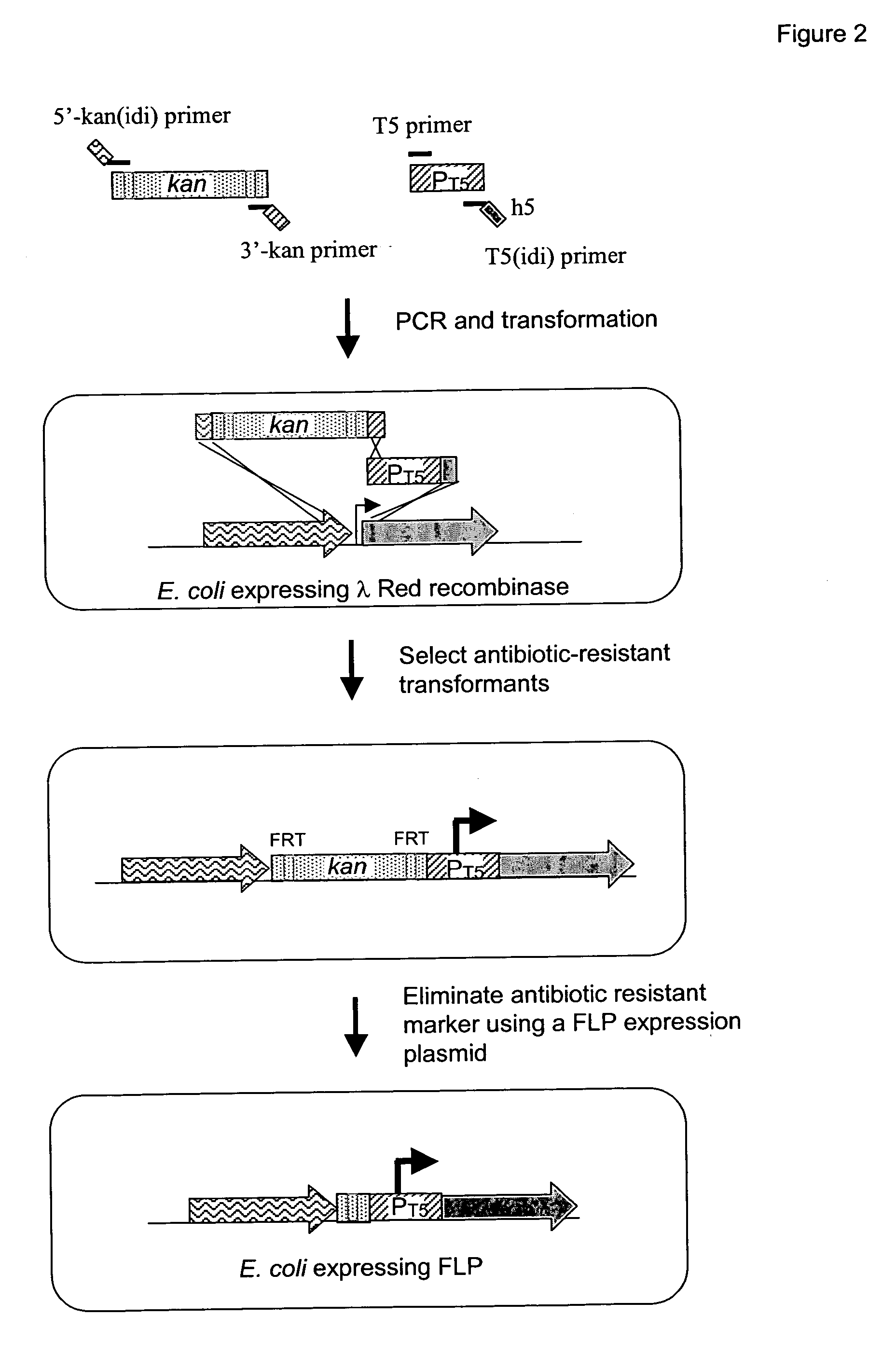
Maize L3 oleosin promoter
InactiveUS6433252B1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesAleuroneEmbryogenesis
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the identification of transgenic seeds. This is accomplished by use of screenable markers linked to aleurone-specific promoters. The screenable markers can be provided as gene fusions with selectable markers, allowing both selection and screening of transformants. The use of aleurone-specific promoters, which also direct expression in embryogenic tissues, allows efficient selection of transgenic cells and the screening of viable transgenic seeds, while avoiding the deleterious effects associated with constitutive expression of screenable marker genes. Screening of transgenic seeds avoids the need for growing and assaying of seeds for transgenes and allows implementation of automated seed screening techniques for the identification of transgenic seeds.
Owner:DEKALB GENETICS CORPORATION +1
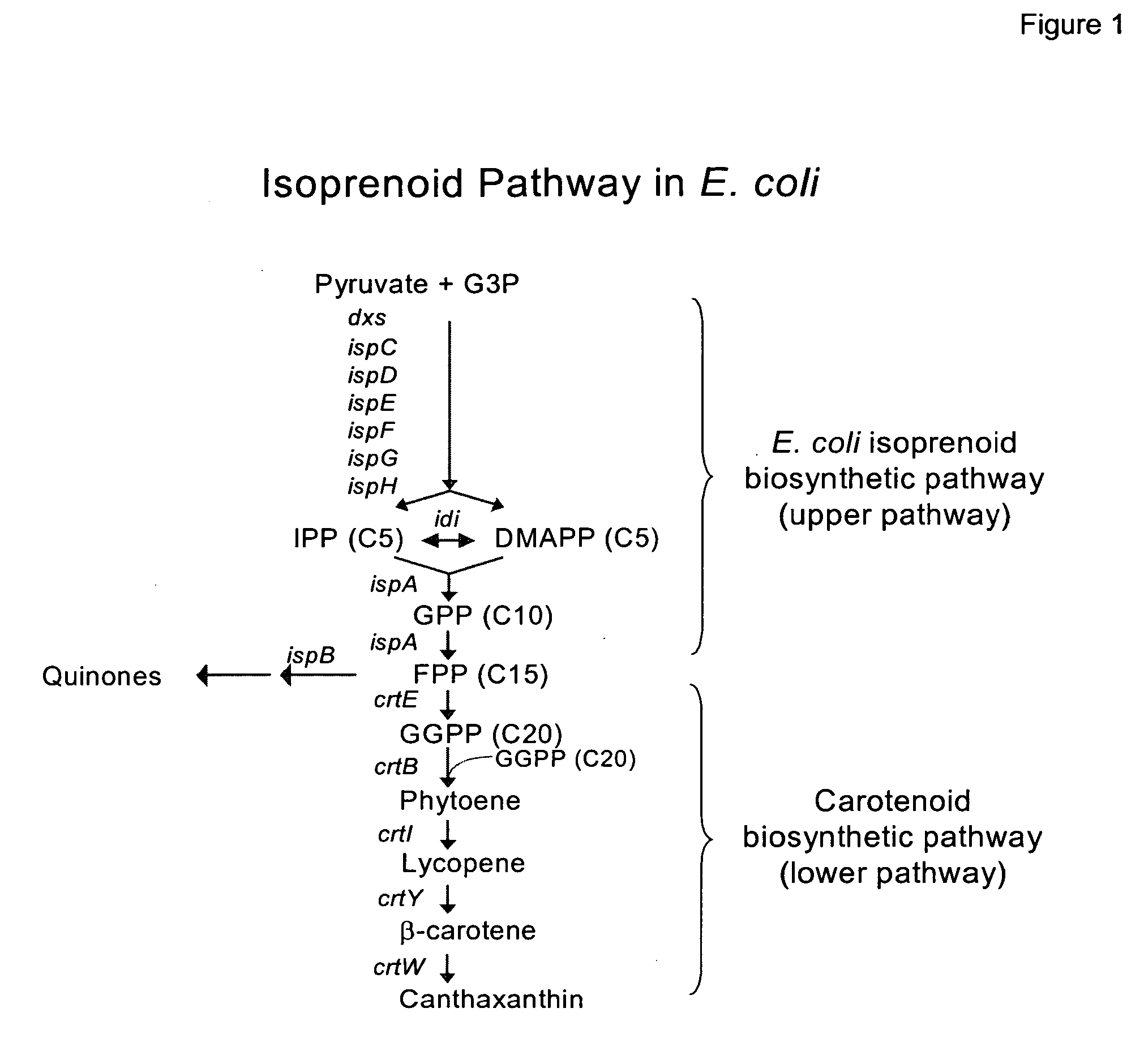
Method to increase hydrophobic compound titer in a recombinant microorganism
InactiveUS20070026484A1Improve compoundImprove the level ofBacteriaUnicellular algaeMicroorganismBiotechnology
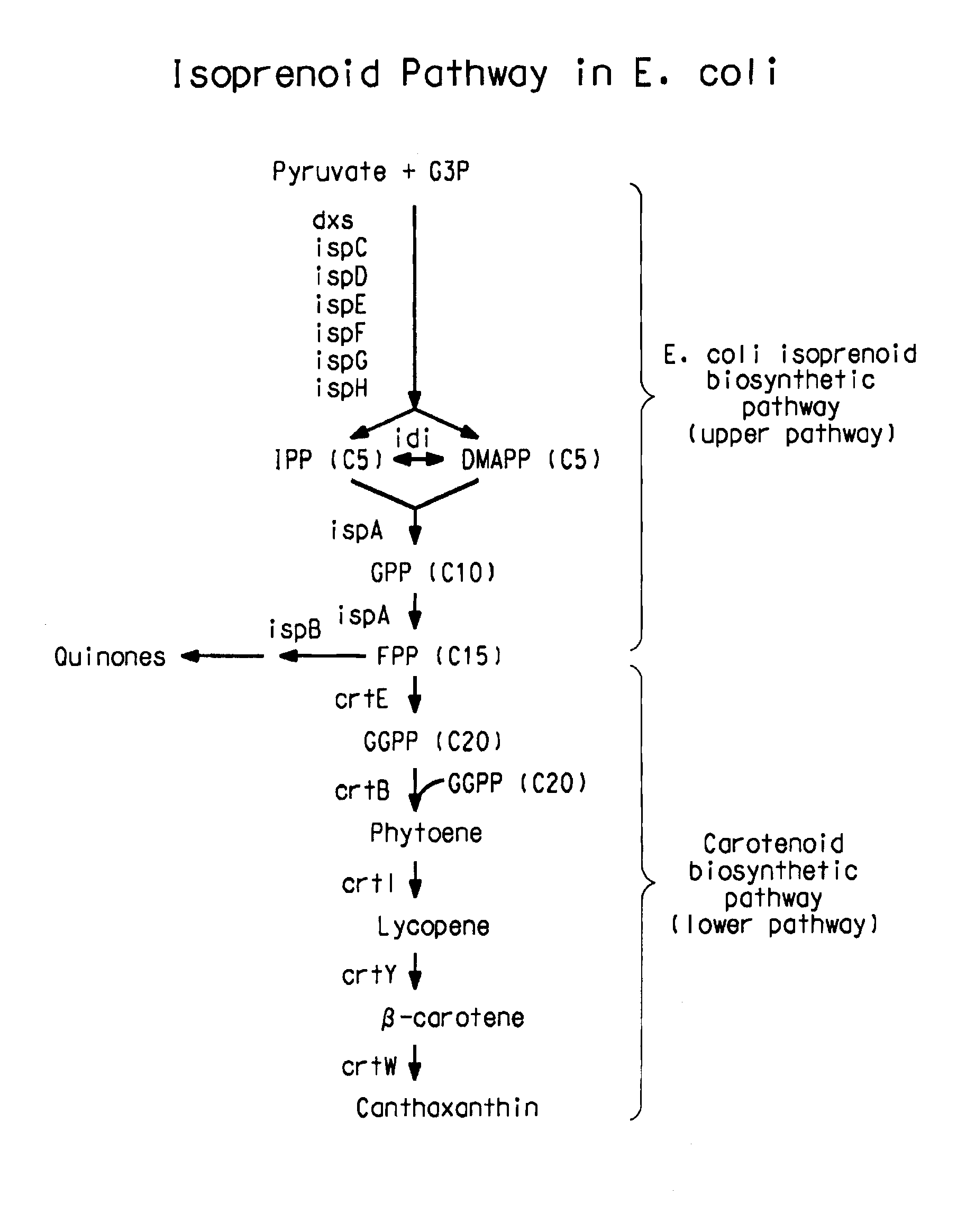
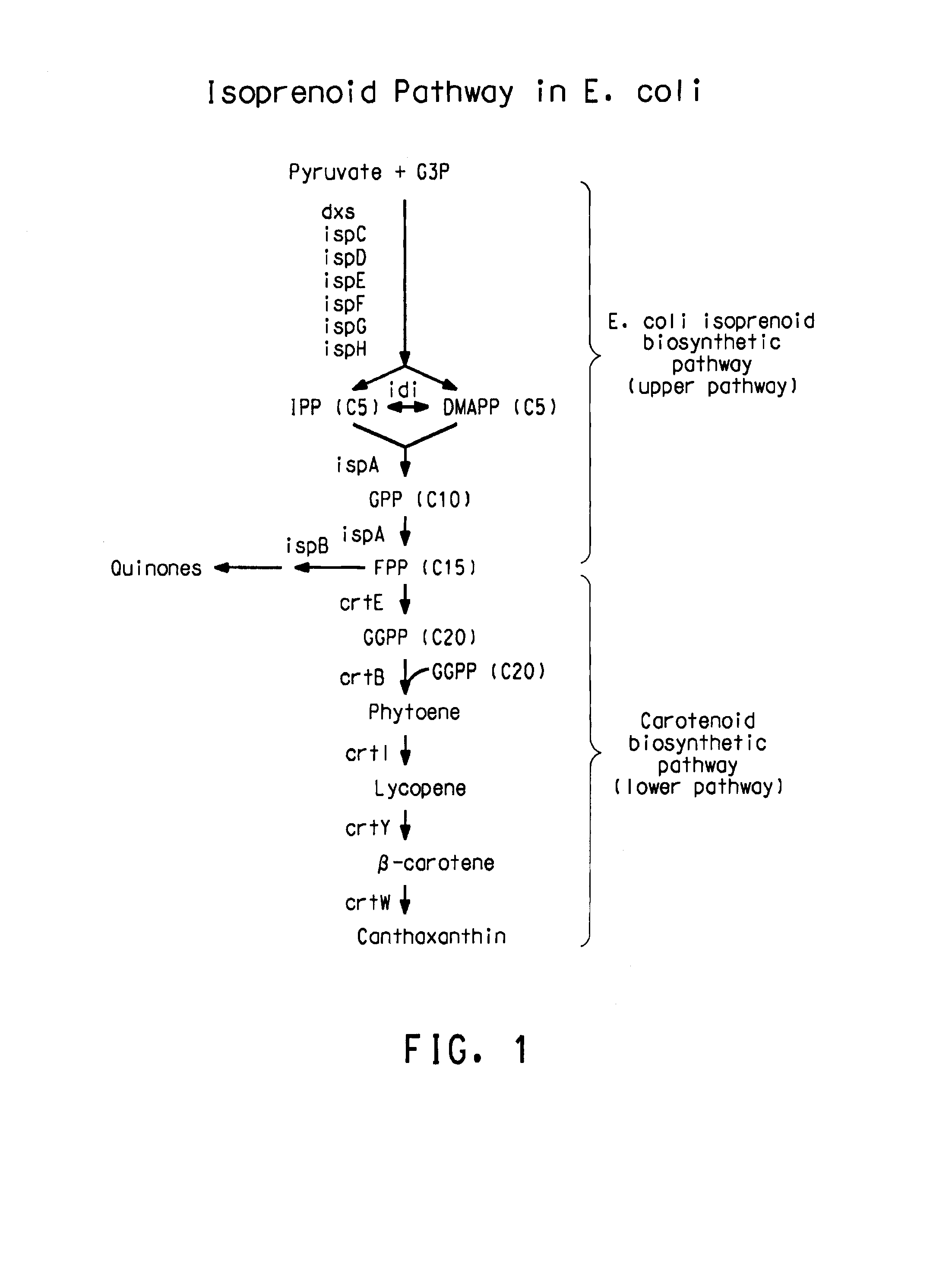
Expression of at least one plant oleosin gene in a microbial cell engineered to produce hydrophobic / lipophilic compounds significantly increases the overall titer of the compound. The hydrophobic nature of the oleosin core is believed to increase the microbial host cell's internal storage capacity for any hydrophobic / lipophilic compound. The method is exemplified using a bacterial host cell engineered to produce significant amount of various carotenoids.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
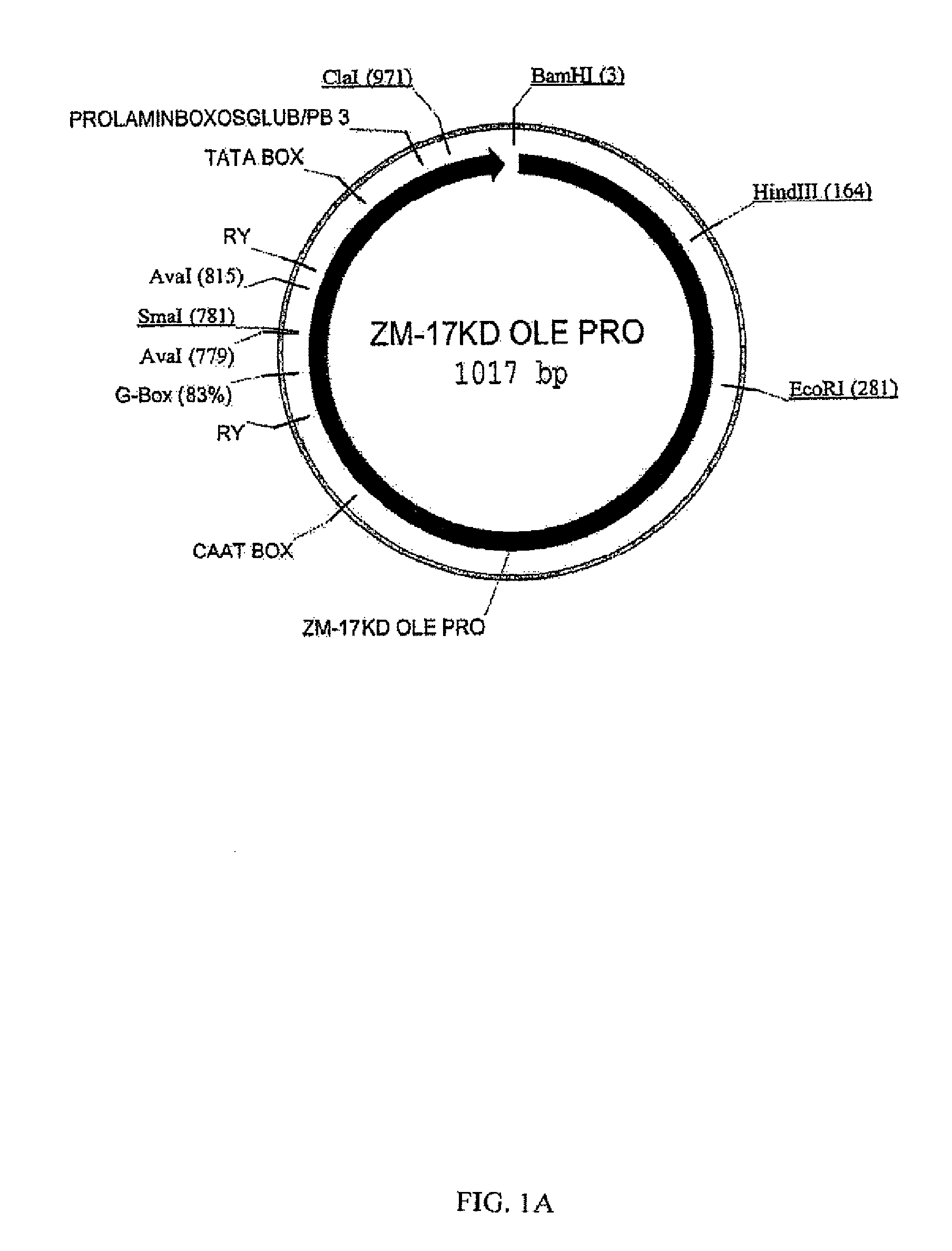
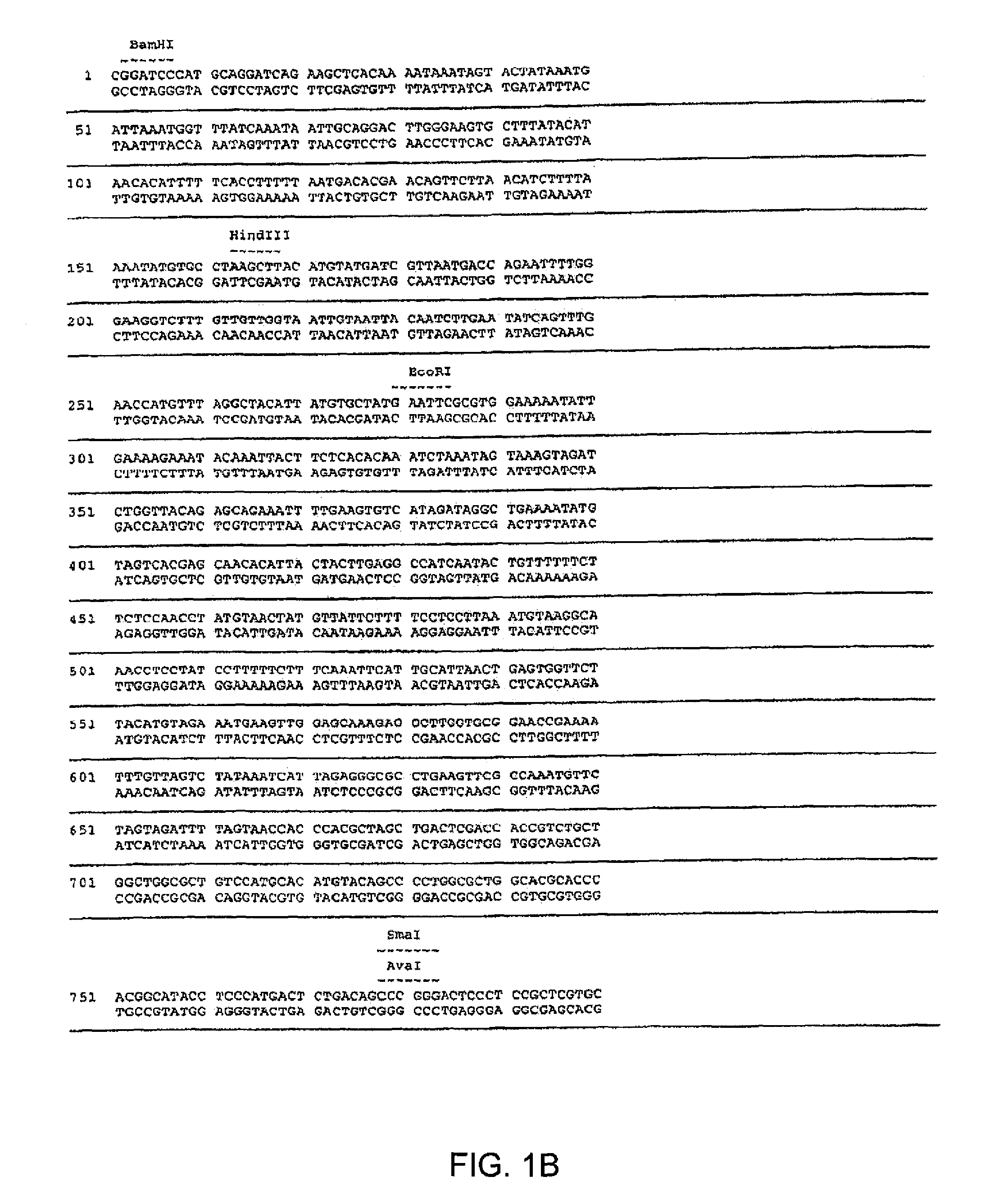
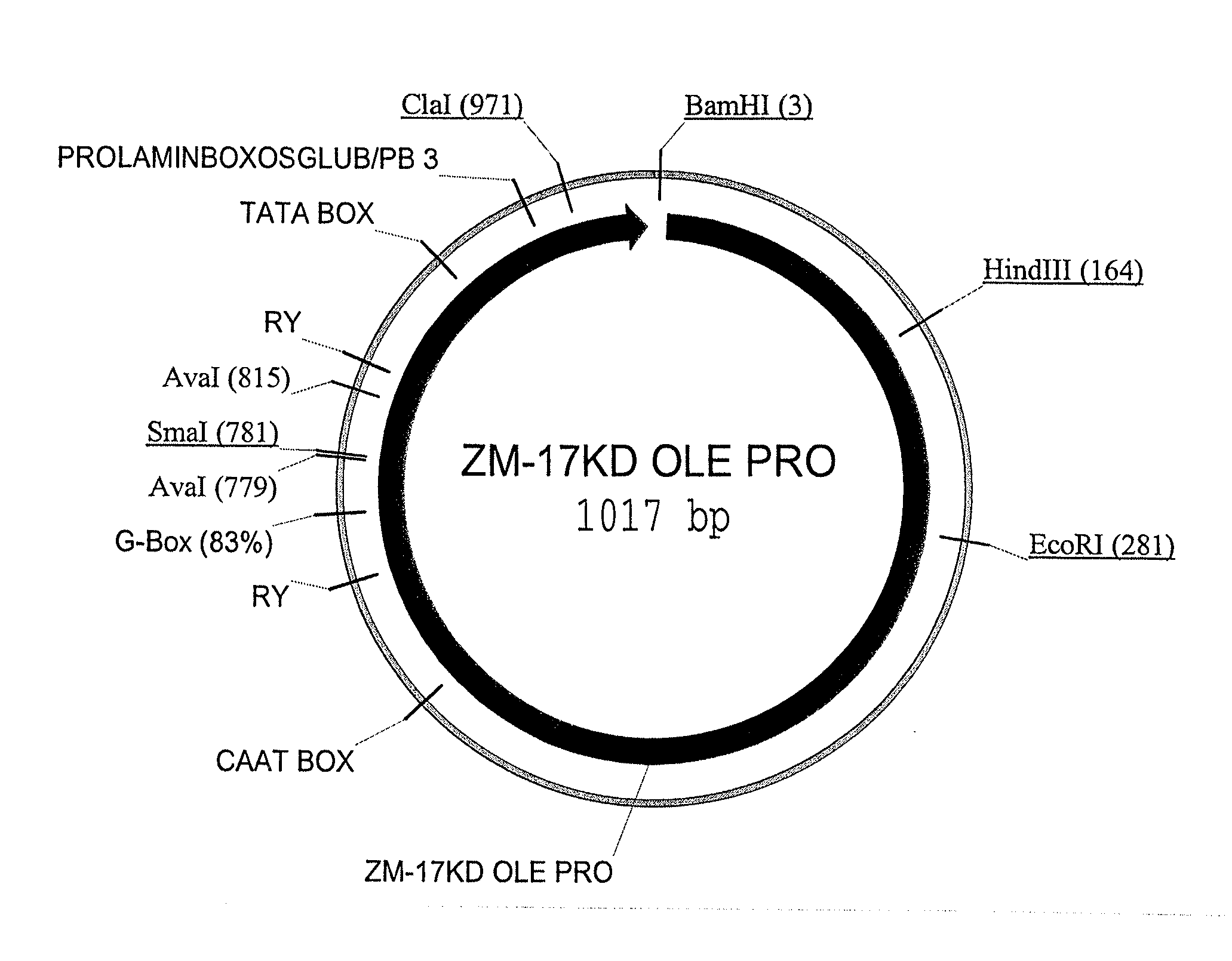
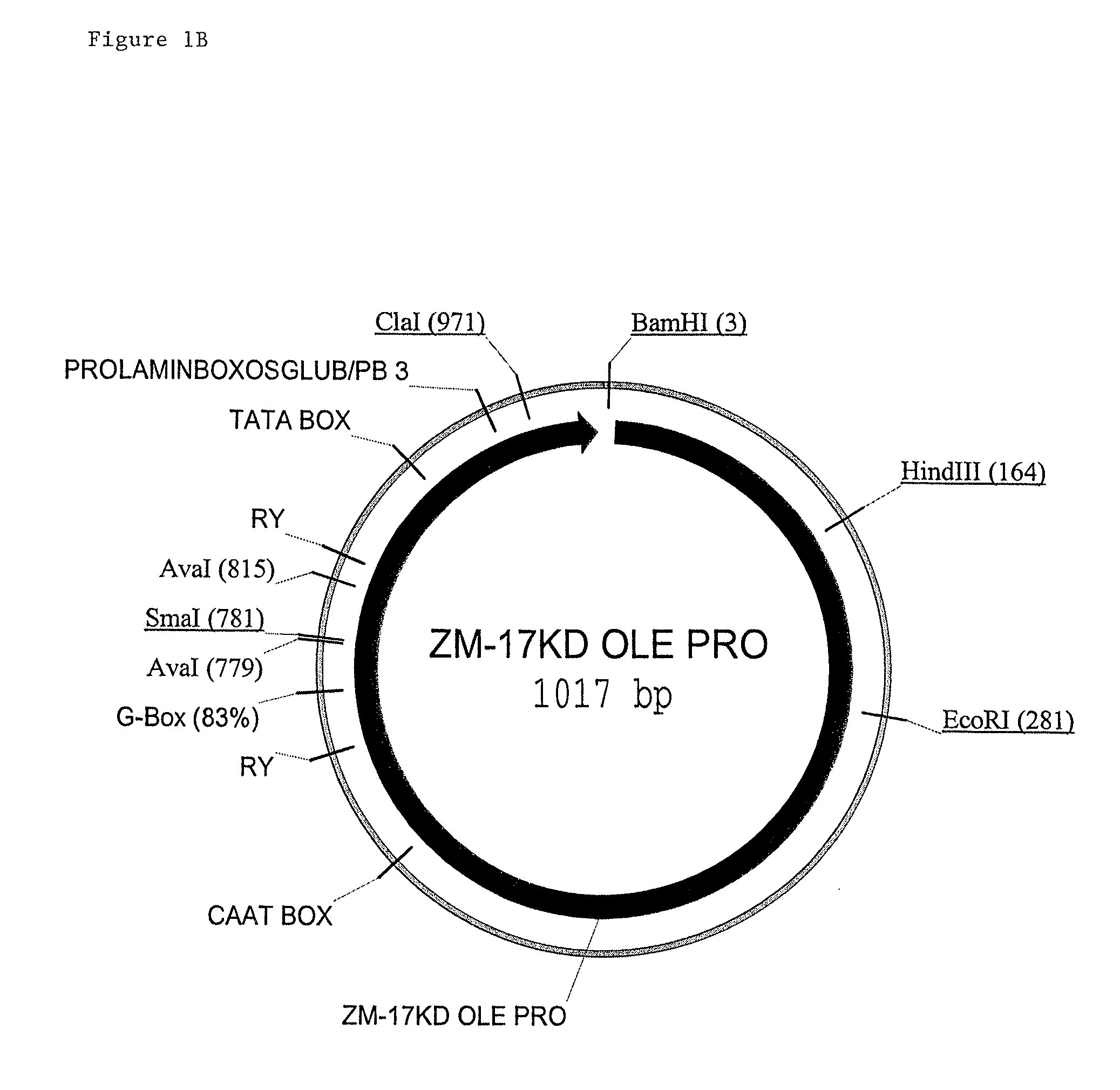
Maize 17KD oleosin seed-preferred regulatory element
The present invention provides compositions and methods for regulating expression of nucleotide sequences of interest in a plant. Compositions are novel nucleotide sequences for a seed-preferred promoter associated with the maize 17 KD OLE (17 kilodalton oleosin) coding region. A method for expressing a nucleotide sequence of interest in a plant using the regulatory sequence disclosed herein is provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Maize 17kd oleosin seed-preferred regulatory element
The present invention provides compositions and methods for regulating expression of nucleotide sequences of interest in a plant. Compositions are novel nucleotide sequences for a seed-preferred promoter associated with the maize 17 KD OLE (17 kilodalton oleosin) coding region. A method for expressing a nucleotide sequence of interest in a plant using the regulatory sequence disclosed herein is provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
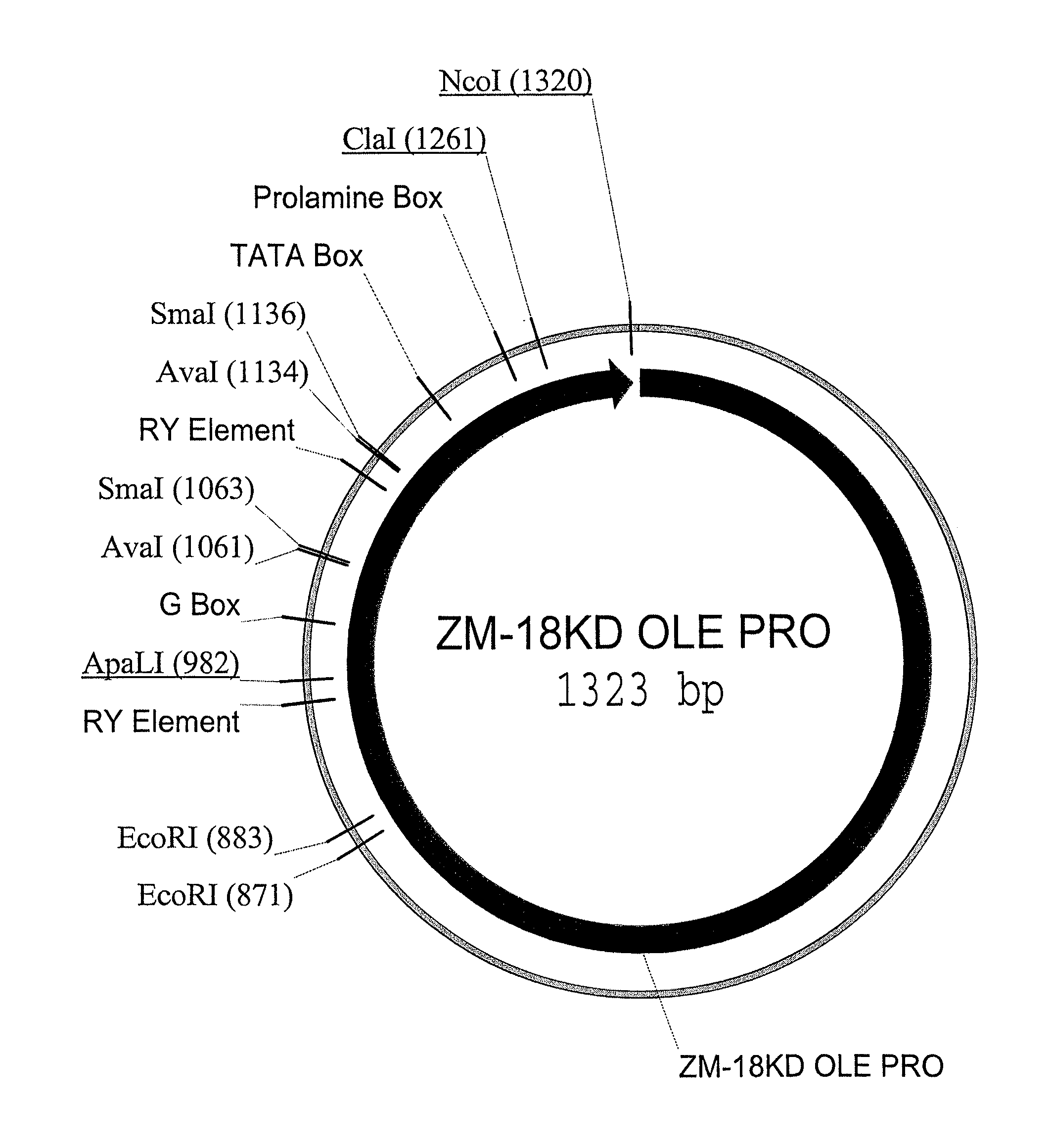
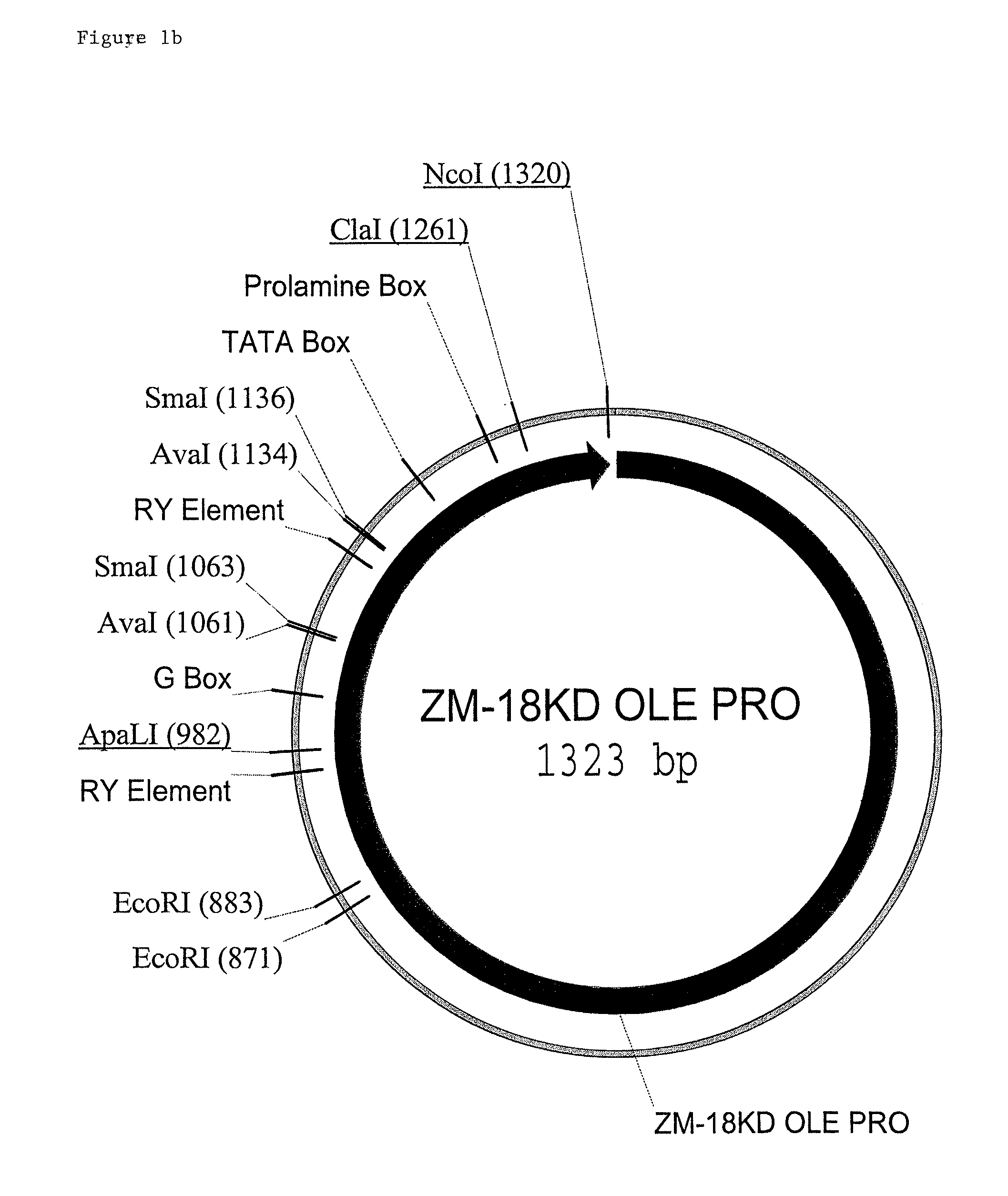
Maize 18kd oleosin seed-preferred regulatory element
InactiveUS20100281570A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesKilodaltonGenetics
The present invention provides compositions and methods for regulating expression of nucleotide sequences of interest in a plant. Compositions are novel nucleotide sequences for a seed-preferred promoter associated with the maize 18 KD OLE (18 kilodalton oleosin) coding region. A method for expressing a nucleotide sequence of interest in a plant using the regulatory sequence disclosed herein is provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Modified oil encapsulating proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120278951A1High oil contentEfficient storageAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulinsBiofuel feedstockIn vivo
The invention provides modified oleosins, including at least one artificially introduced cysteine, and methods and compositions for producing the modified oleosins. Also provided are polynucleotides encoding the modified oleosins, constructs and host cells comprising the polynucleotides, methods for producing oil bodies comprising the modified oleosins, in vivo and in vitro, and methods for producing oil in host cells and plants. The invention also provides methods for increasing the rate of CO2 assimilation in photosynthetic cells and plants, and involves reducing or preventing lipid recycling, and / or expressing modified oleosins with artificially introduced cysteine residues in the photosynthetic cells and plants. Also provided are methods for increasing oil production in plants, via expression of modified oleosins in the non-photosynthetic tissues / organs of plants. The method also optionally includes the step of extrating the oil from the non-photosynthetic tissues / organs of the plant, or processing the oil rich non-photosynthetic tissues / organs into animal or biofuel feedstocks.
Owner:AGRESEARCH LTD
Artificial oil bodies
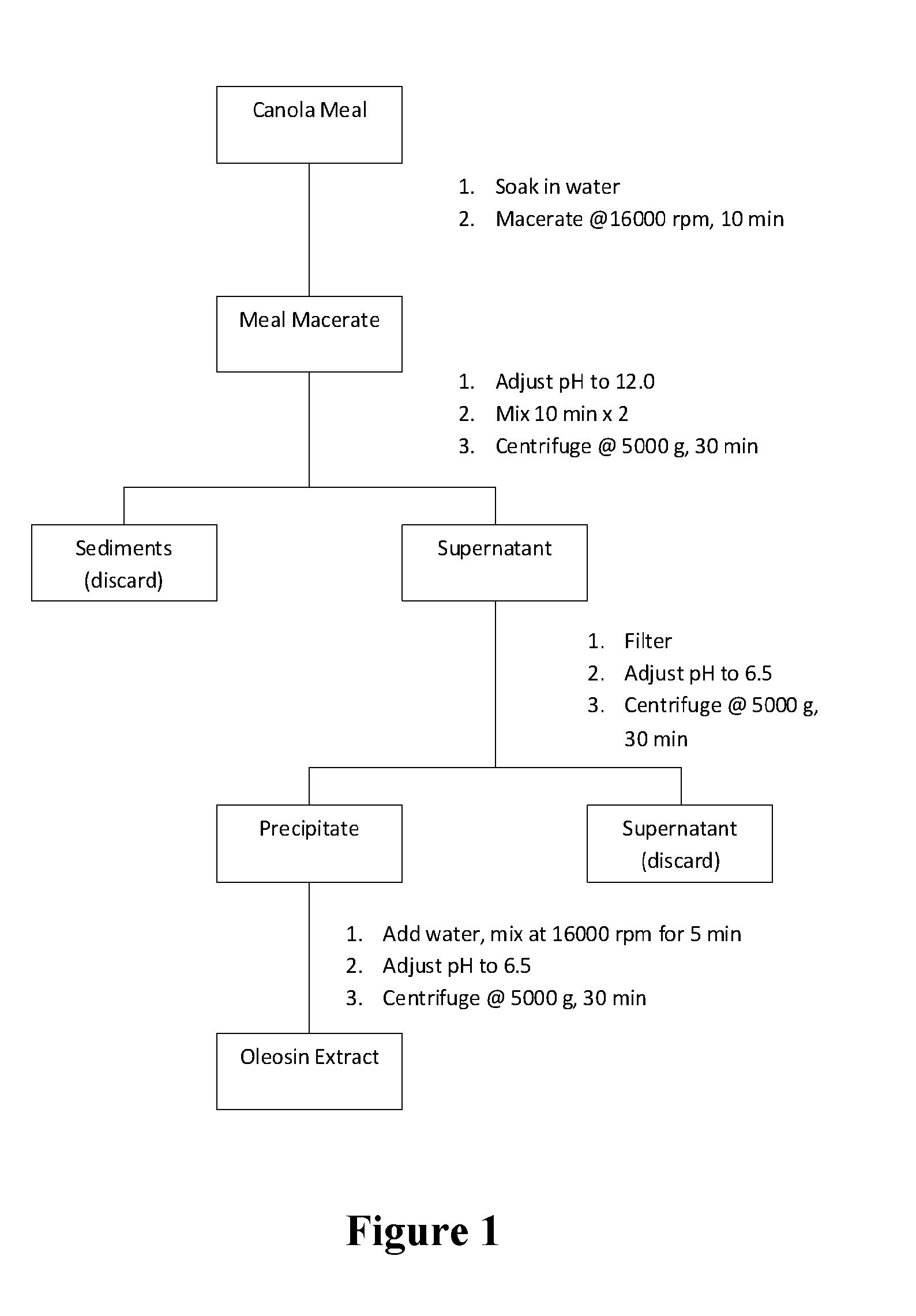
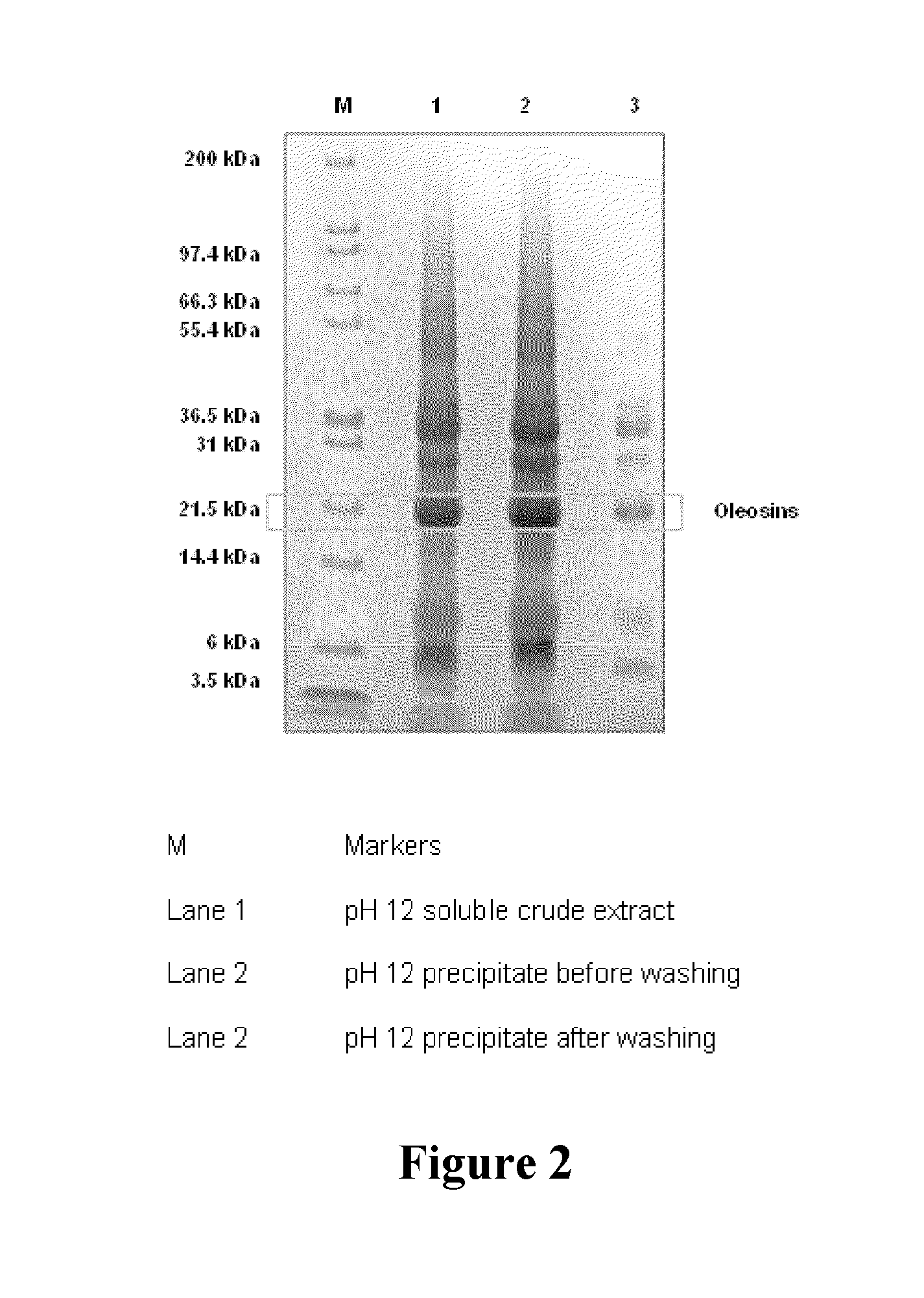
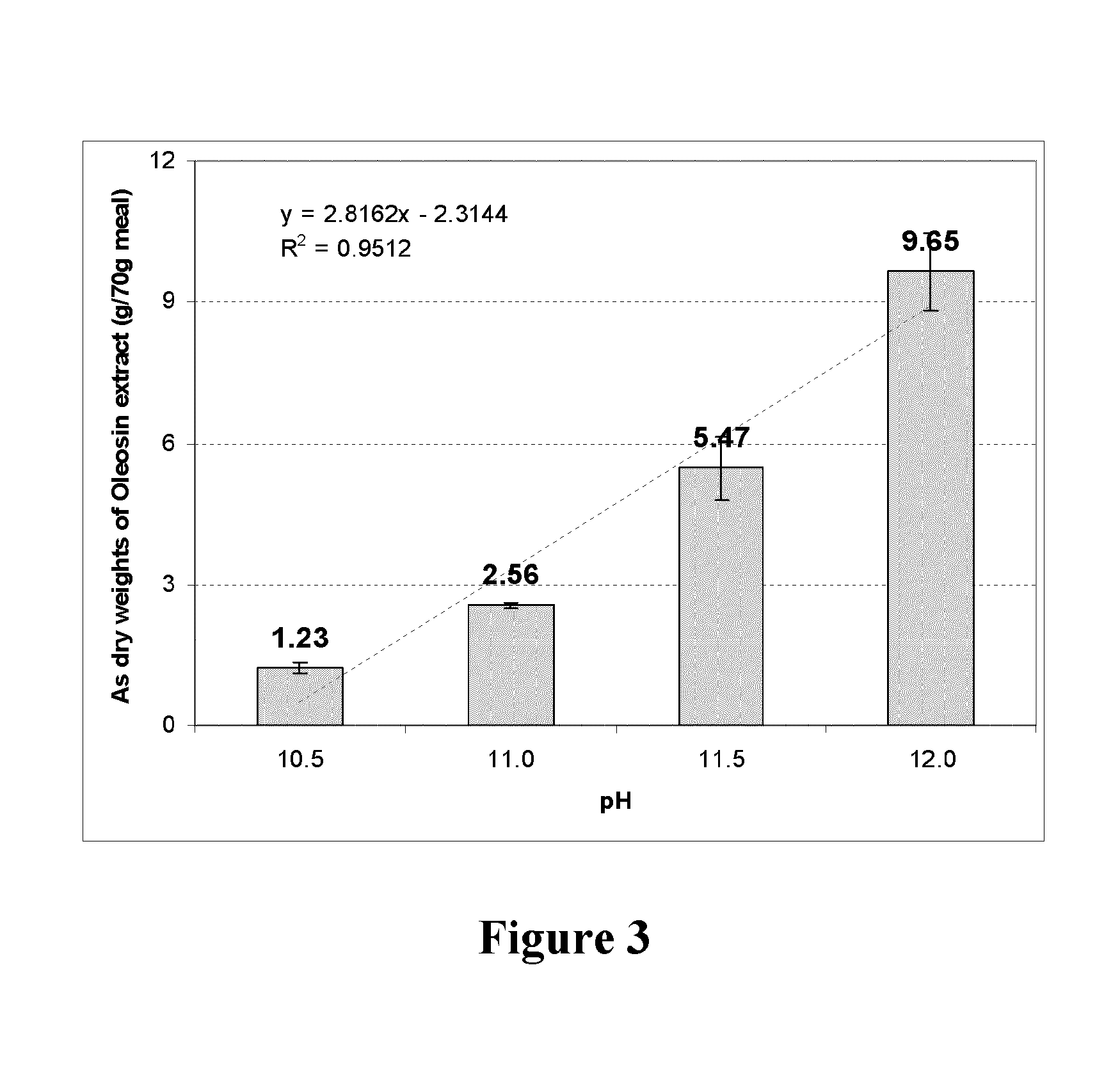
The present invention relates to artificial oil bodies comprising oleosin (which, as presently defined, also encompasses caleosin, steroleosin and polyoleosin), a surfactant such as a phospholipid, and an oil comprising fatty acids, such as polyunsaturated fatty acids having four or more double bonds. The present invention also relates to methods of preparing said artificial oil bodies. These AOBs may further comprise other molecules such as bioactive molecules, used in a wide variety of products, and are particularly useful for producing oxidatively stable oil-in-water emulsions in the absence of added antioxidants. The present invention further encompasses a method for the partial purification of oleosin from a plant extract.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Method to increase hydrophobic compound titer in a recombinant microorganism
InactiveUS7256014B2Improve compoundIncrease the available hydrophobic/lipophilic storage capacityBacteriaUnicellular algaeMicroorganismBiotechnology
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Plant expression carrier and method for cultivating low-phytic-acid rice
ActiveCN102864167AComposite effectsEffects on Phytic Acid SynthesisVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsRice plantsNucleotide
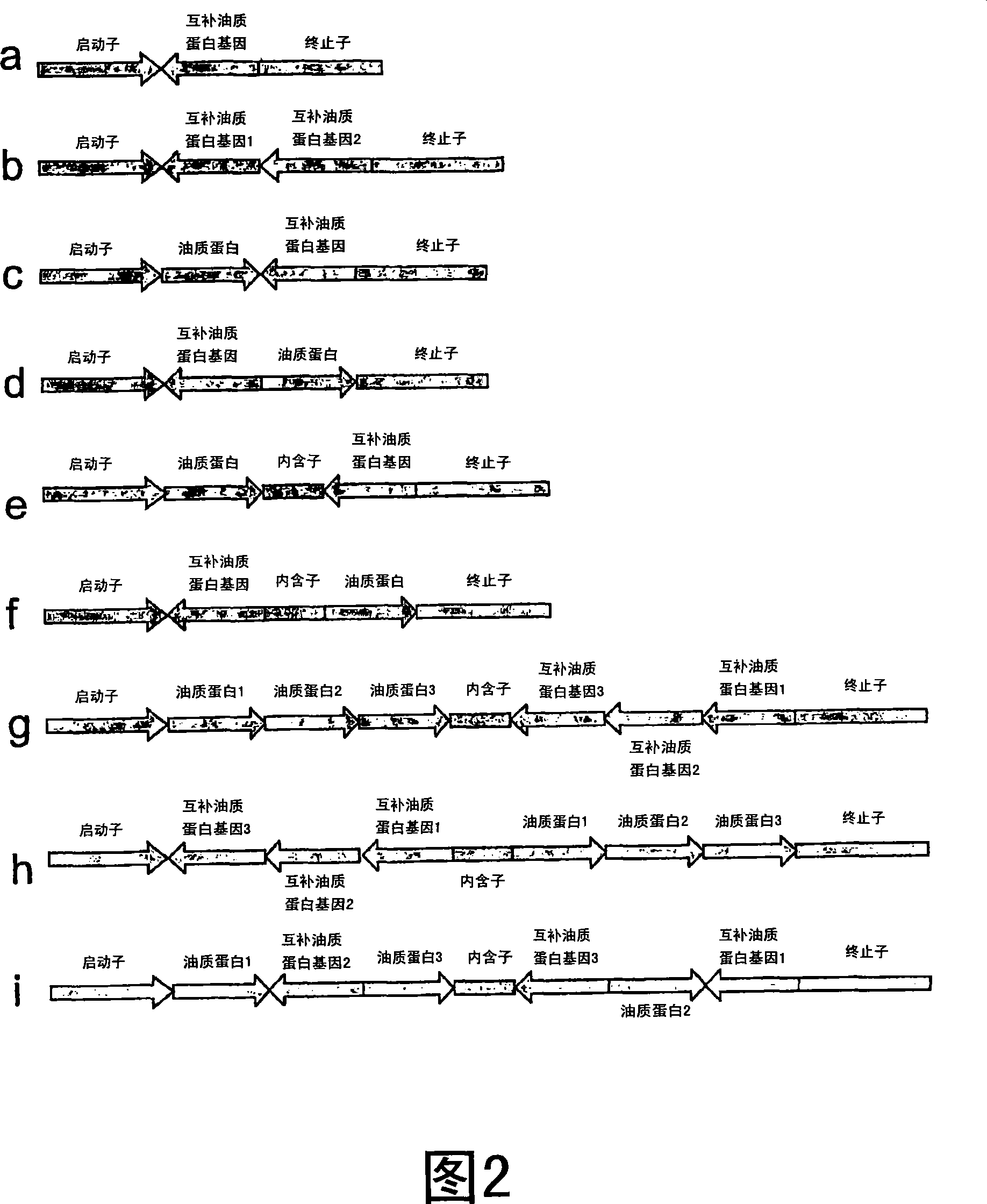
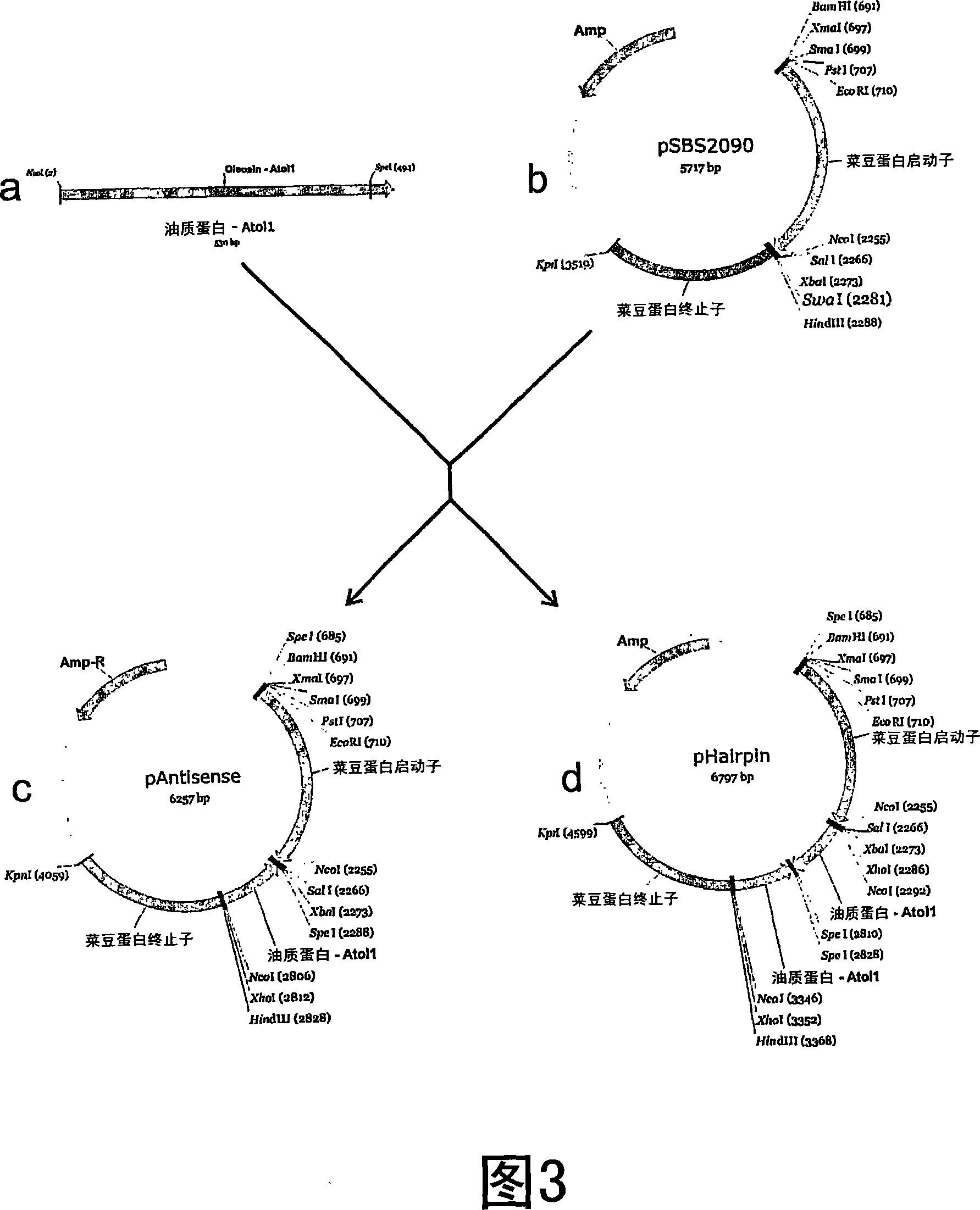
The invention discloses a plant expression carrier and a method for cultivating low-phytic-acid rice. The plant expression carrier comprises a hairpin structure unit inoculated into an original carrier and a specific promoter, wherein the specific promoter is a promoter Oleosin 18, and the nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing the plant expression carrier; (2) performing Agrobacterium-mediated transformation on the plant expression carrier to obtain a rice callus tissue; and (3) transferring the rice callus tissue onto a selective culture medium for further culture, transplanting onto a crop-growing field after seedling differentiation, and screening to obtain the low-phytic-acid rice plant. According to the invention, the seed specific promoter Oleosin 18 is used to control gene expression, so that gene silencing only occurs in seed embryos and aleurone layers, thereby effectively preventing the synthesis of phytic acid in other tissue positions of rice from being influenced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods for the modulation of oleosin expression in plants
InactiveCN101080492AEasy to explainFatty-oils/fats productionFermentationLipid formationBiotechnology
Methods for modulating oleosin expression levels in plants are provided. In particular, it relates to methods for preparing seed-derived products from seeds in which the nutrient stores of the seeds, particularly the content of seed lipids and proteins, have been altered. In particular, the present invention provides methods for the preparation of seed-derived products from seeds wherein the nutrients stored in the seeds are altered by modulating, more particularly inhibiting, oleosin gene expression.
Owner:SEMBIOSYS GENETICS INC +1
Oleosin genes and promoters from coffee
InactiveUS7910718B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyAroma aroma
Owner:NESTEC SA +1
Construction and transform expression method of human alkaline fibroblast growth factor plant expression vector
ActiveCN101323859AEasy to purifyImprove purification yieldFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyPlanting seed
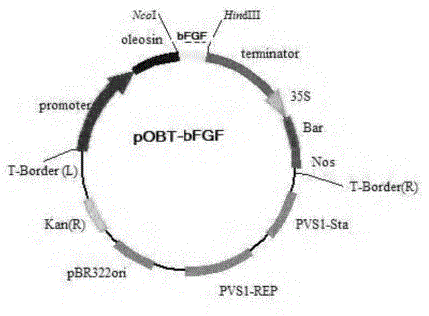
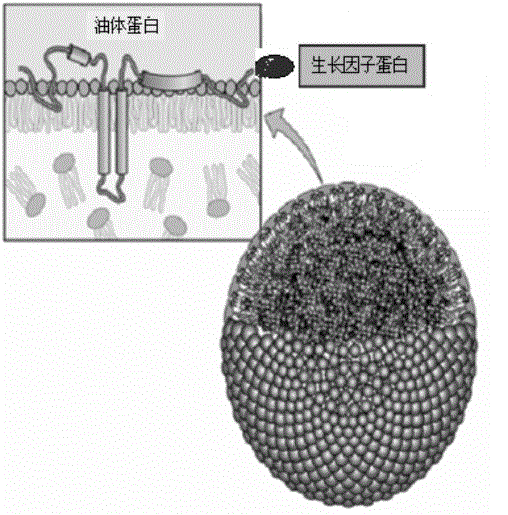
The invention provides an expression vector used for expressing human basic fibroblast growth factors (hbFGF for short). The method adopts a method of gene recombination in vitro, namely, by the fusion of the hbFGF gene and oleosin gene, to construct a plant oleosin expression vector. Arabidopsis thaliana and safflower are transformed by Agrobacterium tume faciens to obtain transgenic plants. Molecular biology proves the integration and expression of a foreign gene. By virtue of activity detection, the obtained recombinant protein has biological activities which are equal to that of a standard plasmid of the hbFGF. The invention also provides a method for expressing the growth factor of a basic fibroblast in a plant seed, which can economically produce the growth factor of the basic fibroblast, thus providing a new way for the drug development of the bFGF.
Owner:吉林农大生物反应器工程有限公司 +1
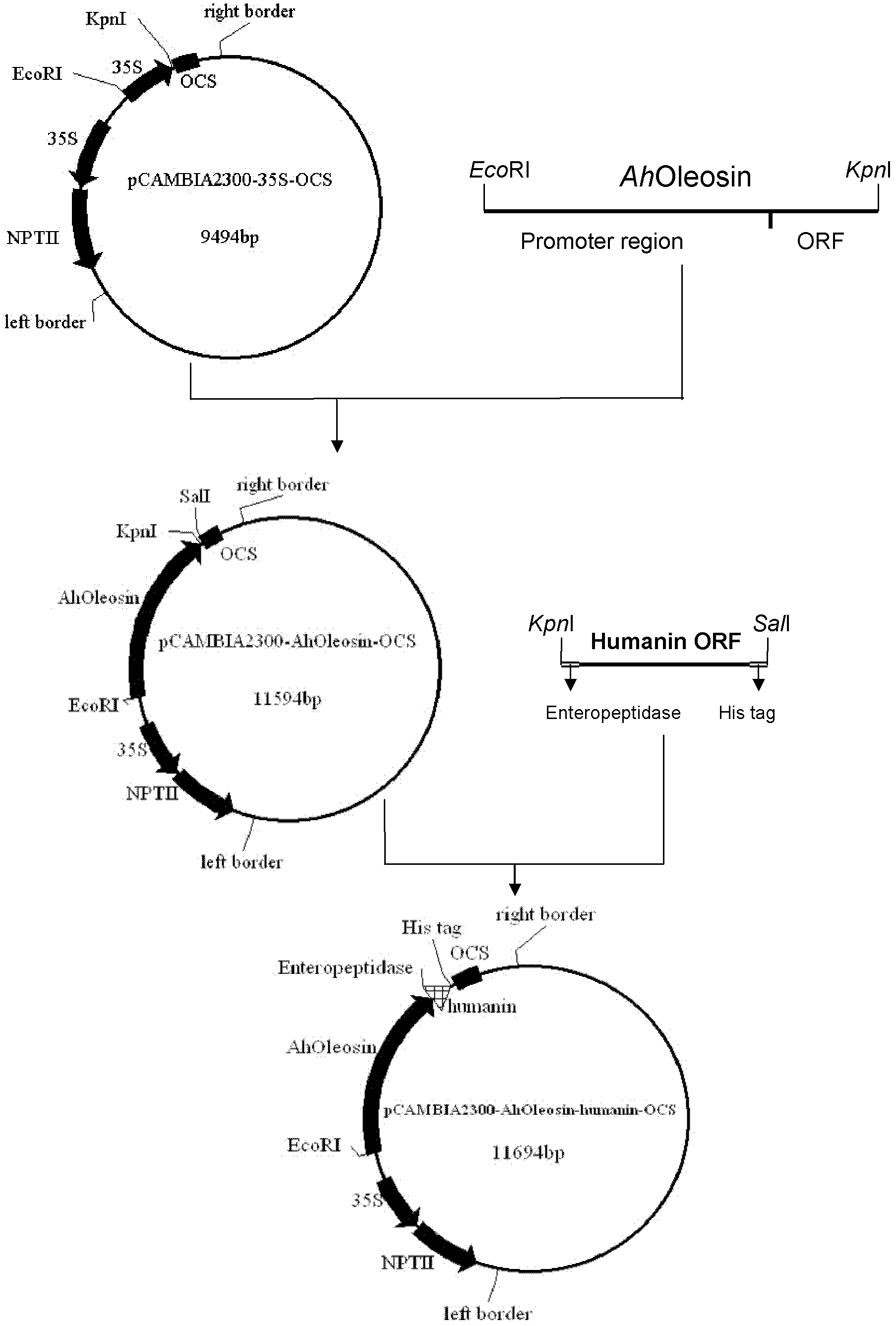
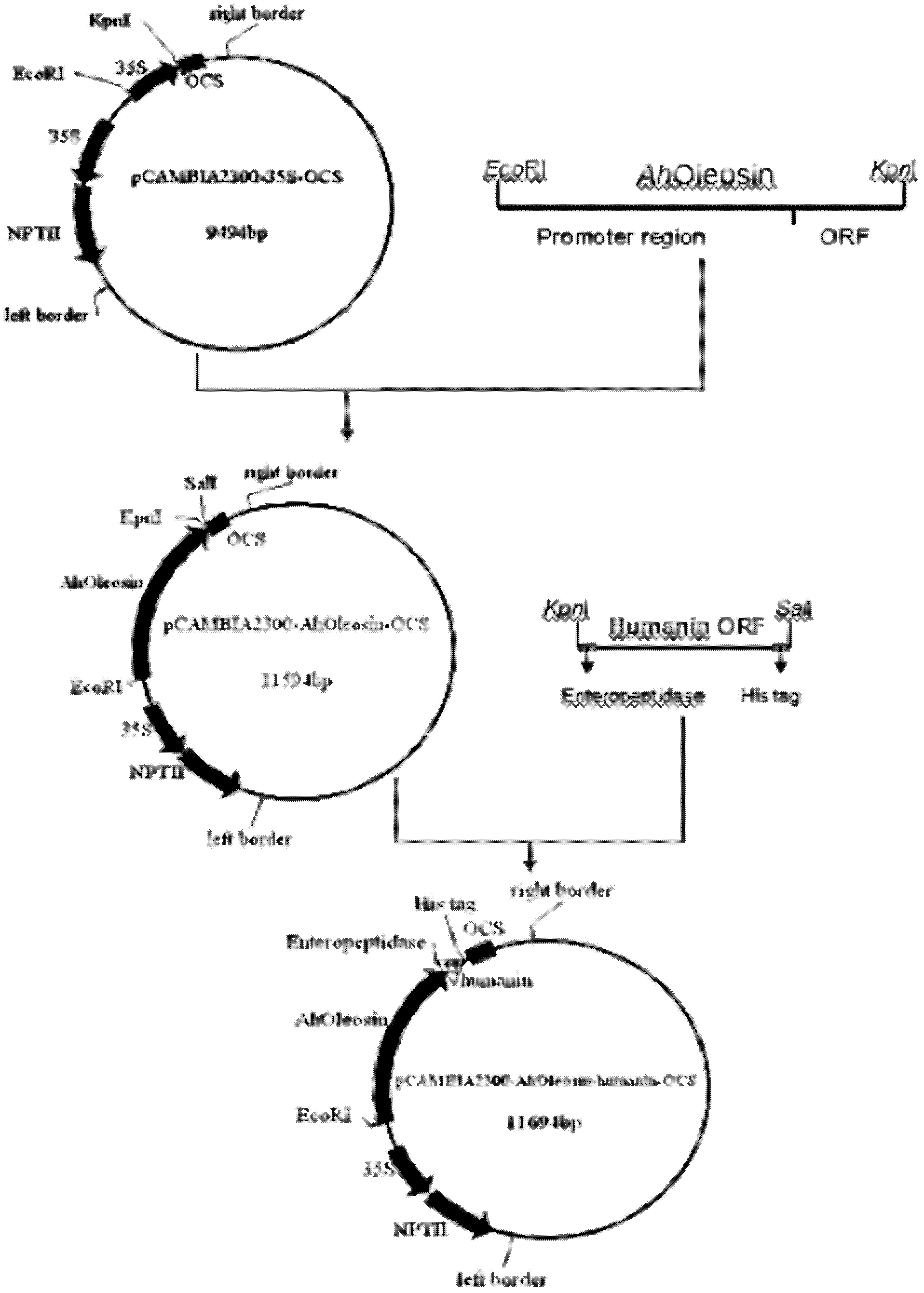
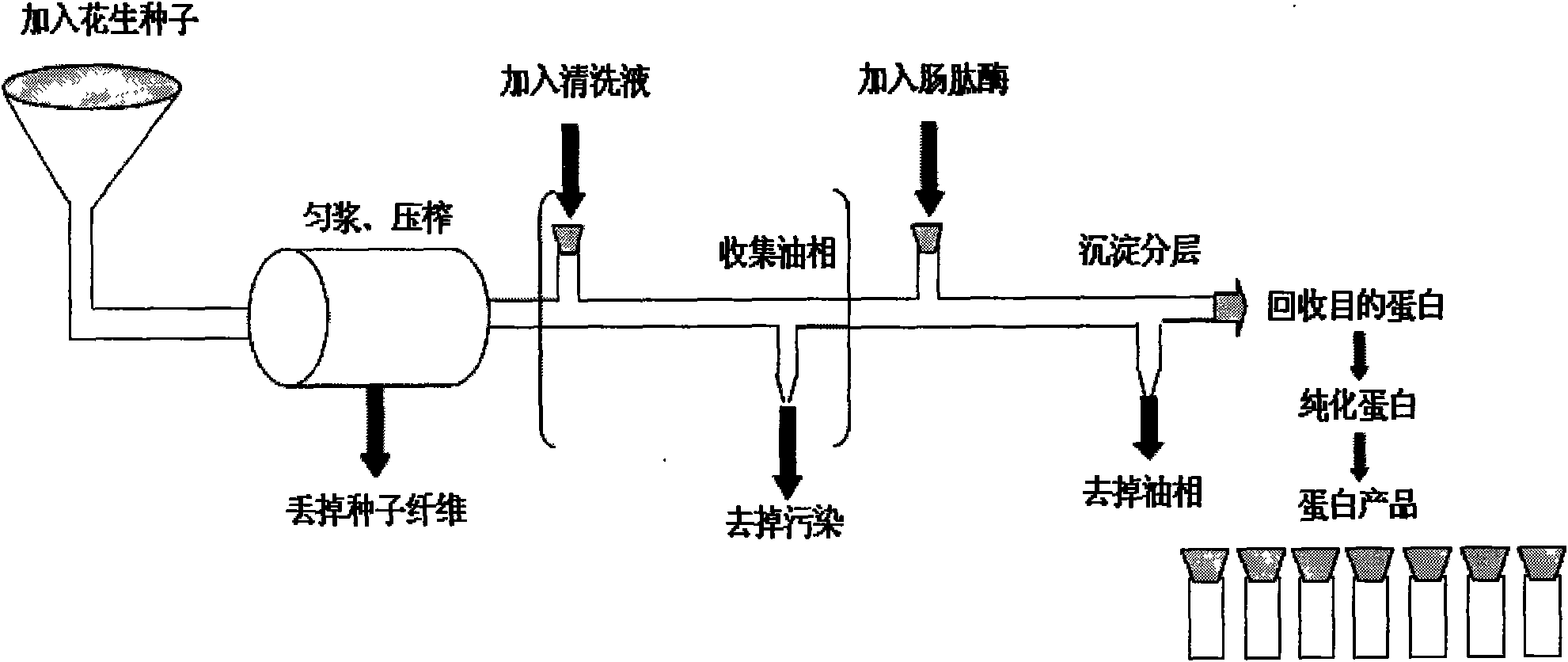
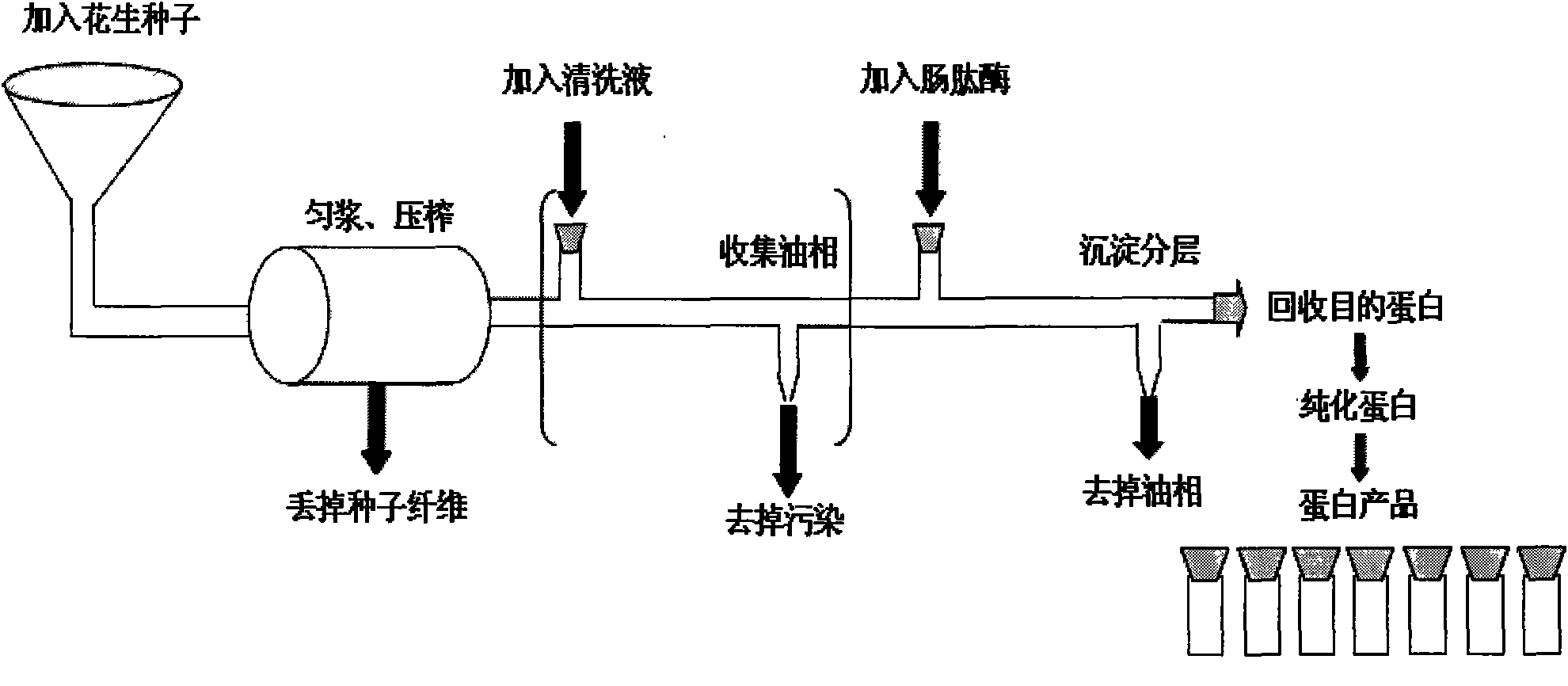
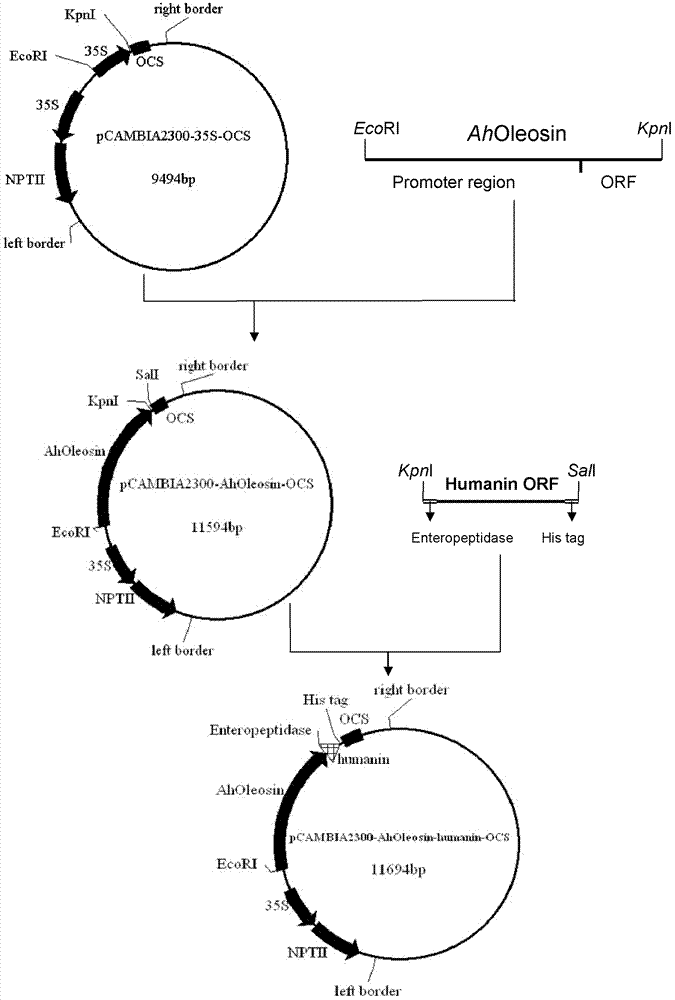
Method for expressing human humanin protein in peanut seed
InactiveCN102321665AHigh oil contentRich in OleosinFermentationGenetic engineeringHumaninEnteropeptidase
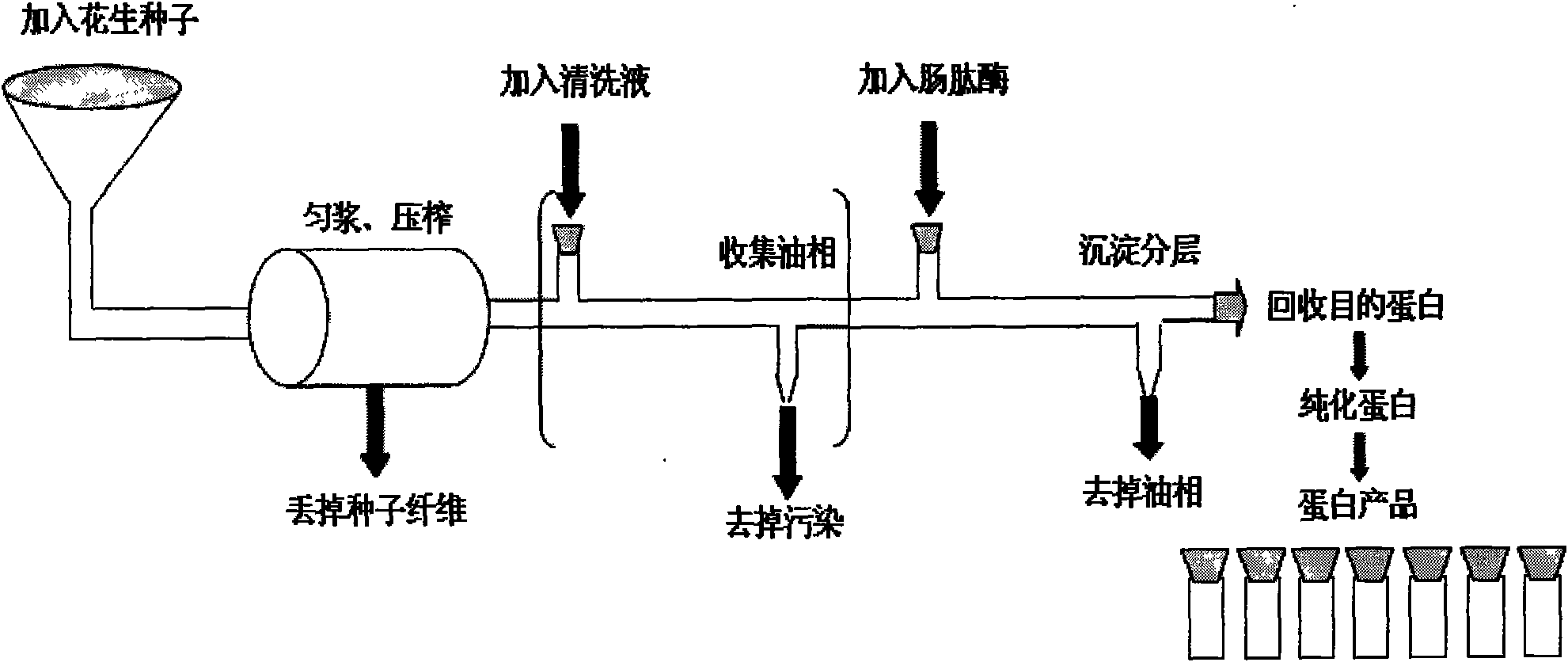
The invention discloses a method for expressing human humanin protein in peanut seeds, which comprises the following steps: connecting humanin protein coding gene to a 3' end of an oleosin gene by a genetic engineering means, establishing an 'oleosin-erepsin-human humanin protein' plant expression vector driven by an oleosin promoter, transforming peanuts to realize high-level expression of recombinant protein in peanut seeds with the accumulation of oil body, then performing centrifugation of fusion protein, digesting the fusion protein by exo-protease, performing centrifugation, removing the oil phase and recovering water phase, performing purification to obtain human humanin protein. The recombinant protein obtained by the method of the invention is safe, has high activity, is very easy to be recovered and purified, can be stored in peanut seeds for a long term, is convenient for transportation, and greatly increases the crop added value.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
Method for improving the carcass quality of an animal
InactiveUS7008664B1Improve carcass qualityFatty acid hydrogenationFatty acid esterificationBiotechnologyACP desaturase
A method for improving the carcass quality of an animal is described. This method invovles the preparation and use of nucleic acid fragments comprising all or substantially all of a corn oleosin promoter, a stearoyl-ACP desaturase and a delta-12 desaturase which can be used individually or in combination to modify the lipid profile of corn are described. Chimeric genes incorporating such nucleic acid fragments and suitable regulatory sequences can be used to create transgenic corn plants having altered lipid profiles are also described.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
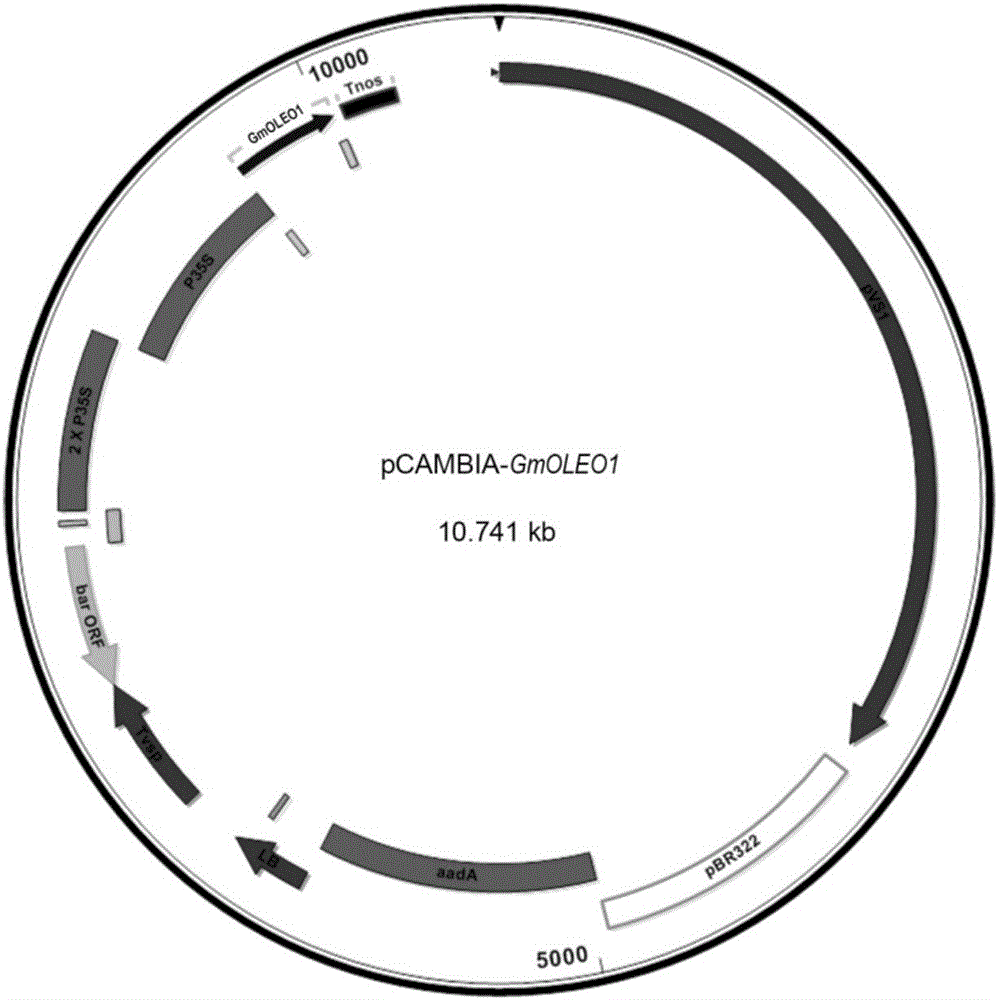
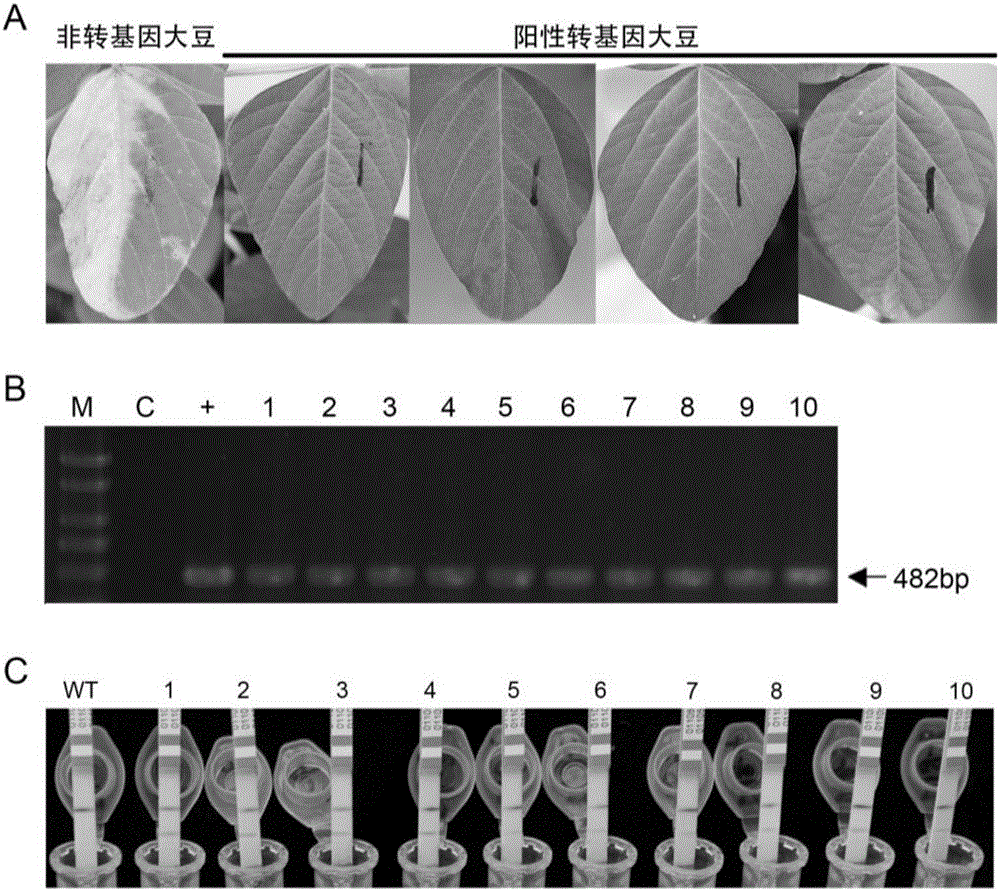
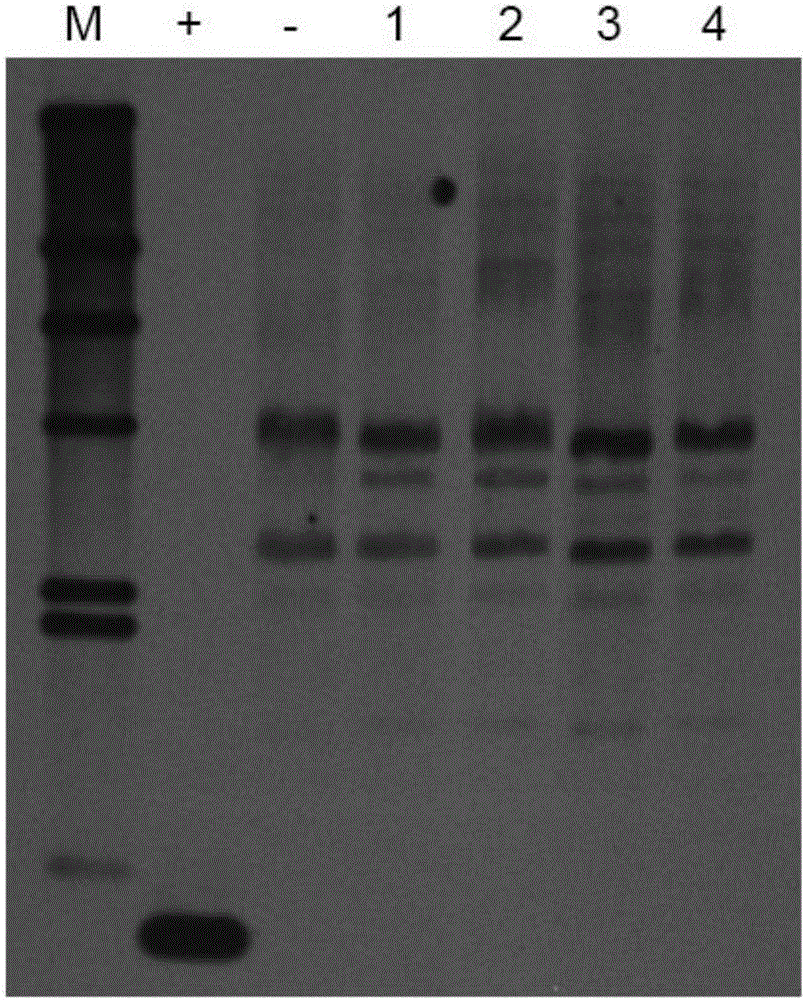
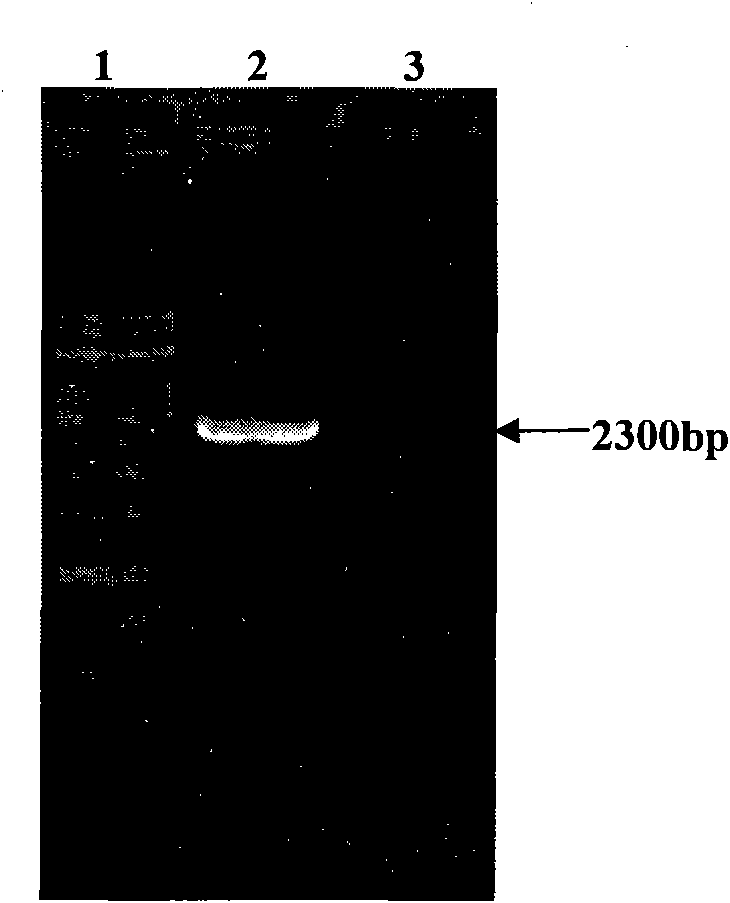
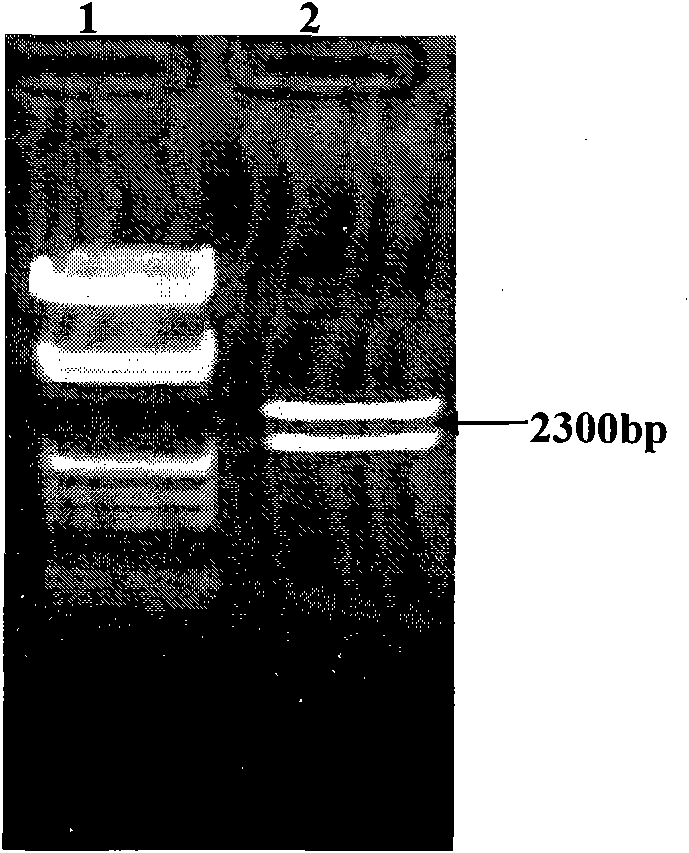
Soybean oleosin gene GmOLEO1 as well as encoded proteins and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and specifically discloses a soybean oleosin gene GmOLEO1 as well as encoded proteins and application thereof. The gene has a nucleotide sequence shown as Seq ID NO.1. The soybean oleosin gene GmOLEO1 is obtained by cloning from soybean genome first, and the gene GmOLEO1 disclosed by the invention is introduced into plant cells by utilizing a plant expression vector, so that a transgenic plant of which the oil content is increased can be obtained. Compared with non-transgenic soybeans, soybeans in which the gene GmOLEO1 disclosed by the invention is overexpressed have the advantage that the oil content of the soybean seeds is obviously improved, and the gene GmOLEO1 plays an important role in the aspect of improving the oil content of plant seeds, particularly the soybean seeds. The achievement of the invention can be applied to regulating the soybean oleosin genes through biotechnologies, has significances for cultivating soybean varieties with high oil content and has excellent application prospects.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
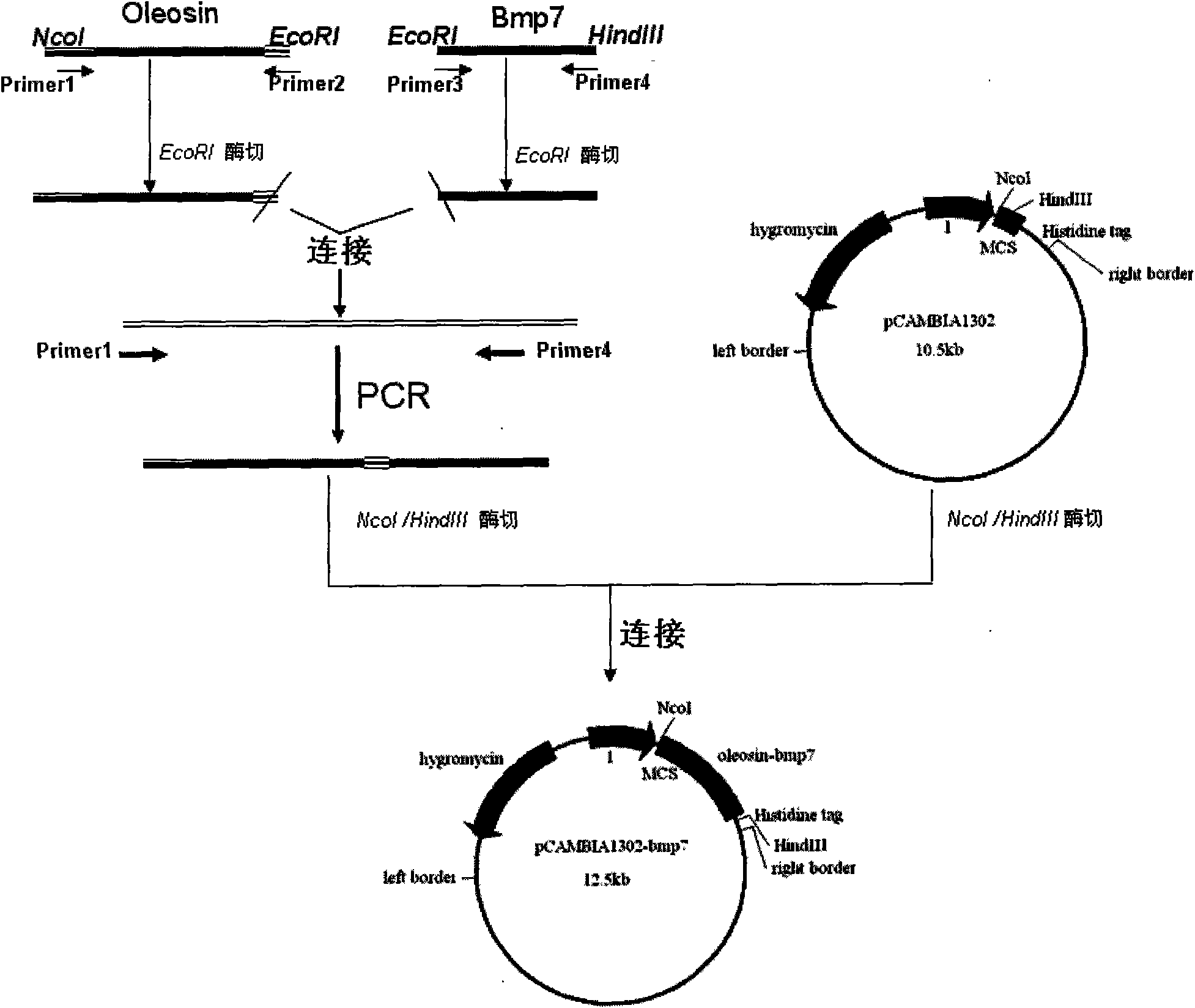
Method for ultrahigh-level and targeting expression of salmon calcitonin protein in oleosin of transgenic rape by using chromosome substitution technology
The invention provides a method for realizing targeting substitution by comprehensively using specific expression and gene targeting of plant oleosin and for ultrahigh-level expression of salmon calcitonin protein in transgenic rapeseeds. According to the invention, rape 5' UTR sequence is obtained by cloning 1900 bp with Race; an inherent endogenous sequence in the genome of rape is substituted by 5' UTR sequence of rape oleosin gene--sesame oleosin gene+CT fusion protein gene'--Pnos-NPTII-Tnos--3' UTR sequence of rape oleosin gene; a transgenic rape plant and a transgenic rape line are obtained by using the method of inplanta. According to detection results, the endogenous sequence in the genome of rape is substituted by a new sequence, which enables targeting expression of a target gene to be successfully realized and ultrahigh-level expression of salmon calcitonin protein in transgenic rapeseeds to be achieved. The method has the following remarkable advantages: the expression level of target protein is high, and the expressed protein is easy to store and purify.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods For The Modulation of Oleosin Expression In Plants
InactiveUS20080104725A1Suppression problemAlters compositionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesLipid formationBiotechnology
Methods to modulate oleosin expression levels in plants are provided. Specifically, methods for preparing seed derived products from seed, in which the composition of seed storage reserves, notably the seed lipid and protein contents, have been altered. In particular the present invention provides methods for preparing seed derived products from seed, in which the seed reserves have been altered by modulation of oleosin gene expression and more particularly the suppression of oleosin gene expression.
Owner:SEMBIOSYS GENETICS INC +1
Novel Vesicles and Nanostructures from Recombinant Proteins
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method for evaluating sensitization of natural bee pollen and fermented bee pollen
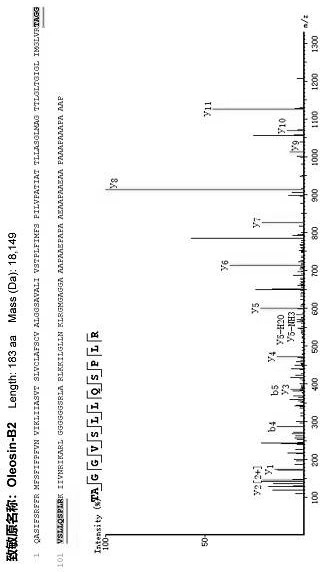
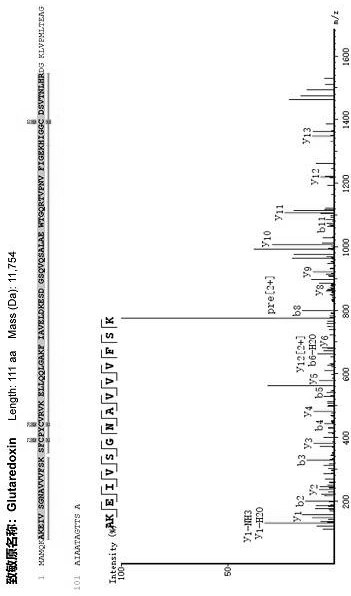
The invention relates to the technical field of food, and particularly relates to a method for evaluating sensitization of natural bee pollen and fermented bee pollen based on oleosin and glutaredoxin characteristic peptide indexes. According to the invention, the oleosin B2 and the glutaredoxin are used as evaluation indexes for evaluating the sensitization of the untreated natural bee pollen or the fermented bee pollen for the first time, and a specific evaluation process is provided according to the evaluation indexes for evaluating the sensitization of the untreated natural bee pollen or the fermented bee pollen. Meanwhile, on the basis of a specific protein evaluation method, the invention further provides a supplementary means for detecting the contents of oligopeptide and amino acid in the methanol extract of the bee pollen, and further verifies the evaluation result of the sensitization of the bee pollen. The evaluation method provided by the invention has the advantages of high accuracy, convenience and rapidness, and provides an evaluation basis for standardized production and quality control of bee pollen.
Owner:BEE RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for expressing human osteogenic protein-1 in peanut seeds
InactiveCN101591671AHigh oil contentStable storageBone-inducing factorOsteogenic factorBiotechnologyHigh level expression
The invention discloses a method for expressing human osteogenic protein-1 in peanut seeds, which comprises the following steps of: utilizing a gene engineering way to connect an osteogenic protein encoding gene to an 3' terminal of an oleosin gene, constructing an 'oleosin-erepsin-human osteogenic protein' plant expression vector driven by an oleosin promoter, transforming peanuts, making recombinant protein perform high-level expression in the peanut seeds along with the accumulation of an oil body, separating and purifying the recombinant protein through floating centrifugation, and then purifying to obtain the protein after the digestion of exoproteinase. The recombinant protein obtained by the method has the advantages of safety, high activity, and easy recovery and purification, can be stored in the peanut seeds for a long time, has convenient transportation, and can increase the added value of farm products.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
Oleosin Genes and Promoters From Coffee
InactiveUS20090229007A1More productiveSuppress gene expressionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesFlavorNucleotide
Owner:NESTEC SA +1
Vegetable oil skin care lotion containing basic fibroblast growth factor active peptide
InactiveCN103333915AEvenly distributedSimple processCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyVegetable oil
The invention discloses a vegetable oil skin care lotion containing basic fibroblast growth factor active peptide. A fusion expression product of oleosin which is inlaid in the surface of oil body and basic fibroblast growth factor is used as an active ingredient in the development of skin care products; so that mixing technologies of basic fibroblast growth factor with an emulsifier (or a protective agent) are simplified, and production cost is reduced. In addition, the bioactivity of basic fibroblast growth factor protein is protected. By taking advantage of the characteristics of oleosin, basic fibroblast growth factor active peptide is encapsulated with vegetable oil, and is fixed on the surface of oil body; and then basic fibroblast growth factor protein can be distributed uniformly in the skin care emulsifier by using emulsifying homogenization; and the effects of basic fibroblast growth factor protein are exerted by transdermal absorption effects of oil body. Preparation technologies of the vegetable oil skin care lotion are simple; efficacy is significant; and cost is reduced.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV +1
Modified oil encapsulating proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS8987551B2Reduces and prevents lipid recyclingIncrease probabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulinsBiofuel feedstockIn vivo
The invention provides modified oleosins, including at least one artificially introduced cysteine, and methods and compositions for producing the modified oleosins. Also provided are polynucleotides encoding the modified oleosins, constructs and host cells comprising the polynucleotides, methods for producing oil bodies comprising the modified oleosins, in vivo and in vitro, and methods for producing oil in host cells and plants. The invention also provides methods for increasing the rate of CO2 assimilation in photosynthetic cells and plants, and involves reducing or preventing lipid recycling, and / or expressing modified oleosins with artificially introduced cysteine residues in the photosynthetic cells and plants. Also provided are methods for increasing oil production in plants, via expression of modified oleosins in the non-photosynthetic tissues / organs of plants. The method also optionally includes the step of extracting the oil from the non-photosynthetic tissues / organs of the plant, or processing the oil rich non-photosynthetic tissues / organs into animal or biofuel feedstocks.
Owner:AGRESEARCH LTD
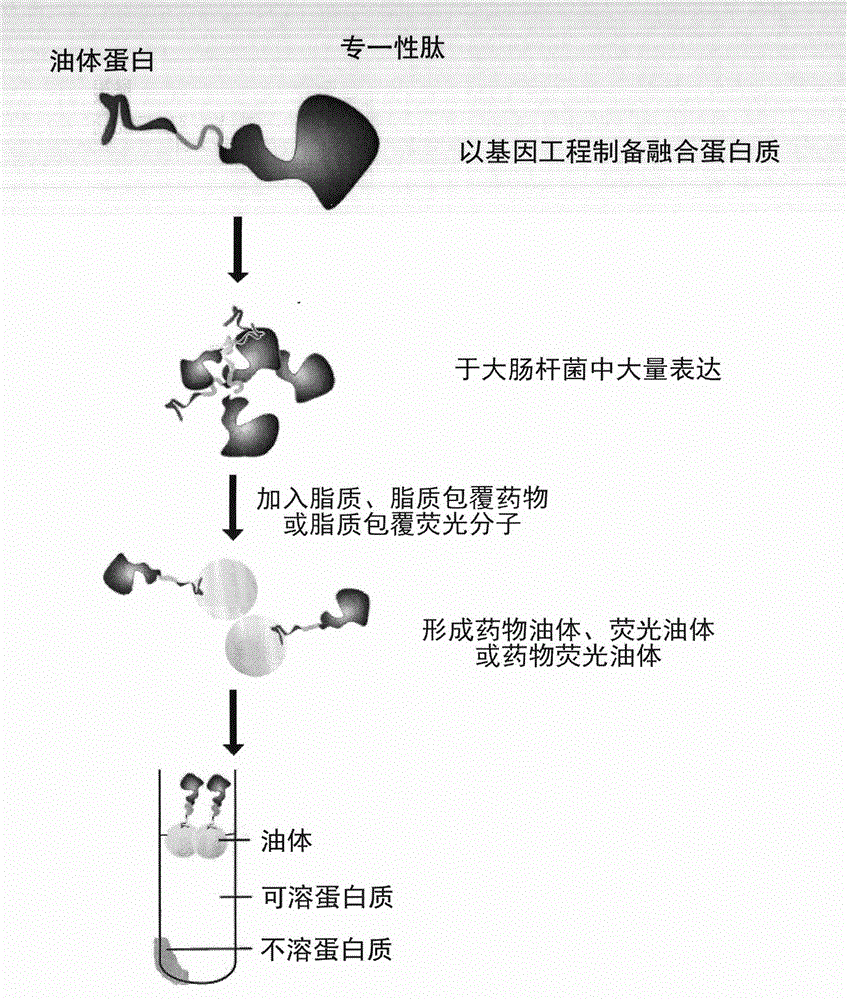
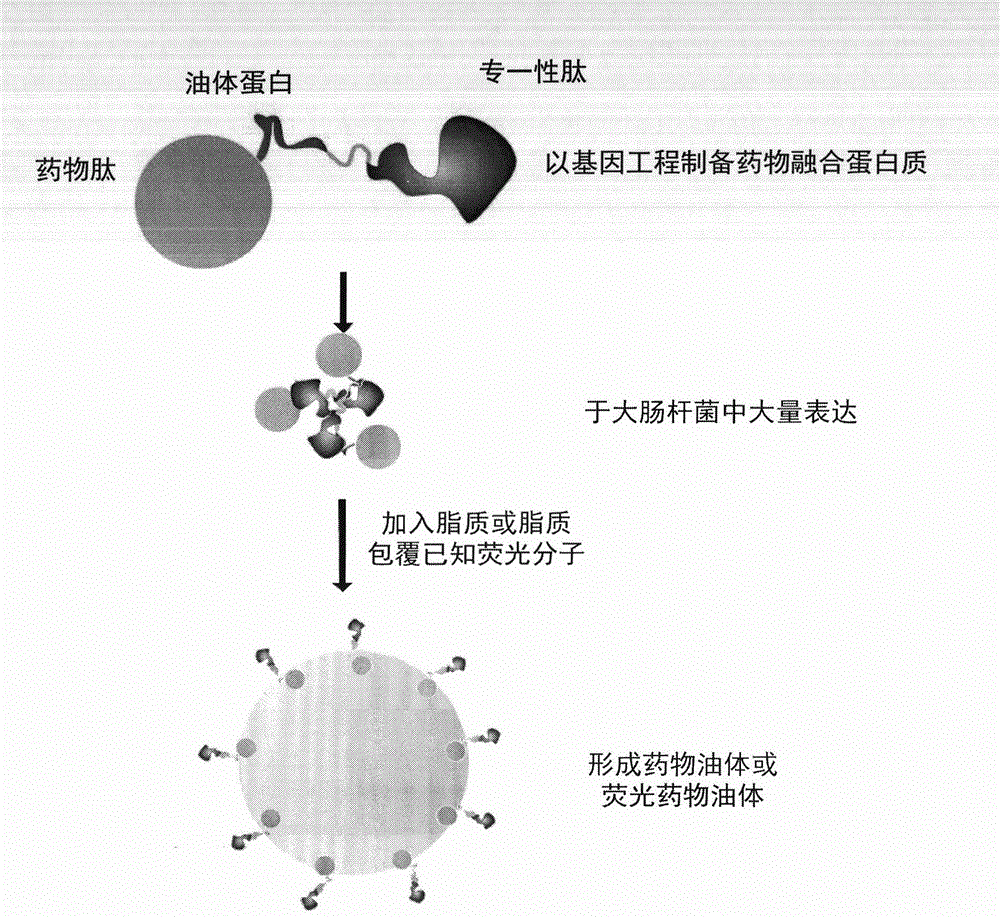
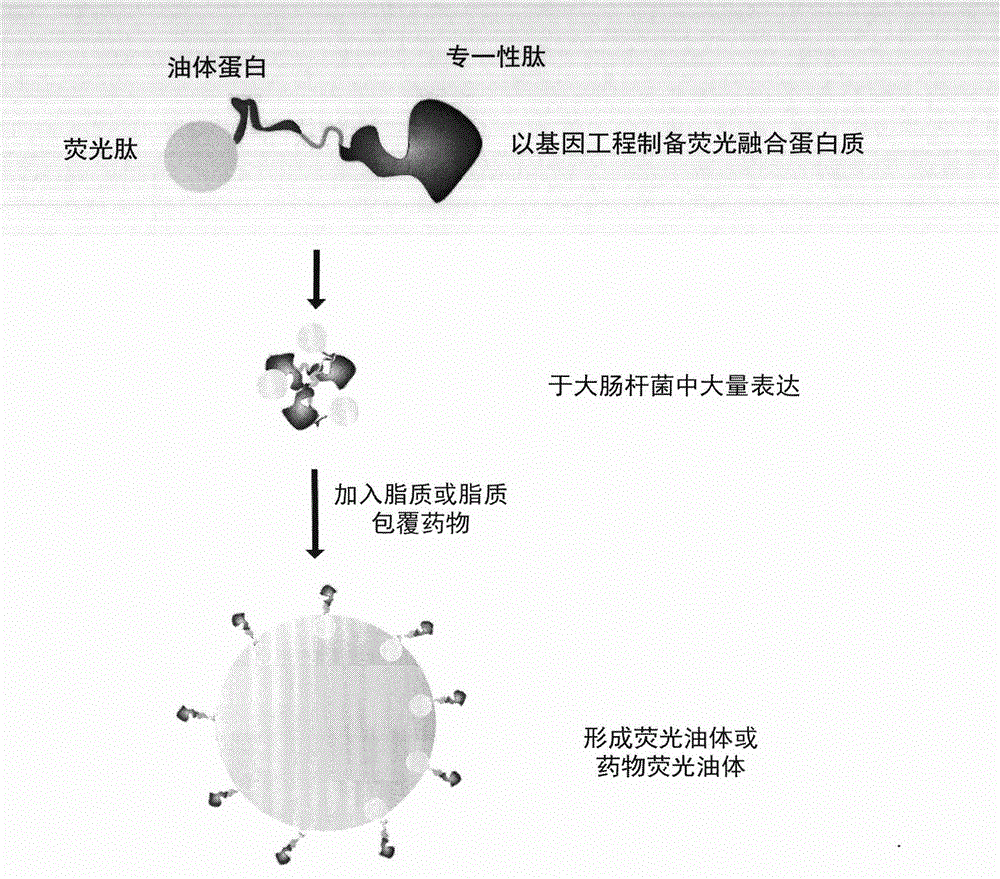
Nano-scale artificial oil body for targeted drug delivery system detection and treatment
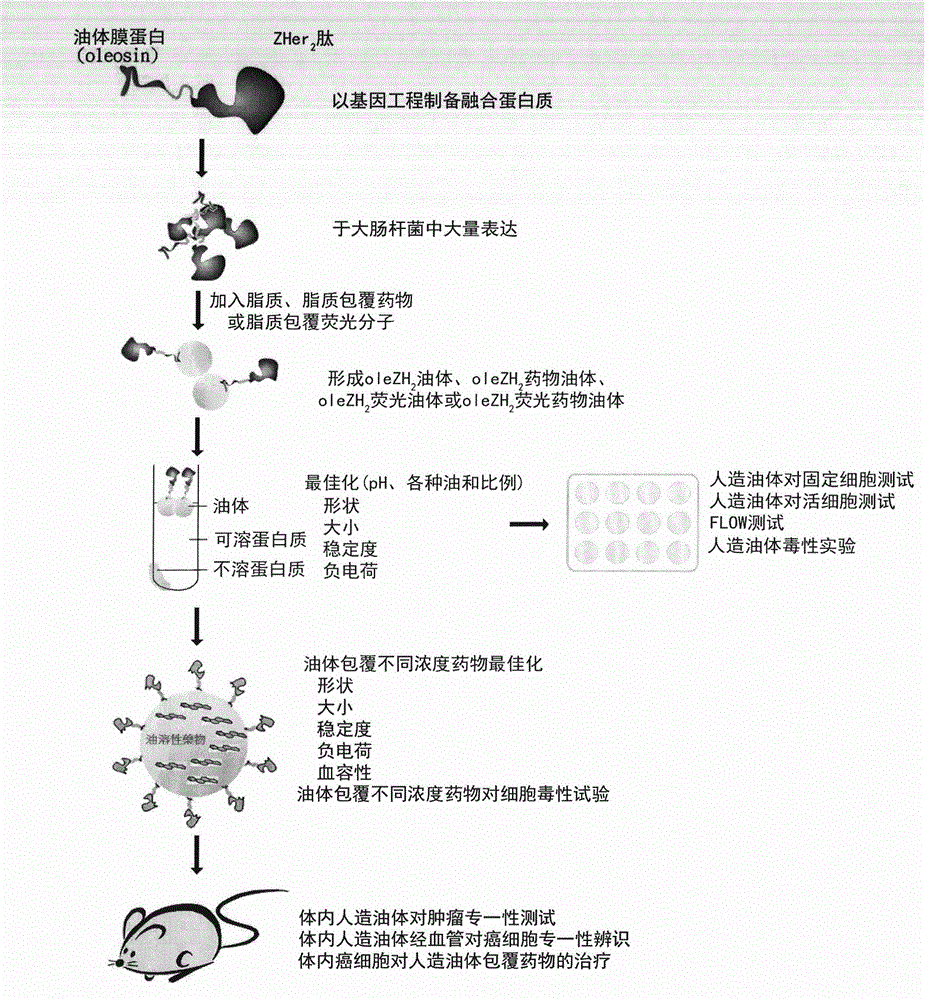
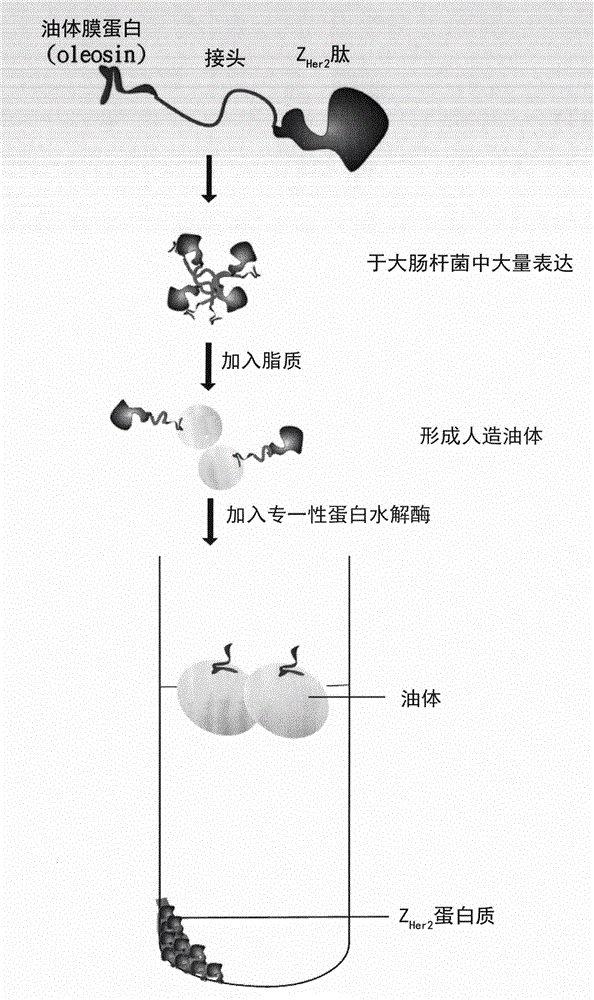
InactiveCN102743327AHigh purityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationFluorescence
The present invention relates to a nano-scale artificial oil body for targeted drug delivery system detection and treatment. The nano-scale artificial oil body comprises: an oleZH2 protein, wherein the oleZH2 protein comprises oleosin and a ZHer2 peptide; a lipid, a lipid-coated liposoluble drug, and a lipid-coated known fluorescence molecule, wherein the materials are prepared into an oleZH2 oil body, an oleZH2 drug oil body and an oleZH2 fluorescence oil body so as to provide an active targeted drug delivery system and a detection system.
Owner:陈致融
Application of soybean seed-specific promoter
InactiveCN110878304AObvious seed-specific featuresEasy to synthesizeVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyTransgene
The invention relates to application of a soybean seed-specific promoter, belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to the application field of changing the seed quality and yield of cash crops. The seed-specific promoter sequence of the invention is as described in SEQ ID NO.1, and the promoter is cloned and specifically expressed in Arabidopsis thaliana seeds. Through promoter predictive analysis, about 2000bp upstream sequences of the soybean oleosin gene are isolated, and the amplified fragment and a pBI101 vector containing a GUS reporter gene are recombined. The function of Arabidopsis thaliana transgene is verified by an Agrobacterium tumefaciens inflorescence infection method, and it is proved that the seed-specific promoter could positively regulate the expression of theoleosin gene, thus providing a favorable tool for improving the seed quality and yield of crops.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
An oleosin 5' regulatory region for the modification of plant seed lipid
The present invention is directed to 5' regulatory regions of an Arabidopsis oleosin gene. The 5' regulatory regions, when operably linked to either the coding sequence of a heterologous gene or a sequence complementary to a native plant gene, direct expression of the coding sequence or complementary sequence in a plant seed. The regulatory regions are useful in expression cassettes and expression vectors for the transformation of plants. Also provided are methods of modulating the levels of a heterologous gene such as a fatty acid synthesis or lipid metabolism gene by transforming a plant with the subject expression cassettes and expression vectors.
Owner:RHONE POULENC AGRO SA
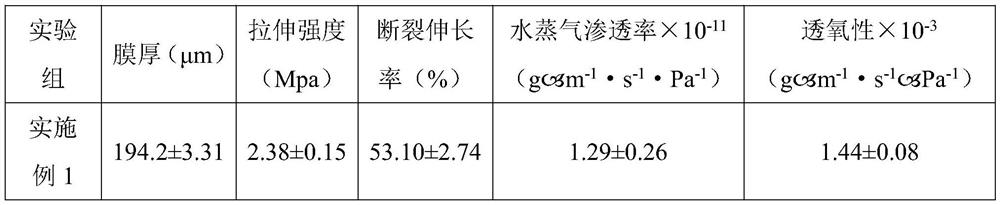
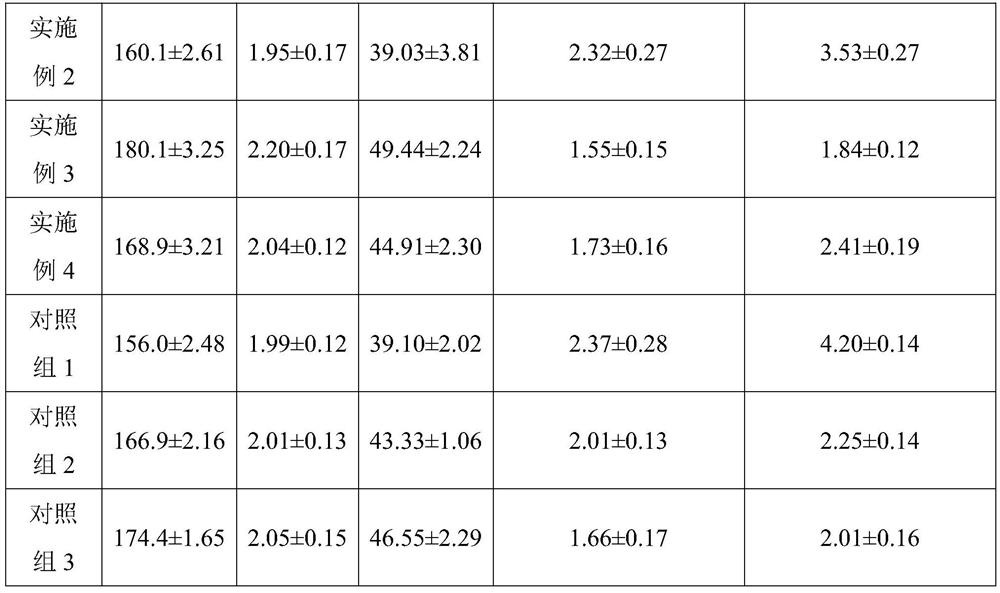
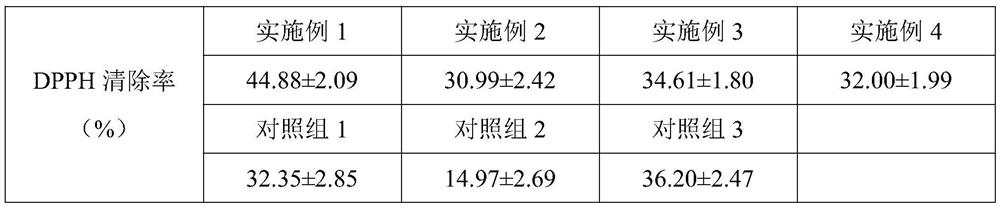
Emulsion film and preparation method thereof
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for expressing human osteogenic protein-1 in peanut seeds
InactiveCN101591671BHigh oil contentStable storageBone-inducing factorOsteogenic factorBiotechnologyEnteropeptidase
The invention discloses a method for expressing human osteogenic protein-1 in peanut seeds, which comprises the following steps of: utilizing a gene engineering way to connect an osteogenic protein encoding gene to an 3' terminal of an oleosin gene, constructing an 'oleosin-erepsin-human osteogenic protein' plant expression vector driven by an oleosin promoter, transforming peanuts, making recombinant protein perform high-level expression in the peanut seeds along with the accumulation of an oil body, separating and purifying the recombinant protein through floating centrifugation, and then purifying to obtain the protein after the digestion of exoproteinase. The recombinant protein obtained by the method has the advantages of safety, high activity, and easy recovery and purification, canbe stored in the peanut seeds for a long time, has convenient transportation, and can increase the added value of farm products.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
Method for expressing human humanin protein in peanut seed
InactiveCN102321665BHigh oil contentRich in OleosinGenetic engineeringFermentationHumaninEnteropeptidase
The invention discloses a method for expressing human humanin protein in peanut seeds, which comprises the following steps: connecting humanin protein coding gene to a 3' end of an oleosin gene by a genetic engineering means, establishing an 'oleosin-erepsin-human humanin protein' plant expression vector driven by an oleosin promoter, transforming peanuts to realize high-level expression of recombinant protein in peanut seeds with the accumulation of oil body, then performing centrifugation of fusion protein, digesting the fusion protein by exo-protease, performing centrifugation, removing the oil phase and recovering water phase, performing purification to obtain human humanin protein. The recombinant protein obtained by the method of the invention is safe, has high activity, is very easy to be recovered and purified, can be stored in peanut seeds for a long term, is convenient for transportation, and greatly increases the crop added value.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com