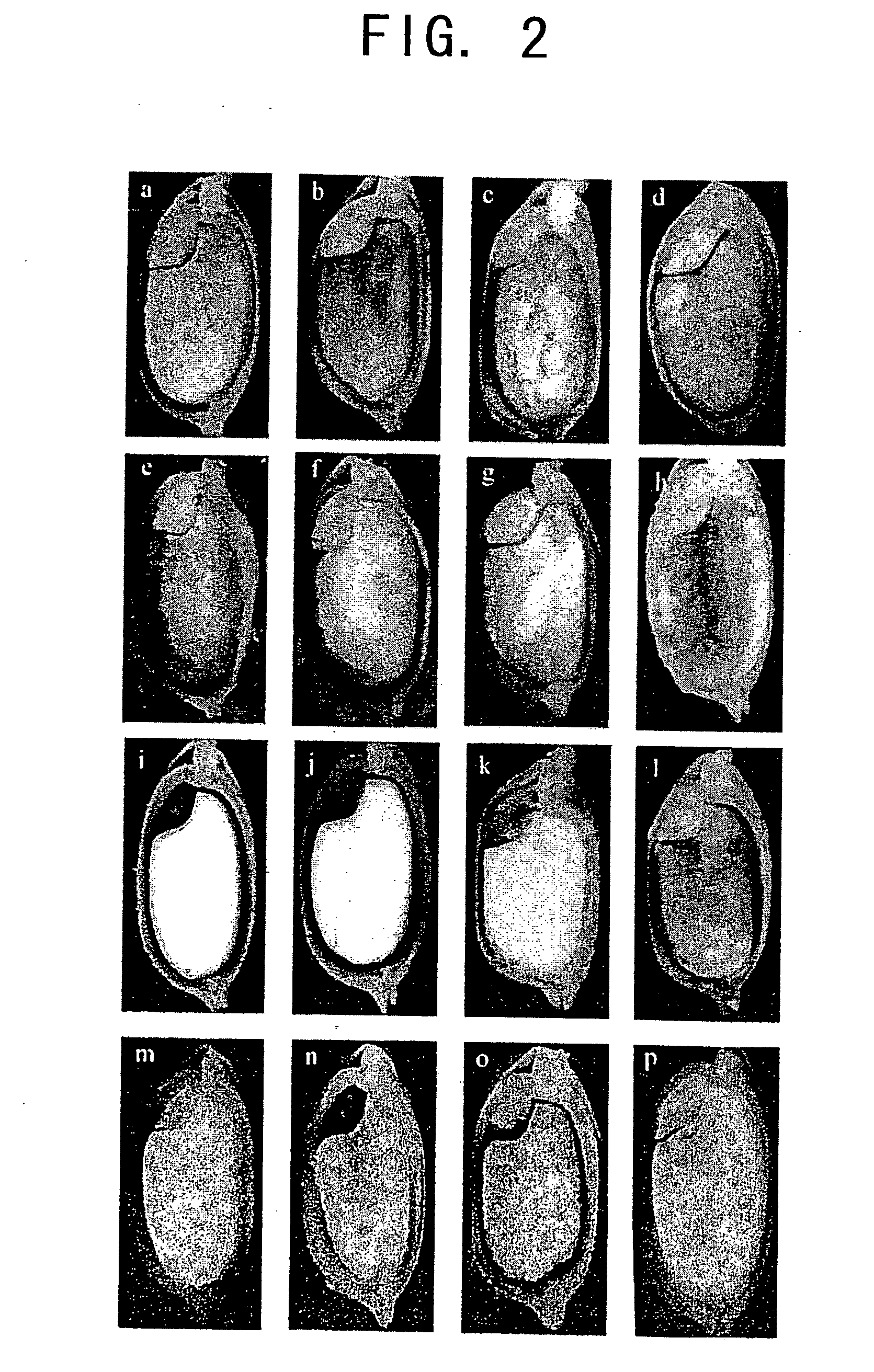
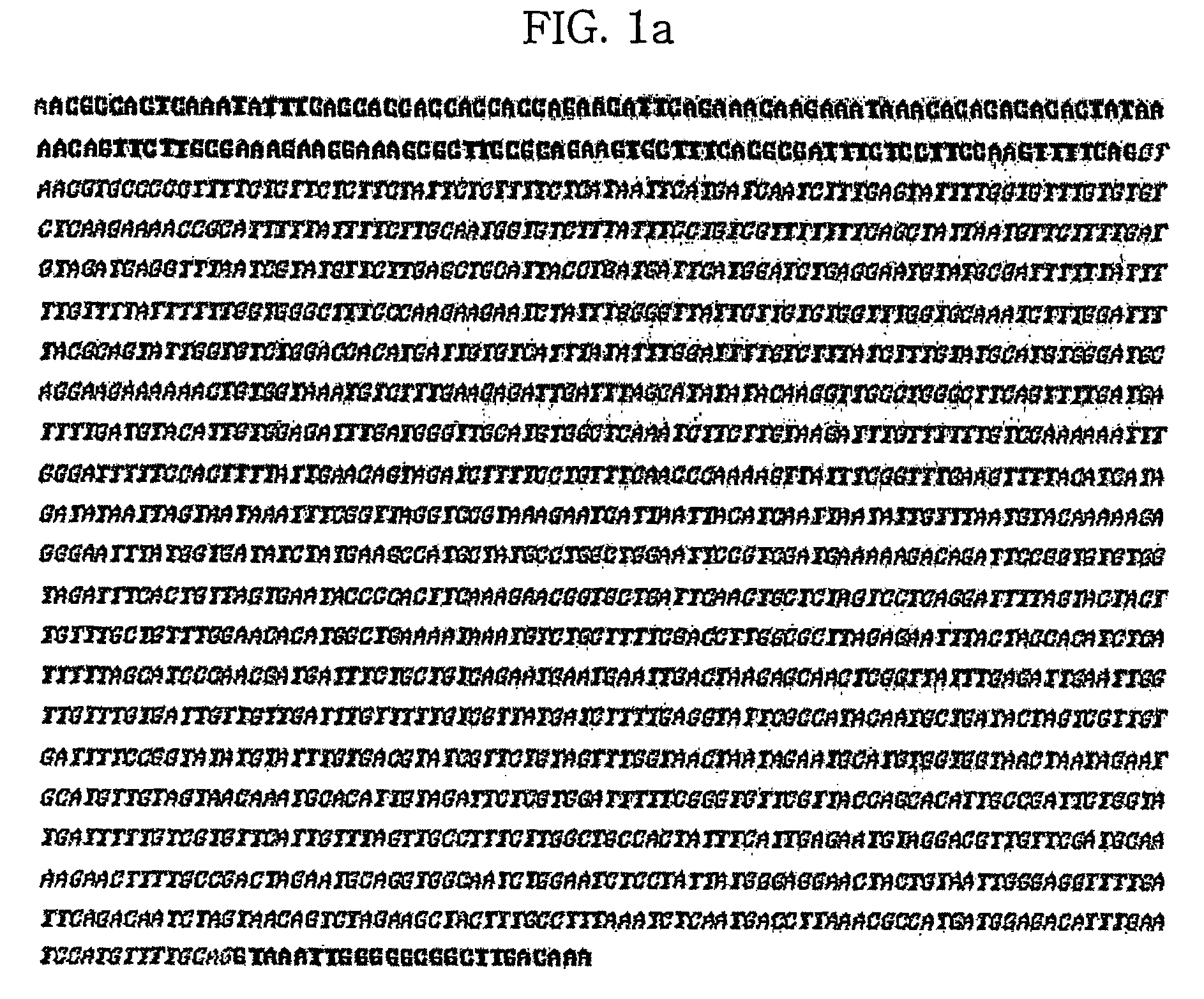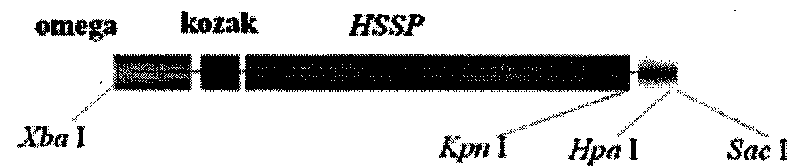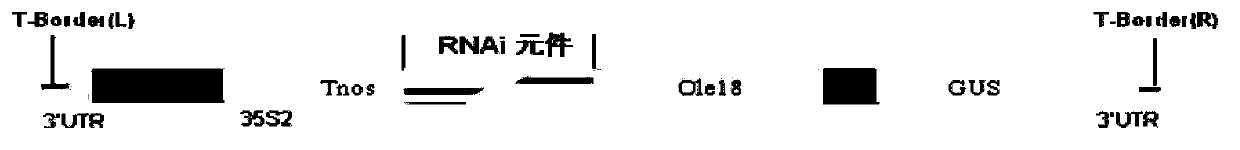Patents
Literature
116 results about "Seed specific" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Seed specific highly effective promoter and its application
The invention discloses a special promoter separated from millet, expressing carrier with nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1 host with the expressing carrier and appliance of the promoter, which is characterized by the following: utilizing Tail-PCR (colored body step moving method); getting the special promoter from gene group DNA; possessing nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1; ;linking downstream of the promoter to non-homologous or homologous gene; constructing plant expressing carrier; transferring host plant; driving the downstream gene to high effective and special express goal protein in the seed; realizing genetic modification of plant; or using as effective tool for studying plant and biological reactor.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Flax (Linum usitatissimum I.) seed-specific promoters
InactiveUS20070192902A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesLipid formationProtein composition
The present invention is directed to promoters of flax conlinin and ω-3 desaturase genes. The promoters guide high levels of the expression exclusively in flax developing seeds. This specific expression pattern concomitant with the biosynthesis of storage lipids and proteins make these promoters particularly useful for seed-specific modification of fatty acid and protein compositions in plant seeds.
Owner:BIORIGINAL FOOD & SCI
Plant seed specific promoters
InactiveUS20030005485A1Improve reliabilityAvoid redundancySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPlanting seedNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to novel seed specific promoter regions. The present invention further provide methods of producing proteins and other products of interest and methods of controlling expression of nucleic acid sequences of interest using the seed specific promoter regions. The present invention also provides methods of identifying and isolating novel seed specific promoters.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
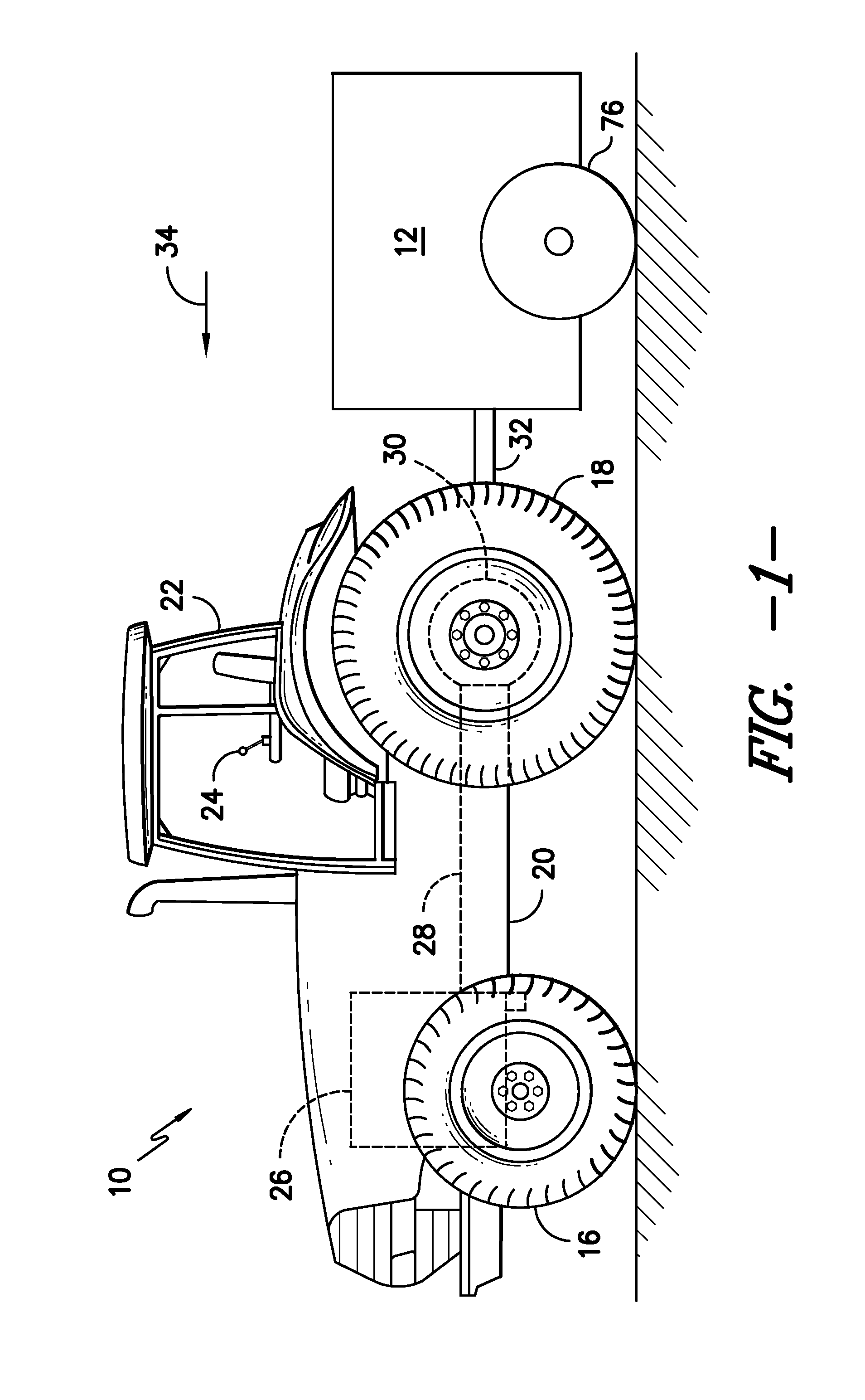
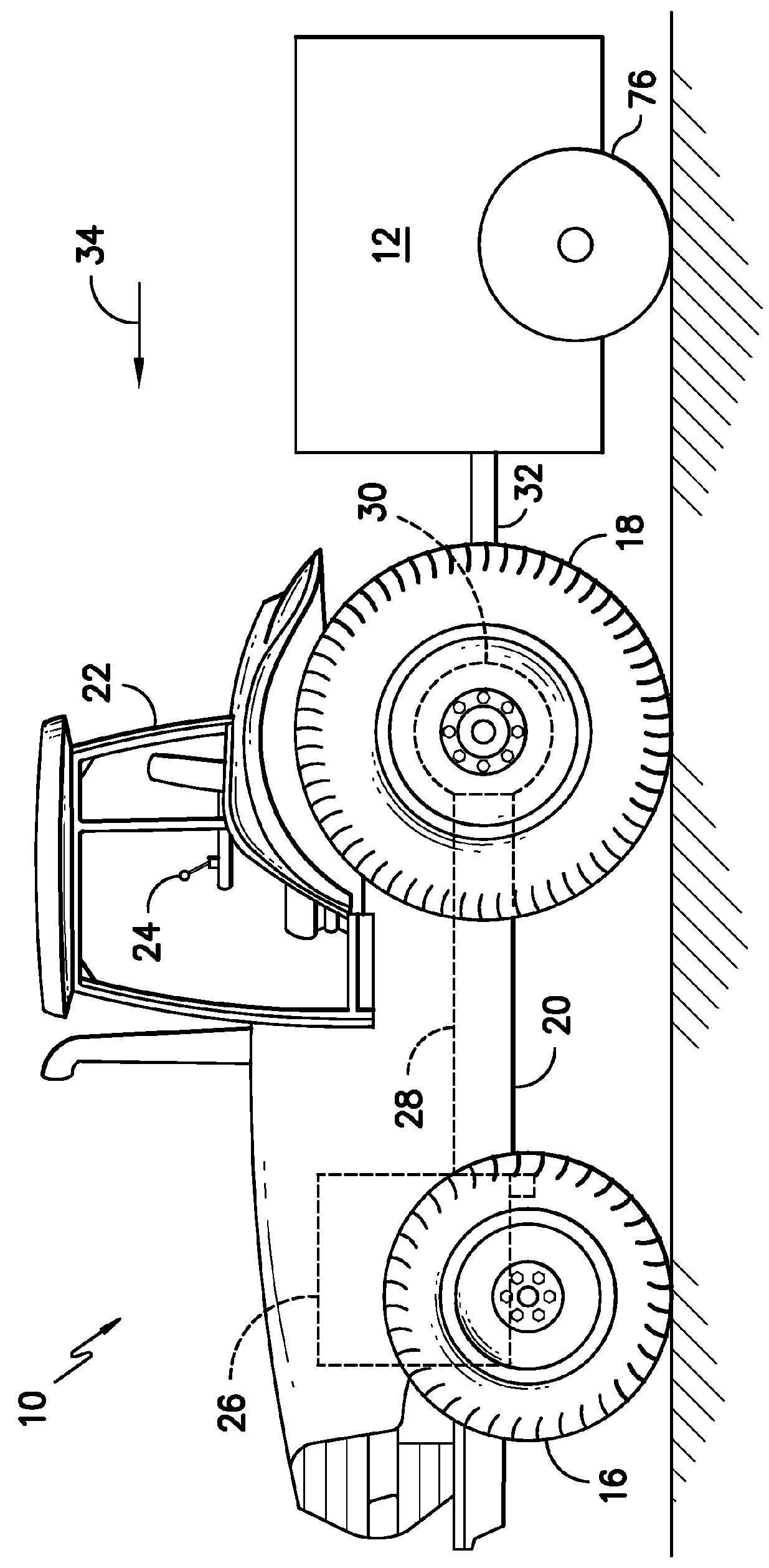
System and Method for Spraying Seeds Dispensed from a Planter
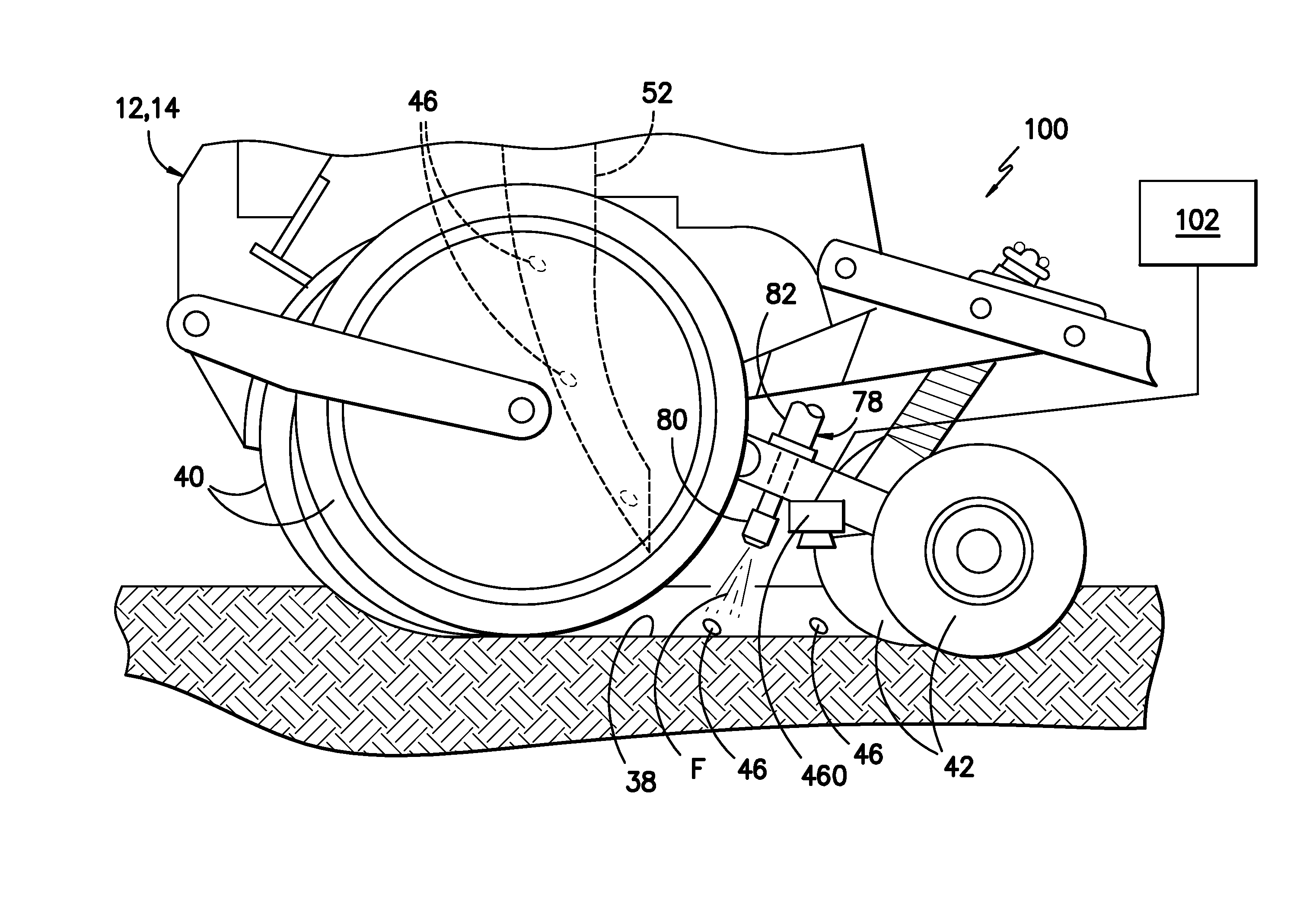
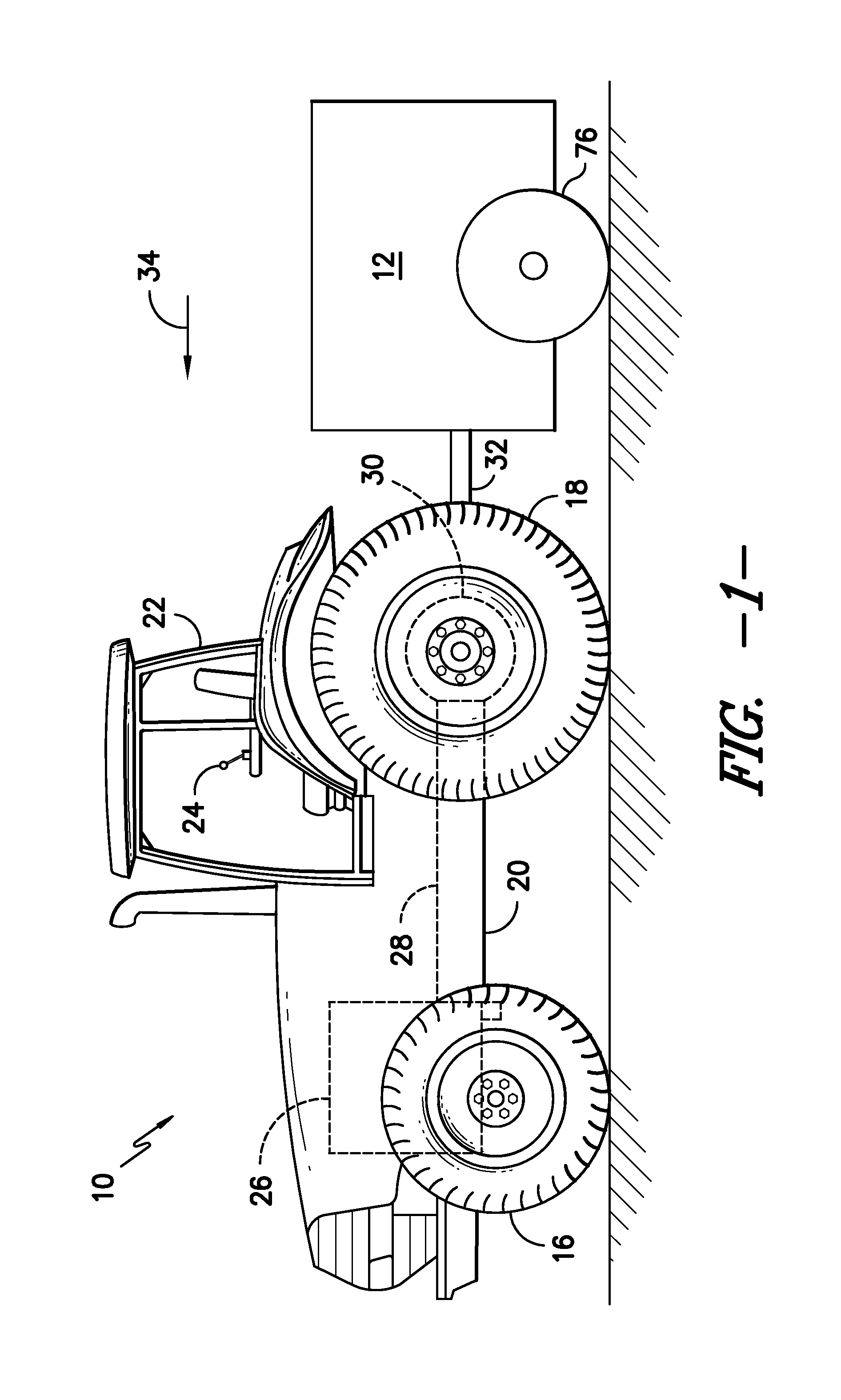
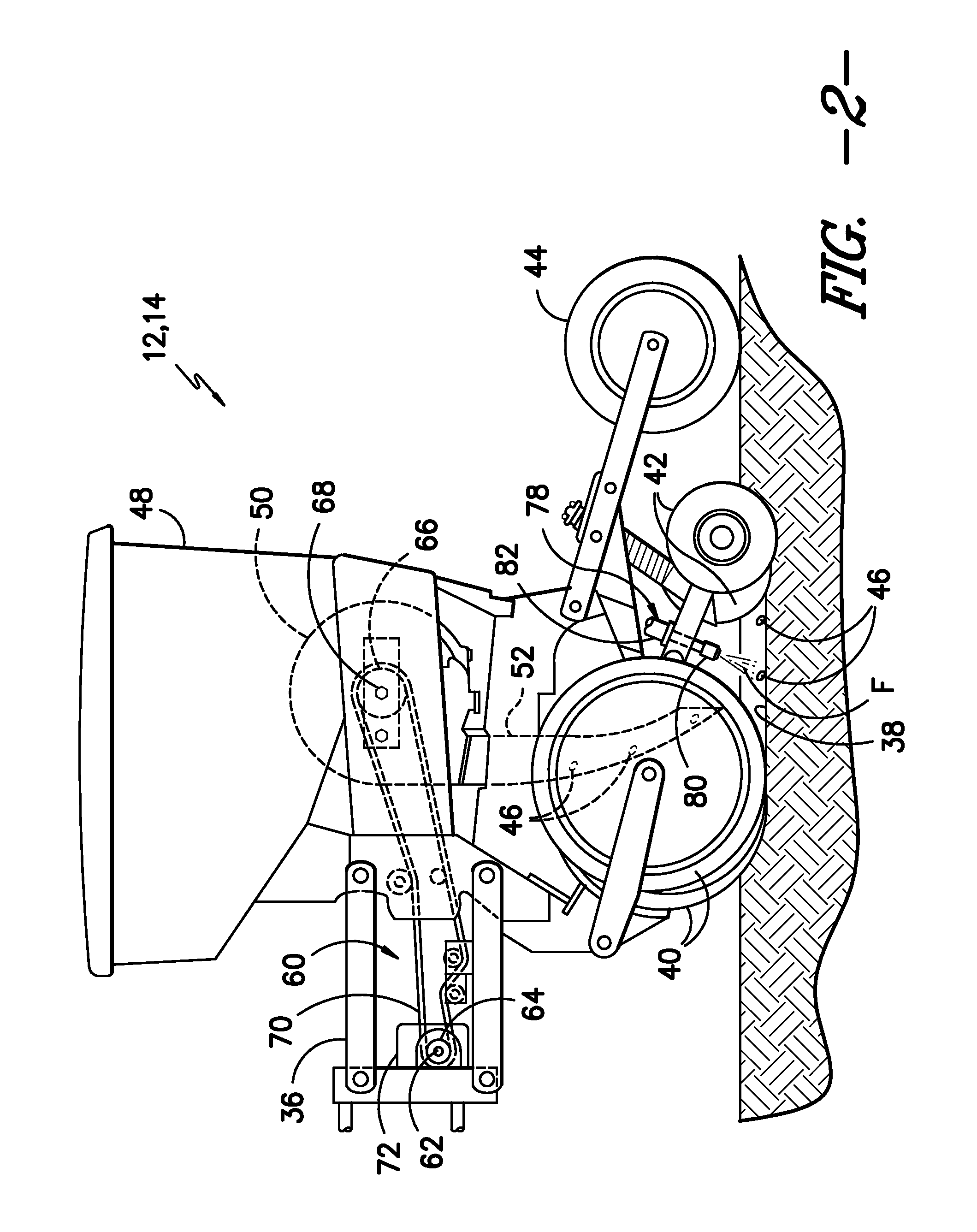
ActiveUS20140048002A1Liquid fertiliser regulation systemsFertilising methodsEngineeringControl valves
In one aspect, a system for providing seed-specific placement of fluid as seeds are planted by a planter is disclosed. The system may generally include a seed meter configured to dispense seeds into a furrow at a seed frequency and a nozzle assembly configured to spray the seeds dispensed into the furrow. The nozzle assembly may include a valve. In addition, the system may include a controller communicatively coupled to the valve. The controller may be configured to determine the seed frequency of the seed meter based on a speed-related parameter of the planter. The controller may also be configured to control the operation of the valve based on the seed frequency such that a metered amount of fluid is sprayed at least one of on or adjacent to each seed.
Owner:CAPSTAN
Flax seed specific promoters
InactiveUS7642346B2Simple methodSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesProtein compositionPlant cell
Novel methods for the expression of non-native genes in flax seeds and the seeds of other plant species are provided. The methods involve the use of seed-specific promoters obtained from flax. Additionally provided are novel flax seed-specific promoters, chimeric nucleic acid constructs comprising novel flax seed-specific promoters, transgenic plant cells, transgenic plants and transgenic plant seeds containing novel flax seed-specific promoters. The promoters and methods are useful, for example, for altering the seed oil and protein composition in flax seed or other plant seeds.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
System and method for spraying seeds dispensed from a planter
In one aspect, a system for providing seed-specific placement of fluid as seeds are planted by a planter is disclosed. The system may generally include a seed meter configured to dispense seeds into a furrow at a seed frequency and a nozzle assembly configured to spray the seeds dispensed into the furrow. The nozzle assembly may include a valve. In addition, the system may include a controller communicatively coupled to the valve. The controller may be configured to determine the seed frequency of the seed meter based on a speed-related parameter of the planter. The controller may also be configured to control the operation of the valve based on the seed frequency such that a metered amount of fluid is sprayed at least one of on or adjacent to each seed.
Owner:CAPSTAN
Gene regulatory region that promotes early seed-specific transcription
InactiveUS7253337B2High expressionProduct can be usedSugar derivativesHydrolasesHigh level expressionNucleic acid sequencing
Nucleic acid sequence capable of regulating transcription during embryogenesis in plants is provided. This sequence may be used in transgenic plants to promote high levels of expression of foreign and endogenous genes in developing seeds to affect seed lipid metabolism, protein or carbohydrate composition and accumulation, or seed development. In addition, these sequences may be useful for the production of modified seed containing novel recombinant proteins which have pharmaceutical, industrial or nutritional value, or novel products like plastics.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Expression of human milk proteins in transgenic plants
The invention is directed to seed and seed extract compositions containing levels of a human milk protein between 3-40% or higher of the total protein weight of the soluble protein extractable from the seed. Also disclosed is a method of producing the seed with high levels of extractable human milk protein. The method includes transforming a monocotyledonous plant with a chimeric gene having a protein-coding sequence encoding a protein normally present in human milk under the control of a seed maturation-specific promoter. The method may further includes a leader DNA sequence encoding a monocot seed-specific transit sequence capable to target a linked milk protein to a storage body.
Owner:VENTRIA BIOSCIENCE
Plant seed specific promoters
InactiveUS7081565B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPlanting seedNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to novel seed specific promoter regions. The present invention further provide methods of producing proteins and other products of interest and methods of controlling expression of nucleic acid sequences of interest using the seed specific promoter regions. The present invention also provides methods of identifying and isolating novel seed specific promoters.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
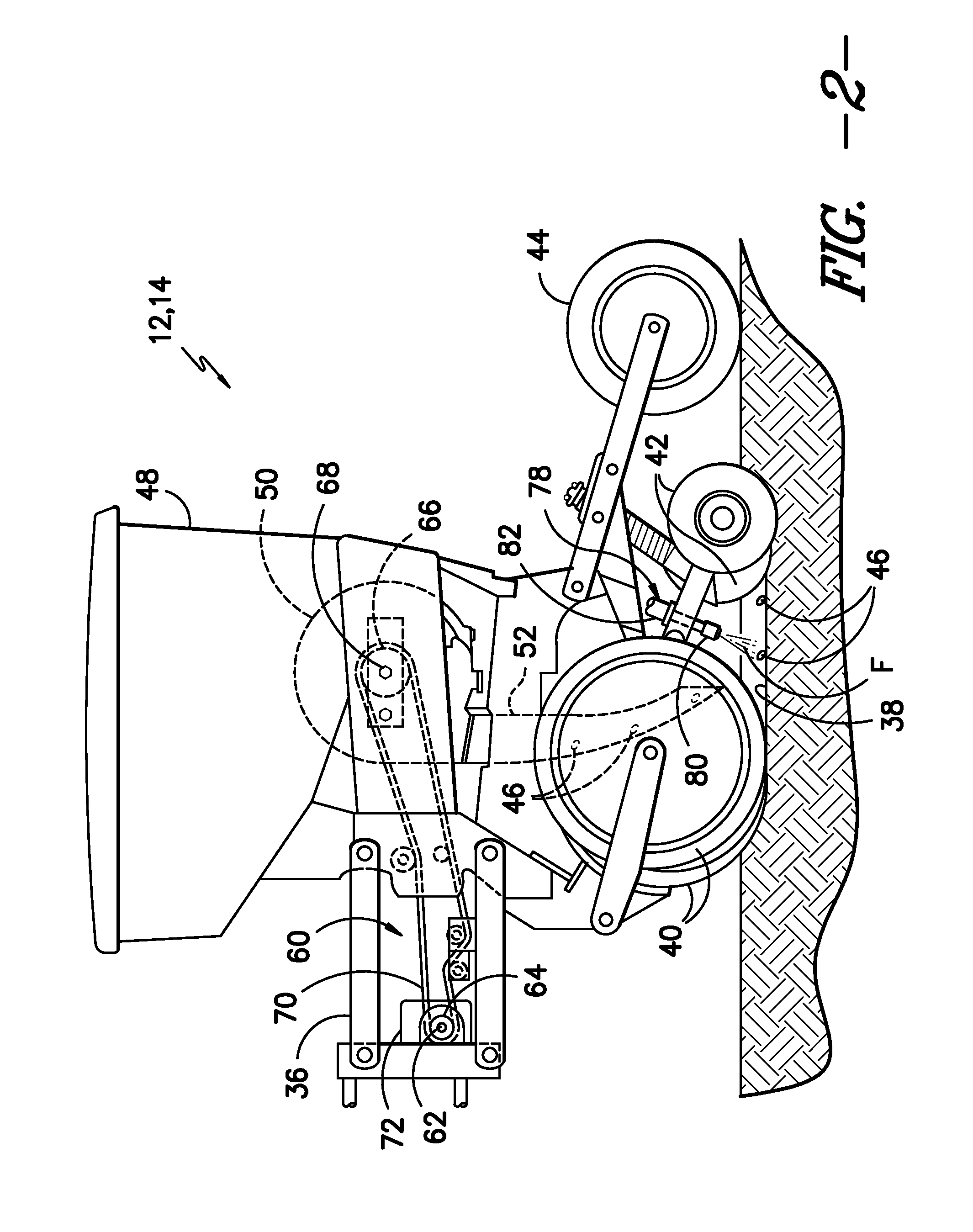
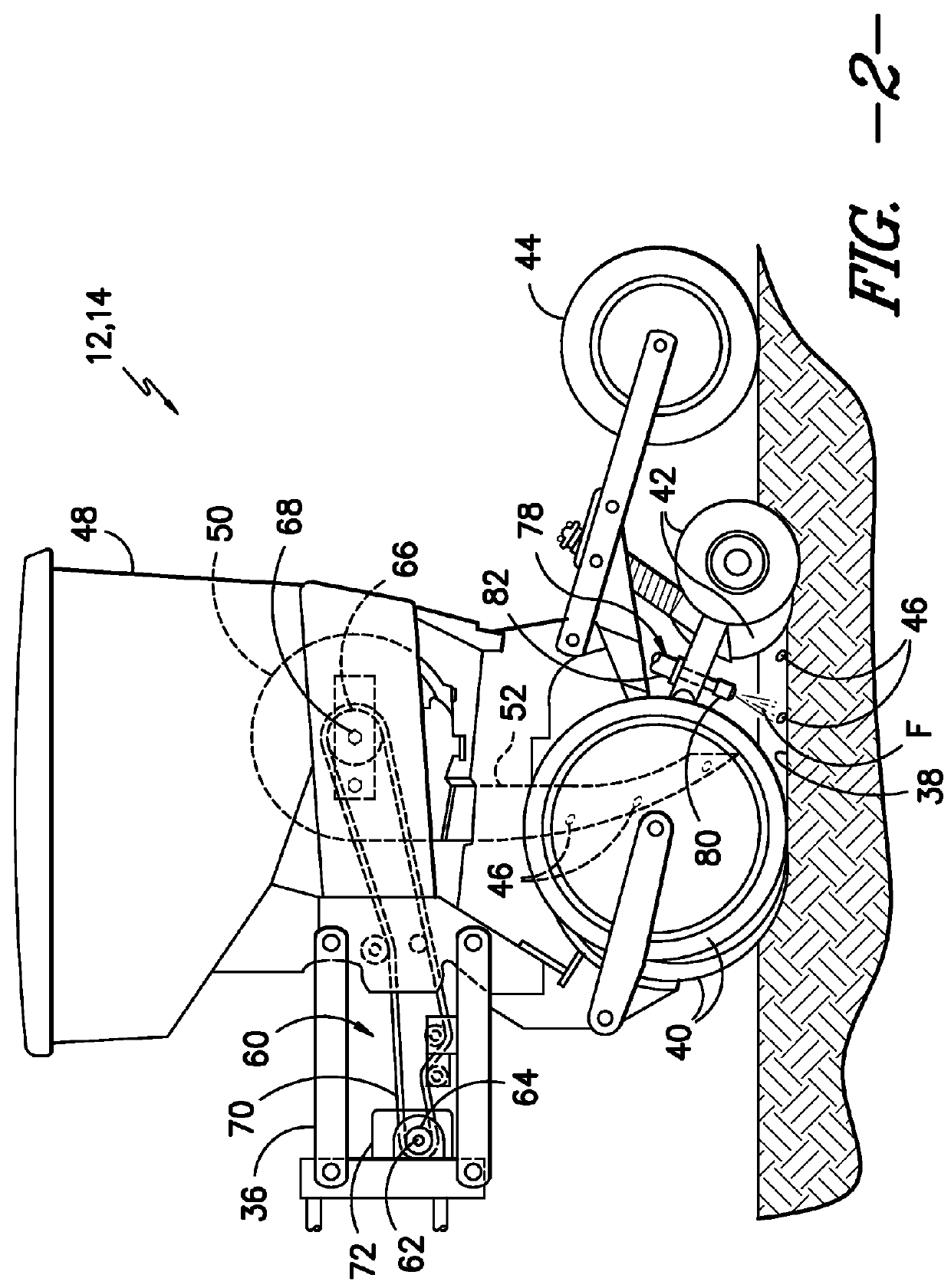
System and method for spraying seeds dispensed from a twin row planter
ActiveUS20160073576A1Liquid fertiliser regulation systemsFertilising methodsEngineeringControl valves
A system for providing seed-specific placement of fluid as seeds are planted by a twin row planter includes a planter row unit, at least one nozzle assembly, and a controller. The planter row unit includes a first seed meter configured to dispense seeds into a first furrow at a seed frequency and a second seed meter configured to dispense seeds into a second furrow at the seed frequency. The nozzle assembly is configured to spray the seeds dispensed into the first and second furrows, and includes a valve. The controller is communicatively coupled to the valve, and is configured to determine the seed frequency of the first and second seed meters based on a speed-related parameter of the planter. The controller is further configured to control operation of the valve based on the seed frequency such that fluid is sprayed at least one of on or adjacent to each seed.
Owner:CAPSTAN
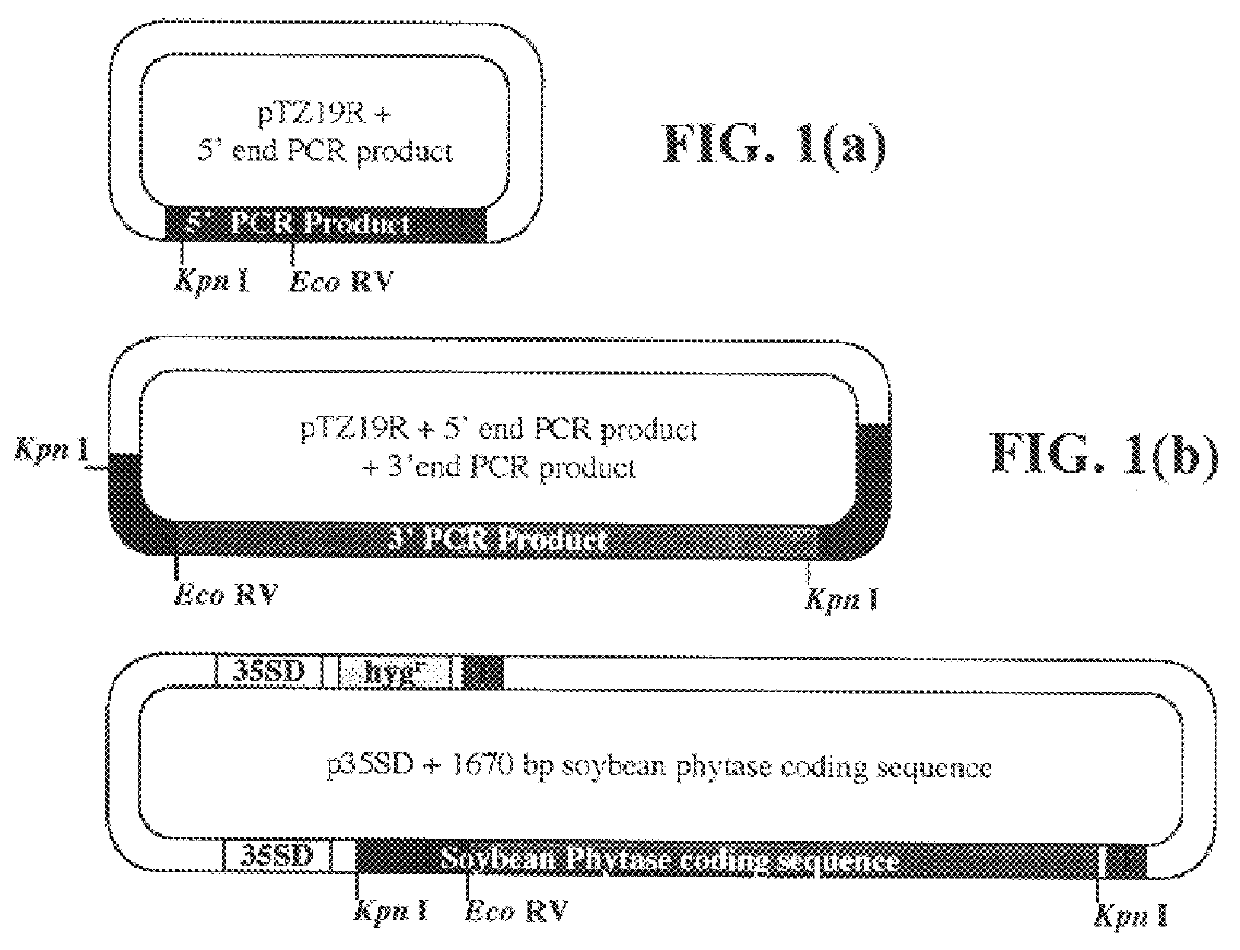
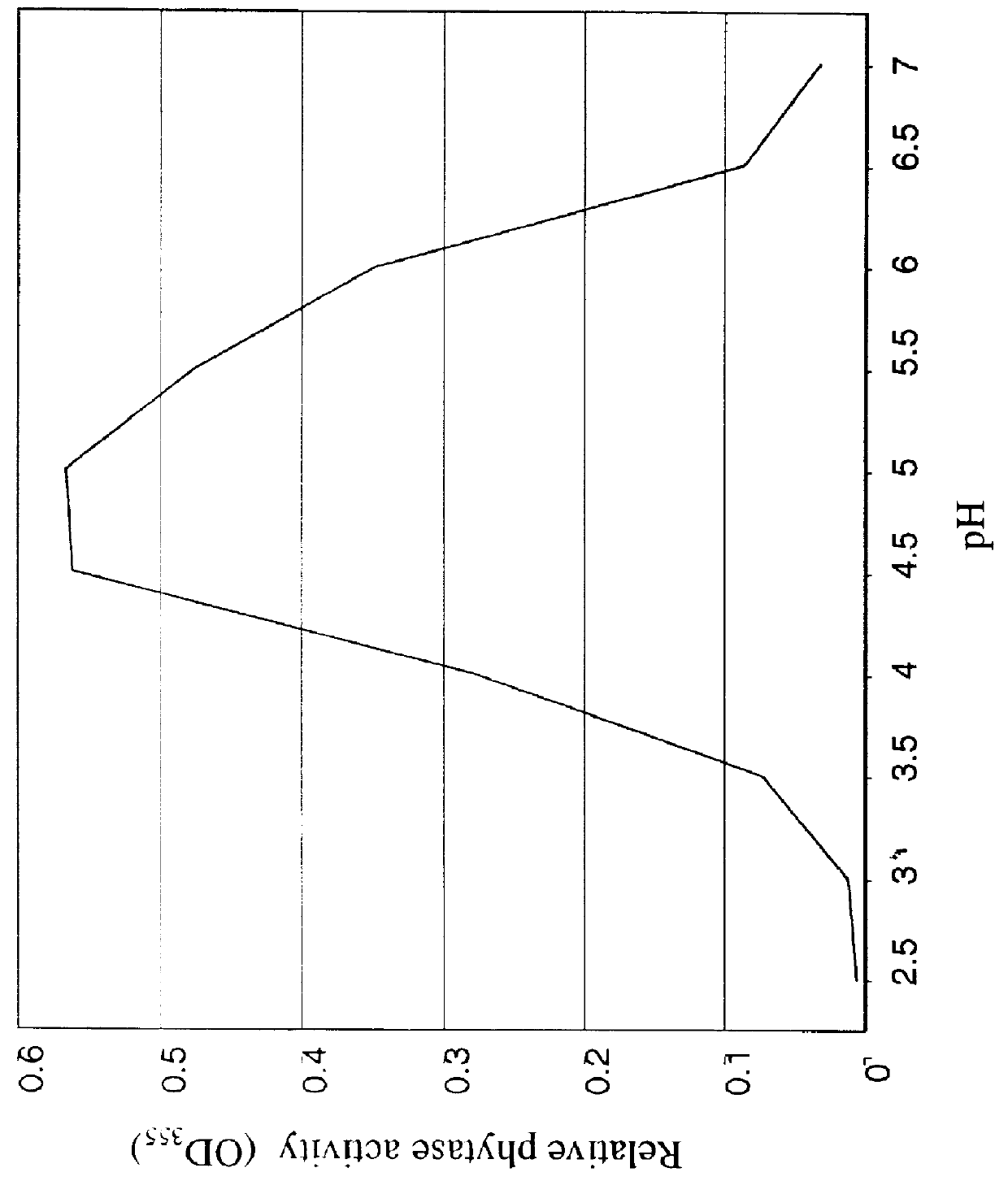
Soybean phytase and nucleic acid encoding the same
Isolated soybean phytase polypeptides and isolated nucleic acids encoding soybean phytases are provided. The invention is also directed to nucleic acid expression constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the isolated soybean phytase nucleic acids, as well as methods for producing recombinant and non-recombinant purified soybean phytase. The invention also relates to transgenic plants expressing the soybean phytase, particularly expression under seed-specific expression control elements.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Plant seed-specific expression promoter derived from sesame and seed-specific expression vector comprising the promoter
Provided are a seed-specific expression promoter derived from sesame microsomal oleic acid desaturase (Si-FAD2) gene, an intron for expression enhancement, a seed-specific expression vector including the promoter and / or the intron, and a transgenic plant transformed with the seed-specific expression vector. Therefore, a useful product can be produced in a seed-specific manner or a common product in a seed can be functionally modified. Also, the promoter can be used together with the intron for expression enhancement, thereby increasing the expression level of an inserted gene in a seed. Therefore, it is very useful in development of a transgenic plant which induces large-scale expression of a foreign gene in a seed-specific manner.
Owner:KOREA CHUNGANG EDUCATIONAL FOUND
BNLEA3-1 promoter
InactiveUS20080244793A1Weakly inducibleSugar derivativesPlant peptidesEscherichia coliNicotiana tabacum
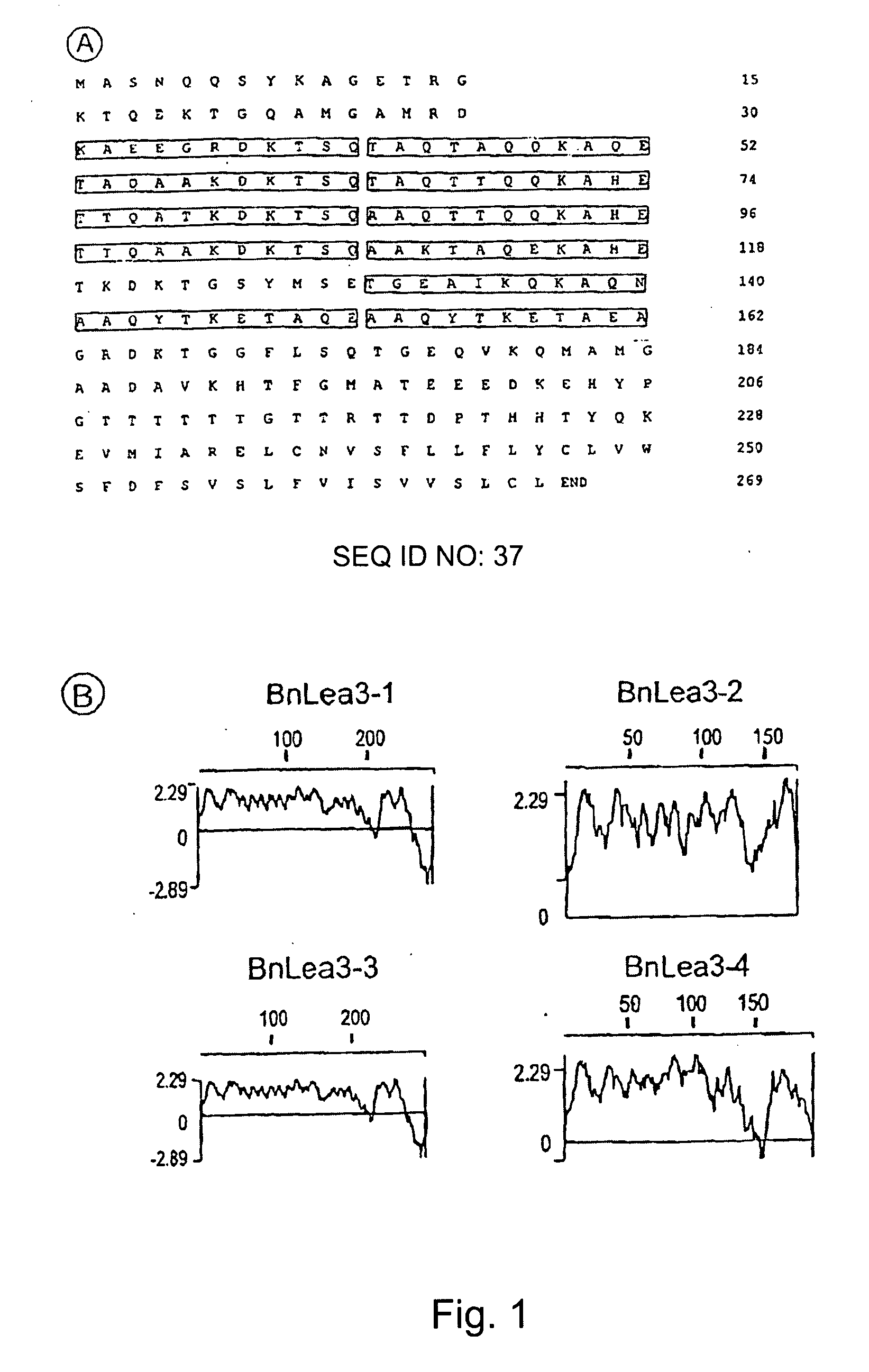
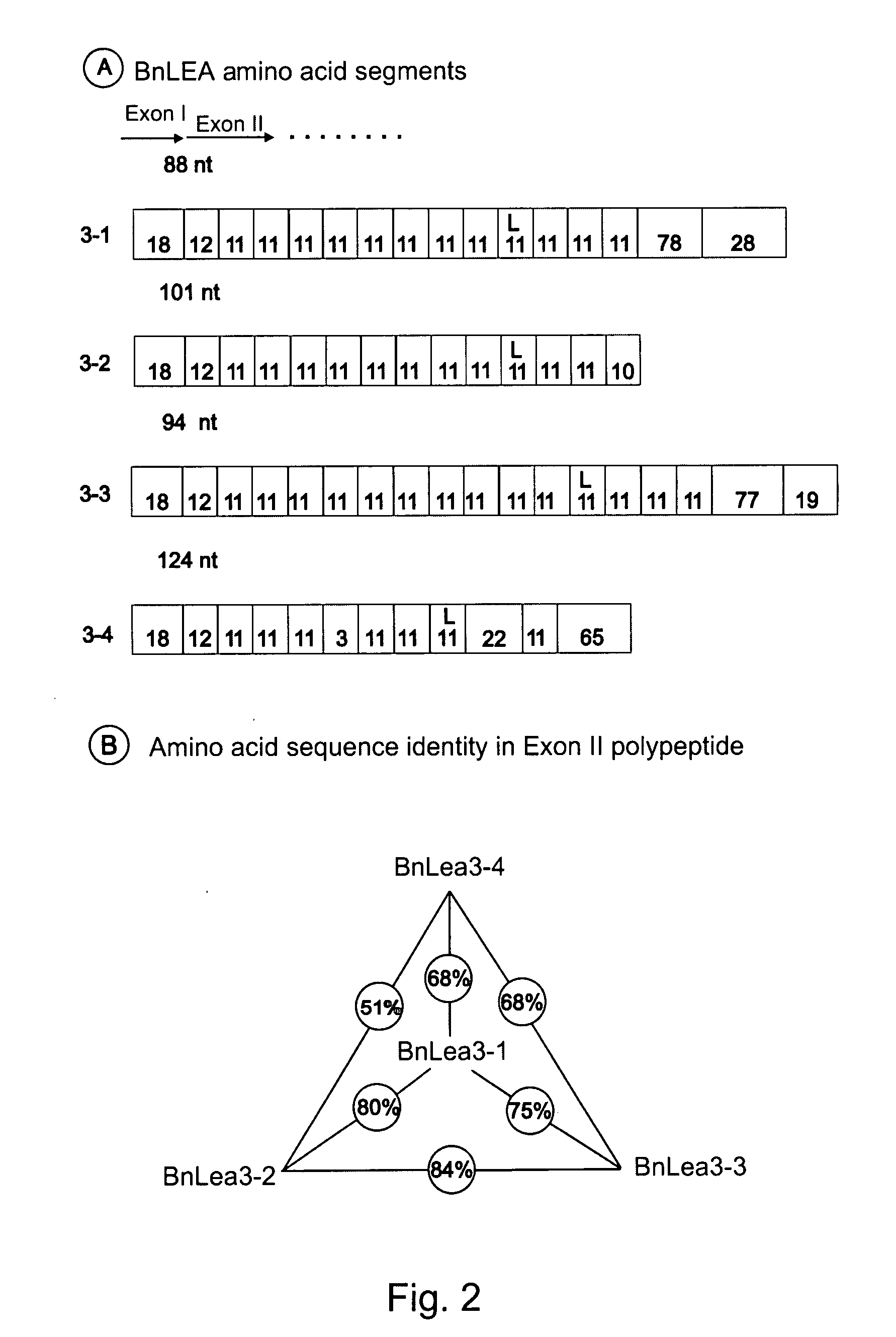
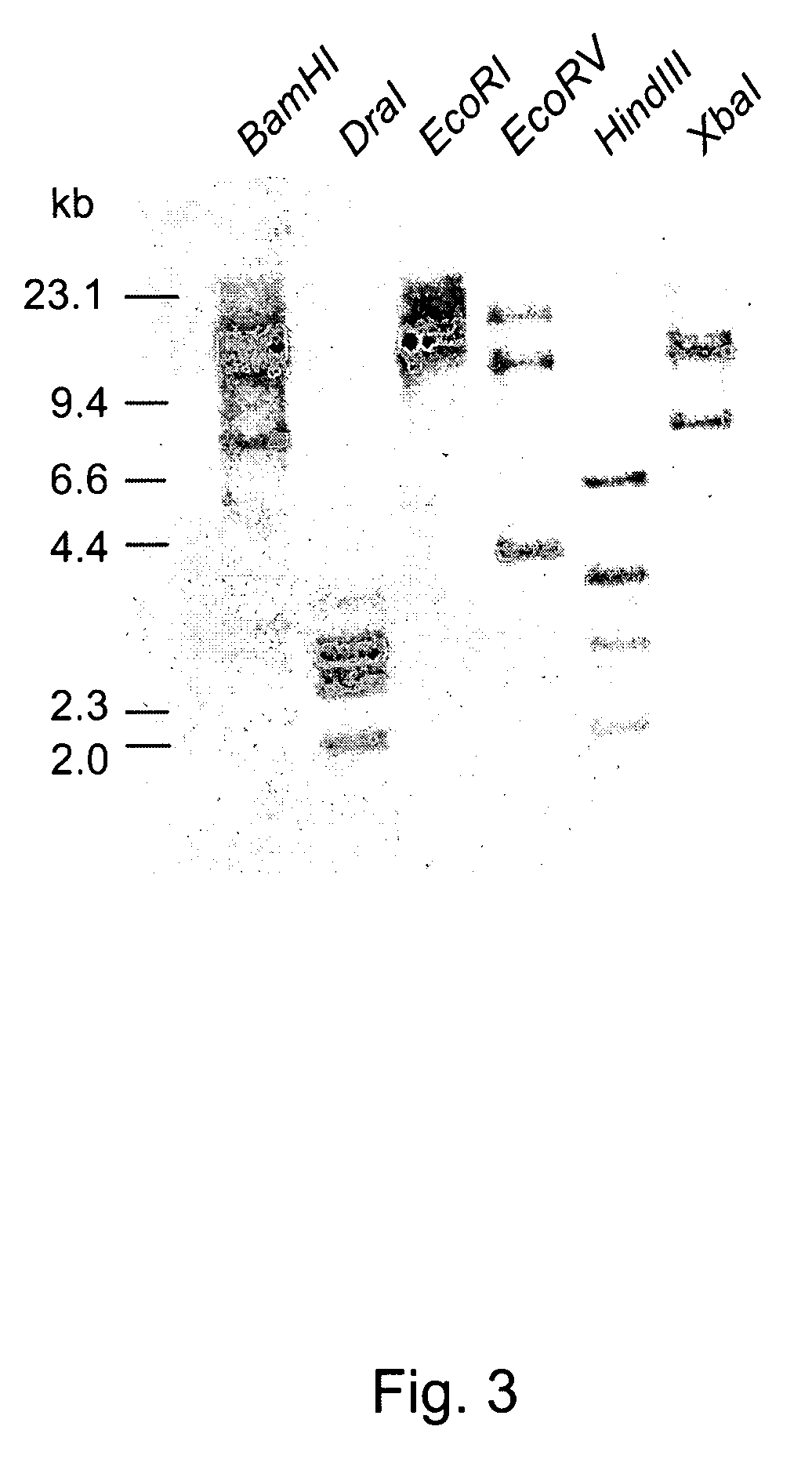
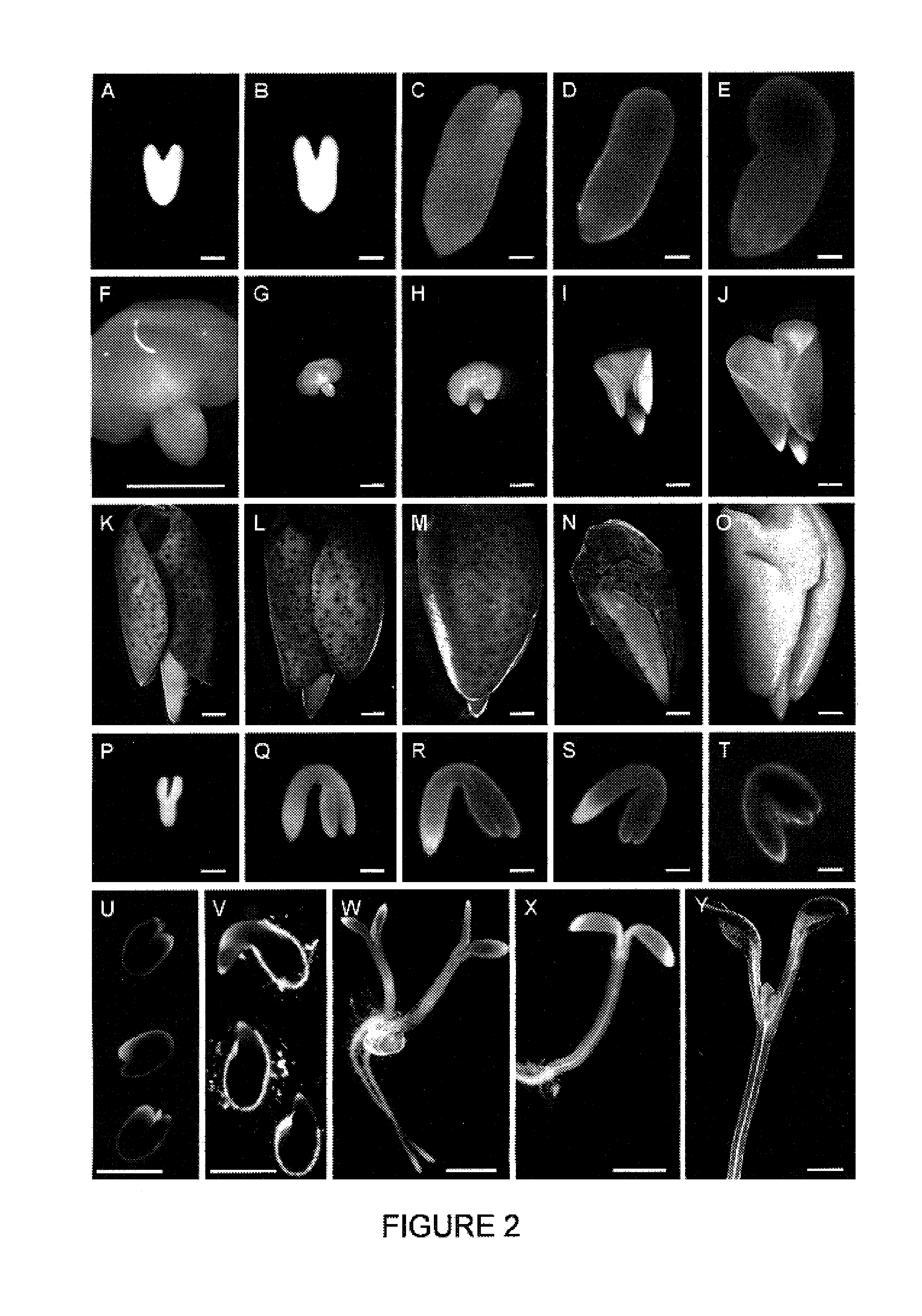
Late embryogenesis abundant (Lea) proteins accumulate in maturing seeds after many of the storage compounds have been synthesized, and they are considered relevant to maturation. We report here the molecular organization and expression of BnLea3-1, a novel Group 3 Lea gene from Brassica napus. BnLea3-1 contains a coding region of 798 bp, sharing 84.4% homology at the amino acid level with Lea76 of B. napus. Two tandem 11-mer repeats are truncated from the coding region of BnLea3-1, compared to the 13 conserved 11-mer repeats of Lea76. Substitutions of consensus residues are found at various positions within the 11-mer repeats. A 1561 bp 5′ flanking promoter fragment of BnLea3-1 fused to E. coli-glucuronidase (GUS) coding region conferred seed-specific GUS expression in stable transgenics of B. napus, tobacco and in transiently-transformed pea. A −137 bp minimal promoter preceding the first transcription start site, identified through progressive deletions from the upstream was sufficient for basal GUS expression in the seeds and in leaves treated with ABA. Deletion studies indicate the presence of enhancing elements located between −137 bp to −742 bp and suppressing elements located between −742 and −1561 bp. BnLea3-1 expression in seeds precedes that of Lea76. Unlike other Group 3 Lea members including HVA1 and Dc3, BnLea3-1 is active in seeds and responsive weakly in vegetative tissues to ABA and methyl jasmonate (MeJA) but not to stress treatments. Possible functions of BnLea3-1 and another member of the Group 3 Lea family BnLea3-2 in embryo development is discussed.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Cotton alpha-globulin promoter for seed-specific expression of transgenes
ActiveUS7626081B2Improve seed qualityInhibit seed germinationSugar derivativesStable introduction of DNAHeterologousFatty acid biosynthesis
The present invention is directed to 5′ regulatory regions of a cotton seed-specific gene, α-globulin. The 5′ regulatory region, or parts thereof, when operably linked to either the coding sequence of a native gene, heterologous gene or a sequence complementary to a native plant gene, direct expression of the coding sequence or complementary sequence in a plant seed. The regulatory regions are useful in expression cassettes and expression vectors for the transformation of plants. Also provided are methods of modulating the levels of a native or heterologous gene such as a fatty acid synthesis or lipid metabolism gene by transforming a plant with the subject expression cassettes and expression vectors.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids, novel biosynthesis genes, and novel plant expression constructs
The present invention relates to a method for the production of unsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds. The invention furthermore relates to the use of nucleic acid sequences SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 11 encoding polypeptides having desaturase activity in the method and for generating a transgenic organism, preferably a transgenic plant or a transgenic microorganism, with an increased content of fatty acids, oils or lipids with unsaturated C18-, C20-, or C22-fatty acids, and to their homologs or derivatives, to gene constructs encompassing these genes, and to their use alone or in combination with biosynthesis genes of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The invention also relates to multiexpression cassettes for seed-specific expression, and to vectors or organisms which encompass a desaturase gene alone or in combination with further desaturases and / or elongase genes or homologs using said expression cassettes.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Plant seed specific promoters
InactiveUS20070022502A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyPlanting seed
The present invention relates to novel seed specific promoter regions. The present invention further provide methods of producing proteins and other products of interest and methods of controlling expression of nucleic acid sequences of interest using the seed specific promoter regions. The present invention also provides methods of identifying and isolating novel seed specific promoters.
Owner:MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Canola oil having increased oleic acid and decreased linolenic acid content
InactiveUS20060137040A1Other foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesAntioxidantAdemetionine
An endogenous oil extracted from Brassica seeds is disclosed that contains, after crushing and extraction, greater than 86% oleic acid and less than 2.5% α-linolenic acid. The oil also contains less than 7% linoleic acid. The Brassica seeds are produced by plants that contain seed-specific inhibition of microsomal oleate desaturase and microsomal linoleate desaturase gene expression. Such inhibition can be created by cosuppression or antisense technology. Such an oil has a very high oxidative stability in the absence of added antioxidants.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Seedling and seed specific expression GmPLPA gene promoter for soybean and application thereof
InactiveCN101914534AAvoid wastingStrong specificity and high efficiencyFungiBacteriaPlant varietySeedling
The invention discloses a seedling and seed specific expression GmPLPA gene promoter for soybean and application thereof. The promoter provided by the invention is a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule shown as a sequence 1 or partial segment of the molecule. The GmPLPA gene promoter is cloned in the soybean for the first time. The promoter of the invention can be applied at a specific stage (such as a seedling stage) of plant development or to a specific texture (such as seed) expression target gene to avoid resource waste caused by the starting of the target gene by a constitutive promoterand has the advantages of high specificity and high efficiency. The promoter provided by the invention can be applied to a new transgenic plant variety with high directive breeding safety and has great value for plant breeding and the research on the function and acting mechanism of the target gene.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Use of a seed specific promoter to drive odp1 expression in cruciferous oilseed plants to increase oil content while maintaining normal germination
ActiveUS20100257635A1High oil contentOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologySucrose synthetase
A recombinant DNA construct comprising a polynucleotide encoding an ODP1 polypeptide operably linked to a sucrose synthase 2 promoter where this construct can be used to increase oil content in the seeds of a cruciferous oilseed plant while maintaining normal germination is disclosed. A method for increasing oil content in the seeds of a cruciferous oilseed plant while maintaining normal germination using this construct is also disclosed.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Artificial sequence for increasing methionine content of soy and plant expression vector thereof
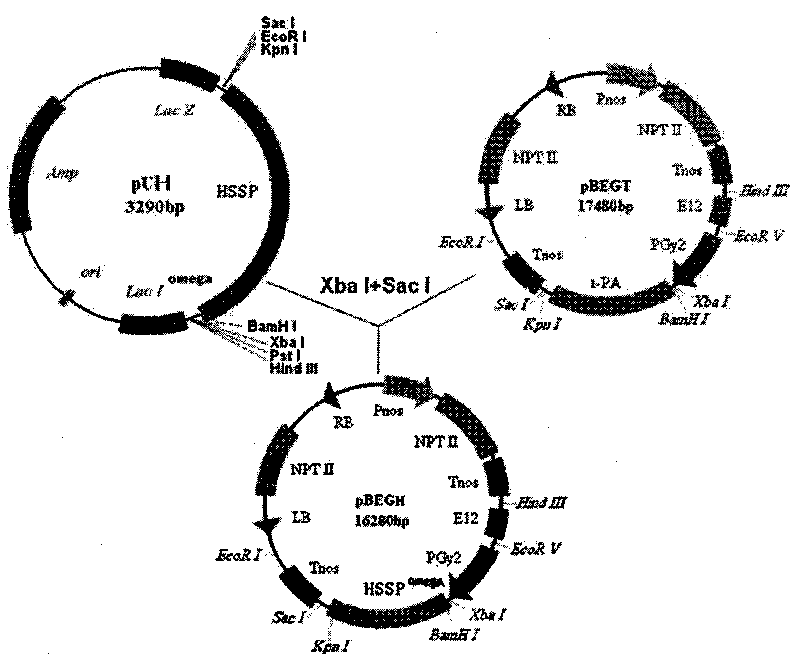
ActiveCN101698841AIncrease methionine contentStable expressionVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyTransgenic technology
The invention relates to an artificial sequence for increasing the methionine content of soy and a plant expression vector thereof, which solve the problem of the poor stability of the prior methods for increasing the methionine content of the soy in the prior transgenic technology. In the artificial sequence HSSP for increasing the methionine content of the soy of the invention, the sequence of the HSSP is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The plant expression vector of the artificial sequence for increasing the methionine content of the soy comprises the artificial sequence HSSP, wherein the upstream of the artificial sequence HSSP of the plant expression vector comprises an E12 enhancer sequence and a seed specific expression promoter PGY2, while the downstream comprises a Tnos terminator sequence. The technical scheme of the invention can be used for cultivating transgenic soy with high methionine content.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Use of a seed specific promoter to drive ODP1 expression in cruciferous oilseed plants to increase oil content while maintaining normal germination
ActiveUS8404926B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologySpore germination
A recombinant DNA construct comprising a polynucleotide encoding an ODP1 polypeptide operably linked to a sucrose synthase 2 promoter where this construct can be used to increase oil content in the seeds of a cruciferous oilseed plant while maintaining normal germination is disclosed. A method for increasing oil content in the seeds of a cruciferous oilseed plant while maintaining normal germination using this construct is also disclosed.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Seed-specific gene promoters and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060191044A1High activitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesForeign proteinPromoter activity
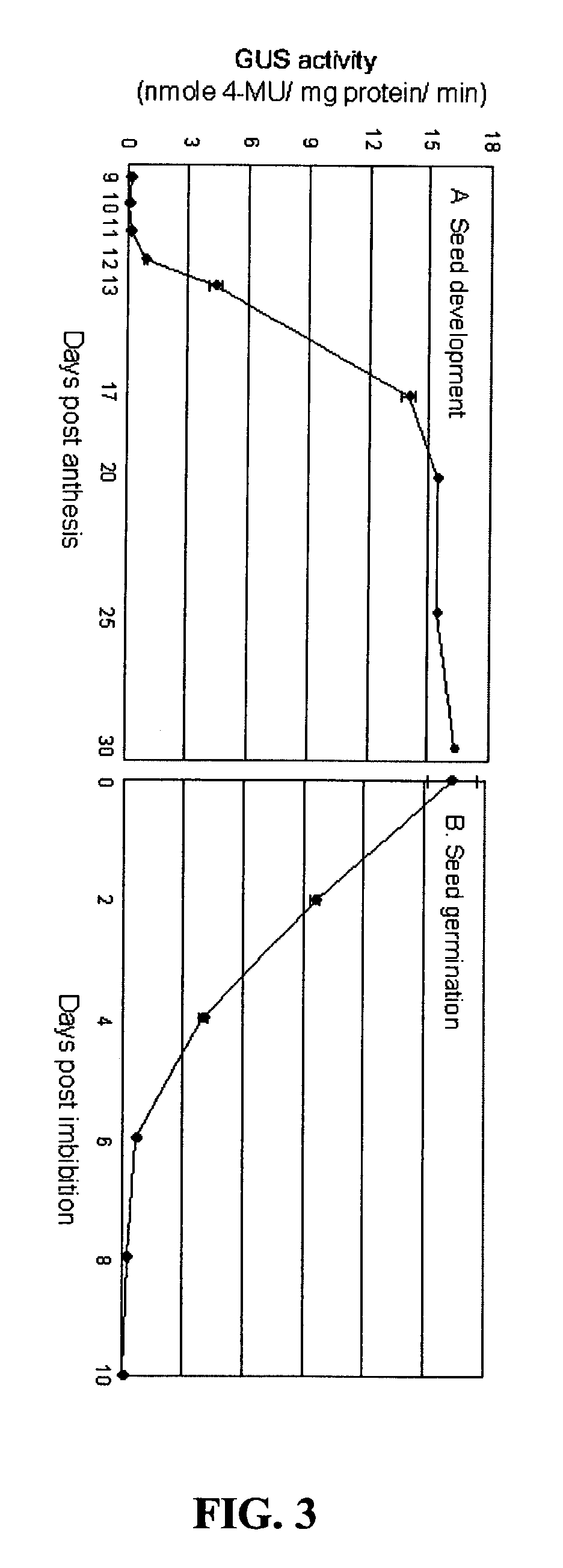
An objective of the present invention is to provide promoters having seed-specific promoter activity, and methods of expressing foreign proteins in seeds. The present inventors isolated the promoters of a number of genes that are expressed in rice seeds, constructed binary vectors in which each promoter is inserted upstream of the GUS reporter gene, and transformed rice using the Agrobacterium method. The inventors then used GUS expression level as an index to examine the site of expression, the expression pattern during seed maturation, and the level of expression in seeds for each promoter. They thus discovered promoters with activity specific to a particular site in seeds, and with higher activity than constitutive promoters and known seed-specific promoters.
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI
Method of increasing lysine content in paddy rice seed and special carrier
InactiveCN1834252AHigh in lysineFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
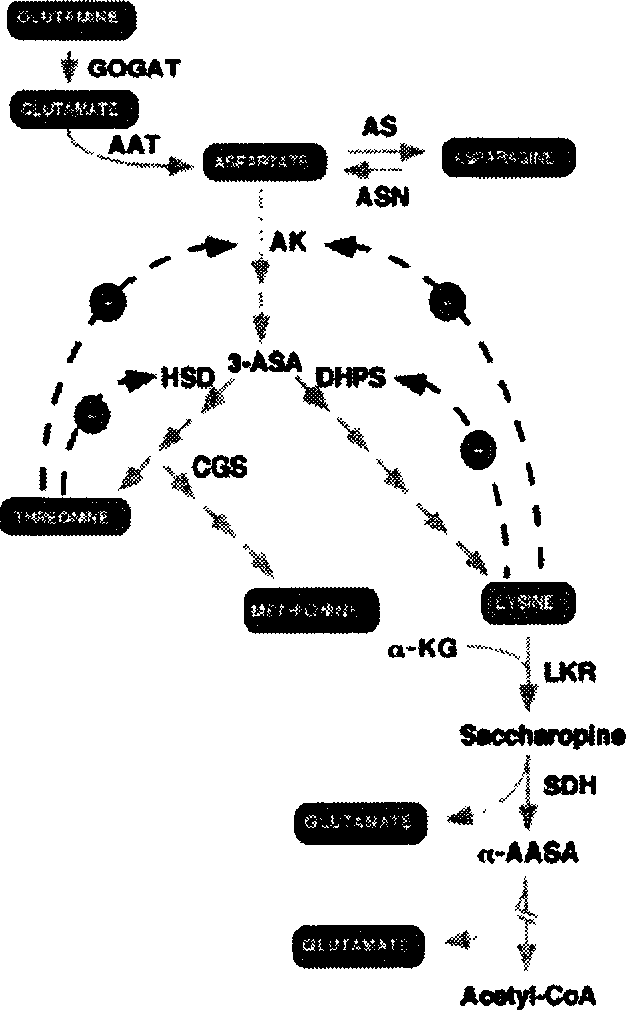
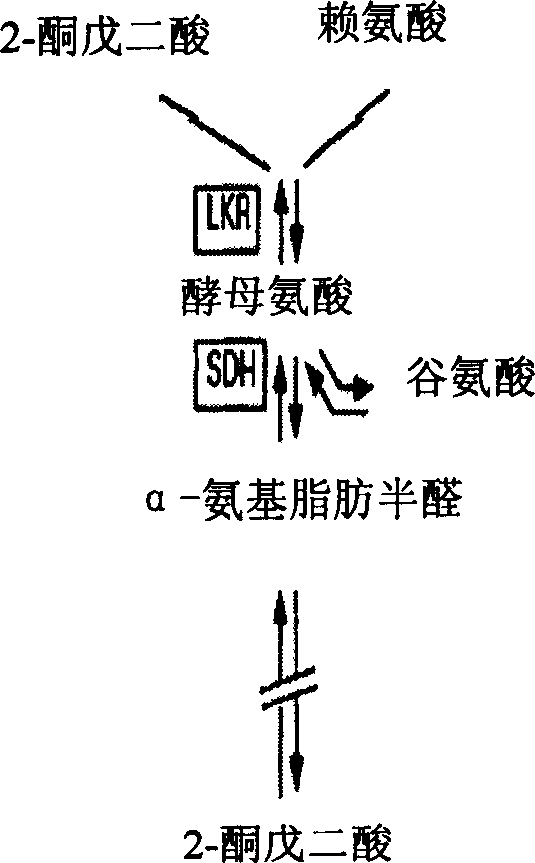
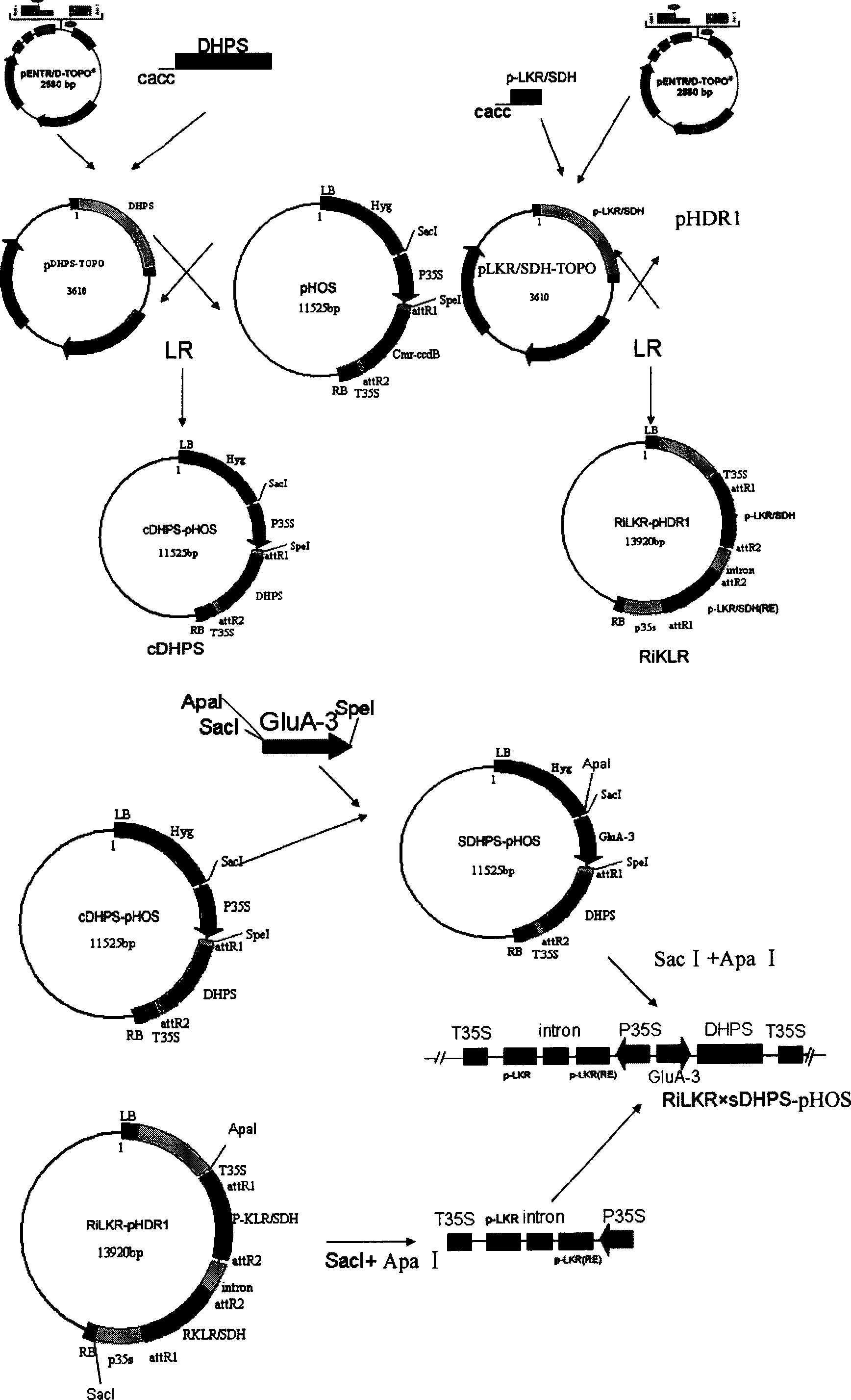
This invention discloses method and carrier for improving the content of lysine in rice seeds. The carrier is a plant expression carrier containing a rice seed specific promoter, dihydropicolinic acid synthetase gene and rice lysine-oxoglutaric acid reductases / saccharopin dehydrogenase gene interfering RNA coding sequence. The said dihydropicolinic acid synthetase gene is located at the downstream of the rice seed specific promoter, and the said rice lysine-oxoglutaric acid reductases / saccharopin dehydrogenase gene interfering RNA coding sequence is located at the downstream of the constitutive promoter. The genetically modified rice strains obtained in this invention have much higher free lysine content in seeds (10 times higher than that of Wild rice). Besides, the exogenous gene has no effect on rice growth. The method and the carrier have important applications in improving the lysine content in rice seeds, and provide a new way for modifying rice and other plants.
Owner:BEIJING KAITUO DNA BIOTECH RES CENT
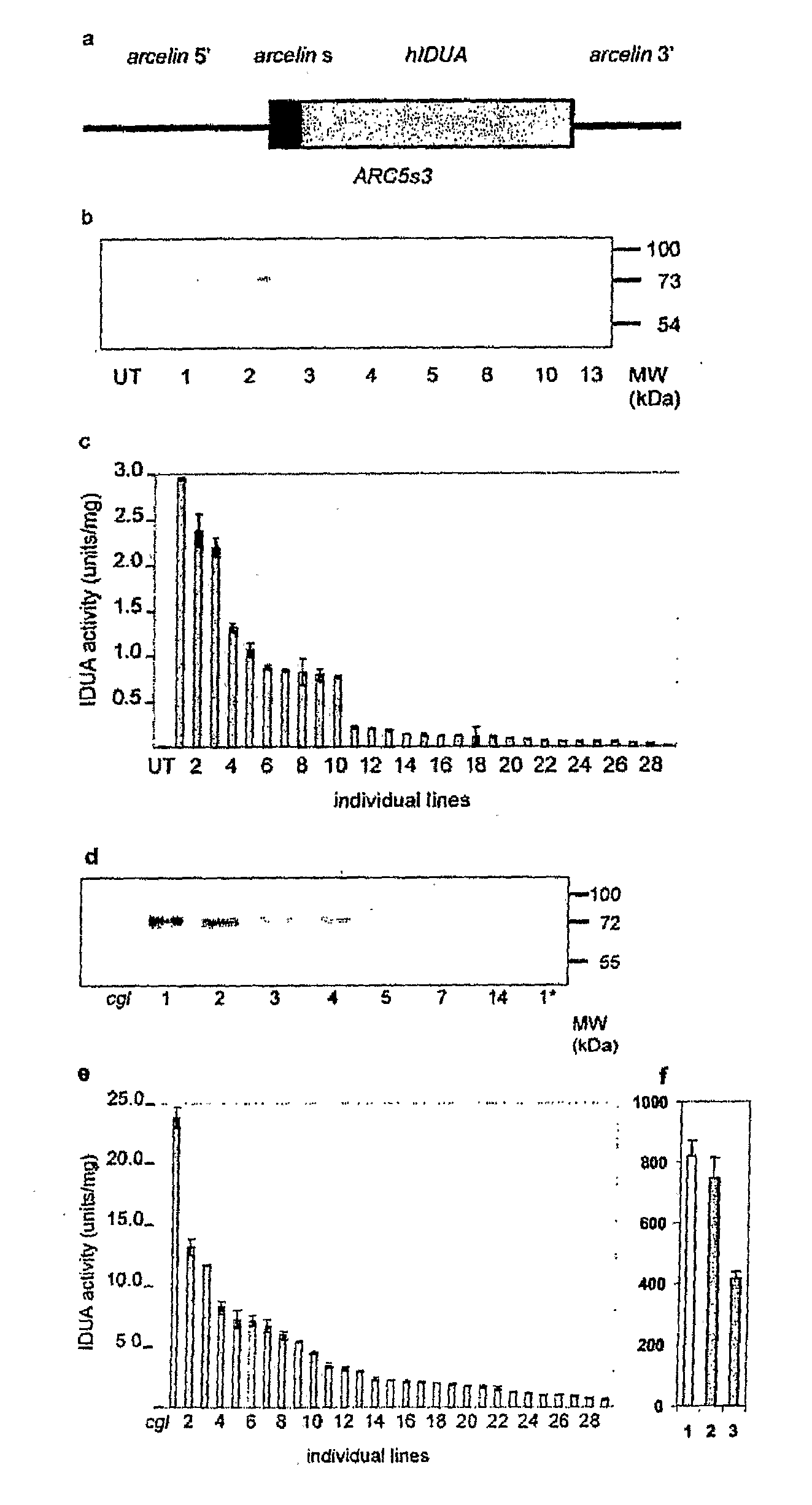
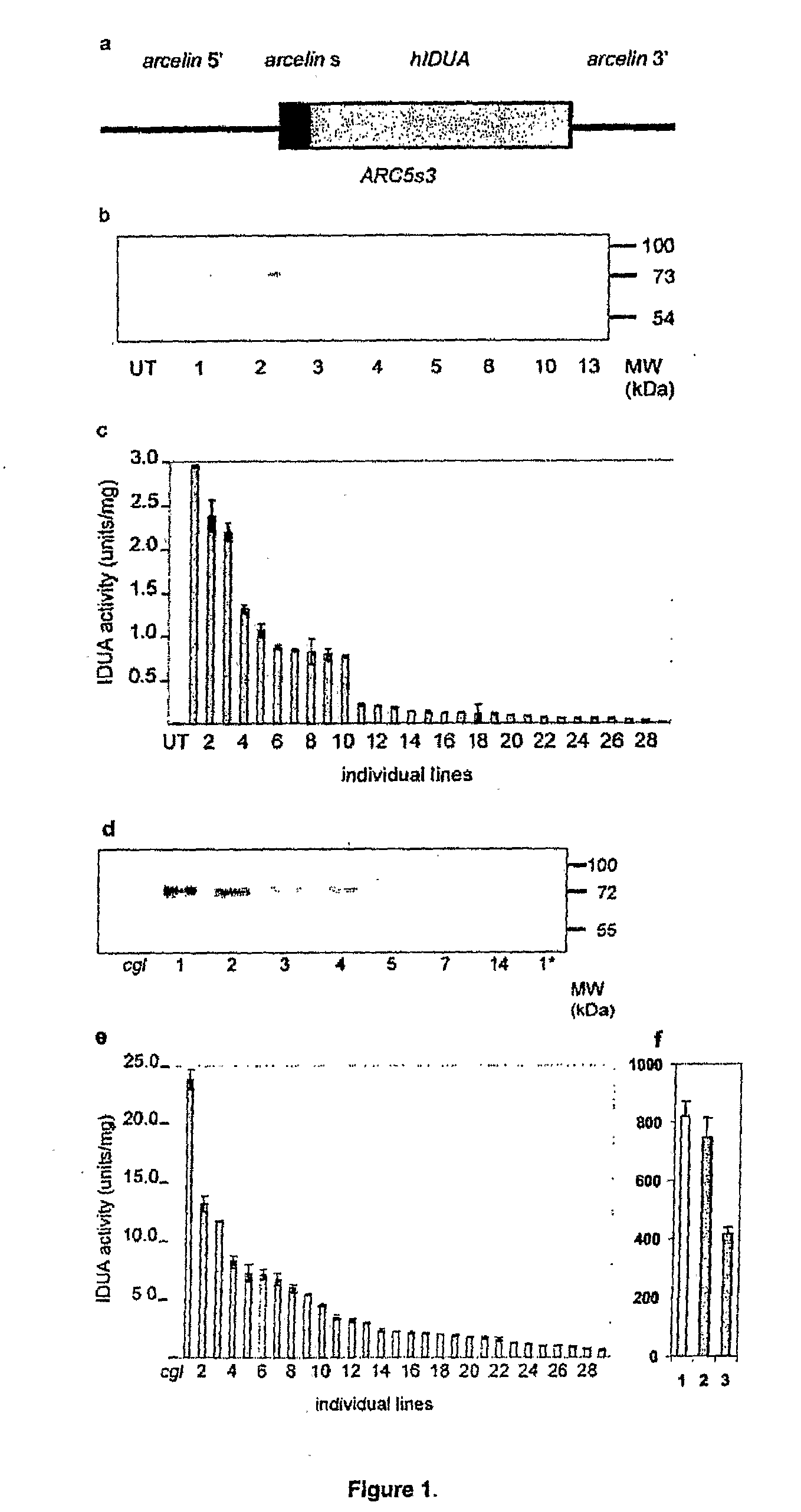
Enhancing vegetative protein production in transgenic plants using seed specific promoters
In various embodiments, the invention provides expression systems for heterologous protein expression in vegetative plant tissues, utilizing plant seed gene components that are adapted to orchestrate high levels of vegetative protein production. The expression systems may include host plant cells having recombinant genomes, and the plant cells may be maintained under protein expressing conditions, for example in tissue culture. The cells may be induced to express an ABD transcription factor, for example by transformation with a vector having a constitutive ABB expression cassette. The recombinant sequences in operative linkage may include an integrated expression promoter responsive to the ABI3 transcription factor, such as an arcelin gene promoter, a vicilin gene promoter and a napin gene promoter. A 5′ untranslated region may include a region of an ABA responsive plant seed gene or an AB 13 responsive plant seed gene. A plant secretion signal peptide coding sequence may be included. An integrated heterologous protein coding region, encoding a recombinant protein, may be provided in an open reading frame with the signal peptide coding sequence. A 3′ untranslated region may be provided having a polyadenylation signal.
Owner:SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY
Seed-specific gene promoters and uses thereof
An objective of the present invention is to provide promoters having seed-specific promoter activity, and methods of expressing foreign proteins in seeds. The present inventors isolated the promoters of a number of genes that are expressed in rice seeds, constructed binary vectors in which each promoter is inserted upstream of the GUS reporter gene, and transformed rice using the Agrobacterium method. The inventors then used GUS expression level as an index to examine the site of expression, the expression pattern during seed maturation, and the level of expression in seeds for each promoter. They thus discovered promoters with activity specific to a particular site in seeds, and with higher activity than constitutive promoters and known seed-specific promoters.
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI
Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids, novel biosynthesis genes, and novel plant expression constructs
The present invention relates to a method for the production of unsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds. The invention furthermore relates to the use of nucleic acid sequences SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 11 encoding polypeptides having desaturase activity in the method and for generating a transgenic organism, preferably a transgenic plant or a transgenic microorganism, with an increased content of fatty acids, oils or lipids with unsaturated C18-, C20-, or C22-fatty acids, and to their homologs or derivatives, to gene constructs encompassing these genes, and to their use alone or in combination with biosynthesis genes of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The invention also relates to multiexpression cassettes for seed-specific expression, and to vectors or organisms which encompass a desaturase gene alone or in combination with further desaturases and / or elongase genes or homologs using said expression cassettes.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Plant expression carrier and method for cultivating low-phytic-acid rice
ActiveCN102864167AComposite effectsEffects on Phytic Acid SynthesisVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsRice plantsNucleotide
The invention discloses a plant expression carrier and a method for cultivating low-phytic-acid rice. The plant expression carrier comprises a hairpin structure unit inoculated into an original carrier and a specific promoter, wherein the specific promoter is a promoter Oleosin 18, and the nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing the plant expression carrier; (2) performing Agrobacterium-mediated transformation on the plant expression carrier to obtain a rice callus tissue; and (3) transferring the rice callus tissue onto a selective culture medium for further culture, transplanting onto a crop-growing field after seedling differentiation, and screening to obtain the low-phytic-acid rice plant. According to the invention, the seed specific promoter Oleosin 18 is used to control gene expression, so that gene silencing only occurs in seed embryos and aleurone layers, thereby effectively preventing the synthesis of phytic acid in other tissue positions of rice from being influenced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Rice seed specific expression promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN105087581AAffect growthBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGenomic clone
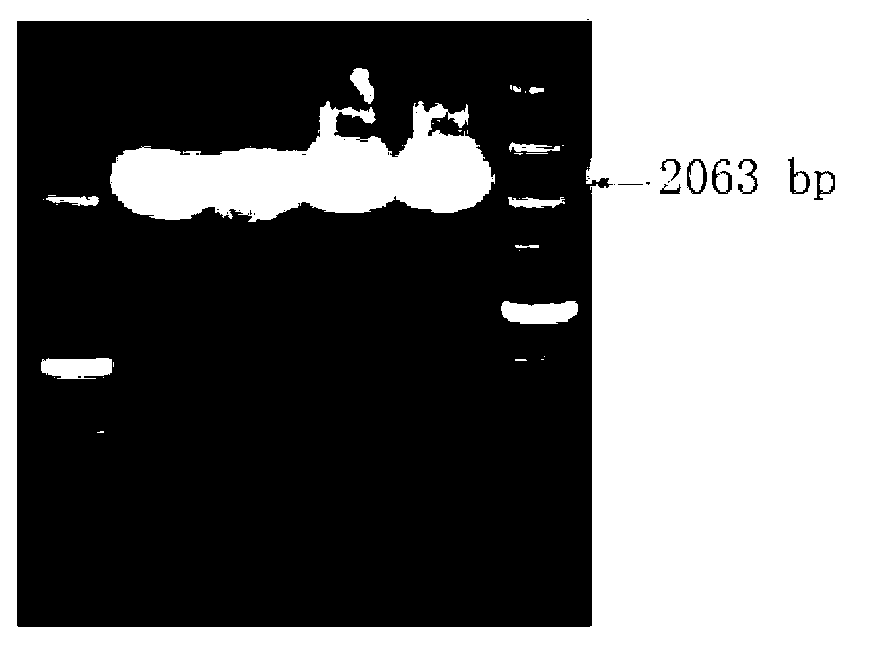
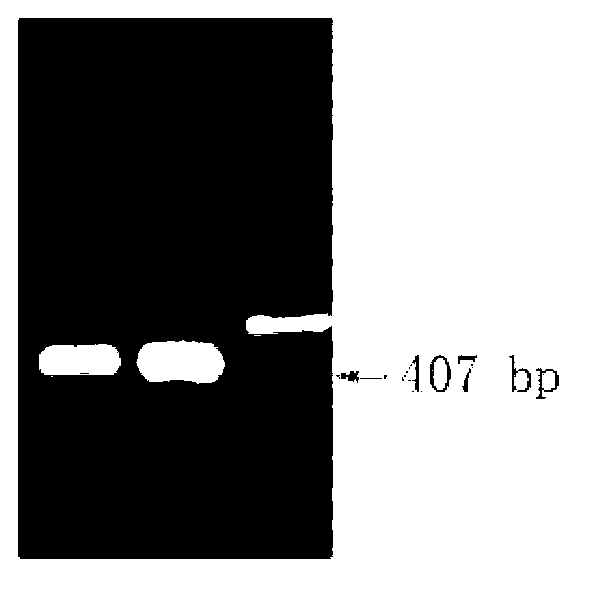
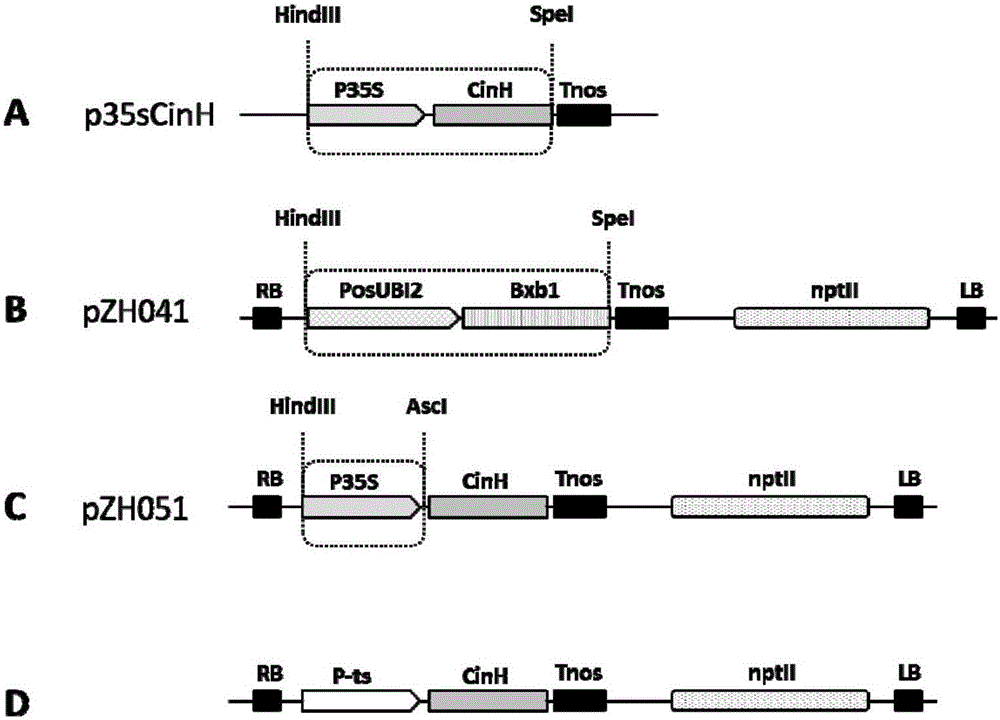
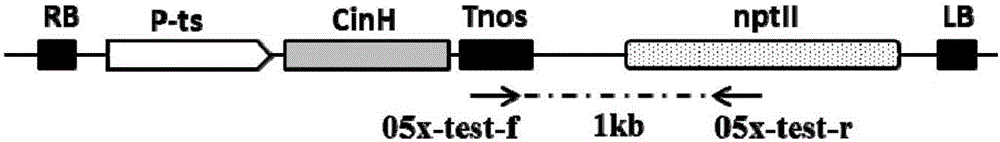
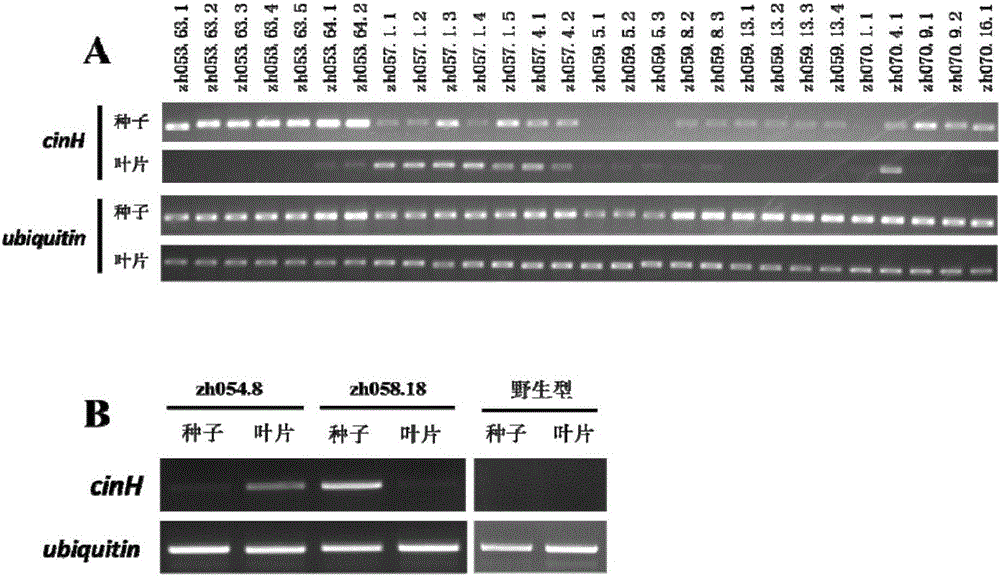
The invention discloses a rice seed specific expression promoter and application thereof. The sequence of the promoter is as shown in any one of SEQ ID NO. 1, SEQ ID NO. 2 and SEQ ID NO. 3, or the promoter has DNA molecule which is hybridized with the DNA sequence as shown in any one of SEQ ID NO. 1, SEQ ID NO. 2 and SEQ ID NO. 3 and has the functions of the promoter. The three promoters screened by the invention can be used for promoting the specific expression of target genes (such as cinH gene) in rice seeds, so that expression products of the target genes are accumulated in a specific special region, and the constitutive expression of the target genes in all tissues of rice is prevented to avoid influence on the growth of plants. The novel promoter disclosed by the invention can be extensive in application and market prospect in agricultural field.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Temporal seed promoters for expressing genes in plants
ActiveUS7179959B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering. More specifically, the present invention relates to seed specific gene expression during a defined period of embryogenesis. The present invention provides promoters capable of transcribing heterologous nucleic acid sequences in seeds, and methods of modifying, producing, and using the same.
Owner:RENESSEN
Regulatory nucleic acid molecules for enhancing seed-specific and/or seed-preferential gene expression in plants
The present invention is in the field of plant molecular biology and provides methods for production of high expressing seed-specific and / or seed-preferential promoters and the production of plants with enhanced seed-specific and / or seed-preferential expression of nucleic acids wherein nucleic acid expression enhancing nucleic acids (NEENAs) are functionally linked to the promoters and / or introduced into plants.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com