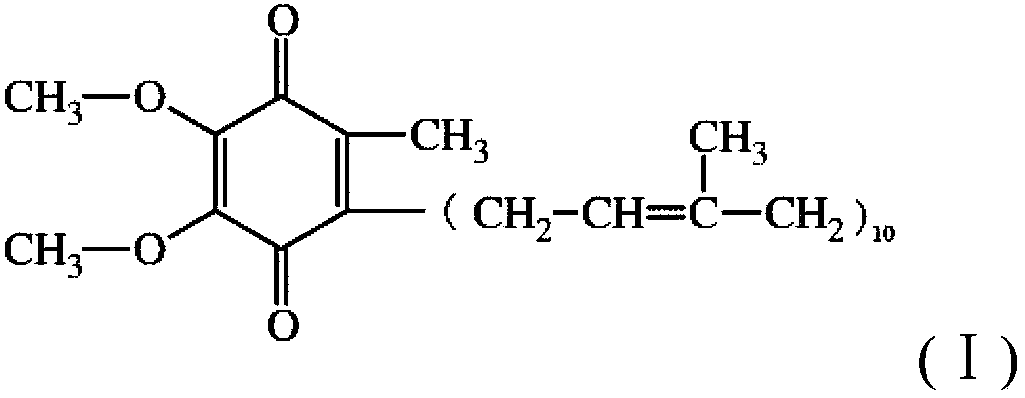
Patents
Literature
340 results about "Homologous gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Seed specific highly effective promoter and its application
The invention discloses a special promoter separated from millet, expressing carrier with nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1 host with the expressing carrier and appliance of the promoter, which is characterized by the following: utilizing Tail-PCR (colored body step moving method); getting the special promoter from gene group DNA; possessing nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1; ;linking downstream of the promoter to non-homologous or homologous gene; constructing plant expressing carrier; transferring host plant; driving the downstream gene to high effective and special express goal protein in the seed; realizing genetic modification of plant; or using as effective tool for studying plant and biological reactor.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Seed specificity highly effective promoter and its application
InactiveCN101063139AReduce adverse effectsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousNucleotide
The invention discloses a special promoter separated from millet, expressing carrier with nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1 host with the expressing carrier and appliance of the promoter, which is characterized by the following: utilizing Tail-PCR (colored body step moving method); getting the special promoter from gene group DNA; possessing nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1; ;linking downstream of the promoter to non-homologous or homologous gene; constructing plant expressing carrier; transferring host plant; driving the downstream gene to high effective and special express goal protein in the seed; realizing genetic modification of plant; or using as effective tool for studying plant and biological reactor.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
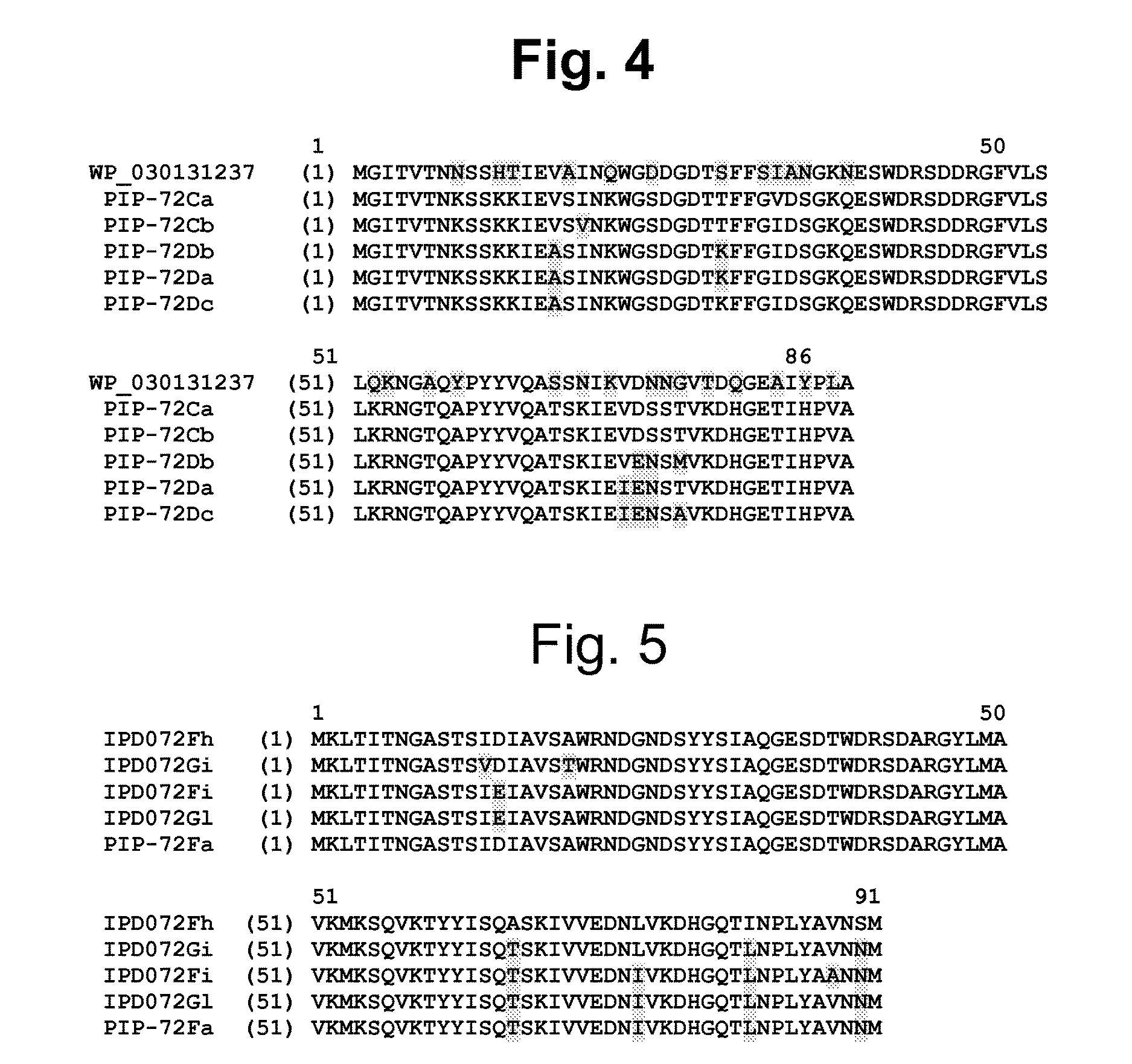
Novel Insecticidal Proteins and Methods for Their Use
ActiveUS20140033361A1Improve pest resistanceImprove toleranceBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyOrder Lepidoptera
Compositions and methods for controlling pests are provided. The methods involve transforming organisms with a nucleic acid sequence encoding an insecticidal protein. In particular, the nucleic acid sequences are useful for preparing plants and microorganisms that possess insecticidal activity. Thus, transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, plant tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions are insecticidal nucleic acids and proteins of bacterial species. The sequences find use in the construction of expression vectors for subsequent transformation into organisms of interest including plants, as probes for the isolation of other homologous (or partially homologous) genes. The pesticidal proteins find use in controlling, inhibiting growth or killing Lepidopteran, Coleopteran, Dipteran, fungal, Hemipteran and nematode pest populations and for producing compositions with insecticidal activity.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC +1
Insecticidal proteins and methods for their use
ActiveUS20160366891A1Improve pest resistanceImprove toleranceBiocideSugar derivativesPopulationNematode
Compositions and methods for controlling pests are provided. The methods involve transforming organisms with a nucleic acid sequence encoding an insecticidal protein. In particular, the nucleic acid sequences are useful for preparing plants and microorganisms that possess insecticidal activity. Thus, transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, plant tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions are insecticidal nucleic acids and proteins of bacterial species. The sequences find use in the construction of expression vectors for subsequent transformation into organisms of interest including plants, as probes for the isolation of other homologous (or partially homologous) genes. The pesticidal proteins find use in controlling, inhibiting growth or killing Lepidopteran, Coleopteran, Dipteran, fungal, Hemipteran and nematode pest populations and for producing compositions with insecticidal activity.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
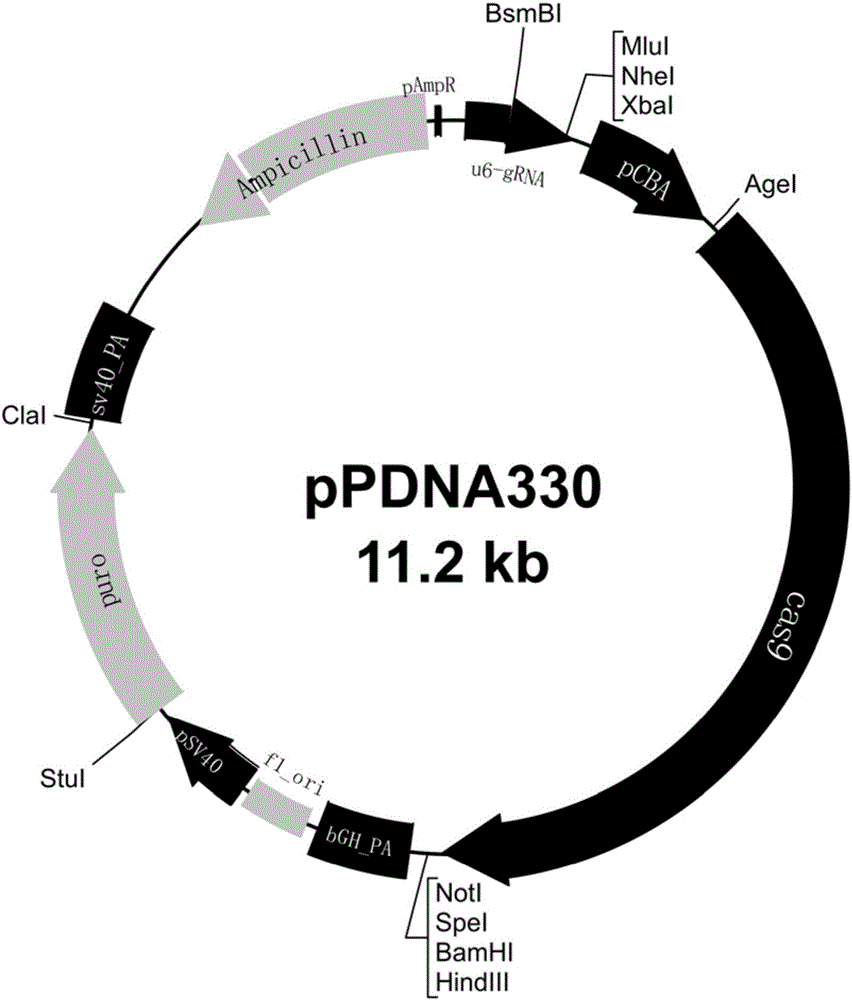
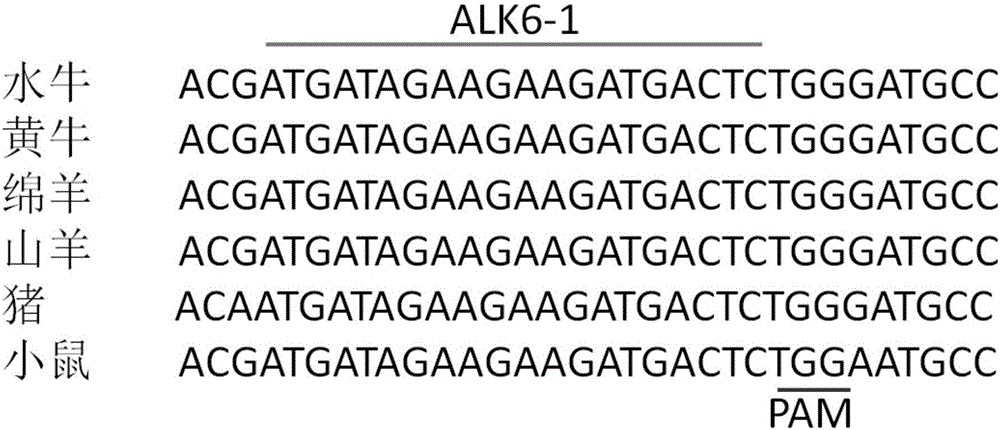
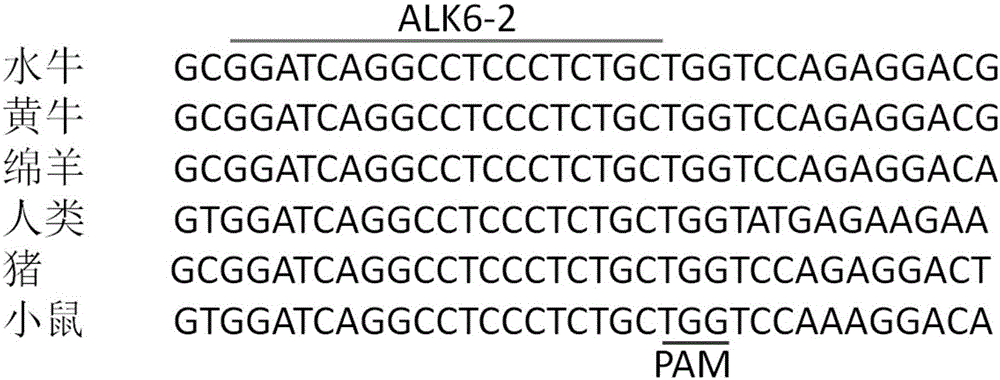
Method for targeted knockout of gene ALK6 by using CRISPR-Cas9
InactiveCN105925608AImprove universalityReduced editing efficiencyNucleic acid vectorReceptors for growth factors/regulatorsDouble strandedTransfection
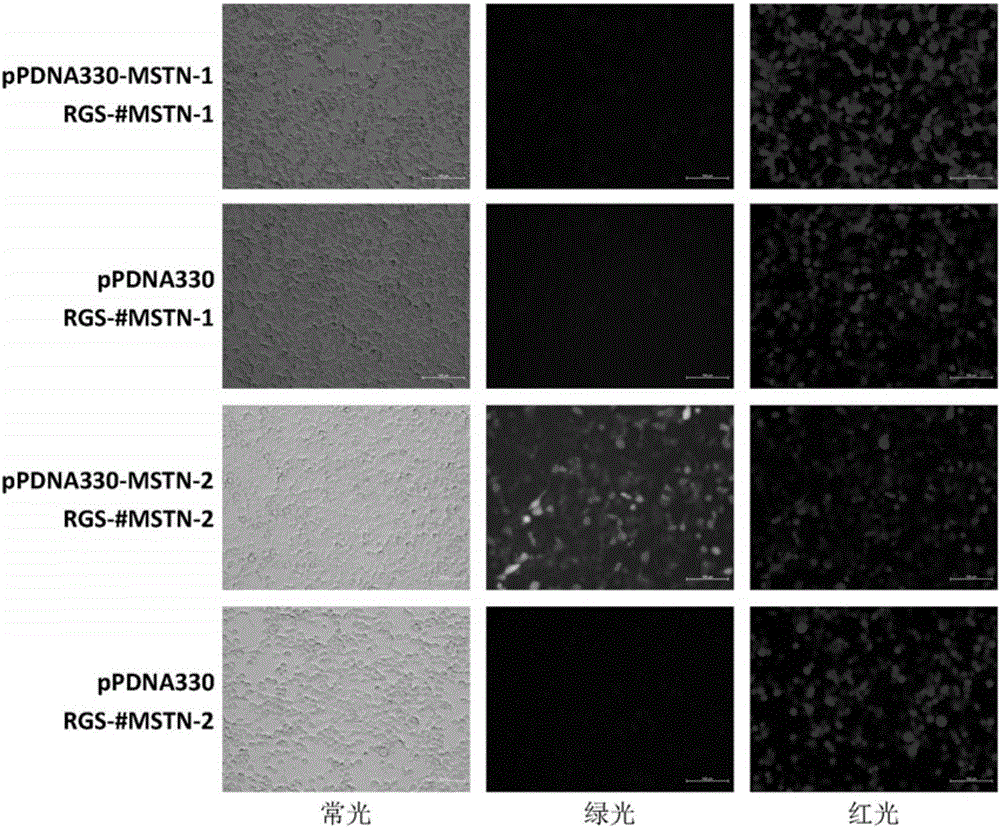
The invention discloses a method for targeted knockout of a gene ALK6 by using CRISPR-Cas9. The method comprises the steps of carrying out homologous comparison on a plurality of species so as to select two pairs of gene ALK6 target sequences, synthesizing DNA double strands, of which two pairs of target sequences are different and expressed proteins are the same and which have the same BsmBI cohesive ends, by using PAM design principles of gRNA, connecting the double strands with plasmid pPDNA330 so as to obtain recombinant vectors carrying ALK6 homologous genes of a plurality of species, detecting gene knockout efficiency of the recombinant vectors by using a fluorescin expression method, carrying out transfection on a vector with higher knockout efficiency with recipient cells of a plurality of species, and carrying out gene knockout and verification, thereby completing simple, efficient and accurate gene knockout of genes ALK6 of a plurality of species.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION BUFFALO INST
Method for knocking out MSTN (myostatin) genes in targeted manner by utilizing CRISPR-Cas9
InactiveCN106119283AImprove universalityReduced editing efficiencyNucleic acid vectorReceptors for growth factors/regulatorsMyostatinDouble strand
The invention discloses a method for knocking out MSTN (myostatin) genes in a targeted manner by utilizing CRISPR-Cas9. According to the method, multiple species are subjected to homology comparison, two pairs of MSTN gene target sequences are selected, two pairs of DNA double strands which have the sequences different from the target sequences, the same expression protein and the same BsmBi sticky ends are synthesized according to the design principle of PAM of gRNA, the double strands are connected with pPDNA330 plasmids, a recombinant vector carrying MSTN homologous genes of multiple species is obtained and is used for detecting the gene knockout efficiency with a fluorescent protein expression method, carrier-transfected receptor cells, having higher knockout efficiency, of multiple species are selected, gene knockout and verification are performed, and simple, efficient and accurate gene knockout on the MSTN genes of the multiple species is completed.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION BUFFALO INST
Insecticidal proteins and methods for their use
ActiveUS20160186204A1Improve pest resistanceImprove toleranceBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyOrder Lepidoptera
Compositions and methods for controlling pests are provided. The methods involve transforming organisms with a nucleic acid sequence encoding an insecticidal protein. In particular, the nucleic acid sequences are useful for preparing plants and microorganisms that possess insecticidal activity. Thus, transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, plant tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions are insecticidal nucleic acids and proteins of bacterial species. The sequences find use in the construction of expression vectors for subsequent transformation into organisms of interest including plants, as probes for the isolation of other homologous (or partially homologous) genes. The pesticidal proteins find use in controlling, inhibiting growth or killing Lepidopteran, Coleopteran, Dipteran, fungal, Hemipteran and nematode pest populations and for producing compositions with insecticidal activity.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Method and system for detection of phenotype genes and analysis of biological information
ActiveCN101930502AReduce misleadingEasy to handleMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsNucleotideData information
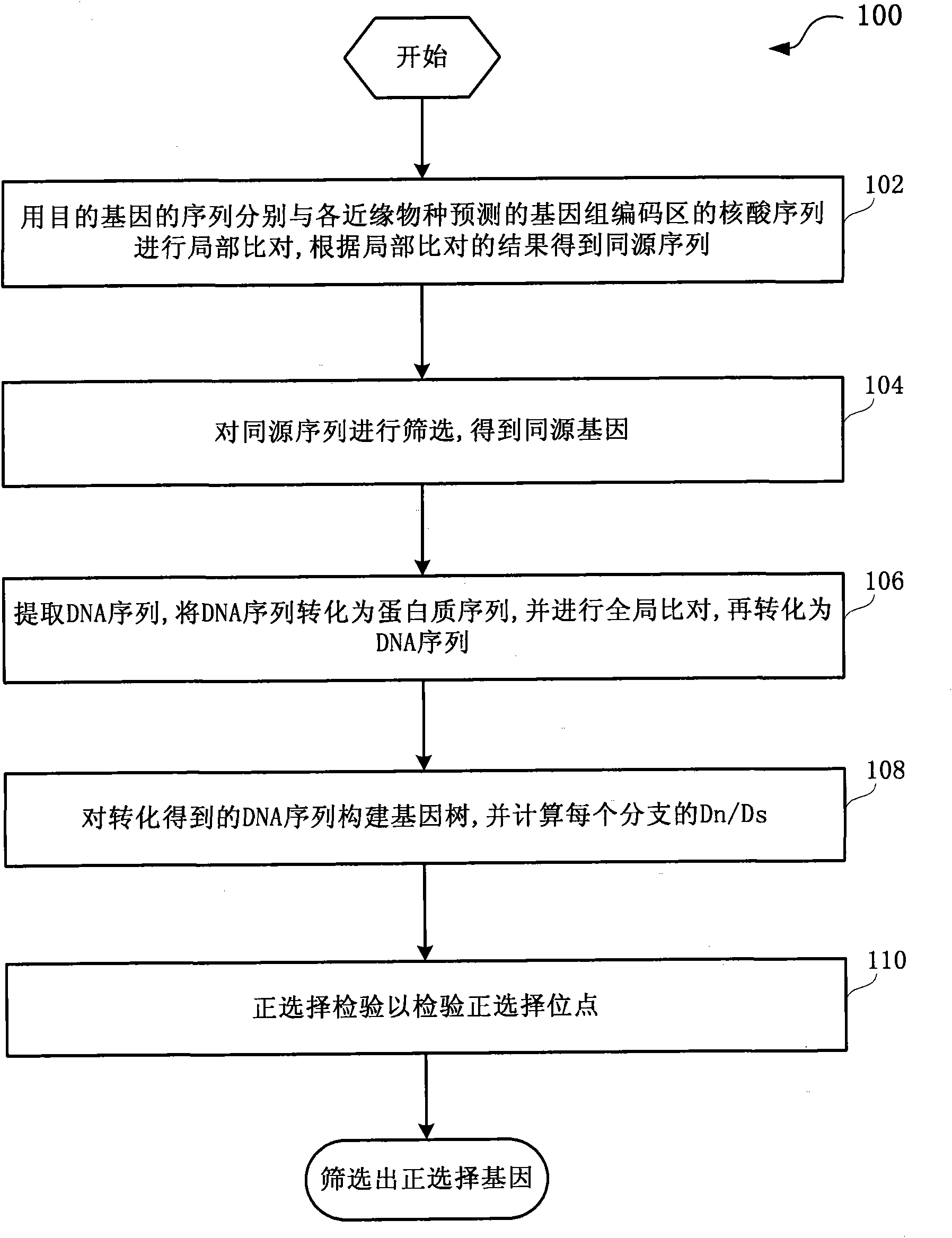
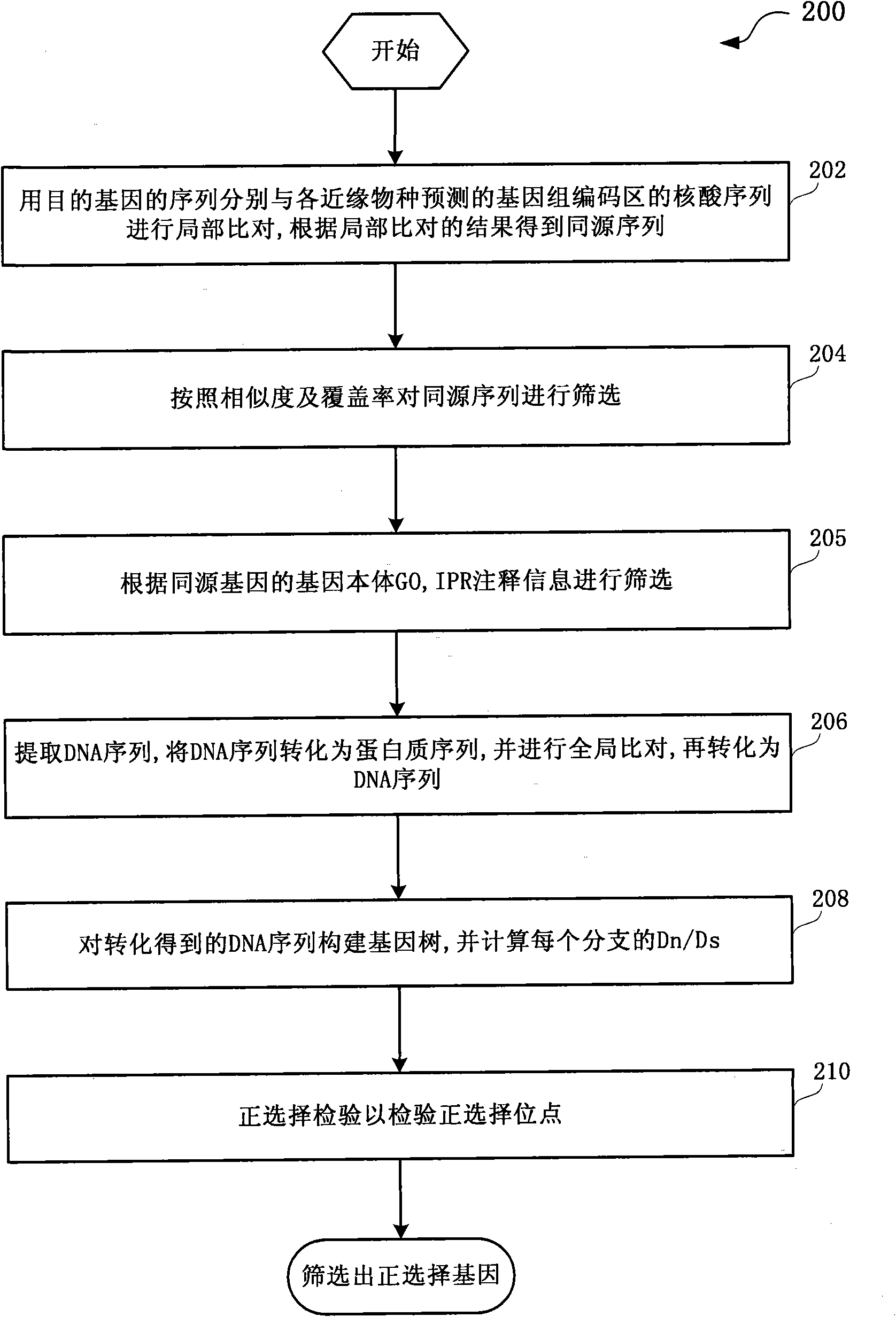
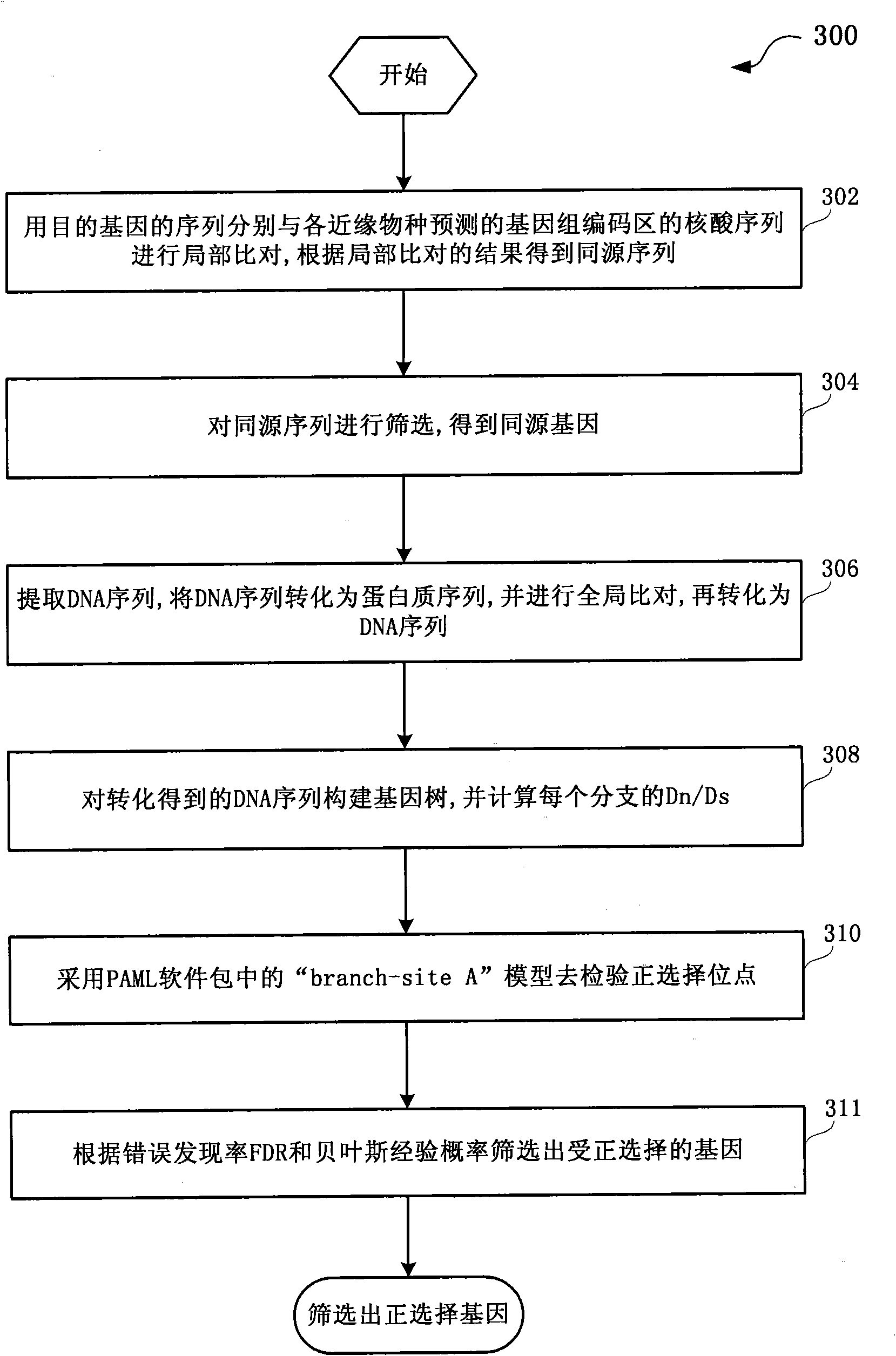
The invention discloses a method and a system for detection of phenotype genes and analysis of biological information. The method comprises the following steps of: performing local comparison between the sequence of target genes and nucleotide sequences of predicted genome coding regions of all allied species respectively, and obtaining a homologous sequence according to the local comparison results; screening the homologous sequence to obtain the homologous genes; extracting a DNA sequence from the homologous genes, converting the DNA sequence into a protein sequence, performing the overall comparison, and then converting the protein sequence into the DNA sequence; constructing a gene tree for the DNA sequence obtained by conversion, and working out Dn / Ds of each branch; and performing positive selection detection and detecting positive selection loci. The method and the system provided by the invention have the advantages of quickly processing a large amount of data information and discovering more accurate information, reducing misguiding of pseudogenes on analysis of biological information and helping to acquire the biological information to explain more biological problems.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Insecticidal proteins and methods for their use
ActiveUS9688730B2Increase productionEnhance the imageBiocideClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyOrder Lepidoptera
Compositions and methods for controlling pests are provided. The methods involve transforming organisms with a nucleic acid sequence encoding an insecticidal protein. In particular, the nucleic acid sequences are useful for preparing plants and microorganisms that possess insecticidal activity. Thus, transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, plant tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions are insecticidal nucleic acids and proteins of bacterial species. The sequences find use in the construction of expression vectors for subsequent transformation into organisms of interest, as probes for the isolation of other homologous (or partially homologous) genes. The insecticidal proteins find use in controlling, inhibiting growth or killing lepidopteran, coleopteran, dipteran, fungal, hemipteran, and nematode pest populations and for producing compositions with insecticidal activity.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Insecticidal proteins and methods of use
ActiveUS9403881B2High insecticidal activityBiocideClimate change adaptationMicroorganismBiological body
Compositions and methods for controlling pests are provided. The methods involve transforming organisms with a nucleic acid sequence encoding an insecticidal protein. In particular, the nucleic acid sequences are useful for preparing plants and microorganisms that possess insecticidal activity. Thus, transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, plant tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions are isolated insecticidal proteins and nucleic acids. The sequences find use in the construction of expression vectors for subsequent transformation into organisms of interest, as probes for the isolation of other homologous (or partially homologous) genes. The insecticidal proteins find use in controlling or killing lepidopteran, coleopteran, dipteran, fungal, hemipteran, and nematode pest populations and for producing compositions with insecticidal activity.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
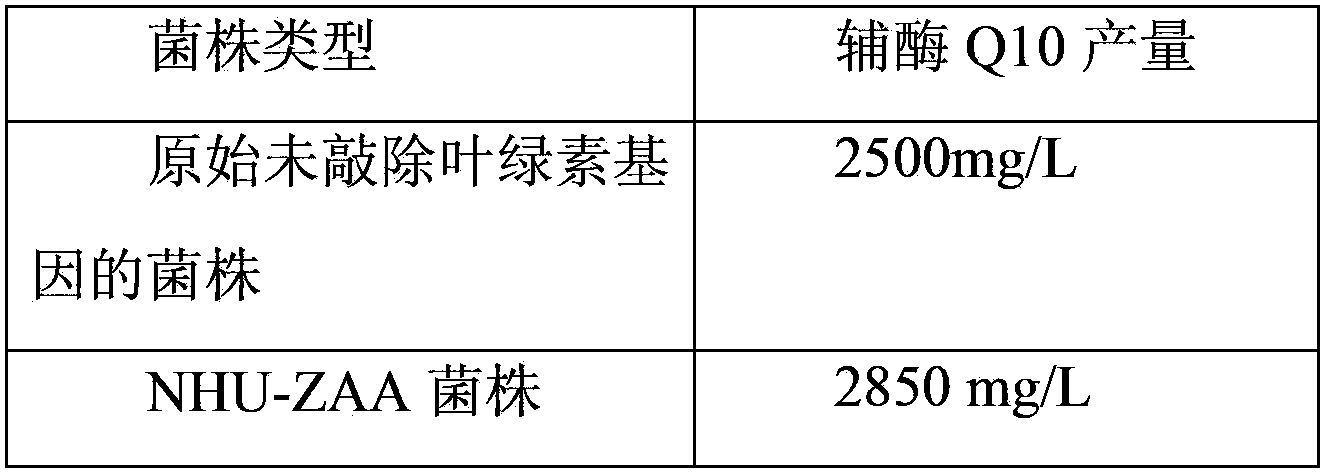
Coenzyme-Q10-production engineered bacteria construction method, engineered bacteria, and application thereof
ActiveCN103509728ALarge amount of synthesisIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGenomic DNA
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and discloses a coenzyme-Q10-production engineered bacteria construction method, engineered bacteria, and an application thereof. The method comprises the steps that: a, total genomic DNA is extracted from Rhodobacter sphaeroides cacterial liquid; b, bchG homologous gene is obtained by amplification with a polymerase chain reaction; c, the amplified homologous gene is connected with broad-host plasmid, such that recombinant vector is constructed; d, the recombinant vector is transferred to Escherichia coli S17-1; and e, the Escherichia coli S17-1 is subjected to conjugal transfer with the Rhodobacter sphaeroides, such that the engineered bacteria with chlorophyll synthesis gene bchG knocked out are obtained. According to the method provided by the invention for improving coenzyme Q10 yield through knocking out Rhodobacter sphaeroides chlorophyll synthesis gene, coenzyme Q10 synthesis capacity can be improved by higher than approximately 15%. The method is suitable for coenzyme Q10 large-scale industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NHU CO LTD +1
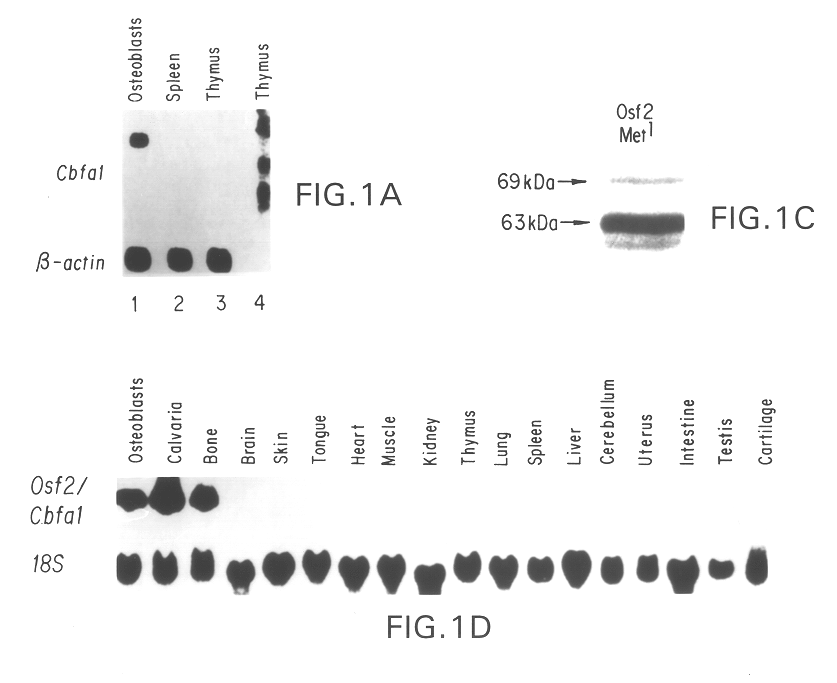
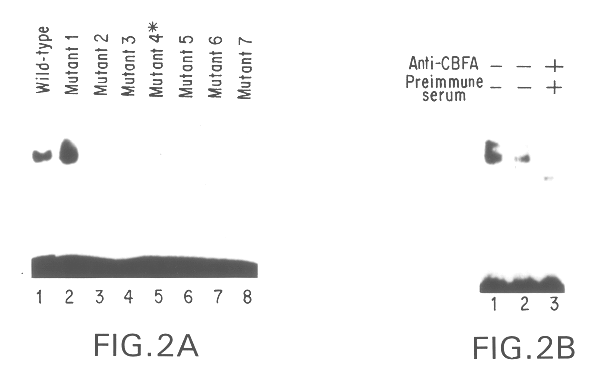
Osf2/Cbfa1 nucleic acids and methods of use therefor
InactiveUS6518063B1Improving immunogenicityIncrease stability and selectivityOrganic active ingredientsNanotechHeterologousNucleotide
Disclosed are methods and compositions comprising a novel osteoblast-specific transcription factor designated Osf2 / Cbfa1. Also disclosed are nucleic acid segments encoding this polypeptide derived from human cell lines, and the use of these polynucleotides in a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Methods, compositions, kits, and devices are also provided for identifying compounds which are inhibitors of osteoblast differentiation, and identifying Osf2 / Cbfa1 polynucleotides and polypeptides in a sample. Also disclosed are nucleic acid compositions comprising an Osf2 promoter, and the use of the promoter in heterologous and homologous gene transcription and protein production.
Owner:TEXAS SYST UNIV OF BOARD OF REGENTS THE
Plant having improved resistivity or sensitivity to 4-hppd inhibitor
ActiveCN103403165AImprove the immunityIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyResistant genes
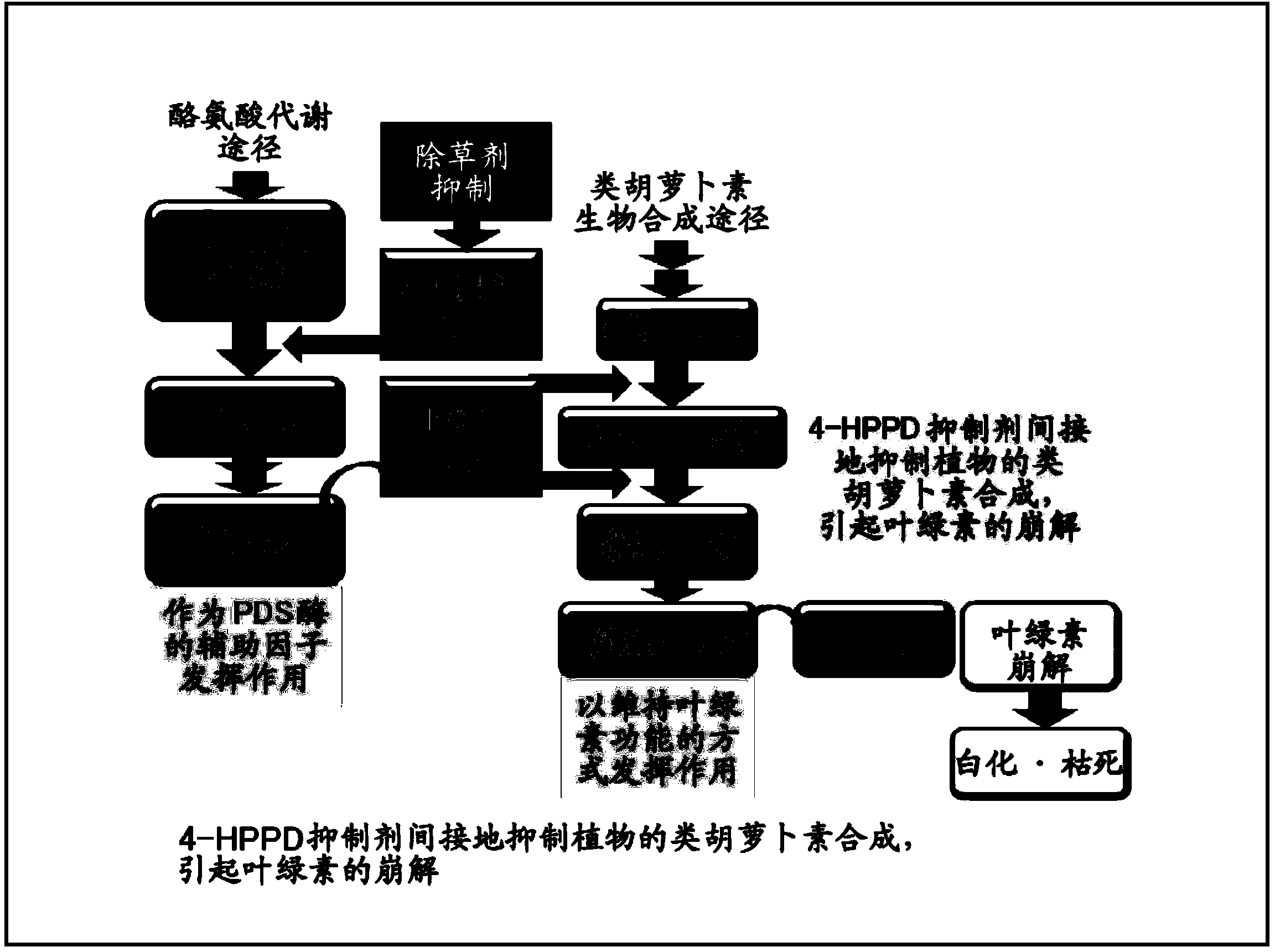
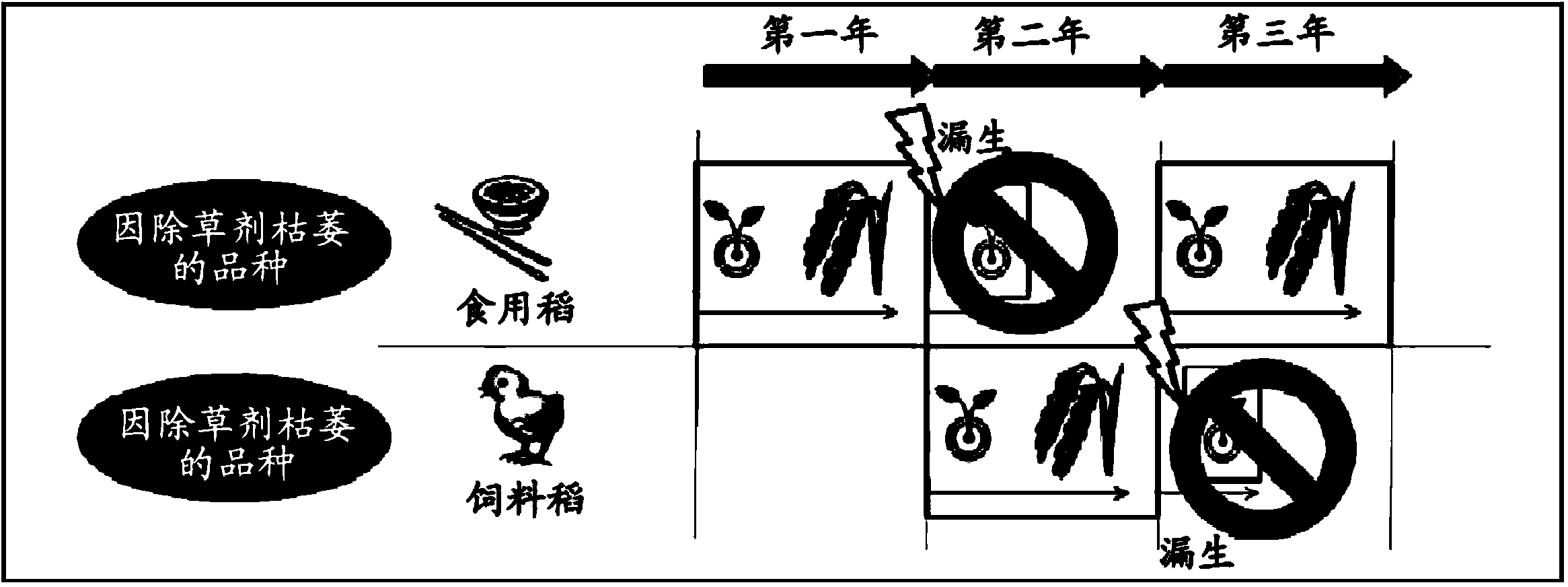
A 4-HPPD inhibitor-resistant gene is identified as a gene (HIS1 gene) which is estimated as an iron- / ascorbic acid-dependent oxidoreductase gene located on the short arm of chromosome-2 of a rice plant, by carrying out QTL analysis using a 4-HPPD inhibitor-sensitive rice plant and a 4-HPPD inhibitor-resistant rice plant or the like. It is also found that a homologous gene (HSL1 gene) to the HIS1 gene is located on chromosome-6 of a rice plant. It is found that a plant having improved resistivity or sensitivity to a 4-HPPD inhibitor can be produced with high efficiency and the resistivity or sensitivity of a plant to a 4-HPPD inhibitor can be determined with high efficiency using the aforementioned genes.
Owner:NAT AGRI & FOOD RES ORG +1
Protein vaccines against poxviruses
InactiveUS20100196491A1High degreeIncreased cross-reactivityPowder deliveryViral antigen ingredientsOpen reading frameMonkeypox
The invention described here entails a protein vaccine against poxviruses which contains at least two purified recombinant monkeypox virus proteins or peptides. The proteins or peptides are encoded by the open reading frames of the monkeypox ortholog genes M1R, A35R, A29L B6R, and orthologs of these proteins or peptides having 90% identity. The invention also entails a vaccine protocol against poxvirus whereby a vaccine is vaccinated with a first vaccine made up of a nucleic acid vaccine of three or more poxvirus virus genes, and subsequently vaccinated with at least one other booster vaccine made up of two or more poxvirus virus proteins.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
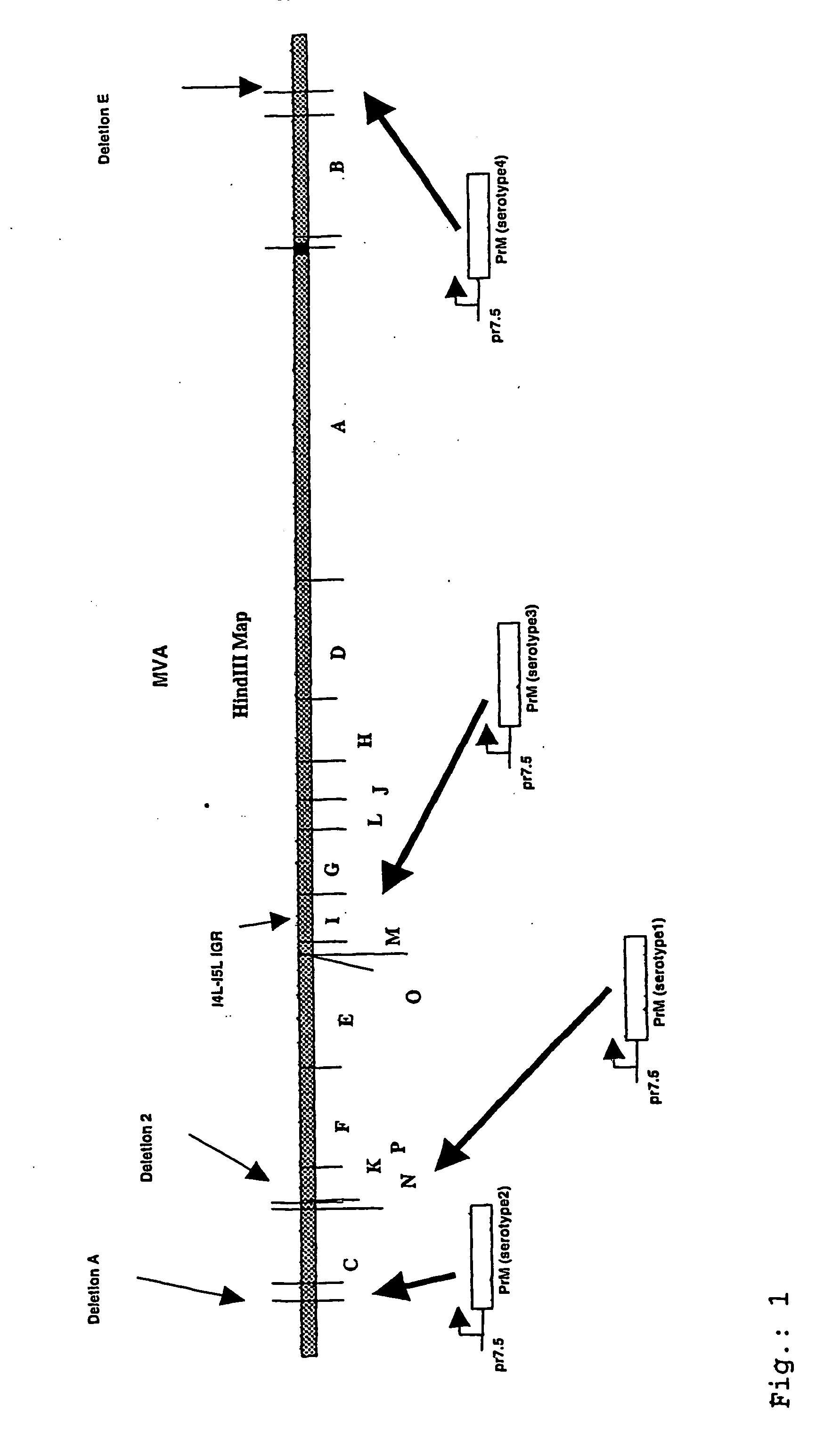
Recombinant poxvirus expressing homologous genes inserted into the foxviral genome
InactiveUS20060165727A1Stable and effective and reliable vaccineReliable vaccinationFungiSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicroorganismViral vector
The sent invention relates to a recombinant poxvirus vector capable of expressing two or more homologous, foreign sequences, which derive from different variants of a microorganism, and which have a homology of 50% or above. The invention further relates to a method for preparing such recombinant poxvirus and the use of such recombinant poxvirus as medicament or vaccine. Additionally, a method for affecting preferably inducing, an immune response in a living animal, including a human, is provided.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
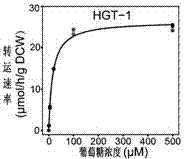
Method for improving expression of filamentous fungi lignocellulosic enzyme line and production of bio-based chemicals
InactiveCN107236757AImprove utilizationPromote degradationFungiDepsipeptidesPenicillinGenetic engineering
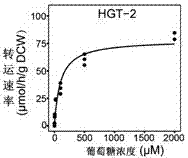
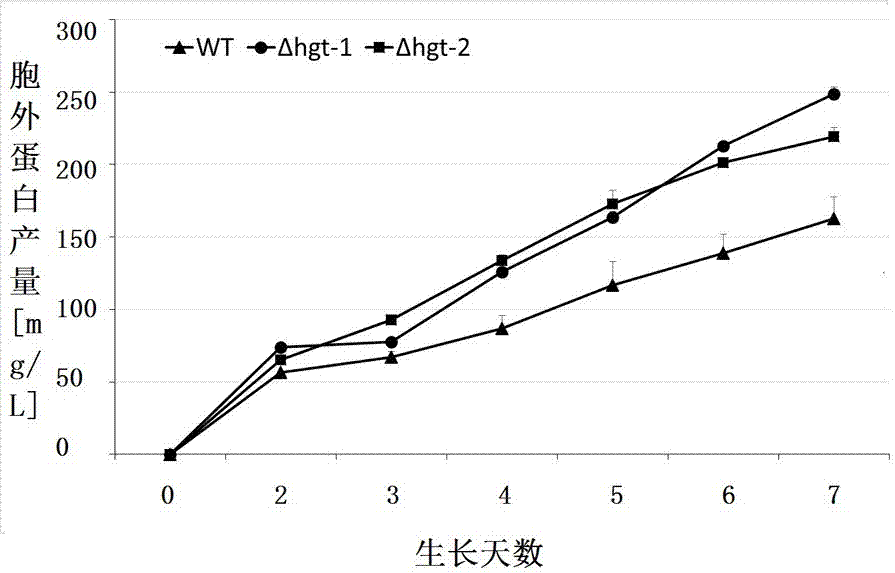
The invention discloses a method for improving production of a lignocellulosic enzyme line from filamentous fungi and an application of the filamentous fungi in fermentation of microbial bio-based chemicals, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the method, high-affinity glucose transporter of the filamentous fungi is transformed by virtue of such genetic engineering approaches as knocking-out, mutation, importing and the like, and an obtained engineering strain has the advantages. The filamentous fungi include, but not limited in, neurospora, myceliophthora, trichoderma, aspergillus, penicillin, fusarium and the like; genes of the transporter include NCU10021 (HGT-1) and a homologous gene thereof as well as NCU04963 (HGT-2) and a homologous gene thereof; any one or two genes are knocked out, or bases of any one or two genes are mutated, or expression of any one or two genes is decreased. The engineering strain, which is obtained by importing the transporter into a microbial strain in an exogenous mode or by changing endogenous expression of the transporter, can gain or enhance a glucose transporting and utilizing capacity, and subsequently, a capacity of producing such bio-based chemicals as organic acid, organic alcohol and the like through fermentation can be gained or improved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Targeted gene deletions for polysaccharide slime formers
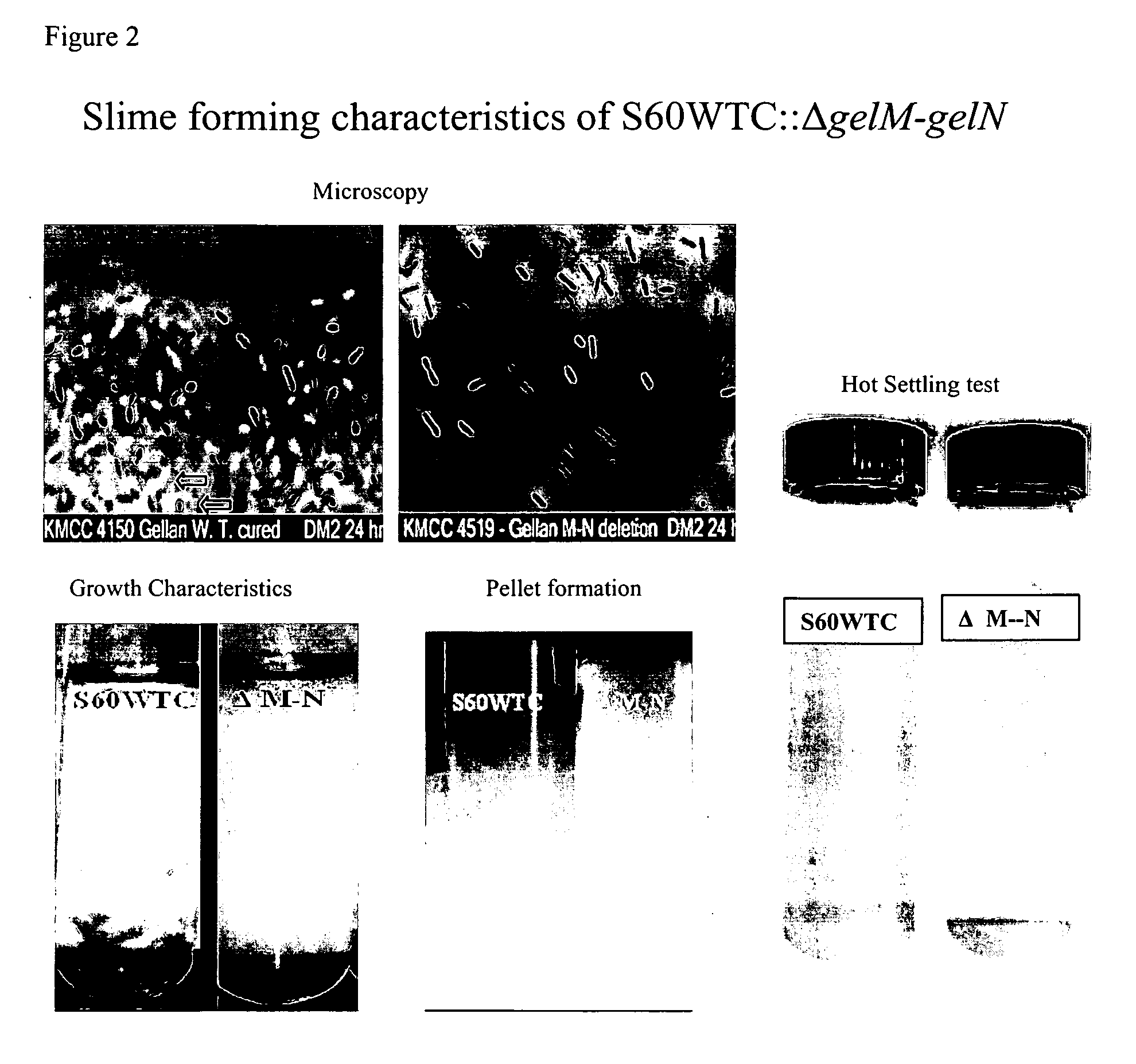
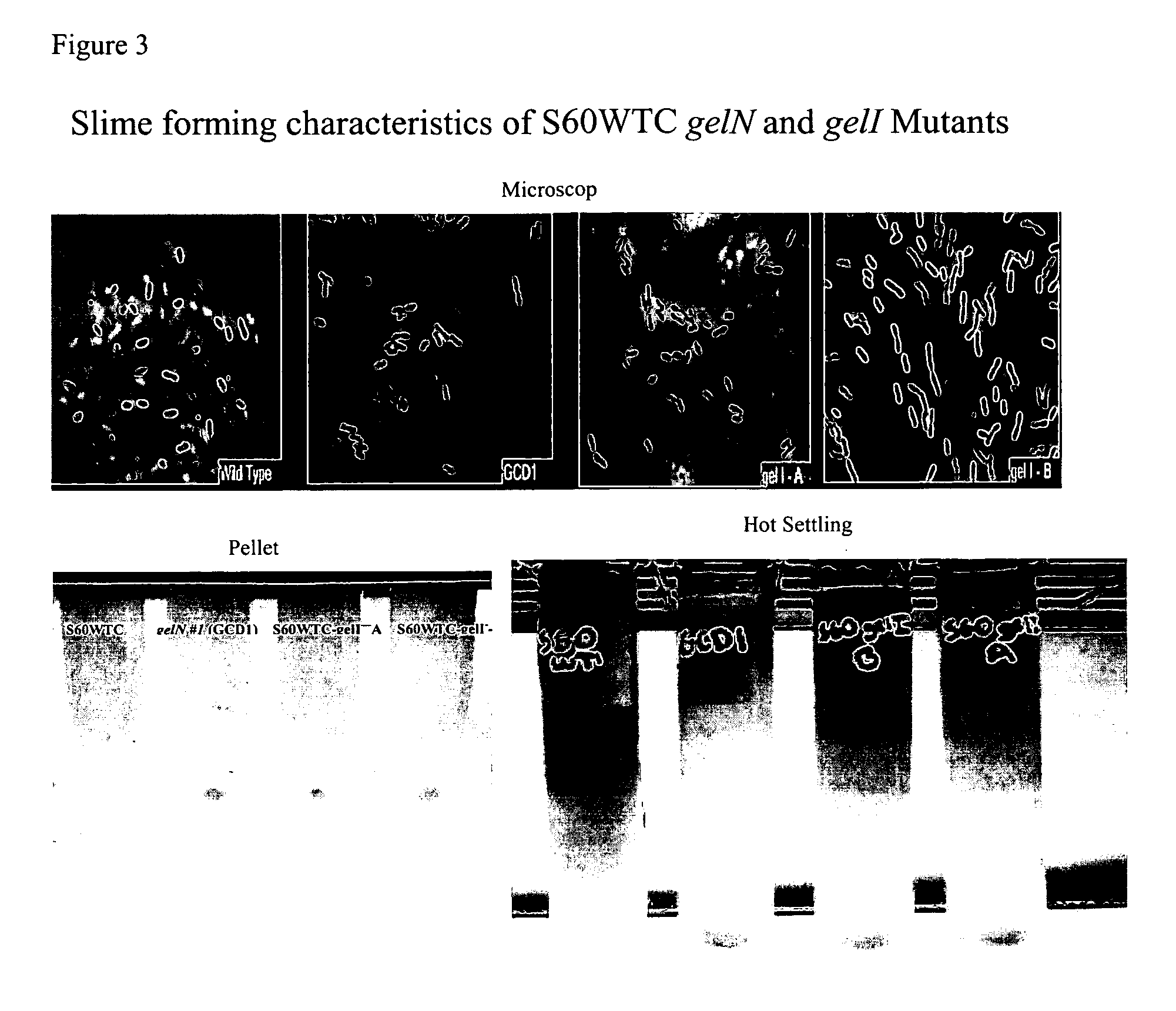
Sphingomonas strains have extracellular polysaccharide (e.g., gellan, diutan) that is firmly attached to the cell surface. This attachment may limit polysaccharide production by impairing uptake of nutrients into the cell or due to limited sites for polysaccharide biosynthesis on the cell surface. Two genes for polysaccharide biosynthesis, designated gelM and gelN in gellan-producing strains and dpsM and dpsN in diutan-producing strains, have been inactivated by deletion mutations and shown to produce polysaccharide that is not firmly attached to the cell surface, i.e., slime form. Another gene for polysaccharide biosynthesis, designated gelI in gellan producing strains, was inactivated by insertion mutation and also shown to produce the slime phenotype. The homologous gene dpsi in the diutan producing strain should also be involved in the attachment of the polysaccharide to the cell surface. The slime characteristic was demonstrated by the ability of the cells to be centrifuged and the lack of cell clumping as seen under the microscope or in diluted suspensions. The diutan slime mutants had somewhat increased productivity and the recovered diutan product had significantly improved rheology. Gellan slime mutants had lower broth viscosity which facilitates mixing during fermentation; however, the recovered gellan product had lower gel strength than the gellan produced from a capsular strain. A deletion in a gene gelR, which encodes a protein with homology to surface proteins and outer membrane proteins and weak homology to proteins with polysaccharide degradation activity, was shown to restore higher gel strength to the slime form of gellan, and to produce gellan of higher gel strength than that of the capsular gellan producing strains.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
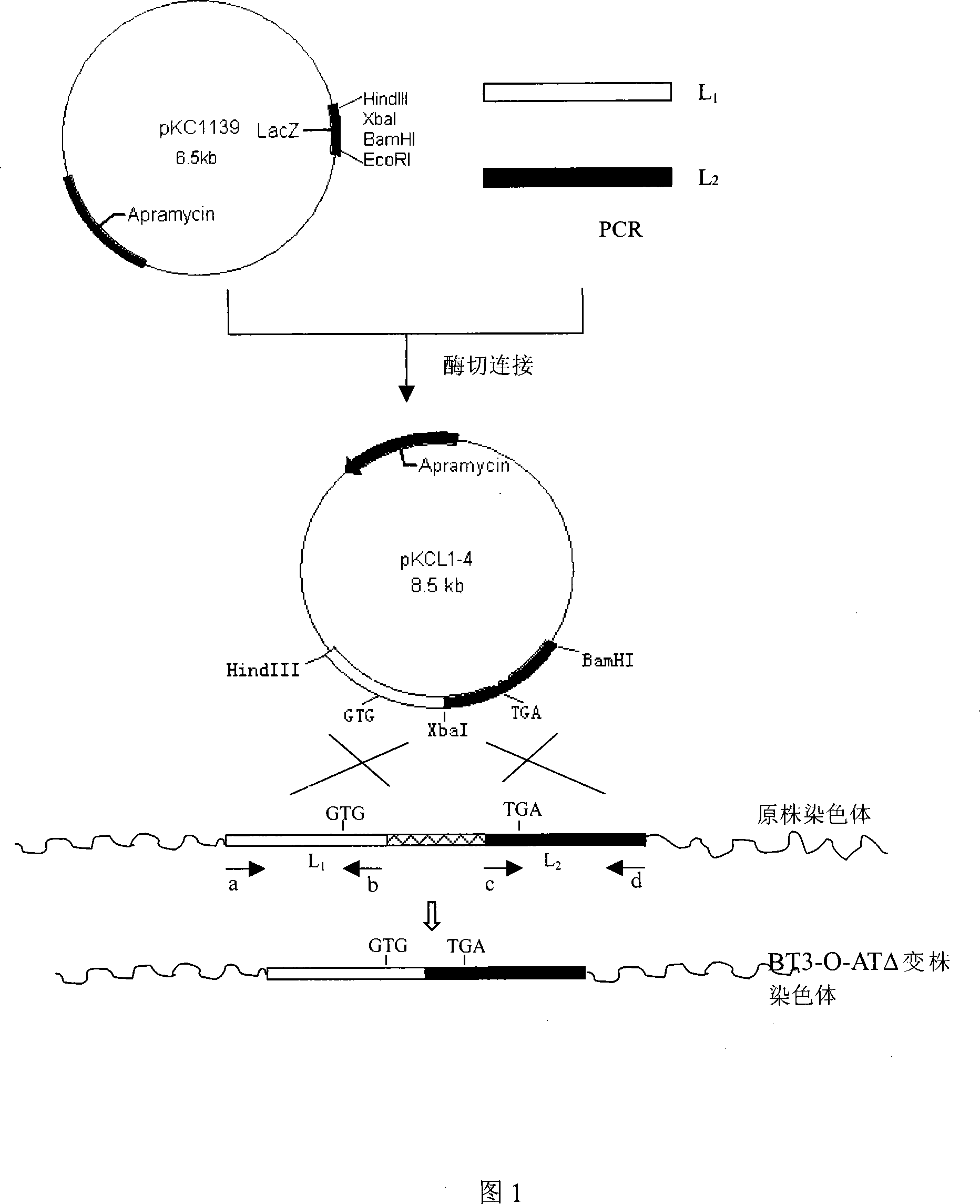
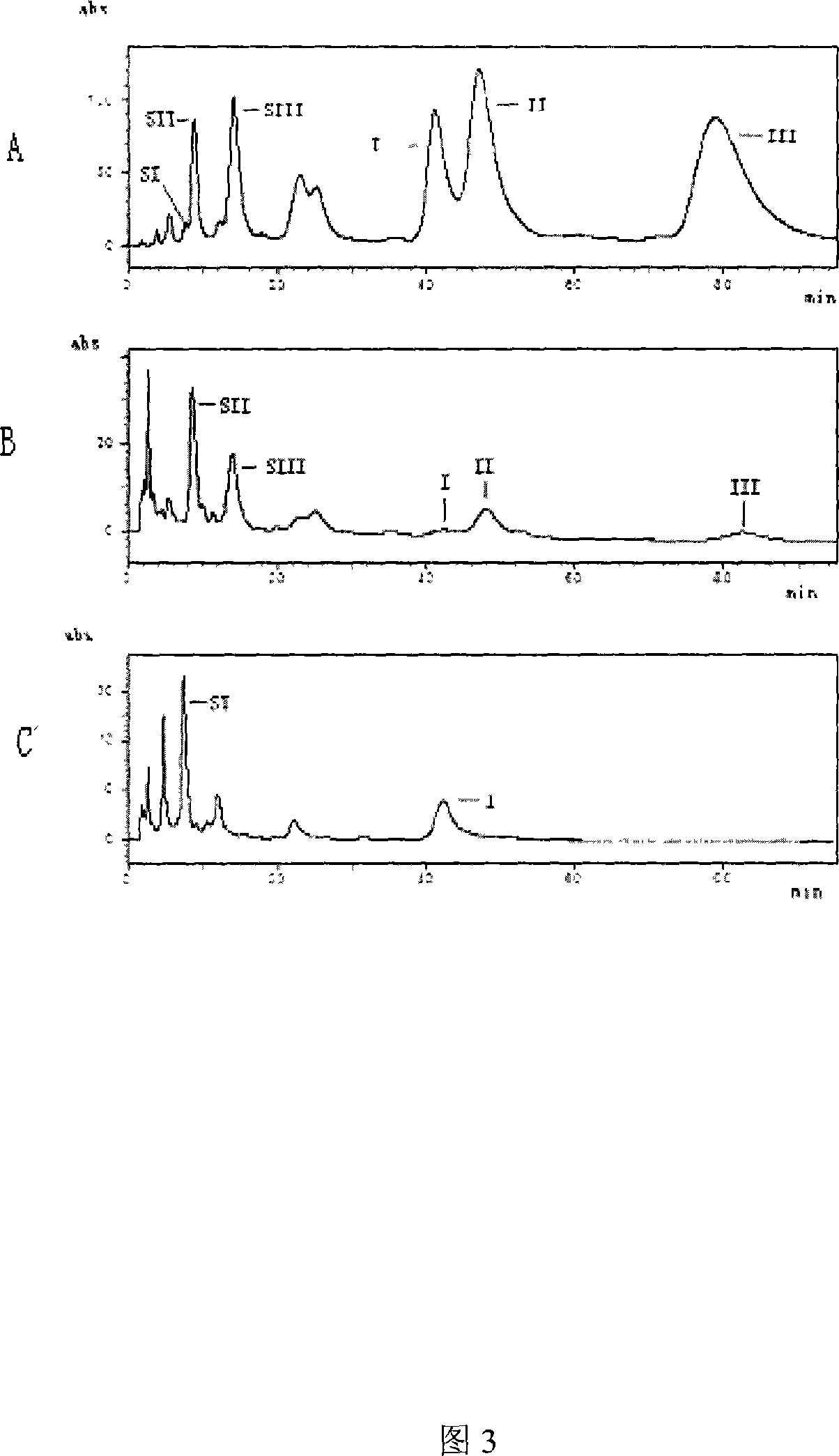
Construction of isovalerylspiramycin I gene engineering strain
InactiveCN101054553AThe fermentation process is simpleSimplified regulation of the fermentation processMicroorganismsRecombinant DNA-technologyBiotechnologyAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to use of gene engineering in modifying antibiotic ingredient, more specificly it refer to blocking and destroying 3-O-acyltransferase which take part in the production of component II and III of bitespiramycin-producing bacteria. The engineered bacteria is obtained by homologous gene double exchange and employs 4'' -isovalerylspiramycin I as main ingredient. The engineered bacteria can simplify the production process, lower the production cost and control the quality standard.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Methods and compositions related thereto for detecting and identifying distinct species of nucleic acids from causative agents
ActiveUS20060088865A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationFamily HerpesviridaeInfectious agent
Methods are described herein for detecting and identifying distinct species of nucleic acids, in a single container, for example, from a certain genus of infectious agents or otherwise causative agents comprising, for example, providing a forward PCR primer common to a homologous gene region between the distinct species, and providing a reverse PCR primer common to a homologous gene region between the distinct species, to thereby define a PCR target region amongst the species, and providing a first oligonucleotide probe specific to a nucleic acid sequence within the target region that is characteristic of a first species, providing a second oligonucleotide probe specific to a nucleic acid sequence within the target region that is characteristic of a second species, wherein the first and second oligonucleotide probes are each detectably labeled with distinctly different detectable labels, conducting a PCR reaction in the container by means of the primers to amplify the target region amongst the species, and detecting the distinct labels, thereby identifying distinct species of nucleic acids corresponding to distinct species of infectious agents. Methods are preferred, for example, wherein the infectious agent is a member of the Herpesviridae family.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
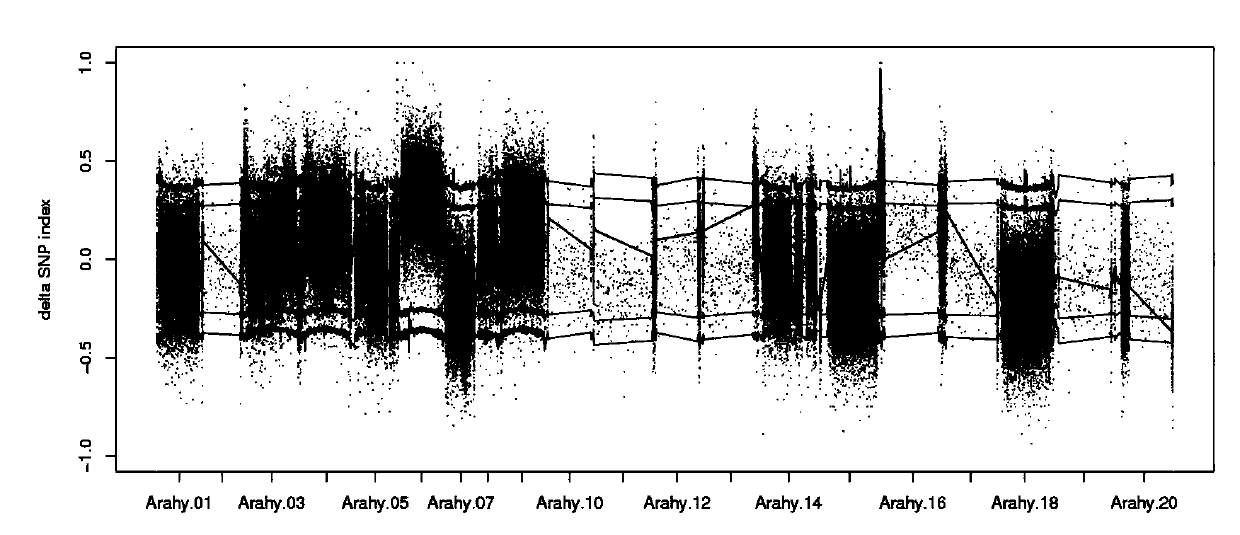
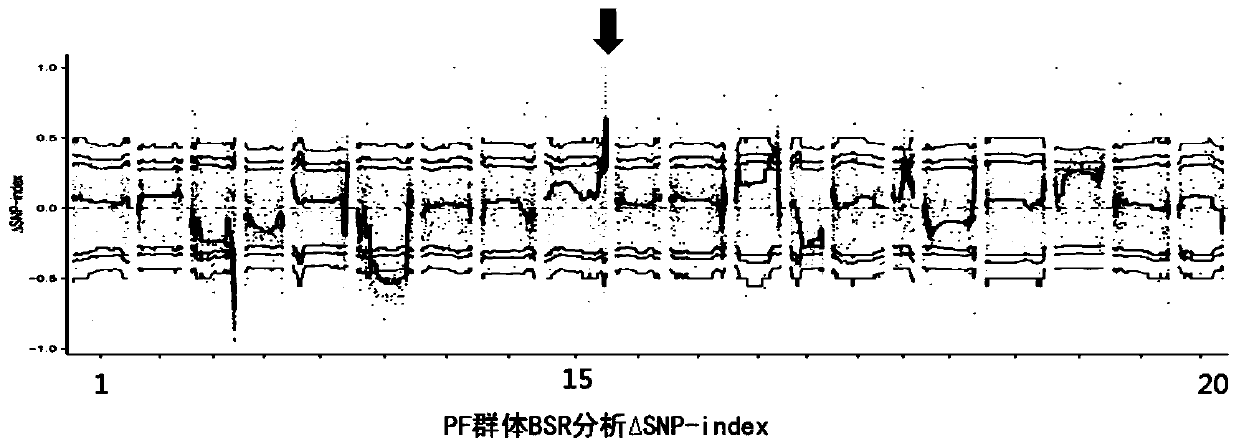
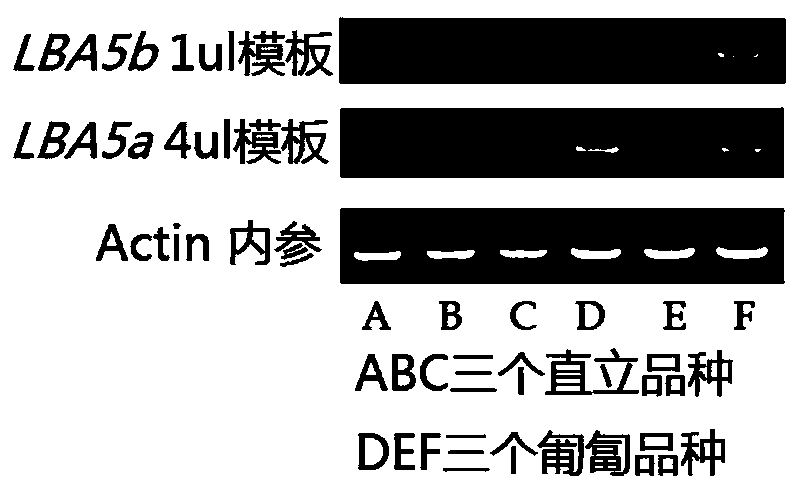
Gene LBA5 for regulating and controlling lateral branch angle, growth habit and plant type of peanut, and application thereof
ActiveCN110592102ARealize reasonable close plantingImprove yield per unit areaPlant peptidesFermentationMain stemHabit
The invention belongs to the technical field of biotechnology and genetic engineering, and provides a gene LBA5 for regulating and controlling a lateral branch angle, growth habit and plant type of apeanut, and application thereof. A major gene LBA5 for controlling the lateral branch angle, growth habit and plant type of the peanut is located and cloned in the peanut, and comprises two homologousgenes LBA5b and LBA5a and promoters thereof; genetic improvement of an included angle between a lateral branch and a main stem of the peanut can be achieved through selection of gene allelic variation via hybridization, backcross and the like; the functions or expression quantity of the gene in a creeping variety peanut can be regulated so that the included angle between the lateral branch and the main stem of the peanut is regulated; and thus, the two homologous genes LBA5b and LBA5a and the promoters thereof of the gene LBA5 can be applied to the genetic improvement and genetic engineeringimprovement of the lateral branch angle, growth habit and plant type of the peanut, even other crops.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Key genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs or combination thereof used for identifying or regulating cell pluripotency
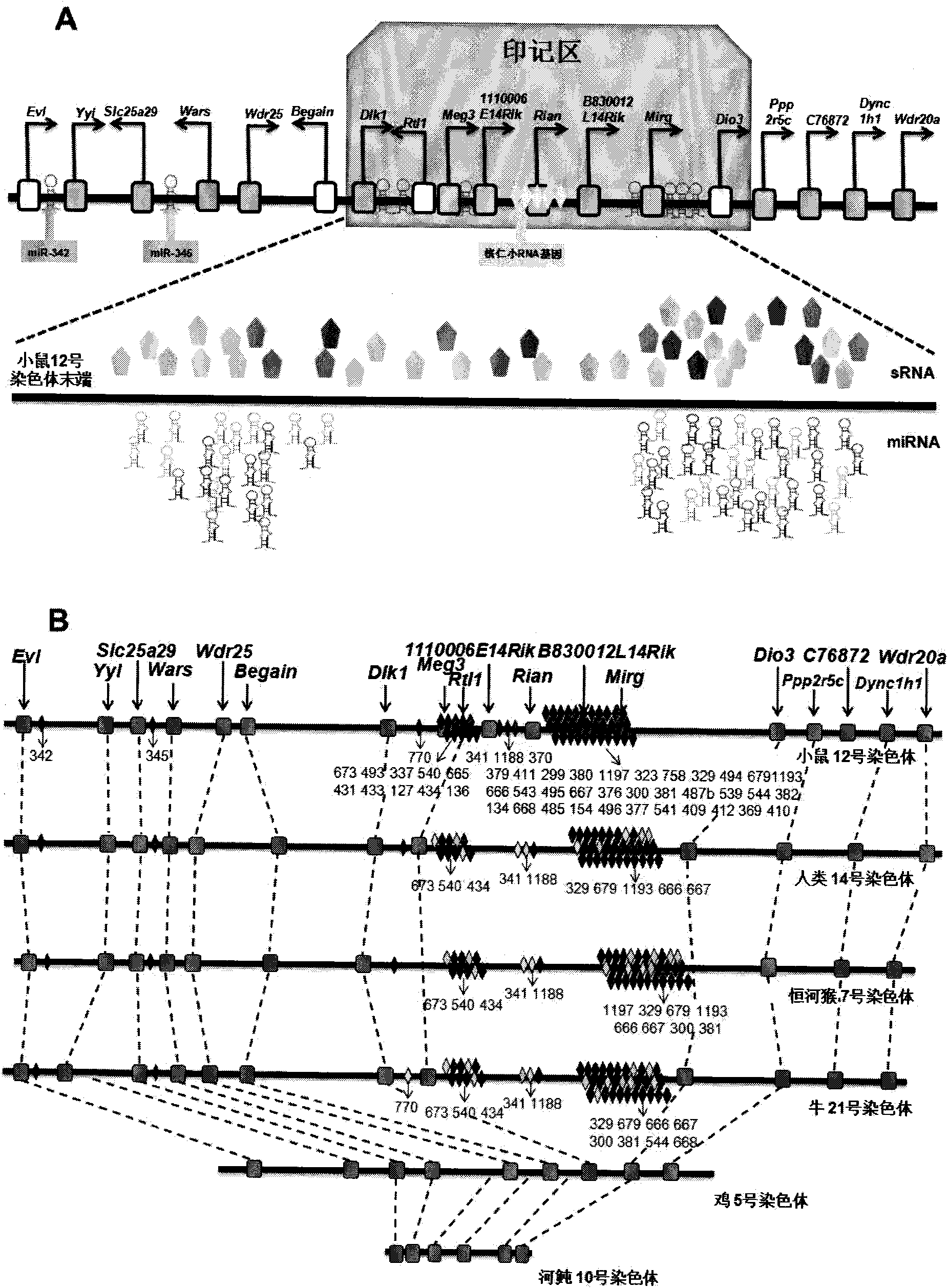
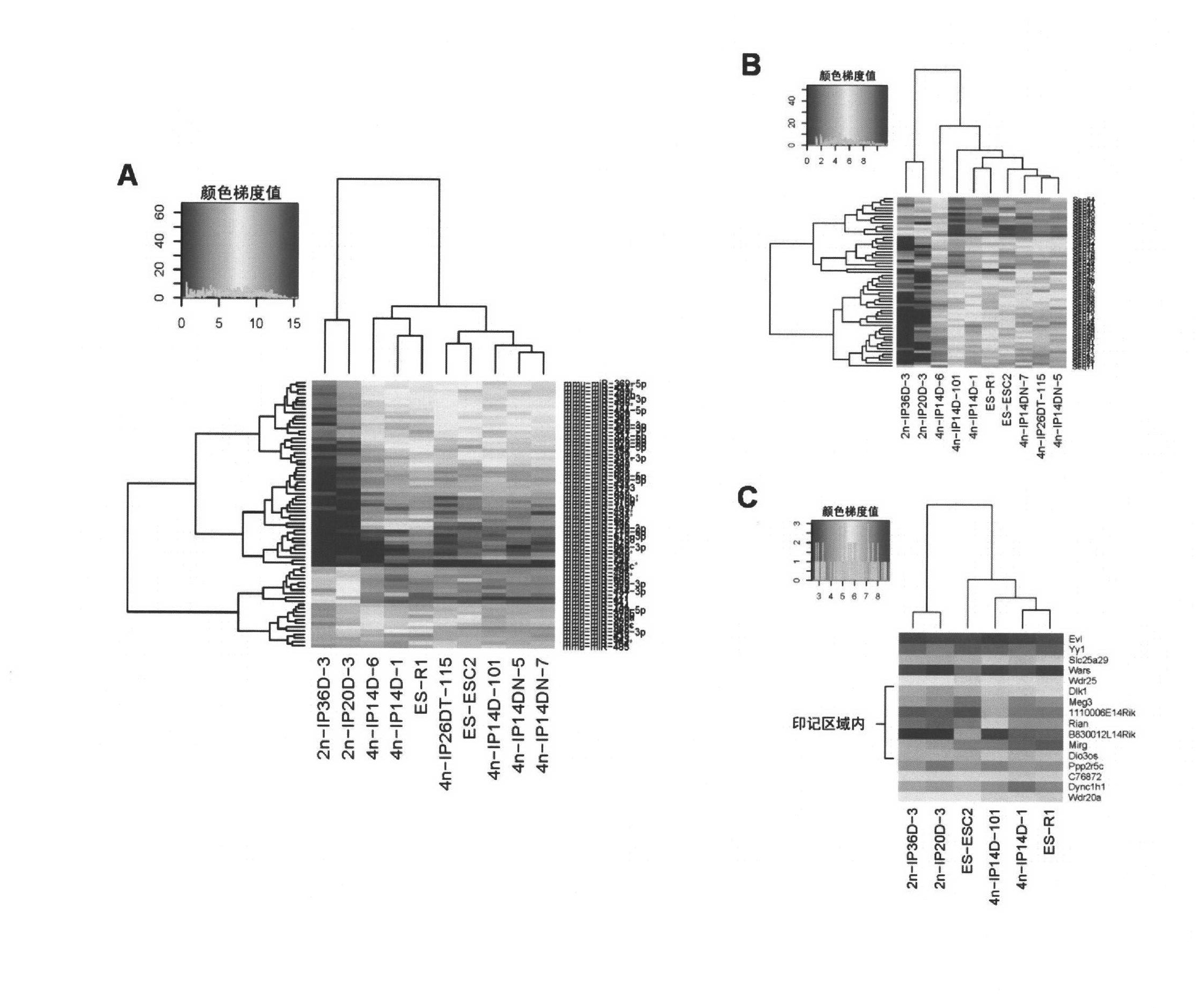
The invention relates to key genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs, or a combination thereof used for identifying or regulating cell pluripotency. The invention is characterized in that the key genes, microRNAs, other non-coding RNAs or a combination is highly expressed in the stem cell with complete pluripotency and the expression is obviously repressed or silent in the stem cell without complete pluripotency. The genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs are the genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs positioned in the chromosome imprinting region named as Dlk1-Dio3 on the long arm of mouse chromosome 12 and the genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs in the genome collinearity regions of other mammals, which have 70%-100% of homology. The invention also relates to applications of the genes, microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs, or the combination thereof used for identifying the pluripotency of the stem cell and regulating cell pluripotency, applications in stem cell typing, applications for regulating the cell pluripotency and the pluripotency state and level of the cell, applications in disease treatment, and applications in the drug target development of tumor treatment or the development of antitumor drugs.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for improving volume of production of rifamycin
InactiveCN101153274AIncrease productionBacteriaGenetic engineeringSecondary metaboliteTwo-component regulatory system
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Efficient gene knockout method of pseudomonas putida KT2440
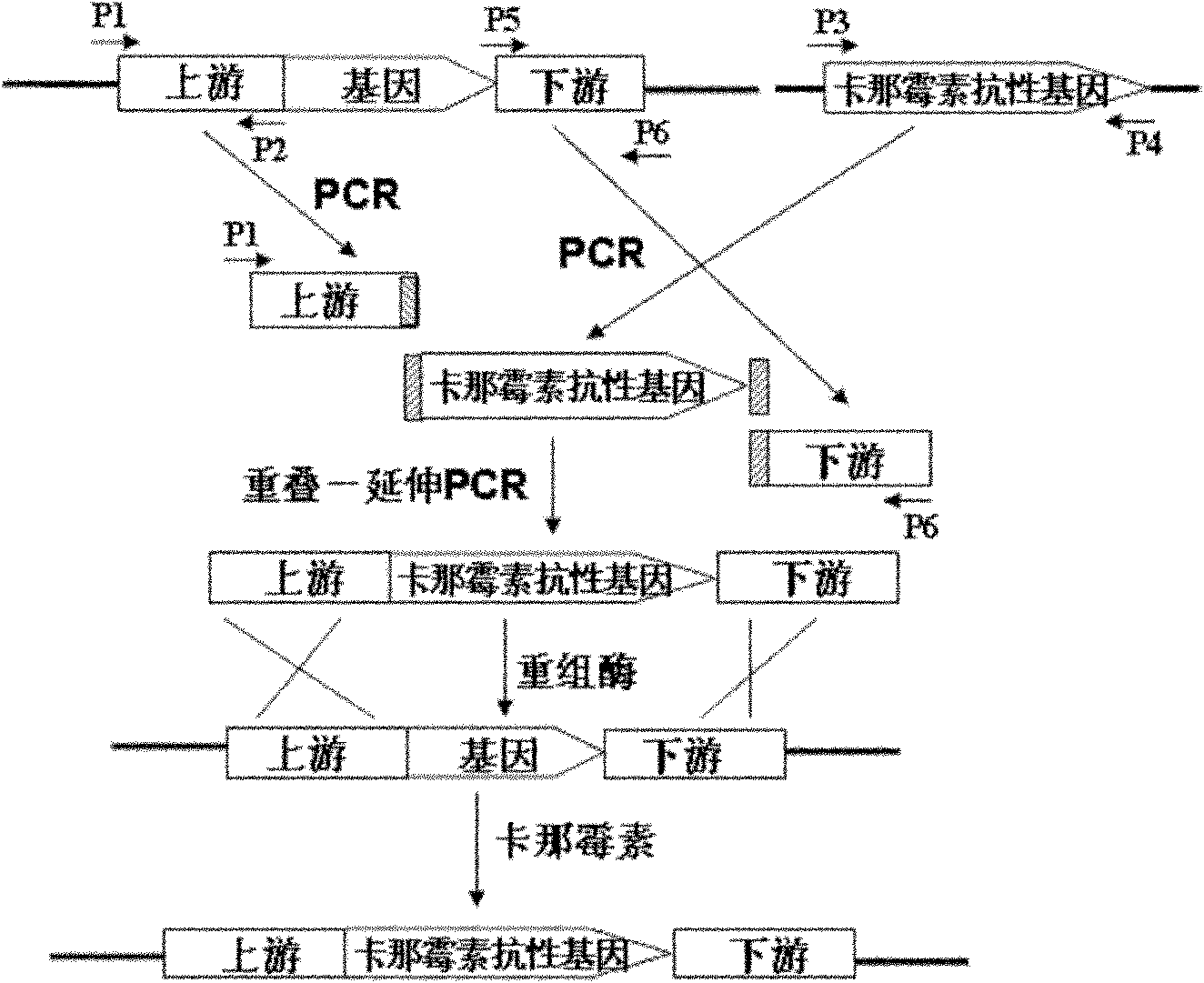
The invention relates to a method for performing gene knockout on pseudomonas putida KT2440 by a recombinant engineering measure. The method comprises the following specific steps of: amplifying through an overlapped-extension polymerase chain reaction so as to obtain a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fragment of which both sides are provided with target genes to be knocked, the upstream and downstream are provided with homologous genes of about 500 base pairs and the middle is provided with a kanamycin resistance gene; electrically transforming the DNA fragment into a pseudomonas putida KT2440 electro-transformation competent cell which is expressed by toluic acid induction recombinase with the final concentration of 2mM; and replacing the target genes by the kanamycin resistance gene through homologous recombination between homologous fragments of a recombinase mediate so as to directly obtain a mutant strain from which target genes are knocked. The method is simple and convenient and can become a genetic operating measure of an environmental microorganism, namely pseudomonas putida KT2440 which has important application value in the aspects of organic compound biodegradation and the like.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Watermelon oxysporum pathogenic FonAGL3 gene as well as deleted DNA fragment, deletion mutant and application thereof
InactiveCN107299105AClear control functionEffectiveness of Good Fusarium Wilt ControlBiocideFungiHygromycin BTreatment effect
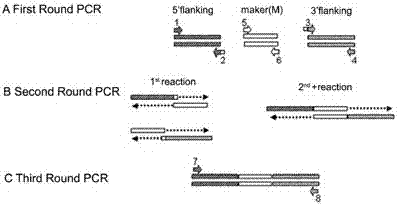
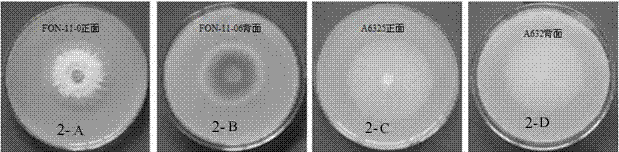
The invention discloses a watermelon oxysporum pathogenic FonAGL3 gene as well as a deleted DNA fragment, a deletion mutant and application thereof, and aims to solve the technical problem of biological prevention and treatment on watermelon oxysporum. A pathogenic gene FonAGL3 derived from watermelon fusarium oxysporum is analyzed and screened by inserting watermelon oxysporum T-DNA into a mutant library, by utilizing the homologous gene replacement principle, DNA fragments of the target gene FonAGL3 are replaced by gene DNA fragments of a resistance gene hygromycin B (HPH), a FonAGL3 gene deletion mutant is obtained by establishing a gene deletion carrier and implementing genetic transformation of a wild strain FON-11-06, and the FonAGL3 mutant bacterium has a good wilt prevention and treatment effect and is environmental-friendly and low in prevention and treatment cost.
Owner:河南省农业科学院园艺研究所 +1
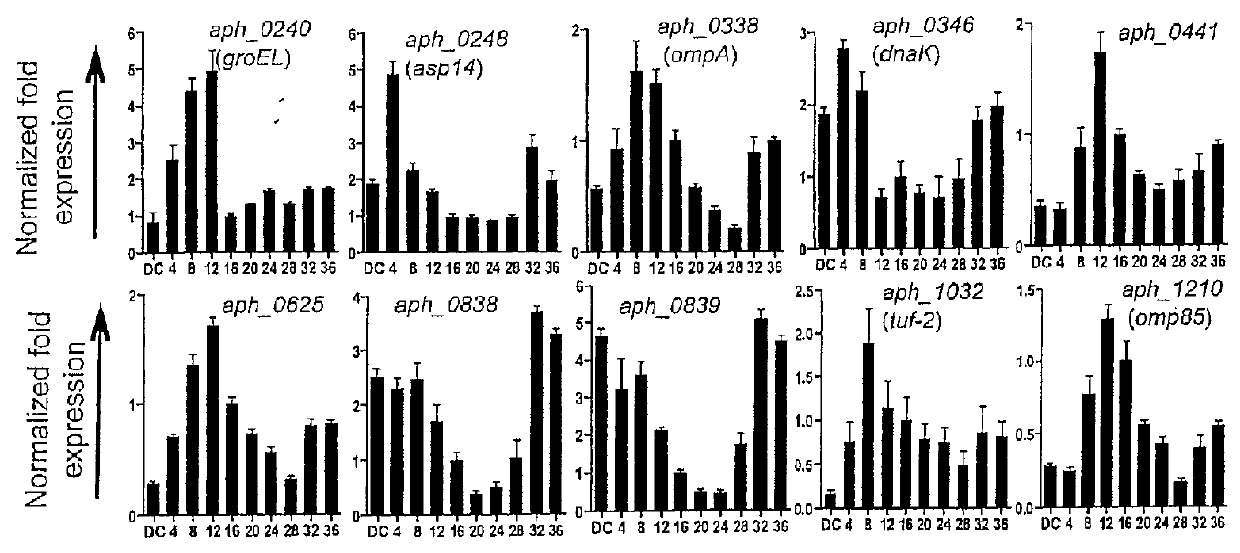
OMPA and ASP14 in vaccine compositions and as diagnostic targets
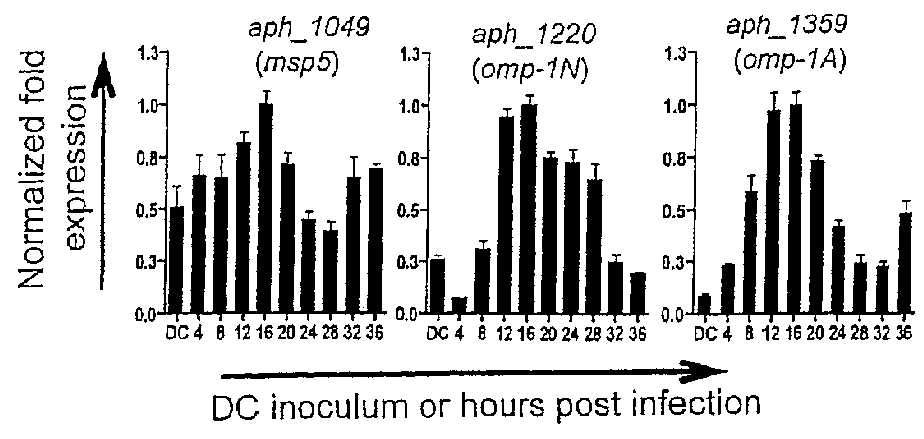
Anaplasma phagocytophilum surface proteins Asp14 and OmpA and homologous genes from Anaplasmatacaea family members are used in compositions suitable for vaccines to treat or prevent infections caused by tick-born bacteria of the Anaplasmatacaea family. Asp14 and / or OmpA proteins or peptide fragments may be used in combination with other Anaplasmatacaea surface proteins to elicit an immune response. Furthermore, antibodies to Asp14 and / or OmpA proteins can be used in diagnostic methods to determine whether an individual has contracted an Anaplasmatacaea infection. Because of the conserved invasin domains in the surface proteins, a wide range of Anaplasmatacaea infections may be diagnosed, treated or prevented using compositions of the invention.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Malus hupehensis MhWRKY40a gene and applications thereof
InactiveCN103387994AImprove germination rateHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySalt resistance
The invention discloses a malus hupehensis MhWRKY40a gene and applications thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the malus hupehensis MhWRKY40a gene is shown as the SEQ ID NO.1. The MhWRKY40a gene is capable of applying to the production of novel species, which are salt resistant and low temperature resistant, and / or plant variety improvement. A novel MhWRKY40a gene is cloned from malus hupehensis for the first time, and the homology between the gene sequence and the arabidopis thaliana, grape and barley is 50.89%. But the protein tertiary structure of the MhWRKY40a is prominently different from the homologous gene of the model plant arabidopis thaliana; the former has 5 beta-folds, while the latter has 4 beta-folds. The MhWRKY40a transgenetic tobacco has the properties of salt resistance and low-temperature resistance, raises the resistance-associated gene expression, and therefore the fact, which the MhWRKY40a gene has the function of improving the salt resistance and low-temperature resistance properties of the plants, is testified.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
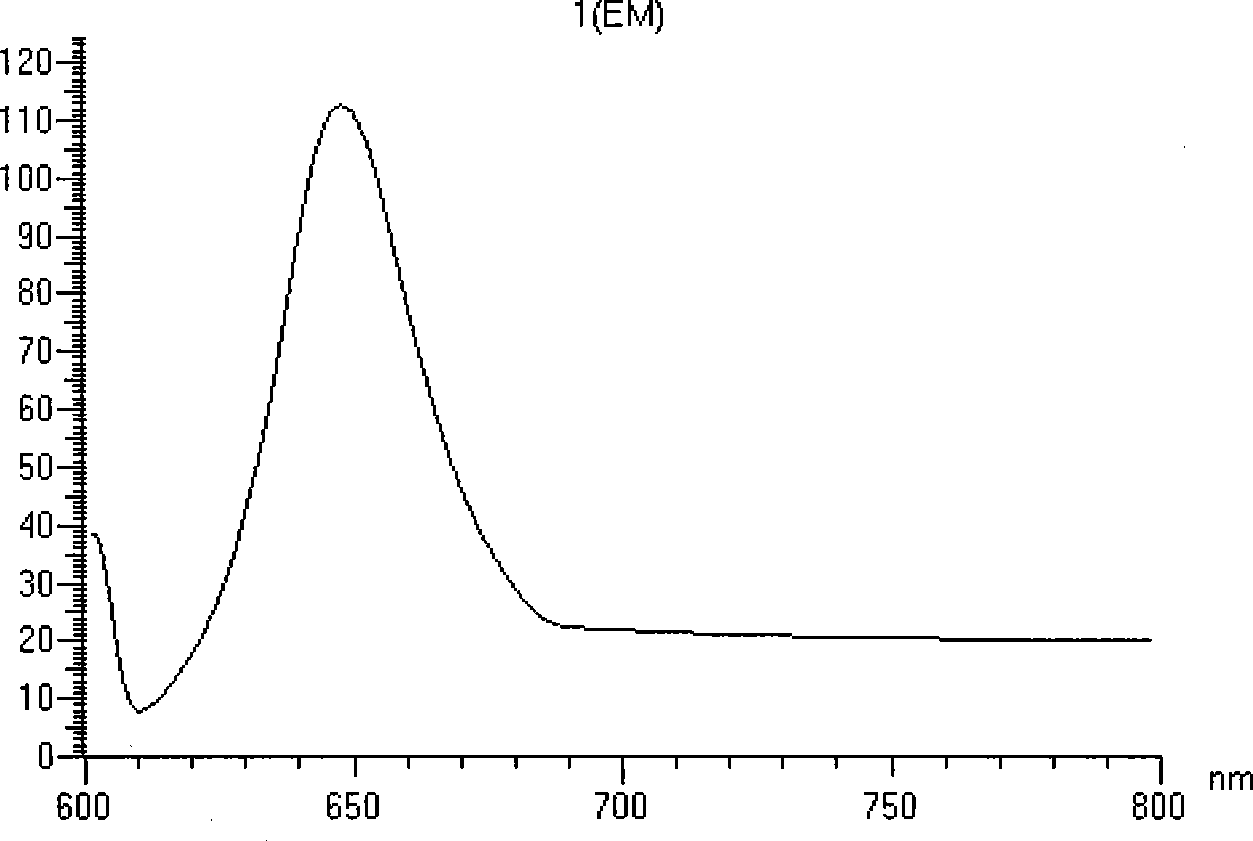
Preparation of allophycocyanin fluorescent protein
InactiveCN101440370ASmall molecular weightSingle ingredientBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFluorescence
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of Arabidopis thaliana transcription factor at3g46080 gene
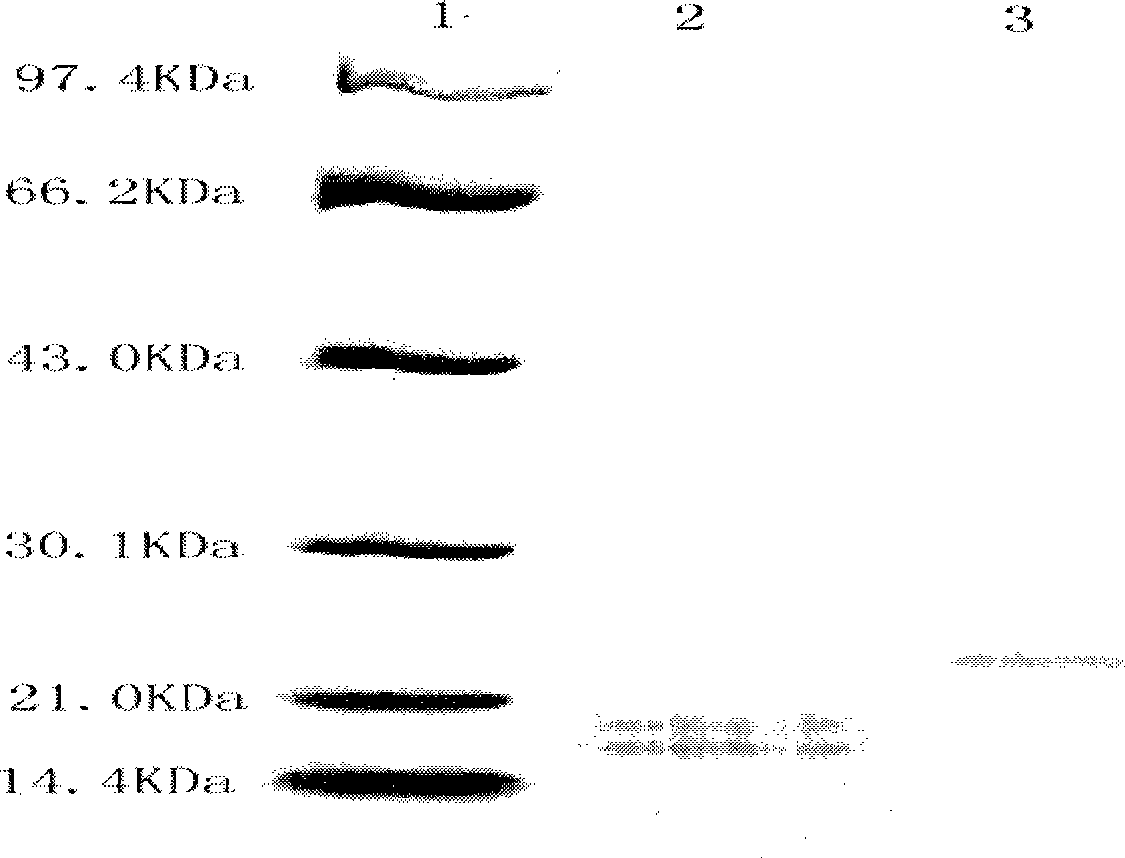
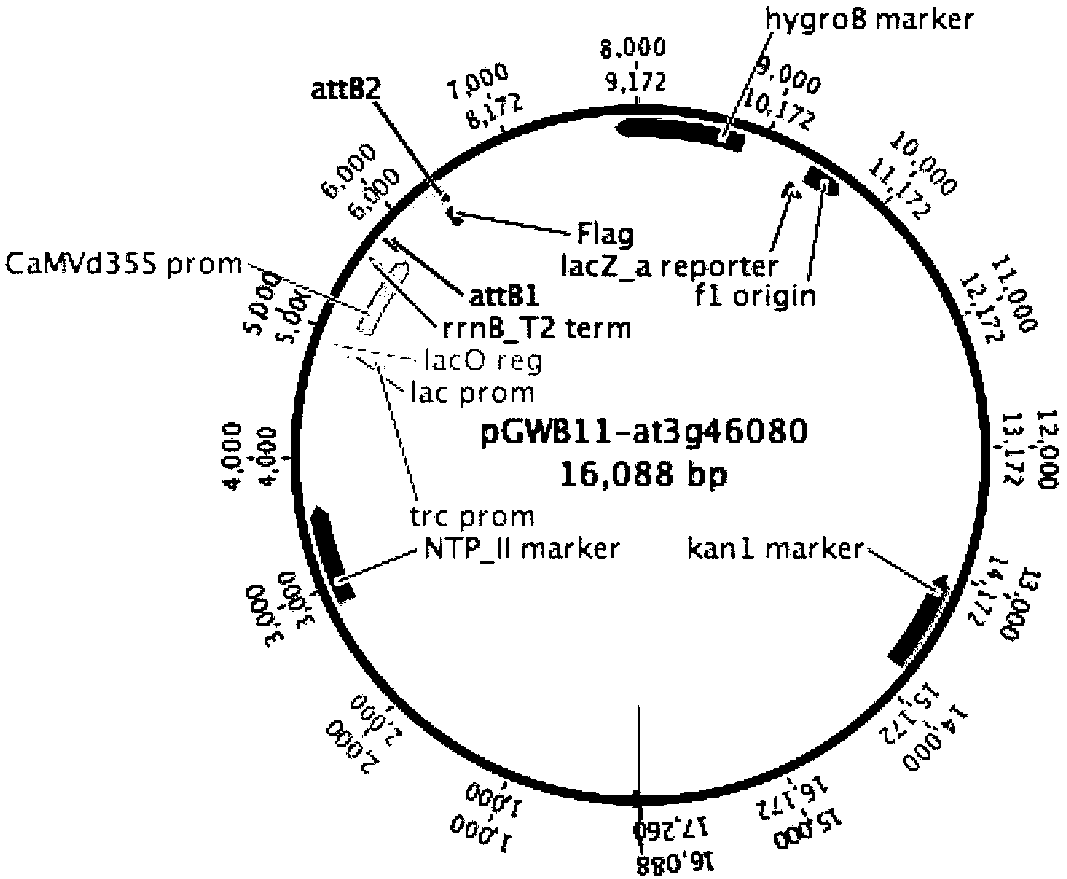
PendingCN110305218AIncrease resistanceAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPlant peptidesDisease phenotypePseudomonas tolaasii
The invention relates to an application of an Arabidopis thaliana transcription factor at3g46080 gene. By constructing a CDS sequence of the Arabidopsis thaliana at3g46080 gene into the upstream of aFLAG protein label by a Gateway technology, Arabidopsis thaliana is conversed, which affects the disease phenotype of Arabidopsis thaliana, screening and identification are carried out, and finally the transgenic plants can be obtained. The analysis of the screened plants carried out so that the plant has enhanced resistance to Pseudomonas lycoposum by Arabidopis thaliana, the gene has the same function for homologous genes in crops, and thus has important significance in production.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Avermectin producing bacteria and preparation method and application thereof
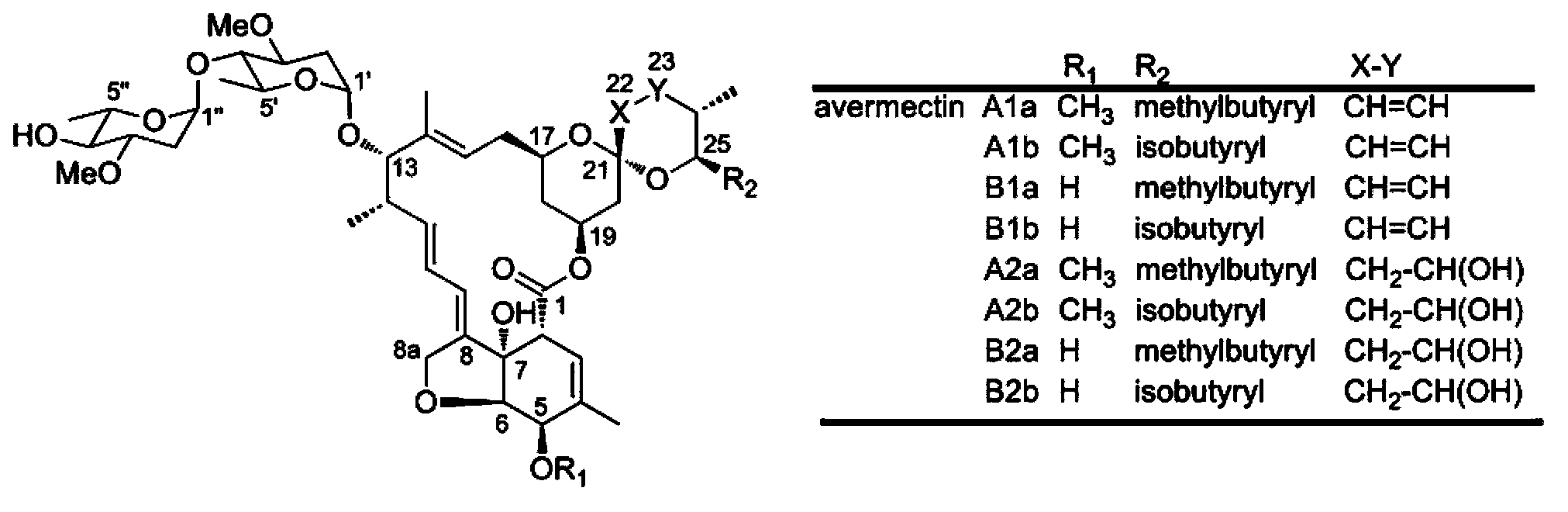
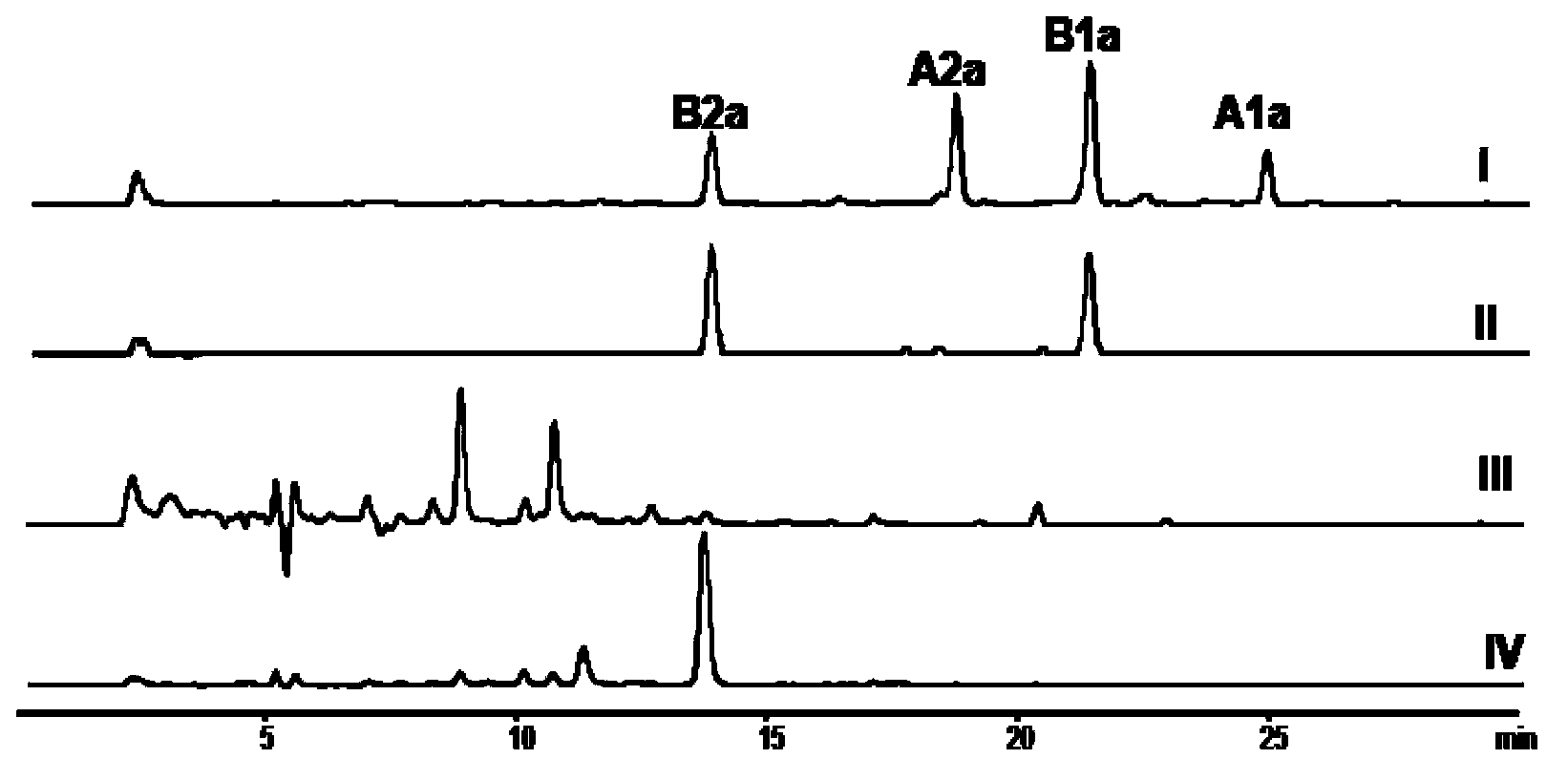
The invention relates to avermectin producing bacteria and a preparation method and application thereof. Specifically, aveD gene in wild type avermectin producing bacteria is inactivated to obtain a strain getting rid of an A component and only producing a B component; by anaplerosis of a homologous gene of the aveC gene (preferably meiC gene in a Meilingmycin biosynthetic gene cluster) on the basis of simultaneous inactivation the aveD gene and aveC gene, 95wt% above of the obtained mutant fermentation product is avermectin B2a. The product avermectin B2a can be used as a precursor for being directly used for large-scale synthesis of high purity avermectin B1a and ivermectin.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Herpesvirus II type polymerase chain reaction (PCR) fluorescent quantitative fast detection kit and method
ActiveCN102337354AImprove accuracyIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceHuman DNA sequencingFluorescence
The invention aims at providing a herpesvirus II type polymerase chain reaction (PCR) fluorescent quantitative fast detection kit, which comprises deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) extraction liquid, PCR reaction liquid, DNA polymerase, a positive quality control article, a weak positive quality control article, a negative quality control article and a quantitative reference article, wherein the PCRreaction liquid comprises a primer and a fluorescent probe. The kit has the beneficial effects that the kit uses the positive comparison and the negative comparison, the accuracy of the kit is improved, and in addition, nucleic acid DNA with the content lower than 5*10<2> gene copy / mL can also be detected. The nucleic acid amplification method has the advantages of high sensitivity, high specificity and good repetitiveness. The invention also uses an arabidopsis inside reference system, and homologous genes do not exist in pure herpesvirus II type genomes and human genomes, so the kit can be used as the inside reference for detecting whether PCR inhibiting substances exist in each PCR reaction, and the accuracy of PCR results is ensured.
Owner:泰普生物科学(中国)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com