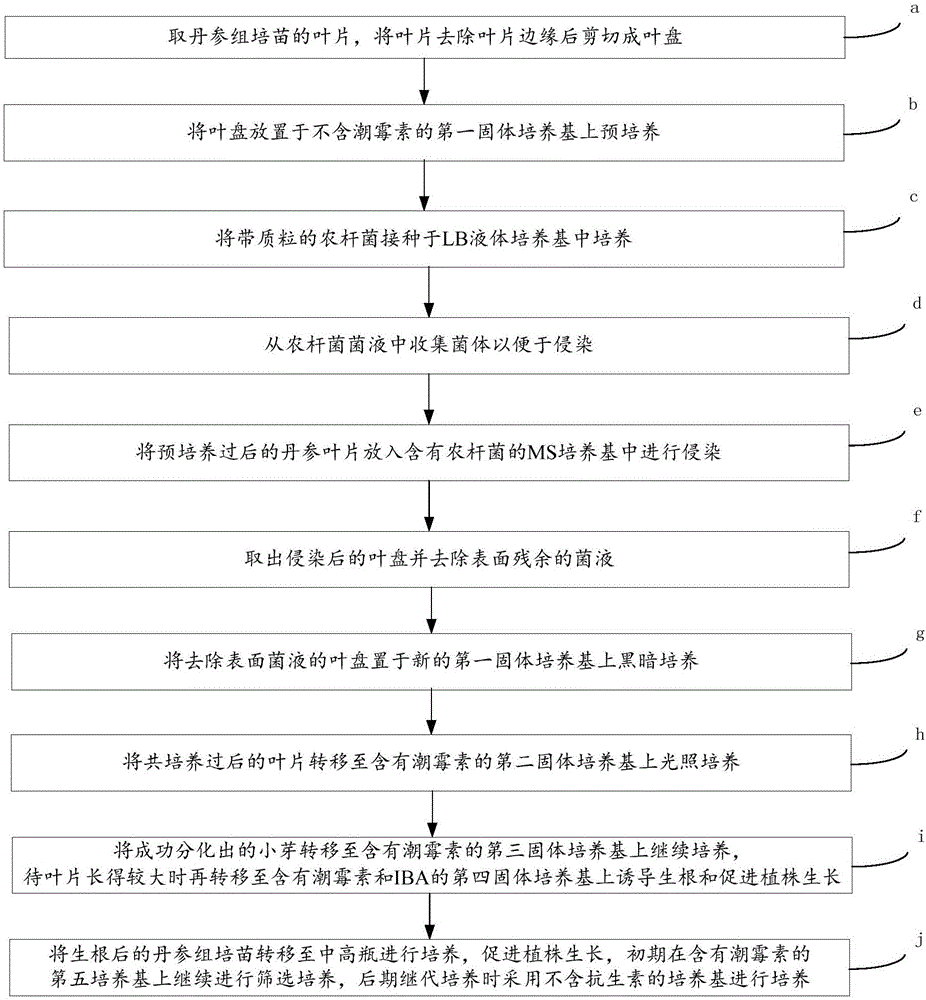
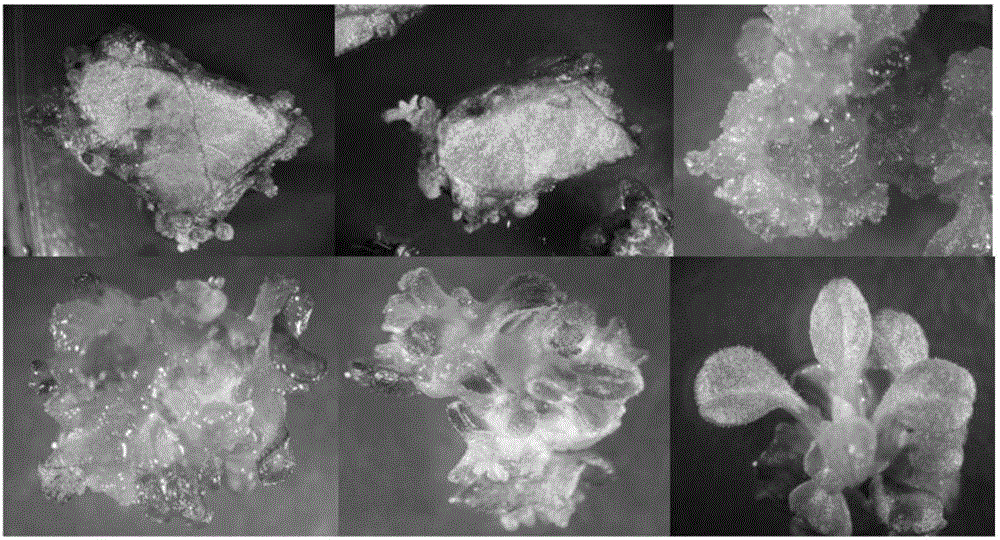
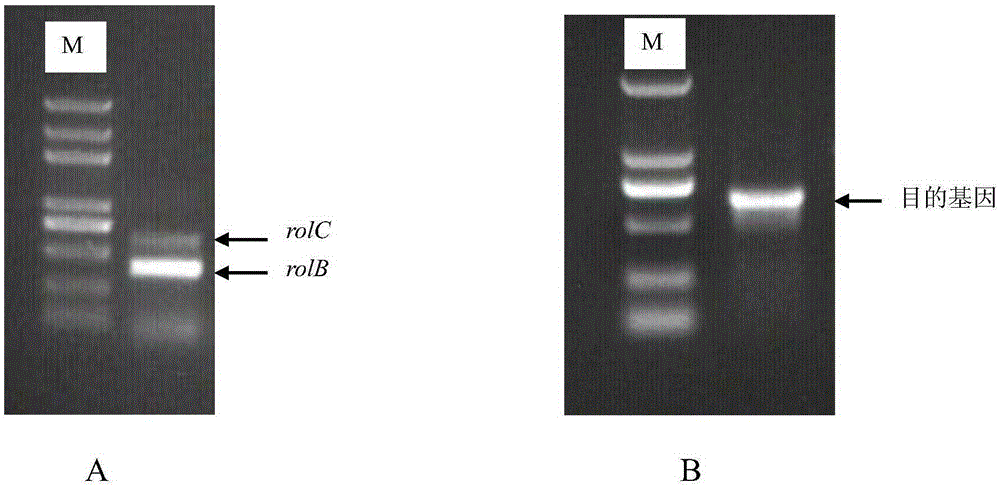
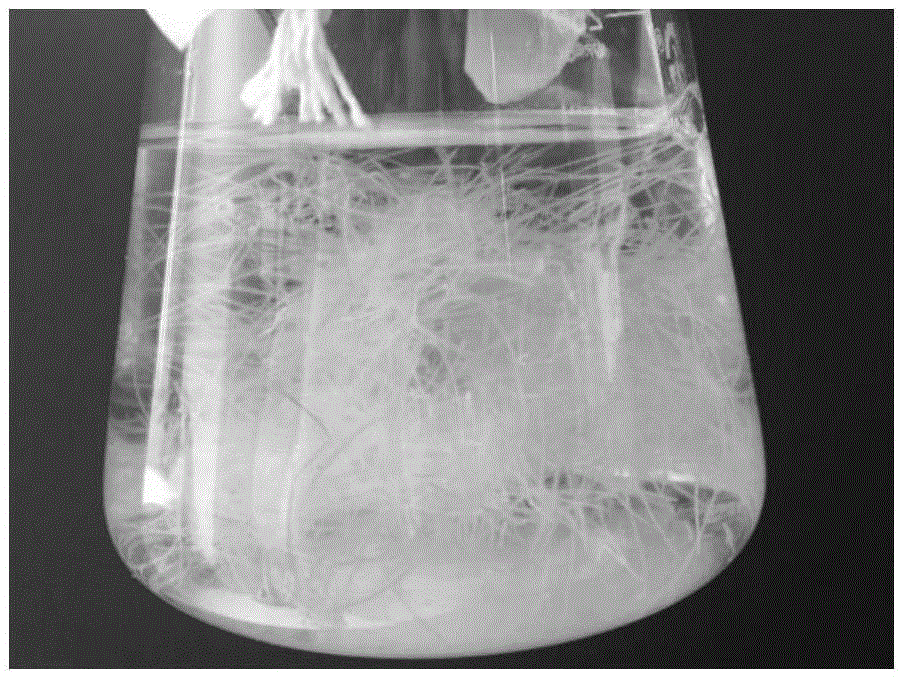
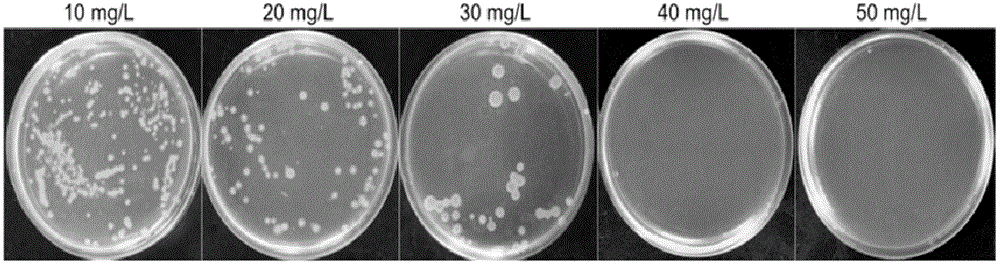
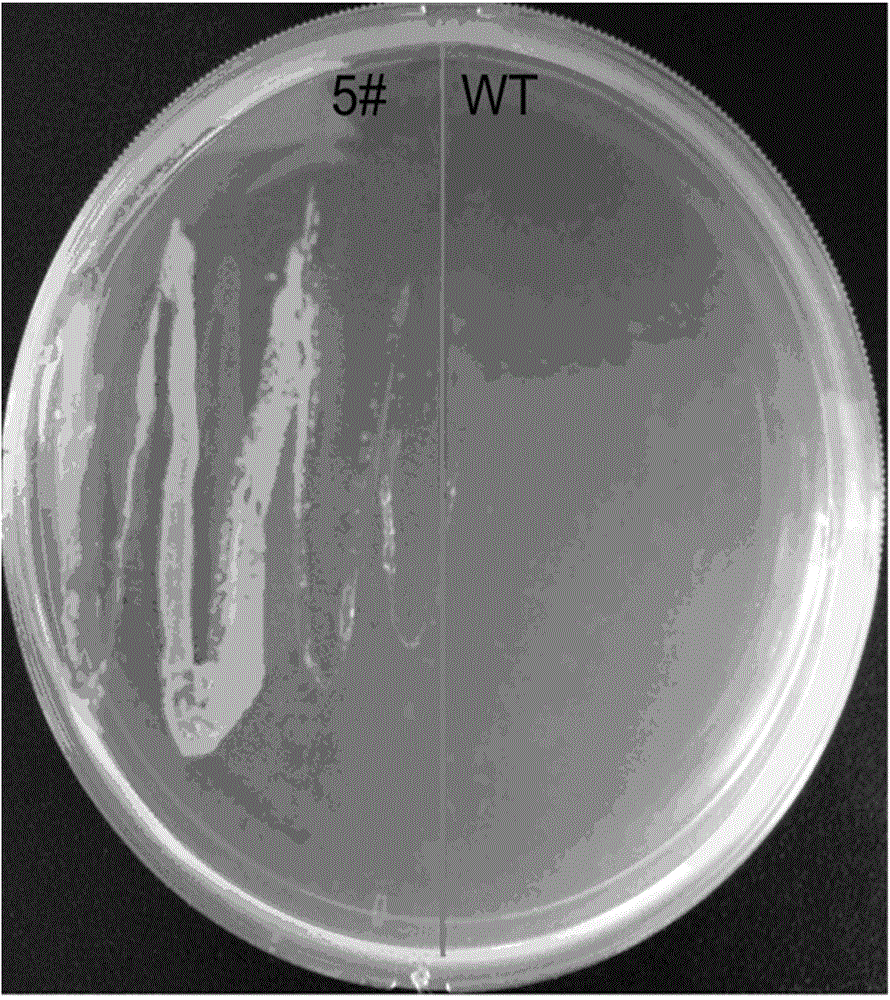
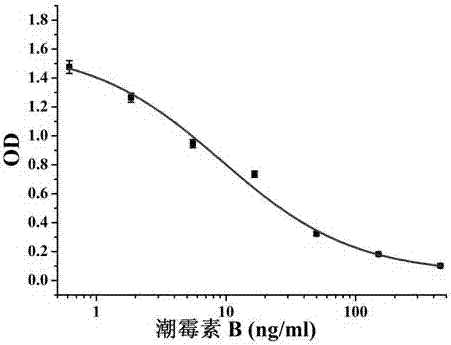
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Hygromycin B" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hygromycin B is an antibiotic produced by the bacterium Streptomyces hygroscopicus. It is an aminoglycoside that kills bacteria, fungi and higher eukaryotic cells by inhibiting protein synthesis.
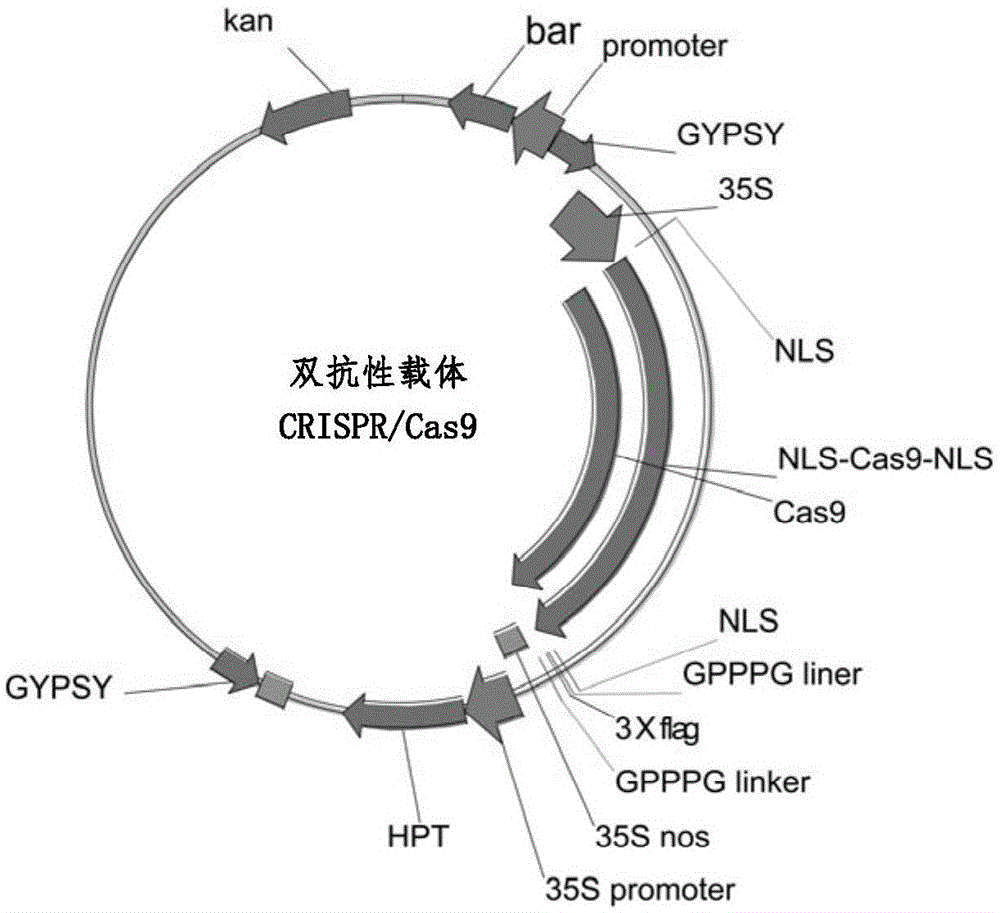
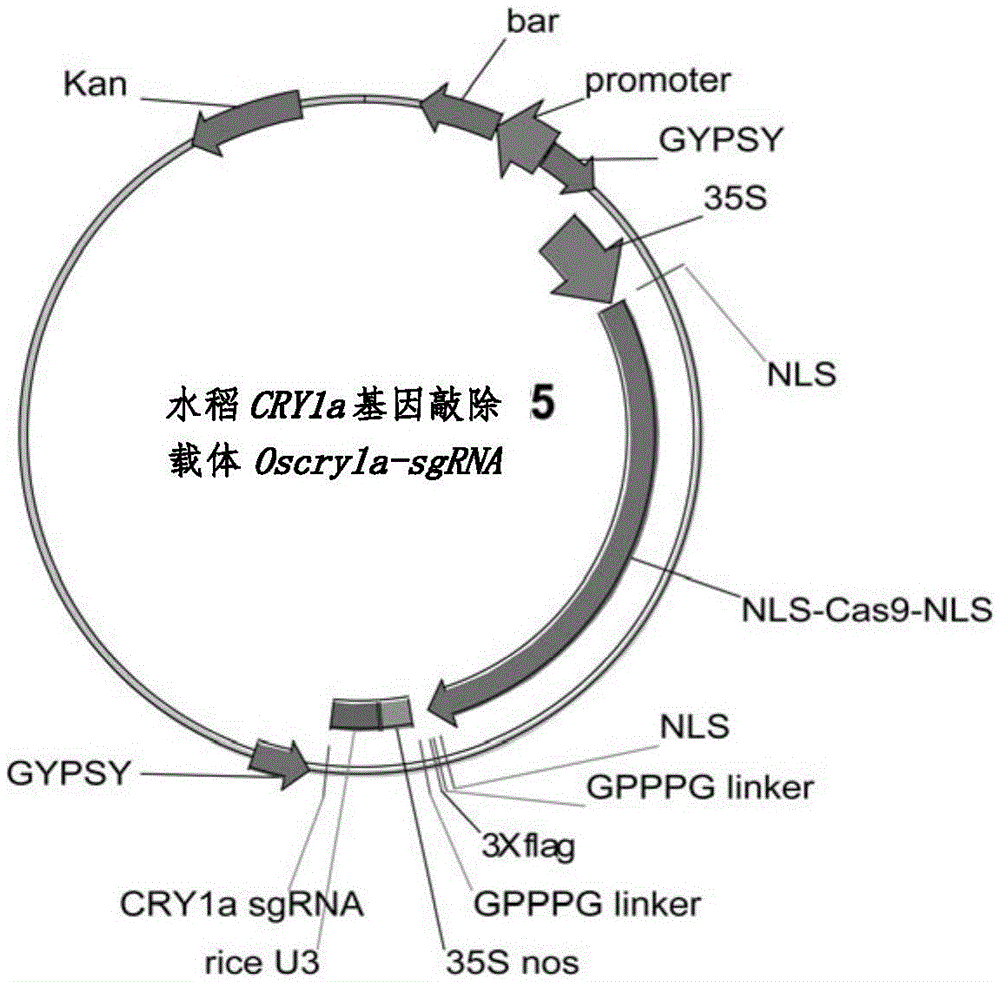
Double resistance CRISPR/Cas9 carrier and application
The invention relates to a double resistance CRISPR / Cas9 carrier and application. The invention provides the double resistance carrier having both hygromycin B resistance and Basta resistance at the same time; the double resistance carrier is obtained by inserting sequences and fragments derived from multiple different carriers into a sequence of a carrier pFGC5941 by enzyme-cutting and linking up, and constructing. Hygromycin B is used for screening in a conversion process, and Basta is used for screening offspring transgenic plants not containing an external source T-DNA sequence in offspring plants. Two resistances, i.e., the hygromycin B and the Basta are used to respectively serve as screening marks of the transgenic plants for the first time, a feasible manner is provided for screening transgenic offspring not containing the external source T-DNA sequence, determining the existence of external source T-DNA by a complex molecular biology detection experiment is avoided, and the offspring transgenic plants not containing the external source T-DNA sequence can be obtained by directly screening the Basta resistance and performing phenotype combination.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for breeding high-producing strain of cellulase by gene knockout
ActiveCN103865949AReduce loadPromote productionFungiMicroorganism based processesHygromycin BAmylase
The invention discloses a method for breeding a high-producing strain of cellulase by gene knockout, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. The method for breeding the high-producing strain of cellulase by gene knockout comprises the step of knocking out an amylase gene of the cellulase producing strain. A high-producing strain of cellulase is aspergillus niger without the amylase gene. An amylase gene knockout plasmid is obtained by connecting the front half part of the recombinant segment amylase gene-hygromycin B-an expression unit of a resistant gene- the rear half part of the amylase gene to a pCAMBIA1300 plasmid. Then, the plasmid is converted into agrobacterium, and the amylase gene is knocked out by agrobacterium-mediated conversion of the aspergillus niger. By using the gene knockout technology, the amylase gene of the aspergillus niger is knocked out. After the amylase gene is knocked out, the cell load is reduced, thereby facilitating production of a lot of cellulase. The cellulase activity of the high-producing strain of cellulase obtained can reach 21U / g.
Owner:中农华威生物制药(湖北)有限公司
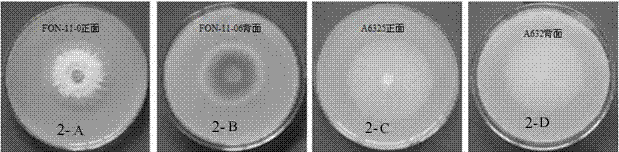
Watermelon oxysporum pathogenic FonAGL3 gene as well as deleted DNA fragment, deletion mutant and application thereof
InactiveCN107299105AClear control functionEffectiveness of Good Fusarium Wilt ControlBiocideFungiHygromycin BTreatment effect
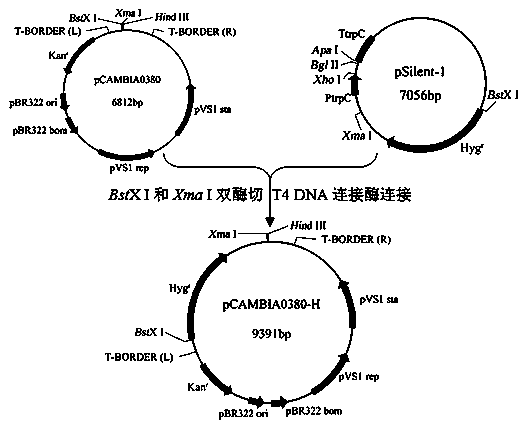
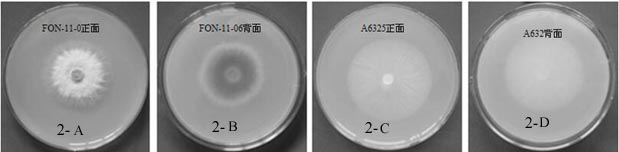
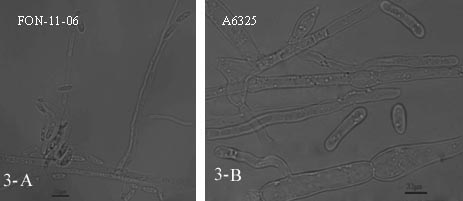
The invention discloses a watermelon oxysporum pathogenic FonAGL3 gene as well as a deleted DNA fragment, a deletion mutant and application thereof, and aims to solve the technical problem of biological prevention and treatment on watermelon oxysporum. A pathogenic gene FonAGL3 derived from watermelon fusarium oxysporum is analyzed and screened by inserting watermelon oxysporum T-DNA into a mutant library, by utilizing the homologous gene replacement principle, DNA fragments of the target gene FonAGL3 are replaced by gene DNA fragments of a resistance gene hygromycin B (HPH), a FonAGL3 gene deletion mutant is obtained by establishing a gene deletion carrier and implementing genetic transformation of a wild strain FON-11-06, and the FonAGL3 mutant bacterium has a good wilt prevention and treatment effect and is environmental-friendly and low in prevention and treatment cost.
Owner:河南省农业科学院园艺研究所 +1
Crystal structure of antibiotics bound to the 30S ribosome and its use
InactiveUS7079956B2High resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesHygromycin BX-ray
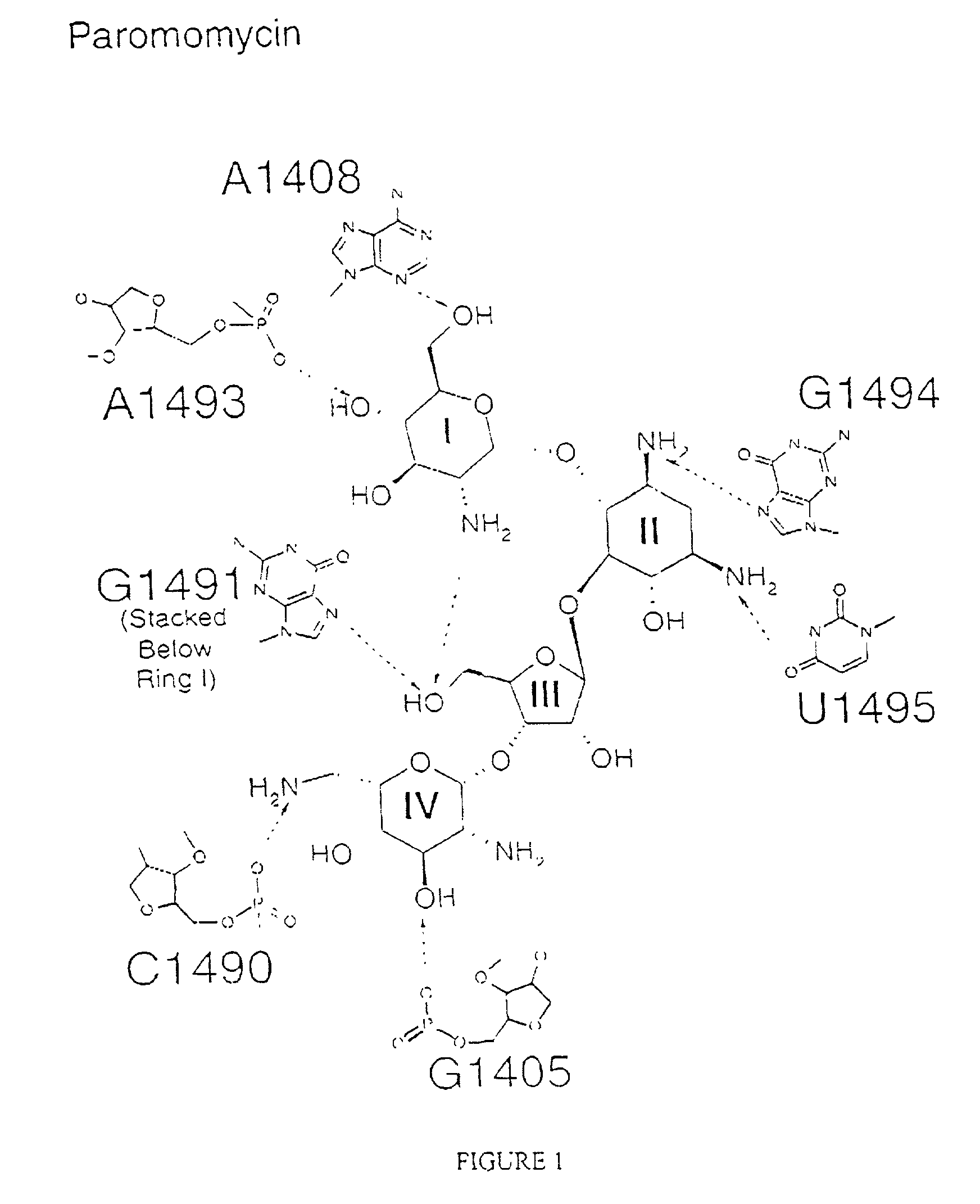
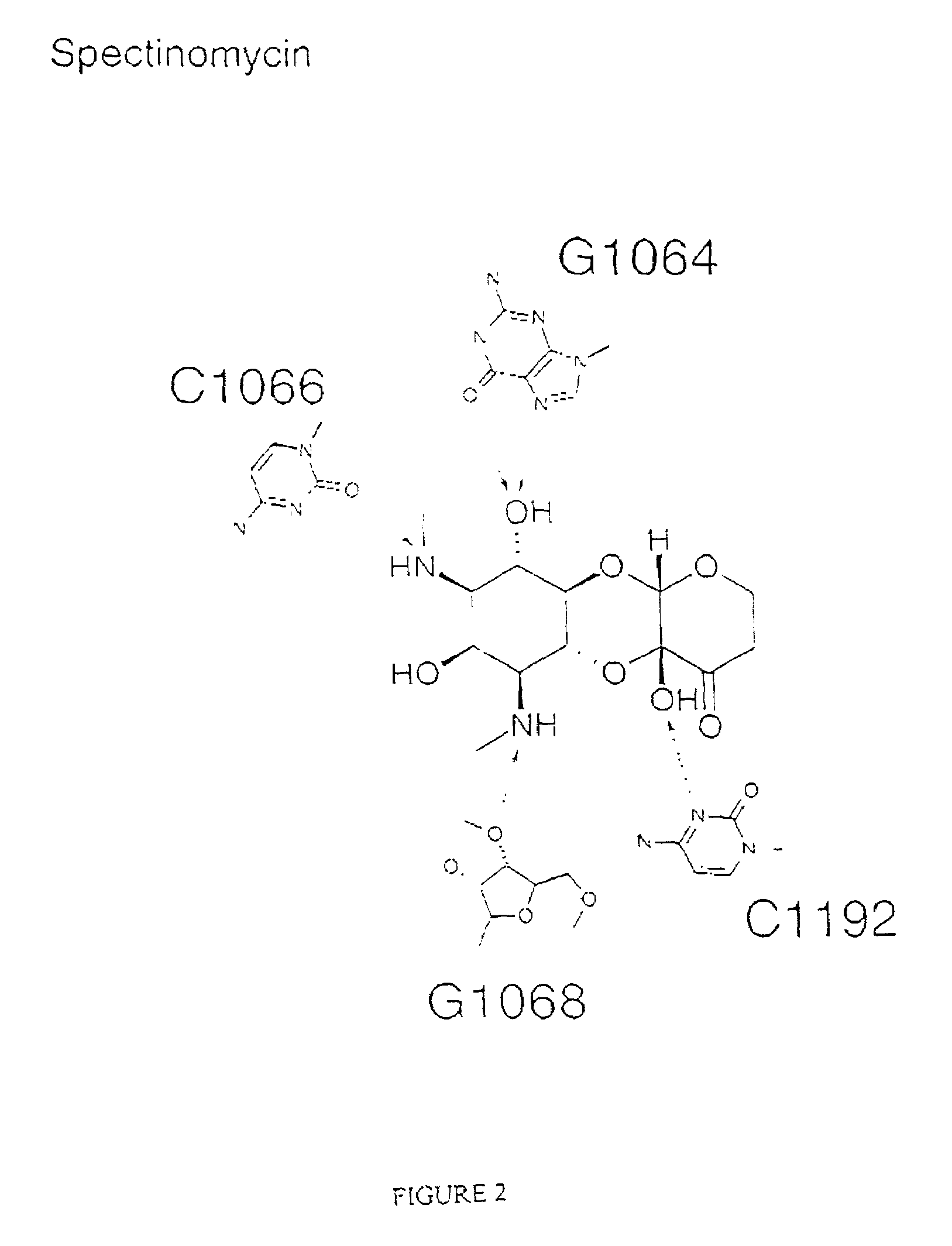
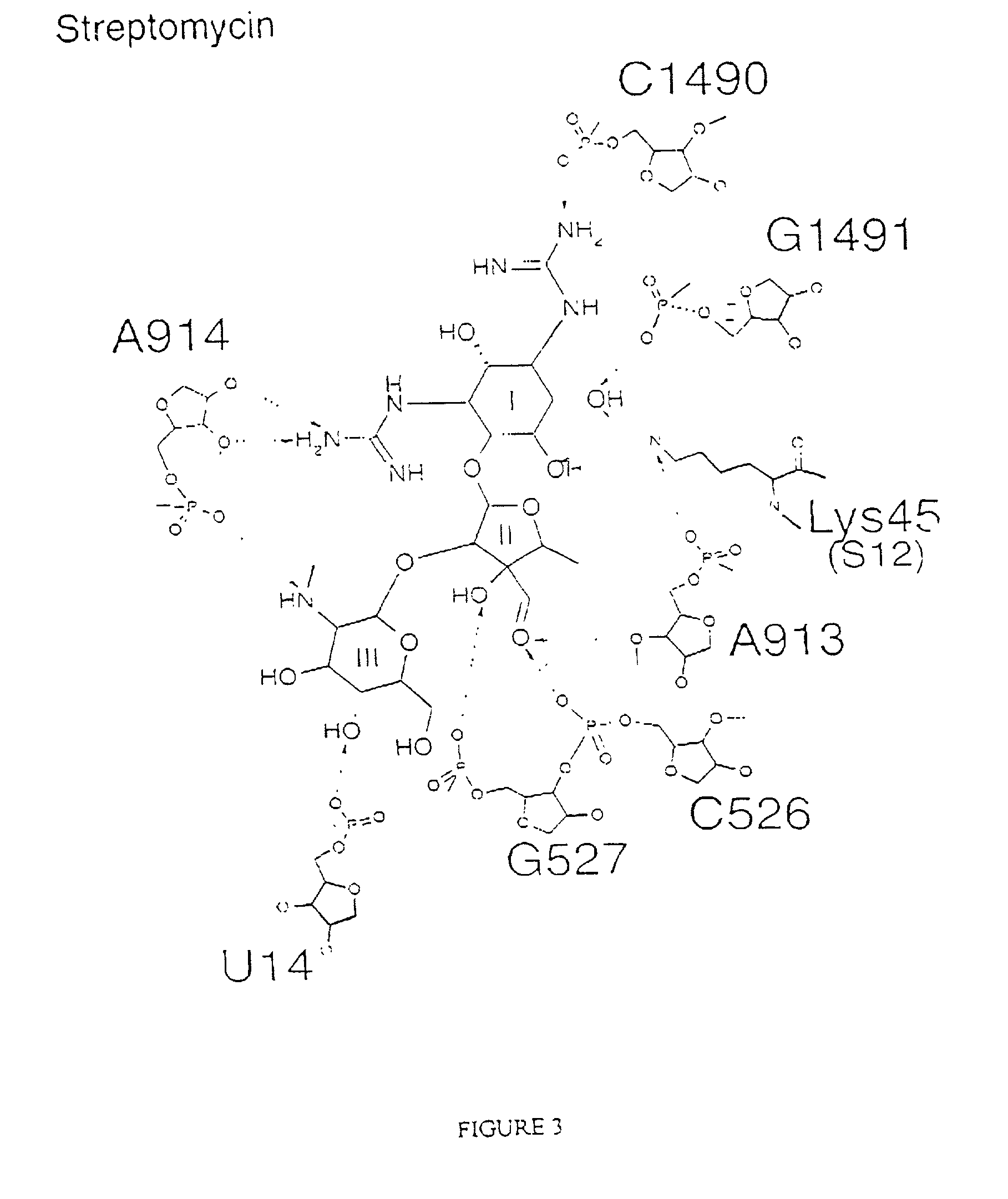
The invention provides high resolution X-ray crystal structures of the 30S ribosome, obtained from Thermus thermophilus 30S subunit, having a tetragonal space group P41212 to which are bound an antibiotic selected from the group paromomycin, streptomycin, spectinomycin, tetracycline, pactamycin and hygromycin B. An advantageous feature of the structure is that it diffracts at about 3 Å resolution. The invention also provides a crystal of 30S having the three dimensional atomic coordinates of the 30S ribosome, the coordinates being provided in any one of tables 1 to 4. The data may be used for the rational design and modelling of inhibitors for the 30S ribosome, which have potential use as antibiotics.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
High-throughput screening system for breeding high-nucleic-acid yeast and application
ActiveCN108893417AEasy to operateAvoid GMO ProblemsFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyHygromycin B
The invention relates to a high-throughput screening system for breeding high-nucleic-acid yeast. The high-throughput screening system comprises reporter plasmid Yep-Hyg B-yeGFP and a host cell containing the Yep-Hyg B-yeGFP, wherein the reporter plasmid Yep-Hyg B-yeGFP is annular and sequentially comprises a YEplac195 plasmid skeleton, a yeast enhanced green fluorescent protein gene yeGFP expression box and a hygromycin B resistance gene expression box from 3' to 5'; the original strain of the host cell is a saccharomyces cerevisiae industrial strain whose nucleic acid content is confirmed tobe higher than a normal value through screening. The invention further discloses application of the screening system in high-nucleic-acid yeast engineering bacterium breeding. The screening system has the advantages that the defect that traditional high-nucleic-acid yeast breeding cannot directly reflect RNA content can be overcome, the instability of the plasmid in the yeast can be utilized to easily eliminate the plasmid through continuous passage, and the system is significant to the application of the high-nucleic-acid yeast in food industry.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for agrobacterium-induced genetic transformation of Ustilaginoidea virens
InactiveCN103834681AShorten the timeImprove conversion rateFungiMicroorganism based processesHygromycin BLoss rate
The invention discloses a method for agrobacterium-induced genetic transformation of Ustilaginoidea virens. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out pre-induction culture on agrobacterium containing a hygromycin B gene and a marker gene, mixing an Ustilaginoidea virens spore liquid and the pre-induced agrobacterium liquid according to a volume ratio of 1: 1 to obtain a mixed bacterium liquid, uniformly coating the mixed bacterium liquid on an acetosyringone-containing modified AIM solid medium flat plate of which the surface is coated with a filter paper, a PVDF film or a nitrocellulose film, carrying out co-culture in the dark at a temperature of 20-24 DEG C for 36-48h, shearing the co-cultured film into small slices, paving the small slices on a modified selective medium CM, and carrying out culture at a temperature of 26 DEG C for 4-5 days to obtain hygromycin B gene-containing Ustilaginoidea virens. The method shortens converter time by 4-5d and has a conversion rate of 91.3%. The transgenic Ustilaginoidea virens has stable offspring, a low gene loss rate and converter stability of 95%.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method for detecting aminoglycosides in milk
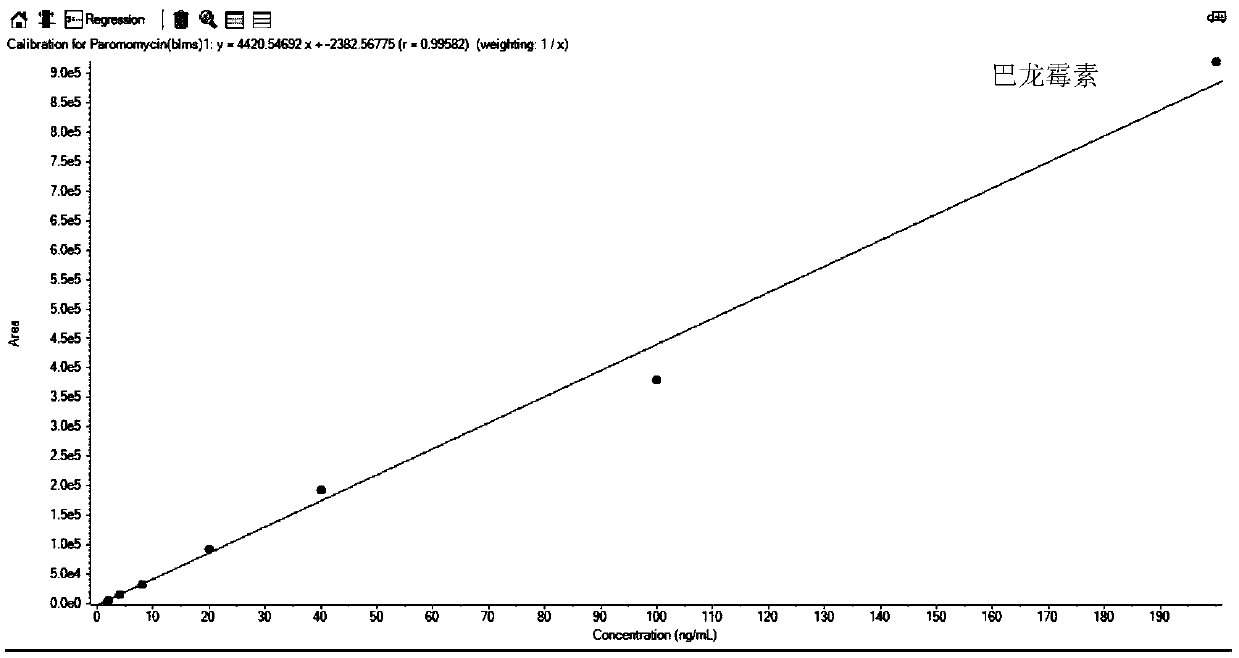
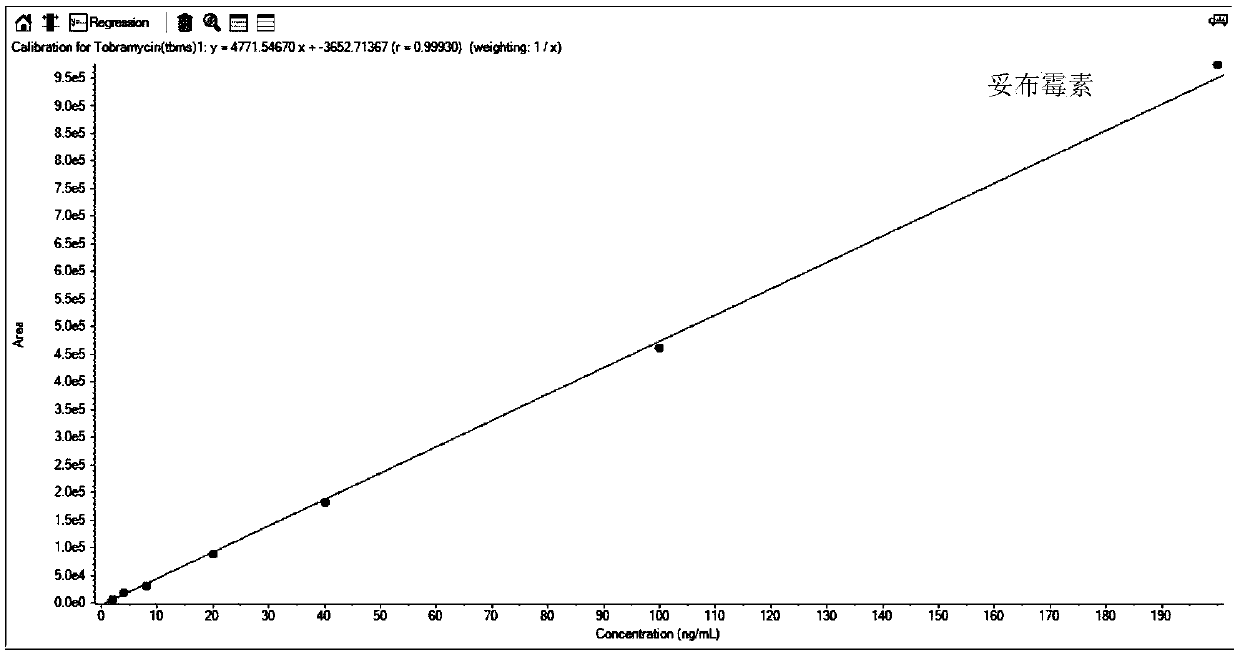
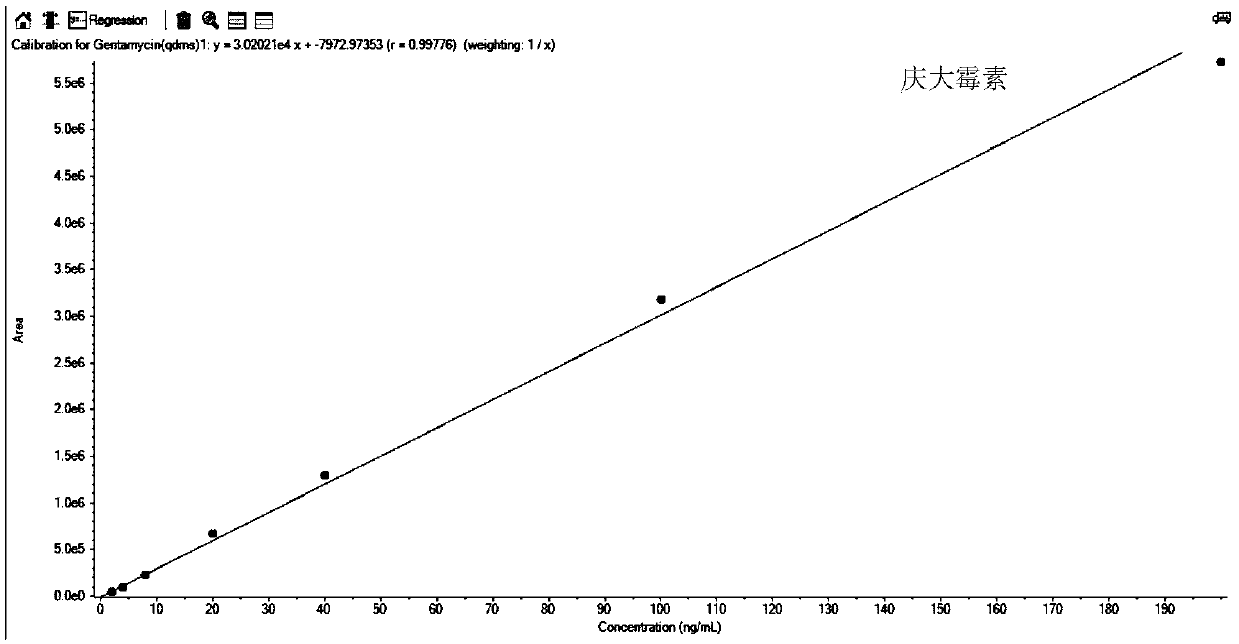
The invention relates to a method for detecting aminoglycosides in milk, which comprises the following steps: (1) extracting; (2) preparing a standard working solution; (3) performing determination bya high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS / MS), wherein the aminoglycosides are paromomycin, tobramycin, gentamicin, kanamycin, amikacin, apramycin, streptomycin, dihydrostreptomycin, neomycin, spectinomycin and hygromycin B. An MIP solid phase extraction column is uses in the step of extracting, thereby simplifying the pretreatment step, reducing the consumption of reagents and the time uses for the pretreatment; a SiELC Obelisc R chromatographic column is used for the separation of 11 kinds of aminoglycosides; and the mobile phase does not require heptafluorobutyric acid and does not contaminate the mass spectrometry.
Owner:上海市农产品质量安全检测中心
Aureobasidium pullulan alb1 gene knockout mutant strain and application thereof
ActiveCN106434394AHigh yieldImprove qualityFungiMicroorganism based processesHygromycin BMicroorganism
The invention discloses aureobasidium pullulan alb1 gene knockout mutant strain. According to the mutant strain, all or part of coding genes in alb1 gene in aureobasidium pullulan strain are knocked out and replaced by a hygromycin B resistance gene cassette. The hygromycin B resistance gene cassette comprises aureobasidium pullulan transcription elongation factor promoter PTEF and hygromycin B resistance gene HrgR; the sequence of the aureobasidium pullulan transcription elongation factor promoter PTEF is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2 in a sequence table; the sequence of the hygromycin B resistance gene HrgR is as shown in SEQ ID NO.3 in the sequence table. The mutant strain is used for the fermentation production of microbial polysaccharide, does not produce melanin, and can obviously the yield and quality of polysaccharide during the purification process.
Owner:SHANDONG ACADEMY OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES +1
Method for improving synthesis of trichodermin from trichoderma brevicompactum
InactiveCN104342461AIncrease productionIncrease concentrationMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyHygromycin B
The invention relates to the fields of microbial technology and biological prevention, and particularly relates to a method for improving synthesis of trichodermin from trichoderma brevicompactum 0248. The concentration of trichodermin in a fermentation liquor can be increased by obtaining hygromycin B resistant gene-containing trichoderma brevicompactum transformed strain AZ1 and adding hygromycin B into a liquid fermentation culture medium. The method provides a reliable method for improving the fermentation unit of the trichoderma brevicompactum.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
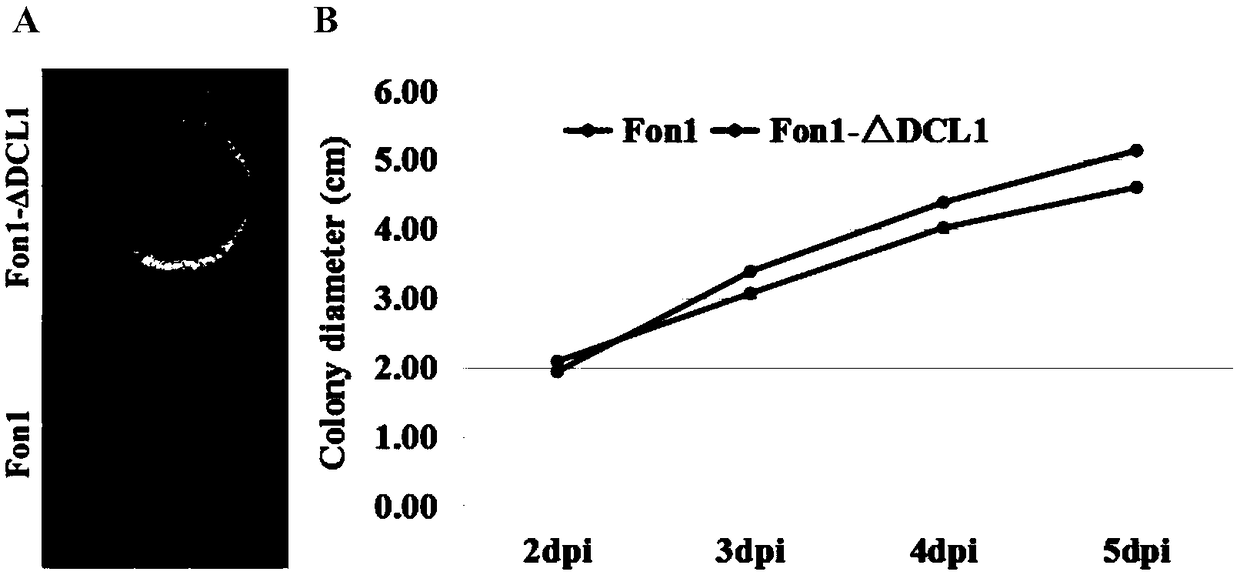
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum RNAi component FonDCL1 gene deletion mutant and construction method thereof
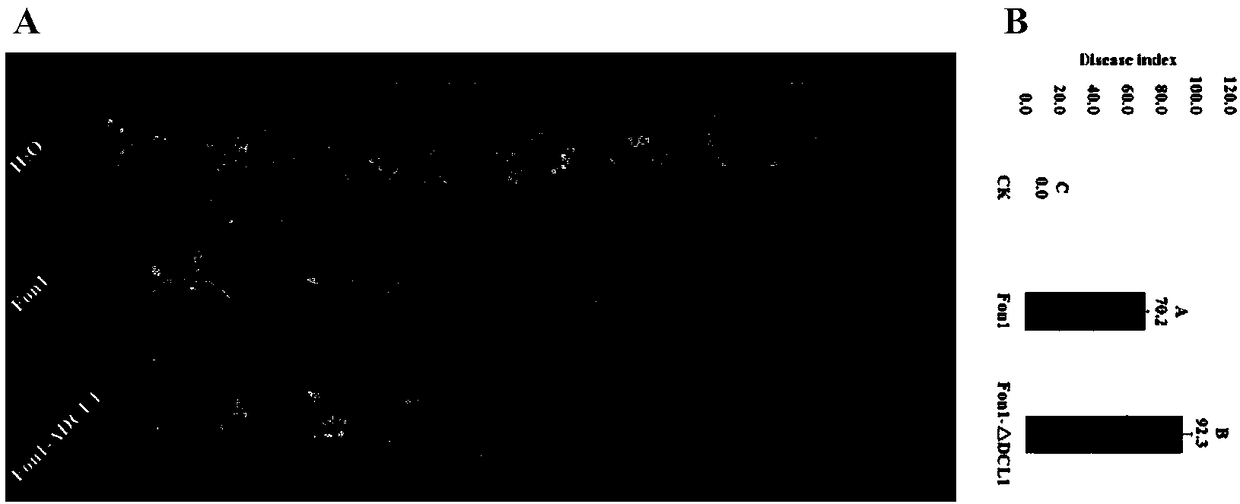
The invention discloses a fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum RNAi component FonDCL1 gene deletion mutant and a construction method thereof. According to the fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum RNAi component FonDCL1 gene deletion mutant and the construction method thereof, according to a reported Dicer like 1 protein sequence, homologous alignment is conducted on a Fon genomic sequence to obtain a fusariumoxysporum f.sp.niveum FonDCL1 gene, by adopting a homologous gene substitution principle, by means of a Split-marker strategy, the target gene FonDCL1 is substituted for a hygromycin B (HPH) gene DNAfragment, and by constructing a homologous gene recombinant fragment, through genetic transformation of a wild strain Fon1, the FonDCL1 gene deletion mutant is obtained. The FonDCL1 mutant has the advantages that the virulence to watermelon seedlings is enhanced, and the FonDCL1 mutant is more sensitive to abiotic stress factors of monensin sodium salt, hydroxycarbamide, a fluorescent whitening agent CFW, Congo red (CR), hydrogen peroxide and the like, so that a research foundation is provided for functional assignment of small RNA generated in processes of self growth and development and watermelon infection of the Fon1.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Flp-In-293 cell line for expressing bovine gamma interferon and establishment method thereof
InactiveCN102321589AVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsHygromycin BLipofectamine
The invention relates to an Flp-In-293 cell line for expressing a bovine gamma interferon. The cell line is named B1 and contains a gene for encoding the bovine gamma interferon. A method for constructing the cell line B1 comprises the following steps of: constructing preBoIFN-gamma fragments which are correctly sequenced into a recombinant plasmid pcDNA5 / FRT-preBoIFN-gamma-FLAG, cotransfecting Flp-In-293 cells by using the recombinant plasmid pcDNA5 / FRT-preBoIFN-gamma-FLAG and a recombinase expression vector pOG44 by a liposomal transfection method, screening positive clones by a dulbecco's modified eagle medium (DMEM) containing 120mu g / mL Hygromycin B, performing amplification culture, subcloning through limiting dilution analysis, and identifying to obtain a recombinant cell line. The bovine gamma interferon secreted by the cell line B1 has extremely high specific activity and stability.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge genetic transformation method
InactiveCN106497972AImprove qualityIncrease concentrationGenetic engineeringFermentationHygromycin BSalvia miltiorrhiza
The invention discloses a salvia miltiorrhiza bunge genetic transformation method which has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation, high repeatability and capability of rapidly and effectively acquiring genetically modified salvia miltiorrhiza bunge plants. At present, most salvia miltiorrhiza bunge plant genetic transformation systems adopt Kanamycin (abbreviated as Kan) for screening. However, inventors find that 99-3 salvia miltiorrhiza bunge leaves are sensitive to the Kanamycin in genetic transformation research for 99-3strain salvia miltiorrhiza bunge subjected to sequencing, leaf growth is easily stopped when the Kanamycin is used as a screening antibiotic, and experimental reproducibility is poor. When 30-60mg / L Hygromycin B (abbreviated as Hyg) is used for screening, positive genetically modified plants are obtained, and positive rate is quite high. In conclusion, the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge plant genetic transformation method taking the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge leaves as explants is efficient, reliable and simple and convenient to operate. The method is mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens, plasmid carrying exogenous genes are transformed into the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge, and the positive genetically modified salvia miltiorrhiza bunge plants are obtained.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
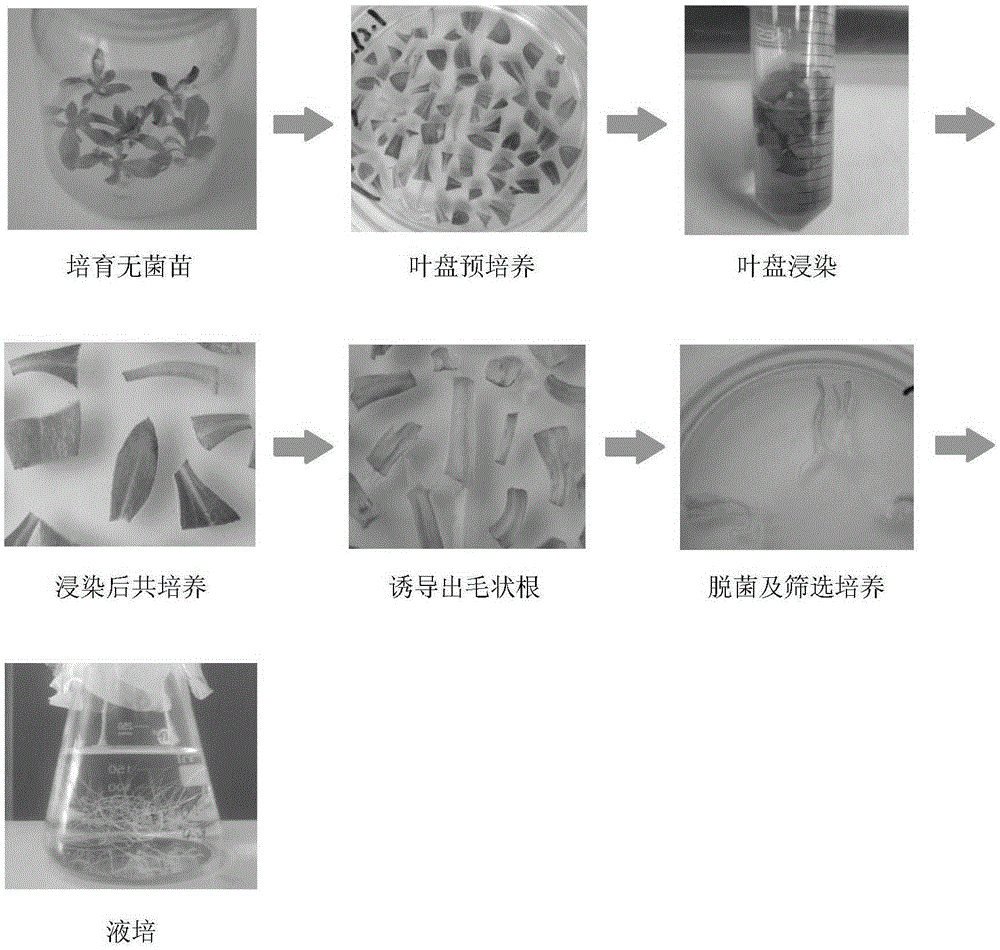
Agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated genetically modified Erigeron breviscapus hairy root transformation method
InactiveCN105255938ASimple operation techniqueVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsHygromycin BLiquid medium
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering in the plant biotechnology, and particularly relates to an agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated genetically modified Erigeron breviscapus hairy root transformation method. Pre-cultivated Erigeron breviscapus aseptic seedling blade explant is soaked in a C58C1 agrobacterium rhizogenes bacterial liquid carrying recombinant plasmid, hairy roots are cultivated on a selection medium containing hygromycin B (Hyb) for selection after infection, co-culture and bacteria removing, and a liquid medium is used for cultivating after a PCR amplification method is used for further identifying genetically modified roots carrying target genes. With the adoption of the technical scheme, the target genes can be guided into Erigeron breviscapus, and compared with genetic transformation of chemical methods of polyethylene glycol and the like, protoplast separation and cultivation segments are reduced; compared with genetic transformation of physical methods of a gene gun and the like, expensive instrument and equipment are not required, and the operation technique is simple.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
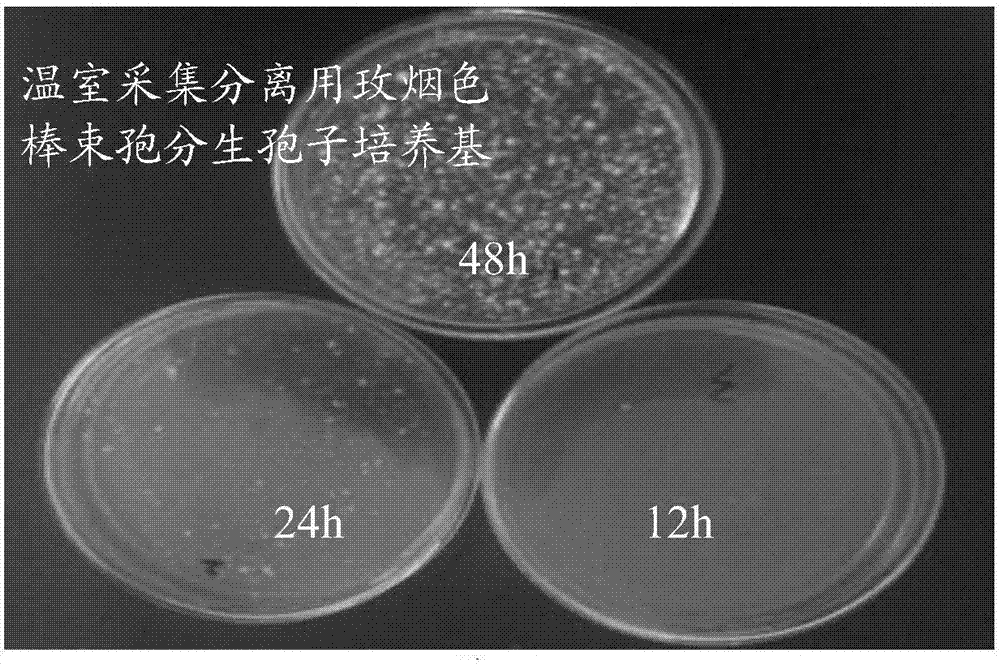
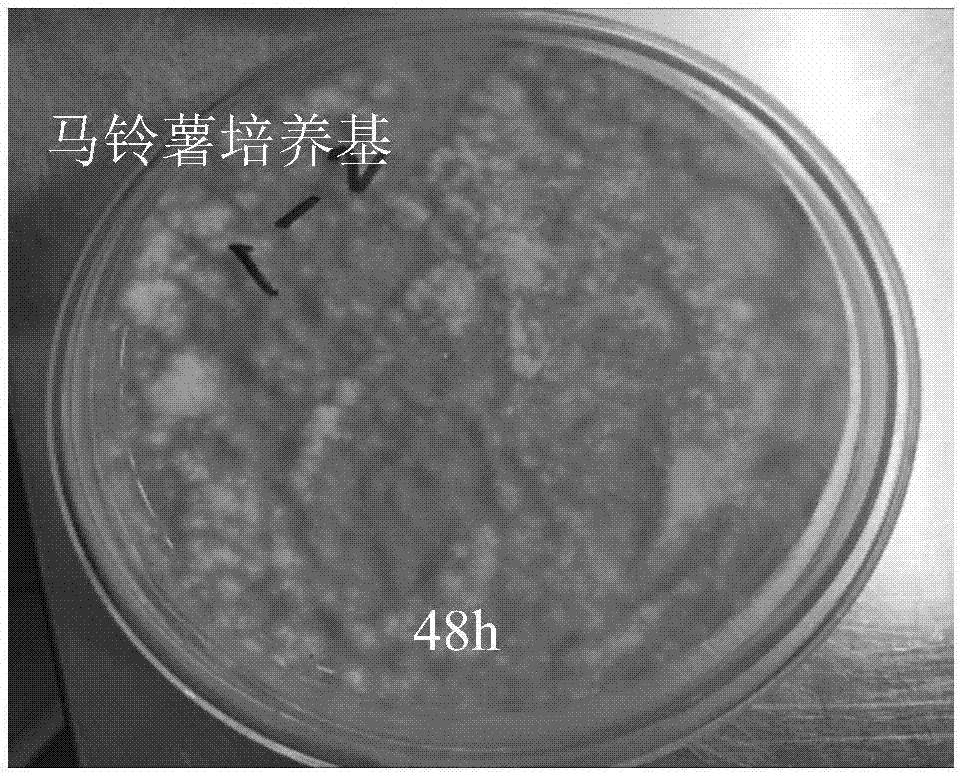
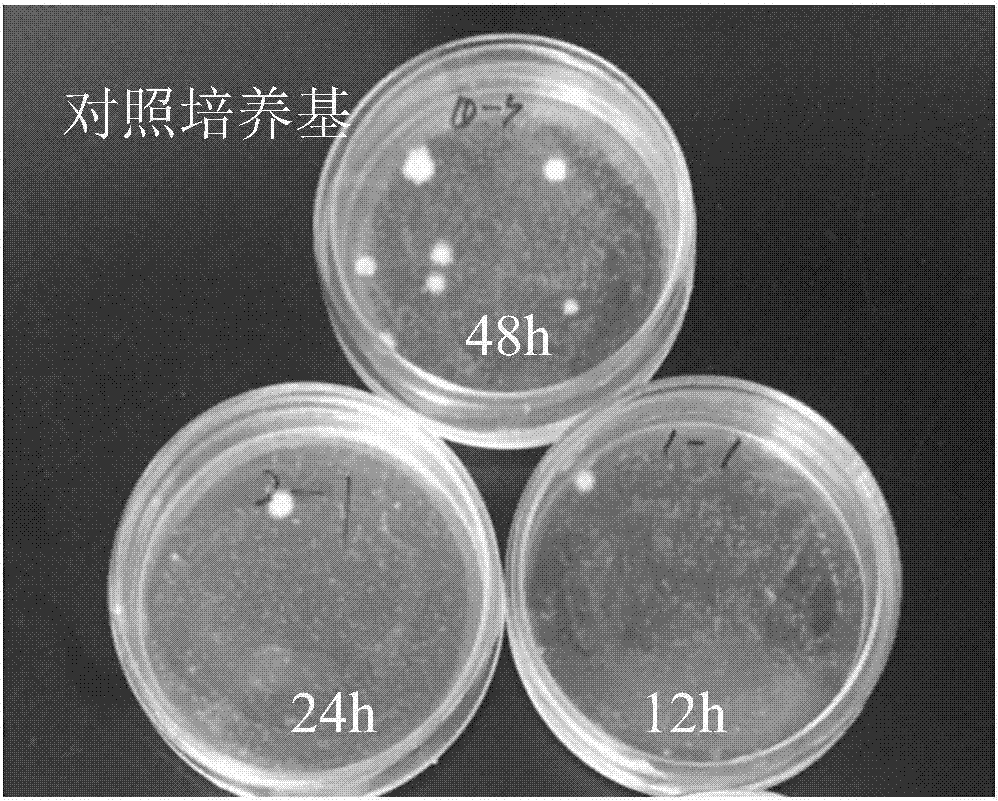
Culture medium for acquiring and isolating conidia of isaria fumosorosea in greenhouses and method for preparing culture medium
ActiveCN106978468AEffective germinationGerminate fastMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisHygromycin BAmpicillin
The invention relates to a culture medium for acquiring and isolating conidia of isaria fumosorosea in greenhouses and a method for preparing the culture medium, and belongs to the field of technologies for isolating and culturing microorganisms. The culture medium for acquiring and isolating the conidia of the isaria fumosorosea in the greenhouses comprises, by weight, 15-20% of potatoes, 1.5-2.0% of sucrose, 25-100 micro-g / ml of ampicillin, 25-100 micro-g / ml of hygromycin B, 1.0-3.0% of agar and the balance distilled water. A pH (potential of hydrogen) value of the culture medium is 7.0-10.0. The culture medium and the method have the advantages that the conidia of the isaria fumosorosea can be acquired and quickly isolated by the culture medium, the quantities of target bacterial colonies on flat plates can be detected, and accordingly diffusion conditions of the conidia of the isaria fumosorosea in control regions can be detected and quantitatively evaluated; the culture medium is high in isolation speed and detection efficiency, and scientific bases can be provided for formulating pest control strategies.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
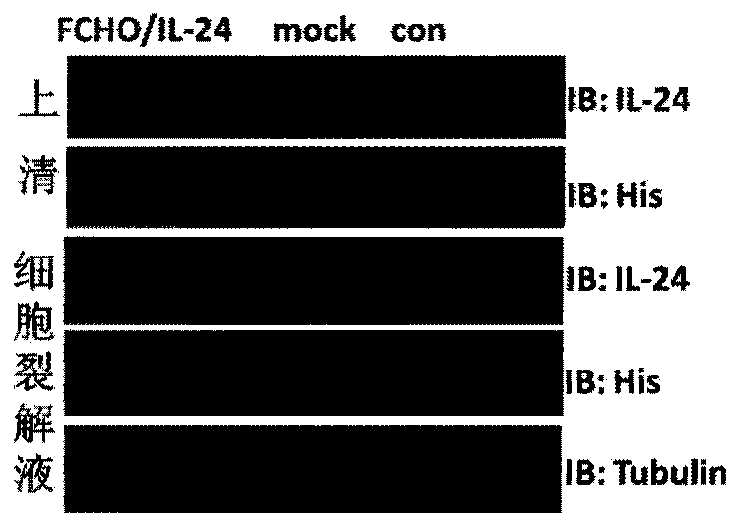
Cell strain capable of stably secreting and expressing IL-24 recombinant protein, and construction and application thereof
InactiveCN103710311AInhibition of clonogenicityPrevent proliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsHygromycin BMelanoma
The invention discloses a cell strain capable of stably secreting and expressing IL-24 recombinant protein, and construction and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of gene engineering. The construction method of the cell strain comprises the following steps: subcloning CDS region sequence of IL-24 gene into pcDNA5 / FRT plasmid of an Flp-In targeted integration system, transfecting into Flp-In-CHO cell together with plasmid pOG44, and screening the stable-expression cell strain by using antibiotic Hygromycin B; purifying the recombinant protein in the cultured supernatant of the cell strain by affinity chromatography; and finally, carrying out in-vivo and in-vitro activity experiments to prove that the recombinant protein has an action on inhibiting esophagus cancer cells and melanoma cells from proliferation and can induce the apoptosis of the esophagus cancer cells and melanoma cells, thereby developing an effective new drug for treating tumors.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL CHINA ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI +1
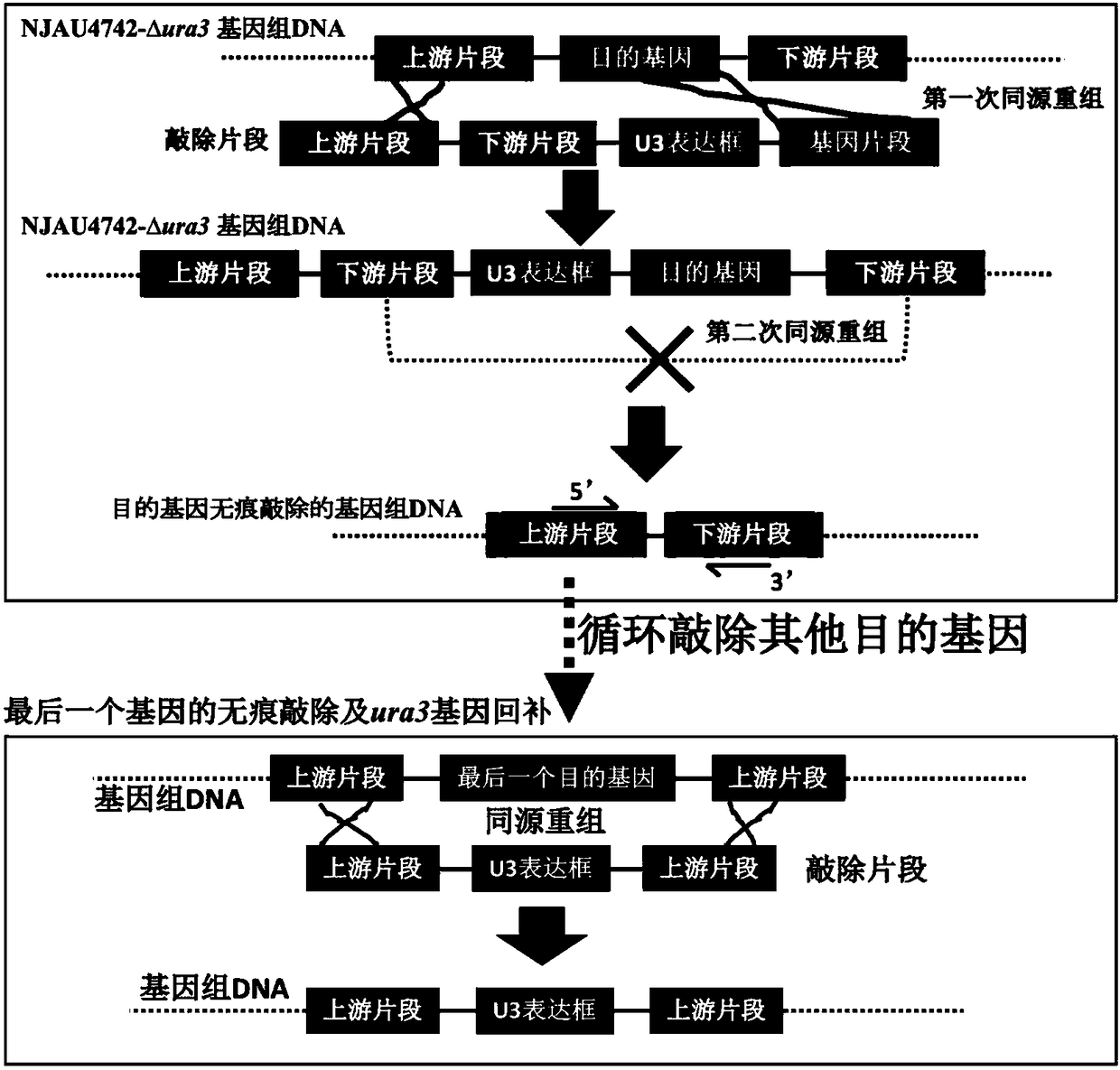
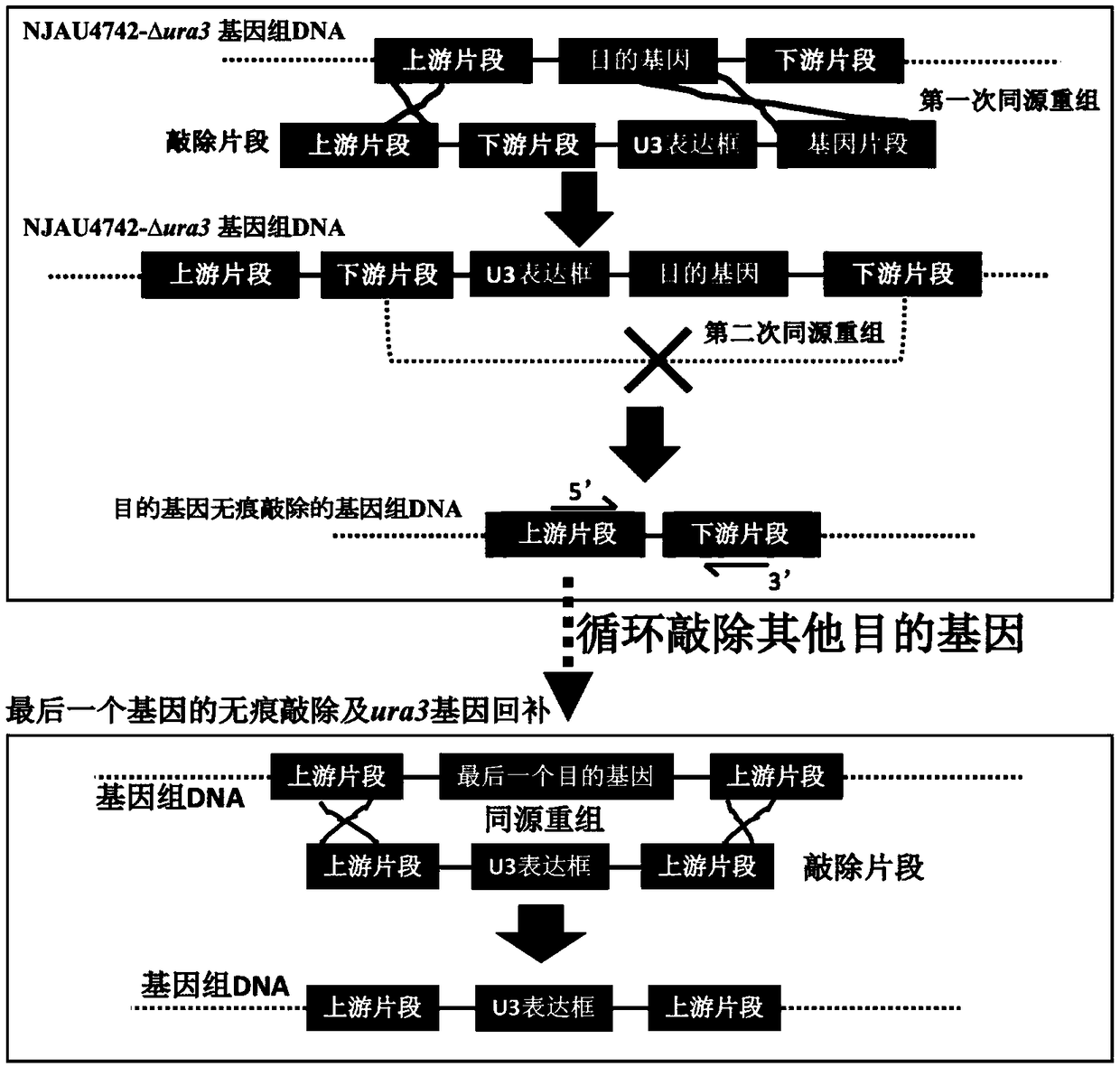
Traceless gene editing method for trichoderma fungi
ActiveCN108384797ASolve scientific research problems that are extremely difficult to operateRealize traceless recyclable operationFungiStable introduction of DNAHygromycin BGene Position
The invention relates to a traceless gene editing method for trichoderma fungi. According to the method, the traceless knockout mutant of the trichoderma guizhouense ura3 gene is obtained through twotimes of homologous recombination events and in combination with the resistance screening strategy of hygromycin B and the lethal strategy of 5-FOA; based on the mutant, the knockout fragment containing the ura3 gene expression cassette is inserted at the position of the target gene through the homologous recombination method, and the mutant having the first-time homologous recombination is screened by utilizing the nutrition defect feature of the ura3 traceless mutant; after the second-time homologous recombination, the ura3 gene and the target gene are removed through recombination, at the time, inverse screening is carried out by utilizing the lethal feature of 5-FOA, and thus the traceless mutant with the target gene completely deleted is obtained. The system is optimized sufficiently,the homologous recombination ratio is 15% or above, the single-gene traceless operating period is shortened to be within 15 days, meanwhile, the traceless overexpression of the target gene can be realized, and no exogenous fragments are introduced during the process.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for transforming gene of crypthecodinium cohnii producing docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
ActiveCN105647956AHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionHygromycin BTransforming Genes
The invention discloses an antibiotic namely hygromycin B that is sensitive to crypthecodinium cohnii producing DHA and a method using hygromycin B as the resistance screening marker to transform the gene of crypthecodinium cohnii. The method comprises the following steps: (1) determining the action concentration of hygromycin B; (2) establishing a gene transformation system; (3) preparing an exogenous gene section; (4) converting crypthecodinium cohnii by the exogenous gene section. According to the method, an exogenous gene can be introduced into cells of crypthecodinium cohnii, and at the same time, hygromycin B is taken as the screening marker to obtain an engineering strain of crypthecodinium cohnii with an exogenous gene. An important technological base is provided for the genetic engineering of crypthecodinium cohnii.
Owner:KUNMING ZAONENG BIOTECH CO LTD
Hybridoma cell strain ZXL-1 secreting specific monoclonal antibody to HB (hygromycin B) and application of hybridoma cell strain ZXL-1
ActiveCN107177559AMeeting the demand for rapid immunoassay productsTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsMicroorganismHygromycin B
The invention discloses a hybridoma cell strain ZXL-1 secreting a specific monoclonal antibody to HB (hygromycin B) and an application of the hybridoma cell strain ZXL-1 and belongs to the technical field of immunodetection. The hybridoma cell strain ZXL-1 secreting the specific monoclonal antibody to the HB has been collected in CGMCC (China general microbiogical culture collection center) of CCCCM (China committee for culture collection of microorganisms) with the collection number of CGMCC No. 13097. The anti-HB monoclonal antibody is obtained from the obtained hybridoma cell strain ZXL-1 specifically secreting the antibody to the HB after ascites preparation and purification. The antibody can be used for immunodetection of HB residues in animal-derived food and meet the market requirement for quick HB immunodetection products at present.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
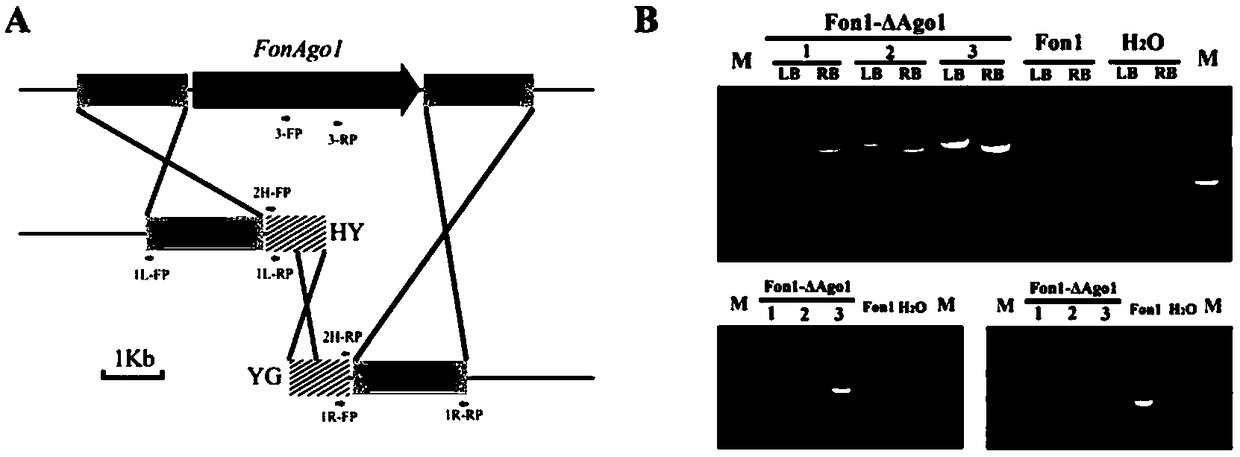
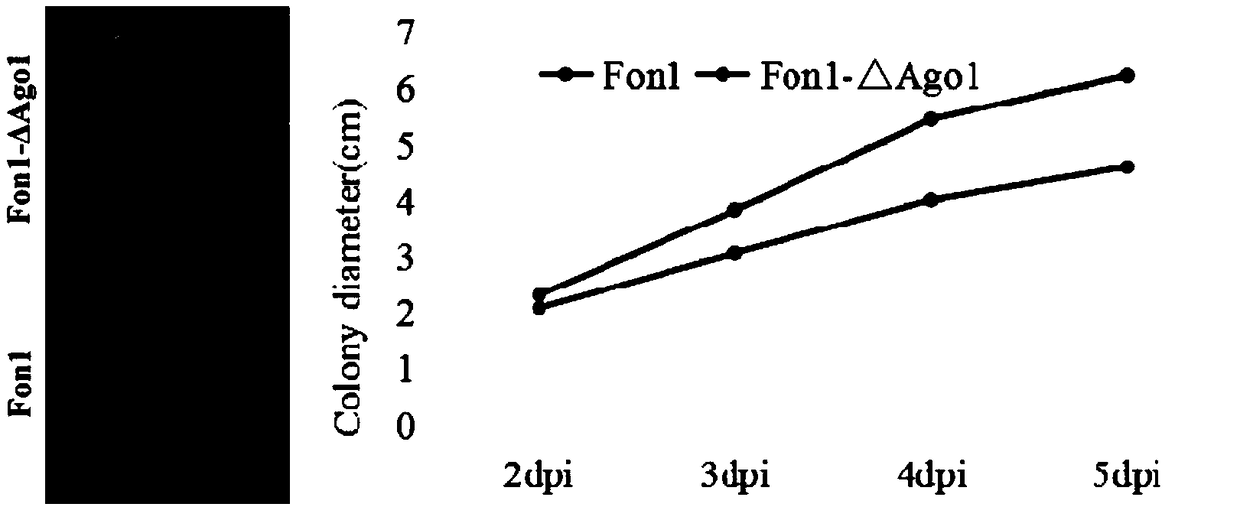
RNAi component FonAgol gene deletion mutant of fusarium oxyspirum f.sp.niveum and construction method of RNAi component FonAgol gene deletion mutant
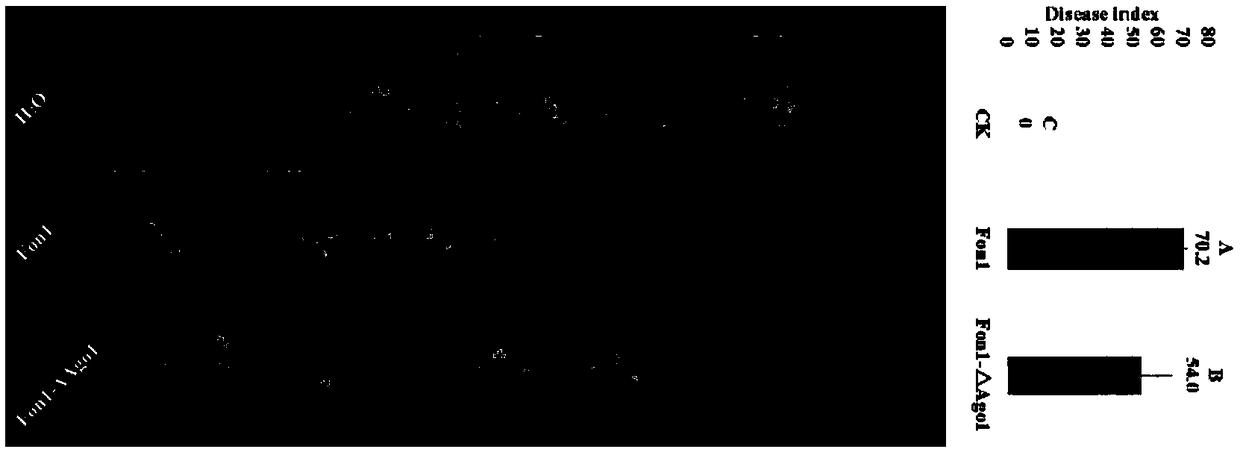
The invention discloses an RNAi component FonAgol gene deletion mutant of fusarium oxyspirum f.sp.niveum and a construction method of the RNAi component FonAgol gene deletion mutant. The RNAi component FonAgol gene deletion mutant and the construction method thereof are characterized in that a reported Argonaute protein sequence is homologously compared with a Fon gemonic sequence to obtain a FonAgol gene of the fusarium oxyspirum f.sp.niveum; a target gene FonAgol is replaced with a DNA fragment of a hygromycin B (HPH) gene by adopting a homologous gene replacement principle and using a Split-marker strategy; a gene deletion mutant of the FonAgol is obtained by constructing a gene homologous recombination fragment and using genetic transformation of a wild strain Fon1. The FonAgol mutanthas the characteristics of higher sensitivity to pathogenicity weakening of watermelon seedlings, abiotic stress factors such as fluorescent brightener CFW, Congo red CR and hydroxycarbamide and the like, which provides a research foundation for growth and development of Fon1 and functional assignment of small RNA produced in the process of infection watermelons.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
High yielding cellulase engineering bacterium and application thereof
InactiveCN104830890AIncrease productionHigh activityFungiMicroorganism based processesAmylaseHygromycin B
The invention relates to a high yielding cellulase engineering bacterium. The high yielding cellulase engineering bacterium is prepared through the following steps: composing a recombinant fragment by using the first half of amylase gene, a hygromycin B resistant gene expression unit and the latter half of the amylase gene, and carrying out enzyme digestion on the recombinant fragment by using a NcoI enzyme solution at 32.3-33.4DEG C; carrying out enzyme digestion on a pCAMIA1300 plasmid by using a NcoI enzyme; connecting the enzyme digested recombinant fragment with the enzyme digested plasmid through a DNA ligase to obtain an amylase gene knockout plasmid; converting Agrobacterium by using the amylase gene knockout plasmid; and carrying out mixing culture on the amylase gene knockout plasmid-containing Agrobacterium and Aspergillus niger, and carrying out hygromycin B resistance screengin to obtain the Aspergillus niger of the knockout amylase gene. The cellulase engineering bacterium provided by the invention substantially improves the output of cellulase, and is suitable for being used in industrial large-scale production.
Owner:上海泰坦科技股份有限公司
Construction and application of model of co-expression uptake of carrier and drug-metabolizing enzyme
ActiveCN103881977APredicted transportForecastMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationHygromycin BMetabolizing enzymes
The invention provides construction of a model of co-expression uptake of a carrier and a drug-metabolizing enzyme. The construction comprises the following steps: amplifying a human gene OAT1cDNA used as a template to obtain a human OAT1 gene segment, connecting the obtained human OAT1 gene segment to a carrier pcDNA3.1(+) to obtain a plasmid pcDNA3.1(+) / OAT1, transfecting MDCK (Madin Darby Canine Kidney) cells, and screening to obtain MDCK-hOAT1 cells in which the OAT1 is highly expressed; connecting a human CYP1A2 gene segment to a carrier pcDNA3.1(+) / Hygro(+) to obtain a plasmid pcDNA3.1 / Hygro(+) / CYP1A2, transfecting the MDCK-hOAT1 cells, screening by using a hygromycin B to obtain cells of co-expression of OAT1 and CYP1A2, then carrying out mRNA verification on the cells and also carrying out functional verification by virtue of a classic substrate and an inhibitor. The cell model can be applied to cellular-level screening based on the medical toxic effects of OAT1 and CYP1A2, and therefore, prediction of the synergistic effect of the two proteins in a medicine disposition process is realized and a basis can be provided for clinical rational medications. The cell model is rational in design and high in repeatability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for constructing rhizopus nigericans CRP genetically engineered bacteria by protoplast transformation
The invention provides a method for exogenous gene genetic transformation of rhizopus nigericans by protoplast transformation technology, which comprises the following steps: treating cell walls of rhizopus nigericans by fungal cell wall degrading enzyme to obtain protoplast, purifying the protoplast, introducing rhizopus oryzae NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase CYPOR (abbreviated as CPR gene) genes into rhizopus nigericans for the first time by using a protoplast transformation method with hygromycin B as a selective marker, so as to obtain the genetically engineered bacteria. The beneficial effects of the invention are that: the method can be used for molecular biology research of rhizopus nigericans, such as the molecular mechanism of the hydroxylation effect of the P450 enzyme system of the bacteria on steroids, and the like; the method can perform genetic engineering of rhizopus nigericans for genetic improvement breeding so as to increase the conversion rate of hydroxylation of steroid substrates by rhizopus nigericans.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii TCTN1 expression plasmid as well as construction method and application thereof
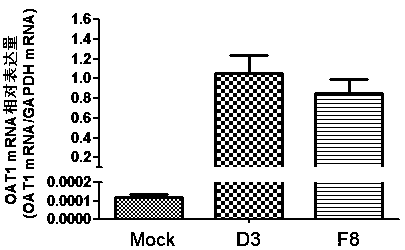
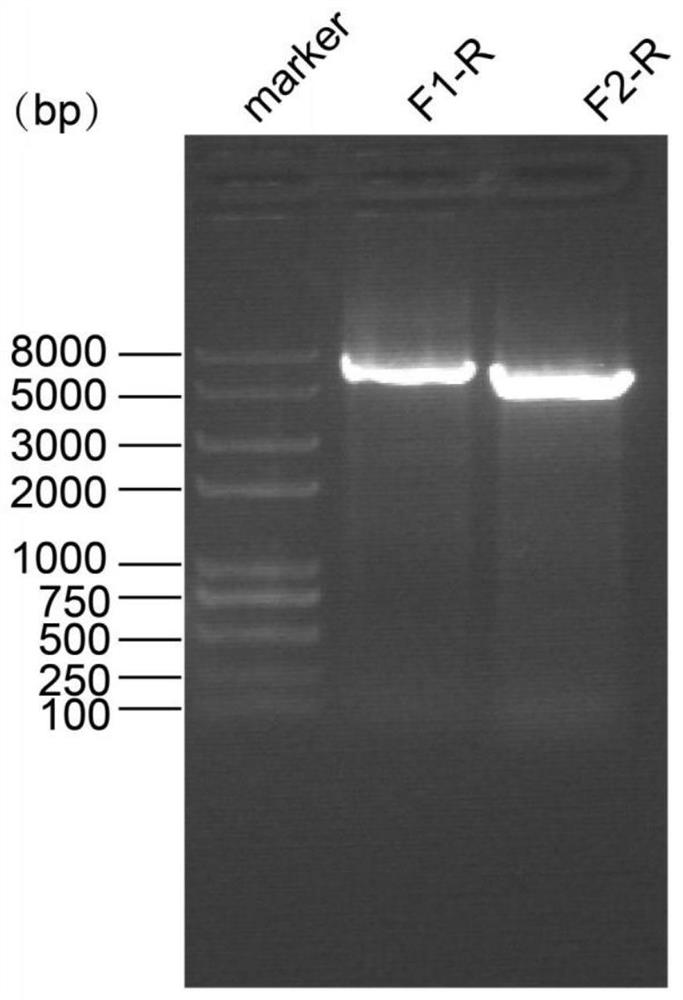
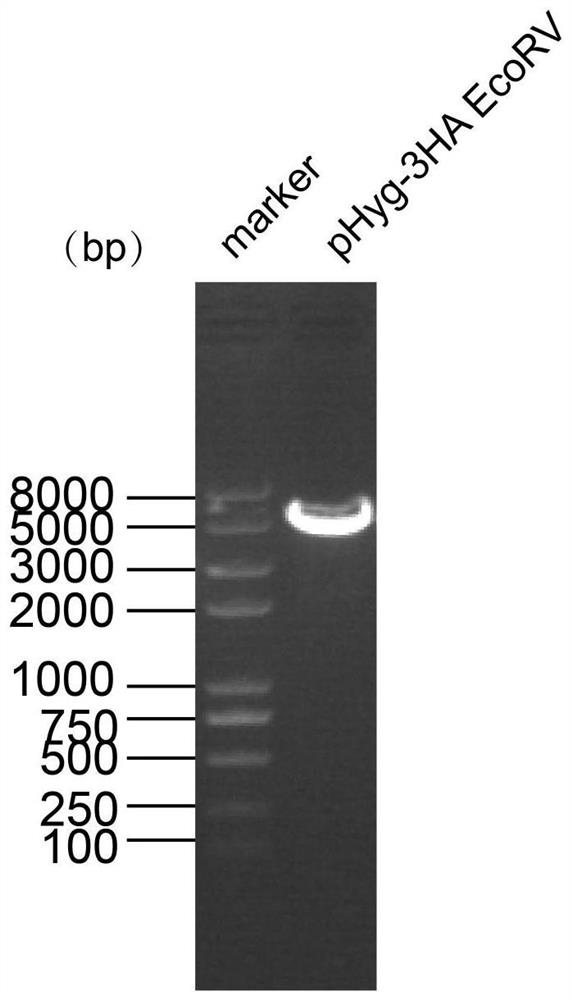
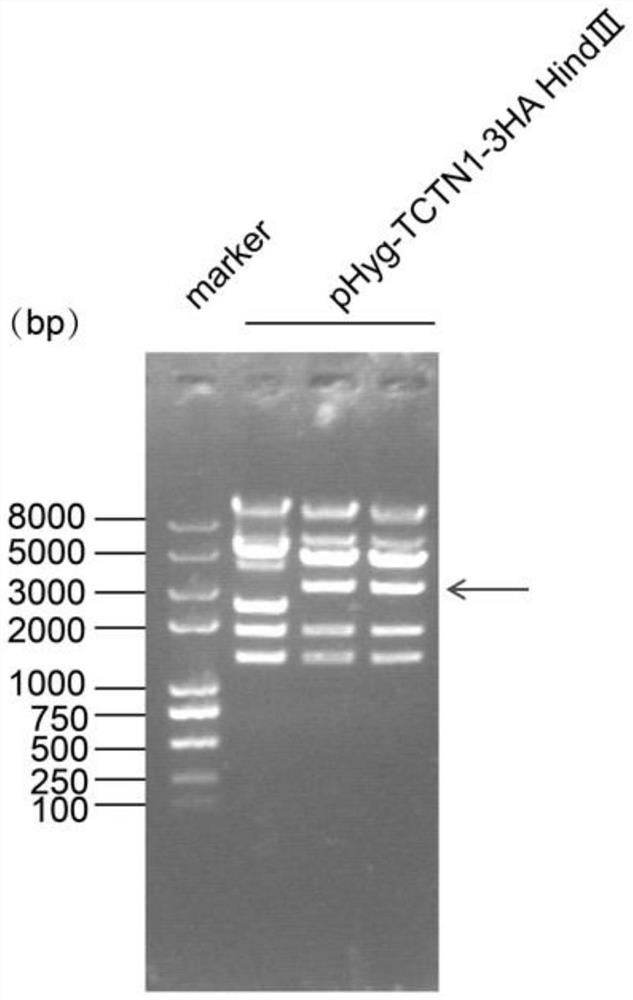
ActiveCN112662697AConducive to research structureGood for studying interactionsHybrid peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionHygromycin BChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a chlamydomonas reinhardtii TCTN1 expression plasmid as well as a construction method and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii TCTN1 expression plasmid is as shown in SEQ ID No.1. The chlamydomonas reinhardtii TCTN1 expression plasmid comprises a hygromycin B screening gene, an endogenous promoter for expressing a TCTN1 gene, TCTN1 gDNA, a 3 * HA tag at the 3'terminal and a terminator rbcS2 for terminating TCTN1 transcription; The construction method comprises the following steps: cloning a chlamydomonas reinhardtii TCTN1 gene segment; constructing a T vector plasmid containing a TCTN1 fragment; obtaining a terminal phosphorylated TCTN1 fragment; preparing a pHyg-3HA vector; and constructing and verifying the plasmid of the pHyg-TCTN1-3HA. According to the expression plasmid of the chlamydomonas TCTN1, algal strains capable of stably expressing the TCTN1-HA fusion protein can be efficiently screened, so that a chlamydomonas cilia transition region is marked, and the structure of the transition region and the function of a complex are known.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application of trichoderma brevicompactum transformant in improvement of trichodermin yield
InactiveCN104293855AIncrease concentrationRaise the fermentation unitFungiMicroorganism based processesHygromycin BBiotechnology
The invention relates to the fields of microbial technologies and biological prevention and control, and particularly relates to an application of a trichoderma brevicompactum 0248 transformant with hygromycin B resistance in improvement of trichodermin yield. Through obtaining the trichoderma brevicompactum transformant containing a hygromycin B resistance gene, and adding hygromycin B to a liquid fermentation culture medium, the concentration of trichodermin in the fermentation liquid is improved. A reliable method is provided for improving the fermentation unit of trichodermin; and an application of the trichoderma brevicompactum transformant with hygromycin B resistance in improvement of the trichodermin yield is provided.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Pathogenic fonagl3 gene of Fusarium wilt of watermelon, its deletion dna fragment, deletion mutant and application thereof
InactiveCN107299105BClear control functionEffectiveness of Good Fusarium Wilt ControlBiocideFungiBiotechnologyHygromycin B
The invention discloses a watermelon oxysporum pathogenic FonAGL3 gene as well as a deleted DNA fragment, a deletion mutant and application thereof, and aims to solve the technical problem of biological prevention and treatment on watermelon oxysporum. A pathogenic gene FonAGL3 derived from watermelon fusarium oxysporum is analyzed and screened by inserting watermelon oxysporum T-DNA into a mutant library, by utilizing the homologous gene replacement principle, DNA fragments of the target gene FonAGL3 are replaced by gene DNA fragments of a resistance gene hygromycin B (HPH), a FonAGL3 gene deletion mutant is obtained by establishing a gene deletion carrier and implementing genetic transformation of a wild strain FON-11-06, and the FonAGL3 mutant bacterium has a good wilt prevention and treatment effect and is environmental-friendly and low in prevention and treatment cost.
Owner:河南省农业科学院园艺研究所 +1
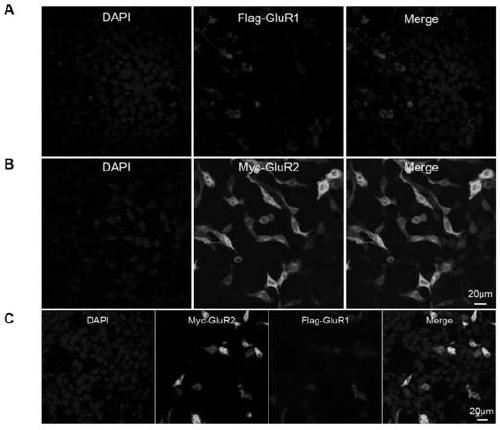
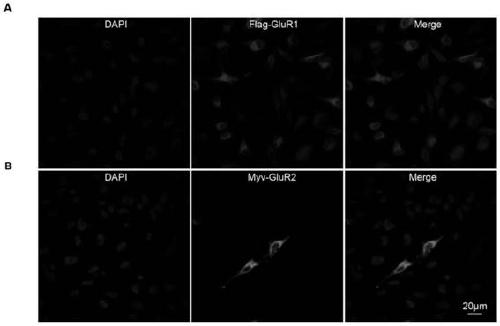
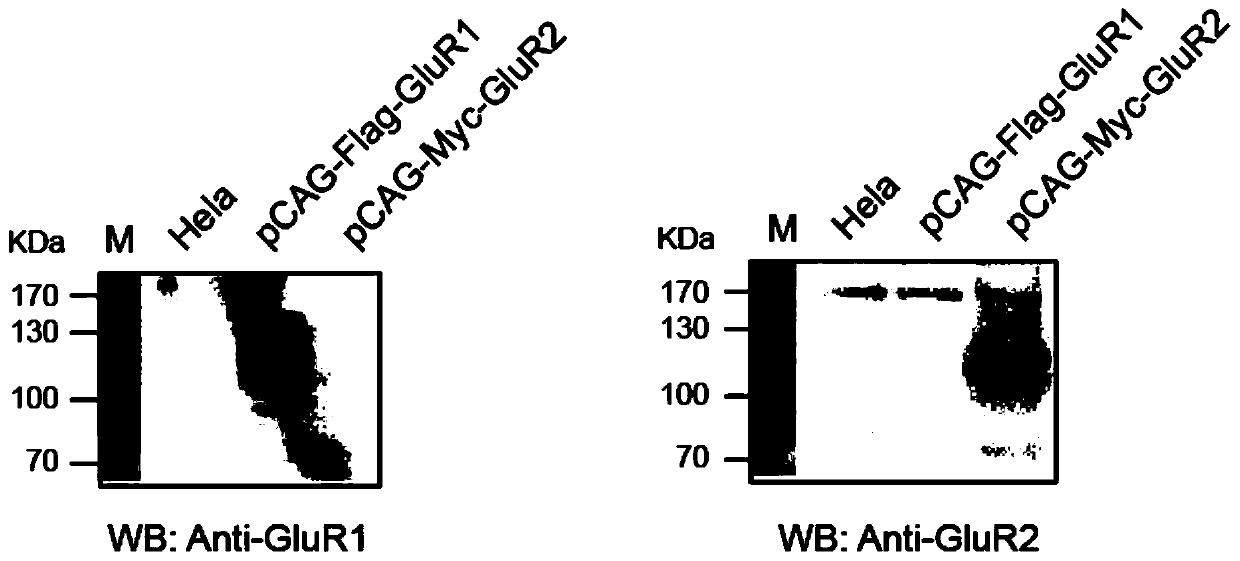
Cell strain capable of stably expressing AMPA receptor GluR1/GluR2, and construction method of cell strain
InactiveCN111269939AStable expressionGenetically modified cellsNucleic acid vectorHygromycin BDisease
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, particularly to a GluR1 / GluR2 cell strain capable of stably expressing an AMPA receptor, and a construction method thereof. Accordingto the construction method disclosed by the invention, a cell strain capable of stably expressing an AMPA receptor GluR1 / GluR2 is prepared. According to the scheme, retrovirus mediated gene expressionis adopted, hygromycin B is added for screening for two weeks, and the cell strain stably expressing the AMPA receptor GluR1 / GluR2 is obtained; after the AMPA receptor GluR1 / GluR2 stably transfectedcell strain is subjected to passage six times, the GluR1 and the GluR2 in the cell strain are still stably expressed, and the GluR1 and the GluR2 interact with each other; and the cell strain can provide basic research materials, experimental tools and carriers for analysis of AMPA receptor functions in diseases such as cerebral apoplexy and the like and probe development.
Owner:湖南大学深圳研究院
A method for constructing Rhizopus niger cpr genetically engineered bacteria by transformation of protoplasts
The invention provides a method for exogenous gene genetic transformation of rhizopus nigericans by protoplast transformation technology, which comprises the following steps: treating cell walls of rhizopus nigericans by fungal cell wall degrading enzyme to obtain protoplast, purifying the protoplast, introducing rhizopus oryzae NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase CYPOR (abbreviated as CPR gene) genes into rhizopus nigericans for the first time by using a protoplast transformation method with hygromycin B as a selective marker, so as to obtain the genetically engineered bacteria. The beneficial effects of the invention are that: the method can be used for molecular biology research of rhizopus nigericans, such as the molecular mechanism of the hydroxylation effect of the P450 enzyme system of the bacteria on steroids, and the like; the method can perform genetic engineering of rhizopus nigericans for genetic improvement breeding so as to increase the conversion rate of hydroxylation of steroid substrates by rhizopus nigericans.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Construction method of Hela cell strain capable of stably expressing H1N1 influenza virus RNPs
InactiveCN106434746ASolve the problem of Hela-RNP cell lineVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsHygromycin BAntibiotic Y
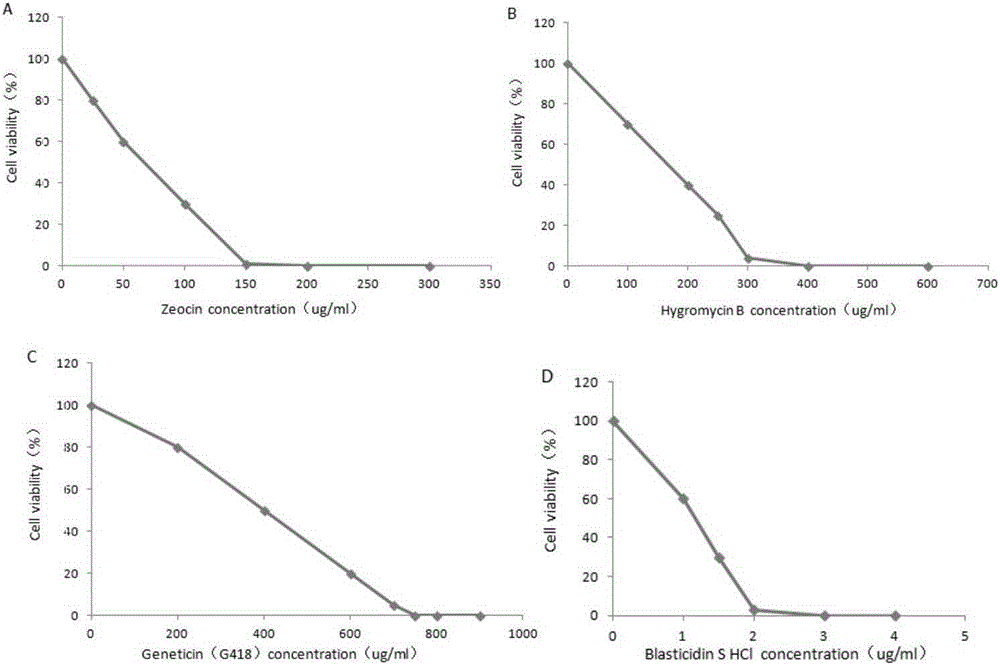
The invention belongs to the field of physical medicine and provides a construction method of a Hela cell strain capable of stably expressing the H1N1 influenza virus RNPs. The method comprises the steps of constructing a recombinant plasmid pcDNA 3.1 / Zeo-PB1, pcDNA 3.1U / Hygro-PB2, pcDNA 3.1 / Neo-PA, and pEF 6 / V5-HisA-NP; acquiring an optimal screening concentration for four antibiotics Zeocin, Hygromycin B, Geneticin, Blasticidin S HCl-infected Hela cells; transfecting the Hela cell strain to the recombinant plasmid pcDNA 3.1 / Zeo-PB1, the pcDNA 3.1U / Hygro-PB2, the pcDNA 3.1 / Neo-PA, and the pEF 6 / V5-HisA-NP in batches, and screening to obtain the cell strain Hela-RNP.
Owner:SHENZHEN CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Aureobasidium pullulans alb1 gene knockout mutant strain and its application
ActiveCN106434394BHigh yieldImprove qualityFungiMicroorganism based processesHygromycin BMicroorganism
The invention discloses aureobasidium pullulan alb1 gene knockout mutant strain. According to the mutant strain, all or part of coding genes in alb1 gene in aureobasidium pullulan strain are knocked out and replaced by a hygromycin B resistance gene cassette. The hygromycin B resistance gene cassette comprises aureobasidium pullulan transcription elongation factor promoter PTEF and hygromycin B resistance gene HrgR; the sequence of the aureobasidium pullulan transcription elongation factor promoter PTEF is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2 in a sequence table; the sequence of the hygromycin B resistance gene HrgR is as shown in SEQ ID NO.3 in the sequence table. The mutant strain is used for the fermentation production of microbial polysaccharide, does not produce melanin, and can obviously the yield and quality of polysaccharide during the purification process.
Owner:SHANDONG ACADEMY OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES +1
A traceless Trichoderma fungal gene editing method
ActiveCN108384797BSolve scientific research problems that are extremely difficult to operateRealize traceless recyclable operationFungiStable introduction of DNAHygromycin BGene Position
The invention relates to a traceless gene editing method for trichoderma fungi. According to the method, the traceless knockout mutant of the trichoderma guizhouense ura3 gene is obtained through twotimes of homologous recombination events and in combination with the resistance screening strategy of hygromycin B and the lethal strategy of 5-FOA; based on the mutant, the knockout fragment containing the ura3 gene expression cassette is inserted at the position of the target gene through the homologous recombination method, and the mutant having the first-time homologous recombination is screened by utilizing the nutrition defect feature of the ura3 traceless mutant; after the second-time homologous recombination, the ura3 gene and the target gene are removed through recombination, at the time, inverse screening is carried out by utilizing the lethal feature of 5-FOA, and thus the traceless mutant with the target gene completely deleted is obtained. The system is optimized sufficiently,the homologous recombination ratio is 15% or above, the single-gene traceless operating period is shortened to be within 15 days, meanwhile, the traceless overexpression of the target gene can be realized, and no exogenous fragments are introduced during the process.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com