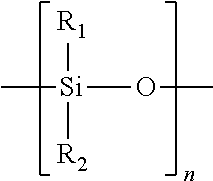
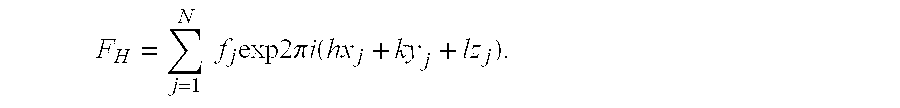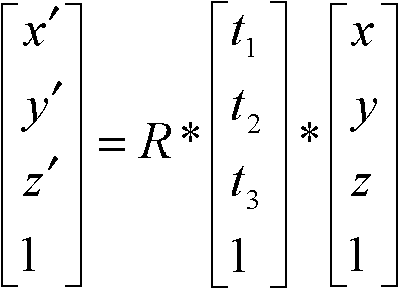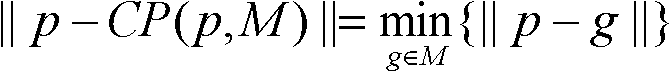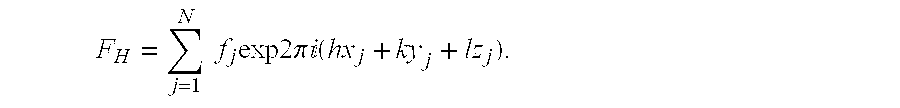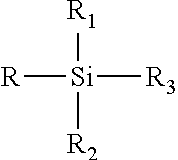Patents
Literature
70 results about "Atomic coordinates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
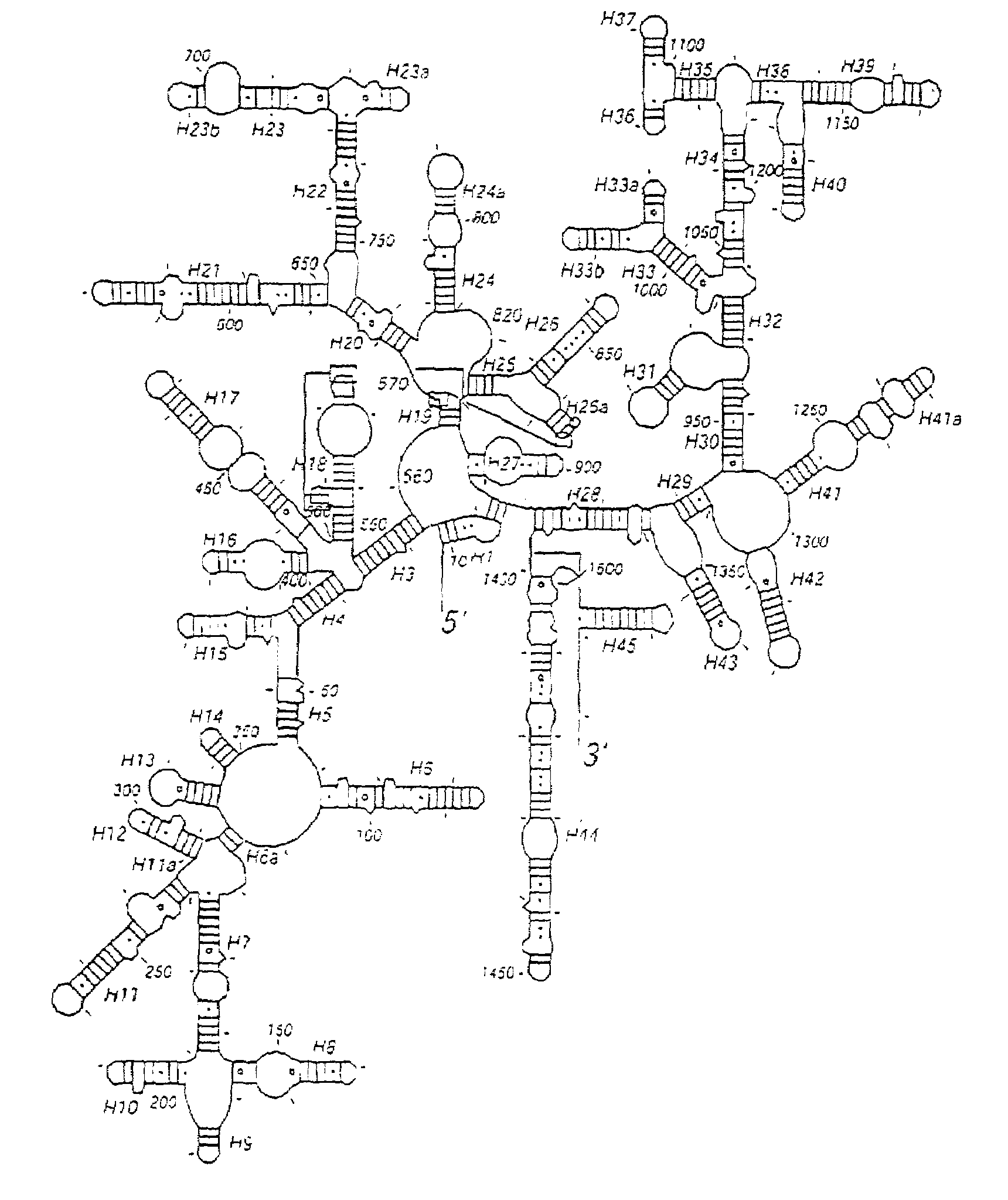
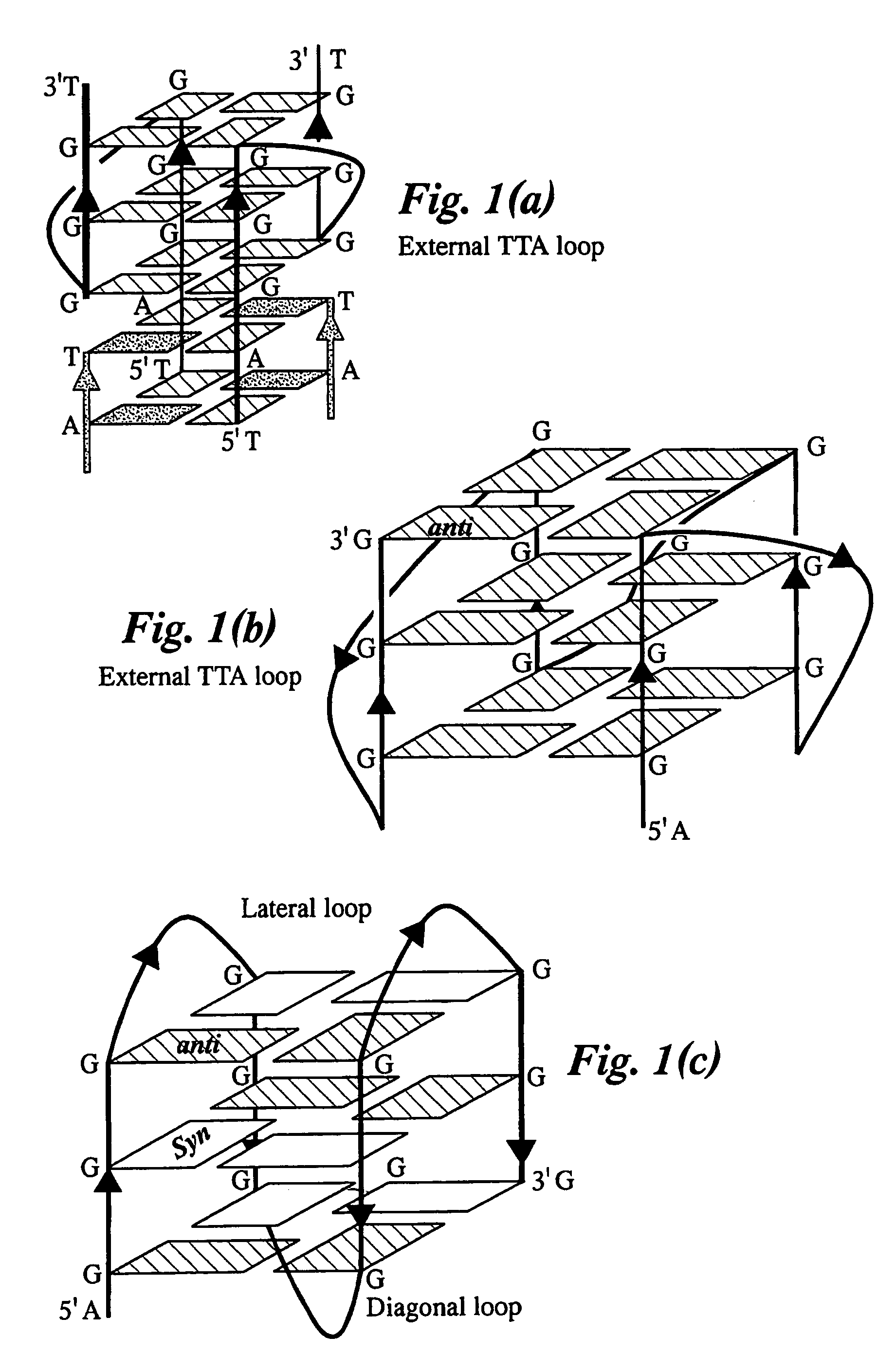
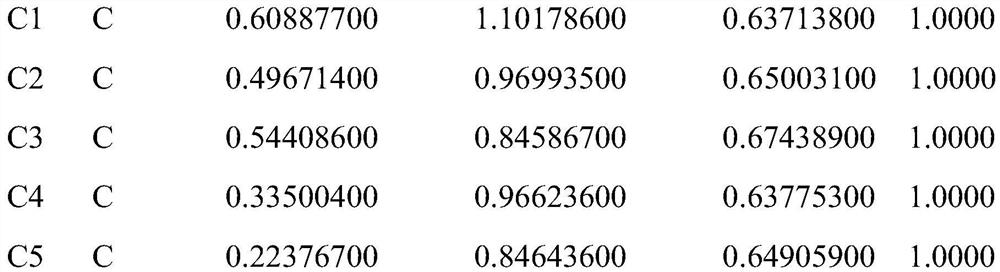
Atomic coordinate files are the data files that specify three-dimensional (3D) molecular structures. At a minimum, they must specify the positions of each atom in space, typically with X, Y and Z Cartesian coordinates, and the chemical element each atom represents.
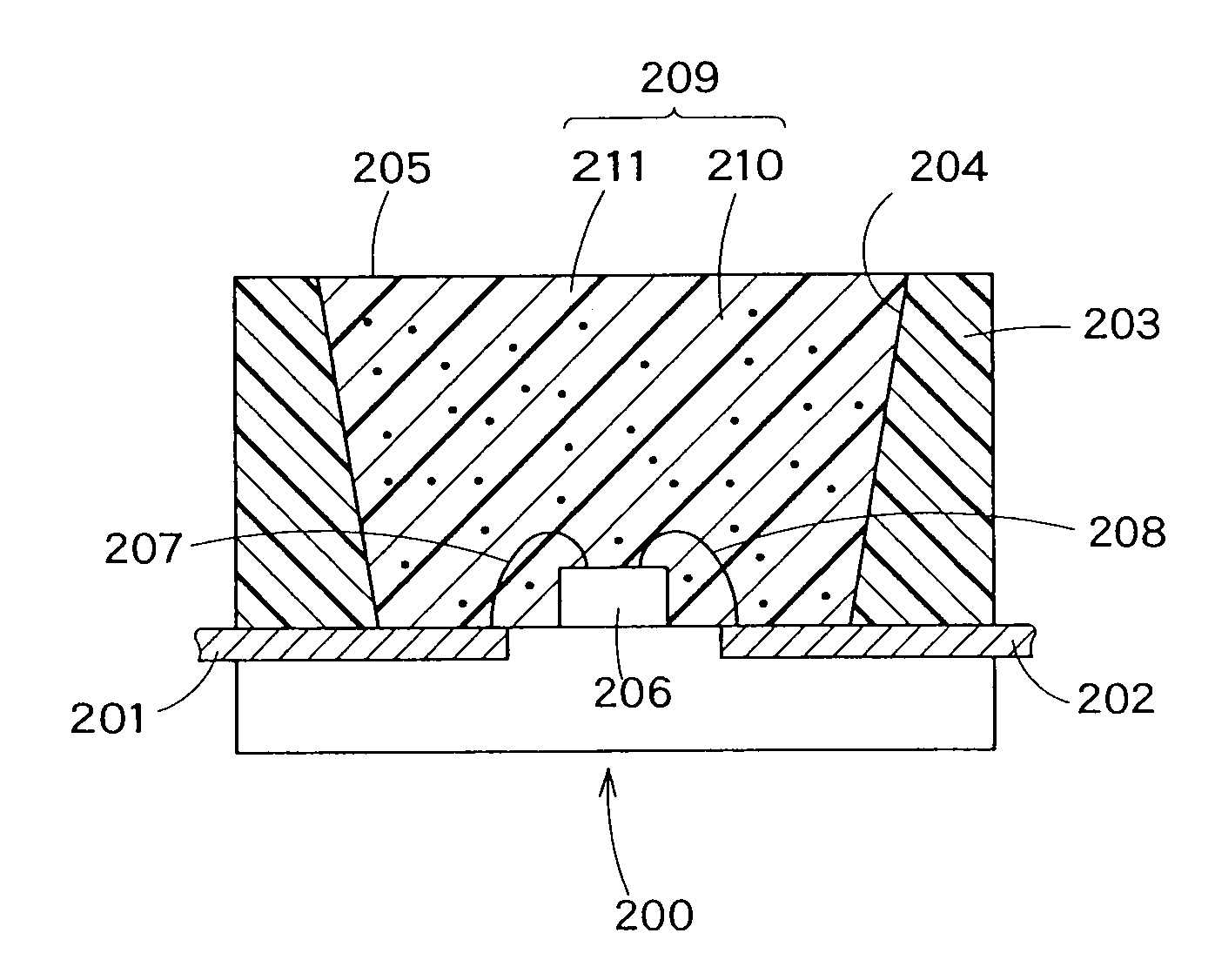
Fluorescent substance and light-emitting device employing the same
ActiveUS20100025632A1Improve quantum efficiencyHigh emission intensitySolid-state devicesLuminescent compositionsQuantum efficiencyFluorescence
The present invention provides a fluorescent substance excellent both in quantum efficiency and in temperature characteristics, and also provides a light-emitting device utilizing the fluorescent substance. This fluorescent substance contains an inorganic compound comprising a metal element M, a trivalent element M1 other than the metal element M, a tetravalent element M2 other than the metal element M, and either or both of O and N. In the inorganic compound, the metal element M is partly replaced with a luminescence center element R. The crystal structure of the fluorescent substance is basically the same as Sr3Al3Si13O2N21, but the chemical bond lengths of M1-N and M2-N are within the range of ±15% based on those of Al—N and Si—N calculated from the lattice constants and atomic coordinates of Sr3Al3Si13O2N21, respectively. The fluorescent substance emits luminescence having a peak in the range of 490 to 580 nm when excited with light of 250 to 500 nm.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
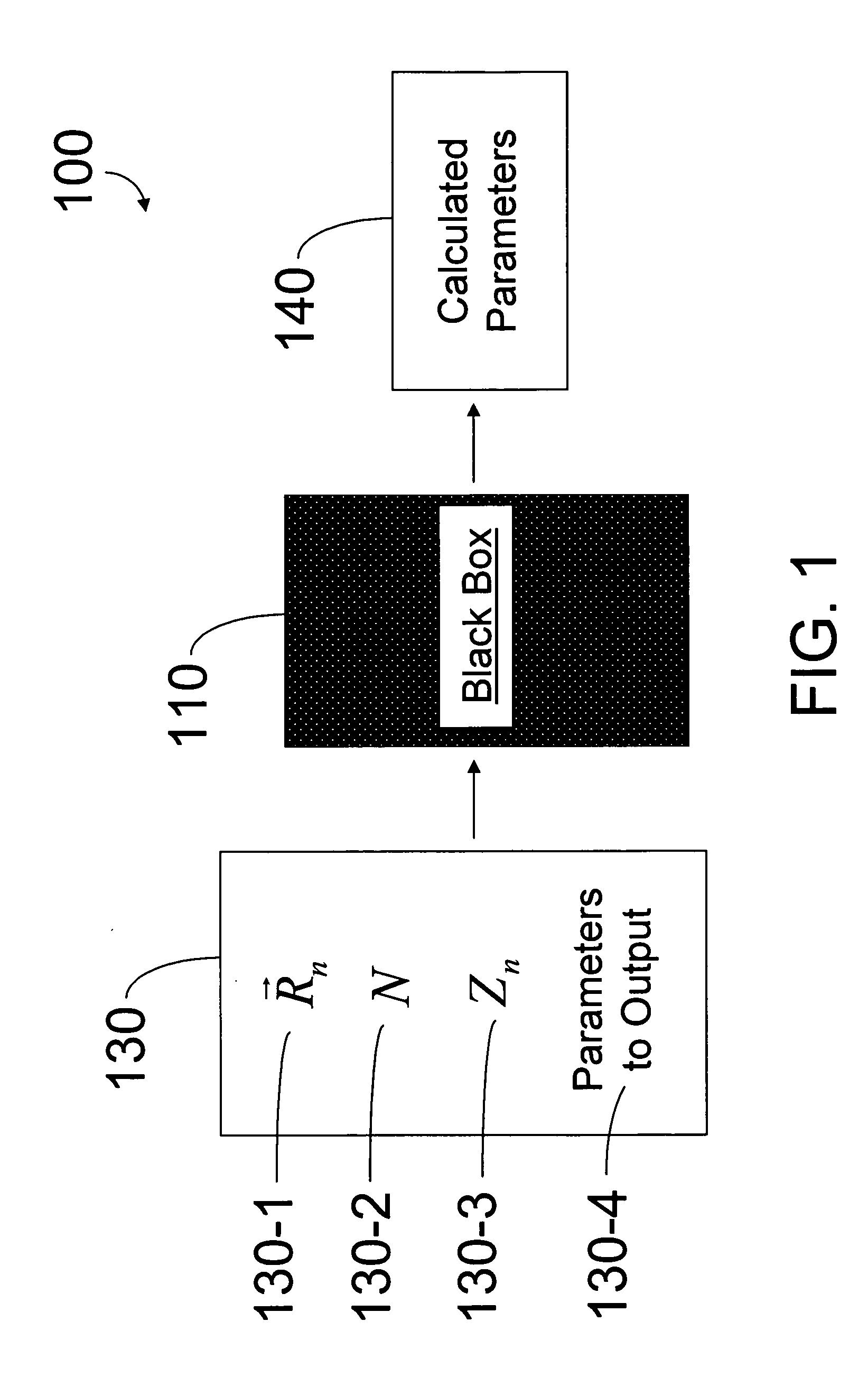
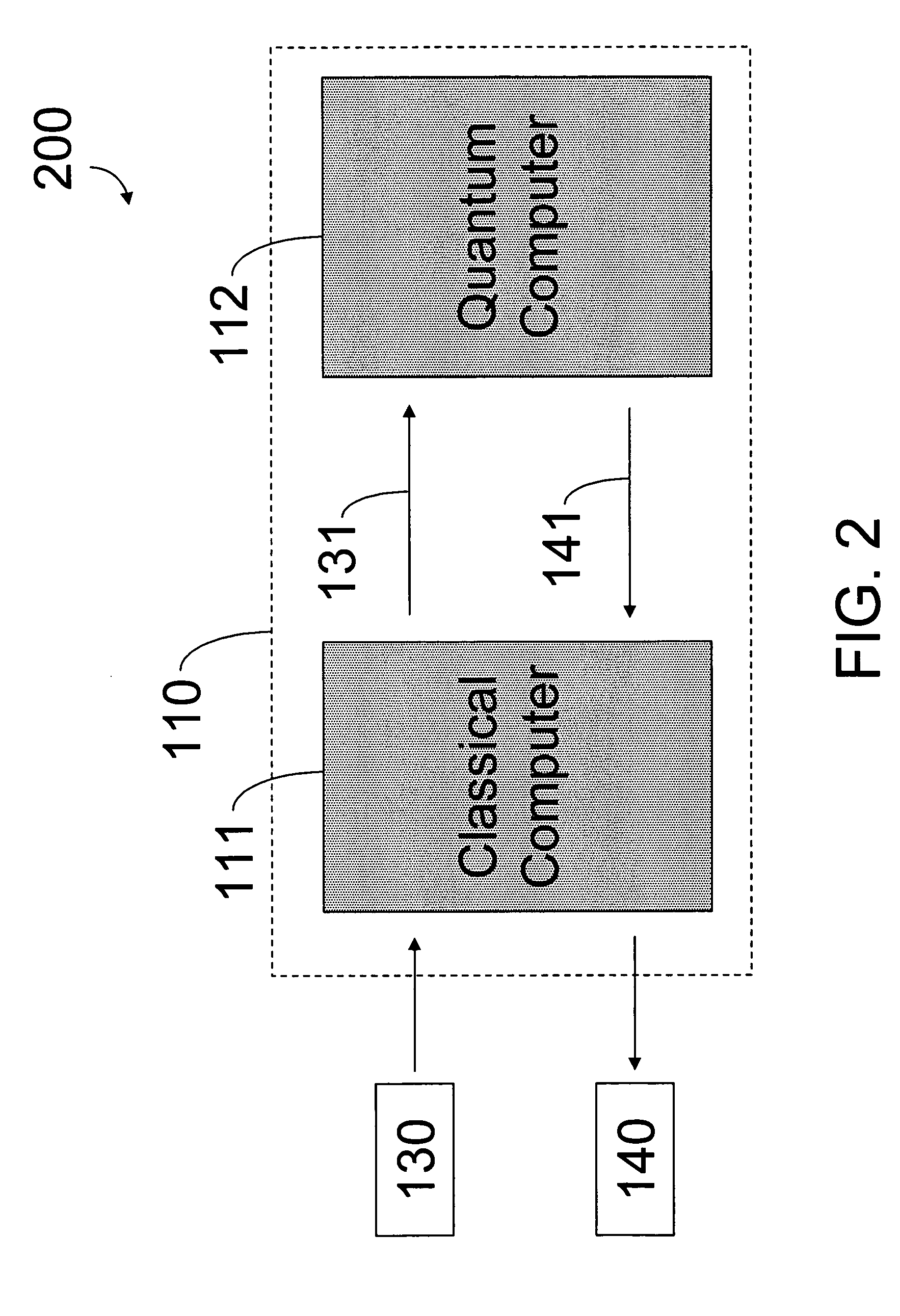
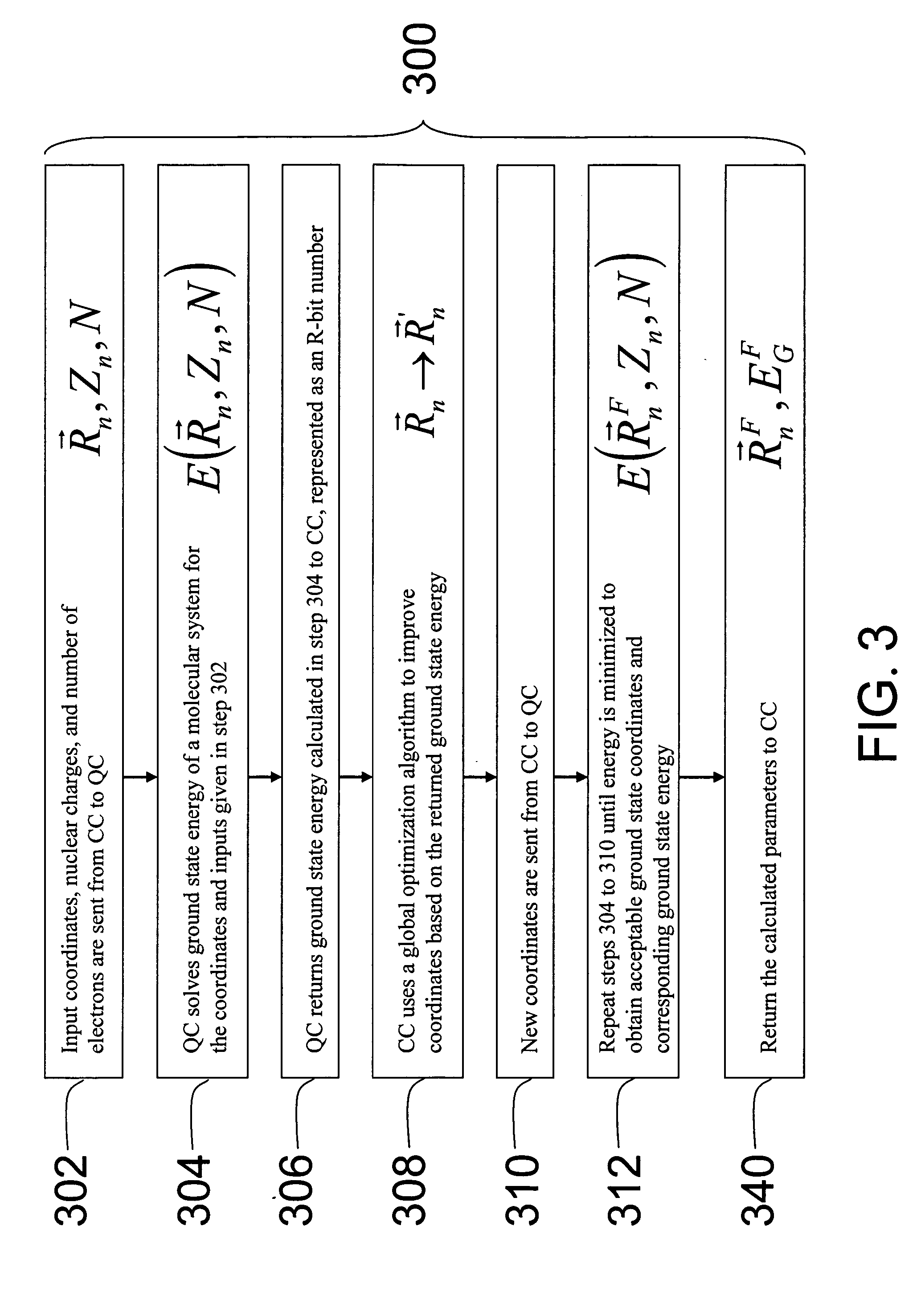
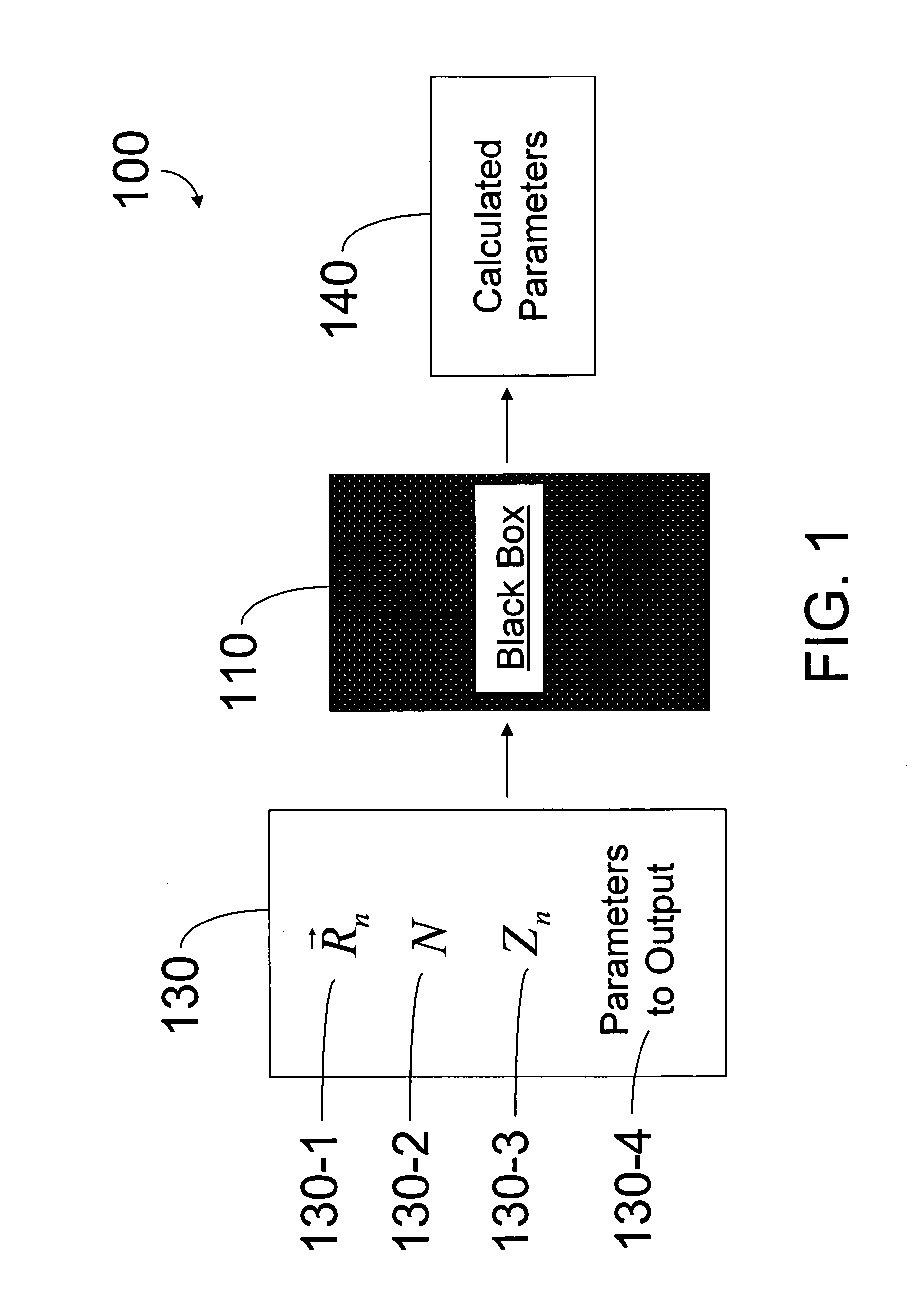
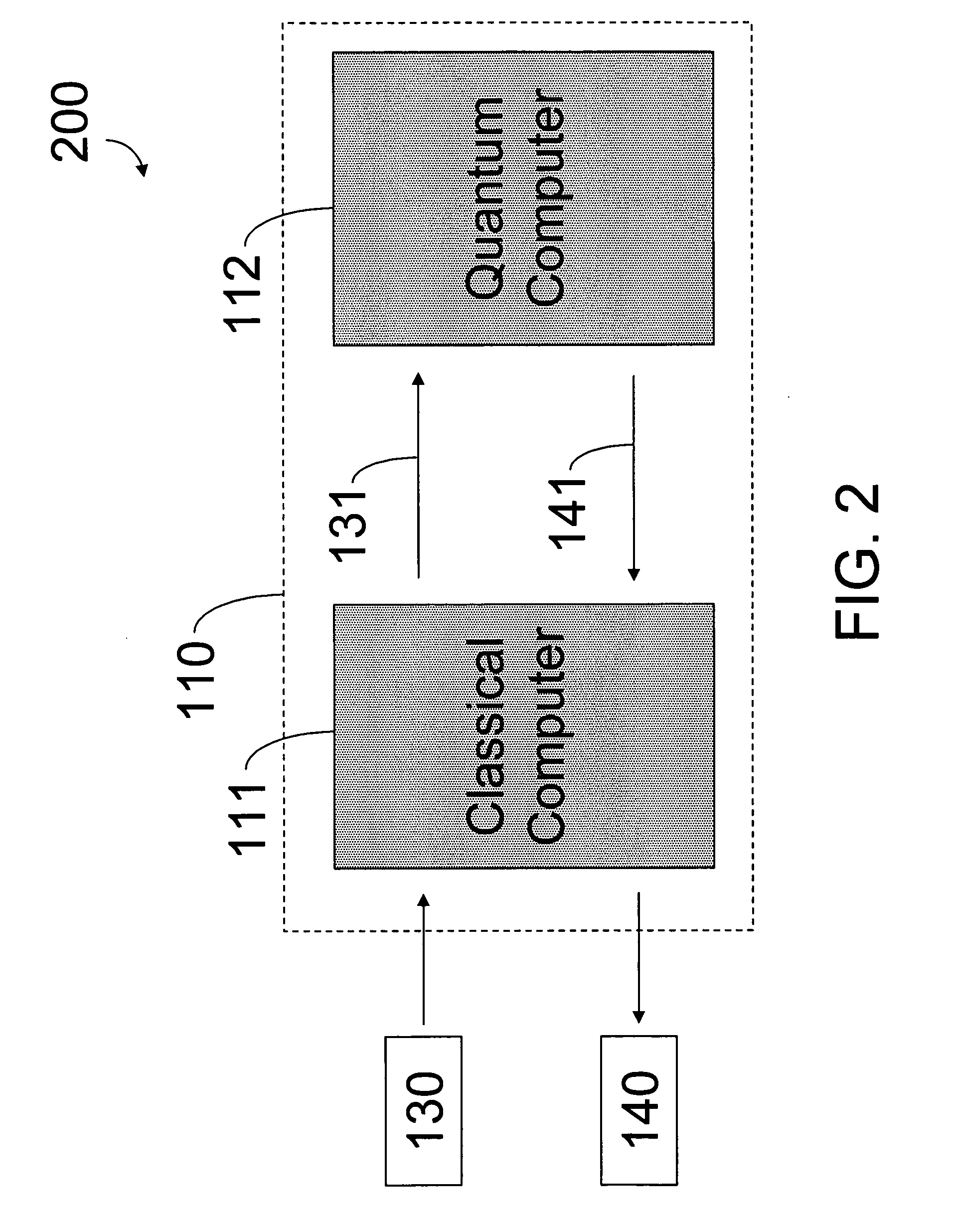
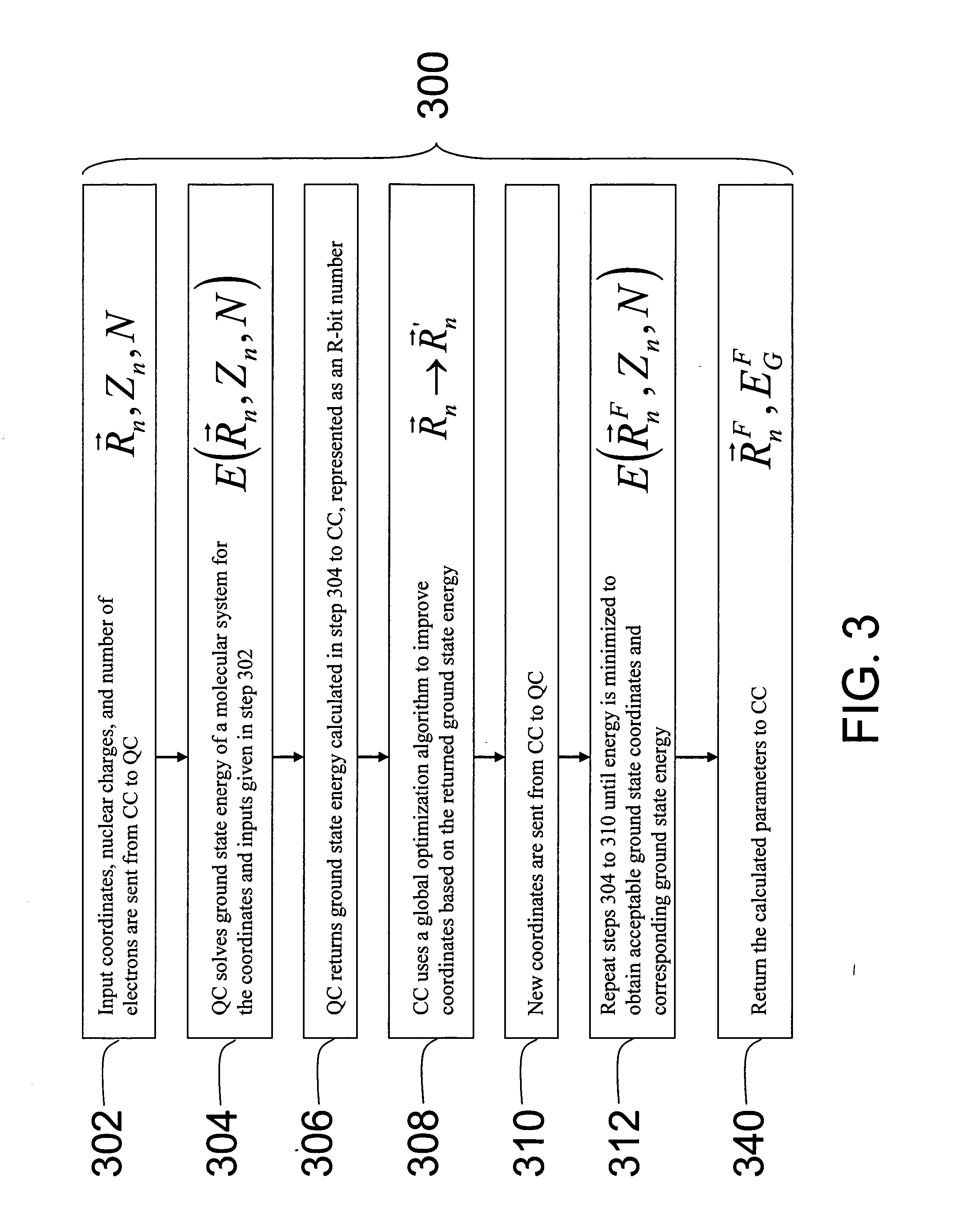
Hybrid classical-quantum computer architecture for molecular modeling
A method of simulating a molecular system using a hybrid computer is provided. The hybrid computer comprises a classical computer and a quantum computer. The method uses atomic coordinates {right arrow over (R)}n and atomic charges Zn of a molecular system to compute a ground state energy of the molecular system using the quantum computer. The ground state energy is returned to the classical computer and the atomic coordinates are geometrically optimized on the classical computer based on information about the returned ground state energy of the atomic coordinates in order to produce a new set of atomic coordinates {right arrow over (R)}′n for the molecular system. These steps are optionally repeated in accordance with a refinement algorithm until a predetermined termination condition is achieved
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
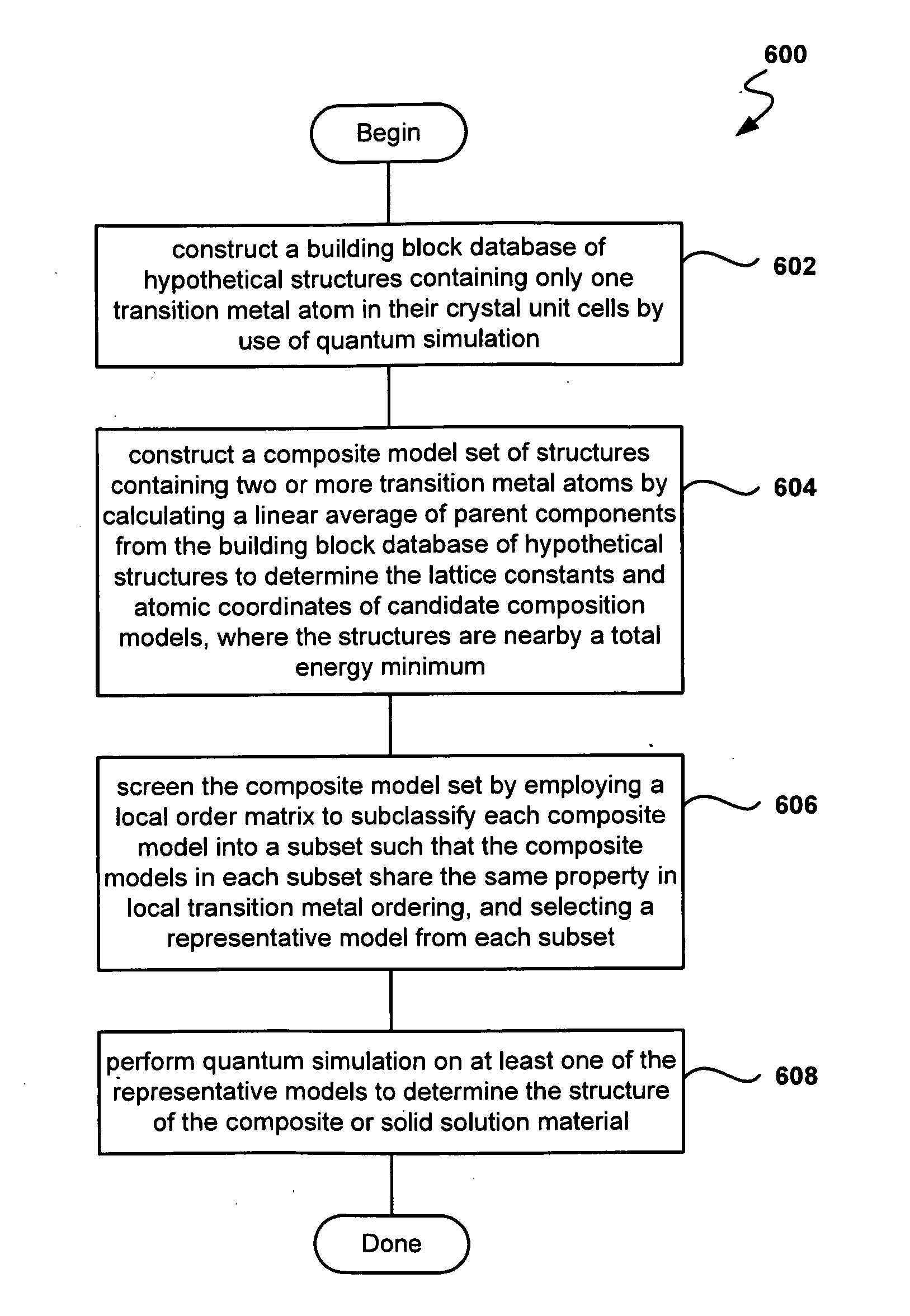
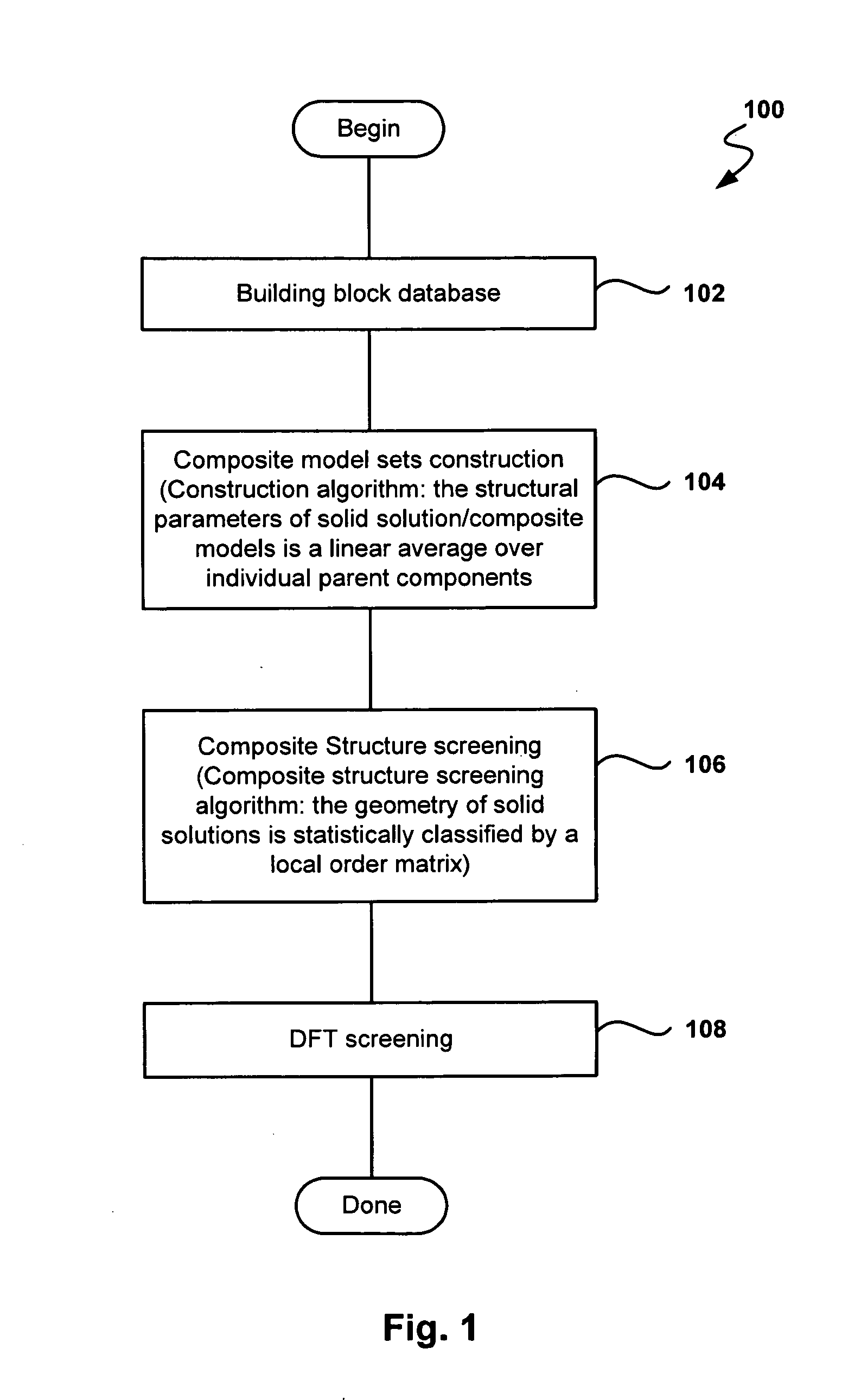
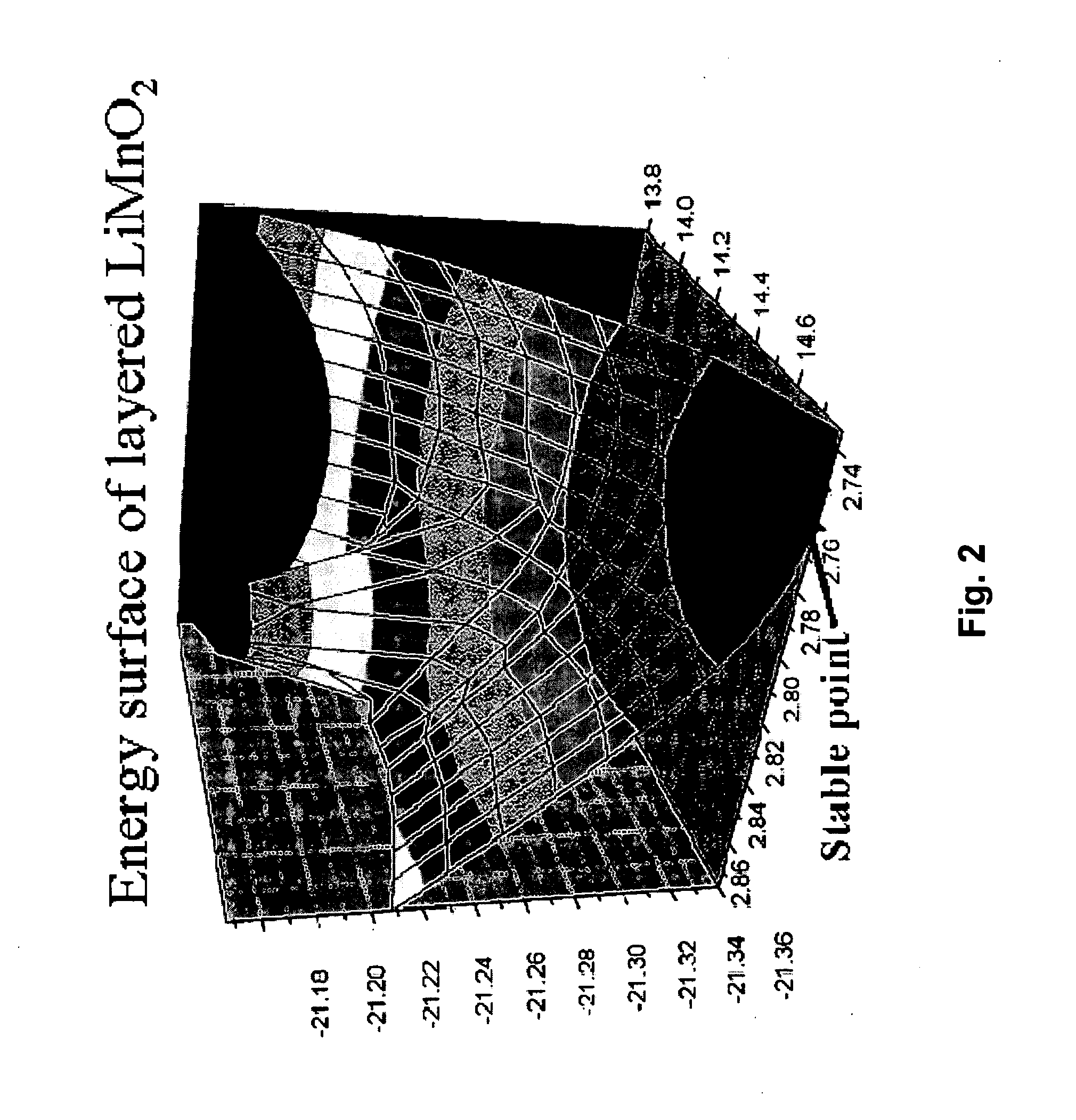
Fast and High-Throughput Search Engine for Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Quantum Simulations
InactiveUS20090157369A1Cell electrodesAnalogue computers for chemical processesTransition metal atomsSolid solution
Provided are methods and systems for determining the structure of a composite or solid solution material for an electrode in lithium-ion batteries. In one embodiment, a method is presented where a building-block database of hypothetical structures containing only one transition metal atom is constructed by use of quantum simulation. Then, a composite model set of structures containing two or more transition metal atoms is constructed by calculating a linear average of parent components from the building-block database of hypothetical structures to determine lattice constants and atomic coordinates of candidates. The composite model set is screened with a local order matrix to subclassify composite models into a subset, such that the composite models share the same property in local transition metal ordering. Still yet, a representative from each subset is selected and a quantum simulation on the representative models is performed to determine the structure of the material.
Owner:EOCELL LTD
Modified chimeric Cry35 proteins
This invention provides modified, insecticidal Cry35 proteins with enhanced properties as compared to wild-type Cry35 proteins. The modifications to these proteins were based in part on analysis of the atomic coordinates and three-dimensional (3D) structure of the ˜45 kDa 149B1 protein and other proteins in the Cry35 class. The subject invention also includes polynucleotides that encode these modified proteins, and transgenic plants that produce these modified proteins. This invention further provides methods of controlling plant pests, including rootworms, with these modified proteins. The modified proteins of the subject invention include chimeric toxins involving exchanged segments, domains, and motifs as discussed herein. The subject invention also provides methods of modifying Cry35 proteins.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
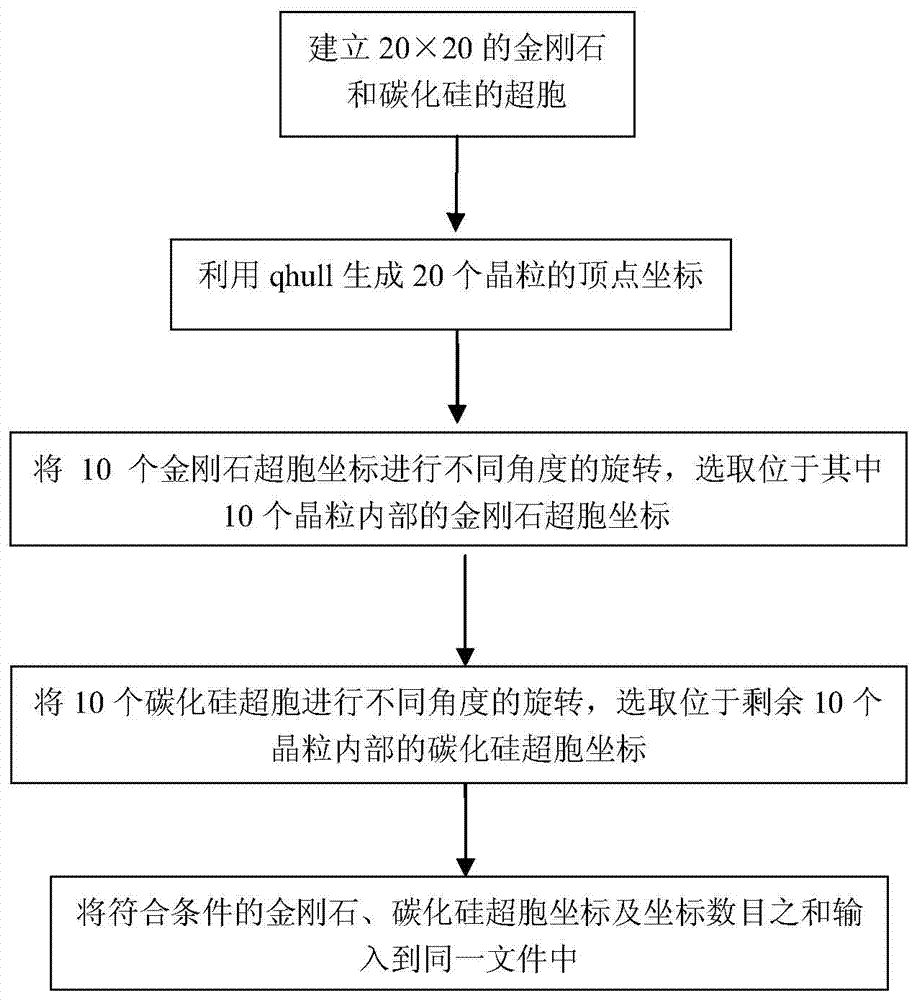
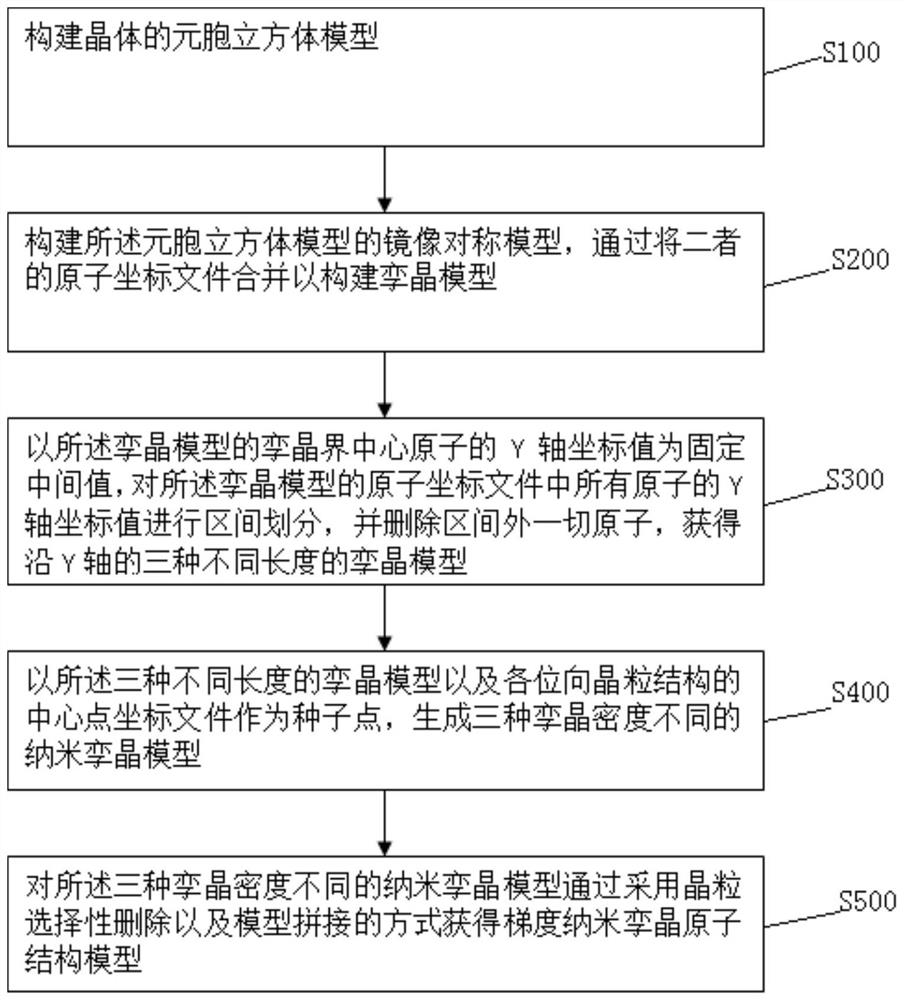
Method for building multiphase polycrystalline atomic structure model
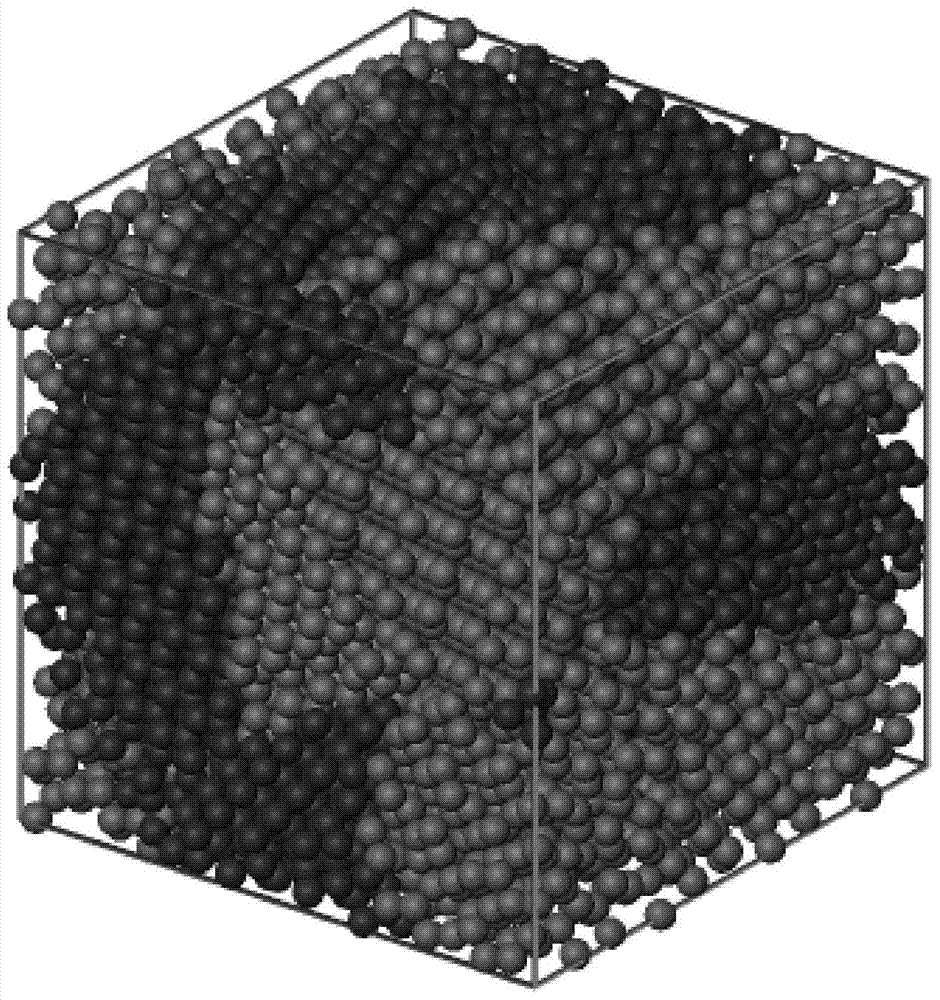
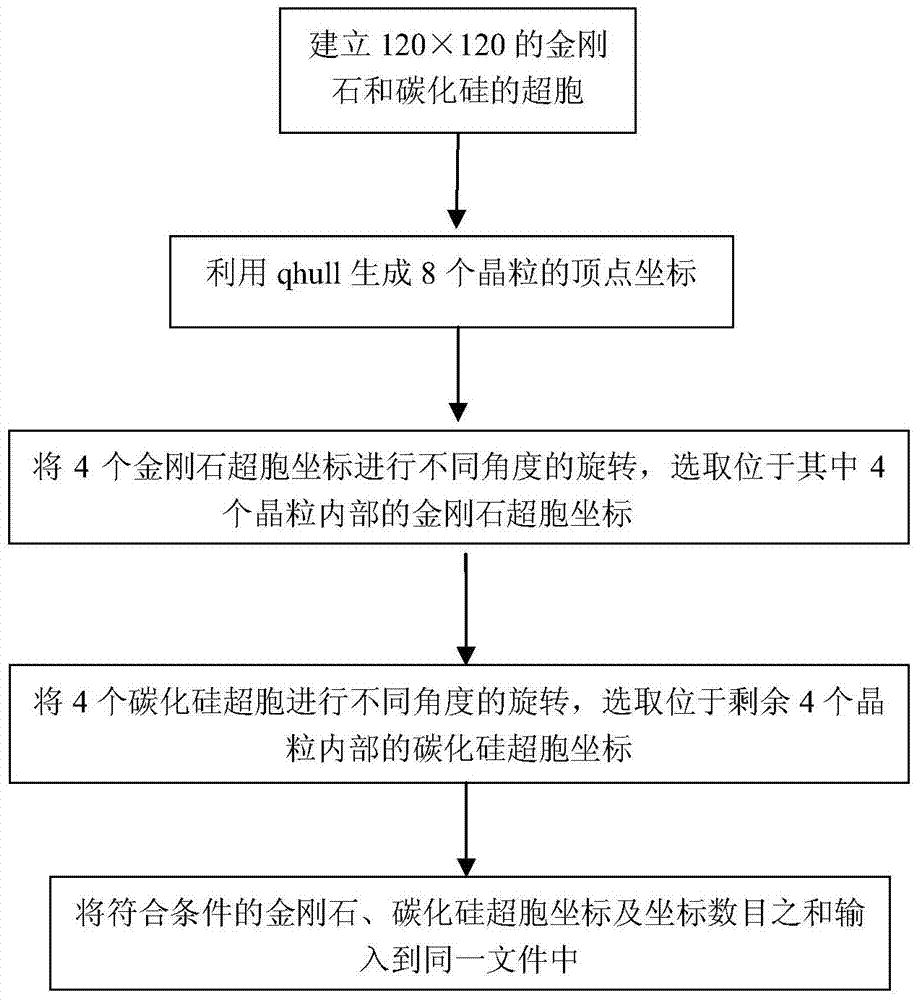
InactiveCN103714579ALow hardware and software requirementsEasy to operate3D modellingComputer sciencePhase number
The invention discloses a method for building a multiphase polycrystalline atomic structure model. The method includes the following steps: 1. preparing an atomic coordinate file of super cell structures of all phases of the built structure; 2. obtaining vertex coordinates of convex polyhedrons of a plurality of crystalline grains of any sizes through Qhull software; 3. rotating the coordinates of a supper cell of a phase at any angle, and through a method for judging inner and outer points of a polyhedron, selecting atomic coordinates of the phase inside the crystalline grain; and determining atomic coordinates of any phase inside any crystalline grain by using the same method; and 4. by controlling the proportion of all phases that fill the crystalline grains, a coordinate file of the multiphase polycrystalline atomic structure model of any phase number, any phase proportion and any crystalline grain size can be obtained by using the step 3. The method in the invention is easy to operate, has relatively low requirements for software and hardware of a computer, and can build a multiphase polycrystalline atomic structure model of a relatively large structure.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Hybrid classical-quantum computer architecture for molecular modeling
A method of simulating a molecular system using a hybrid computer is provided. The hybrid computer comprises a classical computer and a quantum computer. The method uses atomic coordinates {right arrow over (R)}n and atomic charges Zn of a molecular system to compute a ground state energy of the molecular system using the quantum computer. The ground state energy is returned to the classical computer and the atomic coordinates are geometrically optimized on the classical computer based on information about the returned ground state energy of the atomic coordinates in order to produce a new set of atomic coordinates {right arrow over (R)}′n for the molecular system. These steps are optionally repeated in accordance with a refinement algorithm until a predetermined termination condition is achieved
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Method for protein structure alignment
InactiveUS6859736B2Easy to handleHandle protein permutations efficientlyAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingAdditive ingredientField methods
This invention provides a method for protein structure alignment. More particularly, the present invention provides a method for identification, classification and prediction of protein structures. The present invention involves two key ingredients. First, an energy or cost function formulation of the problem simultaneously in terms of binary (Potts) assignment variables and real-valued atomic coordinates. Second, a minimization of the energy or cost function by an iterative method, where in each iteration (1) a mean field method is employed for the assignment variables and (2) exact rotation and / or translation of atomic coordinates is performed, weighted with the corresponding assignment variables.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and apparatus for storing and processing molecular information
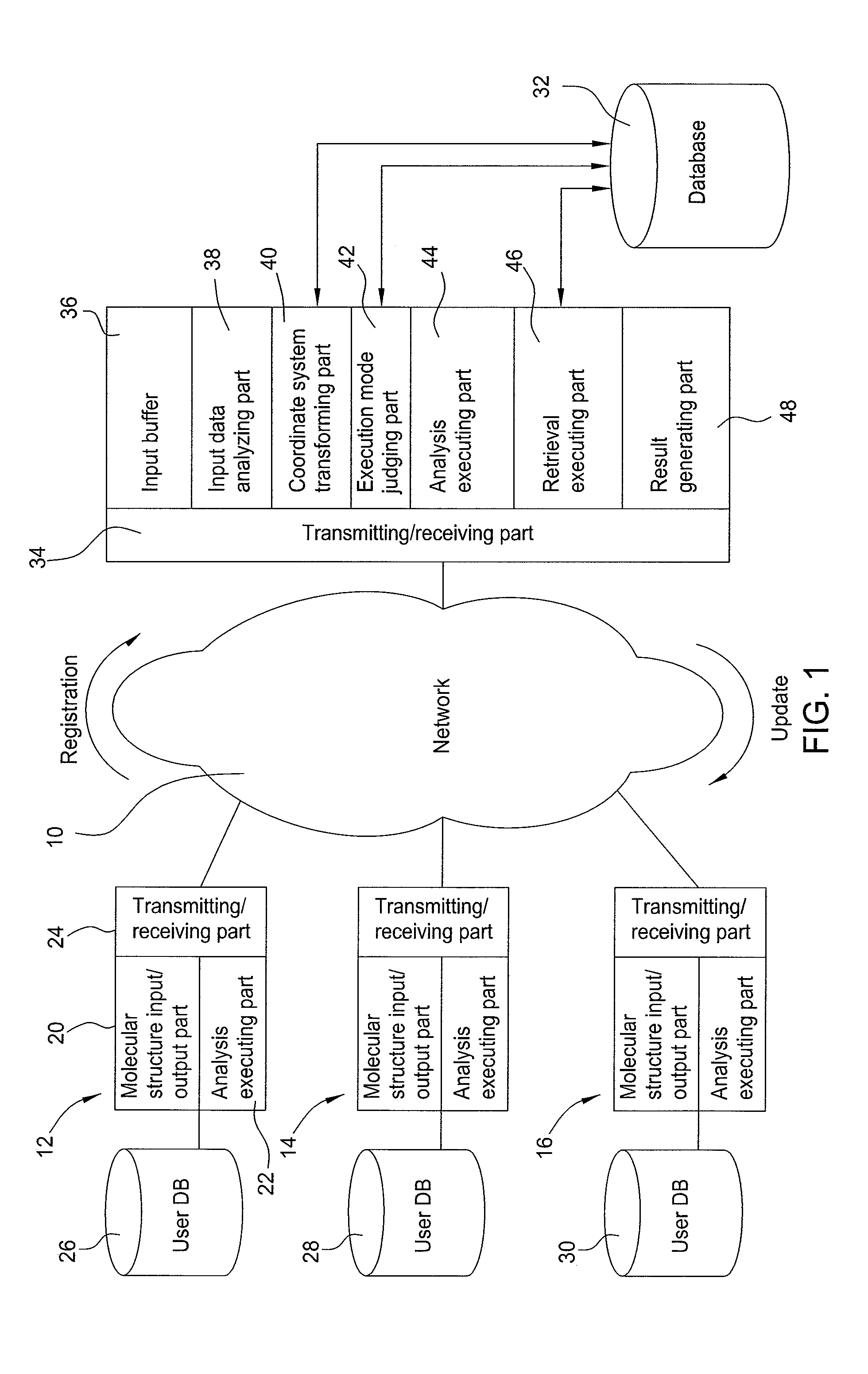
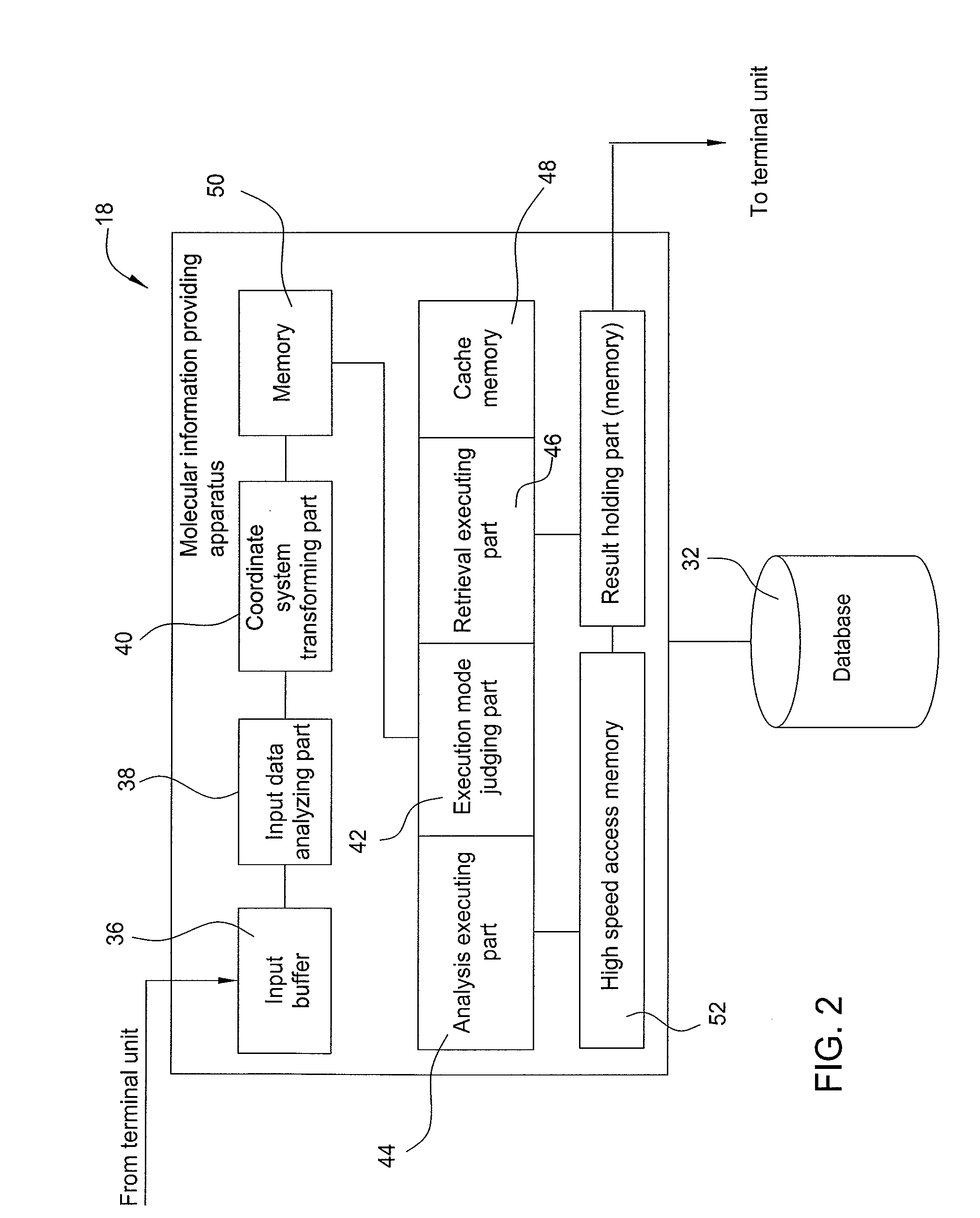
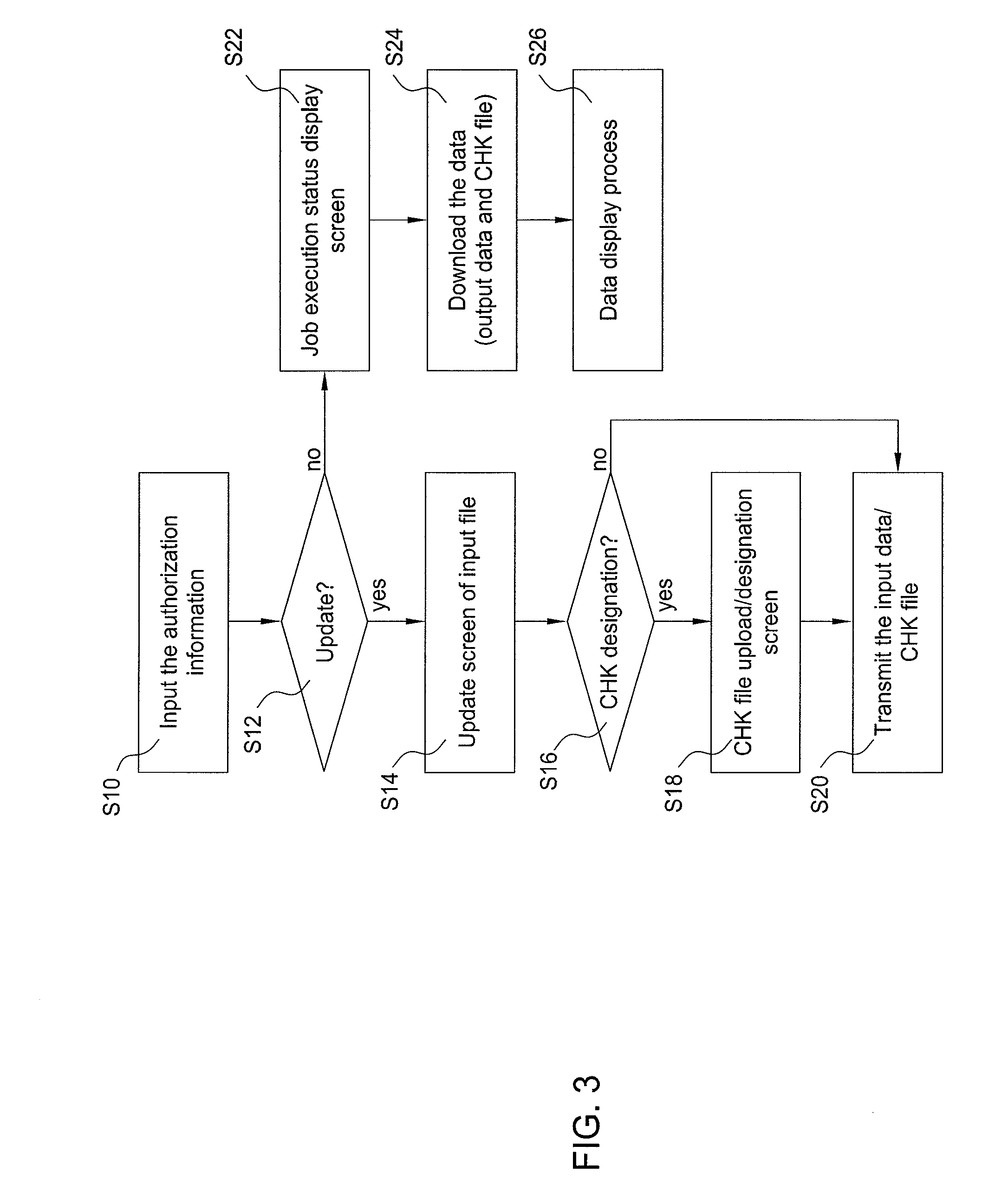
InactiveUS8112231B2Digital data processing detailsCheminformatics data warehousingNetwork connectionTerminal unit
To provide a molecular information providing system that allows the molecular information to be shared by providing high precision information without depending on the format of atomic arrangement notation from a terminal unit.The molecular information providing system of the invention has the terminal units to including molecular structure input / output means, and a molecular information providing apparatus connected via a network to the terminal units and including a database storing a molecular structure, an intermediate representation generated from the molecular structure, and a characteristic decided depending on the molecular structure. The molecular information providing apparatus comprises a coordinate system transforming part for calculating the principal axes of inertia from an atomic arrangement notation specifying the molecular structure, and registering in the database an intermediate representation that is a coordinate transformation of the atomic coordinates into a coordinate system in the directions of the principal axes of inertia, and a retrieval executing part for retrieving the molecular structure stored in the database, employing the intermediate representation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Crystal structure of the 30S ribosome and its use
InactiveUS20050154538A1High resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesImage resolutionX-ray
The invention provides an X-ray crystal structure of the 30S ribosome, obtained from Thermus thermophilus 30S subunit, having a tetragonal space group P41212 with unit cell dimensions of a=401.4±4.0 Å, b=401.4±4.0 Å, c=175.9±5.0 Å. An advantageous feature of the structure is that it diffracts beyond 3 Å resolution. The invention also provides a crystal of 30S having the three dimensional atomic coordinates of the 30S ribosome, the coordinates being provided in Tables 1A and 1B. The data may be used for the rational design and modelling of inhibitors for the 30S ribosome, which have potential use as antibiotics.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND +1
Crystal structure of antibiotics bound to the 30S ribosome and its use
InactiveUS7079956B2High resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesHygromycin BX-ray
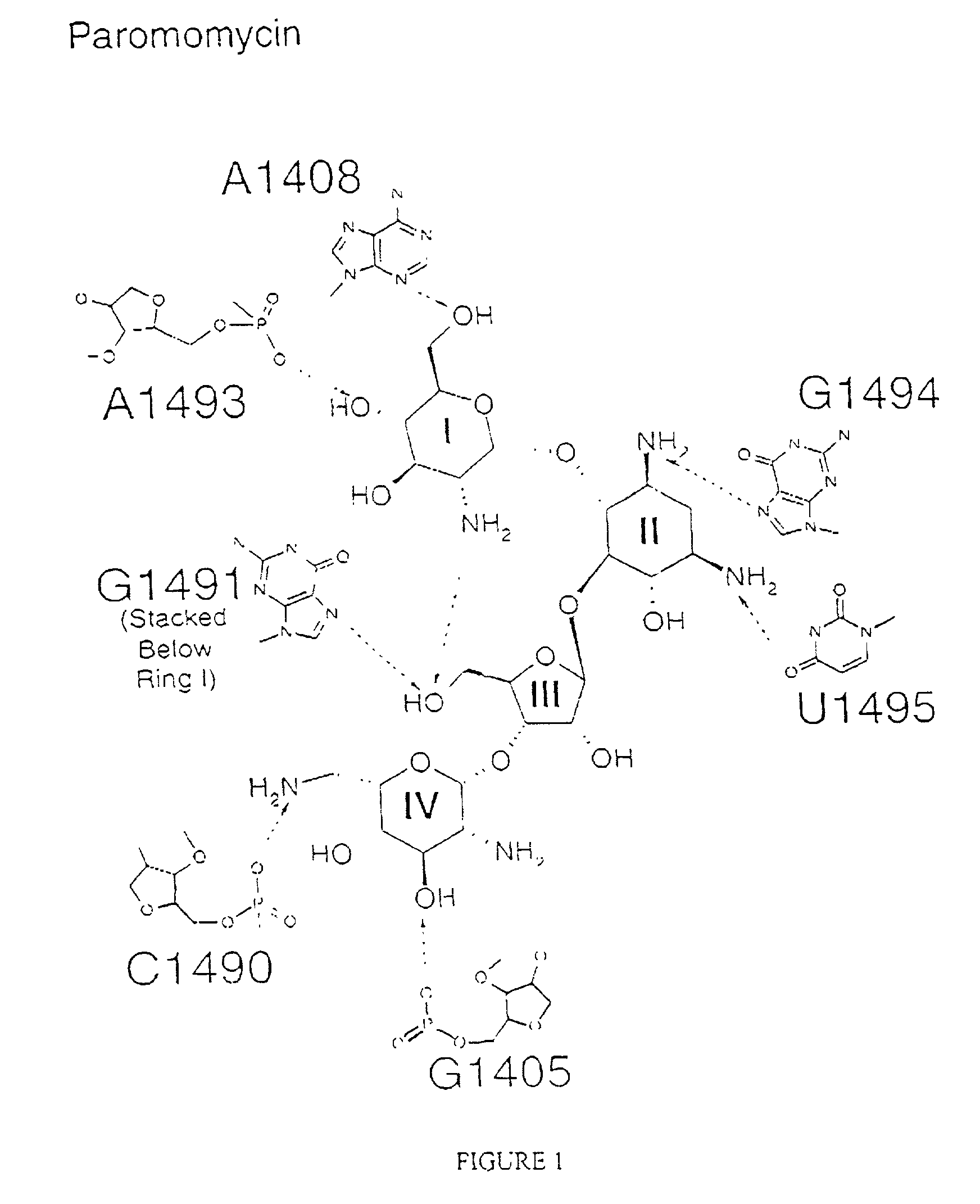
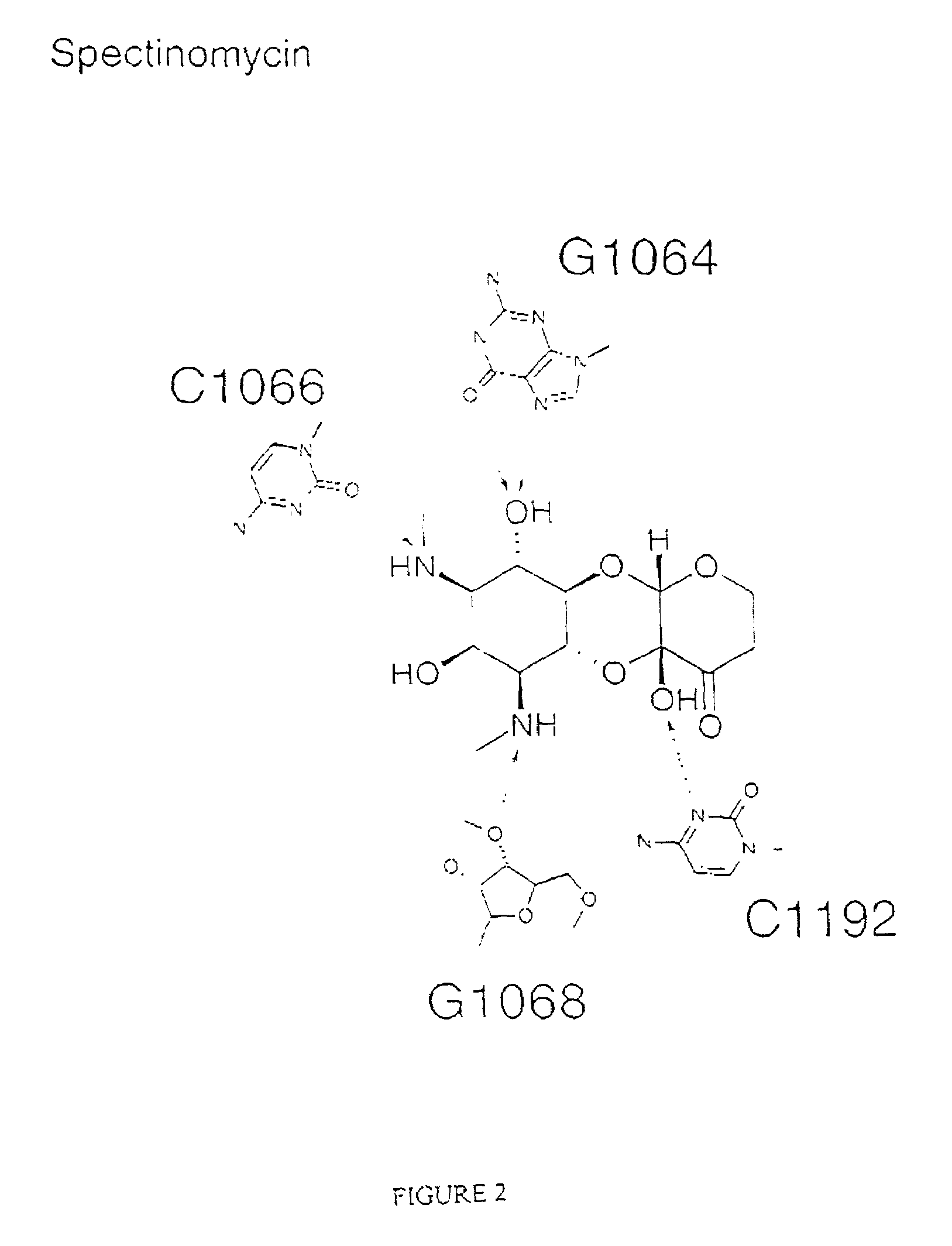
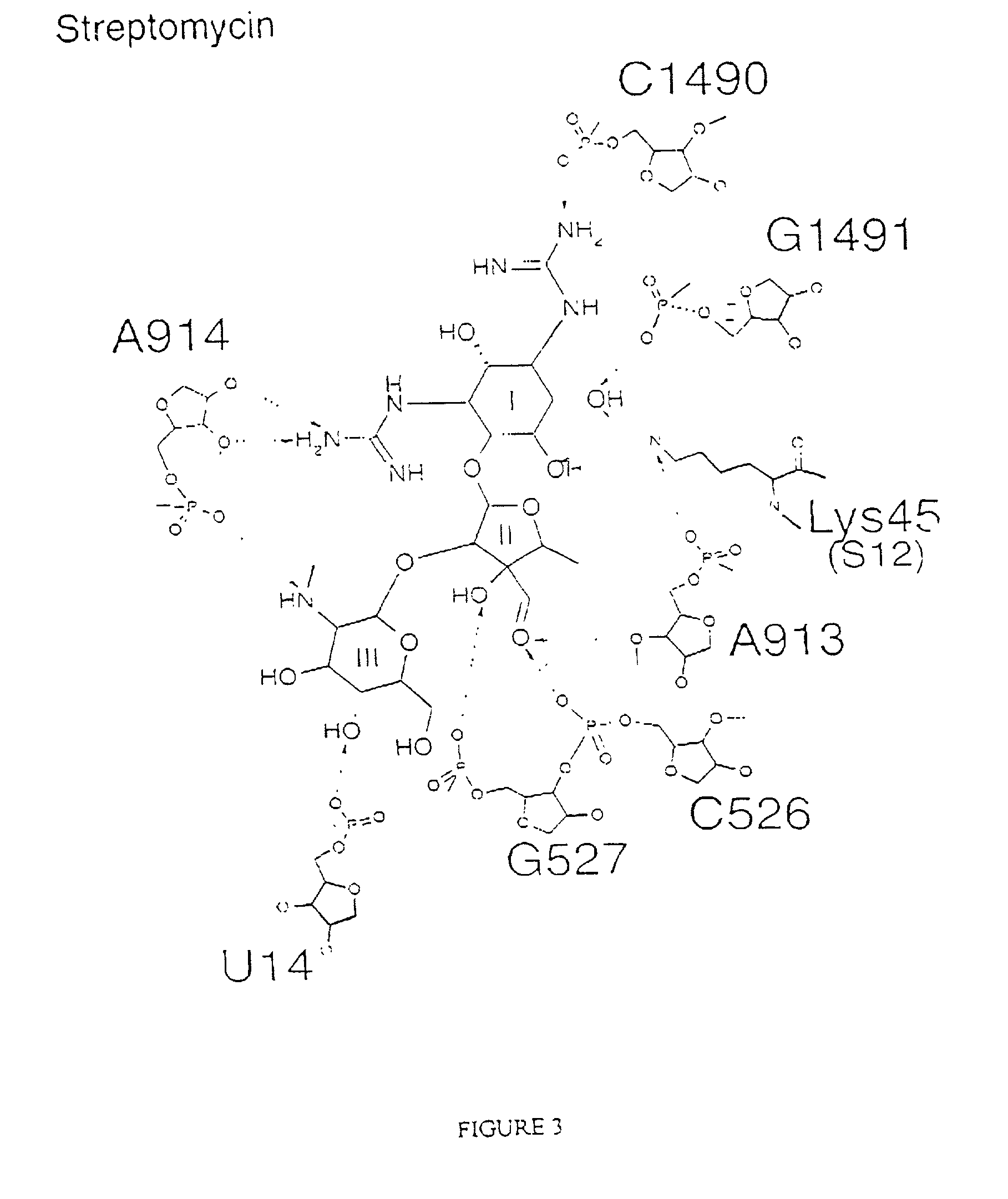
The invention provides high resolution X-ray crystal structures of the 30S ribosome, obtained from Thermus thermophilus 30S subunit, having a tetragonal space group P41212 to which are bound an antibiotic selected from the group paromomycin, streptomycin, spectinomycin, tetracycline, pactamycin and hygromycin B. An advantageous feature of the structure is that it diffracts at about 3 Å resolution. The invention also provides a crystal of 30S having the three dimensional atomic coordinates of the 30S ribosome, the coordinates being provided in any one of tables 1 to 4. The data may be used for the rational design and modelling of inhibitors for the 30S ribosome, which have potential use as antibiotics.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Structure detection method of protein cryoelectron microscopy density map
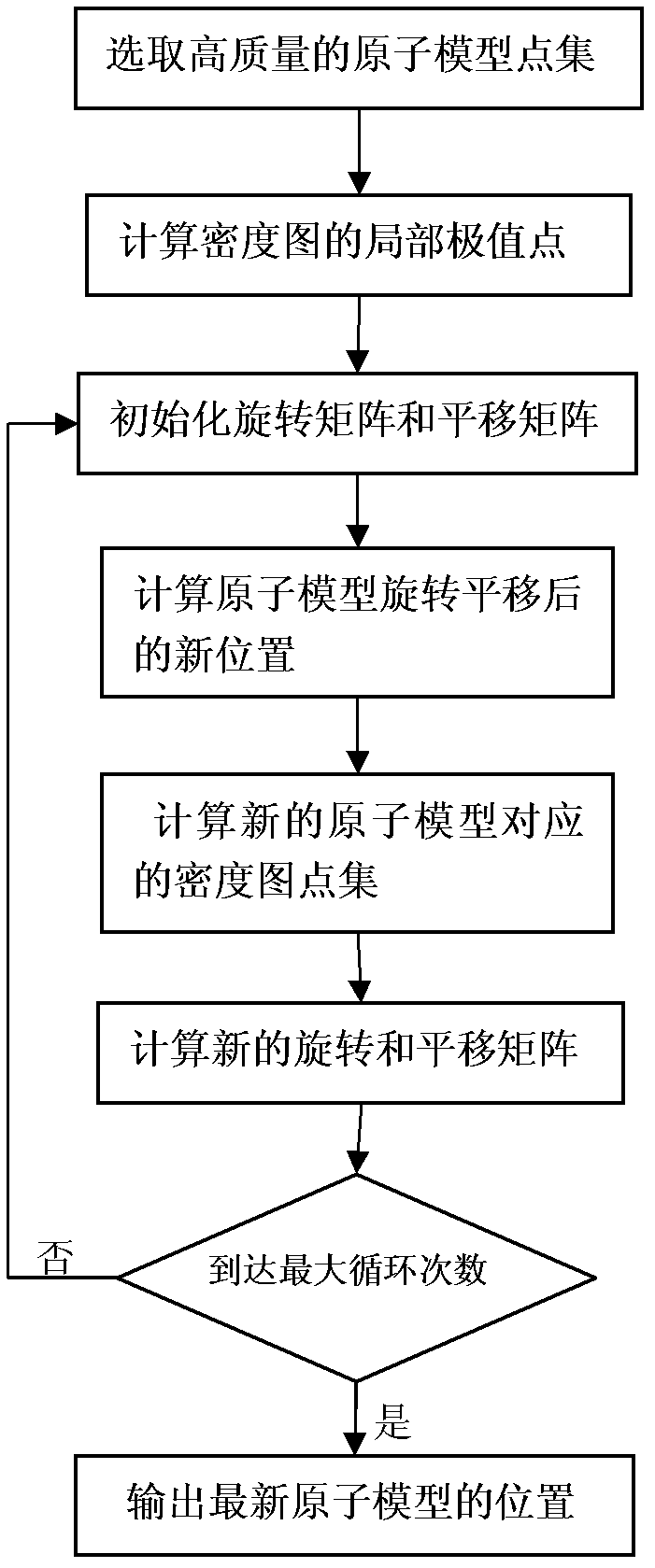
ActiveCN102682223AImprove robustnessSmall amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsQuaternionAlgorithm
The invention discloses a structure detection method of a protein cryoelectron microscopy density map, which belongs to the field of bioinformatics. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) selecting an atom matching conditions in an atom model to indicate the atom model; 2) selecting a key point in a protein cryoelectron microscopy density map to be inspected and adding the key point to a set M; 3) for a point g in the set M, calculating a point g which is closest to the point p in a set M and is used as a corresponding point to the point p, and adding the point g in a set G; 4) calculating a rotation quaternion q and a translation vector t of the atom model according to the sets P and G; 5) calculating a rotation matrix R according to the rotation quaternion q, and calculating the position of each rotated atom coordinate according to R and t, so as to obtain the matching result of the atom model and the density map, and 6) obtaining the structure of the protein cryoelectron microscopy density map to be detected according to the matching result meeting the requirements. The method has the advantages that the robustness is good, the data model is not required to be coincident with density data, the calculated amount is small, and programming is easy to realize.
Owner:COMP NETWORK INFORMATION CENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Complicated function minimal value searching method based on constrained regular pattern
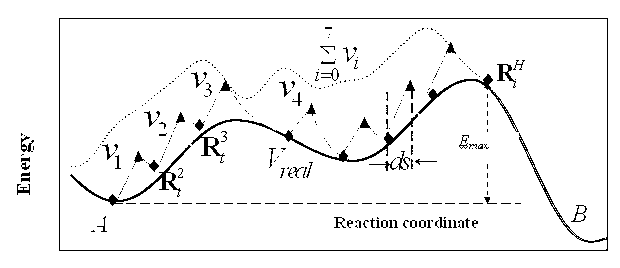
InactiveCN102937946ALow professional background requirementsLittle change in single-step structureComplex mathematical operationsCrystal systemRegular pattern
The invention belongs to the technical fields of computational chemistry and physics and particularly relates to a complicated function minimal value searching method based on a constrained regular pattern. In the complicated function minimal value searching method, an atomic coordinate corresponding to an energy minimal value is solved by virtue of the input atomic coordinate, a known potential energy surface energy function and a first-order derivative of the energy function corresponding to the coordinate. The method comprises the steps: starting from a coordinate system corresponding to one minimal value, carrying out optional generating and analyzing to obtain one constrained regular pattern, realizing a purpose of surpassing an energy maximal value of the potential energy surface by continuously adding bias potential functions and repeating optimizing of the energy minimal value, and finally obtaining the coordinate system corresponding to a new minimal value. The complicated function minimal value searching method based on the constrained regular pattern has the effect that the overall minimal values can be quickly searched, is suitable for complicated function systems, and meanwhile has a function of searching an optimal reaction channel. The complicated function minimal value searching method based on the constrained regular pattern can be used for traversing the potential energy surfaces of complicated molecules and periodic crystal systems.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Crystal structure of the 30s ribosome
The invention provides an X-ray crystal structure of the 30S ribosome, obtained from Thermus thermophilus 30S subunit, having a tetragonal space group P41212 with unit cell dimensions of a=401.4±4.0 Å, b=401.4±4.0 Å, c=175.9±5.0 Å. An advantageous feature of the structure is that it diffracts beyond 3 Å resolution. The invention also provides a crystal of 30S having the three dimensional atomic coordinates of the 30S ribosome, the coordinates being provided in Tables 1A and 1B. The data may be used for the rational design and modelling of inhibitors for the 30S ribosome, which have potential use as antibiotics.
Owner:UTAH UNIVERSIY OF +2
Crystal structure of the 30S ribosome and its use
InactiveUS7606670B2High resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesImage resolutionX-ray
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND +1
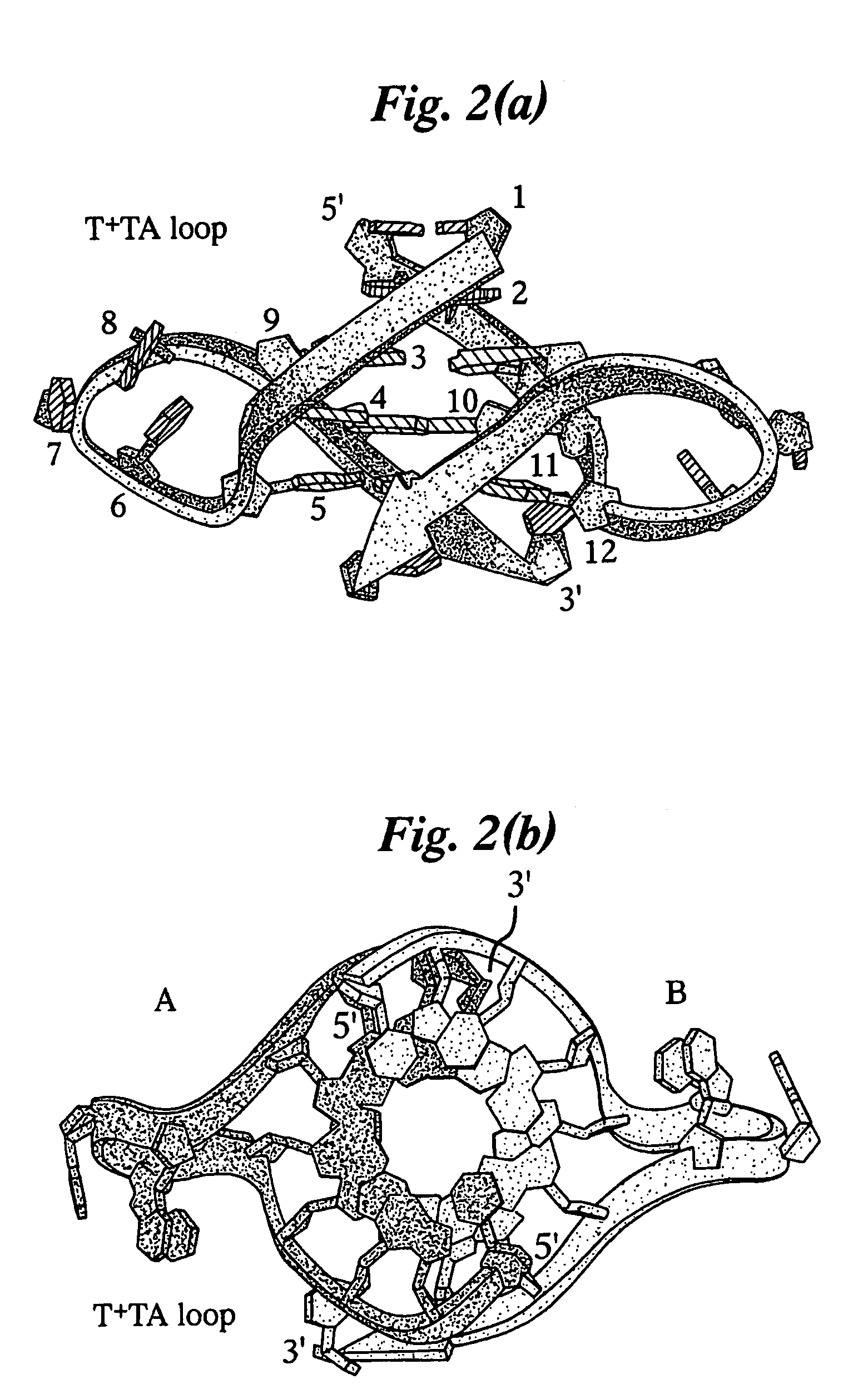
Crystal structure of G-quadruplex containing a potassium ion
The present invention relates to a crystal structure of G-quadruplexes and its use. The invention provides a crystal of an intramolecular G-quadruplex structure having a hexagonal space group P6, and unit cell dimensions a=b=56.7 and c=42.1; α=β=90°, γ=120° and a crystal of G-quadruplex having the three dimensional atomic coordinates of Table 1 or Table 2. These structures may be used in a computer-based method for the analysis of the interaction of a molecular structure with a G-quadruplex.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
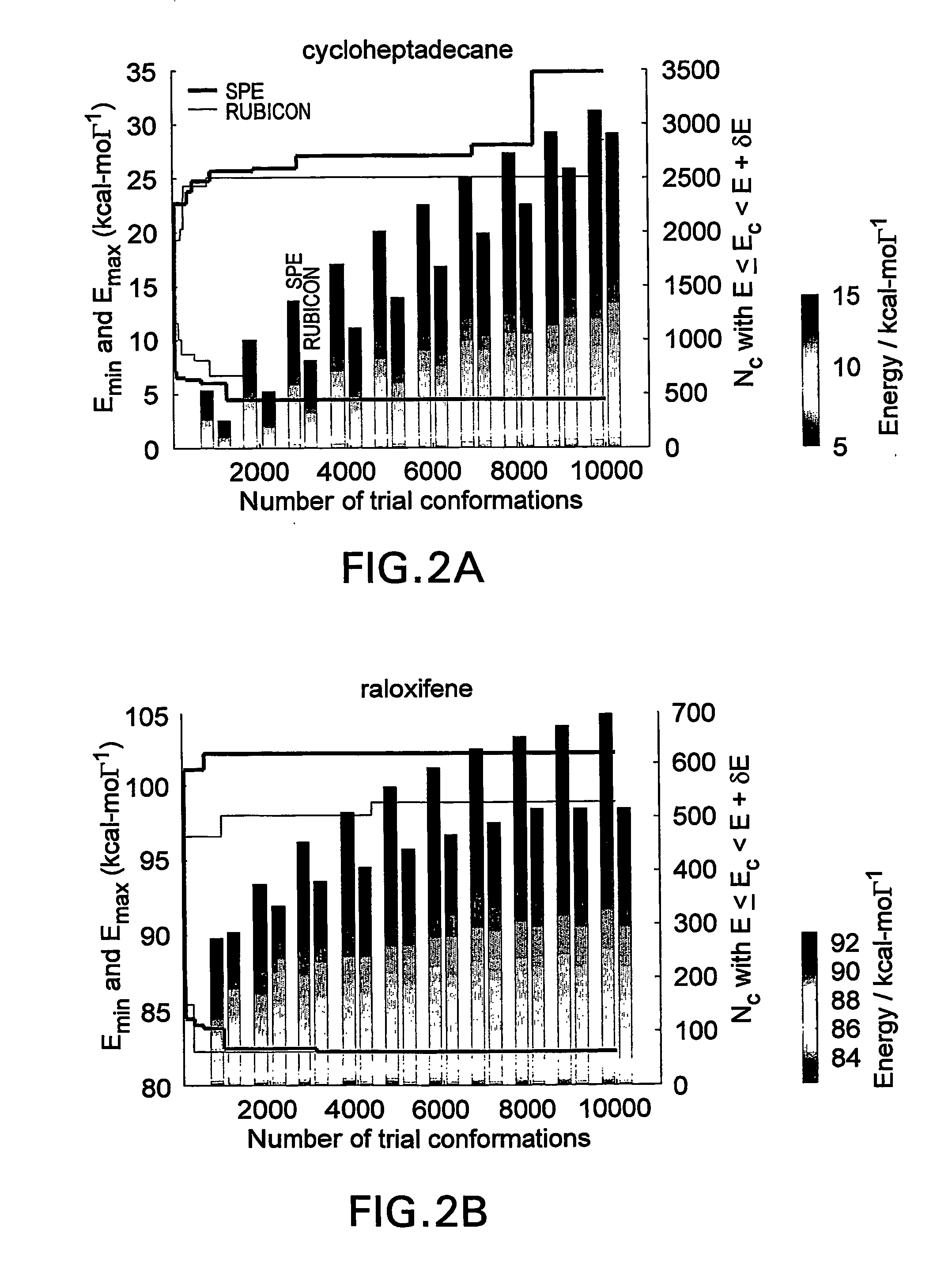
Conformational sampling by self-organization
InactiveUS20060089808A1Biological testingComputational theoretical chemistryLinearityComputer science
A self-organizing method, system, and computer program product for generating molecular conformations that are consistent with a set of distance and / or volume constraints. A stochastic proximity embedding (SPE) algorithm evaluates individual distance and / or volume constraints and adjusts the atomic coordinates to minimize violations of such constraints. The method scales linearly with thenumber of atoms, and produces many more unique conformations at a fraction of the time required by conventional distance geometry algorithms.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON PHARMA RES & DEV LLC
Modulators of phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activator
InactiveUS20080153773A1Inhibiting ATPase activityPreventing modulationBiocideSugar derivativesPhosphoprotein phosphatasePHOSPHOTYROSYL PHOSPHATASE ACTIVATOR
Atomic coordinates for human phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activator (PTPA) and ATPγS bound by PTPA, as well as methods for using these atomic coordinates to prepare ATPase inhibitors of PTPA and ATPase inhibitors prepared using such methods are provided herein. Comprehensive biochemical analyses of the interactions of PTPA with ATP and protein phosphatase 2A are also provided. Compositions including mimetics and small molecules of the invention and, optionally, secondary agents may be used to treat disorders in which PTPA ATPase activity plays a contributing role.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
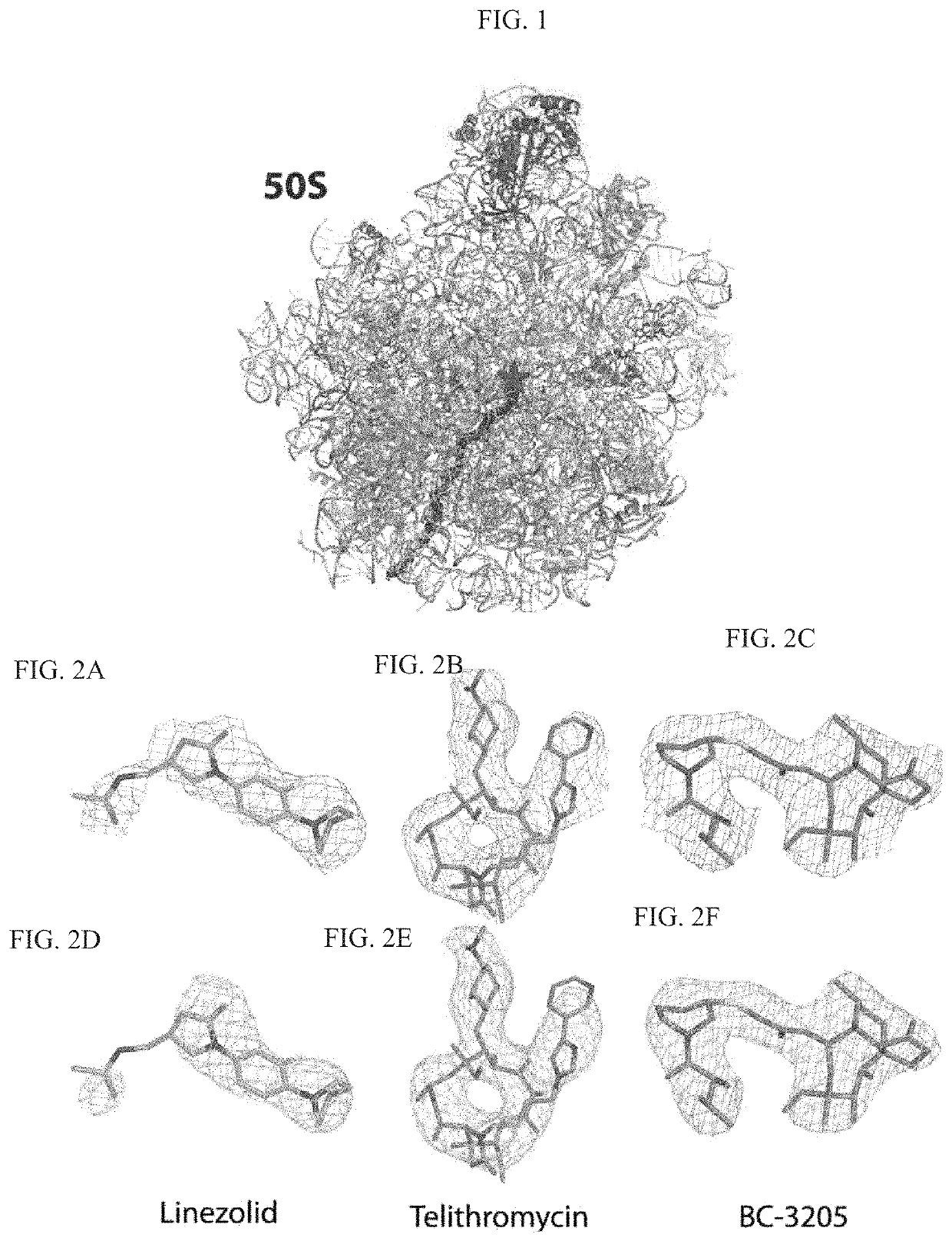
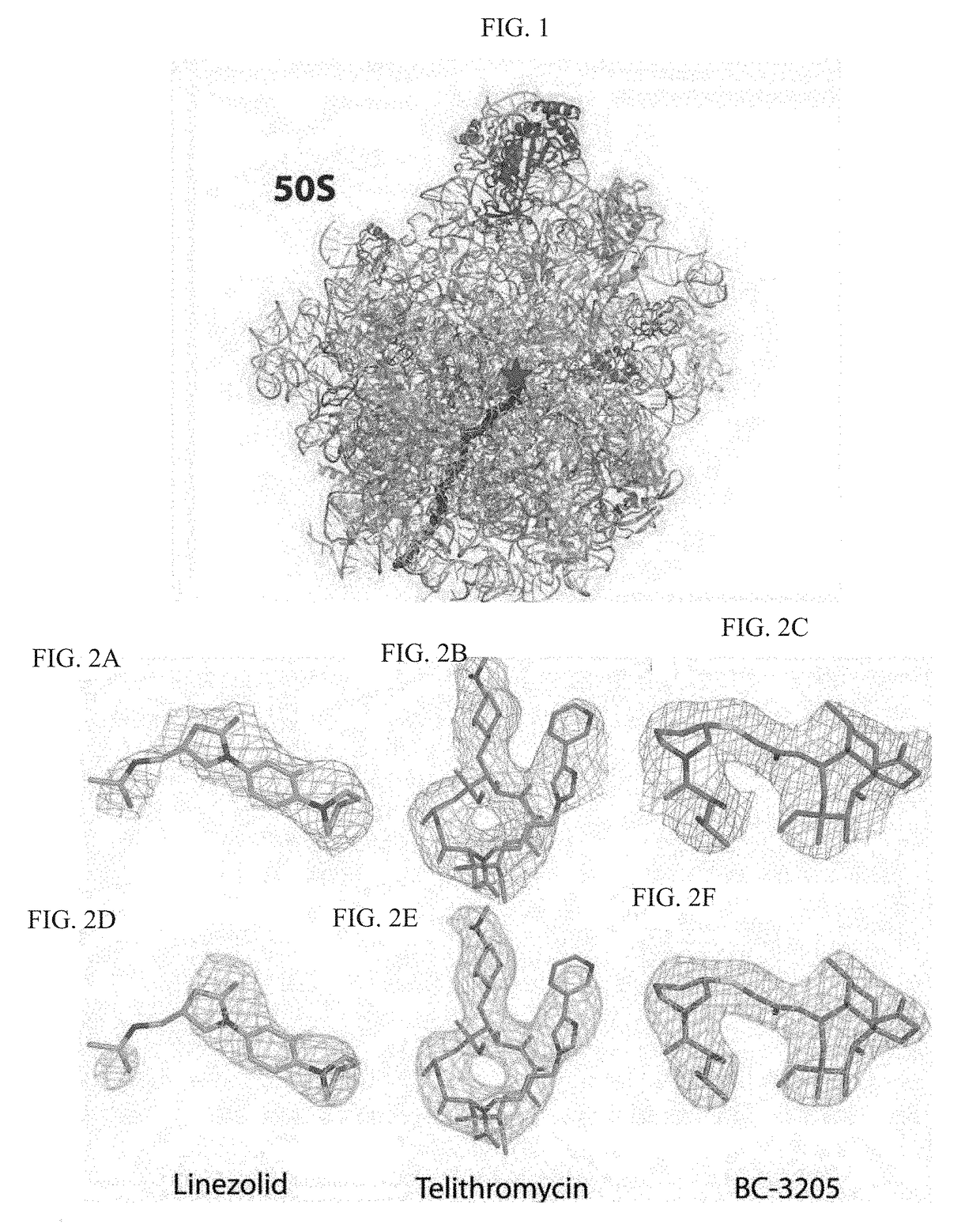
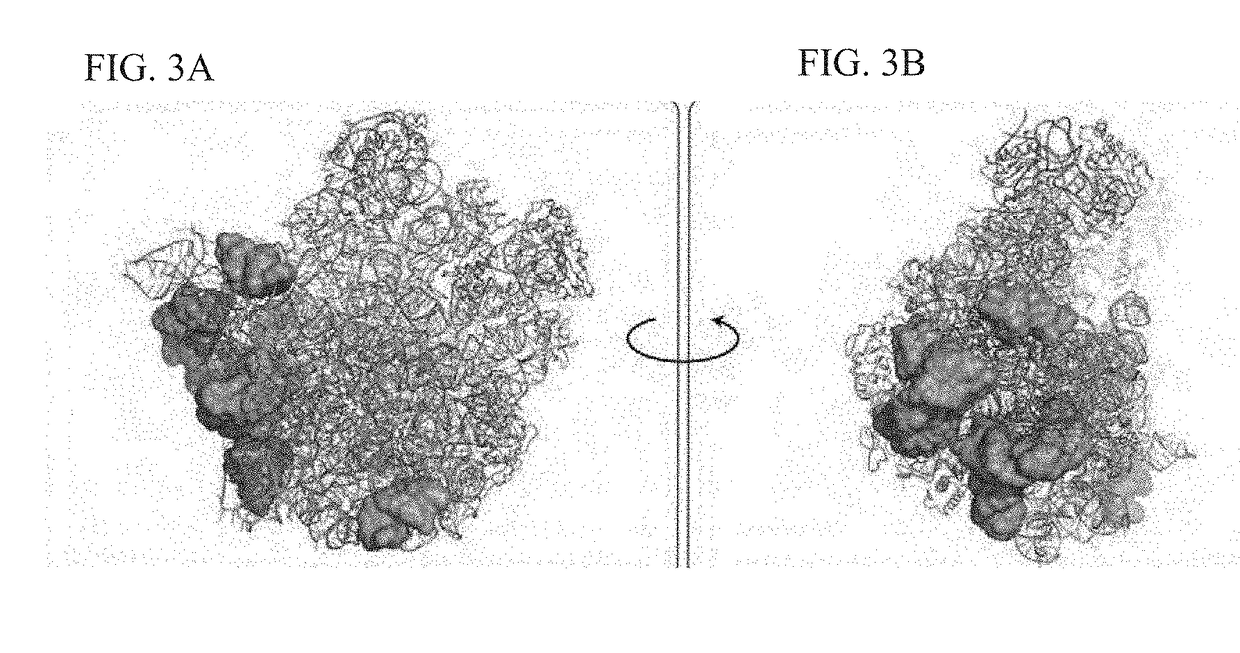
Crystal structure of the large ribosomal subunit from S. aureus
A composition-of-matter comprising a crystallized form of a large ribosomal (50S) subunit of a pathogenic bacterium, and the atomic coordinates of the three-dimensional structure thereof are provided herein, as well as methods for crystallizing the same, and using the atomic coordinates of the same to design de novo ligands with high specificity thereto.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
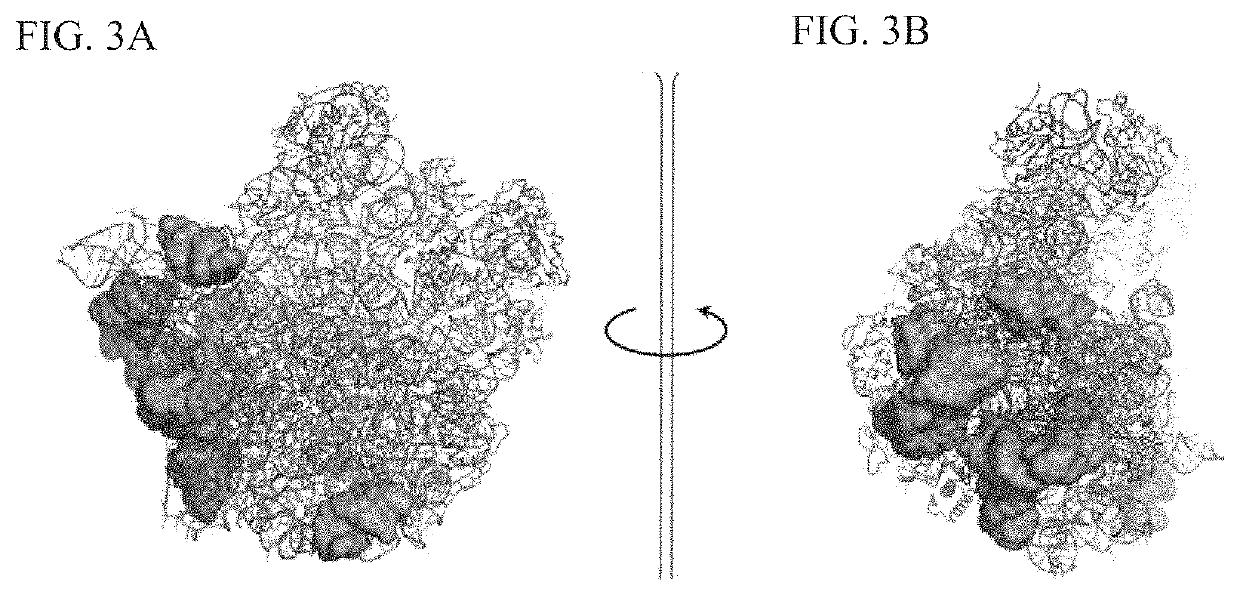
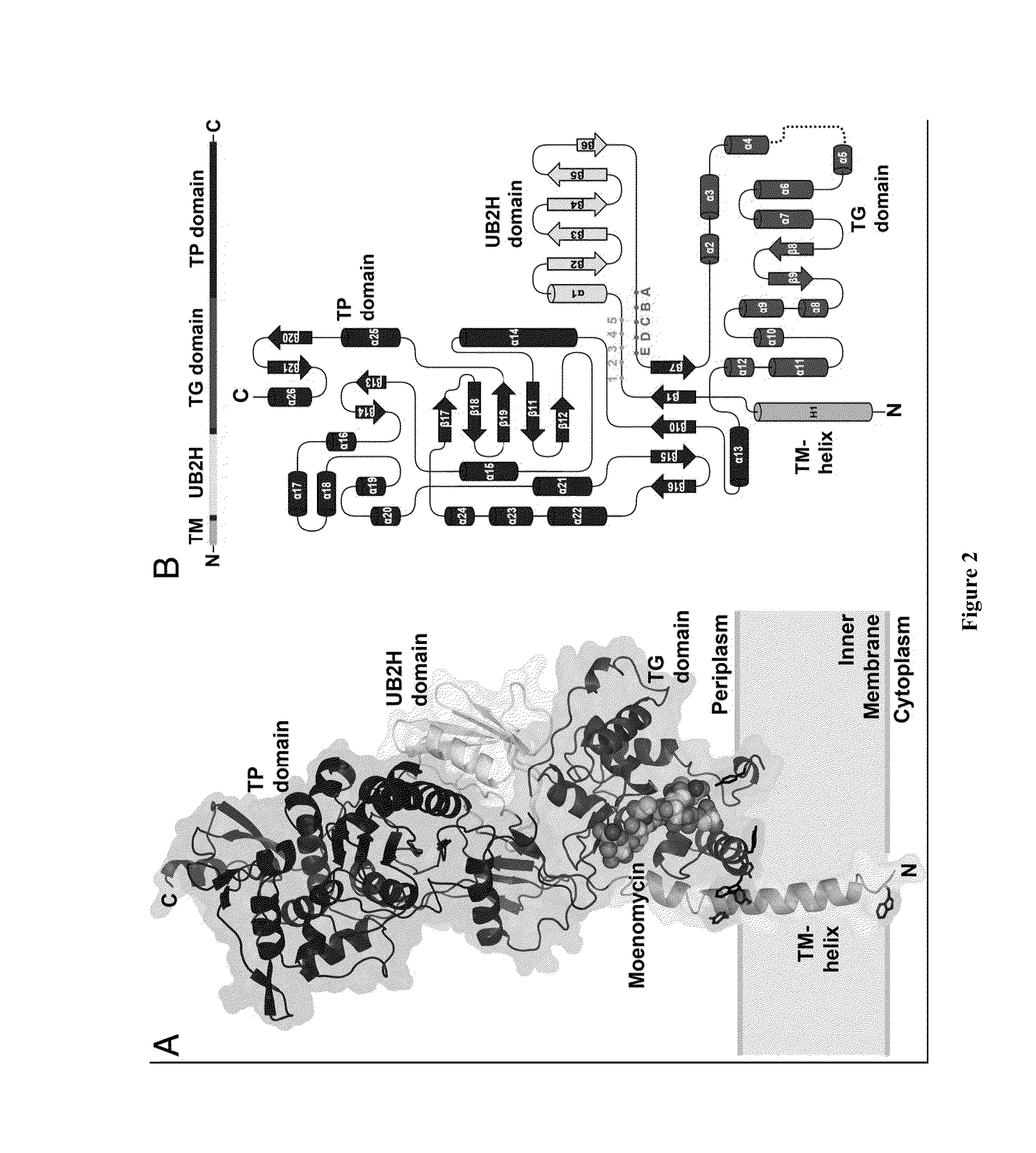
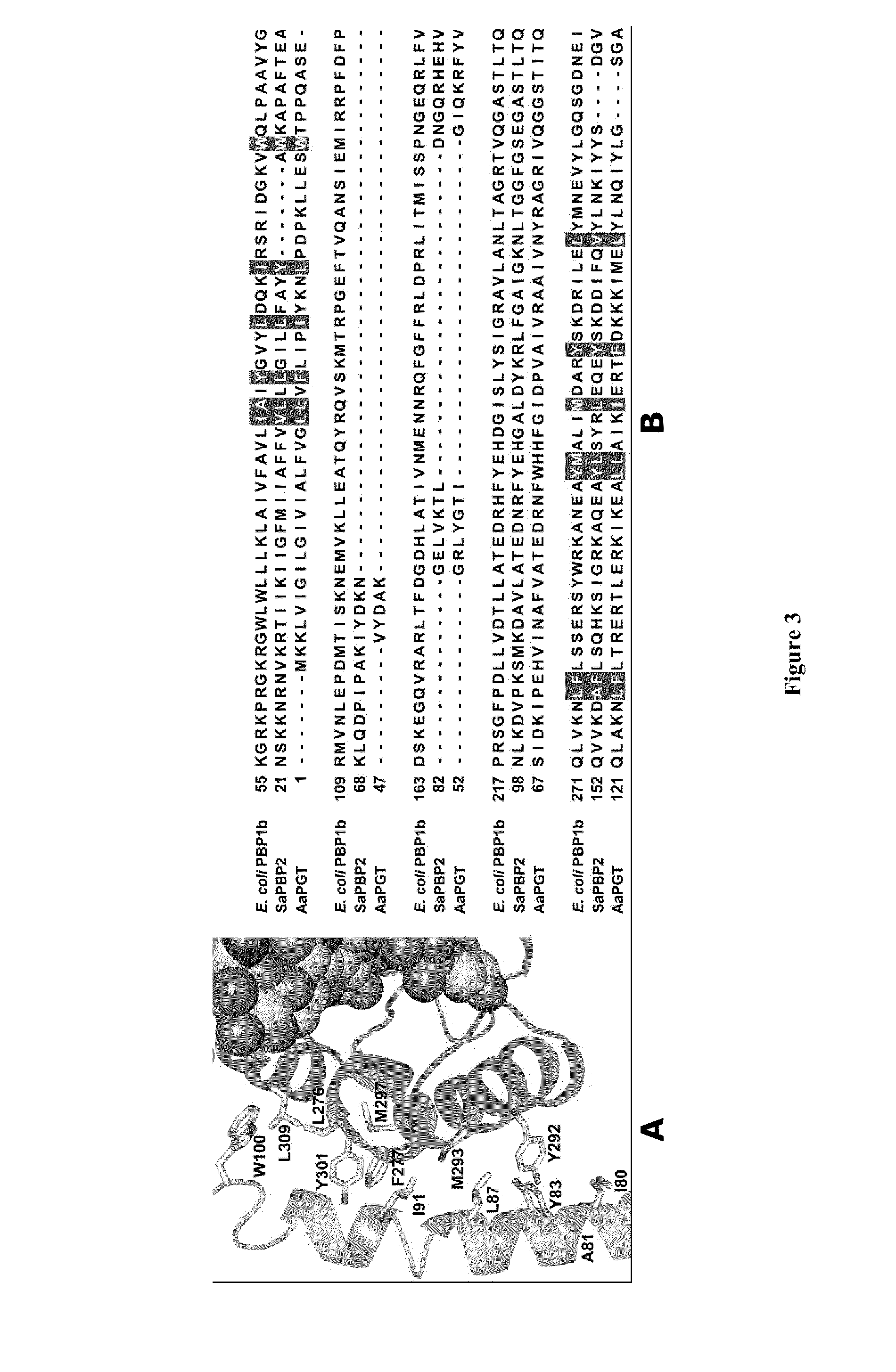
Crystal structure of bifunctional transglycosylase pbp1b from e. coli and inhibitors thereof
InactiveUS20100121107A1Growth inhibitionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionEscherichia coliMoenomycins
The crystal structure at 2.16 Å resolution of the full-length bacterial bifunctional transglycosylase penicillin-binding protein 1b (PBP1b) from Escherichia coli, in complex with its inhibitor moenomycin, is provided. The atomic coordinates of the complex as well as the moenomycin binding site are provided. Three dimensional structures of amino acid residues involved in moenomycin binding and transglycosylation activity are identified. Binding site for peptidoglycan synthesis inhibitors comprising inhibitor-binding site comprises amino acid residues from at least one of transglycosylase (TG), UvrB domain 2 homolog (UB2H) and transmembrane (TM) domains of PBP1b are identified at an atomic level of resolution. Methods for rational drug design based on the atomic coordinates are provided. Methods for screening for antibiotics based on anisotropic binding assay and transglycosylase inhibitor assays are provided. Novel antibiotics based on the screening assays of the invention are disclosed.
Owner:ACAD SINIC +1
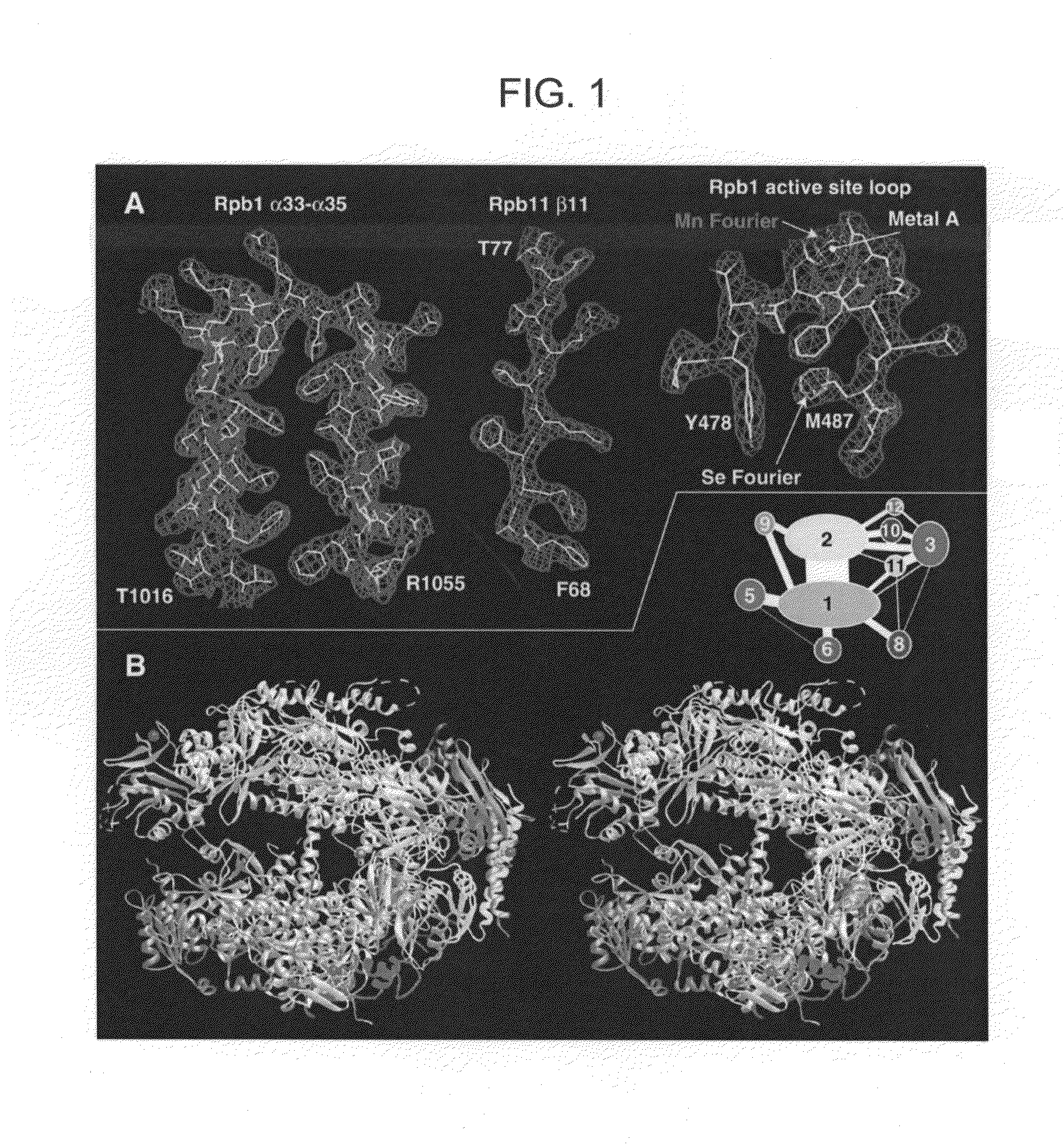
Computer comprising three-dimensional coordinates of a yeast RNA polymerase II
Crystals and structures are provided for an eukaryotic RNA polymerase, and an elongation complex containing a eukaryotic RNA polymerase. The structures and structural coordinates are useful in structural homology deduction, in developing and screening agents that affect the activity of eukaryotic RNA polymerase, and in designing modified forms of eukaryotic RNA polymerase. The structure information may be provided in a computer readable form, e.g. as a database of atomic coordinates, or as a three-dimensional model. The structures are useful, for example, in modeling interactions of the enzyme with DNA, RNA, transcription factors, nucleotides, etc. The structures are also used to identify molecules that bind to or otherwise interact with structural elements in the polymerase.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Crystal space structure transformation method and system
PendingCN112466418ADevelopment is intuitiveOvercome the problem of not being able to find a local optimal solution smoothlyComputational materials scienceInstrumentsSpace groupCrystal cell
The invention discloses a crystal space structure transformation method and system. The method comprises the following steps: reading a crystal file, converting cell parameters, intramolecular atomiccoordinates and space group information in the file into an object-oriented data structure for storage, and converting the object-oriented data structure into a new object data structure, copying cellattributes and space group attributes in a crystal structure in the object-oriented data structure to corresponding attributes in a new crystal structure, reading position information of all atoms ina molecule in the molecular structure, and determining an atomic chain of each atom according to the position information of the atoms; calculating crystal lattice energy, and adjusting cell attribute parameters and flexible bond values according to a set step length; and converting the new object data structure into an object-oriented data structure, and storing the object-oriented data structure. According to the method and the system, the parameter space of the crystal is converted from describing the fractional coordinate of each atom in the crystal cell into describing the relative position between two adjacent atoms in the crystal through conversion, so that the whole parameter space is continuously changed in the crystal evolution process.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZHIYAO TECH CO LTD
Crystal structure of the large ribosomal subunit from s. aureus
A composition-of-matter comprising a crystallized form of a large ribosomal (50S) subunit of a pathogenic bacterium, and the atomic coordinates of the three-dimensional structure thereof are provided herein, as well as methods for crystallizing the same, and using the atomic coordinates of the same to design de novo ligands with high specificity thereto.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
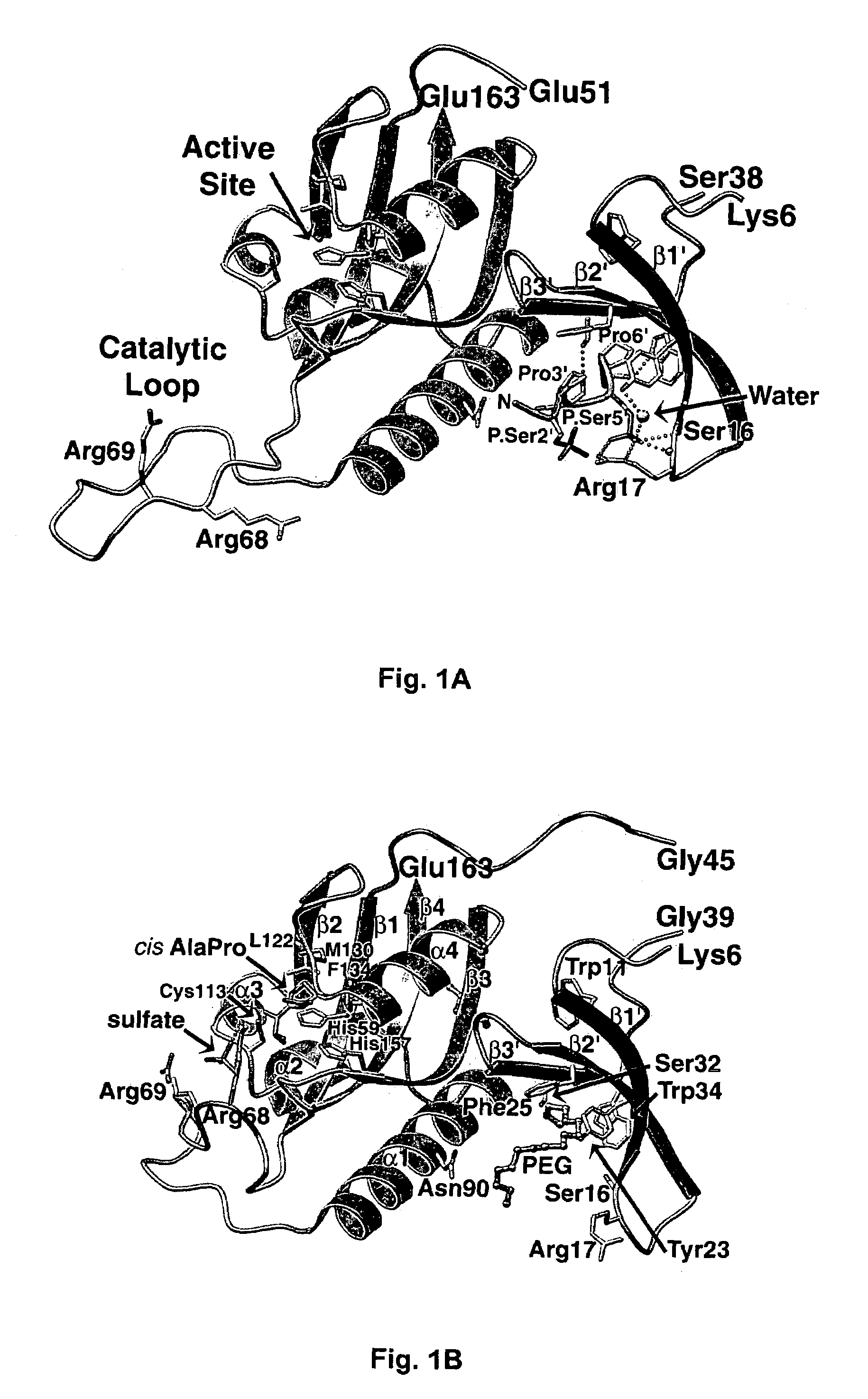
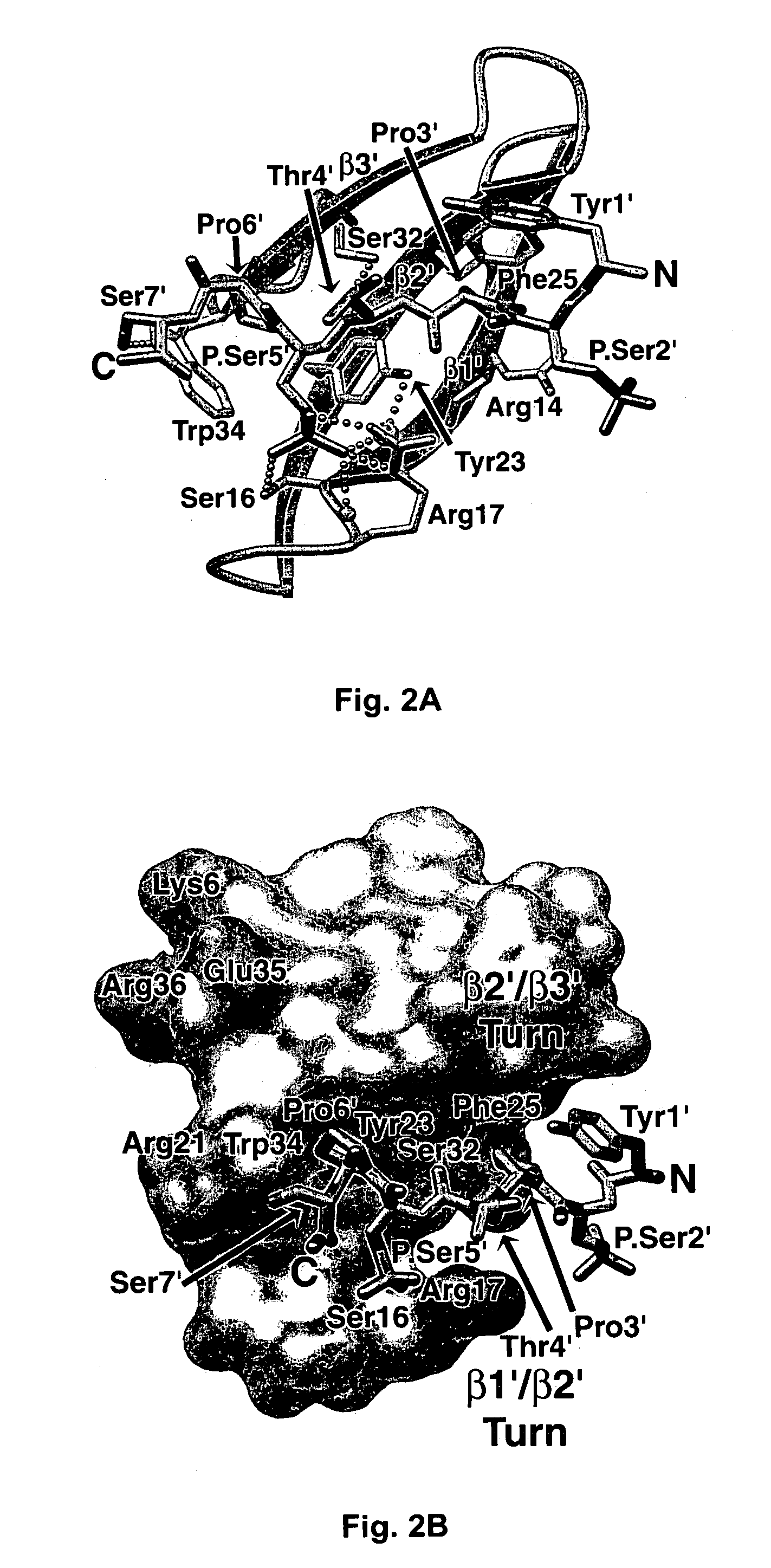
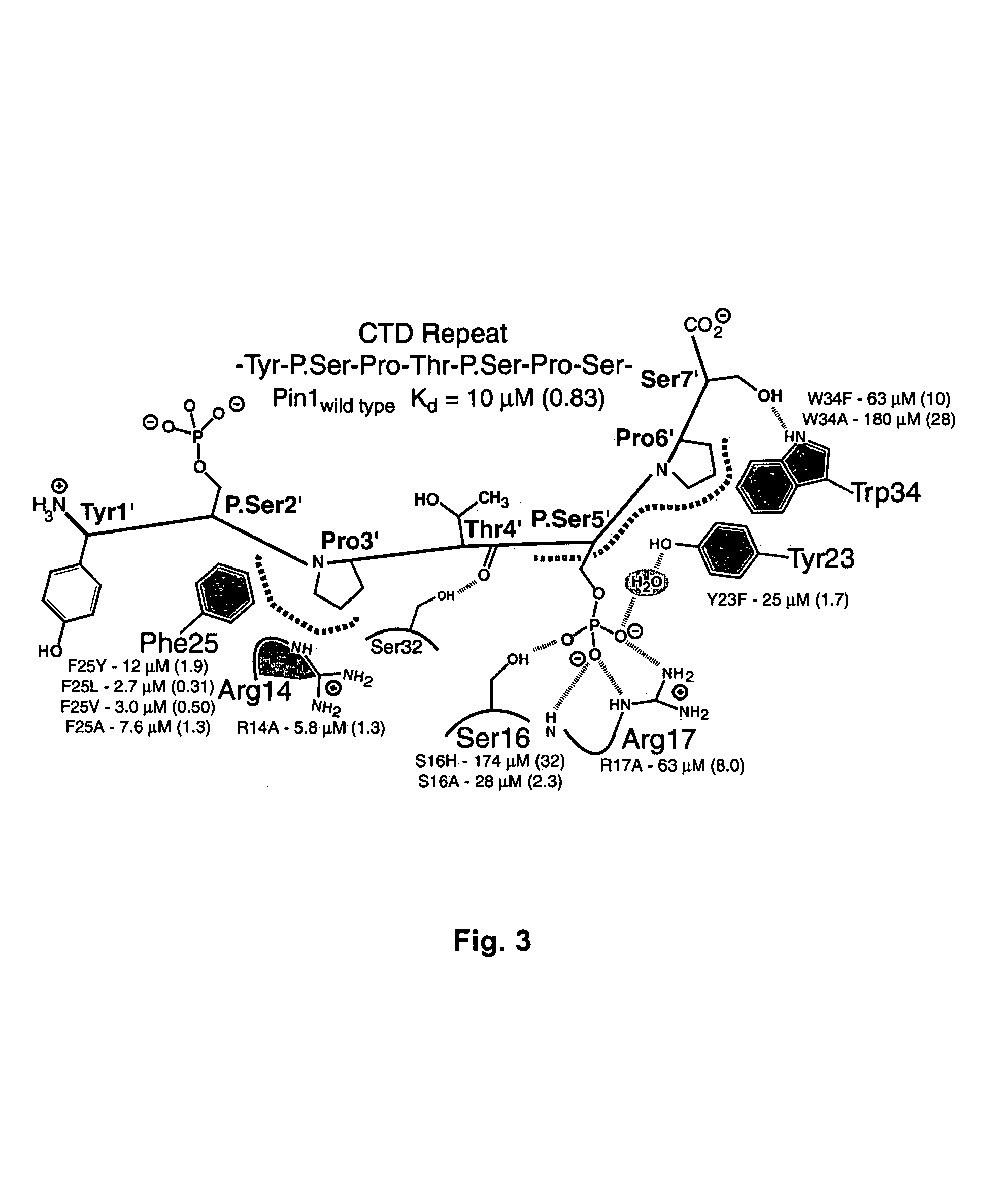
Crystal structure of WW domains and methods of use thereof
A WW domain crystal structure of Pin1 is provided. In addition, methods of using the crystal structure and atomic coordinates for the development of WW domain binding agents is also provided. Also provided are computer programs on computer readable medium for use in developing WW domain binding agents.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
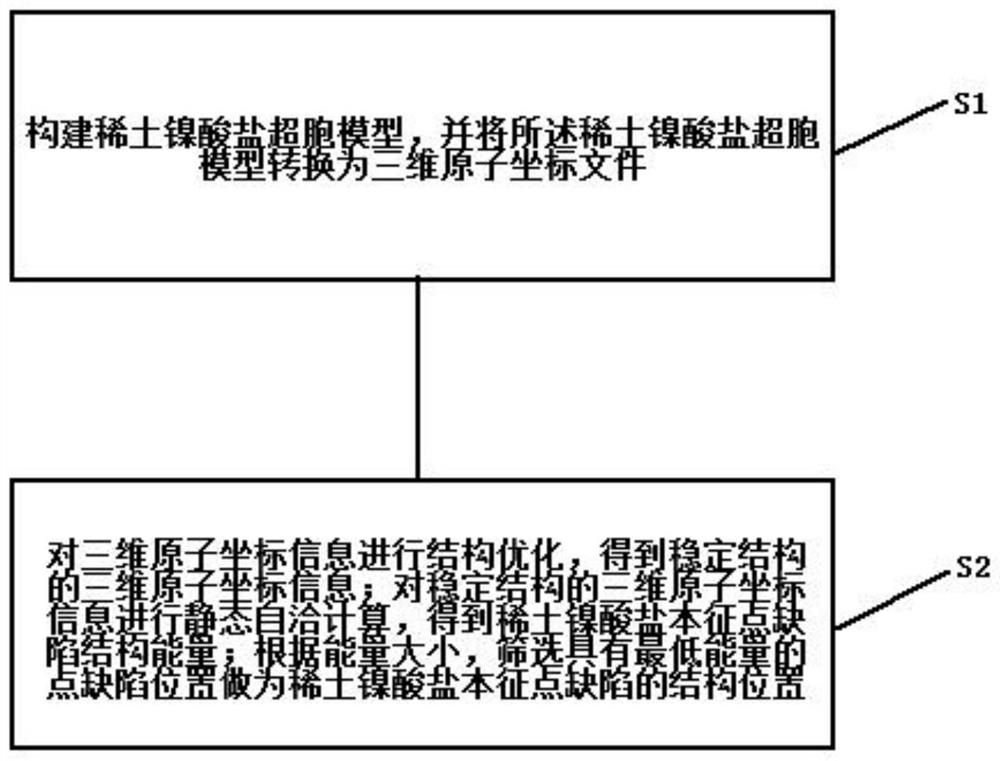
High-throughput screening method for point defects of rare earth nickelate material
InactiveCN112908427AImprove efficiencyLow costMolecular entity identificationIn silico combinatorial chemistryHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsOxidation resistant
The invention discloses a high-throughput screening method for point defects of a rare earth nickelate material. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a rare earth nickelate super-cell model, and converting the rare earth nickelate super-cell model into three-dimensional atomic coordinate information; performing structure optimization on the three-dimensional atomic coordinate information to obtain three-dimensional atomic coordinate information of a stable structure; performing static self-consistent calculation on the three-dimensional atomic coordinate information of the stable structure to obtain rare earth nickelate intrinsic point defect structure energy; and screening the point defect position with the lowest energy as the structure position of the intrinsic point defect of the rare earth nickelate according to the energy size. Through high-throughput screening of defect positions, determination of quantification of rare earth nickelate intrinsic point defect formation energy and simulation of atomic micro-structures and electron behaviors, the method is of great significance in enhancement of oxidation resistance of the rare earth nickelate film, improvement of visible light transmittance and regulation and control of metal insulator transition temperature of the rare earth nickelate; and the method plays a positive role in practical application of a detector and an intelligent window.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method and system for determining the solvent accessible surface area and its derivatives of a molecule
ActiveUS20110218788A1Less memory spaceImprove performanceChemical property predictionAnalogue computers for chemical processesSolventComputer science
A computer-readable storage medium encoded with computer-readable program code for causing a computer to perform a molecular dynamics simulation for determining the solvent accessible surface area of a molecule (M) with respect to atomic coordinates, wherein the molecule (M) comprises a plurality of atoms, a sphere (Bi) is assigned to each atom, and each sphere (Bi) comprises a radius (ρi) and a center position (ri). The program code includes instructions for: determining for each sphere (B) all neighbouring spheres (Bi) that intersect with the sphere (B); defining a set of one or more contours (Cm), such that all intersecting circles of sphere B with spheres Bi intersect on the surface of sphere B; determining for each contour (Cm) an area enclosed by the contour (Cm), wherein the contour (Cm) includes the area on the surface of said sphere (B) that is enclosed by one or more arcs (a1, a2, a3) resulting from an intersection of the surface of said sphere (B) with one of the surface of one intersecting sphere (Bi) or the surfaces of a plurality of intersecting spheres (Bi) that have an overlapping intersection area on the surface of said sphere (B); determining the solvent accessible surface (S) of said sphere (B) as the surface of said sphere (B) subtracted by the area comprised by all contours (Cm) on the surface of said sphere (B); and determining the solvent accessible surface area of the molecule (M) based on a sum of solvent accessible surface areas (Si) of the spheres.
Owner:KARLSRUHER INST FUR TECH
Calculation method and device for atom close-packed surface and two-dimensional dot matrix
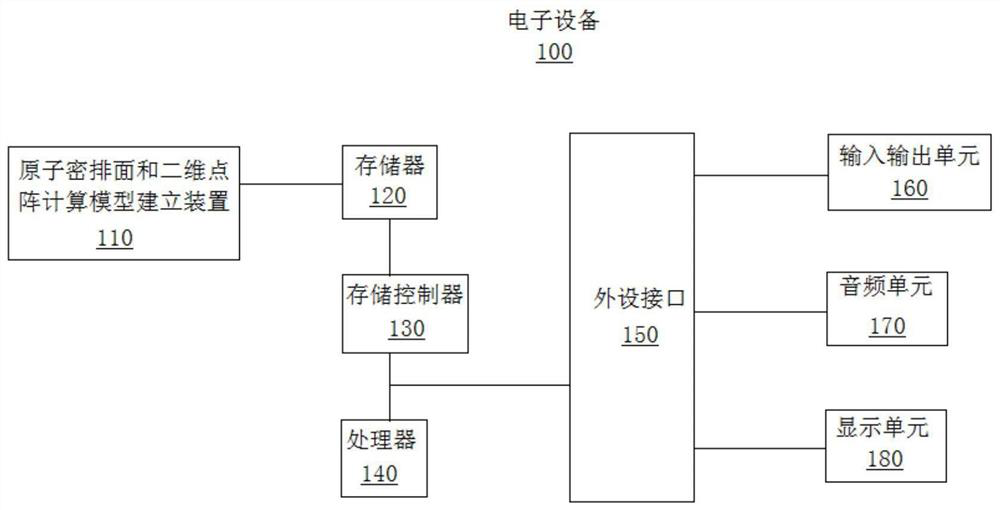
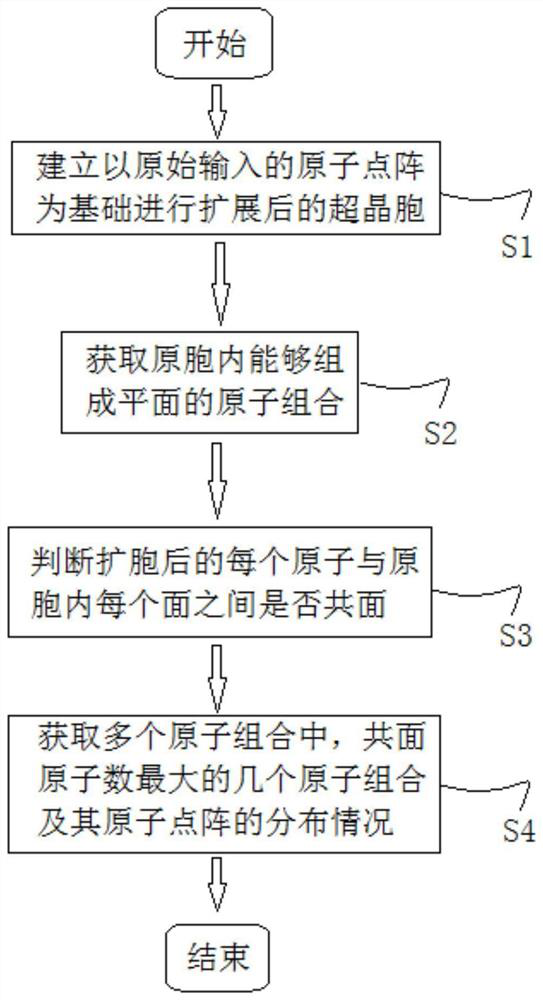
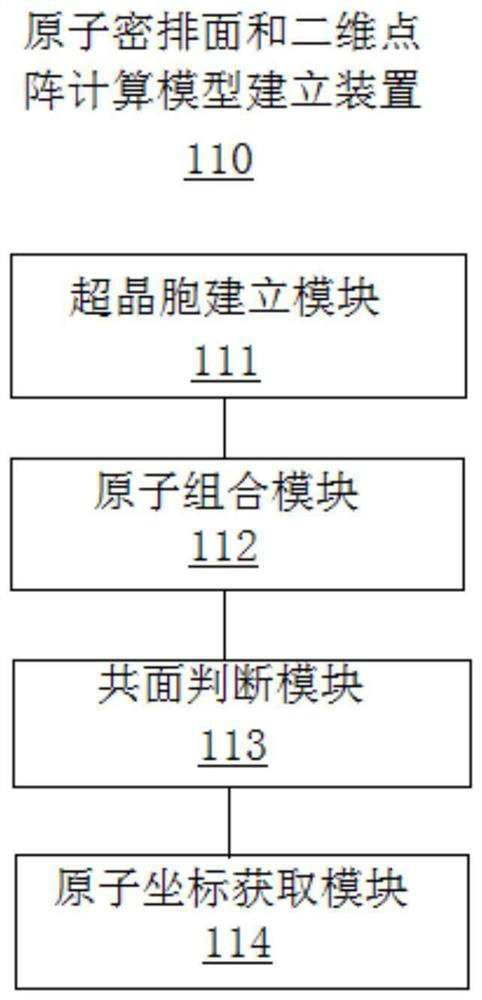
PendingCN113674810AWide applicabilityComputational theoretical chemistryComputational materials scienceDot matrixCondensed matter physics
The invention discloses a calculation method and device for an atom close-packed surface and a two-dimensional dot matrix, and belongs to the technical field of material structure characterization and modeling calculation. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a supercell expanded on the basis of an originally input atomic dot matrix; obtaining atom combinations capable of forming a plane in primitive cells based on an originally input atom dot matrix; judging whether each atom in the expanded supercell and each surface in the primitive cell are coplanar or not; and obtaining the distribution conditions of several atom combinations with the maximum coplane atom number and the atom dot matrix in all atom combinations in the supercell. According to the method, the atomic coordinates of at least one surface with the maximum number of atoms in the same plane and / or close to the maximum number of atoms and the corresponding coplanar atom coordinates in the supercell can be calculated, and the method is suitable for crystal structures except cubic crystals and hexagonal crystals; and a novel mode which is wide in applicability, simple and rapid is provided for obtaining the atom close-packed surface and the two-dimensional dot matrix of the crystal material.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF NEW MATERIALS
Process of Making Alkylaromatics Using EMM-13
This disclosure relates to a process for manufacturing a mono-alkylaromatic aromatic compound, said process comprising contacting a feedstock comprising an alkylatable aromatic compound and an alkylating agent under alkylation reaction conditions with a catalyst comprising EMM-13, wherein said EMM-13 is a molecular sieve comprising a framework of tetrahedral atoms bridged by oxygen atoms, the tetrahedral atom framework being defined by a unit cell with atomic coordinates in nanometers shown in Table 3.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
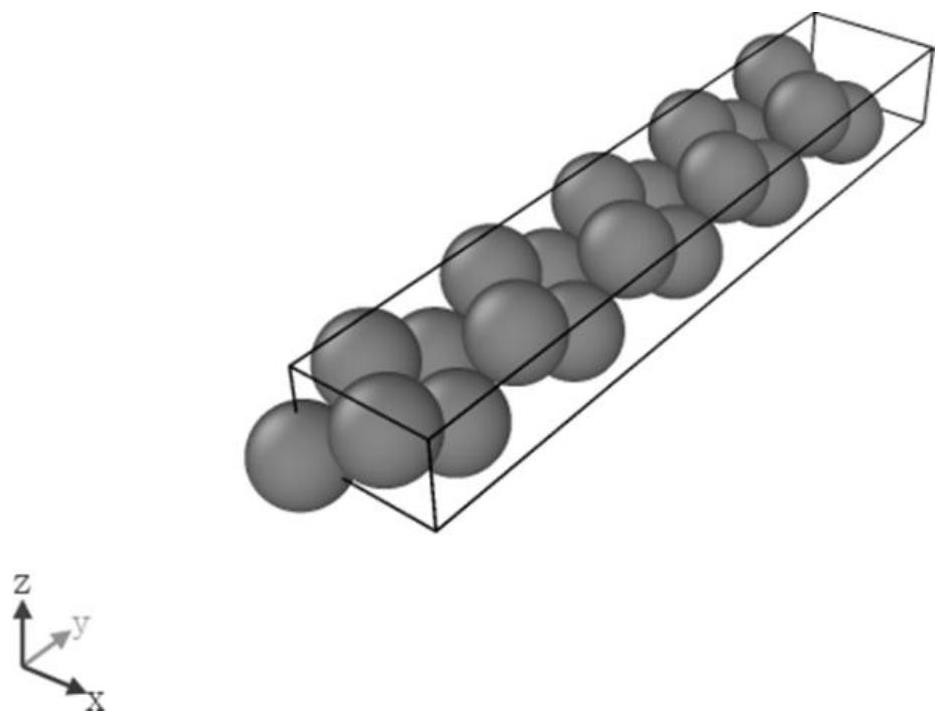
Multi-scale modeling method of gradient nano twin crystal
PendingCN114708920ACheminformatics data warehousingDesign optimisation/simulationGrain structureCrystal density
The invention discloses a multi-scale modeling method for gradient nano twin crystals. The multi-scale modeling method comprises the following steps: constructing a cellular cube model of a crystal; constructing a mirror symmetry model of the cellular cube model, and combining atomic coordinate files of the two to construct a twin crystal model; taking the Y-axis coordinate value of the center atom of the twin boundary of the twin crystal model as a fixed intermediate value, performing interval division on the Y-axis coordinate values of all atoms in the atom coordinate file of the twin crystal model, and deleting all atoms outside the interval to obtain three twin crystal models with different lengths along the Y axis; taking the three twin crystal models with different lengths and the central point coordinate file of each orientation grain structure as seed points to generate three nano twin crystal models with different twin crystal densities; and obtaining a gradient nano-twin crystal atomic structure model for the three nano-twin crystal models with different twin crystal densities by adopting crystal grain selective deletion and model splicing modes.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Hydroalkylation of Aromatic Compounds Using EMM-13
This disclosure relates to a process for manufacturing a mono-cycloalkyl-substituted aromatic compound, said process comprising contacting a feedstock comprising an aromatic compound and hydrogen under hydroalkylation reaction conditions with a catalyst system comprising a molecular sieve, wherein said molecular sieve comprises a framework of tetrahedral atoms bridged by oxygen atoms, the tetrahedral atom framework being defined by a unit cell with atomic coordinates in nanometers shown in Table 2.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Method for predicting adhesive interactions using molecular modeling
InactiveUS7062421B2Chemical property predictionLamination ancillary operationsMolecular modellingComputational chemistry
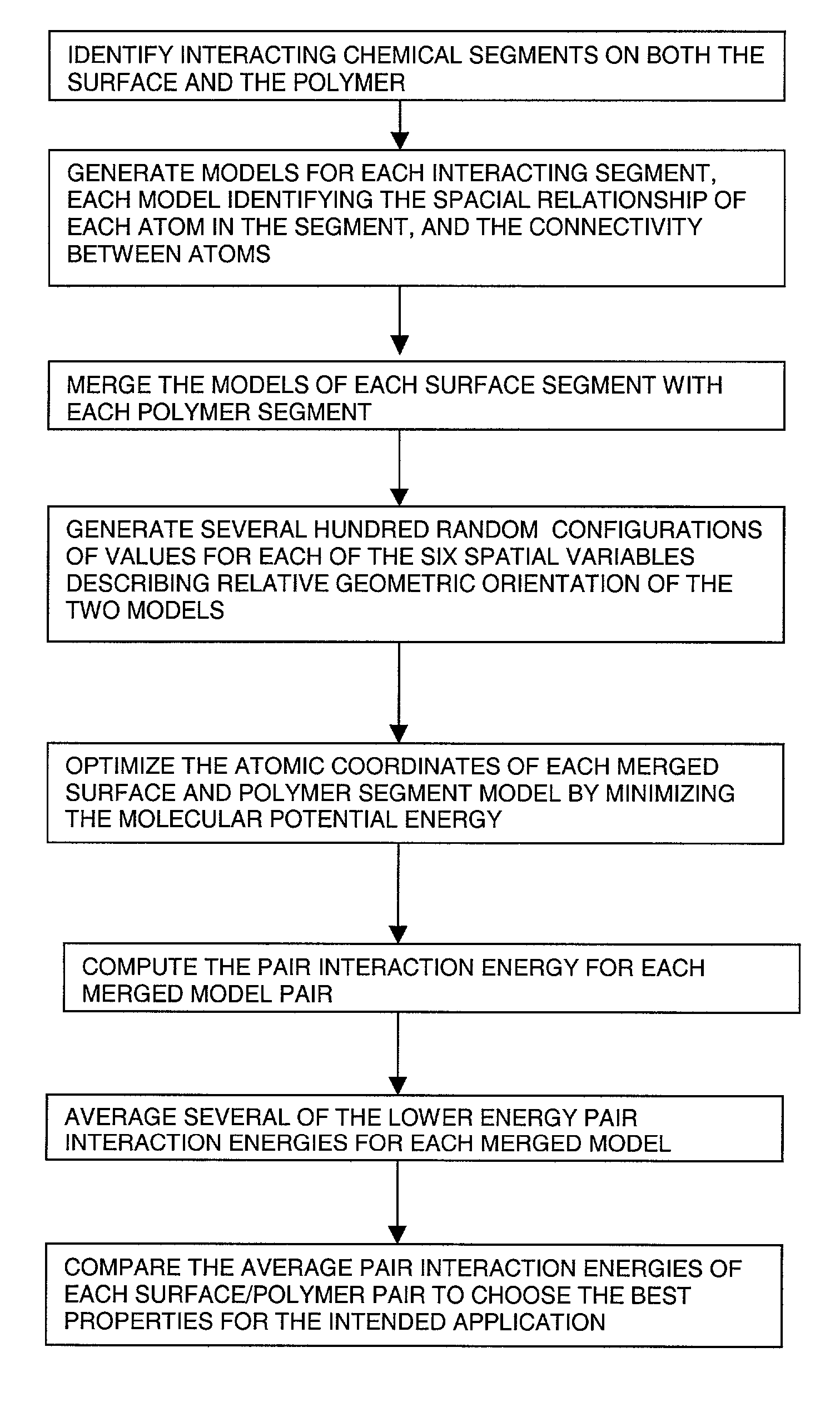
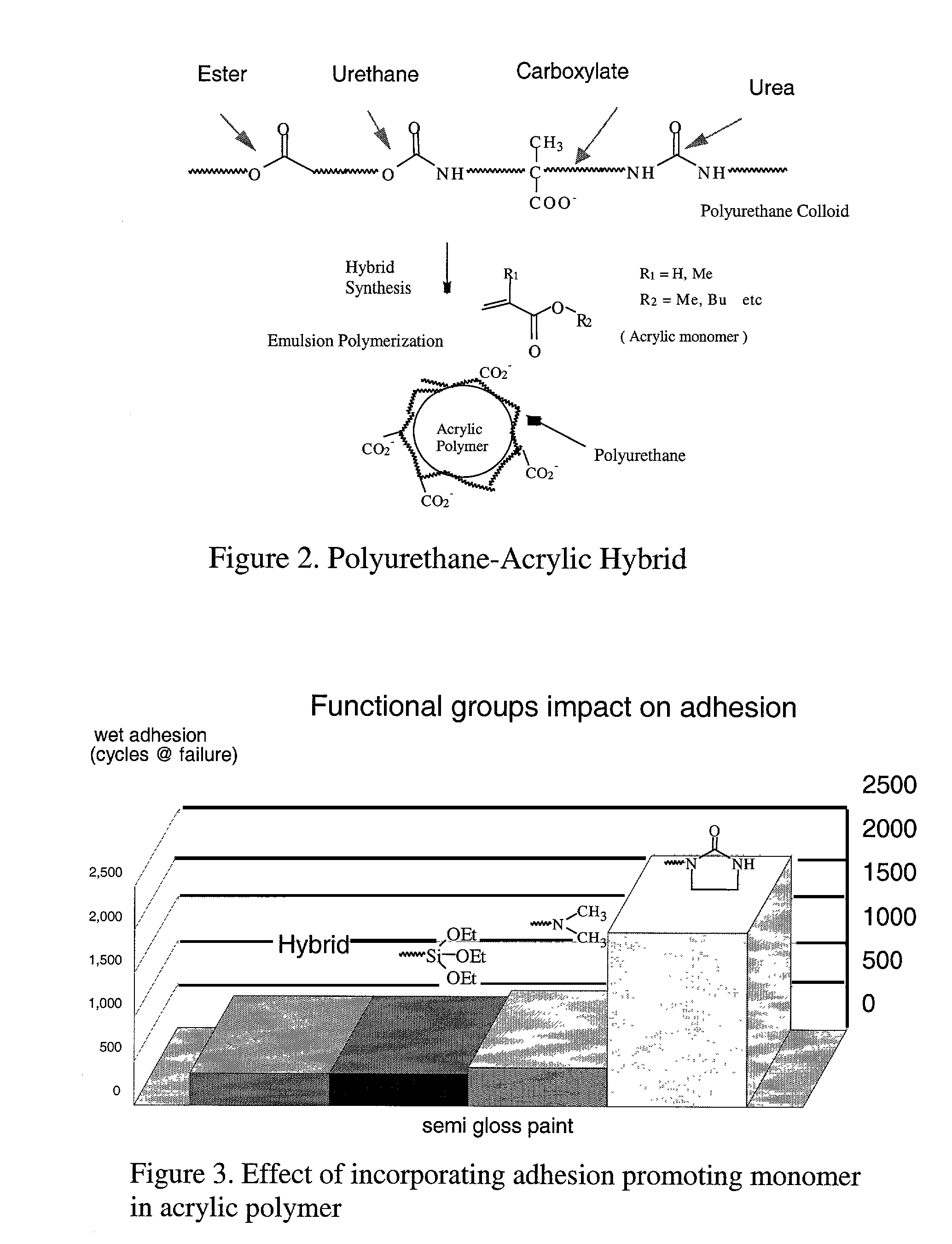
This invention relates to a process for using computerized molecular interaction modeling to predict the adhesive interactions between a substrate and a polymer. The molecular modeling method may be used to predict and select optimal adhesion promoting monomers for use in latex polymer coatings, providing the best wet adhesion to alkyd-coated substrates. The molecular modeling method could also predict substrate polymer pairs having the least affinity, and thus the most useful as a release liner. The method involves the steps of:a) identifying interacting chemical segments on both the surface and the polymer;b) generating models of the interacting segments, said models describing the spatial relationship of each atom in the segment and the connectivity between the atoms;c) merging the models of each surface segment with each polymer segment to describe each possible interacting surface / polymer pair;d) generating several hundred random configurations for each surface / polymer pair merged models, by choosing random values for the six spatial variables, that describe the relative orientations of two objects;e) optimizing the atomic coordinates of each surface / polymer segment interaction model by calculating the minimum of the molecular potential energy;f) computing the pair interaction energy for each merged model pair;g) averaging the pair interaction energies; andh) comparing the average pair interaction energies of each surface / polymer pair to choose the best pair for the intended application.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com