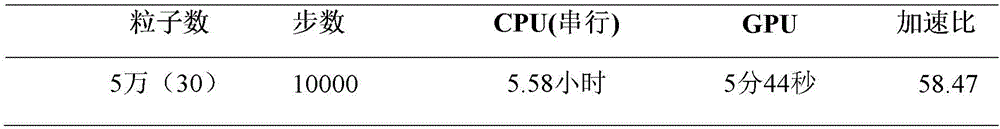
Patents
Literature
533 results about "Molecular dynamics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for studying the physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamic evolution of the system. In the most common version, the trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by numerically solving Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where forces between the particles and their potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanics force fields. The method was originally developed within the field of theoretical physics in the late 1950s but is applied today mostly in chemical physics, materials science and the modelling of biomolecules.
Multi-scale multiphysics coupling simulation method of metal additive manufacturing
ActiveCN107368642AOptimizing manufacturing process parametersImprove manufacturing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsManufacturing technologyFirst principle
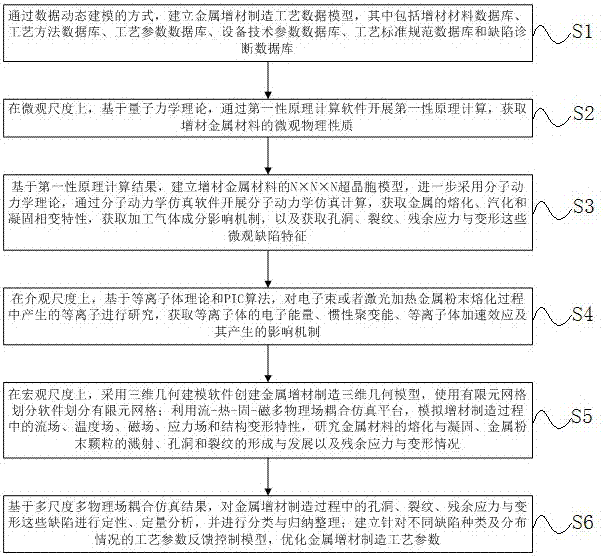
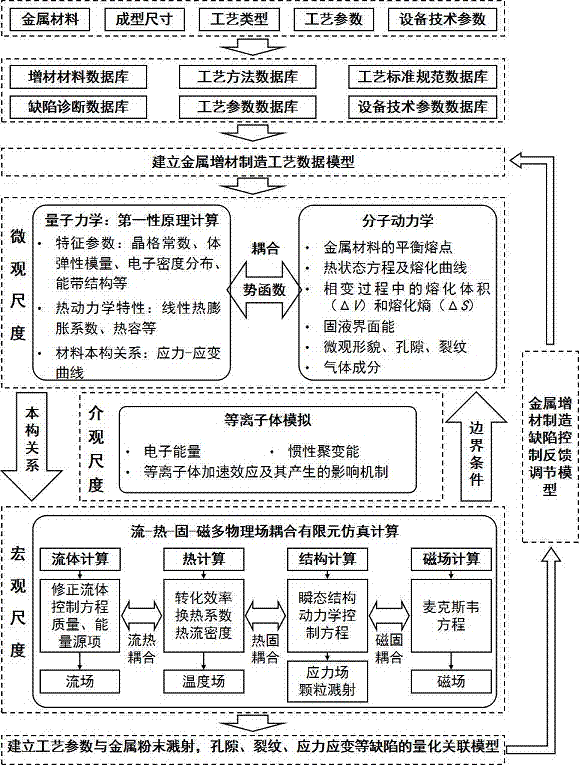
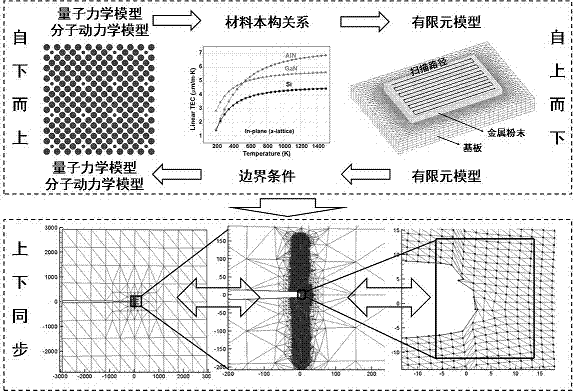
The invention provides a multi-scale multiphysics coupling simulation method of metal additive manufacturing. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a metal additive manufacturing technology data model; S2, carrying out first-principles calculation by calculation software on a microscale through first principles to acquire micro physical properties of additive metal material; S3, establishing an NxNxN super-cell model of the additive metal material, and carrying out molecular dynamics simulation calculation through molecular dynamics simulation software; S4, studying plasma, which is generated in a melting process of metal powder heated by an electron beam or a laser, on a mesoscale; S5, utilizing a flow-heat-solid-magnet multiphysics coupling simulation platform for simulation calculation; and S6, establishing a technology parameter feedback control model for different types and distribution situations of defects, and optimizing metal additive manufacturing technology parameters. The method forms a macro-micro-integration metal additive manufacturing product quality prediction system by means of multi-scale multiphysics coupling simulation.
Owner:湖南珞佳智能科技有限公司
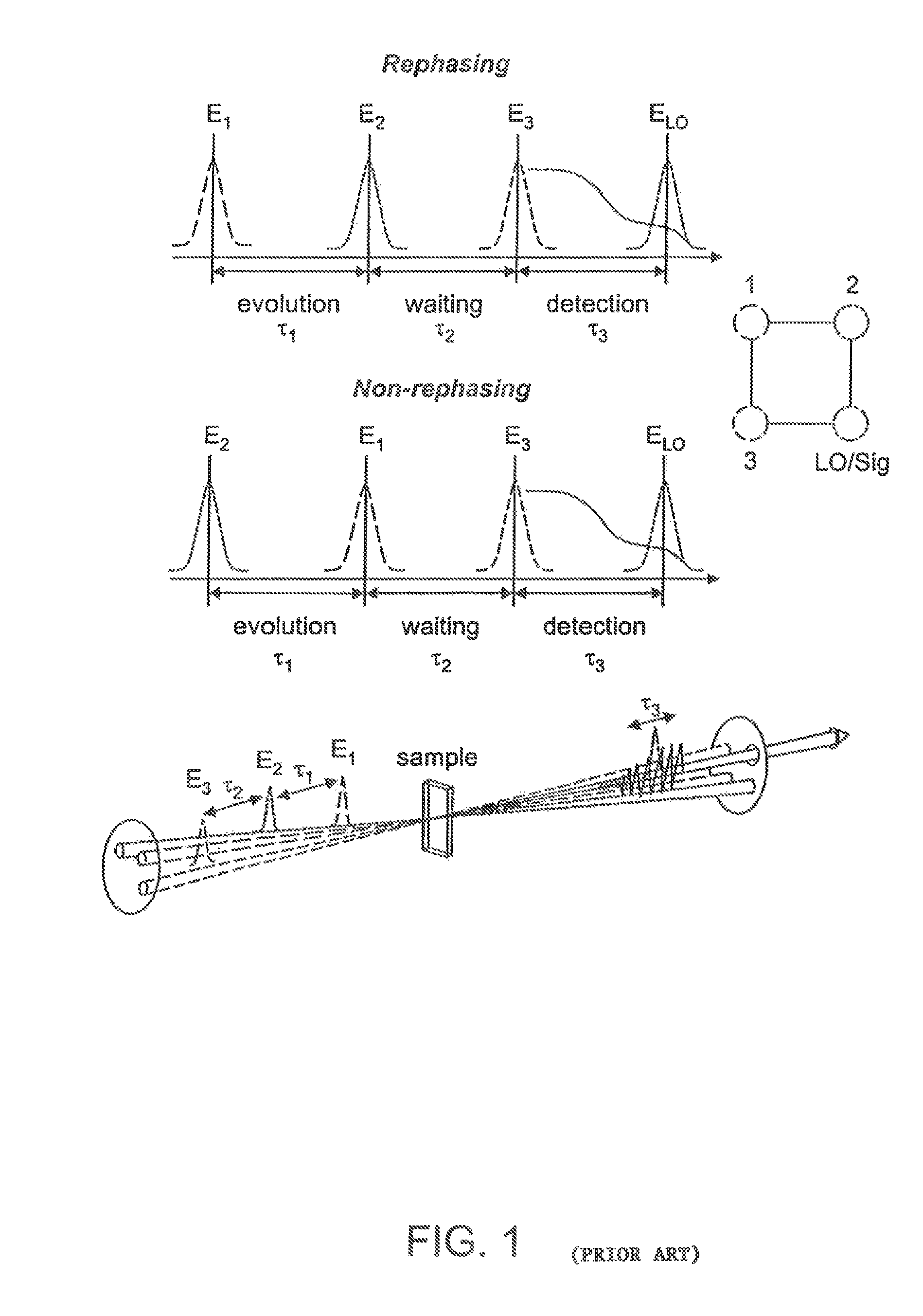
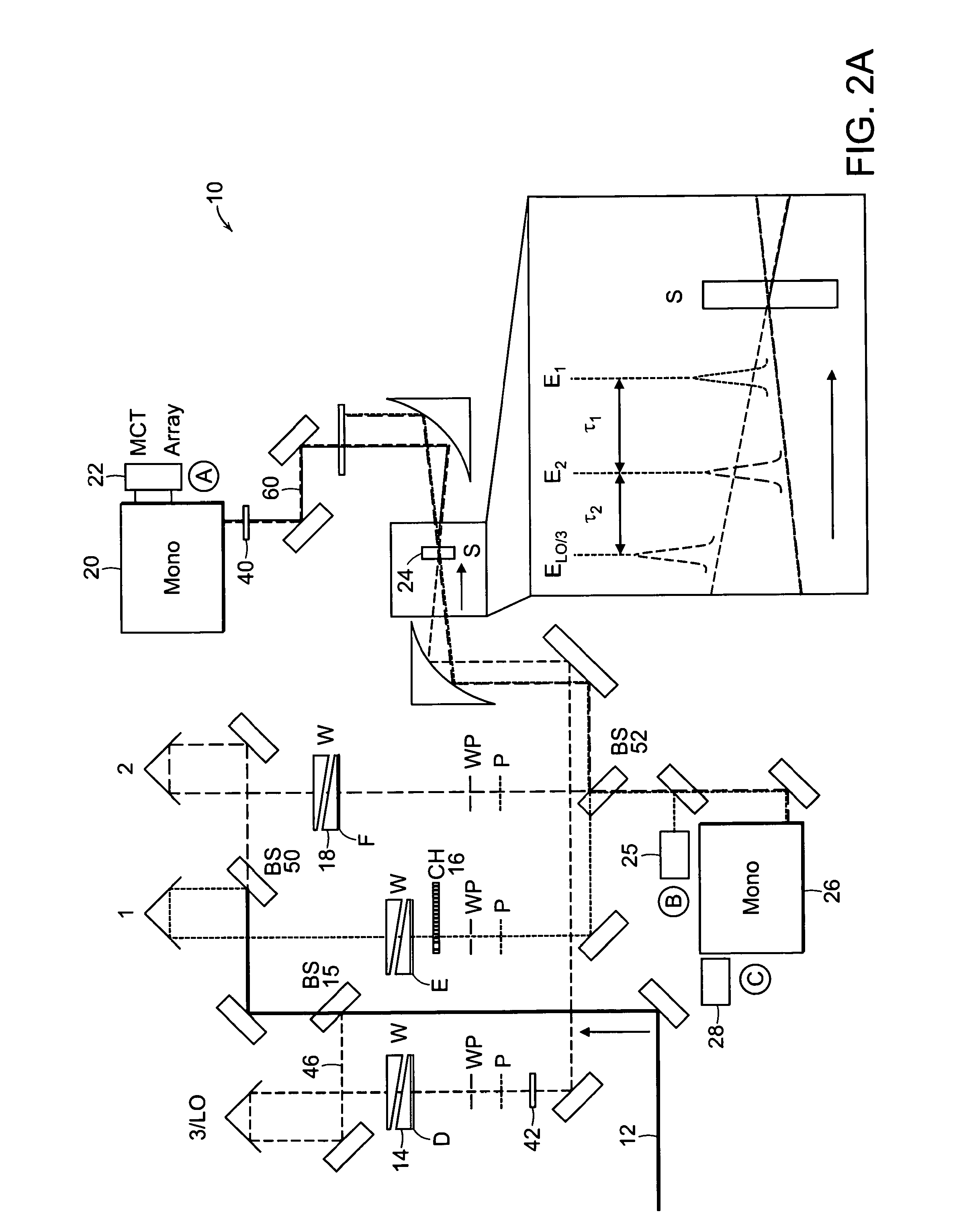
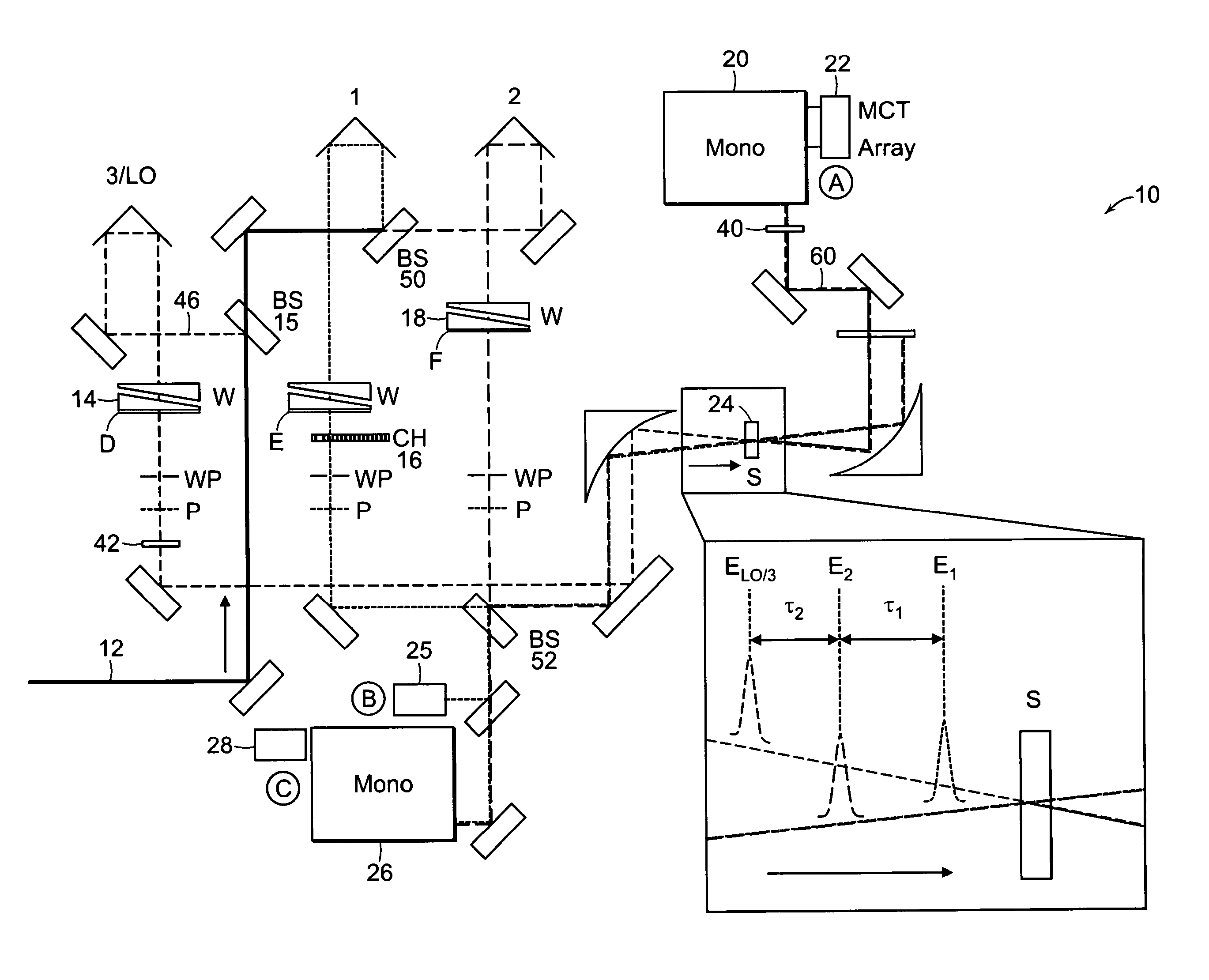
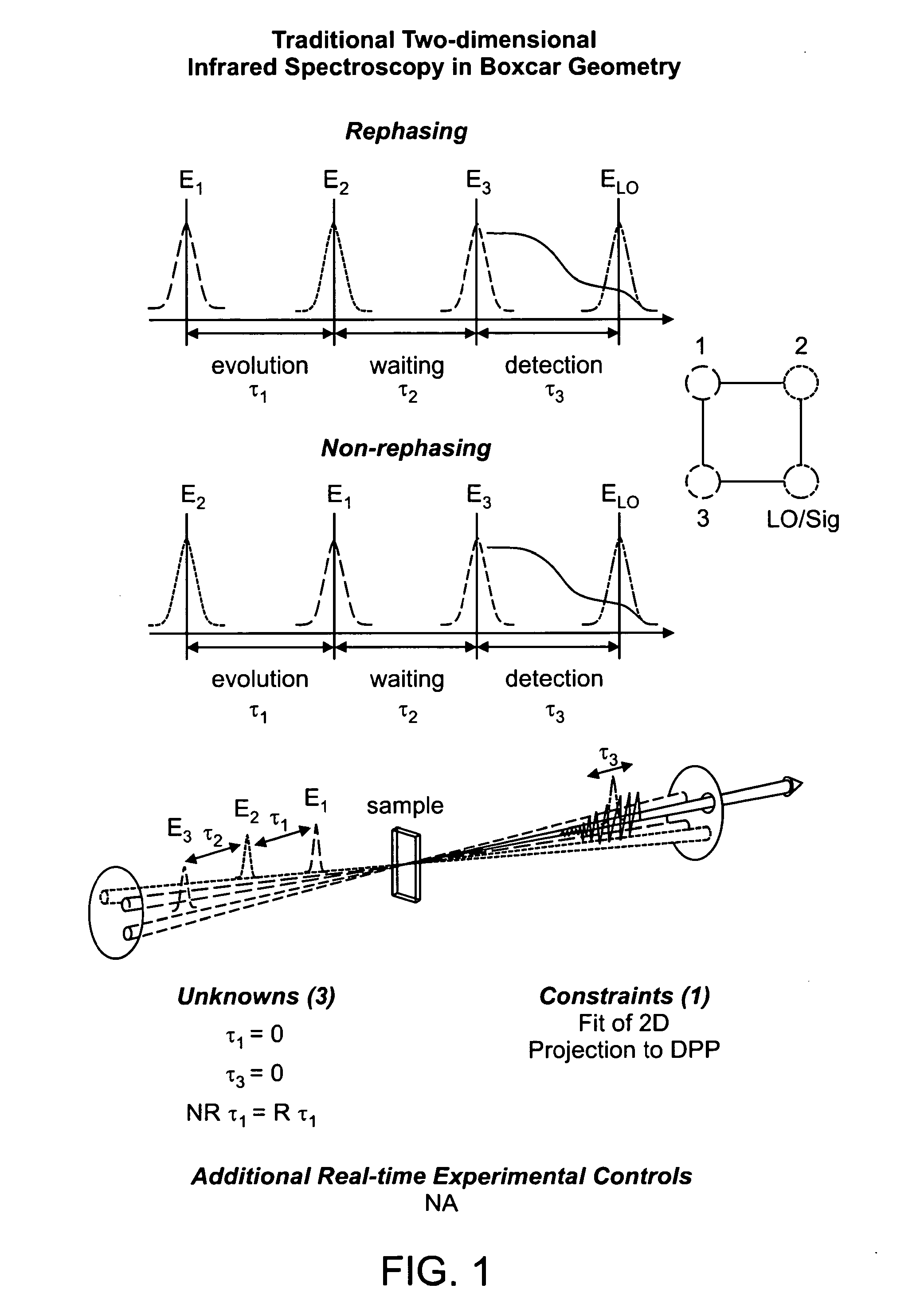
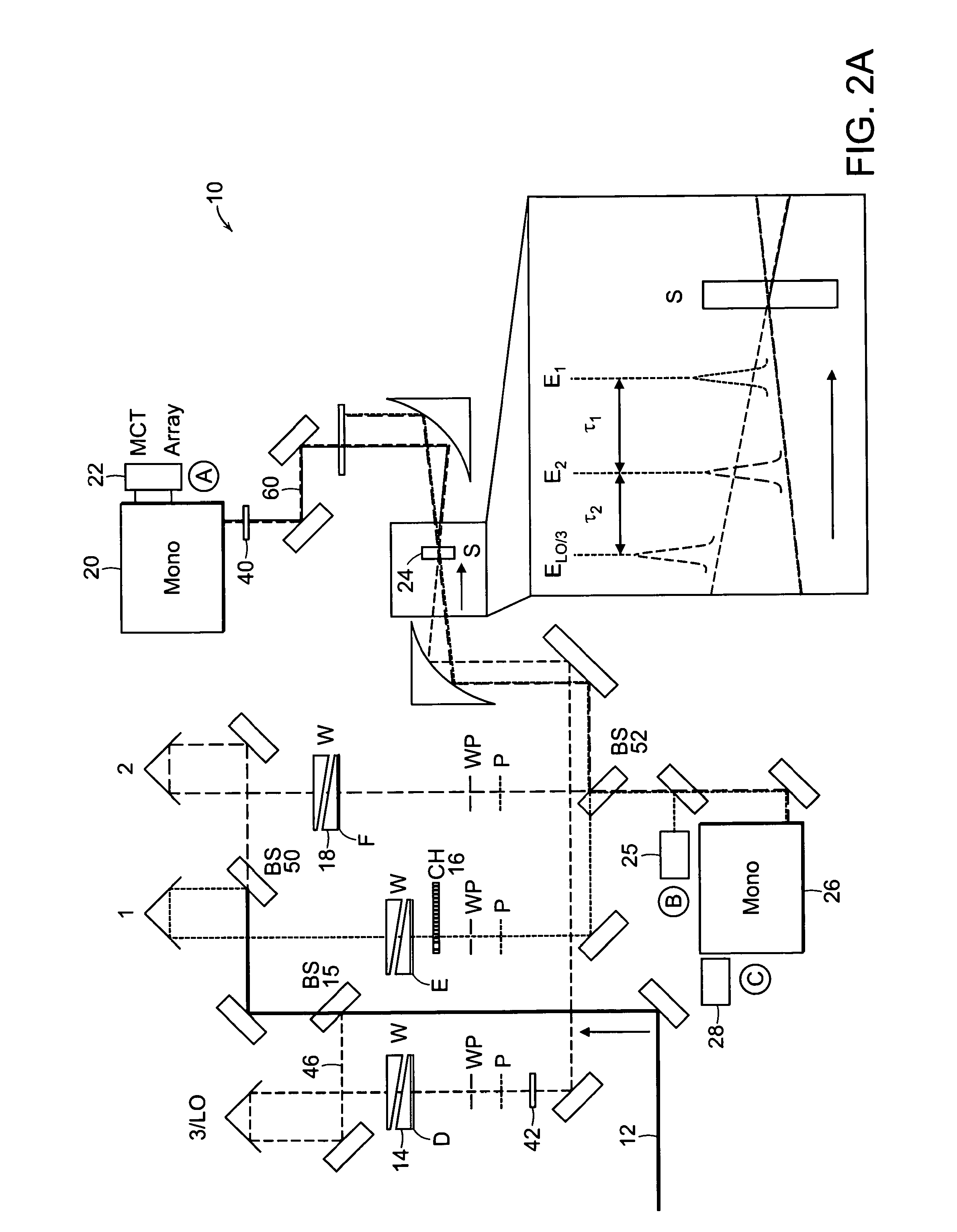
Two-dimensional fourier transform spectrometer
InactiveUS8526002B2Reduce ambiguityReduce subjectivityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFrequency spectrumCoupling
The present invention relates to a system and methods for acquiring two-dimensional Fourier transform (2D FT) spectra. Overlap of a collinear pulse pair and probe induce a molecular response which is collected by spectral dispersion of the signal modulated probe beam. Simultaneous collection of the molecular response, pulse timing and characteristics permit real time phasing and rapid acquisition of spectra. Full spectra are acquired as a function of pulse pair timings and numerically transformed to achieve the full frequency-frequency spectrum. This method demonstrates the ability to acquire information on molecular dynamics, couplings and structure in a simple apparatus. Multi-dimensional methods can be used for diagnostic and analytical measurements in the biological, biomedical, and chemical fields.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method of calculating carrier mobility
InactiveUS20070150206A1High degreeImprove accuracyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic filmCarrier signal
A calculation method for finding the hole mobility or the electron mobility of an organic film. The method includes the steps of: calculating the electron density of a film using semi-empirical quantum molecular dynamics calculations; using the fact that holes and electrons move easily through regions of high electron density to calculate the probability that a hole or an electron will move in an excited state in which an electron is excited from the HOMO (highest occupied molecular orbital) to the LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital) using a Monte Carlo method; and, using the probability as a performance index, calculating the hole mobility from the number of carriers which exist in the HOMO and the orbitals below the HOMO, or calculating the electron mobility from the number of carriers which exist in the LUMO and the orbitals above the LUMO.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Abrasive flow machining numerical simulation research method based on molecular dynamics
InactiveCN104657564AAchieve micromachiningImplementing Molecular Dynamics SimulationsSpecial data processing applicationsEnergy variationMachined surface
The invention relates to an abrasive flow machining numerical simulation research method based on molecular dynamics. According to the method, numerical simulation researches are carried out on a machining course by taking a single abrasive grain as a tool. Specifically, the method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out abrasive flow machining course simulation researches on the basis of molecular dynamics; (2) establishing an abrasive micro-cutting molecular dynamic model; (3) discussing the influence of related parameters on energy change in the machining course and analyzing the quality of a machined surface; and (4) exploring the influence of abrasive machining on an abrasive crystal structure at a micro-scale. According to the method disclosed by the invention, by researching and analyzing a single-abrasive micro-cutting process in the abrasive flow machining course by virtue of a molecular dynamics method, atomic displacement in a Newtonian layer of a workpiece during the abrasive micro-cutting process can be calibrated; and the method can be used for achieving molecular dynamic simulation of abrasive grains and pointing out that bond angle of an abrasive grain can be changed in the course of machining the abrasive grains, so as to lay a theoretical foundation for the subsequent researches on the deformation of the abrasive crystal structure in the abrasive flow machining course.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods, systems, and computer program products for computational analysis and design of amphiphilic polymers
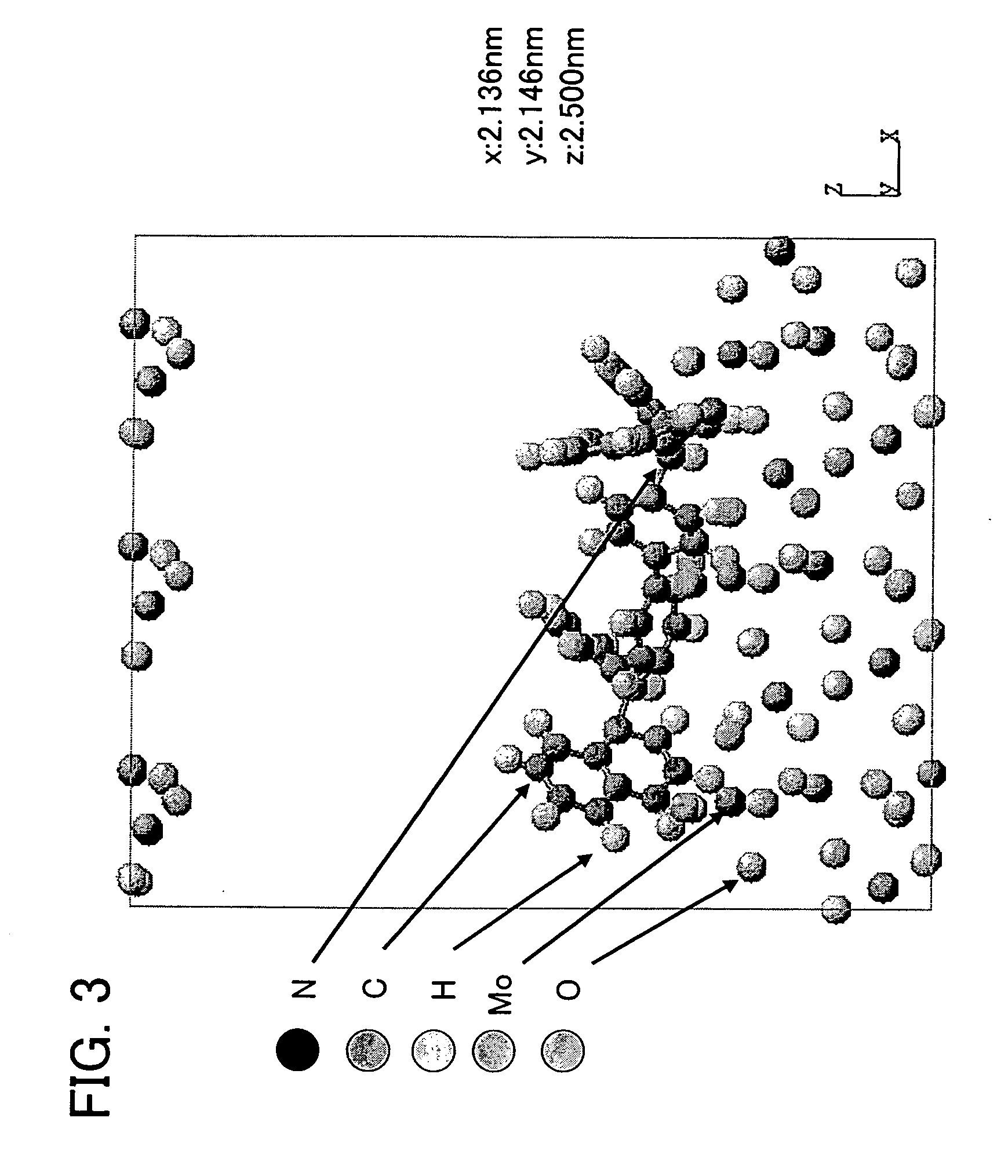
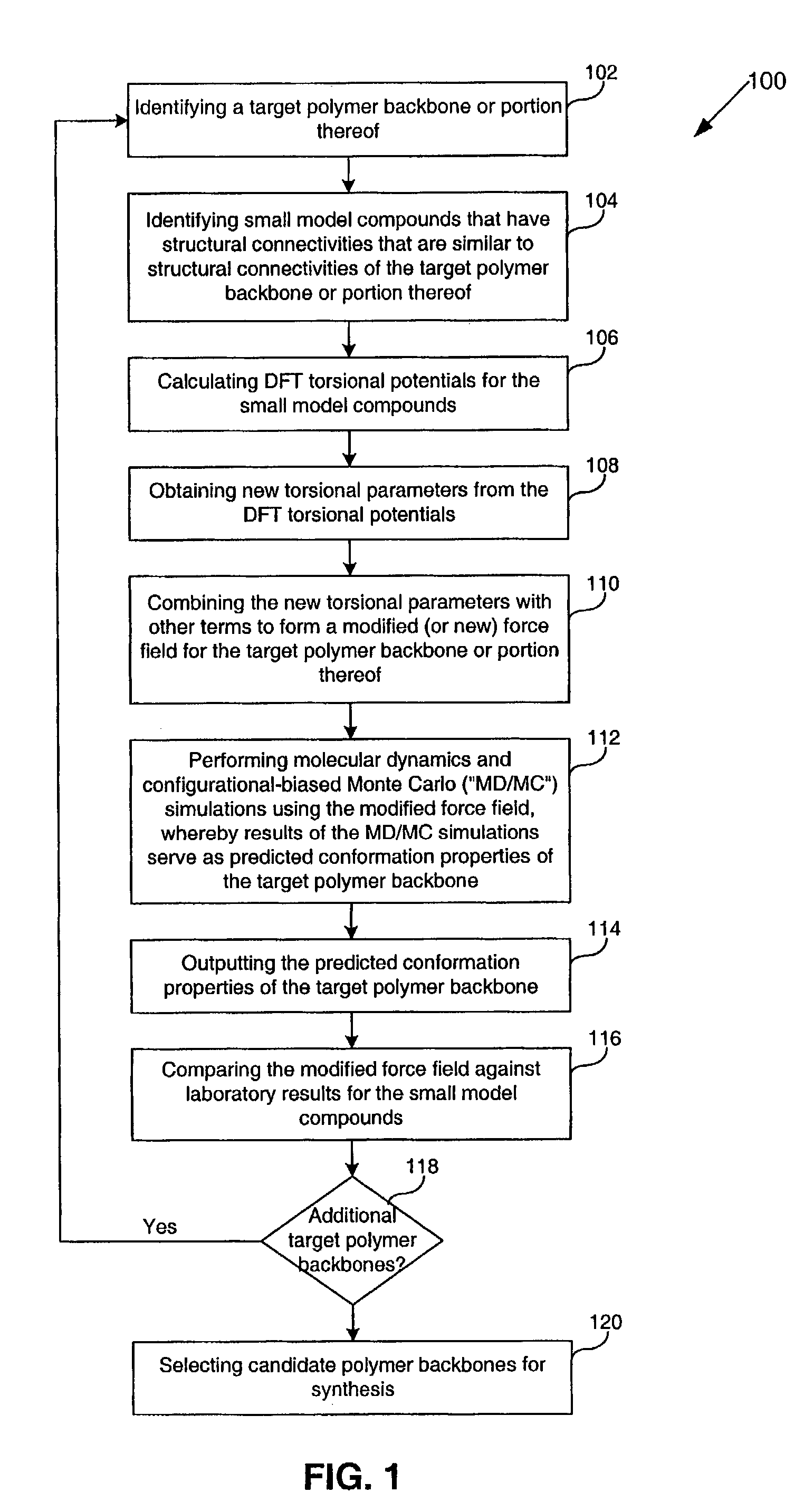
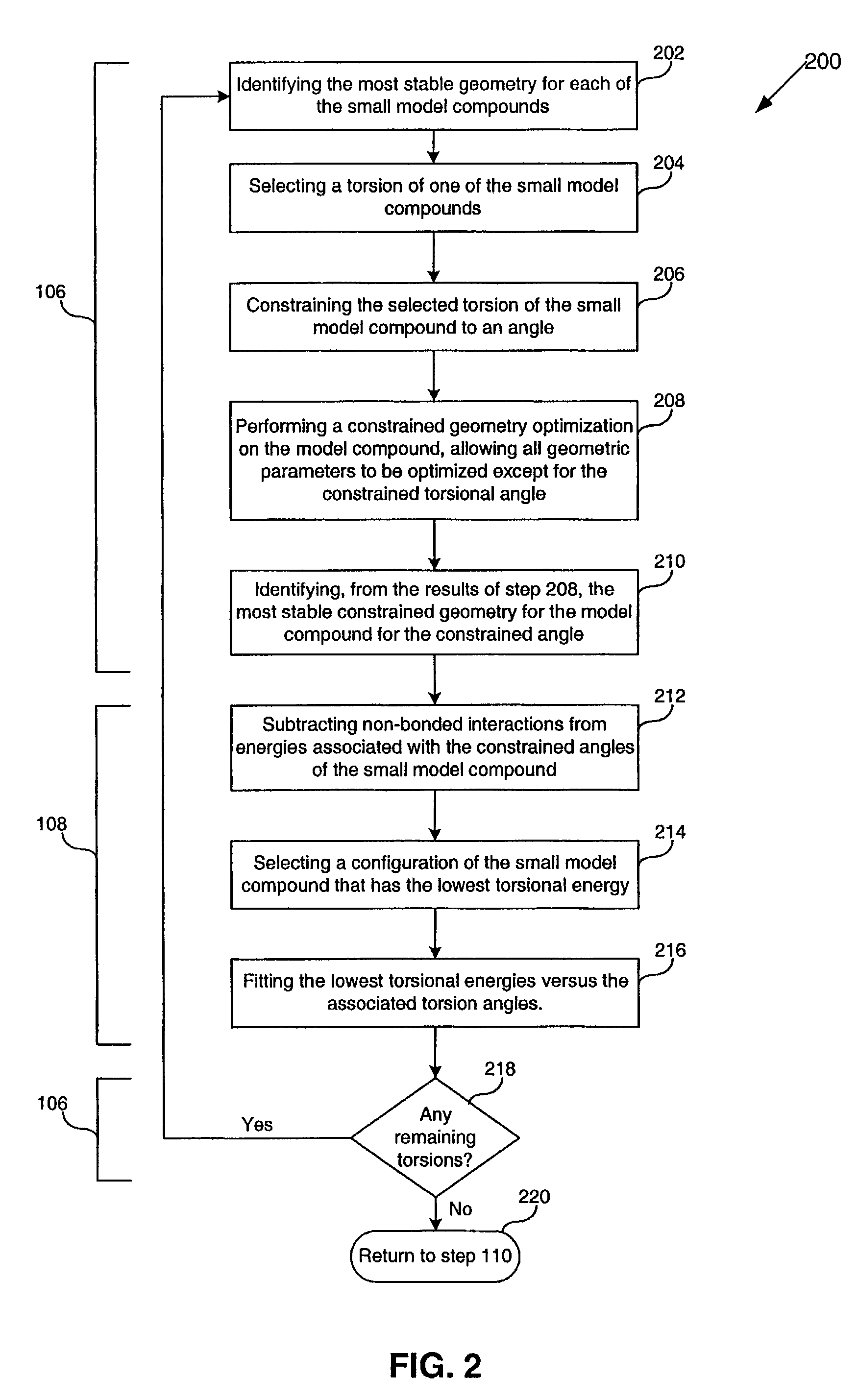
InactiveUS7590517B2Chemical property predictionOrganic chemistry methodsTorsional potentialDensity functional theory
Methods, systems, and computer program products for computational polymer processing including, without limitation, computational amphiphilic polymer design, conformational energy minimization, generation and refinement of torsional parameters for sub-units of potential polymers, generation of modified force field parameters, and prediction of conformational information for potential polymers. A target polymer backbone or portion thereof is identified. Small model compounds that have structural connectivities that are similar to structural connectivities of the target polymer backbone or portion thereof, are identified, whereby the combination of the small model compounds serve as a model of the target polymer or portion thereof. Gradient-corrected density functional theory (“DFT”) torsional potentials are calculated for the small model compounds, wherein energies are calculated at unconstrained and constrained geometries of the selected small model compounds. New torsional parameters are then obtained from the DFT torsional potentials. The new torsional parameters are combined with other terms to form a modified (or new) force field for the target polymer backbone or portion thereof. Molecular dynamics and configurational-biased Monte Carlo (“MD / MC”) simulations are performed using the modified force field, whereby results of the MD / MC simulations serve as predicted conformation properties of the target polymer backbone. The predicted conformation properties for the multiple target polymer backbones are then used to select one or more of the target polymer backbones as candidate amphiphilic polymer backbones for synthesis.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Molecular-dynamics-simulation-based virtual screening method of nuclear receptor mediated endocrine disruption substances
ActiveCN103324861ALow costSimple and fast operationSpecial data processing applicationsPerturbateurs endocriniensDrug biological activity
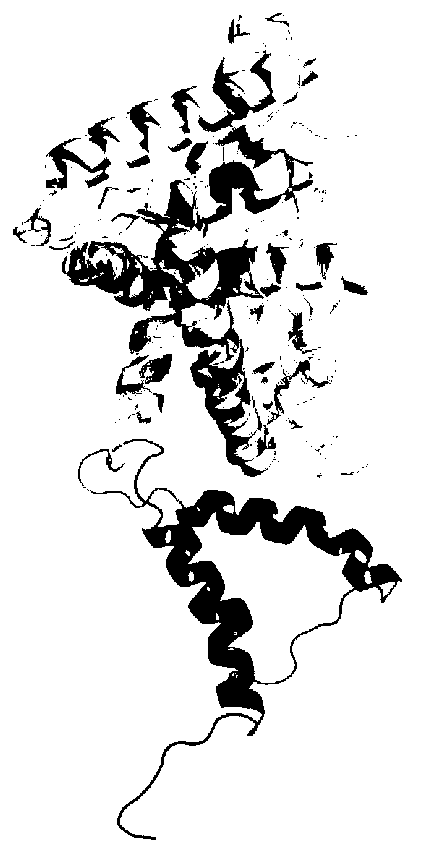
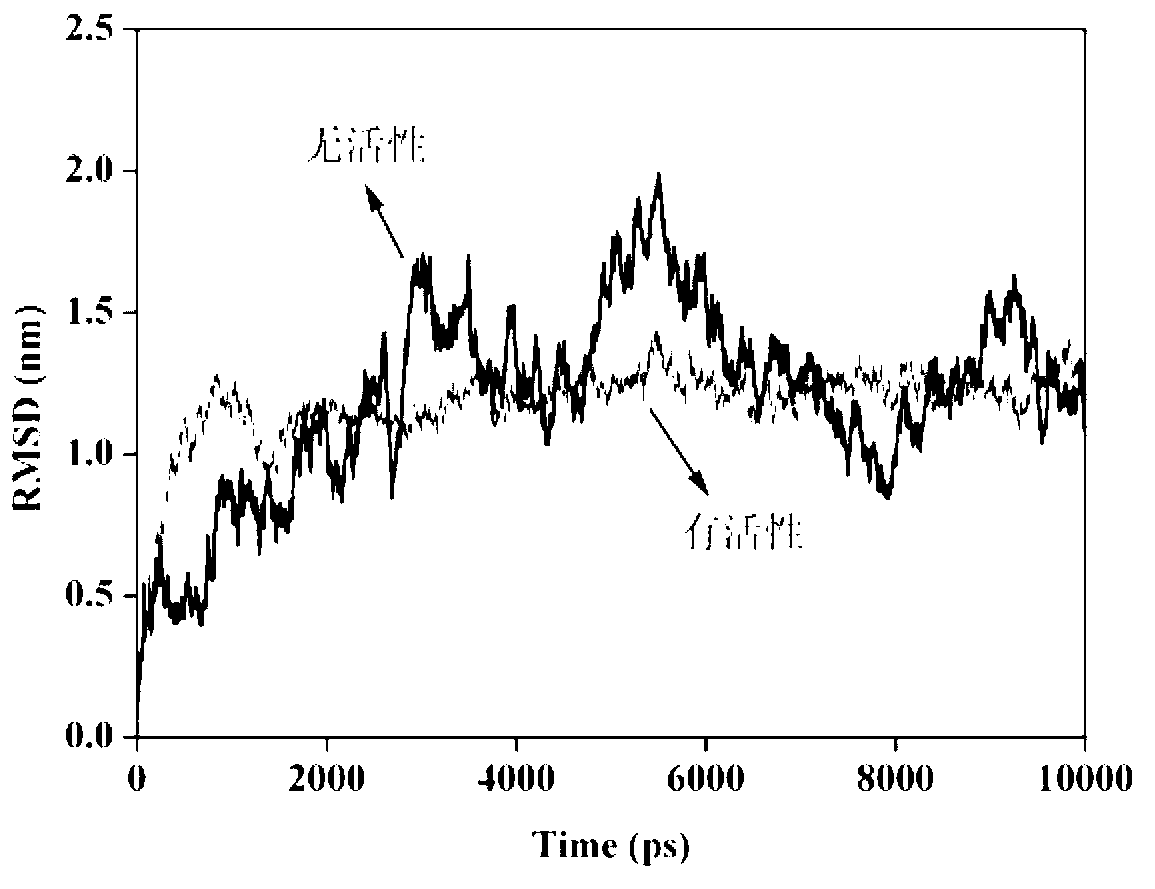
The invention discloses a molecular-dynamics-simulation-based virtual screening method of nuclear receptor mediated endocrine disruption substances, and belongs to the field of virtual screening and activity prediction of environmental suspicious endocrine disruption substances. The molecular-dynamics-simulation-based virtual screening method includes the steps of carrying out butt joint on a receptor file obtained by the fact that optimization and testing or homology modeling are / is carried out on tested small molecules to form a compound, and then using a GROMACS software package to carry out molecular dynamics simulation. Motion trail analysis is carried out on a twelfth helix of a receptor, pollutants with the activity of the receptor are identified through a changing curve of root-mean-square deviation analysis of a space position along with time changes, within the required time, a corresponding helix is regarded to be located to a determined position when the curve tends to be stable, and the receptor has the biological activity. In addition, the located position is inspected to judge whether the activity is fitting or resistance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
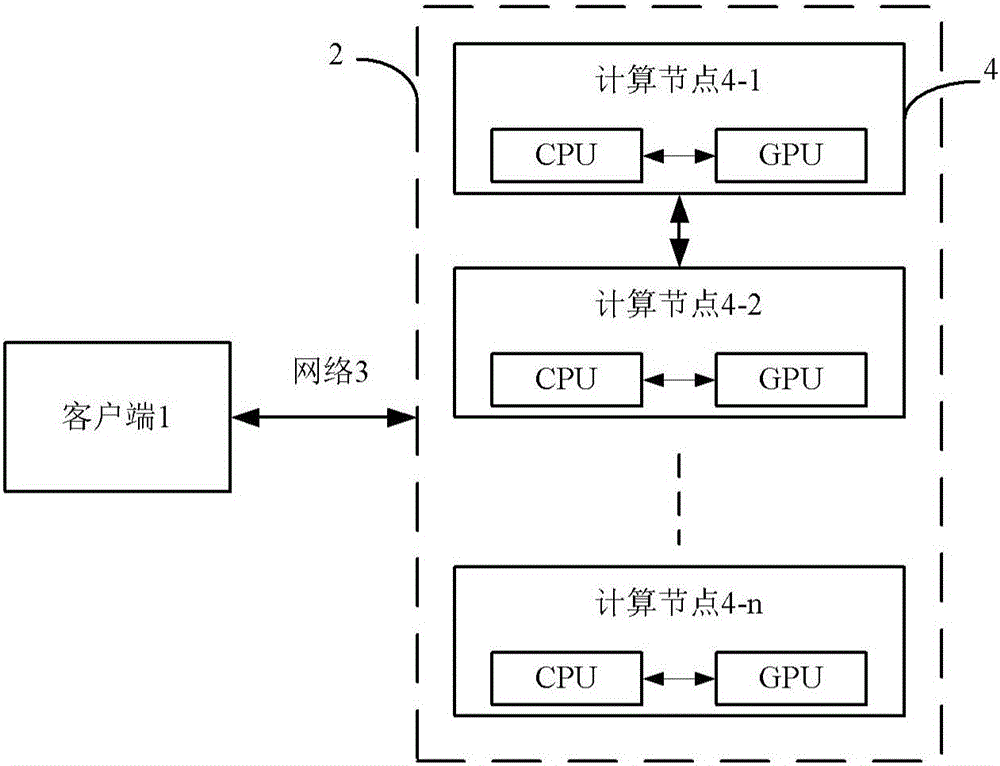
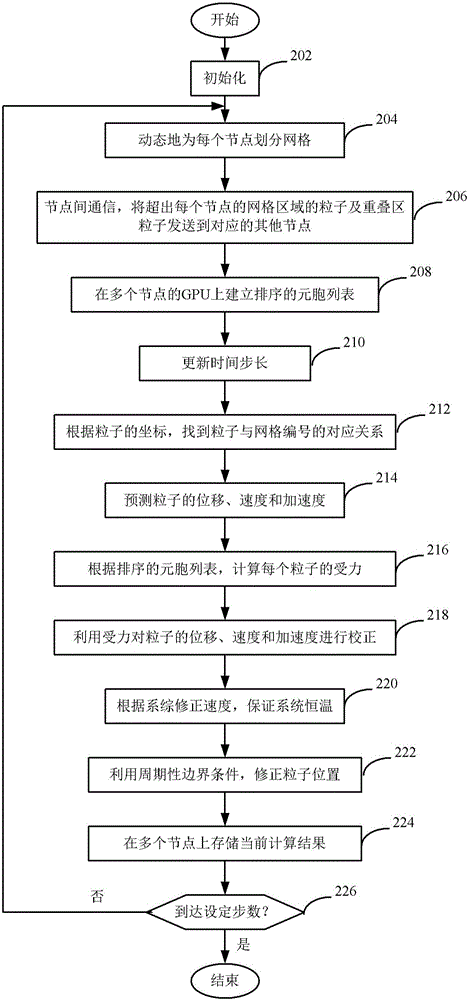
Multi-GPU molecular dynamics simulation method for structural material radiation damage
ActiveCN105787227AReduce energy costsReduce maintenance costsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALTime evolution
The invention discloses a multi-GPU molecular dynamics simulation method for structural material radiation damage. The method comprises the following steps: initializing; dynamically dividing grids for each node; performing inter-node communication; establishing a sorting cellular list on GPU; updating time step; finding the corresponding relationship between particle and grid number according to the coordinate of the particle; forecasting the displacement, speed and accelerated speed of the particle; calculating the stress of each particle; utilizing the stress to rectify the displacement, speed and accelerated speed of the particle; ensuring the constant temperature of the system according to the ensemble correcting speed; utilizing a periodic boundary condition to correct the position of the particle; storing a current calculation result; and iteratively executing the above steps till reaching preset step number. The method can be utilized to high-efficiently and conveniently simulate the material radiation damage process on larger spatial and temporal scale and to explain the long-time evolution law of the radiation damage at micro-scale.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Shale gas reservoir character prediction method
The invention relates to a shale gas reservoir character prediction method. In the method, scanning lines in the horizontal direction are formed through focusing by a reflective mirror in a mirror box with a synchrotron radiation light source. Vertical scanning is achieved through rotating vibration of the reflective mirror for obtaining micro-structure three-dimensional data of a shale gas occurrence porous sample. Three-dimension reconstruction is carried out to the obtained micro-structure three-dimensional data and porosity and an inherent permeability of a shale three-dimensional digital rock core are obtained through calculation in a manner of coupling between molecular dynamics and crystal lattice Boltzmann method and are expressed by mathematic expressions. In the invention a synchrotron radiation light and a computer technology are employed for researching the porosity and the inherent permeability of the shale three-dimensional digital rock core. The method is economic and environmental-protective, is easy to operate, can provide required important evaluation parameters for exploration and development of shale gas, can predict an adsorption / desorption principle of free gas and adsorbed gas in the shale gas, can be used for researching the porosity and the inherent permeability of the shale three-dimensional digital rock core, and provides technical support for development of the shale gas.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
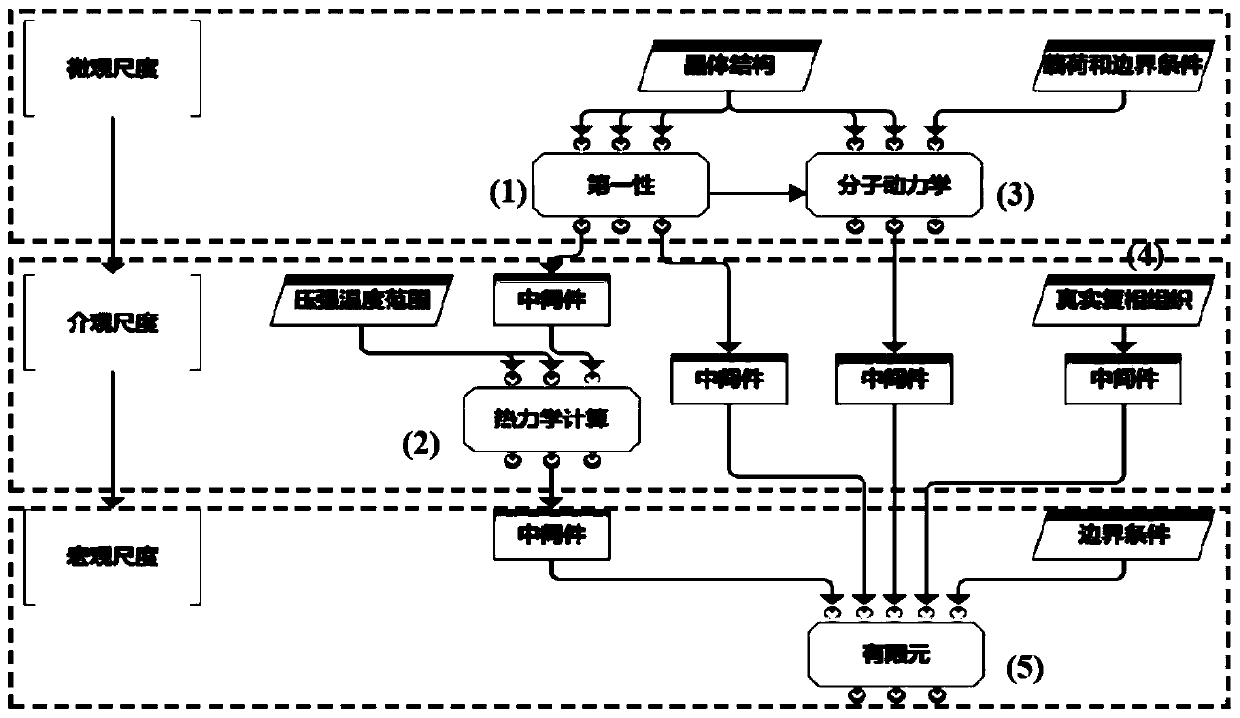
Multi-scale method for simulating mechanical behaviors of multiphase composite materials
PendingUS20210118530A1Plasticity of hard and brittle ceramic phase is negligibleWay accurateChemical property predictionDesign optimisation/simulationMicro structureMacroscopic scale
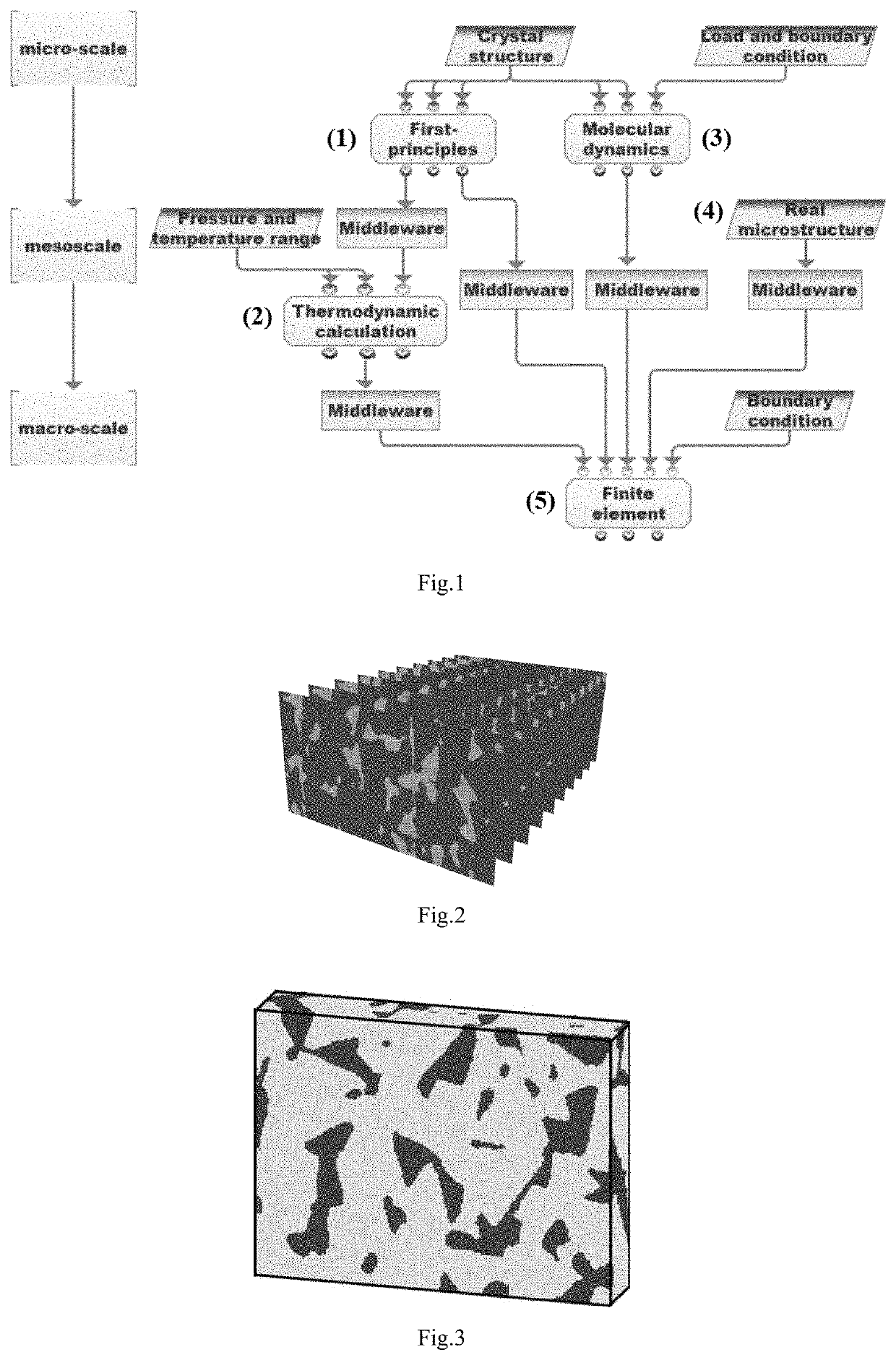
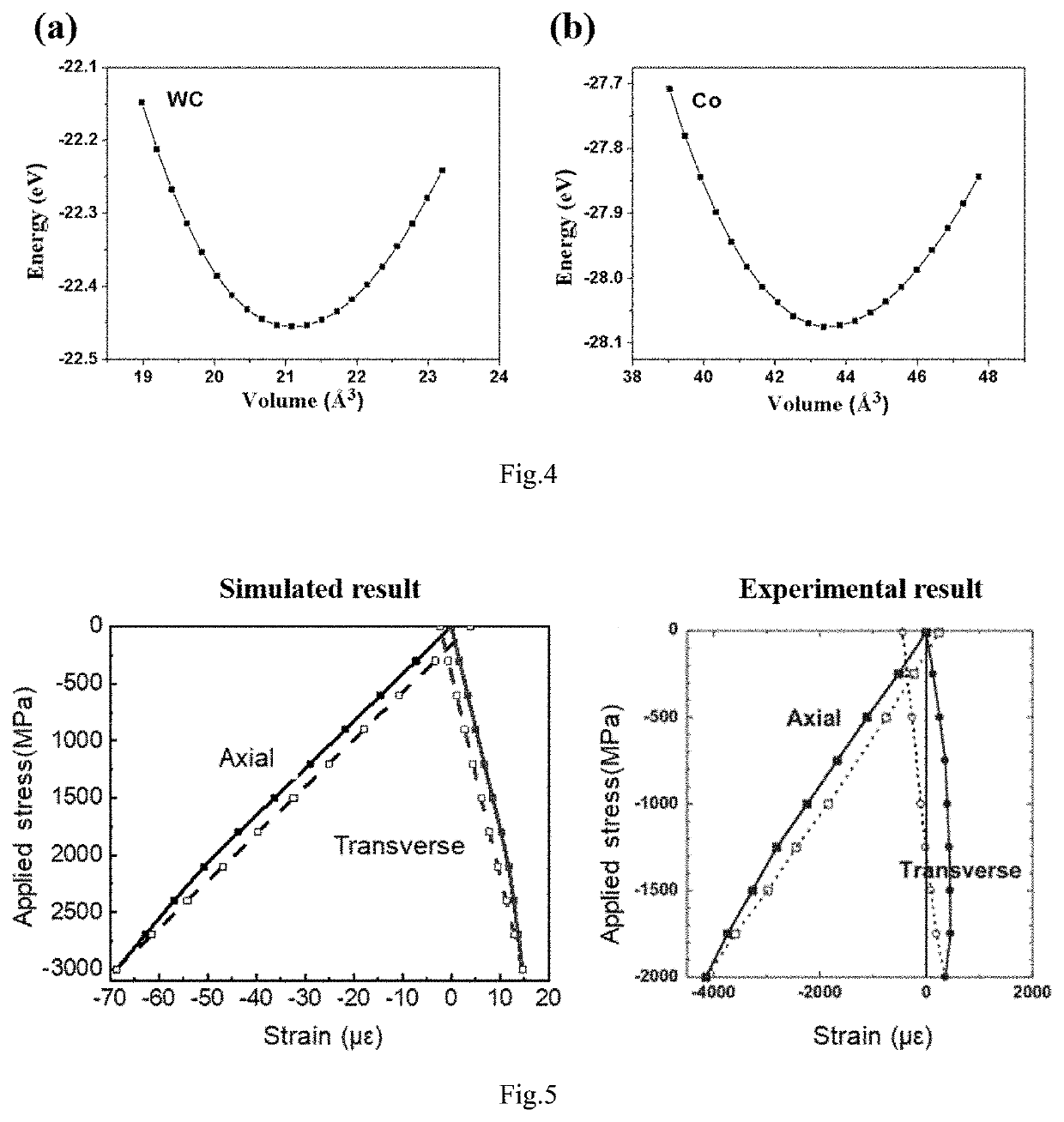
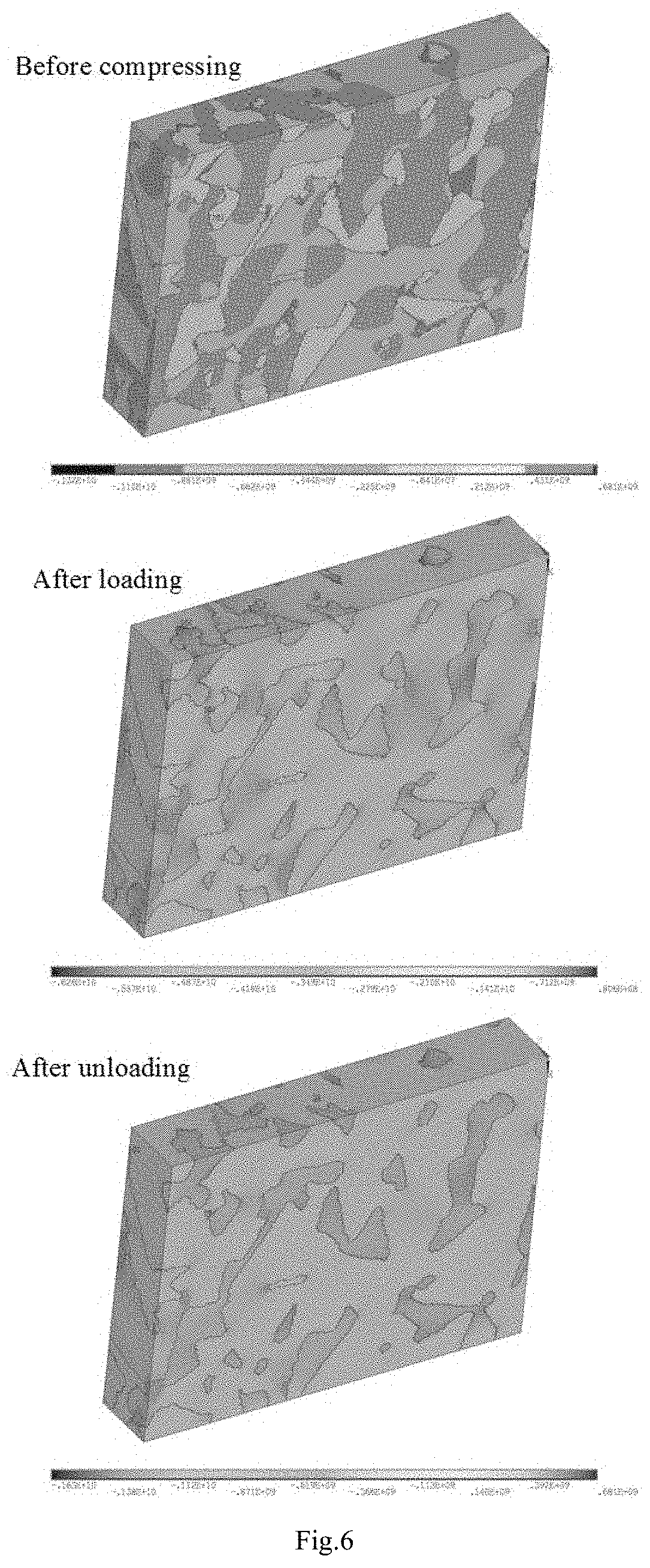
A computer simulation analysis method suitable for describing the mechanical behavior of multiphase composites based on the real microstructure of materials relates to a multidisciplinary field such as computational material science, simulation and high throughput calculation. Through the first-principles calculation under nano scale, the molecular dynamics simulation under micro scale, and the thermodynamic calculation under mesoscopic scale, various physical parameters needed for the finite element simulation under macro scale can be obtained, including the elastic and plastic physical parameters of each phase in the composite at different temperature and different grain sizes. Focused ion beam experiment and image processing are adopted to obtain real material microstructure. Through the parameter coupling and parameter transfer among the calculated results of various scales, combining the microstructure of the material, stress-strain relationship, stress distribution and its evolution law, plastic deformation and other mechanical behaviors of the multiphase composites under complex stress and different temperature can be simulated.
Owner:BEIJING UNIVERSITRY OF TECH
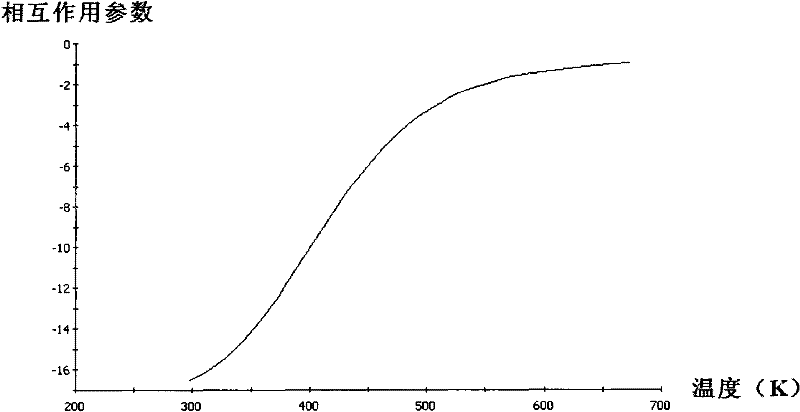
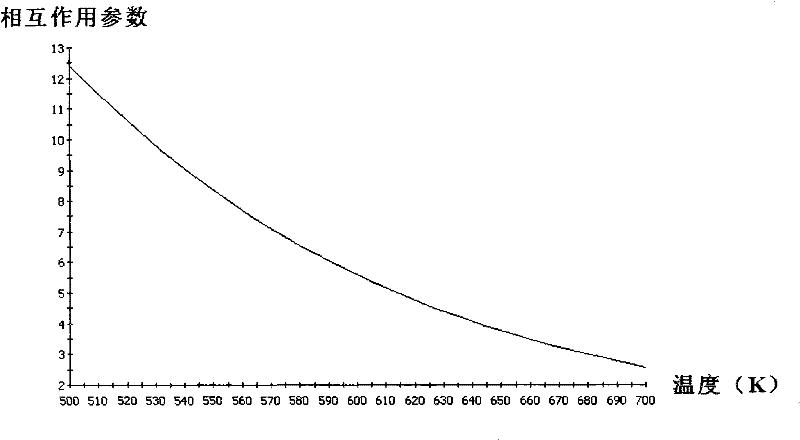
Method for simulating and calculating interaction parameters among chemical components by using computer
InactiveCN102446235ADetermine CompatibilityObvious superiorityComputational theoretical chemistrySpecial data processing applicationsEnergy minimizationSoftware engineering
The invention provides a method for simulating and calculating interaction parameters among chemical components by using a computer. The method comprises the steps of: (1) drawing the molecular formulas of two kinds of components to be simulated by using a Visualizer module of MS (Microsoft) software; (2) performing energy minimization treatment by using Minimize in a Discover module of the MS software; (3) performing structure optimization by using a Focite module of the MS software; (4) performing molecular dynamics structure optimization by using the Discover module of the MS software, analyzing by using analysis in the Discover module to search a conformation with minimal energy; (5) performing Blends computation by using a Blends module of the MS software to obtain a table file; and (6) performing analysis and calculation on the table file by using analysis in the Blends module of the MS software to obtain the interaction parameters of the two kinds of components in different temperature ranges. The method disclosed by the invention has a wide determination range, the interaction parameters of any two kinds of components among heavy oil components can be calculated, and thus, a large amount of experiment cost and labor cost are saved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Multi-scale simulation method for mechanical behaviors of multi-phase composite material
ActiveCN110210103AImprove continuityRealize simulationChemical property predictionDesign optimisation/simulationMacroscopic scaleFirst principle
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
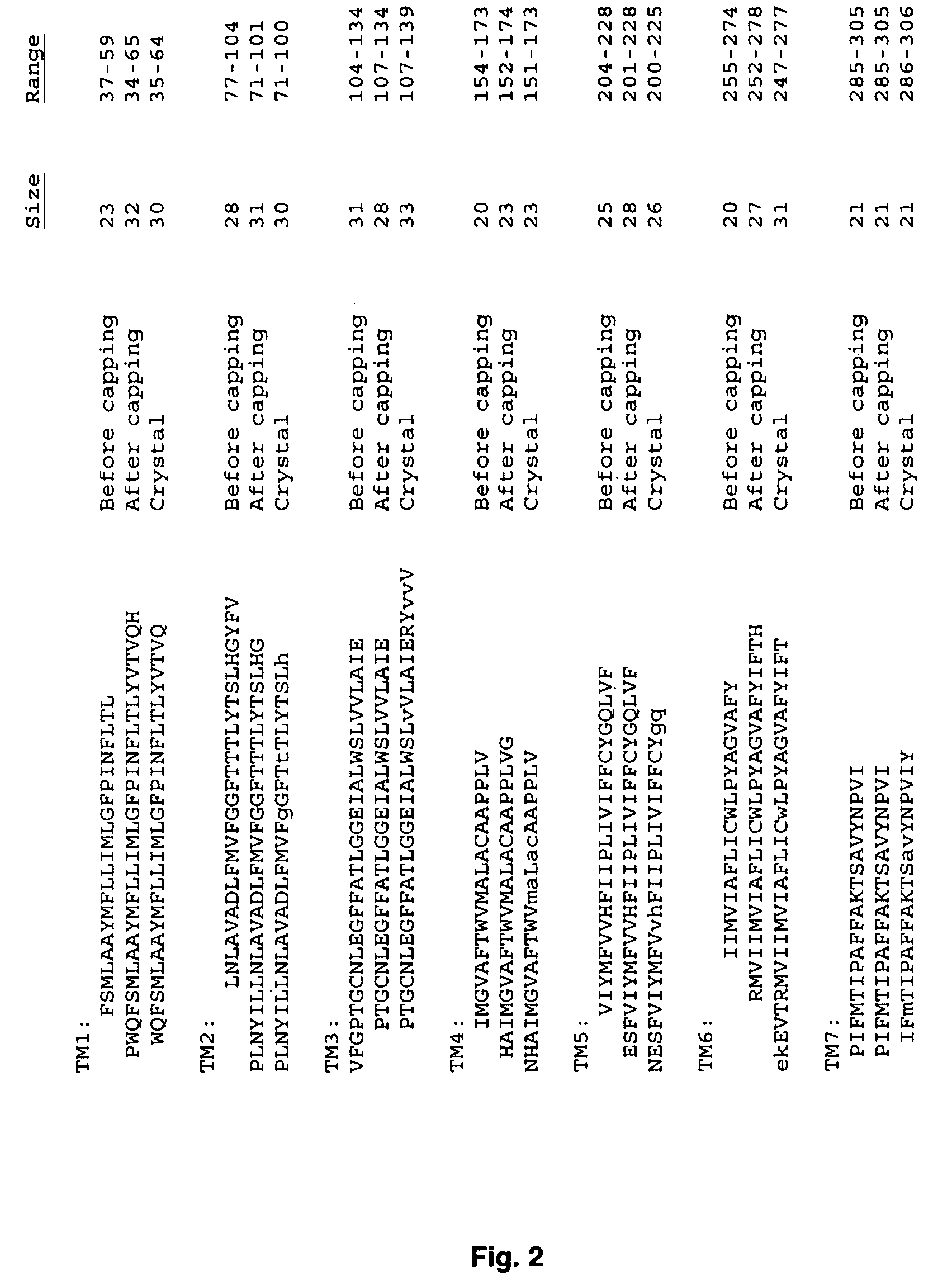
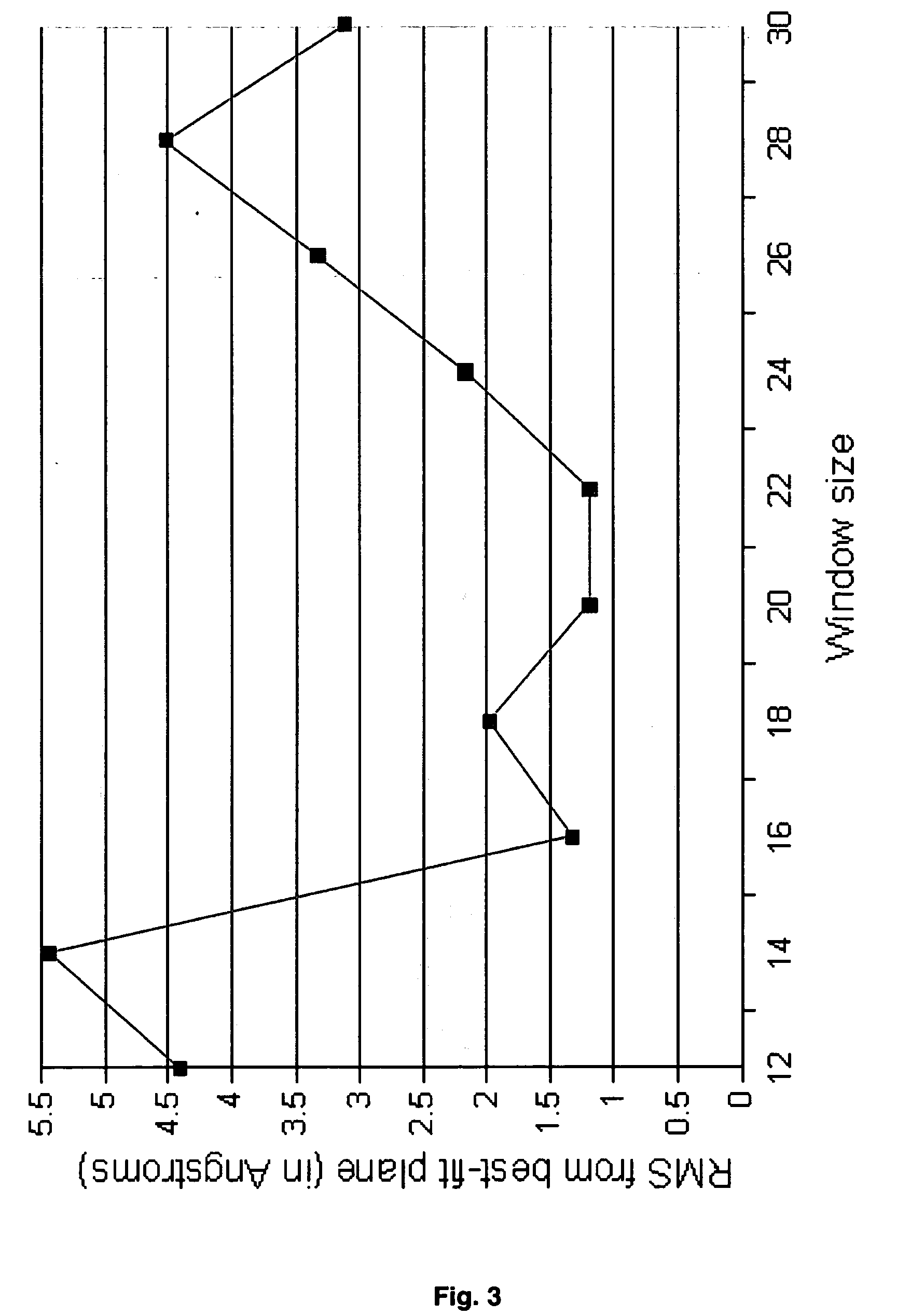
Systems and methods for predicting the structure and function of multipass transmembrane proteins
InactiveUS20050136481A1Fast and accurate procedureMinimizing energyBiological testingSequence analysisProtein structureMolecular modelling
The invention provides computer-implemented methods and apparatus implementing a hierarchical protocol using multiscale molecular dynamics and molecular modeling methods to predict the structure of transmembrane proteins such as G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR), and protein structural models generated according to the protocol. The protocol features a combination of coarse grain sampling methods, such as hydrophobicity analysis, followed by coarse grain molecular dynamics and atomic level molecular dynamics, including accurate continuum solvation. Also included are energy optimization to determine the rotation of helices in the (seven-helical) TM bundle, and optimization of the helix translations along their axes and rotational optimization using hydrophobic moment of the helices, to provide a fast and accurate procedure for predicting GPCR tertiary structure.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
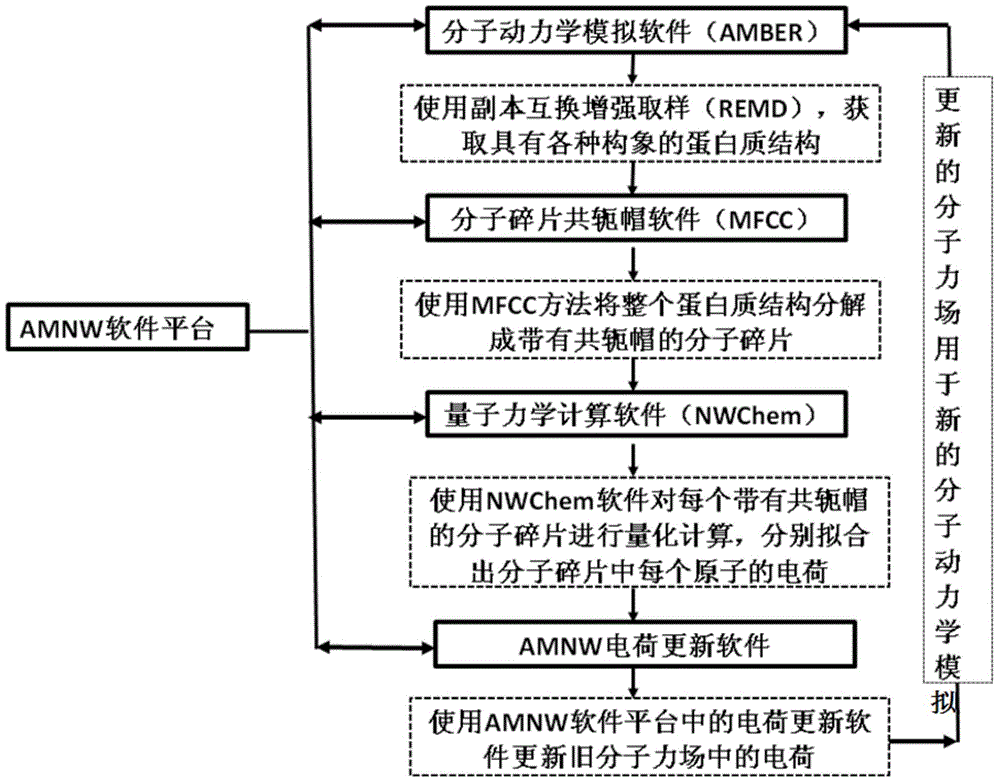
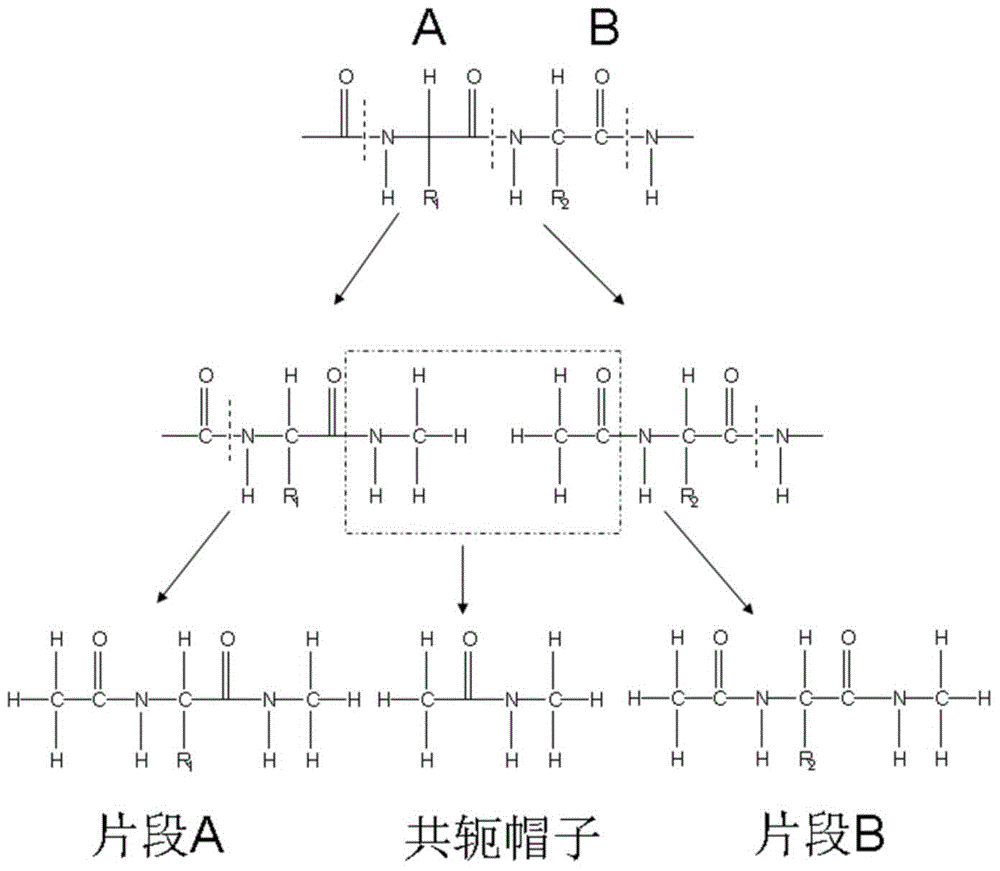
Protein folding parallel predicting method
InactiveCN105787292APolarization cannot be ignoredThe result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsProtein structureAmino acid
The invention relates to a protein folding parallel predicting method. The method includes the following steps: obtaining different protein structures through molecular dynamics simulation; setting different temperatures, and obtaining more protein structures with different conformations; partitioning the protein structures with different conformations through a conjugate cap molecule partitioning method, decomposing amino acids from proteins, and wearing a conjugate cap on each amino acid; calculating out the electrostatic potential of molecular fragments through quantum mechanics software to fit out the electric charge of each atom in each amino acid molecular fragment, and updating the electric charge of atoms in a molecule force field. To research protein folding, the scheme of considering a protein polarization effect and a copy interchange-based method are organically integrated, and then two difficult problems of atom interaction potential and a sampling technique in dynamics simulation can be overcome in order to achieve a good effect in protein folding simulation.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
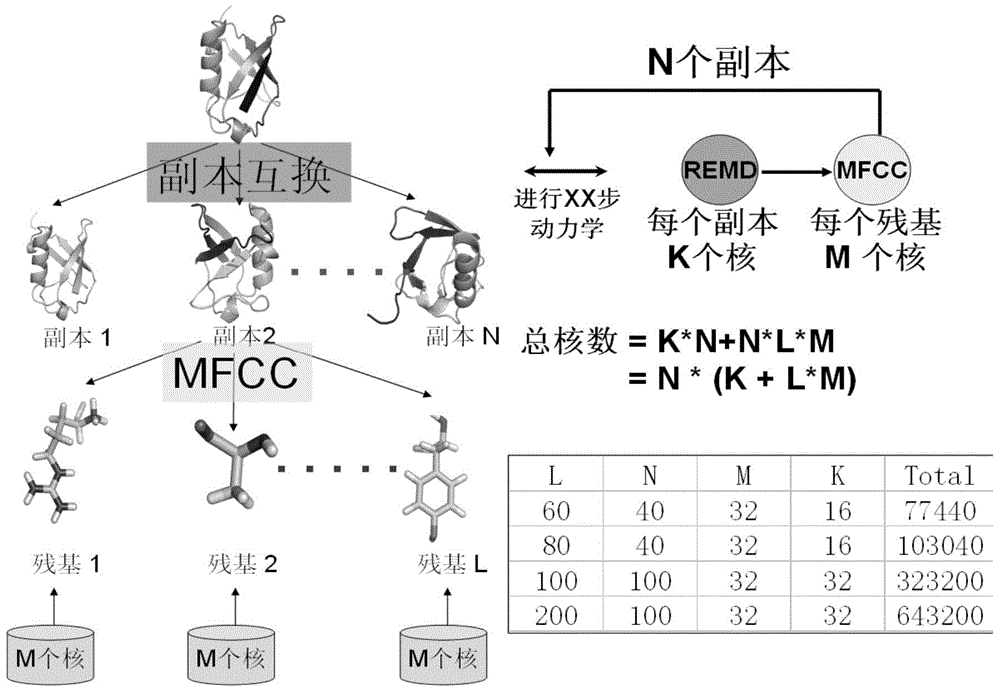
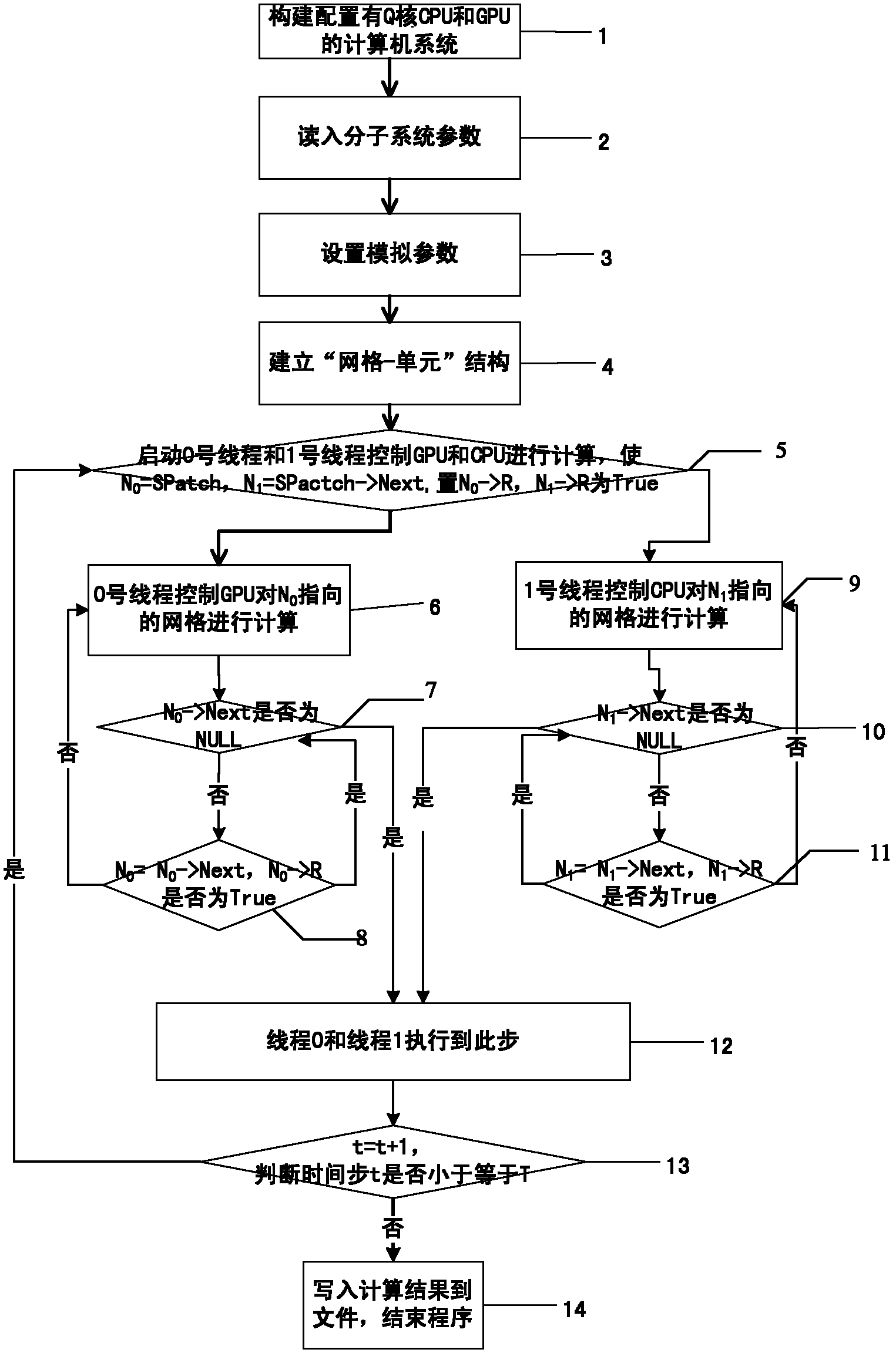
Molecular dynamics accelerating method based on CUP (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) cooperation
InactiveCN102411658AAvoid idle waiting situationsIncrease profitSpecial data processing applicationsFully developedComputerized system
The invention discloses a molecular dynamics accelerating method based on CUP (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) cooperation, which aims to provide a molecular dynamics accelerating method based on CUP and GPU cooperation at a lower cost. The technical scheme is executed by the following steps that: a ''grid-unit'' structure for storing molecular information is built on a to-be-simulated molecular system by a computer configured with a CPU and a GPU; the grids are dynamically applied and processed by the CPU and GPU; when the grids are processed, the CPU processes the grids by regarding cells as the unit; and the whole grid is processed by the GPU for simulating the molecular dynamics by efficient cooperation of CPU and GPU. The molecular dynamics accelerating method disclosed by the invention can balance loads among the CPU cores and avoid the phenomenon that the CPU and GPU are in idle and waiting state in statically distributing the calculating tasks. Therefore, the CPU and GPU can both fully develop the calculating properties. The use ratio of the whole computer system is improved and acceleration of molecular dynamics at lower cost is realized.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Three-dimensional nanometer-grade cutting simulation method based on molecular dynamics
InactiveCN101654222AEffective simulation of machining resultsRealistic display of nanoscale machining resultsNanostructure manufactureSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationDimensional modeling
The invention belongs to the field of nanometer-level ultra-precise processing, in particular to a three-dimensional nanometer-grade cutting simulation method based on molecular dynamics. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a three-dimensional model of a cutter and a working piece; (2) confirming a potential energy function; and (3) performing the three-dimensional nanometer-grade cutting simulation. The three-dimensional model is closer to a practical single-point diamond cutter in shape, thereby more effectively simulating the practical cutting process and more trulypresenting the nanometer-grade cutting mechanism.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
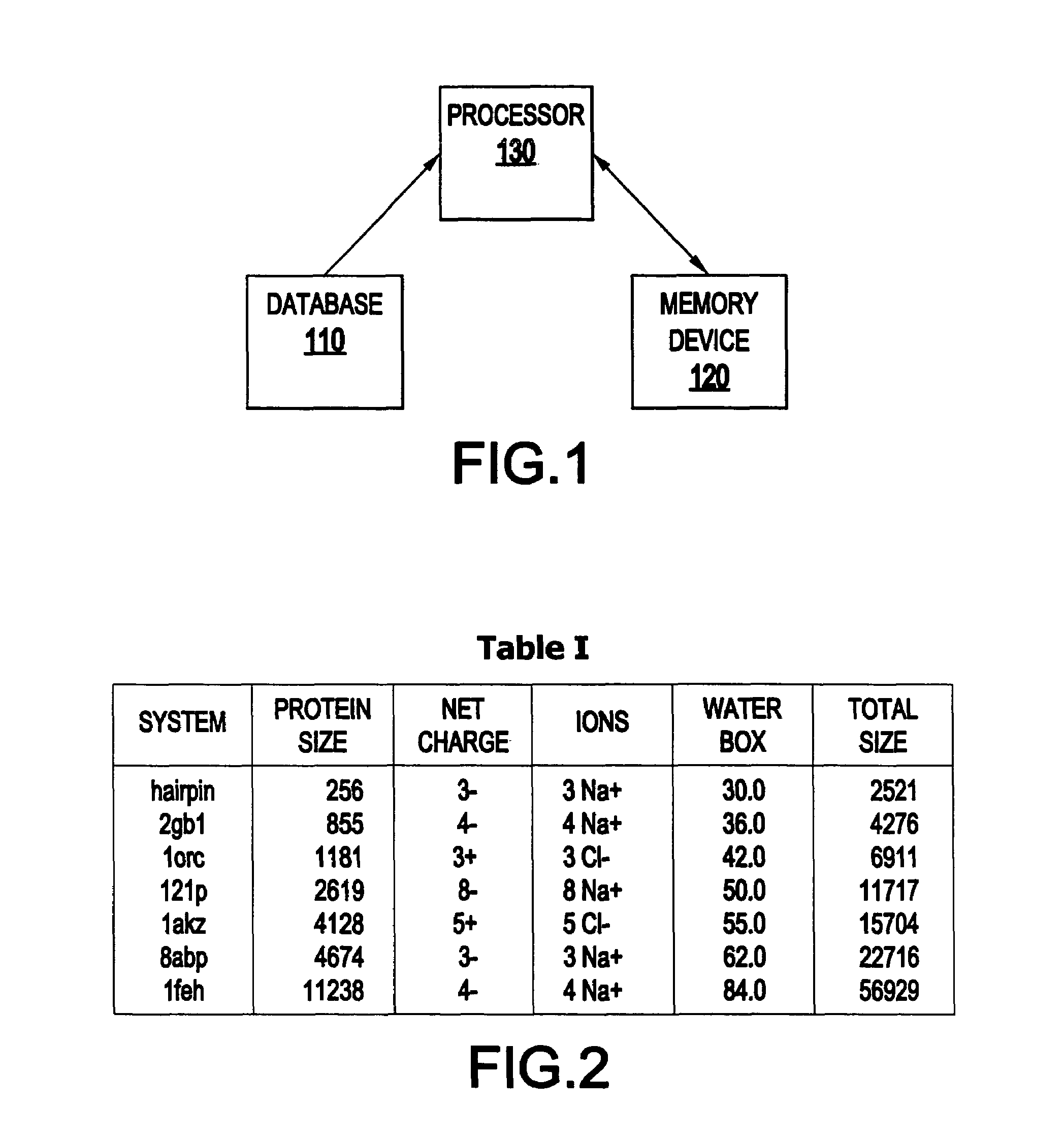
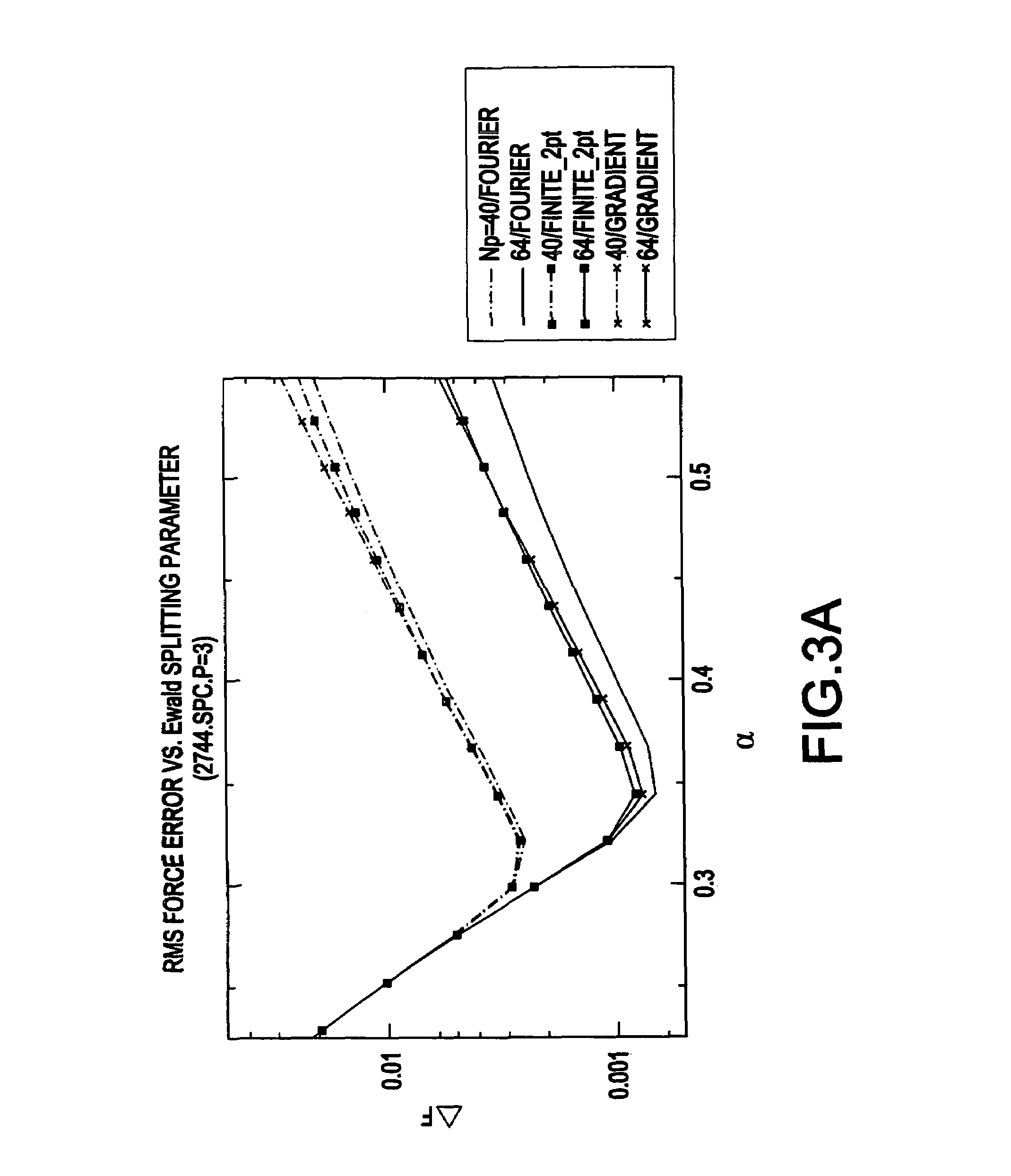
System and method for molecular dynamic simulation
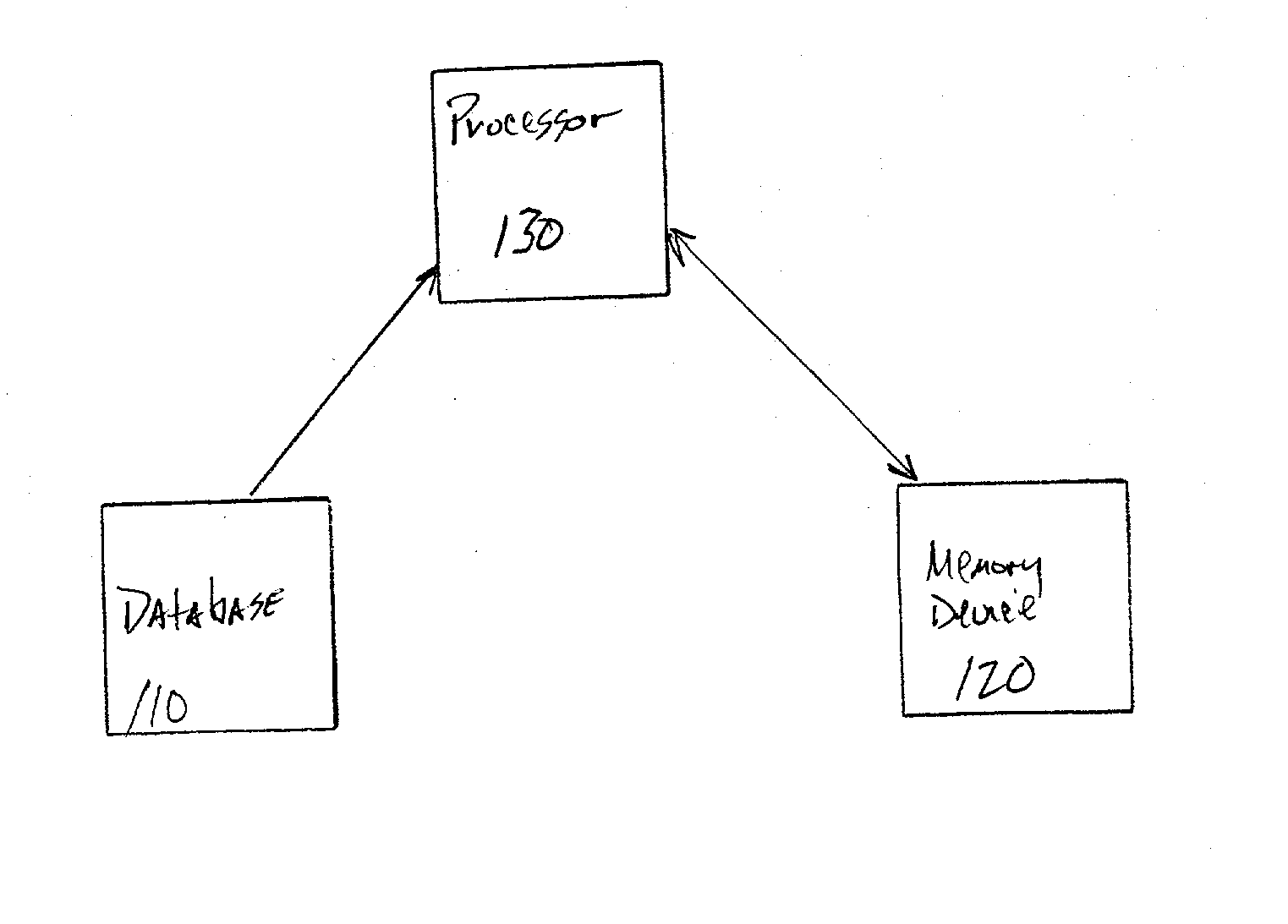
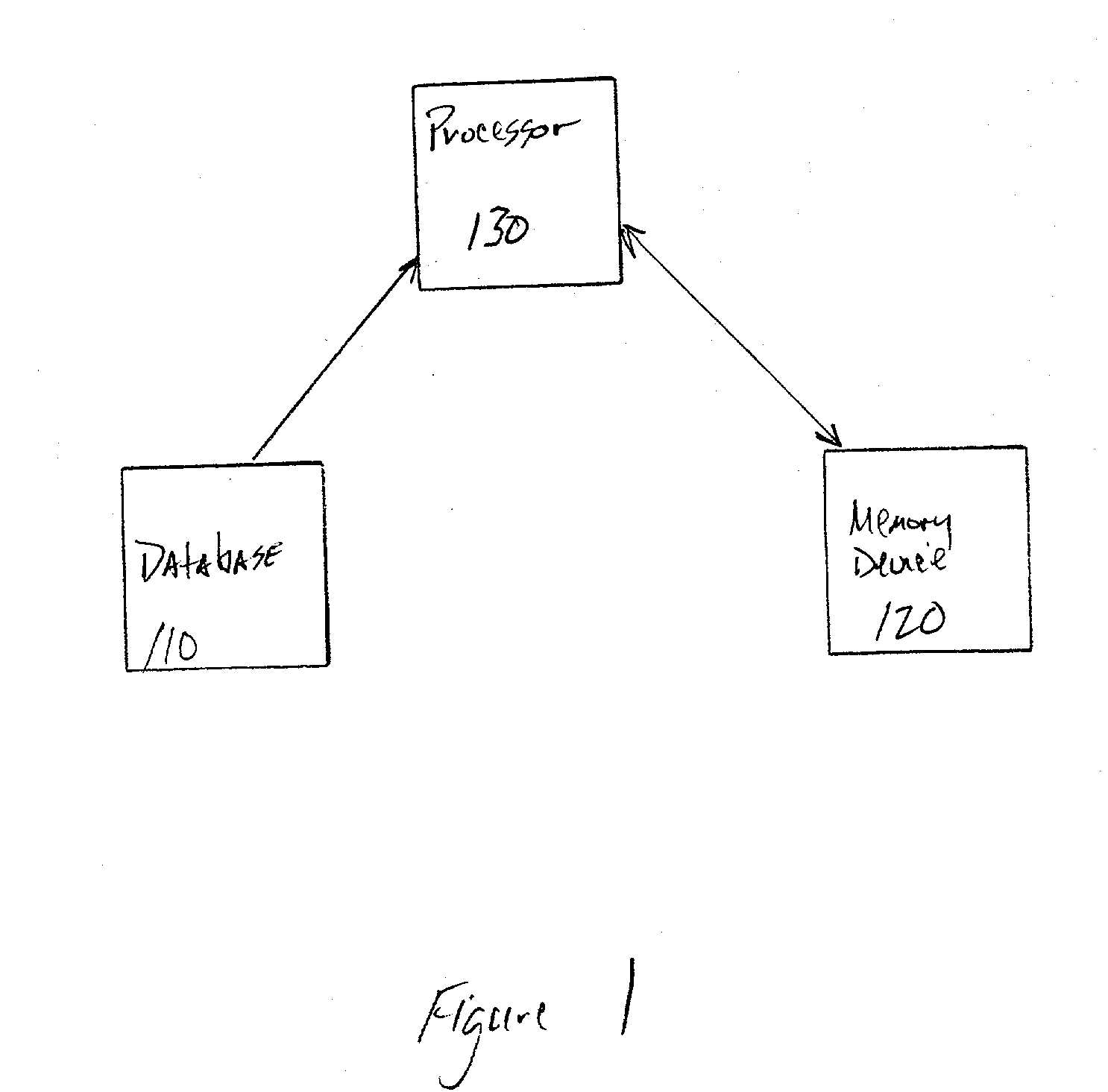
InactiveUS20030014231A1Analogue computers for chemical processesSpecial data processing applicationsProtein solutionProtein molecules
A system and method for molecular dynamic simulation includes a database for storing data pertaining to at least one biomolecular system, a memory device for storing instructions for performing at least one algorithm having an electrostatic interaction calculating function and a multiple time step function, and subdividing forces on a basis of distance over which the forces act, and a processor for processing the data by executing the instructions in order to propagate the biomolecular system from a first set of coordinates to a second set of coordinates. The system and method significantly speed up the molecular dynamics simulation of biomolecular systems in which there are long-range and short-range electrostatic interactions and in which there are fast and slow motions, and make practicable the simulation of large protein solutions and thus, can be used to simulate protein folding and the binding of substrates to protein molecules.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Two-dimensional fourier transform spectrometer
InactiveUS20100171952A1Reduce ambiguityReduce subjectivityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
The present invention relates to a system and methods for acquiring two-dimensional Fourier transform (2D FT) spectra. Overlap of a collinear pulse pair and probe induce a molecular response which is collected by spectral dispersion of the signal modulated probe beam. Simultaneous collection of the molecular response, pulse timing and characteristics permit real time phasing and rapid acquisition of spectra. Full spectra are acquired as a function of pulse pair timings and numerically transformed to achieve the full frequency-frequency spectrum. This method demonstrates the ability to acquire information on molecular dynamics, couplings and structure in a simple apparatus. Multi-dimensional methods can be used for diagnostic and analytical measurements in the biological, biomedical, and chemical fields.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
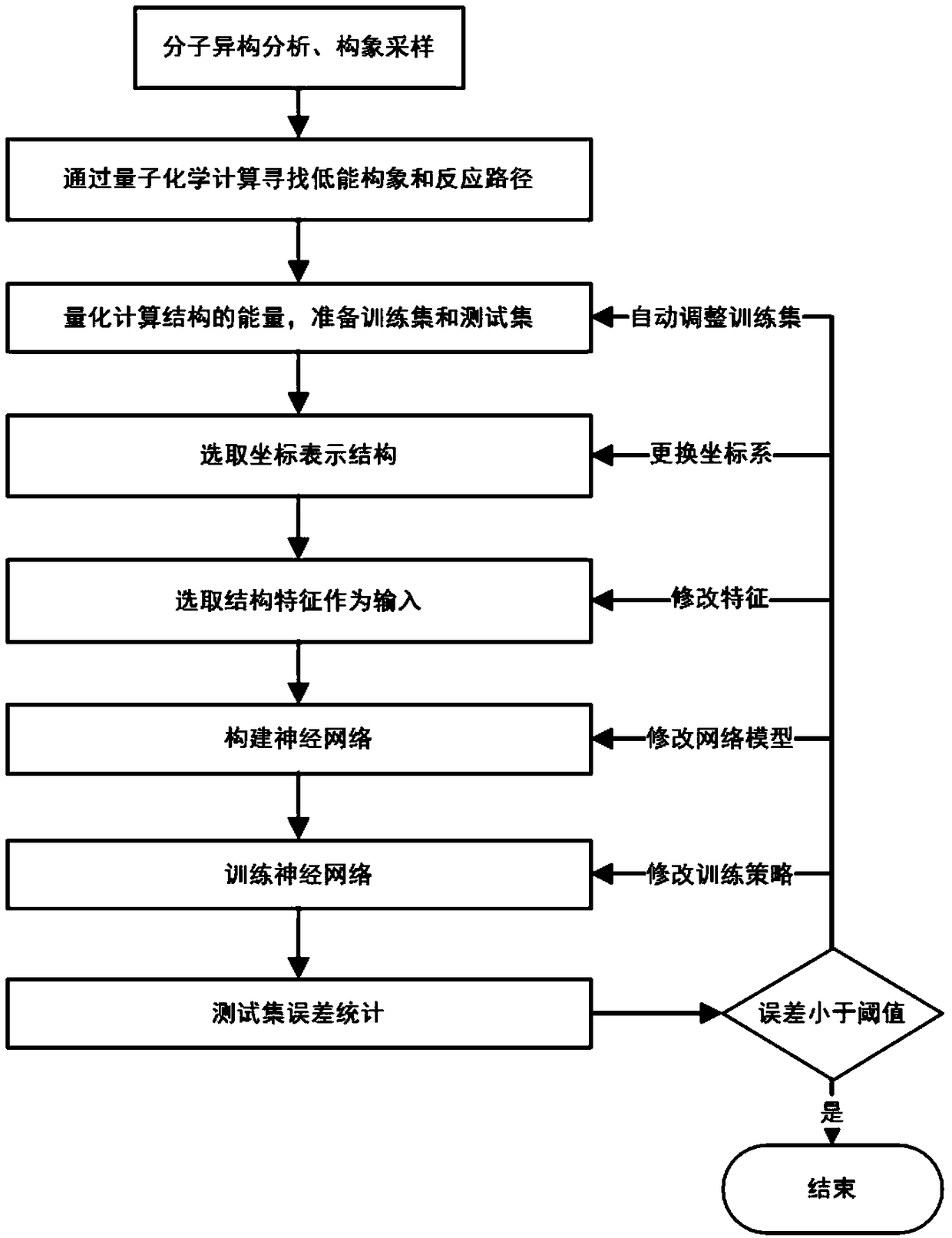
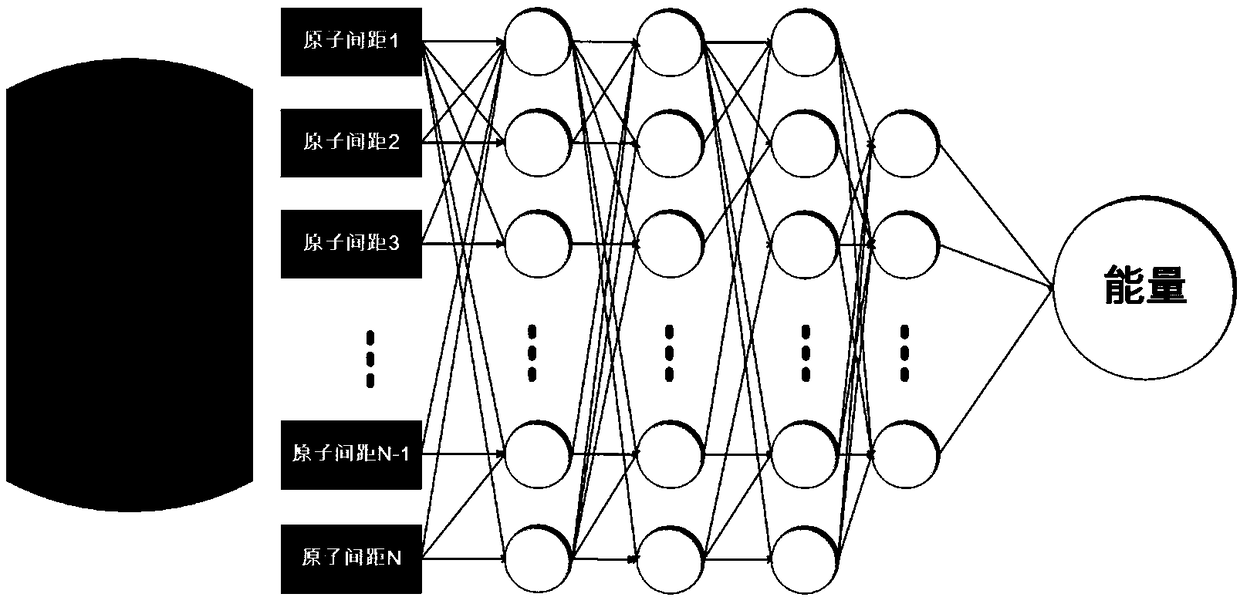
Molecular structure and chemical reaction energy function building method based on neural network
ActiveCN108804869AHigh precisionImprove scalabilitySpecial data processing applicationsQuantum chemistryChemical reaction
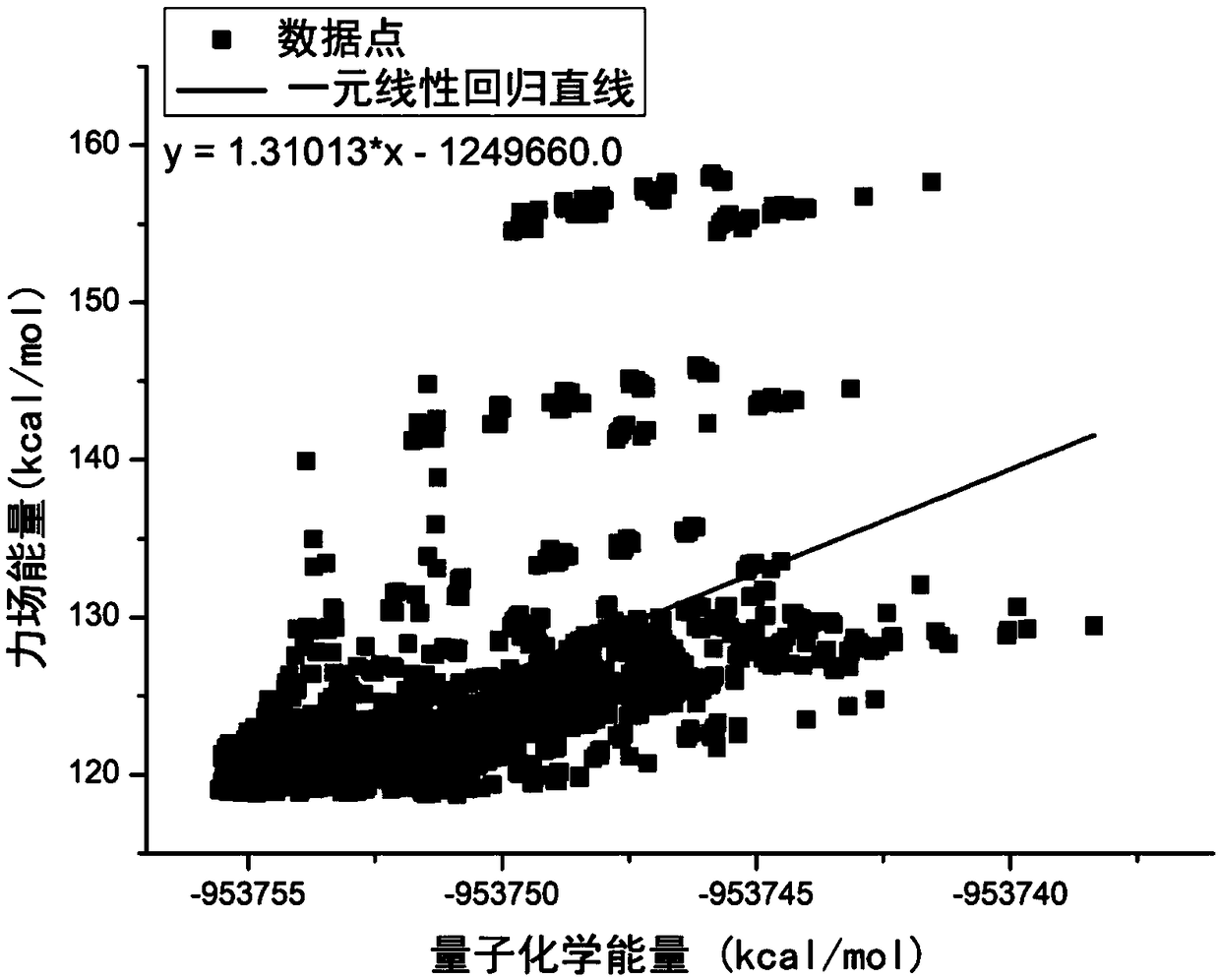
The invention belongs to the technical field of quantum chemistry, and particularly relates to a molecular structure and chemical reaction energy function building method based on a neural network. The method comprises the steps of performing sampling on each degree of freedom of a molecular or chemical reaction; searching for a low-energy conformation structure through quantitative calculation; performing energy calculation on the structure, and preparing a training set and a test set; selecting a proper coordinate representation structure; according to different coordinates, constructing different features to describe the structure; selecting a proper neural network; selecting a proper method to train the neural network; after the training is completed, performing error statistics on thetest set, and when an error is smaller than 1.0 kcal / mol, ending the training; and if the error is greater than 1.0 kcal / mol, following a re-searching model. The precision of obtained conformation energy, reaction energy and the like is higher; the method can be widely applied to the quantum dynamics and molecular dynamics processes; and not only a single molecule conformation but also the chemical reaction including intramolecular or intermolecular bond breaking and generating can be simulated.
Owner:SHENZHEN JINGTAI TECH CO LTD +1
Thermally stable lipase as well as preparation method and applications thereof
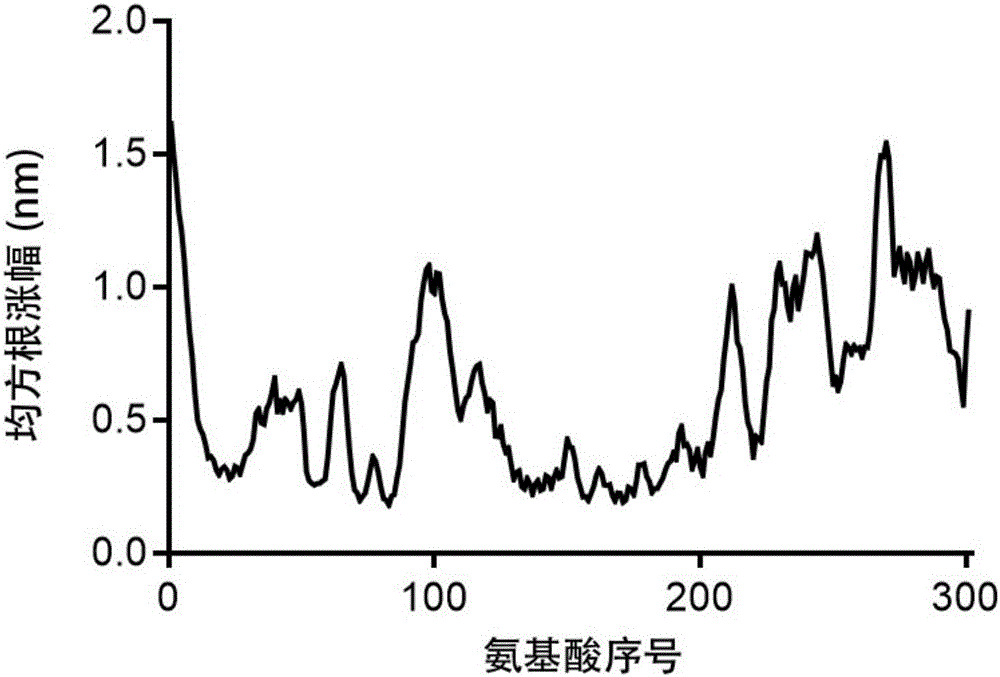
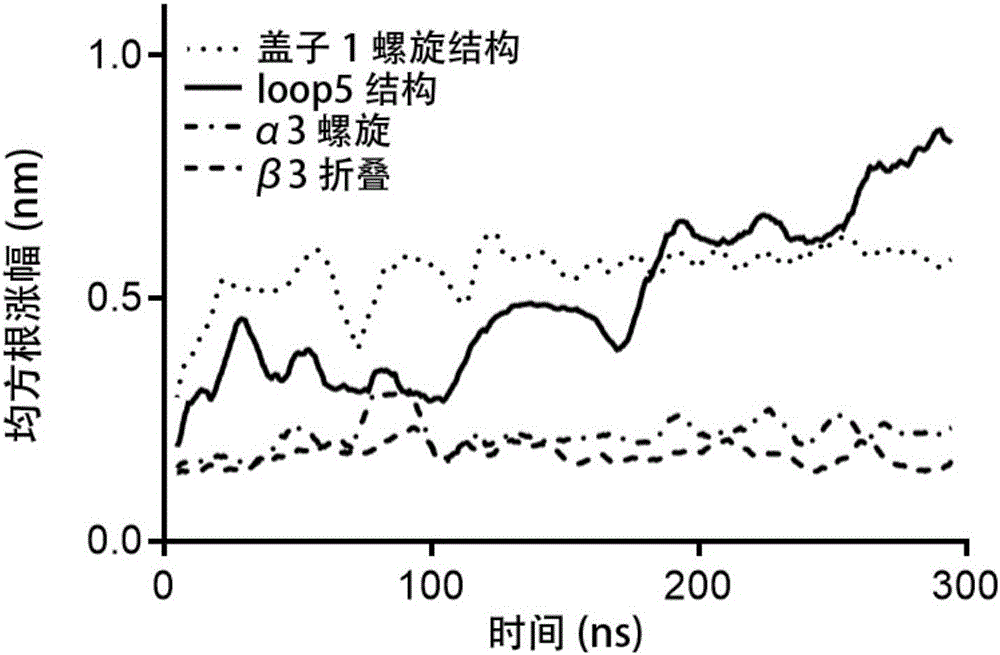
ActiveCN105950585ASave manpower and material resourcesImprove accuracyHydrolasesFermentationHalf-lifeAmino acid
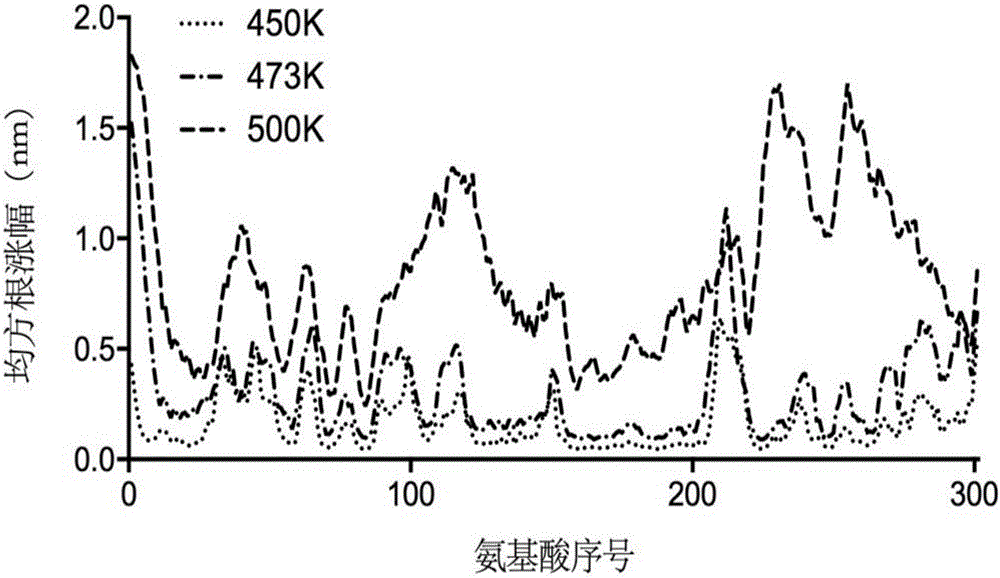
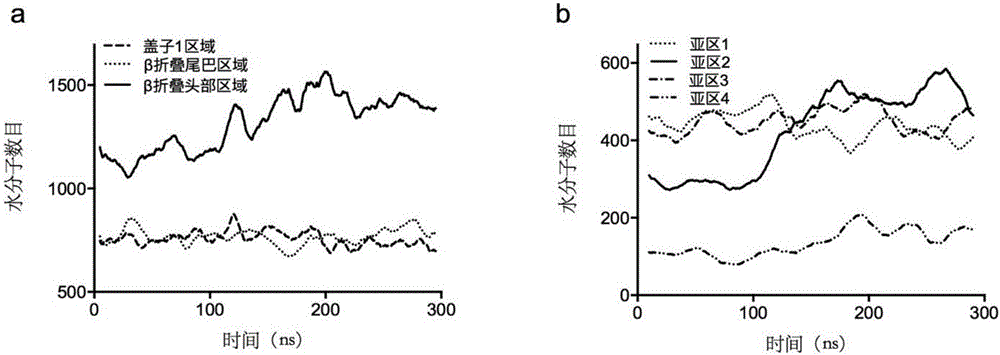
The invention discloses a thermally stable lipase as well as a preparation method and applications of the thermally stable lipase. The lipase is S2-210 lipase with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, S8-214 lipase with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2, S14-216 lipase with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.3, or S191-241 lipase with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.4. According to the thermally stable lipase and the preparation method thereof, the unfolding process of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase 2 is stimulated through the long-time high-temperature molecular dynamics simulation, and the main area of protein unfolding and the critical steps for forming the wet molten-globule state are analyzed, so that the key site for transforming the kinetic stability are effectively screened. The thermally stable lipase is heat-resisting, is long in half-life period, and is particularly suitable for being applied in the industry.
Owner:GUANGDONG RUISHENG TECH GRP CO LTD
Method for calculating force between protein and DNA by computer simulation
InactiveCN101122933AObvious superiorityWide range of measuring objectsSpecial data processing applicationsAnalysis dataResearch Object
The invention discloses a method of computing the interactive force between proteins and DNA through computer simulating. In the method, the NAMD_2.6 computing software and the VMD-1.8.6 analysis software are used for molecule dynamics simulation: firstly the protein structure in the PDB database is made into an appropriate research system, then the system is treated for energy minimization, and when the system is heated to the preset temperature, the system is treated for multi-stage balancing; then molecule dynamics simulation is carried out for the system, the target research objects in the system are marked, SMD simulation is carried out for the system, and finally data are processed and analyzed to acquire change of the interactive force between proteins and DNA, and to calculate the maximum interactive force. The method is characterized by wide range of test objects, easy preparation of experimental material, low requirements to devices, high utilization rate, easy and widely application in the fields of life science, physical chemistry and medicine related to molecule identification and gene representing behaviors.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
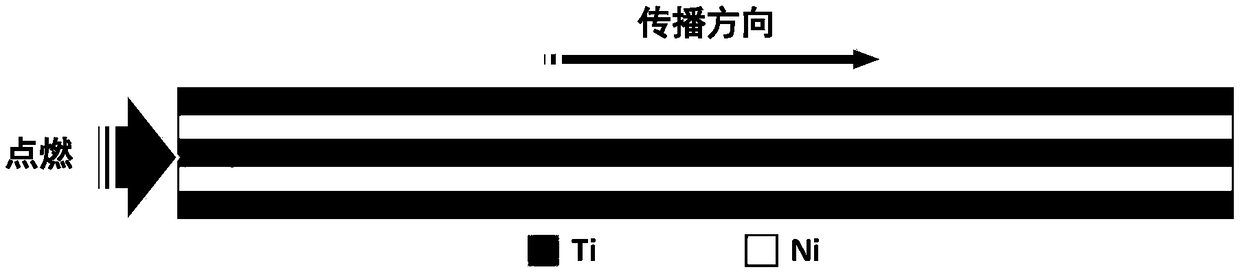
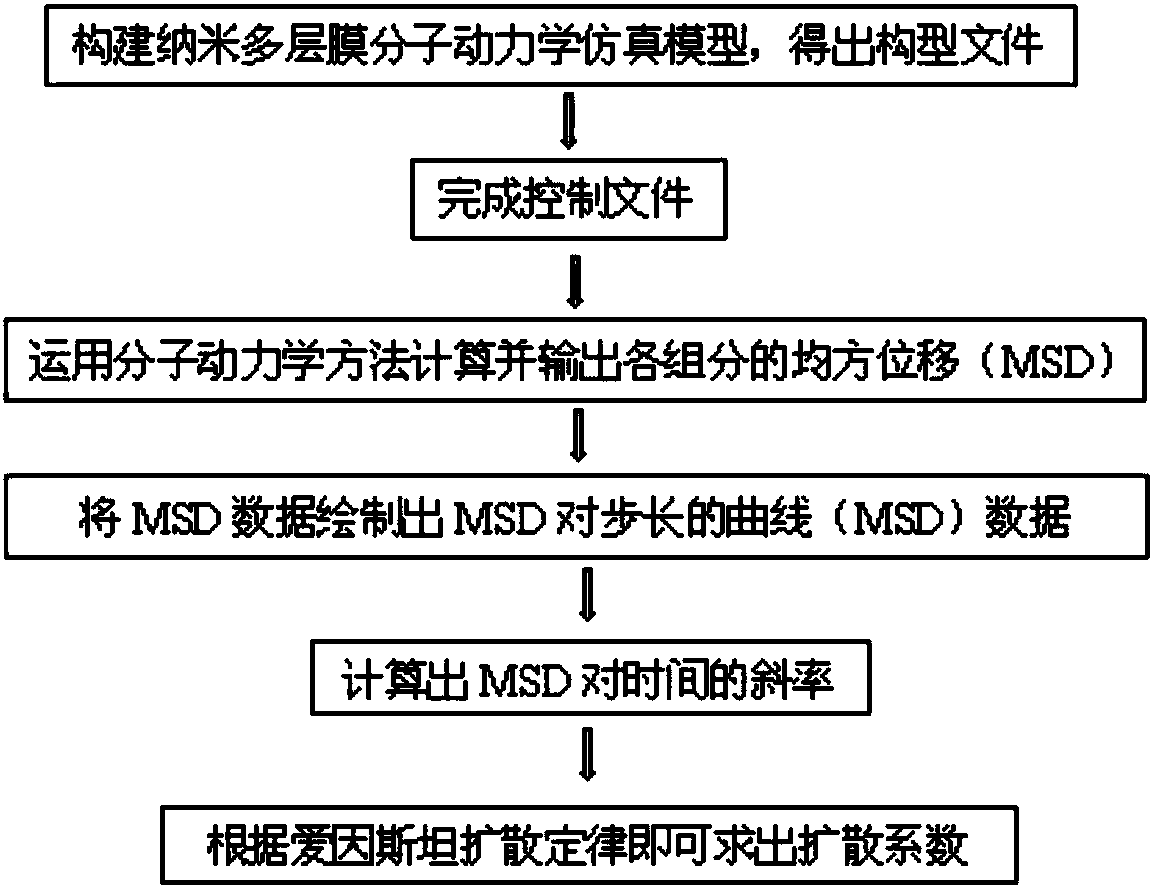
Molecular-dynamics simulation method of predicting diffusion coefficient of combustion process of nano-multilayer film
InactiveCN108491569APlay a guiding roleDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDiffusionMean square
The invention provides a molecular-dynamics simulation method of predicting a diffusion coefficient of a combustion process of a nano-multilayer film. The method comprises the following steps: 1) constructing a nano-multilayer-film molecular-dynamics simulation model, and exporting a configuration file; 2) completing a control file; 3) using a molecular-dynamics method to calculate and output mean-square-displacement (MSD) data of each component; 4), drawing the MSD data as a curve of MSD versus step length; 5) calculating a slope of the MSD versus time; and 6), obtaining the diffusion coefficient by solving according to Einstein's law. According to the method, solving is carried out for the diffusion coefficient of each component of the nano-multilayer film, the problem that real-time atomic diffusion behaviors of the self-propagating reaction combustion process of the nano-multilayer film cannot be tested and analyzed by experiment means is solved, difficulty of program compilation is significantly reduced, atomic behaviors and processes of nano-connection are more accurately understood, and a reference is provided for structure design of nano-multilayer films through study on diffusion coefficients and diffusion behaviors of the multilayer films of different atomic proportions under different temperatures.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
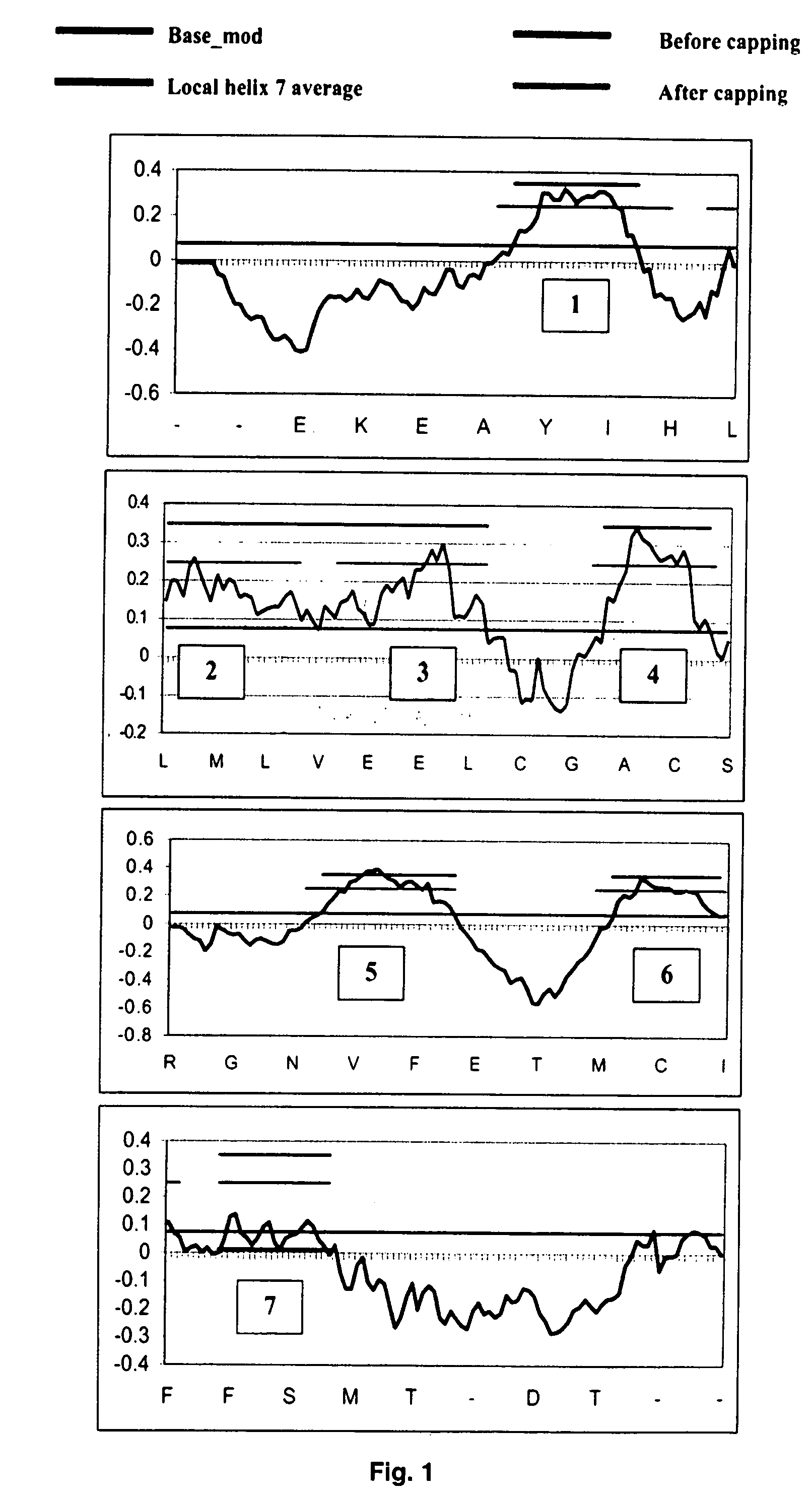
Antibody humanization transformation method
ActiveCN103145834AStable average conformationHigh affinityImmunoglobulinsSpecial data processing applicationsEpitopeSequence analysis
The invention discloses an antibody humanization transformation method. The antibody humanization transformation method comprises the following steps: analyzing an antibody gene sequence; starting antibody Fab isogeny modeling and optimization; ascertaining humanization mutation locus by epitope scanning, simulating virtual mutation molecular dynamics, and confirming key amino acid; the antibody humanization transformation method designs reasonable humanization antibody through the analysis, and further uses the epitope to scan and authenticate antibody humanization degree; and finally authenticates the appetency of the humanization antibody in a biological experiment. The antibody humanization transformation method has the advantages that the antibody humanization transformation method can be used for humanization transformation of mouse sources or source antibodies of other animals, only needs to provide the gene sequence of the antibody Fab, and is not dependent on information of antigen epitope. The humanization antibody designed by the antibody humanization transformation method has higher appetency maintenance, higher humanization degree, is capable of solving a contradiction between antibody appetency and humanization degree to a maximum degree.
Owner:ZHUHAI TRINOMAB BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Heatproof mutation lipase with high catalytic activity as well as preparation method and application of heatproof mutation lipase
ActiveCN106047838ASave manpower and material resourcesQuick filterHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesThermal stabilityMolecular dynamics
The invention discloses heatproof mutation lipase with high catalytic activity as well as a preparation method and an application of the heatproof mutation lipase. The lipase is S118-177 mutation lipase with an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and S122-196 mutation lipase with an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The key unfolding subregion of a lipase lid 1 region is analyzed through long-time high-temperature molecular dynamic simulation of the unfolding process of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase 2, and key mutation sites are effectively screened. The mutation lipase obtained through actual measurement and screening has high heat stability and catalytic activity and is particularly suitable for being applied industrially.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Effect-directed target/non-target androgen disruptor identification method
ActiveCN105891365AReduce complexityImprove accuracyComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementToxicantEnrichment methods
The invention discloses an effect-directed target / non-target identification method for androgen disruptors in complicated environment samples. The effect-directed target / non-target identification method includes the steps of pretreatment and primary separation of the samples, androgen activity test, high-throughput separation and preparation of toxic substances, active component scanning based on high-performance liquid chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry, target androgen disruptor screening and non-target androgen disruptor identification and toxicant confirmation by combining mass spectrum, chromatography and toxic characteristics. The effect-directed target / non-target identification method has the advantages that an SPE (solid phase extraction) column and a preparation and separation series method are used for separation, a high-throughput separation and concentration method is optimized by DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide) serving as a protective agent, target identification of key toxicants is achieved through a target database, and mass spectral characteristic identification based on a high-performance liquid chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry library, chromatographic characteristic identification based on retention time and compound physico-chemical property and toxic characteristic identification based on a molecular dynamics simulation technology are conducted to achieve non-target identification / toxicant confirmation of the key androgen disruptors.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Small-molecular clean fracturing fluid and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105368436ACause blockageCompletely broken glueFluid removalDrilling compositionInorganic saltsFracturing fluid
The invention provides a small-molecular clean fracturing fluid and a preparation method and an application thereof. The fracturing fluid includes a thickening agent, an auxiliary agent, a co-solvent, an activator, an inorganic salt and water, wherein the thickening agent, the auxiliary agent, the co-solvent, the activator and the inorganic salt are each composed of a substance with the molecular weight of less than 500 and the molecular dynamics diameter of less than 60 nm, and the mass ratio of the thickening agent to the auxiliary agent to the co-solvent to the activator to the inorganic salt to water is (0.8-3.5) to (0.01-0.05) to (1.0-3.0) to (0.4-1.5) to (0.1-0.8) to 100. The invention also provides a preparation method for the fracturing fluid. The method comprises the steps: dissolving the inorganic salt in water; mixing the thickening agent, the auxiliary agent and the co-solvent; and adding the thickening agent solution into the salt solution, cooling the mixed solution to room temperature, adding the activator to the mixed solution, aging at room temperature, and thus obtaining the small-molecular clean fracturing fluid. The fracturing fluid provided by the invention has the advantages of wide range of temperature resistance, good shearing property, low cost and simple preparation.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Molecular dynamics-based asphaltene and silicon dioxide interface energy evaluating method
InactiveCN105468840AEasy to implementImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsRoad surfaceSilicon dioxide
The invention relates to a molecular dynamics-based asphaltene and silicon dioxide interface energy evaluating method. The method comprises the steps of building a silicon dioxide supercell model by utilizing Materials Studio software, combining with an asphaltene polymer model to build an asphaltene / silicon dioxide interface model, calculating the interface energy after the system reaches balance by utilizing molecular dynamics and evaluating the adhesion between different aggregates and different asphalt interfaces through comparing the size of the interface energy. By means of the asphaltene and silicon dioxide interface energy obtained through the method disclosed in the invention, the adhesion between the aggregates and the asphalt interfaces can be reflected to a certain extent, the adhesion between the aggregates and the asphalts can further be evaluated, thereby providing help for the selection of asphalt pavement materials and reducing the pavement diseases such as wheel ruts, cracks, water damage and the like to a certain extent through the good adhesion.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
System and method for molecular dynamic simulation
InactiveUS7096167B2Doubles speedStep of become largeComputation using non-denominational number representationBiological testingProtein solutionProtein molecules
A system and method for molecular dynamic simulation includes a database for storing data pertaining to at least one biomolecular system, a memory device for storing instructions for performing at least one algorithm having an electrostatic interaction calculating function and a multiple time step function, and subdividing forces on a basis of distance over which the forces act, and a processor for processing the data by executing the instructions in order to propagate the biomolecular system from a first set of coordinates to a second set of coordinates. The system and method significantly speed up the molecular dynamics simulation of biomolecular systems in which there are long-range and short-range electrostatic interactions and in which there are fast and slow motions, and make practicable the simulation of large protein solutions and thus, can be used to simulate protein folding and the binding of substrates to protein molecules.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Method for researching diffusion properties of atoms in glass system based on molecular dynamics simulation
ActiveCN110021380AReduce experiment costImprove theoretical guidanceChemical property predictionComputational theoretical chemistryMean squareBox model
The invention discloses a method for researching diffusion properties of atoms in a glass system based on molecular dynamics simulation. The method comprises the following steps that a box model of amorphous glass is built; the glass box model is geometrically optimized; molecular dynamics calculation is conducted on the geometrically optimized glass box model, and comprises that 1) high temperature relaxation is conducted, 2) the temperature is lowered from high temperature to low temperature continuously, 3) low temperature relaxation is conducted, and conformation track files under different temperature are output, the conformation track files output under different temperature are subjected to statistical analysis, mean square displacement (MSD) distribution of different atoms is output, and the diffusion coefficients of different atoms are obtained according to Einstein's law. The method adopts a molecular dynamic method to carry out statistical analysis on glass structures underdifferent temperature, solves the problem that the diffusion coefficients of the atoms of the glass under different temperature cannot be tested and analyzed by an experimental means through combination with the Einstein's law, is beneficial for more precise understanding of the diffusion behavior of the atoms in a glass forming process, and provides reference for analyzing and researching the microstructure of the glass.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
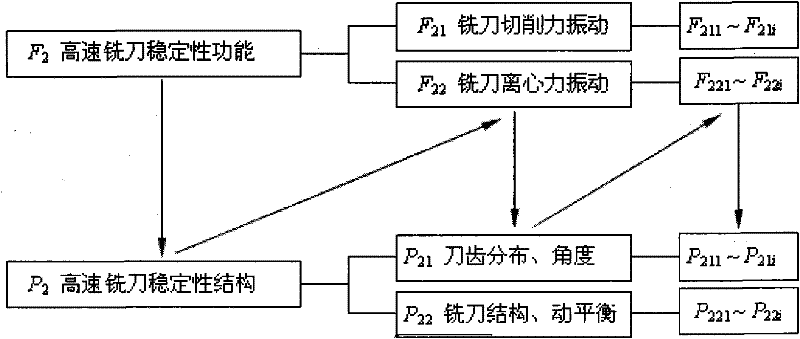
Trans-scale design method of high-speed milling cutter and milling cutter
InactiveCN102126043ASafe cuttingCutting stabilityMilling cuttersDesign matrixGrey correlation analysis
The invention discloses a trans-scale design method of a high-speed milling cutter and the milling cutter. At present, the research of the internal relation among a microstructure, a macrostructure and performance of cutter materials is absent, and scientific evidences of the design and the development of the novel high-speed milling cutter are absent. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) constructing a high-speed milling cutter safety decline behavioral characteristic model; (2) developing the high-speed milling cutter by using a high-speed milling cutter safety stability design model; (3) establishing a high-speed milling cutter safety decline behavioral characteristic model design matrix by a grey correlation analysis method to characterize the relation between milling cutter design parameters and safety decline; (4) establishing a high-speed milling cutter mesoscopic level safety model by a grey cluster analysis method; and (5) researching macroscopic and mesoscopic mechanical characteristics of a high-speed milling cutter component under the condition of presetting an external force boundary, and realizing force connection-based high-speed milling cutter trans-scale correlation through continuous medium-molecular dynamic characteristic zigzag mapping. The method is used for designing the high-speed milling cutter.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for screening anti-androgen activity of flavonoid compounds based on molecular dynamics simulation
InactiveCN106407740ALow costSimple and fast operationSpecial data processing applicationsMolecular structuresReceptor for activated C kinase 1Molecular dynamics
The invention discloses a method for screening anti-androgen activity of flavonoid compounds based on molecular dynamics simulation. The method comprises the following steps: performing butt joint on an optimized tested flavonoid compound structure and a receptor file acquired by homology modeling, then performing molecular dynamics simulation for 20 nanoseconds by using a GROMACS software package, calculating a mean square root deviation of No.12 helix 8-20ns of a flavonoid compound receptor, importing data into a R language package, establishing a distinguishing model for the calculated standard deviation and residues, and removing inactive compounds from the compounds in a fuzzy area by inspecting the movement trajectories of the compounds in the receptor and the calculated mean square root deviation. According to the method disclosed by the invention, quantitative judgment is imported for the first time, the pre-judgment accuracy is improved by the combination of quantitativeness and qualitativeness, the distinction rate of inactive flavonoid and active flavonoid reaches 87.5%, the screening rate of the inactive flavonoid reaches 90%, the laboratory workload can be greatly reduced, the consumption of test products is reduced, resources are saved, and the prediction accuracy of QSAR can also be greatly improved, so QSAR can be really applied.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com