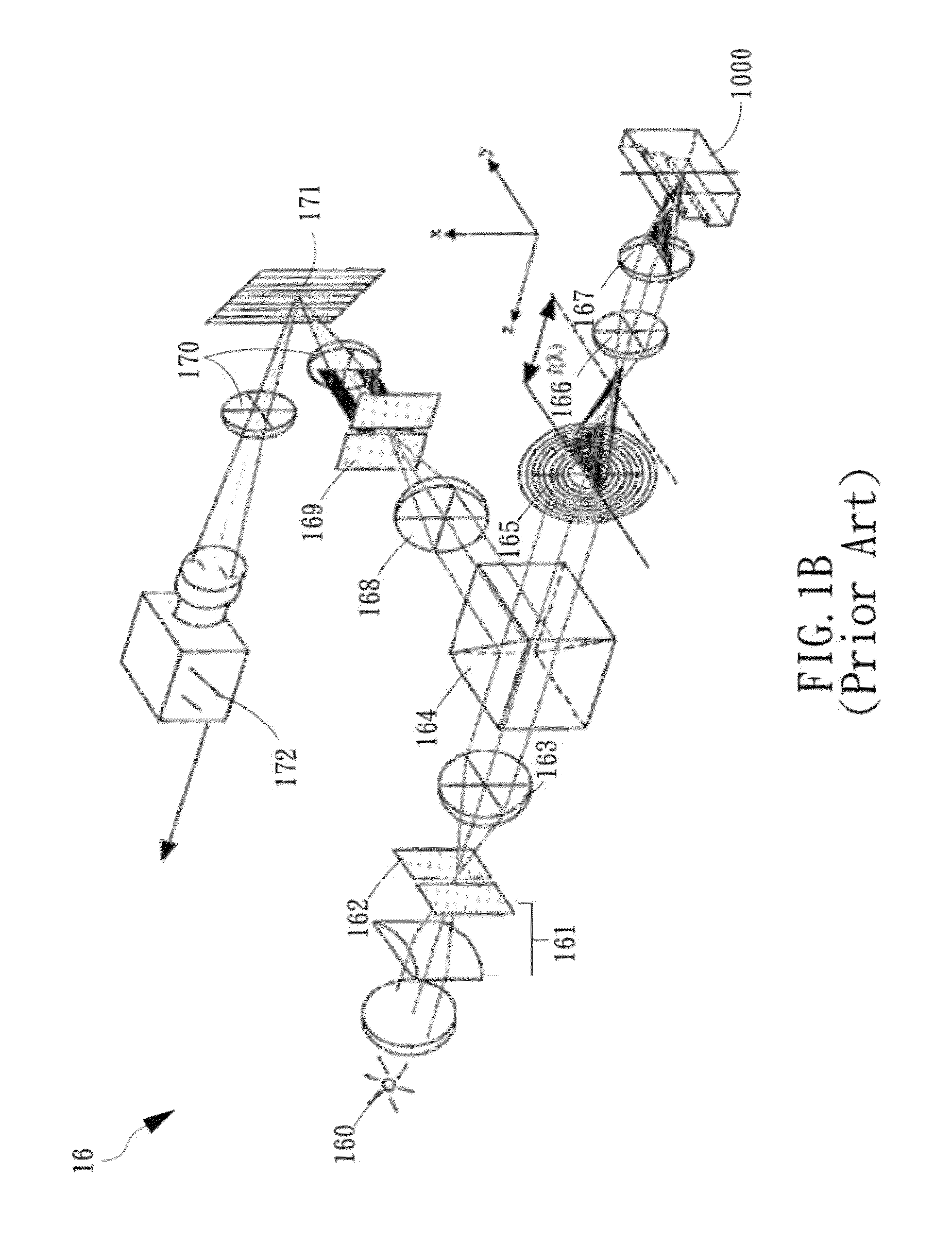
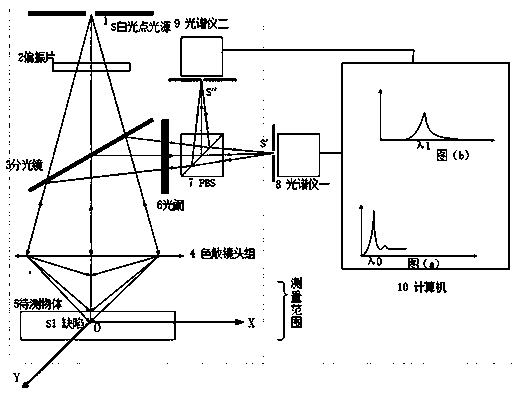
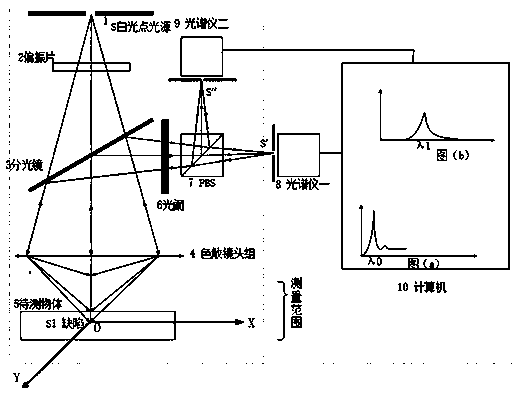
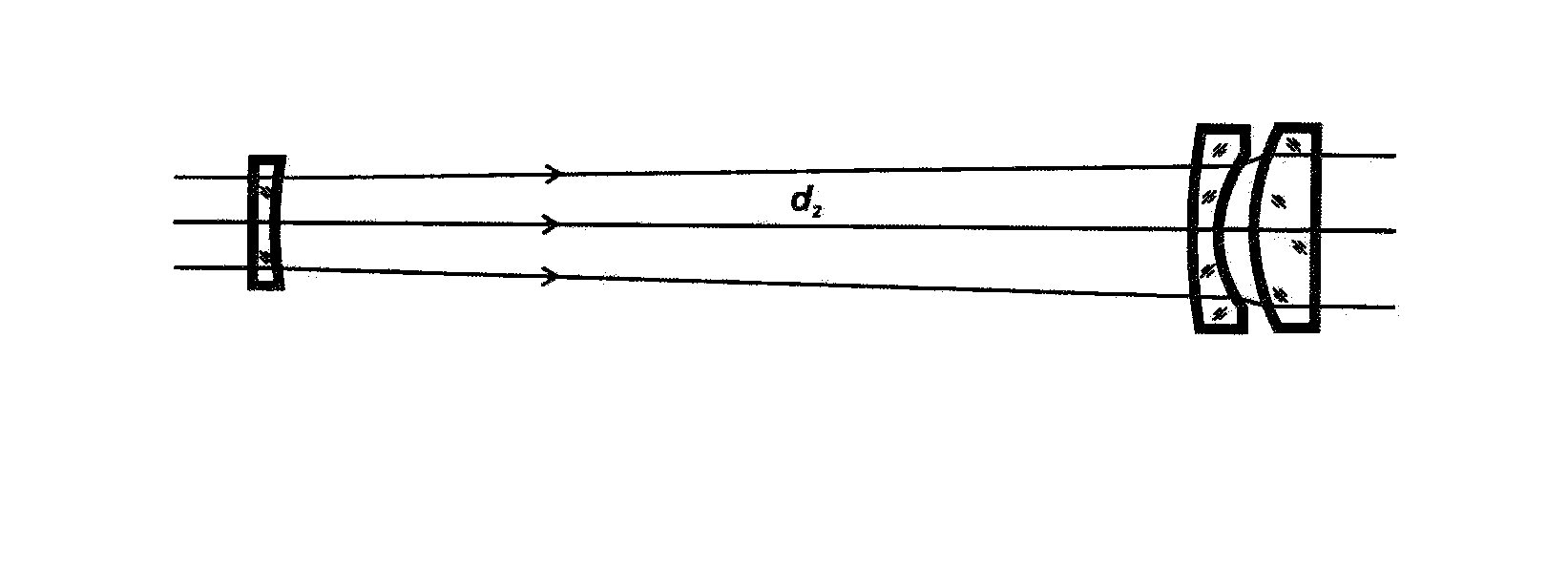
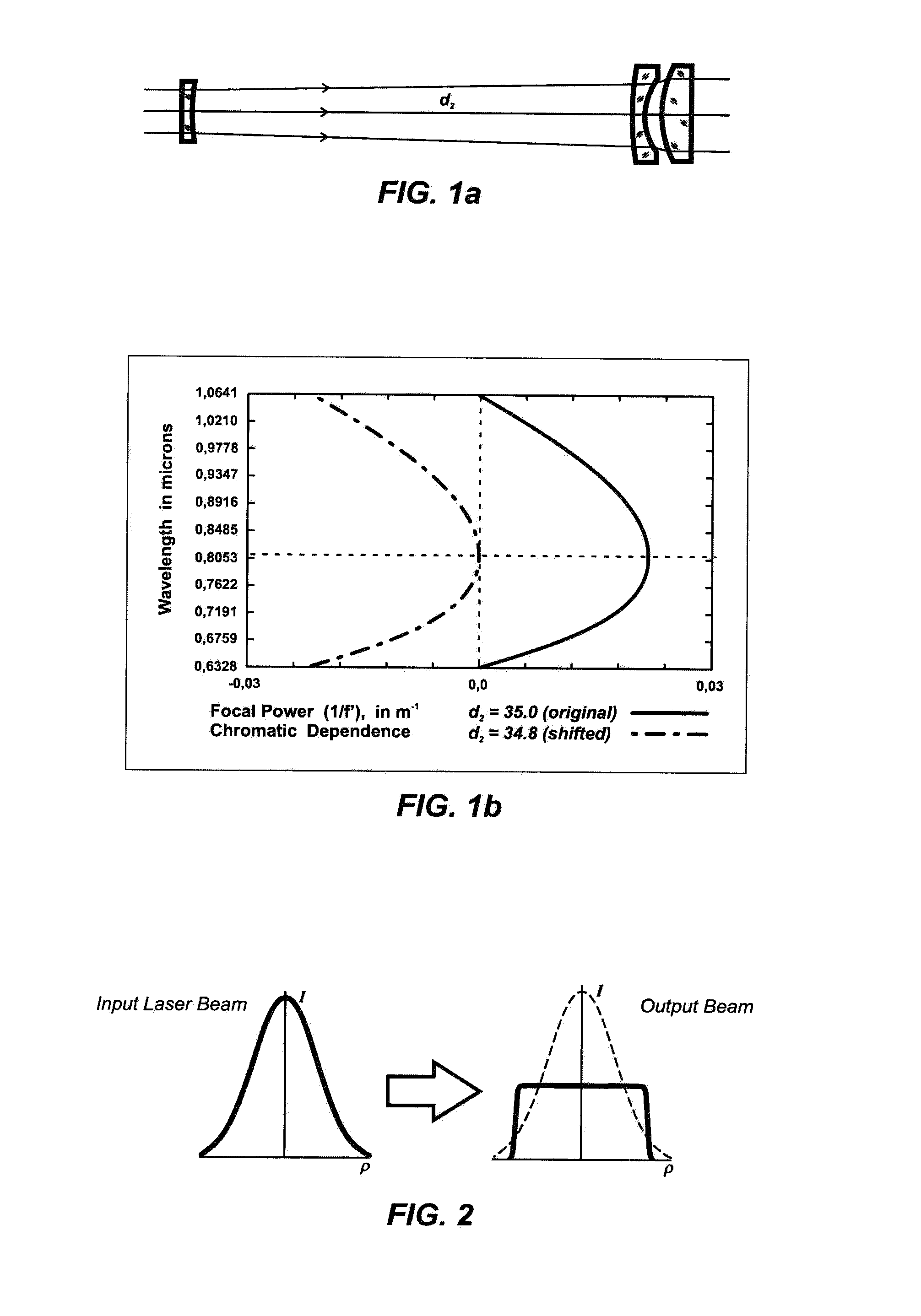
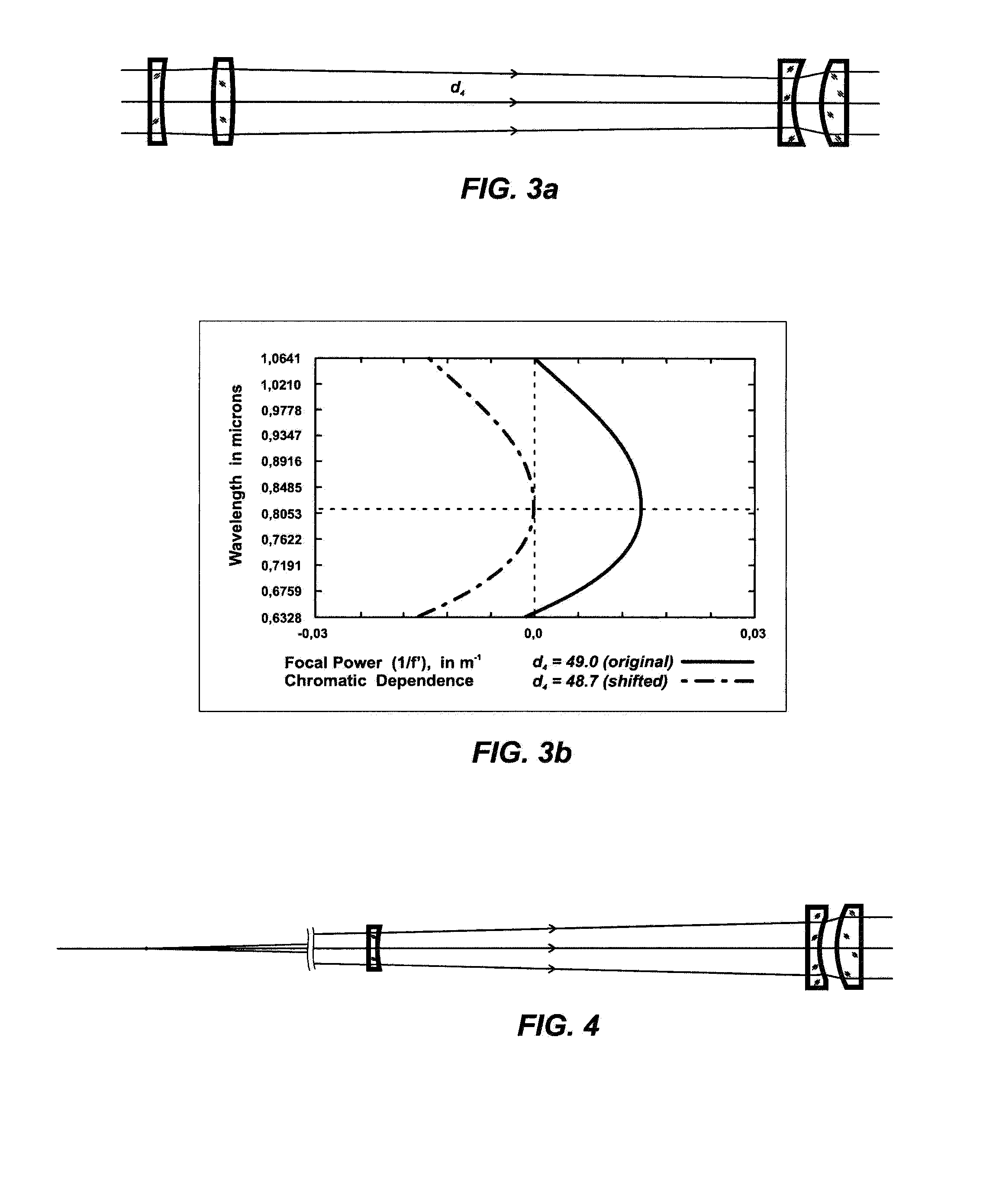
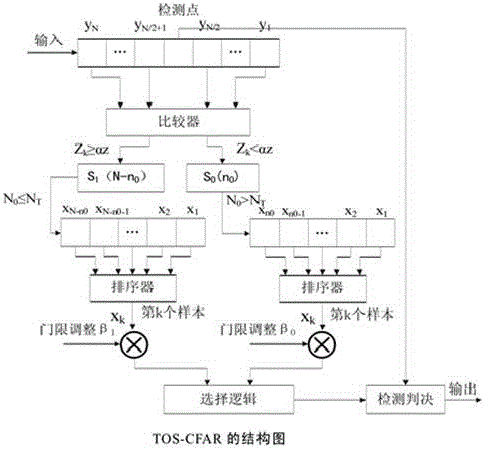
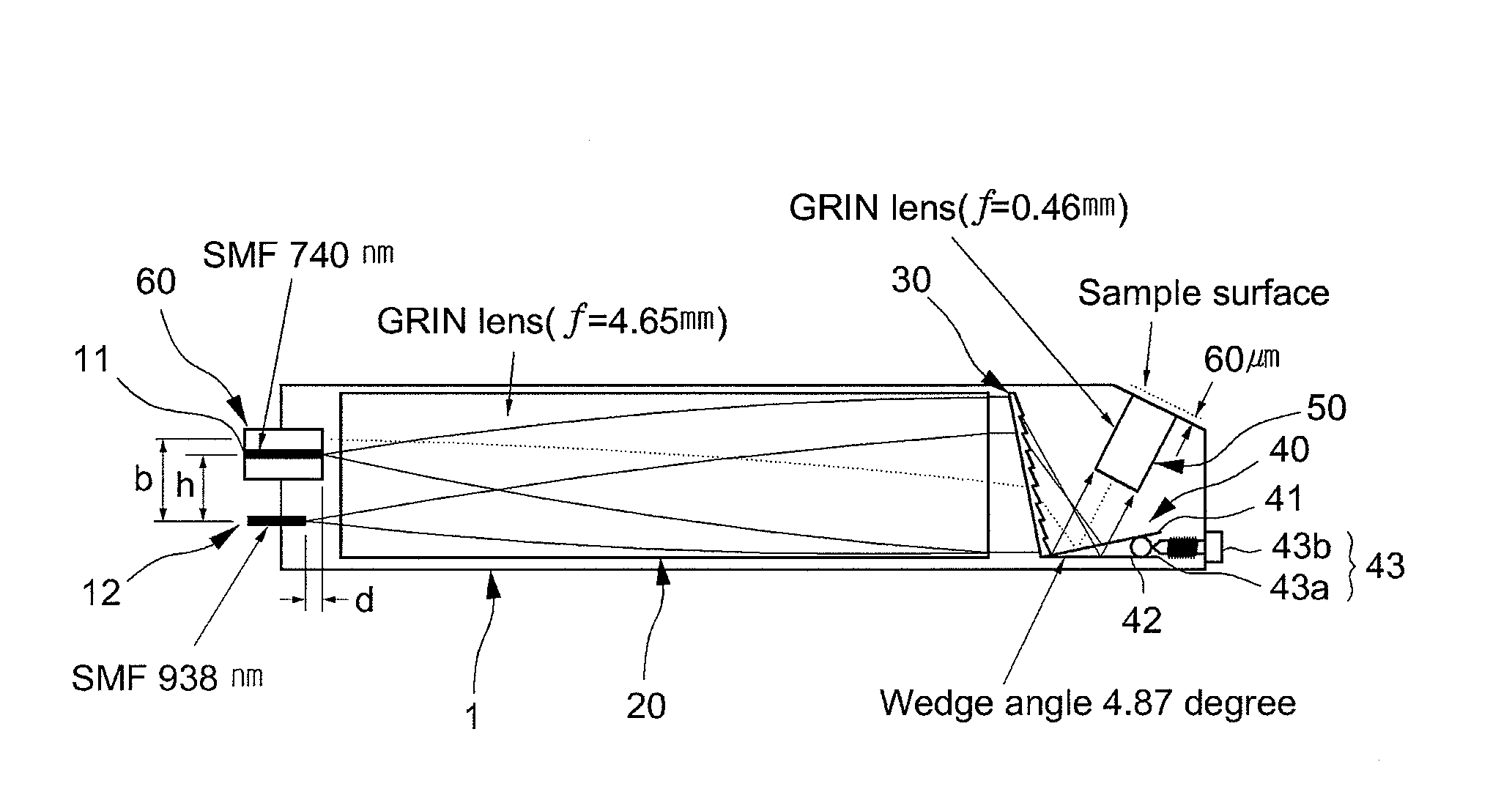
Patents
Literature
119 results about "Spectral dispersion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
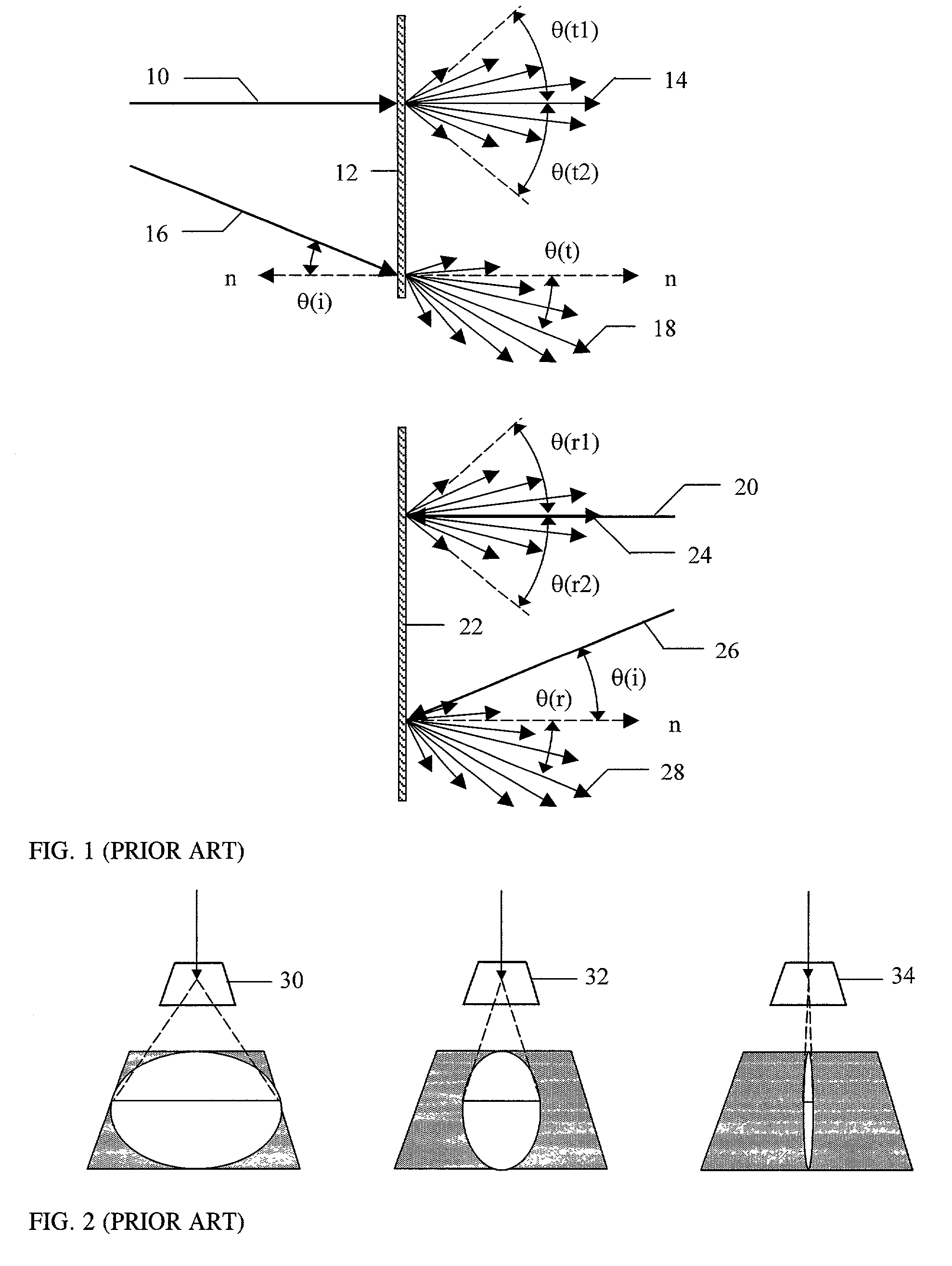
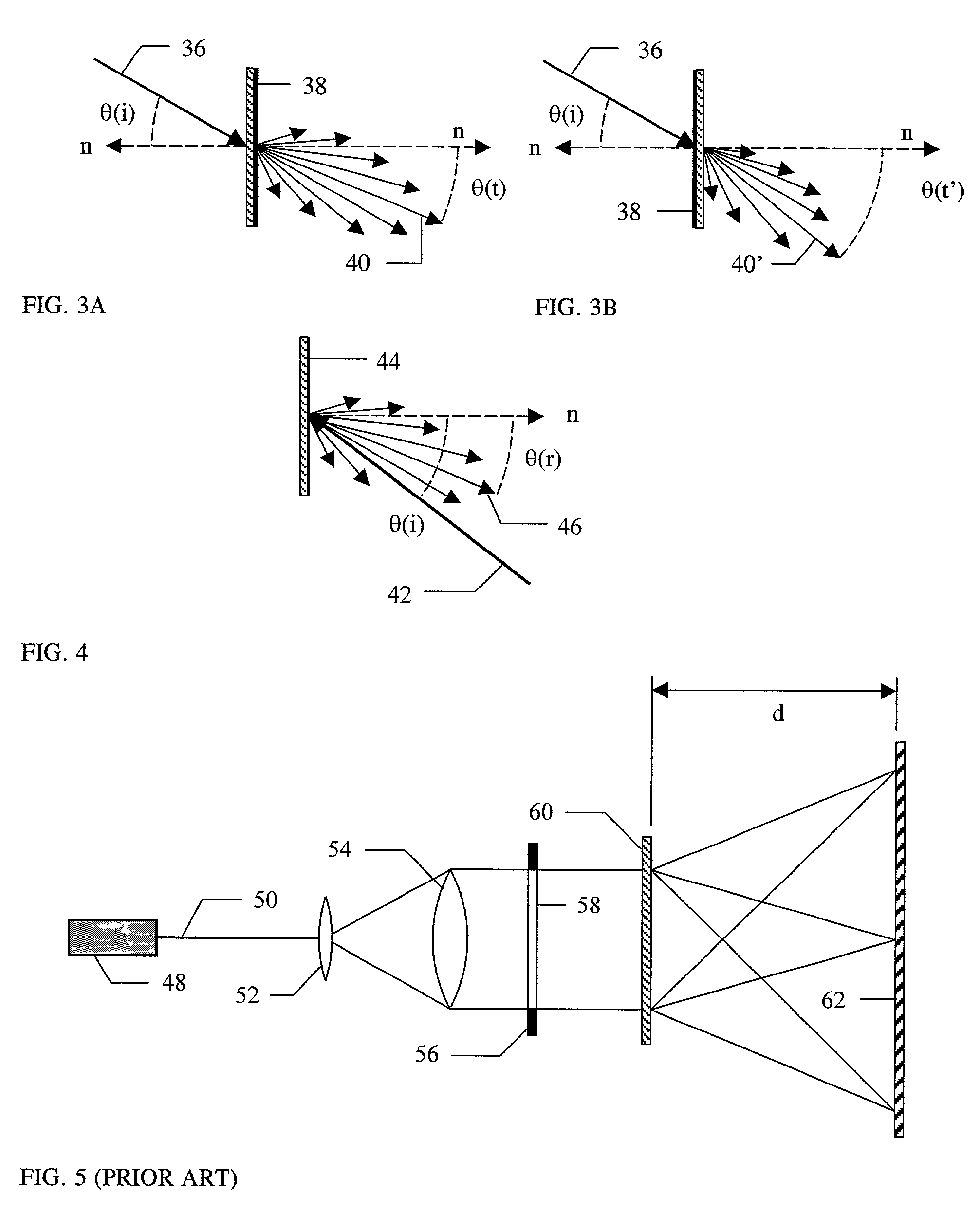
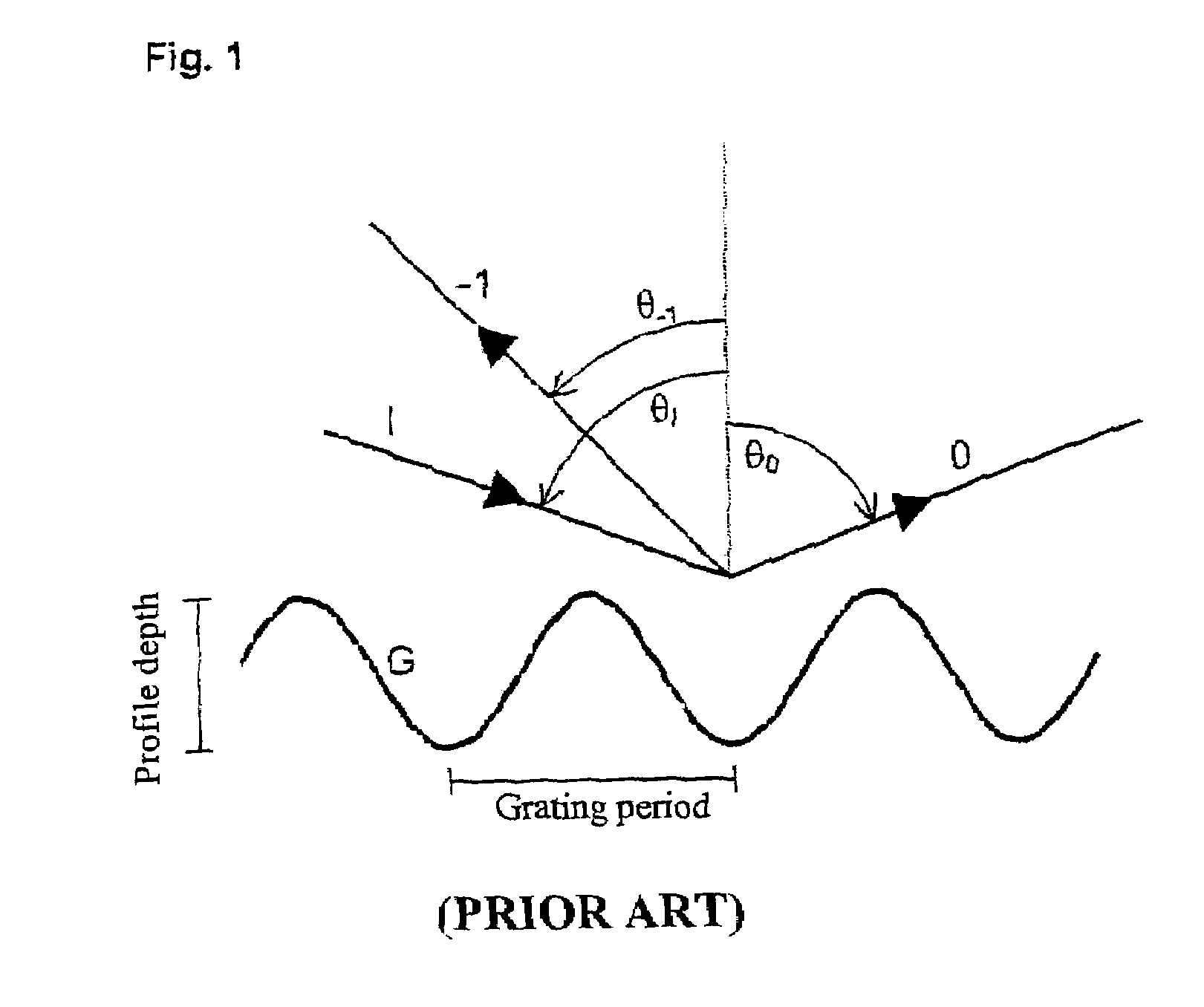
Dispersion and spectral resolution. Two of the most important properties of a spectrograph are the dispersion, which sets the wavelength range of the spectrum, and the spectral resolution, which sets the size of the smallest spectral features that can be studied in the spectrum.
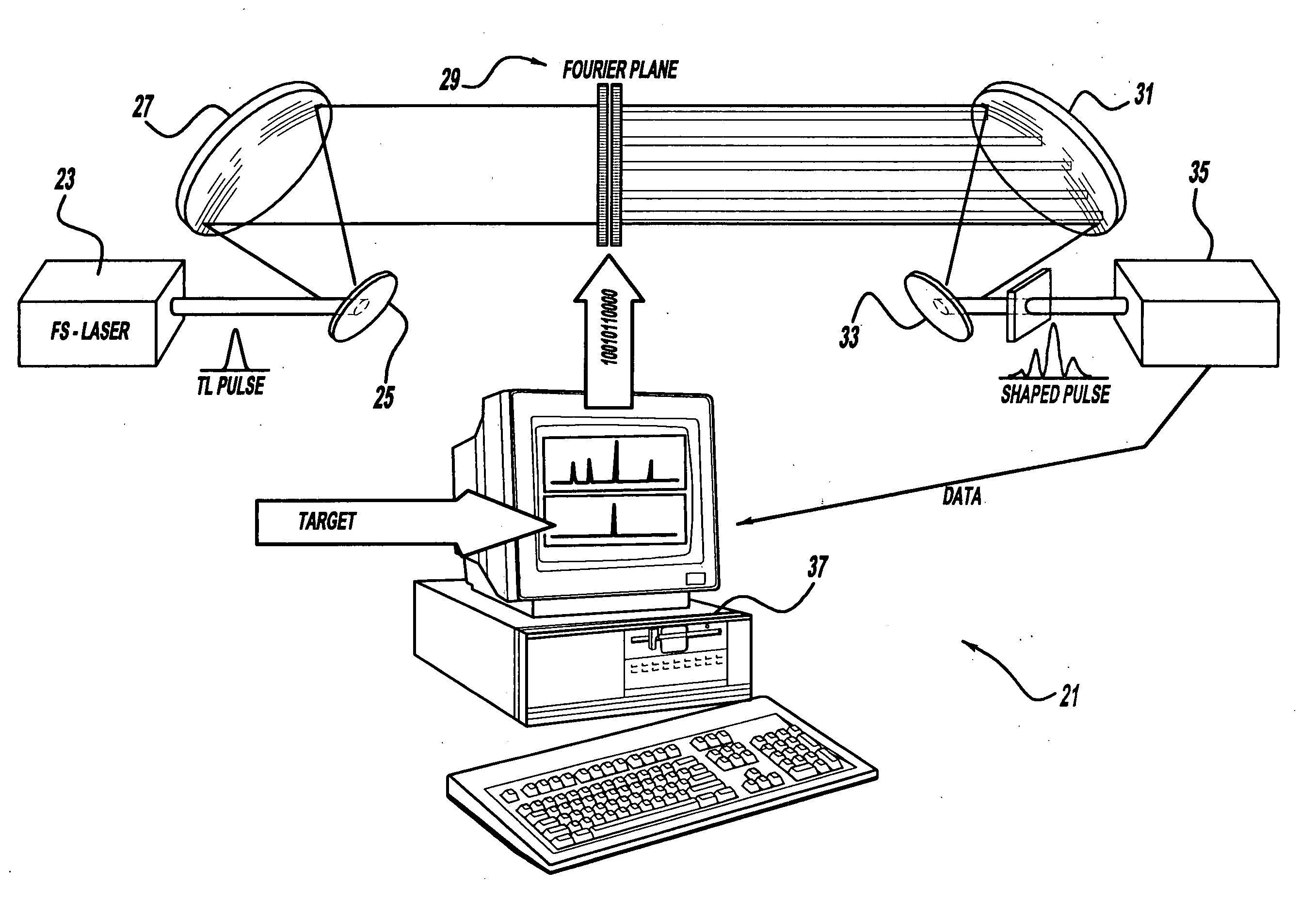
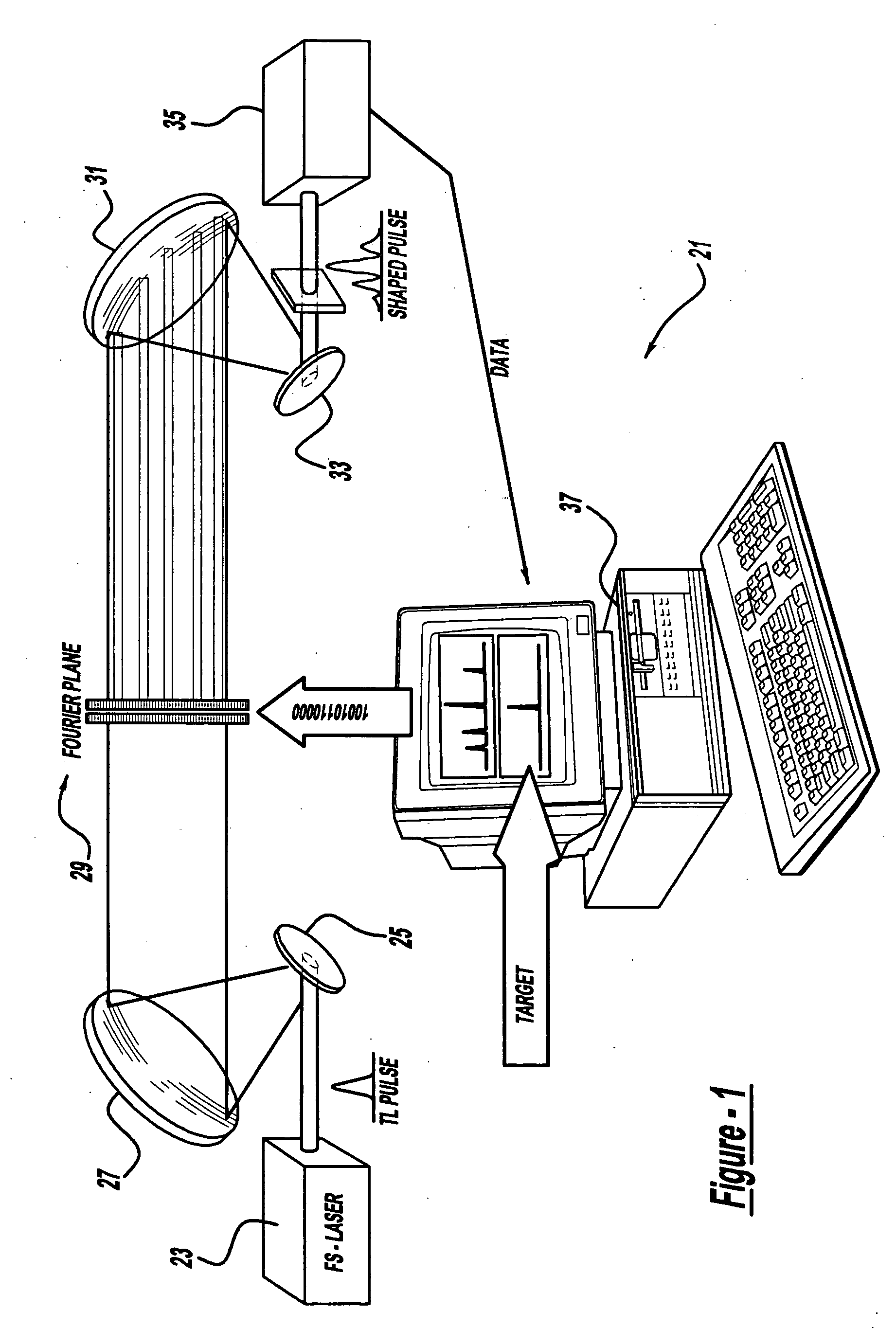
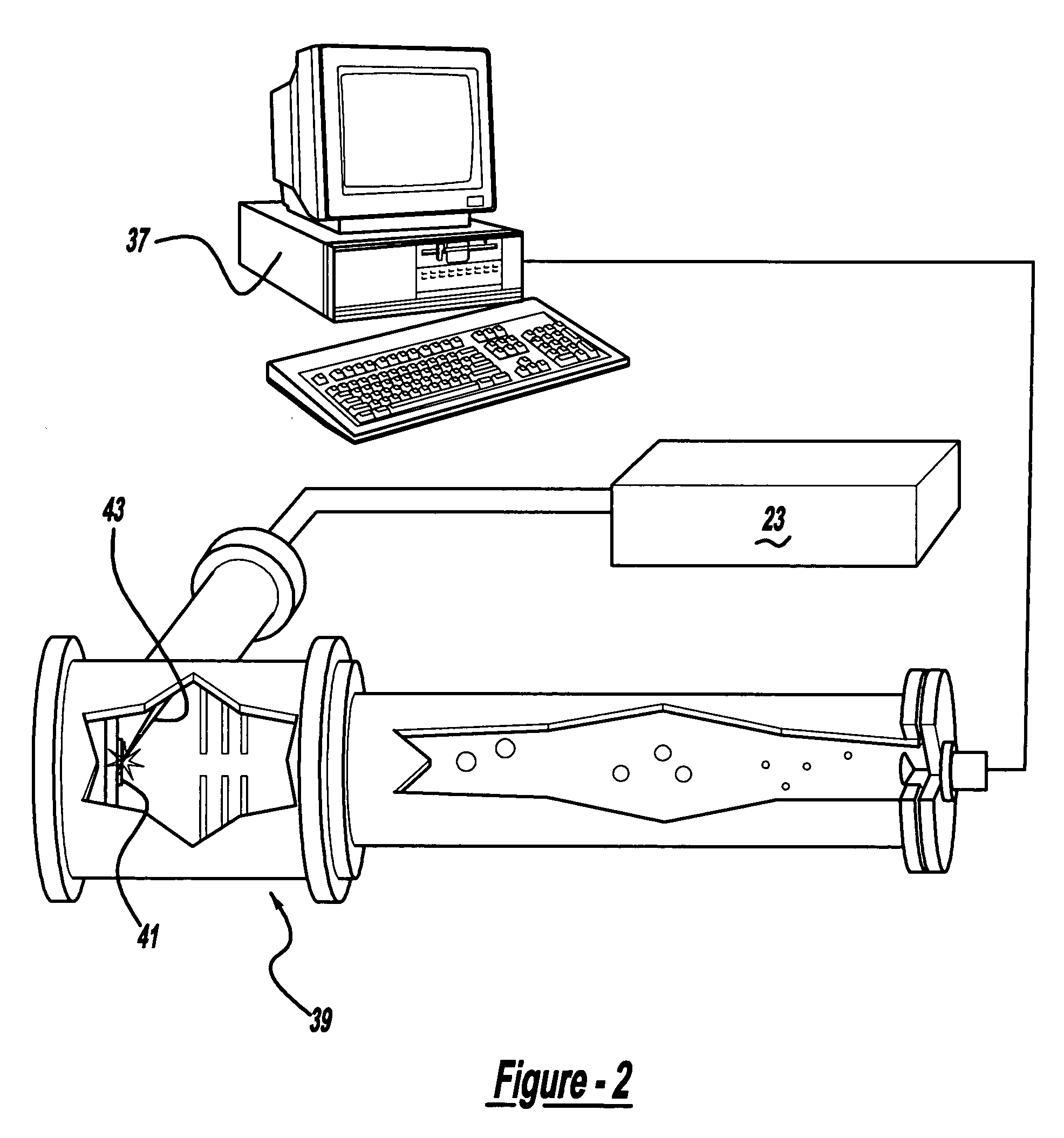
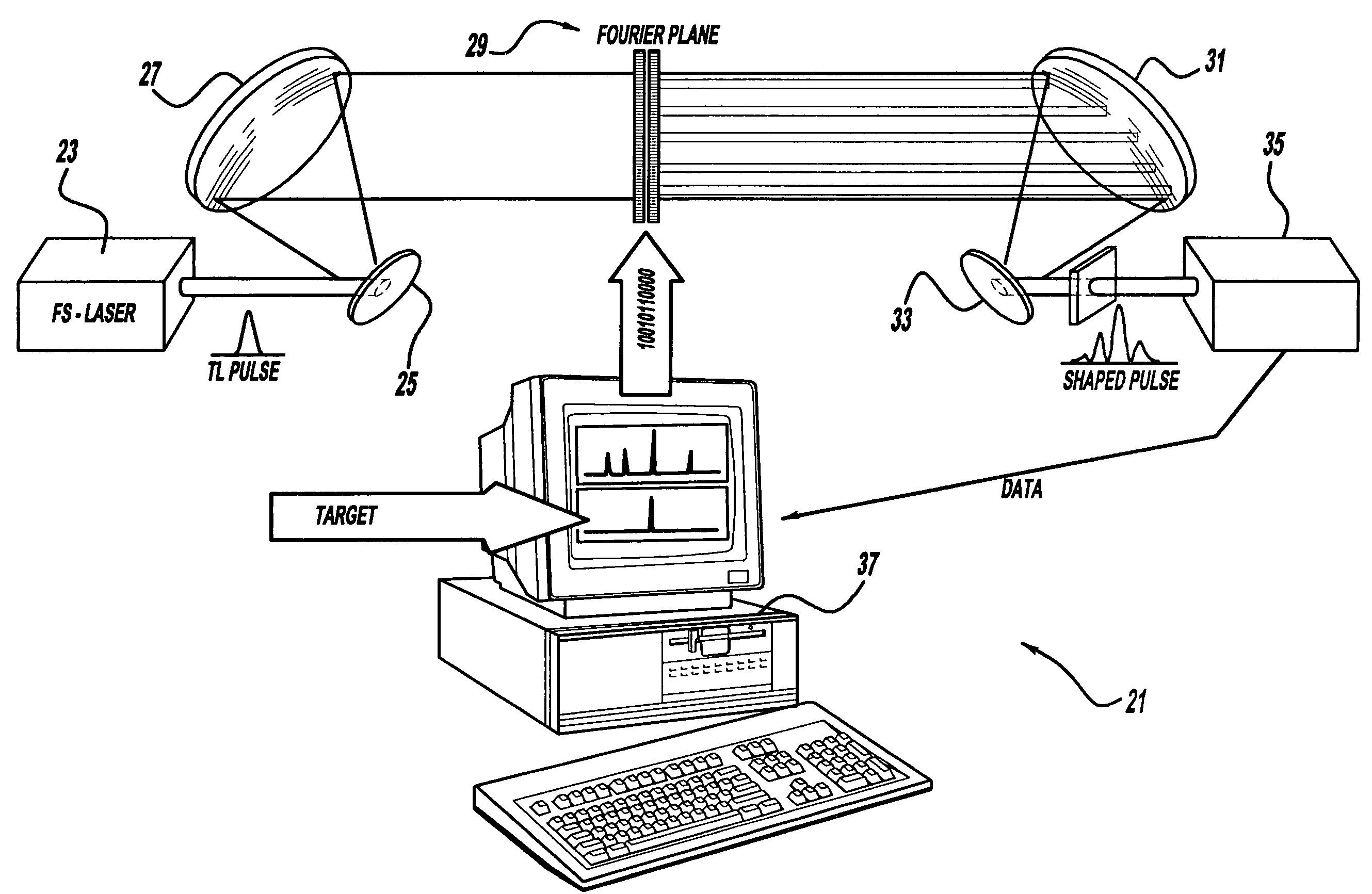
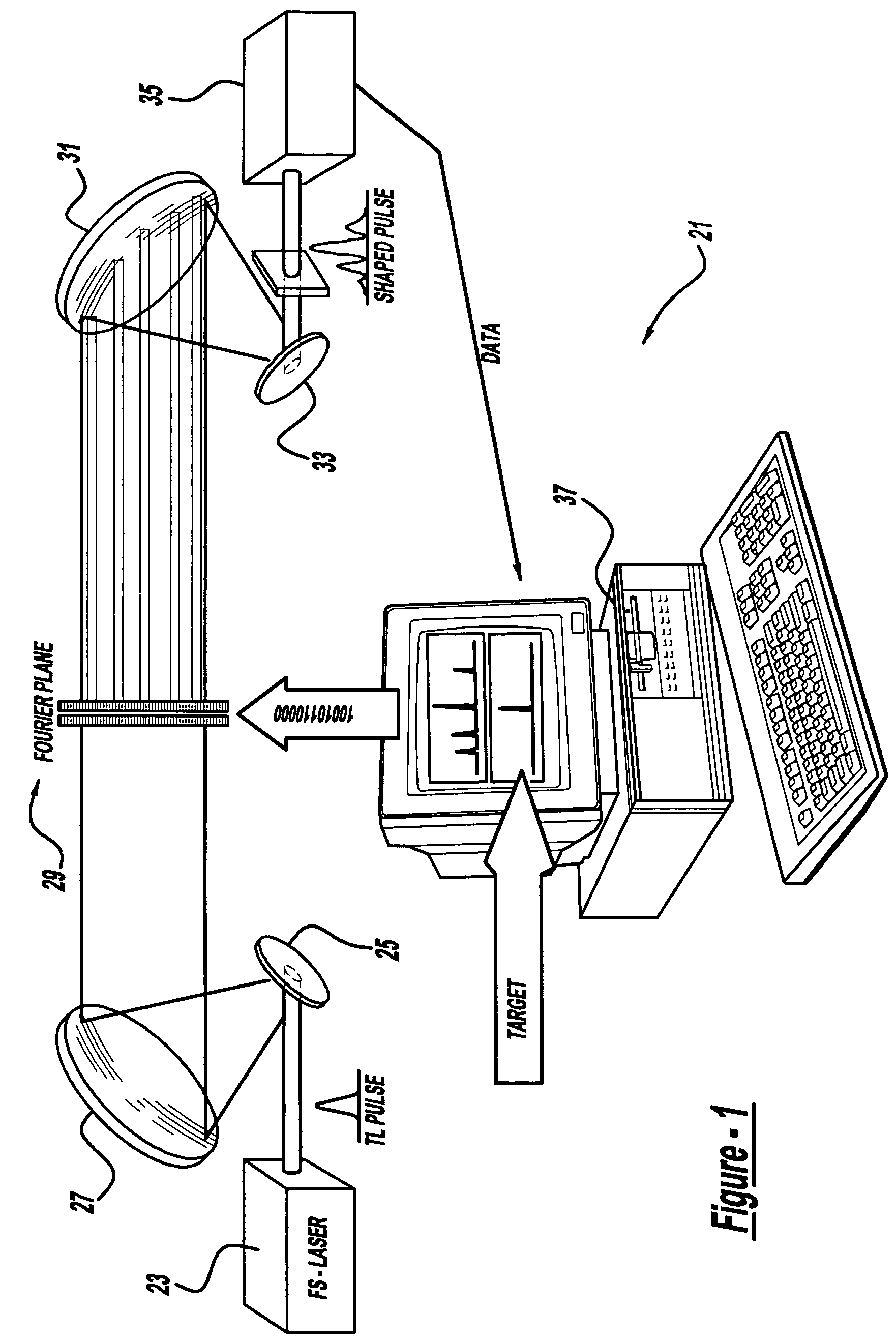
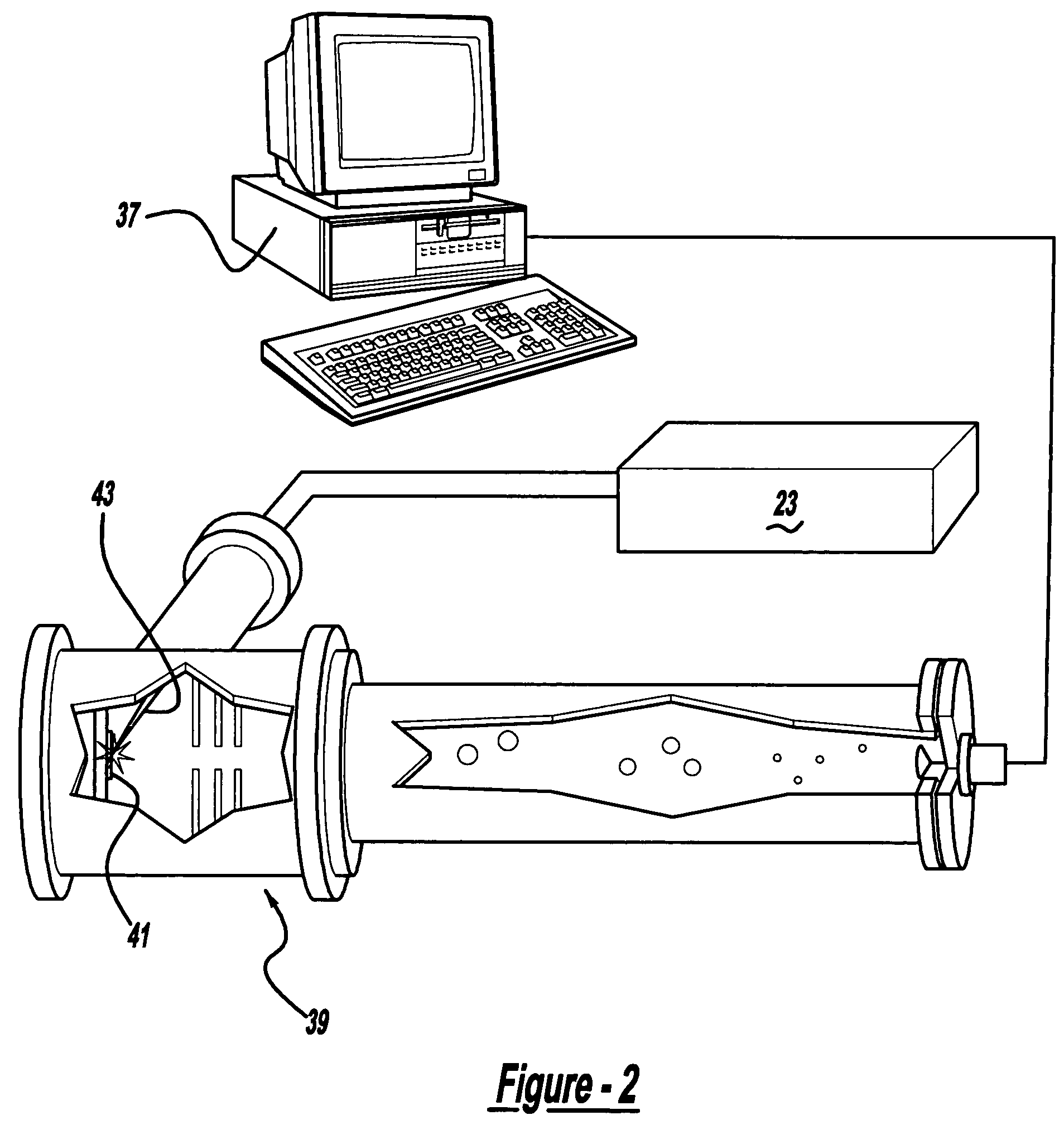
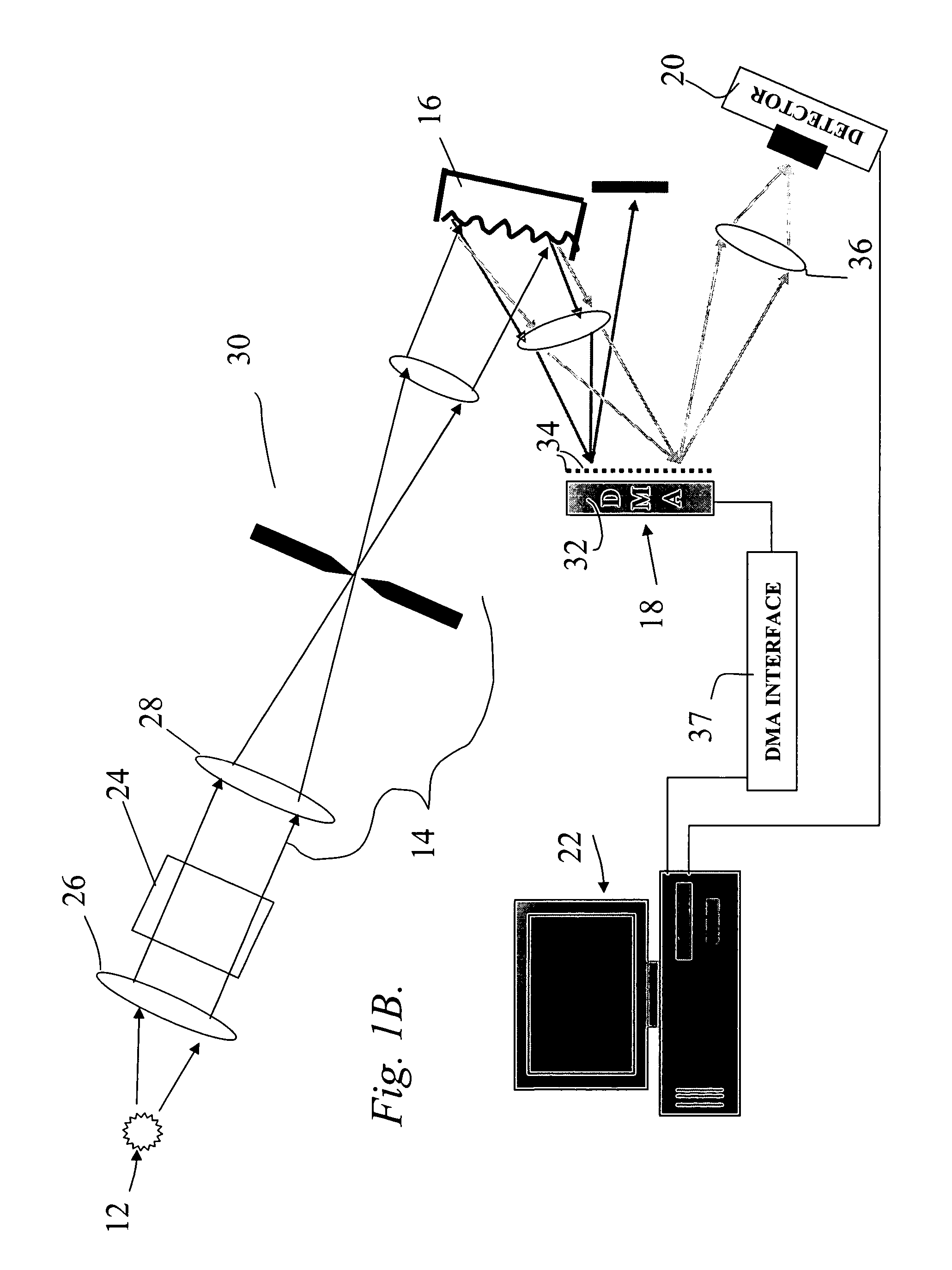
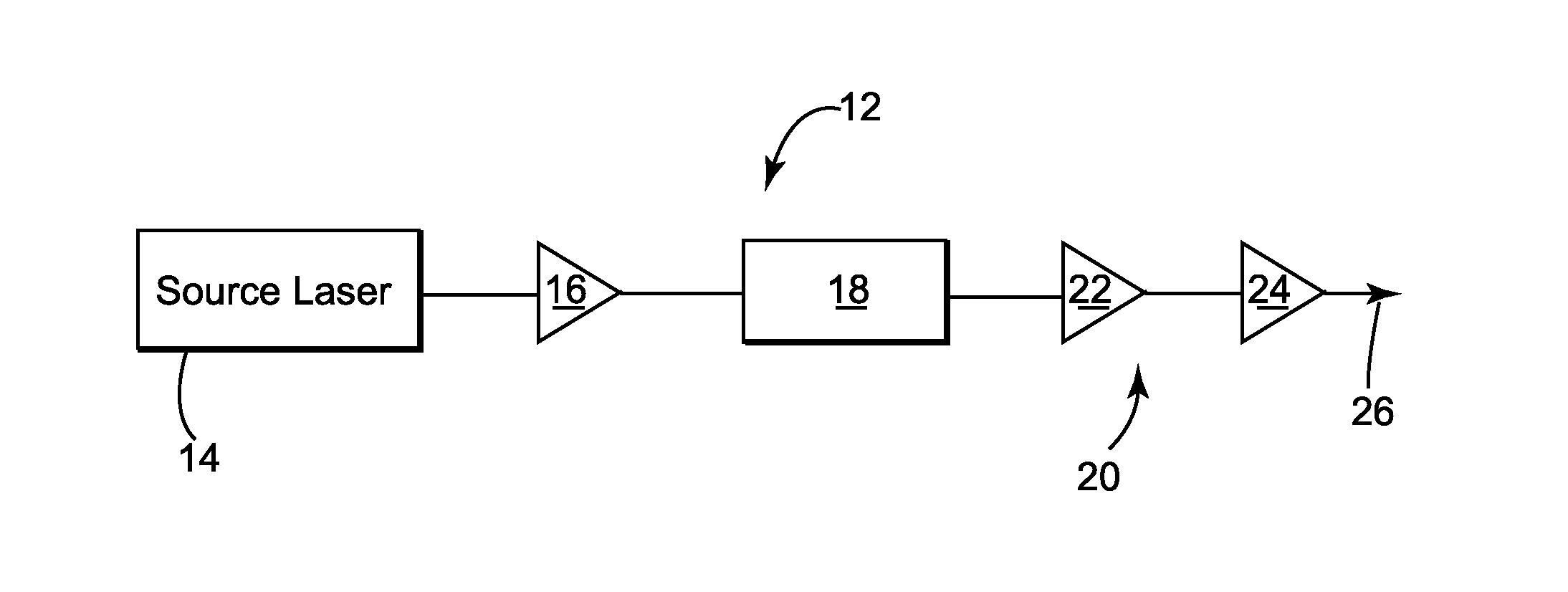
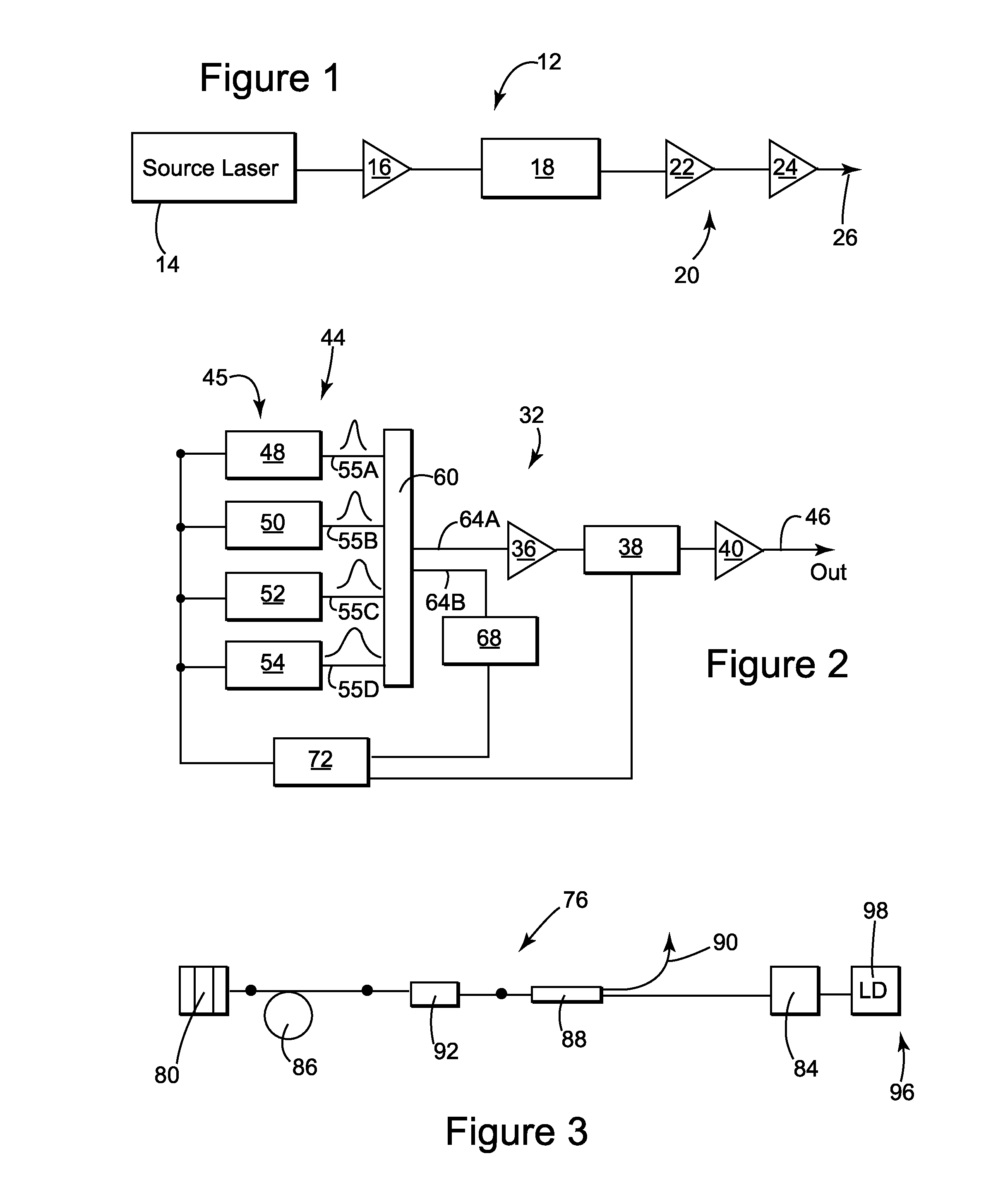
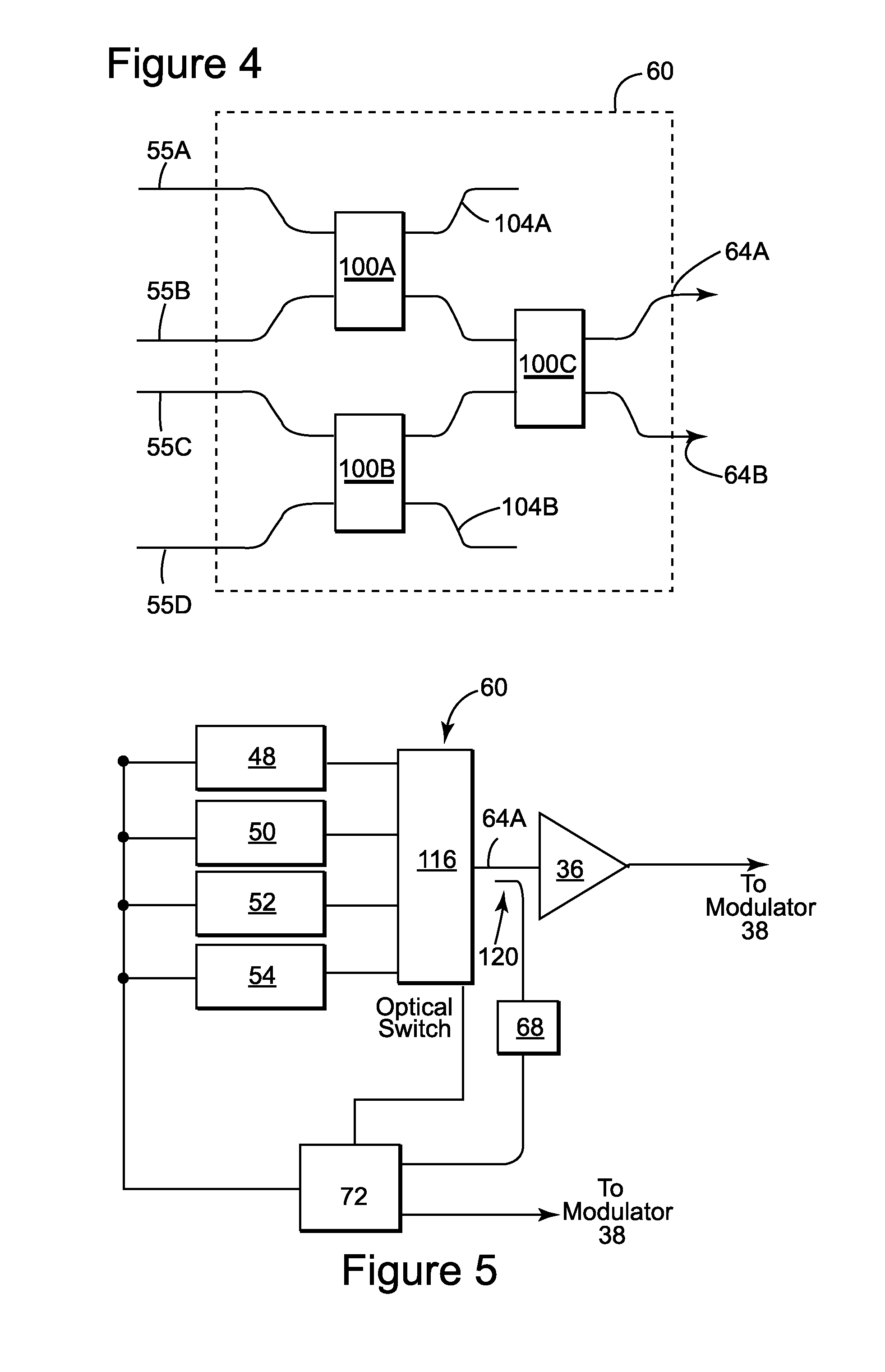
Control system and apparatus for use with ultra-fast laser
InactiveUS20060056468A1Easy to set upEasy to useLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansAudio power amplifierControl system
A control system and apparatus for use with an ultra-fast laser is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the apparatus includes a laser, pulse shaper, detection device and control system. A multiphoton intrapulse interference method is used to characterize the spectral phase of laser pulses and to compensate for any distortions in an additional aspect of the present invention. In another aspect of the present invention, a system employs multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan. Furthermore, another aspect of the present invention locates a pulse shaper and / or MIIPS unit between a spectral dispersion point in a laser oscillator and an output of a laser amplifier.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Control system and apparatus for use with ultra-fast laser
InactiveUS7567596B2Easy to set upEasy to useLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansAudio power amplifierControl system
A control system and apparatus for use with an ultra-fast laser is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the apparatus includes a laser, pulse shaper, detection device and control system. A multiphoton intrapulse interference method is used to characterize the spectral phase of laser pulses and to compensate for any distortions in an additional aspect of the present invention. In another aspect of the present invention, a system employs multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan. Furthermore, another aspect of the present invention locates a pulse shaper and / or MIIPS unit between a spectral dispersion point in a laser oscillator and an output of a laser amplifier.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
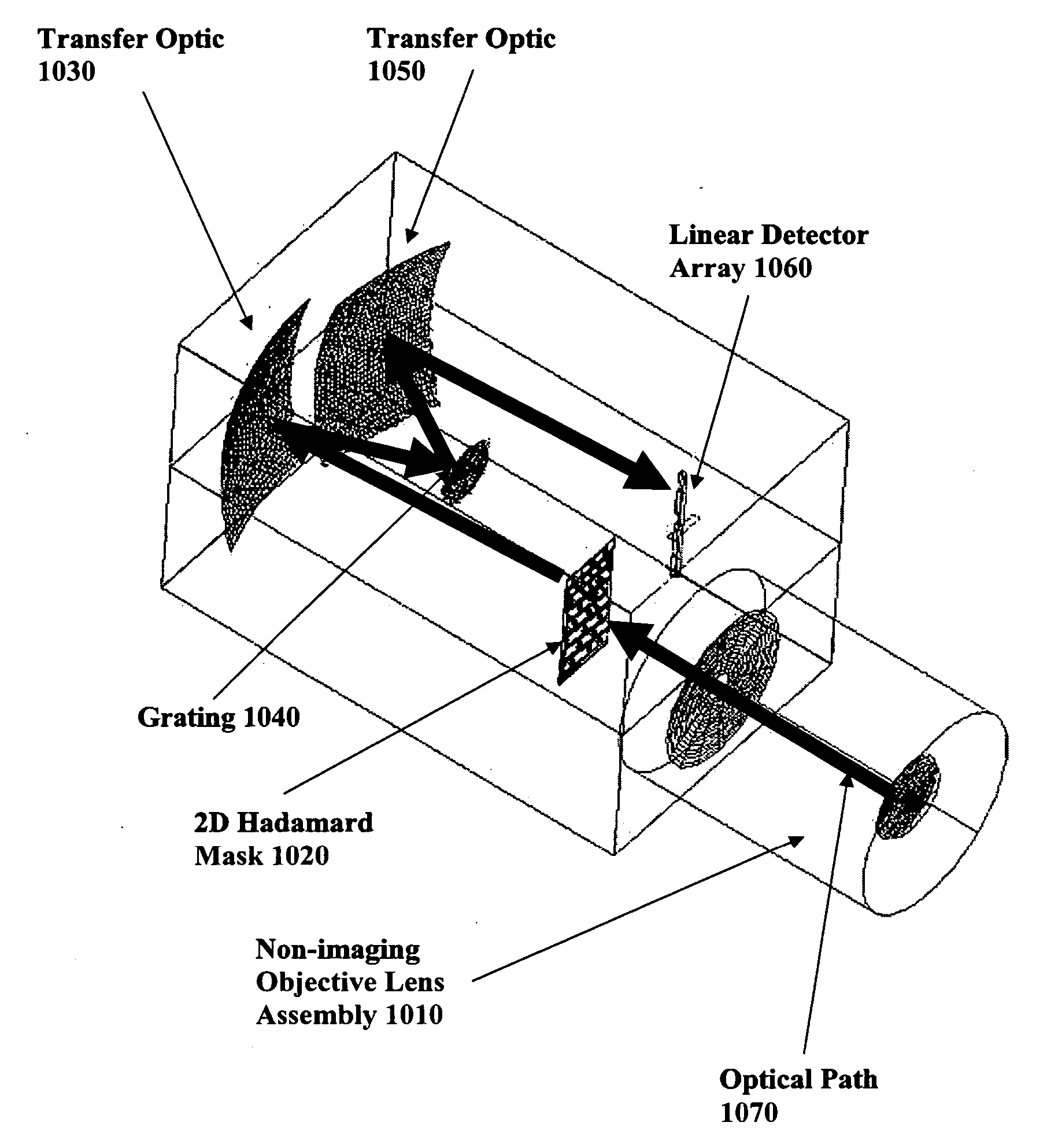
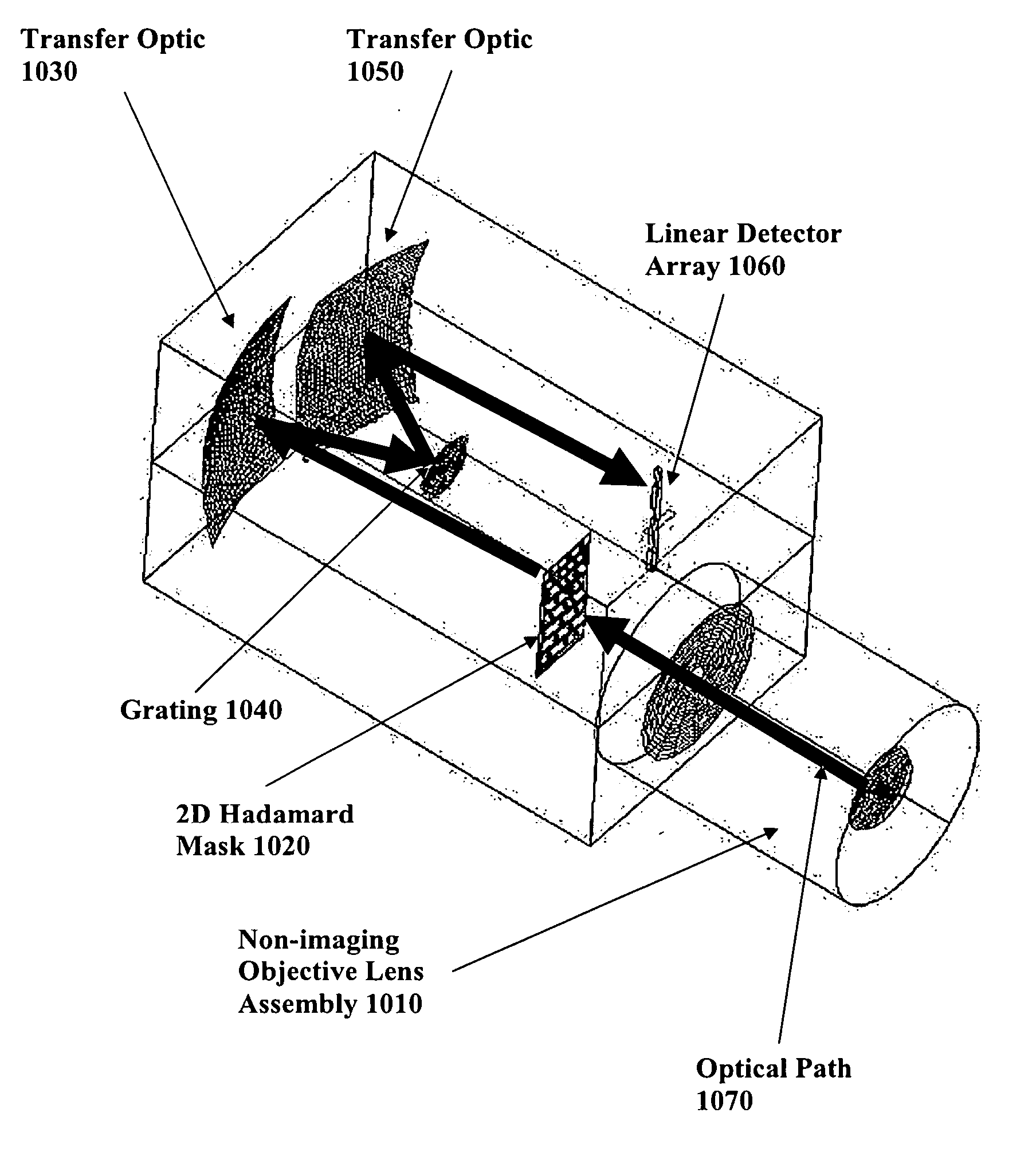
Devices and method for spectral measurements
InactiveUS20050243312A1Quick collectionImprove throughputRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsMeasurement deviceFtir spectra
A spectral measurement device comprising an entrance aperture for receiving an electromagnetic energy and a mask located at the entrance aperture in the form of a two-dimensional encodement pattern. An optical element conditions the electromagnetic energy received from the mask for presentation to the spectral dispersion element and the and a spectral dispersion element disperses the electromagnetic energy in one or more dimensions. Additionally, the optical element conditions the dispersed electromagnetic energy onto an array of detector elements.
Owner:PLAIN SIGHT SYST
Slit-scan multi-wavelength confocal lens module and slit-scan microscopic system and method using the same
ActiveUS20100188742A1Improve performanceMinimized in sizePrismsMicroscopesBroadbandLighting spectrum
The present invention provides a slit-scan multi-wavelength confocal lens module, which utilizes at least two lenses having chromatic aberration for splitting a broadband light into continuously linear spectral lights having different focal length respectively. The present invention utilizes the confocal lens module employing slit-scan confocal principle and chromatic dispersion techniques and the confocal microscopy with optical sectioning ability and high resolution in spectral dispersion to establish a confocal microscopy method and system with long DOF and high resolution, capable of modulating a broadband light to produce the axial chromatic dispersion and focus on different depths toward an object's surface for obtaining the reflected light spectrum from the surface. Thereafter, the spectrum is spatially filtered by a slit and then a peak position with respect to the filtered spectrum along the scanning line is detected by a spectral image sensing unit for generating the sectional profile of the measured surface.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
Devices and method for spectral measurements
InactiveUS20060092414A1Quick collectionImprove throughputRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsMeasurement deviceFtir spectra
A spectral measurement device comprising an entrance aperture for receiving an electromagnetic energy and a mask located at the entrance aperture in the form of a two-dimensional encodement pattern. An optical element conditions the electromagnetic energy received from the mask for presentation to the spectral dispersion element and the and a spectral dispersion element disperses the electromagnetic energy in one or more dimensions. Additionally, the optical element conditions the dispersed electromagnetic energy onto an array of detector elements.
Owner:PLAIN SIGHT SYST
Linear multi-wavelength confocal microscope module and confocal microscopic method and system thereof
ActiveCN101872064AAccurate and fast profile measurementMeasurement rate increaseOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansSpectral dispersionMulti wavelength
The invention provides a linear multi-wavelength confocal microscopic system, which uses more than two chromatic lenses to enable a linear incident light field to generate dispersed rays and to enable rays with different wavelengths to be focused at different positions. Moreover, the invention utilizes a linear multi-wavelength confocal microscope module with a linear scanning confocal principle and a light source dispersion technique to develop a long-field-depth high-definition optical micro-morphological profile microscopic method and a system by using a confocal microscopic technique with optical sectioning capacity and in combination with the high definition of spectral dispersion. The method and the system of the invention use a broadband light source. By adopting a dispersion objective module, the broadband light source is enabled to generate axially dispersed rays which are focused at different depths, the focused surface reflectance spectrum is obtained simultaneously, spatial filtering is conducted through a slit, the peak position of a spectral focusing response curve is accurately sensed by a linear spectral image sensing unit and thereby sectional profile measurement can be finished accurately and rapidly.
Owner:陈亮嘉
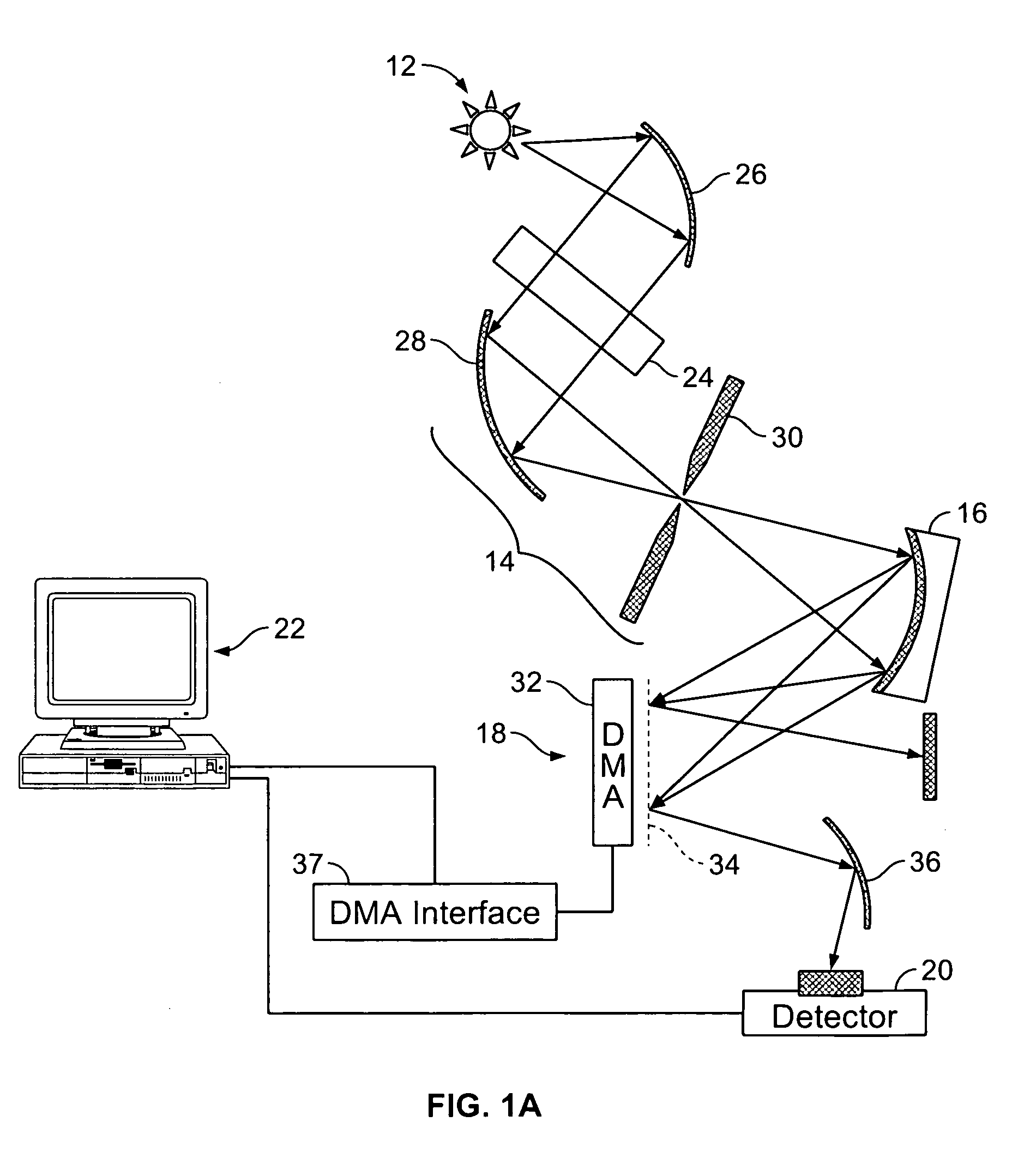
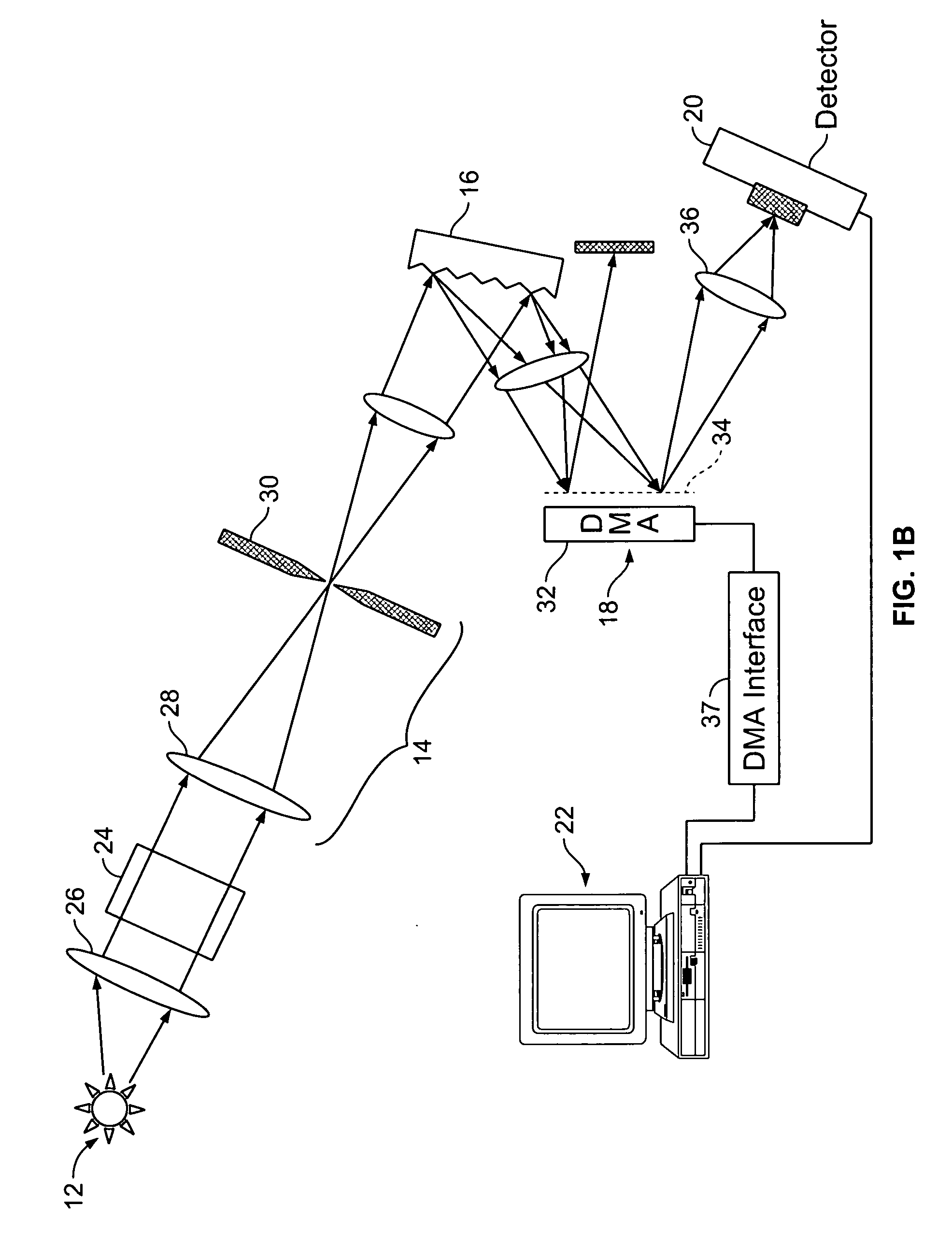
Spectral plane method and apparatus for wavelength-selective optical switching
We describe a variable bandwidth tunable optical spectral filtering device and associated method for selectively directing a portion of a wavelength multiplexed input signal, entering through one or more optical fibers, into one or more output signals provided to one or more optical fibers and / or electronic outputs. The optical filtering is accomplished using free-space diffractive wavelength de-multiplexing optics combined with a fixed (permanent) patterned structure located in the spectrally dispersed image plane. The structure can direct a selected spectral portion of the optical signal to one or more separate outputs, such as an optical fiber or power detector. A single active element in the optical path is used to spatially shift, or steer, the entire input spectrum at the dispersed spectral image plane, to control the portion of the input spectrum illuminating specific features on the permanent patterned structure. In one preferred embodiment, a device with a fixed selective area triangular shaped tilted reflective facet on a flat reflective surface is constructed such that the light reflected off the flat reflective surface and off the triangular reflective facet are selectively multiplexed back and directed to different output fiber ports. Inputs at different angles of incidence on the reflective structures may be deflected by the same structures to different output port fiber ports. A reconfigurable variable-bandwidth tunable optical add / drop multiplexing device is constructed using such a filtering device and an application of such an add / drop multiplexing in a optical transport network is demonstrated.
Owner:WILSON GORDON +1
Two-dimensional fourier transform spectrometer
InactiveUS8526002B2Reduce ambiguityReduce subjectivityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFrequency spectrumCoupling
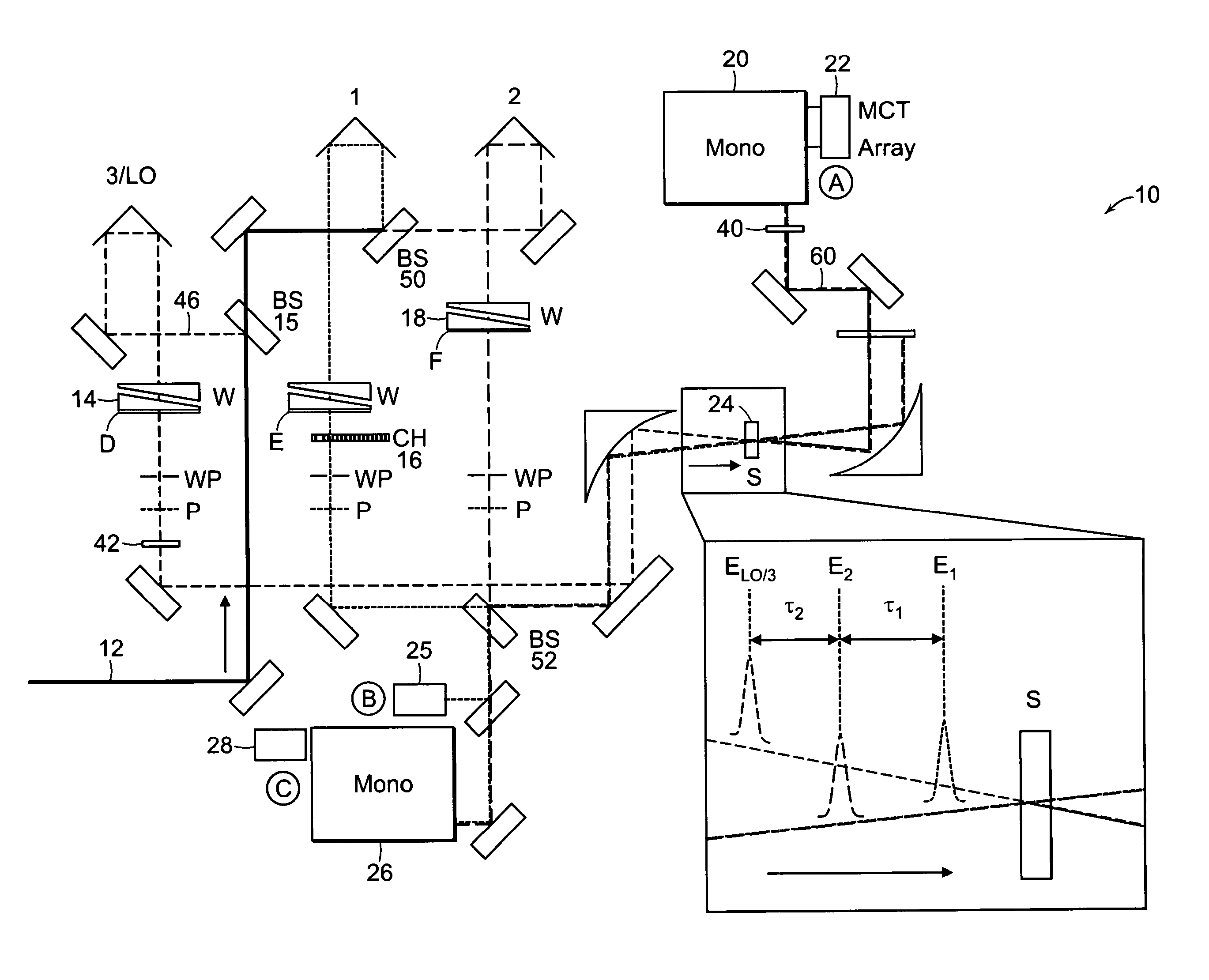
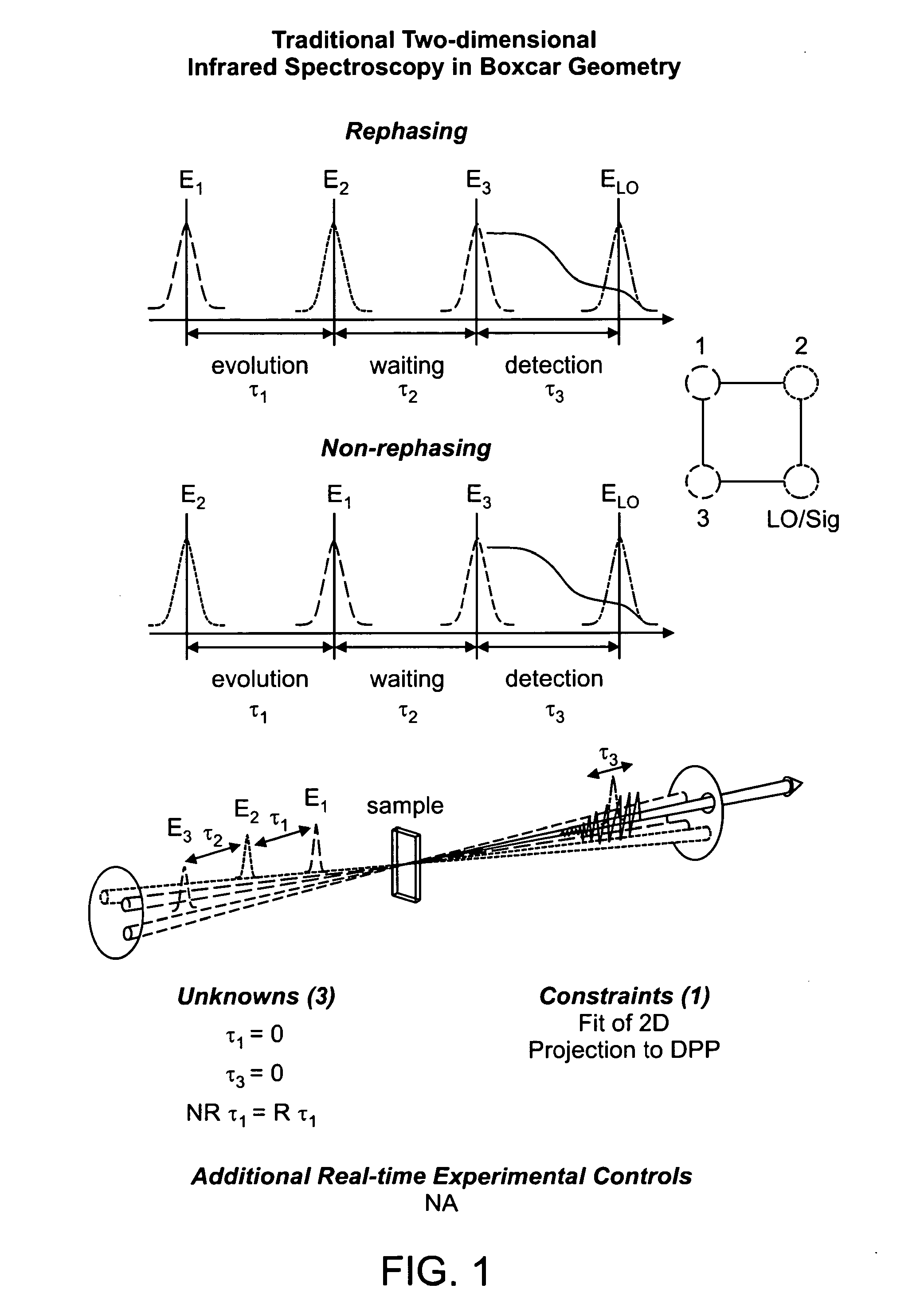
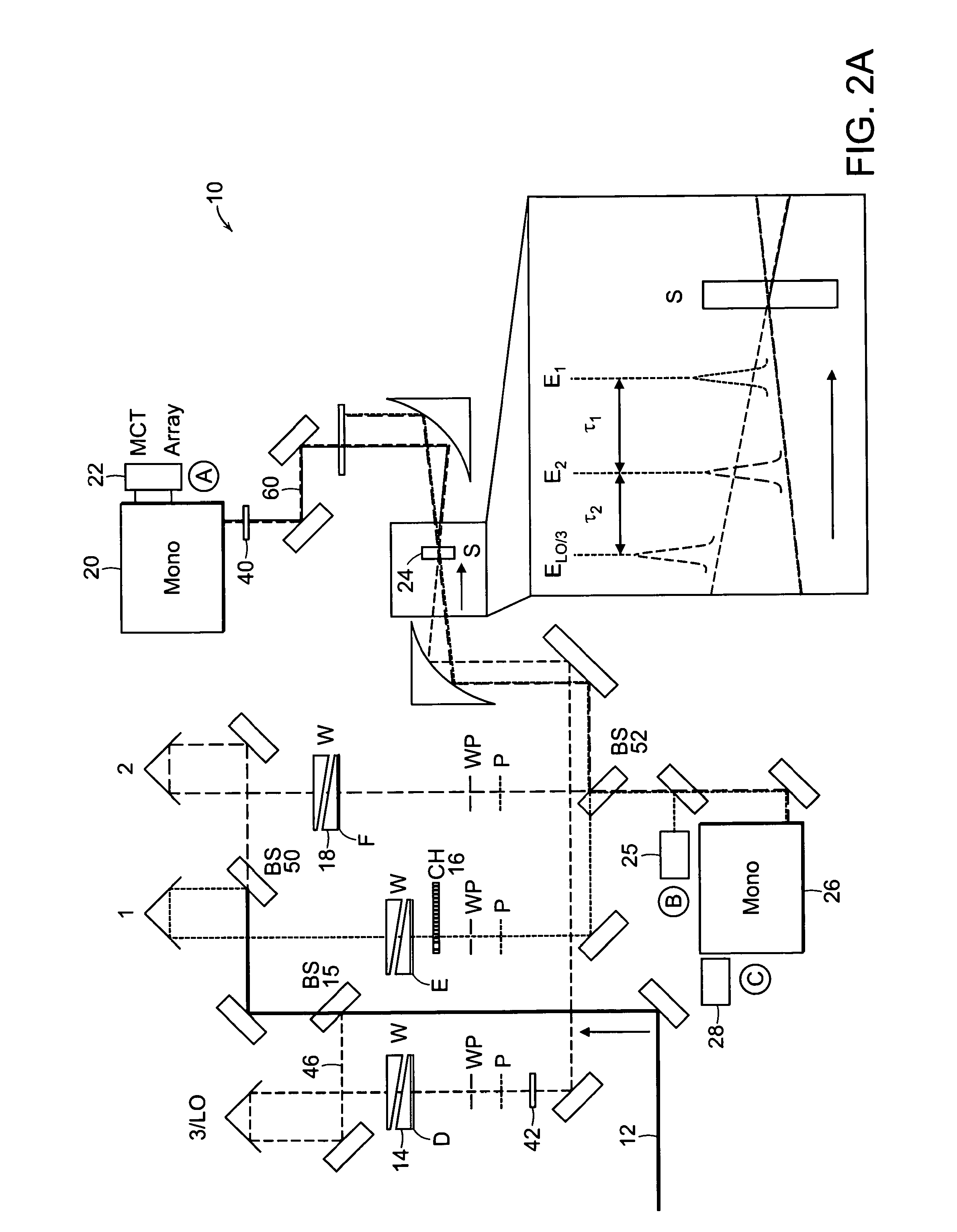
The present invention relates to a system and methods for acquiring two-dimensional Fourier transform (2D FT) spectra. Overlap of a collinear pulse pair and probe induce a molecular response which is collected by spectral dispersion of the signal modulated probe beam. Simultaneous collection of the molecular response, pulse timing and characteristics permit real time phasing and rapid acquisition of spectra. Full spectra are acquired as a function of pulse pair timings and numerically transformed to achieve the full frequency-frequency spectrum. This method demonstrates the ability to acquire information on molecular dynamics, couplings and structure in a simple apparatus. Multi-dimensional methods can be used for diagnostic and analytical measurements in the biological, biomedical, and chemical fields.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
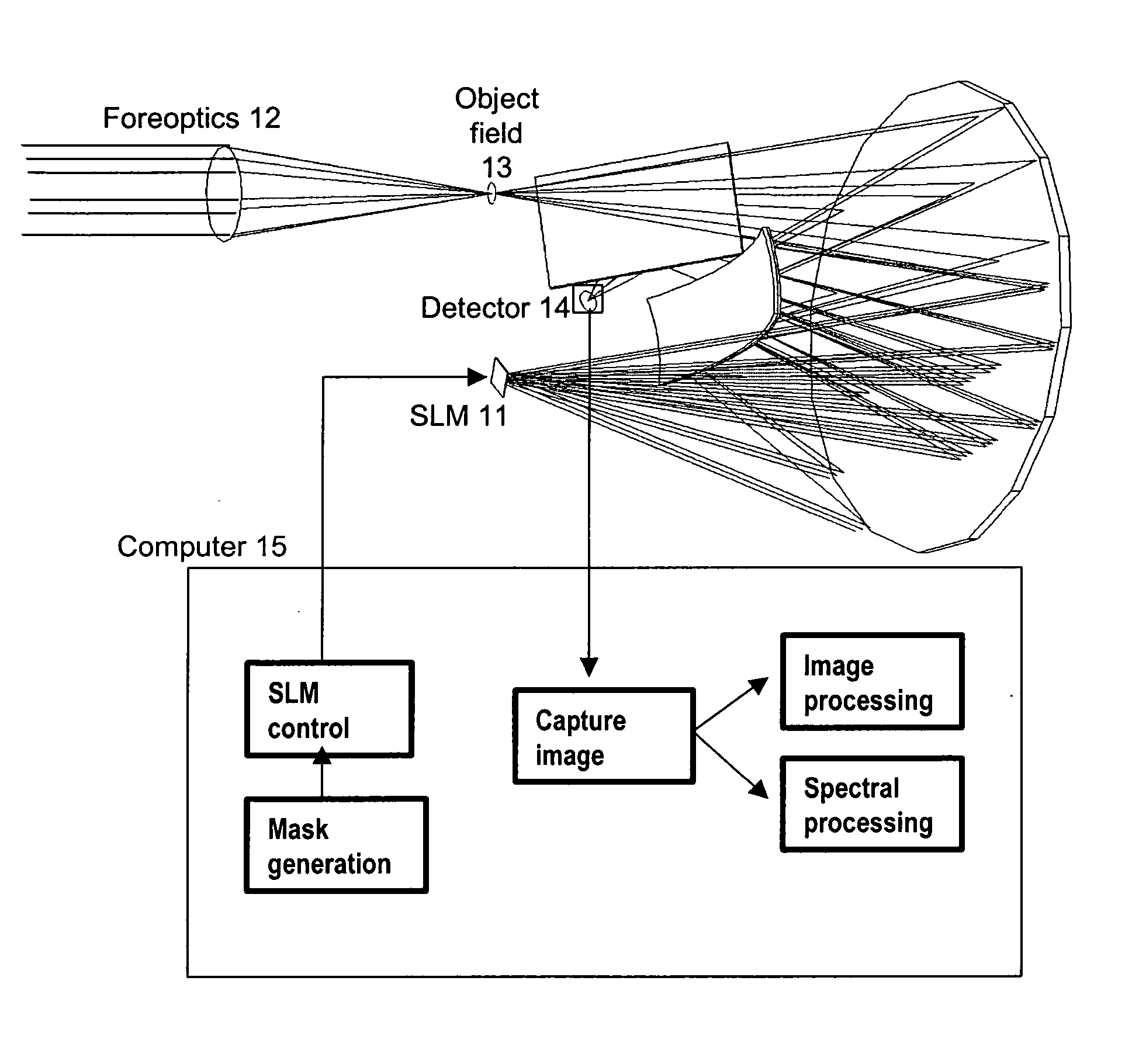
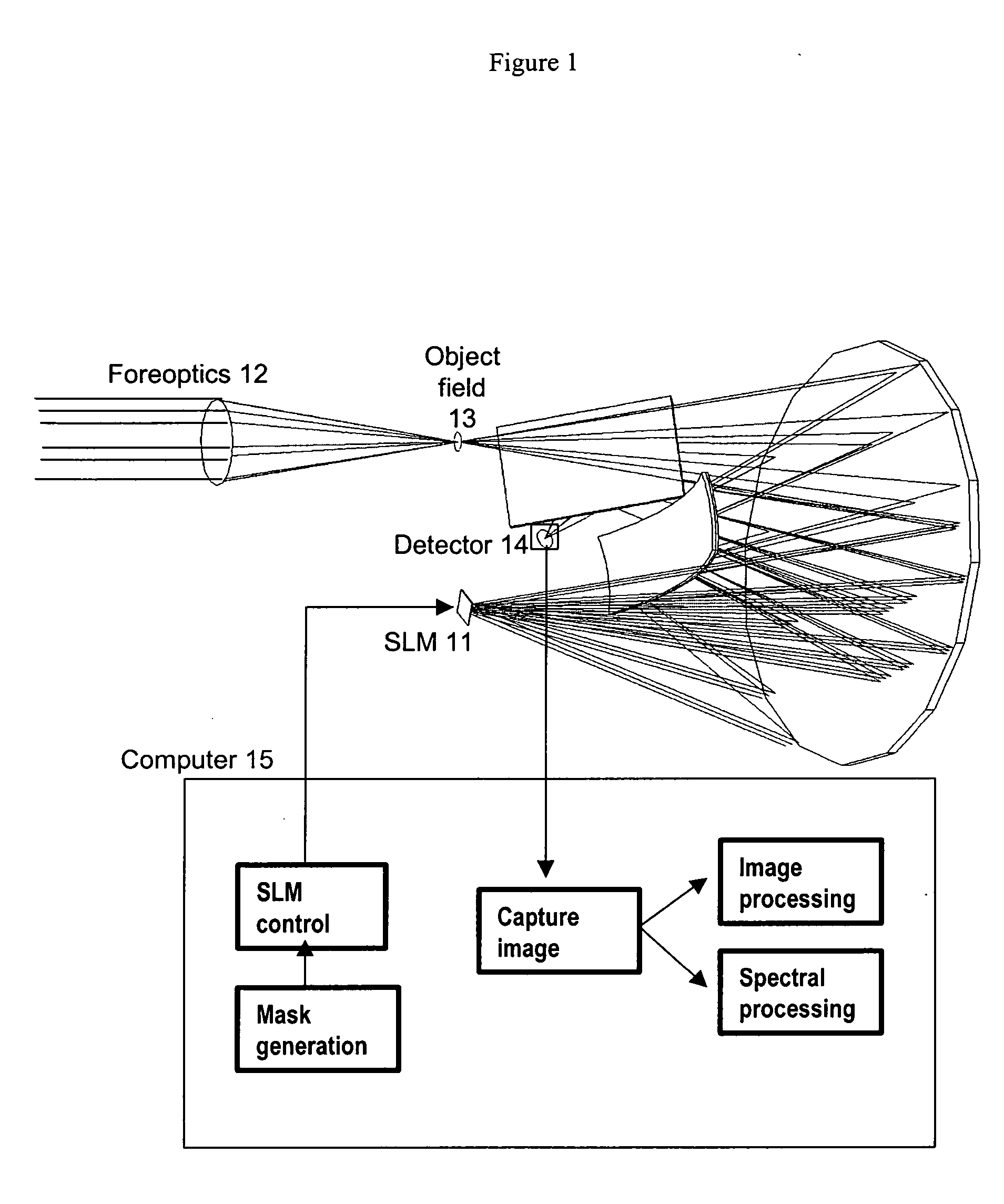
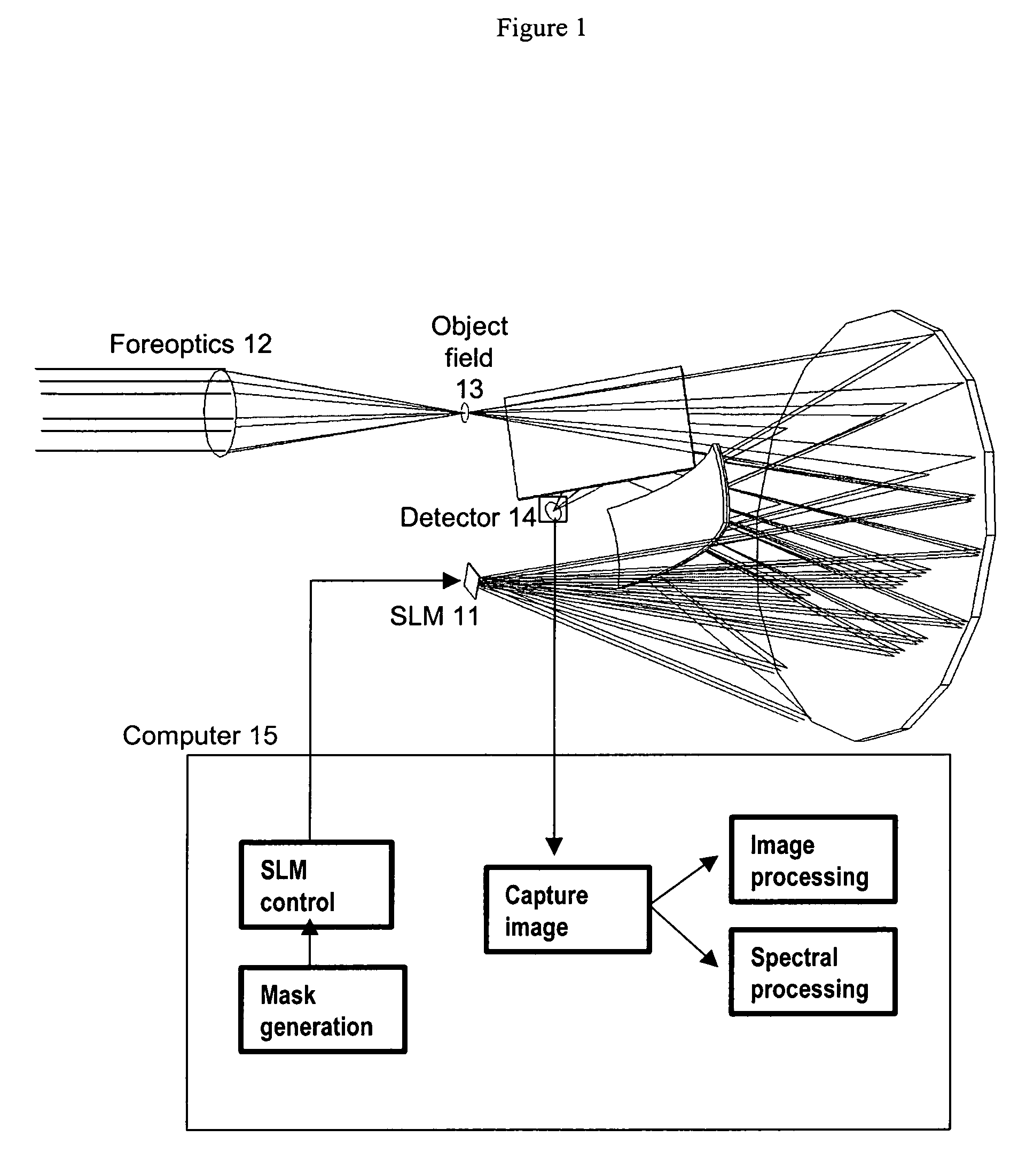
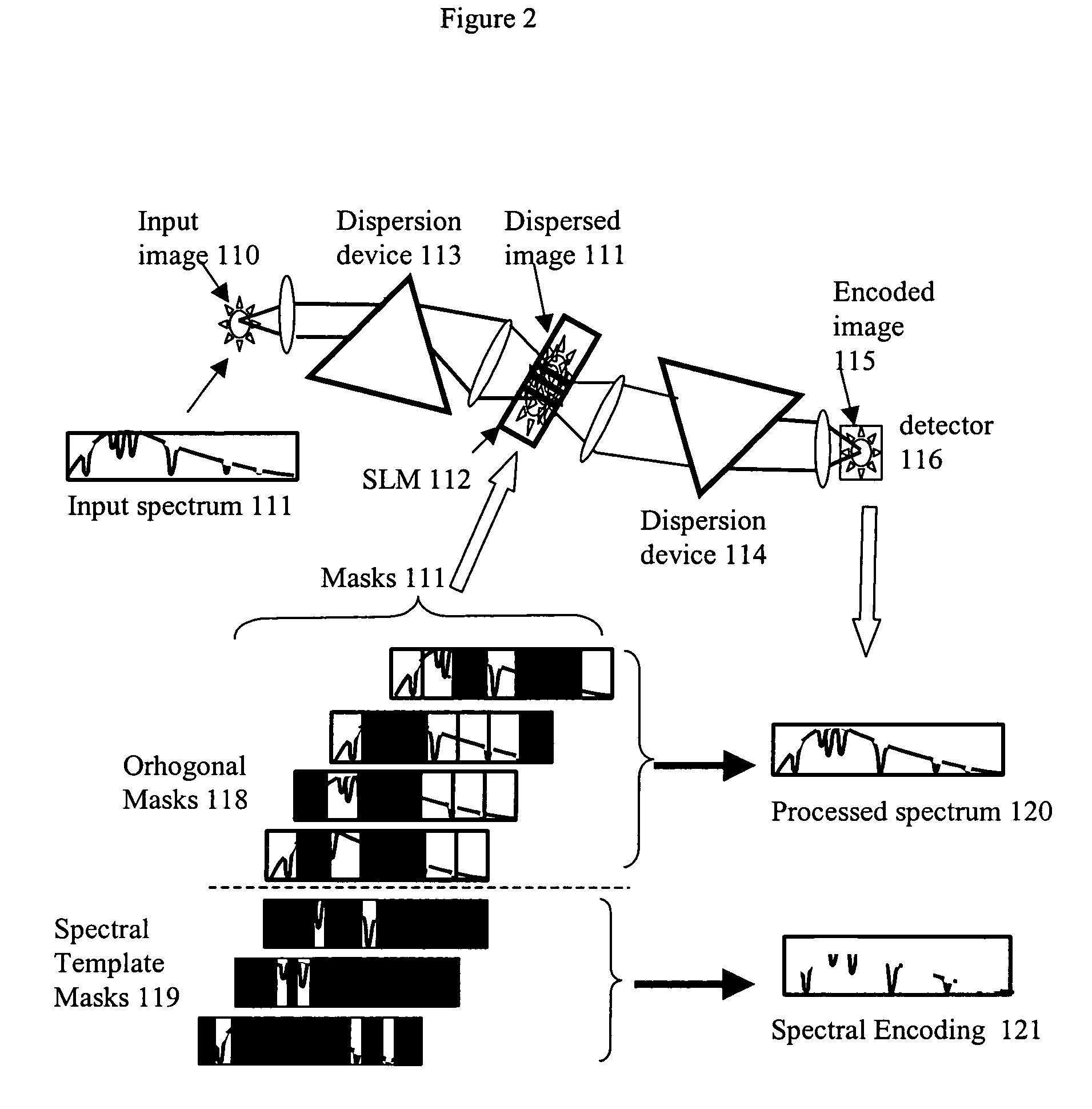
Spectral encoder
ActiveUS20070296969A1Reduce aberrationHigh quality two-dimensional imageRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpatial light modulatorSpectrograph
A spectral encoder for producing spectrally selected images of a radiation field containing multiple spectral components. An imaging spectrograph defines a first optical path that produces from the input radiation field a spectrally dispersed image comprising multiple spectral components displaced along a dispersion direction. Spectral pass bands are encoded on the dispersed image by a programmable spatial light modulator using one or more spatial masks. The imaging spectrograph further defines a second optical path that reverses the spectral dispersion of the first path and produces a spectrally-encoded polychromatic output image containing only those spectral components encoded by the spatial mask. The first and second optical paths share a common dispersing element. A detector records at least one spatial region of the spectrally encoded output image.
Owner:GOLDSTEIN NEIL +6
Light control devices and methods implemented with kinoform diffusers having controllable diffusion characteristics
Kinoform diffusers (82) exhibit controllable diffusion characteristics that include off-axis transmittance and reflectance properties, elimination of zero-order beam, and freedom from spectral dispersion under achromatic illumination. Light control devices (76, 80, 82) implemented with kinoform diffusers having controllable diffusion characteristics provide anisotropic luminous intensity distributions and glare control at high viewing angles while maintaining high luminaire efficiency or daylight utilization.
Owner:LUMEC HLDG ULC
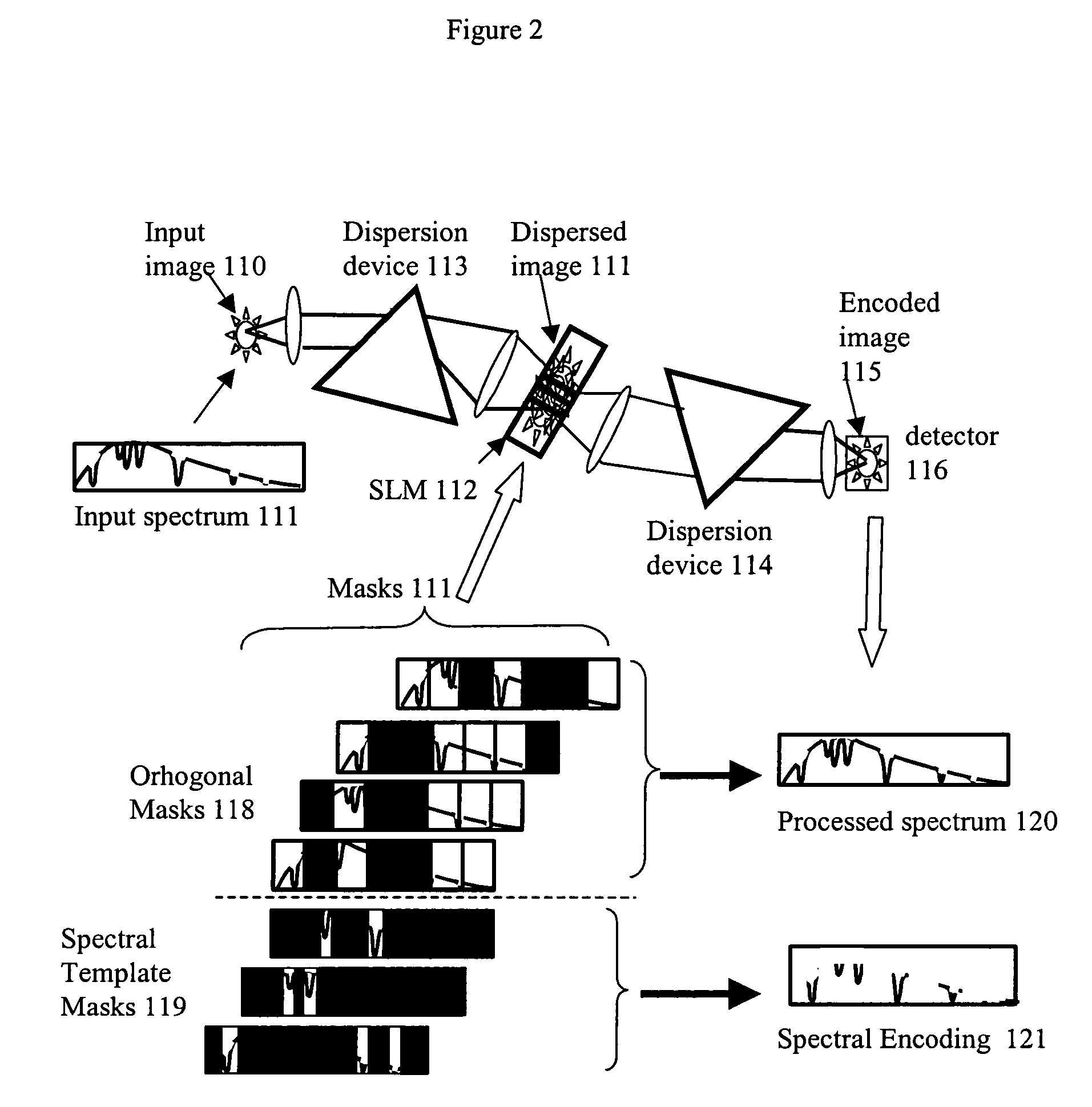
Coding and modulation for hyperspectral imaging
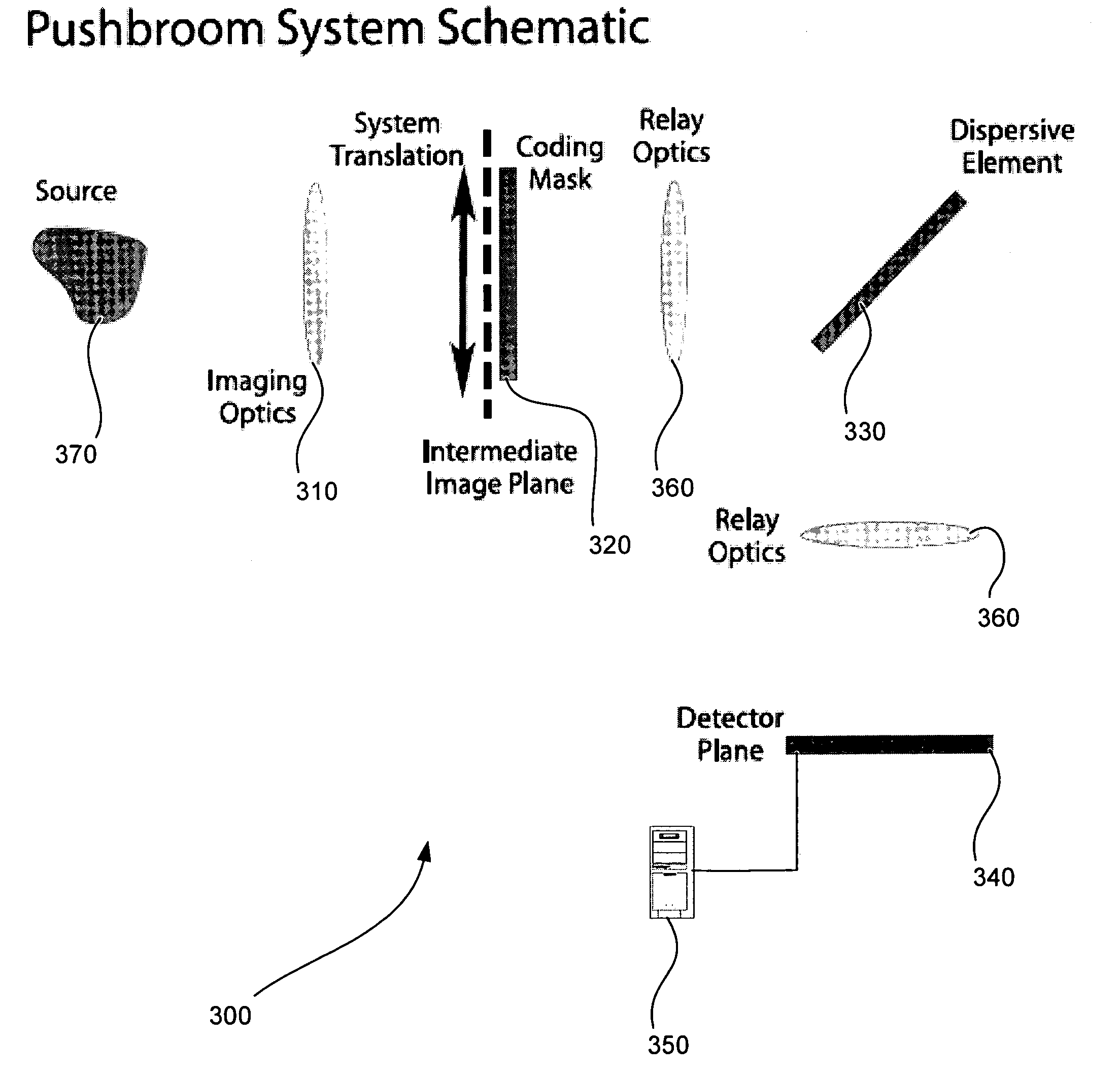
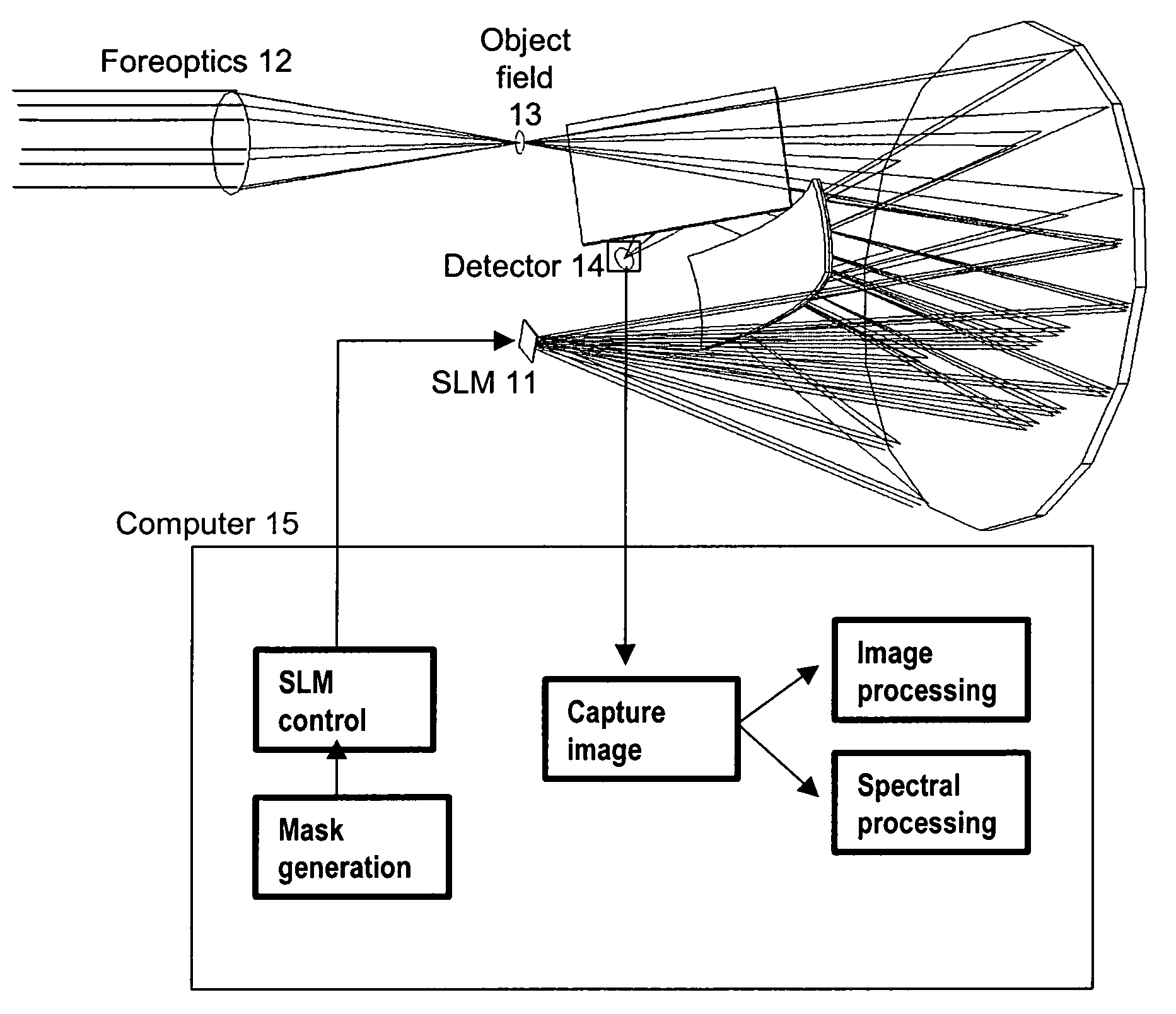
Embodiments of the present invention relate to systems and methods for spectral imaging. In one embodiment, an image of the scene is formed on a coded aperture of a spectrometer. A coded image from the coded aperture is detected on a two-dimensional detector array of the spectrometer through a spectrally dispersive element of the spectrometer. Data from the two-dimensional detector array is collected as the coded image is varied over time. The spectral image is estimated from the data collected and the variation of the coded image over time. The data collected is varied over time through translation, rotation, and defocus.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Mid-infrared hyperspectral spectroscopy systems and methods therefor
ActiveUS9518917B2High sensitivityEfficient emissionsSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyTest sampleHarmonic
MIR spectroscopy systems comprising hierarchical spectral dispersion that enables fine spectral resolution and high sensitivity spectroscopy are disclosed. Hierarchical spectral dispersion is derived by employing at least two diffractive lens arrays, located on either side of a test sample, each receiving input radiation having an input spectral range and distributing the input radiation into a plurality of output signals, each having a fraction of the spectral range of the input radiation. As a result, the signal multiplication factor of the two arrays is multiplied in a manner that mitigates the propagation of wavelength harmonics through the system. In some embodiments, an emitter array comprising a plurality of spectrally selective emitters provides the input MIR radiation to a spectroscopy system. In some embodiments, spectrally selective detectors are used to detect narrow spectral components in the radiation after they have passed through the test sample.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Tunable Pulse Width Laser
ActiveUS20130177031A1Control distortionLong durationLaser using scattering effectsSpectral bandsPulse duration
A method of tuning the time duration of laser output pulses, the method including spectrally dispersing optical pulses and further comprising providing an optical pulse having a time duration and a spectral bandwidth; spectrally dispersing (243, 245) the optical pulse so as to provide a selected change in the time duration of the pulse responsive to the spectral band-width of the pulse; outputting (226) an optical output pulse having a first time duration that is responsive to the selected change in time duration; providing another optical pulse; changing the amount of spectral bandwidth of the another optical pulse (272) to be different than that of the optical pulse or changing the amount of spectral dispersion so that spectrally dispersing the another optical pulse provides a change in time duration that is different than the selected change; and outputting (226) another optical output pulse having a second time duration that is responsive to the different change in time duration, the second time duration of the another optical output pulse being different than the first time duration of the optical output pulse.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
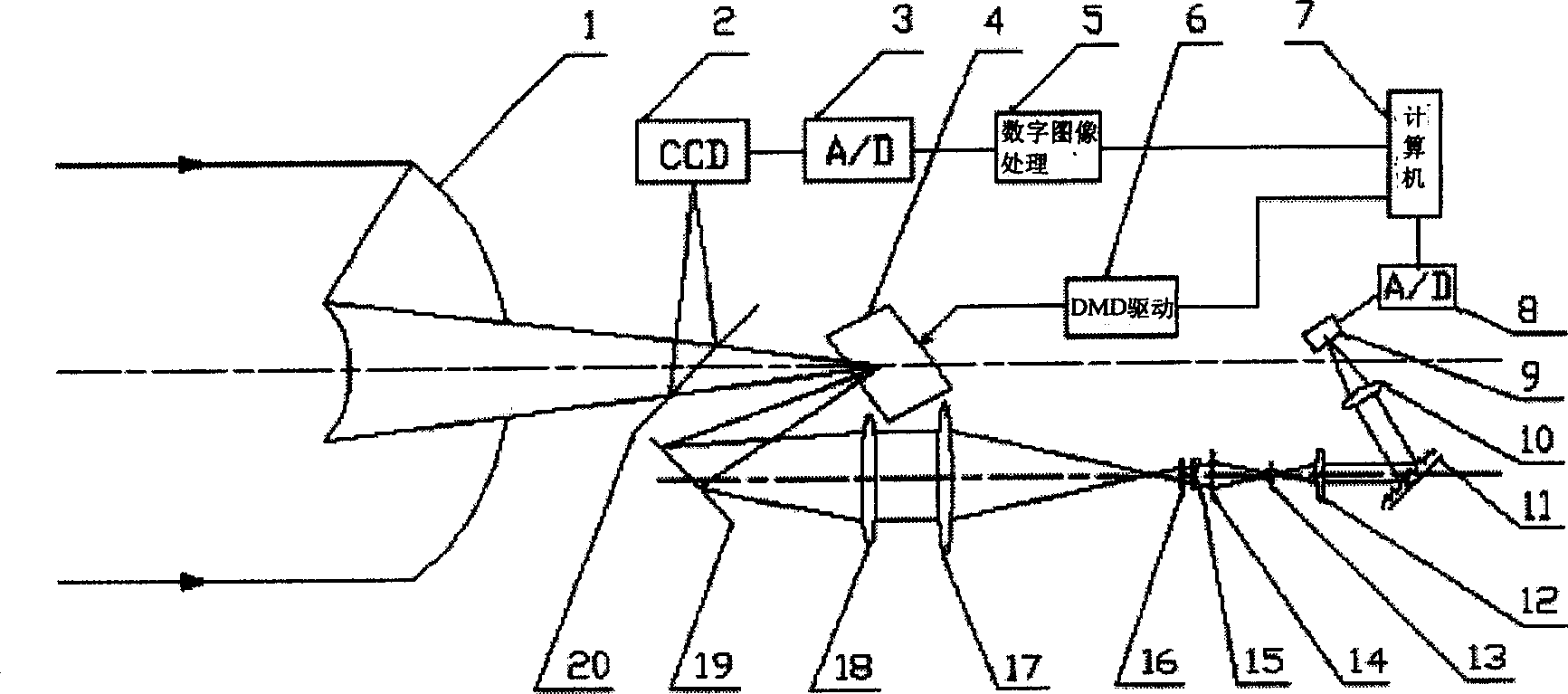
Digital microscope multi-objective imaging spectrometer apparatus
InactiveCN1702452AEliminate the effects ofHigh resolutionColor/spectral properties measurementsPoint objectData acquisition
This invention relates to an optical spectrum instruments of digital microscope multi-imaging, which comprises subsystems of imaging, dimensionality compression, dispersion and collection of spectrum and feedback of digital microscope circuit, wherein, the imaging subsystem comprises pre-telescope, digital microscope, collimation lens and focusing lens; the dimensionality compression subsystem comprises cylindrical micro-lens array and cylindrical lens; feedback subsystem of digital microscope circuit comprises spectroscope, focal plane detector, data gathering chip, digital image processor, computer and digital microscope driver. The invention can rapidly chose a plurality of point objects in large angular field without scanning, and can eliminate the influence of ambient light to improve the system signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Slit-scan multi-wavelength confocal lens module and slit-scan microscopic system and method using the same
ActiveUS8773757B2Improve performanceMinimized in sizePrismsMicroscopesReflectance spectroscopyLighting spectrum
The present invention provides a slit-scan multi-wavelength confocal lens module, utilizing at least two lenses having chromatic aberration for splitting a broadband light into continuously linear spectral lights having different focal length respectively. The present invention utilizes the confocal lens module employing slit-scan confocal principle and chromatic dispersion techniques and the confocal microscopy with optical sectioning ability and high resolution in spectral dispersion to establish a confocal microscopy method and system with long DOF and high resolution, capable of modulating a broadband light to produce the axial chromatic dispersion and focus on different depths toward an object's surface for obtaining the reflected light spectrum from the surface. Thereafter, the spectrum is spatially filtered by a slit and then a peak position with respect to the filtered spectrum along the scanning line is detected by a spectral image sensing unit for generating the sectional profile of the measured surface.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
Detection method and device of optical component surface topography and subsurface defect information
ActiveCN109916909AImprove measurement efficiencyHigh speed scanOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansLength waveTopography
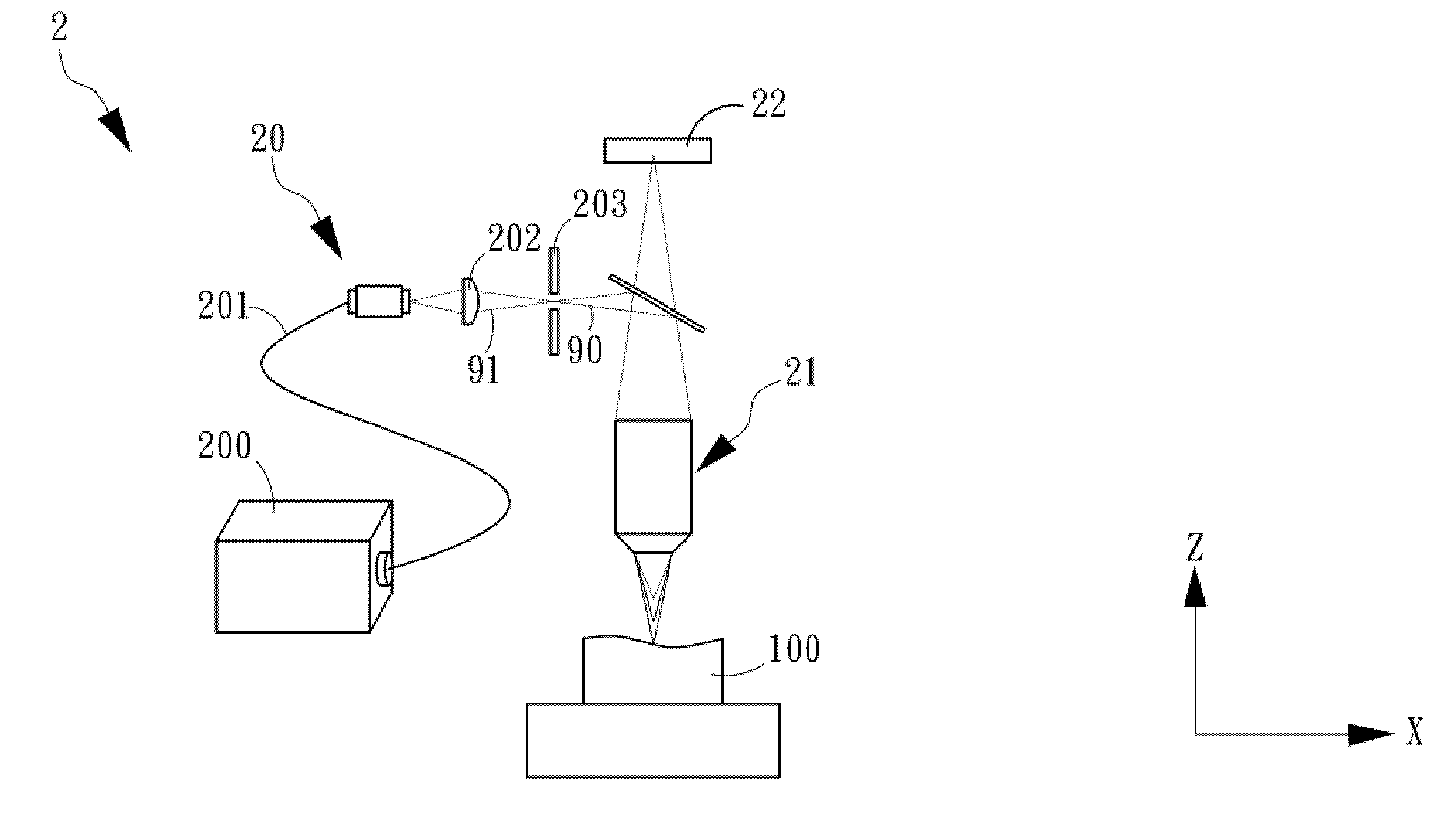
The invention relates to a detection method and device of optical component surface topography and subsurface defect information. The method comprises the following steps that wavelength information is used to measure a distance, one beam of compound color light (white) with a broad spectrum is emitted by a light source, spectral dispersion is generated through a dispersive lens to form monochromatic light with different wavelengths, and a focal point of each wavelength corresponds to one distance value; measurement light is reflected back from a surface of an object, the monochromatic light satisfying a confocal condition can be sensed by a spectrometer through a small hole, and the acquired distance value is converted through calculating the wavelength of the sensed focal point; and thetwo spectrometers are used to receive a surface of a component to be tested and light wave information of an internal defect so as to obtain surface information of the optical component, a position ofthe internal defect, depth information and the like simultaneously.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
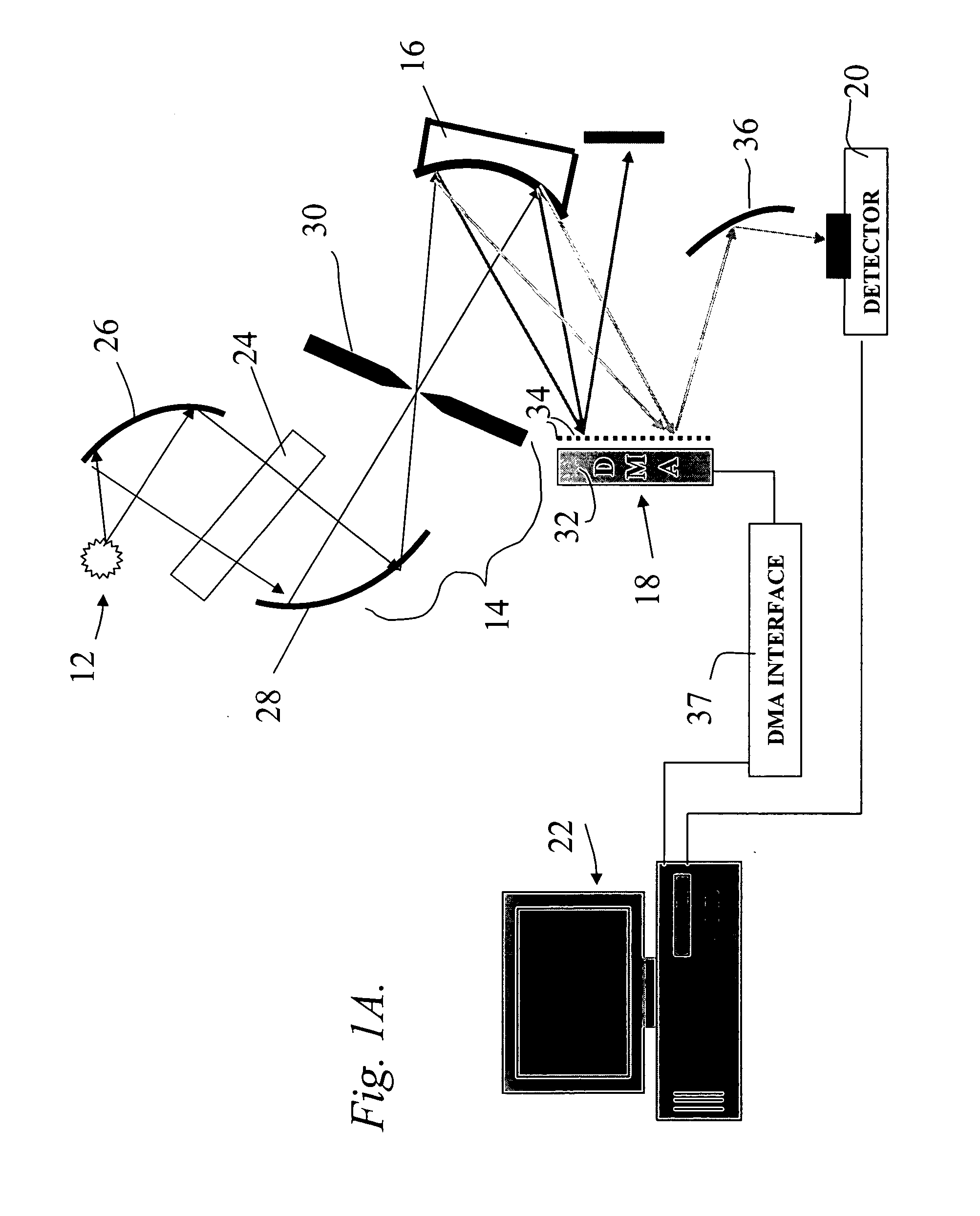
Device and method for optical spectroscopy
InactiveUS7330267B1Improve accuracyImprove performanceOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryQuantum-optical spectroscopyWavefront
The invention relates to an apparatus for optical spectroscopy having means to produce an interference pattern and having a spatially resolving detector which can record the interference pattern produced. In accordance with the invention, the wavefronts of at least one of the part rays involved in the interference pattern is influenced in dependence on the wavelength by spectrally dispersive or diffractive optical elements.
Owner:CAMPUS TECH
Dielectric-coating structure reflecting mirror used for chirp pulse amplification optical spectrum shaping
InactiveCN101140332AAvoid difficultiesSolve practicalityLaser detailsMirrorsHigh power lasersSemiconductor structure
The present invention relates to a chirp pulse amplifying spectrum shaping dielectric film structure reflector, which comprises a transparent substrate, a high reflectance film system, an anaglyph structure and an external protective layer. Wherein, the high reflectance film system is composed of a plurality of staggered dielectric films. A high reflectance film layer and a lower reflectance film layer of the high reflectance film closely contact the anaglyph structure. The anaglyph structure can take a plurality of shapes, such as a micro-lens high transparency film system structure, an air dielectric structure, a glass anaglyph structure or other transparent dielectric structures, including semiconductor structures. As a high-power laser chirp pulse with a plane wave structure vertically casts onto the reflector, the laser passes through the high reflectance film system and the anaglyph structure and all residual lasers are reflected to back of the reflector through the transparent substrate. Reflex intensity distribution is modulated to a needed spectrum distribution structure. The reflector of the present invention can be inserted into any place of an amplifier link and improve capacity to distinguish shaping spectrum chromatic dispersion to a certain level. Scope modulation exceeds 60% without changing phase position, thus adapting to PW devices.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Systems and methods for 4-d hyperspectrial imaging
ActiveCN109196333AEasy accessGet efficient and automatedRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometrySpatial light modulatorExcitation pattern
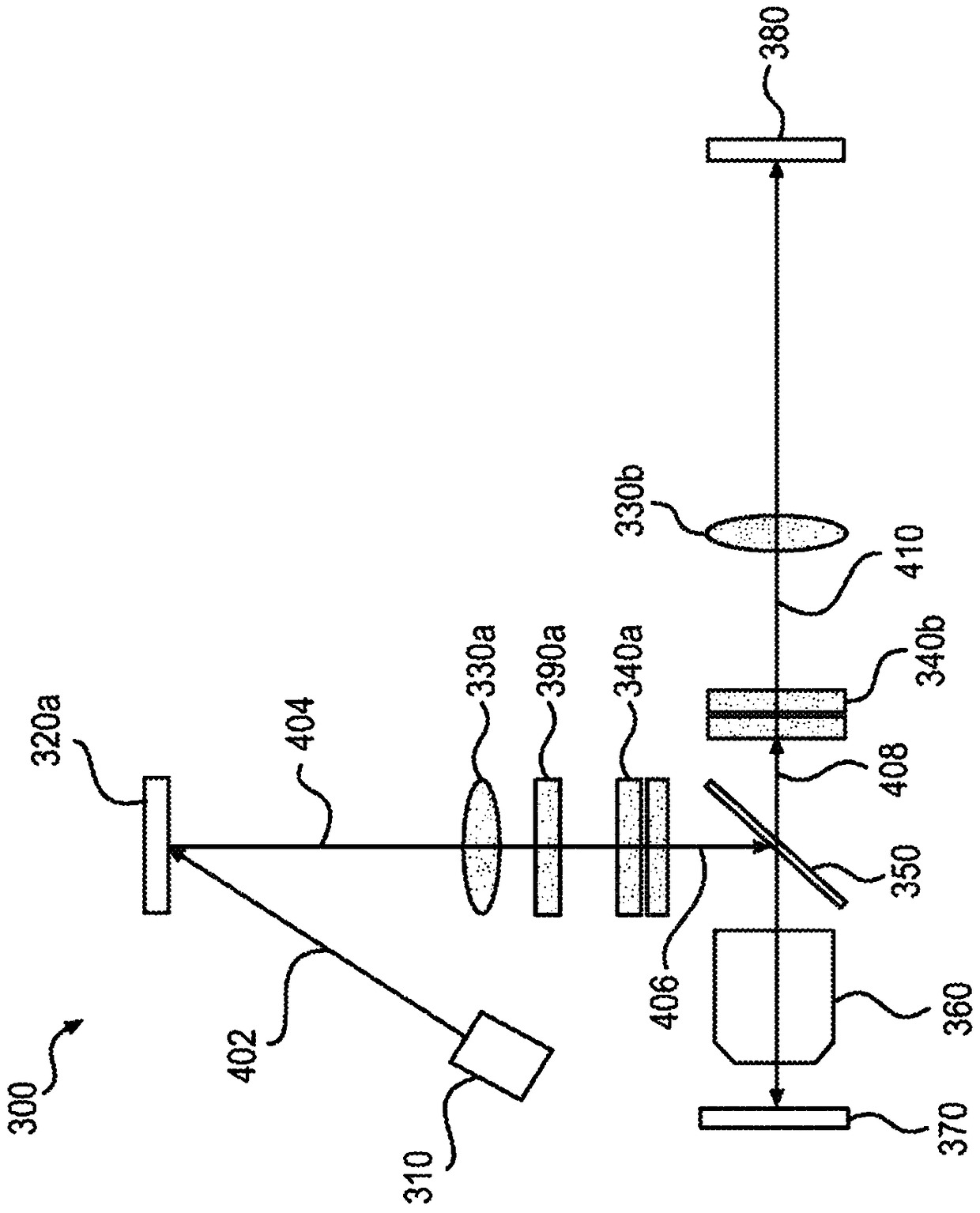
Systems and methods for hyperspectral imaging are described. A hyperspectral imaging system (300), comprising: a sample holder (370) configured to hold a sample; a light source (3010) configured to emit excitation light (402) having one or more wavelengths; a two-dimensional imaging device (380); and an optical system comprising: a first spatial light modulator (320a); a first dispersive element (340a); and a second dispersive element (340b); wherein the optical system is configured to (i) structure the excitation light (402), using the first spatial light modulator (320a), into a predetermined two-dimensional excitation pattern at a conjugate plane of a focal plane in the sample; (ii) spectrally disperse, using the first dispersive element (340a), the excitation light (404); (iii) use excitation pattern (406) to illuminate the sample illuminate the sample in an excitation pattern (406) with the one or more wavelengths dispersed along a first lateral direction within the focal plane; (iv) collect, from the sample, emission light (408); (v) spectrally disperse, using the second dispersive element (340b), the collected emission light (408); and (vi) provide the collected emission light (410) in-focus to the imaging device (380) such that the spectrally dispersed emission light (410) is spectrally dispersed along a second lateral direction.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
Spectrally encoded coherent ant-stokes raman scattering endoscope
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Two-dimensional fourier transform spectrometer
InactiveUS20100171952A1Reduce ambiguityReduce subjectivityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
The present invention relates to a system and methods for acquiring two-dimensional Fourier transform (2D FT) spectra. Overlap of a collinear pulse pair and probe induce a molecular response which is collected by spectral dispersion of the signal modulated probe beam. Simultaneous collection of the molecular response, pulse timing and characteristics permit real time phasing and rapid acquisition of spectra. Full spectra are acquired as a function of pulse pair timings and numerically transformed to achieve the full frequency-frequency spectrum. This method demonstrates the ability to acquire information on molecular dynamics, couplings and structure in a simple apparatus. Multi-dimensional methods can be used for diagnostic and analytical measurements in the biological, biomedical, and chemical fields.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Spectral encoder
ActiveUS7324196B2Improve image qualityReduce aberrationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpatial light modulatorSpectrograph
A spectral encoder for producing spectrally selected images of a radiation field containing multiple spectral components. An imaging spectrograph defines a first optical path that produces from the input radiation field a spectrally dispersed image comprising multiple spectral components displaced along a dispersion direction. Spectral pass bands are encoded on the dispersed image by a programmable spatial light modulator using one or more spatial masks. The imaging spectrograph further defines a second optical path that reverses the spectral dispersion of the first path and produces a spectrally-encoded polychromatic output image containing only those spectral components encoded by the spatial mask. The first and second optical paths share a common dispersing element. A detector records at least one spatial region of the spectrally encoded output image.
Owner:GOLDSTEIN NEIL +6
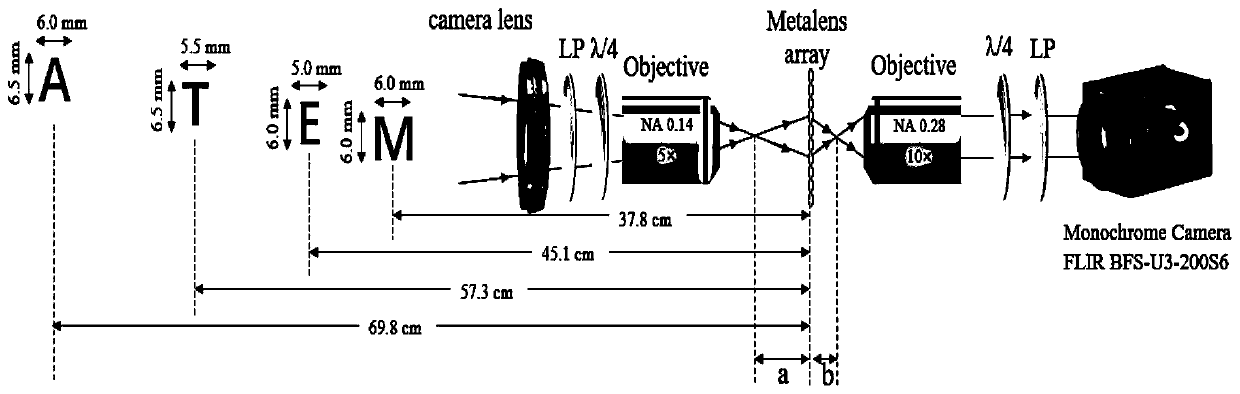
Ultra-compact spectral light field camera system based on super-structured lens array
ActiveCN111426381AReduce process complexitySimple processRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSuperachromatLight-field camera
An ultra-compact spectral light field camera system based on a super-structured lens array comprises a parallel light source lens, linear polaroids, quarter-wave plates, objective lenses, the super-achromatic super-structured lens array and a monochromatic camera which are arranged in sequence. The super-achromatic super-structured lens array is arranged between two pairs of linear polaroids, thequarter-wave plates and objective lens composition structures which are arranged in sequence. The distance a from the image plane of the main lens to the super-structured lens array, the distance b from the super-structured lens array to the re-imaging plane and the focal length f of the super-structured lens meet a certain relation, and the camera is arranged on the image plane and used for receiving images; the super-achromatic super-structured lens array is a two-dimensional lens array plane formed by arranging super-achromatic super-structured lenses on a plane according to a certain rule;the super-achromatic super-structured lenses with off-axis focusing properties are designed, and spectral dispersion is realized by utilizing the change of the focusing positions of the super-achromatic super-structured lenses under different wavelengths.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Achromatic optical system for beam shaping
An achromatic refractive beam shaping optical system that transforms the intensity distribution of a light beam, preferably provides transformation of a beam which intensity distribution described by Gaussian function to a beam of uniform intensity. The system consists of at least two lens groups, one of lens groups is made from at least two lenses having different characteristics, of spectral dispersion, thus achromatic for a certain spectral range optical design providing zero or negligible for practical applications wave aberration is realized. By choosing parameters of lens groups the system can be realized as a telescope of Galilean or Keplerian type, or as a collimator, or as an objective lens. To provide adjustment features one lens group of the system is movable along the optical axis.
Owner:MOLECULAR TECH
Super lateral resolution surface three-dimensional online interference measuring system based on spectral dispersion full field
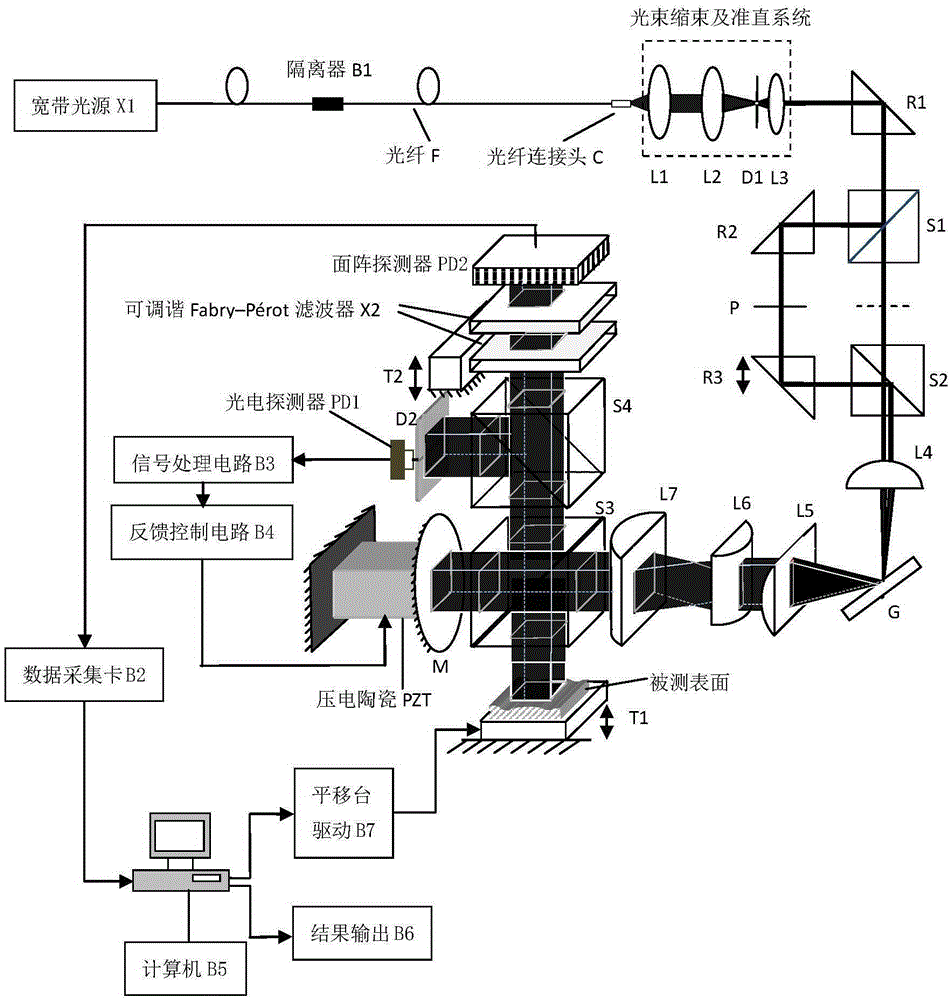
ActiveCN105333816AImprove anti-interference abilityAccurate traceabilityUsing optical meansGratingSignal processing circuits
The invention discloses a super lateral resolution surface three-dimensional online interference measuring system based on a spectral dispersion full field, and belongs to the field of optical measurement. The system is composed of a broadband light source, an isolator, a fiber, a fiber joint, a spherical-surface and cylindrical-surface spectroscopes, spectroscopes, right-angle prisms, diaphragms, a raster, a reflector, a surface array detector, a photoelectric detector, a Fabry-Perot filter, piezoelectric ceramics, a signal processing circuit, a feedback control circuit, a data acquisition card, a computer, translation benches, a translation bench driving part, a result output part and the like. The raster disperses a broadband spectrum to form a mating plate whose wavelength is continuously distributed in a transverse direction, and the mating plat is incident vertically to a measured surface through beam expansion for full-field measurement; a surface provided with a step whose height difference is greater than a half-wavelength and a large-depth-to-width-ratio groove is measured by use of two wavelengths; super lateral resolution measurement is realized by use of the Fabry-Perot filter; and ambient interference is compensated through feedback control, the system is enabled to be suitable for online measurement, the measuring result can be accurately traced to a wavelength reference, and the influence of the drift of a light source spectrum is eliminated.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
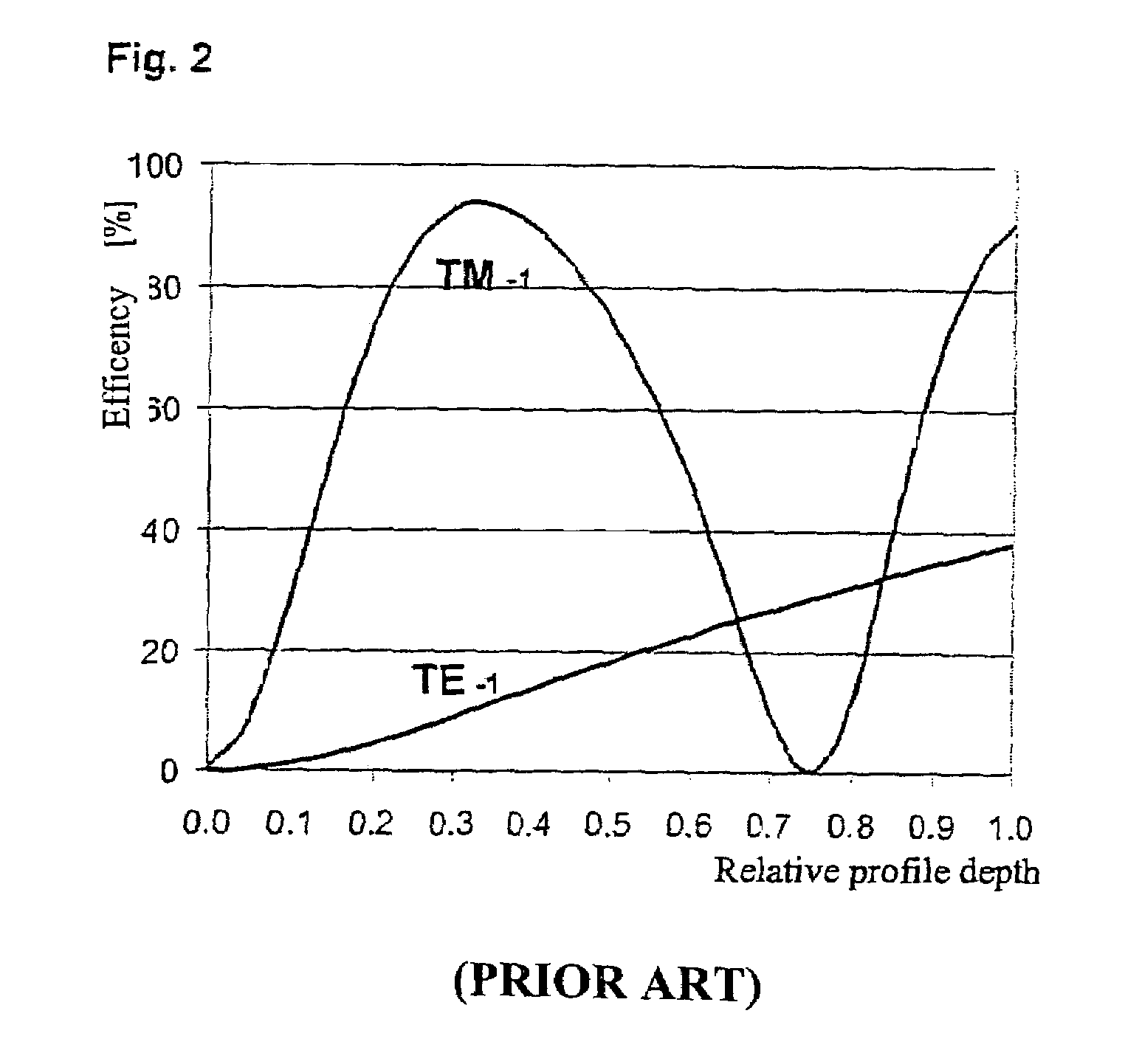
Polarization-dependent grating interferometer for measuring optical profile depth and spectral properties of a sample
InactiveUS7161683B2Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySpectral dispersionOptical polarization
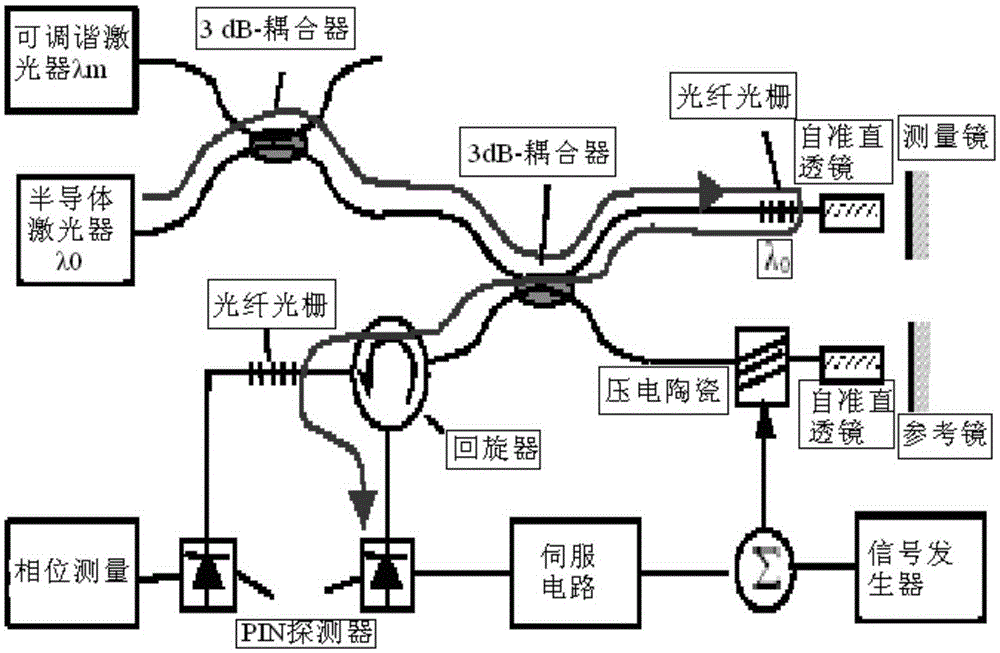
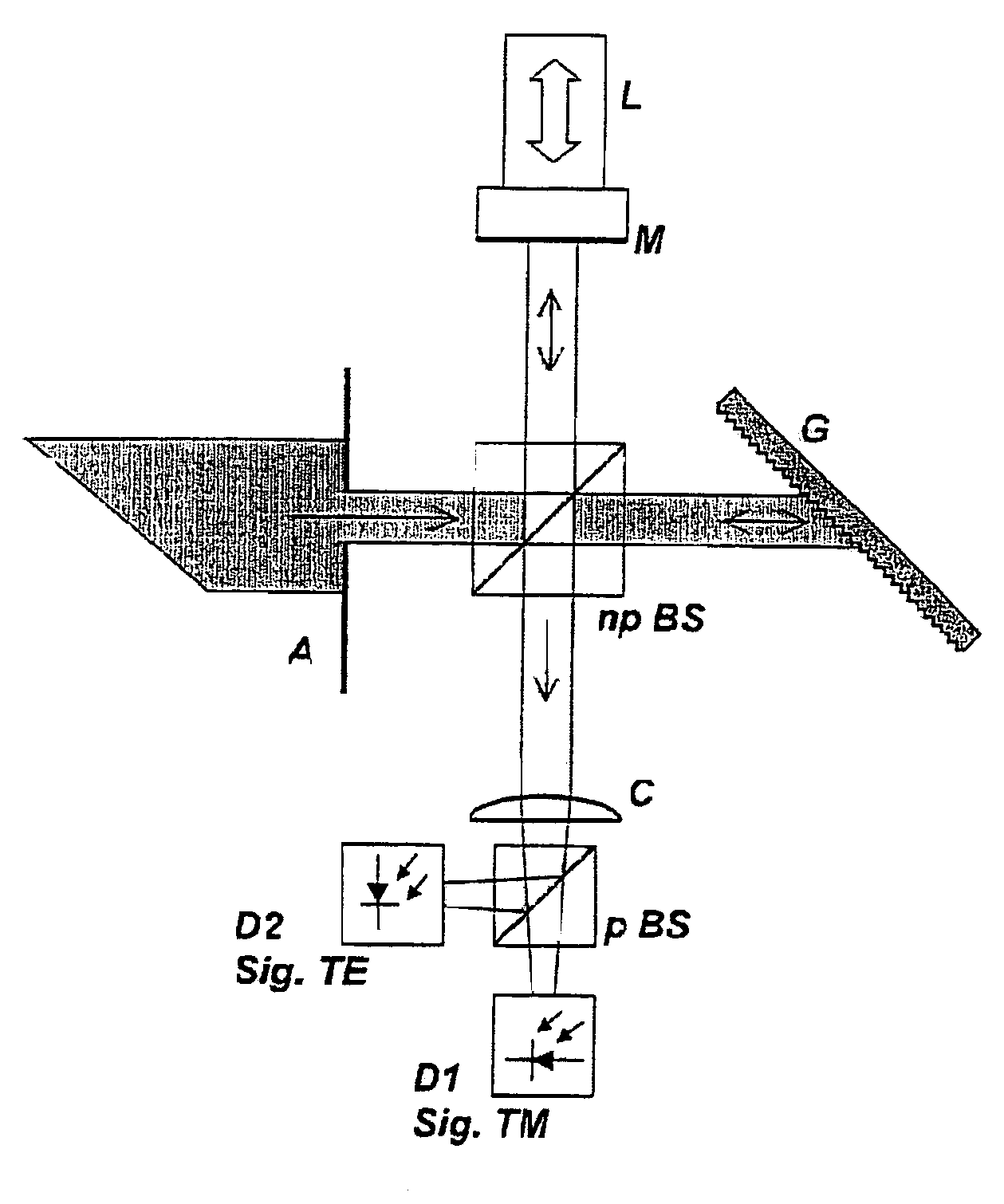
The present invention relates to a spectrally dispersive interferometric optical apparatus having a light source, generating a phase shift, measuring the intensity of the interference signals, selectively measuring the intensity of the interference signal and determining the phase angles and / or a relative phase shift of the intensity of the interference signals. In accordance with the invention, the generating of a phase shift between components of different polarization directions in at least one of the branches of the interferometer includes a diffraction grating. The selective determination of the intensity of the interference signal in dependence on the polarization moreover permits determination of the respective intensity for the TE components and for the TM components of the interference signal with respect to the coordinate system of the diffraction grating.
Owner:CAMPUS TECH
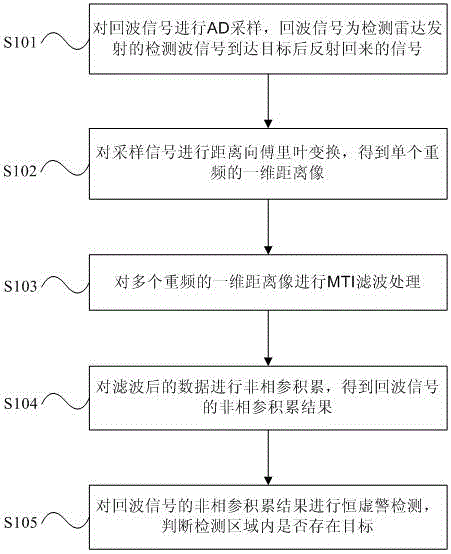
Unmanned area target detection method
InactiveCN106443626AEnhanced inhibitory effectHigh resolutionWave based measurement systemsRadarAzimuth direction
The invention provides an unmanned area target detection method. The unmanned area target detection method comprises the following steps: carrying out AD sampling on echo signals, wherein the echo signals are reflection signals of detection wave signals sent by a detection radar after the detection wave signals reach targets; carrying out range-direction Fourier transform on the sampled signals to obtain a single repetition-frequency one-dimensional range image; carrying out MTI filtering on a plurality of repetition-frequency one-dimensional range images; carrying out non-phase-coherent accumulation on filtered data to obtain non-phase-coherent accumulation results of the echo signals; and carrying out constant false-alarm rate detection on the non-phase-coherent accumulation results of the echo signals and judging whether the targets exist in a detected area. The unmanned area target detection method adopts a dual-delay-line canceller, so that the inhibition capability on zero-frequency clutters can be effectively improved; through the adoption of the azimuth-direction non- phase-coherent accumulation, the azimuth-direction spectral dispersion effect is effectively avoided; in addition, the zero-frequency resolution ratio and the signal-to-clutter ratio of an azimuth Doppler can be further improved by increasing MTI filtering points and non-phase-coherent accumulation points.
Owner:西安思丹德信息技术有限公司
Adama conversion near infrared spectrometer
InactiveCN101419163AIncrease the areaIncrease luminous fluxPhase-affecting property measurementsHadamard transformGrating
The invention provides a novel hadamard transform near-infrared spectrometer, which aims to improve the luminous flux of single micromirrors of a micromirror array of the hadamard transform near-infrared spectrometer further to improve detection sensitivity and signal-to-noise ratio. The hadamard transform near-infrared spectrometer comprises an one-dimensional micromirror array arranged by the micromirrors; the shapes of mirror faces of the micromirrors are strips with long axes and short axes; the one-dimensional micromirror array is formed by the micromirrors which are parallelly and linearly arranged along the short axis direction of the mirror faces of the micromirrors; and the arrangement direction is along a spectral dispersion direction. Lights in different wavelength intervals which are subjected to chromatic dispersion through a preposition optical system and a grating are irradiated to the surfaces of the micromirrors respectively which are parallelly arranged, and are focused on a detector by a postposition optical system through the reflection of the micromirrors. The areas of the single micromirrors are increased, and the luminous flux is increased, so the adoption of the technical proposal can ensure that the detection sensitivity of an instrument is improved, and the signal-to-noise ratio of a detection result is improved by more than 10 times.
Owner:BEIJING CHINAINVENT INSTR TECH
Spectrally encoded coherent Anti-stokes raman scattering endoscope
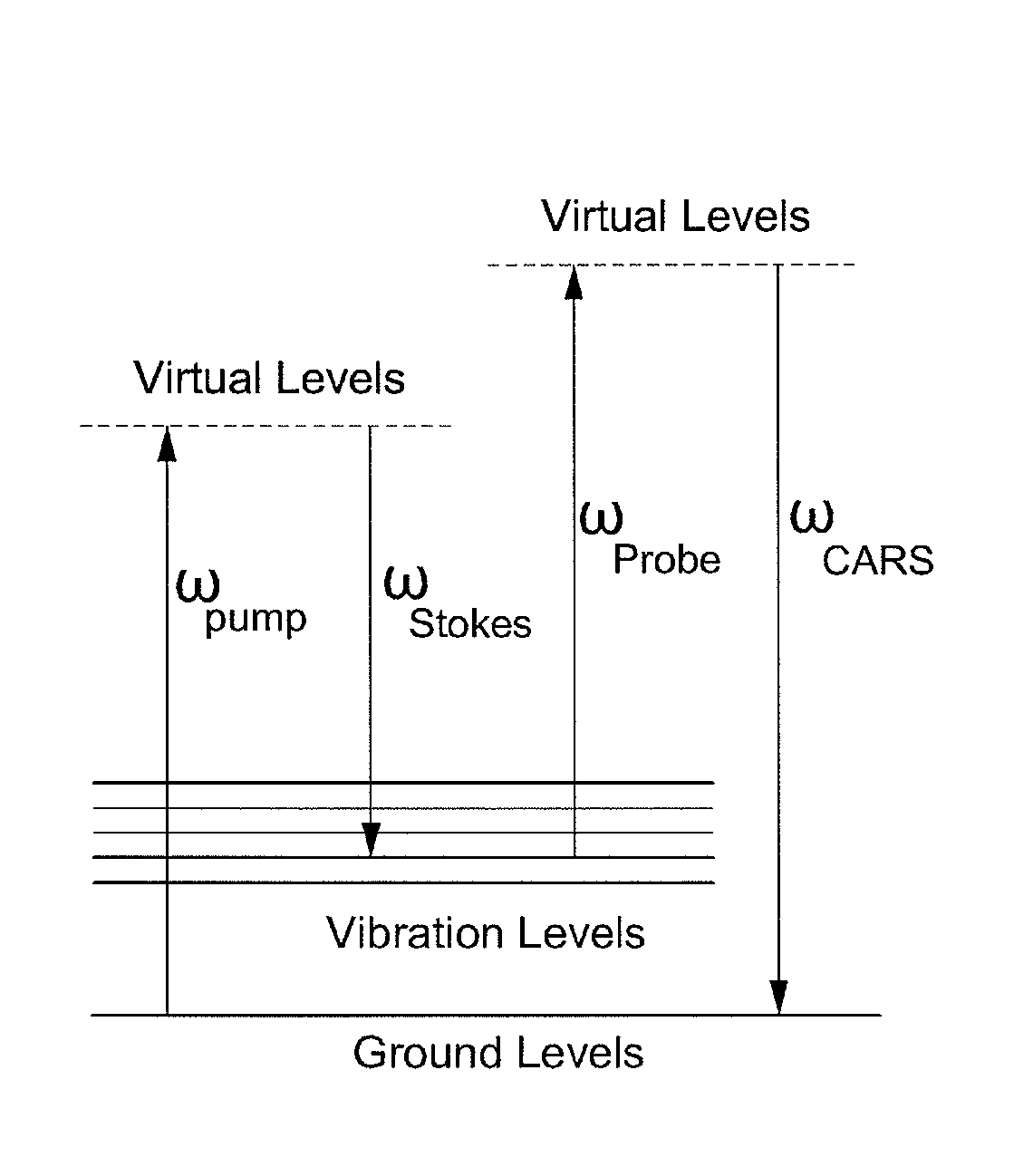
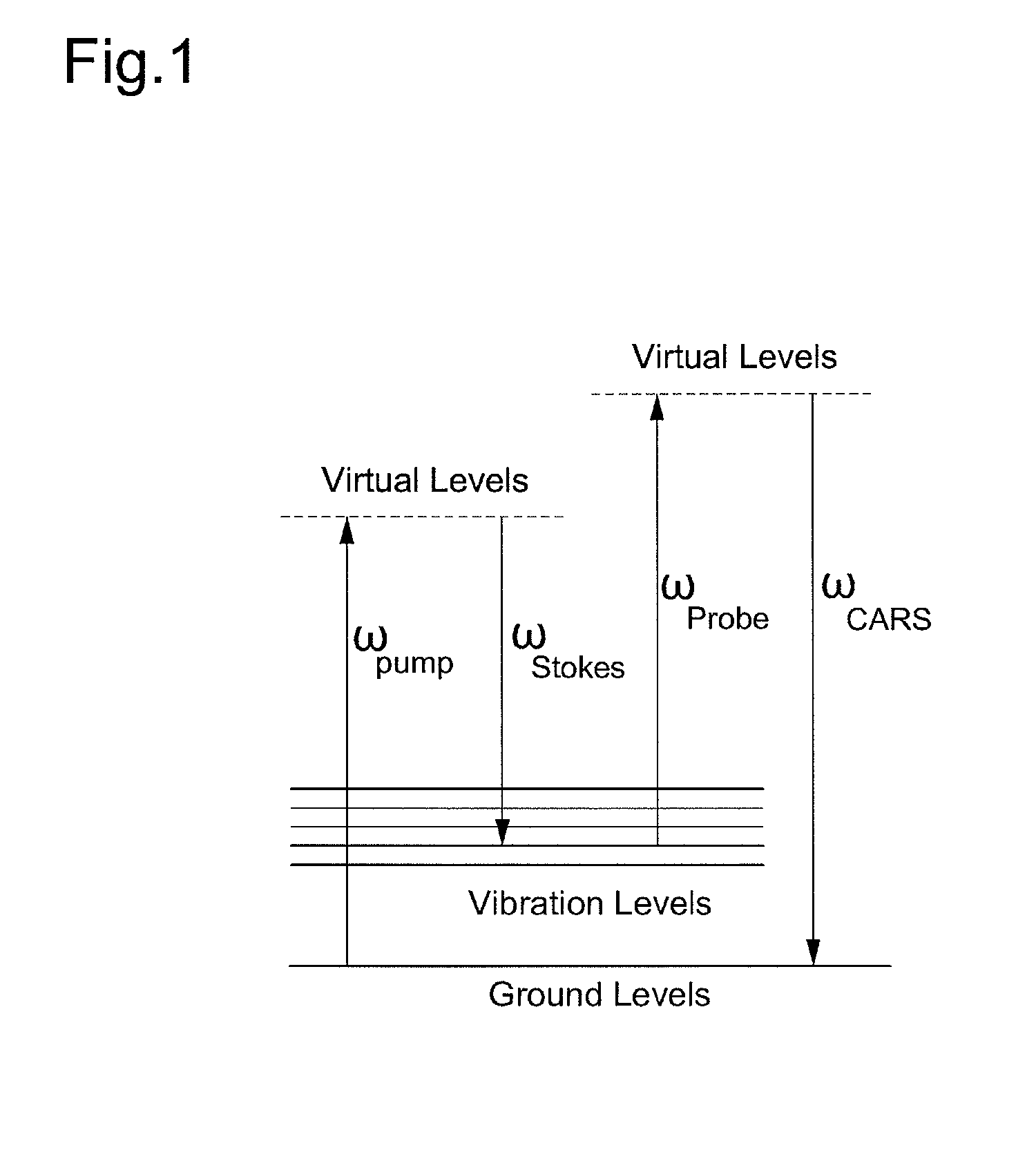
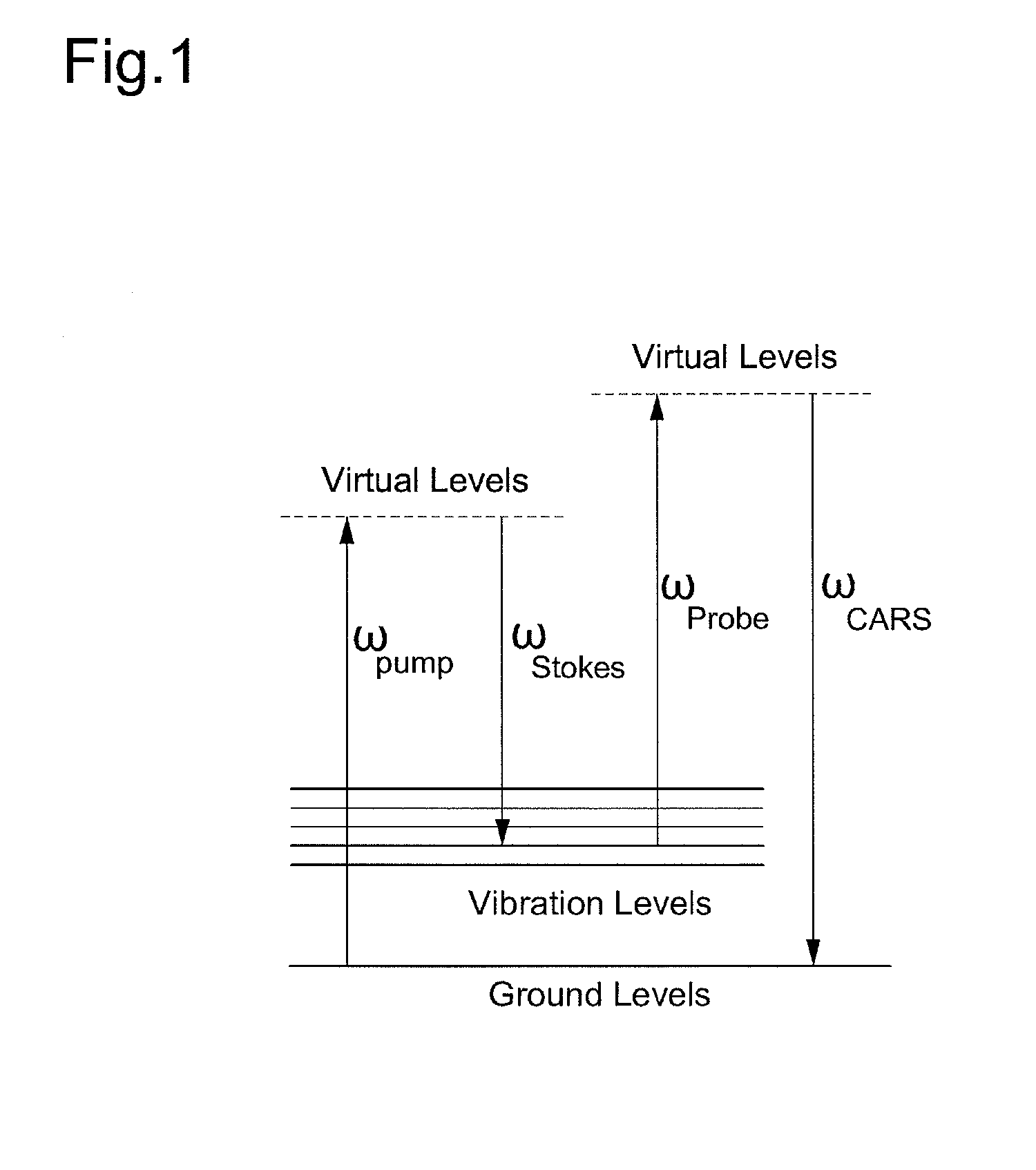
Disclosed is a spectrally encoded coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) endoscope that is capable of spatially encoding spectral dispersions of two light sources having frequency difference as much as a Raman shift and overlapping two laser beams on a position where a sample to be measured is placed, thereby acquiring a spatial distribution of CARS signals.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Large-view field high-resolution spectrometer optical system design method
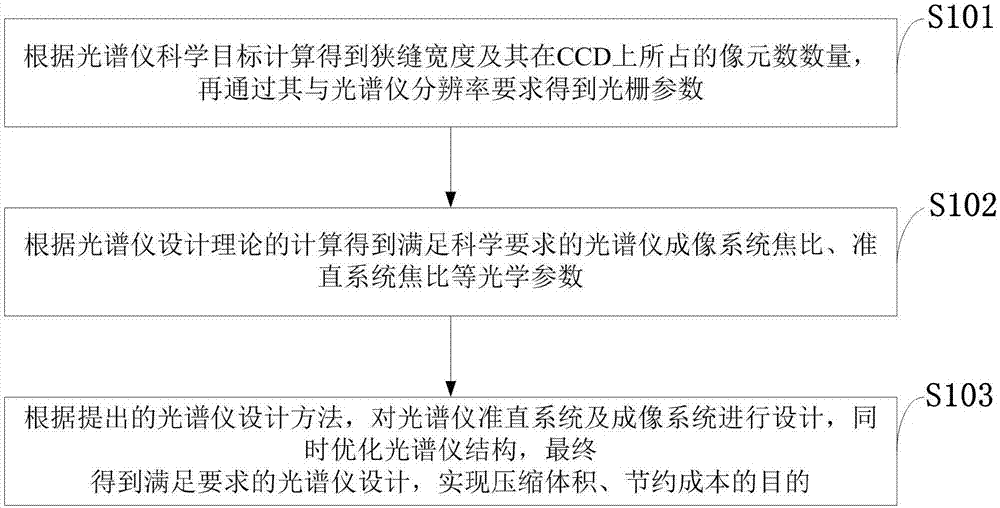
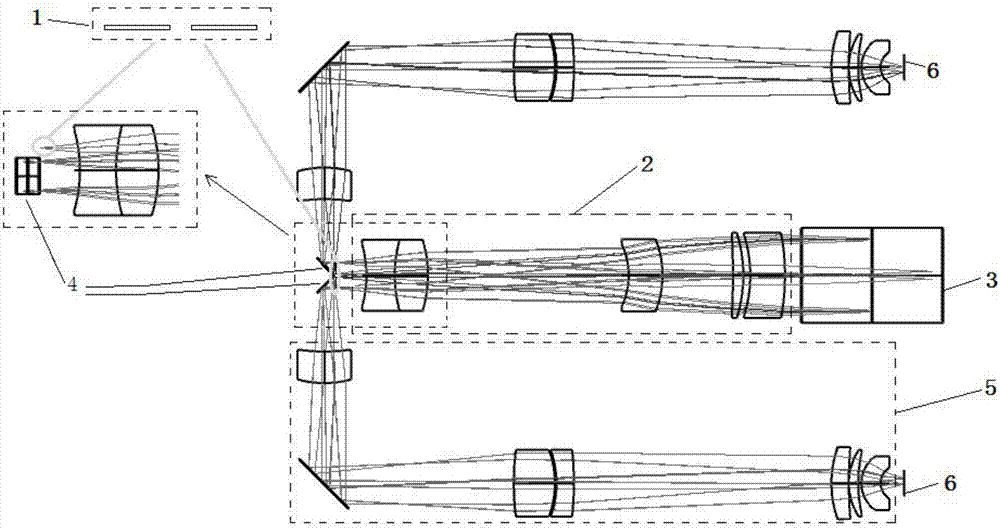
InactiveCN106932098AReduce space layout costsRealize simultaneous acquisitionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsGratingOphthalmology
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical equipment, and discloses a large-view field high-resolution spectrometer optical system design method. The method comprises steps: multiple sections of slits and corresponding field lenses are adopted, and a different field lens carries out reflection and imaging on a sectional slit to a different CCD; light emitted by the slit is collimated through a collimation system and shines on a dispersion element, and spectral dispersion is carried out through the dispersion element; and grating diffraction light after dispersion performs imaging through the collimation system, spatial dislocation exists between the image surface after imaging and the slit of the spectrometer, a field lens is added at the image surface, and an image on a focal plane is imaged on the CCD through the imaging system. The dispersion functions of multiple spectrometers are realized, simultaneous data acquisition by multiple detectors in one spectrometer can be realized, the view field is increased, and the research cost and the space layout cost of multiple spectrometers can be reduced.
Owner:YUNNAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com