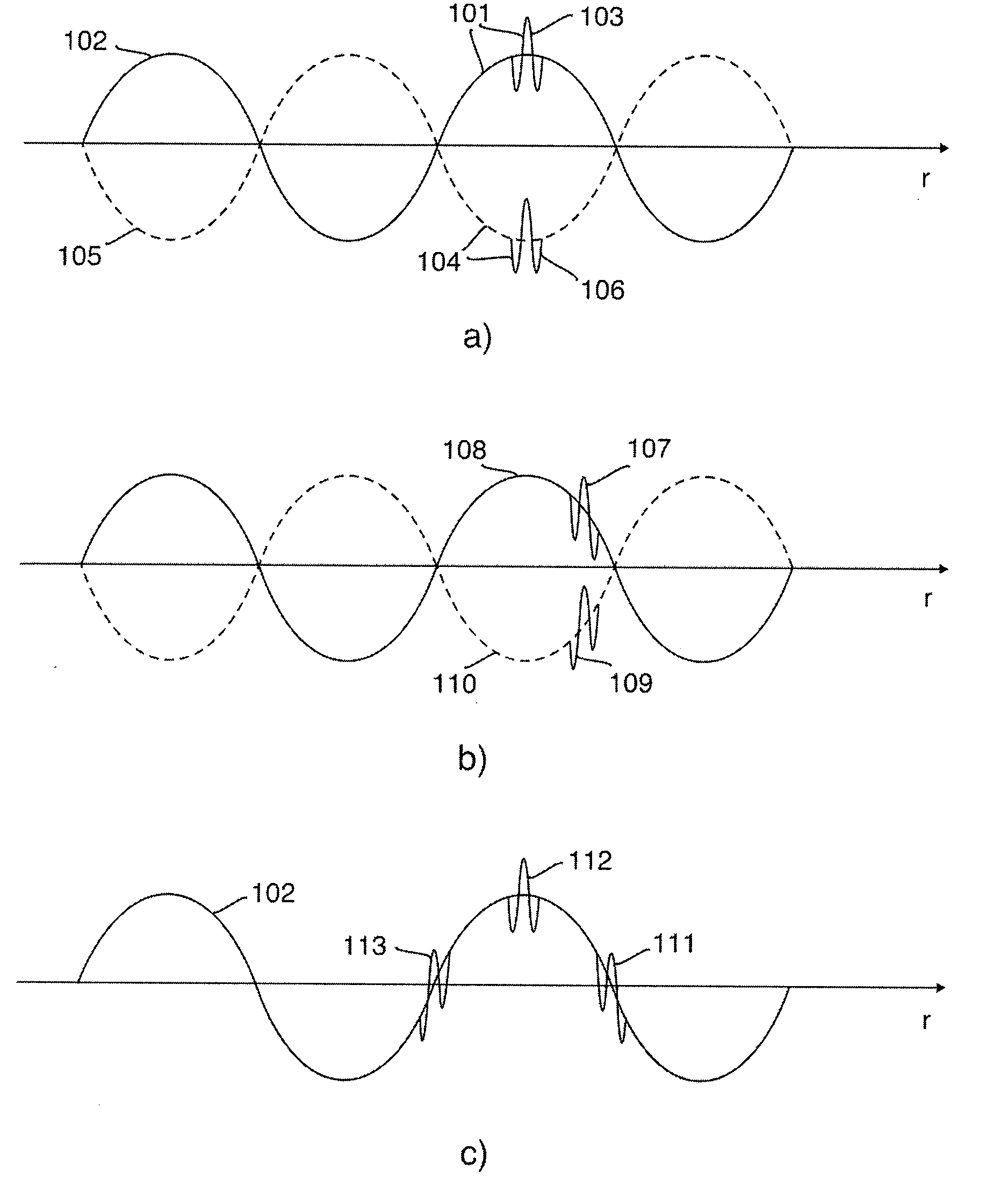
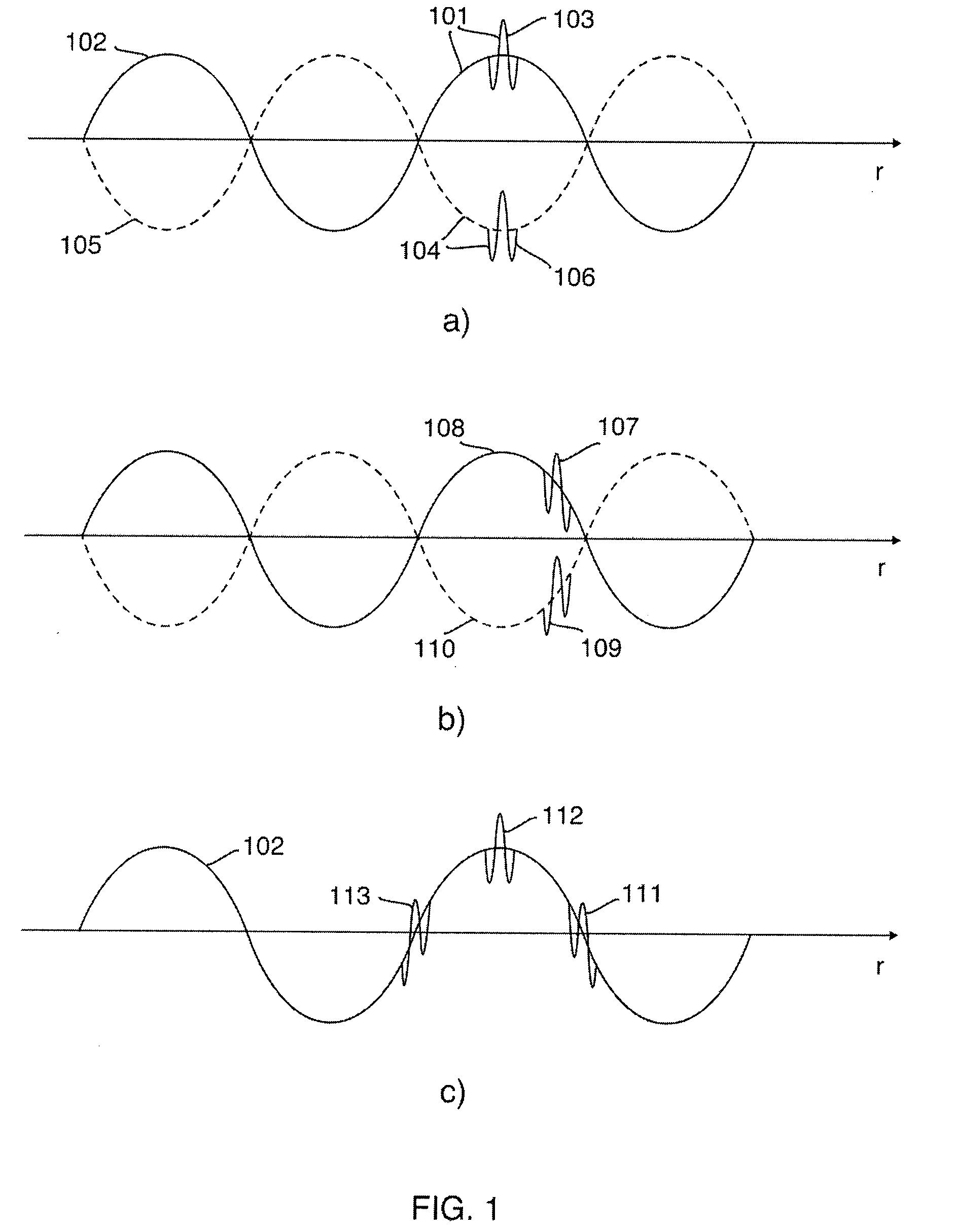
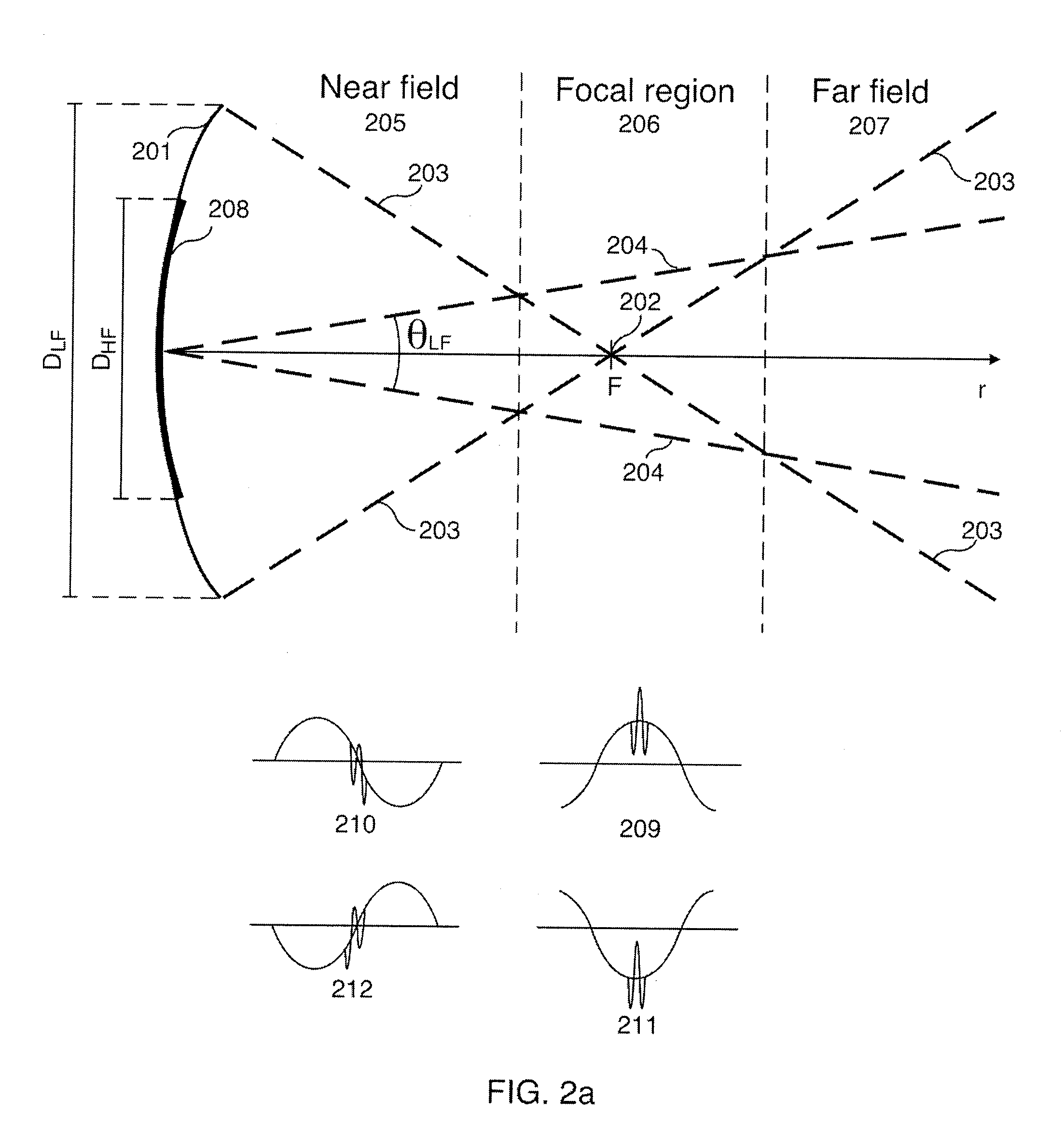
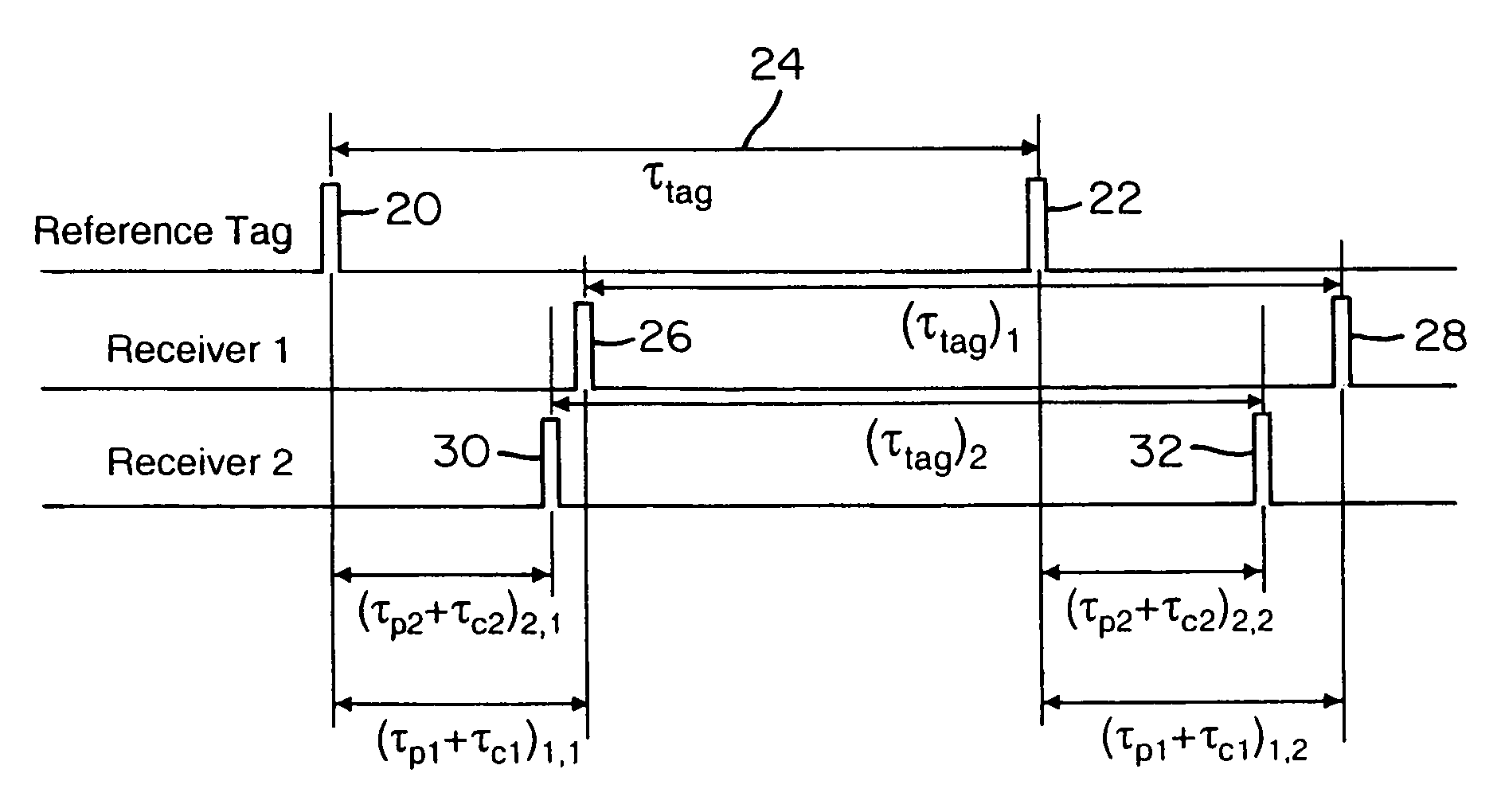
Patents
Literature
424 results about "Pulse pair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods and apparatus for driving electro-optic displays
ActiveUS7952557B2Shorten the overall cycleReduce data volumeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGray levelDisplay device
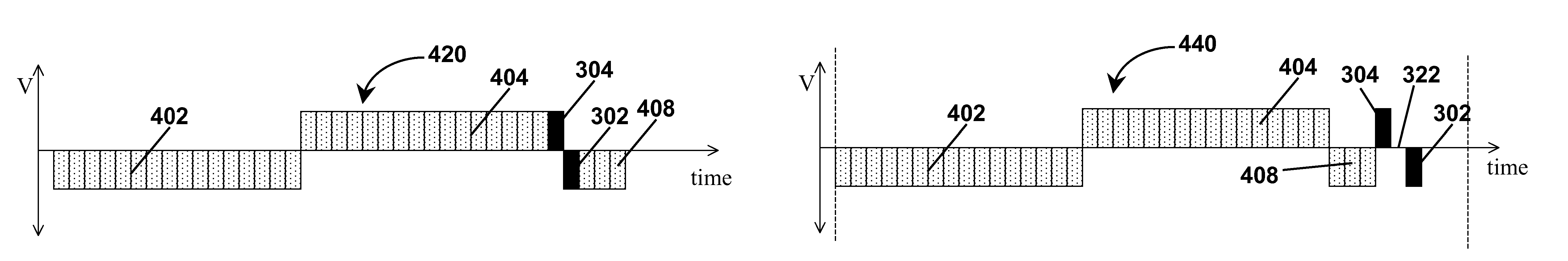
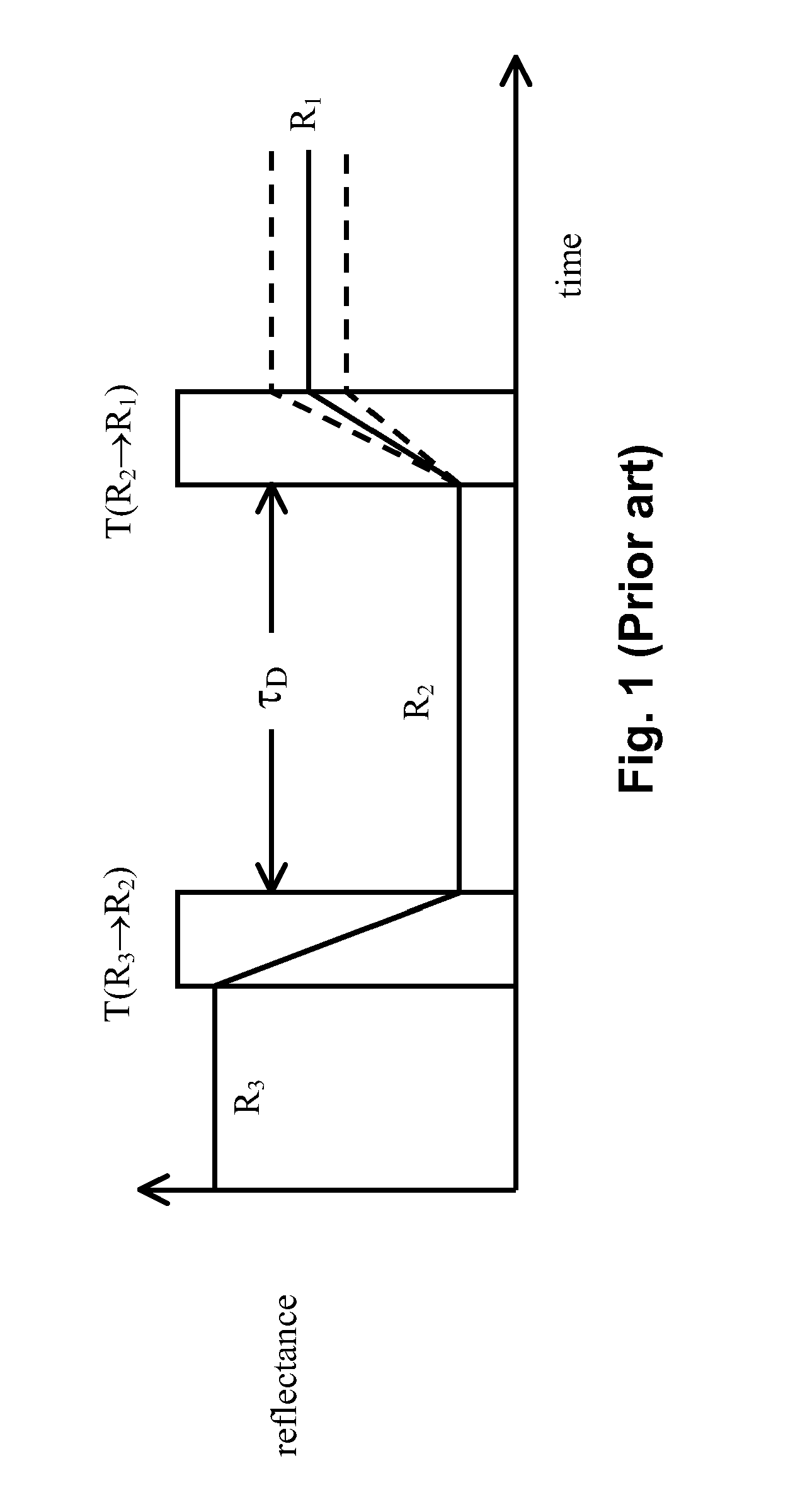
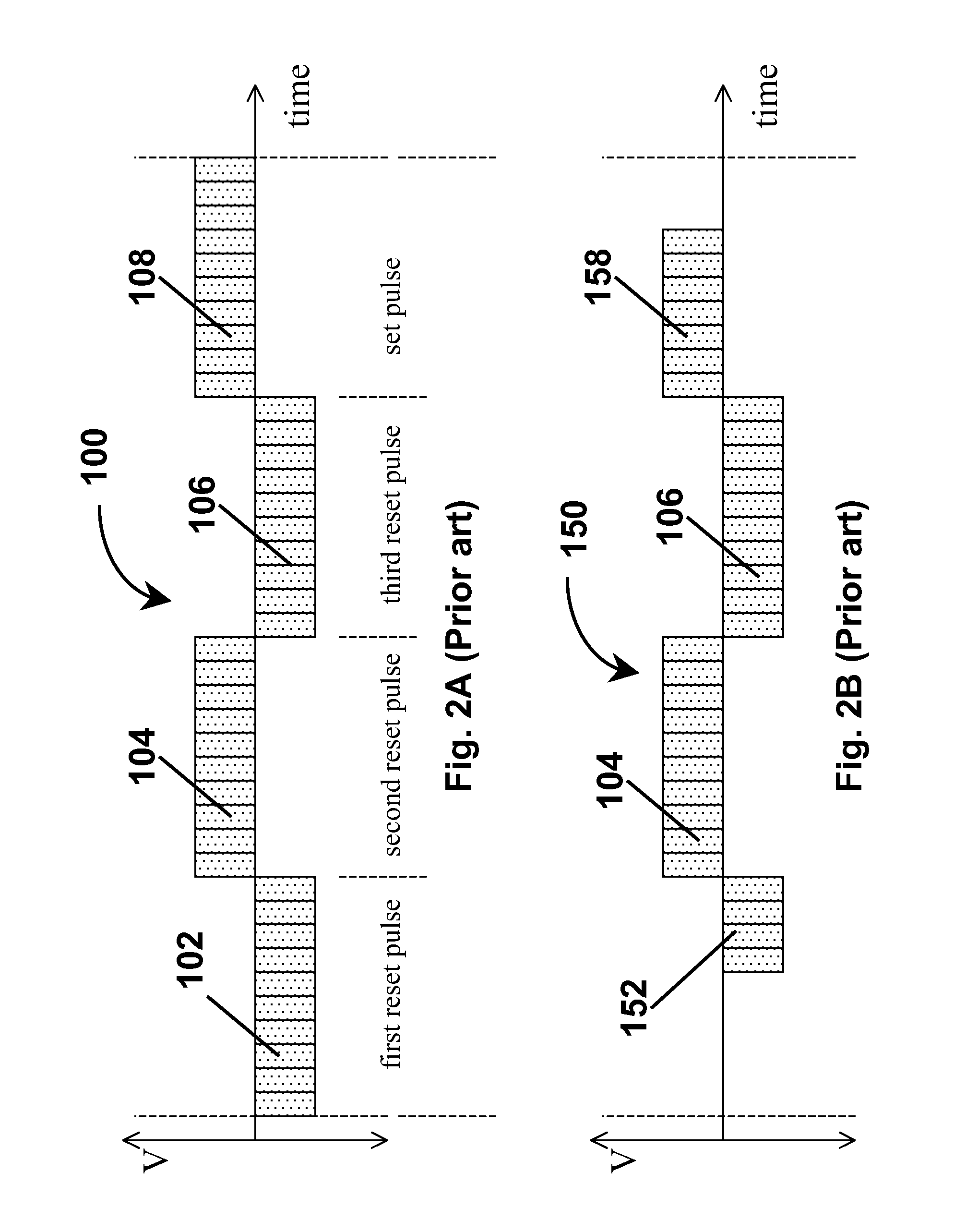
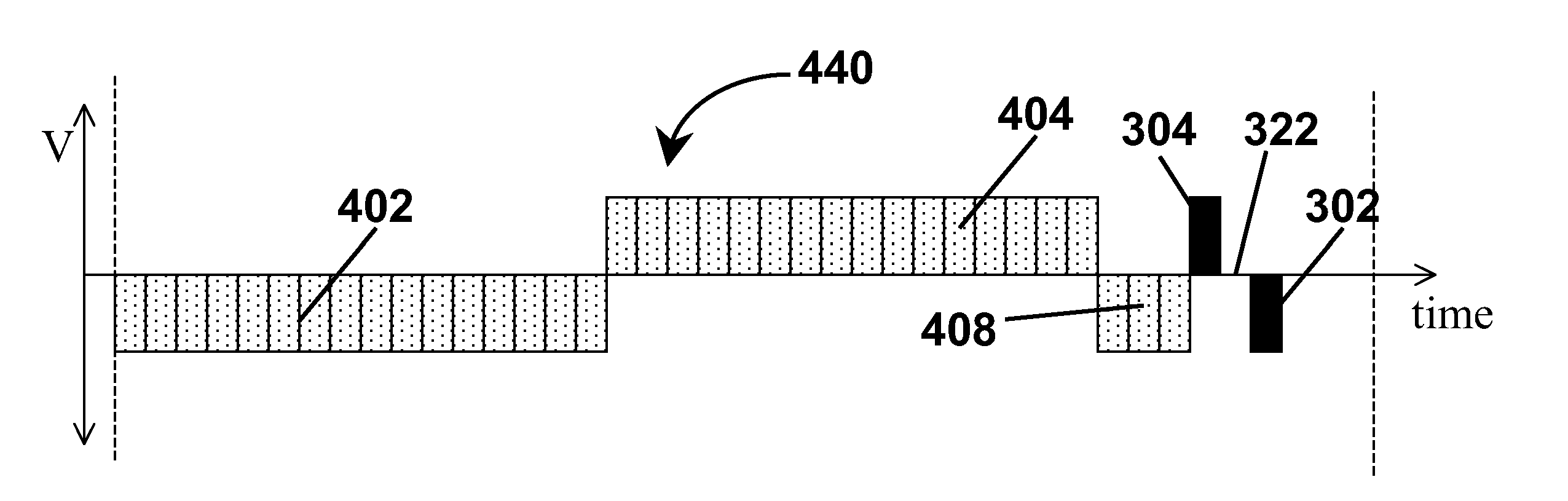
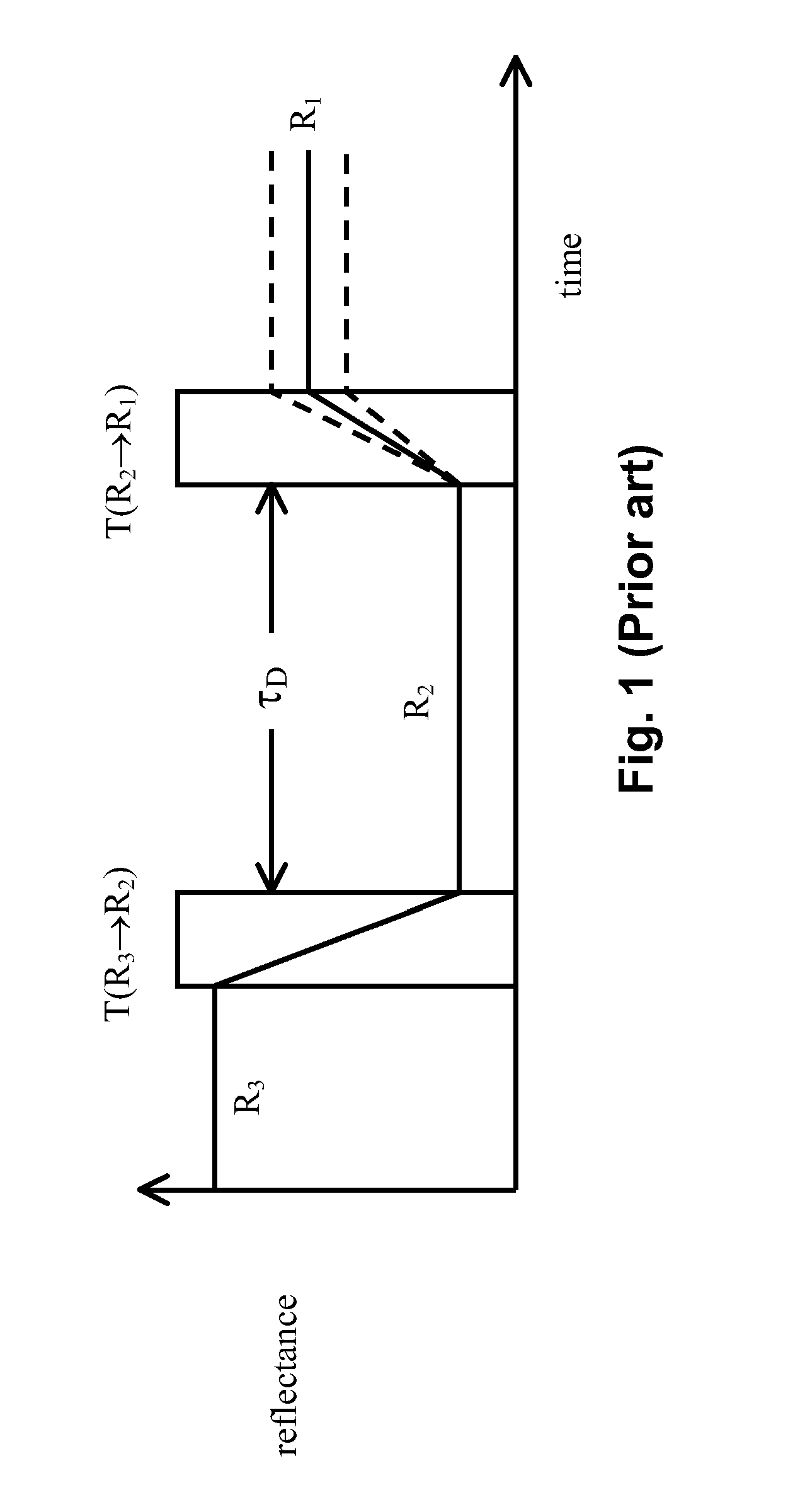
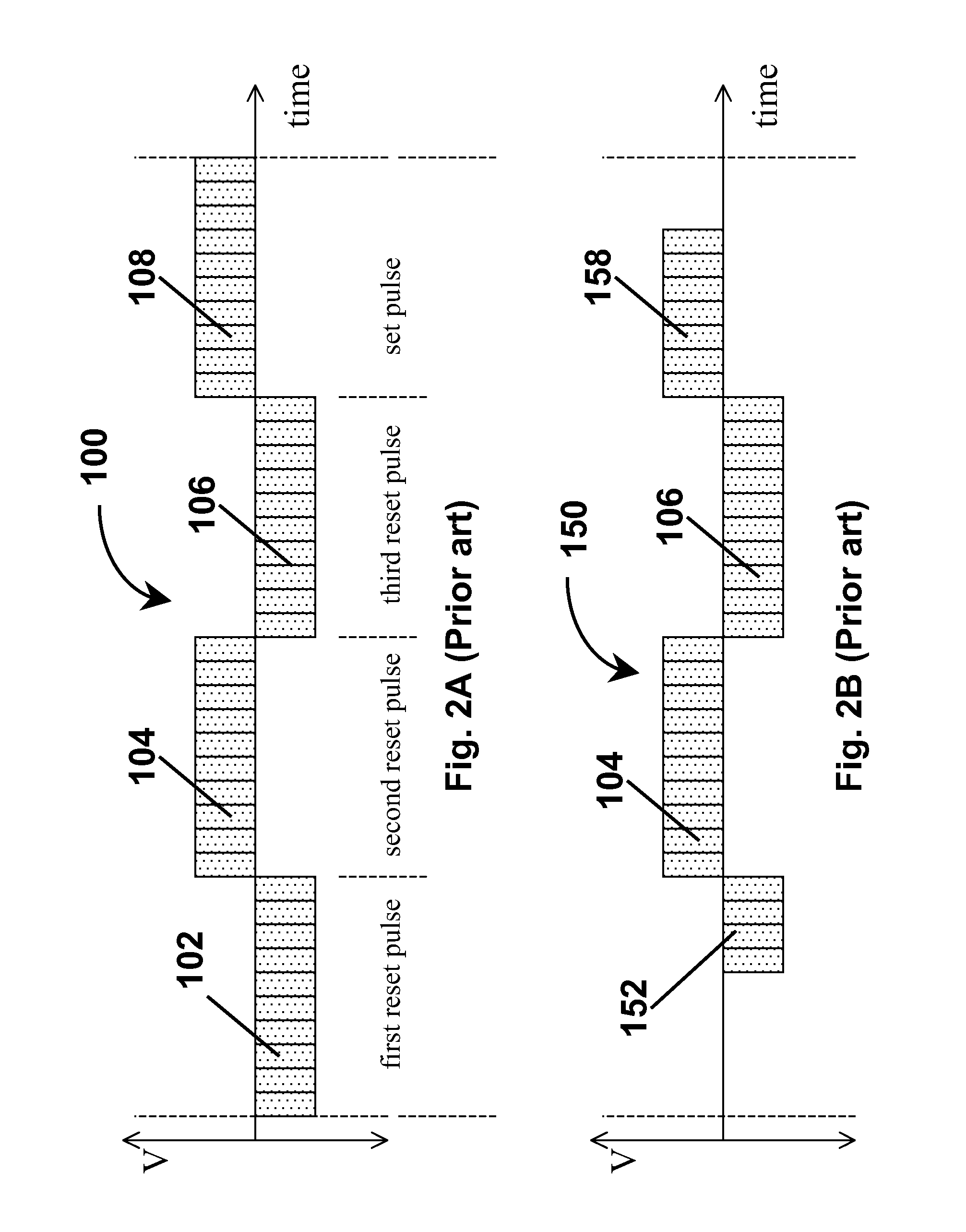
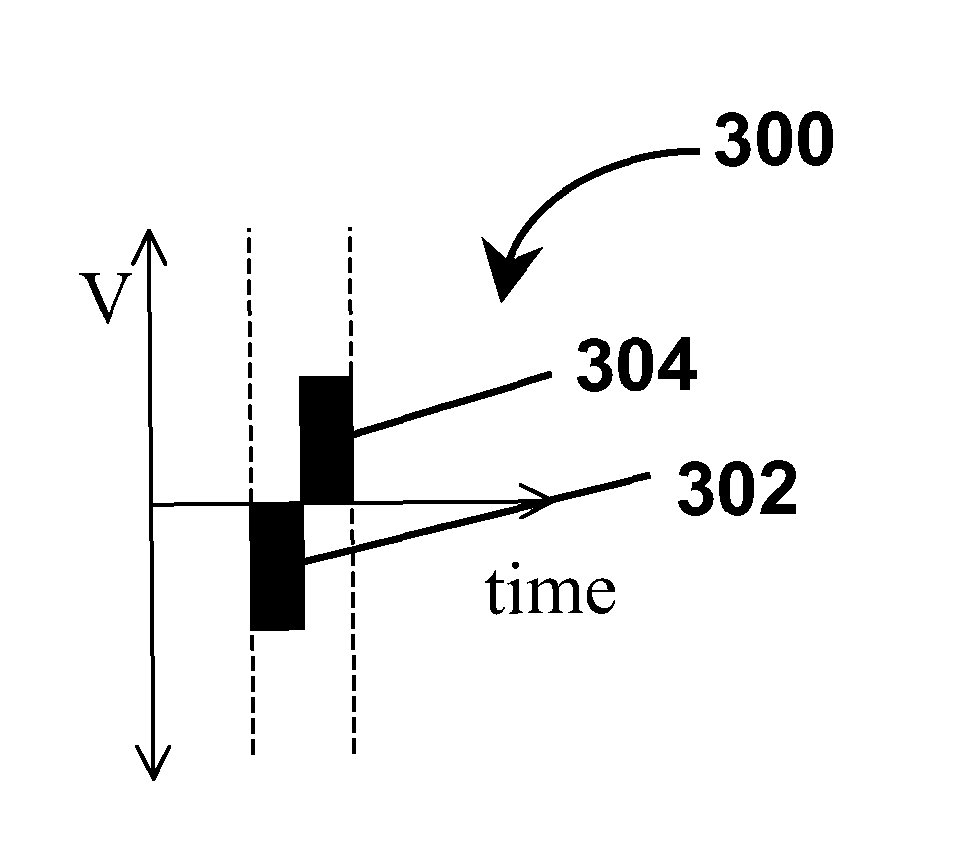
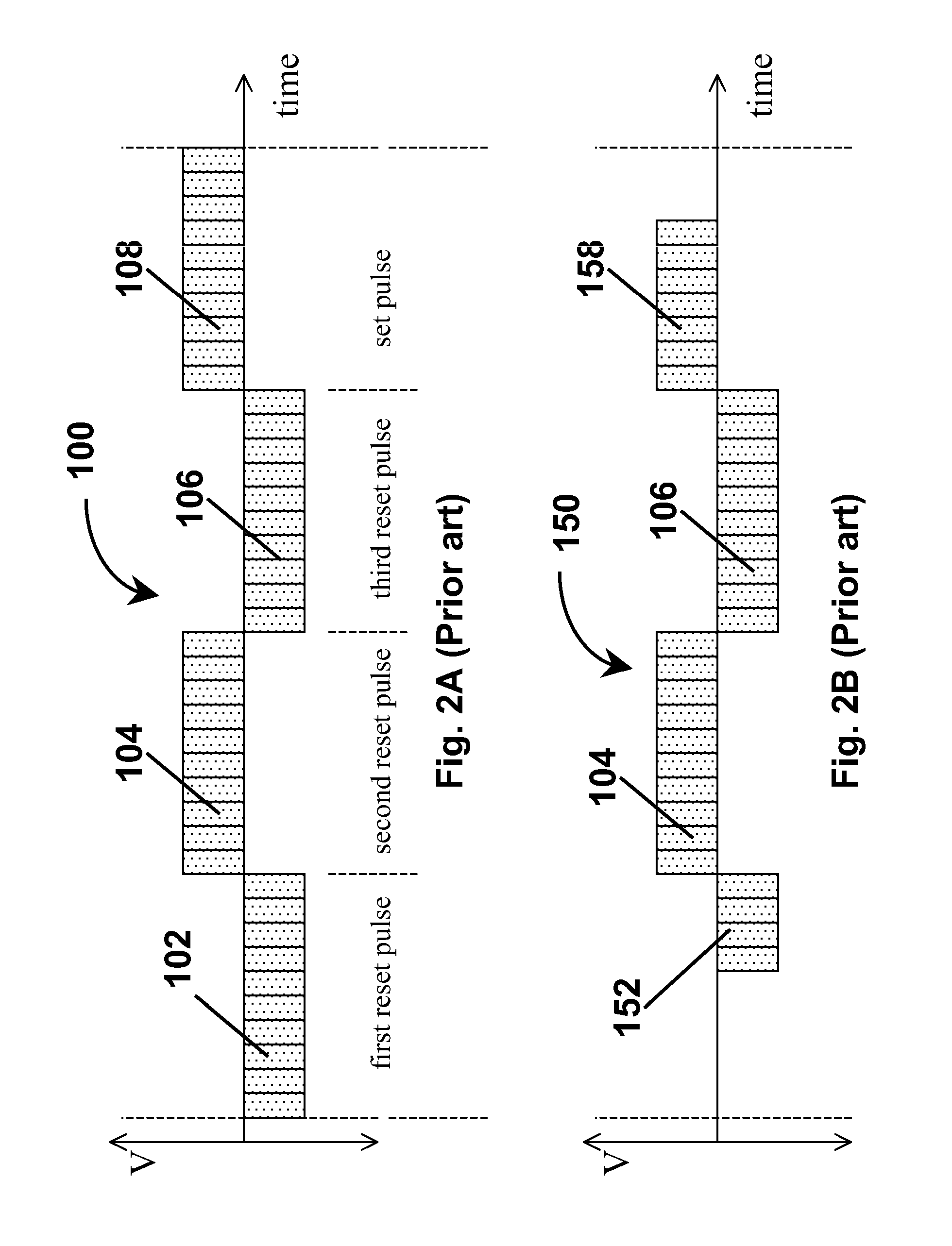
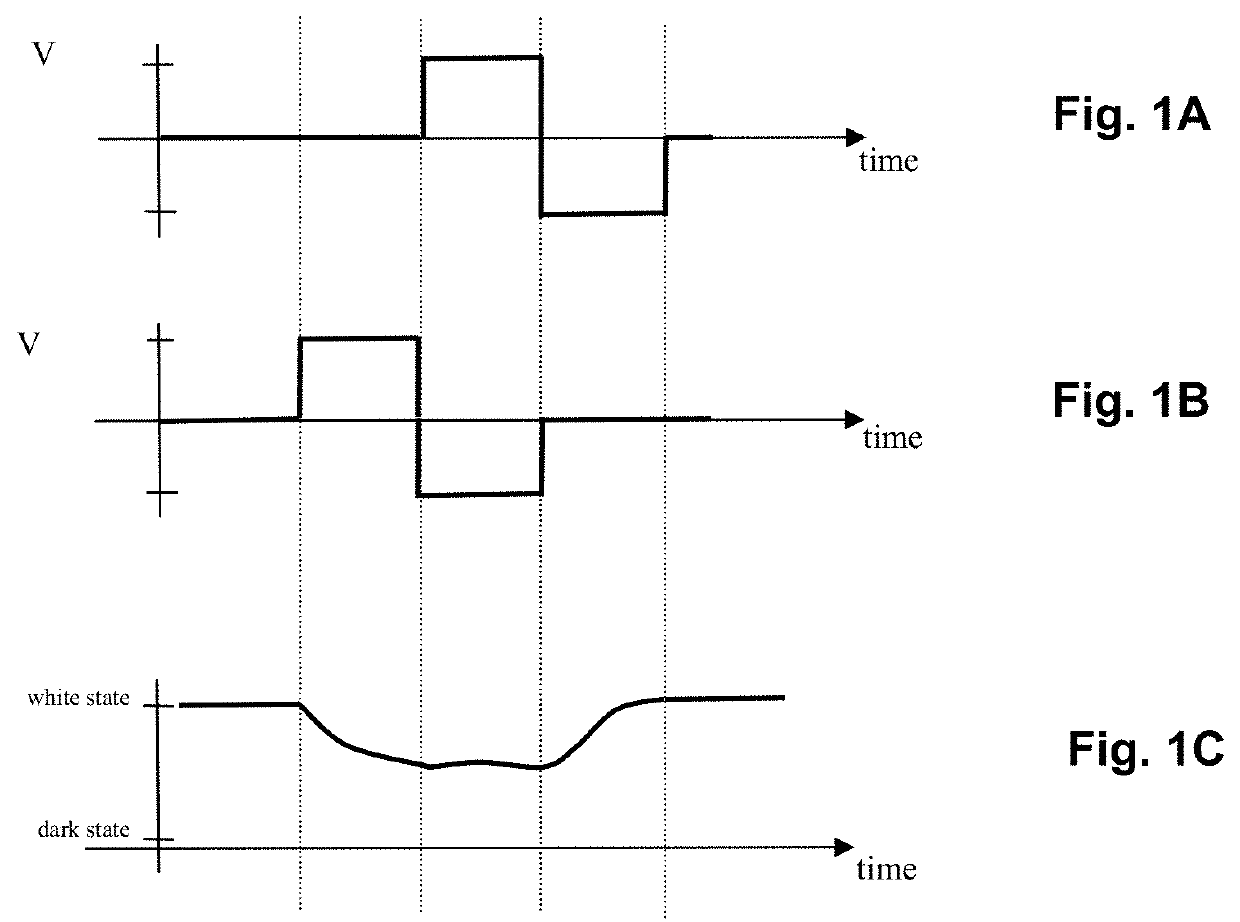
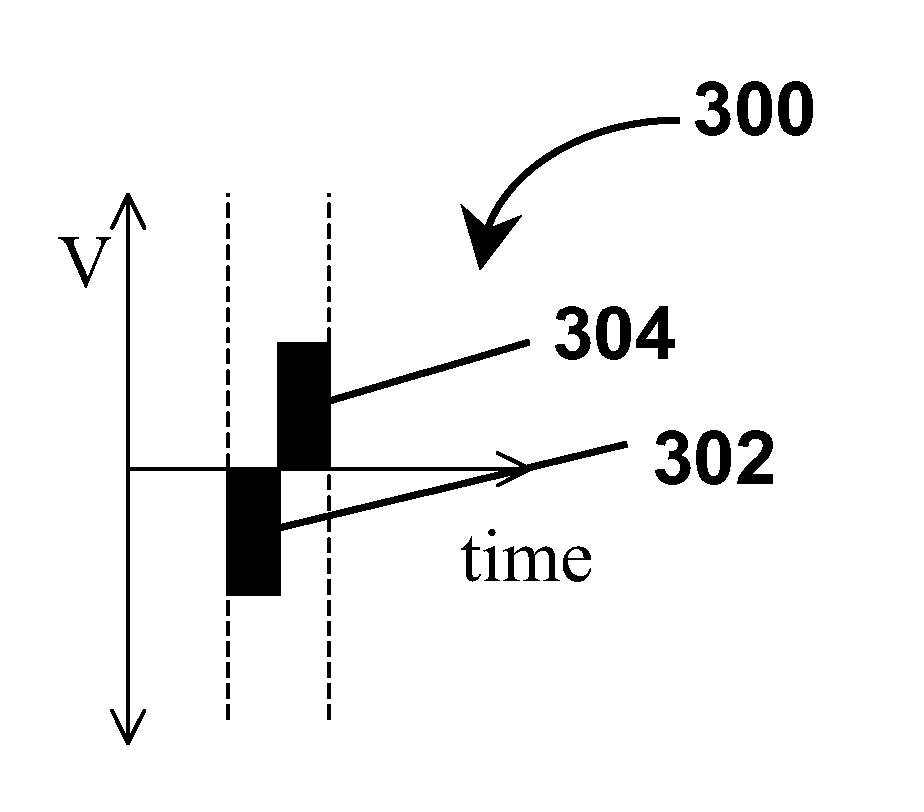
Waveforms for driving electro-optic displays, especially bistable electro-optic displays, are modified by one or more of insertion of at least one balanced pulse pair into a base waveform; excision of at least one balanced pulse pair from the base waveform; and insertion of at least one period of zero voltage into the base waveform. Such modifications permit fine control of gray levels.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods and apparatus for driving electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20050280626A1Reduce in quantityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGray levelDisplay device
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods for driving electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20130194250A1Reduce and eliminate edge artifactImprove visibilityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceComputer vision
A variety of methods for driving electro-optic displays so as to reduce visible artifacts are described. Such methods include (a) applying a first drive scheme to a non-zero minor proportion of the pixels of the display and a second drive scheme to the remaining pixels, the pixels using the first drive scheme being changed at each transition; (b) using two different drive schemes on different groups of pixels so that pixels in differing groups undergoing the same transition will not experience the same waveform; (c) applying either a balanced pulse pair or a top-off pulse to a pixel undergoing a white-to-white transition and lying adjacent a pixel undergoing a visible transition; (d) driving extra pixels where the boundary between a driven and undriven area would otherwise fall along a straight line; and (e) driving a display with both DC balanced and DC imbalanced drive schemes, maintaining an impulse bank value for the DC imbalance and modifying transitions to reduce the impulse bank value.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
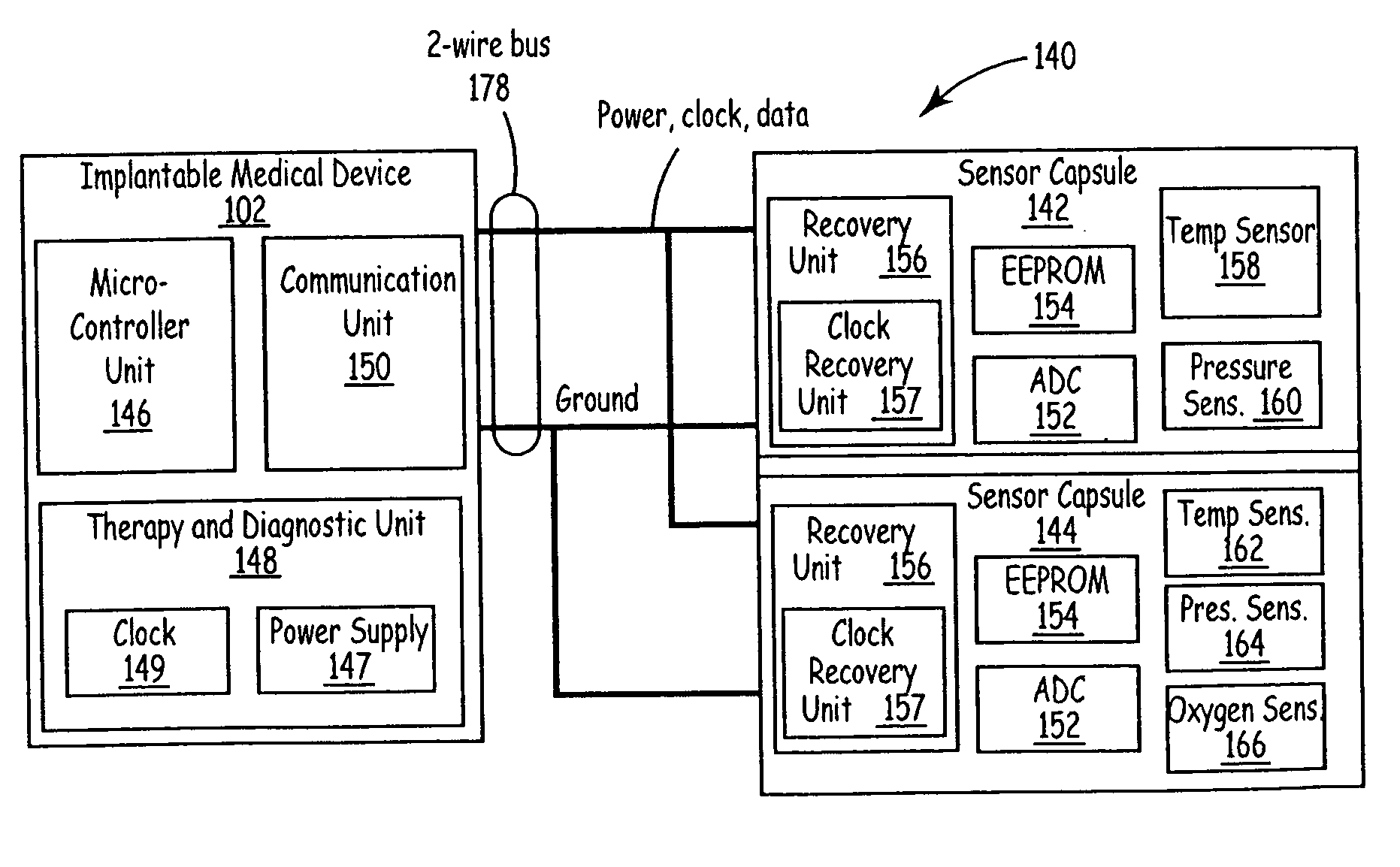
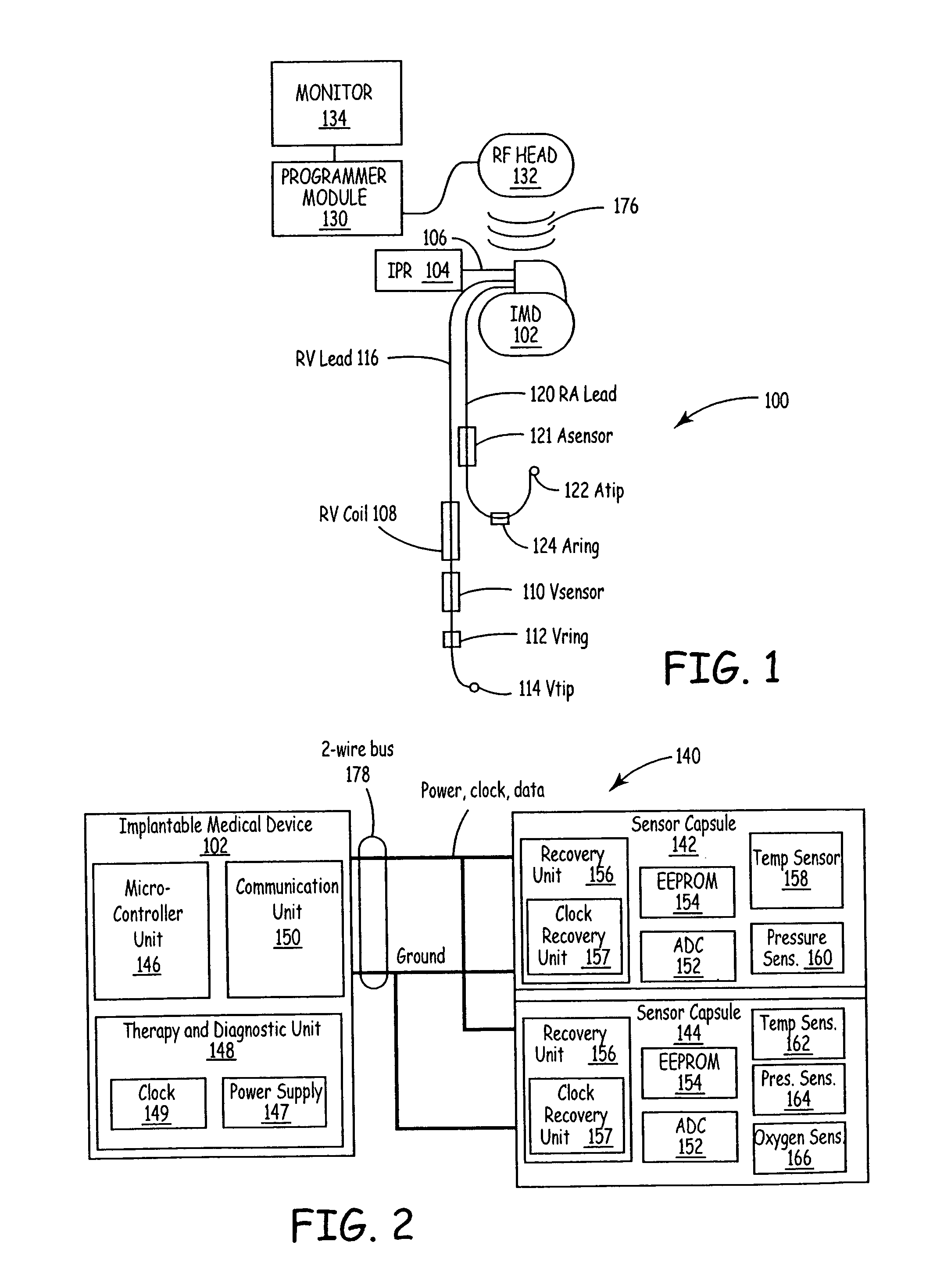
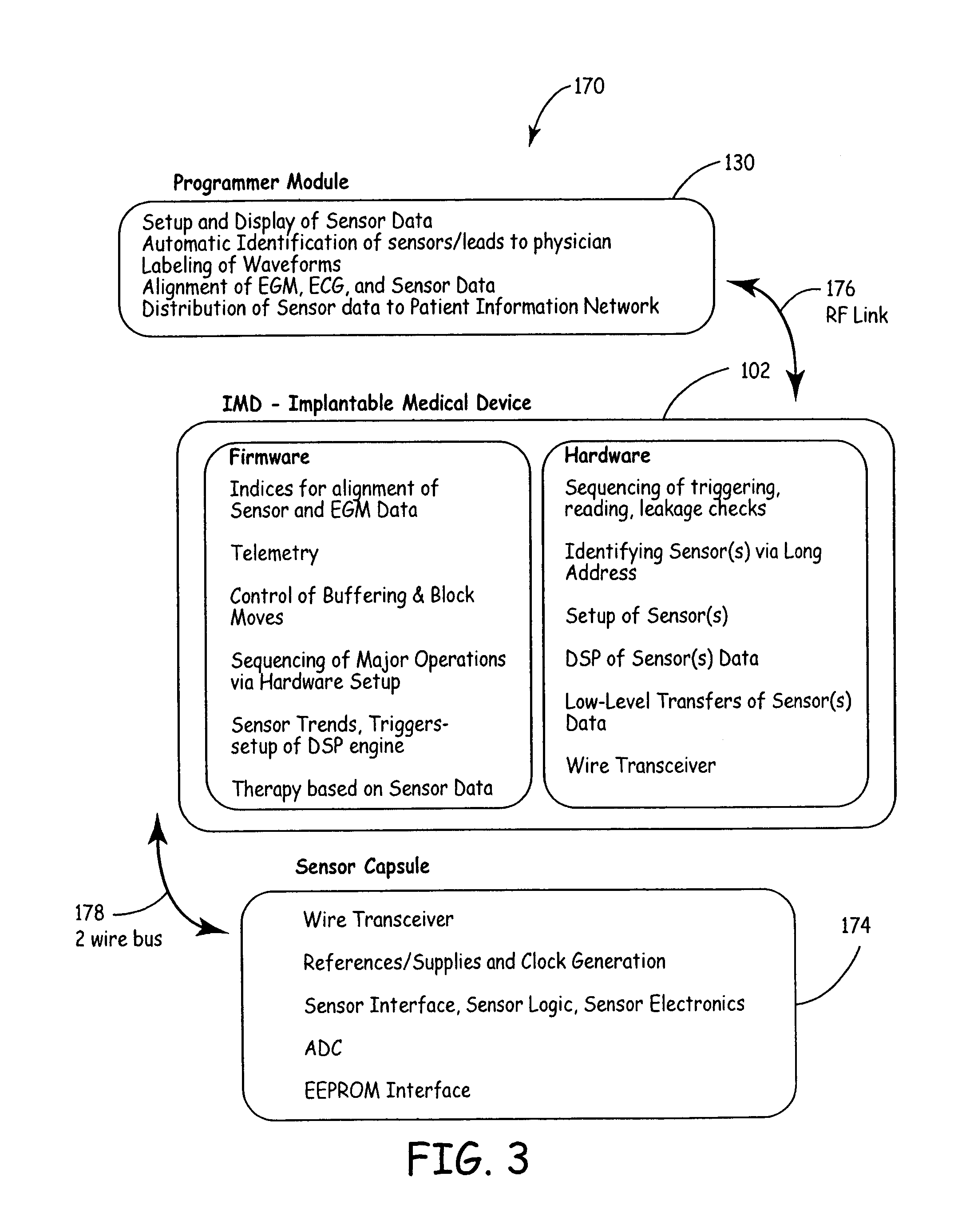
Implantable medical device communication system with pulsed power biasing
InactiveUS7139613B2Improve data communication rateShorten the lengthElectrotherapyArtificial respirationCommunications systemCommunication unit
An implantable medical device communication system communicates information between an implantable medical device and at least one slave device by way of a two-wire bus. Slave devices may include remote sensors, actuators and other implantable medical devices. The implantable medical device includes a communication unit to output commands and power pulses, and receive information from the slave devices over the two-wire bus. The implantable medical device and slaves communicate over the bus by selectively changing one of the lines of the bus between a first and second voltage, the second voltage substantially equal to a reference voltage of the second line, e.g., zero volts. In some embodiments, the power pulses take the form of bipolar pulse pairs. The slave device includes a recovery unit to recover power from the power pulses.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and apparatus for driving electro-optic displays
InactiveUS8593396B2Shorten the overall cycleReduce data volumeCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsGray levelDisplay device
Waveforms for driving electro-optic displays, especially bistable electro-optic displays, are modified by one or more of insertion of at least one balanced pulse pair into a base waveform; excision of at least one balanced pulse pair from the base waveform; and insertion of at least one period of zero voltage into the base waveform. Such modifications permit fine control of gray levels.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Optical signal processing with modelocked lasers
ActiveUS20110080580A1High resolutionMinimize fluctuationLaser detailsRadiation pyrometryFiberTime delays
The invention relates to scanning pulsed laser systems for optical imaging. Coherent dual scanning laser systems (CDSL) are disclosed and some applications thereof. Various alternatives for implementation are illustrated. In at least one embodiment a coherent dual scanning laser system (CDSL) includes two passively modelocked fiber oscillators. In some embodiments an effective CDSL is constructed with only one laser. At least one embodiment includes a coherent scanning laser system (CSL) for generating pulse pairs with a time varying time delay. A CDSL, effective CDSL, or CSL may be arranged in an imaging system for one or more of optical imaging, microscopy, micro-spectroscopy and / or THz imaging.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
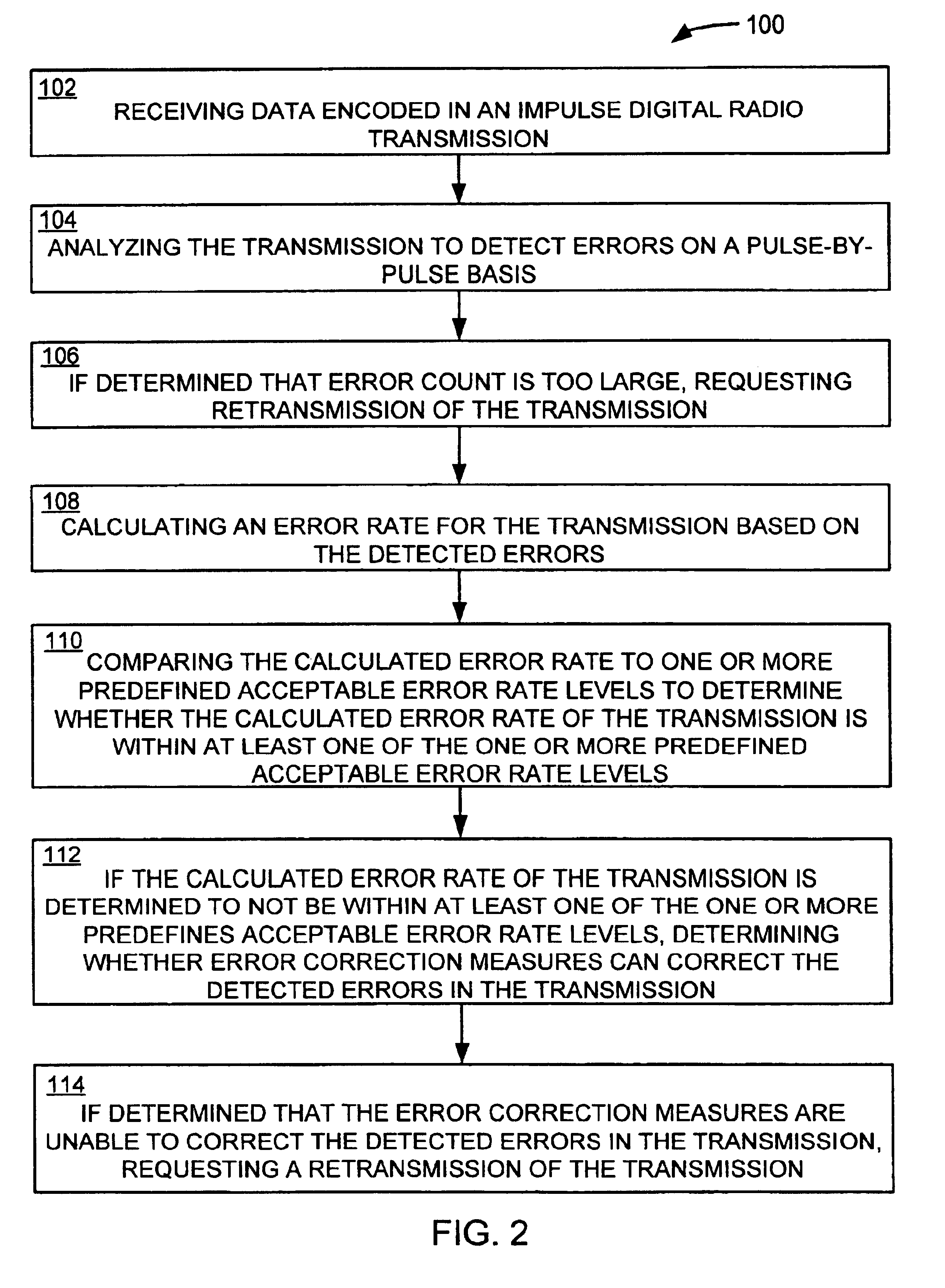
Encoding and decoding ultra-wideband information
InactiveUS6947492B2Reduce disadvantagesDetection errorError prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorUltra-widebandBroadband transmission
A system and a method for encoding and decoding ultra-wideband information are provided. An ultra-wideband transmission is encoded by positioning bipolar pulse pairs. The bipolar pulse pairs assist in detecting errors in the ultra-wideband transmission, before the entire transmission has been received. The transmission is analyzed for errors and an error rate is calculated. The calculated error rate is compared to one or more predefined acceptable error rate levels to determine whether the calculated error rate of the transmission is within at least one of the predefined acceptable error rate levels.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 73
Method for measuring volume of large irregular bulk grain pile based on dynamic three-dimensional laser scanning
The invention relates to a method for measuring the volume of a large irregular bulk grain pile based on dynamic three-dimensional laser scanning. The method comprises the following steps of: arranging a guide rail in the middle of the top of a barn along the width direction, wherein the guide rail is provided with a slide block controlled by a stepping motor, and a laser radar scanner is installed on the slide block; moving the slide block from one end to the other end of the top of the barn at a constant speed to drive the laser radar scanner by the slide block to finish scanning on the surface of the whole bulk grain pile, wherein the laser radar device is a one-dimensional scanning device to realize linear scanning and returning coordinate data, and the master control computer is used for transmitting pulses to the stepping motor and processing the signal; acquiring point cloud data of the surface of the bulk grain pile through the master control computer, determining the distribution density of scanned points for calculating the volume according to an allowed error value of the grain pile measured by the user, and calculating the weight of the grain pile according to the grain density provided by the user; and generating a point cloud graphic matrix attached with coordinates through scanning space morphology by guide rail moving type three-dimensional laser, performing surface fitting to form an irregular bulk grain pile appearance, and thus obtaining the volume of the irregular bulk grain pile. The volume of the large irregular bulk grain pile can be rapidly and effectively measured at high precision, and remote monitoring can be realized; and moreover, the method is low in cost and easy to implement.
Owner:MENG FAN'GANG
Nonlinear Elastic Wave Measurement and Imaging with Two-Frequency Elastic Wave Pulse Complexes
ActiveUS20100036244A1Fast timeSimple processOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsBeam directionTransducer
Methods and instruments for suppression of multiple scattering noise and extraction of nonlinear scattering components with measurement or imaging of a region of an object with elastic waves, where elastic wave pulse complexes are transmitted towards said region where said pulse complexes are composed of a high frequency (HF) and a low frequency (LF) pulse with the same or overlapping beam directions and where the HF pulse is so close to the LF pulse that it observes the modification of the object by the LF pulse at least for a part of the image depth. The frequency and / or amplitude and / or phase of said LF pulse relative to said HF pulse varies for transmitted pulse complexes in order to nonlinearly manipulate the object elasticity observed by the HF pulse along at least parts of its propagation, and where received HF signals are picked up by transducers from one or both of scattered and transmitted components of the transmitted HF pulses. Said received HF signals are processed to form measurement or image signals for display, and where in the process of forming said measurement or image signals said received HF signals are one or both of delay corrected with correction delay in the fast time (depth-time), and pulse distortion corrected in the fast time, and combined in slow time to form noise suppressed HF signals or nonlinear scattering HF signals that are used for further processing to form measurement or image signals. The methods are applicable to elastic waves where the material elasticity is nonlinear in relation to the material deformation.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
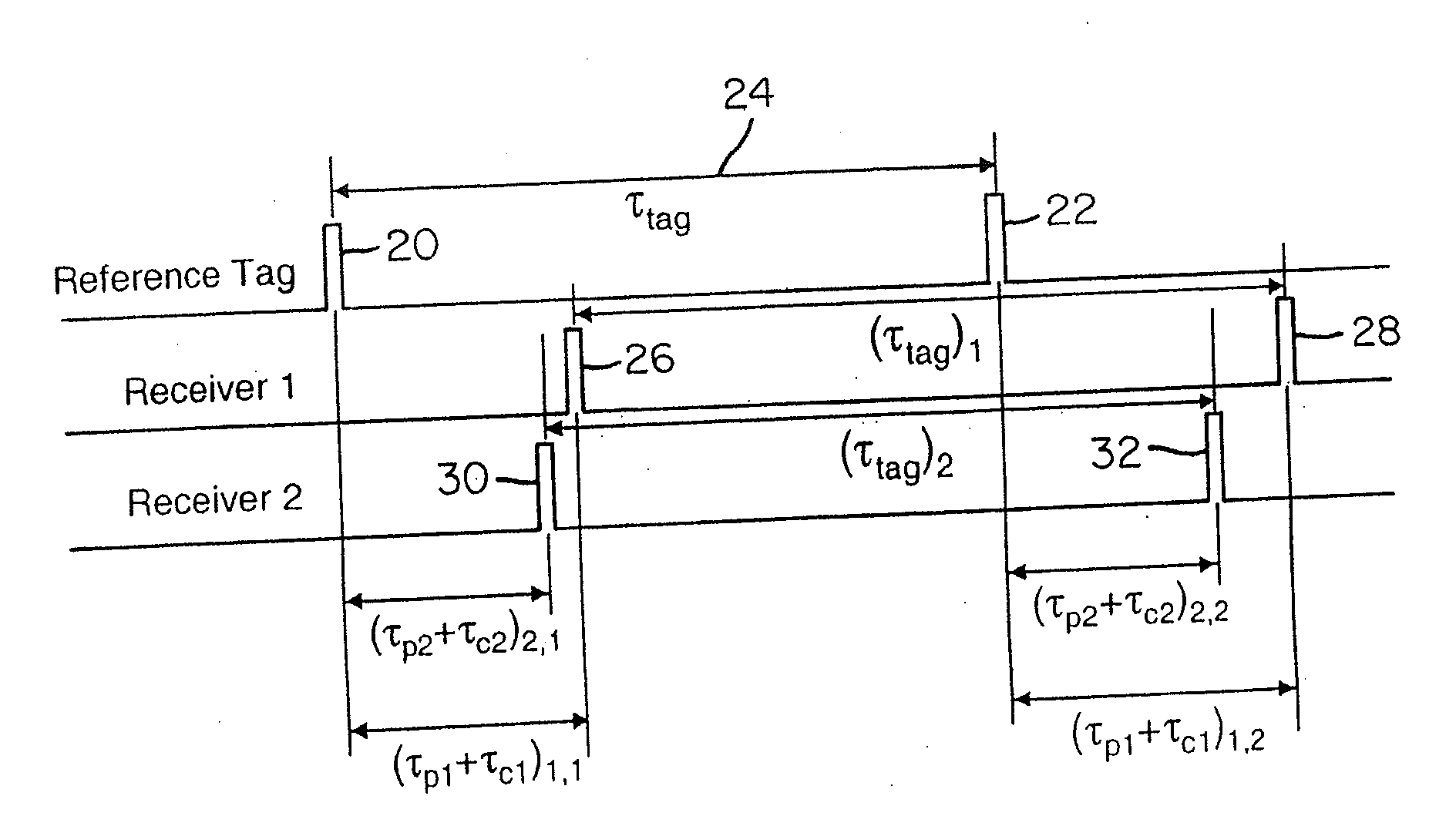
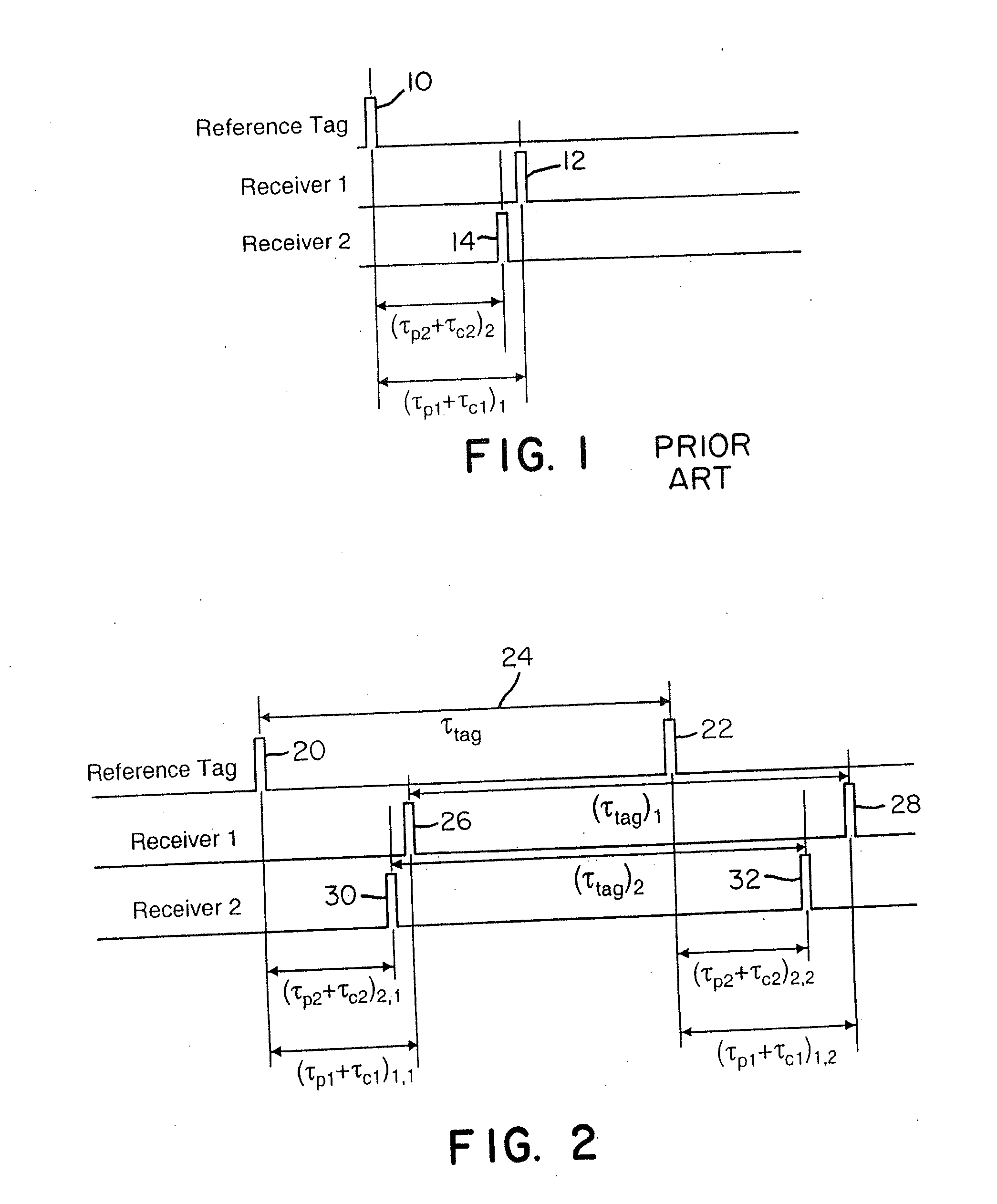
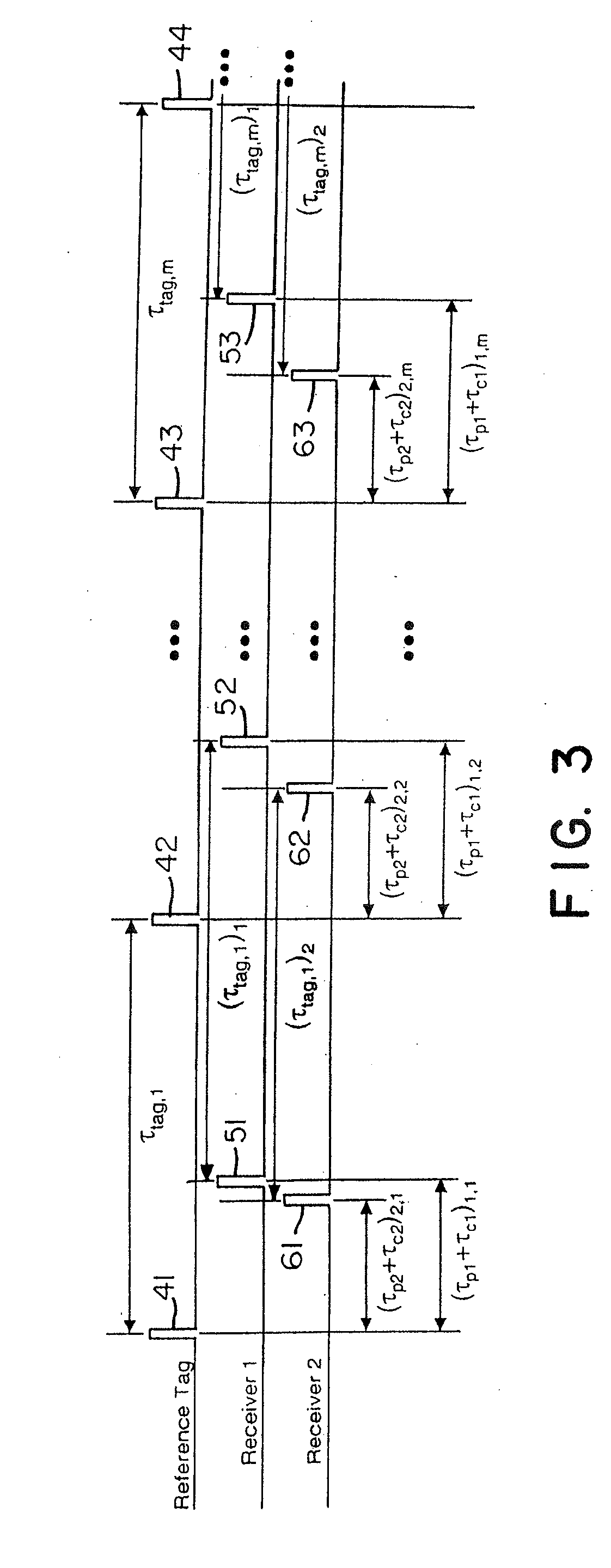
Wireless time reference system and method
ActiveUS7492316B1Accurate measurementDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationClock rateReference intervals
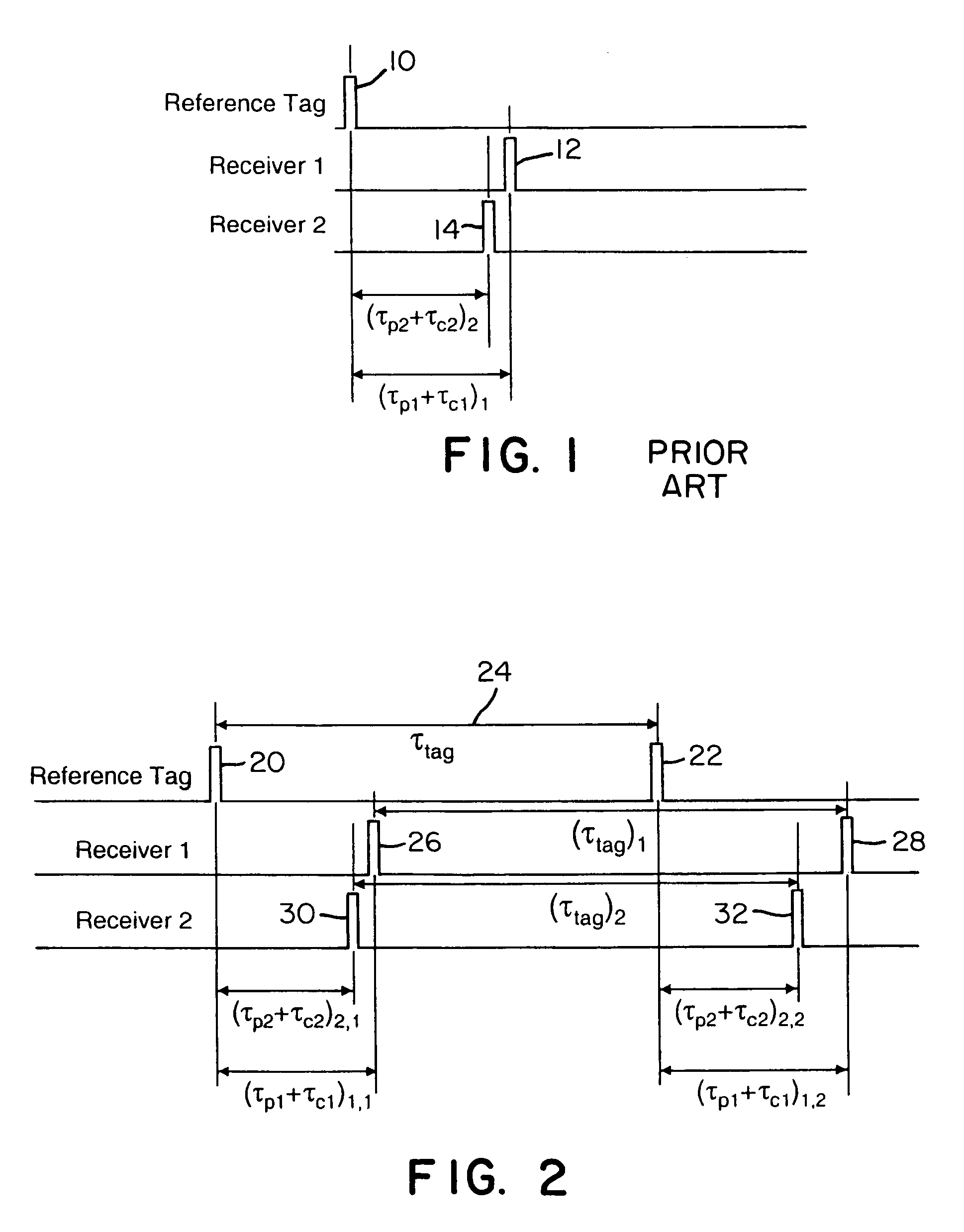
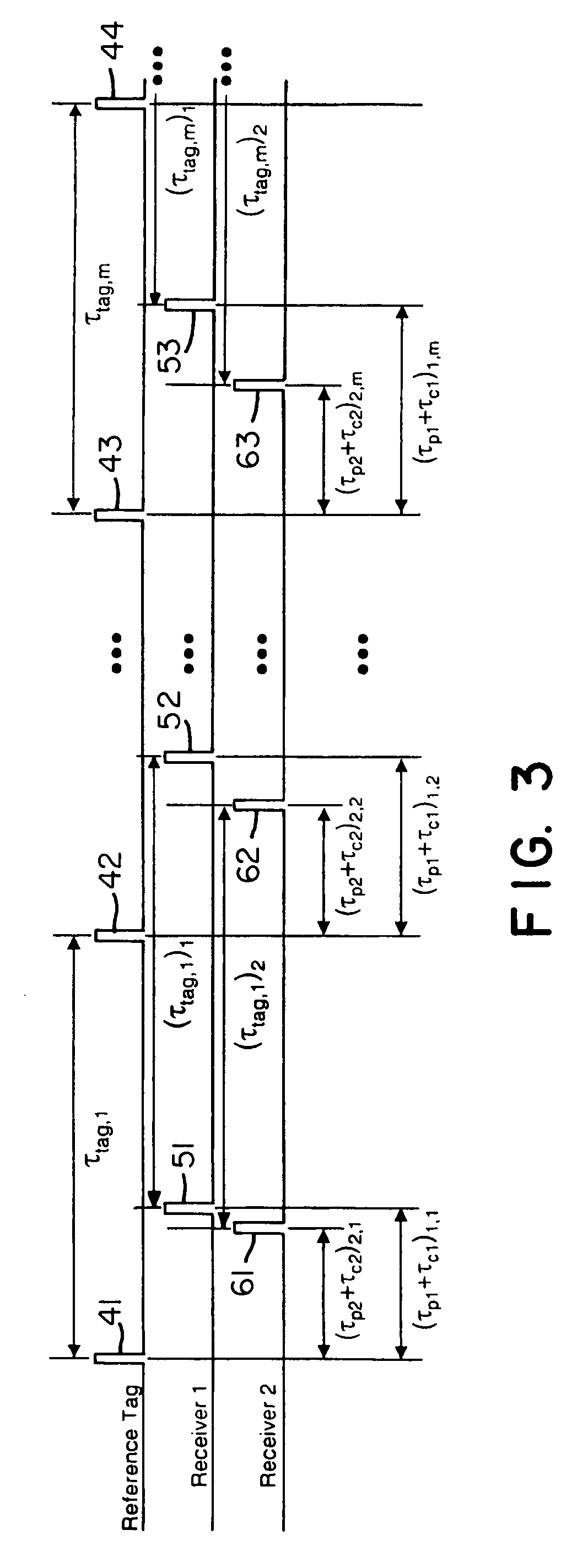
Instead of normalizing time reference of independent spatially-located clocks using a reference tag transmission from known location, the present invention uses an interarrival time interval between a pulse pair of UWB pulses as a timing metric. Thus, a method of synchronizing spatially-located clock or normalizing time indications thereof comprises transmitting a UWB pulse pair, determining at first and second monitoring stations a respective count value indicative of a locally measured time interval between received pulse pairs, determining a ratio between clock counts of first and second monitoring stations, and utilizing the ratio to determine clock skew, e.g., a timing correction to be applied to respective local clocks of the monitoring stations. A corresponding system comprises a reference tag transmitter that transmits a pulse pair of UWB pulses to define a time reference interval, a first independent receiver that receives the pulse pair to generate a first count value indicative an interarrival interval between the pulse pair, a second independent receiver that receives the pulse pair to similarly generate a second count value, and a processor hub responsive to the count values to determine a ratio corresponding to the ratio of respective clock frequencies of the first and second receiver clocks. Once the correction is applied, time-of-arrival information from object tag transmissions may be used to determine object location with sub-foot position accuracies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Methods and apparatus for driving electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20110187684A1Reduce in quantityShorten the overall cycleCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsGray levelDisplay device
Waveforms for driving electro-optic displays, especially bistable electro-optic displays, are modified by one or more of insertion of at least one balanced pulse pair into a base waveform; excision of at least one balanced pulse pair from the base waveform; and insertion of at least one period of zero voltage into the base waveform. Such modifications permit fine control of gray levels.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Differential time domain spectroscopy method for measuring thin film dielectric properties
InactiveUS6556306B2Large dynamic rangeRaise the ratioPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansTime domainDielectric
A non-contact, free-space method for determining the index of refraction of a thin film at a desired angular frequency. The method includes generating an input desired-frequency pulse and an optically detectable probe pulse. The thin film is moved in and out of the path of the input pulse, creating an output pulse that alternates between a transmitted signal, created when the film intercepts the input pulse path, and a reference signal, created when the sample is outside the input pulse path. The output pulse modulates the probe pulse, which is then detected with a photo detector, and the difference between the transmitted signal and the reference signal is calculated. The above steps are repeated over a plurality of delay times between the input pulse and the probe pulse until a complete field waveform of the differential signal is characterized. The index of refraction is calculated as a function of a ratio between the differential signal for the thin film and the reference signal. A complete field waveform of the reference signal may be characterized by repeating the above steps for a reference plate identical to the sample except having a non-transmissive film instead of the thin, transmissive film.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Method and apparatus of detecting states of battery
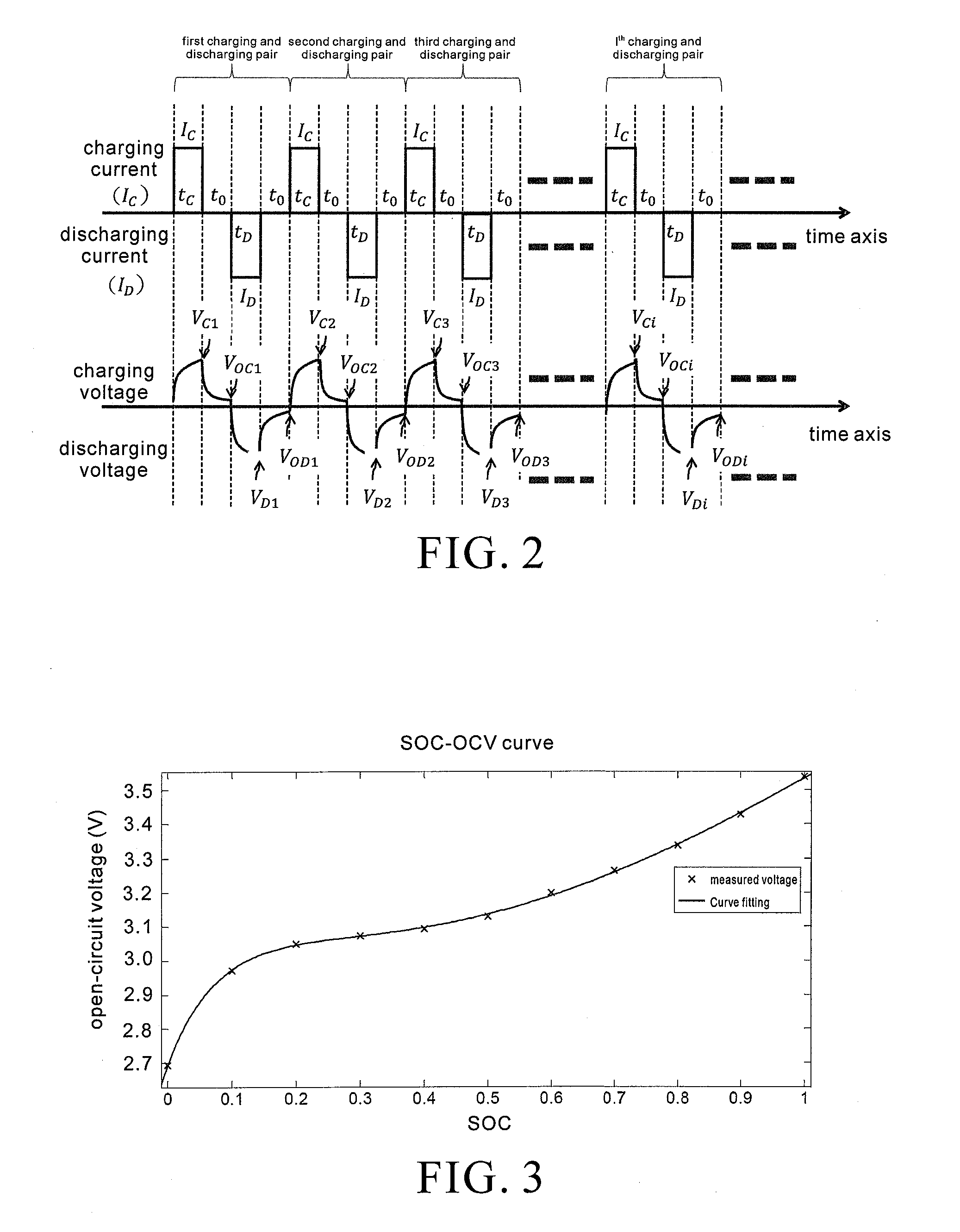
InactiveUS20160178706A1Quick checkElectrical testingSpecial data processing applicationsCapacitanceState of health
A method and apparatus of detecting the states of a battery involve passing test-oriented charging and discharging pulse pair to a battery under test, and retrieving parameters of the battery, such as voltage, current, and temperature, which respond to the charging and discharging pulse pair, so as to estimate the battery states. The battery states include information pertaining to open-circuit voltage, internal resistance, capacitance, state of charge, and state of health of the battery. The battery state-related information is conducive to quick battery state detection and grading.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
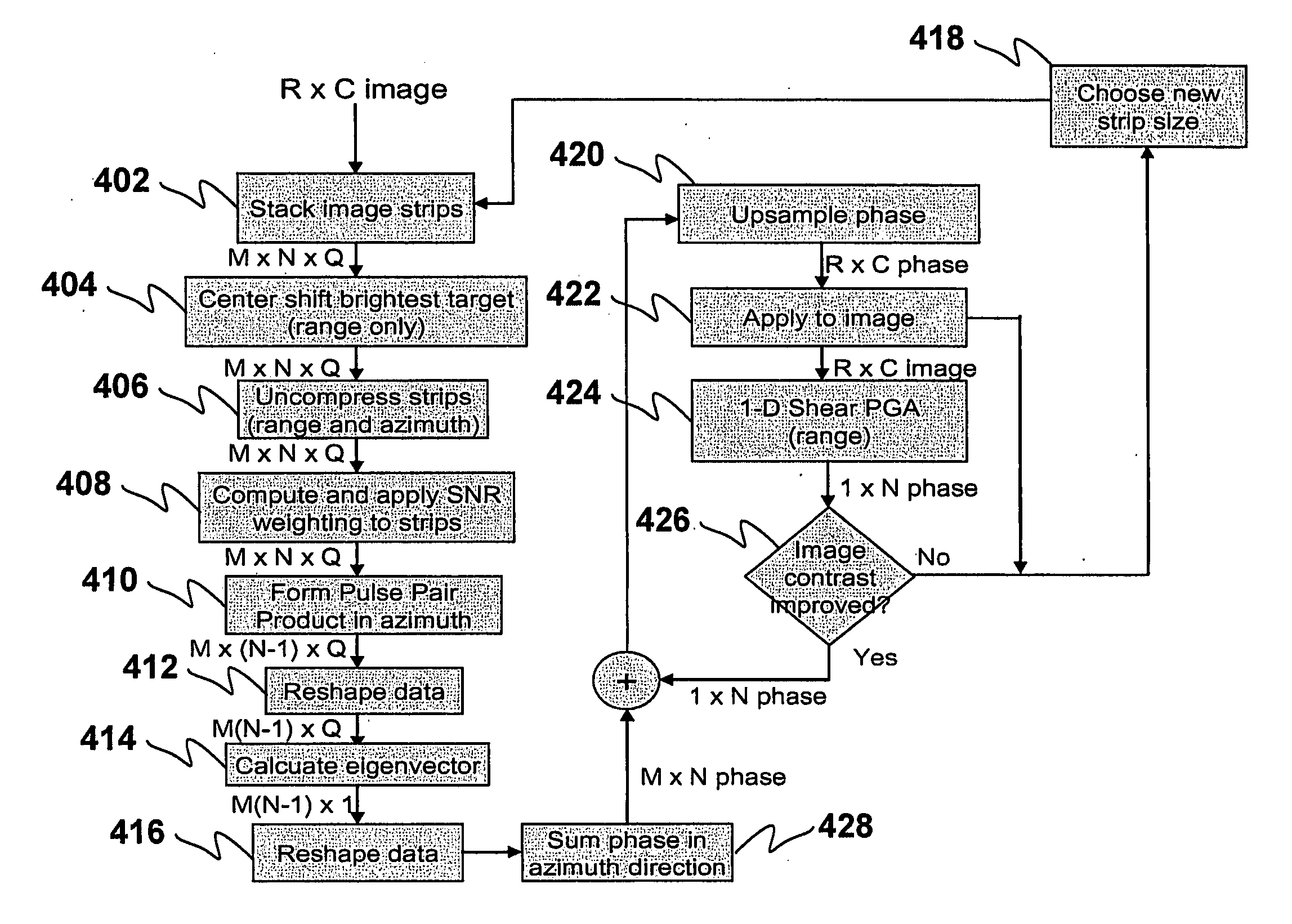
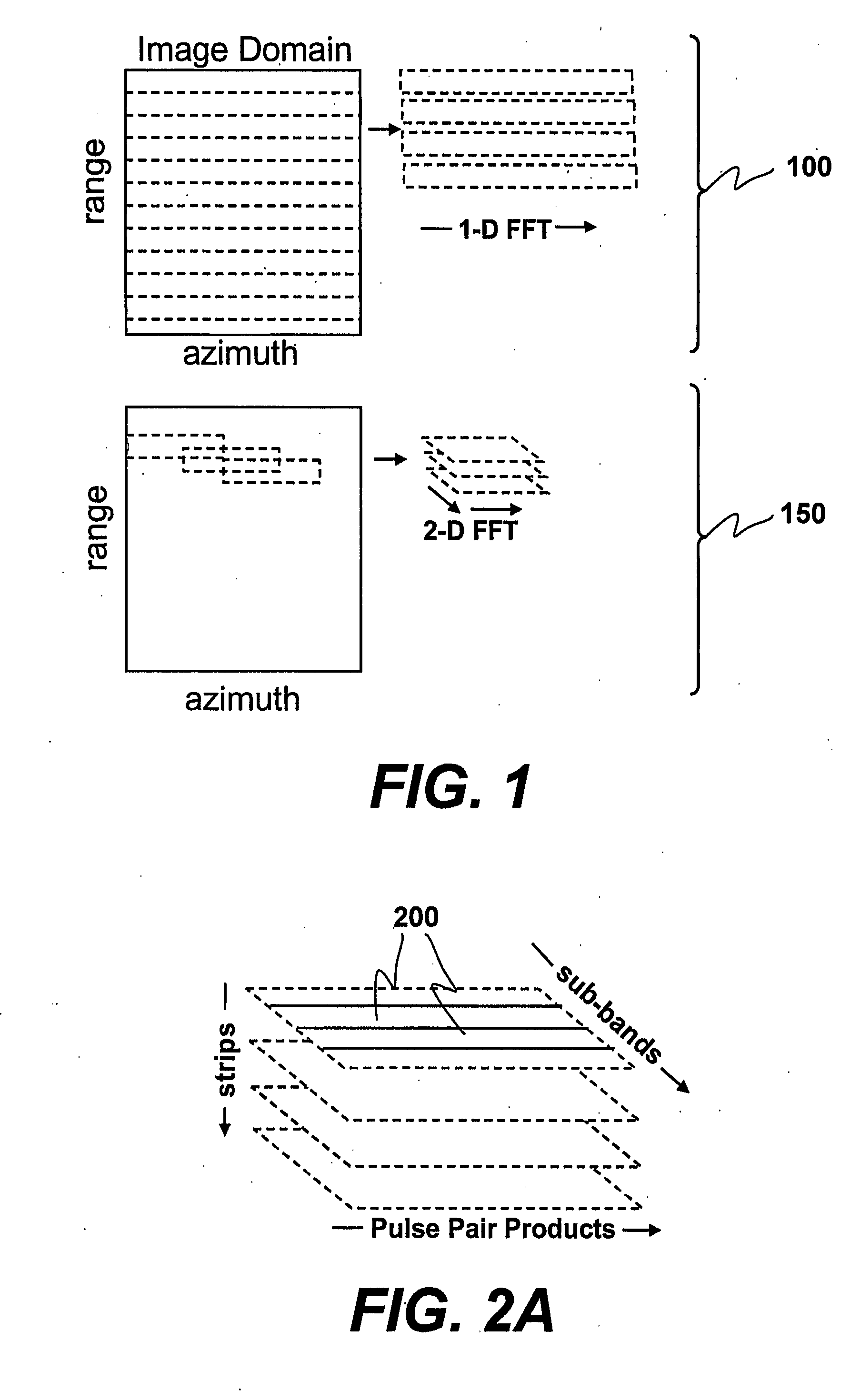
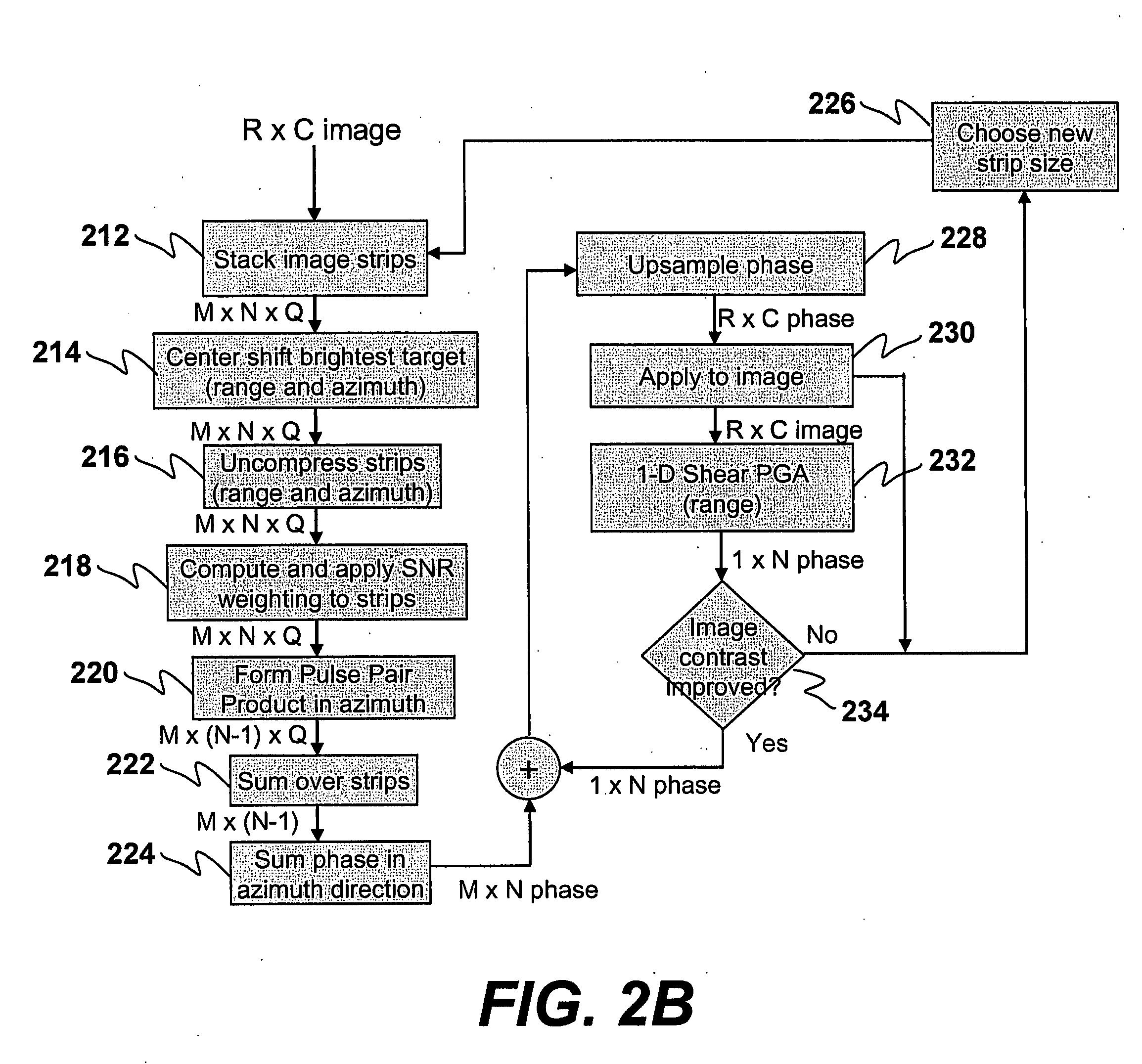
Methods for two-dimensional autofocus in high resolution radar systems
Provided are two-dimensional autofocus methods in a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) system which include: (1) two-dimensional pulse pair product algorithm including shear PGA, eigenvector phase history (“EPH”), shear PGA / EPH); (2) two-dimensional optimization algorithms including parametric one-dimensional estimate / two-dimensional correction, parametric two dimensional estimate / two-dimensional correction, unconstrained two-dimensional nonparametric and constrained two-dimensional nonparametric methods; (3) a two-dimensional geometry filter algorithm; (4) a two-dimensional prominent point processing algorithm; (5) a one-dimensional phase estimate of higher order two dimensional phase errors; and, (6) a fast SHARP parametric autofocus algorithm.
Owner:MAXAR MISSION SOLUTIONS INC
Surgical implement detector utilizing a radio-frequency identification marker
InactiveUS20060187059A1High bandwidthControl moreSurgeryElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingEngineeringFrequency modulation
A radio-frequency surgical implement detection system detects surgical implements in a surgical wound during and at the completion of a surgical procedure. Surgical implements, including surgical sponges or laparotomy pads, gauze pads and metallic surgical instruments, are individually attached to a non battery-powered, encapsulated radio-frequency marker. The marker comprises an integrated chip having a burnt-in memory code, which is broadcast through an antenna using a modulated carrier frequency. The code is received by an interrogating antenna of a detector. The interrogating antenna provides a power pulse, which is received by the antenna of the radio-frequency marker. The power pulse charges a capacitor, which proves power for the read function, carrier frequency modulation function and broadcast function of the integrated chip, permitting each marker-containing implement to be specifically identified.
Owner:FABIAN CARL E
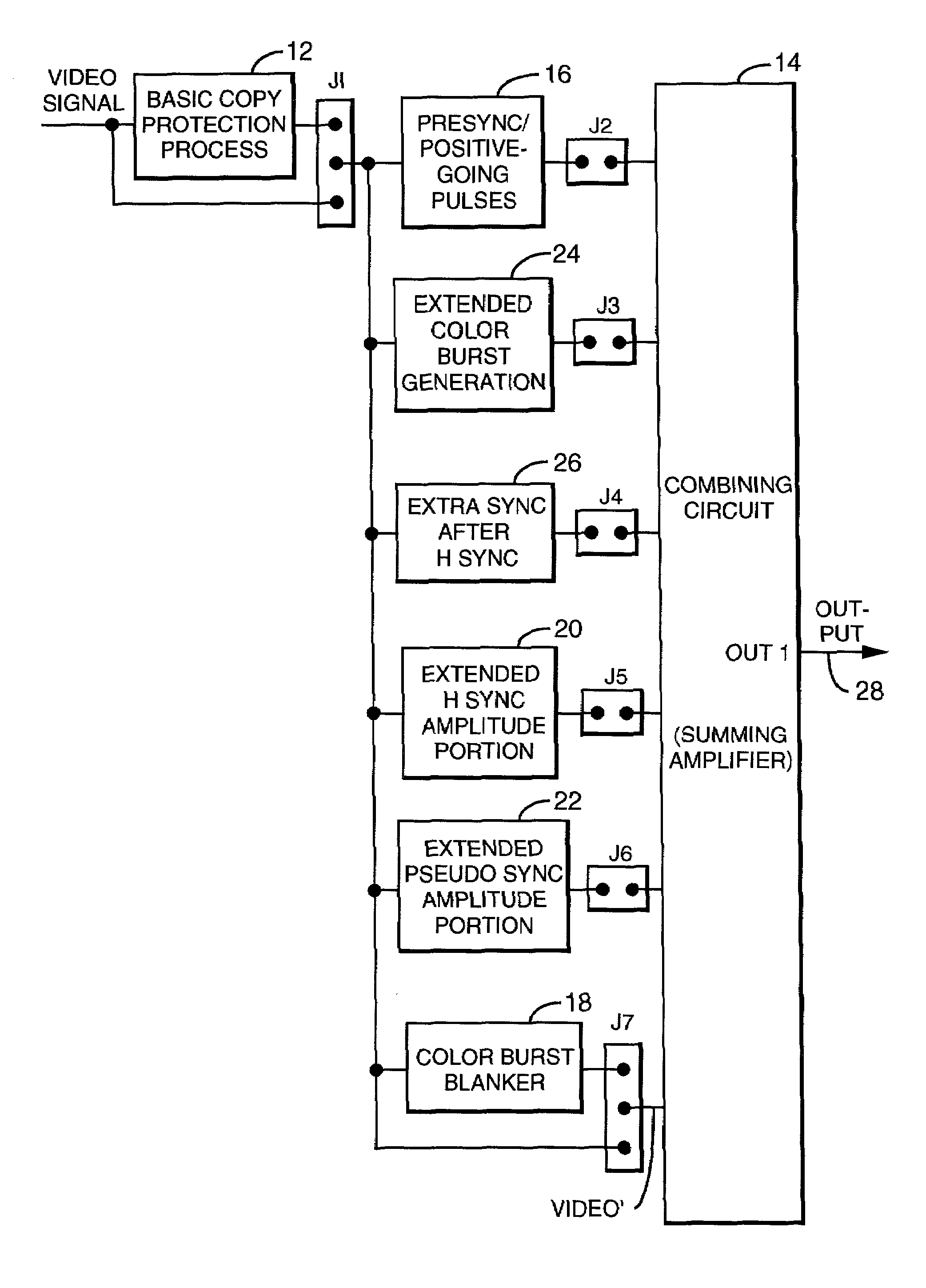
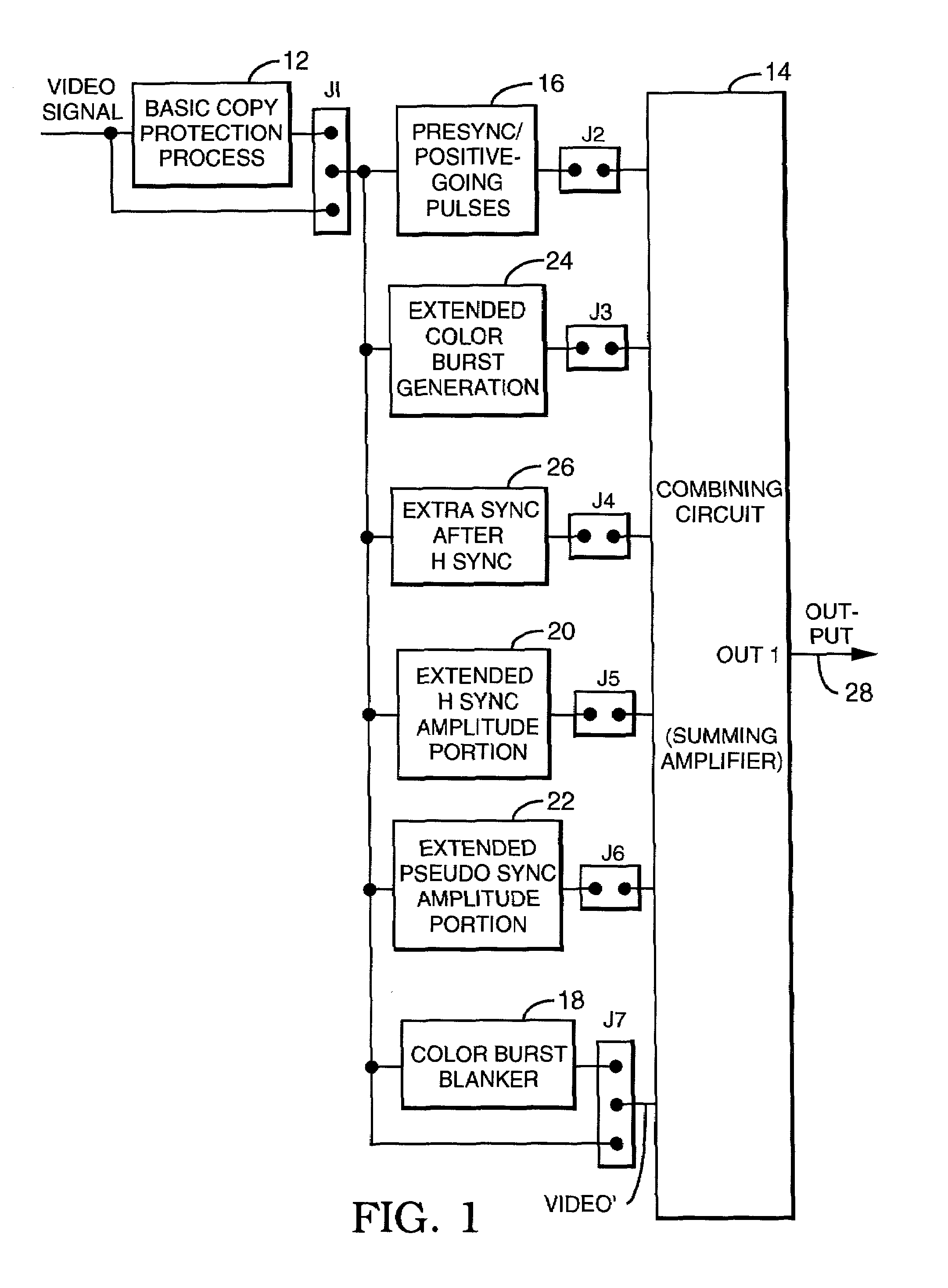
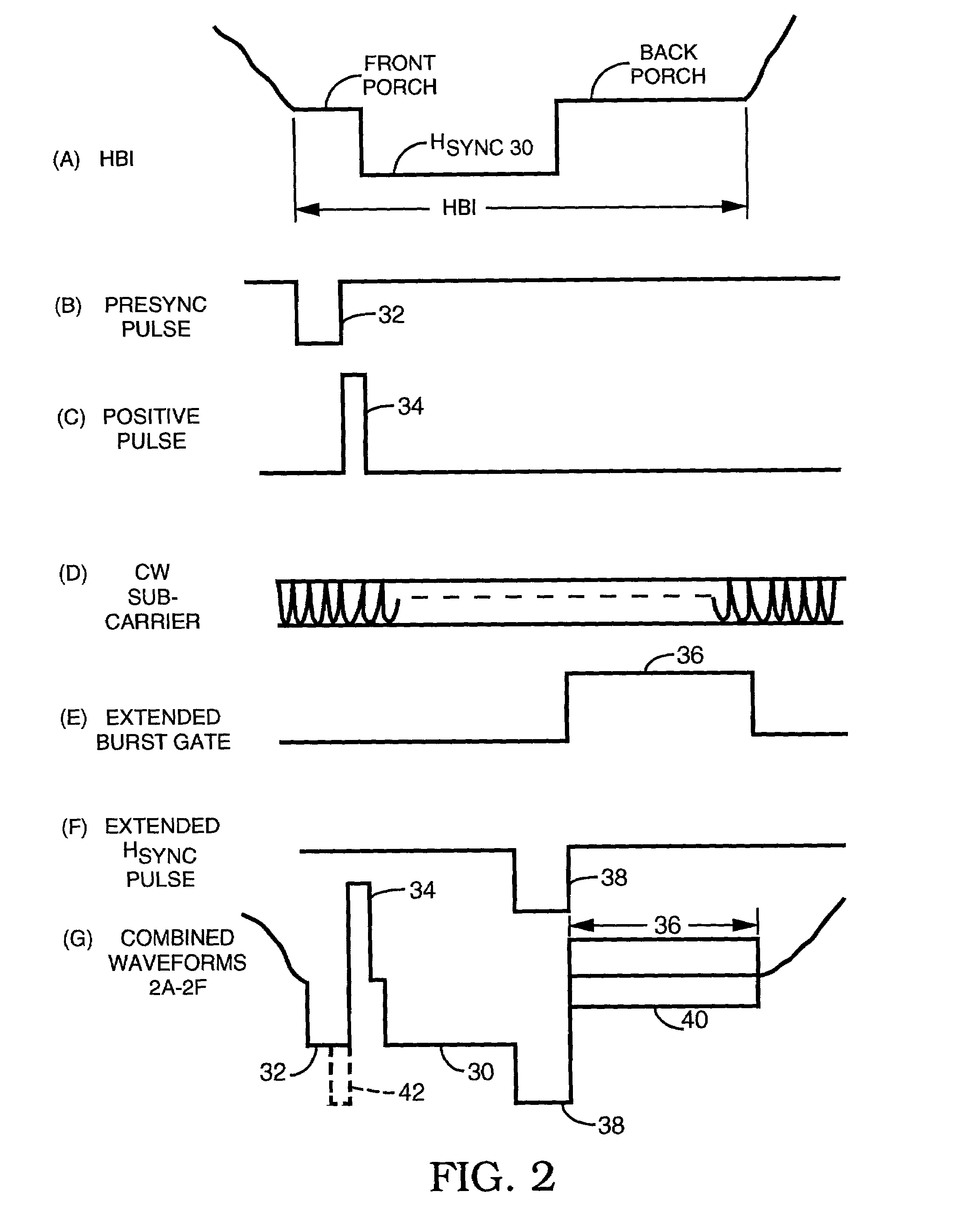
Method and apparatus for synthesizing or modifying a copy protection signal using a lowered signal level portion
InactiveUS7050698B1Maximize the extra darkeningReduced effectTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsUltrasound attenuationPorch
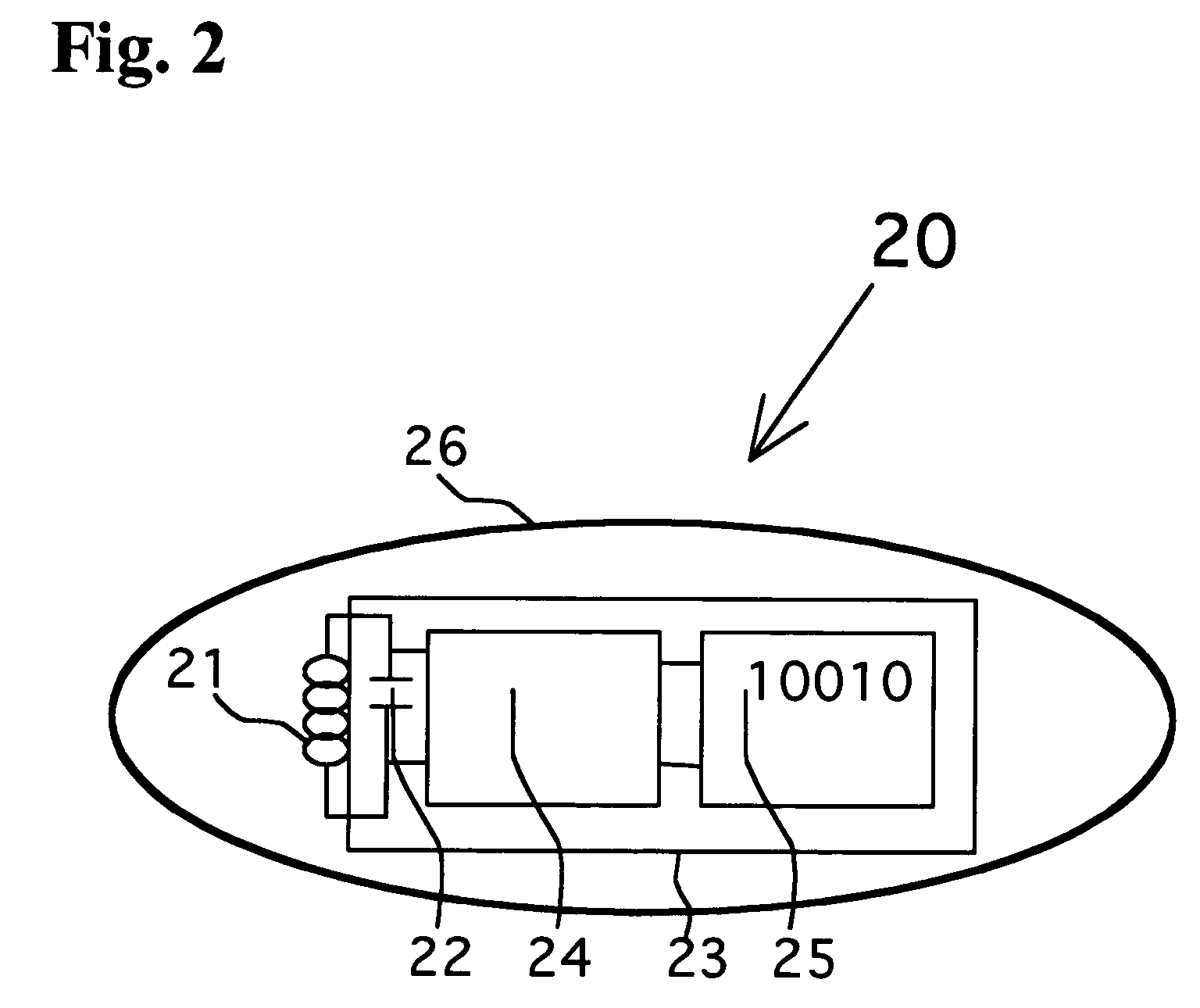
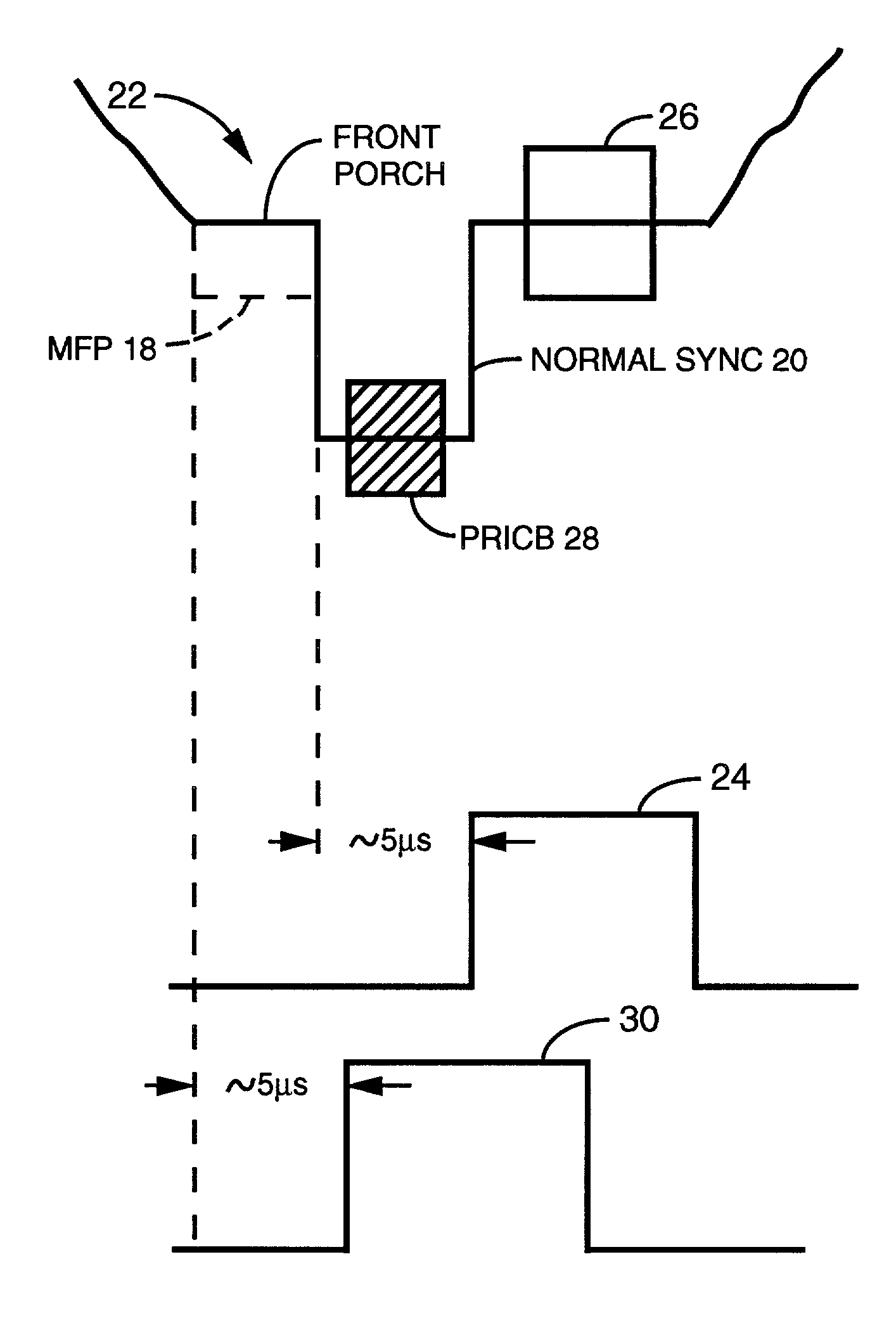
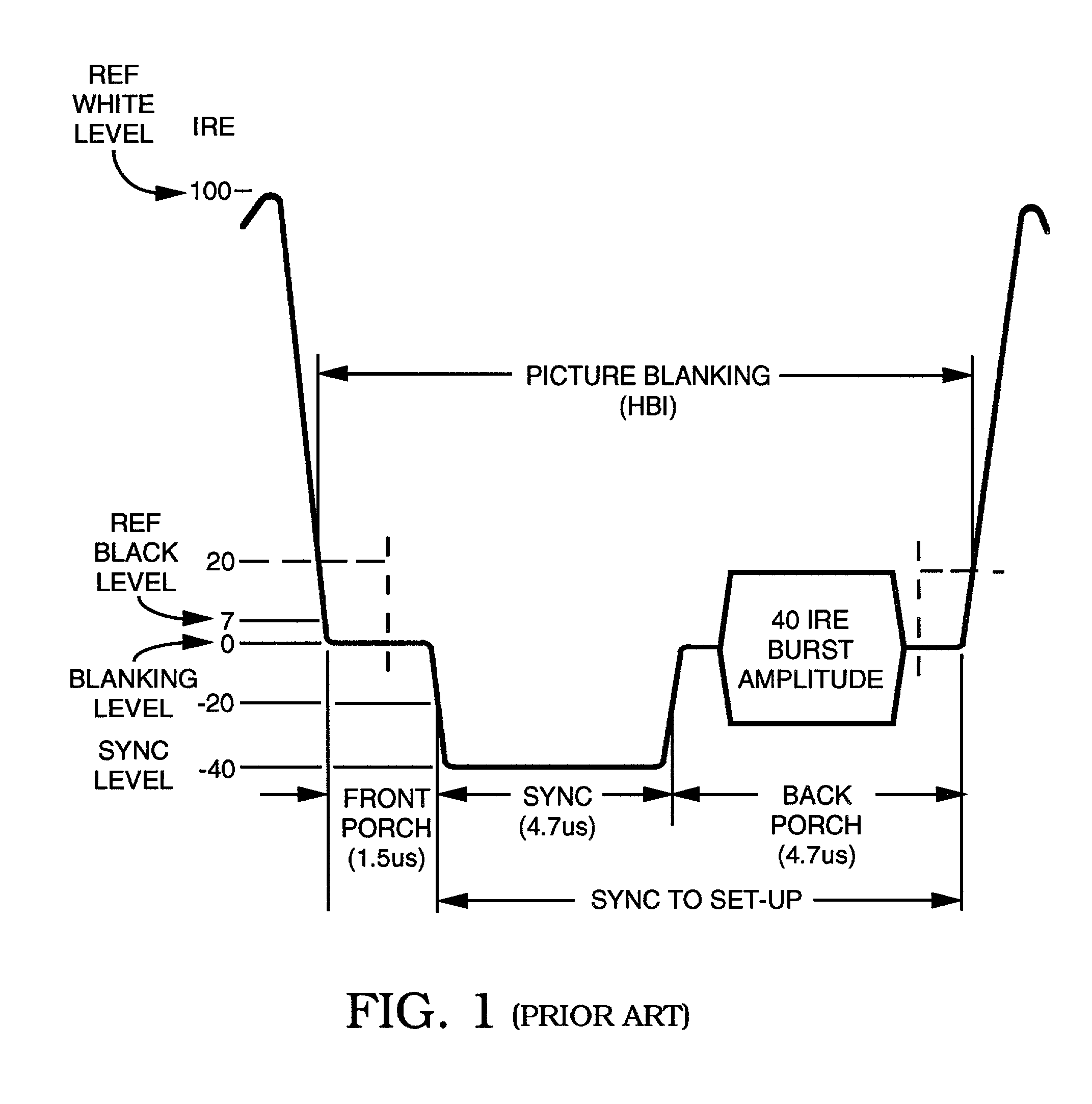
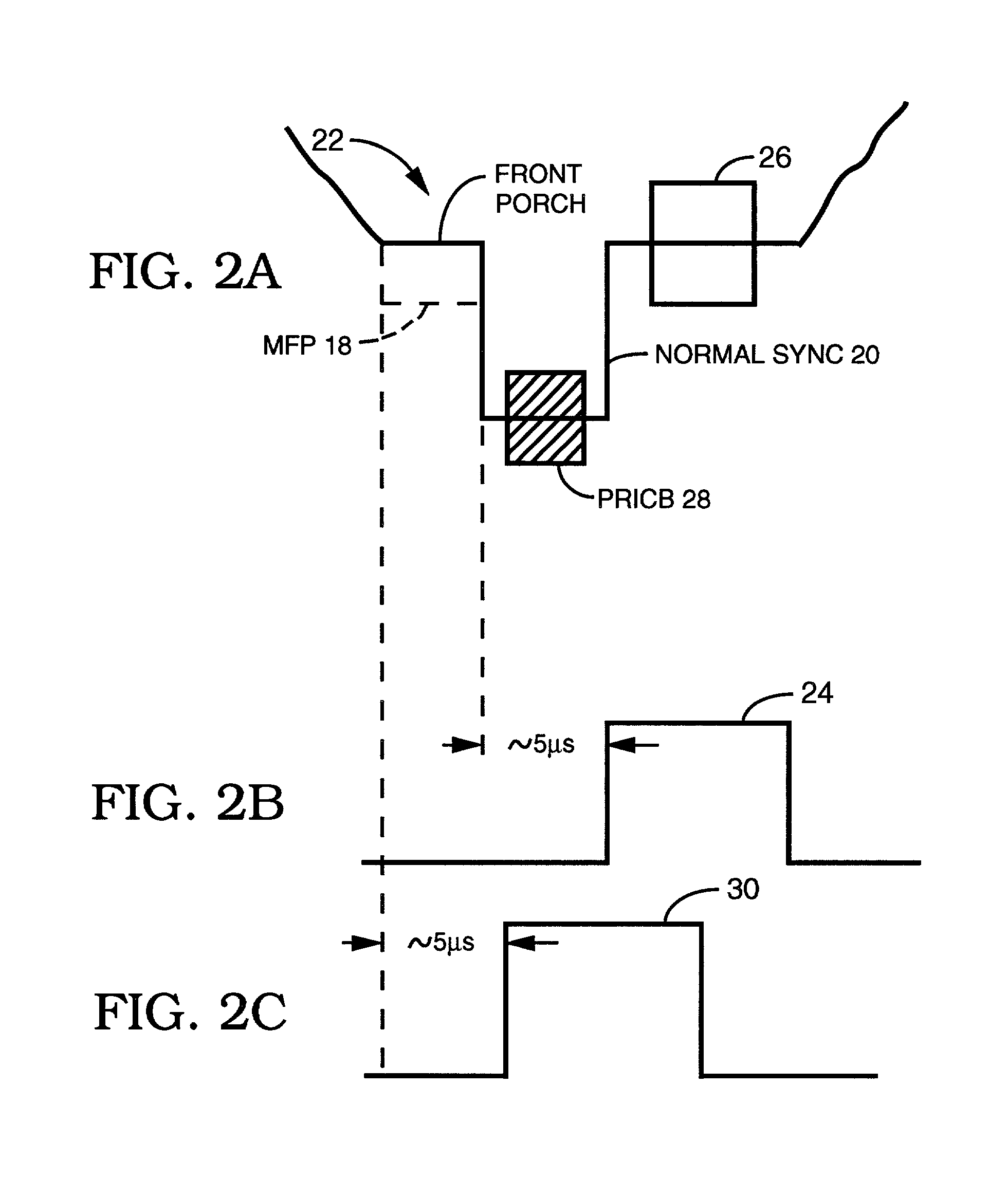
A modified Colorstripe™ copy protection process utilizes a basic anti-copy protection (ACP) signal that causes attenuation of a video signal, wherein, in one embodiment, the process modifies (lowers) the level of a front porch portion and adds an incorrect color signal (color burst) in the region of the sync tip. When an illegal copy is made, a pre-blanked end of line portion causes a TV set to trigger the color burst sample pulse ahead of time and cause the incorrect color signal in the sync tip region to be sampled. Thus, since the sync tip region has incorrect color phase or frequency, the resulting illegal copy will have enhanced color distortions. In other embodiments, other portions of the horizontal blanking interval are lowered in level and incorrect color bursts are added to a portion or portions of the back porch and / or a portion of the front porch.A further embodiment employs lowering a back porch portion above a sync tip level near the beginning of a video line to form a pseudo sync / AGC pulse pair. The various embodiments of the process may include an adaptable process, as well as several alternative ACP signals for use in combination with the process.
Owner:MACROVISION CORP
Two-dimensional fourier transform spectrometer
InactiveUS8526002B2Reduce ambiguityReduce subjectivityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFrequency spectrumCoupling
The present invention relates to a system and methods for acquiring two-dimensional Fourier transform (2D FT) spectra. Overlap of a collinear pulse pair and probe induce a molecular response which is collected by spectral dispersion of the signal modulated probe beam. Simultaneous collection of the molecular response, pulse timing and characteristics permit real time phasing and rapid acquisition of spectra. Full spectra are acquired as a function of pulse pair timings and numerically transformed to achieve the full frequency-frequency spectrum. This method demonstrates the ability to acquire information on molecular dynamics, couplings and structure in a simple apparatus. Multi-dimensional methods can be used for diagnostic and analytical measurements in the biological, biomedical, and chemical fields.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for distributed synchronous clocking
InactiveUS20020031199A1Reduce phase differenceIncrease the number ofRepeater/relay circuitsActive radio relay systemsTelecommunicationsArrival time
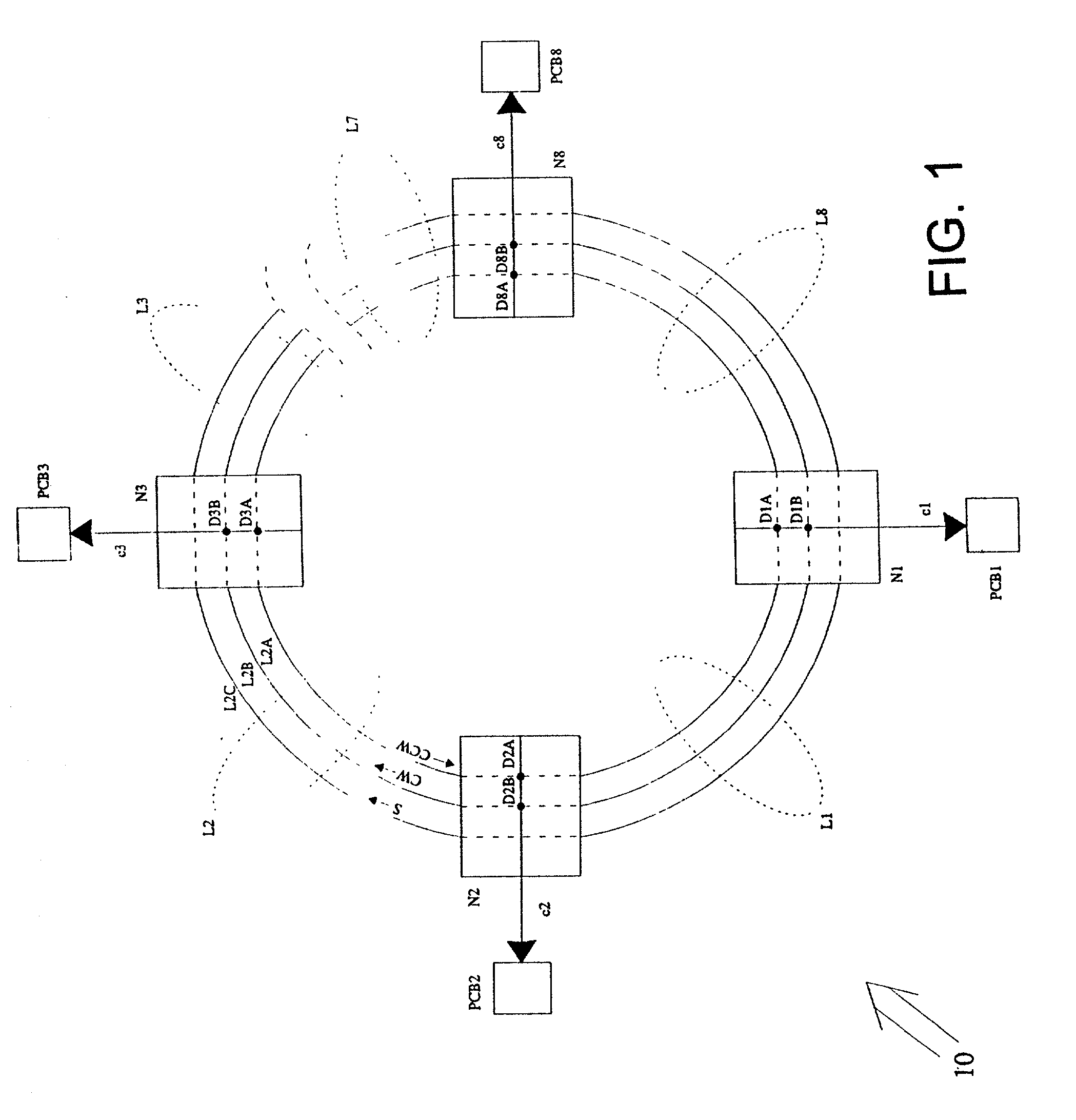
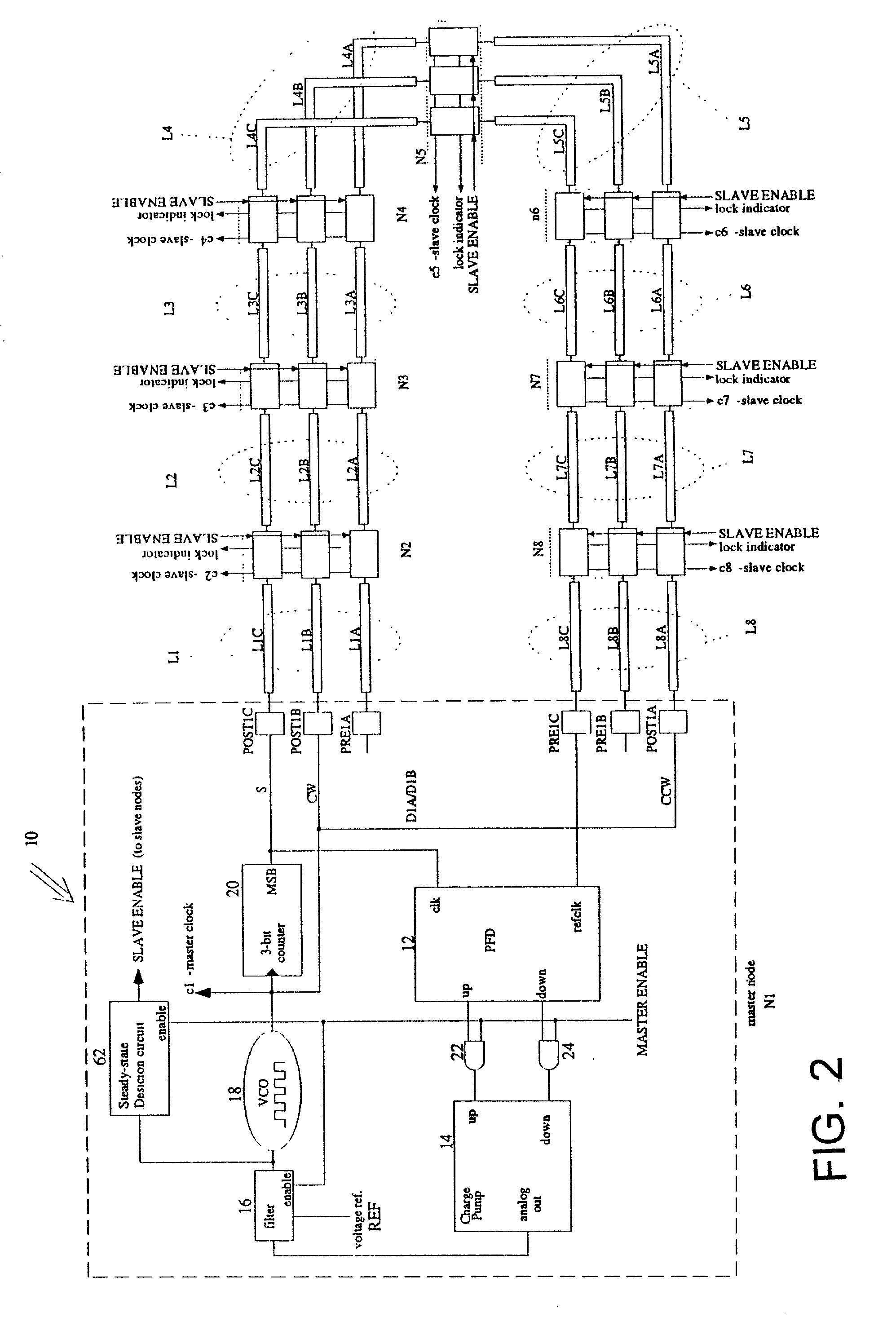
To synchronize clock signals in spatially distributed nodes in a large, synchronous electronic, optical, optoelectronic or wireless system, a master node generates two identical pulse trains and propagates them to a plurality of slave nodes via first and second propagation channels, respectively, so that a pair of pulses, one from each pulse train, arrive at each slave node simultaneously, travelling in opposite directions. Each slave node generates a clock signal event when the pair of pulses arrive substantially simultaneous. When the pulses in the two channels do not arrive simultaneously, the slave node adjusts delays in each propagation channel so as to adjust arrival times of subsequent pairs of pulses. The delays may comprise pre-delays upstream of the detection point and post-delays downstream of the detection point, any increment in a pre-delay being compensated by an equal decrement in the post-delay in the same propagation channel.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
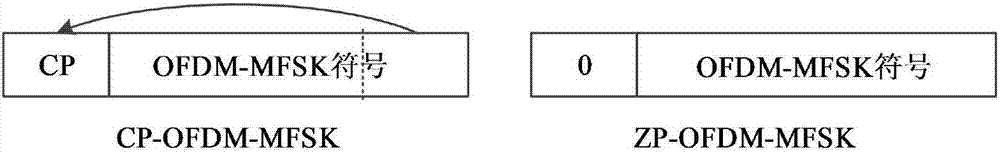
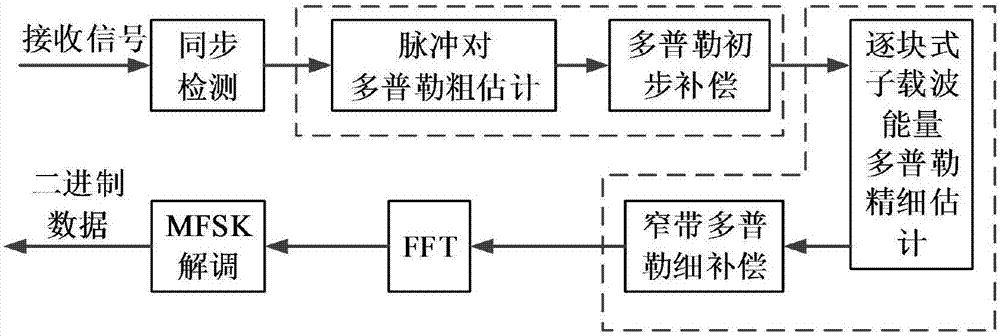
OFDM-MFSK underwater acoustic communication broadband Doppler estimation and compensation method based on sub-carrier energy
ActiveCN107231176AImplement trackingImprove estimation accuracySonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionFrequency-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemEstimation methods
The invention discloses an OFDM-MFSK underwater acoustic communication broadband Doppler estimation and compensation method based on sub-carrier energy, and belongs to the field of the underwater communication. The specific content is as follows: a transmitting end inserts a pulse pair signal between a synchronization signal and the data; a receiving end firstly detects the synchronization signal to complete the Doppler initial compensation; the demodulation is performed on each OFDM-MFSK data block in the data in a way of one data block by one data block to estimate the effective sub-carrier position, and the energy sum of all effective sub-carrier is used as the cost function to perform the search according to the given different Doppler factors, thereby acquiring the fine Doppler factor of the current data block to complete the fine compensation of the Doppler; and finally the receiving data is demodulated. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the accurate estimation and compensation of the broadband Doppler in the underwater OFDM-MFSK communication system is effectively realized, and the problem that the traditional Doppler estimation method is bad in stability and low in estimation precision is solved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Wireless time reference system and method
ActiveUS20090243934A1Accurate measurementDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationClock rateTransmitter
Instead of normalizing time reference of independent spatially-located clocks using a reference tag transmission from known location, the present invention uses an interarrival time interval between a pulse pair of UWB pulses as a timing metric. Thus, a method of synchronizing spatially-located clocks or normalizing time indications thereof comprises transmitting a UWB pulse pair, determining at first and second monitoring stations a respective count value indicative of a locally measured time interval between received pulse pairs, determining a ratio between clock counts of first and second monitoring stations, and utilizing the ratio to determine clock skew, e.g., a timing correction to be applied to respective local clocks of the monitoring stations. A corresponding system comprises a reference tag transmitter that transmits a pulse pair of UWB pulses to define a time reference interval, a first independent receiver that receives, the pulse pair to generate a first count value indicative an interarrival interval between the pulse pair, a second independent receiver that receives the pulse pair to similarly generate a second count value, and a processor hub responsive to the count values to determine a ratio corresponding to the ratio of respective clock frequencies of the first and second receiver clocks. Once the correction is applied, time-of-arrival information from object tag transmissions may be used to determine object location with sub-foot position accuracies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
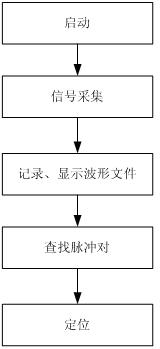
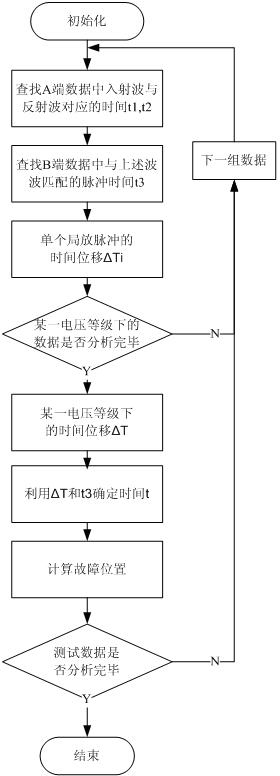
Recognition and location method of oscillatory wave partial discharge in asynchronous double-ended power cable
ActiveCN102288883ANo timing errorEliminate interferenceTesting dielectric strengthData acquisitionEngineering
The invention discloses an oscillation wave partial discharge identifying and positioning method for an asynchronous double-end power cable. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following specific steps: respectively installing oscillation wave partial discharge signal acquisition devices at the two ends of the cable; obtaining the voltage and partial discharge capacity signals at the two ends of the detected cable through data acquisition; recording and converting the corresponding data to obtain a waveform file which is needed for failure positioning; calling a partial discharge positioning algorithm to carry out the failure positioning; and computing the accurate position of a failure point generating partial discharge signals. The positioning analysis result obtained by the invention is more accurate; the error rate is small; the wave velocity does not need to be known, thereby reducing the errors caused by computing the wave velocity; the excessive manual intervention is needed; the problems of large data quantity, inaccuracy in positioning and the like because different pulses under the voltage of each experiment are matched are avoided; and the rapid and accurate failure positioning course of the method is beneficial to the timely repair of faulty lines and the reduction of loss caused by power failure.
Owner:广州安电测控技术有限公司
Method and apparatus for providing or enhancing copy protection by adding selected negative-going and positive-going pulses in a video signal HBI
ActiveUS7236683B2Maximizing video signal copy protectionHigh playabilityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer hardwarePorch
The horizontal blanking interval (HBI) of a normal video signal is modified to enhance the playability of the applied copy protected video signal while maintaining the copy protection effectiveness. As generally known, a copy protected video signal with positive-going pulses in a back porch region causes possible black level depression. The addition of a negative-going pulse and / or negative-going and positive-going pulse pair immediately prior to the H sync signal in the front porch region causes a reduction in such black level depression while resulting in enhanced playability. In other embodiments, an amplitude extending pulse is added to a latter portion of the H sync pulse or to a latter portion of a pseudo sync pulse, to increase the negative-going amplitude of the respective pulse. Various combinations of the added pulses also are possible.
Owner:MACROVISION CORP
Methods for driving electro-optic displays
ActiveUS10672350B2Reduce perceived flashinessReduce artifactsStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
A variety of methods for driving electro-optic displays so as to reduce visible artifacts are described. Such methods include (a) applying a first drive scheme to a non-zero minor proportion of the pixels of the display and a second drive scheme to the remaining pixels, the pixels using the first drive scheme being changed at each transition; (b) using two different drive schemes on different groups of pixels so that pixels in differing groups undergoing the same transition will not experience the same waveform; (c) applying either a balanced pulse pair or a top-off pulse to a pixel undergoing a white-to-white transition and lying adjacent a pixel undergoing a visible transition; (d) driving extra pixels where the boundary between a driven and undriven area would otherwise fall along a straight line; and (e) driving a display with both DC balanced and DC imbalanced drive schemes, maintaining an impulse bank value for the DC imbalance and modifying transitions to reduce the impulse bank value.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Fiber Optic Sensor Thermally Matched Support Tubes for Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing
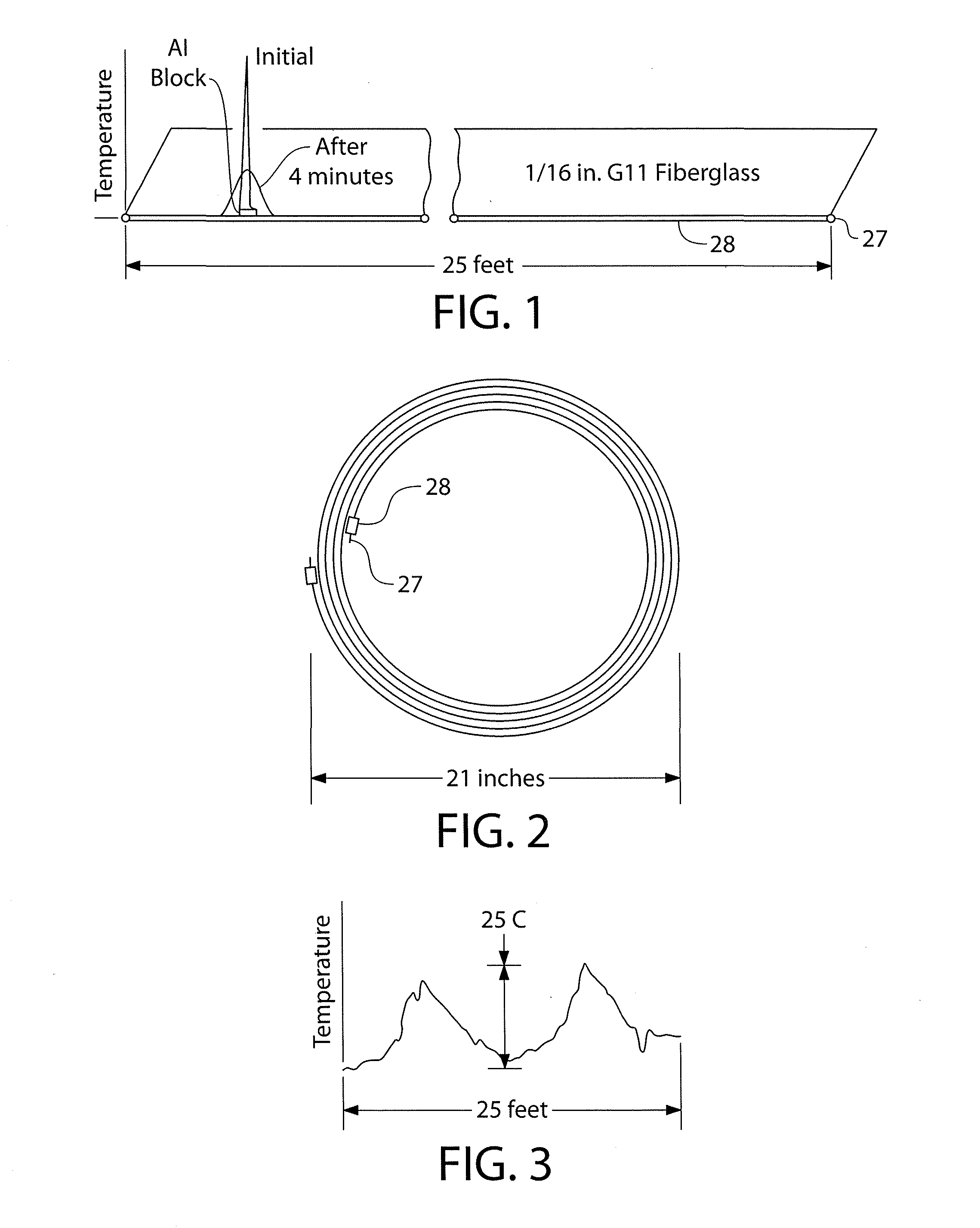
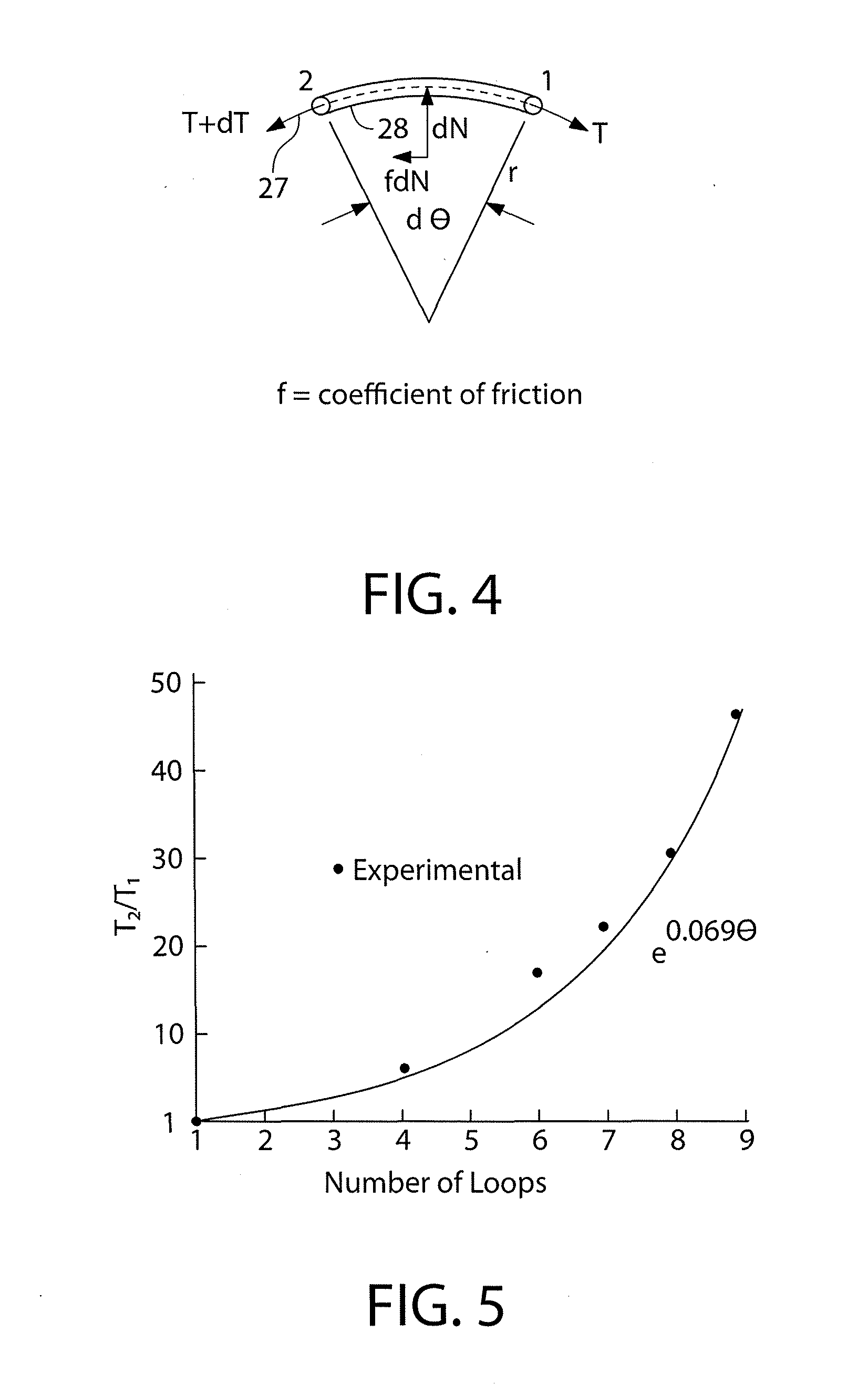
Distributed fiber optic sensor includes a composite support tube that closely matches the coefficient of thermal expansion of the optical sensing fiber contained therewithin for applications including but not limited to Rayleigh back-scattering, (OFDR, Optical Frequency Domain Reflectometry), Brillouin frequency shift (BOTDA, Brillouin Optical Time Domain Analysis, BOTDR, Brillouin Optical Time Domain Reflectometry), Raman (Optical Time Domain Reflectometry), DPP-BOTDA (Differential Pulse Pair Brillouin Optical Time Domain Analysis), Dual-Index BOTDA, PCF (Photonic Crystalline Fibers), and dense packed Fiber Bragg Gratings, both time and wave length modulated are described in detail.
QKD system sending terminal based on phase modulation light source, receiving terminal, QKD system and method thereof
InactiveCN106603161ASimple structureSimplify the control problemPhotonic quantum communicationPhase modulationVoltage
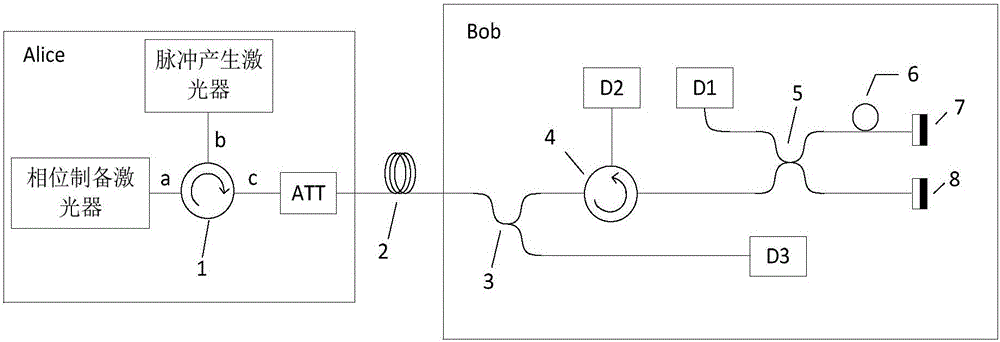
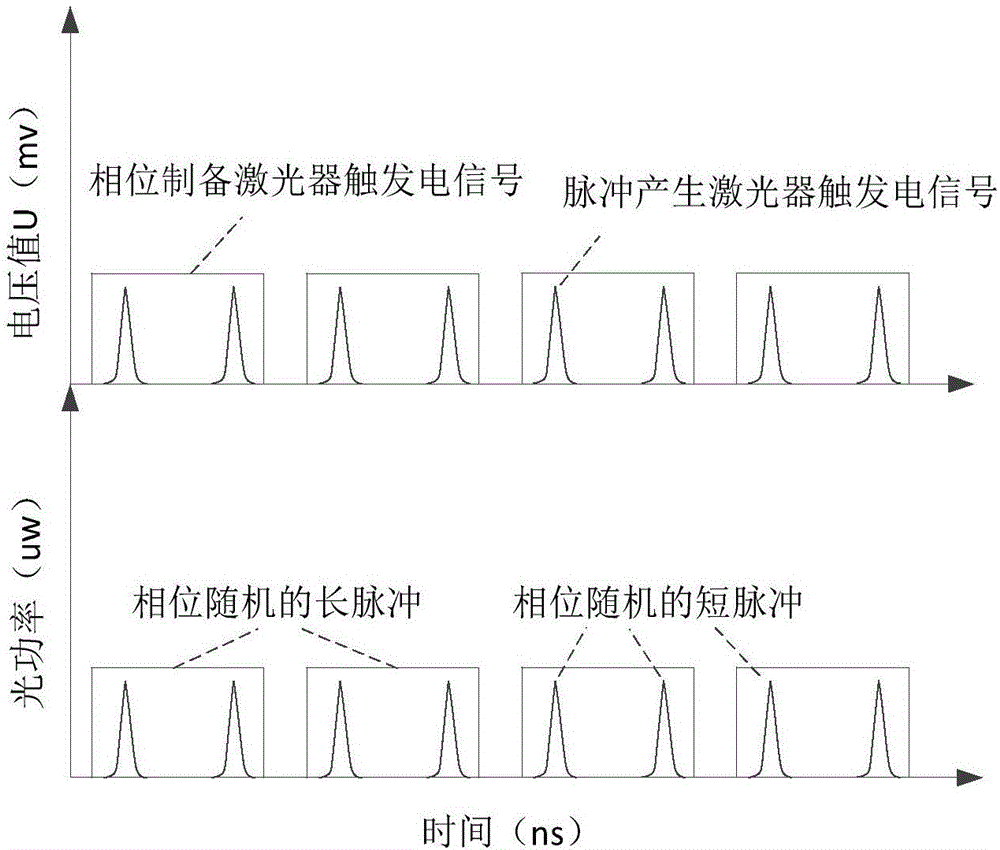
The invention discloses a QKD system sending terminal based on a phase modulation light source, a receiving terminal, a QKD system and a method thereof. By using the QKD system based on the phase modulation light source, at the sending terminal, the phase modulation light source is adopted; and through X basis vector phase coding and Z basis vector time coding modes, a light pulse pair is coded and then the light pulse pair is sent to the receiving terminal. In the invention, the phase modulation light source is used and a low half-wave voltage is possessed so that energy is saved and a possible is provided for a high speed application of the system; and a bias point problem of an intensity modulator does not need to be considered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENZHOU QUANTUM NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Dual head laser system with intra-cavity polarization, and particle image velocimetry system using same
InactiveUS6940888B2Low costEasy to useDevices using optical meansActive medium shape and constructionMetrologyLight beam
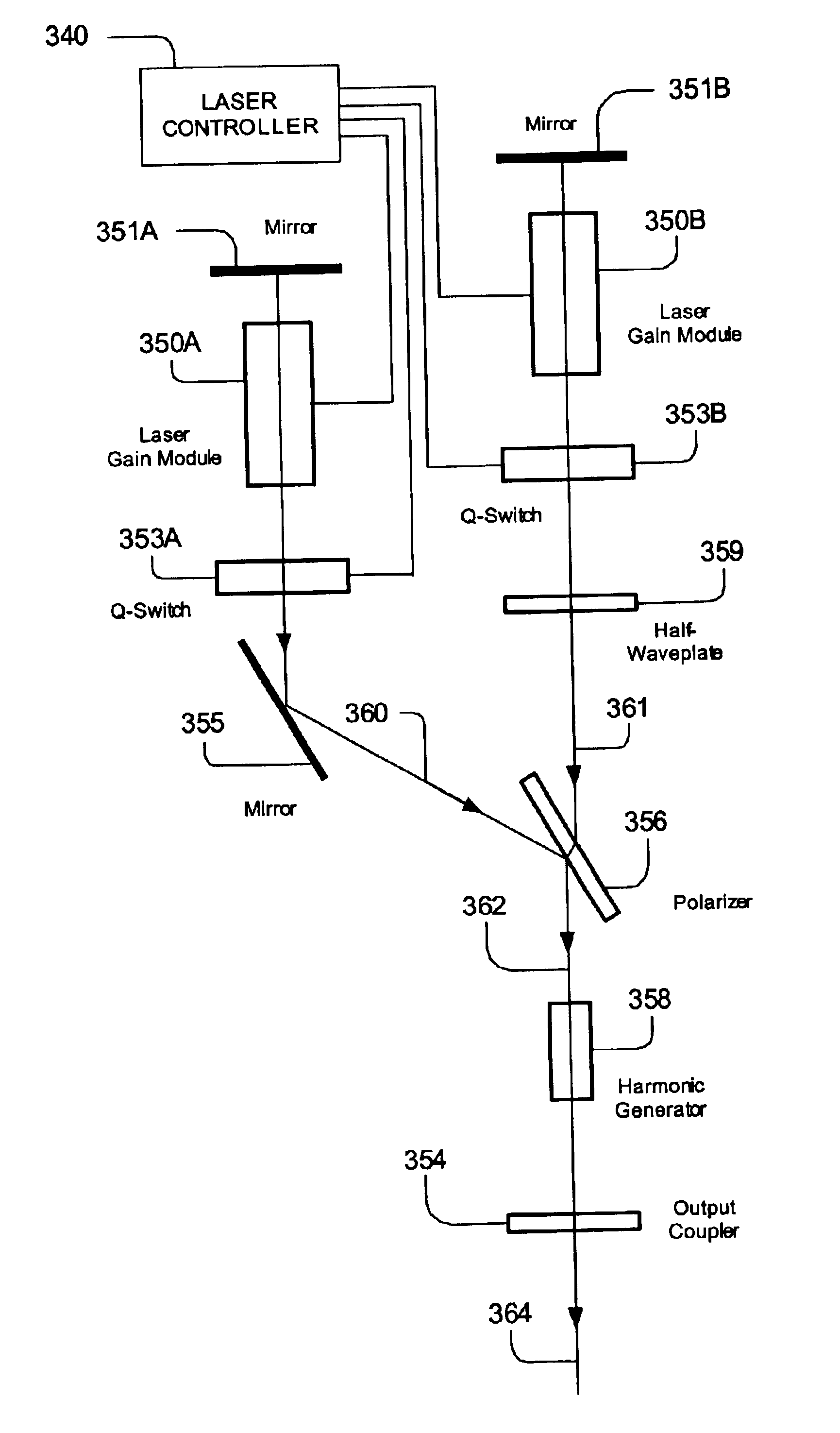
A laser system includes a resonator having two gain modules generating pulses, coupled with intra-cavity polarization into a single beam line, using a single output coupler. A laser controller controls the laser heads to emit pulses in rapid succession, such as pulse pairs separated by a time interval of less than about 1 millisecond, and in some embodiments in a range from about zero (overlapping) to about 100 microseconds. Also a system adapted for metrology using particle image velocimetry PIV uses the resonator. For PIV, optics are provided in the output beam paths which expand the beam to form pulsed illumination sheets. A camera is used to capture images of the pulsed illumination sheets for analysis.
Owner:ELEMENTAL SCI LASERS LLC +1
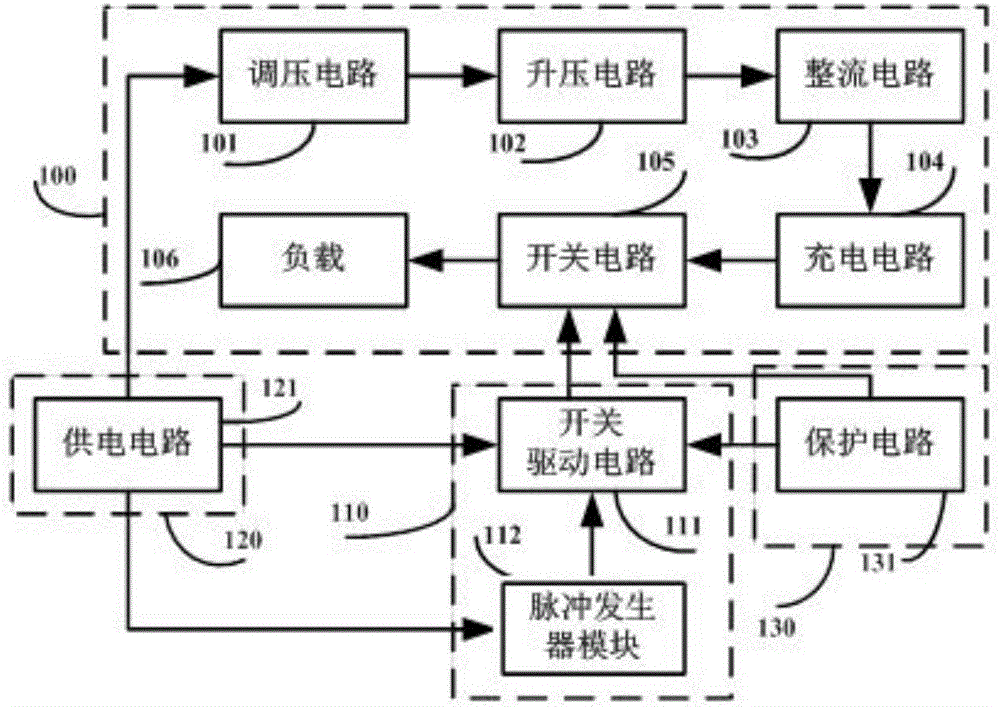
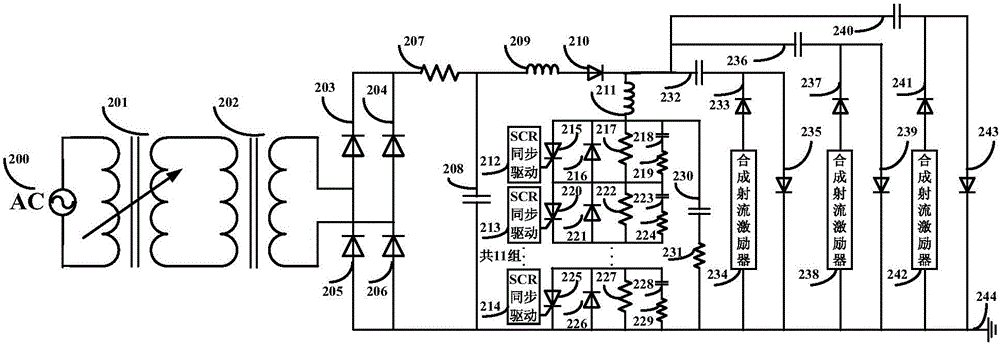
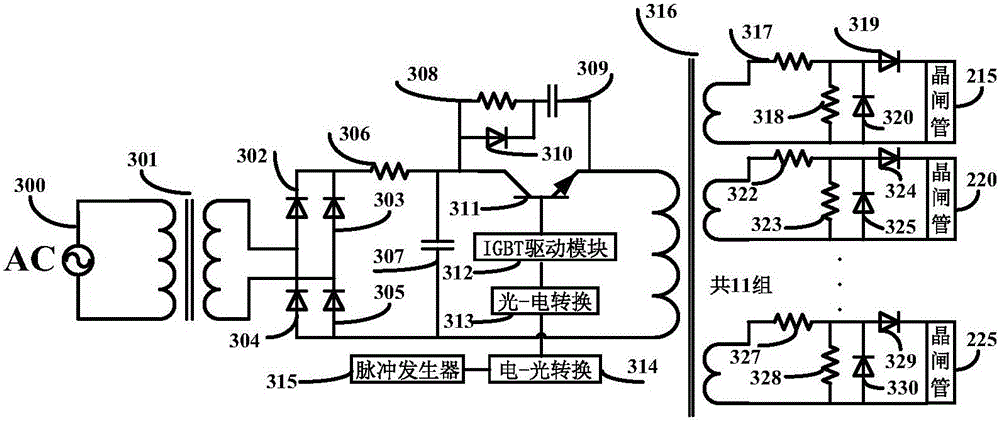
High-voltage pulse power supply for synchronous discharge of multiple spark plasma synthetic jet actuators
The invention discloses a high-voltage pulse power supply for the synchronous discharge of multiple spark plasma synthetic jet actuators, and the power supply comprises a main circuit module which is used for generating multiple synchronous negative high-voltage pulses; a control circuit module which is used for generating an IGBT switch drive signal; a power supply module which is used for supplying power to a main circuit module and a control circuit module; and a protection circuit module, wherein a thyristor switch in the protection circuit module is connected with an IGBT switch in the control circuit module. The power supply module is connected with the main circuit module and the control circuit module. The protection circuit module is connected with the main circuit module and the control circuit module. The control circuit module is connected with the main circuit module. The beneficial effects of the invention are that the structure is simple and compact; the plasma synthetic jet speed is high and the work efficiency is high; the power supply can output multiple 10kV negative high-voltage pulses synchronously to achieve the synchronous excitation of a plurality of spark plasma synthetic jet actuators, achieves the synchronous discharge of the plurality of spark plasma synthetic jet actuators, and enables the discharge current of a single spark plasma synthetic jet actuator to be greater than 100A.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Methods and apparatus for driving electro-optic displays
InactiveUS20140085350A1Shorten the overall cycleReduce data volumeCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsGray levelDisplay device
Waveforms for driving electro-optic displays, especially bistable electro-optic displays, are modified by one or more of insertion of at least one balanced pulse pair into a base waveform; excision of at least one balanced pulse pair from the base waveform; and insertion of at least one period of zero voltage into the base waveform. Such modifications permit fine control of gray levels.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
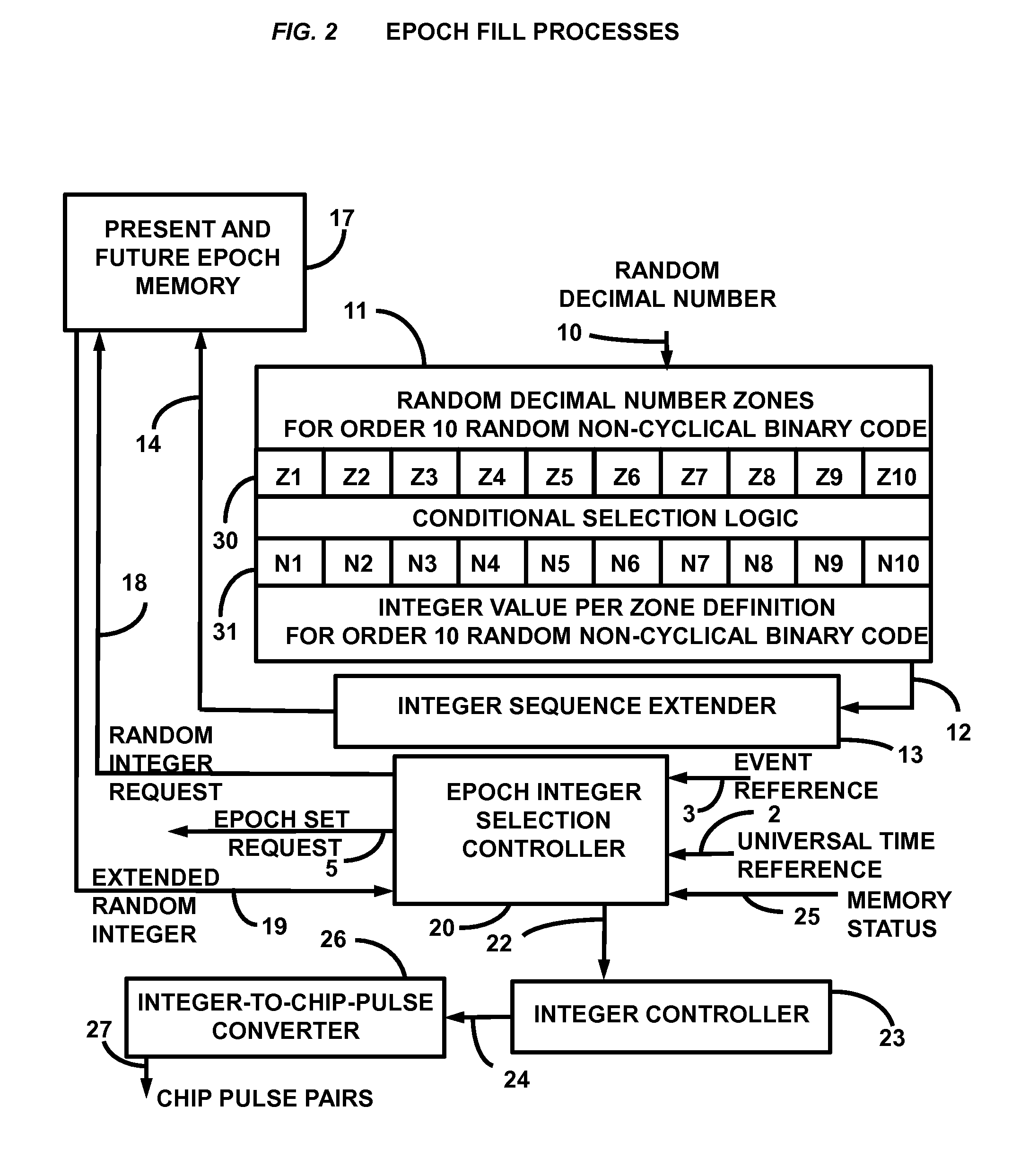
Random Non-Cyclical Binary Code Generator
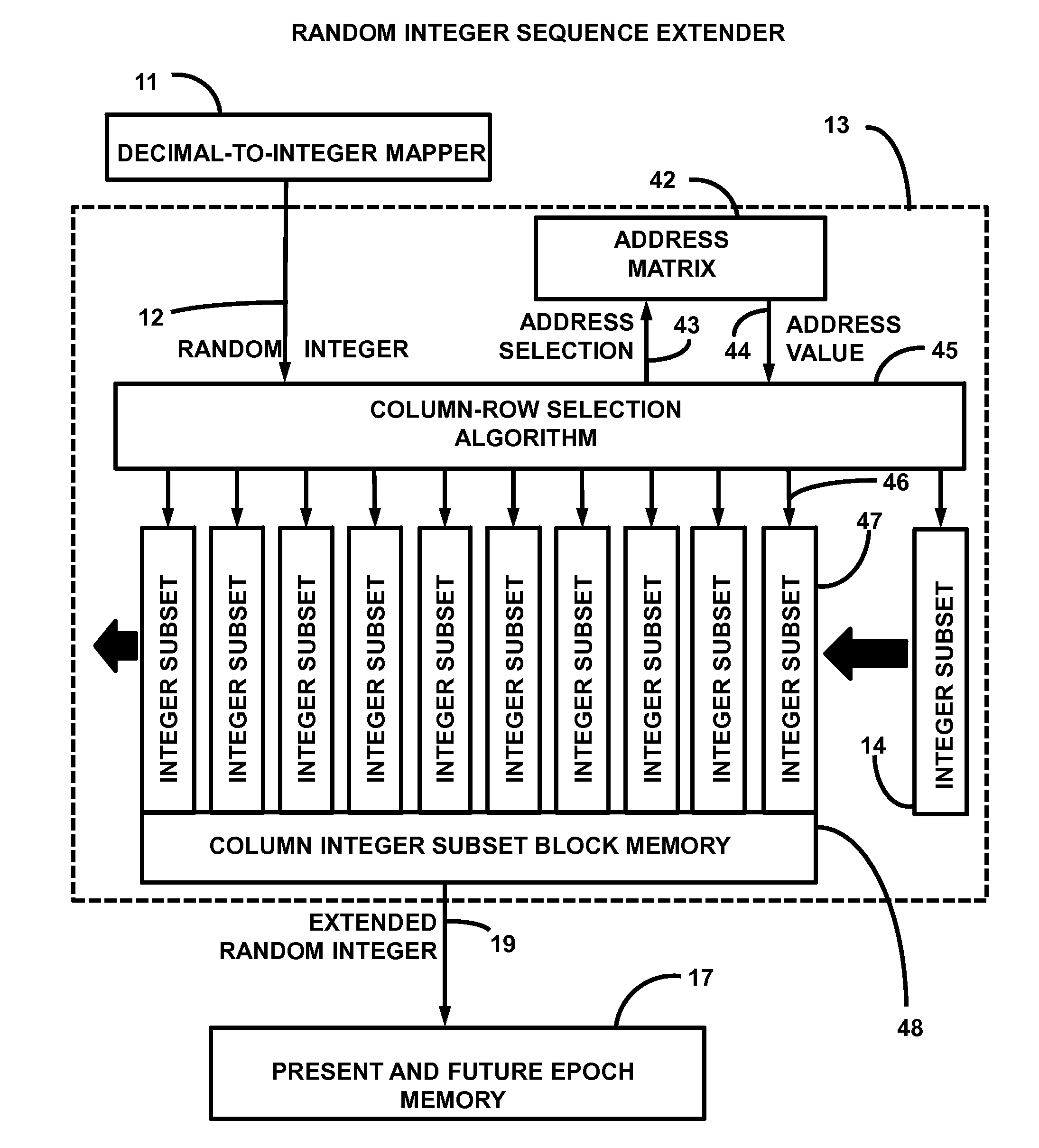
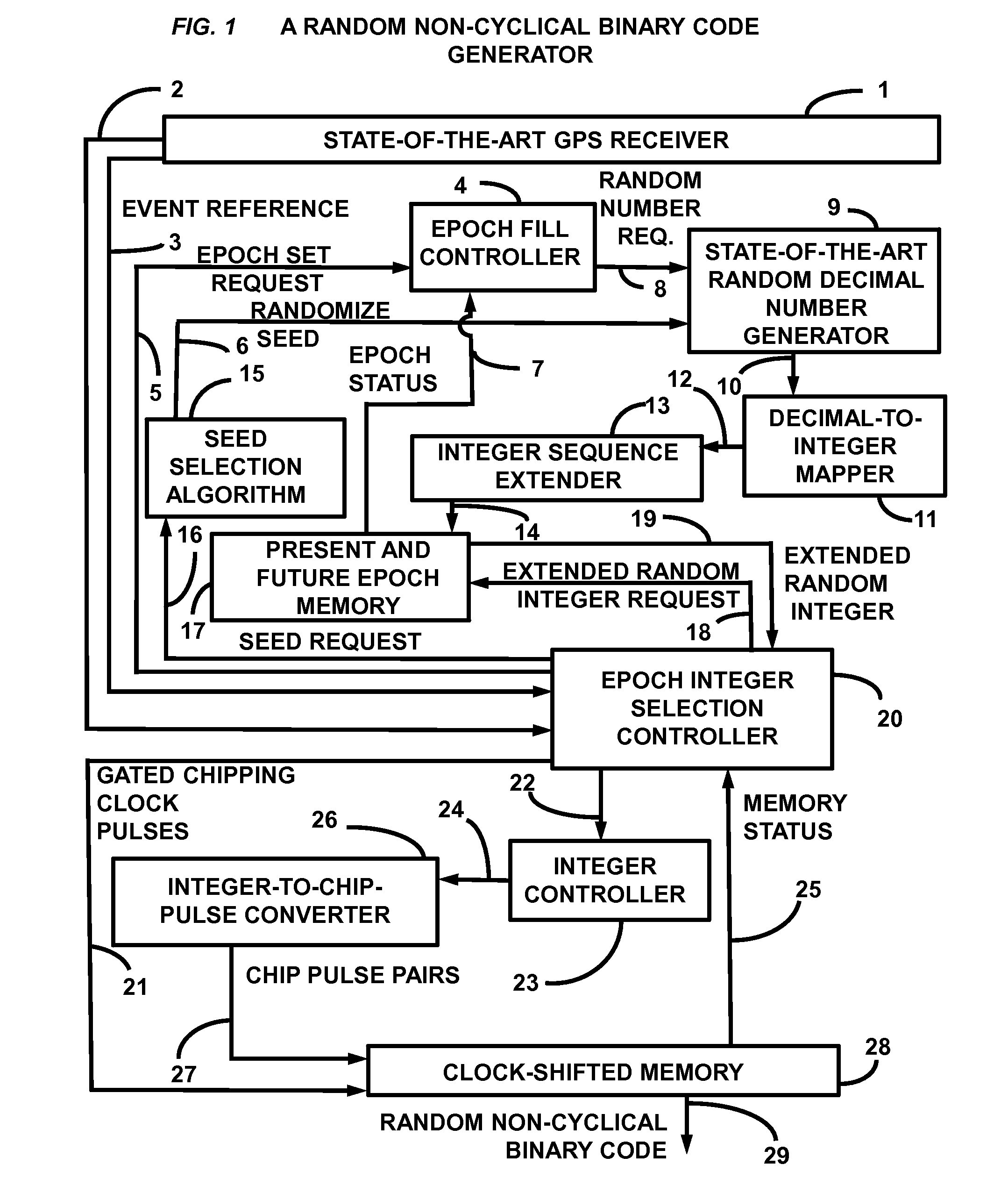
Presented is a random non-cyclical binary code generator for communications systems. A random non-cyclical sequence of integers from a random number generator is extended in length to form an extended integer sequence. This integer set is immediately loaded into a 10-minute epoch memory consistent with 10 minutes of chips. These integers are then synchronously retrieved from memory under GPS time-of-day control. Retrieved integers are immediately converted into pulse pairs of all ones followed by all zeros with each pulse width equal to the integer value in chips. The chips are immediately concatenated to a chipping clock shifting memory wherein each memory location is a unique phase source of the binary code. The memory length in chips is twice the range uncertainty for a 10 MHz chip rate, with the center chip of the shifting memory maintained as the source of universal time synchronized local binary code.
Owner:NEFF RUPERT THEODORE
High-spatial resolution long-distance distributed optical fiber temperature strain sensing system
InactiveCN106525092ASimple structureCompact structureThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansFrequency spectrumSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
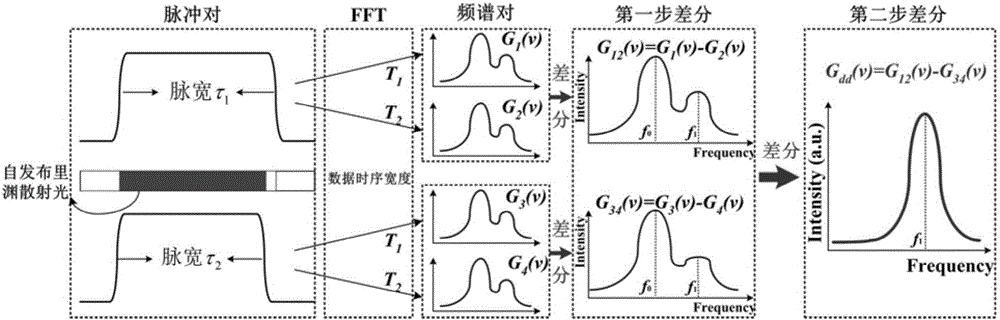
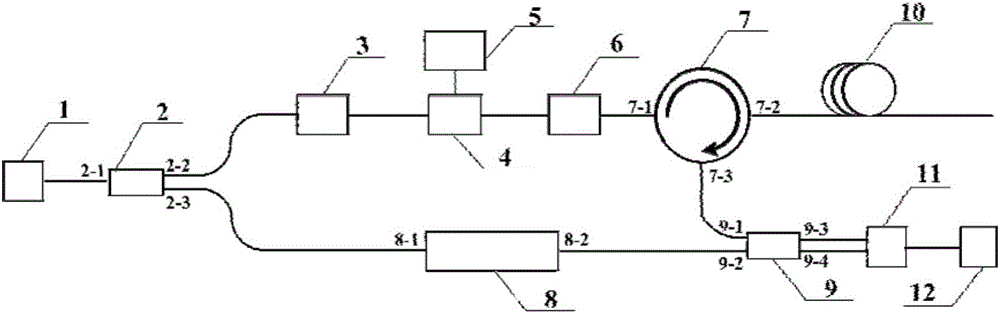
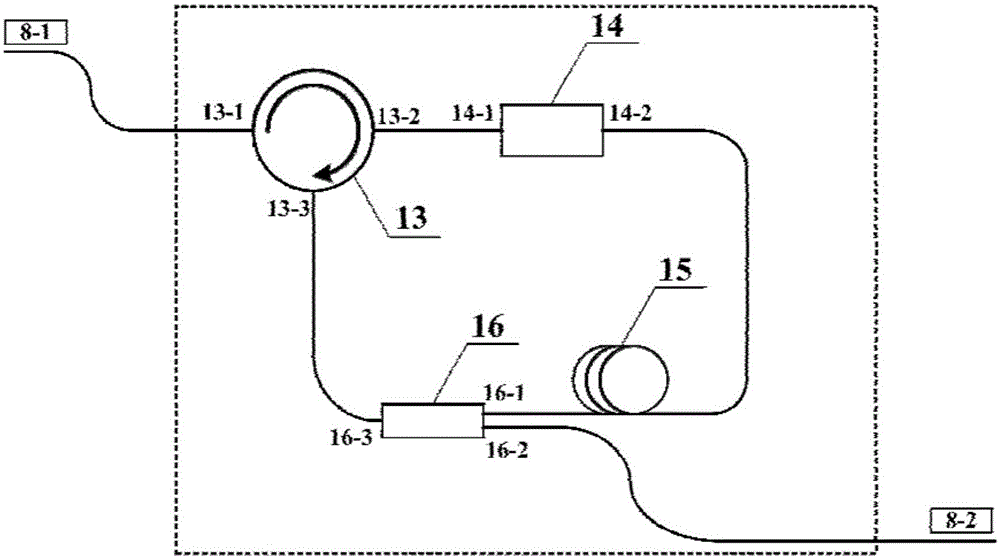
The present invention relates to a high-spatial resolution long-distance distributed optical fiber temperature strain sensing system. The system injects an optical pulse pair of which the pulse widths have a slight difference in a sensing optical fiber based on a pulse pair secondary frequency spectrum differential technology, detects and acquires a time domain brillouin scattering signal generated by each pulse, and adopts two sets of different time window widths to extract the data separately for the spectral analysis, and carries out the secondary frequency spectrum differential operation based on the obtained four sets of brillouin frequency spectrum data, thereby obtaining the space position sensing information covered by the pulse width difference of the optical pulse pair corresponding to the secondary differential brillouin spectrums, and improving the spatial resolution. By designing the pulse widths and the pulse width difference of the optical pulse pair in the system reasonably, the action of a brillouin nonlinear effect is full, and the information within a sensing range of dozens of kilometers is acquired on the condition of keeping a higher signal-to-noise ratio of the system, so that the distributed optical fiber temperature strain sensing system of high spatial resolution (cm magnitude), long distance (greater than 50 kilometers) and high measurement precision (plus or minus 1 DEG C, plus or minus 20 Mu Epsilon) can be realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com