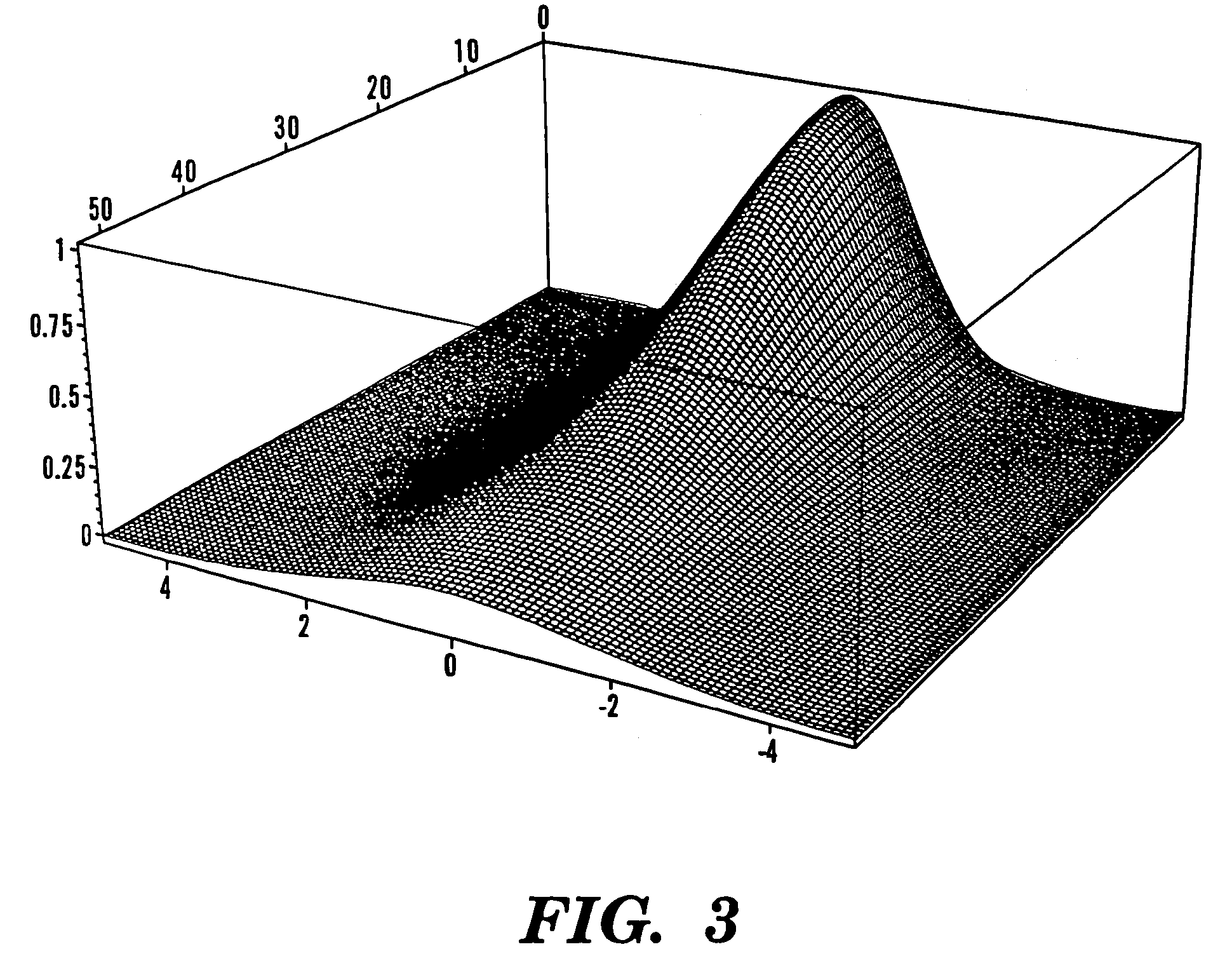
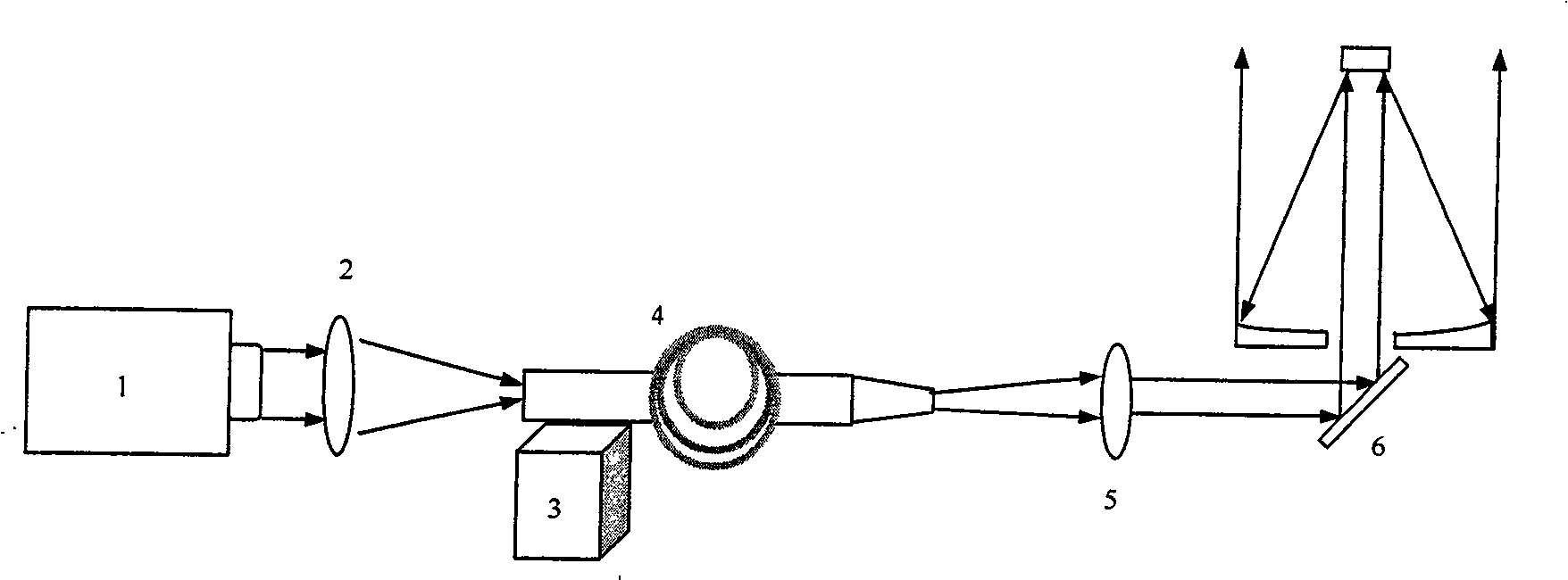
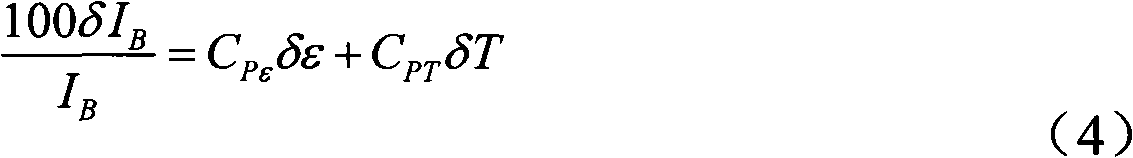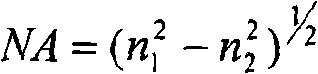Patents
Literature
42 results about "Nonlinear scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
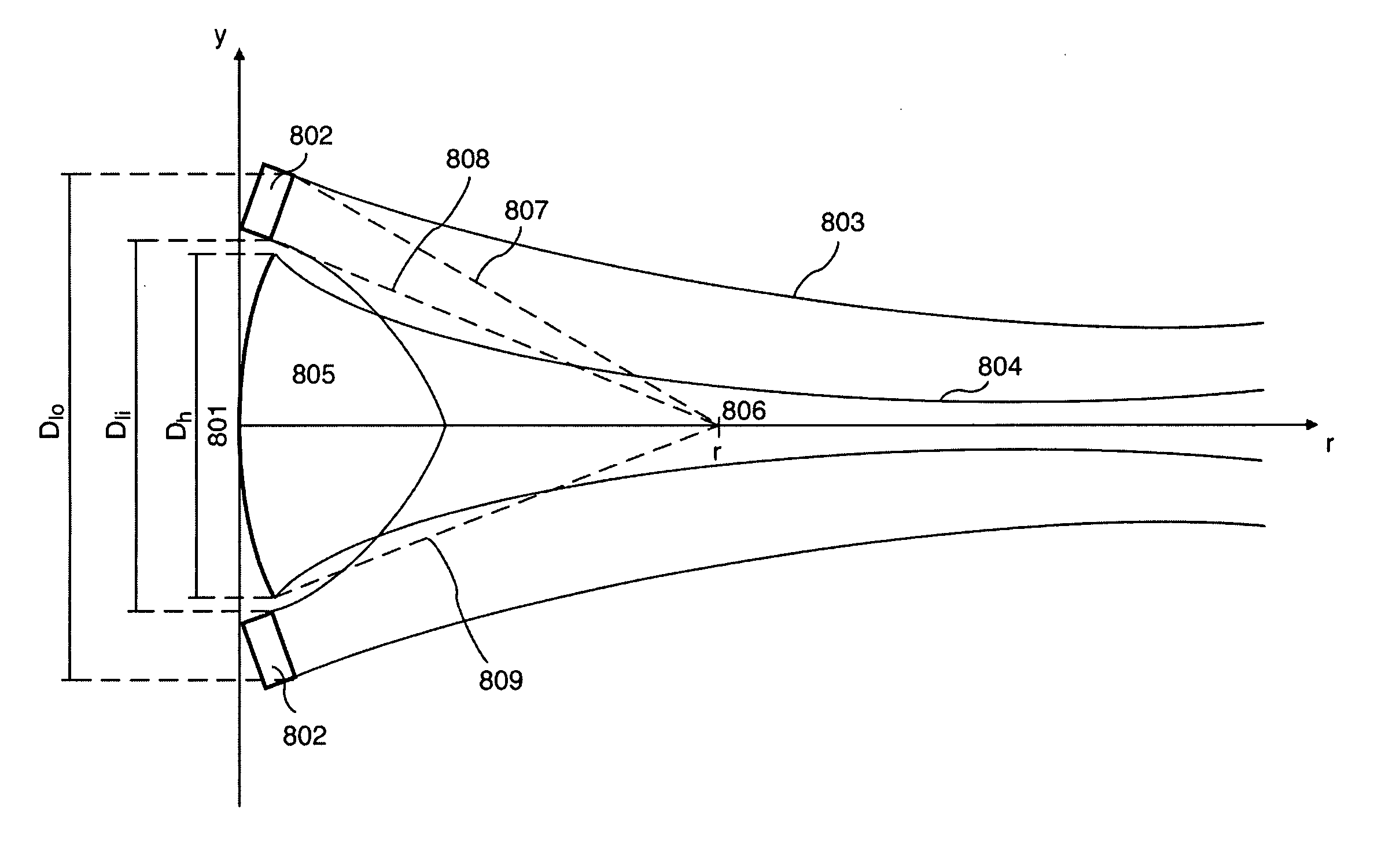
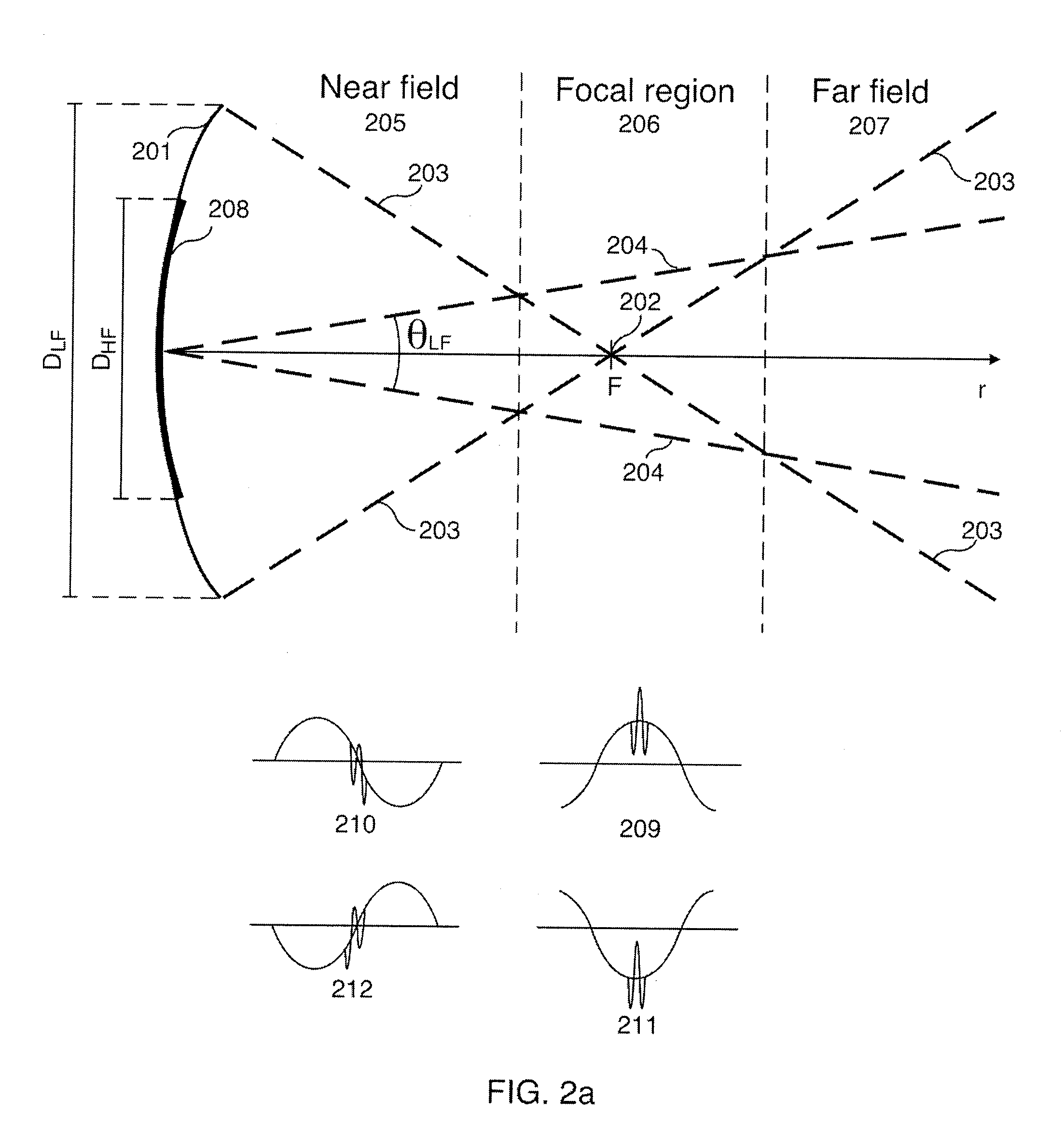
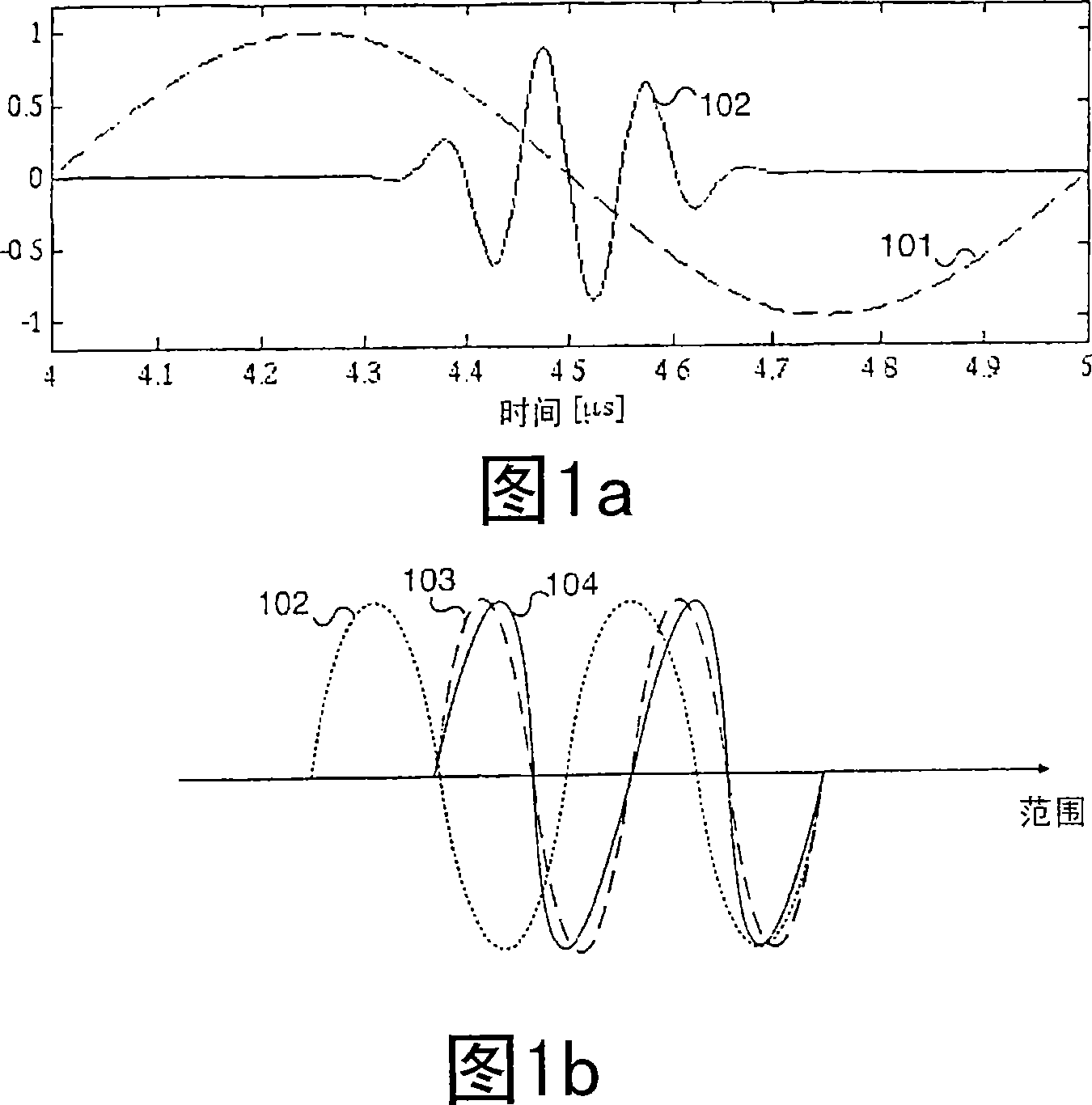
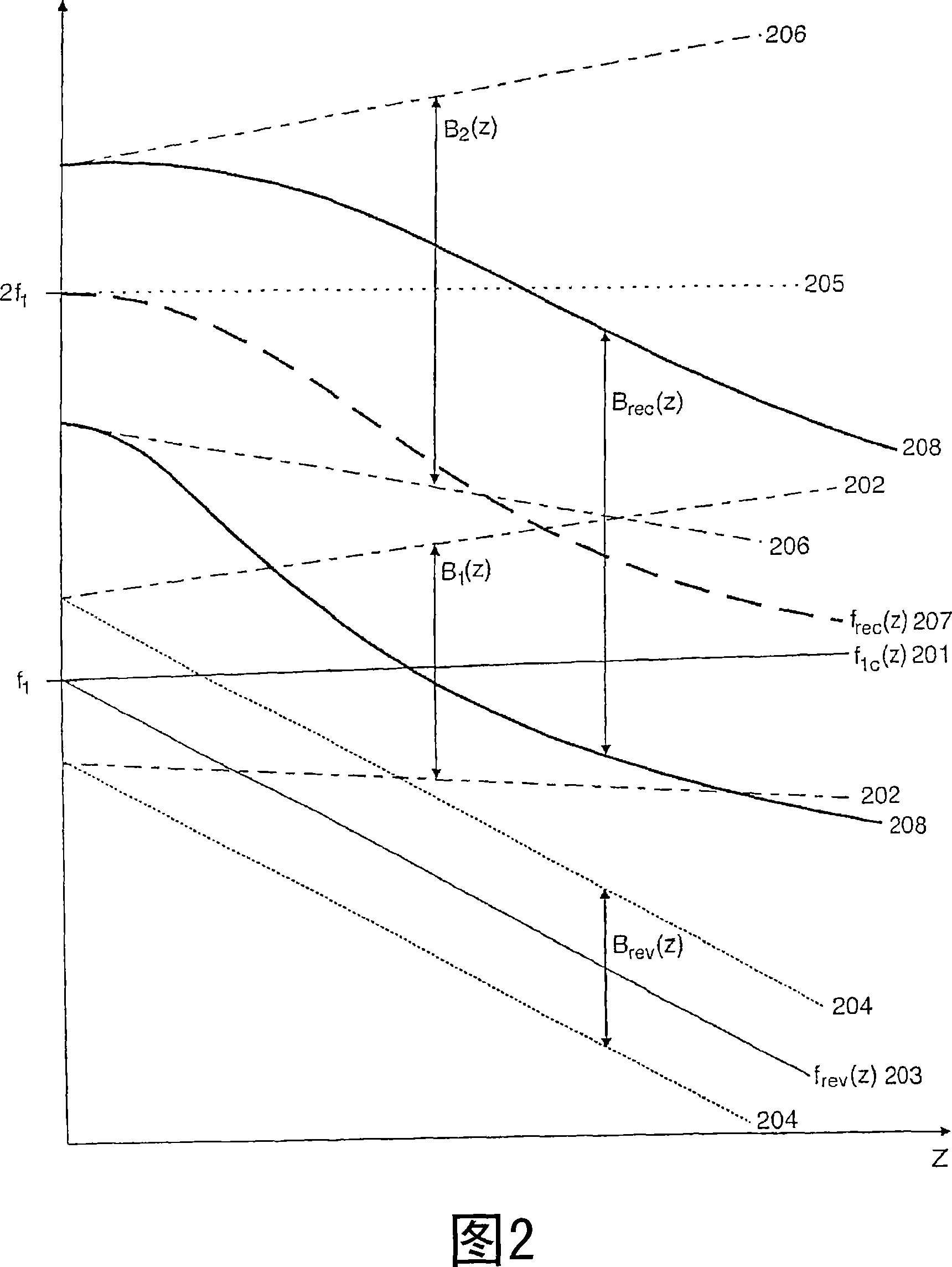
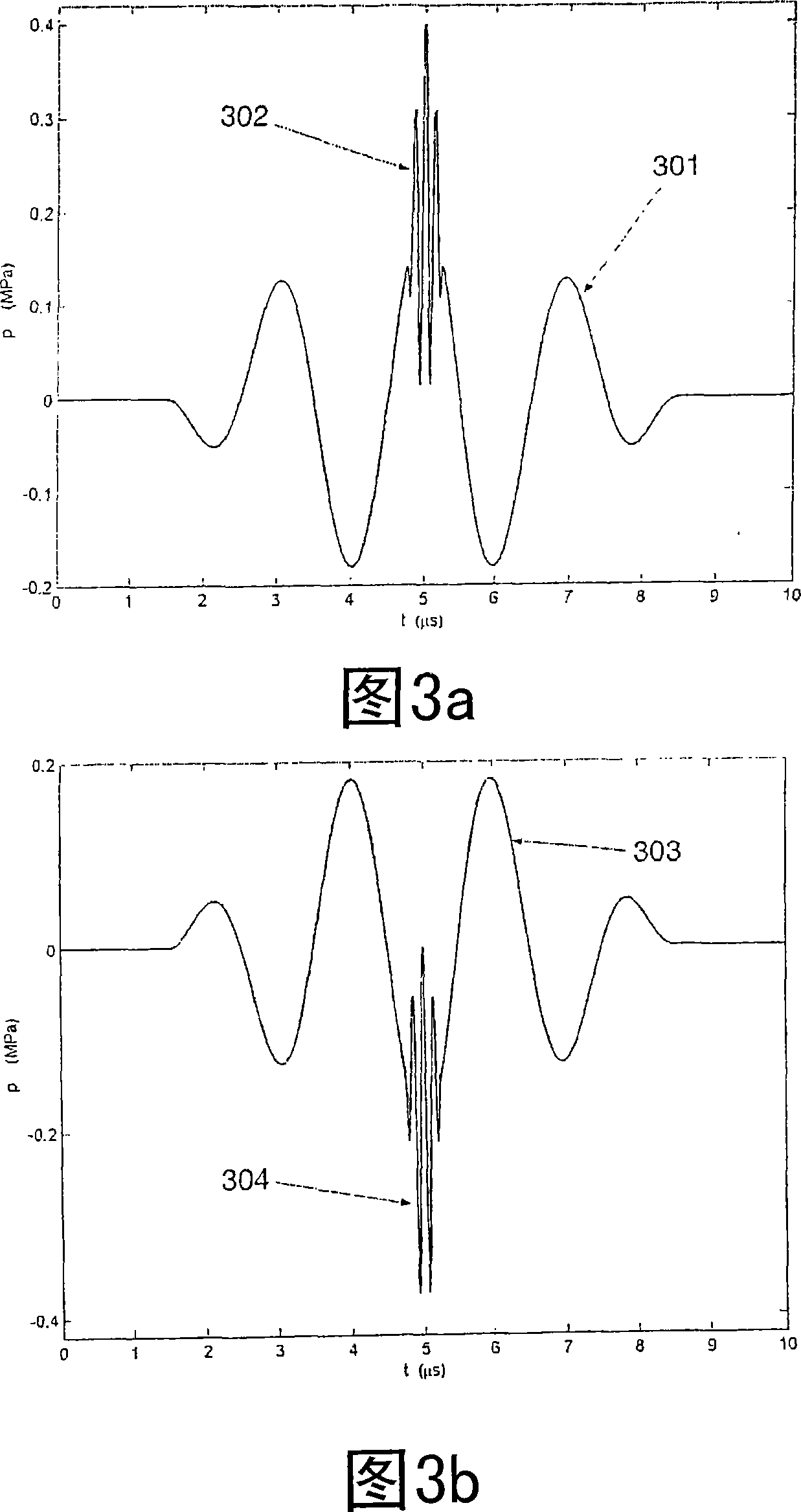
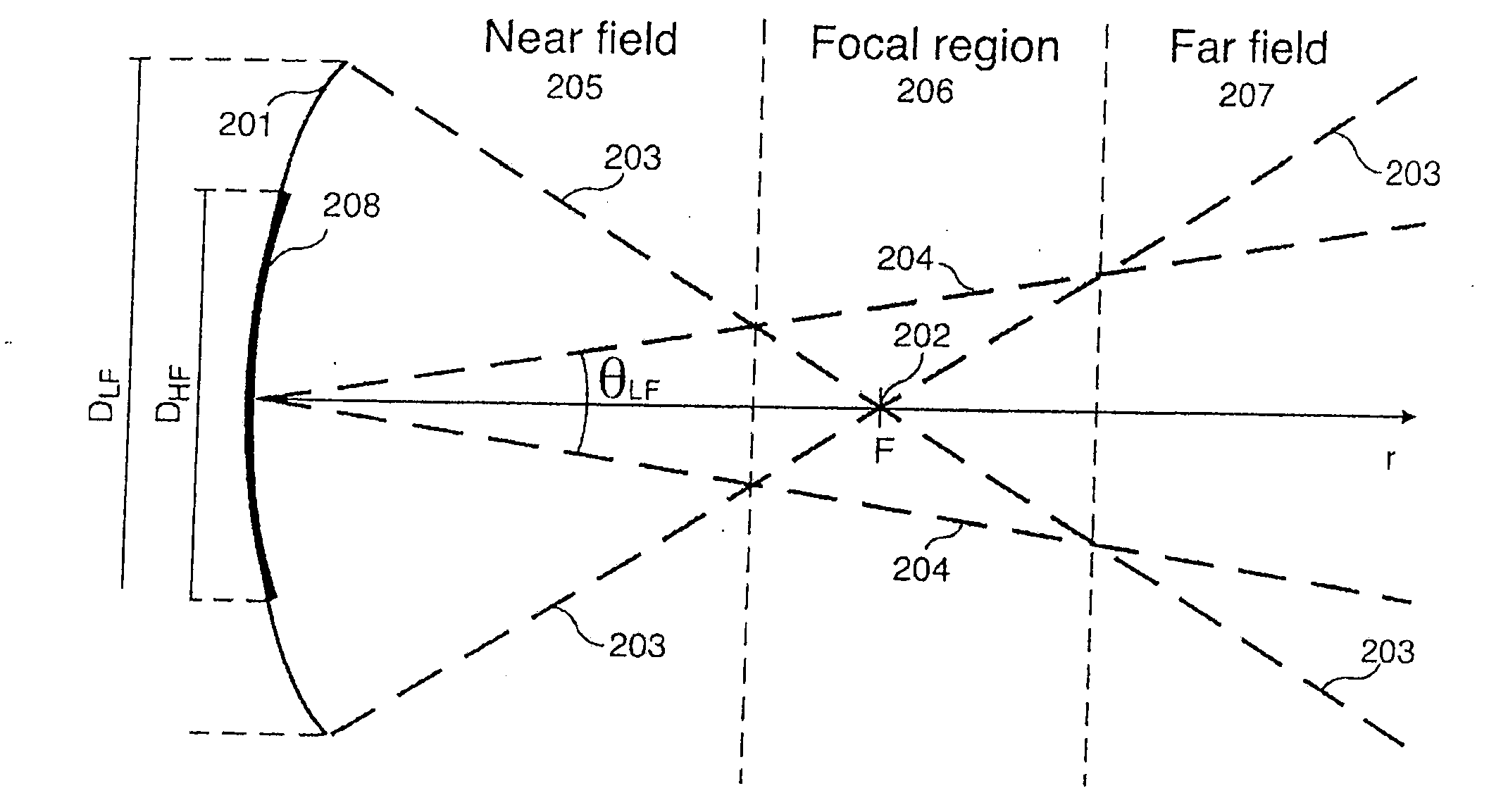
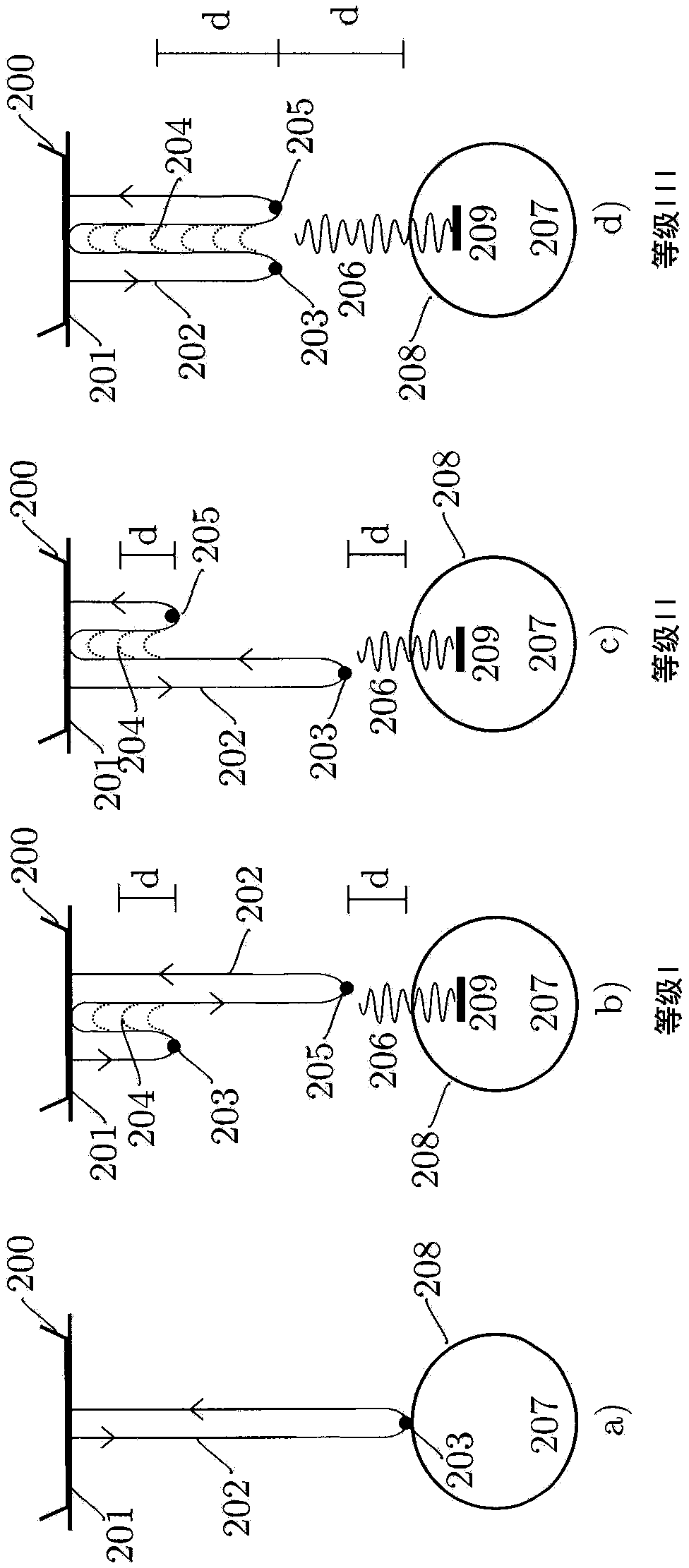
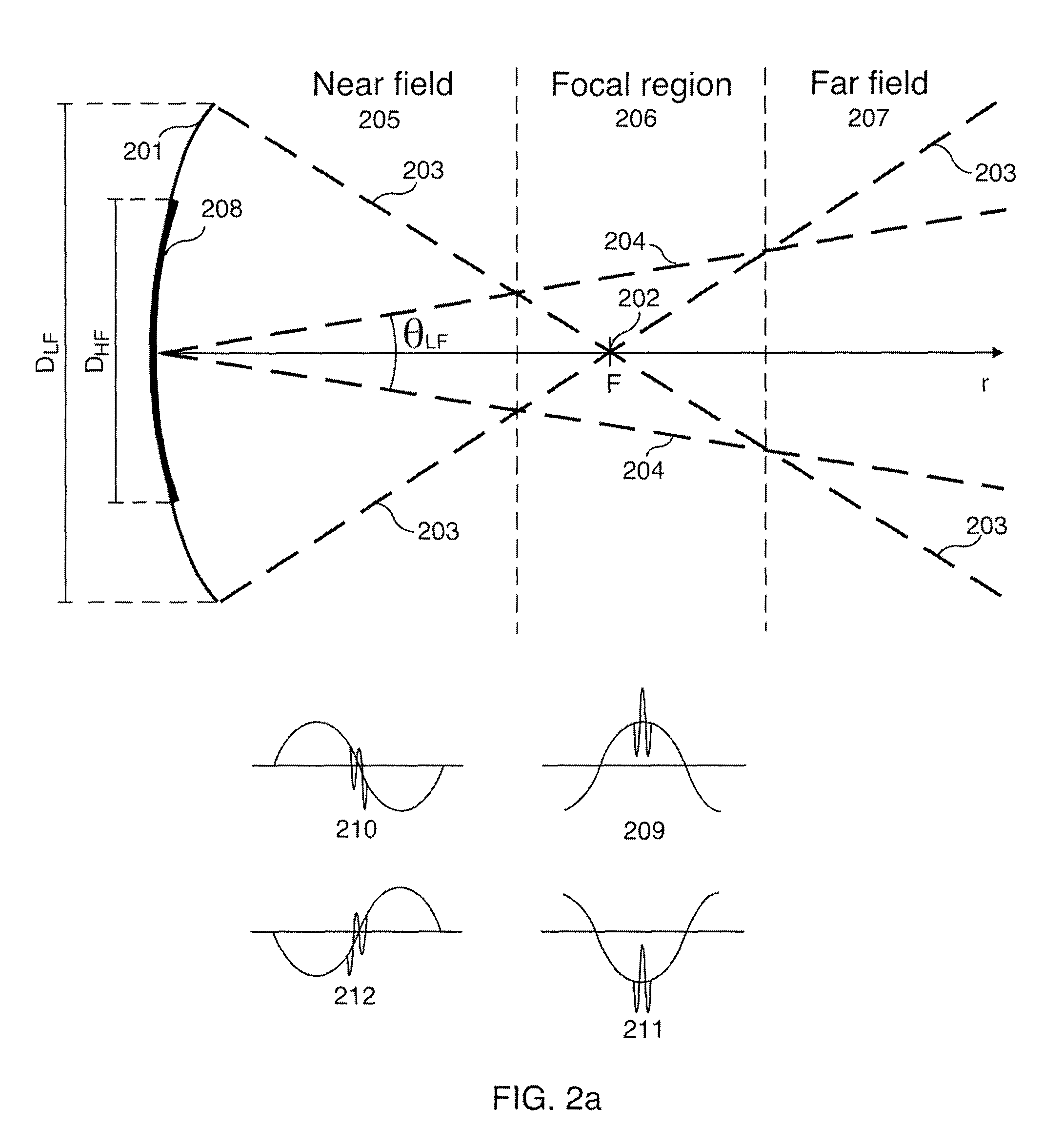
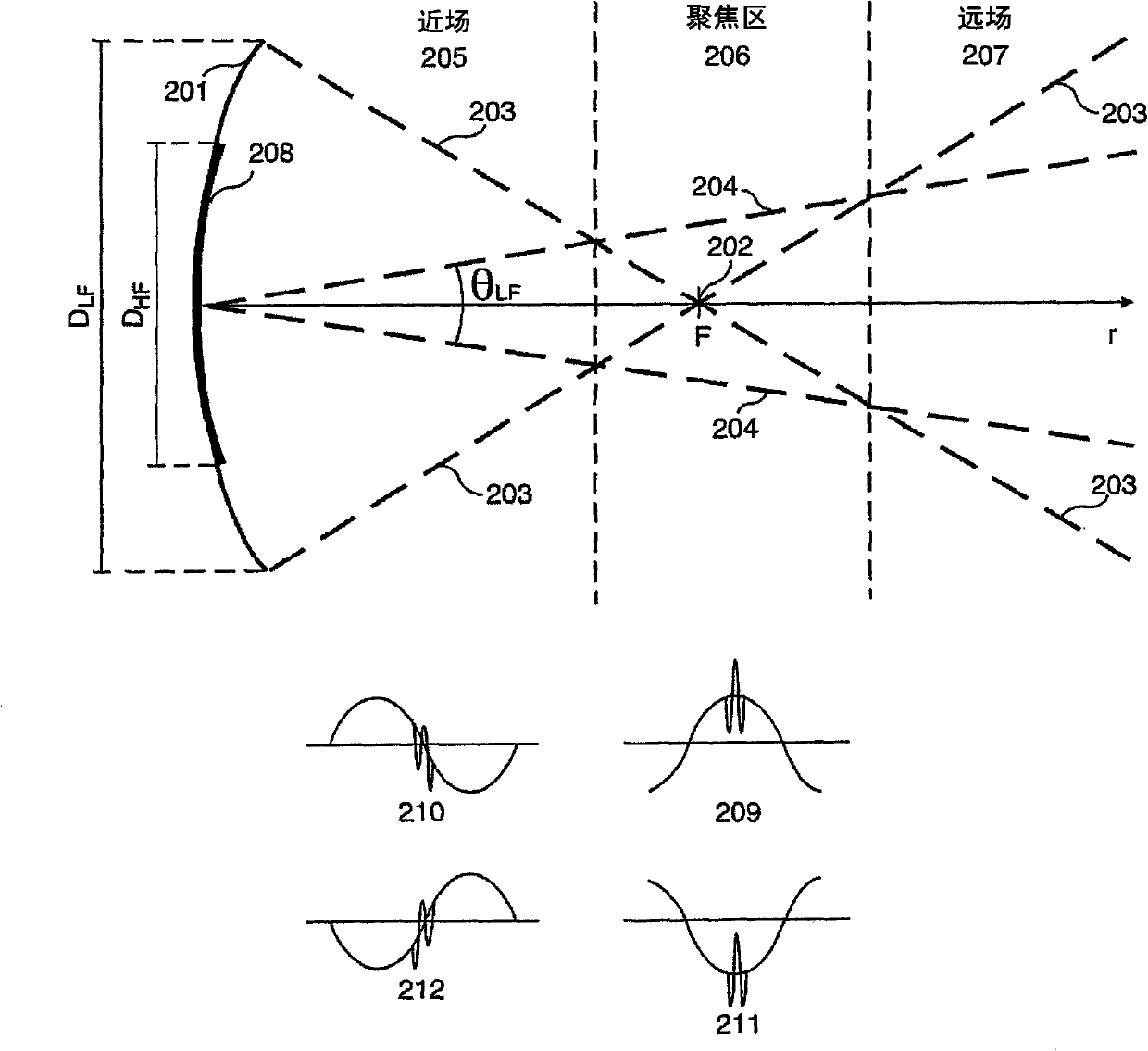
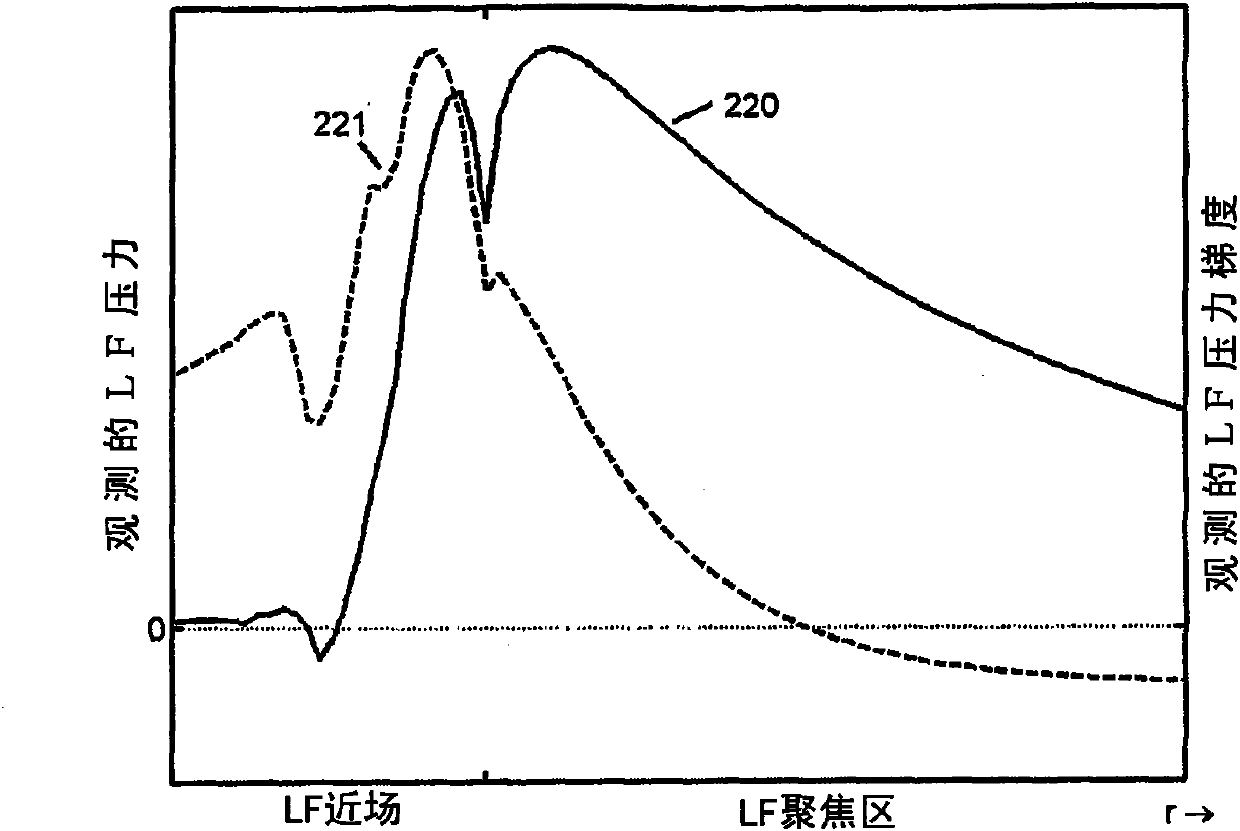
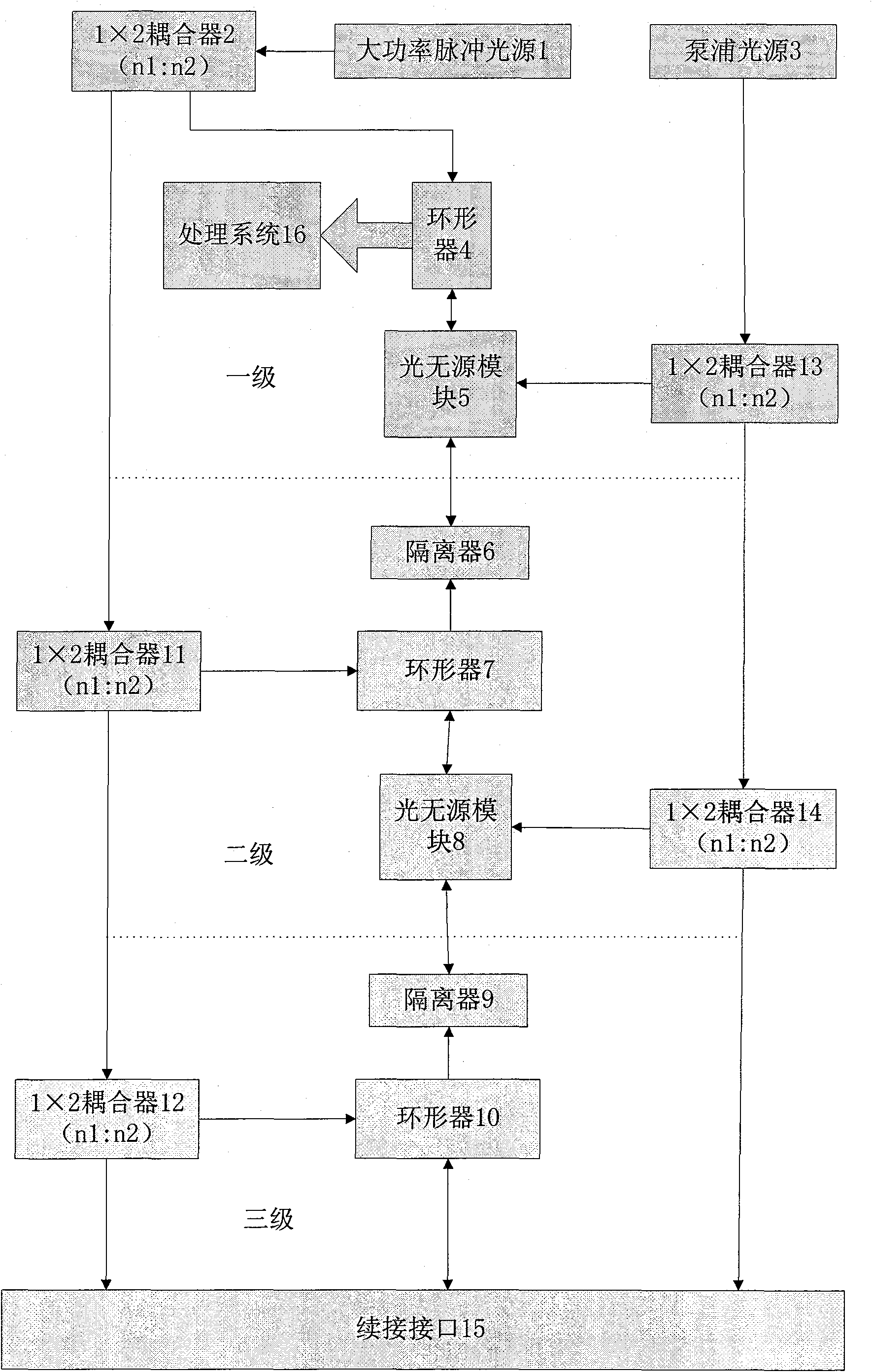
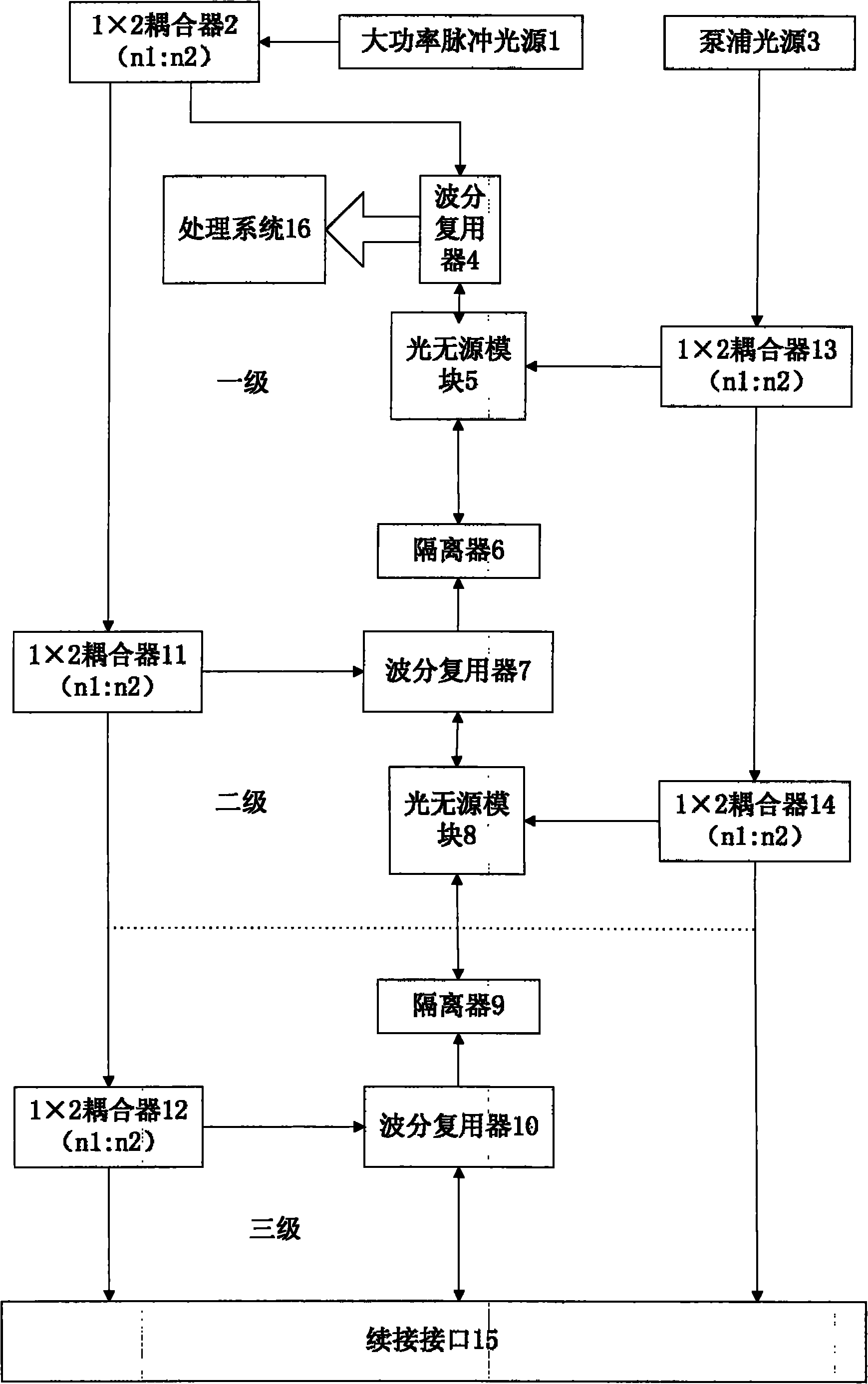
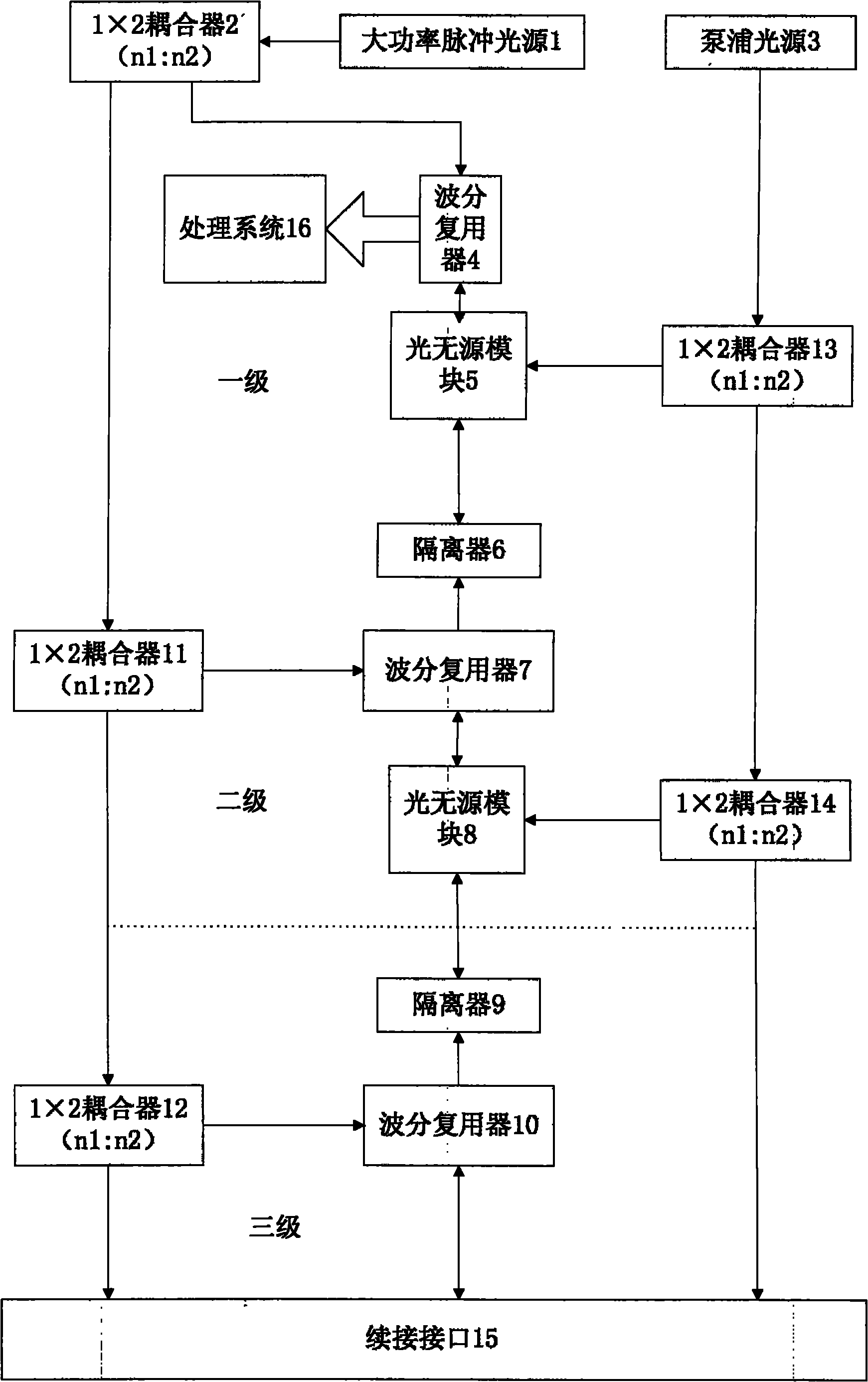
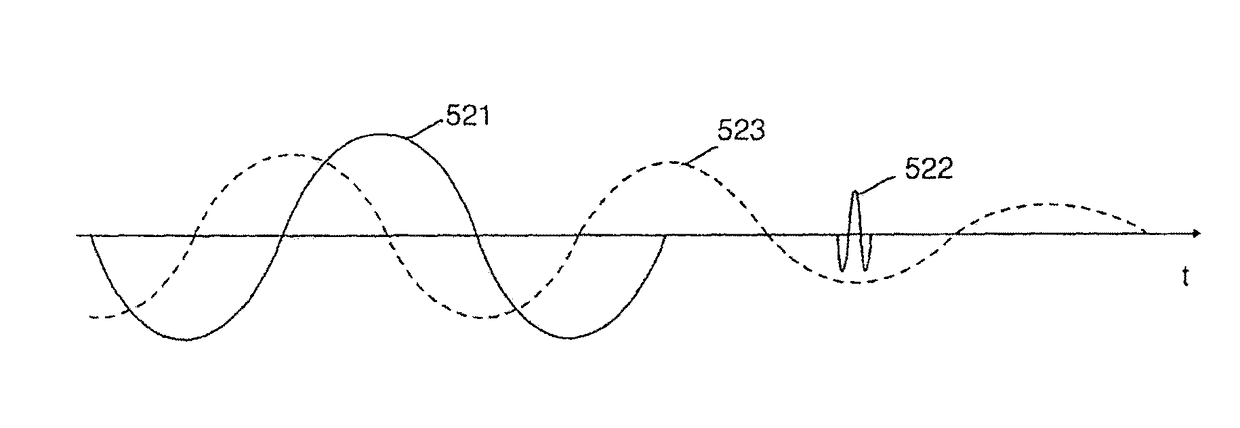
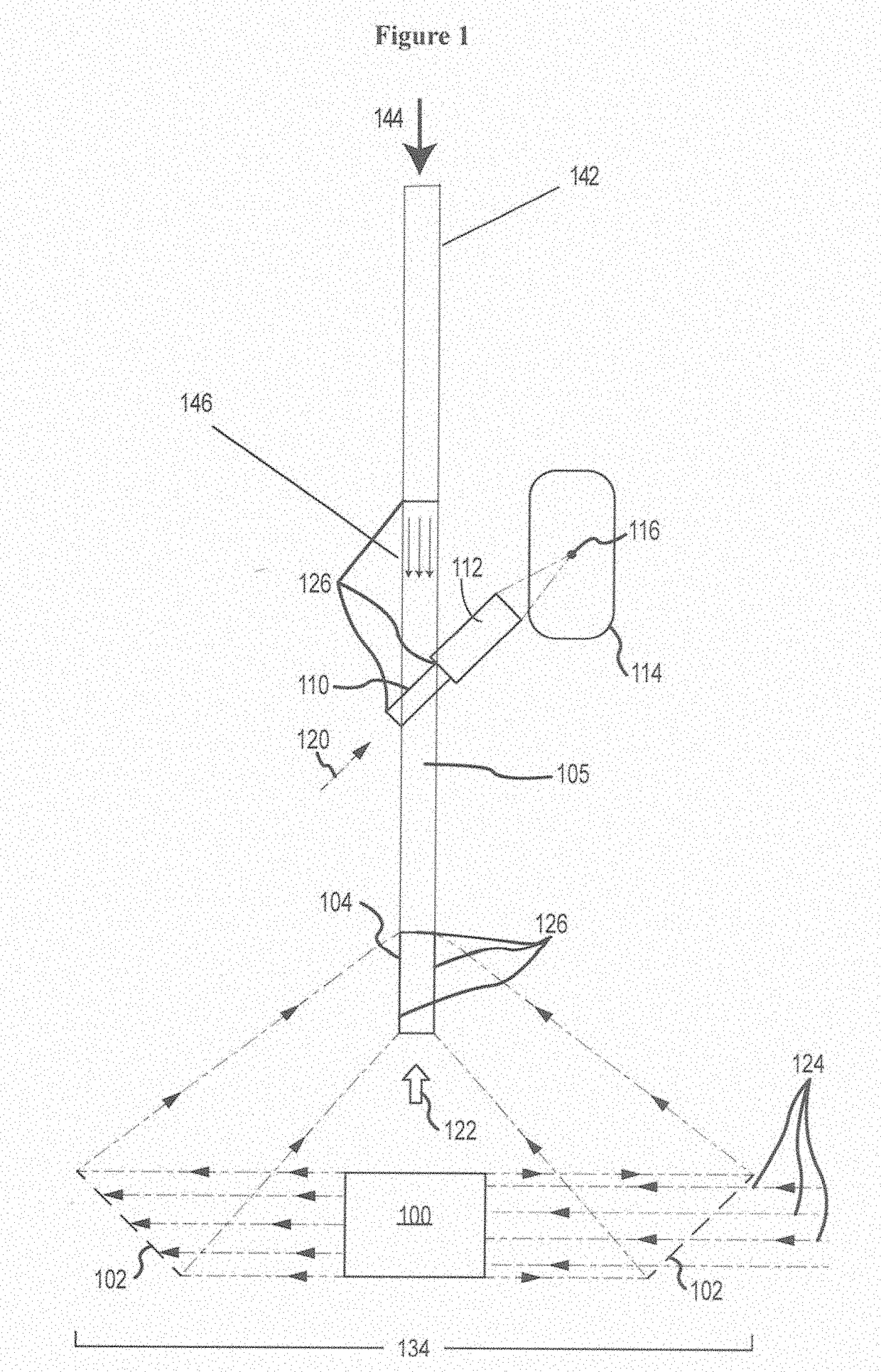
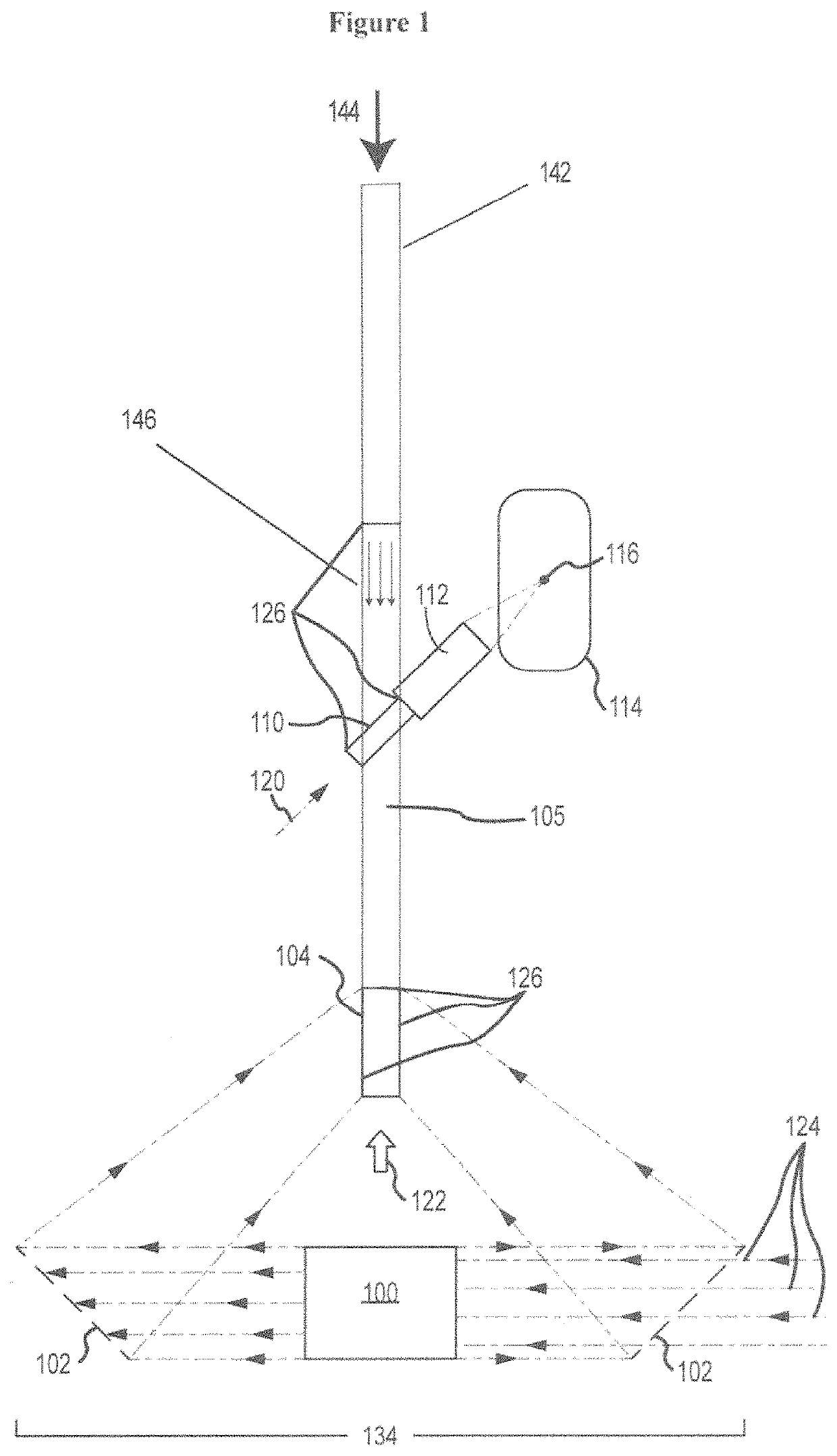
Acoustic imaging by nonlinear low frequency manipulation of high frequency scattering and propagation properties
ActiveUS20060052699A1Easy to measureFrame rateOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryLinearityAcoustical imaging
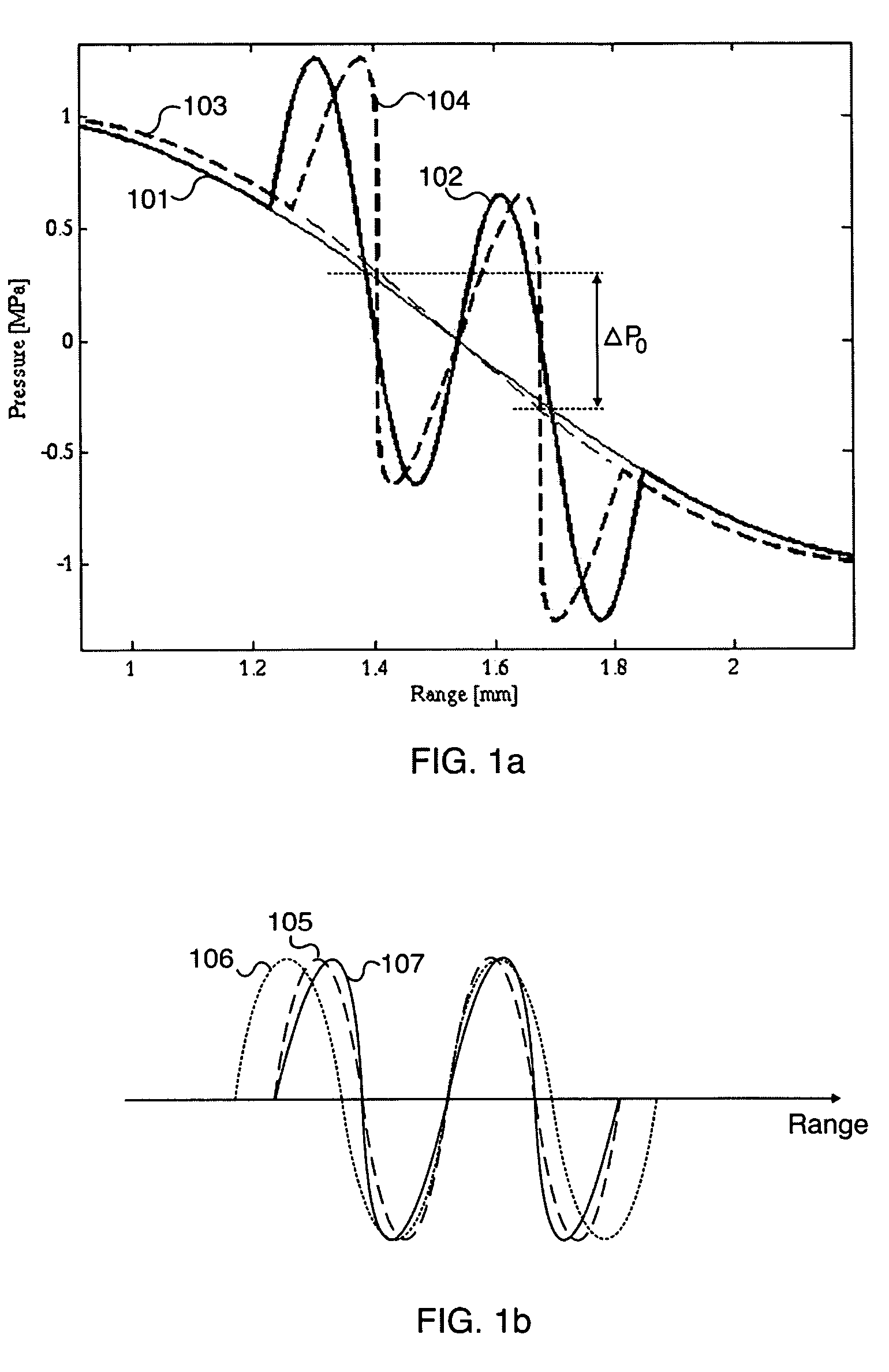
Acoustic imaging provides images with reduced reverberation noise and images of nonlinear scattering and propagation parameters of the object. The received signal from transmitted dual frequency band acoustic pulse complexes is processed with overlapping high and low frequency pulses. The high frequency pulse is used for image reconstruction and the low frequency pulse manipulate the nonlinear scattering and / or propagation properties of the high frequency pulse. The scattered signal from a single dual band pulse complex for filtering in the fast time (depth time) domain provides a signal with suppression of reverberation noise with 1st harmonic sensitivity and increased spatial resolution. Through filtering in the pulse number coordinate and corrections for nonlinear propagation delays, a linear back scattering signal with suppressed pulse reverberation noise, a nonlinear back scattering signal, and quantitative nonlinear forward propagation and scattering parameters are extracted.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
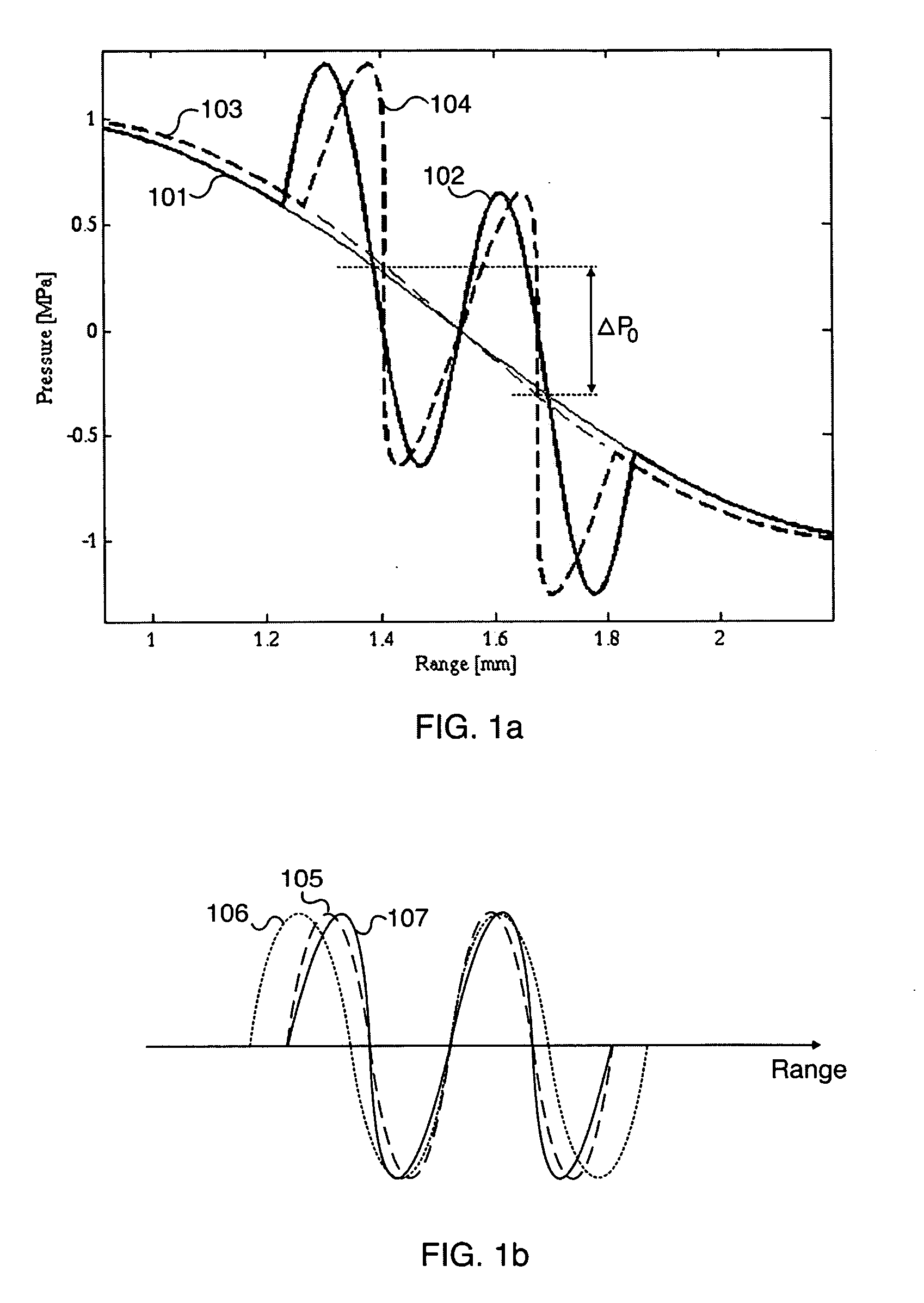
Acoustic imaging by nonlinear low frequency manipulation of high frequency scattering and propagation properties
ActiveUS8038616B2Easy to measureFrame rateMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionWavefront aberrationApproximation property
Methods of acoustic imaging provide images with reduced reverberation noise and images of nonlinear scattering and propagation parameters of the object, and estimation methods of corrections for wave front aberrations produced by spatial variations in the acoustic propagation velocity. The methods are based on processing of the received signal from transmitted dual frequency band acoustic pulse complexes with overlapping high and low frequency pulses. The high frequency pulse is used for the image reconstruction and the low frequency pulse is used to manipulate the nonlinear scattering and / or propagation properties of the high frequency pulse. Through filtering in the pulse number coordinate and corrections for nonlinear propagation delays and optionally also amplitudes, a linear back scattering signal with suppressed pulse reverberation noise, a nonlinear back scattering signal, and quantitative nonlinear forward propagation and scattering parameters are extracted.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
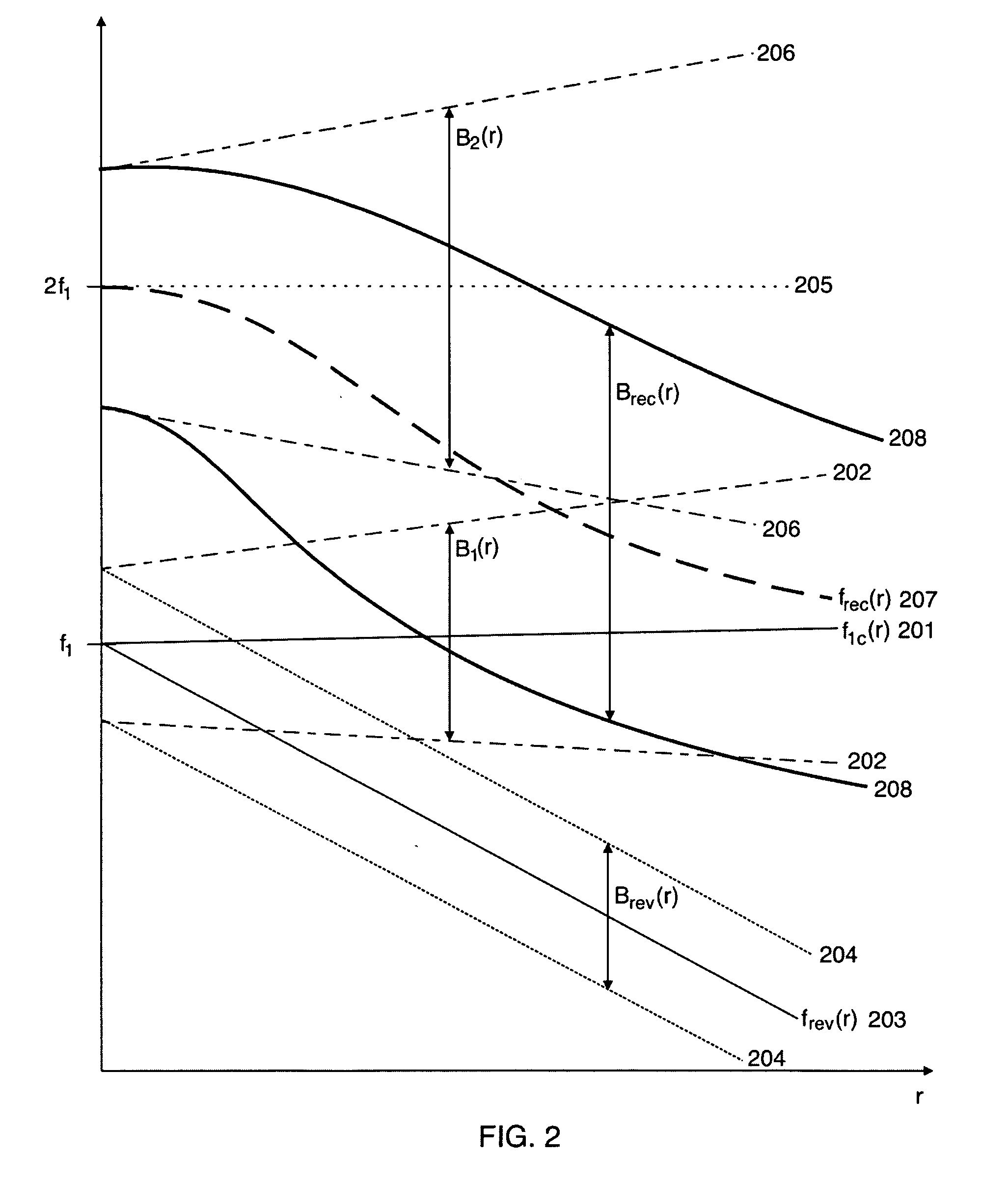
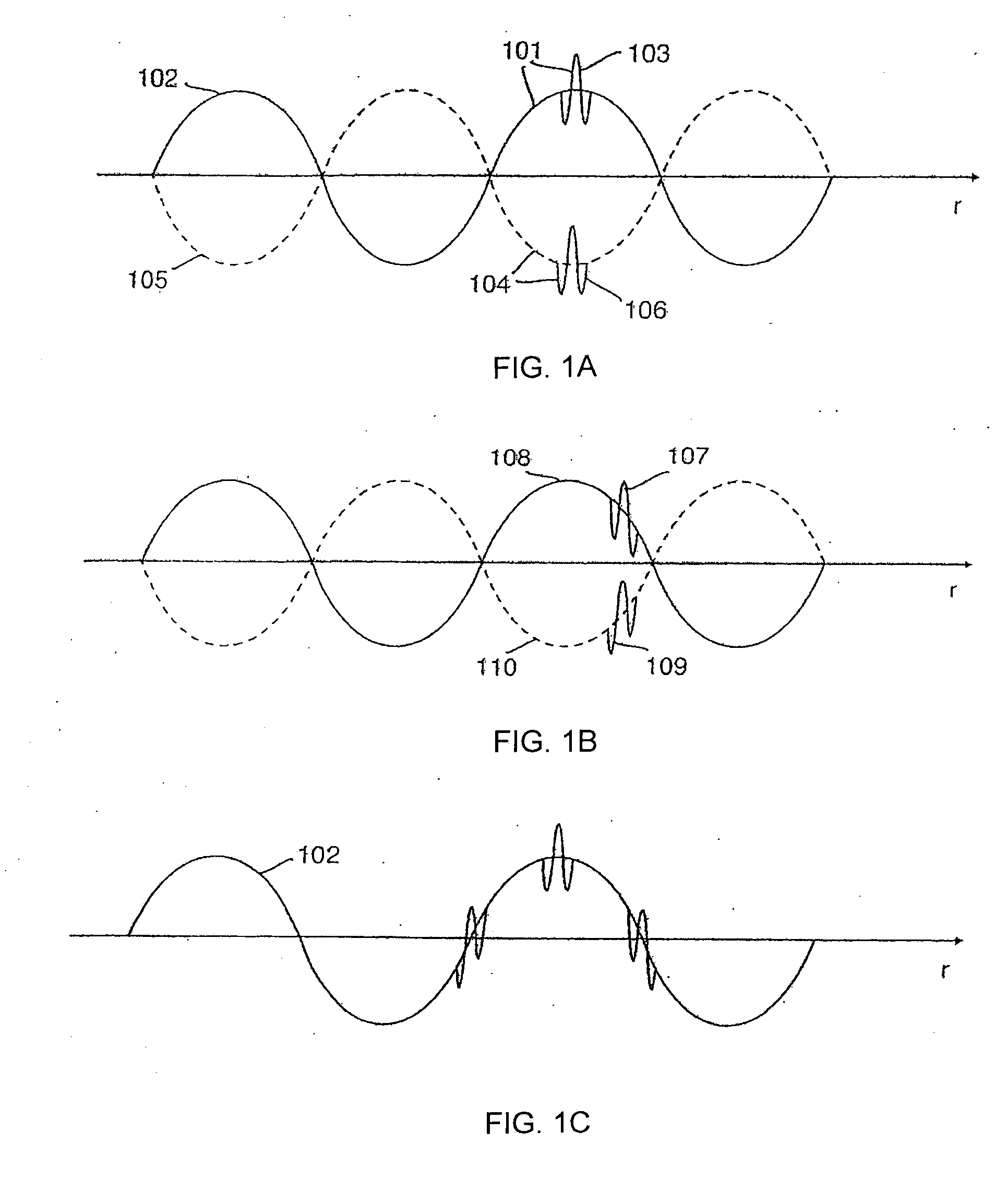
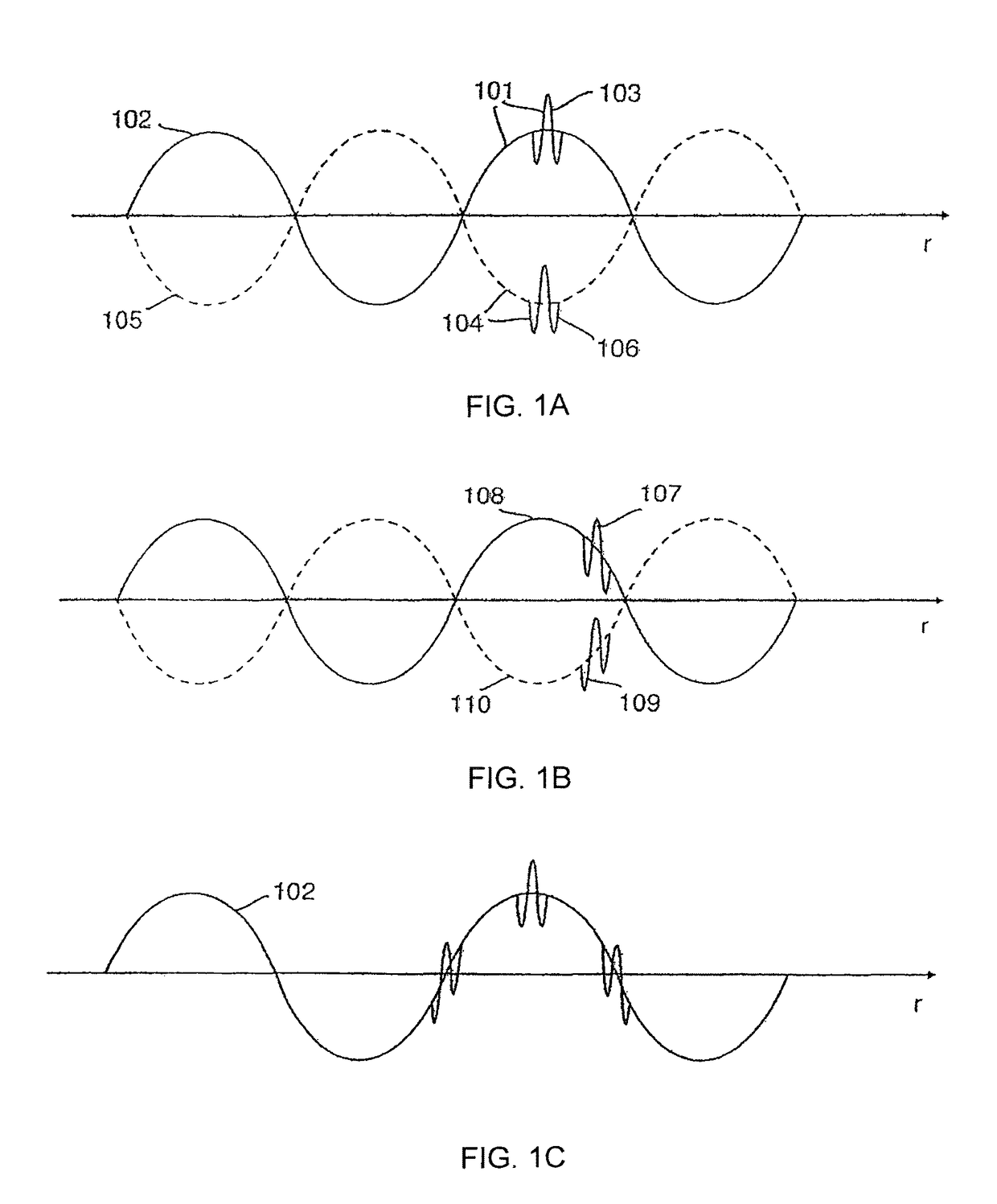
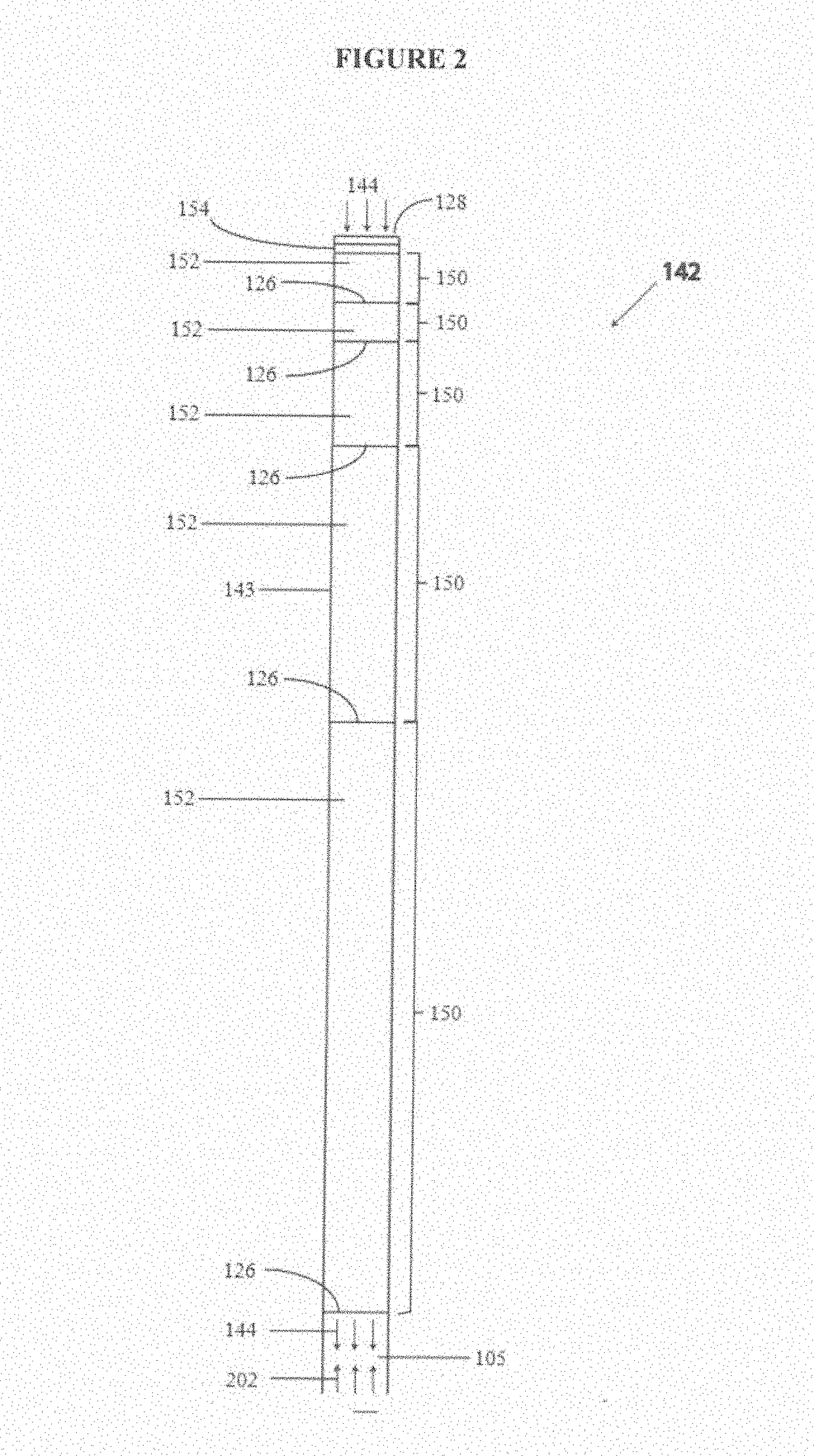
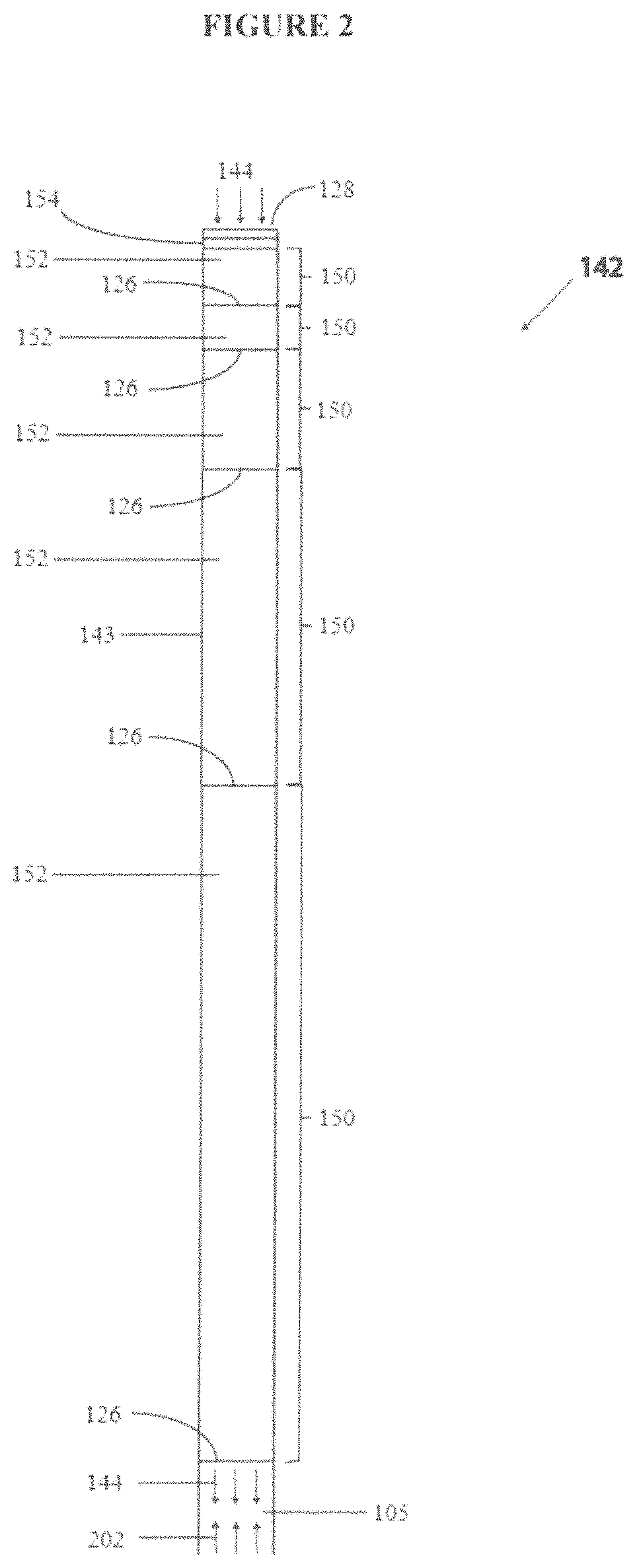
Nonlinear Elastic Wave Measurement and Imaging with Two-Frequency Elastic Wave Pulse Complexes
ActiveUS20100036244A1Fast timeSimple processOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsBeam directionTransducer
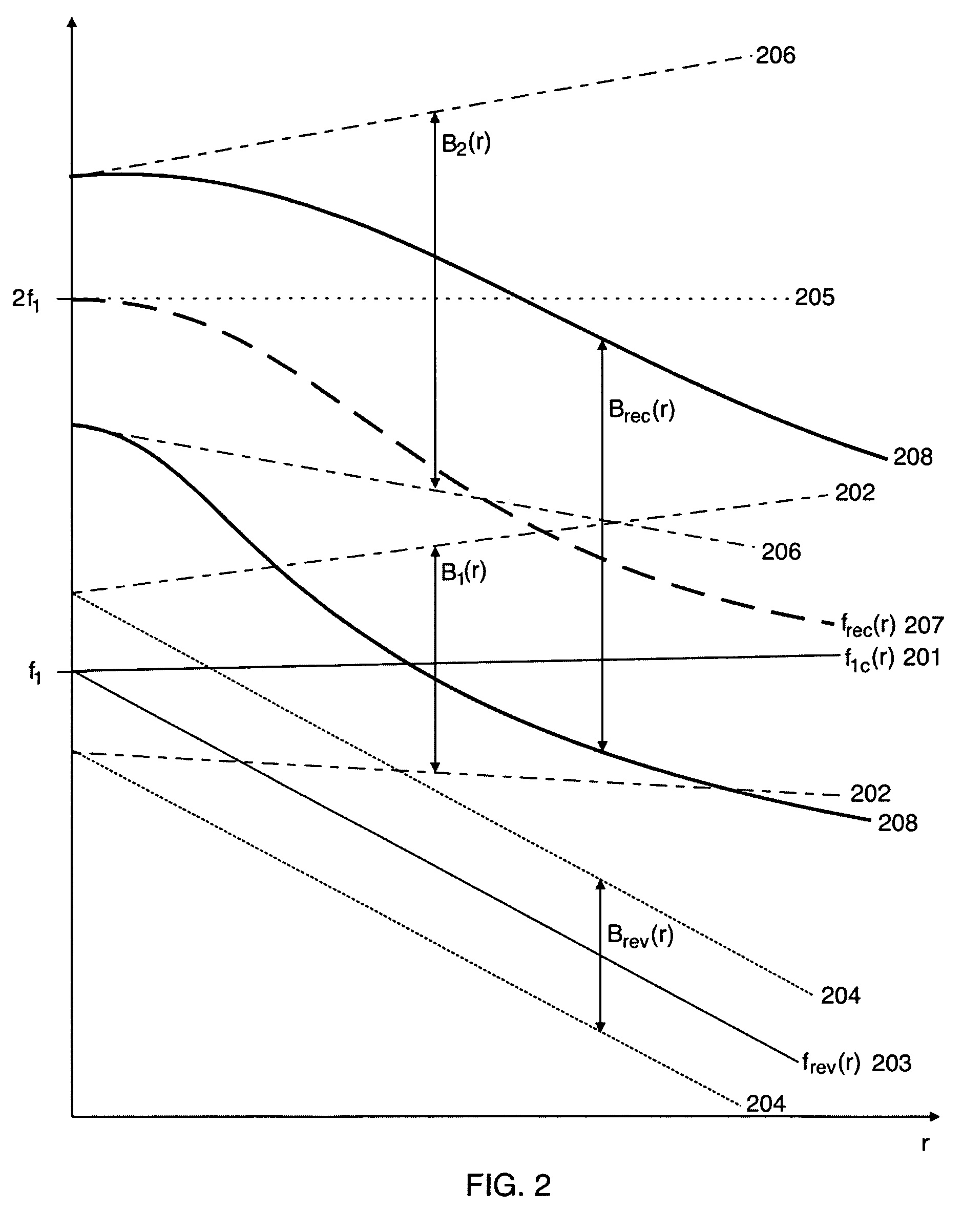
Methods and instruments for suppression of multiple scattering noise and extraction of nonlinear scattering components with measurement or imaging of a region of an object with elastic waves, where elastic wave pulse complexes are transmitted towards said region where said pulse complexes are composed of a high frequency (HF) and a low frequency (LF) pulse with the same or overlapping beam directions and where the HF pulse is so close to the LF pulse that it observes the modification of the object by the LF pulse at least for a part of the image depth. The frequency and / or amplitude and / or phase of said LF pulse relative to said HF pulse varies for transmitted pulse complexes in order to nonlinearly manipulate the object elasticity observed by the HF pulse along at least parts of its propagation, and where received HF signals are picked up by transducers from one or both of scattered and transmitted components of the transmitted HF pulses. Said received HF signals are processed to form measurement or image signals for display, and where in the process of forming said measurement or image signals said received HF signals are one or both of delay corrected with correction delay in the fast time (depth-time), and pulse distortion corrected in the fast time, and combined in slow time to form noise suppressed HF signals or nonlinear scattering HF signals that are used for further processing to form measurement or image signals. The methods are applicable to elastic waves where the material elasticity is nonlinear in relation to the material deformation.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
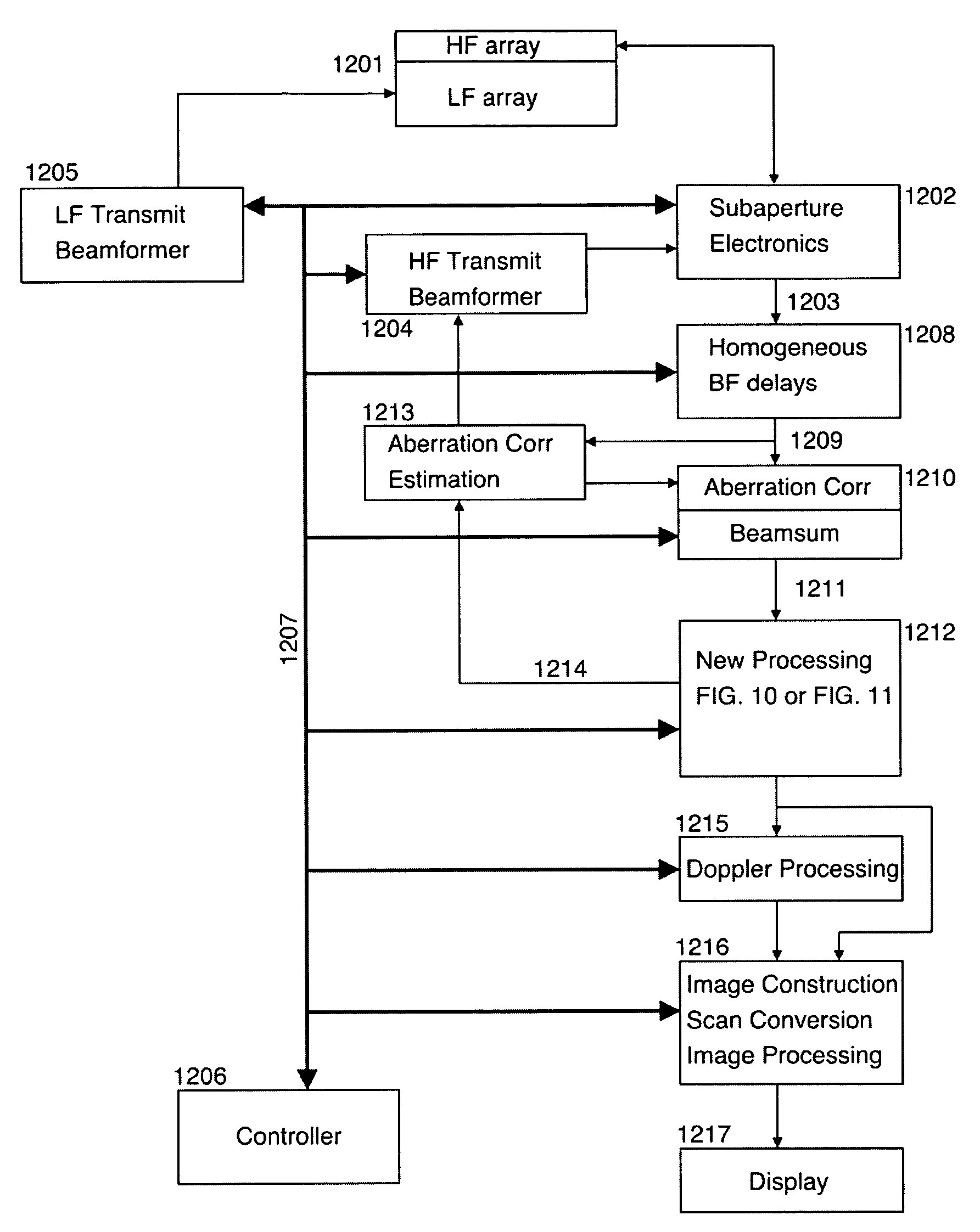
Ultrasound imaging
ActiveCN101023376AImprove the contrast-to-noise ratioSuppression of linear scatter signalsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationCalcification
New methods of ultrasound imaging are presented that provide images with reduced reverberation noise and images of nonlinear scattering and propagation parameters of the object, and estimation of corrections for wave front aberrations produced by spatial variations in the ultrasound propagation velocity. The methods are based on processing of the received signal from transmitted dual frequency band ultrasound pulse complexes with overlapping high and low frequency pulses. The high frequency pulse is used for the image reconstruction and the low frequency pulse is used to manipulate the nonlinear scattering and / or propagation properties of the high frequency pulse. A 1st method uses the scattered signal from a single dual band pulse complex for filtering in the fast time (depth time) to provide a signal with suppression of reverberation noise and with 1st harmonic sensitivity and increased spatial resolution. In other methods two or more dual band pulse complexes are transmitted where the frequency and / or the phase and / or the amplitude of the low frequency pulse vary for each transmitted pulse complex. Through filtering in the pulse number coordinate and corrections of nonlinear propagation delays and optionally also amplitudes, a linear back scattering signal with suppressed pulse reverberation noise, a nonlinear back scattering signal, and quantitative nonlinear scattering and forward propagation parameters are extracted. The reverberation suppressed signals are further useful for estimation of corrections of wave front aberrations, and especially useful with broad transmit beams for multiple parallel receive beams. Approximate estimates of aberration corrections are given. The nonlinear signal is useful for imaging of differences in tissue properties, such as micro-calcifications, in-growth of fibrous tissue or foam cells, or micro gas bubbles as found with decompression or injected as ultrasound contrast agent.
Owner:比约恩・A・J・安杰尔森 +2
Optical fiber delivery and collection system for biological applications such as multiphoton microscopy, spectroscopy, and endoscopy
InactiveUS20050043636A1Improve spatial resolutionEfficient disseminationCladded optical fibreDiagnostics using lightCollection systemSpectroscopy
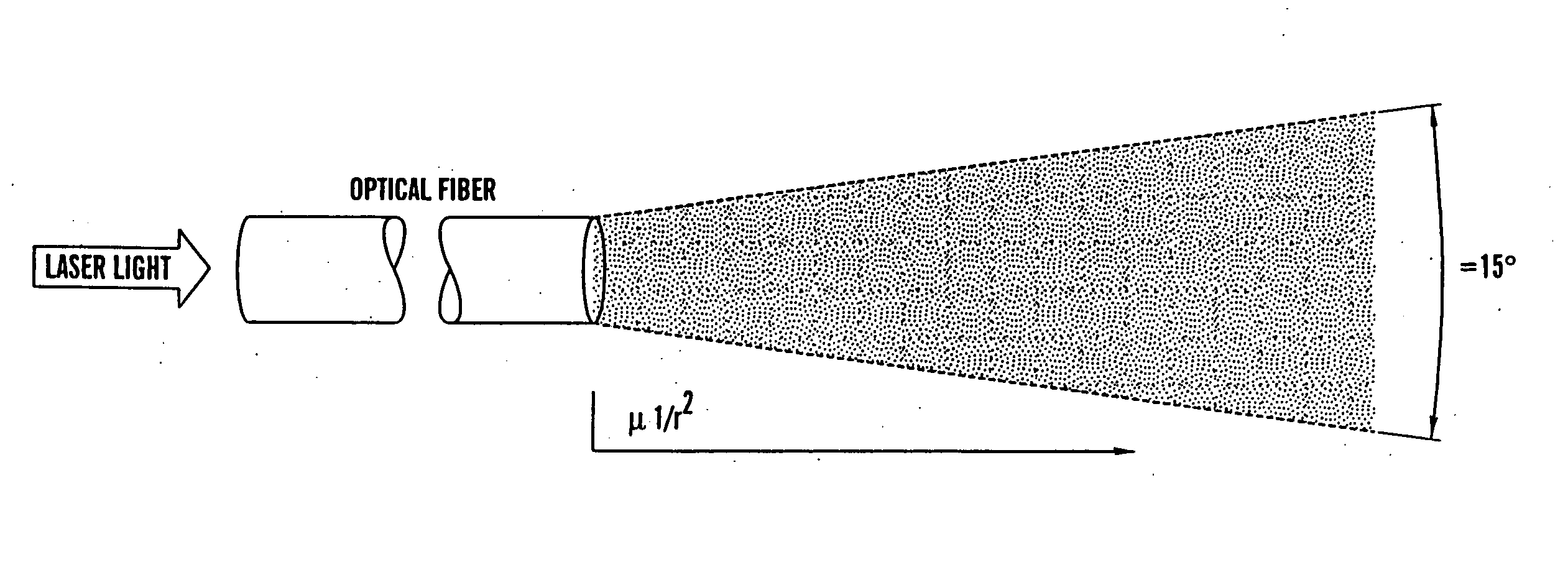
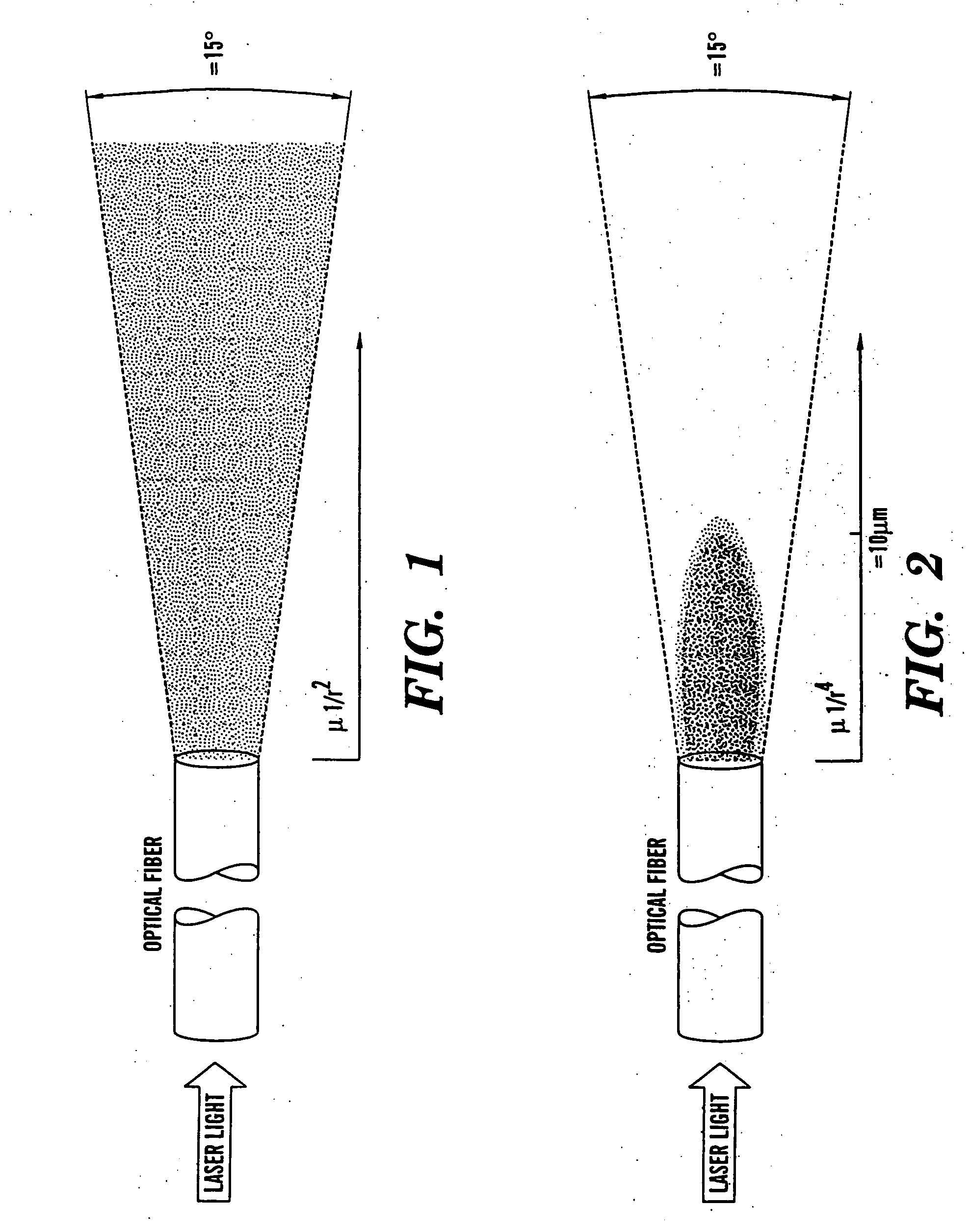
The present invention is directed to a method of applying radiation through an optical fiber for detecting disease within a plant or animal or other penetrable tissue, or imaging a particular tissue of a plant or animal. In addition, fluorescence and nonlinear scattering signals can be detected and localized within a subject by such application of radiation through an optical fiber. The radiation is effective to promote simultaneous multiphoton excitation. The optical fibers are used alone to examine internal regions of tissue, in conjunction with an optical biopsy needle to evaluate sub-surface tissue, or with an endoscope to evaluate tissue within body cavities. The present invention also relates to a device for coupling in radiation from an ultrashort mode-locked laser into the beam path of a microscope.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Temperature-measuring system of distributed fibers
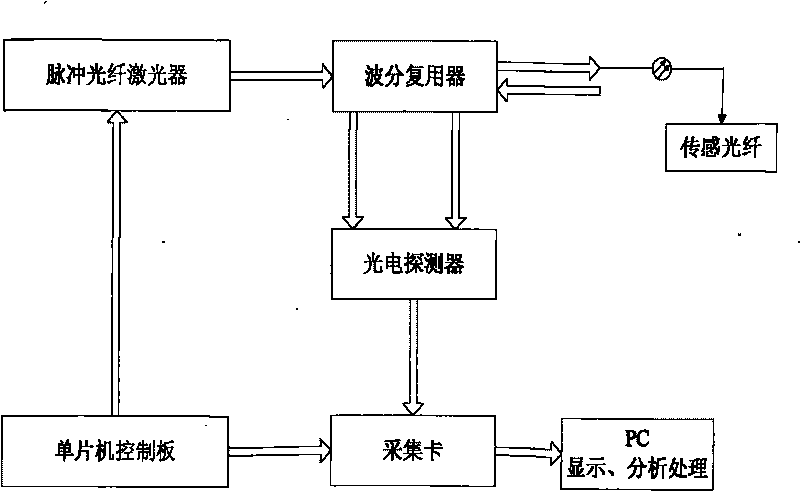
InactiveCN101713689AContinuous Temperature MonitoringIncreased monitoring distance lengthThermometers using physical/chemical changesEquipment temperatureRayleigh scattering
The invention relates to a temperature-measuring system of distributed fibers, aiming at the continuous monitoring of temperature parameters of underground electromechanical transport equipment. The temperature-measuring system of distributed fibers comprises a singlechip control board, a fiber temperature field information acquisition module, a photoelectric detector and a circuit signal post-processing module, wherein the fiber temperature field information acquisition module comprises a pulse fiber laser and a wavelength division multiplexer; the circuit signal post-processing module comprises an acquisition card and a personal computer (PC); the singlechip control board is connected with the pulse fiber laser and the acquisition card by leads; the wavelength division multiplexer is connected with the pulse fiber laser and the photoelectric detector by fibers; incident light emitted by the pulse fiber laser is output to the sensing fiber by the wavelength division multiplexer; the sensing fiber feeds backward scattered light with temperature variance information of mine equipment back to the wavelength division multiplexer; and the wavelength division multiplexer extracts two scattered light beams of anti-Stokes and Stokes from the backward scattered light to restrain Rayleigh scattered light and other non-linear scattered light; and the photoelectric detector is connected with the acquisition card by a lead.
Owner:太原市电子研究设计院
Novel optical fiber Brillouin light time domain analyzer
InactiveCN101324424AHigh gainAvoid difficultiesThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansBeam splitterFiber gratings
The invention discloses an optical fiber Brillouin optical time domain analyzer, which is made based on optical fiber broadband nonlinear light amplification effect and strain, temperature effect and optical light domain analysis principle of coherent amplified Brillouin scattering. The optical fiber Brillouin optical time domain analyzer comprises a narrowband single-frequency fiber laser, a fiber beam splitter, a pulse modulator, two optical fiber circulators, a heterodyne receiver, a digital signal processor, a fiber-grating filter, a monomode fiber and a continuous-operating fiber Raman pump laser. The continuous-operating high-power fiber Raman pump laser is used as the pump light source of the Brillouin optical time domain analyzer, which can overcome the difficulty in strictly locking the frequency of a detection laser and the pump laser of the Brillouin optical time domain analyzer; and boardband fiber nonlinear scattering amplification is used for substituting for narrowband Brillouin amplification to increase the gain of stimulated Brillouin scattering with back amplification, thus improving the S / N ratio of the system, increasing the measurement length, and improving the accuracy for simultaneous measurement of stain and temperature.
Owner:WEIHAI BEIYANG PHOTOELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH
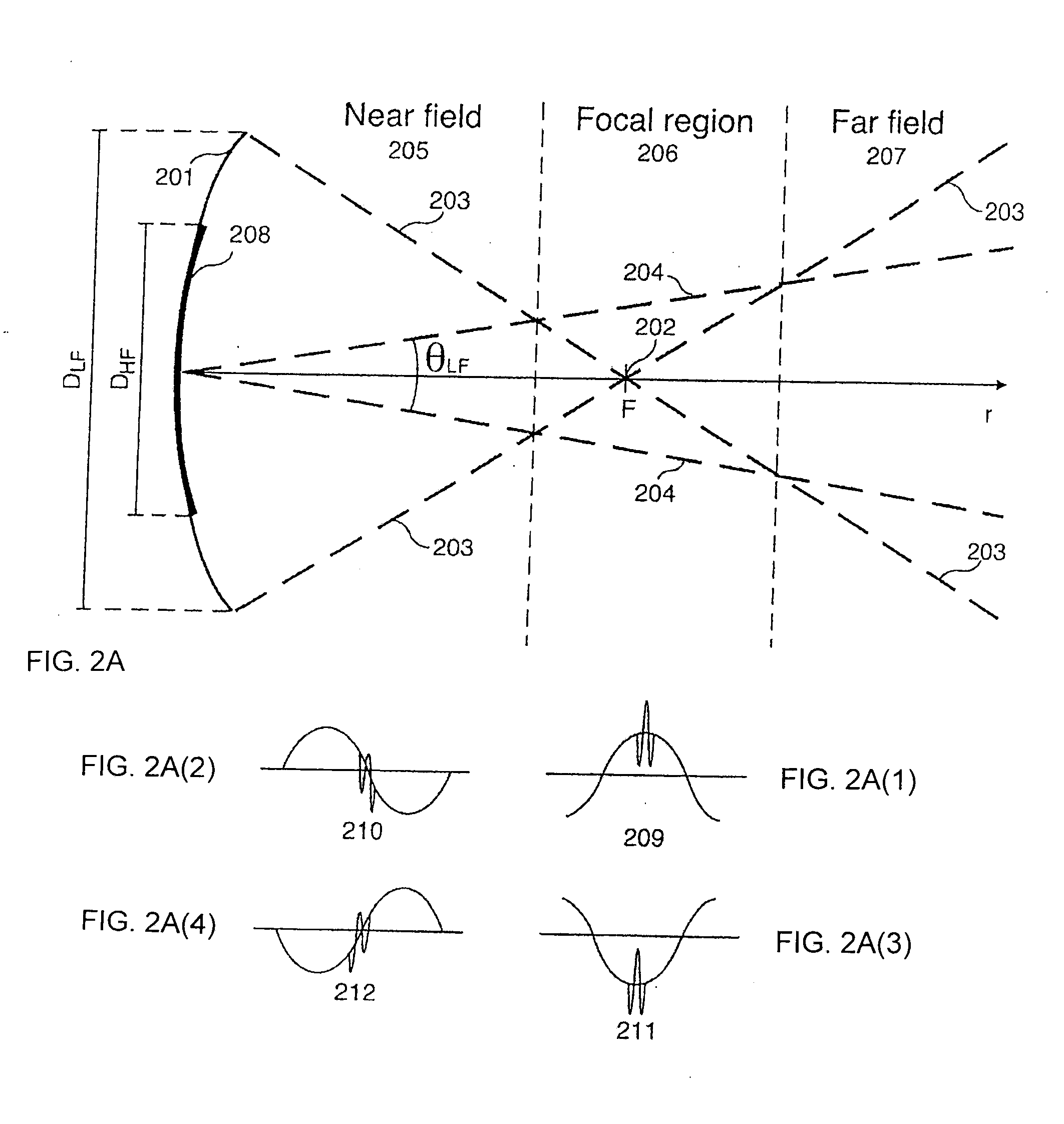
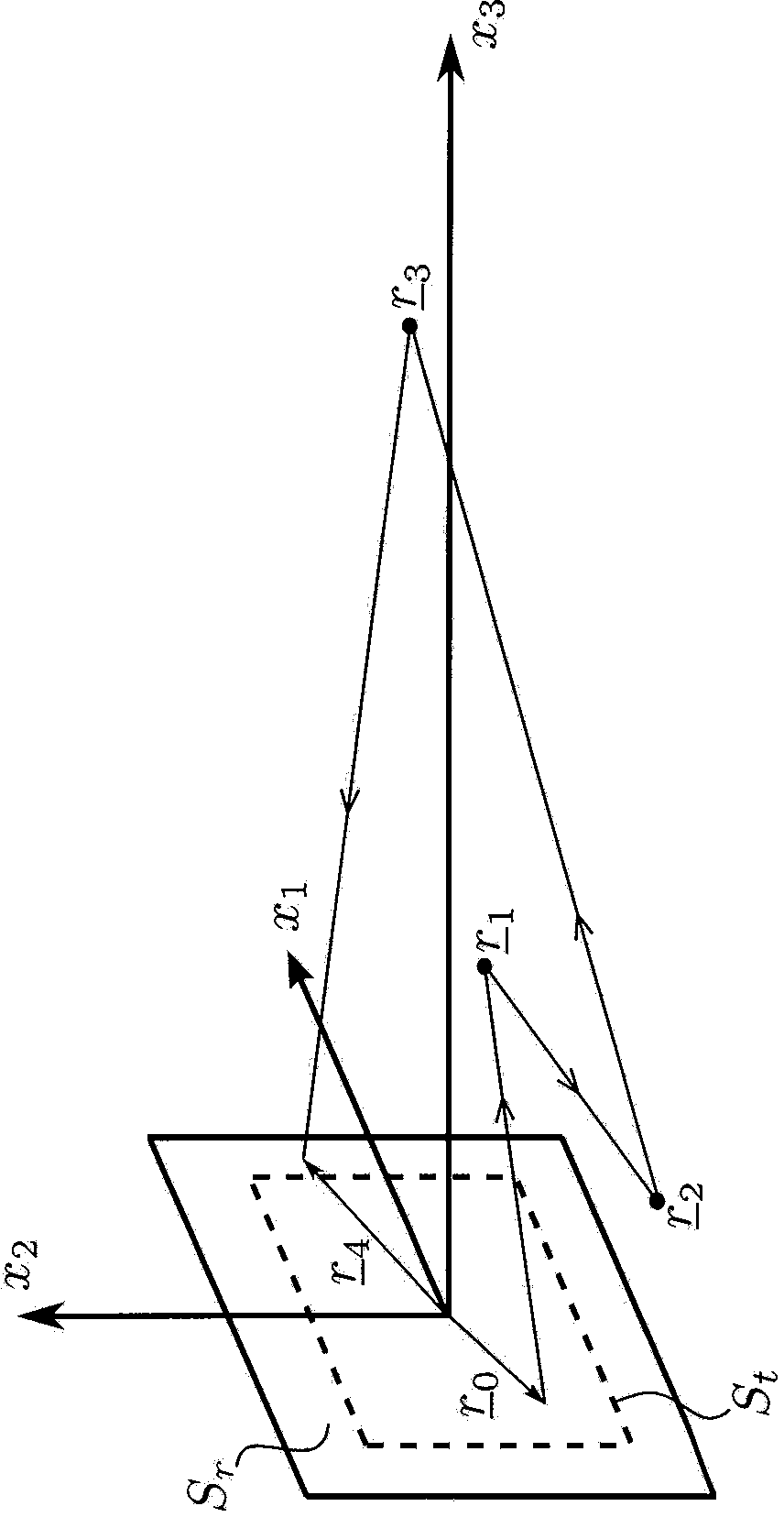
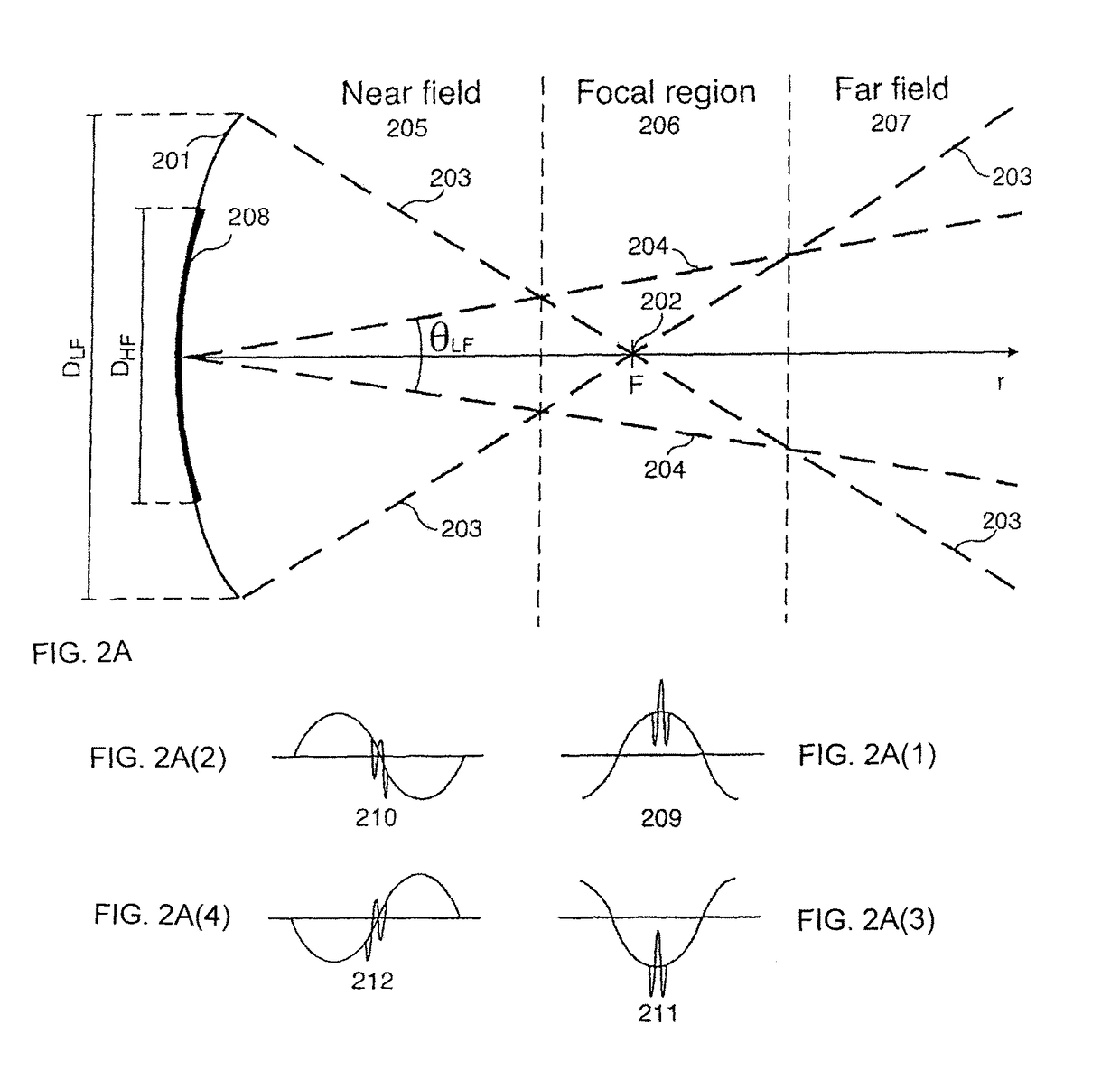
Method for Imaging of Nonlinear Interaction Scattering
ActiveUS20120095699A1Increase ratingsReduce noiseAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesScattering properties measurementsPulsed waveImage signal
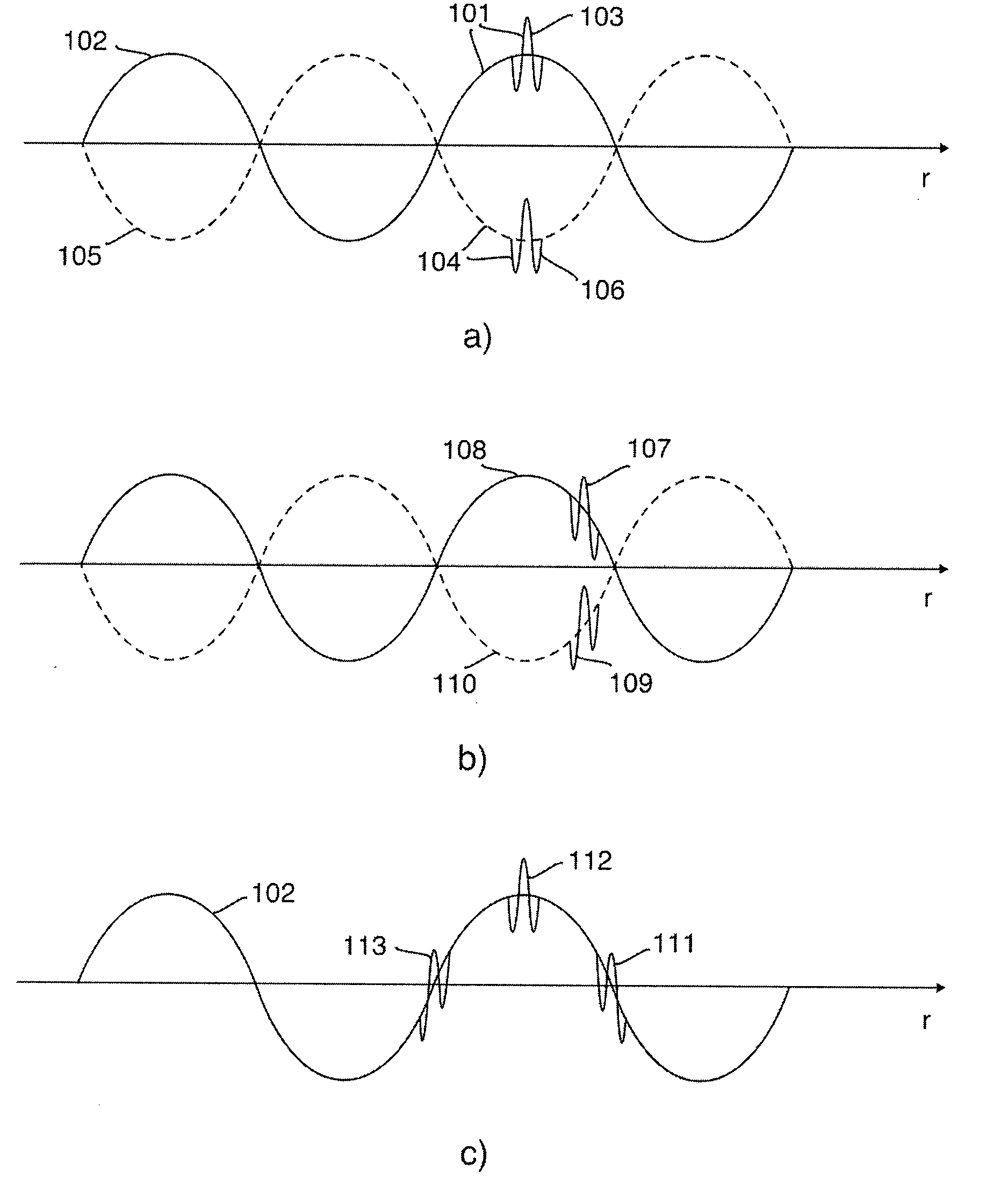
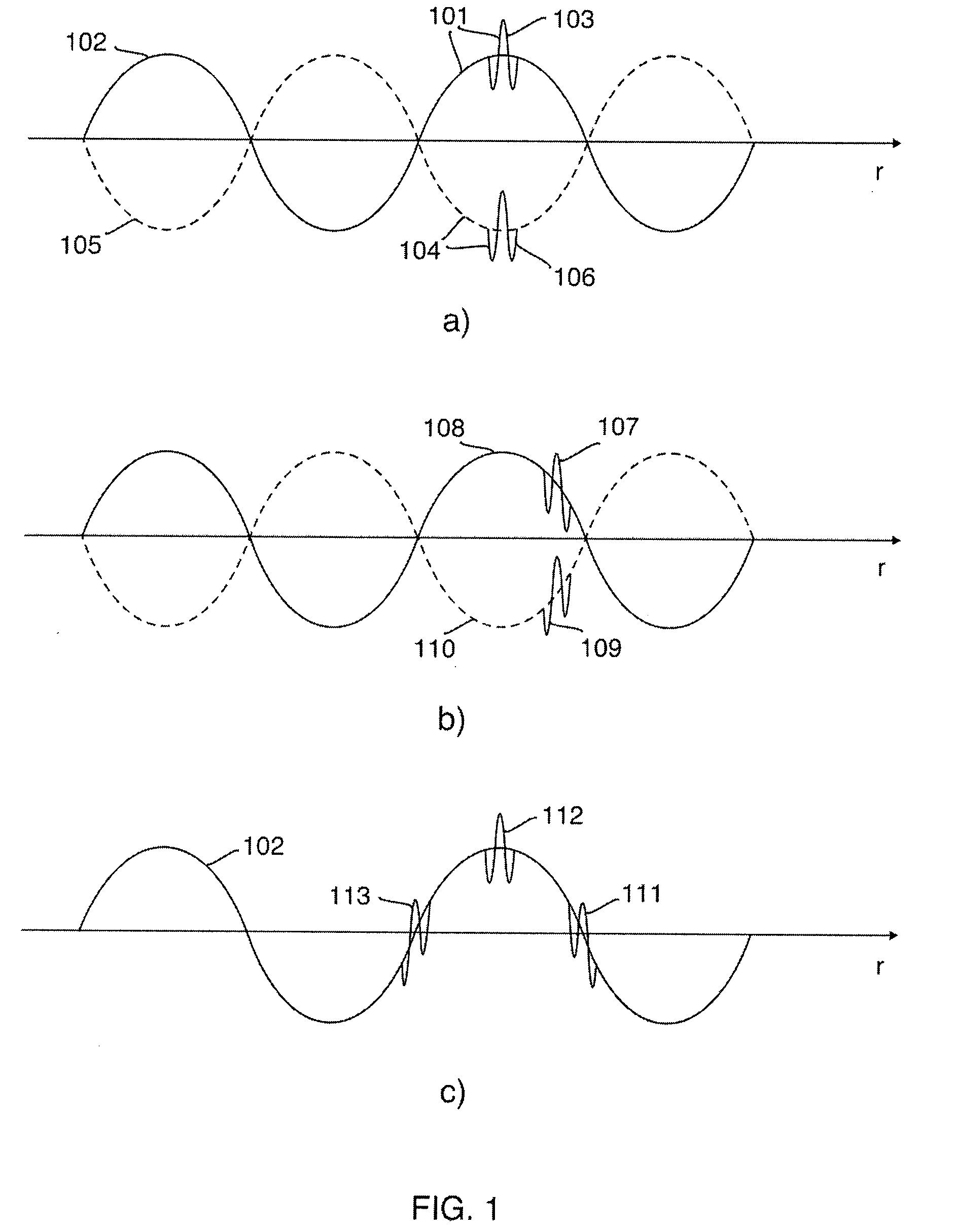
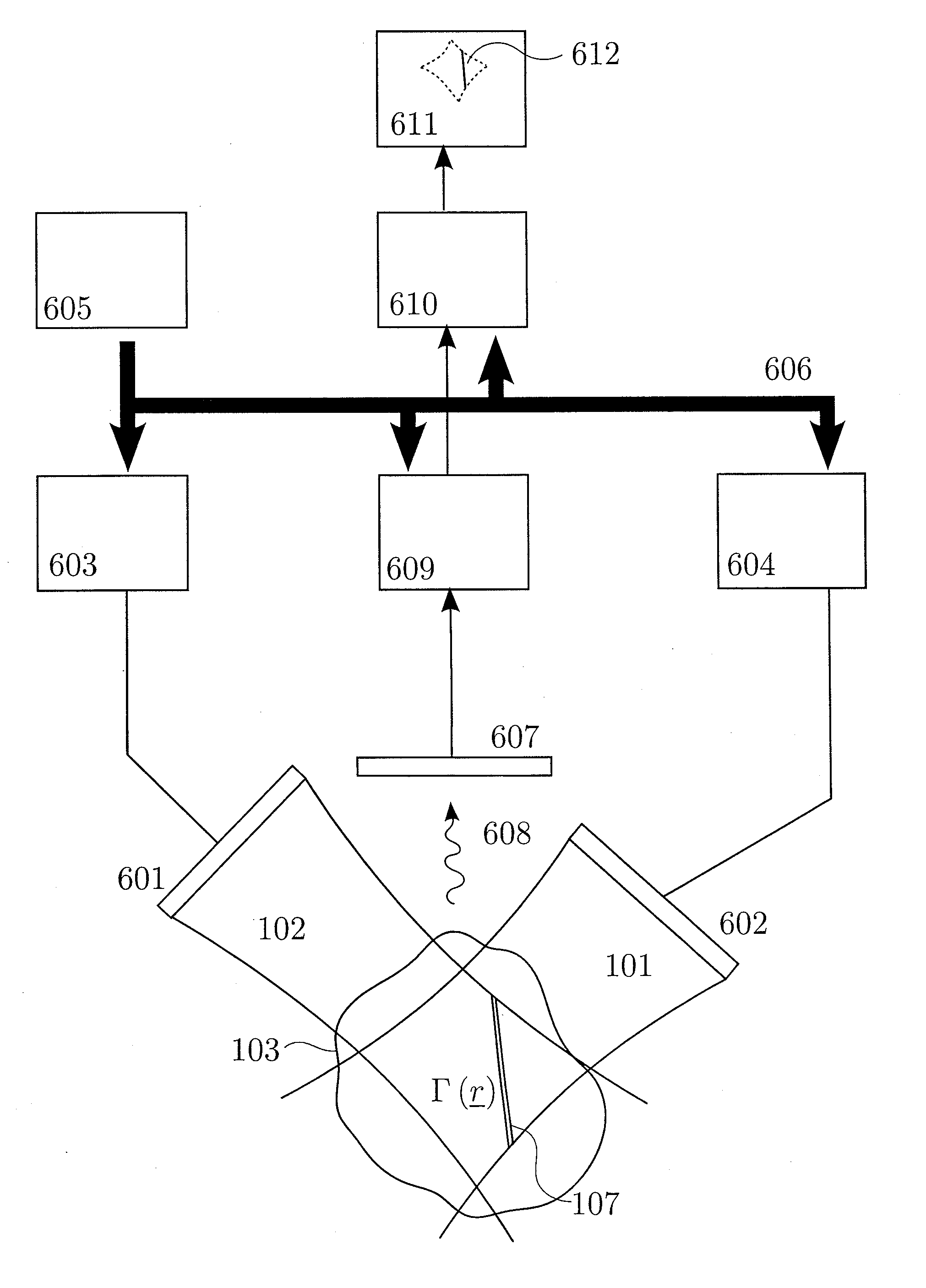
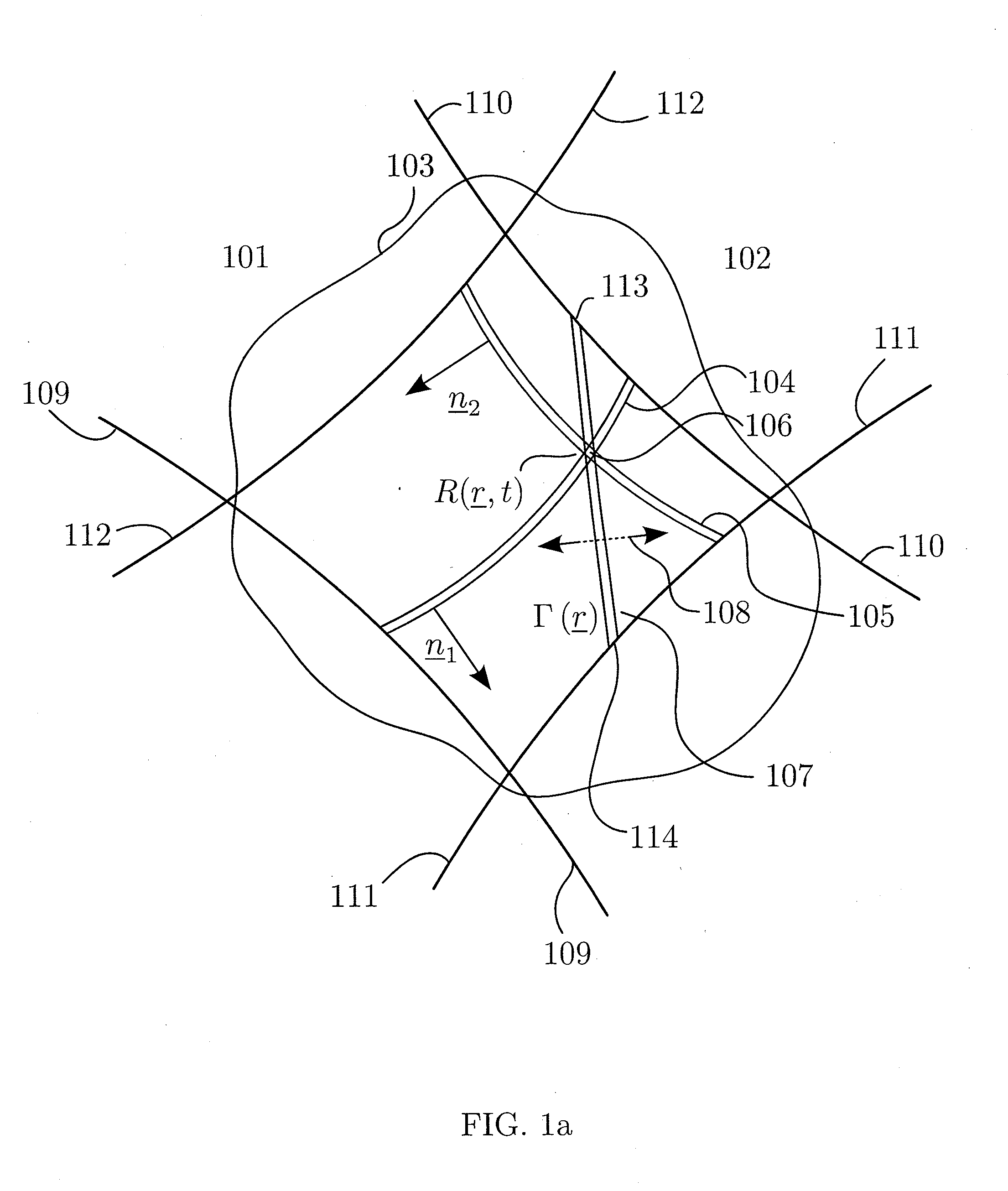
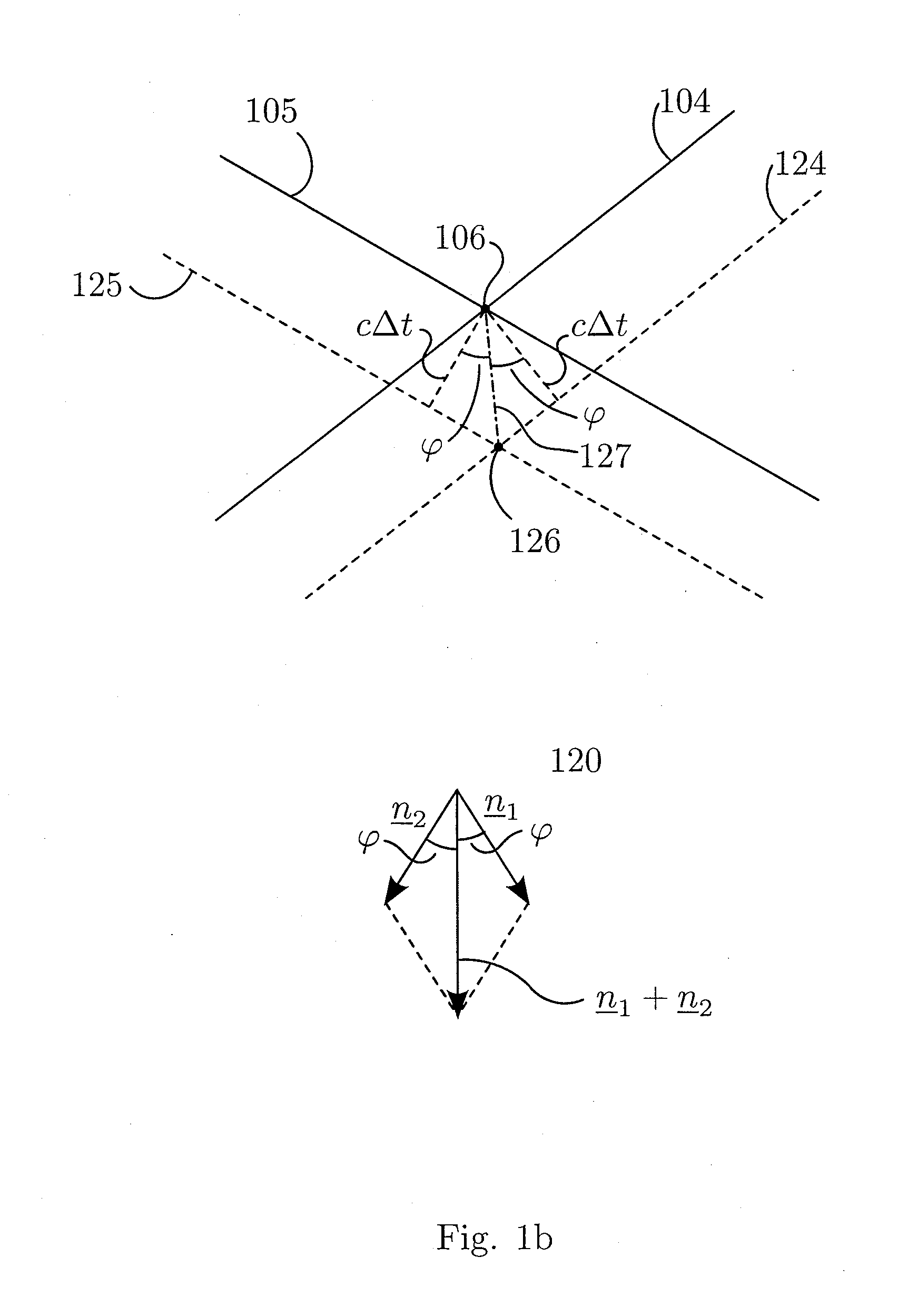
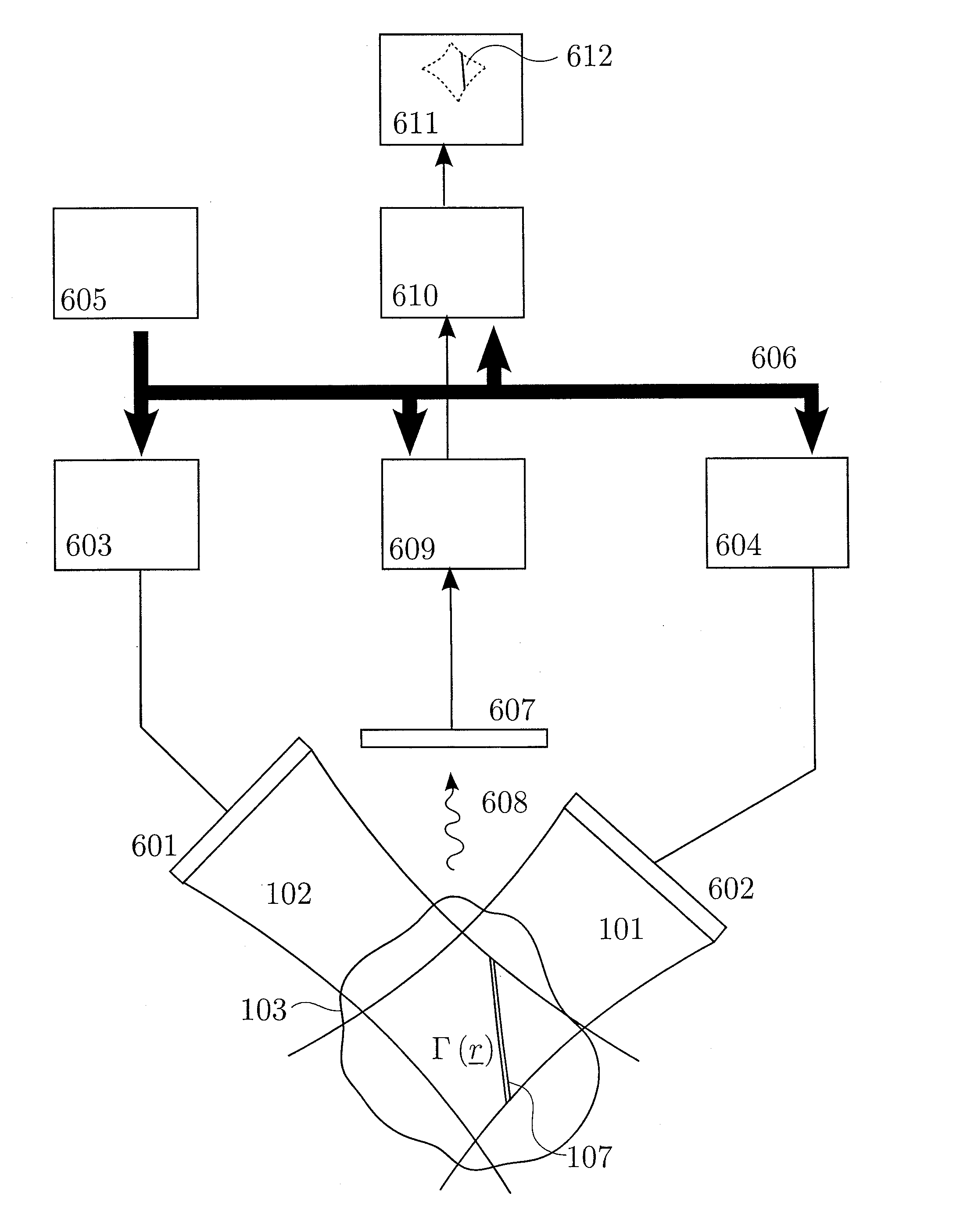
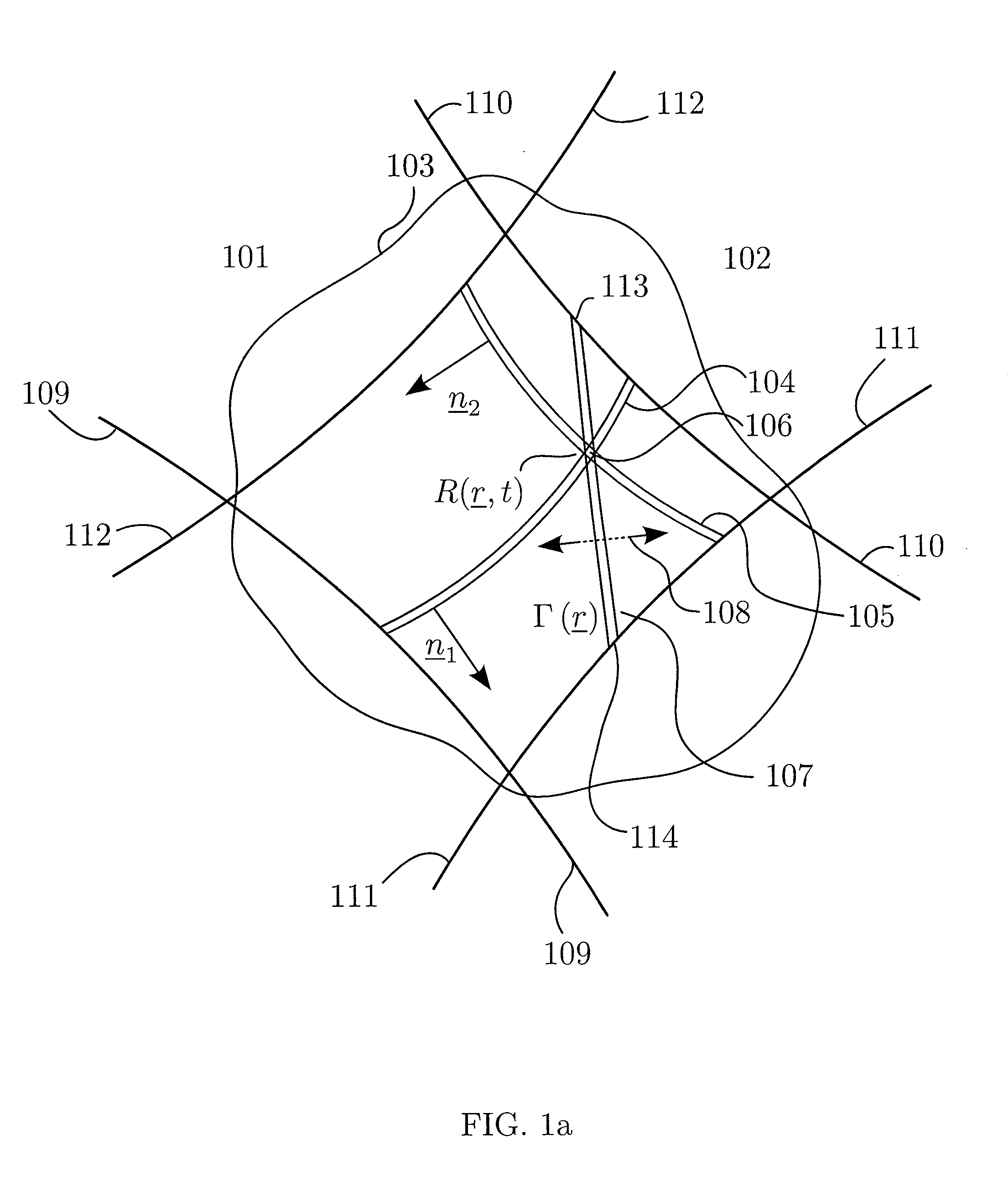
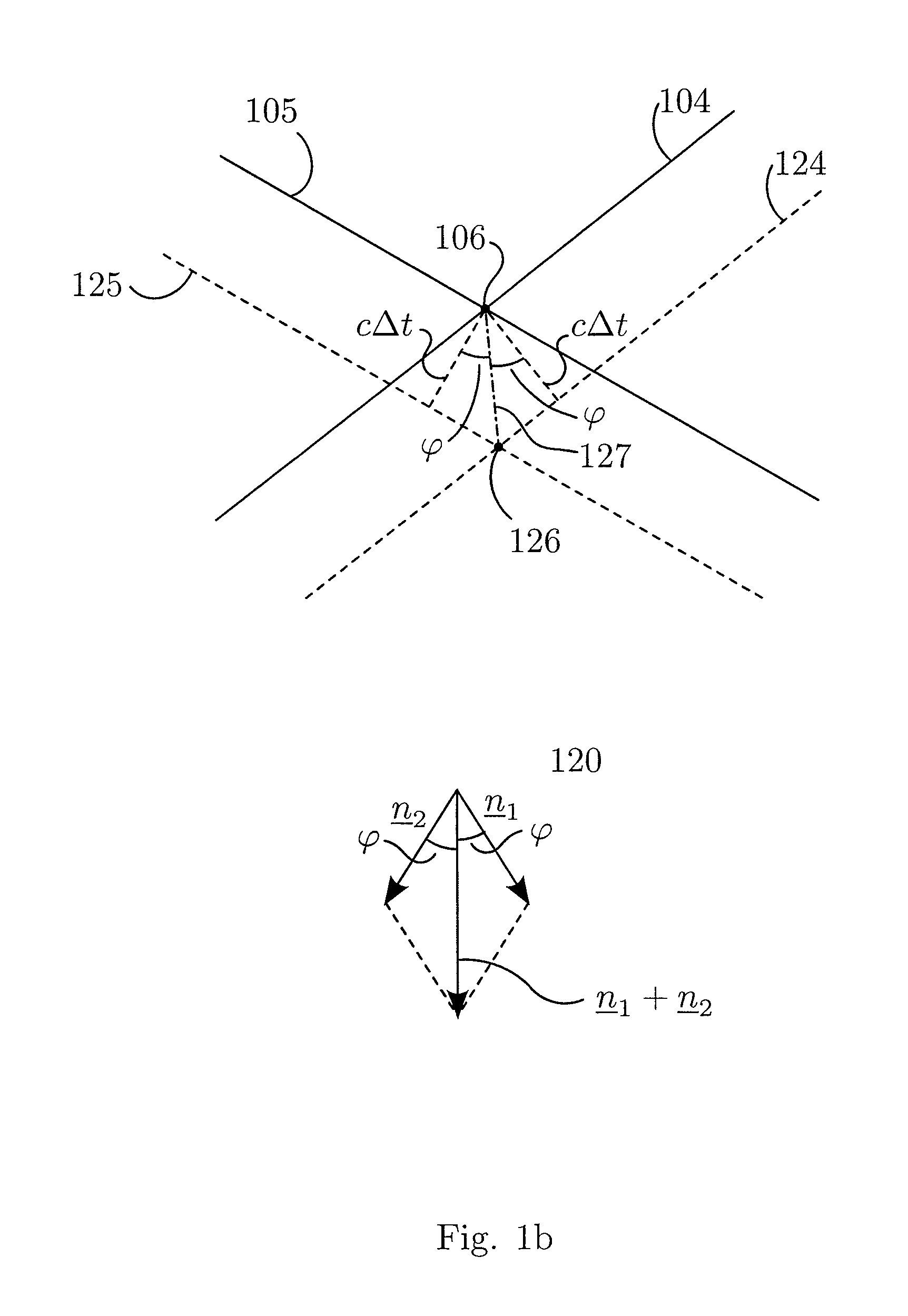
1st and 2nd pulsed waves are transmitted along 1st and 2nd transmit beams where at least one of the beams is broad in at least one direction, and the transmit timing between said 1st and 2nd pulsed waves are selected so that the pulsed wave fronts overlap in an overlap region R(r,t) that propagates along at least one measurement or image curve Γ(r) in the material object. At least the scattered signal produced by nonlinear interaction between said 1st and 2nd waves in the overlap region is received and processed to form a nonlinear interaction scattering image signal along Γ(r). The measurement or image curve Γ(r) can be scanned laterally by either changing of the relative transmit timing between the 1st and 2nd pulsed waves or the direction of at least one of the 1st and 2nd transmit beams, or both. The methods are applicable to image nonlinear scattering sources for both electromagnetic and elastic waves, and combinations of these.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
Measurement and Imaging of Scatterers with Memory of Scatterer Parameters Using at Least Two-Frequency Elastic Wave Pulse Complexes
ActiveUS20140150556A1Solve insufficient capacityImprove performanceMultiple-port networksAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcousticsLow frequency
Measurement or imaging of elastic wave nonlinear scatterers with a memory of scattering parameters comprises selecting LF pulses having characteristics to change the scattering parameters of nonlinear scatterers. A transmit time relation is selected so that the incident HF pulse propagates sufficiently close to the LF pulse that the effect of the incident LF pulse on its scatterer parameters is observed by the HF pulse. At least two elastic wave pulse complexes comprising a high frequency (HF) pulse and a selected low frequency (LF) pulse are transmitted towards the region. Received HF signals are combined to form nonlinear HF signals representing the scatterers with memory, with suppression of received HF signals from other scatterers. At least one of the received HF signals may be corrected by time delay correction and / or speckle correction with a speckle correction filter, determined by movement of the scattering object. Systems are also disclosed.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
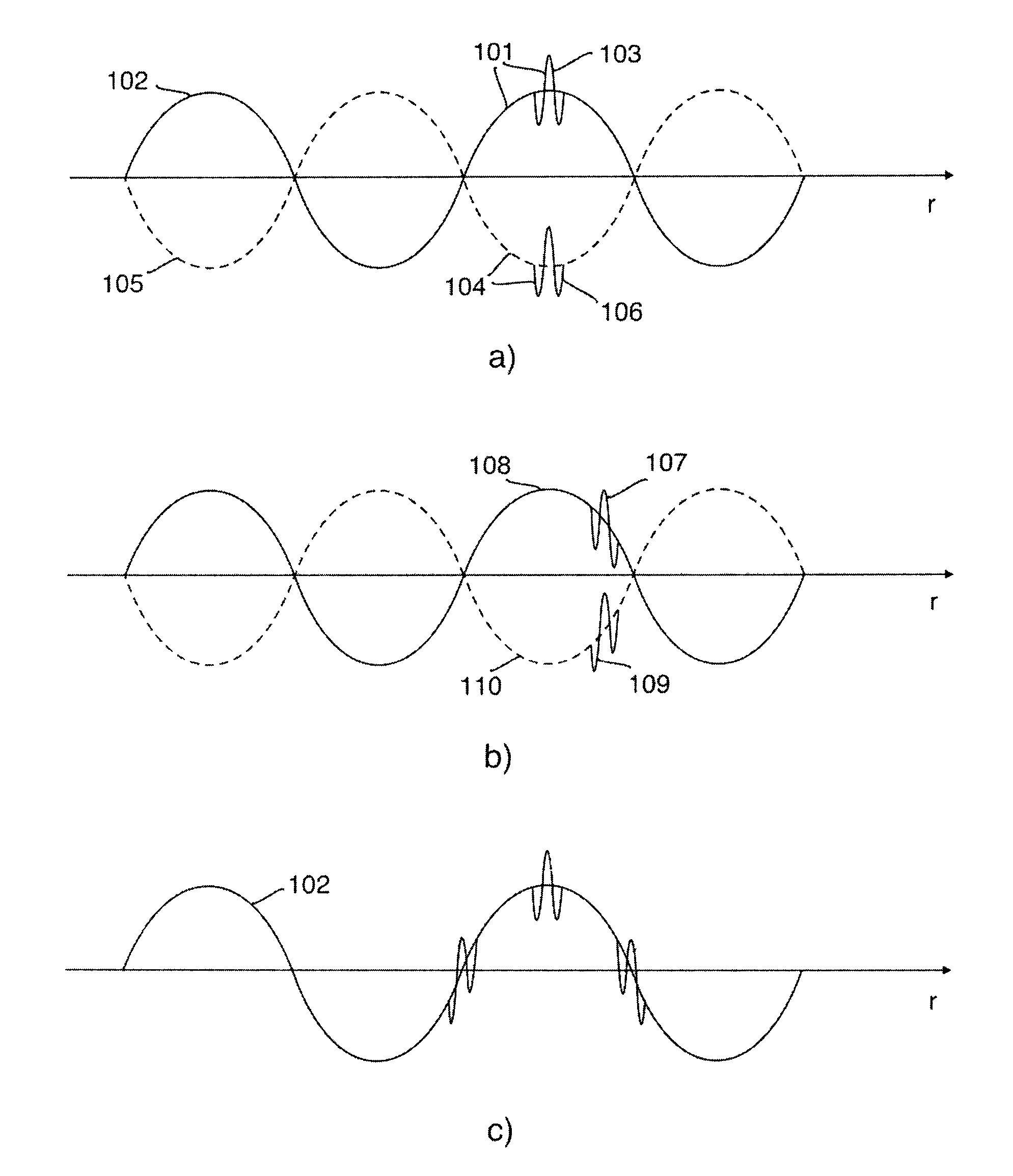
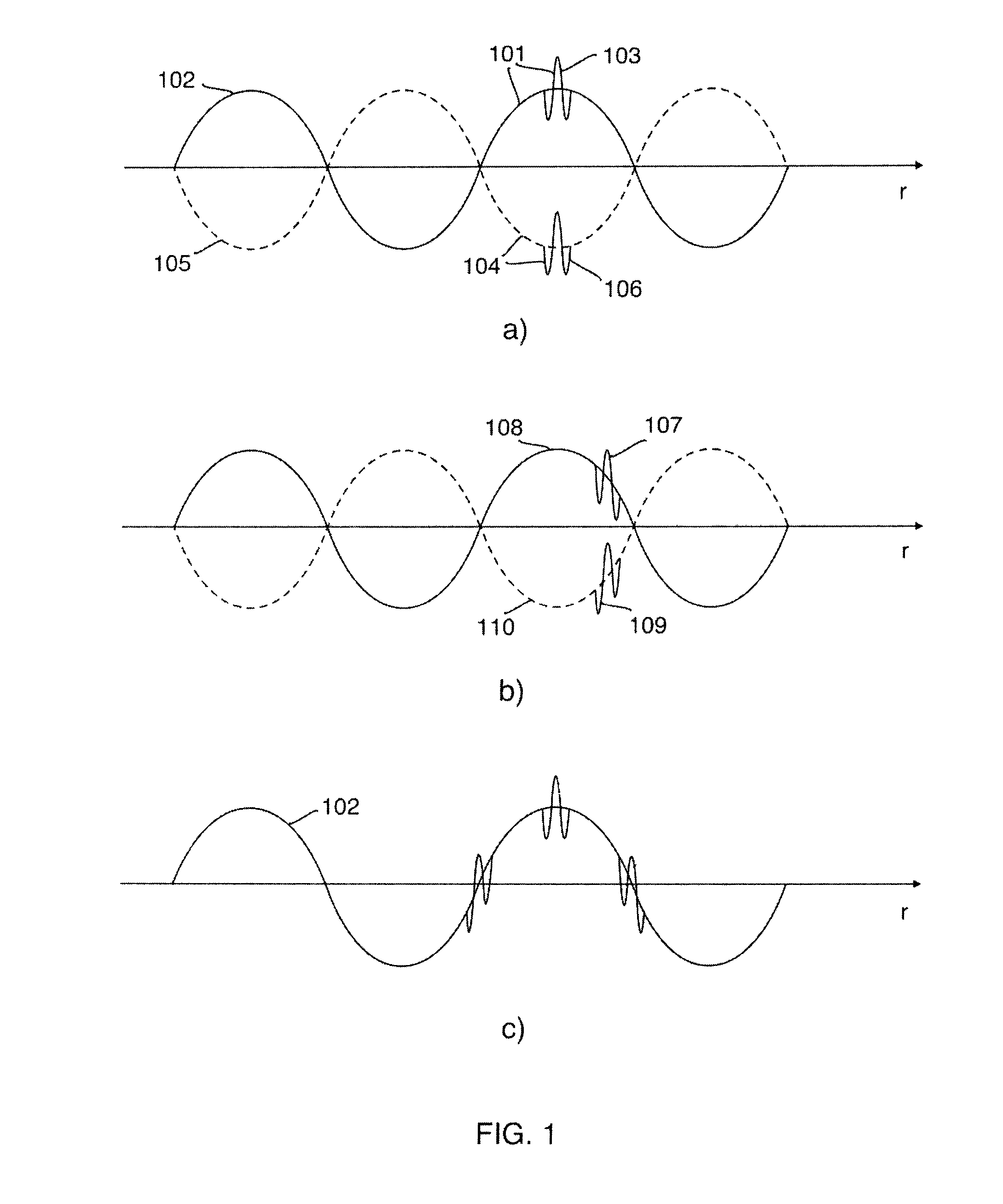
Nonlinear imaging with dual band pulse complexes
InactiveCN104125801AEnhanced Nonlinear Scattering ComponentSuppresses the linear scatter componentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsReverse orderPresent method
The invention presents methods and instrumentation for measurement or imaging of a region of an object with waves of a general nature, for example electromagnetic (EM) and elastic (EL) waves, where the material parameters for wave propagation and scattering in the object depend on the wave field strength. The invention specially addresses suppression of 3rd order multiple scattering noise, referred to as pulse reverberation noise, and also suppression of linear scattering components to enhanced signal components from nonlinear scattering. The pulse reverberation noise is divided into three classes where the invention specially addresses Class I and Class II 3rd order multiple scattering that are generated from the same three scatterers, but in opposite sequence.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
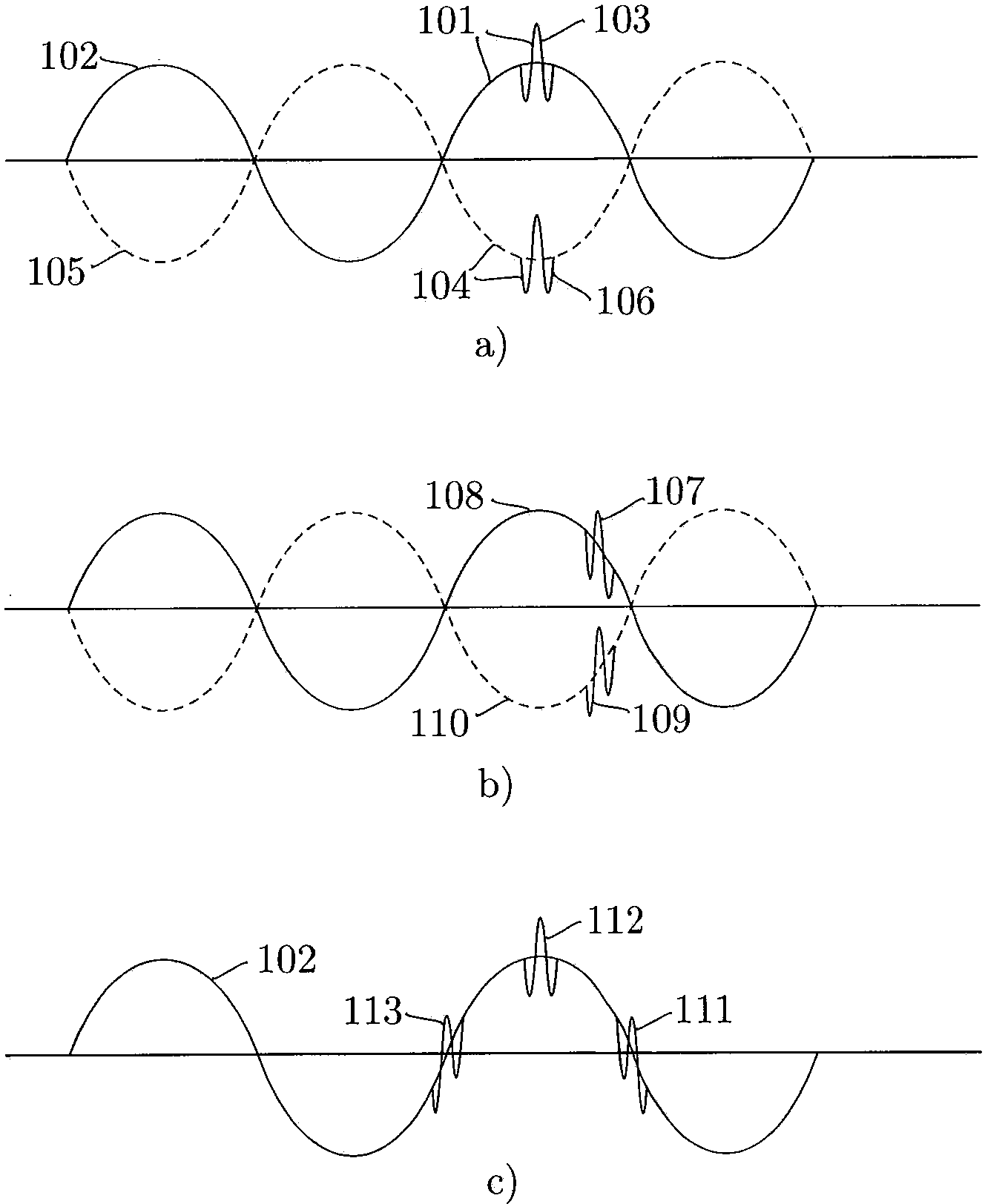
Nonlinear elastic wave measurement and imaging with two-frequency elastic wave pulse complexes
ActiveUS8550998B2Enhance first order scattered HF signalEnhanced signalOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsTransducerBeam direction
Owner:SURF TECH AS
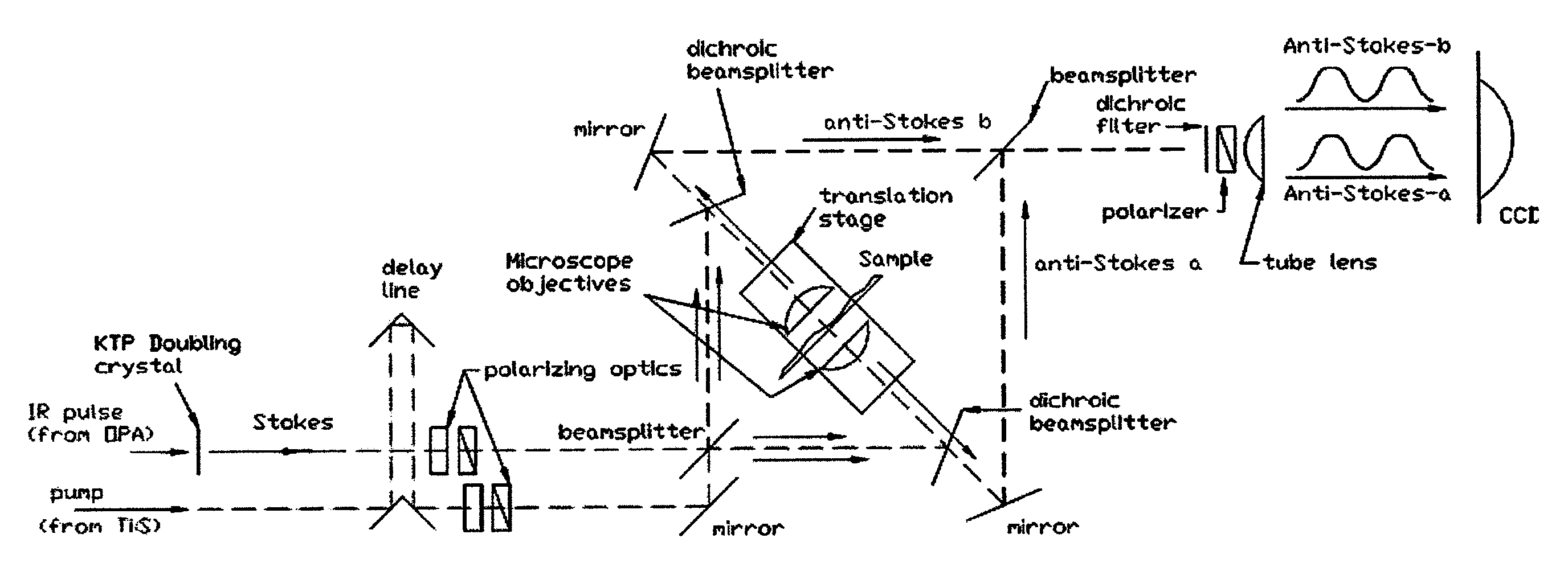
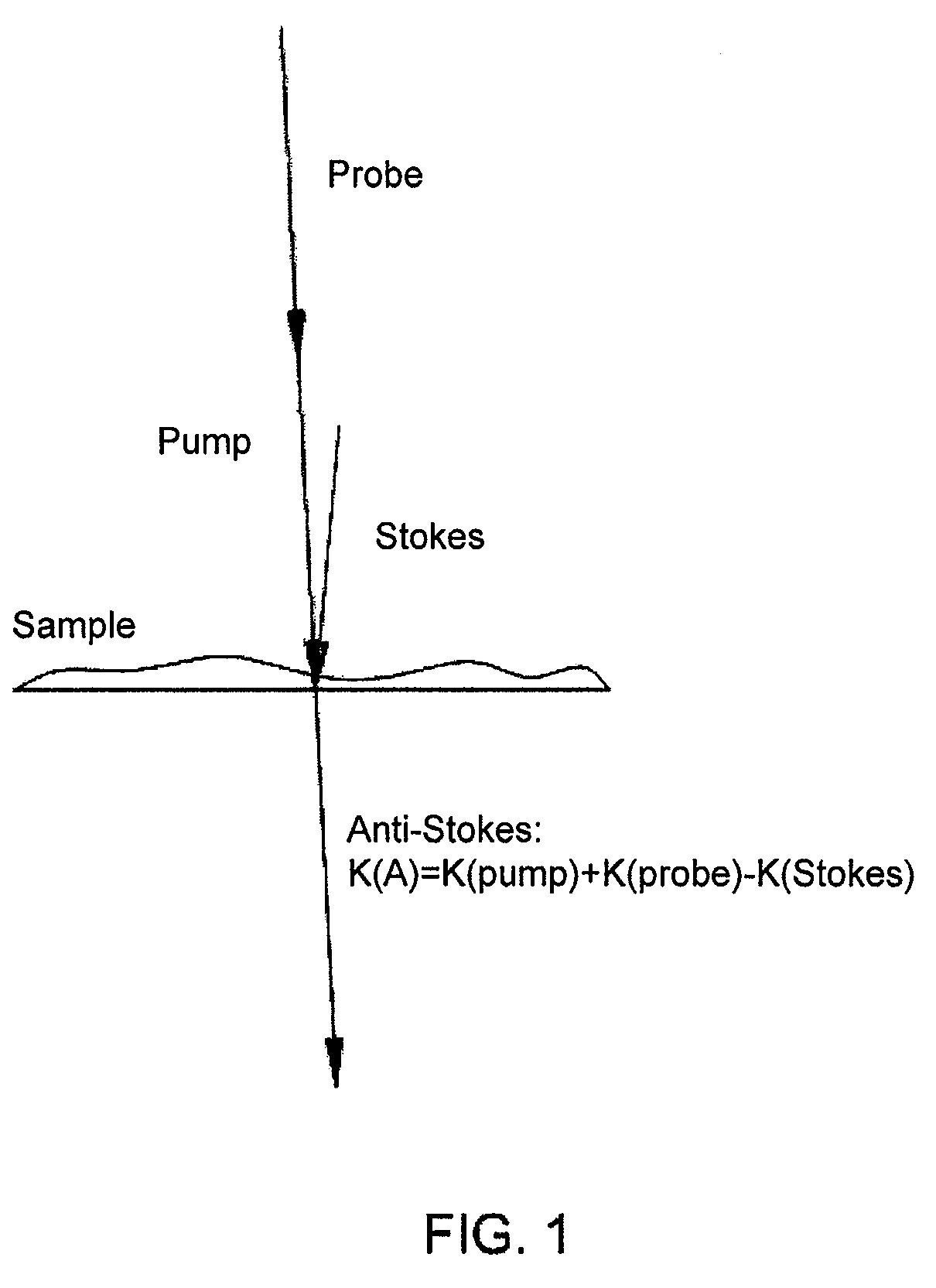
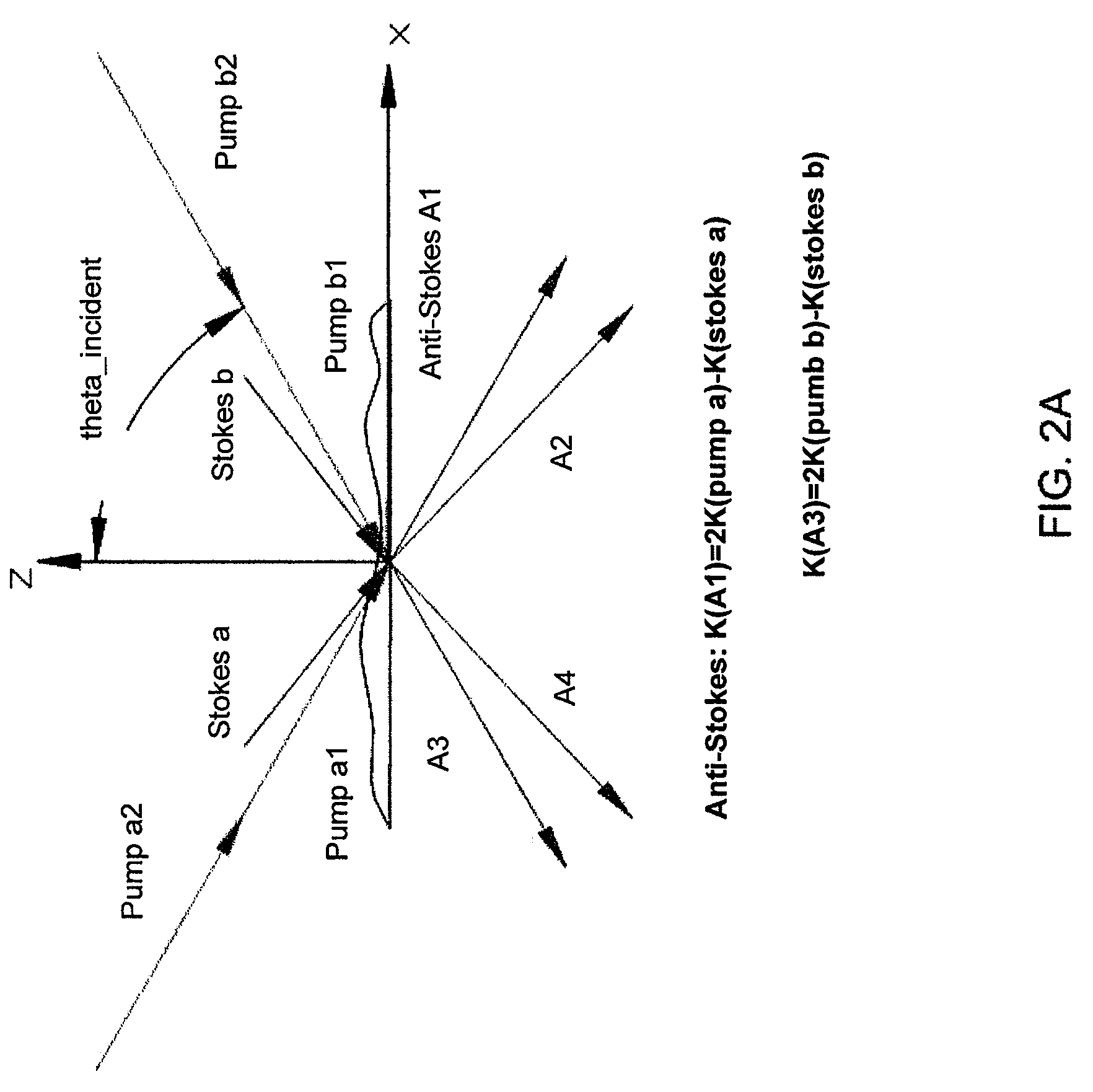
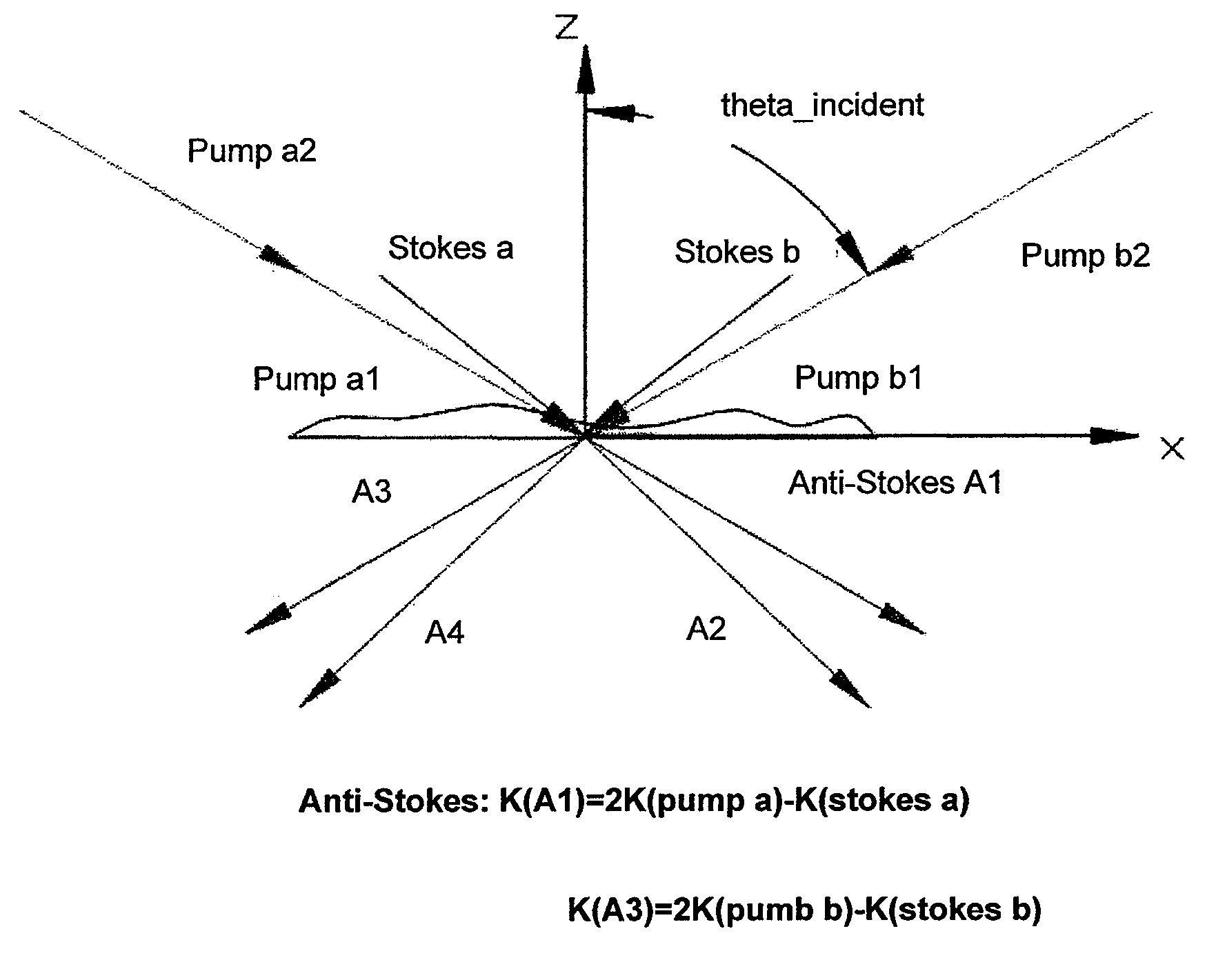
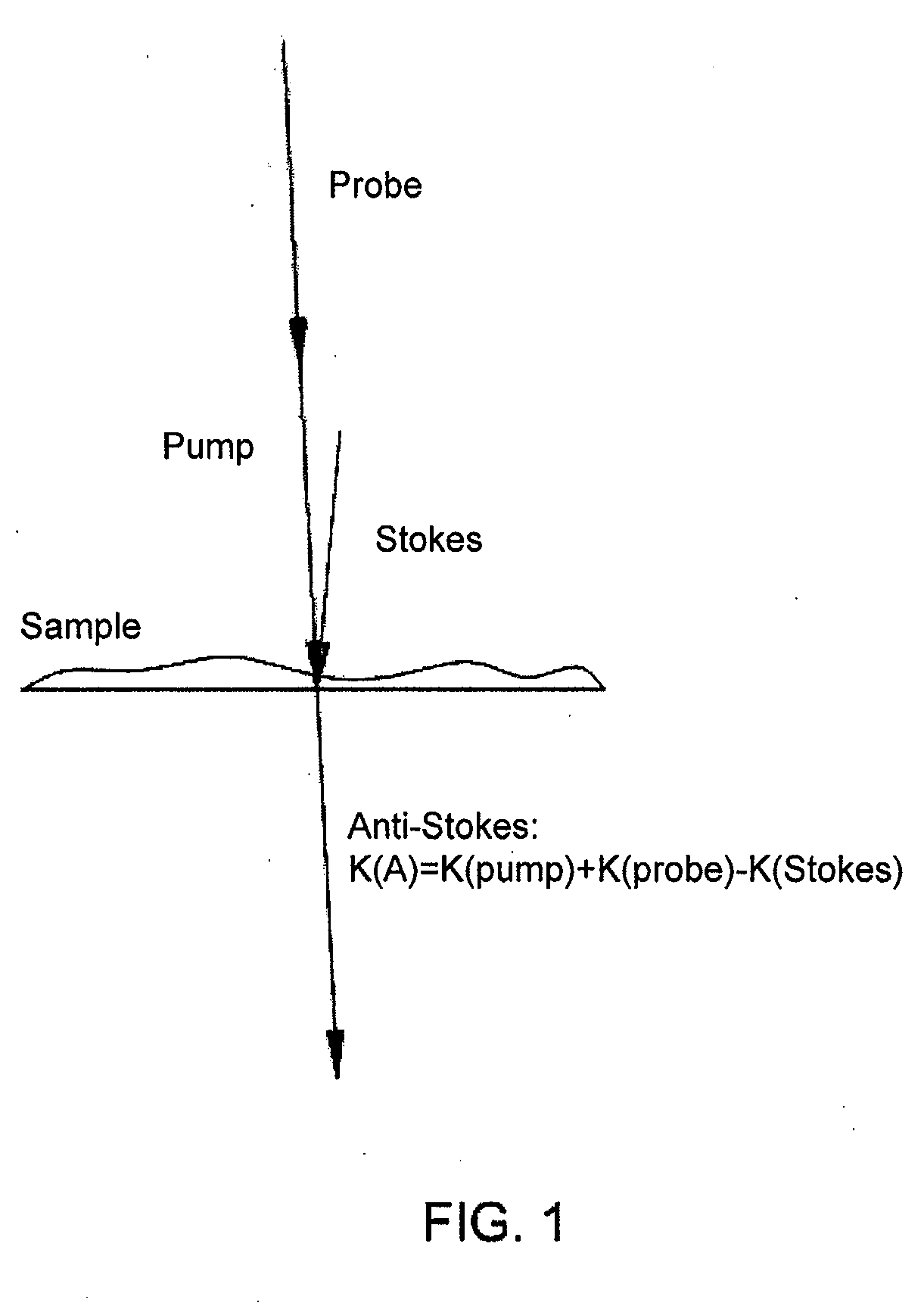
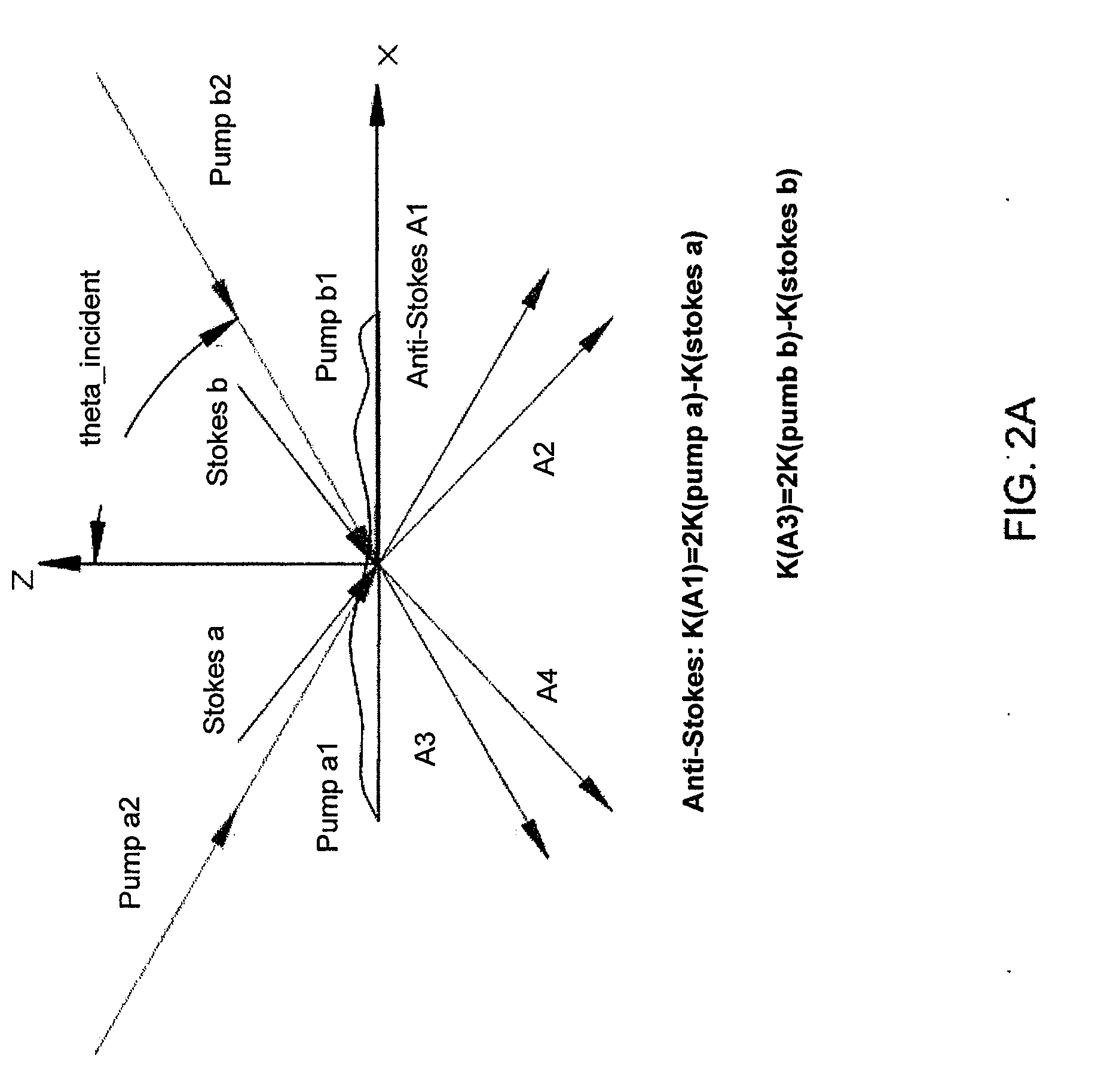
Spatial heterodyne wide-field Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman spectromicroscopy
ActiveUS7573577B2Improve spatial resolutionEasy accessRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryWide fieldSpectroscopie raman
Methods for chemically-resolved optical microscopy are presented. The methods can provide a wide-field, spatial interference imaging using multiple nonlinear scattering channels to produce multiple, spatially coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS).
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Spatial Heterodyne Wide-Field Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Spectromicroscopy
ActiveUS20070121119A1Improve spatial resolutionEasy accessRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryWide fieldParticle physics
Methods for chemically-resolved optical microscopy are presented. The methods can provide a wide-field, spatial interference imaging using multiple nonlinear scattering channels to produce multiple, spatially coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS).
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Nonlinear elastic imaging with two-frequency elastic pulse complexes
Methods and instruments for suppression of multiple scattering noise and extraction of nonlinear scattering components with measurement or imaging of a region of an object with elastic waves, where at least two elastic wave pulse complexes are transmitted towards said region where said pulse complexes are composed of a high frequency (HF) and a low frequency (LF) pulse with the same or overlapping beam directions and where the HF pulse is so close to the LF pulse that it observes the modification of the object by the LF pulse at least for a part of the image depth. The frequency and / or amplitude and / or phase of said LF pulse relative to said HF pulse varies for each transmitted pulse complex in order to nonlinearly manipulate the object elasticity observed by the HF pulse along at least parts of its propagation, and where received HF signals are picked up by transducers from one or both of scattered and transmitted components of the transmitted HF pulses. Said received HF signals are processed to form measurement or image signals for display, and where in the process of forming said measurement or image signals said received HF signals are one or both of delay corrected with correction delay in the fast time (depth-time), and pulse distortion corrected in the fast time, and combined in slow time to form noise suppressed HF signals or nonlinear scattering HF signals that are used for further processing to form measurement or image signals. The methods are applicable to elastic waves where the material elasticity is nonlinear in relation to the material deformation.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
Optical fiber delivery and collection method for biological applications such as multiphoton microscopy, spectroscopy, and endoscopy
InactiveUS7702381B2Efficient collectionRapid in vitro screeningCladded optical fibreDiagnostics using lightDiseaseSpectroscopy
The present invention is directed to a method of applying radiation through an optical fiber for detecting disease within a plant or animal or other penetrable tissue, or imaging a particular tissue of a plant or animal. In addition, fluorescence and nonlinear scattering signals can be detected and localized within a subject by such application of radiation through an optical fiber. The radiation is effective to promote simultaneous multiphoton excitation. The optical fibers are used alone to examine internal regions of tissue, in conjunction with an optical biopsy needle to evaluate sub-surface tissue, or with an endoscope to evaluate tissue within body cavities. The present invention also relates to a device for coupling in radiation from an ultrashort mode-locked laser into the beam path of a microscope.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Laser beam optical fiber transmission device in laser sodium guiding technology
InactiveCN101271176AImprove power conversion efficiencyLarge core diameterGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreFiberLight beam
A laser beam optical fiber transmission device of a laser sodium guide star technology is characterized in that: the device uses a cylindrical multimode optical fiber for producing a conical shape by adopting the melt-pulling method for pulling, then a table is formed by grinding, the device comprises: a cylindrical multimode optical fiber part and a conical table optical fiber part, the conical table optical fiber part is formed at the tail end of the cylindrical multimode optical fiber by direct processing, the other end of the cylindrical multimode optical fiber is an input end of a laser beam, the other end of the conical table optical fiber is an output end of the laser beam, the length of the cylindrical multimode optical fiber is equal to 1 to 1.2 times of the distance from a laser to a transmitting telescope; the radius of a fiber core of the conical table optical fiber which is arranged at the thick end is equal to the radius of the fiber core of the cylindrical multimode optical fiber, and the radius of the fiber core of the conical table optical fiber which is arranged at the thin end meets the single-mode condition for transmitting the laser by the optical fiber. The optical fiber transmission device has the advantages of simple and flexible structure and low cost, the quality of the output light beam is close to the diffraction limit, at the same time, the optical fiber transmission device can effectively overcome the non-linear scattering and other effects during the optical fiber transmission, thus achieving the purpose of transmitting the higher laser power.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
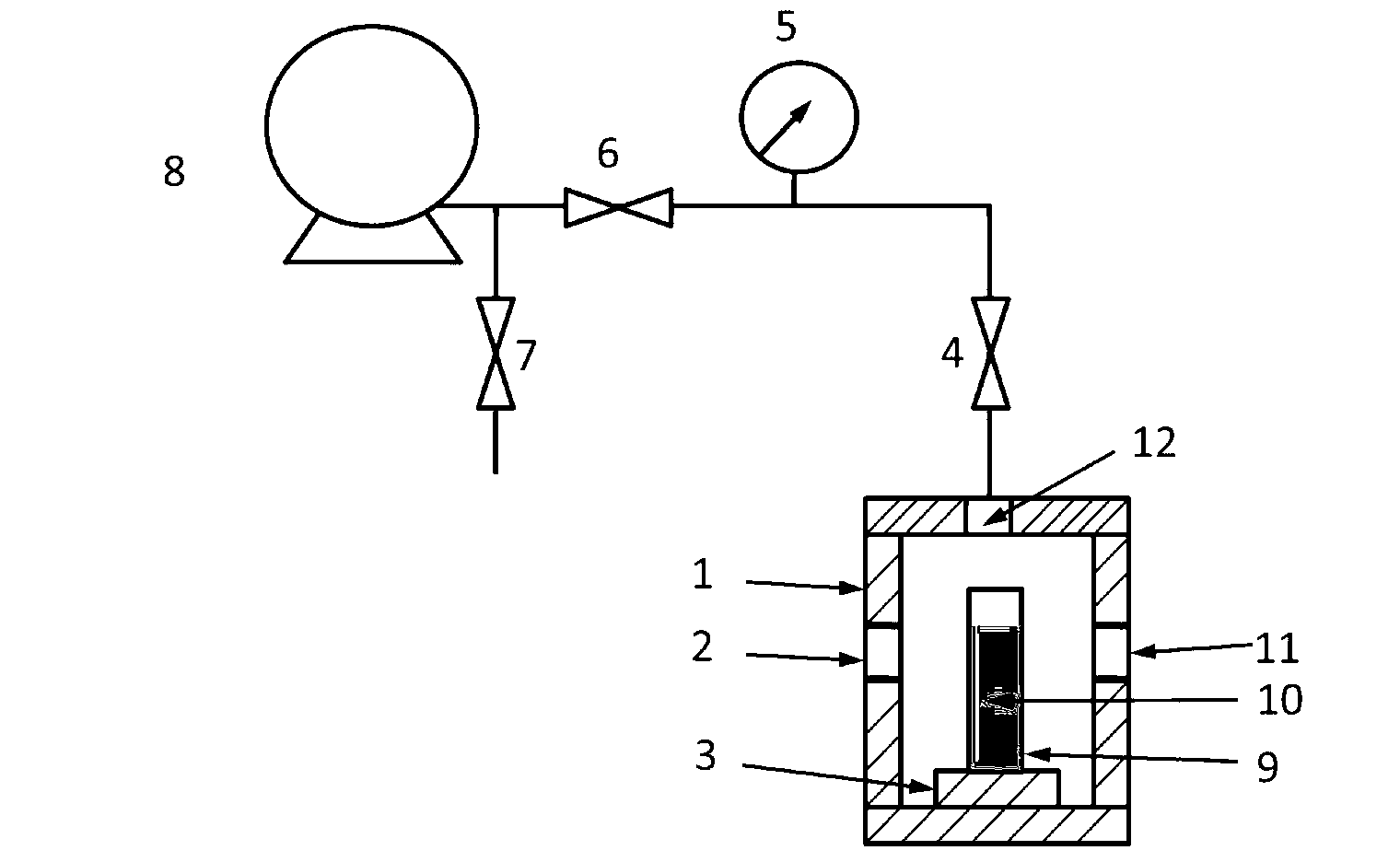
Ultra-long distance distribution type optical fiber sensor and using method thereof
InactiveCN102072741AReduce receiver sensitivityLower requirementSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesContinuous lightHigh energy
The invention discloses an ultra-long distance distribution type optical fiber sensor and a method for measuring temperature and vibration signals. The ultra-long distance distribution type optical fiber sensor adopts a multi-stage relay amplifier, and a high-power pulse light source enters a detecting optical fiber stage by stage through proportional allocation of a plurality of optical fiber couplers and transmission of transmission fibers, and re-amplifies the pulse of the detecting light at a specified length, thereby improving the signal to noise ratio of the system in terms of 'source', being capable of avoiding non-linear scattering caused by overrun light which enters a detecting optical cable directly on one hand, and being capable of reducing higher energy loss caused by continuous light transmission on the other hand. The ultra-long distance distribution type optical fiber sensor adopts the staged design, thereby greatly reducing the requirement on receiving sensitive and dynamic range of a receiving circuit. In addition, the ultra-long distance distribution type optical fiber sensor adopts the expandable design, thereby being capable of conveniently realizing short-distance detection, long-distance detection and ultra-long distance detection in sequence.
Owner:SHANGHAI BOOM FIBER SENSING TECH
Pneumatic-control optical limiter
ActiveCN103197483AEasy to operateWide range of optionsNon-linear opticsBoiling pointScattering effect
A pneumatic-control optical limiter comprises a sealing cavity and a decompress system. Characteristics that nonlinear scattering effect of nonlinear scattering media is relative to solvent boiling point are adopted by the optical limiter; and by means of adjusting air pressure around the nonlinear scattering media, real-time control on response of optical limiting is realized. Real-time and quantitative adjustment on the response of optical limiting can be realized with the pneumatic-control optical limiter which can be applicable to laser protection and laser control of sensitive optical elements.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical transmission line connection system and optical transmission line connection method
InactiveUS20140036258A1Maximizing intensityImprove accuracyUsing optical meansOptical light guidesOptical data transmissionOptical axis
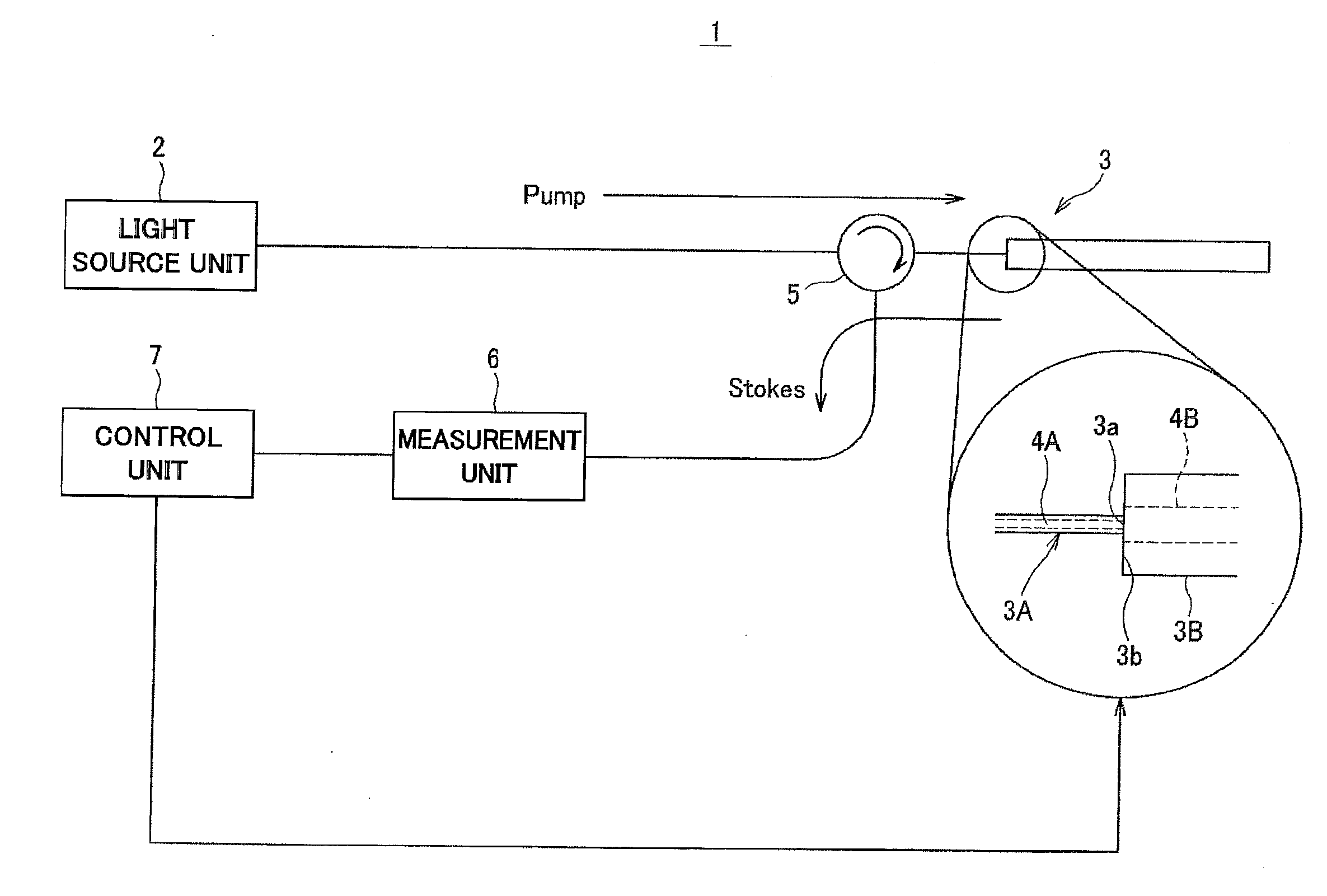
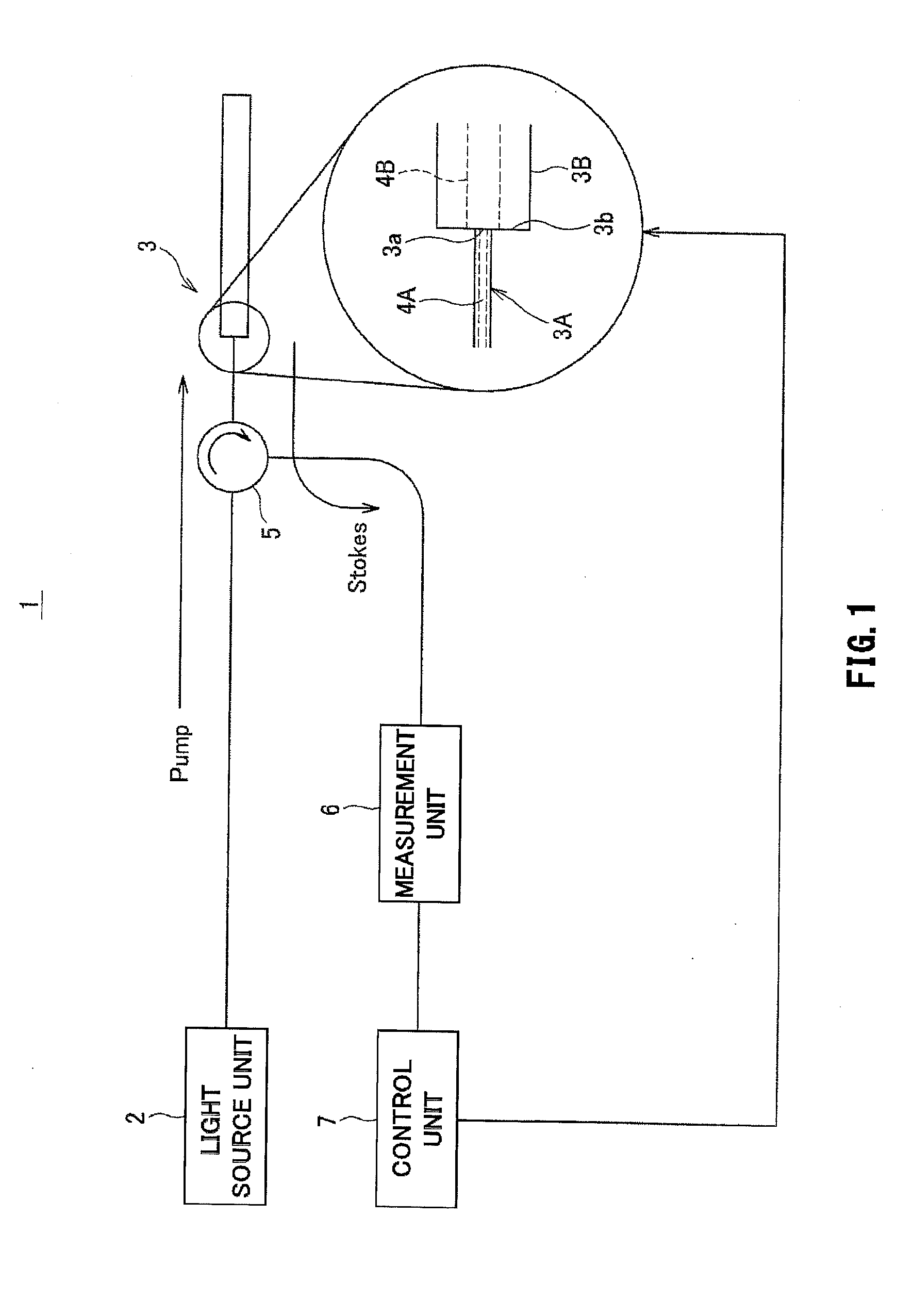
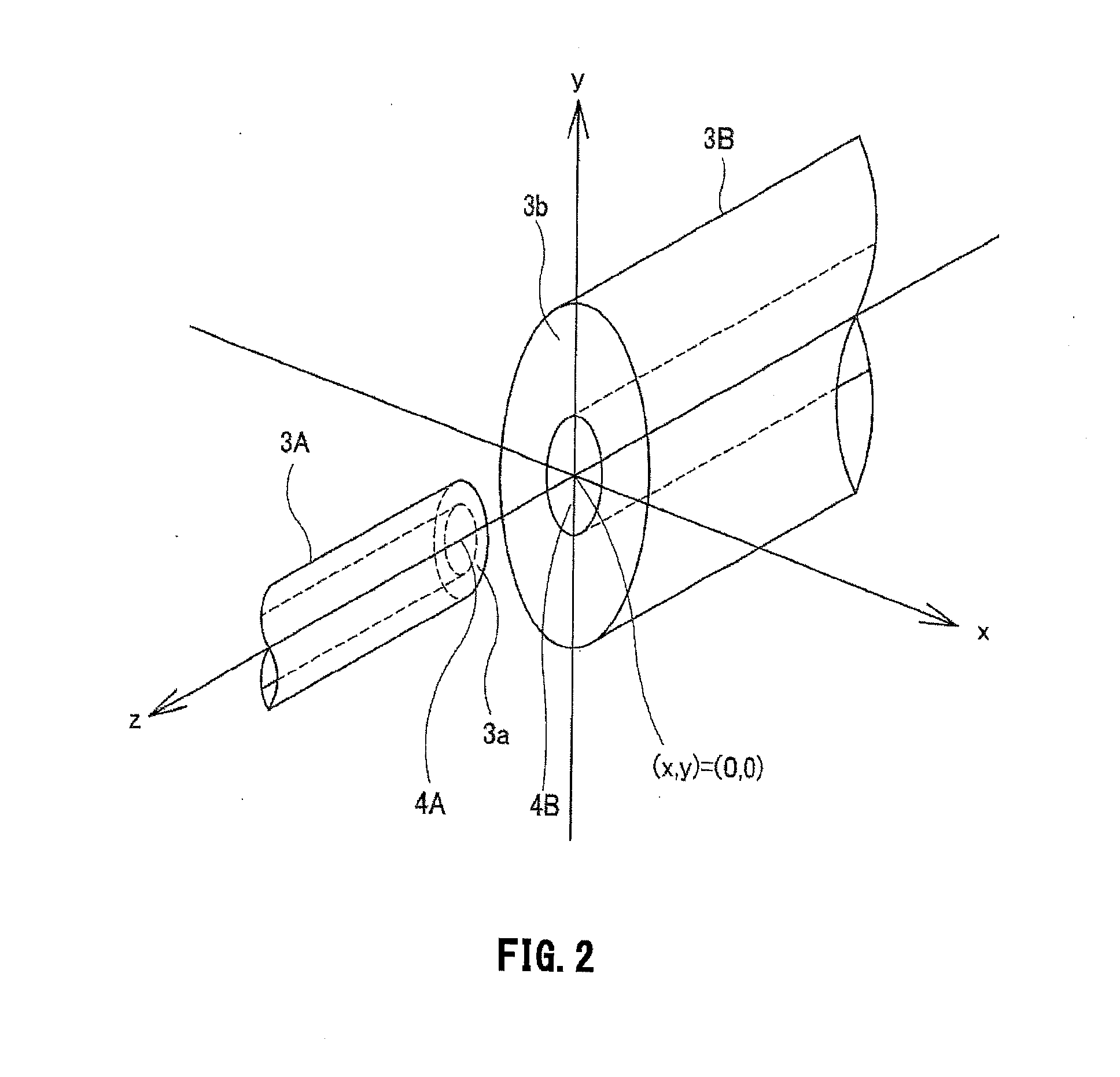
An optical transmission line connection system includes a light source unit that outputs laser light, a pump light generation unit that allows the laser light outputted from the light source unit to pass through one end of an optical transmission line and be made incident on one end of another optical transmission line as pump light, a measurement unit that measures non-linear scattered light components contained in reflected light, and a control unit that evaluates a spectrum of the non-linear scattered components observed by the measurement unit, and controls positions of optical axes of the one end of the one optical transmission line and the one end of the other optical transmission line so as to position the optical axes and maximize an intensity of the non-linear scattered light components.
Owner:TOKYO INST OF TECH
Method for imaging of nonlinear interaction scattering
ActiveUS8793079B2Increase ratingsReduce noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPulsed waveImage signal
1st and 2nd pulsed waves are transmitted along 1st and 2nd transmit beams where at least one of the beams is broad in at least one direction, and the transmit timing between said 1st and 2nd pulsed waves are selected so that the pulsed wave fronts overlap in an overlap region R(r,t) that propagates along at least one measurement or image curve Γ(r) in the material object. At least the scattered signal produced by nonlinear interaction between said 1st and 2nd waves in the overlap region is received and processed to form a nonlinear interaction scattering image signal along Γ(r). The measurement or image curve Γ(r) can be scanned laterally by either changing of the relative transmit timing between the 1st and 2nd pulsed waves or the direction of at least one of the 1st and 2nd transmit beams, or both. The methods are applicable to image nonlinear scattering sources for both electromagnetic and elastic waves, and combinations of these.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
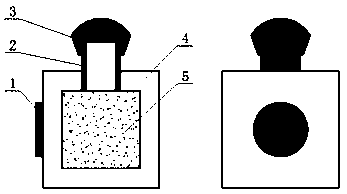
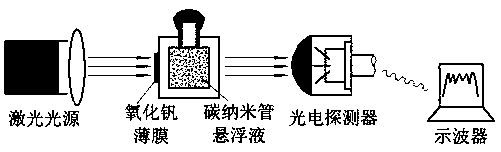
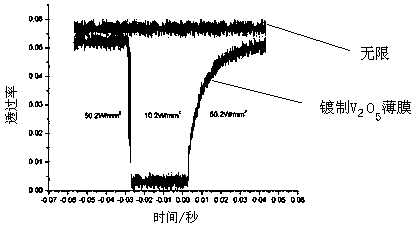
Broadband laser protection method and structure
ActiveCN106403721AStrong laser interference signal attenuationAchieve protectionWeapons typesCarbon nanotubeSapphire
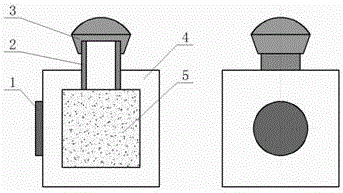
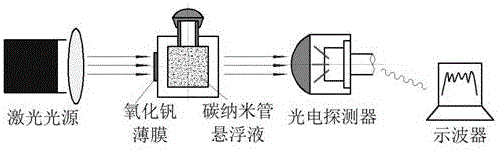
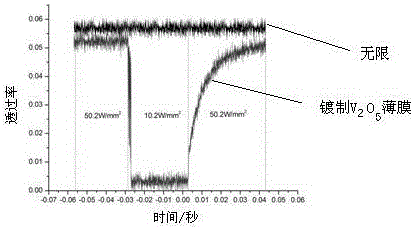
The invention relates to the technical field of surface coatings, nonlinear optics and laser protection, in particular to a broadband laser protection method and structure. The broadband laser protection structure is obtained through the series of steps of preparation of vanadium pentoxide, design of a sapphire shell, preparation of carbon nanotube suspension liquid, and injection and sealing of the suspension liquid. The broadband laser protection structure is widely applied to the technical field of optic intelligent windows and laser protection. The broadband laser protection structure is characterized in that composite multi-element protection is adopted, combined with wave band characteristics of existing various nonlinear optical limiting materials, intensive laser interference signals can be attenuated more effectively through thermally induced phase-transition optical limiting and nonlinear scattering methods, and therefore continuous and adjustable laser protection on the visible light wave band and the near infrared wave band is achieved. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the process is simple, the rate of finished products is high, and the method is mature and reliable.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
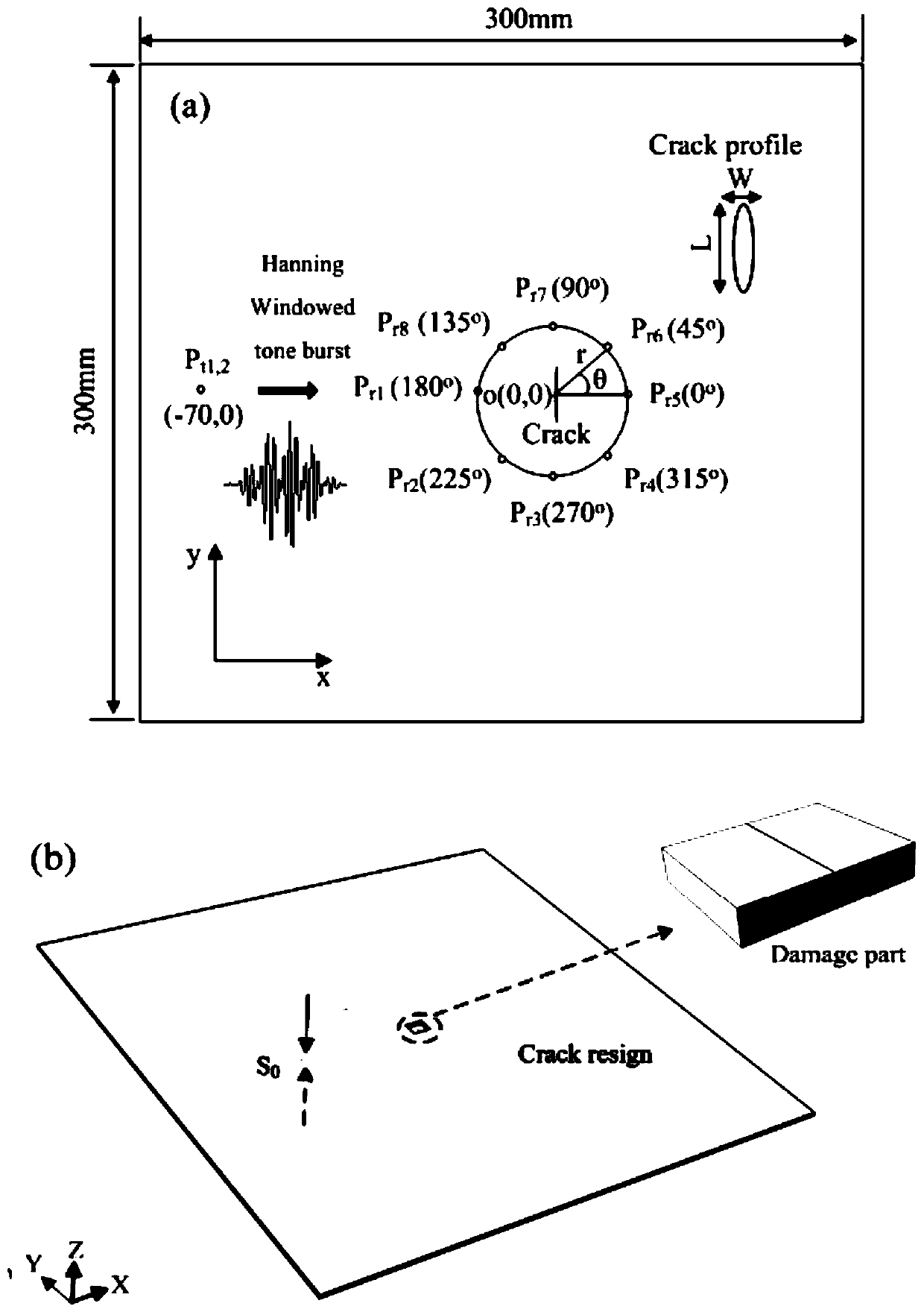
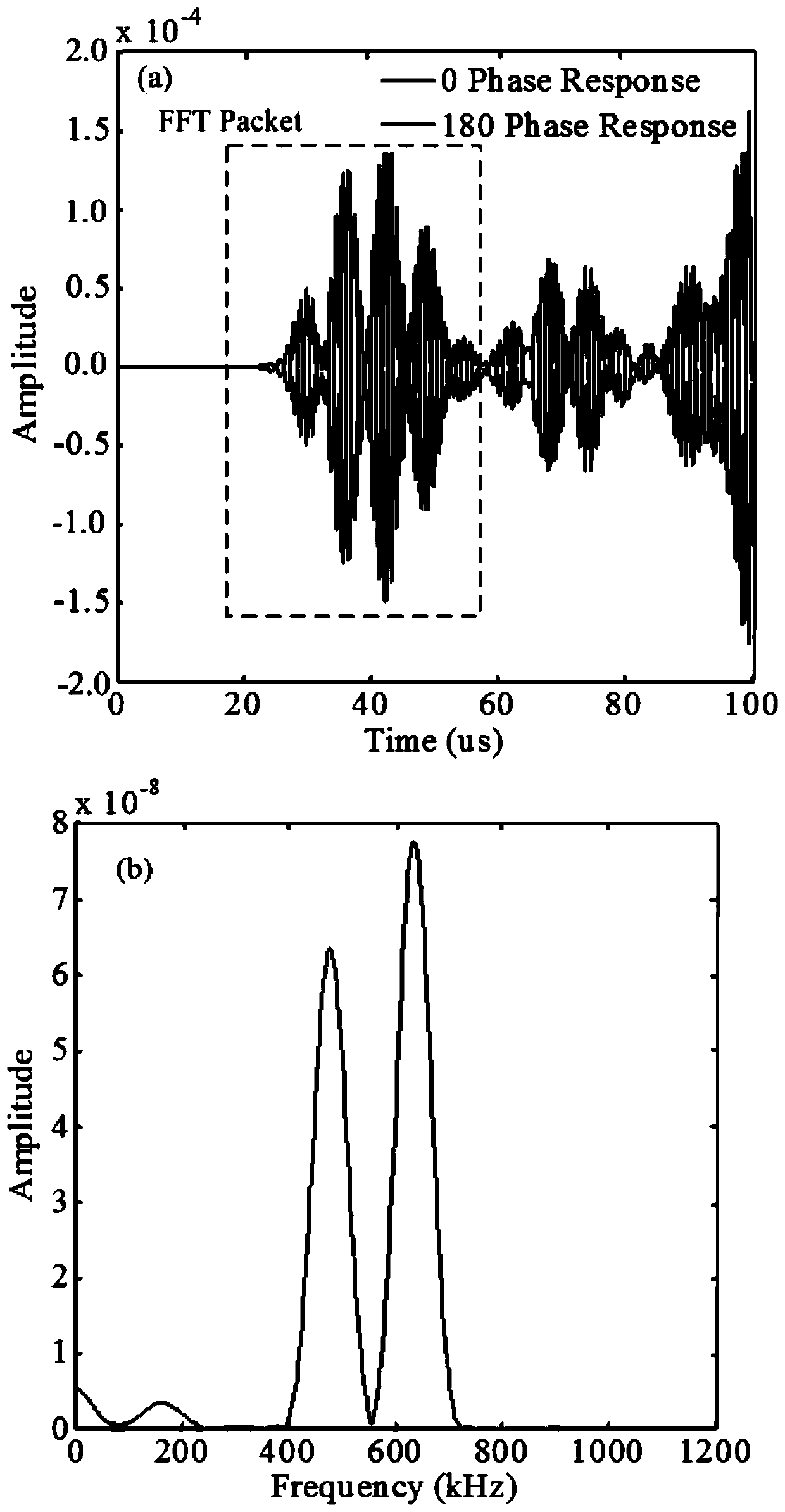
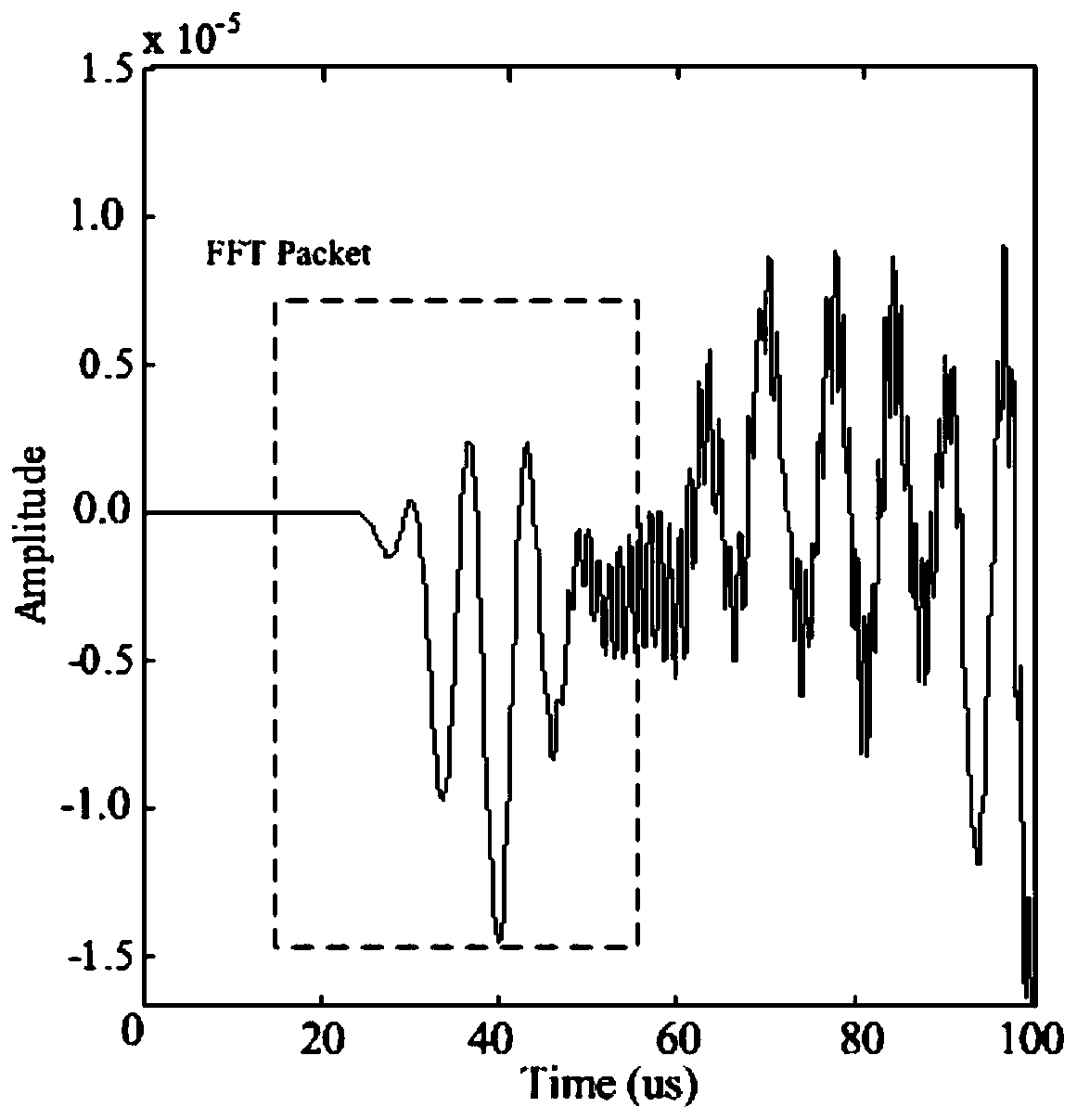
Method for identifying microcrack direction in plate based on nonlinear frequency mixing technology of Lamb waves
ActiveCN111157629AImplement extractionEliminate fundamental frequency componentsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalForward scatterNon linearite
The invention discloses a method for identifying a microcrack direction in a plate based on a nonlinear frequency mixing technology of Lamb waves. The method includes, firstly, extracting a sum frequency signal and a difference frequency signal in a damage response signal by adopting a pulse inversion method; obtaining a directional mode pattern of a nonlinear scattering coefficient beta through the extracted sum frequency signal and difference frequency signal; and determining the maximum forward scattering point and the minimum backward scattering point of the Lamb wave, and taking the direction vertical to the connecting line of the maximum forward scattering point and the minimum backward scattering point of the Lamb wave as the direction of the micro-crack, thereby realizing the identification of the direction of the micro-crack. According to the invention, the Lamb wave excited by frequency mixing interacts with the nonlinear medium to generate a new frequency component; the sumfrequency and difference frequency effective frequency components in the damage response signal are effectively extracted through a pulse inversion method, the microcrack direction is recognized by researching the nonlinear scattering degree of Lamb waves in different directions of the microcrack, and the technical problems that the amplitude is too small, and the sum frequency and difference frequency signals with weak signals are not easy to extract and recognize are effectively solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Measurement and imaging of scatterers with memory of scatterer parameters using at least two-frequency elastic wave pulse complexes
ActiveUS9939413B2Solve insufficient capacityImprove performanceOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationTime delaysDouble frequency
Measurement or imaging of elastic wave nonlinear scatterers with a memory of scattering parameters comprises selecting LF pulses having characteristics to change the scattering parameters of nonlinear scatterers. A transmit time relation is selected so that the incident HF pulse propagates sufficiently close to the LF pulse that the effect of the incident LF pulse on its scatterer parameters is observed by the HF pulse. At least two elastic wave pulse complexes comprising a high frequency (HF) pulse and a selected low frequency (LF) pulse are transmitted towards the region. Received HF signals are combined to form nonlinear HF signals representing the scatterers with memory, with suppression of received HF signals from other scatterers. At least one of the received HF signals may be corrected by time delay correction and / or speckle correction with a speckle correction filter, determined by movement of the scattering object. Systems are also disclosed.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
Preparation method and application of sulfur-nitrogen codoped carbon quantum dots
ActiveCN109337681AHigh nitrogen contentStrong nonlinear scattering performanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsNitrationPhenothiazine
The invention provides a preparation method of sulfur-nitrogen codoped carbon quantum dots. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing phenothiazine, sodium nitrite, dichloromethaneand acetic acid, and performing a nitration reaction to obtain 3,7-dinitrophenothiazine; mixing the 3,7-dinitrophenothiazine and alkaline liquid, sequentially performing a hydrothermal reaction and dialysis to obtain sulfur-nitrogen codoped carbon quantum dots. According to the preparation method, firstly, nitrification is performed on a nitrogen source and a sulfur source, so that the nitrogen content of the carbon quantum dots can be increased; then, the 3,7-dinitrophenothiazine and the alkaline liquid are mixed, and the hydrothermal reaction is performed to obtain the sulfur-nitrogen dopedcarbon quantum dots. The carbon quantum dots have the nitrogen content of 3.45-9.69wt% and the sulfur content of 0.51-0.83wt%, show very strong nonlinear scattering performance and have very good optical limiting performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
One-way waveguide and one-way optical fiber
ActiveCN106353853AEliminate reflectionsEliminate scatterOptical waveguide light guideFibre with gratingsInelastic scatteringTransfer mode
The invention provides a production method of a one-way waveguide. The production method comprises the step of carrying out spiral spatial modulation on Weyl crystals. The Weyl crystals contain Weyl points in an energy band structure. The one-way waveguide produced by adopting the method provided by the invention can eliminate reflection of wave and replace an isolator, also eliminates various types of linear scattering and reduces loss and also inhibits non-linear scattering, so that waveguide signal strength threshold is improved; meanwhile, a transmission mode that any number of group and phase velocities are the same can be realized, so that synchronous transmission of signals is realized.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Ultrasound imaging
InactiveCN101023376BMinimize nonlinear effectsAchieve imagingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationCalcification
Owner:比约恩・A・J・安杰尔森 +2
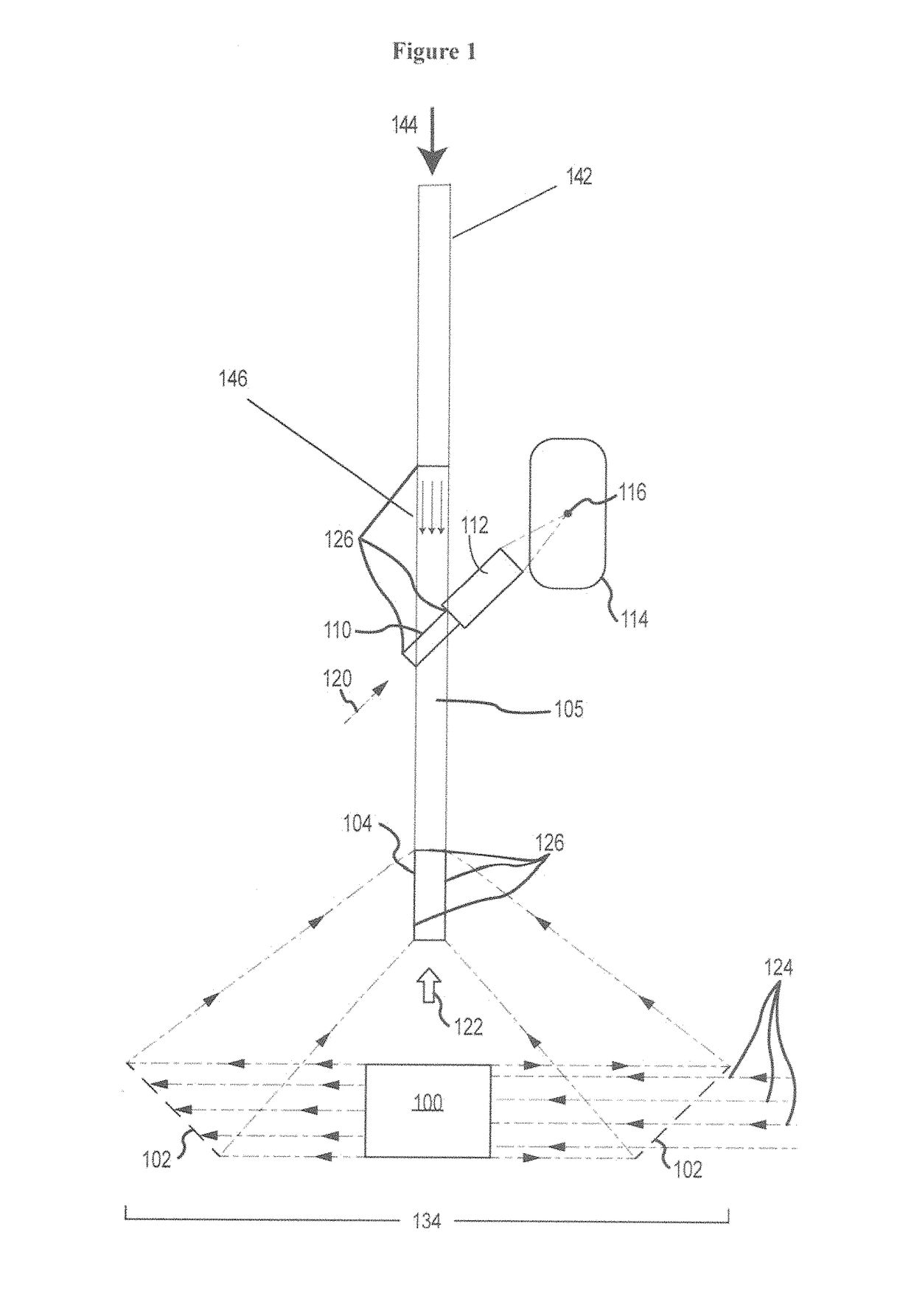
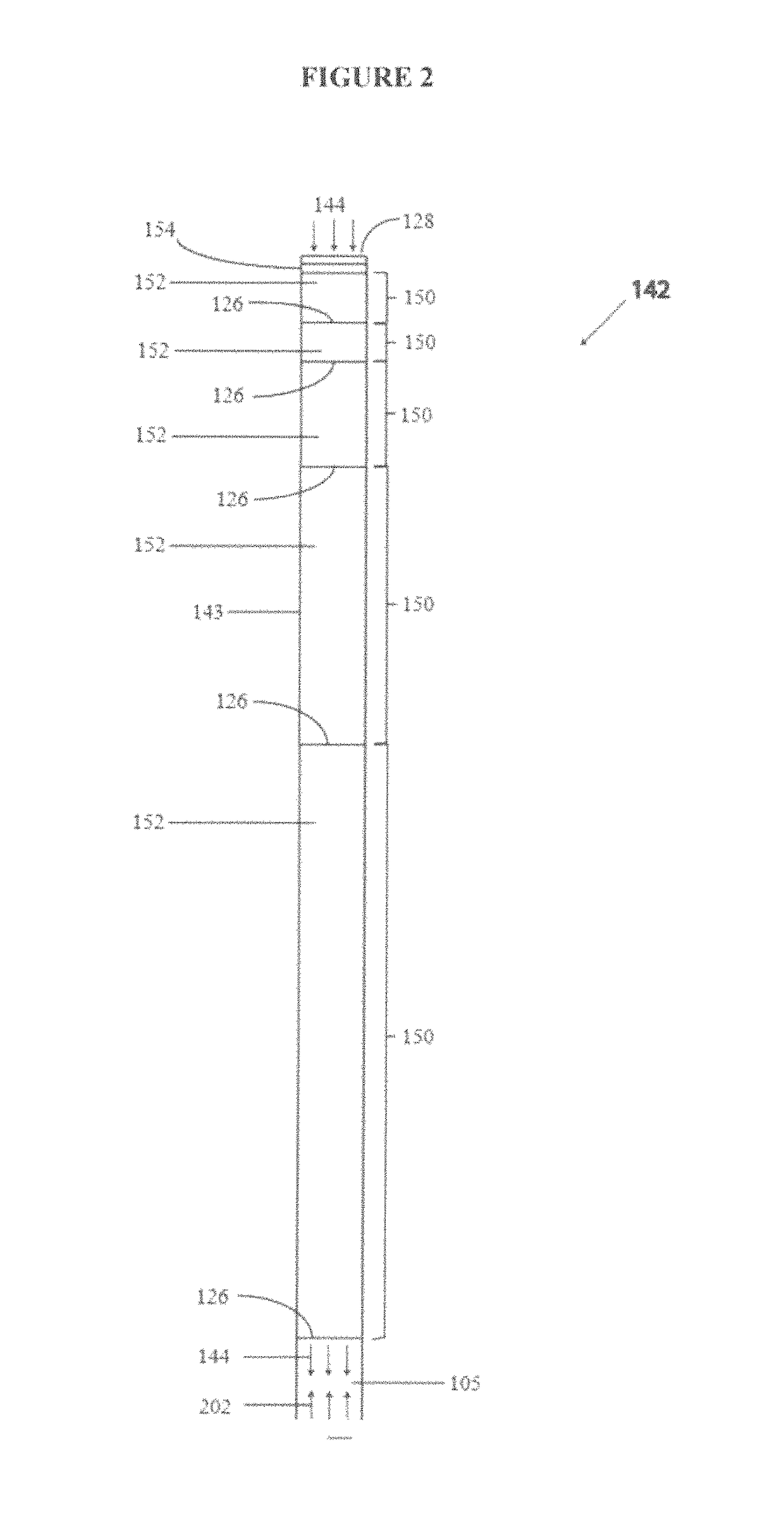
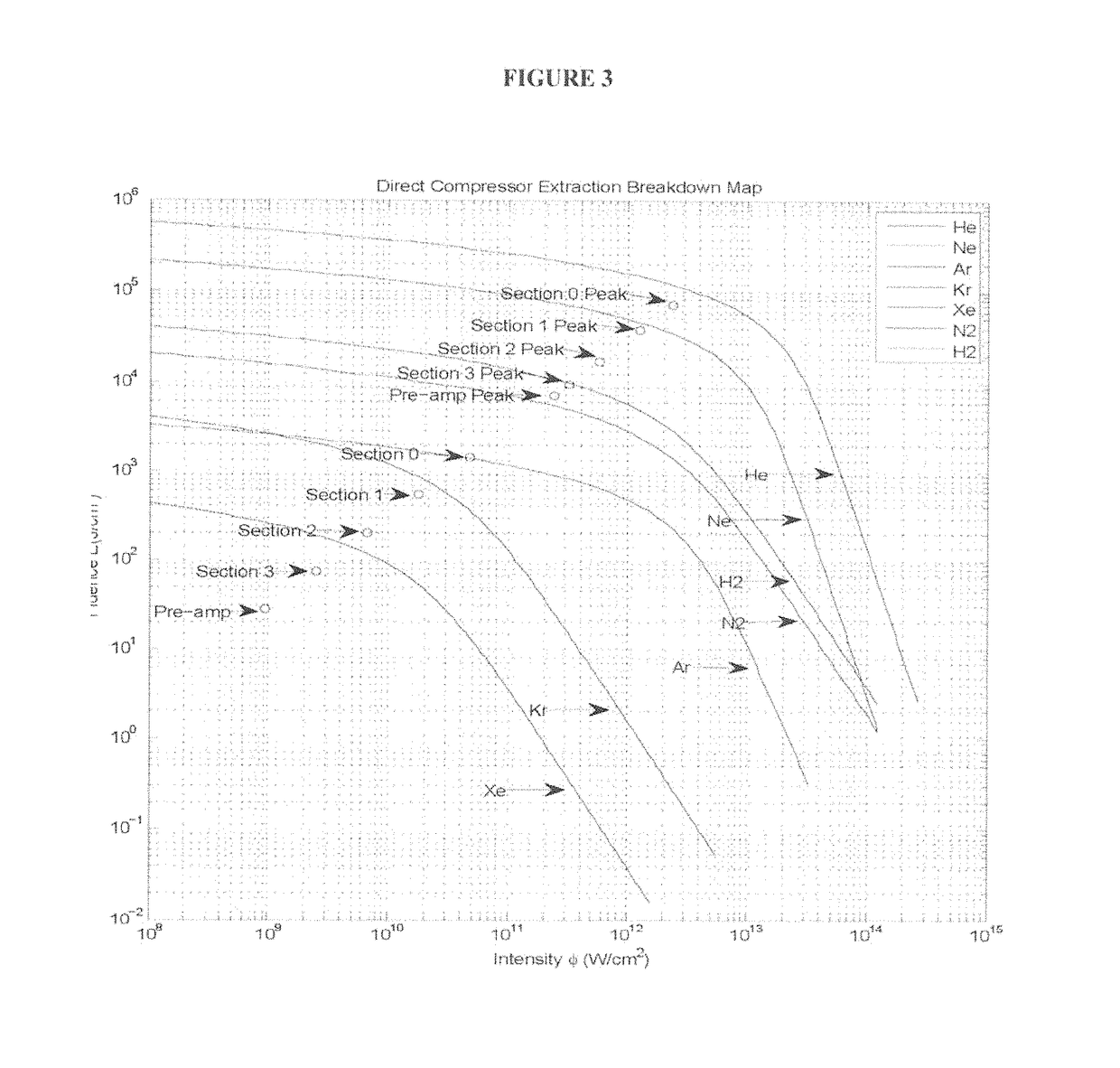
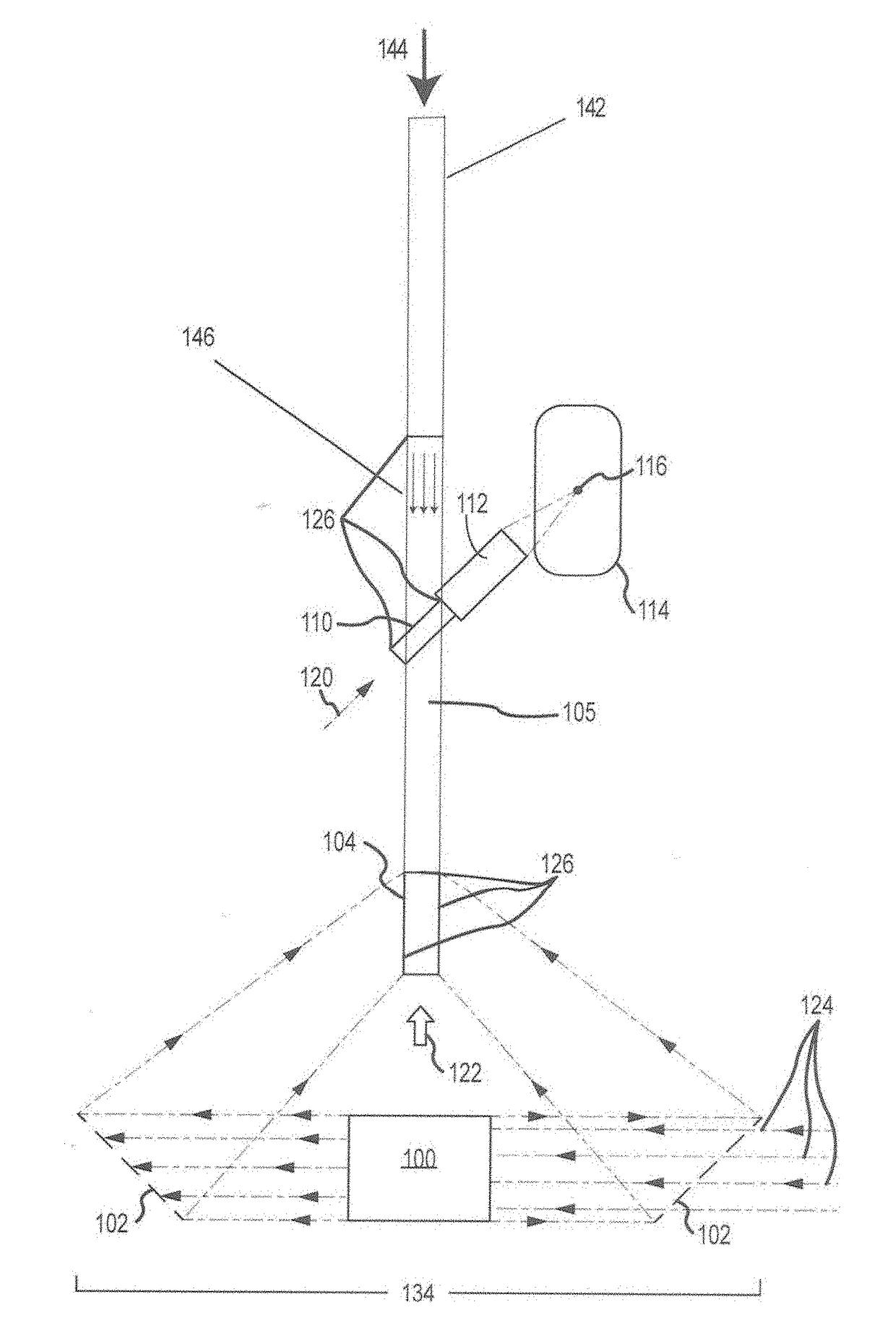
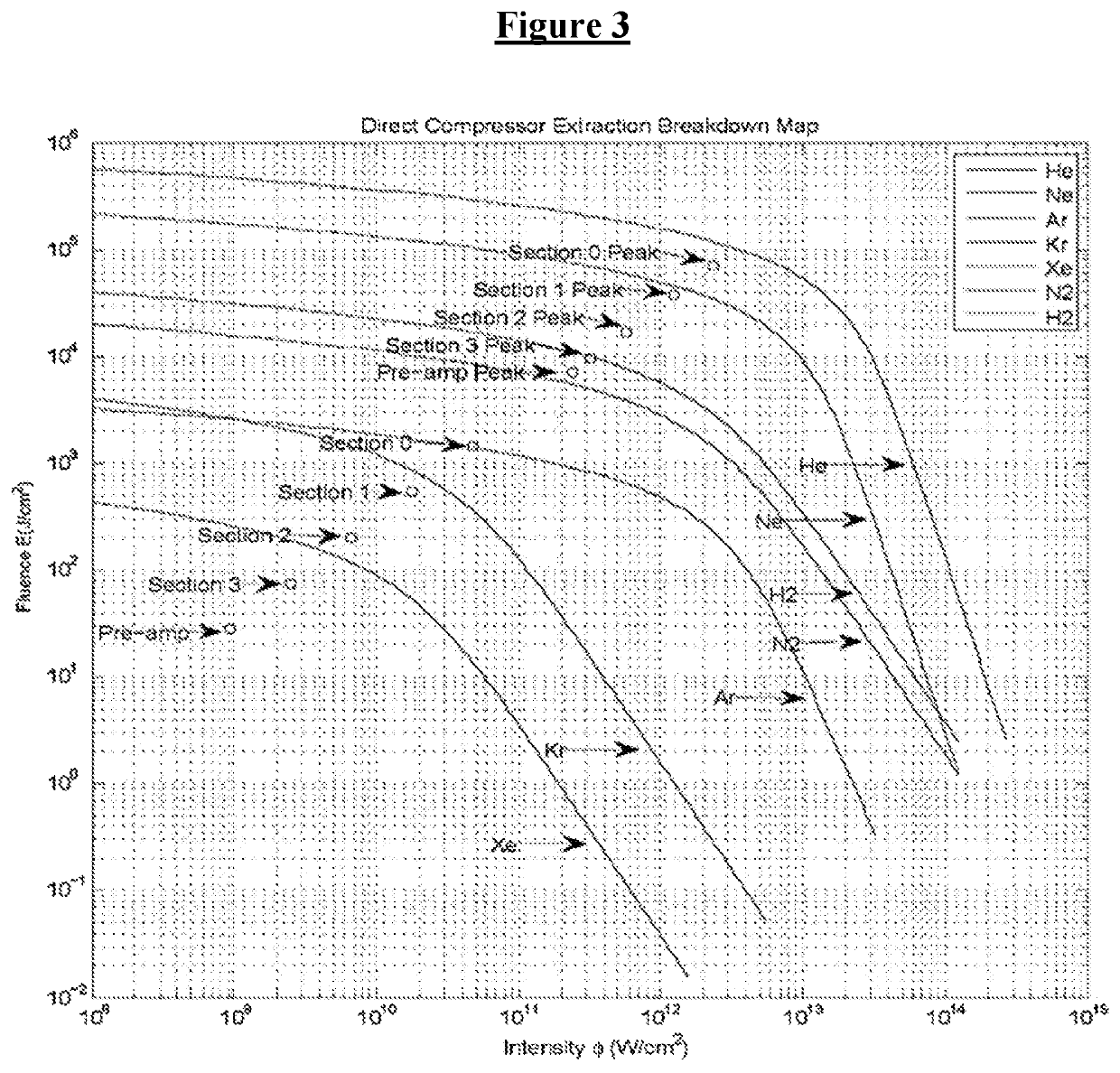
Method for direct compression of laser pulses with large temporal ratios
ActiveUS10170883B1High temporal compression ratioLow costLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsMultiplexingEngineering
The present architecture utilizes a Nonlinear Scattering Aperture Combiner that does not need to be optically multiplexed and then drives a Direct Compressor stage that produces a large temporal compression ratio to pump a Fast Compressor. This eliminates the need for a separate array of ATDMs, multiplexing optical elements, and, at the approximate 107 joule energy output required for ICF, reduces the number of mechanical elements and gas interfaces from the order of 103 to about 10. In addition, this provides a large reduction of the volume of the gas containment region. In order to accomplish this, a technique for transversely segmenting by color and / or polarization of the optical extraction beams of the Direct Compressor has been invented. In particular, it emphasizes the simplicity and uniqueness of design of the Direct Compressor. The Direct Compressor is unique in terms of high fluence, high temporal compression ratios, and high stage gain, leading to a very large reduction in laser costs. It may separately have many other applications than ICF.
Owner:INNOVEN ENERGY
Integration of Direct Compressor with Primary Laser Source and Fast Compressor
ActiveUS20180191120A1High temporal compression ratioLow costNuclear energy generationLaser arrangementsMultiplexingGas compressor
The present architecture utilizes a Nonlinear Scattering Aperture Combiner that does not need to be optically multiplexed and then drives a Direct Compressor stage that produces a large temporal compression ratio to pump a Fast Compressor. This eliminates the need for a separate array of ATDMs, multiplexing optical elements, and, at the approximate 107 joule energy output required for ICF, reduces the number of mechanical elements and gas interfaces from the order of 103 to about 10. In addition, this provides a large reduction of the volume of the gas containment region. In order to accomplish this, a technique for transversely segmenting by color and / or polarization of the optical extraction beams of the Direct Compressor has been invented. In particular, it is directed towards the integration of the Direct Compressor with the Primary Laser Source and Fast Compressor. The embodiments describe how the high operating fluence are addressed in terms of avoiding optical damage and how to integrate the stages in fluid mechanical and optical aspects.
Owner:INNOVEN ENERGY
Integration of direct compressor with primary laser source and fast compressor
ActiveUS10862260B2Big airBig ratioLaser using scattering effectsNuclear energy generationLight beamEngineering
A system and method for integrating a direct compressor with a primary laser source and fast compressor while also reducing the number of mechanical elements and gas interfaces. A nonlinear scattering aperture combiner does not need to be optically multiplexed in order to drive a direct compressor stage, but by producing a large temporal compression ratio it will then pump the fast compressor. In order to accomplish this, a technique for transversely segmenting by color and / or polarization of the optical extraction beams of the direct compressor is utilized.
Owner:INNOVEN ENERGY LLC
A broadband laser protection method and structure
ActiveCN106403721BStrong laser interference signal attenuationAchieve protectionWeapons typesCarbon nanotubeSapphire
The invention relates to the technical field of surface coatings, nonlinear optics and laser protection, in particular to a broadband laser protection method and structure. The broadband laser protection structure is obtained through the series of steps of preparation of vanadium pentoxide, design of a sapphire shell, preparation of carbon nanotube suspension liquid, and injection and sealing of the suspension liquid. The broadband laser protection structure is widely applied to the technical field of optic intelligent windows and laser protection. The broadband laser protection structure is characterized in that composite multi-element protection is adopted, combined with wave band characteristics of existing various nonlinear optical limiting materials, intensive laser interference signals can be attenuated more effectively through thermally induced phase-transition optical limiting and nonlinear scattering methods, and therefore continuous and adjustable laser protection on the visible light wave band and the near infrared wave band is achieved. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the process is simple, the rate of finished products is high, and the method is mature and reliable.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com