Patents
Literature
60 results about "Pulse inversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
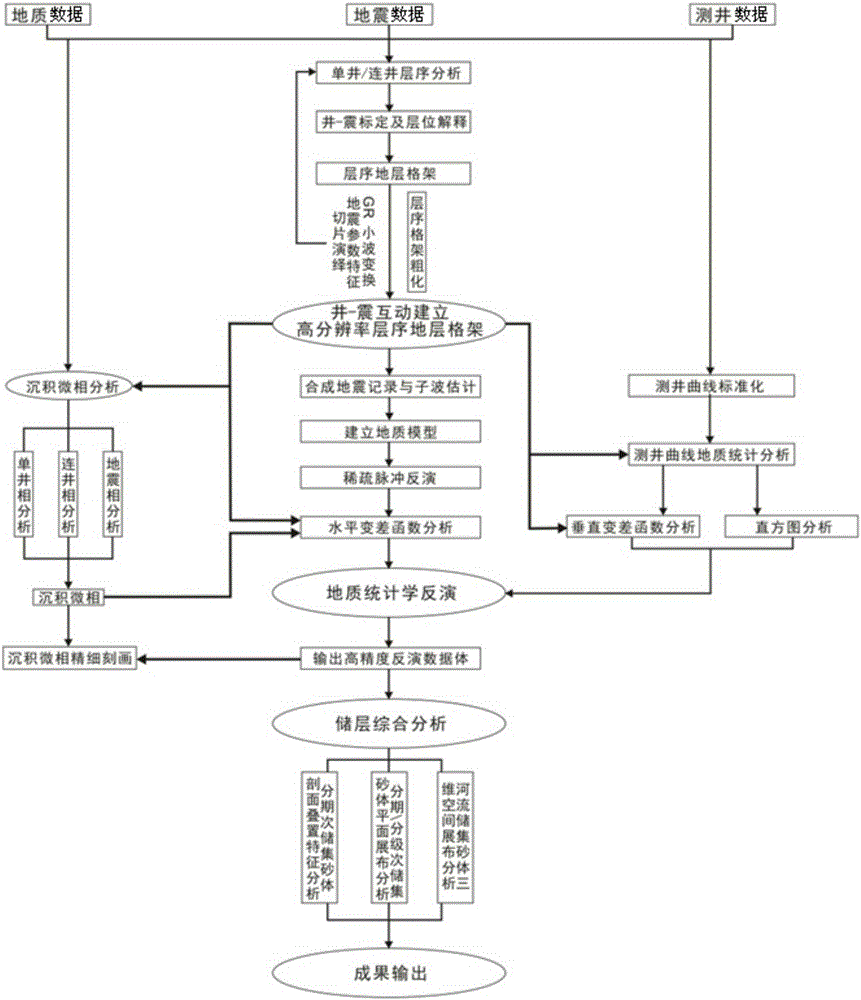
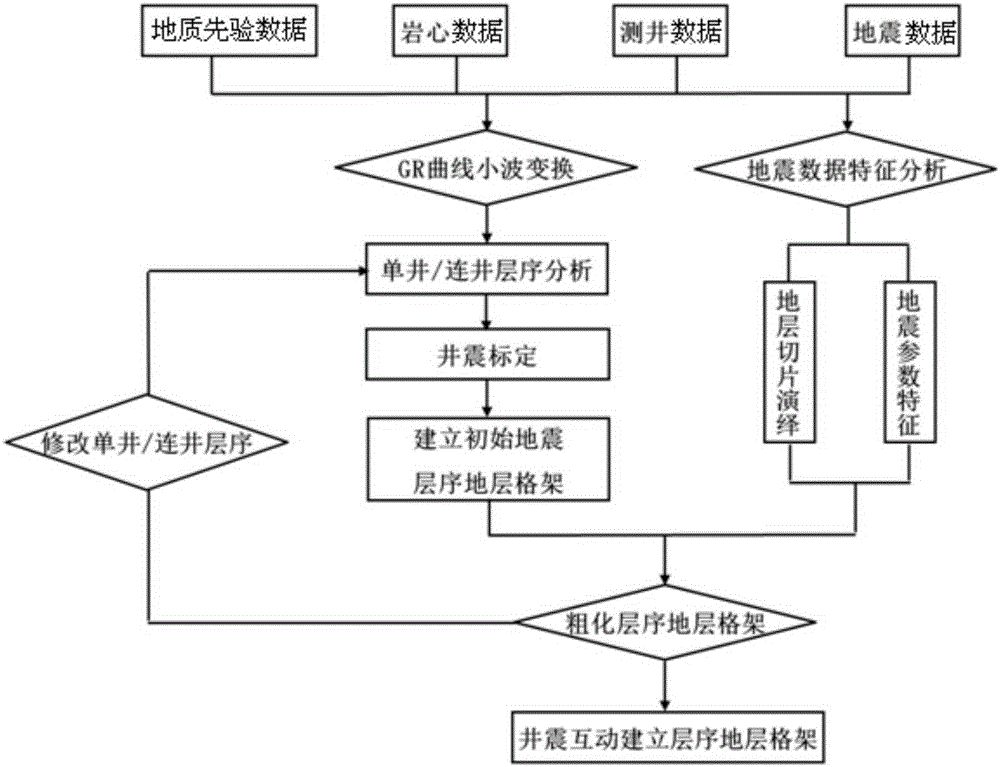
High resolution sequence stratigraphic framework constraint geostatistical inversion method
ActiveCN105182444AIn line with the laws of sedimentary geologyImprove efficiencyGeological measurementsSeismic attributeComputer science
The invention relates to a high resolution sequence stratigraphic framework constraint geostatistical inversion method. The method comprises the steps that well-seismic calibration is carried out, and multi-well wavelets of an optimized target zone are extracted; based on well-seismic calibration, a high resolution sequence stratigraphic framework is established; according to target stratum seismic data, geological priori data and logging data, a geological low frequency model based on the high resolution sequence stratigraphic framework is built; sparse pulse inversion under high resolution sequence stratigraphic framework constraints is carried out to acquire a sparse pulse inversion data body; based on a meandering river geological knowledge base, target stratum logging data and seismic characteristic data are combined; the high resolution sequence stratigraphic framework constraints are used, optimized target stratum sandy land ratio and level range are selected; geostatistical inversion under the high resolution sequence stratigraphic framework constraints is carried out; based on a final geostatistical inversion result, a GR logging curve is used to carry out fine calibration on a reservoir; and seismic attributes extracted from the inversion result are used to predict reservoir sand plane distribution.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Heart imaging with adaptive inversion time
InactiveUS20080242973A1Increase contrastLong period of timeElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsResonanceInversion Time
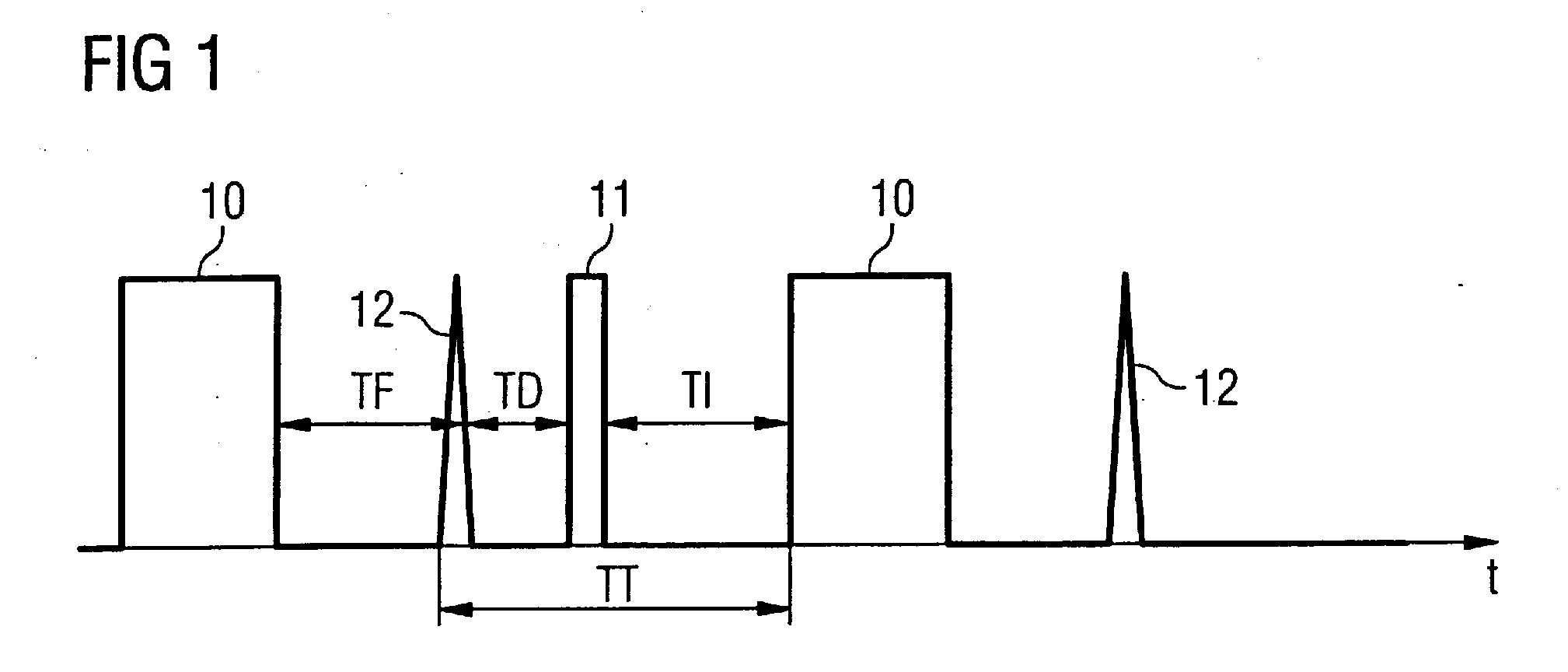
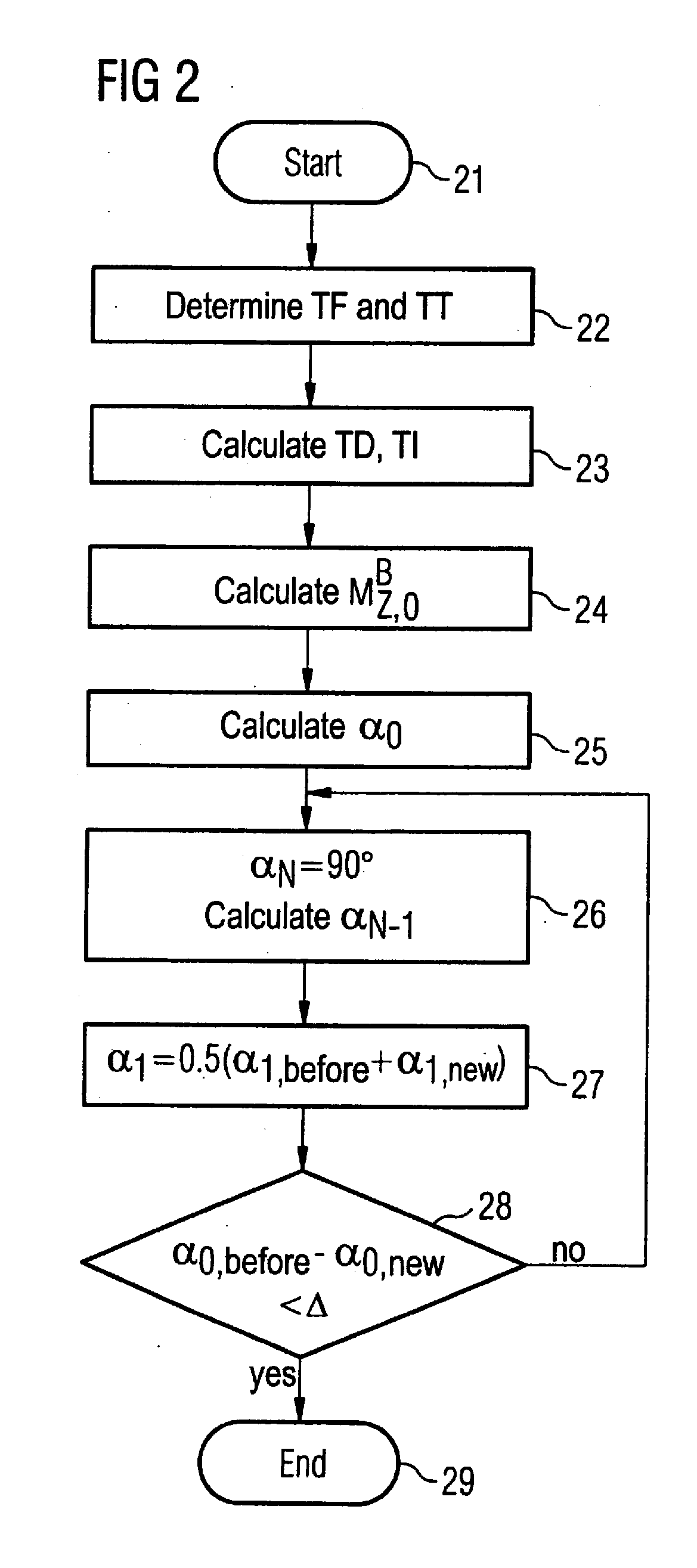
In a method for acquisition of magnetic resonance images of the heart, MR signals of the heart are acquired using an imaging sequence, wherein the magnetization is inverted by an RF inversion pulse before the acquisition of the MR signals; and of the heart activity is detected, and the point in time of the switching of the RF inversion pulse dependent on the detected heart activity.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Point constraint Bayes sparse pulse inversion method
InactiveCN103792571AHigh-resolutionImprove accuracySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingImage resolutionIterative method
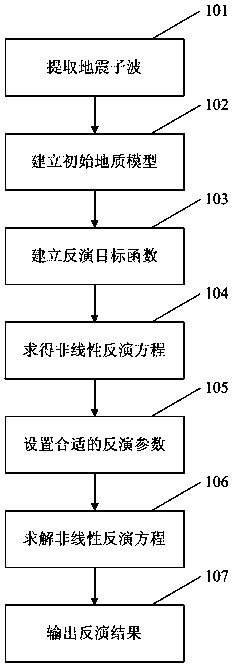
The invention provides a point constraint Bayes sparse pulse inversion method. The point constraint Bayes sparse pulse inversion method comprises steps that: step 1, seismic wavelets are extracted; step2, an initial geology model is established; step 3, an inversion target function is established; step 4, derivation of each item of the inversion target function is carried out to acquire a non-linear inversion equation; step 5, inversion parameters are set; step 6, the non-linear inversion equation is solved through an iterative method; and step 7, a reservoir high-resolution inversion result is outputted. The point constraint Bayes sparse pulse inversion method integrates the random inversion with the traditional sparse pulse inversion, improves the inversion result resolution and further improves accuracy and stability of the inversion result, and thereby more abundant information is provided for reservoir description.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
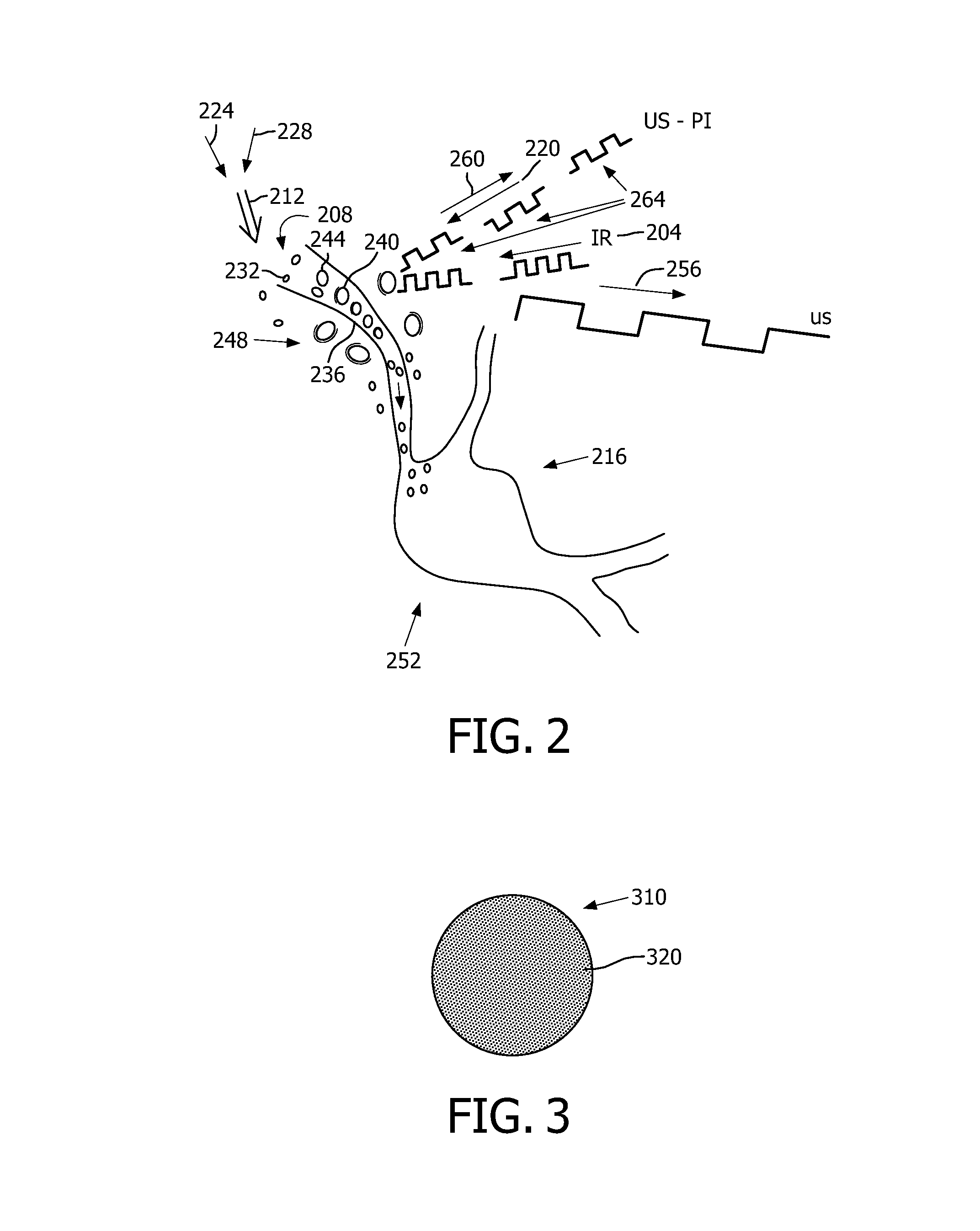
Real-time extracting device and detection method for focused ultrasonic cavitation and microbubbles thereof
InactiveCN101530320AAchieving real-time identification detectionHas inhibitory effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBroadband noiseUltrasonic cavitation
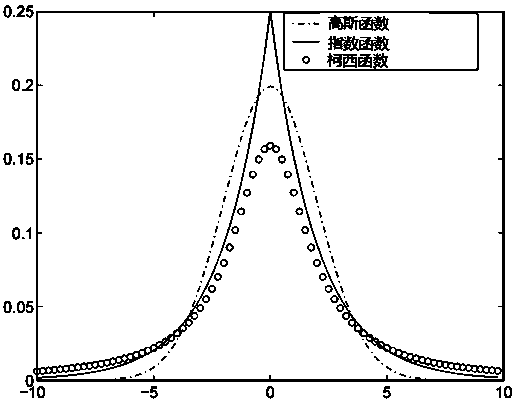
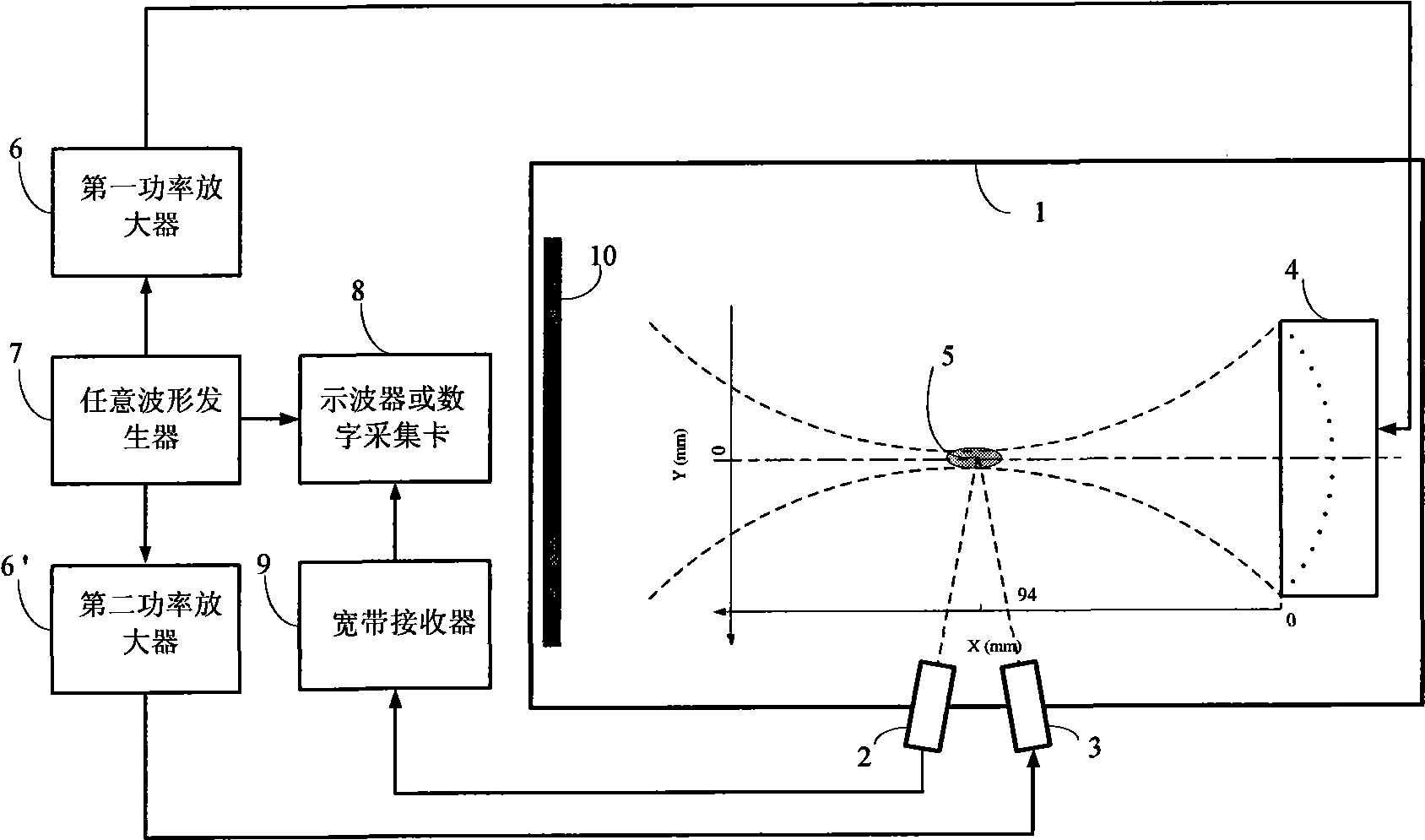
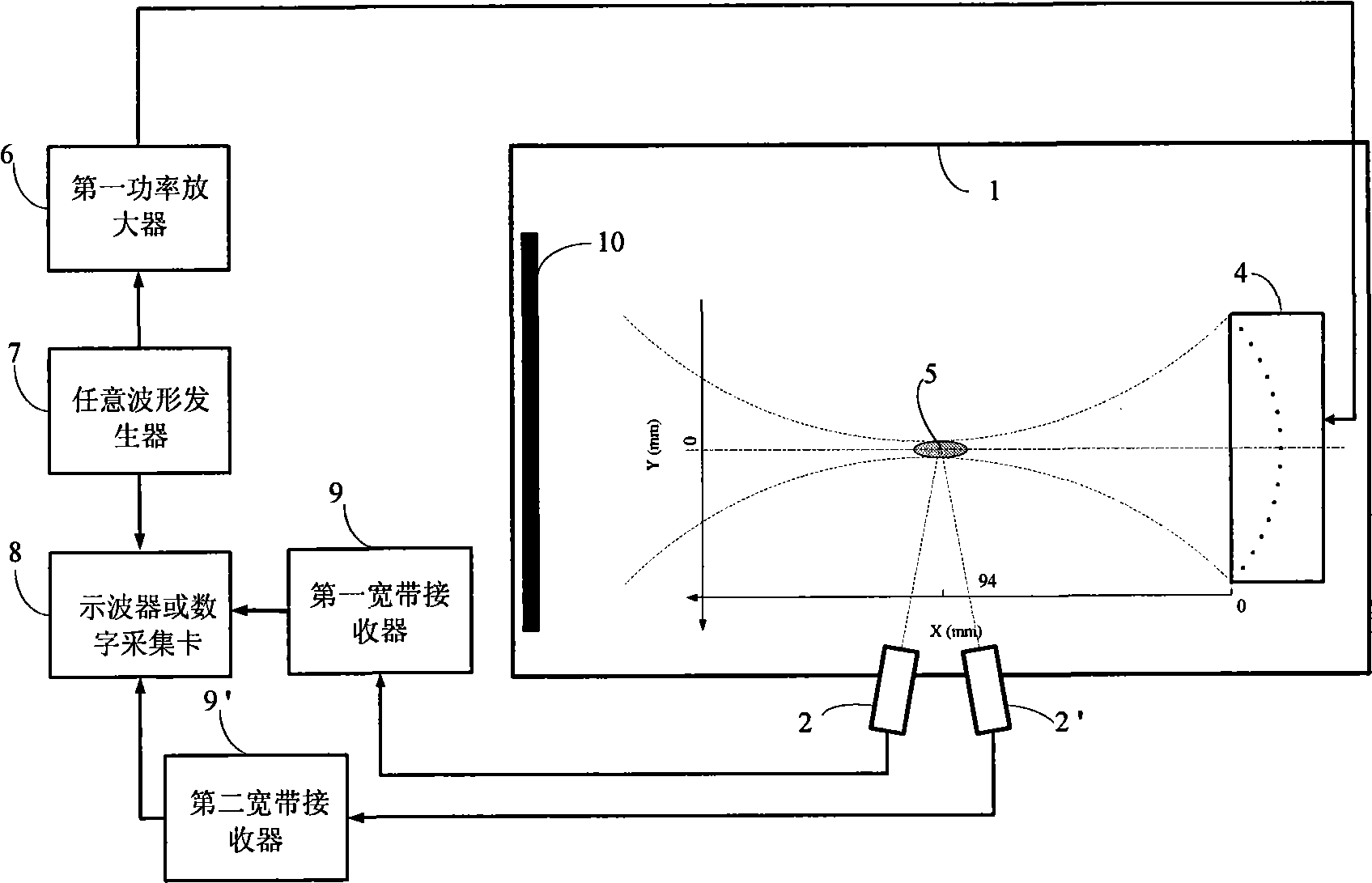
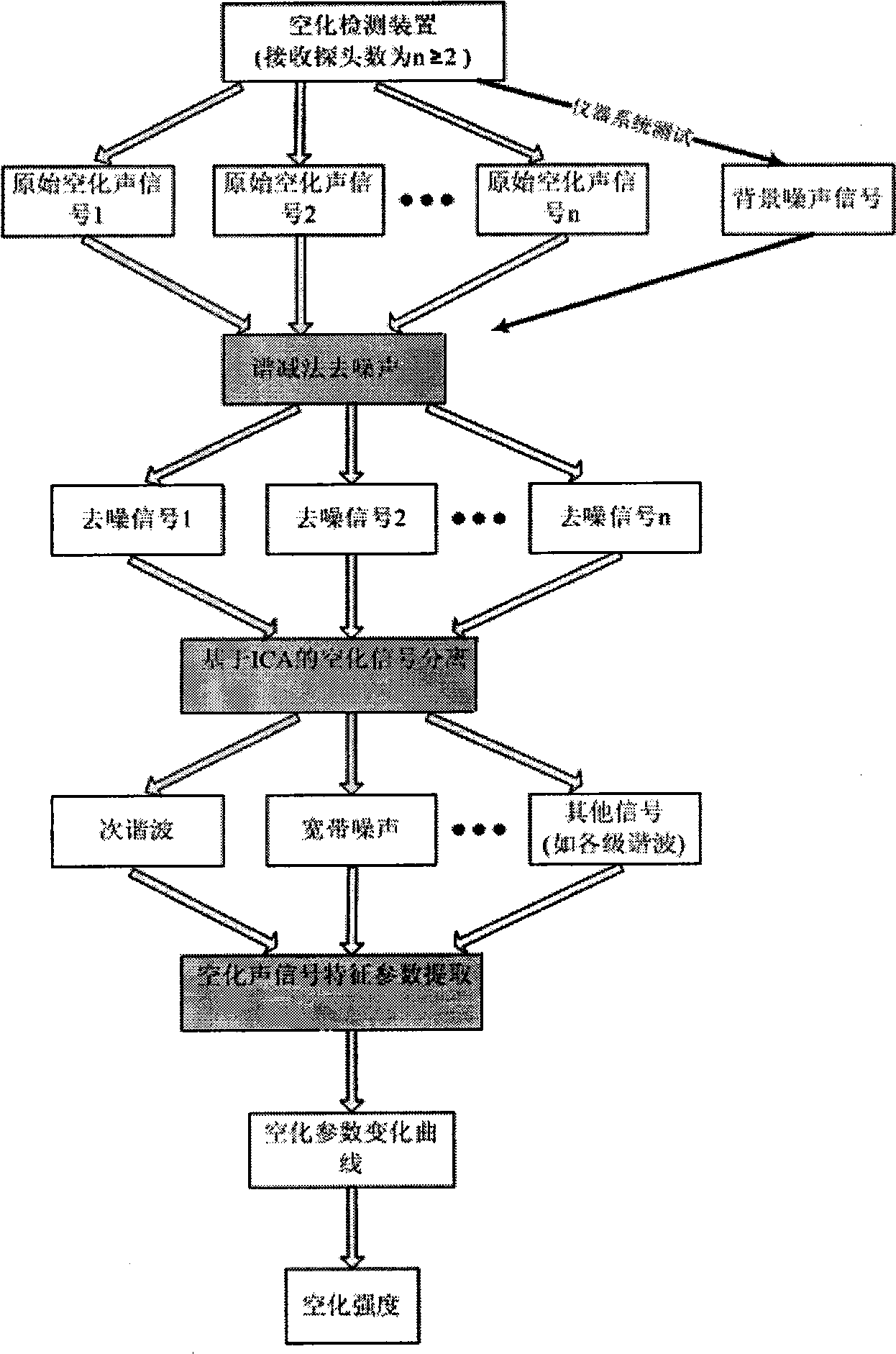
The invention belongs to the technical field of ultrasonic cavitation detection and signal analysis, and relates to a method and a device for separating and detecting focused ultrasonic cavitation signals. An ultrasonic transducer of a device emits cavitation detecting signals in a pulse-inversion mode, and another ultrasonic transducer receives acoustic signals diffused by ultrasonic cavitation and movement of microbubbles; a transducer of another device generates cavitation signals in the pulse-inversion mode; for each cavitation detecting experiment, the detection method extracts background signals when the cavitation does not happen, respectively calculates power spectrums of the acquired cavitation acoustic signals and the background signals, calculates the subtracted power spectrum estimation and phase position estimation, and converts the power spectrum estimation and the phase position estimation into time domain signals to filter noise of a system; and an ICA method separates target signals such as broadband noise component, subharmonic and the like in cavitation acoustic signals from other signal components and extracts characteristic parameters of the cavitation acoustic signals. The detection method has high sensitivity and can perform quantitative analysis.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Seismic frequency-broadening processing-based phase-controlled random inversion thin reservoir prediction method
ActiveCN106154323AImprove forecast reliabilityHigh-resolutionSeismic signal processingImage resolutionPhase control
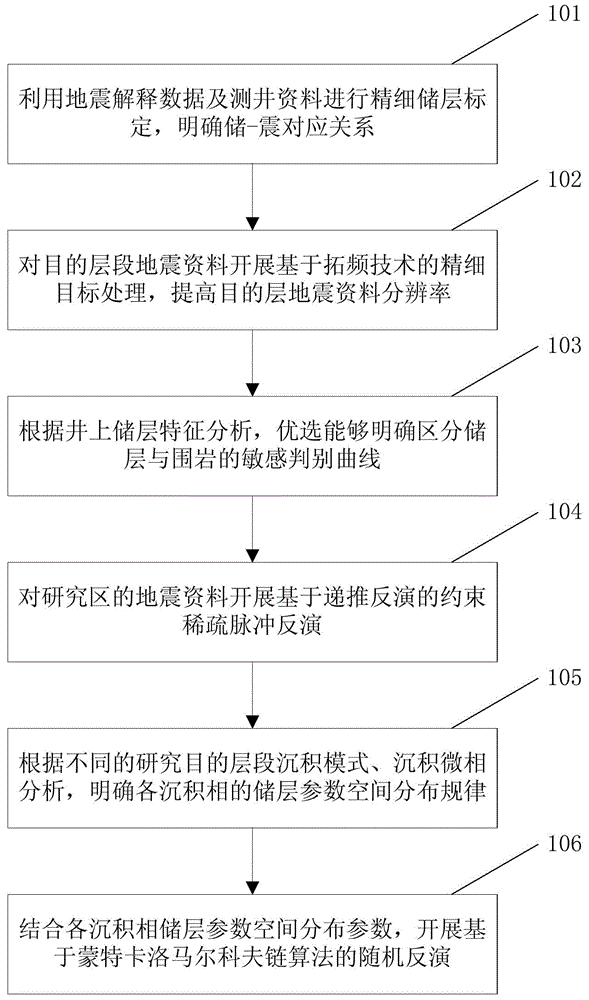
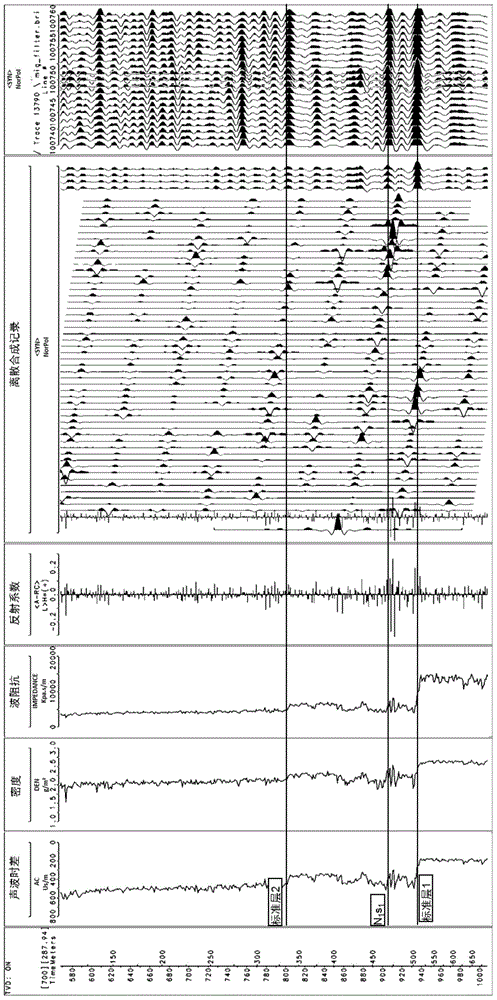
The invention provides a seismic frequency-broadening processing-based phase-controlled random inversion thin reservoir prediction method. The method includes the following steps that: seismic interpretation data and logging information are utilized to carry out fine reservoir calibration, and response characteristics of a reservoir on a seismic profile are clarified; frequency-broadening technology-based fine target processing is carried out on target stratum seismic data, and therefore, the resolution of the target stratum seismic data can be improved, a sensitive discriminant curve which can clearly distinguish the reservoir from surrounding rock is selected according to ground reservoir characteristic analysis; recursive inversion-based constrained sparse pulse inversion is carried out on the seismic data of a research region; reservoir parameter spatial distribution rules of various sedimentary facies are clarified; and based on deterministic inversion data and the reservoir parameter spatial distribution rules of the sedimentary facies, Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm-based random inversion is carried out. With the seismic frequency-broadening processing-based phase-controlled random inversion thin reservoir prediction method of the invention adopted, an inversion effect can be optimal, and the reliability of the prediction of the thin reservoir is improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
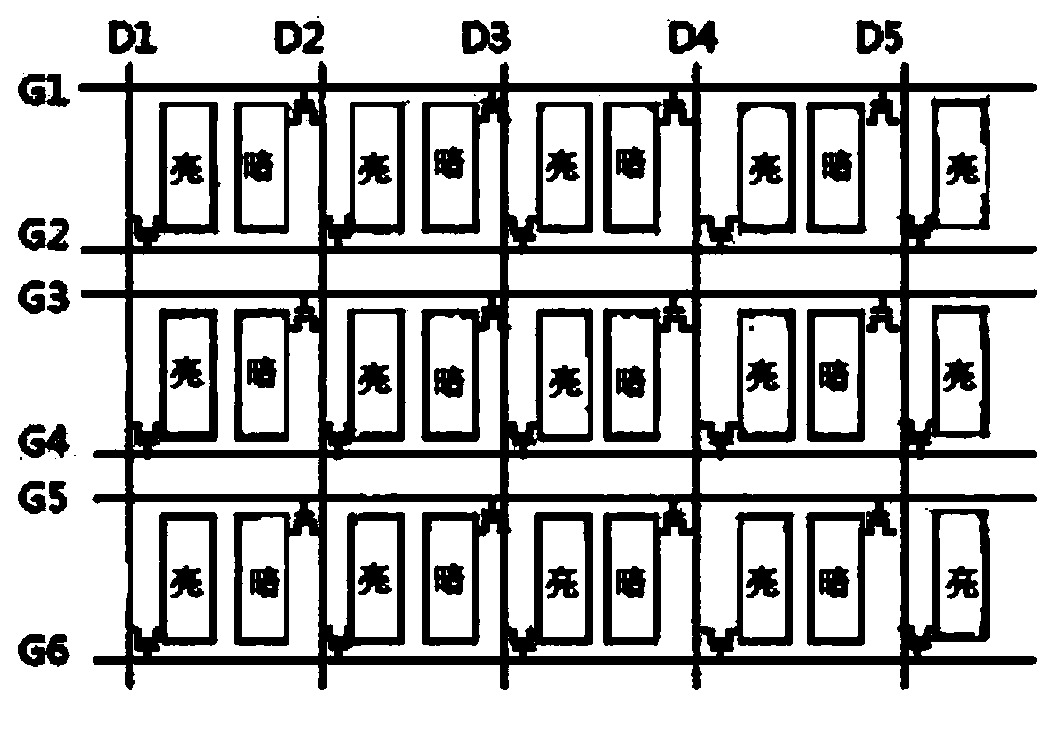
Method and device for driving HSD liquid crystal display panel
The invention discloses a method for driving an HSD liquid crystal display panel. The method comprises the steps that a sequence scanning pulse signal is provided for a grid line of the liquid crystal display panel so as to open TFT elements corresponding to pixel units in each line respectively; a square wave data signal is provided for a data line of the liquid crystal display panel so as to charge the pixel units connected with drain electrodes of the TFT elements through the square wave data signal when the TFT elements are opened, wherein the polarity of the square wave data signal reverses once every time the square wave data signal passes through 2n+1 scanning pulses, and n is an integer greater than or equal to 1. A device corresponding to the method comprises a liquid crystal display unit, a scanning drive unit, a data signal drive unit and a time sequence control unit. The method enables the pixel units with different brightness levels on the two sides of the data line to be located on the two sides of the data line in a staggered mode; staggered arrangement of the pixel units with the different brightness levels in space overcomes the display defect of perpendicular bright lines and dark lines on the panel.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Non-linear ultrasonic diagnostic imaging using intermodulation component signals
InactiveCN1976635AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationUltrasonic imaging
An ultrasonic imaging system transmits waveforms containing first and second major frequency components which are intermodulated by passage through a nonlinear medium or interaction with a contrast agent microbubble to produce a difference frequency component. In an illustrated embodiment the second major frequency is twice the frequency of the first major frequency, resulting in a difference frequency signal at the first major frequency. Two differently modulated transmit waveforms are transmitted and the difference frequency component is separated by pulse inversion.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for tissue harmonic imaging with natural (tissue) decoded coded excitation
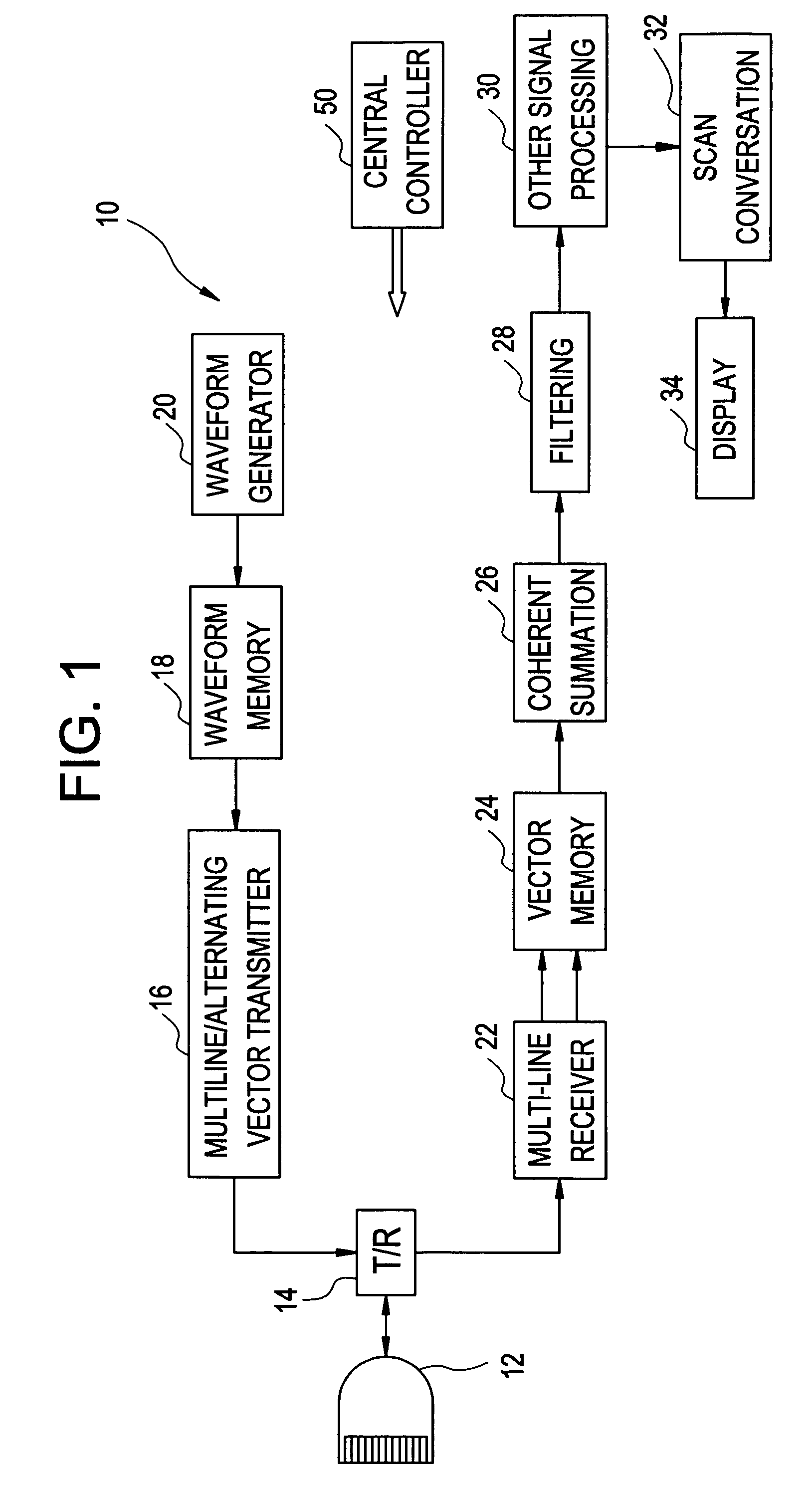
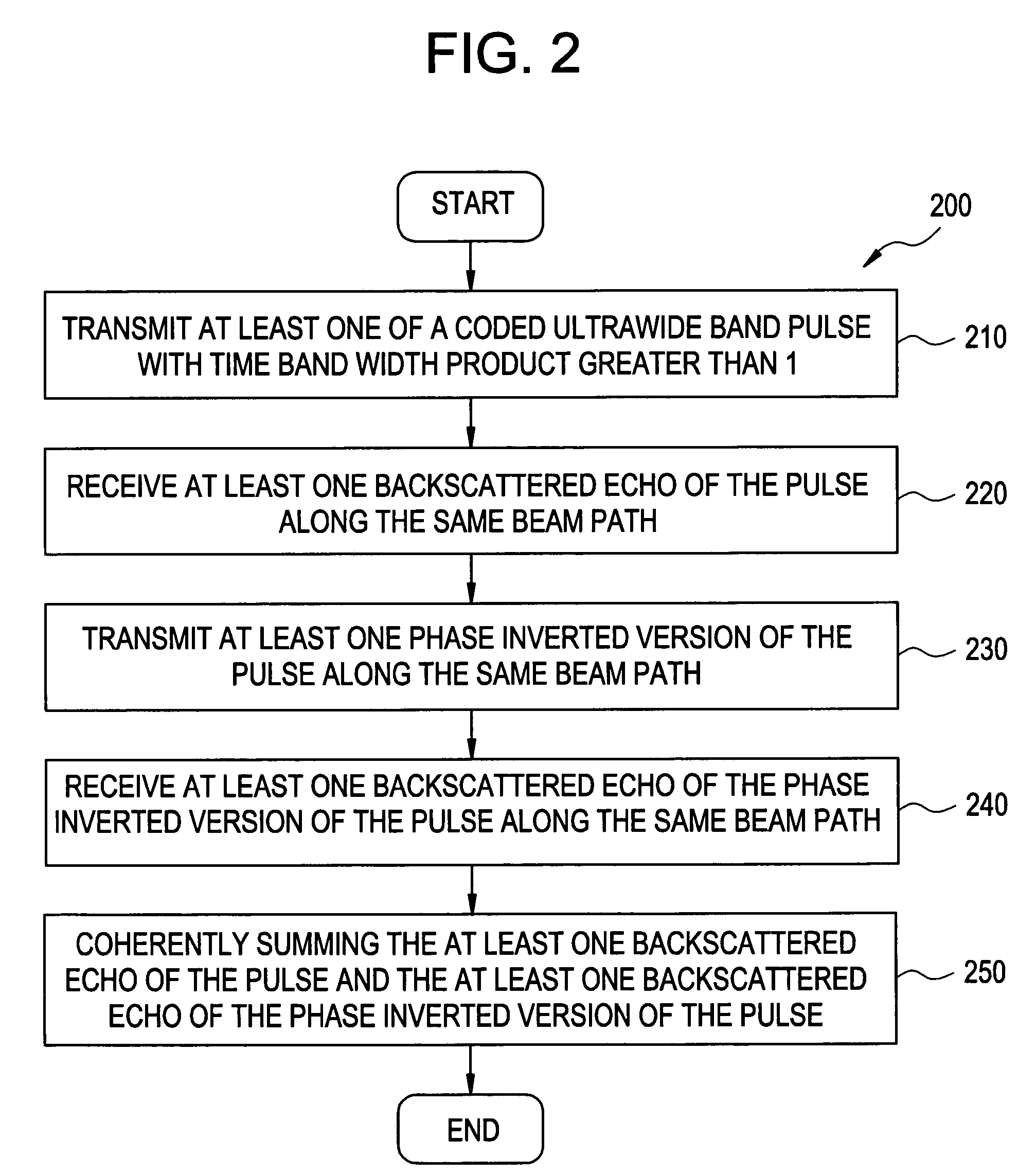
InactiveUS20050054925A1Avoid frame rate dropImproves harmonic imaging performanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationHarmonic
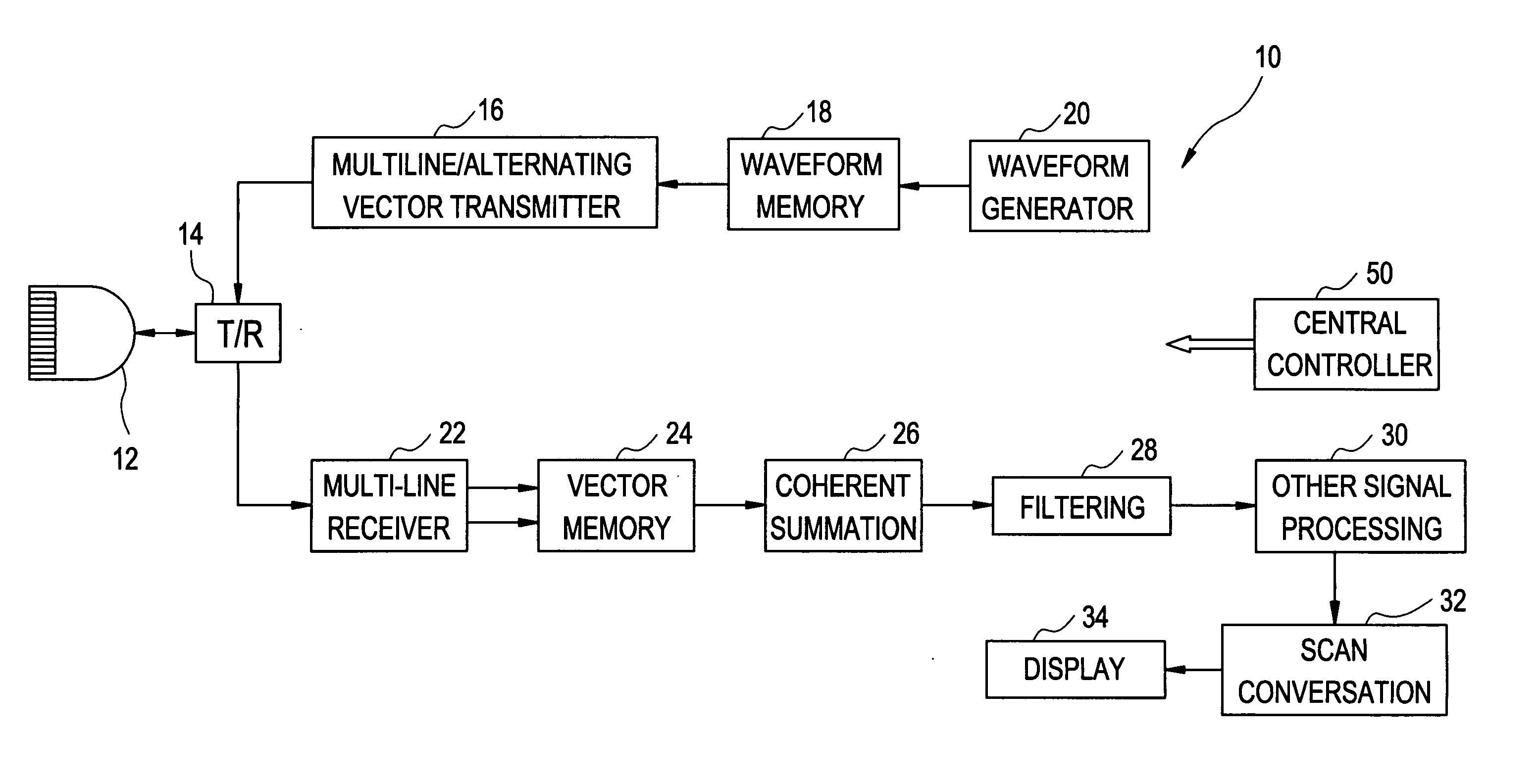
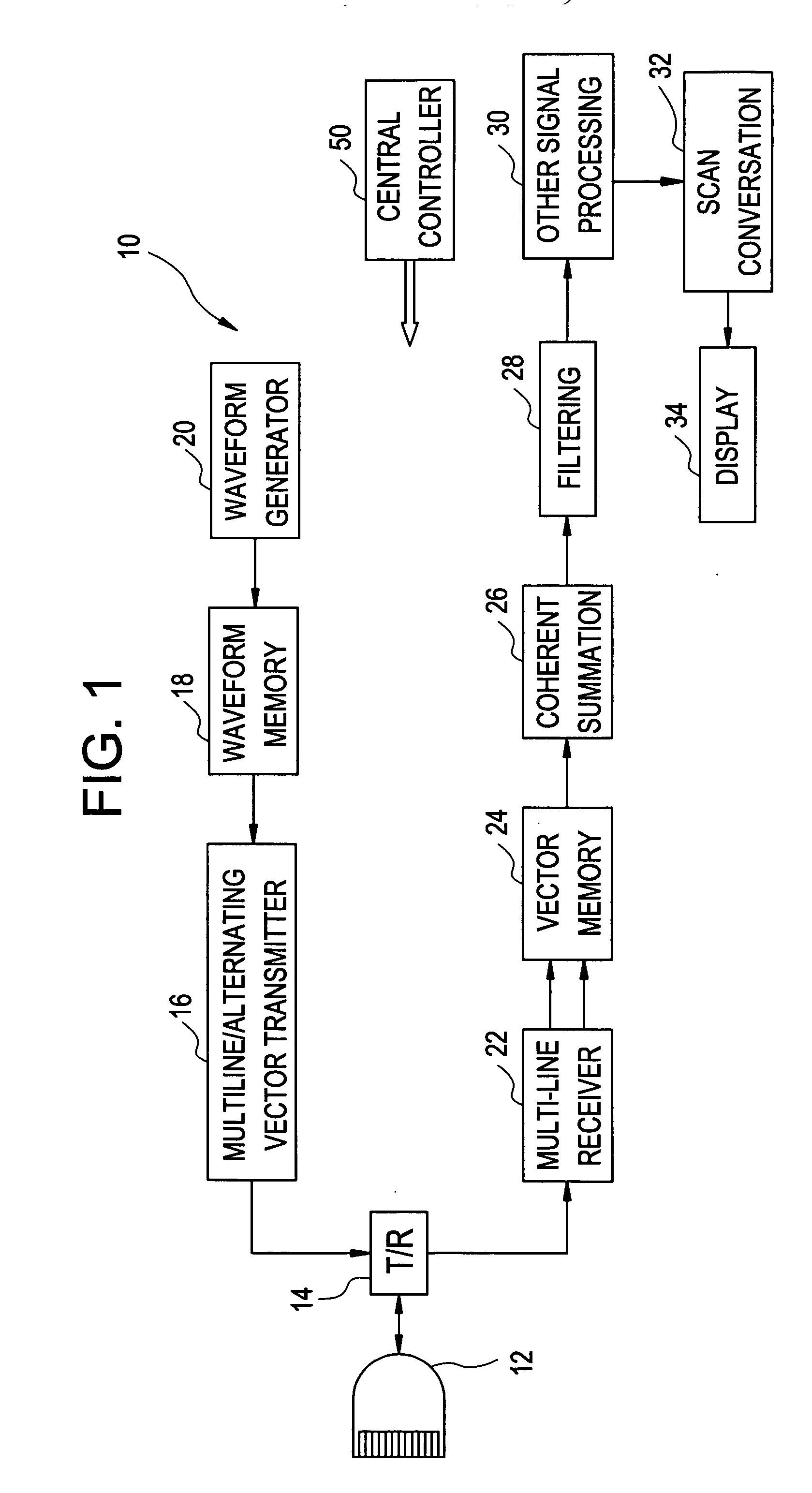
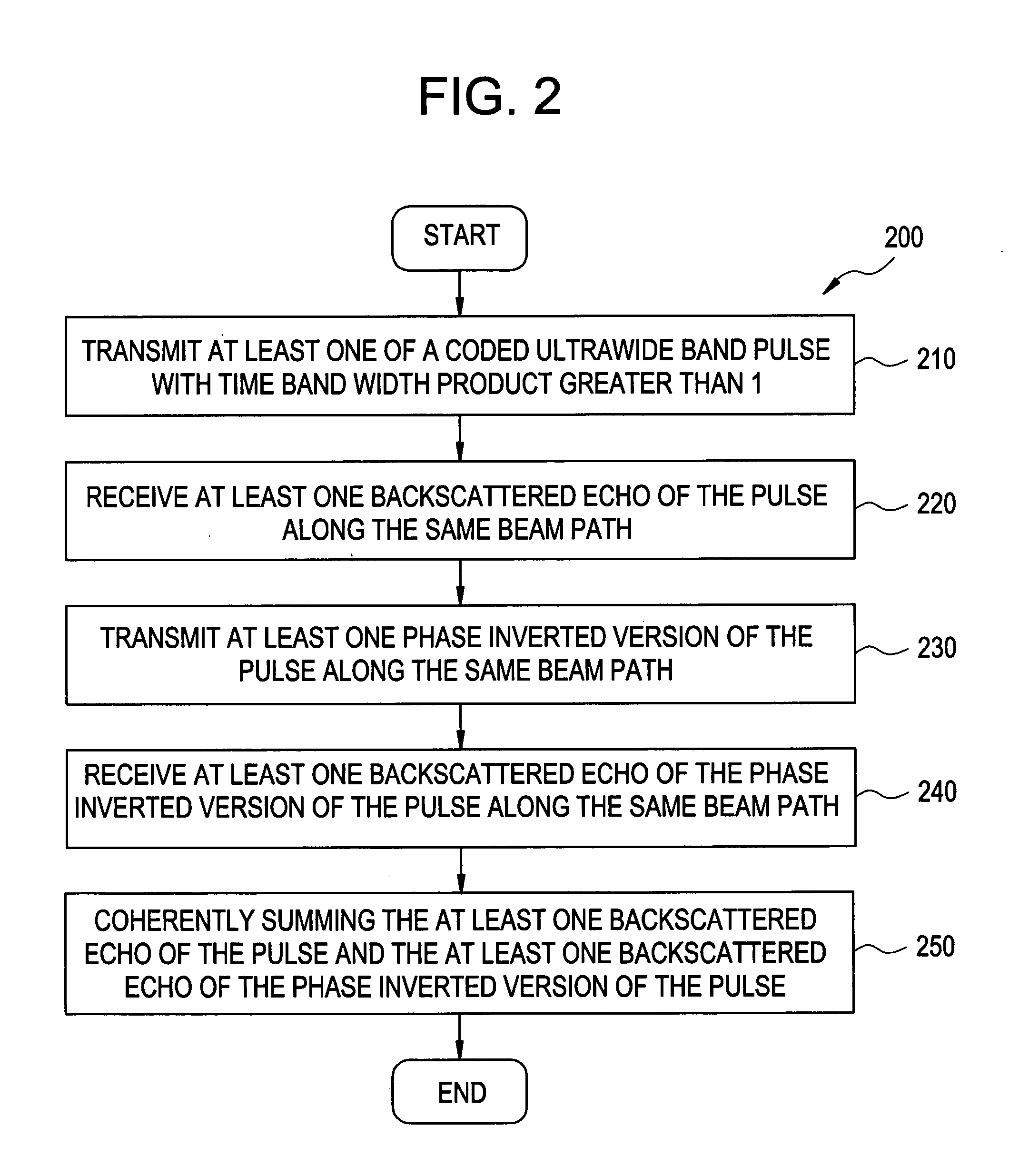
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus providing tissue harmonic imaging using an ultrasound machine. Coded pulses and the phase inverted version of the said coded pulses with time bandwidth greater than 1 are transmitted into the tissue. Backscattered echoes are received and filtered before or after coherent summation. Decoding / compressing of the received echoes of the coded pulses is implemented naturally through the propagation of the specially designed ultrawide band (>80%) waveforms inside tissue and pulse inversion. Costly decoding / compression filter are not necessary.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYSTEMS INC
Direction Fourier coefficient-based elastic impedance inversion method and system
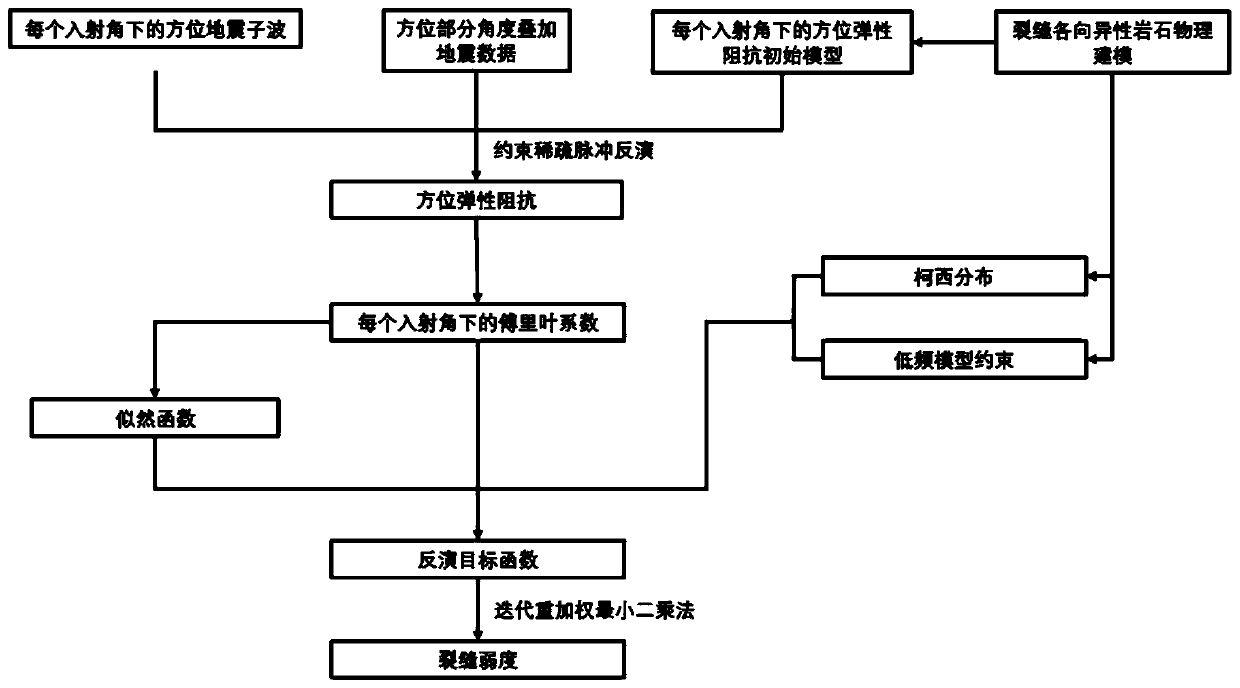
The invention proposes a direction Fourier coefficient-based elastic impedance inversion method and system. The direction Fourier coefficient-based elastic impedance inversion method comprises the steps of superposing earthquake data by a direction part, and obtaining direction elastic impedance by constraint sparse pulse inversion; and extracting Fourier coefficients under different incident angles according to all direction elastic impedance obtained by inversion, and performing further inversion to obtain crack normal weakness and crack tangential weakness for representing crack developmentdegree by the extracted second-order term and four-order term Fourier coefficient. The method proposed by the invention has certain noise resistance. Model test and actual application verify the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Transcranial low-frequency ultrasonic linear frequency-modulation pulse inversion micro-bubble imaging method
ActiveCN107714091AHigh sensitivityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsMicro bubbleSonification
The invention provides a transcranial low-frequency ultrasonic linear frequency-modulation pulse inversion micro-bubble imaging method. A special transcranial low-frequency ultrasonic linear array transducer transmits linear frequency-modulating linear scanning acoustic beams or wide wave beams opposite in phase; ultrasonic echo signals received by corresponding array elements are sampled and converted into radio frequency data; pulse compression is conducted on the radio frequency data, and two sets of radio frequency data undergoing the pulse compression and being opposite in phase are superposed; the superposed radio frequency data undergoes delayed correction and then undergoes compressive self-adapting wave beam forming; the signals obtained through wave beam forming sequentially undergo envelope detection and logarithm compression. The method utilizes low-frequency linear frequency-modulating signals and multi-angle composite imaging technology to jointly break through ultrasonicsignal blocking and shielding of the skull and achieves high-sensitivity ultrasonic imaging of encephalic tissues. The problem is solved that ultrasonic signals are severely attenuated after passingthe skull, so that transcranial ultrasonic detection depth is limited and the inside of the skull is difficult to detect and image.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Wave impedance inversion method based on improved damped least square method
A wave impedance inversion method based on an improved damped least square method belongs to the field of geophysical inversion, and particularly relates to wave impedance inversion technology in oiland gas geophysical exploration. The invention aims to provide an improved wave impedance inversion method, which is used to establish a wave impedance inversion objective function in the sense of least squares and reduce the calculation cost of the Jacobian matrix in the traditional least square method, and can solve the non-positive singular problems of the Jacobian matrix to optimize the iterative method of damping coefficients, so that the algorithm has better stability and global convergence, and the inversion results are more reliable. The implementation process comprises the following steps of (1) constructing an inversion objective function according to the convolution model and the sparsely constrained pulse inversion theory; (2) establishing an initial model based on the log dataand horizon Information; (3) setting the algorithm and model parameters; (4) putting the initial model into the objective function to iterate; (5) obtaining the best matching reflection coefficient under the comprehensive constraint of three data bodies of model constraint, sparse constraint and seismic data constraint; (6) solving the wave impedance by using the recursive method; and (7) addinghigh and low frequency compensation to get the broadband wave impedance value.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method and apparatus for tissue harmonic imaging with natural (tissue) decoded coded excitation
InactiveUS7037265B2Inhibition rateImprove imaging effectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationHarmonic
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus providing tissue harmonic imaging using an ultrasound machine. Coded pulses and the phase inverted version of the said coded pulses with time bandwidth greater than 1 are transmitted into the tissue. Backscattered echoes are received and filtered before or after coherent summation. Decoding / compressing of the received echoes of the coded pulses is implemented naturally through the propagation of the specially designed ultrawide band (>80%) waveforms inside tissue and pulse inversion. Costly decoding / compression filter are not necessary.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYSTEMS INC
Micro-elasticity imaging method based on tissue microbubble dynamics model
ActiveCN103330576AControl importHigh detection sensitivityOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesSonificationDynamic models
The invention provides a micro-elasticity imaging method based on a tissue microbubble dynamics model. According to the invention, a mother wavelet which has strong correlation with a microbubble signal and weak correlation with a tissue signal is established according to that microbubble vibration is influenced by characteristics of a surrounding tissue, and a tissue microbubble dynamics model can be used for establishing the relation of a microbubble vibration signal and tissue elasticity, the microbubble signal is detected for imaging through a pulse inversion and wavelet transform combined imaging algorithm, and when the detection signal is the closest to a model signal, the maximum tissue contrast ratio can be obtained, so that the elasticity parameters of the tissue within the range of a dozen to tens of microns around the tissue are obtained in a reverse derivation manner. The method can be applied to real-time monitoring on a high-intensity focused ultrasound therapeutic process and elasticity detection of a biological thin-layer tissue, can overcome the limitations that the general elasticity imaging requires external pressure, and is influenced by boundary conditions easily, and effectively improves the imaging resolution to the micron level from the millimeter level.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for identifying microcrack direction in plate based on nonlinear frequency mixing technology of Lamb waves
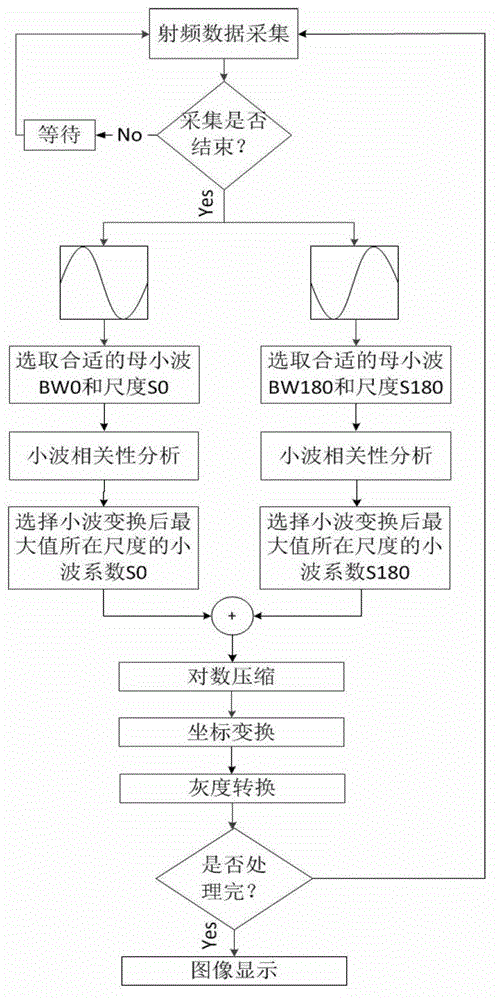
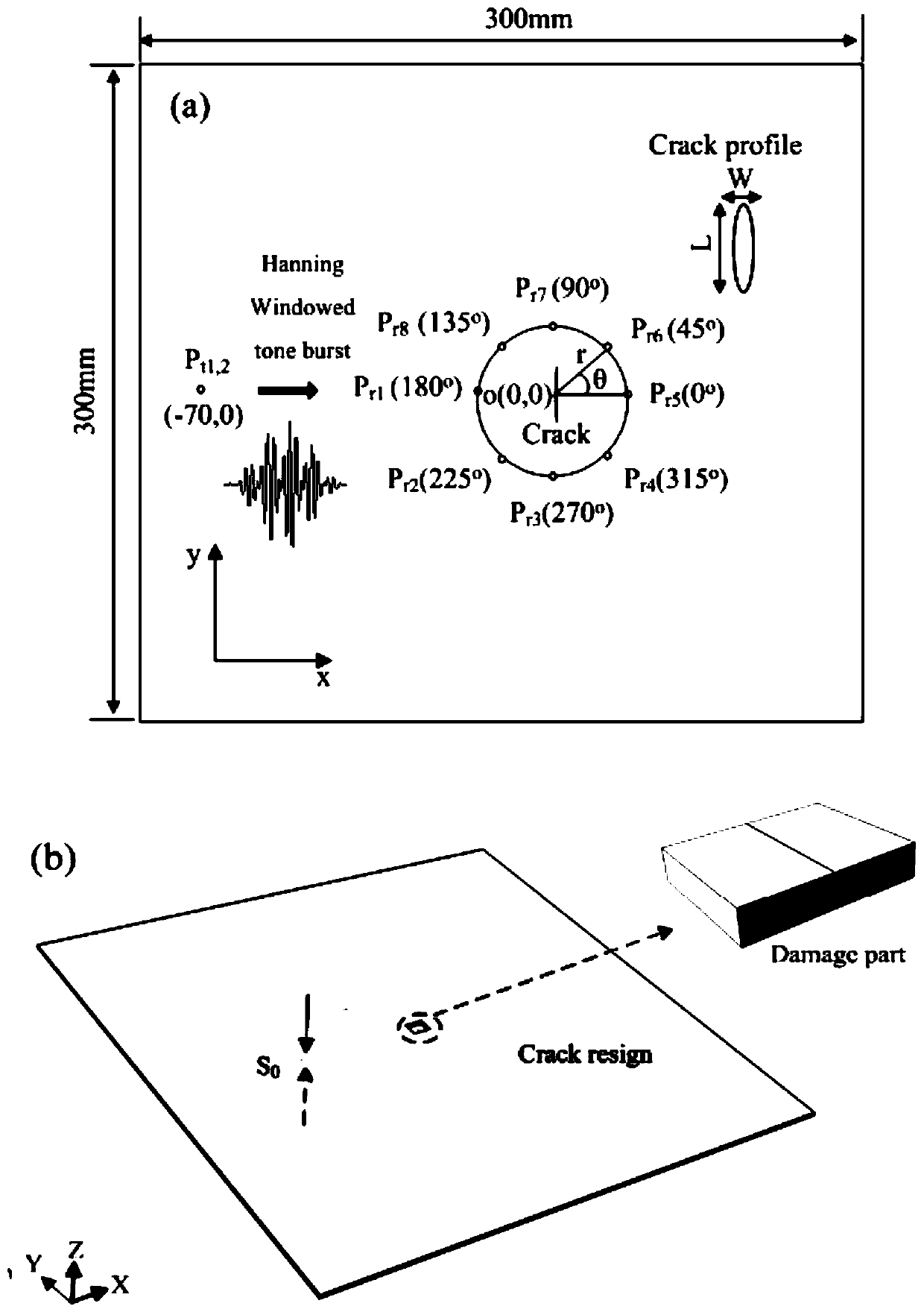
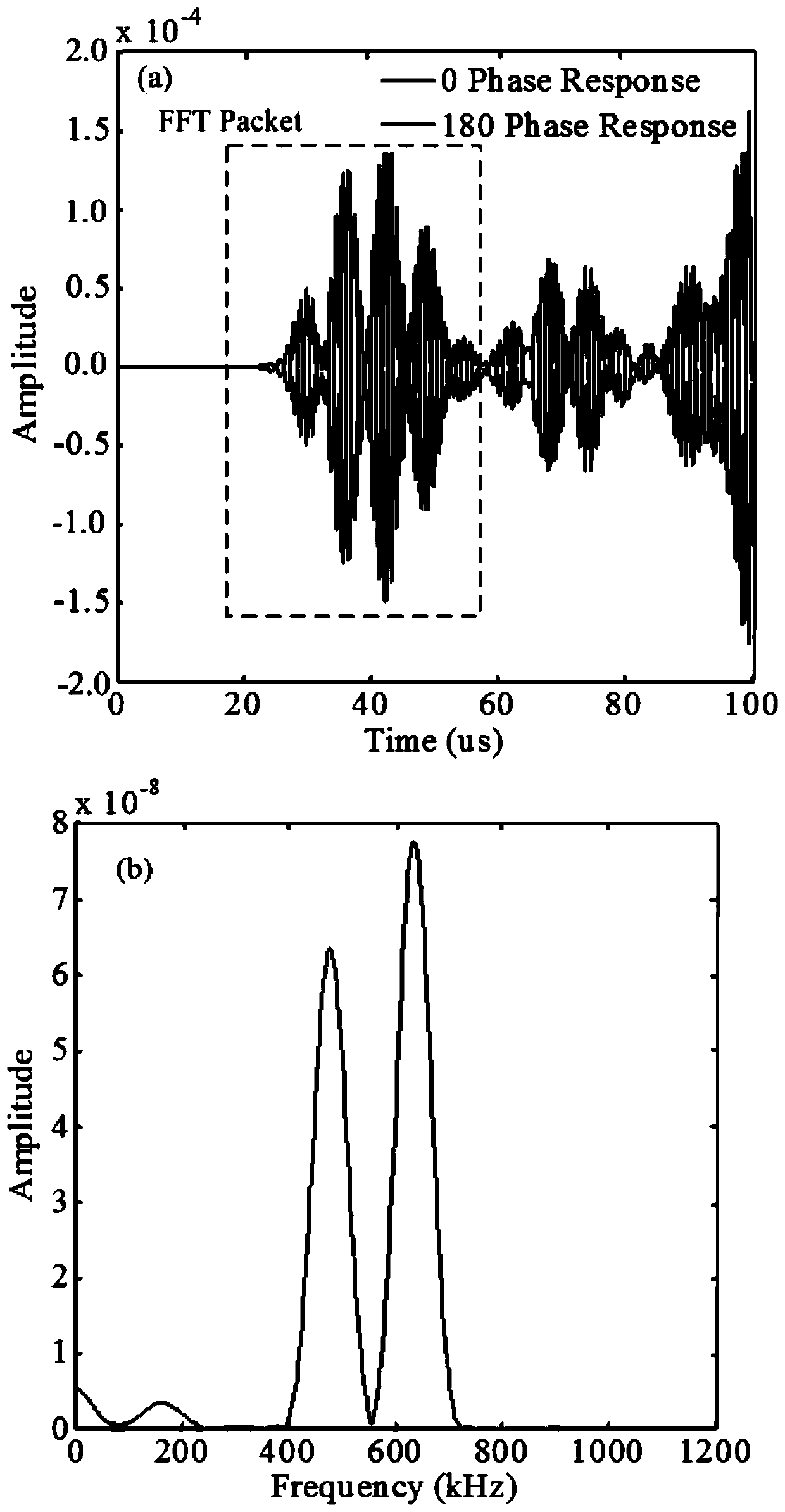
ActiveCN111157629AImplement extractionEliminate fundamental frequency componentsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalForward scatterNon linearite
The invention discloses a method for identifying a microcrack direction in a plate based on a nonlinear frequency mixing technology of Lamb waves. The method includes, firstly, extracting a sum frequency signal and a difference frequency signal in a damage response signal by adopting a pulse inversion method; obtaining a directional mode pattern of a nonlinear scattering coefficient beta through the extracted sum frequency signal and difference frequency signal; and determining the maximum forward scattering point and the minimum backward scattering point of the Lamb wave, and taking the direction vertical to the connecting line of the maximum forward scattering point and the minimum backward scattering point of the Lamb wave as the direction of the micro-crack, thereby realizing the identification of the direction of the micro-crack. According to the invention, the Lamb wave excited by frequency mixing interacts with the nonlinear medium to generate a new frequency component; the sumfrequency and difference frequency effective frequency components in the damage response signal are effectively extracted through a pulse inversion method, the microcrack direction is recognized by researching the nonlinear scattering degree of Lamb waves in different directions of the microcrack, and the technical problems that the amplitude is too small, and the sum frequency and difference frequency signals with weak signals are not easy to extract and recognize are effectively solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Anisotropy parameter inversion method based on transmission equation
ActiveCN105487110AHigh inversion stabilityImprove signal-to-noise ratioSeismic signal processingGreek letter epsilonTransmission coefficient
The invention provides an anisotropy parameter inversion method based on a transmission equation, and belongs to the field of physical geography inversion. The method comprises the steps: (1) selecting post-stack seismic data volumes corresponding to any three different azimuth angles, calculating and obtaining reflection coefficients corresponding to the three different azimuth angles through employing a sparse pulse inversion method; (2) respectively calculating transmission coefficients corresponding to the three reflection coefficients; (3) analyzing a pre-stack azimuth path set, and obtaining incident angle information, wherein the incident angle information comprises a maximum incident angle i2, a maximum incident angle i1, and an interval; (4) calculating and obtaining anisotropy parameters delta epsilon (V) and delta delta (V) through the azimuth angle information and the transmission coefficient information.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Broadband blended fundamental and harmonic frequency ultrasonic diagnostic imaging
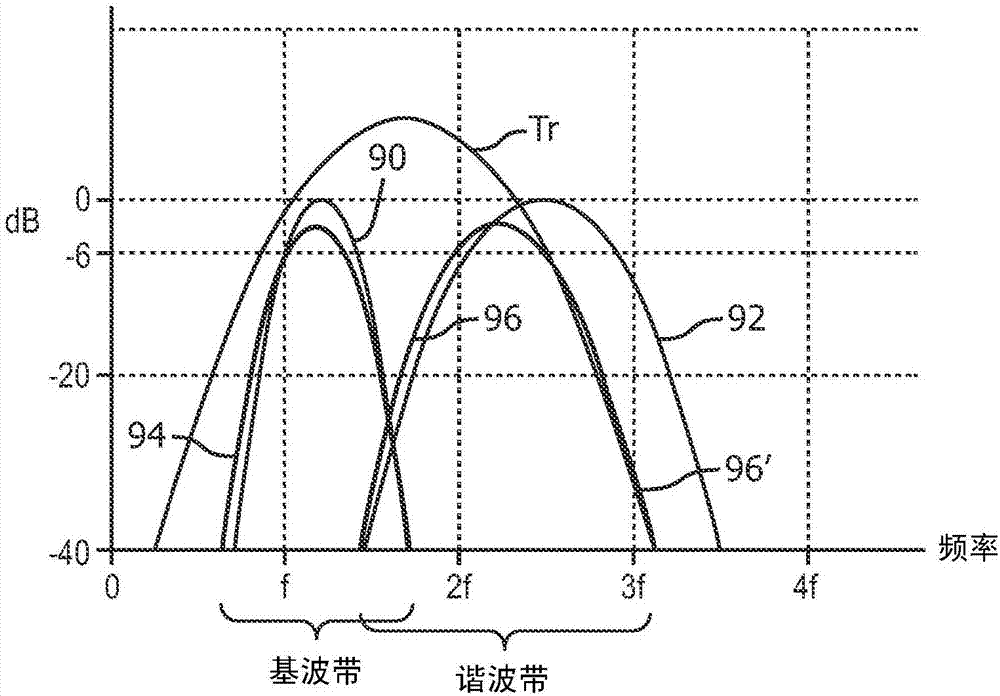
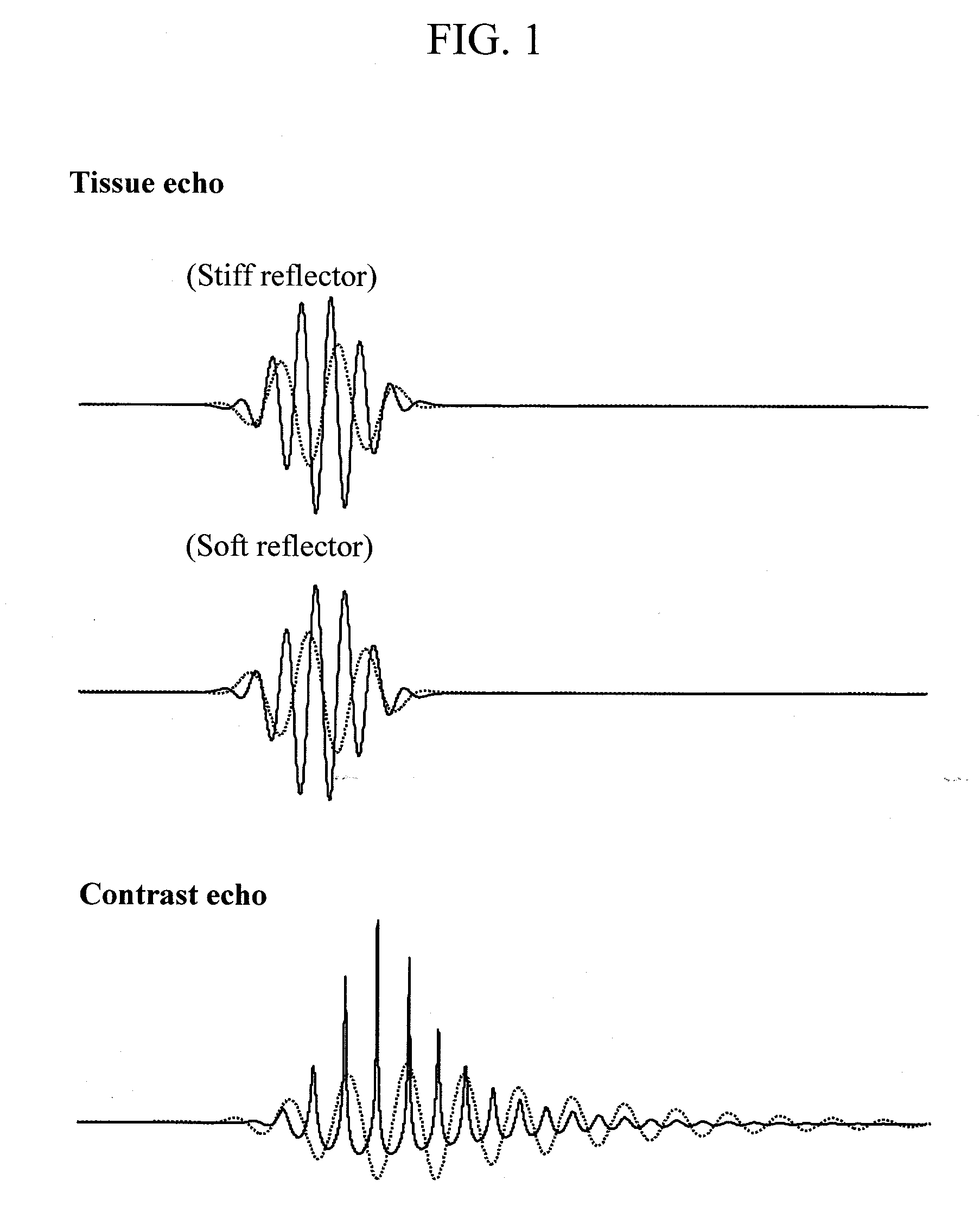
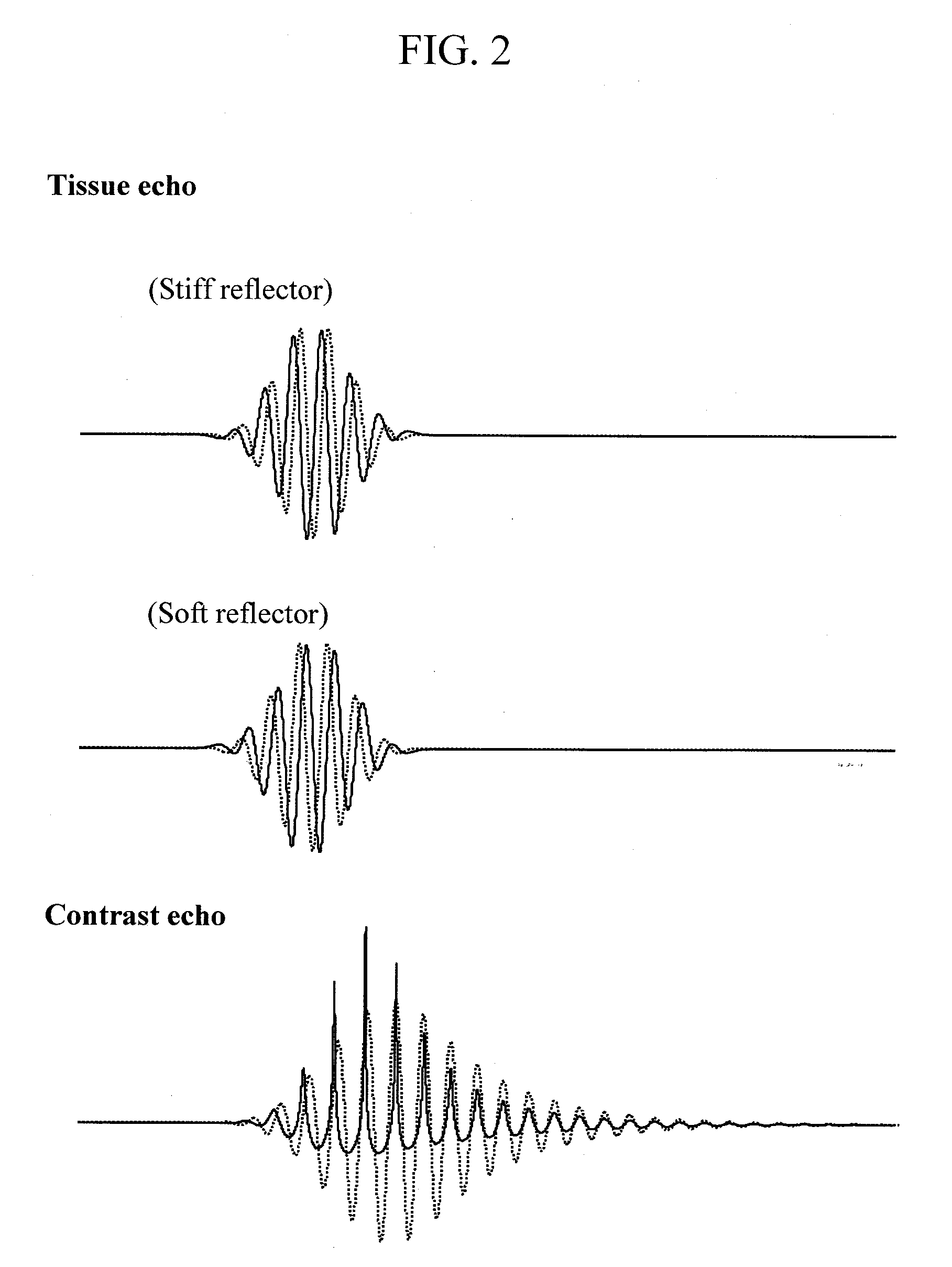
An ultrasound system is described which produces blended fundamental and harmonic frequency images. Successively transmitted, differently modulated pulses are transmitted by an ultrasound probe and both fundamental and harmonic frequencies are received in response. The echo signals received from the two pulses are processed by pulse inversion, producing cleanly separated bands of fundamental and harmonic signals in which undesired components have been cancelled. Since the two bands have been separated by signal cancellation rather than filtering, the two bands are allowed to overlap, providing broadband signals in each band. The bands are filtered by bandpass filtering to define the fundamental and harmonic signals to be imaged. The signals are detected, and the detected signals are combined after weighting to produce a blended fundamental / harmonic image.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Ultrasonic diagnostic contrast imaging at moderate MI levels
InactiveCN1976636AAvoid damageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationImage contrast
A method and device for imaging contrast agents which oscillate nonlinearly in a nondestructive mode at an MI in excess of 0.1 is described. Three transmit pulses are transmitted in each beam direction which are differently modulated. In an illustrated embodiment the transmit pulses are symmetrically differently phase modulated at 0 degrees, 120 degrees and 240 degrees. The echoes received in response to each transmit pulse are stored and combined by a pulse inversion processor. Pulse inversion processing results in separation of the third harmonic to the relative exclusion of the first and second harmonic signal components. Third harmonic images of the contrast image are formed which exhibit a relatively low tissue background.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
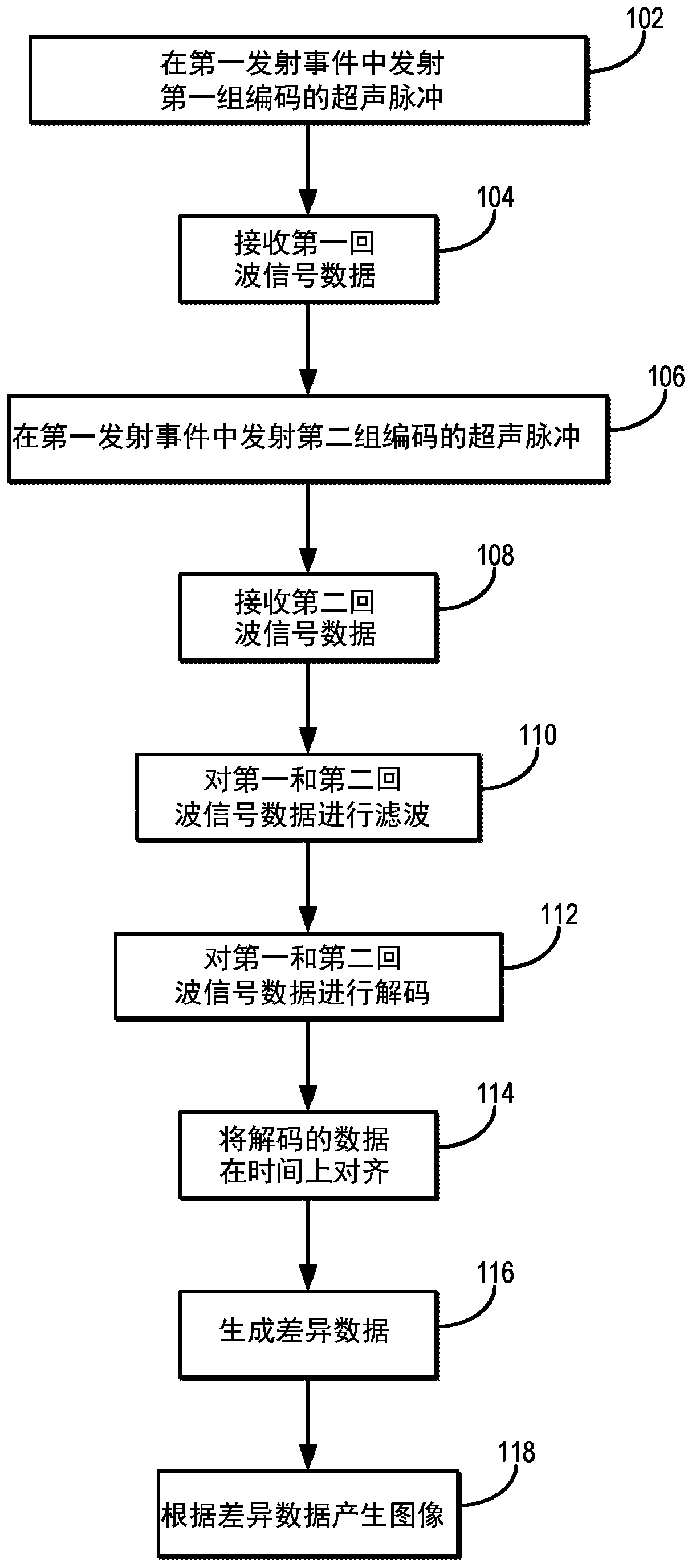
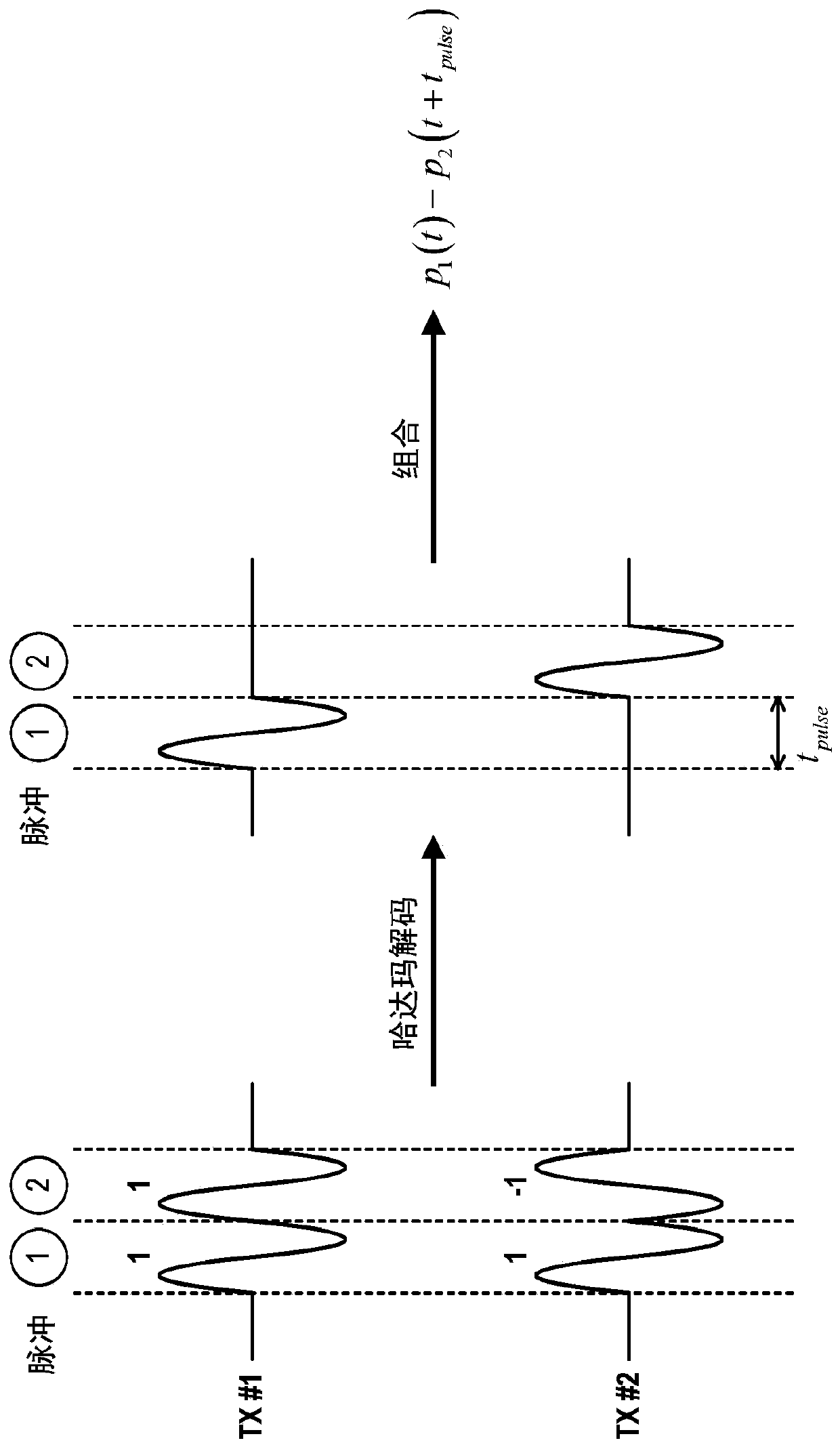
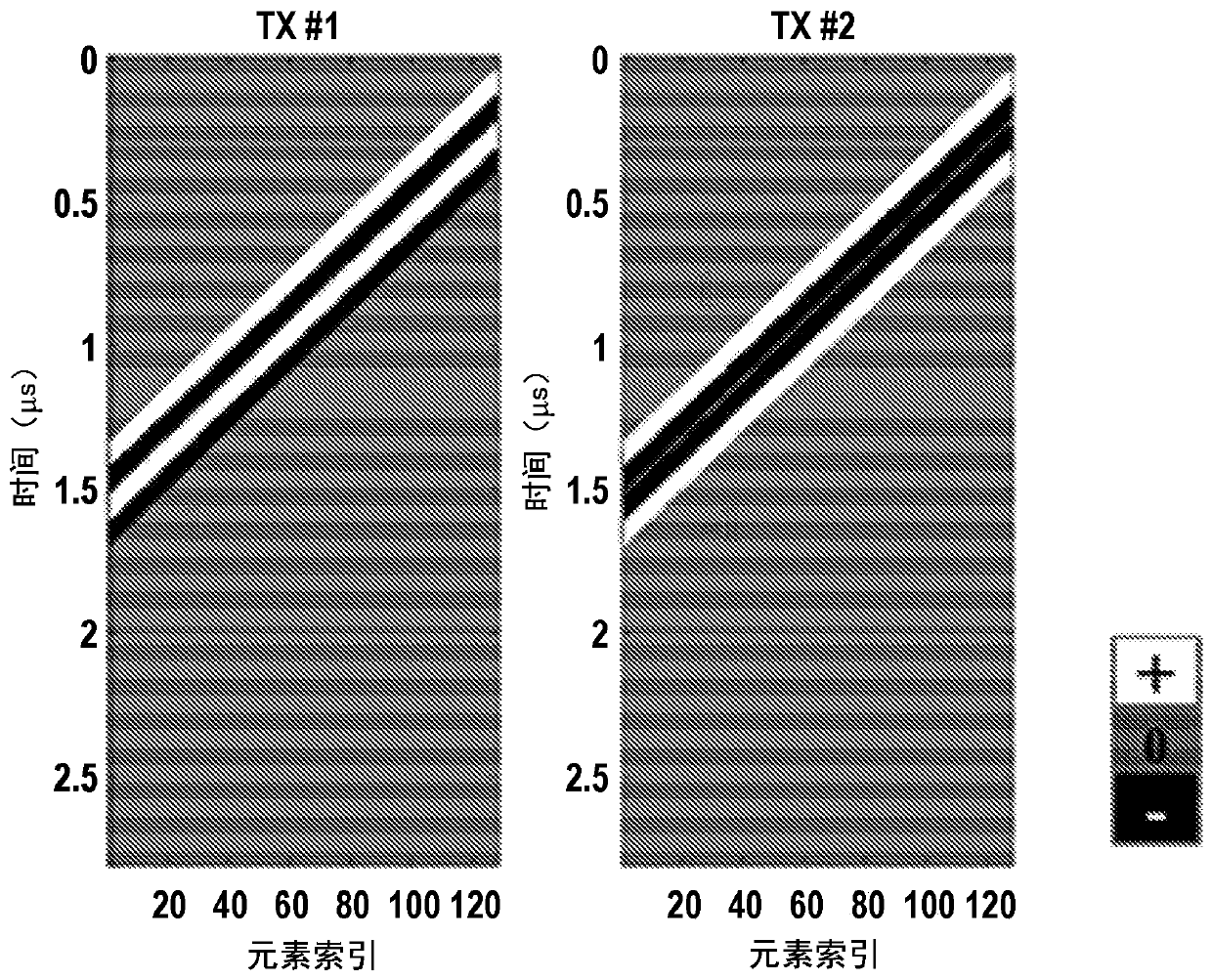
Methods for encoded multi-pulse contrast enhanced ultrasound imaging
PendingCN110998361AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingContrast enhance ultrasound
Methods for contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging that implement coded multi-pulses in each of two or more different transmission events are described. Data acquired in response to the two different transmission events are decoded and combined. In some embodiments, the coded multi-pulses include two or more consecutive Hadamard encoded ultrasound pulses. In other embodiments, multiplane wave pulsescan be used. Such multiplane wave pulses can be coded using Hadamard encoding, as one example. In addition, the multiplane wave pulses can be further coded using amplitude modulation, pulse inversion, or pulse inversion amplitude modulation techniques.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
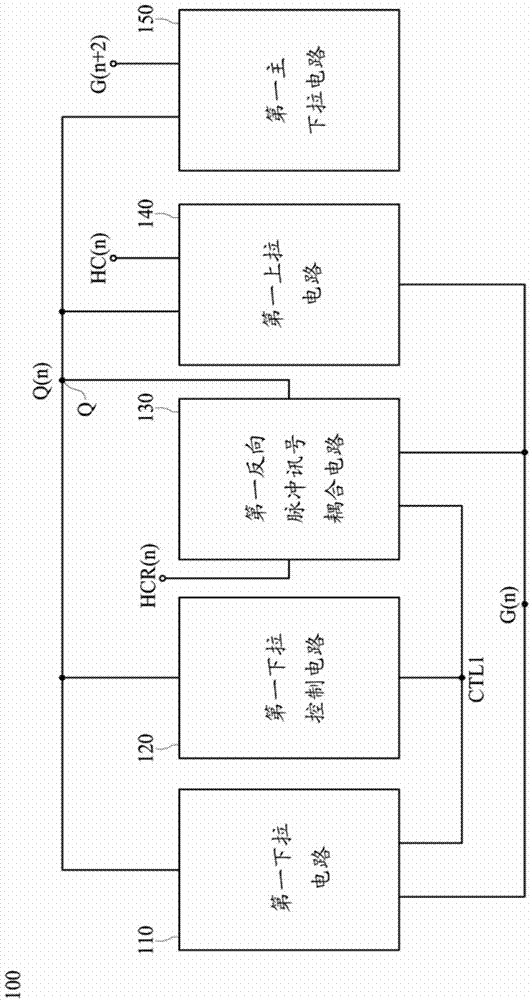
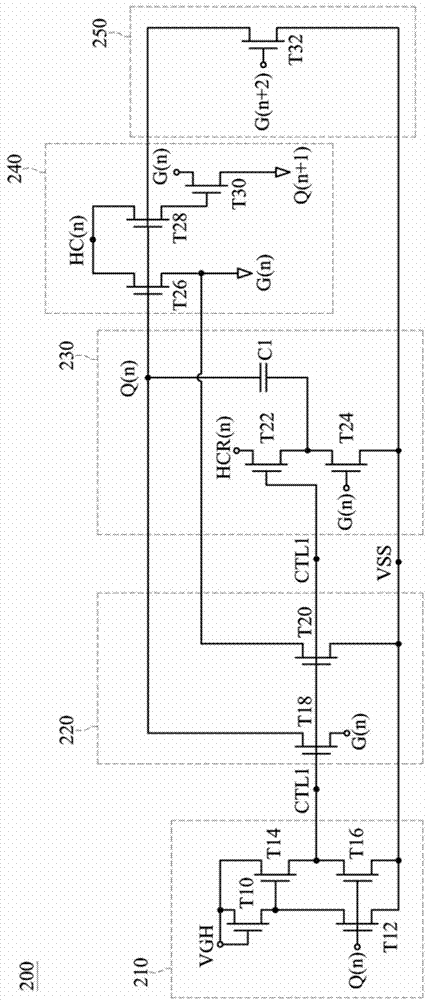
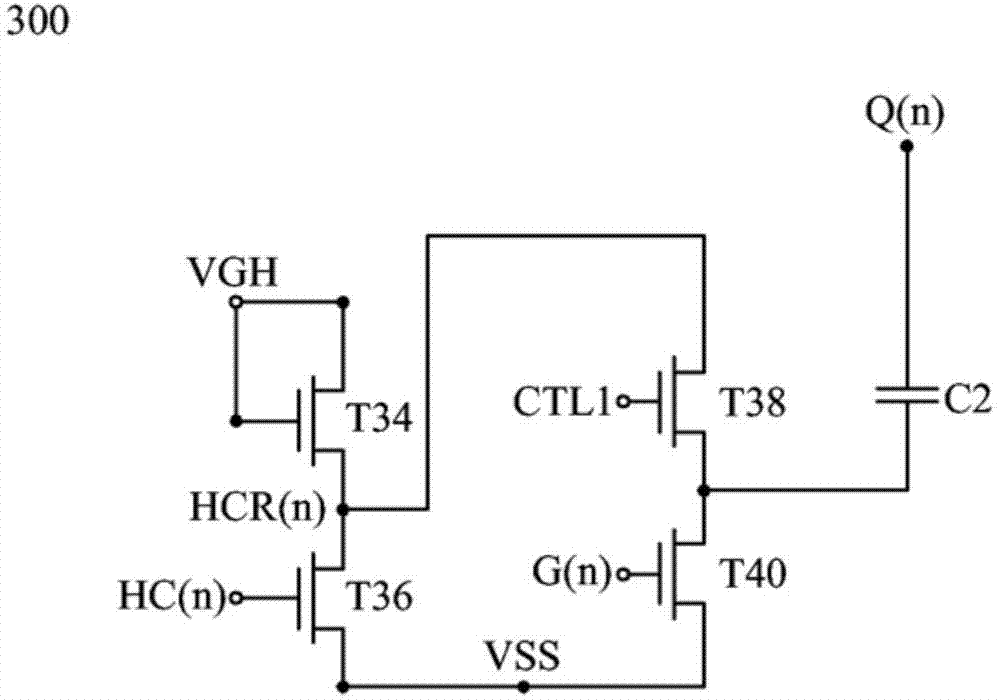
Shifting register circuit
ActiveCN103578403AReduce coupling effectAffects the voltage levelStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerControl signal
The invention discloses a shifting register circuit comprising a pull-down control circuit, a pull-down circuit, a pulse inversion signal coupling circuit, a main pull-down circuit, and a pull-up circuit. The pull-down control circuit is electrically connected with the pull-down circuit and the pulse inversion signal coupling circuit. The pull-down circuit is electrically connected with the pull-up circuit by a driving signal and a grid electrode signal. The main pull-down circuit is electrically connected with the pull-up circuit, and the pull-up circuit is connected with a pulse signal and the driving signal to output a grid control signal. The pulse inversion signal coupling circuit can be used to output the pulse inversion signal to offset the surge of the driving signal timely.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
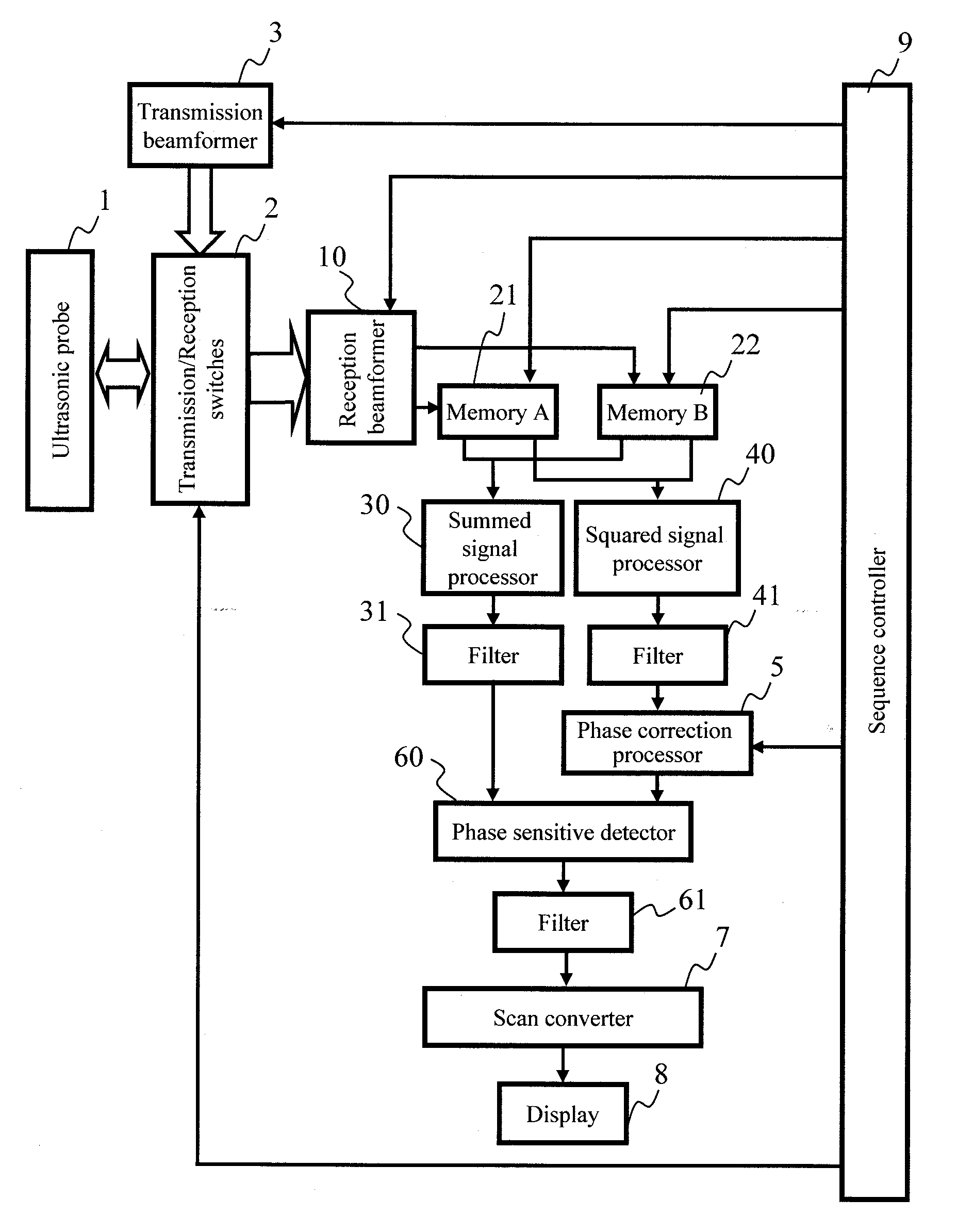
Ultrasonic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20100280376A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingImage resolution
An echo signal reflected from a microbubble contrast agent is discriminated from an echo signal generated upon reflection of a nonlinearly propagated transmission pulse from the body tissues without degradation of the axial resolution, by performing transmission / reception twice or less which would hardly decrease the imaging speed. By detecting a difference in phase of the second harmonic component based on the fundamental component included in the echo signal, an echo signal generated upon nonlinear reflection from a microbubble contrast agent is discriminated from an echo signal generated upon linear reflection of a nonlinearly propagated transmission pulse from the body tissues. The phase of the second harmonic component is detected through phase sensitive detection in which the square of the fundamental component is used as a reference wave. Concurrently, a pulse inversion method is used to extract the second harmonic component included in the original echo signal, whereby degradation of the axial resolution is prevented.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
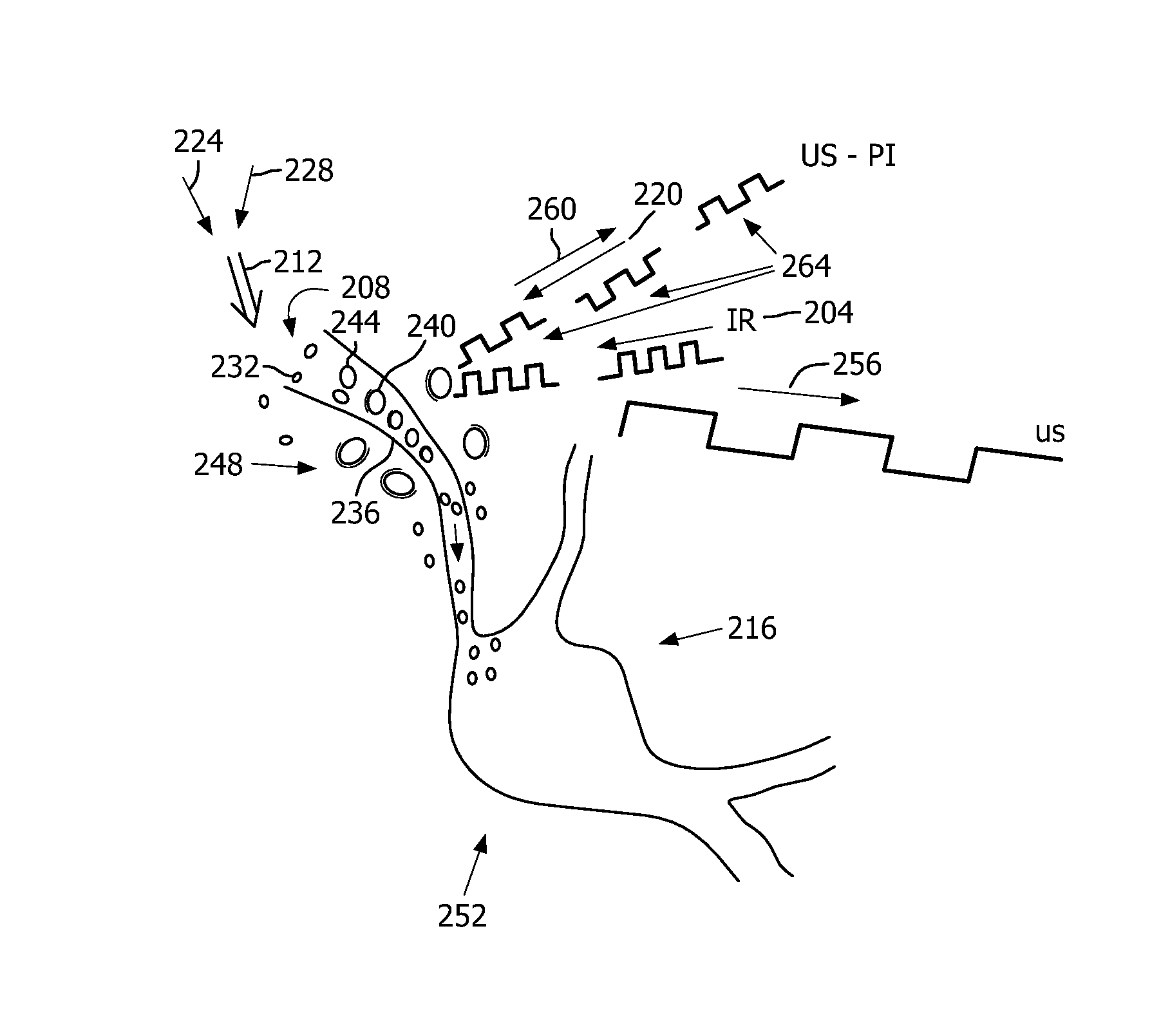
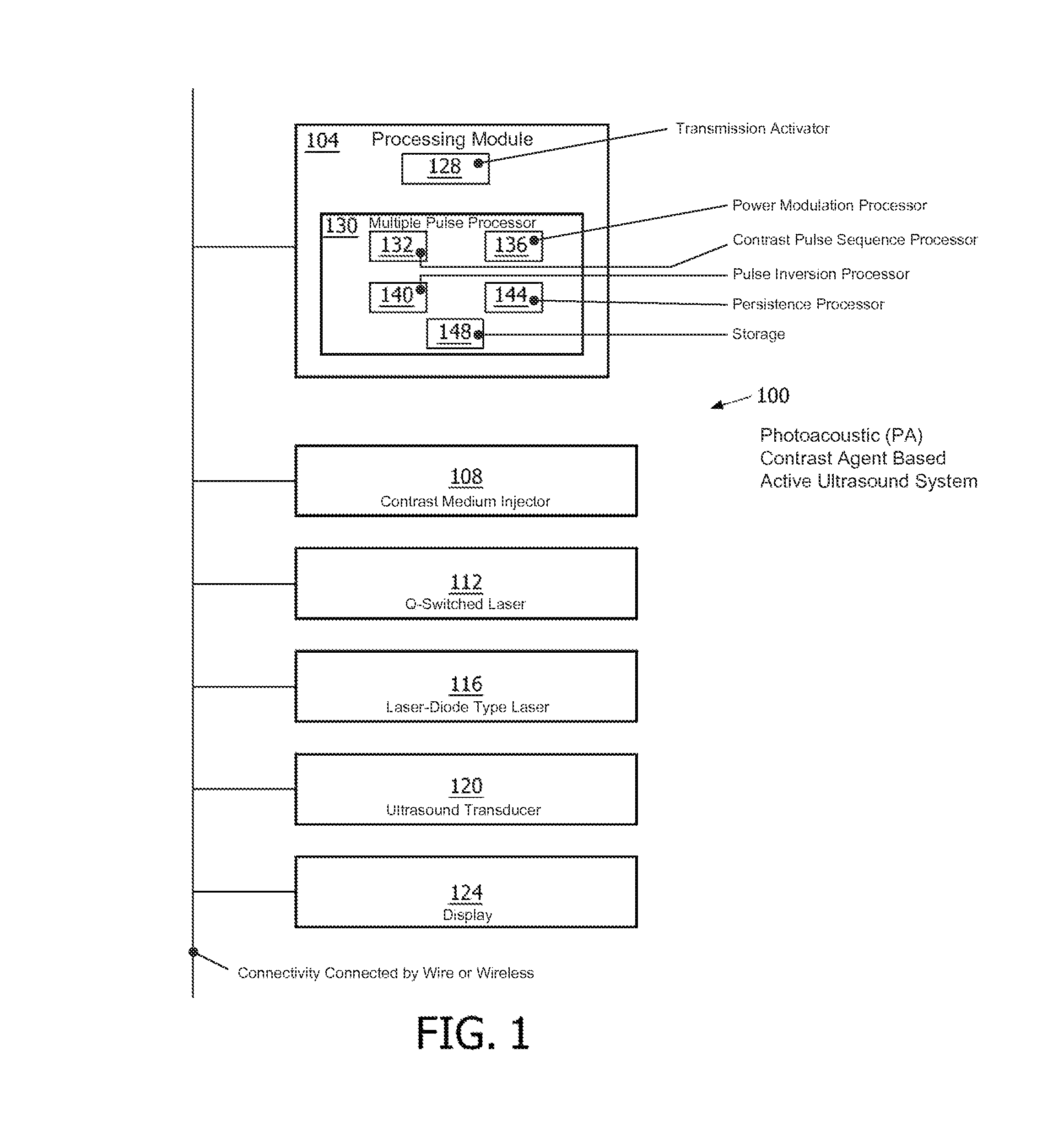
Photoacoustic contrast agent based active ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS9037218B2Effective imagingSufficiently stableOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasound contrast mediaBiological activation
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
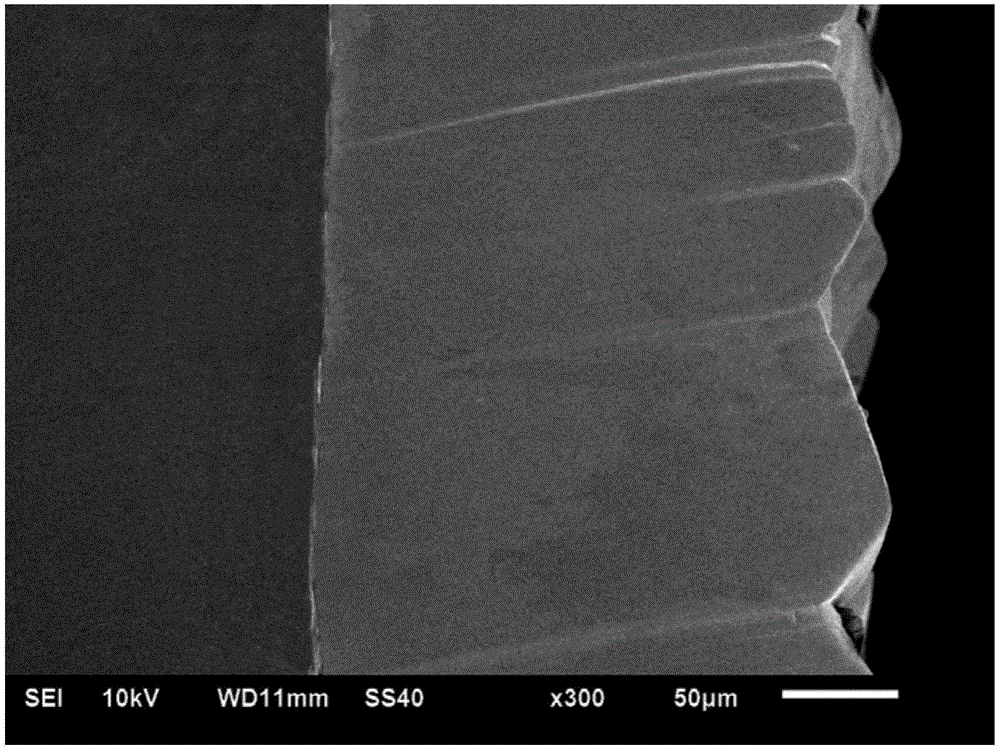
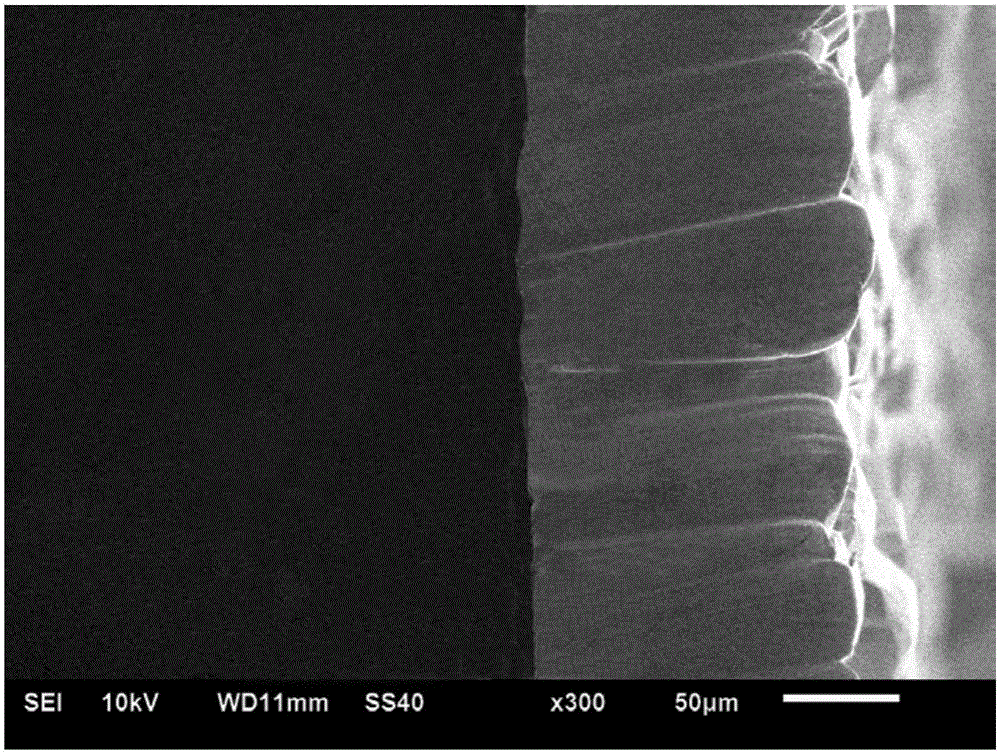
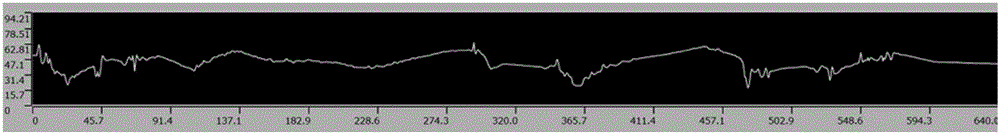
Method for pulse inversion electrodeposition of thick tungsten coating layer
ActiveCN105200471AUnaltered surface qualityNo change in surface roughnessCrazingConcentration polarization
The invention discloses a method for pulse inversion electrodeposition of a thick tungsten coating layer. The method comprises the steps of pretreatment, molten smelt preparation, pulse inversion electrodeposition and ultrasonic cleaning. The method improves the electrodeposition efficiency without changing the quality of the surface of the tungsten coating layer, and controls the roughness of the surface of the tungsten coating layer, so the surface of the produced thick tungsten coating layer has compact structure, good flatness and no cracks; and compared with a single phase pulse electrodeposition technology, a pulse inversion technology adopted in the invention allows the projecting part of the coating layer to be strong dissolved and leveled through highly-uneven anode current distribution caused by reverse current, so the cathode surface metal ion concentration rapidly rises, and the concentration polarization is reduced, thereby the surface of the tungsten coating layer produced in the invention is flattened, and the electrodeposition efficiency is increased. The thickness of the tungsten coating layer produced after pulse inversion electrodeposition for 10h reaches 220[mu]m, and the surface roughness is 6.673[mu]m; and the pulse inversion electrodeposition technology improves the electrodeposition rate without reducing the quality of the surface of the coating layer.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Low-frequency transcranial dedicated ultrasonic transducer and application thereof
InactiveCN108175439AImprove fitStrong penetrating powerOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsImaging qualityArray element
The invention provides a low-frequency transcranial dedicated ultrasonic transducer and application thereof. The provided ultrasonic transducer is a 1.5D linear array transducer or area array transducer with a center frequency between 1.6MHz and 2.3MHz and a liner array with the number of array elements of 128-256, the size of the transducer can better fit a temporal bone for imaging, according toimaging experiments of the ultrasonic transducer, the penetrability is better, the sound pressure after passing through a skull is stronger, the imaging effect is better, and the imaging definition can be better improved so that the transducer can be used as the transcranial dedicated ultrasonic transducer. By means of the low-frequency transcranial dedicated ultrasonic transducer, B-mode imagingcan be conducted by the low-frequency transcranial dedicated ultrasonic transducer, imaging in manners of plane wave, linear frequency modulation, broad focus and the like can also be conducted, andthe low-frequency transcranial dedicated ultrasonic transducer can be applied to transcranial B-mode imaging, transcranial Doppler imaging and transcranial pulse-inversion imaging to improve imaging quality.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Ultrasound System and Method, and Ultrasound Probe
ActiveUS20160120516A1Quality improvementHigh-quality ultrasound imageOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationAudio power amplifier
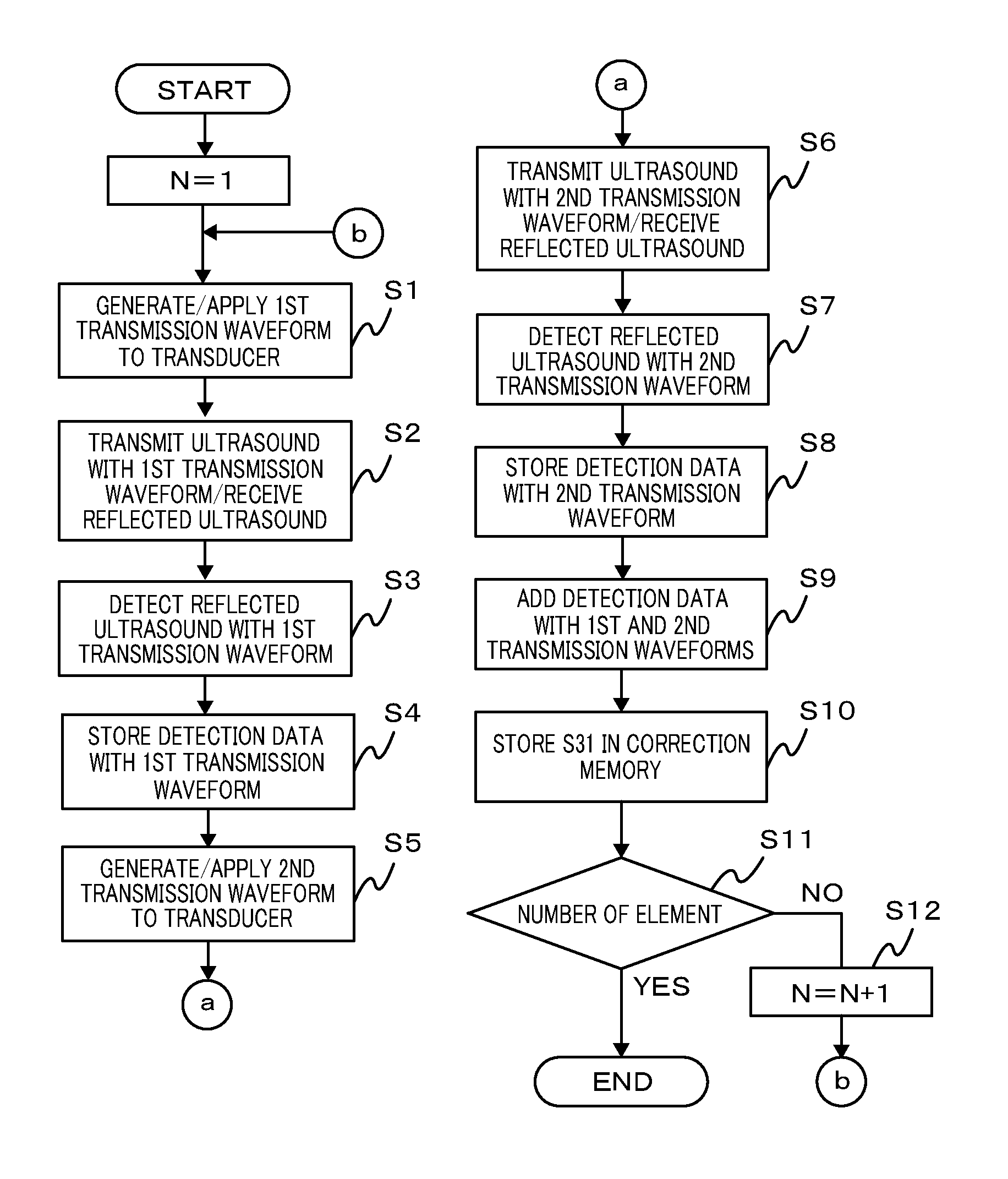
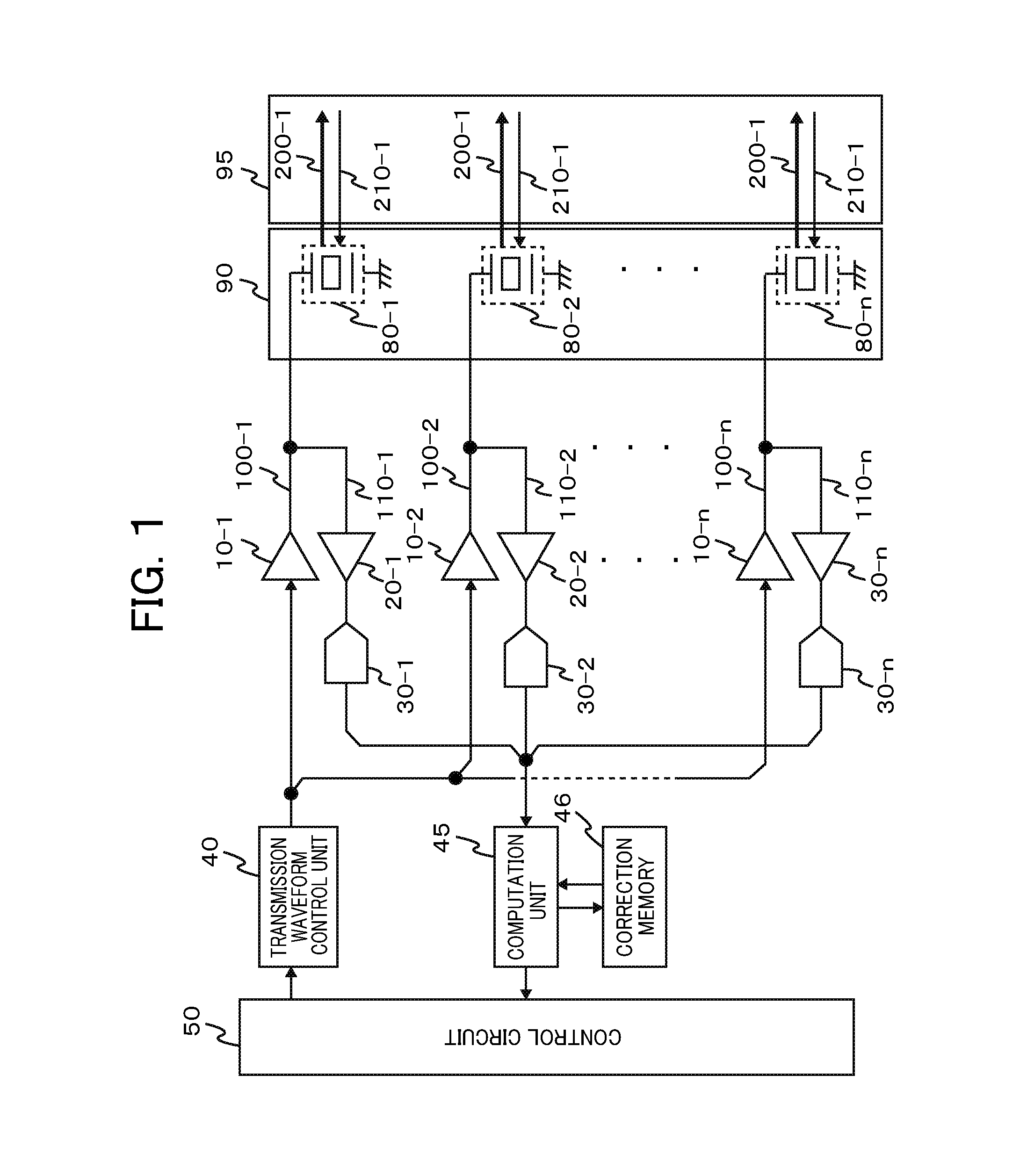
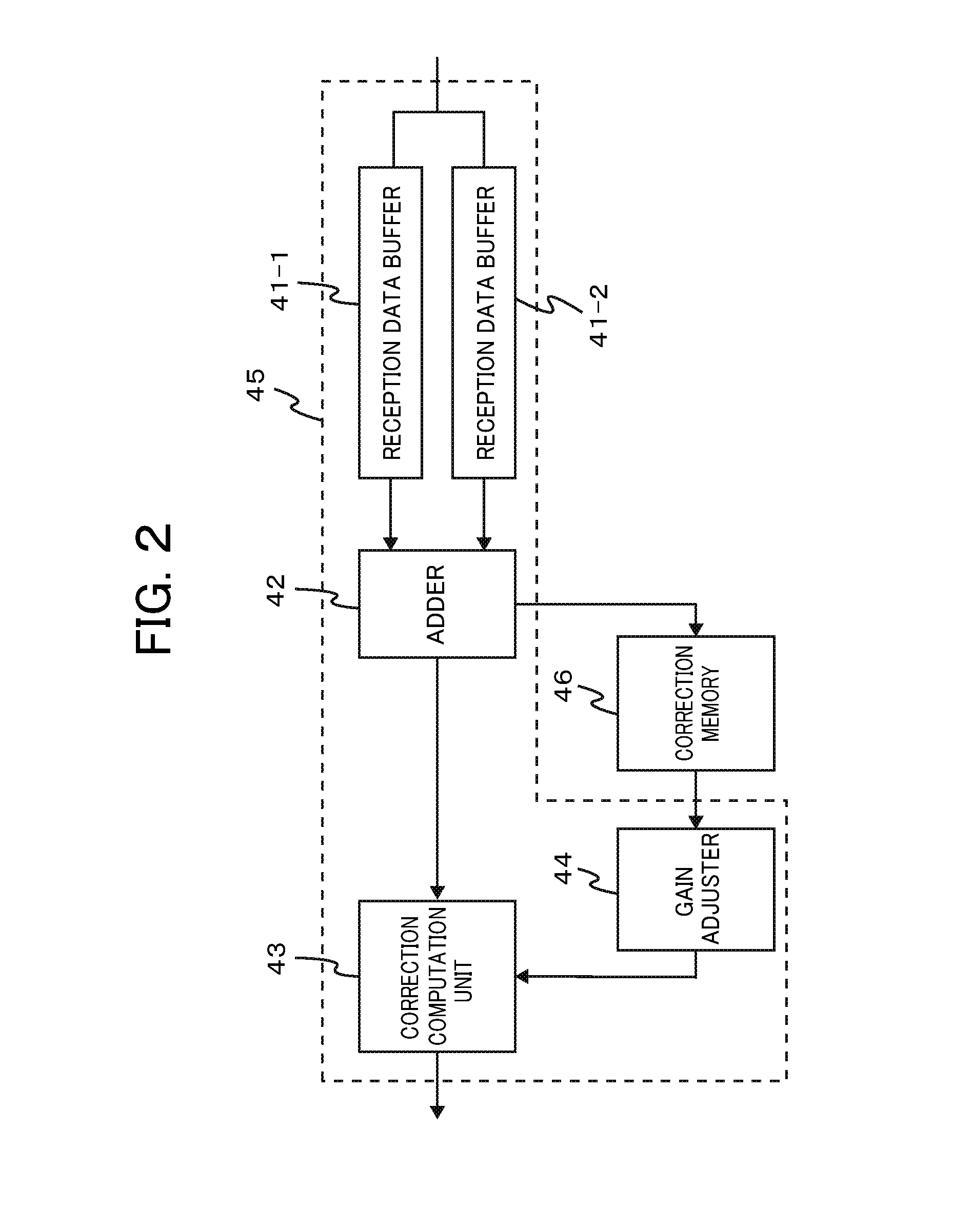
An objective of the present invention is to provide an ultrasound system which can correct a positive-negative asymmetry in pulse inversion (PI) and obtain a high-image quality ultrasound image. To carryout an asymmetry correction of a transmission assembly circuit comprising an oscillation adjustment amplifier (10) and an ultrasound oscillator array (90), correction data obtained in a calibration mode is stored in a correction memory (46), and positive-negative asymmetry of an overall receiving assembly circuit comprising a computation unit (45) is corrected in a diagnostic mode of the device using the correction data.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
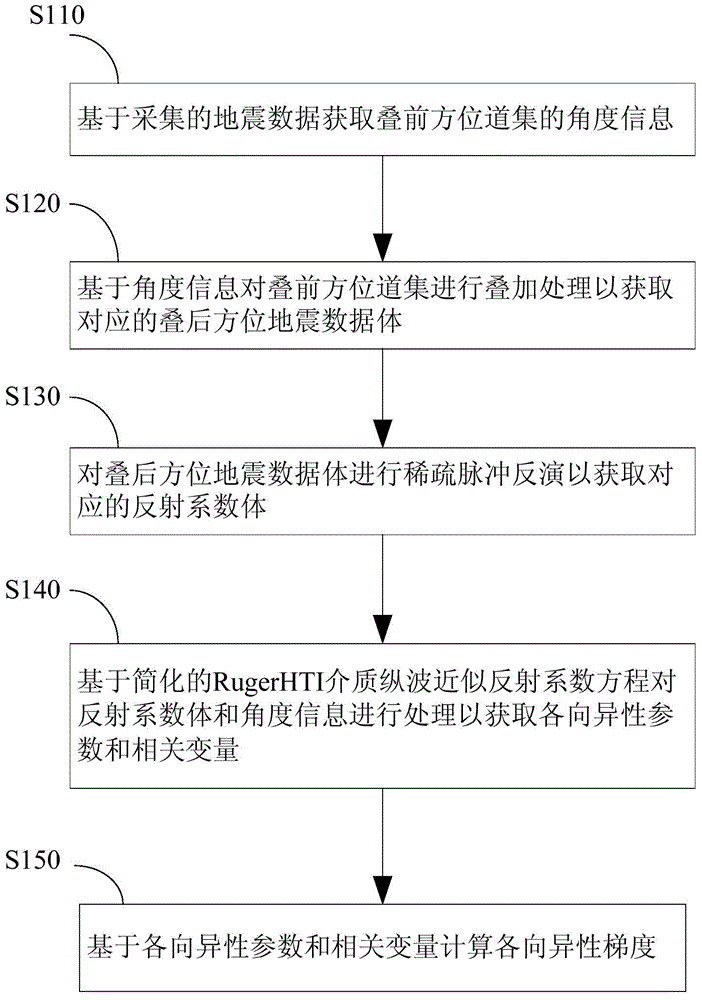
Method for calculating crack anisotropism gradient
ActiveCN105487113AAvoid direct impactEven energy distributionSeismic signal processingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Longitudinal wave
The invention discloses a method for calculating crack anisotropism gradient. The method comprises: based on acquired seismic data, obtaining angle information of pre-stack azimuth gather; based on the angle information, performing superposition processing on the pre-stack azimuth gather, to obtain corresponding post-stack azimuth seismic data cube; performing sparse pulse inversion on the post-stack azimuth seismic data volume, to obtain corresponding reflection coefficient body; based on a simplified Ruger HTI medium longitudinal wave approximate reflection coefficient equation, processing the reflection coefficient body and the angle information, to obtain a longitudinal wave variable coefficient difference value of the upper layer and the lower layer of a HTI medium and correlated variables; and based on the longitudinal wave variable coefficient difference value of the upper layer and the lower layer of the HTI medium and the correlated variables, calculating the anisotropism gradient. The method is based on post-stack azimuth data, and the high-quality part of the seismic data is selected to be used as inversion input data, thereby preventing direct influence of post-stack azimuth data on calculation results. The inversion method is high in stability and high in signal to noise ratio.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Real-time extracting device and detection method for focused ultrasonic cavitation and microbubbles thereof
InactiveCN101530320BAchieving real-time identification detectionHas inhibitory effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBroadband noiseUltrasonic cavitation
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
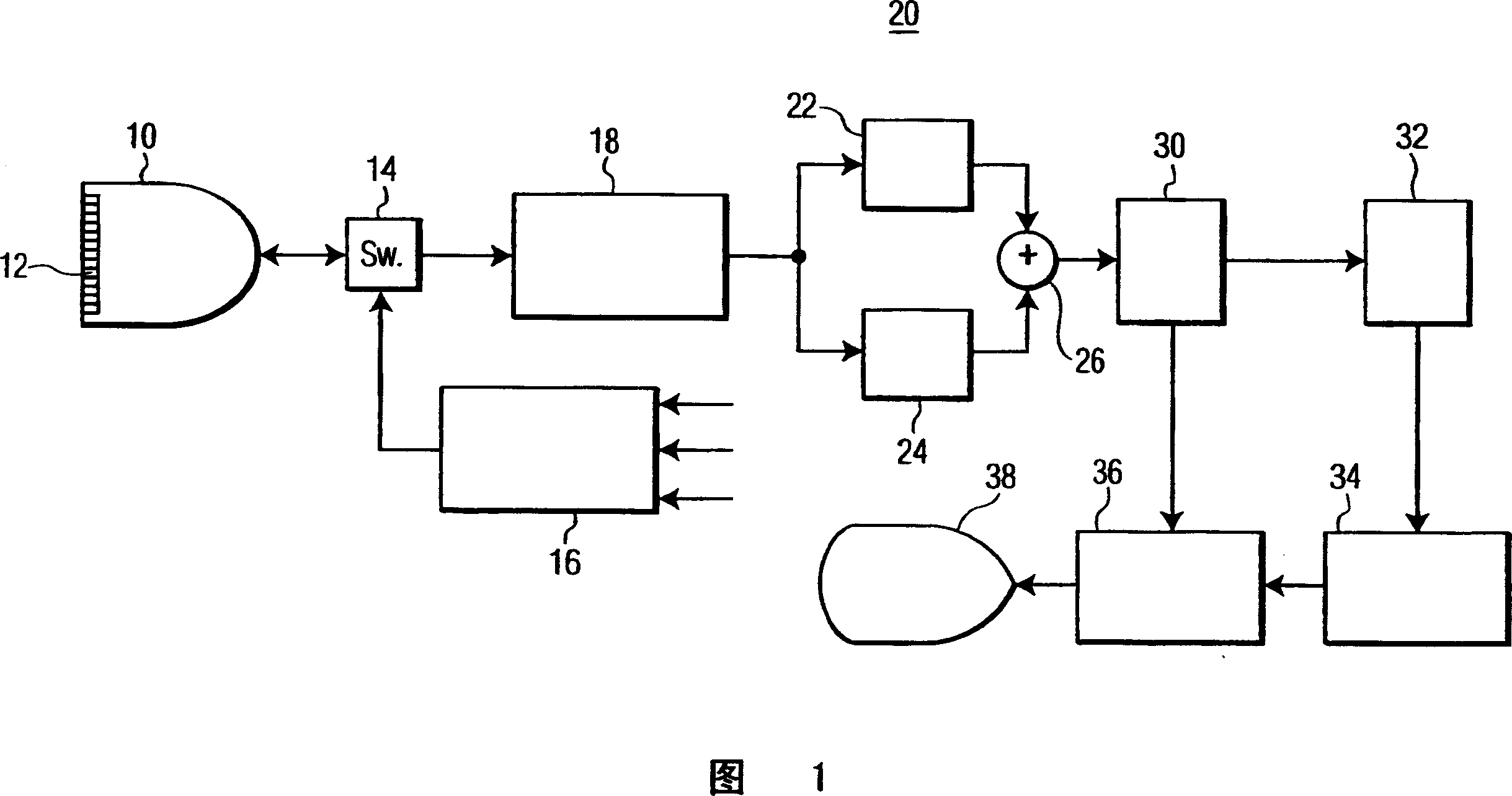
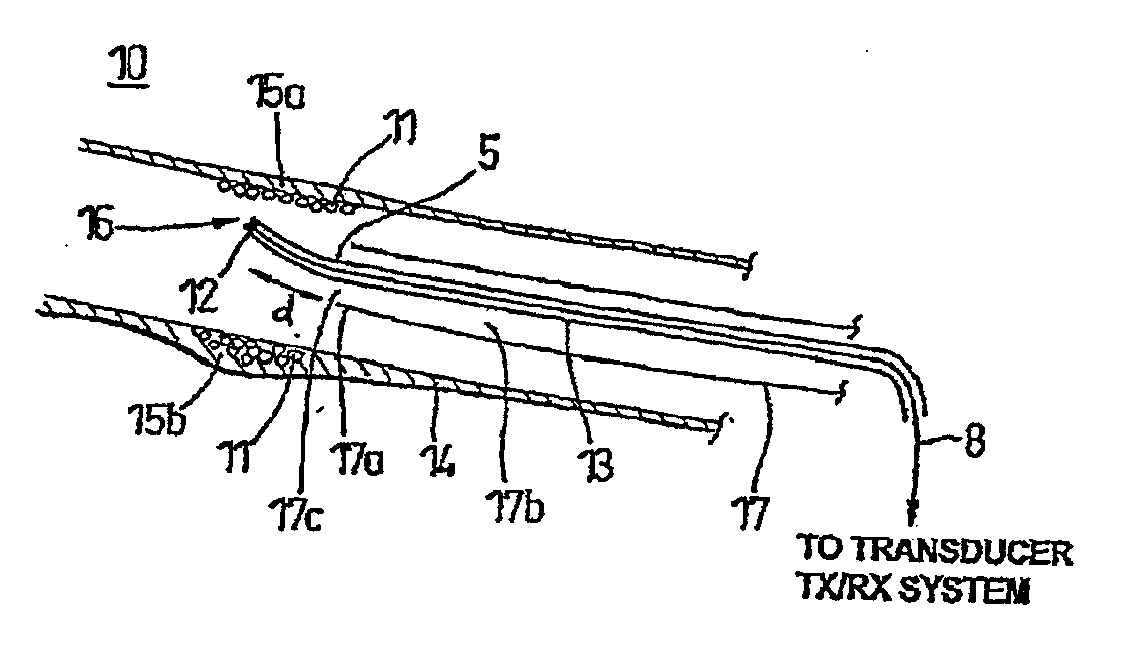
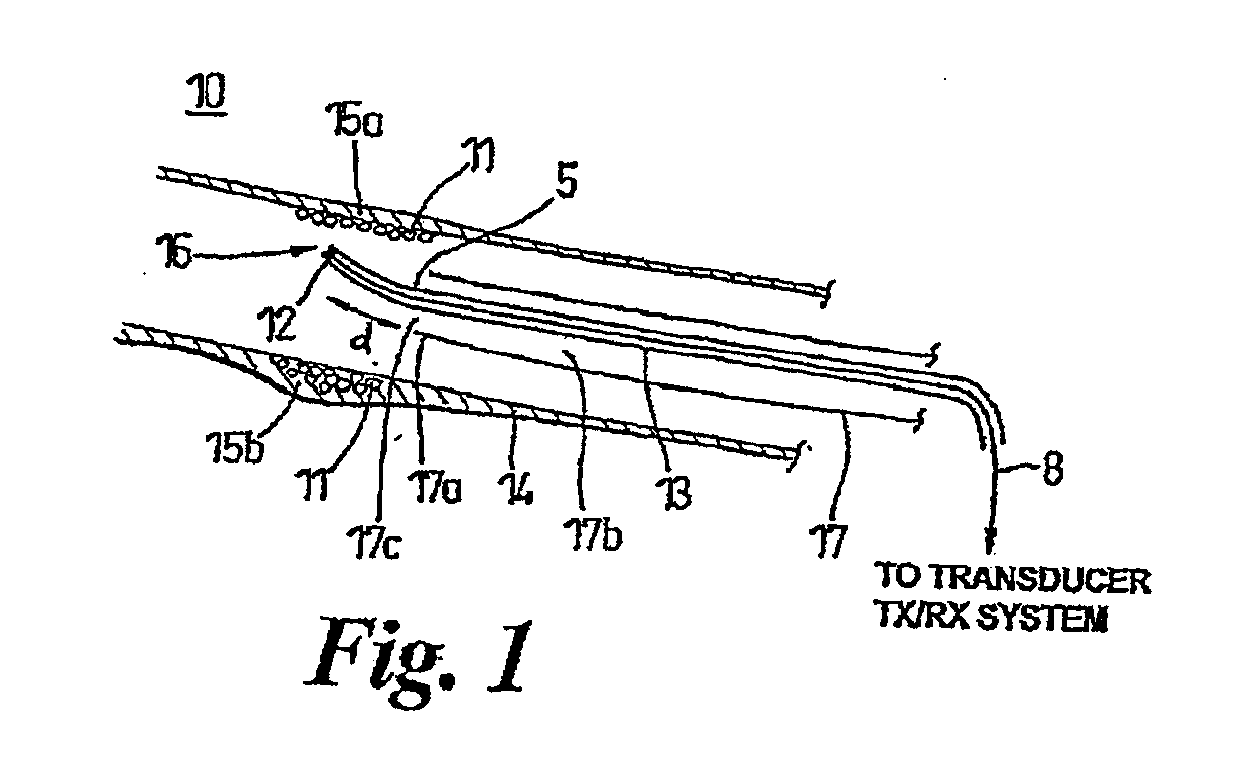
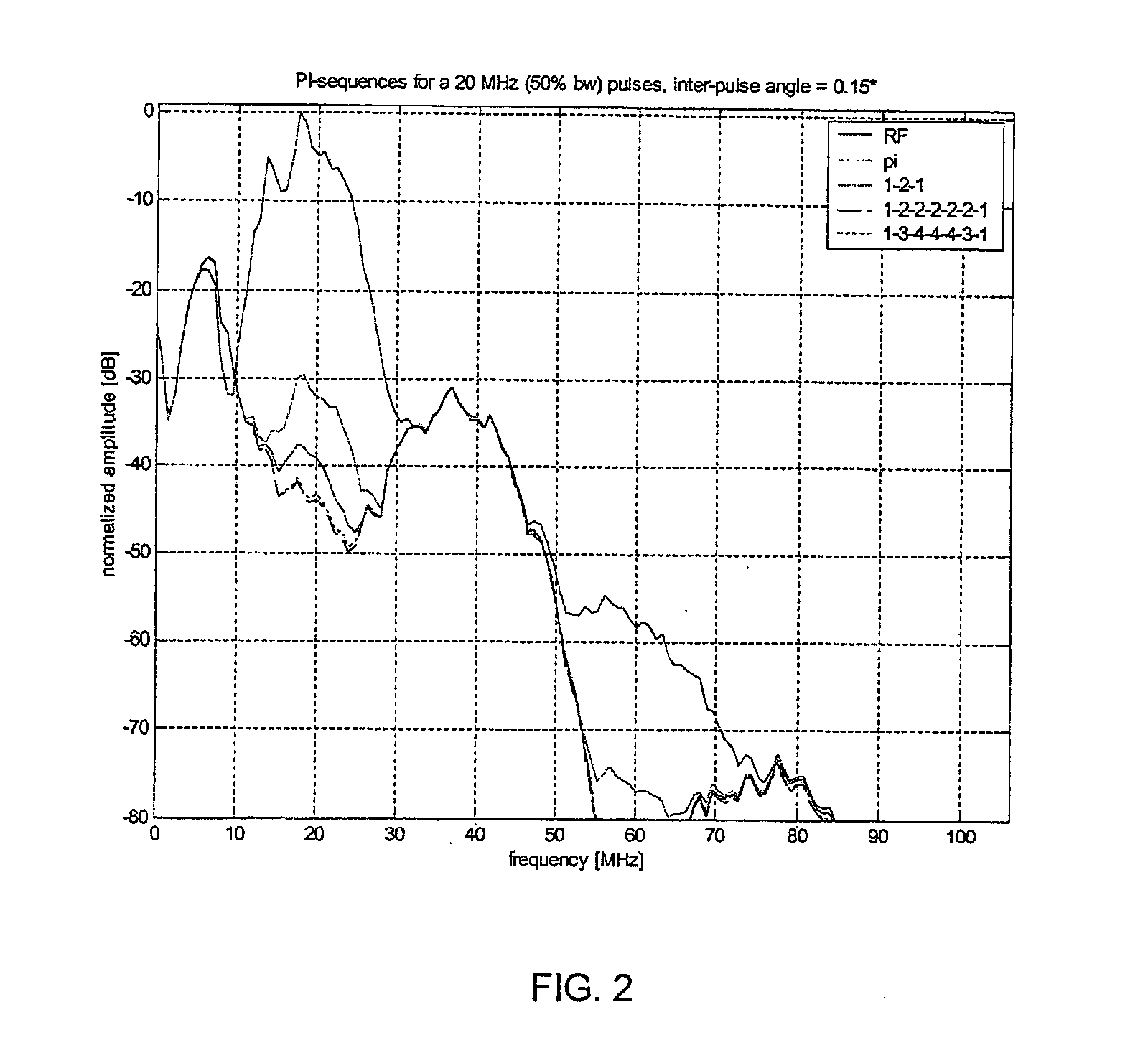
Pulse Inversion Sequences For Nonlinear Imaging
InactiveUS20080077018A1Reduce the impactReduce impactUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterTransducerElectrical polarity
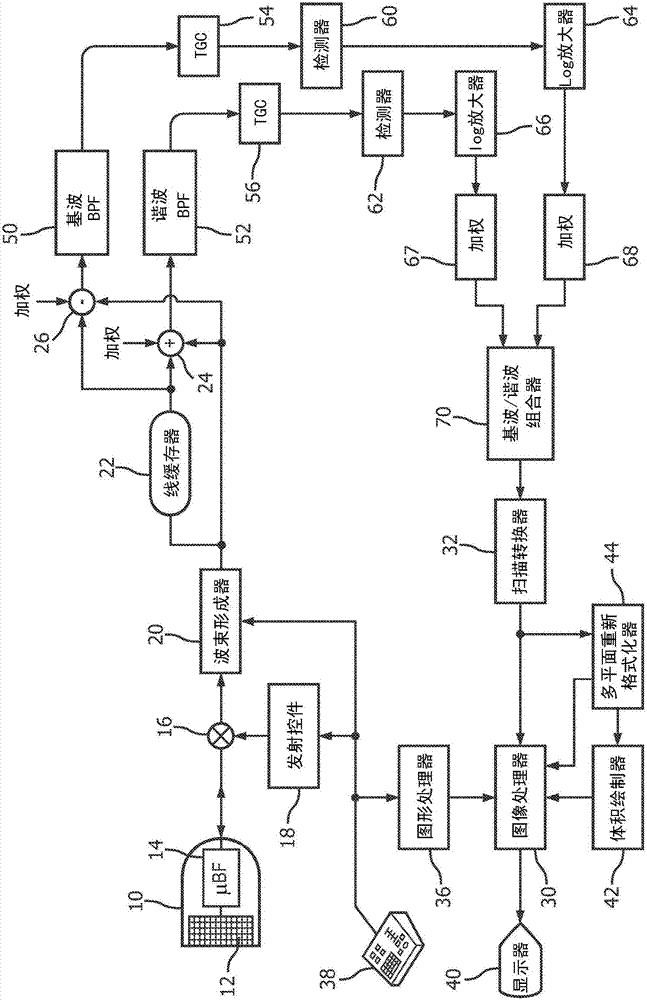
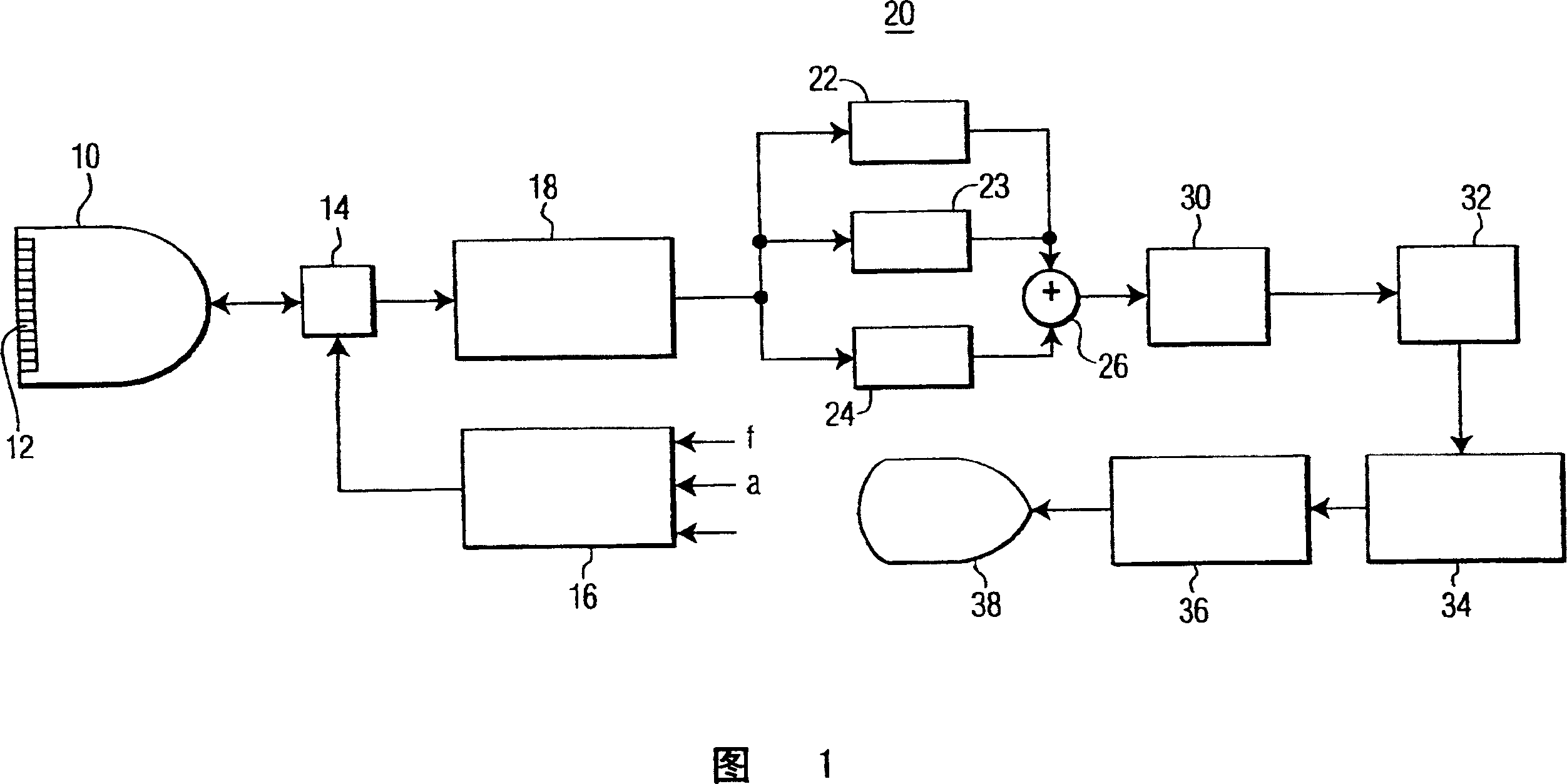
Provided herein are Pulse-Inversion (PI) sequences that provide for fundamental frequency suppression in nonlinear imaging applications. In an embodiment, a weighting scheme is applied to the received echo pulses resulting from transmit pulses of alternating polarity to reduce the effect of transducer motion. In an embodiment, a three-pulse weighting scheme is applied to a PI sequence. In other embodiments, different combinations of the three-pulse weighting scheme are applied to a PI sequence.
Owner:STICHTING VOOR DE TECH WETENSCHAPPEN
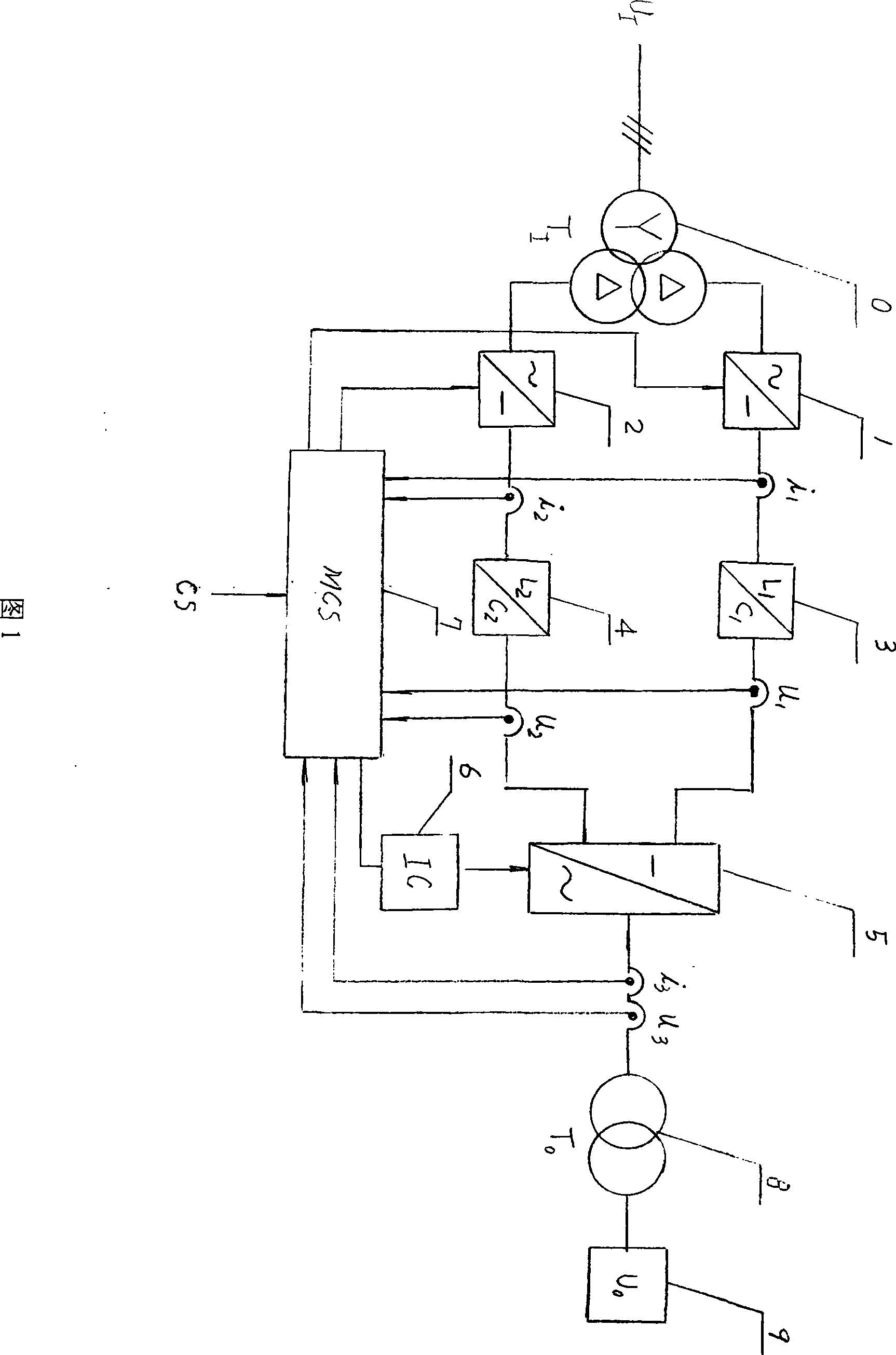
Computer controlled large power narrow pulse system
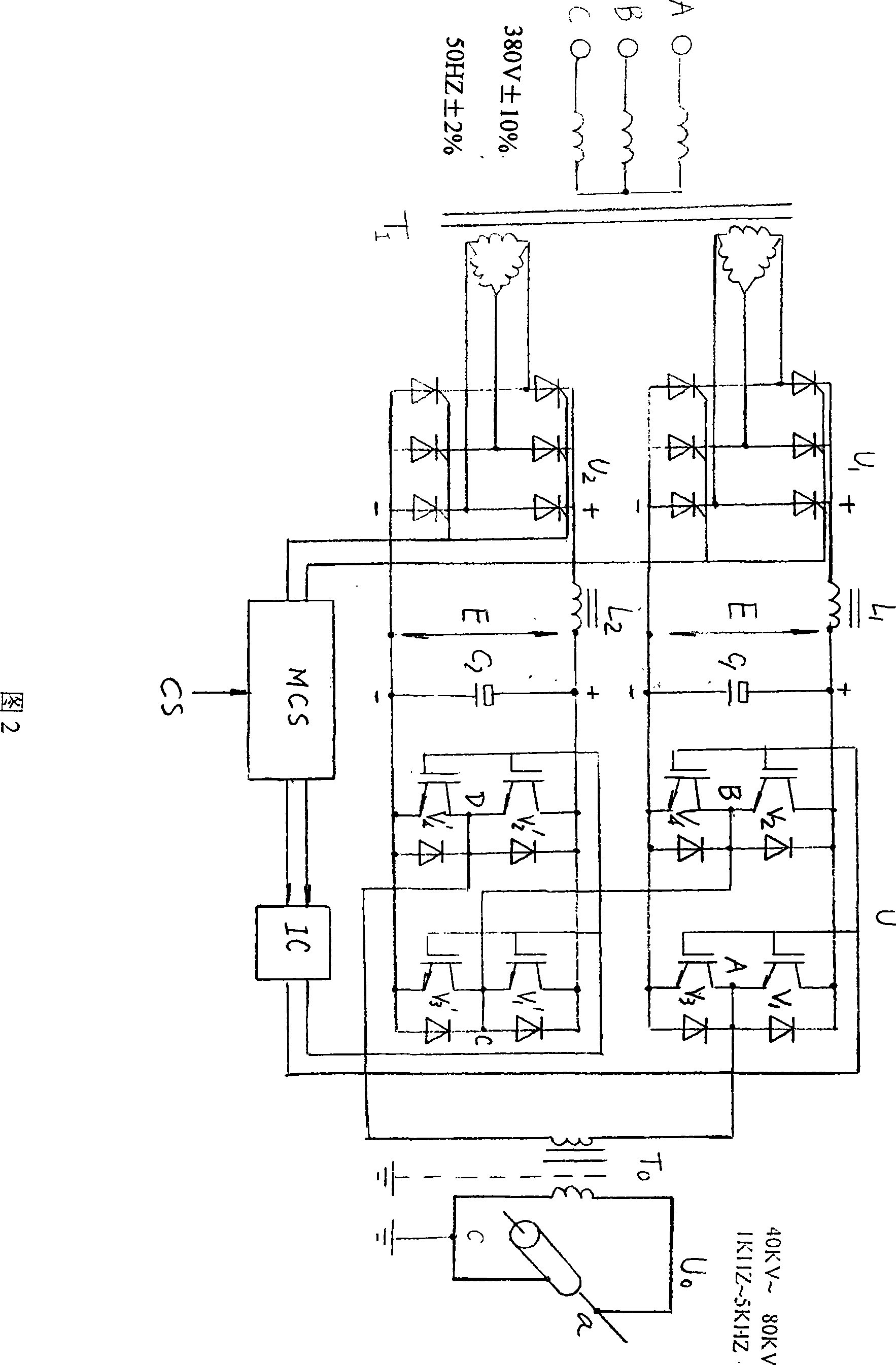
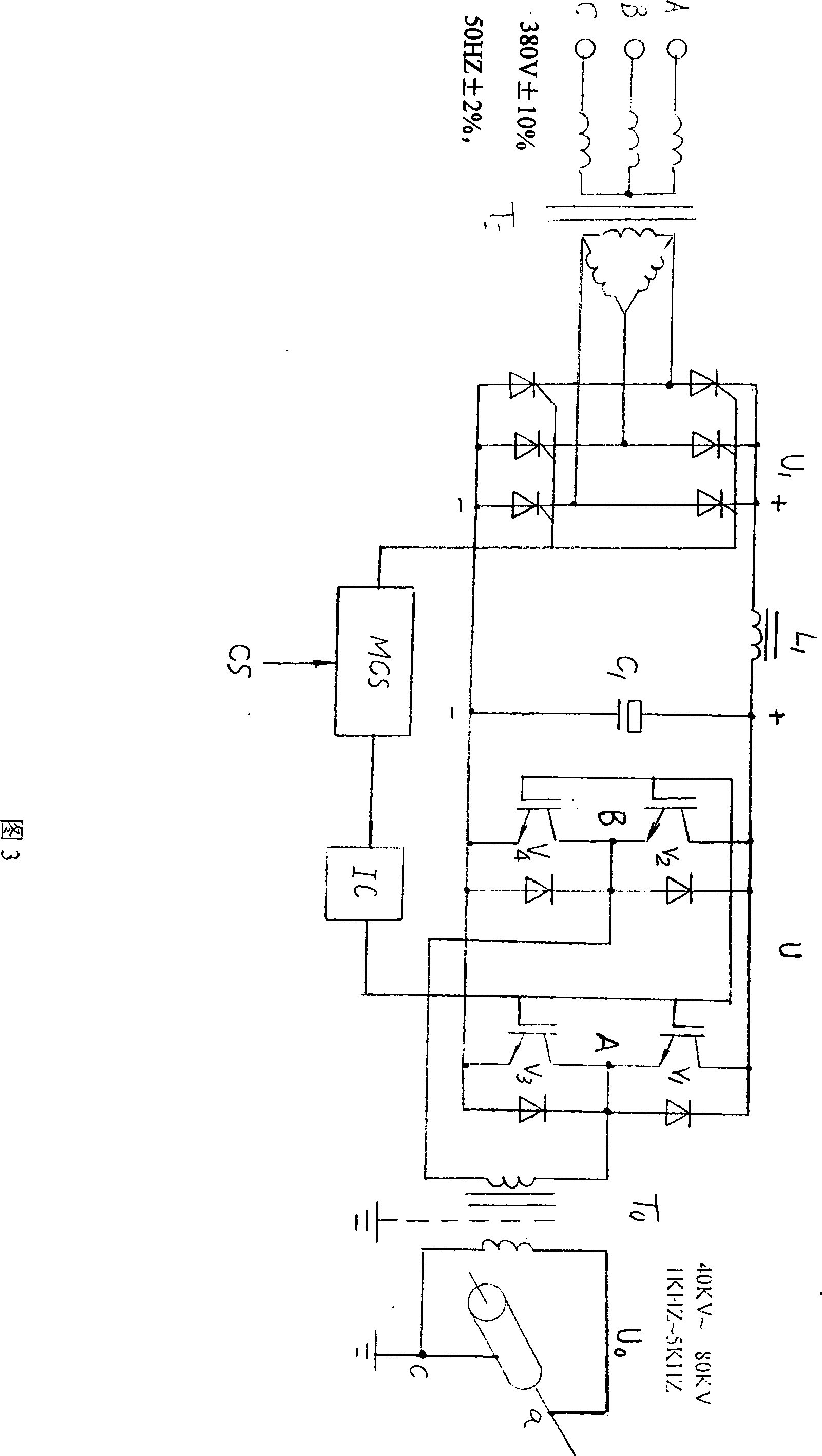
A computer-controlled large-power narrow-pulse system belongs to the high-new technical field of bioengineering and suits bioengineering use. The system is composed of a three-phase isolating transformer (0), thyristor current inverting power devices (1, 2), filter devices (3, 4), a large-power narrow-pulse inversion sub-system (5), a power pulse drive device (6), a computer digital control sub-system (7), a high-frequency high-voltage transformation device (8) and an electric field device. The large-power narrow-pulse inversion sub-system is composed of insulated gate bipolar transistors IGBT serving as the power switch elements, and has the advantages that the IGBT can be integrated and can apply soft switching technique. The computer can control on and off of the power switch elements IGBT according to application software, and can control the thyristor current inverting power devices to convert a controllable DC voltage to an alternating high-frequency pulse voltage, which is outputted after being boosted by the high-frequency high-voltage transformation device. The input power is a three-phase AC voltage with a magnitude of 380-10% to 380+10% and a frequency of 50-2% to 50+2%, and the output voltage has a magnitude of 40 KV to 80 KV, a frequency of 1 KHz to 5 KHz, a power number of 10 KW and a pulse width of ns to mus. The computer-controlled large-power narrow-pulse system has the advantages of high voltage, large power, high frequency, narrow pulse, and computer-controllable pulse parameter, and can save the energy resources to achieve large social and economic benefits.
Owner:王强 +1
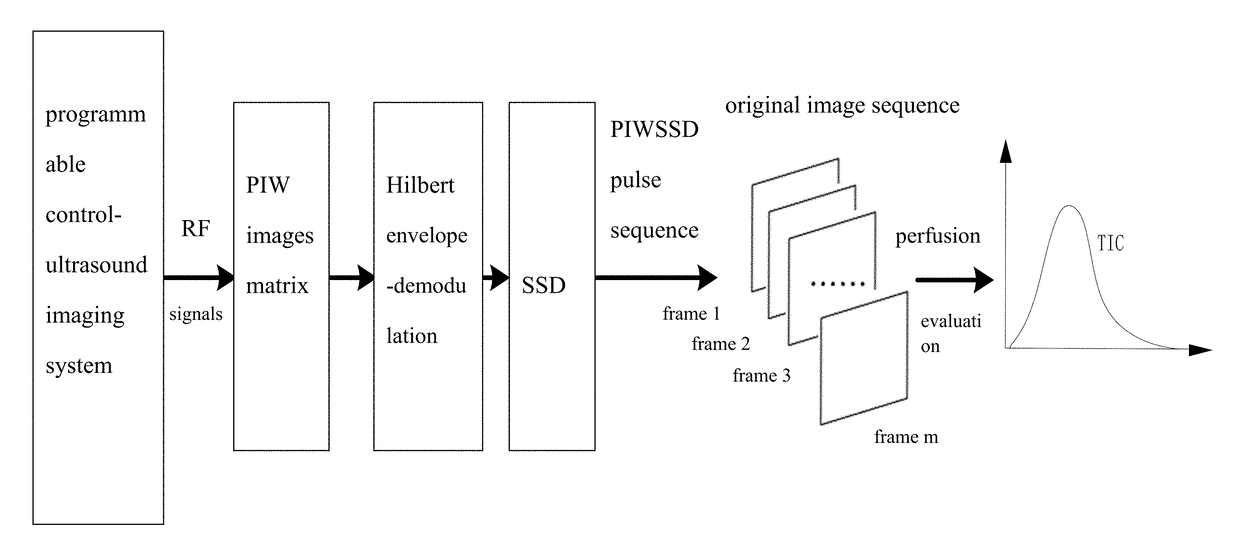
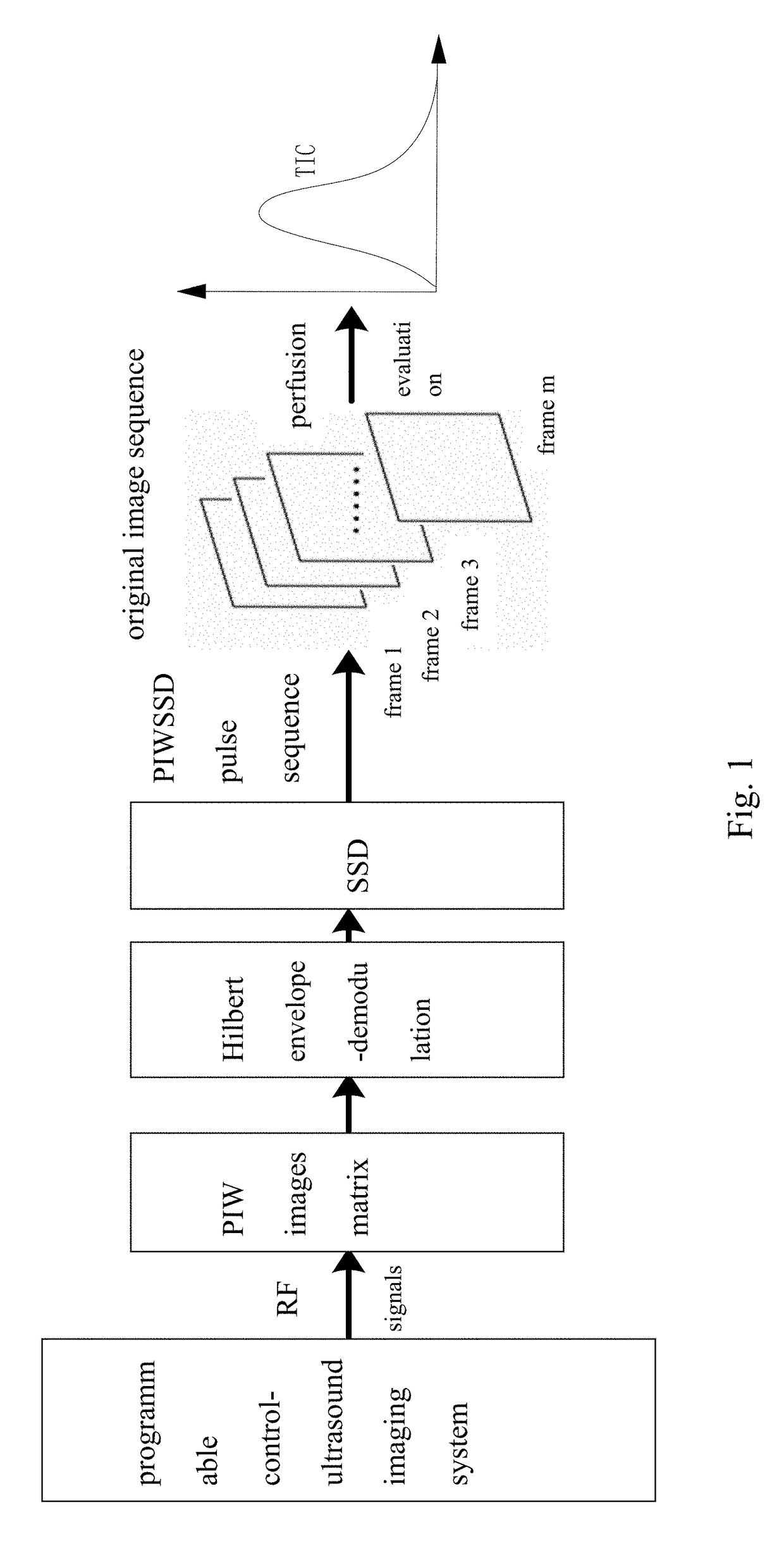
Contrast imaging method based on wide beam and method for extracting perfusion time-intensity curve
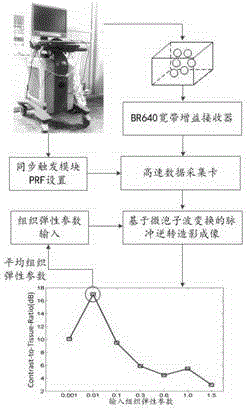
ActiveUS9788815B2Rapidly and accurately extractingReduce contrastBlood flow measurement devicesHealth-index calculationWide beamPerfusion
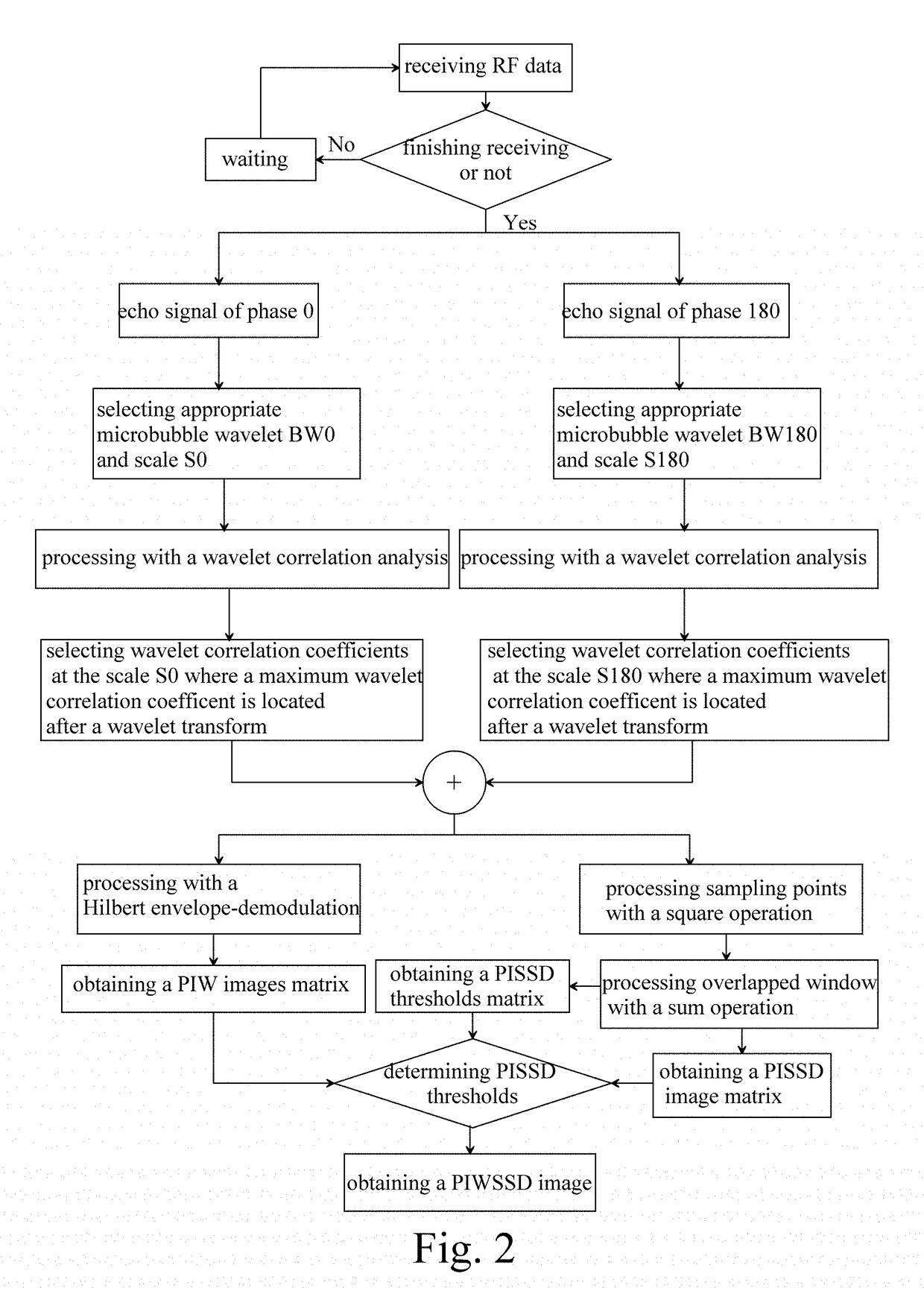
A contrast imaging method based on a wide beam and a method for extracting a perfusion time-intensity curve (TIC) are provided to increase contrast-to-tissue ratio (CTR) through the contrast imaging method based on the wide beam via a pulse inversion microbubble wavelet transform sum squared differences decorrelation (PIWSSD). An auto adaptive analysis method about rapidly and accurately extracting a TIC tendency of the contrast imaging method based on the wide beam is also provided to overcome limitations of a decrease in the CTR of the contrast imaging based on the wide beam and a decrease in SCR of the perfusion TIC. The present invention plays an important role in effectively reducing an ultrasound contrast imaging acoustic power and a contrast microbubble perfusion concentration, reducing potential threat to human body, acquiring a contrast image with the high CTR, and accurately evaluating and diagnosing blood perfusion.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Methods and systems for motion corrected wide-band pulse inversion ultrasonic imaging
ActiveUS20210068792A1Organ movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsBroadband pulseUltrasonic imaging
Systems and methods are provided for motion corrected wide-band pulse inversion ultrasonic imaging. A first pulse is transmitted, a second pulse is then transmitted after a delay, with the second pulse having different polarity. Echoes of the first pulse and the second pulse are received, using a reception bandwidth that enables capturing at least a portion of a fundamental portion of each pulse. The echoes are processed, and corresponding ultrasound images are generated based on processing. The processing includes determining displacement data between the first pulse echo and the echo of the second pulse for at least one structure in an imaged area; determining one or more displacement corrections based on the displacement data; applying at least one displacement correction to at least one of the first pulse echo and the echo of the second pulse; and combining the first pulse echo and the echo of the second pulse.
Owner:GE PRECISION HEALTHCARE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com