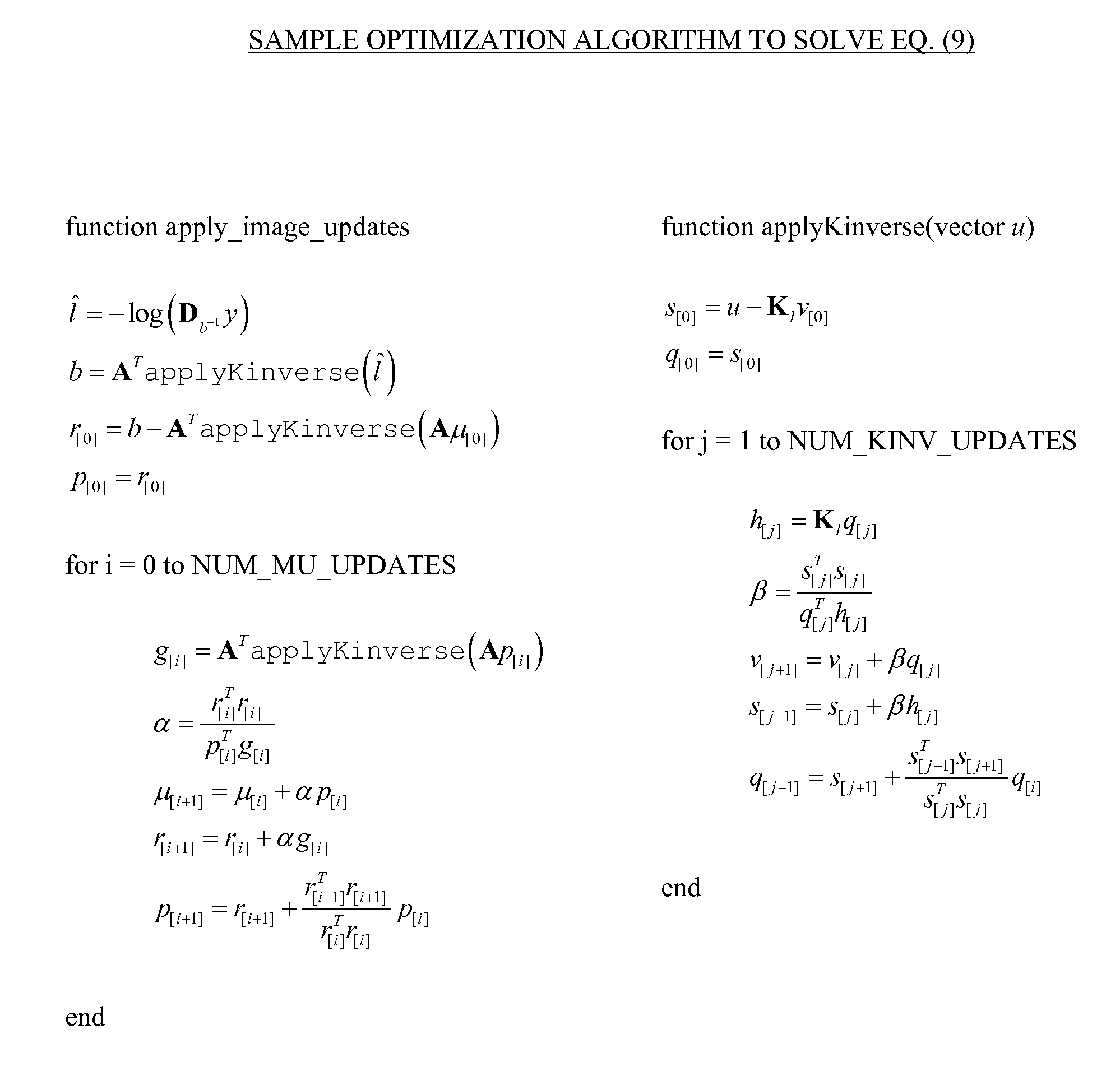Patents
Literature
72 results about "Temporal bone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
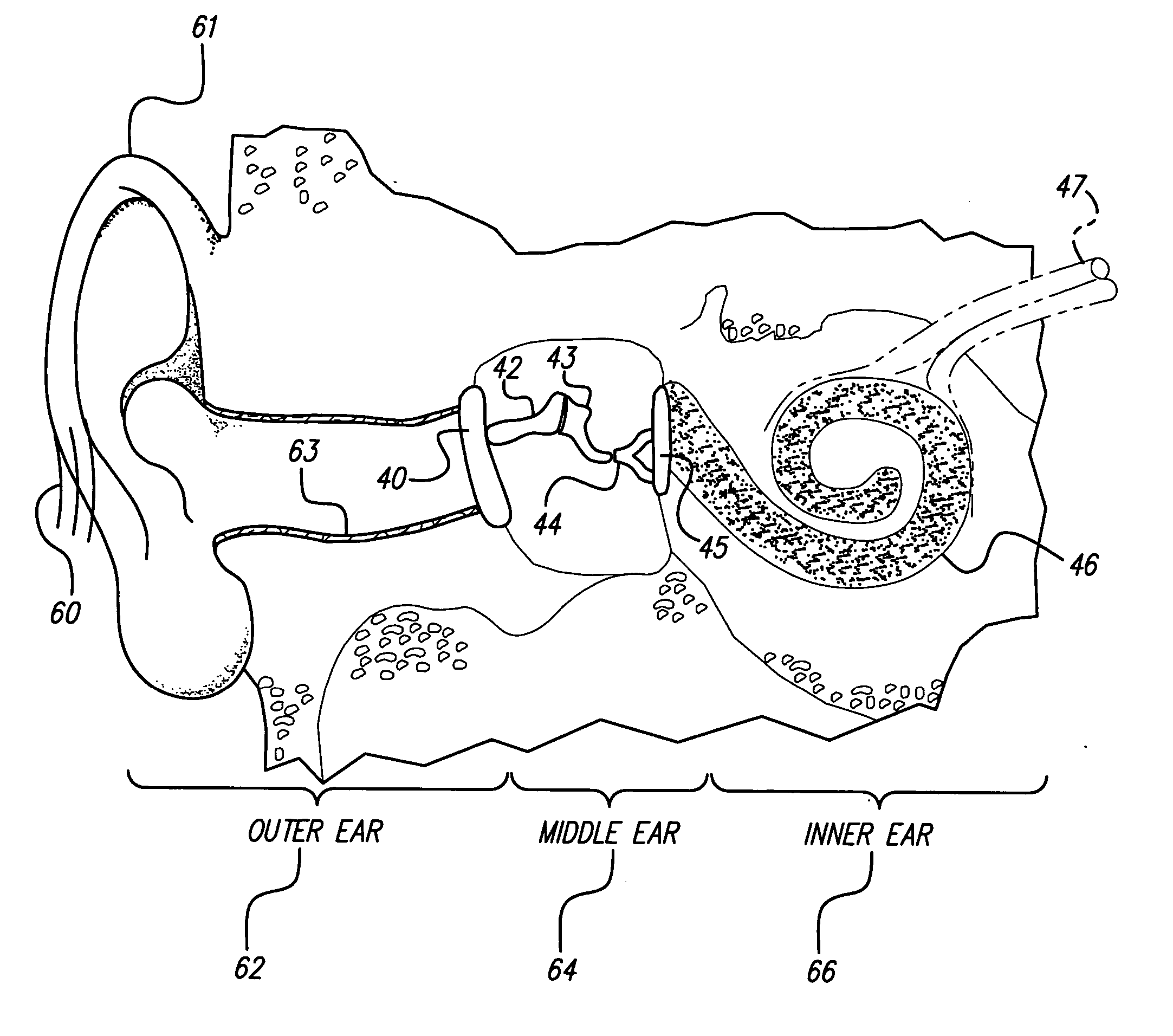
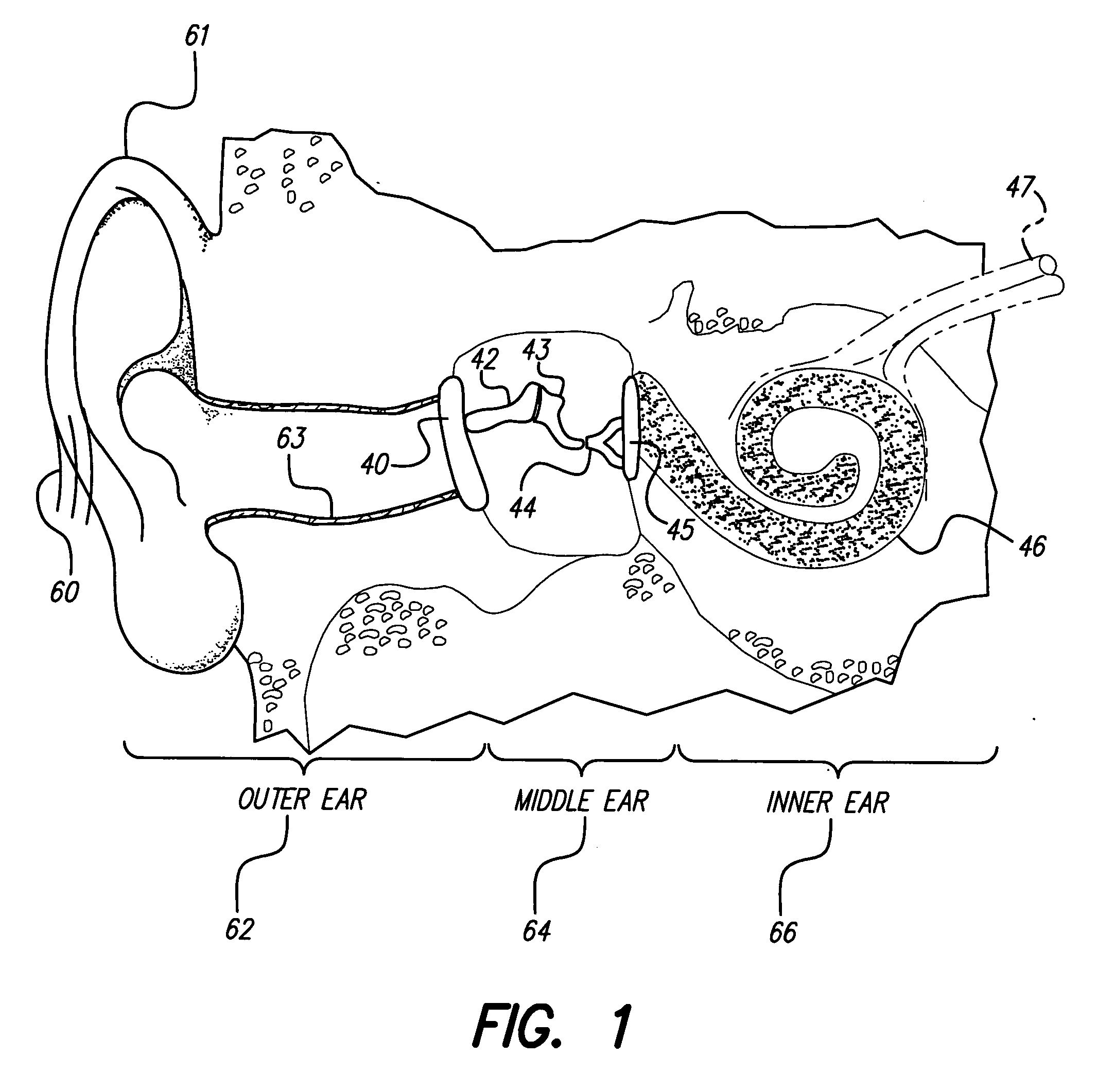
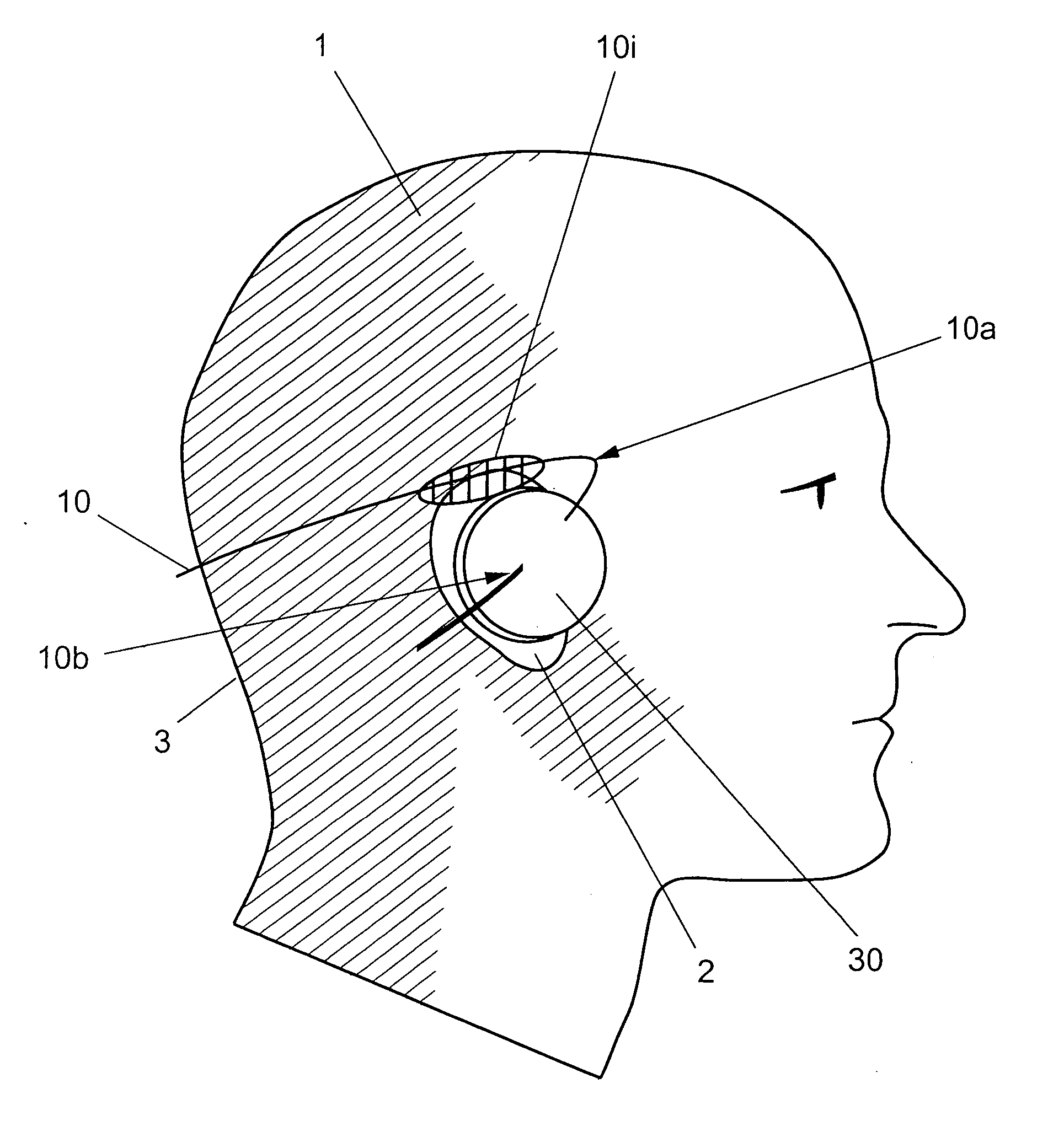
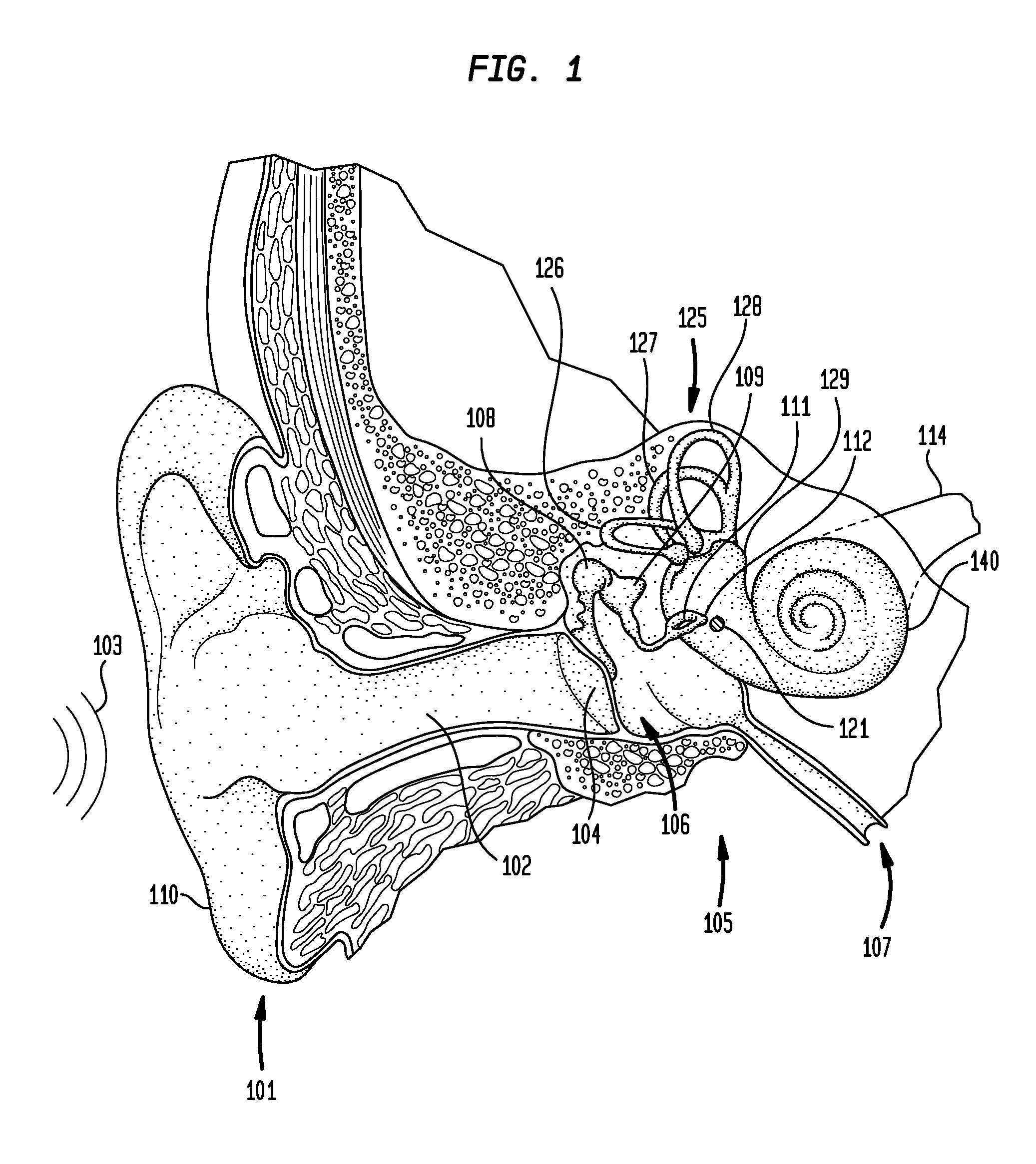
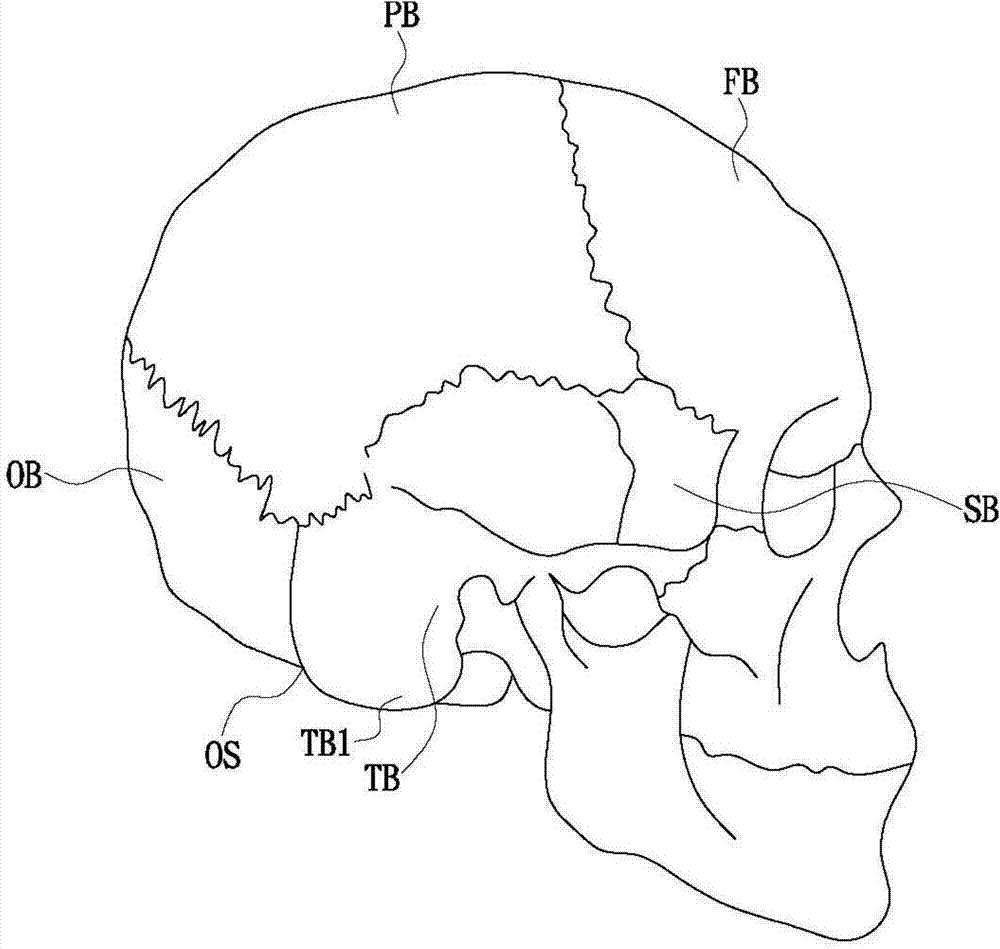
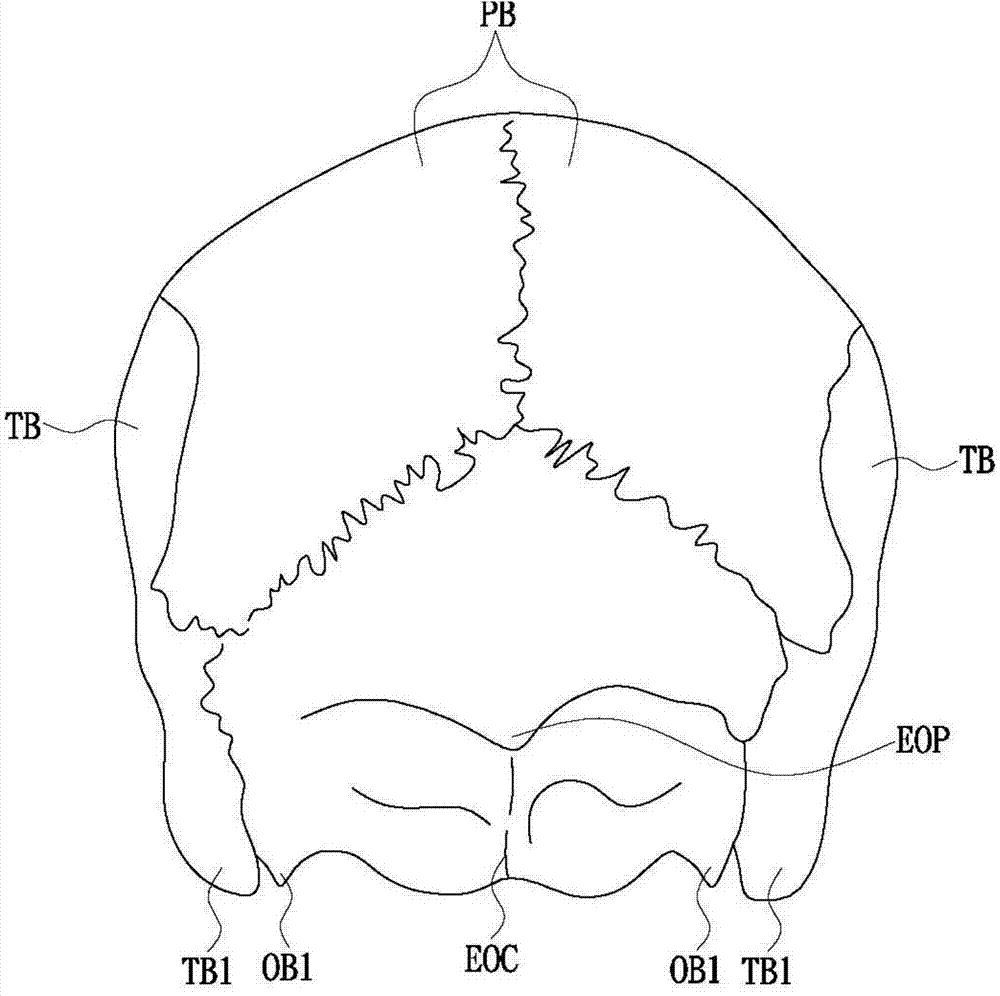
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples, and house the structures of the ears. The lower seven cranial nerves and the major vessels to and from the brain traverse the temporal bone.
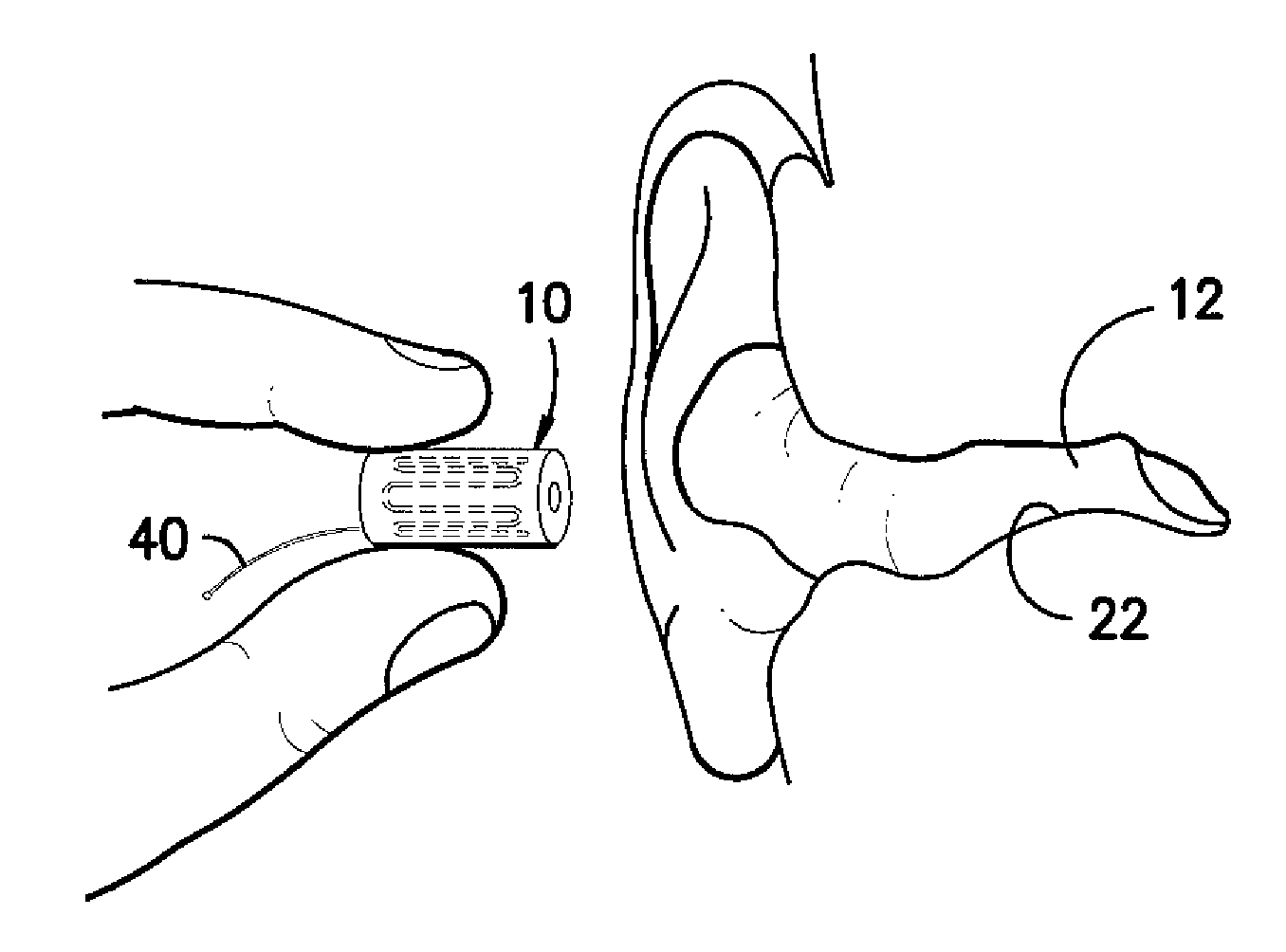
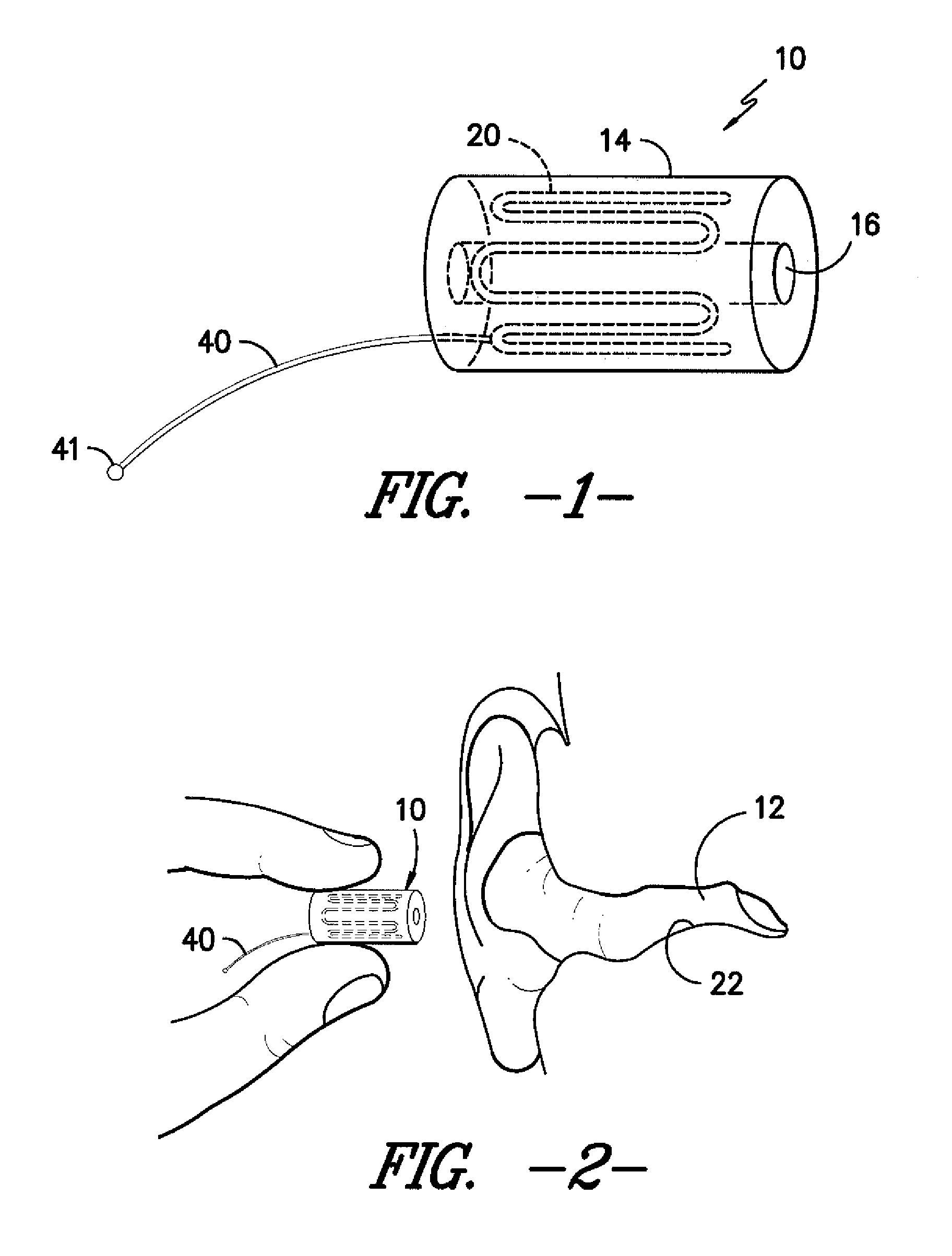
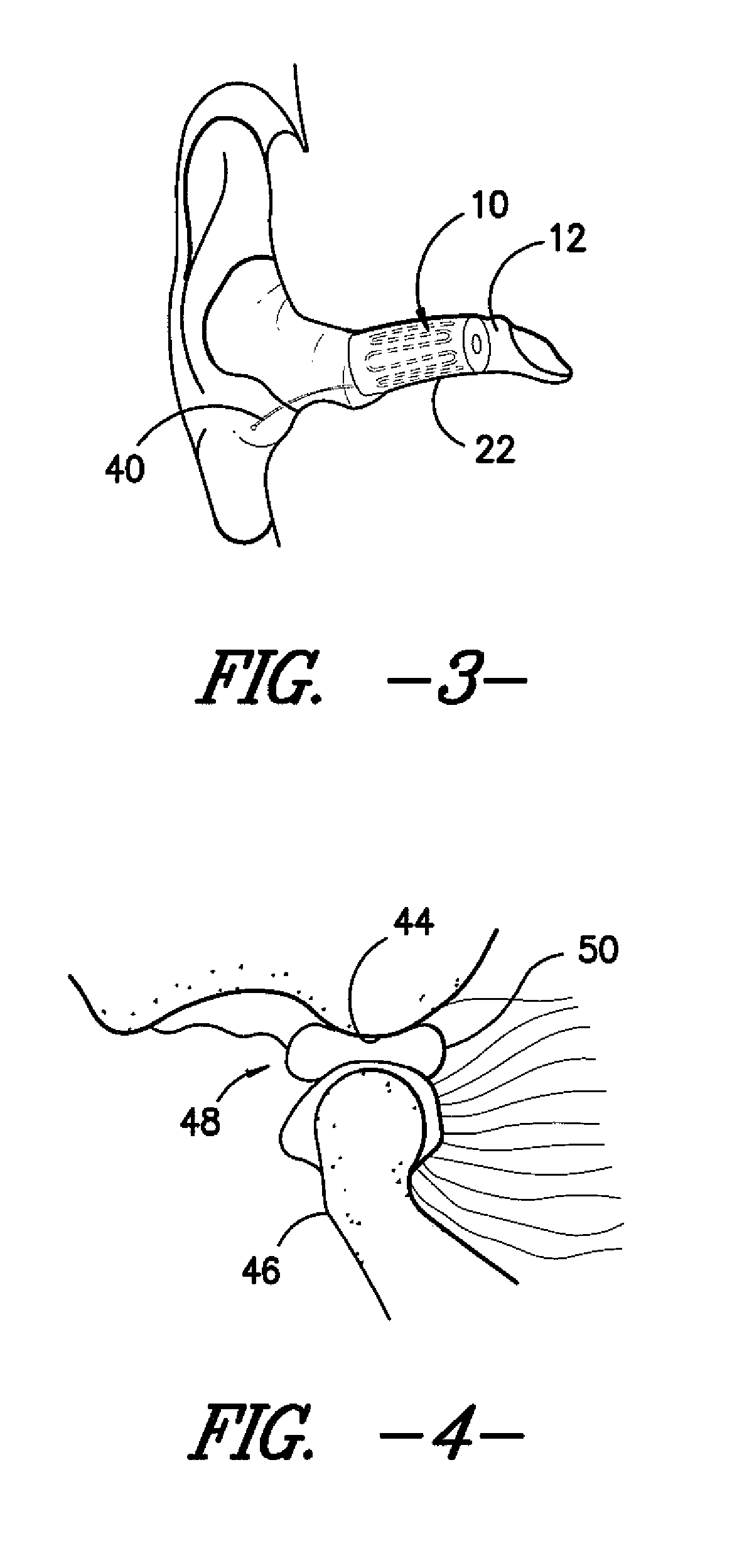
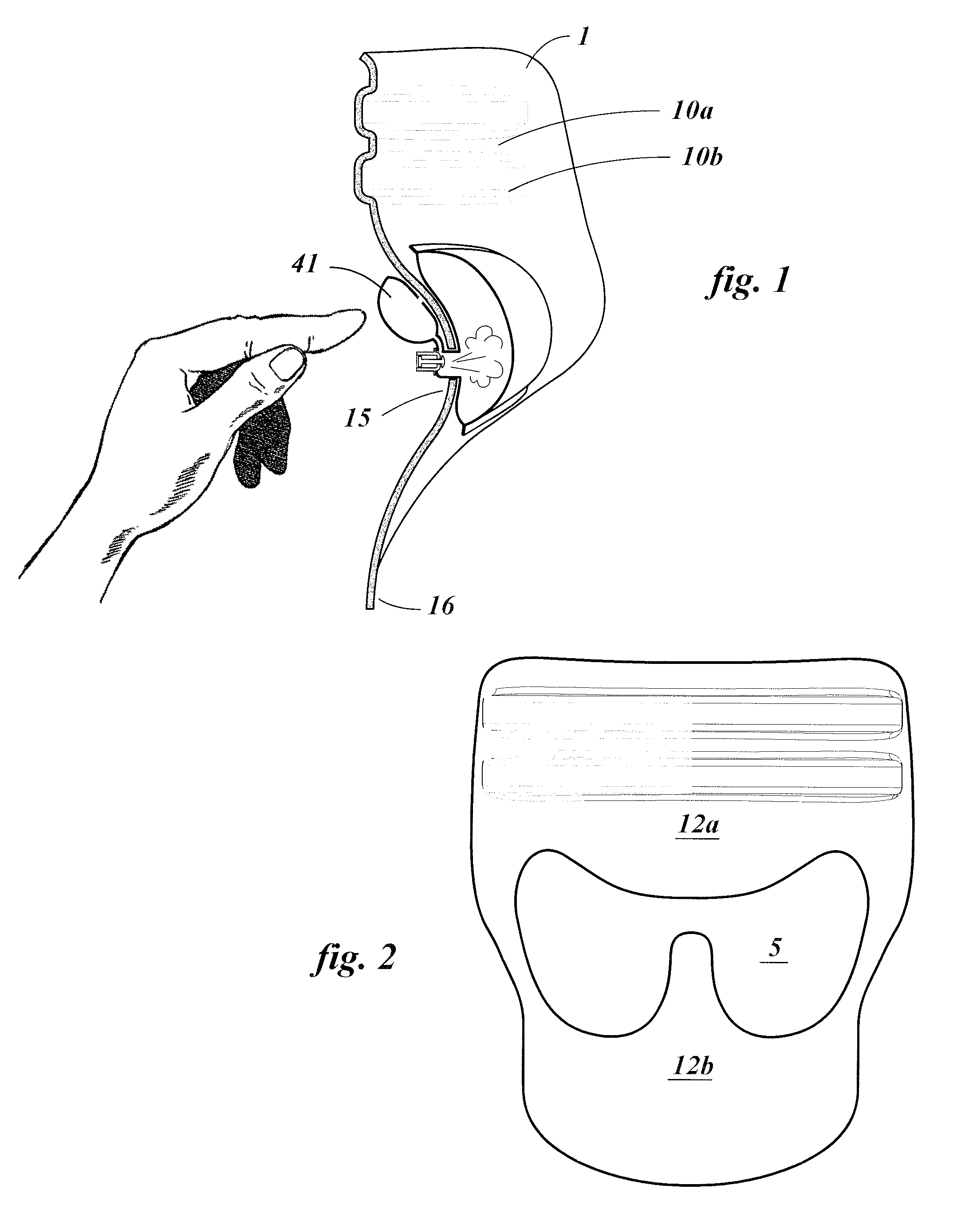
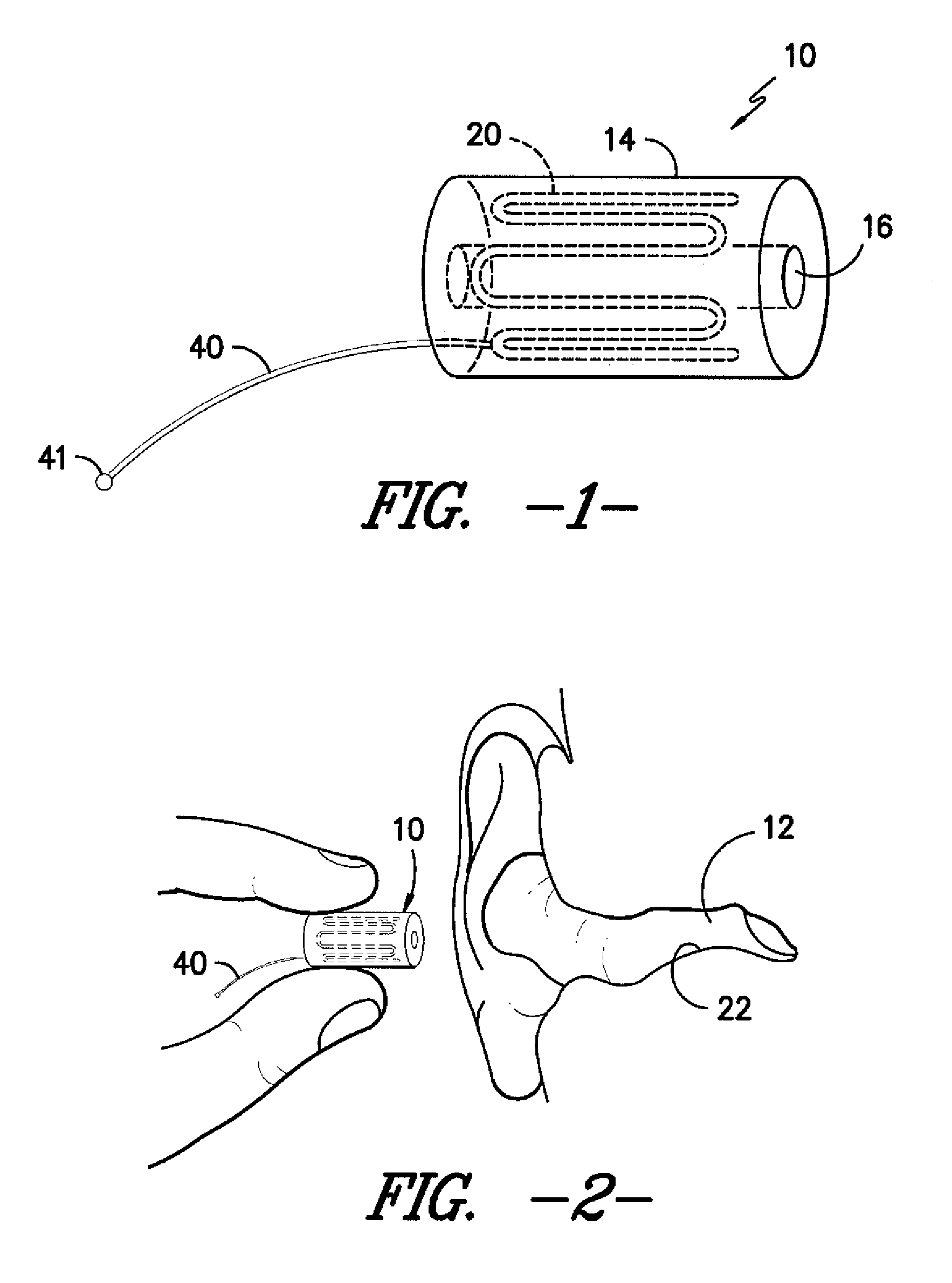
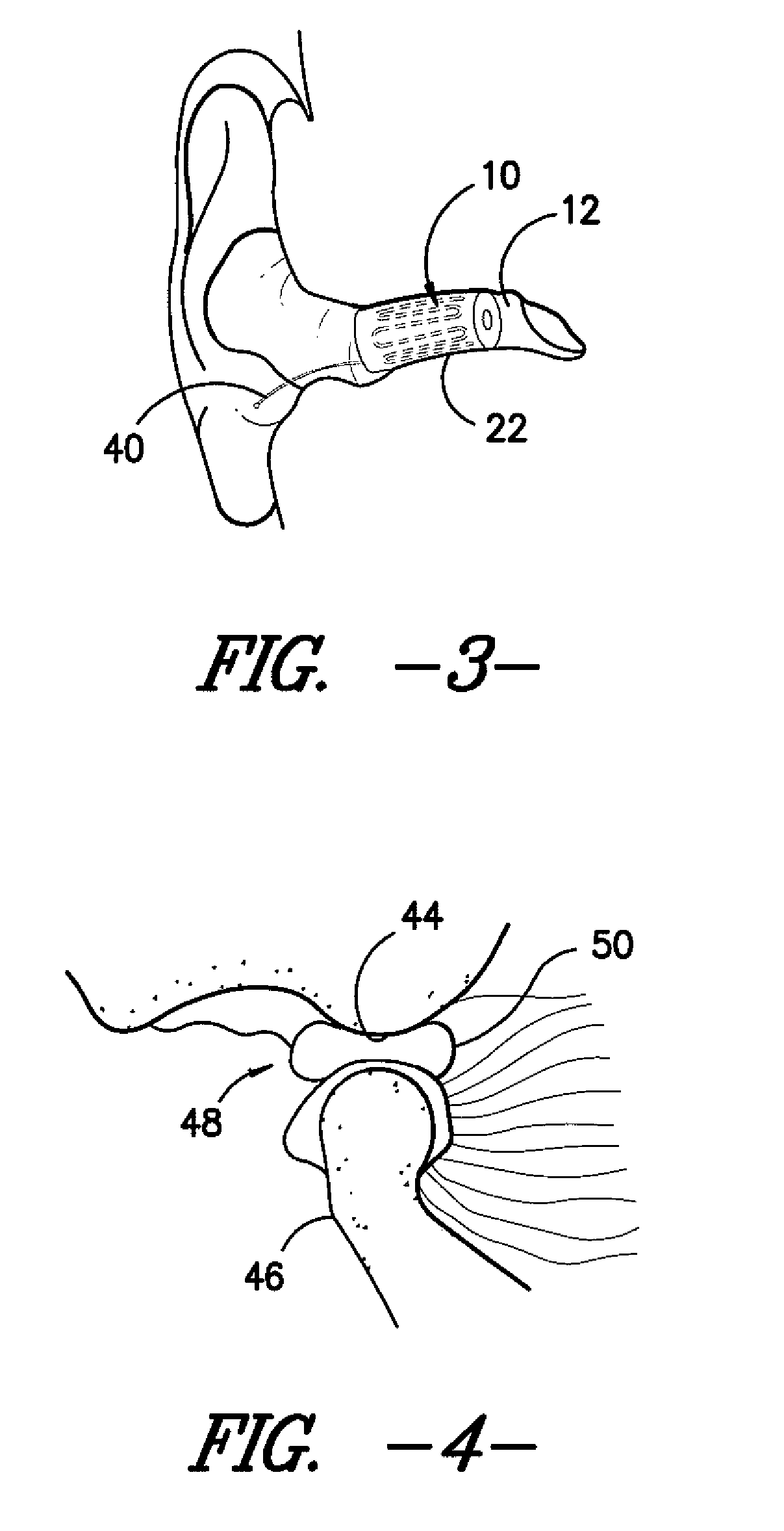
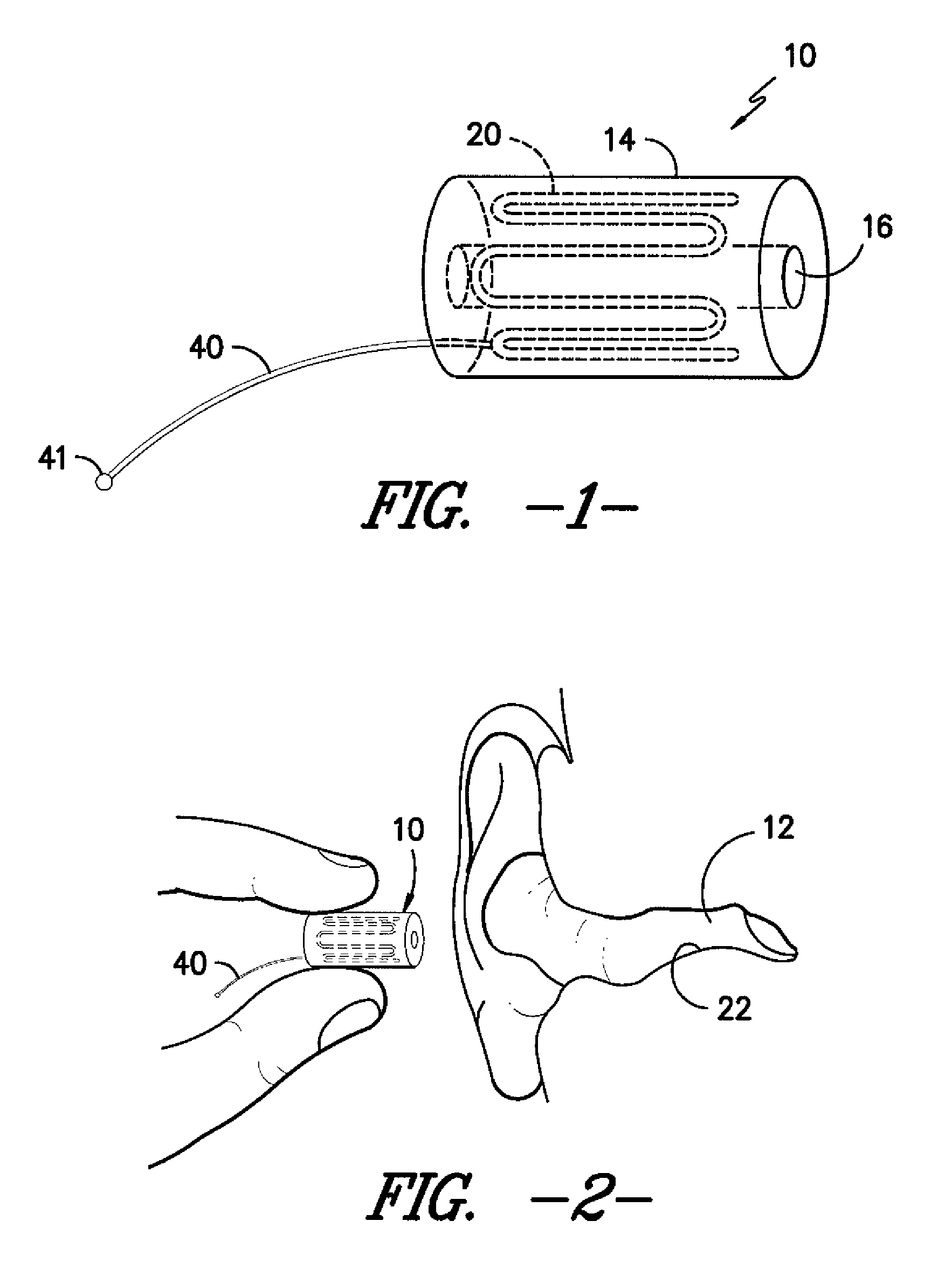
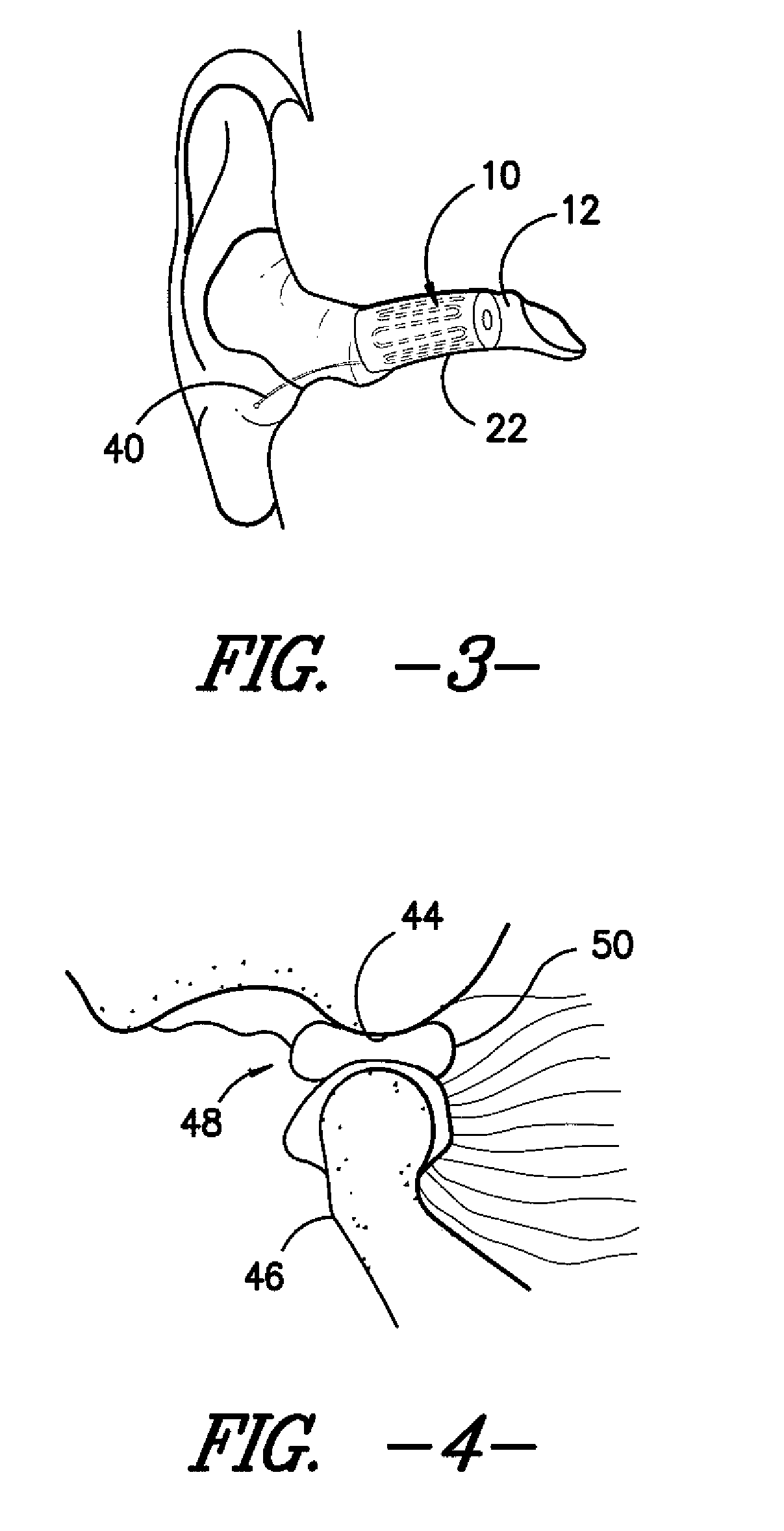
Ear insert for relief of tmj discomfort and headaches
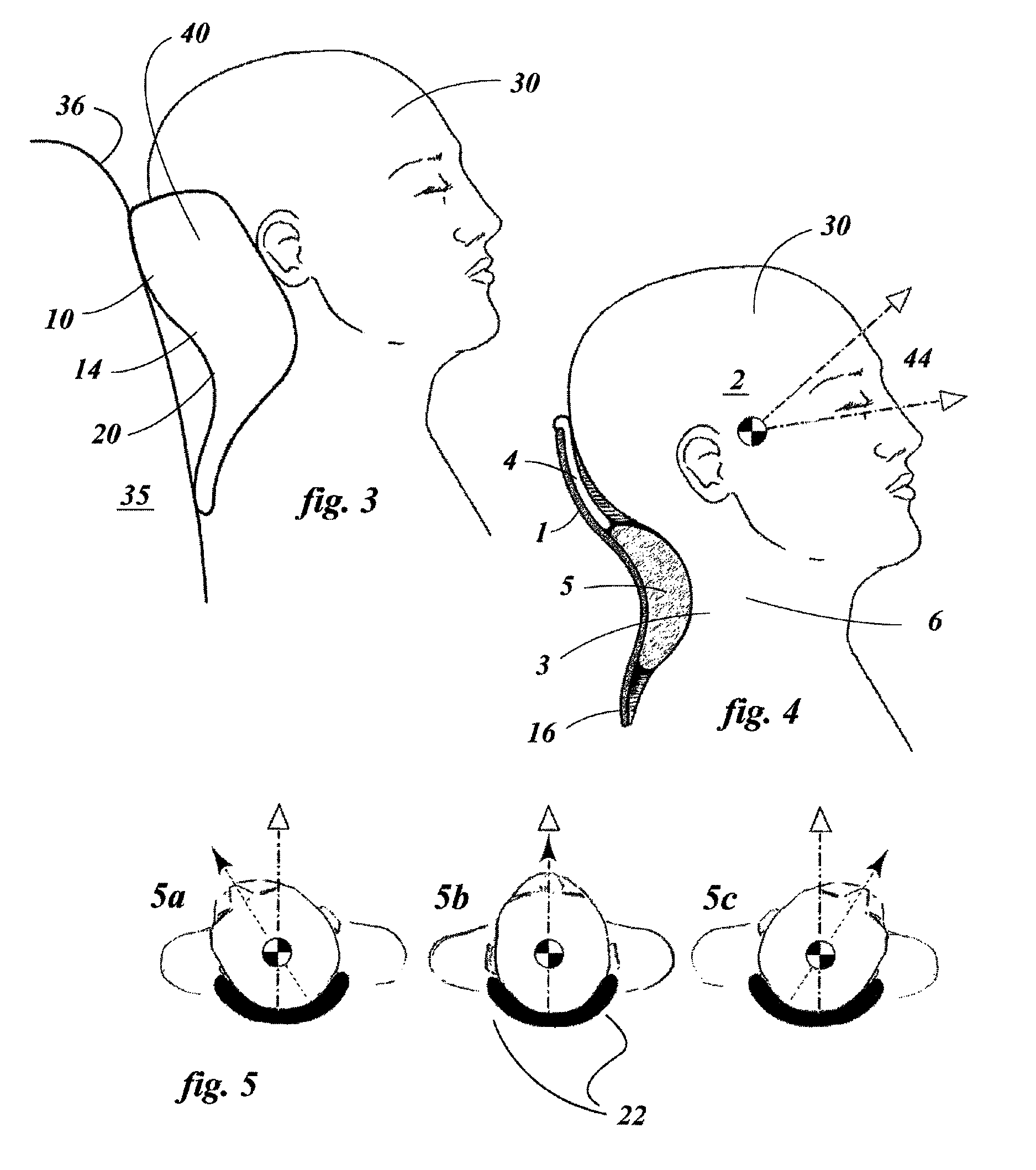
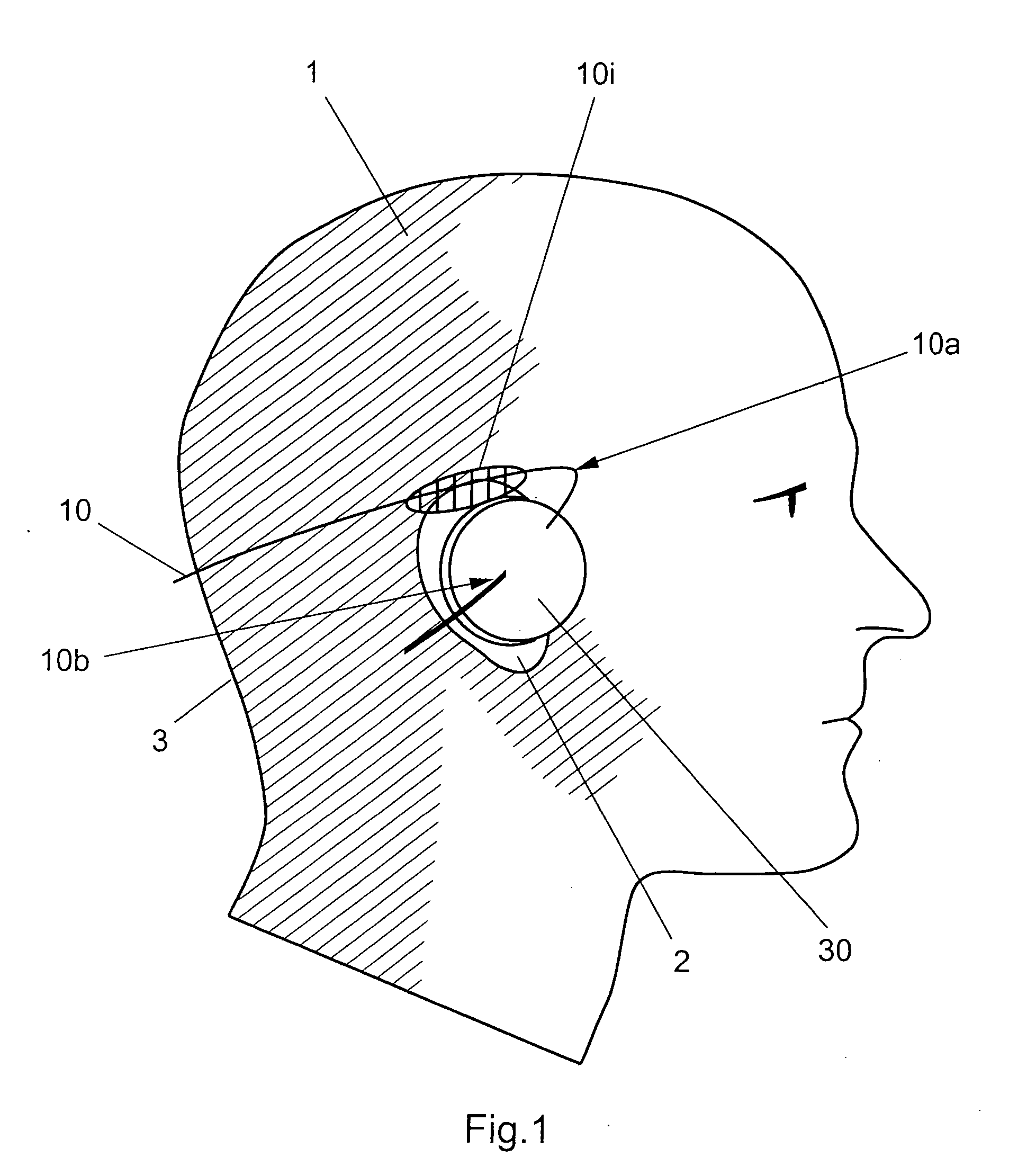
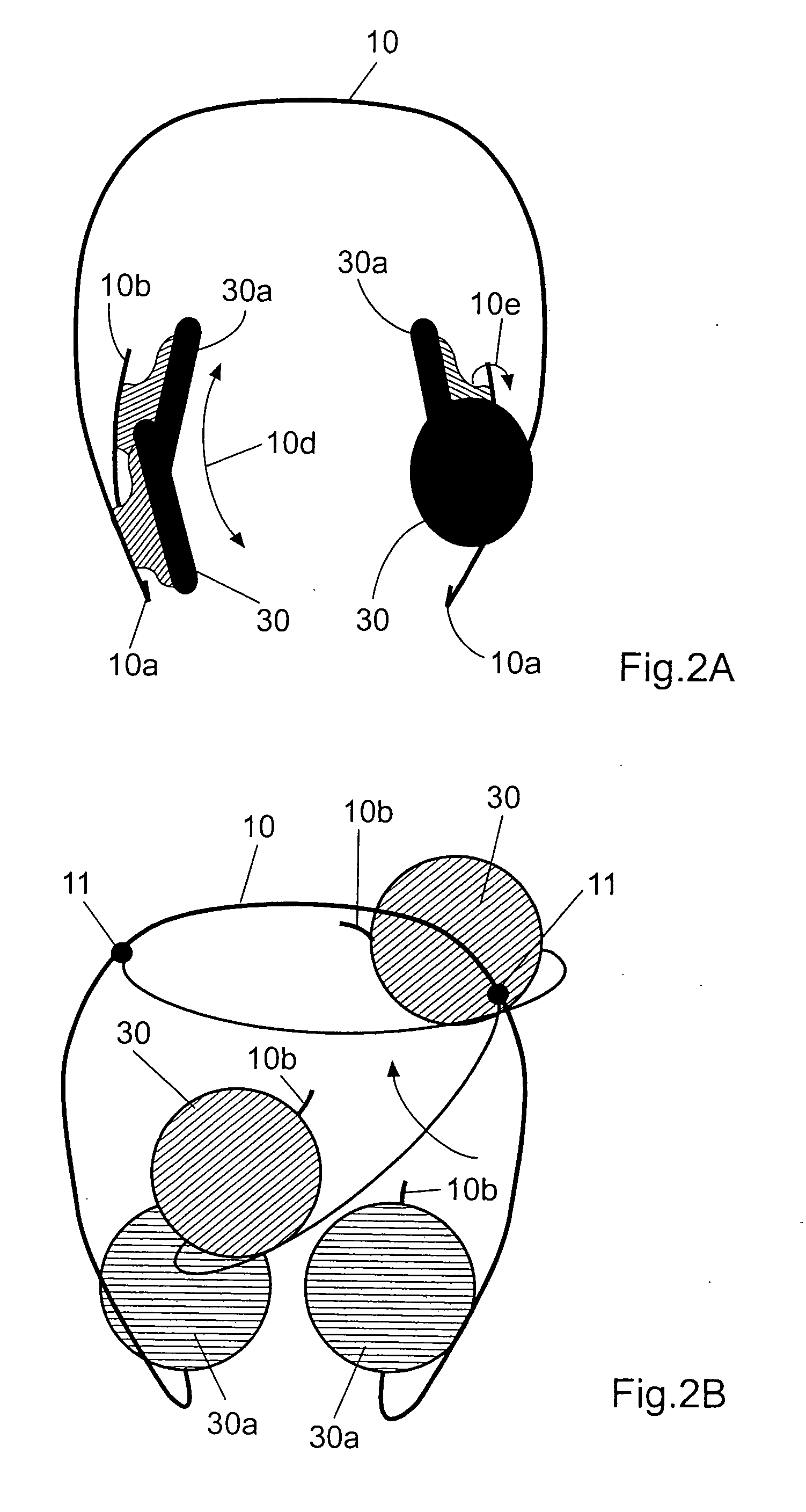
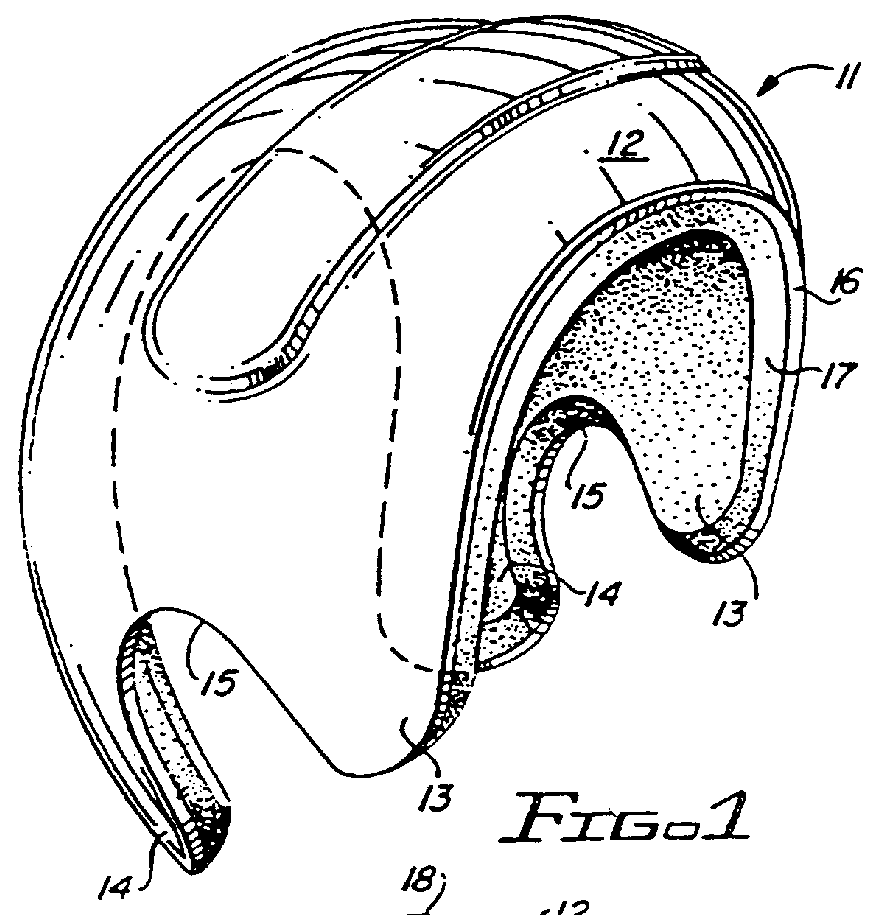
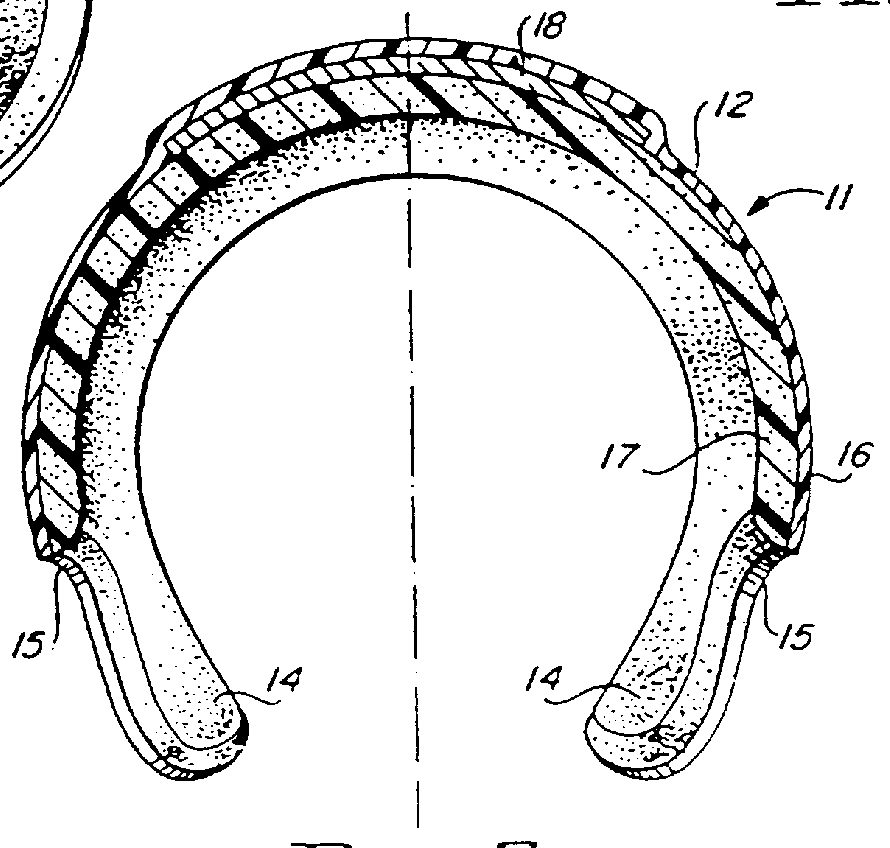
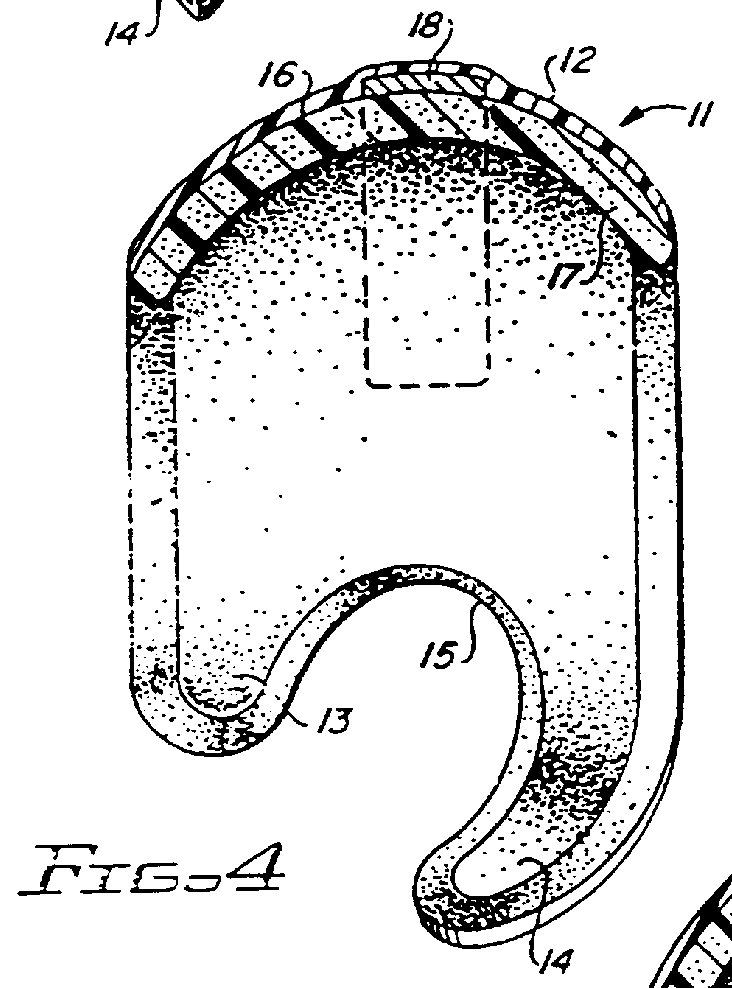
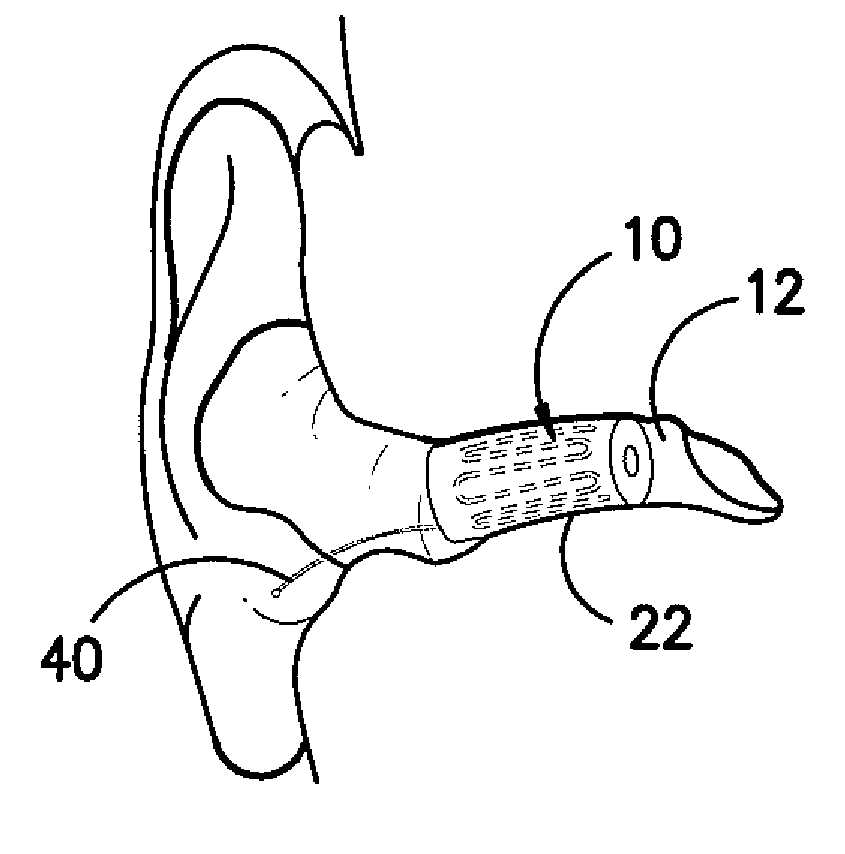
An expansible ear canal insert for treating TMJ disorders and headaches which acts directly on the TMJ and associated ligament and muscle structures to reduce stress and loads placed on the articulator disc located between the temporal bone and the mandible, as well as supportive muscles and ligaments near the TMJ. The insert is adapted to expand by application of body heat. In the expanded condition, the insert provides support to the TMJ and associated ligament and muscle structures.
Owner:RENEW GRP
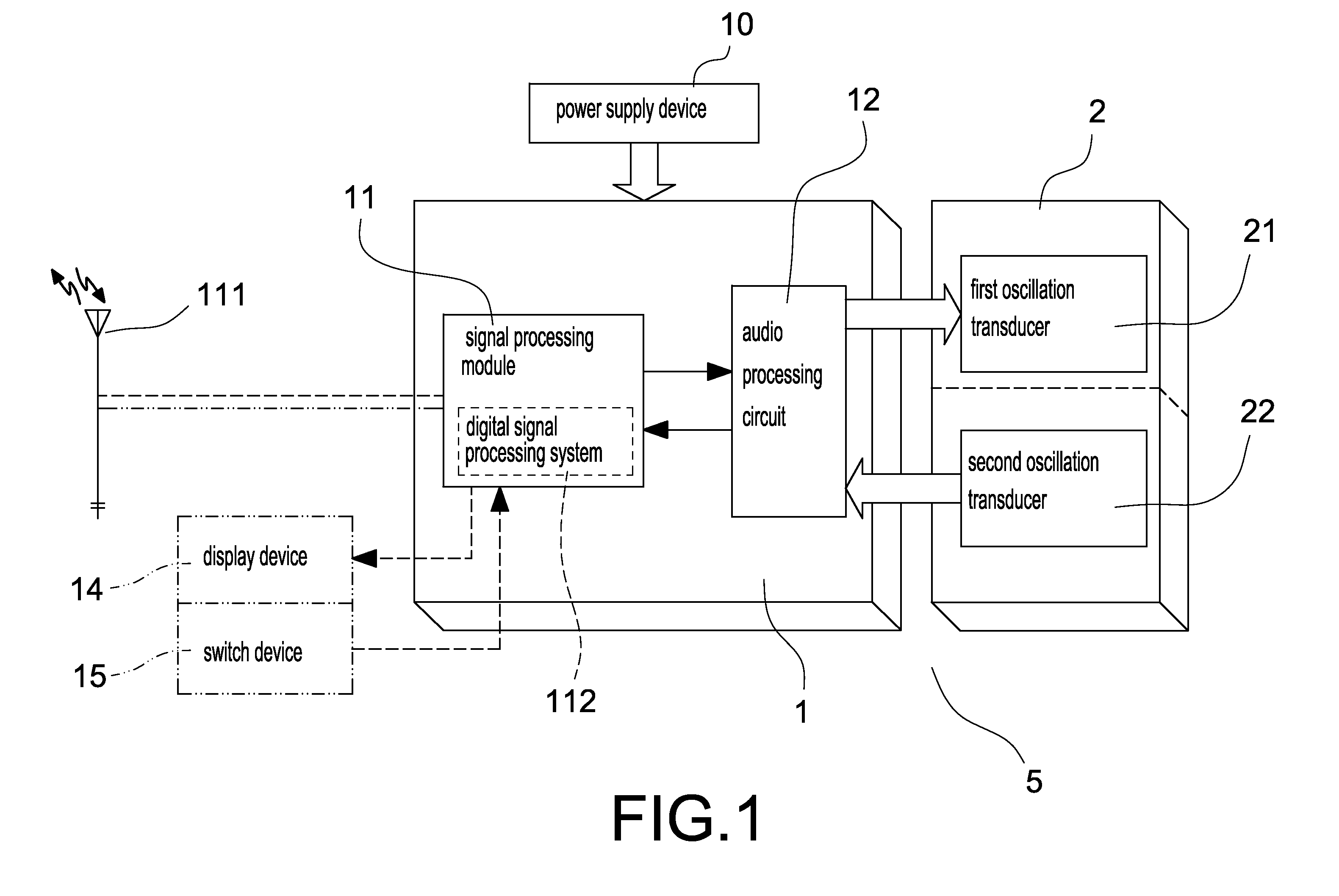
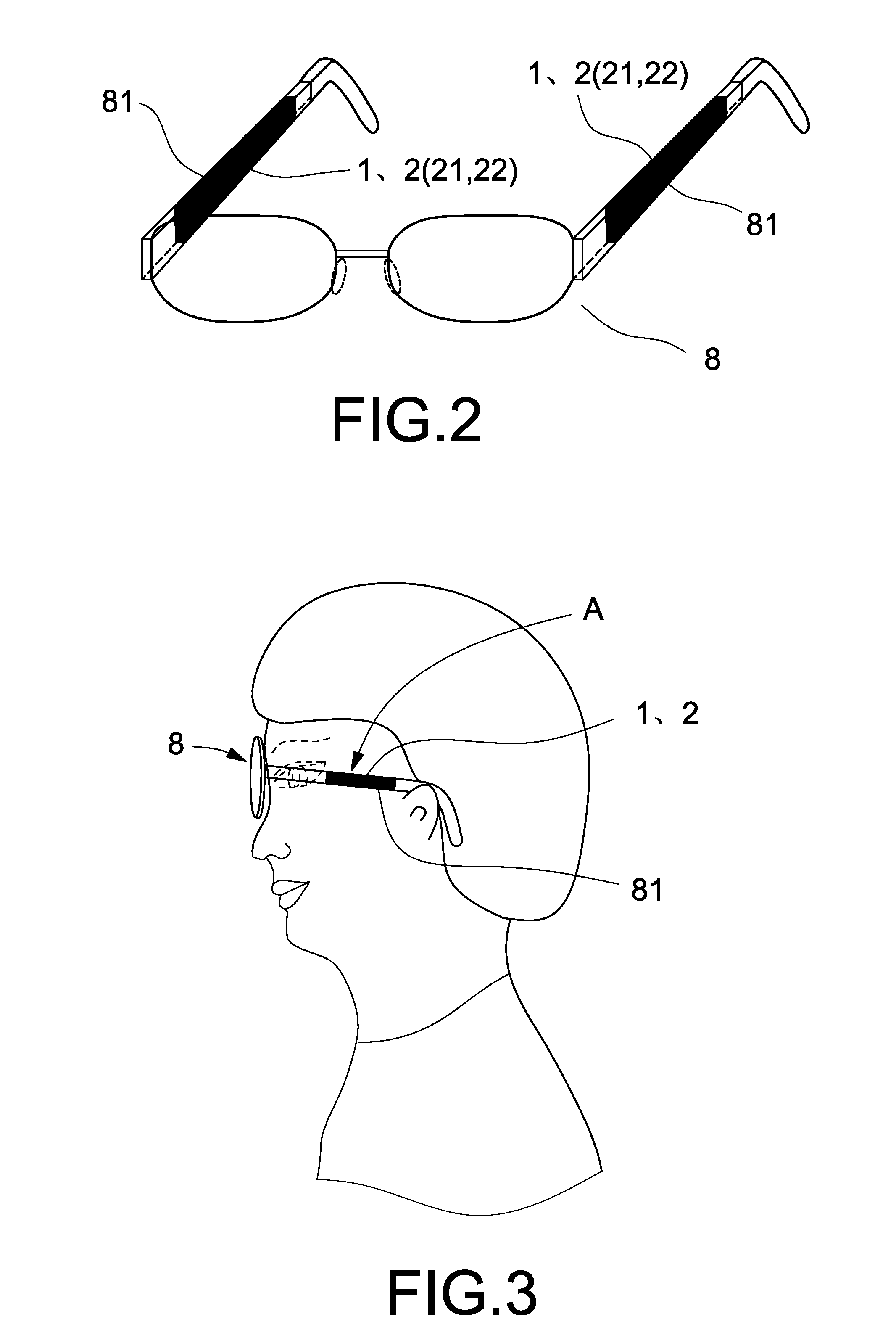
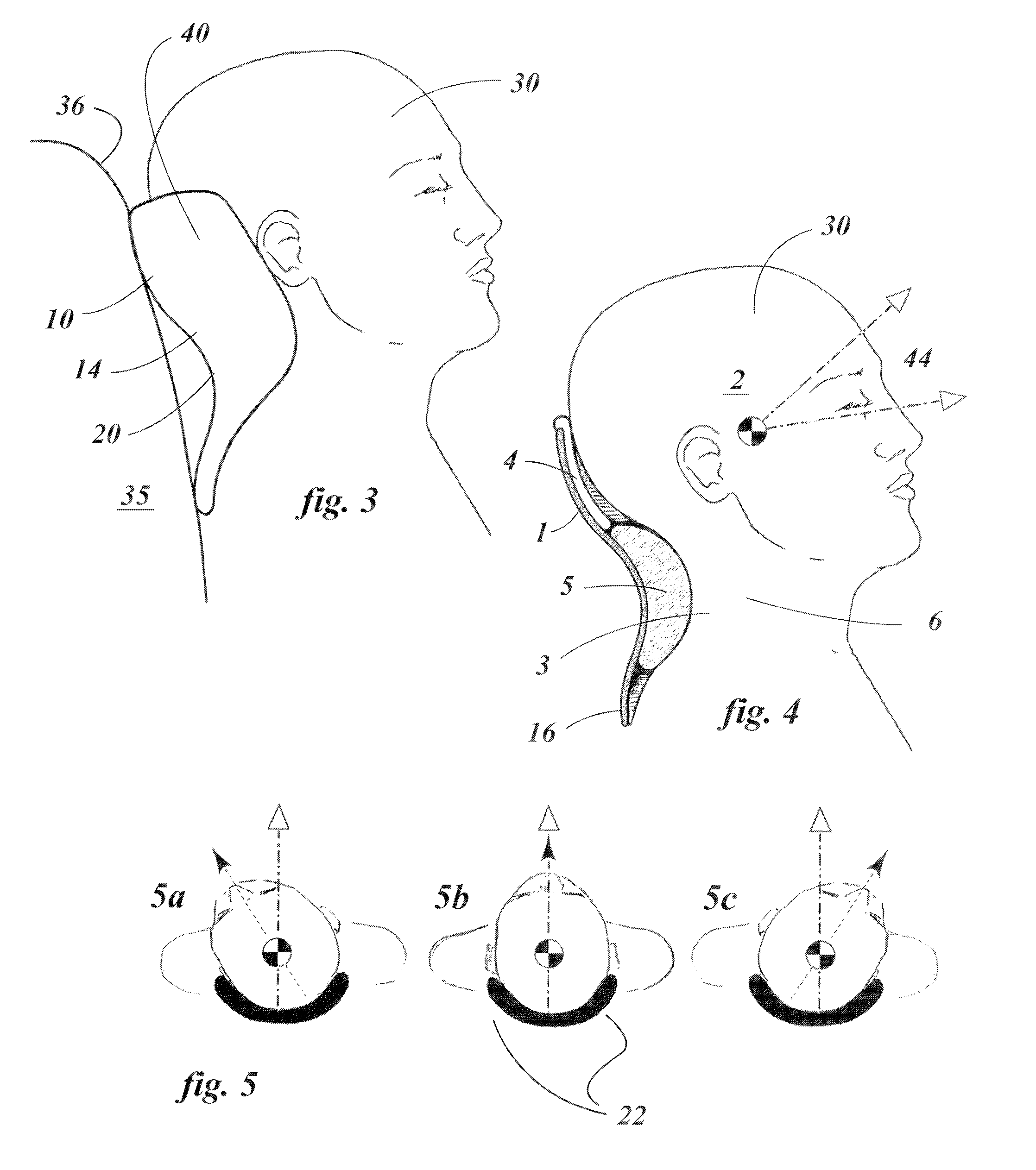
Spheno-temporal bone conduction communication equipment and/or hearing aid equipment
InactiveUS20110224481A1Eliminating external noise interferenceImprove ease of useNon-optical adjunctsDeaf-aid setsEngineeringBone conduction hearing
A spheno-temporal bone conduction communication equipment and / or hearing aid includes a system device, a bone skin conduction oscillator and a carrier device for supporting said abovementioned devices. The carrier device has a structural body, and the structural body allows the supported bone skin conduction oscillator in close contact with the spheno-temporal bone. The bone skin conduction oscillator contains a transducer, and the transducer converts an electrical signal into an acoustic oscillating wave and transmits the acoustic oscillating wave into the inner ear via spheno-temporal bone, or receives an acoustic oscillating wave produced by vibration of the skull when speaking and converts it into an electrical signal. The equipment implements bone conduction transmission of the acoustic oscillating wave via spheno-temporal bone, and can be used in bone conduction speaker, bone conduction microphone, bone conduction multimedia device, bone conduction hearing aid device or bone conduction communication device. The equipment can be used with a nasal bone conduction device, can avoid the defect of much external noise when using air conduction mode and overcome shortcomings of the structure easy to slide and inconvenience to add the component when using commonly used bone conduction.
Owner:NEOVICTORY TECH
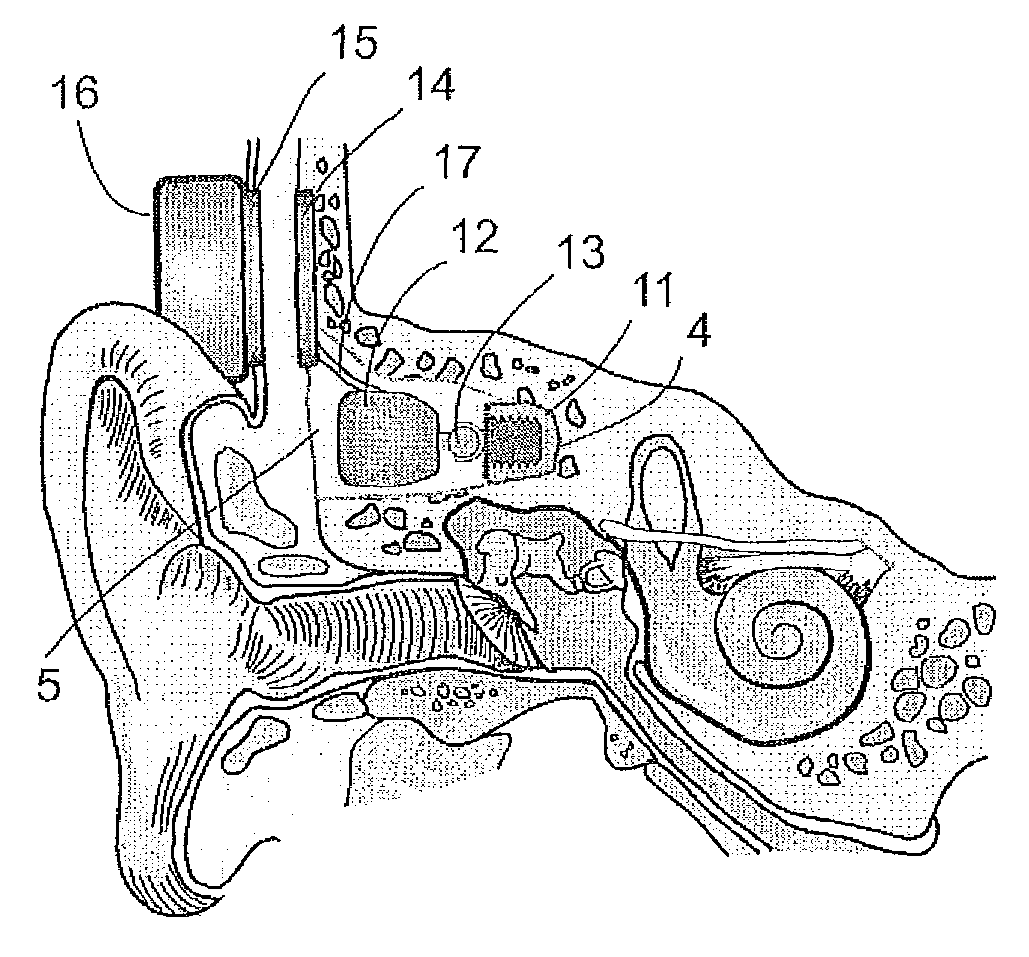
Implantable transducer
ActiveUS20090209806A1Easy to disassembleFastening effect becomes relatively lowElectrotherapyBone conduction transducer hearing devicesTransducerSkull bone
A method and device for connecting a bone conductor transducer contained in a housing to the skull bone for the transmission of vibrations characterized by, that the housing has at least one surface, which is placed against the bottom plane of a recess shaped in the temporal bone with a static force exceeding the dynamic signal forces.
Owner:OSSEOFON
Dental implants with external polygonal head
PCT No. PCT / ES97 / 00178 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 24, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 24, 1999 PCT Filed Jul. 15, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 03129 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 29, 1998The invention comprises the following elements: cervico-anatomical orientation posts (FIGS. 1-8) used in the first surgical operation, in order to help replace the dental pieces to be restored; cervico-anatomical temporal healing pillars, of the direct or indirect type (FIGS. 9-12) whose design is intended to provide the gingival tissues with the morphology necessary in the healing phase and the ideal housing for the artificial tooth. Transporter (FIGS. 13 and 14), this being the element which evaluates the orientation, depth and inclination of the implants; direct and indirect cervico-anatomical transfer pins (FIGS. 16-18), which copy the exact intraoral position of the implants and the peri-implantory soft tissues; parallelizer (FIGS. 19 and 20) which replicate the position of the polygonal head of the implant; hexagonal base (FIGS. 23 and 24) for angle pillars; surgical guides (FIGS. 25-36) presenting the directing piece, patterns, tubular parts for bone drilling and direction posts.
Owner:SALA MESEGUER JUAN CARLOS
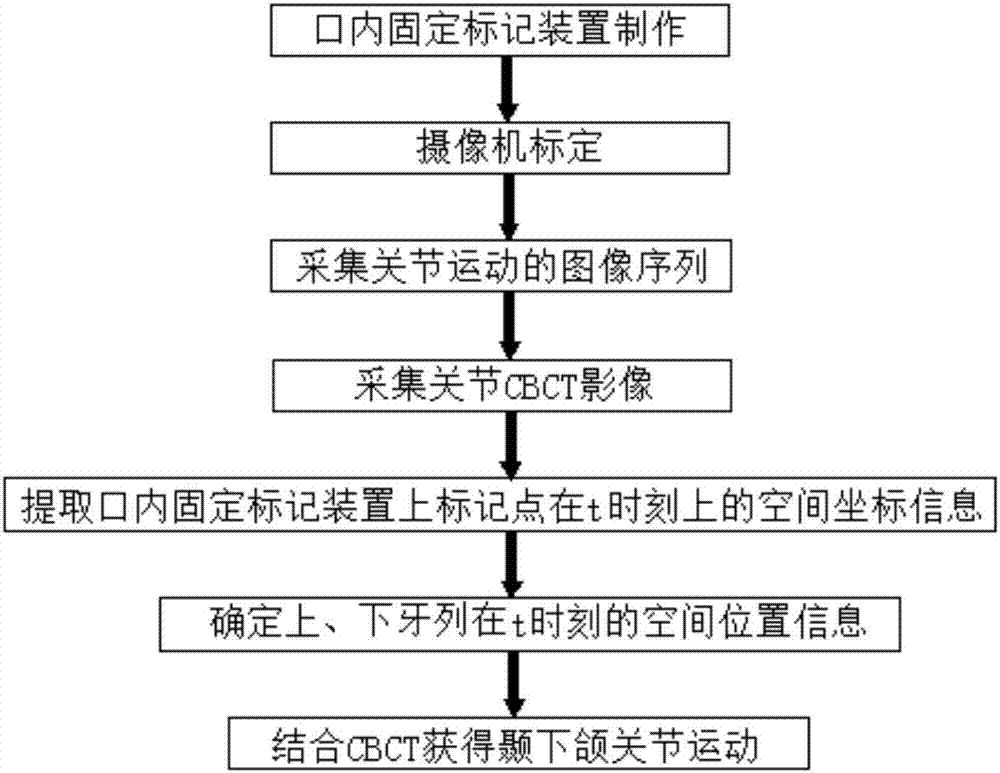
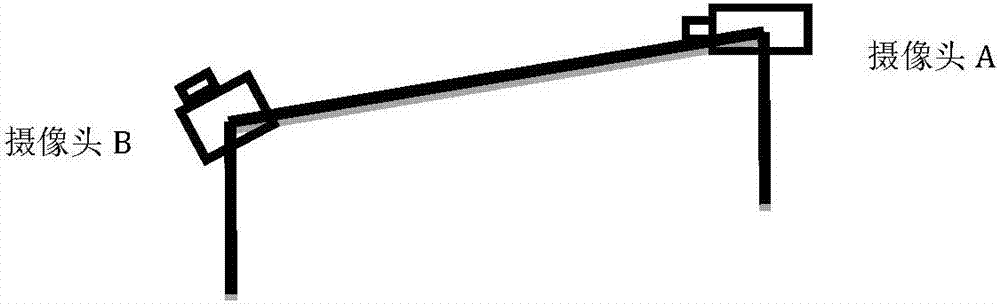
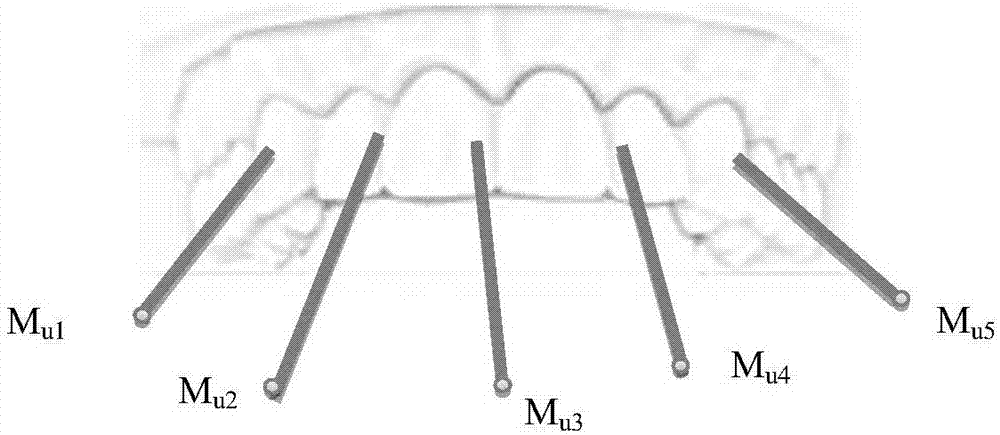
Temporomandibular joint movement reconstruction method and system thereof
ActiveCN106875432AIncreased means of diagnosisImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyTemporomandibular Joint Diseases
The invention provides a temporomandibular joint movement reconstruction method and a system thereof. The method is characterized by collecting an image sequence of a mark point track of open and close mouth mandible movements of a photographed person; determining three-dimensional coordinates of all the mark points on an intraoral fixed mark device in each frame of image, acquiring a movement track of each mark point in a space, and collecting a CBCT image of the intraoral fixed mark device and collecting a CBCT image of the photographed person; registering the mark point of the CBCT image of the intraoral fixed mark device with the mark point acquired by a camera through photographing, and acquiring a transformation matrix of a mark point movement; and using the transformation matrix to carry out rigid body transformation on the CBCT image of the photographed person, acquiring a CBCT image sequence of the photographed person and acquiring a temporomandibular movement image. In the invention, real movement conditions of mandible condyle process and a temporal bone joint surface of a human-body temporomandibular joint can be acquired, the method and the system can be used for auxiliary diagnosis of a temporomandibular joint disease and dynamic analysis of joint motion, temporomandibular joint diagnosis means are increased, doctor diagnosis accuracy and efficiency can be increased, and medical quality and efficiency can be increased too.
Owner:南京市图研医疗科技有限公司
Butterfly temporal bone conductive communication and/or hear-assisting device
InactiveCN101753221AIncrease in sizeIncrease the areaNon-optical adjunctsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersNoseBone conduction hearing
The invention relates to a butterfly temporal bone conductive communication and / or hear-assisting device which is provided with a system device, a bone skin conduction and oscillation device and a vehicle device loading the system device and the bone skin conduction and oscillation device; wherein the vehicle device is provided with a structural body which can closely contact the bone skin conduction and oscillation device and the butterfly temporal bone at the butterfly temporal bone part; in addition, the bone skin conduction and oscillation device comprises a energy converter for converting electric signals and sound oscillation waves, which can transmit sound oscillation waves to inner ear through the butterfly temporal bone by means of bone conduction and receive the oscillation waves generated by a sounding vibrating skull and convert the oscillation waves into electric signals; on the basis, since bone conductive communication of sound oscillation waves can be carried out at the butterfly temporal bone part, according to applications, the vehicle device can be used as a bone conduction loudspeaker, a bone conduction microphone, a bone conduction multi-media device or a bone conduction communication device; if a peripheral external audio acquisition device is added, the vehicle device can be used as a bone conduction hear-assisting device or a bone conduction communication hear-assisting device; if a nose bone conduction device is added, the vehicle device can be used as a nose butterfly temporal bone conduction communication or communication hear-assisting device for reducing external noise of an air conduction mode and conveniences brought about by structural sliding in frequently-used bone skin conduction mode or by additional installation of construction members.
Owner:NEOVICTORY TECH
Travel pillow providing head and neck alignment during use
Disclosed is a travel pillow for providing the head and neck alignment of a human user resting against a seat back. The travel pillow has an interior shell of a semi-stiff unitary construction. There is a head support region defining a head supporting space for supporting the user's head, a neck support region defining a neck supporting space for supporting the user's neck posteriorly, an enlarged portion bridging together the head support region and the neck support region, the enlarged portion varying in radius from the head support region to the neck support region all elements functioning together as a single unit to maintain the columnar alignment of the user's head directly above the user's neck, and lobes extending upwardly on either side of the head support region to support the head at the intersection of the occipital bone, parietal bone and temporal bones on either side of the head to prevent lateral bending of the neck. The pillow is placed between the user and the seat back, wherein the pillow is held in place during use by the user's weight resting against the seat back. The head support region may be sized and shaped to match the approximate shape of the back of the user's head. The head support region may be transversely curved about the user's vertebral axis and is cut away at the user's occiput such that the user's head rests directly against the seat headrest.
Owner:TANSINGCO EDWARD
Stimulation using a microstimulator to treat tinnitus
InactiveUS20070021804A1Good curative effectLittle to accommodateHead electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsNervous systemMiddle ear
An implantable microstimulator and a stimulating electrode are implanted to treat tinnitus. The microstimulator is connected to the stimulating electrode via a short, flexible lead. The electrode is implanted in the promontory of the cochlea or in the cochlear round window niche to deliver electrical stimulation to the auditory nervous system and thereby suppress or mask the tinnitus. The microstimulator may be surgically implanted through the ear canal, via a mastoidectomy or through the middle fossa, i.e., a supra-meatal approach. The microstimulator may be placed in middle ear cavity, a bony recess created in the bone surrounding the middle ear, the mastoid, the cochlea or a part of the temporal bone. In addition, the system may further include a test electrode, a test stimulator and a remote programming device that employs a bi-directional radio-frequency communication link to control and program the microstimulator and the test stimulator.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
Heaphone with behind-the-head headband
InactiveUS20070071269A1Minimum contact pressureImprove acousticsInterconnection arrangementsBroadcast circuit arrangementsTransducerEngineering
There is provided a headphone with a behind-the-head headband comprising at least one transducer and a behind-the-head headband for receiving the transducer. The behind-the-head headband further comprises first and second contact locations for resting against a temporal bone of a wearer of the headphone. The spacing between the transducer and the first or second contact location can be adjusted. By virtue of the possibility of adjusting the spacing with respect to the contact location the transducer can be positioned exactly over the auditory channel of the headphone wearer without pressure points on the ear.
Owner:SENNHEISER ELECTRONICS GMBH & CO KG
Travel pillow providing head and neck alignment during use
InactiveUS20110094035A1Prevent lateral bendingRelieve painPillowsVehicle seatsHuman useRight parietal bone
Disclosed is a travel pillow for providing the head and neck alignment of a human user resting against a seat back. The travel pillow has an interior shell of a semi-stiff unitary construction. There is a head support region defining a head supporting space for supporting the user's head, a neck support region defining a neck supporting space for supporting the user's neck posteriorly, an enlarged portion bridging together the head support region and the neck support region, the enlarged portion varying in radius from the head support region to the neck support region all elements functioning together as a single unit to maintain the columnar alignment of the user's head directly above the user's neck, and lobes extending upwardly on either side of the head support region to support the head at the intersection of the occipital bone, parietal bone and temporal bones on either side of the head to prevent lateral bending of the neck. The pillow is placed between the user and the seat back, wherein the pillow is held in place during use by the user's weight resting against the seat back. The head support region may be sized and shaped to match the approximate shape of the back of the user's head. The head support region may be transversely curved about the user's vertebral axis and is cut away at the user's occiput such that the user's head rests directly against the seat headrest.
Owner:TANSINGCO EDWARD
Implantable transducer
ActiveUS8241201B2Easy to disassembleHighly preventive effectElectrotherapyBone conduction transducer hearing devicesTransducerSkull bone
A method and device for connecting a bone conductor transducer contained in a housing to the skull bone for the transmission of vibrations characterized by, that the housing has at least one surface, which is placed against the bottom plane of a recess shaped in the temporal bone with a static force exceeding the dynamic signal forces.
Owner:OSSEOFON AB
Hearing aid
ActiveUS20180160242A1Prevent movementAvoid contactIn the ear hearing aidsBone conduction transducer hearing devicesMedicineBone implant
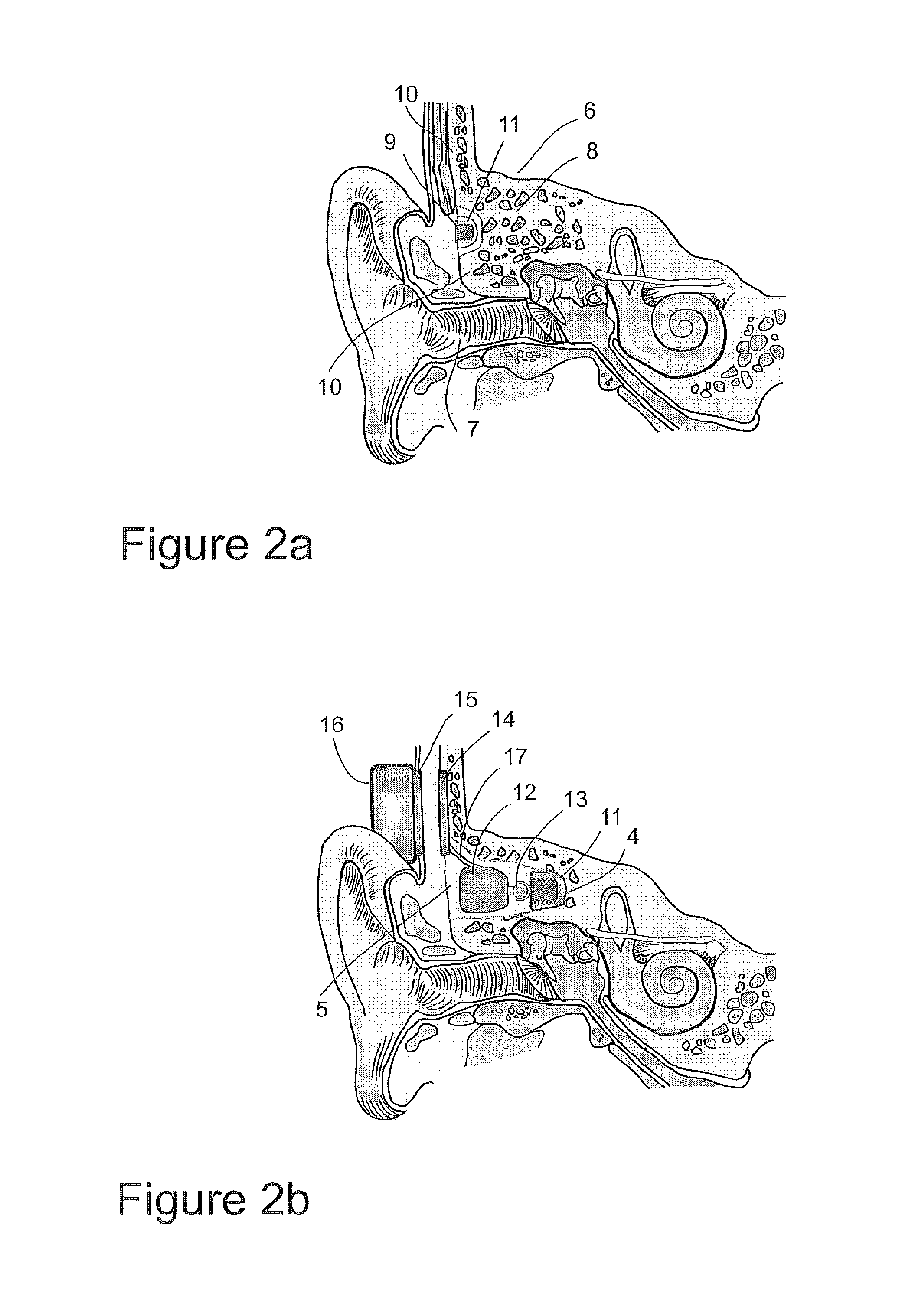
Apparatus for assisting hearing, the apparatus comprising: an in-ear component for insertion into the ear canal and comprising an electromagnet; and a bone implant for mounting in the temporal bone bordering the ear canal, the bone implant comprising a housing and a magnetic mass suspended within the housing such that vibrations of the magnetic mass are mechanically coupled into the housing; wherein the in-ear component is configured to drive its electromagnet so as to, when the in-ear component is located in an ear canal with the electromagnet adjacent to the bone implant, cause the magnetic mass to vibrate within the housing.
Owner:SRIS TECH LTD
Cranial remodeling orthosis
A cranial remodeling orthosis is shaped to extend across the top of the head with depending regions closely confining the temporal bone regions and the mastoid process regions of the cranium. The orthosis is self-suspending and preferably includes an elastic band for imparting ear-to-ear rigidity to the device.
Owner:CRANIAL TECH
Ear insert for relief of tmj discomfort and headaches
InactiveUS20110066176A1Reduce loadReduce stressDevices for pressing relfex pointsSurgeryDental ArticulatorsHeadaches
An expansible ear canal insert for treating TMJ disorders and headaches which acts directly on the TMJ and associated ligament and muscle structures to reduce stress and loads placed on the articulator disc located between the temporal bone and the mandible, as well as supportive muscles and ligaments near the TMJ. The insert is adapted to expand by application of body heat. In the expanded condition, the insert provides support to the TMJ and associated ligament and muscle structures.
Owner:RENEW GRP
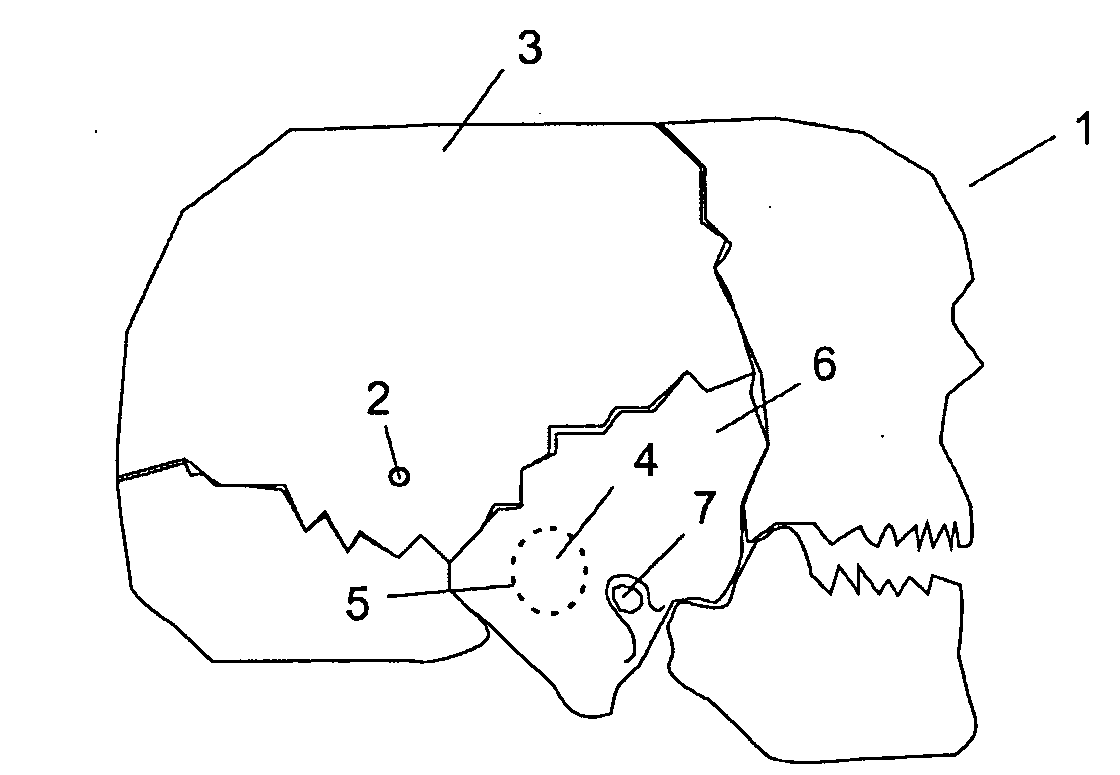
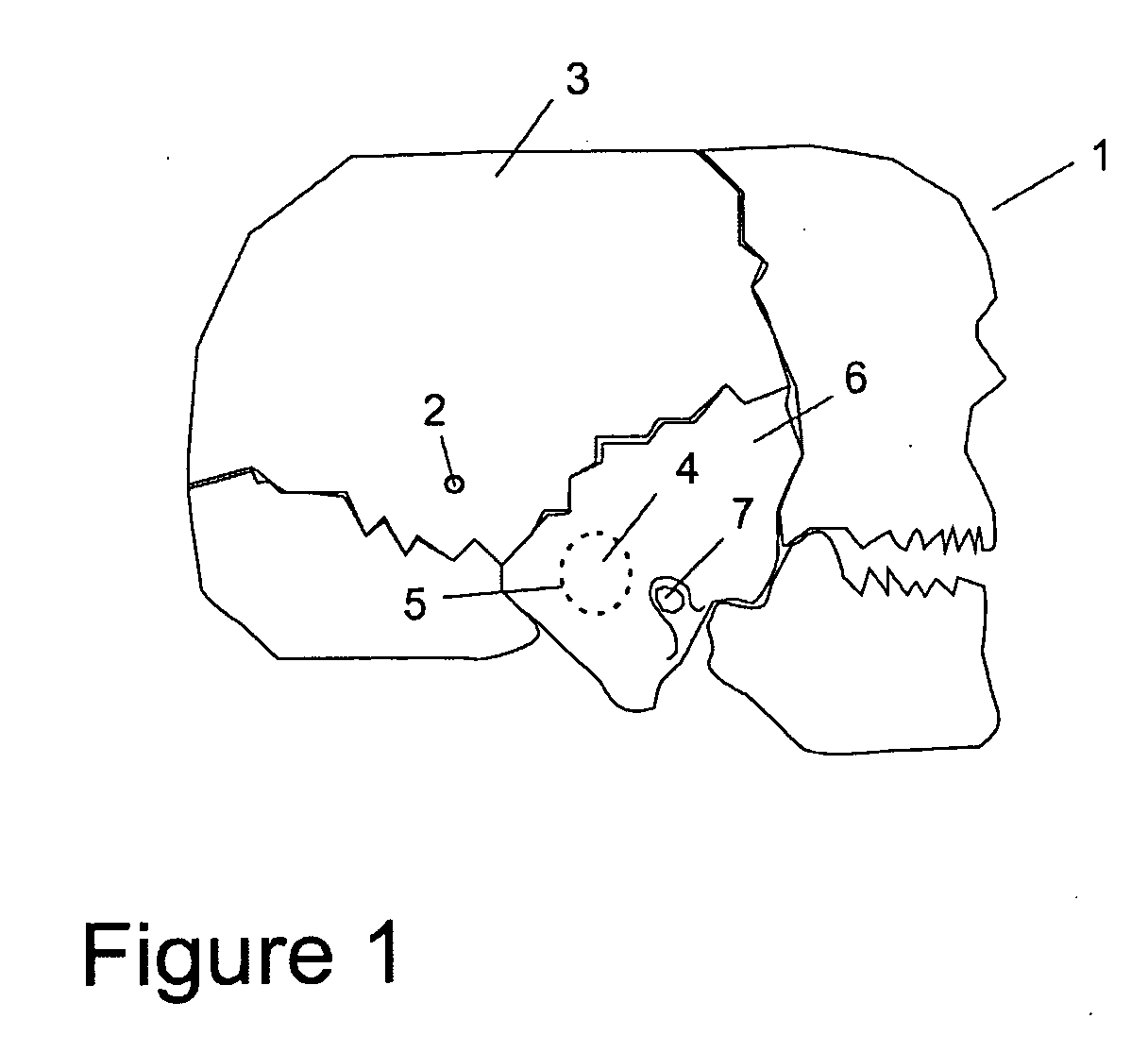
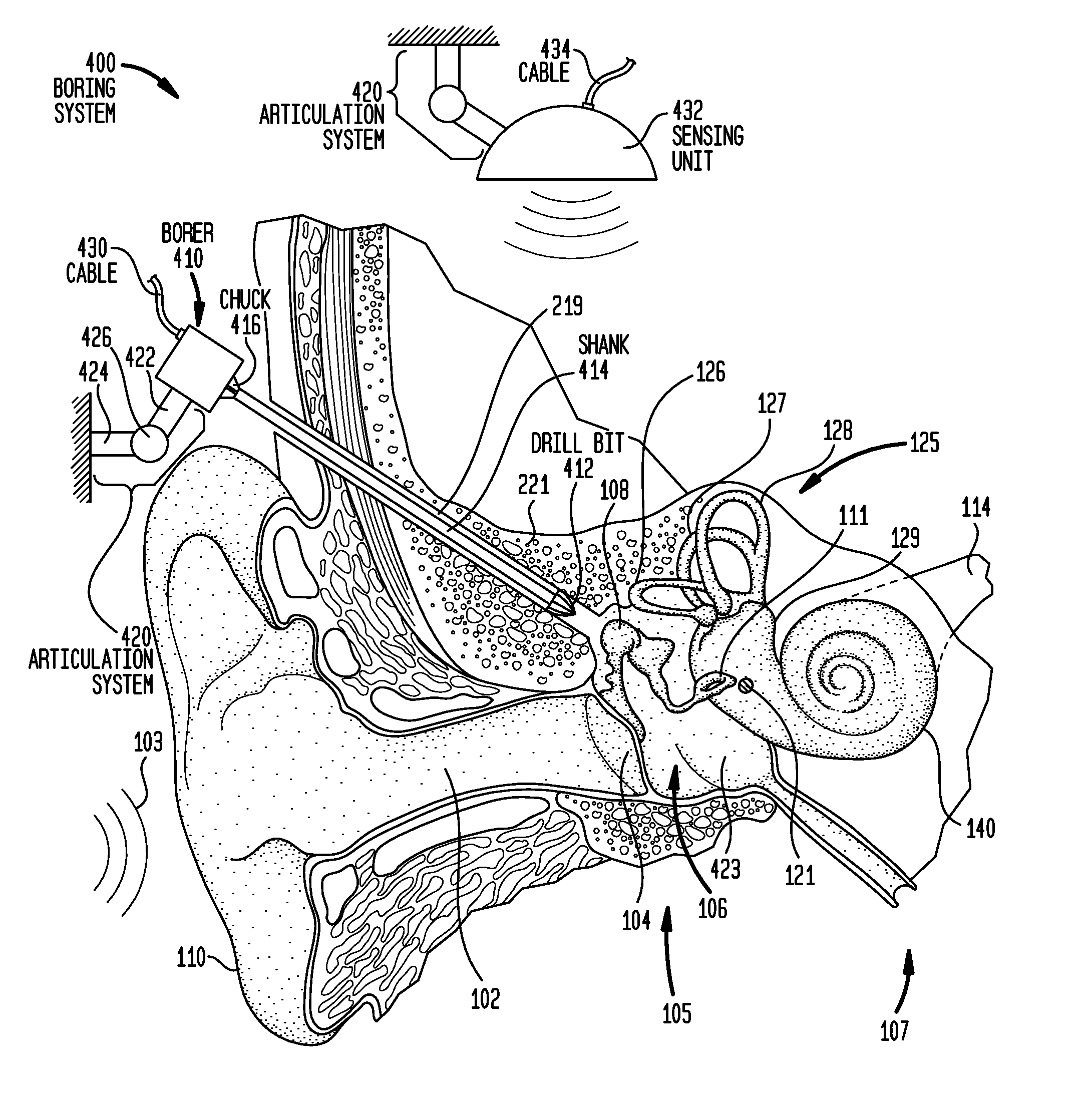
Implantation of a hearing prosthesis
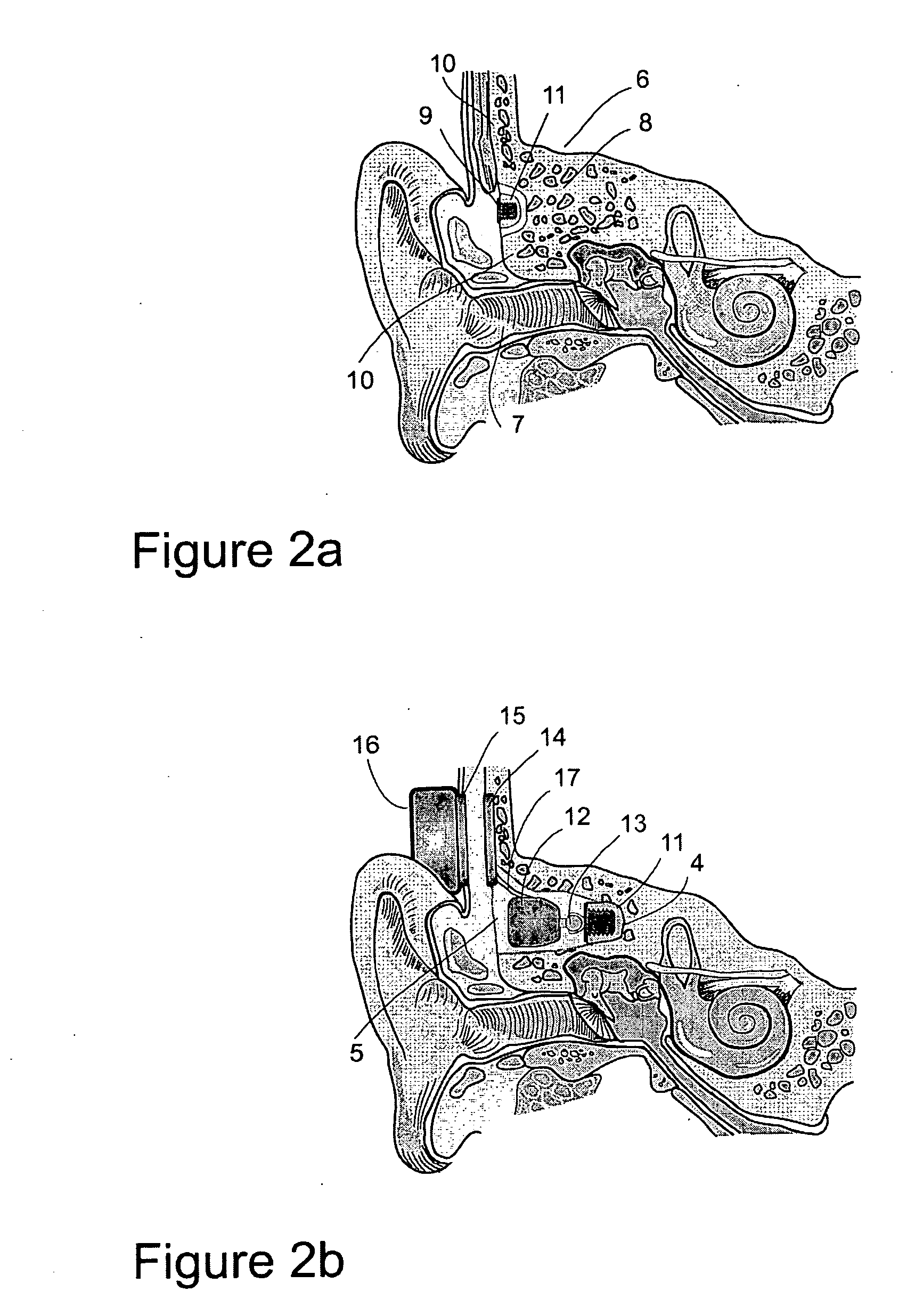
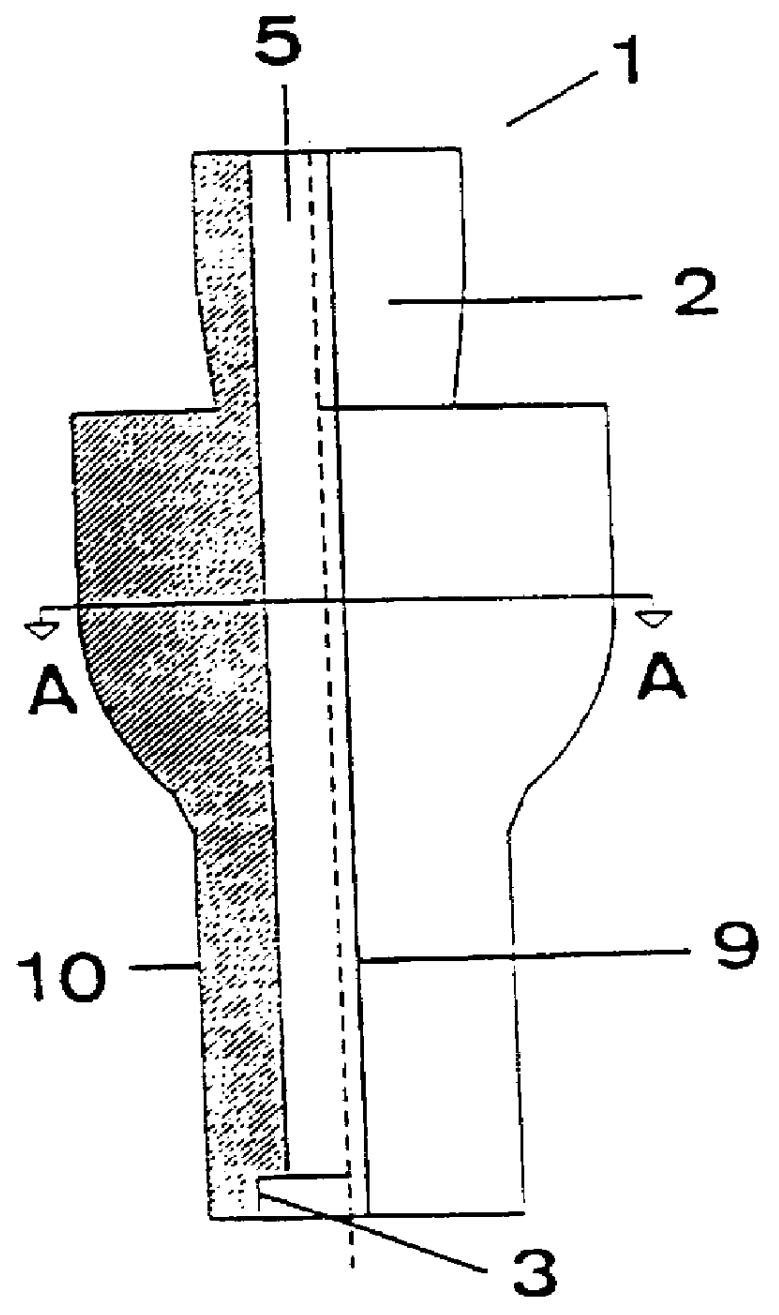
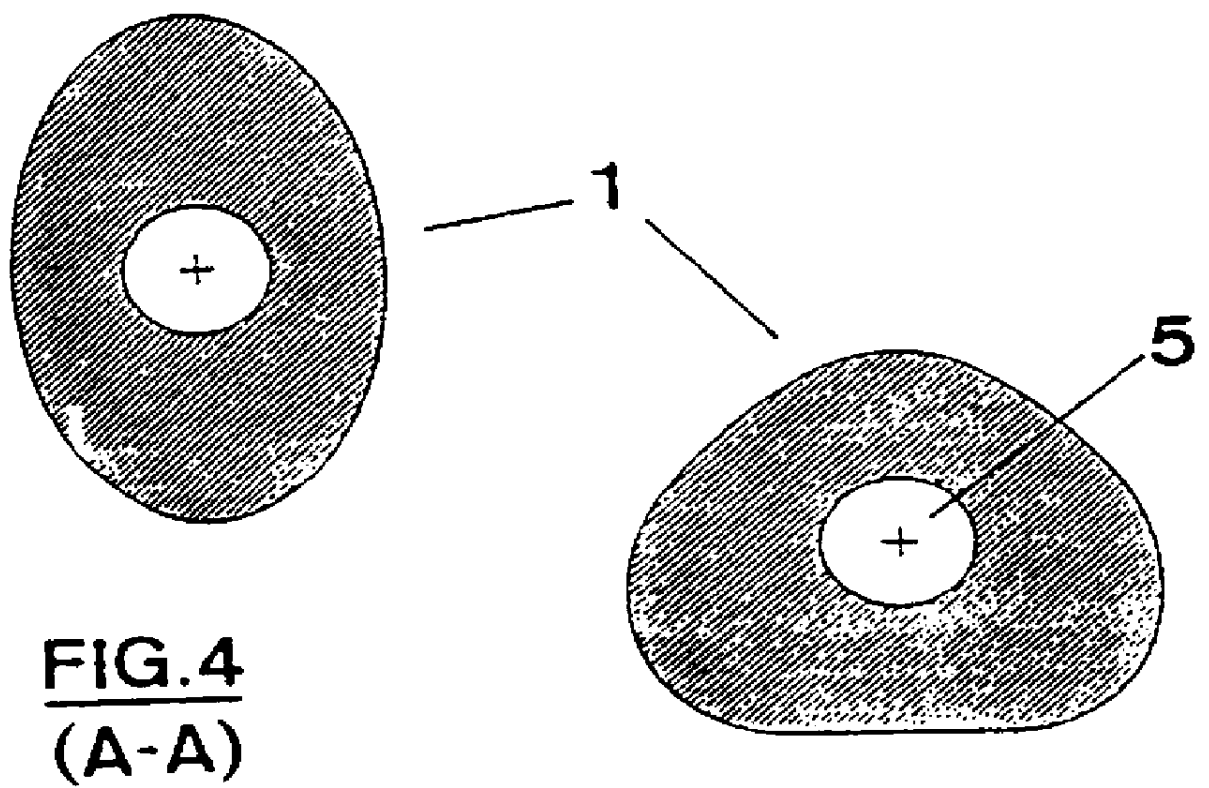
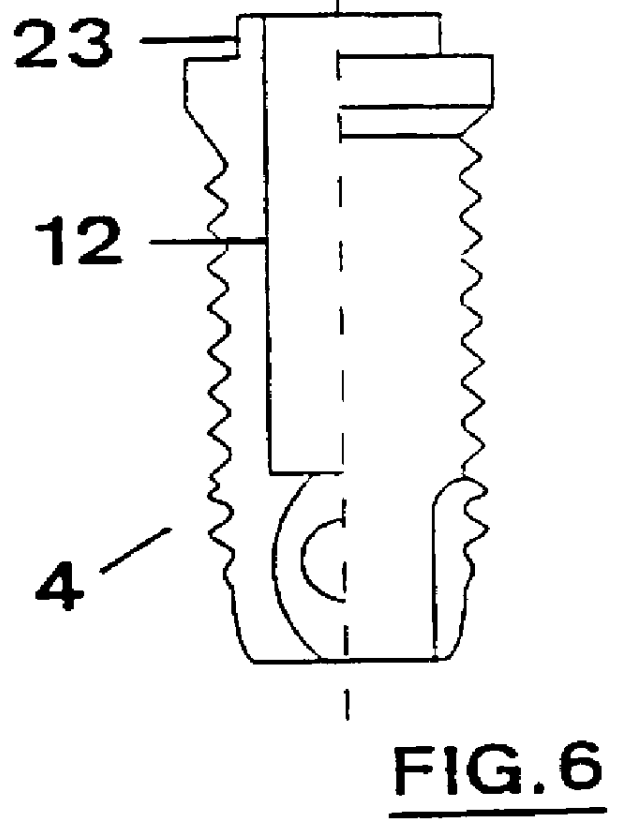
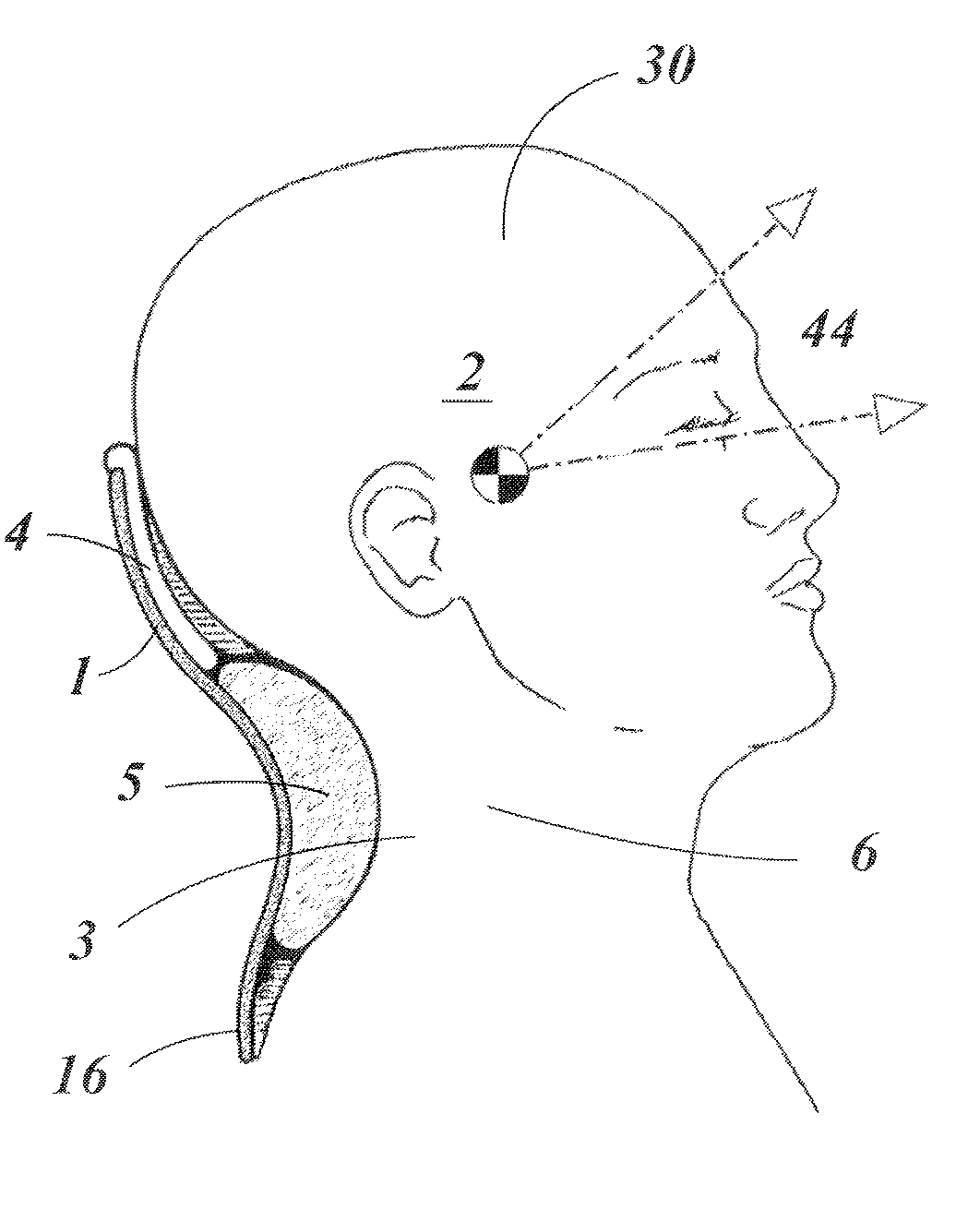
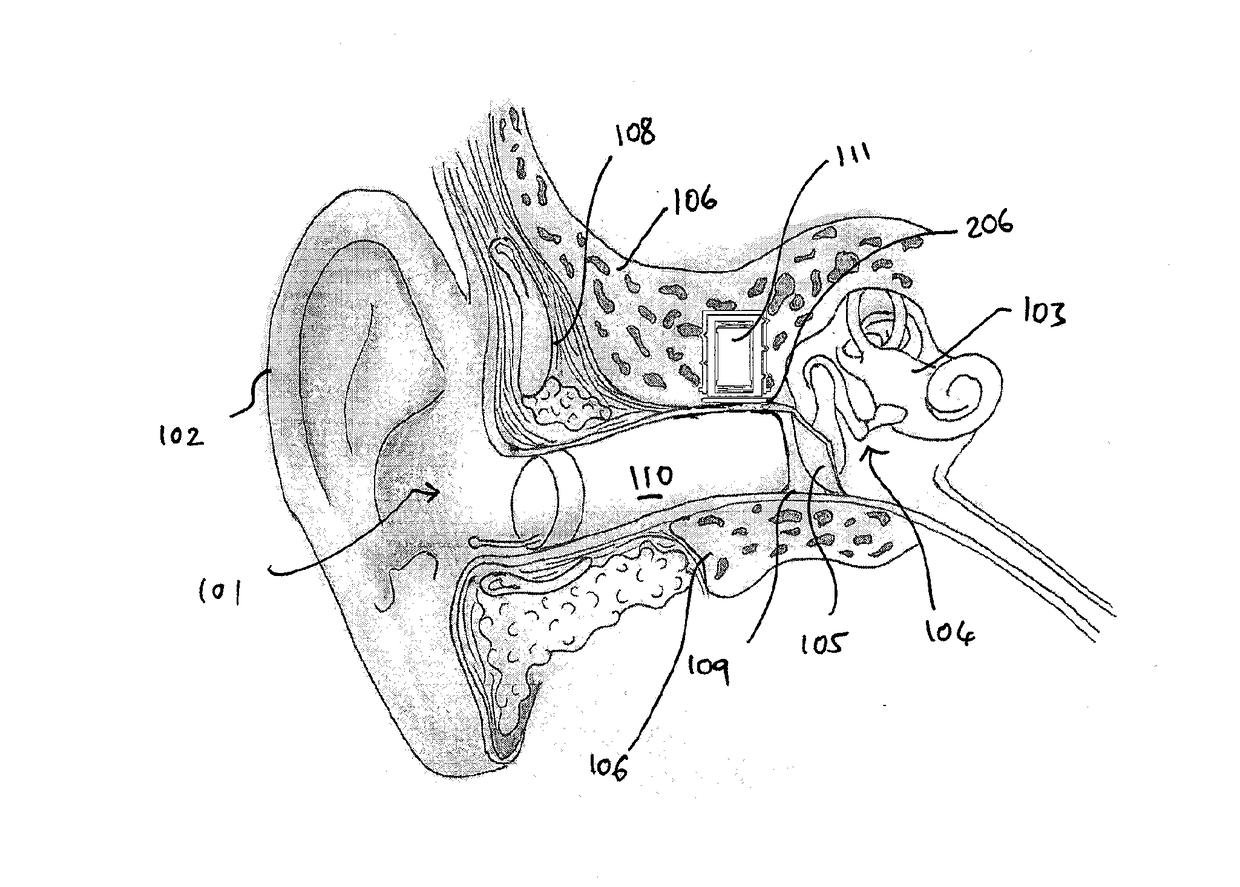
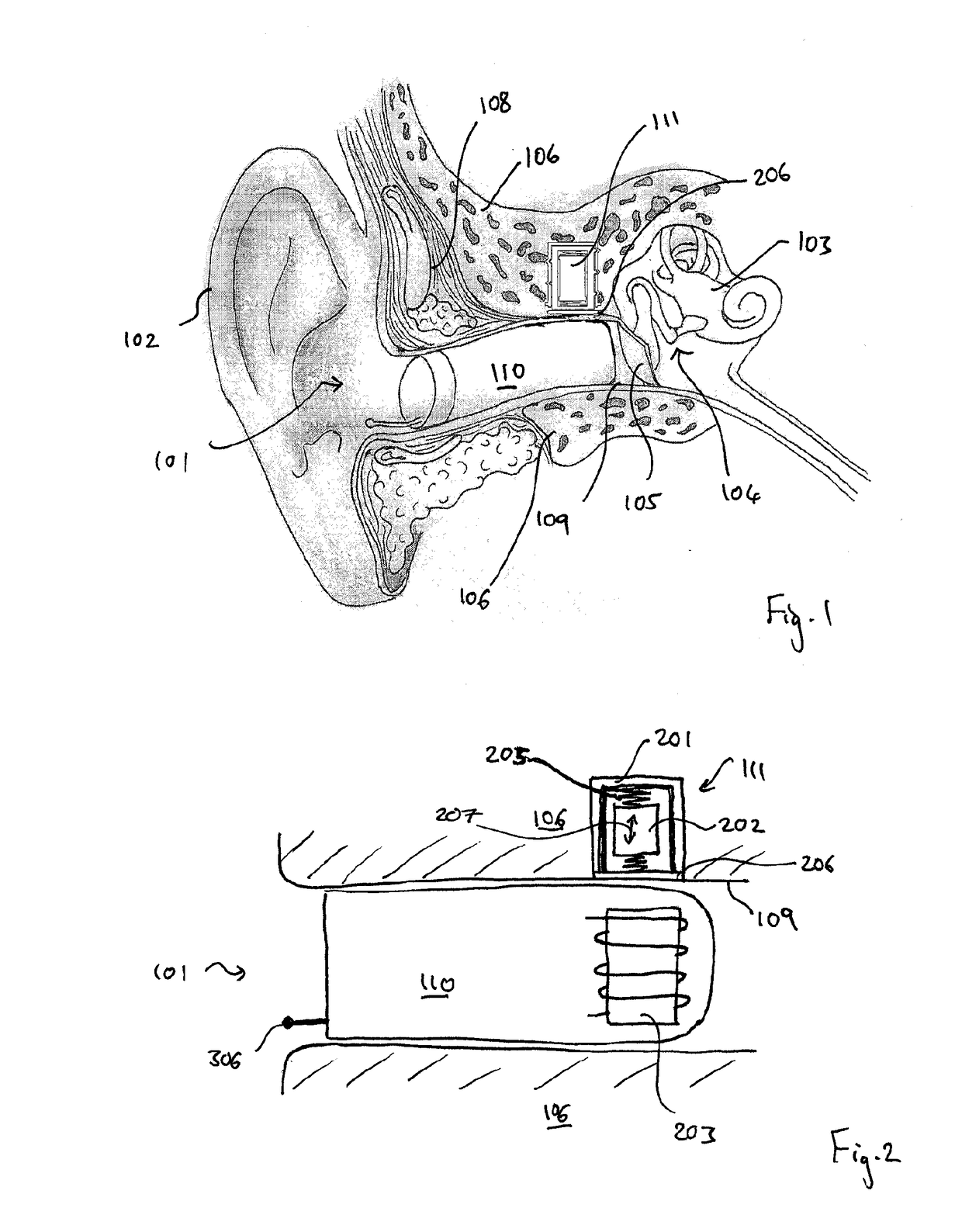
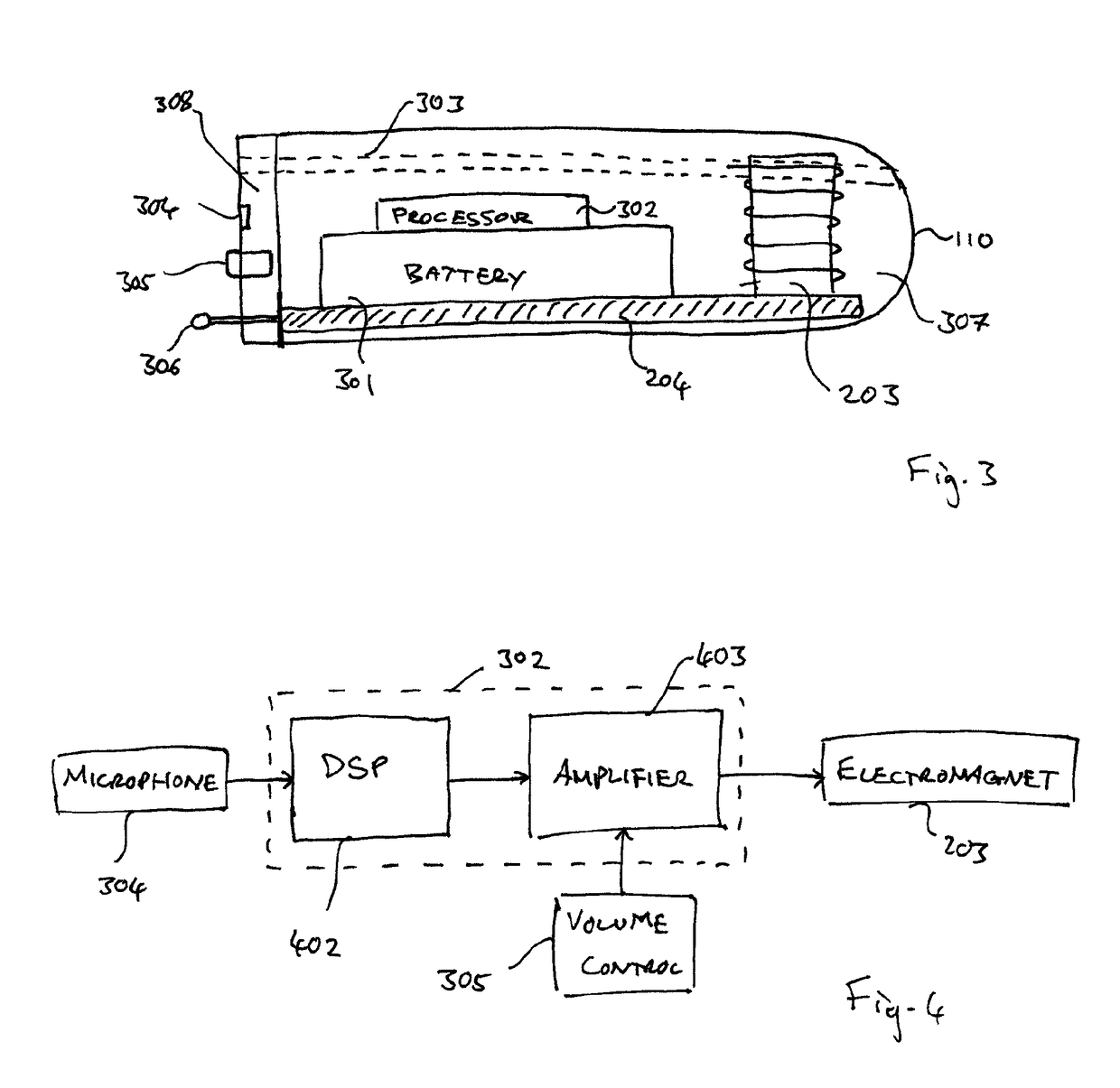
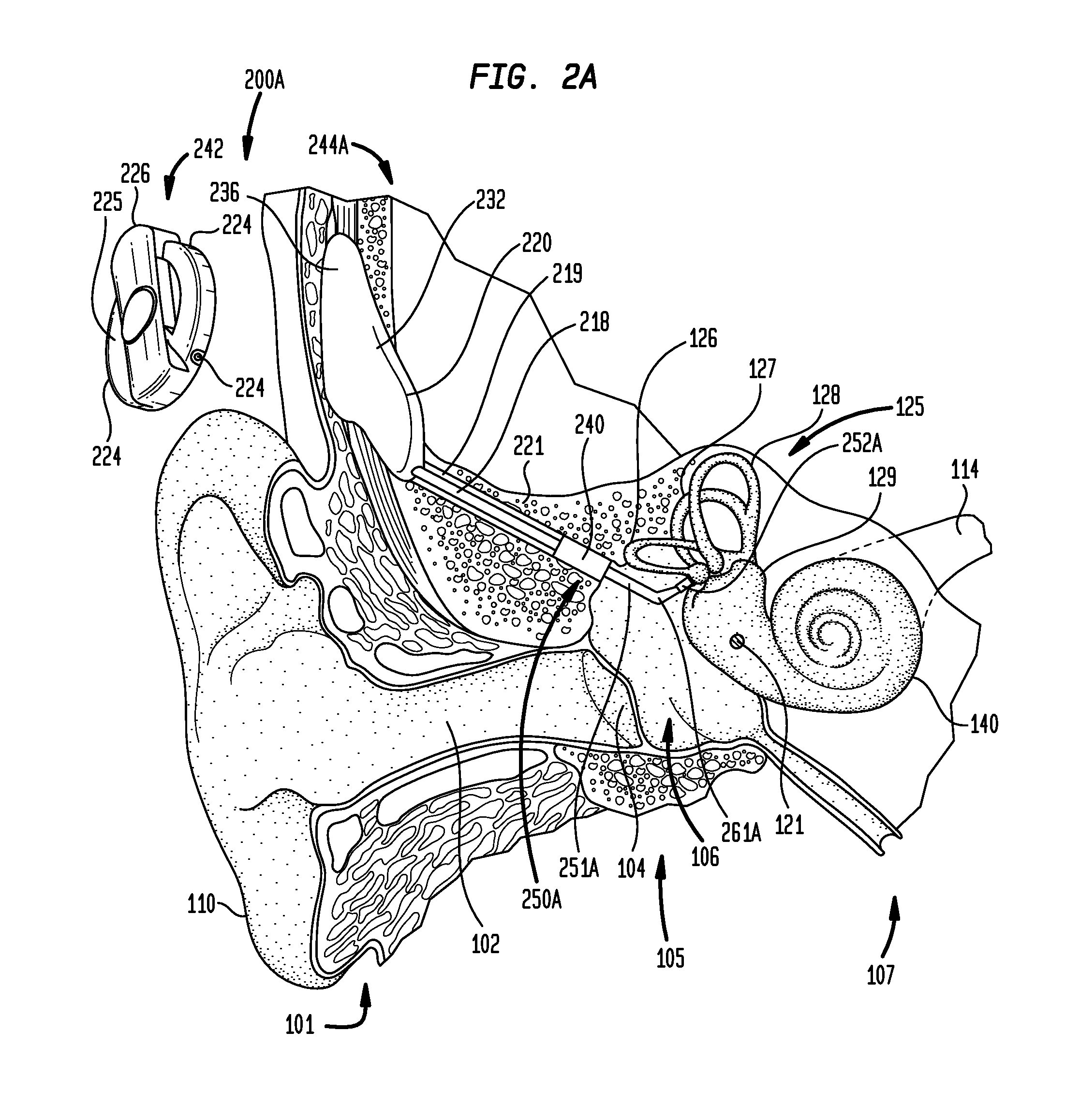
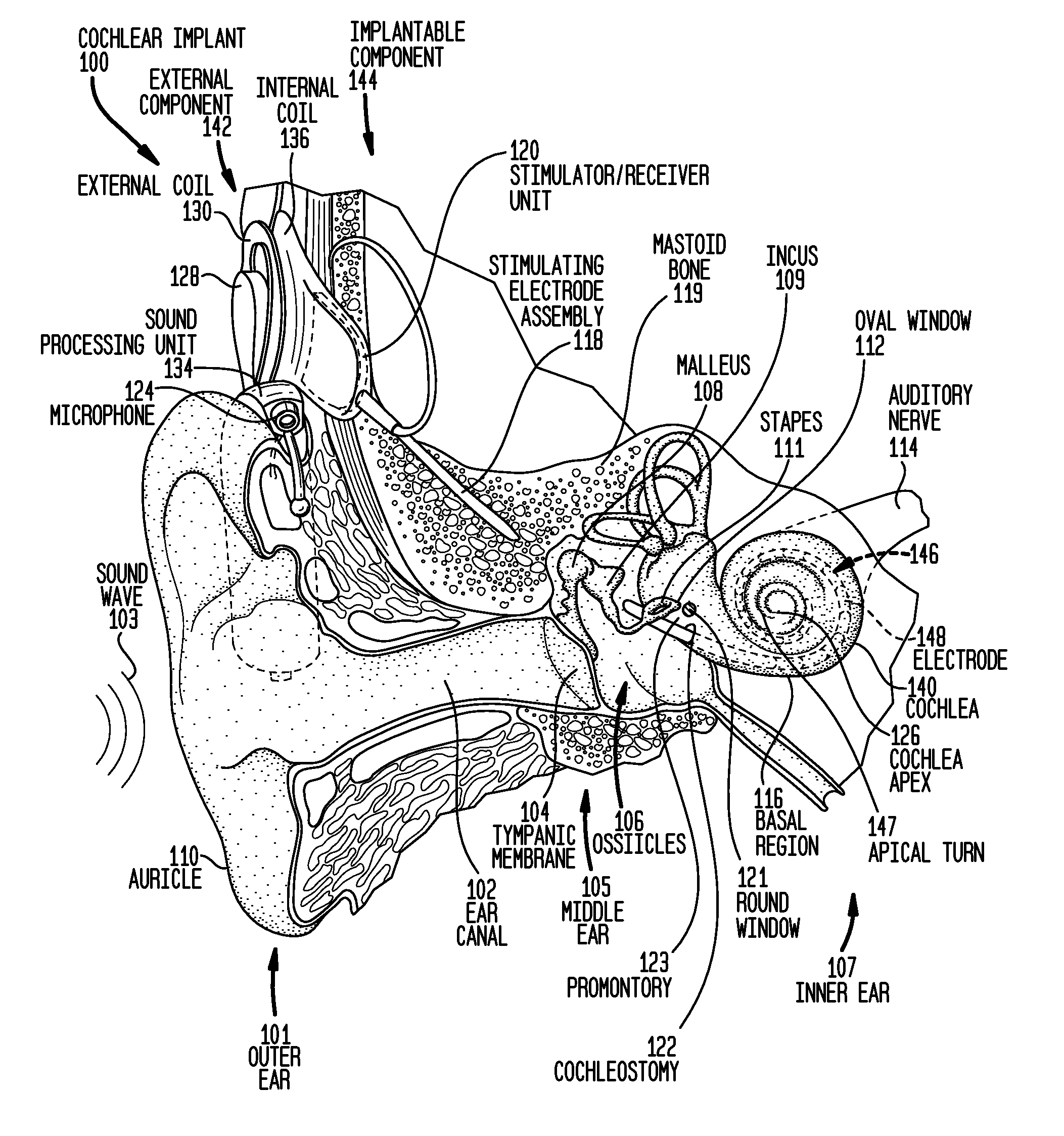
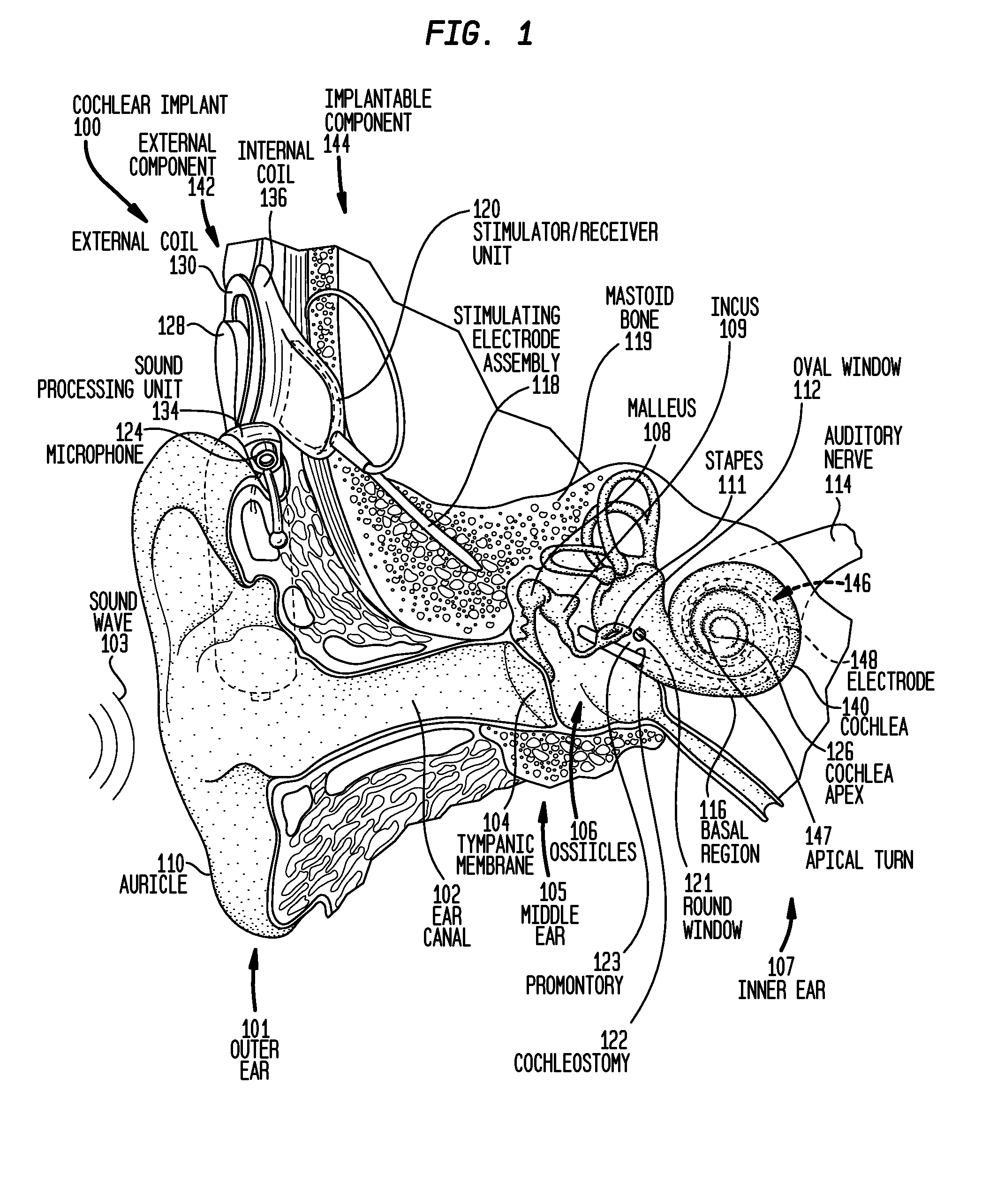
A method of implanting a hearing prosthesis in a recipient, including boring an artificial passageway into the temporal bone to a middle ear cavity based on a virtual model of at least a portion of a recipient's temporal bone.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
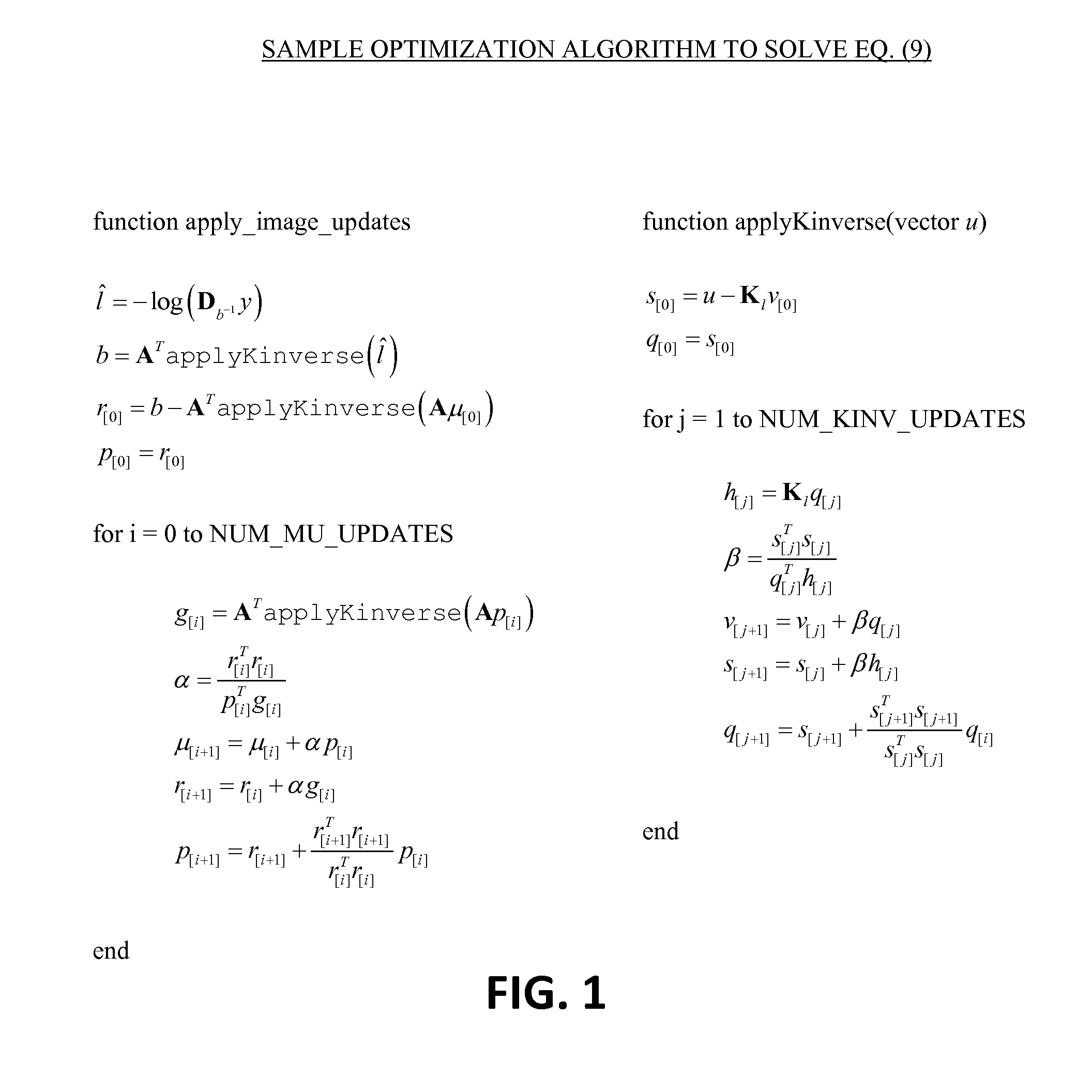
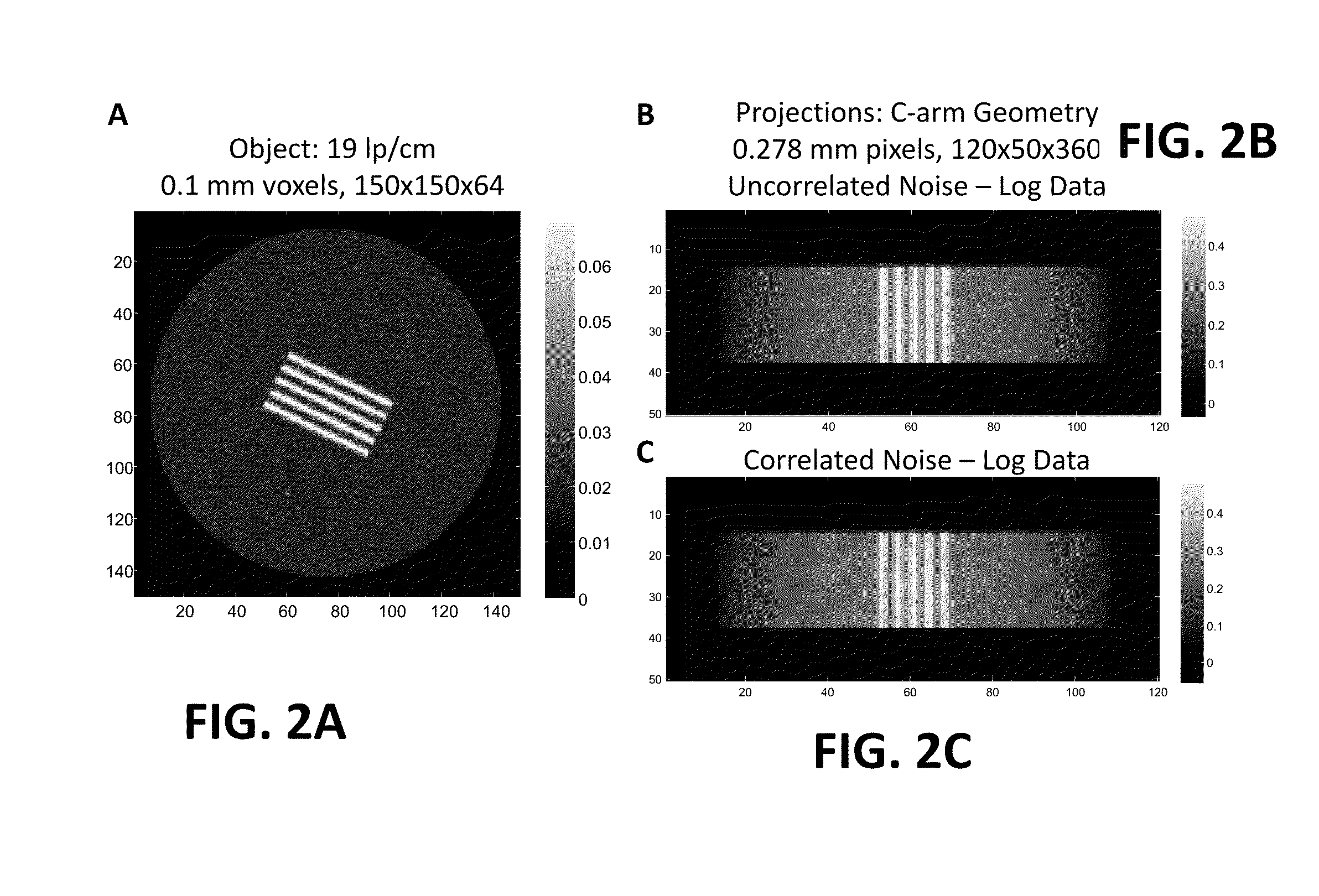
Model-based tomographic reconstruction with correlated measurement noise
The present invention is directed to a novel tomographic reconstruction framework that explicitly models the covariance of the measurements in the forward model using a mean measurement model and a noise model. This more accurate model can result in improved image quality, increased spatial resolution, and enhanced detectability—in particular, for imaging scenarios where there are features on the order of the correlation length in the projection data. Applications where these methods might have particular benefit include high resolution CBCT applications as in CBCT mammography (where very fine calcifications are difficult to resolve due to detector blur and correlation), musculoskeletal imaging (where fine bone details are important to the imaging task), or in temporal bone imaging where the fine detail structures of the inner ear are also difficult to resolve with standard imaging techniques.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
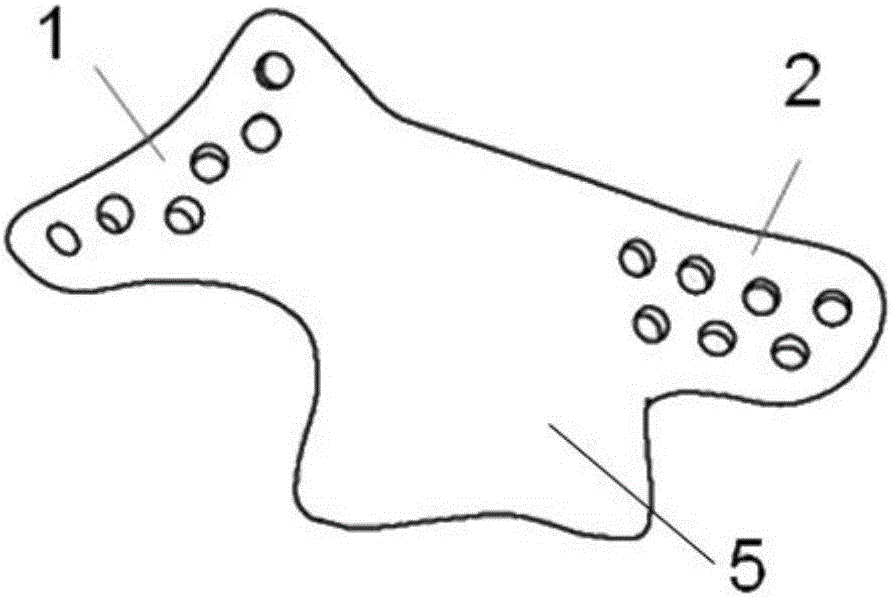
Head relaxing pillow
ActiveUS20150245967A1Reduce stressIncrease loopPillowsOperating chairsTemporal boneBiomedical engineering
Owner:HORNG SY WEN +1
Rat primary auditory cortex microelectrode array implantation fixation operation method
The invention belongs to the research field of electro-neurophysiology, and particularly relates to a rat primary auditory cortex microelectrode array implantation fixation operation method for auditory sense cognitive research. The method comprises the following steps of: fixing a wire electrode part and an electrode connector part of a microelectrode array in a double ectopia way, i.e. fixing the wire electrode on an auditory cortex temporal bone through an electrode landing device, and then buckling the wire electrode to fix the electrode connector onto a parietal bone so as to complete implantation fixation of the auditory cortex microelectrode array. According to the method, the operation is simple, electrodes can be carried stably, the reliability of signal acquisition is high, the requirement of an auditory sense cognitive research under a freetime state of a rat is met, and the experimental animal cost of correlational researches is reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Concussion retarding orthotic and method of producing the orthotic
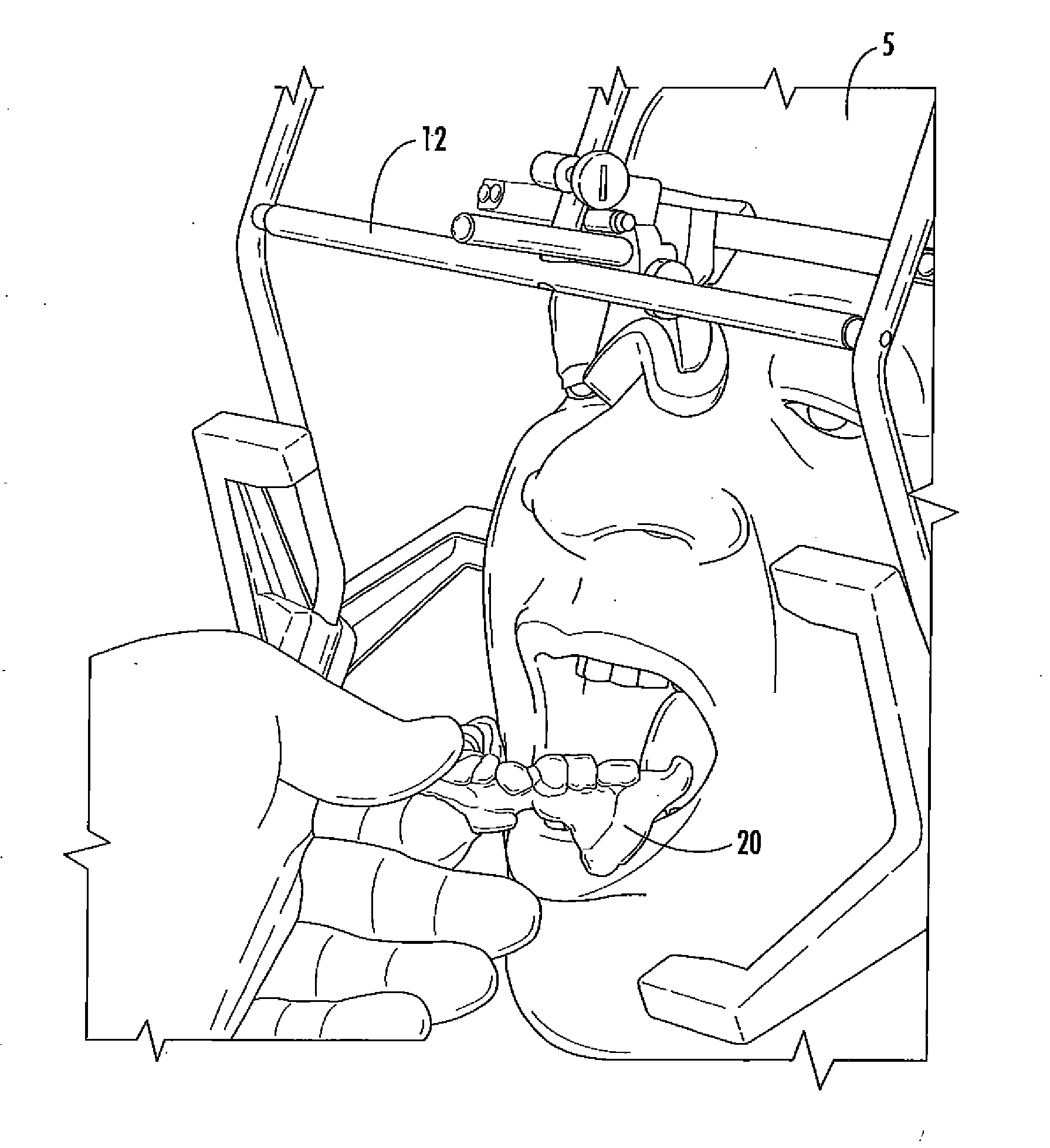
ActiveUS20140360511A1Alleviate concussionEfficiently dissipatedTeeth fillingWristbandsMaxilla/MaxillaryEngineering
A maxillary, mandibular, or dual concussion orthotic that substantially reduces concussion resulting from forces applied to the lower jaw, and a method of producing the orthotic. The orthotic device produced according to the method described herein is objectively measured and produced to physiological parameters for an individual user. The orthotic is constructed so that the mandibular teeth are firmly indexed into the orthotic to hold the mandible in a specific position relative to the maxilla. The upper and lower jaws are positioned by the orthotic to act as a unit, and cooperate with the orthotic to effectively dissipate concussive forces and provide spacing of the temporomandibular joint, resulting in the decompression of the joint to mitigate transmission of concussive forces from the condyles of the mandible to the temporal bones of the skull.
Owner:MOHLER CHRISTOPHER EDWARD
Method and apparatus for picking up auditory evoked potentials
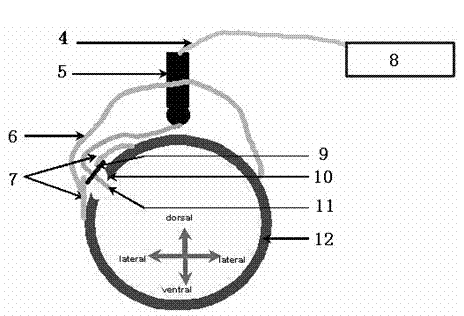
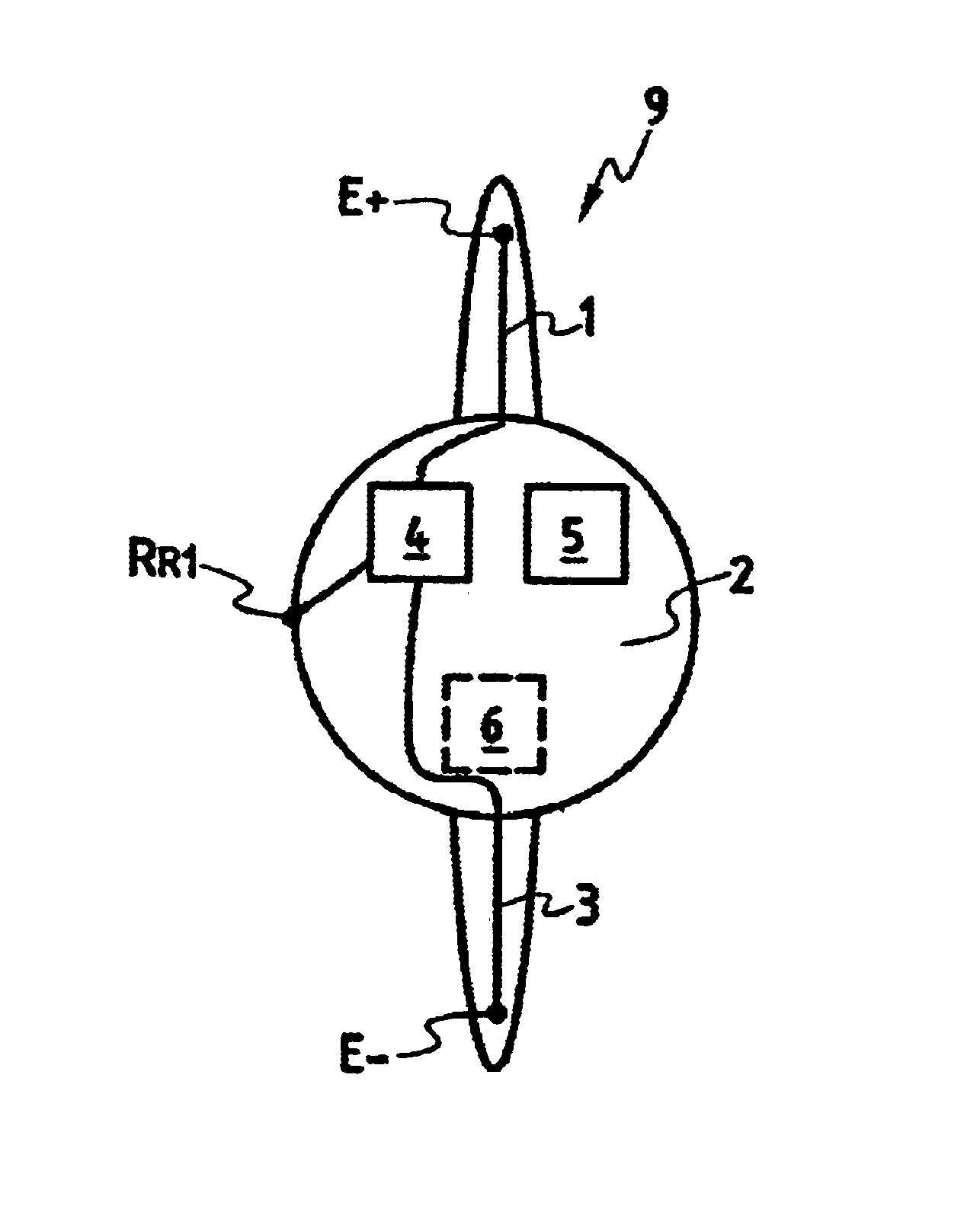
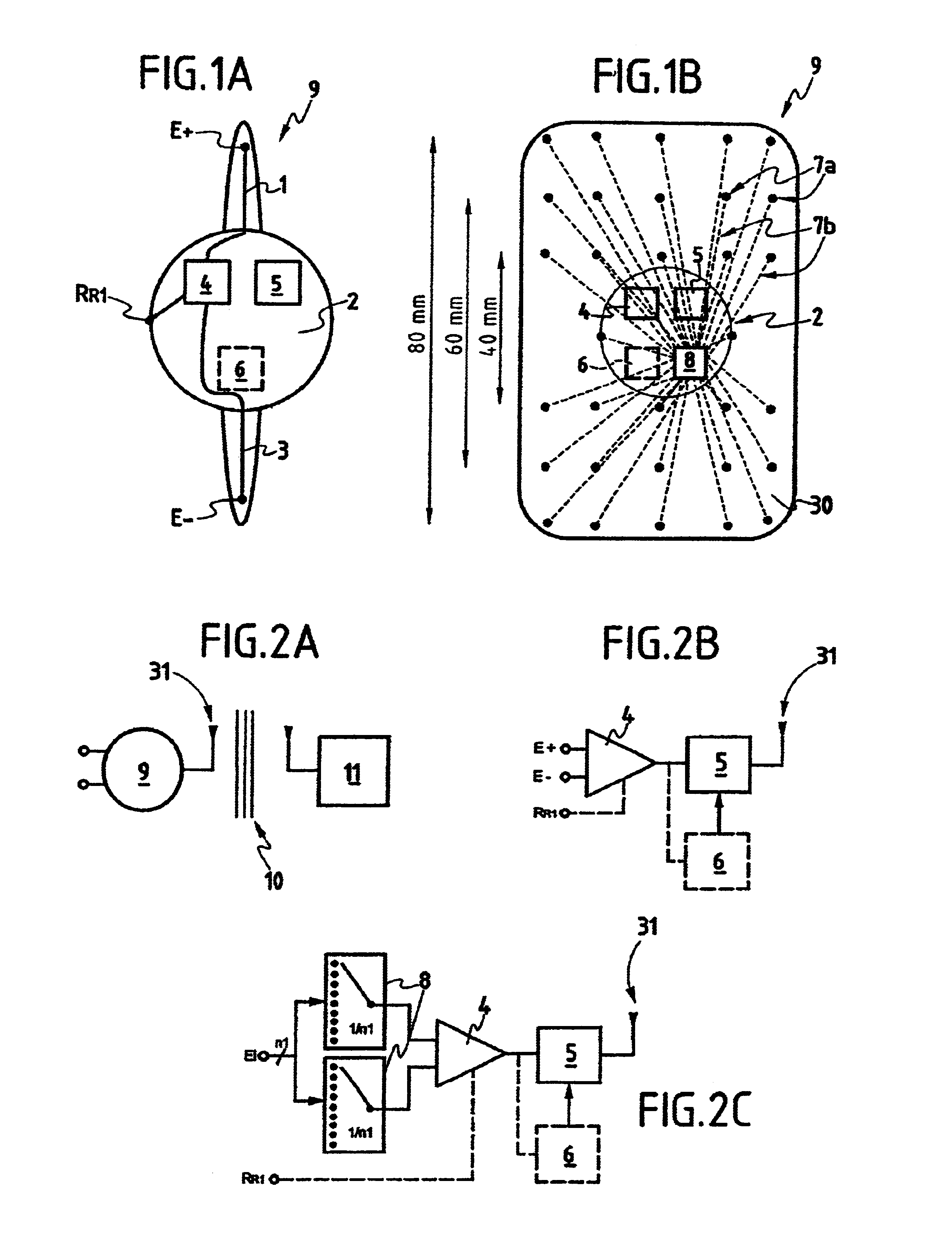
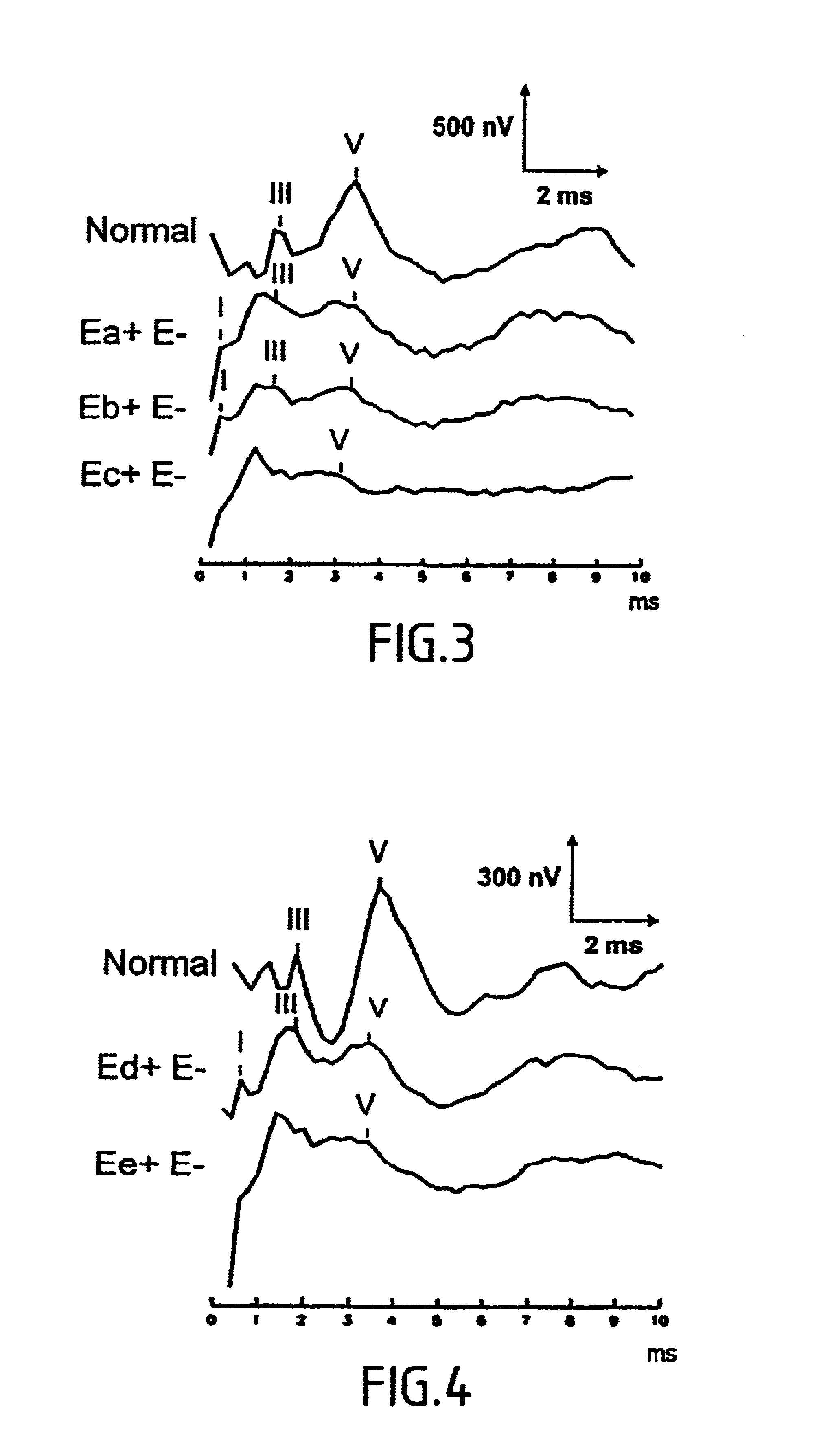
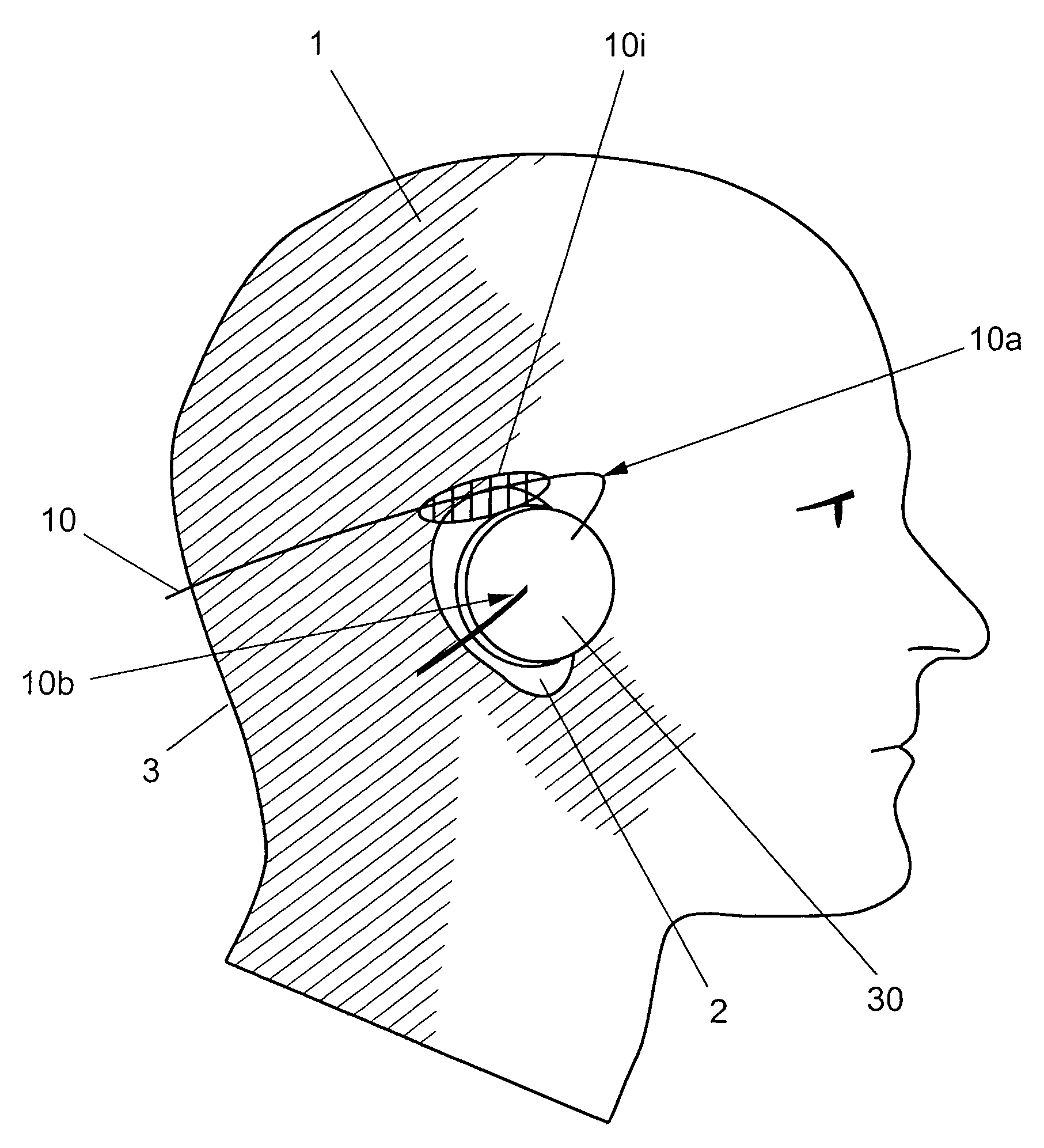
InactiveUS6944502B2Constant timeImprove accuracyElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyAuditory systemTemporo-occipital area
The present invention relates to a device for picking up biological electrical signals, and more precisely auditory evoked potentials generated by acoustic and / or electrical and / or mechanical stimulation of the cochlea, or of a portion of the auditory system in man or animal. The device for measuring or picking up auditory evoked potentials is surgically implantable in the temporo-occipital area and comprises at least two extracochlear pickup electrodes connected to the inputs of a differential amplifier.
Owner:NEURELEC FIFTY PERCENT INTEREST
Headphone with behind-the-head headband
InactiveUS7406180B2Minimum contact pressureImprove acousticsInterconnection arrangementsBroadcast circuit arrangementsTransducerEngineering
There is provided a headphone with a behind-the-head headband comprising at least one transducer and a behind-the-head headband for receiving the transducer. The behind-the-head headband further comprises first and second contact locations for resting against a temporal bone of a wearer of the headphone. The spacing between the transducer and the first or second contact location can be adjusted. By virtue of the possibility of adjusting the spacing with respect to the contact location the transducer can be positioned exactly over the auditory channel of the headphone wearer without pressure points on the ear.
Owner:SENNHEISER ELECTRONICS GMBH & CO KG
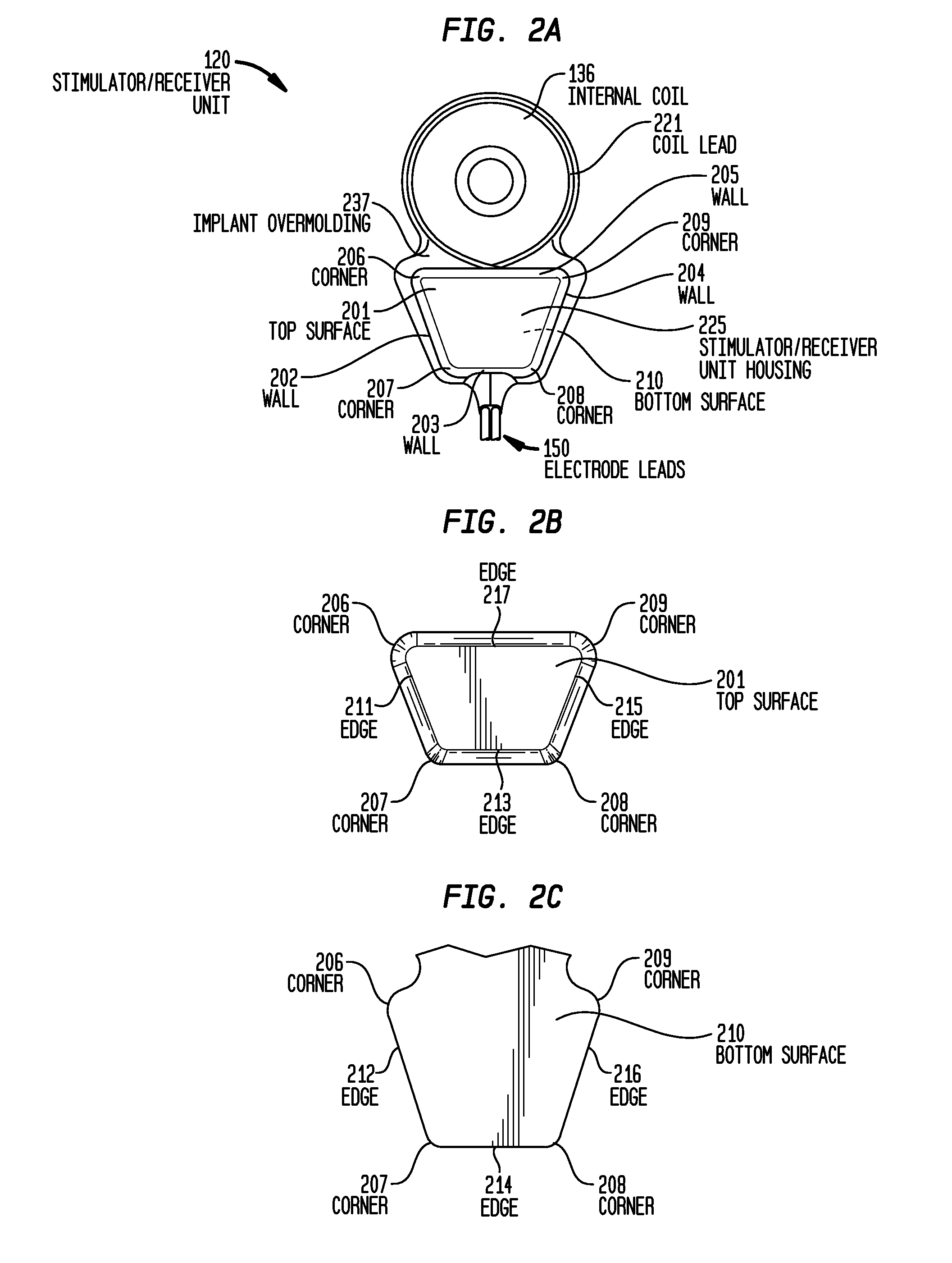
Implantable device migration control
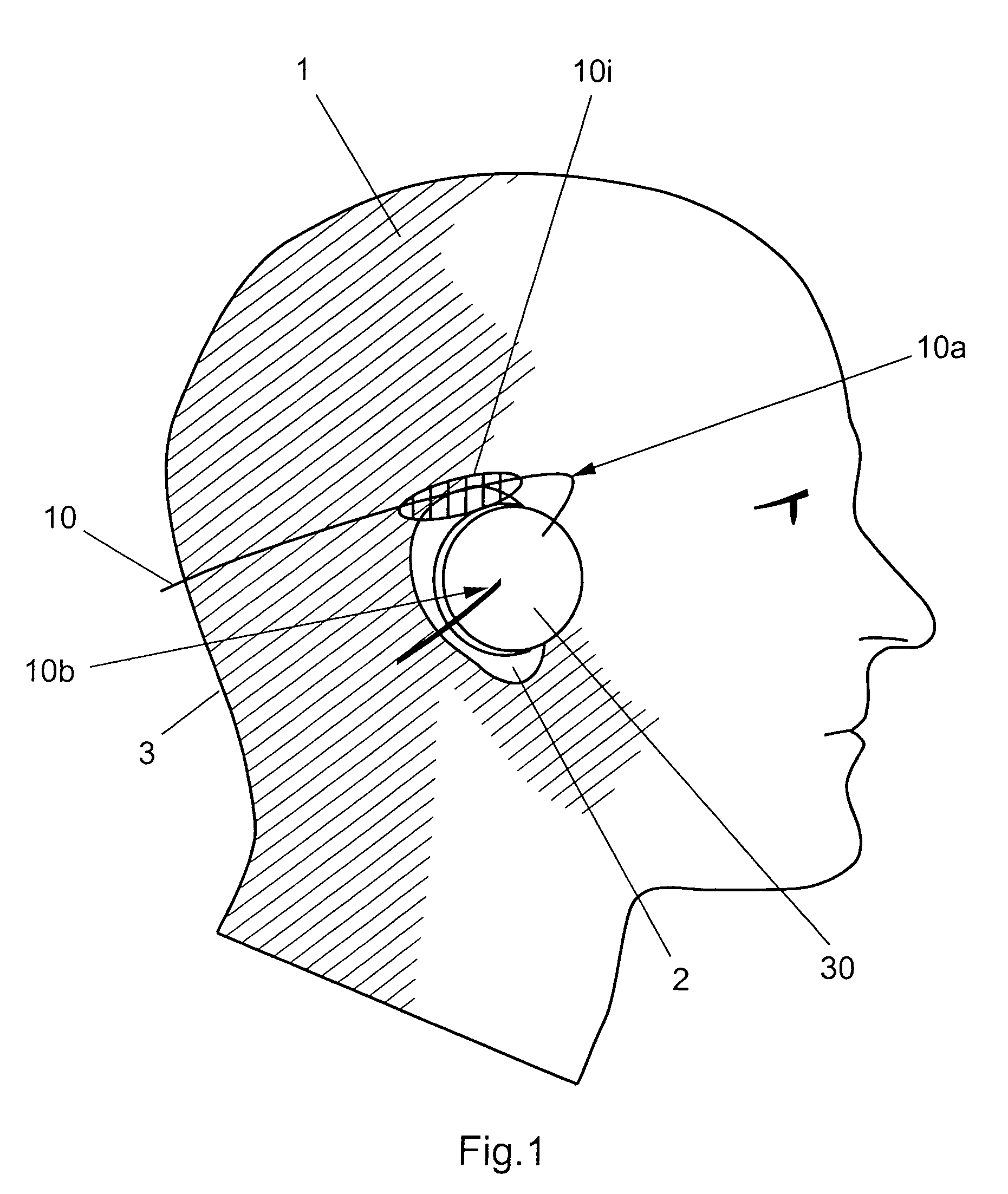
Devices and methods are disclosed for a stimulator unit in a medical device, such as an implantable component of a cochlear implant. In embodiments, the stimulator unit comprises a bottom wall configured to be substantially contacting a temporal bone of a recipient, and a top wall positioned opposite the bottom wall, wherein a cross section of the stimulator unit has an outer profile substantially parallel to the bottom wall and the top wall.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Artificial cochlea cranked electrode and implanting method thereof
ActiveCN104622601AImprove reliabilityImprove securityEar treatmentProsthesisColloidal silicaElectrode array
The invention provides an artificial cochlea cranked electrode. The artificial cochlea cranked electrode comprises an electrode array link, and the electrode array link is bent into a cochlea shape and then is packed into a cranked electrode array link body through a colloidal silica body. The cranked electrode array link body is provided with a guide hose enabling the cranked electrode array link body to be straight, a horn mouth is formed in the tail end of the guide hose, and the guide hose is provided with a tearable structure penetrating through the head end and the tail end of the guide hose. The invention further provides an implanting method of the artificial cochlea cranked electrode. The implanting method comprises the steps that the horn mouth in the tail end of the guide hose of the artificial cochlea cranked electrode abuts against a windowing hole of the temporal bone of the human body, the artificial cochlea cranked electrode is slowly pushed into the temporal bone through the windowing hole of the temporal bone, the guide hose is made to gradually crack from the tearable structure, and the cranked electrode array link body is made to gradually recover the bent state and is matched with the human body cochlea completely; the cracked guide hose is taken out of the earhole, and then the cranked artificial cochlea is implanted. The artificial cochlea cranked electrode is simple in structure, convenient to implant, safe, reliable, high in language distinguishing ability, small in power consumption and long in service life.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV +1
Phased array head temporal bone imager
InactiveCN105147330AObserve the flow in real timeReduce inspection costsOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesParenchymaDisplay device
The invention relates to a phased array head temporal bone imager. The phased array head temporal bone imager comprises a displayer body, a main input device, an ultrasonic probe, an auxiliary input device, an outer shell, an ultrasonic main machine, a machine body, a power source, a PC host, a CD driver, a displayer guide column, a displayer bottom cover, a displayer arm and a displayer support. When the phased array head temporal bone imager is in practical use, the 2-MHz low-frequency phased array probe is adopted to penetrate through the head temporal bone to observe a brain tissue structure, intracranial vessels and vessel conditions of a wemes ring of the brainstem, and intracranial lesions are diagnosed through the brain parenchyma, the brain vessels and Doppler frequency spectrum waveforms of the brain parenchyma and the brain vessels. When used for detection, the phased array head temporal bone imager is direct, easy, convenient, free of radiation and low in detection cost. Meanwhile, blood flowing and pulsation can be observed in real time, and analysis and diagnosis are carried out in cooperation with the conditions such as the rigidity of the vessels and the blood concentration.
Owner:苏州斯科特医学影像科技有限公司
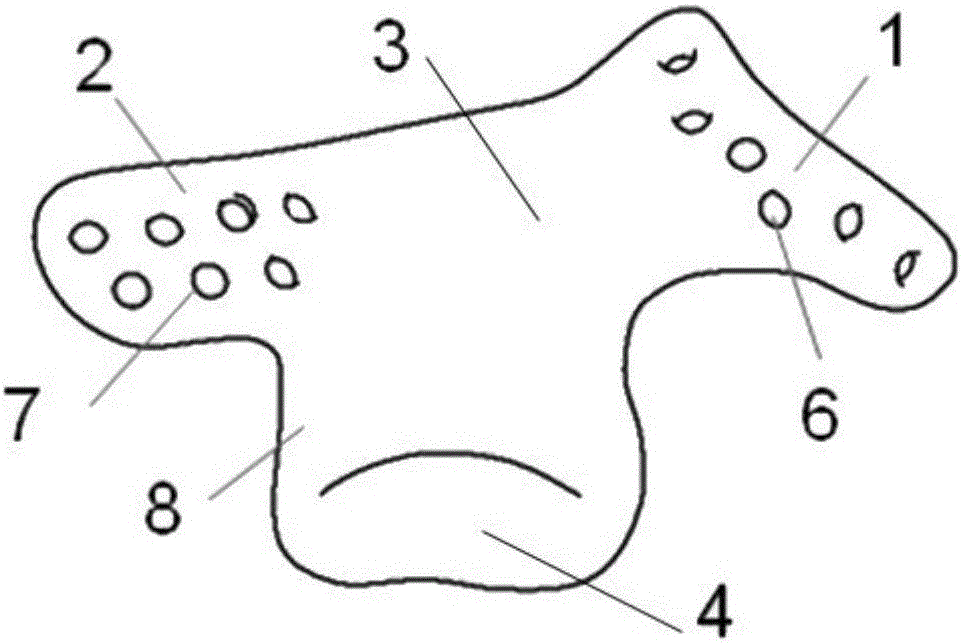
Head relaxing pillow
ActiveCN104720471APromote circulationPillowsDevices for pressing relfex pointsOccipital boneTemporal bone
It is an objective of the present invention to provide a head relaxing pillow. The pillow is made of an elastic material and includes a supporting main body, two contact portions, and a pressing portion. The top of the supporting main body is designed to support the neck of a user who lies face up. The bottom of the supporting main body is concavely provided with a recess. The supporting main body is provided with two sunken portions which are adjacent to two corresponding ends of the supporting main body respectively. Each contact portion has one end connected to one of the two corresponding ends of the supporting main body. The other end of each contact portion extends far from the supporting main body. The pressing portion extends from one side of the supporting main body and is located between the contact portions. When the user is lying, face up, such that his neck is resting on the supporting main body, the user's temporal bones correspond in position to the sunken portions respectively. Meanwhile, the supporting main body is deformed toward the recess due to the weight of the user's neck, such that the other ends of the contact portions may support the support the parietal bones of the user and the pressing portion may press against the occipital bone of the head of the user. Thus, the gaps in the user's skull are allowed to open slightly to lower the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid in the skull and thereby enhance circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Owner:洪斯文 +1
After-brain-surgery cranial nerve care device
ActiveCN110215362AClose contactProtective structureNursing bedsAmbulance serviceCranial nervesSphenoid bone
The invention discloses an after-brain-surgery cranial nerve care device which comprises an inner layer protection cushion, a middle layer air bag, an outer layer cooling shell and a bottom fixing ring. The inner layer protection cushion comprises a frontal bone cushion, a parietal bone cushion, an occipital bone cushion, a temporal bone cushion and a sphenoid bone cushion which are fixedly connected with one another through locking and fixing devices. The cushions, the middle layer air bag and the outer layer cooling shell form a three-layer protection structure. Through the after-brain-surgery cranial nerve care device, by simulating a human brain skeleton structure, by means of the split type structural design, the product makes closer contact with the head, and the after-brain-surgerycranial nerve care device is convenient to detach and assembly; through the middle layer air bag, the after-brain-surgery cranial nerve care device can massage and protect the head bone through compression or depressurization in use; the inner layer protection cushion is made of silica gel and can make soft contact with the head, and therefore pressure sores are prevented, the brain tissue structure is protected, and the safety protection capacity of the product is improved.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Intracerebral Blood Flow Measuring Device
InactiveUS20080021335A1Efficient use ofEasy to measureBlood flow measurement devicesCatheterCBF - Cerebral blood flowTemporal bone
It is intended to standardize MCAO model and to further improve the reproducibility and reliability thereof. There is provided a probe holding device (10) which includes a probe holding member (14) for holding a blood flowmeter probe (12), and such device is used together with the blood flowmeter probe when measuring intracerebral blood flow. While holding the blood flowmeter, the probe holding member can be disposed in a position of being adjacent to and outside temporal bones.
Owner:HARADA HIDEKI
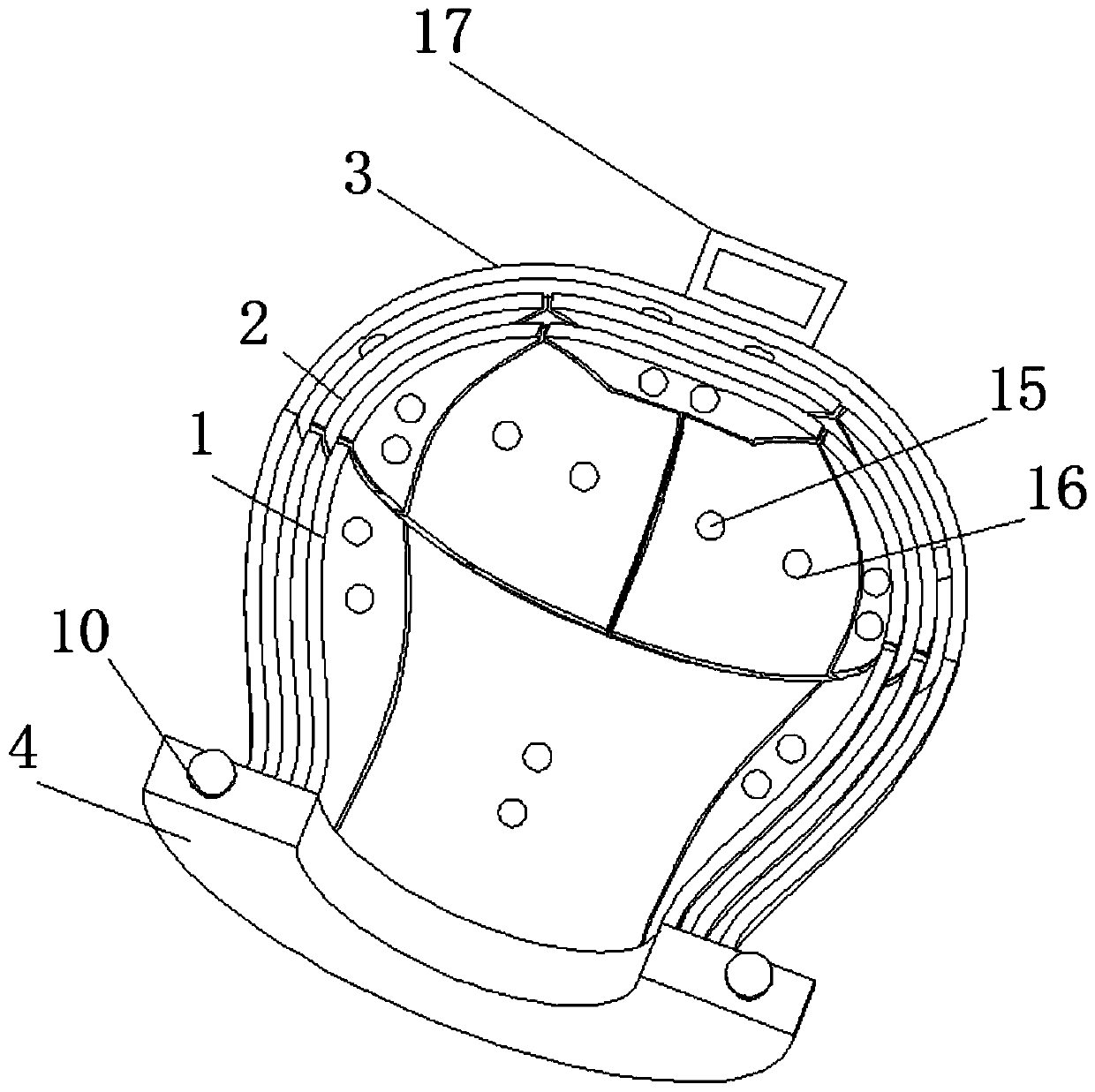
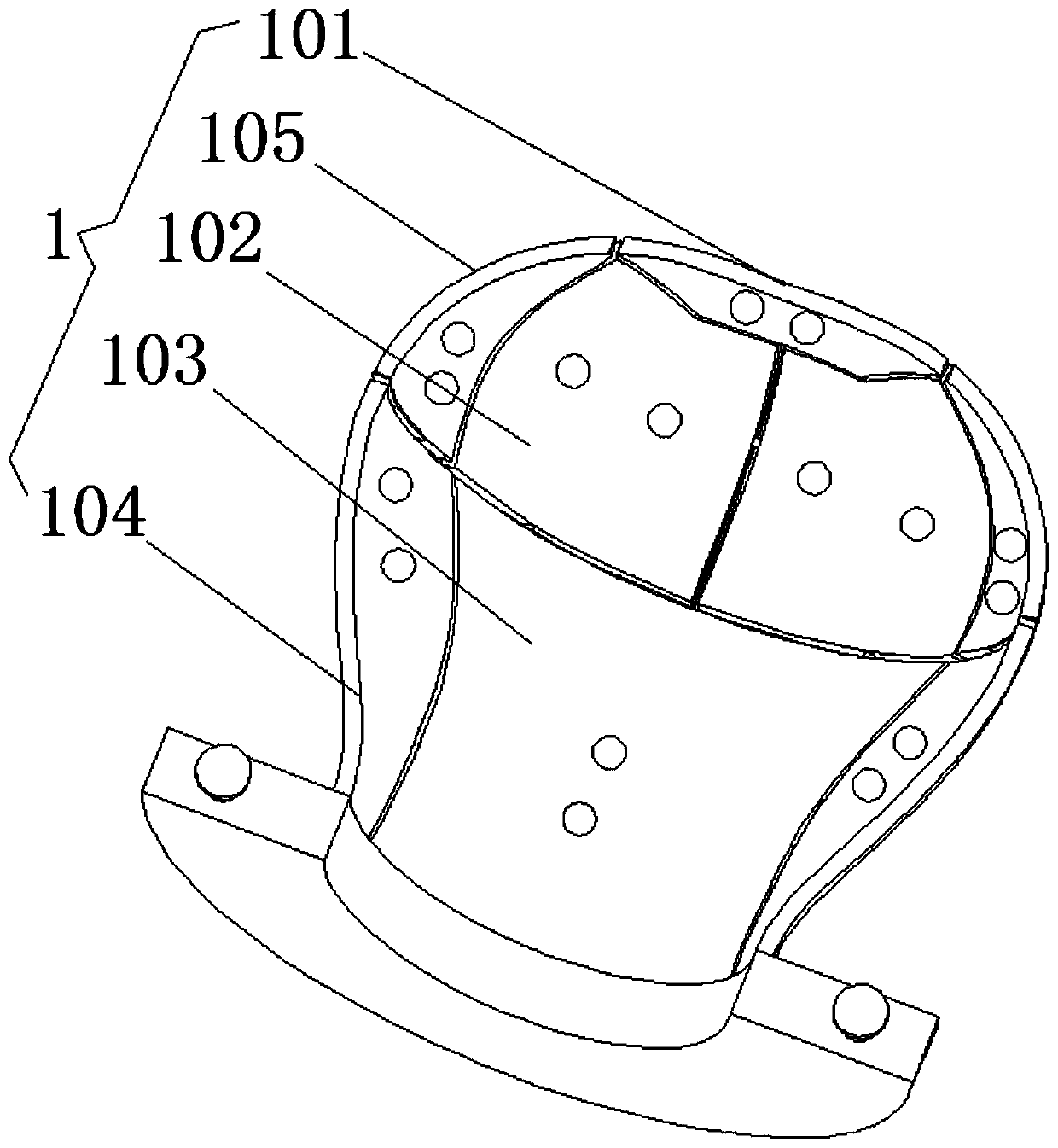
Temporal bone model for surgery training and forming method thereof
ActiveCN107993547AHigh degree of simulationImprove training effectEducational modelsTraining periodBone Cortex
The invention discloses a temporal bone model for surgery training and a forming method thereof, which belong to the technical field of ear surgery training aids. The temporal bone model for surgery training comprises a cortical bone, a cancellous bone, a semicircular canal, an ear bone and a face neural tube, wherein the cancellous bone is of a porous structure; the semicircular canal and the face neural tube are of cavity structures; the ear bone is of a solid structure; the semicircular canal, the ear bone and the face neural tube are integrally formed by adopting aluminum oxide ceramics through 3D (Three-dimensional) printing; the cancellous bone is prepared from three raw materials: mixed powder, water and graphite powder; the mixed powder is prepared from mixing 85 percent by weightof clay and 15 percent by weight of feldspar powder; the cortical bone is prepared from two raw materials: mixed powder and water. The invention provides the temporal bone model for surgery training and the forming method thereof. The temporal bone model for surgery training is higher in biofidelity, lower in manufacturing cost, and capable of greatly improving a surgery training effect, shortening a doctor training period, reducing doctor training cost, and benefitting patients.
Owner:上海璞临医疗科技有限公司
Zygomatic arch temporal-mandibular joint glenoid fossa combined remediation prosthesis
InactiveCN105943200AAvoid risk of injuryImprove accuracyJoint implantsExternal Auditory CanalsJaw bone
The invention discloses a zygomatic arch temporal-mandibular joint glenoid fossa combined remediation prosthesis, and the prosthesis comprises a zygomatic bone fixing pterygoid lamina which contacts with a zygomatic bone and is fixed on the zygomatic bone, a temporal bone fixing pterygoid lamina which contacts with the temporal bone and is fixed on the temporal bone, a zygomatic arch connection part, and a skull base projection part which contacts with a skull base. The zygomatic bone fixing pterygoid lamina, the temporal bone fixing pterygoid lamina and the zygomatic arch connection part are respectively connected with the zygomatic arch connection part. The skull base projection part is provided with a glenoid fossa recessed part and baffle plates disposed at two ends of the glenoid fossa recessed part. The prosthesis can be used for repairing the combined loss, caused by the temporal-mandibular joint tumour and congenital malformation, of the zygomatic arch and a temporal-mandibular joint fossa, is more attached to a jaw bone, reduces unnecessary bone grinding, avoids the risks of damages to a skull base and an external auditory canal, greatly reduces the operation time, improves the fixing accuracy and stability, and can achieve the precise restoration of the combine loss of a zygomatic arch temporal-mandibular joint glenoid fossa of a Chinese.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Ear insert for relief of TMJ discomfort and headaches
InactiveUS8758436B2Reduce loadReduce stressDevices for pressing relfex pointsSurgeryDental ArticulatorsLigament structure
An expansible ear canal insert for treating TMJ disorders and headaches which acts directly on the TMJ and associated ligament and muscle structures to reduce stress and loads placed on the articulator disc located between the temporal bone and the mandible, as well as supportive muscles and ligaments near the TMJ. The insert is adapted to expand by application of body heat. In the expanded condition, the insert provides support to the TMJ and associated ligament and muscle structures.
Owner:RENEW GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com